Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32 - EXHIBIT 32 - ENTERPRISE BANCORP INC /MA/ | ebtc123119-ex32.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - ENTERPRISE BANCORP INC /MA/ | ebtc123119-ex312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - ENTERPRISE BANCORP INC /MA/ | ebtc123119-ex311.htm |
| EX-23 - EXHIBIT 23 - ENTERPRISE BANCORP INC /MA/ | ebtc12311910kex23.htm |
| EX-21 - EXHIBIT 21 - ENTERPRISE BANCORP INC /MA/ | ebtc12311910kex21.htm |
| EX-4.4 - EXHIBIT 4.4 - ENTERPRISE BANCORP INC /MA/ | ebtc12311910kex44.htm |
| EX-4.3 - EXHIBIT 4.3 - ENTERPRISE BANCORP INC /MA/ | ebtc12311910kex43.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
ý | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019
OR
¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission file number 001-33912
Enterprise Bancorp, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Massachusetts | 04-3308902 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation of organization) | (IRS Employer Identification No.) | |
222 Merrimack Street, Lowell, Massachusetts | 01852 | |
(Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip code) | |
(978) 459-9000
Registrant's telephone number, including area code
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Exchange Act:
Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered | ||
Common Stock, $0.01 par value per share | EBTC | NASDAQ Stock Market | ||
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Exchange Act:
NONE
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. o Yes ý No
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. o Yes ý No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. ý Yes o No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). ý Yes o No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company or an emerging growth company. See definition of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and "emerging growth company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act (Check one):
Large accelerated filer o | Accelerated filer x | |
Non-accelerated filer o | Smaller reporting company o | Emerging growth company o |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act) o Yes ý No
State the aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was last sold, or the average bid price and asked price of such common equity, as of the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter: $2,086,685 ($31.71 per share) as of June 28, 2019, the last trading day of the registrant’s most recently completed second quarter.
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the registrant's classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date:
March 2, 2020, Common Stock, par value $0.01, 11,840,547 shares outstanding
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant’s definitive proxy statement for its annual meeting of stockholders to be held on May 5, 2020 are incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K.
ENTERPRISE BANCORP, INC.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page Number | |||
2
PART I
Item 1. | Business |
Organization
Enterprise Bancorp, Inc. ("the Company," "Enterprise," "us," "we," or "our") is a Massachusetts corporation organized in 1996, which operates as the parent holding company of Enterprise Bank and Trust Company, commonly referred to as Enterprise Bank ('the Bank"). Substantially all of the Company’s operations are conducted through the Bank and its subsidiaries. The Bank, a Massachusetts trust company and state chartered commercial bank that commenced banking operations in 1989, has five wholly owned subsidiaries that are included in the Company’s consolidated financial statements:
• | Enterprise Insurance Services, LLC, organized in 2000 in the State of Delaware for the purpose of engaging in insurance sales activities; |
• | Enterprise Wealth Services, LLC, organized in 2000 in the State of Delaware for the purpose of offering non-deposit investment products and services, under the name of "Enterprise Wealth Services;" and |
• | Three Massachusetts security corporations, Enterprise Security Corporation (2005), Enterprise Security Corporation II (2007) and Enterprise Security Corporation III (2007), which hold various types of qualifying securities. The security corporations are limited to conducting securities investment activities that the Bank itself would be allowed to conduct under applicable laws. |
Enterprise's headquarters are located at 222 Merrimack Street in Lowell, Massachusetts.
The services offered through the Bank and its subsidiaries are managed as one strategic unit and represent the Company's only reportable operating segment.
All material intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
The Company's common stock trades on the NASDAQ Global Market under the trading symbol "EBTC."
Market Area
The Company's primary market area is the Greater Merrimack Valley, Nashoba Valley and North Central regions of Massachusetts and Southern New Hampshire (Southern Hillsborough and Rockingham counties). As of December 31, 2019, Enterprise had 24 full-service branches located in the Massachusetts communities of Lowell (2), Acton, Andover, Billerica (2), Chelmsford (2), Dracut, Fitchburg, Lawrence, Leominster, Methuen, Tewksbury (2), Tyngsborough and Westford and in the New Hampshire communities of Derry, Hudson, Nashua (2), Pelham, Salem and Windham. Our 25th branch in Lexington, MA also recently opened in early March 2020 and our 26th branch in North Andover, MA is scheduled to open in summer 2020.
Management actively seeks to strengthen the Company's market position by capitalizing on market opportunities to grow all business lines and the continued pursuit of organic growth and strategic expansion within existing and into neighboring geographic markets.
Products and Services
The Company principally is engaged in the business of gathering deposits from the general public and investing primarily in commercial loans and investment securities and utilizing the resulting cash flows to conduct operations, expand service and product offerings, expand the branch network, and pay dividends to stockholders. Through the Bank and its subsidiaries, the Company offers a range of commercial, residential and consumer loan products, deposit products and cash management services, electronic and digital banking options, commercial insurance services, as well as wealth management, wealth services, and trust services. The integrated branch network serves all product channels with knowledgeable service providers and well-appointed facilities. Management continually examines new products and technologies in order to maintain a highly competitive mix of offerings and state-of-the-art delivery channels in order to tailor product lines to customers' needs. These products and services are outlined below.
The Company's business is not dependent on one, or a few, customers, or upon a particular industry, the loss of which would have a material adverse impact on the financial condition or operations of the Company.
3
Lending Products
General
The Company specializes in lending to business entities, non-profit organizations, professional practices and individuals. The Company's primary lending focus is on the development of high-quality commercial relationships achieved through active business development efforts, long-term relationships with established commercial businesses, strong community involvement, and focused marketing strategies. Commercial loans may include commercial real estate mortgage loans, construction and land development loans, secured and unsecured commercial loans and lines of credit, and letters of credit. Consumer or "retail" loans may include conventional residential mortgage loans, home equity loans and lines, residential construction loans on owner-occupied primary and secondary residences, and secured and unsecured personal loans and lines of credit. The Company manages its loan portfolio to avoid concentration by industry, relationship size, and source of repayment to lessen its credit risk exposure.
Interest rates charged on loans may be fixed or variable; variable rate loans may have fixed initial periods before periodic rate adjustments begin. Individual rates offered are dependent on the associated degree of credit risk, term, underwriting and servicing costs, loan amount, and the extent of other banking relationships maintained with the borrower, and may be subject to interest rate floors. Rates are also subject to competitive pressures, the current interest-rate environment, availability of funds, and government regulations. The Company has a "Back-to-Back Swap" program whereby the Bank enters into an interest rate swap with a qualified commercial banking customer and simultaneously enters into an equal and opposite interest rate swap with a swap counterparty. The customer interest-rate swap agreement allows commercial banking customers to convert a floating-rate loan payment to a fixed-rate payment. The transaction structure effectively minimizes the Bank's net interest rate risk exposure resulting from such transactions.
Enterprise employs a seasoned commercial lending staff, with commercial lenders supporting each of the Bank's branch locations. An internal loan review function assesses the compliance of commercial loan originations with the Company's internal policies and underwriting guidelines and monitors the ongoing credit quality of the loan portfolio. The credit risk management function monitors a wide variety of individual borrower and industry factors; and the Company's internal loan credit risk rating system classifies loans depending on risk of loss characteristics. The Company also contracts with an external loan review company to review, on a pre-determined schedule, the internal credit ratings assigned to loans in the commercial loan portfolio. The review is focused on the non-criticized segment of the portfolio, based on the type, size, credit rating, and overall risk of the loan and generally encompasses 55% or more of the commercial portfolio. This same company is also contracted to perform limited stress testing on the commercial real estate loan portfolio on an annual basis.
The Company's internal residential origination and underwriting staff originate residential loans and are responsible for compliance with residential lending regulations, consumer protection and internal policy guidelines. The Company contracts with an external loan review company to complete a regular quality control review in accordance with secondary market underwriting requirements for residential mortgage loans sold. The sample reviewed is based on loan volume originated since the prior review. Additionally, the Company's internal compliance department monitors the residential loan origination activity for regulatory compliance.
A management loan review committee, consisting of senior lending officers, credit, loan workout, loan operations, risk management and accounting personnel, is responsible for setting loan policy and procedures, as well as reviewing loans on the internal "watched asset list" and classified loan report. An internal credit review committee, consisting of senior lending officers and credit review personnel, meets to review loan requests related to borrowing relationships of certain dollar levels, as well as other borrower relationships recommended for discussion by committee members.
The Loan Committee of the Company's Board of Directors (the "Board") approves loan relationships exceeding certain prescribed dollar limits. The Board's Loan Committee reviews current portfolio statistics, problem credits, construction loan reviews, watched assets, loan delinquencies, and the allowance for loan losses, as well as current market conditions and issues relating to the construction and real estate development industry and the reports from the external loan review company. The Board's Loan Committee is also responsible for approval of the loan policy and credit-related charge-offs recommended by management, subject to final approval by the full Board.
4
At December 31, 2019, the Bank's statutory lending limit, based on 20% of capital (capital stock plus surplus and undivided profits, but excluding other comprehensive income), to any individual borrower and related entities was approximately $60.1 million, subject to certain exceptions provided under applicable law.
See also Item 1A, "Risk Factors," and "Credit Risk," contained under the heading "Financial Condition," in Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," in this annual report on Form 10-K ("this Form 10-K") for further discussion on a variety of risks and uncertainties that may affect the Company's loan portfolio.
Commercial Real Estate, Commercial and Industrial, and Commercial Construction Loans
Commercial real estate loans include loans secured by both owner-use and non-owner occupied (investor) real estate. These loans are typically secured by a variety of commercial and industrial property types, including one-to-four and multi-family apartment buildings, office, industrial, or mixed-use facilities, strip shopping centers, or other commercial properties, and are generally guaranteed by the principals of the borrower. Commercial real estate loans generally have repayment periods of approximately 15 to 25 years. Variable interest-rate loans have a variety of adjustment terms and underlying interest-rate indices and are generally fixed for an initial period before periodic rate adjustments begin.
Commercial and industrial loans include seasonal and formula-based revolving lines of credit, working capital loans, equipment financing, formula-based lines of credit, and term loans. Also included in commercial and industrial loans are loans partially guaranteed by the U.S. Small Business Administration ("SBA"), and loans under various other government and municipal programs and agencies. Commercial and industrial credits may be unsecured loans and lines to financially strong borrowers, loans secured in whole or in part by real estate unrelated to the principal purpose of the loan or secured by inventories, equipment, or receivables, and are generally guaranteed by the principals of the borrower. Variable rate loans and lines in this portfolio have interest rates that are periodically adjusted, with loans generally having fixed initial periods. Revolving lines of credit are written on demand and are subject to annual credit review. Commercial and industrial loans have average repayment periods of 1 to 7 years.
Commercial construction loans include the development of residential housing and condominium projects, the development of commercial and industrial use property, and loans for the purchase and improvement of raw land. These loans are secured in whole or in part by underlying real estate collateral and are generally guaranteed by the principals of the borrowers. In
many cases, these loans move into the permanent commercial real estate portfolio when the construction phase is completed. Construction lenders work to cultivate long-term relationships with established developers. The Company limits the amount of financing provided to any single developer for the construction of properties built on a speculative basis. Funds for construction projects are disbursed as pre-specified stages of construction are completed. Regular site inspections are performed, prior to advancing additional funds, at each construction phase, either by experienced construction lenders on staff or by independent outside inspection companies. Commercial construction loans generally are variable rate loans and lines with interest rates that are periodically adjusted and generally have terms of 1 to 3 years.
From time to time, the Company participates with other banks in the financing of certain commercial projects. Participating loans with other institutions provide banks the opportunity to retain customer relationships and reduce credit risk exposure among each participating bank, while providing customers with larger credit vehicles than the individual bank might be willing or able to offer independently. In some cases, the Company may act as the lead lender, originating and servicing the loans, but participating out a portion of the funding to other banks. In other cases, the Company may participate in loans originated by other institutions. In each case, the participating bank funds a percentage of the loan commitment and takes on the related pro-rata risk. In each case in which the Company participates in a loan, the rights and obligations of each participating bank are divided proportionately among the participating banks in an amount equal to their share of ownership and with equal priority among all banks. Each participation is governed by individual participation agreements executed by the lead bank and the participant at loan origination. When the participation qualifies as a sale under U.S. generally accepted accounting procedures ("GAAP"), the balances participated out to other institutions are not carried as assets on the Company's consolidated financial statements. The Company performs an independent credit analysis of each commitment and a review of the participating institution prior to participation in the loan, and an annual review thereafter of each participating institution. Loans originated by other banks in which the Company is a participating institution are carried in the loan portfolio at the Company’s pro-rata share of ownership.
In addition, the Company participates in various community development loan funds in which local banks contribute to a loan pool that is independently managed. These loan pools make small dollar loans available to local businesses and start-ups that might otherwise not qualify for traditional small business loans directly from banks, with the potential risk spread among the
5
participating banks. The goal of these partnerships with community development loan funds is to stimulate local economic development, create jobs, and help small businesses and entrepreneurs to become more viable, bankable and an integrated part of the local community.
Letters of credit are conditional commitments issued by the Company to guarantee the financial obligation or performance of a customer to a third party. The credit risk involved in issuing letters of credit is essentially the same as that involved in extending loan facilities to customers. If the letter of credit is drawn upon, a loan is created for the customer, generally a commercial loan, with the same criteria associated with similar commercial loans.
Residential Loans
Enterprise originates conventional mortgage loans on one-to-four family residential properties. These properties may serve as the borrower's primary residence, or as vacation homes or investment properties. Loan-to-value policy limits vary, generally from 75% for multi-family, owner-occupied properties, up to 97% for single family, owner-occupied properties, with mortgage insurance coverage required for loan-to-value ratios greater than 80% based on program parameters. In addition, financing is provided for the construction of owner-occupied primary and secondary residences. Residential mortgage loans may have terms of up to 30 years at either fixed or adjustable rates of interest. Fixed and adjustable rate residential mortgage loans are generally originated using secondary market underwriting and documentation standards.
Depending on the current interest-rate environment, management projections of future interest rates and the overall asset-liability management program of the Company, management may elect to sell those fixed and adjustable rate residential mortgage loans which are eligible for sale in the secondary market or hold some or all of this residential loan production for the Company's portfolio. Mortgage loans are generally not pooled for sale, but instead sold on an individual basis. The Company may retain or sell the servicing when selling the loans. Loans sold are subject to standard secondary market underwriting and eligibility representations and warranties over the life of the loan and are subject to an early payment default period covering the first four payments for certain loan sales. Loans classified as held for sale are carried as a separate line item on the balance sheet.
Home Equity Loans and Lines of Credit ("Home equity")
Home equity term loans are originated for one-to-four family residential properties with maximum original loan-to-value ratios generally up to 80% of the automated valuation or appraised value of the property securing the loan. Home equity loan payments consist of monthly principal and interest based on amortization ranging from 3 to 15 years. The rates may be variable or fixed.
The Company also originates home equity revolving lines of credit for one-to-four family residential properties with maximum original loan-to-value ratios generally up to 80% of the automated valuation or appraised value of the property securing the loan. Home equity lines generally have interest rates that adjust monthly based on changes in the Wall Street Journal Prime Rate, although minimum rates may be applicable. Some home equity line rates may be fixed for a period of time and then adjusted monthly thereafter. The payment schedule for home equity lines requires interest only payments for the first ten years of the lines. Generally, at the end of ten years, the line may be frozen to future advances, and principal plus interest payments are collected over a 15-year amortization schedule or, for eligible borrowers meeting certain requirements, the line availability may be extended for an additional interest only period.
Consumer Loans
Consumer loans consist primarily of secured or unsecured personal loans, loans under energy efficiency financing programs in conjunction with Massachusetts public utilities, and overdraft protection lines on checking accounts extended to individual customers. The aggregate amounts of overdrawn deposit accounts are reclassified as loan balances.
Credit Risk and Allowance for Loan Losses
Information regarding the Company's credit risk and allowance for loan losses is contained in Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," contained in the section "Financial Condition," under "Loans," in the subsections "Credit Risk," "Asset Quality," and "Allowance for Loan Losses" of this Form 10-K.
6
Deposit Products
Deposits have traditionally been the principal source of the Company's funds. Enterprise offers a broad selection of competitive commercial and retail deposit products, including transactional checking accounts, non-transactional savings and money market accounts, commercial sweep products, and term certificates of deposit ("CDs") typically ranging from 1 month to 36 months. The Company caters its deposit product offerings to commercial businesses, professionals, municipalities, and individuals. As a member of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (the "FDIC"), the Bank's depositors are provided deposit protection up to the maximum FDIC insurance coverage limits.
In addition to the deposit products noted above, the Company also provides customers the ability to allocate checking deposits, money markets, and CDs balances to nationwide networks of reciprocating FDIC insured banks. Deposits are placed into nationwide networks in increments that are eligible for FDIC insurance. This allows the Company to offer enhanced FDIC insurance coverage on larger deposit balances by placing the "excess" funds in FDIC insured accounts or term CDs issued by other banks participating in the networks. In exchange, the other institutions place dollar-for-dollar matching reciprocal and insurable deposits with the Company via the networks. Essentially, the equivalent of the original deposit comes back to the Company and is available to fund local loan growth. The original funds placed into the networks are not carried as deposits on the Company's Consolidated Balance Sheet, however the network's reciprocal dollar deposits are carried within the appropriate product category under customer deposits on the Consolidated Balance Sheet.
Management determines the interest rates offered on deposit accounts based on current and expected economic conditions, competition, liquidity needs, the volatility of existing deposits, the asset-liability position of the Company and the overall objectives of the Company regarding the growth and retention of relationships. Low-cost checking deposits are an important component of the Company's core funding strategy.
Enterprise may also utilize brokered deposits, mainly term products, from several available sources, as part of the Company's asset-liability management strategy and as an alternative to borrowed funds to support asset growth in excess of internally generated deposits. Brokered deposits along with borrowed funds are referred to as wholesale funding.
Cash Management Services
In addition to the lending and deposit products discussed above, commercial banking and municipal customers may take advantage of cash management services and products that enhance the reporting on and acceptance of deposited funds, the use of those funds for such purposes as payments, disbursements and overnight investment through the use of investment sweep services including third party FDIC enhanced money markets or third party non-deposit mutual funds. Management believes that commercial customers benefit from the flexibility of these products, while retaining conservative investment options of high quality and safety. The balances swept on a daily basis into mutual funds do not represent obligations of the Company and are not insured by the FDIC.
Product Delivery Channels
In addition to traditional product access channels, customers may access their bank accounts securely via the internet through personal computers or any mobile device. Various electronic banking capabilities are delivered through the Bank's online website and mobile apps allowing customers to view account balances, transactions, check images and statements, as well as perform internal and external account transfers, pay bills, and make person-to-person payments and conduct check deposits.
Online and mobile banking tools utilize multiple layers of customer authentication including device, geographic and biometric recognition, personal access ID’s and passwords, as well as digital signatures for certain transactions.
Wealth Management and Wealth Services
The Company provides a range of wealth advisory and management services delivered via two channels, Enterprise Wealth Management and Enterprise Wealth Services.
Wealth advisory and management services include customized investment management and trust services provided under the label "Enterprise Wealth Management" to individuals, family groups, commercial businesses, trusts, foundations, non-profit organizations, and endowments.
7
Enterprise Wealth Management primarily utilizes an open-architecture approach to client investment management. The philosophy is to identify and select high performing mutual funds and independent investment management firms on behalf of our clients. The Company partners with investment research and due diligence firms to strengthen strategic development and provide performance monitoring capabilities. These firms perform detailed research and due diligence reviews and provide objective analysis of each independent management firm based on key criteria, and maintains ongoing oversight and monitoring of their performance. This due diligence is intended to enable the Company to customize investment portfolios to meet each customer’s financial objectives and deliver superior long-term performance.
Enterprise Wealth Management also offers the flexibility of an individually-managed portfolio for clients who prefer customized asset management with a variety of investment options, which includes our Large Cap Core Equity Strategy, a proprietary blend of value and growth stocks.
Enterprise Wealth Services provides brokerage and management services through a third-party arrangement with Commonwealth Financial Network, a licensed securities brokerage firm, with products designed primarily for the individual investor. Retirement plan services are offered through third-party arrangements with leading 401(k) plan providers.
The Enterprise Wealth Management Committee ("EWMC") of the Board is responsible for overseeing that the fiduciary and investment activities of the Enterprise Wealth Management and Services department are consistent with those powers delegated by the Board and overseeing that prudent care and discretion are followed in the management of client assets including client and Bank risk exposure. EWMC is also responsible for reviewing investment performance of investment advisors, strategic planning initiatives and results, and proposed new products or services, among other responsibilities.
Insurance Services
Enterprise Insurance Services, LLC engages in insurance sales activities through a third-party arrangement with HUB International New England, LLC ("HUB"), a full-service insurance agency with offices in Massachusetts and New Hampshire and a part of HUB International Limited, which operates throughout the United States and Canada. Enterprise Insurance Services provides, through HUB, a full array of insurance products tailored to serve the specific insurance needs of businesses in a range of industries operating in the Company's market area.
Investment Activities
The Company's investment portfolio activities are an integral part of the overall asset-liability management program of the Company. The investment function provides readily available funds to support loan growth, as well as to meet withdrawals and maturities of deposits, and attempts to provide maximum return consistent with liquidity constraints and general prudence, including diversification and safety of investments. In addition to the Bank, the Company holds investment securities in three Massachusetts security corporation subsidiaries in order to provide enhanced tax savings associated with certain state tax policies related to investment income.
The securities in which the Company may invest are limited by regulation. In addition, an internal investment policy restricts investments in debt securities to high-quality securities within prescribed categories as approved by the Board. Management utilizes an outside registered investment adviser to manage the corporate and municipal bond portfolios within prescribed guidelines set by management. The Company's internal investment policy also sets sector limits as a percentage of the total portfolio, identifies acceptable and unacceptable investment practices, and denotes approved security dealers. The effect of changes in interest rates, market values, timing of principal payments and credit risk are considered when purchasing securities.
Cash equivalents are defined as highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less, that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash and present insignificant risk of changes in value due to changes in interest rates. The Company's cash and cash equivalents may be comprised of cash and due from banks, interest-earning deposits (deposit accounts, excess reserve cash balances, money markets and money market mutual fund accounts and short-term U.S. Agency Discount Notes) and overnight and term federal funds sold ("fed funds") to money center banks.
The Company primarily invests in debt securities, with a small portion of the portfolio invested in equities. As of the balance sheet dates reflected in this annual report, all of the debt securities within the Company's investment portfolio were classified as available-for-sale and carried at fair value, with changes in fair value reflected in other comprehensive income. The equity securities are carried at fair value, with changes in fair value recognized in net income.
8
Management reports investment transactions, portfolio allocation, effective duration, fair value at risk and projected cash flows to the Board on a periodic basis. Credit risk inherent in the portfolio is closely monitored by management and presented at least annually to the Board. The Board also approves the Company's internal investment policy annually and ongoing investment strategy.
The Company is required to purchase Federal Home Loan Bank of Boston ("FHLB") stock at par value in association with the Bank's outstanding advances from the FHLB; this stock is classified as a restricted investment and carried at cost which management believes approximates fair value.
See also "Impairment Review of Investment Securities," contained under the heading "Accounting Policies/Critical Accounting Estimates," in Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," of this Form 10-K for further discussion on the determination and recognition of impairment.
Other Sources of Funds
As discussed above, deposit gathering has been the Company's principal source of funds. Asset growth in excess of deposits may be funded through cash flows from our loan and investment portfolios, or the following sources:
Borrowed Funds
Total borrowing capacity includes borrowing arrangements at the FHLB and the Federal Reserve Bank ("FRB") Discount Window and borrowing arrangements with correspondent banks.
Membership in the FHLB provides borrowing capacity based on qualifying collateral balances pre-pledged to the FHLB, including certain residential loans, home equity lines, commercial loans, U.S. government and agency securities and certain municipal securities.
Borrowings from the FHLB typically are utilized to fund short-term liquidity needs or specific lending projects under the FHLB's community development programs. The FHLB funding facility is an integral component of the Company's asset-liability management program.
The FRB Discount Window borrowing capacity is based on the pledge of qualifying collateral balances to the FRB. Collateral pledged for this FRB facility consists primarily of certain municipal and corporate securities held in the Company's investment portfolio. Additional types of collateral are available to increase borrowing capacity with the FRB if necessary.
Pre-established non-collateralized overnight borrowing arrangements with large national and regional correspondent banks provide additional overnight and short-term borrowing capacity for the Company and are classified as "other borrowings" under Borrowed Funds on the Company's balance sheets.
Subordinated Debt
The Company had $14.9 million of outstanding subordinated debt at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively which consisted of $15.0 million in aggregate principal amount of Fixed-to-Floating Rate Subordinated Notes (the "Notes"), net of amortized deferred-issuance costs, issued in January 2015 in a private placement to an accredited investor. See also Note 8, "Borrowed Funds and Subordinated Debt" to the Company's consolidated financial statements contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below, for further information regarding the Company's subordinated debt.
Capital Resources
Capital planning by the Company and the Bank considers current needs and anticipated future growth. Ongoing sources of capital include the retention of earnings, less dividends paid, proceeds from the exercise of employee stock options and proceeds from purchases of shares pursuant to the Company's dividend reinvestment plan and direct stock purchase plan (together, the "DRSPP"). Additional sources of capital for the Company and the Bank have been proceeds from the issuance of common stock and proceeds from the issuance of subordinated debt. The Company believes its current capital is adequate to support ongoing operations.
9
The Company is subject to the regulatory capital framework known as the "Basel III Rules" which include risk-based capital ratio requirements which were fully phased-in January 1, 2019. Management believes, as of December 31, 2019, that the Company and the Bank met all capital adequacy requirements to which they were subject under Basel III. As of December 31, 2019, the Company met the definition of "well-capitalized" under the applicable Federal Reserve Board regulations and the Bank qualified as "well-capitalized" under the prompt corrective action regulations of Basel III and the FDIC.
See also "Capital Requirements," and "Capital Requirements under Basel III," under the heading "Supervision and Regulation," contained below, for further information regarding the Company's and the Bank's regulatory capital requirements. See Note 11, "Stockholders' Equity," to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below, for further information regarding the Company's stockholder's equity and capital ratios.
Patents, Trademarks, etc.
The Company holds several registered service marks and trademarks related to product names and corporate branding. The Company holds no other patents, registered trademarks, licenses (other than licenses required to be obtained from appropriate banking regulatory agencies), franchises or concessions that are material to its business.
Employees
At December 31, 2019, the Company employed 538 full-time equivalent employees. None of the employees are presently represented by a union or covered by a collective bargaining agreement. Management believes its employee relations are excellent.
Company Websites
The Company currently uses outside vendors to design, support and host its two primary internet websites: www.enterprisebanking.com, for general banking products and services and Company information, as noted below, and www.enterprisewealth.com, for wealth advisory and management services offered by the Bank. The underlying structure of the websites allows for ongoing maintenance to be performed by third parties, and updates of information to be performed by authorized Company personnel. The information contained on or accessible from our websites does not constitute a part of this report and is not incorporated by reference.
The Bank's websites provide information on the Company and its products and services. Users have the ability to securely open various deposit accounts, as well as the ability to submit mortgage loan applications online and, via a link, to access their bank accounts and perform various financial transactions, or access various wealth account reports and statements using a secure online banking platform.
The Bank's website also provides the access point to a variety of specified banking services and information, various financial management tools, and Company investor and corporate information, which includes a corporate governance page. The Company's corporate governance page includes the Corporate Governance Guidelines, Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, and Whistleblower and Non-Retaliation policy, as well as the charters of the Board's Audit, Compensation, and Corporate Governance/Nominating committees.
In the Investor Relations section of the Bank's website, under the SEC Filings tab, the Company makes available copies of the Company's annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q ("Form 10-Q"), proxy statements and current reports on Form 8-K ("Form 8-K"). Additionally, the site includes current registration statements that the Company has been required to file in connection with the issuance of its shares. The Company similarly makes available all insider stock ownership and transaction reports filed with the SEC by executive officers, directors and any 10% or greater stockholders under Section 16 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act") (Forms 3, 4 and 5). Access to all of these reports is made available free of charge and is essentially simultaneous with the SEC's posting of these reports on its EDGAR system through the SEC's website (www.sec.gov).
10
Competition
Enterprise faces robust competition to attract and retain customers within existing and neighboring geographic markets. The Company's ability to achieve its long-term strategic growth and market share objectives will depend in part upon management's continued success in differentiating the Company in the marketplace and its ability to strengthen its competitive position. National and larger regional banks and financial institutions have a local presence in the Company's market area. These larger institutions have certain competitive advantages, including greater financial resources and the ability to make larger loans to a single borrower. Numerous local savings banks, commercial banks, cooperative banks and credit unions also compete in the Company's market area. The expanded commercial lending capabilities of credit unions and the shift to commercial lending by traditional savings banks means that both types of traditionally consumer-orientated institutions now compete for the Company's targeted commercial customers. In addition, the non-taxable status of credit unions allows them certain advantages as compared to taxable institutions such as Enterprise. Competition for loans, deposits and cash management services, wealth advisory assets, and insurance business also comes from other businesses that provide financial services, including consumer finance companies, mortgage brokers and lenders, private lenders, insurance companies, securities brokerage firms, institutional mutual funds, registered investment advisors, internet-based banks, non-bank electronic payment and funding channels, and other financial intermediaries. The evolving financial technology ("Fintech") industry also aims to compete with traditional banking services and delivery methods, although the industry offers opportunities for strategic partnerships, it is also a source for direct competition. Consolidation within the industry and customer disenfranchisement with larger national/international banks are expected to continue to have an impact on the regional competitive market.
The Company faces increasing competition within its marketplace on the pricing and terms of loans. This is expected to be an ongoing competitive challenge; however, the Company is committed to maintaining asset quality and focuses its sales efforts on building long-term relationships, rather than competing for individual transactions or easing loan terms.
The Company actively seeks to increase deposit market share and strengthen its competitive position with an unwavering commitment to providing an enhanced customer experience and through continuous reviews of deposit product offerings, cash management and ancillary services and state-of-the-art secure delivery channels, targeted to businesses, non-profits, professional practice groups, municipalities and consumers' needs.
Enterprise carefully plans market expansion through active development of new branch locations, identifying markets strategically located to complement existing locations while expanding the Company's geographic market footprint.
The increased use and advances in technology and data analytics and storage, such as internet and mobile banking, non-bank electronic payment channels, electronic transaction processing, digital currency, and cloud-computing and storage, among others are expected to have a significant impact on the future competitive landscape confronting financial service businesses.
In addition, the cost of compliance with new government regulations, changes in tax legislation and the interest-rate environment continue to impact competition and consolidation within the industry in various ways, with some participants better equipped to manage these changes than others based on size, depth of resources, or competitive product positioning, among other factors. See also "Supervision and Regulation" below, and Item 1A, "Risk Factors," of this Form 10-K for further discussion on how laws and regulations and other factors may affect the Company's competitive position, growth and/or profitability.
Supervision and Regulation
General
Set forth below is a summary description of the significant elements of the laws and regulations applicable to the Company and the Bank. The description is qualified in its entirety by reference to the full text of the statutes, regulations and policies that are described. Moreover, these statutes, regulations and policies are continually under review by the U.S. Congress and state legislatures and federal and state regulatory agencies. A change in statutes, regulations or regulatory policies applicable to the Company or its principal subsidiary, the Bank, could have a material effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
11
Regulatory Agencies
As a registered bank holding company, the Company is subject to the supervision and regulation of the Federal Reserve Board and, acting under delegated authority, the FRB pursuant to the Bank Holding Company Act, as amended (the "Bank Holding Company Act"). The Massachusetts Division of Banks (the "Division") also retains supervisory jurisdiction over the Company.
As a Massachusetts state-chartered bank, the Bank is subject to the supervision and regulation of the Division and, with respect to the Bank's New Hampshire branching operations, the New Hampshire Banking Department. As a state-chartered bank that accepts deposits and is not a member of the Federal Reserve System, the Bank is also subject to the supervision and regulation of the FDIC.
Bank Holding Company Regulation
As a registered bank holding company, the Company is required to furnish to the FRB annual and quarterly reports of its financial condition and results of operations and may also be required to furnish such additional information and reports as the Federal Reserve Board or the FRB may require.
Acquisitions by Bank Holding Companies
Under the Bank Holding Company Act, the Company must obtain the prior approval of the Federal Reserve Board or, acting under delegated authority, the FRB before (1) acquiring direct or indirect ownership or control of any class of voting securities of any bank or bank holding company if, after the acquisition, the Company would directly or indirectly own or control 5% or more of such class; (2) acquiring all or substantially all of the assets of another bank or bank holding company; or (3) merging or consolidating with another bank holding company. The Company's acquisition of or merger with another bank holding company or acquisition of another bank would also require the prior approval of the Division.
Under the Bank Holding Company Act, any company must obtain approval of the Federal Reserve Board or, acting under delegated authority, the FRB, prior to acquiring control of the Company or the Bank. For purposes of the Bank Holding Company Act, "control" is defined as ownership of 25% or more of any class of voting securities of the Company or the Bank, the ability to control the election of a majority of the directors, or the exercise of a controlling influence over management or policies of the Company or the Bank.
Control Acquisitions
The Change in Bank Control Act, as amended (the "Change in Bank Control Act"), and the related regulations of the Federal Reserve Board require any person or groups of persons acting in concert (except for companies required to make application under the Bank Holding Company Act), to file a written notice with the Federal Reserve Board or, acting under delegated authority, the appropriate Federal Reserve Bank, before the person or group acquires control of the Company. The Change in Bank Control Act defines "control" as the direct or indirect power to vote 25% or more of any class of voting securities or to direct the management or policies of a bank holding company or an insured bank. A rebuttable presumption of control arises under the Change in Bank Control Act where a person or group controls 10% or more, but less than 25%, of a class of the voting stock of a company or insured bank which is a reporting company under the Exchange Act, such as the Company, or such ownership interest is greater than the ownership interest held by any other person or group.
In addition, the Change in Bank Control Act prohibits any entity from acquiring 25% (or 5% in the case of an acquirer that is a bank holding company) or more of a bank holding company's or bank's voting securities, or otherwise obtaining control or a controlling influence over a bank holding company or bank without the approval of the Federal Reserve Board. On September 22, 2008, the Federal Reserve Board issued a policy statement on equity investments in bank holding companies and banks, which allows the Federal Reserve Board to generally be able to conclude that an entity's investment is not "controlling" if the investment in the form of voting and nonvoting shares represents in the aggregate (i) less than one-third of the total equity of the banking organization (and less than one-third of any class of voting securities, assuming conversion of all convertible nonvoting securities held by the entity) and (ii) less than 15% of any class of voting securities of the banking organization.
Under the Change in Bank Control Act and applicable Massachusetts law, any person or group of persons acting in concert would also be required to file a written notice with the FDIC and the Division before acquiring any such direct or indirect control of the Bank.
12
Permissible Activities
The Bank Holding Company Act also limits the investments and activities of bank holding companies. In general, a bank holding company is prohibited from acquiring direct or indirect ownership or control of more than 5% of the voting shares of a company that is not a bank or a bank holding company or from engaging directly or indirectly in activities other than those of banking, managing or controlling banks, providing services for its subsidiaries, and various non-bank activities that are deemed to be closely related to banking. The activities of the Company are subject to these legal and regulatory limitations under the Bank Holding Company Act and the implementing regulations of the Federal Reserve Board.
In connection with the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the "Dodd-Frank Act"), Section 13 of the Bank Holding Company Act, commonly known as the "Volcker Rule," was amended to generally prohibit banking entities from engaging in the short-term proprietary trading of securities and derivatives for their own account and bar them from having certain relationships with hedge funds or private equity funds. However, Section 203 of the Economic Growth, Regulatory Relief, and Consumer Protection Act, (the "EGRRCPA"), exempts community banks from the restrictions of the Volcker Rule if (i) the community bank, and every entity that controls it, has total consolidated assets equal to or less than $10 billion; and (ii) trading assets and liabilities of the community bank, and every entity that controls it, is equal to or less than 5% of its total consolidated assets. As the consolidated assets of the Company are less than $10 billion and the Company does not currently exceed the 5% threshold, this aspect of the Volcker Rule does not have any impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements at this time.
A bank holding company may also elect to become a "financial holding company," by which a qualified parent holding company of a banking institution may engage, directly or through its non-bank subsidiaries, in any activity that is financial in nature or incidental to such financial activity or in any other activity that is complementary to a financial activity and does not pose a substantial risk to the safety and soundness of depository institutions or the financial system generally. These activities include securities underwriting and dealing, insurance underwriting and making merchant banking investments. A bank holding company will be able to successfully elect to be regulated as a financial holding company if all of its depository institution subsidiaries meet certain prescribed standards pertaining to management, capital adequacy and compliance with the Community Reinvestment Act, as amended (the "Community Reinvestment Act"), such as being "well-managed" and "well-capitalized," and must have a Community Reinvestment Act rating of at least "satisfactory." Financial holding companies remain subject to regulation and oversight by the Federal Reserve Board. The Company believes that the Bank, which is the Company's sole depository institution subsidiary, presently satisfies all of the requirements that must be met to enable the Company to successfully elect to become a financial holding company. However, the Company has no current intention of seeking to become a financial holding company. Such a course of action may become necessary or appropriate at some time in the future depending upon the Company's strategic plan.
Source of Strength
Under the Federal Reserve Board's "source-of-strength" doctrine, a bank holding company is required to act as a source of financial and managerial strength to any of its subsidiary banks. The holding company is expected to commit resources to support its subsidiary bank, including at times when the holding company may not be in a financial position to provide such support. A bank holding company's failure to meet its source-of-strength obligations may constitute an unsafe and unsound practice or a violation of the Federal Reserve Board's regulations, or both. The source-of-strength doctrine most directly affects bank holding companies in situations where the bank holding company's subsidiary bank fails to maintain adequate capital levels. This doctrine was codified by the Dodd-Frank Act, but the Federal Reserve Board has not yet adopted regulations to implement this requirement.
Imposition of Liability for Undercapitalized Subsidiaries
Bank regulators are required to take "prompt corrective action" to resolve problems associated with insured depository institutions whose capital declines below certain levels. In the event an institution becomes "undercapitalized," it must submit a capital restoration plan to its regulators. The capital restoration plan will not be accepted by the regulators unless each company having control of the undercapitalized institution guarantees the subsidiary's compliance with the capital restoration plan up to a certain specified amount. Any such guarantee from a depository institution's holding company is entitled to a priority of payment in bankruptcy.
The aggregate liability of the holding company of an undercapitalized bank is limited to the lesser of 5% of the institution's assets at the time it became undercapitalized or the amount necessary to cause the institution to be "adequately capitalized."
13
The bank regulators have greater power in situations where an institution becomes "significantly" or "critically" undercapitalized or fails to submit a capital restoration plan. For example, a bank holding company controlling such an institution can be required to obtain prior Federal Reserve Board approval of proposed dividends, or it may be required to consent to a consolidation or to divest the troubled institution or other affiliates.
Safety and Soundness
The federal banking agencies have adopted the Interagency Guidelines for Establishing Standards for Safety and Soundness. The guidelines establish general standards relating to internal controls and information systems, internal audit systems, loan documentation, credit underwriting, interest-rate exposure, asset growth, asset quality, earnings and compensation, and fees and benefits. In general, these guidelines require, among other things, appropriate systems and practices to identify and manage the risk and exposures specified in the guidelines. These guidelines also prohibit excessive compensation as an unsafe and unsound practice and describe compensation as excessive when the amounts paid are unreasonable or disproportionate to the services performed by an executive officer, employee, director or principal stockholder.
Bank holding companies are not permitted to engage in unsafe or unsound banking practices. The Federal Reserve Board has the power to order a bank holding company to terminate any activity or investment, or to terminate its ownership or control of any subsidiary, when it has reasonable cause to believe that the continuation of such activity or investment or such ownership or control constitutes a serious risk to the financial safety, soundness, or stability of any subsidiary bank of the bank holding company. The Federal Reserve Board also has the authority to prohibit activities of non-banking subsidiaries of bank holding companies which represent unsafe and unsound banking practices or which constitute violations of laws or regulations.
For example, the Federal Reserve Board's Regulation Y requires a holding company to give the Federal Reserve Board prior notice of any redemption or repurchase of its own equity securities, if the consideration to be paid, together with the consideration paid for any repurchases in the preceding year, is equal to 10% or more of the bank holding company's consolidated net worth. There is an exception for bank holding companies that are well-managed, well-capitalized, and not subject to any unresolved supervisory issues. The Federal Reserve Board may oppose the transaction if it believes that the transaction would constitute an unsafe or unsound practice or would violate any law or regulation. As another example, a holding company may not impair its subsidiary bank's soundness by causing it to make funds available to non-banking subsidiaries or their customers if the Federal Reserve Board believes it not prudent to do so.
The Federal Reserve Board can assess civil money penalties for activities conducted on a knowing and reckless basis, if such unsafe and unsound activities caused a substantial loss to a depository institution. The Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery and Enforcement Act ("FIRREA") expanded the Federal Reserve's authority to prohibit activities of bank holding companies and their non-banking subsidiaries which represent unsafe and unsound banking practices, or which constitute violations of laws or regulations. FIRREA increased the amount of civil money penalties which the Federal Reserve can assess for activities conducted on a knowing and reckless basis, if those activities caused a substantial loss to a depository institution. The penalties can be as high as $1 million for each day the activity continues. FIRREA also expanded the scope of individuals and entities against which such penalties may be assessed.
Capital Requirements
The federal banking agencies have adopted risk-based capital guidelines for bank holding companies and banks that are expected to provide a measure of capital that reflects the degree of risk associated with a banking organization's operations for both transactions reported on the consolidated balance sheet as assets, such as loans, and those recorded as off-balance sheet items, such as commitments, letters of credit and recourse arrangements. The risk-based guidelines apply on a consolidated basis to bank holding companies with consolidated assets of $3 billion or more or with a material amount of equity securities outstanding that are registered with the SEC.
Pursuant to federal regulations, banks and bank holding companies must maintain capital levels commensurate with the level of risk to which they are exposed, including the volume and severity of problem loans. For example, bank holding companies experiencing internal growth or making acquisitions are expected to maintain strong capital positions substantially above the minimum supervisory levels, without significant reliance on intangible assets. The federal banking agencies may change existing capital guidelines or adopt new capital guidelines in the future and have required many banks and bank holding companies subject to enforcement actions to maintain capital ratios in excess of the minimum ratios otherwise required to be deemed well-capitalized, in which case the affected institution may no longer be deemed well-capitalized and may be subject to restrictions on various activities, including a bank's ability to accept or renew brokered deposits.
14
Under these capital guidelines, a banking organization is required to maintain certain minimum capital ratios, which are obtained by dividing its qualifying capital by its total risk-adjusted assets and off-balance sheet items. In general, the dollar amounts of assets and certain off-balance sheet items are "risk-adjusted" and assigned to various risk categories. In addition to such risk adjusted capital requirements, banking organizations are also required to maintain an additional minimum "leverage" capital ratio, which is calculated based on average total assets without any adjustment for risk being made to the value of the assets.
Qualifying capital is classified depending on the type of capital as follows:
"Tier 1 capital" consists of common equity, retained earnings, qualifying non-cumulative perpetual preferred stock, a limited amount of qualifying cumulative perpetual preferred stock and minority interests in the equity accounts of consolidated subsidiaries, less goodwill and certain other intangible assets. In determining bank holding company compliance with holding company level capital requirements, qualifying Tier 1 capital may count trust preferred securities, subject to certain criteria and quantitative limits for inclusion of restricted core capital elements in Tier 1 capital, provided that the bank holding company has total assets of less than $15 billion and such trust preferred securities were issued before May 19, 2010;
"Tier 2 capital" includes, among other things, hybrid capital instruments, perpetual debt, mandatory convertible debt securities, qualifying term subordinated debt, preferred stock that does not qualify as Tier 1 capital, and a limited amount of allowance for loan and lease losses.
Capital Requirements under Basel III
The rules adopted by the regulators implementing the international regulatory capital framework, referred to as the "Basel III Rules," apply to both depository institutions and (subject to certain exceptions not applicable to the Company) their holding companies. Although parts of the Basel III Rules apply only to large, complex financial institutions, substantial portions of the Basel III Rules apply to the Company and the Bank. Under the Basel III Rules, which generally became effective January 1, 2015, and were fully phased in effective January 1, 2019, a bank holding company must satisfy certain capital levels in order to comply with the prompt corrective action framework and to avoid limitations on capital distributions and discretionary bonus payments.
The Basel III Rules also establish a "capital conservation buffer" of 2.5% above the regulatory minimum risk-based capital requirements. An institution will be subject to limitations on certain activities, including payment of dividends, share repurchases and discretionary bonuses to executive officers, if its capital level is below the buffered ratio.
The Basel III minimum capital ratios, as applicable to the Company and the Bank in 2019, with the full capital conservation buffer are summarized in the table below.
Basel III Minimum for Capital Adequacy Purposes | Basel III Additional Capital Conservation Buffer | Basel III Ratio with Capital Conservation Buffer | ||||
Total Risk Based Capital (total capital to risk weighted assets) | 8.00% | 2.50% | 10.50% | |||
Tier 1 Risk Based Capital (tier 1 to risk weighted assets) | 6.00% | 2.50% | 8.50% | |||
Tier 1 Leverage Ratio (tier 1 to average assets) | 4.00% | —% | 4.00% | |||
Common Equity Tier 1 Risk Based Capital (CET1 to risk weighted assets) | 4.50% | 2.50% | 7.00% | |||
Under the Basel III Rules, higher or more sensitive risk weights are assigned to various categories of assets, including, certain credit facilities that finance the acquisition, development or construction of real property, certain exposures or credits that are 90 days past due or on non-accrual, foreign exposures and certain corporate exposures. In addition, these rules include greater recognition of collateral and guarantees, and revised capital treatment for derivatives and repo-style transactions.
In addition, the Basel III Rules include certain exemptions to address concerns about the regulatory burden on community banks. For example, banking organizations with less than $15 billion in consolidated assets as of December 31, 2009 are permitted to include in Tier 1 capital trust preferred securities and cumulative perpetual preferred stock issued and included in
15
Tier 1 capital prior to May 19, 2010 on a permanent basis, without any phase out. Community banks were also allowed to elect, on a one-time basis in their March 31, 2015 quarterly filings, to permanently opt-out of the requirement to include most accumulated other comprehensive income ("AOCI") components in the calculation of CET1 capital and, in effect, retain the AOCI treatment under the previous capital rules. Under the Basel III Rules, in 2015 the Company made such election to permanently exclude AOCI from capital.
Management believes, as of December 31, 2019, that the Company met all capital adequacy requirements to which it was subject under Basel III. As of December 31, 2019, the Company met the definition of "well-capitalized" under the applicable Federal Reserve Board regulations.
