Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - LYDALL INC /DE/ | ldl-20161231exhibit321.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - LYDALL INC /DE/ | ldl-20161231exhibit312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - LYDALL INC /DE/ | ldl-201612x31exhibit311.htm |
| EX-24.1 - EXHIBIT 24.1 - LYDALL INC /DE/ | ldl-201612x31exhibit241.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 - LYDALL INC /DE/ | ldl-20161231exhibit231.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EXHIBIT 21.1 - LYDALL INC /DE/ | ldl-201612x31exhibit211.htm |
| EX-10.6 - EXHIBIT 10.6 - LYDALL INC /DE/ | ldl-201612x31exhibit106.htm |
UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
ý ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2016
OR
o TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 1-7665
Lydall, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Delaware | 06-0865505 | |
(State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
One Colonial Road, Manchester, Connecticut | 06042 | |
(Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (860) 646-1233
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
Common Stock, $.01 par value | New York Stock Exchange | |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No ý
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes o No ý
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of the registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ý
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
Large accelerated filer o | Non-accelerated filer o (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Accelerated filer ý | Smaller reporting company o | |||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No ý
On June 30, 2016, the aggregate market value of the Registrant’s voting stock held by nonaffiliates was $633,528,229 based on the New York Stock Exchange closing price on that date. For purposes of this calculation, the Registrant has assumed that its directors and executive officers are affiliates.
On February 15, 2017, there were 17,234,146 shares of Common Stock outstanding, exclusive of treasury shares.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Part III incorporates information by reference to the definitive Proxy Statement to be distributed in connection with the Registrant’s
Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on April 28, 2017.
The exhibit index is located on pages 42 – 44.
INDEX TO ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K
Year Ended December 31, 2016
Page Number | ||
PART I | ||
PART II | ||
PART III | ||
PART IV | ||
The information called for by Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14, to the extent not included in this document, is incorporated herein by reference to such information included in the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission and distributed in connection with Lydall, Inc.’s 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on April 28, 2017.
i
CAUTIONARY NOTE CONCERNING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Lydall, Inc. and its subsidiaries are hereafter collectively referred to as “Lydall,” the “Company” or the “Registrant.” Lydall and its subsidiaries’ names, abbreviations thereof, logos, and product and service designators are all either the registered or unregistered trademarks or trade names of Lydall and its subsidiaries.
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). Any statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K that are not statements of historical fact may be deemed to be forward-looking statements. All such forward-looking statements are intended to provide management’s current expectations for the future operating and financial performance of the Company based on current assumptions relating to the Company’s business, the economy and future conditions. Forward-looking statements generally can be identified through the use of words such as “believes,” “anticipates,” “may,” “should,” “will,” “plans,” “projects,” “expects,” “expectations,” “estimates,” “forecasts,” “predicts,” “targets,” “prospects,” “strategy,” “signs” and other words of similar meaning in connection with the discussion of future operating or financial performance. Forward-looking statements may include, among other things, statements relating to future sales, earnings, cash flow, results of operations, uses of cash and other measures of financial performance. Because forward-looking statements relate to the future, they are subject to inherent risks, uncertainties and changes in circumstances that are difficult to predict. Accordingly, the Company’s actual results may differ materially from those contemplated by the forward-looking statements. Investors, therefore, are cautioned against relying on any of these forward-looking statements. They are neither statements of historical fact nor guarantees or assurances of future performance. Forward-looking statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K include, among others, statements relating to:
• | Overall economic, business and political conditions and the effects on the Company’s markets; |
• | Outlook for the fiscal year 2017; |
• | Expected vehicle production in the North American, European or Asian markets; |
• | Growth opportunities in markets served by the Company; |
• | Ability to integrate the Texel and Gutsche businesses which were acquired in the second half of 2016; |
• | Expected future financial and operating performance of Texel and Gutsche; |
• | Expected gross margin, operating margin and working capital improvements from the application of Lean Six Sigma; |
• | Product development and new business opportunities; |
• | Future strategic transactions, including but not limited to: acquisitions, joint ventures, alliances, licensing agreements and divestitures; |
• | Pension plan funding; |
• | Future cash flow and uses of cash; |
• | Future amounts of stock-based compensation expense; |
• | Future earnings and other measurements of financial performance; |
• | Ability to meet cash operating requirements; |
• | Future levels of indebtedness and capital spending; |
• | Ability to meet financial covenants in the Company's amended revolving credit facility; |
• | Future impact of the variability of interest rates and foreign currency exchange rates; |
• | Expected future impact of recently issued accounting pronouncements upon adoption; |
• | Future effective income tax rates and realization of deferred tax assets; |
• | Estimates of fair values of reporting units and long-lived assets used in assessing goodwill and long-lived assets for possible impairment; and |
• | The expected outcomes of legal proceedings and other contingencies, including environmental matters |
ii
All forward-looking statements are inherently subject to a number of risks and uncertainties that could cause the actual results of the Company to differ materially from those reflected in forward-looking statements made in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, as well as in press releases and other statements made from time to time by the Company’s authorized officers. Such risks and uncertainties include, among others, worldwide economic cycles and political changes that affect the markets which the Company’s businesses serve, which could have an effect on demand for the Company’s products and impact the Company’s profitability; disruptions in the global credit and financial markets, including diminished liquidity and credit availability; changes in international trade agreements including tariff regulation and trade restrictions; swings in consumer confidence and spending; unstable economic growth; volatility in foreign currency exchange rates; raw material pricing and supply issues; fluctuations in unemployment rates; retention of key employees; increases in fuel prices; and outcomes of legal proceedings, claims and investigations as well as other risks and uncertainties identified in Part I, Item 1A — Risk Factors of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The Company does not assume any obligation to update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
iii
PART I
Item 1. | BUSINESS |
Lydall, Inc. has been incorporated in Delaware since 1987 after originally being incorporated in Connecticut in 1969. The principal executive offices are located in Manchester, Connecticut. The Company designs and manufactures specialty engineered filtration media, industrial thermal insulating solutions, automotive thermal and acoustical barriers for filtration/separation and thermal/acoustical applications.
Lydall serves a number of markets. The Company’s products are primarily sold directly to customers through an internal sales force and distributed via common carrier. The majority of products are sold to original equipment manufacturers and tier-one suppliers. The Company differentiates itself through high-quality, specialty engineered innovative products, application engineering and exceptional customer service. Lydall has a number of domestic and foreign competitors for its products, most of whom are either privately owned or divisions of larger companies.
The Company’s Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and Proxy Statements are made available free of charge through the Investor Relations Section of the Company’s Internet website at www.lydall.com after such material is electronically filed with, or furnished to, the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “Commission”) and are also available on the Commission’s website at www.sec.gov. Information found on these websites is not part of this Form 10-K. Additionally, the public may read and copy any materials the Company files with the Commission at the Commission’s Public Reference room located at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. The public may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the Commission at 1-800-SEC-0330.
SEGMENTS
The Company’s reportable segments are Performance Materials, Technical Nonwovens, Thermal/Acoustical Metals, and Thermal/Acoustical Fibers. The Performance Materials segment reports the results of the Filtration, Thermal Insulation and Life Sciences Filtration businesses. The Technical Nonwovens segment reports the results of Lydall's Industrial Filtration and Advanced Materials products. The Thermal/Acoustical Metals segment reports the results of Lydall’s metal parts and related tooling and the Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment reports the results of Lydall’s fiber parts and related tooling, with both used primarily in automotive applications. Other Products and Services (“OPS”) was the Life Sciences Vital Fluids business, that was divested by Lydall on January 30, 2015. For additional information regarding the Company’s reportable segments, please refer to Note 10 in the Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Performance Materials Segment
The Performance Materials segment includes filtration media solutions primarily for air, fluid power, and industrial applications (“Filtration”), thermal insulation solutions for building products, appliances, and energy and industrial markets (“Thermal Insulation”) and air and liquid life science applications (“Life Sciences Filtration”). Filtration products include LydAir® MG (Micro-Glass) Air Filtration Media, LydAir® MB (Melt Blown) Air Filtration Media, LydAir® SC (Synthetic Composite) Air Filtration Media, and Arioso™ Membrane Composite Media. These products constitute the critical media component of clean-air systems for applications in clean-space, commercial, industrial and residential HVAC, power generation, and industrial processes. Lydall leverages its extensive technical expertise and applications knowledge into a suite of media products covering the vast liquid filtration landscape across the engine and industrial fields. The LyPore® Liquid Filtration Media series address a variety of application needs in fluid power including hydraulic filters, air-water and air-oil coalescing, industrial fluid processes and diesel fuel filtration.
Thermal Insulation products are high performance nonwoven veils, papers, mats and specialty composites for the building products, appliance, and energy and industrial markets. The Manniglas® Thermal Insulation brand is diverse in its product application ranging from high temperature seals and gaskets in ovens and ranges to specialty veils for HVAC and cavity wall insulation. The appLY® Mat Needled Glass Mats have been developed to expand Lydall’s high temperature technology portfolio for broad application into the appliance market and supplements the Lytherm® Insulation Media product brand, traditionally utilized in the industrial market for kilns and furnaces used in metal processing. Lydall’s Cryotherm® Super-Insulating Media, CRS-Wrap® Super-Insulating Media and Cryo-Lite™ Cryogenic Insulation products are industry standards for state-of-the-art cryogenic insulation designs used by manufacturers of cryogenic equipment for liquid gas storage, piping, and transportation.
1
Life Sciences is comprised of products which have been designed to meet the stringent requirements of critical applications including biopharmaceutical pre-filtration and clarification, lateral flow diagnostic and analytical testing, respiratory protection, potable water filtration and high purity process filtration such as that found in food and beverage and medical applications. Lydall also offers ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene membranes under the Solupor® trade name. These specialty microporous membranes are utilized in various markets and applications including air and liquid filtration and transdermal drug delivery. Solupor® membranes incorporate a unique combination of high mechanical strength, chemical inertness, gamma stability and very high porosity making them ideal for many applications.
Net sales from the Performance Materials segment represented 19.6% of Lydall’s net sales in 2016 compared with 19.3% in 2015 and 21.6% in 2014. Net sales generated by the foreign operations of the Performance Materials segment accounted for 35.3%, 33.9% and 34.2% of segment net sales in 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively.
Technical Nonwovens Segment
On February 20, 2014, the Company acquired certain industrial filtration businesses from Andrew Industries Limited, which was reported as a separate reportable segment ("Industrial Filtration") from the acquisition date through the second quarter of 2016. Beginning with third quarter 2016 reporting, the Company's Industrial Filtration segment was renamed Technical Nonwovens.
On July 7, 2016, the Company completed an acquisition of the nonwoven and coating materials businesses primarily operating under the Texel brand (“Texel”) from ADS, Inc. (“ADS”), a Canadian based corporation. The Texel operations manufacture nonwoven needle punch materials and predominantly serve the geosynthetic, liquid filtration, and other industrial markets.
On December 31, 2016, the Company completed an acquisition of the nonwoven needle punch materials businesses, operating under the Gutsche (“Gutsche”) brand, a German based corporation. The Gutsche operations manufacture nonwoven needle punch materials and predominantly serve the industrial filtration and high performance nonwoven markets.
The Technical Nonwovens segment primarily produces needle punch nonwoven solutions for a myriad of industries and applications. Industrial filtration products include nonwoven rolled-good felt media and filter bags used primarily in industrial air and liquid filtration applications. Nonwoven filter media is the most effective solution to satisfy increasing emission control regulations in a wide range of industries, including power, cement, steel, asphalt, incineration, mining, food, and pharmaceutical. Advanced materials products include nonwoven rolled-good media used in commercial applications and predominantly serves the geosynthetic, automotive, industrial, medical, and safety apparel markets. The automotive media is provided to Tier I/II suppliers as well as the Company's Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment.
Technical Nonwovens products are manufactured and sold globally under the leading brands of Lydall Industrial Filtration, Southern Felt, Gutsche, and Texel. These products include air and liquid filtration media sold under the brand names Fiberlox® high performance filtration felts, Checkstatic™ conductive filtration felts, Microfelt® high efficiency filtration felts, Pleatlox® pleatable filtration felts, Ultratech™ PTFE filtration felts, Powertech® and Powerlox® power generation filtration felts, Microcap® high efficiency liquid filtration felts, Duotech membrane composite filtration felts, along with our porotex® family of high temperature filtration felts including microvel® and optivel® products. Technical Nonwovens Advanced Materials products are sold under the brand names Thermofit® thermo-formable products, Ecoduo® recycled content materials, Duotex® floor protection products, and Versaflex® composite molding materials. Technical Nonwovens also offers extensive finishing and coating capabilities which provide custom engineered properties tailored to meet the most demanding applications. The business leverages a wide range of fiber types and extensive technical capabilities to provide products that meet our customers’ needs across a variety of applications providing both high performance and durability.
Technical Nonwovens segment net sales represented 27.4% of the Company's net sales in 2016, 26.5% in 2015 and 20.9% in 2014. Net sales generated by foreign operations of the Technical Nonwovens segment accounted for 55.4%, 40.9% and 48.8% of segment net sales in 2016, 2015 and 2014 respectively.
2
Thermal/Acoustical Metals Segment
The Thermal/Acoustical Metals segment offers a full range of innovative engineered products tailored for the transportation sector to thermally shield sensitive components from high heat, improve exhaust gas treatment and lower harmful emissions as well as assist in the reduction of powertrain and road noise. Products are found in the underbody (tunnel, fuel tank, rear muffler, spare tire) and underhood (outer dash, powertrain, catalytic converter, turbo charger, and manifolds) of cars, trucks, SUVs, heavy duty trucks and recreational vehicles.
Products are formed on production lines capable of efficiently combining multiple layers of metal and insulation media to provide an engineered thermal and acoustical shielding solution for an array of application areas in the global automotive and truck markets. The flux® product family in Thermal/Acoustical Metals includes several patented or IP-rich products that address applications which include: Direct Exhaust Mount heat shields, which are fastened to high temperature components like catalytic converters, turbochargers or exhaust manifolds using aluminized and stainless steel high performance and high temperature heat insulating materials; Powertrain heat shields that absorb noise at the source and do not contribute to the engine's noise; and durable, thermally robust solutions for temperature sensitive plastic components such as fuel tanks that are in proximity to high temperature heat sources.
Thermal/Acoustical Metals segment net sales represented 30.9% of the Company’s net sales in 2016, 30.7% in 2015 and 30.7% in 2014. Net sales generated by foreign operations of the Thermal/Acoustical Metals segment accounted for 49.8%, 54.9% and 58.2% of segment net sales in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
The operating results include allocations of certain costs shared between the Thermal/Acoustical Metals and Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segments.
Thermal/Acoustical Fibers Segment
The Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment offers innovative engineered products to assist primarily in noise vibration and harshness (NVH) abatement within the transportation sector. Products are found in the interior (dash insulators, cabin flooring), underbody (wheel well, aerodynamic belly pan, fuel tank, exhaust) and under hood (engine compartment) of cars, trucks, SUVs, heavy duty trucks and recreational vehicles.
Products offer thermal and acoustical insulating solutions comprised of organic and inorganic fiber composites for the automotive and truck markets primarily in North America. Lydall’s dBCore® is a lightweight acoustical composite that emphasizes absorption principles over heavy-mass type systems. Lydall’s dBLyte® is a high-performance acoustical barrier with sound absorption and blocking properties and can be used throughout a vehicle’s interior to minimize intrusive noise from an engine compartment and road. Lydall’s ZeroClearance® is an innovative thermal solution that utilizes an adhesive backing for attachment and is used to protect vehicle components from excessive heat. Lydall’s specially engineered products provide a solution that provides weight reduction, superior noise suppression, and increased durability over conventional designs.
Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment net sales represented 26.4% of the Company’s net sales in 2016, 26.5% in 2015 and 24.0% in 2014. There are no net sales generated by foreign operations, as the Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment only produces domestically.
The operating results include allocations of certain costs shared between the Thermal/Acoustical Fibers and Thermal/Acoustical Metals segments.
Other Products and Services (“OPS”)
On January 30, 2015, the Company sold all of the outstanding shares of common stock of its Life Sciences Vital Fluids business for a cash purchase price of $30.1 million. The disposition was completed pursuant to a Stock Purchase and Sale Agreement, dated January 30, 2015, by and among the Company, and the Buyer. The Company recognized an after-tax gain on the sale of this business of approximately $11.8 million in the first quarter of 2015.
OPS net sales were 0.3% of the Company’s net sales in 2015 and 3.7% in 2014.
3
GENERAL BUSINESS INFORMATION
Lydall holds a number of patents, trademarks and licenses. While no single patent, trademark or license is critical to the success of Lydall, together these intangible assets are of considerable value to the Company.
Typically, the Company’s business can be slightly stronger in the first half of the calendar year given the timing of customer order patterns and planned customer shutdowns in North America and Europe that typically occur in the third and fourth quarters of each year. Lydall maintains levels of inventory and grants credit terms that are normal within the industries it serves. The Company uses a wide range of raw materials in the manufacturing of its products, including aluminum and other metals to manufacture most of its automotive heat shields and various glass and petroleum derived fibers in its Performance Materials, Technical Nonwovens, and Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segments. The majority of raw materials used are generally available from a variety of suppliers.
Sales to Ford Motor Company accounted for 19.6%, 18.2% and 16.5% of Lydall’s net sales in the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. No other customers accounted for more than 10% of Lydall's net sales in such years. Foreign and export sales were 46.9% of net sales in 2016, 44.2% in 2015, and 46.2% in 2014. Foreign sales were $212.5 million, $179.6 million and $190.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Export sales primarily to Canada, Mexico, Asia and Europe were $53.2 million, $52.5 million, and $57.6 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The increase in foreign sales during 2016, compared to 2015, was primarily related to the acquisition of Texel on July 7, 2016.
Foreign operations generated operating income of $4.9 million, $6.4 million, and $6.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Total foreign assets were $317.8 million, $144.2 million, and $155.9 million at December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The increase in foreign assets in 2016 compared to 2015 was primarily due to the acquisitions of Texel and Gutsche. For further detail regarding revenue and financial information about the Company’s geographic areas, see Note 10 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
The Company invested $9.0 million in 2016, $8.5 million in 2015, and $9.0 million in 2014, or approximately 2% of net sales in 2016, 2015 and 2014, in research and development to create new products and to improve existing products. All amounts were expensed as incurred. Most of the investment in research and development is application specific. There were no customer-sponsored research and development activities during the past three years.
Backlog at January 31, 2017 was $95.9 million. Lydall’s backlog was $94.9 million at December 31, 2016, $72.2 million at December 31, 2015, and $74.8 million at December 31, 2014. The increase in backlog at year-end 2016 compared to year-end 2015 was primarily driven by the addition of the Texel and Gutsche businesses. Thermal/Acoustical Metals and Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment backlog, which comprises the majority of total backlog, may be impacted by various assumptions, including future automotive production volume estimates, changes in program launch timing and changes in customer development plans. The Company believes that global automotive orders for a two month period represent a reasonable timeframe to be deemed as firm orders and are included as Thermal/Acoustical Metals and Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment backlog. There are minimal seasonal aspects to Lydall’s backlog.
No material portion of Lydall’s business is subject to renegotiation of profits or termination of contracts or subcontracts at the election of any governmental body.
Lydall believes that its plants and equipment are overall, in substantial compliance with applicable federal, state and local provisions that have been enacted or adopted regulating the discharge of materials into the environment, or otherwise relating to the protection of the environment (See Item 3, Legal Proceedings).
As of December 31, 2016, Lydall employed approximately 2,700 people. Three unions with contracts expiring on September 30, 2020 represent approximately 60 employees in the United States. All employees at the facilities in France and the Netherlands are covered under a National Collective Bargaining Agreement. Certain salaried and all hourly employees in Germany, the United Kingdom, China and Canada are also covered under some form of a National Collective Bargaining Agreement. Lydall considers its employee relationships to be satisfactory.
There are no significant anticipated operating risks related to foreign investment law, expropriation, or availability of material, labor or energy. The foreign and domestic operations attempt to limit foreign currency exchange transaction risk by completing transactions in functional currencies whenever practical or through the use of foreign currency forward exchange contracts when deemed appropriate.
4
Item 1A. | RISK FACTORS |
The reader should carefully review and consider the risk factors discussed below. Any and all of these risk factors could materially affect the Company’s business, financial condition, future results of operations or cash flows and possibly lead to a decline in Lydall’s stock price. The risks, uncertainties and other factors described below constitute all material risk factors known to management as of the date of this report.
Global political or economic changes may negatively impact Lydall’s business - Ongoing instability or changes in a country's or region's economic or political conditions could adversely affect demand for the Company’s products and impact profitability. Among other factors, political conflicts or changes, disruptions in the global credit and financial markets, including diminished liquidity and credit availability, changes in international trade agreements, including tariffs regulation and trade restrictions, swings in consumer confidence and spending, unstable economic growth and fluctuations in unemployment rates causing economic instability could have a negative impact on the Company’s results of operations, financial condition and liquidity. These factors also make it difficult to accurately forecast and plan future business activities.
The Company’s foreign and export sales were 46.9% of net sales in 2016, 44.2% in 2015, and 46.2% in 2014. If the global economy were to take a significant downturn, depending on the length, duration and severity of such downturn, the Company’s business and financial statements could be adversely affected.
The Company’s Thermal/Acoustical Metals and Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segments are tied primarily to general economic and automotive industry conditions - The Company’s Thermal/Acoustical Metals and Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segments are suppliers in the automotive market. Sales to the automotive market accounted for 56.2% of the Company’s net sales in 2016, 56.6% in 2015, and 54.1% in 2014. The segments' net sales from products manufactured in North America were 73.1%, 70.6%, and 67.4% in 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively, with the remainder manufactured in Europe and Asia. These segments are closely tied to general economic and automotive industry conditions as demand for vehicles depends largely on the strength of the economy, employment levels, consumer confidence levels, the availability and cost of credit, the cost of fuel, legislative and regulatory oversight and trade agreements. These factors have had, and could continue to have, a substantial impact on these segments. Adverse developments could reduce demand for new vehicles, causing Lydall’s customers to reduce their vehicle production in North America, Europe and Asia and, as a result, demand for Company products would be adversely affected.
The Company’s quarterly operating results may fluctuate; as a result, the Company may fail to meet or exceed the expectations of research analysts or investors, which could cause Lydall’s stock price to decline - The Company’s quarterly results are subject to significant fluctuations. Operating results have fluctuated as a result of many factors, including size and timing of orders and shipments, loss of significant customers, product mix, technological change, operational efficiencies and inefficiencies, competition, changes in deferred tax asset valuation allowances, strategic initiatives, severance and recruiting charges, asset impairment, penalties or fines and general economic conditions. In addition, lower revenues may cause asset utilization to decrease, resulting in the under absorption of the Company’s fixed costs, which could negatively impact gross margins. Additionally, the Company’s gross margins vary among its product groups and have fluctuated from quarter to quarter as a result of shifts in product mix. Any and all of these factors could affect the Company’s business, financial condition, future results of operations or cash flows and possibly lead to a decline in Lydall’s stock price.
Implementation of the Company’s strategic initiatives may not be successful - As part of Lydall’s business strategy, the Company continues to review various strategic and business opportunities to grow the business and to assess the profitability and growth potential for each of its existing businesses. The Company may incur significant professional services expenses associated with the review and potential implementation of strategic business opportunities. The Company cannot predict with certainty whether any recent or future strategic transactions will be beneficial to the Company. Among other things, future performance could be impacted by the Company’s ability to:
• | Identify and effectively complete strategic transactions; |
• | Obtain adequate financing to fund strategic initiatives; |
• | Successfully integrate and manage acquired businesses that involve numerous operational and financial risks, including difficulties in the integration of acquired operations, diversion of management's attention from other |
5
business concerns, managing assets in multiple geographic regions and potential loss of key employees and key customers of acquired operations;
• | Improve operating margins through its Lean Six Sigma initiatives which are intended to improve processes and work flow, improve customer service, reduce costs and leverage synergies across the Company; and |
• | Successfully invest and deploy capital investments to support our business and commitments to our customers. |
In order to meet its strategic objectives, the Company may also divest assets and/or businesses. Successfully executing such a strategy depends on various factors, including effectively transferring assets, liabilities, contracts, facilities and employees to any purchaser, identifying and separating the intellectual property to be divested from the intellectual property that the Company wishes to retain, reducing or eliminating fixed costs previously associated with the divested assets or business, and collecting the proceeds from any divestitures.
The Company may not have adequate cash to fund its operating requirements - The principal source of the Company’s liquidity is operating cash flows. Other significant factors that affect the overall management of liquidity include capital expenditures, investments in businesses, acquisitions, income tax payments, pension funding, share repurchases, outcomes of contingencies and availability of lines of credit and long-term financing. The Company’s liquidity can be impacted by the Company’s ability to:
• | Manage working capital and the level of future profitability. The consolidated cash balance is impacted by capital equipment and inventory investments that may be made in response to changing market conditions; |
• | Satisfy covenants and other obligations under its existing credit facility, which could limit or prohibit Lydall’s ability to borrow funds. Additionally, these debt covenants and other obligations could limit the Company’s ability to make acquisitions, incur additional debt, make investments, or consummate asset sales and obtain additional financing from other sources. |
The Company incurred a substantial amount of additional indebtedness which could have an adverse effect on the Company’s financial health and make it more difficult for Lydall to obtain additional financing in the future - The Company financed the Texel and Gutsche acquisitions with available cash and borrowings of $85.0 million and $31.6 million, respectively, under the Amended Credit Facility executed on July 7, 2016. Incurring additional debt to fund the acquisitions' purchase price may have an adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition and may limit Lydall’s ability to obtain any necessary financing in the future for working capital, capital expenditures, future acquisitions, debt service requirements or other purposes. Additionally, the Company may not be able to generate sufficient cash flow or otherwise obtain funds necessary to meet the additional debt obligations. Any default under the Amended Credit Facility would likely result in the acceleration of the repayment obligations to our lenders.
The Company is subject to the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and similar worldwide anti-bribery laws, which impose restrictions on the Company and violations of which may carry substantial fines and penalties and result in criminal sanctions - The U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and anti-bribery laws in other jurisdictions, including anti-bribery legislation in the United Kingdom, generally prohibit companies and their intermediaries from making improper payments for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business or other commercial advantage. The Company’s policies mandate compliance with these anti-bribery laws, violations of which often carry substantial fines and penalties and could result in criminal sanctions against the Company, Lydall’s officers or employees. The Company cannot assure that its internal control policies and procedures always will protect it from reckless or other inappropriate acts committed by the Company’s affiliates, employees or agents. Violations of these laws, or allegations of such violations, could have a material adverse effect on Lydall’s business, or financial statements and could possibly lead to a decline in Lydall's stock price.
Raw material pricing, supply issues, and disruptions in transportation networks could affect all of the Company’s businesses - The Thermal/Acoustical Metals segment uses aluminum and other metals to manufacture most of its automotive heat shields. The Thermal/Acoustical Fibers and Technical Nonwovens segments use various petroleum-derivative fibers in manufacturing products, and the Performance Materials segment uses various glass-derivative fibers in manufacturing products. If the prices of these raw materials, or any other raw materials used in the Company’s businesses increase, the Company may not have the ability to pass incremental cost increases on to its customers. In addition, an interruption in the ability of the Company to source such materials could negatively impact operations and sales.
6
Impairment of the Company’s goodwill or other long-lived assets has required, and may in the future require recording significant charges to earnings - The Company reviews its long-lived assets for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable. Goodwill is also tested by the Company for impairment during the fourth quarter of each year. Factors that may be considered a change in circumstances, indicating that the carrying value of goodwill or other long-lived assets may not be recoverable, include, but are not limited to, a decline in the Company’s stock price and market capitalization, reduced future cash flow estimates, and slower growth rates.
Volatility in the securities markets, interest rates, actuarial assumptions and other factors could substantially increase the Company’s costs and funding for its domestic defined benefit pension plan - The Company’s domestic defined benefit pension plan is funded with trust assets invested in a diversified portfolio of securities. Changes in interest rates, mortality rates, investment returns, and the market value of plan assets may affect the funded status and cause volatility in the net periodic benefit cost and future funding requirements of such plan. A significant increase in benefit plan liabilities or future funding requirements could have a negative impact on the Company’s financial statements.
The Company is involved in certain legal proceedings and may become involved in future legal proceedings all of which could give rise to liability - The Company is involved in legal proceedings that, from time to time, may be material. These proceedings may include, without limitation, commercial or contractual disputes, intellectual property matters, personal injury claims, stockholder claims, and employment matters. No assurances can be given that such proceedings and claims will not have a material adverse impact on the Company’s financial statements.
The Company is subject to legal and compliance risks and oversight on a global basis and developments in these risks and related matters could have a material adverse effect on Lydall's consolidated financial position, results of operations or liquidity - The Company is subject to a variety of laws and regulations that govern our business both in the United States and internationally, including antitrust laws. Violations of these laws and regulations can result in significant fines, penalties or other damages being imposed by regulatory authorities. Expenses and fines arising out of or related to these investigations and related claims can also be significant. Despite meaningful measures that we undertake to seek to ensure lawful conduct, which include training and internal control policies, these measures may not always prevent our employees or agents from violating the laws and regulations. As a result, we could be subject to criminal and civil penalties, disgorgement, further changes or enhancements to our procedures, policies and controls, personnel changes or other remedial actions. For example, the Company agreed in principle with the German Cartel Office to pay a settlement amount of €3.3 million (approximately $3.5 million as of December 31, 2016) in connection with an investigation relating to violations of German anti-trust laws by and among certain European automotive heat shield manufacturers, including Lydall Gerhardi. Violations of laws, or allegations of such violations, could disrupt our operations, involve significant management distraction and result in a material adverse effect on our competitive position, results of operations, cash flows or financial condition.
Regulations related to conflict minerals could adversely impact the Company’s business - The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act contains provisions designed to improve transparency and accountability concerning the supply of certain minerals, known as conflict minerals, originating from the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and adjoining countries. In August 2012, the SEC promulgated disclosure and reporting requirements for companies who use conflict minerals in their products. These requirements may result in changes to the sourcing practices of the Company’s customers which may require the identification and qualification of alternate sourcing for the components of products Lydall manufactures, which could impact the availability of, or cause increases in the price of, materials used in our products. As there may be only a limited number of suppliers offering “conflict free” conflict minerals, there can be no assurance that the Company will be able to obtain necessary conflict free minerals from such suppliers in sufficient quantities or at competitive prices.
Changes in tax rates and exposure to additional income tax liabilities - The Company is subject to risks with respect to changes in tax law and rates, changes in rules related to accounting for income taxes, or adverse outcomes from tax audits that are in process or future tax audits in various jurisdictions in which the Company operates. As a result of political changes in the U.S., changes to tax policy and tax rates are considered likely and, depending on the nature of these changes, could have a significant impact on the Company's business and financial results. In addition, certain jurisdictions have statutory rates greater than or less than the United States statutory rate. Changes in the mix and source of earnings between jurisdictions could have a significant impact on the Company’s overall effective tax rate.
