Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.2 - EX-32.2 - AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC | d787677dex322.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC | d787677dex321.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC | d787677dex312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC | d787677dex311.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EX-21.1 - AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC | d787677dex211.htm |
| EX-10.1 - EX-10.1 - AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC | d787677dex101.htm |
| EX-4.1 - EX-4.1 - AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC | d787677dex41.htm |
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| ☑ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019
OR
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15 (d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from ________ to ________
Commission File Number: 0-26486
Auburn National Bancorporation, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in charter)
| Delaware | 63-0885779 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
| 100 N. Gay Street, Auburn, Alabama | 36830 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (334) 821-9200
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12 (b) of the Act:
| Title of Each Class |
Trading Symbol |
Name of Exchange on which Registered | ||
| Common Stock, par value $0.01 | AUBN | Nasdaq Global Market |
Securities registered to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☑
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☑
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of
Regulation S-T
(§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (Section 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☑
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large Accelerated filer ☐ |
Accelerated filer ☑ |
Non-accelerated filer ☐ |
Smaller reporting company ☑ | Emerging Growth Company ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has selected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. Yes ☐ No ☑
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☑
State the aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was last sold, or the average bid and asked price of such common equity as of the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter: $76,043,895 as of June 30, 2019.
APPLICABLE ONLY TO CORPORATE REGISTRANTS
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the registrant’s classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date: 3,566,146 shares of common stock as of March 05, 2020.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders, scheduled to be held May 12, 2020, are incorporated by reference into Part II, Item 5 and Part III of this Form 10-K.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
SPECIAL CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Various of the statements made herein under the captions “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations”, “Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk”, “Risk Factors” and elsewhere, are “forward-looking statements” within the meaning and protections of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933 and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”).
Forward-looking statements include statements with respect to our beliefs, plans, objectives, goals, expectations, anticipations, assumptions, estimates, intentions and future performance, and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors, which may be beyond our control, and which may cause the actual results, performance, achievements or financial condition of the Company to be materially different from future results, performance, achievements or financial condition expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. You should not expect us to update any forward-looking statements.
All statements other than statements of historical fact are statements that could be forward-looking statements. You can identify these forward-looking statements through our use of words such as “may,” “will,” “anticipate,” “assume,” “should,” “indicate,” “would,” “believe,” “contemplate,” “expect,” “estimate,” “continue,” “plan,” “point to,” “project,” “could,” “intend,” “target” and other similar words and expressions of the future. These forward-looking statements may not be realized due to a variety of factors, including, without limitation:
| ● | the effects of future economic, business and market conditions and changes, foreign, domestic and locally, including seasonality, including as a result of natural disasters or climate change, such as rising sea and water levels, hurricanes and tornados, coronavirus or other epidemics or pandemics; |
| ● | the effects of war or other conflicts, acts of terrorism, or other events that may affect general economic conditions; |
| ● | governmental monetary and fiscal policies; |
| ● | legislative and regulatory changes, including changes in banking, securities and tax laws, regulations and rules and their application by our regulators, including capital and liquidity requirements, and changes in the scope and cost of FDIC insurance; |
| ● | the failure of assumptions and estimates, as well as differences in, and changes to, economic, market and credit conditions, including changes in borrowers’ credit risks and payment behaviors from those used in our loan portfolio reviews; |
| ● | the risks of changes in interest rates on the levels, composition and costs of deposits, loan demand, and the values and liquidity of loan collateral, securities, and interest-sensitive assets and liabilities, and the risks and uncertainty of the amounts realizable; |
| ● | changes in borrower credit risks and payment behaviors; |
| ● | changes in the availability and cost of credit and capital in the financial markets, and the types of instruments that may be included as capital for regulatory purposes; |
| ● | changes in the prices, values and sales volumes of residential and commercial real estate; |
| ● | the effects of competition from a wide variety of local, regional, national and other providers of financial, investment and insurance services, including the disruption effects of financial technology and other competitors who are not subject to the same regulations as the Company and the Bank; |
| ● | the failure of assumptions and estimates underlying the establishment of allowances for possible loan losses and other asset impairments, losses valuations of assets and liabilities and other estimates; |
| ● | The costs of redeveloping our headquarters and the timing and amount of rental income upon completion of the project; |
3
Table of Contents
| ● | the risks of mergers, acquisitions and divestitures, including, without limitation, the related time and costs of implementing such transactions, integrating operations as part of these transactions and possible failures to achieve expected gains, revenue growth and/or expense savings from such transactions; |
| ● | changes in technology or products that may be more difficult, costly, or less effective than anticipated; |
| ● | cyber-attacks and data breaches that may compromise our systems, our vendor systems or customers’ information; |
| ● | the risks that our deferred tax assets (“DTAs”), if any, could be reduced if estimates of future taxable income from our operations and tax planning strategies are less than currently estimated, and sales of our capital stock could trigger a reduction in the amount of net operating loss carry-forwards that we may be able to utilize for income tax purposes; and |
| ● | other factors and risks described under “Risk Factors” herein and in any of our subsequent reports that we make with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “Commission” or “SEC”) under the Exchange Act. |
All written or oral forward-looking statements that are made by us or are attributable to us are expressly qualified in their entirety by this cautionary notice. We have no obligation and do not undertake to update, revise or correct any of the forward-looking statements after the date of this report, or after the respective dates on which such statements otherwise are made.
Auburn National Bancorporation, Inc. (the “Company”) is a bank holding company registered with the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (the “Federal Reserve”) under the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, as amended (the “BHC Act”). The Company was incorporated in Delaware in 1990, and in 1994 it succeeded its Alabama predecessor as the bank holding company controlling AuburnBank, an Alabama state member bank with its principal office in Auburn, Alabama (the “Bank”). The Company and its predecessor have controlled the Bank since 1984. As a bank holding company, the Company may diversify into a broader range of financial services and other business activities than currently are permitted to the Bank under applicable laws and regulations. The holding company structure also provides greater financial and operating flexibility than is presently permitted to the Bank.
The Bank has operated continuously since 1907 and currently conducts its business primarily in East Alabama, including Lee County and surrounding areas. The Bank has been a member of the Federal Reserve System since April 1995. The Bank’s primary regulators are the Federal Reserve and the Alabama Superintendent of Banks (the “Alabama Superintendent”). The Bank has been a member of the Federal Home Loan Bank of Atlanta (the “FHLB”) since 1991.
General
The Company’s business is conducted primarily through the Bank and its subsidiaries. Although it has no immediate plans to conduct any other business, the Company may engage directly or indirectly in a number of activities that the Federal Reserve has determined to be so closely related to banking or managing or controlling banks as to be a proper incident thereto.
The Company’s principal executive offices are located at 100 N. Gay Street, Auburn, Alabama 36830, and its telephone number at such address is (334) 821-9200. The Company maintains an Internet website at www.auburnbank.com. The Company’s website and the information appearing on the website are not included or incorporated in, and are not part of, this report. The Company files annual, quarterly and current reports, proxy statements, and other information with the SEC. You may read and copy any document we file with the SEC at the SEC’s public reference room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, DC 20549. Please call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 for more information on the operation of the public reference rooms. The SEC maintains an Internet site at www.sec.gov that contains reports, proxy, and other information, where SEC filings are available to the public free of charge.
4
Table of Contents
Services
The Bank offers checking, savings, transaction deposit accounts and certificates of deposit, and is an active residential mortgage lender in its primary service area. The Bank’s primary service area includes the cities of Auburn and Opelika, Alabama and nearby surrounding areas in East Alabama, primarily in Lee County. The Bank also offers commercial, financial, agricultural, real estate construction and consumer loan products and other financial services. The Bank is one of the largest providers of automated teller services in East Alabama and operates ATM machines in 13 locations in its primary service area. The Bank offers Visa® Checkcards, which are debit cards with the Visa logo that work like checks but can be used anywhere Visa is accepted, including ATMs. The Bank’s Visa Checkcards can be used internationally through the Plus® network. The Bank offers online banking, bill payment and other electronic services through its Internet website, www.auburnbank.com. Our online banking services, bill payment and electronic services are subject to certain cybersecurity risks. See “Risk Factors – Our information systems may experience interruptions and security breaches.”
Competition
The banking business in East Alabama, including Lee County, is highly competitive with respect to loans, deposits, and other financial services. The area is dominated by a number of regional and national banks and bank holding companies that have substantially greater resources, and numerous offices and affiliates operating over wide geographic areas. The Bank competes for deposits, loans and other business with these banks, as well as with credit unions, mortgage companies, insurance companies, and other local and nonlocal financial institutions, including institutions offering services through the mail, by telephone and over the Internet. As more and different kinds of businesses enter the market for financial services, competition from nonbank financial institutions may be expected to intensify further.
Among the advantages that larger financial institutions have over the Bank are their ability to finance extensive advertising campaigns, to diversify their funding sources, and to allocate and diversify their assets among loans and securities of the highest yield in locations with the greatest demand. Many of the major commercial banks or their affiliates operating in the Bank’s service area offer services which are not presently offered directly by the Bank and they typically have substantially higher lending limits than the Bank.
Banks also have experienced significant competition for deposits from mutual funds, insurance companies and other investment companies and from money center banks’ offerings of high-yield investments and deposits. Certain of these competitors are not subject to the same regulatory restrictions as the Bank.
Selected Economic Data
Lee County’s population was estimated to be 163,941 in 2018, and has increased approximately 16.9% from 2010 to 2018. The largest employers in the area are Auburn University, East Alabama Medical Center, a Wal-Mart Distribution Center, Mando America Corporation, and Briggs & Stratton. Auto manufacturing and related suppliers are increasingly important along Interstate Highway 85 to the east and west of Auburn. Kia Motors has a large automobile factory in nearby West Point, Georgia, and Hyundai Motors has a large automobile factory in Montgomery, Alabama.
Between 2010 and 2018, the Auburn-Opelika MSA grew 16.9%, the second fastest growing MSA in Alabama. The U.S. Census Bureau estimates that the Auburn-Opelika MSA population will grow 5.41% from 2020 to 2025. During the same time, the U.S. Census Bureau estimates that household income will increase 13.70%, to $66,363, which is approximately the same as the Birmingham-Hoover MSA.
Loans and Loan Concentrations
The Bank makes loans for commercial, financial and agricultural purposes, as well as for real estate mortgages, real estate acquisition, construction and development and consumer purposes. While there are certain risks unique to each type of lending, management believes that there is more risk associated with commercial, real estate acquisition, construction and development, agricultural and consumer lending than with residential real estate mortgage loans. To help manage these risks, the Bank has established underwriting standards used in evaluating each extension of credit on an individual basis, which are substantially similar for each type of loan. These standards include a review of the economic conditions affecting the borrower, the borrower’s financial strength and capacity to repay the debt, the underlying collateral and the borrower’s past credit performance. We apply these standards at the time a loan is made and monitor them periodically throughout the life of the loan. See “Lending Practices” for a discussion of regulatory guidance on commercial real estate lending.
5
Table of Contents
The Bank has loans outstanding to borrowers in all industries within our primary service area. Any adverse economic or other conditions affecting these industries would also likely have an adverse effect on the local workforce, other local businesses, and individuals in the community that have entered into loans with the Bank. For example, the auto manufacturing business and its suppliers have positively affected our local economy, but automobile manufacturing is cyclical and adversely affected by increases in interest rates. Decreases in automobile sales, including adverse changes due to interest rate increases, could adversely affect nearby Kia and Hyundai automotive plants and their suppliers’ local spending and employment, and could adversely affect economic conditions in the markets we serve. However, management believes that due to the diversified mix of industries located within the Bank’s primary service area, adverse changes in one industry may not necessarily affect other area industries to the same degree or within the same time frame. The Bank’s primary service area also is subject to both local and national economic conditions and fluctuations. While most loans are made within our primary service area, some residential mortgage loans are originated outside the primary service area, and the Bank from time to time has purchased loan participations from outside its primary service area.
Employees
At December 31, 2019, the Company and its subsidiaries had 163.5 full-time equivalent employees, including 39 officers.
Statistical Information
Certain statistical information is included in response to Item 7 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Certain statistical information is also included in response to Item 6, Item 7A and Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
SUPERVISION AND REGULATION
The Company and the Bank are extensively regulated under federal and state laws applicable to banks and bank holding companies. The supervision, regulation and examination of the Company and the Bank and their respective subsidiaries by the bank regulatory agencies are primarily intended to maintain the safety and soundness of depository institutions and the federal deposit insurance system, as well as the protection of depositors, rather than holders of Company capital stock and other securities. Any change in applicable law or regulation may have a material effect on the Company’s business. The following discussion is qualified in its entirety by reference to the particular statutory and regulatory provisions referred to below.
Bank Holding Company Regulation
The Company, as a bank holding company, is subject to supervision, regulation and examination by the Federal Reserve under the BHC Act. Bank holding companies generally are limited to the business of banking, managing or controlling banks, and certain related activities. The Company is required to file periodic reports and other information with the Federal Reserve. The Federal Reserve examines the Company and its subsidiaries. The State of Alabama currently does not regulate bank holding companies.
The BHC Act requires prior Federal Reserve approval for, among other things, the acquisition by a bank holding company of direct or indirect ownership or control of more than 5% of the voting shares or substantially all the assets of any bank, or for a merger or consolidation of a bank holding company with another bank holding company. The BHC Act generally prohibits a bank holding company from acquiring direct or indirect ownership or control of voting shares of any company that is not a bank or bank holding company and from engaging directly or indirectly in any activity other than banking or managing or controlling banks or performing services for its authorized subsidiary. A bank holding company may, however, engage in or acquire an interest in a company that engages in activities that the Federal Reserve has determined by regulation or order to be so closely related to banking or managing or controlling banks as to be a proper incident thereto.
6
Table of Contents
Bank holding companies that are and remain “well-capitalized” and “well-managed,” as defined in Federal Reserve Regulation Y, and whose insured depository institution subsidiaries maintain “satisfactory” or better ratings under the Community Reinvestment Act of 1977 (the “CRA”), may elect to become “financial holding companies.” Financial holding companies and their subsidiaries are permitted to acquire or engage in activities such as insurance underwriting, securities underwriting, travel agency activities, broad insurance agency activities, merchant banking and other activities that the Federal Reserve determines to be financial in nature or complementary thereto. In addition, under the BHC Act’s merchant banking authority and Federal Reserve regulations, financial holding companies are authorized to invest in companies that engage in activities that are not financial in nature, as long as the financial holding company makes its investment, subject to limitations, including a limited investment term, no day-to-day management, and no cross-marketing with any depositary institutions controlled by the financial holding company. The Federal Reserve recommended repeal of the merchant banking powers in its September 16, 2016 study pursuant to Section 620 of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 (the “Dodd-Frank Act”). The Company has not elected to become a financial holding company, but it may elect to do so in the future.
Financial holding companies continue to be subject to Federal Reserve supervision, regulation and examination, but the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act of 1999 (the “GLB Act”) applies the concept of functional regulation to subsidiary activities. For example, insurance activities would be subject to supervision and regulation by state insurance authorities.
The BHC Act permits acquisitions of banks by bank holding companies, subject to various restrictions, including that the acquirer is “well capitalized” and “well managed”. Under the Alabama Banking Code, with the prior approval of the Alabama Superintendent, an Alabama bank may acquire and operate one or more banks in other states pursuant to a transaction in which the Alabama bank is the surviving bank. In addition, one or more Alabama banks may enter into a merger transaction with one or more out-of-state banks, and an out-of-state bank resulting from such transaction may continue to operate the acquired branches in Alabama. The Dodd-Frank Act permits banks, including Alabama banks, to branch anywhere in the United States.
The Company is a legal entity separate and distinct from the Bank. Various legal limitations restrict the Bank from lending or otherwise supplying funds to the Company. The Company and the Bank are subject to Sections 23A and 23B of the Federal Reserve Act and Federal Reserve Regulation W thereunder. Section 23A defines “covered transactions,” which include extensions of credit, and limits a bank’s covered transactions with any affiliate to 10% of such bank’s capital and surplus. All covered and exempt transactions between a bank and its affiliates must be on terms and conditions consistent with safe and sound banking practices, and banks and their subsidiaries are prohibited from purchasing low-quality assets from the bank’s affiliates. Finally, Section 23A requires that all of a bank’s extensions of credit to its affiliates be appropriately secured by permissible collateral, generally United States government or agency securities. Section 23B of the Federal Reserve Act generally requires covered and other transactions among affiliates to be on terms and under circumstances, including credit standards, that are substantially the same as or at least as favorable to the bank or its subsidiary as those prevailing at the time for similar transactions with unaffiliated companies.
Federal Reserve policy and the Federal Deposit Insurance Act, as amended by the Dodd-Frank Act, require a bank holding company to act as a source of financial and managerial strength to its FDIC-insured bank subsidiaries and to take measures to preserve and protect such bank subsidiaries in situations where additional investments in a bank subsidiary may not otherwise be warranted. In the event an FDIC-insured subsidiary becomes subject to a capital restoration plan with its regulators, the parent bank holding company is required to guarantee performance of such plan up to 5% of the bank’s assets, and such guarantee is given priority in bankruptcy of the bank holding company. In addition, where a bank holding company has more than one bank or thrift subsidiary, each of the bank holding company’s subsidiary depository institutions may be responsible for any losses to the FDIC’s Deposit Insurance Fund (“DIF”), if an affiliated depository institution fails. As a result, a bank holding company may be required to loan money to a bank subsidiary in the form of subordinate capital notes or other instruments which qualify as capital under bank regulatory rules. However, any loans from the holding company to such subsidiary banks likely will be unsecured and subordinated to such bank’s depositors and to other creditors of the bank. See “Capital.”
As a result of legislation in 2014 and 2018, the Federal Reserve has revised its Small Bank Holding Company Policy Statement (the “Small BHC Policy”) to expand it to include thrift holding companies and increase the size of “small” for qualifying bank and thrift holding companies from $500 million to up to $3 billion of pro forma consolidated assets.
The Federal Reserve confirmed in 2018 that the Company is eligible for treatment as a small banking holding company under the Small BHC Policy. As a result, unless and until the Company fails to qualify under the Small BHC Policy, the Company’s capital adequacy will continue to be evaluated on a bank only basis. See “Capital.”
7
Table of Contents
Bank Regulation
The Bank is a state bank that is a member of the Federal Reserve. It is subject to supervision, regulation and examination by the Federal Reserve and the Alabama Superintendent, which monitor all areas of the Bank’s operations, including loans, reserves, mortgages, issuances and redemption of capital securities, payment of dividends, establishment of branches, capital adequacy and compliance with laws. The Bank is a member of the FDIC and, as such, its deposits are insured by the FDIC to the maximum extent provided by law, and is subject to various FDIC regulations. See “FDIC Insurance Assessments.”
Alabama law permits statewide branching by banks. The powers granted to Alabama-chartered banks by state law include certain provisions designed to provide such banks competitive equality with national banks.
The Federal Reserve has adopted the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council’s (“FFIEC”) rating system, which assigns each financial institution a confidential composite “CAMELS” rating based on an evaluation and rating of six essential components of an institution’s financial condition and operations: Capital Adequacy, Asset Quality, Management, Earnings, Liquidity and Sensitivity to market risk, as well as the quality of risk management practices. For most institutions, the FFIEC has indicated that market risk primarily reflects exposures to changes in interest rates. When regulators evaluate this component, consideration is expected to be given to: management’s ability to identify, measure, monitor and control market risk; the institution’s size; the nature and complexity of its activities and its risk profile; and the adequacy of its capital and earnings in relation to its level of market risk exposure. Market risk is rated based upon, but not limited to, an assessment of the sensitivity of the financial institution’s earnings or the economic value of its capital to adverse changes in interest rates, foreign exchange rates, commodity prices or equity prices; management’s ability to identify, measure, monitor and control exposure to market risk; and the nature and complexity of interest rate risk exposure arising from non-trading positions. Composite ratings are based on evaluations of an institution’s managerial, operational, financial and compliance performance. The composite CAMELS rating is not an arithmetical formula or rigid weighting of numerical component ratings. Elements of subjectivity and examiner judgment, especially as these relate to qualitative assessments, are important elements in assigning ratings. The federal bank regulatory agencies are reviewing the CAMELS rating system and their consistency.
The GLB Act and related regulations require banks and their affiliated companies to adopt and disclose privacy policies, including policies regarding the sharing of personal information with third parties. The GLB Act also permits bank subsidiaries to engage in “financial activities” similar to those permitted to financial holding companies. In December 2015, Congress amended the GLB Act as part of the Fixing America’s Surface Transportation Act. This amendment provided financial institutions that meet certain conditions an exemption to the requirement to deliver an annual privacy notice. On August 10, 2018, the federal Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (“CFPB”) announced that it had finalized conforming amendments to its implementing regulation, Regulation P.
A variety of federal and state privacy laws govern the collection, safeguarding, sharing and use of customer information, and require that financial institutions have policies regarding information privacy and security. Some state laws also protect the privacy of information of state residents and require adequate security of such data, and certain state laws may, in some circumstances, require us to notify affected individuals of security breaches of computer databases that contain their personal information. These laws may also require us to notify law enforcement, regulators or consumer reporting agencies in the event of a data breach, as well as businesses and governmental agencies that own data.
Community Reinvestment Act and Consumer Laws
The Bank is subject to the provisions of the CRA and the Federal Reserve’s regulations thereunder. Under the CRA, all FDIC-insured institutions have a continuing and affirmative obligation, consistent with their safe and sound operation, to help meet the credit needs for their entire communities, including low- and moderate-income neighborhoods. The CRA requires a depository institution’s primary federal regulator to periodically assess the institution’s record of assessing and meeting the credit needs of the communities served by that institution, including low- and moderate-income neighborhoods. The bank regulatory agency’s CRA assessment is publicly available. Further, consideration of the CRA is required of any FDIC-insured institution that has applied to: (i) charter a national bank; (ii) obtain deposit insurance coverage for a newly-chartered institution; (iii) establish a new branch office that accepts deposits; (iv) relocate an office; or (v) merge or consolidate with, or acquire the assets or assume the liabilities of, an FDIC-insured financial institution. In the case of bank holding company applications to acquire a bank or other bank holding company, the Federal Reserve will assess the records of each subsidiary depository institution of the applicant bank holding company, and such records may be the basis for denying the application. A less than satisfactory CRA rating will slow, if not preclude, acquisitions, and new branches and other expansion activities and may prevent a company from becoming a financial holding company.
8
Table of Contents
CRA agreements with private parties must be disclosed and annual CRA reports must be made to a bank’s primary federal regulator. A financial holding company election, and such election and financial holding company activities are permitted to be continued, only if any affiliated bank has not received less than a “satisfactory” CRA rating. The federal CRA regulations require that evidence of discriminatory, illegal or abusive lending practices be considered in the CRA evaluation.
The OCC and the FDIC have new CRA rules proposed. The proposal seeks comments on ways to increase lending and services to people and in low- and moderate-income areas and clarify and expand the types of activities eligible for CRA consideration, in light of changes in the banking. The Federal Reserve has not joined this proposal and has its own views of the CA and how to join the OCC in the publication of modernizing CRA, tailoring the CRA regulations for banks of different sizes and improving the consistency and predictability of CRA evaluations and ratings.
The Bank is also subject to, among other things, the Equal Credit Opportunity Act (the “ECOA”) and the Fair Housing Act and other fair lending laws, which prohibit discrimination based on race or color, religion, national origin, sex and familial status in any aspect of a consumer or commercial credit or residential real estate transaction. The Department of Justice (the “DOJ”), and the federal bank regulatory agencies have issued an Interagency Policy Statement on Discrimination in Lending to provide guidance to financial institutions in determining whether discrimination exists, how the agencies will respond to lending discrimination, and what steps lenders might take to prevent discriminatory lending practices. The DOJ has prosecuted what it regards as violations of the ECOA, the Fair Housing Act, and the fair lending laws, generally.
The federal bank regulators have updated their guidance several times on overdrafts, including overdrafts incurred at automated teller machines and point of sale terminals. Overdrafts also have been a CFPB concern. Among other things, the federal regulators require banks to monitor accounts and to limit the use of overdrafts by customers as a form of short-term, high-cost credit, including, for example, giving customers who overdraw their accounts on more than six occasions where a fee is charged in a rolling 12 month period a reasonable opportunity to choose a less costly alternative and decide whether to continue with fee-based overdraft coverage. It also encourages placing appropriate daily limits on overdraft fees, and asks banks to consider eliminating overdraft fees for transactions that overdraw an account by a de minimis amount. Overdraft policies, processes, fees and disclosures are frequently the subject of litigation against banks in various jurisdictions. The federal bank regulators continue to consider responsible small dollar lending, including overdrafts and related fee issues. The CFPB proposed on February 6, 2019 to rescind its mandatory underwriting standards for loans covered by its 2017 Payday, Vehicle Title and Certain High-Cost Installment Loans rule, and has separately proposed delaying the effectiveness of such 2017 rule.
The CFPB has a broad mandate to regulate consumer financial products and services, whether or not offered by banks or their affiliates. The CFPB has the authority to adopt regulations and enforce various laws, including fair lending laws, the Truth in Lending Act, the Electronic Funds Transfer Act, mortgage lending rules, the Truth in Savings Act, the Fair Credit Reporting Act and Privacy of Consumer Financial Information rules. Although the CFPB does not examine or supervise banks with less than $10 billion in assets, banks of all sizes are affected by the CFPB’s regulations, and the precedents set in CFPB enforcement actions and interpretations.
Residential Mortgages
CFPB regulations require that lenders determine whether a consumer has the ability to repay a mortgage loan. These regulations establish certain minimum requirements for creditors when making ability to repay determinations, and provide certain safe harbors from liability for mortgages that are “qualified mortgages” and are not “higher-priced.” Generally, these CFPB regulations apply to all consumer, closed-end loans secured by a dwelling including home-purchase loans, refinancing and home equity loans—whether first or subordinate lien. Qualified mortgages must generally satisfy detailed requirements related to product features, underwriting standards, and requirements where the total points and fees on a mortgage loan cannot exceed specified amounts or percentages of the total loan amount. Qualified mortgages must have: (1) a term not exceeding 30 years; (2) regular periodic payments that do not result in negative amortization, deferral of principal repayment, or a balloon payment; (3) and be supported with documentation of the borrower and its credit. We focus our residential mortgage origination on qualified mortgages and those that meet our investors’ requirements, but we may make loans that do not meet the safe harbor requirements for “qualified mortgages.”
The Economic Growth, Regulatory Relief, and Consumer Protection Act of 2018 (the “2018 Growth Act”) provides that certain residential mortgages held in portfolio by banks with less than $10 billion in consolidated assets automatically are deemed “qualified mortgages.” This relieves smaller institutions from many of the requirements to satisfy the criteria listed above for “qualified mortgages.” Mortgages meeting the “qualified mortgage” safe harbor may not have negative amortization, must follow prepayment penalty limitations included in the Truth in Lending Act, and may not have fees greater than 3% of the total value of the loan.
9
Table of Contents
The Bank generally services the loans it originates, including those it sells. The CFPB’s mortgage servicing standards include requirements regarding force-placed insurance, certain notices prior to rate adjustments on adjustable rate mortgages, and periodic disclosures to borrowers. Servicers are prohibited from processing foreclosures when a loan modification is pending, and must wait until a loan is more than 120 days delinquent before initiating a foreclosure action. Servicers must provide borrowers with direct and ongoing access to its personnel, and provide prompt review of any loss mitigation application. Servicers must maintain accurate and accessible mortgage records for the life of a loan and until one year after the loan is paid off or transferred. These standards increase the cost and compliance risks of servicing mortgage loans, and the mandatory delays in foreclosures could result in loss of value on collateral or the proceeds we may realize from a sale of foreclosed property.
The Federal Housing Finance Authority (“FHFA”) updated, effective January 1, 2016, The Federal National Mortgage Association’s (“Fannie Mae’s”) and the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (“Freddie Mac’s”) (individually and collectively, “GSE”) repurchase rules, including the kinds of loan defects that could lead to a repurchase request to, or alternative remedies with, the mortgage loan originator or seller. These rules became effective January 1, 2016. FHFA also has updated these GSEs’ representations and warranties framework and provided an independent dispute resolution (“IDR”) process to allow a neutral third party to resolve demands after the GSEs’ quality control and appeal processes have been exhausted.
The Bank is subject to the CFPB’s integrated disclosure rules under the Truth in Lending Act and the Real Estate Settlement Procedures Act, referred to as “TRID”, for credit transactions secured by real property. The TRID rules adversely affected our mortgage originations in 2016, when we revised our systems and processes to comply with these rules. Our residential mortgage strategy, product offerings, and profitability may change as these regulations are interpreted and applied in practice, and may also change due to any restructuring of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac as part of the resolution of their conservatorships. The 2018 Growth Act reduced the scope of TRID rules by eliminating the wait time for a mortgage, if an additional creditor offers a consumer a second offer with a lower annual percentage rate. Congress encouraged federal regulators to provide better guidance on TRID in an effort to provide a clearer understanding for consumers and bankers alike. The law also provides partial exemptions from the collection, recording and reporting requirements under Sections 304(b)(5) and (6) of the Home Mortgage Disclosure Act (“HMDA”), for those banks with fewer than 500 closed-end mortgages or less than 500 open-end lines of credit in both of the preceding two years, provided the bank’s rating under the CRA for the previous two years has been at least “satisfactory.” On August 31, 2018, the CFPB issued an interpretive and procedural rule to implement and clarify these requirements under the 2018 Growth Act.
Anti-Money Laundering and Sanctions
The International Money Laundering Abatement and Anti-Terrorism Funding Act of 2001 specifies “know your customer” requirements that obligate financial institutions to take actions to verify the identity of the account holders in connection with opening an account at any U.S. financial institution. Bank regulators are required to consider compliance with anti-money laundering laws in acting upon merger and acquisition and other expansion proposals under the BHC Act and the Bank Merger Act, and sanctions for violations of this Act can be imposed in an amount equal to twice the sum involved in the violating transaction, up to $1 million.
Under the Uniting and Strengthening America by Providing Appropriate Tools Required to Intercept and Obstruct Terrorism Act of 2001 (the “USA PATRIOT Act”), financial institutions are subject to prohibitions against specified financial transactions and account relationships as well as to enhanced due diligence and “know your customer” standards in their dealings with foreign financial institutions and foreign customers.
The USA PATRIOT Act requires financial institutions to establish anti-money laundering programs, and sets forth minimum standards, or “pillars” for these programs, including:
| ● | the development of internal policies, procedures, and controls; |
| ● | the designation of a compliance officer; |
| ● | an ongoing employee training program; |
| ● | an independent audit function to test the programs; and |
| ● | ongoing customer due diligence and monitoring. |
10
Table of Contents
New federal Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (“FinCEN”) rules effective May 2018 require banks to know the beneficial owners of customers that are not natural persons, update customer information in order to develop a customer risk profile, and generally monitor such matters.
The United States has imposed various sanctions upon various foreign countries, such as Iran, North Korea, Russia and Venezuela, and their certain government officials and persons. Banks are required to comply with these sanctions, which require additional customer screening and transaction monitoring.
Other Laws and Regulations
The Company is also required to comply with various corporate governance and financial reporting requirements under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, as well as related rules and regulations adopted by the SEC, the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board and Nasdaq. In particular, the Company is required to report annually on internal controls as part of its annual report pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
The Company has evaluated its controls, including compliance with the SEC rules on internal controls, and expects to continue to spend significant amounts of time and money on compliance with these rules. If the Company fails to comply with these internal control rules in the future, it may materially adversely affect its reputation, its ability to obtain the necessary certifications to its financial statements, its relations with its regulators and other financial institutions with which it deals, and its ability to access the capital markets and offer and sell Company securities on terms and conditions acceptable to the Company. The Company’s assessment of its financial reporting controls as of December 31, 2019 are included in this report with no material weaknesses reported.
Payment of Dividends and Repurchases of Capital Instruments
The Company is a legal entity separate and distinct from the Bank. The Company’s primary source of cash is dividends from the Bank. Prior regulatory approval is required if the total of all dividends declared by a state member bank (such as the Bank) in any calendar year will exceed the sum of such bank’s net profits for the year and its retained net profits for the preceding two calendar years, less any required transfers to surplus. During 2019, the Bank paid cash dividends of approximately $8.6 million to the Company. At December 31, 2019, the Bank could have declared and paid additional dividends of approximately $8.0 million without prior regulatory approval.
In addition, the Company and the Bank are subject to various general regulatory policies and requirements relating to the payment of dividends, including requirements to maintain capital above regulatory minimums. The appropriate federal and state regulatory authorities are authorized to determine when the payment of dividends would be an unsafe or unsound practice, and may prohibit such dividends. The Federal Reserve has indicated that paying dividends that deplete a state member bank’s capital base to an inadequate level would be an unsafe and unsound banking practice. The Federal Reserve has indicated that depository institutions and their holding companies should generally pay dividends only out of current year’s operating earnings.
Federal Reserve Supervisory Letter SR-09-4 (February 24, 2009), as revised December 21, 2015, applies to dividend payments, stock redemptions and stock repurchases. Prior consultation with the Federal Reserve supervisory staff is required before:
| ● | redemptions or repurchases of capital instruments when the bank holding company is experiencing financial weakness; and |
| ● | redemptions and purchases of common or perpetual preferred stock which would reduce such Tier 1 capital at end of the period compared to the beginning of the period. |
11
Table of Contents
Bank holding company directors must consider different factors to ensure that its dividend level is prudent relative to maintaining a strong financial position, and is not based on overly optimistic earnings scenarios, such as potential events that could affect its ability to pay, while still maintaining a strong financial position. As a general matter, the Federal Reserve has indicated that the board of directors of a bank holding company should consult with the Federal Reserve and eliminate, defer or significantly reduce the bank holding company’s dividends if:
| ● | its net income available to shareholders for the past four quarters, net of dividends previously paid during that period, is not sufficient to fully fund the dividends; |
| ● | its prospective rate of earnings retention is not consistent with its capital needs and overall current and prospective financial condition; or |
| ● | It will not meet, or is in danger of not meeting, its minimum regulatory capital adequacy ratios. |
The Basel III Capital Rules further limit permissible dividends, stock repurchases and discretionary bonuses by the Company and the Bank, respectively, unless the Company and the Bank meet capital conservation buffer requirement effective January 1, 2019. See “Basel III Capital Rules.”
Regulatory Capital Changes
Simplification
The federal bank regulators issued final rules on July 22, 2029 simplifying their capital rules. The last of these changes become effective on April 1, 2020. The principal changes for standardized approaches institutions, such the Company and the Bank are:
| ● | Deductions from capital for certain items, such as temporary difference DTAs, MSAs and investments in unconsolidated were decreased to those amounts that individually exceed 25% of CET1; |
| ● | Institutions can elect to deduct investments in unconsolidated subsidiaries or subject them to capital requirements; and |
| ● | Minority interests would be includable up to 10% of (i) CET1 capital, (ii) Tier 1 capital and (iii) total capital. |
HVCRE
In December 2019, the federal banking regulators published a final rule, effective April 1, 2020, to implement the “high volatility commercial real estate,” or “HVCRE” changes in Section 214 of the 2018 Growth Act. The new rules define HVCRE loans as loans secured by land or improved real property that:
| ● | finance or refinance the acquisition, development, or construction of real property; |
| ● | the purpose of such loans must be to acquire, develop, or improve such real property into income producing property; and |
| ● | the repayment of the loan must depend on the future income or sales proceeds from, or refinancing of, such real property. |
Various exclusions from HVCRE are specified. Banking institutions and their holding companies are required to assign 150% risk weight to HVCRE loans.
12
Table of Contents
Community Capital Rule
On October 29, 2019, the federal banking regulators adopted, effective January 1, 2020, an optional community banking leverage ratio framework applicable to depository institutions and their holding companies intended to reduce regulatory burdens for qualifying community banking organizations that do not use advanced approaches capital measures, and that have:
| ● | less than $10 billion of assets; |
| ● | a leverage ratio greater than 9%; |
| ● | off-balance sheet exposures of 25% or less of total consolidated assets; and |
| ● | trading assets plus trading liabilities of less than 5% of total consolidated assets. |
The leverage ratio would be Tier 1 capital divided by average total consolidated assets, taking into account the capital simplification discussed above and the CECL related capital transitions.
The community bank leverage ratio will be the sole capital measure, and electing institutions will not have to calculate or use any other capital measure. It is estimated that 85% of depository institutions will be eligible to use this rule. The Company expect they would be eligible to make such election, if they determined it desirable. After preliminary consideration, the Company believes that it would still need to calculate the regulatory capital ratios, which investors would find helpful in comparing the Company to others.