Community Bank Leverage Ratio
On September 17, 2019, the federal banking agencies jointly finalized a rule to be effective January 1, 2020 and intended to simplify the regulatory capital requirements described above for qualifying community banking organizations that opt into the Community Bank Leverage Ratio ("CBLR") framework, as required by Section 201 of the EGRRCPA. Under the final rule, if a qualifying community banking organization opts into the CBLR framework and meets all requirements under the framework, it will be considered to have met the well-capitalized ratio requirements under the Prompt Corrective Action regulations described below and will not be required to report or calculate risk-based capital. In order to qualify for the CBLR framework, a community banking organization must have a tier 1 leverage ratio of greater than 9%, less than $10 billion in total consolidated assets, and limited amounts of off-balance-sheet exposures and trading assets and liabilities. The Company and the Bank will continue to follow Basel III capital requirements as described above.
Regulatory Restrictions on Dividends
The Company is regarded as a legal entity separate and distinct from the Bank. The principal source of the Company's revenues is dividends received from the Bank. Both Massachusetts and federal law limit the payment of dividends by the Company. Under Massachusetts law, the Company is generally prohibited from paying a dividend or making any other distribution if, after making such distribution, it would be unable to pay its debts as they become due in the usual course of business, or if its total assets would be less than the sum of its total liabilities plus the amount that would be needed if it were dissolved at the time of the distribution, to satisfy any preferential rights on dissolution of holders of preferred stock ranking senior in right of payment to the capital stock on which the applicable distribution is made. The Federal Reserve Board also has further authority to prohibit dividends by bank holding companies if their actions constitute unsafe or unsound practices.
The Federal Reserve Board policy statement and supervisory guidance on the payment of cash dividends by bank holding companies, expresses the view that a bank holding company should pay cash dividends only to the extent that, (1) the company's net income for the past year is sufficient to cover the cash dividends, (2) the rate of earnings retention is consistent with the company's capital needs, asset quality, and overall financial condition, and (3) the minimum regulatory capital adequacy ratios are met. It is also the Federal Reserve Board's policy that bank holding companies should not maintain dividend levels that undermine their ability to serve as a source of strength to their banking subsidiaries.
Bank Regulation
The Bank is subject to the supervision and regulation of the Division and the FDIC, and, with respect to its New Hampshire branching operations, of the New Hampshire Banking Department. Federal and Massachusetts laws and regulations that specifically apply to the Bank's business and operations cover, among other matters, the scope of its business, the nature of its investments, its reserves against deposits, the timing of the availability of deposited funds, its activities relating to dividends, investments, loans, the nature and amount of and collateral for certain loans, borrowings, capital requirements, certain check-clearing activities, branching, and mergers and acquisitions. The Bank is also subject to federal and state laws and regulations that restrict or limit loans or extensions of credit to, or other transactions with, "insiders," including executive officers, directors and principal stockholders, and loans or extension of credit by banks to affiliates or purchases of assets from, or other transactions with, affiliates, including parent holding companies.
The FDIC and the Division may exercise extensive discretion in connection with their supervisory and enforcement activities and examination policies, including policies with respect to the classification of assets and the establishment of adequate loan loss reserves for regulatory purposes. If as a result of an examination, the Division or the FDIC should determine that the financial condition, capital resources, asset quality, earnings prospects, management, liquidity, sensitivity to market risk, or other aspects of the Bank's operations are unsatisfactory or that the Bank or its management is violating or has violated any law
16
or regulation, the Division and the FDIC have authority to undertake a variety of enforcement measures of varying degrees of severity, including the following:
• | Requiring the Bank to take affirmative action to correct any conditions resulting from any violation or practice; |
• | Directing the Bank to increase capital and maintain higher specific minimum capital ratios, which may preclude the Bank from being deemed to be well-capitalized and restrict its ability to engage in various activities; |
• | Restricting the Bank's growth geographically, by products and services, or by mergers and acquisitions; |
• | Requiring the Bank to enter into an informal or formal enforcement action to take corrective measures and cease unsafe and unsound practices, including requesting the board of directors to adopt a binding resolution, sign a memorandum of understanding or enter into a consent order; |
• | Requiring prior approval for any changes in senior management or the board of directors; |
• | Removing officers and directors and assessing civil monetary penalties; and |
• | Taking possession of, closing and liquidating the Bank or appointing the FDIC as receiver under certain circumstances. |
Permissible Activities
Under the Federal Deposit Insurance Act, as amended (the "FDIA"), and applicable Massachusetts law, the Bank may generally engage in any activity that is permissible under Massachusetts law and either is permissible for national banks or the FDIC has determined does not pose a significant risk to the FDIC's Deposit Insurance Fund ("DIF"). In addition, the Bank may also form, subject to the approvals of the Division and the FDIC, "financial subsidiaries" to engage in any activity that is financial in nature or incidental to a financial activity. In order to qualify for the authority to form a financial subsidiary, the Bank is required to satisfy certain conditions, some of which are substantially similar to those that the Company would be required to satisfy in order to elect to become a financial holding company. The Company believes that the Bank would be able to satisfy all of the conditions that would be required to form a financial subsidiary, although the Bank has no current intention of doing so. Such a course of action may become necessary or appropriate at some time in the future depending upon the Bank's strategic plan.
Capital Adequacy Requirements
The FDIC monitors the capital adequacy of the Bank by using a combination of risk-based guidelines and leverage ratios. The FDIC considers the Bank's capital levels when taking action on various types of applications and when conducting supervisory activities related to the safety and soundness of the Bank and the banking system. As noted above, the Basel III Rules require banks to maintain four minimum capital standards: (1) a Tier 1 capital to adjusted total assets ratio, or "leverage capital ratio," of at least 4.0%, (2) a Tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets ratio, or "Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio," of at least 6.0%, (3) a total risk-based capital (Tier 1 plus Tier 2) to risk-weighted assets ratio, or "total risk-based capital ratio," of at least 8.0%, and (4) a CET1 capital ratio of 4.5%, which are the same minimum capital standards to which the Company is held on a consolidated basis. In addition, the FDIC's prompt corrective action standards discussed below, in effect, increase the minimum regulatory capital ratios for banking organizations in order to be considered "well capitalized." Higher capital levels may be required if warranted by the particular circumstances or risk profiles of individual institutions, or if required by the banking regulators due to the economic conditions impacting our market. For example, FDIC regulations provide that higher capital may be required to take adequate account of, among other things, interest-rate risk and the risks posed by concentrations of credit, nontraditional activities or securities trading activities.
Management believes, as of December 31, 2019, that Bank exceeded its minimum capital requirements and met all capital adequacy requirements to which it was subject under Basel III.
17
Prompt Corrective Action
The federal banking agencies define five categories in which an insured depository institution will be placed, based on the level of its capital ratios: well-capitalized, adequately capitalized, undercapitalized, significantly undercapitalized, and critically undercapitalized. Insured depository institutions are required to meet the following capital levels in order to qualify as "well-capitalized:" (i) a Total risk-based capital ratio of 10%; (ii) a Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio of 8%; (iii) a Tier 1 leverage ratio of 5%; and (iv) a CET1 risk-based capital ratio of 6.5%. Accordingly, a financial institution may be considered "well-capitalized" under the prompt corrective action framework, but not satisfy the full Basel III capital ratios.
The Bank's regulatory capital ratios were in excess of the levels established for "well-capitalized" institutions as of December 31, 2019. As noted above, as of December 31, 2019, management believes the Bank satisfied all capital adequacy requirements under Basel III.
A bank that may otherwise meet the minimum requirements to be classified as well-capitalized, adequately capitalized, or undercapitalized but may be treated instead as though it were in the next lower capital category if the appropriate federal banking agency, after notice and opportunity for hearing, determines that an unsafe or unsound condition, or an unsafe or unsound practice, warrants such treatment. Under the prompt corrective action regulations, a bank that is deemed to be undercapitalized or in a lesser capital category will be required to submit to its primary federal banking regulator a capital restoration plan and to comply with the plan.
Any bank holding company that controls a subsidiary bank that has been required to submit a capital restoration plan will be required to provide assurances of compliance by the bank with the capital restoration plan, subject to limitations on the bank holding company's aggregate liability in connection with providing such required assurances. Failure to restore capital under a capital restoration plan can result in the bank being placed into receivership if it becomes critically undercapitalized. A bank subject to prompt corrective action also may affect its parent holding company in other ways. These include possible restrictions or prohibitions on dividends or subordinated debt payments to the parent holding company by the bank, as well as limitations on other transactions between the bank and the parent holding company. In addition, the Federal Reserve Board may impose restrictions on the ability of the bank holding company itself to pay dividends or require divestiture of holding company affiliates that pose a significant risk to the subsidiary bank, or require divestiture of the undercapitalized subsidiary bank. At each successive lower capital category, an insured bank may be subject to increased operating restrictions by its primary federal banking regulator.
Branching
Massachusetts law provides that a Massachusetts banking company may be "eligible" to submit a notice to the Division and the FDIC to establish a branch within the Commonwealth. A bank is "eligible" to submit a notice to establish a branch in the Commonwealth if the following conditions are met: (i) the bank has received a "satisfactory" or higher Community Reinvestment Act (the "CRA") rating at its most recent CRA examination by the Division or federal regulator; (ii) the bank is "adequately capitalized" as defined under the provisions of the Federal Deposit Insurance Act and the FDIC's Capital Adequacy Regulations; and (iii) the bank has not been notified that it is in troubled condition by the Division or any federal regulatory agency. A bank must also submit a notice to the Division to relocate or close an existing branch. The Division and the FDIC consider several factors when making a decision to approve the notice, including financial condition, capital adequacy, earnings prospects, the needs of the community, and whether competition would be adversely affected.
Previously, under the Riegle-Neal Interstate Banking and Branching Efficiency Act of 1994, (the "Riegle-Neal Act"), a bank's ability to branch into a particular state was largely dependent upon whether the state "opted in" to de novo interstate branching. Many states did not "opt-in," which resulted in branching restrictions in those states. The Dodd-Frank Act amended the Riegle-Neal legal framework for interstate branching to permit national banks and state banks to establish branches in any state if that state would permit the establishment of the branch by a state bank chartered in that state. The Bank may, therefore, also establish branches in any other state if that state would permit the establishment of a branch by a state bank chartered in that state. In this case, the Bank would also be required to file a notice with the Division, the FDIC and potentially the banking authority of the state into which the Bank intends to branch.
Deposit Insurance
The FDIC insures the deposits of federally insured banks, such as the Bank, and thrifts, up to prescribed statutory limits of $250,000 for each depositor, through the DIF and safeguards the safety and soundness of the banking and thrift industries. The
18
amount of FDIC assessments paid by each insured depository institution is based on its relative risk of default as measured by regulatory capital ratios and other supervisory factors.
At least semi-annually, the FDIC will update its loss and income projections for the DIF and, if needed, will increase or decrease assessment rates, following notice-and-comment rulemaking, if required. However, if there are additional bank or financial institution failures or if the FDIC otherwise determines to increase assessment rates, the Bank may be required to pay higher FDIC insurance premiums. Additionally, under the FDIA, the FDIC may terminate deposit insurance upon a finding that the institution has engaged in unsafe and unsound practices, is in an unsafe or unsound condition to continue operations, or has violated any applicable law, regulation, rule, order or condition imposed by the FDIC.
The Bank is generally unable to control the amount of premiums that it is required to pay for FDIC insurance. In connection with the Dodd Frank Act's requirement that insurance assessments be based on assets, in July 2016, the FDIC redefined its deposit insurance premium assessment base to be an institution's average consolidated total assets minus average tangible equity and revised its deposit insurance assessment rate schedule. In addition, the FDIC is considering, and is expected to adopt, a final rule to apply the CBLR framework to the deposit insurance assessment system.
On September 30, 2018, the DIF reserve ratio reached 1.36%. Because the reserve ratio exceeded the targeted 1.35%, two deposit assessment changes occurred under FDIC regulations: (1) surcharges on large banks ended, and the last surcharge on large banks was collected on December 28, 2018; and (2) small banks were awarded assessment credits for the portion of their assessment that contributed to the growth in the reserve ratio from 1.15% to 1.35%, to be applied when the reserve ratio is at least 1.38%. The DIF ratio exceeded 1.38% at both June30, 2019 and September 30, 2019. The Bank's assessment credit as calculated by the FDIC was $683 thousand and was fully utilized towards the Bank's September 2019 and a portion of the December 2019 quarterly Deposit Insurance Assessments.
In addition, all FDIC-insured institutions have historically been required to pay assessments to the FDIC to fund interest payments on bonds issued by the Financing Corporation ("FICO"), an agency of the federal government established to recapitalize the predecessor to the DIF. The FICO bonds matured in September 2019 and the last FICO assessment was collected on the March 29, 2019 FDIC Quarterly Assessment Invoice. These assessments were included in the Company's Deposit Insurance Premiums on the Consolidated Statements of Income.
Restrictions on Dividends and Other Capital Distributions
The Company's ability to pay dividends on its shares depends primarily on dividends it receives from the Bank. Both Massachusetts and federal law limit the payment of dividends by the Bank. Under FDIC regulations and applicable Massachusetts law, the dollar amount of dividends and any other capital distributions that the Bank may make depends upon its capital position and recent net income. Any dividend payment that would exceed the total of the Bank's net profits for the current year plus its retained net profits of the preceding two years would require the Massachusetts Division of Banks' approval. Applicable provisions of the FDIA also prohibits a bank from paying any dividends on its capital stock if the bank is in default on the payment of any assessment to the FDIC or if the payment of dividends would otherwise cause the bank to become undercapitalized. Any restrictions, regulatory or otherwise, on the ability of the Bank to pay dividends to the Company may restrict the ability of the Company to pay dividends to the holders of its common stock. However, if the Bank's capital becomes impaired or the FDIC or Division otherwise determines that the Bank needs more than normal supervision, the Bank may be prohibited or otherwise limited from paying any dividends or making any other capital distributions.
The statutory term "net profits" essentially equates with the accounting term "net income" and is defined under the Massachusetts banking statutes to mean the remainder of all earnings from current operations plus actual recoveries on loans and investments and other assets after deducting from such total all current operating expenses, actual losses, accrued dividends on any preferred stock and all federal and state taxes.
19
Community Reinvestment Act
The Community Reinvestment Act of 1977 and the regulations issued thereunder are intended to encourage banks to help meet the credit needs of their entire assessment area, including low-and moderate-income neighborhoods, consistent with the safe and sound operations of such banks. The CRA requires the FDIC and the Division evaluate the record of each financial institution in meeting such credit needs. The CRA evaluation is also considered by the bank regulatory agencies in evaluating approvals for mergers, acquisitions, and applications to open, relocate or close a branch or facility. Failure to adequately meet the criteria within CRA guidelines could impose additional requirements and limitations on the Bank. Additionally, the Bank must publicly disclose the ability to request the Bank's CRA Performance Evaluation and other various related documents. The Bank received a rating of "High Satisfactory" by the Division and "Satisfactory" by the FDIC on its most recent Community Reinvestment Act examination.
On December 12, 2019, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency and the FDIC issued a joint proposal to revamp how the agencies will assess banks' performance under the CRA. Among other changes, the proposal (i) expands the concept of assessment area ("AA") to include geographies outside of a bank's current AAs and in which the bank receives at least 5% of its retail deposits and (ii) introduces a series of objective tests for determining a bank's presumptive CRA rating. The proposal will be most noteworthy for banks with at least $500 million in total assets and with significant retail deposits sourced outside of their current AAs. The Company and the Bank will continue to monitor this proposal.
Restrictions on Transactions with Affiliates and Loans to Insiders
Transactions between the Bank and its affiliates are subject to the provisions of Section 23A and 23B of the Federal Reserve Act (the "Affiliates Act"), as such provisions are made applicable to state non-member banks by Section 18(i) of the Federal Deposit Insurance Act. Affiliates of a bank include, among other entities, the bank's holding company and companies that are under common control with the bank.
These provisions place limits on the amount of:
• | loans or extensions of credit to affiliates; |
• | investment in affiliates; |
• | assets that may be purchased from affiliates, except for real and personal property exempted by the Federal Reserve Board; |
• | the amount of loans or extensions of credit to third parties collateralized by the securities or obligations of affiliates; and |
• | the guarantee, acceptance or letter of credit issued on behalf of an affiliate. |
The total amount of the above transactions is limited in amount, as to any one affiliate, to 10% of the Bank's capital and surplus and, as to all affiliates combined, to 20% of its capital and surplus. In addition to the limitation on the amount of these transactions, each of the above transactions must also meet specified collateral requirements and the types of permissible collateral may be limited. The Bank must also comply with other provisions designed to avoid the purchase or acquisition of low-quality assets from affiliates. The Dodd-Frank Act expanded the scope of Section 23A, which now includes investment funds managed by an institution as an affiliate, as well as other procedural and substantive hurdles.
The Bank is also subject to Section 23B of the Federal Reserve Act which, among other things, prohibits the Bank from engaging in any transaction with an affiliate unless the transaction is on terms substantially the same, or at least as favorable to the Bank or its subsidiaries, as those prevailing at the time for comparable transactions with non-affiliated companies. The Federal Reserve Board has also issued Regulation W which codifies prior regulations under the Affiliates Act and interpretive guidance with respect to affiliate transactions.
Under both Massachusetts and federal law, the Bank is also subject to restrictions on extensions of credit to its executive officers, directors, principal stockholders and their related interests. These extensions of credit (1) must be made on substantially the same terms, including interest rates and collateral, as those prevailing at the time for comparable transactions with third parties, (2) must follow the credit underwriting procedures at least as stringent as those applicable to comparable transactions with third parties, and (3) must not involve more than the normal risk of repayment or present other unfavorable features. The Dodd-Frank Act expanded coverage of transactions with insiders by including credit exposure arising from derivative transactions (which are also covered by the expansion of Section 23A). The Dodd-Frank Act prohibits an insured depository institution from purchasing or selling an asset to an executive officer, director, or principal stockholder (or any related interest of such a person) unless the transaction is on market terms, and, if the transaction exceeds 10% of the institution's capital, it is approved in advance by a majority of the disinterested directors.
20
Concentrated Commercial Real Estate Lending Regulations
The federal banking agencies, including the FDIC, have promulgated guidance governing financial institutions with concentrations in commercial real estate lending. The guidance provides that a bank has a concentration in commercial real estate lending if (i) total reported loans for construction, land development, and other land represent 100% or more of total capital or (ii) total reported loans secured by multifamily and non-farm nonresidential properties (excluding loans secured by owner-occupied properties) and loans for construction, land development, and other land represent 300% or more of total capital and the bank's commercial real estate loan portfolio has increased 50% or more during the prior 36 months. If a concentration is present, management must employ heightened risk management practices that address the following key elements: including board and management oversight and strategic planning, portfolio management, development of underwriting standards, risk assessment and monitoring through market analysis and stress testing, and maintenance of increased capital levels as needed to support the level of commercial real estate lending. As of December 31, 2019, the Bank's concentrations of commercial real estate loans fall near or slightly above the established levels and the Company believes its credit risk administration to be consistent with heightened risk management regulatory guidance.
The Basel III Rules also require loans categorized as "high-volatility commercial real estate," or HVCRE, to be assigned a 150% risk weighting and require additional capital support. However, the EGRRCPA prohibits federal banking regulators from imposing this higher capital standards on HVCRE exposures unless they are for higher risk loans for acquisition, development or construction, or ADC, and clarifying ADC status.
On November 20, 2019, federal banking regulators jointly issued a final rule revising the definition of a HVCRE exposure and providing interpretations of certain aspects of Acquisition Development and Construction loans. The interpretation under this final rule will take effect on April 1, 2020 and may impact the Banks' Consolidated Report of Condition and Income.
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act
The Dodd-Frank Act implemented significant changes to the regulation of the financial services industry and includes the following provisions that have affected or are likely to affect the Company:
• | Repeal of the federal prohibitions on the payment of interest on demand deposits effective July 21, 2011, thereby permitting, but not requiring, depository institutions to pay interest on business transaction and other accounts. |
• | Imposition of comprehensive regulation of the over-the-counter derivatives market, including provisions that effectively prohibit insured depository institutions from conducting certain derivatives activities from within the institution. |
• | Implementation of corporate governance revisions, including proxy access requirements for all publicly traded companies. |
• | Increase in the Federal Reserve Board's examination authority with respect to bank holding companies' non-banking subsidiaries. |
• | Limitations on the amount of any interchange fee charged by a debit card issuer to be reasonable and proportional to the cost incurred by the issuer. The interchange rate cap has been set at $0.24 per transaction. While these restrictions do not apply to banks like Enterprise with less than $10 billion in assets, the rule could affect the competitiveness of debit cards issued by smaller banks. We believe that market forces may erode the effectiveness of this exemption now that merchants can select more than one network for transaction routing. |
• | Significant increases in the regulation of mortgage lending and servicing by banks and non-banks. In particular, requirements that mortgage originators act in the best interests of a consumer and seek to ensure that a consumer will have the capacity to repay a loan that the consumer enters into; requirements that mortgage originators be properly qualified, registered, and licensed and comply with any regulations designed by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau ("CFPB") to monitor their operations; mandates of comprehensive additional and enhanced residential mortgage loan related disclosures, both prior to loan origination and after; mandates of additional appraisal practices for loans secured by residential dwellings, including potential additional appraisals at the banks cost; mandates of additional collection and reporting requirements on transactions that are reportable under the Home Mortgage Disclosure Act; additional restrictions on the compensation of loan originators; and requirements that mortgage loan securitizers retain a certain amount of risk (as established by the regulatory agencies). However, mortgages that conform to the new regulatory standards as "qualified residential mortgages" will not be subject to risk retention requirements. |
Although the majority of the Dodd-Frank Act's rulemaking requirements have been met with finalized rules, approximately one-fifth of the rulemaking requirements are either still in the proposal stage or have not yet been proposed. On May 24, 2018,
21
the EGRRCPA amended provisions in the Dodd-Frank Act with the intent to relieve the regulatory burden on community banks. A theme of the EGRRCPA is to provide broad exemption for smaller banking institutions from certain requirements of the Dodd-Frank Act, by raising the level of consolidated assets an institution must have before it becomes subject to certain regulatory requirements. A number of changes made by the EGRRCPA require agency implementation either through rule making procedures or other action by the federal banking regulators. For those regulations that have been implemented, most will have little to no impact on the Company. However, the Company may be impacted by future agency rulemaking in connection with implementation of the EGRRCPA and it is difficult to anticipate the continued impact this expansive legislation may have on the Company, its customers and the financial industry generally.
For more information on the EGRRCPA, please see the following sections "Permissible Activities, Community Bank Leverage Ratio, and Concentrated Commercial Real Estate Lending Regulations," above, and "Consumer Financial Protection Bureau and HMDA," below.
Consumer Financial Protection Bureau
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau was created under the Dodd-Frank Act to centralize responsibility for consumer financial protection with broad rulemaking, supervision and enforcement authority for a wide range of consumer protection laws that would apply to all banks and thrifts, including the Equal Credit Opportunity Act, Truth-in Lending Act ("TILA"), Real Estate Settlement Procedures Act ("RESPA"), Fair Credit Reporting Act, Fair Debt Collection Act, the Consumer Financial Privacy provisions of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act and certain other statutes. Banking institutions with total assets of $10 billion or less, such as the Bank, remain subject to the supervision and enforcement of their primary federal banking regulator with respect to the federal consumer financial protection laws and such additional regulations as may be adopted by the CFPB.
The "Ability-to-Repay/Qualified Mortgage" rules, which amended TILA's implementing regulation, Regulation Z generally requires creditors to make a reasonable, good faith determination of a consumer's ability to repay for certain consumer credit transactions secured by a dwelling and establishes certain protections from liability under this requirement for "qualified mortgages." The EGRRCPA provides that for certain insured depository institutions and insured credit unions with less than $10 billion in total consolidated assets, mortgage loans that are originated and retained in portfolio will automatically be deemed to satisfy the "ability to repay" requirement. To qualify for this treatment, the insured depository institutions and credit unions must meet conditions relating to prepayment penalties, points and fees, negative amortization, interest-only features and documentation.
Home Mortgage Disclosure Act ("HMDA")
On October 15, 2015, pursuant to section 1094 of the Dodd-Frank Act, the CFPB issued amended rules in regard to the collection, reporting and disclosure of certain residential mortgage transactions under the Home Mortgage Disclosure Act (the "HMDA Rules"). The Dodd-Frank Act mandated additional loan data collection points in addition to authorizing the Bureau to require other data collection points under implementing Regulation C. Most of the provisions of the HMDA Rule went into effect on January 1, 2018 and apply to data collected in 2018 and reporting in 2019 and later years. The HMDA Rule adopts a uniform loan volume threshold for all financial institutions, modifies the types of transactions that are subject to collection and reporting, expands the loan data information being collected and reported, and modifies procedures for annual submission and annual public disclosures. EGRRCPA amended provisions of the HMDA rule to exempt certain insured institutions from most of the expanded data collection requirements required of the Dodd- =Frank Act. Institutions originating fewer than 500 dwelling secured closed-end mortgage loans or fewer than 500 dwelling secured open-end lines are exempt from the expanded data collection requirements that went into effect January 1, 2018. The Bank does not receive this reporting relief based on the number of dwelling secured mortgage loans reported annually.
UDAP and UDAAP
Banking regulatory agencies have increasingly used a general consumer protection statute to address "unethical" or otherwise "bad" business practices that may not necessarily fall directly under the purview of a specific banking or consumer finance law. The law of choice for enforcement against such business practices has been Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act, referred to as the FTC Act, which is the primary federal law that prohibits unfair or deceptive acts or practices, referred to as UDAP, and unfair methods of competition in or affecting commerce. "Unjustified consumer injury" is the principal focus of the FTC Act. Prior to the Dodd-Frank Act, there was little formal guidance to provide insight to the parameters for compliance with UDAP laws and regulations. However, UDAP laws and regulations have been expanded under the Dodd-Frank Act to apply to "unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices," referred to as UDAAP, which have been delegated to the CFPB for rule-making. The federal banking agencies have the authority to enforce such rules and regulations.
22
Incentive Compensation
In June 2010, the Federal Reserve Board, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency and the FDIC issued comprehensive final guidance on incentive compensation policies intended to ensure that the incentive compensation policies of banking organizations do not undermine the safety and soundness of such organizations by encouraging excessive risk-taking. The guidance, which covers all employees that have the ability to materially affect the risk profile of an organization, either individually or as part of a group, is based upon the key principles that a banking organization's incentive compensation arrangements should (i) provide incentives that do not encourage risk-taking beyond the organization's ability to effectively identify and manage risks, (ii) be compatible with effective internal controls and risk management, and (iii) be supported by strong corporate governance, including active and effective oversight by the organization's board of directors.
The Federal Reserve Board will review, as part of the regular, risk-focused examination process, the incentive compensation arrangements of banking organizations, such as the Company, that are not "large, complex banking organizations." The findings of the supervisory initiatives will be included in reports of examination. Enforcement actions may be taken against a banking organization if its incentive compensation arrangements, or related risk management control or governance processes, pose a risk to the organization's safety and soundness and the organization is not taking prompt and effective measures to correct the deficiencies.
In addition, publicly traded companies are required by the SEC to give stockholders a non-binding vote on executive compensation at least every three years and on so-called "golden parachute" payments in connection with approvals of mergers and acquisitions unless previously voted on by stockholders. Also, certain publicly traded companies are required to disclose the ratio of the compensation of its chief executive officer ("CEO") to the median compensation of its employees.
The Dodd-Frank Act directs the federal banking regulators to promulgate rules prohibiting excessive compensation paid to executives of depository institutions and their holding companies with assets in excess of $1 billion, regardless of whether the company is publicly traded or not. In May 2016, the federal banking regulators, joined by the SEC, proposed such a rule that is tailored based on the asset size of the institution. All covered financial institutions would be subject to a prohibition on paying compensation, fees, and benefits that are "unreasonable" or "disproportionate" to the value of the services performed by a person covered by the proposed rule (generally, senior executive officers and employees who are significant risk-takers). Moreover, the proposed rule includes a new requirement which provides that an incentive-based compensation arrangement must (i) include financial and non-financial measures of performance, (ii) be designed to allow non-financial measures of performance to override financial measures of performance, when appropriate (so called safety and soundness factors), and (iii) be subject to adjustment to reflect actual losses, inappropriate risk taking, compliance deficiencies, or other measures or aspects of financial and non-financial performance. Finally, the Dodd-Frank Act gives the SEC authority to prohibit broker discretionary voting on elections of directors and executive compensation matters.
Technology Risk Management and Consumer Privacy
State and federal banking regulators have issued various policy statements emphasizing the importance of technology risk management and supervision in evaluating the safety and soundness of depository institutions with respect to banks that contract with third-party vendors to provide data processing and core banking functions. The use of technology-related products, services, delivery channels and processes expose a bank to various risks, particularly operational, privacy, security, strategic, reputation and compliance risk. Banks are generally expected to prudently manage technology-related risks as part of their comprehensive risk management policies by identifying, measuring, monitoring and controlling risks associated with the use of technology.
Under Section 501 of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, the federal banking agencies have established appropriate standards for financial institutions regarding the implementation of safeguards to protect the security and confidentiality of customer records and information, protection against any anticipated threats or hazards to the security or integrity of such records and protection against unauthorized access to or use of such records or information in a way that could result in substantial harm or inconvenience to a customer. Among other matters, the rules require each bank to implement a comprehensive written information security program that includes administrative, technical and physical safeguards relating to customer information. In addition, Massachusetts has established Standards for the Protection of Personal Information which create minimum standards to be met in connection with the safeguarding of personal information and outline the content and timing of disclosures required following a system breach or compromise.
Under the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, a financial institution must also provide its customers with a notice of privacy policies and practices. Section 502 prohibits a financial institution from disclosing nonpublic personal information about a customer to non-
23
affiliated third parties unless the institution satisfies various notice and opt-out requirements and the customer has not elected to opt out of the disclosure. Under Section 504, the agencies are authorized to issue regulations as necessary to implement notice requirements and restrictions on a financial institution's ability to disclose nonpublic personal information about customers to non-affiliated third parties. Under the final rule the regulators adopted, all banks must develop initial and annual privacy notices which describe in general terms the bank's information sharing practices. Banks that share nonpublic personal information about customers with non-affiliated third parties must also provide customers with an opt-out notice and a reasonable period of time for the customer to opt out of any such disclosure (with certain exceptions). Limitations are placed on the extent to which a bank can disclose an account number or access code for credit card, deposit or transaction accounts to any nonaffiliated third-party for use in marketing.
Bank Secrecy Act, and Anti-Money Laundering
Our Company and the Bank are also subject to the Bank Secrecy Act, as amended by the Uniting and Strengthening America by Providing Appropriate Tools Required to Intercept and Obstruct Terrorism Act of 2001 (the "USA PATRIOT Act"), which gives the federal government powers to address money laundering and terrorist threats through enhanced domestic security measures, expanded surveillance powers, and mandatory transaction reporting obligations. The Bank Secrecy Act imposes an affirmative obligation on the Bank to report currency transactions that exceed certain thresholds and to report other transactions determined to be suspicious. Financial institutions must take reasonable steps to conduct enhanced scrutiny of account relationships to guard against money laundering and to report any suspicious information maintained by financial institutions. The Bank Secrecy Act requires that all banking institutions develop and provide for the continued administration of a program reasonably designed to assure and monitor compliance with certain record-keeping and reporting requirements regarding both domestic and international currency transactions. These programs must, at a minimum, provide for a system of internal controls to assure ongoing compliance, provide for independent testing of such systems and compliance, designate individuals responsible for such compliance and provide appropriate personnel training.
The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network issued a final rule regarding customer due diligence requirements for covered financial institutions in connection with their Bank Secrecy Act and Anti-Money Laundering policies, that became effective in May 2018. The final rule adds a requirement to understand the nature and purpose of customer relationships and identify the "beneficial owner" (25% or more ownership interest) of legal entity customers. Bank regulators routinely examine institutions for compliance with these obligations and they must consider an institution's anti-money laundering compliance when considering regulatory applications filed by the institution, including applications for bank mergers and acquisitions. The regulatory authorities have imposed "cease and desist" orders and civil money penalty sanctions against institutions found to be violating these obligations.
USA PATRIOT Act and Know-Your-Customer
Under the USA PATRIOT Act, financial institutions are subject to prohibitions against specified financial transactions and account relationships, as well as enhanced due diligence and "know your customer" standards intended to detect, and prevent, the use of the United States financial system for money laundering and terrorist financing activities. The USA PATRIOT Act requires financial institutions, including banks, to establish anti-money laundering programs, including providing for a system of internal controls, designating individuals responsible for compliance, including employee training and independent audit requirements, meet minimum standards specified by the act, follow minimum standards for customer identification and maintenance of customer identification records, and regularly compare customer lists against lists of suspected terrorists, terrorist organizations and money launderers.
Other Operations and Consumer Compliance Laws
The Bank must comply with numerous federal anti-money laundering and consumer protection statutes and implement regulations, including but not limited to the Truth in Savings Act, Electronic Funds Transfer Act, Expedited Funds Availability Act, the Equal Credit Opportunity Act, the Federal Housing Act, the National Flood Insurance Act and various other federal and state privacy protection laws. Failure to comply in any material respect with any of these laws could subject the Bank to lawsuits and could also result in administrative penalties, including fines and reimbursements. The Company and the Bank are also subject to federal and state laws prohibiting unfair or fraudulent business practices, untrue or misleading advertising and unfair competition. These laws and regulations mandate certain disclosure requirements and regulate the manner in which financial institutions must deal with customers when taking deposits, making loans, collecting loans, and providing other services. Failure to comply in any material respect with any of these laws and regulations could subject the Bank to various penalties, including but not limited to enforcement actions, injunctions, fines or criminal penalties, punitive damages to consumers, and the loss of certain contractual rights.
24
Other Pending and Proposed Legislation
From time to time, various legislative and regulatory initiatives are introduced in Congress, as well as by regulatory agencies. Such initiatives may include proposals to expand or contract the powers of bank holding companies and depository institutions or proposals to substantially change the financial institution regulatory system. Such legislation could change banking statutes and the operating environment of the Company or Bank in substantial and unpredictable ways. If enacted, such legislation could increase or decrease the cost of doing business, limit or expand permissible activities or affect the competitive balance among banks, savings associations, credit unions, and other financial institutions. The Company cannot predict whether any such legislation will be enacted, and, if enacted, the effect that it, or any implementing regulations, would have on the financial condition or results of operations of the Company. A change in statutes, regulations or regulatory policies applicable to the company or our subsidiaries could have a material effect on the Company's business, financial condition and results of operations.
The Company maintains a Compliance Management Program designed to meet regulatory and legislative requirements. See Key Risk Areas, below under the heading "Risk Management Framework."
See also Item 1A, "Risk Factors," of this Form 10-K for further discussion on how new laws and regulations may affect the Company's business, financial condition and results of operations.
Risk Management Framework
In addition to the risks discussed below, numerous other factors that could adversely affect the Company's future results of operations and financial condition, and its reputation and business model are addressed in Item 1A, "Risk Factors" of this Form 10-K. This Risk Management Framework discussion should be read in conjunction with Item 1A of this Form 10-K.
Management utilizes a comprehensive risk management framework which enables the aggregation of risk across the Company and provides reasonable assurance that management has the tools, programs and processes in place to support informed decision making, anticipate risks before they materialize and maintain the Company's risk profile consistent with its strategic planning, and applicable laws and regulations.
The Company's enterprise risk management framework provides a structured approach for identifying, assessing and managing risks across the Company in a coordinated manner, which includes, but is not limited to: credit risk, market and interest rate risk, legal and regulatory compliance risk, reputational risk, strategic risk, capital risk, compensation risk, liquidity management, information security, internal controls over financial reporting, physical security, loss and fraud prevention, policy reviews, vendor management (direct and indirect vendors) and contract management, business continuity planning, short and long-term capital projects and facility planning, and corporate governance.
The Company promotes proactive risk management by all Enterprise employees with clear ownership and accountability. Managers in each line of business have responsibility for identifying, assessing and managing the risks in their areas. The Risk Management department is responsible for providing guidance, oversight and input on remediation to business lines to provide reasonable assurance that risk assessments and mitigating controls and procedures are properly designed and functioning with in their areas. The Risk Management department also independently monitors operational risk, including information security, third-party risk management, disaster recovery and business continuity planning. In addition, the Internal Audit department, which is independent of management, through reviews and testing, confirms appropriate risk management controls, processes and systems are in place and functioning effectively. The Company also maintains a package of commercial insurance policies with national insurers, which provides for a broad range of insurance coverage for a variety of risk factors, at levels deemed appropriate by management. Policies are reviewed annually, or as circumstances change, by management for necessary updates and adjustments in coverage.
The CEO has overall responsibility for risk management and manages strategic and reputational risks. The Chief Risk Officer, who also serves as the Information Security Officer, is responsible for establishing and maintaining oversight of the Company's enterprise risk management framework and also oversees operational, legal and compliance risk. The Chief Financial Officer is responsible for overseeing and managing market, interest rate, liquidity, and capital risk management activities, and also evaluating the effectiveness of the design of internal controls over financial reporting. The Credit Director and Chief Lending Officer are responsible for overseeing and managing credit risk. The Chief Information Officer is responsible for technology administration including technology governance, architecture, infrastructure and application support, and the Chief Human Resources Officer is responsible for compensation risk management. Periodic reports
25
relating to the Company's risk profile are provided to the Board for analysis and review. Additional risk assessments and management reporting is provided to management and the Board or its committees as deemed necessary.
Key Risk Areas
Compliance risk includes the threat of fines, civil money penalties, lawsuits and restricted growth opportunities resulting from violations and/or non-conformance with laws, rules, regulations, prescribed practices, internal policies and procedures, or ethical standards. The Company maintains a Compliance Management Program (the "CMP") designed to meet regulatory and legislative requirements. The CMP provides a framework for tracking and implementing regulatory changes, monitoring the effectiveness of policies and procedures, conducting compliance risk assessments, managing customer complaints and educating employees in matters relating to regulatory compliance. The Audit Committee of the Board oversees the effectiveness of the CMP.
Operational risk includes the threat of loss from inadequate or failed internal processes, people, systems or external events, due to, among other things: fraud or error; the inability to deliver products or services; failure to maintain a competitive position; lack of, or insufficient information security, cybersecurity or physical security; inadequate procedures or controls followed by third-party service providers; or violations of ethical standards. In addition to intensive and ongoing employee training, and employee and customer awareness campaigns, controls to manage operational risk include, but are not limited to, technology administration, information security, third-party management, and disaster recovery and business continuity planning.
• | The Company's technology administration includes policies and guidelines for the design, procurement, installation, management and acceptable use of hardware, software and network devices. The Company's project management standards are designed to provide risk-based oversight, coordinate and communicate ideas, and to prioritize and manage project implementation in a manner consistent with corporate objectives. |
• | The Company has implemented layered security approaches for all electronic delivery channels to detect, prevent and respond to rising cybersecurity risks. Management utilizes a combination of third-party information security assessments, key technologies and ongoing internal and external evaluations to provide a level of protection of non-public personal information, to continually monitor and attempt to safeguard information on its operating systems and those of third-party service providers, and to quickly detect attacks. The Company also utilizes firewall technology and a combination of software and third-party monitoring to detect intrusion, and cybersecurity threats, guard against unauthorized access, and continuously identify and prevent computer viruses on the Company's information systems. To minimize debit card losses, the Company works with a third-party provider to establish parameters for allowable transaction activity, monitor transactions, and alert customers of potentially fraudulent activity. |
• | The Company has a third-party risk management program designed to enable management to determine what risk, if any, a particular vendor and indirect vendors or subcontractors, exposes the Company to, and to rate and mitigate that risk by properly performing initial and ongoing due diligence when selecting or maintaining relationships with critical third-party providers and their subcontractors, for both on-premise and off-premise technology solutions. |
• | The Company's Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Program consists of the information and procedures required to enable a rapid recovery from an occurrence that would disable the Company's operations for an extended period, due to circumstances such as: loss of personnel; loss of data and/or loss of facilities under various scenarios, including unintentional, malicious or criminal intentions; or loss of access to, or the physical destruction or damage of facilities, infrastructure or systems; or denial of access to our systems or information by outside parties. The plan, which is reviewed annually, establishes responsibility for assessing a disruption of business, contains alternative strategies for the continuance of critical business functions during an emergency, assigns responsibility for restoring services, and sets priorities by which critical services will be restored. A bank-owned and maintained secondary data center location provides the Company back-up network processing capabilities if needed. |
• | The Company has developed an Incident Response Plan in order to guide its actions in responding to real and suspected information security incidents. This includes unlawful, unauthorized, or unacceptable actions that involve a computer system or a computer network such as Distributed Denial of Service attacks, Corporate Account Takeover schemes, or ransomware. Additionally, an event that disrupts one of the Bank's service |
26
channels, whether as a result of a security incident or not, is also considered an incident requiring a response under this program. These disclosure controls and procedures compel the Company to make appropriate accurate and timely disclosures of material events and incidents to both customers and regulatory authorities. The reaction to an incident aims to reduce potential damage and loss and to protect and restore confidence through timely communication and the restoration of normal operating conditions for computers, services and information.
• | The Bank Technology Committee of the Board oversees the technology and cybersecurity strategies and their alignment with business strategies. The Committee also oversees the effectiveness of the information security program and monitors the results of third-party testing and risk assessments and responses to breaches of customer data, among other project management, cybersecurity and business continuity oversight functions. |
Credit risk management is reviewed in detail in Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," in the section 'Loans," under the heading "Credit Risk" of this Form 10-K. The Loan Committee of the Board oversees the effectiveness of the credit risk management.
Liquidity management is reviewed in Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," in the section entitled "Financial Condition" under the heading "Liquidity" of this Form 10-K.
Interest rate risk is reviewed in detail under Item 7A, "Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk," of this Form 10-K below.
The Board of Directors oversees the Company's asset–liability management, which includes managing interest rate risk and liquidity.
For information regarding capital planning, current capital framework requirements applicable to the Company and the Bank and their respective capital levels at December 31, 2019, see the section within Item 1, "Business," entitled "Capital Resources" and the sections within "Supervision and Regulation" entitled "Capital Requirements" and "Capital Requirements under Basel III" and for the Bank "Capital Adequacy Requirements" of this Form 10-K and also see Note 11, "Stockholders' Equity," to the consolidated financial statements contained in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" of this Form 10-K.
The Company maintains a set of internal controls over financial reporting designed to provide reasonable assurance to management that the information required to be disclosed in reports it files with or furnishes to the SEC is prepared and fairly presented based on properly recorded, processed, and summarized information. The Audit Committee of the Board oversees the effectiveness of the internal controls over financial reporting. See Item 9A, "Controls and Procedures," of this Form 10-K for management's reports on its evaluation of disclosure controls and internal controls over financial reporting.
Any system of controls or contingency plan, however well designed and operated, is based in part on certain assumptions and has inherent limitations and may not prevent or detect all risks, and therefore can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurances that the objectives of the controls and procedures will be met. Any breakdown in the integrity of the design or functioning of the control, or the Company's inability to identify, respond and correct such breakdown, could subject the Company to increased costs and additional regulatory scrutiny, or result in loss of customer business, expose customers' personal information to unauthorized parties, damage the Company's reputation, and expose the Company to regulatory enforcement actions, civil litigation and possible financial liability, additional expenses, or losses, any of which could have a material adverse effect on the Company's business, financial condition and results of operations.
Item 1A. | Risk Factors |
An investment in the Company's common stock is subject to a variety of risks and uncertainties including, without limitation, those set forth below, any of which could cause the Company's actual results to vary materially from recent results or from the other forward-looking statements that the Company may make from time to time in news releases, periodic reports and other written or oral communications. This annual report on Form 10-K is qualified in its entirety by these risk factors.
Realization of any of the risks outlined in the following sections, or additional risks and uncertainties that management is not aware of, or may deem immaterial, may impair the Company's business in a variety of ways, including, but not limited to, any one or a combination of the following consequences: loss of assets; an interruption in the ability to conduct transactions; loss of
27
customer business; loss of key personnel; additional regulatory scrutiny and potential enforcement actions and/or penalties against the Company or the Bank; limit the payment of dividends; damage the Company's reputation; expose the Company to civil litigation and possible financial liability; result in unanticipated charges against capital; increase operational costs; decrease revenue; restrict funding sources, which could adversely impact the Company's ability to meet cash needs; be required to liquidate investments or other assets; limit growth; close locations or reduce staffing; or limit permissible activities. As a result, the Company's overall business, financial condition, results of operations, capital position, liquidity position, and financial performance could be materially and adversely affected. If this were to happen, the value of the Company's common stock could decline significantly, and stockholders could lose some or all their investment.
The material risks and uncertainties that management believes may affect the Company are outlined below. These risks and uncertainties are not listed in any order of priority and are not necessarily the only ones facing the Company.
RISK MANAGEMENT CONTROLS
Risk Management Controls and Procedures Could Fail or Be Circumvented
Management regularly reviews and updates the Company's internal controls, corporate governance policies, compensation policies, Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and security controls to prevent and detect errors, theft, fraud or robbery from both internal and external sources. Any system of controls, however well designed and operated, is based in part on certain assumptions and can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurances that the objectives of the system are met. The Company is at risk of any circumvention of the Company's internal controls and procedures, whether intentional or unintentional, or failure to comply with regulations related to controls and procedures, or failure to adequately document executed controls and procedures, or a physical theft or robbery, whether by employees, management, directors, or external elements, or any illegal activity conducted by a Bank customer or employee.
See also “Risk Management Framework,” contained above in Item 1, “Business,” of this Form 10-K for further information regarding the Company's operational risk management, information security and technology practices, the Company's Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Plan and third-party risk management.
LENDING
There are inherent risks associated with the Company's lending activities. These risks include, among other things, the impact of changes in the economic conditions in the market areas in which the Company operates and changes in interest rates. In addition, the Company may be impacted by the following risks associated with its lending activities:
Commercial Lending Generally Involves a Higher Degree of Risk than Retail Residential Mortgage Lending
The Company's loan portfolio consists primarily of commercial real estate, commercial and industrial, and commercial construction loans. These types of loans are generally viewed as having more risk of default than owner-occupied residential real estate loans or consumer loans, and typically have larger balances. The underlying commercial real estate values, the actual costs necessary to complete a construction project, or customer cash flow and payment expectations on such loans can be more easily influenced by adverse conditions in the related industries, the real estate market or in the economy in general and are dependent on the skills and experience of the business' management team.
The Company May Need to Increase its Allowance for Loan Losses
The determination of the appropriate level of the allowance for loan losses inherently involves a high degree of subjectivity and requires the Company to make significant estimates of current credit risks and non-performing trends, all of which may undergo material changes. In addition, bank regulatory agencies periodically review the Company's allowance for loan losses and may require an increase in the provision for loan losses or the recognition of further loan charge-offs, based on judgments that may differ from those of the Company's management.
On January 1, 2020, the Company adopted CECL which will impact the way all banking organizations estimate their allowance for loan losses.
See Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” Item (v) “Recent Accounting Pronouncements,” to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below, under the section “Accounting pronouncements not yet adopted by the Company” for further information regarding Accounting Standards Update No. 2016-13, “Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments”
28
Increases in the Company's Non-performing Assets Could Adversely Affect the Company's Results of Operations and Financial Condition in the Future
Non-performing assets adversely affect our net income in various ways. No interest income is recorded on non-accrual loans or other real estate owned, thereby adversely affecting income and returns on assets and equity. In addition, loan administration and workout costs increase, including significant time commitments from management and staff, resulting in additional reductions of earnings. When taking collateral in foreclosures and similar proceedings, the Company is required to carry the property or loan at its then-estimated fair value less estimated cost to sell, which, when compared to the carrying value of the loan, may result in a loss. In addition, any errors in documentation or previously unknown defects in deeds may impact the Company's ability to perfect title of the collateral in foreclosure. These non-performing loans and other real estate owned assets also increase the Company's risk profile and the capital that regulators believe is appropriate in light of such risks and have an impact on the Company's FDIC risk-based deposit insurance premium rate.
The Company's Use of Appraisals in Deciding Whether to Make a Loan Does Not Ensure the Value of the Collateral
In considering whether to make a loan secured by real property or other business assets, the sale of which may provide ultimate recovery of the outstanding balance of the loan, the Company generally requires an internal evaluation or independent appraisal of the collateral supporting the loan. However, these assessment methods are only an estimate of the value of the collateral at the time the assessment is made and involve estimates and assumptions. An error in fact, estimate or judgment could adversely affect the reliability of the valuation. Furthermore, changes in those estimates due to the economic environment and events occurring after the initial assessment, may cause the value of the collateral to differ significantly from the initial valuations. As a result, the value of collateral securing a loan may be less than estimated at the time of assessment, and if a default occurs the Company may not recover the outstanding balance of the loan.
The Company is Subject to Environmental Risks Associated with Real Estate Held as Collateral or Occupied
When a borrower defaults on a loan secured by real property, the Company may purchase the property in foreclosure or accept a deed to the property surrendered by the borrower. The Company may also take over the management of commercial properties whose owners have defaulted on loans. The Company also occupies owned and leased premises where branches and other bank facilities are located. While the Company’s lending, foreclosure and facilities policies and guidelines are intended to exclude properties with an unreasonable risk of contamination, hazardous substances could exist on some of the properties that the Company may own, acquire, manage or occupy. Environmental laws could force the Company to clean up the properties at the Company’s expense. It may cost much more to clean a property than the property is worth, and it may be difficult or impossible to sell contaminated properties. The Company could also be liable for pollution generated by a borrower’s operations if the Company takes a role in managing those operations after a default.
Concentrations in Commercial Real Estate Loans are Subject to Heightened Risk Management and Regulatory Review
If a concentration in commercial real estate lending is present, as measured under government banking regulations, management must employ heightened risk management lending practices that address the following key elements: board and management oversight and strategic planning, portfolio management, development of underwriting standards, portfolio risk assessment and monitoring through market analysis and stress testing, and maintenance of increased capital levels as needed to support the level of commercial real estate lending. If a concentration is determined to exist, the Company may incur additional operating expenses in order to comply with additional risk management practices and increased capital requirements.
See also “Loans,” including the subsections “Credit Risk,” and “Asset Quality,” included in the section entitled “Financial Condition,” contained in Item 7, “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” of this Form 10-K for further information regarding the Company's commercial loan portfolio and credit risk.
ECONOMICS & FINANCIAL MARKETS
The Company's Profitability Depends Significantly on Economic Conditions in the Company's Primary Market Areas
The Company's financial results are impacted by the general economic conditions of the primary market areas in which the Company operates. Any weakening in general economic conditions in the New England region, or any long-term deterioration of the regional economy could negatively impact the Company’s financial results.
The Company's Investment Portfolio Could Incur Losses or Fair Value Could Deteriorate
There are inherent risks associated with the Company's investment activities. These risks include the impact from changes in interest rates, weakness in real estate, municipalities, government sponsored enterprises, or other industries, the impact of changes in income tax rates on the value of tax-exempt securities, adverse changes in regional or national economic conditions, and general turbulence in domestic and foreign financial markets, among other things. If an investment's value
29
is deemed other-than-temporarily impaired, then the Company is required to write down the fair value of the debt security which may involve a charge to earnings. These conditions could adversely impact the ultimate collectability of the Company's investments.
The Company is Subject to Interest Rate Risk
The Company's earnings and cash flows are largely dependent upon its net interest income, meaning the difference between interest income earned on interest-earning assets and interest expense paid on interest-bearing liabilities. Changes in interest rates could negatively impact the demand for bank products and adversely impact earnings. Interest rates are highly sensitive to many factors that are beyond the Company's control, including monetary policy of the U.S. federal government, inflation and deflation, volatility of domestic and global financial markets, including credit markets, and competition. In addition, certain assets may have interest rate caps and floors, which restrict the level of interest rate movement that the Company can impose.
Uncertainty related to the London Interbank Offer Rate ("LIBOR") and its replacement
In July 2017, the Financial Conduct Authority (the authority that regulates LIBOR) announced it intends to stop compelling banks to submit rates for the calculation of LIBOR after December 31, 2021. The Federal Reserve Board and the New York Federal Reserve Bank have jointly formed a committee known as the Alternative Reference Rates Committee (the "ARRC") to help ensure a successful transition from LIBOR. While there is no consensus on what rate or rates may become accepted alternatives to LIBOR, the ARRC has proposed the Secured Overnight Financing Rate ("SOFR") as the alternative rate for use in derivatives and other financial contracts currently being indexed to LIBOR. SOFR is a daily index of the interest rate banks and hedge funds pay to borrow money overnight, secured by U.S. Treasury securities. Currently no forward-looking term index (like LIBOR) yet exists and the development of a SOFR-based term rate is ongoing. Historically, SOFR has been lower than LIBOR because it does not take into account bank credit risk. Accordingly, a credit spread adjustment is being considered. Since the proposed SOFR is calculated differently than LIBOR, payments under contracts referencing the new rates may differ from those referencing LIBOR. At this time, it is not possible to predict whether SOFR will attain market traction as a LIBOR replacement tool, and the future of LIBOR is still uncertain.
A relatively small portion of the Company's assets and liabilities are indexed to LIBOR and the transition to an alternative rate is not expected to have a material impact on the Company's earnings.
See also “Impairment Review of Investment Securities,” included in the section entitled “Accounting Policies/Critical Accounting Estimates,” contained in Item 7, “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” of this Form 10-K, Item (d), “Restricted Cash and Investments” and Item (e), “Investments,” included in Note 1, “Summary of Significant Account Policies,” to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below. See Item 7A, “Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk,” of this Form 10-K for further discussions related to the Company's management of interest-rate risk.
LIQUIDITY
Deposit Outflows May Increase Reliance on Borrowings and Brokered Deposits as Sources of Funds
The Company has traditionally funded asset growth principally through deposits and borrowings. As a general matter, deposits are typically a lower cost source of funds than external wholesale funding (e.g., brokered deposits and borrowed funds), because interest rates paid for deposits are typically less than interest rates charged for wholesale funding. If the balance of the Company's deposits decreases relative to the Company's overall banking operations, the Company may have to rely more heavily on wholesale funding or other sources of external funding or may have to increase deposit rates to maintain deposit levels in the future.
Sources of External Funding Could Become Restricted and Impact the Company's Liquidity
If, as a result of general economic conditions or other events, sources of external funding become restricted or are eliminated, the Company may not be able to raise adequate funds, or may incur substantially higher funding costs in order to raise the necessary funds to support the Company's operations and growth, or may be required to restrict operations or the payment of dividends.
See also “Other Sources of Funds,” contained in Item 1, “Business,” of this Form 10-K and “Liquidity,” included in the section entitled “Financial Condition,” contained in Item 7, “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” of this Form 10-K for further information regarding the Company's sources of contingent liquidity.
30
TECHNOLOGY & INFORMATION SYSTEMS
The Company is Subject to Technology Related Risk
The use of technology related products, services, delivery channels, access points and processes expose the Company to various risks, particularly operational, privacy, cybersecurity, strategic, reputation and compliance risk. Banks are required to prudently manage technology-related risks as part of their comprehensive risk management policies by identifying, measuring, monitoring and controlling risks associated with the use of technology.
Failure to Keep Pace with Technological Change Could Affect the Company's Profitability
The banking industry is continually undergoing rapid technological change with frequent introductions of new technology-driven products, services and delivery channels. Failure to successfully plan or keep pace with technological changes affecting the banking industry, or failure to adequately train and educate staff and customers on the use and risks of new technologies, or failure to comply adequately with regulatory guidance regarding protection of information security systems could have a material adverse effect on the Company's business and, in turn, the Company's financial condition and results of operations. In addition, there may be significant time and expenses associated with upgrading and implementing new technology, technology compliance and information security processes.
Information Systems Could Experience an Interruption, Failure, Breach in Security, or Cyber-Attack
The Company relies heavily on public utilities infrastructures and internal information and operating systems to conduct its business, and these systems could fail in a variety of ways. In addition, the use of networked operating systems exposes the Company to the increased sophistication and activity of cyber-criminals. A cyber incident is considered to be any adverse event that threatens the confidentiality, integrity or availability of the information resources of the Company. These incidents may be an intentional attack or an unintentional event and could involve gaining unauthorized access directly to our information systems, or indirectly through our vendors and customers systems, for purposes of misappropriating assets, stealing confidential corporate information or customers' Personally Identifiable Financial Information, corrupting data or causing operational disruption. The Company's independent third-party service providers or their subcontractors may also have access to customers' personal information and therefore also expose the Company to cybersecurity risk. Additionally, vendors' and customers' home, business or mobile information systems are at risk of fraudulent corporate account takeovers which the Company may not be able to detect. There is no guarantee the Company's counter-actions will be successful or that the Company will have the resources or technical expertise to anticipate, detect or prevent rapidly evolving types of cyber-attacks.
The occurrence of any failures or disruptions of infrastructure, or breakdown, breach, failures or interruptions of the Company's information systems, access points (or those of third-party service providers and customers), or the Company's inability to detect, respond, disclose and correct such occurrence or infiltration in a timely manner, could result in an interruption in our ability to conduct transactions for an indeterminable length of time, could expose customers' personal information to unauthorized parties, increase the risk of fraud or customer identity theft, subject the Company to increased operational costs to detect and rectify the situation, damage the Company's reputation and deter customers from using the Company's services, subject the Company to additional regulatory scrutiny, and expose the Company to civil litigation and possible financial liability.
OPERATIONS
The Company Operates in a Competitive Industry and Market Area
The Company faces substantial competition in all areas of its operations from a variety of different competitors, several of which are larger and have more financial resources than the Company. Competitors within the Company's market area include national, regional, other community banks, internet based banks and credit unions, and various types of other non-bank financial institutions, including, consumer finance companies, mortgage brokers and lenders, private lenders, insurance companies, securities brokerage firms, institutional mutual funds, registered investment advisors, other financial intermediaries and non-bank electronic payment and funding channels. The evolving Fintech industry also aims to compete with traditional banking services, and delivery methods, although the industry offers opportunities for strategic partnerships, it is also a source for direct competition. Some of these competitors are not subject to the same degree of government regulation as the Company and thus may have a competitive advantage over the Company. If due to the inability to compete successfully within the Company's target banking markets, the Company encounters difficulties attracting and retaining customers it would have a material adverse effect on the Company's growth and profitability.
The Company May Experience a Prolonged Interruption in its Ability to Conduct Business
The Company relies heavily on its personnel and facilities to conduct its business. A material loss of people or core
31
operating facilities, for any number of reasons including natural disasters or pandemics, could result in interruptions in customer services and our ability to conduct transactions, loss of customer business and damage the Company's reputation.
The Company Relies on External Service Providers
The Company relies on independent third-party firms, including indirect vendors utilized by such third parties, to provide critical services necessary to conducting its business. These services include but are not limited to: electronic funds delivery networks; check clearing houses; electronic banking services; wealth advisory, management and custodial services; wealth brokerage services; correspondent banking services; information security assessments and technology support services; and loan underwriting and review services. The occurrence of any failures or interruptions of the independent firms' systems or in their delivery of services, or failure to perform in accordance with contracted service level agreements, for any number of reasons could also impact the Company's ability to conduct business and process transactions.
The Company Relies on Financial Counterparty Relationships
The Company routinely executes transactions with counterparties in the financial services industry, in order to maintain correspondent bank relationships, liquidity, manage certain loan participations, mortgage sales activities, interest-rate swaps, engage in securities transactions, and engage in other financial activities with counterparties that are customary to our industry. Many of these transactions expose the Company to counterparty credit, liquidity and/or reputation risk in the event of default by the counterparty, or negative publicity or public complaints, whether real or perceived, about one or more of the Company's financial counterparties, or the financial services industry in general. Although the Company seeks to manage these risks through internal controls and procedures, the Company may experience loss or interruption of business, damage to its reputation, or incur additional costs or liabilities as a result of unforeseen events with these counterparties.
Investment Management Practices and Aggregate Assets Under Management Expose the Company to Financial, Operational and Legal Risk
The Company's Enterprise Wealth Management and Enterprise Wealth Services channels derive their revenues primarily from investment management fees based on assets under management. The Company's ability to maintain or increase investment assets under management is subject to a number of factors, including changes in client investment preferences, investment decisions by us or our third party service provider partners, and various economic conditions, among other factors. Wealth management and wealth services clients can terminate their relationships with us, reduce their aggregate assets under management, or shift their funds to other types of accounts with different rate structures for any number of reasons. Investment performance is one of the most important factors in retaining existing clients and competing for new wealth management clients. Financial markets are affected by many factors, any of which could adversely impact the fair value of customer portfolios. Even when market conditions are generally favorable, our investment performance may be adversely affected by the investment style of our wealth management and investment advisors and the investment decisions that they make.
Any decrease in assets under management, could reduce related fee income. Poor investment performance, whether real or perceived, in either relative or absolute terms, could impair our ability to attract and retain funds from existing and new clients, damage the company’s reputation and expose the Company to litigation and possible financial liability, among other factors.
The Company's Insurance Coverage May Not be Adequate to Prevent Additional Liabilities or Expenses
The Company works with an independent third-party insurance advisor to obtain insurance policies that provide coverage for a variety of business risks at coverage levels that compare favorably to bench-marked coverage for loss exposures that are faced by similarly sized financial institutions. However, there is no guarantee that the circumstances of an incident will meet the criteria for insurance coverage under a specific policy, and despite the insurance policies in place the Company may experience a loss incident or event which could have a material adverse effect on the Company's business, reputation, financial condition and results of operations.
Slower than Expected Growth in New Branches and Products Could Adversely Affect the Company's Profitability
The Company has placed a strategic emphasis on expanding the Bank's branch network and market share through organic growth within existing and into neighboring geographic markets. However, in the future the Company could explore growth opportunities through acquisition of other banks, financial services companies or lines of business. New branches and new products and services require a significant investment of both financial and personnel resources. Lower or slower than expected loan and deposit growth in new branches and/or lower than expected fee or other income generated from new branches could decrease anticipated revenues, increase costs and reduce net income generated by such investments.
32
Any potential future acquisitions could adversely affect the Company's profitability based on management's ability to successfully complete such acquisitions and integration of the acquired businesses and increase the risk of losing key employees and customers. In addition, branch openings, relocations, and closings require the approval of various state and federal regulatory agencies, which may or may not approve the Company's application for a branch. Adding new branches in existing or new market areas could also divert resources from current core operations and thereby further adversely affect the Company's growth and profitability.
The Company May Not be Able to Attract, Retain or Develop Key Personnel
The Company's success and growth strategy depends, in large part, on its ability to attract, retain and develop top performing banking professional within our markets, and its ability to successfully identify and develop personnel for succession to key executive management positions and to the board of directors. The inability to do so could have a material adverse impact on the Company’s business because of the loss of their skills, knowledge of the Company's market, years of industry or business experience and the difficulty of promptly finding qualified replacements.
See the section entitled “Competition,” contained in Item 1, “Business,” of this Form 10-K for additional information regarding the competitive issues facing the Company.
REGULATION
The Company is Subject to Extensive Government Regulation and Supervision
The Company and the Bank are also subject to a variety of federal and state laws and regulations that are primarily intended to protect depositors' funds, the FDIC insurance fund and the banking system as a whole, not the interests of stockholders. These regulations, including bank regulatory reform, tax policy and corporate governance rules, affect the Company's lending practices, capital structure, investment practices, dividend policy, growth, and net income, among other things. Federal and state laws and regulations may not always align in principle or statue, and preemptive federal laws may be more or less restrictive than those of a state. The Company cannot predict what legislation will be enacted, and, if enacted, the effect that it, or any implementing regulations, would have on the financial condition or results of operations of the Company. If enacted, such legislation could increase or decrease the cost of doing business, limit or expand permissible activities or affect the competitive balance among banks, savings associations, credit unions, and other financial institutions.
See also the section entitled “Supervision and Regulation,” contained in Item 1, “Business,” of this Form 10-K for additional information regarding the supervisory and regulatory issues facing the Company and the Bank.
ESTIMATES AND ASSUMPTIONS
The Company's Financial Condition and Results of Operation Rely in Part on Management Estimates and Assumptions
In preparing the financial statements in conformity with GAAP, management is required to exercise judgment in determining many of the methodologies, estimates and assumptions to be utilized. These estimates and assumptions affect the reported values of assets and liabilities at the balance sheet date and income and expenses for the years then ended. Changes in those estimates resulting from continuing change in the economic environment and other factors will be reflected in the financial statements and results of operations in future periods. As future events and their effects cannot be determined with precision, actual results could differ significantly from these estimates and be adversely affected should the assumptions and estimates used be incorrect or change over time due to changes in circumstances. The three most significant areas in which management applies critical assumptions and estimates are the estimates of the allowance for loan losses, impairment review of investment securities and the impairment review of goodwill.
The Net Deferred Tax Assets (“DTAs”) May be Determined to be Unrealizable in Future Periods
In making its assessment on the future realizability of net DTAs, management considers all available positive and negative evidence, including recent financial operations, projected future taxable income, and recoverable past income tax paid. If in the future, management believes based upon historical and expected future earnings that it is more likely than not that the Company will not generate sufficient taxable income to utilize the DTA balance, then a valuation allowance would be booked against the DTA, with the write down offset to current earnings. Factors beyond management's control can affect future levels of taxable income and there can be no assurances that sufficient taxable income will be generated to fully realize the DTAs in the future.
See also “Accounting Policies/Critical Accounting Estimates,” contained in Item 7, “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” of this Form 10-K for further information regarding significant areas that
33
management applies estimates and assumptions and Item (v), “Recent Accounting Pronouncements,” included in Note 1, “Summary of Significant Account Policies,” to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below.
REPUTATION
Damage to the Company's Reputation Could Affect the Company's Profitability and Stockholders' Value
The Company is dependent on its reputation within its market area as a trusted and responsible financial company for all aspects of its business with customers, employees, vendors, third-party service providers, and others with whom the Company conducts business or potential future business. Any negative publicity or public complaints, whether real or perceived, disseminated by word of mouth, by the general media, by electronic or social networking means, or by other methods, could harm the Company's reputation.
The Company is Exposed to Legal Claims and Litigation
The Company is subject to legal challenges under a variety of circumstances in the course of its normal business practices. Regardless of the scope or the merits of any claims by potential or actual litigants, the Company may have to engage in litigation that could be expensive, time-consuming, disruptive to the Company's operations, and distracting to management. Whether claims or legal action are founded or unfounded, if such claims and legal actions are not resolved in a manner favorable to the Company, they may result in significant financial liability, damage the Company's reputation, subject the Company to additional regulatory scrutiny and restrictions, and/or adversely affect the market perception of our products and services, as well as impact customer demand for those products and services.
COMMON STOCK, STOCKHOLDER’S EQUITY, CAPITAL
The Trading Volume in the Company's Common Stock is Less Than That of Larger Companies
Although the Company's common stock is listed for trading on the NASDAQ Global Market, the trading volume in the Company's common stock is substantially less than that of larger companies. Given the lower trading volume of the Company's common stock, significant purchases or sales of the Company's common stock, or the expectation of such purchases or sales, could cause significant movement in the Company's stock price.
The Market Price of the Company's Common Stock Could be Affected by General Industry Issues
The banking industry may be more affected than other industries by certain economic, credit, regulatory or information security issues. Although the Company itself may or may not be directly impacted by such issues, the Company's stock price may move up or down due to the influence, both real and perceived, of these issues, among others, on the banking industry in general. Investment in the Company's stock is not insured against loss by the FDIC or any other public or private entity.
Stockholder Dilution Could Occur if Additional Stock is Issued in the Future
If the Company's Board should determine in the future that there is a need to obtain additional capital through the issuance of additional shares of the Company's common stock or securities convertible into shares of common stock, or if the Board decides to grant additional stock awards or options for the purchase of shares of common stock, the issuance of such additional shares, stock awards and/or the issuance of additional shares upon the exercise of such options would expose existing stockholders' ownership interest to dilution.
The Company's Capital Levels Could Fall Below Regulatory Minimums
If the Company's regulatory capital levels decline, or if regulatory requirements increase, and the Company is unable to raise additional capital to offset that decline or meet the increased requirements, then its regulatory capital ratios may fall below regulatory minimum capital adequacy levels.
The Company's failure to remain “well-capitalized” for bank regulatory purposes could affect customer confidence, restrict the Company's ability to grow (both assets and branching activity), increase the Company's costs of funds and FDIC insurance expense, prohibit the Company's ability to pay dividends on common shares, and restrict its ability to make acquisitions, among other impacts. Under FDIC rules, if the Bank ceases to be a “well-capitalized” institution, its ability to accept brokered deposits and the interest rates that it pays may be restricted.
The Company's Articles of Organization, By-Laws and Stockholders Rights Plan as Well as Certain Banking and Corporate Laws Could Have an Anti-Takeover Effect
Although management believes that certain anti-takeover strategies are in the best interest of the Company and its
34
stockholders, provisions of the Company's articles of organization, by-laws, and stockholders rights plan and certain federal and state banking laws and state corporate laws, including regulatory approval requirements for any acquisition of control of the Company, could make it more difficult for a third-party to acquire the Company, even if doing so would be perceived to be beneficial to the Company's stockholders. The combination of these provisions is intended to prohibit a non-negotiated merger, or other business combination involving an acquisition of the Company, which, in turn, could adversely affect the market price of the Company's common stock.
Directors and Executive Officers Own a Significant Portion of Common Stock
The Company's directors and executive officers, as a group, beneficially own approximately 17% of the Company's outstanding common stock as of December 31, 2019. Management views this ownership commitment by insiders as an integral component of maintaining the Company's local and community-based ownership. However, as a result of this combined ownership interest, the directors and executive officers have the ability, if they vote their shares in a like manner, to significantly influence the outcome of all matters submitted to stockholders for approval, including the election of directors.
The Company Relies on Dividends from the Bank for Substantially All of its Revenue
Holders of the Company’s common stock are entitled to receive dividends only when, and if declared by our Board. Although the Company has historically declared cash dividends on our common stock, we are not required to do so, and our Board may reduce or eliminate our common stock dividend in the future.
The Company is a separate and distinct legal entity from the Bank. It receives substantially all its revenue from dividends paid by the Bank. These dividends are the principal source of funds used to pay dividends on the Company’s common stock and interest and principal on the Company’s subordinated debt. Various federal and state laws and regulations limit the amount of dividends that the Bank may pay to the Company, and certain regulators may prohibit the Bank or the Company from paying future dividends if deemed an unsafe or unsound practice. If the Bank, due to its capital position, inadequate net income levels, or otherwise, is unable to pay dividends to the Company, then the Company will be unable to service its debt, pay obligations or pay dividends on the Company’s common stock, which could have a material adverse effect on the market price of the Company’s common stock.
See the sections entitled “Supervision and Regulation” and “Capital Resources,” contained in Item 1, “Business,” of this Form 10-K for additional information regarding regulatory capital requirements for the Company and the Bank. See also the section entitled “Dividends,” contained in Item 5, “Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities” of this Form 10-K below.
Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments |
None.
Item 2. | Properties |
The Company's main office and operational support offices are located in Lowell, Massachusetts. The main Lowell campus consists of four buildings, three of which are owned, with ample on-site customer parking. The Company purchased one of the previously leased buildings in its main campus in 2019. The Company also owns and maintains a back-up operations/data facility in the Merrimack Valley region of Massachusetts. As of December 31, 2019, the Company had 24 full-service branch banking offices serving the Greater Merrimack Valley, Nashoba Valley and North Central regions of Massachusetts, and Southern New Hampshire (Southern Hillsborough and Rockingham counties). Our 25th branch in Lexington, MA recently opened in early March 2020 and our 26th branch in North Andover, MA is anticipated to open in summer 2020. The Company also has several ATMs at remote locations within its primary customer service area.
The Company believes that all of its facilities are well maintained and suitable for the purpose for which they are used. However, the Company regularly looks for opportunities to improve its facilities and locations.
At December 31, 2019, the Company had 15 operating real estate leases. See also Note 6, "Leases" to the Company's consolidated financial statements contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below for further information regarding the Company's leases and lease obligations.
35
Item 3. | Legal Proceedings |
There are no material pending legal proceedings to which the Company or its subsidiaries are a party or to which any of its property is subject, other than ordinary routine litigation incidental to the business of the Company. Management does not believe resolution of any present litigation will have a material adverse effect on the business, consolidated financial condition or results of operations of the Company.
Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures |
Not Applicable.
PART II
Item 5.Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Market for Common Stock
The Company's common stock trades on the NASDAQ Global Market under the trading symbol "EBTC."
As of March 2, 2020, there were 1,244 registered stockholders of the Company's common stock and 11,840,547 shares of the Company's common stock outstanding.
Dividends
In 2019, quarterly dividends of $0.16 per share were paid to the Company's stockholders in March, June, September and December. Total 2019 dividends of $0.64 per share compared to total dividends of $0.58 per share were paid to the Company's stockholders on a quarterly basis in 2018.
The Company maintains a DRSPP. The DRSPP enables stockholders, at their discretion, to continue to elect to reinvest cash dividends paid on their shares of the Company's common stock by purchasing additional shares of common stock from the Company at a purchase price equal to fair market value. Under the DRSPP, stockholders and new investors also have the opportunity to purchase shares of the Company's common stock without brokerage fees, subject to monthly minimums and maximums. See Note 11, "Stockholders' Equity," to the consolidated financial statements in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below for further information regarding the share purchase option under the DRSPP.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company declared $7.5 million in cash dividends to holders of common stock. Stockholders utilized the dividend reinvestment portion of the DRSPP to purchase an aggregate of 39,176 shares of the Company's common stock totaling $1.2 million. In 2018, the Company declared $6.8 million in cash dividends to holders of common stock. Stockholders utilized the dividend reinvestment portion of the DRSPP to purchase 37,999 shares of the Company's common stock totaling $1.3 million.
On January 21, 2020, the Company announced a quarterly dividend of $0.175 per share, which was paid on March 2, 2020 to stockholders of record as of February 10, 2020.
See the sections within Item 1, "Business," under the heading "Supervision and Regulation" entitled "Regulatory Restrictions on Dividends" and "Restrictions on Dividends and Other Capital Distributions," of this Form 10-K for information on factors that could impact the payment of dividends.
36
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
The following table provides information as of December 31, 2019, with respect to the Company's 2009 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended, and its 2016 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended, which together constitute all of the Company's existing equity compensation plans that have been previously approved by the Company's stockholders. The 2009 plan expired in 2019 and is closed for future grants, although awards previously granted under the 2009 plan remain outstanding and may be exercised through 2028.
Plan Category | Number of Securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights | Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights | Number of Securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in second column from left) | |||||||
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | 159,372 | $ | 23.45 | 271,838 | ||||||
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | — | — | — | |||||||
TOTAL | 159,372 | $ | 23.45 | 271,838 | ||||||
Repurchases of Common Stock
During the three months ended December 31, 2019, the Company did not repurchase any shares of its common stock.
37
Performance Graph
The following graph compares the cumulative total shareholder return (which assumes the reinvestment of all dividends) on the Company's common stock with the cumulative total return reflected by a broad-based equity market index and an appropriate published industry index. This graph shows the changes over the five-year period ended on December 31, 2019 in the value of $100 invested in (i) the Company's common stock, (ii) the Standard & Poor's 500 Index, and (iii) the SNL Bank $1B to $5B index.
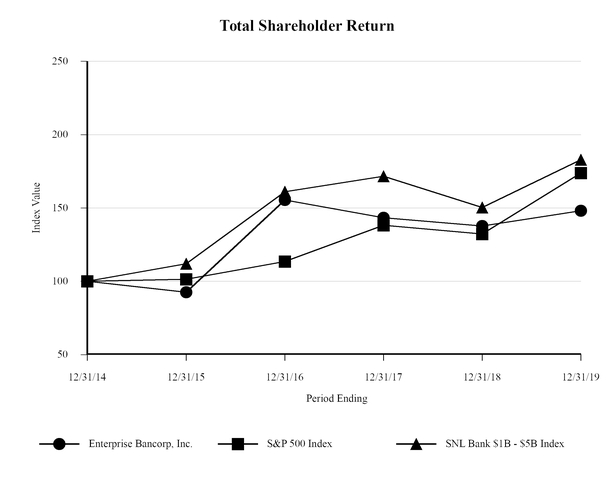
Period Ending | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Index | 12/31/14 | 12/31/15 | 12/31/16 | 12/31/17 | 12/31/18 | 12/31/19 | ||||||||||||||||||
Enterprise Bancorp, Inc. | $ | 100.00 | $ | 92.56 | $ | 155.49 | $ | 143.30 | $ | 137.67 | $ | 148.10 | ||||||||||||
S&P 500 Index | 100.00 | 101.38 | 113.51 | 138.29 | 132.23 | 173.86 | ||||||||||||||||||
SNL Bank $1B - $5B Index | 100.00 | 111.94 | 161.04 | 171.69 | 150.42 | 182.85 | ||||||||||||||||||
38
Item 6. | Selected Financial Data |
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands, except per share data) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
EARNINGS DATA | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest income | $ | 115,857 | $ | 108,835 | $ | 97,522 | $ | 86,792 | $ | 78,294 | ||||||||||
Provision for loan losses | 1,180 | 2,250 | 1,430 | 2,993 | 3,267 | |||||||||||||||
Net interest income after provision for loan loss | 114,677 | 106,585 | 96,092 | 83,799 | 75,027 | |||||||||||||||
Non-interest income | 16,173 | 14,940 | 14,958 | 13,639 | 13,139 | |||||||||||||||
Net gains (losses) on sales of available for sale securities | 146 | (2,950 | ) | 716 | 802 | 1,828 | ||||||||||||||
Non-interest expense | 86,415 | 80,878 | 76,145 | 70,328 | 65,732 | |||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 44,581 | 37,697 | 35,621 | 27,912 | 24,262 | |||||||||||||||
Provision for income taxes | 10,381 | 8,816 | 16,228 | 9,161 | 8,114 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 34,200 | $ | 28,881 | $ | 19,393 | $ | 18,751 | $ | 16,148 | ||||||||||
COMMON SHARE DATA | ||||||||||||||||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 2.90 | $ | 2.47 | $ | 1.68 | $ | 1.71 | $ | 1.56 | ||||||||||
Diluted earnings per share | 2.89 | 2.46 | 1.66 | 1.70 | 1.55 | |||||||||||||||
Book value per share at year end | 25.09 | 21.80 | 19.97 | 18.72 | 17.38 | |||||||||||||||
Dividends paid per share | $ | 0.64 | $ | 0.58 | $ | 0.54 | $ | 0.52 | $ | 0.50 | ||||||||||
Basic weighted average shares outstanding | 11,789,570 | 11,679,520 | 11,568,430 | 10,966,333 | 10,323,016 | |||||||||||||||
Diluted weighted average shares outstanding | 11,829,818 | 11,750,462 | 11,651,763 | 11,039,511 | 10,389,934 | |||||||||||||||
YEAR END BALANCE SHEET AND OTHER DATA | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 3,235,049 | $ | 2,964,358 | $ | 2,817,564 | $ | 2,526,269 | $ | 2,285,531 | ||||||||||
Loans serviced for others | 95,905 | 89,232 | 89,059 | 80,996 | 71,272 | |||||||||||||||
Investment assets under management | 916,623 | 800,751 | 844,977 | 725,338 | 678,377 | |||||||||||||||
Total assets under management(1) | $ | 4,247,577 | $ | 3,854,341 | $ | 3,751,600 | $ | 3,332,603 | $ | 3,035,180 | ||||||||||
Total loans | $ | 2,565,459 | $ | 2,387,506 | $ | 2,269,904 | $ | 2,022,729 | $ | 1,859,962 | ||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses | 33,614 | 33,849 | 32,915 | 31,342 | 29,008 | |||||||||||||||
Investment securities | 505,255 | 432,921 | 405,206 | 374,790 | 300,358 | |||||||||||||||
Interest-earning deposits | 23,867 | 19,255 | 14,496 | 17,428 | 19,177 | |||||||||||||||
Customer deposits | 2,786,730 | 2,507,999 | 2,293,872 | 2,209,559 | 1,911,378 | |||||||||||||||
Total deposits (including brokered deposits) | 2,786,730 | 2,564,782 | 2,441,362 | 2,268,921 | 2,018,148 | |||||||||||||||
Borrowed funds | 96,173 | 100,492 | 89,000 | 10,671 | 53,671 | |||||||||||||||
Subordinated debt | 14,872 | 14,860 | 14,847 | 14,834 | 14,822 | |||||||||||||||
Total stockholders' equity | 296,641 | 255,297 | 231,810 | 214,786 | 180,327 | |||||||||||||||
RATIOS | ||||||||||||||||||||
Return on average total assets | 1.10 | % | 1.00 | % | 0.73 | % | 0.78 | % | 0.76 | % | ||||||||||
Return on average stockholders' equity | 12.31 | % | 12.15 | % | 8.58 | % | 9.33 | % | 9.29 | % | ||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses to total loans | 1.31 | % | 1.42 | % | 1.45 | % | 1.55 | % | 1.56 | % | ||||||||||
Stockholders' equity to total assets | 9.17 | % | 8.61 | % | 8.23 | % | 8.50 | % | 7.89 | % | ||||||||||
Dividend payout ratio | 22.07 | % | 23.48 | % | 32.14 | % | 30.41 | % | 32.05 | % | ||||||||||
(1) Loans serviced for others and investment assets under management are not carried as assets on the Company's Consolidated Balance Sheet, and as such total assets under management is not a financial measurement recognized under GAAP.
39
Item 7. | Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
Management's discussion and analysis should be read in conjunction with the Company's (also referred to herein as "Enterprise," "us," "we," or "our") consolidated financial statements and notes thereto, contained in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," and the other financial and statistical information contained in this Form 10-K.
Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
This Form 10-K contains certain forward-looking statements concerning plans, objectives, future events or performance and assumptions and other statements. These statements are not statements of historical fact. Forward-looking statements may be identified by reference to a future period or periods or by use of forward-looking terminology such as "will," "should," "could," "anticipates," "believes," "expects," "intends," "may," "plans," "pursue," "views" and similar terms or expressions.
Various statements contained in Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," and Item 7A, "Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk," of this Form 10-K are forward-looking statements, including, but not limited to statements related to management's views on:
• | the banking environment and the economy; |
• | competition and market expansion opportunities; |
• | the interest-rate environment, credit risk and the level of future non-performing assets and charge-offs; |
• | potential asset and deposit growth, future non-interest expenditures and non-interest income growth; |
• | expansion strategy; and |
• | borrowing capacity. |
The Company cautions readers that such forward-looking statements reflect numerous assumptions made by management, which are inherently uncertain and beyond the Company's control, and involve a number of risks and uncertainties that could cause the Company's actual results to differ materially from those expressed in, or implied by, the forward-looking statement. Accordingly, we caution you that any such forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and not to place undue reliance on any such forward-looking information and statements. Any forward-looking statements in this Form 10-K are based on information available to the Company as of the date of this Form 10-K, and the Company undertakes no obligation to publicly update or otherwise revise any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by applicable law. The following important factors, among others, including those listed in our Item 1A - Risk Factors of this Form 10-K could cause the Company's results for subsequent periods to differ materially from those expressed in any forward-looking statement made herein:
(i) | failure of risk management controls and procedures; |
(ii) | risk specific to commercial loans and borrowers and the adequacy of the allowance for loan losses; |
(iii) | changes in the business cycle and downturns in the local, regional or national economies, including deterioration in the local real estate market, could negatively impact credit and/or asset quality and result in credit losses and increases in the Company's allowance for loan losses; |
(iv) | deterioration of securities markets could adversely affect the value or credit quality of the Company's assets and the availability of funding sources necessary to meet the Company's liquidity needs; |
(v) | changes in interest rates could negatively impact net interest income; |
(vi) | liquidity risks; |
(vii) | technology-related risk, including technological changes and technology service interruptions or failure could adversely impact the Company's operations and increase technology-related expenditures; |
(viii) | cybersecurity risk including security breaches and identity theft could impact the Company's reputation, increase regulatory oversight and impact the financial results of the Company; |
(ix) | increasing competition from larger regional and out-of-state banking organizations as well as non-bank providers of various financial services could adversely affect the Company's competitive position within its market area and reduce demand for the Company's products and services; |
(x) | our ability to retain and increase our aggregate assets under management; |
(xi) | our ability to enter new markets successfully and capitalize on growth opportunities, including the receipt of required regulatory approvals; |
(xii) | damage to our reputation in the markets we serve; |
(xiii) | exposure to legal claims and litigation; |
40
(xiv) | the inability to raise capital, on terms favorable to us, could cause us to fall below regulatory minimum capital adequacy levels and consequently restrict our business and operations; |
(xv) | changes in laws and regulations that apply to the Company's business and operations, and any additional regulations, or repeals that may be forthcoming as a result thereof, could cause the Company to incur additional costs and adversely affect the Company's business environment, operations and financial results; |
(xvi) | future regulatory compliance costs, including any increase caused by new regulations imposed by the government's current administration; and |
(xvii) | changes in accounting and/or auditing standards, policies and practices, as may be adopted or established by the regulatory agencies, FASB, or the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board could negatively impact the Company's financial results. |
The risks and uncertainties described in the documents that the Company files or furnishes to the SEC, including those discussed above in Item 1A, "Risk Factors," of this Form 10-K which could have a material adverse effect on the Company's business, financial condition and results of operations.
Overview
Executive Summary
Net income for the year ended December 31, 2019 amounted to $34.2 million, an increase of $5.3 million compared to the year ended December 31, 2018. Diluted earnings per share were $2.89 for the year ended December 31, 2019, compared to $2.46 for the year ended December 31, 2018.
The increase in our 2019 earnings compared to 2018 is largely attributable to solid loan and customer deposit (total deposits excluding brokered deposits) growth and the continuation of positive credit metrics. For 2019, total assets, total loans and total customer deposits increased 9%, 7% and 11%, respectively, compared to December 31, 2018. Strategically, the Company operates with a long-term mindset that is focused on growing organically and supporting growth by continually investing in our people, products, services, technology, digital transformation, and both new and existing branches. Our 25th branch in Lexington, MA recently opened in early March 2020 and our 26th branch in North Andover, MA is scheduled to open in summer 2020.
Composition of Earnings
The Company's earnings are largely dependent on its net interest income, which is primarily the difference between interest earned on loans and investments and the cost of funding (primarily deposits and borrowings). Net interest income expressed as a percentage of average interest-earning assets is referred to as net interest margin ("Margin"). Margin presented on a tax equivalent basis by factoring in adjustments associated with tax exempt loans and investments interest income is referred to as tax equivalent net interest margin ("T/E Margin").
Net interest income for the year ended December 31, 2019 amounted to $115.9 million, an increase of $7.0 million, or 6%, compared to the year ended December 31, 2018. The increase in net interest income was due largely to interest-earning asset growth, primarily in loans. Average loan balances (including loans held for sale) increased $128.4 million, or 6%, for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to the same 2018 respective period average. T/E Margin was 3.95% for the year ended December 31, 2019, compared to 3.97% for the year ended December 31, 2018. The decrease resulted from the cost of funds increasing more than interest earning asset yields. T/E Margin was 3.93% for the three months ended December 31, 2019. In the latter half of the year, T/E Margin was impacted by declining interest rates driven by three reductions in the fed funds rate from August through October 2019.
The re-pricing frequency of the Company's assets and liabilities are not identical, and therefore subject the Company to the risk of adverse changes in interest rates. This is often referred to as "interest-rate risk" and is reviewed in more detail in Item 7A, "Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk," of this Form 10-K.
The allowance for loan losses to total loans ratio was 1.31% at December 31, 2019, compared to 1.42% at December 31, 2018. For the years ended December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the provisions to the allowance for loan losses amounted to $1.2 million and $2.3 million, respectively. The decrease in the provision for loan losses for 2019 compared to the prior year was due primarily to generally positive credit metrics, partially offset by the impact of loan growth in 2019. Affecting the provision for loan losses for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to the prior year were:
41
• | The ratio of impaired and classified loans to total loans amounted to 2.25% at December 31, 2019, compared to 2.41% at December 31, 2018. |
• | The provision for loan loss related to impaired and classified loans was lower in 2019 than in 2018, contributing to a decrease in the overall provision. |
• | Loan growth for the year ended December 31, 2019 was $178.0 million, compared to $117.6 million during the year ended December 31, 2018. |
• | The allowance allocated to non-classified loans was relatively flat for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to 2018, as provisions necessary for loan growth were largely offset by continued positive credit and economic metrics. |
See also "Credit Risk," "Asset Quality," and "Allowance for Loan Losses," included in the "Loans" section within "Financial Condition" below, for further information regarding loan quality statistics and the allowance for loan losses.
Non-interest income for the year ended December 31, 2019 amounted to $16.3 million, an increase of $4.3 million, or 36%, compared to the year ended December 31, 2018. Non-interest income increased for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to the prior year, due primarily to $2.9 million in realized losses on a discretionary partial restructure of the bond portfolio in 2018. Other changes included increases in deposit and interchange fees in 2019, as well as net gains on equity securities, which are included in other income, compared with net losses on equity securities in the comparable 2018 period, due primarily to fair value adjustments.
Non-interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2019 amounted to $86.4 million, an increase of $5.5 million, or 7%, compared to the year ended December 31, 2018. Increases in non-interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2019 primarily related to the Company's strategic growth initiatives, particularly salaries and employee benefits and technology and telecommunications expenses. Technology initiatives include the Company's multi-year digital transformation strategy to enhance operating efficiency and customer experience. Partially offsetting these expenses was a reduction in deposit insurance premiums primarily resulting from a Small Bank Assessment Credit from the FDIC Deposit Insurance Fund of $683 thousand for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Sources and Uses of Funds
The Company's primary sources of funds are customer deposits, FHLB borrowings, current earnings and proceeds from the sales, maturities and pay-downs on loans and investment securities. The Company may also, from time to time, utilize brokered deposits and overnight borrowings from correspondent banks. Additionally, funding for the Company may be generated through equity transactions, including the dividend reinvestment and direct stock purchase plan or exercise of stock options, and occasionally the issuance of debt securities or common stock. The Company's sources of funds are intended to be used to conduct operations and to support growth, by funding loans, and investing in securities, to expand the branch network, and to pay dividends to stockholders.
The investment portfolio is primarily used to provide liquidity, manage the Company's asset-liability position and to invest excess funds, providing additional sources of revenue. Total investments, a component of interest-earning assets, amounted to $505.3 million at December 31, 2019, an increase of $72.3 million, or 17%, since December 31, 2018 and comprised 16% of total assets at December 31, 2019 and 15% of total assets at December 31, 2018.
Enterprise's main asset strategy is to grow loans, the largest component of interest-earning assets, with a focus on high quality commercial lending relationships. Total loans, comprising 79% of total assets at December 31, 2019 and 81% of total assets at December 31, 2018, amounted to $2.57 billion at December 31, 2019, compared to $2.39 billion at December 31, 2018, an increase of $178.0 million, or 7%. Total commercial loans amounted to $2.21 billion, or 86% of gross loans, at December 31, 2019, which was consistent with the composition at December 31, 2018.
Management's preferred strategy for funding asset growth is to grow relationship-based customer deposit balances, preferably comprised of non-interest checking accounts, interest-bearing checking accounts and traditional savings accounts. Asset growth in excess of transactional deposits is typically funded through non-transactional deposits (comprised of money market accounts, commercial tiered rate or "investment savings" accounts and term CDs) and wholesale funding (brokered deposits and borrowed funds).
42
At December 31, 2019, customer deposits amounted to $2.79 billion, or 86% of total assets, compared to $2.51 billion, or 85% of total assets at December 31, 2018. Since December 31, 2018, customer deposits increased $278.7 million, or 11%, primarily in money market and checking accounts. See "Deposits" under "Financial Condition" contained in this Item 7 of this Form 10-K for a further breakdown of deposit growth.
Wholesale funding amounted to $96.2 million at December 31, 2019, or 3% of total assets, compared to $157.3 million at December 31, 2018, or 5% of total assets, a decrease of $61.1 million, or 39%. At December 31, 2019, wholesale funding consisted of FHLB advances only, primarily in overnight or short-term borrowings. At December 31, 2018, wholesale funding included brokered CDs of $56.8 million and FHLB advances of $100.5 million. The Company's level of wholesale funding has decreased since December 31, 2018 as increases in customer deposit balances have exceeded loan growth.
Culture and Organic Growth Strategy
The Company's business model is to provide a full range of diversified financial products and services through a highly trained team of knowledgeable banking professionals who have in-depth understanding of our markets and a commitment to open and honest communication with clients.
Management believes the Company has differentiated itself from the competition by building a strong reputation within the local market as a customer-centric, community rooted, and commercially focused community bank, offering competitive products, delivering exceptional customer service and being a community leader in our markets.
The Company's banking professionals are dedicated to upholding the Company's core values, including significant and active involvement in many charitable and civic organizations, and community development programs throughout our service area. This long-held commitment to community not only contributes to the welfare of the communities we serve, it also helps to fuel the local economy, creating new businesses and jobs, and has led to a strong referral network with local businesses, non-profit organizations and community leaders.
Management believes the Company's employee-centric culture, commitment to community, robust product and service lines, including commercial lending, cash management, wealth management and trust services and commercial insurance, delivered by a knowledgeable and dedicated team of community bankers, makes the Enterprise team stand out among the competition.
Management further believes that Enterprise is well equipped to capitalize on market opportunities to grow the commercial and residential loan portfolios through strong business development and referral efforts, while utilizing a disciplined and reliable credit management approach, which has served to provide consistent quality asset growth over varying economic cycles during the Company's history.
The Company’s loan growth initiatives are executed through a seasoned lending team possessing a broad breadth of business acumen and experience, supported by a highly qualified and experienced commercial credit review function.
Management maintains a long-term focus and continues to invest in strategic growth initiatives, including investments in employee hiring, training and development, community relations, technology and digital transformation, and branch evolution and expansion.
The Company has an ongoing commitment to continually improving the customer experience, and internal efficiencies and productivity, using scalable technology and digitization. As part of the Company's multi-year digital transformation strategy, new technology-driven products, services, delivery channels, and process automation are continually introduced.
