Attached files
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
[X] ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended September 30, 2019
[ ] TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15 (d) OF THE EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
Commission File number: 000-55088
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION |
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) |
Nevada |
| 33-1227980 |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
| (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
930 Tahoe Blvd. Suite 802-16, Incline Village, NV 89451 |
(Address of principal executive offices) |
(775) 473-4744 |
(Registrant's telephone number) |
(Former name, former address and former fiscal year, if changed since last report) |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: None
Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered |
|
|
|
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes [ ] No [X]
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes [ ] No [X]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the past 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes [X] No [ ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes [X] No [ ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See definition of "large accelerated filer", "accelerated filer," "smaller reporting company," and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
[ ] | Accelerated filer | [ ] | |
Non-accelerated filer | [X] | Smaller reporting company | [X] |
Emerging growth company | [ ] |
|
|
1
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act [ ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act) Yes [ ] No [X]
State the aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was last sold, or the average bid and asked price of such common equity, as of the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter. $22,182,023 as of March 31, 2019
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the registrant’s classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date. 166,234,301 as of December 20, 2019
2
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This annual report on Form 10-K (this “Report”) contains forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements are contained principally in the “Business” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” sections of this Report. These statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors which may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from any future results, performances or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terms such as “anticipates”, “believes”, “seeks”, “could”, “estimates”, “expects”, “intends”, “may”, “plans”, “potential”, “predicts”, “projects”, “should”, “would” and similar expressions intended to identify forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements reflect our current views with respect to future events and are based on assumptions and subject to risks and uncertainties. Given these uncertainties, you should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. Such statements may include, but are not limited to, information related to: anticipated operating results; relationships with our customers; consumer demand; financial resources and condition; changes in revenues; changes in profitability; changes in accounting treatment; cost of sales; selling, general and administrative expenses; interest expense; the ability to produce the liquidity or enter into agreements to acquire the capital necessary to continue our operations and take advantage of opportunities; legal proceedings and claims. Also, forward-looking statements represent our estimates and assumptions only as of the date of this Report. You should read this Report and the documents that we reference and file or furnish as exhibits to this Report completely and with the understanding that our actual future results may be materially different from what we expect. Except as required by law, we assume no obligation to update any forward-looking statements publicly, or to update the reasons actual results could differ materially from those anticipated in any forward-looking statements, even if new information becomes available in the future.
PRESENTATION OF INFORMATION
Except as otherwise indicated by the context, references in this Report to “ABMC”, “we”, “us”, “our” and the “Company” are to the combined business of American Battery Metals Corporation and its consolidated subsidiaries.
This Report includes our audited consolidated financial statements as at and for the years ended September 30, 2019 and 2018. These financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (“US GAAP”). All financial information in this Report is presented in US dollars, unless otherwise indicated, and should be read in conjunction with our audited consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto included in this Report.
3
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| ||
|
|
|
Item 1. | Business | 5 |
Item 1A. | Risk Factors | 7 |
Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments | 7 |
Item 2. | Properties | 8 |
Item 3. | Legal Proceedings | 15 |
Item 4 | Mine Safety Disclosures | 15 |
|
|
|
PART II |
| |
|
|
|
Item 5. | Market for Registrant's Common Equity and Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities | 16 |
Item 6. | Selected Financial Data | 19 |
Item 7. | Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 19 |
Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk | 21 |
Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | 21 |
Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure | 22 |
Item 9A | Control and Procedures | 22 |
Item 9B. | Other Information | 22 |
|
|
|
PART III |
| |
|
|
|
Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance | 23 |
Item 11. | Executive Compensation | 25 |
Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters | 26 |
Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence | 26 |
Item 14. | Principal Accounting Fees and Services | 26 |
|
|
|
PART IV |
| |
|
|
|
Item 15. | Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules | 27 |
Item 16. | Form 10-K Summary | 28 |
| Signatures | 28 |
4
PART I
Background
We are a start-up company, engaged in the exploration, mining, extraction and recycling of battery metals. We were incorporated under the laws of the State of Nevada on October 6, 2011 for the purpose of acquiring rights to mineral properties with the eventual objective of being a producing mineral company, if and when it ever occurs. We have limited operating history and have not yet generated or realized any revenues from our activities. Our principal executive offices are located at 930 Tahoe Blvd., Suite 802-16, Incline Village, NV 89451.
We are actively exploring and drilling for lithium-rich brines and deposits from the Company’s claims covering 30,000 acres in Railroad Valley, Nevada.
In our laboratory located in Silver Springs, Nevada, we have started developing a proprietary extraction technology to harvest lithium from brine for refinement into battery-grade lithium carbonate or lithium hydroxide.
In an incubator space provided by BASF Corporation and located in Greentown, Massachusetts, we began, in the first quarter of the 2020 fiscal year, to develop a closed-loop battery recycling process that separates and recovers each individual elemental metal from end-of-life batteries, as well as from defects and waste from battery manufacturing facilities. These recovered metals will be refined up to battery-grade specifications and then sold.
Currently, the Board of Directors (consisting of Mr. Douglas Cole, Mr. Douglas MacLellan and Mr. William Hunter) are involved in guiding the Company’s goals and objectives to solely focus on the exploration, extraction and recycling of Lithium (Li) and other battery metal deposits in the State of Nevada, primarily through new capital commitments which Mr. Cole is actively seeking.
On August 8, 2016, the Company formed Lithortech Resources Inc. as a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company to serve as its operating subsidiary for lithium resource exploration and development. On June 29, 2018, the Company changed the name of Lithortech Resources to LithiumOre Corp. (“LithiumOre”).
On May 3, 2019, the Company changed its name to American Battery Metals Corporation (“ABMC”) and reorganized into three divisions; Battery Metals Mining, Battery Metals Extraction and Battery Metals Recycling. ABMC currently has 1,300 mining claims on 30,000 acres in the area known as the Western Nevada Basin, situated in Railroad Valley in Nye County, Nevada (the “WNB Claim”). In the second half of 2017, we engaged experts to evaluate the region and the WNB Claim to target onsite exploration efforts and determined that the claims of the WNB Claim were appropriate for the Company’s planned exploration, which we began in the first half of 2019. With many features similar to Clayton Valley and with no exploration work targeting lithium to date, Railroad Valley represents a new and untested target for lithium brine. The Railroad Valley brine exploration can build on both the dense existing oil field data and the experiences at Clayton Valley and other Lithium brine basins to target potential brine aquifers. Please see the Company’s website for more information: www.batterymetals.com.
The growth in demand for lithium batteries is predicted by industry researchers to outpace lithium production in the coming decade. Lithium-ion batteries for the automotive industry are expected to advance demand beyond current supply. These industry trends support and validate the Company’s new business model.
The Company is currently a pre-revenue organization and we do not anticipate earning revenues until such time as we have undertaken sufficient exploration work to identify lithium and or other battery metals reserves. Exploration work will take several years and there is no certainty we will ever reach a production stage. Our Company is considered to be in the exploration stage due to not having done exploration work which would result in a development decision.
Market and Industry
Lithium is extracted from primarily two sources: pegmatite crystals and lithium salts from brine pools. Currently, the world’s top producers of Lithium are located in Australia, Chile, Argentina, and China.
In 2018, worldwide Lithium production totaled approximately 85,000 metric tons, with the top 3 countries contributing roughly 89% of the global production. Most of the world’s lithium supply is produced by three companies: Albemarle Corporation, FMC Corporation, and Chile’s Sociedad Quimica Y Minera de Chile (SQM). Ganfeng and Tianqi of China are major players.
5
Much of the current production of Lithium in Australia is derived from conventional mining techniques of ancient Precambrian rocks containing Lithium ore which is crushed and fed into capital intensive processing plants which upgrade the lithium mineral using gravity, flotation, magnetic and roasting purification processes.
Alternatively, Lithium production from Chile and Argentina uses a much less capital intense extraction method. Lithium is located beneath various salt flats. The Lithium is leached from nearby source rocks and becomes concentrated in salty brines just under the surface. The Lithium enriched brines are then pumped up to settle in multiple of shallow surface evaporation pools which produces a thicker Lithium rich liquid. That liquid is treated with sodium carbonate, which creates lithium carbonate.
Lithium is a soft silver-white metal. With an atomic number of 3, it is the lightest of the all metals. Lightweight Lithium has many applications but the metal is a perfect replacement of the much heavier Nickel used in most large batteries. Lithium-ion batteries also have a high charge density, a longer life and are rechargeable.
The Lithium market has typically been dominated by the ceramic and medical sectors, however recently the demand for Lithium for the battery markets- to fuel electric vehicles and energy storage applications- outstripped any other sector.
The primary lithium-ion battery manufacturers by capacity are: CATL, BYD, Tesla, Panasonic of Japan, and LG Chem of South Korea.
Lithium is not currently traded on any commodity exchanges, but rather is usually distributed in a chemical form such as lithium carbonate (Li2CO3) and sold directly to end users for a negotiated price per ton of Lithium carbonate.
General Market Analysis
Lithium-ion batteries have become the rechargeable battery of choice in cell phones, computers, electric cars and now larger scale electric storage. The growth in demand for lithium batteries is predicted to far outpace lithium production in the coming decade; in particular, Lithium-ion batteries for the automotive industry is expected to continue to drive demand beyond supply.
Recently, Japan and South Korea have both recorded high levels of Lithium-ion battery exports as auto companies’ ramp up battery consumption to power all-electric vehicle sales. China has the most electric vehicles on the road, but both European and North American auto manufacturers are committed to significantly increasing EV sales by 2025. In November 2019, Ford unveiled its long awaited fully electric Mustang-styled SUV.
Goldman Sachs predicted that the market consumption could very well triple from the current production by 2025. Just a 1% increase of Electric Vehicles hitting the market could increase lithium demand by roughly half of the current production of lithium today.
SQM’s CEO Patricio de Solminihac said in a 2018 interview with Reuters that the company would invest $525 million in order to expand its lithium production in Chile through 2021, due to the high demand for electric vehicle batteries. FMC and Albemarle have decided not to wait either. FMC announced in May 2017 it would triple its production of lithium hydroxide by 2019, increasing to 30,000 tons from 10,000. Albemarle also announced it would be increasing production of lithium carbonate to 70,000 tons from 24,000 over a few years.
Tesla’s mile long Gigafactory started producing powerful Lithium-ion batteries in January 2017 with its partner Panasonic. The Gigafactory will supply batteries for the 500,000 cars Tesla hopes to produce by the end of the decade, as well as to power homes. Also, Chrysler, Dodge, Ford, GM, BMW, Volkswagen, Mercedes-Benz, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Saturn, Tesla and Toyota have all announced plans to build lithium-ion battery powered cars. After Tesla released the Model 3 in July 2017, there have been over 500,000 reservations for the vehicle and production is starting 2 years ahead of schedule. Elon Musk has stated that Tesla will have to acquire the entire lithium market to meet the current demands. Thus, the global lithium market is approaching shortages, which has made it a useful commodity and mineral explorers have launched efforts to locate and bring new suppliers to the marketplace.
Lithium brine exploration and development has proven to be much more cost effective and faster to be put into production than the hard rock mine counterparts. Lithium brine deposits are considered placer deposits and are easier to gain mining permits for. Brine is also a liquid which means that drilling to find it is more akin to drilling for water or oil. It’s also typically located relatively close to surface, which limits the depth of required drilling. Once a Lithium Brine is found, the reserve data is more straightforward to understand and quantify.
As the brines are found in large flat areas, the construction of numerous flat evaporation pools or direct solvent extraction can be achieved at relatively low cost. Environmental impact is minimized as the excess residual brines can be pumped back into the salt flats.
6
In Summary:
Historically, lithium demand came from industrial sectors manufacturing greases, glass, and ceramics. The processing of lithium for industrial applications requires lower specification products.
The introduction of the lithium-ion battery for consumer electronics, EV, and energy storage applications changed the demand dynamic; the batteries for e-mobility and energy storage now dominate current and future demand for lithium. Electric vehicles will continue to require vast amounts of lithium with higher grade and purities.
Electric Vehicle OEM are increasingly quality-conscious, and develop close relationships to the modern “megafactories” that supply them with battery cells. In order to consistently supply the desired high nickel cathodes, megafactories need high purity raw materials - particularly lithium - to create low impurity lithium hydroxide.
In the United States, there are not currently enough chemical producers in operation to meet existing or future standards; battery grade hydroxide production is quite small as compared to the whole lithium supply chain. To meet market demand, this segment must quickly grow in the short term, at an estimated rate of 35-40% between now and 2025.
In 2019, explanations for the drop in the price of lithium were erroneously attributed to the “oversupply myth.” The reality is that there is not “too much lithium” in production but rather that there is not enough battery grade lithium hydroxide to meet market demand to fuel the explosive projections for Electric Vehicles.
Existing producers know that aside from handling and limited shelf life, consistently producing battery grade hydroxide within "spec,” while meeting the qualification challenges going forward will require significantly more high-grade lithium products. This will require new resources of raw materials, which demands investment in new exploration and mining projects.
Competition
We compete with other mining/exploration and battery recycling companies, many of which possess greater financial resources and technical facilities than we do, in connection with the acquisition of suitable exploration properties, building and operating process plants and in connection with the engagement of qualified personnel. The lithium exploration/mining and battery recycling industries are fragmented, and we are a very small participant in these sectors. Many of our competitors have been in business longer than we have and have established more strategic partnerships and relationships and have greater financial accessibility than we have.
While we compete with other exploration companies in acquiring suitable properties, we believe that there would be readily available purchasers of lithium and other precious metals if they were to be produced from any of our leased properties. The price of precious metals can be affected by a number of factors beyond our control, including:
fluctuations in the market prices for lithium;
fluctuating supplies of lithium;
fluctuating demand for lithium; and
mining activities of others.
If lithium mineralization that is determined to be of economic grade and in sufficient quantity to justify production were located, additional capital would be required to develop, mine and sell our production.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
Not required.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
Not applicable.
7
Description of Properties
LithiumOre, the Company’s wholly owned subsidiary, currently has 1,040 placer mining claims on over 20,000 acres in the area known as the Western Nevada Basin, situated in Railroad Valley in Nye County, Nevada. We do not currently have any partnership agreements or royalty agreements in connection with such claims.
We own a 120-acre property with water rights, in the town of Duckwater, NV near Railroad Valley, which we acquired for exploratory purposes and was fully impaired in prior years. It will act as a base for such operations for the Company.
We lease from the Bureau of Land Management our Western Nevada Basin Claim where we are exploring and drilling for possible lithium-rich brine.
The Western Nevada Basin (WNB) Claim is located in east central Nye County, Nevada (Figure 1) approximately 93 miles northeast of the county seat of Tonopah, NV, the major commercial center for the region; 56 miles southwest of the town of Ely, NV and 120 miles northeast of the village of Silver Peak the only currently operating Lithium producer in the State.
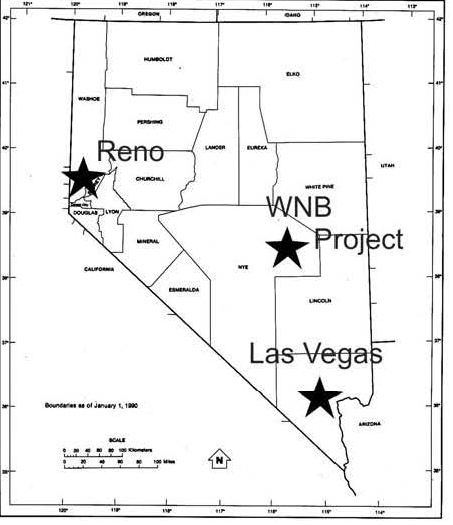
Figure 1. Location Map. The Western Nevada Basin Claim is located within the central portion of the Railroad Valley, approximately 169 miles north-northwest of Las Vegas, NV and 234 miles east-southeast of Reno, NV.