Capital
The Federal Reserve has risk-based capital guidelines for bank holding companies and state member banks, respectively. These guidelines required at year end 2018 a minimum ratio of capital to risk-weighted assets (including certain off-balance sheet activities, such as standby letters of credit) and capital conservation buffer of 9.875%. Tier 1 capital includes common equity and related retained earnings and a limited amount of qualifying preferred stock, less goodwill and certain core deposit intangibles. Voting common equity must be the predominant form of capital. Tier 2 capital consists of non–qualifying preferred stock, qualifying subordinated, perpetual, and/or mandatory convertible debt, term subordinated debt and intermediate term preferred stock, up to 45% of pretax unrealized holding gains on available for sale equity securities with readily determinable market values that are prudently valued, and a limited amount of general loan loss allowance. Tier 1 and Tier 2 capital equals total capital.
In addition, the Federal Reserve has established minimum leverage ratio guidelines for bank holding companies not subject to the Small BHC Policy, and state member banks, which provide for a minimum leverage ratio of Tier 1 capital to adjusted average quarterly assets (“leverage ratio”) equal to 4%. However, bank regulators expect banks and bank holding companies to operate with a higher leverage ratio. The guidelines also provide that institutions experiencing internal growth or making acquisitions will be expected to maintain strong capital positions substantially above the minimum supervisory levels without significant reliance on intangible assets. Higher capital may be required in individual cases and depending upon a bank holding company’s risk profile. All bank holding companies and banks are expected to hold capital commensurate with the level and nature of their risks including the volume and severity of their problem loans. Lastly, the Federal Reserve’s guidelines indicate that the Federal Reserve will continue to consider a “tangible Tier 1 leverage ratio” (deducting all intangibles) in evaluating proposals for expansion or new activity. The level of Tier 1 capital to risk-adjusted assets is becoming more widely used by the bank regulators to measure capital adequacy. The Federal Reserve has not advised the Company or the Bank of any specific minimum leverage ratio or tangible Tier 1 leverage ratio applicable to them. Under Federal Reserve policies, bank holding companies are generally expected to operate with capital positions well above the minimum ratios. The Federal Reserve believes the risk-based ratios do not fully take into account the quality of capital and interest rate, liquidity, market and operational risks. Accordingly, supervisory assessments of capital adequacy may differ significantly from conclusions based solely on the level of an organization’s risk-based capital ratio.
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation Improvement Act of 1991 (“FDICIA”), among other things, requires the federal banking agencies to take “prompt corrective action” regarding depository institutions that do not meet minimum capital requirements. FDICIA establishes five capital tiers: “well capitalized,” “adequately capitalized,” “undercapitalized,” “significantly undercapitalized” and “critically undercapitalized.” A depository institution’s capital tier will depend upon how its capital levels compare to various relevant capital measures and certain other factors, as established by regulation. See “Prompt Corrective Action Rules.”
13
Table of Contents
Basel III Capital Rules
The Federal Reserve and the other bank regulators adopted in June 2013 final capital rules for bank holding companies and banks implementing the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision’s “Basel III: A Global Regulatory Framework for more Resilient Banks and Banking Systems.” These new U.S. capital rules are called the “Basel III Capital Rules,” and generally were fully phased-in on January 1, 2019.
The Basel III Capital Rules limit Tier 1 capital to common stock and noncumulative perpetual preferred stock, as well as certain qualifying trust preferred securities and cumulative perpetual preferred stock issued before May 19, 2010, each of which were grandfathered in Tier 1 capital for bank holding companies with less than $15 billion in assets. The Company had no qualifying trust preferred securities or cumulative preferred stock outstanding at December 31, 2019. The Basel III Capital Rules also introduced a new capital measure, “Common Equity Tier I Capital” or “CET1.” CET1 includes common stock and related surplus, retained earnings and, subject to certain adjustments, minority common equity interests in subsidiaries. CET1 is reduced by deductions for:
| ● | Goodwill and other intangibles, other than mortgage servicing assets (“MSRs”), which are treated separately, net of associated deferred tax liabilities (“DTLs”); |
| ● | Deferred tax assets (“DTAs”) arising from operating losses and tax credit carryforwards net of allowances and DTLs; |
| ● | Gains on sale from any securitization exposure; and |
| ● | Defined benefit pension fund net assets (i.e., excess plan assets), net of associated DTLs. |
The Company made a one-time election in 2015 and, as a result, CET1 will not be adjusted for certain accumulated other comprehensive income (“AOCI”).
Additional “threshold deductions” of the following that are individually greater than 10% of CET1 or collectively greater than 15% of CET1 (after the above deductions are also made):
| ● | MSAs, net of associated DTLs; |
| ● | DTAs arising from temporary differences that could not be realized through net operating loss carrybacks, net of any valuation allowances and DTLs; and |
| ● | Significant common stock investments in unconsolidated financial institutions, net of associated DTLs. |
As discussed below, recent regulations change these items to simplify and improve their capital treatment.
Noncumulative perpetual preferred stock and Tier 1 minority interest not included in CET1, subject to limits, will qualify as additional Tier I capital. All other qualifying preferred stock, subordinated debt and qualifying minority interests will be included in Tier 2 capital.
In addition to the minimum risk-based capital requirements, a new “capital conservation buffer” of CET1 capital of at least 2.5% of total risk weighted assets, will be required. The capital conservation buffer will be calculated as the lowest of:
| ● | the banking organization’s CET1 capital ratio minus 4.5%; |
| ● | the banking organization’s tier 1 risk-based capital ratio minus 6.0%; and |
| ● | the banking organization’s total risk-based capital ratio minus 8.0%. |
14
Table of Contents
Full compliance with the capital conservation buffer is required by January 1, 2019. At such time, permissible dividends, stock repurchases and discretionary bonuses will be limited to the following percentages based on the capital conservation buffer as calculated above, subject to any further regulatory limitations, including those based on risk assessments and enforcement actions:
|
Buffer % |
Buffer % Limit | |
| More than 2.50% |
None | |
|
> 1.875% - 2.50% |
60.0% | |
|
> 1.250% - 1.875% |
40.0% | |
|
> 0.625% - 1.250% |
20.0% | |
|
£ 0.625 |
- 0 - | |
The various capital elements and total capital under the Basel III Capital Rules, at January 1, 2018 were and as fully phased in on January 1, 2019 are:
| Fully Phased In | ||||
| January 1, 2018 | January 1, 2019 | |||
| Minimum CET1 |
4.50% | 4.50% | ||
| CET1 Conservation Buffer |
1.875% | 2.50% | ||
| Total CET1 |
6.375% | 7.0% | ||
| Deductions from CET1 |
100% | 100% | ||
| Minimum Tier 1 Capital |
6.0% | 6.0% | ||
| Minimum Tier 1 Capital plus conservation buffer |
7.875% | 8.5% | ||
| Minimum Total Capital |
8.0% | 8.0% | ||
|
Minimum Total Capital plus |
9.875% | 10.5% | ||
Changes in Risk-Weightings
The Basel III Capital Rules significantly change the risk weightings used to determine risk weighted capital adequacy. Among various other changes, the Basel III Capital Rules apply a 250% risk-weighting to MSRs, DTAs that cannot be realized through net operating loss carry-backs and significant (greater than 10%) investments in other financial institutions. A 150% risk-weighted category applies to “high volatility commercial real estate loans,” or “HVCRE,” which are credit facilities for the acquisition, construction or development of real property, excluding one-to-four family residential properties or commercial real estate projects where: (i) the loan-to-value ratio is not in excess of interagency real estate lending standards; and (ii) the borrower has contributed capital equal to not less than 15% of the real estate’s “as completed” value before the loan was made.
The Basel III Capital Rules also changed some of the risk weightings used to determine risk-weighted capital adequacy. Among other things, the Basel III Capital Rules:
| ● | Assigned a 250% risk weight to MSRs; |
| ● | Assigned up to a 1,250% risk weight to structured securities, including private label mortgage securities, trust preferred CDOs and asset backed securities; |
| ● | Retained existing risk weights for residential mortgages, but assign a 100% risk weight to most commercial real estate loans and a 150% risk-weight for HVCRE; |
| ● | Assigned a 150% risk weight to past due exposures (other than sovereign exposures and residential mortgages); |
| ● | Assigned a 250% risk weight to DTAs, to the extent not deducted from capital (subject to certain maximums); |
15
Table of Contents
| ● | Retained the existing 100% risk weight for corporate and retail loans; and |
| ● | Increased the risk weight for exposures to qualifying securities firms from 20% to 100%. |
HVCRE loans currently have a risk weight of 150%. Section 214 of the 2018 Growth Act, restricts the federal bank regulators from applying this risk weight except to certain ADC loans. The federal bank regulators issued a notice of a proposed rule on September 18, 2018 to implement Section 214 of the 2018 Growth Act, by revising the definition HVCRE. If this proposal is adopted, it is expected that this proposal could reduce the Company’s risk weighted assets and thereby may increase the Company’s risk-weighted capital.
CECL
The Financial Accounting Standards Board’s (the “FASB”) Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2016-13 “Financial Instruments – Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments” on June 16, 2016, which changed the loss model to take into account current expected credit losses (“CECL”). The Federal Reserve and the other federal banking agencies adopted rules effective on April 1, 2019 that allows banking organizations to phase in the regulatory capital effect of a reduction in retained earnings upon adoption of CECL over a three year period. CECL is effective for the Company beginning January 1, 2023, and its effects upon the Company have not yet been determined.
Prompt Corrective Action Rules
All of the federal bank regulatory agencies’ regulations establish risk-adjusted measures and relevant capital levels that implement the “prompt corrective action” standards. The relevant capital measures are the total risk-based capital ratio, Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio, Common Equity Tier 1 capital ratio, as well as, the leverage capital ratio. Under the regulations, a state member bank will be:
| ● | well capitalized if it has a total risk-based capital ratio of 10% or greater, a Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio of 8% or greater, a Common Equity Tier 1 capital ratio of 6.5% or greater, a leverage capital ratio of 5% or greater and is not subject to any written agreement, order, capital directive or prompt corrective action directive by a federal bank regulatory agency to maintain a specific capital level for any capital measure; |
| ● | “adequately capitalized” if it has a total risk-based capital ratio of 8% or greater, a Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio of 6% or greater, a Common Equity Tier 1 capital ratio of 4.5% or greater, and generally has a leverage capital ratio of 4% or greater; |
| ● | “undercapitalized” if it has a total risk-based capital ratio of less than 8%, a Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio of less than 6%, a Common Equity Tier 1 capital ratio of less than 4.5% or generally has a leverage capital ratio of less than 4%; |
| ● | “significantly undercapitalized” if it has a total risk-based capital ratio of less than 6%, a Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio of less than 4%, a Common Equity Tier 1 capital ratio of less than 3%, or a leverage capital ratio of less than 3%; or |
| ● | “critically undercapitalized” if its tangible equity is equal to or less than 2% to total assets. |
The federal bank regulatory agencies have authority to require additional capital, and have indicated that higher capital levels may be required in light of market conditions and risk.
Depository institutions that are “adequately capitalized” for bank regulatory purposes must receive a waiver from the FDIC prior to accepting or renewing brokered deposits, and cannot pay interest rates or brokered deposits that exceeds market rates by more than 75 basis points. Banks that are less than “adequately capitalized” cannot accept or renew brokered deposits. FDICIA generally prohibits a depository institution from making any capital distribution (including paying dividends) or paying any management fee to its holding company, if the depository institution thereafter would be “undercapitalized”. Institutions that are “undercapitalized” are subject to growth limitations and are required to submit a capital restoration plan for approval.
16
Table of Contents
A depository institution’s parent holding company must guarantee that the institution will comply with such capital restoration plan. The aggregate liability of the parent holding company is limited to the lesser of 5% of the depository institution’s total assets at the time it became undercapitalized and the amount necessary to bring the institution into compliance with applicable capital standards. If a depository institution fails to submit an acceptable plan, it is treated as if it is “significantly undercapitalized”. If the controlling holding company fails to fulfill its obligations under FDICIA and files (or has filed against it) a petition under the federal Bankruptcy Code, the claim against the holding company’s capital restoration obligation would be entitled to a priority in such bankruptcy proceeding over third party creditors of the bank holding company.
Significantly undercapitalized depository institutions may be subject to a number of requirements and restrictions, including orders to sell sufficient voting stock to become “adequately capitalized”, requirements to reduce total assets, and cessation of receipt of deposits from correspondent banks. “Critically undercapitalized” institutions are subject to the appointment of a receiver or conservator. Because the Company and the Bank exceed applicable capital requirements, Company and Bank management do not believe that the provisions of FDICIA have had or are expected to have any material effect on the Company and the Bank or their respective operations.
Section 201 of the 2018 Growth Act provides that banks and bank holding companies with consolidated assets of less than $10 billion that meet a “community bank leverage ratio,” established by the federal bank regulators between 8% and 10%, are deemed to satisfy applicable risk-based capital requirements necessary to be considered “well capitalized.” The federal banking agencies have the discretion to determine that an institution does not qualify for such treatment due to its risk profile. An institution’s risk profile may be assessed by its off-balance sheet exposure, trading of assets and liabilities, notional derivatives’ exposure, and other methods. On November 21, 2018, the federal banking agencies issued for public comment a proposal under which a community banking organization would be eligible to elect the community bank leverage ratio framework if it has less than $10 billion in total consolidated assets, limited amounts of certain assets and off-balance sheet exposures, and a community bank leverage ratio greater than 9%. A qualifying community banking organization that has chosen the proposed framework would not be required to calculate the existing risk-based and leverage capital requirements. This proposal further provides that an institution would be considered to be “well-capitalized” under the agencies’ prompt corrective action rules, provided it has a community bank leverage ratio greater than 9%.
FDICIA
FDICIA directs that each federal bank regulatory agency prescribe standards for depository institutions and depository institution holding companies relating to internal controls, information systems, internal audit systems, loan documentation, credit underwriting, interest rate exposure, asset growth composition, a maximum ratio of classified assets to capital, minimum earnings sufficient to absorb losses, a minimum ratio of market value to book value for publicly traded shares, safety and soundness, and such other standards as the federal bank regulatory agencies deem appropriate.
Enforcement Policies and Actions
The Federal Reserve and the Alabama Superintendent monitor compliance with laws and regulations. The CFPB monitors compliance with laws and regulations applicable to consumer financial products and services. Violations of laws and regulations, or other unsafe and unsound practices, may result in these agencies imposing fines, penalties and/or restitution, cease and desist orders, or taking other formal or informal enforcement actions. Under certain circumstances, these agencies may enforce these remedies directly against officers, directors, employees and others participating in the affairs of a bank or bank holding company, in the form of fines, penalties, or the recovery, or claw-back, of compensation. The federal prudential banking regulators have been bringing more enforcement actions recently.
Fiscal and Monetary Policy
Banking is a business that depends on interest rate differentials. In general, the difference between the interest paid by a bank on its deposits and its other borrowings, and the interest received by a bank on its loans and securities holdings, constitutes the major portion of a bank’s earnings. Thus, the earnings and growth of the Company and the Bank, as well as the values of, and earnings on, its assets and the costs of its deposits and other liabilities are subject to the influence of economic conditions generally, both domestic and foreign, and also to the monetary and fiscal policies of the United States and its agencies, particularly the Federal Reserve. The Federal Reserve regulates the supply of money through various means, including open market dealings in United States government securities, the setting of discount rate at which banks may borrow from the Federal Reserve, and the reserve requirements on deposits.
17
Table of Contents
The Federal Reserve has been paying interest on depository institutions’ required and excess reserve balances since October 2008. The payment of interest on excess reserve balances was expected to give the Federal Reserve greater scope to use its lending programs to address conditions in credit markets while also maintaining the federal funds rate close to the target rate established by the Federal Open Market Committee. The Federal Reserve has indicated that it may use this authority to implement a mandatory policy to reduce excess liquidity, in the event of inflation or the threat of inflation.
In April 2010, the Federal Reserve Board amended Regulation D (Reserve Requirements of Depository Institutions) authorizing the Reserve Banks to offer term deposits to certain institutions. Term deposits, which are deposits with specified maturity dates, will be offered through a Term Deposit Facility. Term deposits will be one of several tools that the Federal Reserve could employ to drain reserves when policymakers judge that it is appropriate to begin moving to a less accommodative stance of monetary policy.
In 2011, the Federal Reserve repealed its historical Regulation Q to permit banks to pay interest on demand deposits. The Federal Reserve also engaged in several rounds of quantitative easing (“QE”) to reduce interest rates by buying bonds, and “Operation Twist” to reduce long term interest rates by buying long term bonds, while selling intermediate term securities. Beginning December 2013, the Federal Reserve began to taper the level of bonds purchased, but continues to reinvest the principal of its securities as these mature.
The Federal Reserve adopted, in September 2014, a normalization of monetary policy that includes gradually raising the Federal Reserve’s target range for the Federal Funds rate to more normal levels and gradually reducing the Federal Reserve’s holdings of U.S. government and agency securities. The Federal Reserve’s target Federal Funds rate has increased nine times since December 2015 in 25 basis point increments from 0.25% to 2.50% on December 30, 2018. Although the Federal Reserve considers the target Federal Funds rate its primary means of monetary policy normalization, in September 2017 it began reducing its securities holdings by not reinvesting the principal of maturing securities, subject to certain monthly caps on amounts not reinvested. In 2019, due to various factors, the Federal Reserve stopped further increases in its target Federal Funds rate, and decreased the targeted federal funds three times by 25 basis points. The adverse economic effects of the coronavirus may cause the Federal Reserve to further loosen monetary policy.
The nature and timing of any changes in monetary policies and their effect on the Company and the Bank cannot be predicted. The turnover of a majority of the Federal Reserve Board and the members of its FOMC and the appointment of a new Federal Reserve Chairman may result in changes in policy and the timing and amount of monetary policy normalization.
FDIC Insurance Assessments
The Bank’s deposits are insured by the FDIC’s DIF, and the Bank is subject to FDIC assessments for its deposit insurance, as well as assessments by the FDIC to pay interest on Financing Corporation (“FICO”) bonds.
Since 2011, and as discussed above under “Recent Regulatory Developments”, the FDIC has been calculating assessments based on an institution’s average consolidated total assets less its average tangible equity (the “FDIC Assessment Base”) in accordance with changes mandated by the Dodd-Frank Act. The FDIC changed its assessment rates which shifted part of the burden of deposit insurance premiums toward depository institutions relying on funding sources other than deposits.
In 2016, the FDIC again changed its deposit insurance pricing and eliminated all risk categories and now uses “financial ratios method” based on CAMELS composite ratings to determine assessment rates for small established institutions with less than $10 billion in assets (“Small Banks”). The financial ratios method sets a maximum assessment for CAMELS 1 and 2 rated banks, and set minimum assessments for lower rated institutions. All basis points are annual amounts.
The following table shows the FDIC assessment schedule for 2018 applicable to Small Banks, such as the Bank.
|
Established Small Institution CAMELS Composite
| ||||||
| 1 or 2 | 3 | 4 or 5 | ||||
| Initial Base Assessment Rule
|
3 to 16 basis points
|
6 to 30 basis points
|
16 to 30 basis points
| |||
| Unsecured Debt Adjustment
|
-5 to 0 basis points
|
-5 to 0 basis points
|
-5 to 0 basis points
| |||
| Total Base Assessment Rate |
1.5 to 16 basis points | 3 to 30 basis points | 11 to 30 basis points | |||
18
Table of Contents
On March 15, 2016 the FDIC implemented Dodd-Frank Act provisions by raising the DIF’s minimum Reserve Ratio from 1.15% to 1.35%. The FDIC imposed a 4.5 basis point annual surcharge on insured depository institutions with total consolidated assets of $10 billion or more (“Large Banks”). The new rules grant credits to smaller banks for the portion of their regular assessments that contribute to increasing the reserve ratio from 1.15% to 1.35%.
The FDIC’s reserve ratio reached 1.36% on September 30, 2018, exceeding the minimum requirement. As a result, deposit insurance surcharges on Large Banks ceased, and smaller banks will receive credits against their deposit assessments from the FDIC for their portion of assessments that contributed to the growth in the reserve ratio from 1.15% to 1.35%. The Bank’s credit was $0.2 million, and credits will be received and applied against the Bank’s deposit insurance assessment each quarter that the reserve ratio exceeds 1.36%.
Prior to June 30, 2016, when the new assessment system became effective, the Bank’s overall rate for assessment calculations was 9 basis points or less, which was within the range of assessment rates for the lowest “risk category” under the former FDIC assessment rules. In 2019 and 2018, the Company recorded FDIC insurance premiums expenses of $0.1 million and $0.2 million, respectively.
In addition, all FDIC-insured institutions are required to pay a pro rata portion of the interest due on FICO bonds, which mature during 2017 through 2019. FICO assessments are set by the FDIC quarterly on each institution’s FDIC Assessment Base. The FICO Assessment rate was 0.560 basis points in the first quarter of 2017, and 0.540 basis points through December 31, 2017. FICO assessments have been set at 0.460 basis points in the first quarter of 2018, 0.440 basis points in the second quarter of 2018 and 0.320 basis points for the third and fourth quarters of 2018. FICO assessments of approximately $20 thousand and $2 thousand were paid to the FDIC in 2018 and 2019, respectively. The final FICO assessments were paid in the second quarter of 2019.
Lending Practices
The federal bank regulatory agencies released guidance in 2006 on “Concentrations in Commercial Real Estate Lending” (the “Guidance”). The Guidance defines CRE loans as exposures secured by raw land, land development and construction (including 1-4 family residential construction), multi-family property, and non-farm nonresidential property where the primary or a significant source of repayment is derived from rental income associated with the property (that is, loans for which 50% or more of the source of repayment comes from third party, non-affiliated, rental income) or the proceeds of the sale, refinancing, or permanent financing of this property. Loans to REITs and unsecured loans to developers that closely correlate to the inherent risks in CRE markets would also be considered CRE loans under the Guidance. Loans on owner occupied CRE are generally excluded. In December 2015, the Federal Reserve and other bank regulators issued an interagency statement to highlight prudent risk management practices from existing guidance that regulated financial institutions and made recommendations regarding maintaining capital levels commensurate with the level and nature of their CRE concentration risk.
The Guidance requires that appropriate processes be in place to identify, monitor and control risks associated with real estate lending concentrations. This could include enhanced strategic planning, CRE underwriting policies, risk management, internal controls, portfolio stress testing and risk exposure limits as well as appropriately designed compensation and incentive programs. Higher allowances for loan losses and capital levels may also be required. The Guidance is triggered when either:
| ● | Total reported loans for construction, land development, and other land of 100% or more of a bank’s total capital; or |
| ● | Total reported loans secured by multifamily and nonfarm nonresidential properties and loans for construction, land development, and other land are 300% or more of a bank’s total risk-based capital. |
This Guidance was supplemented by the Interagency Statement on Prudent Risk Management for Commercial Real Estate Lending (December 18, 2015). The Guidance also applies when a bank has a sharp increase in CRE loans or has significant concentrations of CRE secured by a particular property type.
19
Table of Contents
The Guidance did not apply to the Bank’s CRE lending activities during 2018 or 2019. At December 31, 2019, the Bank had outstanding $32.8 million in construction and land development loans and $270.3 million in total CRE loans (excluding owner occupied), which represent approximately 33.7% and 277.8%, respectively, of the Bank’s total risk-based capital at December 31, 2019. The Company has always had significant exposures to loans secured by commercial real estate due to the nature of its markets and the loan needs of both its retail and commercial customers. The Company believes its long term experience in CRE lending, underwriting policies, internal controls, and other policies currently in place, as well as its loan and credit monitoring and administration procedures, are generally appropriate to manage its concentrations as required under the Guidance.
In 2013, the Federal Reserve and other banking regulators issued their “Interagency Guidance on Leveraged Lending” highlighting standards for originating leveraged transactions and managing leveraged portfolios, as well as requiring banks to identify their highly leveraged transactions, or HLTs. The Government Accountability Office issued a statement on October 23, 2017 that this guidance constituted a “rule” for purposes of the Congressional Review Act, which provides Congress with the right to review the guidance and issue a joint resolution for signature by the President disapproving it. No such action was taken, and instead, the federal bank regulators issued a September 11, 2018 “Statement Reaffirming the Role of Supervisory Guidance.” This Statement indicated that guidance does not have the force or effect of law or provide the basis for enforcement actions, but this guidance can outline supervisory agencies’ views of supervisory expectations and priorities, and appropriate practices. The federal bank regulators continue to identify elevated risks in leveraged loans and shared national credits.
The Bank did not have any loans at year-end 2019 or 2018 that were leveraged loans subject to the Interagency Guidance on Leveraged Lending or that were shared national credits.
Other Dodd-Frank Act Provisions
In addition to the capital, liquidity and FDIC deposit insurance changes discussed above, some of the provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act we believe may affect us are set forth below.
Executive Compensation
The Dodd-Frank Act provides shareholders of all public companies with a say on executive compensation. Under the Dodd-Frank Act, each company must give its shareholders the opportunity to vote on the compensation of its executives, on a non-binding advisory basis, at least once every three years. The Dodd-Frank Act also adds disclosure and voting requirements for golden parachute compensation that is payable to named executive officers in connection with sale transactions.
The SEC is required under the Dodd-Frank Act to issue rules obligating companies to disclose in proxy materials for annual shareholders meetings, information that shows the relationship between executive compensation actually paid to their named executive officers and their financial performance, taking into account any change in the value of the shares of a company’s stock and dividends or distributions. The Dodd-Frank Act also provides that a company’s compensation committee may only select a consultant, legal counsel or other advisor on methods of compensation after taking into consideration factors to be identified by the SEC that affect the independence of a compensation consultant, legal counsel or other advisor.
Section 954 of the Dodd-Frank Act added section 10D to the Exchange Act. Section 10D directs the SEC to adopt rules prohibiting a national securities exchange or association from listing a company unless it develops, implements, and discloses a policy regarding the recovery or “claw-back” of executive compensation in certain circumstances. The policy must require that, in the event an accounting restatement due to material noncompliance with a financial reporting requirement under the federal securities laws, the company will recover from any current or former executive officer any incentive-based compensation (including stock options) received during the three year period preceding the date of the restatement, which is in excess of what would have been paid based on the restated financial statements. There is no requirement of wrongdoing by the executive, and the claw-back is mandatory and applies to all executive officers. Section 954 augments section 304 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which requires the CEO and CFO to return any bonus or other incentive or equity-based compensation received during the 12 months following the date of similarly inaccurate financial statements, as well as any profit received from the sale of employer securities during the period, if the restatement was due to misconduct. Unlike section 304, under which only the SEC may seek recoupment, the Dodd-Frank Act requires the Company to seek the return of compensation.
20
Table of Contents
The SEC adopted rules in September 2013 to implement pay ratios pursuant to Section 953 of the Dodd-Frank Act, which apply to fiscal year 2017 annual reports and proxy statements. The SEC proposed Rule 10D-1 under Section 954 on July 1, 2015 which would direct Nasdaq and the other national securities exchanges to adopt listing standards requiring companies to adopt policies requiring executive officers to pay back erroneously awarded incentive-based compensation. In February 2017, the acting SEC Chairman indicated interest in reconsidering the pay ratio rule.
The Dodd-Frank Act, Section 955, requires the SEC, by rule, to require that each company disclose in the proxy materials for its annual meetings whether an employee or board member is permitted to purchase financial instruments designed to hedge or offset decreases in the market value of equity securities granted as compensation or otherwise held by the employee or board member. The SEC proposed implementing rules in February 2015, though the rules have not been implemented to date.
Section 956 of the Dodd-Frank Act prohibits incentive-based compensation arrangements that encourage inappropriate risk taking by covered financial institutions, are deemed to be excessive, or that may lead to material losses. In June 2010, the federal bank regulators adopted Guidance on Sound Incentive Compensation Policies, which, although targeted to larger, more complex organizations than the Company, includes principles that have been applied to smaller organizations similar to the Company. This Guidance applies to incentive compensation to executives as well as employees, who, “individually or a part of a group, have the ability to expose the relevant banking organization to material amounts of risk.” Incentive compensation should:
| ● | Provide employees incentives that appropriately balance risk and reward; |
| ● | Be compatible with effective controls and risk-management; and |
| ● | Be supported by strong corporate governance, including active and effective oversight by the organization’s board of directors. |
The federal bank regulators, the SEC and other regulators proposed regulations implementing Section 956 in April 2011, which would have been applicable to, among others, depository institutions and their holding companies with $1 billion or more in assets. An advance notice of a revised proposed joint rulemaking under Section 956 was published by the financial services regulators in May 2016, but these rules have not been adopted.
Debit Card Interchange Fees
The “Durbin Amendment” to the Dodd-Frank Act provides for a set of new rules requiring that interchange transaction fees for electronic debit transactions be “reasonable” and proportional to certain costs associated with processing the transactions. The Federal Reserve has established standards for assessing whether interchange fees are reasonable and proportional, which a Federal District Court ruled were improperly adopted. This decision in NACS v. Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, was reversed by the District of Columbia Circuit Court of Appeals in 2014 and the Supreme Court declined to hear an appeal on January 20, 2015. The Durbin Amendment is not applicable to banks with assets less than $10 billion.
Other Legislative and Regulatory Changes
Various legislative and regulatory proposals, including substantial changes in banking, and the regulation of banks, thrifts and other financial institutions, compensation, and the regulation of financial markets and their participants and financial instruments, and the regulators of all of these, as well as the taxation of these entities, are being considered by the executive branch of the federal government, Congress and various state governments, including Alabama.
The President has frozen new rulemaking generally, and on February 3, 2017 issued an executive order containing “Core Principles for Regulating the United States Financial System” (“Core Principles”). The Core Principles direct the Secretary of the Treasury to consult with heads of Financial Stability Oversight Council’s members and report to the President within 120 days and periodically thereafter on how laws and government policies promote the Core Principles and to identify laws, regulations, guidance and reporting that inhibit financial services regulation in a manner consistent with the Core Principles. Another executive order required the repeal of two existing rules for any new significant regulatory proposal. Although this executive order does not apply to the SEC, the federal bank regulators or the CFPB, these independent agencies were encouraged to seek cost savings that would offset the costs of new significant regulatory actions. The federal regulators and the White House, pursuant to a Fall 2019 executive order, are considering further clarification as to the effect of guidance and whether it creates the basis for enforcement actions.
21
Table of Contents
The 2018 Growth Act, which, was enacted on May 24, 2018, amends the Dodd-Frank Act, the BHC Act, the Federal Deposit Insurance Act and other federal banking and securities laws to provide regulatory relief in these areas:
| ● | consumer credit and mortgage lending; |
| ● | capital requirements; |
| ● | Volcker Rule compliance; |
| ● | stress testing and enhanced prudential standards; |
| ● | increased the asset threshold under the Federal Reserve’s Small BHC Policy from $1 billion to $3 billion; and |
| ● | capital formation. |
On July 6, 2018, the Federal Reserve, OCC and FDIC issued an interagency statement describing their interim positions on regulations affected by the 2018 Growth Act that remain in effect until the agencies amend their regulations to conform to that Act.
We believe the 2018 Growth Act has positively affected our business. The following provisions of the 2018 Growth Act may be especially helpful to banks of our size as regulations adopted in 2019 became effective:
| ● | “qualifying community banks,” defined as institutions with total consolidated assets of less than $10 billion, which meet a “community bank leverage ratio” of 8.00% to 10.00%, may be deemed to have satisfied applicable risk based capital requirements as well as the capital ratio requirements; |
| ● | section 13(h) of the BHC Act, or the “Volcker Rule,” is amended to exempt from the Volcker Rule, banks with total consolidated assets valued at less than $10 billion (“community banking organizations”), and trading assets and liabilities comprising not more than 5.00% of total assets; |
| ● | “reciprocal deposits” will not be considered “brokered deposits” for FDIC purposes, provided such deposits do not exceed the lesser of $5 billion or 20% of the bank’s total liabilities; and |
The Volcker Rule change may enable us to invest in certain collateralized loan obligations that are treated as “covered funds” prohibited to banking entities by the Volcker Rule. Reciprocal deposits, such as CDARs, may expand our funding sources without being subjected to FDIC limitations and potential insurance assessments increases for brokered deposits. The FDIC announced on December 19, 2018 a final rules that change existing rules to comply with the 2018 Growth Act’s reciprocal deposits provisions effective March 26, 2019. Well-capitalized and well-rated banks are not required to treat reciprocal deposits as brokered deposits up to the lesser of 20% of total liabilities or $5 billion. Banks that are not both well-capitalized and well-rated may exclude reciprocal deposits under certain circumstances. The December 19, 2018 release also included a proposal seeking comments on the brokered deposits and related interest rates restrictions rules. Reciprocal deposits, such as CDARs, may expand our funding sources without being subjected to FDIC limitations and potential insurance assessments increases for brokered deposits.
On July 9, 2019, the federal banking agencies, together with the SEC and the Commodities Futures Trading Commission (“CFTC”), issued a final rule excluding qualifying community banking organizations from the Volcker Rule pursuant to the 2018 Growth Act. The Volcker Rule change may enable us to invest in certain collateralized loan obligations that are treated as “covered funds” and other investments prohibited to banking entities by the Volcker Rule.
The applicable agencies also issued final rules simplifying the Volcker Rule proprietary trading restrictions effective January 1, 2020. On January 30, 2020, these agencies released a proposal to simplify the Volcker Rule’s covered fund provisions.
The FDIC announced on December 19, 2018 a final rule allows reciprocal deposits to be excluded from “brokered deposits” up to the lesser of $5 billion or 20% of their total liabilities. Institutions that are not both well capitalized and well rated are permitted to exclude reciprocal deposits from brokered deposits in certain circumstances.
The FDIC issued a proposal on brokered deposits on December 12, 2019. This proposal substantially modifies the framework for brokered deposits by establishing a new framework for analyzing whether deposits placed through deposit placement arrangements qualify as brokered deposits.
22
Table of Contents
Certain of these new rules, and proposals, if adopted, these proposals could significantly change the regulation or operations of banks and the financial services industry. New regulations and statutes are regularly proposed that contain wide-ranging proposals for altering the structures, regulations and competitive relationships of the nation’s financial institutions.
Any of the following risks could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition and an investment in our stock. The risks discussed below also include forward-looking statements, and our actual results may differ substantially from those discussed in these forward-looking statements.
Market conditions and economic cyclicality may adversely affect our industry.
We are exposed to the U.S. economy and market conditions generally. Local employment and local economic conditions may be affected increasingly because of the growth of automobile manufacturing and related suppliers located in our markets and nearby. These businesses are adversely affected by higher interest rates and experience cyclicality of sales.