Realization of deferred tax assets is not assured - The Company maintains valuation allowances against certain deferred tax assets where realization is not reasonably assured. The Company evaluates the likelihood of the realization of all deferred tax assets and reduces the carrying amount to the extent it believes a portion will not be realized.
7
Changes in these assessments can result in an increase or reduction to valuation allowances on deferred tax assets and could have a significant impact on the Company’s overall effective tax rate.
The Company’s future success depends upon its ability to continue to innovate, improve its existing products, develop and market new products, and identify and enter new markets - Improved performance and growth are partially dependent on improvements to existing products and new product introductions planned for the future. Delays in improving or developing products and long customer qualification cycles may impact the success of new product programs. The degree of success of new product programs could impact the Company’s future results. Developments by other companies of new or improved products, processes or technologies may make our products or proposed products obsolete or less competitive and may negatively impact our net sales. Accordingly, our ability to compete is in part dependent on our ability to continually offer enhanced and improved products that meet the changing requirements of our customers. If we fail to develop new products or enhance existing products, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
The Company’s foreign operations expose it to business, economic, political, legal, regulatory and other risks - The Company believes that in order to be competitive and grow its businesses, it needs to maintain significant foreign operations. Foreign sales were $212.5 million, $179.6 million and $190.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively. Foreign operations are subject to inherent risks including political and economic conditions in various countries, unexpected changes in regulatory requirements (including tariff regulations and trade restrictions), longer accounts receivable collection cycles and potentially adverse tax consequences. The Company has little control over most of these risks and may be unable to anticipate changes in international economic and political conditions and, therefore, unable to alter its business practices in time to avoid the adverse effect of any of these possible changes.
Foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations and limitations on repatriation of earnings may affect the Company’s results of operations - The Company’s financial results are exposed to currency exchange rate fluctuations and an increased proportion of its assets, liabilities and expenses are denominated in non-U.S. dollar currencies. During 2016, there was significant volatility in foreign currencies that impacted the Company, primarily the British Pound Sterling, Euro, Chinese Yuan and Canadian Dollar. The Company’s foreign and domestic operations seek to limit foreign currency exchange transaction risk by completing transactions in functional currencies whenever practical or through the use of foreign currency forward exchange contracts when deemed appropriate. If the Company does not successfully hedge its currency exposure, changes in the rate of exchange between these currencies and the U.S. dollar may negatively impact the Company. Translation of the results of operations and financial condition of its foreign operations into U.S. dollars may be affected by exchange rate fluctuations. Additionally, limitations on the repatriation of earnings, including imposition or increase of withholding and other taxes on remittances, may limit or negatively impact the Company’s ability to redeploy or distribute cash. The Company receives a material portion of its revenue from foreign operations. Foreign operations generated approximately 37.5%, 34.2% and 35.5% of total net sales in 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively.
The Company’s manufacturing processes are subject to inherent risk - The Company operates a number of manufacturing facilities and relies upon an effective workforce and properly performing machinery and equipment. The workforce may experience a relatively high turnover rate, causing inefficiencies associated with retraining and rehiring. The equipment and systems necessary for such operations may break down, perform poorly or fail, and possibly cause higher manufacturing costs. Manufacturing processes affect the Company’s ability to deliver quality products on a timely basis, and delays in delivering products to customers could result in the Company incurring penalties from customers.
Increases in energy pricing can affect all of the Company’s businesses - Higher energy costs at the Company’s manufacturing plants or higher energy costs passed on from the Company’s vendors could impact the Company’s profitability.
The Company’s resources are limited and may impair its ability to capitalize on changes in technology, competition and pricing - The industries in which the Company sells its products are highly competitive and many of the competitors are affiliated with entities that are substantially larger and that have greater financial, technical and marketing resources. The Company’s more limited resources and relatively diverse product mix may limit or impair its ability to capitalize on changes in technology, competition and pricing.
The Company’s products may fail to perform as expected, subjecting it to warranty or other claims from its customers -If such failure results in, or is alleged to result in, bodily injury and/or property damage or other losses, the Company
8
may be subject to product liability lawsuits, U.S. Food and Drug Administration product recalls and other claims, any of which could have a material adverse impact on results of operations and cash flows.
If the Company does not retain its key employees, the Company’s ability to execute its business strategy could be adversely affected - The Company’s success, in part, depends on key managerial, engineering, sales and marketing and technical personnel and its ability to continue to attract and retain additional personnel. The loss of certain key personnel could have a material, adverse effect upon the Company’s business and results of operations. There is no assurance that the Company can retain its key employees or that it can attract competent and effective new or replacement personnel in the future.
The Company’s current reserve levels may not be adequate to cover potential exposures - Estimates and assumptions may affect the reserves that the Company has established to cover uncollectible accounts receivable, excess or obsolete inventory, income tax valuation and fair market value write downs of certain assets and various liabilities. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
The Company is subject to environmental laws and regulations that could increase its expense and affect operating results - The Company is subject to federal, state, local, and foreign environmental, health and safety laws and regulations that affect operations. New and changing environmental laws and regulations may impact the products manufactured and sold to customers. In order to maintain compliance with such laws and regulations, the Company must devote significant resources and maintain and administer adequate policies, procedures and oversight. Should the Company fail to do these things, it could be negatively impacted by lower net sales, fines, legal costs, and clean-up requirements.
We may incur liabilities under various government statutes for the investigation and cleanup of contaminants previously released into the environment. We do not anticipate that compliance with current provisions relating to the protection of the environment or that any payments we may be required to make for cleanup liabilities will have a material adverse effect upon our cash flows, competitive position, financial condition or results of operations. Current and on-going environmental matters are further addressed in Item 3, Legal Proceedings, Item 7, Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations and Note 12 to the Consolidated Financial Statements in our 2016 Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The Company may be unable to adequately protect its intellectual property, which may limit its ability to compete effectively - The Company owns intellectual property, including patents and trademarks, which play an important role in helping the Company to maintain its competitive position in a number of markets. The Company is subject to risks with respect to (i) changes in the intellectual property landscape of markets in which it competes; (ii) the potential assertion of intellectual property-related claims against the Company; (iii) the failure to maximize or successfully assert its intellectual property rights; and (iv) significant technological developments by others.
Disruptions may occur to the Company’s operations relating to information technology - The capacity, reliability and security of the Company’s information technology (“IT”) hardware and software infrastructure and the ability to expand and update this infrastructure in response to the Company’s changing needs are important to the operation of the businesses. Also, any inadequacy, interruption, loss of data, integration failure or security failure of the Company’s IT technology could harm its ability to effectively operate its business, which could adversely impact the Company’s results of operations and cash flows.
Increased cybersecurity requirements, vulnerabilities, threats and more sophisticated and targeted computer crime could pose a risk to the Company’s systems, networks, and data - Increased global cybersecurity vulnerabilities, threats and more sophisticated and targeted cyber-related attacks pose a risk to the security of the Company’s systems and networks and the confidentiality, availability and integrity of the Company’s data. While the Company attempts to mitigate these risks by employing a number of measures, including employee training, monitoring and testing, and maintenance of protective systems and contingency plans, the Company remains vulnerable to additional known or unknown threats. The Company also may have access to sensitive, confidential or personal data or information in certain of Lydall’s businesses that is subject to privacy and security laws, regulations and customer-imposed controls. Despite efforts made by the Company to protect sensitive, confidential or personal data or information, the Company may be vulnerable to security breaches, theft, misplaced or lost data, programming errors, employee errors and/or malfeasance that could potentially lead to the compromising of sensitive, confidential or personal data or information and could adversely impact the Company's results of operations and cash flows. In addition, a cyber-related attack could result in other negative consequences, including loss of information, damage to the Company’s reputation or competitiveness, remediation or increased protection costs, litigation or regulatory action.
9
The Company could be subject to work stoppages or other business interruptions as a result of its unionized work force - A portion of the Company’s hourly employees are represented by various union locals and covered by collective bargaining agreements. These agreements contain various expiration dates and must be renegotiated upon expiration. Specifically, three union contracts expiring on September 30, 2020 represent approximately 60 employees in the United States. If the Company is unable to negotiate any of its collective bargaining agreements on satisfactory terms prior to expiration, the Company could experience disruptions in its operations which could have a material adverse effect on operations.
The Company could be negatively affected as a result of the actions of activist stockholders - Over the last few years, proxy contests and other forms of stockholder activism have been directed against numerous public companies. The Company could become engaged in a solicitation, or proxy contest, or experience other stockholder activism, in the future. Activist stockholders may advocate for certain governance and strategic changes at the Company. In the event of stockholder activism, particularly with respect to matters which our Board of Directors, in exercising their fiduciary duties, disagree with or have determined not to pursue, our business could be adversely affected because responding to actions by activist stockholders can be costly and time-consuming, disrupting our operations and diverting the attention of management, and perceived uncertainties as to our future direction may result in the loss of potential business opportunities and may make it more difficult to attract and retain qualified personnel, business partners and customers.
The Company may be unable to realize expected benefits from cost reduction and restructuring efforts and profitability may be hurt or business otherwise might be adversely affected - In order to operate more efficiently and control costs, the Company announces from time to time restructuring plans, which include workforce reductions as well as facility consolidations and other cost reduction initiatives. These plans are intended to generate operating expense savings through direct cost and indirect overhead expense reductions as well as other savings. The Company may undertake workforce reductions or restructuring actions in the future. These types of cost reduction and restructuring activities are complex. If the Company does not successfully manage current restructuring activities, or any other restructuring activities that it may undertake in the future, expected efficiencies and benefits might be delayed or not realized, and our operations and business could be disrupted. Risks associated with these actions and other workforce management issues include unforeseen delays in implementation of anticipated workforce reductions, additional unexpected costs, adverse effects on employee morale and the failure to meet operational targets due to the loss of employees, any of which may impair our ability to achieve anticipated cost reductions or may otherwise harm the business, which could have a material adverse effect on competitive position, results of operations, cash flows or financial condition.
The Company may not be able to implement effective internal controls, procedures and policies for the acquired Texel and Gutsche businesses as required by Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 within the time periods prescribed thereby - The Company plans to fully evaluate the internal controls of the Texel and Gutsche businesses and any subsequently acquired companies, and then implement a standard framework established by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (COSO) of the Treadway Commission in internal control - integrated framework (2013 Framework) of internal controls at those acquired businesses. The Company cannot provide assurance that it will be able to provide a report that contains no material weaknesses with respect to the Texel and Gutsche businesses or any other acquisition.
10
Item 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
Item 2. | PROPERTIES |
The principal properties of the Company as of December 31, 2016 are situated at the following locations and have the following characteristics:
Location | Primary Business Segment/General Description | Type of Interest | ||
Hamptonville, North Carolina | Thermal/Acoustical Metals and Fibers – Product Manufacturing | Owned | ||
Yadkinville, North Carolina | Thermal/Acoustical Fibers – Product Manufacturing | Leased | ||
Meinerzhagen, Germany | Thermal/Acoustical Metals – Product Manufacturing | Owned | ||
Saint-Nazaire, France | Thermal/Acoustical Metals – Product Manufacturing | Owned | ||
Taicang, China | Thermal/Acoustical Metals – Product Manufacturing | Leased | ||
Green Island, New York | Performance Materials – Specialty Media Manufacturing | Owned | ||
Rochester, New Hampshire | Performance Materials – Specialty Media Manufacturing | Owned | ||
Saint-Rivalain, France | Performance Materials – Specialty Media Manufacturing | Owned | ||
St. Elzear, Quebec, Canada | Technical Nonwovens - Filtration Media Manufacturing | Owned | ||
St. Marie, Quebec, Canada | Technical Nonwovens - Filtration Media Manufacturing | Owned | ||
Rossendale, United Kingdom | Technical Nonwovens - Filtration Media Manufacturing | Owned | ||
Shanghai, China | Technical Nonwovens - Filtration Media Manufacturing | Leased | ||
North Augusta, South Carolina | Technical Nonwovens - Filtration Media Manufacturing | Owned | ||
Fulda, Germany | Technical Nonwovens - Filtration Media Manufacturing | Leased | ||
Dingshan, China | Technical Nonwovens - Filtration Media Manufacturing | Leased | ||
Manchester, Connecticut | Corporate Office | Owned | ||
For additional information regarding lease obligations, see Note 12 to the Consolidated Financial Statements. The Company considers its properties to be in good operating condition and suitable and adequate for its present needs. In addition to the properties listed above, the Company has several leases for sales offices and warehouses in the United States, Europe and Asia, which the Company believes are immaterial individually and in the aggregate.
11
Item 3. | LEGAL PROCEEDINGS |
The Company is subject to legal proceedings, claims, investigations and inquiries that arise in the ordinary course of business such as, but not limited to, actions with respect to commercial, intellectual property, employment, personal injury, and environmental matters. The Company believes that it has meritorious defenses against the claims currently asserted against it and intends to defend them vigorously. While the outcome of litigation is inherently uncertain and the Company cannot be sure that it will prevail in any of the cases, subject to the matter referenced below, the Company is not aware of any matters pending that are expected to have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
As previously disclosed, Lydall Gerhardi GmbH Co. & KG (“Lydall Gerhardi”), an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Lydall, Inc. (“Lydall,” “we” or “our”) and part of Lydall’s Thermal/Acoustical Metals reporting segment, has been cooperating with the German Federal Cartel Office, Bundeskartellamt (“German Cartel Office”) since May 2014 in connection with an investigation relating to violations of German anti-trust laws by and among certain European automotive heat shield manufacturers, including Lydall Gerhardi.
In December 2016, Lydall Gerhardi agreed in principle with the German Cartel Office to pay a settlement amount of €3.3 million (approximately $3.5 million as of December 31, 2016) to definitively conclude this matter. The Company recorded the expense of €3.3 million (approximately $3.5 million as of December 31, 2016) in December 2016 and expects to enter into a formal settlement agreement with the German Cartel Office and remit payment in the quarter ending March 31, 2017.
In the fourth quarter of 2016, as part of a groundwater discharging permitting process, water samples collected from wells and process water basins at the Company’s Rochester, New Hampshire manufacturing facility, within the Performance Materials segment, showed concentrations of Perfluorinated Compounds (“PFCs”) in excess of state ambient groundwater quality standards.
In January 2017, the Company received a notification from the State of New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services (“NHDES”) naming Lydall Performance Materials, Inc. a responsible party with respect to the discharge of a regulated contaminant and as such, is required to take action to investigate and remediate the impacts in accordance with standards established by the NHDES. The Company will conduct a site investigation, the scope of which is in the planning stage, in order to assess the extent of potential soil and groundwater contamination and develop a remedial action, if necessary. The Company does not know the scope or extent of its obligations, if any, that may arise from the site investigation and therefore is unable to estimate the cost of any corrective action, if required. Accordingly the Company cannot assure that the costs of any future corrective action at this location would not have a material effect on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
Item 4. | MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES |
Not applicable.
12
EXECUTIVE OFFICERS OF THE REGISTRANT
The executive officers of Lydall, Inc. or its subsidiaries, together with the offices presently held by them, their business experience since January 1, 2012, and their age as of March 3, 2017, the record date of the Company’s 2017 Annual Meeting, are as follows:
Name | Age | Position and Date of Appointment | Other Business Experience Since 2012 | |||
Dale G. Barnhart | 64 | President, Chief Executive Officer (August 27, 2007) | Not applicable | |||
Scott M. Deakin | 50 | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (September 8, 2015) | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, Ensign-Bickford Industries, Inc. (2009 – 2015), a diversified global manufacturer with operating segments that serve the aerospace & defense, life science, specialty chemicals and food & flavoring industries. | |||
Joseph A. Abbruzzi | 58 | President, Technical Nonwovens, (February 20, 2014); formerly Sr. Vice President, General Manager, Lydall Thermal/Acoustical Fibers (March 14, 2011) | Not applicable | |||
William M. Feld | 54 | Vice President, General Manager, Lydall Thermal/Acoustical Fibers (February 24, 2014); formerly Vice President of Operations, Performance Materials (December 10, 2012), formerly Director Engineering, Lydall Thermal/Acoustical Metals (July 11, 2011) | Not applicable | |||
William J. Hume | 54 | Senior Vice President, General Manager, Lydall Thermal/Acoustical Metals (August 19, 2014); formerly Senior Vice President, General Manager, Charter Medical Ltd. (January 2, 2012), formerly Director Lean Six Sigma, Lydall, Inc. (September 12, 2011), formerly General Manager, Affinity, a former subsidiary of Lydall,Inc. (March 9, 2009) | Not applicable | |||
James V. Laughlan | 44 | Vice President, Chief Accounting Officer and Treasurer (March 26, 2013); formerly Chief Accounting Officer, Controller and Treasurer (July 27, 2012); formerly Chief Accounting Officer and Controller (March 29, 2010) | Not applicable | |||
Paul A. Marold | 55 | President, Performance Materials (February 15, 2016) | Chief Operating Officer, Sontara, a division of Jacob Holm & Sons (2014-2016), a global manufacturer of spunlace nonwoven fabrics and finished goods; Senior Vice President, Growth & Innovation, Clarcor, Inc. (2013-2014), a global manufacturer of filtration products; President, Clarcor Air Filtration Products (2011-2013), a manufacturer of air filtration products. | |||
13
Chad A. McDaniel | 43 | Senior Vice President, Chief Administrative Officer, General Counsel and Secretary (May 13, 2015); formerly Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary (May 10, 2013) | Director, Chase Corporation (2016), NYSE: CCF, a manufacturer of protective materials for high reliability applications; Associate General Counsel, United Technologies Corporation (“UTC”), Sikorsky Aircraft division (2012 – 2013), Director; Executive Assistant to the President, UTC Fire & Security division (2010 – 2012); UTC is a manufacturer of high-technology products and services for the global aerospace and building systems industries. | |||
There is no family relationship among any of the Company’s directors or executive officers.
14
Item 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
PRICE RANGE OF COMMON STOCK AND DIVIDEND HISTORY
The Company’s Common Stock is traded on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) under the symbol LDL. The table below shows the range of reported sale prices on the NYSE Composite Tape for the Company’s Common Stock for the periods indicated. As of December 31, 2016, 11,434 stockholders of record held 17,232,146 shares of Lydall’s Common Stock, $.01 par value.
High | Low | Close | ||||||||||
2016 | ||||||||||||
First Quarter | $ | 35.10 | $ | 25.41 | $ | 32.52 | ||||||
Second Quarter | 40.22 | 32.01 | 38.56 | |||||||||
Third Quarter | 53.30 | 37.96 | 51.13 | |||||||||
Fourth Quarter | 64.85 | 44.14 | 61.85 | |||||||||
2015 | ||||||||||||
First Quarter | $ | 33.10 | $ | 27.19 | $ | 31.72 | ||||||
Second Quarter | 32.75 | 26.13 | 29.56 | |||||||||
Third Quarter | 30.71 | 25.28 | 28.49 | |||||||||
Fourth Quarter | 38.86 | 28.16 | 35.48 | |||||||||
The Company does not pay a cash dividend on its Common Stock. The Company’s Amended Credit Facility entered into on July 7, 2016, places no restrictions on cash dividend payments, so long as the payments do not place the Company in default.
ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
The Company acquired 34,068 shares through withholding during 2016, pursuant to provisions in agreements with recipients of restricted stock granted under the Company’s equity compensation plans, which allow the Company to withhold the number of shares having fair value equal to each recipient’s tax withholding due. The following table details the activity for the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2016.
Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased | Average Price Paid per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | Maximum Number of Shares That May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs | ||||||||
Activity October 1, 2016 - October 31, 2016 | — | $ | — | — | — | |||||||
Activity November 1, 2016 - November 30, 2016 | 629 | $ | 51.90 | — | — | |||||||
Activity December 1, 2016 - December 31, 2016 | 4,553 | $ | 61.95 | — | — | |||||||
Total | 5,182 | — | — | — | ||||||||
15
PERFORMANCE GRAPH
The following performance graph and related information shall not be deemed to be “soliciting material” or “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act, nor shall such information be incorporated by reference into any filing of Lydall, Inc. under the Exchange Act, except to the extent that the Company specifically incorporates it by reference in such filing.
The following graph compares the cumulative total return on Lydall’s shares over the past five years with the cumulative total return on shares of companies comprising the Standard & Poor’s Smallcap 600 Index and the Russell 2000 Index. Cumulative total return is measured assuming an initial investment of $100 on December 31, 2011, including reinvestment of dividends, if any. Due to the diversity of niche businesses that the Company participates in, it is difficult to identify a reasonable peer group or one industry or line-of-business index for comparison purposes. Thus, Lydall has chosen to compare its performance to the Standard & Poor’s Smallcap 600 Index and to the Russell 2000 Index, which are comprised of issuers with generally similar market capitalizations to that of the Company.
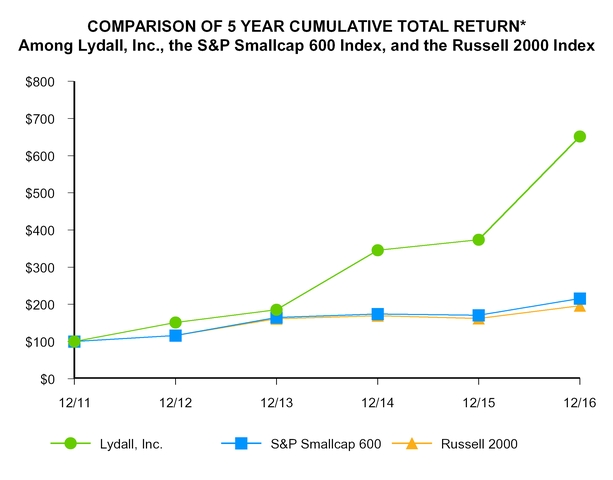
12/11 | 12/12 | 12/13 | 12/14 | 12/15 | 12/16 | |||||||||||||
Lydall, Inc. | 100.00 | 151.11 | 185.67 | 345.84 | 373.87 | 651.74 | ||||||||||||
S&P Smallcap 600 | 100.00 | 116.33 | 164.38 | 173.84 | 170.41 | 215.67 | ||||||||||||
Russell 2000 | 100.00 | 116.35 | 161.52 | 169.43 | 161.95 | 196.45 | ||||||||||||
* | $100 invested on 12/31/11 in stock or index, including reinvestment of dividends. Fiscal year ending December 31. |
16
Item 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
FIVE-YEAR SUMMARY
In thousands except per share amounts and ratio data | 2016 (1) | 2015 (2) | 2014 (3) | 2013 | 2012 (4) | ||||||||||||||
Financial results for the year | |||||||||||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 566,852 | $ | 524,505 | $ | 535,829 | $ | 397,969 | $ | 378,924 | |||||||||
Gross margin | 24.4 | % | 23.4 | % | 21.5 | % | 21.4 | % | 20.5 | % | |||||||||
Operating margin | 9.7 | % | 10.0 | % | 6.4 | % | 7.2 | % | 5.6 | % | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 37,187 | $ | 46,259 | $ | 21,847 | $ | 19,155 | $ | 16,806 | |||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | $ | 19,559 | $ | 17,275 | $ | 17,646 | $ | 12,703 | $ | 13,682 | |||||||||
Capital expenditures | $ | 28,159 | $ | 21,555 | $ | 19,001 | $ | 13,826 | $ | 11,404 | |||||||||
Common stock per share data | |||||||||||||||||||
Basic net income | $ | 2.20 | $ | 2.76 | $ | 1.31 | $ | 1.16 | $ | 1.01 | |||||||||
Diluted net income | $ | 2.16 | $ | 2.71 | $ | 1.28 | $ | 1.14 | $ | 0.99 | |||||||||
Financial position | |||||||||||||||||||
Working capital | $ | 165,162 | $ | 158,303 | $ | 140,229 | $ | 123,577 | $ | 105,451 | |||||||||
Property, plant and equipment, net | $ | 160,795 | $ | 114,433 | $ | 115,357 | $ | 78,863 | $ | 76,254 | |||||||||
Goodwill | $ | 63,606 | $ | 16,841 | $ | 21,943 | $ | 18,589 | $ | 18,282 | |||||||||
Other intangible assets, net | $ | 41,447 | $ | 5,399 | $ | 7,841 | $ | 3,510 | $ | 3,825 | |||||||||
Total assets | $ | 527,029 | $ | 358,260 | $ | 361,770 | $ | 274,685 | $ | 251,916 | |||||||||
Long-term debt, net of current maturities | $ | 128,141 | $ | 20,156 | $ | 40,315 | $ | 1,051 | $ | 1,646 | |||||||||
Total stockholders’ equity | $ | 273,456 | $ | 245,225 | $ | 212,599 | $ | 200,087 | $ | 174,496 | |||||||||
Total debt to total capitalization | 32.0 | % | 7.7 | % | 16.1 | % | 0.8 | % | 1.4 | % | |||||||||
Please read Part II, Item 7 (Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations) of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for specific changes in the Company and its markets that provide context to the above data for the years 2014 through 2016 including, without limitation, discussions concerning (i) how global economic uncertainties have affected the Company’s results; (ii) the impact of the acquisitions and divestitures; (iii) the impact of foreign currency translation; (iv) asset impairment charges; (v) pension settlement charges; (vi) the German Cartel settlement and (vii) the Company’s effective tax rate.
(1) During 2016, the Company completed the acquisitions of the Texel and Gutsche businesses. The results of Texel and Gutsche, from their respective acquisition dates on July 7, 2016 and December 31, 2016, have been included within the Company's Consolidated Financial Statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2016 and are contributing to the increases in the balance sheet line items above.
(2) On January 30, 2015, the Company sold all of the outstanding shares of common stock of its Life Sciences Vital Fluids business, reported as Other Products and Services. As a result, the Company recognized a gain on the sale of $18.6 million, reported as non-operating income, and net income of $11.8 million, or $0.69 per diluted share, for the year ended December 31, 2015.
(3) During 2014, the Company completed the acquisition of the filtration businesses of Andrews Industries, Limited on February 20, 2014. The results of these businesses were included within the Company's Consolidated Financial Statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2014.
(4) The Company's 2012 results include the recording of an asset impairment charge of $1.8 million, or $0.07 per diluted share, associated with the abandonment of an ERP project, and the impact of valuation allowance reversal on a foreign tax credit carryover of $3.9 million or $0.23 per diluted share.
17
Item 7. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
Overview and Outlook
Lydall, Inc. and its subsidiaries (collectively, the “Company” or “Lydall”) designs and manufactures specialty engineered nonwoven filtration media, industrial thermal insulating solutions, and thermal and acoustical barriers for filtration/separation and heat abatement and sound dampening applications. Lydall principally conducts its business through four reportable segments: Performance Materials, Technical Nonwovens, Thermal/Acoustical Metals and Thermal/Acoustical Fibers, with sales globally.
The Performance Materials segment includes filtration media solutions primarily for air, fluid power, and industrial applications (“Filtration”), thermal insulation solutions for building products, appliances, and energy and industrial markets (“Thermal Insulation”) and air and liquid life science applications (“Life Sciences Filtration”).
The Technical Nonwovens segment primarily produces needle punch nonwoven solutions for myriad industries and applications. Products are manufactured and sold globally under the leading brands of Lydall Industrial Filtration, Southern Felt, Gutsche, and Texel. The Industrial Filtration products include nonwoven rolled-good felt media and filter bags used primarily in industrial air and liquid filtration applications. Nonwoven filter media is the most effective solution to satisfy increasing emission control regulations in a wide range of industries, including power, cement, steel, asphalt, incineration, mining, food, and pharmaceutical. The Advanced Materials products include nonwoven rolled-good media used in commercial applications and predominantly serves the geosynthetic, automotive, industrial,medical, and safety apparel markets. The automotive media is provided to Tier I/II suppliers and as well as the Company's Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment.
The Thermal/Acoustical Metals ("T/A Metals") segment offers a full range of innovative engineered products tailored for the transportation sector to thermally shield sensitive components from high heat, improve exhaust gas treatment and lower harmful emissions as well as assist in the reduction of powertrain and road noise. Lydall products are found in the underbody (tunnel, fuel tank, rear muffler, spare tire) and underhood (outer dash, powertrain, catalytic converter, turbo charger and manifolds) of cars, trucks, SUVs, heavy duty trucks and recreational vehicles.
The Thermal/Acoustical Fibers ("T/A Fibers") segment offers innovative engineered products to assist primarily in noise vibration and harshness (NVH) abatement within the transportation sector. Lydall products are found in the interior (dash insulators, cabin flooring), underbody (wheel well, aerodynamic belly pan, fuel tank, exhaust) and under hood (engine compartment) of cars, trucks, SUVs, heavy duty trucks and recreational vehicles.
Financial Highlights
Below are financial highlights comparing Lydall’s 2016 results to its 2015 results:
• | Consolidated net sales were $566.9 million in 2016, compared to $524.5 million in 2015, an increase of $42.3 million, or 8.1%, with the increase nearly all attributable to the acquisition of Texel on July 7, 2016. The change in consolidated net sales is summarized in the following table. |
Components | Change in Net Sales | Percent Change | |||||
Acquisition of Texel (July 7, 2016) | $ | 40,923 | 7.8 | % | |||
Parts, volume and pricing change | 7,761 | 1.5 | % | ||||
Change in tooling sales | 274 | 0.1 | % | ||||
Divestiture of Life Sciences Vital Fluids (January 30, 2015) | (1,671 | ) | (0.3 | )% | |||
Foreign currency translation | (4,940 | ) | (0.9 | )% | |||
Total | $ | 42,347 | 8.1 | % | |||
• | Gross margin increased 100 basis points to 24.4% in 2016 compared to 23.4% in 2015 primarily due to improved mix of products, lower raw material costs and improved absorption of fixed costs, partially offset by the negative impact of 30 basis points from a purchase accounting adjustment related to inventory step-up associated with |
18
the Texel business included in the Technical Nonwovens segment. The gross margin improvement was principally led by the Performance Materials, T/A Fibers and Technical Nonwovens segments, partially offset by lower gross margin in the T/A Metals segment due to operating inefficiencies.
