Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-12.1 - EXHIBIT 12.1 - PBF Holding Co LLC | exhibit121-earningstofixed.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - PBF Holding Co LLC | a12311610kexhibit322.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - PBF Holding Co LLC | a12311610kexhibit321.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - PBF Holding Co LLC | a12311610kexhibit312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - PBF Holding Co LLC | a12311610kexhibit311.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EXHIBIT 21.1 - PBF Holding Co LLC | listofsubsidiaries-exhibit.htm |
| EX-10.35 - EXHIBIT 10.35 - PBF Holding Co LLC | a12311610kexhibit1035.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark one)
x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended: December 31, 2016
Or
¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 001-35764
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
PBF FINANCE CORPORATION
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
DELAWARE | 27-2198168 | |
DELAWARE | 45-2685067 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
One Sylvan Way, Second Floor Parsippany, New Jersey | 07054 | |
(Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrants’ telephone number, including area code: (973) 455-7500
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: None.
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None.
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. ¨Yes xNo
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. ¨Yes xNo
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports); and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. ¨ Yes x No (Note: As of January 1, 2017, the registrant was no longer subject to the filing requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act other than with respect to this Form 10-K; however, the registrant filed all reports required to be filed during the period it was subject to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act.)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). x Yes o No
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer | Accelerated filer | Non-accelerated filer (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | ||||
¨ | ¨ | x | ¨ | ||||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). ¨ Yes x No
There is no trading in the membership interests of PBF Holding LLC or the common stock of PBF Finance Corporation and therefore an aggregate market value based on such is not determinable.
PBF Holding Company LLC has no common stock outstanding. As of March 8, 2017 100% of the membership interests of PBF Holding Company LLC were owned by PBF Energy Company LLC, and PBF Finance Corporation had 100 shares of common stock outstanding, all of which were held by PBF Holding Company LLC.
PBF Finance Corporation meets the conditions set forth in General Instruction (I)(1)(a) and (b) of Form 10-K and is therefore filing this form with the reduced disclosure format.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
PBF Energy Inc., the managing member of our direct parent PBF Energy Company LLC, will file with the Securities and Exchange Commission a definitive Proxy Statement for its 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders. Portions of the Proxy Statement of PBF Energy Inc. are incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K to the extent stated herein.
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Explanatory Note
This Form 10-K is filed by PBF Holding Company LLC (“PBF Holding”) and PBF Finance Corporation (“PBF Finance”). PBF Holding is a wholly-owned subsidiary of PBF Energy Company LLC (“PBF LLC”) and is the parent company for PBF LLC's refinery operating subsidiaries. PBF Finance is a wholly-owned subsidiary of PBF Holding. PBF Holding is an indirect subsidiary of PBF Energy Inc. (“PBF Energy”), which is the sole managing member of, and owner of an equity interest representing approximately 96.5% of the outstanding economic interests in PBF LLC as of December 31, 2016. PBF Energy operates and controls all of the business and affairs and consolidates the financial results of PBF LLC and its subsidiaries. PBF Holding, together with its consolidated subsidiaries, owns and operates oil refineries and related facilities in North America.
2
PART I
In this Annual Report on Form 10-K, unless the context otherwise requires, references to the “Company,” “we,” “our” or “us” refer to PBF Holding, and, in each case, unless the context otherwise requires, its consolidated subsidiaries. References to “subsidiary guarantors” refer to PBF Services Company LLC, PBF Power Marketing LLC, Paulsboro Natural Gas Pipeline Company LLC, Paulsboro Refining Company LLC (“Paulsboro Refining”), Toledo Refining Company LLC (“Toledo Refining” or “TRC”), Delaware City Refining Company LLC (“Delaware City Refining” or “DCR”), PBF Investments LLC (“PBF Investments”), Chalmette Refining, L.L.C. (“Chalmette Refining”), PBF Western Region LLC ("PBF Western Region"), Torrance Refining Company LLC ("Torrance Refining") and Torrance Logistics Company LLC ("Torrance Logistics"), which are the subsidiaries of PBF Holding that guarantee PBF Holding's 8.25% Senior Secured Notes due 2020 (the “2020 Senior Secured Notes”) and 7.0% Senior Secured Notes due 2023 (the “2023 Senior Secured Notes”, and together with the 2020 Senior Secured Notes, the “Senior Secured Notes”) on a joint and several basis.
In this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we make certain forward-looking statements, including statements regarding our plans, strategies, objectives, expectations, intentions, and resources. You should read our forward-looking statements together with our disclosures under the heading: “Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.” When considering forward-looking statements, you should keep in mind the risk factors and other cautionary statements set forth in this Annual Report on Form 10-K under “Risk Factors” in Item 1A.
ITEM. 1 BUSINESS
Overview
We are one of the largest independent petroleum refiners and suppliers of unbranded transportation fuels, heating oil, petrochemical feedstocks, lubricants and other petroleum products in the United States. We sell our products throughout the Northeast, Midwest, Gulf Coast and West Coast of the United States, as well as in other regions of the United States and Canada, and are able to ship products to other international destinations. We were formed in 2008 to pursue acquisitions of crude oil refineries and downstream assets in North America. As of December 31, 2016, we own and operate five domestic oil refineries and related assets, which we acquired in 2010, 2011, 2015 and 2016. Our refineries have a combined processing capacity, known as throughput, of approximately 900,000 barrels per day (" bpd"), and a weighted-average Nelson Complexity Index of 12.2. The Company’s five oil refineries are aggregated into one reportable segment.
PBF Energy Inc.'s Public Offerings
We are a Delaware limited liability company and a holding company for our operating subsidiaries. PBF Finance is a wholly-owned subsidiary of PBF Holding. We are a wholly-owned subsidiary of PBF LLC, and PBF Energy is the sole managing member of, and owner of an equity interest as of December 31, 2016 representing approximately 96.5% of the outstanding economic interests in PBF LLC.
On December 18, 2012, our indirect parent, PBF Energy completed its initial public offering. As a result of PBF Energy's initial public offering and related organization transactions, PBF Energy became the sole managing member of PBF LLC and operates and controls all of its business and affairs and consolidates the financial results of PBF LLC and its subsidiaries, including PBF Holding and PBF Finance. PBF Energy completed secondary offerings of its Class A common stock in 2013, 2014, and 2015. On October 13, 2015, PBF Energy completed a public offering of an aggregate of 11,500,000 shares of Class A common stock (the “October 2015 Equity Offering”) and on December 19, 2016, PBF Energy completed a public offering of 10,000,000 shares of Class A common stock (the "December 2016 Equity Offering"). As of December 31, 2016, PBF Energy held 109,204,047 PBF LLC Series C Units and its current and former executive officers and directors and certain employees and others beneficially held 3,920,902 PBF LLC Series A Units, and the holders of PBF Energy's issued and outstanding shares of Class A common stock have 96.5% of the voting power in PBF Energy and the members of PBF LLC other than PBF Energy through their holdings of Class B common stock have the remaining 3.5% of the voting power.
3
PBF Holding Refineries
Our five refineries are located in Delaware City, Delaware, Paulsboro, New Jersey, Toledo, Ohio, New Orleans, Louisiana and Torrance, California. Each of these refineries is briefly described in the table below:
Refinery | Region | Nelson Complexity | Throughput Capacity (in barrels per day) | PADD | Crude Processed (1) | Source (1) | |||
Delaware City | East Coast | 11.3 | 190,000 | 1 | medium and heavy sour crude | water, rail | |||
Paulsboro | East Coast | 13.2 | 180,000 | 1 | medium and heavy sour crude | water, rail | |||
Toledo | Mid-Continent | 9.2 | 170,000 | 2 | light, sweet crude | pipeline, truck, rail | |||
Chalmette | Gulf Coast | 12.7 | 189,000 | 3 | light and heavy crude | water, pipeline | |||
Torrance | West Coast | 14.9 | 155,000 | 5 | heavy and medium crude | pipeline, water, truck | |||
________
(1) Reflects the typical crude and feedstocks and related sources utilized under normal operating conditions and prevailing market environments.
On July 1, 2016, we closed our acquisition of the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets (the “Torrance Acquisition”). The Torrance refinery is strategically positioned in Southern California with advantaged logistics connectivity that offers flexible raw material sourcing and product distribution opportunities primarily in the California, Las Vegas and Phoenix area markets.
In addition to refining assets, the Torrance Acquisition included a number of high-quality logistics assets including a sophisticated network of crude and products pipelines, product distribution terminals and refinery crude and product storage facilities. The most significant of the logistics assets is a 189-mile crude gathering and transportation system which delivers San Joaquin Valley crude oil directly from the field to the refinery. Additionally, the transaction included several pipelines which provide access to sources of crude oil including the Ports of Long Beach and Los Angeles, as well as clean product outlets with a direct pipeline supplying jet fuel to the Los Angeles airport. The Torrance refinery also has crude and product storage facilities with approximately 8.6 million barrels of shell capacity.
Public Offerings of PBFX and Subsequent Drop-Down Transactions
PBF Logistics LP ("PBFX" or the "Partnership") is an affiliate of ours. PBFX is a fee-based, growth-oriented, Delaware master limited partnership formed by PBF Energy to own or lease, operate, develop and acquire crude oil and refined petroleum products terminals, pipelines, storage facilities and similar logistics assets. PBFX engages in the receiving, handling, storing and transferring of crude oil, refined products and intermediates from sources located throughout the United States and Canada for PBF Energy in support of certain of its refineries, as well as for third party customers. As of December 31, 2016, a substantial majority of PBFX’s revenue is derived from long-term, fee-based commercial agreements with us, which include minimum volume commitments, for receiving, handling, storing and transferring crude oil and refined products. PBF Energy also has agreements with PBFX that establish fees for certain general and administrative services and operational and maintenance services provided by us to PBFX.
PBF Logistics GP LLC (“PBF GP”) serves as the general partner of PBFX. PBF GP is wholly-owned by PBF LLC. On May 14, 2014, PBFX completed its initial public offering (the “PBFX Offering”). In connection with the PBFX Offering, we contributed to PBFX the assets and liabilities of certain crude oil terminaling assets. In a series of additional transactions subsequent to the PBFX Offering, we distributed certain additional assets to PBF LLC, which in turn contributed those assets to PBFX. See "Agreements with PBFX" below as well as "Note
4
12 - Related Party Transactions" to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
See “Item 1A. Risk Factors” and “Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.”
Recent Developments
Contribution Agreement
On February 15, 2017, PBF LLC entered into a contribution agreement with PBFX pursuant to which PBF LLC has agreed to contribute to PBFX all of the issued and outstanding limited liability company interests of Paulsboro Natural Gas Pipeline Company LLC ("PNGPC"), a wholly-owned subsidiary of PBF Holding. PNGPC owns and operates an existing interstate natural gas pipeline that originates in Delaware County, Pennsylvania, and terminates at the delivery point to our Paulsboro Refinery. PNGPC has Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (“FERC”) approval for, and is in the process of constructing, a new 24” pipeline (the “New Pipeline”) to replace the existing pipeline, which will be abandoned. In consideration for the PNGPC limited liability company interests, at closing, PBFX delivered (i) an intercompany promissory note in an amount to be determined based on the amounts expended through the closing date with respect to the New Pipeline and the abandonment of the existing line, (ii) an expansion rights and right of first refusal agreement in favor of PBF LLC with respect to the New Pipeline and (iii) an assignment and assumption agreement with respect to certain outstanding litigation involving PNGPC and the existing pipeline. The transaction closed on February 28, 2017.
Storage Services Agreement
On February 15, 2017, we entered into a ten-year storage services agreement (the “Chalmette Storage Agreement”) with PBFX’s wholly-owned subsidiary, PBFX Operating Company ("PBFX Op Co"), under which PBFX, through PBFX Op Co, will provide storage services to us upon the earlier of November 1, 2017 and the completion of construction of a new tank at our Chalmette Refinery. PBFX Op Co and Chalmette Refining have entered into a twenty-year lease for the premises upon which the tank will be located and a project management agreement pursuant to which our subsidiary, Chalmette Refining, will manage the construction of the tank.
Available Information
Our website address is www.pbfenergy.com. Information contained on our website is not part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and any other materials filed with (or furnished to) the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) by us are available on our website (under “Investors”) free of charge, soon after we file or furnish such material.
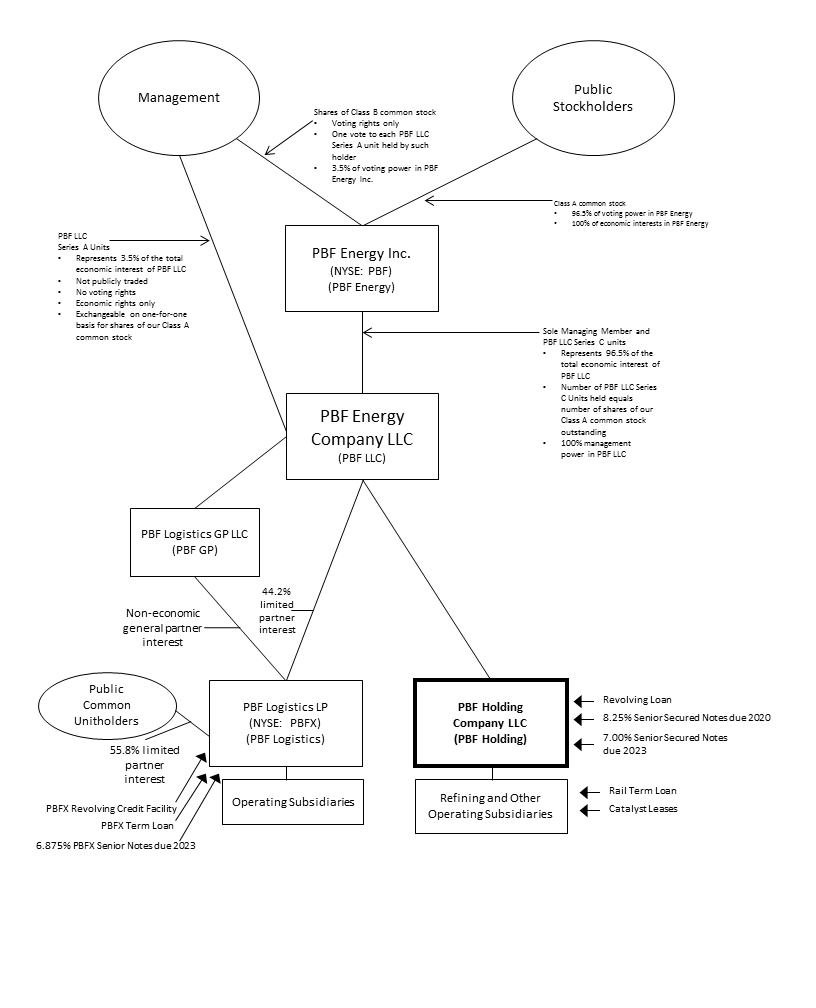
The diagram below depicts our organizational structure as of December 31, 2016:
5
6
Refining Operations
We own and operate five refineries providing geographic and market diversity. We produce a variety of products at each of our refineries, including gasoline, ULSD, heating oil, jet fuel, lubricants, petrochemicals and asphalt. We sell our products throughout the Northeast, Midwest, Gulf Coast and West Coast of the United States, as well as in other regions of the United States and Canada, and are able to ship products to other international destinations.
Delaware City Refinery
Overview. The Delaware City refinery is located on an approximately 5,000-acre site, with access to waterborne cargoes and an extensive distribution network of pipelines, barges and tankers, truck and rail. Delaware City is a fully integrated operation that receives crude via rail at its crude unloading facilities, or ship or barge at its docks located on the Delaware River. The crude and other feedstocks are transported, via pipes, to an extensive tank farm where they are stored until processing. In addition, there is a 15-lane, 50,000 bpd capacity truck loading rack located adjacent to the refinery and a 23-mile interstate pipeline that are used to distribute clean products, which were transferred to PBFX in conjunction with its acquisition of the Delaware City Products Pipeline and Truck Rack (as defined in "Note 12 - Related Party Transactions" to the consolidated financial statements) in May 2015.
As a result of its configuration and process units, Delaware City has the capability of processing a slate of heavy crudes with a high concentration of high sulfur crudes and is one of the largest and most complex refineries on the East Coast. The Delaware City refinery is one of two heavy crude coking refineries, the other being Paulsboro, on the East Coast of the United States with coking capacity equal to approximately 25% of crude capacity.
The Delaware City refinery primarily processes a variety of medium to heavy, sour crude oils, but can run light, sweet crude oils as well. The refinery has large conversion capacity with its 82,000 bpd fluid catalytic cracking unit ("FCC unit"), 47,000 bpd fluid coking unit ("FCU") and 18,000 bpd hydrocracking unit with vacuum distillation. Hydrogen is provided via the refinery’s steam methane reformer and continuous catalytic reformer.
The following table approximates the Delaware City refinery’s major process unit capacities. Unit capacities are shown in barrels per stream day.
Refinery Units | Nameplate Capacity | |
Crude Distillation Unit | 190,000 | |
Vacuum Distillation Unit | 102,000 | |
Fluid Catalytic Cracking Unit | 82,000 | |
Hydrotreating Units | 160,000 | |
Hydrocracking Unit | 18,000 | |
Catalytic Reforming Unit | 43,000 | |
Benzene / Toluene Extraction Unit | 15,000 | |
Butane Isomerization Unit | 6,000 | |
Alkylation Unit | 11,000 | |
Polymerization Unit | 16,000 | |
Fluid Coking Unit | 47,000 | |
Feedstocks and Supply Arrangements. We purchase all of our crude and feedstock needs independently from a variety of suppliers on the spot market or through term agreements. Prior to 2016, we had a crude and feedstock supply agreement with Statoil pursuant to which we directed Statoil to purchase waterborne crude and other feedstocks for Delaware City and Statoil purchased these products on the spot market or through term agreements. Accordingly, Statoil entered into, on our behalf, hedging arrangements to protect against changes in prices between the time of purchase and the time of processing the feedstocks. In addition to procurement, Statoil
7
arranged transportation and insurance for these waterborne deliveries of crude and feedstock supply and we paid Statoil a per barrel fee for their procurement and logistics services.
Refined Product Yield and Distribution. The Delaware City refinery predominantly produces gasoline, jet fuel, ULSD and ultra-low sulfur heating oil as well as certain other products. We market and sell all of our refined products independently to a variety of customers on the spot market or through term agreements.
Inventory Intermediation Agreement. On June 26, 2013, we entered into an Inventory Intermediation Agreement with J. Aron ("Inventory Intermediation Agreement") to support the operations of the Delaware City refinery. Pursuant to the Inventory Intermediation Agreement, J. Aron purchased certain of the finished and intermediate products (collectively the “Products”) located at the refinery upon termination of a previous product offtake agreement. J. Aron purchases the Products produced and delivered into the refinery's storage tanks on a daily basis. J. Aron further agrees to sell to us on a daily basis the Products delivered out of the refinery's storage tanks. On May 29, 2015, we entered into amended and restated inventory intermediation agreements for both the Delaware City and Paulsboro refineries (the "A&R Intermediation Agreements") with J. Aron pursuant to which certain terms of the existing Inventory Intermediation Agreements were amended, including, among other things, pricing and an extension of the term for a period of two years from the original expiry date of July 1, 2015 subject to certain early termination rights. In addition, the A&R Intermediation Agreements include one-year renewal clauses upon six months' advance notice by mutual consent of both parties. The A&R Intermediation Agreements have not been renewed and are scheduled to expire July 1, 2017. If we are unable to negotiate and extension with J. Aron or enter into an alternative intermediation agreement, we will have to repurchase the inventories outstanding under the A&R Intermediation Agreement at that time.
Tankage Capacity. The Delaware City refinery has total storage capacity of approximately 10.0 million barrels. Of the total, approximately 3.6 million barrels of storage capacity are dedicated to crude oil and other feedstock storage with the remaining approximately 6.4 million barrels allocated to finished products, intermediates and other products.
Energy and Other Utilities. Under normal operating conditions, the Delaware City refinery consumes approximately 65,000 MMBTU per day of natural gas supplied via pipeline from third parties. The Delaware City refinery has a 280 MW power plant located on-site that consists of two natural gas-fueled turbines with combined capacity of approximately 140 MW and four turbo-generators with combined nameplate capacity of approximately 140 MW. Collectively, this power plant produces electricity in excess of Delaware City’s refinery load of approximately 90 MW. Excess electricity is sold into the Pennsylvania-New Jersey-Maryland, or PJM, grid. Steam is primarily produced by a combination of three dedicated boilers, two heat recovery steam generators on the gas turbines, and is supplemented by secondary boilers at the FCC and Coker.
Paulsboro Refinery
Overview. The Paulsboro refinery is located on approximately 950 acres on the Delaware River in Paulsboro, New Jersey, just south of Philadelphia and approximately 30 miles away from Delaware City. Paulsboro receives crude and feedstocks via its marine terminal on the Delaware River. Paulsboro is one of two operating refineries on the East Coast with coking capacity, the other being Delaware City. The Paulsboro refinery primarily processes a variety of medium and heavy, sour crude oils but can run light, sweet crude oils as well.
The following table approximates the Paulsboro refinery’s major process unit capacities. Unit capacities are shown in barrels per stream day.
8
Refinery Units | Nameplate Capacity | |
Crude Distillation Units | 168,000 | |
Vacuum Distillation Units | 83,000 | |
Fluid Catalytic Cracking Unit | 55,000 | |
Hydrotreating Units | 141,000 | |
Catalytic Reforming Unit | 32,000 | |
Alkylation Unit | 11,000 | |
Lube Oil Processing Unit | 12,000 | |
Delayed Coking Unit | 27,000 | |
Propane Deasphalting Unit | 11,000 | |
Feedstocks and Supply Arrangements. We have a contract with Saudi Aramco pursuant to which we have been purchasing up to approximately 100,000 bpd of crude oil from Saudi Aramco that is processed at Paulsboro. The crude purchased under this contract is priced off ASCI.
Refined Product Yield and Distribution. The Paulsboro refinery predominantly produces gasoline, diesel fuels and jet fuel and also manufactures Group I base oils or lubricants and asphalt. We market and sell all of our refined products independently to a variety of customers on the spot market or through term agreements under which we sell approximately 35% of our Paulsboro refinery's gasoline production.
Inventory Intermediation Agreement. On June 26, 2013, the Company entered into an Inventory Intermediation Agreement with J. Aron to support the operations of the Paulsboro refinery, which commenced upon the termination of the previous product offtake agreement. Pursuant to the Inventory Intermediation Agreement, J. Aron purchases the Products produced and delivered into the refinery's storage tanks on a daily basis. J. Aron further agrees to sell to us on a daily basis the Products delivered out of the refinery's storage tanks. On May 29, 2015, the Company and J. Aron amended the Inventory Intermediation Agreement pursuant to which certain terms of the existing inventory intermediation agreements were amended, including, among other things, pricing and an extension of the term for a period of two years from the original expiry date of July 1, 2015 subject to certain early termination rights. In addition, the A&R Intermediation Agreements include one-year renewal clauses upon six months' advance notice by mutual consent of both parties. The A&R Intermediation Agreements have not been renewed and are scheduled to expire July 1, 2017. If we are unable to negotiate and extension with J. Aron or enter into an alternative intermediation agreement, we will have to repurchase the inventories outstanding under the A&R Intermediation Agreement at that time.
Tankage Capacity. The Paulsboro refinery has total storage capacity of approximately 7.5 million barrels. Of the total, approximately 2.1 million barrels are dedicated to crude oil storage with the remaining 5.4 million barrels allocated to finished products, intermediates and other products.
Energy and Other Utilities. Under normal operating conditions, the Paulsboro refinery consumes approximately 30,000 MMBTU per day of natural gas supplied via pipeline from third parties. The Paulsboro refinery is virtually self-sufficient for its electrical power requirements. The refinery supplies approximately 90% of its 63 MW load through a combination of four generators with a nameplate capacity of 78 MW, in addition to a 30 MW gas turbine generator and two 15 MW steam turbine generators located at the Paulsboro utility plant. In the event that Paulsboro requires additional electricity to operate the refinery, supplemental power is available through a local utility. Paulsboro is connected to the grid via three separate 69 KV aerial feeders and has the ability to run entirely on imported power. Steam is primarily produced by three boilers, each with continuous rated capacity of 300,000-lb/hr at 900-psi. In addition, Paulsboro has a heat recovery steam generator and a number of waste heat boilers throughout the refinery that supplement the steam generation capacity. Paulsboro’s current hydrogen needs are met by the hydrogen supply from the reformer. In addition, the refinery employs a standalone steam methane reformer that is capable of producing 10 MMSCFD of 99% pure hydrogen. This ancillary hydrogen plant is utilized as a back-up source of hydrogen for the refinery’s process units.
9
Toledo Refinery
Overview. Toledo primarily processes a slate of light, sweet crudes from Canada, the Mid-Continent, the Bakken region and the U.S. Gulf Coast. The Toledo refinery is located on a 282-acre site near Toledo, Ohio, approximately 60 miles from Detroit. Crude is delivered to the Toledo refinery through three primary pipelines: (1) Enbridge from the north, (2) Capline from the south and (3) Mid-Valley from the south. Crude is also delivered to a nearby terminal by rail and from local sources by truck to a truck unloading facility within the refinery.
The following table approximates the Toledo refinery’s major process unit capacities. Unit capacities are shown in barrels per stream day.
Refinery Units | Nameplate Capacity | |
Crude Distillation Unit | 170,000 | |
Fluid Catalytic Cracking Unit | 79,000 | |
Hydrotreating Units | 95,000 | |
Hydrocracking Unit | 45,000 | |
Catalytic Reforming Units | 45,000 | |
Alkylation Unit | 10,000 | |
Polymerization Unit | 7,000 | |
UDEX Unit | 16,300 | |
Feedstocks and Supply Arrangements. We currently fully source our own crude oil needs for Toledo. Previously, we had a crude oil acquisition agreement with a third party that expired on July 31, 2014.
Refined Product Yield and Distribution. Toledo produces finished products including gasoline and ULSD, in addition to a variety of high-value petrochemicals including benzene, toluene, xylene, nonene and tetramer. Toledo is connected, via pipelines, to an extensive distribution network throughout Ohio, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Michigan, Pennsylvania and West Virginia. The finished products are transported on pipelines owned by Sunoco Logistics Partners L.P. and Buckeye Partners. In addition, we have proprietary connections to a variety of smaller pipelines and spurs that help us optimize our clean products distribution. A significant portion of Toledo’s gasoline and ULSD are distributed through the approximately 36 terminals in this network.
We have an agreement with Sunoco whereby Sunoco purchases gasoline and distillate products representing approximately one-third of the Toledo refinery’s gasoline and distillates production. The agreement had an initial three year term, subject to certain early termination rights. In March 2017, the agreement was renewed and extended for another two year term. We sell the bulk of the petrochemicals produced at the Toledo refinery through short-term contracts or on the spot market and the majority of the petrochemical distribution is done via rail.
Tankage Capacity. The Toledo refinery has total storage capacity of approximately 4.5 million barrels. The Toledo refinery receives its crude through pipeline connections and a truck rack. Of the total, approximately 1.3 million barrels are dedicated to crude oil storage with the remaining 3.2 million barrels allocated to intermediates and products. A portion of storage capacity dedicated to crude oil and finished products was transferred to PBFX in conjunction with its acquisition of the Toledo Storage Facility (as defined in "Note 12 - Related Party Transactions" to the consolidated financial statements) in December 2014.
Energy and Other Utilities. Under normal operating conditions, the Toledo refinery consumes approximately 20,000 MMBTU per day of natural gas supplied via pipeline from third parties. The Toledo refinery purchases its electricity from the PJM grid and has a long-term contract to purchase hydrogen and steam from a local third party supplier. In addition to the third party steam supplier, Toledo consumes a portion of the steam that is generated by its various process units.
10
Chalmette Refinery
Acquisition. On November 1, 2015, we acquired from ExxonMobil Oil Corporation ("ExxonMobil"), Mobil Pipe Line Company and PDV Chalmette, L.L.C., the ownership interests of Chalmette Refining, L.L.C. (“Chalmette Refining”), which owns the Chalmette refinery and related logistics assets (collectively, the "Chalmette Acquisition"). The aggregate purchase price for the Chalmette Acquisition was $322.0 million in cash, plus inventory and final working capital of $246.0 million.
Overview. The Chalmette refinery is located on a 400-acre site near New Orleans, Louisiana. It is a dual-train coking refinery and is capable of processing both light and heavy crude oil though its 189,000 bpd crude units and downstream units. Chalmette Refining owns 100% of the MOEM Pipeline, providing access to the Empire Terminal, as well as the CAM Connection Pipeline, providing access to the Louisiana Offshore Oil Port facility through a third party pipeline. Chalmette Refining also owns 80% of each of the Collins Pipeline Company and T&M Terminal Company, both located in Collins, Mississippi, which provide a clean products outlet for the refinery to the Plantation and Colonial Pipelines. Also included in the acquisition were a marine terminal capable of importing waterborne feedstocks and loading or unloading finished products; a clean products truck rack which provides access to local markets; and a crude and product storage facility.
The following table approximates the Chalmette refinery’s major process unit capacities. Unit capacities are shown in barrels per stream day.
Refinery Units | Nameplate Capacity | |
Crude Distillation Unit | 189,000 | |
Fluid Catalytic Cracking Unit | 72,000 | |
Hydrotreating Units | 158,000 | |
Delayed Coker | 29,000 | |
Catalytic Reforming Unit | 22,000 | |
Alkylation Unit | 15,000 | |
Feedstocks and Supply Arrangements. In connection with the Chalmette Acquisition on November 1, 2015, we entered into a crude supply arrangement with PDVSA that has a ten year term with a renewal option for an additional five years, subject to certain early termination rights. The pricing for the crude supply is market based and is agreed upon on a quarterly basis by both parties. Additionally, we obtain crude and feedstocks from other sources through connections to the CAM and MOEM Pipelines as well as ship docks and truck racks.
Refined Product Yield and Distribution. The Chalmette refinery primarily processes a variety of light and heavy crude oils. The Chalmette refinery predominantly produces gasoline, diesel fuels and jet fuel and also manufactures high-value petrochemicals including benzene and xylene. Products produced at the Chalmette refinery are transferred to customers through pipelines, the marine terminal and truck rack. The majority of our clean products are delivered to customers via pipelines. Our ownership of the Collins Pipeline and T&M Terminal provides Chalmette with strategic access to Southeast and East Coast markets through third party logistics. We have an offtake agreement with ExxonMobil pursuant to which ExxonMobil purchases approximately 50% of the 14,000 barrel per day capacity. This agreement had an initial term of one year from the date of the Chalmette Acquisition continuing thereafter subject to the right of either party to cancel with six months' written notice. As of December 31, 2016, no notice of cancellation had been given by either party.
Tankage Capacity. Chalmette has a total tankage capacity of approximately 7.5 million barrels. Of this total, approximately 2.1 million barrels are allocated to crude oil storage with the remaining 5.4 million barrels allocated to intermediates and products.
Energy and Other Utilities. Under normal operating conditions, the Chalmette refinery consumes approximately 30,000 MMBTU per day of natural gas supplied via pipeline from third parties. The Chalmette
11
refinery purchases its electricity from a local utility and has a long-term contract to purchase hydrogen and steam from third party suppliers.
Torrance Refinery
Acquisition. On July 1, 2016, we acquired from ExxonMobil Oil Corporation and its subsidiary, Mobil Pacific Pipe Line Company, the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets (collectively, the "Torrance Acquisition"). Subsequent to the closing of the Torrance Acquisition, Torrance Refining and Torrance Logistics are indirect wholly-owned subsidiaries of PBF Holding. The aggregate purchase price for the Torrance Acquisition was approximately $521.4 million in cash after post-closing purchase price adjustments, plus final working capital of $450.6 million.
Overview. The Torrance refinery is located on 750 acres in Torrance, California. It is a high-conversion crude, delayed-coking refinery. It is capable of processing both heavy and medium crude oil though its crude unit and downstream units. In addition to refining assets, the Torrance Acquisition included a number of high-quality logistics assets including a sophisticated network of crude and products pipelines, product distribution terminals and refinery crude and product storage facilities. The most significant of the logistics assets is a crude gathering and transportation system which delivers San Joaquin Valley crude oil directly from the field to the refinery. Additionally, included in the transaction are several pipelines which provide access to sources of crude oil including the Ports of Long Beach and Los Angeles, as well as clean product outlets with a direct pipeline supplying jet fuel to the Los Angeles airport.
The following table approximates the Torrance refinery’s major process unit capacities. Unit capacities are shown in barrels per stream day.
Refinery Units | Nameplate Capacity | |
Crude Distillation Unit | 156,000 | |
Vacuum Distillation Unit | 102,000 | |
Fluid Catalytic Cracking Unit | 88,000 | |
Hydrotreating Units | 151,000 | |
Hydrocracking Unit | 23,000 | |
Alkylation Unit | 27,000 | |
Delayed Coker | 53,000 | |
Feedstocks and Supply Arrangements. The Torrance refinery primarily processes a variety of medium and heavy crude oils. In connection with the closing of the Torrance Acquisition, we entered into a crude supply agreement with ExxonMobil for approximately 60,000 bpd of crude oil that can be processed at our Torrance refinery. This crude supply agreement has a five year term with an automatic renewal feature unless either party gives thirty-six months prior written notice. Additionally, we obtain crude and feedstocks from other sources through connections to third party pipelines as well as ship docks and truck racks.
Refined Product Yield and Distribution. The Torrance refinery predominantly produces gasoline, jet fuel and diesel fuels. Products produced at the Torrance refinery are transferred to customers through pipelines, the marine terminal and truck rack. The majority of clean products are delivered to customers via pipelines. We have an offtake agreement with ExxonMobil pursuant to which ExxonMobil purchases approximately 50% of our gasoline production. This offtake agreement has an initial term of three years from the date of the Torrance Acquisition at which time it will automatically renew for another three year term unless either party gives six months' written notice of its intent to terminate the agreement.
Tankage Capacity. Torrance has a total tankage capacity of approximately 8.6 million barrels. Of this total, approximately 2.1 million barrels are allocated to crude oil storage with the remaining 6.5 million barrels allocated to intermediates and products.
12
Energy and Other Utilities. Under normal operating conditions, the Torrance refinery consumes approximately 42,000 MMBTU per day of natural gas supplied via pipeline from third parties. The Torrance refinery generates some power internally using a combination of steam and gas turbines and purchases any additional needed power from the local utility. The Torrance refinery has a long-term contract to purchase hydrogen and steam from a third party supplier.
Principal Products
Our refineries make various grades of gasoline, distillates (including diesel fuel, jet fuel, and ULSD) and other products from crude oil, other feedstocks, and blending components. We sell these products through our commercial accounts, and sales with major oil companies. For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, gasoline and distillates accounted for 88.1%, 88.0% and 86.0% of our revenues, respectively.
Customers
We sell a variety of refined products to a diverse customer base. The majority of our refined products are primarily sold through short-term contracts or on the spot market. However, we do have product offtake arrangements for a portion of our clean products. For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, no single customer accounted for 10% or more of our revenues, respectively. As of December 31, 2016, no single customer accounted for 10% or more of our total trade accounts receivable. ExxonMobil and its affiliates represented approximately 18% of our total trade accounts receivable as of December 31, 2015.
Seasonality
Demand for gasoline and diesel is generally higher during the summer months than during the winter months due to seasonal increases in highway traffic and construction work. Decreased demand during the winter months can lower gasoline and diesel prices. As a result, our operating results for the first and fourth calendar quarters may be lower than those for the second and third calendar quarters of each year. Refining margins remain volatile and our results of operations may not reflect these historical seasonal trends.
Competition
The refining business is very competitive. We compete directly with various other refining companies on the East, Gulf and West Coasts and in the Mid-Continent, with integrated oil companies, with foreign refiners that import products into the United States and with producers and marketers in other industries supplying alternative forms of energy and fuels to satisfy the requirements of industrial, commercial and individual consumers. Some of our competitors have expanded the capacity of their refineries and internationally new refineries are coming on line which could also affect our competitive position.
Profitability in the refining industry depends largely on refined product margins, which can fluctuate significantly, as well as crude oil prices and differentials between the prices of different grades of crude oil, operating efficiency and reliability, product mix and costs of product distribution and transportation. Certain of our competitors that have larger and more complex refineries may be able to realize lower per-barrel costs or higher margins per barrel of throughput. Several of our principal competitors are integrated national or international oil companies that are larger and have substantially greater resources. Because of their integrated operations and larger capitalization, these companies may be more flexible in responding to volatile industry or market conditions, such as shortages of feedstocks or intense price fluctuations. Refining margins are frequently impacted by sharp changes in crude oil costs, which may not be immediately reflected in product prices.