We believe the following, among other things, may affect us in 2019:
| ● | We expect to face continued high levels of regulation of our industry as a result of rulemaking and other initiatives by the U.S. government and its regulatory agencies. Compliance with such laws and regulations may increase our costs, reduce our profitability, and limit our ability to pursue business opportunities and serve customers’ needs. In addition to 2018 Growth Act, various pending bills in Congress and statements by our regulators have provided some, and may provide further regulatory relief for banking organizations of our size. We believe that comprehensive regulatory relief will be slow and contentious. We are uncertain about the scope, nature and timing of any regulatory relief, and its effect on us. |
| ● | The Federal Reserve adopted in September 2014 a normalization of monetary policy (the “Federal Reserve Normalization Policy”), which included gradually raising the Federal Reserve’s target range for the Federal Funds rate to more normal levels and gradually reducing the Federal Reserve’s holdings of U.S. government and agency securities. The Federal Reserve’s target Federal Funds rate increased nine times since December 2015 in 25 basis point increments from 0.25% to 2.50% on December 20, 2018. Although the Federal Reserve considers the target Federal Funds rate its primary means of monetary policy normalization, in September 2017, it also began reducing its securities holdings by not reinvesting the principal of maturing securities, subject to certain monthly caps on amounts not reinvested. Such reduction may also push interest rates higher and reduce liquidity in the financial system. Beginning August 1, 2019, the Federal Reserve reduced its target Federal Funds rate in 25 basis point in each of August, September and October 2019, and was 1.50% - 1.75% as of December 31, 2019. Moreover, at the conclusion of the Federal Reserve’s Federal Open Market Committee (“FOMC”) meeting in July 2019, the FOMC announced that it intended to cease the reduction in the Federal Reserve’s securities portfolio. The nature and timing of any future changes in monetary policies and their effect on us and the Bank cannot be predicted. If the coronavirus pandemic, or other events, has sufficient adverse effects on the United States economy, the FOMC may determine to further reduce interest rates to stimulate the economy. |
| ● | Market developments, including employment and price levels, stock market volatility and declines, and tax changes, such as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “2017 Tax Act”), may affect consumer confidence levels from time to time in different directions, and may cause adverse changes in payment behaviors and payment rates, causing increases in delinquencies and default rates, which could affect our charge-offs and provisions for credit losses. |
| ● | Our ability to assess the creditworthiness of our customers and those we do business with, and to estimate the values of our assets and collateral for loans may be impaired if the models and approaches we use become less predictive of future behaviors and valuations. The process we use to estimate losses inherent in our credit exposure or estimate the value of certain assets requires difficult, subjective, and complex judgments, including forecasts of economic conditions and how those economic predictions might affect the ability of our borrowers to repay their loans or the value of assets. |
23
Table of Contents
| ● | The 2017 Tax Act substantially limits the deductibility of all state and local taxes for U.S. taxpayers, including property taxes, lowers the cap on residential mortgage indebtedness for which U.S. taxpayers may deduct interest. These changes could have adverse effects on home sales, the volume of new mortgage and home equity loans and the values and salability of residences held as collateral for loans. |
| ● | Our ability to borrow from and engage in other business with other financial institutions on favorable terms or at all could be adversely affected by disruptions in the capital markets or other events, including, among other things, investor expectations and changes in regulations. |
| ● | Failures of other financial institutions in our markets and increasing consolidation of financial services companies as a result of market conditions could increase our deposits and assets and necessitate additional capital, and could have unexpected adverse effects upon us and our business. |
| ● | The “Volcker Rule,” including final regulations adopted in December 2013, may indirectly affect us adversely by reducing market liquidity and securities inventories at those institutions where we buy and sell securities for our portfolio and increasing the bid-ask spreads on securities we purchase or sell. These rules have decreased the range of permissible investments, such as certain collateralized loan obligation (“CLO”) interests, which we could otherwise use to diversify our assets and for asset/liability management. The 2018 Growth Act removed Volcker Rule restrictions generally on banks under $10 billion in assets. In July 2019, the federal banking agencies issued a final rule to exclude community banking organizations, such as the Company and the Bank, from the Volcker Rule. |
The soundness of other financial institutions could adversely affect us.
We have exposure to many different industries and counterparties, and routinely execute transactions with counterparties in the financial services industry, including brokers and dealers, central clearinghouses, commercial banks, and investment funds, our correspondent banks and other financial institutions. Our ability to engage in routine investment and banking transactions, as well as the quality and values of our investments in equity securities and obligations of other financial institutions, could be adversely affected by the actions, financial condition, and profitability of such other financial institutions with which we deal, including, without limitation, the FHLB and our correspondent banks. At December 31, 2019, the amortized cost of the Bank’s investments in FHLB and our correspondent bank’s common stock was approximately $1.1 million. Financial services institutions are interrelated as a result of shared credits, trading, clearing, counterparty and other relationships. As a result, defaults by, or even rumors or questions about, one or more financial institutions, or the financial services industry generally, have led to market-wide liquidity problems, losses of depositor, creditor or counterparty confidence in certain institutions and could lead to losses or defaults by other institutions, and in some cases, failure of such institutions. Any losses, defaults by, or failures of, the institutions we do business with could adversely affect our holdings of the debt of and equity in, such other institutions, our participation interests in loans originated by other institutions, and our business, including our liquidity, financial condition and earnings.
Nonperforming and similar assets take significant time to resolve and may adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
At December 31, 2019, our nonaccrual loans totaled $0.2 million, or 0.04% of total loans. We had no properties held as other real estate owned (“OREO”) at December 31, 2019. Our non-performing assets may adversely affect our net income in various ways. We do not record interest income on nonaccrual loans or OREO and these assets require higher loan administration and other costs, thereby adversely affecting our income. Decreases in the value of these assets, or the underlying collateral, or in the related borrowers’ performance or financial condition, whether or not due to economic and market conditions beyond our control, could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition. In addition, the resolution of nonperforming assets requires commitments of time from management, which can xxx be detrimental to the performance of their other responsibilities. There can be no assurance that we will not experience increases in nonperforming loans in the future.
24
Table of Contents
Our allowance for loan losses may prove inadequate or we may be negatively affected by credit risk exposures.
We periodically review our allowance for loan losses for adequacy considering economic conditions and trends, collateral values and credit quality indicators, including past charge-off experience and levels of past due loans and nonperforming assets. We cannot be certain that our allowance for loan losses will be adequate over time to cover credit losses in our portfolio because of unanticipated adverse changes in the economy, market conditions or events adversely affecting specific customers, industries or markets, and changes in borrower behaviors. If the credit quality of our customer base materially decreases, if the risk profile of the market, industry or group of customers changes materially or weaknesses in the real estate markets worsen, borrower payment behaviors change, or if our allowance for loan losses is not adequate, our business, financial condition, including our liquidity and capital, and results of operations could be materially adversely affected. CECL is effective for the Company beginning January 1, 2023, and its effects upon the Company have not yet been determined.
Changes in the real estate markets, including the secondary market for residential mortgage loans, may continue to adversely affect us.
Notwithstanding changes made by the 2018 Growth Act, the effects of the CFPB changes to mortgage and servicing rules effective at the beginning of 2014, the CFPB’s TRID rules for closed end credit transactions secured by real property that became effective in October 2015, enforcement actions, reviews and settlements, changes in the securitization rules under the Dodd-Frank Act, including the risk retention rules that became effective on December 24, 2016, and the Basel III Rules could have serious adverse effects on the mortgage markets and our mortgage operations.
The TRID rules have affected our current and proposed mortgage business and have increased our costs as a result of our compliance efforts. In addition, the CFPB’s regulations that lenders determine whether a consumer has the ability to repay a mortgage loan have limited the secondary market for and liquidity of many mortgage loans that are not “qualified mortgages.”
Increasing interest rates and the 2017 Tax Act’s limitations on the deductibility of residential mortgage interest and state and local property and other taxes could adversely affect consumer behaviors and the volumes of housing sales, mortgage and home equity loan originations, as well as the value and liquidity of residential property held as collateral by lenders such as the Bank, and the secondary markets for residential loans. Acquisition, construction and development loans for residential development may be similarly adversely affected.
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, have been in conservatorship since September 2008, although the U.S. Treasury released a plan in September 2019 for housing finance reform that includes recommendations related to ending Fannie Mae’s and Freddie Mac’s conservatorship, and the FHFA established 2020 performance objectives that include preparing for Fannie Mae’s and Freddie Mac’s eventual exit from conservatorship. The timing and effects of their resolution cannot be predicted. Minimal capital, the levels of risky assets at the FHA, and its relatively low capital and reserves for losses, the current levels of home sales, and the risks of interest rates increasing materially from historically low levels, as well as the 2017 Tax Act, could also have serious adverse effects on the mortgage markets and our mortgage operations. Such adverse effects could include, among other things, price reductions in single family home values, further adversely affecting the liquidity and value of collateral securing commercial loans for residential acquisition, construction and development, as well as residential mortgage loans that we hold, mortgage loan originations and gains on sale of mortgage loans. In the event our allowance for loan losses is insufficient to cover such losses, if any, our earning, capital and liquidity could be adversely affected.
Significant ongoing disruptions in the secondary market for residential mortgage loans have limited the market for and liquidity of most mortgage loans other than conforming Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, and FHA loans. Declines in real estate values, low home sales volumes, financial stress on borrowers as a result of job losses or reduced incomes, interest rate changes, generally, including resets on adjustable rate mortgage loans, maturities of second lien mortgages or other factors have adversely affected borrowers during recent years. Changes in interest rate and mortgage loan rules, could result in fewer mortgage originations, higher delinquencies and greater charge-offs in future periods, as well as increased regulation capital requirement which would adversely affect our financial condition, including capital and liquidity, and our results of operations. In the event our allowance for loan losses is insufficient to cover such losses, if any, our earnings, capital and liquidity could be adversely affected.
25
Table of Contents
On February 5, 2020, the Federal Housing Finance Authority (“FHFA”), which regulates Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, announced the transition from mortgages based on the London Interbank Offering Rate, or LIBOR, as follows:
| ● | New language will be required for single-family Uniform Adjustable Rate Mortgage (“ARM”) instruments closed on or after June 1, 2020; |
| ● | All LIBOR-based single-family and multifamily ARMs must have loan application dates on or before September 30, 2020 to be eligible for acquisition; and |
| ● | Acquisitions of single-family and multifamily LIBOR ARMs will cease on or before December 31, 2020. |
The effects of these changes could adversely affect Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac and the cost and availability of credit in the markets for these types of mortgages.
Weaknesses in real estate markets may adversely affect the length of time and costs required to manage and dispose of, and the values realized from the sale of our OREO.
We may be contractually obligated to repurchase mortgage loans we sold to third parties on terms unfavorable to us.
As a routine part of its business, the Company originates mortgage loans that it subsequently sells in the secondary market, including to governmental agencies and GSEs, such as Fannie Mae. In connection with the sale of these loans, the Company makes customary representations and warranties, the breach of which may result in the Company being required to repurchase the loan or loans. Furthermore, the amount paid may be greater than the fair value of the loan or loans at the time of the repurchase. Although mortgage loan repurchase requests made to us have been limited, if these increased notwithstanding new repurchase procedures adopted in late 2015 and early 2016 by the FHFA, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, we may have to establish reserves for possible repurchases and adversely affect our results of operation and financial condition.
Mortgage servicing rights requirements may change and require us to incur additional costs and risks.
The CFPB’s residential mortgage servicing standards include servicing requirements, require servicer activities and delay foreclosures, among other things. These may adversely affect our costs to service residential mortgage loans, and together with the Basel III Rules, may decrease the returns on our MSRs. The CFPB and the bank regulators continue to bring enforcement actions and develop proposals, rules and practices that could increase the costs of providing mortgage servicing. This could reduce our income from servicing these types of loans and make it more difficult and costly to timely realize the value of collateral securing such loans upon a borrower default.
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac restructuring may adversely affect the mortgage markets and our sales of mortgages we originated.
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac remain in conservatorship, and although legislation has been introduced at various times to restructure Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to take them out of conservatorship and substantially change the way they conduct business in the future, no proposal has been enacted. Through 2017, all of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac’s earnings above a specified capital reserve have been swept into the U.S. Treasury and have not been available to build Fannie Mae’s or Freddie Mac’s capital. At the end of 2017, the capital reserve was increased to $3 billion for each of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
In February 2018, Fannie Mae reported that the 2017 Tax Act had reduced its DTAs, and that it had a net worth deficit of $3.7 billion as of December 31, 2017. To eliminate its net worth deficit, the Treasury Department provided Fannie Mae with $3.7 billion of capital in the first quarter of 2018. Fannie Mae reported that it had a net worth of $14.6 billion as of December 31, 2019. Freddie Mac had a net worth deficit of $312 million at December 31, 2017, and the Treasury Department provided Freddie Mac with $312 million of capital in the first quarter of 2018. Freddie Mac reported that it had a net worth of $9.1 billion as of December 31, 2019. The U.S. Treasury’s housing finance reform plan that includes recommendations related to ending Fannie Mae’s and Freddie Mac’s conservatorship, including permitting Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to retain up to $25 billion and $20 billion in profits, and the FHFA established 2020 performance objectives that include preparing for their eventual exit from conservatorship.
26
Table of Contents
Since Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac dominate the residential mortgage markets, any changes in their structure and operations, as well as their respective restructurings and capital, could adversely affect the primary and secondary mortgage markets, and our residential mortgage businesses, our results of operations and the returns on capital deployed in these businesses.
Our concentration of commercial real estate loans could result in further increased loan losses, and adversely affect our business, earnings, and financial condition.
Commercial real estate, or CRE, is cyclical and poses risks of possible loss due to concentration levels and risks of the assets being financed, which include loans for the acquisition and development of land and residential construction. The federal bank regulatory agencies released guidance in 2006 on “Concentrations in Commercial Real Estate Lending.” The guidance defines CRE loans as exposures secured by raw land, land development and construction (including 1-4 family residential construction), multi-family property, and non-farm non-residential property, where the primary or a significant source of repayment is derived from rental income associated with the property (that is, loans for which 50% or more of the source of repayment comes from third party, non-affiliated, rental income) or the proceeds of the sale, refinancing, or permanent financing of the property. Loans to REITs and unsecured loans to developers that closely correlate to the inherent risks in CRE markets would also be considered CRE loans under the guidance. Loans on owner occupied commercial real estate are generally excluded from CRE for purposes of this guidance. Excluding owner occupied commercial real estate, we had 52.3% of our portfolio in CRE loans at year-end 2019 compared to 50.9% at year-end 2018. The banking regulators continue to give CRE lending scrutiny and require banks with higher levels of CRE loans to implement improved underwriting, internal controls, risk management policies and portfolio stress testing, as well as higher levels of allowances for possible losses and capital levels as a result of CRE lending growth and exposures. Lower demand for CRE, and reduced availability of, and higher interest rates and costs for, CRE lending could adversely affect our CRE loans and sales of our OREO, and therefore our earnings and financial condition, including our capital and liquidity.
Our ability to realize our deferred tax assets may be reduced in the future if our estimates of future taxable income from our operations and tax planning strategies do not support this amount, and the amount of net operating loss carry-forwards realizable for income tax purposes may be reduced under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code by sales of our capital securities.
We are allowed to carry-back losses for two years for Federal income tax purposes. As of December 31, 2019, we had a net deferred tax liability of $0.9 million with gross deferred tax assets of $1.7 million. These and future deferred tax assets may be further reduced in the future if our estimates of future taxable income from our operations and tax planning strategies do not support the amount of the deferred tax asset. The amount of net operating loss carry-forwards realizable for income tax purposes potentially could be further reduced under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code by a significant offering and/or other sales of our capital securities. The Basel III Rules reduce the regulatory capital benefits of deferred tax assets, also.
Our future success is dependent on our ability to compete effectively in highly competitive markets.
The East Alabama banking markets in which we do business are highly competitive and our future growth and success will depend on our ability to compete effectively in these markets. We compete for loans, deposits and other financial services in our markets with other local, regional and national commercial banks, thrifts, credit unions, mortgage lenders, and securities and insurance brokerage firms. Marketplace lenders operating nationwide over the internet are growing rapidly. Many of our competitors offer products and services different from us, and have substantially greater resources, name recognition and market presence than we do, which benefits them in attracting business. In addition, larger competitors may be able to price loans and deposits more aggressively than we are able to and have broader and more diverse customer and geographic bases to draw upon. The Dodd-Frank Act allows others to branch into our markets more easily from other states. Failures of other banks with offices in our markets could also lead to the entrance of new, stronger competitors in our markets.
Our success depends on local economic conditions where we operate.
Our success depends on the general economic conditions in the geographic markets we serve in Alabama. The local economic conditions in our markets have a significant effect on our commercial, real estate and construction loans, the ability of borrowers to repay these loans and the value of the collateral securing these loans. Adverse changes in the economic conditions of the Southeastern United States in general, or in one or more of our local markets could negatively affect our results of operations and our profitability. Our local economy is also affected by the growth of automobile manufacturing and related suppliers located in our markets and nearby. Auto sales are cyclical and are affected adversely by higher interest rates.
27
Table of Contents
Our cost of funds may increase as a result of general economic conditions, interest rates, inflation and competitive pressures.
Although the Federal Reserve raised the target federal Funds rate nine times between December 2015 and January 2018 and has been selling securities in accordance with efforts to normalize monetary policy until it changed to more accommodating policy in Summer 2019. At that time, the Federal Reserve stopped selling securities from its portfolio and reduced interest rates 75 basis points over three months keep interest rates relatively low, and the federal government continues large deficit spending. Our costs of funds may increase as a result of general economic conditions, interest rates and competitive pressures, and potential inflation resulting from continued government deficit spending, the effects of the 2017 Tax Act and monetary policies. Traditionally, we have obtained funds principally through local deposits and borrowings from other institutional lenders. Generally, we believe local deposits are a cheaper and more stable source of funds than borrowings because interest rates paid for local deposits are typically lower than interest rates charged for borrowings from other institutional lenders. Increases in interest rates may cause consumers to shift their funds to more interest bearing instruments and to increase the competition for and costs of deposits. If customers move money out of bank deposits and into other investment assets or from transaction deposits to higher interest bearing time deposits, we could lose a relatively low cost source of funds, increasing our funding costs and reducing our net interest income and net income. Additionally, any such loss of funds could result in lower loan originations and growth, which could materially and adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Our profitability and liquidity may be affected by changes in interest rates and interest rate levels, the shape of the yield curve and economic conditions.
Our profitability depends upon net interest income, which is the difference between interest earned on interest-earning assets, such as loans and investments, and interest expense on interest-bearing liabilities, such as deposits and borrowings. Net interest income will be adversely affected if market interest rates change where the interest we pay on deposits and borrowings increases faster than the interest earned on loans and investments. Interest rates, and consequently our results of operations, are affected by general economic conditions (national, international and local) and fiscal and monetary policies, as well as expectations of these rates and policies and the shape of the yield curve. Our income is primarily driven by the spread between these rates. As a result, a steeper yield curve, meaning long-term interest rates are significantly higher than short-term interest rates, would provide the Bank with a better opportunity to increase net interest income. Conversely, a flattening yield curve could pressure our net interest margin as our cost of funds increases relative to the spread we can earn on our assets. In addition, net interest income could be affected by asymmetrical changes in the different interest rate indexes, given that not all of our assets or liabilities are priced with the same index. The 2019 rate reductions by the Federal Reserve and the effects of the coronavirus pandemic have reduced market rates, which may adversely affect our net interest income and our results of operations.
The production of mortgages and other loans and the value of collateral securing our loans are dependent on demand within the markets we serve, as well as interest rates.
Increases in interest rates generally decrease the market values of fixed-rate, interest-bearing investments and loans held, the value of mortgage and other loans produced and the value of loans sold, mortgage loan activities and the collateral securing our loans, and therefore may adversely affect our liquidity and earnings, to the extent not offset by potential increases in our net interest margin and the value of our mortgage servicing rights.
The 2017 Tax Act, including its limitations on the deductibility of residential mortgage interest, state and local taxes and business interest expenses and other changes, could have mixed effects on economic activity and reduce the demand for loans and increase competition among lenders for loans. This Act could promote inflation and higher interest rates, including as a result of increased fiscal deficits.
The Company is an entity separate and distinct from the Bank.
The Company is an entity separate and distinct from the Bank. Company transactions with the Bank are limited by Sections 23A and 23B of the Federal Reserve Act and Federal Reserve Regulation W. We depend upon the Bank’s earnings and dividends, which are limited by law and regulatory policies and actions, for cash to pay the Company’s debt and corporate obligations, and to pay dividends to our shareholders. If the Bank’s ability to pay dividends to the Company was terminated or limited, the Company’s liquidity and financial condition could be materially and adversely affected.
28
Table of Contents
Liquidity risks could affect operations and jeopardize our financial condition.
Liquidity is essential to our business. An inability to raise funds through deposits, borrowings, proceeds from loan repayments or sales proceeds from maturing loans and securities, and other sources could have a substantial negative effect on our liquidity. Our funding sources include federal funds purchased, securities sold under repurchase agreements, core and non-core deposits, and short- and long-term debt. We maintain a portfolio of securities that can be used as a source of liquidity. We are also members of the FHLB and the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta, where we can obtain advances collateralized with eligible assets. There are other sources of liquidity available to the Company or the Bank should they be needed, including our ability to acquire additional non-core deposits. We may be able, depending upon market conditions, to otherwise borrow money or issue and sell debt and preferred or common securities in public or private transactions. Our access to funding sources in amounts adequate to finance or capitalize our activities on terms which are acceptable to us could be impaired by factors that affect us specifically or the financial services industry or the economy in general. General conditions that are not specific to us, such as disruptions in the financial markets or negative views and expectations about the prospects for the financial services industry could adversely affect us.
We are subject to extensive regulation that could limit or restrict our activities and adversely affect our earnings.
We and our subsidiaries are regulated by several regulators, including the Federal Reserve, the Alabama Superintendent, the SEC and the FDIC. Our success is affected by state and federal regulations affecting banks and bank holding companies, and the securities markets, and our costs of compliance could adversely affect our earnings. Banking regulations are primarily intended to protect depositors, and the FDIC Deposit Insurance Fund (“DIF”), not shareholders. The financial services industry also is subject to frequent legislative and regulatory changes and proposed changes. In addition, the interpretations of regulations by regulators may change and statutes may be enacted with retroactive impact. From time to time, regulators raise issues during examinations of us which, if not determined satisfactorily, could have a material adverse effect on us. Compliance with applicable laws and regulations is time consuming and costly and may affect our profitability.
The current President and members of his political party in Congress have promoted and supported regulatory relief for the banking industry. The nature, effects and timing of administrative and legislative change, including the 2018 Growth Act, and possible changes in regulations or regulatory approach, as a result of the 2020 elections, cannot be predicted. The federal bank regulators and the Treasury Department, as well as the Congress and the President, are evaluating the regulation of banks, other financial services providers and the financial markets and such changes, if any, could require us to maintain more capital and liquidity, and restrict our activities, which could adversely affect our growth, profitability and financial condition. Our consumer finance products, including residential mortgage loans, are subject to CFPB regulations and evolving standards reflecting CFPB releases, rule-making and enforcement actions.
Changes in accounting and tax rules applicable to banks could adversely affect our financial conditions and results of operations.
From time to time, the FASB and the SEC change the financial accounting and reporting standards that govern the preparation of our financial statements. These changes can be difficult to predict and can materially impact how we record and report our financial condition and results of operations. In some cases, we could be required to apply a new or revised standard retroactively, resulting in us restating prior period financial statements. The FASB’s new guidance under ASU No. 2016-13 includes significant changes to the manner in which banks’ allowance for loan losses will be calculated beginning January 1, 2023. Instead of using historical losses, the CECL model will be forward-looking with respect to expected losses over the life of loans and other instruments, and could materially affect our results of operations and financial condition, including the variability of our results of operations and our regulatory capital, notwithstanding a three-year phase-in of CECL for regulatory capital purposes.
29
Table of Contents
The 2017 Tax Act may have adverse effects on certain of our customers and our businesses.
The 2017 Tax Act benefits the Bank by reducing the maximum U.S. corporate income tax rate on its taxable income from 35% to 21%. This benefit may be diminished by the complexity, uncertainty and possible adverse effects of this legislation on certain of our borrowers, including limitations on the deductibility of:
| • | residential mortgage interest; |
| • | state and local taxes, including property taxes; and |
| • | business interest expenses. |
These changes may adversely affect borrowers’ cash flows and the values and liquidity of collateral we hold to secure our loans. Fewer borrowers may be able to meet the CFPB’s “ability to repay” standards under the Truth in Lending Act and CFPB regulations, which include the borrower’s ability to pay taxes and assessments. Demand for loans by qualified borrowers could be reduced, and therefore competition among lenders could increase. Customer behaviors toward incurring and repaying debt could also change as a result of the 2017 Tax Act. As a result, the 2017 Tax Act could materially and adversely affect our business and results of operations, at least before taking into account our lower U.S. corporate income tax rate.
We are required to maintain capital to meet regulatory requirements, and if we fail to maintain sufficient capital, our financial condition, liquidity and results of operations would be adversely affected.
We and the Bank must meet regulatory capital requirements and maintain sufficient liquidity, including liquidity at the Company, as well as the Bank. If we fail to meet these capital and other regulatory requirements, including more rigorous requirements arising from our regulators’ implementation of Basel III, our financial condition, liquidity and results of operations would be materially and adversely affected. Our failure to remain “well capitalized” and “well managed”, including meeting the Basel III capital conservation buffers, for bank regulatory purposes could affect customer confidence, our ability to grow, our costs of funds and FDIC insurance, our ability to raise brokered deposits, our ability to pay dividends on our common stock and our ability to make acquisitions, and we would no longer meet the requirements for becoming a financial holding company. These could also affect our ability to use discretionary bonuses to attract and retain quality personnel. The Basel III Capital Rules include a minimum ratio of common equity tier 1 capital, or CET1, to risk-weighted assets of 4.5% and a capital conservation buffer of 2.5% of risk-weighted assets. See “Supervision and Regulation—Basel III Capital Rules.” Although we currently have capital ratios that exceed all these minimum levels and a strategic plan to maintain these levels, we or the Bank may be unable to continue to satisfy the capital adequacy requirements for the following reasons:
| • | losses and/or increases in the Bank’s credit risk assets and expected losses resulting from the deterioration in the creditworthiness of borrowers and the issuers of equity and debt securities; |
| • | difficulty in refinancing or issuing instruments upon redemption or at maturity of such instruments to raise capital under acceptable terms and conditions; |
| • | declines in the value of our securities portfolios; |
| • | revisions to the regulations or their application by our regulators that increase our capital requirements; |
| • | reductions in the value of our DTAs; and other adverse developments; and |
| • | unexpected growth and an inability to increase capital timely. |
30
Table of Contents
A failure to remain “well capitalized,” for bank regulatory purposes, including meeting the Basel III Capital Rule’s conservation buffer, could adversely affect customer confidence, and our:
| • | ability to grow; |
| • | the costs of and availability of funds; |
| • | FDIC deposit insurance premiums; |
| • | ability to raise or replace brokered deposits; |
| • | ability to make acquisitions or engage in new activities; |
| • | flexibility if we become subject to prompt corrective action restrictions; |
| • | ability to make discretionary bonuses to attract and retain quality personnel; |
| • | ability to make payments of principal and interest on our capital instruments; and |
| • | ability to pay dividends on our capital stock. |
The Dodd-Frank Act restricts our future issuance of trust preferred securities and cumulative preferred securities as eligible Tier 1 risk-based capital for purposes of the regulatory capital guidelines for bank holding companies.
We repurchased and retired all our outstanding trust preferred securities in 2018, and the Dodd-Frank Act does not permit us to issue new trust preferred securities as Tier 1 capital. Accordingly, should we determine it is advisable, or should our regulators require us, based upon new capital or liquidity regulations or otherwise, to raise additional Tier 1 risk-based capital, we would not be able to issue additional trust preferred securities. Under the Federal Reserve’s Small BHC Policy, the Company could issue senior or secured debt, the proceeds of which could be down-streamed as capital to the Bank as capital. We also could issue noncumulative preferred stock or common equity. To the extent we issue new equity, it could result in dilution to our existing shareholders. To the extent we issue preferred stock, dividends on the preferred stock, unlike distributions paid on trust preferred securities, would not be tax deductible. Dividends on preferred stock, if any, would be payable prior to payment of dividends on our common stock.
We may need to raise additional capital in the future, but that capital may not be available when it is needed or on favorable terms.
We anticipate that our current capital resources will satisfy our capital requirements for the foreseeable future under currently effective rules. We may, however, need to raise additional capital to support our growth or currently unanticipated losses, or to meet the needs of our communities, resulting from failures or cutbacks by our competitors, and the Basel III Rules. Our ability to raise additional capital, if needed, will depend, among other things, on conditions in the capital markets at that time, which are limited by events outside our control, and on our financial performance. If we cannot raise additional capital on acceptable terms when needed, our ability to further expand our operations through internal growth and acquisitions could be limited.
Future acquisitions and expansion activities may disrupt our business, dilute shareholder value and adversely affect our operating results.
We regularly evaluate potential acquisitions and expansion opportunities, including new branches and other offices. To the extent that we grow through acquisitions, we cannot assure you that we will be able to adequately or profitably manage this growth. Acquiring other banks, branches, or businesses, as well as other geographic and product expansion activities, involve various risks including:
| ● | risks of unknown or contingent liabilities; |
| ● | unanticipated costs and delays; |
| ● | risks that acquired new businesses will not perform consistent with our growth and profitability expectations; |
31
Table of Contents
| ● | risks of entering new markets or product areas where we have limited experience; |
| ● | risks that growth will strain our infrastructure, staff, internal controls and management, which may require additional personnel, time and expenditures; |
| ● | exposure to potential asset quality issues with acquired institutions; |
| ● | difficulties, expenses and delays of integrating the operations and personnel of acquired institutions; |
| ● | potential disruptions to our business; |
| ● | possible loss of key employees and customers of acquired institutions; |
| ● | potential short-term decreases in profitability; and |
| ● | diversion of our management’s time and attention from our existing operations and business. |
Attractive acquisition opportunities may not be available to us in the future.
While we seek continued organic growth, we also may consider the acquisition of other businesses. We expect that other banking and financial companies, many of which have significantly greater resources, will compete with us to acquire financial services businesses. This competition could increase prices for potential acquisitions that we believe are attractive. Also, acquisitions are subject to various regulatory approvals. If we fail to receive the appropriate regulatory approvals, we will not be able to consummate an acquisition that we believe is in our best interests, and regulatory approvals could contain conditions that reduce the anticipated benefits of any transaction. Among other things, our regulators consider our capital, liquidity, profitability, regulatory compliance and levels of goodwill and intangibles when considering acquisition and expansion proposals. Any acquisition could be dilutive to our earnings and shareholders’ equity per share of our common stock.
Technological changes affect our business, and we may have fewer resources than many competitors to invest in technological improvements.
The financial services industry is undergoing rapid technological changes with frequent introductions of new technology driven products and services and a growing demand for mobile and user-based banking applications. In addition to allowing us to analyze our customers better, the effective use of technology may increase efficiency and may enable financial institutions to reduce costs, risks associated with fraud and compliance with anti-money laundering and other laws, and various operational risks. Largely unregulated “fintech” businesses have increased their participation in the lending and payments businesses, and have increased competition in these businesses. Our future success will depend, in part, upon our ability to use technology to provide products and services that meet our customers’ preferences and create additional efficiencies in operations, while avoiding cyber-attacks and disruptions, and data breaches. We may need to make significant additional capital investments in technology, including cyber and data security, and we may not be able to effectively implement new technology-driven products and services, or such technology may prove less effective than anticipated. Many larger competitors have substantially greater resources to invest in technological improvements and, increasingly, non-banking firms are using technology to compete with traditional lenders for loans and other banking services.
32
Table of Contents
Operational risks are inherent in our businesses.
Operational risks and losses can result from internal and external fraud; gaps or weaknesses in our risk management or internal audit procedures; errors by employees or third parties, including our vendors, failure to document transactions properly or to obtain proper authorization; failure to comply with applicable regulatory requirements and conduct of business rules in the various jurisdictions where we do business or have customers; failures in the models we generate and rely on; equipment failures, including those caused by natural disasters or by electrical, telecommunications or other essential utility outages; business continuity and data security system failures, including those caused by computer viruses, cyberattacks, unforeseen problems encountered while implementing major new computer systems or, upgrades or patches to existing systems or inadequate access to data or poor response capabilities in light of such business continuity and data security system failures; or the inadequacy or failure of systems and controls, including those of our vendors or counterparties. In addition, we face certain risks inherent in the ownership and operation of our bank premises and other real-estate, including liability for “slip and fall” and other accidents on our properties. Although we have implemented risk controls and loss mitigation actions, and substantial resources are devoted to developing efficient procedures, identifying and rectifying weaknesses in existing procedures and training staff, it is not possible to be certain that such actions have been or will be effective in controlling each of the operational risks faced by us.
Potential gaps in our risk management policies and internal audit procedures may leave us exposed unidentified or unanticipated risk, which could negatively affect our business.
Our enterprise risk management and internal audit program is designed to mitigate material risks and loss to us. We have developed and continue to develop risk management and internal audit policies and procedures to reflect the ongoing review of our risks and expect to continue to do so in the future. Nonetheless, our policies and procedures may not be comprehensive and may not identify every risk to which we are exposed, and our internal audit process may fail to detect such weaknesses or deficiencies in our risk management framework. Many of our methods for managing risk and exposures use observed historical market behavior to model or project potential future exposure. Models used by our business are based on assumptions and projections. These models may not operate properly or our inputs and assumptions may be inaccurate. As a result, these methods may not fully predict future exposures, which can be significantly greater than historical measures indicate. Other risk management methods depend upon the evaluation of information regarding markets, clients, or other matters that are publicly available or otherwise accessible to us. This information may not always be accurate, complete, up-to-date or properly evaluated. Furthermore, there can be no assurance that we can effectively review and monitor all risks or that all of our employees will closely follow our risk management policies and procedures, nor can there be any assurance that our risk management policies and procedures will enable us to accurately identify all risks and limit our exposures based on our assessments. In addition, we may have to implement more extensive and perhaps different risk management policies and procedures under new or pending regulations. All of these could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
Any failure to protect the confidentiality of customer information could adversely affect our reputation and have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Various federal and state laws enforced by the bank regulators and other agencies protect the privacy and security of customers’ non-public personal information. Many of our employees have access to, and routinely process personal information of clients through a variety of media, including information technology systems. We rely on various internal processes and controls to protect the confidentiality of client information that is accessible to, or in the possession of, us and our employees. It is possible that an employee could, intentionally or unintentionally, disclose or misappropriate confidential client information or our data could be the subject of a cybersecurity attack. Such personal data could also be compromised by third party hackers via intrusions into our systems or those of service providers or persons we do business with such as credit bureaus, data processors and merchants who accept credit or debit cards for payment. If we fail to maintain adequate internal controls, or if our employees fail to comply with our policies and procedures, misappropriation or intentional or unintentional inappropriate disclosure or misuse of client information could occur. Such internal control inadequacies or non-compliance could materially damage our reputation, lead to civil or criminal penalties, or both, which, in turn, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our information systems may experience interruptions and security breaches.
We rely heavily on communications and information systems, including those provided by third-party service providers, to conduct our business. Any failure, interruption, or security breach of these systems could result in failures or disruptions which could affect our customers’ privacy and our customer relationships, generally. Our business continuity plans, including those of our service providers, to provide back-up and restore service may not be effective in the case of widespread outages due to severe weather, natural disasters, pandemics and epidemics or power failures.
33
Table of Contents
Our systems and networks, as well as those of our third-party service providers, are subject to security risks and could be susceptible to cyber-attacks, such as denial of service attacks, hacking, terrorist activities or identity theft. Although we do not believe that we and our third-party service providers have been subject to a cyber-attack, other financial service institutions and their service providers have reported security breaches in their websites or other systems, some of which have involved sophisticated and targeted attacks, including use of stolen access credentials, malware, ransomware, phishing, structured query language injection attacks and distributed denial-of-service attacks, among other means. Such cyber-attacks may also be directed at disrupting the operations of public companies or their business partners, which are intended to effect unauthorized fund transfers, obtain unauthorized access to confidential information, to destroy data, disable or degrade service, or sabotage systems, often through the introduction of computer viruses or malware, cyberattacks and other means. Denial of service attacks have been launched against a number of financial services institutions, and we may be subject to these types of attacks in the future. Hacking and identity theft risks, in particular, could cause serious reputational harm. Cyber threats are rapidly evolving and we may not be able to anticipate or prevent all such attacks and could be held liable for any security breach or loss.
Despite our cybersecurity policies and procedures and our Board of Director’s and Management’s efforts to monitor and ensure the integrity of our and our service providers’ systems, we may not be able to anticipate all types of security threats, nor may we be able to implement preventive measures effective against all such security threats. The techniques used by cyber criminals change frequently, may not be recognized until launched and can originate from a wide variety of sources, including outside groups such as external service providers, organized crime affiliates, terrorist organizations or hostile foreign governments. These risks may increase in the future as the use of mobile banking and other internet-based products and services continues to grow.
Security breaches or failures may have serious adverse financial and other consequences, including significant legal and remediation costs, disruptions to operations, misappropriation of confidential information, damage to systems operated by us or our third-party service providers, as well as damages to our customers and our counterparties. In addition to the immediate costs of any failure, interruption or security breach, including those at our third-party service providers, these events could damage our reputation, result in a loss of customer business, subject us to additional regulatory scrutiny, or expose us to civil litigation and possible financial liability, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Severe weather, natural disasters, pandemics, epidemics, acts of war or terrorism or other external events could have significant effects on our business.