8
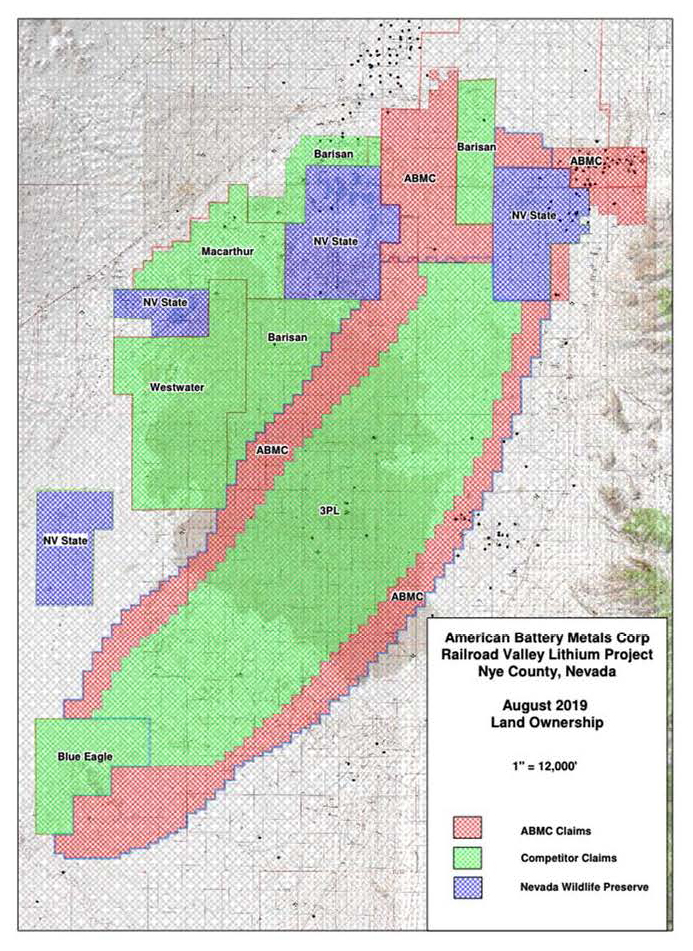
Figure 2. The Western Nevada Basin Claim covers just over 30,000 acres. It consists of a total of one thousand three hundred (1,300) placer claims. Each claim covers approximately 20 acres and was laid out by aliquot parts as required by the Bureau of Land Management.
Lithium is a locatable mineral according to the Code of Federal Regulations. Rights to Lithium are to be held by lode claims where it occurs in bedrock and by placer claims where it occurs in sediments. A body of legal precedence set during the original development of lithium brines in the area provides that lithium in valley sediments by nature of the unconsolidated host rock are staked by and produced from placer claims.
The WNB Claim is held by 1,300 twenty-acre placer claims, which are located on public Federal lands managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM). The placer claims are located on U.S. Surveyed lands and fit to aliquot parts.
In Nevada the claim staking procedure requires recording documents with both the county Recorder’s Office and the state BLM office. Claims must be held by posts at the claims four corners and Notice of Location which describe the claims legal description of location and owner. The claims are required to be recorded at the county courthouse within the proper jurisdiction within 90 days from the staking date.
Placer claims on Federal lands are held to a September 1 to August 31 assessment year when Intent to Hold or Proof of Labor documents need to be filed with the county for the annual assessment work. The pertinent documents are filed with the Nye County Recorder’s Office.
9
260 claims were staked by the third Party, Plateau Ventures LLC of Moab, Utah and 1,040 claims were staked by 3 Proton Lithium, Inc. of Carson City, Nevada. Official rights to the claims by ABMC are subject to Quit Claim Deed Transfer Approval by BLM. ABMC received full entitlement to its claims in the Western Nevada Basin by way of the Quit Claim Deeds on January 2, 2017 (260 claims), August 13, 2018, (40 claims) and August 28, 2018 (1,000 claims). The current annual maintenance fee is $155 per 20-acre (or a portion thereof) placer claim (http://www.blm.gov/ca/st/en/info/iac/miningfacts.html). Payment of those fees allows the claim to stay on the BLM active database. Non-payment results in the claims moving to ‘closed’ status.
Before August 31st of each year, a payment of $155 per claim is made to the BLM to hold the claims in good standing for the following assessment year. The total cost for the 1,300 WNB Claims was $203,260. In August 2017, the Company paid $42,060 to the BLM for 260 Claims. In August 2018, the Company paid $6,200 to the BLM for 40 Claims, and $155,000 to the BLM for 1,000 Claims. These fees were also paid in 2018 and 2019 in order to maintain the current mining claims. When fees are paid a claim is deemed ‘active’. Active and approved claims are Before October 31st of each year, it is necessary to make a payment to Nye County, NV, of $10 per claim to file an affidavit of assessment fees paid and notice of intent to hold the claims into the next assessment year. The total cost for the current 1,300 WNB claims is $13,000. Payments to the County of $15,586 are current as of October 31, 2019.
As public lands, there is right of free access and both surface and mineral rights are held by the Federal government. Public records (Management, Bureau of Land) show no military withdrawals or Areas of Critical Environmental Concern. The Railroad Valley Wildlife Management Area is located to the west of the WNB claim boundary and has no effect on any planned work on the WNB claim area.
There is free access to the Federal land in Railroad Valley and there are no restrictions on casual prospecting. New exploration drilling will trigger a permitting process. There are two major levels of permitting: Notice of Intent (NOI) and Plan of Operations (POO). Historically, if the proposed disturbance was less than 5 acres or 1,000 tons, then the work can proceed under a NOI if there are no complications such as ancient ruins or endangered species. Application for a NOI is relatively simple with requirements like bonding the access route and re-seeding afterwards. A NOI is valid for two years and may be renewed every two years. Maintaining it requires maintaining bonds and reclaiming any new disturbance which includes re-seeding vegetation in disturbed areas when the work is complete. A POO is more complicated requiring more in-depth studies including an archeological survey, and comprehensive environmental assessments as required by the National Environmental Protection Act. The BLM may respond within 15 days to a NOI application whereas a POO may require several months to years for final acceptance.
Any drilling planned will require a NOI filed with the Tonopah office of the BLM. To the best of the Company’s knowledge, there are no known environmental liabilities to which the property is subject or other significant factors and risks that may affect access, title, or the right or ability to perform work on the property. The NOI permit for the drilling site was approved on July 13, 2018.
Accessibility
The main route of access to the WNB project is Nevada State U.S. Route 6 which provides all year access to Railroad Valley and the project area. U.S. Route 6 provides direct access to the two nearby commercial centers; Tonopah, located southwest of the project at the junction of Routes 6 and 95, approximately 90 minutes away, and Ely, a slightly larger commercial center with a population of over 4,200 approximately, located northeast of the project approximately 60 minutes away. US Highway 95 is the main highway linking Las Vegas and Reno, the two largest metropolitan areas in Nevada.
Climate
Railroad Valley is in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada Mountains. The region is arid to almost semiarid. Winters are cold while summers are hot. Average annual precipitation is approximately 5 inches; however, variations occur at differing altitudes. Exploration can be conducted in the spring, summer, and fall seasons.
Local Resources
The Railroad Valley contains several small communities; which include Currant, Crows Nest, Green Springs, Lockes, and Nyala. Electrical power is available within the valley area.
The larger population centers of Ely and Tonopah are connected via U.S. Route 6 to the project area. Tonopah has a population of approximately 2,500 and is the governmental center for the region. Ely has a population of approximately 4,200 and is the closest commercial center. Groceries, hardware, a bank and a choice of motels and restaurants are available in both Ely and Tonopah.
The area has a long history of mining. Mining personnel can be sourced mostly from the larger towns of Tonopah or Ely.
10
Infrastructure
A reasonable network of 4x4, graded and paved roads connects the claim area to the rest of Nevada. Electrical power is available at several sites throughout the valley and could easily provide power to any operation at the project area. The nearest rail and large commercial airline service are in Las Vegas, NV approximately 169 miles to the south.
Physiography
Railroad Valley is one of the longest topographically closed drainage basins in Nevada, extending more than 110 miles in a north-south direction and up to 20 miles wide. This valley is one of the Central Nevada Desert Basins in the Tonopah Basin. The southern end of the valley begins near Gray Top Mountain (7,036 feet) and stretches north all the way to Mount Hamilton (10,745 feet). The mountain masses are dominated by the White Pine, Grant and Quinn Canyon ranges east of the valley.
Railroad Valley comprises an area of approximately 2,750 square miles. Two large flat areas occur within the valley. The claims are located on the large Northern flat area of the valley floor at elevations generally of 4400 – 4700 feet. The valley floor is characterized by subdued topography with washes eroding into slightly older valley-fill sediments.
The claims are located on the flat areas where vegetation is scarce. There is sufficient surface area for recovery and processing facilities within the Claims.
Geologic Setting
The claims are located in the Basin and Range physiographic province which stretches from southern Oregon and Idaho to Mexico. It is characterized by extreme elevation changes between mountains and flat intermountain valleys or basins.
Plate tectonics powered by crustal spreading broadly generates two types of forces: compression as plates are moved together and extension as those forces relax. Compression was the dominant geologic force affecting the western United States beginning about 200 million years ago as the Pacific Ocean plate moved eastward under the North American continental plate. Those forces compressed the overlying pile of sedimentary rocks accumulated over hundreds of millions of years into a thick stack reaching up to elevations of 14,000 feet, similar to the altiplano of Mexico and South America which formed at the same time from similar forces. That highland plateau stretched west – east from the Sierra Nevada Mountains in California to the Wasatch Range in Utah.
Extension became the dominant force beginning in the Eocene - Oligocene epochs approximately 55 to 25 million years ago. Also, the relative movement of the tectonic plates changed about 30 million years ago with the movement becoming more oblique to the continent. This relaxed the compressional forces and also tended to ‘tear’ the crust apart, creating diagonal extensions.
The resulting compressional and extensional tectonics have created throughout Nevada a classical Basin and Range province consisting of narrow, N- to NE-trending, fault block mountain chains separated by flat linear valleys. This geological pattern is repeated across the State and has created a number of currently arid, ‘trapped’ or closed basins with respect to drainage that have the potential of containing Lithium Brine deposits.
Geology of Lithium Brines
Lithium brine deposits are accumulations of saline groundwater that are enriched in dissolved lithium. All producing lithium brine deposits share a number of first-order characteristics:
(1) arid climate;
(2) closed basin containing a salt flat (also known as a Playa or Salar);
(3) tectonically driven subsidence;
(4) associated igneous or geothermal activity;
(5) suitable lithium source-rocks;
(6) one or more adequate aquifers; and
(7) sufficient time to concentrate a brine.
The single most important factor determining if a nonmarine basin can accumulate lithium brine is whether or not the basin is closed.
Lithium enriched brines are formed by complex processes that include: evaporation, re-mobilization, salt and lithium clay dissolution and precipitation. In essence, lithium is liberated through weathering or derived from hydrothermal fluids from a variety of rock sources within a closed basin where Lithium, a lightweight element, cannot escape.
11
Lithium is highly soluble and, unlike sodium (Na), potassium (K), or calcium (Ca), does not readily produce evaporite minerals when concentrated by evaporation. Instead it ends up in residual brines in the shallow subsurface. Economic brines have Li concentrations in the range of 200 to 4,000 milligrams per liter (mg/l). 1 mg/l = 1 ppm.
Clayton Valley contains the only currently producing Lithium Brine project in Nevada. Production has been on-going since 1967. The production at Clayton Valley is located approximately 120 miles west of the Railroad Valley. Evidence from Clayton Valley suggests that felsic vitric tuffs are a particularly favorable primary source of Lithium as well, uplifted Neogene lake beds from earlier in the basin’s history, which have been altered to hectorite, may provide a source of Lithium.
Geology of Railroad Valley
Railroad Valley has produced about 44 million barrels of oil (MMBO) from nine petroleum fields and has been extensively studied to determine relations between structure and oil production. Several interpretations of basin configuration have evolved, based on improved seismic acquisition and processing and better understanding of deformation styles and kinetics.
Oil was first discovered at Railroad Valley by Shell Oil in 1954. Their first discovery well reached a depth of 10,360 feet and it was determined that there were commercial oil reserves at intervals between 6,450 and 6,730 feet. The valley area is essentially wedge shaped with the wedge increasing in thickness from west to east. A low-angle attenuation fault has been reported to underlie Railroad Valley which has been interpreted to be a result of asymmetric arching rather than a series of down-to-the-west high-angle normal faults.
The stratigraphy of the valley is known to contain Paleozoic platform carbonate rocks, Tertiary volcanic rocks, and Tertiary lacustrine sediments. In comparison to Clayton Valley, the Railroad Valley has a large endowment of Neogene volcanic flows and tophaceous rocks.
Oil exploration has reported several laterally continuous thick Lithium brine horizons throughout Railroad Valley. Testing for Lithium from the brines was not conducted by the oil industry. Good reservoir rocks for oil may not represent good reservoir hosts for Lithium. The underlying brine-waters of the Railroad Valley were at one time examined as a potential reservoir for Las Vegas.
Volcanic rocks form a large part of the Neogene rock sequence: ash-flow tuffs and basalt flows from major calderas in eastern and central Nevada. Thickness of the volcanic section can vary greatly because of Neogene erosion and faulting. The thickness of ash flow tuffs in Railroad Valley can range from less than 1,000 ft to more than 3,000 ft. These rocks have shown good porosity and may represent an enormous source for Lithium.
Tertiary lacustrine formations consist of varying proportions of fresh-water carbonate, shale, sandstone, and volcanic debris. To date, oil production from Tertiary lacustrine reservoirs is limited, but there is production from the Sheep Pass Formation in the Eagle Springs field, and formerly there was production from Currant field; both in Railroad Valley.
The northern Playa area of Railroad Valley contained a large lake during the Pleistocene Epoch, more than 7,000 years ago. The lake has subsequently evaporated within the valley; however, at one point it reportedly covered an area of over 525 square miles and attained a maximum depth of 315 feet. The large Railroad Valley north playa today is partly covered by young erosional alluvium.
Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves
The Railroad Valley has demonstrated enrichment in Lithium in the nearby dry sediments as evidenced from the NURE sample database from the U.S. Geologic Survey. However, the project is at an exploration stage. There are no lithium brine mineral resources or reserves for the property.
Exploration and Development
Exploration and Development would consist of direct sampling and analysis of Lithium both laterally and vertically across the project area from both volcanic horizons and underground Brines contained within the Playa. Drilling and mobilization represent the largest costs of the program. Every effort would be made to minimize costs and maximize the sampling of brine from either re-entry and perforation of ‘shut-in’ oil wells or testing of current water wells in the project area.
Exploration Time Table
The work for the initial phase exploration program will be designed over the following four to five months. Surficial sampling will be performed from February to March 2020 and Drilling and sampling from April to June. Analytical analysis will follow each program.
12
We began and completed the drilling of the initial test and production hole in May 2019. The breakdown of the exploration timetable and budget is as follows:
Exploration Activity | Estimated Timetable | Budget |
Oil and Water Well Testing | 2016-2018 | $300,000 (approximately) |
Surface Sampling | 2016-2018 | $100,000 (approximately) |
Geophysics | Ongoing | $44,200 |
Drilling | Ongoing | $705,280 |
Geochemistry | Ongoing for 2 years | $300,000 yearly |
Production | In development, 6-18 months | TBD |
Current and Prior Program Phases
Phase 1 Exploration of Potential Development Areas (2016 - 2018)
(a)Oil and water well testing in partnership with 3PL Operating Inc.
(b)Surface sampling conducted by our chief geologist Greg Kuzma (June 2016 to present day)
(c)Geophysical survey conducted by Zonge International Inc. (3/6/19 – present)
Phase 2 Beginning Exploration and Production Drilling (May 2019)
(a)Initial test and production drilling hole conducted by Welsco Inc. under the supervision of chief drilling engineer George Scheid.
Phase 3 Studying Geochemistry of Initial Drilling Results (June 2019)
(a)Chemistry, led by chief chemist Axel Drefahl
Current Exploration Plans
As stated above we began the drilling of the initial test and production hole in May 2019 and we intend to continue exploration upon the Company obtaining necessary financing for such exploration. The Company intends to fund the exploration program through a series of equity or debt private placements to accredited investors or through the seeking of joint venture partners.
Exploratory Team
Below are individuals and companies that the Company currently intends to use for exploration work and their qualifications.
Welsco Drilling Corp - Drilling Contractor:
Welsco Drilling Corporation brings 50 years of experience conducting geothermal, water well, and mineral exploration to our project. Welsco began operation with an old cable tool back in 1973. The Corporation continued to drill water wells and provide pump services until the early 80s where work began with its first geothermal steam project. Since that time Welsco has honed its skills in the Geothermal Steam arena, has completed a multitude of water well projects and has added a 24-hour pump service.
John Young and Matt Dusenberry – Permitting
John Young has been the Principal Environmental Services Specialist at Great Basin Environmental Services, LLC for over 5 years, providing environmental permitting and consulting services to the exploration and mining industry. Before that, he was vice president of Mining and Minerals at Tetra Tech, a leading provider of consulting and engineering services. He is a successful mining professional with a diverse background in planning and managing mineral exploration, mine development, remediation, reclamation, and mine closure operations. He has experience in construction, drilling, remediation, mine closure, reclamation, environmental permitting, environmental compliance, NEPA, and regulatory oversight. He has experience with precious metals, base metals, and industrial mineral and is a National Instrument 43-101 Compliant Qualified Party.