Branch evolution includes enhancing our highly-personalized customer interactions, updating technology and delivery methods, and ongoing facility improvements and renovations. New and renovated branches exhibit a modern, open-concept lobby with advanced technology, such as cash recyclers. These branches are supported by our “Universal Bankers,” who are crossed-trained to fully serve customer needs, and have on-site commercial lenders.
The Company also continually looks to develop new branch locations within, and to complement, our existing footprint. In early March 2020, Enterprise opened its new Lexington, MA location. Additionally, our 26th branch is scheduled to open in North Andover, MA in the summer of 2020.
While management recognizes that such investments increase expenses in the short term, Enterprise believes that such initiatives are a critical investment in the long-term growth and earnings potential of the Company and will help the Company to capitalize on current opportunities in the marketplace for community banks such as Enterprise. However, lower than
43
expected returns on these investments, such as slower than anticipated loan and deposit growth in new branches and/or lower than expected adoption rates or income generated from new technology or initiatives, could decrease anticipated revenues and net income on such investments in the future.
Financial Condition
Total assets increased $270.7 million, or 9%, since December 31, 2018, to $3.24 billion at December 31, 2019. The balance sheet composition and changes since December 31, 2018 are discussed below.
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents may be comprised of cash on hand and cash items due from banks, interest-earning deposits (deposit accounts, excess reserve cash balances, money markets, and money market mutual funds accounts) and federal funds sold ("fed funds"). Cash and cash equivalents amounted to 2% of total assets at both December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018. Balances in cash and cash equivalents will fluctuate due primarily to the timing of net cash flows from deposits, borrowings, loans and investments, and the immediate liquidity needs of the Company.
Investments
At December 31, 2019, the fair value of the investment portfolio amounted to $505.3 million, an increase of $72.3 million, or 17%, since December 31, 2018. The increase was primarily due to the investment of funds from growth in customer deposits, the 2018 partial bond portfolio restructure, and increases in market values. The investment portfolio represented 16% of total assets at December 31, 2019 and 15% of total assets at December 31, 2018. As of December 31, 2019, the investment portfolio was primarily comprised of debt securities, with a small portion of the portfolio invested in equity securities. At both December 31, 2019 and 2018, all investments were carried at fair value and debt securities were classified as available-for-sale.
See Note 2, "Investment Securities," and Note 16, "Fair Value Measurements," to the Company's consolidated financial statements contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below, for further information regarding the Company's unrealized gains and losses on debt securities, including information about investments in an unrealized loss position for which impairment has or has not been recognized, and investments pledged as collateral, as well as the Company's fair value measurements for investments.
Debt Securities
The following table summarizes the fair value of debt securities at the dates indicated:
December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | |||||||||||||||
Federal agency obligations(1) | $ | 1,004 | 0.2 | % | $ | 7,975 | 1.9 | % | $ | 51,717 | 12.8 | % | |||||||||
Residential federal agency MBS(1) | 192,658 | 38.2 | % | 172,726 | 40.0 | % | 140,154 | 34.6 | % | ||||||||||||
Commercial federal agency MBS(1) | 114,635 | 22.7 | % | 93,979 | 21.8 | % | 66,500 | 16.4 | % | ||||||||||||
Municipal securities taxable | 81,687 | 16.2 | % | 34,741 | 8.1 | % | 11,420 | 2.8 | % | ||||||||||||
Municipal securities tax exempt | 100,038 | 19.8 | % | 107,302 | 24.8 | % | 122,926 | 30.4 | % | ||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 14,311 | 2.8 | % | 13,806 | 3.2 | % | 11,542 | 2.8 | % | ||||||||||||
CDs(2) | 455 | 0.1 | % | 944 | 0.2 | % | 947 | 0.2 | % | ||||||||||||
Total debt securities | $ | 504,788 | 100.0 | % | $ | 431,473 | 100.0 | % | $ | 405,206 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||
(1) | These categories may include investments issued or guaranteed by government sponsored enterprises such as Fannie Mae ("FNMA"), Freddie Mac ("FHLMC"), Federal Farm Credit Bank ("FFCB"), or one of several Federal Home Loan Banks, as well as investments guaranteed by Ginnie Mae ("GNMA"), a wholly-owned government entity. |
(2) | CDs represent term deposits issued by banks that are subject to FDIC insurance and purchased on the open market. |
44
The majority of residential and commercial federal agency MBS categories were collateralized mortgage obligations ("CMOs") issued by U.S. agencies. The remaining MBS investments totaled $23.5 million, $23.9 million and $35.0 million at December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
Net unrealized gains on the debt securities portfolio amounted to $13.5 million at December 31, 2019 compared to net unrealized losses of $1.7 million at December 31, 2018. The Company attributes the increase in net unrealized gains as compared to the net unrealized losses of 2018 to decreases in market yields and restructuring of the debt security portfolio in the fourth quarter of 2018, which overall raised portfolio yields. Unrealized gains or losses on debt securities are carried on the balance sheet and will be recognized in the statements of income if the investments are sold. Should an investment be deemed to have Other than temporary impairment or "OTTI", the Company is required to write-down the fair value of the investment. See "Impairment Review of Investment Securities" under the heading "Accounting Policies/Critical Accounting Estimates" in this Item 7 of this Form 10-K for additional information regarding the accounting for OTTI.
In 2019 and 2018, the Company purchased debt securities totaling $120.0 million and $195.4 million, respectively. The Company also had principal pay downs, calls and maturities totaling $48.8 million during the year ended December 31, 2019 compared with $42.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2018.
During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company realized net gains of $146 thousand on sales of debt securities with an amortized cost of approximately $11.6 million. For the year ended December 31, 2018, the Company realized net losses of $3.0 million on sales of debt securities with an amortized cost of approximately $122.7 million. These losses resulted primarily from a partial, discretionary restructure of the bond portfolio that was undertaken to improve future earnings by selling lower yielding bonds and reinvesting into slightly longer, higher yielding bonds.
The contractual maturity distribution as of December 31, 2019 of the debt securities portfolio with the weighted average tax equivalent yield for each category is set forth below:
Under 1 Year | >1 – 5 Years | >5 – 10 Years | Over 10 Years | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Amount | Yield | Amount | Yield | Amount | Yield | Amount | Yield | ||||||||||||||||||||
At amortized cost: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Federal agency obligations | $ | 999 | 2.56 | % | $ | — | — | % | $ | — | — | % | $ | — | — | % | ||||||||||||
Residential federal agency MBS | 2 | 2.71 | % | — | — | % | 6,406 | 2.87 | % | 183,984 | 2.81 | % | ||||||||||||||||
Commercial federal agency MBS | 990 | 3.17 | % | 51,578 | 2.88 | % | 58,614 | 3.03 | % | — | — | % | ||||||||||||||||
Municipal securities taxable | — | — | % | 3,865 | 3.17 | % | 71,129 | 3.16 | % | 4,101 | 2.84 | % | ||||||||||||||||
Municipal securities tax exempt | 1,419 | 3.61 | % | 9,524 | 3.49 | % | 45,548 | 3.02 | % | 38,851 | 2.68 | % | ||||||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 2,766 | 2.70 | % | 6,728 | 2.79 | % | 4,332 | 3.61 | % | — | — | % | ||||||||||||||||
CDs | 454 | 2.30 | % | — | — | % | — | — | % | — | — | % | ||||||||||||||||
Total debt securities | $ | 6,630 | 2.92 | % | $ | 71,695 | 2.97 | % | $ | 186,029 | 3.08 | % | $ | 226,936 | 2.78 | % | ||||||||||||
At fair value: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total debt securities | $ | 6,660 | $ | 73,737 | $ | 193,368 | $ | 231,023 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Scheduled contractual maturities shown above may not reflect the actual maturities of the investments. The actual MBS/CMO cash flows likely will be faster than presented above due to prepayments and amortization. Similarly, included in the table above are callable securities, comprised of municipal securities and corporate bonds, with a fair value of $91.0 million, which can be redeemed by the issuer prior to the maturity presented above. Management considers these factors when evaluating the interest-rate risk in the Company's asset-liability management program.
Equity Securities
The Company held equity securities with a fair value of $467 thousand and $1.4 million at December 31, 2019, and December 31, 2018, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company's net gains on equity securities recorded in the Consolidated Statement of Income was $367 thousand. During the year ended December 31, 2018, the net losses on equity securities recorded in the Consolidated Statement of Income was $204 thousand.
45
Federal Home Loan Bank Stock
The Bank is required to purchase stock of the FHLB at par value in association with advances from the FHLB; this stock is classified as a restricted investment and carried at cost, which management believes approximates fair value. The Company's investment in FHLB stock was $4.5 million and $5.4 million at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively.
See also Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," Item (d) "Restricted Cash and Investments" to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," of this Form 10-K below, for further information regarding the Company's investment in FHLB stock.
Loans
This discussion should be read in conjunction with the material presented in Item 1, "Business," under the heading "Lending Products" of this Form 10-K.
Total loans represented 79% of total assets at December 31, 2019 and 81% of total assets at December 31, 2018. Total loans increased $178.0 million, or 7%, for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to December 31, 2018. The mix of loans within the portfolio remained relatively unchanged with commercial loans amounting to approximately 86% of gross loans at December 31, 2019 and 2018, reflecting a continued focus on commercial loan growth.
The following table sets forth the loan balances by certain loan categories at the dates indicated and the percentage of each category to gross loans:
December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 1,394,179 | 54.3 | % | $ | 1,303,879 | 54.6 | % | $ | 1,201,351 | 52.9 | % | $ | 1,038,082 | 51.3 | % | $ | 936,921 | 50.3 | % | |||||||||||||||
Commercial & industrial | 501,227 | 19.5 | % | 514,253 | 21.5 | % | 498,802 | 21.9 | % | 490,799 | 24.2 | % | 458,553 | 24.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial construction | 317,477 | 12.4 | % | 234,430 | 9.8 | % | 274,905 | 12.1 | % | 213,447 | 10.5 | % | 202,993 | 10.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total commercial loans | 2,212,883 | 86.2 | % | 2,052,562 | 85.9 | % | 1,975,058 | 86.9 | % | 1,742,328 | 86.0 | % | 1,598,467 | 85.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Residential mortgages | 247,373 | 9.6 | % | 231,501 | 9.7 | % | 195,492 | 8.6 | % | 180,560 | 8.9 | % | 169,188 | 9.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Home equity loans and lines | 98,252 | 3.8 | % | 96,116 | 4.0 | % | 91,706 | 4.0 | % | 91,065 | 4.5 | % | 83,373 | 4.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Consumer | 10,054 | 0.4 | % | 10,241 | 0.4 | % | 10,293 | 0.5 | % | 10,845 | 0.6 | % | 10,747 | 0.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total retail loans | 355,679 | 13.8 | % | 337,858 | 14.1 | % | 297,491 | 13.1 | % | 282,470 | 14.0 | % | 263,308 | 14.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Gross loans | 2,568,562 | 100.0 | % | 2,390,420 | 100.0 | % | 2,272,549 | 100.0 | % | 2,024,798 | 100.0 | % | 1,861,775 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Deferred fees, net | (3,103 | ) | (2,914 | ) | (2,645 | ) | (2,069 | ) | (1,813 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total loans | 2,565,459 | 2,387,506 | 2,269,904 | 2,022,729 | 1,859,962 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses | (33,614 | ) | (33,849 | ) | (32,915 | ) | (31,342 | ) | (29,008 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loans | $ | 2,531,845 | $ | 2,353,657 | $ | 2,236,989 | $ | 1,991,387 | $ | 1,830,954 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2019, commercial real estate loans increased $90.3 million, or 7%, compared to December 31, 2018. Commercial real estate loans are typically secured by a variety of owner-use and non-owner occupied (investor) commercial and industrial property types including one-to-four and multi-family apartment buildings, office, industrial or mixed-use facilities, strip shopping centers or other commercial properties and are generally guaranteed by the principals of the borrower.
Commercial and industrial loans decreased $13.0 million, or 3%, as of December 31, 2019 compared to December 31, 2018. These loans include seasonal and formula-based revolving lines of credit, working capital loans, equipment financing, and term loans. Also included in commercial and industrial loans are loans partially guaranteed by the SBA, and loans under various programs and agencies. Commercial and industrial credits may be unsecured loans and lines to financially strong borrowers, loans secured in whole or in part by real estate unrelated to the principal purpose of the loan or secured by inventories, equipment, or receivables, and are generally guaranteed by the principals of the borrower.
Commercial construction loans increased by $83.0 million, or 35%, as of December 31, 2019 compared to December 31, 2018. Commercial construction loans include the development of residential housing and condominium projects, the development of commercial and industrial use property and loans for the purchase and improvement of raw land. These loans are secured in whole or in part by underlying real estate collateral and are generally guaranteed by the principals of the borrowers. In many
46
cases, these loans move into the permanent commercial real estate portfolio when the construction phase is completed. The increase since December 31, 2018 was due primarily to funding of new and existing loans across a variety of projects including residential housing and condominium projects, and development of commercial use property.
Total retail loan balances increased by $17.8 million, or 5%, as of December 31, 2019 compared to December 31, 2018. Residential secured one-to-four family mortgage loans continue to make up the largest portion of the retail segment. The increase since December 31, 2018 was primarily due to an increase in originations of adjustable rate residential mortgages which are typically held in our portfolio rather than sold.
At December 31, 2019, commercial loan balances participated out to various banks amounted to $80.2 million, compared to $72.1 million at December 31, 2018. These balances participated out to other institutions are not carried as assets on the Company's financial statements. Commercial loans originated by other banks in which the Company is a participating institution are carried at the pro-rata share of ownership and amounted to $104.3 million and $63.5 million at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. In each case, the participating bank funds a percentage of the loan commitment and takes on the related pro-rata risk. The rights and obligations of each participating bank are divided proportionately among the participating banks in an amount equal to their share of ownership and with equal priority among all banks. Each participation is governed by individual participation agreements executed by the lead bank and the participant at loan origination. Participating loans with other institutions provide banks the opportunity to retain customer relationships and reduce credit risk exposure among each participating bank, while providing customers with larger credit vehicles than the individual bank might be willing or able to offer independently.
See also Note 3, "Loans," to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below, for information on related party loans, loans serviced for others and loans pledged as collateral.
The following table sets forth the scheduled maturities of commercial real estate, commercial and industrial and commercial construction loans in the Company's portfolio at December 31, 2019. The table also sets forth the dollar amount of loans which are scheduled to mature after one year which have fixed or adjustable rates.
(Dollars in thousands) | Commercial real estate | Commercial & industrial | Commercial construction | |||||||||
Amounts due(1): | ||||||||||||
One year or less, and demand notes | $ | 68,342 | $ | 246,087 | $ | 150,921 | ||||||
After one year through five years | 249,559 | 132,558 | 54,164 | |||||||||
Beyond five years | 1,076,278 | 122,582 | 112,392 | |||||||||
$ | 1,394,179 | $ | 501,227 | $ | 317,477 | |||||||
Interest rate terms on amounts due after one year: | ||||||||||||
Fixed | $ | 45,229 | $ | 119,541 | $ | 2,933 | ||||||
Adjustable(2) | $ | 1,280,608 | $ | 135,599 | $ | 163,623 | ||||||
(1) | Scheduled contractual maturities may not reflect the actual maturities of loans. The average maturity of loans may be shorter than their contractual terms principally due to prepayments and demand features. |
(2) | Adjustable rate loans may have fixed initial periods before periodic rate adjustments begin. |
Credit Risk
Inherent in the lending process is the risk of loss due to customer non-payment, or "credit risk." The Company's commercial lending focus may entail significant additional credit risks compared to long-term financing on existing, owner-occupied residential real estate. The Company seeks to lessen its credit risk exposure by managing its loan portfolio to avoid concentration by industry, relationship size and source of repayment, and through sound underwriting practices and the credit risk management function; however, management recognizes that loan losses will occur and that the amount of these losses will fluctuate depending on the risk characteristics of the loan portfolio and economic conditions.
The credit risk management function focuses on a wide variety of factors, including, among others, current and expected economic conditions, the real estate market, the financial condition of borrowers, the ability of borrowers to adapt to changing conditions or circumstances affecting their business and the continuity of borrowers' management teams. Early detection of
47
credit issues is critical to minimize credit losses. Accordingly, management regularly monitors these factors, among others, through ongoing credit reviews by the Credit Department, an external loan review service, reviews by members of senior management, as well as reviews by the Loan Committee and the Board. This review includes the assessment of internal credit quality indicators such as, among others, the risk classification of individual loans, individual review of larger and higher risk problem assets, the level of delinquent loans and non-performing loans, impaired and restructured loans, the level of foreclosure activity, net charge-offs, commercial concentrations by industry and property type and by real estate location, as well as trends in the general levels of these indicators and the growth and composition of the loan portfolio. In addition, management monitors expansion in the Company's geographic market areas, the experience level of lenders and any changes in underwriting criteria, and the strength of the local and national economy, including general conditions in the multi-family, commercial real estate and development and construction markets in the Company's local region.
The Company's loan risk rating system classifies loans depending on risk of loss characteristics. The classifications range from "substantially risk free" for the highest quality loans and loans that are secured by cash collateral, through a satisfactory range of "minimal," "moderate," "better than average," and "average" risk, to the regulatory problem-asset classifications of "criticized," for loans that may need additional monitoring, and the more severe adverse classifications of "substandard," "doubtful," and "loss" based on criteria established under banking regulations. Loans which are evaluated to be of weaker credit quality are placed on the "watch credit list" and reviewed on a more frequent basis by management. Loans classified as "substandard" include those characterized by the distinct possibility that the Company will sustain some loss if the deficiencies are not corrected. Loans classified as "doubtful" have all the weaknesses inherent in a substandard rated loan with the added characteristic that the weaknesses make collection or full payment from liquidation, on the basis of currently existing facts, conditions, and values, highly questionable and improbable. Loans classified as "loss" are generally considered uncollectible at present, although long term recovery of part or all of loan proceeds may be possible. These "loss" loans would require a specific loss reserve or charge-off. Adversely classified loans may be accruing or in non-accrual status and may be additionally designated as impaired or restructured, or some combination thereof.
Loans on which the accrual of interest has been discontinued are designated as non-accrual loans and the classified portions are credit downgraded to one of the adversely classified categories noted above. Accrual of interest on loans is generally discontinued when a loan becomes contractually past due, with respect to interest or principal, by 90 days, or when reasonable doubt exists as to the full and timely collection of interest or principal. When a loan is placed on non-accrual status, all interest previously accrued but not collected is reversed against current period interest income. Interest accruals are resumed on such loans only when payments are brought current and have remained current for a period of 180 days or when, in the judgment of management, the collectability of both principal and interest is reasonably assured. Interest payments received on loans in a non-accrual status are generally applied to principal on the books of the Company.
Impaired loans are individually significant loans for which management considers it probable that not all amounts due (principal and interest) will be collected in accordance with the original contractual terms. Impaired loans include loans that have been modified in a troubled debt restructuring ("TDR"), see "TDR" below. Impaired loans are individually evaluated and exclude large groups of smaller-balance homogeneous loans, such as residential mortgage loans and consumer loans, which are collectively evaluated for impairment, and loans that are measured at fair value, unless the loan is amended in a TDR.
Management does not set any minimum delay of payments as a factor in reviewing for impaired classification. Management considers the individual payment status, net worth and earnings potential of the borrower, and the value and cash flow of the collateral as factors to determine if a loan will be paid in accordance with its contractual terms.
Loans are designated as a TDR when, as part of an agreement to modify the original contractual terms of the loan as a result of financial difficulties of the borrower, the Bank grants the borrower a concession on the terms that would not otherwise be considered. Typically, such concessions may consist of one or a combination of the following: a reduction in interest rate to a below market rate, taking into account the credit quality of the note, extension of additional credit based on receipt of adequate collateral, or a deferment or reduction of payments (principal or interest), which materially alters the Bank's position or significantly extends the note's maturity date, such that the present value of cash flows to be received is materially less than those contractually established at the loan’s origination. All loans that are modified are reviewed by the Company to identify if a TDR has occurred. TDR loans are included in the impaired loan category and as such, these loans are individually reviewed and evaluated.
Impaired loans are individually evaluated for credit loss and a specific allowance reserve is assigned for the amount of the estimated probable credit loss. When a loan is deemed to be impaired, management estimates the probable credit loss by comparing the loan's carrying value against either: (1) the present value of the expected future cash flows discounted at the loan's effective interest rate; (2) the loan's observable market price; or (3) the expected realizable fair value of the collateral, in
48
the case of collateral dependent loans. Impaired loans are charged-off, in whole or in part, when management believes that the recorded investment in the loan is uncollectible.
An impaired or TDR loan classification will be considered for upgrade based on the borrower's sustained performance over time and their improving financial condition. Consistent with the criteria for returning non-accrual loans to accrual status, the borrower must demonstrate the ability to continue to service the loan in accordance with the original or modified terms and, in the judgment of management, the collectability of the remaining balances, both principal and interest, are reasonably assured. In the case of TDR loans having had a modified interest rate, that rate must be at, or greater than, a market rate for a similar credit at the time of modification for an upgrade to be considered.
Real estate acquired by the Company through foreclosure proceedings, or the acceptance of a deed in lieu of foreclosure, is classified as other real estate owned ("OREO"). When property is acquired, it is recorded at the estimated fair value of the property acquired, less estimated costs to sell, establishing a new cost basis. The estimated fair value is based on market appraisals and the Company's internal analysis. Any loan balance in excess of the estimated realizable fair value on the date of transfer is charged to the allowance for loan losses on that date. All costs incurred thereafter in maintaining the property, as well as subsequent declines in fair value are charged to non-interest expense.
Non-performing assets are comprised of non-accrual loans, deposit account overdrafts that are more than 90 days past due and OREO. The designation of a loan or other asset as non-performing does not necessarily indicate that loan principal and interest will ultimately be uncollectible. However, management recognizes the greater risk characteristics of these assets and therefore considers the potential risk of loss on assets included in this category in evaluating the adequacy of the allowance for loan losses. The level of delinquent and non-performing assets is largely a function of economic conditions and the overall banking environment and the individual business circumstances of borrowers. Despite prudent loan underwriting, adverse changes within the Company's market area, or deterioration in local, regional or national economic conditions, could negatively impact the Company's level of non-performing assets in the future.
Asset Quality
At December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company had adversely classified loans (loans carrying "substandard," "doubtful" or "loss" classifications) amounting to $37.1 million and $35.5 million, respectively. The increase in adversely classified loans was due to several commercial relationships which were credit downgraded during the year due to individual business circumstances. These additions to adversely classified loans were partially offset by credit upgrades, payoffs and charge-offs. Total adversely classified loans amounted to 1.45% of total loans at December 31, 2019, compared to 1.49% at December 2018.
Adversely classified loans included in the balances above that were performing but possessed potential weaknesses and, as a result, could ultimately become non-performing loans amounted to $22.4 million at December 31, 2019 and $23.8 million December 31, 2018. The remaining balances of adversely classified loans were non-accrual loans amounting to $14.7 million and $11.7 million at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively.
Total impaired loans amounted to $31.9 million and $31.5 million at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. Total accruing impaired loans amounted to $17.1 million and $19.7 million at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively, while non-accrual impaired loans amounted to $14.8 million and $11.8 million as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively.
In management's opinion, the majority of impaired loan balances at December 31, 2019 and 2018 were supported by expected future cash flows or, for those collateral dependent loans, the net realizable value of the underlying collateral. Based on management's assessment at December 31, 2019, impaired loans totaling $29.5 million required no specific reserves and impaired loans totaling $2.4 million required specific reserve allocations of $1.0 million. At December 31, 2018, impaired loans totaling $26.4 million required no specific reserves and impaired loans totaling $5.1 million required specific reserve allocations of $2.2 million. The decline in specific reserves since December 31, 2018 was due primarily to the charge-off of a previously impaired commercial relationship. Management closely monitors impaired relationships for the individual business circumstances, and underlying collateral or credit deterioration to determine if additional reserves are necessary.
Total TDR loans included in the impaired loan amounts above as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 were $21.1 million and $23.1 million, respectively. TDR loans on accrual status amounted to $17.1 million and $19.4 million at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. TDR loans included in non-performing loans amounted to $4.0 million and $3.7 million at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. The Company continues to work with
49
customers and enters into loan modifications (which may or may not be TDRs) to the extent deemed to be necessary or appropriate while attempting to achieve the best mutual outcome given the individual financial circumstances and prospects of the borrower.
At December 31, 2019, accruing loans past due 60-89 days increased $7.6 million from December 31, 2018, due primarily to three commercial relationships that are closely monitored by management for further deterioration. These relationships contain commercial real estate, commercial and industrial, and commercial construction loans. Approximately 50% of the December 31, 2019 outstanding balance of loans past due 60-89 days related to a single relationship which is anticipated to be paid-in-full in the first quarter of 2020.
The Company carried no OREO property at December 31, 2019 or December 31, 2018. There was one property added to OREO in 2019 that was subsequently sold resulting in net gains of $34 thousand. There were no write-downs of OREO during 2019 or 2018, and there were no sales of OREO during 2018.
The following table sets forth information regarding non-performing assets, TDR loans and delinquent loans 60-89 days past due as to interest or principal, held by the Company at the dates indicated:
December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
Non-accrual loan summary: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 8,280 | $ | 6,894 | $ | 6,751 | $ | 4,876 | $ | 8,506 | ||||||||||
Commercial and industrial | 3,285 | 3,417 | 1,294 | 3,174 | 4,323 | |||||||||||||||
Commercial construction | 1,735 | 176 | 193 | 519 | 335 | |||||||||||||||
Residential mortgages | 411 | 763 | 262 | 289 | 366 | |||||||||||||||
Home equity | 1,040 | 514 | 463 | 616 | 288 | |||||||||||||||
Consumer | 20 | 17 | 34 | — | 19 | |||||||||||||||
Total non-accrual loans | 14,771 | 11,781 | 8,997 | 9,474 | 13,837 | |||||||||||||||
Overdrafts > 90 days past due | — | 3 | 35 | 11 | 8 | |||||||||||||||
Total non-performing loans | 14,771 | 11,784 | 9,032 | 9,485 | 13,845 | |||||||||||||||
OREO | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Total non-performing assets | $ | 14,771 | $ | 11,784 | $ | 9,032 | $ | 9,485 | $ | 13,845 | ||||||||||
Total Loans | $ | 2,565,459 | $ | 2,387,506 | $ | 2,269,904 | $ | 2,022,729 | $ | 1,859,962 | ||||||||||
Accruing TDR loans not included above | $ | 17,103 | $ | 19,389 | $ | 17,356 | $ | 22,418 | $ | 10,053 | ||||||||||
Delinquent loans 60-89 days past due and still accruing | $ | 7,776 | $ | 205 | $ | 1,026 | $ | 940 | $ | 2,021 | ||||||||||
Loans 60-89 days past due and still accruing to total loans | 0.30 | % | 0.01 | % | 0.05 | % | 0.05 | % | 0.11 | % | ||||||||||
Adversely classified loans to total loans | 1.45 | % | 1.49 | % | 1.16 | % | 1.70 | % | 1.33 | % | ||||||||||
Non-performing loans to total loans | 0.58 | % | 0.49 | % | 0.40 | % | 0.47 | % | 0.74 | % | ||||||||||
Non-performing assets to total assets | 0.46 | % | 0.40 | % | 0.32 | % | 0.38 | % | 0.61 | % | ||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses | $ | 33,614 | $ | 33,849 | $ | 32,915 | $ | 31,342 | $ | 29,008 | ||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses to non-performing loans | 227.57 | % | 287.25 | % | 364.43 | % | 330.44 | % | 209.52 | % | ||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses to total loans | 1.31 | % | 1.42 | % | 1.45 | % | 1.55 | % | 1.56 | % | ||||||||||
Allowance for Loan Losses
The allowance for loan losses is an estimate of probable credit loss inherent in the loan portfolio as of the specified balance sheet dates. On a quarterly basis, management prepares an estimate of the allowance necessary to cover estimated probable credit losses. The Company maintains the allowance at a level that it deems adequate to absorb all reasonably anticipated probable losses from specifically known and other probable credit risks associated with the portfolio.
Except for loans specifically identified as impaired, as discussed above, the estimate is a two-tiered approach that allocates loan loss reserves to "regulatory problem asset" loans by classified credit rating and to non-classified loans by credit type. The
50
general loss allocations take into account quantitative historic loss experience, qualitative factors, as well as regulatory guidance and industry data. The allowance for loan losses is established through a provision for loan losses, which is a direct charge to earnings. Loan losses are charged against the allowance when management believes that the collectability of the loan principal is unlikely. Recoveries on loans previously charged-off are credited to the allowance.
In making its assessment on the adequacy of the allowance, management considers several quantitative and qualitative factors that could have an effect on the credit quality of the portfolio. Management closely monitors the credit quality of individual delinquent and non-performing relationships, the levels of impaired and adversely classified loans, net charge-offs, the growth and composition of the loan portfolio, expansion in geographic market area, the experience level of lenders and any changes in underwriting criteria, and the strength of the local and national economy, among other factors.
The level of delinquent and non-performing assets is largely a function of economic conditions and the overall banking environment and the individual business circumstances of borrowers. Despite prudent loan underwriting, adverse changes within the Company’s market area, or deterioration in local, regional or national economic conditions, could negatively impact management's estimate of probable credit losses.
Management continues to closely monitor the necessary allowance levels, including specific reserves. The allowance for loan losses to total loans ratio was 1.31% at December 31, 2019 compared to 1.42% at December 31, 2018. Continued general positive credit metrics, partially offset by the impact of loan growth in 2019 have contributed to the decline in the allowance to total loans ratio since the prior year.
Based on the foregoing, as well as management's judgment as to the existing credit risks inherent in the loan portfolio, as discussed above under the headings "Credit Risk" and "Asset Quality," management believes that the Company's allowance for loan losses is adequate to absorb probable losses from specifically known and other probable credit risks associated with the portfolio as of December 31, 2019.
The following table sets forth the allocation of the Company's allowance for loan losses among the categories of loans and the percentage of loans in each category to gross loans for the periods ending on the respective dates indicated:
December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Allowance allocation | Loan category as % of gross loans | Allowance allocation | Loan category as % of gross loans | Allowance allocation | Loan category as % of gross loans | Allowance allocation | Loan category as % of gross loans | Allowance allocation | Loan category as % of gross loans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comml real estate | $ | 18,338 | 54.3 | % | $ | 18,014 | 54.6 | % | $ | 17,545 | 52.9 | % | $ | 14,902 | 51.3 | % | $ | 13,514 | 50.3 | % | |||||||||||||||
Comml and industrial | 9,129 | 19.5 | % | 10,493 | 21.5 | % | 9,669 | 21.9 | % | 11,204 | 24.2 | % | 9,758 | 24.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Comml constr | 4,149 | 12.4 | % | 3,307 | 9.8 | % | 3,947 | 12.1 | % | 3,406 | 10.5 | % | 3,905 | 10.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Resid: mortg and home equity | 1,731 | 13.4 | % | 1,789 | 13.7 | % | 1,512 | 12.6 | % | 1,594 | 13.4 | % | 1,601 | 13.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Consumer | 267 | 0.4 | % | 246 | 0.4 | % | 242 | 0.5 | % | 236 | 0.6 | % | 230 | 0.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 33,614 | 100.0 | % | $ | 33,849 | 100.0 | % | $ | 32,915 | 100.0 | % | $ | 31,342 | 100.0 | % | $ | 29,008 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
The allocation of the allowance for loan losses above reflects management's judgment of the relative risks of the various categories of the Company's loan portfolio. This allocation should not be considered an indication of the future amounts or types of possible loan charge-offs.
See also Note 4, "Allowance for Loan Losses," to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below, for further information regarding credit quality and the allowance for loan losses.
51
The following table summarizes the activity in the allowance for loan losses for the periods indicated:
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
Balance at beginning of year | $ | 33,849 | $ | 32,915 | $ | 31,342 | $ | 29,008 | $ | 27,121 | ||||||||||
Provision charged to operations | 1,180 | 2,250 | 1,430 | 2,993 | 3,267 | |||||||||||||||
Recoveries on charged-off loans: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | — | 51 | 193 | 20 | 74 | |||||||||||||||
Commercial and industrial | 734 | 278 | 550 | 681 | 279 | |||||||||||||||
Commercial construction | — | — | — | — | 25 | |||||||||||||||
Residential mortgages | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Home equity | 9 | 55 | 4 | 3 | 15 | |||||||||||||||
Consumer | 35 | 47 | 8 | 5 | 16 | |||||||||||||||
Total recovered | $ | 778 | $ | 431 | $ | 755 | $ | 709 | $ | 409 | ||||||||||
Charged-off loans: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | — | — | 178 | 328 | 133 | |||||||||||||||
Commercial and industrial | 2,069 | 1,593 | 348 | 980 | 1,571 | |||||||||||||||
Commercial construction | — | — | — | 5 | — | |||||||||||||||
Residential mortgages | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Home equity | — | — | — | 6 | — | |||||||||||||||
Consumer | 124 | 154 | 86 | 49 | 85 | |||||||||||||||
Total charged-off | $ | 2,193 | $ | 1,747 | $ | 612 | $ | 1,368 | $ | 1,789 | ||||||||||
Net loans charged-off (recovered) | $ | 1,415 | $ | 1,316 | $ | (143 | ) | $ | 659 | $ | 1,380 | |||||||||
Balance at December 31 | $ | 33,614 | $ | 33,849 | $ | 32,915 | $ | 31,342 | $ | 29,008 | ||||||||||
Average loans outstanding | $ | 2,430,912 | $ | 2,303,708 | $ | 2,130,048 | $ | 1,919,826 | $ | 1,740,962 | ||||||||||
Net loans charged-off (recovered) to average loans | 0.06 | % | 0.06 | % | (0.01 | )% | 0.03 | % | 0.08 | % | ||||||||||
Recoveries to charge-offs | 35.48 | % | 24.67 | % | 123.37 | % | 51.83 | % | 22.86 | % | ||||||||||
Net loans charged-off (recovered) to allowance | 4.21 | % | 3.89 | % | (0.43 | )% | 2.10 | % | 4.76 | % | ||||||||||
Deposits
Total deposits amounted to $2.79 billion as of December 31, 2019, an increase of $221.9 million, or 9%, compared to December 31, 2018. Total deposits as a percentage of total assets were 86% at December 31, 2019 and 87% at December 31, 2018. As of December 31, 2019, customer deposits amounted to $2.79 billion, an increase of $278.7 million, or 11%, since December 31, 2018.
52
The following table sets forth deposit balances by certain categories at the dates indicated and the percentage of each deposit category to total deposits:
December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | December 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Amount | % of Total | Amount | % of Total | Amount | % of Total | |||||||||||||||
Non-interest checking | $ | 794,583 | 28.5 | % | $ | 765,029 | 29.8 | % | $ | 705,846 | 28.9 | % | |||||||||
Interest-bearing checking | 467,988 | 16.8 | % | 403,497 | 15.8 | % | 391,111 | 16.0 | % | ||||||||||||
Total checking | 1,262,571 | 45.3 | % | 1,168,526 | 45.6 | % | 1,096,957 | 44.9 | % | ||||||||||||
Savings | 203,236 | 7.3 | % | 193,214 | 7.5 | % | 193,385 | 7.9 | % | ||||||||||||
Money markets | 1,009,972 | 36.2 | % | 862,028 | 33.6 | % | 807,931 | 33.1 | % | ||||||||||||
Total savings/money markets | 1,213,208 | 43.5 | % | 1,055,242 | 41.1 | % | 1,001,316 | 41.0 | % | ||||||||||||
CDs | 310,951 | 11.2 | % | 284,231 | 11.1 | % | 195,599 | 8.0 | % | ||||||||||||
Total customer deposits | 2,786,730 | 100.0 | % | 2,507,999 | 97.8 | % | 2,293,872 | 93.9 | % | ||||||||||||
Brokered deposits(1) | — | — | % | 56,783 | 2.2 | % | 147,490 | 6.1 | % | ||||||||||||
Total deposits | $ | 2,786,730 | 100.0 | % | $ | 2,564,782 | 100.0 | % | $ | 2,441,362 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||
(1) | Brokered CDs $250,000 and under. |
Total customer deposits include reciprocal deposits from checking, money market deposits and CDs received from participating banks in nationwide deposit networks as a result of our customers electing to participate in Company offered programs which allow for enhanced FDIC insurance. Essentially, the equivalent of the original customers' deposited funds comes back to the Company and are carried within the appropriate category under total customer deposits. The Company's balances in these reciprocal products were $419.7 million, $342.4 million and $249.6 million at December 31, 2019, December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, respectively.
Increases in customer deposits during the year were attributed to sales and marketing efforts, product capabilities and market expansion. Checking deposits, a strong source of low-cost funding for the Company, increased $94.0 million, or 8%, through December 31, 2019 compared to December 31, 2018. Savings and money market account balances increased by $158.0 million, or 15%, at December 31, 2019 compared to December 31, 2018, primarily due to increases in money market balances. CD balances also increased $26.7 million, or 9%, through December 31, 2019.
Management may, from time-to-time utilize brokered deposits as cost effective wholesale funding sources to support continued loan growth. Brokered deposits may be comprised of non-reciprocal insured overnight or selected term funding gathered from nationwide bank networks or from large money center banks; however, at December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, brokered deposits were comprised only of brokered CDs. As of December 31, 2019, the Company had no brokered deposits. See also "Wholesale Funding" below.
The following table shows the scheduled maturities of CDs greater than $250,000:
(Dollars in thousands) | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | ||||||
Due in three months or less | $ | 22,515 | $ | 9,435 | ||||
Due in greater than three months through six months | 15,476 | 12,353 | ||||||
Due in greater than six months through twelve months | 29,325 | 18,012 | ||||||
Due in greater than twelve months | 22,884 | 29,231 | ||||||
Total CDs | $ | 90,200 | $ | 69,031 | ||||
53
The table below sets forth a comparison of the Company's average deposits and average rates paid for the periods indicated, as well as the percentage of each deposit category to total average deposits. The annualized average rate on total deposits reflects both interest-bearing and non-interest-bearing deposits.
Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Average Balance | Avg Rate | % of Total | Average Balance | Avg Rate | % of Total | Average Balance | Avg Rate | % of Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
Non-interest checking | $ | 790,915 | — | % | 28.6 | % | $ | 744,820 | — | % | 28.8 | % | $ | 697,247 | — | % | 29.8 | % | ||||||||||||
Interest checking | 434,074 | 0.38 | % | 15.7 | % | 391,209 | 0.30 | % | 15.1 | % | 357,252 | 0.14 | % | 15.3 | % | |||||||||||||||
Savings | 204,977 | 0.18 | % | 7.4 | % | 197,420 | 0.13 | % | 7.6 | % | 195,465 | 0.15 | % | 8.3 | % | |||||||||||||||
Money market | 1,020,363 | 1.14 | % | 36.9 | % | 867,318 | 0.61 | % | 33.5 | % | 827,867 | 0.32 | % | 35.4 | % | |||||||||||||||
Total interest-bearing non-term deposits | 1,659,414 | 0.82 | % | 60.0 | % | 1,455,947 | 0.46 | % | 56.2 | % | 1,380,584 | 0.25 | % | 59.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
CDs | 300,810 | 1.99 | % | 10.8 | % | 242,077 | 1.46 | % | 9.4 | % | 170,427 | 0.84 | % | 7.3 | % | |||||||||||||||
Total non-brokered deposits | 2,751,139 | 0.71 | % | 99.4 | % | 2,442,844 | 0.42 | % | 94.4 | % | 2,248,258 | 0.22 | % | 96.1 | % | |||||||||||||||
Brokered deposits | 15,466 | 1.88 | % | 0.6 | % | 145,645 | 1.70 | % | 5.6 | % | 91,522 | 1.22 | % | 3.9 | % | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 2,766,605 | 0.72 | % | 100.0 | % | $ | 2,588,489 | 0.49 | % | 100.0 | % | $ | 2,339,780 | 0.26 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||||
Borrowed Funds
Borrowed funds, comprised of FHLB borrowings and other borrowings, amounted to $96.2 million at December 31, 2019, compared to $100.5 million at December 31, 2018, decreasing $4.3 million, or 4%. The Company's primary borrowing source is the FHLB, but the Company may choose to borrow from other established business partners. Outstanding borrowings from the FHLB typically have been comprised of overnight or short-term borrowings, which represents the majority of the balance at December 31, 2019, and term advances linked to outstanding commercial loans under various community reinvestment programs of the FHLB. At December 31, 2019 and 2018, borrowed funds consisted of FHLB borrowings only. For additional information on the composition of borrowed funds, including weighted average rates and maturities, and maximum borrowing outstanding at any month end, see Note 8, "Borrowed Funds and Subordinated Debt," to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K.
At December 31, 2019, the Bank had the capacity to borrow additional funds from the FHLB of up to approximately $535.0 million and the capacity to borrow from the FRB Discount Window of approximately $175.0 million.
The table below shows the comparison of the Company's average borrowed funds and average rates paid for the periods indicated:
Year ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Average Balance | Average Cost | Average Balance | Average Cost | Average Balance | Average Cost | |||||||||||||||
FHLB advances | $ | 15,885 | 2.42 | % | $ | 22,250 | 1.72 | % | $ | 49,546 | 1.19 | % | |||||||||
Other borrowed funds | 55 | 2.64 | % | — | — | % | — | — | % | ||||||||||||
Total borrowed funds | $ | 15,940 | 2.42 | % | $ | 22,250 | 1.72 | % | $ | 49,546 | 1.19 | % | |||||||||
The category "Other borrowed funds" represents overnight advances from the FRB or borrowings from correspondent banks.
54
Wholesale Funding
Wholesale funding, includes brokered deposits and borrowed funds, amounted to $96.2 million at December 31, 2019, compared to $157.3 million at December 31, 2018. Since December 31, 2018, wholesale funding has decreased $61.1 million, as customer deposit growth has exceeded loan growth.
The following table sets forth the breakout of wholesale funding by composition at the dates indicated and the percentage of each category to total wholesale funding:
December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | December 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | |||||||||||||||
Brokered deposits | $ | — | — | % | $ | 56,783 | 36.1 | % | $ | 147,490 | 62.4 | % | |||||||||
Borrowed funds | 96,173 | 100.0 | % | 100,492 | 63.9 | % | 89,000 | 37.6 | % | ||||||||||||
Wholesale funding | $ | 96,173 | 100.0 | % | $ | 157,275 | 100.0 | % | $ | 236,490 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||
See "Liquidity," below, for additional information.
Subordinated Debt
The Company had outstanding subordinated debt of $14.9 million (net of deferred issuance costs) at both December 31, 2019, and December 31, 2018, which consisted of $15.0 million in aggregate principal amount of Fixed-to-Floating Rate Subordinated Notes (the "Notes") issued in January 2015, in a private placement to an accredited investor. See also Note 8, "Borrowed Funds and Subordinated Debt," to the Company's consolidated financial statements contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below, for further information regarding the Company's subordinated debt.
Liquidity
Liquidity is the ability to meet cash needs arising from, among other things, fluctuations in loans, investments, deposits and borrowings. Liquidity management is the coordination of activities so that cash needs are anticipated and met readily and efficiently. The Company's liquidity policies are set and monitored by the Company's Board. The duties and responsibilities related to asset-liability management matters are also covered by the Board. The Company's asset-liability objectives are to engage in sound balance sheet management strategies, maintain liquidity, provide and enhance access to a diverse and stable source of funds, provide competitively priced and attractive products to customers and conduct funding at a low-cost relative to current market conditions. Funds gathered are used to support current commitments, to fund earning asset growth, and to take advantage of selected leverage opportunities.
The Company's liquidity is maintained by projecting cash needs, balancing maturing assets with maturing liabilities, monitoring various liquidity ratios, monitoring deposit flows, maintaining cash flow within the investment portfolio, and maintaining wholesale funding resources.
At December 31, 2019, the Company's wholesale funding sources primarily included borrowing capacity at the FHLB and brokered deposits. In addition, the Company maintains overnight fed fund purchase arrangements with correspondent banks and has access to the FRB Discount Window.
Management believes that the Company has adequate liquidity to meet its obligations. However, if general economic conditions or other events causes these sources of external funding to become restricted or are eliminated, the Company may not be able to raise adequate funds or may incur substantially higher funding costs or operating restrictions in order to raise the necessary funds to support the Company's operations and growth.
The Company has in the past also increased capital and liquidity by offering shares of the Company's common stock for sale to its existing stockholders and new investors and through the issuance of subordinated debt. For additional information on the Company's capital planning, see the section entitled "Capital Resources" contained in Item 1, "Business" of this Form 10-K.
55
Capital Adequacy
The Company is subject to various regulatory capital requirements administered by the federal banking agencies. The Company's capital policies and capital levels are monitored on a quarterly basis and capital planning is reviewed at least annually by the Board.
Failure to meet minimum capital requirements can initiate or result in certain mandatory and possible additional discretionary supervisory actions by regulators, which if undertaken, could have a material adverse effect on the Company's consolidated financial condition. At December 31, 2019, the capital levels of both the Company and the Bank complied with all applicable minimum capital requirements of the Federal Reserve Board and the FDIC, respectively. Additionally, the Company met the definition of "well-capitalized" under the applicable Federal Reserve Board regulations and the Bank qualified as "well-capitalized" under the prompt corrective action regulations of Basel III and the FDIC.
See also "Capital Resources," and within the "Supervision and Regulation," section "Capital Requirements," "Capital Requirements under Basel III," and for the Bank "Capital Adequacy Requirements" all contained in Item 1, and Note 11, "Stockholders' Equity," to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below, for additional information regarding the capital requirements applicable to the Company and the Bank and their respective capital levels at December 31, 2019.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
The Company is required to make future cash payments under various contractual obligations. The following table summarizes the contractual cash obligations at December 31, 2019:
Payments Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Total | With-in 1 Year | >1 – 3 Years | >3 – 5 Years | After 5 Years | |||||||||||||||
Contractual Cash Obligations: | ||||||||||||||||||||
CDs | $ | 310,951 | $ | 229,616 | $ | 78,204 | $ | 2,907 | $ | 224 | ||||||||||
FHLB borrowings | 96,173 | 95,697 | — | — | 476 | |||||||||||||||
Subordinated debt | 15,000 | — | — | — | 15,000 | |||||||||||||||
Supplemental retirement plans | 2,492 | 276 | 552 | 552 | 1,112 | |||||||||||||||
Operating lease obligations | 29,579 | 1,242 | 2,487 | 2,507 | 23,343 | |||||||||||||||
Vendor contracts | 15,807 | 7,364 | 5,709 | 2,541 | 193 | |||||||||||||||
Total contractual obligations | $ | 470,002 | $ | 334,195 | $ | 86,952 | $ | 8,507 | $ | 40,348 | ||||||||||
See also Note 7, "Deposits," Note 8, "Borrowed Funds and Subordinated Debt," Note 6, "Leases," and Note 12, "Employee Benefit Plans," to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below, for further information regarding non-term deposits and CDs, FHLB Borrowings and Subordinated Debt, operating lease obligations. and supplement retirement plans.