Severe weather and natural disasters, including hurricanes, tornados, drought and floods, epidemics and pandemics, acts of war or terrorism or other external events could have a significant effect on our ability to conduct business. Such events could affect the stability of our deposit base; impair the ability of borrowers to repay outstanding loans, impair the value of collateral securing loans, cause significant property damage, result in loss of revenue and/or cause us to incur additional expenses. Although management has established disaster recovery and business continuity policies and procedures, the occurrence of any such event could have a material adverse effect on our business, which, in turn, could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
The coronavirus or COVID-19 pandemic, trade wars, tariffs, and similar events and disputes, domestic and international, have adversely affected, and may continue to adversely affect economic activity globally, nationally and locally. Market interest rates have declined significantly, with the 10 year Treasury bond falling below 1.00% on March 3, 2020 for the first time. Such events also may adversely affect business and consumer confidence, generally. We and our customers, and our respective suppliers, vendors and processors may be adversely affected. Any such adverse changes may adversely affect our profitability, growth asset quality and financial condition.
The Federal Reserve stated on February 28, 2020 that it was closely monitoring coronavirus developments and their effects on the economic outlook, and would act appropriately to support the economy. On March 3, 2020, the Federal Reserve reduced the target federal funds rate by 50 basis points to 1.00% to 1.25%. The Federal Reserve also announced it was purchasing Treasury bills into the second quarter of 2020, conducting overnight repurchase agreement operations at least through April 2020, and will continue to reinvest amounts of principal received by the Federal Reserve on its portfolio of treasury and agency debt and mortgage-backed securities. Lastly, the Federal Reserve also reduced the interest it pays on excess reserves from 1.60% to 1.10%. We expect that such reductions in interest rates will adversely affect our net interest income and margins, and our profitability.
34
Table of Contents
Our associates may take excessive risks which could negatively affect our financial condition and business.
As a banking enterprise, we are in the business of accepting certain risks. The associates who conduct our business, including executive officers and other members of management, sales intermediaries, investment professionals, product managers, and other associates, do so in part by making decisions and choices that involve exposing us to risk. We endeavor, in the design and implementation of our compensation programs and practices, to avoid giving our associates incentives to take excessive risks; however, associates may nonetheless take such risks and our policies and procedures, generally. Similarly, although we employ controls and procedures designed to prevent employee misconduct, to monitor associates’ business decisions and prevent them from taking excessive risks, these controls and procedures may not be effective. If our associates take excessive risks, the impact of those risks could harm our reputation and have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and business operations.
A substantial legal liability or a significant federal, state or other regulatory action against us, as well as regulatory inquiries or investigations, could harm our reputation, result in material fines or penalties, result in significant legal costs, divert management resources away from our business, and otherwise have a material adverse effect on our ability to expand on our existing business, financial condition and results of operations. Even if we ultimately prevail in the litigation, regulatory action or investigation, our ability to attract new customers, retain our current customers and recruit and retain employees could be materially and adversely affected. Regulatory inquiries and litigation may also adversely affect the prices or volatility of our securities specifically, or the securities of our industry, generally.
We may be unable to attract and retain key people to support our business.
Our success depends, in large part, on our ability to attract and retain key people. We compete with other financial services companies for people primarily on the basis of compensation and benefits, support services and financial position. Intense competition exists for key employees with demonstrated ability, and we may be unable to hire or retain such employees. Effective succession planning is also important to our long-term success. The unexpected loss of services of one or more of our key personnel and failure to ensure effective transfer of knowledge and smooth transitions involving key personnel could have a material adverse effect on our business due to loss of their skills, knowledge of our business, their years of industry experience and the potential difficulty of promptly finding qualified replacement employees.
Proposed rules implementing the executive compensation provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act may limit the type and structure of compensation arrangements into which we may enter with certain of our employees and officers. In addition, proposed rules under the Dodd-Frank Act would prohibit the payment of “excessive compensation” to our executives. These restrictions could negatively affect our ability to compete with other companies in recruiting and retaining key personnel.
The Federal Reserve may require us to commit capital resources to support the Bank.
As a matter of policy, the Federal Reserve, which examines us, expects a bank holding company to act as a source of financial and managerial strength to a subsidiary bank and to commit resources to support such subsidiary bank. The Federal Reserve may require a bank holding company to make capital injections into a troubled subsidiary bank. In addition, the Dodd-Frank Act amended the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation Act to require that all companies that control a FDIC-insured depository institution serve as a source of financial strength to their depository institution subsidiaries. Under this requirement, we could be required to provide financial assistance to the Bank should it experience financial distress, even if further investment was not otherwise warranted. See “Supervision and Regulation.”
Our ability to continue to pay dividends to shareholders in the future is subject to our profitability, capital, liquidity and regulatory requirements and these limitations may prevent or limit future dividends.
Cash available to pay dividends to our shareholders is derived primarily from dividends paid to the Company by the Bank. The ability of the Bank to pay dividends, as well as our ability to pay dividends to our shareholders, will continue to be subject to and limited by applicable laws limiting dividend payments by the Bank, the results of operations of our subsidiaries and our need to maintain appropriate liquidity and capital at all levels of our business consistent with regulatory requirements and the needs of our businesses. See “Supervision and Regulation”.
35
Table of Contents
A limited trading market exists for our common shares, which could lead to price volatility.
Your ability to sell or purchase common shares depends upon the existence of an active trading market for our common stock. Although our common stock is quoted on the Nasdaq Global Market under the trading symbol “AUBN,” the volume of trades on any given day has been limited historically. As a result, you may be unable to sell or purchase shares of our common stock at the volume, price and time that you desire. Additionally, whether the purchase or sales prices of our common stock reflects a reasonable valuation of our common stock also is affected by an active trading market, and thus the price you receive for a thinly-traded stock such as common stock, may not reflect its true or intrinsic value. The limited trading market for our common stock may cause fluctuations in the market value of our common stock to be exaggerated, leading to price volatility in excess of that which would occur in a more active trading market.
Our operations are subject to risk of loss from unfavorable fiscal, monetary and political developments in the U.S.
Our businesses and earnings are affected by the fiscal, monetary and other policies and actions of various U.S. governmental and regulatory authorities. Changes in these are beyond our control and are difficult to predict and, consequently, changes in these policies could have negative effects on our activities and results of operations. Failures of the executive and legislative branches to agree on spending plans and budgets previously have led to Federal government shutdowns, which may adversely affect the U.S. economy. Additionally, any prolonged government shutdown may inhibit our ability to evaluate the economy, generally, and affect government workers who are not paid during such events, and where the absence of government services and data could adversely affect consumer and business sentiment, our local economy and our customers and therefore our business.
Litigation and regulatory investigations are increasingly common in our businesses and may result in significant financial losses and/or harm to our reputation.
We face risks of litigation and regulatory investigations and actions in the ordinary course of operating our businesses, including the risk of class action lawsuits. Plaintiffs in class action and other lawsuits against us may seek very large and/or indeterminate amounts, including punitive and treble damages. Due to the vagaries of litigation, the ultimate outcome of litigation and the amount or range of potential loss at particular points in time may be difficult to ascertain. We do not have any material pending litigation or regulatory matters affecting us.
Failures to comply with the fair lending laws, CFPB regulations or the Community Reinvestment Act, or CRA, could adversely affect us.
The Bank is subject to, among other things, the provisions of the Equal Credit Opportunity Act, or ECOA, and the Fair Housing Act, both of which prohibit discrimination based on race or color, religion, national origin, sex and familial status in any aspect of a consumer, commercial credit or residential real estate transaction. The DOJ and the federal bank regulatory agencies have issued an Interagency Policy Statement on Discrimination in Lending to provide guidance to financial institutions in determining whether discrimination exists and how the agencies will respond to lending discrimination, and what steps lenders might take to prevent discriminatory lending practices. Failures to comply with ECOA, the Fair Housing Act and other fair lending laws and regulations, including CFPB regulations, could subject us to enforcement actions or litigation, and could have a material adverse effect on our business financial condition and results of operations. Our Bank is also subject to the CRA and periodic CRA examinations. The CRA requires us to serve our entire communities, including low- and moderate-income neighborhoods. Our CRA ratings could be adversely affected by actual or alleged violations of the fair lending or consumer financial protection laws. Even though we have maintained an “satisfactory” CRA rating since 2000, we cannot predict our future CRA ratings. Violations of fair lending laws or if our CRA rating falls to less than “satisfactory” could adversely affect our business, including expansion through branching or acquisitions.
36
Table of Contents
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM 2. DESCRIPTION OF PROPERTY
The Bank conducts its business from its main office and eight full-service branches. The Bank also operates a commercial loan production office in Phenix City, Alabama. The bank owns its main office building, which is located in downtown Auburn, Alabama, and has approximately 16,150 square feet of space. The original building was constructed in 1964, and an addition was completed in 1981. Portions of the building have been renovated to accommodate growth and changes in the Bank’s operational structure and to adapt to technological changes. The main office offers the full line of the Bank’s services and has one ATM. The Bank completed construction on a new drive-through facility located on the main office campus in October 2012. This drive-through facility has five drive-through lanes, including an ATM, and a walk-up teller window.
The Bank also owns a commercial office building, the AuburnBank Center (the “Center”), which is located next to the Bank’s main office. The Center has approximately 23,000 square feet of space. The Bank’s mortgage servicing, data processing activities, and other operations, are located in the Center. In total, the main office and Center parking lots provide parking for approximately 196 vehicles.
In January 2019, the Bank purchased a parcel that adjoins the Center in order to improve ingress and egress to the Bank’s main campus, which comprises over 5 acres in downtown Auburn and includes the Bank’s main office building, drive-through facility, and the Center. The building improvements on this adjoining parcel will be demolished as part of the Bank’s plan to redevelop its main campus. Phase I of this redevelopment plan will include the construction of a new headquarters building and a parking deck. Construction is scheduled to begin during the second half of 2020. Upon completion of construction, the Bank’s main office branch and all of its back-office operations will be located in the new headquarters building. Any unused office/retail space in this new building will be available for lease to third parties. During construction, the Bank will temporarily relocate its main office branch to the Center.
The Opelika branch is located in Opelika, Alabama. This branch, built in 1991, is owned by the Bank and has approximately 4,000 square feet of space. This branch offers the full line of the Bank’s services and has drive-through windows and an ATM. This branch offers parking for approximately 36 vehicles.
The Bank’s Notasulga branch was opened in August 2001. This branch is located in Notasulga, Alabama, about 15 miles west of Auburn, Alabama. This branch is owned by the Bank and has approximately 1,344 square feet of space. The Bank leased the land for this branch from a third party. In May 2019, the Bank’s land lease renewed for another one year term. This branch offers the full line of the Bank’s services including safe deposit boxes and a drive-through window. This branch offers parking for approximately 11 vehicles, including a handicapped ramp.
In November 2002, the Bank opened a loan production office in Phenix City, Alabama, about 35 miles south of Auburn, Alabama. In November 2019, the Bank renewed its lease for another year.
In February 2009, the Bank opened a branch located on Bent Creek Road in Auburn, Alabama. This branch is owned by the Bank and has approximately 4,000 square feet of space. This branch offers the full line of the Bank’s services and has drive-through windows and a drive-up ATM. This branch offers parking for approximately 29 vehicles.
In December 2011, the Bank opened a branch located on Fob James Drive in Valley, Alabama, about 30 miles northeast of Auburn, Alabama. This branch is owned by the Bank and has approximately 5,000 square feet of space. This branch offers the full line of the Bank’s services and has drive-through windows and a drive-up ATM. This branch offers parking for approximately 35 vehicles. Prior to December 2011, the Bank leased office space for a loan production office in Valley, Alabama. The loan production office was originally opened in September 2004.
In February 2015, the Bank relocated its Auburn Kroger branch to a new location within the Corner Village Shopping Center, in Auburn, Alabama. In February 2015, the Bank entered into a new lease agreement for five years with options for two 5-year extensions. In February 2020, the Bank exercised its option to extend the lease for another five years. The Bank leases approximately 1,500 square feet of space for the Corner Village branch. Prior to relocation, the Bank’s Auburn Kroger branch was located in the Kroger supermarket in the same shopping center. The Auburn Kroger branch was originally opened in August 1988. The Corner Village branch offers the full line of the Bank’s deposit and other services including an ATM, except safe deposit boxes.
37
Table of Contents
In September 2015, the Bank relocated its Auburn Wal-Mart Supercenter branch to a new location the Bank purchased in December 2014 at the intersection of S. Donahue Avenue and E. University Drive in Auburn, Alabama. The South Donahue branch, built in 2015, has approximately 3,600 square feet of space. Prior to relocation, the Bank’s Auburn Wal-Mart Supercenter branch was located inside the Wal-Mart shopping center on the south side of Auburn, Alabama. The Auburn Wal-Mart Supercenter branch was originally opened in September 2000. The South Donahue branch offers the full line of the Bank’s services and has drive-through windows and an ATM. This branch offers parking for approximately 28 vehicles.
In May 2017, the Bank relocated its Opelika Kroger branch to a new location the Bank purchased in August 2016 near the Tiger Town Retail Shopping Center and the intersection of U.S. Highway 280 and Frederick Road in Opelika, Alabama. The Tiger Town branch, built in 2017, has approximately 5,500 square feet of space. Prior to relocation, the Bank’s Opelika Kroger branch was located inside the Kroger supermarket in the Tiger Town retail center in Opelika, Alabama. The Opelika Kroger branch was originally opened in July 2007. The Tiger Town branch offers the full line of the Bank’s services and has drive-through windows and an ATM. This branch offers parking for approximately 36 vehicles.
In September 2018, the Bank opened a mortgage loan production office on East Samford Avenue in Auburn, Alabama. The location has approximately 2,500 square feet of space and is leased through 2028. The mortgage loan production office was previously located in the Center on the Bank’s main campus. This location offers parking for approximately 16 vehicles.
In the normal course of its business, the Company and the Bank from time to time are involved in legal proceedings. The Company’s management believe there are no pending or threatened legal proceedings that, upon resolution, are expected to have a material adverse effect upon the Company’s or the Bank’s financial condition or results of operations.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
38
Table of Contents
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
The Company’s Common Stock is listed on the Nasdaq Global Market, under the symbol “AUBN”. As of March 5, 2020, there were approximately 3,566,146 shares of the Company’s Common Stock issued and outstanding, which were held by approximately 376 shareholders of record. The following table sets forth, for the indicated periods, the high and low closing sale prices for the Company’s Common Stock as reported on the Nasdaq Global Market, and the cash dividends declared to shareholders during the indicated periods.
| Closing | Cash | |||||||||||||
| Price | Dividends | |||||||||||||
| Per Share (1) | Declared | |||||||||||||
| High |
Low |
|||||||||||||
| 2019 |
||||||||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 39.43 | $ | 30.61 | $ | 0.25 | ||||||||
| Second Quarter |
39.55 | 31.06 | 0.25 | |||||||||||
| Third Quarter |
47.38 | 32.33 | 0.25 | |||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter |
53.90 | 40.00 | 0.25 | |||||||||||
| 2018 |
||||||||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 39.25 | $ | 35.50 | $ | 0.24 | ||||||||
| Second Quarter |
50.99 | 37.40 | 0.24 | |||||||||||
| Third Quarter |
53.50 | 38.31 | 0.24 | |||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter |
41.50 | 28.88 | 0.24 | |||||||||||
| (1) The price information represents actual transactions. |
| |||||||||||||
The Company has paid cash dividends on its capital stock since 1985. Prior to this time, the Bank paid cash dividends since its organization in 1907, except during the Depression years of 1932 and 1933. Holders of Common Stock are entitled to receive such dividends as may be declared by the Company’s Board of Directors. The amount and frequency of cash dividends will be determined in the judgment of the Board based upon a number of factors, including the Company’s earnings, financial condition, capital requirements and other relevant factors. The Board currently intends to continue its present dividend policies.
Federal Reserve policy could restrict future dividends on our Common Stock, depending on our earnings and capital position and likely needs. See “Supervision and Regulation – Payment of Dividends” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations – Capital Adequacy”.
The amount of dividends payable by the Bank is limited by law and regulation. The need to maintain adequate capital in the Bank also limits dividends that may be paid to the Company.
39
Table of Contents
Performance Graph
The following performance graph compares the cumulative, total return on the Company’s Common Stock from December 31, 2014 to December 31, 2019, with that of the Nasdaq Composite Index and SNL Southeast Bank Index (assuming a $100 investment on December 31, 2014). Cumulative total return represents the change in stock price and the amount of dividends received over the indicated period, assuming the reinvestment of dividends.
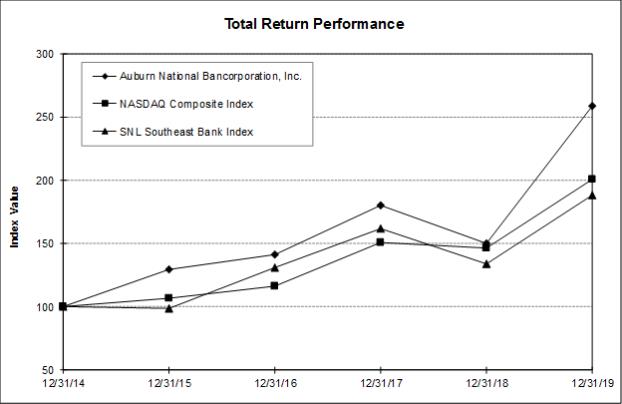
| Period Ending | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Index |
12/31/14 | 12/31/15 | 12/31/16 | 12/31/17 | 12/31/18 | 12/31/19 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Auburn National Bancorporation, Inc. |
100.00 | 129.59 | 141.36 | 180.33 | 150.26 | 258.45 | ||||||||||||||||||
| NASDAQ Composite Index |
100.00 | 106.96 | 116.45 | 150.96 | 146.67 | 200.49 | ||||||||||||||||||
| SNL Southeast Bank Index |
100.00 | 98.44 | 130.68 | 161.65 | 133.56 | 188.08 | ||||||||||||||||||
40
Table of Contents
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
| Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased |
Average Price Paid per Share |
Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs |
The
Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Under the Plans or Programs(1) | ||||
|
October 1 – October 31, 2019 |
–– | –– | –– | 2,279,285 | ||||
|
November 1 – November 30, 2019 |
–– | –– | –– | 2,279,285 | ||||
|
December 1 – December 31, 2019 |
–– | –– | –– | 2,279,285 | ||||
|
Total |
–– | –– | –– | 2,279,285 |
| 1) | The Company approved a $5 million stock repurchase program adopted on January 15, 2019. As of December 31, 2019, the approximate remaining dollar value of shares that may be purchased under the program was $2.3 million. |
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
See the information included under Part III, Item 12, which is incorporated in response to this item by reference.
Unregistered Sale of Equity Securities
Not applicable.
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
See Table 2 “Selected Financial Data” and general discussion in Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations”.
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following is a discussion of our financial condition at December 31, 2019 and 2018 and our results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018. The purpose of this discussion is to provide information about our financial condition and results of operations which is not otherwise apparent from the consolidated financial statements. The following discussion and analysis should be read along with our consolidated financial statements and the related notes included elsewhere herein. In addition, this discussion and analysis contains forward-looking statements, so you should refer to Item 1A, “Risk Factors” and “Special Cautionary Notice Regarding Forward-Looking Statements”.
OVERVIEW
The Company was incorporated in 1990 under the laws of the State of Delaware and became a bank holding company after it acquired its Alabama predecessor, which was a bank holding company established in 1984. The Bank, the Company’s principal subsidiary, is an Alabama state-chartered bank that is a member of the Federal Reserve System and has operated continuously since 1907. Both the Company and the Bank are headquartered in Auburn, Alabama. The Bank conducts its business primarily in East Alabama, including Lee County and surrounding areas. The Bank operates full-service branches in Auburn, Opelika, Notasulga and Valley, Alabama. The Bank also operates loan production offices in Auburn and Phenix City, Alabama.
41
Table of Contents
Summary of Results of Operations
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands, except per share data) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net interest income (a) |
$ | 26,621 | $ | 26,183 | ||||||
| Less: tax-equivalent adjustment |
557 | 613 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net interest income (GAAP) |
26,064 | 25,570 | ||||||||
| Noninterest income |
5,494 | 3,325 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total revenue |
31,558 | 28,895 | ||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
(250 | ) | — | |||||||
| Noninterest expense |
19,697 | 17,874 | ||||||||
| Income tax expense |
2,370 | 2,187 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 9,741 | $ | 8,834 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Basic and diluted net earnings per share |
$ | 2.72 | $ | 2.42 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| (a) Tax-equivalent. See “Table 1 - Explanation of Non-GAAP Financial Measures”. |
| |||||||||
Financial Summary
The Company’s net earnings were $9.7 million for the full year 2019, compared to $8.8 million for the full year 2018. Basic and diluted net earnings per share were $2.72 per share for the full year 2019, compared to $2.42 per share for the full year 2018.
Net interest income (tax-equivalent) was $26.6 million in 2019, a 2% increase compared to $26.2 million in 2018. This increase was primarily due to loan growth and increases in short-term market interest rates. Average loans grew 4% to $474.3 million in 2019, compared to $456.3 million in 2018. The Company’s net interest margin (tax-equivalent) increased to 3.43% in 2019, compared to 3.40% in 2018 as yields on earning assets improved.
The Company recorded a negative provision for loan losses of $0.3 million in 2019 compared to no provision for loan losses during 2018. The provision for loan losses is based upon various estimates and judgements, including the absolute level of loans, loan growth, credit quality and the amount of net charge-offs. Annualized net charge-offs as a percent of average loans were 0.03% in 2019 compared to annualized net recoveries of 0.01% in 2018.
Noninterest income was $5.5 million in 2019 compared to $3.3 million in 2018. The increase was primarily due to a $1.7 million payment received by the Company that resulted from the termination of a loan guarantee program operated by the State of Alabama and a $0.3 million pre-tax gain from an insurance recovery received in the first quarter of 2019. Mortgage lending income also increased $0.2 million, or 32%, as pricing margins improved and lower interest rates for mortgage loans positively affected refinance activity.
Noninterest expense was $19.7 million in 2019 compared to $17.9 million in 2018. This increase in noninterest expense was primarily due to increases in salaries and benefits expense of $1.3 million and $0.5 million of various expenses related to the planned redevelopment of the Company’s headquarters in downtown Auburn, including professional fees, temporary relocation costs, and revised depreciation estimates. The Company expects it will incur additional expense in 2020 related to this redevelopment project.
Income tax expense was $2.4 million in 2019 and $2.2 million in 2018 reflecting an effective tax rate of 19.57% and 19.84%, respectively.
The Company paid cash dividends of $1.00 per share in 2019, an increase of 4.2% from 2018. At December 31, 2019, the Bank’s regulatory capital ratios were well above the minimum amounts required to be “well capitalized” under current regulatory standards with a total risk-based capital ratio of 19.69%, a tier 1 leverage ratio of 11.23% and common equity tier 1 (“CET1”) of 18.78% at December 31, 2019.
42
Table of Contents
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The accounting and financial reporting policies of the Company conform with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles and with general practices within the banking industry. In connection with the application of those principles, we have made judgments and estimates which, in the case of the determination of our allowance for loan losses, our assessment of other-than-temporary impairment, recurring and non-recurring fair value measurements, the valuation of other real estate owned, and the valuation of deferred tax assets, were critical to the determination of our financial position and results of operations. Other policies also require subjective judgment and assumptions and may accordingly impact our financial position and results of operations.
Allowance for Loan Losses
The Company assesses the adequacy of its allowance for loan losses prior to the end of each calendar quarter. The level of the allowance is based upon management’s evaluation of the loan portfolio, past loan loss experience, current asset quality trends, known and inherent risks in the portfolio, adverse situations that may affect a borrower’s ability to repay (including the timing of future payment), the estimated value of any underlying collateral, composition of the loan portfolio, economic conditions, industry and peer bank loan loss rates and other pertinent factors, including regulatory recommendations. This evaluation is inherently subjective as it requires material estimates including the amounts and timing of future cash flows expected to be received on impaired loans that may be susceptible to significant change. Loans are charged off, in whole or in part, when management believes that the full collectability of the loan is unlikely. A loan may be partially charged-off after a “confirming event” has occurred which serves to validate that full repayment pursuant to the terms of the loan is unlikely.
The Company deems loans impaired when, based on current information and events, it is probable that the Company will be unable to collect all amounts due according to the contractual terms of the loan agreement. Collection of all amounts due according to the contractual terms means that both the interest and principal payments of a loan will be collected as scheduled in the loan agreement.
An impairment allowance is recognized if the fair value of the loan is less than the recorded investment in the loan. The impairment is recognized through the allowance. Loans that are impaired are recorded at the present value of expected future cash flows discounted at the loan’s effective interest rate, or if the loan is collateral dependent, impairment measurement is based on the fair value of the collateral, less estimated disposal costs.
The level of allowance maintained is believed by management to be adequate to absorb probable losses inherent in the portfolio at the balance sheet date. The allowance is increased by provisions charged to expense and decreased by charge-offs, net of recoveries of amounts previously charged-off.
In assessing the adequacy of the allowance, the Company also considers the results of its ongoing internal, independent loan review process. The Company’s loan review process assists in determining whether there are loans in the portfolio whose credit quality has weakened over time and evaluating the risk characteristics of the entire loan portfolio. The Company’s loan review process includes the judgment of management, the input from our independent loan reviewers, and reviews that may have been conducted by bank regulatory agencies as part of their examination process. The Company incorporates loan review results in the determination of whether or not it is probable that it will be able to collect all amounts due according to the contractual terms of a loan.
As part of the Company’s quarterly assessment of the allowance, management divides the loan portfolio into five segments: commercial and industrial, construction and land development, commercial real estate, residential real estate, and consumer installment loans. The Company analyzes each segment and estimates an allowance allocation for each loan segment.
The allocation of the allowance for loan losses begins with a process of estimating the probable losses inherent for these types of loans. The estimates for these loans are established by category and based on the Company’s internal system of credit risk ratings and historical loss data. The estimated loan loss allocation rate for the Company’s internal system of credit risk grades is based on its experience with similarly graded loans. For loan segments where the Company believes it does not have sufficient historical loss data, the Company may make adjustments based, in part, on loss rates of peer bank groups. At December 31, 2019 and 2018, and for the years then ended, the Company adjusted its historical loss rates for the commercial real estate portfolio segment based, in part, on loss rates of peer bank groups.
43
Table of Contents
The estimated loan loss allocation for all five loan portfolio segments is then adjusted for management’s estimate of probable losses for several “qualitative and environmental” factors. The allocation for qualitative and environmental factors is particularly subjective and does not lend itself to exact mathematical calculation. This amount represents estimated probable inherent credit losses which exist, but have not yet been identified, as of the balance sheet date, and are based upon quarterly trend assessments in delinquent and nonaccrual loans, credit concentration changes, prevailing economic conditions, changes in lending personnel experience, changes in lending policies or procedures and other influencing factors. These qualitative and environmental factors are considered for each of the five loan segments and the allowance allocation, as determined by the processes noted above, is increased or decreased based on the incremental assessment of these factors.
The Company regularly re-evaluates its practices in determining the allowance for loan losses. Since the fourth quarter of 2016, the Company has increased its look-back period each quarter to incorporate the effects of at least one economic downturn in its loss history. The Company believes the extension of its look-back period is appropriate due to the risks inherent in the loan portfolio. Absent this extension, the early cycle periods in which the Company experienced significant losses would be excluded from the determination of the allowance for loan losses and its balance would decrease. For the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company increased its look-back period to 43 quarters to continue to include losses incurred by the Company beginning with the first quarter of 2009. The Company will likely continue to increase its look-back period to incorporate the effects of at least one economic downturn in its loss history. Other than expanding the look-back period each quarter, the Company has not made any material changes to its methodology that would impact the calculation of the allowance for loan losses or provision for loan losses for the periods included in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and statements of earnings.
Assessment for Other-Than-Temporary Impairment of Securities
On a quarterly basis, management makes an assessment to determine whether there have been events or economic circumstances to indicate that a security on which there is an unrealized loss is other-than-temporarily impaired. For equity securities with an unrealized loss, the Company considers many factors including the severity and duration of the impairment; the intent and ability of the Company to hold the security for a period of time sufficient for a recovery in value; and recent events specific to the issuer or industry. Equity securities for which there is an unrealized loss that is deemed to be other-than-temporary are written down to fair value with the write-down recorded as a realized loss in securities gains (losses).
For debt securities with an unrealized loss, an other-than-temporary impairment write-down is triggered when (1) the Company has the intent to sell a debt security, (2) it is more likely than not that the Company will be required to sell the debt security before recovery of its amortized cost basis, or (3) the Company does not expect to recover the entire amortized cost basis of the debt security. If the Company has the intent to sell a debt security or if it is more likely than not that it will be required to sell the debt security before recovery, the other-than-temporary write-down is equal to the entire difference between the debt security’s amortized cost and its fair value. If the Company does not intend to sell the security or it is not more likely than not that it will be required to sell the security before recovery, the other-than-temporary impairment write-down is separated into the amount that is credit related (credit loss component) and the amount due to all other factors. The credit loss component is recognized in earnings and is the difference between the security’s amortized cost basis and the present value of its expected future cash flows. The remaining difference between the security’s fair value and the present value of future expected cash flows is due to factors that are not credit related and is recognized in other comprehensive income, net of applicable taxes.
Fair Value Determination
U.S. GAAP requires management to value and disclose certain of the Company’s assets and liabilities at fair value, including investments classified as available-for-sale and derivatives. ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures, which defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value in accordance with U.S. GAAP and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. For more information regarding fair value measurements and disclosures, please refer to Note 15, Fair Value, of the consolidated financial statements that accompany this report.
Fair values are based on active market prices of identical assets or liabilities when available. Comparable assets or liabilities or a composite of comparable assets in active markets are used when identical assets or liabilities do not have readily available active market pricing. However, some of the Company’s assets or liabilities lack an available or comparable trading market characterized by frequent transactions between willing buyers and sellers. In these cases, fair value is estimated using pricing models that use discounted cash flows and other pricing techniques. Pricing models and their underlying assumptions are based upon management’s best estimates for appropriate discount rates, default rates, prepayments, market volatility and other factors, taking into account current observable market data and experience.
44
Table of Contents
These assumptions may have a significant effect on the reported fair values of assets and liabilities and the related income and expense. As such, the use of different models and assumptions, as well as changes in market conditions, could result in materially different net earnings and retained earnings results.
Other Real Estate Owned
Other real estate owned (“OREO”), consists of properties obtained through foreclosure or in satisfaction of loans and is reported at the lower of cost or fair value, less estimated costs to sell at the date acquired with any loss recognized as a charge-off through the allowance for loan losses. Additional OREO losses for subsequent valuation adjustments are determined on a specific property basis and are included as a component of other noninterest expense along with holding costs. Any gains or losses on disposal of OREO are also reflected in noninterest expense. Significant judgments and complex estimates are required in estimating the fair value of OREO, and the period of time within which such estimates can be considered current is significantly shortened during periods of market volatility. As a result, the net proceeds realized from sales transactions could differ significantly from appraisals, comparable sales, and other estimates used to determine the fair value of other OREO.
Deferred Tax Asset Valuation
A valuation allowance is recognized for a deferred tax asset if, based on the weight of available evidence, it is more-likely-than-not that some portion or the entire deferred tax asset will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income and tax planning strategies in making this assessment. Based upon the level of taxable income over the last three years and projections for future taxable income over the periods in which the deferred tax assets are deductible, management believes it is more likely than not that we will realize the benefits of these deductible differences at December 31, 2019. The amount of the deferred tax assets considered realizable, however, could be reduced if estimates of future taxable income are reduced.
Average Balance Sheet and Interest Rates
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||||||||||
| Average | Yield/ | Average | Yield/ | |||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | Balance | Rate | Balance | Rate | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
| Loans and loans held for sale |
$ | 474,259 | 4.83% | $ | 457,610 | 4.76% | ||||||||||
| Securities - taxable |
178,410 | 2.24% | 181,485 | 2.23% | ||||||||||||
| Securities - tax-exempt (a) |
66,628 | 3.99% | 71,065 | 4.11% | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
| Total securities |
245,038 | 2.72% | 252,550 | 2.76% | ||||||||||||
| Federal funds sold |
20,223 | 2.09% | 28,689 | 1.93% | ||||||||||||
| Interest bearing bank deposits |
36,869 | 2.16% | 31,339 | 1.81% | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
| Total interest-earning assets |
776,389 | 3.97% | 770,188 | 3.88% | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
| Deposits: |
||||||||||||||||
| NOW |
134,430 | 0.53% | 125,533 | 0.34% | ||||||||||||
| Savings and money market |
218,630 | 0.44% | 220,810 | 0.39% | ||||||||||||
| Certificates of deposits |
170,835 | 1.46% | 184,010 | 1.27% | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
| Total interest-bearing deposits |
523,895 | 0.80% | 530,353 | 0.68% | ||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings |
1,443 | 0.49% | 2,634 | 0.68% | ||||||||||||
| Long-term debt |
— | 0.00% | 1,022 | 4.50% | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
| Total interest-bearing liabilities |
525,338 | 0.80% | 534,009 | 0.69% | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
| Net interest income and margin (a) |
$ | 26,621 | 3.43% | $ | 26,183 | 3.40% | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
(a) Tax-equivalent. See “Table 1 - Explanation of Non-GAAP Financial Measures”.
45
Table of Contents
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Net Interest Income and Margin
Net interest income (tax-equivalent) was $26.6 million in 2019, compared to $26.2 million in 2018. This increase was due to improvement in the Company’s net interest margin (tax-equivalent) and balance sheet growth.
The tax-equivalent yield on total interest-earning assets increased by 9 basis points in 2019 from 2018 to 3.97%. Expansion of our earning asset yields was primarily driven by loan growth and increases in short-term market interest rates, which positively impacted the yields on our short-term assets, including federal funds sold and interest bearing bank deposits.
The cost of total interest-bearing liabilities increased 11 basis points in 2019 from 2018 to 0.80%. The increase in our funding costs was primarily due to higher prevailing market interest rates.
The Company continues to deploy various asset liability management strategies to manage its risk to interest rate fluctuations. The Company’s net interest margin could experience pressure due to reduced earning asset yields, increased competition for quality loan opportunities, and possible increases in our costs of funds. Management anticipates the Company’s net interest income and margin will likely decrease in 2020 compared to 2019 as the Company’s ability to lower its deposit costs will likely continue to lag the current decrease in earning asset yields.
Provision for Loan Losses
The Company recorded a negative provision for loan losses of $0.3 million in 2019, compared to no provision for loan losses in 2018. The negative provision was primarily related to a decline in total loans outstanding at December 31, 2019 and more specifically the construction and land development loan portfolio segment.
Based upon its assessment of the loan portfolio, management adjusts the allowance for loan losses to an amount it believes to be appropriate to adequately cover probable losses in the loan portfolio. The Company’s allowance for loan losses to total loans decreased to 0.95% at December 31, 2019 from 1.00% at December 31, 2018. Based upon our evaluation of the loan portfolio, management believes the allowance for loan losses to be adequate to absorb our estimate of probable losses existing in the loan portfolio at December 31, 2019. While our policies and procedures used to estimate the allowance for loan losses, as well as the resultant provision for loan losses charged to operations, are believed adequate by management and are reviewed from time to time by our regulators, they are based on estimates and judgment and are therefore approximate and imprecise. Factors beyond our control, such as conditions in the local and national economy, a local real estate market or particular industry conditions exist which may negatively and materially affect our asset quality and the adequacy of our allowance for loan losses and, thus, the resulting provision for loan losses.
Noninterest Income
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Service charges on deposit accounts |
$ | 717 | $ | 749 | ||||
| Mortgage lending |
866 | 655 | ||||||
| Bank-owned life insurance |
437 | 435 | ||||||
| Gain from loan guarantee program |
1,717 | — | ||||||
| Securities losses, net |
(123 | ) | — | |||||
| Other |
1,880 | 1,486 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Total noninterest income |
$ | 5,494 | $ | 3,325 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The Company’s income from mortgage lending is primarily attributable to the (1) origination and sale of new mortgage loans and (2) servicing of mortgage loans. Origination income, net, is comprised of gains or losses from the sale of the mortgage loans originated, origination fees, underwriting fees and other fees associated with the origination of loans, which are netted against the commission expense associated with these originations. The Company’s normal practice is to originate mortgage loans for sale in the secondary market and to either sell or retain the MSRs when the loan is sold.
MSRs are recognized based on the fair value of the servicing right on the date the corresponding mortgage loan is sold. Subsequent to the date of transfer, the Company has elected to measure its MSRs under the amortization method. Servicing fee income is reported net of any related amortization expense.