• | Operating income was $54.8 million, or 9.7% of net sales in 2016, compared to $52.5 million, or 10.0% of net sales in 2015; The increase in operating income of $2.3 million is summarized in the following table: |
Components | Change in Operating Income | Percent Change | ||||
Sales/operational | $ | 5,775 | 11.0% | |||
Increase in acquisition related expenses | (3,702 | ) | (7.1)% | |||
German Cartel settlement | (3,479 | ) | (6.6)% | |||
Acquisition/Divestiture, net | 2,415 | 4.6% | ||||
Long-lived asset impairment charge (2015) | 1,354 | 2.6% | ||||
Impact of foreign currency translation | (48 | ) | (0.1)% | |||
Total | 2,315 | 4.4% | ||||
• | The sales/operational component of the change in consolidated operating income was primarily attributed to the T/A Fibers and Performance Materials segments, which increased $4.4 million and $4.2 million, respectively, in 2016 compared to 2015 due to increased net sales and improved gross margins, partially offset by increased corporate office expenses. |
• | Net income was $37.2 million, or $2.16 per diluted share, compared to $46.3 million, or $2.71 per diluted share in 2015. |
2016 Net income:
◦ | Included $3.5 million, or $0.20 per diluted share, related to the German Cartel settlement expense |
◦ | Included $2.9 million, or $0.17 per diluted share, related to acquisition costs |
◦ | Included $1.4 million, or $0.08 per diluted share, related to inventory step-up adjustments on acquisitions |
2015 Net income:
◦ | Included $11.8 million, or $0.69 per diluted share, from the sale of the Life Sciences Vital Fluids business on January 30, 2015 |
◦ | Included $1.4 million, or $0.08 per diluted share, related to the long-lived asset impairment charge |
Acquisitions
On July 7, 2016, the Company completed an acquisition of the nonwoven and coating materials businesses primarily operating under the Texel brand (“Texel”) from ADS, Inc. (“ADS”), a Canadian based corporation. The Texel operations manufacture nonwoven needle punch materials and predominantly serve the geosynthetic, liquid filtration, and other industrial markets. The acquired businesses are included in the Company's Technical Nonwovens reporting segment.
On December 31, 2016, the Company completed an acquisition of the nonwoven needle punch materials businesses, operating under the Gutsche (“Gutsche”) brand, a German based corporation. The Gutsche operations manufacture nonwoven needle punch materials and predominantly serve the industrial filtration and high performance nonwoven markets. The acquired businesses are included in the Company's Technical Nonwovens reporting segment.
Liquidity
On July 7, 2016, the Company amended its $100 million senior secured revolving credit facility to increase the available borrowing from $100 million to $175 million, added a fourth lender and extended the maturity date from January 31, 2019 to July 7, 2021. The Company borrowed $116.6 million from this amended credit facility (for a total of $126.6 million outstanding as of December 31, 2016) to fund the Texel and Gutsche acquisitions. As a result, the Company’s leverage ratio at December 31, 2016 was 1.6 to 1.0, which was below the maximum allowed ratio of debt to EBITDA of 3.0 to 1.0. The amended credit facility provides additional capacity to support organic growth programs, fund capital investments and continue the pursuit of attractive acquisitions intended to drive profitable growth.
19
• | The Company generated cash from operating activities of $69.7 million in 2016 compared to $36.1 million in 2015, an increase of $33.6 million driven by improved operating performance, working capital management and cash flows from the Texel acquisition. |
Outlook
Entering 2017, overall demand in the Company's end markets remains solid, including early signs of stabilization and improvement in the power generation and energy space where Technical Nonwovens has faced market weakness since early 2016. The Company is encouraged by improving order activity and increased backlog entering the year in these industrial filtration focused applications. The Company expects demand in its automotive segments to be steady with recent periods as the Company benefits from the relative strength of the platforms it serves. In the Performance Materials segment, the Company expects improved demand to continue in its filtration markets, and in the insulation space, the Company is experiencing early signs of increased quoting activity in liquid natural gas and energy related applications. Operationally, a critical focus area for the Company is to ensure that the productivity improvements and corrective actions the Company has been putting in place in the Thermal/Acoustical Metals segment are executed effectively and sustained so the Company is able to realize operating improvement. And finally, the Company remains focused on the integration of the Texel and Gutsche businesses.
20
CONSOLIDATED RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Net Sales
In thousands of dollars | 2016 | Percent Change | 2015 | Percent Change | 2014 | |||||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 566,852 | 8.1 | % | $ | 524,505 | (2.1 | )% | $ | 535,829 | ||||||||
Net sales in 2016 increased $42.3 million, or 8.1%, compared to 2015. This increase was primarily related to greater net sales in the Technical Nonwovens segment of $16.4 million, or 11.8%, including $40.9 million of net sales from Texel since the acquisition date, which occurred on July 7, 2016, partially offset by lower net sales from segment legacy products of $24.5 million. The increase in net sales for the Technical Nonwovens segment included the negative impact of foreign currency translation of $4.3 million, or 3.1%, in 2016 compared to 2015. There were no Texel sales included in the Technical Nonwovens segment in 2015. The T/A Metals segment reported sales growth of $14.0 million, or 8.7%, including the negative impact of foreign currency translation of $0.6 million, or 0.4%, in 2016 compared to 2015, and the T/A Fibers segment reported net sales growth of $10.7 million, or 7.7%. The Performance Materials segment reported growth in net sales of $9.7 million, or 9.5%, in 2016 compared to 2015, with minimal impact of foreign currency translation. Net sales in the Life Sciences Vital Fluids business decreased by $1.7 million in 2016 compared to 2015 as the business was sold on January 30, 2015.
Net sales in 2015 decreased $11.3 million, or 2.1%, compared to 2014 as volume increases in the T/A Fibers, T/A Metals and Technical Nonwovens segments were offset by unfavorable foreign currency translation, a divestiture of the Life Sciences Vital Fluids business, and lower net sales from the Performance Materials segment. Life Sciences Vital Fluids business net sales decreased $18.0 million as the business was sold on January 30, 2015, and net sales in the Performance Materials segment decreased by $14.4 million, or 12.4%, in 2015 compared to 2014. The T/A Metals segment reported lower net sales of $3.3 million, which included unfavorable foreign currency translation of $17.1 million, or 10.4%. These decreases were partially offset by growth in Technical Nonwovens segment net sales of $26.9 million, or 24.0%, including the negative impact of foreign currency translation of $2.3 million, or 2.0%, in 2015 compared to 2014, as the segment was created upon the acquisition of the filtration businesses of Andrews Industries, Limited on February 20, 2014. The T/A Fibers segment reported sales growth of $10.2 million, or 7.9%, in 2015 compared to 2014.
Cost of Sales
In thousands of dollars | 2016 | Percent Change | 2015 | Percent Change | 2014 | |||||||||||||
Cost of sales | $ | 428,310 | 6.5 | % | $ | 402,008 | (4.5 | )% | $ | 420,851 | ||||||||
Cost of sales in 2016 increased $26.3 million, or 6.5%, compared to 2015. The increase was due to increased sales volumes across all of the Company's segments, which included the Texel acquisition since July 7, 2016 in the Technical Nonwovens segment, and a $2.0 million purchase accounting adjustment to cost of sales related to inventory step-up. Also contributing to the increase in cost of sales for 2016 compared to 2015 was higher labor and overhead costs in the T/A Metals segment due to operating inefficiencies. These increases to cost of sales were partially offset by improved mix of products as well as lower raw material sourcing costs primarily in the Technical Nonwovens, T/A Fibers and Performance Materials segments and lower overhead costs in the Performance Materials segment. Foreign currency translation reduced cost of sales by $4.2 million, or 1.0%, in 2016 compared to 2015.
Cost of sales in 2015 decreased $18.8 million, or 4.5%, compared to 2014. The decrease was primarily due to foreign currency translation of $21.9 million, or 5.2%, in the Company's T/A Metals, Performance Materials and Technical Nonwovens segments and lower cost of sales of $12.5 million from the divested Life Sciences Vital Fluids business which was sold on January 30, 2015. These decreases to cost of sales were partially offset by increases in cost of sales of $18.0 million in the Technical Nonwovens segment, as the segment was created upon the acquisition of the filtration businesses of Andrews Industries, Limited on February 20, 2014. Also, cost of sales increased by $1.8 million in the T/A Fibers segment due to higher sales volumes. The increases to cost of sales in the Technical Nonwovens and T/A Fibers segments were partially offset by lower raw material sourcing costs and improved product mix.
21
Gross Profit
In thousands of dollars | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Gross profit | $ | 138,542 | $ | 122,497 | $ | 114,978 | |||||
Gross margin | 24.4 | % | 23.4 | % | 21.5 | % | |||||
The increase in gross margin by 100 basis points in 2016 compared to 2015 was primarily attributable to the Performance Materials segment as a result of favorable mix of product sales and improved absorption of fixed costs on higher sales volumes, increasing consolidated gross margin by approximately 60 basis points. Additionally, the T/A Fibers segment favorably impacted consolidated gross margin by approximately 50 basis points, primarily as a result of lower raw material costs, improved material productivity and favorable product mix, partially offset by lower pricing. The Technical Nonwovens segment favorably impacted consolidated gross margin by approximately 30 basis points, which included the negative impact of a $2.0 million, or 30 basis point, purchase accounting adjustment relating to inventory step-up in 2016, offset by lower raw material costs and favorable product mix. The T/A Metals segment negatively impacted consolidated gross margin by approximately 60 basis points, primarily as a result of higher labor and overhead costs, including inefficiencies associated with new platform launches, partially offset by favorable product mix in 2016 compared to 2015.
The increase in gross margin by 190 basis points in 2015 compared to 2014 was primarily attributable to improved gross margin in the T/A Fibers segment, which favorably impacted consolidated gross margin by approximately 110 basis points, as a result of lower raw material costs, a favorable mix of product sales and labor efficiencies. Gross margin improved in the Industrial Filtration segment in 2015 compared to 2014 impacting consolidated gross margin by 50 basis points primarily due to the negative impact in 2014 of a $2.1 million, or 40 basis points, inventory purchase accounting adjustment associated with the Andrews Industries acquisition. The Life Sciences Vital Fluids business, which was sold in the first quarter of 2015, negatively impacted consolidated gross margin by approximately 25 basis points in 2015 compared to 2014.
Selling, Product Development and Administrative Expenses
In thousands of dollars | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Selling, product development and administrative expenses | $ | 83,750 | $ | 70,020 | $ | 80,930 | |||||
Percentage of net sales | 14.8 | % | 13.3 | % | 15.1 | % | |||||
Selling, product development and administrative expenses in 2016 increased by $13.7 million, or 19.6%, compared to 2015. Contributing to this increase was the acquisition of Texel in 2016 that increased expenses by $4.4 million, as there were no Texel expenses in 2015. All other selling, product development and administrative expenses increased $9.4 million, or 13.4%, in 2016 compared to 2015. This increase included $3.7 million of corporate office acquisition related expenses associated with the Texel and Gutsche acquisitions and a $3.5 million settlement charge in the fourth quarter of 2016 in connection with the German Cartel office investigation relating to violations of German anti-trust laws within the Company's T/A Metals segment. The remaining increase in expenses was due to higher salaries and benefits of $2.9 million, including $1.4 million of stock based compensation, primarily at the Company's corporate headquarters and higher accrued incentive compensation expense of $1.2 million, primarily driven by improved performance in the Company's Performance Materials segment. These increases were partially offset by a $1.4 million long-lived asset impairment charge in the Performance Materials segment related to intangible assets at the Company's Solutech operation in the fourth quarter of 2015 and decreased selling, product development and administrative expenses of $0.4 million related to the Life Sciences Vital Fluids business as a result of the sale of that business on January 30, 2015.
Selling, product development and administrative expenses in 2015 decreased by $10.9 million, or 13.5%, compared to 2014. This decrease was due in part to a non-cash pension plan settlement charge of $4.9 million in 2014. Additionally, sales commission expense in 2015 decreased by $3.5 million compared to 2014, primarily related to a $2.9 million commission settlement within the T/A Metals segment, as the Company terminated a long-standing third party commercial sales agreement in the second quarter of 2014. Also contributing to the decreased expenses were transaction related expenses of $2.6 million incurred in 2014 related to the acquisition of the filtration businesses of Andrews Industries, Limited and decreased accrued incentive compensation expenses of $1.2 million in 2015 compared to 2014 as fewer targets were achieved in the Company's 2015 annual incentive plan. Selling, product development and administrative expenses also decreased $4.0 million in 2015 as a result of the sale of the Life Sciences Vital Fluids business on January 30, 2015. These decreased expenses were partially offset by a $1.4 million long-lived asset
22
impairment charge in the Performance Materials segment related to intangible assets at the Company's Solutech operation. The Technical Nonwovens segment selling, product development and administrative expenses increased $1.9 million in 2015 compared to 2014, primarily due to the inclusion of this business for twelve months in 2015 compared to 2014, as the business was acquired on February 20, 2014. Additionally, other selling, product development and administrative expenses associated with pre-acquisition businesses increased in 2015, compared to 2014, related to higher salaries of $0.6 million, higher severance expenses of $0.6 million, recruiting expenses of $0.5 million and higher product development expenses of $0.6 million in 2015 compared to 2014.
Gain on Sale of Business
In thousands of dollars | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Gain on sale of business | $ | — | $ | (18,647 | ) | $ | — | ||||
On January 30, 2015, the Company sold all of the outstanding shares of common stock of its Life Sciences Vital Fluids business, reported as Other Products and Services, for a cash purchase price of $30.1 million. The disposition was completed pursuant to a Stock Purchase and Sale Agreement, dated January 30, 2015, by and among the Company, and the buyer. The Company recognized a pre-tax gain on the sale of $18.6 million, reported as non-operating income for the year ended December 31, 2015. Net of income taxes, the Company reported a gain on sale of $11.8 million.
Interest Expense
In thousands of dollars | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Interest expense | $ | 1,068 | $ | 755 | $ | 1,093 | |||||
Weighted average interest rate during the year | 1.4 | % | 1.3 | % | 1.5 | % | |||||
The increase in interest expense in 2016 compared to 2015 was due to higher average borrowings under the Company's Amended Credit Facility used to finance both the Texel and Gutsche acquisitions on July 7, 2016 and December 31, 2016, respectively.
The decrease in interest expense in 2015 compared to 2014 was due to lower average outstanding borrowings under the Company's Amended Credit Facility and lower borrowing rates compared to 2014. Borrowings under the Company's Amended Credit Facility are associated with the acquisition of Industrial Filtration on February 20, 2014.
Other Income and Expense
In thousands of dollars | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Other (income) expense, net | $ | (1,215 | ) | $ | (654 | ) | $ | (701 | ) | ||
The increase in other income, net in 2016 compared to 2015 was primarily related to higher foreign currency transaction gains associated with the revaluation of cash, trade payables and receivables and intercompany loans denominated in currencies other than the functional currency of the Company's subsidiaries, primarily driven by the devaluation of the British Pound Sterling.
The decrease in other income, net in 2015 compared to 2014 primarily relates to a decrease in foreign currency transaction gains due to the settlement of certain intercompany loans denominated in currencies other than the local functional currency, offset by an increase in foreign currency transaction gains associated with intercompany balances and trade payables and receivables denominated in currencies other than the local functional currency.
Income Taxes
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Effective income tax rate | 32.4 | % | 34.9 | % | 35.1 | % | ||
The Company’s effective tax rate for 2016 of 32.4% was positively impacted by a favorable mix of taxable income generated from countries with lower tax rates compared to that of the United States, resulting in a tax benefit of $1.3 million. The Company also recorded a tax benefit of $1.5 million attributable to the Domestic Production Activities Deduction and a tax benefit of $1.1 million related to stock based compensation. These favorable adjustments were partially offset by tax expense of $1.2 million related to a nondeductible German Cartel settlement and a net increase
23
in valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets of $0.7 million, primarily related to tax valuation allowances of $0.5 million recorded against certain net deferred tax assets in the Netherlands and China, as future realization of the assets is not reasonably assured.
In 2015, the effective tax rate of 34.9% was positively impacted by a favorable mix of taxable income generated from countries with lower tax rates compared to that of the United States, resulting in a tax benefit of $1.0 million. The Company also recorded a tax benefit of $1.2 million attributable to the Domestic Production Activities Deduction and a tax benefit of $1.1 million related to research and development credits. These favorable adjustments were partially offset by tax expense of $0.9 million related to a net increase in valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets and by a $0.6 million reduction to state deferred tax assets as a result of state tax law changes that led the Company to deem the asset unrealizable in future periods. The net increase in valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets of $0.9 million in 2015 was primarily related to tax valuation allowances of $0.8 million recorded against certain net deferred tax assets in the Netherlands and China, as future realization of the assets is not reasonably assured.
In 2014, the effective tax rate of 35.1% was positively impacted by a favorable mix of taxable income generated from countries with lower tax rates compared to that of the United States resulting in a tax benefit of $1.2 million and a tax benefit of $0.9 million attributable to the Domestic Production Activities Deduction. These favorable adjustments were partially offset by tax expense of $0.8 million related to nondeductible transaction costs from the Industrial Filtration acquisition, and a net increase in tax valuation allowances of $0.2 million.
The Company and its subsidiaries file a consolidated federal income tax return, as well as returns required by various state and foreign jurisdictions. In the normal course of business, the Company is subject to examination by taxing authorities, including such major jurisdictions as the United States, China, France, Germany, Hong Kong, the Netherlands, Canada and the United Kingdom. Within the next fiscal year, the Company expects to conclude certain income tax matters through the year ended December 31, 2013 and it is reasonably expected that unrecognized benefits of $0.5 million may be recognized. The total amount of net unrecognized tax benefits that would affect the effective tax rate if recognized was $3.2 million as of December 31, 2016. However, $1.3 million of the unrecognized tax benefits, if recognized, would be offset in pre-tax income by the reversal of indemnification assets due to the Company. The Company is no longer subject to U.S. federal examinations for years before 2013, state and local examinations for years before 2012, and non-U.S. income tax examinations for years before 2003.
24
SEGMENT RESULTS
Consolidated Net Sales | For the Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Performance Materials Segment: | |||||||||||
Filtration | $ | 70,430 | $ | 62,716 | $ | 71,648 | |||||
Thermal Insulation | 27,783 | 28,311 | 31,404 | ||||||||
Life Sciences Filtration | 12,915 | 10,451 | 12,814 | ||||||||
Performance Materials Segment net sales | 111,128 | 101,478 | 115,866 | ||||||||
Technical Nonwovens Segment (1): | |||||||||||
Industrial Filtration | 90,415 | 113,044 | 92,721 | ||||||||
Advanced Materials (2) | 65,090 | 26,089 | 19,499 | ||||||||
Technical Nonwovens Segment net sales | 155,505 | 139,133 | 112,220 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Metals Segment: | |||||||||||
Metal parts | 156,187 | 141,117 | 145,135 | ||||||||
Tooling | 18,787 | 19,815 | 19,130 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Metals Segment net sales | 174,974 | 160,932 | 164,265 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Fibers Segment: | |||||||||||
Fiber parts | 144,345 | 135,595 | 124,458 | ||||||||
Tooling | 5,067 | 3,152 | 4,133 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Fibers Segment net sales | 149,412 | 138,747 | 128,591 | ||||||||
Other Products and Services: | |||||||||||
Life Sciences Vital Fluids (3) | — | 1,671 | 19,682 | ||||||||
Other Products and Services net sales | — | 1,671 | 19,682 | ||||||||
Eliminations and Other (2) | (24,167 | ) | (17,456 | ) | (4,795 | ) | |||||
Consolidated Net Sales | $ | 566,852 | $ | 524,505 | $ | 535,829 | |||||
Operating Income | For the Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Performance Materials Segment | $ | 12,339 | $ | 6,790 | $ | 9,706 | |||||
Technical Nonwovens Segment (1) | 15,584 | 13,431 | 6,412 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Metals Segment | 11,562 | 15,517 | 13,823 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Fibers Segment | 41,452 | 37,086 | 29,167 | ||||||||
Other Products and Services: | |||||||||||
Life Sciences Vital Fluids (3) | — | 118 | 1,582 | ||||||||
Corporate Office Expenses | (26,145 | ) | (20,465 | ) | (26,642 | ) | |||||
Consolidated Operating Income | $ | 54,792 | $ | 52,477 | $ | 34,048 | |||||
(1) | The Technical Nonwovens segment reports results of Texel for the period following the date of acquisition of July 7, 2016 through Deember 31, 2016. |
(2) | Included in the Technical Nonwovens segment and Eliminations and Other is $18.2 million, $13.8 million and $1.0 million in intercompany sales to the T/A Fibers segment for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. |
(3) | Other Products and Services reports results for the period preceding the date of disposition of the Life Sciences Vital Fluids business on January 30, 2015. |
Performance Materials Segment
Segment net sales increased $9.7 million, or 9.5%, in 2016 compared to 2015. Filtration product net sales and life sciences product net sales increased $7.7 million, or 12.3% and $2.5 million, or 23.6%, respectively, in 2016 compared to 2015. The increase in filtration product net sales was primarily due to higher overall demand and share gains for filtration products, particularly in North America and Europe, as well as net sales from new product development in
25
Europe. The increase in life sciences product net sales was primarily due to a termination buy in advance of product discontinuance. These increases were partially offset by lower net sales of thermal insulation products of $0.5 million, or 1.9%, in 2016 compared to 2015, primarily the result of continued lower demand globally for cryogenic insulation products serving the liquid natural gas market which were negatively impacted by lower oil prices. Foreign currency translation had a minimal impact on net sales for 2016 compared to 2015.
The Performance Materials segment reported operating income of $12.3 million, or 11.1% of net sales in 2016, compared to operating income of $6.8 million, or 6.7% of net sales in 2015. The increase in operating income was primarily the result of higher gross profit of $5.7 million due to gross margin improvement of 290 basis points as a result of a favorable mix of product sales and improved absorption of overhead costs due to improved demand for products. Segment selling, product development and administrative expenses increased $0.1 million in 2016 compared to 2015 as increases in 2016 of $1.5 million, primarily related to accrued incentive compensation and to a lesser extent salaries, were nearly offset by lower expense as a result of a long-lived asset impairment charge of $1.4 million, related to intangible assets at the Company's Solutech operation in 2015. Increased accrued incentive compensation was due to improved performance in the segment against annual incentive plan targets.
Segment net sales decreased $14.4 million, or 12.4%, in 2015 compared to 2014, due to decreased sales volumes of $7.4 million, or 6.4%, and the negative impact of foreign currency translation of $7.0 million, or 6.0%. Filtration product net sales decreased by $8.9 million, or 12.5%, primarily due to unfavorable foreign currency translation and to a lesser extent, lower demand for air filtration products, particularly in Asia and North America. Net sales of thermal insulation products were lower by $3.1 million, or 9.8%, in 2015 compared to 2014 due to lower demand in North America and Asia. Lower insulation product net sales were primarily the result of lower oil prices causing less demand globally for the segment's cryogenic insulation products serving the liquid natural gas market. Net sales of life sciences products were lower by $2.4 million, or 18.4%, in 2015 compared to 2014, due to lower demand for water purification and life protection application products in large part due to the timing of customer orders.
The Performance Materials segment reported operating income of $6.8 million, or 6.7% of net sales in 2015, compared to operating income of $9.7 million, or 8.4% of net sales in 2014. The decrease in operating income was primarily the result of lower gross profit of $2.8 million due to lower segment net sales as well as a long-lived asset impairment charge of $1.4 million, related to intangible assets at the Company's Solutech operation, recorded in selling, product development and administrative expenses. Segment selling, product development and administrative expenses also decreased $1.3 million in 2015 compared to 2014, primarily related to lower accrued incentive compensation and lower salaries expense. Foreign currency translation had minimal impact on operating income in 2015 compared to 2014.
Technical Nonwovens Segment
Segment net sales increased by $16.4 million, or 11.8%, in 2016 compared to 2015. The increase in segment net sales was due to the acquisition of Texel which occurred on July 7, 2016. As a result, Texel net sales of $40.9 million since the date of the acquisition were included in 2016 net sales, including $5.9 million in industrial filtration products and $35.0 million in advanced materials products. Legacy segment net sales decreased $24.5 million, or 17.6%, in 2016 compared to 2015. Sales of legacy industrial filtration products decreased $28.5 million in 2016 compared to 2015 primarily due to lower demand in the global power generation markets, as well as general softness in China. These decreases were partially offset by higher net sales of advanced materials products of $4.0 million, primarily from automotive rolled-good material for use in the T/A Fibers segment manufacturing process in 2016 compared to 2015. Foreign currency translation had a negative impact on segment net sales of $4.3 million, or 3.1%, in 2016 compared to 2015.
The Technical Nonwovens segment reported operating income of $15.6 million, or 10.0%, of segment net sales in 2016, compared to operating income of $13.4 million, or 9.7% of segment net sales in 2015. The increase in segment operating income of $2.2 million in 2016 was from the acquisition of Texel, which included the negative impact of a $2.0 million purchase accounting adjustment to cost of sales related to inventory step-up. The increase in operating margin by 30 basis points in 2016 compared to 2015 was primarily attributable to lower raw material costs and a favorable product mix. Segment selling, product development and administrative expenses increased $3.3 million due to Texel expenses, partially offset by lower legacy business expenses related to lower professional service costs of $0.3 million, lower salaries of $0.3 million, lower other administrative costs of $0.3 million and lower accrued incentive compensation of $0.2 million. Foreign currency translation had a minimal impact on operating income in 2016 compared to 2015.
26
Segment net sales increased by $26.9 million, or 24.0% in 2015 compared to 2014, primarily due to a $12.8 million increase in net sales of automotive rolled-good materials to the T/A Fibers segment for use in the T/A Fibers segment manufacturing process. Additionally, segment net sales increased due to the reporting of a full twelve months of segment net sales in 2015 compared to 2014 as the business was acquired on February 20, 2014. Foreign currency translation had a negative impact on segment net sales of $2.3 million, or 2.0%, in 2015 compared to 2014, primarily impacting segment net sales in Europe.
The Technical Nonwovens segment reported operating income of $13.4 million, or 9.7% of segment net sales in 2015, compared to operating income of $6.4 million, or 5.7% of segment net sales in 2014. The increase in operating income of $7.0 million in 2015 was due to improved sales volume, due to the reporting of a full quarter of operating income in the first quarter of 2015 compared to the first quarter of 2014 as the business was acquired on February 20, 2014, and a $2.1 million purchase accounting adjustment in cost of sales in 2014 related to inventory step-up. After considering the impact of the inventory step-up adjustment in 2014, the increase in operating margin in 2015 of approximately 190 basis points compared to 2014 was primarily related to the sale of automotive rolled-goods to the T/A Fibers segment, lower raw material costs and a favorable mix of product sales. Foreign currency translation had minimal impact on operating income in 2015 compared to 2014.
Thermal/Acoustical Metals Segment
Segment net sales increased by $14.0 million, or 8.7%, in 2016 compared to 2015. Parts net sales increased by $15.1 million, or 10.7%, in 2016 compared to 2015, due to increased demand and new platform launches from customers served by the Company's North American and Chinese automotive operations, offset to some extent by lower market share related to customers served by the Company's European automotive operations. The increase in segment net sales was partially offset by a decrease in tooling net sales of $1.0 million, or 5.2%, in 2016 compared to 2015. Foreign currency translation negatively impacted net sales by $0.6 million, or 0.4%, in 2016 compared to 2015.
The Thermal/Acoustical Metals segment reported 2016 operating income of $11.6 million, or 6.6% of net sales, compared to $15.5 million, or 9.6% of net sales, in 2015. The decrease of $3.9 million was principally due to an increase in selling, product development and administrative costs of $4.0 million in 2016 compared to 2015, primarily related to a $3.5 million settlement agreed to in the fourth quarter of 2016 with the German Cartel Office. In addition, salaries and benefits increased $0.6 million in 2016 compared to 2015. The decrease in operating income as a percentage of net sales of 300 basis points was primarily due to lower gross margins of approximately 140 basis points due to operating inefficiencies causing higher labor and overhead costs to meet increased demand in North America and changing product mix in Europe. Foreign currency translation had a minimal impact on operating income in 2016 compared to 2015.
Segment net sales decreased by $3.3 million, or 2.0%, in 2015 compared to 2014. Foreign currency translation negatively impacted net sales by $17.1 million, or 10.4%, in 2015 compared to 2014. Automotive parts net sales decreased by $4.0 million, or 2.8%, in 2015 compared to 2014, due to unfavorable foreign currency translation of $14.7 million, or 10.1% of net sales. Excluding the negative impact of foreign currency translation, automotive part net sales increased by $10.7 million, or 7.4%, compared to 2014, due to increased demand from customers served by the Company's European and, to a lesser extent, North American and Chinese automotive operations. Tooling net sales increased by $0.7 million, or 3.6%, in 2015 compared to 2014. Excluding the negative impact of foreign currency translation, tooling net sales increased $3.1 million, or 16.3%, due to the timing of new product launches.
The Thermal/Acoustical Metals segment reported 2015 operating income of $15.5 million, or 9.6% of net sales, compared to $13.8 million, or 8.4% of net sales, in 2014. The increase of $1.7 million was due to a decrease in selling, product development and administrative costs of $3.0 million in 2015 compared to 2014. This decrease was primarily related to a $2.9 million commission settlement associated with the 2014 termination of a long-standing third party commercial sales agreement in Europe, and a decrease in professional service expenses of $0.4 million. Partially offsetting the reduction in expenses was foreign currency translation which had a negative impact on operating income of $1.6 million, or 1.0% of net sales in 2015 compared to 2014. Operational inefficiencies at the Company's Chinese facility resulted in a negative impact to operating margin of approximately 120 and 140 basis points in 2015 and 2014, respectively.
27
Thermal/Acoustical Fibers Segment
Segment net sales increased by $10.7 million, or 7.7%, in 2016 compared to 2015. Parts net sales increased by $8.8 million, or 6.5%, in 2016 compared to 2015. The increase in parts net sales was driven by higher consumer demand for vehicles in North America on Lydall's existing platforms and new platform awards and to a lesser extent, the impact of a key customer planned shut-down in the beginning of 2015. Tooling net sales increased $1.9 million, or 60.8%, in 2016 compared to 2015 due to timing of new product launches. Domestic automobile production increased 2.0% in 2016 compared to 2015.
The Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment reported 2016 operating income of $41.5 million, or 27.7% of net sales, compared to operating income of $37.1 million, or 26.7%, in 2015. The increase in operating income was primarily attributable to increased parts net sales and gross margin improvement of approximately 150 basis points as a result of lower raw material sourcing costs, improved material productivity and favorable mix of product sales, partially offset by lower pricing with customers. Segment selling, product development and administrative expenses increased by $1.2 million in 2016 compared to 2015 primarily due to higher salaries and benefits of $0.8 million and increased product development expenses of $0.3 million.
Segment net sales increased by $10.2 million, or 7.9%, in 2015 compared to 2014. Automotive parts net sales increased by $11.1 million, or 8.9%, in 2015 compared to 2014. Higher volumes of parts net sales were primarily due to increased consumer demand for vehicles in North America on Lydall’s existing platforms and new platform awards. Tooling net sales decreased $1.0 million, or 23.7%, in 2015 compared to 2014 due to timing of new product launches. Domestic automobile production increased 2.7% in 2015 compared to 2014.
The Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment reported 2015 operating income of $37.1 million, or 26.7% of net sales, compared to operating income of $29.2 million, or 22.7%, in 2014. The increase in operating income was primarily attributable to increased parts net sales and gross margin improvement of approximately 400 basis points as a result of lower raw material costs, favorable mix of product sales, improved absorption of fixed costs and labor efficiencies. Segment selling, product development and administrative expenses increased by $0.4 million in 2015 compared to 2014 primarily due to increased salaries and product development expenses. Segment selling, product development and administrative expenses as a percentage of net sales was 5.1% in both 2015 and 2014.
Other Products and Services
On January 30, 2015, the Company sold all of the outstanding shares of common stock of its Life Sciences Vital Fluids business for a cash purchase price of $30.1 million. The disposition was completed pursuant to a Stock Purchase and Sale Agreement, dated January 30, 2015, by and among the Company, and the buyer. The Company recognized a pre-tax gain on the sale of $18.6 million, reported as non-operating income in the first quarter of 2015. Net of income taxes, the Company reported a gain on sale of $11.8 million.
Life Sciences Vital Fluids net sales in 2015 decreased by $18.0 million in 2015 compared to 2014. Life Sciences Vital Fluids reported operating income of $0.1 million, or 7.1% of net sales, in 2015 compared to operating income of $1.6 million, or 8.0% of net sales, in 2014. The decreases in net sales and operating income were due to the sale of this business in the first quarter of 2015.
Corporate Office Expenses
The increase in corporate office expenses of $5.7 million in 2016 compared to 2015 was primarily due to $3.7 million of acquisition related expenses, which included costs associated with the Texel and Gutsche acquisitions. Other items contributing to the increase in corporate office expenses were higher salaries and benefits of $1.6 million, including stock based compensation of $1.0 million, higher accrued incentive compensation of $0.3 million and increases in other administrative expenses of $0.1 million in 2016 compared to 2015.
The decrease in corporate office expenses of $6.2 million in 2015 compared to 2014 was primarily due to a non-cash pension plan settlement charge of $4.9 million in 2014 associated with a voluntary one-time lump sum payment option elected by certain former U.S. employees under the Company's domestic defined benefit pension plan and $2.6 million of transaction related costs incurred in 2014 associated with the Andrews Industries acquisition on February 20, 2014. Accrued incentive compensation also decreased $0.4 million in 2015 compared to 2014 as fewer targets were achieved in the Company's 2015 annual incentive plan. These decreased costs were offset by increased salaries of $0.7 million,
28
other employee benefits of $0.3 million, recruiting expenses of $0.3 million, and increases in other administrative costs of $0.4 million.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
For the Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
In thousands except ratio data | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 71,934 | $ | 75,909 | $ | 62,051 | ||||||
Cash provided by operating activities | $ | 69,727 | $ | 36,110 | $ | 41,628 | ||||||
Cash (used for) provided by investing activities | $ | (177,708 | ) | $ | 7,905 | $ | (93,489 | ) | ||||
Cash provided by (used for) financing activities | $ | 106,375 | $ | (26,707 | ) | $ | 42,549 | |||||
Depreciation and amortization | $ | 19,559 | $ | 17,275 | $ | 17,646 | ||||||
Capital expenditures | $ | (25,466 | ) | $ | (20,645 | ) | $ | (13,971 | ) | |||
Total debt | $ | 128,775 | $ | 20,479 | $ | 40,930 | ||||||
Total capitalization (debt plus equity) | $ | 402,231 | $ | 265,704 | $ | 253,529 | ||||||
Total debt to total capitalization | 32.0 | % | 7.7 | % | 16.1 | % | ||||||
The Company assesses its liquidity in terms of its ability to generate cash to fund operating, investing and financing activities. The principal source of liquidity is operating cash flows. In addition to operating cash flows, other significant factors that affect the overall management of liquidity include capital expenditures, investments in businesses, strategic transactions, income tax payments, debt service payments, outcomes of contingencies, foreign currency exhange rates and pension funding. The Company manages worldwide cash requirements by considering available funds among domestic and foreign subsidiaries. The Company expects to finance its 2017 operating cash and capital spending requirements from existing cash balances, cash provided by operating activities and through borrowings under the Amended Credit Facility, as needed.
At December 31, 2016, the Company held $71.9 million in cash and cash equivalents, including $19.2 million in the U.S. with the remaining held by foreign subsidiaries.
Operating Cash Flows
Net cash provided by operating activities in 2016 was $69.7 million compared with $36.1 million in 2015, an increase of $33.6 million driven by improved operating performance, working capital management and cash flows from the Texel acquisition. In 2016, net income and non-cash adjustments were $61.9 million compared to $52.9 million in 2015. Net operating assets and liabilities in 2016 decreased $7.8 million since December 31, 2015, compared to an increase in net operating assets and liabilities in 2015 of $16.8 million since December 31, 2014. The decrease in net operating assets and liabilities in 2016 was primarily due to a $3.4 million increase in other, net, an increase of $3.5 million in accounts payable and an increase in accrued payroll and other compensation of $1.8 million, partially offset by increased prepaid expenses and other current assets of $3.4 million. The increase in other, net, was primarily the result of an accrual of $3.5 million recorded in the fourth quarter of 2016 for the settlement of the German Cartel Office investigation which is expected to be paid in the first quarter of 2017. The increase in accounts payable was primarily driven by the timing of inventory purchases and payments for capital expenditures within the fourth quarter of 2016.
Net cash provided by operating activities in 2015 was $36.1 million compared with $41.6 million in 2014. In 2015, net income and non-cash adjustments were $52.9 million compared to $48.0 million in 2014. Net operating assets and liabilities in 2015 increased $16.8 million since December 31, 2014, compared to an increase in net operating assets and liabilities in 2014 of $6.4 million since December 31, 2013. The increase in net operating assets and liabilities in 2015 was primarily due to a $4.8 million decrease in benefit plan liabilities resulting from cash contributions to the Company's domestic pension plan as well as a $3.4 million decrease in accrued payroll and other compensation mainly due to the timing of payroll and lower accruals related to the Company's annual incentive bonus program. Further contributing to the increase in operating assets and liabilities in 2015 was a $4.9 million decrease in accounts payable primarily due to timing of payments to vendors and higher accounts receivable of $2.8 million due to greater sales in the fourth quarter of 2015 compared to the fourth quarter of 2014.
29
Investing Cash Flows
Net cash used for investing activities was $177.7 million in 2016 compared to net cash provided by investing activities of $7.9 million in 2015. Investing activities in 2016 consisted of cash outflows of $101.1 million to fund the Texel acquisition, net of cash acquired of $1.6 million, and cash outflows of $51.1 million to fund the Gutsche acquisition, net of cash acquired of $9.4 million. Cash outflows for capital expenditures in 2016 were $25.5 million compared to $20.6 million in 2015, with the increase coming primarily within the Company's T/A Fibers and T/A Metals segments to support facility and new product platform expansion projects. In 2015, the Company received $28.6 million in proceeds from the sale of the Life Sciences Vital Fluids business, net of transaction expenses.
Net cash provided by investing activities was $7.9 million in 2015 compared to net cash used of $93.5 million in 2014. In 2015, the Company received $28.6 million in proceeds from the sale of the Life Sciences Vital Fluids business, net of transaction expenses. Cash outflows for capital expenditures in 2015 were $20.6 million compared to $14.0 million in 2014 primarily related to capital spending in the Company's T/A Fibers and T/A Metals North American manufacturing facilities. In 2014, the Company paid $79.4 million, net of cash acquired, for the Industrial Filtration businesses of Andrews Industries, Limited.
Financing Cash Flows
In 2016, net cash provided by financing activities was $106.4 million compared with net cash used for financing activities of $26.7 million in 2015. In 2016, the Company borrowed $116.6 million against its Amended Credit Facility to fund the purchase of the Texel and Gutsche businesses. Debt repayments were $10.3 million and $20.6 million in 2016 and 2015, respectively. The Company acquired $1.1 million in company stock through its equity compensation plans in 2016 compared to $8.7 million in company stock through its stock repurchase and equity compensation plans in 2015. The Company also received $1.2 million from the exercise of stock options during 2016, compared to $1.5 million during 2015.
In 2015, net cash used for financing activities was $26.7 million compared with net cash provided by financing activities of $42.5 million in 2014. In 2014, the Company borrowed $60.0 million against its prior Amended Credit Facility to fund the purchase of the Industrial Filtration businesses of Andrews Industries, Limited. Debt repayments were $20.6 million and $20.7 million in 2015 and 2014, respectively. The Company acquired $8.7 million in company stock through its stock repurchase and equity compensation plans in 2015, compared to $0.7 million in 2014. The Company also received $1.5 million from the exercise of stock options during 2015, compared to $2.5 million during 2014.
Financing Arrangements
On July 7, 2016, the Company amended its $100.0 million senior secured revolving credit facility (“Amended Credit Facility”) which increased the available borrowing from $100 million to $175 million, added a fourth lender and changed the maturity date from January 31, 2019 to July 7, 2021. The Amended Credit Facility is secured by substantially all of the assets of the Company. The Company entered into this Amended Credit Facility in part to fund a majority of the 2016 acquisitions and provide additional capacity to support organic growth programs, fund capital investments and continue pursuits of attractive acquisitions.
Under the terms of the Amended Credit Facility, the lenders are providing a $175 million revolving credit facility to the Company, under which the lenders may make revolving loans and issue letters of credit to or for the benefit of the Company and its subsidiaries. The Company may request the Amended Credit Facility be increased by an aggregate amount not to exceed $50 million through an accordion feature, subject to specified conditions.
The Amended Credit Facility contains a number of affirmative and negative covenants, including financial and operational covenants. The Company is required to meet a minimum interest coverage ratio. The interest coverage ratio requires that, at the end of each fiscal quarter, the ratio of consolidated EBIT to Consolidated Interest Charges, both as defined in the Amended Credit Facility, may not be less than 2.0 to 1.0 for the immediately preceding 12 month period. In addition, the Company must maintain a Consolidated Leverage Ratio, as defined in the Amended Credit Facility, as of the end of each fiscal quarter of no greater than 3.0 to 1.0. The Company must also meet minimum consolidated EBITDA as of the end of each fiscal quarter for the preceding 12 month period of $30.0 million. The Company was in compliance with all covenants during 2016 and at December 31, 2016.
Interest is charged on borrowings at the Company’s option of either: (i) Base Rate plus the Applicable Rate, or (ii) the Eurodollar Rate plus the Applicable Rate. The Base Rate is a fluctuating rate equal to the highest of (a) the federal
30
funds rate plus 0.50%, (b) the prime rate as set by Bank of America, and (c) the Eurocurrency Rate plus 1.00%. The Eurocurrency Rate means (i) if denominated in LIBOR quoted currency, a fluctuating LIBOR per annum rate equal to the London Interbank Offered Rate; (ii) if denominated in Canadian Dollars, the rate per annum equal to the Canadian Dealer Offered Rate; or (iii) the rate per annum as designated with respect to such alternative currency at the time such alternative currency is approved by the Lenders. The Applicable Rate is determined based on the Company’s Consolidated Leverage Ratio (as defined in the Amended Credit Agreement). The Applicable Rate added to the Base Rate Committed Loans ranges from 15 basis points to 100 basis points, and the Applicable Rate added to Eurocurrency Rate Committed Loans and Letters of Credit ranges from 75 basis points to 175 basis points. The Company pays a quarterly fee ranging from 17.5 basis points to 30 basis points on the unused portion of the $175 million available under the Amended Credit Facility. At December 31, 2016, the Company had borrowing availability of $44.6 million under the Amended Credit Facility net of $126.6 million of borrowings outstanding and standby letters of credit outstanding of $3.8 million.
In addition to the amounts outstanding under the Amended Credit Facility, the Company has various acquired foreign credit facilities totaling approximately $10.5 million. At December 31, 2016, the Company's foreign subsidiaries had $1.4 million in borrowings outstanding as well as $2.3 million in standby letters of credit outstanding.
Future Cash Requirements
The Company manages worldwide cash requirements considering available funds among domestic and foreign subsidiaries. The Company expects to fund its operating cash requirements from existing cash balances, cash generated by operations, and through borrowings, as needed, under its existing domestic and foreign credit facilities. The Company continually explores its core markets for suitable acquisitions, joint ventures, alliances and licensing agreements. If completed, such activities would be financed with existing cash balances, cash generated from operations, under the credit facilities described under “Financing Arrangements” above or other forms of financing, as required.
At December 31, 2016, total indebtedness was $128.8 million, of which $126.6 million was a domestic revolver loan, $1.4 million was borrowings under foreign credit facilities and $0.8 million was capital leases, or 32.0% of the Company’s total capital structure. Cash requirements for 2017 are expected to include the funding of ongoing operations, capital expenditures, payments due on capital and operating leases, pension plan contributions, income tax payments and optional prepayments on the revolver loan. Capital spending for 2017 is expected to be approximately $33 million to $38 million.
The funded status of the Company's domestic defined benefit pension plan is dependent upon many factors, including returns on invested assets, levels of market interest rates, mortality rates and levels of contributions to the plan. The Company is not obligated to make any minimum contributions during the 2017 plan year but expects to contribute approximately $3.0 million to $4.0 million to its defined benefit pension plan in 2017. See Note 8 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding the Company’s pension plans.
As discussed in Item 3, Legal Proceedings, Lydall Gerhardi agreed with the German Cartel Office to pay a settlement amount of €3.3 million (approximately $3.5 million as of December 31, 2016) and expects to make this payment in the quarter ending March 31, 2017.
31
Contractual Obligations
The following table summarizes the Company’s significant contractual obligations as of December 31, 2016 and the effect of such contractual obligations are expected to have on the Company’s liquidity and cash flows in future periods. For recent financing activity please refer to “Financing Arrangements” above.
Payments Due by Period | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In thousands | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | After 5 years | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||
Contractual Obligations: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating leases | 5,169 | 3,363 | 1,680 | 1,251 | 1,177 | 2,823 | 15,463 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Capital leases* | 244 | 244 | 241 | 35 | — | — | 764 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Long-term debt* | 2,802 | 2,402 | 2,402 | 2,402 | 126,923 | 416 | 137,347 | ||||||||||||||||||||
German Cartel settlement | 3,479 | — | — | — | — | — | 3,479 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total Contractual Obligations | $ | 11,694 | $ | 6,009 | $ | 4,323 | $ | 3,688 | $ | 128,100 | $ | 3,239 | $ | 157,053 | |||||||||||||
* | Includes estimated interest payments | |
The Company has capital lease agreements for machinery and equipment at multiple operations requiring monthly principal and interest payments through 2020. Operating leases are primarily related to buildings, office equipment, vehicles and machinery.
With the exception of the revolver loan, the Company’s long-term debt payments and interest rates relating to its foreign debt and capital lease obligations debt were fixed as of December 31, 2016. Refer to Note 6 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional discussion on long-term debt. Actual payments may vary significantly from those included in the table above depending on future debt levels, timing of debt repayments and sources of funding utilized.
In addition to the above contractual obligations, the Company utilizes letters of credit in the ordinary course of business for security deposit requirements. Outstanding letters of credit were $6.1 million and $1.9 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
The above table does not reflect net tax contingencies of $3.2 million, the timing of which is uncertain. Refer to Note 11 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional discussion on unrecognized tax benefits.
Purchase orders or contracts for normal purchases of raw materials and other goods and services are not included in the table above. The Company is not able to determine the aggregate amount of such purchase orders that represent contractual obligations, as purchase orders may represent authorizations to purchase rather than binding agreements. For purposes of this table, contractual obligations for purchase of goods or services are defined as agreements that are enforceable and legally binding on the Company and that specify all significant terms, including: fixed or minimum quantities to be purchased; fixed, minimum or variable price provisions; and the approximate timing of the transactions. The Company does not have significant agreements for the purchase of raw materials or other goods specifying minimum quantities or set prices that exceed expected requirements.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES
The preparation of the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Note 1 in Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements describes the significant accounting policies used in the preparation of the Consolidated Financial Statements. The Company’s management is required to make judgments about and estimates of the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain. Actual results could differ from management’s estimates. The most significant areas involving management judgments and estimates are described below.
32
Goodwill
The Company had goodwill of $63.6 million at December 31, 2016 and $16.8 million at December 31, 2015. Goodwill is not amortized, but rather is subject to impairment tests annually or more frequently when an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying value. The identification and measurement of goodwill impairment involves the estimation of the fair value of reporting units, including related goodwill. The Company’s reporting units are operating segments or components of operating segments for which discrete financial information is available and segment management regularly reviews the operating results of that reporting unit.
During the fourth quarter of 2016, the Company performed its annual impairment analysis of the $12.8 million of goodwill in the Performance Materials reporting unit and $50.8 million of goodwill in Technical Nonwovens reporting unit. The Company used the qualitative method to analyze the goodwill for the Performance Materials and Technical Nonwovens reporting units. When considering capital markets environment, economic conditions, industry trends, results of operations, and other factors, the Company determined that it is not more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. For the Performance Materials reporting unit, the Company also considered changes in assumptions used in the Company's most recent quantitative annual testing, including results of operations, the magnitude of excess of fair value over carrying value and other factors. As a result, the Company concluded that the Performance Materials and Technical Nonwovens reporting unit goodwill was not impaired.
In the event that the Company’s operating results in the future do not meet current expectations, management, based upon conditions at the time, would consider taking restructuring or other actions as necessary to maximize profitability. Future cash flows can be affected by numerous factors including changes in economic, industry or market conditions, changes in the underlying business or products of the reporting unit, changes in competition and changes in technology. Any changes in key assumptions about the business and its prospects, changes in any of the factors discussed above or other factors could affect the fair value of one or more of the reporting units resulting in an impairment charge.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Long-lived assets are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets may not be recoverable. Determination of recoverability is based on the Company’s judgment and estimates of undiscounted future cash flows resulting from the use of the assets and their eventual disposition. Measurement of an impairment loss for long-lived assets that management expects to hold and use is based on the fair value of the assets. If the carrying values of the assets are determined to be impaired, then the carrying values are reduced to their estimated fair values. The fair values of the impaired assets are determined based on applying a combination of market approaches, including independent appraisals when appropriate, the income approach, which utilizes cash flow projections, and the cost approach.
During the first quarter of 2016, the Company performed an impairment analysis for long-lived assets Company’s DSM Solutech B.V. (“Solutech”) operation, included in the Performance Materials segment. In March 2016, the Solutech operation became aware of a reduction of demand with certain customers that impacted the outlook for both its Arioso and Solupor membrane product lines that prompted management to adjust its long term revenue projections. These events resulted in a net decrease in forecasted revenue and cash flows. Based on these events and combined with historical operating losses, the Company determined that it was appropriate to test the Solutech asset group for recoverability as of March 31, 2016.
Patents, with a remaining useful life of approximately 8 years, and machinery and equipment primarily comprise the carrying value of the asset group of $1.9 million. To determine the recoverability of the Solutech asset group the Company completed an undiscounted cash flow analysis and compared it to the asset group carrying value. This analysis was primarily dependent on the expectations for net sales over the period when the business has technological exclusivity provided by its patents. Future cash flows are dependent on the success of commercialization efforts of Solutech products by OEMs, the quality of Solutech products and technology advancements and management’s ability to manage costs.
The impairment test performed at the end of the first quarter of 2016 concluded that the Solutech asset group was not recoverable as the resulting undiscounted cash flows were less than their carrying amount. Accordingly, in accordance with ASC 360 “Impairment of Long-Lived Assets,” the Company estimated the fair value of the Solutech long-lived assets and, based on these fair value estimates, determined that the long-lived assets were not impaired.
33
Determining fair value is judgmental in nature and requires the use of significant estimates and assumptions considered to be Level 3 inputs including royalty rates, long-term growth rates and discount rates. The fair value of the Solutech patents, was determined using the relief from royalty method, which is a form of the income approach that focused on the level of royalty payments that the user of an intangible asset would have to pay a third party for the use of the asset if it were not owned by the user. Under this approach, revenue associated with the associated technology was projected over the expected remaining useful life of the asset, with a royalty rate applied to the expected revenue. The estimated fair value of machinery and equipment was based on the cost approach. Under the cost approach, the determination of fair value considered the replacement cost of the assets with adjustments in value for physical deterioration, functional obsolescence, and economic obsolescence, all Level 3 inputs.
During the remainder of 2016, the Company continued to monitor the recoverability of the long-lived assets at the Solutech operation as a result of historical operating losses and negative cash flows. Future cash flows are dependent on the success of commercialization efforts of Solutech products by OEMs, and management’s ability to manage costs. A marginal reduction in expected future revenue or the inability to manage identified cost cutting measures could result in an impairment charge. In the event that Solutech's cash flows in the future do not meet current expectations, management, based upon conditions at the time, would consider taking actions as necessary to improve cash flow. A thorough analysis of all the facts and circumstances existing at the time would need to be performed to determine if recording an impairment loss was appropriate.
Pensions
Pension cost and the related obligations recognized in the Consolidated Financial Statements are determined on an actuarial basis. The determination of such amounts is made in consultation with the Company’s outside actuaries based on information and assumptions provided by the Company. A substantial portion of the Company’s pension amounts relate to its domestic defined benefit pension plan. Pension plans outside the United States were not significant at December 31, 2016. The domestic defined benefit pension plan, which covers certain domestic Lydall employees, is noncontributory and benefits are based on either years of service or eligible compensation paid while a participant is in a plan. The plan has been closed to new employees for several years and benefits under the pension plan are no longer accruing.
A significant element in determining the Company’s pension cost is the expected return on plan assets. Based on a review of market trends, actual returns on plan assets and other factors, including the allocation of the Company’s investments between equity and fixed income funds, the Company’s expected long-term rate of return on plan assets was 6.30% at December 31, 2016, which will be utilized for determining 2017 pension cost. An expected long-term rate of return of 7.00% was used for determining 2016 pension expense and 7.25% in determining 2015 and 2014 pension expense. In determining the expected return on plan assets, the Company considers the relative weighting of plan assets, the historical performance of marketable debt and equity securities and economic and other indicators of future performance. Investment management objectives include maintaining an adequate level of diversification to balance market risk and to provide sufficient liquidity for near-term payments of benefits accrued under the plan and to pay the expenses of administration. The investment plan assets are stated at fair value, which is based on quoted market prices in an active market. The expected long-term rate of return on assets is applied to the value of plan assets at the beginning of the year and this produces the expected return on plan assets that is included in the determination of pension cost for that year. The difference between this expected return and the actual return on plan assets is deferred, within certain parameters, as discussed below. The Company continually evaluates its expected long-term rate of return and will adjust such rate as deemed appropriate.
At the end of each year, the Company determines the discount rate to be used to calculate the present value of plan liabilities, as well as the following year’s pension cost. The discount rate is an estimate of the current interest rate at which the pension liabilities could be effectively settled at the end of the year. The Company based its discount rate assumption on an analysis which included the selection of a bond portfolio comprised of high quality fixed income investments whose cash flows would provide for the projected benefit payments of the plan. The discount rate is then developed as the single rate that equates the market value of the bond portfolio to the discounted value of the plan’s benefit payments. At December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company determined this rate to be 4.21% and 4.56%, respectively. Increases or decreases in the discount rate result in decreases and increases, respectively, in the projected benefit obligation. Actuarial losses, related to the decrease in discount rate at December 31, 2016, increased the pension plan liability $2.1 million and decreased other comprehensive income net-of-tax by $1.3 million. The net effect on pension liabilities from changes in the discount rate is deferred within certain parameters, as discussed below.
34
Pension accounting guidance requires that gains or losses be deferred unless the unrecognized net gain or loss at the end of a year exceeds a “corridor” (as defined in the pension accounting guidance). If the deferred gain or loss exceeds the corridor at the end of the year, then the amount in excess of the corridor is amortized over a period equal to the average remaining service period of active employees expected to receive benefits. Since benefit accruals were frozen on certain domestic defined benefit pension plans on June 30, 2006, these plan participants are considered inactive participants. Therefore, the gain/loss amortization for these plans is amortized over the average remaining life expectancy of all plan participants. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the net deferred loss exceeded the corridor. Consequently, pension cost for 2017 will include amortization of a portion of the deferred loss in excess of the corridor. The amount of amortization in future years will be dependent on changes in the components of the deferred loss amount, particularly actual return on plan assets in relation to the estimated return on plan assets, as well as future increases or decreases in the discount rate.
In 2014, the Society of Actuaries issued an updated set of mortality tables and improvement scale collectively known as RP-2014 and MP-2014, respectively. The Company reviewed the findings and recommendations of these reports with their actuary. Based on that review, the Company elected to utilize the Society of Actuaries' base mortality scale RP-2014 with the BB-2D mortality improvement scale, as the Company believes the BB-2D mortality improvement table more accurately reflects recent rates of mortality improvement since 2006 for the general population compared to the MP-2014 table. In 2016, the Society of Actuaries updated the mortality improvement table to MP-2016. The Company evaluated the MP-2016 table and determined the change would be insignificant so the mortality assumption remained the same using the RP-2014 mortality scale with the BB-2D mortality improvement scale.
A one-quarter percentage point change in the assumed long-term rate of return on the Company’s domestic pension plan as of December 31, 2016 would impact the Company’s 2017 pre-tax income by approximately $0.1 million. A one-quarter percentage point decrease in the discount rate on the Company’s domestic pension plan as of December 31, 2016 would have a minimal impact on the Company’s 2017 pre-tax income. The Company reviews these and other assumptions at least annually.
For the year ended December 31, 2016, the Company recognized pension expense related to its domestic defined benefit pension plan of $0.7 million as a result of the expected return on assets being lower than the aggregate of interest cost and the amortization of actuarial loss.
During 2014, the Company offered a voluntary one-time lump sum payment option to certain former U.S. employees who were vested defined benefit plan participants and not currently receiving monthly payments from the Company's domestic pension plan. This one-time lump sum payout of $10.3 million required a re-measurement of the domestic pension plan and a partial plan settlement charge, which resulted in a non-cash pre-tax loss of $4.9 million in 2014 net periodic pension benefit expense. The non-cash charge was required to accelerate the recognition of a portion of the previously unrecognized actuarial losses in the domestic pension plan.
As discussed above, the Company’s discount rate was 4.21% at December 31, 2016 and will be used for purposes of determining 2017 pension cost. Pension expense for 2017 is expected to be in the range of $0.7 million to $0.8 million. The Company contributed $3.6 million to its domestic defined benefit pension plan during 2016 and expects to contribute approximately $3.0 million to $4.0 million in 2017.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes following ASC 740 (Accounting for Income Taxes) recognizing deferred tax assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates for the effect of temporary differences between book and tax basis of recorded assets and liabilities. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance if it is more likely than not that some or all of a deferred tax asset will not be realized.
In assessing the need for a valuation allowance, the Company analyzes historical financial results by jurisdiction and estimates future taxable income, considering the feasibility of ongoing tax planning strategies and the realizable benefit of tax loss carryforwards. Valuation allowances related to deferred tax assets can be impacted by changes in tax law, changes in statutory tax rates and future levels of taxable income. In the event the Company was to determine that it would not be able to realize all or a portion of its deferred tax assets in the future, the Company would reduce such amounts through a charge to income in the period that such determination was made. Conversely, if the Company was to determine that it would be able to realize its deferred tax assets in the future in excess of the net carrying amounts, the Company would decrease the recorded valuation allowance and record an increase to income in the period that such determination was made.
35
As of December 31, 2016 the Company has not paid U.S. income taxes on approximately $17.2 million of undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries. The Company’s intention is to reinvest these earnings indefinitely. The Company estimates that the amount of tax that would be payable on the undistributed earnings if repatriated to the United States would fall in the range of $0.4 million to $2.3 million, based on current facts, but depending on the timing and extent of the repatriation. This amount may vary in the future due to a variety of factors including future tax law changes, future earnings and statutory taxes paid by foreign subsidiaries, and ongoing tax planning strategies by the Company.
The Company and its subsidiaries file a consolidated federal income tax return, as well as returns required by various state and foreign jurisdictions. In the normal course of business, the Company is subject to examination by taxing authorities, including such major jurisdictions as the United States, China, France, Germany, Hong Kong, the Netherlands, Canada and the United Kingdom. Within the next fiscal year, the Company expects to conclude certain income tax matters through the year ended December 31, 2013 and it is reasonably expected that net unrecognized benefits of $0.5 million may be recognized. The total amount of net unrecognized tax benefits that would affect the effective tax rate if recognized was $3.2 million as of December 31, 2016. However, $1.3 million of the unrecognized tax benefits, if recognized, would be offset in pre-tax income by the reversal of indemnification assets due to the Company. The Company is no longer subject to U.S. federal examinations for years before 2013, state and local examinations for years before 2012, and non-U.S. income tax examinations for years before 2003.
Equity Compensation Plans
The Company accounts for awards of equity instruments under the fair value method of accounting and recognizes such amounts in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The Company recognizes expense on a straight-line basis over the vesting period of the entire award. Prior to January 1, 2016, stock compensation expense included estimated effects of forfeitures. Upon adoption of ASU 2016-09, Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting, in the first quarter of 2016, an accounting policy election was made to account for forfeitures as they occur. Compensation expense for performance based awards is based upon the service period and management’s assessment of the probability of achieving the performance goals and adjusted based upon actual achievement. The Company estimates the fair value of option grants based on the Black Scholes option-pricing model. Expected volatility and expected term are based on historical information. The calculation assumes that future volatility and expected term are not likely to materially differ from the Company’s historical stock price volatility and historical exercise data, respectively.
The fair value of each option granted is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following weighted-average assumptions for the years ended December 31:
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Risk-free interest rate | 1.8 | % | 1.8 | % | 1.6 | % | ||
Expected life | 5.5 years | 5.5 years | 5.1 years | |||||
Expected volatility | 42 | % | 43 | % | 46 | % | ||
Expected dividend yield | — | % | — | % | — | % | ||
Contingencies and Environmental Obligations
The Company makes judgments and estimates in accordance with applicable accounting rules when it establishes reserves for legal proceedings, claims, investigations, environmental obligations and other contingent matters. Provisions for such matters are charged to expense when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and reasonable estimates of the liability can be made. Estimates of environmental liabilities are based on a variety of matters, including, but not limited to, the stage of investigation, the stage of the remedial design, evaluation of existing remediation technologies, and presently enacted laws and regulations. The amount and timing of all future expenses related to legal proceedings, claims, investigations, environmental obligations and other contingent matters may vary significantly from the Company's estimates.
RECENTLY ISSUED ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
See Note 15 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding accounting standards issued by the FASB but not effective until after December 31, 2016.
36
OTHER KEY FINANCIAL ITEMS
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements — Other than operating leases, the Company does not have any other material off-balance sheet financing arrangements.
Inflation — Inflation generally affects the Company through its costs of labor, equipment, energy and raw materials. The increased costs of these items have generally been offset by price increases, operating improvements and other cost-saving initiatives. The Company also has certain arrangements in which it can pass through inflation on raw material costs to its customers.
Item 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
Lydall’s limited market risk exposures relate to changes in foreign currency exchange rates and interest rates.