The Company is also party to financial instruments with off-balance sheet risk in the normal course of business to meet the financing needs of its customers. The instruments involve, to varying degrees, elements of credit risk in excess of the amount recognized in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The contractual amounts of these instruments reflect the extent of involvement the Company has in the particular classes of financial instruments.
56
The following table summarizes the contractual commitments at December 31, 2019:
Commitment Expiration — By Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Total | With-in 1 Year | >1 – 3 Years | >3 – 5 Years | After 5 Years | |||||||||||||||
Other Commitments: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Unadvanced loans and lines | $ | 905,245 | $ | 587,119 | $ | 182,863 | $ | 44,406 | $ | 90,857 | ||||||||||
Commitments to originate loans | 25,930 | 25,930 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Letters of credit | 25,284 | 17,260 | 7,984 | 40 | — | |||||||||||||||
Commitments to originate loans for sale | 1,095 | 1,095 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Commitments to sell loans | 1,696 | 1,696 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Customer related interest-rate swaps notional amount(1) | 22,775 | — | 1,921 | — | 20,854 | |||||||||||||||
Total commitments | $ | 982,025 | $ | 633,100 | $ | 192,768 | $ | 44,446 | $ | 111,711 | ||||||||||
(1) | Offsetting positions to these interest-rate swaps offered to commercial loan customers are entered into with a counterparty. Notional principal amounts are not actually exchanged. |
See also Note 10, "Commitments, Contingencies and Financial Instruments with Off-Balance Sheet Risk and Concentrations of Credit Risk," to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below, for further information regarding unadvanced loans and lines, commitments to originate loans, letters of credit and commitments to originate loans for sale or to sell loans. See Note 9, "Derivatives and Hedging Activities," to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below, for further information regarding customer related interest-rate swaps.
Assets Under Management
Total assets under management, includes total assets, loans serviced for others and investment assets under management. Loans serviced for others and investment assets under management are not carried as assets on the Company's Consolidated Balance Sheet, and as such, total assets under management is not a financial measurement recognized under GAAP, however management believes its disclosure provides information useful in understanding the trends in total assets under management.
The Company provides a wide range of wealth management and wealth services, including brokerage, trust, and investment management. Also included in the investment assets under management total are customers' commercial sweep arrangements that are invested in third-party money market mutual funds.
Investment assets under management, which are reflected at fair market value, increased $115.9 million, or 14%, for the year ended December 31, 2019 since December 31, 2018 and increased $71.6 million, or 8%, since December 31, 2017. The increase since December 31, 2018 in investment assets under management was primarily due to increases in market values.
Total assets under management increased $393.2 million, or 10%, for the year ended December 31, 2019 since December 31, 2018 and $496.0 million, or 13% since December 31, 2017.
The following table sets forth the value of assets under management and its components at the dates indicated:
December 31, | ||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Total assets | $ | 3,235,049 | $ | 2,964,358 | $ | 2,817,564 | ||||||
Loans serviced for others | 95,905 | 89,232 | 89,059 | |||||||||
Investment assets under management | 916,623 | 800,751 | 844,977 | |||||||||
Total assets under management | $ | 4,247,577 | $ | 3,854,341 | $ | 3,751,600 | ||||||
57
Results of Operations
COMPARISON OF YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018
Unless otherwise indicated, the reported results are for the year ended December 31, 2019 with the "same period," the "comparable year" and "prior year" being the year ended December 31, 2018. Average yields are presented on a tax equivalent basis.
Net Income
The Company's net income for the year ended December 31, 2019 amounted to $34.2 million, an increase of $5.3 million compared to the year ended December 31, 2018. Diluted earnings per share for 2019 were $2.89 for the year ended December 31, 2019, as compared to $2.46 for the year ended December 31, 2018.
Net Interest Income and Margin
The Company's net interest income for the year ended December 31, 2019 amounted to $115.9 million, an increase of $7.0 million, or 6%, compared to the year ended December 31, 2018. The increase in net interest income over the comparable year was due largely to interest-earning asset growth, primarily in loans. The Company's Margin was 3.89% for years ended December 31, 2019 and was 3.91% for year ended December 31, 2018.
Tax equivalent net interest income for the years ended December 31, 2019 was $117.4 million compared to $110.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2018, an increase of $6.8 million, or 6%. T/E Margin was 3.95% for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to 3.97% for the year ended December 31, 2018. The decrease resulted from the cost of funds increasing more than interest earning asset yields. T/E Margin was 3.93% for the three months ended December 31, 2019. In the latter half of the year, T/E Margin was impacted by declining rates driven by three reductions in the fed funds rate from August through October 2019.
Interest and Dividend Income
For the year ended December 31, 2019, total interest and dividend income amounted to $137.1 million, an increase of $14.2 million, or 12%, compared to the prior year. The increase was driven by increases in both average balances and yields. Average balances of interest-earning assets increased $189.4 million, or 7%, and the average yields on interest-earning assets increased 18 basis points, both mainly attributable to loans and loans held for sale. The increase in loan yields since the prior period is primarily attributable to market rate increases, including the prime rate throughout 2018, which positively impacted yields in 2019. Declines in market rates in the second half of 2019, including three recent reductions in the Prime Rate, have lowered loan yields relative to earlier in the year but on a year-to-date basis remain at levels that exceed the comparable prior year period.
Interest Expense
For the year ended December 31, 2019, total interest expense amounted to $21.3 million, an increase of $7.2 million, or 51%, compared to the prior year primarily due to increases in deposit market rates during 2018 and the first half of 2019. The average cost of funding, including the impact of non-interest deposit accounts, increased 22 basis points. The average cost of checking, saving and money market accounts increased 36 basis points and the average cost of CDs increased 53 basis points. Partially offsetting the increase in interest expense were lower average balances on brokered CDs as maturing balances were not renewed in 2019 due to increases in lower-costing deposits.
Non-interest deposit accounts are an important component of the Company's core funding strategy. The average balance of non-interest checking deposits increased $46.1 million, or 6%, as compared to the same period in 2018. This non-interest-bearing funding source represented 29% of total average deposit balances for both the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Interest rate risk is reviewed in detail under the heading Item 7A, "Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk," of this Form 10-K below.
58
Rate/Volume Analysis
The following table sets forth, on a tax-equivalent basis, the extent to which changes in interest rates and changes in the average balances of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities have affected interest income and expense for the period indicated. For each category of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities, information is provided on changes attributable to: (1) volume (change in average portfolio balance multiplied by prior year average rate); and (2) interest rate (change in average interest rate multiplied by prior year average balance). Changes attributable to the combined impact of volume and rate have been allocated proportionately based on absolute value to the changes due to volume and the changes due to rate.
December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 vs 2018 | |||||||||||
Increase (Decrease) due to | |||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Net Change | Volume | Rate | ||||||||
Interest Income | |||||||||||
Loans and loans held for sale (tax equivalent) | $ | 10,929 | $ | 6,212 | $ | 4,717 | |||||
Investment securities (tax equivalent) | 2,225 | 870 | 1,355 | ||||||||
Other interest-earning assets(1) | 806 | 715 | 91 | ||||||||
Total interest-earning assets (tax equivalent) | 13,960 | 7,797 | 6,163 | ||||||||
Interest Expense | |||||||||||
Interest checking, savings, and money market | 6,893 | 1,044 | 5,849 | ||||||||
CDs | 2,469 | 989 | 1,480 | ||||||||
Brokered CDs | (2,181 | ) | (2,419 | ) | 238 | ||||||
Borrowed funds | 2 | (127 | ) | 129 | |||||||
Subordinated debt | — | 1 | (1 | ) | |||||||
Total interest-bearing funding | 7,183 | (512 | ) | 7,695 | |||||||
Change in net interest income (tax equivalent) | $ | 6,777 | $ | 8,309 | $ | (1,532 | ) | ||||
____________________
(1) | Income on other interest-earning assets includes interest on deposits, and fed funds sold, and dividends on FHLB stock. |
The table on the following page presents the Company's average balance sheet, net interest income and average rates for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017:
59
Average Balances, Interest and Average Yields | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2019 | Year ended December 31, 2018 | Year ended December 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Average Balance | Interest(1) | Average Yield(1) | Average Balance | Interest(1) | Average Yield (1) | Average Balance | Interest(1) | Average Yield(1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loans and loans held for sale(2) (tax equivalent) | $ | 2,432,195 | $ | 122,635 | 5.04 | % | $ | 2,303,781 | $ | 111,706 | 4.85 | % | $ | 2,130,752 | $ | 97,741 | 4.59 | % | |||||||||||||||
Investment securities(3) (tax equivalent) | 462,017 | 14,160 | 3.06 | % | 431,835 | 11,935 | 2.76 | % | 379,324 | 10,242 | 2.70 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Other interest-earning assets(4) | 80,740 | 1,891 | 2.34 | % | 49,970 | 1,085 | 2.17 | % | 30,225 | 428 | 1.42 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total interest-earning assets (tax equivalent) | 2,974,952 | 138,686 | 4.66 | % | 2,785,586 | 124,726 | 4.48 | % | 2,540,301 | 108,411 | 4.27 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Other assets | 138,205 | 98,148 | 107,729 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 3,113,157 | $ | 2,883,734 | $ | 2,648,030 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Liabilities and stockholders' equity: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest checking, savings and money market | $ | 1,659,414 | 13,650 | 0.82 | % | $ | 1,455,947 | 6,757 | 0.46 | % | $ | 1,380,584 | 3,448 | 0.25 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
CDs | 300,810 | 6,000 | 1.99 | % | 242,077 | 3,531 | 1.46 | % | 170,427 | 1,433 | 0.84 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Brokered CDs | 15,466 | 291 | 1.88 | % | 145,645 | 2,472 | 1.70 | % | 91,522 | 1,114 | 1.22 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Borrowed funds | 15,940 | 385 | 2.42 | % | 22,250 | 383 | 1.72 | % | 49,546 | 590 | 1.19 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Subordinated debt(5) | 14,866 | 925 | 6.22 | % | 14,853 | 925 | 6.23 | % | 14,840 | 925 | 6.23 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total interest-bearing funding | 2,006,496 | 21,251 | 1.06 | % | 1,880,772 | 14,068 | 0.75 | % | 1,706,919 | 7,510 | 0.44 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest-rate spread (tax equivalent) | 3.60 | % | 3.73 | % | 3.83 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Non-interest checking | 790,915 | — | 744,820 | — | 697,247 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total deposits, borrowed funds and subordinated debt | 2,797,411 | 21,251 | 0.76 | % | 2,625,592 | 14,068 | 0.54 | % | 2,404,166 | 7,510 | 0.31 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Other liabilities | 37,913 | 20,459 | 17,919 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total liabilities | 2,835,324 | 2,646,051 | 2,422,085 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stockholders' equity | 277,833 | 237,683 | 225,945 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $ | 3,113,157 | $ | 2,883,734 | $ | 2,648,030 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest income (tax equivalent) | 117,435 | 110,658 | 100,901 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest margin (tax equivalent) | 3.95 | % | 3.97 | % | 3.97 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Less tax equivalent adjustment | 1,578 | 1,823 | 3,379 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest income | $ | 115,857 | $ | 108,835 | $ | 97,522 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest margin | 3.89 | % | 3.91 | % | 3.84 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1) | Average yields and interest income are presented on a tax equivalent basis, calculated using a U.S federal income tax rate of 21% in both 2019 and 2018, and 35% in 2017, based on tax equivalent adjustments associated with tax exempt loans and investments interest income. |
(2) | Average loans and loans held for sale include non-accrual loans and are net of average deferred loan fees. |
(3) | Average investment balances are presented at average amortized cost. |
(4) | Average other interest-earning assets includes interest-earning deposits, fed funds sold, and FHLB stock. |
(5) | The subordinated debt is net of average deferred debt issuance costs. |
60
Provision for Loan Losses
The provision for loan losses amounted to $1.2 million and $2.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, a decrease of $1.1 million compared to 2018. The decrease in the provision for loan losses for 2019 compared to the prior year was due primarily to continued generally positive credit metrics, partially offset by the impact of loan growth in 2019.
In determining the provision to the allowance for loan losses, management takes into consideration the level of loan growth and an estimate of credit risk, which includes such items as adversely classified and non-performing loans, the estimated specific reserves needed for impaired loans, the level of net charge-offs, and the estimated impact of current economic conditions on credit quality. The provision reflects management’s estimate of the loan loss allowance necessary to support the level of credit risk inherent in the portfolio during the period.
See also "Credit Risk," "Asset Quality," and "Allowance for Loan Losses" included in the section entitled "Financial Condition," contained in this Item 7 of this Form 10-K above, for further information regarding the provision for loan losses.
Non-Interest Income
Non-interest income for the year ended December 31, 2019 amounted to $16.3 million, an increase of $4.3 million, or 36%, compared to 2018.
The following table sets forth the components of non-interest income and the related changes for the periods indicated:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | Change | % Change | |||||||||||
Wealth management fees | $ | 5,494 | $ | 5,624 | $ | (130 | ) | (2 | )% | ||||||
Deposit and interchange fees | 6,870 | 6,234 | 636 | 10 | % | ||||||||||
Income on bank-owned life insurance, net | 638 | 672 | (34 | ) | (5 | )% | |||||||||
Net gains (losses) on sales of available-for-sale securities | 146 | (2,950 | ) | 3,096 | (105 | )% | |||||||||
Net gains on sales of loans | 469 | 260 | 209 | 80 | % | ||||||||||
Other income | 2,702 | 2,150 | 552 | 26 | % | ||||||||||
Total non-interest income | $ | 16,319 | $ | 11,990 | $ | 4,329 | 36 | % | |||||||
Deposit and interchange fee increases were primarily attributable to increases in debit card usage, as well as increases in business checking and overdraft fees compared to 2018. Deposit and interchange fees include servicing fees received on customer deposit accounts and income derived from the use of debit cards by bank customers and the use of the Company's ATM by non-bank customers.
Net gains (losses) on sales of available-for-sale securities increased due primarily to $2.9 million in realized losses on a discretionary partial restructure of the bond portfolio in 2018.
Net gains on sales of loans increased due to the higher volume of loans sold in 2019, primarily from lower interest rates in the second half of 2019.
Other income increased primarily due to net gains on equity securities compared with net losses on equity securities in the comparable 2018 period, due primarily to fair value adjustments. None of the remaining components were individually significant to the year-over-year increase.
Non-Interest Expense
Non-interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2019 amounted to $86.4 million, an increase of $5.5 million, or 7%, compared to the prior year.
61
The following table sets forth the components of non-interest expense and the related changes for the periods indicated:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | Change | % Change | |||||||||||
Salaries and employee benefits | $ | 56,059 | $ | 51,442 | $ | 4,617 | 9 | % | |||||||
Occupancy and equipment expenses | 8,417 | 8,526 | (109 | ) | (1 | )% | |||||||||
Technology and telecommunications expenses | 7,590 | 6,382 | 1,208 | 19 | % | ||||||||||
Advertising and public relations expenses | 2,962 | 3,182 | (220 | ) | (7 | )% | |||||||||
Audit, legal and other professional fees | 2,039 | 1,725 | 314 | 18 | % | ||||||||||
Deposit insurance premiums | 876 | 1,697 | (821 | ) | (48 | )% | |||||||||
Supplies and postage expenses | 971 | 989 | (18 | ) | (2 | )% | |||||||||
Other operating expenses | 7,501 | 6,935 | 566 | 8 | % | ||||||||||
Total non-interest expense | $ | 86,415 | $ | 80,878 | $ | 5,537 | 7 | % | |||||||
Salaries and employee benefits increased primarily to support the Company's strategic growth and market expansion initiatives since the prior year.
The increase in technology and telecommunications expenses is primarily due to higher infrastructure costs and expenses associated with the Company's multi–year digital transformation strategy to enhance operating efficiency and customer experience.
Deposit insurance premiums decreased primarily resulting from a Small Bank Assessment Credit from the FDIC Deposit Insurance Fund of $683 thousand for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Other operating expenses is comprised of a variety of miscellaneous expenses, none of which were individually significant to the year-over-year increase.
Income Tax Expense
The effective tax rate for the year ended December 31, 2019 was 23.3% and for the year ended December 31, 2018 was 23.4%. Refer to Note 14, "Income Taxes," to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K, for additional information about the Company's tax positions.
Results of Operations Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2018 and 2017
For a comparison of the results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, see Part II, Item 7 Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2018, as filed with SEC on March 13, 2019.
62
Accounting Policies/Critical Accounting Estimates
The Company's significant accounting policies are described in Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," to the consolidated financial statements contained in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" of this Form 10-K. In applying these accounting policies, management is required to exercise judgment in determining many of the methodologies, assumptions and estimates to be utilized. Certain of the critical accounting estimates are more dependent on such judgment and in some cases may contribute to volatility in the Company's reported financial performance should the assumptions and estimates used be incorrect or change over time due to changes in circumstances. The three most significant areas in which management applies critical assumptions and estimates include the areas described further below.
Allowance for Loan Losses
The allowance for loan losses is an estimate of probable credit loss inherent in the loan portfolio as of the specified balance sheet dates. The allowance for loan losses is established through a provision for loan losses, a direct charge to earnings. Loan losses are charged against the allowance when management believes that the collectability of the loan principal is unlikely. Recoveries on loans previously charged-off are credited to the allowance. The Company maintains the allowance at a level that it deems adequate to absorb all reasonably anticipated probable losses from specifically known and other credit risks associated with the portfolio. Arriving at an appropriate level of allowance for loan losses involves a high degree of management judgment.
The Company uses a systematic methodology to measure the amount of estimated loan loss exposure inherent in the portfolio for purposes of establishing a sufficient allowance for loan losses. The methodology makes use of specific reserves for loans individually evaluated and deemed impaired, and general reserves for larger groups of homogeneous loans, which are collectively evaluated relying on a combination of qualitative and quantitative factors that may affect credit quality of the pool.
Management believes that the Company's allowance for loan losses is adequate to absorb probable losses from specifically known and other probable credit risks associated with the portfolio as of the balance sheet dates reflected in this annual report. While management uses available information to recognize losses on loans, future additions to the allowance may be necessary. In addition, various regulatory agencies, as an integral part of their examination process, periodically review the Company's allowance for loan losses. Such agencies may require the Company to recognize additions to the allowance based on judgments different from those of management.
Management's assessment of the adequacy of the allowance for loan losses is contained under "Loans" with the subheadings "Credit Risk," "Asset Quality," and "Allowance for Loan Losses," included in the section "Financial Condition," contained in this Item 7 of this Form 10-K.
On January 1, 2020, the Company adopted ASU No. 2016-13, "Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments," also referred to as CECL. See Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," Item (v) "Recent Accounting Pronouncements," under the heading "Accounting pronouncements not yet adopted by the Company" to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below, for information regarding the Company's adoption of CECL.
Impairment Review of Investment Securities
There are inherent risks associated with the Company's investment activities that could adversely impact the fair value and the ultimate collectability of the Company's investments. The Company primarily invests in debt securities. At December 31, 2019, the Company also held immaterial amounts of equity securities and FHLB stock.
Management regularly reviews the portfolio for debt securities with unrealized losses to determine if any of the unrealized losses are OTTI. The determination of OTTI involves a high degree of judgment. While management uses available information to measure OTTI at the balance sheet date, future write-downs may be necessary based on extended duration of current unrealized losses, changing market conditions, or circumstances surrounding individual issuers.
If a debt investment is deemed to have an unrealized loss that is OTTI, the Company is required to write-down the investment. For debt securities, OTTI is generally recognized through a charge to earnings as of the balance sheet date, while non-OTTI unrealized losses are recognized in other comprehensive income. Unrealized losses on debt securities are deemed OTTI if (1) the Company intends to sell the security, (2) it is more likely than not that the Company will be required to sell the security
63
before recovery, or (3) a credit loss exists, and the Company does not expect to recover the entire amortized cost. For debt securities that have a credit loss, any portion of the loss related to other factors is recorded in other comprehensive income. Once written-down, the previous charge may not be recovered through earnings until sale or maturity, if in excess of its new cost basis. Any OTTI charges, depending upon the magnitude of the charges, could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition and results of operations.
Based on this impairment review, management determined that there were no debt securities carried in the Company's investment securities portfolio at December 31, 2019 that were deemed other-than-temporarily impaired.
Management's assessment of impairment of the unrealized losses on debt securities in the investment portfolio is contained in Note 2, "Investment Securities," to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below.
At December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, in accordance with GAAP, the Company's equity securities were carried at fair value, with changes in fair value recognized in the Company's Consolidated Statement of Income in the "Other income" line item.
For information of the Company's OTTI assessment of FHLB stock, see Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," Item (d), "Restricted Cash and Investments," to the Company’s consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below for further information.
Impairment Review of Goodwill
In accordance with GAAP, the Company does not amortize goodwill and instead, at least annually, evaluates whether the carrying value of goodwill has become impaired. A determination that goodwill has become impaired results in an immediate write-down of goodwill to its determined value with a resulting charge to the Company's Consolidated Statement of Income. Goodwill is evaluated at the reporting unit level. In the case of the Company, the services offered through the Bank and subsidiaries are managed as one strategic unit and represent the Company's only reportable operating segment.
The Company has the option to perform either (1) a qualitative assessment of whether it is "more likely than not" that the reporting unit's fair value is less than its book value, or (2) a quantitative assessment.
1. | Management's qualitative assessment would take into consideration, among other items, macroeconomic conditions, industry and market considerations, cost or margin factors, financial performance and share price. Based on the qualitative assessment, if the Company were to conclude: (a) it is "more likely than not" that the fair value of a reporting unit exceeds its book value, goodwill is deemed not impaired, or (b) it is "more likely than not" that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its book value, a quantitative goodwill analysis must be performed. |
2. | The Company may elect to forgo the qualitative assessment and perform the quantitative analysis even if management does not believe that is "more likely than not" that goodwill is impaired. The quantitative goodwill analysis compares the fair value of the reporting unit with its book value, including goodwill. If the fair value of the reporting unit equals or exceeds its book value, goodwill is deemed not impaired. If the book value of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value, a goodwill impairment loss is recognized for the difference between these amounts, not exceeding the goodwill carrying amount. |
At December 31, 2019, based on the Company's quantitative analysis, goodwill was deemed not to be impaired.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," Item (v) "Recent Accounting Pronouncements," to the Company's consolidated financial statements, contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K below, for information regarding recent accounting pronouncements.
64
Impact of Inflation and Changing Prices
The Company's asset and liability structure is substantially different from that of an industrial company in that virtually all assets and liabilities of the Company are monetary in nature. Management believes the impact of inflation on financial results depends upon the Company's ability to react to changes in interest rates and by such reaction, reduce the inflationary impact on performance. Interest rates do not necessarily move in the same direction, or at the same magnitude, as the prices of other goods and services. As discussed previously, management seeks to manage the relationship between interest rate-sensitive assets and liabilities in order to protect against wide net interest income fluctuations, including those resulting from inflation.
Various information shown elsewhere in this annual report will assist in the understanding of how well the Company is positioned to react to changing interest rates and inflationary trends. In particular, additional information related to the margin sensitivity analysis is contained in Item 7A of this Form 10-K below and other maturity and repricing information of the Company's interest rate-sensitive assets and liabilities is contained in this Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" of this Form 10-K under the heading "Financial Condition" in this report.
Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk |
Interest Margin Sensitivity Analysis
The Company's primary market risk is interest-rate risk. Oversight of interest-rate risk management is the responsibility of the Board. Annually, the Board reviews and approves the Company's asset-liability management policy, which provides management with guidelines for controlling interest-rate risk, as measured through net interest income sensitivity to changes in interest rates, within certain tolerance levels. The Board also establishes and monitors guidelines for the Company's liquidity, capital ratios and asset-liability management.
The Company's asset-liability management strategies and guidelines are reported to the Board on a periodic basis. These strategies and guidelines are revised based on changes in interest-rate levels, general economic conditions, competition in the marketplace, the current interest-rate risk position of the Company, anticipated growth and other factors.
One of the principal factors in maintaining planned levels of net interest income is the ability to design effective strategies to manage the impact of interest rate changes on future net interest income. Quarterly, management completes a net interest income sensitivity analysis and reports the results to the Board. This analysis includes a simulation of the Company's net interest income under various interest-rate scenarios and assumes no future growth (i.e.; static balance sheet). Variations in the interest-rate environment affect numerous factors, including prepayment speeds, reinvestment rates, maturities of investments (due to call provisions), ability to attract deposits and other funding, and interest rates on various asset and liability accounts. Results of this analysis are also impacted by changes in liquidity, such as fluctuations in the balances of short-term investments and overnight borrowings.
The Company can be subject to margin compression depending on the economic environment and the shape of the yield curve. Under the Company's current balance sheet position, the Company's margin generally performs slightly better over time in a rising rate environment, while it generally decreases in a declining rate environment and when the yield curve is flattening or inverted.
In a flattening yield curve scenario, margin compression occurs as the spread between the cost of funding and the yield on interest-earning assets narrows. Under this scenario the degree of margin compression is highly dependent on the Company's ability to fund asset growth through lower cost deposits. However, if the curve is flattening, while short-term rates are rising, the adverse impact on margin may be somewhat delayed, as increases in the Prime Rate will initially result in the Company's asset yields re-pricing more quickly than funding costs.
In an inverted yield curve situation, shorter-term rates exceed longer-term rates, and the impact on margin is similar but more adverse than the flat curve scenario. Again, however, the extent of the impact on margin is highly dependent on the Company's balance sheet mix.
In a declining rate environment, margin compression will eventually occur when the yield on interest-earning assets decrease more than funding costs. The primary causes would be the impact of interest rate decreases (including decreases in the Prime Rate) on adjustable rate loans and the fact that decreases in deposit rates may be limited or lag decreases in the Prime Rate.
65
At December 31, 2019, the Company's interest-rate risk exposure continues to be margin compression that may result from changes in interest rates and/or changes in the mix of the Company's balance sheet components. This would include the mix of fixed versus variable rate loans and investments within assets, and higher cost versus lower cost deposits and overnight borrowings versus term borrowings and certificates of deposit within liabilities. Refer to the heading "Results of Operations" contained within Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" of this Form 10-K for further discussion of margin.
The following table summarizes the projected cumulative net interest income and the percent changes compared to the rates unchanged scenario, for a 24-month period as of December 31, 2019. These results, which are subject to various assumptions as noted above, including a static balance sheet with parallel yield curve shifts and gradual interest rate changes.
December 31, 2019 | ||||||||
24 Months | ||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Net interest income | Percentage Change | ||||||
Changes in interest rates | ||||||||
Rates Rise 400 Basis Points | $ | 237,216 | 0.77 | % | ||||
Rates Rise 200 Basis Points | 237,369 | 0.83 | % | |||||
Rates Unchanged | 235,414 | — | % | |||||
Rates Decline 200 Basis Points | 225,422 | (4.24 | )% | |||||
In the declining rate scenario noted, net interest income is projected to decrease as funding costs are at low levels and do not decline as significantly as asset yields.
In the 200 and 400 basis point rising rate scenarios noted, net interest income is projected to increase slightly in the first 24 months primarily due to loan yields increasing more significantly than funding costs. Net interest income increases further beyond a 24 month period as loan yields continue to reprice higher, resulting in increases of 6.67% and 11.87%, respectively, in a 60 month period.
66
Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements
Page | |
67
ENTERPRISE BANCORP, INC.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
As of December 31,
(Dollars in thousands, except per share data) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Assets | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents: | ||||||||
Cash and due from banks | $ | 39,927 | $ | 43,865 | ||||
Interest-earning deposits | 23,867 | 19,255 | ||||||
Total cash and cash equivalents | 63,794 | 63,120 | ||||||
Investments: | ||||||||
Debt securities at fair value | 504,788 | 431,473 | ||||||
Equity securities at fair value | 467 | 1,448 | ||||||
Total investment securities at fair value | 505,255 | 432,921 | ||||||
Federal Home Loan Bank ("FHLB") stock | 4,484 | 5,357 | ||||||
Loans held for sale | 601 | 701 | ||||||
Loans, less allowance for loan losses of $33,614 at December 31, 2019 and $33,849 at December 31, 2018 | 2,531,845 | 2,353,657 | ||||||
Premises and equipment, net | 45,419 | 37,588 | ||||||
Lease right-of-use asset | 19,048 | — | ||||||
Accrued interest receivable | 12,295 | 11,462 | ||||||
Deferred income taxes, net | 8,732 | 11,747 | ||||||
Bank-owned life insurance | 30,776 | 30,138 | ||||||
Prepaid income taxes | 572 | 732 | ||||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets | 6,572 | 11,279 | ||||||
Goodwill | 5,656 | 5,656 | ||||||
Total assets | $ | 3,235,049 | $ | 2,964,358 | ||||
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity | ||||||||
Liabilities | ||||||||
Deposits: | ||||||||
Customer deposits | $ | 2,786,730 | $ | 2,507,999 | ||||
Brokered deposits | — | 56,783 | ||||||
Total deposits | 2,786,730 | 2,564,782 | ||||||
Borrowed funds | 96,173 | 100,492 | ||||||
Subordinated debt | 14,872 | 14,860 | ||||||
Lease liability | 18,104 | — | ||||||
Accrued expenses and other liabilities | 21,683 | 27,948 | ||||||
Accrued interest payable | 846 | 979 | ||||||
Total liabilities | 2,938,408 | 2,709,061 | ||||||
Commitments and Contingencies | ||||||||
Stockholders' Equity | ||||||||
Preferred stock, $0.01 par value per share; 1,000,000 shares authorized; no shares issued | — | — | ||||||
Common stock $0.01 par value per share; 40,000,000 shares authorized; 11,825,331 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 and 11,708,218 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2018 | 118 | 117 | ||||||
Additional paid-in capital | 94,170 | 91,281 | ||||||
Retained earnings | 191,843 | 165,183 | ||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | 10,510 | (1,284 | ) | |||||
Total stockholders' equity | 296,641 | 255,297 | ||||||
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $ | 3,235,049 | $ | 2,964,358 | ||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
68
ENTERPRISE BANCORP, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Income
Years Ended December 31,
(Dollars in thousands, except per share data) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Interest and dividend income: | ||||||||||||
Loans and loans held for sale | $ | 122,082 | $ | 111,090 | $ | 96,559 | ||||||
Investment securities | 13,135 | 10,728 | 8,045 | |||||||||
Other interest-earning assets | 1,891 | 1,085 | 428 | |||||||||
Total interest and dividend income | 137,108 | 122,903 | 105,032 | |||||||||
Interest expense: | ||||||||||||
Deposits | 19,941 | 12,760 | 5,995 | |||||||||
Borrowed funds | 385 | 383 | 590 | |||||||||
Subordinated debt | 925 | 925 | 925 | |||||||||
Total interest expense | 21,251 | 14,068 | 7,510 | |||||||||
Net interest income | 115,857 | 108,835 | 97,522 | |||||||||
Provision for loan losses | 1,180 | 2,250 | 1,430 | |||||||||
Net interest income after provision for loan losses | 114,677 | 106,585 | 96,092 | |||||||||
Non-interest income: | ||||||||||||
Wealth management fees | 5,494 | 5,624 | 5,149 | |||||||||
Deposit and interchange fees | 6,870 | 6,234 | 6,011 | |||||||||
Income on bank-owned life insurance, net | 638 | 672 | 701 | |||||||||
Net gains (losses) on sales of available-for-sale debt securities | 146 | (2,950 | ) | (2,550 | ) | |||||||
Net gains on sales of available-for-sale equity securities | — | — | 3,266 | |||||||||
Net gains on sales of loans | 469 | 260 | 460 | |||||||||
Other income | 2,702 | 2,150 | 2,637 | |||||||||
Total non-interest income | 16,319 | 11,990 | 15,674 | |||||||||
Non-interest expense: | ||||||||||||
Salaries and employee benefits | 56,059 | 51,442 | 48,613 | |||||||||
Occupancy and equipment expenses | 8,417 | 8,526 | 7,960 | |||||||||
Technology and telecommunications expenses | 7,590 | 6,382 | 6,372 | |||||||||
Advertising and public relations expenses | 2,962 | 3,182 | 2,621 | |||||||||
Audit, legal and other professional fees | 2,039 | 1,725 | 1,565 | |||||||||
Deposit insurance premiums | 876 | 1,697 | 1,535 | |||||||||
Supplies and postage expenses | 971 | 989 | 999 | |||||||||
Other operating expenses | 7,501 | 6,935 | 6,480 | |||||||||
Total non-interest expense | 86,415 | 80,878 | 76,145 | |||||||||
Income before income taxes | 44,581 | 37,697 | 35,621 | |||||||||
Provision for income taxes | 10,381 | 8,816 | 16,228 | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 34,200 | $ | 28,881 | $ | 19,393 | ||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 2.90 | $ | 2.47 | $ | 1.68 | ||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 2.89 | $ | 2.46 | $ | 1.66 | ||||||
Basic weighted average common shares outstanding | 11,789,570 | 11,679,520 | 11,568,430 | |||||||||
Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding | 11,829,818 | 11,750,462 | 11,651,763 | |||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
69
ENTERPRISE BANCORP, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income
Years Ended December 31,
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 34,200 | $ | 28,881 | $ | 19,393 | ||||||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of taxes: | ||||||||||||
Gross unrealized holding gains (losses) on available-for-sale securities arising during the period | 15,330 | (5,143 | ) | 2,424 | ||||||||
Income tax (expense) benefit | (3,422 | ) | 1,162 | (855 | ) | |||||||
Net unrealized holding gains (losses), net of tax | 11,908 | (3,981 | ) | 1,569 | ||||||||
Less: Reclassification adjustment for net gains (losses) included in net income | ||||||||||||
Net realized gains (losses) on sales of available-for-sale securities during the period | 146 | (2,950 | ) | 716 | ||||||||
Income tax (expense) benefit | (32 | ) | 669 | (247 | ) | |||||||
Reclassification adjustment for gains (losses) realized, net of tax | 114 | (2,281 | ) | 469 | ||||||||
Total other comprehensive income (loss), net | 11,794 | (1,700 | ) | 1,100 | ||||||||
Comprehensive income | $ | 45,994 | $ | 27,181 | $ | 20,493 | ||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
70
ENTERPRISE BANCORP, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders' Equity
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
Common Stock | Additional Paid-in Capital | Retained Earnings | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income/(Loss) | Total Stockholders’ Equity | |||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands, except share data) | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2016 | 11,475,742 | $ | 115 | $ | 85,421 | $ | 130,008 | $ | (758 | ) | $ | 214,786 | |||||||||||
Net income | 19,393 | 19,393 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Cumulative effect adjustment for adoption of new accounting pronouncements | 13 | (87 | ) | 74 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net | 1,100 | 1,100 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Common stock dividend declared ($0.54 per share) | (6,241 | ) | (6,241 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued under dividend reinvestment plan | 44,752 | — | 1,494 | 1,494 | |||||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued, other | 2,798 | — | 96 | 96 | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | 58,037 | 1 | 1,757 | 1,758 | |||||||||||||||||||
Net settlement for employee taxes on restricted stock and options | (15,185 | ) | — | (931 | ) | (931 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Stock option exercised, net | 43,709 | — | 355 | 355 | |||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2017 | 11,609,853 | $ | 116 | $ | 88,205 | $ | 143,073 | $ | 416 | $ | 231,810 | ||||||||||||
Net income | 28,881 | 28,881 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive income, net | (1,700 | ) | (1,700 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Common stock dividend declared ($0.58 per share) | (6,771 | ) | (6,771 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued under dividend reinvestment plan | 37,999 | — | 1,328 | 1,328 | |||||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued, other | 3,440 | — | 121 | 121 | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | 51,107 | 1 | 1,878 | 1,879 | |||||||||||||||||||
Net settlement for employee taxes on restricted stock and options | (15,106 | ) | — | (559 | ) | (559 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Stock options exercised, net | 20,925 | — | 308 | 308 | |||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2018 | 11,708,218 | $ | 117 | $ | 91,281 | $ | 165,183 | $ | (1,284 | ) | $ | 255,297 | |||||||||||
Net income | 34,200 | 34,200 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net | 11,794 | 11,794 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Common stock dividend declared ($0.64 per share) | (7,540 | ) | (7,540 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued under dividend reinvestment plan | 39,176 | — | 1,169 | 1,169 | |||||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued, other | 2,305 | — | 69 | 69 | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | 61,318 | 1 | 1,868 | 1,869 | |||||||||||||||||||
Net settlement for employee taxes on restricted stock and options | (8,223 | ) | — | (402 | ) | (402 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Stock options exercised, net | 22,537 | — | 185 | 185 | |||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2019 | 11,825,331 | $ | 118 | $ | 94,170 | $ | 191,843 | $ | 10,510 | $ | 296,641 | ||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
71
ENTERPRISE BANCORP, INC
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Years Ended December 31,
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 34,200 | $ | 28,881 | $ | 19,393 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Provision for loan losses | 1,180 | 2,250 | 1,430 | |||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 6,142 | 6,836 | 7,028 | |||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 1,872 | 1,848 | 1,753 | |||||||||
Income on bank-owned life insurance, net | (638 | ) | (672 | ) | (701 | ) | ||||||
Net (gains) losses on sales of debt securities | (146 | ) | 2,950 | 2,550 | ||||||||
Net (gains) losses on equity securities | (367 | ) | 204 | (3,266 | ) | |||||||
Mortgage loans originated for sale | (25,562 | ) | (13,026 | ) | (19,820 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from mortgage loans sold | 26,131 | 12,793 | 21,641 | |||||||||
Net gains on sales of loans | (469 | ) | (260 | ) | (460 | ) | ||||||
Net gains on sales of OREO | (34 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Changes in: | ||||||||||||
Decrease (increase) in other assets | 136 | (1,815 | ) | 6,026 | ||||||||
Increase in other liabilities | 1,174 | 1,812 | 2,357 | |||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 43,619 | 41,801 | 37,931 | |||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from sales of debt securities | 13,623 | 129,862 | 119,526 | |||||||||
Purchase of debt securities | (126,872 | ) | (208,978 | ) | (186,628 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from maturities, calls and pay-downs of investment securities | 48,805 | 42,278 | 32,643 | |||||||||
Net proceeds from the sale (purchases) of equity securities | 1,348 | (1,631 | ) | 13,680 | ||||||||
Net proceeds (purchases of) from sales of FHLB capital stock | 873 | (142 | ) | (3,121 | ) | |||||||
Net increase in loans | (179,623 | ) | (118,918 | ) | (247,032 | ) | ||||||
Additions to premises and equipment, net | (12,498 | ) | (5,297 | ) | (8,211 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from OREO sales | 289 | — | — | |||||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (254,055 | ) | (162,826 | ) | (279,143 | ) | ||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||
Net increase in deposits | 221,948 | 123,420 | 172,441 | |||||||||
Net (decrease) increase in borrowed funds | (4,319 | ) | 11,492 | 78,329 | ||||||||
Cash dividends paid, net of DRP | (6,371 | ) | (5,443 | ) | (4,747 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from issuance of common stock | 69 | 121 | 96 | |||||||||
Net settlement for employee taxes on restricted stock and options | (402 | ) | (559 | ) | (931 | ) | ||||||
Net proceeds from stock option exercises | 185 | 308 | 355 | |||||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | 211,110 | 129,339 | 245,543 | |||||||||
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | 674 | 8,314 | 4,331 | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 63,120 | 54,806 | 50,475 | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 63,794 | $ | 63,120 | $ | 54,806 | ||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
72
(1) | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
(a) Organization of the Company and Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements of Enterprise Bancorp, Inc. ("the Company," "Enterprise," "we," or "our"), a Massachusetts corporation, include the accounts of the Company and its wholly owned subsidiary, Enterprise Bank and Trust Company, commonly referred to as Enterprise Bank ("the Bank"). The Bank is a Massachusetts trust company and state chartered commercial bank organized in 1989. Substantially all of the Company's operations are conducted through the Bank and its subsidiaries.
The Bank's subsidiaries include Enterprise Insurance Services, LLC and Enterprise Wealth Services, LLC, both organized under the laws of the State of Delaware, engage in insurance sales activities and offer non-deposit investment products and services, respectively. In addition, the Bank has the following subsidiaries that are incorporated in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts and classified as security corporations in accordance with applicable Massachusetts General Laws: Enterprise Security Corporation; Enterprise Security Corporation II; and Enterprise Security Corporation III. The security corporations, which hold various types of qualifying securities, are limited to conducting securities investment activities that the Bank itself would be allowed to conduct under applicable laws.
The Company's headquarters and the Bank's main office are located at 222 Merrimack Street in Lowell, Massachusetts. At December 31, 2019, the Company had 24 full-service branch banking offices serving the Greater Merrimack Valley, Nashoba Valley and North Central regions of Massachusetts and Southern New Hampshire (Southern Hillsborough and Rockingham counties). The Company also opened a branch in Lexington, Massachusetts in early March 2020 and is scheduled to open a branch in North Andover, Massachusetts in summer 2020. Through the Bank and its subsidiaries, the Company offers a range of commercial, residential and consumer loan products, deposit products and cash management services, electronic and digital banking options, and commercial insurance services. The Company also provides a range of wealth management, wealth services and trust services delivered via two channels, Enterprise Wealth Management and Enterprise Wealth Services. The services offered through the Bank and its subsidiaries are managed as one strategic unit and represent the Company's only reportable operating segment.
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (the "FDIC") and the Massachusetts Division of Banks (the "Division") have regulatory authority over the Bank. The Bank is also subject to certain regulatory requirements of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (the "Federal Reserve Board") and, with respect to its New Hampshire branch operations, the New Hampshire Banking Department. The business and operations of the Company are subject to the regulatory oversight of the Federal Reserve Board. The Division also retains supervisory jurisdiction over the Company.
The accompanying audited consolidated financial statements and notes thereto have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP") and the instructions for SEC Form 10-K through the rules and interpretive releases of the SEC under federal securities law. In the opinion of management, the accompanying audited consolidated financial statements reflect all necessary adjustments consisting of normal recurring accruals for a fair presentation. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. Certain previous years' amounts in the consolidated financial statements, and notes thereto, have been reclassified to conform to the current year's presentation.
The Company has evaluated subsequent events and transactions from December 31, 2019 through the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K was filed with the SEC for potential recognition or disclosure as required by GAAP and determined that there were no material subsequent events requiring recognition or disclosure.
(b) Uses of Estimates
In preparing the consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP, management is required to exercise judgment in determining many of the methodologies, assumptions and estimates to be utilized. These assumptions and estimates affect the reported values of assets and liabilities as of the balance sheet dates and income and expenses for the years then ended. As future events and their effects cannot be determined with precision, actual results could differ significantly from these estimates should the assumptions and estimates used be incorrect or change over time due to
73
changes in circumstances. Changes in those estimates resulting from continuing changes in the economic environment and other factors will be reflected in the consolidated financial statements and results of operations in future periods. The three most significant areas in which management applies critical assumptions and estimates are the estimates of the allowance for loan losses, impairment review of investment securities and the impairment review of goodwill.
(c) Cash and cash equivalents
Cash equivalents are defined as highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less, that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash and present insignificant risk of changes in value due to changes in interest rates. The Company's cash and cash equivalents may be comprised of cash on hand and cash items due from banks, interest-earning deposits (deposit accounts, excess reserve cash balances, money markets, and money market mutual fund accounts) and federal funds ("fed funds") sold. Balances in cash and cash equivalents will fluctuate due primarily to the timing of net cash flows from deposits, borrowings, loans and investments, and the immediate liquidity needs of the Company.
(d) Restricted Cash and Investments
Certain of the Company's derivative agreements contain provisions for collateral to be posted if the derivative exposure exceeds a threshold amount. When the Company has pledged cash as collateral for this purpose, the cash is carried as restricted cash within "interest-earning deposits." See Note 9, "Derivatives and Hedging Activities," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K below for more information about the Company's collateral related to its derivatives.
The Bank is also required by the Federal Reserve Bank of Boston ("FRB") to maintain in reserves certain amounts of vault cash and/or deposits with the FRB. The average daily cash balance on hand for FRB reserve requirements included in "Cash and Due from Banks" was approximately $2.3 million and $9.0 million, based on the two-week computation periods encompassing December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
As a member of the FHLB, the Company is required to purchase certain levels of FHLB capital stock at par value in association with outstanding advances from the FHLB. From time-to-time, the FHLB may initiate the repurchase, at par value, of "excess" levels of its capital stock held by member banks. This stock is classified as a restricted investment and is carried at cost, which management believes approximates fair value. FHLB stock represents the only restricted investment held by the Company.
Management regularly reviews its holdings of FHLB stock for other-than-temporary impairment ("OTTI"). Based on management's periodic review, the Company has not recorded any OTTI charges on this investment to date. If it was determined that a write-down of FHLB stock was required, impairment would be recognized through a charge to earnings.
See Note 2, "Investment Securities," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for additional information on management's OTTI review.
(e) Investments
Investments in debt securities that are intended to be held for indefinite periods of time, but which may not be held to maturity or on a long-term basis are considered to be "available-for-sale" and are carried at fair value. Net unrealized appreciation and depreciation on investments available-for-sale, net of applicable income taxes, are reflected as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). Included as available-for-sale are debt securities that are purchased in connection with the Company's asset-liability risk management strategy and that may be sold in response to changes in interest rates, resultant prepayment risk and other related factors. In instances where the Company has the positive intent to hold debt securities to maturity, these securities will be classified as held-to-maturity and carried at amortized cost. As of the balance sheet dates, all of the Company's debt securities were classified as available-for-sale and carried at fair value.
74
There are inherent risks associated with the Company's investment activities that could adversely impact the fair value and the ultimate collectability of the Company's investments. Management regularly reviews the debt portfolio for securities with unrealized losses to determine if any of the unrealized losses are OTTI. The determination of OTTI involves a high degree of judgment. While management uses available information to measure OTTI at the balance sheet date, future write-downs may be necessary based on extended duration of current unrealized losses, changing market conditions, or circumstances surrounding individual issuers.
If a debt investment is deemed to have an unrealized loss that is OTTI, the Company is required to write-down the investment. For debt securities, OTTI is generally recognized through a charge to earnings as of the balance sheet date, while non-OTTI unrealized losses are recognized in other comprehensive income. Unrealized losses on debt securities are deemed OTTI if (1) the Company intends to sell the security, (2) it is more likely than not that the Company will be required to sell the security before recovery, or (3) a credit loss exists and the Company does not expect to recover the entire amortized cost. For debt securities that have a credit loss, any portion of the loss related to other factors is recorded in other comprehensive income. Once written-down, the previous charge on debt securities may not be recovered through earnings until sale or maturity, if in excess of its new cost basis. Any OTTI charges, depending upon the magnitude of the charges, could have a material adverse effect on the Company's financial condition and results of operations. See also Note 2, "Investment Securities," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K below, for further information on management's OTTI assessment.
At December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company's equity securities were accounted for under ASC Topic 321, "Investments-Equity Securities," and are recorded on the Company's Consolidated Balance Sheet at fair value with changes in fair value recognized in the Company's Consolidated Income Statement as a component of "Other income." The net gains and losses on equity securities that will be recognized as a component of "Other income" in the future will depend on the amount of dollars invested in equities, the magnitude of changes in equity markets and amount of gains or losses realized through equity sales.