46
Table of Contents
The Company evaluates MSRs for impairment on a quarterly basis. Impairment is determined by grouping MSRs by common predominant characteristics, such as interest rate and loan type. If the aggregate carrying amount of a particular group of MSRs exceeds the group’s aggregate fair value, a valuation allowance for that group is established. The valuation allowance is adjusted as the fair value changes. An increase in mortgage interest rates typically results in an increase in the fair value of the MSRs while a decrease in mortgage interest rates typically results in a decrease in the fair value of MSRs.
The following table presents a breakdown of the Company’s mortgage lending income for 2019 and 2018.
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Origination income |
$ | 545 | $ | 311 | ||||
| Servicing fees, net |
321 | 344 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Total mortgage lending income |
$ | 866 | $ | 655 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The increase in mortgage lending income was primarily due to improved pricing margins and an increase in the level of refinance activity. The Company’s income from mortgage lending typically fluctuates as mortgage interest rates change and is primarily attributable to the origination and sale of new mortgage loans.
In 2019, the Company recognized a gain of $1.7 million resulting from the termination of a Loan Guarantee Program (the “Program”) operated by the State of Alabama. For more information regarding the Program, please refer to Note 5, Loans and Allowance for Loan Losses, of the consolidated financial statements that accompany this report.
The increase in other noninterest income was primarily due to a $0.3 million gain from an insurance recovery received in the first quarter of 2019.
Noninterest Expense
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Salaries and benefits |
$ | 11,931 | $ | 10,653 | ||||
| Net occupancy and equipment |
1,907 | 1,465 | ||||||
| Professional fees |
1,014 | 902 | ||||||
| FDIC and other regulatory assessments |
181 | 310 | ||||||
| Other |
4,664 | 4,544 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Total noninterest expense |
$ | 19,697 | $ | 17,874 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The increase in salaries and benefits expense in 2019 over 2018 was due to a variety of factors, including an increase in the number of employees, routine annual wage increases, incentive accrual increases, an increase in the employer matching contribution percentage under the Company’s 401(k) Plan, and an increase in severance pay.
The increase in net occupancy and equipment expense and professional fees expense was primarily due to $0.5 million of various expenses related to the planned redevelopment of the Company’s headquarters in downtown Auburn. This amount includes revised depreciation estimates of $0.2 million. For more information regarding changes in accounting estimates, please refer to Note 1, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, of the consolidated financial statements that accompany this report.
The decrease in FDIC and other regulatory assessments expense was primarily due to the Bank receiving an assessment credit of approximately $0.2 million to offset future assessments in connection with the FDIC Deposit Insurance Fund exceeding its target ratio of 1.35% as of September 30, 2018. The Deposit Insurance Fund ratio was 1.36% at December 31, 2018, below the 1.38% threshold required for assessment credits to be applied. The Deposit Insurance Fund ratio was again below 1.38% at June 30, 2019, so assessment credit were applied against our assessment due for the third and fourth quarters of 2019. Future expense may continue to be reduced by these assessment credits depending on the level of the Deposit Insurance Fund, until they are fully utilized.
47
Table of Contents
Income Tax Expense
Income tax expense was $2.4 million in 2019 compared to $2.2 million in 2018. The Company’s effective income tax rate was 19.57% in 2019, compared to 19.84% in 2018.
BALANCE SHEET ANALYSIS
Securities
Securities available-for-sale were $235.9 million at December 31, 2019, a decrease of $3.9 million, or 2%, compared to $239.8 million as of December 31, 2018. This decline was primarily due to a decrease of $11.7 million in the amortized cost basis of securities available-for-sale as proceeds from sales, calls, and maturities were not reinvested. This decrease was offset by an increase in the fair value of securities available-for-sale of $7.8 million. The average tax-equivalent yields earned on total securities were 2.72% in 2019 and 2.76% in 2018.
The following table shows the carrying value and weighted average yield of securities available-for-sale as of December 31, 2019 according to contractual maturity. Actual maturities may differ from contractual maturities of residential mortgage-backed securities (“RMBS”) because the mortgages underlying the securities may be called or prepaid with or without penalty.
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 year | 1 to 5 | 5 to 10 | After 10 | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | or less | years | years | years | Fair Value | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency obligations |
$ | 4,993 | 27,245 | 18,470 | — | 50,708 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS |
— | 560 | 4,510 | 118,207 | 123,277 | |||||||||||||||||||
| State and political subdivisions |
— | 1,355 | 6,166 | 54,396 | 61,917 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total available-for-sale |
$ | 4,993 | 29,160 | 29,146 | 172,603 | 235,902 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weighted average yield: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency obligations |
1.63% | 1.78% | 2.26% | — | 1.94% | |||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS |
— | 3.42% | 2.50% | 2.64% | 2.63% | |||||||||||||||||||
| State and political subdivisions |
— | 4.06% | 2.32% | 3.07% | 3.01% | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total available-for-sale |
1.63% | 1.92% | 2.31% | 2.77% | 2.58% | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loans
| December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 56,782 | 63,467 | 59,086 | 49,850 | 52,479 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Construction and land development |
32,841 | 40,222 | 39,607 | 41,650 | 43,694 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
270,318 | 261,896 | 239,033 | 220,439 | 203,853 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Residential real estate |
92,575 | 102,597 | 106,863 | 110,855 | 116,673 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
8,866 | 9,295 | 9,588 | 8,712 | 10,220 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total loans |
461,382 | 477,477 | 454,177 | 431,506 | 426,919 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Less: unearned income |
(481 | ) | (569 | ) | (526 | ) | (560 | ) | (509) | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans, net of unearned income |
$ | 460,901 | 476,908 | 453,651 | 430,946 | 426,410 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total loans, net of unearned income, were $460.9 million at December 31, 2019, a decrease of $16.0 million, or 3%, from $476.9 million at December 31, 2018. Four loan categories represented the majority of the loan portfolio at December 31, 2019: commercial real estate mortgage loans (59%), residential real estate mortgage loans (20%), commercial and industrial loans (12%) and construction and land development loans (7%). Approximately 23% of the Company’s commercial real estate loans were classified as owner-occupied at December 31, 2019.
48
Table of Contents
Within its residential real estate mortgage portfolio, the Company had junior lien mortgages of approximately $10.8 million, or 2%, and $12.3 million, or 3%, of total loans, net of unearned income at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. For residential real estate mortgage loans with a consumer purpose, approximately $0.8 million and $0.5 million required interest-only payments at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The Company’s residential real estate mortgage portfolio does not include any option ARM loans, subprime loans, or any material amount of other high-risk consumer mortgage products.
Purchased loan participations included in the Company’s loan portfolio were approximately $1.4 million and $5.4 million as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. All purchased loan participations are underwritten by the Company independent of the selling bank. In addition, all loans, including purchased participations, are evaluated for collectability during the course of the Company’s normal loan review procedures. If the Company deems a participation loan impaired, it applies the same accounting policies and procedures described under “Critical Accounting Policies – Allowance for Loan Losses”.
The average yield earned on loans and loans held for sale was 4.83% in 2019 and 4.76% in 2018.
The specific economic and credit risks associated with our loan portfolio include, but are not limited to, the effects of current economic conditions on our borrowers’ cash flows, real estate market sales volumes, valuations, and availability and cost of financing for properties, real estate industry concentrations, deterioration in certain credits, interest rate fluctuations, reduced collateral values or non-existent collateral, title defects, inaccurate appraisals, financial deterioration of borrowers, fraud, and any violation of applicable laws and regulations.
The Company attempts to reduce these economic and credit risks by adhering to loan to value guidelines for collateralized loans, investigating the creditworthiness of borrowers and monitoring borrowers’ financial positions. Also, we establish and periodically review our lending policies and procedures. Banking regulations limit a bank’s credit exposure by prohibiting unsecured loan relationships that exceed 10% of its capital accounts; or 20% of capital accounts, if loans in excess of 10% are fully secured. Under these regulations, we are prohibited from having secured loan relationships in excess of approximately $19.5 million. Furthermore, we have an internal limit for aggregate credit exposure (loans outstanding plus unfunded commitments) to a single borrower of $17.5 million. Our loan policy requires that the Loan Committee of the Board of Directors approve any loan relationships that exceed this internal limit. At December 31, 2019, the Bank had no loan relationships exceeding our internal limit.
We periodically analyze our commercial loan portfolio to determine if a concentration of credit risk exists in any one or more industries. We use classification systems broadly accepted by the financial services industry in order to categorize our commercial borrowers. Loan concentrations to borrowers in the following classes exceeded 25% of the Bank’s total risk-based capital at December 31, 2019 (and related balances at December 31, 2018).
| December 31 | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Multi-family residential properties |
$ | 44,839 | $ | 40,455 | ||||||||
| Hotel/motel |
43,719 | 47,936 | ||||||||||
| Lessors of 1-4 family residential properties |
43,652 | 46,374 | ||||||||||
| Shopping centers |
30,407 | 35,789 | ||||||||||
| Office buildings |
29,548 | 25,421 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Allowance for Loan Losses
The Company maintains the allowance for loan losses at a level that management believes appropriate to adequately cover the Company’s estimate of probable losses in the loan portfolio. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, the allowance for loan losses was $4.4 million and $4.8 million, which management believed to be adequate at each of the respective dates. The judgments and estimates associated with the determination of the allowance for loan losses are described under “Critical Accounting Policies”.
49
Table of Contents
A summary of the changes in the allowance for loan losses and certain asset quality ratios for each of the five years in the five year period ended December 31, 2019 is presented below.
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses: |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of period |
$ | 4,790 | 4,757 | 4,643 | 4,289 | 4,836 | ||||||||||||||||
| Charge-offs: |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
(364 | ) | (52 | ) | (449 | ) | (97 | ) | (100 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
— | (38 | ) | — | (194 | ) | (866 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Residential real estate |
(6 | ) | (26 | ) | (107 | ) | (182 | ) | (89 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
(38 | ) | (52 | ) | (40 | ) | (67 | ) | (59 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total charge-offs |
(408 | ) | (168 | ) | (596 | ) | (540 | ) | (1,114 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Recoveries: |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
117 | 70 | 461 | 29 | 22 | |||||||||||||||||
| Construction and land development |
— | — | 347 | 1,212 | 17 | |||||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
1 | 19 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Residential real estate |
109 | 79 | 115 | 127 | 313 | |||||||||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
27 | 33 | 87 | 11 | 15 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total recoveries |
254 | 201 | 1,010 | 1,379 | 367 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net (charge-offs) recoveries |
(154 | ) | 33 | 414 | 839 | (747 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
(250 | ) | — | (300 | ) | (485 | ) | 200 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ending balance |
$ | 4,386 | 4,790 | 4,757 | 4,643 | 4,289 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| as a % of loans |
0.95 | % | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.08 | 1.01 | ||||||||||||||||
| as a % of nonperforming loans |
2,345 | % | 2,691 | 160 | 196 | 158 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net charge-offs (recoveries) as a % of average loans |
0.03 | % | (0.01 | ) | (0.09 | ) | (0.19 | ) | 0.18 | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
As noted under “Critical Accounting Policies”, management assesses the adequacy of the allowance prior to the end of each calendar quarter. The level of the allowance is based upon management’s evaluation of the loan portfolios, past loan loss experience, known and inherent risks in the portfolio, adverse situations that may affect the borrower’s ability to repay (including the timing of future payment), the estimated value of any underlying collateral, composition of the loan portfolio, economic conditions, industry and peer bank loan quality indications and other pertinent factors. This evaluation is inherently subjective as it requires various material estimates and judgments including the amounts and timing of future cash flows expected to be received on impaired loans that may be susceptible to significant change. The ratio of our allowance for loan losses to total loans outstanding was 0.95% at December 31, 2019, compared to 1.00% at December 31, 2018. In the future, the allowance to total loans outstanding ratio will increase or decrease to the extent the factors that influence our quarterly allowance assessment in their entirety either improve or weaken.
Net charge-offs were $0.2 million, or 0.03%, of average loans in 2019, compared to net recoveries of $33 thousand, or 0.01% of average loans, in 2018.
Our regulators, as an integral part of their examination process, periodically review the Company’s allowance for loan losses, and may require the Company to make additional provisions to the allowance for loan losses based on their judgment about information available to them at the time of their examinations.
Nonperforming Assets
At December 31, 2019 the Company had $0.2 million in nonperforming assets compared to $0.4 million at December 31, 2018.
50
Table of Contents
The table below provides information concerning total nonperforming assets and certain asset quality ratios.
| December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||
| Nonperforming assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nonperforming (nonaccrual) loans |
$ | 187 | 178 | 2,972 | 2,370 | 2,714 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other real estate owned |
— | 172 | — | 152 | 252 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total nonperforming assets |
$ | 187 | 350 | 2,972 | 2,522 | 2,966 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| as a % of loans and other real estate owned |
0.04 | % | 0.07 | 0.66 | 0.59 | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||||
| as a % of total assets |
0.02 | % | 0.04 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.36 | ||||||||||||||||
| Nonperforming loans as a % of total loans |
0.04 | % | 0.04 | 0.66 | 0.55 | 0.64 | ||||||||||||||||
| Accruing loans 90 days or more past due |
$ | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
The table below provides information concerning the composition of nonaccrual loans at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
| December 31 | ||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
| Nonaccrual loans: |
||||||||||
| Residential real estate |
187 | 178 | ||||||||
| Total nonaccrual loans / nonperforming loans |
$ | 187 | 178 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
The Company discontinues the accrual of interest income when (1) there is a significant deterioration in the financial condition of the borrower and full repayment of principal and interest is not expected or (2) the principal or interest is more than 90 days past due, unless the loan is both well-secured and in the process of collection. At December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, the Company had $0.2 million in loans on nonaccrual.
Due to the weakening credit status of a borrower, the Company may elect to formally restructure certain loans to facilitate a repayment plan that minimizes the potential losses that we might incur. Restructured loans, or troubled debt restructurings (“TDRs”), are classified as impaired loans, and if the loans are on nonaccrual status as of the date of restructuring, the loans are included in the nonaccrual loan balances noted above. Nonaccrual loan balances do not include loans that have been restructured that were performing as of the restructure date. At December 31, 2019 the Company had no accruing TDRs compared to $0.2 million in accruing TDRs at December 31, 2018.
At December 31, 2019 and 2018, there were no loans 90 days past due and still accruing interest.
The table below provides information concerning the composition of OREO at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
| December 31 | ||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
| Other real estate owned: |
||||||||||
| Residential |
$ | — | 172 | |||||||
| Total other real estate owned |
$ | — | 172 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
Potential Problem Loans
Potential problem loans represent those loans with a well-defined weakness and where information about possible credit problems of borrowers has caused management to have serious doubts about the borrower’s ability to comply with present repayment terms. This definition is believed to be substantially consistent with the standards established by the Federal Reserve, the Company’s primary regulator, for loans classified as substandard, excluding nonaccrual loans. Potential problem loans, which are not included in nonperforming assets, amounted to $4.4 million, or 1.0% of total loans at December 31, 2019, compared to $6.5 million, or 1.4% of total loans at December 31, 2018.
51
Table of Contents
The table below provides information concerning the composition of potential problem loans at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
| December 31 | ||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
| Potential problem loans: |
||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 266 | 522 | |||||||
| Construction and land development |
1,043 | 741 | ||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
99 | 688 | ||||||||
| Residential real estate |
2,899 | 4,506 | ||||||||
| Consumer installment |
64 | 71 | ||||||||
| Total potential problem loans |
$ | 4,371 | 6,528 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
At December 31, 2019, approximately $1.1 million or 26.7% of total potential problem loans were past due at least 30 but less than 90 days.
The following table is a summary of the Company’s performing loans that were past due at least 30 days but less than 90 days as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
| December 31 | ||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
| Performing loans past due 30 to 89 days: |
||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 24 | 100 | |||||||
| Construction and land development |
456 | 225 | ||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
— | — | ||||||||
| Residential real estate |
1,608 | 1,740 | ||||||||
| Consumer installment |
64 | 41 | ||||||||
| Total performing loans past due 30 to 89 days |
$ | 2,152 | 2,106 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
Deposits
| December 31 | ||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
| Noninterest bearing demand |
$ | 196,218 | 201,648 | |||||||
| NOW |
138,315 | 120,769 | ||||||||
| Money market |
160,934 | 161,464 | ||||||||
| Savings |
61,486 | 59,075 | ||||||||
| Certificates of deposit under $100,000 |
59,516 | 62,207 | ||||||||
| Certificates of deposit and other time deposits of $100,000 or more |
107,683 | 108,620 | ||||||||
| Brokered certificates of deposit |
— | 10,410 | ||||||||
| Total deposits |
$ | 724,152 | 724,193 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
Total deposits were $724.2 million at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. Decreases of $5.4 million in noninterest-bearing deposits were offset by increases in interest-bearing deposits of $5.4 million during 2019. Of the $5.4 million increase in interest-bearing deposits, $17.5 million was due to increases in NOW accounts and $2.4 million in savings accounts. These increases were partially offset by decreases of $10.4 million in brokered certificates of deposit and $3.6 million in retail certificates of deposit.
The average rates paid on total interest-bearing deposits were 0.80% in 2019 and 0.68% in 2018. Noninterest bearing deposits were 27% and 28% of total deposits at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
52
Table of Contents
Other Borrowings
Other borrowings generally consist of short-term borrowings and long-term debt. Short-term borrowings generally consist of federal funds purchased and securities sold under agreements to repurchase with an original maturity of one year or less. The Bank had available federal fund lines totaling $41.0 million with none outstanding at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. Securities sold under agreements to repurchase totaled $1.1 million and $2.3 million at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
The average rates paid on short-term borrowings was 0.49% and 0.68% in 2019 and 2018, respectively. Information concerning the average balances, weighted average rates, and maximum amounts outstanding for short-term borrowings during the two-year period ended December 31, 2019 is included in Note 9 to the accompanying consolidated financial statements included in this annual report.
The Company had no long-term debt outstanding at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. On April 27, 2018, the Company formally redeemed all of the issued and outstanding junior subordinated debentures, which were previously presented as long-term debt. The average rate paid on long-term debt in 2018 was 4.50%.
CAPITAL ADEQUACY
The Company’s consolidated stockholders’ equity was $98.3 million and $89.1 million as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The change from December 31, 2018 was primarily driven by net earnings of $9.7 million and other comprehensive gain due to the change in unrealized gains on securities available-for-sale, net of tax, of $5.8 million, partially offset by cash dividends paid of $3.5 million and stock repurchases of $2.7 million, representing 77,907 shares.
The Bank’s Tier 1 leverage ratio was 11.23%, Common Equity Tier 1 (“CET1”) risk-based capital ratio was 17.28%, Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio was 17.28%, and total risk-based capital ratio was 18.12% at December 31, 2019. These ratios exceed the minimum regulatory capital percentages of 5.0% for Tier 1 leverage ratio, 6.5% for CET1 risk-based capital ratio, 8.0% for Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio, and 10.0% for total risk-based capital ratio to be considered “well capitalized.” Based on current regulatory standards, the Bank is classified as “well capitalized.”
MARKET AND LIQUIDITY RISK MANAGEMENT
Management’s objective is to manage assets and liabilities to provide a satisfactory, consistent level of profitability within the framework of established liquidity, loan, investment, borrowing, and capital policies. The Bank’s Asset Liability Management Committee (“ALCO”) is charged with the responsibility of monitoring these policies, which are designed to ensure an acceptable asset/liability composition. Two critical areas of focus for ALCO are interest rate risk and liquidity risk management.
Interest Rate Risk Management
In the normal course of business, the Company is exposed to market risk arising from fluctuations in interest rates because assets and liabilities may mature or reprice at different times. For example, if liabilities reprice faster than assets, and interest rates are generally rising, earnings will initially decline. In addition, assets and liabilities may reprice at the same time but by different amounts. For example, when the general level of interest rates is rising, the Company may increase rates paid on interest bearing demand deposit accounts and savings deposit accounts by an amount that is less than the general increase in market interest rates. Also, short-term and long-term market interest rates may change by different amounts. For example, a flattening yield curve may reduce the interest spread between new loan yields and funding costs. Further, the remaining maturity of various assets and liabilities may shorten or lengthen as interest rates change. For example, if long-term mortgage interest rates decline sharply, mortgage-backed securities in the securities portfolio may prepay earlier than anticipated, which could reduce earnings. Interest rates may also have a direct or indirect effect on loan demand, loan losses, mortgage origination volume, the fair value of MSRs and other items affecting earnings.
ALCO measures and evaluates the interest rate risk so that we can meet customer demands for various types of loans and deposits. ALCO determines the most appropriate amounts of on-balance sheet and off-balance sheet items. Measurements used to help manage interest rate sensitivity include an earnings simulation and an economic value of equity model.
53
Table of Contents
Earnings simulation. Management believes that interest rate risk is best estimated by our earnings simulation modeling. On at least a quarterly basis, the following 12 month time period is simulated to determine a baseline net interest income forecast and the sensitivity of this forecast to changes in interest rates. The baseline forecast assumes an unchanged or flat interest rate environment. Forecasted levels of earning assets, interest-bearing liabilities, and off-balance sheet financial instruments are combined with ALCO forecasts of market interest rates for the next 12 months and other factors in order to produce various earnings simulations and estimates.
To help limit interest rate risk, we have guidelines for earnings at risk which seek to limit the variance of net interest income from gradual changes in interest rates. For changes up or down in rates from management’s flat interest rate forecast over the next 12 months, policy limits for net interest income variances are as follows:
| ● | +/- 20% for a gradual change of 400 basis points |
| ● | +/- 15% for a gradual change of 300 basis points |
| ● | +/- 10% for a gradual change of 200 basis points |
| ● | +/- 5% for a gradual change of 100 basis points |
The following table reports the variance of net interest income over the next 12 months assuming a gradual change in interest rates up or down when compared to the baseline net interest income forecast at December 31, 2019.
| Changes in Interest Rates | Net Interest Income % Variance | |||
| 400 basis points |
0.42 % | |||
| 300 basis points |
0.55 | |||
| 200 basis points |
0.54 | |||
| 100 basis points |
0.32 | |||
| (100) basis points |
(1.27) | |||
| (200) basis points |
(1.99) | |||
| (300) basis points |
NM | |||
| (400) basis points |
NM | |||
NM=not meaningful
At December 31, 2019, our earnings simulation model indicated that we were in compliance with the policy guidelines noted above.
Economic Value of Equity. Economic value of equity (“EVE”) measures the extent that estimated economic values of our assets, liabilities and off-balance sheet items will change as a result of interest rate changes. Economic values are estimated by discounting expected cash flows from assets, liabilities and off-balance sheet items, which establishes a base case EVE. In contrast with our earnings simulation model which evaluates interest rate risk over a 12 month timeframe, EVE uses a terminal horizon which allows for the re-pricing of all assets, liabilities, and off-balance sheet items. Further, EVE is measured using values as of a point in time and does not reflect any actions that ALCO might take in responding to or anticipating changes in interest rates, or market and competitive conditions.
To help limit interest rate risk, we have stated policy guidelines for an instantaneous basis point change in interest rates, such that our EVE should not decrease from our base case by more than the following:
| ● | 45% for an instantaneous change of +/- 400 basis points |
| ● | 35% for an instantaneous change of +/- 300 basis points |
| ● | 25% for an instantaneous change of +/- 200 basis points |
| ● | 15% for an instantaneous change of +/- 100 basis points |
54
Table of Contents
The following table reports the variance of EVE assuming an immediate change in interest rates up or down when compared to the baseline EVE at December 31, 2019.
| Changes in Interest Rates | EVE % Variance | |||
| 400 basis points |
(24.09) % | |||
| 300 basis points |
(16.16) | |||
| 200 basis points |
(9.74) | |||
| 100 basis points |
(3.62) | |||
| (100) basis points |
(1.33) | |||
| (200) basis points |
(4.08) | |||
| (300) basis points |
NM | |||
| (400) basis points |
NM | |||
NM=not meaningful
At December 31, 2019, our EVE model indicated that we were in compliance with the policy guidelines noted above.
Each of the above analyses may not, on its own, be an accurate indicator of how our net interest income will be affected by changes in interest rates. Income associated with interest-earning assets and costs associated with interest-bearing liabilities may not be affected uniformly by changes in interest rates. In addition, the magnitude and duration of changes in interest rates may have a significant impact on net interest income. For example, although certain assets and liabilities may have similar maturities or periods of repricing, they may react in different degrees to changes in market interest rates, and other economic and market factors, including market perceptions. Interest rates on certain types of assets and liabilities fluctuate in advance of changes in general market rates, while interest rates on other types of assets and liabilities may lag behind changes in general market rates. In addition, certain assets, such as adjustable rate mortgage loans, have features (generally referred to as “interest rate caps and floors”) which limit changes in interest rates. Prepayment and early withdrawal levels also could deviate significantly from those assumed in calculating the maturity of certain instruments. The ability of many borrowers to service their debts also may decrease during periods of rising interest rates or economic stress, which may differ across industries and economic sectors. ALCO reviews each of the above interest rate sensitivity analyses along with several different interest rate scenarios in seeking satisfactory, consistent levels of profitability within the framework of the Company’s established liquidity, loan, investment, borrowing, and capital policies.
The Company may also use derivative financial instruments to improve the balance between interest-sensitive assets and interest-sensitive liabilities and as one tool to manage interest rate sensitivity while continuing to meet the credit and deposit needs of our customers. From time to time, the Company may enter into interest rate swaps (“swaps”) to facilitate customer transactions and meet their financing needs. These swaps qualify as derivatives, but are not designated as hedging instruments. At December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company had no derivative contracts to assist in managing interest rate sensitivity.
Liquidity Risk Management
Liquidity is the Company’s ability to convert assets into cash equivalents in order to meet daily cash flow requirements, primarily for deposit withdrawals, loan demand and maturing obligations. Without proper management of its liquidity, the Company could experience higher costs of obtaining funds due to insufficient liquidity, while excessive liquidity can lead to a decline in earnings due to the cost of foregoing alternative higher-yielding investment opportunities.
Liquidity is managed at two levels. The first is the liquidity of the Company. The second is the liquidity of the Bank. The management of liquidity at both levels is essential, because the Company and the Bank are separate and distinct legal entities with different funding needs and sources, and each are subject to regulatory guidelines and requirements. The Company depends upon dividends from the Bank for liquidity to pay its operating expenses, debt obligations and dividends. The Bank’s payment of dividends depends on its earnings, liquidity, capital and the absence of any regulatory restrictions.
The primary source of funding and liquidity for the Company has been dividends received from the Bank. If needed, the Company could also issue common stock or other securities. Primary uses of funds by the Company include dividends paid to stockholders and stock repurchases.
55
Table of Contents
Primary sources of funding for the Bank include customer deposits, other borrowings, repayment and maturity of securities, and sale and repayment of loans. The Bank has access to federal funds lines from various banks and borrowings from the Federal Reserve discount window. In addition to these sources, the Bank has participated in the FHLB’s advance program to obtain funding for its growth. Advances include both fixed and variable terms and are taken out with varying maturities. As of December 31, 2019, the Bank had a remaining available line of credit with the FHLB totaling $246.7 million. As of December 31, 2019, the Bank also had $41.0 million of federal funds lines, with none outstanding. Primary uses of funds include repayment of maturing obligations and growing the loan portfolio.
The following table presents additional information about our contractual obligations as of December 31, 2019, which by their terms had contractual maturity and termination dates subsequent to December 31, 2019:
| Payments due by period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 year | 1 to 3 | 3 to 5 | More than | |||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | Total | or less | years | years | 5 years | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Contractual obligations: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Deposit maturities (1) |
$ | 724,152 | 649,693 | 62,075 | 12,384 | — | ||||||||||||||
| Operating lease obligations |
788 | 99 | 150 | 153 | 386 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 724,940 | 649,792 | 62,225 | 12,537 | 386 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
(1) Deposits with no stated maturity (demand, NOW, money market, and savings deposits) are presented in the “1 year or less” column
Management believes that the Company and the Bank have adequate sources of liquidity to meet all known contractual obligations and unfunded commitments, including loan commitments and reasonable borrower, depositor, and creditor requirements over the next 12 months.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
At December 31, 2019, the Bank had outstanding standby letters of credit of $1.9 million and unfunded loan commitments outstanding of $60.6 million. Because these commitments generally have fixed expiration dates and many will expire without being drawn upon, the total commitment level does not necessarily represent future cash requirements. If needed to fund these outstanding commitments, the Bank has the ability to liquidate federal funds sold or securities available-for-sale, or on a short-term basis to borrow and purchase federal funds from other financial institutions.
Residential mortgage lending and servicing activities
Since 2009, we have primarily sold residential mortgage loans in the secondary market to Fannie Mae while retaining the servicing of these loans. The sale agreements for these residential mortgage loans with Fannie Mae and other investors include various representations and warranties regarding the origination and characteristics of the residential mortgage loans. Although the representations and warranties vary among investors, they typically cover ownership of the loan, validity of the lien securing the loan, the absence of delinquent taxes or liens against the property securing the loan, compliance with loan criteria set forth in the applicable agreement, compliance with applicable federal, state, and local laws, among other matters.
As of December 31, 2019, the unpaid principal balance of residential mortgage loans, which we have originated and sold, but retained the servicing rights was $271.5 million. Although these loans are generally sold on a non-recourse basis, except for breaches of customary seller representations and warranties, we may have to repurchase residential mortgage loans in cases where we breach such representations or warranties or the other terms of the sale, such as where we fail to deliver required documents or the documents we deliver are defective. Investors also may require the repurchase of a mortgage loan when an early payment default underwriting review reveals significant underwriting deficiencies, even if the mortgage loan has subsequently been brought current. Repurchase demands are typically reviewed on an individual loan by loan basis to validate the claims made by the investor and to determine if a contractually required repurchase event has occurred. We seek to reduce and manage the risks of potential repurchases or other claims by mortgage loan investors through our underwriting, quality assurance and servicing practices, including good communications with our residential mortgage investors.
56
Table of Contents
The Company was not required to repurchase any loans during 2019 as a result of representation and warranty provisions contained in the Company’s sale agreements with Fannie Mae. During 2018, the Company was required to repurchase one loan with an aggregate principal balance of $53 thousand that was current as to principal and interest at the time of repurchase. At December 31, 2019, the Company had no pending repurchase or make-whole requests related to representation and warranty provisions.
We service all residential mortgage loans originated and sold by us to Fannie Mae. As servicer, our primary duties are to: (1) collect payments due from borrowers; (2) advance certain delinquent payments of principal and interest; (3) maintain and administer any hazard, title, or primary mortgage insurance policies relating to the mortgage loans; (4) maintain any required escrow accounts for payment of taxes and insurance and administer escrow payments; and (5) foreclose on defaulted mortgage loans or take other actions to mitigate the potential losses to investors consistent with the agreements governing our rights and duties as servicer.
The agreement under which we act as servicer generally specifies a standard of responsibility for actions taken by us in such capacity and provides protection against expenses and liabilities incurred by us when acting in compliance with the respective servicing agreements. However, if we commit a material breach of our obligations as servicer, we may be subject to termination if the breach is not cured within a specified period following notice. The standards governing servicing and the possible remedies for violations of such standards are determined by servicing guides issued by Fannie Mae as well as the contract provisions established between Fannie Mae and the Bank. Remedies could include repurchase of an affected loan.
Although to date repurchase requests related to representation and warranty provisions, and servicing activities have been limited, it is possible that requests to repurchase mortgage loans may increase in frequency if investors more aggressively pursue all means of recovering losses on their purchased loans. As of December 31, 2019, we believe that this exposure is not material due to the historical level of repurchase requests and loss trends, the results of our quality control reviews, and the fact that 99% of our residential mortgage loans serviced for Fannie Mae were current as of such date. We maintain ongoing communications with our investors and will continue to evaluate this exposure by monitoring the level and number of repurchase requests as well as the delinquency rates in our investor portfolios.
Effects of Inflation and Changing Prices
The consolidated financial statements and related consolidated financial data presented herein have been prepared in accordance with GAAP and practices within the banking industry which require the measurement of financial position and operating results in terms of historical dollars without considering the changes in the relative purchasing power of money over time due to inflation. Unlike most industrial companies, virtually all the assets and liabilities of a financial institution are monetary in nature. As a result, interest rates have a more significant impact on a financial institution’s performance than the effects of general levels of inflation.
CURRENT ACCOUNTING DEVELOPMENTS
The following ASUs have been issued by the FASB but are not yet effective.
| ● | ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments – Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments; |
| ● | ASU 2018-13, Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosure Framework – Changes to the Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurement; and |
| ● | ASU 2018-15, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other – Internal Use Software (Subtopic 350-40): Customer’s Accounting for Implementation Costs Incurred in a Cloud Computing Arrangement that is a Service Contract. |
57
Table of Contents
Information about these pronouncements is described in more detail below.
ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): - Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments, amends guidance on reporting credit losses for assets held at amortized cost basis and available for sale debt securities. For assets held at amortized cost basis, the new standard eliminates the probable initial recognition threshold in current GAAP and, instead, requires an entity to reflect its current estimate of all expected credit losses using a broader range of information regarding past events, current conditions and forecasts assessing the collectability of cash flows. The allowance for credit losses is a valuation account that is deducted from the amortized cost basis of the financial assets to present the net amount expected to be collected. For available for sale debt securities, credit losses should be measured in a manner similar to current GAAP, however the new standard will require that credit losses be presented as an allowance rather than as a write-down. The new guidance affects entities holding financial assets and net investment in leases that are not accounted for at fair value through net income. The amendments affect loans, debt securities, trade receivables, net investments in leases, off-balance sheet credit exposures, reinsurance receivables, and any other financial assets not excluded from the scope that have the contractual right to receive cash. The Company has developed an implementation team that is following a general timeline. The team has been working with an advisory consultant, with whom a third-party software license has been purchased. The Company’s preliminary evaluation indicates the provisions of ASU No. 2016-13 are expected to impact the Company’s consolidated financial statements, in particular the level of the reserve for credit losses. The Company is continuing to evaluate the extent of the potential impact and expects that portfolio composition and economic conditions at the time of adoption will be a factor. In November 2019, the FASB issued guidance to defer the effective dates for private companies, not-for-profit organizations, and certain smaller reporting companies applying standards on current expected credit losses. As a result of this delay, the Company’s effective dated for ASU 2016-13 was delayed to fiscal year beginning after December 15, 2022 including interim periods within those fiscal years.
ASU 2018-13, Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosure Framework – Changes to the Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurement, improves the disclosure requirements on fair value measurements by eliminating the requirements to disclose (i) the amount of and reasons for transfers between Level 1 and Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy; (ii) the policy for timing of transfers between levels; and (iii) the valuation processes for Level 3 fair value measurements. This ASU also added specific disclosure requirements for fair value measurements for public entities including the requirement to disclose the changes in unrealized gains and losses for the period included in other comprehensive income for recurring Level 3 fair value measurements and the range and weighted average of significant unobservable inputs used to develop Level 3 fair value measurements.
The amendments in this ASU are effective for all entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, and all interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted upon issuance of the ASU. Entities are permitted to early adopt amendments that remove or modify disclosures and delay the adoption of the additional disclosures until their effective date. The Company adopted this ASU on January 1, 2020. Adoption of this guidance did not have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
ASU 2018- 15, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other – Internal Use Software (Subtopic 350-40): Customer’s Accounting for Implementation Costs Incurred in a Cloud Computing Arrangement that is a Service Contract aligns the requirements for capitalizing implementation costs incurred in a hosting arrangement that is a service contract with the requirements for capitalizing implementation costs incurred to develop or obtain internal-use software (and hosting arrangements that include internal-use software license). This ASU requires entities to use the guidance in FASB ASC 350-40, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other - Internal Use Software, to determine whether to capitalize or expense implementation costs related to the service contract. This ASU also requires entities to (i) expense capitalized implementation costs of a hosting arrangement that is a service contract over the term of the hosting arrangement; (ii) present the expense related to the capitalized implementation costs in the same line item on the income statement as fees associated with the hosting element of the arrangement; (iii) classify payments for capitalized implementation costs in the statement of cash flows in the same manner as payments made for fees associated with the hosting element; and (iv) present the capitalized implementation costs in the same balance sheet line item that a prepayment for the fees associated with the hosting arrangement would be presented.
The amendments in this ASU are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019 and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The Company adopted this ASU on January 1, 2020. Adoption of this guidance did not have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
58
Table of Contents
Table 1 – Explanation of Non-GAAP Financial Measures
In addition to results presented in accordance with GAAP, this annual report on Form 10-K includes certain designated net interest income amounts presented on a tax-equivalent basis, a non-GAAP financial measure, including the presentation of total revenue and the calculation of the efficiency ratio.