FOREIGN CURRENCY RISK
The Company has operations in Germany, France, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, China and Canada, in addition to the United States. As a result of this, the Company’s financial results are affected by factors such as changes in foreign currency exchange rates or economic conditions in the foreign markets where the Company manufactures and distributes its products. The Company’s currency exposure is to the US Dollar, the Euro, the British Pound Sterling, the Japanese Yen, the Chinese Yuan, the Hong Kong Dollar and the Canadian Dollar. The Company’s foreign and domestic operations attempt to limit foreign currency exchange transaction risk by completing transactions in local functional currencies, whenever practicable. The Company may periodically enter into foreign currency forward exchange contracts to mitigate exposure to foreign currency volatility. In addition, the Company utilizes bank loans and other debt instruments throughout its operations. To mitigate foreign currency risk, such debt is denominated primarily in the functional currency of the operation maintaining the debt.
The Company also has exposure to fluctuations in currency risk on intercompany loans that the Company makes to certain of its subsidiaries. The Company may periodically enter into foreign currency forward contracts which are intended to offset the impact of foreign currency movements on the underlying intercompany loan obligations.
INTEREST RATE RISK
The Company’s interest rate exposure is most sensitive to fluctuations in interest rates in the United States and Europe, which impact interest paid on its debt. In July 2016 and December 2016, the Company borrowed $85.0 million and $31.6 million, respectively, to fund the Texel and Gutsche acquisitions, from its Amended Credit Facility, with a variable interest rate. The Company has debt with variable rates of interest based generally on LIBOR. Increases in interest rates could therefore significantly increase the associated interest payments that the Company is required to make on this debt. From time to time, the Company may enter into interest rate swap agreements to manage interest rate risk. The Company has assessed its exposure to changes in interest rates by analyzing the sensitivity to Lydall’s earnings assuming various changes in market interest rates. Assuming a hypothetical increase of one percentage point in interest rates on the $126.6 million outstanding borrowings as of December 31, 2016, the Company’s net income would decrease by an estimated $0.9 million over a twelve-month period.
The weighted average interest rate on long-term debt was 1.4% for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with 1.3% and 1.5% for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Item 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
The response to this Item is contained under Item 15. “Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.”
37
Item 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
None.
Item 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Under the supervision and with the participation of management, including the Company’s President and Chief Executive Officer and its Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, the Company has, pursuant to Rule 13a-15(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of its disclosure controls and procedures (as defined under Rule 13a-15(e) of the Exchange Act). Based upon that evaluation, the Company’s President and Chief Executive Officer and its Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, as of December 31, 2016, the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures are effective.
Changes in Internal Controls Over Financial Reporting
There has been no change in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act) that occurred during the fiscal quarter ended December 31, 2016 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. As part of its ongoing integration activities, the Company will complete an assessment of existing controls and incorporate its controls and procedures into the technical nonwovens businesses ("Technical Nonwovens") acquired from ADS and Gutsche in July 2016 and December 2016, respectively.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The Company’s management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external reporting purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Due to its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements.
The Company acquired Texel and Gutsche for $102.7 million and $57.6 million, respectively. The Company excluded Texel and Gutsche from its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016 because they were acquired by the Company in purchase business combinations in 2016. Texel accounted for 12.9% of the Company’s total consolidated assets as of December 31, 2016 and 7.2% of the Company’s total consolidated revenue for the year then ended. Gutsche accounted for 7.1% of the Company’s total consolidated assets as of December 31, 2016.
Management has assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016. In making its assessment, management has utilized the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013 Framework). Management concluded that based on its assessment, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2016. The effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which appears herein.
Item 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION |
None.
38
PART III
Item 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
Information required by this Item is incorporated by reference from the sections entitled “Proposal 1 — Election of Directors,” “Corporate Governance” and “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” of the definitive Proxy Statement of Lydall to be filed with the Commission within 120 days of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016 in connection with the Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on April 28, 2017 (the “2017 Proxy Statement”). Information regarding the Executive Officers of the Company is contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The Company’s Code of Ethics and Business Conduct for all employees and its Code of Ethics for the Chief Executive Officer, Senior Financial Officers and all Accounting and Financial Personnel can be obtained free of charge on the Company’s website under the Corporate Governance section or by contacting the Office of the General Counsel, P.O. Box 151, One Colonial Road, Manchester, CT 06045-0151.
The Company intends to post on its website all disclosures that are required by law or New York Stock Exchange listing standards concerning any amendments to, or waivers from, the provisions of these documents.
Item 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
Information required by this Item is incorporated by reference from the sections entitled “2016 Director Compensation,” “Compensation Discussion and Analysis,” “Executive Compensation Tables,” “Corporate Governance — Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” and “Compensation Discussion and Analysis — Compensation Committee Report on Executive Compensation” of the 2017 Proxy Statement.
Item 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
Certain information required by this Item is incorporated by reference from the section entitled “Securities Ownership of Directors, Certain Officers and 5% Beneficial Owners” of the 2017 Proxy Statement.
The following table provides information about the Company’s Common Stock that may be issued upon exercise of options and rights under all of the Company’s existing equity compensation plans at December 31, 2016. The number of securities remaining available for issuance at December 31, 2016 was 832,631 and includes shares that may be issued as restricted stock, performance shares and other stock awards.
Plan Category | Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights (a) | Weighted average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights (b) | Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a)) (c) | ||||||
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | 723,293 | $ | 14.95 | 832,631 | |||||
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | — | — | — | ||||||
Total | 723,293 | $ | 14.95 | 832,631 | |||||
39
Item 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
Information required by this Item is incorporated by reference from the sections entitled “Corporate Governance — Independence Determination,” “Related Party Transactions,” and “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” of the 2017 Proxy Statement.
Item 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES |
Information required by this Item is incorporated by reference from the sections entitled “Proposal 4 — Ratification of Appointment of Independent Auditors,” and “Principal Fees and Services” of the 2017 Proxy Statement.
40
PART IV
Item 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
Page | |
1. Financial Statements: | |
Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 | |
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 | |
Consolidated Balance Sheets at December 31, 2016 and 2015 | |
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 | |
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2016 | |
2. Financial Statement Schedule: | |
Schedule II — Valuation and Qualifying Accounts for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 | |
Other schedules for which provision is made in the applicable accounting regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission are not required under the related instructions, are inapplicable or are presented in “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” and therefore have been omitted.
41
a) 3. Exhibits Included Herein or Incorporated by Reference:
2.1 | Share Purchase Agreement, dated July 7, 2016, by and among ADS, Inc. and Lydall Canada Acquisition Corp., filed as Exhibit 2.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated July 12, 2016 and incorporated herein by reference. The Registrant will supplementally furnish any omitted schedules to the Commission upon request. | |
2.2 | Sale and Purchase Agreement dated February 20, 2014, by and among the Andrew Industries Limited, Lydall Inc. and Lydall UK Ltd., filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated February 24, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference. The Registrant will supplementally furnish any omitted schedules to the Commission upon request. | |
3.1 | Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Registrant, as amended through the date of filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, filed as Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated April 30, 2015 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
3.2 | Bylaws of the Registrant, as amended and restated as of August 1,2015, filed as Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated August 5, 2015 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
4.1 | Certain long-term debt instruments, each representing indebtedness in an amount equal to or less than 10 percent of the Registrant’s total consolidated assets, have not been filed as exhibits to this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The Registrant will file these instruments with the Commission upon request. | |
10.1* | Employment Agreement with Dale G. Barnhart dated July 31, 2007, filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated August 3, 2007 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
10.2* | Employment Agreement with Chad A. McDaniel dated May 8, 2013, filed as Exhibit 10.5 to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K dated March 5, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.3* | Employment Agreement with Joseph A. Abbruzzi dated March 31, 2014, filed as Exhibit 10.6 to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K dated March 3, 2015 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.4* | Employment Agreement with James V. Laughlan dated August 3, 2015, filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant's Form 8-K dated August 5, 2015 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.5* | Employment Agreement with Scott M. Deakin dated August 21, 2015, filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant's Form 8-K dated August 21, 2015 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.6* | Employment Agreement with Paul A. Marold dated February 18, 2016, filed herewith. | |
10.7* | Indemnification Agreement with Dale G. Barnhart dated July 31, 2007, filed as Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated August 3, 2007 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
10.8* | Lydall, Inc. Annual Incentive Performance Program adopted March 30, 2016 and effective January 1, 2016, filed as Exhibit 99.1 to the Registrant's Form 8-K dated April 1, 2016 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.9 | Form of Indemnification Agreement between Lydall, Inc. and non-employee directors, filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated June 19, 2009 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
10.10* | Amended and Restated Lydall 2003 Stock Incentive Compensation Plan, filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated May 2, 2011 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
10.11* | Lydall 2012 Stock Incentive Plan, filed as Exhibit A to the Registrant’s Definitive Proxy Statement dated March 16, 2012 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
10.12* | Form of Restricted Share Award Agreement to Non-Employee Directors (Under the Lydall 2012 Stock Incentive Plan), filed as Exhibit 10.9 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q dated August 1, 2012 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
10.13* | Form of Non-Qualified/Incentive Stock Option Agreement (Under the Lydall 2012 Stock Incentive Plan) for U.S. employees, filed as Exhibit 10.4 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q dated August 1, 2012 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
10.14* | Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement (Under the Lydall 2012 Stock Incentive Plan) for U.S. Employees, filed as Exhibit 10.8 to the Registrant’s to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q dated August 1, 2012 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
10.15* | Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement (Under the Lydall 2012 Stock Incentive Plan) for Netherland employees, filed as Exhibit 10.10 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q dated August 1, 2012 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
10.16* | Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement (Under the Lydall 2012 Stock Incentive Plan) for French employees, filed as Exhibit 10.11 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q dated August 1, 2012 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
42
10.17* | Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement (Under the Lydall 2012 Stock Incentive Plan) for German employees, filed as Exhibit 10.12 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q dated August 1, 2012 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
10.18* | Form of Lydall, Inc. Performance Share Award Agreement (Three-Year Period) for U.S. employees, filed as Exhibit 10.18 to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K dated March 3, 2015 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.19* | Form of Lydall, Inc. Performance Share Award Agreement (Three-Year Period) for French employees, filed as Exhibit 10.6 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q dated August 1, 2012 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
10.20* | Form of Lydall, Inc. Performance Share Award Agreement (Three-Year Period) for German employees, filed as Exhibit 10.7 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q dated August 1, 2012 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
10.21* | Form of Lydall, Inc. Performance Share Award Agreement (One-Year Period), filed as Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K dated February 26, 2010 and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
10.22 | Joinder and Second Amendment and Reaffirmation of Guaranty Agreement, dated July 7, 2016, by and among Lydall, Inc., as borrower, and Bank of America, N.A., as Agent for the Lenders, filed as Exhibit 99.2 to the Registrant's From 8-K dated July 12, 2016 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.23 | Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated February 18, 2014, by and between Lydall, Inc., as borrower, and Bank of America, N.A., as Agent for the Lenders, filed as Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated February 24, 2014 and incorporated herein by this reference, as further amended by Amendment No. 1 to the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated May 5, 2015, filed as Exhibit 99.1 to the Registrant's Form 8-K dated May 6, 2015 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.24 | Amended and Restated Guaranty Agreement, dated February 18, 2014, by and among Lydall Thermal/Acoustical, Inc., Lydall Filtration/Separation, Inc., Lydall International, Inc., and Bank of America, N.A., filed as Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated February 24, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.25 | Amended and Restated Security Agreement, dated February 18, 2014, by and between Lydall, Inc., and Bank of America, N.A., filed as Exhibit 10.4 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated February 24, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference, as further amended by that certain Amendment to the Amended and Restated Security Agreements, the Amended and Restated Domain Name Collateral Assignment and Security Agreement and Partial Release dated January 30, 2015, filed as Exhibit 10.34 to the Registrant's Annual Report on From 10-K dated March 3, 2015 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.26 | Amended and Restated Security Agreement, dated February 18, 2014, by and between Lydall Thermal/Acoustical, Inc., and Bank of America, N.A., filed as Exhibit 10.5 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated February 24, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference, as further amended by that certain Amendment to the Amended and Restated Security Agreements, the Amended and Restated Domain Name Collateral Assignment and Security Agreement and Partial Release dated January 30, 2015, filed as Exhibit 10.34 to the Registrant's Annual Report on From 10-K dated March 3, 2015 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.27 | Amended and Restated Security Agreement, dated February 18, 2014, by and between Lydall Filtration/Separation, Inc., and Bank of America, N.A. filed as Exhibit 10.6 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated February 24, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.28 | Amended and Restated Security Agreement, dated February 18, 2014, by and between Lydall International, Inc., and Bank of America, N.A., filed as Exhibit 10.7 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K dated February 24, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.29 | Amendment to the Amended and Restated Security Agreements, the Amended and Restated Domain Name Collateral Assignment and Security Agreement and Partial Release dated January 30, 2015 by and among Lydall, Inc., Lydall Thermal/Acoustical, Inc. and Bank of America, filed as Exhibit 10.34 to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K dated March 3, 2015 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.30* | Amendment No. 1 to the Agreement, dated February 24, 2016, between the Company and Chad A. McDaniel, amending that certain Employment Agreement dated May 8, 2013, filed as Exhibit 10.5 to the Registrant's Annual Report on From 10-K dated February 24, 2016 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.31* | Amendment No. 1 to the Agreement, dated February 24, 2016, between the Company and Joseph A. Abbruzzi, amending that certain Employment Agreement dated March 31, 2014, filed as Exhibit 10.6 to the Registrant's Annual Report on From 10-K dated February 24, 2016 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
43
10.32* | Amendment No. 1 to the Agreement, dated February 24, 2016, between the Company and James V. Laughlan, amending that certain Employment Agreement dated August 3, 2015, filed as Exhibit 10.7 to the Registrant's Annual Report on From 10-K dated February 24, 2016 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
10.33* | Amendment No. 1 to the Agreement, dated February 24, 2016, between the Company and Scott M. Deakin, amending that certain Employment Agreement dated August 21, 2015, filed as Exhibit 10.8 to the Registrant's Annual Report on From 10-K dated February 24, 2016 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
14.1 | Lydall’s Code of Ethics and Business Conduct, as amended, and the supplemental Code of Ethics for the Chief Executive Officer, Senior Financial Officers and All Accounting and Financial Personnel, as amended, each can be accessed on Lydall’s website at www.lydall.com under the Corporate Governance section. | |
21.1 | List of subsidiaries of the Registrant, filed herewith. | |
23.1 | Consent of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, filed herewith. | |
24.1 | Power of Attorney, dated February 17, 2017 authorizing Scott M. Deakin to sign this Annual Report on Form 10-K on behalf of each member of the Board of Directors indicated therein, filed herewith. | |
31.1 | Certification Pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) and Rule 15d-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as principal executive officer, filed herewith. | |
31.2 | Certification Pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) and Rule 15d-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as principal executive officer, filed herewith. | |
32.1 | Certifications Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, furnished herewith. | |
101.INS | XBRL Instance Document | |
101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | |
101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | |
101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | |
101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | |
101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | |
* | Management contract or compensatory plan. | |
44
Item 16. | FORM 10-K SUMMARY |
Not applicable.
45
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, Lydall, Inc. has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
LYDALL, INC. | |||
February 22, 2017 | By: | /s/ Scott M. Deakin | |
Scott M. Deakin Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) | |||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of Lydall, Inc. in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature | Title | Date | ||
/s/ Dale G. Barnhart | President, Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) | February 22, 2017 | ||
Dale G. Barnhart | ||||
/s/ Scott M. Deakin | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) | February 22, 2017 | ||
Scott M. Deakin | ||||
/s/ James V. Laughlan | Vice President, Chief Accounting Officer, and Treasurer (Principal Accounting Officer) | February 22, 2017 | ||
James V. Laughlan | ||||
/s/ Scott M. Deakin | February 22, 2017 | |||
Scott M. Deakin | ||||
Attorney-in-fact for: | ||||
Kathleen Burdett | Director | |||
W. Leslie Duffy | Chairman of the Board of Directors | |||
Matthew T. Farrell | Director | |||
Marc T. Giles | Director | |||
William D. Gurley | Director | |||
Suzanne Hammett | Director | |||
S. Carl Soderstrom, Jr. | Director | |||
46
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and
Stockholders of Lydall, Inc.:
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements listed in the index appearing under item 15(a)(1) present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Lydall, Inc. and its subsidiaries at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2016 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In addition, in our opinion, the financial statement schedule listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(2) presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein when read in conjunction with the related consolidated financial statements. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework 2013 issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company's management is responsible for these financial statements and financial statement schedule, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements, on the financial statement schedule, and on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed the manner in which it accounts for share based compensation due to the adoption of ASU 2016-09, Improvements to Employee Share Based Payment Accounting in 2016. As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed the manner in which it accounts for the classification of deferred taxes due to the adoption of ASU 2015-17, Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes in 2016.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
F-1
As described in Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting appearing under item 9A, management has excluded the businesses of both Texel and Gutsche from its assessment of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016 because such businesses were acquired by the Company in purchase business combinations during 2016. We have also excluded both Texel and Gutsche from our audit of internal control over financial reporting. Texel is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Lydall whose total assets and total net sales represent 12.9% and 7.2%, respectively, of the related consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the year ended December 31, 2016. Gutsche is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Lydall whose total assets and total net sales represent 7.1% and 0%, respectively, of the related consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the year ended December 31, 2016.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP |
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP |
Hartford, Connecticut |
February 22, 2017 |
F-2
Lydall, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
For the years ended December 31, | |||||||||||
In thousands except per share data | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Net sales | $ | 566,852 | $ | 524,505 | $ | 535,829 | |||||
Cost of sales | 428,310 | 402,008 | 420,851 | ||||||||
Gross profit | 138,542 | 122,497 | 114,978 | ||||||||
Selling, product development and administrative expenses | 83,750 | 70,020 | 80,930 | ||||||||
Operating income | 54,792 | 52,477 | 34,048 | ||||||||
Gain on sale of business | — | (18,647 | ) | — | |||||||
Interest expense | 1,068 | 755 | 1,093 | ||||||||
Other income, net | (1,215 | ) | (654 | ) | (701 | ) | |||||
Income before income taxes | 54,939 | 71,023 | 33,656 | ||||||||
Income tax expense | 17,821 | 24,764 | 11,809 | ||||||||
Income from equity method investment | (69 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Net income | $ | 37,187 | $ | 46,259 | $ | 21,847 | |||||
Earnings per common share: | |||||||||||
Basic | $ | 2.20 | $ | 2.76 | $ | 1.31 | |||||
Diluted | $ | 2.16 | $ | 2.71 | $ | 1.28 | |||||
Weighted average common shares outstanding | 16,871 | 16,746 | 16,662 | ||||||||
Weighted average common shares and equivalents outstanding | 17,241 | 17,084 | 17,003 | ||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-3
Lydall, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the years ended December 31, | |||||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 37,187 | $ | 46,259 | $ | 21,847 | |||||
Other comprehensive loss income: | |||||||||||
Change in pension plans, net of income taxes of $1,409, $55 and $1,595, respectively | (2,400 | ) | (90 | ) | (2,603 | ) | |||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments | (10,965 | ) | (10,334 | ) | (12,714 | ) | |||||
Total other comprehensive loss, net of tax | (13,365 | ) | (10,424 | ) | (15,317 | ) | |||||
Comprehensive income | $ | 23,822 | $ | 35,835 | $ | 6,530 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-4
Lydall, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, | |||||||
In thousands of dollars and shares | 2016 | 2015 | |||||
Assets | |||||||
Current assets: | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 71,934 | $ | 75,909 | |||
Accounts receivable, (net of allowance for doubtful receivables of $1,429 and $1,251, respectively) | 103,316 | 82,149 | |||||
Inventories | 66,146 | 46,530 | |||||
Taxes receivable | 3,883 | 4,194 | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 10,327 | 10,521 | |||||
Total current assets | 255,606 | 219,303 | |||||
Property, plant and equipment, net | 160,795 | 114,433 | |||||
Goodwill | 63,606 | 16,841 | |||||
Other intangible assets, net | 41,447 | 5,399 | |||||
Other assets, net | 5,575 | 2,284 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 527,029 | $ | 358,260 | |||
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity | |||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||
Current portion of long-term debt | $ | 634 | $ | 323 | |||
Accounts payable | 56,346 | 42,470 | |||||
Accrued payroll and other compensation | 14,016 | 10,210 | |||||
Accrued taxes | 6,460 | 1,200 | |||||
Other accrued liabilities | 12,988 | 6,797 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 90,444 | 61,000 | |||||
Long-term debt | 128,141 | 20,156 | |||||
Deferred tax liabilities | 15,849 | 14,997 | |||||
Benefit plan liabilities | 14,729 | 14,222 | |||||
Other long-term liabilities | 4,410 | 2,660 | |||||
Commitments and Contingencies (Note 12) | |||||||
Stockholders’ equity: | |||||||
Preferred stock (par value $0.01 per share; authorized 500 shares; none issued or outstanding) (Note 7) | — | — | |||||
Common stock (par value $0.01 per share; authorized 30,000 shares; issued 24,858 and 24,732 shares, respectively) (Note 7) | 249 | 247 | |||||
Capital in excess of par value | 82,387 | 76,746 | |||||
Retained earnings | 325,466 | 288,358 | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (47,950 | ) | (34,585 | ) | |||
Treasury stock, 7,626 and 7,592 shares of common stock, respectively, at cost | (86,696 | ) | (85,541 | ) | |||
Total stockholders’ equity | 273,456 | 245,225 | |||||
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $ | 527,029 | $ | 358,260 | |||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-5
Lydall, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the years ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 37,187 | $ | 46,259 | $ | 21,847 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided | ||||||||||||
by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Gain on sale of business | — | (18,647 | ) | — | ||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 19,559 | 17,275 | 17,646 | |||||||||
Inventory step-up amortization | 1,954 | — | 2,053 | |||||||||
Long-lived asset impairment charge | — | 1,354 | — | |||||||||
Deferred income taxes | (1,172 | ) | 3,585 | (1,477 | ) | |||||||
Stock-based compensation | 4,359 | 2,827 | 2,787 | |||||||||
Pension settlement charge | — | — | 4,914 | |||||||||
Income from equity method investment | (69 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||
Loss on disposition of property, plant and equipment | 60 | 288 | 241 | |||||||||
Accounts receivable | 379 | (2,749 | ) | (7,189 | ) | |||||||
Inventories | 500 | 479 | 4,539 | |||||||||
Taxes receivable | 1,169 | 276 | (4,129 | ) | ||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets | (3,355 | ) | (1,337 | ) | (2,318 | ) | ||||||
Accounts payable | 3,505 | (4,886 | ) | 1,167 | ||||||||
Accrued payroll and other compensation | 1,770 | (3,416 | ) | 3,299 | ||||||||
Benefit plan liabilities | 487 | (4,778 | ) | (3,563 | ) | |||||||
Other, net | 3,394 | (420 | ) | 1,811 | ||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 69,727 | 36,110 | 41,628 | |||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||||||
Business acquisitions, net of cash acquired | (152,242 | ) | — | (79,407 | ) | |||||||
Capital expenditures | (25,466 | ) | (20,645 | ) | (13,971 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from sale of business, net | — | 28,550 | — | |||||||||
Acquisition earn out payments | — | — | (111 | ) | ||||||||
Net cash (used for) provided by investing activities | (177,708 | ) | 7,905 | (93,489 | ) | |||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from borrowings | 116,600 | — | 60,000 | |||||||||
Debt repayments | (10,328 | ) | (20,571 | ) | (20,646 | ) | ||||||
Common stock issued | 1,194 | 1,521 | 2,457 | |||||||||
Common stock repurchased | (1,091 | ) | (8,701 | ) | (748 | ) | ||||||
Excess tax benefit on stock awards | — | 1,044 | 1,486 | |||||||||
Net cash provided by (used for) financing activities | 106,375 | (26,707 | ) | 42,549 | ||||||||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | (2,369 | ) | (3,450 | ) | (4,044 | ) | ||||||
(Decrease) Increase in cash and cash equivalents | (3,975 | ) | 13,858 | (13,356 | ) | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 75,909 | 62,051 | 75,407 | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 71,934 | $ | 75,909 | $ | 62,051 | ||||||
Supplemental Schedule for Cash Flow Information | ||||||||||||
Cash paid during the year for: | ||||||||||||
Interest | $ | 787 | $ | 632 | $ | 875 | ||||||
Income taxes, net | $ | 15,739 | $ | 20,180 | $ | 14,679 | ||||||
Non-cash capital expenditures of $8.6 million, $5.9 million and $5.0 million were included in accounts payable at December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 respectively.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-6
Lydall, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
In thousands of dollars and shares | Common Stock Shares | Common Stock Amount | Capital in Excess of Par Value | Retained Earnings | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss | Treasury Stock | Total Stockholders' Equity | |||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2013 | 24,098 | $ | 2,410 | $ | 62,284 | $ | 220,252 | $ | (8,844 | ) | $ | (76,015 | ) | $ | 200,087 | |||||||||||
Net income | 21,847 | 21,847 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | (15,317 | ) | (15,317 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock repurchased | (748 | ) | (748 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock issued under employee plans | 524 | 52 | 2,405 | 2,457 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Excess tax benefit on stock awards | 1,486 | 1,486 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 2,535 | 2,535 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock issued to directors | 9 | 1 | 251 | 252 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2014 | 24,631 | 2,463 | 68,961 | 242,099 | (24,161 | ) | (76,763 | ) | 212,599 | |||||||||||||||||
Net income | 46,259 | 46,259 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | (10,424 | ) | (10,424 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock repurchased | (8,778 | ) | (8,778 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock issued under employee plans | 91 | (2 | ) | 1,700 | 1,698 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Excess tax benefit on stock awards | 1,044 | 1,044 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 2,477 | 2,477 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock issued to directors | 10 | 350 | 350 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Change in par value | (2,214 | ) | 2,214 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2015 | 24,732 | 247 | 76,746 | 288,358 | (34,585 | ) | (85,541 | ) | 245,225 | |||||||||||||||||
Net Income | 37,187 | 37,187 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | (13,365 | ) | (13,365 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock repurchased | (1,155 | ) | (1,155 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock issued under employee plans | 119 | 2 | 1,156 | 1,158 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 4,009 | 4,009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock issued to directors | 7 | 350 | 350 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Recently adopted accounting standards | 126 | (79 | ) | 47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2016 | 24,858 | $ | 249 | $ | 82,387 | $ | 325,466 | $ | (47,950 | ) | $ | (86,696 | ) | $ | 273,456 | |||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
F-7
Lydall, Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Significant Accounting Policies
Business — Lydall, Inc. and its subsidiaries (the “Company” or “Lydall”) design and manufacture specialty engineered nonwoven filtration media, industrial thermal insulating solutions, and thermal and acoustical barriers for filtration/separation and heat abatement and sound dampening applications.
On July 7, 2016, the Company completed an acquisition of the nonwoven and coating materials businesses primarily operating under the Texel brand (“Texel”) from ADS, Inc. (“ADS”), a Canadian based corporation. The Texel operations manufacture nonwoven needle punch materials and predominantly serve the geosynthetic, liquid filtration, and other industrial markets. The acquired businesses are included in the Company's Technical Nonwovens reporting segment.
On December 31, 2016, the Company completed an acquisition of the nonwoven needle punch materials businesses, operating under the Gutsche (“Gutsche”) brand, a German based corporation. The Gutsche operations manufacture nonwoven needle punch materials and predominantly serve the industrial filtration and high performance nonwoven markets. The acquired businesses are included in the Company's Technical Nonwovens reporting segment.
Principles of consolidation — The Consolidated Financial Statements include the accounts of Lydall, Inc. and its wholly owned subsidiaries. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated.
Estimates and assumptions — The preparation of the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the financial statement dates and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Risks and uncertainties — Worldwide economic cycles and political changes affect the markets that the Company’s businesses serve and affect demand for Lydall’s products and impact profitability. Among other factors, disruptions in the global credit and financial markets, including diminished liquidity and credit availability, swings in consumer confidence and spending, unstable economic growth and fluctuations in unemployment rates has caused economic instability and can have a negative impact on the Company’s results of operations, financial condition and liquidity.
Cash and cash equivalents — Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand and highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less at the date of purchase.
Concentrations of credit risk — Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist principally of cash and cash equivalents and trade accounts receivable. The Company places its cash and cash equivalents in high-quality financial institutions. Concentrations of credit risk with respect to trade accounts receivable are limited by the large number of customers comprising the Company’s customer base and their dispersion across many different industries and geographies. At December 31, 2016, Ford Motor Company ("Ford") represented 14.2% of total accounts receivable. No other customers accounted for more than 10.0% of total accounts receivable at December 31, 2016 and 2015. Foreign and export sales were 46.9% of the Company’s net sales in 2016, 44.2% in 2015, and 46.2% in 2014. Export sales primarily to Canada, Mexico, Asia and Europe were $53.2 million, $52.5 million, and $57.6 million in 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively. The Company performs ongoing credit evaluations of its customers’ financial condition and generally does not require collateral. Sales to the automotive market, included in the Thermal/Acoustical Metals and Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segments, were 56.2% of the Company’s net sales in 2016, 56.6% in 2015, and 54.1% in 2014. Sales to Ford were 19.6%, 18.2%, and 16.5% of Lydall’s 2016, 2015, and 2014 net sales, respectively. No other customers accounted for more than 10% of total net sales in 2016, 2015, and 2014.
Inventories — Inventories are valued at lower of cost or market, cost being determined using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) cost method. Inventories in excess of requirements for current or anticipated orders have been written down to net realizable value.
Pre-production design and development costs — The Company enters into contractual agreements with certain customers to design and develop molds, dies and tools (collectively, “tooling”). All such tooling contracts relate to parts
F-8
that the Company will supply to customers under long-term supply agreements. Tooling costs are accumulated in work-in process inventory and are charged to operations as the related revenue from the tooling is recognized. Revenue is recognized as tooling is delivered and accepted by the customer. The Company also may progress bill on certain tooling being constructed. These billings are recorded as progress billings (a reduction of the associated work-in-process inventory) until the appropriate revenue recognition criteria have been met.
Periodically, the Company enters into contractually guaranteed reimbursement arrangements as a mechanism to collect amounts due from customers from tooling sales. Under these arrangements, amounts due from tooling sales are collected as parts are delivered over the part supply arrangement, in accordance with the specific terms of the arrangement. The amounts due from the customer in such transactions are recorded in “Prepaid expenses and other current assets, net” or “Other assets, net” based upon the expected term of the reimbursement arrangement.