13
Matt Dusenberry obtained an M.S. in land Rehabilitation from Montana State University and has more than 7 years’ experience including mine permitting and environmental design, laboratory and field instrumentation, and soil and groundwater data collection, analysis and research. Matt has assisted with development of approximately 10 integrated permit application documents. He has prepared AutoCAD drawings, narrative plans, and detailed databases in Excel to support permitting of mining operations on Bureau of land Management and private lands in Nevada. He has assisted principals in preparing a plan of operations, environmental assessment, water pollution control permits, reclamation plans and cost estimates to support financial assurance and bonding, an environmental assessment, air emissions inventories and permit applications, Spill Prevention Control and Countermeasures Plans (SPCC), and Stormwater Pollution Prevention Plans (SWPPP) for both copper and gold mining operations in Nevada. Matt assisted with a comprehensive review of international reclamation and closure practices and standards for a major international gold mining company, performed a geotechnical investigation of faults in California and conducted vegetation surveys in Nevada.
Chris Facque – Water Rights Manager
Chris Facque is the lead Water Right Specialist with Farr West Engineering. Chris manages the water rights for a variety of clients throughout Nevada. He is experienced in all aspects of water rights, including research, permit filings, title assignment, survey monitoring and mapping, forfeiture prevention, proofs, and permit compliance. Chris graduated with a degree in Political Science at the University of Nevada, Reno (UNR) in 2005. In 2005 Chris began working for Tri State Surveying, Ltd., increasing the depth of his knowledge while working on several Northern Nevada water rights projects. Chris is proficient in drafting water rights maps, and is a Certified Survey Technician through the National Society of Professional Surveyors. Chris has worked with several Nevada County Recorders and other agencies, including the Truckee Carson Irrigation District, the Southern Nevada Water Authority and California Water Resources Control Board. Over the course of his 10 year involvement with water rights, he has acquired extensive experience in managing water rights projects from agricultural to mining to wildlife.
Zonge International – Geophysical Survey Operator
The company was formed in 1972 by Kenneth L. Zonge who developed the complex resistivity (CR) investigation method, demonstrated its uses for natural-resource exploration, and became the first to build a microprocessor-based electromagnetic (EM) receiver in the early 1970s. Today, Zonge serves as a resource to exploration managers, engineers and independent consultants in three application areas— exploration, environmental and geotechnical. The company performs hundreds of projects each year involving seismic, magnetics, gravity and other geophysical methods, in addition to the EM methods it helped establish. Formerly Zonge Engineering and Research Organization, the company changed its name to Zonge International in 2011.
George Scheid- Chief Drilling Engineer:
Mr. Scheid currently serves as Senior Driller Project Manager at Teton Energy Services and brings more than 30 years of experience managing onsite drilling operations in the exploration and mining industry. For the last 14 years he has worked as drilling project manager, first with Omat Nevada, then with Thermasource, Inc, where he managed onsite drilling and work-over projects. He reviewed and evaluated mud reports, bit records, and drilling operations to prepare daily status reports for distribution and made real-time adjustments to equipment and strategies relevant to drilling conditions.
Greg Kuzma- Chief Geologist:
Mr. Kuzma is the Director of Exploration for the Company. Mr. Kuzma is a graduate of the University of Southern California and is a well-respected and highly skilled exploration geologist with over 30 years’ experience. Mr. Kuzma has consulted with numerous mining groups and spent 12 years as Senior Project Geologist in Nevada for Teck Resources. Mr. Kuzma has extensive experience in the Southwest United States, Mexico, El Salvador and Argentina. He has evaluated, designed, managed and implemented over 40 drill programs within Nevada’s Great Basin.
Ross Leisinger - Geologist:
Mr. Leisinger has more than 30 years of experience in the exploration and mining industry and has participated in numerous projects from initial project conception through production. He also has decades of experience liaising with local and federal authorities as well as establishing and operating mining businesses in Nevada and abroad.
14
Vincent Ramirez – Engineer and Advisor:
Mr. Ramirez is the CEO of 3PLOperating Co., Inc. a private mining group company, and was the former Chairman of Vostochnaya Transnational, Lead Exploration and Operations Geologist for Shell Oil and Exploration Geologist for Shell Western E&P Inc. Vincent Ramirez has an M.A. degree in Geology from UC Santa Barbara. He has drilled 61 oil and gas wildcats worldwide, including 44 discoveries. While at Shell Oil, Vincent also was the Operations Manager for the San Joaquin Basin, and he was the appointed Structural Geology instructor at the Shell Research Lab. Vincent discovered and developed several oil fields in central Siberia during 10 years with the Lundin Group. During this time, he transformed an oil company from bankruptcy to $850 Million in value, drilled the highest-producing well in Russia (11,500 BOPD), and drilled the first multi-lateral wells in Russia, while overseeing 350 employees as CEO. He has published extensively on structural geology subjects, including the San Andreas Fault, Ridge Basin, the California Coast Ranges, and Obduction Tectonics.
Axel Drefahl – Chief Chemist
Dr. Axel Drefahl is ABMC’s director of chemistry/extraction. His interests include understanding nanostructure diversity and how it inspires and launches smart and flexible applications towards a sustainable future. His previous work includes roles as a metallurgical research scientist at Cycladex and a cheminformatician at Axeleratio, and metallurgical assay chemist and informatician at Comstock Mining Inc. He is also the project founder at CurlySMILES, a chemical line notation which extends SMILES with annotations for storage, retrieval and modeling of interlinked, coordinated, assembled and adsorbed molecules in supramolecular structures and nanodevices. Axel’s work comprises web design and software development for virtual, high-throughput screening, combinatorial materials design and problem-driven nanostructure-search algorithms. He received his Ph.D. in Cheminformatics/Molecular Modeling from Technical University Munich in 1989 and continued his post-doctorate at Stanford University.
William Hunter – Director, and CFO of AMCI, previous head of mining for Jefferies:
Mr. Hunter received his B.S. from DePaul University in Chicago and an MBA with distinction from the Kellstadt School of Business at DePaul University. Mr. Hunter is an experienced financial executive with over 20 years of advisory and capital markets experience. Bill led the Americas Banking team at Nomura where he advised Mitsui in their acquisition of a minority interest in the Moatize Coal Mining complex from Vale and Globe Specialty Metals in their $3.1 billion ‘merger of equals’ transaction with FerroAtlantica. Before Nomura he led the team at Jefferies and did numerous transactions for companies like Alpha Natural Resources, Fortescue Metals Group and Murray Energy.
Other Mineral Properties
We are not contemplating any other mineral properties at this time.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
In January 2018, the Company filed a complaint in Nevada seeking the return or cancellation of 16 million common shares which the Company believes were fraudulently issued as well as claims against the former CEO of the Company, Craig Alford. As a result, the Company entered into agreements to cancel eleven million shares (of which ten million shares have already been cancelled). The remaining five million shares were cancelled and reissued after the Company determined that the recipients provided proper consideration for such shares. The litigation continues against Alford and certain other relief defendants. Alford has filed a counterclaim against the Company for amounts allegedly owed to him that the Company believes is entirely without merit.
In March 2019, a shareholder of the Company filed a lawsuit against the Company seeking removal of a securities law restrictive legend and damages related thereto. The Company is defending the claim. Other than the preceding, to the best of our knowledge, we are not currently a party to any legal proceedings that, individually or in the aggregate, are deemed to be material to our financial condition or results of operations.
We are required by Section 78.090 of the Nevada Revised Statutes (the "NRS") to maintain a registered agent in the State of Nevada. Our registered agent for this purpose is United Corporate Services, Inc., 2520 St Rose Pkwy Suite 319, Henderson, NV 89074. All legal process and any demand or notice authorized by law to be served upon us may be served upon our registered agent in the State of Nevada in the manner provided in NRS 14.020(2).
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
15
PART II
Item 5. Market for Common Equity and Related Stockholder Matters
Market Information
Our shares of common stock are eligible for quotation on the OTC Markets Group under the symbol “ABML.” Quotations for our securities represent inter-dealer prices, without retail markups, markdowns or commissions and may not necessarily represent actual transactions.
On December 20, 2019, the closing price of our Common Stock as reported by the OTC Markets Group was $0.029 per share.
Holders
As of December 20, 2019, we have approximately 52 shareholders including our directors and officers. One such holder is Cede & Co., a nominee for Depository Trust Company, or DTC. Shares of Common Stock that are held by financial institutions as nominees for beneficial owners are deposited into participant accounts at DTC, and are considered to be held of record by Cede & Co. as one stockholder.
Dividends
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our capital stock. We currently intend to retain all available funds and any future earnings to support our operations and finance the growth and development of our business. We do not intend to pay cash dividends on our common stock for the foreseeable future. Any future determination related to dividend policy will be made at the discretion of our Board of Directors. The Nevada Revised Statutes, however, prohibits us from declaring dividends where, after giving effect to the distribution of the dividend:
we would not be able to pay our debts as they become due in the usual course of business; or
our total assets would be less than the sum of our total liabilities plus the amount that would be needed to satisfy the rights of stockholders who have preferential rights superior to those receiving the distribution, unless otherwise permitted under our Articles of Incorporation.
Stock Options, Warrants and Rights
As at September 30, 2019, ABMC has potentially issuable shares of common stock as follows:
8,925,334 potentially issuable shares of common stock from share purchase warrants issued with an exercise price that ranges from $0.001 to $0.10 per share; and
In addition, the Company had 11,168,816 shares issuable based on convertible notes which have a conversion price based on a discount to the market price of the Company’s stock prior to conversion.
Penny Stock
Our common stock is subject to the provisions of Section 15(g) of the Exchange Act and Rule 15g-9 thereunder, commonly referred to as the “penny stock rule”. Section 15(g) sets forth certain requirements for transactions in penny stock, and Rule 15g-9(d) incorporates the definition of “penny stock” that is found in Rule 3a51-1 of the Exchange Act. The SEC generally defines a penny stock to be any equity security that has a market price less than US$5.00 per share, subject to certain exceptions. We are subject to the SEC’s penny stock rules. Since our common stock is deemed to be penny stock, trading in the shares of our common stock is subject to additional sales practice requirements on broker dealers who sell penny stock to persons other than established customers and accredited investors. “Accredited investors” are generally persons with assets in excess of US$1,000,000 or annual income exceeding US$200,000 or US$300,000 together with their spouse. For transactions covered by these rules, broker dealers must make a special suitability determination for the purchase of securities and must have the purchaser’s written consent to the transaction prior to the purchase. Additionally, for any transaction involving a penny stock, unless exempt, the rules require the delivery, prior to the first transaction, of a risk disclosure document prepared by the SEC relating to the penny stock market. A broker-dealer also must disclose the commissions payable to both the broker-dealer and the registered representative and current quotations for the securities. Finally, monthly statements must be sent disclosing recent price information for penny stocks held in an account and information to the limited market in penny stocks. Consequently, these rules may restrict the ability of broker-dealer to trade and/or maintain a market in our common stock and may affect the ability of our stockholders to sell their shares.
16
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
As of the date of this Report, we do not have any compensation plans under which our equity securities are authorized for issuance. We intend to adopt an equity compensation plan in which our directors, officers, employees and consultants will be eligible to participate. However, no formal steps have yet been taken to adopt such a plan.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
On July 8, 2019, the Company issued 1,650,000 common shares with a fair value of $396,000 for consulting services.
On July 9, 2019, the Company issued a 10% Convertible Promissory Note in the principal amount of $160,000 with a purchase price of $160,000 to Odyssey Capital Funding LLC. The note is due July 9, 2020. The holder shall have the right from time to time, and at any time to convert all or any amount of the outstanding and unpaid principal amount of the note into fully paid and non-assessable shares of common stock. The conversion price is equal to 60% of the lowest closing bid price of the Company’s common stock during the fifteen (15) trading day period ending on the latest complete trading day prior to the conversion date. The note may be prepaid until 180 days from the issuance date at a price of 120% - 140% of the face amount plus any accrued interest as of the date of prepayment. The default rate on the note is 24% per annum.
On July 11, 2019, the Company issued a 12% Convertible Promissory Note in the principal amount of $50,000 with a purchase price of $50,000 to Sunshine Equity Partners LLC. The note is due July 11, 2020. The holder shall have the right from time to time, and at any time during the period beginning on the issue date and ending on the later of (i) the maturity date and (ii) the date of payment the date of payment of the default amount, each in respect of the remaining outstanding principal amount of this note to convert all or any amount of the outstanding and unpaid principal amount of the note into fully paid and non-assessable shares of common stock. The conversion price is equal to 60% of the lowest trading price of common stock during the twenty (20) trading day period ending on the latest complete trading day prior to the conversion date. The note may be prepaid until 180 days from the issuance date at a price of 115% - 140% of the face amount plus any accrued interest as of the date of prepayment. The default rate on the note is 22% per annum.
On July 15, 2019, the Company issued 1,352,240 common shares with a fair value of $311,015 as part of a conversion of $190,000 of convertible notes payable, $11,192 of accrued interest and derivative liability of $133,574.
On July 29, 2019, the Company issued a 12% Convertible Promissory Note in the principal amount of $53,000 with a purchase price of $53,000 to Power Up Lending Group Ltd. The note is due June 15, 2020. The holder shall have the right from time to time, and at any time during the period beginning one hundred seventy (170) days from the issue date and ending on the later of (i) the maturity date and (ii) the date of payment the date of payment of the default amount, each in respect of the remaining outstanding principal amount of this note to convert all or any amount of the outstanding and unpaid principal amount of the note into fully paid and non-assessable shares of common stock. The conversion price is equal to 61% of the lowest closing bid price of common stock during the ten (10) trading day period ending on the latest complete trading day prior to the conversion date. The note may be prepaid until 170 days from the issuance date at a price of 115% - 140% of the face amount plus any accrued interest as of the date of prepayment. The default rate on the note is 22% per annum.
On August 1, 2019, the Company issued a 10% Convertible Promissory Note in the principal amount of $175,000 with a purchase price of $175,000 to Auctus Fund, LLC. The note is due August 1, 2020. The holder shall have the right from time to time, and at any time during the period beginning on the issue date and ending on the later of (i) the maturity date and (ii) the date of payment the date of payment of the default amount, each in respect of the remaining outstanding principal amount of this note to convert all or any amount of the outstanding and unpaid principal amount of the note into fully paid and non-assessable shares of common stock. The conversion price is equal to 68% of the lowest volume weighted average price of common stock during the twenty (20) trading day period ending on the latest complete trading day prior to the conversion date. The note may be prepaid until 180 days from the issuance date at a price of 115% - 135% of the face amount plus any accrued interest as of the date of prepayment. The default rate on the note is 24% per annum.
On August 1, 2019, the Company issued 300,000 common shares with a fair value of $54,000 for consulting services.
On August 8, 2019, the Company issued a 10% Convertible Promissory Note in the principal amount of $105,000 with a purchase price of $105,000 to Adar Alef, LLC. The note is due August 8, 2020. The holder shall have the right from time to time, and at any time to convert all or any amount of the outstanding and unpaid principal amount of the note into fully paid and non-assessable shares of common stock. The conversion price is equal to 60% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common stock during the prior fifteen (15) trading day period including the conversion date. The note may be prepaid until 180 days from the issuance date at a price of 120% - 140% of the face amount plus any accrued interest as of the date of prepayment. The default rate on the note is 24% per annum.
17
On August 12, 2019, the Company issued a 10% Convertible Promissory Note in the principal amount of $105,000 with a purchase price of $105,000 to Black Ice Advisors, LLC. The note is due August 12, 2020. The holder shall have the right from time to time, and at any time to convert all or any amount of the outstanding and unpaid principal amount of the note into fully paid and non-assessable shares of common stock. The conversion price is equal to 60% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common stock during the prior fifteen (15) trading day period including the conversion date. The note may be prepaid until 180 days from the issuance date at a price of 115% - 140% of the face amount plus any accrued interest as of the date of prepayment. The default rate on the note is 24% per annum.
On August 21, 2019, the Company issued 1,500,000 common shares with a fair value of $226,500 for consulting services including 1,000,000 common shares with a fair value of $151,000 to the Chief Executive Officer of the Company.
On August 28, 2019, the Company issued a 10% Convertible Promissory Note in the principal amount of $110,000 with a purchase price of $100,000 to LG Capital Funding, LLC. The note is due August 28, 2020. The holder shall have the right from time to time, and at any time to convert all or any amount of the outstanding and unpaid principal amount of the note into fully paid and non-assessable shares of common stock. The conversion price is equal to 60% of the lowest closing bid price of the Company’s common stock during the prior twenty (20) trading day period including the conversion date. The note may be prepaid until 180 days from the issuance date at a price of 120% - 140% of the face amount plus any accrued interest as of date of prepayment. The default rate on the note is 24% per annum.
On August 28, 2019, the Company issued a 10% Convertible Promissory Note in the principal amount of $35,200 with a purchase price of $32,000 to BHP Capital NY Inc. The note is due May 28, 2020. The holder shall have the right from time to time, and at any time during the period beginning on the issue date and ending on the later of (i) the maturity date and (ii) the date of payment the date of payment of the default amount, each in respect of the remaining outstanding principal amount of this note to convert all or any amount of the outstanding and unpaid principal amount of the note into fully paid and non-assessable shares of common stock. The conversion price is equal to 62% of the lowest trading price of common stock during the twenty (20) trading day period ending on the latest complete trading day prior to the conversion date. The note may be prepaid until 180 days from the issuance date at a price of 115% - 135% of the face amount plus any accrued interest as of the date of prepayment. The default rate on the note is 22% per annum.