The Company believes the presentation of net interest income on a tax-equivalent basis provides comparability of net interest income from both taxable and tax-exempt sources and facilitates comparability within the industry. Although the Company believes these non-GAAP financial measures enhance investors’ understanding of its business and performance, these non-GAAP financial measures should not be considered an alternative to GAAP. The reconciliation of these non-GAAP financial measures from GAAP to non-GAAP is presented below.
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net interest income (GAAP) |
$ | 26,064 | 25,570 | 24,526 | 22,732 | 22,718 | ||||||||||||||||
| Tax-equivalent adjustment |
557 | 613 | 1,205 | 1,276 | 1,342 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net interest income (Tax-equivalent) |
$ | 26,621 | 26,183 | 25,731 | 24,008 | 24,060 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
59
Table of Contents
Table 2 - Selected Financial Data
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands, except per share amounts) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income statement |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax-equivalent interest income (a) |
$ | 30,804 | 29,859 | 29,325 | 28,092 | 28,495 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total interest expense |
4,183 | 3,676 | 3,594 | 4,084 | 4,435 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax equivalent net interest income (a) |
26,621 | 26,183 | 25,731 | 24,008 | 24,060 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
(250) | — | (300) | (485) | 200 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total noninterest income |
5,494 | 3,325 | 3,441 | 3,383 | 4,532 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total noninterest expense |
19,697 | 17,874 | 16,784 | 15,348 | 16,372 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings before income taxes and tax-equivalent adjustment |
12,668 | 11,634 | 12,688 | 12,528 | 12,020 | |||||||||||||||||
| Tax-equivalent adjustment |
557 | 613 | 1,205 | 1,276 | 1,342 | |||||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
2,370 | 2,187 | 3,637 | 3,102 | 2,820 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 9,741 | 8,834 | 7,846 | 8,150 | 7,858 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Per share data: |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted net earnings |
$ | 2.72 | 2.42 | 2.15 | 2.24 | 2.16 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared |
$ | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.88 | ||||||||||||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted |
3,581,476 | 3,643,780 | 3,643,616 | 3,643,504 | 3,643,428 | |||||||||||||||||
| Shares outstanding |
3,566,146 | 3,643,868 | 3,643,668 | 3,643,523 | 3,643,478 | |||||||||||||||||
| Book value |
$ | 27.57 | 24.44 | 23.85 | 22.55 | 21.94 | ||||||||||||||||
| Common stock price |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| High |
$ | 53.90 | 53.50 | 40.25 | 31.31 | 30.39 | ||||||||||||||||
| Low |
30.61 | 28.88 | 30.75 | 24.56 | 23.15 | |||||||||||||||||
| Period-end |
$ | 53.00 | 31.66 | 38.90 | 31.31 | 29.62 | ||||||||||||||||
| To earnings ratio |
19.49 | x | 13.08 | 18.09 | 13.98 | 13.78 | ||||||||||||||||
| To book value |
192 | % | 130 | 163 | 139 | 135 | ||||||||||||||||
| Performance ratios: |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Return on average equity |
10.35 | % | 10.14 | 9.17 | 9.65 | 9.98 | ||||||||||||||||
| Return on average assets |
1.18 | % | 1.08 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.98 | ||||||||||||||||
| Dividend payout ratio |
36.76 | % | 39.67 | 42.79 | 40.18 | 40.74 | ||||||||||||||||
| Average equity to average assets |
11.39 | % | 10.63 | 10.30 | 10.14 | 9.79 | ||||||||||||||||
| Asset Quality: |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses as a % of: |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans |
0.95 | % | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.08 | 1.01 | ||||||||||||||||
| Nonperforming loans |
2,345 | % | 2,691 | 160 | 196 | 158 | ||||||||||||||||
| Nonperforming assets as a % of: |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans and other real estate owned |
0.04 | % | 0.07 | 0.66 | 0.59 | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
0.02 | % | 0.04 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.36 | ||||||||||||||||
| Nonperforming loans as % of loans |
0.04 | % | 0.04 | 0.66 | 0.55 | 0.64 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net charge-offs (recoveries) as a % of average loans |
0.03 | % | (0.01) | (0.09) | (0.19) | 0.18 | ||||||||||||||||
| Capital Adequacy (c): |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| CET 1 risk-based capital ratio |
17.28 | % | 16.49 | 16.42 | 16.44 | 15.28 | ||||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio |
17.28 | % | 16.49 | 16.98 | 17.00 | 16.57 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total risk-based capital ratio |
18.12 | % | 17.38 | 17.91 | 17.95 | 17.44 | ||||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 leverage ratio |
11.23 | % | 11.33 | 10.95 | 10.27 | 10.35 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other financial data: |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net interest margin (a) |
3.43 | % | 3.40 | 3.29 | 3.05 | 3.17 | ||||||||||||||||
| Effective income tax rate |
19.57 | % | 19.84 | 31.67 | 27.57 | 26.41 | ||||||||||||||||
| Efficiency ratio (b) |
61.33 | % | 60.57 | 57.53 | 56.03 | 57.26 | ||||||||||||||||
| Selected period end balances: |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Securities |
$ | 235,902 | 239,801 | 257,697 | 243,572 | 241,687 | ||||||||||||||||
| Loans, net of unearned income |
460,901 | 476,908 | 453,651 | 430,946 | 426,410 | |||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses |
4,386 | 4,790 | 4,757 | 4,643 | 4,289 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
828,570 | 818,077 | 853,381 | 831,943 | 817,189 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total deposits |
724,152 | 724,193 | 757,659 | 739,143 | 723,627 | |||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt |
— | — | 3,217 | 3,217 | 7,217 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity |
98,328 | 89,055 | 86,906 | 82,177 | 79,949 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
(a) Tax-equivalent. See “Table 1 - Explanation of Non-GAAP Financial Measures”.
(b) Efficiency ratio is the result of noninterest expense divided by the sum of noninterest income and tax-equivalent net interest income.
(c) Regulatory capital ratios presented are for the Company’s wholly-owned subsidiary, AuburnBank.
60
Table of Contents
Table 3 - Average Balance and Net Interest Income Analysis
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest | Interest | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average | Income/ | Yield/ | Average | Income/ | Yield/ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | Balance | Expense | Rate | Balance | Expense | Rate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-earning assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans and loans held for sale (1) |
$ | 474,259 | $ | 22,930 | 4.83% | $ | 457,610 | $ | 21,766 | 4.76% | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Securities - taxable |
178,410 | 4,000 | 2.24% | 181,485 | 4,051 | 2.23% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Securities - tax-exempt (2) |
66,628 | 2,656 | 3.99% | 71,065 | 2,921 | 4.11% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total securities |
245,038 | 6,656 | 2.72% | 252,550 | 6,972 | 2.76% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Federal funds sold |
20,223 | 423 | 2.09% | 28,689 | 554 | 1.93% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest bearing bank deposits |
36,869 | 795 | 2.16% | 31,339 | 567 | 1.81% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total interest-earning assets |
776,389 | 30,804 | 3.97% | 770,188 | 29,859 | 3.88% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
14,037 | 13,802 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other assets |
36,119 | 35,539 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 826,545 | $ | 819,529 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NOW |
$ | 134,430 | 710 | 0.53% | $ | 125,533 | 428 | 0.34% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Savings and money market |
218,630 | 969 | 0.44% | 220,810 | 855 | 0.39% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Certificates of deposits |
170,835 | 2,497 | 1.46% | 184,010 | 2,329 | 1.27% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total interest-bearing deposits |
523,895 | 4,176 | 0.80% | 530,353 | 3,612 | 0.68% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings |
1,443 | 7 | 0.49% | 2,634 | 18 | 0.68% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt |
— | — | 0.00% | 1,022 | 46 | 4.50% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total interest-bearing liabilities |
525,338 | 4,183 | 0.80% | 534,009 | 3,676 | 0.69% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noninterest-bearing deposits |
203,828 | 195,924 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other liabilities |
3,228 | 2,489 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity |
94,151 | 87,107 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total liabilities and and stockholders’ equity |
$ | 826,545 | $ | 819,529 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net interest income and margin |
$ | 26,621 | 3.43% | $ | 26,183 | 3.40% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1) Average loan balances are shown net of unearned income and loans on nonaccrual status have been included in the computation of average balances.
(2) Yields on tax-exempt securities have been computed on a tax-equivalent basis using an income tax rate of 21%.
61
Table of Contents
Table 4 - Volume and Rate Variance Analysis
| Years ended December 31, 2019 vs. 2018 | Years ended December 31, 2018 vs. 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net | Due to change in | Net | Due to change in | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | Change | Rate (2) | Volume (2) | Change | Rate (2) | Volume (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans and loans held for sale |
$ | 1,164 | 358 | 806 | $ | 985 | 247 | 738 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Securities - taxable |
(51 | ) | 18 | (69) | (178 | ) | 171 | (349) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Securities - tax-exempt (1) |
(265 | ) | (88 | ) | (177) | (624 | ) | (673 | ) | 49 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total securities |
(316 | ) | (70 | ) | (246) | (802 | ) | (502 | ) | (300) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Federal funds sold |
(131 | ) | 46 | (177) | 213 | 284 | (71) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest bearing bank deposits |
228 | 109 | 119 | 138 | 319 | (181) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total interest income |
$ | 945 | 443 | 502 | $ | 534 | 348 | 186 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NOW |
$ | 282 | 235 | 47 | $ | 180 | 181 | (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Savings and money market |
114 | 124 | (10) | 3 | 39 | (36) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Certificates of deposits |
168 | 361 | (193) | (22 | ) | 161 | (183) | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total interest-bearing deposits |
564 | 720 | (156) | 161 | 381 | (220) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings |
(11 | ) | (5 | ) | (6) | — | 6 | (6) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt |
(46 | ) | — | (46) | (79 | ) | 20 | (99) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total interest expense |
507 | 715 | (208) | 82 | 407 | (325) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net interest income |
$ | 438 | (272 | ) | 710 | $ | 452 | (59 | ) | 511 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Yields on tax-exempt securities have been computed on a tax-equivalent basis using an income tax rate of 21% for 2019 and 2018 and 34% for 2017. |
| (2) | Changes that are not solely a result of volume or rate have been allocated to volume. |
62
Table of Contents
Table 5 - Loan Portfolio Composition
| December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 56,782 | 63,467 | 59,086 | 49,850 | 52,479 | ||||||||||||||||
| Construction and land development |
32,841 | 40,222 | 39,607 | 41,650 | 43,694 | |||||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
270,318 | 261,896 | 239,033 | 220,439 | 203,853 | |||||||||||||||||
| Residential real estate |
92,575 | 102,597 | 106,863 | 110,855 | 116,673 | |||||||||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
8,866 | 9,295 | 9,588 | 8,712 | 10,220 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total loans |
461,382 | 477,477 | 454,177 | 431,506 | 426,919 | |||||||||||||||||
| Less: unearned income |
(481 | ) | (569 | ) | (526 | ) | (560 | ) | (509) | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans, net of unearned income |
460,901 | 476,908 | 453,651 | 430,946 | 426,410 | |||||||||||||||||
| Less: allowance for loan losses |
(4,386 | ) | (4,790 | ) | (4,757 | ) | (4,643 | ) | (4,289) | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans, net |
$ | 456,515 | 472,118 | 448,894 | 426,303 | 422,121 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
63
Table of Contents
Table 6 - Loan Maturities and Sensitivities to Changes in Interest Rates
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 year | 1 to 5 | After 5 | Adjustable | Fixed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | or less | years | years | Total | Rate | Rate | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 18,555 | 12,398 | 25,829 | 56,782 | 10,552 | 46,230 | 56,782 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction and land development |
26,102 | 6,599 | 140 | 32,841 | 12,179 | 20,662 | 32,841 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
25,607 | 114,382 | 130,329 | 270,318 | 7,328 | 262,990 | 270,318 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Residential real estate |
8,013 | 27,337 | 57,225 | 92,575 | 41,652 | 50,923 | 92,575 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
3,304 | 4,959 | 603 | 8,866 | 369 | 8,497 | 8,866 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total loans |
$ | 81,581 | 165,675 | 214,126 | 461,382 | 72,080 | 389,302 | 461,382 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
64
Table of Contents
Table 7 - Allowance for Loan Losses and Nonperforming Assets
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of period |
$ | 4,790 | 4,757 | 4,643 | 4,289 | 4,836 | ||||||||||||||
| Charge-offs: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
(364 | ) | (52 | ) | (449 | ) | (97 | ) | (100) | |||||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
— | (38 | ) | — | (194 | ) | (866) | |||||||||||||
| Residential real estate |
(6 | ) | (26 | ) | (107 | ) | (182 | ) | (89) | |||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
(38 | ) | (52 | ) | (40 | ) | (67 | ) | (59) | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total charge-offs |
(408 | ) | (168 | ) | (596 | ) | (540 | ) | (1,114) | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Recoveries: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
117 | 70 | 461 | 29 | 22 | |||||||||||||||
| Construction and land development |
— | — | 347 | 1,212 | 17 | |||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
1 | 19 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Residential real estate |
109 | 79 | 115 | 127 | 313 | |||||||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
27 | 33 | 87 | 11 | 15 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total recoveries |
254 | 201 | 1,010 | 1,379 | 367 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net (charge-offs) recoveries |
(154 | ) | 33 | 414 | 839 | (747) | ||||||||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
(250 | ) | — | (300 | ) | (485 | ) | 200 | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Ending balance |
$ | 4,386 | 4,790 | 4,757 | 4,643 | 4,289 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| as a % of loans |
0.95 | % | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.08 | 1.01 | ||||||||||||||
| as a % of nonperforming loans |
2,345 | % | 2,691 | 160 | 196 | 158 | ||||||||||||||
| Net charge-offs (recoveries) as % of average loans |
0.03 | % | (0.01 | ) | (0.09 | ) | (0.19 | ) | 0.18 | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Nonperforming assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Nonaccrual/nonperforming loans |
$ | 187 | 178 | 2,972 | 2,370 | 2,714 | ||||||||||||||
| Other real estate owned |
— | 172 | — | 152 | 252 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total nonperforming assets |
$ | 187 | 350 | 2,972 | 2,522 | 2,966 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| as a % of loans and other real estate owned |
0.04 | % | 0.07 | 0.66 | 0.59 | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||
| as a % total assets |
0.02 | % | 0.04 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.36 | ||||||||||||||
| Nonperforming loans as a % of total loans |
0.04 | % | 0.04 | 0.66 | 0.55 | 0.64 | ||||||||||||||
| Accruing loans 90 days or more past due |
$ | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
65
Table of Contents
Table 8 - Allocation of Allowance for Loan Losses
| December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | Amount | %* | Amount | %* | Amount | %* | Amount | %* | Amount | %* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 577 | 12.3 | $ | 778 | 13.3 | $ | 653 | 13.0 | $ | 540 | 11.6 | $ | 523 | 12.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction and land development |
569 | 7.1 | 700 | 8.4 | 734 | 8.7 | 812 | 9.7 | 669 | 10.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
2,289 | 58.6 | 2,218 | 54.9 | 2,126 | 52.7 | 2,071 | 51.0 | 1,879 | 47.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Residential real estate |
813 | 20.1 | 946 | 21.5 | 1,071 | 23.5 | 1,107 | 25.7 | 1,059 | 27.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
138 | 1.9 | 148 | 1.9 | 173 | 2.1 | 113 | 2.0 | 159 | 2.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total allowance for loan losses |
$ | 4,386 | $ | 4,790 | $ | 4,757 | $ | 4,643 | $ | 4,289 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
* Loan balance in each category expressed as a percentage of total loans.
66
Table of Contents
Table 9 - CDs and Other Time Deposits of $100,000 or More
| (Dollars in thousands) | December 31, 2019 | |||
|
|
||||
| Maturity of: |
||||
| 3 months or less |
$ | 13,910 | ||
| Over 3 months through 6 months |
7,318 | |||
| Over 6 months through 12 months |
39,867 | |||
| Over 12 months |
46,588 | |||
|
|
||||
| Total CDs and other time deposits of $100,000 or more |
$ | 107,683 | ||
|
|
||||
67
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Auburn National Bancorporation, Inc.
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Auburn National Bancorporation, Inc. and its subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of earnings, comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for the years then ended, and the related notes to the consolidated financial statements and schedules (collectively, the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013, and our report dated March 6, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Elliott Davis, LLC
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2015.
Greenville, South Carolina
March 6, 2020
69
Table of Contents
AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Balance Sheets
| December 31 | ||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands, except share data) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
$ | 15,172 | $ | 13,043 | ||||||
| Federal funds sold |
25,944 | 26,918 | ||||||||
| Interest bearing bank deposits |
51,327 | 25,115 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
92,443 | 65,076 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Securities available-for-sale |
235,902 | 239,801 | ||||||||
| Loans held for sale |
2,202 | 383 | ||||||||
| Loans, net of unearned income |
460,901 | 476,908 | ||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses |
(4,386 | ) | (4,790) | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Loans, net |
456,515 | 472,118 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Premises and equipment, net |
14,743 | 13,596 | ||||||||
| Bank-owned life insurance |
19,202 | 18,765 | ||||||||
| Other assets |
6,872 | 8,338 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 827,879 | $ | 818,077 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Liabilities: |
||||||||||
| Deposits: |
||||||||||
| Noninterest-bearing |
$ | 196,218 | $ | 201,648 | ||||||
| Interest-bearing |
527,934 | 522,545 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total deposits |
724,152 | 724,193 | ||||||||
| Federal funds purchased and securities sold under agreements to repurchase |
1,069 | 2,300 | ||||||||
| Accrued expenses and other liabilities |
4,330 | 2,529 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total liabilities |
729,551 | 729,022 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity: |
||||||||||
| Preferred stock of $.01 par value; authorized 200,000 shares; |
— | — | ||||||||
| Common stock of $.01 par value; authorized 8,500,000 shares; |
39 | 39 | ||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
3,784 | 3,779 | ||||||||
| Retained earnings |
101,801 | 95,635 | ||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net |
2,059 | (3,763) | ||||||||
| Less treasury stock, at cost - 390,989 shares and 313,267 shares at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively |
(9,355 | ) | (6,635) | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity |
98,328 | 89,055 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
$ | 827,879 | $ | 818,077 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
70
Table of Contents
AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Earnings
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Interest income: |
||||||||||
| Loans, including fees |
$ | 22,930 | $ | 21,766 | ||||||
| Securities: |
||||||||||
| Taxable |
4,000 | 4,051 | ||||||||
| Tax-exempt |
2,099 | 2,308 | ||||||||
| Federal funds sold and interest bearing bank deposits |
1,218 | 1,121 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total interest income |
30,247 | 29,246 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Interest expense: |
||||||||||
| Deposits |
4,176 | 3,612 | ||||||||
| Short-term borrowings |
7 | 18 | ||||||||
| Long-term debt |
— | 46 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total interest expense |
4,183 | 3,676 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net interest income |
26,064 | 25,570 | ||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
(250 | ) | — | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for loan losses |
26,314 | 25,570 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Noninterest income: |
||||||||||
| Service charges on deposit accounts |
717 | 749 | ||||||||
| Mortgage lending |
866 | 655 | ||||||||
| Bank-owned life insurance |
437 | 435 | ||||||||
| Gain from loan guarantee program |
1,717 | — | ||||||||
| Other |
1,880 | 1,486 | ||||||||
| Securities losses, net |
(123 | ) | — | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total noninterest income |
5,494 | 3,325 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Noninterest expense: |
||||||||||
| Salaries and benefits |
11,931 | 10,653 | ||||||||
| Net occupancy and equipment |
1,907 | 1,465 | ||||||||
| Professional fees |
1,014 | 902 | ||||||||
| FDIC and other regulatory assessments |
181 | 310 | ||||||||
| Other |
4,664 | 4,544 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total noninterest expense |
19,697 | 17,874 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Earnings before income taxes |
12,111 | 11,021 | ||||||||
| Income tax expense |
2,370 | 2,187 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 9,741 | $ | 8,834 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net earnings per share: |
||||||||||
| Basic and diluted |
$ | 2.72 | $ | 2.42 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding: |
||||||||||
| Basic and diluted |
3,581,476 | 3,643,780 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
71
Table of Contents
AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 9,741 | $ | 8,834 | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: |
||||||||||
| Unrealized net holding gain (loss) on securities |
5,730 | (3,197) | ||||||||
| Reclassification adjustment for net loss on securities recognized in net earnings |
92 | — | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) |
5,822 | (3,197) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Comprehensive income |
$ | 15,563 | $ | 5,637 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
72
Table of Contents
AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity
| (Dollars in thousands, except share data) | Common
Shares
Outstanding |
Common
Stock |
Additional
paid-in
capital |
Retained
earnings |
Accumulated
other
comprehensive
income (loss) |
Treasury
stock |
Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2017 |
3,643,668 | $ | 39 | 3,771 | 90,299 | (566 | ) | (6,637 | ) | $ | 86,906 | |||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
— | — | — | 8,834 | — | — | 8,834 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss |
— | — | — | — | (3,197 | ) | — | (3,197 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends paid ($0.96 per share) |
— | — | — | (3,498 | ) | — | — | (3,498 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sale of treasury stock |
200 | — | 8 | — | — | 2 | 10 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2018 |
3,643,868 | $ | 39 | $ | 3,779 | $ | 95,635 | $ | (3,763 | ) | $ | (6,635 | ) | $ | 89,055 | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
— | — | — | 9,741 | — | — | 9,741 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income |
— | — | — | — | 5,822 | — | 5,822 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends paid ($1.00 per share) |
— | — | — | (3,575 | ) | — | — | (3,575 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Stock repurchases |
(77,907 | ) | — | — | — | — | (2,721 | ) | (2,721 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sale of treasury stock |
185 | — | 5 | — | — | 1 | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2019 |
3,566,146 | $ | 39 | $ | 3,784 | $ | 101,801 | $ | 2,059 | $ | (9,355 | ) | $ | 98,328 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
73
Table of Contents
AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 9,741 | $ | 8,834 | ||||||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
(250 | ) | — | |||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
1,157 | 938 | ||||||||||||
| Premium amortization and discount accretion, net |
1,853 | 2,025 | ||||||||||||
| Deferred tax (benefit) expense |
(153 | ) | 71 | |||||||||||
| Net loss on securities available for sale |
123 | — | ||||||||||||
| Net gain on sale of loans held for sale |
(545 | ) | (311) | |||||||||||
| Net gain on other real estate owned |
(59 | ) | — | |||||||||||
| Loans originated for sale |
(30,407 | ) | (27,681) | |||||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of loans |
28,892 | 29,323 | ||||||||||||
| Increase in cash surrender value of bank owned life insurance |
(437 | ) | (435) | |||||||||||
| Net increase in other assets |
(872 | ) | (221) | |||||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in accrued expenses and other liabilities |
1,807 | (402) | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
$ | 10,850 | $ | 12,141 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from sales of securities available-for-sale |
36,462 | 8,770 | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from maturities of securities available-for-sale |
55,078 | 22,673 | ||||||||||||
| Purchase of securities available-for-sale |
(81,843 | ) | (19,841) | |||||||||||
| Decrease (increase) in loans, net |
15,771 | (24,749) | ||||||||||||
| Net purchases of premises and equipment |
(1,809 | ) | (240) | |||||||||||
| Decrease (increase) in FHLB stock |
32 | (20) | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of other real estate owned |
394 | 1,353 | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
$ | 24,085 | $ | (12,054) | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||||||||
| Net (decrease) increase in noninterest-bearing deposits |
(5,430 | ) | 7,731 | |||||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in interest-bearing deposits |
5,389 | (41,197) | ||||||||||||
| Net decrease in federal funds purchased and securities sold under agreements to repurchase |
(1,231 | ) | (358) | |||||||||||
| Repayments or retirement of long-term debt |
— | (3,217) | ||||||||||||
| Stock repurchases |
(2,721 | ) | — | |||||||||||
| Dividends paid |
(3,575 | ) | (3,498) | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Net cash used in financing activities |
$ | (7,568 | ) | $ | (40,539) | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 27,367 | $ | (40,452) | ||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period |
65,076 | 105,528 | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period |
$ | 92,443 | $ | 65,076 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
| |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: |
||||||||||||||
| Cash paid (received) during the period for: |
||||||||||||||
| Interest |
$ | 4,092 | $ | 3,616 | ||||||||||
| Income taxes |
2,295 | 2,688 | ||||||||||||
| Gain from loan guarantee program |
(1,717 | ) | — | |||||||||||
| Supplemental disclosure of non-cash transactions: |
||||||||||||||
| Initial recognition of operating lease right of use assets |
$ | 891 | $ | n/a | ||||||||||
| Initial recognition of operating lease liabilities |
889 | n/a | ||||||||||||
| Real estate acquired through foreclosure |
82 | 1,525 | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
74
Table of Contents
AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
NOTE 1: SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Nature of Business
Auburn National Bancorporation, Inc. (the “Company”) is a bank holding company whose primary business is conducted by its wholly-owned subsidiary, AuburnBank (the “Bank”). AuburnBank is a commercial bank located in Auburn, Alabama. The Bank provides a full range of banking services in its primary market area, Lee County, which includes the Auburn-Opelika Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Basis of Presentation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. Auburn National Bancorporation Capital Trust I was an affiliate of the Company and was included in these consolidated financial statements pursuant to the equity method of accounting. On April 27, 2018, the Trust was dissolved. Significant intercompany transactions and accounts are eliminated in consolidation.
Revenue Recognition
On January 1, 2018, the Company implemented ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, codified at ASC 606. The Company adopted ASC 606 using the modified retrospective transition method. The majority of the Company’s revenue stream is generated from interest income on loans and deposits which are outside the scope of ASC 606.
The Company’s sources of income that fall within the scope of ASC 606 include service charges on deposits, investment services, interchange fees and gains and losses on sales of other real estate, all of which are presented as components of noninterest income. The following is a summary of the revenue streams that fall within the scope of ASC 606:
| ● | Service charges on deposits, investment services, ATM and interchange fees – Fees from these services are either transaction-based, for which the performance obligations are satisfied when the individual transaction is processed, or set periodic service charges, for which the performance obligations are satisfied over the period the service is provided. Transaction-based fees are recognized at the time the transaction is processed, and periodic service charges are recognized over the service period. |
| ● | Gains on sales of other real estate – A gain on sale should be recognized when a contract for sale exists and control of the asset has been transferred to the buyer. ASC 606 lists several criteria required to conclude that a contract for sale exists, including a determination that the institution will collect substantially all of the consideration to which it is entitled. In addition to the loan-to-value, the analysis is based on various other factors, including the credit quality of the borrower, the structure of the loan, and any other factors that may affect collectability. |
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of the balance sheet date and the reported amounts of income and expense during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates. Material estimates that are particularly susceptible to significant change in the near term include the determination of the allowance for loan losses, fair value measurements, valuation of other real estate owned, and valuation of deferred tax assets.
75
Table of Contents
Change in Accounting Estimate
During the fourth quarter of 2019, the Company reassessed its estimate of the useful lives of certain fixed assets. The Company revised its original useful life estimate for certain land improvements, buildings and improvements and furniture, fixtures and equipment, with a carrying value of $0.5 million at December 31, 2019, to correspond with estimated demolition dates planned as part of the redevelopment project for our main campus. This is considered a change in accounting estimate, per ASC 250-10, where adjustments should be made prospectively. The effects of this change in accounting estimate on the 2019 consolidated financial statements was a decrease in net earnings of $0.2 million, or $0.04 per share.
Reclassifications
Certain amounts reported in the prior period have been reclassified to conform to the current-period presentation. These reclassifications had no impact on the Company’s previously reported net earnings or total stockholders’ equity.
Subsequent Events
The Company has evaluated the effects of events or transactions through the date of this filing that have occurred subsequent to December 31, 2019. The Company does not believe there are any material subsequent events that would require further recognition or disclosure.
Accounting Standards Adopted in 2019
In 2019, the Company adopted new guidance related to the following Accounting Standards Update (“Update” or “ASU”):
| ● | ASU 2016-02, Leases; and |
| ● | ASU 2017-02, Targeted Improvements to Accounting for Hedging Activities. |
Information about these pronouncements is described in more detail below.
ASU 2016-02, Leases, requires lessees to recognize the assets and liabilities that arise from leases on the balance sheet. A lessee should recognize in the statement of financial position a liability to make lease payments (the lease liability) and a right-of-use asset representing its right to use the underlying asset for the lease term. In July 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-10 and 2018-11, which are designed to make targeted improvements to and clarifications regarding ASU 2016-02. The Company adopted ASU No. 2016-02 on January 1, 2019. ASU No. 2016-02 did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements due to the fact the Company does not have any material leases.
ASU 2017-12, Targeted Improvements to Accounting for Hedging Activities, improves the transparency and understandability of information conveyed to financial statement users about an entity’s risk management activities by better aligning the entity’s financial reporting for hedging relationships with those risk management activities and reduces the complexity of and simplifies the application of hedge accounting by preparers. The Company adopted ASU No. 2017-12 on January 1, 2019. ASU No. 2017-12 did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Cash Equivalents
Cash equivalents include cash on hand, cash items in process of collection, amounts due from banks, including interest bearing deposits with other banks, and federal funds sold.
76
Table of Contents
Securities
Securities are classified based on management’s intention at the date of purchase. At December 31, 2019, all of the Company’s securities were classified as available-for-sale. Securities available-for-sale are used as part of the Company’s interest rate risk management strategy, and they may be sold in response to changes in interest rates, changes in prepayment risks or other factors. All securities classified as available-for-sale are recorded at fair value with any unrealized gains and losses reported in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of the deferred income tax effects. Interest and dividends on securities, including the amortization of premiums and accretion of discounts are recognized in interest income over the estimated life of the security using the effective interest method. Realized gains and losses from the sale of securities are determined using the specific identification method.
On a quarterly basis, management makes an assessment to determine whether there have been events or economic circumstances to indicate that a security on which there is an unrealized loss is other-than-temporarily impaired.
For debt securities with an unrealized loss, an other-than-temporary impairment write-down is triggered when (1) the Company has the intent to sell a debt security, (2) it is more likely than not that the Company will be required to sell the debt security before recovery of its amortized cost basis, or (3) the Company does not expect to recover the entire amortized cost basis of the debt security. If the Company has the intent to sell a debt security or if it is more likely than not that it will be required to sell the debt security before recovery, the other-than-temporary write-down is equal to the entire difference between the debt security’s amortized cost and its fair value. If the Company does not intend to sell the security or it is not more likely than not that it will be required to sell the security before recovery, the other-than-temporary impairment write-down is separated into the amount that is credit related (credit loss component) and the amount due to all other factors. The credit loss component is recognized in earnings, as a realized loss in securities gains (losses), and is the difference between the security’s amortized cost basis and the present value of its expected future cash flows. The remaining difference between the security’s fair value and the present value of future expected cash flows is due to factors that are not credit related and is recognized in other comprehensive income, net of applicable taxes.
Loans held for sale
Loans originated and intended for sale in the secondary market are carried at the lower of cost or estimated fair value in the aggregate. Loan sales are recognized when the transaction closes, the proceeds are collected, and ownership is transferred. Continuing involvement, through the sales agreement, consists of the right to service the loan for a fee for the life of the loan, if applicable. Gains on the sale of loans held for sale are recorded net of related costs, such as commissions, and reflected as a component of mortgage lending income in the consolidated statements of earnings.
In the course of conducting the Bank’s mortgage lending activities of originating mortgage loans and selling those loans in the secondary market, the Bank makes various representations and warranties to the purchaser of the mortgage loans. Every loan closed by the Bank’s mortgage center is run through a government agency automated underwriting system. Any exceptions noted during this process are remedied prior to sale. These representations and warranties also apply to underwriting the real estate appraisal opinion of value for the collateral securing these loans. Failure by the Company to comply with the underwriting and/or appraisal standards could result in the Company being required to repurchase the mortgage loan or to reimburse the investor for losses incurred (make whole requests) if such failure cannot be cured by the Company within the specified period following discovery.
Loans
Loans are reported at their outstanding principal balances, net of any unearned income, charge-offs, and any deferred fees or costs on originated loans. Interest income is accrued based on the principal balance outstanding. Loan origination fees, net of certain loan origination costs, are deferred and recognized in interest income over the contractual life of the loan using the effective interest method. Loan commitment fees are generally deferred and amortized on a straight-line basis over the commitment period, which results in a recorded amount that approximates fair value.
The accrual of interest on loans is discontinued when there is a significant deterioration in the financial condition of the borrower and full repayment of principal and interest is not expected or the principal or interest is more than 90 days past due, unless the loan is both well-collateralized and in the process of collection. Generally, all interest accrued but not collected for loans that are placed on nonaccrual status is reversed against current interest income. Interest collections on nonaccrual loans are generally applied as principal reductions. The Company determines past due or delinquency status of a loan based on contractual payment terms.
77
Table of Contents
A loan is considered impaired when it is probable the Company will be unable to collect all principal and interest payments due according to the contractual terms of the loan agreement. Individually identified impaired loans are measured based on the present value of expected payments using the loan’s original effective rate as the discount rate, the loan’s observable market price, or the fair value of the collateral if the loan is collateral dependent. If the recorded investment in the impaired loan exceeds the measure of fair value, a valuation allowance may be established as part of the allowance for loan losses. Changes to the valuation allowance are recorded as a component of the provision for loan losses.
Impaired loans also include troubled debt restructurings (“TDRs”). In the normal course of business, management may grant concessions to borrowers who are experiencing financial difficulty. The concessions granted most frequently for TDRs involve reductions or delays in required payments of principal and interest for a specified time, the rescheduling of payments in accordance with a bankruptcy plan or the charge-off of a portion of the loan. In most cases, the conditions of the credit also warrant nonaccrual status, even after the restructuring occurs. As part of the credit approval process, the restructured loans are evaluated for adequate collateral protection in determining the appropriate accrual status at the time of restructuring. TDR loans may be returned to accrual status if there has been at least a six-month sustained period of repayment performance by the borrower.
Allowance for Loan Losses
The allowance for loan losses is maintained at a level that management believes is adequate to absorb probable losses inherent in the loan portfolio. Loan losses are charged against the allowance when they are known. Subsequent recoveries are credited to the allowance. Management’s determination of the adequacy of the allowance is based on an evaluation of the portfolio, current economic conditions, growth, composition of the loan portfolio, homogeneous pools of loans, risk ratings of specific loans, historical loan loss factors, identified impaired loans and other factors related to the portfolio. This evaluation is performed quarterly and is inherently subjective, as it requires various material estimates that are susceptible to significant change, including the amounts and timing of future cash flows expected to be received on any impaired loans. In addition, regulatory agencies, as an integral part of their examination process, will periodically review the Company’s allowance for loan losses, and may require the Company to record additions to the allowance based on their judgment about information available to them at the time of their examinations.
Premises and Equipment
Land is carried at cost. Land improvements, buildings and improvements, and furniture, fixtures, and equipment are carried at cost, less accumulated depreciation computed on a straight-line method over the useful lives of the assets or the expected terms of the leases, if shorter. Expected terms include lease option periods to the extent that the exercise of such options is reasonably assured.
Nonmarketable equity investments
Nonmarketable equity investments include equity securities that are not publicly traded and securities acquired for various purposes. The Bank is required to maintain certain minimum levels of equity investments with certain regulatory and other entities in which the Bank has an ongoing business relationship based on the Bank’s common stock and surplus (with regard to the relationship with the Federal Reserve Bank) or outstanding borrowings (with regard to the relationship with the Federal Home Loan Bank of Atlanta). These nonmarketable equity securities are accounted for at cost which equals par or redemption value. These securities do not have a readily determinable fair value as their ownership is restricted and there is no market for these securities. These securities can only be redeemed or sold at their par value and only to the respective issuing government supported institution or to another member institution. The Company records these nonmarketable equity securities as a component of other assets, which are periodically evaluated for impairment. Management considers these nonmarketable equity securities to be long-term investments. Accordingly, when evaluating these securities for impairment, management considers the ultimate recoverability of the par value rather than by recognizing temporary declines in value.
