Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - PHARMACYCLICS INC | form8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.9 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex999to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.4 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex994to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.8 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex998to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.6 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex996to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.1 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex991to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.2 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex992to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.5 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex995to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.7 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex997to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.12 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9912to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.18 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9918to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.15 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9915to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.10 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9910to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.16 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9916to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.13 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9913to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.14 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9914to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.17 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9917to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.11 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9911to8k207380_11052012.htm |
Exhibit 99.3
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma Oral Presentation
Title: The Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Inhibitor Ibrutinib Promotes High Response Rate, Durable Remissions, and Is Tolerable in Treatment Naïve (TN) and Relapsed or Refractory (RR) CLL or SLL Patients Including Patients with High-Risk (HR) Disease: New and Updated Results of 116 Patients in a Phase Ib/II Study
Session: 642. CLL - Therapy, excluding Transplantation: New Targeted Therapies
Date/Time: Sunday, December 9, 2012 Presentation Time: 5:00 PM
Location: Georgia World Congress Center, Thomas Murphy Ballroom 4
Presenter: John Byrd
John C. Byrd, MD1, Richard R. Furman, MD2, Steven Coutre, MD3, Ian W. Flinn, MD, PhD4,5, Jan A. Burger, MD, PhD6, Kristie A. Blum, MD7*, Jeff P. Sharman, MD8*, Barbara Grant, MD9*, Jeffrey A. Jones, MD, MPH7, William G. Wierda, MD, Ph.D.10, Weiqiang Zhao, MD PhD11*, Nyla A. Heerema, PhD11, Amy J. Johnson, PhD12, Anh Tran13*, Fong Clow, ScD14*, Lori Kunkel, MD15, Danelle F. James, M.D13 and Susan O'Brien, MD16*
1Division of Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
2Weill Medical College of Cornell University, New York, NY
3Stanford Univ. School of Med., Stanford, CA
4Sarah Cannon Research Institute, Nashville, TN
5Tennessee Oncology PLLC, Nashville, TN
6Department of Leukemia, The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
7Hematology, The Ohio State University-James Cancer Center, Columbus, OH
8Willamette Valley Cancer Institute and Research Center/US Oncology Research, Eugene, OR
9Vermont Cancer Center, University of Vermont, Burlington, VT
10Department of Leukemia, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
11Pathology, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
12Internal Medicine, Division of Hematology, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
13Pharmacyclics, Inc, Sunnyvale, CA
14Pharmacyclics, Sunnyvale, CA
15Pharmacyclics, Inc., Sunnyvale, CA
16Department of Leukemia, University of Texas, M D Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
ABSTRACT:
Background: BTK is an essential mediator of B-cell receptor signaling in normal and transformed B-cells. Ibrutinib (PCI-32765), an oral inhibitor to BTK, promotes apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, migration and adhesion in CLL cells. Chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) treatment approaches such as fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and rituximab have markedly improved outcomes of younger, fit patients (pts) as initial or second-line therapy. While effective, fludarabine-based therapy is less well tolerated in the elderly and carries significant risk of cellular immune suppression and myelosupression that limit protracted use. Additionally, virtually all pts eventually relapse after fludarabine-based CIT and effective salvage regimens that induce durable remissions are lacking. Herein, we present mature data from a large (n=116 pts) multi-cohort Phase Ib/II trial of ibrutinib in treatment-naive (TN) or relapsed/refractory (RR) CLL/SLL. Pts experienced a high frequency of disease control extending beyond 22 months in both TN and RR CLL/SLL including those with high risk genomic features.
Methods: Pts who were TN (all age >=65 years), RR (>= 2 prior therapies including a purine analog), or high-risk (HR) (relapse within 2 years following combination CIT or del 17p) were enrolled into 5 cohorts evaluating oral ibrutinib at fixed doses of 420mg or 840mg daily until disease progression (PD).
|
Cohort
|
Population
|
Dose
mg/day
|
Group
Size
|
|
1
|
relapsed/refractory
|
420
|
27
|
|
2
|
treatment-naïve; aged ≥ 65 years
|
420
|
26
|
|
3
|
relapsed/refractory
|
840
|
34
|
|
4
|
High Risk - relapsed or refractory
|
420
|
24
|
|
5
|
treatment-naïve; aged ≥ 65 years
|
840
|
5a
|
aCohort closed prior to full accrual after comparable activity and safety between doses was shown in R/R pts.
Primary objective was to determine the safety of the two dosing regimens. Secondary objectives were to assess efficacy, PK/PD and long-term safety. Overall Response rate (ORR) inclusive of complete and partial responses (CR and PR respectively) was assessed per IWCLL guidelines. In addition, those pts who achieved a PR with the exception of lymphocytosis were categorized as PR with lymphocytosis.