The following tooling related assets were included in the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2016 and 2015:
December, 31 | |||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | |||||
Inventories, net of progress billings and reserves | $ | 9,388 | $ | 9,220 | |||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets, net | 258 | 266 | |||||
Total tooling related assets | $ | 9,646 | $ | 9,486 | |||
Amounts included in “Prepaid expenses and other current assets, net” include the short-term portion of receivables due under contractually guaranteed reimbursement arrangements. Included in the inventory balance was an offset for progress billings of $0.9 million and $0.3 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Company owned tooling is recorded in “Property, plant and equipment, net” at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015.
Property, plant and equipment — Property, plant, and equipment are stated at cost. Assets held under capital leases are recorded at the lower of the net present value of the minimum lease payments or the fair value of the leased asset at the inception of the lease. Property, plant and equipment, including property, plant and equipment under capital leases, are depreciated over their estimated useful lives using the straight-line method. Leasehold improvements are depreciated on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease or the life of the asset, whichever is shorter. The cost and accumulated depreciation amounts applicable to assets sold or otherwise disposed of are removed from the asset and accumulated depreciation accounts and any net gain or loss is included in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Expenses for maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred.
Goodwill and other intangible assets — Goodwill represents costs in excess of fair values assigned to the underlying net assets of acquired companies. Goodwill and other intangible assets with indefinite lives are not amortized but are subject to annual impairment tests. All other intangible assets are amortized over their estimated useful lives, which range from 4 to 14 years. In performing impairment tests, the Company considers discounted cash flows and other market factors as best evidence of fair value. There are inherent uncertainties and management judgment required in these analyses.
Valuation of long-lived assets — The Company evaluates the recoverability of long-lived assets, or asset groups, whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that carrying amounts may not be recoverable. Should such evaluations indicate that the related future undiscounted cash flows are not sufficient to recover the carrying values of the assets, such carrying values would be reduced to fair value and this adjusted carrying value would become the assets’ new cost basis. Fair value is determined primarily using future anticipated cash flows that are directly associated with, and that are expected to arise as a direct result of the use and eventual disposition of the asset, or asset group, as well as market conditions and other factors. There are inherent uncertainties and management judgment required in these analyses.
Contingencies and environmental obligations — The Company makes judgments and estimates in accordance with applicable accounting rules when it establishes reserves for legal proceedings, claims, investigations, environmental obligations and other contingent matters. Provisions for such matters are charged to expense when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and reasonable estimates of the liability can be made. Estimates of environmental liabilities are based on a variety of matters, including, but not limited to, the stage of investigation, the stage of the remedial design, evaluation of existing remediation technologies, and presently enacted laws and
F-9
regulations. The amount and timing of all future expenses related to legal proceedings, claims, investigations, environmental obligations and other contingent matters may vary significantly from estimates.
Employer sponsored benefit plans — The Company recognizes the funded status of its domestic defined benefit pension plan. Net benefit obligations are calculated based on actuarial valuations using key assumptions related to discount rates, mortality rates and expected return on plan assets.
Derivative instruments — Derivative instruments are measured at fair value and recognized as either assets or liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheet in either current or non-current other assets or other accrued liabilities or other long-term liabilities depending upon maturity and commitment. For derivative instruments that are designated and qualify as a fair value hedge, the gain or loss on the derivative as well as the offsetting loss or gain on the hedged item attributable to the hedged risk are recognized in the Consolidated Statement of Operations. For derivative instruments that are designated and qualify as a cash flow hedge, the effective portion of the gain or loss on the derivative is reported as a component of other comprehensive income and reclassified into earnings in the same period or periods in which the hedge transaction affects earnings. In general, the types of risks being hedged by the Company are related to the variability of future cash flows caused by changes in foreign currency exchange rates and hedging the impact of variability of foreign exchange rates on recorded intercompany assets or liabilities. Lydall’s objective for entering into derivative instruments has always been for risk management purposes. The Company does not engage in derivative instruments for speculative purposes. Lydall has historically not been a party to a significant number of derivative instruments.
Revenue recognition — The Company recognizes revenue (1) once evidence of an arrangement exists; (2) product delivery has occurred; (3) pricing is fixed or determinable; and (4) collection is reasonably assured. The four criteria required to recognize revenue are considered to be met, and the passage of title to the customer occurs, at the respective FOB point and, therefore, revenue is recognized at that time. The Company’s standard sales and shipping terms are FOB shipping point, therefore, substantially all revenue is recognized upon shipment. However, the Company conducts business with certain customers on FOB destination terms and in these instances revenue is recognized upon receipt by the customer. The Company generally does not provide specific customer inspection or acceptance provisions in its sales terms, with the exception of tooling sales discussed in “Pre-production design and development costs” above.
Sales returns and allowances are recorded as identified or communicated by the customer and internally approved. The Company does not provide customers with general rights of return for products sold; however, in limited circumstances, the Company will allow sales returns and allowances from customers if the products sold do not conform to specifications.
Shipping and handling costs consist primarily of costs incurred to deliver products to customers and internal costs related to preparing products for shipment and are recorded in cost of sales. Amounts billed to customers as shipping and handling are classified as revenue.
Research and development — Research and development costs are charged to expense as incurred and amounted to $9.0 million in 2016, $8.5 million in 2015, and $9.0 million in 2014. Research and development costs were primarily comprised of development personnel salaries, prototype material costs and testing and trials of new products.
Earnings per share — Basic earnings per common share are equal to net income divided by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per common share are equal to net income divided by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period, including the effect of stock options and stock awards, if such effect is dilutive.
Income taxes — The provision for income taxes is based upon income reported in the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements. Deferred income taxes reflect the impact of temporary differences between the amounts of income and expense recognized for financial reporting purposes and such amounts recognized for tax purposes. In the event the Company was to determine that it would not be able to realize all or a portion of its deferred tax assets in the future, the Company would record a valuation allowance through a charge to income in the period that such determination was made. Conversely, if the Company was to determine that it would be able to realize its deferred tax assets in the future in excess of the net carrying amounts, the Company would decrease the recorded valuation allowance and record an increase to income in the period that such determination was made.
F-10
Translation of foreign currencies — Assets and liabilities of foreign subsidiaries are translated at exchange rates prevailing on the balance sheet date. Revenues and expenses are translated at average exchange rates prevailing during the period. Any resulting translation gains or losses are reported in other comprehensive income (loss).
Stock options and share grants — The Company accounts for awards of equity instruments under the fair value method of accounting and recognizes such amounts in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The Company recognizes expense on a straight-line basis over the vesting period of the entire award. Prior to January 1, 2016, stock-based compensation expense included estimated effects of forfeitures. Upon adoption of ASU 2016-09, Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting, in 2016, an accounting policy election was made to account for forfeitures as they occur. The Company estimates the fair value of option grants based on the Black Scholes option-pricing model. Expected volatility and expected term are based on historical information. The calculation assumes that future volatility and expected term are not likely to materially differ from the Company’s historical stock price volatility and historical exercise data, respectively. Compensation expense for all restricted stock awards is recorded based on the market value of the stock on the grant date and recognized as expense over the vesting period of the award. Compensation expense for performance-based restricted stock is also impacted by the probability of achieving the performance targets.
Recently Adopted Accounting Standards
Effective January 1, 2016, the Company adopted the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2014-12, “Compensation - Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Accounting for Share-Based Payments When the Terms of an Award Provide That a Performance Target Could be Achieved after the Requisite Service Period". This ASU affects entities that grant their employees share-based payments in which terms of the award provide that a performance target that affects vesting could be achieved after the requisite service period. The amendments in this ASU require that a performance target that affects vesting and that could be achieved after the requisite service period be treated as a performance condition. The adoption of this ASU did not have any impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
Effective January 1, 2016, the Company adopted ASU No. 2015-07, "Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosures for Investments in Certain Entities That Calculate Net Asset Value per Share (or Its Equivalent)". This ASU eliminates the requirement to categorize investments measured using the net asset value (NAV) practical expedient in the fair value hierarchy table. The adoption of this standard was applied retrospectively to the investments eligible for the NAV practical expedient. The adoption of the updates in ASU 2015-07 did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements other than the disclosure and presentation of certain investments of the Company’s pension plan that are measured using the NAV practical expedient. Refer to Note 8 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Effective January 1, 2016, the Company adopted ASU No. 2015-17, "Income Taxes (Topic 740): Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes". This ASU requires an entity to classify all deferred tax assets and liabilities, along with any related valuation allowance, as noncurrent on the balance sheet. The Company adopted this standard prospectively during the quarter ended March 31, 2016. The adoption of this standard resulted in the reclassification of $4.6 million from current deferred income tax assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheet as of March 31, 2016 to noncurrent deferred income tax assets. Prior periods were not retrospectively adjusted.
Effective January 1, 2016, the Company adopted ASU No. 2016-09, "Compensation - Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting". This ASU simplifies several aspects of the accounting for share-based payment transactions, including the income tax consequences, classification of awards as either equity or liabilities, classification on the statement of cash flows, and accounting for forfeitures. The Company adopted this accounting standard update in the first quarter of 2016. As a result of the adoption of this ASU, the Company recognized excess tax benefits from stock award exercises and vesting as a discrete tax benefit of $1.1 million during the year ended December 31, 2016. In addition, as a result of this change, excess tax benefits were excluded from the calculation of assumed proceeds in the Company’s calculation of diluted weighted shares. The Company applied these changes prospectively, and therefore prior periods have not been adjusted. As permitted by this ASU, the Company has made an accounting policy election to record forfeitures as they occur rather than estimating expected forfeitures and, as a result, the cumulative effect of this change in accounting principle of $0.1 million was recorded as an adjustment to retained earnings as of January 1, 2016. The ASU permits equity classification of awards for tax withholding up to the maximum individual tax rate in a given jurisdiction for the net settlement of an award. The Company is currently evaluating its policy on tax withholding for award net settlement.
F-11
Effective January 1, 2016, the Company adopted ASU No. 2015-16, “Business Combinations (Topic 805): Simplifying the Accounting for Measurement-Period Adjustments”. This ASU eliminates the requirement to restate prior period financial statements for measurement period adjustments. The amendments also require that the cumulative impact of a measurement period adjustment (including the impact on prior periods) be recognized in the reporting period in which the adjustment is identified. The adoption of this ASU did not have any impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
Effective December 31, 2016, the Company adopted ASU 2014-15, “Presentation of Financial Statements - Going Concern (Subtopic 205-40)”, which requires an evaluation every reporting period, including interim periods, of whether there is substantial doubt about an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern and provide certain footnote disclosures depending on the result of such evaluation. The adoption of this guidance did not have an impact on the consolidated financial position, results of operations, cash flows or related disclosures.
2. Acquisitions and Divestitures
Acquisitions
On December 31, 2016, the Company completed an acquisition of the nonwoven needle punch materials businesses, which include MGF Gutsche & Co GmbH KG, FRG and Gutsche Environmental Technology (Yixing) Co. Ltd., China, operating under Gutsche (“Gutsche”), a German based corporation. The Gutsche operations manufacture nonwoven needle punch materials and predominantly serve the industrial filtration and high performance nonwoven markets. The Company acquired one hundred percent of Gutsche for $57.6 million, net of a receivable of $3.0 million related to an estimated post-closing purchase price adjustment. The purchase price was financed with a combination of cash on hand and $31.6 million of borrowings through the Company's amended $175 million credit facility. The assets and liabilities of Gutsche have been included in the Consolidated Balance Sheet at December 31, 2016. The acquired businesses are included in the Company's Technical Nonwovens reporting segment.
On July 7, 2016, the Company completed an acquisition of the nonwoven and coating materials businesses primarily operating under Texel from ADS, a Canadian based corporation. The Texel operations manufacture nonwoven needle punch materials and predominantly serve the geosynthetic, liquid filtration, and other industrial markets. The Company acquired one hundred percent of Texel for $102.7 million in cash, including a post-closing working capital adjustment. The purchase price was financed with a combination of cash on hand and $85.0 million of borrowings through the Company’s amended $175 million credit facility. As part of the acquisition, the Company acquired a fifty percent interest in a joint venture, Afitex Texel Geosynthetiques, Inc., with a fair value of $0.6 million. The joint venture is accounted for under the equity method of accounting. The operating results of the Texel business have been included in the Consolidated Statements of Operations since July 7, 2016, the date of the acquisition and are reported within the Technical Nonwovens segment.
During the year ended December 31, 2016 the Company incurred $3.7 million of acquisition related costs, related to the acquisitions of Texel and Gutsche. These transaction costs include legal fees and other professional services fees to complete the transaction. These corporate office expenses have been recognized in the Company’s Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations as selling, product development and administrative expenses.
From the date of the acquisition through December 31, 2016, Texel reported net sales and operating income of $40.9 million and $2.5 million, respectively. Operating income from the date of the acquisition through the year ended December 31, 2016 included $2.0 million of purchase accounting inventory fair value step-up adjustments in cost of sales upon the sale of inventory. The total purchase accounting inventory fair value step-up adjustment included in the balance sheet at the acquisition date was $2.4 million. The Company did not report net sales or operating income for Gutsche as the acquisition took place on December 31, 2016.
On February 20, 2014, the Company completed the acquisition of certain industrial filtration businesses of Andrew Industries Limited, an Altham, United Kingdom based corporation. The Industrial Filtration business serves a global customer base in the manufacture of non-woven felt filtration media and filter bags used primarily in industrial air filtration applications including power, cement, asphalt, incineration, food and pharmaceutical. The Company acquired the Industrial Filtration business for $86.9 million in cash (including cash acquired of $7.5 million and a post-closing adjustment payment of $0.2 million to Andrew Industries Limited) and with no debt being acquired. The purchase price was financed with a combination of cash on hand and $60.0 million of borrowings through the Company’s amended $100 million credit facility.
F-12
Divestiture
On January 30, 2015, the Company sold all of the outstanding shares of common stock of its Life Sciences Vital Fluids business, reported as Other Products and Services, for a cash purchase price of $30.1 million. The disposition was completed pursuant to a Stock Purchase and Sale Agreement, dated January 30, 2015, by and among the Company, and the buyer. The Company recognized a pre-tax gain on the sale of $18.6 million, reported as non-operating income in the first quarter of 2015. Net of income taxes, the Company reported a gain on sale of $11.8 million.
In accordance with the revised accounting guidance for reporting discontinued operations, the Company did not report Life Sciences Vital Fluids as a discontinued operation as it would not be considered a strategic shift in Lydall's business. Accordingly, the operating results of Life Sciences Vital Fluids are included in the operating results of the Company through the sale date and in all periods presented in 2014.
The following table summarizes the fair values of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of the 2016 acquisitions:
In thousands | Texel | Gutsche | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 1,610 | $ | 9,400 | ||||
Accounts Receivable | 13,355 | 7,736 | ||||||
Inventories | 17,525 | 6,417 | ||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 2,469 | 1,125 | ||||||
Non-current environmental indemnification receivable (Note 12) | 925 | — | ||||||
Property, plant and equipment, net | 31,525 | 7,969 | ||||||
Investment in joint venture | 616 | — | ||||||
Goodwill (Note 5) | 28,655 | 19,331 | ||||||
Other intangible assets, net (Note 5) | 22,887 | 15,622 | ||||||
Other long-term assets | — | 1,545 | ||||||
Total assets acquired | 119,567 | 69,145 | ||||||
Current liabilities | (8,520 | ) | (8,376 | ) | ||||
Long-term environmental remediation liability (Note 12) | (925 | ) | — | |||||
Other long-term liabilities | — | (2,742 | ) | |||||
Deferred tax liabilities | (7,413 | ) | (470 | ) | ||||
Total liabilities assumed | (16,858 | ) | (11,588 | ) | ||||
Net assets acquired | $ | 102,709 | $ | 57,557 | ||||
The final purchase price allocation related to Texel reflects post-closing adjustments pursuant to the terms of the Stock Purchase Agreement. The final purchase price allocation for Gutsche remains subject to post-closing adjustments pursuant to the terms of the Share Purchase Agreement.
The following table reflects the unaudited pro forma operating results of the Company for years ended December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, which give effect to the acquisitions of Texel and Gutsche as if they had occurred on January 1, 2015. The pro forma information includes the historical financial results of the Company and the acquired businesses. The pro forma results are not necessarily indicative of the operating results that would have occurred had the acquisition been effective January 1, 2015, nor are they intended to be indicative of results that may occur in the future. The pro forma information does not include the effects of any synergies related to the acquisitions.
F-13
(Unaudited Pro Forma) | ||||||||
For The Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Net Sales | $ | 654,877 | $ | 651,252 | ||||
Net Income | $ | 43,559 | $ | 47,956 | ||||
Earnings per share: | ||||||||
Basic | $ | 2.58 | $ | 2.86 | ||||
Diluted | $ | 2.53 | $ | 2.81 | ||||
Pro forma earnings during the year ended December 31, 2016 were adjusted to exclude non-recurring items such as acquisition-related costs of $4.3 million and expense related to the fair value adjustment to inventory of $2.0 million. No amount was included in the pro forma earnings during the year ended December 31, 2016 related to inventory fair value adjustments which would have been recognized in cost of sales as the corresponding inventory would have been completely sold during 2015. Pro forma earnings during the year ended December 31, 2016 were adjusted to include additional expense of $3.9 million related to the amortization of the acquired intangible assets recognized at fair value in purchase accounting, additional depreciation expense of $1.2 million resulting from increased basis of property, plant and equipment, and additional interest expense of $0.8 million associated with borrowings under the Company’s Amended Credit Facility. Customer freight billings of $0.9 million were reclassed from costs of sales to net sales for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Pro forma earnings during the year ended December 31, 2015 were adjusted to include acquisition-related costs of $0.8 million, expense of $3.2 million related to the amortization of the fair value adjustments to inventory, $3.5 million of additional amortization of the acquired intangible assets recognized at fair value in purchase accounting, additional depreciation expense of $2.1 million resulting from increased basis of property, plant and equipment, as well as $1.2 million of interest expense associated with borrowings under the Company’s Amended Credit Facility. Customer freight billings of $1.6 million were reclassed from costs of sales to net sales for the year ended December 31, 2015.
3. Inventories
Inventories as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 were as follows:
December 31, | |||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | |||||
Raw materials | $ | 24,518 | $ | 17,128 | |||
Work in process | 17,161 | 14,670 | |||||
Finished goods | 25,360 | 15,048 | |||||
67,039 | 46,846 | ||||||
Less: Progress billings | (893 | ) | (316 | ) | |||
Total inventories | $ | 66,146 | $ | 46,530 | |||
Included in work in process is gross tooling inventory of $10.3 million and $9.5 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Tooling inventory, net of progress billings, was $9.4 million and $9.2 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
F-14
4. Property, Plant and Equipment, Net
Property, plant and equipment as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 were as follows:
Estimated Useful Lives | December 31, | ||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Land | – | $ | 3,981 | $ | 2,636 | ||||
Buildings and improvements | 10-35 years | 74,397 | 55,887 | ||||||
Machinery and equipment | 5-25 years | 226,675 | 195,125 | ||||||
Office equipment | 2-8 years | 31,504 | 30,622 | ||||||
Vehicles | 3-6 years | 1,553 | 864 | ||||||
Assets under capital leases: | |||||||||
Land | – | 226 | 546 | ||||||
Buildings and improvements | 10-35 years | 4,806 | 4,798 | ||||||
343,142 | 290,478 | ||||||||
Accumulated depreciation | (196,251 | ) | (185,356 | ) | |||||
Accumulated amortization of capital leases | (2,915 | ) | (2,829 | ) | |||||
143,976 | 102,293 | ||||||||
Construction in progress | 16,819 | 12,140 | |||||||
Total property, plant and equipment, net | $ | 160,795 | $ | 114,433 | |||||
Depreciation expense was $17.8 million in 2016, $16.4 million in 2015, and $16.7 million in 2014.
5. Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Gross and net carrying amounts of goodwill at December 31, 2016 and 2015 were as follows:
In thousands | Performance Materials | Technical Nonwovens | Thermal/ Acoustical Metals | Totals | |||||||||||
Goodwill | $ | 12,898 | $ | 3,943 | $ | 12,160 | $ | 29,001 | |||||||
Accumulated amortization/impairment | — | — | (12,160 | ) | (12,160 | ) | |||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2015 | 12,898 | 3,943 | — | 16,841 | |||||||||||
Goodwill | 12,777 | 50,829 | 12,160 | 75,766 | |||||||||||
Accumulated amortization/impairment | — | — | (12,160 | ) | (12,160 | ) | |||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2016 | $ | 12,777 | $ | 50,829 | $ | — | $ | 63,606 | |||||||
The changes in the carrying amounts of goodwill in 2015 and 2016 were as follows:
In thousands | Performance Materials | Technical Nonwovens | Other Products and Services | Totals | |||||||||||
Balance at January 1, 2014 | $ | 13,340 | $ | 3,943 | $ | 4,660 | $ | 21,943 | |||||||
Goodwill adjustment | — | — | (4,660 | ) | (4,660 | ) | |||||||||
Currency translation adjustment | (442 | ) | — | — | (442 | ) | |||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2015 | 12,898 | 3,943 | — | 16,841 | |||||||||||
Goodwill addition | — | 47,987 | — | 47,987 | |||||||||||
Currency translation adjustment | (121 | ) | (1,101 | ) | — | (1,222 | ) | ||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2016 | $ | 12,777 | $ | 50,829 | $ | — | $ | 63,606 | |||||||
F-15
Goodwill Associated with Acquisitions and Divestitures
The goodwill addition of $48.0 million in 2016 within the Technical Nonwovens segment results from the acquisitions of Texel on July 7, 2016 and Gutsche on December 31, 2016. The amount allocated to goodwill is reflective of the benefits the Company expects to realize from its entrance into the geosynthetic market, expansion in the liquid filtration and other industrial markets and Texel's and Gutsche's assembled workforce. None of the goodwill associated with the Texel acquisition is expected to be deductible for income tax purposes. Of the $19.3 million of goodwill associated with the Gutsche acquisition at December 31, 2016, $16.3 million is expected to be deductible for income tax purposes.
The goodwill adjustment in 2015 associated with Other Products and Services of $4.7 million was the result of the sale of the Company's Life Sciences Vital Fluids business on January 30, 2015.
Goodwill Impairment Testing
During the fourth quarter of 2016, the Company performed its annual impairment analysis of the $12.8 million of goodwill in the Performance Materials reporting unit (PM reporting unit) and $50.8 million in the Technical Nonwovens reporting unit. The Company used the qualitative method to analyze the goodwill for the Performance Materials and Technical Nonwovens reporting units. When considering capital markets environment, economic conditions, industry trends, results of operations, and other factors, the Company determined that it is not more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit was less than its carrying amount. For the Performance Materials reporting unit the Company also considered changes in assumptions used in the Company's most recent quantitative annual testing, including results of operations, the magnitude of excess of fair value over carrying value and other factors. As a result, the Company concluded that the Performance Materials and Technical Nonwovens reporting unit goodwill was not impaired.
Other Intangible Assets
The table below presents the gross carrying amount and, as applicable, the accumulated amortization of the Company’s acquired intangible assets other than goodwill included in “Other intangible assets, net” in the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2016 and 2015:
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||
In thousands | Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | ||||||||||||
Amortized intangible assets | ||||||||||||||||
Customer relationships | $ | 36,131 | $ | (1,284 | ) | $ | 2,412 | $ | (411 | ) | ||||||
Patents | 4,028 | (3,300 | ) | 4,137 | (3,272 | ) | ||||||||||
Technology | 2,500 | (477 | ) | 2,500 | (310 | ) | ||||||||||
Trade names | 3,912 | (394 | ) | 220 | (82 | ) | ||||||||||
License agreements | 583 | (583 | ) | 771 | (771 | ) | ||||||||||
Other | 536 | (205 | ) | 392 | (187 | ) | ||||||||||
Total amortized intangible assets | $ | 47,690 | $ | (6,243 | ) | $ | 10,432 | $ | (5,033 | ) | ||||||
In connection with the acquisition of Texel on July 7, 2016, the Company recorded intangible assets of $22.9 million, which included $20.8 million of customer relationships and $2.1 million of trade names. As of December 31, 2016, the weighted average useful lives of the acquired assets were 14 years and 5 years, respectively.
In connection with the acquisition of Gutsche on December 31, 2016, the Company recorded intangible assets of $15.6 million, which included $13.8 million of customer relationships, $1.7 million of trade names and $0.1 million of backlog. As of December 31, 2016, the weighted average useful lives of the acquired assets were 13 years, 5 years and 1 year, respectively.
Amortization of all intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 was $1.5 million, $0.8 million, and $0.9 million, respectively. Estimated amortization expense for intangible assets is expected to be $4.3 million, $5.5 million, $5.2 million, $4.9 million and $4.1 million for each of the years ending December 31, 2017 through 2021, respectively. As of December 31, 2016, the weighted average useful life of intangible assets was approximately 12 years.
F-16
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
During the first quarter of 2016, the Company performed an impairment analysis for long-lived assets Company’s DSM Solutech B.V. (“Solutech”) operation, included in the Performance Materials segment. In March 2016, the Solutech operation became aware of a reduction of demand with certain customers that impacted the outlook for both its Arioso and Solupor membrane product lines that prompted management to adjust its long term revenue projections. These events resulted in a net decrease in forecasted revenue and cash flows. Based on these events and combined with historical operating losses, the Company determined that it was appropriate to test the Solutech asset group for recoverability in the first quarter of 2016.
Patents, with a remaining useful life of approximately 8 years, and machinery and equipment primarily comprise the carrying value of the asset group of $1.9 million. To determine the recoverability of the Solutech asset group the Company completed an undiscounted cash flow analysis and compared it to the asset group carrying value. This analysis was primarily dependent on the expectations for net sales over the period when the business has technological exclusivity provided by its patents. Future cash flows are dependent on the success of commercialization efforts of Solutech products by OEMs, the quality of Solutech products and technology advancements and management’s ability to manage costs.
The impairment test performed at the end of the first quarter of 2016 concluded that the Solutech asset group was not recoverable as the resulting undiscounted cash flows were less than their carrying amount. Accordingly, in accordance with ASC 360 “Impairment of Long-Lived Assets,” the Company estimated the fair value of the Solutech long-lived assets and, based on these fair value estimates, determined that the long-lived assets were not impaired.
Determining fair value is judgmental in nature and requires the use of significant estimates and assumptions considered to be Level 3 inputs including royalty rates, long-term growth rates and discount rates. The fair value of the Solutech patents, was determined using the relief from royalty method, which is a form of the income approach that focused on the level of royalty payments that the user of an intangible asset would have to pay a third party for the use of the asset if it were not owned by the user. Under this approach, revenue associated with the associated technology was projected over the expected remaining useful life of the asset, with a royalty rate applied to the expected revenue. The estimated fair value of machinery and equipment was based on the cost approach. Under the cost approach, the determination of fair value considered the replacement cost of the assets with adjustments in value for physical deterioration, functional obsolescence, and economic obsolescence, all Level 3 inputs.
During the remainder of 2016, the Company continued to monitor the recoverability of the long-lived assets at the Solutech operation as a result of historical operating losses and negative cash flows. Future cash flows are dependent on the success of commercialization efforts of Solutech products by OEMs, and management’s ability to manage costs. A marginal reduction in expected future revenue or the inability to manage identified cost cutting measures could result in an impairment charge. In the event that Solutech's cash flows in the future do not meet current expectations, management, based upon conditions at the time, would consider taking actions as necessary to improve cash flow. A thorough analysis of all the facts and circumstances existing at the time would need to be performed to determine if recording an impairment loss was appropriate.
6. Long-term Debt and Financing Arrangements
On July 7, 2016, the Company amended its $100.0 million senior secured revolving credit facility (“Amended Credit Facility”) which increased the available borrowing from $100 million to $175 million, added a fourth lender and extended the maturity date to July 7, 2021. The Amended Credit Facility is secured by substantially all of the assets of the Company. Under the terms of the Amended Credit Facility, the lenders are providing a $175 million revolving credit facility to the Company, under which the lenders may make revolving loans and issue letters of credit to or for the benefit of the Company and its subsidiaries. The Company may request the Amended Credit Facility be increased by an aggregate amount not to exceed $50 million through an accordion feature, subject to specified conditions.
The Amended Credit Facility contains a number of affirmative and negative covenants, including financial and operational covenants. The Company is required to meet a minimum interest coverage ratio. The interest coverage ratio requires that, at the end of each fiscal quarter, the ratio of consolidated EBIT to Consolidated Interest Charges, both as defined in the Amended Credit Facility, may not be less than 2.0 to 1.0 for the immediately preceding 12 month period. In addition, the Company must maintain a Consolidated Leverage Ratio, as defined in the Amended Credit Facility, as of the end of each fiscal quarter of no greater than 3.0 to 1.0. The Company must also meet minimum
F-17
consolidated EBITDA as of the end of each fiscal quarter for the preceding 12 month period of $30.0 million. The Company was in compliance with all covenants during 2016 and at December 31, 2016.
Interest is charged on borrowings at the Company’s option of either: (i) Base Rate plus the Applicable Rate, or (ii) the Eurodollar Rate plus the Applicable Rate. The Base Rate is a fluctuating rate equal to the highest of (a) the federal funds rate plus 0.50%, (b) the prime rate as set by Bank of America, and (c) the Eurocurrency Rate plus 1.00%. The Eurocurrency Rate means (i) if denominated in LIBOR quoted currency, a fluctuating LIBOR per annum rate equal to the London Interbank Offered Rate; (ii) if denominated in Canadian Dollars, the rate per annum equal to the Canadian Dealer Offered Rate; or (iii) the rate per annum as designated with respect to such alternative currency at the time such alternative currency is approved by the Lenders. The Applicable Rate is determined based on the Company’s Consolidated Leverage Ratio (as defined in the Amended Credit Agreement). The Applicable Rate added to the Base Rate Committed Loans ranges from 15 basis points to 100 basis points, and the Applicable Rate added to Eurocurrency Rate Committed Loans and Letters of Credit ranges from 75 basis points to 175 basis points. The Company pays a quarterly fee ranging from 17.5 basis points to 30 basis points on the unused portion of the $175 million available under the Amended Credit Facility.
At December 31, 2016, the Company had borrowing availability of $44.6 million under the Amended Credit Facility net of $126.6 million of borrowings outstanding and standby letters of credit outstanding of $3.8 million. In addition to the amounts outstanding under the Amended Credit Facility, the Company has various acquired foreign credit facilities totaling approximately $10.5 million. At December 31, 2016, the Company's foreign subsidiaries had $1.4 million in borrowings outstanding as well as $2.3 million in standby letters of credit outstanding.
The Company had a capital lease agreement for the land and building at the St. Nazaire, France operating facility, included in the Thermal/Acoustical Metals segment, requiring monthly principal and interest payments through July 2016. The capital lease provided an option for the Company to purchase the land and building at the end of the lease for a nominal amount, which the Company exercised in the third quarter of 2016. The Company also has capital lease agreements for machinery and equipment at multiple operations requiring monthly principal and interest payments through 2020.