The refining industry is highly competitive with respect to feedstock supply. Unlike certain of our competitors that have access to proprietary controlled sources of crude oil production available for use at their own refineries, we obtain all of our crude oil and substantially all other feedstocks from unaffiliated sources. The availability and cost of crude oil is affected by global supply and demand. We have no crude oil reserves and are not engaged in the exploration or production of crude oil. We believe, however, that we will be able to obtain adequate crude oil and other feedstocks at generally competitive prices for the foreseeable future.
13
Agreements with PBFX
Beginning with the completion of the PBFX Offering, we have entered into a series of agreements with PBFX, including commercial and operational agreements. Each of these agreements and their impact to our operations is outlined below.
Contribution Agreements
Immediately prior to the closing of the contribution agreements, which PBF LLC entered into with PBFX (as defined in the table below, and collectively referred to as the “Contribution Agreements”), we contributed certain assets to PBF LLC. PBF LLC in turn contributed those assets to PBFX pursuant to the Contribution Agreements. Certain proceeds received by PBF LLC from PBFX in accordance with the Contribution Agreements were subsequently contributed by PBF LLC to us. The Contribution Agreements include the following:
Contribution Agreement | Contribution Date | Assets Contributed |
Contribution Agreement I | 5/8/2014 | DCR Rail Terminal and the Toledo Truck Terminal |
Contribution Agreement II | 9/30/2014 | DCR West Rack |
Contribution Agreement III | 12/11/2014 | Toledo Storage Facility |
Contribution Agreement IV | 5/5/2015 | Delaware City Products Pipeline and Truck Rack |
Contribution Agreement V | 8/31/2016 | Torrance Valley Pipeline |
Pursuant to Contribution Agreement V on August 31, 2016, PBF Holding contributed 50% of the issued and outstanding limited liability company interests of TVPC to PBF LLC. PBFX then acquired 50% of the issued and outstanding limited liability company interests of Torrance Valley Pipeline Company LLC (“TVPC”). TVPC's assets consist of the Torrance Valley Pipeline which include the M55, M1 and M70 pipeline systems, including 11 pipeline stations with storage capacity and truck unloading capability at two of the stations.
PBFX Operating Company LP ("PBFX Op Co"), PBFX’s wholly-owned subsidiary, serves as TVPC's managing member. PBFX, through its ownership of PBFX Op Co, has the sole ability to direct the activities of TVPC that most significantly impact its economic performance. Accordingly, PBFX, and not PBF Holding, is considered to be the primary beneficiary for accounting purposes and as a result PBFX fully consolidates TVPC. Subsequent to the Contribution Agreement V, we record an investment in equity method investee on its balance sheet for the 50% of TVPC that we own. The carrying value of our equity method investment in TVPC was $179.9 million and $0 million at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Our equity investment in TVPC is included in the Non-Guarantor financial position and results of PBF Holding disclosed in "Note 22 - Condensed Consolidating Financial Statements of PBF Holding" to the consolidated financial statements as this subsidiary is not a guarantor of the Senior Secured Notes.
Commercial Agreements
PBFX currently derives a substantial majority of its revenue from long-term, fee-based agreements with us relating to assets associated with the Contribution Agreements described above, PBF Holding entered into long-term, fee-based commercial agreements with PBFX, supported by contractual fee escalations for inflation adjustments and certain increases in operating costs. We believe the terms and conditions under these agreements, as well as the Omnibus Agreement (as defined below) and the Services Agreement (as defined below) each with PBFX, are generally no less favorable to either party than those that could have been negotiated with unaffiliated parties with respect to similar services.
These commercial agreements (as defined in the table below) with PBFX relating to the Contributed Assets include:
14
Service Agreements | Initiation Date | Initial Term | Renewals (a) | Minimum Volume Commitments ("MVC") | Force Majeure |
Transportation and Terminaling | |||||
Delaware City Rail Terminaling Services Agreement | 5/8/2014 | 7 years, 8 months | 2 x 5 | 85,000 bpd | PBFX or PBF Holding can declare |
Toledo Truck Unloading & Terminaling Services Agreement | 5/8/2014 | 7 years, 8 months | 2 x 5 | 5,500 bpd | |
Delaware West Ladder Rack Terminaling Services Agreement | 10/1/2014 | 7 years, 3 months | 2 x 5 | 40,000 bpd | |
Toledo Storage Facility Storage and Terminaling Services Agreement- Terminaling Facility (b) | 12/12/2014 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 4,400 bpd | |
Delaware Pipeline Services Agreement | 5/15/2015 | 10 years, 8 months | 2 x 5 | 50,000 bpd | |
Delaware Pipeline Services Agreement- Magellan Connection | 11/1/2016 | 2 years, 5 months | - | 14,500 bpd | |
Delaware City Truck Loading Services Agreement- Gasoline (c) | 5/15/2015 | 10 years, 8 months | 2 x 5 | 30,000 bpd | |
Delaware City Truck Loading Services Agreement- Liquefied Petroleum Gases (“LPGs”) (c) | 5/15/2015 | 10 years, 8 months | 2 x 5 | 5,000 bpd | |
Torrance Valley Pipeline Transportation Services Agreement- North Pipeline | 8/31/2016 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 50,000 bpd | |
Torrance Valley Pipeline Transportation Services Agreement- South Pipeline | 8/31/2016 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 70,000 bpd | |
Torrance Valley Pipeline Transportation Services Agreement- Midway Storage Tank | 8/31/2016 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 55,000 barrels (d) | |
Torrance Valley Pipeline Transportation Services Agreement- Emido Storage Tank | 8/31/2016 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 900,000 barrels per month | |
Torrance Valley Pipeline Transportation Services Agreement- Belridge Storage Tank | 8/31/2016 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 770,000 barrels per month | |
Storage | |||||
Toledo Storage Facility Storage and Terminaling Services Agreement- Storage Facility (b) | 12/12/2014 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 3,849,271 barrels (d) | PBFX or PBF Holding can declare |
____________________
(a) | PBF Holding has the option to extend the agreements for up to two additional five-year terms. |
(b) | The Toledo Storage Facility Storage and Terminaling Services Agreement- Terminaling Facility and the Toledo Storage Facility Storage and Terminaling Services Agreement- Storage Facility are referred to herein collectively as the “Toledo Storage Facility Storage and Terminaling Services Agreement." |
(c) | The Delaware City Truck Loading Services Agreement- Gasoline and the Delaware City Truck Loading Services Agreement- LPGs are referred to herein collectively as the “Delaware City Truck Loading Services Agreement." |
(d) | Reflects the overall capacity of the storage facility. The storage MVC is subject to effective operating capacity of each tank which can be impacted by routine tank maintenance and other factors. |
15
In addition, we have commercial agreements in place with PBFX with respect to the East Coast Terminals having terms ranging from approximately three months to five years and include:
• | tank lease agreements, under which PBFX provides tank lease services to us at the East Coast Terminals, with MVCs of total aggregate shell capacity; and |
• | terminaling service agreements, under which PBFX provides terminaling and other services to us at the East Coast Terminals. The terminaling service agreements have no MVCs and are billed based on actual volumes throughput, other than a terminaling services agreement between us and PBFX's East Coast Terminals' located at Paulsboro, New Jersey which has a 15,000 bpd MVC. |
Omnibus Agreement
PBFX entered into an omnibus agreement with PBF GP, PBF LLC and us at the closing of the PBFX Offering for the provision of executive management services and support for accounting and finance, legal, human resources, information technology, environmental, health and safety, and other administrative functions, as well as (i) PBF LLC’s agreement not to compete with PBFX under certain circumstances, subject to certain exceptions, (ii) PBFX's right of first offer for ten years to acquire certain logistics assets retained by PBF Energy following the PBFX Offering, including certain logistics assets that PBF LLC or its subsidiaries may construct or acquire in the future, subject to certain exceptions, and (iii) a license to use the PBF Logistics trademark and name.
On August 31, 2016, we entered into the Fourth Amended and Restated Omnibus Agreement (as amended, the "Omnibus Agreement") with PBFX in connection with the TVPC Acquisition resulting in an increase to the annual administrative fee to approximately $4.0 million.
Services Agreement
In connection with the PBFX Offering, PBF Holding and certain of its subsidiaries entered into an operation and management services and secondment agreement with PBFX, pursuant to which we and our subsidiaries provide PBFX with the personnel necessary for PBFX to perform its obligations under its commercial agreements. PBFX reimburses us for the use of such employees and the provision of certain infrastructure-related services to the extent applicable to its operations, including storm water discharge and waste water treatment, steam, potable water, access to certain roads and grounds, sanitary sewer access, electrical power, emergency response, filter press, fuel gas, API solids treatment, fire water and compressed air.
On August 31, 2016, we entered into the Fourth Amended and Restated Services Agreement (as amended, the "Services Agreement") with PBFX in connection with the TVPC Acquisition resulting in an increase to the annual fee to approximately $6.4 million.
The Services Agreement will terminate upon the termination of the Omnibus Agreement, provided that PBFX may terminate any service on 30 days’ notice.
Corporate Offices
We currently lease approximately 58,000 square feet for our principal corporate offices in Parsippany, New Jersey. The lease for our principal corporate offices expires in 2019. Functions performed in the Parsippany office include overall corporate management, refinery and HSE management, planning and strategy, corporate finance, commercial operations, logistics, contract administration, marketing, investor relations, governmental affairs, accounting, tax, treasury, information technology, legal and human resources support functions.
We lease approximately 4,000 square feet for our regional corporate office in Long Beach, California. The lease for our Long Beach office expires in 2021. Functions performed in the Long Beach office include overall regional corporate management, planning and strategy, commercial operations, logistics, contract administration, marketing and governmental affairs functions.
16
Employees
As of December 31, 2016, we had approximately 3,136 employees. At Paulsboro, 287 of our 461 employees are covered by a collective bargaining agreement. In addition, 1,267 of our 2,272 employees at Delaware City, Toledo, Chalmette and Torrance are covered by a collective bargaining agreement. None of our corporate employees are covered by a collective bargaining agreement. We consider our relations with the represented employees to be satisfactory. At Delaware City, Toledo, Chalmette and Torrance, most hourly employees are covered by a collective bargaining agreement through the United Steel Workers ("USW"). The agreements with the USW covering Delaware City, Chalmette and Torrance are scheduled to expire in January 2019; the agreement with the USW covering Toledo is scheduled to expire in February 2019. Similarly, at Paulsboro hourly employees are represented by the Independent Oil Workers ("IOW") under a contract scheduled to expire in March 2019.
Environmental, Health and Safety Matters
Our refineries, pipelines and related operations are subject to extensive and frequently changing federal, state and local laws and regulations, including, but not limited to, those relating to the discharge of materials into the environment or that otherwise relate to the protection of the environment, waste management and the characteristics and the compositions of fuels. Compliance with existing and anticipated laws and regulations can increase the overall cost of operating the refineries, including remediation, operating costs and capital costs to construct, maintain and upgrade equipment and facilities. Permits are also required under these laws for the operation of our refineries, pipelines and related operations and these permits are subject to revocation, modification and renewal. Compliance with applicable environmental laws, regulations and permits will continue to have an impact on our operations, results of operations and capital requirements. We believe that our current operations are in substantial compliance with existing environmental laws, regulations and permits.
Our operations and many of the products we manufacture are subject to certain specific requirements of the Clean Air Act (the "CAA") and related state and local regulations. The CAA contains provisions that require capital expenditures for the installation of certain air pollution control devices at our refineries. Subsequent rule making authorized by the CAA or similar laws or new agency interpretations of existing rules, may necessitate additional expenditures in future years.
In 2010, New York State adopted a Low-Sulfur Heating Oil mandate that, beginning July 1, 2012, requires all heating oil sold in New York State to contain no more than 15 parts per million ("PPM") sulfur. Since July 1, 2012, other states in the Northeast market began requiring heating oil sold in their state to contain no more than 15 PPM sulfur. Currently, all of the Northeastern states and Washington DC have adopted sulfur controls on heating oil. Most of the Northeastern states will require heating oil with 15 PPM or less sulfur by July 1, 2018 (except for Pennsylvania and Maryland - where 500 PPM sulfur is required). All of the heating oil we currently produce meets these specifications. The mandate and other requirements do not currently have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
The EPA issued the final Tier 3 Gasoline standards on March 3, 2014 under the Clean Air Act. This final rule establishes more stringent vehicle emission standards and further reduces the sulfur content of gasoline starting in January of 2017. The new standard is set at 10 PPM sulfur in gasoline on an annual average basis starting January 1, 2017, with a credit trading program to provide compliance flexibility. The EPA responded to industry comments on the proposed rule and maintained the per gallon sulfur cap on gasoline at the existing 80 PPM cap. The standards set by the new rule are not expected to have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
The EPA published the final 2014-2016 standards under the Renewable Fuels Standard ("RFS") late in 2015. The EPA proposed the 2017 standards in May of 2016 and issued final 2017 RFS standards in November 2016, in line with the deadline for issuing such standards. The final standards for 2017 are in fact slightly more aggressive than were originally proposed in May of 2016. It is not clear that renewable fuel producers will be able to produce the volumes of these fuels required for blending in 2017. The final 2017 cellulosic standard is at approximately 135% of the 2016 standard and the renewable fuel industry was only on pace to make approximately 75% of the
17
lower 2016 standard. It is quite likely that cellulosic RIN production will be lower than needed forcing obligated parties to purchase cellulosic “waiver credits” to comply in 2017 (the waiver credit option by regulation is only available for the cellulosic standard). The advanced and total renewable RIN requirements were raised slightly (by 7% and 3% respectively) above the original proposed level in May 2016. Analysts had been expecting that the EPA might, in fact, lower these standards. Production of advanced RINs has been well below what is needed for compliance in 2016. Obligated parties will likely be relying on the nesting feature of the biodiesel RIN to comply with the advanced standard in 2017. While the total renewable RIN production was adequate for 2016 needs, the new 2017 standard will put obligated parties up against the E10 blendwall leaving little flexibility. Compliance in 2017 will likely rely on obligated parties drawing down the supply of excess RINs collectively known as the “RIN bank” and could tighten the RIN market potentially raising RIN prices further. Industry organizations pointed out these issues with the May 2016 proposal to the EPA in commenting on the proposed standards. The EPA decided to ignore these arguments and raised the requirements in support of renewable fuel producers. We are currently evaluating the final standards, including any possible changes to the program following a new presidential administration, and they may have a material impact on our cost of compliance with RFS 2.
On December 1, 2015 the EPA finalized revisions to an existing air regulation concerning Maximum Achievable Control Technologies ("MACT") for Petroleum Refineries. The regulation requires additional continuous monitoring systems for eligible process safety valves relieving to atmosphere, minimum flare gas heat (Btu) content, and delayed coke drum vent controls to be installed by January 30, 2019. In addition, a program for ambient fence line monitoring for benzene will need to be implemented by January 30, 2018. We are currently evaluating the final standards to evaluate the impact of this regulation, and at this time we do not anticipate it will have a material impact on the our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
As a result of the Torrance Acquisition, we are subject to greenhouse gas emission control regulations in the state of California pursuant to Assembly Bill 32 ("AB 32"). AB 32 imposes a statewide cap on greenhouse gas emissions, including emissions from transportation fuels, with the aim of returning the state to 1990 emission levels by 2020. AB 32 is implemented through two market mechanisms including the Low Carbon Fuel Standard ("LCFS") and Cap and Trade. We are responsible for the AB 32 obligations related to the Torrance refinery beginning on July 1, 2016 and must purchase emission credits to comply with these obligations. Additionally, in September 2016, the state of California enacted Senate Bill 32 ("SB 32") which further reduces greenhouse gas emissions targets to 40 percent below 1990 levels by 2030. We expect to recover the majority of these costs from our customers, and as such do not expect this obligation to materially impact our financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. To the degree there are unfavorable changes to AB 32 or SB 32 regulations or we are unable to recover such compliance costs from customers, these regulations could have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations, and liquidity.
We are subject to obligations to purchase Renewable Identification Numbers ("RINs") required to comply with the RFS. In late 2015, the EPA initiated enforcement proceedings against companies it believes produced invalid RINs. On October 13, 2016, we and our subsidiaries Toledo Refining Company LLC and Delaware City Refining Company LLC were notified by the EPA that its records indicated that these entities used potentially invalid RINs. The EPA directed each of the subsidiaries to resubmit reports to remove the potentially invalid RINs and to replace the invalid RINs with valid RINs with the same D Code. The invalid RINs have been retired and we do not expect any settlement with the EPA to resolve this matter to be material.
As of January 1, 2011, we are required to comply with the EPA’s Control of Hazardous Air Pollutants From Mobile Sources, or MSAT2, regulations on gasoline that impose reductions in the benzene content of our produced gasoline. We purchase benzene credits to meet these requirements. Our planned capital projects will reduce the amount of benzene credits that we need to purchase. In addition, the renewable fuel standards mandate the blending of prescribed percentages of renewable fuels (e.g., ethanol and biofuels) into our produced gasoline and diesel. These new requirements, other requirements of the CAA and other presently existing or future environmental regulations may cause us to make substantial capital expenditures as well as the purchase of credits at significant cost, to enable our refineries to produce products that meet applicable requirements.
18
Our operations are also subject to the federal Clean Water Act (the "CWA"), the federal Safe Drinking Water Act (the "SDWA") and comparable state and local requirements. The CWA, the SDWA and analogous laws prohibit any discharge into surface waters, ground waters, injection wells and publicly-owned treatment works except in strict conformance with permits, such as pre-treatment permits and discharge permits, issued by federal, state and local governmental agencies. Federal waste-water discharge permits and analogous state waste-water discharge permits are issued for fixed terms and must be renewed.
We generate wastes that may be subject to the federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (the "RCRA") and comparable state and local requirements. The EPA and various state agencies have limited the approved methods of disposal for certain hazardous and non-hazardous wastes.
The EPA published a Final Rule to the CWA Section 316(b) in August 2014 regarding cooling water intake structures, which includes requirements for petroleum refineries. The purpose of this rule is to prevent fish from being trapped against cooling water intake screens (impingement) and to prevent fish from being drawn through cooling water systems (entrainment). Facilities will be required to implement Best Technology Available ("BTA") as soon as possible, but gives state agencies the discretion to establish implementation time lines. We continue to evaluate the impact of this regulation, and at this time do not anticipate it having a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
The federal Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act of 1980 ("CERCLA"), also known as "Superfund," imposes liability, without regard to fault or the legality of the original conduct, on certain classes of persons who are considered to be responsible for the release of a “hazardous substance” into the environment. These persons include the current or former owner or operator of the disposal site or sites where the release occurred and companies that disposed of or arranged for the disposal of the hazardous substances. Under CERCLA, such persons may be subject to joint and several liability for investigation and the costs of cleaning up the hazardous substances that have been released into the environment, for damages to natural resources and for the costs of certain health studies. As discussed more fully below, certain of our sites are subject to these laws and we may be held liable for investigation and remediation costs or claims for natural resource damages. It is not uncommon for neighboring landowners and other third parties to file claims for personal injury and property damage allegedly caused by hazardous substances or other pollutants released into the environment. Analogous state laws impose similar responsibilities and liabilities on responsible parties. In our current normal operations, we have generated waste, some of which falls within the statutory definition of a “hazardous substance” and some of which may have been disposed of at sites that may require cleanup under Superfund.
As is the case with all companies engaged in industries similar to ours, we face potential exposure to future claims and lawsuits involving environmental matters. These matters include soil and water contamination, air pollution, personal injury and property damage allegedly caused by substances which we manufactured, handled, used, released or disposed of.
Current and future environmental regulations are expected to require additional expenditures, including expenditures for investigation and remediation, which may be significant, at our refineries and at our other facilities. To the extent that future expenditures for these purposes are material and can be reasonably determined, these costs are disclosed and accrued.
Our operations are also subject to various laws and regulations relating to occupational health and safety. We maintain safety training and maintenance programs as part of our ongoing efforts to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations. Compliance with applicable health and safety laws and regulations has required and continues to require substantial expenditures.
In connection with each of our acquisitions, we assumed certain environmental remediation obligations. The more significant of these are discussed below.
In connection with the Paulsboro refinery acquisition, we assumed certain environmental remediation obligations. The environmental liability of $10.8 million recorded as of December 31, 2016 ($10.4 million as of
19
December 31, 2015) represents the present value of expected future costs discounted at a rate of 8.0%. As of December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, this liability is self-guaranteed by us.
In connection with the acquisition of the Delaware City assets, Valero Energy Corporation ("Valero") remains responsible for certain pre-acquisition environmental obligations up to $20.0 million and the predecessor to Valero in ownership of the refinery retains other historical obligations.
In connection with the acquisition of the Delaware City assets and the Paulsboro refinery, we and Valero purchased ten year, $75.0 million environmental insurance policies to insure against unknown environmental liabilities at each site. In connection with the Toledo refinery acquisition, Sunoco, Inc. (R&M) ("Sunoco") remains responsible for environmental remediation for conditions that existed on the closing date for twenty years from March 1, 2011, subject to certain limitations.
In connection with the acquisition of the Chalmette refinery, we obtained $3.9 million in financial assurance (in the form of a surety bond) to cover estimated potential site remediation costs associated with an agreed to Administrative Order of Consent with the EPA. The estimated cost assumes remedial activities will continue for a minimum of 30 years. Further, in connection with the acquisition of the Chalmette refinery, we purchased a ten year, $100.0 million environmental insurance policy to insure against unknown environmental liabilities at the refinery.
As of November 1, 2015, we acquired Chalmette Refining, which was in discussions with the Louisiana Department of Environmental Quality ("LDEQ") to resolve self-reported deviations from refinery operations relating to certain Clean Air Act Title V permit conditions, limits and other requirements. LDEQ commenced an enforcement action against Chalmette Refining on November 14, 2014 by issuing a Consolidated Compliance Order and Notice of Potential Penalty (the "Order") covering deviations from 2009 and 2010. Chalmette Refining and LDEQ subsequently entered into a dispute resolution agreement, the enforcement of which has been suspended while negotiations are ongoing, which may include the resolution of deviations outside the periods covered by the Order. It is possible that LDEQ will assess an administrative penalty against Chalmette Refining, but any such amount is not expected to be material to us.
On January 24, 2017, in connection with a Clean Air Act inspection in May 2014 by the EPA to determine compliance with 40 CFR Subpart 68 Chemical Accident Prevention Provisions, the EPA notified the Chalmette refinery of its intent to bring an enforcement action on two (2) findings from the audit. No settlement or penalty demand has been received to date. It is possible that the EPA will assess penalties in these matters in excess of $0.1 million but any such amount is not expected to be material to us, individually or in the aggregate.
On December 23, 2016, the Delaware City refinery received a Notice of Violation (“NOV”) from DNREC concerning a potential violation of the DNREC order authorizing the shipment of crude oil by barge from the Refinery. The NOV alleges that DCR made shipments to locations other than the Paulsboro refinery in violation of the order and requests certain additional information but no penalties have been assessed at this time. On December 28, 2016, DNREC issued a Coastal Zone Act permit (the “Ethanol Permit”) to DCR allowing the utilization of existing tanks and existing marine loading equipment at their existing facilities to enable denatured ethanol to be loaded from storage tanks to marine vessels and shipped to offsite facilities. On January 13, 2017, the issuance of the Ethanol Permit was appealed by two environmental groups. On February 27, 2017, the Coastal Zone Industrial Board held a public hearing and dismissed the appeal, determining that the appellants did not have standing. The release of the Board decision is pending.
On February 3, 2011, the EPA sent a request for information pursuant to Section 114 of the Clean Air Act to the Paulsboro refinery with respect to compliance with EPA standards governing flaring. The refinery and the EPA have recently reached a settlement pursuant to which the Paulsboro refinery will pay a penalty of approximately $0.2 million.
On February 14, 2017, the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (“NJDEP”) submitted a proposed Administrative Consent Order (“ACO”) which covers air emission violations from 2013 through 2016
20
and work practice standards that were not subject to an affirmative defense at the Paulsboro refinery (“PRC”). In settlement of the violations, the NJDEP has proposed that PRC pay a civil administrative penalty of $0.3 million, which includes $0.1 million for a supplemental environmental project. If the offer is accepted, the remaining $0.2 million shall be remitted by PRC within 30 days of receipt of the offer. This amount is not material to the Company, individually or in the aggregate.
In connection with the acquisition of the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets, we assumed certain pre-existing environmental liabilities totaling $142.5 million as of December 31, 2016, related to certain environmental remediation obligations to address existing soil and groundwater contamination and monitoring activities, which reflects the estimated cost of the remediation obligations. In addition, in connection with the acquisition of the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets, we purchased a ten year, $100.0 million environmental insurance policy to insure against unknown environmental liabilities. Furthermore, in connection with the acquisition, we assumed responsibility for certain specified environmental matters that occurred prior to our ownership of the refinery. Specifically, we assumed responsibility for (i) a Notice of Violation ("NOV") issued on March 12, 2015 by the Southern California Air Quality Management District ("SCAQMD") relating to self-reported Title V deviations for the Torrance Refinery for compliance year 2012, (ii) a NOV issued on March 10, 2016 for self-reported Title V deviations for the Torrance Refinery for compliance year 2013, (iii) a NOV issued on March 10, 2016 for self-reported Title V deviations for the Torrance Refinery for compliance year 2014 and (iv) a NOV issued on March 10, 2016 for self-reported Title V deviations for the Torrance Refinery for compliance year 2015. Following the closing of the acquisition, the Torrance refinery has received a number of NOVs. On September 6, 2016, a NOV was issued to the Torrance refinery by the SCAQMD for the July 11, 2016 FCCU shutdown and startup. The NOV alleges that the facility operated equipment while it bypassed associated air pollution control equipment in violation of our facility permit to operate. Opacity from FCCU 2F-7 exceeded 40 percent on July 11, 2016 and July 14, 2016, aggregate over 3 minutes in one continuous hour. In addition, on October 13, 2016, a NOV was issued by the SCAQMD for an alleged nuisance created from flaring associated with the October 11, 2016 Southern California Edison power disruption. On January 4, 2017, a NOV was also issued for an alleged discharge of air contaminants from Tank 1340x113 that caused a nuisance to a considerable number of persons or to the public. On January 13, 2017, a NOV was issued by the City of Torrance for allegedly failing to report a release or threatened release of hazardous material. On January 7, 2017, the Torrance refinery allegedly experienced a third release (January 3, January 4 and January 7) in a week of untreated Naphtha gas due to the generation of higher capacity from the Coker Unit. On February 28, 2017, in review of the fire occurring at the refinery on February 18, 2017, the City of Torrance Fire Department issued a NOV to the Torrance refinery requiring the refinery to comply with California Fire Code Section 104.7.2 and provide a technical opinion and report with respect to the refinery’s process safety risk assessment plan. With the exception of the October 13th NOV, no settlement or penalty demand has been received to date with respect to these notices. The proposed penalty for the October 13th NOV is less than $0.1 million. It is possible that SCAQMD and/or the City of Torrance will assess penalties in the other matters in excess of $0.1 million but any such amount is not expected to be material to us, individually or in the aggregate.
We cannot predict what additional health, safety and environmental legislation or regulations will be enacted or become effective in the future or how existing or future laws or regulations will be administered or interpreted with respect to our operations. Compliance with more stringent laws or regulations or adverse changes in the interpretation of existing requirements or discovery of new information such as unknown contamination could have an adverse effect on the financial position and the results of our operations and could require substantial expenditures for the installation and operation of systems and equipment that we do not currently possess.
21
GLOSSARY OF SELECTED TERMS
Unless otherwise noted or indicated by context, the following terms used in this Annual Report on Form 10-K have the following meanings:
“AB 32” refers to the greenhouse gas emission control regulations in the state of California to comply with Assembly Bill 32.
“ASCI” refers to the Argus Sour Crude Index, a pricing index used to approximate market prices for sour, heavy crude oil.
“Bakken” refers to both a crude oil production region generally covering North Dakota, Montana and Western Canada, and the crude oil that is produced in that region.
“barrel” refers to a common unit of measure in the oil industry, which equates to 42 gallons at 1 atmosphere pressure.
“blendstocks” refers to various compounds that are combined with gasoline or diesel from the crude oil refining process to make finished gasoline and diesel; these may include natural gasoline, FCC unit gasoline, ethanol, reformate or butane, among others.
“bpd” refers to an abbreviation for barrels per day.
“CAA” refers to the Clean Air Act.
“CAM Pipeline” or "CAM Connection Pipeline" refers to the Clovelly-Alliance-Meraux pipeline in Louisiana.
“CAPP” refers to the Canadian Association of Petroleum Producers.
"CARB" refers to the California Air Resources Board; gasoline and diesel fuel sold in the state of California are regulated by CARB and require stricter quality and emissions reduction performance than required by other states.
“catalyst” refers to a substance that alters, accelerates, or instigates chemical changes, but is not produced as a product of the refining process.
“coke” refers to a coal-like substance that is produced from heavier crude oil fractions during the refining process.
“complexity” refers to the number, type and capacity of processing units at a refinery, measured by the Nelson Complexity Index, which is often used as a measure of a refinery’s ability to process lower quality crude in an economic manner.
“crack spread” refers to a simplified calculation that measures the difference between the price for light products and crude oil. For example, we reference (a) the 2-1-1 crack spread, which is a general industry standard utilized by our Delaware City, Paulsboro and Chalmette refineries that approximates the per barrel refining margin resulting from processing two barrels of crude oil to produce one barrel of gasoline and one barrel of heating oil or ULSD, and (b) the 4-3-1 crack spread, which is a benchmark utilized by our Toledo and Torrance refineries that approximates the per barrel refining margin resulting from processing four barrels of crude oil to produce three barrels of gasoline and one-half barrel of jet fuel and one-half barrel of ULSD.
“Dated Brent” refers to Brent blend oil, a light, sweet North Sea crude oil, characterized by API gravity of 38° and a sulfur content of approximately 0.4 weight percent that is used as a benchmark for other crude oils.
“distillates” refers primarily to diesel, heating oil, kerosene and jet fuel.
22
“downstream” refers to the downstream sector of the energy industry generally describing oil refineries, marketing and distribution companies that refine crude oil and sell and distribute refined products. The opposite of the downstream sector is the upstream sector, which refers to exploration and production companies that search for and/or produce crude oil and natural gas underground or through drilling or exploratory wells.
“EPA” refers to the United States Environmental Protection Agency.
“ethanol” refers to a clear, colorless, flammable oxygenated liquid. Ethanol is typically produced chemically from ethylene, or biologically from fermentation of various sugars from carbohydrates found in agricultural crops and cellulosic residues from crops or wood. It is used in the United States as a gasoline octane enhancer and oxygenate.
“feedstocks” refers to crude oil and partially refined petroleum products that are processed and blended into refined products.
“FASB” refers to the Financial Accounting Standards Board which develops GAAP.
“FCC” refers to fluid catalytic cracking.
“FCU” refers to fluid coking unit.
“FERC” refers to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission.
“GAAP” refers to U.S. generally accepted accounting principles developed by the Financial Accounting Standards Board for nongovernmental entities.
“GHG” refers to greenhouse gas.
“Group I base oils or lubricants” refers to conventionally refined products characterized by sulfur content less than 0.03% with a viscosity index between 80 and 120. Typically, these products are used in a variety of automotive and industrial applications.
“heavy crude oil” refers to a relatively inexpensive crude oil with a low API gravity characterized by high relative density and viscosity. Heavy crude oils require greater levels of processing to produce high value products such as gasoline and diesel.
“IPO” refers to the initial public offering of PBF Energy’s Class A common stock which closed on December 18, 2012.
“J. Aron” refers to J. Aron & Company, a subsidiary of The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc.
“KV” refers to Kilovolts.
“LCM” refers to a GAAP requirement for inventory to be valued at the lower of cost or market.
“light crude oil” refers to a relatively expensive crude oil with a high API gravity characterized by low relative density and viscosity. Light crude oils require lower levels of processing to produce high value products such as gasoline and diesel.
“light products” refers to the group of refined products with lower boiling temperatures, including gasoline and distillates.
“light-heavy differential” refers to the price difference between light crude oil and heavy crude oil.
“LLS” refers to Light Louisiana Sweet benchmark for crude oil reflective of Gulf coast economics for light sweet domestic and foreign crudes.
23
“LPG” refers to liquefied petroleum gas.
“Maya” refers to Maya crude oil, a heavy, sour crude oil characterized by an API gravity of approximately 22° and a sulfur content of approximately 3.3 weight percent that is used as a benchmark for other heavy crude oils.
“MLP” refers to master limited partnership.
“MMbbls” refers to an abbreviation for million barrels.
“MMBTU” refers to million British thermal units.
“MMSCFD” refers to million standard cubic feet per day.
“MOEM Pipeline” refers to a pipeline that originates at a terminal in Empire, Louisiana approximately 30 miles north of the mouth of the Mississippi River. The MOEM Pipeline is 14 inches in diameter, 54 miles long and transports crude from South Louisiana to the Chalmette refinery and transports Heavy Louisiana Sweet (HLS) and South Louisiana Intermediate (SLI) crude.
“MSCG” refers to Morgan Stanley Capital Group Inc.
“MW” refers to Megawatt.
“Nelson Complexity Index” refers to the complexity of an oil refinery as measured by the Nelson Complexity Index, which is calculated on an annual basis by the Oil and Gas Journal. The Nelson Complexity Index assigns a complexity factor to each major piece of refinery equipment based on its complexity and cost in comparison to crude distillation, which is assigned a complexity factor of 1.0. The complexity of each piece of refinery equipment is then calculated by multiplying its complexity factor by its throughput ratio as a percentage of crude distillation capacity. Adding up the complexity values assigned to each piece of equipment, including crude distillation, determines a refinery’s complexity on the Nelson Complexity Index. A refinery with a complexity of 10.0 on the Nelson Complexity Index is considered ten times more complex than crude distillation for the same amount of throughput.
“NYH” refers to the New York Harbor market value of petroleum products.
“NYMEX” refers to the New York Mercantile Exchange.
“NYSE” refers to the New York Stock Exchange.
“PADD” refers to Petroleum Administration for Defense Districts.
“Platts” refers to Platts, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies.
“PPM” refers to parts per million.
“RINS” refers to renewable fuel credits required for compliance with the Renewable Fuels Standard.
“refined products” refers to petroleum products, such as gasoline, diesel and jet fuel, that are produced by a refinery.
“sour crude oil” refers to a crude oil that is relatively high in sulfur content, requiring additional processing to remove the sulfur. Sour crude oil is typically less expensive than sweet crude oil.
“Saudi Aramco” refers to Saudi Arabian Oil Company.
“SEC” refers to the United States Securities and Exchange Commission.
“Statoil” refers to Statoil Marketing and Trading (US) Inc.
24
“Sunoco” refers to Sunoco, Inc. (R&M).
“sweet crude oil” refers to a crude oil that is relatively low in sulfur content, requiring less processing to remove the sulfur than sour crude oil. Sweet crude oil is typically more expensive than sour crude oil.
“Syncrude” refers to a blend of Canadian synthetic oil, a light, sweet crude oil, typically characterized by API gravity between 30° and 32° and a sulfur content of approximately 0.1-0.2 weight percent.
“throughput” refers to the volume processed through a unit or refinery.
“turnaround” refers to a periodically required shutdown and comprehensive maintenance event to refurbish and maintain a refinery unit or units that involves the inspection of such units and occurs generally on a periodic cycle.
“ULSD” refers to ultra-low-sulfur diesel.
“Valero” refers to Valero Energy Corporation.
“WCS” refers to Western Canadian Select, a heavy, sour crude oil blend typically characterized by API gravity between 20° and 22° and a sulfur content of approximately 3.5 weight percent that is used as a benchmark for heavy Western Canadian crude oil.
“WTI” refers to West Texas Intermediate crude oil, a light, sweet crude oil, typically characterized by API gravity between 38° and 40° and a sulfur content of approximately 0.3 weight percent that is used as a benchmark for other crude oils.
“WTS” refers to West Texas Sour crude oil, a sour crude oil characterized by API gravity between 30° and 33° and a sulfur content of approximately 1.28 weight percent that is used as a benchmark for other sour crude oils.
“yield” refers to the percentage of refined products that is produced from crude oil and other feedstocks.
25
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
Risks Relating to Our Business and Industry
You should carefully read the risks and uncertainties described below. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only ones facing our company. Additional risks and uncertainties may also impair our business operations. If any of the following risks actually occur, our business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows would likely suffer.
The price volatility of crude oil, other feedstocks, blendstocks, refined products and fuel and utility services may have a material adverse effect on our revenues, profitability, cash flows and liquidity.