Transfers of Financial Assets
Transfers of an entire financial asset (i.e. loan sales), a group of entire financial assets, or a participating interest in an entire financial asset (i.e. loan participations sold) are accounted for as sales when control over the assets have been surrendered. Control over transferred assets is deemed to be surrendered when (1) the assets have been isolated from the Company, (2) the transferee obtains the right (free of conditions that constrain it from taking that right) to pledge or exchange the transferred assets, and (3) the Company does not maintain effective control over the transferred assets through an agreement to repurchase them before their maturity.
78
Table of Contents
Mortgage Servicing Rights
The Company recognizes as assets the rights to service mortgage loans for others, known as MSRs. The Company determines the fair value of MSRs at the date the loan is transferred. An estimate of the Company’s MSRs is determined using assumptions that market participants would use in estimating future net servicing income, including estimates of prepayment speeds, discount rate, default rates, cost to service, escrow account earnings, contractual servicing fee income, ancillary income, and late fees.
Subsequent to the date of transfer, the Company has elected to measure its MSRs under the amortization method. Under the amortization method, MSRs are amortized in proportion to, and over the period of, estimated net servicing income. The amortization of MSRs is analyzed monthly and is adjusted to reflect changes in prepayment speeds, as well as other factors. MSRs are evaluated for impairment based on the fair value of those assets. Impairment is determined by stratifying MSRs into groupings based on predominant risk characteristics, such as interest rate and loan type. If, by individual stratum, the carrying amount of the MSRs exceeds fair value, a valuation allowance is established through a charge to earnings. The valuation allowance is adjusted as the fair value changes. MSRs are included in the other assets category in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Securities sold under agreements to repurchase
Securities sold under agreements to repurchase generally mature less than one year from the transaction date. Securities sold under agreements to repurchase are reflected as a secured borrowing in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets at the amount of cash received in connection with each transaction.
Income Taxes
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are the expected future tax amounts for the temporary differences between carrying amounts and tax bases of assets and liabilities, computed using enacted tax rates. A valuation allowance, if needed, reduces deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized. The net deferred tax asset is reflected as a component of other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Income tax expense or benefit for the year is allocated among continuing operations and other comprehensive income (loss), as applicable. The amount allocated to continuing operations is the income tax effect of the pretax income or loss from continuing operations that occurred during the year, plus or minus income tax effects of (1) changes in certain circumstances that cause a change in judgment about the realization of deferred tax assets in future years, (2) changes in income tax laws or rates, and (3) changes in income tax status, subject to certain exceptions. The amount allocated to other comprehensive income (loss) is related solely to changes in the valuation allowance on items that are normally accounted for in other comprehensive income (loss) such as unrealized gains or losses on available-for-sale securities.
In accordance with ASC 740, Income Taxes, a tax position is recognized as a benefit only if it is “more likely than not” that the tax position would be sustained in a tax examination, with a tax examination being presumed to occur. The amount recognized is the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than 50% likely of being realized on examination. For tax positions not meeting the “more likely than not” test, no tax benefit is recorded. It is the Company’s policy to recognize interest and penalties related to income tax matters in income tax expense. The Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries file a consolidated income tax return.
Fair Value Measurements
ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements, which defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value in U.S. generally accepted accounting principles and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. ASC 820 applies only to fair-value measurements that are already required or permitted by other accounting standards. The definition of fair value focuses on the exit price, i.e., the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date, not the entry price, i.e., the price that would be paid to acquire the asset or received to assume the liability at the measurement date. The statement emphasizes that fair value is a market-based measurement; not an entity-specific measurement. Therefore, the fair value measurement should be determined based on the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability. For more information related to fair value measurements, please refer to Note 15, Fair Value.
79
Table of Contents
NOTE 2: BASIC AND DILUTED NET EARNINGS PER SHARE
Basic net earnings per share is computed by dividing net earnings by the weighted average common shares outstanding for the year. Diluted net earnings per share reflect the potential dilution that could occur upon exercise of securities or other rights for, or convertible into, shares of the Company’s common stock. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, the Company had no such securities or other rights issued or outstanding, and therefore, no dilutive effect to consider for the diluted net earnings per share calculation.
The basic and diluted net earnings per share computations for the respective years are presented below.
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Basic and diluted: |
||||||||||
| Net earnings |
$ |
9,741 | $ | 8,834 | ||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding |
3,581,476 | 3,643,780 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net earnings per share |
$ | 2.72 | $ | 2.42 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
NOTE 3: RESTRICTED CASH BALANCES
Regulation D of the Federal Reserve Act requires that banks maintain reserve balances with the Federal Reserve Bank based principally on the type and amount of their deposits. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Bank did not have a required reserve balance at the Federal Reserve Bank.
NOTE 4: SECURITIES
At December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, all securities within the scope of ASC 320, Investments – Debt and Equity Securities were classified as available-for-sale. The fair value and amortized cost for securities available-for-sale by contractual maturity at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, are presented below.
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 year | 1 to 5 | 5 to 10 | After 10 | Fair | Gross Unrealized | Amortized | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | or less | years | years | years | Value | Gains | Losses | Cost | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency obligations (a) |
$ | 4,993 | 27,245 | 18,470 | — | 50,708 | 215 | 98 | $ | 50,591 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS (a) |
— | 560 | 4,510 | 118,207 | 123,277 | 798 | 261 | 122,740 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State and political subdivisions |
— | 1,355 | 6,166 | 54,396 | 61,917 | 2,104 | 9 | 59,822 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total available-for-sale |
$ | 4,993 | 29,160 | 29,146 | 172,603 | 235,902 | 3,117 | 368 | $ | 233,153 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency obligations (a) |
$ | 14,437 | 19,865 | 16,869 | — | 51,171 | 25 | 1,200 | $ | 52,346 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS (a) |
— | — | 8,368 | 110,230 | 118,598 | 65 | 3,738 | $ | 122,271 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| State and political subdivisions |
— | 3,682 | 7,726 | 58,624 | 70,032 | 518 | 692 | $ | 70,206 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total available-for-sale |
$ | 14,437 | 23,547 | 32,963 | 168,854 | 239,801 | 608 | 5,630 | $ | 244,823 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(a) Includes securities issued by U.S. government agencies or government sponsored entities. Expected maturities of these securities may differ from contractual maturities because issues may have the right to call or repay obligations with or without prepayment penalties.
Securities with aggregate fair values of $147.8 million and $133.1 million at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, were pledged to secure public deposits, securities sold under agreements to repurchase, Federal Home Loan Bank (“FHLB”) advances, and for other purposes required or permitted by law.
Included in other assets on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets are nonmarketable equity investments. The carrying amounts of nonmarketable equity investments were $1.4 million at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. Nonmarketable equity investments include FHLB of Atlanta stock, Federal Reserve Bank (“FRB”) stock, and stock in a privately held financial institution.
80
Table of Contents
Gross Unrealized Losses and Fair Value
The fair values and gross unrealized losses on securities at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, segregated by those securities that have been in an unrealized loss position for less than 12 months and 12 months or more are presented below.
| Less than 12 Months | 12 Months or Longer | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | Fair
Value |
Unrealized
Losses |
Fair
Value |
Unrealized
Losses |
Fair
Value |
Unrealized
Losses |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency obligations |
$ | 24,734 | 97 | 4,993 | 1 | 29,727 | $ | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS |
40,126 | 98 | 21,477 | 163 | 61,603 | 261 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| State and political subdivisions |
2,741 | 9 | — | — | 2,741 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 67,601 | 204 | 26,470 | 164 | 94,071 | $ | 368 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agency obligations |
$ | 4,724 | 28 | 44,307 | 1,172 | 49,031 | $ | 1,200 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Agency RMBS |
12,325 | 238 | 99,184 | 3,500 | 111,509 | 3,738 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| State and political subdivisions |
14,840 | 181 | 14,384 | 511 | 29,224 | 692 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 31,889 | 447 | 157,875 | 5,183 | 189,764 | $ | 5,630 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
For the securities in the previous table, the Company does not have the intent to sell and has determined it is not more likely than not that the Company will be required to sell the security before recovery of the amortized cost basis, which may be maturity. On a quarterly basis, the Company assesses each security for credit impairment. For debt securities, the Company evaluates, where necessary, whether credit impairment exists by comparing the present value of the expected cash flows to the securities’ amortized cost basis.
In determining whether a loss is temporary, the Company considers all relevant information including:
| ● | the length of time and the extent to which the fair value has been less than the amortized cost basis; |
| ● | adverse conditions specifically related to the security, an industry, or a geographic area (for example, changes in the financial condition of the issuer of the security, or in the case of an asset-backed debt security, in the financial condition of the underlying loan obligors, including changes in technology or the discontinuance of a segment of the business that may affect the future earnings potential of the issuer or underlying loan obligors of the security or changes in the quality of the credit enhancement); |
| ● | the historical and implied volatility of the fair value of the security; |
| ● | the payment structure of the debt security and the likelihood of the issuer being able to make payments that increase in the future; |
| ● | failure of the issuer of the security to make scheduled interest or principal payments; |
| ● | any changes to the rating of the security by a rating agency; and |
| ● | recoveries or additional declines in fair value subsequent to the balance sheet date. |
Agency obligations
The unrealized losses associated with agency obligations were primarily driven by changes in interest rates and not due to the credit quality of the securities. These securities were issued by U.S. government agencies or government-sponsored entities and did not have any credit losses given the explicit government guarantee or other government support.
Agency residential mortgage-backed securities (“RMBS”)
The unrealized losses associated with agency RMBS were primarily driven by changes in interest rates and not due to the credit quality of the securities. These securities were issued by U.S. government agencies or government-sponsored entities and did not have any credit losses given the explicit government guarantee or other government support.
81
Table of Contents
Securities of U.S. states and political subdivisions
The unrealized losses associated with securities of U.S. states and political subdivisions were primarily driven by changes in interest rates and were not due to the credit quality of the securities. Some of these securities are guaranteed by a bond insurer, but management did not rely on the guarantee in making its investment decision. These securities will continue to be monitored as part of the Company’s quarterly impairment analysis, but are expected to perform even if the rating agencies reduce the credit rating of the bond insurers. As a result, the Company expects to recover the entire amortized cost basis of these securities.
The carrying values of the Company’s investment securities could decline in the future if the financial condition of an issuer deteriorates and the Company determines it is probable that it will not recover the entire amortized cost basis for the security. As a result, there is a risk that other-than-temporary impairment charges may occur in the future.
Other-Than-Temporarily Impaired Securities
Credit-impaired debt securities are debt securities where the Company has written down the amortized cost basis of a security for other-than-temporary impairment and the credit component of the loss is recognized in earnings. At December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, the Company had no credit-impaired debt securities and there were no additions or reductions in the credit loss component of credit-impaired debt securities during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Realized Gains and Losses
The following table presents the gross realized gains and losses on sales related to securities.
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Gross realized gains |
$ | 120 | — | |||||||
| Gross realized losses |
(243) | — | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Realized losses, net |
$ | (123) | — | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
NOTE 5: LOANS AND ALLOWANCE FOR LOAN LOSSES
| December 31 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 56,782 | $ | 63,467 | ||||||
| Construction and land development |
32,841 | 40,222 | ||||||||
| Commercial real estate: |
||||||||||
| Owner occupied |
60,893 | 56,413 | ||||||||
| Multifamily |
44,839 | 40,455 | ||||||||
| Other |
164,586 | 165,028 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total commercial real estate |
270,318 | 261,896 | ||||||||
| Residential real estate: |
||||||||||
| Consumer mortgage |
48,923 | 56,223 | ||||||||
| Investment property |
43,652 | 46,374 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total residential real estate |
92,575 | 102,597 | ||||||||
| Consumer installment |
8,866 | 9,295 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total loans |
461,382 | 477,477 | ||||||||
| Less: unearned income |
(481) | (569) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Loans, net of unearned income |
$ | 460,901 | $ | 476,908 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
Loans secured by real estate were approximately 85.8% of the total loan portfolio at December 31, 2019. At December 31, 2019, the Company’s geographic loan distribution was concentrated primarily in Lee County, Alabama and surrounding areas.
82
Table of Contents
In accordance with ASC 310, Receivables, a portfolio segment is defined as the level at which an entity develops and documents a systematic method for determining its allowance for loan losses. As part of the Company’s quarterly assessment of the allowance, the loan portfolio is disaggregated into the following portfolio segments: commercial and industrial, construction and land development, commercial real estate, residential real estate and consumer installment. Where appropriate, the Company’s loan portfolio segments are further disaggregated into classes. A class is generally determined based on the initial measurement attribute, risk characteristics of the loan, and an entity’s method for monitoring and determining credit risk.
The following describe the risk characteristics relevant to each of the portfolio segments.
Commercial and industrial (“C&I”) — includes loans to finance business operations, equipment purchases, or other needs for small and medium-sized commercial customers. Also included in this category are loans to finance agricultural production. Generally the primary source of repayment is the cash flow from business operations and activities of the borrower.
Construction and land development (“C&D”) — includes both loans and credit lines for the purpose of purchasing, carrying and developing land into commercial developments or residential subdivisions. Also included are loans and lines for construction of residential, multi-family and commercial buildings. Generally the primary source of repayment is dependent upon the sale or refinance of the real estate collateral.
Commercial real estate (“CRE”) — includes loans disaggregated into three classes: (1) owner occupied (2) multi-family and (3) other.
| ● | Owner occupied – includes loans secured by business facilities to finance business operations, equipment and owner-occupied facilities primarily for small and medium-sized commercial customers. Generally the primary source of repayment is the cash flow from business operations and activities of the borrower, who owns the property. |
| ● | Multifamily – primarily includes loans to finance income-producing multi-family properties. Loans in this class include loans for 5 or more unit residential property and apartments leased to residents. Generally, the primary source of repayment is dependent upon income generated from the real estate collateral. The underwriting of these loans takes into consideration the occupancy and rental rates, as well as the financial health of the borrower. |
| ● | Other – primarily includes loans to finance income-producing commercial properties. Loans in this class include loans for neighborhood retail centers, hotels, medical and professional offices, single retail stores, industrial buildings, and warehouses leased generally to local businesses and residents. Generally the primary source of repayment is dependent upon income generated from the real estate collateral. The underwriting of these loans takes into consideration the occupancy and rental rates as well as the financial health of the borrower. |
Residential real estate (“RRE”) — includes loans disaggregated into two classes: (1) consumer mortgage and (2) investment property.
| ● | Consumer mortgage – primarily includes first or second lien mortgages and home equity lines to consumers that are secured by a primary residence or second home. These loans are underwritten in accordance with the Bank’s general loan policies and procedures which require, among other things, proper documentation of each borrower’s financial condition, satisfactory credit history and property value. |
| ● | Investment property – primarily includes loans to finance income-producing 1-4 family residential properties. Generally the primary source of repayment is dependent upon income generated from leasing the property securing the loan. The underwriting of these loans takes into consideration the rental rates as well as the financial health of the borrower. |
Consumer installment — includes loans to individuals both secured by personal property and unsecured. Loans include personal lines of credit, automobile loans, and other retail loans. These loans are underwritten in accordance with the Bank’s general loan policies and procedures which require, among other things, proper documentation of each borrower’s financial condition, satisfactory credit history, and if applicable, property value.
83
Table of Contents
The following is a summary of current, accruing past due and nonaccrual loans by portfolio class as of December 31, 2019 and 2018.
| (In thousands) | Current | Accruing
30-89 Days
Past Due |
Accruing
Greater than
90 days |
Total
Accruing
Loans |
Non-
Accrual |
Total
Loans |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 56,758 | 24 | — | 56,782 | — | $ | 56,782 | ||||||||||||||||
| Construction and land development |
32,385 | 456 | — | 32,841 | — | 32,841 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner occupied |
60,893 | — | — | 60,893 | — | 60,893 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Multifamily |
44,839 | — | — | 44,839 | — | 44,839 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other |
164,586 | — | — | 164,586 | — | 164,586 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total commercial real estate |
270,318 | — | — | 270,318 | — | 270,318 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Residential real estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer mortgage |
47,151 | 1,585 | — | 48,736 | 187 | 48,923 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Investment property |
43,629 | 23 | — | 43,652 | — | 43,652 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total residential real estate |
90,780 | 1,608 | — | 92,388 | 187 | 92,575 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
8,802 | 64 | — | 8,866 | — | 8,866 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 459,043 | 2,152 | — | 461,195 | 187 | $ | 461,382 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 63,367 | 100 | — | 63,467 | — | $ | 63,467 | ||||||||||||||||
| Construction and land development |
39,997 | 225 | — | 40,222 | — | 40,222 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner occupied |
56,413 | — | — | 56,413 | — | 56,413 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Multifamily |
40,455 | — | — | 40,455 | — | 40,455 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other |
165,028 | — | — | 165,028 | — | 165,028 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total commercial real estate |
261,896 | — | — | 261,896 | — | 261,896 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Residential real estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer mortgage |
54,446 | 1,599 | — | 56,045 | 178 | 56,223 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Investment property |
46,233 | 141 | — | 46,374 | — | 46,374 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total residential real estate |
100,679 | 1,740 | — | 102,419 | 178 | 102,597 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
9,254 | 41 | — | 9,295 | — | 9,295 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 475,193 | 2,106 | — | 477,299 | 178 | $ | 477,477 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
The gross interest income which would have been recorded under the original terms of those nonaccrual loans had they been accruing interest, amounted to approximately $9 thousand and $12 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Allowance for Loan Losses
The allowance for loan losses as of and for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, is presented below.
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| (In thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Beginning balance |
$ | 4,790 | $ | 4,757 | ||||
| Charged-off loans |
(408) | (168) | ||||||
| Recovery of previously charged-off loans |
254 | 201 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Net (charge-offs) recoveries |
(154) | 33 | ||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
(250) | — | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Ending balance |
$ | 4,386 | $ | 4,790 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
84
Table of Contents
The Company assesses the adequacy of its allowance for loan losses prior to the end of each calendar quarter. The level of the allowance is based upon management’s evaluation of the loan portfolio, past loan loss experience, current asset quality trends, known and inherent risks in the portfolio, adverse situations that may affect a borrower’s ability to repay (including the timing of future payment), the estimated value of any underlying collateral, composition of the loan portfolio, economic conditions, industry and peer bank loan loss rates and other pertinent factors, including regulatory recommendations. This evaluation is inherently subjective as it requires material estimates including the amounts and timing of future cash flows expected to be received on impaired loans that may be susceptible to significant change. Loans are charged off, in whole or in part, when management believes that the full collectability of the loan is unlikely. A loan may be partially charged-off after a “confirming event” has occurred which serves to validate that full repayment pursuant to the terms of the loan is unlikely.
The Company deems loans impaired when, based on current information and events, it is probable that the Company will be unable to collect all amounts due according to the contractual terms of the loan agreement. Collection of all amounts due according to the contractual terms means that both the interest and principal payments of a loan will be collected as scheduled in the loan agreement.
An impairment allowance is recognized if the fair value of the loan is less than the recorded investment in the loan. The impairment is recognized through the allowance. Loans that are impaired are recorded at the present value of expected future cash flows discounted at the loan’s effective interest rate, or if the loan is collateral dependent, impairment measurement is based on the fair value of the collateral, less estimated disposal costs.
The level of allowance maintained is believed by management to be adequate to absorb probable losses inherent in the portfolio at the balance sheet date. The allowance is increased by provisions charged to expense and decreased by charge-offs, net of recoveries of amounts previously charged-off.
In assessing the adequacy of the allowance, the Company also considers the results of its ongoing internal, independent loan review process. The Company’s loan review process assists in determining whether there are loans in the portfolio whose credit quality has weakened over time and evaluating the risk characteristics of the entire loan portfolio. The Company’s loan review process includes the judgment of management, the input from our independent loan reviewers, and reviews that may have been conducted by bank regulatory agencies as part of their examination process. The Company incorporates loan review results in the determination of whether or not it is probable that it will be able to collect all amounts due according to the contractual terms of a loan.
As part of the Company’s quarterly assessment of the allowance, management divides the loan portfolio into five segments: commercial and industrial, construction and land development, commercial real estate, residential real estate, and consumer installment loans. The Company analyzes each segment and estimates an allowance allocation for each loan segment.
The allocation of the allowance for loan losses begins with a process of estimating the probable losses inherent for these types of loans. The estimates for these loans are established by category and based on the Company’s internal system of credit risk ratings and historical loss data. The estimated loan loss allocation rate for the Company’s internal system of credit risk grades is based on its experience with similarly graded loans. For loan segments where the Company believes it does not have sufficient historical loss data, the Company may make adjustments based, in part, on loss rates of peer bank groups. At December 31, 2019 and 2018, and for the years then ended, the Company adjusted its historical loss rates for the commercial real estate portfolio segment based, in part, on loss rates of peer bank groups.
The estimated loan loss allocation for all five loan portfolio segments is then adjusted for management’s estimate of probable losses for several “qualitative and environmental” factors. The allocation for qualitative and environmental factors is particularly subjective and does not lend itself to exact mathematical calculation. This amount represents estimated probable inherent credit losses which exist, but have not yet been identified, as of the balance sheet date, and are based upon quarterly trend assessments in delinquent and nonaccrual loans, credit concentration changes, prevailing economic conditions, changes in lending personnel experience, changes in lending policies or procedures and other influencing factors. These qualitative and environmental factors are considered for each of the five loan segments and the allowance allocation, as determined by the processes noted above, is increased or decreased based on the incremental assessment of these factors.
85
Table of Contents
The Company regularly re-evaluates its practices in determining the allowance for loan losses. Since the fourth quarter of 2016, the Company has increased its look-back period each quarter to incorporate the effects of at least one economic downturn in its loss history. The Company believes the extension of its look-back period is appropriate due to the risks inherent in the loan portfolio. Absent this extension, the early cycle periods in which the Company experienced significant losses would be excluded from the determination of the allowance for loan losses and its balance would decrease. For the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company increased its look-back period to 43 quarters to continue to include losses incurred by the Company beginning with the first quarter of 2009. The Company will likely continue to increase its look-back period to incorporate the effects of at least one economic downturn in its loss history. Other than expanding the look-back period each quarter, the Company has not made any material changes to its methodology that would impact the calculation of the allowance for loan losses or provision for loan losses for the periods included in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and statements of earnings.
The following table details the changes in the allowance for loan losses by portfolio segment for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
| (in thousands) | Commercial and industrial |
Construction and land Development |
Commercial Real Estate |
Residential Real Estate |
Consumer Installment |
Total | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2017 |
$ | 653 | 734 | 2,126 | 1,071 | 173 | $ | 4,757 | ||||||||||||||||
| Charge-offs |
(52) | — | (38 | ) | (26 | ) | (52 | ) | (168) | |||||||||||||||
| Recoveries |
70 | — | 19 | 79 | 33 | 201 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net recoveries (charge-offs) |
18 | — | (19 | ) | 53 | (19 | ) | 33 | ||||||||||||||||
| Provision |
107 | (34 | ) | 111 | (178 | ) | (6 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2018 |
$ | 778 | 700 | 2,218 | 946 | 148 | $ | 4,790 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charge-offs |
(364) | — | — | (6 | ) | (38 | ) | (408) | ||||||||||||||||
| Recoveries |
117 | — | 1 | 109 | 27 | 254 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net (charge-offs) recoveries |
(247) | — | 1 | 103 | (11 | ) | (154) | |||||||||||||||||
| Provision |
46 | (131 | ) | 70 | (236 | ) | 1 | (250) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2019 |
$ | 577 | 569 | 2,289 | 813 | 138 | $ | 4,386 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
The following table presents an analysis of the allowance for loan losses and recorded investment in loans by portfolio segment and impairment methodology as of December 31, 2019 and 2018.
| Collectively evaluated (1) | Individually evaluated (2) | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance | Recorded | Allowance | Recorded | Allowance | Recorded | |||||||||||||||||||||
| for loan | investment | for loan | investment | for loan | investment | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | losses | in loans | losses | in loans | losses | in loans | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 577 | 56,683 | — | 99 | 577 | 56,782 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Construction and land development |
569 | 32,841 | — | — | 569 | 32,841 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
2,289 | 270,318 | — | — | 2,289 | 270,318 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Residential real estate |
813 | 92,575 | — | — | 813 | 92,575 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
138 | 8,866 | — | — | 138 | 8,866 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 4,386 | 461,283 | — | 99 | 4,386 | 461,382 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 778 | 63,467 | — | — | 778 | 63,467 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Construction and land development |
700 | 40,222 | — | — | 700 | 40,222 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
2,218 | 261,739 | — | 157 | 2,218 | 261,896 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Residential real estate |
946 | 102,597 | — | — | 946 | 102,597 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
148 | 9,295 | — | — | 148 | 9,295 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 4,790 | 477,320 | — | 157 | 4,790 | 477,477 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Represents loans collectively evaluated for impairment in accordance with ASC 450-20, Loss Contingencies (formerly FAS 5), and pursuant to amendments by ASU 2010-20 regarding allowance for unimpaired loans. |
| (2) | Represents loans individually evaluated for impairment in accordance with ASC 310-30, Receivables (formerly FAS 114), and pursuant to amendments by ASU 2010-20 regarding allowance for impaired loans. |
86
Table of Contents
Credit Quality Indicators
The credit quality of the loan portfolio is summarized no less frequently than quarterly using categories similar to the standard asset classification system used by the federal banking agencies. The following table presents credit quality indicators for the loan portfolio segments and classes. These categories are utilized to develop the associated allowance for loan losses using historical losses adjusted for qualitative and environmental factors and are defined as follows:
| ● | Pass – loans which are well protected by the current net worth and paying capacity of the obligor (or guarantors, if any) or by the fair value, less cost to acquire and sell, of any underlying collateral. |
| ● | Special Mention – loans with potential weakness that may, if not reversed or corrected, weaken the credit or inadequately protect the Company’s position at some future date. These loans are not adversely classified and do not expose an institution to sufficient risk to warrant an adverse classification. |
| ● | Substandard Accruing – loans that exhibit a well-defined weakness which presently jeopardizes debt repayment, even though they are currently performing. These loans are characterized by the distinct possibility that the Company may incur a loss in the future if these weaknesses are not corrected. |
| ● | Nonaccrual – includes loans where management has determined that full payment of principal and interest is in doubt. |
| (In thousands) | Pass | Special Mention |
Substandard Accruing |
Nonaccrual | Total loans | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 54,340 | 2,176 | 266 | — | $ | 56,782 | |||||||||||||
| Construction and land development |
31,798 | — | 1,043 | — | 32,841 | |||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner occupied |
59,898 | 917 | 78 | — | 60,893 | |||||||||||||||
| Multifamily |
44,839 | — | — | — | 44,839 | |||||||||||||||
| Other |
163,716 | 849 | 21 | — | 164,586 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total commercial real estate |
268,453 | 1,766 | 99 | — | 270,318 | |||||||||||||||
| Residential real estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer mortgage |
45,247 | 962 | 2,527 | 187 | 48,923 | |||||||||||||||
| Investment property |
42,331 | 949 | 372 | — | 43,652 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total residential real estate |
87,578 | 1,911 | 2,899 | 187 | 92,575 | |||||||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
8,742 | 60 | 64 | — | 8,866 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 450,911 | 5,913 | 4,371 | 187 | $ | 461,382 | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 61,568 | 1,377 | 522 | — | $ | 63,467 | |||||||||||||
| Construction and land development |
39,481 | — | 741 | — | 40,222 | |||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner occupied |
55,942 | 154 | 317 | — | 56,413 | |||||||||||||||
| Multifamily |
40,455 | — | — | — | 40,455 | |||||||||||||||
| Other |
163,449 | 1,208 | 371 | — | 165,028 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total commercial real estate |
259,846 | 1,362 | 688 | — | 261,896 | |||||||||||||||
| Residential real estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer mortgage |
50,903 | 1,374 | 3,768 | 178 | 56,223 | |||||||||||||||
| Investment property |
45,463 | 173 | 738 | — | 46,374 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total residential real estate |
96,366 | 1,547 | 4,506 | 178 | 102,597 | |||||||||||||||
| Consumer installment |
9,149 | 75 | 71 | — | 9,295 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 466,410 | 4,361 | 6,528 | 178 | $ | 477,477 | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
87
Table of Contents
During the fourth quarter of 2019, the Company recognized a gain of $1.7 million resulting from the termination of a Loan Guarantee Program (the “Program”) operated by the State of Alabama. The payment of $1.7 million received by the Company in October 2019 was recorded as a gain and included in noninterest income on the accompanying consolidated statements of earnings. The Program required a 1% fee on the commitment balance at origination and in return the Company received a guarantee of up to 50% of losses in the event of the borrower’s default. As of December 31, 2019, the Company had 5 loans outstanding totaling $10.2 million that were enrolled in the Program prior to its termination by the State of Alabama. Despite being enrolled in the Program, these loans would have met the Company’s normal loan underwriting criteria at origination. At December 31, 2019, all of these loans were categorized as Pass within the Company’s credit quality asset classification.
Impaired loans
The following table presents details related to the Company’s impaired loans. Loans which have been fully charged-off do not appear in the following table. The related allowance generally represents the following components which correspond to impaired loans:
| ● | Individually evaluated impaired loans equal to or greater than $500 thousand secured by real estate (nonaccrual construction and land development, commercial real estate, and residential real estate). |
| ● | Individually evaluated impaired loans equal to or greater than $250 thousand not secured by real estate (nonaccrual commercial and industrial and consumer loans). |
The following table sets forth certain information regarding the Company’s impaired loans that were individually evaluated for impairment at December 31, 2019 and 2018.
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | Unpaid principal balance (1) |
Charge-offs and payments applied (2) |
Recorded investment (3) |
Related allowance |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
| With no allowance recorded: |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 335 | (236 | ) | $ | 99 | — | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Total impaired loans |
$ | 335 | (236 | ) | $ | 99 | $ | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Unpaid principal balance represents the contractual obligation due from the customer. |
| (2) | Charge-offs and payments applied represents cumulative charge-offs taken, as well as interest payments that have been applied against the outstanding principal balance. |
| (3) | Recorded investment represents the unpaid principal balance less charge-offs and payments applied; it is shown before any related allowance for loan losses. |
| December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | Unpaid principal balance (1) |
Charge-offs and payments applied (2) |
Recorded investment (3) |
Related allowance |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
| With no allowance recorded: |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner occupied |
$ | 157 | — | $ | 157 | — | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Total commercial real estate |
157 | — | 157 | — | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Total impaired loans |
$ | 157 | — | $ | 157 | $ | — | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Unpaid principal balance represents the contractual obligation due from the customer. |
| (2) | Charge-offs and payments applied represents cumulative charge-offs taken, as well as interest payments that have been applied against the outstanding principal balance. |
| (3) | Recorded investment represents the unpaid principal balance less charge-offs and payments applied; it is shown before any related allowance for loan losses. |
88
Table of Contents
The following table provides the average recorded investment in impaired loans and the amount of interest income recognized on impaired loans after impairment by portfolio segment and class.
| Year ended December 31, 2019 | Year ended December 31, 2018 | |||||||||||||||
| Average | Total interest | Average | Total interest | |||||||||||||
| recorded | income | recorded | income | |||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | investment | recognized | investment | recognized | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Impaired loans: |
| |||||||||||||||
| Commercial and industrial |
$ | 8 | — | $ | 9 | — | ||||||||||
| Commercial real estate: |
||||||||||||||||
| Owner occupied |
24 | 9 | 166 | 9 | ||||||||||||
| Other |
— | — | 1,145 | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Total commercial real estate |
24 | 9 | 1,311 | 9 | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 32 | 9 | $ | 1,320 | 9 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Troubled Debt Restructurings
Impaired loans also include troubled debt restructurings (“TDRs”). In the normal course of business, management may grant concessions to borrowers who are experiencing financial difficulty. A concession may include, but is not limited to, delays in required payments of principal and interest for a specified period, reduction of the stated interest rate of the loan, reduction of accrued interest, extension of the maturity date or reduction of the face amount or maturity amount of the debt. A concession has been granted when, as a result of the restructuring, the Bank does not expect to collect all amounts due, including interest at the original stated rate. A concession may have also been granted if the debtor is not able to access funds elsewhere at a market rate for debt with similar risk characteristics as the restructured debt. In determining whether a loan modification is a TDR, the Company considers the individual facts and circumstances surrounding each modification. In determining the appropriate accrual status at the time of restructure, the Company evaluates whether a restructured loan has adequate collateral protection, among other factors.
Similar to other impaired loans, TDRs are measured for impairment based on the present value of expected payments using the loan’s original effective interest rate as the discount rate, or the fair value of the collateral, less selling costs if the loan is collateral dependent. If the recorded investment in the loan exceeds the measure of fair value, impairment is recognized by establishing a valuation allowance as part of the allowance for loan losses or a charge-off to the allowance for loan losses. In periods subsequent to the modification, all TDRs are evaluated individually, including those that have payment defaults, for possible impairment.
At December 31, 2019 the Company had no TDRs. The following is a summary of accruing and nonaccrual TDRs and the related loan losses, by portfolio segment and class at December 31, 2018.
| TDRs | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | Accruing | Nonaccrual | Total | Related
Allowance |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner occupied |
$ | 157 | — | 157 | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total commercial real estate |
157 | — | 157 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 157 | — | 157 | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
At December 31, 2019, there were no significant outstanding commitments to advance additional funds to customers whose loans had been restructured.
89
Table of Contents
There were no loans modified in a TDR during the year ended December 31, 2019. The following table summarizes loans modified in a TDR during the year ended December 31, 2018 both before and after modification.
| ($ in thousands) | Number of contracts |
Pre- modification outstanding recorded investment |
Post- modification outstanding recorded investment |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate: |
||||||||||||||||
| Other |
2 | $ | 1,447 | 1,447 | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Total commercial real estate |
2 | 1,447 | 1,447 | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Total |
2 | $ | 1,447 | 1,447 | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Two loans were modified in a TDR during the year ended December 31, 2018. The only concessions granted by the Company were related to either a delay in the required payment of principal and/or interest or the interest rate at renewal was considered to be less than a market rate.
During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company had no loans modified in a TDR within the previous 12 months for which there was a payment default. The following table summarizes the recorded investment in loans modified in a TDR within the previous twelve months for which there was a payment default (defined as 90 days or more past due) during the year ended December 31, 2018.
| ($ in thousands) | Number of Contracts |
Recorded investment (1) |
||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| December 31, 2018 |
||||||||||
| Commercial real estate: |
||||||||||
| Other |
1 | $ | 1,259 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total commercial real estate |
1 | 1,259 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total |
1 | $ | 1,259 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| (1) | Amount as of applicable month end during the respective year for which there was a payment default. |
NOTE 6: PREMISES AND EQUIPMENT
Premises and equipment at December 31, 2019 and 2018 is presented below.
| December 31 | ||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Land and improvements |
$ | 9,874 | 8,444 | |||||||
| Buildings and improvements |
10,094 | 9,871 | ||||||||
| Furniture, fixtures, and equipment |
3,109 | 2,953 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total premises and equipment |
23,077 | 21,268 | ||||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation |
(8,334) | (7,672) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Premises and equipment, net |
$ | 14,743 | 13,596 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
Depreciation expense was approximately $662 thousand and $435 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, and is a component of net occupancy and equipment expense in the consolidated statements of earnings.
NOTE 7: MORTGAGE SERVICING RIGHTS, NET
MSRs are recognized based on the fair value of the servicing rights on the date the corresponding mortgage loans are sold. An estimate of the Company’s MSRs is determined using assumptions that market participants would use in estimating future net servicing income, including estimates of prepayment speeds, discount rate, default rates, cost to service, escrow account earnings, contractual servicing fee income, ancillary income, and late fees. Subsequent to the date of transfer, the Company has elected to measure its MSRs under the amortization method. Under the amortization method, MSRs are amortized in proportion to, and over the period of, estimated net servicing income. Servicing fee income is recorded net of related amortization expense and recognized in earnings as part of mortgage lending income.
90
Table of Contents
The Company has recorded MSRs related to loans sold without recourse to Fannie Mae. The Company generally sells conforming, fixed-rate, closed-end, residential mortgages to Fannie Mae. MSRs are included in other assets on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
The Company evaluates MSRs for impairment on a quarterly basis. Impairment is determined by stratifying MSRs into groupings based on predominant risk characteristics, such as interest rate and loan type. If, by individual stratum, the carrying amount of the MSRs exceeds fair value, a valuation allowance is established. The valuation allowance is adjusted as the fair value changes. Changes in the valuation allowance are recognized in earnings as a component of mortgage lending income.