On August 28, 2019, the Company issued a 10% Convertible Promissory Note in the principal amount of $35,200 with a purchase price of $32,000 to Jefferson Street Capital LLC. The note is due May 28, 2020. The holder shall have the right from time to time, and at any time during the period beginning on the issue date and ending on the later of (i) the maturity date and (ii) the date of payment the date of payment of the default amount, each in respect of the remaining outstanding principal amount of this note to convert all or any amount of the outstanding and unpaid principal amount of the note into fully paid and non-assessable shares of common stock. The conversion price is equal to 68% of the lowest trading price of common stock during the twenty (20) trading day period ending on the latest complete trading day prior to the conversion date. The note may be prepaid until 180 days from the issuance date at a price of 115% - 135% of the face amount plus any accrued interest as of the date of prepayment. The default rate on the note is 22% per annum.
On September 13, 2019, the Company issued 200,000 common shares with a fair value of $14,000 for consulting services.
On September 17, 2019, the Company issued a 10% Convertible Promissory Note in the principal amount of $150,000 with a purchase price of $141,000 to EMA Financial, LLC. The note is due January 17, 2021. The holder shall have the right from time to time, and at any time to convert all or any amount of the outstanding and unpaid principal amount of the note into fully paid and non-assessable shares of common stock. The conversion price is equal 68% of the lowest traded price for the Common Stock during the twenty (20) consecutive trading days on which at least 100 shares of Common Stock were traded including and immediately preceding the conversion date. The note may be prepaid until 180 days from the issuance date at a price of 115% - 135% of the face amount plus any accrued interest as of the date of prepayment. The default rate on the note is 24% per annum.
On September 24, 2019, the Company issued a 12% Convertible Promissory Note in the principal amount $48,000 with a purchase price of $48,000 to Power Up Lending Group Ltd. The note is due September 24, 2020. The holder shall have the right from time to time, and at any time during the period beginning one hundred seventy (170) days from the issue date and ending on the later of (i) the maturity date and (ii) the date of payment the date of payment of the default amount, each in respect of the remaining outstanding principal amount of this note to convert all or any amount of the outstanding and unpaid principal amount of the note into fully paid and non-assessable shares of common stock. The conversion price is equal to 61% of the lowest closing bid price of common stock during the ten (10) trading day period ending on the latest complete trading day prior to the conversion date. The note may be prepaid until 170 days from the issuance date at a price of 115% - 140% of the face amount plus any accrued interest as of the date of prepayment. The default rate on the note is 22% per annum.
From July 1, 2019 through September 30, 2019, the Company issued 12,793,165 common shares for the conversions of $825,975 in principal of convertible notes and $66,561 of accrued interest.
18
The foregoing securities were issued under Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and/or Rule 506 of Regulation D under the Securities Act. In the case of the promissory notes, each investor represented that it was an accredited investor, as defined in Rule 501 of Regulation D, and that it was acquiring the securities for its own account, not as nominee or agent, and not with a view to the resale or distribution of any part thereof in violation of the Securities Act. Any proceeds issued from the above issuances were used for working capital purposes of the Company.
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and “Affiliated Purchasers”
We did not purchase any shares of our common stock or other securities during the year ended September 30, 2019.
ITEM 6. Selected Financial Data
Not required.
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Conditions and Results of Operations
You should read the following discussion of our financial condition and results of operations in conjunction with the financial statements and the notes thereto included elsewhere in the Form 10-K. The following discussion contains forward-looking statements that reflect our plans, estimates and beliefs. Our actual results could differ materially from those discussed in the forward-looking statements. Factors that could cause or contribute to these differences include those discussed below and elsewhere in this Form 10-K.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Working Capital
| September 30, 2019 $ |
| September 30, 2018 $ |
Current Assets | 57,444 |
| 308,769 |
Current Liabilities | 4,879,614 |
| 2,741,281 |
Working Capital (Deficit) | (4,822,170) |
| (2,432,512) |
Cash Flows
| September 30, 2019 $ |
| September 30, 2018 $ |
Cash Flows used in Operating Activities | (3,432,069) |
| (993,422) |
Cash Flows used in Investing Activities | - |
| (10,200) |
Cash Flows from Financing Activities | 3,316,671 |
| 1,117,250 |
Net increase (decrease) in Cash During Period | (115,398) |
| 113,628 |
Operating Revenues
During the years ended September 30, 2019 and 2018, the Company did not record any revenues from operations.
Operating Expenses and Net Loss
During the year ended September 30, 2019, the Company incurred operating expenses of $10,486,623 compared to $5,588,730 during the year ended September 30, 2018. The increase in operating expenses is due to an increase in exploration costs of $809,382 relating to the Company’s additional work on the Nye County property, an increase of $3,057,834 of management and consulting fees which includes stock-based compensation costs, an increase of $131,324 for general and administrative expenses as the Company had more operating activity in the current year compared to the prior year, an increase of $451,254 of payroll costs for employees used by the Company, and $678,976 increase in legal fees due to use of a full time lawyer during the year and for the overall increase in business activity in the Company during the year. The increases were offset by a decrease of $153,200 for an impairment loss recorded in fiscal 2018 relating to capitalized mineral properties that were not supportable.
19
The Company incurred a net loss of $12,625,204 for the year ended September 30, 2019 compared to a net loss of $6,048,092 for the year ended September 30, 2018. In addition to operating expenses, the Company incurred interest and accretion expense of $2,241,933 during the year ended September 30, 2019 compared to $293,401 for the year ended September 30, 2018. The increase is due to the fact that the Company entered into more convertible notes during the current year which resulted in more interest expense and a larger accretion amount given that the majority of the convertible notes had variable conversion rates resulting in derivative liabilities. The Company also recorded a loss of $218,922 for the change in the fair value of derivative liabilities compared to $165,961 for the year ended September 30, 2018 due in part to a larger convertible note balance which resulted in more variations in the fair value of the derivative liabilities on a period-to-period basis. Finally, the Company recorded a gain on the settlement of debt of $571,962 due to the full conversion and settlement of outstanding convertible notes payable due in part to a large derivative liability balance which would reverse upon full conversion of the notes.
The Company incurred a net loss of $12,625,204, or $0.11 loss per share, during the year ended September 30, 2019 compared to a net loss of $6,048,092, or $0.07 loss per share, during the year ended September 30, 2018.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of September 30, 2019, the Company had cash of $7,371 and total assets of $92,694 compared to cash of $122,769 and total assets of $308,769 as at September 30, 2018. The decrease in cash and total assets was due to the fact that the Company used the financing from convertible notes for operating activities including work spent on the Company’s mineral properties and overhead costs.
As of September 30, 2019, the Company had total liabilities of $4,880,156 compared to total liabilities of $2,741,281 as at September 30, 2018. The increase in total liabilities is due to an increase in the derivative liabilities of $2,636,227 due to an increase in the number of convertible notes outstanding during the current year and the fact that the majority of the convertible notes in fiscal 2019 had variable conversion rates. The increase was offset by a decrease in the carrying value of convertible notes payable of $448,762 due in part to a greater amount of convertible notes being entered into near the end of the fiscal year which resulted in a full discount of the carrying value due to the fair value of the derivative liability at the onset of the convertible note. As at September 30, 2019, the Company had total face value of convertible debentures of $3,643,259 compared to total face value of convertible notes of $1,380,822 at September 30, 2018. In addition, the Company had an increase of $76,018 in accounts payable and accrued liabilities offset by a decrease of $124,608 in amounts due to related parties which are related to timing differences between payment of outstanding obligations as they become due.
As of September 30, 2019, the Company has a working capital deficit of $4,822,170 compared to a working capital deficit of $2,432,512 as at September 30, 2018. The increase in the working capital deficit is due to the use of convertible debentures to pay for operating expenditures which increases the overall working capital deficit as the Company is still in development stage and has not commenced any cash flows from its operations.
During the year ended September 30, 2019, the Company issued 26,700,000 common shares with a fair value of $7,093,110 for services and 22,396,684 common shares with a fair value of $3,141,894 for the conversion of outstanding notes payable. Furthermore, the Company cancelled 10,0000,000 common shares and issued 250,000 common shares as part of its joint venture agreement with CINC Industries Inc. During the year ended September 30, 2018, the Company issued 1,000,000 common shares with a fair value of $143,000 to acquire mineral properties located in Nye County, Nevada, issued 500,000 common shares as a donation with a fair value of $75,000, issued 716,666 common shares for the issuance of convertible notes and exercise of cashless warrants, issued 31,340,000 common shares for services with a fair value of $3,199,950, and issued 4,874,783 common shares pursuant to the conversion of notes payable with a fair value of $560,550. In addition, the Company also cancelled 3,600,000 common shares and replaced those shares with the issuance of 3,600,000 share purchase warrants.
Cashflows from Operating Activities
During the year ended September, 30 2019, the Company used $3,432,069 of cash for operating activities compared to $993,422 of cash for operating activities during the year ended September 30, 2018. The increase in the use of cash for operating activities was due to additional costs incurred during the year due to an overall increase in day-to-day transactions and costs.
Cashflows from Investing Activities
During the year ended September 30, 2019, the Company used cash of $nil for investing activities compared to use of $10,200 for acquisition of mineral properties during the year ended September 30, 2018.
20
Cashflows from Financing Activities
During the year ended September 30, 2019, the Company received $4,800,502 of cash from issuance of notes payable less repayment of $1,483,831 compared to proceeds of $1,117,250 of cash from financing activities from notes payable during the year ended September 30, 2018.
Going Concern
We have not attained profitable operations and are dependent upon obtaining financing to pursue any extensive acquisitions and activities. For these reasons, our auditors stated in their report on our audited financial statements that they have substantial doubt that we will be able to continue as a going concern without further financing.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have no significant off-balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our financial condition, changes in financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures or capital resources that are material to stockholders.
Future Financings
We will continue to rely on equity sales of our common shares in order to continue to fund our business operations. Issuances of additional shares will result in dilution to existing stockholders. There is no assurance that we will achieve any additional sales of the equity securities or arrange for debt or other financing to fund planned acquisitions and exploration activities.
Critical Accounting Policies
Our financial statements and accompanying notes have been prepared in accordance with United States generally accepted accounting principles applied on a consistent basis. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods.
We regularly evaluate the accounting policies and estimates that we use to prepare our financial statements. A complete summary of these policies is included in the notes to our financial statements. In general, management's estimates are based on historical experience, on information from third party professionals, and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the facts and circumstances. Actual results could differ from those estimates made by management.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
The Company has implemented all new accounting pronouncements that are in effect. These pronouncements did not have any material impact on the financial statements unless otherwise disclosed, and the Company does not believe that there are any other new accounting pronouncements that have been issued that might have a material impact on its financial position or results of operations.
Item 7a. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
21
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Consolidated Financial Statements
For the Years Ended September 30, 2019 and 2018
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | F-1 |
Consolidated Balance Sheets | F-2 |
Consolidated Statements of Operations | F-3 |
Consolidated Statement of Stockholders’ Deficit | F-4 |
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | F-5 |
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements | F-6 |
22
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To The Board of Directors and Stockholders of
American Battery Metals Corporation
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of American Battery Metals Corporation (formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.) (the “Company”) as of September 30, 2019 and 2018, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended September 30, 2019 (collectively referred to as the consolidated financial statements). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of September 30, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended September 30, 2019, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Consideration of the Company’s Ability to Continue as a Going Concern
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has not generated sufficient cash flows from operations to fund its business operations. This factor, among others, raises substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans in regard to this matter are also described in Note 1. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/Pinnacle Accountancy Group of Utah
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2016
Farmington, Utah
December 27, 2019
F-1
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Consolidated Balance Sheets
| September 30, 2019 $ |
| September 30, 2018 $ |
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash | 7,371 |
| 122,769 |
Prepaid expenses | 50,073 |
| 186,000 |
|
|
|
|
Total current assets | 57,444 |
| 308,769 |
|
|
|
|
Investment in joint venture | 35,250 |
| – |
|
|
|
|
Total assets | 92,694 |
| 308,769 |
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 585,797 |
| 509,779 |
Due to related parties | 458,269 |
| 582,877 |
Derivative liability | 3,437,200 |
| 800,973 |
Notes payable, net of unamortized discount of $3,094,911 and $533,170, respectively | 398,348 |
| 847,652 |
|
|
|
|
Total current liabilities | 4,879,614 |
| 2,741,281 |
|
|
|
|
Notes payable, non-current portion, net of unamortized discount of $149,458 and $nil, respectively | 542 |
| – |
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities | 4,880,156 |
| 2,741,281 |
|
|
|
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common Stock Authorized: 500,000,000 common shares with a par value of $0.001 per share |
|
|
|
Issued and outstanding: 132,678,133 and 93,331,449 common shares, respectively | 132,678 |
| 93,331 |
Additional paid-in capital | 44,970,398 |
| 34,739,491 |
Deficit | (49,890,538) |
| (37,265,334) |
|
|
|
|
Total stockholders’ deficit | (4,787,462) |
| (2,432,512) |
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity (deficit) | 92,694 |
| 308,769 |
(The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements)
F-2
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Consolidated Statements of Operations
| For the year ended September 30, 2019 $ |
| For the year ended September 30, 2018 $ |
Revenues | – |
| – |
|
|
|
|
Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exploration costs | 1,037,035 |
| 227,653 |
General and administrative | 9,449,588 |
| 5,207,877 |
Impairment of mineral property | – |
| 153,200 |
|
|
|
|
Net loss before other income (expense) | (10,486,623) |
| (5,588,730) |
|
|
|
|
Other income (expense) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest expense | (2,491,621) |
| (293,401) |
Change in fair value of derivative liability | (218,922) |
| (165,961) |
Gain on settlement of debt | 571,962 |
| – |
|
|
|
|
Total other income (expense) | (2,138,581) |
| (459,362) |
|
|
|
|
Net loss | (12,625,204) |
| (6,048,092) |
Net loss per share, basic and diluted | (0.11) |
| (0.07) |
Weighted average shares outstanding, basic and diluted | 112,948,676 |
| 82,297,005 |
(The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements)
F-3
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Consolidated Statement of Stockholders’ Deficit
| Common Shares |
| Additional Paid-In Capital $ |
| Deficit $ |
| Total $ | |
| Number | Amount $ | .+ |
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, September 30, 2017 | 58,500,000 | 58,500 |
| 29,892,737 |
| (31,217,242) |
| (1,266,005) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued to acquire mineral property | 1,000,000 | 1,000 |
| 142,000 |
| – |
| 143,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued for services | 31,340,000 | 31,340 |
| 3,168,610 |
| – |
| 3,199,950 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued for conversion of notes payable and accrued interest | 4,874,783 | 4,874 |
| 555,676 |
| – |
| 560,550 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued as donation | 500,000 | 500 |
| 74,500 |
| – |
| 75,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued for interest expense | 50,000 | 50 |
| 7,450 |
| – |
| 7,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued for warrant exercise | 666,666 | 667 |
| (667) |
| – |
| – |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share cancellation | (3,600,000) | (3,600) |
| 3,600 |
| – |
| – |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fair value of share purchase warrants | – | – |
| 887,007 |
| – |
| 887,007 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fair value of beneficial conversion feature | – | – |
| 8,578 |
| – |
| 8,578 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss for the year | – | – |
| – |
| (6,048,092) |
| (6,048,092) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, September 30, 2018 | 93,331,449 | 93,331 |
| 34,739,491 |
| (37,265,334) |
| (2,432,512) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued for services | 26,700,000 | 26,700 |
| 7,066,410 |
| – |
| 7,093,110 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued for joint venture | 250,000 | 250 |
| 35,000 |
| – |
| 35,250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cancellation of shares | (10,000,000) | (10,000) |
| 10,000 |
| – |
| – |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares issued pursuant to note conversion | 22,396,684 | 22,397 |
| 3,119,497 |
| – |
| 3,141,894 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss for the year | – | – |
| – |
| (12,625,204) |
| (12,625,204) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, September 30, 2019 | 132,678,133 | 132,678 |
| 44,970,398 |
| (49,890,538) |
| (4,787,462) |
(The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements)
F-4
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
| For the year ended September 30, 2019 |
| For the year ended September 30, 2018 |
Operating Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss | (12,625,204) |
| (6,048,092) |
|
|
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
|
|
|
Accretion expense | 2,241,933 |
| 194,234 |
Change in fair value of derivative liability | 218,922 |
| 165,961 |
Discount on convertible notes payable | 198,602 |
| – |
Fair value of share purchase warrants issued | – |
| 887,007 |
Gain on settlement of debt | (571,962) |
| – |
Impairment of mineral property | – |
| 153,200 |
Shares issued as a donation | – |
| 75,000 |
Shares issued for interest expense | – |
| 7,500 |
Shares issued for services | 7,093,110 |
| 3,199,950 |
|
|
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
Prepaid expenses | 135,927 |
| (133,500) |
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 199,813 |
| 140,687 |
Due to related parties | (124,608) |
| 364,631 |
|
|
|
|
Net Cash Used In Operating Activities | (3,432,069) |
| (993,422) |
|
|
|
|
Investing Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mineral property costs | – |
| (10,200) |
|
|
|
|
Net Cash Used In Investing Activities | – |
| (10,200) |
|
|
|
|
Financing Activities |
|
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of convertible notes payable | 4,800,502 |
| 1,117,250 |
Repayment on notes payable | (1,483,831) |
| – |
|
|
|
|
Net Cash Provided By Financing Activities | 3,316,671 |
| 1,117,250 |
|
|
|
|
Change in Cash | (115,398) |
| 113,628 |
Cash – Beginning of Period | 122,769 |
| 9,141 |
Cash – End of Period | 7,371 |
| 122,769 |
|
|
|
|
Non-cash investing and financing activities: |
|
|
|
Discount on convertible debenture | 198,602 |
| 74,033 |
Original issue discount on convertible debentures | 99,750 |
| 70,750 |
Shares issued on the exercise of cashless warrants | – |
| 667 |
Shares issued for joint venture | 35,250 |
| – |
Shares issued to settle accrued interest | 123,795 |
| 43,371 |
Shares issued for acquisition of mineral property | – |
| 143,000 |
Shares issued for conversion of debt | 3,018,099 |
| 517,179 |
(The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements)
F-5
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
1. Organization and Nature of Operations
American Battery Metals Corporation (formerly Oroplata Resources Inc.) (“the Company”) was incorporated under the laws of the state of Nevada on October 6, 2011 for the purpose of acquiring and developing mineral properties. The Company had a wholly-owned subsidiary called Oroplata Exploraciones E Ingenieria SRL, which was incorporated in the Dominican Republic on January 10, 2012. The Company has no current intention to operate under this subsidiary. On July 26, 2016, the Company incorporated LithiumOre Corporation (formerly Lithortech Resources Inc.), a Nevada company, as a wholly-owned subsidiary. On July 5, 2019, the Company incorporated ABMC AG, LLC, a Nevada company as a wholly-owned subsidiary. The Company currently holds mineral rights in the Western Nevada Basin of Nye County in the state of Nevada. The Company once owned mineral rights in the Dominican Republic but has no information as to whether those mineral rights have expired and currently has no intention of pursuing such claims.