Results:
|
Study Population
(N=116)
|
Treatment naive , age >= 65yrs
(cohort 2 & 5)
|
Relapsed or Refractory
(cohort 1 & 3)
|
High risk
(cohort 4)
|
|
Number of pts
|
31
|
61
|
24
|
|
Median f/u, months
(range)
|
16.6 (1.4, 23.2)
|
17.3 (0.3, 22.4)
|
10.3 (1.1, 11.5)
|
|
Age (range)
|
71 (65, 84)
|
64 (40, 81)
|
68 (37, 82)
|
|
Median # prior Tx
(range)
|
0
|
4 (1,12)
|
4 (1,11)
|
|
Hgb <11 g/dl OR Plt <100,000 µL
|
61%
|
57%
|
63%
|
|
b2M >3 mg/L
|
8/ 31 (26%)
|
30/ 57 (53%)
|
9/ 23 (39%)
|
|
IgVH unmutated (UM)
|
17/ 31 ( 55%)
|
50/ 58 (86%)
|
19/ 23 ( 83%)
|
|
del 17p
|
2/ 30 ( 7%)
|
21/ 57 ( 37%)
|
7/ 23 ( 30%)
|
|
del 11q
|
1/ 30 ( 3%)
|
23/ 57 ( 40%)
|
8/ 23 ( 35%)
|
|
Best Response by Cohort:
|
|||
|
IWCLL ORR (CR + PR)
|
71%
|
67%
|
50%
|
|
CR
|
10%
|
3%
|
0
|
|
PR
|
61%
|
64%
|
50%
|
|
PR with lymphocytosis
|
10%
|
20%
|
29%
|
|
SD
|
13%
|
5%
|
8%
|
|
PD
|
0
|
2%
|
4%
|
|
Not evaluable
|
6%
|
7%
|
8%
|
The majority of AEs have been Gr ≤ 2 in severity, most commonly diarrhea (54%), fatigue (29%), upper respiratory tract infection (29%), rash (28%), nausea (26%) and arthralgias (25%). Hematologic toxicity ≥ Gr 3 was relatively infrequent. There was no evidence of cumulative toxicity or long-term safety concerns with a median follow-up of 16 months for the 116 treated pts. Treatment discontinuation for AE occurred in 7/116 pts across cohorts. Serial evaluation of serum immunoglobulins revealed a significant increase in IgA at 3, 6, and 12 months (P < 0.005 at each time point) with no decline in IgG or IgM.
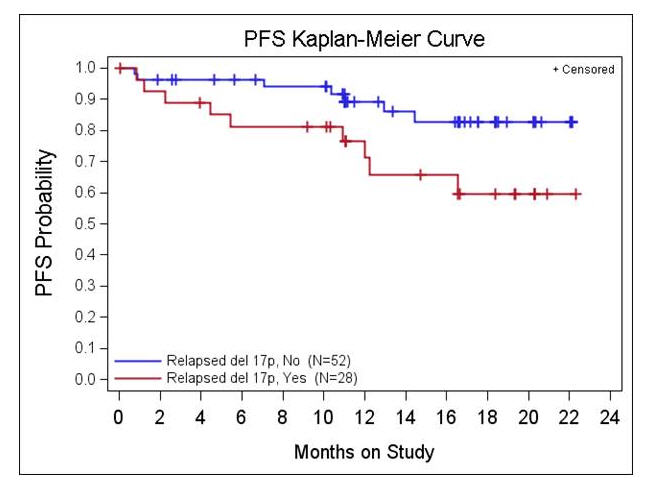
Responses were observed independent of poor-risk factors including advanced stage disease, prior lines of therapy, b2M, or cytogenetics (e.g. ORR in del 17p R/R (cohorts 1 & 3) 67%). Interestingly, 56/69 relapsed pts with UM IgVH developed treatment related lymphocytosis compared to 11/11 pts with mutated (M) IgVH that resolved more rapidly (median time to normalization 6.2 vs 14.8 months) and normalized more frequently (86% vs 55% P<0.04) compared to those with M IgVH.
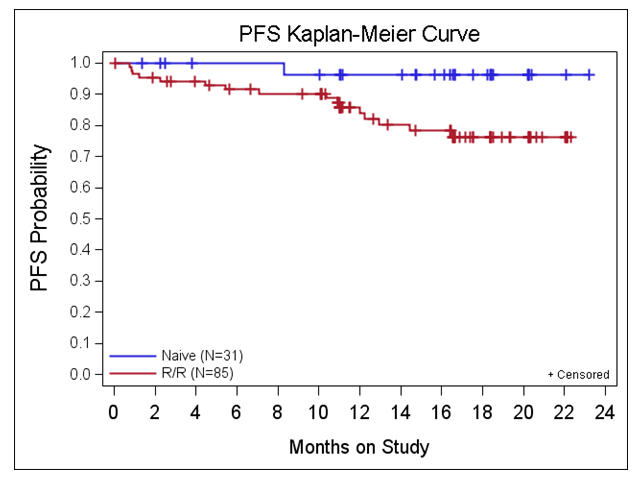
Estimated 22 month PFS for the 85 RR and HR pts is 76% and for the 31 TN pts is 96%. Estimated 22 month OS for 85 R/R and HR pts is 85% and for the 31 TN pts is 96%. Median PFS and OS have not been met for any of the cohorts including pts with high-risk factors (see Figure- PFS by 17p del status).
Conclusions: Ibrutinib monotherapy is highly active, well tolerated, and induces durable remissions in pts with RR CLL including those with high-risk disease and in older TN pts warranting phase III evaluation in these populations.
Disclosures: Byrd: Pharmacyclics: Research Funding. Off Label Use: Ibrutinib is not approved for the treatment of NHL. Burger: Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding. Sharman: Celgene: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria; Calistoga: Honoraria; Portola pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Tran: pharmacyclics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Clow: Pharmacyclics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Kunkel: Onyx Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. James: Pharmacyclics: Employment, Equity Ownership. O'Brien: Pharmacyclics: Research Funding.
