Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - PHARMACYCLICS INC | form8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.9 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex999to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.4 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex994to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.8 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex998to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.6 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex996to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.1 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex991to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.2 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex992to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.5 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex995to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.7 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex997to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.3 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex993to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.12 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9912to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.18 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9918to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.15 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9915to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.10 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9910to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.16 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9916to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.13 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9913to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.14 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9914to8k207380_11052012.htm |
| EX-99.11 - PHARMACYCLICS INC | ex9911to8k207380_11052012.htm |
Exhibit 99.17
B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Poster Presentation
Title: Activity of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Inhibitor Ibrutinib (PCI-32765) in B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-ALL)
Session: 612. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia - Pathophysiology & Clinical Studies: Poster II
Date/Time: Sunday, December 9, 2012, 6:00 PM - 8:00 PM
Location: Georgia World Congress Center, Hall B1-B2
Presenter: Ekaterina Kim
Ekaterina Kim, MS1*, Stefan Koehrer, MD1*, Nathalie Y Rosin, PhD1*, Deborah A. Thomas, MD1, Farhad Ravandi, MD1, Steven M. Kornblau, MD, PhD2, Hagop M. Kantarjian, MD3, Susan O'Brien, MD1, Zeev Estrov, MD, PhD1, Joseph J. Buggy, PhD4* and Jan A. Burger, MD, PhD3
1The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Department of Leukemia, Houston, TX
2The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Department of Leukemia, Houston, TX
3Department of Leukemia, The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
4Pharmacyclics, Inc., Sunnyvale, CA
ABSTRACT:
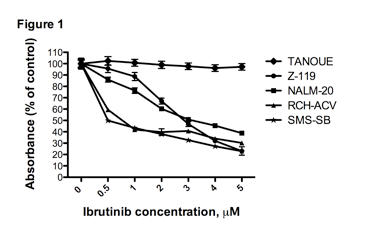
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a member of the TEC family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases and is predominantly expressed in hematopoietic cells, except in T cells. BTK plays a prominent role in B cell receptor (BCR) signaling and several other pathways, including CXCR4 signaling, which is essential for lymphocyte homing. BTK activation downstream of the BCR leads to proliferation, differentiation, and survival of B cells. Functional BTK is necessary for normal B cell development, defective BTK result in a primary immunodeficiency called X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA). Because of the restricted expression and the B cell phenotype in BTK-deficient mice and XLA patients, BTK has become a promising therapeutic target in mature B cell malignancies. Ibrutinib is a selective, orally bioavailable, covalent BTK inhibitor currently studied in clinical trials in patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) and other mature B cell malignancies. The importance of BTK in B-ALL is controversial. Initial study in childhood B-ALL revealed normal BTK protein levels, and gene expression profiling data from the St. Jude's group revealed BTK expression in B-ALL, but not in T-ALL. Other studies revealed abnormally spliced BTK mRNA and truncated BTK protein lacking kinase activity in some B-ALL samples. To explore the pre-clinical activity of ibrutinib in B-ALL, we used a panel of 14 B-ALL cell lines, representing pro-B (CD10+/-, TdT+, cyt Igμ-), pre-B (CD10+, TdT+, cyt Igμ+) and mature (CD10+/-, TdT-, surf IgM+) phenotypes. The panel included 4 Ph+/BCR-ABL1+ cell lines (Z-119, NALM-20, NALM-21, TOM-1). Western blot analysis revealed BTK expression in 12 out of 14 lines, while phospho-BTK (Y223) was present only in half of the cases. Effects of ibrutinib on B-ALL proliferation were tested in XTT assays, using increasing concentrations of ibrutinib (0.5 – 5 μM). All B-ALL cells responded to ibrutinib except for BTK-negative TANOUE cells. All other B-ALL cells displayed decreased proliferation with variable half maximal inhibitory concentrations of ibrutinib (IC50). The most sensitive cell lines (RCH-ACV, SMS-SB) had IC50 of < 1 µM; all BCR-ABL1+ cells showed IC50 < 3.5 μM (see Figure). We also analyzed inhibitory effects of ibrutinib on B-ALL cell proliferation by serial automated cell counting, which confirmed the XTT assay data. B-ALL cells viability was determined after incubation with ibrutinib, which induced only minor decreases after 3 days of incubation. Preliminary data with primary B-ALL samples revealed BTK protein expression in 5 out of 5 samples. In co-culture with KUSA-H1 stromal cells, primary B-ALL cells showed moderate levels of apoptosis, ranging from 10 – 25% after 3 days of incubation with 1 μM ibrutinib, which is similar to levels of ibrutinib-induced apoptosis in CLL. Collectively, these data demonstrate that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib can interfere with B-ALL cell proliferation and survival, providing a rationale for clinical testing of this novel, well-tolerated targeted agent in patients with relapsed B-ALL.
Disclosures: O'Brien: Pharmacyclics: Research support Other. Buggy: Pharmacyclics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Burger: Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding.