Our revenues, profitability, cash flows and liquidity from operations depend primarily on the margin above operating expenses (including the cost of refinery feedstocks, such as crude oil, intermediate partially refined petroleum products, and natural gas liquids that are processed and blended into refined products) at which we are able to sell refined products. Refining is primarily a margin-based business and, to increase profitability, it is important to maximize the yields of high value finished products while minimizing the costs of feedstock and operating expenses. When the margin between refined product prices and crude oil and other feedstock costs contracts, our earnings, profitability and cash flows are negatively affected. Refining margins historically have been volatile, and are likely to continue to be volatile, as a result of a variety of factors, including fluctuations in the prices of crude oil, other feedstocks, refined products and fuel and utility services. An increase or decrease in the price of crude oil will likely result in a similar increase or decrease in prices for refined products; however, there may be a time lag in the realization, or no such realization, of the similar increase or decrease in prices for refined products. The effect of changes in crude oil prices on our refining margins therefore depends in part on how quickly and how fully refined product prices adjust to reflect these changes.
In addition, the nature of our business requires us to maintain substantial crude oil, feedstock and refined product inventories. Because crude oil, feedstock and refined products are commodities, we have no control over the changing market value of these inventories. Our crude oil, feedstock and refined product inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market value under the last-in-first-out (“LIFO”) inventory valuation methodology. If the market value of our crude oil, feedstock and refined product inventory declines to an amount less than our LIFO cost, we would record a write-down of inventory and a non-cash impact to cost of sales. For example, during the year ended December 31, 2016, we recorded an adjustment to value our inventories to the lower of cost or market which increased operating income and net income by $521.3 million, respectively, reflecting the net change in the lower of cost or market inventory reserve from $1,117.3 million at December 31, 2015 to $596.0 million at December 31, 2016.
Prices of crude oil, other feedstocks, blendstocks, and refined products depend on numerous factors beyond our control, including the supply of and demand for crude oil, other feedstocks, gasoline, diesel, ethanol, asphalt and other refined products. Such supply and demand are affected by a variety of economic, market, environmental and political conditions.
Our direct operating expense structure also impacts our profitability. Our major direct operating expenses include employee and contract labor, maintenance and energy. Our predominant variable direct operating cost is energy, which is comprised primarily of fuel and other utility services. The volatility in costs of fuel, principally natural gas, and other utility services, principally electricity, used by our refineries and other operations affect our operating costs. Fuel and utility prices have been, and will continue to be, affected by factors outside our control, such as supply and demand for fuel and utility services in both local and regional markets. Natural gas prices have historically been volatile and, typically, electricity prices fluctuate with natural gas prices. Future increases in fuel and utility prices may have a negative effect on our refining margins, profitability and cash flows.
Our profitability is affected by crude oil differentials and related factors, which fluctuate substantially.
A significant portion of our profitability is derived from the ability to purchase and process crude oil feedstocks that historically have been cheaper than benchmark crude oils, such as the heavy, sour crude oils
26
processed at our Delaware City, Paulsboro, Chalmette and Torrance refineries. For our Toledo refinery, historically crude prices have been slightly above the WTI benchmark, however, that premium to WTI typically results in favorable refinery production yield. For all locations, these crude oil differentials can vary significantly from quarter to quarter depending on overall economic conditions and trends and conditions within the markets for crude oil and refined products. Any change in these crude oil differentials may have an impact on our earnings. Our rail investment and strategy to acquire cost advantaged Mid-Continent and Canadian crude, which are priced based on WTI, could be adversely affected when the Dated Brent/WTI or related differential narrows. A narrowing of the WTI/Dated Brent differential may result in our Toledo refinery losing a portion of its crude oil price advantage over certain of our competitors, which negatively impacts our profitability. In addition, the narrowing of the WTI/WCS differential, which is a proxy for the difference between light U.S. and heavy Canadian crude oil, may reduce our refining margins and adversely affect our profitability and earnings. Divergent views have been expressed as to the expected magnitude of changes to these crude differentials in future periods. Any further or continued narrowing of these differentials could have a material adverse effect on our business and profitability.
Additionally, governmental and regulatory actions, including recent initiatives by the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries to restrict crude oil production levels and executive actions by the new U.S. presidential administration to advance certain energy infrastructure projects such as the Keystone XL pipeline, may continue to impact crude oil prices and crude oil differentials. Any increase in crude oil prices or unfavorable movements in crude oil differentials due to such actions or changing regulatory environment may negatively impact our ability to acquire crude oil at economical prices and could have a material adverse effect on our business and profitability.
The repeal of the crude oil export ban in the United States may affect our profitability.
In December 2015, the United States Congress passed and the President signed the 2016 Omnibus Appropriations bill which included a repeal of the ban on the export of crude oil produced in the United States. The crude export ban was established by the Energy Policy and Conservation Act in 1975 to reduce reliance on foreign oil producing countries. While there are differing views on the magnitude of the impact of lifting the crude export ban on crude oil prices, most economists believe the export ban repeal will eventually lead to higher crude oil prices and narrowing Dated Brent/WTI differentials and in turn higher gasoline prices in the United States. Crude oil is our most significant input cost and there is no guaranty that increases in our crude oil costs will be offset by corresponding increases in the selling prices of our refined products. As a result, an increase in crude oil prices resulting from the repeal of the crude oil export ban may reduce our profitability.
Our recent historical earnings have been concentrated and may continue to be concentrated in the future.
Our five refineries have similar throughput capacity, however, favorable market conditions due to, among other things, geographic location, crude and refined product slates, and customer demand, may cause an individual refinery to contribute more significantly to our earnings than others for a period of time. For example, our Toledo, Ohio refinery in the past has produced a substantial portion of our earnings. As a result, if there were a significant disruption to operations at this refinery, our earnings could be materially adversely affected (to the extent not recoverable through insurance) disproportionately to Toledo’s portion of our consolidated throughput. The Toledo refinery, or one of our other refineries, may continue to disproportionately affect our results of operations in the future. Any prolonged disruption to the operations of such refinery, whether due to labor difficulties, destruction of or damage to such facilities, severe weather conditions, interruption of utilities service or other reasons, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations or financial condition.
A significant interruption or casualty loss at any of our refineries and related assets could reduce our production, particularly if not fully covered by our insurance. Failure by one or more insurers to honor its coverage commitments for an insured event could materially and adversely affect our future cash flows, operating results and financial condition.
Our business currently consists of owning and operating five refineries and related assets. As a result, our operations could be subject to significant interruption if any of our refineries were to experience a major accident,
27
be damaged by severe weather or other natural disaster, or otherwise be forced to shut down or curtail production due to unforeseen events, such as acts of God, nature, orders of governmental authorities, supply chain disruptions impacting our crude rail facilities or other logistical assets, power outages, acts of terrorism, fires, toxic emissions and maritime hazards. Any such shutdown or disruption would reduce the production from that refinery. There is also risk of mechanical failure and equipment shutdowns both in general and following unforeseen events. Further, in such situations, undamaged refinery processing units may be dependent on or interact with damaged sections of our refineries and, accordingly, are also subject to being shut down. In the event any of our refineries is forced to shut down for a significant period of time, it would have a material adverse effect on our earnings, our other results of operations and our financial condition as a whole.
As protection against these hazards, we maintain insurance coverage against some, but not all, such potential losses and liabilities. We may not be able to maintain or obtain insurance of the type and amount we desire at reasonable rates. As a result of market conditions, premiums and deductibles for certain of our insurance policies may increase substantially. In some instances, certain insurance could become unavailable or available only for reduced amounts of coverage. For example, coverage for hurricane damage can be limited, and coverage for terrorism risks can include broad exclusions. If we were to incur a significant liability for which we were not fully insured, it could have a material adverse effect on our financial position.
Our insurance program includes a number of insurance carriers. Significant disruptions in financial markets could lead to a deterioration in the financial condition of many financial institutions, including insurance companies and, therefore, we may not be able to obtain the full amount of our insurance coverage for insured events.
Our refineries are subject to interruptions of supply and distribution as a result of our reliance on pipelines and railroads for transportation of crude oil and refined products.
Our Toledo, Chalmette and Torrance refineries receive a significant portion of their crude oil through pipelines. These pipelines include the Enbridge system, Capline and Mid-Valley pipelines for supplying crude to our Toledo refinery, the MOEM and CAM pipelines for supplying crude to our Chalmette refinery and the San Joaquin Pipeline, San Ardo and Coastal Pipeline systems for supplying crude to our Torrance refinery. Additionally, our Toledo, Chalmette and Torrance refineries deliver a significant portion of the refined products through pipelines. These pipelines include pipelines such as the Sunoco Logistics Partners L.P. and Buckeye Partners L.P. pipelines at Toledo, the Collins Pipeline at our Chalmette refinery and Jet Pipeline to the Los Angeles International Airport, the Product Pipeline to Vernon and the Product Pipeline to Atwood at our Torrance refinery. We could experience an interruption of supply or delivery, or an increased cost of receiving crude oil and delivering refined products to market, if the ability of these pipelines to transport crude oil or refined products is disrupted because of accidents, weather interruptions, governmental regulation, terrorism, other third party action or casualty or other events.
The Delaware City rail unloading facilities allow our East Coast refineries to source WTI-based crudes from Western Canada and the Mid-Continent, which may provide significant cost advantages versus traditional Brent-based international crudes in certain market environments. Any disruptions or restrictions to our supply of crude by rail due to problems with third party logistics infrastructure or operations or as a result of increased regulations, could increase our crude costs and negatively impact our results of operations and cash flows.
In addition, due to the common carrier regulatory obligation applicable to interstate oil pipelines, capacity allocation among shippers can become contentious in the event demand is in excess of capacity. Therefore, nominations by new shippers or increased nominations by existing shippers may reduce the capacity available to us. Any prolonged interruption in the operation or curtailment of available capacity of the pipelines that we rely upon for transportation of crude oil and refined products could have a further material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
28
We may have capital needs for which our internally generated cash flows and other sources of liquidity may not be adequate.
If we cannot generate sufficient cash flows or otherwise secure sufficient liquidity to support our short-term and long-term capital requirements, we may not be able to meet our payment obligations or our future debt obligations, comply with certain deadlines related to environmental regulations and standards, or pursue our business strategies, including acquisitions, in which case our operations may not perform as we currently expect. We have substantial short-term capital needs and may have substantial long term capital needs. Our short-term working capital needs are primarily related to financing certain of our refined products inventory not covered by our various supply and Inventory Intermediation Agreements. Pursuant to the Inventory Intermediation Agreements, J. Aron purchases and holds title to certain of the intermediate and finished products produced by the Delaware City and Paulsboro refineries and delivered into the tanks at the refineries (or at other locations outside of the refineries as agreed upon by both parties). Furthermore, J. Aron agrees to sell the intermediate and finished products back to us as they are discharged out of the refineries' tanks (or other locations outside of the refineries as agreed upon by both parties). On May 29, 2015, we entered into amended and restated inventory intermediation agreements with J. Aron pursuant to which certain terms of the existing inventory intermediation agreements were amended, including, among other things, pricing and an extension of the term for a period of two years from the original expiry date of July 1, 2015, subject to certain early termination rights. In addition, the A&R Intermediation Agreements for both the Delaware City and Paulsboro refineries with J. Aron include one-year renewal clauses upon six months' advance notice by mutual consent of both parties. The A&R Intermediation Agreements have not been renewed and are scheduled to expire July 1, 2017. If we are unable to negotiate an extension with J. Aron or enter into an alternative intermediation agreement, we will have to repurchase the inventories outstanding under the A&R Intermediation Agreement at that time.
If we cannot adequately handle our crude oil and feedstock requirements or if we are required to obtain our crude oil supply at our other refineries without the benefit of the existing supply arrangements or the applicable counterparty defaults in its obligations, our crude oil pricing costs may increase as the number of days between when we pay for the crude oil and when the crude oil is delivered to us increases. Termination of our A&R Intermediation Agreements with J. Aron would require us to finance our refined products inventory covered by the agreements at terms that may not be as favorable. Additionally, we are obligated to repurchase from J. Aron all volumes of products located at the refineries’ storage tanks (or at other locations outside of the refineries as agreed upon by both parties) upon termination of these agreements, which may have a material adverse impact on our working capital and financial condition. Further, if we are not able to market and sell our finished products to credit worthy customers, we may be subject to delays in the collection of our accounts receivable and exposure to additional credit risk. Such increased exposure could negatively impact our liquidity due to our increased working capital needs as a result of the increase in the amount of crude oil inventory and accounts receivable we would have to carry on our balance sheet. Our long-term needs for cash include those to support ongoing capital expenditures for equipment maintenance and upgrades during turnarounds at our refineries and to complete our routine and normally scheduled maintenance, regulatory and security expenditures.
In addition, from time to time, we are required to spend significant amounts for repairs when one or more processing units experiences temporary shutdowns. We continue to utilize significant capital to upgrade equipment, improve facilities, and reduce operational, safety and environmental risks. In connection with the Paulsboro and Torrance acquisitions, we assumed certain significant environmental obligations, and may similarly do so in future acquisitions. We will likely incur substantial compliance costs in connection with new or changing environmental, health and safety regulations. See “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition.” Our liquidity condition will affect our ability to satisfy any and all of these needs or obligations.
We may not be able to obtain funding on acceptable terms or at all because of volatility and uncertainty in the credit and capital markets. This may hinder or prevent us from meeting our future capital needs.
In the recent past, global financial markets and economic conditions have been, and may continue to be, subject to disruption and volatile due to a variety of factors, including uncertainty in the financial services sector, low consumer confidence, falling commodity prices, geopolitical issues and the generally weak economic
29
conditions. In addition, the fixed income markets have experienced periods of extreme volatility that have negatively impacted market liquidity conditions. As a result, the cost of raising money in the debt and equity capital markets has increased substantially at times while the availability of funds from those markets diminished significantly. In particular, as a result of concerns about the stability of financial markets generally and the solvency of lending counterparties specifically, the cost of obtaining money from the credit markets may increase as many lenders and institutional investors increase interest rates, enact tighter lending standards, refuse to refinance existing debt on similar terms or at all and reduce or, in some cases, cease to provide funding to borrowers. Due to these factors, we cannot be certain that new debt or equity financing will be available on acceptable terms. If funding is not available when needed, or is available only on unfavorable terms, we may be unable to meet our obligations as they come due. Moreover, without adequate funding, we may be unable to execute our growth strategy, complete future acquisitions, take advantage of other business opportunities or respond to competitive pressures, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our revenues and results of operations.
Competition from companies who produce their own supply of feedstocks, have extensive retail outlets, make alternative fuels or have greater financial and other resources than we do could materially and adversely affect our business and results of operations.
Our refining operations compete with domestic refiners and marketers in regions of the United States in which we operate, as well as with domestic refiners in other regions and foreign refiners that import products into the United States. In addition, we compete with other refiners, producers and marketers in other industries that supply their own renewable fuels or alternative forms of energy and fuels to satisfy the requirements of our industrial, commercial and individual consumers. Certain of our competitors have larger and more complex refineries, and may be able to realize lower per-barrel costs or higher margins per barrel of throughput. Several of our principal competitors are integrated national or international oil companies that are larger and have substantially greater resources than we do and access to proprietary sources of controlled crude oil production. Unlike these competitors, we obtain substantially all of our feedstocks from unaffiliated sources. We are not engaged in the petroleum exploration and production business and therefore do not produce any of our crude oil feedstocks. We do not have a retail business and therefore are dependent upon others for outlets for our refined products. Because of their integrated operations and larger capitalization, these companies may be more flexible in responding to volatile industry or market conditions, such as shortages of crude oil supply and other feedstocks or intense price fluctuations.
Newer or upgraded refineries will often be more efficient than our refineries, which may put us at a competitive disadvantage. We have taken significant measures to maintain our refineries including the installation of new equipment and redesigning older equipment to improve our operations. However, these actions involve significant uncertainties, since upgraded equipment may not perform at expected throughput levels, the yield and product quality of new equipment may differ from design specifications and modifications may be needed to correct equipment that does not perform as expected. Any of these risks associated with new equipment, redesigned older equipment or repaired equipment could lead to lower revenues or higher costs or otherwise have an adverse effect on future results of operations and financial condition. Over time, our refineries or certain refinery units may become obsolete, or be unable to compete, because of the construction of new, more efficient facilities by our competitors.
Any political instability, military strikes, sustained military campaigns, terrorist activity, or changes in foreign policy could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Any political instability, military strikes, sustained military campaigns, terrorist activity, or changes in foreign policy in areas or regions of the world where we acquire crude oil and other raw materials or sell our refined petroleum products may affect our business in unpredictable ways, including forcing us to increase security measures and causing disruptions of supplies and distribution markets. We may also be subject to United States trade and economic sanctions laws, which change frequently as a result of foreign policy developments, and which may necessitate changes to our crude oil acquisition activities. Further, like other industrial companies, our facilities may be the target of terrorist activities. Any act of war or terrorism that resulted in damage to any of our refineries
30
or third-party facilities upon which we are dependent for our business operations could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Economic turmoil in the global financial system has had and may in the future have an adverse impact on the refining industry.
Our business and profitability are affected by the overall level of demand for our products, which in turn is affected by factors such as overall levels of economic activity and business and consumer confidence and spending. Declines in global economic activity and consumer and business confidence and spending during the recent global downturn significantly reduced the level of demand for our products. Reduced demand for our products has had and may continue to have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. In addition, downturns in the economy impact the demand for refined fuels and, in turn, result in excess refining capacity. Refining margins are impacted by changes in domestic and global refining capacity, as increases in refining capacity can adversely impact refining margins, earnings and cash flows.
Our business is indirectly exposed to risks faced by our suppliers, customers and other business partners. The impact on these constituencies of the risks posed by economic turmoil in the global financial system have included or could include interruptions or delays in the performance by counterparties to our contracts, reductions and delays in customer purchases, delays in or the inability of customers to obtain financing to purchase our products and the inability of customers to pay for our products. Any of these events may have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
We must make substantial capital expenditures on our operating facilities to maintain their reliability and efficiency. If we are unable to complete capital projects at their expected costs and/or in a timely manner, or if the market conditions assumed in our project economics deteriorate, our financial condition, results of operations or cash flows could be materially and adversely affected.
Delays or cost increases related to capital spending programs involving engineering, procurement and construction of new facilities (or improvements and repairs to our existing facilities and equipment, including turnarounds) could adversely affect our ability to achieve targeted internal rates of return and operating results. Such delays or cost increases may arise as a result of unpredictable factors in the marketplace, many of which are beyond our control, including:
• | denial or delay in obtaining regulatory approvals and/or permits; |
• | unplanned increases in the cost of construction materials or labor; |
• | disruptions in transportation of modular components and/or construction materials; |
• | severe adverse weather conditions, natural disasters or other events (such as equipment malfunctions, explosions, fires or spills) affecting our facilities, or those of vendors and suppliers; |
• | shortages of sufficiently skilled labor, or labor disagreements resulting in unplanned work stoppages; |
• | market-related increases in a project’s debt or equity financing costs; and/or |
• | non-performance or force majeure by, or disputes with, vendors, suppliers, contractors or sub-contractors involved with a project. |
Our refineries contain many processing units, a number of which have been in operation for many years. Equipment, even if properly maintained, may require significant capital expenditures and expenses to keep it operating at optimum efficiency. One or more of the units may require unscheduled downtime for unanticipated maintenance or repairs that are more frequent than our scheduled turnarounds for such units. Scheduled and unscheduled maintenance could reduce our revenues during the period of time that the units are not operating.
Our forecasted internal rates of return are also based upon our projections of future market fundamentals, which are not within our control, including changes in general economic conditions, available alternative supply and customer demand. Any one or more of these factors could have a significant impact on our business. If we were unable to make up the delays associated with such factors or to recover the related costs, or if market conditions change, it could materially and adversely affect our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
31
Acquisitions that we may undertake in the future involve a number of risks, any of which could cause us not to realize the anticipated benefits.
We may not be successful in acquiring additional assets, and any acquisitions that we do consummate may not produce the anticipated benefits or may have adverse effects on our business and operating results. We may selectively consider strategic acquisitions in the future within the refining and mid-stream sector based on performance through the cycle, advantageous access to crude oil supplies, attractive refined products market fundamentals and access to distribution and logistics infrastructure. Our ability to do so will be dependent upon a number of factors, including our ability to identify acceptable acquisition candidates, consummate acquisitions on acceptable terms, successfully integrate acquired assets and obtain financing to fund acquisitions and to support our growth and many other factors beyond our control. Risks associated with acquisitions include those relating to the diversion of management time and attention from our existing business, liability for known or unknown environmental conditions or other contingent liabilities and greater than anticipated expenditures required for compliance with environmental, safety or other regulatory standards or for investments to improve operating results, and the incurrence of additional indebtedness to finance acquisitions or capital expenditures relating to acquired assets. We may also enter into transition services agreements in the future with sellers of any additional refineries we acquire. Such services may not be performed timely and effectively, and any significant disruption in such transition services or unanticipated costs related to such services could adversely affect our business and results of operations. In addition, it is likely that, when we acquire refineries, we will not have access to the type of historical financial information that we will require regarding the prior operation of the refineries. As a result, it may be difficult for investors to evaluate the probable impact of significant acquisitions on our financial performance until we have operated the acquired refineries for a substantial period of time.
Our business may suffer if any of our senior executives or other key employees discontinues employment with us. Furthermore, a shortage of skilled labor or disruptions in our labor force may make it difficult for us to maintain labor productivity.
Our future success depends to a large extent on the services of our senior executives and other key employees. Our business depends on our continuing ability to recruit, train and retain highly qualified employees in all areas of our operations, including engineering, accounting, business operations, finance and other key back-office and mid-office personnel. Furthermore, our operations require skilled and experienced employees with proficiency in multiple tasks. The competition for these employees is intense, and the loss of these executives or employees could harm our business. If any of these executives or other key personnel resigns or becomes unable to continue in his or her present role and is not adequately replaced, our business operations could be materially adversely affected.
A portion of our workforce is unionized, and we may face labor disruptions that would interfere with our operations.
At Delaware City, Toledo, Chalmette and Torrance, most hourly employees are covered by a collective bargaining agreement through the United Steel Workers ("USW"). The agreements with the USW covering Delaware City, Chalmette and Torrance are scheduled to expire in January 2019 and the agreement with the USW covering Toledo is scheduled to expire in February 2019. Similarly, at Paulsboro hourly employees are represented by the Independent Oil Workers ("IOW") under a contract scheduled to expire in March 2019. Future negotiations after 2019 may result in labor unrest for which a strike or work stoppage is possible. Strikes and/or work stoppages could negatively affect our operational and financial results and may increase operating expenses at the refineries.
Our hedging activities may limit our potential gains, exacerbate potential losses and involve other risks.
We may enter into commodity derivatives contracts to hedge our crude price risk or crack spread risk with respect to a portion of our expected gasoline and distillate production on a rolling basis. Consistent with that policy we may hedge some percentage of future crude supply. We may enter into hedging arrangements with the intent to secure a minimum fixed cash flow stream on the volume of products hedged during the hedge term and to protect against volatility in commodity prices. Our hedging arrangements may fail to fully achieve these objectives for a variety of reasons, including our failure to have adequate hedging arrangements, if any, in effect at any particular
32
time and the failure of our hedging arrangements to produce the anticipated results. We may not be able to procure adequate hedging arrangements due to a variety of factors. Moreover, such transactions may limit our ability to benefit from favorable changes in crude oil and refined product prices. In addition, our hedging activities may expose us to the risk of financial loss in certain circumstances, including instances in which:
• | the volumes of our actual use of crude oil or production of the applicable refined products is less than the volumes subject to the hedging arrangement; |
• | accidents, interruptions in feedstock transportation, inclement weather or other events cause unscheduled shutdowns or otherwise adversely affect our refineries, or those of our suppliers or customers; |
• | changes in commodity prices have a material impact on collateral and margin requirements under our hedging arrangements, resulting in us being subject to margin calls; |
• | the counterparties to our derivative contracts fail to perform under the contracts; or |
• | a sudden, unexpected event materially impacts the commodity or crack spread subject to the hedging arrangement. |
As a result, the effectiveness of our hedging strategy could have a material impact on our financial results. See “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.”
In addition, these hedging activities involve basis risk. Basis risk in a hedging arrangement occurs when the price of the commodity we hedge is more or less variable than the index upon which the hedged commodity is based, thereby making the hedge less effective. For example, a NYMEX index used for hedging certain volumes of our crude oil or refined products may have more or less variability than the actual cost or price we realize for such crude oil or refined products. We may not hedge all the basis risk inherent in our hedging arrangements and derivative contracts.
Our commodity derivative activities could result in period-to-period earnings volatility.
We do not apply hedge accounting to all of our commodity derivative contracts and, as a result, unrealized gains and losses will be charged to our earnings based on the increase or decrease in the market value of such unsettled positions. These gains and losses may be reflected in our income statement in periods that differ from when the settlement of the underlying hedged items are reflected in our income statement. Such derivative gains or losses in earnings may produce significant period-to-period earnings volatility that is not necessarily reflective of our underlying operational performance.
The adoption of derivatives legislation by the United States Congress could have an adverse effect on our ability to use derivatives contracts to reduce the effect of commodity price, interest rate and other risks associated with our business.
The United States Congress in 2010 passed the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, or the Dodd-Frank Act, which, among other things, established federal oversight and regulation of the over-the-counter derivatives market and entities that participate in that market. In connection with the Dodd-Frank Act, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission, or the CFTC, has proposed rules to set position limits for certain futures and option contracts, and for swaps that are their economic equivalent, in the major energy markets. The legislation and related regulations may also require us to comply with margin requirements and with certain clearing and trade-execution requirements if we do not satisfy certain specific exceptions. The legislation may also require the counterparties to our derivatives contracts to transfer or assign some of their derivatives contracts to a separate entity, which may not be as creditworthy as the current counterparty. The legislation and related regulations could significantly increase the cost of derivatives contracts (including through requirements to post collateral), materially alter the terms of derivatives contracts, reduce the availability of derivatives to protect against risks we encounter, reduce our ability to monetize or restructure our existing derivatives contracts, and increase our exposure to less creditworthy counterparties. If we reduce our use of derivatives as a result of the legislation and regulations, our results of operations may become more volatile and our cash flows may be less predictable, which could adversely
33
affect our ability to plan for and fund capital expenditures. Any of these consequences could have a material adverse effect on us, our financial condition and our results of operations.
Our operations could be disrupted if our critical information systems are hacked or fail, causing increased expenses and loss of sales.
Our business is highly dependent on financial, accounting and other data processing systems and other communications and information systems, including our enterprise resource planning tools. We process a large number of transactions on a daily basis and rely upon the proper functioning of computer systems. If a key system was hacked or otherwise interfered with by an unauthorized access, or was to fail or experience unscheduled downtime for any reason, even if only for a short period, our operations and financial results could be affected adversely. Our systems could be damaged or interrupted by a security breach, cyber-attack, fire, flood, power loss, telecommunications failure or similar event. We have a formal disaster recovery plan in place, but this plan may not prevent delays or other complications that could arise from an information systems failure. Further, our business interruption insurance may not compensate us adequately for losses that may occur. Finally, federal legislation relating to cyber-security threats could impose additional requirements on our operations.
Product liability claims and litigation could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
Product liability is a significant commercial risk. Substantial damage awards have been made in certain jurisdictions against manufacturers and resellers based upon claims for injuries and property damage caused by the use of or exposure to various products. Failure of our products to meet required specifications or claims that a product is inherently defective could result in product liability claims from our shippers and customers, and also arise from contaminated or off-specification product in commingled pipelines and storage tanks and/or defective fuels. Product liability claims against us could have a material adverse effect on our business or results of operations.
We may incur significant liability under, or costs and capital expenditures to comply with, environmental and health and safety regulations, which are complex and change frequently.
Our operations are subject to federal, state and local laws regulating, among other things, the use and/or handling of petroleum and other regulated materials, the emission and discharge of materials into the environment, waste management, and remediation of discharges of petroleum and petroleum products, characteristics and composition of gasoline and distillates and other matters otherwise relating to the protection of the environment and the health and safety of the surrounding community. For example, the SCAQMD recently announced that it will consider banning the use of modified hydrofluoric acid, also known as MHF, in California. We utilize MHF in the manufacturing of gasoline at our Torrance refinery. If MHF usage is limited or restricted by the SCAQMD,our current operations would be adversely affected, which could have a material adverse affect on our business, financial condition, cash flows and results of operations. Our operations are also subject to extensive laws and regulations relating to occupational health and safety.
We cannot predict what additional environmental, health and safety legislation or regulations may be adopted in the future, or how existing or future laws or regulations may be administered or interpreted with respect to our operations. Many of these laws and regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, and the cost of compliance with these requirements can be expected to increase over time.
Certain environmental laws impose strict, and in certain circumstances, joint and several, liability for costs of investigation and cleanup of such spills, discharges or releases on owners and operators of, as well as persons who arrange for treatment or disposal of regulated materials at, contaminated sites. Under these laws, we may incur liability or be required to pay penalties for past contamination, and third parties may assert claims against us for damages allegedly arising out of any past or future contamination. The potential penalties and clean-up costs for past or future releases or spills, the failure of prior owners of our facilities to complete their clean-up obligations, the liability to third parties for damage to their property, or the need to address newly-discovered information or conditions that may require a response could be significant, and the payment of these amounts could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, cash flows and results of operations.
34
Environmental clean-up and remediation costs of our sites and environmental litigation could decrease our net cash flow, reduce our results of operations and impair our financial condition.
We are subject to liability for the investigation and clean-up of environmental contamination at each of the properties that we own or operate and at off-site locations where we arrange for the treatment or disposal of regulated materials. We may become involved in future litigation or other proceedings. If we were to be held responsible for damages in any litigation or proceedings, such costs may not be covered by insurance and may be material. Historical soil and groundwater contamination has been identified at each of our refineries. Currently remediation projects are underway in accordance with regulatory requirements at our refineries. In connection with the acquisitions of certain of our refineries, the prior owners have retained certain liabilities or indemnified us for certain liabilities, including those relating to pre-acquisition soil and groundwater conditions, and in some instances we have assumed certain liabilities and environmental obligations, including certain existing and potential remediation obligations. If the prior owners fail to satisfy their obligations for any reason, or if significant liabilities arise in the areas in which we assumed liability, we may become responsible for remediation expenses and other environmental liabilities, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition. As a result, in addition to making capital expenditures or incurring other costs to comply with environmental laws, we also may be liable for significant environmental litigation or for investigation and remediation costs and other liabilities arising from the ownership or operation of these assets by prior owners, which could materially adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flow. See “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Contractual Obligations and Commitments” and “Item 1. Business—Environmental, Health and Safety Matters.”
We may also face liability arising from current or future claims alleging personal injury or property damage due to exposure to chemicals or other regulated materials, such as asbestos, benzene, silica dust and petroleum hydrocarbons, at or from our facilities. We may also face liability for personal injury, property damage, natural resource damage or clean-up costs for the alleged migration of contamination from our properties. A significant increase in the number or success of these claims could materially adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flow.
Regulation of emissions of greenhouse gases could force us to incur increased capital and operating costs and could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
Both houses of Congress have actively considered legislation to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases (“GHGs”), such as carbon dioxide and methane, including proposals to: (i) establish a cap and trade system, (ii) create a federal renewable energy or “clean” energy standard requiring electric utilities to provide a certain percentage of power from such sources, and (iii) create enhanced incentives for use of renewable energy and increased efficiency in energy supply and use. In addition, the EPA is taking steps to regulate GHGs under the existing federal Clean Air Act (the “CAA”). The EPA has already adopted regulations limiting emissions of GHGs from motor vehicles, addressing the permitting of GHG emissions from stationary sources, and requiring the reporting of GHG emissions from specified large GHG emission sources, including refineries. These and similar regulations could require us to incur costs to monitor and report GHG emissions or reduce emissions of GHGs associated with our operations. In addition, various states, individually as well as in some cases on a regional basis, have taken steps to control GHG emissions, including adoption of GHG reporting requirements, cap and trade systems and renewable portfolio standards (such as AB 32 regulations in California). Efforts have also been undertaken to delay, limit or prohibit the EPA and possibly state action to regulate GHG emissions, and it is not possible at this time to predict the ultimate form, timing or extent of federal or state regulation. In addition, it is currently uncertain how the new presidential administration will address GHG emissions. In the event we do incur increased costs as a result of increased efforts to control GHG emissions, we may not be able to pass on any of these costs to our customers. Such requirements also could adversely affect demand for the refined petroleum products that we produce. Any increased costs or reduced demand could materially and adversely affect our business and results of operation.
Requirements to reduce emissions could result in increased costs to operate and maintain our facilities as well as implement and manage new emission controls and programs put in place. For example, AB 32 in California
35
requires the state to reduce its GHG emissions to 1990 levels by 2020. Additionally, in September 2016, the state of California enacted Senate Bill 32 which further reduces greenhouse gas emissions targets to 40 percent below 1990 levels by 2030. Two regulations implemented to achieve these goals are Cap-and-Trade and the LCFS. In 2012, the California Air Resource Board ("CARB") implemented Cap-and-Trade. This program currently places a cap on GHGs and we are required to acquire a sufficient number of credits to cover emissions from our refineries and our in-state sales of gasoline and diesel. In 2009, CARB adopted the LCFS, which requires a 10% reduction in the carbon intensity of gasoline and diesel by 2020. Compliance is achieved through blending lower carbon intensity biofuels into gasoline and diesel or by purchasing credits. Compliance with each of these programs is facilitated through a market-based credit system. If sufficient credits are unavailable for purchase or we are unable to pass through costs to our customers, we have to pay a higher price for credits or if we are otherwise unable to meet our compliance obligations, our financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Climate change could have a material adverse impact on our operations and adversely affect our facilities.
Some scientists have concluded that increasing concentrations of GHGs in the Earth's atmosphere may produce climate changes that have significant physical effects, such as increased frequency and severity of storms, droughts, floods and other climatic events. We believe the issue of climate change will likely continue to receive scientific and political attention, with the potential for further laws and regulations that could materially adversely affect our ongoing operations.
In addition, as many of our facilities are located near coastal areas, rising sea levels may disrupt our ability to operate those facilities or transport crude oil and refined petroleum products. Extended periods of such disruption could have an adverse effect on our results of operation. We could also incur substantial costs to protect or repair these facilities.
Renewable fuels mandates may reduce demand for the refined fuels we produce, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition. The market prices for RINs have been volatile and may harm our profitability.
Pursuant to the Energy Policy Act of 2005 and the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007, the EPA has issued Renewable Fuel Standards, or RFS, implementing mandates to blend renewable fuels into the petroleum fuels produced and sold in the United States. Under RFS, the volume of renewable fuels that obligated refineries must blend into their finished petroleum fuels increases annually over time until 2022. In addition, certain states have passed legislation that requires minimum biodiesel blending in finished distillates. On October 13, 2010, the EPA raised the maximum amount of ethanol allowed under federal law from 10% to 15% for cars and light trucks manufactured since 2007. The maximum amount allowed under federal law currently remains at 10% ethanol for all other vehicles. Existing laws and regulations could change, and the minimum volumes of renewable fuels that must be blended with refined petroleum fuels may increase. Because we do not produce renewable fuels, increasing the volume of renewable fuels that must be blended into our products displaces an increasing volume of our refinery’s product pool, potentially resulting in lower earnings and profitability. In addition, in order to meet certain of these and future EPA requirements, we may be required to purchase renewable fuel credits, known as “RINS,” which may have fluctuating costs. We have seen a fluctuation in the cost of RINs, required for compliance with the RFS. We incurred approximately $347.5 million in RINs costs during the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to $171.6 million and $115.7 million during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The fluctuations in our RINs costs are due primarily to volatility in prices for ethanol-linked RINs and increases in our production of on-road transportation fuels since 2012. Our RINs purchase obligation is dependent on our actual shipment of on-road transportation fuels domestically and the amount of blending achieved which can cause variability in our profitability.
Our pipelines are subject to federal and/or state regulations, which could reduce profitability and the amount of cash we generate.
Our transportation activities are subject to regulation by multiple governmental agencies. The regulatory burden on the industry increases the cost of doing business and affects profitability. Additional proposals and
36
proceedings that affect the oil industry are regularly considered by Congress, the states, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, the United States Department of Transportation, and the courts. We cannot predict when or whether any such proposals may become effective or what impact such proposals may have. Projected operating costs related to our pipelines reflect the recurring costs resulting from compliance with these regulations, and these costs may increase due to future acquisitions, changes in regulation, changes in use, or discovery of existing but unknown compliance issues.
We are subject to strict laws and regulations regarding employee and process safety, and failure to comply with these laws and regulations could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition and profitability.
We are subject to the requirements of the Occupational Safety & Health Administration, or OSHA, and comparable state statutes that regulate the protection of the health and safety of workers. In addition, OSHA requires that we maintain information about hazardous materials used or produced in our operations and that we provide this information to employees, state and local governmental authorities, and local residents. Failure to comply with OSHA requirements, including general industry standards, process safety standards and control of occupational exposure to regulated substances, could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition and the cash flows of the business if we are subjected to significant fines or compliance costs.
Compliance with and changes in tax laws could adversely affect our performance.