The following table details the changes in amortized MSRs and the related valuation allowance for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Beginning balance |
$ | 1,441 | 1,644 | |||||||
| Additions, net |
241 | 208 | ||||||||
| Amortization expense |
(383) | (411) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Ending balance |
$ | 1,299 | 1,441 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Valuation allowance included in MSRs, net: |
||||||||||
| Beginning of period |
$ | — | — | |||||||
| End of period |
— | — | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Fair value of amortized MSRs: |
||||||||||
| Beginning of period |
$ | 2,697 | 2,528 | |||||||
| End of period |
2,111 | 2,697 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
Data and assumptions used in the fair value calculation related to MSRs at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, are presented below.
| December 31 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Unpaid principal balance |
$ | 274,227 | 289,981 | |||||||
| Weighted average prepayment speed (CPR) |
11.6 | % | 8.3 | |||||||
| Discount rate (annual percentage) |
10.0 | % | 10.0 | |||||||
| Weighted average coupon interest rate |
3.9 | % | 3.9 | |||||||
| Weighted average remaining maturity (months) |
255 | 250 | ||||||||
| Weighted average servicing fee (basis points) |
25.0 | 25.0 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
At December 31, 2019, the weighted average amortization period for MSRs was 5.5 years. Estimated amortization expense for each of the next five years is presented below.
| (Dollars in thousands) | December 31, 2019 | |||
|
|
||||
| 2020 |
$ | 220 | ||
| 2021 |
182 | |||
| 2022 |
151 | |||
| 2023 |
126 | |||
| 2024 |
105 | |||
|
|
||||
91
Table of Contents
NOTE 8: DEPOSITS
At December 31, 2019, the scheduled maturities of certificates of deposit and other time deposits are presented below.
| (Dollars in thousands) | December 31, 2019 | |||
|
|
||||
| 2020 |
$ | 92,740 | ||
| 2021 |
25,432 | |||
| 2022 |
36,643 | |||
| 2023 |
5,812 | |||
| 2024 |
6,572 | |||
|
|
||||
| Total certificates of deposit and other time deposits |
$ | 167,199 | ||
|
|
||||
Additionally, at December 31, 2019 and 2018, approximately $57.4 million and $59.4 million, respectively, of certificates of deposit and other time deposits were issued in denominations greater than $250 thousand.
At December 31, 2019 and 2018, the amount of deposit accounts in overdraft status that were reclassified to loans on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets was not material.
NOTE 9: SHORT-TERM BORROWINGS
At December 31, 2019 and 2018, the composition of short-term borrowings is presented below.
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||||||||||
| Weighted | Weighted | |||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | Amount | Avg. Rate | Amount | Avg. Rate | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Federal funds purchased: |
||||||||||||||||
| As of December 31 |
$ | — | — | $ | — | — | ||||||||||
| Average during the year |
1 | 2.58 % | 2 | 2.50 % | ||||||||||||
| Maximum outstanding at any month-end |
— | — | ||||||||||||||
| Securities sold under agreements to repurchase: |
||||||||||||||||
| As of December 31 |
$ | 1,069 | 0.50 % | $ | 2,300 | 0.50 % | ||||||||||
| Average during the year |
1,442 | 0.50 % | 2,632 | 0.50 % | ||||||||||||
| Maximum outstanding at any month-end |
2,261 | 3,241 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Federal funds purchased represent unsecured overnight borrowings from other financial institutions by the Bank. The Bank had available federal fund lines totaling $41.0 million with none outstanding at December 31, 2019.
Securities sold under agreements to repurchase represent short-term borrowings with maturities less than one year collateralized by a portion of the Company’s securities portfolio. Securities with an aggregate carrying value of $2.6 million and $5.6 million at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, were pledged to secure securities sold under agreements to repurchase.
NOTE 10: LEASE COMMITMENTS
We lease certain office facilities and office equipment under operating leases. Rent expense for all operating leases totaled $0.2 million for both the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018. On January 1, 2019, we adopted a new accounting standard which required the recognition of certain operating leases on our balance sheet as lease right of use assets (reported as component of other assets) and related lease liabilities (reported as a component of accrued expenses and other liabilities). At December 31, 2019, aggregate lease right of use assets and lease liabilities amounted to $785 thousand and $788 thousand, respectively. Rent expense includes amounts related to items that are not included in the determination of lease right of use assets including expenses related to short-term leases totaling $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2019.
92
Table of Contents
Lease payments under operating leases that were applied to our operating lease liability totaled $129 thousand during the year ended December 31, 2019. The following table reconciles future undiscounted lease payments due under non-cancelable operating leases (those amounts subject to recognition) to the aggregate operating lease liability as of December 31, 2019:
| (Dollars in thousands) | Remaining lease payments |
|||
|
|
||||
| 2020 |
$ | 106 | ||
| 2021 |
93 | |||
| 2022 |
93 | |||
| 2023 |
93 | |||
| 2024 |
93 | |||
| Thereafter |
416 | |||
|
|
||||
| Total undiscounted operating lease liabilities |
$ | 894 | ||
| Imputed interest |
106 | |||
|
|
||||
| Total operating lease liabilities included in the accompanying balance sheet |
$ | 788 | ||
|
|
||||
| Weighted-average lease terms in years |
8.89 | |||
| Weighted-average discount rate |
3.40 % | |||
|
|
||||
NOTE 11: OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
Comprehensive income is defined as the change in equity from all transactions other than those with stockholders, and it includes net earnings and other comprehensive income (loss). Other comprehensive income (loss) for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, is presented below.
| Pre-tax | Tax benefit | Net of | ||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | amount | (expense) | tax amount | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| 2019: |
||||||||||||
| Unrealized net holding gain on securities |
$ | 7,651 | (1,921) | 5,730 | ||||||||
| Reclassification adjustment for net loss on securities recognized in net earnings |
123 | (31) | 92 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income |
$ | 7,774 | (1,952) | 5,822 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| 2018: |
||||||||||||
| Unrealized net holding loss on securities |
$ | (4,269) | 1,072 | (3,197) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss |
$ | (4,269) | 1,072 | (3,197) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
NOTE 12: INCOME TAXES
For the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 the components of income tax expense from continuing operations are presented below.
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Current income tax expense: |
||||||||||
| Federal |
$ | 1,939 | 1,685 | |||||||
| State |
584 | 431 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total current income tax expense |
2,523 | 2,116 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Deferred income tax (benefit) expense: |
||||||||||
| Federal |
(136) | 56 | ||||||||
| State |
(17) | 15 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total deferred income tax (benefit) expense |
(153) | 71 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total income tax expense |
$ | 2,370 | 2,187 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
93
Table of Contents
Total income tax expense differs from the amounts computed by applying the statutory federal income tax rate of 21% to earnings before income taxes. A reconciliation of the differences for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, is presented below.
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||||||||||||
| Percent of | Percent of | |||||||||||||||||
| pre-tax | pre-tax | |||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | Amount | earnings | Amount | earnings | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings before income taxes |
$ |
12,111 | 11,021 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Income taxes at statutory rate |
2,543 | 21.0 | % | 2,315 | 21.0 % | |||||||||||||
| Tax-exempt interest |
(508) | (4.1 | ) | (515) | (4.7) | |||||||||||||
| State income taxes, net of federal tax effect |
440 | 3.6 | 361 | 3.3 | ||||||||||||||
| Bank-owned life insurance |
(92) | (0.8 | ) | (92) | (0.8) | |||||||||||||
| Other |
(13) | (0.1 | ) | 118 | 1.0 | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Total income tax expense |
$ | 2,370 | 19.6 | % | 2,187 | 19.8 % | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
The Company had a net deferred tax liability of $9 thousand included in other liabilities and a net deferred tax asset of $1.8 million included in other assets on the consolidated balance sheets at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The tax effects of temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of the deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities at December 31, 2019 and 2018 are presented below:
| December 31 | ||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Deferred tax assets: |
||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses |
$ |
1,102 | 1,203 | |||||||
| Unrealized loss on securities |
— | 1,262 | ||||||||
| Accrued bonus |
296 | 8 | ||||||||
| Right of use liability |
198 | — | ||||||||
| Other |
88 | 127 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total deferred tax assets |
1,684 | 2,600 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities: |
||||||||||
| Premises and equipment |
315 | 280 | ||||||||
| Unrealized gain on securities |
690 | — | ||||||||
| Originated mortgage servicing rights |
326 | 362 | ||||||||
| Right of use asset |
197 | — | ||||||||
| Other |
165 | 168 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Total deferred tax liabilities |
1,693 | 810 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net deferred tax (liability) asset |
$ |
(9 | ) | 1,790 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
A valuation allowance is recognized for a deferred tax asset if, based on the weight of available evidence, it is more-likely-than-not that some portion of the entire deferred tax asset will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income and tax planning strategies in making this assessment. Based upon the level of historical taxable income and projection for future taxable income over the periods which the temporary differences resulting in the remaining deferred tax assets are deductible, management believes it is more-likely-than-not that the Company will realize the benefits of these deductible differences at December 31, 2019. The amount of the deferred tax assets considered realizable, however, could be reduced in the near term if estimates of future taxable income are reduced.
94
Table of Contents
The change in the net deferred tax asset for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, is presented below.
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net deferred tax (liability) asset: |
||||||||||
| Balance, beginning of year |
$ | 1,790 | 789 | |||||||
| Deferred tax benefit (expense) related to continuing operations |
153 | (71) | ||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity, for accumulated other comprehensive (income) loss |
(1,952 | ) | 1,072 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Balance, end of year |
$ | (9 | ) | 1,790 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
ASC 740, Income Taxes, defines the threshold for recognizing the benefits of tax return positions in the financial statements as “more-likely-than-not” to be sustained by the taxing authority. This section also provides guidance on the de-recognition, measurement, and classification of income tax uncertainties in interim periods. As of December 31, 2019, the Company had no unrecognized tax benefits related to federal or state income tax matters. The Company does not anticipate any material increase or decrease in unrecognized tax benefits during 2020 relative to any tax positions taken prior to December 31, 2019. As of December 31, 2019, the Company has accrued no interest and no penalties related to uncertain tax positions. It is the Company’s policy to recognize interest and penalties related to income tax matters in income tax expense.
The Company and its subsidiaries file consolidated U.S. federal and State of Alabama income tax returns. The Company is currently open to audit under the statute of limitations by the Internal Revenue Service and the State of Alabama for the years ended December 31, 2016 through 2019.
NOTE 13: EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLAN
The Company sponsors a qualified defined contribution retirement plan, the Auburn National Bancorporation, Inc. 401(k) Plan (the “Plan”). Effective January 1, 2019, the Plan was amended and restated. As part of this amendment and restatement, eligible employees may contribute up to 100% of eligible compensation, subject to statutory limits upon completion of 2 months of service. Furthermore, the Company now allows employer Safe Harbor contributions. Participants are immediately vested in employer Safe Harbor contributions. Effective January 1, 2019, the Company’s matching contributions on behalf of participants were equal to $1.00 for each $1.00 contributed by participants, up to 3% of the participants’ eligible compensation, and $0.50 for every $1.00 contributed by participants, up to 5% of the participants’ eligible compensation, for a maximum matching contribution of 4% of the participants’ eligible compensation. Prior to January 1, 2019, the Company made matching contributions on behalf of participants equal to $0.50 for each $1.00 contributed by participants, up to 6% of the participant’s eligible compensation, for a maximum matching contribution of 3% of the participants’ eligible compensation. Company matching contributions to the Plan were $264 thousand and $131 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, and are included in salaries and benefits expense.
NOTE 14: COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENT LIABILITIES
Credit-Related Financial Instruments
The Company is party to credit related financial instruments with off-balance sheet risk in the normal course of business to meet the financing needs of its customers. These financial instruments include commitments to extend credit and standby letters of credit. Such commitments involve, to varying degrees, elements of credit and interest rate risk in excess of the amount recognized in the consolidated balance sheets.
The Company’s exposure to credit loss is represented by the contractual amount of these commitments. The Company follows the same credit policies in making commitments as it does for on-balance sheet instruments.
At December 31, 2019 and 2018, the following financial instruments were outstanding whose contract amount represents credit risk:
| December 31 | ||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Commitments to extend credit |
$ | 60,564 | $ | 61,889 | ||||
| Standby letters of credit |
1,921 | 7,026 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
95
Table of Contents
Commitments to extend credit are agreements to lend to a customer as long as there is no violation of any condition established in the agreement. Commitments generally have fixed expiration dates or other termination clauses and may require payment of a fee. The commitments for lines of credit may expire without being drawn upon. Therefore, total commitment amounts do not necessarily represent future cash requirements. The amount of collateral obtained, if it is deemed necessary by the Company, is based on management’s credit evaluation of the customer.
Standby letters of credit are conditional commitments issued by the Company to guarantee the performance of a customer to a third party. The credit risk involved in issuing letters of credit is essentially the same as that involved in extending loan facilities to customers. The Company holds various assets as collateral, including accounts receivable, inventory, equipment, marketable securities, and property to support those commitments for which collateral is deemed necessary. The Company has recorded a liability for the estimated fair value of these standby letters of credit in the amount of $39 thousand and $73 thousand at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Contingent Liabilities
The Company and the Bank are involved in various legal proceedings, arising in connection with their business. In the opinion of management, based upon consultation with legal counsel, the ultimate resolution of these proceeding will not have a material adverse effect upon the consolidated financial condition or results of operations of the Company and the Bank.
NOTE 15: FAIR VALUE
Fair Value Hierarchy
“Fair value” is defined by ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures, as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction occurring in the principal market (or most advantageous market in the absence of a principal market) for an asset or liability at the measurement date. GAAP establishes a fair value hierarchy for valuation inputs that gives the highest priority to quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs. The fair value hierarchy is as follows:
Level 1—inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices, unadjusted, for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
Level 2—inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active, or inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly.
Level 3—inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and reflect the Company’s own assumptions about the inputs market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability.
Level changes in fair value measurements
Transfers between levels of the fair value hierarchy are generally recognized at the end of the reporting period. The Company monitors the valuation techniques utilized for each category of financial assets and liabilities to ascertain when transfers between levels have been affected. The nature of the Company’s financial assets and liabilities generally is such that transfers in and out of any level are expected to be infrequent. For the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, there were no transfers between levels and no changes in valuation techniques for the Company’s financial assets and liabilities.
96
Table of Contents
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis
Securities available-for-sale
Fair values of securities available for sale were primarily measured using Level 2 inputs. For these securities, the Company obtains pricing from third party pricing services. These third party pricing services consider observable data that may include broker/dealer quotes, market spreads, cash flows, market consensus prepayment speeds, benchmark yields, reported trades for similar securities, credit information and the securities’ terms and conditions. On a quarterly basis, management reviews the pricing received from the third party pricing services for reasonableness given current market conditions. As part of its review, management may obtain non-binding third party broker quotes to validate the fair value measurements. In addition, management will periodically submit pricing provided by the third party pricing services to another independent valuation firm on a sample basis. This independent valuation firm will compare the price provided by the third-party pricing service with its own price and will review the significant assumptions and valuation methodologies used with management.
The following table presents the balances of the assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, by caption, on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets by ASC 820 valuation hierarchy (as described above).
| Quoted Prices in | Significant | |||||||||||||||
| Active Markets | Other | Significant | ||||||||||||||
| for | Observable | Unobservable | ||||||||||||||
| Identical Assets | Inputs | Inputs | ||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | Amount | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019: |
||||||||||||||||
| Securities available-for-sale: |
||||||||||||||||
| Agency obligations |
$ | 50,708 | — | 50,708 | — | |||||||||||
| Agency RMBS |
123,277 | — | 123,277 | — | ||||||||||||
| State and political subdivisions |
61,917 | — | 61,917 | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Total securities available-for-sale |
235,902 | — | 235,902 | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Total assets at fair value |
$ | 235,902 | — | 235,902 | — | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018: |
||||||||||||||||
| Securities available-for-sale: |
||||||||||||||||
| Agency obligations |
$ | 51,171 | — | 51,171 | — | |||||||||||
| Agency RMBS |
118,598 | — | 118,598 | — | ||||||||||||
| State and political subdivisions |
70,032 | — | 70,032 | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Total securities available-for-sale |
239,801 | — | 239,801 | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Total assets at fair value |
$ | 239,801 | — | 239,801 | — | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis
Loans held for sale
Loans held for sale are carried at the lower of cost or fair value. Fair values of loans held for sale are determined using quoted market secondary market prices for similar loans. Loans held for sale are classified within Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy.
Impaired Loans
Loans considered impaired under ASC 310-10-35, Receivables, are loans for which, based on current information and events, it is probable that the Company will be unable to collect all principal and interest payments due in accordance with the contractual terms of the loan agreement. Impaired loans can be measured based on the present value of expected payments using the loan’s original effective rate as the discount rate, the loan’s observable market price, or the fair value of the collateral less selling costs if the loan is collateral dependent.
97
Table of Contents
The fair value of impaired loans were primarily measured based on the value of the collateral securing these loans. Impaired loans are classified within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy. Collateral may be real estate and/or business assets including equipment, inventory, and/or accounts receivable. The Company determines the value of the collateral based on independent appraisals performed by qualified licensed appraisers. These appraisals may utilize a single valuation approach or a combination of approaches including comparable sales and the income approach. Appraised values are discounted for costs to sell and may be discounted further based on management’s historical knowledge, changes in market conditions from the date of the most recent appraisal, and/or management’s expertise and knowledge of the customer and the customer’s business. Such discounts by management are subjective and are typically significant unobservable inputs for determining fair value. Impaired loans are reviewed and evaluated on at least a quarterly basis for additional impairment and adjusted accordingly, based on the same factors discussed above.
Other real estate owned
Other real estate owned, consisting of properties obtained through foreclosure or in satisfaction of loans, are initially recorded at the lower of the loan’s carrying amount or the fair value less costs to sell upon transfer of the loans to other real estate. Subsequently, other real estate is carried at the lower of carrying value or fair value less costs to sell. Fair values are generally based on third party appraisals of the property and are classified within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy. The appraisals are sometimes further discounted based on management’s historical knowledge, and/or changes in market conditions from the date of the most recent appraisal, and/or management’s expertise and knowledge of the customer and the customer’s business. Such discounts are typically significant unobservable inputs for determining fair value. In cases where the carrying amount exceeds the fair value, less costs to sell, a loss is recognized in noninterest expense.
Mortgage servicing rights, net
Mortgage servicing rights, net, included in other assets on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets, are carried at the lower of cost or estimated fair value. MSRs do not trade in an active market with readily observable prices. To determine the fair value of MSRs, the Company engages an independent third party. The independent third party’s valuation model calculates the present value of estimated future net servicing income using assumptions that market participants would use in estimating future net servicing income, including estimates of prepayment speeds, discount rate, default rates, cost to service, escrow account earnings, contractual servicing fee income, ancillary income, and late fees. Periodically, the Company will review broker surveys and other market research to validate significant assumptions used in the model. The significant unobservable inputs include prepayment speeds or the constant prepayment rate (“CPR”) and the weighted average discount rate. Because the valuation of MSRs requires the use of significant unobservable inputs, all of the Company’s MSRs are classified within Level 3 of the valuation hierarchy.
98
Table of Contents
The following table presents the balances of the assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, by caption, on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and by ASC 820 valuation hierarchy (as described above):
| Quoted Prices in
|
||||||||||||||||
| Active Markets
|
Other
|
Significant
|
||||||||||||||
| for
|
Observable
|
Unobservable
|
||||||||||||||
| Identical Assets
|
Inputs
|
Inputs
|
||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | Amount | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019: |
||||||||||||||||
| Loans held for sale |
$ | 2,202 | — | 2,202 | — | |||||||||||
| Loans, net(1) |
99 | — | — | 99 | ||||||||||||
| Other assets (2) |
1,299 | — | — | 1,299 | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Total assets at fair value |
$ | 3,600 | — | 2,202 | 1,398 | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018: |
||||||||||||||||
| Loans held for sale |
$ | 383 | — | 383 | — | |||||||||||
| Loans, net(1) |
157 | — | — | 157 | ||||||||||||
| Other real estate owned |
172 | — | — | 172 | ||||||||||||
| Other assets (2) |
1,441 | — | — | 1,441 | ||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Total assets at fair value |
$ | 2,153 | — | 383 | 1,770 | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Loans considered impaired under ASC 310-10-35 Receivables. This amount reflects the recorded investment in impaired loans, net of any related allowance for loan losses. |
| (2) | Represents other real estate owned and MSRs, net, both of which are carried at lower of cost or estimated fair value. |
At December 31, 2019 and 2018 and for the years then ended, the Company had no Level 3 assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis. For Level 3 assets measured at fair value on a non-recurring basis as of December 31, 2019, the significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurements are presented below.
| (Dollars in thousands) | Carrying Amount |
Valuation Technique | Significant Unobservable Input | Weighted Average of Input |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| December 31, 2019: |
||||||||||||||||
| Nonrecurring: |
||||||||||||||||
| Impaired loans |
$ | 99 | Appraisal | Appraisal discounts (%) | 10.0% | |||||||||||
| Mortgage servicing rights, net |
1,299 | Discounted cash flow | Prepayment speed or CPR (%) | 11.6% | ||||||||||||
| Discount rate (%) | 10.0% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018: |
||||||||||||||||
| Nonrecurring: |
||||||||||||||||
| Impaired loans |
$ | 157 | Appraisal | Appraisal discounts (%) | 10.0% | |||||||||||
| Other real estate owned |
172 | Appraisal | Appraisal discounts (%) | 10.0% | ||||||||||||
| Mortgage servicing rights, net |
1,441 | Discounted cash flow | Prepayment speed or CPR (%) | 8.3% | ||||||||||||
| Discount rate (%) | 10.0% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
99
Table of Contents
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
ASC 825, Financial Instruments, requires disclosure of fair value information about financial instruments, whether or not recognized on the face of the balance sheet, for which it is practicable to estimate that value. The assumptions used in the estimation of the fair value of the Company’s financial instruments are explained below. Where quoted market prices are not available, fair values are based on estimates using discounted cash flow analyses. Discounted cash flows can be significantly affected by the assumptions used, including the discount rate and estimates of future cash flows. The following fair value estimates cannot be substantiated by comparison to independent markets and should not be considered representative of the liquidation value of the Company’s financial instruments, but rather are a good-faith estimate of the fair value of financial instruments held by the Company. ASC 825 excludes certain financial instruments and all nonfinancial instruments from its disclosure requirements.
The following methods and assumptions were used by the Company in estimating the fair value of its financial instruments:
Loans, net
Fair values for loans were calculated using discounted cash flows. The discount rates reflected current rates at which similar loans would be made for the same remaining maturities. Expected future cash flows were projected based on contractual cash flows, adjusted for estimated prepayments. The fair value of loans was measured using an exit price notion.
Loans held for sale
Fair values of loans held for sale are determined using quoted market secondary market prices for similar loans.
Time Deposits
Fair values for time deposits were estimated using discounted cash flows. The discount rates were based on rates currently offered for deposits with similar remaining maturities.
| Fair Value Hierarchy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | Carrying
amount |
Estimated
fair value |
Level 1
inputs |
Level 2
inputs |
Level 3
Inputs |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial Assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans, net (1) |
$ | 456,515 | $ | 453,705 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 453,705 | ||||||||||||||
| Loans held for sale |
2,202 | 2,251 | — | 2,251 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Financial Liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time Deposits |
$ | 167,199 | $ | 168,316 | $ | — | $ | 168,316 | $ | — | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial Assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans, net (1) |
$ | 472,118 | $ | 465,456 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 465,456 | ||||||||||||||
| Loans held for sale |
383 | 397 | — | 397 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Financial Liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time Deposits |
$ | 181,237 | $ | 181,168 | $ | — | $ | 181,168 | $ | — | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1) Represents loans, net of unearned income and the allowance for loan losses. The fair value of loans was measured using an exit price notion.
100
Table of Contents
NOTE 16: RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
The Bank has made, and expects in the future to continue to make in the ordinary course of business, loans to directors and executive officers of the Company, the Bank, and their affiliates. In management’s opinion, these loans were made in the ordinary course of business at normal credit terms, including interest rate and collateral requirements, and do not represent more than normal credit risk. An analysis of such outstanding loans is presented below.
| (Dollars in thousands) | Amount | |||
|
|
||||
| Loans outstanding at December 31, 2018 |
$ | 8,207 | ||
| New loans/advances |
1,559 | |||
| Repayments |
(6,617) | |||
|
|
||||
| Loans outstanding at December 31, 2019 |
$ | 3,149 | ||
|
|
||||
During 2019 and 2018, certain executive officers and directors of the Company and the Bank, including companies with which they are affiliated, were deposit customers of the bank. Total deposits for these persons at December 31, 2019 and 2018 amounted to $19.1 million and $19.8 million, respectively.
NOTE 17: REGULATORY RESTRICTIONS AND CAPITAL RATIOS
As required by the Economic Growth, Regulatory Relief, and Consumer Protection Act in August 2018, the Federal Reserve Board issued an interim final rule that expanded applicability of the Board’s small bank holding company policy statement. The interim final rule raised the policy statement’s asset threshold from $1 billion to $3 billion in total consolidated assets for a bank holding company or savings and loan holding company that: (1) is not engaged in significant nonbanking activities; (2) does not conduct significant off-balance sheet activities; and (3) does not have a material amount of debt or equity securities, other than trust-preferred securities, outstanding. The interim final rule provides that, if warranted for supervisory purposes, the Federal Reserve may exclude a company from the threshold increase. Management believes the Company meets the conditions of the Federal Reserve’s small bank holding company policy statement and is therefore excluded from consolidated capital requirements at December 31, 2019.
The Bank remains subject to regulatory capital requirements administered by the federal banking agencies. Failure to meet minimum capital requirements can initiate certain mandatory - and possibly additional discretionary - actions by regulators that, if undertaken, could have a direct material effect on the Company’s financial statements. Under capital adequacy guidelines and the regulatory framework for prompt corrective action, the Bank must meet specific capital guidelines that involve quantitative measures of their assets, liabilities and certain off-balance sheet items as calculated under regulatory accounting practices. The capital amounts and classification are also subject to qualitative judgments by the regulators about components, risk weightings and other factors.
As of December 31, 2019, the Bank is “well capitalized” under the regulatory framework for prompt corrective action. To be categorized as “well capitalized,” the Bank must maintain minimum common equity Tier 1, total risk-based, Tier 1 risk-based, and Tier 1 leverage ratios as set forth in the table. Management has not received any notification from the Bank’s regulators that changes the Bank’s regulatory capital status.
101
Table of Contents
The actual capital amounts and ratios and the aforementioned minimums as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 are presented below.
| Minimum for capital | Minimum to be | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Actual |
adequacy purposes |
well capitalized |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At December 31, 2019: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 Leverage Capital |
$ | 92,778 | 11.23% | $ | 33,043 | 4.00% | $ | 41,303 | 5.00% | |||||||||||||||
| Common Equity Tier 1 Capital |
$ | 92,778 | 17.28% | $ | 24,162 | 4.50% | $ | 34,901 | 6.50% | |||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 Risk-Based Capital |
$ | 92,778 | 17.28% | $ | 32,216 | 6.00% | $ | 42,955 | 8.00% | |||||||||||||||
| Total Risk-Based Capital |
$ | 97,291 | 18.12% | $ | 42,955 | 8.00% | $ | 53,693 | 10.00% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At December 31, 2018: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 Leverage Capital |
$ | 91,719 | 11.33% | $ | 32,368 | 4.00% | $ | 40,461 | 5.00% | |||||||||||||||
| Common Equity Tier 1 Capital |
$ | 91,719 | 16.49% | $ | 25,031 | 4.50% | $ | 36,156 | 6.50% | |||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 Risk-Based Capital |
$ | 91,719 | 16.49% | $ | 33,375 | 6.00% | $ | 44,500 | 8.00% | |||||||||||||||
| Total Risk-Based Capital |
$ | 96,661 | 17.38% | $ | 44,500 | 8.00% | $ | 55,625 | 10.00% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends paid by the Bank are a principal source of funds available to the Company for payment of dividends to its stockholders and for other needs. Applicable federal and state statutes and regulations impose restrictions on the amounts of dividends that may be declared by the subsidiary bank. State law and Federal Reserve policy restrict the Bank from declaring dividends in excess of the sum of the current year’s earnings plus the retained net earnings from the preceding two years without prior approval. In addition to the formal statutes and regulations, regulatory authorities also consider the adequacy of the Bank’s total capital in relation to its assets, deposits, and other such items. Capital adequacy considerations could further limit the availability of dividends from the Bank. At December 31, 2019, the Bank could have declared additional dividends of approximately $8.0 million without prior approval of regulatory authorities. As a result of this limitation, approximately $86.8 million of the Company’s investment in the Bank was restricted from transfer in the form of dividends.
NOTE 18: AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION (PARENT COMPANY)
The Parent Company’s condensed balance sheets and related condensed statements of earnings and cash flows are as follows:
CONDENSED BALANCE SHEETS
| December 31 | ||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
$ | 4,119 | 1,941 | |||||
| Investment in bank subsidiary |
94,837 | 87,956 | ||||||
| Other assets |
625 | 626 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 99,581 | 90,523 | |||||
|
|
||||||||
| Liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accrued expenses and other liabilities |
$ | 1,253 | 1,468 | |||||
|
|
||||||||
| Total liabilities |
1,253 | 1,468 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity |
98,328 | 89,055 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
$ | 99,581 | 90,523 | |||||
|
|
||||||||
102
Table of Contents
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF EARNINGS
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Income: |
||||||||
| Dividends from bank subsidiary |
$ | 8,574 | 6,533 | |||||
| Noninterest income |
346 | 149 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Total income |
8,920 | 6,682 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Expense: |
||||||||
| Interest expense |
— | 51 | ||||||
| Noninterest expense |
212 | 237 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Total expense |
212 | 288 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Earnings before income tax expense (benefit) and equity in undistributed earnings of bank subsidiary |
8,708 | 6,394 | ||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) |
26 | (28) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Earnings before equity in undistributed earnings of bank subsidiary |
8,682 | 6,422 | ||||||
| Equity in undistributed earnings of bank subsidiary |
1,059 | 2,412 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 9,741 | 8,834 | |||||
|
|
||||||||
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| Year ended December 31 | ||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 9,741 | 8,834 | |||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||
| Net decrease in other assets |
7 | 1,134 | ||||||||
| Net decrease in other liabilities |
(215) | (70) | ||||||||
| Equity in undistributed earnings of bank subsidiary |
(1,059) | (2,412) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
8,474 | 7,486 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||||
| Repayments or retirement of long-term debt |
— | (3,217) | ||||||||
| Dividends paid |
(3,575) | (3,498) | ||||||||
| Stock repurchases |
(2,721) | — | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net cash used in financing activities |
(6,296) | (6,715) | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents |
2,178 | 771 | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period |
1,941 | 1,170 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period |
$ | 4,119 | 1,941 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
103
Table of Contents
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
Not applicable.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
As required by Rule 13a-15(b) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”), the Company’s management, under the supervision and with the participation of its principal executive and principal financial officer, conducted an evaluation as of the end of the period covered by this report, of the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Exchange Act. Based on that evaluation, and the results of the audit process described below, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the Company’s reports under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and regulations, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to the Company’s management, including the Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding disclosure.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting. Internal control is designed to provide reasonable assurance to the Company’s management and board of directors regarding the preparation of reliable published financial statements. Internal control over financial reporting includes self-monitoring mechanisms, and actions are taken to correct deficiencies as they are identified.
Because of inherent limitations in any system of internal control, no matter how well designed, misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and not be detected, including the possibility of the circumvention or overriding of controls. Accordingly, even effective internal control over financial reporting can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation. Further, because of changes in conditions, internal control effectiveness may vary over time.
Management assessed the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019. This assessment was based on criteria for effective internal control over financial reporting described in “Internal Control – Integrated Framework” issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework). Based on this assessment, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer assert that the Company maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019 based on the specified criteria.
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019 has been audited by Elliott Davis, LLC, the independent registered public accounting firm who also has audited the Company’s consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Elliott Davis, LLC’s attestation report on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting appears on the following page and is incorporated by reference herein.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
During the period covered by this report, there has not been any change in the Company’s internal controls over financial reporting that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal controls over financial reporting.
104
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Auburn National Bancorporation, Inc.
Opinion on the Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Auburn National Bancorporation, Inc. and its subsidiaries’ (the “Company”) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013. In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on the criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 and the related consolidated statements of earnings, comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows of the Company for the years then ended, and the related notes to the consolidated financial statements and our report dated March 6, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of consolidated financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of consolidated financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Elliott Davis, LLC
Greenville, South Carolina
March 6, 2020
105
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS AND EXECUTIVE OFFICERS OF THE REGISTRANT
Information required by this item is set forth under the headings “Proposal One: Election of Directors - Information about Nominees for Directors,” and “Executive Officers,” “Additional Information Concerning the Company’s Board of Directors and Committees,” “Executive Compensation,” “Audit Committee Report” and “Compliance with Section 16(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934” in the Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference.
The Board of Directors has adopted a Code of Conduct and Ethics applicable to the Company’s directors, officers and employees, including the Company’s principal executive officer, principal financial and principal accounting officer, controller and other senior financial officers. The Code of Conduct and Ethics, as well as the charters for the Audit Committee, Compensation Committee, and the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee, can be found by hovering over the heading “About Us” on the Company’s website, www.auburnbank.com, and then clicking on “Investor Relations”, and then clicking on “Governance Documents”. In addition, this information is available in print to any shareholder who requests it. Written requests for a copy of the Company’s Code of Conduct and Ethics or the Audit Committee, Compensation Committee, or Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee Charters may be sent to Auburn National Bancorporation, Inc., 100 N. Gay Street, Auburn, Alabama 36830, Attention: Marla Kickliter, Senior Vice President of Compliance and Internal Audit. Requests may also be made via telephone by contacting Marla Kickliter, Senior Vice President of Compliance and Internal Audit, or Laura Carrington, Vice President of Human Resources, at (334) 821-9200.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
Information required by this item is set forth under the headings “Additional Information Concerning the Company’s Board of Directors and Committees – Board Compensation,” and “Executive Officers” in the Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
Information required by this item is set forth under the headings “Proposal One: Election of Directors - Information about Nominees for Directors and Executive Officers” and “Stock Ownership by Certain Persons” in the Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
Information required by this item is set forth under the headings “Additional Information Concerning the Company’s Board of Directors and Committees – Committees of the Board of Directors – Independent Directors Committee” and “Certain Transactions and Business Relationships” in the Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
Information required by this item is set forth under the heading “Independent Public Accountants” in the Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference.
107
Table of Contents
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
| (a) | List of all Financial Statements |
The following consolidated financial statements and report of independent registered public accounting firm of the Company are included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K:
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2019 and 2018
Consolidated Statements of Earnings for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document | |||
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | |||
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | |||
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | |||
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | |||
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | |||
| * | The certifications attached as exhibits 32.1 and 32.2 to this annual report on Form 10-K are “furnished” to the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and shall not be deemed “filed” by the Company for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. |
108
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the City of Auburn, State of Alabama, on March 6, 2020.
| AUBURN NATIONAL BANCORPORATION, INC. | ||
| (Registrant) | ||
| By: | /S/ ROBERT W. DUMAS | |
| Robert W. Dumas Chairman, President and CEO | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature |
Title |
Date | ||
| /S/ ROBERT W. DUMAS Robert W. Dumas |
Chairman of the Board, President and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) |
March 6, 2020 | ||
| /S/ DAVID A. HEDGES David A. Hedges |
EVP, Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) |
March 6, 2020 | ||
| /S/ C. WAYNE ALDERMAN C. Wayne Alderman |
Director | March 6, 2020 | ||
| /S/ TERRY W. ANDRUS Terry W. Andrus |
Director | March 6, 2020 | ||
| /S/ J. TUTT BARRETT J. Tutt Barrett |
Director | March 6, 2020 | ||
| /S/ LAURA COOPER Laura Cooper |
Director | March 6, 2020 | ||
| /S/ WILLIAM F. HAM, JR. William F. Ham, Jr. |
Director | March 6, 2020 | ||
| /S/ DAVID E. HOUSEL David E. Housel |
Director | March 6, 2020 | ||
| /S/ ANNE M. MAY Anne M. May |
Director | March 6, 2020 | ||
| /S/ EDWARD LEE SPENCER, III Edward Lee Spencer, III |
Director | March 6, 2020 | ||
| /S/ PATRICIA WADE Dr. Patricia Wade |
Director | March 6, 2020 | ||
110