Total outstanding debt consists of:
December 31, | |||||||||||
In thousands | Effective Rate | Maturity | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Revolver Loan, due July 7, 2021 | 1.77% | 2021 | $ | 126,600 | $ | 20,000 | |||||
Commerzbank Loan, due January 2, 2017 | 3.40% | 2017 | 400 | — | |||||||
Sparkasse Loan, due December 31, 2024 | 0.80% | 2024 | 1,030 | — | |||||||
Capital Lease, land and building, St. Nazaire, France | 5.44% | 2016 | — | 277 | |||||||
Capital Lease, manufacturing equipment, Hamptonville, North Carolina | 1.65% | 2020 | 156 | 202 | |||||||
Capital Lease, manufacturing equipment, Fulda, Germany | 2.08% | 2019 | 409 | — | |||||||
Capital Lease, manufacturing equipment, Fulda, Germany | 2.09% | 2019 | 180 | — | |||||||
128,775 | 20,479 | ||||||||||
Less portion due within one year | (634 | ) | (323 | ) | |||||||
Total long-term debt | $ | 128,141 | $ | 20,156 | |||||||
As of December 31, 2016, total debt maturing in 2017, 2019, 2020, 2021 and 2024 is $0.4 million, $0.6 million, $0.2 million, $126.6 million, and $1.0 million, respectively.
The weighted average interest rate on long-term debt was 1.4% for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with 1.3% and 1.5% for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
The fair values of the Company’s long-term debt are determined using discounted cash flows based upon the Company’s estimated current interest cost for similar type borrowings or current market value, which falls under Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy. The carrying values of the long-term debt approximate fair market value.
F-18
7. Capital Stock
At the 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders in April 2015, the Company's stockholders approved an amendment to the Company's Restated Articles of Incorporation as detailed below:
Preferred Stock — The Company decreased the par value of its preferred stock from $1.00 to $0.01. None of the 500,000 authorized shares have been issued.
Common Stock — In 2015, the Company decreased the per share par value of its common stock from $0.10 to $0.01 which resulted in a reclassification of approximately $2.2 million from common stock to capital in excess of par value. As of December 31, 2016, 11,434 Lydall stockholders of record held 17,232,146 shares of Common Stock.
Dividend policy — The Company does not pay a cash dividend on its common stock. The Company’s Amended Credit Facility does not place any restrictions on cash dividend payments, so long as the payments do not place the Company in default.
8. Employer Sponsored Benefit Plan
The Company maintains a domestic defined benefit pension plan, which covers certain domestic Lydall employees, is noncontributory and benefits are based on either years of service or eligible compensation paid while a participant is in a plan. The plan has been closed to new employees for several years and benefits under the pension plan are no longer accruing. The Company’s funding policy for its domestic defined benefit pension plan is to fund not less than the ERISA minimum funding standard and not more than the maximum amount that can be deducted for federal income tax purposes.
Plan assets and benefit obligations of the domestic defined benefit pension plan are as follows:
December 31, | |||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | |||||
Change in benefit obligation: | |||||||
Net benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | 48,081 | $ | 50,827 | |||
Interest cost | 2,139 | 2,066 | |||||
Actuarial loss (gain) | 2,062 | (2,430 | ) | ||||
Gross benefits paid | (2,196 | ) | (2,382 | ) | |||
Net benefit obligation at end of year | $ | 50,086 | $ | 48,081 | |||
Change in plan assets: | |||||||
Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | $ | 35,413 | $ | 33,275 | |||
Actual return on plan assets | 221 | (1,106 | ) | ||||
Contributions | 3,600 | 5,626 | |||||
Gross benefits paid | (2,196 | ) | (2,382 | ) | |||
Fair value of plan assets at end of year | $ | 37,038 | $ | 35,413 | |||
Net benefit obligation in excess of plan assets | $ | (13,048 | ) | $ | (12,668 | ) | |
Balance sheet amounts: | |||||||
Noncurrent liabilities | $ | (13,048 | ) | $ | (12,668 | ) | |
Total liabilities | $ | (13,048 | ) | $ | (12,668 | ) | |
Amounts recognized in accumulated other comprehensive income, net of tax consist of: | |||||||
Net actuarial loss | $ | 19,689 | $ | 17,313 | |||
Net amount recognized | $ | 19,689 | $ | 17,313 | |||
At December 31, 2016, in addition to the accrued benefit liability of $13.0 million recognized for the Company’s domestic defined benefit pension plan, the Company also had foreign regulatory labor agreements with an accrued benefit liability of $1.5 million and accumulated other comprehensive loss, net of tax, of $0.4 million. At December 31, 2015, in addition to the accrued benefit liability of $12.7 million recognized for the Company’s domestic defined benefit
F-19
pension plan, the Company also had an accrued benefit liability of $1.4 million and accumulated other comprehensive loss, net of tax, related to foreign regulatory labor agreements of $0.4 million.
The domestic defined benefit pension plan liability, net of tax, included in other comprehensive income increased by $2.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 and increased by $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. These changes are mainly due to changes in pension assumptions, primarily the discount rates.
Aggregated information for the domestic defined benefit pension plan with an accumulated benefit obligation in excess of plan assets is provided in the tables below:
December 31, | |||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | |||||
Projected benefit obligation | $ | 50,086 | $ | 48,081 | |||
Accumulated benefit obligation | $ | 50,086 | $ | 48,081 | |||
Fair value of plan assets | $ | 37,038 | $ | 35,413 | |||
Components of net periodic benefit cost for the domestic pension plan:
December 31, | |||||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Interest cost | $ | 2,139 | $ | 2,066 | $ | 2,348 | |||||
Expected return on plan assets | (2,419 | ) | (2,360 | ) | (2,798 | ) | |||||
Amortization of actuarial net loss | 933 | 897 | 725 | ||||||||
Pension settlement cost | — | — | 4,914 | ||||||||
Total net periodic benefit cost | $ | 653 | $ | 603 | $ | 5,189 | |||||
On April 1, 2014, the Company offered a voluntary one-time lump sum payment option to certain former U.S. employees who were vested defined benefit plan participants and not currently receiving monthly payments from the Company's domestic pension plan. This payout required a re-measurement of the domestic pension plan and a partial plan settlement charge, which resulted in a non-cash pre-tax loss of $4.9 million in net periodic pension benefit expense, which was recorded in selling, product development and administrative expenses in 2014, with an offset to accumulated other comprehensive loss in shareholder’s equity, net of $1.9 million tax benefit. The non-cash charge was required to accelerate the recognition of a portion of the previously unrecognized actuarial losses in the domestic pension plan.
It is estimated that $1.1 million of actuarial net loss will be amortized from accumulated other comprehensive loss into net periodic benefit costs for the domestic pension plan in 2017.
The major assumptions used in determining the year-end benefit obligation and annual net cost for the domestic pension plan are presented in the following table:
Benefit Obligation | Net Cost | |||||||||||||
For the years ended December 31, | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
Discount rate | 4.21 | % | 4.56 | % | 4.56 | % | 4.16 | % | 5.09 | % | ||||
Expected return on plan assets | 6.30 | % | 7.00 | % | 7.00 | % | 7.25 | % | 7.25 | % | ||||
Plan Assets
The domestic defined benefit pension plan is administered by an Administrative Committee and an Investment Committee, which are appointed by the Board of Directors. The Investment Committee’s responsibilities are to establish a funding policy for the Lydall Pooled Pension Investment Trust (“the Trust”) and to appoint and oversee the investment advisors responsible for the Trust’s investments. The Investment Committee is a named fiduciary under the plan with respect to management of the Trust’s investments. The assets of the domestic defined benefit pension plan are invested in the Trust for the purpose of investment diversification. In determining the expected return on plan assets, the Investment Committee considers the relative weighting of plan assets, the historical performance of marketable debt and equity securities and economic and other indicators of future performance.
F-20
Investment management objectives include maintaining an adequate level of diversification to balance market risk and to provide sufficient liquidity for near-term payments of benefits accrued under the domestic pension plan and to pay the expenses of administration. The long-term investment objective of the Trust is to achieve a total return equal to or greater than the Trust’s actuarially assumed rate of return, currently 6.30%. Though it is the intent of the Investment Committee to achieve income and growth, that intent does not include taking extraordinary risks or engaging in investment activities not commonly considered prudent under the standards imposed by ERISA. The Investment Committee defines risk as the probability of not meeting the Trust’s objectives and the probability of not meeting the Trust’s liability requirements. The allowable investments include: securities, mutual funds, sub-advisers, independent investment managers and/or programs, and cash or cash equivalents. Prohibited investments include: single strategy hedge funds, investment in individual securities, direct investment in venture capital, CMO derivatives and commodities.
The Investment Committee’s target asset allocation seeks to control risk through portfolio diversification and takes into account, among other factors, objectives discussed above, current funding levels, cash flow conditions and economic and industry trends. In developing strategic asset allocation guidelines for the portfolio, an emphasis was placed on the long-term characteristics of individual asset classes, and the benefits of diversification among multiple asset classes. Investment decisions are based on the returns and risk relative to the Plan's liabilities, an approach commonly referred to as liability-driven investing. This approach does not preclude taking risk; instead, it reframes risk from a total-return framework to one mindful of liability-driven investing as the funded status of the domestic defined benefit pension plan improves.
The following table presents the target allocation of pension plan assets for 2017 and the actual allocation of plan assets as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 by major asset category:
Target Allocation | Actual Allocation of Plan Assets December 31, | ||||||
Asset Category | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||
Domestic equities | 25% - 35% | 30 | % | 42 | % | ||
International equities | 25% - 35% | 30 | % | 27 | % | ||
Fixed income | 25% - 35% | 28 | % | 28 | % | ||
Hedge fund of funds | 5% - 15% | 10 | % | — | % | ||
Real estate investment trusts | 0% | — | % | — | % | ||
Cash and cash equivalents | 0% - 5% | 2 | % | 3 | % | ||
Domestic and international equities consist primarily of mutual funds valued at the closing price reported in the active market in which individual securities are traded. Equity securities include investments in domestic and international mutual funds with a blend of small, mid and large cap investments. Emerging market equities are to comprise no more than 25% of the international equities allocation. Equity securities held by the Trust are publicly traded in active markets and are classified within Level 1 of the fair value hierarchy.
Fixed income consists of long duration fixed income held in proprietary funds pooled with other investor accounts which use the net asset value (NAV) per share practical expedient to measure fair value. The total nets assets of the fund are calculated at the close of trading by the fund’s custodian. The net asset value per share is calculated by dividing the total net assets of the fund by the number of units outstanding on the valuation date. Such investments are not classified in the fair value hierarchy. Fixed income investments provide a moderate return and are aligned with the interest rate risk of the Plan's obligations.
Hedge funds are pooled funds that employ a range of investment strategies including equity and fixed income, credit driven, macro and multi oriented strategies. The hedge funds are measured at fair value the NAV practical expedient and are not classified in the fair value hierarchy. Generally, underlying investments held by the Funds which are publicly traded are valued at their current observable market values. Other investments are valued using procedures established by the portfolio manager. Hedge funds are incorporated to diversify the portfolio and to diminish equity volatility.
Cash and cash equivalents include investments readily converted to cash valued in the active market in which the funds were traded and are classified within Level 1 of the fair value hierarchy.
F-21
The investments of the Trust are stated at fair value. Fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. The asset’s fair value measurement level within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of any input that is significant to the fair value measurement. Valuation techniques used need to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The framework for measuring fair value provides a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value. The hierarchy gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1 measurements) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3 measurements). Effective December 31, 2016, the Company adopted ASU No. 2015-07, “Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosures for Investments in Certain Entities That Calculate Net Asset Value per Share”, which removed from the fair value hierarchy, investments for which the practical expedient is used to measure fair value at NAV. The fixed income long duration fund and the hedge fund of funds were measured at fair value using the NAV practical expedient and are included as a reconciling item to the fair value table.
The following tables set forth the fair value of the Trust’s assets by major asset category as of December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015:
December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||
In thousands | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Measured at NAV | Total | |||||||||||||
Domestic equity | $ | 10,964 | $ | — | $ | — | — | $ | 10,964 | |||||||||
International equity | 10,944 | — | — | — | 10,944 | |||||||||||||
Fixed income | — | — | — | 10,499 | 10,499 | |||||||||||||
Hedge fund of funds | — | — | — | 3,863 | 3,863 | |||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | 768 | — | — | — | 768 | |||||||||||||
Total Assets at Fair Value | $ | 22,676 | $ | — | $ | — | 14,362 | $ | 37,038 | |||||||||
December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||
In thousands | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Measured at NAV | Total | |||||||||||||
Domestic equity | $ | 14,789 | $ | — | $ | — | — | $ | 14,789 | |||||||||
International equity | 9,383 | — | — | — | 9,383 | |||||||||||||
Fixed income | 9,949 | — | — | — | 9,949 | |||||||||||||
Real estate investment trusts | 195 | — | — | — | 195 | |||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | 1,097 | — | — | — | 1,097 | |||||||||||||
Total Assets at Fair Value | $ | 35,413 | $ | — | $ | — | — | $ | 35,413 | |||||||||
Estimated Future Contributions and Benefit Payments
The Company expects to contribute approximately $3.0 million to $4.0 million in cash to its domestic defined benefit pension plan in 2017. Estimated future benefit payments for the next 10 years are as follows:
In thousands | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022-2026 | |||||||||||||||||
Benefit payments | $ | 2,422 | $ | 2,500 | $ | 2,632 | $ | 2,773 | $ | 2,856 | $ | 14,742 | |||||||||||
Employee Savings Plan
The Company also sponsors a 401(k) Plan. Employer contributions to this plan amounted to $2.5 million in 2016, $2.3 million in 2015, and $2.1 million in 2014. Matching contributions by the Company are made on employee pretax contributions up to five percent of compensation, with the first three percent matched at 100% and the next two percent matched at 50%.
F-22
9. Equity Compensation Plans
As of December 31, 2016, the Company’s equity compensation plans consisted of the 2003 Stock Incentive Compensation Plan (the “2003 Plan”) and the 2012 Stock Incentive Plan (the “2012 Plan” and together with the 2003 Plan, the “Plans”) under which incentive and non-qualified stock options and time and performance based restricted shares have been granted to employees and directors from authorized but unissued shares of common stock or treasury shares. The 2003 Plan is not active, but continues to govern all outstanding awards granted under the plan until the awards themselves are exercised or terminate in accordance with their terms. The 2012 Plan, approved by stockholders on April 27, 2012, authorized 1,750,000 shares of common stock for awards. The 2012 Plan also authorizes an additional 1,200,000 shares of common stock to the extent awards granted under prior stock plans that were outstanding as of April 27, 2012 are forfeited. The 2012 Plan provides for the following type of awards: options, restricted stock, restricted stock units and other stock-based awards.
The Company accounts for the expense of all share-based compensation by measuring the awards at fair value on the date of grant. The Company recognizes expense on a straight-line basis over the vesting period of the entire award. Options issued by the Company under its stock option plans have a term of ten years and generally vest ratably over a period of three to four years. Time-based restricted stock grants are expensed over the vesting period of the award, which is typically two to four years. The number of performance based restricted shares that vest or forfeit depend upon achievement of certain targets during the performance period. Prior to January 1, 2016, stock-based compensation expense included estimated effects of forfeitures. Upon adoption of ASU 2016-09, Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting, in 2016, an accounting policy election was made to account for forfeitures as they occur. Compensation expense for performance based awards is recorded based upon the service period and management’s assessment of the probability of achieving the performance goals and will be adjusted based upon actual achievement. Stock options issued under the current plan must have an exercise price that may not be less than the fair market value of the Company’s Common Stock on the date of grant. The Plans provide for automatic acceleration of vesting in the event of a change in control of the Company. Upon the exercise of a stock option under the Plans, shares are issued from authorized shares or treasury shares held by the Company.
The Company incurred compensation expense of $4.4 million, $2.8 million, and $2.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively, for all stock-based compensation plans, including restricted stock awards. No compensation costs were capitalized as part of inventory. The associated tax benefit realized was $1.9 million, $1.5 million, and $2.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively.
Stock Options
The fair value of each option granted was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following weighted-average assumptions for the years ended December 31:
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Risk-free interest rate | 1.8 | % | 1.8 | % | 1.6 | % | ||
Expected life | 5.5 years | 5.5 years | 5.1 years | |||||
Expected volatility | 42 | % | 43 | % | 46 | % | ||
Expected dividend yield | — | % | — | % | — | % | ||
F-23
The following is a summary of the option activity as of December 31, 2016 and changes during the year then ended:
In thousands except per share amounts and years | |||||||||||
Shares | Weighted-Average Exercise Price | Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Term (years) | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | ||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2015 | 463 | $ | 20.15 | ||||||||
Granted | 57 | $ | 52.22 | ||||||||
Exercised | (76) | $ | 15.18 | ||||||||
Forfeited/Cancelled | (17) | $ | 19.31 | ||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2016 | 427 | $ | 25.32 | 6.9 | $ | 15,694 | |||||
Options exercisable at December 31, 2016 | 240 | $ | 15.66 | 5.5 | $ | 11,097 | |||||
Unvested at December 31, 2016 | 187 | $ | 37.74 | 8.8 | $ | 4,597 | |||||
The Company granted 56,580, 91,900, and 131,800 stock options during 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively. The weighted-average grant-date fair value of options granted during the years 2016, 2015, and 2014 was $21.11, $15.28, and $11.85, respectively. There were 76,333 options exercised in 2016, 166,175 options exercised in 2015, and 277,006 options exercised in 2014. The intrinsic value for options exercised during 2016 was $2.4 million and the associated tax benefit realized from stock options exercised was $0.7 million. The total intrinsic value for options exercised during 2015 was $3.5 million and the associated tax benefit realized from stock options exercised was $1.1 million. The total intrinsic value for options exercised during 2014 was $5.0 million and the associated tax benefit realized from stock options exercised was $1.8 million. The amount of cash received from the exercise of stock options was $1.2 million in 2016, $1.5 million in 2015, and $2.5 million in 2014. At December 31, 2016, the total unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested stock option awards was approximately $2.8 million, with a weighted average expected amortization period of 3.0 years.
Restricted Stock
The following is a summary of the Company’s unvested restricted shares for the year ended and as of December 31, 2016:
In thousands except per share amounts | |||||
Outstanding Restricted Shares | Shares | Weighted-Average Grant-Date Fair Value | |||
Nonvested at December 31, 2015 | 343 | $ | 24.01 | ||
Granted | 84 | $ | 49.70 | ||
Vested | (98) | $ | 16.96 | ||
Forfeited/Cancelled | (33) | $ | 20.92 | ||
Nonvested December 31, 2016 | 296 | $ | 34.01 | ||
Restricted stock includes both performance-based and time-based awards. Compensation for restricted stock is recorded based on the market value of the stock on the grant date and amortized to expense over the vesting period of the award. The Company granted 44,423, 38,170, and 204,800 shares of performance-based restricted stock during 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively. The Company granted 31,455 shares of time-based restricted stock in 2016, 33,755 shares in 2015, and 48,649 in 2014. The Company granted 8,570 time-based restricted stock units in 2016. The weighted average fair value per share of restricted stock granted was $49.70, $34.09, and $22.93 during 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively. During 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively, there were 33,800, 147,187 and 6,212 shares of restricted stock forfeited. The fair value of awards for which restrictions lapsed during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 was $3.4 million, $1.4 million, and $2.2 million, respectively. At December 31, 2016, the total unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested restricted stock awards was approximately $5.8 million, with a weighted average expected amortization period of 2.4 years.
F-24
Stock Repurchases
During the year ended December 31, 2016, the Company acquired 34,068 shares of common stock valued at $1.2 million, through withholding, pursuant to provisions in agreements with recipients of restricted stock granted under the Company's equity compensation plans, which allow the Company to withhold the number of shares having fair value equal to each recipient's tax withholding due.
10. Segment Information
On December 31, 2016, the Company completed an acquisition of the nonwoven needle punch materials businesses, which include MGF Gutsche & Co GmbH KG, FRG and Gutsche Environmental Technology (Yixing) Co. Ltd., China, operating under Gutsche (“Gutsche”), a German based corporation. The Gutsche operations manufacture nonwoven needle punch materials and predominantly serve the industrial filtration and high performance nonwoven markets. The acquired businesses are included in the Company's Technical Nonwovens reporting segment.
On July 7, 2016, the Company completed an acquisition of the nonwoven and coating materials businesses primarily operating under the Texel brand (“Texel”) from ADS, Inc. (“ADS”), a Canadian based corporation. The Texel operations manufacture nonwoven needle punch materials and predominantly serve the geosynthetic, liquid filtration, and other industrial markets. The acquired businesses are included in the Company's Technical Nonwovens reporting segment.
On February 20, 2014, the Company acquired the Industrial Filtration business from Andrew Industries Limited, which is being reported as a separate reportable segment (now known as Technical Nonwovens) since the acquisition date. Segment information is consistent with how management reviews the businesses, makes investing and resource allocation decisions and assesses operating performance.
The Company’s reportable segments are Performance Materials, Technical Nonwovens, Thermal/Acoustical Metals, and Thermal/Acoustical Fibers. Other Products and Services (“OPS”) included Life Sciences Vital Fluids, which was sold on January 30, 2015.
Performance Materials Segment
The Performance Materials segment includes filtration media solutions primarily for air, fluid power, and industrial applications (“Filtration”), thermal insulation solutions for building products, appliances, and energy and industrial markets (“Thermal Insulation”) and air and liquid life science applications (“Life Sciences Filtration”). Filtration products include LydAir® MG (Micro-Glass) Air Filtration Media, LydAir® MB (Melt Blown) Air Filtration Media, LydAir® SC (Synthetic Composite) Air Filtration Media, and Arioso™ Membrane Composite Media. These products constitute the critical media component of clean-air systems for applications in clean-space, commercial, industrial and residential HVAC, power generation, and industrial processes. Lydall has leveraged its extensive technical expertise and applications knowledge into a suite of media products covering the vast liquid filtration landscape across the engine and industrial fields. The LyPore® Liquid Filtration Media series address a variety of application needs in fluid power including hydraulic filters, air-water and air-oil coalescing, industrial fluid processes and diesel fuel filtration.
Thermal Insulation products are high performance nonwoven veils, papers, mats and specialty composites for the building products, appliance, and energy and industrial markets. The Manniglas® Thermal Insulation brand is diverse in its product application ranging from high temperature seals and gaskets in ovens and ranges to specialty veils for HVAC and cavity wall insulation. The appLY® Mat Needled Glass Mats have been developed to expand Lydall’s high temperature technology portfolio for broad application into the appliance market and supplements the Lytherm® Insulation Media product brand, traditionally utilized in the industrial market for kilns and furnaces used in metal processing. Lydall’s Cryotherm® Super-Insulating Media, CRS-Wrap® Super-Insulating Media and Cryo-Lite™ Cryogenic Insulation products are industry standards for state-of-the-art cryogenic insulation designs used by manufacturers of cryogenic equipment for liquid gas storage, piping, and transportation.
Life Sciences is comprised of products which have been designed to meet the stringent requirements of critical applications including biopharmaceutical pre-filtration and clarification, lateral flow diagnostic and analytical testing, respiratory protection, potable water filtration and high purity process filtration such as that found in food and beverage and medical applications. Lydall also offers ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene membranes under the Solupor® trade name. These specialty microporous membranes are utilized in various markets and applications including air and liquid filtration and transdermal drug delivery. Solupor® membranes incorporate a unique combination of high
F-25
mechanical strength, chemical inertness, gamma stability and very high porosity making them ideal for many applications.
Technical Nonwovens Segment
The Technical Nonwovens segment primarily produces needle punch nonwoven solutions for myriad industries and applications. Products are manufactured and sold globally under the leading brands of Lydall Industrial Filtration, Southern Felt, Gutsche, and Texel. The Industrial Filtration products include nonwoven rolled-good felt media and filter bags used primarily in industrial air and liquid filtration applications. Nonwoven filter media is the most effective solution to satisfy increasing emission control regulations in a wide range of industries, including power, cement, steel, asphalt, incineration, mining, food, and pharmaceutical. The Advanced Materials products include nonwoven rolled-good media used in commercial applications and predominantly serves the geosynthetics, automotive, industrial,medical, and safety apparel markets. The automotive media is provided to Tier I/II suppliers and as well as the Company's Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment.
Technical Nonwovens segment products include air and liquid filtration media sold under the brand names Fiberlox® high performance filtration felts, Checkstatic™ conductive filtration felts, Microfelt® high efficiency filtration felts, Pleatlox® pleatable filtration felts, Ultratech™ PTFE filtration felts, Powertech® and Powerlox® power generation filtration felts, Microcap® high efficiency liquid filtration felts, Duotech membrane composite filtration felts, along with our porotex® family of high temperature filtration felts including microvel® and optivel® products. Technical Nonwovens Advanced Materials products are sold under the brand names Thermofit® thermo-formable products, Ecoduo® recycled content materials, Duotex® floor protection products, and Versaflex® composite molding materials. Technical Nonwovens also offers extensive finishing and coating capabilities which provide custom engineered properties tailored to meet the most demanding applications. The business leverages a wide range of fiber types and extensive technical capabilities to provide products that meet our customers’ needs across a variety of applications providing both high performance and durability.
Thermal/Acoustical Metals Segment
The Thermal/Acoustical Metals segment offers a full range of innovative engineered products tailored for the transportation sector to thermally shield sensitive components from high heat, improve exhaust gas treatment and lower harmful emissions as well as assist in the reduction of powertrain and road noise. Lydall products are found in the underbody (tunnel, fuel tank, rear muffler, spare tire) and underhood (outer dash, powertrain, catalytic converter, turbo charger, manifolds) of cars, trucks, SUVs, heavy duty trucks and recreational vehicles.
Thermal/Acoustical Metals segment products are formed on production lines capable of efficiently combining multiple layers of metal and thermal - acoustical insulation media to provide an engineered thermal and acoustical shielding solution for an array of application areas in the global automotive and truck markets. The flux® product family in Thermal/Acoustical Metals includes several patented or IP-rich products that address applications which include: Direct Exhaust Mount heat shields, which are assembled to high temperature components like catalytic converters, turbochargers or exhaust manifolds using aluminized and stainless steel high performance and high temperature heat insulating materials; Powertrain heat shields that absorb noise at the source and do not contribute to the engines noise; and durable, thermally robust solutions for temperature sensitive plastic components such as fuel tanks that are in proximity to high temperature heat sources.
Thermal/Acoustical Fibers Segment
The Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment offers innovative engineered products to assist primarily in noise vibration and harshness (NVH) abatement within the transportation sector. Lydall products are found in the interior (dash insulators, cabin flooring), underbody (wheel well, aerodynamic belly pan, fuel tank, exhaust) and under hood (engine compartment) of cars, trucks, SUVs, heavy duty trucks and recreational vehicles.
Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment products offer thermal and acoustical insulating solutions comprised of organic and inorganic fiber composites for the automotive and truck markets primarily in North America. Lydall’s dBCore® is a lightweight acoustical composite that emphasizes absorption principles over heavy-mass type systems. Lydall’s dBLyte® is a high-performance acoustical barrier with sound absorption and blocking properties and can be used throughout a vehicle’s interior to minimize intrusive noise from an engine compartment and road. Lydall’s ZeroClearance® is an innovative thermal solution that utilizes an adhesive backing for attachment and is used to
F-26
protect vehicle components from excessive heat. Lydall’s specially engineered products provide a solution that provides weight reduction, superior noise suppression, and increased durability over conventional designs.
Thermal/Acoustical Metals segment and Thermal/Acoustical Fibers segment operating results include allocations of certain costs shared between the segments.
Other Products and Services
The Life Sciences Vital Fluids business offered specialty products for blood filtration devices, blood transfusion single-use containers and the design and manufacture of single-use solutions for cell growth, frozen storage and fluid handling, as well as equipment for bioprocessing applications.
On January 30, 2015, the Company sold all of the outstanding shares of common stock of its Life Sciences Vital Fluids business for a cash purchase price of $30.1 million. The disposition was completed pursuant to a Stock Purchase and Sale Agreement, dated January 30, 2015, by and among the Company, and the buyer. The Company recognized an after-tax gain on the sale of this business of approximately $11.8 million in the first quarter of 2015.
Net sales by segment and for OPS, as well as reconciling items, to equal consolidated net sales for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 were as follows:
Consolidated Net Sales | For the Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Performance Materials Segment: | |||||||||||
Filtration | $ | 70,430 | $ | 62,716 | $ | 71,648 | |||||
Thermal Insulation | 27,783 | 28,311 | 31,404 | ||||||||
Life Sciences Filtration | 12,915 | 10,451 | 12,814 | ||||||||
Performance Materials Segment net sales | 111,128 | 101,478 | 115,866 | ||||||||
Technical Nonwovens Segment (1): | |||||||||||
Industrial Filtration | 90,415 | 113,044 | 92,721 | ||||||||
Advanced Materials (2) | 65,090 | 26,089 | 19,499 | ||||||||
Technical Nonwovens net sales | 155,505 | 139,133 | 112,220 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Metals Segment: | |||||||||||
Metal parts | 156,187 | 141,117 | 145,135 | ||||||||
Tooling | 18,787 | 19,815 | 19,130 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Metals Segment net sales | 174,974 | 160,932 | 164,265 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Fibers Segment: | |||||||||||
Fiber parts | 144,345 | 135,595 | 124,458 | ||||||||
Tooling | 5,067 | 3,152 | 4,133 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Fibers Segment net sales | 149,412 | 138,747 | 128,591 | ||||||||
Other Products and Services: | |||||||||||
Life Sciences Vital Fluids (3) | — | 1,671 | 19,682 | ||||||||
Other Products and Services net sales | — | 1,671 | 19,682 | ||||||||
Eliminations and Other (2) | (24,167 | ) | (17,456 | ) | (4,795 | ) | |||||
Consolidated Net Sales | $ | 566,852 | $ | 524,505 | $ | 535,829 | |||||
F-27
Operating income by segment and for OPS and Corporate Office Expenses for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 were as follows:
Operating Income | For the Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Performance Materials Segment | $ | 12,339 | $ | 6,790 | $ | 9,706 | |||||
Technical Nonwovens Segment (1) | 15,584 | 13,431 | 6,412 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Metals Segment | 11,562 | 15,517 | 13,823 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Fibers Segment | 41,452 | 37,086 | 29,167 | ||||||||
Other Products and Services (3) | — | 118 | 1,582 | ||||||||
Corporate Office Expenses | (26,145 | ) | (20,465 | ) | (26,642 | ) | |||||
Consolidated Operating Income | $ | 54,792 | $ | 52,477 | $ | 34,048 | |||||
Operating results in 2016 were negatively impacted by $3.7 million of acquisition related expenses within Corporate Office Expenses, $3.5 million related to a settlement with the German Cartel Office in the T/A Metals segment and a $2.0 million purchase accounting adjustment related to inventory step-up in the Technical Nonwovens segment. Operating results in 2015 were negatively impacted by a $1.4 million long-lived asset impairment charge within the Performance Materials segment and unfavorable foreign currency translation of $2.0 million impacting the Performance Materials, T/A Metals and Industrial Filtration segments. Operating results in 2014 were negatively impacted by $2.1 million of purchase accounting adjustments relating to inventory step-up for the Technical Nonwovens segment and a $2.9 million sales commission settlement within the T/A Metals segment. Corporate Office Expenses in 2014 were negatively impacted by a $4.9 million non-cash pension plan settlement charge and $2.6 million of transaction related costs.