Going Concern
These consolidated financial statements have been prepared on a going concern basis, which implies that the Company will continue to realize its assets and discharge its liabilities in the normal course of business. As at September 30, 2019, the Company has not earned revenue, has a working capital deficit of $4,822,170, and an accumulated deficit of $49,890,538. The continuation of the Company as a going concern is dependent upon the continued financial support from its management, and its ability to identify future investment opportunities and obtain the necessary debt or equity financing, and generating profitable operations from the Company’s future operations. If the Company is able to obtain financing, there is no certainty that terms will be favorable to the Company. These factors raise substantial doubt regarding the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. These unaudited consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments to the recoverability and classification of recorded asset amounts and classification of liabilities that might be necessary should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern.
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
(a)Basis of Presentation
The financial statements of the Company have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“US GAAP”) and are expressed in U.S. dollars. The Company’s fiscal year end is September 30.
These consolidated financial statements and related notes are presented in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States and are expressed in U.S. dollars. These consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries, Oroplata Exploraciones E Ingenieria SRL (See Note 1 regarding this subsidiary) and LithiumOre Corporation (formerly Lithortech Resources Inc) and ABMC AG, LLC. All inter-company accounts and transactions have been eliminated on consolidation.
(b)Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid instruments with a maturity of three months or less at the time of issuance to be cash equivalents. As of September 30, 2019, and 2018, there were no cash equivalents.
(c)Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with US GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. The Company regularly evaluates estimates and assumptions related to the fair value of stock-based compensation, recoverability of long-lived assets, valuation of derivative liability, and deferred income tax asset valuation allowances.
F-6
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
(c)Use of Estimates (continued)
The Company bases its estimates and assumptions on current facts, historical experience and various other factors that it believes to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities and the accrual of costs and expenses that are not readily apparent from other sources. The actual results experienced by the Company may differ materially and adversely from the Company’s estimates. To the extent there are material differences between the estimates and the actual results, future results of operations will be affected.
(d)Long-Lived Assets
Long-lived assets, such as property and equipment, mineral properties, and purchased intangibles with finite lives (subject to amortization), are evaluated for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the asset may not be recoverable in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification topic 360 “Property, Plant, and Equipment”. Circumstances which could trigger a review include, but are not limited to: significant decreases in the market price of the asset; significant adverse changes in the business climate or legal factors; accumulation of costs significantly in excess of the amount originally expected for the acquisition or construction of the asset; current period cash flow or operating losses combined with a history of losses or a forecast of continuing losses associated with the use of the asset; and current expectation that the asset will more likely than not be sold or disposed significantly before the end of its estimated useful life.
Recoverability of assets is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by an asset. If the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its estimated future cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized as the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the estimated fair value of the asset. The estimated fair value is determined using a discounted cash flow analysis. Any impairment in value is recognized as an expense in the period when the impairment occurs. Asset Retirement Obligations
The Company follows the provisions of ASC 410, Asset Retirement and Environmental Obligations, which establishes standards for the initial measurement and subsequent accounting for obligations associated with the sale, abandonment or other disposal of long-lived tangible assets arising from the acquisition, construction or development and for normal operations of such assets.
(e)Loss per Share
The Company computes net income (loss) per share in accordance with ASC 260, Earnings per Share. ASC 260 requires presentation of both basic and diluted earnings per share (“EPS”) on the face of the income statement. Basic EPS is computed by dividing net income (loss) available to common shareholders (numerator) by the weighted average number of shares outstanding (denominator) during the period. Diluted EPS gives effect to all dilutive potential common shares outstanding during the period using the treasury stock method and convertible preferred stock using the if-converted method. In computing diluted EPS, the average stock price for the period is used in determining the number of shares assumed to be purchased from the exercise of stock options or warrants. Diluted EPS excludes all dilutive potential shares if their effect is anti-dilutive. At September 30, 2018, the Company has 20,094,150 (2018 – 8,925,334) potentially dilutive shares, which their inclusion in EPS would be anti-dilutive due to the Company’s net loss.
(f)Foreign Currency Translation
The Company’s functional and reporting currency is the United States dollar. Foreign currency transactions, if any, would primarily be undertaken in Canadian dollars. Foreign currency transactions are translated to United States dollars in accordance with ASC 830, Foreign Currency Translation Matters as follows:
1.Monetary assets and liabilities at the rate of exchange in effect at the balance sheet date
2.Equity at historical rates
3.Revenue and expense items at the average rate of exchange prevailing during the period
F-7
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
(f)Foreign Currency Translation (continued)
Adjustments arising from such translations are deferred until realization and are included as a separate component of stockholders’ equity as a component of comprehensive income or loss. Therefore, translation adjustments are not included in determining net income (loss) but reported as other comprehensive income. Gains and losses from foreign currency transactions are included in earnings in the period of settlement.
(g)Comprehensive Loss
ASC 220, Comprehensive Income, establishes standards for the reporting and display of comprehensive loss and its components in the financial statements. As at September 30, 2019 and 2018, the Company has no items representing comprehensive income or loss.
(h)Revenue Recognition
Revenue from the sale of minerals will be recognized when a contract is in place and minerals are delivered to the customer.
(i)Financial Instruments
Pursuant to ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures, an entity is required to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs when measuring fair value. ASC 820 establishes a fair value hierarchy based on the level of independent, objective evidence surrounding the inputs used to measure fair value. A financial instrument’s categorization within the fair value hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. ASC 820 prioritizes the inputs into three levels that may be used to measure fair value:
Level 1
Level 1 applies to assets or liabilities for which there are quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2
Level 2 applies to assets or liabilities for which there are inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in markets with insufficient volume or infrequent transactions (less active markets); or model-derived valuations in which significant inputs are observable or can be derived principally from, or corroborated by, observable market data.
Level 3
Level 3 applies to assets or liabilities for which there are unobservable inputs to the valuation methodology that are significant to the measurement of the fair value of the assets or liabilities.
If the inputs used to measure the financial assets and liabilities fall within more than one level described above, the categorization is based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement of the instrument.
F-8
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
(i)Financial Instruments (continued)
The following table provides a summary of the fair value of the Company’s derivative liabilities as of September 30, 2019 and September 30, 2018:
| Fair value measurements on a recurring basis | ||||||||||
| Level 1 |
| Level 2 |
| Level 3 | ||||||
As of September 30, 2019: |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
Derivative liabilities |
| $ | - |
|
| $ | - |
|
| $ | 3,437,200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of September 30, 2018: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Derivative liabilities |
| $ | - |
|
| $ | - |
|
| $ | 800,973 |
(j)Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes using the asset and liability method in accordance with ASC 740, Accounting for Income Taxes. The asset and liability method provides that deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the expected future tax consequences of temporary differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities, and for operating loss and tax credit carryforwards.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using the currently enacted tax rates and laws that will be in effect when the differences are expected to reverse. The Company records a valuation allowance to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount that is believed more likely than not to be realized.
Due to the Company’s net loss position from inception on October 6, 2011 to September 30, 2019, there was no provision for income taxes recorded. As a result of the Company’s losses to date, there exists doubt as to the ultimate realization of the deferred tax assets. Accordingly, a valuation allowance equal to the total deferred tax assets has been recorded at September 30, 2019 and 2018.
(k)Stock-based Compensation
The Company records stock-based compensation in accordance with ASC 718, Compensation – Stock Compensation using the fair value method. All transactions in which goods or services are the consideration received for the issuance of equity instruments are accounted for based on the fair value of the consideration received or the fair value of the equity instrument issued, whichever is more reliably measurable. Equity instruments issued to employees and the cost of the services received as consideration are measured and recognized based on the fair value of the equity instruments issued on the grant date. As at September 30, 2019 and 2018, the Company did not grant any stock options.
(l)Mineral Property Costs
Mineral property acquisition costs are capitalized as incurred. Exploration and evaluation costs are expensed as incurred until proven and probable reserves are established. The Company assesses the carrying costs for impairment under ASC 360, “Property, Plant, and Equipment” at each fiscal quarter end. When it has been determined that a mineral property can be economically developed as a result of establishing proven and probable reserves, the costs then incurred to develop such property, are capitalized. Such costs will be amortized using the units-of-production method over the estimated life of the probable reserve. If mineral properties are subsequently abandoned or impaired, any capitalized costs will be charged to operations.
(m)Advertising and Marketing Costs
The Company expenses advertising and marketing development costs as incurred.
F-9
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
3.Convertible Notes Payable
(a)On February 16, 2017, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds up to $250,000. The aggregate principal amount owed of $250,000 is secured, bears interest at 10%, is due one year after the date of funding for each tranche, and is convertible into common shares of the Company at $0.10 per share. In September 2017, the conversion price was amended to $0.115 per share. On December 11, 2017, the due date for all tranches was extended to December 11, 2018. On May 23, 2018, the Company issued 817,391 common shares for the conversion of $94,000 of note payable and $nil of interest payable. On November 6, 2018, the Company issued 443,478 common shares for the conversion of $38,822 of note payable. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $38,822), and accrued interest of $29,999 (September 30, 2018 - $29,999) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities.
(b)On July 25, 2017, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds up to $550,000. On July 25, 2017 the Company received proceeds of $44,000, net of issuance fees of $4,000. On August 17, 2017, the Company received proceeds of $110,000, net of issuance fees of $10,000. The aggregate principal amount owed of $154,000 is secured, bears interest at 10%, is due one year after the date of funding for each tranche, and is convertible into common shares of the Company at $0.115 per share. On October 23, 2017, the Company received proceeds of $82,500, net of issuance costs of $7,500. On December 1, 2017, the Company received proceeds of $55,000, net of issuance costs of $5,000. On December 11, 2017, the due date was extended to December 11, 2018. On December 15, 2017, the Company received proceeds of $55,000, net of issuance costs of $5,000. On February 9, 2018, the Company received proceeds of $56,100, net of issuance costs of $5,100. On November 20, 2018, the Company issued 420,870 common shares for the conversion of $44,000 of note payable and $4,400 of accrued interest. On December 13, 2018, the Company issued 448,696 common shares for the conversion of $51,600 of note payable. On December 21, 2018, the Company issued 420,870 common shares for the conversion of $48,400 of notes payable. On February 7, 2019, the Company issued 434,783 common shares for the conversion of $39,000 of notes payable. On June 24, 2019, the Company issued 869,565 common shares for the conversion of $100,000 of notes payable. On June 24, 2019, the Company issued 1,414,000 common shares for the conversion of $136,100 of notes payable. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $397,825), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $4,775), and accrued interest of $24,596 (September 30, 2018 - $28,060) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities.
(c)On April 3, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for $85,800, net of an original issue discount of $7,800. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, is due on January 15, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at $0.15 per share until October 3, 2018 (180 days following the issuance date of the loan) when the conversion price is equal to 75% of the lowest closing bid price during the fifteen trading days prior to conversion. Upon the due date on January 15, 2019, if the loan remains unpaid, the interest will increase to 22% per annum. During the year ended September 30, 2019, the Company issued 1,105,708 common shares for the conversion of $85,800 of note payable and $4,680 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $82,892), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $2,908), and accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $5,106) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities.
(d)On April 9, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for $150,000, net of an original issue discount of $2,500, of which $75,000 is a front-end note and $75,000 is a back-end note. The amounts owing are unsecured, bear interest at 10% per annum, are due on April 8, 2019, and are convertible into common shares at 66% of the lowest trading price for the twenty trading days prior to conversion. During the year ended September 30, 2019, the Company issued 2,044,753 common shares for the conversion of $150,000 of notes payable and $6,562 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $13,524), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $136,476), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $7,125) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $170,764).
F-10
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
3.Convertible Notes Payable (continued)
(e)On April 20, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for $58,800, net of an original issue discount of $5,800. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, is due on January 30, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at $0.15 per share until October 20, 2018 (180 days following the issuance date of the loan) when the conversion price is equal to 75% of the lowest trading price during the fifteen trading days prior to conversion. Upon the due date on January 30, 2019, if the loan remains unpaid, the interest will increase to 22% per annum. On October 25, 2018, the Company issued 869,285 common shares for the conversion of $58,800 of note payable and $3,180 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $56,317), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $2,483), and accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $3,170) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities.
(f)On May 25, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for $150,000, net of an original issue discount of $2,500, of which $75,000 is a front-end note and $75,000 is a back-end note. The amounts owing are unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, and are due on May 25, 2019, and are convertible into common shares at 66% of the lowest trading price for the twenty trading days prior to conversion. On January 8, 2019, the Company issued 708,006 common shares for the conversion of $75,000 of note payable and $4,438 of accrued interest. On February 22, 2019, the Company issued 629,833 common shares for the conversion of $75,000 of note payable and $4,438 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $129,177), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $20,823), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $5,301) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $168,191).
(g)On June 11, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for $60,500 net of an original issue discount of $5,500. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, is due on March 30, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at $0.15 per share until November 11, 2018 (180 days following the issuance date of the loan) when the conversion price is equal to 75% of the lowest trading price during the fifteen trading days prior to conversion. Upon the due date on March 30, 2019, if the loan remains unpaid, the interest will increase to 22% per annum. On December 7, 2018, the Company repaid $60,500 of note payable and $3,600 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $54,591), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $5,909), and accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $2,228) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities.
(h)On June 18, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds up to $165,000. On June 26, 2018, the Company received proceeds of $55,000, net of an original issue discount of $5,500. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, is due on June 18, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at 65% of the lowest trading price for the twenty trading days prior to conversion. Upon the due date on June 18, 2019, if the loan remains unpaid, the interest will increase to 15% per annum. On December 12, 2018, the Company repaid $55,000 of note payable and $2,658 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $1,900), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $53,100), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $1,567) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $92,012).
(i)On June 29, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds of $82,500, net of an original issue discount of $7,500. On July 17, 2018, the Company received the proceeds of the loan. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, is due on March 29, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at the lesser of (i) $0.15 per common share, (ii) 75% of the lowest trading price for the fifteen trading days prior to the date of the note, or (iii) 75% of the lowest trading price for the fifteen trading days prior to conversion. Upon the due date on March 29, 2019, if the loan remains unpaid, the interest will increase to 24% per annum. On January 9, 2019, the Company repaid $67,500 of notes payable and $4,699 of accrued interest. On January 14, 2019, the Company issued 180,180 common shares for the conversion of $15,000 of notes payable. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $16,550), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $65,950), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $2,495) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30 2018 - $87,288). Refer to Note 9(h).