Investment securities' discounts are accreted and premiums are amortized over the period of estimated principal repayment using methods that approximate the interest method. Gains or losses on the sale of investment securities are recognized on the trade date on a specific identification basis.
(f) Loans Held for Sale
Depending on the current interest-rate environment, management projections of future interest rates and the overall asset-liability management program of the Company, management may elect to sell those fixed and adjustable rate residential mortgage loans which are eligible for sale in the secondary market or hold some or all of this residential loan production for the Company's portfolio. Mortgage loans are generally not pooled for sale, but instead sold on an individual basis. Enterprise may retain or sell the servicing when selling the loans. Loans sold are subject to standard secondary market underwriting and eligibility representations and warranties over the life of the loan and are subject to an early payment default period covering the first four payments for certain loan sales. Loans held for sale are carried at the lower of aggregate amortized cost or fair value. Fair value is based on comparable market prices for loans with similar rates and terms. When loans are sold, a gain or loss is recognized to the extent that the sales proceeds plus unamortized fees and costs exceed, or are less than, the carrying value of the loans. Gains and losses are determined using the specific identification method.
(g) Loans
Loans made by the Company to businesses, non-profits and professional practices include commercial real estate mortgage loans, construction and land development loans, secured and unsecured commercial loans and lines of credit, and letters of credit. Loans made to individuals include conventional residential mortgage loans, home equity loans and lines, residential construction loans on owner-occupied primary and secondary residences, and secured and unsecured personal loans and lines of credit. Most loans granted by the Company are collateralized by real estate or equipment and/or are guaranteed by the principals of the borrower. The ability and willingness of the single family residential and consumer borrowers to honor their repayment commitments is generally dependent on the level of overall economic activity and real estate values within the borrowers' geographic areas. The ability and willingness of commercial real estate, commercial and construction loan borrowers to honor their repayment commitments is
75
generally dependent on the health of the real estate sector in the borrowers' geographic areas and the general economy, among other factors.
Loans are reported at the principal amount outstanding, net of deferred origination fees and costs. The aggregate amounts of overdrawn deposit accounts are reclassified as loan balances. Loan origination fees received, offset by direct loan origination costs, are deferred and amortized using the straight-line method over three to five years for lines of credit and demand notes or over the life of the related loans using the level-yield method for all other types of loans. When loans are paid off, the unamortized fees and costs are recognized as an adjustment to interest income.
From time to time, the Company participates with other banks in the financing of certain commercial projects. In each case in which the Company participates in a loan, the rights and obligations of each participating bank are divided proportionately among the participating banks in an amount equal to their share of ownership and with equal priority among all banks. Each participation is governed by individual participation agreements executed by the lead bank and the participants at loan origination. When the participation qualifies as a sale under GAAP, the balances participated out to other institutions are not carried as assets on the Company's consolidated financial statements. The Company performs an independent credit analysis of each commitment and a review of the participating institution prior to participation in the loan, and an annual review thereafter of each participating institution. Loans originated by other banks in which the Company is the participating institution are carried in the loan portfolio at the Company's pro rata share of ownership. See also Note 3, "Loans," to the Company's consolidated financial statements, under "Loan Portfolio Classifications," of this Form 10-K for further information about the Company's participation loans.
(h) Allowance for Loan Losses
The allowance for loan losses is an estimate of probable credit losses inherent in the loan portfolio as of the specified balance sheet dates. The Company maintains the allowance at a level that it deems adequate to absorb all reasonably anticipated probable losses from specifically known and other credit risks associated with the portfolio.
The allowance for loan losses is established through a provision for loan losses, a direct charge to earnings. Loan losses are charged against the allowance when management believes that the collectability of the loan principal is unlikely. Recoveries on loans previously charged-off are credited to the allowance.
The Company uses a systematic methodology to measure the amount of estimated loan loss exposure inherent in the portfolio for purposes of establishing a sufficient allowance for loan losses. The methodology uses a two-tiered approach that makes use of specific reserves for loans individually evaluated and deemed impaired and general reserves for larger groups of homogeneous loans, which are collectively evaluated relying on a combination of qualitative and quantitative factors that may affect credit quality of the pool.
On a quarterly basis, the Company prepares an estimate of the allowance necessary to cover estimated credit risk inherent in the portfolio as of the specified balance sheet dates. The adequacy of the allowance for loan losses is reviewed and evaluated on a regular basis by an internal management committee and the full Board.
While management uses available information to recognize losses on loans, future additions to the allowance may be necessary. In addition, various regulatory agencies, as an integral part of their examination process, periodically review the Company's allowance for loan losses. Such agencies may require the Company to recognize additions to the allowance based on judgments different from those of management.
See also Note 4, "Allowance for Loan Losses," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for additional accounting policies related to non-accrual, impaired and troubled debt restructured loans and to the allowance for loan losses.
On January 1, 2020, the Company adopted ASU No. 2016-13, "Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments," commonly referred to as CECL. See Item (v) "Recent Accounting Pronouncements," below under the heading "Accounting pronouncements not yet adopted by the Company" in this Note 1 of this Form 10-K for additional information.
76
(i) Other Real Estate Owned
Real estate acquired by the Company through foreclosure proceedings or the acceptance of a deed in lieu of foreclosure is classified as other real estate owned ("OREO"). When property is acquired, it is recorded at estimated fair value of the property acquired, less estimated costs to sell, establishing a new cost basis and carried on the Consolidated Balance Sheet in the line item "Prepaid expenses and other assets." The estimated fair value is based on market appraisals and the Company's internal analysis. Any loan balance in excess of the estimated realizable fair value on the date of transfer is charged to the allowance for loan losses on that date. All costs incurred thereafter in maintaining the property, as well as subsequent declines in fair value are charged to non-interest expense.
(j) Premises and Equipment
Land is carried at cost. All other premises and equipment costs are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation or amortization is computed on a straight-line basis over the lesser of the estimated useful lives of the asset or the respective lease term (including renewal options reasonably certain to be exercised) for leasehold improvements generally as follows:
Bank premises, land improvements, and leasehold improvements | 10 to 39 years | |
Computer software and equipment | 3 to 5 years | |
Furniture, fixtures and equipment | 3 to 10 years | |
(k) Leases
On January 1, 2019, the Company adopted ASU No. 2016-02, "Leases (Topic 842)." Under this ASU, as amended, lessees are required to recognize lease ROU assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet for all leases with terms longer than 12 months. The lease liability represents the present value of the future lease payments. The (right-of-use or "ROU") asset includes the lease liability, lease prepayments and initial direct costs, less fixed payment lease liabilities. For the Company, this ASU primarily impacted operating leases on our facilities, mainly branch leases, and as a result the Company recorded, on its Consolidated Balance Sheet a lease liability of $18.0 million and ROU asset of $19.0 million on January 1, 2019 related to these leases.
Upon adoption of this ASU, the Company elected the following practical expedients:
•to not reassess, among other things, the historical lease classification, and
•to use hindsight to assess lease terms and impairment of the initial ROU asset.
The Company excludes leases with a term of 12 months or less from the recorded lease liability and ROU asset and accounts for lease and non-lease components (such as common area maintenance) separately. In order to calculate the lease liability, the Company used its incremental borrowing rate as the discount rate to determine the net present value of the lease liability. In determining the term of a lease, the Company included option renewal periods that it considered reasonably certain to be exercised, which generally resulted in the inclusion of all lease option renewal periods.
The Company recognizes lease expense on a straight-line basis in the "Occupancy and Equipment Expenses" line item within the non-interest expense section of the Consolidated Statement of Income.
(l) Bank Owned Life Insurance
The Company has purchased bank-owned life insurance ("BOLI") as an investment vehicle, on certain current and former senior and executive officers, utilizing the earnings on BOLI to offset the cost of the Company's benefit plans. The cash surrender value carried on the Consolidated Balance Sheets at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, amounted to $30.8 million and $30.1 million, respectively. There are no associated surrender charges under the outstanding policies.
77
Information on the Company's benefit plans is contained in Note 12, "Employee Benefit Plans," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below.
(m) Impairment of Long-Lived Assets Other than Goodwill
The Company reviews long-lived assets, including premises and equipment, for impairment on an ongoing basis or whenever events or changes in business circumstances indicate that the remaining useful life may warrant revision or that the carrying amount of the long-lived asset may not be fully recoverable. If impairment is determined to exist, any related impairment loss is recognized through a charge to earnings. Impairment losses on assets disposed of, if any, are based on the estimated proceeds to be received, less cost of disposal.
(n) Goodwill
Goodwill carried on the Company's consolidated financial statements was $5.7 million at both December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018. This asset is related to the Company's acquisition of two branch offices in July 2000.
In accordance with GAAP, the Company does not amortize goodwill and instead, at least annually, evaluates whether the carrying value of goodwill has become impaired. A determination that goodwill has become impaired results in an immediate write-down of goodwill to its determined value with a resulting charge to the Company's Consolidated Statement of Income. Goodwill is evaluated at the reporting unit level. In the case of the Company, the services offered through the Bank and subsidiaries are managed as one strategic unit and represent the Company’s only reportable operating segment.
The Company has the option to perform either (1) a qualitative assessment of whether it is "more likely than not" that the reporting unit's fair value is less than its book value, or (2) a quantitative assessment.
1.Management's qualitative assessment would take into consideration, among other items, macroeconomic conditions, industry and market considerations, cost or margin factors, financial performance and share price. Based on the qualitative assessment, if the Company were to conclude: a) it is "more likely than not" that the fair value of a reporting unit exceeds its book value, goodwill is deemed not impaired, or b) it is "more likely than not" that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its book value, a quantitative goodwill analysis must be performed.
2.The Company may elect to forgo the qualitative assessment and perform the quantitative analysis even if management believes that is "more likely than not" that goodwill is not impaired. The quantitative goodwill analysis compares the fair value of the reporting unit with its book value, including goodwill. If the fair value of the reporting unit equals or exceeds its book value, goodwill is deemed not impaired. If the book value of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value, a goodwill impairment loss is recognized for the difference between these amounts, not exceeding the goodwill carrying amount.
At December 31, 2019, based on the Company's quantitative analysis, goodwill was deemed not impaired.
(o) Investment Assets Under Management
Investment assets under management, consisting of assets managed through Enterprise Wealth Management and Enterprise Wealth Services and commercial sweep products, totaled $916.6 million and $800.8 million at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. Securities and other property held in a fiduciary or agency capacity are not included in the Consolidated Balance Sheets because they are not assets of the Company. See Item (q), "Revenue Recognition-ASC Topic 606," below in this Note 1, of this Form 10-K for information on the Company's accounting policies for wealth management fees.
78
(p) Derivatives
The Company recognizes all derivatives as either assets or liabilities on its Consolidated Balance Sheet and measures those instruments at fair value.
The Company has a "Back-to-Back Swap" program whereby the Bank enters into an interest-rate swap with a qualified commercial banking customer and simultaneously enters into an equal and opposite interest-rate swap with a swap counterparty. The customer interest-rate-swap agreement allows commercial banking customers to convert a floating-rate loan payment to a fixed-rate payment. The transaction structure effectively minimizes the Bank's net interest rate risk exposure resulting from such transactions. Customer-related credit risk is minimized by the cross collateralization of the loan and the interest-rate-swap agreement.
Back-to-Back Swaps are not speculative but rather, result from a service the Company provides to certain customers. Back-to-Back Swaps do not meet hedge accounting requirements and therefore changes in the fair value of both the customer swaps and the counterparty swaps, which have an offsetting relationship, are recognized directly in earnings. See also Note 9, "Derivatives and Hedging Activities," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for more information about the Company's derivatives.
Interest-rate lock commitments related to the origination of mortgage loans that will be sold are considered derivative instruments. The commitments to sell loans are also considered derivative instruments. The Company generally does not pool mortgage loans for sale, but instead, sells the loans on an individual basis. To reduce the net interest rate exposure arising from its loan sale activity, the Company enters into the commitment to sell these loans at essentially the same time that the interest-rate lock commitment is quoted on the origination of the loan. The Company estimates the fair value of these derivatives based on current secondary mortgage market prices. At December 31, 2019 and 2018, the estimated fair value of the Company's interest-rate lock commitments and commitments to sell these mortgage loans were deemed immaterial.
The Company may use interest-rate-contract swaps as part of its interest-rate risk management strategy. Interest-rate- swap agreements are entered into as hedges against future interest-rate fluctuations on specifically identified assets or liabilities. The Company did not have derivative fair value hedges or derivative cash flow hedges at December 31, 2019 or 2018.
(q) Revenue Recognition-Accounting Standard Codification ("ASC") Topic 606
While the majority of the Company's revenue is generated from contracts with customers, our primary sources of revenue, interest and dividend income (primarily loan interest income), are outside of the scope of ASC 606, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers-Topic 606," and are accounted for under other ASC topics. The core principles of this standard require an entity to recognize revenue to depict the transfer of goods and services to customers as performance obligations are satisfied.
The primary areas of income within the scope of ASC 606, wealth management fees and deposit and interchange fees, are components of non-interest income on the Company's Consolidated Statements of Income, and are discussed below.
Wealth management fees consist of income generated through Enterprise Wealth Management and Enterprise Wealth Services. Enterprise Wealth Management income is primarily generated by managing customers' financial assets. Revenue is recognized as our performance obligation is completed each month. Enterprise Wealth Services revenue is generated through a third-party arrangement to refer, manage and service customers. For new sales and referrals along with transactional type charges, the performance obligation is based on a point in time and the payment is received and revenue is recognized in the same month as the revenue generating activity. For managing and servicing customers, revenue is recognized when our performance obligation is completed each month.
Deposit and interchange fees are comprised of deposit account related charges and income generated from electronic payment interchanges. Deposit account charges consist of certain transactional analysis fees net of earning balance credits, monthly account service fees, and transactional fees such as overdraft fees. Analysis and monthly account
79
services fees are recognized over the period the service is performed. For transactional fees, the performance obligation and the revenue are recognized at a point of time and payment is typically received as the service is rendered. Interchange income is generated primarily from retail debit card transactions processed through the card payment network. The performance obligation and the revenue are recognized when the service is performed.
The following non-interest income components are not subject to ASC 606: income on bank-owned life insurance ("BOLI"), net gains/losses on investment securities, and net gains on sales of loans, and are covered under other ASC topics. The remaining revenue items in non-interest income are not material.
See Item (e), "Investments," Item (f), "Loans Held for Sale," and Item (g), "Loans," above in this Note 1, of this Form 10-K for additional accounting policies on revenue recognition related to income generated on investments, gains and losses on securities, net gains on loans held for sale, and loans.
(r) Stock-Based Compensation
The Company's consolidated financial statements include stock-based compensation expense for the portion of stock option awards and stock awards for which the requisite service has been rendered during the period. The compensation expense has been recorded based on the estimated grant-date fair value of the stock option awards, or in the case of stock awards, the market value of the common stock on the date of grant. Expense adjustments are made for actual forfeitures as they occur.
The Company will recognize the remaining estimated compensation expense for the portion of outstanding awards and compensation expense for any future awards, net of actual forfeitures, as the requisite service is rendered (i.e., on a straight-line basis over the remaining vesting period of each award) or as performance objectives are met. Stock awards that do not require future service ("vested awards") will be expensed immediately. Stock-based compensation also includes Director stock compensation for stock awards and stock in lieu of cash fees, both included in other operating expenses.
See Note 13, "Stock-Based Compensation," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for further information on the Company's stock-based compensation.
(s) Income Taxes
The Company and its subsidiaries file income tax returns in the U.S. federal jurisdiction and in the states of Massachusetts and New Hampshire within the directives of the respective enacted tax legislation. The Company uses the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax expense or benefit attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax basis of assets and liabilities. The deferred tax assets and liabilities are reflected at currently enacted income tax rates applicable to the period in which the deferred tax assets or liabilities are expected to be realized or settled. As changes in tax laws or rates are enacted, deferred tax assets and liabilities will be adjusted accordingly through the provision for income taxes in the period that includes the enactment date.
The Company's policy is to classify interest resulting from underpayment of income taxes as income tax expense in the first period the interest would begin accruing according to the provisions of the relevant tax law. The Company classifies penalties resulting from underpayment of income taxes as income tax expense in the period for which the Company claims or expects to claim an uncertain tax position or in the period in which the Company's judgment changes regarding an uncertain tax position.
The income tax provisions will differ from the expense that would result from applying the federal statutory rate to income before taxes, due primarily to the impact of state tax expense, tax-exempt interest from certain investment securities, loans and BOLI and the tax impact from equity compensation activity.
The Company did not have any unrecognized tax benefits accrued as income tax liabilities or receivables or as deferred tax items at December 31, 2019 or December 31, 2018. The Company is subject to U.S. federal and state income tax examinations by taxing authorities for the 2016 through 2019 tax years.
80
See also Note 14, "Income Taxes," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for further information about the Company's income taxes and deferred tax assets.
(t) Earnings per Share
Basic earnings per share are calculated by dividing net income available to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding (including participating securities) during the year. The Company's only participating securities are unvested restricted stock awards that contain non-forfeitable rights to dividends. Diluted earnings per share reflects the effect on weighted average shares outstanding of the number of additional shares outstanding if dilutive stock options were converted into common stock using the treasury stock method.
(u) Reporting Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income is defined as all changes to stockholders' equity except investments by and distributions to stockholders. Net income is one component of comprehensive income, with other components referred to in the aggregate as other comprehensive income. The Company's only other comprehensive income component is the net unrealized holding gains or losses on available-for-sale securities, net of deferred income taxes. After 2017, the Company's available for sale securities were comprised only of debt securities. Pursuant to GAAP, the Company initially excludes these unrealized holding gains and losses from net income; however, they are later reported as reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive income into net income when the debt securities are sold.
When debt securities are sold, the reclassification of realized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities are included on the Consolidated Statements of Income under the "non-interest income" subheading on the line item "net gains/losses on sales of available for sale securities" and the related income tax expense is included in the line item "provision for income taxes," both of which are also detailed on the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income under the subheading "reclassification adjustment for net gains/losses included in net income."
(v) Recent Accounting Pronouncements
The tables below summarize recent accounting pronouncements issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") that were either recently adopted by the Company or have not yet been adopted. For pronouncements not yet adopted, the effective date listed below is in line with the required adoption date for public business entities, such as the Company, though certain accounting pronouncements may permit early adoption. For more detailed information regarding these pronouncements, refer to the FASB's Accounting Standards Updates ("ASU").
81
Accounting pronouncements adopted by the company | ||
Standard/Adoption Date | Description | Effect on Financial Statements or Other Significant Matters |
ASU 2016-02, Leases (ASC Topic 842) January 1, 2019 | This ASU supersedes previous leasing guidance in Topic 840, and lessees are now required to recognize lease ROU assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet for all leases with terms longer than 12 months. | See item (k) in this Note 1 of this Form 10-K above, for further information on the impact of the standard's adoption on the Company. |
ASU 2017-02, Derivatives and Hedging (ASC Topic 815): Targeted Improvements to Accounting for Hedging Activities January 1, 2019 | The objective of the ASU is to better align hedge accounting with an organization's risk management activities in the financial statements. In addition, the ASU simplifies the application of hedge accounting guidance in areas where practice issues exist. The amendments expand the strategies that qualify for hedge accounting, change how many hedging relationships are presented in the financial statements and simplify the application of hedge accounting in certain situations, reducing the operational complexities associated with certain existing strategies. New or modified disclosures are required, primarily for fair value and cash flow hedges. | In 2019, the Company did not hold any instruments that met hedge accounting requirements and therefore the adoption of this ASU in January 2019 did not have an impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements, results of operations or disclosures for the periods covered by this Form 10-K. In February 2020, the Company executed three pay fixed, received float interest-rate swap hedges. |
ASU No. 2018-07, Compensation-Stock-Based Compensation (ASU Topic 718): Improvements to Non-employee Shared-Based Payment Accounting January 1, 2019 | The amendments in the ASU expand the scope of Topic 718 to include share-based payment transactions for acquiring goods and services from non-employees except for share-based payments used to effectively provide (1) financing to the issuer or (2) awards granted in conjunction with selling goods or services to customers as part of a contract. Additionally, Topic 718 has been updated for specific guidance on inputs to an option pricing model and the attribution of cost (that is, the period of time over which share-based payment awards vest and the pattern of cost recognition over that period). | The adoption of this standard in January 2019 did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements, results of operations or disclosures. See Note 11, "Stockholders' Equity" of this Form 10-K. |
ASU No. 2017-04, Intangibles-Goodwill and Other (ASU Topic 350)- Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment October 1, 2019 | The main provision in this ASU eliminated Step 2 of the goodwill impairment test and instead requires an entity to perform its annual, or interim, goodwill impairment test by comparing the fair value of the reporting unit with its carrying amount. An impairment charge would be recognized for the amount the carrying value exceeds the reporting unit's fair value as long as the amount recognized does not exceed the amount of goodwill allocated to the reporting unit. | The Company early adopted this ASU in the third quarter of 2019, before the effective date of January 1, 2020. See Item (n) "Goodwill" in this Note 1 of this Form 10-K above for more information on the Company's goodwill impairment review process. The adoption of this ASU did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements and results of operations. |
82
Accounting pronouncements not yet adopted by the Company | ||
Standard/Anticipated Adoption Date | Description | Effect on Financial Statements or Other Significant Matters |
ASU No. 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments January 1, 2020 | The amendments in this ASU require a financial asset (or a group of financial assets) measured at amortized cost basis to be presented at the net amount expected to be collected. Previously, when credit losses were measured under GAAP, an entity generally only considered past events and current conditions in measuring the incurred loss and generally recognition of the full amount of credit losses was delayed until the loss was probable of occurring. The amendments in this ASU eliminate the probable initial recognition threshold in current GAAP and, instead, reflect an entity's current estimate of all expected credit losses (CECL). The measurement of expected credit losses is based on relevant information about past events, including historical experience, current conditions, and reasonable and supportable forecasts that affect the collectability of the report amount. An entity must use judgment in determining the relevant information and estimation methods that are appropriate in its circumstances. The Statement of Income reflects the measurement of credit losses for newly recognized financial assets, as well as the expected increases or decreases of expected credit losses that have taken place during the period. The allowance for credit losses is a valuation account that is deducted from the amortized cost basis of the financial asset(s) to present the net carrying value at the amount expected to be collected on the financial asset. Credit losses on available-for-sale debt securities should be measured in a manner similar to current GAAP. However, the amendments in this ASU require that credit losses be presented as an allowance rather than as a write-down. Unlike current GAAP, the ASU provides for reversals of credit losses in future period net income in situations where the estimate of loss declines. An entity will apply the amendments in this ASU through a cumulative-effect adjustment to retained earnings as of the beginning of the first reporting period in which the guidance is effective (that is, a modified-retrospective approach). | The Company adopted this standard on January 1, 2020 and based on the implementation process to date estimates the cumulative effect adjustment to retained earnings to be approximately $0 to $3 million, after tax. The Company is finalizing its assessment of the impact of the adoption of ASU No. 2016-13. The foregoing observations are subject to change as management completes the implementation review of CECL in the first quarter of 2020. |
ASU No. 2018-13, Fair Value Measurement (ASU Topic 820)-Disclosure Framework-Changes to the Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurement January 1, 2020 | The amendments in this ASU modify the disclosure requirements primarily related to level 3 fair value measurements of the fair value hierarchy. | The adoption of ASU No. 2018-13 in January 2020 did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements and results of operations because this ASU primarily relates to disclosure requirements. |
83
Accounting pronouncements not yet adopted by the Company (continued) | ||
Standard/Anticipated Adoption Date | Description | Effect on Financial Statements or Other Significant Matters |
ASU No.2018-15, Intangibles-Goodwill and Other- Internal-Use Software (ASU Subtopic 350-40): Customer's Accounting for Implementation Costs Incurred in a Cloud Computing Arrangement That is a Service Contract January 1, 2020 | The major provision in the amendments in this ASU require an entity to capitalize certain implementation costs incurred in a hosting arrangement that is a service contract in accordance with current GAAP for internal-use software and expense these costs over the term of the hosting arrangement. Additionally, these capitalized implementation costs are required to be reviewed for impairment in accordance with current GAAP for internal-use software. The amendments in this ASU should be applied either retrospectively or prospectively to all implementation costs incurred after the date of adoption. | The adoption of ASU No. 2018-15 in January 2020 did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements and results of operations. |
ASU No. 2018-14, Compensation-Retirement Benefits-Defined Benefit Plans-General (ASU Subtopic 715-20) - Disclosure Framework- Changes to the Disclosure Requirements for Defined Benefit Plans January 1, 2021 | The amendments in this ASU modify the disclosure requirements on defined benefit plans including requiring disclosures about significant gains and losses related to changes in the benefit obligation. | The adoption of ASU No. 2018-14 will not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements and results of operations because this ASU primarily relates to disclosure requirements and the balances of the benefit plans impacted by this ASU are immaterial to the Company. |
(2) | Investment Securities |
As of December 31, 2019, and 2018, the investment portfolio was primarily comprised of debt securities, with a small portion of the portfolio invested in equity securities.
See also Item (d), "Restricted Cash and Investments" and Item (e), "Investments," contained in Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained above, for further information regarding the accounting for the Company's investments portfolio and FHLB Stock. See Note 16, "Fair Value Measurements," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for further information regarding the Company's fair value measurements for investment securities.
84
Debt Securities
The amortized cost and fair values of debt securities at December 31, 2019 and 2018 are summarized as follows:
2019 | ||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Amortized cost | Unrealized gains | Unrealized losses | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
Federal agency obligations(1) | $ | 999 | $ | 5 | $ | — | $ | 1,004 | ||||||||
Residential federal agency MBS(1) | 190,392 | 2,599 | 333 | 192,658 | ||||||||||||
Commercial federal agency MBS(1) | 111,182 | 3,453 | — | 114,635 | ||||||||||||
Municipal securities taxable | 79,095 | 2,726 | 134 | 81,687 | ||||||||||||
Municipal securities tax exempt | 95,342 | 4,696 | — | 100,038 | ||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 13,826 | 485 | — | 14,311 | ||||||||||||
CDs(2) | 454 | 1 | — | 455 | ||||||||||||
Total debt securities, at fair value | $ | 491,290 | $ | 13,965 | $ | 467 | $ | 504,788 | ||||||||
2018 | ||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Amortized cost | Unrealized gains | Unrealized losses | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
Federal agency obligations(1) | $ | 7,994 | $ | — | $ | 19 | $ | 7,975 | ||||||||
Residential federal agency MBS(1) | 174,701 | 633 | 2,608 | 172,726 | ||||||||||||
Commercial federal agency MBS(1) | 93,800 | 609 | 430 | 93,979 | ||||||||||||
Municipal securities taxable | 34,491 | 448 | 198 | 34,741 | ||||||||||||
Municipal securities tax exempt | 107,256 | 674 | 628 | 107,302 | ||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 13,967 | 24 | 185 | 13,806 | ||||||||||||
CDs(2) | 950 | — | 6 | 944 | ||||||||||||
Total debt securities, at fair value | $ | 433,159 | $ | 2,388 | $ | 4,074 | $ | 431,473 | ||||||||
(1) | These categories may include investments issued or guaranteed by government sponsored enterprises such as Fannie Mae ("FNMA"), Freddie Mac ("FHLMC"), Federal Farm Credit Bank ("FFCB"), or one of several Federal Home Loan Banks, as well as, investments guaranteed by Ginnie Mae ("GNMA"), a wholly-owned government entity. |
(2) | CDs represent term deposits issued by banks that are subject to FDIC insurance and purchased on the open market. |
The majority of residential and commercial federal agency MBS categories were collateralized mortgage obligations ("CMOs") issued by U.S. agencies. The remaining MBS investments totaled $23.5 million, and $23.9 million at December 31, 2019, and 2018, respectively.
As of the dates reflected in the tables above, all of the Company's debt securities were classified as available-for-sale and carried at fair value.
Net unrealized appreciation and depreciation on debt securities available-for-sale, net of applicable income taxes, are reflected as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). The net unrealized gain or loss in the Company's debt security portfolio fluctuates as market interest rates rise and fall. Due to the fixed rate nature of this portfolio, as market rates fall the value of the portfolio rises, and as market rates rise, the value of the portfolio declines. The unrealized gains or losses on debt securities will also decline as the securities approach maturity. Unrealized losses on debt securities that are deemed OTTI are generally charged to earnings, as described further in Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," of this Form 10-K under Item (e), "Investments." Gains or losses will be recognized in the Consolidate Statement of Income if the securities are sold.
85
The following tables summarize debt securities with unrealized losses, due to the fair values having declined below the amortized costs of the individual investments, by the duration of their continuous unrealized loss positions at December 31, 2019 and 2018:
2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Less than 12 months | 12 months or longer | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | # of holdings | ||||||||||||||||||||
Residential federal agency MBS | $ | 36,464 | $ | 263 | $ | 5,060 | $ | 70 | $ | 41,524 | $ | 333 | 11 | ||||||||||||||
Municipal securities taxable | 16,826 | 134 | — | — | 16,826 | 134 | 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total temporarily impaired debt securities | $ | 53,290 | $ | 397 | $ | 5,060 | $ | 70 | $ | 58,350 | $ | 467 | 26 | ||||||||||||||
2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Less than 12 months | 12 months or longer | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | # of holdings | ||||||||||||||||||||
Federal agency obligations | $ | 997 | $ | 1 | $ | 6,978 | $ | 18 | $ | 7,975 | $ | 19 | 3 | ||||||||||||||
Residential federal agency MBS | 26,147 | 597 | 81,158 | 2,011 | 107,305 | 2,608 | 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial federal agency MBS | 3,258 | 11 | 18,717 | 419 | 21,975 | 430 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Municipal securities taxable | 491 | 9 | 8,730 | 189 | 9,221 | 198 | 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Municipal securities tax exempt | 14,545 | 99 | 32,535 | 529 | 47,080 | 628 | 69 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 5,277 | 36 | 5,653 | 149 | 10,930 | 185 | 63 | ||||||||||||||||||||
CDs | — | — | 944 | 6 | 944 | 6 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total temporarily impaired debt securities | $ | 50,715 | $ | 753 | $ | 154,715 | $ | 3,321 | $ | 205,430 | $ | 4,074 | 187 | ||||||||||||||
During the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company did not record any OTTI on its investments in debt securities and at December 31, 2019, management did not consider any debt securities to have OTTI. Management regularly reviews the portfolio for debt securities with unrealized losses that are other-than-temporarily impaired.
The process for assessing investments for OTTI may vary depending on the type of debt security. In assessing the Company's investments in federal agency mortgage-backed securities and federal agency obligations, the contractual cash flows of these investments are guaranteed by the respective government sponsored enterprise (FHLMC, FNMA, FFCB, or FHLB) or wholly-owned government corporation (GNMA). Accordingly, it is expected that the securities would not be settled at a price less than the par value of the Company's investments. Management's assessment of other debt securities within the portfolio includes reviews of market pricing, ongoing credit quality evaluations, assessment of the investments' materiality, and duration of the investments' unrealized loss position. In addition, the Company utilizes an outside registered investment adviser to manage the corporate and municipal bond portfolios, within prescribed guidelines set by management, and to provide assistance in assessing the credit risk of those portfolios. At December 31, 2019, the Company's corporate and municipal bond portfolios did not contain any securities below investment grade, as reported by major credit rating agencies.
The contractual maturity distribution at December 31, 2019 of total debt securities was as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | Amortized Cost | Fair Value | ||||||
Due in one year or less | $ | 6,630 | $ | 6,660 | ||||
Due after one, but within five years | 71,695 | 73,737 | ||||||
Due after five, but within ten years | 186,029 | 193,368 | ||||||
Due after ten years | 226,936 | 231,023 | ||||||
Total debt securities | $ | 491,290 | $ | 504,788 | ||||
86
Scheduled contractual maturities shown above may not reflect the actual maturities of the investments. The actual MBS/CMO cash flows likely will be faster than presented above due to prepayments and amortization. Similarly, included in the table above are callable securities, comprised of municipal securities and corporate bonds, with a fair value of $91.0 million, which can be redeemed by the issuers prior to the maturity presented above. Management considers these factors when evaluating the interest-rate risk in the Company's asset-liability management program.
From time to time the Company may pledge debt securities as collateral for deposit account balances of municipal customers, and for borrowing capacity with the FHLB and the FRB. The fair value of debt securities pledged as collateral for these purposes was $503.5 million and $424.7 million at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Sales of debt securities, for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018, and 2017 are summarized as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Amortized cost of debt securities sold(1) | $ | 11,621 | $ | 122,652 | $ | 133,812 | ||||||
Gross realized gains on sales(2) | 149 | 25 | 38 | |||||||||
Gross realized losses on sales | (3 | ) | (2,975 | ) | (2,588 | ) | ||||||
Total proceeds from sales of debt securities | $ | 11,767 | $ | 119,702 | $ | 131,262 | ||||||
(1) Amortized cost of investments sold is determined on a specific identification basis and includes pending trades based on trade date, if applicable.
(2) Immaterial amount of capital gain distributions realized from mutual funds included in 2018.
Tax-exempt interest earned on the municipal securities portfolio was $3.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2019, $4.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2018, and $4.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2017.
The average balance of tax-exempt investments was $99.8 million and $119.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively.
Equity Securities
As of December 31, 2019, the Company held equity securities with a fair value of $467 thousand, compared to $1.4 million equity securities held at December 31, 2018. At December 31, 2019, the equity portfolio consisted primarily of investments in common stock of individual entities in the financial services industry. Also included in the equity portfolio at December 31, 2019 were investments with a fair value of $135 thousand held in conjunction with the Company's supplemental executive retirement and deferred compensation plan.
Gains and losses on equity securities at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 are summarized as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Net gains (losses) recognized during the period on equity securities | $ | 367 | $ | (204 | ) | |||
Less: Net gains (losses) recognized on equity securities sold during the period | 159 | — | ||||||
Unrealized gains (losses) recognized during the reporting period on equity securities still held at year end | $ | 208 | $ | (204 | ) | |||
In the first quarter of 2018, the Company adopted ASU 2016-01, "Financial Instruments - Overall (Subtopic 825-10): Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities," and as a result, changes in fair value of the equity securities are recognized in the Company's Consolidated Statement of Income in the "Other income" line item. For the year ended December 31, 2017, the amortized cost of equity securities sold based on trade date, if applicable, amounted to $10.9 million, resulting in net realized gains of $3.3 million.
87
(3) Loans
The Company specializes in lending to business entities, non-profit organizations, professional practices and individuals. The Company's primary lending focus is on the development of high-quality commercial relationships achieved through active business development efforts, long-term relationships with established commercial developers, strong community involvement and focused marketing strategies. Commercial loans may include commercial real estate mortgage loans, construction and land development loans, secured and unsecured commercial loans and lines of credit, and letters of credit. Consumer or "retail" loans include conventional residential mortgage loans, home equity loans and lines, residential construction loans on owner-occupied primary and secondary residences, and secured and unsecured personal loans and lines of credit. The Company manages its loan portfolio to avoid concentration by industry, relationship size and source of repayment to lessen its credit risk exposure.
See also Note 4, "Allowance for Loan Losses," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for information on the Company's credit risk management, non-accrual, impaired and troubled debt restructured loans and the allowance for loan losses. See Note 16, "Fair Value Measurements," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for further information regarding the Company's fair value measurements for loans, and Note 9, "Derivatives and Hedging Activities," to these consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for information regarding interest-rate swap agreements related to certain commercial loans. For additional information on unadvanced loans and lines, commitments to originate loans, letters of credit and commitments to originate loans for sale or to sell loans see Note 10, "Commitments, Contingencies and Financial Instruments with Off-Balance Sheet Risk and Concentrations of Credit Risk" of this Form 10-K, contained below.
Loan Portfolio Classifications
Major classifications of loans at the periods indicated were as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | ||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 1,394,179 | $ | 1,303,879 | ||||
Commercial and industrial | 501,227 | 514,253 | ||||||
Commercial construction | 317,477 | 234,430 | ||||||
Total commercial loans | 2,212,883 | 2,052,562 | ||||||
Residential mortgages | 247,373 | 231,501 | ||||||
Home equity loans and lines | 98,252 | 96,116 | ||||||
Consumer | 10,054 | 10,241 | ||||||
Total retail loans | 355,679 | 337,858 | ||||||
Gross loans | 2,568,562 | 2,390,420 | ||||||
Deferred loan origination fees, net | (3,103 | ) | (2,914 | ) | ||||
Total loans | 2,565,459 | 2,387,506 | ||||||
Allowance for loan losses | (33,614 | ) | (33,849 | ) | ||||
Net loans | $ | 2,531,845 | $ | 2,353,657 | ||||
Commercial loans originated by other banks in which the Company is a participating institution are carried at the pro-rata share of ownership and amounted to $104.3 million at December 31, 2019 and $63.5 million at December 31, 2018. See also "Loans serviced for others" below for information related to commercial loans participated out to various other institutions.
88
Related Party Loans
Certain of the Company's directors, officers, principal stockholders and their associates are credit customers of the Company in the ordinary course of business. In addition, certain directors are also directors, trustees, officers or stockholders of corporations and non-profit entities or members of partnerships that are customers of the Bank and that enter into loan and other transactions with the Bank in the ordinary course of business. All loans and commitments included in such transactions are on such terms, including interest rates, repayment terms and collateral, as those prevailing at the time for comparable transactions with persons who are not affiliated with the Bank and do not involve more than a normal risk of collectability or present other features unfavorable to the Bank.
As of December 31, 2019, and 2018, the outstanding loan balances to directors, officers, principal stockholders and their associates were $47.9 million and $50.2 million, respectively. All loans to these related parties were current and accruing at those dates. Unadvanced portions of lines of credit available to these individuals were $32.1 million and $9.8 million, as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. During 2019, new loans and net increases in loan balances or lines of credit under existing commitments of $23.8 million were made and principal paydowns of $3.7 million were received. During 2018, new loans and net increases in loan balances or lines of credit under existing commitments of $13.3 million were made and principal paydowns of $4.1 million were received.
Loans serviced for others
At December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company was servicing residential mortgage loans owned by investors amounting to $15.7 million and $17.2 million, respectively. Additionally, the Company was servicing commercial loans originated by the Company and participated out to various other institutions amounting to $80.2 million and $72.1 million at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. See the discussion above under the heading "Loan Portfolio Classifications" for further information regarding commercial participations.
Loans serving as collateral
Loans designated as qualified collateral and pledged to the FHLB for borrowing capacity for the periods indicated are summarized below:
(Dollars in thousands) | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | ||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 246,865 | $ | 311,024 | ||||
Residential mortgages | 231,028 | 220,815 | ||||||
Home equity | 7,676 | 8,382 | ||||||
Total loans pledged to FHLB | $ | 485,569 | $ | 540,221 | ||||
Tax-Exempt Interest
Tax-exempt interest earned on qualified commercial loans was $2.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2019, $2.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2018, and $2.1 million for the year ended and December 31, 2017. Average tax-exempt loan balances were $59.2 million and $66.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
See also Note 4, "Allowance for Loan Losses," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for information on the Company's credit risk management, non-accrual, impaired and troubled debt restructured loans and the allowance for loan losses. See Note 9, "Derivatives and Hedging Activities," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for information regarding interest-rate swap agreements related to certain commercial loans, and see Note 16, "Fair Value Measurements," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for further information regarding the Company's fair value measurements for loans.
89
(4) | Allowance for Loan Losses |
Inherent in the lending process is the risk of loss due to customer non-payment, or "credit risk." The Company's commercial lending focus may entail significant additional credit risks compared to long-term financing on existing, owner-occupied residential real estate. The Company seeks to lessen its credit risk exposure by managing its loan portfolio to avoid concentration by industry, relationship size and source of repayment, and through sound underwriting practices and the credit risk management function; however, management recognizes that loan losses will occur and that the amount of these losses will fluctuate depending on the risk characteristics of the loan portfolio and economic conditions.
In making its assessment on the adequacy of the allowance, management considers several quantitative and qualitative factors that could have an effect on the credit quality of the portfolio including: the risk classification of individual loans; individual review of larger and higher risk problem assets; the level of delinquent loans and non-performing loans; impaired and restructured loans; the level of foreclosure activity; net charge-offs; commercial concentrations by industry and property type and by real estate location; the growth and composition of the loan portfolio; as well as trends in the general levels of these indicators. In addition, management monitors expansion in geographic market area, the experience level of lenders and any changes in underwriting criteria, the strength of the local and national economy, including general conditions in the multi-family, commercial real estate and development and construction markets in the Company's local region.
Allowance for probable loan losses methodology
On a quarterly basis, management prepares an estimate of the allowance necessary to cover estimated probable credit losses. The Company uses a systematic methodology to measure the amount of estimated loan loss exposure inherent in the portfolio for purposes of establishing a sufficient allowance for loan losses. The methodology makes use of specific reserves for loans individually evaluated and deemed impaired, and general reserves for larger pools of homogeneous loans, which are collectively evaluated relying on a combination of qualitative and quantitative factors that may affect credit quality of the pool.
Specific Reserves for loans individually evaluated for impairment
When a loan is deemed to be impaired, management estimates the credit loss by comparing the loan's carrying value against either (1) the present value of the expected future cash flows discounted at the loan's effective interest rate; (2) the loan's observable market price; or (3) the expected realizable fair value of the collateral, in the case of collateral dependent loans. A specific allowance is assigned to the impaired loan for the amount of estimated credit loss. Impaired loans are charged-off, in whole or in part, when management believes that the recorded investment in the loan is uncollectible.
General Reserves for loans collectively evaluated for impairment
In assessing the general reserves management has segmented the portfolio for groups of loans with similar risk characteristics, by I. Non-adversely classified loans, and II. Regulatory problem-asset segments. These groups are further subdivided by loan category or internal risk rating, respectively. The general loss allocation factors take into account the quantitative historic loss experience, qualitative or environmental factors such as those identified above, as well as regulatory guidance and industry data.
I.Non-adversely classified loans by credit type:
Management has established the modified historic loss factor for non-adversely classified loan segments by first calculating net charge-offs over a period of time, divided by the average loan balance over that same period. The time period utilized equates to the estimated loss emergence period for each loan segment. This average period may be changed from time to time to be reflective of the most appropriate corresponding conditions (market, economic, etc.). These historic loss factors are then adjusted up or down based on management's assessment of current qualitative factors that are likely to cause estimated credit losses as of the evaluation date to differ from the segment's historical loss experience. These key qualitative factors include the following broad categories:
90
• | Several key areas of expansion and growth, including geographic market, changes in lending staff, new or expanded product lines, changes in composition and portfolio concentrations; |
• | Changes in the credit trend and current volume and severity of past due loans, non-accrual loans and the severity of adversely classified and impaired loans compared to historical levels; and |
• | The current economic environment and conditions (local, state and national) and their general implications to each loan category. |
Management weighs the current effect of each of these areas on each particular non-adversely classified loan segment in determining the allowance allocation factors. Management must exercise significant judgment when evaluating the effect of these qualitative factors on the amount of the allowance for loan losses on the non-adversely classified segments because data may not be reasonably available or directly applicable to determine the precise impact of a factor on the collectability of the loan portfolio as of the evaluation date. The methodology contemplates a range of acceptable levels for these factors due to the subjective nature of the factors and the qualitative considerations related to the inherent credit risk in the portfolio.
II.Regulatory problem-assets segments by credit rating:
For determining the reserve percentages for problem-loans, management has segmented the portfolio following the regulatory problem-asset segments by risk rating: Criticized; Substandard; Doubtful; or Loss, after excluding loans that are individually evaluated for impairment. The modified historic loss factor for problem loan segments was determined by first tracking a sampling of these loans over a period of time, to determine the ultimate resolution. Those balances resulting in charge-offs were calculated as a percentage of the segment's loan balance and an average was calculated over that same period. This average period may be changed from time to time to be reflective of the most appropriate corresponding conditions (market, economic, etc.). These historic loss factors are then adjusted up or down based on management's assessment of current qualitative factors that are likely to cause estimated credit losses as of the evaluation date to differ from the segment's historical loss experience. Management also utilizes regulatory guidance and industry data in relation to the Company's own portfolio statistics as a basis for assessing the reasonableness of the allocation factors for each class of regulatory problem-assets.
Management recognizes that additional issues may also impact the estimate of credit losses to some degree. From time to time management will re-evaluate the qualitative factors, regulatory guidance, and industry data in use in order to consider the impact of other issues which, based on changing circumstances, may become more significant in the future.
The balances of loans as of December 31, 2019 by portfolio classification and evaluation method are summarized as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | Loans individually evaluated for impairment | Loans collectively evaluated for impairment | Gross Loans | |||||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 17,515 | $ | 1,376,664 | $ | 1,394,179 | ||||||
Commercial and industrial | 9,332 | 491,895 | 501,227 | |||||||||
Commercial construction | 3,347 | 314,130 | 317,477 | |||||||||
Residential mortgages | 1,229 | 246,144 | 247,373 | |||||||||
Home equity | 411 | 97,841 | 98,252 | |||||||||
Consumer | 44 | 10,010 | 10,054 | |||||||||
Total gross loans | $ | 31,878 | $ | 2,536,684 | $ | 2,568,562 | ||||||
91
The balances of loans as of December 31, 2018 by portfolio classification and evaluation method are summarized as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | Loans individually evaluated for impairment | Loans collectively evaluated for impairment | Gross Loans | |||||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 16,318 | $ | 1,287,561 | $ | 1,303,879 | ||||||
Commercial and industrial | 12,053 | 502,200 | 514,253 | |||||||||
Commercial construction | 1,736 | 232,694 | 234,430 | |||||||||
Residential mortgages | 893 | 230,608 | 231,501 | |||||||||
Home equity | 514 | 95,602 | 96,116 | |||||||||
Consumer | 16 | 10,225 | 10,241 | |||||||||
Total gross loans | $ | 31,530 | $ | 2,358,890 | $ | 2,390,420 | ||||||
Credit Risk Management
As noted above, the credit risk management function focuses on a wide variety of factors and early detection of credit issues is critical to minimize credit losses. Accordingly, management regularly monitors these factors, among others, through ongoing credit reviews by the Credit Department, an external loan review service, reviews by members of senior management as well as reviews by the Loan Committee and the Board. This review includes the assessment of internal credit quality indicators such as, among others, the risk classification of adversely classified loans, past due and non-accrual loans, impaired and restructured loans, and the level of foreclosure activity. These credit quality indicators are discussed below.
Credit Quality Indicators
Adversely classified loans
The Company's loan risk rating system classifies loans depending on risk of loss characteristics. The classifications range from "substantially risk free" for the highest quality loans and loans that are secured by cash collateral, through a satisfactory range of "minimal," "moderate," "better than average," and "average" risk, to the regulatory problem-asset classifications of "criticized," for loans that may need additional monitoring, and the more severe adverse classifications of "substandard," "doubtful," and "loss" based on criteria established under banking regulations. Loans which are evaluated to be of weaker credit quality are placed on the "watch credit list" and reviewed on a more frequent basis by management.