Total assets by segment and for OPS and the Corporate Office were as follows at December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014:
Total Assets | December 31, | ||||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Performance Materials Segment | $ | 66,965 | $ | 66,706 | $ | 71,325 | |||||
Technical Nonwovens Segment (1),(4) | 268,104 | 89,566 | 100,201 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Metals Segment | 119,494 | 111,195 | 106,210 | ||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Fibers Segment | 47,097 | 38,881 | 33,109 | ||||||||
Other Products and Services (3) | — | — | 11,580 | ||||||||
Corporate Office | 25,369 | 51,912 | 39,345 | ||||||||
Total Assets | $ | 527,029 | $ | 358,260 | $ | 361,770 | |||||
Total capital expenditures and depreciation and amortization by segment and for OPS and the Corporate Office for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 were as follows:
Capital Expenditures | Depreciation and Amortization | ||||||||||||||||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||
Performance Materials Segment | $ | 4,098 | $ | 3,519 | $ | 4,124 | $ | 4,023 | $ | 4,499 | $ | 4,654 | |||||||||||
Technical Nonwovens Segment (1) | 1,248 | 968 | 1,804 | 6,778 | 4,996 | 4,536 | |||||||||||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Metals Segment | 15,425 | 11,494 | 8,544 | 5,094 | 4,233 | 4,578 | |||||||||||||||||
Thermal/Acoustical Fibers Segment | 6,899 | 4,807 | 3,296 | 2,570 | 2,400 | 2,166 | |||||||||||||||||
Other Products and Services (3) | — | 22 | 574 | — | 45 | 804 | |||||||||||||||||
Corporate Office | 489 | 745 | 659 | 1,094 | 1,102 | 908 | |||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 28,159 | $ | 21,555 | $ | 19,001 | $ | 19,559 | $ | 17,275 | $ | 17,646 | |||||||||||
F-28
Net sales by geographic area for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 and long-lived asset information by geographic area as of December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 were as follows:
Net Sales | Long-Lived Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||
United States (3) | $ | 354,371 | $ | 344,950 | $ | 345,864 | $ | 88,918 | $ | 76,502 | $ | 72,832 | |||||||||||
France | 52,042 | 47,495 | 52,534 | 12,692 | 12,899 | 13,861 | |||||||||||||||||
Germany (4) | 63,301 | 68,861 | 77,896 | 15,649 | 10,149 | 12,366 | |||||||||||||||||
United Kingdom | 23,871 | 26,598 | 26,387 | 4,903 | 6,399 | 7,601 | |||||||||||||||||
Canada (1) | 40,871 | — | — | 30,911 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
China (4) | 30,361 | 33,885 | 29,401 | 11,996 | 9,953 | 11,225 | |||||||||||||||||
Other | 2,035 | 2,716 | 3,747 | 1,301 | 815 | 795 | |||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 566,852 | $ | 524,505 | $ | 535,829 | $ | 166,370 | $ | 116,717 | $ | 118,680 | |||||||||||
(1) | Technical Nonwovens segment includes results of Texel for the period following the date of acquisition of July 7, 2016 through December 31, 2016. |
(2) | Included in the Technical Nonwovens segment and Eliminations and Other is $18.2 million, $13.8 million and $1.0 million of intercompany sales to the T/A Fibers segment for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. |
(3) | Other Products and Services reports results for the period preceding the date of disposition of the Vital Fluids Life Sciences business on January 30, 2015. |
(4) | Technical Nonwovens segment includes results of Gutsche as of acquisition date of December 31, 2016. |
Foreign sales are based on the country in which the sales originated (i.e., where the Company’s legal entity is domiciled). Sales to Ford Motor Company in 2016, 2015, and 2014 were $110.9 million, $95.4 million, and $88.4 million, respectively, and accounted for 19.6%, 18.2%, and 16.5% of Lydall’s net sales in the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively. These sales were reported in the Thermal/Acoustical Metal and Thermal/Acoustical Fiber segments. No other customers accounted for more than 10.0% of total net sales in 2016, 2015, and 2014.
11. Income Taxes
The provision for income taxes consists of the following:
For the years ended December 31, | |||||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Current: | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | 15,376 | $ | 18,291 | $ | 8,069 | |||||
State | 1,513 | 1,204 | 1,334 | ||||||||
Foreign | 2,104 | 1,684 | 3,883 | ||||||||
Total Current | 18,993 | 21,179 | 13,286 | ||||||||
Deferred: | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | (594 | ) | $ | 1,583 | $ | (42 | ) | |||
State | 601 | 1,696 | (1,626 | ) | |||||||
Foreign | (1,179 | ) | 306 | 191 | |||||||
Total Deferred | (1,172 | ) | 3,585 | (1,477 | ) | ||||||
Provision for income taxes | $ | 17,821 | $ | 24,764 | $ | 11,809 | |||||
F-29
The following is a reconciliation of the difference between the actual provision for income taxes and the provision computed by applying the federal statutory tax rate on earnings:
For the years ended December 31, | ||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Statutory federal income tax rate | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||
State income taxes | 2.1 | 2.9 | 0.8 | |||||
Valuation allowances for deferred tax assets, including state | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | |||||
Research and development credits | (1.2 | ) | (1.5 | ) | (0.5 | ) | ||
Capitalized transaction costs | 0.7 | — | 2.0 | |||||
Domestic production activities deduction | (2.7 | ) | (1.6 | ) | (2.6 | ) | ||
Stock based compensation | (2.1 | ) | (0.2 | ) | (0.1 | ) | ||
German Cartel settlement | 2.2 | — | — | |||||
Foreign income taxed at lower rates | (2.4 | ) | (1.3 | ) | (3.5 | ) | ||
Other | (0.5 | ) | 0.3 | 2.7 | ||||
Effective income tax rate | 32.4 | % | 34.9 | % | 35.1 | % | ||
In 2016, the effective tax rate of 32.4% was positively impacted by a favorable mix of taxable income generated from countries with lower tax rates compared to that of the United States, resulting in a tax benefit of $1.3 million. The Company also recorded a tax benefit of $1.5 million attributable to the Domestic Production Activities Deduction and a tax benefit of $1.1 million related to stock based compensation. These favorable adjustments were partially offset by tax expense of $1.2 million related to a nondeductible German Cartel settlement and a net increase in valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets of $0.7 million, primarily related to tax valuation allowances of $0.5 million recorded against certain net deferred tax assets in the Netherlands and China, as future realization of the assets is not reasonably assured.
In 2015, the effective tax rate of 34.9% was positively impacted by a favorable mix of taxable income generated from countries with lower tax rates compared to that of the United States, resulting in a tax benefit of $1.0 million. The Company also recorded a tax benefit of $1.2 million attributable to the Domestic Production Activities Deduction and a tax benefit of $1.1 million related to research and development credits. These favorable adjustments were partially offset by tax expense of $0.9 million related to a net increase in valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets and by a $0.6 million reduction to state deferred tax assets as a result of state tax law changes that led the Company to deem the asset unrealizable in future periods. The net increase in valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets of $0.9 million in 2015 was primarily related to tax valuation allowances of $0.8 million recorded against certain net deferred tax assets in the Netherlands and China, as future realization of the assets is not reasonably assured.
In 2014, the effective tax rate of 35.1% was positively impacted by a favorable mix of taxable income generated from countries with lower tax rates compared to that of the United States resulting in a tax benefit of $1.2 million and a tax benefit of $0.9 million attributable to the Domestic Production Activities Deduction. These favorable adjustments were partially offset by tax expense of $0.8 million related to nondeductible transaction costs from the Industrial Filtration acquisition, and a net increase in tax valuation allowances of $0.2 million.
The Company maintains valuation allowances against certain deferred tax assets where realization is not reasonably assured. The Company evaluates the likelihood of the realization of deferred tax assets and reduces the carrying amount to the extent it believes a portion will not be realized. The Company’s effective tax rates in future periods could be affected by earnings being lower or higher than anticipated in countries where tax rates differ from the United States federal rate, the relative impact of permanent tax adjustments on higher or lower earnings from domestic operations, changes in net deferred tax asset valuation allowances, completion of acquisitions or divestitures, changes in tax rates or tax laws and the outcome of tax audits.
F-30
The following schedule presents net current and net long-term deferred tax assets and liabilities by tax jurisdiction as of December 31, 2016 and 2015:
2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||
Deferred Tax Assets | Deferred Tax Assets | ||||||||||||||
In thousands | Current | Long-term | Current | Long-term | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 3,684 | $ | — | |||||||
State | — | — | 147 | 134 | |||||||||||
Foreign | — | 248 | 782 | — | |||||||||||
Totals | $ | — | $ | 248 | $ | 4,613 | $ | 134 | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||
Deferred Tax Liabilities | Deferred Tax Liabilities | ||||||||||||||
In thousands | Current | Long-term | Current | Long-term | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | — | $ | 7,705 | $ | — | $ | 12,504 | |||||||
State | — | 531 | — | — | |||||||||||
Foreign | — | 7,613 | — | 2,493 | |||||||||||
Totals | $ | — | $ | 15,849 | $ | — | $ | 14,997 | |||||||
Net deferred tax assets (liabilities) consist of the following as of December 31, 2016 and 2015:
December 31, | |||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | |||||
Deferred tax assets: | |||||||
Accounts receivable | $ | 225 | $ | 218 | |||
Inventories | 743 | 741 | |||||
Net operating loss carryforwards | 3,851 | 4,213 | |||||
Other accrued liabilities | 4,592 | 2,745 | |||||
Pension | 3,545 | 3,684 | |||||
Tax Credits | 1,687 | 1,634 | |||||
Total deferred tax assets | 14,643 | 13,235 | |||||
Deferred tax liabilities: | |||||||
Intangible assets | 4,224 | 4,077 | |||||
Property, plant and equipment | 21,117 | 15,101 | |||||
Total deferred tax liabilities | 25,341 | 19,178 | |||||
Valuation allowance | 4,903 | 4,307 | |||||
Net deferred tax liabilities | $ | (15,601 | ) | $ | (10,250 | ) | |
For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, income before income taxes was derived from the following sources:
For the years ended December 31, | |||||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
United States | $ | 53,356 | $ | 64,923 | $ | 27,463 | |||||
Foreign | 1,583 | 6,100 | 6,193 | ||||||||
Total income before income taxes | $ | 54,939 | $ | 71,023 | $ | 33,656 | |||||
At December 31, 2016, the Company had approximately $4.0 million of state net operating loss carryforward which expires in 2035 and 2036. The Company has not recorded a deferred tax asset for this carryforward as the Company anticipates paying a non-income based franchise tax for the foreseeable future in the applicable jurisdiction. In addition, at December 31, 2016, the Company had $2.5 million of state tax credit carry forwards that expire between 2017 and 2032. As of December 31, 2016, the Company has provided a valuation reserve against $2.3 million of its state tax
F-31
credit carryforwards. The Company also has $5.7 million of foreign net operating loss carryovers in China, $0.2 million of net operating loss carryovers in the United Kingdom and $9.4 million of net operating loss carryovers in the Netherlands. The Netherlands’ net operating losses expire between the years 2017 and 2025 and the China net operating losses expire between the years 2017 and 2021. The Company has recorded a valuation allowance against $9.4 million of its net operating losses in the Netherlands and $4.6 million of its net operating losses in China as future realization is not reasonably assured. The Company evaluates and weighs the positive and negative evidence present at each period. The Company will continue to monitor the realization criteria based on future operating results.
As of December 31, 2016 the Company has not paid U.S. income taxes on approximately $17.2 million of undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries. The Company’s intention is to reinvest these earnings indefinitely. The Company estimates that the amount of tax that would be payable on the undistributed earnings if repatriated to the United States would fall in the range of $0.4 million to $2.3 million, based on current facts, but depending on the timing and extent of the repatriation. This amount may vary in the future due to a variety of factors including future tax law changes, future earnings and statutory taxes paid by foreign subsidiaries, and ongoing tax planning strategies by the Company.
The Company and its subsidiaries file a consolidated federal income tax return, as well as returns required by various state and foreign jurisdictions. In the normal course of business, the Company is subject to examination by taxing authorities, including such major jurisdictions as the United States, China, France, Germany, Hong Kong, the Netherlands, Canada and the United Kingdom. Within the next fiscal year, the Company expects to conclude certain income tax matters through the year ended December 31, 2013 and it is reasonably expected that net unrecognized benefits of $0.5 million may be recognized. The total amount of unrecognized tax benefits that would affect the effective tax rate if recognized is $3.2 million as of December 31, 2016. However, $1.3 million of the unrecognized tax benefits, if recognized, would be offset in pre-tax income by the reversal of indemnification assets due to the Company. The Company is no longer subject to U.S. federal examinations for years before 2013, state and local examinations for years before 2012, and non-U.S. income tax examinations for years before 2003.
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows:
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | |||||
Unrecognized tax benefits at beginning of year | $ | 1,657 | $ | 2,272 | |||
Decreases relating to positions taken in prior periods | (63 | ) | — | ||||
Increases relating to current period | 1,678 | 49 | |||||
Decreases due to settlements with tax authorities | — | (336 | ) | ||||
Decreases due to lapse of statute of limitations | (53 | ) | (328 | ) | |||
Unrecognized tax benefits at end of year | $ | 3,219 | $ | 1,657 | |||
The Company recognizes the interest accrued and the penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as a component of tax expense.
12. Commitments and Contingencies
Leases
The Company has operating leases that resulted in expense of $5.4 million in 2016, $5.1 million in 2015, and $6.4 million in 2014. These contracts include building, office equipment, vehicle and machinery leases that require payment of property taxes, insurance, repairs and other operating costs.
F-32
Approximate future minimum lease payments under noncancelable leases are:
Payments due by period | |||||||||||
In thousands | Operating Lease Payments | Capital Lease Payments | Total | ||||||||
2017 | $ | 5,169 | $ | 244 | $ | 5,413 | |||||
2018 | 3,363 | 244 | 3,607 | ||||||||
2019 | 1,680 | 241 | 1,921 | ||||||||
2020 | 1,251 | 35 | 1,286 | ||||||||
2021 | 1,177 | — | 1,177 | ||||||||
Thereafter | 2,823 | — | 2,823 | ||||||||
Total | 15,463 | 764 | 16,227 | ||||||||
Interest on capital leases | — | (19 | ) | (19 | ) | ||||||
Total | $ | 15,463 | $ | 745 | $ | 16,208 | |||||
Commitments and Contingencies
The Company is subject to legal proceedings, claims, investigations and inquiries that arise in the ordinary course of business such as, but not limited to, actions with respect to commercial, intellectual property, employment, personal injury and environmental matters. While the outcome of any matter is inherently uncertain and the Company cannot be sure that it will prevail in any of the cases, subject to the matter referenced below, the Company is not aware of any matters pending that are expected to be material with respect to the Company’s business, financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
As previously disclosed, Lydall Gerhardi GmbH Co. & KG (“Lydall Gerhardi”), an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Lydall, Inc. (“Lydall”) and part of Lydall’s Thermal/Acoustical Metals reporting segment, has been cooperating with the German Federal Cartel Office, Bundeskartellamt (“German Cartel Office”) since May 2014 in connection with an investigation relating to violations of German anti-trust laws by and among certain European automotive heat shield manufacturers, including Lydall Gerhardi.
In December 2016, Lydall Gerhardi agreed in principle with the German Cartel Office to pay a settlement amount of €3.3 million (approximately $3.5 million as of December 31, 2016) to definitively conclude this matter. The Company recorded the expense of €3.3 million (approximately $3.5 million as of December 31, 2016) in December 2016 and expects to enter into a formal settlement agreement with the German Cartel Office and remit payment in the quarter ending March 31, 2017.
Environmental Obligations
The Company has elected to remediate environmental contamination discovered prior to the closing of the Texel acquisition at a certain property in the province of Quebec, Canada (“the Property”) that was acquired by Lydall. The Company records accruals for environmental costs when such losses are probable and reasonably estimable. While the Company is currently in the process of determining the final scope and timing of the remediation project, it estimates the cost of the remediation project to range between $0.9 million and $1.5 million based on information provided from and the results of investigatory work performed by a third party environmental service firm. Based upon this range of estimated remediation costs, the Company recorded an environmental liability of $0.9 million (which is fully offset as described below) within other long-term liabilities on the Company's balance sheet at December 31, 2016, representing the minimum amount in the range as no other amount within the range represents a better estimate at this time.
Pursuant to the Share Purchase Agreement, ADS has agreed to indemnify the Company from all costs and liabilities associated with the contamination and remediation work, including the costs of preparation and approval of the remediation plan and other reports in relation therewith. This indemnity was secured by an environmental escrow account, which was established in the amount of $3.0 million Canadian Dollars ($2.2 million U.S. Dollars as of December 31, 2016). Should the costs and liabilities exceed the environmental escrow amount, the Company also has access to the general indemnity escrow account, which was established in the amount of $14.0 million Canadian Dollars ($10.4 million U.S. Dollars as of December 31, 2016). Based on the foregoing, an indemnification asset of $0.9 million was also recorded in other assets as the Company believes collection from ADS is probable. The accrual for remediation
F-33
costs will be adjusted as further information develops, estimates change and payments to vendors are made for remediation, with an off-setting adjustment to the indemnification asset from ADS if collection is deemed probable.
In the fourth quarter of 2016, as part of a groundwater discharging permitting process, water samples collected from wells and process water basins at the Company’s Rochester New Hampshire manufacturing facility, within the Performance Materials segment, showed concentrations of Perfluorinated Compounds (“PFCs”) in excess of state ambient groundwater quality standards. In January 2017, the Company received a notification from the State of New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services (“NHDES”) naming Lydall Performance Materials, Inc. a responsible party with respect to the discharge of regulated contaminants and as such, is required to take action to investigate and remediate the impacts in accordance with standards established by the NHDES. The Company will conduct a site investigation, the scope of which is in the planning stage, in order to assess the extent of potential soil and groundwater contamination and develop a remedial action, if necessary. The Company does not know the scope or extent of its future obligations, if any, that may arise from the site investigation and therefore is unable to estimate the cost of any corrective action. Accordingly the Company cannot assure that the costs of any future corrective action at this location would not have a material effect on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations or liquidity. Provisions for such matters are charged to expense when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and reasonable estimates of the liability can be made. Estimates of environmental liabilities are based on a variety of matters, including, but not limited to, the stage of investigation, the stage of the remedial design, evaluation of existing remediation technologies, and presently enacted laws and regulations. In future periods, a number of factors could significantly impact any estimates of environmental remediation costs.
13. Earnings Per Share
The following table provides a reconciliation of weighted-average shares used to determine basic and diluted earnings per share.
For the years ended December 31, | ||||||||
In thousands | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||
Basic average common shares outstanding | 16,871 | 16,746 | 16,662 | |||||
Effect of dilutive options and restricted stock awards | 370 | 338 | 341 | |||||
Diluted average common shares outstanding | 17,241 | 17,084 | 17,003 | |||||
For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, stock options for 0.1 million, 0.1 million, and less than 0.1 million shares of Common Stock, respectively, were not considered in computing diluted earnings per common share as the stock options were considered anti-dilutive.
14. Quarterly Financial Information (Unaudited)
The following table summarizes quarterly financial results for 2016 and 2015. In management’s opinion, all material adjustments necessary for a fair statement of the information for such quarters have been reflected.
1st Quarter | 2nd Quarter | 3rd Quarter | 4th Quarter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In thousands except per share data | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 129,700 | $ | 127,306 | $ | 137,235 | $ | 134,561 | $ | 155,725 | $ | 131,240 | $ | 144,192 | $ | 131,398 | |||||||||||||||
Gross profit | $ | 32,377 | $ | 27,700 | $ | 35,990 | $ | 33,889 | $ | 38,193 | $ | 31,691 | $ | 31,982 | $ | 29,217 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 9,169 | $ | 18,937 | $ | 10,813 | $ | 10,817 | $ | 12,785 | $ | 11,186 | $ | 4,420 | $ | 5,319 | |||||||||||||||
Earnings per common share: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.54 | $ | 1.12 | $ | 0.64 | $ | 0.65 | $ | 0.76 | $ | 0.67 | $ | 0.26 | $ | 0.32 | |||||||||||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.54 | $ | 1.11 | $ | 0.63 | $ | 0.64 | $ | 0.75 | $ | 0.66 | $ | 0.26 | $ | 0.31 | |||||||||||||||
The table above includes the quarterly results of Texel since the acquisition date of July 7, 2016. The Gutsche acquisition was on December 31, 2016, therefore, there no operating results from Gutsche are included in the above table.
F-34
Gross profit during the quarters ended September 30, 2016 and December 31, 2016 were negatively impacted by purchase accounting adjustments of $1.6 million and $0.3 million, respectively, related to the acquisition of Texel. These purchase accounting adjustments reduced net income by $1.2 million and $0.2 million during the quarters ended September 30, 2016 and December 31, 2016, respectively. (See Note 2)
Net income during the quarters ended March 31, 2016, June 30, 2016, September 30, 2016 and December 31, 2016 was negatively impacted by corporate acquisition expenses for Texel and Gutsche of $0.4 million, $1.1 million, $0.8 million and $0.8 million, respectively. Net income during the quarter ended December 31, 2016 was negatively impacted by a $3.5 million German Cartel settlement expense within the T/A Metals segment.
During the quarter ended December 31, 2016, the Company recorded out of period adjustments reducing gross profit by $0.9 million and net income by $0.6 million to correct inventory and cost of sales errors within the T/A Metals and Technical Nonwovens segments. These errors resulted in the overstatement of gross profit by $0.5 million and net income by $0.3 million in the second quarter of 2016 and overstatement of gross profit by $0.4 million and net income by $0.3 million in the third quarter of 2016. The Company evaluated the impact of these errors and determined them to be immaterial to all quarters in 2016.
Net income during the quarter ended March 31, 2015 was positively impacted by an after-tax gain of $11.8 million due to the sale of Life Sciences Vital Fluids. Net income during the quarter ended September 30, 2015 was positively impacted by discrete tax benefits of $1.2 million, related to the completion of a tax credit project and the release of reserves for previously uncertain tax positions. Net income during the quarter ended December 31, 2015 was negatively impacted by a $1.4 million long-lived asset impairment charge related to Solutech and $1.2 million of a discrete income tax charges related to changes in state tax legislation. During the quarter ended December 31, 2015, the Company identified an error in its income tax expense related to a state tax credit carryforward that resulted in the overstatement of net income by $0.4 million for the quarter ended September 30, 2015. The correction of this error was recorded during the quarter ended December 31, 2015 and reduced net income by $0.4 million, or $0.02 per share. The Company evaluated the impact of the error and determined it to be immaterial to both the third and fourth quarters of 2015.
15. Recently Issued Accounting Standards
In February 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2016-02, "Leases (Topic 842)". This ASU requires entities that lease assets with lease terms of more than 12 months to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities created by those leases on their balance sheets. The ASU will also require new qualitative and quantitative disclosures to help investors and other financial statement users better understand the amount, timing, and uncertainty of cash flows arising from leases. This ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the method and impact the adoption of ASU 2016-02 will have on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606)." The objective of this standard update is to remove inconsistent practices with regard to revenue recognition between US GAAP and IFRS. The standard intends to improve comparability of revenue recognition practices across entities, industries, jurisdictions and capital markets. ASU 2014-09 is effective for the Company’s interim and annual reporting periods beginning January 1, 2018, and is to be adopted using either a full retrospective or modified retrospective transition method with early adoption permitted for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016. The Company anticipates adopting the ASU 2014-09 under the modified retrospective transition method, with the cumulative effect of initially adopting this standard recognized through retained earnings at the date of adoption.
The Company has developed a project plan that includes a phased approach to implementing this standard update. During 2016, the Company substantially completed phase one, the assessment phase which includes an initial diagnosis of the standard on the Company’s revenue recognition practices. During 2017, the Company will complete the second phase which includes conversion activities, such as establishing policies, identifying system impacts, integration of the standard update into financial reporting processes and systems, and developing an understanding of the financial impact of this statement on the Company’s consolidated financial statements. The Company anticipates the transition to the new standard will result in changes to revenue recognition practices but the Company will be unable to quantify that impact until the final phase of the project has been completed.
Subsequent to the issuance of ASU No. 2014-09, the FASB has issued the following updates: ASU 2016-08, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) - Principal versus Agent Considerations (Reporting Revenue Gross versus
F-35
Net).”; ASU 2016-10, " Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) - Identifying Performance Obligations and Licensing."; and ASU 2016-12, " Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) - Narrow-Scope Improvements and Practical Expedients." The amendments in these updates affect the guidance contained within ASU 2014-09 and will be assessed as part of the Company's revenue recognition project plan.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13, "Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Statements", which requires entities to measure all expected credit losses for financial assets held at the reporting date based on historical experience, current conditions, and reasonable and supportable forecasts. Entities will now use forward-looking information to better form their credit loss estimates. The ASU also requires enhanced disclosures to help financial statement users better understand significant estimates and judgments used in estimating credit losses. The broad scope of this ASU includes trade receivables. This ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019. Early adoption is permitted beginning after December 15, 2018. The Company is currently evaluating the method and impact the adoption of ASU 2016-13 will have on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-15, "Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments", which provides guidance on eight specific cash flow classification issues. Current GAAP does not include specific guidance on these eight cash flow classification issues. This ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact the adoption of ASU 2016-15 will have on the Company’s statement of cash flows and disclosures.
In October 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-16, “Income Taxes (Topic 740): Intra-Entity Transfers of Assets Other Than Inventory” as part of the Board’s initiative to reduce complexity in accounting standards. This ASU eliminates an exception in ASC 740, which prohibits the immediate recognition of income tax consequences of intra-entity asset transfers other than inventory. This ASU requires entities to recognize the immediate current and deferred income tax effects of intra-entity asset transfers. This ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact the adoption of ASU 2016-16 will have on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-18, "Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Restricted Cash", which clarifies guidance and presentation related to restricted cash in the statement of cash flows, including stating that restricted cash should be included within cash and cash equivalents on the statement of cash flows. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact the adoption of ASU 2016-18 will have on the Company’s statements of cash flows and disclosures.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-01, "Business Combinations (Topic 805): Clarifying the Definition of a Business", which adds guidance to assist entities with evaluating whether transactions should be accounted for as acquisitions (or disposals) of assets or businesses. The definition of a business affects many areas of accounting including acquisitions, disposals, goodwill, and consolidation. The amendments of this ASU provide a screen to determine when an integrated set of assets and activities is not a business. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017. The Company is currently evaluating the impact the adoption of ASU 2017-01 will have on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-04, "Intangibles - Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment", which eliminates Step 2 from the goodwill impairment test. Instead, an entity should perform its annual or interim goodwill impairment test by comparing the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying amount and recognize an impairment charge for the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the reporting unit's fair value, not to exceed the total amount of goodwill allocated to the reporting unit. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019. Early adoption is permitted for interim or annual goodwill impairment tests performed on testing dates after January 1, 2017. The Company is currently evaluating the impact the adoption of ASU 2017-04 will have on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
F-36
16. Changes in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The following table discloses the changes by classification within accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) for the period ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
In thousands | Foreign Currency Translation Adjustment | Defined Benefit Pension Adjustment | Total Accumulated Other Comprehensive (Loss) Income | ||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2013 | $ | 6,128 | $ | (14,972 | ) | $ | (8,844 | ) | |||
Other Comprehensive loss | (12,714 | ) | (6,099 | ) | (a) | (18,813 | ) | ||||
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss | — | 3,496 | (b) | 3,496 | |||||||
Balance at December 31, 2014 | $ | (6,586 | ) | $ | (17,575 | ) | $ | (24,161 | ) | ||
Other Comprehensive loss | (10,334 | ) | (637 | ) | (a) | (10,971 | ) | ||||
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss | — | 547 | (b) | 547 | |||||||
Balance at December 31, 2015 | $ | (16,920 | ) | $ | (17,665 | ) | $ | (34,585 | ) | ||
Other Comprehensive loss | (10,965 | ) | (2,969 | ) | (a) | (13,934 | ) | ||||
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss | 569 | (b) | 569 | ||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2016 | $ | (27,885 | ) | $ | (20,065 | ) | $ | (47,950 | ) | ||
(a) Amount represents actuarial (losses) gains arising from the Company’s postretirement benefit obligation. This amount was $(3.0) million, net of $1.6 million tax benefit, for 2016, $(0.6) million, net of a $0.4 million tax benefit, for 2015 and $(6.1) million, net of $3.7 million tax benefit in 2014. (See Note 8)
(b) Amount represents the amortization of actuarial losses to pension expense arising from the Company’s postretirement benefit obligation. This amount was $0.6 million, net of $0.4 million tax benefit in 2016, $0.5 million, net of $0.3 million tax benefit in 2015, and $3.5 million, net of $2.1 million tax benefit, which included $3.0 million, net of $1.9 million tax benefit for pension settlement costs in 2014. (See Note 8)
F-37
Schedule II
LYDALL, INC.
VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED December 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
In thousands | Balance at January 1, | Charges to Costs and Expenses | Charges (Deductions) to Other Accounts | Deductions | Balance at December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Allowance for doubtful receivables | $ | 1,251 | $ | 941 | $ | (123 | ) | 2 | $ | (640 | ) | 1 | $ | 1,429 | |||||||
Tax valuation allowances | 4,307 | 762 | (140 | ) | 2 | (26 | ) | 3 | 4,903 | ||||||||||||
2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Allowance for doubtful receivables | $ | 709 | $ | 855 | $ | (53 | ) | 2 | $ | (260 | ) | 1 | $ | 1,251 | |||||||
Tax valuation allowances | 3,727 | 1,615 | (272 | ) | 2,4 | (763 | ) | 3 | 4,307 | ||||||||||||
2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Allowance for doubtful receivables | $ | 480 | $ | 384 | $ | (39 | ) | 2 | $ | (116 | ) | 1 | $ | 709 | |||||||
Tax valuation allowances | 3,315 | 1,120 | 193 | (901 | ) | 3 | 3,727 | ||||||||||||||
1. | Uncollected receivables written off and recoveries. |
2. | Foreign currency translation and other adjustments. |
3. | Reduction to income tax expense. |
4. | Adjustments relating to the acquisition of Industrial Filtration. |
S-1