F-11
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
3.Convertible Notes Payable (continued)
(j)On June 29, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds of $27,500. On July 17, 2018, the Company received proceeds of $25,000, net of an original issue discount of $2,500. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, is due on March 29, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at the lesser of (i) $0.15 per common share, (ii) 75% of the lowest trading price for the fifteen trading days prior to the date of the note, or (iii) 75% of the lowest trading price for the fifteen trading days prior to conversion. Upon the due date on March 29, 2019, if the loan remains unpaid, the interest will increase to 24% per annum. On January 9, 2019, the Company repaid $12,500 of notes payable and $1,575 of accrued interest. On January 11, 2019, the Company issued 180,181 common shares for the conversion of $15,000 of notes payable. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $669), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $26,831), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $835) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $29,335). Refer to Note 9(g).
(k)On June 29, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds of $27,500. On August 31, 2018, the Company received proceeds of $25,000, net of an original issue discount of $2,500. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, is due on June 18, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at 65% of the lowest trading price for the twenty trading days prior to conversion. Upon the due date on June 18, 2019, if the loan remains unpaid, the interest will increase to 15% per annum. On March 19, 2019, the Company issued 110,000 common shares for conversion of $9,400 of notes payable. On May 8, 2019, the Company issued 184,930 common shares for conversion of $18,100 of notes payable and $1,742 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $306), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $27,194), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $306) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $51,080).
(l)On July 10, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds of $58,800. On July 12, 2018, the Company received proceeds of $50,000, net of an original issue discount of $5,800. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, is due on April 30, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at $0.15 per common share until January 10, 2019 when the conversion price is equal to 75% of the lowest trading price for the fifteen trading days prior to conversion. Upon the due date on April 30, 2019, if the loan remains unpaid, the interest will increase to 22% per annum. On January 4, 2019, the Company repaid $58,800 of notes payable and $3,499 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $54,618), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $4,182), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $1,604) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities.
(m)On September 10, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds of $53,000. On July 12, 2018, the Company received proceeds of $47,200, net of an original issue discount of $5,800. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, is due on June 30, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at the lesser of (i) $0.15 per common share, (ii) 61% of the lowest trading price for the fifteen trading days prior to the date of the note, or (iii) 61% of the lowest trading price for the fifteen trading days prior to conversion. Upon the due date on June 30, 2019, if the loan remains unpaid, the interest will increase to 22% per annum. On February 19, 2019, the Company repaid $53,000 of notes payable and $2,809 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $353), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $52,647), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $353) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $52,223).
F-12
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
3.Convertible Notes Payable (continued)
(n)On September 27, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds of $130,000. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, is due on September 27, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at the lesser of (i) $0.15 per common share, (ii) 60% of the lowest trading price for the fifteen trading days prior to the date of the note, or (iii) 60% of the lowest trading price for the fifteen trading days prior to conversion. Upon the due date on September 27, 2019, if the loan remains unpaid, the interest will increase to 22% per annum. On March 21, 2019, the Company repaid $130,000 of notes payable and $6,283 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $108), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $129,892), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $108) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $150,080).
(o)On October 16, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds of $43,000. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 22% per annum, is due on July 30, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at 61% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common stock in the ten trading days prior to the date of the notice of conversion. On March 26, 2019, the Company repaid $43,000 of notes payable and $4,204 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(p)On October 22, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds of $27,500. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, is due on June 18, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at 61% of the lower of the lowest trading price or closing price of the Company’s common stock in the twenty trading days prior to the date of the notice of conversion. If the conversion price is lower than $0.10 per share, an additional discount of 15% is added to the conversion price. On March 26, 2019, the Company repaid $27,500 of the notes payable and $1,184 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(q)On December 6, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds of $55,000. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, is due on September 30, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at 68% of the lowest trading price for the Company’s common stock in the twenty trading days prior to the date of the notice of conversion. On May 29, 2019, the Company repaid $55,000 of the notes payable and $3,190 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(r)On December 6, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds of $265,000. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, is due on December 6, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at 68% of the lowest trading price for the Company’s common stock in the twenty trading days prior to the date of the notice of conversion. On June 7, 2019, the Company repaid $265,000 of the notes payable and $12,923 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(s)On December 10, 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with a non-related party for proceeds of $265,000. The amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, is due on December 10, 2019, and is convertible into common shares at 68% of the lowest trading price for the Company’s common stock in the twenty trading days prior to the date of the notice of conversion. On June 11, 2019, the Company issued 552,381 shares for $75,000 of notes payable and $3,842 of accrued interest. On July 15, 2019, the Company issued 1,352,240 shares for $190,000 of notes payable and $11,192 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
F-13
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
3.Convertible Notes Payable (continued)
(t)On January 2, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $55,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, and is due on June 18, 2019. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 65% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. On July 15, 2019, the Company issued 650,000 shares for $17,375 of notes payable. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $5,087 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $32,538 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $4,015 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $57,213 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(u)On January 3, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $54,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, and is due on January 3, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 66% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. On August 30, 2019, the Company repaid $47,766 of notes payable and $2,234 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $6,061 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $173 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $1,388 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $6,168 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(v)On January 4, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $55,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum which increases to 22% per annum if the note is in default, and is due on October 30, 2019. The note is convertible into common shares of the Company at 61% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the ten trading days prior to the date of conversion. On June 28, 2019, the Company repaid $55,000 of notes payable and $3,190 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(w)On January 9, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $220,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, and is due on January 9, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 66% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. During the year ended September 30, 2019, the Company issued 2,852,379 shares for $165,000 of notes payable and accrued interest of $10,563. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $33,549 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $21,451 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $4,088 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $48,047 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(x)On January 9, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $220,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, and is due on January 9, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 66% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. During the year ended September 30, 2019, the Company issued 2,997,561 shares for $120,000 of notes payable and accrued interest of $8,171. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $55,054 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $44,946 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $7,211 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $98,753 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(y)On January 11, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $82,500. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum which increases to 24% per annum if the note is in default, and is due on October 11, 2019. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. During the year ended September 30, 2019, the Company issued 988,687 shares for $70,000 of notes payable. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
F-14
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
3.Convertible Notes Payable (continued)
(z)On January 11, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $110,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum which increases to 24% per annum if the note is in default, and is due on October 11, 2019. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. During the year ended September 30, 2019, the Company issued 1,602,691 shares for $110,000 of notes payable and $6,347 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(aa)On February 19, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $63,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum which increases to 22% per annum if the note is in default, and is due on December 15, 2019. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 61% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the ten trading days prior to the date of conversion. On August 8, 2019, the Company repaid $63,000 of notes payable and $3,570 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(bb)On March 18, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $270,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on March 18, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $33,264 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $236,736 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $14,475 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $240,091 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(cc)On March 18, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $270,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on March 18, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $33,264 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $236,736 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $14,475 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $240,091 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(dd)On March 26, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $53,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum which increases to 22% per annum if the note is in default, and is due on February 15, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. On September 24, 2019, the Company repaid $53,000 of notes payable and $3,162 of accrued interest. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $nil (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(ee)On April 8, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $38,500. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum which increases to 24% per annum if the note is in default, and is due on January 8, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $5,208 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $33,292 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $1,839 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $31,405 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
F-15
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
3.Convertible Notes Payable (continued)
(ff)On April 8, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $38,500. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum which increases to 24% per annum if the note is in default, and is due on January 8, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $5,208 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $33,292 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $1,839 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $31,405 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(gg)On May 1, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $325,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on May 1, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $22,805 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $302,195 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $13,451 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $284,348 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(hh)On May 1, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $325,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on May 1, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $22,805 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $302,195 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $13,451 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $284,348 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(ii)On May 29, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $325,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on May 29, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $16,726 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $308,274 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $10,924 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $289,004 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(jj)On June 3, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $55,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum which increases to 22% per annum if the note is in default, and is due on March 30, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 61% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the ten trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $3,488 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $51,512 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $2,145 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $56,840 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(kk)On June 11, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $105,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on June 11, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $35,858 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $69,142 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $3,179 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $93,716 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
F-16
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
3.Convertible Notes Payable (continued)
(ll)On June 12, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $55,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum which increases to 22% per annum if the note is in default, and is due on March 12, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $3,075 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $51,925 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $1,980 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $46,520 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(mm)On June 12, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $55,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum which increases to 22% per annum if the note is in default, and is due on March 12, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $3,075 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $51,925 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $1,980 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $46,520 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(nn)On June 13, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $75,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum which increases to 15% per annum if the note is in default, and is due on June 17, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 65% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $2,862 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $72,138 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $2,229 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $71,671 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(oo)On June 21, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $270,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on June 17, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $56,011 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $213,989 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $7,425 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $239,317 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(pp)On June 27, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $98,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on June 27, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 66% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common share for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $2,692 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $95,308 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $2,532 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $91,469 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(qq)On June 27, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $58,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum and is due on June 27, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 61% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the ten trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $1,798 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $56,202 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $1,798 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $59,759 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
F-17
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
3.Convertible Notes Payable (continued)
(rr)On July 9, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $160,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on July 9, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 60% of the lowest closing bid price of the Company’s common shares for the fifteen trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $3,600 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $156,400 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $3,600 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $169,527 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(ss)On July 11, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $50,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum and is due on July 11, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 60% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $1,317 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $48,683 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $1,317 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $54,669 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(tt)On July 29, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $53,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum and is due on June 15, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 61% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the ten trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $1,078 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $51,922 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $1,078 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $55,136 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(uu)On August 1, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $175,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on August 1, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest closing bid price of the Company’s common shares for the twenty prior trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $34,136 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $140,864 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $2,868 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $158,571 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(vv)On August 8, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $105,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on August 8, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 60% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the prior fifteen trading days including the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $1,517 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $103,483 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $1,517 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $113,820 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(ww)On August 12, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $105,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on August 12, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 60% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the prior fifteen trading days including the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $1,400 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $103,600 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $1,400 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $113,725 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
F-18
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
3.Convertible Notes Payable (continued)
(xx)On August 28, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $35,200. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum and is due on May 28, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 62% of the lower of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common stock in the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion and the lowest trading price of the Company’s common stock in the twenty days prior to the date of issuance. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $375 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $34,825 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $375 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $35,083 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(yy)On August 28, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $35,200. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum and is due on May 28, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lower of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common stock in the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion and the lowest trading price of the Company’s common stock in the twenty days prior to the date of issuance. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $5,869 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $29,331 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $375 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $30,617 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(zz)On August 28, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $110,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on August 28, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at 60% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common stock in the twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $978 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $109,022 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $978 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $121,624 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(aaa)On September 17, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $150,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on January 17, 2021. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at the lower of the closing common stock price and 68% of the lowest trading price in the prior twenty trading days on which at least 100 common shares of the Company were traded including the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $92 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $54,908 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $542 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $152,239 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(bbb)On September 22, 2019, the Company issued the second tranche of the convertible note payable dated June 13, 2019 for $55,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum and is due on September 24, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at the lower of the closing common stock price and 65% of the lowest trading price in the prior twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $92 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $54,908 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $92 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $59,287 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
(ccc)On September 24, 2019, the Company issued a convertible note payable for $48,000. Under the terms of the note, the amount owing is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum and is due on September 24, 2020. The note is also convertible into common shares of the Company at the lower of the closing common stock price and 61% of the lowest trading price in the prior twenty trading days prior to the date of conversion. As at September 30, 2019, the carrying value of the note payable is $96 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), the unamortized discount on the note is $47,904 (September 30, 2018 - $nil), accrued interest of $96 (September 30, 2018 - $nil) has been recorded in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, and had a derivative liability of $56,217 (September 30, 2018 - $nil).
F-19
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
4.Related Party Transactions
(a)As of September 30, 2019, the Company owes $120,146 (September 30, 2018 - $120,146) to the former Chief Executive Officer and Director of the Company for advances to the Company to fund day-to-day operations. The amounts owing are unsecured, non-interest bearing, and due on demand.
(b)As of September 30, 2019, the Company owes $85,500 (September 30, 2018 - $85,500) to the former Chief Executive Officer and Director of the Company for advances to the Company to fund day-to-day operations and accrued management fees. The amounts owing are unsecured, non-interest bearing, and due on demand.
(c)As of September 30, 2019, the Company owes $221,897 (September 30, 2018 - $280,639) to the Chief Executive Officer of the Company for accrued management fees. The amounts owing are unsecured, non-interest bearing, and due on demand.
(d)As of September 30, 2019, the Company owes $30,726 (September 30, 2018 – $96,592) to directors of the Company for accrued management fees. The amounts owing are unsecured, non-interest bearing, and due on demand.
5.Investment in Joint Venture
On October 8, 2018, the Company entered into a joint venture agreement with CINC Industries Inc. (“CINC”), a Nevada company, for a period of five years whereby the joint venture will propagate the sale of a new process for extraction of lithium salt from salt brine solutions using CINC’s existing and future processing equipment. As part of the joint venture, each of CINC and the Company holds a 50% interest in the joint venture. No entity has been formed to serve as the joint venture entity and there has been no activity in the joint venture during the year ended September 30, 2019.
CINC is responsible for completing testing on the pilot project, providing training to the Company for use of its processing equipment, manufacturing up to 20 test units, and support and product development, as well as shared costs on other personnel utilized in the joint venture company. The Company is responsible for the initial funding for all equipment and associated expenses, the cost of the lease space, and marketing and sales of the joint venture agreement.
The joint venture is committed to acquiring a minimum amount of processing equipment, goods, accessories, and/or materials totaling: (i) $1,000,000 by October 8, 2020; (ii) $3,000,000 by October 8, 2021; (iii) $6,000,000 by October 8, 2022; and (v) $10,000,000 by October 8, 2023. In the event that the joint venture fails to meet the minimum amounts above, the Company will lose the exclusive right to market, promote and sell the processing equipment provided by CINC. As part of the joint venture agreement, the Company issued 250,000 common shares to CINC with a fair value of $35,250. Refer to Note 7.
As at September 30, 2019, the Company is raising additional financing to fund the future day-to-day operations of the joint venture as noted above.
6.Derivative Liabilities
The Company records the fair value of the conversion price of the convertible debentures as disclosed in Note 4 in accordance with ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging. The fair value of the derivatives was calculated using a multi-nominal lattice model. The fair value of the derivative liabilities is revalued on each balance sheet date with corresponding gains and losses recorded in the consolidated statement of operations. For the year ended September 30, 2019, the Company recorded a loss on the change in the fair value of derivative liability of $218,922 (2018 - $165,961). As at September 30, 2019, the Company recorded a derivative liability of $3,437,200 (September 30, 2018 - $800,973).
F-20
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
6.Derivative Liabilities (continued)
The following inputs and assumptions were used to value the derivative liabilities outstanding during the years ended September 30, 2019 and 2018:
| September 30, 2019 |
| September 30, 2018 |
Expected volatility | 75-151% |
| 133-156% |
Risk free rate | 1.75% |
| 2.59% |
Expected life (in years) | 0.2-1.0 |
| 0.5-1.0 |
A summary of the activity of the derivative liability is shown below:
|
| $ |
Balance, September 30, 2017 |
| - |
Derivative additions associated with convertible notes |
| 1,035,610 |
Adjustment for conversion |
| (400,598) |
Mark-to-market adjustment at September 30, 2018 |
| 165,961 |
Balance, September 30, 2018 |
| 800,973 |
Derivative additions associated with convertible notes |
| 3,772,666 |
Adjustment for conversion |
| (1,355,361) |
Mark to market adjustment at September 30, 2019 |
| 218,922 |
|
|
|
Balance, September 30, 2019 |
| 3,437,200 |
7.Common Shares
The Company’s authorized common stock consists of 500,000,000 shares of common stock, with par value of $0.001.
Year Ended September 30, 2018
On December 5, 2017, the Company issued 578,696 common shares as part of a conversion of $66,550 of convertible notes payable and accrued interest.
On December 18, 2017, the Company cancelled 1,000,000 common shares issued to the Chief Executive Officer of the Company which was previously issued in error.
On December 29, 2017, the Company issued 19,700,000 common shares with a fair value of $1,970,000 for services, including 5,000,000 common shares to the Chief Executive Officer of the Company, and 4,000,000 common shares to directors of the Company. In addition, the Company also issued 1,000,000 common shares to the Chief Executive Officer of the Company to replace the common shares that were previously issued in error and cancelled on December 18, 2017.
On January 29, 2018, the Company issued 3,600,000 common shares with a fair value of $360,000 to the directors of the Company for director fees with a fair value of $180,000, of which $45,000 has been recorded in prepaid expense as at September 30, 2018. In addition, the Company issued 2,400,000 common shares for consulting services with a fair value of $240,000, of which $60,000 has been recorded as prepaid expense as at September 30, 2018
On January 29, 2018, the Company issued 1,440,000 common shares for professional fees with a fair value of $144,000.