We are subject to extensive tax liabilities, including federal, state, local and foreign taxes such as income, excise, sales/use, payroll, franchise, property, gross receipts, withholding and ad valorem taxes. New tax laws and regulations and changes in existing tax laws and regulations are continuously being enacted or proposed that could result in increased expenditures for tax liabilities in the future. These liabilities are subject to periodic audits by the respective taxing authorities, which could increase our tax liabilities. Subsequent changes to our tax liabilities as a result of these audits may also subject us to interest and penalties. There can be no certainty that our federal, state, local or foreign taxes could be passed on to our customers.
Furthermore, the new presidential administration has called for substantial change to fiscal and tax policies, which may include comprehensive tax reform. We cannot predict the impact, if any, of these changes to our business. However, it is possible that some of these changes could adversely affect our business. Until we know what changes are enacted, we will not know whether in total we are negatively impacted by, the changes.
Changes in our credit profile could adversely affect our business.
Changes in our credit profile could affect the way crude oil suppliers view our ability to make payments and induce them to shorten the payment terms for our purchases or require us to post security or letters of credit prior to payment. Due to the large dollar amounts and volume of our crude oil and other feedstock purchases, any imposition by our suppliers of more burdensome payment terms on us may have a material adverse effect on our liquidity and our ability to make payments to our suppliers. This, in turn, could cause us to be unable to operate one or more of our refineries at full capacity.
Changes in laws or standards affecting the transportation of North American crude oil by rail could significantly impact our operations, and as a result cause our costs to increase.
Investigations into past rail accidents involving the transport of crude oil have prompted government agencies and other interested parties to call for increased regulation of the transport of crude oil by rail including in the areas of crude oil constituents, rail car design, routing of trains and other matters. Recent regulation governing shipments of petroleum crude oil by rail requires shippers to properly test and classify petroleum crude oil and further requires shippers to treat Class 3 petroleum crude oil transported by rail in tank cars as a Packing Group I or II hazardous material only. The DOT recently issued additional rules and regulation that require rail carriers to provide certain notifications to State agencies along routes utilized by trains over a certain length carrying crude oil, enhance safety training standards under the Rail Safety Improvement Act of 2008, require each railroad or contractor to develop and submit a training program to perform regular oversight and annual written reviews and establish enhanced
37
tank car standards and operational controls for high-hazard flammable trains. The new rules and any further changes in law, regulations or industry standards that require us to reduce the volatile or flammable constituents in crude oil that is transported by rail, alter the design or standards for rail cars we use, change the routing or scheduling of trains carrying crude oil, or any other changes that detrimentally affect the economics of delivering North American crude oil by rail to our, or subsequently to third party, refineries, could increase our costs, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our ability to service our indebtedness.
We could incur substantial costs or disruptions in our business if we cannot obtain or maintain necessary permits and authorizations or otherwise comply with health, safety, environmental and other laws and regulations.
Our operations require numerous permits and authorizations under various laws and regulations. These authorizations and permits are subject to revocation, renewal or modification and can require operational changes to limit impacts or potential impacts on the environment and/or health and safety. A violation of authorization or permit conditions or other legal or regulatory requirements could result in substantial fines, criminal sanctions, permit revocations, injunctions, and/or facility shutdowns. In addition, major modifications of our operations could require modifications to our existing permits or upgrades to our existing pollution control equipment. Any or all of these matters could have a negative effect on our business, results of operations and cash flows.
We may incur significant liability under, or costs and capital expenditures to comply with, environmental and health and safety regulations, which are complex and change frequently.
Our operations are subject to federal, state and local laws regulating, among other things, the handling of petroleum and other regulated materials, the emission and discharge of materials into the environment, waste management, and remediation of discharges of petroleum and petroleum products, characteristics and composition of gasoline and distillates and other matters otherwise relating to the protection of the environment. Our operations are also subject to extensive laws and regulations relating to occupational health and safety.
We cannot predict what additional environmental, health and safety legislation or regulations may be adopted in the future, or how existing or future laws or regulations may be administered or interpreted with respect to our operations. Many of these laws and regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, and the cost of compliance with these requirements can be expected to increase over time.
Certain environmental laws impose strict, and in certain circumstances joint and several liability for, costs of investigation and cleanup of such spills, discharges or releases on owners and operators of, as well as persons who arrange for treatment or disposal of regulated materials at contaminated sites. Under these laws, we may incur liability or be required to pay penalties for past contamination, and third parties may assert claims against us for damages allegedly arising out of any past or future contamination. The potential penalties and clean-up costs for past or future releases or spills, the failure of prior owners of our facilities to complete their clean-up obligations, the liability to third parties for damage to their property, or the need to address newly-discovered information or conditions that may require a response could be significant, and the payment of these amounts could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our operating results are seasonal and generally lower in the first and fourth quarters of the year for our refining operations. We depend on favorable weather conditions in the spring and summer months.
Demand for gasoline products is generally higher during the summer months than during the winter months due to seasonal increases in highway traffic and construction work. Varying vapor pressure requirements between the summer and winter months also tighten summer gasoline supply. As a result, our operating results are generally lower for the first and fourth quarters of each year.
38
We may not be able to successfully integrate the Chalmette Refinery or the Torrance Refinery into our business, or realize the anticipated benefits of these acquisitions.
Following the completion of the Chalmette and Torrance Acquisitions, the integration of these businesses into our operations may be a complex and time-consuming process that may not be successful. Prior to the completion of the Chalmette Acquisition we did not have any operations in the Gulf Coast and prior to the Torrance Acquisition we did not have any operations in the West Coast. This may add complexity to effectively overseeing, integrating and operating these refineries and related assets. Even if we successfully integrate these businesses into our operations, there can be no assurance that we will realize the anticipated benefits and operating synergies. Our estimates regarding the earnings, operating cash flow, capital expenditures and liabilities resulting from these acquisitions may prove to be incorrect. These acquisitions involve risks, including:
• | unexpected losses of key employees, customers and suppliers of the acquired operations; |
• | challenges in managing the increased scope, geographic diversity and complexity of our operations; |
• | diversion of management time and attention from our existing business; |
• | liability for known or unknown environmental conditions or other contingent liabilities and greater than anticipated expenditures required for compliance with environmental, safety or other regulatory standards or for investments to improve operating results; and |
• | the incurrence of additional indebtedness to finance acquisitions or capital expenditures relating to acquired assets. |
In connection with our recently completed Chalmette and Torrance Acquisitions, we did not have access to the type of historical financial information that we may require regarding the prior operation of the refineries. As a result, it may be difficult for investors to evaluate the probable impact of these significant acquisitions on our financial performance until we have operated the acquired refineries for a substantial period of time.
Risks Related to Our Indebtedness
Our substantial indebtedness could adversely affect our financial condition and prevent us from fulfilling our obligations under our indebtedness.
Our substantial indebtedness may significantly affect our financial flexibility in the future. As of December 31, 2016, we have total long-term debt, including affiliate notes payable, of 1,688.1 million, excluding deferred debt issuance costs of $25.3 million, substantially all of which is secured, and we could incur an additional $534.6 million of senior secured indebtedness under our existing debt agreements. We may incur additional indebtedness in the future. Our strategy includes executing future refinery and logistics acquisitions. Any significant acquisition would likely require us to incur additional indebtedness in order to finance all or a portion of such acquisition. The level of our indebtedness has several important consequences for our future operations, including that:
• | a significant portion of our cash flow from operations will be dedicated to the payment of principal of, and interest on, our indebtedness and will not be available for other purposes; |
• | covenants contained in our existing debt arrangements limit our ability to borrow additional funds, dispose of assets and make certain investments; |
• | these covenants also require us to meet or maintain certain financial tests, which may affect our flexibility in planning for, and reacting to, changes in our industry, such as being able to take advantage of acquisition opportunities when they arise; |
• | our ability to obtain additional financing for working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions, general corporate and other purposes may be limited; and |
• | we may be at a competitive disadvantage to those of our competitors that are less leveraged; and we may be more vulnerable to adverse economic and industry conditions. |
Our substantial indebtedness increases the risk that we may default on our debt obligations, certain of which contain cross-default and/or cross-acceleration provisions. We have significant principal payments due under our debt instruments. Our and our subsidiaries’ ability to meet their principal obligations will be dependent upon our
39
future performance, which in turn will be subject to general economic conditions, industry cycles and financial, business and other factors affecting our operations, many of which are beyond our control. Our business may not continue to generate sufficient cash flow from operations to repay our substantial indebtedness. If we are unable to generate sufficient cash flow from operations, we may be required to sell assets, to refinance all or a portion of our indebtedness or to obtain additional financing. Refinancing may not be possible and additional financing may not be available on commercially acceptable terms, or at all.
Despite our level of indebtedness, we and our subsidiaries may be able to incur substantially more debt, which could exacerbate the risks described above.
We and our subsidiaries may be able to incur substantial additional indebtedness in the future including additional secured debt. Although our debt instruments and financing arrangements contain restrictions on the incurrence of additional indebtedness, these restrictions are subject to a number of qualifications and exceptions, and the indebtedness incurred in compliance with these restrictions could be substantial. To the extent new debt is added to our currently anticipated debt levels, the substantial leverage risks described above would increase. Also, these restrictions do not prevent us from incurring obligations that do not constitute indebtedness.
Restrictive covenants in our debt instruments may limit our ability to undertake certain types of transactions.
Various covenants in our debt instruments and other financing arrangements may restrict our and our subsidiaries’ financial flexibility in a number of ways. Our indebtedness subjects us to significant financial and other restrictive covenants, including restrictions on our ability to incur additional indebtedness, place liens upon assets, pay dividends or make certain other restricted payments and investments, consummate certain asset sales or asset swaps, conduct businesses other than our current businesses, or sell, assign, transfer, lease, convey or otherwise dispose of all or substantially all of our assets. Some of these debt instruments also require our subsidiaries to satisfy or maintain certain financial condition tests in certain circumstances. Our subsidiaries’ ability to meet these financial condition tests can be affected by events beyond our control and they may not meet such tests.
Provisions in our indentures could discourage an acquisition of us by a third party.
Certain provisions of our indentures could make it more difficult or more expensive for a third party to acquire us. Upon the occurrence of certain transactions constituting a “change in control” as described in the indentures governing the Senior Secured Notes (as defined below), holders of our notes could require us to repurchase all outstanding notes at 101% of the principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, at the date of repurchase.
Our future credit ratings could adversely affect our ability to obtain credit in the future.
Our senior secured debt is rated BBB- by Standard & Poor’s Rating Services and B1 by Moody's Investors Service. Any adverse effect on our credit rating may increase our cost of borrowing or hinder our ability to raise financing in the capital markets, which would impair our ability to grow our business and make cash distributions to our shareholders.
Risks Related to Our Organizational Structure
Under a tax receivable agreement, PBF Energy is required to pay the pre-IPO owners of PBF LLC for certain realized or assumed tax benefits it may claim arising in connection with its initial public offering and future exchanges of PBF LLC Series A Units for shares of its Class A common stock and related transactions. The indenture governing the notes allows us, under certain circumstances, to make distributions sufficient for PBF Energy to pay its obligations arising from the tax receivable agreement, and such amounts are expected to be substantial.
PBF Energy entered into a tax receivable agreement that provides for the payment from time to time (“On-Going Payments”) by PBF Energy to the holders of PBF LLC Series A Units and PBF LLC Series B Units for certain tax benefits it may claim arising in connection with its prior offerings and future exchanges of PBF LLC
40
Series A Units for shares of its Class A Common Stock and related transactions, and the amounts it may pay could be significant.
PBF Energy’s payment obligations under the tax receivable agreement are PBF Energy’s obligations and not obligations of PBF Holding, PBF Finance, or any of PBF Holding’s other subsidiaries. However, because PBF Energy is primarily a holding company with limited operations of its own, its ability to make payments under the tax receivable agreement is dependent on our ability to make future distributions to it. The indentures governing the Senior Secured Notes allow us to make tax distributions (as defined in the indenture), and it is expected that PBF Energy’s share of these tax distributions will be in amounts sufficient to allow PBF Energy to make On-Going Payments. The indentures governing the Senior Secured Notes also allow us to make a distribution sufficient to allow PBF Energy to make any payments required under the tax receivable agreement upon a change in control, so long as we offer to purchase all of the Senior Secured Notes outstanding at a price in cash equal to 101% of the aggregate principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon, if any. If PBF Energy’s share of the distributions it receives under these specific provisions of the indentures is insufficient to satisfy its obligations under the tax receivable agreement, PBF Energy may cause us to make distributions in accordance with other provisions of the indentures in order to satisfy such obligations. In any case, based on our estimates of PBF Energy’s obligations under the tax receivable agreement, the amount of our distributions on account of PBF Energy’s obligations under the tax receivable agreement are expected to be substantial.
For example, with respect to On-Going Payments, assuming no material changes in the relevant tax law, and that PBF Energy earns sufficient taxable income to realize all tax benefits that are subject to the tax receivable agreement, we expect that PBF Energy On-Going Payments under the tax receivable agreement relating to exchanges that occurred prior to that date to aggregate $611.4 million and to range over the next 5 years from approximately $39.6 million to $60.0 million per year and decline thereafter. Further On-Going Payments by PBF Energy in respect of subsequent exchanges of PBF LLC Series A Units would be in addition to these amounts and are expected to be substantial as well. With respect to the Change of Control Payment, assuming that the market value of a share of PBF Energy’s Class A common stock equals $27.88 per share of Class A common stock (the closing price on December 31, 2016) and that LIBOR were to be 1.85%, we estimate as of December 31, 2016 that the aggregate amount of these accelerated payments would have been approximately $551.6 million if triggered immediately on such date. Our existing indebtedness may limit our ability to make distributions to PBF LLC, and in turn to PBF Energy to pay these obligations. These provisions may deter a potential sale of us to a third party and may otherwise make it less likely a third party would enter into a change of control transaction with PBF Energy or us.
The foregoing numbers are merely estimates—the actual payments could differ materially. For example, it is possible that future transactions or events could increase or decrease the actual tax benefits realized and the corresponding payments. Moreover, payments under the tax receivable agreement will be based on the tax reporting positions that PBF Energy determines in accordance with the tax receivable agreement. Neither PBF Energy nor any of its subsidiaries will be reimbursed for any payments previously made under the tax receivable agreement if the Internal Revenue Service subsequently disallows part or all of the tax benefits that gave rise to such prior payments.
Risks Related to Our Affiliation with PBFX
We depend upon PBFX for a substantial portion of our refineries’ logistics needs and have obligations for minimum volume commitments in our commercial agreements with PBFX.
We depend on PBFX to receive, handle, store and transfer crude oil and petroleum products for us from our operations and sources located throughout the United States and Canada in support of certain of our refineries under long-term, fee-based commercial agreements with us. These commercial agreements have an initial term of approximately seven to ten years and generally include minimum quarterly commitments and inflation escalators. If we fail to meet the minimum commitments during any calendar quarter, we will be required to make a shortfall payment quarterly to PBFX equal to the volume of the shortfall multiplied by the applicable fee.
41
PBFX’s operations are subject to all of the risks and operational hazards inherent in receiving, handling, storing and transferring crude oil and petroleum products, including: damages to its facilities, related equipment and surrounding properties caused by floods, fires, severe weather, explosions and other natural disasters and acts of terrorism; mechanical or structural failures at PBFX’s facilities or at third-party facilities on which its operations are dependent; curtailments of operations relative to severe seasonal weather; inadvertent damage to our facilities from construction, farm and utility equipment; and other hazards. Any of these events or factors could result in severe damage or destruction to PBFX’s assets or the temporary or permanent shut-down of PBFX’s facilities. If PBFX is unable to serve our logistics needs, our ability to operate our refineries and receive crude oil and distribute products could be adversely impacted, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
All of the executive officers and a majority of the directors of PBF GP are also current or former officers of PBF Energy. Conflicts of interest could arise as a result of this arrangement.
PBF Energy indirectly owns and controls PBF GP, and appoints all of its officers and directors. All of the executive officers and a majority of the directors of PBF GP are also current or former officers or directors of PBF Energy. These individuals will devote significant time to the business of PBFX. Although the directors and officers of PBF GP have a fiduciary duty to manage PBF GP in a manner that is beneficial to PBF Energy, as directors and officers of PBF GP they also have certain duties to PBFX and its unit holders. Conflicts of interest may arise between PBF Energy and its affiliates, including PBF GP, on the one hand, and PBFX and its unit holders, on the other hand. In resolving these conflicts of interest, PBF GP may favor its own interests and the interests of PBFX over the interests of PBF Energy and its subsidiaries. In certain circumstances, PBF GP may refer any conflicts of interest or potential conflicts of interest between PBFX, on the one hand, and PBF Energy, on the other hand, to its conflicts committee (which must consist entirely of independent directors) for resolution, which conflicts committee must act in the best interests of the public unit holders of PBFX. As a result, PBF GP may manage the business of PBFX in a way that may differ from the best interests of PBF Energy or us.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
See “Item 1. Business”.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
On July 24, 2013, the Delaware Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control ("DNREC") issued a Notice of Administrative Penalty Assessment and Secretary’s Order to Delaware City Refining for alleged air emission violations that occurred during the re-start of the refinery in 2011 and subsequent to the re-start. The penalty assessment seeks $460,200 in penalties and $69,030 in cost recovery for DNREC’s expenses associated with investigation of the incidents. We dispute the amount of the penalty assessment and allegations made in the order, and are in discussions with DNREC to resolve the assessment. It is possible that DNREC will assess a penalty in this matter but any such amount is not expected to be material to the Company.
As of November 1, 2015, the Company acquired Chalmette Refining, which was in discussions with the Louisiana Department of Environmental Quality ("LDEQ") to resolve self-reported deviations from refinery operations relating to certain Clean Air Act Title V permit conditions, limits and other requirements. LDEQ commenced an enforcement action against Chalmette Refining on November 14, 2014 by issuing a Consolidated Compliance Order and Notice of Potential Penalty (the "Order") covering deviations from 2009 and 2010. Chalmette Refining and LDEQ subsequently entered into a dispute resolution agreement, the enforcement of which has been suspended while negotiations are ongoing, which may include the resolution of deviations outside the periods covered by the Order. In February 2017, Chalmette Refining and the LDEQ met to resolve the issues under the Order, including the assessment of an administrative penalty against Chalmette Refining. Although a resolution
42
has not been finalized, the administrative penalty is anticipated to be approximately $0.7 million, including beneficial environmental projects. To the extent the administrative penalty exceeds such amount, it is not expected to be material to the Company.
On January 24, 2017, in connection with a Clean Air Act inspection in May 2014 by the EPA to determine compliance with 40 CFR Subpart 68 Chemical Accident Prevention Provisions, the EPA notified the Chalmette refinery of its intent to bring an enforcement action on two (2) findings from the audit. No settlement or penalty demand has been received to date. It is possible that the EPA will assess penalties in these matters in excess of $0.1 million but any such amount is not expected to be material to the Company, individually or in the aggregate.
On December 23, 2016, the Delaware City Refinery received a Notice of Violation (“NOV”) from DNREC concerning a potential violation of the DNREC order authorizing the shipment of crude oil by barge from the refinery. The NOV alleges that DCR made shipments to locations other than the Paulsboro refinery in violation of the order and requests certain additional information. The Delaware City refinery responded to the NOV on February 7, 2017, maintaining that no violations occurred. Although no penalties have been assessed at this time, DNREC has reserved the right to assess penalties. On December 28, 2016, DNREC issued a Coastal Zone Act permit (the “Ethanol Permit”) to DCR allowing the utilization of existing tanks and existing marine loading equipment at their existing facilities to enable denatured ethanol to be loaded from storage tanks to marine vessels and shipped to offsite facilities. On January 13, 2017, the issuance of the Ethanol Permit was appealed by two environmental groups. On February 27, 2017, the Coastal Zone Industrial Board held a public hearing and dismissed the appeal, determining that the appellants did not have standing. The release of the Board decision is pending.
On February 3, 2011, the EPA sent a request for information pursuant to Section 114 of the Clean Air Act to the Paulsboro refinery with respect to compliance with EPA standards governing flaring. The refinery and the EPA have recently reached a settlement pursuant to which the Paulsboro refinery will pay a penalty of approximately $0.2 million.
On February 14, 2017, the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (“NJDEP”) submitted a proposed Administrative Consent Order (“ACO”) which covers air emission violations from 2013 through 2016 and work practice standards that were not subject to an affirmative defense at the Paulsboro refinery (“PRC”). In settlement of the violations, the NJDEP has proposed that PRC pay a civil administrative penalty of $0.3 million, which includes $0.1 million for a supplemental environmental project. If the offer is accepted, the remaining $0.2 million shall be remitted by PRC within 30 days of receipt of the offer. This amount is not material to the Company, individually or in the aggregate.
In connection with the acquisition of the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets, we assumed certain pre-existing environmental liabilities totaling $142.5 million as of December 31, 2016, related to certain environmental remediation obligations to address existing soil and groundwater contamination and monitoring activities, which reflects the estimated cost of the remediation obligations. In addition, in connection with the acquisition of the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets, we purchased a ten year, $100.0 million environmental insurance policy to insure against unknown environmental liabilities. Furthermore, in connection with the acquisition, we assumed responsibility for certain specified environmental matters that occurred prior to our ownership of the refinery. Specifically, we assumed responsibility for (i) a Notice of Violation ("NOV") issued on March 12, 2015 by the Southern California Air Quality Management District ("SCAQMD") relating to self-reported Title V deviations for the Torrance Refinery for compliance year 2012, (ii) a NOV issued on March 10, 2016 for self-reported Title V deviations for the Torrance Refinery for compliance year 2013, (iii) a NOV issued on March 10, 2016 for self-reported Title V deviations for the Torrance Refinery for compliance year 2014 and (iv) a NOV issued on March 10, 2016 for self-reported Title V deviations for the Torrance Refinery for compliance year 2015. Following the closing of the acquisition, the Torrance refinery has received a number of NOVs. On September 6, 2016, a NOV was issued to the Torrance refinery by the SCAQMD for the July 11, 2016 FCCU shutdown and startup. The NOV alleges that the facility operated equipment while it bypassed associated air pollution control equipment in violation of our facility permit to operate. Opacity from FCCU 2F-7 exceeded 40 percent on July 11, 2016 and July 14, 2016, aggregate over 3 minutes in one continuous hour. In addition, on
43
October 13, 2016, a NOV was issued by the SCAQMD for an alleged nuisance created from flaring associated with the October 11, 2016 Southern California Edison power disruption. On January 4, 2017, a NOV was also issued for an alleged discharge of air contaminants from Tank 1340x113 that caused a nuisance to a considerable number of persons or to the public. On January 13, 2017, a NOV was issued by the City of Torrance for allegedly failing to report a release or threatened release of hazardous material. On January 7, 2017, the Torrance refinery allegedly experienced a third release (January 3, January 4 and January 7) in a week of untreated Naphtha gas due to the generation of higher capacity from the Coker Unit. On February 28, 2017, in review of the fire occurring at the refinery on February 18, 2017, the City of Torrance Fire Department issued a NOV to the Torrance refinery requiring the refinery to comply with California Fire Code Section 104.7.2 and provide a technical opinion and report with respect to the refinery’s process safety risk assessment plan. With the exception of the October 13th NOV, no settlement or penalty demand has been received to date with respect to these notices. The proposed penalty for the October 13th NOV is less than $0.1 million. It is possible that SCAQMD and/or the City of Torrance will assess penalties in the other matters in excess of $0.1 million but any such amount is not expected to be material to us, individually or in the aggregate.
On September 2, 2011, prior to the Company’s ownership of the Chalmette refinery, the plaintiff in Vincent Caruso, et al. v. Chalmette Refining, L.L.C., filed an action on behalf of himself and other Louisiana residents who live or own property in St. Bernard Parish and Orleans Parish and whose property was allegedly contaminated and who allegedly suffered any personal or property damages as a result of an emission of spent catalyst, sulfur dioxide and hydrogen sulfide from the Chalmette refinery on September 6, 2010. Plaintiffs claim to have suffered injuries, symptoms, and property damage as a result of the release. Plaintiffs seek to recover unspecified damages, interest and costs. In August 2015, there was a mini-trial for four plaintiffs for property damage relating to home and vehicle cleaning. On April 12, 2016, the trial court rendered judgment limiting damages ranging from $100 to $500 for home cleaning and $25 to $75 for vehicle cleaning to the four plaintiffs. The trial court found Chalmette Refining and co-defendant Eaton Corporation (“Eaton”), to be solitarily liable for the damages. Chalmette Refining and Eaton filed an appeal in August 2016 of the judgment on the mini-trial, which appeal is pending. There is no stay pending appeal. The potential class members have not been identified as the parties are negotiating a claims process for claims such as home cleaning, vehicle cleaning, and alleged personal injury. The claims process would also include a class notice to identify potential class members. Depending upon the ultimate class size and the nature of the claims, the outcome may have a material adverse effect on the Company's financial condition, or cash flows.
The Company is subject to obligations to purchase RINs required to comply with the RFS. In late 2015, the EPA initiated enforcement proceedings against companies it believes produced invalid RINs. On October 13, 2016, PBF Holding and its subsidiaries Toledo Refining Company LLC and Delaware City Refining Company LLC were notified by the EPA that its records indicated that these entities used potentially invalid RINs. The EPA directed each of the subsidiaries to resubmit reports to remove the potentially invalid RINs and to replace the invalid RINs with valid RINs with the same D Code. The invalid RINs have been retired and the Company does not expect any settlement with the EPA to resolve this matter to be material.
On February 14, 2017, the plaintiff in Adam Trotter v. ExxonMobil Corp., ExxonMobil Oil Corp., ExxonMobil Refining and Supply Company, et. al., filed a civil action against the Company in the Superior Court of the State of California, County of Los Angeles, Southwest District, claiming public nuisance, battery, a violation of civil rights under 42 U.S.C. §1983, intentional infliction of emotional distress, negligence and strict liability in tort and injuries and symptoms resulting from the February 18, 2015 electrostatic precipitator ("ESP") explosion at the Torrance Refinery which was then owned and operated by Exxon. The City of Torrance and the SCAQMD are also named as defendants in the lawsuit. The Company was served with the lawsuit on February 22, 2017 and has not had an opportunity to evaluate the merits of plaintiff’s claims. To the extent that plaintiff’s claims relate to the ESP explosion, Exxon has retained responsibility for any liabilities that would arise from the lawsuit.
On February 17, 2017, in Arnold Goldstein, et al. v. Exxon Mobil Corporation, et al., the Company’s parents, PBF Energy Inc. and PBF Energy Company LLC, the Company and the Company’s subsidiaries, PBF Energy Western Region LLC and Torrance Refining Company LLC and the manager of the Company’s Torrance refinery along with Exxon Mobil Corporation were named as defendants in a class action and representative action complaint
44
filed on behalf of Arnold Goldstein, John Covas, Gisela Janette La Bella and others similarly situated. The complaint was filed in the Superior Court of the State of California, County of Los Angeles and alleges negligence, strict liability, ultrahazardous activity, a continuing private nuisance, a permanent private nuisance, a continuing public nuisance, a permanent public nuisance and trespass resulting from the February 18, 2015 electrostatic precipitator ("ESP") explosion at the Torrance Refinery which was then owned and operated by Exxon. The operation of the Torrance Refinery by the PBF entities subsequent to the Company’s acquisition in July 2016 is also referenced in the complaint. The Company was served with the lawsuit on March 1, 2017 and has not had an opportunity to evaluate the merits of the plaintiffs’ claims. To the extent that plaintiffs’ claims relate to the ESP explosion, Exxon has retained responsibility for any liabilities that would arise from the lawsuit pursuant to the agreement relating to the acquisition of the Torrance Refinery. The Company cannot currently estimate the amount of its potential liability.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURE
None.
45
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS, AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market Information
We are a privately-owned company with no established public trading market for our membership units.
Holders
At December 31, 2016, 100% of our outstanding membership interests was held by PBF LLC. PBF Finance had 100 shares of common stock outstanding, all of which were held by us. None of the membership interests are publicly traded, and none were issued or sold in 2016.
Dividend and Distribution Policy
We made cash distributions to PBF LLC in the amount of $139.4 million during 2016, which in turn made cash distributions (including tax distributions) of an equivalent amount to its members including PBF Energy.
We currently intend to make quarterly cash distributions in amounts sufficient for PBF LLC to make tax distributions to its members and may make additional distributions to the extent necessary for PBF Energy to declare and pay a quarterly cash dividend of approximately $0.30 per share on its Class A common stock. The declaration, amount and payment of this and any other future distributions by us will be at the sole discretion of our board of directors and the board of directors of PBF Energy, which is the sole managing member of our sole member (PBF LLC), and we are not obligated under any applicable laws, governing documents or any contractual agreements with PBF LLC's existing owners or otherwise to declare or pay any dividends or other distributions (other than the obligations of PBF LLC to make tax distributions to its members).
We are a holding company and all of our operations are conducted through our subsidiaries. We have no independent means of generating revenue other than through assets owned by our subsidiaries. In order for us to make any distributions, we will need to cause our subsidiaries to make distributions to us. We and our subsidiaries are generally prohibited under Delaware law from making a distribution to a member to the extent that, at the time of the distribution, after giving effect to the distribution, liabilities of the limited liability company (with certain exceptions) exceed the fair value of its assets. As a result, we may be unable to obtain cash from our subsidiaries to satisfy our obligations and make distributions to PBF LLC.
Our ability to pay dividends and make distributions to PBF LLC is, and in the future may be, limited by covenants in our Revolving Loan, our Senior Secured Notes and other debt instruments. Subject to certain exceptions, the Revolving Loan and the indentures governing the Senior Secured Notes prohibit us from making distributions to PBF LLC if certain defaults exist. In addition, both the indentures and the Revolving Loan contain additional restrictions limiting our ability to make distributions to PBF LLC.
Based upon our operating results for the year ended December 31, 2016, we were permitted, under our Revolving Loan, Senior Secured Notes and other debt instruments, to make distributions to PBF LLC so that PBF LLC could make tax distributions to its members and make quarterly distributions to its members in an amount sufficient for PBF Energy to declare and pay a quarterly dividend of $0.30 per share on its Class A common stock. Our ability to comply with the foregoing limitations and restrictions is, to a significant degree, subject to our operating results, which are dependent on a number of factors outside of our control. As a result, we cannot assure you that we will be able to continue to make distributions. See “Item 1A. Risk Factors”
PBF Holding paid $139.4 million in distributions to PBF LLC during the year ended December 31, 2016. PBF LLC used $123.4 million of this amount in total to make four separate non-tax distributions of $0.30 per unit ($1.20 per unit in total) to its members, of which $117.5 million was distributed to PBF Energy and the balance was distributed to PBF LLC’s other members. PBF Energy used this $117.5 million to pay four separate equivalent
46
cash dividends of $0.30 per share of Class A common stock on November 22, 2016, August 23, 2016, May 31, 2016, and March 8, 2016. PBF LLC used the remaining $16.0 million distributions from PBF Holding to make tax distributions to its members, including to PBF Energy.
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The following table presents selected historical consolidated financial and other data of PBF Holding. The selected historical consolidated financial data for each of the fiscal years ended as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 and for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2016 have been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements, included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The selected historical consolidated financial data as of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 and for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 have been derived from the audited financial statements of PBF Holding not included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. As a result of the Chalmette and Torrance acquisitions, the historical consolidated financial results of PBF Holding only include the results of operations for Chalmette and Torrance from November 1, 2015 and July 1, 2016 forward, respectively.
The historical consolidated financial data and other statistical data presented below should be read in conjunction with “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” and our consolidated financial statements and the related notes thereto, included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
47
The following tables reflect our financial and operating highlights (amounts in thousands) for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||
Statement of operations data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 15,908,537 | $ | 13,123,929 | $ | 19,828,155 | $ | 19,151,455 | $ | 20,138,687 | ||||||||||
Costs, expenses and other: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Cost of sales, excluding depreciation | 13,765,088 | 11,611,599 | 18,514,054 | 17,803,314 | 18,269,078 | |||||||||||||||
Operating expenses, excluding depreciation | 1,390,582 | 889,368 | 880,701 | 812,652 | 738,824 | |||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses (1) | 149,643 | 166,904 | 140,150 | 95,794 | 120,443 | |||||||||||||||
Equity (income) loss in investee | (5,679 | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Loss (gain) on sale of asset | 11,374 | (1,004 | ) | (895 | ) | (183 | ) | (2,329 | ) | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization expense | 209,840 | 191,110 | 178,996 | 111,479 | 92,238 | |||||||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 387,689 | 265,952 | 115,149 | 328,399 | 920,433 | |||||||||||||||
Other income (expense): | ||||||||||||||||||||
Change in fair value of contingent consideration | — | — | — | — | (2,768 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Change in fair value of catalyst lease | 1,422 | 10,184 | 3,969 | 4,691 | (3,724 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense, net | (129,536 | ) | (88,194 | ) | (98,001 | ) | (94,214 | ) | (108,629 | ) | ||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 259,575 | 187,942 | 21,117 | 238,876 | 805,312 | |||||||||||||||
Income tax expense | 23,689 | 648 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Net Income | 235,886 | 187,294 | 21,117 | 238,876 | 805,312 | |||||||||||||||
Less income attributable to noncontrolling interest | 269 | 274 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Net income attributable to PBF Holding LLC | $ | 235,617 | $ | 187,020 | $ | 21,117 | $ | 238,876 | $ | 805,312 | ||||||||||
Balance sheet data (at end of period) : | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 6,566,897 | $ | 5,082,722 | $ | 4,013,762 | $ | 4,192,504 | $ | 4,085,264 | ||||||||||
Total debt (2) | 1,601,836 | 1,272,937 | 750,349 | 747,576 | 729,980 | |||||||||||||||
Total equity | 2,588,933 | 1,821,284 | 1,630,516 | 1,772,153 | 1,751,654 | |||||||||||||||
Other financial data : | ||||||||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures (3) | $ | 1,498,191 | $ | 979,481 | $ | 625,403 | $ | 415,702 | $ | 222,688 | ||||||||||
(1) | Includes acquisition related expenses consisting primarily of consulting and legal expenses related to the Torrance Acquisition and other pending and non-consummated acquisitions of $13.6 million in 2016, as well as the Chalmette Acquisition and other pending and non-consummated acquisitions of $5.8 million in 2015. |
(2) | Total debt, excluding debt issuance costs and affiliate notes payable, includes current maturities and our Delaware Economic Development Authority Loan (which was fully converted to a grant as of December 31, 2016). |
(3) | Includes expenditures for construction in progress, property, plant and equipment (including railcar purchases), deferred turnaround costs and other assets, excluding the proceeds from sales of assets. |
48
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following review of our results of operations and financial condition should be read in conjunction with Items 1, 1A, and 2, “Business, Risk Factors, and Properties,” Item 6, “Selected Financial Data,” and Item 8, “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data,” respectively, included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains certain “forward-looking statements” of expected future developments that involve risk and uncertainties. You can identify forward-looking statements because they contain words such as “believes,” “expects,” “may,” “should,” “seeks,” “approximately,” “intends,” “plans,” “estimates,” or “anticipates” or similar expressions that relate to our strategy, plans or intentions. All statements we make relating to our estimated and projected earnings, margins, costs, expenditures, cash flows, growth rates and financial results or to our expectations regarding future industry trends are forward-looking statements. In addition, we, through our senior management, from time to time make forward-looking public statements concerning our expected future operations and performance and other developments. These forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that may change at any time, and, therefore, our actual results may differ materially from those that we expected. We derive many of our forward-looking statements from our operating budgets and forecasts, which are based upon many detailed assumptions. While we believe that our assumptions are reasonable, we caution that it is very difficult to predict the impact of known factors, and, of course, it is impossible for us to anticipate all factors that could affect our actual results.