Loans classified as substandard include those loans characterized by the distinct possibility that the Company will sustain some loss if the deficiencies are not corrected. These loans are inadequately protected by the sound net worth and paying capacity of the borrower; repayment has become increasingly reliant on collateral liquidation or reliance on guaranties; credit weaknesses are well-defined; borrower cash flow is insufficient to meet the required debt service specified in the loan terms and to meet other obligations, such as trade debt and tax payments.
Loans classified as doubtful have all the weaknesses inherent in a substandard rated loan with the added characteristic that the weaknesses make collection or full payment from liquidation, on the basis of currently existing facts, conditions, and values, highly questionable and improbable. The probability of loss is extremely high, but because of certain important and reasonably specific pending factors which may work to the advantage and strengthening of the loan, its classification as an estimated loss is deferred until more exact status may be determined.
Loans classified as loss are generally considered uncollectible at present, although long term recovery of part or all of loan proceeds may be possible. These "loss" loans would require a specific loss reserve or charge-off.
92
Adversely classified loans may be accruing or in non-accrual status and may be additionally designated as impaired or restructured, or some combination thereof.
The following tables present the Company's credit risk profile for each portfolio classification by internally assigned adverse risk rating category as of the periods indicated:
December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Adversely Classified | Not Adversely Classified | Gross Loans | |||||||||||||||||
Substandard | Doubtful | Loss | ||||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 16,664 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,377,515 | $ | 1,394,179 | ||||||||||
Commercial and industrial | 10,900 | 2,370 | — | 487,957 | 501,227 | |||||||||||||||
Commercial construction | 4,836 | — | — | 312,641 | 317,477 | |||||||||||||||
Residential mortgages | 1,825 | — | — | 245,548 | 247,373 | |||||||||||||||
Home equity | 455 | — | — | 97,797 | 98,252 | |||||||||||||||
Consumer | 69 | 3 | — | 9,982 | 10,054 | |||||||||||||||
Total gross loans | $ | 34,749 | $ | 2,373 | $ | — | $ | 2,531,440 | $ | 2,568,562 | ||||||||||
December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Adversely Classified | Not Adversely Classified | Gross Loans | |||||||||||||||||
Substandard | Doubtful | Loss | ||||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 17,714 | $ | 240 | $ | — | $ | 1,285,925 | $ | 1,303,879 | ||||||||||
Commercial and industrial | 12,821 | — | — | 501,432 | 514,253 | |||||||||||||||
Commercial construction | 2,262 | — | — | 232,168 | 234,430 | |||||||||||||||
Residential mortgages | 1,820 | — | — | 229,681 | 231,501 | |||||||||||||||
Home equity | 561 | — | — | 95,555 | 96,116 | |||||||||||||||
Consumer | 35 | 8 | — | 10,198 | 10,241 | |||||||||||||||
Total gross loans | $ | 35,213 | $ | 248 | $ | — | $ | 2,354,959 | $ | 2,390,420 | ||||||||||
Total adversely classified loans amounted to 1.45% of total loans at December 31, 2019, compared to 1.49% at December 31, 2018.
Past due and non-accrual loans
Loans on which the accrual of interest has been discontinued are designated as non-accrual and the classified portions are credit downgraded to one of the adversely classified categories noted above. Accrual of interest on loans is generally discontinued when a loan becomes contractually past due, with respect to interest or principal, by 90 days, or when reasonable doubt exists as to the full and timely collection of interest or principal. Interest payments received on loans in a non-accrual status are generally applied to principal on the books of the Company. When a loan is placed on non-accrual status, all interest previously accrued but not collected is reversed against current period interest income. Interest accruals are resumed on such loans only when payments are brought current and have remained current for a period of 180 days and when, in the judgment of management, the collectability of both principal and interest is reasonably assured.
93
The following tables present an age analysis of past due loans by portfolio classification as of the dates indicated:
Balance at December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Past Due 30-59 Days | Past Due 60-89 Days | Past Due 90 Days or More | Total Past Due Loans | Current Loans | Gross Loans | Non-accrual Loans | |||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 1,469 | $ | 3,914 | $ | 4,158 | $ | 9,541 | $ | 1,384,638 | $ | 1,394,179 | $ | 8,280 | ||||||||||||||
Commercial and industrial | 576 | 1,034 | 265 | 1,875 | 499,352 | 501,227 | 3,285 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial construction | 576 | 3,325 | 1,735 | 5,636 | 311,841 | 317,477 | 1,735 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Residential mortgages | 700 | 283 | 623 | 1,606 | 245,767 | 247,373 | 411 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Home equity | 645 | — | 169 | 814 | 97,438 | 98,252 | 1,040 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Consumer | 12 | — | 6 | 18 | 10,036 | 10,054 | 20 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total gross loans | $ | 3,978 | $ | 8,556 | $ | 6,956 | $ | 19,490 | $ | 2,549,072 | $ | 2,568,562 | $ | 14,771 | ||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Past Due 30-59 Days | Past Due 60-89 Days | Past Due 90 Days or More | Total Past Due Loans | Current Loans | Gross Loans | Non-accrual Loans | |||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 7,596 | $ | 21 | $ | 3,821 | $ | 11,438 | $ | 1,292,441 | $ | 1,303,879 | $ | 6,894 | ||||||||||||||
Commercial and industrial | 619 | 17 | 2,299 | 2,935 | 511,318 | 514,253 | 3,417 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial construction | 4,319 | — | — | 4,319 | 230,111 | 234,430 | 176 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Residential mortgages | 114 | — | 377 | 491 | 231,010 | 231,501 | 763 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Home equity | 14 | 168 | 209 | 391 | 95,725 | 96,116 | 514 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Consumer | 23 | 31 | 6 | 60 | 10,181 | 10,241 | 20 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total gross loans | $ | 12,685 | $ | 237 | $ | 6,712 | $ | 19,634 | $ | 2,370,786 | $ | 2,390,420 | $ | 11,784 | ||||||||||||||
At December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, all loans past due 90 days or more were carried as non-accrual, in addition to those loans that were less than 90 days past due where reasonable doubt existed as to the full and timely collection of interest or principal that have also been designated as non-accrual, despite their payment due status shown in the tables above.
Non-accrual loans that were not adversely classified amounted to $84 thousand at December 31, 2019 and $81 thousand at December 31, 2018. These balances primarily represented the guaranteed portions of non-performing SBA loans. The majority of the non-accrual loan balances were also carried as impaired loans during the periods noted and are discussed further below.
The ratio of non-accrual loans to total loans amounted to 0.58% and 0.49% at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively.
The Company's obligation to fulfill the additional funding commitments on impaired loans is generally contingent on the borrower's compliance with the terms of the credit agreement. If the borrower is not in compliance, additional funding commitments may or may not be made at the Company's discretion. At December 31, 2019, additional funding commitments for non-accrual loans were not material.
94
The reduction in interest income for the years ended December 31, associated with non-accruing loans is summarized as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Income that would have been recognized if non-accrual loans had been current | $ | 1,893 | $ | 2,106 | $ | 1,906 | ||||||
Less income recognized | 244 | 833 | 990 | |||||||||
Reduction in interest income | $ | 1,649 | $ | 1,273 | $ | 916 | ||||||
Impaired loans
Impaired loans are individually significant loans for which management considers it probable that not all amounts due (principal and interest) will be collected in accordance with the original contractual terms. Impaired loans include loans that have been modified in a troubled debt restructuring ("TDR"), see "Troubled debt restructurings" below. Impaired loans are individually evaluated and exclude large groups of smaller-balance homogeneous loans, such as residential mortgage loans and consumer loans, which are collectively evaluated for impairment, and loans that are measured at fair value, unless the loan is amended in a TDR.
Management does not set any minimum delay of payments as a factor in reviewing for impaired classification. Management considers the individual payment status, net worth and earnings potential of the borrower, and the value and cash flow of the collateral as factors to determine if a loan will be paid in accordance with its contractual terms. An impaired or TDR loan classification will be considered for upgrade based on the borrower's sustained performance over time and their improving financial condition. Consistent with the criteria for returning non-accrual loans to accrual status, the borrower must demonstrate the ability to continue to service the loan in accordance with the original or modified terms and, in the judgment of management, the collectability of the remaining balances, both principal and interest, are reasonably assured. In the case of TDR loans having had a modified interest rate, that rate must be at, or greater than, a market rate for a similar credit at the time of modification for an upgrade to be considered.
Impaired loans are individually evaluated for credit loss and a specific allowance reserve is assigned for the amount of the estimated probable credit loss. Refer to heading "Allowance for probable loan losses methodology" contained within this Note 4 of this Form 10-K for further discussion of management's methodology used to estimate specific reserves for impaired loans.
The carrying value of impaired loans amounted to $31.9 million and $31.5 million at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. Total accruing impaired loans amounted to $17.1 million and $19.7 million at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively, while non-accrual impaired loans amounted to $14.8 million and $11.8 million as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively.
The following tables set forth the recorded investment in impaired loans and the related specific allowance allocated by portfolio classification as of the dates indicated:
Balance at December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Unpaid contractual principal balance | Total recorded investment in impaired loans | Recorded investment with no allowance | Recorded investment with allowance | Related specific allowance | |||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 18,537 | $ | 17,515 | $ | 17,129 | $ | 386 | $ | 31 | ||||||||||
Commercial and industrial | 11,455 | 9,332 | 7,405 | 1,927 | 974 | |||||||||||||||
Commercial construction | 3,359 | 3,347 | 3,347 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Residential mortgages | 1,331 | 1,229 | 1,229 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Home equity | 607 | 411 | 411 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Consumer | 44 | 44 | — | 44 | 44 | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 35,333 | $ | 31,878 | $ | 29,521 | $ | 2,357 | $ | 1,049 | ||||||||||
95
Balance at December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Unpaid contractual principal balance | Total recorded investment in impaired loans | Recorded investment with no allowance | Recorded investment with allowance | Related specific allowance | |||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 17,140 | $ | 16,318 | $ | 15,948 | $ | 370 | $ | 55 | ||||||||||
Commercial and industrial | 12,538 | 12,053 | 7,752 | 4,301 | 2,140 | |||||||||||||||
Commercial construction | 1,804 | 1,736 | 1,736 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Residential mortgages | 970 | 893 | 473 | 420 | 13 | |||||||||||||||
Home equity | 685 | 514 | 514 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Consumer | 16 | 16 | — | 16 | 16 | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 33,153 | $ | 31,530 | $ | 26,423 | $ | 5,107 | $ | 2,224 | ||||||||||
The following table presents the average recorded investment in impaired loans by portfolio classification and the related interest recognized during the year ends indicated:
December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Average recorded investment | Interest income recognized | Average recorded investment | Interest income recognized | Average recorded investment | Interest income (loss) recognized | ||||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 17,033 | $ | 509 | $ | 13,971 | $ | 385 | $ | 14,473 | $ | 363 | ||||||||||||
Commercial and industrial | 11,135 | 385 | 11,801 | 373 | 12,272 | 370 | ||||||||||||||||||
Commercial construction | 2,158 | 81 | 1,691 | 93 | 1,818 | 92 | ||||||||||||||||||
Residential mortgages | 1,024 | 18 | 644 | — | 320 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
Home equity | 447 | — | 498 | — | 482 | (1 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Consumer | 28 | — | 56 | — | 25 | (1 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 31,825 | $ | 993 | $ | 28,661 | $ | 851 | $ | 29,390 | $ | 825 | ||||||||||||
All payments received on impaired loans in non-accrual status are applied to principal. Interest income that was not recognized on loans that were deemed impaired as of December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, amounted to $1.0 million, $1.1 million, and $890 thousand, respectively. At December 31, 2019, additional funding commitments for impaired loans was not material. The Company's obligation to fulfill the additional funding commitments on impaired loans is generally contingent on the borrower's compliance with the terms of the credit agreement. If the borrower is not in compliance, additional funding commitments may or may not be made at the Company's discretion.
Troubled debt restructurings
Loans are designated as a TDR when, as part of an agreement to modify the original contractual terms of the loan as a result of financial difficulties of the borrower, the Bank grants the borrower a concession on the terms, that would not otherwise be considered. Typically, such concessions may consist of one or a combination of the following: a reduction in interest rate to a below market rate, taking into account the credit quality of the note; extension of additional credit based on receipt of adequate collateral; or a deferment or reduction of payments (principal or interest) which materially alters the Bank's position or significantly extends the note's maturity date, such that the present value of cash flows to be received is materially less than those contractually established at the loan's origination. All loans that are modified are reviewed by the Company to identify if a TDR has occurred. TDR loans are included in the impaired loan category and, as such, these loans are individually reviewed and evaluated, and a specific reserve is assigned for the amount of the estimated probable credit loss.
Total TDR loans, included in the impaired loan balances above, as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, were $21.1 million and $23.1 million, respectively. TDR loans on accrual status amounted to $17.1 million and $19.4 million at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. TDR loans included in non-performing loans amounted to $4.0 million and $3.7 million at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. The Company
96
continues to work with customers and enters into loan modifications (which may or may not be TDRs) to the extent deemed to be necessary or appropriate while attempting to achieve the best mutual outcome given the individual financial circumstances and future prospects of the borrower.
At December 31, 2019, additional funding commitments for TDR loans was not material. The Company's obligation to fulfill the additional funding commitments on TDR loans is generally contingent on the borrower's compliance with the terms of the credit agreement. If the borrower is not in compliance, additional funding commitments may or may not be made at the Company's discretion.
Loans modified as TDRs during the years indicated, by portfolio classification, are detailed below:
December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Number of restructurings | Pre-modification outstanding recorded investment | Post-modification outstanding recorded investment | Number of restructurings | Pre-modification outstanding recorded investment | Post-modification outstanding recorded investment | ||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | 3 | $ | 2,047 | $ | 1,620 | 4 | $ | 2,342 | $ | 2,349 | ||||||||||||
Commercial and industrial | 11 | 505 | 319 | 10 | 1,283 | 921 | ||||||||||||||||
Commercial construction | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Residential mortgages | 1 | 315 | 311 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Home equity | — | — | — | 2 | 112 | 92 | ||||||||||||||||
Consumer | 3 | 34 | 31 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Total | 18 | $ | 2,901 | $ | 2,281 | 16 | $ | 3,737 | $ | 3,362 | ||||||||||||
There were no subsequent charge-offs associated with the new TDRs noted in the table above during 2019 and $109 thousand subsequent charge-offs in 2018.
Interest payments received on non-accruing 2019 and 2018 TDR loans which were applied to principal and not recognized as interest income were not material.
Payment defaults by portfolio classification, during the years indicated, on loans modified as TDRs within the preceding twelve months are detailed below:
December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Number of TDRs that defaulted | Post-modification outstanding recorded investment | Number of TDRs that defaulted | Post-modification outstanding recorded investment | ||||||||||
Commercial real estate | 1 | $ | 1,400 | 1 | $ | 82 | ||||||||
Commercial and industrial | 3 | 79 | 3 | 273 | ||||||||||
Commercial construction | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Residential mortgages | 1 | 311 | — | — | ||||||||||
Home equity | — | — | 2 | 92 | ||||||||||
Consumer | 1 | 4 | — | — | ||||||||||
Total | 6 | $ | 1,794 | 6 | $ | 447 | ||||||||
97
The following table sets forth the post modification balances of TDRs listed by type of modification for TDRs that occurred during the periods indicated:
December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Number of restructurings | Amount | Number of restructurings | Amount | ||||||||||
Loan advances with adequate collateral | — | $ | — | 1 | $ | 240 | ||||||||
Extended maturity date | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Temporary payment reduction and payment re-amortization of remaining principal over extended term | 10 | 112 | 8 | 304 | ||||||||||
Temporary interest-only payment plan | 4 | 400 | 3 | 2,349 | ||||||||||
Other payment concessions | 4 | 1,769 | 4 | 469 | ||||||||||
Total | 18 | $ | 2,281 | 16 | $ | 3,362 | ||||||||
Amount of specific reserves included in the allowance for loan losses associated with TDRs listed above | $ | 320 | $ | 425 | ||||||||||
See "Financial Condition" in Item 2, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," within the "Loans" section under the headings "Credit Risk" and "Allowance for Loan Losses" of this Form 10-K for additional information about changes in the Company's credit quality indicators since December 31, 2018.
Other real estate owned ("OREO")
The Company carried no OREO at December 31, 2019 or December 31, 2018. During the year ended December 31, 2019, there was one property added to OREO that was subsequently sold resulting in net gains of $34 thousand. There were no sales of OREO during 2018 and 2017, and there were no write downs of OREO during 2019, 2018 or 2017.
At both December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company had no consumer mortgage loans secured by residential real estate properties for which formal foreclosure proceedings were in process according to local requirements of the applicable jurisdictions.
Allowance for loan loss activity
The allowance for loan losses is established through a provision for loan losses, a direct charge to earnings. Loan losses are charged against the allowance when management believes that the collectability of the loan principal is unlikely. Recoveries on loans previously charged-off are credited to the allowance.
The allowance for loan losses amounted to $33.6 million at December 31, 2019, compared to $33.8 million at December 31, 2018. The allowance for loan losses to total loans ratio was 1.31% at December 31, 2019, compared to 1.42% at December 31, 2018. Based on management's judgment as to the existing credit risks inherent in the loan portfolio, as discussed above under the heading "Credit Quality Indicators," management believes that the Company's allowance for loan losses is adequate to absorb probable losses from specifically known and other probable credit risks associated with the portfolio as of December 31, 2019.
98
Changes in the allowance for loan losses for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 are summarized as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Balance at beginning of year | $ | 33,849 | $ | 32,915 | $ | 31,342 | ||||||
Provision | 1,180 | 2,250 | 1,430 | |||||||||
Recoveries | 778 | 431 | 755 | |||||||||
Less: Charge-offs | 2,193 | 1,747 | 612 | |||||||||
Balance at end of year | $ | 33,614 | $ | 33,849 | $ | 32,915 | ||||||
Changes in the allowance for loan losses by portfolio classification for the year ended December 31, 2019 are presented below:
(Dollars in thousands) | Cmml Real Estate | Cmml and Industrial | Cmml Constr | Resid. Mortgage | Home Equity | Cnsmr | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
Beginning Balance | $ | 18,014 | $ | 10,493 | $ | 3,307 | $ | 1,160 | $ | 629 | $ | 246 | $ | 33,849 | ||||||||||||||
Provision | 324 | (29 | ) | 842 | 35 | (102 | ) | 110 | 1,180 | |||||||||||||||||||
Recoveries | — | 734 | — | — | 9 | 35 | 778 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Less: Charge-offs | — | 2,069 | — | — | — | 124 | 2,193 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Ending Balance | $ | 18,338 | $ | 9,129 | $ | 4,149 | $ | 1,195 | $ | 536 | $ | 267 | $ | 33,614 | ||||||||||||||
Ending allowance balance: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allocated to loans individually evaluated for impairment | $ | 31 | $ | 974 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 44 | $ | 1,049 | ||||||||||||||
Allocated to loans collectively evaluated for impairment | $ | 18,307 | $ | 8,155 | $ | 4,149 | $ | 1,195 | $ | 536 | $ | 223 | $ | 32,565 | ||||||||||||||
Changes in the allowance for loan losses by portfolio classification for the year ended December 31, 2018 are presented below:
(Dollars in thousands) | Cmml Real Estate | Cmml and Industrial | Cmml Constr | Resid. Mortgage | Home Equity | Cnsmr | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
Beginning Balance | $ | 17,545 | $ | 9,669 | $ | 3,947 | $ | 904 | $ | 608 | $ | 242 | $ | 32,915 | ||||||||||||||
Provision | 418 | 2,139 | (640 | ) | 256 | (34 | ) | 111 | 2,250 | |||||||||||||||||||
Recoveries | 51 | 278 | — | — | 55 | 47 | 431 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Less: Charge-offs | — | 1,593 | — | — | — | 154 | 1,747 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Ending Balance | $ | 18,014 | $ | 10,493 | $ | 3,307 | $ | 1,160 | $ | 629 | $ | 246 | $ | 33,849 | ||||||||||||||
Ending allowance balance: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allocated to loans individually evaluated for impairment | $ | 55 | $ | 2,140 | $ | — | $ | 13 | $ | — | $ | 16 | $ | 2,224 | ||||||||||||||
Allocated to loans collectively evaluated for impairment | $ | 17,959 | $ | 8,353 | $ | 3,307 | $ | 1,147 | $ | 629 | $ | 230 | $ | 31,625 | ||||||||||||||
99
(5) | Premises and Equipment |
Premises and equipment at December 31, 2019 and 2018 are summarized as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Land and land improvements | $ | 8,435 | $ | 6,722 | ||||
Bank premises and leasehold improvements | 48,184 | 42,658 | ||||||
Computer software and equipment | 12,652 | 10,054 | ||||||
Furniture, fixtures and equipment | 21,406 | 21,568 | ||||||
Total premises and equipment, before accumulated depreciation | 90,677 | 81,002 | ||||||
Less accumulated depreciation | (45,258 | ) | (43,414 | ) | ||||
Total premises and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation | $ | 45,419 | $ | 37,588 | ||||
Total depreciation expense related to premises and equipment amounted to $4.7 million for both the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
(6) | Leases |
For the Company, material leases consisted of operating leases on our facilities, mainly branch leases; leases 12-months or less and immaterial equipment leases have been excluded. As of December 31, 2019, the Company had 15 operating real estate leases. The Company's leased facilities are contracted under various non-cancelable operating leases, most of which provide options to the Company to extend the lease periods and include periodic rent adjustments. While the Company typically exercises its option to extend lease terms, the lease contains provisions that allow the Company, upon notification, to terminate the lease at the end of the lease term, or any option period. Several real estate leases also provide the Company the right of first refusal should the property be offered for sale. During the third quarter of 2019, the Company finalized the purchase of one of the leased buildings in its main campus.
Lease expense for the year ended December 31, 2019 was $1.4 million. Variable lease costs and short-term lease expenses during this period were immaterial.
The weighted average remaining lease term for operating leases at December 31, 2019 was 27.3 years and the weighted average discount rate was 3.79%.
At December 31, 2019, the remaining undiscounted cash flows by year of these lease liabilities were as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | Operating Leases | |||
2020 | $ | 1,242 | ||
2021 | 1,242 | |||
2022 | 1,245 | |||
2023 | 1,252 | |||
2024 | 1,255 | |||
Thereafter | 23,343 | |||
Total lease payments | $ | 29,579 | ||
Less: Imputed interest | 11,475 | |||
Total lease liability | $ | 18,104 | ||
In addition, the Company currently collects rent through non-cancellable leases for a small portion of the overall square-footage within its Lowell, Massachusetts campus headquarters and at one of its branch locations. These leases are deemed immaterial.
100
Prior to adoption of ASU No. 2016-02, "Leases (Topic 842)," total rent expense was $1.4 million for both the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017.
See also Item (k), "Leases," contained in Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained above, for further information regarding the accounting for the Company's leases.
(7) | Deposits |
Deposits at December 31, are summarized as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Non-interest checking | $ | 794,583 | $ | 765,029 | ||||
Interest-bearing checking | 467,988 | 403,497 | ||||||
Savings | 203,236 | 193,214 | ||||||
Money market | 1,009,972 | 862,028 | ||||||
CDs $250,000 or less | 220,751 | 215,200 | ||||||
CDs greater than $250,000 | 90,200 | 69,031 | ||||||
Total customer deposits | 2,786,730 | 2,507,999 | ||||||
Brokered deposits(1) | — | 56,783 | ||||||
Total deposits | $ | 2,786,730 | $ | 2,564,782 | ||||
(1) Brokered CDs which are $250,000 and under.
Total customer deposits include reciprocal balances from checking, money market deposits and CDs received from participating banks in nationwide deposit networks as a result of our customers electing to participate in Company offered programs which allow for enhanced FDIC insurance. Essentially, the equivalent of the customers' original deposited funds comes back to the Company and are carried within the appropriate category under total customer deposits. The Company's balances in these reciprocal products were $419.7 million and $342.4 million at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively.
The aggregate amounts of overdrawn deposits that have been reclassified as loan balances were $348 thousand and $470 thousand at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
The following table shows the scheduled maturities of CDs (December 31, 2018 includes brokered CDs with weighted average remaining lives of less than six months):
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Due in less than twelve months | $ | 229,616 | $ | 223,611 | ||||
Due in over one year through two years | 69,357 | 93,770 | ||||||
Due in over two years through three years | 8,847 | 16,228 | ||||||
Due in over three years through four years | 2,101 | 5,216 | ||||||
Due in over four years through five years | 806 | 1,885 | ||||||
Due in over five years | 224 | 304 | ||||||
Total CDs | $ | 310,951 | $ | 341,014 | ||||
See also Note 16, "Fair Value Measurements," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for further information regarding the Company's fair value measurements for deposits.
101
(8) | Borrowed Funds and Subordinated Debt |
Borrowed funds and subordinated debt outstanding at December 31, for the years indicated are summarized as follows:
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Amount | Average Rate | Amount | Average Rate | Amount | Average Rate | |||||||||||||||
Borrowed funds | $ | 96,173 | 1.86 | % | $ | 100,492 | 2.67 | % | $ | 89,000 | 1.54 | % | |||||||||
Subordinated debt | 14,872 | 6.22 | % | 14,860 | 6.23 | % | 14,847 | 6.23 | % | ||||||||||||
Total borrowed funds and subordinated debt | $ | 111,045 | 2.44 | % | $ | 115,352 | 3.13 | % | $ | 103,847 | 2.21 | % | |||||||||
At December 31, 2019, 2018, and 2017, borrowed funds were comprised solely of FHLB borrowings.
The contractual maturity distribution as of December 31, 2019, of borrowed funds with the weighted average cost for each category is set forth below:
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Balance | Rate | Balance | Rate | Balance | Rate | |||||||||||||||
Overnight | $ | 92,000 | 1.85 | % | $ | 100,000 | 2.68 | % | $ | 39,000 | 1.59 | % | |||||||||
Within 12 months | 3,697 | 2.22 | % | — | — | % | 50,000 | 1.50 | % | ||||||||||||
Over 5 years | 476 | — | % | 492 | — | % | — | — | % | ||||||||||||
At December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the FHLB borrowings, excluding overnight advances, were related to specific lending projects under the FHLB's community development programs.
Maximum FHLB and other borrowings outstanding at any month end during 2019, 2018, and 2017 were $96.2 million, $100.5 million, and $149.3 million, respectively.
The following table summarizes the average balance and average cost of borrowed funds for the years indicated:
Year ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Average Balance | Average Cost | Average Balance | Average Cost | Average Balance | Average Cost | |||||||||||||||
FHLB advances | $ | 15,885 | 2.42 | % | $ | 22,250 | 1.72 | % | $ | 49,546 | 1.19 | % | |||||||||
Other borrowings | 55 | 2.64 | % | — | — | % | — | — | % | ||||||||||||
Total borrowed funds | $ | 15,940 | 2.42 | % | $ | 22,250 | 1.72 | % | $ | 49,546 | 1.19 | % | |||||||||
The Company's primary borrowing source is the FHLB, however the Company may choose to borrow from other established business partners. "Other borrowings" represents overnight advances from the FRB or federal funds purchased from correspondent banks.
As a member of the FHLB, the Bank has the potential capacity to borrow an amount up to the value of its discounted qualified collateral. Borrowings from the FHLB are secured by certain securities from the Company's investment portfolio not otherwise pledged and certain residential and commercial real estate loans. At December 31, 2019, based on qualifying collateral less outstanding advances, the Bank had the capacity to borrow additional funds from the FHLB of up to approximately $535.0 million. In addition, based on qualifying collateral, the Bank had the capacity to borrow funds from the FRB Discount Window up to approximately $175.0 million at December 31, 2019. The Bank also has pre-approved borrowing arrangements with large correspondent banks to provide overnight and short-term borrowing capacity.
102
The Company had outstanding subordinated debt of $14.9 million (net of deferred issuance costs) at both December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, and $14.8 million at December 31, 2017, which consisted of $15.0 million in aggregate principal amount of Fixed-to-Floating Rate Subordinated Notes (the "Notes"), issued in January 2015, in a private placement to an accredited investor. The Notes are intended to qualify as Tier 2 capital for regulatory purposes, mature on January 30, 2030 (the "Maturity Date") and are callable by the Company, subject to regulatory approval, at a premium beginning January 30, 2020, and at par beginning January 30, 2025. The Notes pay interest at a fixed rate of 6.00% per annum through January 30, 2025, and beginning on January 31, 2025 through the Maturity Date, or any early redemption date, the interest rate on the Notes will adjust monthly at an interest rate of 3.90% plus 30-day LIBOR. Original debt issuance costs were $190 thousand and have been netted against the subordinated debt on the consolidated balance sheet in accordance with accounting guidance. These costs are being amortized to interest expense over the life of the Notes.
See also Note 16, "Fair Value Measurements," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for further information regarding the Company's fair value measurements for borrowed funds and subordinated debt.
See Note 2, "Investment Securities," and Note 3, "Loans," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained above, for further information regarding securities and loans pledged for borrowed funds. Refer to the "Borrowed Funds" and "Liquidity" sections in the "Financial Condition" section in Item 2, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operation," of this Form 10-K for additional information about other sources of funding available to the Company.
(9) | Derivatives and Hedging Activities |
At December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company had ten and eight interest-rate swaps, respectively, from Back-to-Back swap transactions. Each Back-to-Back swap consists of two interest-rate swaps (a customer swap and offsetting counterparty swap). The notional asset amount of these swaps totaled $22.8 million and $18.8 million at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively, with a corresponding notional liability of the same value. Due to the offsetting nature of Back-to-Back swaps, there were no net gains or losses recognized in net income on Back-to-Back swaps during the years ended December 31, 2019, December 31, 2018 or December 31, 2017.
Asset derivatives are included in the line item "Prepaid expenses and other assets," and liability derivatives are included in the "Accrued expenses and other liabilities" line item on the Consolidated Balance Sheets, respectively. Interest-rate swaps with the counterparty are subject to master netting agreements, while interest-rate swaps with customers are not.
The table below presents the fair value and classification of the Company's derivative financial instruments for the periods presented:
As of December 31, 2019 | As of December 31, 2018 | |||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Asset Derivatives | Liability Derivatives | Asset Derivatives | Liability Derivatives | ||||||||||||
Interest-rate contracts - pay floating, received fixed | $ | 625 | $ | 187 | $ | 45 | $ | 723 | ||||||||
Interest-rate contracts - pay fixed, receive floating | — | 438 | 678 | — | ||||||||||||
Total interest-rate swaps | $ | 625 | $ | 625 | $ | 723 | $ | 723 | ||||||||
By using derivative financial instruments, the Company exposes itself to counterparty-credit risk. Credit risk is the risk of failure by the counterparty to perform under the terms of the derivative contract. When the fair value of a derivative contract is positive, the counterparty owes the Company, which creates credit risk for the Company. When the fair value of a derivative is negative, the Company owes the counterparty and, therefore, it does not possess credit risk. The credit risk in derivative instruments is mitigated by entering into transactions with highly-rated counterparties that management believes to be creditworthy. Additionally, counterparty interest-rate swaps contain provisions for collateral to be posted if the derivative exposure exceeds a threshold amount.
103
The Company has one counterparty and it was rated A and A2 by Standard & Poor's and Moody's, respectively, at December 31, 2019. The Company had no credit risk exposure at December 31, 2019 and $678 thousand in credit risk exposure at December 31, 2018 relating to interest-rate swaps with counterparties. When the Company has credit risk exposure, collateral is received from the counterparty and held by the Company. Collateral held by the Company is restricted and not considered an asset of the Company. Therefore, it is not carried on the Company's Consolidated Balance Sheet. If the Company posts collateral, the cash is restricted, it is considered an asset of the Company and is carried on the Company's Consolidated Balance Sheet. The Company posted cash collateral of $850 thousand at December 31, 2019, while at December 31, 2018 the Company held cash collateral of $850 thousand.
The table below present the Company's liability derivative positions and the potential effect of those netting arrangements on its financial position, as of the period presented. As noted above, interest-rate swaps with customers are not subject to master netting agreements and therefore are not included in the table
below.
As of December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Gross Amounts of Recognized Liabilities | Gross Amounts Offset in the Consolidated Balance Sheet | Net Amounts of Liabilities Presented in the Consolidated Balance Sheet | |||||||||
Liabilities Derivatives | ||||||||||||
Interest-rate contracts - pay fixed, receive floating | $ | 625 | $ | 187 | $ | 438 | ||||||
The table below present the Company's asset derivative positions and the potential effect of those netting arrangements on its financial position, as of the period presented. As noted above, interest-rate swaps with customers are not subject to master netting agreements and therefore are not included in the table below.
As of December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Gross Amounts of Recognized Assets | Gross Amounts Offset in the Consolidated Balance Sheet | Net Amounts of Assets Presented in the Consolidated Balance Sheet | |||||||||
Asset Derivatives | ||||||||||||
Interest-rate contracts - pay fixed, receive floating | $ | 723 | $ | 45 | $ | 678 | ||||||
The Company's interest-rate swaps with counterparties contain credit-risk-related contingent provisions. These provisions provide the counterparty with the right to terminate its derivative positions and require the Company to settle its obligations under the agreements if the Company defaults on certain of its indebtedness.
The Company also participates in loans originated by third party banks, where the originating bank utilizes a back-to-back interest-rate swap structure; however, the Company is not a party to the swap agreements. Under the terms of the loan participations, the Company has accepted contingent liabilities that would only be realized if the swaps were terminated early and there were outstanding losses not covered by the underlying borrowers and the borrowers' pledged collateral. If applicable, the Company's swap-loss exposure would be equal to a percentage of the originating bank's swap loss based on the ratio of the Company's loan participation to the underlying loan. At both December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company had one participation loan where the originating bank utilizes a back-to-back interest-rate swap structure. At December 31, 2019, management considers the risk of material swap loss exposure related to this participation loan to be unlikely based on the swap market value, as well as the borrower's financial and collateral strength.
104
See also Note 10, "Commitments, Contingencies and Financial Instruments with Off-Balance Sheet Risk and Concentrations of Credit Risk," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for further information on the Company's commitments and contingencies.
(10) | Commitments, Contingencies and Financial Instruments with Off-Balance Sheet Risk and Concentrations of Credit Risk |
The Company is party to financial instruments with off-balance sheet risk in the normal course of business to meet the financing needs of its customers. These financial instruments include commitments to originate loans, letters of credit, and unadvanced portions of loans and lines of credit.
The instruments involve, to varying degrees, elements of credit risk in excess of the amount recognized in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The contractual amounts of these instruments reflect the extent of involvement the Company has in the particular classes of financial instruments.
The Company's exposure to credit loss in the event of nonperformance by the other party to the financial instrument for loan commitments and letters of credit is represented by the contractual amounts of those instruments. The Company uses the same credit policies in making commitments and conditional obligations as it does for on-balance sheet instruments.
Financial instruments with off-balance sheet credit risk at December 31, 2019 and 2018 are as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Commitments to originate loans | $ | 25,930 | $ | 71,586 | ||||
Commitments to originate residential mortgages loans for sale | 1,095 | — | ||||||
Commitments to sell residential mortgage loans | 1,696 | 701 | ||||||
Letters of credit | 25,284 | 23,482 | ||||||
Unadvanced portions of commercial real estate loans | 20,486 | 39,311 | ||||||
Unadvanced portions of commercial loans and lines | 472,419 | 453,381 | ||||||
Unadvanced portions of construction loans (commercial & residential) | 294,744 | 240,019 | ||||||
Unadvanced portions of home equity lines | 113,387 | 100,227 | ||||||
Unadvanced portions of consumer loans | 4,209 | 4,270 | ||||||
Commitments to originate loans are agreements to lend to a customer provided there is no violation of any condition established in the contract. Commitments generally have fixed expiration dates or other termination clauses and may require payment of a fee by the customer. Since some of the commitments are expected to expire without being drawn upon, the total commitment amounts do not necessarily represent future cash requirements. The Company evaluates each customer's credit worthiness on a case-by-case basis. The amount of collateral obtained, if deemed necessary by the Company upon extension of credit, is based on management’s credit evaluation of the borrower.
The Company originates residential mortgage loans intended for sale under agreements to sell such loans on an individual loan basis and may retain or sell the servicing when selling the loans. Loans sold are subject to standard secondary market underwriting and eligibility representations and warranties over the life of the loan and are subject to an early payment default period covering the first four payments for certain loan sales.
Letters of credit are conditional commitments issued by the Company to guarantee the financial obligation or performance of a customer to a third party. The credit risk involved in issuing letters of credit is essentially the same as that involved in extending loan facilities to customers. If the letter of credit is drawn upon, a loan is created for the customer, generally a commercial loan, with the same criteria associated with similar commercial loans.
Unadvanced portions of loans and lines of credit represent credit extended to customers but not yet drawn upon and are secured or guaranteed under preexisting loan agreements and credit evaluations having taken into consideration the full commitment amount.
105
See also Note 9, "Derivatives and Hedging Activities," and Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," under Item (p), "Derivatives," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained above, for information on the Company's interest-rate lock commitments, interest-rate swaps, and participation in loans originated by third-party banks with potential contingent liabilities.
There are no material pending legal proceedings to which the Company or its subsidiaries are a party or to which any of its property is subject, other than ordinary and routine litigation incidental to the business of the Company. Management does not believe resolution of any present litigation will have a material adverse effect on the consolidated financial condition or results of operations of the Company.
(11) | Stockholders' Equity |
Shares Authorized and Share Issuance
The Company's authorized capital is divided into common stock and preferred stock. The Company is authorized to issue 40,000,000 shares of common stock, with a par value of $0.01 per share, and as of December 31, 2019 had 11,825,331 shares issued and outstanding. Holders of common stock are entitled to one vote per share and are entitled to receive dividends if, as and when declared by the Board. Dividend and liquidation rights of the common stock may be subject to the rights of any outstanding preferred stock. The Company is also authorized to issue 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock, with a par value of $0.01 per share. No preferred stock has been issued as of the date of this Form 10-K.
The Company has a stockholders' rights plan. Under the plan, each share of common stock includes a right to purchase under certain circumstances one one-hundredth of a share of the Company's Series A Junior Participating Preferred Stock, par value $0.01 per share, at a purchase price of $122.50 per one one-hundredth of a preferred share, subject to adjustment, or, in certain circumstances, to receive cash, property, shares of common stock or other securities of the Company. The rights are not presently exercisable and remain attached to the shares of common stock until the occurrence of certain triggering events that would ordinarily be associated with an unsolicited acquisition or attempted acquisition of 10% or more of the Company's outstanding shares of common stock. The rights have no voting or dividend privileges, and unless and until they become exercisable, have no dilutive effect on the earnings of the Company. The rights will expire, unless earlier redeemed, exchanged, or otherwise rescinded by the Company, on January 13, 2028.
The Company's stock incentive plans permit the Board to grant, under various terms, stock options (for the purchase of newly issued shares of common stock), common stock, restricted stock awards, restricted stock units and stock appreciation rights to officers and other employees, non-employee directors and consultants.
The Company issues stock options and restricted stock awards to officers and other employees and restricted stock awards and stock compensation in lieu of cash fees to non-employee directors. The restricted stock awards allow for the non-forfeitable receipt of dividends, and the voting of all shares, whether or not vested, throughout the vesting periods at the same proportional level as common shares outstanding. The unvested restricted stock awards are the Company's only participating securities and are included in shares outstanding. Unvested participating restricted awards amounted to 102,056 shares and 91,708 shares as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. See Item (t), "Earnings per Share," contained in Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained above, and Note 15, "Earnings per Share," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for additional information regarding unvested participating restricted awards and the Company's earnings per share calculation.
Upon vesting, restricted stock awards may be net settled to cover payment for employee tax obligations, resulting in shares of common stock being reacquired by the Company and returned to the pool of shares reserved for issuance under the incentive plans. In accordance with Massachusetts law, shares reacquired by the Company will be treated as authorized but unissued shares.
The Company's stock incentive plans also allow for newly issued shares of common stock to be issued without restrictions to officers and other employees, non-employee directors and consultants. From time to time, the Company issues shares to community members for consulting on regional advisory councils and grants shares of fully vested
106
stock as employee anniversary awards. These shares vest immediately and the cost, which is based on the market price on the date of grant and deemed to be immaterial, is expensed in the period in which the services are rendered. See Note 13, "Stock-Based Compensation," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for further information regarding the Company's stock incentive plans.
In addition, the Company maintains a dividend reinvestment and direct stock purchase plan ("DRSPP") which enables stockholders, at their discretion, to elect to reinvest cash dividends paid on their shares of the Company's common stock by purchasing additional shares of common stock from the Company at a purchase price equal to fair market value. Under the DRSPP, stockholders and new investors also have the opportunity to purchase shares of the Company's common stock without brokerage fees, subject to monthly minimums and maximums. During the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018, and 2017, the direct purchase component of the DRSPP was used by stockholders to purchase 1,609, 2,652 and 2,014 shares of the Company's common stock totaling $48 thousand, $94 thousand, and $70 thousand, respectively. See "Dividends" below for further information about the dividend reinvestment portion of the DRSPP.
Capital Raised and Capital Adequacy Requirements
Capital planning by the Company and the Bank considers current needs and anticipated future growth. Ongoing sources of capital include the retention of earnings, less dividends paid, proceeds from the exercise of employee stock options and proceeds from purchases of shares pursuant to the DRSPP. Additional sources of capital for the Company and the Bank have been proceeds from the issuance of common stock and proceeds from the issuance of subordinated debt. The Company believes its current capital is adequate to support ongoing operations.
Management believes, as of December 31, 2019, that the Company and the Bank met all capital adequacy requirements to which they were subject. As of December 31, 2019, and December 31, 2018, the Company met the definition of "well-capitalized" under the applicable Federal Reserve Board regulations and the Bank qualified as "well-capitalized" under the prompt corrective action regulations of Basel III and the FDIC.
The Company's and the Bank's actual capital amounts and ratios are presented as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 in the tables below:
Actual | Minimum Capital for Capital Adequacy Purposes(1) | Minimum Capital To Be Well Capitalized(2) | |||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | |||||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||
The Company | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total Capital (to risk weighted assets) | $ | 328,961 | 11.88 | % | $ | 221,435 | 8.00 | % | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||
Tier 1 Capital (to risk weighted assets) | 280,475 | 10.13 | % | 166,077 | 6.00 | % | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||
Tier 1 Capital (to average assets) or Leverage Ratio | 280,475 | 8.86 | % | 126,661 | 4.00 | % | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||
Common equity tier 1 capital (to risk-weighted assets) | 280,475 | 10.13 | % | 124,557 | 4.50 | % | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||
The Bank | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total Capital (to risk weighted assets) | $ | 328,489 | 11.87 | % | $ | 221,435 | 8.00 | % | $ | 276,794 | 10.00 | % | |||||||||
Tier 1 Capital (to risk weighted assets) | 294,875 | 10.65 | % | 166,077 | 6.00 | % | 221,435 | 8.00 | % | ||||||||||||
Tier 1 Capital (to average assets) or Leverage Ratio | 294,875 | 9.31 | % | 126,661 | 4.00 | % | 158,326 | 5.00 | % | ||||||||||||
Common equity tier 1 capital (to risk-weighted assets) | 294,875 | 10.65 | % | 124,557 | 4.50 | % | 179,916 | 6.50 | % | ||||||||||||
107
Actual | Minimum Capital for Capital Adequacy Purposes(1) | Minimum Capital To Be Well Capitalized(2) | |||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | |||||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||
The Company | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total Capital (to risk weighted assets) | $ | 297,402 | 11.77 | % | $ | 202,172 | 8.00 | % | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||
Tier 1 Capital (to risk weighted assets) | 250,925 | 9.93 | % | 151,629 | 6.00 | % | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||
Tier 1 Capital (to average assets) or Leverage Ratio | 250,925 | 8.56 | % | 117,198 | 4.00 | % | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||
Common equity tier 1 capital (to risk-weighted assets) | 250,925 | 9.93 | % | 113,722 | 4.50 | % | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||
The Bank | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total Capital (to risk weighted assets) | $ | 297,162 | 11.76 | % | $ | 202,172 | 8.00 | % | $ | 252,715 | 10.00 | % | |||||||||
Tier 1 Capital (to risk weighted assets) | 265,545 | 10.51 | % | 151,629 | 6.00 | % | 202,172 | 8.00 | % | ||||||||||||
Tier 1 Capital (to average assets) or Leverage Ratio | 265,545 | 9.06 | % | 117,198 | 4.00 | % | 146,498 | 5.00 | % | ||||||||||||
Common equity tier 1 capital (to risk-weighted assets) | 265,545 | 10.51 | % | 113,722 | 4.50 | % | 164,265 | 6.50 | % | ||||||||||||
(1) | Before application of the capital conservation buffer of 2.50% as of December 31, 2019 and 1.875% as of December 31, 2018, see discussion below. |
(2) | For the Bank to qualify as "well-capitalized," it must maintain at least the minimum ratios listed under the regulatory prompt corrective action framework. This framework does not apply to the Company. |
The Company is subject to the Basel III capital ratio requirements which include a "capital conservation buffer" of 2.50% above the regulatory minimum risk-based capital adequacy requirements shown above. The capital conservation buffer requirement, which had a phase in implementation period, was fully implemented on January 1, 2019. If a banking organization dips into its capital conservation buffer it may be restricted in its activities, including its ability to pay dividends and discretionary bonus payments to its executive officers. Both the Company's and the Bank's actual ratios, as outlined in the table above, exceeded the Basel III risk-based capital requirement with the capital conservation buffer as of December 31, 2019.
The Basel III minimum capital ratio requirements as applicable to the Company and the Bank with the capital conversation buffer are summarized in the table below:
Basel III Minimum for Capital Adequacy Purposes | Basel III Additional Capital Conservation Buffer | Basel III "Adequate" Ratio with Capital Conservation Buffer | ||||
Total Capital (to risk weighted assets) | 8.00% | 2.50% | 10.50% | |||
Tier 1 Capital (to risk weighted assets) | 6.00% | 2.50% | 8.50% | |||
Tier 1 Capital (to average assets) or Leverage Ratio | 4.00% | — | 4.00% | |||
Common equity tier 1 capital (to risk-weighted assets) | 4.50% | 2.50% | 7.00% | |||
Failure to meet minimum capital requirements can initiate or result in certain mandatory and possibly additional discretionary supervisory actions by regulators that, if undertaken, could have a material adverse effect on the Company's consolidated financial statements. Under applicable capital adequacy requirements and the regulatory framework for prompt corrective action applicable to the Bank, the Company must meet specific capital guidelines that involve quantitative measures of the Company's assets, liabilities and certain off-balance sheet items as calculated under regulatory accounting practices. The Company's capital amounts and classifications are also subject to qualitative judgments by the regulators about components, risk weightings, and other factors.
108
See also "Supervision and Regulation," contained in Item 1, "Business," of this Form 10-K for further information on the Company's Basel III and capital requirements.