On February 2, 2018, the Company issued 578,696 common shares as part of a conversion of $66,550 of convertible notes payable and accrued interest.
On March 8, 2018, the Company issued 2,000,000 common shares to officers of the Company for management fees with a fair value of $190,000, of which 1,000,000 common shares were issuable on each of January 1, 2018 and June 1, 2018.
F-21
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
7.Common Shares (continued)
On March 8, 2018, the Company issued 350,000 common shares for consulting services with a fair value of $33,250.
On April 19, 2018, the Company issued 717,391 common shares as part of a conversion of $82,500 of convertible notes payable and accrued interest.
On May 11, 2018, the Company issued 1,052,174 common shares as part of a conversion of $121,100 of convertible notes payable and accrued interest.
On May 23, 2018, the Company issued 817,391 common shares as part of a conversion of $94,000 of convertible notes payable and accrued interest.
On June 22, 2018, the company issued 666,666 common shares for proceeds of $667 pursuant to the exercise of warrants.
On July 9, 2018, the Company issued 1,850,000 restricted common shares with a fair value of $262,700 as compensation to various advisors.
On July 18, 2018, the Company issued 500,000 restricted common shares with a fair value of $75,000 as a donation.
On July 18, 2018, pursuant to the terms of a convertible note agreement, the Company issued 12,500 restricted common shares with a fair value of $1,875 for payment of interest. Refer to Note 3(k).
On July 18, 2018, pursuant to the terms of a convertible note agreement, the Company issued 37,500 restricted common shares with a fair value of $5,625 for payment of interest. Refer to Note 3(l).
On August 30, 2018, the Company issued 1,130,435 common shares as part of a conversion of $130,000 of convertible notes payable and accrued interest.
On September 4, 2018, the Company issued 1,000,000 common shares with a fair value of $143,000 in exchange for the acquisition of 1,000 land claims. Refer to Note 3.
On September 24, 2018, the Company cancelled 3,600,000 common shares that were previously issued to a non-related party.
Year Ended September 30, 2019
On October 8, 2018, the Company issued 2,500,000 common shares with a fair value of $357,500 for services, including 1,000,000 common shares to the Chief Executive Officer of the Company and 1,000,000 shares to a director of the Company.
On October 10, 2018, the Company issued 250,000 common shares with a fair value of $35,250 as part of the joint venture agreement with CINC.
On October 11, 2018, the Company issued 193,986 common shares with a fair value of $22,308 for the conversion of $20,000 of notes payable resulting in a loss on settlement of debt of $2,308.
On October 12, 2018, the Company issued 240,096 common shares with a fair value of $27,611 for the conversion of $20,000 of notes payable resulting in a loss on settlement of debt of $7,611.
On October 15, 2018, the Company issued 216,086 common shares with a fair value of $21,047 for the conversion of $18,000 of notes payable resulting in a loss on settlement of debt of $3,047.
On October 16, 2018, the Company issued 280,505 common shares with a fair value of $40,673 for the conversion of 20,000 of notes payable resulting in a loss on settlement of debt of $20,673.
F-22
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
7.Common Shares (continued)
Year Ended September 30, 2019 (continued)
On October 16, 2018, the Company issued 100,000 common shares with a fair value of $14,500 for consulting services.
On October 17, 2018, the Company issued 175,035 common shares with a fair value of $25,800 for the conversion of $7,800 of notes payable and $4,680 of accrued interest resulting in a loss on settlement of debt of $13,320.
On October 19, 2018, the Company issued 550,000 common shares with a fair value of $90,750 for consulting services.
On October 23, 2018, the Company issued 150,000 common shares with a fair value of $42,000 for consulting services.
On October 25, 2018, the Company issued 869,285 common shares with a fair value of $139,086 for the conversion of $58,800 of notes payable and $3,180 of accrued interest resulting in a loss on settlement of debt of $77,106.
On October 26, 2018, the Company issued 414,785 common shares with a fair value of $66,366 for the conversion of $25,000 of notes payable and $1,281 of accrued interest resulting in a loss on settlement of debt of $40,085.
On November 7, 2018, the Company issued 443,478 common shares with a fair value of $51,000 as part of a conversion of notes payable at $0.115 per share.
On November 13, 2018, the Company issued 833,895 common shares with a fair value of $179,287 for the conversion of $50,000 of notes payable and accrued interest of $2,836 resulting in a loss on settlement of debt of $126,451.
On November 19, 2018, the Company issued 796,073 common shares with a fair value of $151,254 for the conversion of $75,000 of notes payable and accrued interest of $2,445 resulting in a loss on settlement of debt of $73,809.
On November 21, 2018, the Company issued 420,870 common shares with a fair value of $48,400 for the conversion of notes payable at $0.115 per share.
On December 18, 2018, the Company issued 448,696 common shares with a fair value of $51,600 for the conversion of notes payable at $0.115 per share.
On December 26, 2018, the Company issued 420,870 common shares with a fair value of $48,400 for the conversion of notes payable at $0.115 per share.
On January 8, 2019, the Company issued 708,006 common shares with a fair value of $207,446 upon the conversion of $75,000 of convertible notes payable $4,438 of accrued interest, and derivative liability of $138,845 resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $10,837.
On January 11, 2019, the Company issued 12,700,000 common shares with a fair value of $4,362,320 for services, including 2,000,000 common shares with a fair value of $703,600 to the Chief Executive Officer of the Company, and 4,000,000 common shares with a fair value of $1,407,200 to directors of the Company.
On January 11, 2019, the Company issued 300,000 common shares with a fair value of $105,540 for consulting services.
On January 11, 2019, the Company issued 180,181 common shares with a fair value of $62,234 upon the conversion of $15,000 of convertible notes payable, resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $159.
On January 14, 2019, the Company issued 180,180 common shares with a fair value of $62,234 upon the conversion of $15,000 of convertible notes payable and derivative liability of $47,316, resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $82.
F-23
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
7.Common Shares (continued)
Year Ended September 30, 2019 (continued)
On February 7, 2019, the Company issued 434,783 common shares with a fair value of $50,000 for the conversion of $39,000 of notes payable and $11,000 of accrued interest at $0.115 per share.
On February 22, 2019, the Company issued 629,833 common shares with a fair value of $135,414 upon the conversion of $75,000 of convertible notes payable, $4,438 of accrued interest, and $59,352 of derivative liability resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $3,376.
On February 27, 2019, the Company cancelled 10,000,000 common shares that were previously issued for consulting services.
On February 27, 2019, the Company issued 6,100,000 common shares with a fair value of $1,220,000 for consulting services, including 1,000,000 common shares with a fair value of $200,000 to a director of the Company.
On February 28, 2019, the Company issued 750,000 common shares with a fair value of $151,500 for consulting services.
On March 19, 2019, the Company issued 110,000 common shares with a fair value of $24,090 for the conversion of $9,400 of convertible notes payable and derivative liability of $14,750, resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $60.
April 23, 2019, the Company issued 300,000 common shares with a fair value of $74,250 for consulting services.
On May 8, 2019, the Company issued 184,930 common shares with a fair value of $48,082 for the conversion of $18,100 of convertible notes payable, $1,742 of accrued interest, and derivative liability of $22,363, resulting in a loss on settlement of debt of $5,377.
On June 11, 2019, the Company issued 552,381 common shares with a fair value of $132,516 for the conversion of $75,000 of convertible notes payable, $3,842 of accrued interest and derivative liability of $61,803, resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $8,129.
On June 11, 2019, the Company issued 869,565 common shares with a fair value of $100,000 as part of a conversion of notes payable at $0.115 per share.
On July 8, 2019, the Company issued 1,650,000 common shares with a fair value of $396,000 for consulting services.
On July 15, 2019, the Company issued 1,352,240 common shares with a fair value of $311,015 as part of a conversion of $190,000 of convertible notes payable, $11,192 of accrued interest and derivative liability of $133,574, resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $23,750.
On July 19, 2019, the Company issued 1,414,000 common shares with a fair value of $162,610 as part of the conversion of $136,100 of convertible notes payable and $26,510 of accrued interest.
On July 30, 2019, the Company issued 160,552 common shares with a fair value of $27,294 for the settlement of $15,000 of convertible notes payable, conversion fees of $500, accrued interest of $9, and derivative liability of $12,388 resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $603.
On July 31, 2019, the Company issued 129,453 common shares with a fair value of $23,302 for the settlement of $12,500 of convertible notes payable and $10,853 of derivative liability resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $51.
On August 1, 2019, the Company issued 300,000 common shares with a fair value of $54,000 for consulting services.
F-24
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
7.Common Shares (continued)
Year Ended September 30, 2019 (continued)
On August 8, 2019, the Company issued 196,711 common shares with a fair value of $34,424 for the settlement of $20,000 of convertible notes payable, conversion fees of $500, and derivative liability of $13,998 resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $74.
On August 12, 2019, the Company issued 167,946 common shares with a fair value of $28,551 for the settlement of $17,500 of convertible notes payable and $11,110 of derivative liability resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $59.
On August 21, 2019, the Company issued 1,500,000 common shares with a fair value of $226,500 for consulting services including 1,000,000 common shares with a fair value of $151,000 to the Chief Executive Officer of the Company.
On August 22, 2019, the Company issued 1,233,035 common shares with a fair value of $188,038 for the conversion of $110,000 of convertible notes payable, $6,781 of accrued interest, and $76,580 of derivative liability resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $5,323.
On August 27, 2019, the Company issued 310,606 common shares with a fair value of $34,167 for the conversion of $20,000 of convertible notes payable, conversion fees of $500, and derivative liability of $13,717 resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $50.
On August 27, 2019, the Company issued 303,030 common shares with a fair value of $33,333 for the conversion of $20,000 of convertible notes payable and $13,383 of derivative liability resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $50.
On September 3, 2019, the Company issued 507,826 common shares with a fair value of $49,513 for the settlement of $30,000 of convertible notes payable, conversion fees of $500, and derivative liability of $19,078 resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $65.
On September 3, 2019, the Company issued 249,727 common shares with a fair value of $24,348 for the settlement of $15,000 of convertible notes payable, $988 of accrued interest, and $9,149 of derivative liability resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $789.
On September 5, 2019, the Company issued 504,919 common shares with a fair value of $40,394 for the settlement of $25,000 of convertible notes payable, $1,660 of accrued interest, and $15,344 of derivative liability resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $1,610.
On September 6, 2019, the Company issued 388,257 common shares with a fair value of $29,090 for the settlement of $20,000 of convertible notes payable, conversion fees of $500, and derivative liability of $8,620 resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $40.
On September 9, 2019, the Company issued 622,086 common shares with a fair value of $42,862 for the settlement of $25,000 of convertible notes payable, $1,688 of accrued interest, and $17,260 of derivative liability resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $1,086.
On September 11, 2019, the Company issued 426,997 common shares with a fair value of $43,554 for the settlement of $15,000 of convertible notes payable, $500 of conversion fees, and $28,080 of derivative liability resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $26.
On September 11, 2019, the Company issued 471,763 common shares with a fair value of $48,120 for the settlement of $12,500 of convertible notes payable, $500 of conversion fees, and $2,913 of accrued interest and derivative liability resulting in a loss on settlement of debt of $32,207.
F-25
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
7.Common Shares (continued)
Year Ended September 30, 2019 (continued)
On September 11, 2019, the Company issued 650,000 common shares with a fair value of $66,300 for the settlement of $17,375 of convertible notes payable, $500 of conversion fees, and $49,683 of derivative liability resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $1,258.
On September 13, 2019, the Company issued 200,000 common shares with a fair value of $14,000 for consulting services.
On September 16, 2019, the Company issued 736,532 common shares with a fair value of $51,395 for the settlement of $30,000 of convertible notes payable, $2,100 of accrued interest, and $24,312 of derivative liability resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $5,017.
On September 17, 2019, the Company issued 1,619,344 common shares with a fair value of $100,399 for the settlement of $55,000 of convertible notes payable, $3,782 of accrued interest, and $50,872 of derivative liability resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $9,255.
On September 17, 2019, the Company issued 463,843 common shares with a fair value of $28,758 for the settlement of $10,000 of convertible notes payable, $500 of conversion fees, $6,338 of accrued interest, and $1,487 of derivative liability resulting in a loss on settlement of debt of $10,433.
On September 18, 2019, the Company issued 884,298 common shares with a fair value of $79,587 for the settlement of $30,000 of convertible notes payable, $2,100 of accrued interest, and $50,051 of derivative liability resulting in a gain on settlement of debt of $2,564.
8.Share Purchase Warrants
| Number of warrants |
| Weighted average exercise price $ |
Balance, September 30, 2018 and 2019 | 8,683,334 |
| 0.09 |
Additional information regarding share purchase warrants as of September 30, 2019, is as follows:
|
| Outstanding and exercisable | ||
Range of Exercise Prices $ |
| Number of Warrants |
| Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (years) |
0.001 |
| 1,333,334 |
| 0.7 |
0.01 |
| 3,600,000 |
| 4.7 |
0.10 |
| 1,000,000 |
| 0.5 |
0.15 |
| 750,000 |
| 1.5 |
0.10 |
| 2,000,000 |
| 1.6 |
0.50 |
| 242,000 |
| 1.8 |
| 8,925,334 |
| 4.1 | |
F-26
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
9.Income Taxes
The Company has $18,126,542 of net operating losses carried forward to offset taxable income in future years which expire commencing in fiscal 2032. The income tax benefit differs from the amount computed by applying the US federal income tax rate which was 34% until January 1, 2018, when the income tax rate decreased to 21% to net loss before income taxes. As at September 30, 2019 and 2018, the Company had no uncertain tax positions.
| September 30, 2019 $ |
| September 30, 2018 $ |
Net loss before taxes | 12,625,204 |
| 6,048,092 |
Statutory rate | 21% |
| 24.3% |
|
|
|
|
Computed expected tax recovery | 2,651,293 |
| 1,475,301 |
Permanent differences and other | (396,668) |
| (309,483) |
Change in tax rates | – |
| (390,471) |
Change in valuation allowance | (2,254,625) |
| (775,347) |
|
|
|
|
Income tax provision | – |
| – |
The significant components of deferred income tax assets and liabilities as at September 30, 2019 and 2018 after applying enacted corporate income tax rates are as follows:
| 2019 $ |
| 2018 $ |
Net operating losses carried forward | 3,806,574 |
| 1,551,949 |
Valuation allowance | (3,806,574) |
| (1,551,949) |
|
|
|
|
Net deferred tax asset | – |
| – |
10.Subsequent Events
(a)Subsequent to September 30, 2019, the Company issued 27,996,168 common shares pursuant to the conversion of convertible debentures and 5,560,000 common shares for services, including 1,000,000 common shares issued to a director of the Company.
(b)On September 13, 2019, the Company issued a convertible promissory note for $175,000 for which net proceeds of $170,000 was not received until October 10, 2019. The amounts are unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, and is due on September 13, 2020. The note is convertible into common shares of the Company at 68% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the prior twenty trading days prior to notice of conversion.
(c)On October 15, 2019, the Company issued a convertible promissory note for $52,000, which is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, and is due on October 15, 2020. The note is convertible into common shares of the Company at 66% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the prior twenty trading days prior to notice of conversion.
(d)On October 15, 2019, the Company issued a convertible promissory note for $29,150, which is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, and is due on October 15, 2020. The note is convertible into common shares of the Company at 61% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the prior twenty trading days prior to notice of conversion.
F-27
AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION
(formerly Oroplata Resources, Inc.)
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
For the year ended September 30, 2019
10.Subsequent Events (continued)
(e)On October 15, 2019, the Company issued a convertible promissory note for $29,150, which is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, and is due on October 15, 2020. The note is convertible into common shares of the Company at 61% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the prior twenty trading days prior to notice of conversion.
(f)On October 29, 2019, the Company issued a convertible promissory note for $20,000, which is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, and is due on October 29, 2020. The note is convertible into common shares of the Company at 65% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the prior twenty trading days prior to notice of conversion.
(g)On October 31, 2019, the Company issued a convertible promissory note for $43,000, which is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, and is due on October 31, 2020. The note is convertible into common shares of the Company at 61% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the prior ten trading days prior to notice of conversion.
(h)On November 4, 2019, the Company issued a convertible promissory note for $113,000, which is unsecured, bears interest at 10% per annum, and is due on November 4, 2020. The note is convertible into common shares of the Company at 60% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the prior fifteen trading days prior to notice of conversion.
(i)On December 4, 2019, the Company issued a convertible promissory note for $46,200, which is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, and is due on December 4, 2020. The note is convertible into common shares of the Company at 61% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the prior twenty trading days prior to notice of conversion.
(j)On December 9, 2019, the Company issued a convertible promissory note for $47,300, which is unsecured, bears interest at 12% per annum, and is due on December 9, 2020. The note is convertible into common shares of the Company at 61% of the lowest trading price of the Company’s common shares for the prior twenty trading days prior to notice of conversion.