Important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from our expectations, which we refer to as “cautionary statements,” are disclosed under “Item 1A. Risk Factors,” and “Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. All forward-looking information in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and subsequent written and oral forward-looking statements attributable to us, or persons acting on our behalf, are expressly qualified in their entirety by the cautionary statements. Some of the factors that we believe could affect our results include:
•supply, demand, prices and other market conditions for our products, including volatility in commodity prices;
• the effects of competition in our markets;
•changes in currency exchange rates, interest rates and capital costs;
• adverse developments in our relationship with both our key employees and unionized employees;
•our ability to operate our businesses efficiently, manage capital expenditures and costs (including general and administrative expenses) and generate earnings and cash flow;
•our substantial indebtedness;
•our supply and inventory intermediation arrangements expose us to counterparty credit and performance risk;
•termination of our A&R Intermediation Agreements with J. Aron, which could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, as we would be required to finance our intermediate and refined products inventory covered by the agreements. Additionally, we are obligated to repurchase from J. Aron certain intermediates and finished products located at the Paulsboro and Delaware City refineries’ storage tanks upon termination of these agreements;
•restrictive covenants in our indebtedness that may adversely affect our operational flexibility or ability to make distributions;
•our assumptions regarding payments arising under PBF Energy's tax receivable agreement and other arrangements relating to PBF Energy;
•our expectations and timing with respect to our acquisition activity;
49
•our expectations with respect to our capital improvement and turnaround projects;
•the status of an air permit to transfer crude through the Delaware City refinery's dock;
•the impact of disruptions to crude or feedstock supply to any of our refineries, including disruptions due to problems at PBFX or with third party logistics infrastructure or operations, including pipeline, marine and rail transportation;
•the impact of current and future laws, rulings and governmental regulations, including the implementation of rules and regulations regarding transportation of crude oil by rail;
•the effectiveness of our crude oil sourcing strategies, including our crude by rail strategy and related commitments;
•adverse impacts related to recent legislation by the federal government lifting the restrictions on exporting U.S. crude oil;
•adverse impacts from changes in our regulatory environment, such as the effects of compliance with the California Global Warming Solutions Act (also referred to as "AB32"), or from actions taken by environmental interest groups;
•market risks related to the volatility in the price of RINs required to comply with the Renewable Fuel Standards and GHG emission credits required to comply with various GHG emission programs, such as AB32;
•our ability to successfully integrate the completed acquisitions of Chalmette Refining and related logistics assets and the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets into our business and realize the benefits from such acquisitions;
•liabilities arising from the Chalmette Acquisition and/or Torrance Acquisition that are unforeseen or exceed our expectations; and
•any decisions we continue to make with respect to our energy-related logistical assets that may be transferred to PBFX.
We caution you that the foregoing list of important factors may not contain all of the material factors that are important to you. In addition, in light of these risks and uncertainties, the matters referred to in the forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K may not in fact occur. Accordingly, investors should not place undue reliance on those statements.
Our forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Except as required by applicable law, including the securities laws of the United States, we do not intend to update or revise any forward-looking statements. All subsequent written and oral forward-looking statements attributable to us or persons acting on our behalf are expressly qualified in their entirety by the foregoing.
Explanatory Note
This Annual Report on Form 10-K is filed by PBF Holding and PBF Finance. PBF Finance is a wholly-owned subsidiary of PBF Holding. PBF Holding is a wholly-owned subsidiary of PBF LLC and is the parent company for PBF LLC's refinery operating subsidiaries. PBF Holding is an indirect subsidiary of PBF Energy, which is the sole managing member of, and owner of an equity interest representing approximately 96.5% of the outstanding economic interests in PBF LLC as of December 31, 2016. PBF Energy operates and controls all of the business and affairs and consolidates the financial results of PBF LLC and its subsidiaries. PBF Holding, together with its consolidated subsidiaries, owns and operates oil refineries and related facilities in North America.
Unless the context indicates otherwise, the terms “we,” “us,” and “our” refer to PBF Holding and its consolidated subsidiaries.
50
Executive Summary
We were formed in March 2008 to pursue the acquisitions of crude oil refineries and downstream assets in North America. We currently own and operate five domestic oil refineries and related assets located in Toledo, Ohio, Delaware City, Delaware, Paulsboro, New Jersey, New Orleans, Louisiana and Torrance, California. Our refineries have a combined processing capacity, known as throughput, of approximately 900,000 bpd, and a weighted average Nelson Complexity Index of 12.2. Our five oil refineries are all engaged in the refining of crude oil and other feedstocks into petroleum products, and are aggregated into one reportable segment.
Factors Affecting Comparability
Our results over the past three years have been affected by the following events, the understanding of which will aid in assessing the comparability of our period to period financial performance and financial condition.
Torrance Acquisition
On July 1, 2016, we acquired from ExxonMobil and its subsidiary, Mobil Pacific Pipeline Company (together, the “Torrance Sellers”), the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets. The Torrance refinery, located on 750 acres in Torrance, California, is a high-conversion 155,000 barrel per day, delayed-coking refinery with a Nelson Complexity of 14.9. The facility is strategically positioned in Southern California with advantaged logistics connectivity that offers flexible raw material sourcing and product distribution opportunities primarily in the California, Las Vegas and Phoenix area markets. The Torrance Acquisition increased our total throughput capacity to approximately 900,000 bpd.
In addition to refining assets, the Torrance Acquisition included a number of high-quality logistics assets consisting of a sophisticated network of crude and products pipelines, product distribution terminals and refinery crude and product storage facilities. The most significant of the logistics assets is a 189-mile crude gathering and transportation system which delivers San Joaquin Valley crude oil directly from the field to the refinery. Additionally, included in the transaction were several pipelines which provide access to sources of crude oil including the Ports of Long Beach and Los Angeles, as well as clean product outlets with a direct pipeline supplying jet fuel to the Los Angeles airport. The Torrance refinery also has crude and product storage facilities with approximately 8.6 million barrels of shell capacity.
The purchase price for the assets was approximately $521.4 million in cash after post-closing purchase price adjustments, plus final working capital of $450.6 million. The purchase price and fair value allocation may be subject to adjustment pending completion of the final valuation which was in process as of December 31, 2016. In addition, we assumed certain pre-existing environmental and regulatory emission credit obligations in connection with the Torrance Acquisition. The transaction was financed through a combination of cash on hand, including proceeds from PBF Energy's October 2015 Equity Offering and the 2023 Senior Secured Notes offering, and borrowings under our Revolving Loan.
TVPC Contribution Agreement
On August 31, 2016, PBFX entered into a contribution agreement (the "TVPC Contribution Agreement") between PBFX and PBF LLC. Pursuant to the TVPC Contribution Agreement, PBF Holding distributed to PBF LLC and PBFX acquired from PBF LLC 50% of the issued and outstanding limited liability company interests of Torrance Valley Pipeline Company LLC (“TVPC”), whose assets consist of the 189 mile San Joaquin Valley Pipeline system, including the M55, M1 and M70 Pipeline System, including 11 pipeline stations with storage capability and truck unloading capability at two of the stations (collectively, the “Torrance Valley Pipeline”). The total consideration paid to PBF LLC was $175.0 million, which was funded by PBFX with $20.0 million of cash on hand, $76.2 million in proceeds from the sale of marketable securities, and $78.8 million in net proceeds from the PBFX equity offering completed in August 2016.
PBFX Operating Company LP ("PBFX Op Co"), PBFX’s wholly-owned subsidiary, serves as TVPC's managing member. PBFX, through its ownership of PBFX Op Co, has the sole ability to direct the activities of
51
TVPC that most significantly impact its economic performance. PBFX, and not PBF Holding, is considered to be the primary beneficiary for accounting purposes, and as a result fully consolidates the net assets and results of operations of TVPC, with the 50% of TVPC it does not own recorded as noncontrolling interests and net income attributable to noncontrolling interests. Accordingly, PBF Holding deconsolidated TVPC and has recognized an equity investment in TVPC for its 50% noncontrolling interest.
Chalmette Acquisition
On November 1, 2015, we acquired from ExxonMobil Oil Corporation, Mobil Pipe Line Company and PDV Chalmette, Inc., 100% of the ownership interests of Chalmette Refining, which owns the Chalmette refinery and related logistics assets. The Chalmette refinery, located outside of New Orleans, Louisiana, is a dual-train coking refinery and is capable of processing both light and heavy crude oil. Subsequent to the closing of the Chalmette Acquisition, Chalmette Refining is a wholly-owned subsidiary of ours.
Chalmette Refining owns 100% of the MOEM Pipeline, providing access to the Empire Terminal, as well as the CAM Connection Pipeline, providing access to the Louisiana Offshore Oil Port facility through a third party pipeline. Chalmette Refining also owns 80% of each of the Collins Pipeline Company and T&M Terminal Company, both located in Collins, Mississippi, which provide a clean products outlet for the refinery to the Plantation and Colonial Pipelines. Also included in the acquisition are a marine terminal capable of importing waterborne feedstocks and loading or unloading finished products; a clean products truck rack which provides access to local markets; and a crude and product storage facility.
The aggregate purchase price for the Chalmette Acquisition was $322.0 million in cash, plus inventory and working capital of $246.0 million, which was finalized in the first quarter of 2016. The transaction was financed through a combination of cash on hand and borrowings under our Revolving loan.
Amended and Restated Asset Based Revolving Credit Facility
On an ongoing basis, the Revolving Loan is available to be used for working capital and other general corporate purposes. On August 15, 2014, the agreement was amended and restated to, among other things, increase the maximum availability to $2.50 billion and extend its maturity to August 2019. The amended and restated Revolving Loan includes an accordion feature which allows for aggregate commitments of up to $2.75 billion. In November and December 2015, PBF Holding increased the maximum availability under the Revolving Loan to $2.60 billion and $2.64 billion, respectively, in accordance with its accordion feature. The commitment fees on the unused portions, the interest rate on advances and the fees for letters of credit have also been reduced in the amended and restated Revolving Loan.
As noted in "Note 3 - Acquisitions" to the consolidated financial statements, we drew down under our Revolving Loan to partially fund the Torrance Acquisition and $350.0 million remains outstanding as of December 31, 2016.
Senior Secured Notes Offering
On November 24, 2015, we and PBF Finance Corporation issued $500.0 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2023 Senior Secured Notes. The net proceeds were approximately $490.0 million after deducting the initial purchasers’ discount and offering expenses. We used the proceeds for general corporate purposes, including to fund a portion of the purchase price for the Torrance Acquisition.
PBF Rail Revolving Credit Facility
Effective March 25, 2014, PBF Rail Logistics Company LLC (“PBF Rail”), an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of PBF Holding, entered into a $250.0 million secured revolving credit agreement (the “Rail Facility”). The primary purpose of the Rail Facility was to fund the acquisition by PBF Rail of coiled and insulated crude tank cars and non-coiled and non-insulated general purpose crude tank cars before December 2015.
52
As noted in "Note 9 - Credit Facility and Long-term Debt" to the consolidated financial statements, the Rail Facility was amended on two occasions in 2015 and 2016 and on December 22, 2016, the Rail Facility was terminated and replaced with the PBF Rail Term Loan (as described below).
PBF Rail Term Loan
On December 22, 2016, PBF Rail entered into a $35.0 million term loan (the “PBF Rail Term Loan”) with DVB Bank SE (“DVB”). The PBF Rail Term Loan amortizes monthly over its five year term and bears interest at the one month LIBOR plus 2.0%. As security for the PBF Rail Term Loan, PBF Rail pledged, among other things, (i) certain eligible railcars; (ii) the Debt Service Reserve Account; and (iii) our member interest in PBF Rail. Additionally, the PBF Rail Term Loan contains customary terms, events of default and covenants for transactions of this nature. PBF Rail may at any time repay the PBF Rail Term Loan without penalty in the event that railcars collateralizing the loan are sold, scrapped or otherwise removed from the collateral pool.
J. Aron Intermediation Agreements
On May 29, 2015, we entered into amended and restated inventory intermediation agreements with J. Aron pursuant to which certain terms of the existing inventory intermediation agreements were amended, including, among other things, pricing and an extension of the term for a period of two years from the original expiry date of July 1, 2015, subject to certain early termination rights. In addition, the A&R Intermediation Agreements include one-year renewal clauses by mutual consent of both parties. The A&R Intermediation Agreements have not been renewed and are scheduled to expire on July 1, 2017. If we are unable to negotiate an extension with J. Aron or enter into an alternative intermediation agreement, we will have to repurchase the inventories outstanding under the A&R Intermediation Agreement at that time.
Pursuant to each A&R Intermediation Agreement, J. Aron continues to purchase and hold title to certain of the intermediate and finished products produced by the Paulsboro and Delaware City refineries, respectively, and delivered into tanks at the Refineries. Furthermore, J. Aron agrees to sell the Products back to Paulsboro refinery and Delaware City refinery as the Products are discharged out of the refineries' tanks. J. Aron has the right to store the products purchased in tanks under the A&R Intermediation Agreements and will retain these storage rights for the term of the agreements. PBF Holding continues to market and sell the products independently to third parties.
Crude Oil Acquisition Agreements
We currently purchase all of our crude and feedstock needs independently from a variety of suppliers on the spot market or through term agreements for our Delaware City refinery. We have a contract with Saudi Aramco pursuant to which we have been purchasing up to approximately 100,000 bpd of crude oil from Saudi Aramco that is processed at our Paulsboro refinery. Prior to December 31, 2015, we had a crude oil supply contract with a third-party for our Delaware City refinery. We currently fully source our own crude oil needs for our Toledo refinery. Prior to July 31, 2014, we had a crude oil acquisition agreement with a third party that expired on July 31, 2014. In connection with the Chalmette Acquisition we entered into a contract with PDVSA for the supply of 40,000 to 60,000 bpd of crude oil that can be processed at any of our East or Gulf Coast refineries. In connection with the closing of the Torrance Acquisition, we entered into a crude supply agreement with ExxonMobil for approximately 60,000 bpd of crude oil that can be processed at our Torrance refinery.
Renewable Fuels Standard
We have seen fluctuations in the cost of renewable fuel credits, known as RINs, required for compliance with the RFS. We incurred approximately $347.5 million in RINs costs during the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to $171.6 million and $115.7 million during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The fluctuations in RINs costs are due primarily to volatility in prices for ethanol-linked RINs and increases in our production of on-road transportation fuels since 2012. Our RINs purchase obligation is dependent on our actual shipment of on-road transportation fuels domestically and the amount of blending achieved.
53
Agreements with PBFX
PBFX is a fee-based, growth-oriented, publicly traded Delaware master limited partnership formed by our indirect parent company, PBF Energy, to own or lease, operate, develop and acquire crude oil and refined petroleum products terminals, pipelines, storage facilities and similar logistics assets. PBFX engages in the receiving, handling, storing and transferring of crude oil, refined products and intermediates from sources located throughout the United States and Canada for PBF Energy in support of certain of its refineries.
Beginning with the completion of the PBFX Offering, we have entered into a series of agreements with PBFX, including contribution, commercial and operational agreements. Each of these agreements and their impact to our operations is described in "Item 1. Business" and "Note 12 - Related Party Transactions" in our consolidated financial statements.
A summary of revenue and expense transactions with PBFX is as follows (in millions):
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
Revenues under affiliate agreements: | ||||||||||||
Services Agreement | $ | 5.1 | $ | 4.5 | $ | 2.3 | ||||||
Omnibus Agreement | 4.8 | 5.3 | 3.6 | |||||||||
Total expenses under commercial agreements | 175.4 | 142.1 | 59.4 | |||||||||
Factors Affecting Operating Results
Overview
Our earnings and cash flows from operations are primarily affected by the relationship between refined product prices and the prices for crude oil and other feedstocks. The cost to acquire crude oil and other feedstocks and the price of refined petroleum products ultimately sold depends on numerous factors beyond our control, including the supply of, and demand for, crude oil, gasoline, diesel and other refined petroleum products, which, in turn, depend on, among other factors, changes in global and regional economies, weather conditions, global and regional political affairs, production levels, the availability of imports, the marketing of competitive fuels, pipeline capacity, prevailing exchange rates and the extent of government regulation. Our revenue and operating income fluctuate significantly with movements in industry refined petroleum product prices, our materials cost fluctuate significantly with movements in crude oil prices and our other operating expenses fluctuate with movements in the price of energy to meet the power needs of our refineries. In addition, the effect of changes in crude oil prices on our operating results is influenced by how the prices of refined products adjust to reflect such changes.
Crude oil and other feedstock costs and the prices of refined petroleum products have historically been subject to wide fluctuation. Expansion and upgrading of existing facilities and installation of additional refinery distillation or conversion capacity, price volatility, international political and economic developments and other factors beyond our control are likely to continue to play an important role in refining industry economics. These factors can impact, among other things, the level of inventories in the market, resulting in price volatility and a reduction or increase in product margins. Moreover, the industry typically experiences seasonal fluctuations in demand for refined petroleum products, such as for gasoline and diesel, during the summer driving season and for home heating oil during the winter.
Benchmark Refining Margins
In assessing our operating performance, we compare the refining margins (revenue less materials cost) of each of our refineries against a specific benchmark industry refining margin based on crack spreads. Benchmark refining margins take into account both crude and refined petroleum product prices. When these prices are combined in a formula they provide a single value—a gross margin per barrel—that, when multiplied by throughput, provides an approximation of the gross margin generated by refining activities.
54
The performance of our East Coast refineries generally follows the Dated Brent (NYH) 2-1-1 benchmark refining margin. Our Toledo refinery generally follows the WTI (Chicago) 4-3-1 benchmark refining margin. Our Chalmette refinery generally follows the LLS (Gulf Coast) 2-1-1 benchmark refining margin. Our Torrance refinery generally follows the ANS (West Coast) 4-3-1 benchmark refining margin.
While the benchmark refinery margins presented below under “Results of Operations—Market Indicators” are representative of the results of our refineries, each refinery’s realized gross margin on a per barrel basis will differ from the benchmark due to a variety of factors affecting the performance of the relevant refinery to its corresponding benchmark. These factors include the refinery’s actual type of crude oil throughput, product yield differentials and any other factors not reflected in the benchmark refining margins, such as transportation costs, storage costs, credit fees, fuel consumed during production and any product premiums or discounts, as well as inventory fluctuations, timing of crude oil and other feedstock purchases, a rising or declining crude and product pricing environment and commodity price management activities. As discussed in more detail below, each of our refineries, depending on market conditions, has certain feedstock-cost and product-value advantages and disadvantages as compared to the refinery’s relevant benchmark.
Credit Risk Management
Credit risk refers to the risk that a counterparty will default on its contractual obligations resulting in financial loss to us. Our exposure to credit risk is reflected in the carrying amount of the receivables that are presented in our balance sheet. To minimize credit risk, all customers are subject to extensive credit verification procedures and extensions of credit above defined thresholds are to be approved by the senior management. Our intention is to trade only with recognized creditworthy third parties. In addition, receivable balances are monitored on an ongoing basis. We also limit the risk of bad debts by obtaining security such as guarantees or letters of credit.
Other Factors
We currently source our crude oil for the Paulsboro, Delaware City, Toledo, Chalmette and Torrance refineries on a global basis through a combination of market purchases and short-term purchase contracts, and through our crude oil supply agreements with Saudi Aramco, PDVSA and ExxonMobil. We have been purchasing up to approximately 100,000 bpd of crude oil from Saudi Aramco that is processed at Paulsboro. We have a contract with PDVSA for the supply of 40,000 to 60,000 bpd of crude oil that can be processed at any of our East or Gulf Coast refineries. Additionally, we have a supply agreement with ExxonMobil for approximately 60,000 bpd of crude oil that can be processed at our Torrance refinery. We believe purchases based on market pricing has given us flexibility in obtaining crude oil at lower prices and on a more accurate “as needed” basis. Since our Paulsboro and Delaware City refineries access their crude slates from the Delaware River via ship or barge and through our rail facilities at Delaware City, these refineries have the flexibility to purchase crude oils from the Mid-Continent and Western Canada, as well as a number of different countries.
In the past several years, we expanded and upgraded the existing on-site railroad infrastructure at the Delaware City refinery. Currently, crude oil delivered by rail to this facility is consumed at our Delaware City and Paulsboro refineries. The Delaware City rail unloading facility, which was transferred to PBFX in 2014, allows our East Coast refineries to source WTI-based crude oils from Western Canada and the Mid-Continent, which we believe, at times, may provide cost advantages versus traditional Brent-based international crude oils. In support of this rail strategy, we have at times entered into agreements to lease or purchase crude railcars. A portion of these railcars were purchased via the Rail Facility entered into during 2014, which was terminated in connection with the execution of the PBF Rail Term Loan in 2016. Certain of these railcars were subsequently sold to a third party, which has leased the railcars back to us for periods of between four and seven years. In 2016, we sold approximately 120 of these railcars to optimize our railcar portfolio. Our railcar fleet, at times, provides transportation flexibility within our crude oil sourcing strategy that allows our East Coast refineries to process cost advantaged crude from Canada and the Mid-Continent.
Our operating cost structure is also important to our profitability. Major operating costs include costs relating to employees and contract labor, energy, maintenance and environmental compliance, and emission control
55
regulations, including the cost of RINs required for compliance with the Renewable Fuels Standard. The predominant variable cost is energy, in particular, the price of utilities, natural gas, electricity and chemicals.
Our operating results are also affected by the reliability of our refinery operations. Unplanned downtime of our refinery assets generally results in lost margin opportunity and increased maintenance expense. The financial impact of planned downtime, such as major turnaround maintenance, is managed through a planning process that considers such things as the margin environment, the availability of resources to perform the needed maintenance and feed logistics, whereas unplanned downtime does not afford us this opportunity.
Refinery-Specific Information
The following section includes refinery-specific information related to our operations, crude oil differentials, ancillary costs, and local premiums and discounts.
Delaware City Refinery. The benchmark refining margin for the Delaware City refinery is calculated by assuming that two barrels of Dated Brent crude oil are converted into one barrel of gasoline and one barrel of diesel. We calculate this benchmark using the NYH market value of reformulated blendstock for oxygenate blending ("RBOB") and ULSD against the market value of Dated Brent and refer to the benchmark as the Dated Brent (NYH) 2-1-1 benchmark refining margin. Our Delaware City refinery has a product slate of approximately 53% gasoline, 30% distillate (consisting of jet fuel, ULSD and ultra-low sulfur heating oil), 1% high-value petrochemicals, with the remaining portion of the product slate comprised of lower-value products (6% black oil, 4% petroleum coke, 3% LPGs and 3% other). For this reason, we believe the Dated Brent (NYH) 2-1-1 is an appropriate benchmark industry refining margin. The majority of Delaware City revenues are generated off NYH-based market prices.
The Delaware City refinery’s realized gross margin on a per barrel basis has historically differed from the Dated Brent (NYH) 2-1-1 benchmark refining margin due to the following factors:
• | the Delaware City refinery processes a slate of primarily medium and heavy sour crude oils, which has constituted approximately 65% to 70% of total throughput. The remaining throughput consists of sweet crude oil and other feedstocks and blendstocks. In addition, we have the capability to process a significant volume of light, sweet crude oil depending on market conditions. Our total throughput costs have historically priced at a discount to Dated Brent; and |
• | as a result of the heavy, sour crude slate processed at Delaware City, we produce lower value products including sulfur, carbon dioxide and petroleum coke. These products are priced at a significant discount to gasoline, ULSD and heating oil and represent approximately 5% to 7% of our total production volume. |
Paulsboro Refinery. The benchmark refining margin for the Paulsboro refinery is calculated by assuming that two barrels of Dated Brent crude oil are converted into one barrel of gasoline and one barrel of diesel. We calculate this benchmark using the NYH market value of RBOB and ULSD diesel against the market value of Dated Brent and refer to the benchmark as the Dated Brent (NYH) 2-1-1 benchmark refining margin. Our Paulsboro refinery has a product slate of approximately 38% gasoline, 32% distillate (comprised of jet fuel, ULSD and ultra-low sulfur heating oil), 5% high-value Group I lubricants and 10% asphalt, with the remaining portion of the product slate comprised of lower-value products (6% black oil, 4% petroleum coke, 4% LPGs and 1% other). For this reason, we believe the Dated Brent (NYH) 2-1-1 is an appropriate benchmark industry refining margin. The majority of Paulsboro revenues are generated off NYH-based market prices.
The Paulsboro refinery’s realized gross margin on a per barrel basis has historically differed from the Dated Brent (NYH) 2-1-1 benchmark refining margin due to the following factors:
• | the Paulsboro refinery has generally processed a slate of primarily medium and heavy sour crude oils, which has historically constituted approximately 70% to 80% of total throughput. The remaining throughput consists of sweet crude oil and other feedstocks and blendstocks; |
56
• | as a result of the heavy, sour crude slate processed at Paulsboro, we produce lower value products including sulfur and petroleum coke. These products are priced at a significant discount to gasoline and heating oil and represent approximately 3% to 5% of our total production volume; and |
• | the Paulsboro refinery produces Group I lubricants which carry a premium sales price to gasoline and distillates. |
Toledo Refinery. The benchmark refining margin for the Toledo refinery is calculated by assuming that four barrels of WTI crude oil are converted into three barrels of gasoline, one-half barrel of ULSD and one-half barrel of jet fuel. We calculate this refining margin using the Chicago market values of conventional blendstock for oxygenate blending ("CBOB") and ULSD and the United States Gulf Coast value of jet fuel against the market value of WTI crude oil and refer to this benchmark as the WTI (Chicago) 4-3-1 benchmark refining margin. Our Toledo refinery has a product slate of approximately 54% gasoline, 35% distillate (comprised of jet fuel and ULSD), 5% high-value petrochemicals (including nonene, tetramer, benzene, xylene and toluene) with the remaining portion of the product slate comprised of lower-value products (5% LPGs and 1% other). For this reason, we believe the WTI (Chicago) 4-3-1 is an appropriate benchmark industry refining margin. The majority of Toledo revenues are generated off Chicago-based market prices.
The Toledo refinery’s realized gross margin on a per barrel basis has historically differed from the WTI (Chicago) 4-3-1 benchmark refining margin due to the following factors:
• | the Toledo refinery processes a slate of domestic sweet and Canadian synthetic crude oil. Historically, Toledo’s blended average crude costs have been higher than the market value of WTI crude oil; |
• | the Toledo refinery configuration enables it to produce more barrels of product than throughput which generates a pricing benefit; and |
• | the Toledo refinery generates a pricing benefit on some of its refined products, primarily its petrochemicals. |
Chalmette Refinery. The benchmark refining margin for the Chalmette refinery is calculated by assuming two barrels of Light Louisiana Sweet ("LLS") crude oil are converted into one barrel of gasoline and one barrel of diesel. We calculate this benchmark using the US Gulf Coast market value of 87 conventional gasoline and ULSD against the market value of LLS and refer to this benchmark as the LLS (Gulf Coast) 2-1-1 benchmark refining margin. Our Chalmette refinery has a product slate of approximately 48% gasoline, 31% distillate (comprised of ULSD, heating oil, and light cycle oil), 5% high-value petrochemicals (including benzene and xylenes) with the remaining portion of the product slate comprised of lower-value products (10% black oil, 5% petroleum coke and 1% other). For this reason, we believe the LLS (Gulf Coast) 2-1-1 is an appropriate benchmark industry refining margin. The majority of Chalmette revenues are generated off Gulf Coast-based market prices.
The Chalmette refinery’s realized gross margin on a per barrel basis has historically differed from the LLS (USGC) 2-1-1 benchmark refining margin due to the following factors:
• | The Chalmette refinery has generally processed a slate of primarily medium and heavy sour crude oils, which has historically constituted approximately 60% to 70% of total throughput. The remaining throughput consists of sweet crude oil and other feedstocks and blendstocks; and |
• | as a result of the heavy, sour crude slate processed at Chalmette, we produce lower-value products including sulfur and petroleum coke. These products are priced at a significant discount to gasoline and heating oil and represent approximately 4% to 6% of our total production volume. |
A project underway to restart an idled naphtha hydrotreater, reformer and light-ends recovery unit will increase high-octane, ultra-low sulfur reformate and chemicals production. A new crude oil tank being constructed will allow gasoline and diesel export opportunities and reduce Renewable Identification Numbers (“RINs”) compliance costs. Both projects are expected to be completed in the third quarter of 2017.
57
Torrance Refinery. The benchmark refining margin for the Torrance refinery is calculated by assuming that four barrels of Alaskan North Slope (“ANS”) crude oil are converted into three barrels of gasoline, one-half barrel of diesel and one-half barrel of jet fuel. We calculate this benchmark using the West Coast Los Angeles market value of California reformulated blendstock for oxygenate blending (CARBOB), California Air Resources Board (CARB) diesel and jet fuel and refer to the benchmark as the ANS (WCLA) 4-3-1 benchmark refining margin. Our Torrance Refinery has a product slate of approximately 62% gasoline and 25% distillate (comprised of jet fuel, ULSD and marine diesel) with the remaining portion of the product slate comprised of lower-value products (8% petroleum coke, 2% LPG, 2% black oil and 1% other). For this reason, we believe the ANS (West Coast) 4-3-1 is an appropriate benchmark industry refining margin. The majority of Torrance revenues are generated off West Coast Los Angeles-based market prices.
The Torrance refinery’s realized gross margin on a per barrel basis has historically differed from the ANS (WCLA) 4-3-1 benchmark refining margin due to the following factors:
• | The Torrance Refinery has generally processed a slate of primarily heavy sour crude oils, which has historically constituted approximately 80% to 90% of total throughput. The Torrance crude slate has the lowest API gravity (typically an American Petroleum Institute ("API") gravity of less than 20 degrees) of all of our refineries. The remaining throughput consists of other feedstocks and blendstocks; and |
• | as a result of the heavy, sour crude slate processed at Torrance, we produce lower-value products including petroleum coke and sulfur. These products are priced at a significant discount to gasoline and diesel and represent approximately 9% to 11% of our total production volume. |
58
Results of Operations
The following tables reflect our consolidated financial and operating highlights for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 (amounts in thousands).
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 15,908,537 | $ | 13,123,929 | $ | 19,828,155 | ||||||
Cost of sales, excluding depreciation | 13,765,088 | 11,611,599 | 18,514,054 | |||||||||
2,143,449 | 1,512,330 | 1,314,101 | ||||||||||
Operating expenses, excluding depreciation | 1,390,582 | 889,368 | 880,701 | |||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 149,643 | 166,904 | 140,150 | |||||||||
Equity (income) loss in investee | (5,679 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Loss (gain) on sale of assets | 11,374 | (1,004 | ) | (895 | ) | |||||||
Depreciation and amortization expense | 209,840 | 191,110 | 178,996 | |||||||||
Income from operations | 387,689 | 265,952 | 115,149 | |||||||||
Change in fair value of catalyst leases | 1,422 | 10,184 | 3,969 | |||||||||
Interest expense, net | (129,536 | ) | (88,194 | ) | (98,001 | ) | ||||||
Income before income taxes | 259,575 | 187,942 | 21,117 | |||||||||
Income tax expense | 23,689 | 648 | — | |||||||||
Net Income | 235,886 | 187,294 | 21,117 | |||||||||
Less: net income attributable to noncontrolling interest | 269 | 274 | — | |||||||||
Net income attributable to PBF Holding LLC | $ | 235,617 | $ | 187,020 | $ | 21,117 | ||||||
Gross margin | $ | 548,862 | $ | 441,539 | $ | 267,987 | ||||||
Gross refining margin (1) | 2,143,449 | 1,512,330 | 1,314,101 | |||||||||
——————————
(1) | See Non-GAAP financial measures below. |
59
Operating Highlights
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
Key Operating Information | ||||||||||||
Production (bpd in thousands) | 734.3 | 511.9 | 452.1 | |||||||||
Crude oil and feedstocks throughput (bpd in thousands) | 727.7 | 516.4 | 453.1 | |||||||||
Total crude oil and feedstocks throughput (millions of barrels) | 266.4 | 188.4 | 165.4 | |||||||||
Gross margin per barrel of throughput | $ | 2.06 | $ | 2.34 | $ | 1.60 | ||||||
Gross refining margin, excluding special items, per barrel of throughput (1) | $ | 6.09 | $ | 10.29 | $ | 12.11 | ||||||
Refinery operating expense, excluding depreciation, per barrel of throughput | $ | 5.22 | $ | 4.72 | $ | 5.34 | ||||||
Crude and feedstocks (% of total throughput) (2) | ||||||||||||
Heavy Crude | 26 | % | 14 | % | 14 | % | ||||||
Medium Crude | 37 | % | 49 | % | 44 | % | ||||||
Light Crude | 25 | % | 26 | % | 33 | % | ||||||
Other feedstocks and blends | 12 | % | 11 | % | 9 | % | ||||||
Total throughput | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | ||||||
Yield (% of total throughput) | ||||||||||||
Gasoline and gasoline blendstocks | 50 | % | 49 | % | 47 | % | ||||||
Distillates and distillate blendstocks | 31 | % | 35 | % | 36 | % | ||||||
Lubes | 1 | % | 1 | % | 2 | % | ||||||
Chemicals | 3 | % | 3 | % | 3 | % | ||||||
Other | 15 | % | 12 | % | 12 | % | ||||||
Total yield | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | ||||||
(1) See Non-GAAP Financial measures below. | ||||||||||||
(2) We define heavy crude oil as crude oil with American Petroleum Institute (API) gravity less than 24 degrees. We define medium crude oil as crude oil with API gravity between 24 and 35 degrees. We define light crude oil as crude oil with API gravity higher than 35 degrees. | ||||||||||||
60
The table below summarizes certain market indicators relating to our operating results as reported by Platts.
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
(dollars per barrel, except as noted) | ||||||||||||
Dated Brent Crude | $ | 43.91 | $ | 52.56 | $ | 98.95 | ||||||
West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude oil | $ | 43.34 | $ | 48.71 | $ | 93.28 | ||||||
Light Louisiana Sweet (LLS) crude oil | $ | 45.03 | $ | 52.36 | $ | 96.92 | ||||||
Alaska North Slope (ANS) crude oil | $ | 43.67 | $ | 52.44 | $ | 97.52 | ||||||
Crack Spreads | ||||||||||||
Dated Brent (NYH) 2-1-1 | $ | 13.49 | $ | 16.35 | $ | 12.92 | ||||||
WTI (Chicago) 4-3-1 | $ | 12.38 | $ | 17.91 | $ | 15.92 | ||||||
LLS (Gulf Coast) 2-1-1 | $ | 10.75 | $ | 14.39 | $ | 16.95 | ||||||
ANS (West Coast) 4-3-1 | $ | 16.46 | $ | 26.46 | $ | 15.59 | ||||||
Crude Oil Differentials | ||||||||||||
Dated Brent (foreign) less WTI | $ | 0.56 | $ | 3.85 | $ | 5.66 | ||||||
Dated Brent less Maya (heavy, sour) | $ | 7.36 | $ | 8.45 | $ | 13.08 | ||||||
Dated Brent less WTS (sour) | $ | 1.42 | $ | 3.59 | $ | 11.62 | ||||||
Dated Brent less ASCI (sour) | $ | 3.92 | $ | 4.57 | $ | 6.49 | ||||||
WTI less WCS (heavy, sour) | $ | 12.57 | $ | 11.87 | $ | 19.45 | ||||||
WTI less Bakken (light, sweet) | $ | 1.32 | $ | 2.89 | $ | 5.47 | ||||||
WTI less Syncrude (light, sweet) | $ | (2.01 | ) | $ | (1.45 | ) | $ | 2.25 | ||||
WTI less ANS (light, sweet) | $ | (0.33 | ) | $ | (3.73 | ) | $ | (4.24 | ) | |||
Natural gas (dollars per MMBTU) | $ | 2.55 | $ | 2.63 | $ | 4.26 | ||||||
2016 Compared to 2015
Overview— Our net income was $235.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to $187.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2015.
Our results for the year ended December 31, 2016 were positively impacted by a non-cash special item consisting of an inventory LCM adjustment of approximately $521.3 million whereas our results for the year ended December 31, 2015 were negatively impacted by an inventory LCM adjustment of approximately $427.2 million. These LCM adjustments were recorded due to significant changes in the price of crude oil and refined products in the periods presented. Excluding the impact of the net change in LCM reserve, our results for the year ended December 31, 2016 were negatively impacted by unfavorable movements in certain crude oil differentials, lower crack spreads, increased costs to comply with the RFS, and increased interest costs, partially offset by positive earnings contributions from the Chalmette and Torrance refineries and higher throughput in the Mid-Continent. Throughput volumes for 2015 in the Mid-Continent were impacted by unplanned downtime in the second quarter of 2015.
Revenues— Revenues totaled $15.9 billion for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to $13.1 billion for the year ended December 31, 2015, an increase of approximately $2.8 billion or 21.2%. Revenues per barrel were $59.72 and $69.66 for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, a decrease of 14.3% directly related to lower hydrocarbon commodity prices. For the year ended December 31, 2016, the total throughput rates at our East Coast, Mid-Continent and Gulf Coast refineries averaged approximately 327,000 bpd, 159,100 bpd and 169,300 bpd, respectively. For the period from its acquisition on July 1, 2016 through December 31, 2016, our West Coast refinery's throughput averaged 143,900 bpd. For the year ended December 31, 2015, the total throughput rates at our East Coast and Mid-Continent, refineries averaged approximately 330,700 bpd and 153,800 bpd, respectively. For the period from its acquisition on November 1, 2015 through December 31, 2015, our Gulf
61
Coast refinery's throughput averaged 190,800 bpd. The slight decrease in throughput rates at our East Coast refineries in 2016 compared to 2015 is primarily due to weather-related unplanned downtime at our Delaware City refinery in the first quarter of 2016, partially offset by downtime at our Delaware City refinery in 2015. The increase in throughput rates at our Mid-Continent refinery in 2016 is due to unplanned downtime in the second quarter of 2015. Our Gulf Coast and West Coast refineries were not acquired until the fourth quarter of 2015 and the third quarter of 2016, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2016, the total refined product barrels sold at our East Coast, Mid-Continent, and Gulf Coast refineries averaged approximately 364,100 bpd, 171,800 bpd and 206,400 bpd, respectively. For the period from its acquisition on July 1, 2016 through December 31, 2016, refined product barrels sold at our West Coast refinery averaged approximately 179,200 bpd. For the year ended December 31, 2015, the total refined product barrels sold at our East Coast and Mid-Continent refineries averaged approximately 366,100 bpd and 162,600 bpd, respectively. For the period from its acquisition on November 1, 2015 through December 31, 2015, the total refined product barrels sold at our Gulf Coast refinery averaged 216,100 bpd. Total refined product barrels sold were higher than throughput rates, reflecting sales from inventory as well as sales and purchases of refined products outside the refineries.