Dividends
Neither the Company nor the Bank may declare or pay dividends on its stock if the effect thereof would cause stockholders' equity to be reduced below applicable regulatory capital requirements or if such declaration and payment would otherwise violate regulatory requirements.
As the principal asset of the Company, the Bank currently provides the only source of cash for the payment of dividends by the Company. Under Massachusetts law, trust companies such as the Bank may pay dividends only out of "net profits" and only to the extent that such payments will not impair the Bank's capital stock. Any dividend payment that would exceed the total of the Bank's net profits for the current year plus its retained net profits of the preceding two years would require the Massachusetts Division of Banks' approval. Applicable provisions of the FDIC Improvement Act also prohibit a bank from paying any dividends on its capital stock if the bank is in default on the payment of any assessment to the FDIC or if the payment of dividends would otherwise cause the bank to become undercapitalized. Any restrictions, regulatory or otherwise, on the ability of the Bank to pay dividends to the Company may restrict the ability of the Company to pay dividends to the holders of its common stock.
The statutory term "net profits" essentially equates with the accounting term "net income" and is defined under the Massachusetts banking statutes to mean the remainder of all earnings from current operations plus actual recoveries on loans and investments and other assets after deducting from such total all current operating expenses, actual losses, accrued dividends on any preferred stock and all federal and state taxes.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company declared $7.5 million in cash dividends and stockholders utilized the dividend reinvestment portion of the DRSPP to purchase an aggregate of 39,176 shares of the Company's common stock totaling $1.2 million. In 2018, the Company declared $6.8 million in cash dividends and stockholders utilized the dividend reinvestment portion of the DRSPP to purchase 37,999 shares of the Company's common stock totaling $1.3 million. In 2017, the Company declared $6.2 million in cash dividends and stockholders utilized the dividend reinvestment portion of the DRSPP to purchase 44,752 shares of the Company's common stock totaling $1.5 million. See "Shares Authorized and Share Issuance" above in this Note 11 of this Form 10-K for more information on the DRSPP, including the direct stock purchase component of the plan.
(12) | Employee Benefit Plans |
Defined Contribution Plans
The Company has a 401(k) defined contribution employee benefit plan. The 401(k) plan allows eligible employees to contribute a percentage of their earnings to the plan. A portion of an employee's contribution, as determined by the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors, is matched by the Company. In 2019 and 2018, the Company's percentage match was 70% up to the first 6% contributed by the employee, while in 2017, the Company's percentage match was 60% up to the first 6% contributed by the employee.
All eligible employees, at least 18 years of age and completing 1 hour of service, may participate in the 401(k) plan. Since the fourth quarter of 2017, vesting for the Company's 401(k) retirement plan matching contribution is based on years of service with participants becoming 25% vested on the anniversary of their hire date and each subsequent year until they are 100% vested following four years of service. Unvested amounts not distributable to an employee following termination of employment are used to offset plan expenses and the Company's matching contributions.
The Company's expense for the 401(k) plan match was $1.5 million, $1.3 million and $965 thousand, respectively, for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018, and 2017.
Additionally, on December 11, 2018, the Board approved and adopted the Enterprise Bank Supplemental Executive Retirement and Deferred Compensation Plan. The plan is unfunded and is maintained for the purpose of providing deferred compensation to a certain group of management employees. Total expenses for the deferred compensation plan were $322 thousand and $120 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
109
Supplemental Employee Retirement Plan ("SERP")
The Company has salary continuation agreements with two of its current executive officers and one former executive officer. These salary continuation agreements provide for predetermined fixed-cash supplemental retirement benefits to be provided for a period of 20 years after each individual reaches a defined "benefit age." The individuals covered under the SERP have reached the defined benefit age and are receiving payments under the plan. Additionally, the Company has not recognized service costs in the current or prior year as each officer had previously attained their individually defined benefit age and was fully vested under the plan.
This non-qualified plan represents a direct liability of the Company, and as such has no specific assets set aside to settle the benefit obligation. The aggregate amount accrued, or the "accumulated benefit obligation," is equal to the present value of the benefits to be provided to the employee or any beneficiary. Because the Company's benefit obligations provide for predetermined fixed-cash payments, the Company does not have any unrecognized costs to be included as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income.
The amounts charged to expense for the SERP are included in the table below. The Company anticipates accruing an additional $80 thousand to the SERP for the year ending December 31, 2020.
The following table provides a reconciliation of the changes in the supplemental retirement benefit obligation and the net periodic benefit cost for the years ended December 31:
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Reconciliation of benefit obligation: | ||||||||||||
Benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | 2,174 | $ | 2,372 | $ | 2,502 | ||||||
Net periodic benefit cost: | ||||||||||||
Interest cost | 84 | 110 | 110 | |||||||||
Actuarial loss (gain) | 82 | (32 | ) | 36 | ||||||||
Net periodic benefit costs | $ | 166 | $ | 78 | $ | 146 | ||||||
Benefits paid | (276 | ) | (276 | ) | (276 | ) | ||||||
Benefit obligation at end of year | $ | 2,064 | $ | 2,174 | $ | 2,372 | ||||||
Funded status: | ||||||||||||
Accrued liability as of December 31 | $ | (2,064 | ) | $ | (2,174 | ) | $ | (2,372 | ) | |||
Discount rate used for benefit obligation(1) | 4.00 | % | 4.75 | % | 4.50 | % | ||||||
(1) | Management utilizes the Moody's 20 year AA corporate bond rates to establish the reasonableness of the discount rate used. The Company reviews and periodically updates the discount rate to reflect changes in bond market rates. The impact of the discount rate change is reflected as the actuarial gain or loss. |
110
SERP benefits expected to be paid in each of the next five years and in the aggregate five years thereafter:
(Dollars in thousands) | |||
2020 | $ | 276 | |
2021 | 276 | ||
2022 | 276 | ||
2023 | 276 | ||
2024 | 276 | ||
2025-2029 | 1,088 | ||
Supplemental Life Insurance
The Company has provided supplemental life insurance through split-dollar life insurance arrangements for certain executive and senior officers on whom the Bank owns BOLI. See Item (l), "Bank Owned Life Insurance," in Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained above, for further information regarding BOLI.
These arrangements provide a death benefit to the officer's designated beneficiaries that extend to postretirement periods for some of the supplemental life insurance plans. The Company has recognized a liability for these future postretirement benefits.
These non-qualified plans represent a direct liability of the Company, and, as such, the Company has no specific assets set aside to settle the benefit obligation. The funded status is the aggregate amount accrued, or the "accumulated postretirement benefit obligation," which is the present value of the post-retirement benefits associated with this arrangement.
The following table provides a reconciliation of the changes in the post-retirement supplemental life insurance plan obligation and the net periodic benefit cost for the years ended December 31:
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Reconciliation of benefit obligation: | ||||||||||||
Benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | 2,084 | $ | 2,032 | $ | 1,895 | ||||||
Net periodic benefit cost: | ||||||||||||
Service cost | (16 | ) | (13 | ) | (11 | ) | ||||||
Interest cost | 95 | 94 | 91 | |||||||||
Actuarial loss (gain) | 261 | (29 | ) | 57 | ||||||||
Total net period cost | $ | 340 | $ | 52 | $ | 137 | ||||||
Benefit obligation at end of year | $ | 2,424 | $ | 2,084 | $ | 2,032 | ||||||
Funded status: | ||||||||||||
Accrued liability as of December 31 | $ | (2,424 | ) | $ | (2,084 | ) | $ | (2,032 | ) | |||
Discount rate used for benefit obligation(1) | 4.00 | % | 4.75 | % | 4.50 | % | ||||||
(1) | Management utilizes the Moody's 20 year AA corporate bond rates to establish the reasonableness of the discount rate used. The Company reviews and periodically updates the discount rate to reflect changes in bond market rates. The impact of the discount rate change is reflected as the actuarial gain or loss. |
The amounts charged to expense for supplemental life insurance are included in the table above. The Company anticipates accruing an additional $92 thousand to the plan for the year ending December 31, 2020.
111
See also Note 13, "Stock-Based Compensation," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained below, for further information regarding employee benefits offered in the form of stock options and stock awards.
(13) | Stock-Based Compensation |
The Company currently has one active stock incentive plan: The Enterprise Bancorp, Inc. 2016 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended. The 2016 plan permits the Board to grant, under various terms, common stock, both incentive and non-qualified stock options (for the purchase of newly issued shares of common stock), restricted stock, restricted stock units and stock appreciation rights to officers and other employees, directors and consultants. Option exercises and restricted stock vestings may be net exercised or net settled to cover option costs and employee tax obligations under the terms of the respective plan. As of December 31, 2019, 271,838 shares remained available for future grants under the 2016 plan.
Additionally, the Enterprise Bancorp, Inc 2009 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended, expired in March 2019 with 87,849 unissued shares. As such, the 2009 plan is closed for future grants, although awards previously granted under the 2009 plan remain outstanding and may be exercised through 2028.
The Company's stock-based compensation expense related to these plans includes stock options and stock awards to officers and other employees included in salary and benefits expense, and stock awards and stock compensation in lieu of cash fees to non-employee directors both included in other operating expenses. Total stock-based compensation expense was $1.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 and $1.8 million for both the years ended December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017. The total tax benefit recognized related to the stock-based compensation expense was $526 thousand, $519 thousand and $716 thousand for the years ended 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
A tax benefit associated with employee exercises and vesting of stock compensation of approximately $137 thousand was recorded as a reduction of the Company's income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2019, compared with $302 thousand and $922 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, respectively. These amounts, treated as discrete tax items in the period in which they occur, will vary from year to year as a function of the volume of share-based payments vested or exercised and the then current market price of the Company's stock in comparison to the compensation cost recognized in the Company's consolidated financial statements.
Stock Option Awards
Stock options granted generally vest 50% in year two and 50% in year four, on or about the anniversary date of the awards. Vested stock options are only exercisable while the employee remains employed with the Company and for a limited time thereafter. For all awards, if a grantee's employment or other service relationship, such as service as a director, is terminated for any reason, then any stock options granted that have not vested at the time of such termination generally must be forfeited, unless the Compensation Committee or the Board, as the case may be, waives such forfeiture requirement.
Under the terms of the plans, stock options may not be granted at less than 100% of the fair market value of the shares on the date of grant and may not have a term of more than ten years. Any shares of common stock reserved for issuance pursuant to stock options granted under the plans that are returned to the Company unexercised shall remain available for issuance under such plan, while the plan is effective. For participants owning 10% or more of the Company's outstanding common stock (of which there are currently none), incentive stock options may not be granted at less than 110% of the fair market value of the shares on the date of grant and may not have an expiration term of more than five years.
112
The Company utilizes the Black-Scholes option valuation model in order to determine the per share grant date fair value of stock option grants.
The table below provides a summary of the stock options granted, including the weighted average fair value, the fair value as a percentage of the market value of the underlying stock at the date of grant and the average assumptions used in the model for the years indicated:
Stock Option Awards | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Stock options granted | 23,218 | 14,755 | 15,009 | |||||||||
Term in years | 10 | 10 | 10 | |||||||||
Weighted average assumptions used in the fair value model: | ||||||||||||
Expected volatility | 33 | % | 37 | % | 40 | % | ||||||
Expected dividend yield | 2.75 | % | 2.10 | % | 2.09 | % | ||||||
Expected life in years | 6.5 | 6.5 | 7.0 | |||||||||
Risk-free interest rate | 2.58 | % | 2.86 | % | 2.35 | % | ||||||
Weighted average market price on date of grants | $ | 29.84 | $ | 34.33 | $ | 30.46 | ||||||
Per share weighted average fair value | $ | 8.70 | $ | 11.98 | $ | 11.34 | ||||||
Fair value as a percentage of market value at grant date | 29 | % | 35 | % | 37 | % | ||||||
The expected volatility is the anticipated variability in the Company's share price over the expected life of the stock option and is based on the Company's historical volatility.
The expected dividend yield is the Company's projected dividends based on historical annualized dividend yield to coincide with volatility divided by its share price at the date of grant.
The expected life represents the period of time that the stock option is expected to be outstanding. The Company utilized the simplified method, under which the expected term equals the vesting term plus the contractual term divided by 2.
The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Department of the Treasury rate in effect at the time of grant for a period equivalent to the expected life of the stock option.
Stock option transactions during the year ended December 31, 2019 are summarized as follows:
(Dollars in thousands, except per share data) | Options | Weighted Average Exercise Price Per Share | Weighted Average Remaining Life in Years | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | |||||||||
Outstanding December 31, 2018 | 183,845 | $ | 20.90 | 4.9 | $ | 2,102 | |||||||
Granted | 23,218 | 29.84 | |||||||||||
Exercised | 47,142 | 16.61 | |||||||||||
Forfeited/Expired | 549 | 26.33 | |||||||||||
Outstanding December 31, 2019 | 159,372 | $ | 23.45 | 5.8 | $ | 1,667 | |||||||
Vested and Exercisable at December 31, 2019 | 100,233 | $ | 20.11 | 4.6 | $ | 1,379 | |||||||
113
The aggregate intrinsic value in the table above represents the difference between the closing price of the Company's common stock on December 31, 2019 and the exercise price, multiplied by the number of stock options. If the closing price was less than the exercise price of the stock option, no intrinsic value was assigned to the grant. At December 31, 2019, all of the vested and exercisable stock options were in-the money. The intrinsic value of stock options vested and exercisable represents the total pretax intrinsic value that would have been received by the stock option holders had all in-the-money vested stock option holders exercised their options on December 31, 2019. The intrinsic value will change based on the fair market value of the Company's stock.
Cash received from stock option exercises was $185 thousand, $308 thousand and $355 thousand in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The total intrinsic value of stock options exercised was $659 thousand, $452 thousand and $1.6 million in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. Cash paid by the Company for the net settlement of stock options to cover employee tax obligations was $157 thousand, $39 thousand, and $386 thousand in 2019, 2018, and 2017 respectively.
Stock option activity during the year ended December 31, 2019 for unvested options are summarized as follows:
Unvested Options | Options | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | |||||
Unvested December 31, 2018 | 56,008 | $ | 10.00 | ||||
Granted | 23,218 | 8.70 | |||||
Vested | 19,613 | 9.56 | |||||
Forfeited | 474 | 9.14 | |||||
Unvested December 31, 2019 | 59,139 | $ | 9.64 | ||||
The total fair value of stock options vested (based on grant date fair value) during the years ended December 31, 2019, December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017 was $187 thousand, $236 thousand, and $246 thousand, respectively.
Compensation expense recognized in association with the stock option awards amounted to $190 thousand, $200 thousand and $204 thousand for the years ended 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The total tax benefit recognized related to the stock option expense was $54 thousand, $56 thousand, and $83 thousand for the years ended 2019, 2018, and 2017, respectively.
As of December 31, 2019, there was $320 thousand of unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to non-vested stock options. That cost is expected to be recognized over the remaining weighted average vesting period of 2.5 years.
Stock Awards
Restricted stock awards are granted at the market price of the Company's common stock on the date of the grant. Employee restricted stock awards generally vest over four years in equal portions beginning on or about the first anniversary date of the restricted stock award or are performance based restricted stock awards that vest upon the Company achieving certain predefined performance objectives. Non-employee director restricted stock awards generally vest over two years in equal portions beginning on or about the first anniversary date of the restricted stock award.
114
The table below provides a summary of restricted stock awards granted during the years indicated:
Restricted Stock Awards (number of underlying shares) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Two-year vesting | 8,368 | 7,280 | 6,944 | |||||||||
Four-year vesting | 22,403 | 16,666 | 16,253 | |||||||||
Performance-based vesting | 24,427 | 20,559 | 25,623 | |||||||||
Total restricted stock awards | 55,198 | 44,505 | 48,820 | |||||||||
Weighted average grant date fair value | $ | 29.84 | $ | 34.33 | $ | 30.46 | ||||||
If a grantee's employment or other service relationship, such as service as a director, is terminated for any reason, then any shares of restricted stock granted that have not vested as of the time of such termination generally must be forfeited, unless the Compensation Committee or the Board, as the case may be, waives such forfeiture requirement.
The restricted stock awards allow for the non-forfeitable receipt of dividends, and the voting of all shares, whether or not vested, throughout the vesting periods at the same proportional level as common shares outstanding.
Upon vesting, restricted stock awards may be net settled to cover payment for employee tax obligations, resulting in shares of common stock being reacquired by the Company. In 2019, 2018, and 2017 the Company paid $245 thousand, $520 thousand and $545 thousand, respectively, to net settle the vesting of restricted stock awards to cover employee tax obligations.
Any shares that are returned to the Company prior to vesting or as payment for employee tax obligations upon vesting shall remain available for issuance under such plan, while the plan is still effective.
The following table sets forth a summary of the activity for the Company's restricted stock awards:
(Dollars in thousands, except per share data) | Restricted Stock | Weighted Average Grant Price Per Share | |||||
Unvested December 31, 2018 | 91,708 | $ | 30.39 | ||||
Granted | 55,198 | 29.84 | |||||
Vested/released | 43,348 | 28.30 | |||||
Forfeited | 1,502 | 30.40 | |||||
Unvested December 31, 2019 | 102,056 | $ | 30.98 | ||||
Stock-based compensation expense recognized in association with the restricted stock awards amounted to $1.4 million for both the years ended December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, and $1.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2017. The total tax benefit recognized related to restricted stock award compensation expense was $401 thousand, $393 thousand, and $518 thousand for the years ended 2019, 2018, and 2017, respectively.
As of December 31, 2019, there remained $1.7 million of unrecognized compensation expense related to the restricted stock awards. That cost is expected to be recognized over the remaining weighted average vesting period of 2.2 years.
The total fair value of restricted stock awards vested (based on grant date fair value) during the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 was $1.2 million, $1.7 million and $1.4 million, respectively.
Stock in Lieu of Directors' Fees
In addition to restricted stock awards discussed above, the non-employee members of the Company's Board may opt to receive newly issued shares of the Company's common stock in lieu of cash compensation for attendance at Board and Board Committee meetings. These shares are issued annually each January for Board meetings held in the previous year. Directors must make an irrevocable election to receive shares of common stock in lieu of cash fees prior to
115
December 31st of the preceding year. Directors are granted shares of common stock in lieu of cash fees based on an average quarterly close price of the Company's common stock on the NASDAQ Global Market during the year. Prior to the 2018 election, Directors were granted shares of common stock in lieu of cash fees at a per share issuance price which reflected the market value of the Company's common stock on the first business day of the year.
The 2019 stock in lieu of directors' fees expense was $253 thousand, which represented 8,346 shares issued to Directors in January 2020, at a price of $30.35 per share, and was based on the Company's average quarterly close price in 2019. In 2018 the corresponding expense was $250 thousand, which represented 7,470 shares issued to Directors in January 2019, at a price of $33.50 per share, which reflected the fair value of the common stock on January 2, 2018. In the 2017, the corresponding expense was $281 thousand, which represented 7,326 shares issued to Directors in January 2018, at a price of $38.39 per share, which reflected the fair value of the common stock on January 3, 2017. The total tax benefit recognized related to the stock in lieu of directors' fees for meeting attendance was $71 thousand, $70 thousand and $115 thousand, for the years ended 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
See also Note 11, "Stockholders' Equity," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained above, under the caption "Shares authorized and share issuance," for further information regarding the Company's stock awards.
(14) | Income Taxes |
The components of income tax expense for the years ended December 31, were calculated using the asset and liability method as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Current tax expense: | ||||||||||||
Federal | $ | 7,728 | $ | 6,485 | $ | 8,222 | ||||||
State | 3,028 | 2,835 | 2,271 | |||||||||
Total current tax expense | 10,756 | 9,320 | 10,493 | |||||||||
Deferred tax (benefit) expense: | ||||||||||||
Federal | (339 | ) | (392 | ) | 5,646 | |||||||
State | (36 | ) | (112 | ) | 89 | |||||||
Total deferred tax (benefit) expense | (375 | ) | (504 | ) | 5,735 | |||||||
Total income tax expense | $ | 10,381 | $ | 8,816 | $ | 16,228 | ||||||
The provision for income taxes differs from the amount computed by applying the statutory U.S. federal income tax rate of 21% for 2019 and 2018, and 35% for 2017 to income before taxes as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Computed income tax expense at statutory rate | $ | 9,362 | $ | 7,916 | $ | 12,467 | ||||||
State income taxes, net of federal tax benefit | 2,364 | 2,151 | 1,534 | |||||||||
Tax-exempt income, net of disallowance | (894 | ) | (1,034 | ) | (1,665 | ) | ||||||
Bank-owned life insurance income, net | (134 | ) | (141 | ) | (245 | ) | ||||||
Impact of change in federal statutory rate on deferred tax assets | — | — | 4,761 | |||||||||
Tax benefit from stock compensation | (137 | ) | (302 | ) | (922 | ) | ||||||
Other | (180 | ) | 226 | 298 | ||||||||
Total income tax expense | $ | 10,381 | $ | 8,816 | $ | 16,228 | ||||||
Effective income tax rate | 23.3 | % | 23.4 | % | 45.6 | % | ||||||
116
The change in income tax expense and the effective income tax rate from the 2017 levels was primarily related to the 2017 Tax Act. The value of the Company's 2017 net deferred tax assets declined, due to the new lower federal tax rate at which they will be recovered, with the offset charged to Federal tax expense. This non-cash expense for the Company was approximately $4.8 million.
At December 31, the tax effects of each type of income and expense item that give rise to deferred taxes are as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Deferred tax asset: | ||||||||
Allowance for loan losses | $ | 9,383 | $ | 9,515 | ||||
Depreciation | 2,355 | 2,118 | ||||||
Net unrealized losses on equity securities | — | 43 | ||||||
Net unrealized losses on debt securities | — | 402 | ||||||
Supplemental employee retirement plans | 695 | 611 | ||||||
Non-accrual interest | 793 | 624 | ||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 573 | 555 | ||||||
Lease liability | 5,054 | — | ||||||
Other | 334 | 359 | ||||||
Total | 19,187 | 14,227 | ||||||
Deferred tax liability: | ||||||||
Goodwill | 1,579 | 1,590 | ||||||
Net unrealized gains on equity securities | 37 | — | ||||||
Net unrealized gains on debt securities | 2,988 | — | ||||||
Deferred origination costs | 725 | 721 | ||||||
Lease ROU asset | 5,054 | — | ||||||
Other | 72 | 169 | ||||||
Total | 10,455 | 2,480 | ||||||
Net deferred tax asset | $ | 8,732 | $ | 11,747 | ||||
Deferred income taxes are recognized based on the expected future tax consequences of differences between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities, calculated using currently enacted tax rates. Management records net deferred tax assets to the extent we believe these assets will more likely than not be realized. In making this determination, we consider all available positive and negative evidence, including recent financial operations and projected future taxable income. Management believes based upon positive historical and expected future earnings that it is more likely than not the Company will generate sufficient taxable income to realize the deferred tax asset existing at December 31, 2019. However, factors beyond management's control, such as the general state of the economy, can affect future levels of taxable income and there can be no assurances that sufficient taxable income will be generated to fully realize the deferred tax assets in the future.
The Company paid total income taxes in 2019, 2018, and 2017 of $10.6 million, $8.7 million, and $10.5 million, respectively.
The Company did not have any unrecognized tax benefits accrued as income tax liabilities or receivables or as deferred tax items at December 31, 2019 or December 31, 2018.
The Company invests in qualified affordable housing projects as a limited partner. In 2019, 2018 and 2017, the Company recognized $71 thousand of Federal Low Income Housing tax credits per year. The Company anticipates
117
that it will receive additional tax credits related to the Federal Low Income Housing Tax Credit program in the amount of $177 thousand which are expected to be realized over the next 3 years.
(15) | Earnings per Share |
The table below presents the increase in average shares outstanding, using the treasury stock method, for the diluted earnings per share calculation for the years indicated:
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
Basic weighted average common shares outstanding | 11,789,570 | 11,679,520 | 11,568,430 | ||||||
Dilutive shares | 40,248 | 70,942 | 83,333 | ||||||
Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding | 11,829,818 | 11,750,462 | 11,651,763 | ||||||
There were 52,219 ,29,260 and 14,678 stock options outstanding at December 31, 2019, December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, respectively, that were determined to be anti-dilutive and therefore excluded from the calculation of dilutive shares for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018, and 2017. These stock options, which were not dilutive at that date, may potentially dilute earnings per share in the future.
See Note 11, "Stockholders' Equity," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained above, under the caption "Shares authorized and share issuance," for information regarding the Company's participating securities and see Item (t), "Earnings per Share," contained in Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained above, for additional information regarding the earnings per share calculation.
(16) | Fair Value Measurements |
The FASB defines the fair value of an asset or liability to be the price which a seller would receive in an orderly transaction between market participants (an exit price) and also establishes a fair value hierarchy segregating fair value measurements using three levels of inputs: (Level 1) quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities; (Level 2) significant other observable inputs, including quoted prices for similar items in active markets, quoted prices for identical or similar items in markets that are not active, inputs such as interest rates and yield curves, volatilities, prepayment speeds, credit risks and default rates which provide a reasonable basis for fair value determination or inputs derived principally from observed market data; and (Level 3) significant unobservable inputs for situations in which there is little, if any, market activity for the asset or liability. Unobservable inputs must reflect reasonable assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability, which are developed based on the best information available under the circumstances.
118
The following tables summarize significant assets and liabilities carried at fair value and placement in the fair value hierarchy at the dates specified:
December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||
Fair Value Measurements using: | ||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Fair Value | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | ||||||||||||
Assets measured on a recurring basis: | ||||||||||||||||
Debt securities | $ | 504,788 | $ | — | $ | 504,788 | $ | — | ||||||||
Equity securities | 467 | 467 | — | — | ||||||||||||
FHLB stock | 4,484 | — | 4,484 | — | ||||||||||||
Interest-rate swaps | 625 | — | 625 | — | ||||||||||||
Assets measured on a non-recurring basis: | ||||||||||||||||
Impaired loans (collateral dependent) | 1,268 | — | — | 1,268 | ||||||||||||
Liabilities measured on a recurring basis: | ||||||||||||||||
Interest-rate swaps | $ | 625 | $ | — | $ | 625 | $ | — | ||||||||
December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||
Fair Value Measurements using: | ||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Fair Value | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | ||||||||||||
Assets measured on a recurring basis: | ||||||||||||||||
Debt securities | $ | 431,473 | $ | — | $ | 431,473 | $ | — | ||||||||
Equity securities | 1,448 | 1,448 | — | — | ||||||||||||
FHLB stock | 5,357 | — | 5,357 | — | ||||||||||||
Interest-rate swaps | 723 | — | 723 | — | ||||||||||||
Assets measured on a non-recurring basis: | ||||||||||||||||
Impaired loans (collateral dependent) | 2,574 | — | — | 2,574 | ||||||||||||
Liabilities measured on a recurring basis: | ||||||||||||||||
Interest-rate swaps | $ | 723 | $ | — | $ | 723 | $ | — | ||||||||
The Company did not transfer any assets between the fair value measurement levels during the years ended December 31, 2019 or December 31, 2018.
All of the Company's debt securities are considered "available-for-sale" and are carried at fair value. The debt security category above includes federal agency obligations, commercial and residential federal agency MBS, municipal securities, corporate bonds, and CDs, as held at those dates. The Company utilizes third-party pricing vendors to provide valuations on its debt securities. Fair values provided by the vendors were generally determined based upon pricing matrices utilizing observable market data inputs for similar or benchmark securities in active markets and/or based on a matrix pricing methodology which employs The Bond Market Association's standard calculations for cash flow and price/yield analysis, live benchmark bond pricing and terms/condition data available from major pricing sources. Therefore, management regards the inputs and methods used by third-party pricing vendors to be "Level 2 inputs and methods" as defined in the "fair value hierarchy." The Company periodically obtains a second price from an impartial third-party on debt securities to assess the reasonableness of prices provided by the primary independent pricing vendor.
119
The Company's equity portfolio fair value is measured based on quoted market prices for the shares; therefore, these securities are categorized as Level 1 within the fair value hierarchy.
The Bank is required to purchase FHLB stock at par value in association with advances from the FHLB. The stock is issued, redeemed, repurchased and transferred by the FHLB only at their fixed par value. This stock is classified as a restricted investment and carried at FHLB par value which management believes approximates fair value; therefore, these securities are categorized as Level 2 measures. See Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," Item (d), "Restricted Cash and Investments," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, contained above, for further information regarding the Company's fair value assessment of FHLB capital stock.
Impaired loan balances in the table above represent those collateral dependent commercial loans where management has estimated the probable credit loss by comparing the loan's carrying value against the expected realizable fair value of the collateral (appraised value, or internal analysis, less estimated cost to sell, adjusted as necessary for changes in relevant valuation factors subsequent to the measurement date). Certain inputs used in these assessments, and possible subsequent adjustments, are not always observable, and therefore, collateral dependent loans are categorized as Level 3 within the fair value hierarchy. A specific allowance is assigned to the collateral dependent loan for the amount of management's estimated probable credit loss. The specific allowances assigned to the collateral dependent impaired loans amounted to $564 thousand at December 31, 2019 compared to $1.6 million at December 31, 2018.
The fair values for the interest-rate swap assets and liabilities represent a FASB Level 2 measurement and are based on settlement values adjusted for credit risks and observable market interest-rate curves. The settlement values are based on discounted cash flow analysis, a widely accepted valuation technique, reflecting the contractual terms of the derivatives, including the period to maturity, and uses observable market-based inputs, including interest-rate curves. Credit risk adjustments consider factors such as the likelihood of default by the Company and its counterparties, its net exposures and remaining contractual life. The change in value of interest-rate swap assets and liabilities attributable to credit risk was not significant during the reported periods. Refer also to Note 9, "Derivatives and Hedging Activities," to the Company's consolidated financial statements of this Form 10-K, for additional information on the Company's interest-rate swaps.
Letters of credit are conditional commitments issued by the Company to guarantee the financial obligation or performance of a customer to a third party. The fair value of these commitments was estimated to be the fees charged to enter into similar agreements, and accordingly these fair value measures are deemed to be FASB Level 2 measurements. In accordance with the FASB, the estimated fair values of these commitments are carried on the Consolidated Balance Sheet as a liability and amortized to income over the life of the letters of credit, which are typically one year. The estimated fair value of these commitments carried on the Consolidated Balance Sheet at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 were deemed immaterial.
Interest-rate lock commitments related to the origination of mortgage loans that will be sold are considered derivative instruments. The commitments to sell loans are also considered derivative instruments. The Company generally does not pool mortgage loans for sale, but instead sells the loans on an individual basis. To reduce the net interest rate exposure arising from its loan sale activity, the Company enters into the commitment to sell these loans at essentially the same time that the interest-rate lock commitment is quoted on the origination of the loan. The Company estimates the fair value of these derivatives based on current secondary mortgage market prices. These commitments are accounted for in accordance with FASB guidance. The fair values of the Company's derivative instruments are deemed to be FASB Level 2 measurements. At December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the estimated fair value of the Company's interest-rate lock commitments and commitments to sell these mortgage loans were deemed immaterial.
120
The following table presents additional quantitative information about assets measured at fair value on a non-recurring basis for which the Company utilized Level 3 inputs (significant unobservable inputs for situations in which there is little, if any, market activity for the asset or liability) to determine fair value as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018:
Fair Value | ||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | Valuation Technique | Unobservable Input | Unobservable Input Value or Range | |||||||
Assets measured on a non-recurring basis: | ||||||||||||
Impaired loans (collateral dependent) | $1,268 | $ | 2,574 | Appraisal of Collateral | Appraisal adjustments(1) | 5% - 50% | ||||||
(1) | Appraisals may be adjusted by management for qualitative factors such as economic conditions and estimated liquidation expenses. |
Estimated Fair Values of Assets and Liabilities
In addition to disclosures regarding the measurement of assets and liabilities carried at fair value on the Consolidated Balance Sheet, the Company is also required to disclose fair value information about financial instruments for which it is practicable to estimate that value, whether or not recognized on the consolidated balance sheet.
The carrying values, estimated fair values and placement in the fair value hierarchy of the Company's financial instruments for which fair value is only disclosed but not recognized on the Consolidated Balance Sheet at the dates indicated are summarized as follows:
December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Fair value measurement | ||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Carrying Amount | Fair Value | Level 1 Inputs | Level 2 Inputs | Level 3 Inputs | |||||||||||||||
Financial assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Loans held for sale | $ | 601 | $ | 609 | $ | — | $ | 609 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Loans, net | 2,531,845 | 2,542,577 | — | — | 2,542,577 | |||||||||||||||
Financial liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
CDs (including brokered) | 310,951 | 311,975 | — | 311,975 | — | |||||||||||||||
Borrowed funds | 96,173 | 96,045 | — | 96,045 | — | |||||||||||||||
Subordinated debt | 14,872 | 14,957 | — | — | 14,957 | |||||||||||||||
December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Fair value measurement | ||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Carrying Amount | Fair Value | Level 1 Inputs | Level 2 Inputs | Level 3 Inputs | |||||||||||||||
Financial assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Loans held for sale | $ | 701 | $ | 710 | $ | — | $ | 710 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Loans, net | 2,353,657 | 2,331,076 | — | — | 2,331,076 | |||||||||||||||
Financial liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
CDs (including brokered) | 341,014 | 339,308 | — | 339,308 | — | |||||||||||||||
Borrowed funds | 100,492 | 100,312 | — | 100,312 | — | |||||||||||||||
Subordinated debt | 14,860 | 14,300 | — | — | 14,300 | |||||||||||||||
Excluded from the tables above are certain financial instruments with carrying values that approximated their fair value at the dates indicated, as they were short-term in nature or payable on demand. These include cash and cash
121
equivalents and non-term deposit accounts. The respective carrying values of these instruments would all be classified within Level 1 of their fair value hierarchy.
Also excluded from these tables are the fair values of commitments for unused portions of lines of credit and commitments to originate loans that were short-term, at current market rates and estimated to have no significant change in fair value.
(17)Supplemental Cash Flow Information
The supplemental cash flow information for the years indicated is as follows:
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Supplemental financial data: | ||||||||||||
Cash paid for: interest | $ | 21,384 | $ | 13,567 | $ | 7,295 | ||||||
Cash paid for: income taxes | 10,557 | 8,694 | 10,459 | |||||||||
Cash paid for: lease liability | 1,205 | — | — | |||||||||
Supplemental schedule of non-cash activity: | ||||||||||||
Net purchases of investment securities not yet settled | 810 | 5,794 | 9,154 | |||||||||
Transfer from loans to other real estate owned | 255 | — | — | |||||||||
ROU lease assets: operating leases(1) | 19,635 | — | — | |||||||||
_________________________________________
(1) | This represents the ROU lease asset that was recorded upon adoption of ASC 842 and new leases added in the current year. |
(18)Parent Company Only Financial Statements
Balance Sheets
December 31, | ||||||||
(Dollars in thousands, except per share data) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Assets | ||||||||
Cash | $ | 353 | $ | 123 | ||||
Investment in subsidiaries | 311,040 | 269,917 | ||||||
Other assets | 201 | 198 | ||||||
Total assets | $ | 311,594 | $ | 270,238 | ||||
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity | ||||||||
Liabilities | ||||||||
Subordinated debt | $ | 14,872 | $ | 14,860 | ||||
Accrued interest payable | 78 | 78 | ||||||
Other liabilities | 3 | 3 | ||||||
Total liabilities | 14,953 | 14,941 | ||||||
Stockholders' equity: | ||||||||
Preferred stock, $0.01 par value per share; 1,000,000 shares authorized; no shares issued | — | — | ||||||
Common stock $0.01 par value per share; 40,000,000 shares authorized; 11,825,331 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 and 11,708,218 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2018 | 118 | 117 | ||||||
Additional paid-in capital | 94,170 | 91,281 | ||||||
Retained earnings | 191,843 | 165,183 | ||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | 10,510 | (1,284 | ) | |||||
Total stockholders' equity | 296,641 | 255,297 | ||||||
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $ | 311,594 | $ | 270,238 | ||||
122
Parent Company Only Financial Statements
Statements of Income
For the years ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Equity in undistributed net income of subsidiaries | $ | 29,329 | $ | 25,635 | $ | 16,922 | ||||||
Dividends distributed by subsidiaries | 5,700 | 4,100 | 3,000 | |||||||||
Total income | 35,029 | 29,735 | 19,922 | |||||||||
Interest expense | 925 | 925 | 925 | |||||||||
Other operating expenses | 226 | 216 | 245 | |||||||||
Total operating expenses | 1,151 | 1,141 | 1,170 | |||||||||
Income before income taxes | 33,878 | 28,594 | 18,752 | |||||||||
Benefit from income taxes | (322 | ) | (287 | ) | (641 | ) | ||||||
Net income | $ | 34,200 | $ | 28,881 | $ | 19,393 | ||||||
Statements of Cash Flows
For the years ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 34,200 | $ | 28,881 | $ | 19,393 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Equity in undistributed net income of subsidiaries | (29,329 | ) | (25,635 | ) | (16,922 | ) | ||||||
Payment from subsidiary bank for stock compensation expense | 1,869 | 1,879 | 1,758 | |||||||||
Changes in: | ||||||||||||
(Increase) decrease in other assets | (3 | ) | 213 | 832 | ||||||||
Decrease in other liabilities | 12 | 13 | 14 | |||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 6,749 | 5,351 | 5,075 | |||||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||
Cash dividends paid, net of DRP | (6,371 | ) | (5,443 | ) | (4,747 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from issuance of common stock | 69 | 121 | 96 | |||||||||
Net settlement for employee tax withholdings on restricted stock and options | (402 | ) | (559 | ) | (931 | ) | ||||||
Net proceeds from exercise of stock options | 185 | 308 | 355 | |||||||||
Net cash used in financing activities | (6,519 | ) | (5,573 | ) | (5,227 | ) | ||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 230 | (222 | ) | (152 | ) | |||||||
Cash at beginning of year | 123 | 345 | 497 | |||||||||
Cash at end of year | $ | 353 | $ | 123 | $ | 345 | ||||||
The Parent Company's Statements of Comprehensive Income and Statements of Changes in Stockholders' Equity are identical to the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income and the Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders' Equity and therefore are not presented here.
123
(19) | Quarterly Results of Operations (Unaudited) |
2019 | ||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands, except share data) | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | ||||||||||||
Interest and dividend income | $ | 33,297 | $ | 34,301 | $ | 34,848 | $ | 34,662 | ||||||||
Interest expense | 5,213 | 5,523 | 5,427 | 5,088 | ||||||||||||
Net interest income | 28,084 | 28,778 | 29,421 | 29,574 | ||||||||||||
Provision for loan losses | (400 | ) | 955 | 1,025 | (400 | ) | ||||||||||
Net interest income after provision for loan losses | 28,484 | 27,823 | 28,396 | 29,974 | ||||||||||||
Non-interest income | 3,837 | 3,893 | 4,149 | 4,294 | ||||||||||||
Net gains (losses) on sales of available-for-sale debt securities | (1 | ) | 147 | — | — | |||||||||||
Non-interest expense | 20,850 | 21,753 | 21,098 | 22,714 | ||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 11,470 | 10,110 | 11,447 | 11,554 | ||||||||||||
Provision for income taxes | 2,774 | 2,347 | 2,445 | 2,815 | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 8,696 | $ | 7,763 | $ | 9,002 | $ | 8,739 | ||||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 0.74 | $ | 0.66 | $ | 0.76 | $ | 0.74 | ||||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 0.74 | $ | 0.66 | $ | 0.76 | $ | 0.74 | ||||||||
2018 | ||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands, except share data) | First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | ||||||||||||
Interest and dividend income | $ | 28,771 | $ | 30,320 | $ | 31,348 | $ | 32,464 | ||||||||
Interest expense | 2,756 | 3,102 | 3,936 | 4,274 | ||||||||||||
Net interest income | 26,015 | 27,218 | 27,412 | 28,190 | ||||||||||||
Provision for loan losses | 1,600 | 300 | 750 | (400 | ) | |||||||||||
Net interest income after provision for loan losses | 24,415 | 26,918 | 26,662 | 28,590 | ||||||||||||
Non-interest income | 3,790 | 3,733 | 3,758 | 3,659 | ||||||||||||
Net gains (losses) on sales of available-for-sale debt securities | 1 | — | (34 | ) | (2,917 | ) | ||||||||||
Non-interest expense | 19,447 | 20,808 | 19,975 | 20,648 | ||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 8,759 | 9,843 | 10,411 | 8,684 | ||||||||||||
Provision for income taxes | 1,934 | 2,269 | 2,429 | 2,184 | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 6,825 | $ | 7,574 | $ | 7,982 | $ | 6,500 | ||||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 0.59 | $ | 0.65 | $ | 0.68 | $ | 0.56 | ||||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 0.58 | $ | 0.64 | $ | 0.68 | $ | 0.55 | ||||||||
124
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Enterprise Bancorp, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Enterprise Bancorp, Inc. and its subsidiaries (the Company) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, changes in stockholders' equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes to the consolidated financial statements (collectively, the financial statements). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013, and our report dated March 10, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ RSM US LLP
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2015.
Boston, Massachusetts
March 10, 2020
125
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Enterprise Bancorp, Inc.
Opinion on the Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Enterprise Bancorp, Inc. and its subsidiaries’ (the Company) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013. In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, changes in stockholder’s equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes to the consolidated financial statements (collectively the financial statements) of the Company and our report dated March 10, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ RSM US LLP
Boston, Massachusetts
March 10, 2020
126
Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
None.
Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company maintains a set of disclosure controls and procedures and internal controls designed to ensure that the information required to be disclosed in reports that it files or furnishes to the SEC under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act"), is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC's rules and forms.
The Company carried out an evaluation as of the end of the period covered by this Form 10-K, under the supervision and with the participation of the Company's management, including its principal executive officer and principal financial officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of the Company's disclosure controls and procedures pursuant to Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(b). Based upon that evaluation, the Company's principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that the Company's disclosure controls and procedures are effective as of December 31, 2019.
Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The Company's management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. The Company's internal control system was designed to provide reasonable assurance to the Company's management and Board regarding the preparation and fair presentation of published financial statements. All internal control systems, however, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations and may not prevent or detect misstatement. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
The Company's management assessed the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019. In making this assessment, it used the 2013 criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in "Internal Control-Integrated Framework." Based on management's assessment, the Company believes that, as of December 31, 2019, the Company's internal control over financial reporting is effective based on these criteria.
The Company's independent registered public accounting firm has issued a report on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting, which appears on page 126 of this Form 10-K.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There has been no change in the Company's internal control over financial reporting that has occurred during the Company's most recent fiscal quarter (i.e., the three months ended December 31, 2019) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. | Other Information |
None.
Part III
Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14.
The information required in Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14 of this Part III of this Form 10-K is incorporated herein by reference to the Company's definitive proxy statement for its annual meeting of stockholders to be held on May 5, 2020, which it expects to file with the SEC within 95 days of the end of the fiscal year covered by this Form 10-K. For additional information on availability of the Company's corporate governance guidelines, see the section titled "Company Website," contained in Item 1, "Business," of this Form 10-K.
127
Part IV
Item 15. | Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules |
(a) | The following documents are filed as part of this annual report: |
(1) | Financial Statements |
See Index to Consolidated Financial Statements contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K above.
(2) | Financial Statement Schedules |
None (information included in consolidated financial statements)
(3) | Exhibits |
Exhibit No. and Description
3.1.1 |
3.1.2 |
3.1.3 |
3.2 |
4.1 |
4.2 |
4.3* |
4.4* |
10.1 |
10.2.1 |
10.2.2 |
128
10.3.1 |
10.3.2 |
10.4.1 |
10.4.2 |
10.4.3 |
10.5.1 |
10.5.2 |
10.5.3 |
10.6.1 |
10.6.2 |
10.7.1 |
10.8.1 |
10.8.2 |
10.9.1 |
129
10.09.2 |
10.10.1 |
10.10.2 |
10.10.3 |
10.11.1 |
10.11.2 |
10.11.3 |
10.12 |
10.13 |
10.14 |
10.15.1 |
10.15.2 |
21.0* |
23.0* |
31.1* |
31.2* |
32.0* |
130
101* | Interactive data files pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T: The following materials from Enterprise Bancorp, Inc.'s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019 were formatted in XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language): |
(i) Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018,
(ii) Consolidated Statements of Income for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017,
(iii) Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017,
(iv) Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017,
(v) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, and
(vi) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
* Filed herewith
(b) | Exhibits required by Item 601 of Regulation S-K |
The exhibits listed above either have been previously filed and are incorporated herein by reference to the applicable prior filing or are filed herewith.
(c) | Additional Financial Statement Schedules |
None.
Item 16. | Form 10-K Summary |
None.
ENTERPRISE BANCORP, INC.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
ENTERPRISE BANCORP, INC. | ||
March 10, 2020 | By: | /s/ Joseph R. Lussier |
Joseph R. Lussier | ||
Executive Vice President, | ||
Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
/s/ George L. Duncan | Chairman | March 10, 2020 | ||
George L. Duncan | ||||
/s/ Kenneth S. Ansin | Director | March 10, 2020 | ||
Kenneth S. Ansin | ||||
/s/ Gino J. Baroni | Director | March 10, 2020 | ||
Gino J. Baroni | ||||
131
/s/ John P. Clancy, Jr. | Director, Chief Executive Officer | March 10, 2020 | ||
John P. Clancy, Jr. | ||||
/s/ John R. Clementi | Director | March 10, 2020 | ||
John R. Clementi | ||||
/s/ James F. Conway, III | Lead Director, Vice Chairman | March 10, 2020 | ||
James F. Conway, III | ||||
/s/ Carole A. Cowan | Director | March 10, 2020 | ||
Carole A. Cowan | ||||
/s/ Normand E. Deschene | Director | March 10, 2020 | ||
Normand E. Deschene | ||||
/s/ John T. Grady, Jr. | Director | March 10, 2020 | ||
John T. Grady, Jr. | ||||
/s/ Mary Jane King | Director | March 10, 2020 | ||
Mary Jane King | ||||
/s/ John A. Koutsos | Director, Secretary | March 10, 2020 | ||
John A. Koutsos | ||||
/s/ Joseph C. Lerner | Director | March 10, 2020 | ||
Joseph C. Lerner | ||||
/s/ Shelagh E. Mahoney | Director | March 10, 2020 | ||
Shelagh E. Mahoney | ||||
/s/ Richard W. Main | Director, President | March 10, 2020 | ||
Richard W. Main | ||||
/s/ Jacqueline F. Moloney | Director | March 10, 2020 | ||
Jacqueline F. Moloney | ||||
/s/ Luis M. Pedroso | Director | March 10, 2020 | ||
Luis M. Pedroso | ||||
/s/ Michael T. Putziger | Director | March 10, 2020 | ||
Michael T. Putziger | ||||
/s/ Carol L. Reid | Director | March 10, 2020 | ||
Carol L. Reid | ||||
/s/ Joseph R. Lussier | Executive Vice President, Chief | March 10, 2020 | ||
Joseph R. Lussier | Financial Officer and Treasurer | |||
132
/s/ Michael K. Sullivan | Controller of the Bank | March 10, 2020 | ||
Michael K. Sullivan | ||||
133