F-28
Item 9. Changes In and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
(a) Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company maintains disclosure controls and procedures designed to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed in reports filed pursuant to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In addition, The Company contracts with an independent firm to review and test its internal controls. A control system, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met.
As of September 30, 2019, the Company’s management carried out an evaluation of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934. Based on that evaluation, it was concluded the disclosure controls and procedures were not effective as of September 30, 2019.
(b) Report of Management on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(f) of the Exchange Act. The Company has designed internal controls to provide reasonable, but not absolute, assurance that financial statements are prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP. The Company assesses the effectiveness of internal controls based on the criteria set forth in the 2013 Internal Control - Integrated Framework developed by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this evaluation, management has concluded that the Company’s internal controls over financial reporting was not effective as of September 30, 2019.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. It should be noted that any system of internal control, however well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, and not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the system will be met. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
None.
22
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The following table sets forth the names and ages of our current directors and executive officers, the principal offices and positions held by each person:
Name |
| Age |
| Positions |
William Hunter |
| 51 |
| Director |
Douglas MacLellan |
| 64 |
| Director |
Douglas Cole |
| 64 |
| Director, Chairman, CEO, CFO, Secretary |
William Hunter, Director
Mr. Hunter, age 51, received his B.Sc. from DePaul University in Chicago and an MBA with distinction from the Kellstadt School of Business at DePaul University. Mr. Hunter is currently the CFO of AMCI Group and CEO and board member of AMCI Acquisition Corp (Nasdaq: AMCIU). He is a seasoned financial executive with over 20 years of advisory and capital markets experience and has been involved in over $20 billion of transactions throughout his career in the natural resources and industrial industries. Prior to joining AMCI, Mr. Hunter led the Americas Banking team at Nomura where he advised Mitsui in their acquisition of a minority interest in the Moatize Coal Mining complex from Vale and Globe Specialty Metals in their $3.1 billion ‘merger of equals’ transaction with FerroAtlantica. Before Nomura he led industrial and natural resource teams at Jefferies, TD Securities and BMO Nesbitt Burns.
There have been no transactions since the beginning of the Company's last fiscal year, and there are no currently proposed transactions, in which the Company was or is to be a participant and in which Mr. Hunter (or any member of his immediate family) had or will have any interest, that are required to be reported under Item 404(a) of Regulation S-K. The appointment of Mr. Hunter was not pursuant to any arrangement or understanding between him and any person, other than a director or executive officer of the Company acting in his or her official capacity.
Douglas MacLellan, Director
Mr. MacLellan, age 64, currently serves as Chairman of the Board of eWellness Healthcare Corporation (OTCQB: EWLL), since May 2013. From November 2009 to December 2017 Mr. MacLellan was an independent director and Chairman of the Audit Committee of ChinaNet Online Holdings, Inc. (NASDAQ: CNET) a media development, advertising and communications company. From June 2011 to present Mr. MacLellan has been Chairman of Innovare Products, Inc., a privately held company that develops innovative consumer products. From May 2014 to October 2016, Mr. MacLellan was a member of the Board as an independent director of Jameson Stanford Resources Corporation (OTCBB: JMSN) an early stage mining company. From September 1992 through April 2014, Mr. MacLellan held various Board positions and was Chairman and chief executive officer at Radient Pharmaceuticals Corporation. (OTCQB: RXPC.PK), a vertically integrated specialty pharmaceutical company. He also continued to serve as president and chief executive officer for the MacLellan Group, an international financial advisory firm from March 1992 through January 2016. From August 2005 to May 2009, Mr. MacLellan was co-founder and vice chairman at Ocean Smart, Inc., a Canadian based aquaculture company. From February 2002 to September 2006, Mr. MacLellan served as chairman and cofounder at Broadband Access MarketSpace, Ltd., a China based IT advisory firm, and was also co-founder at Datalex Corp., a software and IT company specializing in mainframe applications, from February 1997 to May 2002. Mr. MacLellan was educated at the University of Southern California in economics and international relations.
There have been no transactions since the beginning of the Company's last fiscal year, and there are no currently proposed transactions, in which the Company was or is to be a participant and in which Mr. MacLellan (or any member of his immediate family) had or will have any interest, that are required to be reported under Item 404(a) of Regulation S-K. The appointment of Mr. MacLellan was not pursuant to any arrangement or understanding between him and any person, other than a director or executive officer of the Company acting in his or her official capacity.
23
Douglas Cole, Director, CEO, CFO, Controller, Secretary
Mr. Cole, age 64, has been a Partner overseeing all ongoing deal activities with Objective Equity LLC since 2005, a boutique investment bank focused on the high technology, data analytics and the mining sector. Mr. Cole currently serves on the Board of Directors of eWellness Healthcare Corporation (EWLL). Since 1977 Mr. Cole has held various executive roles, including Chairman, Executive Vice Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and President of multiple public corporations. From May 2000 to September 2005, he was also the Director of Lair of the Bear, The University of California Family Camp located in Pinecrest, California. During the period between 1991 and 1996 he was the CEO of HealthSoft and he also founded and operated Great Bear Technology, which acquired Sony Image Soft and Starpress, then went public and eventually sold to Graphix Zone. In 1995 Mr. Cole was honored by NEA, a leading venture capital firm, as CEO of the year. In 1997 Mr. Cole became CEO of NetAmerica until merging in 1999. Since 1982 he has been very active with the University of California, Berkeley mentoring early-stage technology companies. Mr. Cole has extensive experience in global M&A and global distributions. He obtained his BA in Social Sciences from UC Berkeley in 1978.
There have been no transactions since the beginning of the Company's last fiscal year, and there are no currently proposed transactions, in which the Company was or is to be a participant and in which Mr. Cole (or any member of his immediate family) had or will have any interest, that are required to be reported under Item 404(a) of Regulation S-K. The appointment of Mr. Cole was not pursuant to any arrangement or understanding between him and any person, other than a director or executive officer of the Company acting in his or her official capacity.
Director Qualifications
We believe that our directors should have the highest professional and personal ethics and values, consistent with our longstanding values and standards. They should have broad experience at the policy-making level in business or banking. They should be committed to enhancing stockholder value and should have sufficient time to carry out their duties and to provide insight and practical wisdom based on experience. Their service on other boards of public companies should be limited to a number that permits them, given their individual circumstances, to perform responsibly all director duties for us. Each director must represent the interests of all stockholders. When considering potential director candidates, the Board also considers the candidate’s character, judgment, diversity, age and skills, including financial literacy and experience in the context of our needs and the needs of the Board.
Family Relationships
Involvement in Certain Legal Proceedings
Our directors and executive officers have not been involved in any of the following events during the past ten years:
Any bankruptcy petition filed by or against such person or any business of which such person was a general partner or executive officer either at the time of the bankruptcy or within two years prior to that time;
Any conviction in a criminal proceeding or being subject to a pending criminal proceeding (excluding traffic violations and other minor offenses);
Being subject to any order, judgment, or decree, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any court of competent jurisdiction, permanently or temporarily enjoining him from or otherwise limiting his involvement in any type of business, securities or banking activities or to be associated with any person practicing in banking or securities activities;
Being found by a court of competent jurisdiction in a civil action, the SEC or the Commodity Futures Trading Commission to have violated a Federal or state securities or commodities law, and the judgment has not been reversed, suspended, or vacated;
Being subject of, or a party to, any Federal or state judicial or administrative order, judgment decree, or finding, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, relating to an alleged violation of any Federal or state securities or commodities law or regulation, any law or regulation respecting financial institutions or insurance companies, or any law or regulation prohibiting mail or wire fraud or fraud in connection with any business entity; or
Being subject of or party to any sanction or order, not subsequently reversed, suspended, or vacated, of any self-regulatory organization, any registered entity or any equivalent exchange, association, entity or organization that has disciplinary authority over its members or persons associated with a member.
Code of Ethics
The Company has not adopted a Code of Ethics and Business Conduct. Management intends to adopt a Code of Ethics and Business Conduct in the near future.
24
Term of Office
Our directors are appointed to hold office until the next annual general meeting of our stockholders or until removed from office in accordance with our Bylaws. Our officers are appointed by our Board and hold office until removed by the Board, absent an employment agreement.
Conflicts of Interest
Since we do not have an audit or compensation committee comprised of independent directors, the functions that would have been performed by such committees are performed by our directors. The Board has not established an audit committee and does not have an audit committee financial expert, nor has the Board established a nominating committee. The Board is of the opinion that such committees are not necessary since the Company is in the early stages of operations. The Company has three directors, two of which are not involved in the management of the Company, and to date, such directors have been performing the functions of such committees. The involvement of the two non-management directors mitigates some potential conflict of interest issues.
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Compliance Reporting
Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act requires a company’s directors and officers, and persons who own more than 10% of any class of a company’s equity securities which are registered under Section 12 of the Exchange Act, to file with the SEC reports of ownership on Form 3 and reports of changes in ownership on Forms 4 and 5. Such officers, directors and 10% stockholders are also required to furnish the company with copies of all Section 16(a) reports they file. Based solely on our review of the copies of such forms received by us and on written representations from certain reporting persons as of September 30, 2018, we do not believe that all Section 16(a) reports applicable to our officers, directors and 10% stockholders with respect to our fiscal year ended September 30, 2018 have been filed.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
Summary Compensation Table
Name and Principal Position | Fiscal Year Ended 9/30 | Salary ($) | Bonus ($) | Stock Awards ($) | Option Awards ($) | Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation ($) | Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Earnings ($) | All Other Compensation ($) | Total ($) | |
Douglas Cole CEO, CFO, and Chairman of the Board | 2018 | 57,692 | - | 210,000 | - | - | - | - | 267,692 | |
2019 | 250,000 | - | 1,237,600 | - | - | - | - | 1,487,600 | ||
Douglas MacLellan Director | 2018 | 9,500 | - | 120,000 | - | - | - | - | 129,500 | |
2019 | 57,500 | - | 886,600 | - | - | - | - | 944,100 | ||
William Hunter Director | 2018 | 10,000 | - | 220,000 | - | - | - | - | 230,000 | |
2019 | 65,000 |
| 903,600 |
|
|
|
| 968,600 | ||
Greg Kuzma Former Director | 2018 | 25,000 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 25,000 | |
2019 | 60,000 | - | 175,900 | - | - | - | - | 235,900 | ||
Outstanding Equity Awards
Since incorporation on October 6, 2011, to September 30, 2019, we have not granted any stock options or stock appreciation rights to our executive officer or directors.
25
Compensation of Directors and Officers
As of September 30, 2019, we had no standard arrangement to compensate our directors for their services in the capacity as a director. On December 29, 2017, the Company entered into consulting agreements with each of the directors and entered into an employment agreement with its sole executive officer, Douglas Cole All travel and lodging expenses associated with corporate matters are reimbursed by us, if and when incurred.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management
The following table sets forth certain information as of December 20, 2019 regarding the beneficial ownership of our common stock and preferred stock, based on 166,234,301 shares of Common Stock issued and outstanding and 300,000 shares of preferred stock issued and outstanding, by (i) each person or entity who, to our knowledge, owns more than 5% of our common stock or preferred stock and (ii) each executive officer and director. Unless otherwise indicated in the footnotes to the following table, each person named in the table has sole voting and investment power and that person’s address is deemed to be the address of our principal executive offices.
Shares of common stock subject to options, warrants, or other rights currently exercisable or exercisable within 60 days of December 20, 2019, are deemed to be beneficially owned and outstanding for computing the share ownership and percentage of the stockholder holding such options, warrants or other rights, but are not deemed outstanding for computing the percentage of any other stockholder.
| Number of Shares of Common Stock Beneficially Owned |
| Percentage of Common Stock Beneficially Owned |
| Number of Shares of Preferred Stock Beneficially Owned1 |
| Percentage of Preferred Stock Beneficially Owned | |
William Hunter |
| 8,200,000 |
| 5.17% |
| 100,000 |
| 33% |
Douglas Cole |
| 13,200,000 |
| 8.33% |
| 100,000 |
| 33% |
Douglas MacLellan |
| 7,200,000 |
| 4.54% |
| 100,000 |
| 33% |
1 Each share of preferred stock entitles the holder to cast 1,000 votes and such shares vote with the common stock as a single class.
There are no arrangements known to the Company which may at a subsequent date result in a change-in-control.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions and Director Independence
Related Party Transactions
During the past two fiscal years, there have been no transactions, whether directly or indirectly, between us and any of our respective officers, directors, beneficial owners of more than 5% of our outstanding Common Stock or their family members, that exceeded the lesser of $120,000 or 1% of the average of our total assets at year-end for the last two completed fiscal years.
Director Independence
William Hunter, Douglas MacLellan and Douglas Cole are not independent within the meaning of Section 5605 of NASDAQ.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
The aggregate fees billed for the two most recently completed fiscal years for professional services rendered by the principal accountant for the audit of our annual financial statements and review of the financial statements that are normally provided by the accountant in connection with statutory and regulatory filings or engagements for those fiscal periods were as follows:
|
| Year Ended September 30, 2019 |
| Year Ended September 30, 2018 |
Audit Fees | $ | 17,000 | $ | 14,500 |
Audit-Related Fees |
| - |
| - |
Tax Fees |
| - |
| - |
All Other Fees |
| - |
| - |
Total | $ | 17,000 | $ | 14,500 |
26
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.
The following exhibits are either provided with this Annual Report or are incorporated herein by reference:
Description | Filed Herein | Incorporated Date | By Form | Reference Exhibit | |
Articles of Incorporation, as amended | x |
|
|
| |
Bylaws |
| May 22, 2013 | S-1 | 3.2 | |
Certificate of Designation of Preferences, Rights and Limitations of Series A Preferred Stock |
| October 8, 2019 | 8-K | 3.1 | |
Securities Purchase Agreement by and between American Battery Metals Corporation and Odyssey Capital Funding LLC dated July 9, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Convertible Promissory Note of American Battery Metals Corporation in favor of Odyssey Capital Funding LLC dated July 9, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Securities Purchase Agreement by and between American Battery Metals Corporation and Sunshine Equity Partners LLC dated July 11, 2019 | x |
|
|
| |
Convertible Promissory Note of American Battery Metals Corporation in favor of Sunshine Equity Partners LLC dated July 11, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Securities Purchase Agreement by and between American Battery Metals Corporation and Power Up Lending Group Ltd. dated July 29, 2019 | x |
|
|
| |
Convertible Promissory Note of American Battery Metals Corporation in favor of Power Up Lending Group Ltd. dated July 29, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Securities Purchase Agreement by and between American Battery Metals Corporation and Auctus Fund, LLC dated August 1, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Convertible Promissory Note of American Battery Metals Corporation in favor of Auctus Fund, LLC dated August 1, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Securities Purchase Agreement by and between American Battery Metals Corporation and Adar Alef, LLC dated August 8, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Convertible Promissory Note of American Battery Metals Corporation in favor of Adar Alef, LLC dated August 8, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Securities Purchase Agreement by and between American Battery Metals Corporation and Black Ice Advisors, LLC dated August 12, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Convertible Promissory Note of American Battery Metals Corporation in favor of Black Ice Advisors, LLC dated August 12, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Securities Purchase Agreement by and between American Battery Metals Corporation and LG Capital Funding, LLC dated August 28, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Convertible Promissory Note of American Battery Metals Corporation in favor of LG Capital Funding, LLC dated August 28, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Securities Purchase Agreement by and between American Battery Metals Corporation and BHP Capital NY Inc. dated August 28, 2019. | x |
|
|
|
27
Convertible Promissory Note of American Battery Metals Corporation in favor of BHP Capital NY Inc. dated August 28, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Securities Purchase Agreement by and between American Battery Metals Corporation and Jefferson Street Capital LLC dated August 28, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Convertible Promissory Note of American Battery Metals Corporation in favor of Jefferson Street Capital LLC dated August 28, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Securities Purchase Agreement by and between American Battery Metals Corporation and Power Up Lending Group Ltd. dated September 24, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Convertible Promissory Note of American Battery Metals Corporation in favor of Power Up Lending Group Ltd. dated September 24, 2019. | x |
|
|
| |
Certification of Chief Executive Officer as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | x |
|
|
| |
Certification of Chief Executive Officer as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | x |
|
|
| |
101 | INS XBRL Instant Document. | x |
|
|
|
101 | SCH XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | x |
|
|
|
101 | CAL XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | x |
|
|
|
101 | LAB XRBL Taxonomy Label Linkbase Document | x |
|
|
|
101 | PRE XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | x |
|
|
|
101 | DEF XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | x |
|
|
|
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary.
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
|
|
| AMERICAN BATTERY METALS CORPORATION (Registrant) |
| |
|
|
|
|
Date: December 27, 2019 | By: | /s/ Douglas D Cole |
|
|
| Douglas D Cole |
|
|
| Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer |
|
|
|
|
|
28