Gross Margin— Gross margin, including refinery operating expenses and depreciation, totaled $548.9 million, or $2.06 per barrel of throughput, for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to $441.5 million, or $2.34 per barrel of throughput for the year ended December 31, 2015, an increase of approximately $107.3 million. Gross refining margin (as defined below in Non-GAAP Financial Measures) totaled $2,143.4 million, or $8.05 per barrel of throughput ($1,622.1 million or $6.09 per barrel of throughput excluding the impact of special items) for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to $1,512.3 million, or $8.02 per barrel of throughput ($1,939.6 million or $10.29 per barrel of throughput excluding the impact of special items) for the year ended December 31, 2015, an increase of approximately $631.1 million or a decrease of approximately $317.5 million excluding special items. Excluding the impact of special items, gross margin and gross refining margin decreased due to unfavorable movements in certain crude differentials, lower crack spreads as persistent above-average refined product inventory levels weighed on margins, and increased costs to comply with the RFS, partially offset by higher throughput rates in the Mid-Continent and positive margin contributions from the Chalmette and Torrance refineries acquired in the fourth quarter of 2015 and third quarter of 2016, respectively. Costs to comply with our obligation under the RFS totaled $236.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 (excluding our Gulf Coast and West Coast refineries, whose costs to comply with RFS totaled $111.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2016) compared to $163.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 (excluding our Gulf Coast, whose costs to comply with RFS totaled $8.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2015). In addition, gross margin and gross refining margin were positively impacted by a non-cash LCM adjustment of approximately $521.3 million resulting from the change in crude oil and refined product prices from the end of 2015 to the end of 2016 which, in addition to remaining below historical costs, increased since the prior year. The non-cash LCM adjustment decreased gross margin and gross refining margin by approximately $427.2 million in the year ended December 31, 2015.
Average industry refining margins in the Mid-Continent were weaker during the year ended December 31, 2016, as compared to the same period in 2015. The WTI (Chicago) 4-3-1 industry crack spread was $12.38 per barrel, or 30.9% lower, in the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to $17.91 per barrel in the same period in 2015. Our margins were negatively impacted from our refinery specific crude slate in the Mid-Continent which was impacted by a declining WTI/Bakken differential and a declining WTI/Syncrude differential, which averaged a premium of $2.01 per barrel for the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to a premium of $1.45 per barrel in the same period in 2015.
The Dated Brent (NYH) 2-1-1 industry crack spread was approximately $13.49 per barrel, or 17.5% lower in the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to $16.35 per barrel in the same period in 2015. The Dated Brent/WTI differential and Dated Brent/Maya differential were $3.29 and $1.09 lower, respectively, in the year ended December 31, 2016, as compared to the same period in 2015. In addition, the WTI/Bakken differential was approximately $1.57 per barrel less favorable in the year December 31, 2016 as compared to the same period in 2015. Reductions in these benchmark crude differentials typically result in higher crude costs and negatively impact our earnings.
62
Operating Expenses— Operating expenses totaled $1,390.6 million, or $5.22 per barrel of throughput, for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to $889.4 million, or $4.72 per barrel of throughput, for the year ended December 31, 2015, an increase of $501.2 million, or 56.4%. The increase in operating expenses was mainly attributable to the operating expenses associated with the Chalmette and Torrance refineries and related logistics assets. For the year ended December 31, 2016 and for the period from its acquisition on November 1, 2015 to December 31, 2015, the Chalmette refinery and related logistics assets incurred operating expenses of approximately $343.9 million and $52.1 million, respectively. In the period from its acquisition on July 1, 2016 to December 31, 2016, the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets incurred operating expenses of approximately $250.5 million. Total operating expenses at our refineries, excluding our Chalmette and Torrance refineries, decreased slightly for the year ended December 31, 2016, primarily due to lower energy costs and maintenance costs. The reduction in energy costs was mainly due to lower natural gas prices while the reduction in maintenance costs was mainly due to timing of repairs and certain non-recurring maintenance costs incurred in 2015. These reductions were partially offset by higher employee-related expenses, primarily attributable to merit increases in salaries.
General and Administrative Expenses— General and administrative expenses totaled $149.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to $166.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, a decrease of $17.3 million or 10.3%. The decrease in general and administrative expenses primarily relates to reduced employee related expenses of $39.3 million mainly due to lower incentive compensation expenses, partially offset by $12.9 million in additional outside services and other costs to support our acquisitions and related integration activities, and an increase of $9.1 million in equity compensation expense related to incremental grants in 2016 and accelerated vesting of awards due to retirements. Our general and administrative expenses are comprised of the personnel, facilities and other infrastructure costs necessary to support our refineries.
Loss (gain) on Sale of Assets— There was a loss of $11.4 million on the sale of assets for the year ended December 31, 2016 relating to the sale of non-refining assets as compared to a gain of $1.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 which related to the sale of railcars which were subsequently leased back.
Depreciation and Amortization Expense— Depreciation and amortization expense totaled $209.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to $191.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, an increase of $18.7 million. The increase was a result of additional depreciation expense associated with the assets acquired in the Chalmette and Torrance Acquisitions and a general increase in our fixed asset base due to capital projects and turnarounds completed since 2015.
Change in Fair Value of Catalyst Leases— Change in the fair value of catalyst leases represented a gain of $1.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to a gain of $10.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. These gains relate to the change in value of the precious metals underlying the sale and leaseback of our refineries’ precious metals catalyst, which we are obligated to return or repurchase at fair market value on the lease termination dates.
Interest Expense, net— Interest expense totaled $129.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to $88.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, an increase of $41.3 million. This increase is mainly attributable to higher interest costs associated with the issuance of the 2023 Senior Secured Notes in November 2015, increased interest expense related to the affiliate notes payable and the drawdown on our Revolving Loan to partially fund the Torrance Acquisition in July 2016, partially offset by lower letter of credit fees. Interest expense includes interest on long-term debt and notes payable, costs related to the sale and leaseback of our precious metals catalyst, financing costs associated with the A&R Inventory Intermediation Agreements with J. Aron, letter of credit fees associated with the purchase of certain crude oils, and the amortization of deferred financing costs.
Income Tax Expense— As PBF Holding is a limited liability company treated as a “flow-through” entity for income tax purposes our consolidated financial statements generally do not include a benefit or provision for income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 apart from the income tax attributable to two subsidiaries of Chalmette Refining and a wholly-owned Canadian subsidiary, PBF Energy Limited ("PBF Ltd.") that are treated as C-Corporations for income tax purposes. The two Chalmette subsidiaries incurred approximately
63
$1.4 million of income tax expense and PBF Holding incurred income tax benefit of approximately $8.4 million attributable to PBF Ltd for the year ended December 31, 2016. In addition, we recorded $30.7 million of incremental income tax expense in 2016 relating to a correction of prior period income taxes.
2015 Compared to 2014
Overview—Net income was $187.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to $21.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Our results for the year ended December 31, 2015 were negatively impacted by a non-cash special item consisting of an inventory LCM adjustment of approximately $427.2 million whereas our results for the year ended December 31, 2014 were negatively impacted by an inventory LCM adjustment of approximately $690.1 million. These LCM charges were recorded due to significant declines in the price of crude oil and refined products in 2015 and 2014. Our throughput rates during the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to December 31, 2014 were higher due to the acquisition of the Chalmette refinery on November 1, 2015 as well as an approximate 40-day plant-wide planned turnaround at our Toledo Refinery completed in the fourth quarter of 2014. Our results for the year ended December 31, 2015 were positively impacted by higher throughput volumes, lower non-cash special items for LCM charges and higher crack spreads for the East Coast and in the Mid-Continent partially offset by unfavorable movements in certain crude differentials.
Revenues—Revenues totaled $13.1 billion for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to $19.8 billion for the year ended December 31, 2014, a decrease of approximately $6.7 billion, or 33.8%. Revenues per barrel were $69.66 and $119.89 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, a decrease of 41.9% directly related to lower hydrocarbon commodity prices. For the year ended December 31, 2015, the total throughput rates in the East Coast and Mid-Continent refineries averaged approximately 330,700 bpd and 153,800 bpd, respectively. For the period from its acquisition on November 1, 2015 through December 31, 2015, our Gulf Coast refinery's throughput averaged 190,800 bpd. For the year ended December 31, 2014, the total throughput rates at our East Coast and Mid-Continent refineries averaged approximately 325,300 bpd, and 127,800 bpd, respectively. The increase in throughput rates at our East Coast refineries in 2015 compared to 2014 was primarily due to higher run rates as a result of favorable market economics partially offset by unplanned downtime at our Delaware City refinery in 2015. The increase in throughput rates at our Mid-Continent refinery in 2015 compared to 2014 was primarily due to an approximate 40-day plant-wide planned turnaround completed in the fourth quarter of 2014. For the year ended December 31, 2015, the total refined product barrels sold at our East Coast and Mid-Continent refineries averaged approximately 366,100 bpd and 162,600 bpd, respectively. For the period from its acquisition on November 1, 2015 through December 31, 2015, the total refined product barrels sold at our Gulf Coast refinery averaged 216,100 bpd. For the year ended December 31, 2014, the total refined product barrels sold at our East Coast and Mid-Continent refineries averaged approximately 350,800 bpd and 144,100 bpd, respectively. Total refined product barrels sold were higher than throughput rates, reflecting sales from inventory as well as sales and purchases of refined products outside the refineries.
Gross Margin— Gross margin, including refinery operating expenses and depreciation, totaled $441.5 million, or $2.34 per barrel of throughput, for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to $268.0 million, or $1.60 per barrel of throughput, for the year ended December 31, 2014, an increase of $173.6 million. Gross refining margin (as defined below in Non-GAAP Financial Measures) totaled $1,512.3 million, or $8.02 per barrel of throughput, ($1,939.6 million or $10.29 per barrel of throughput excluding the impact of special items) for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to $1,314.1 million, or $7.94 per barrel of throughput ($2,004.2 million, or $12.11 per barrel of throughput excluding the impact of special items) for the year ended December 31, 2014, an increase of $198.2 million and a decrease of $64.7 million excluding special items. Excluding the impact of special items, gross refining margin decreased due to the narrowing of certain crude differentials partially offset by higher throughput rates, reflecting the impact from the Chalmette Acquisition, and favorable movements in crack spreads. Excluding the impact of special items, gross margin was relatively consistent with the prior year.
Average industry refining margins in the U.S. Mid-Continent were generally improved during the year ended December 31, 2015, as compared to the same period in 2014. The WTI (Chicago) 4-3-1 industry crack spread was
64
approximately $17.91 per barrel or 12.5% higher in the year ended December 31, 2015, as compared to the same period in 2014. The price of WTI versus Dated Brent and other crude discounts narrowed during the year ended December 31, 2015, and our refinery specific crude slate in the Mid-Continent faced an adverse WTI/Syncrude differential, which averaged a premium of $1.45 per barrel for the year ended December 31, 2015 as compared to a discount of $2.25 per barrel in the same period in 2014.
The Dated Brent (NYH) 2-1-1 industry crack spread was approximately $16.35 per barrel, or 26.5% higher in the year ended December 31, 2015, as compared to the same period in 2014. However, the WTI/Dated Brent differential was $1.81 lower in the year ended December 31, 2015, as compared to the same period in 2014, and the WTI/Bakken differential was $2.58 per barrel less favorable for the same periods. The Dated Brent/Maya differential was approximately $4.63 per barrel less favorable in the year ended December 31, 2015 as compared to the same period in 2014. Additionally, the decrease in the Dated Brent/Maya crude differential, our proxy for the light/heavy crude differential, had a negative impact on our East Coast refineries, which can process a large slate of medium and heavy, sour crude oil that is priced at a discount to light, sweet crude oil. However, the lower flat price of crude oil during 2015 as compared to 2014 resulted in improved margins on certain lower value products we produce.
Operating Expenses—Operating expenses totaled $889.4 million, or $4.72 per barrel of throughput, for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to $880.7 million, or $5.34 per barrel of throughput, for the year ended December 31, 2014, an increase of $8.7 million, or 1.0%. The increase in operating expenses is mainly attributable to an increase of approximately $45.8 million in maintenance costs, primarily driven by the Chalmette Acquisition in 2015 and general repairs at the Delaware City and Paulsboro refineries, an increase of $17.3 million in employee compensation primarily driven by additional headcount and $14.9 million of increased catalyst and chemicals costs partially offset by net reduced energy and utility costs of $64.4 million due to lower natural gas prices and $4.4 million lower other fixed charges. Our operating expenses principally consist of salaries and employee benefits, maintenance, energy and catalyst and chemicals costs at our refineries. Although operating expenses increased on an overall basis, refinery operating expenses per barrel decreased as a result of higher throughput volumes.
General and Administrative Expenses—General and administrative expenses totaled $166.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to $140.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, an increase of $26.7 million or 19.1%. The increase in general and administrative expenses primarily relates to higher employee compensation expense of $13.3 million, mainly related to higher headcount and higher incentive compensation expenses, higher outside services fees of $3.0 million related to professional, legal and engineering consultants attributable to the Chalmette Acquisition, and higher equity compensation expense of $1.3 million. Our general and administrative expenses are comprised of the personnel, facilities and other infrastructure costs necessary to support our refineries.
Gain on Sale of Assets—Gain on sale of assets for the year ended December 31, 2015 was $1.0 million which related to the sale of railcars which were subsequently leased back to us, compared to a gain of $0.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, for the sale of railcars.
Depreciation and Amortization Expense—Depreciation and amortization expense totaled $191.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to $179.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, an increase of $12.1 million. The increase was largely driven by our increased fixed asset base due to capital projects and turnarounds completed during 2014 and 2015 as well as the acquisition of the Chalmette refinery in 2015. These general increases were partially offset by reduction in impairment charges. In 2014, we recorded a $28.5 million impairment related to an abandoned capital project at our Delaware City refinery during that year whereas we did not record any significant impairment charges in the year ended December 31, 2015.
Change in Fair Value of Catalyst Leases— Change in the fair value of catalyst leases represented a gain of $10.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to a gain of $4.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. This gain relates to the change in value of the precious metals underlying the sale and leaseback of our refineries’ precious metals catalyst, which we are obligated to return or repurchase at fair market value on the lease termination dates.
65
Interest Expense, net— Interest expense totaled $88.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to $98.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, a decrease of $9.8 million. The decrease is mainly attributable to the termination of our crude and feeedstock supply agreement with MSCG, effective July 31, 2014. Interest expense includes interest on long-term debt including the Senior Secured Notes and credit facility, costs related to the sale and leaseback of our precious metals catalyst, interest expense incurred in connection with our crude and feedstock supply agreement with Statoil up to its expiration on December 31, 2015, financing costs associated with the Inventory Intermediation Agreements with J. Aron, letter of credit fees associated with the purchase of certain crude oils, and the amortization of deferred financing fees.
Income Tax Expense— As PBF Holding is a limited liability company treated as a “flow-through” entity for income tax purposes our consolidated financial statements do not include a benefit or provision for income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 apart from the income tax attributable to two subsidiaries of Chalmette Refining that are treated as C-Corporations for income tax purposes.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
Management uses certain financial measures to evaluate our operating performance that are calculated and presented on the basis of methodologies other than in accordance with GAAP (“Non-GAAP”). These measures should not be considered a substitute for, or superior to, measures of financial performance prepared in accordance with GAAP, and our calculations thereof may not be comparable to similarly entitled measures reported by other companies.
Special Items
The non-GAAP measures presented include EBITDA excluding special items, and gross refining margin excluding special items. The special items for the periods presented relate to an LCM adjustment. LCM is a GAAP guideline related to inventory valuation that requires inventory to be stated at the lower of cost or market. Our inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market. Cost is determined by the last-in, first-out (“LIFO”) inventory valuation methodology, in which the most recently incurred costs are charged to cost of sales and inventories are valued at base layer acquisition costs. Market is determined based on an assessment of the current estimated replacement cost and net realizable selling price of the inventory. In periods where the market price of our inventory declines substantially, cost values of inventory may exceed market values. In such instances, we record an adjustment to write down the value of inventory to market value in accordance with GAAP. In subsequent periods, the value of inventory is reassessed and a LCM adjustment is recorded to reflect the net change in the LCM inventory reserve between the prior period and the current period. Although we believe that non-GAAP financial measures, excluding the impact of special items, provide useful supplemental information to investors regarding the results and performance of our business and allow for helpful period-over-period comparisons, such non-GAAP measures should only be considered as a supplement to, and not as a substitute for, or superior to, the financial measures prepared in accordance with GAAP.
Gross Refining Margin
Gross refining margin is defined as gross margin excluding depreciation and operating expense related to the refineries. We believe gross refining margin is an important measure of operating performance and provides useful information to investors because it is a helpful metric comparison to the industry refining margin benchmarks, as the refining margin benchmarks do not include a charge for refinery operating expenses and depreciation expense. In order to assess our operating performance, we compare our gross refining margin (revenue less cost of sales) to industry refining margin benchmarks and crude oil prices as defined in the table below.
Gross refining margin should not be considered an alternative to gross margin, operating income, net cash flows from operating activities or any other measure of financial performance or liquidity presented in accordance with GAAP. Gross refining margin presented by other companies may not be comparable to our presentation, since each company may define this term differently. The following table presents a reconciliation of gross refining
66
margin to the most directly comparable GAAP financial measure, gross margin, on a historical basis, as applicable, for each of the periods indicated (in thousands except per barrel amounts):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||
$ | per barrel of throughput | $ | per barrel of throughput | $ | per barrel of throughput | ||||||||||||||||
Reconciliation of gross margin to gross refining margin: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Gross margin | $ | 548,862 | $ | 2.06 | $ | 441,539 | $ | 2.34 | $ | 267,987 | $ | 1.60 | |||||||||
Add: Refinery operating expense | 1,390,582 | 5.22 | 889,368 | 4.72 | 880,701 | 5.34 | |||||||||||||||
Add: Refinery depreciation expense | 204,005 | 0.77 | 181,423 | 0.96 | 165,413 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||
Gross refining margin | $ | 2,143,449 | $ | 8.05 | $ | 1,512,330 | $ | 8.02 | $ | 1,314,101 | $ | 7.94 | |||||||||
Special items: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Add: Non-cash LCM inventory adjustment (1) | (521,348 | ) | (1.96 | ) | 427,226 | 2.27 | 690,110 | 4.17 | |||||||||||||
Gross refining margin excluding special items | $ | 1,622,101 | $ | 6.09 | $ | 1,939,556 | $ | 10.29 | $ | 2,004,211 | $ | 12.11 | |||||||||
(1) During the year ended December 31, 2016, we recorded an adjustment to value our inventories to the lower of cost or market which resulted in a net pre-tax benefit of $521.3 million reflecting the change in the lower of cost or market inventory reserve from $1,117.3 million at December 31, 2015 to $596.0 million at December 31, 2016. During the year ended December 31, 2015, we recorded an adjustment to value our inventories to the lower of cost or market which resulted in a net pre-tax charge of $427.2 million reflecting the change in the lower of cost or market inventory reserve from $690.1 million at December 31, 2014 to $1,117.3 million at December 31, 2015. During the year ended December 31, 2014, we recorded an adjustment to value our inventory to the lower of cost or market which resulted in a net pre-tax charge of $690.1 million. The net impact of these LCM inventory adjustments are included in operating income, but are excluded from the operating results presented in the table in order to make such information comparable between periods. | |||||||||||||||||||||
EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA
Our management uses EBITDA (earnings before interest, income taxes, depreciation and amortization) and Adjusted EBITDA as measures of operating performance to assist in comparing performance from period to period on a consistent basis and to readily view operating trends, as a measure for planning and forecasting overall expectations and for evaluating actual results against such expectations, and in communications with our board of directors, creditors, analysts and investors concerning our financial performance. Our outstanding indebtedness for borrowed money and other contractual obligations also include similar measures as a basis for certain covenants under those agreements which may differ from the Adjusted EBITDA definition described below.
EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA are not presentations made in accordance with GAAP and our computation of EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA may vary from others in our industry. In addition, Adjusted EBITDA contains some, but not all, adjustments that are taken into account in the calculation of the components of various covenants in the agreements governing the Senior Secured Notes and other credit facilities. EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA should not be considered as alternatives to operating income (loss) or net income (loss) as measures of operating performance. In addition, EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA are not presented as, and should not be considered, an alternative to cash flows from operations as a measure of liquidity. Adjusted EBITDA is defined as EBITDA before adjustments for items such as equity-based compensation expense, gains (losses) from certain derivative activities and contingent consideration, the non-cash change in the deferral of gross profit related to the sale of certain finished products and the write down of inventory to the LCM. Other companies, including other companies in our industry, may calculate EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA differently than we do, limiting their usefulness as a comparative measure. EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA also have limitations as analytical tools and should not be
67
considered in isolation, or as a substitute for analysis of our results as reported under GAAP. Some of these limitations include that EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA:
• | does not reflect depreciation expense or our cash expenditures, or future requirements, for capital expenditures or contractual commitments; |
• | does not reflect changes in, or cash requirements for, our working capital needs; |
• | does not reflect our interest expense, or the cash requirements necessary to service interest or principal payments, on our debt; |
• | does not reflect realized and unrealized gains and losses from certain hedging activities, which may have a substantial impact on our cash flow; |
• | does not reflect certain other non-cash income and expenses; and |
• | excludes income taxes that may represent a reduction in available cash. |
The following tables reconcile net income as reflected in our results of operations to EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA for the periods presented (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||
Reconciliation of net income to EBITDA: | |||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 235,886 | $ | 187,294 | $ | 21,117 | |||||||
Add: Depreciation and amortization expense | 209,840 | 191,110 | 178,996 | ||||||||||
Add: Interest expense, net | 129,536 | 88,194 | 98,001 | ||||||||||
Add: Income tax expense (benefit) | 23,689 | 648 | — | ||||||||||
EBITDA | $ | 598,951 | $ | 467,246 | $ | 298,114 | |||||||
Special Items: | |||||||||||||
Add: Non-cash LCM inventory adjustment (1) | (521,348 | ) | 427,226 | 690,110 | |||||||||
EBITDA excluding special items | $ | 77,603 | $ | 894,472 | $ | 988,224 | |||||||
Reconciliation of EBITDA to Adjusted EBITDA: | |||||||||||||
EBITDA | $ | 598,951 | $ | 467,246 | $ | 298,114 | |||||||
Add: Stock based compensation | 18,296 | 9,218 | 6,095 | ||||||||||
Add: Non-cash LCM inventory adjustment | (521,348 | ) | 427,226 | 690,110 | |||||||||
Add: Non-cash change in fair value of catalyst lease obligations | (1,422 | ) | (10,184 | ) | (3,969 | ) | |||||||
Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 94,477 | $ | 893,506 | $ | 990,350 | |||||||
(1) During the year ended December 31, 2016, we recorded an adjustment to value our inventories to the lower of cost or market which resulted in a net pre-tax benefit of $521.3 million reflecting the change in the lower of cost or market inventory reserve from $1,117.3 million at December 31, 2015 to $596.0 million at December 31, 2016. During the year ended December 31, 2015, we recorded an adjustment to value our inventories to the lower of cost or market which resulted in a net pre-tax charge of $427.2 million reflecting the change in the lower of cost or market inventory reserve from $690.1 million at December 31, 2014 to $1,117.3 million at December 31, 2015. During the year ended December 31, 2014, we recorded an adjustment to value our inventory to the lower of cost or market which resulted in a net pre-tax charge of $690.1 million. The net impact of these LCM inventory adjustments are included in operating income, but are excluded from the operating results presented in the table in order to make such information comparable between periods. | |||||||||||||
68
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
Our primary sources of liquidity are our cash flows from operations and borrowing availability under our credit facilities, as more fully described below. We believe that our cash flows from operations and available capital resources will be sufficient to meet our and our subsidiaries' capital expenditure, working capital, distribution payments and debt service requirements for the next twelve months. On July 1, 2016, we closed the Torrance Acquisition with a combination of cash on hand, including proceeds from a capital contribution made in connection with PBF Energy's October 2015 Equity Offering and our 2023 Senior Secured Notes Offering, and borrowings under our Revolving Loan. However, our ability to generate sufficient cash flow from operations depends, in part, on petroleum oil market pricing and general economic, political and other factors beyond our control. We are in compliance as of December 31, 2016 with all of the covenants, including financial covenants, in all of our debt agreements.
Cash Flow Analysis
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
Net cash provided by operating activities was $551.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to net cash provided by operating activities of $652.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. Our operating cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2016 included our net income of $235.9 million, depreciation and amortization of $218.9 million, change in the fair value of our inventory repurchase obligations of $29.5 million, pension and other post retirement benefits costs of $38.0 million, deferred income tax expense of $19.8 million, stock-based compensation of $18.3 million and a loss on sale of assets of $11.4 million, partially offset by net non-cash benefits relating to an LCM adjustment of $521.3 million, equity income from our investment in TVPC of $5.7 million and the changes in the fair value of our catalyst lease of $1.4 million. In addition, net changes in working capital reflected sources of cash of $508.3 million driven by timing of inventory purchases and collections of accounts receivable. Our operating cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2015 included our net income of $187.3 million, plus net non-cash charges relating to an LCM adjustment of $427.2 million, depreciation and amortization of $199.4 million, change in the fair value of our inventory repurchase obligations of $63.4 million, pension and other post retirement benefits costs of $27.0 million, and stock-based compensation of $9.2 million, partially offset by the changes in the fair value of our catalyst lease of $10.2 million, and gain on sales of assets of $1.0 million. In addition, net changes in working capital reflected uses of cash of $249.9 million driven by timing of inventory purchases and collections of accounts receivable.
Net cash provided by operating activities was $652.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to net cash provided by operating activities of $495.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. Our operating cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2014 included our net income of $21.1 million, plus net non-cash charges relating to an LCM adjustment of $690.1 million, depreciation and amortization of $186.4 million, pension and other post retirement benefits costs of $22.6 million, and stock-based compensation of $6.1 million, partially offset by the change in the fair value of our inventory repurchase obligations of $93.2 million, change in the fair value of our catalyst lease of $4.0 million, and gain on sales of assets of $0.9 million. In addition, net changes in working capital reflected uses of cash of $332.5 million driven by timing of inventory purchases and collections of accounts receivable as well as payments associated with the terminations of the MSCG offtake and Statoil supply agreement.
Cash Flows from Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities was $1,473.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to net cash used in investing activities of $811.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The net cash flows used in investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2016 was comprised of cash outflows of $971.9 million used to fund the Torrance Acquisition, capital expenditures totaling $282.4 million, expenditures for turnarounds of $198.7 million, expenditures for other assets of $42.5 million and the final working capital settlement related
69
to the acquisition of the Chalmette refinery of $2.7 million, partially offset by $24.7 million in proceeds from the sale of assets. The net cash flows used in investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2015 was comprised of $565.3 million used in the acquisition of the Chalmette refinery, capital expenditures totaling $352.4 million, expenditures for turnarounds of $53.6 million, and expenditures for other assets of $8.2 million, partially offset by $168.3 million in proceeds from the sale of assets.
Net cash used in investing activities was $811.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to net cash used in investing activities of $422.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The net cash used in investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2014 was comprised of capital expenditures totaling $470.5 million, expenditures for turnarounds of $137.7 million, and expenditures for other assets of $17.3 million, partially offset by $202.7 million in proceeds from the sale of assets.
Cash Flows from Financing Activities
Net cash provided by financing activities was $633.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to net cash provided by financial activities of $855.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. For the year ended December 31, 2016, net cash provided by financing activities consisted primarily of net proceeds from the Revolving Loan of $350.0 million, a contribution from our parent of $450.3 million, proceeds from the PBF Rail Term Loan of $35.0 million and proceeds from catalyst leases of $15.6 million, partially offset by distributions to members of $139.4 million, repayments of the Rail Facility of $67.5 million and net repayments of the affiliate note payable of $10.1 million. For the year ended December 31, 2015, net cash provided by financing activities consisted primarily of $500.0 million in proceeds from the 2023 Senior Secured Notes, capital contributions of $345.0 million, proceeds from affiliate notes payable of $347.8 million, and net proceeds from the Rail Facility of $30.1 million, partially offset by distribution to members of $350.7 million and deferred financing costs and other of $17.1 million .
Net cash provided by financing activities was $855.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to net cash provided by financing activities of $68.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. For the year ended December 31, 2014, net cash provided by financing activities consisted primarily of capital contributions of $328.7 million, proceeds from affiliate notes payable of $90.6 million, net proceeds from the Rail Facility of $37.3 million, partially offset by distributions to members of $361.4 million, net repayments of the Revolving Loan of $15.0 million and $11.7 million for deferred financing costs and other.
70
Capitalization
Our capital structure was comprised of the following as of December 31, 2016 (in millions):
December 31, 2016 | |||
Debt, including current maturities: | |||
8.25% Senior Secured Notes due 2020 | $ | 670.9 | |
7.00% Senior Secured Notes due 2023 | 500.0 | ||
Revolving Loan | 350.0 | ||
PBF Rail Term Loan | 35.0 | ||
Catalyst leases | 46.0 | ||
Total debt | 1,601.9 | ||
Unamortized deferred financing costs | (25.3 | ) | |
Total debt, net of unamortized deferred financing costs | 1,576.6 | ||
Affiliate notes payable | 86.3 | ||
Total Equity | 2,588.9 | ||
Total Capitalization | $ | 4,251.8 | |
Total Debt to Capitalization Ratio | 39 | % | |
Our total debt, net of unamortized deferred financing costs to capitalization ratio was 39% and 48% at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
2016 Debt Transactions
As noted in "Note 9 - Credit Facility and Long-term Debt" to the consolidated financial statements, on December 22, 2016, the PBF Rail Facility was repaid in full and terminated in connection with the execution of a term loan (as described below).
On December 22, 2016, PBF Rail entered into a $35.0 million term loan (the “PBF Rail Term Loan”) with DVB Bank SE (“DVB”). The PBF Rail Term Loan amortizes monthly over its five year term and bears interest at the one month LIBOR plus 2.0%. As security for the PBF Rail Term Loan, PBF Rail pledged, among other things: (i) certain eligible railcars; (ii) the Debt Service Reserve Account; and (iii) our member interest in PBF Rail. Additionally, the PBF Rail Term Loan contains customary terms, events of default and covenants for transactions of this nature. PBF Rail may at any time repay the PBF Rail Term Loan without penalty in the event that railcars collateralizing the loan are sold, scrapped or otherwise removed from the collateral pool.
The 7.00% Senior Secured Notes due 2023 (the "2023 Senior Secured Notes") were issued on November 24, 2015 and included a registration payment arrangement whereby we agreed to use commercially reasonable efforts to consummate an offer to exchange the 2023 Senior Secured Notes for an issue of registered notes with terms substantially identical to the notes not later than 365 days after the date of the original issuance of the notes. This registration statement was declared effective on December 1, 2016 and the exchange was consummated on January 19, 2017. Because the exchange offer was not consummated by November 24, 2016, additional interest was added at a rate of 0.25% per annum for the period from November 24, 2016 through the consummation of the exchange. As a result, we recognized approximately $0.1 million of additional interest expense in 2016.
During 2016, we borrowed under our Revolving Loan to partially fund the Torrance Acquisition (as discussed in "Note 3 - Acquisitions" to the consolidated financial statements).
71
Revolving Credit Facilities Overview
Our primary sources of liquidity are cash flows from operations with additional sources available under borrowing capacity from our revolving line of credit. As of December 31, 2016, we had $626.7 million of cash and cash equivalents and $350.0 million outstanding under our Revolving Loan. We believe available capital resources will be adequate to meet our capital expenditure, working capital and debt service requirements. We had available capacity under our revolving credit facility as follows at December 31, 2016 (in millions):
Total Capacity | Amount Borrowed as of December 31, 2016 | Outstanding Letters of Credit | Available Capacity | Expiration date | ||||||||||||||
PBF Holding Revolving Loan (a) | $ | 2,635.0 | $ | 350.0 | $ | 412.0 | $ | 534.6 | August 2019 | |||||||||
(a) | The amount available for borrowings and letters of credit under the Revolving Loan is calculated according to a “borrowing base” formula based on (i) 90% of the book value of eligible accounts receivable with respect to investment grade obligors plus (ii) 85% of the book value of eligible accounts receivable with respect to non-investment grade obligors plus (iii) 80% of the cost of eligible hydrocarbon inventory plus (iv) 100% of cash and cash equivalents in deposit accounts subject to a control agreement. The borrowing base is subject to customary reserves and eligibility criteria and in any event cannot exceed $2.635 billion. |
Additional Information on Indebtedness
Our debt, including our revolving credit facility, term loan and senior secured notes, include certain typical financial covenants and restrictions on our subsidiaries' ability to, among other things, incur or guarantee new debt, engage in certain business activities including transactions with affiliates and asset sales, make investments or distributions, engage in mergers or pay dividends in certain circumstances. These covenants are subject to a number of important exceptions and qualifications. For further discussion of our indebtedness and these covenants and restrictions, see "Note 9 - Credit Facilities and Long-term Debt" to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this annual report.
We are in compliance with our covenants as of December 31, 2016.
Cash Balances
As of December 31, 2016, our cash and cash equivalents totaled $626.7 million.
Liquidity
As of December 31, 2016, our total liquidity was approximately $1,161.3 million, compared to total liquidity of approximately $1,514.5 million as of December 31, 2015. Total liquidity is the sum of our cash and cash equivalents plus the amount of availability under the Revolving Loan.
Working Capital
Working capital at December 31, 2016 was $1,111.0 million, consisting of $3,154.3 million in total current assets and $2,043.3 million in total current liabilities. Working capital at December 31, 2015 was $1,120.6 million, consisting of $2,580.9 million in total current assets and $1,460.3 million in total current liabilities.
Crude and Feedstock Supply Agreements
We have acquired crude oil for our Paulsboro and Delaware City refineries under supply agreements whereby Statoil generally purchased the crude oil requirements for each refinery on our behalf and under our direction. Our agreements with Statoil for Paulsboro and Delaware City were terminated effective March 31, 2013 and December 31, 2015, respectively, at which time we began to source Paulsboro’s and Delaware City's crude oil and feedstocks independently. Additionally, for our purchases of crude oil under our agreement with Saudi Aramco, similar to our purchases of other foreign waterborne crudes, we posted letters of credit and arranged for shipment. We paid for the crude when we were invoiced and the letters of credit were lifted.
72
We had a similar supply agreement with MSCG, which was terminated effective July 31, 2014, to supply the crude oil requirements for our Toledo refinery, under which we took title to MSCG’s crude oil at certain interstate pipeline delivery locations. Payment for the crude oil under the Toledo supply agreement was due three days after it was processed by us or sold to third parties. We did not have to post letters of credit for these purchases and the Toledo supply agreement allowed us to price and pay for our crude oil as it was processed, which reduced the time we were exposed to market fluctuations. We recorded an accrued liability at each period-end for the amount we owed MSCG for the crude oil that we owned but had not processed. Subsequent to the term of the MSCG supply agreement, we have sourced all of our Toledo crude oil needs independently, which has increased the volumes of crude oil we own.
We have crude and feedstock supply agreements with PDVSA to supply 40,000 to 60,000 bpd of crude oil that can be processed at any of our East and Gulf Coast refineries.
In connection with the closing of the Torrance Acquisition, we entered into a crude supply agreement with ExxonMobil for approximately 60,000 bpd of crude oil that can be processed at our Torrance refinery.
Inventory Intermediation Agreements
We entered into two separate Inventory Intermediation Agreements with J. Aron, which were amended and restated on May 29, 2015, expiring two years from the original expiry date of July 1, 2015, subject to certain early termination rights. In addition, the A&R Intermediation Agreements include one-year renewal clauses by mutual consent of both parties.
Pursuant to each A&R Intermediation Agreement, J. Aron will continue to purchase and hold title to certain of the intermediate and finished products produced by the Paulsboro and Delaware City refineries, respectively, and delivered into tanks at the refineries. Furthermore, J. Aron agrees to sell the Products back to Paulsboro refinery and Delaware City refinery as the Products are discharged out of the Refineries' tanks. J. Aron has the right to store the Products purchased in tanks under the A&R Intermediation Agreements and will retain these storage rights for the term of the agreements. PBF Holding will continue to market and sell independently to third parties. The A&R Intermediation Agreements for both the Delaware City and Paulsboro refineries with J. Aron include one-year renewal clauses upon six months' advance notice by mutual consent of both parties. The A&R Intermediation Agreements have not been renewed and are scheduled to expire July 1, 2017. If we are unable to negotiate an extension with J. Aron or enter into an alternative intermediation agreement, we will have to repurchase the inventories outstanding under the A&R Intermediation Agreement at that time.
At December 31, 2016, the LIFO value of intermediates and finished products owned by J. Aron included within inventory on our balance sheet was $352.5 million. We accrue a corresponding liability for such intermediates and finished products.
Capital Spending
Net capital spending was $1,473.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, which primarily included turnaround costs, safety related enhancements, facility improvements at the refineries, the Torrance Acquisition and the final working capital settlement associated with the Chalmette Acquisition. We currently expect to spend an aggregate of approximately between $575.0 to $600.0 million in net capital expenditures during 2017 for facility improvements and refinery maintenance and turnarounds. Significant capital spending plans for 2017 include turnarounds for the FCC at our Delaware City refinery, several units at our Torrance refinery and several units at our Chalmette refinery, as well as expenditures to meet Tier 3 requirements.
On July 1, 2016 we acquired the Torrance refinery and related logistic assets. The purchase price for the Torrance Acquisition was approximately $521.4 million in cash after post-closing purchase price adjustments, plus final working capital of $450.6 million. The purchase price and fair value allocation may be subject to adjustment pending completion of the final valuation which was still in process as of December 31, 2016. The transaction was financed through a combination of cash on hand, including proceeds from a capital contribution made in connection
73
with PBF Energy's October 2015 Equity Offering and the 2023 Senior Secured Notes Offering, and borrowings under our Revolving Loan.
74
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
The following table summarizes our material contractual payment obligations as of December 31, 2016:
Payments due by period | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total | Less than 1 year | 1-3 Years | 3-5 Years | More than 5 years | ||||||||||||||||
Long-term debt (a) | $ | 1,692,767 | $ | 9,798 | $ | 472,469 | $ | 710,500 | $ | 500,000 | ||||||||||
Interest payments on debt facilities (a) | 472,490 | 101,893 | 200,808 | 99,789 | 70,000 | |||||||||||||||
Operating Leases (b) | 436,667 | 111,184 | 187,740 | 105,322 | 32,421 | |||||||||||||||
Purchase obligations (c): | ||||||||||||||||||||
Crude Supply and Inventory Intermediation Agreements | 8,137,912 | 2,268,826 | 3,560,062 | 2,309,024 | — | |||||||||||||||
Other Supply and Capacity Agreements | 1,269,562 | 187,443 | 328,399 | 195,324 | 558,396 | |||||||||||||||
Minimum volume commitments with PBFX (d) | 1,469,766 | 208,319 | 411,344 | 409,116 | 440,987 | |||||||||||||||
Construction obligations | 33,927 | 33,927 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Environmental obligations (e) | 159,111 | 9,981 | 22,037 | 10,250 | 116,843 | |||||||||||||||
Pension and post-retirement obligations (f) | 263,723 | 13,413 | 17,648 | 19,012 | 213,650 | |||||||||||||||
Total contractual cash obligations | $ | 13,935,925 | $ | 2,944,784 | $ | 5,200,507 | $ | 3,858,337 | $ | 1,932,297 | ||||||||||
(a) Long-term Debt and Interest Payments on Debt Facilities
Long-term obligations represent (i) the repayment of the outstanding borrowings under the Revolving Loan; (ii) the repayment of indebtedness incurred in connection with the Senior Secured Notes; (iii) the repayment of our catalyst lease obligations on their maturity dates; (iv) the repayment of outstanding amounts under the PBF Rail Term Loan; and (v) the repayment of outstanding affiliate notes payable with PBF LLC and PBF Energy.
Interest payments on debt facilities include cash interest payments on the Senior Secured Notes, catalyst lease obligations, PBF Rail Term Loan, our affiliate notes payable with PBF Energy and PBF LLC, plus cash payments for the commitment fee on the unused Revolving Loan and letter of credit fees on the letters of credit outstanding at December 31, 2016. With the exception of our catalyst leases, we have no long-term debt maturing before 2019 as of December 31, 2016.
(b) Operating Leases
We enter into operating leases in the normal course of business, some of these leases provide us with the option to renew the lease or purchase the leased item. Future operating lease obligations would change if we chose to exercise renewal options and if we enter into additional operating lease agreements. Certain of our lease obligations contain a fixed and variable component. The table above reflects the fixed component of our lease obligations. The variable component could be significant. Our operating lease obligations are further explained in the Commitments and Contingencies footnote to our financial statements, “Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” In support of our rail strategy, we have at times entered into agreements to lease or purchase crude railcars. A portion of these railcars were purchased via the Rail Facility entered into during 2014, which was repaid in full and terminated in connection with the execution of the PBF Rail Term Loan in 2016. Certain of these railcars were subsequently sold to third parties, which have leased the railcars back to us for periods of between four and seven years.
75
(c) Purchase Obligations
We have obligations to repurchase certain intermediates and refined products under separate inventory intermediation agreements with J. Aron as further explained in the Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, Inventories and Accrued Expenses footnotes to our financial statements, “Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” Additionally, purchase obligations under "Crude Supply and Inventory Intermediation Agreements" include commitments to purchase crude oil from certain counterparties under supply agreements entered into to ensure adequate supplies of crude oil for our refineries. These obligations are based on aggregate minimum volume commitments at 2016 year end market prices.
Payments under "Other Supply and Capacity Agreements" include contracts for the transportation of crude oil and supply of hydrogen, steam, or natural gas to certain of our refineries, contracts for the treatment of wastewater, and contracts for pipeline capacity. We enter into these contracts to facilitate crude oil deliveries and to ensure an adequate supply of energy or essential services to support our refinery operations. Substantially all of these obligations are based on fixed prices. Certain agreements include fixed or minimum volume requirements, while others are based on our actual usage. The amounts included in this table are based on fixed or minimum quantities to be purchased and the fixed or estimated costs based on market conditions as of December 31, 2016.
(d) Minimum commitments with PBFX
We have minimum obligations under our commercial agreements entered into with PBFX. PBFX receives, handles and transfers crude oil and receives, stores and delivers crude oil, refined products and intermediates from sources located throughout the United States and Canada in support of certain of our refineries. Refer to "Note 12 - Related Party Transactions” to our Consolidated Financial Statements for a detailed explanation of each of these agreements.
Included in the table above are our obligations related to the minimum commitments required under these commercial agreements. Any incremental volumes above any minimums throughput under these agreements would increase our obligations. Our obligation with respect to the Toledo Tank Farm Storage and Terminaling Agreement is based on the estimated shell capacity of the storage tanks to be utilized.
(e) Environmental Obligations
In connection with the Paulsboro acquisition, we assumed certain environmental remediation obligations to address existing soil and groundwater contamination at the site and recorded as a liability in the amount of $10.8 million which reflects the present value of the current estimated cost of the remediation obligations assumed based on investigative work to-date. The undiscounted estimated costs related to these environmental remediation obligations were $16.7 million as of December 31, 2016.
In connection with the acquisition of the Delaware City assets, the prior owners remain responsible, subject to certain limitations, for certain pre-acquisition environmental obligations, including ongoing soil and groundwater remediation at the site.
In connection with the Delaware City assets and Paulsboro refinery acquisitions, we, along with the seller, purchased two individual ten-year, $75.0 million environmental insurance policies to insure against unknown environmental liabilities at each site.
In connection with the acquisition of Toledo, the seller initially retains, subject to certain limitations, remediation obligations which will transition to us over a 20-year period.
In connection with the acquisition of the Chalmette refinery, the sellers provided $3.9 million financial assurance in the form of a surety bond to cover estimated potential site remediation costs associated with an agreed to Administrative Order of Consent with the EPA. Additionally, we purchased a ten year $100.0 million environmental insurance policy to insure against unknown environmental liabilities at the site.
76
In connection with the Torrance Acquisition, we assumed certain environmental remediation obligations to address existing soil and groundwater contamination at the site and recorded a liability of $142.5 million as of December 31, 2016, which reflects the current estimated cost of the remediation obligations, expected to be paid out over an average period of approximately 20 years. Additionally, we purchased a ten year $100.0 million environmental insurance policy to insure against unknown environmental liabilities.
In connection with the acquisition of all of our refineries, we assumed certain environmental obligations under regulatory orders unique to each site, including orders regulating air emissions from each facility.
(f) Pension and Post-retirement Obligations
Pension and post-retirement obligations include only those amounts we expect to pay out in benefit payments and are further explained at the Employee Benefit Plans footnote to our financial statements, “Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
(g) Tax Receivable Agreement Obligations
The Contractual Obligations and Commitments Table above does not include tax distributions or other distributions that we expect to make on account of PBF Energy’s obligations under the tax receivable agreement that PBF Energy entered into with the members of PBF LLC other than PBF Energy in connection with PBF Energy’s initial public offering.
PBF Energy used a portion of the proceeds from its IPO to purchase PBF LLC Series A Units from the members of PBF LLC other than PBF Energy. In addition, the members of PBF LLC other than PBF Energy may (subject to the terms of the exchange agreement) exchange their PBF LLC Series A Units for shares of Class A common stock of PBF Energy on a one-for-one basis. As a result of both the purchase of PBF LLC Series A Units and subsequent secondary offerings and exchanges, PBF Energy is entitled to a proportionate share of the existing tax basis of the assets of PBF LLC. Such transactions have resulted in increases in the tax basis of the assets of PBF LLC that otherwise would not have been available. Both this proportionate share and these increases in tax basis may reduce the amount of tax that PBF Energy would otherwise be required to pay in the future. These increases in tax basis have reduced the amount of the tax that PBF Energy would have otherwise been required to pay and may also decrease gains (or increase losses) on the future disposition of certain capital assets to the extent tax basis is allocated to those capital assets. PBF Energy entered into a tax receivable agreement with the current and former members of PBF LLC other than PBF Energy that provides for the payment by PBF Energy to such members of 85% of the amount of the benefits, if any, that PBF Energy is deemed to realize as a result of (i) these increases in tax basis and (ii) certain other tax benefits related to entering into the tax receivable agreement, including tax benefits attributable to payments under the tax receivable agreement. These payment obligations are obligations of PBF Energy and not of PBF Holding or any of its subsidiaries.
PBF Energy expects to obtain funding for these payments by causing its subsidiaries to make cash distributions to PBF LLC, which, in turn, will distribute such amounts, generally as tax distributions, on a pro-rata basis to its owners, which as of December 31, 2016 include the members of PBF LLC other than PBF Energy holding a 3.5% interest and PBF Energy holding a 96.5% interest. The members of PBF LLC other than PBF Energy may continue to reduce their ownership in PBF LLC by exchanging their PBF LLC Series A Units for shares of PBF Energy Class A common stock. Such exchanges may result in additional increases in the tax basis of PBF Energy’s investment in PBF LLC and require PBF Energy to make increased payments under the tax receivable agreement. Required payments under the tax receivable agreement also may increase or become accelerated in certain circumstances, including certain changes of control.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have no off-balance sheet arrangements as of December 31, 2016, other than outstanding letters of credit in the amount of approximately $412.0 million and operating leases.
During 2015, in aggregate we sold 1,122 of our owned crude railcars and concurrently entered into lease
77
agreements for the same railcars. The lease agreements have varying terms from five to seven years. We received an aggregate cash payment for the railcars of approximately $168.3 million and expect to make payments totaling $99.4 million over the term of the lease for these railcars. In 2016, we sold approximately 120 of these railcars to optimize our railcar portfolio.
During the year ended December 31, 2016, we had additional railcar leases outstanding with terms of up to 10 years. We expect to make lease payments of $18.6 million over the remaining term of these additional agreements.
Critical Accounting Policies
The following summary provides further information about our critical accounting policies that involve critical accounting estimates and should be read in conjunction with "Note 2 - Summary of Significant Accounting Policies" to our consolidated financial statements, “Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” The following accounting policies involve estimates that are considered critical due to the level of subjectivity and judgment involved, as well as the impact on our financial position and results of operations. We believe that all of our estimates are reasonable. Unless otherwise noted, estimates of the sensitivity to earnings that would result from changes in the assumptions used in determining our estimates is not practicable due to the number of assumptions and contingencies involved, and the wide range of possible outcomes.
Inventory
Inventories are carried at the lower of cost or market. The cost of crude oil, feedstocks, blendstocks and refined products is determined under the LIFO method using the dollar value LIFO method with increments valued based on average cost during the year. The cost of supplies and other inventories is determined principally on the weighted average cost method. In addition, the use of the LIFO inventory method may result in increases or decreases to cost of sales in years that inventory volumes decline as the result of charging cost of sales with LIFO inventory costs generated in prior periods. At December 31, 2016 and 2015, market values had fallen below historical LIFO inventory costs and, as a result, we recorded lower of cost or market inventory valuation reserves of $596.0 million and $1,117.3 million, respectively. The $596.0 million as of December 31, 2016, or a portion thereof, is subject to reversal as a reduction to cost of products sold in subsequent periods as inventories giving rise to the reserve are sold, and a new reserve is established. Such a reduction to cost of products sold could be significant if inventory values return to historical cost price levels. Additionally, further decreases in overall inventory values could result in additional charges to cost of products sold should the lower of cost or market inventory valuation reserve be increased.
Our Delaware City refinery acquired a portion of its crude oil from Statoil under our crude supply agreement whereby we took title to the crude oil as it was delivered to our processing units. We had risk of loss while the Statoil inventory was in our storage tanks. We were obligated to purchase all of the crude oil held by Statoil on our behalf upon termination of the agreements. As a result of the purchase obligations, we recorded the inventory of crude oil and feedstocks in the refinery’s storage facilities. The purchase obligations contained derivatives that changed in value based on changes in commodity prices. Such changes were included in our cost of sales. Our agreement with Statoil for our Delaware City refinery terminated effective December 31, 2015, at which time we began to source crude oil and feedstocks internally. Our agreement with Statoil for Paulsboro terminated effective March 31, 2013, at which time we began to source crude oil and feedstocks independently.
Prior to July 31, 2014, our Toledo refinery acquired substantially all of its crude oil from MSCG under a crude oil acquisition agreement whereby we took legal title to the crude oil at certain interstate pipeline delivery locations. We recorded an accrued liability at each period-end for the amount we owed MSCG for the crude oil that we owned but had not processed. The accrued liability was based on the period-end market value, as it represented our best estimate of what we would pay for the crude oil. We terminated this crude oil acquisition agreement effective July 31, 2014 and began to source our crude oil needs independently.
78
Environmental Matters
Liabilities for future clean-up costs are recorded when environmental assessments and/or clean-up efforts are probable and the costs can be reasonably estimated. Other than for assessments, the timing and magnitude of these accruals generally are based on the completion of investigations or other studies or a commitment to a formal plan of action. Environmental liabilities are based on best estimates of probable future costs using currently available technology and applying current regulations, as well as our own internal environmental policies. The actual settlement of our liability for environmental matters could materially differ from our estimates due to a number of uncertainties such as the extent of contamination, changes in environmental laws and regulations, potential improvements in remediation technologies and the participation of other responsible parties. Additionally, in connection with the Torrance Acquisition on July 1, 2016, we assumed certain pre-existing environmental liabilities. While we believe that our current estimates of the amounts and timing of the costs related to the remediation of these liabilities are reasonable, we have had limited experience with these environmental obligations due to our short operating history. It is possible that our estimates of the costs and duration of the environmental remediation activities related to these liabilities could materially change.
Business Combinations
We use the acquisition method of accounting for the recognition of assets acquired and liabilities assumed in business combinations at their estimated fair values as of the date of acquisition. Any excess consideration transferred over the estimated fair values of the identifiable net assets acquired is recorded as goodwill. Significant judgment is required in estimating the fair value of assets acquired. As a result, in the case of significant acquisitions, we obtain the assistance of third-party valuation specialists in estimating fair values of tangible and intangible assets based on available historical information and on expectations and assumptions about the future, considering the perspective of marketplace participants. While management believes those expectations and assumptions are reasonable, they are inherently uncertain. Unanticipated market or macroeconomic events and circumstances may occur, which could affect the accuracy or validity of the estimates and assumptions.
Deferred Turnaround Costs
Refinery turnaround costs, which are incurred in connection with planned major maintenance activities at our refineries, are capitalized when incurred and amortized on a straight-line basis over the period of time estimated until the next turnaround occurs (generally three to five years). While we believe that the estimates of time until the next turnaround are reasonable, it should be noted that factors such as competition, regulation or environmental matters could cause us to change our estimates thus impacting amortization expense in the future.
Derivative Instruments
We are exposed to market risk, primarily related to changes in commodity prices for the crude oil and feedstocks we use in the refining process as well as the prices of the refined products we sell. The accounting treatment for commodity contracts depends on the intended use of the particular contract and on whether or not the contract meets the definition of a derivative. Non-derivative contracts are recorded at the time of delivery.
All derivative instruments that are not designated as normal purchases or sales are recorded in our balance sheet as either assets or liabilities measured at their fair values. Changes in the fair value of derivative instruments that either are not designated or do not qualify for hedge accounting treatment or normal purchase or normal sale accounting are recognized in income. Contracts qualifying for the normal purchases and sales exemption are accounted for upon settlement. We elect fair value hedge accounting for certain derivatives associated with our inventory repurchase obligations.
Derivative accounting is complex and requires management judgment in the following respects: identification of derivatives and embedded derivatives; determination of the fair value of derivatives; identification of hedge relationships; assessment and measurement of hedge ineffectiveness; and election and designation of the normal purchases and sales exception. All of these judgments, depending upon their timing and effect, can have a significant impact on earnings.
79
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In August 2015, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2015-14, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Deferral of the Effective Date” (“ASU 2015-14”), which defers the effective date of ASU 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers” (“ASU 2014-09”) for all entities by one year. Additional ASUs have been issued in 2016 that provide certain implementation guidance related to ASU 2014-09 (collectively, we refer to ASU 2014-09 and these additional ASUs as the "Updated Revenue Recognition Guidance").The Updated Revenue Recognition Guidance will replace most existing revenue recognition guidance in GAAP when it becomes effective. Under ASU 2015-14, this guidance becomes effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017 and permits the use of either the retrospective or modified retrospective transition method. Under ASU 2015-14, early adoption is permitted only as of annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim reporting periods within that reporting period. We have established a working group to assess the Updated Revenue Recognition Guidance, including its impact on our business processes, accounting systems, controls and financial statement disclosures. Our preliminary expectation is that we will adopt this guidance using the modified retrospective method whereby a cumulative effect adjustment is recognized upon adoption and the Updated Revenue Recognition Guidance is applied prospectively. It is not anticipated that we will early adopt this new guidance. The working group is in the early stages of its implementation plan and continues to evaluate the impact of this new standard on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures. Although our analysis of the new standard is still in process and interpretative and industry specific guidance is still developing, we currently do not expect the new standard to have a material impact on the amount or timing of revenues recognized for the majority of our revenue arrangements.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, "Leases (Topic 842)" ("ASU 2016-02"), to increase the transparency and comparability about leases among entities. The new guidance requires lessees to recognize a lease liability and a corresponding lease asset for virtually all lease contracts. It also requires additional disclosures about leasing arrangements. ASU 2016-02 is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2018, and requires a modified retrospective approach to adoption. Early adoption is permitted. We have established a working group to study the new guidance in ASU 2016-02. This working group was formed during 2016 and has recommended that we adopt this guidance using the modified retrospective method whereby a cumulative effect adjustment is recognized upon adoption and the new guidance in ASU 2016-02 is applied prospectively. It is not anticipated that we will early adopt this new guidance. The working group continues to evaluate the impact of this new standard on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures. At this time, we have identified that the most significant impacts of this new guidance will be to bring nearly all leases on our balance sheet with “right of use assets” and “lease obligation liabilities” as well as accelerating the interest expense component of financing leases.
Refer to "Note 2 - Summary of Significant Accounting Policies" for additional Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
We are exposed to market risks, including changes in commodity prices and interest rates. Our primary commodity price risk is associated with the difference between the prices we sell our refined products and the prices we pay for crude oil and other feedstocks. We may use derivative instruments to manage the risks from changes in the prices of crude oil and refined products, natural gas, interest rates, or to capture market opportunities.
Commodity Price Risk
Our earnings, cash flow and liquidity are significantly affected by a variety of factors beyond our control, including the supply of, and demand for, crude oil, other feedstocks, refined products and natural gas. The supply of and demand for these commodities depend on, among other factors, changes in domestic and foreign economies, weather conditions, domestic and foreign political affairs, planned and unplanned downtime in refineries, pipelines and production facilities, production levels, the availability of imports, the marketing of competitive and alternative fuels, and the extent of government regulation. As a result, the prices of these commodities can be volatile. Our
80
revenues fluctuate significantly with movements in industry refined product prices, our cost of sales fluctuates significantly with movements in crude oil and feedstock prices and our operating expenses fluctuate with movements in the price of natural gas. We manage our exposure to these commodity price risks through our supply and offtake agreements as well as through the use of various commodity derivative instruments.
We may use non-trading derivative instruments to manage exposure to commodity price risks associated with the purchase or sale of crude oil and feedstocks, finished products and natural gas outside of our supply and offtake agreements. The derivative instruments we use include physical commodity contracts and exchange-traded and over-the-counter financial instruments. We mark-to-market our commodity derivative instruments and recognize the changes in their fair value in our statements of operations.
At December 31, 2016 and 2015, we had gross open commodity derivative contracts representing 8.8 million barrels and 44.2 million barrels, respectively, with an unrealized net loss of $3.5 million and net gain of $46.1 million, respectively. The open commodity derivative contracts as of December 31, 2016 expire at various times during 2017.
We carry inventories of crude oil, intermediates and refined products (“hydrocarbon inventories”) on our balance sheet, the values of which are subject to fluctuations in market prices. Our hydrocarbon inventories totaled approximately 29.4 million barrels and 26.8 million barrels at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The average cost of our hydrocarbon inventories was approximately $80.50 and $83.55 per barrel on a LIFO basis at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, excluding the impact of LCM adjustments of approximately $596.0 million and $1,117.3 million, respectively. During 2016 and 2015, the market prices of our inventory declined to a level below our average cost and we wrote down the carrying value of our hydrocarbon inventories to market.
Our predominant variable operating cost is energy, which is comprised primarily of natural gas and electricity. We are therefore sensitive to movements in natural gas prices. Assuming normal operating conditions, we annually consume a total of approximately 68 million MMBTUs of natural gas amongst our five refineries. Accordingly, a $1.00 per MMBTU change in natural gas prices would increase or decrease our natural gas costs by approximately $68 million.
Compliance Program Price Risk
We are exposed to market risks related to the volatility in the price of RINs required to comply with the Renewable Fuel Standard. Our overall RINs obligation is based on a percentage of our domestic shipments of on-road fuels as established by the EPA. To the degree we are unable to blend the required amount of biofuels to satisfy our RINs obligation, we must purchase RINs on the open market. To mitigate the impact of this risk on our results of operations and cash flows we may purchase RINs when the price of these instruments is deemed favorable.
In addition, we are exposed to risks associated with complying with federal and state legislative and regulatory measures to address greenhouse gas and other emissions. Requirements to reduce emissions could result in increased costs to operate and maintain our facilities as well as implement and manage new emission controls and programs put in place. For example, AB 32 in California requires the state to reduce its GHG emissions to 1990 levels by 2020.
Interest Rate Risk
The maximum availability under our Revolving Loan is $2.64 billion. Borrowings under the Revolving Loan bear interest either at the Alternative Base Rate plus the Applicable Margin or at the Adjusted LIBOR Rate plus the Applicable Margin, all as defined in the Revolving Loan. The Applicable Margin ranges from 1.50% to 2.25% for Adjusted LIBOR Rate Loans and from 0.50% to 1.25% for Alternative Base Rate Loans, depending on the Company's debt rating. If this facility were fully drawn, a 1.0% change in the interest rate would increase or decrease our interest expense by approximately $26.4 million annually.
In addition, we entered into the PBF Rail Term Loan in December 22, 2016 which bears interest at the one
81
month LIBOR plus 200 basis points. A 1.0% change in the interest rate would increase or decrease our interest expense by approximately $0.4 million, assuming all $35.0 million remained outstanding.
We also have interest rate exposure in connection with our J. Aron Inventory Intermediation Agreements under which we pay a time value of money charge based on LIBOR.
Credit Risk
We are subject to risk of losses resulting from nonpayment or nonperformance by our counterparties. We will continue to closely monitor the creditworthiness of customers to whom we grant credit and establish credit limits in accordance with our credit policy.
Concentration Risk
For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, no single customer accounted for 10% or more of our total sales.
No single customer accounted for 10% or more of our total trade accounts receivable as of December 31, 2016. ExxonMobil and its affiliates represented approximately 18% of our total trade accounts receivable as of December 31, 2015.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
The information required by this item is set forth beginning on page F-1 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management has evaluated, with the participation of our principal executive and principal financial officers, the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as amended (the “Exchange Act”)) as of the end of the period covered by this report, and has concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures are effective to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or furnish under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the SEC's rules and forms including, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or furnish under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive and principal financial officers, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosures.
Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act. The Company’s internal control system is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America. Due to its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
82
On July 1, 2016, we completed the acquisition of the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets. We are in the process of integrating the related Torrance operations, including internal controls over financial reporting and, therefore, management's evaluation and conclusion as to the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K excludes any evaluation of the internal controls over financial reporting of the acquired Torrance refinery and related logistics assets. We expect the integration of the related Torrance operations, including internal controls over financial reporting to be complete in the year ending December 31, 2017. The Torrance refinery and related logistics assets account for 15% of the Company's total assets and 12% of total revenues of the Company as of and for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, using the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013). Based on such assessment, we conclude that as of December 31, 2016, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting is effective.
This Annual Report on Form 10-K does not include an attestation report of our independent registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting as permitted by Item 308(b) of Regulation S-K for non-accelerated filers.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
On July 1, 2016, we completed the acquisition of the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets. We are in the process of integrating Torrance's operations, including internal controls over financial reporting. There has been no other change in our internal controls over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2016 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal controls over our financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
None.
PART III
Explanatory Note:
We are a limited liability company wholly owned and controlled by PBF LLC. PBF Energy is the sole managing member of PBF LLC. Our directors and executive officers are the executive officers of PBF Energy. The compensation paid to these executive officers is for services provided to both entities (i.e., they are not separately compensated for their services as an officer or director of PBF Holding). PBF Holding does not file a proxy statement. If the information were required it would be identical (other than as expressly set forth below) to the information contained in Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14 of Annual Report on Form 10-K of PBF Energy that will appear in the Proxy Statement of PBF Energy furnished to its stockholders in connection with its 2016 Annual Meeting. Such information is incorporated by reference in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
83
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERANCE
Directors and Executive Officers of PBF Holding
The following is a list of our directors and executive officers as of March 8, 2017:
Name | Age (as of December 31, 2016) | Position | |||
Thomas J. Nimbley | 65 | Chief Executive Officer | |||
Matthew C. Lucey | 43 | President | |||
Erik Young | 39 | Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer | |||
Jeffrey Dill | 55 | President, Western Region | |||
Thomas L. O'Connor | 44 | Senior Vice President, Commercial | |||
Herman Seedorf | 65 | Senior Vice President of Refining | |||
Paul Davis | 54 | Senior Vice President, Western Region Commercial Operations | |||
Trecia Canty | 47 | Senior Vice President, General Counsel | |||
Messrs. Nimbley and Lucey and Ms. Canty serve as the sole directors of PBF Holding and PBF Finance. We believe that each of their experience as executive officers of PBF Holding make them qualified to serve as its directors.
Thomas J. Nimbley has served as the Chairman of the Board of Directors of PBF Energy since July 2016 and on our Board of Directors since October 2012 and during the period from April 2010 to January 2011. He has served as our and PBF Energy's Chief Executive Officer since June 2010 and was Executive Vice President, Chief Operating Officer from March 2010 through June 2010. In his capacity as Chief Executive Officer, Mr. Nimbley also serves as a director and the Chief Executive Officer of certain of our subsidiaries and our affiliates, including Chairman of the Board of PBF GP. Prior thereto, he served as a Principal for Nimbley Consultants LLC from June 2005 to March 2010, where he provided consulting services and assisted on the acquisition of two refineries. He previously served as Senior Vice President and head of Refining for Phillips Petroleum Company (“Phillips”) and subsequently Senior Vice President and head of Refining for ConocoPhillips (“ConocoPhillips”) domestic refining system (13 locations) following the merger of Phillips and Conoco Inc. Before joining Phillips at the time of its acquisition of Tosco Corporation ("Tosco") in September 2001, Mr. Nimbley served in various positions with Tosco and its subsidiaries starting in April 1993.
Matthew C. Lucey has served as our and PBF Energy's President since January 2015 and was Executive Vice President from April 2014 to December 2014. Mr. Lucey served as Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer from April 2010 to March 2014. Mr. Lucey joined us as Vice President, Finance in April 2008. Mr. Lucey has also served as one of our directors since joining us. Mr. Lucey is also a director of certain of PBF Energy's subsidiaries, including PBF GP. Prior thereto, Mr. Lucey served as a Managing Director of M.E. Zukerman & Co., a New York-based private equity firm specializing in several sectors of the broader energy industry, from 2001 to 2008. Before joining M.E. Zukerman & Co., Mr. Lucey spent six years in the banking industry.
Erik Young has served as our and PBF Energy's Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer since April 2014 after joining us in December 2010 as Director, Strategic Planning where he was responsible for both corporate development and capital markets initiatives. Mr. Young is also a director of certain of PBF Energy's subsidiaries, including PBF GP. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Young spent eleven years in corporate finance, strategic planning and mergers and acquisitions roles across a variety of industries. He began his career in investment banking before joining J.F. Lehman & Company, a private equity investment firm, in 2001.
Jeffrey Dill has served as our and PBF Energy's President, PBF Energy Western Region LLC since September 2015 and was our and PBF Energy's Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary for more than five years
84
prior thereto. Mr. Dill is also a director of certain of PBF Energy's subsidiaries. Previously he served as Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary for Maxum Petroleum, Inc., a national marketer and logistics company for petroleum products and Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary at Neurogen Corporation, a drug discovery and development company, from March 2006 to December 2007. Mr. Dill has close to 20 years' experience providing business and legal support to refining, transportation and marketing organizations in the petroleum industry, including positions at Premcor Inc. ("Premcor"), ConocoPhillips, Tosco and Unocal Corporation.
Thomas L. O’Connor has served as our and PBF Energy Senior Vice President, Commercial since September 2015. Mr. O'Connor joined us and PBF Energy as Senior Vice President in September 2014 with responsibility for business development and growing the business of PBFX, and from January to September 2015, served as Co-Head of commercial activities. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. O'Connor worked at Morgan Stanley since 2000 in various positions, most recently as a Managing Director and Global Head of Crude Oil Trading and Global Co-Head of Oil Flow Trading. Prior to joining Morgan Stanley, Mr. O'Connor worked for Tosco from 1995 to 2000 in the Atlantic Basin Fuel Oil and Feedstocks group.
Herman Seedorf serves as our and PBF Energy's Senior Vice President of Refining. Mr. Seedorf originally joined PBF Energy in February of 2011 as the Delaware City Refinery Plant Manager and became Senior Vice President, Eastern Region Refining, in September of 2013. Prior to 2011, Mr. Seedorf served as the refinery manager of the Wood River Refinery in Roxana, Illinois, and also as an officer of the joint venture between ConocoPhillips and Cenovus Energy Inc. Mr. Seedorf's oversight responsibilities included the development and execution of the multi-billion dollar upgrade project which enabled the expanded processing of Canadian crude oils. He also served as the refinery manager of the Bayway Refinery in Linden, New Jersey for four years during the time period that it was an asset of Tosco. Mr. Seedorf began his career in the petroleum industry with Exxon Corporation (“Exxon”) in 1980.
Paul Davis has served as our and PBF Energy Senior Vice President, Western Region Commercial Operations since September 2015. Mr. Davis joined us in April 2012 and has been head of PBF's commercial operations related to crude oil and refinery feedstock sourcing since May of 2013 and, from January 2015 to September 2015, served as our Co-Head of Commercial. Previously, Mr. Davis was responsible for managing the U.S. clean products commercial operations for Hess Energy Trading Company (“HETCO”) from 2006 to 2012. Prior to that, Mr. Davis was responsible for Premcor’s U.S. Midwest clean products disposition group. Mr. Davis has over 29 years of experience in commercial operations in crude oil and refined products, including 16 years with the ExxonMobil Corporation in various operational and commercial positions, including sourcing refinery feedstocks and crude oil and the disposition of refined petroleum products, as well as optimization roles within refineries.
Trecia Canty has served as our Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary since September 2015. In her role, Ms. Canty is responsible for the Legal Department and Contracts Administration. Ms. Canty has also served as one of our directors since May 2016. Previously, Ms. Canty was named Vice President, Senior Deputy General Counsel and Assistant Secretary in October 2014 and led the Company's commercial and finance legal operations since joining us in November 2012. Ms. Canty is also a director of certain of PBF Energy's subsidiaries. Prior to joining the Company, Ms. Canty served as Associate General Counsel, Corporate and Assistant Secretary of Southwestern Energy Company, where her responsibilities included finance and mergers and acquisitions, securities and corporate compliance and corporate governance. She also provided legal support to the midstream marketing and logistics businesses. Prior to joining Southwestern Energy Company in 2004, she was an associate with Cleary, Gottlieb, Steen & Hamilton.
Corporate Governance Matters
PBF Energy, our indirect parent, has adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics that applies to our principal executive officer, principal financial officer and principal accounting officer. The Code of Business Conduct and Ethics is available at www.pbfenergy.com under the heading “Investors”. Any amendments to the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics or any grant of a waiver from the provisions of the Code of Business Conduct
85
and Ethics requiring disclosure under applicable Securities and Exchange Commission rules will be disclosed on such website.
Additional information required by this Item will be contained in PBF Energy's 2017 Proxy Statement, incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
Compensation of Directors of PBF Holding Company LLC
Directors of PBF Holding receive no separate compensation for service on the board of directors or committees thereof.
Additional information required under this Item will be contained in PBF Energy’s 2017 Proxy Statement, incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
As of December 31, 2016, 100% of the membership interests of PBF Holding were owned by PBF LLC, and PBF Finance had 100 shares of common stock outstanding, all of which were held by PBF Holding. Refer to Note 14 “Equity Structure” of our Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
The stockholders of PBF Energy may be deemed to beneficially own an interest in our membership interests by virtue of their beneficial ownership of shares of Class A common stock of PBF Energy. PBF Energy reports separately on the beneficial ownership of its officers, directors and significant stockholders. For additional information, we refer you to PBF Energy’s 2017 Proxy Statement, which is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
Refer to Note 10 “Affiliate Notes Payable”, Note 12 “Related Party Transactions” and Note 21 “Subsequent Events” of our Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
86
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
Deloitte & Touche LLP (“Deloitte”) is our independent registered public accounting firm. Our audit fees are determined as part of the overall audit fees for PBF Energy and are approved by the audit committee of the board of directors of PBF Energy. PBF Energy reports separately on the fees and services of its principal accountants. For additional information, we refer you to PBF Energy’s 2017 Proxy Statement, which is incorporated herein by reference.
The following table presents fees billed for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 for professional services performed by Deloitte.
2016 | 2015 | |||||
Audit Fees and Expenses (1) | $ | 3,988,690 | $ | 3,365,000 | ||
Audit-related Fees (2) | 867,767 | 2,001,184 | ||||
Tax Fees (3) | — | 92,605 | ||||
All Other Fees | — | — | ||||
Total Fees and Expenses | $ | 4,856,457 | $ | 5,458,789 | ||
(1) Represents the aggregate fees for professional services rendered by Deloitte in connection with its audits of PBF Holding and its indirect parent, PBF Energy's consolidated financial statements, including the audits of internal control over financial reporting of PBF Energy, and reviews of the condensed consolidated financial statements included in Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q. | ||||||
(2) Represents fees for professional services rendered in connection with various filings for PBF Energy and its subsidiaries, including (i) services rendered in connection with the PBF Energy public offerings in 2016 and 2015, secondary offerings in 2015, and the 2023 Senior Secured Notes offering and related notes registration in 2016, (ii) audits performed related to the Delaware City Products Pipeline and Truck Rack and PBF LLC in 2015, and (iii) consultations on accounting issues. | ||||||
(3) Represents fees associated with tax services rendered for income tax planning and sales, use and excise tax matters. | ||||||
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a) 1. Financial Statements. The consolidated financial statements of PBF Holding Company LLC and subsidiaries, required by Part II, Item 8, are included in Part IV of this report. See Index to Consolidated Financial Statements beginning on page F-1.
2. Financial Statement Schedules and Other Financial Information. No financial statement schedules are submitted because either they are inapplicable or because the required information is included in the consolidated financial statements or notes thereto.
3. Exhibits. Filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K are the following exhibits:
Number | Description | |
2.1 | Contribution Agreement dated as of August 31, 2016 by and between PBF Energy Company LLC and PBF Logistics LP (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Current Report on Form 8-K dated September 7, 2016 (File No. 001-35764) ) | |
2.2 | Sale and Purchase Agreement by and between PBF Holding Company LLC and ExxonMobil Oil Corporation and its subsidiary, Mobil Pacific Pipeline Company as of September 29, 2015(incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated October 1, 2015 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
2.3 | Sale and Purchase Agreement by and between PBF Holding Company LLC, ExxonMobil Oil Corporation, Mobil Pipe Line Company and PDV Chalmette, L.L.C. as of June 17, 2015 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated June 17, 2015 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
87
3.1 | Certificate of Formation of PBF Holding Company LLC (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 filed with PBF Holding Company LLC’s Registration Statement on Form S-4 (Registration No. 333-186007)) | |
3.2 | Limited Liability Company Agreement of PBF Holding Company LLC (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 filed with PBF Holding Company LLC’s Registration Statement on Form S-4 (Registration No. 333-186007)) | |
3.3 | Certificate of Incorporation of PBF Finance Corporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 filed with PBF Holding Company LLC’s Registration Statement on Form S-4 (Registration No. 333-186007)) | |
3.4 | Bylaws of PBF Finance Corporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.4 filed with PBF Holding Company LLC’s Registration Statement on Form S-4 (Registration No. 333-186007)) | |
4.1 | Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of July 29, 2016, by and among PBF Holding Company LLC, the Guarantors named on the signature page thereto and Wilmington Trust, National Association (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated November 4, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
4.2 | First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of July 29, 2016, among PBF Western Region LLC, Torrance Refining Company LLC, Torrance Logistics Company LLC, Wilmington Trust, National Association and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated November 4, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
4.3 | Indenture dated as of November 24, 2015, among PBF Holding Company LLC, PBF Finance Corporation, the Guarantors named on the signature pages thereto, Wilmington Trust, National Association, as Trustee and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as Paying Agent, Registrar, Transfer Agent, Authenticating Agent and Notes Collateral Agent and Form of 7.00% Senior Secured Note (included as Exhibit A) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated November 30, 2015 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
4.4 | Registration Rights Agreement dated November 24, 2015, among PBF Holding Company LLC and PBF Finance Corporation, the Guarantors named therein and UBS Securities LLC, as Representative of the several Initial Purchasers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated November 30, 2015 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
4.5 | Indenture, dated as of February 9, 2012, among PBF Holding Company LLC, PBF Finance Corporation, the Guarantors party thereto, Wilmington Trust, National Association and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Registration No. 333-177933)) | |
4.6 | First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of November 13, 2015, among Chalmette Refining, L.L.C., Wilmington Trust, National Association and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.7 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Annual Report on Form 10-K dated February 29, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
4.7 | Second Supplemental Indenture, dated as of November 16, 2015, by and among PBF Holding Company LLC, PBF Finance Corporation, the Guarantors named on the signature page thereto and Wilmington Trust, National Association (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.8 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s December 31, 2015 Form 10-K (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.1 ** | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement for Employees, under PBF Energy Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Current Report on Form 8-K dated October 28, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.2 ** | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement for Employees, under PBF Energy Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated November 4, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
88
10.3 | Fourth Amended and Restated Omnibus Agreement dated as of August 31, 2016 among PBF Holding Company LLC, PBF Energy Company LLC, PBF Logistics GP LLC and PBF Logistics LP (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Current Report on Form 8-K dated September 7, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.4 | Fourth Amended and Restated Operation and Management Services and Secondment Agreement dated as of August 31, 2016 among PBF Holding Company LLC, Delaware City Refining Company LLC, Toledo Refining Company LLC, Torrance Refining Company LLC, Torrance Logistics Company LLC, PBF Logistics GP LLC , PBF Logistics LP, Delaware City Terminaling Company LLC, Delaware Pipeline Company LLC, Delaware City Logistics Company LLC, Toledo Terminaling Company LLC and PBFX Operating Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Current Report on Form 8-K dated September 7, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.5 | Transportation Services Agreement dated as of August 31, 2016 among PBF Holding Company LLC and Torrance Valley Pipeline Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Current Report on Form 8-K dated September 7, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.6 | Pipeline Service Order dated as of August 31, 2016, by and between Torrance Valley Pipeline Company LLC, and PBF Holding Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Current Report on Form 8-K dated September 7, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.7 | Pipeline Service Order dated as of August 31, 2016, by and between Torrance Valley Pipeline Company LLC, and PBF Holding Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Current Report on Form 8-K dated September 7, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.8 | Dedicated Storage Service Order dated as of August 31, 2016, by and between Torrance Valley Pipeline Company LLC, and PBF Holding Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Current Report on Form 8-K dated September 7, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.9 | Throughput Storage Service Order dated as of August 31, 2016, by and between Torrance Valley Pipeline Company LLC, and PBF Holding Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Current Report on Form 8-K dated September 7, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.10 | Joinder Agreement to the Amended and Restated ABL Security Agreement dated as of July 1, 2016, among Torrance Refining Company LLC and UBS AG, Stamford Branch, as Administrative Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated November 4, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.11 | Joinder Agreement to the Amended and Restated ABL Security Agreement dated as of July 1, 2016, among PBF Western Region LLC, Torrance Logistics Company LLC and UBS AG, Stamford Branch, as Administrative Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated November 4, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.12 | Joinder Agreement to the Third Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement dated as of July 1, 2016, among PBF Holding Company LLC, the Guarantors named on the signature pages thereto including Torrance Refining Company LLC and UBS AG, Stamford Branch, as Administrative Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated November 4, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.13 | Joinder Agreement to the Third Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement dated as of July 1, 2016, among PBF Holding Company LLC, the Guarantors named on the signature pages thereto including PBF Western Region LLC, Torrance Logistics Company LLC and UBS AG, Stamford Branch, as Administrative Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated November 4, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.14 | Consulting Agreement between PBF Investments LLC and Thomas D. O'Malley effective July 1, 2016 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 27, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
89
10.15 ** | Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement for Directors under PBF Energy Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated May 5, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.16 | Contribution Agreement dated as of May 5, 2015 by and between PBF Energy Company LLC and PBF Logistics LP (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 5, 2015 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.17 | Third Amended and Restated Omnibus Agreement dated as of May 15, 2015 among PBF Holding Company LLC, PBF Energy Company LLC, PBF Logistics GP LLC and PBF Logistics LP (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 12, 2015 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.18 | Third Amended and Restated Operation and Management Services and Secondment Agreement dated as of May 15, 2015 among PBF Holding Company LLC, Delaware City Refining Company LLC, Toledo Refining Company LLC, PBF Logistics GP LLC , PBF Logistics LP, Delaware City Terminaling Company LLC, Delaware Pipeline Company LLC, Delaware City Logistics Company LLC and Toledo Terminaling Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 12, 2015 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.19 | Delaware Pipeline Services Agreement dated as of May 15, 2015 among PBF Holding Company LLC and Delaware Pipeline Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 12, 2015 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.20 | Delaware City Truck Loading Services Agreement dated as of May 15, 2015 among PBF Holding Company LLC and Delaware City Logistics Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 12, 2015 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.21** | Employment Agreement dated as of September 4, 2014 between PBF Investments LLC and Thomas O'Connor (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Annual Report on Form 10-K dated February 29, 2016 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.22† | Inventory Intermediation Agreement dated as of May 29, 2015 (as amended) between J. Aron & Company and PBF Holding Company LLC and Paulsboro Refining Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated August 6, 2015 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.23† | Inventory Intermediation Agreement dated as of May 29, 2015 (as amended) between J. Aron & Company and PBF Holding Company LLC and Delaware City Refining Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated August 6, 2015 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.24 | Third Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement, dated as of August 15, 2014, among PBF Holding Company LLC, Delaware City Refining Company LLC, Paulsboro Refining Company LLC, Toledo Refining Company LLC and UBS Securities LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated November 7, 2014 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.25 | Contribution, Conveyance and Assumption Agreement dated as of May 14, 2014 by and among PBF Logistics LP, PBF Logistics GP LLC, PBF Energy Inc., PBF Energy Company LLC, PBF Holding Company LLC, Delaware City Refining Company LLC, Delaware City Terminaling Company LLC and Toledo Refining Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 14, 2014 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.26 | Delaware City Rail Terminaling Services Agreement, dated as of May 14, 2014 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 14, 2014 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
90
10.27 | Amended and Restated Toledo Truck Unloading & Terminaling Agreement effective as of June 1, 2014 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated August 7, 2014 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.27.1 | Assignment and Amendment of Amended and Restated Toledo Truck Unloading & Terminaling Agreement dated as of December 12, 2014 by and between PBF Holding Company LLC, PBF Logistics LP and Toledo Terminaling Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 filed with PBF Logistics LP's Current Report on Form 8-K dated December 16, 2014 (File No. 001-36446)) | |
10.28 | Contribution Agreement, dated as of September 16, 2014 among PBF Energy Company LLC and PBF Logistics LP (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated September 19, 2014 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.29 | Delaware City West Ladder Rack Terminaling Services Agreement, dated as of October 1, 2014 among PBF Holding Company LLC and Delaware City Terminaling Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated October 2, 2014 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.30 | Contribution Agreement, dated as of December 2, 2014 by and between PBF Energy Company LLC and PBF Logistics LP (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated December 5, 2014 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.31 | Storage and Terminaling Services Agreement dated as of December 12, 2014 among PBF Holding Company LLC and Toledo Terminaling Company LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 16, 2014 (File No. 001-36446)) | |
10.32** | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement dated as of December 17, 2012, between PBF Investments LLC and Thomas J. Nimbley (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated December 18, 2012 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.33** | Second Amended and Restated Employment Agreement, dated as of December 17, 2012, between PBF Investments LLC and Matthew C. Lucey (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated December 18, 2012 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.34** | Employment Agreement dated as of April 1, 2014 between PBF Investments LLC and Erik Young. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated May 7, 2014 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.35*/** | Second Amended and Restated Employment Agreement, dated as of September 29, 2015, between PBF Investments LLC and Jeffrey Dill | |
10.36** | Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement for Directors under the PBF Energy Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 filed with PBF Energy Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q dated November 7, 2014 (File No. 001-35764)) | |
10.37** | Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement under the PBF Energy Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.28 filed with PBF Energy Inc.’s Amendment No. 6 to Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Registration No. 333-177933)) | |
12.1* | Computation of Ratios of Earnings to Fixed Charge of PBF Holding Company LLC | |
21.1* | Subsidiaries of PBF Holding Company LLC | |
24.1* | Power of Attorney (included on signature page) | |
31.1* | Certification by Chief Executive Officer of PBF Holding Company LLC pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a), as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
91
31.2* | Certification by Chief Financial Officer of PBF Holding Company LLC pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a), as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
32.1*(1) | Certification by Chief Executive Officer of PBF Holding Company LLC pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
32.2*(1) | Certification by Chief Financial Officer of PBF Holding Company LLC pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
101.INS | XBRL Instance Document. | |
101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. | |
101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. | |
101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. | |
101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. | |
101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. | |
——————————
* | Filed herewith. |
** | Indicates management compensatory plan or arrangement. |
† | Confidential treatment has been granted by the SEC as to certain portions, which portions have been omitted and filed separately with the SEC. |
(1) | This exhibit should not be deemed to be “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act. |
92
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
F- 1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To PBF Energy Inc., the Managing Member of
PBF Holding Company LLC
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of PBF Holding Company LLC and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, changes in equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2016. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of PBF Holding Company LLC and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2016, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Parsippany, New Jersey
March 8, 2017
F- 2
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands)
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | ||||||
ASSETS | |||||||
Current assets: | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 626,705 | $ | 914,749 | |||
Accounts receivable | 615,881 | 454,759 | |||||
Accounts receivable - affiliate | 7,631 | 3,438 | |||||
Inventories | 1,863,560 | 1,174,272 | |||||
Prepaid expense and other current assets | 40,536 | 33,701 | |||||
Total current assets | 3,154,313 | 2,580,919 | |||||
Property, plant and equipment, net | 2,728,699 | 2,211,090 | |||||
Investment in equity method investee | 179,882 | — | |||||
Deferred charges and other assets, net | 504,003 | 290,713 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 6,566,897 | $ | 5,082,722 | |||
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | |||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 530,365 | $ | 314,843 | |||
Accounts payable - affiliate | 37,863 | 23,949 | |||||
Accrued expenses | 1,462,729 | 1,117,435 | |||||
Deferred revenue | 12,340 | 4,043 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 2,043,297 | 1,460,270 | |||||
Delaware Economic Development Authority loan | — | 4,000 | |||||
Long-term debt | 1,576,559 | 1,236,720 | |||||
Affiliate notes payable | 86,298 | 470,047 | |||||
Deferred tax liabilities | 45,699 | 20,577 | |||||
Other long-term liabilities | 226,111 | 69,824 | |||||
Total liabilities | 3,977,964 | 3,261,438 | |||||
Commitments and contingencies (Note 13) | |||||||
Equity: | |||||||
Member's equity | 2,155,863 | 1,479,175 | |||||
Retained earnings | 446,519 | 349,654 | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (25,962 | ) | (24,770 | ) | |||
Total PBF Holding Company LLC equity | 2,576,420 | 1,804,059 | |||||
Noncontrolling interest | 12,513 | 17,225 | |||||
Total equity | 2,588,933 | 1,821,284 | |||||
Total liabilities and equity | $ | 6,566,897 | $ | 5,082,722 | |||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F- 3
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in thousands)
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 15,908,537 | $ | 13,123,929 | $ | 19,828,155 | ||||||
Cost, expenses and other | ||||||||||||
Cost of sales, excluding depreciation | 13,765,088 | 11,611,599 | 18,514,054 | |||||||||
Operating expenses, excluding depreciation | 1,390,582 | 889,368 | 880,701 | |||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 149,643 | 166,904 | 140,150 | |||||||||
Equity income in investee | (5,679 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Loss (gain) on sale of assets | 11,374 | (1,004 | ) | (895 | ) | |||||||
Depreciation and amortization expense | 209,840 | 191,110 | 178,996 | |||||||||
Total costs, expenses and other | 15,520,848 | 12,857,977 | 19,713,006 | |||||||||
Income from operations | 387,689 | 265,952 | 115,149 | |||||||||
Other income (expense) | ||||||||||||
Change in fair value of catalyst lease | 1,422 | 10,184 | 3,969 | |||||||||
Interest expense, net | (129,536 | ) | (88,194 | ) | (98,001 | ) | ||||||
Income before income taxes | 259,575 | 187,942 | 21,117 | |||||||||
Income tax expense | 23,689 | 648 | — | |||||||||
Net income | 235,886 | 187,294 | 21,117 | |||||||||
Less income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 269 | 274 | — | |||||||||
Net income attributable to PBF Holding Company LLC | $ | 235,617 | $ | 187,020 | $ | 21,117 | ||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F- 4
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(in thousands)
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 235,886 | $ | 187,294 | $ | 21,117 | |||||
Other comprehensive (loss) income: | |||||||||||
Unrealized (loss) gain on available for sale securities | (42 | ) | 124 | 127 | |||||||
Net (loss) gain on pension and other post-retirement benefits | (2,550 | ) | 1,982 | (12,465 | ) | ||||||
Total other comprehensive (loss) income | (2,592 | ) | 2,106 | (12,338 | ) | ||||||
Comprehensive income | 233,294 | 189,400 | 8,779 | ||||||||
Less: comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 269 | 274 | — | ||||||||
Comprehensive income attributable to PBF Holding Company LLC | $ | 233,025 | $ | 189,126 | $ | 8,779 | |||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F- 5
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
(in thousands)
Member's Equity | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss | Retained Earnings | Noncontrolling Interest | Total Equity | ||||||||||||||||
Balance, January 1, 2014 | $ | 933,164 | $ | (14,538 | ) | $ | 853,527 | $ | — | $ | 1,772,153 | |||||||||
Member distributions | — | — | (361,352 | ) | — | (361,352 | ) | |||||||||||||
Capital contributions | 328,664 | — | — | — | 328,664 | |||||||||||||||
Distribution of assets to PBF LLC | (126,280 | ) | — | — | — | (126,280 | ) | |||||||||||||
Stock based compensation | 6,095 | — | — | — | 6,095 | |||||||||||||||
Exercise of options and other | 2,457 | — | — | — | 2,457 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | 21,117 | — | 21,117 | |||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss | — | (12,338 | ) | — | — | (12,338 | ) | |||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2014 | 1,144,100 | (26,876 | ) | 513,292 | — | 1,630,516 | ||||||||||||||
Member distributions | — | — | (350,658 | ) | — | (350,658 | ) | |||||||||||||
Capital contributions | 345,000 | — | — | — | 345,000 | |||||||||||||||
Distribution of assets to PBF LLC | (19,233 | ) | — | — | — | (19,233 | ) | |||||||||||||
Stock based compensation | 9,218 | — | — | — | 9,218 | |||||||||||||||
Exercise of options and other | 90 | — | — | — | 90 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | 187,020 | 274 | 187,294 | |||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive income | — | 2,106 | — | — | 2,106 | |||||||||||||||
Noncontrolling interest acquired in Chalmette Acquisition | — | — | — | 16,951 | 16,951 | |||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2015 | 1,479,175 | (24,770 | ) | 349,654 | 17,225 | 1,821,284 | ||||||||||||||
Member distributions | — | — | (139,434 | ) | — | (139,434 | ) | |||||||||||||
Capital contributions | 830,247 | — | — | — | 830,247 | |||||||||||||||
Distribution of assets to PBF LLC | (172,743 | ) | — | — | — | (172,743 | ) | |||||||||||||
Stock based compensation | 18,296 | — | — | — | 18,296 | |||||||||||||||
Exercise of options and other | 886 | — | — | — | 886 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | 235,617 | 269 | 235,886 | |||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive income | — | (2,592 | ) | — | — | (2,592 | ) | |||||||||||||
Other | 2 | 1,400 | 682 | (4,981 | ) | (2,897 | ) | |||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2016 | $ | 2,155,863 | $ | (25,962 | ) | $ | 446,519 | $ | 12,513 | $ | 2,588,933 | |||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F- 6
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | |||||||||||
Net income | $ | 235,886 | $ | 187,294 | $ | 21,117 | |||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operations: | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 218,933 | 199,383 | 186,412 | ||||||||
Stock-based compensation | 18,296 | 9,218 | 6,095 | ||||||||
Change in fair value of catalyst lease obligation | (1,422 | ) | (10,184 | ) | (3,969 | ) | |||||
Deferred income taxes | 19,802 | — | — | ||||||||
Non-cash change inventory repurchase obligations | 29,453 | 63,389 | (93,246 | ) | |||||||
Non-cash lower of cost or market inventory adjustment | (521,348 | ) | 427,226 | 690,110 | |||||||
Pension and other post retirement benefits costs | 37,987 | 26,982 | 22,600 | ||||||||
Equity (income) loss in investee | (5,679 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Loss (gain) on sale of assets | 11,374 | (1,004 | ) | (895 | ) | ||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||
Accounts receivable | (161,122 | ) | 97,636 | 45,378 | |||||||
Due to/from affiliates | 9,721 | 12,104 | 8,407 | ||||||||
Inventories | 236,602 | (271,892 | ) | (394,031 | ) | ||||||
Prepaid expense and other current assets | (5,783 | ) | (631 | ) | 23,686 | ||||||
Accounts payable | 213,514 | (25,015 | ) | (67,111 | ) | ||||||
Accrued expenses | 227,986 | (37,737 | ) | 59,899 | |||||||
Deferred revenue | 8,297 | 2,816 | (6,539 | ) | |||||||
Other assets and liabilities | (20,878 | ) | (27,182 | ) | (2,225 | ) | |||||
Net cash provided by operations | 551,619 | 652,403 | 495,688 | ||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | |||||||||||
Acquisition of Torrance refinery and related logistics assets | (971,932 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Acquisition of Chalmette refinery, net of cash acquired | (2,659 | ) | (565,304 | ) | — | ||||||
Expenditures for property, plant and equipment | (282,430 | ) | (352,365 | ) | (470,460 | ) | |||||
Expenditures for deferred turnaround costs | (198,664 | ) | (53,576 | ) | (137,688 | ) | |||||
Expenditures for other assets | (42,506 | ) | (8,236 | ) | (17,255 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from sale of assets | 24,692 | 168,270 | 202,654 | ||||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (1,473,499 | ) | (811,211 | ) | (422,749 | ) | |||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | |||||||||||
Contributions from PBF LLC | 450,300 | 345,000 | 328,664 | ||||||||
Distributions to members | (139,434 | ) | (350,658 | ) | (361,352 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from affiliate notes payable | 43,396 | 347,783 | 90,631 | ||||||||
Repayment of affiliate notes payable | (53,524 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Proceeds from revolver borrowings | 550,000 | 170,000 | 395,000 | ||||||||
Repayments of revolver borrowings | (200,000 | ) | (170,000 | ) | (410,000 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from Rail Facility revolver borrowings | — | 102,075 | 83,095 | ||||||||
Repayments of Rail Facility revolver borrowings | (67,491 | ) | (71,938 | ) | (45,825 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from PBF Rail Term Loan | 35,000 | — | — | ||||||||
Proceeds from 2023 Senior Secured Notes | — | 500,000 | — | ||||||||
Additional catalyst lease | 15,589 | — | — | ||||||||
Deferred financing costs and other | — | (17,108 | ) | (11,719 | ) | ||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | 633,836 | 855,154 | 68,494 | ||||||||
Net (decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents | (288,044 | ) | 696,346 | 141,433 | |||||||
Cash and equivalents, beginning of period | 914,749 | 218,403 | 76,970 | ||||||||
Cash and equivalents, end of period | $ | 626,705 | $ | 914,749 | $ | 218,403 | |||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F- 7
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS (Continued)
(in thousands)
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
Supplemental cash flow disclosure | |||||||||||
Non-cash activities: | |||||||||||
Conversion of affiliate notes payable to capital contribution | $ | 379,947 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Conversion of Delaware Economic Development Authority loan to grant | 4,000 | 4,000 | 4,000 | ||||||||
Accrued construction in progress and unpaid fixed assets | 34,055 | 7,974 | 33,296 | ||||||||
Distribution of assets to PBF Energy Company LLC | 172,743 | 19,233 | 126,280 | ||||||||
Cash paid during the year for: | |||||||||||
Interest (including capitalized interest of $8,333, $3,529 and $7,487 in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively) | $ | 116,880 | $ | 83,371 | $ | 96,346 | |||||
Income taxes | 2,449 | — | — | ||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F- 8
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
1. DESCRIPTION OF THE BUSINESS AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
Description of the Business
PBF Holding Company LLC (“PBF Holding” or the “Company”), a Delaware limited liability company, together with its consolidated subsidiaries, owns and operates oil refineries and related facilities in North America. PBF Holding is a wholly-owned subsidiary of PBF Energy Company LLC (“PBF LLC”). PBF Energy Inc. (“PBF Energy”) is the sole managing member of, and owner of an equity interest representing approximately 96.5% of the outstanding economic interest, in PBF LLC as of December 31, 2016. PBF Investments LLC ("PBF Investments"), Toledo Refining Company LLC ("Toledo Refining" or "TRC"), Paulsboro Refining Company LLC ("Paulsboro Refining" or "PRC"), Delaware City Refining Company LLC (“Delaware City Refining” or “DCR”), Chalmette Refining, L.L.C. (“Chalmette Refining”), PBF Western Region LLC (“PBF Western Region”), Torrance Refining Company LLC ("Torrance Refining") and Torrance Logistics Company LLC are PBF LLC's principal operating subsidiaries and are all wholly-owned subsidiaries of PBF Holding. Collectively, PBF Holding and its consolidated subsidiaries are referred to hereinafter as the “Company”.
On May 14, 2014, PBF Logistics LP (“PBFX”), a Delaware master limited partnership, completed its initial public offering (the “PBFX Offering”) of 15,812,500 common units. PBF Logistics GP LLC (“PBF GP”) serves as the general partner of PBFX. PBF GP is wholly-owned by PBF LLC. In connection with the PBFX Offering, PBF Holding distributed to PBF LLC the assets and liabilities of certain crude oil terminaling assets, which were immediately contributed by PBF LLC to PBFX. PBF Holding and PBF LLC entered into additional transactions with PBFX since the PBFX Offering as described in "Note 12 - Related Party Transactions”).
Substantially all of the Company’s operations are in the United States. The Company’s oil refineries are all engaged in the refining of crude oil and other feedstocks into petroleum products, and have been aggregated to form one reportable segment. To generate earnings and cash flows from operations, the Company is primarily dependent upon processing crude oil and selling refined petroleum products at margins sufficient to cover fixed and variable costs and other expenses. Crude oil and refined petroleum products are commodities; and factors largely out of the Company’s control can cause prices to vary over time. The potential margin volatility can have a material effect on the Company’s financial position, earnings and cash flow.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principles of Consolidation and Presentation
These consolidated financial statements include the accounts of PBF Holding and its consolidated subsidiaries. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Reclassification
Certain amounts previously reported in the Company's consolidated financial statements for prior periods have been reclassified to conform to the 2016 presentation. These reclassifications include certain details about accrued expenses and deferred charges and other assets in those respective footnotes.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States ("GAAP") requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses and the related disclosures. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
F- 9
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Business Combinations
We use the acquisition method of accounting for the recognition of assets acquired and liabilities assumed in business combinations at their estimated fair values as of the date of acquisition. Any excess consideration transferred over the estimated fair values of the identifiable net assets acquired is recorded as goodwill. Significant judgment is required in estimating the fair value of assets acquired. As a result, in the case of significant acquisitions, we obtain the assistance of third-party valuation specialists in estimating fair values of tangible and intangible assets based on available historical information and on expectations and assumptions about the future, considering the perspective of marketplace participants. While management believes those expectations and assumptions are reasonable, they are inherently uncertain. Unanticipated market or macroeconomic events and circumstances may occur, which could affect the accuracy or validity of the estimates and assumptions.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less to be cash equivalents. The carrying amount of the cash equivalents approximates fair value due to the short-term maturity of those instruments.
Concentrations of Credit Risk
For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 no single customer amounted to greater than or equal to 10% of the Company's revenues.
No single customer accounted for 10% or more of our total trade accounts receivable as of December 31, 2016. Following the Chalmette Acquisition on November 1, 2015, ExxonMobil Oil Corporation and its affiliates represented approximately 18% of our total trade accounts receivable as of December 31, 2015.
Revenue, Deferred Revenue and Accounts Receivable
The Company sells various refined products primarily through its refinery subsidiaries and recognizes revenue related to the sale of products when there is persuasive evidence of an agreement, the sales prices are fixed or determinable, collectability is reasonably assured and when products are shipped or delivered in accordance with their respective agreements. Revenue for services is recorded when the services have been provided. Certain of the Company's refineries have product offtake agreements with third-parties under which these third parties purchase a portion of the refineries' daily gasoline production. The refineries also sell their products through short-term contracts or on the spot market.
On May 29, 2015, PBF Holding entered into amended and restated inventory intermediation agreements (the "A&R Intermediation Agreements") with J. Aron & Company, a subsidiary of The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. ("J. Aron") pursuant to which certain terms of the existing inventory intermediation agreements were amended, including, among other things, pricing and an extension of the term for a period of two years from the original expiry date of July 1, 2015, subject to certain early termination rights. In addition, the A&R Intermediation Agreements include one-year renewal clauses by mutual consent of both parties.
Pursuant to each A&R Intermediation Agreement, J. Aron, will continue to purchase and hold title to certain of the intermediate and finished products (the "Products") produced by the Paulsboro and Delaware City refineries (the "Refineries"), respectively, and delivered into tanks at the Refineries. Furthermore, J. Aron agrees to sell the Products back to Paulsboro refinery and Delaware City refinery as the Products are discharged out of the Refineries' tanks. These purchases and sales are settled monthly at the daily market prices related to those products. These transactions are considered to be made in contemplation of each other and, accordingly, do not result in the recognition of a sale when title passes from the refineries to J. Aron. Additionally, J. Aron has the right to store the Products purchased in tanks under the A&R Intermediation Agreements and will retain these storage rights for the term of the agreements. PBF Holding will continue to market and sell the Products independently to third parties.
F- 10
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Accounts receivable are carried at invoiced amounts. An allowance for doubtful accounts is established, if required, to report such amounts at their estimated net realizable value. In estimating probable losses, management reviews accounts that are past due and determines if there are any known disputes. There was no allowance for doubtful accounts at December 31, 2016 and 2015.
Excise taxes on sales of refined products that are collected from customers and remitted to various governmental agencies are reported on a net basis.
Inventory
Inventories are carried at the lower of cost or market. The cost of crude oil, feedstocks, blendstocks and refined products are determined under the last-in first-out (“LIFO”) method using the dollar value LIFO method with increments valued based on average purchase prices during the year. The cost of supplies and other inventories is determined principally on the weighted average cost method.
The Company had the obligation to purchase and sell feedstocks under a supply agreement with Statoil for its Delaware City refinery. This Crude Supply Agreement expired on December 31, 2015. The Company's Paulsboro refinery also had a crude supply agreement with Statoil that was terminated in March 2013. Prior to the expiration or termination of these agreements, Statoil purchased the refineries' production of certain feedstocks or purchased feedstocks from third parties on the refineries' behalf. The Company took title to the crude oil as it was delivered to the processing units, in accordance with the Crude Supply Agreement; however, the Company was obligated to purchase all the crude oil held by Statoil on the Company’s behalf upon termination of the agreement at the then market price. The Paulsboro crude supply agreement also included an obligation to purchase a fixed volume of feedstocks from Statoil on the later of maturity or when the arrangement is terminated based on a forward market price of West Texas Intermediate crude oil. As a result of the purchase obligations, the Company recorded the inventory of crude oil and feedstocks in the refineries’ storage facilities. The Company determined the purchase obligations were contracts that contain derivatives that changed in value based on changes in commodity prices. Such changes in the fair value of these derivatives were included in cost of sales.
Prior to July 31, 2014, the Company’s Toledo refinery acquired substantially all of its crude oil from Morgan Stanley Capital Group, Inc. ("MSCG") under a crude oil acquisition agreement (the “Toledo Crude Oil Acquisition Agreement”). Under the Toledo Crude Oil Acquisition Agreement, the Company took title to crude oil at various pipeline locations for delivery to the refinery or sale to third parties. The Company recorded the crude oil inventory when it received title. Payment for the crude oil was due to MSCG under the Toledo Crude Oil Acquisition Agreement three days after the crude oil was delivered to the Toledo refinery processing units or upon sale to a third party. The Company terminated the Toledo Crude Oil Acquisition Agreement effective July 31, 2014 and began to source its crude oil needs independently.
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment additions are recorded at cost. The Company capitalizes costs associated with the preliminary, pre-acquisition and development/construction stages of a major construction project. The Company capitalizes the interest cost associated with major construction projects based on the effective interest rate of total borrowings. The Company also capitalizes costs incurred in the acquisition and development of software for internal use, including the costs of software, materials, consultants and payroll-related costs for employees incurred in the application development stage.
F- 11
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the following estimated useful lives:
Process units and equipment | 5-25 years | |
Pipeline and equipment | 5-25 years | |
Buildings | 25 years | |
Computers, furniture and fixtures | 3-7 years | |
Leasehold improvements | 20 years | |
Railcars | 50 years | |
Maintenance and repairs are charged to operating expenses as they are incurred. Improvements and betterments, which extend the lives of the assets, are capitalized.
Deferred Charges and Other Assets, Net
Deferred charges and other assets include refinery turnaround costs, catalyst, precious metals catalyst, linefill, deferred financing costs and intangible assets. Refinery turnaround costs, which are incurred in connection with planned major maintenance activities, are capitalized when incurred and amortized on a straight-line basis over the period of time estimated to lapse until the next turnaround occurs (generally 3 to 5 years).
Precious metals catalyst and linefill are considered indefinite-lived assets as they are not expected to deteriorate in their prescribed functions. Such assets are assessed for impairment in connection with the Company’s review of its long-lived assets as indicators of impairment develop.
Deferred financing costs are capitalized when incurred and amortized over the life of the loan (generally 1 to 8 years).
Intangible assets with finite lives primarily consist of catalyst, emission credits and permits and are amortized over their estimated useful lives (generally 1 to 10 years).
Long-Lived Assets and Definite-Lived Intangibles
The Company reviews its long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable. Impairment is evaluated by comparing the carrying value of the long-lived assets to the estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to result from use of the assets and their ultimate disposition. If such analysis indicates that the carrying value of the long-lived assets is not considered to be recoverable, the carrying value is reduced to the fair value.
Impairment assessments inherently involve judgment as to assumptions about expected future cash flows and the impact of market conditions on those assumptions. Although management would utilize assumptions that it believes are reasonable, future events and changing market conditions may impact management’s assumptions, which could produce different results.
Investments in Equity Method Investments
For equity investments that are not required to be consolidated under the variable or voting interest model, the Company evaluates the level of influence it is able to exercise over an entity’s operations to determine whether to use the equity method of accounting.The Company's judgment regarding the level of control over an equity method investment includes considering key factors such as its ownership interest, participation in policy-making and other significant decisions and material intercompany transactions. Amounts recognized for equity method investments are included in equity method investments in the consolidated balance sheet and adjusted for the Company's shares of the net earnings and losses of the investee and cash distributions, which are included in the consolidated statements of operations and the consolidated statements of cash flows. Amounts recognized for earnings in excess of distributions of the Company's equity method investments are included in the operating section of the consolidated statements of cash flows. The Company evaluates its equity method investments for impairment whenever events
F- 12
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amounts of such investments may be impaired. A loss is recorded in earnings in the current period to write down the carrying value of the investment to fair value if a decline in the value of an equity method investment is determined to be other than temporary.
Asset Retirement Obligations
The Company records an asset retirement obligation at fair value for the estimated cost to retire a tangible long-lived asset at the time the Company incurs that liability, which is generally when the asset is purchased, constructed, or leased. The Company records the liability when it has a legal or contractual obligation to incur costs to retire the asset and when a reasonable estimate of the fair value of the liability can be made. If a reasonable estimate cannot be made at the time the liability is incurred, the Company will record the liability when sufficient information is available to estimate the liability’s fair value. Certain of the Company’s asset retirement obligations are based on its legal obligation to perform remedial activity at its refinery sites when it permanently ceases operations of the long-lived assets. The Company therefore considers the settlement date of these obligations to be indeterminable. Accordingly, the Company cannot calculate an associated asset retirement liability for these obligations at this time. The Company will measure and recognize the fair value of these asset retirement obligations when the settlement date is determinable.
Environmental Matters
Liabilities for future remediation costs are recorded when environmental assessments and/or remedial efforts are probable and the costs can be reasonably estimated. Other than for assessments, the timing and magnitude of these accruals generally are based on the completion of investigations or other studies or a commitment to a formal plan of action. Environmental liabilities are based on best estimates of probable future costs using currently available technology and applying current regulations, as well as the Company’s own internal environmental policies. The measurement of environmental remediation liabilities may be discounted to reflect the time value of money if the aggregate amount and timing of cash payments of the liabilities are fixed or reliably determinable. The actual settlement of the Company’s liability for environmental matters could materially differ from its estimates due to a number of uncertainties such as the extent of contamination, changes in environmental laws and regulations, potential improvements in remediation technologies and the participation of other responsible parties.
Stock-Based Compensation
Stock-based compensation includes the accounting effect of options to purchase PBF Energy Class A common stock granted by PBF Energy to certain PBF Holding employees, Series A warrants issued or granted by PBF LLC to employees in connection with their acquisition of PBF LLC Series A units, options to acquire Series A units of PBF LLC granted by PBF LLC to certain employees, Series B units of PBF LLC that were granted to certain members of management and restricted PBF LLC Series A Units and restricted PBF Energy Class A common stock granted to certain directors and officers. The estimated fair value of the options to purchase PBF Energy Class A common stock and the PBF LLC Series A warrants and options, is based on the Black-Scholes option pricing model and the fair value of the PBF LLC Series B units is estimated based on a Monte Carlo simulation model. The estimated fair value is amortized as stock-based compensation expense on a straight-line method over the vesting period and included in general and administration expense with forfeitures recognized in the period they occur.
Income Taxes
As PBF Holding is a limited liability company treated as a “flow-through” entity for income tax purposes, there is no benefit or provision for federal or state income tax in the accompanying financial statements apart from the income taxes attributable to two subsidiaries acquired in connection with the acquisition of Chalmette Refining that are treated as C-corporations for tax purposes.
The Federal tax returns for all years since 2013 and state tax returns for all years since 2012 or 2013 are subject to examination by the respective tax authorities.
F- 13
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Pension and Other Post-Retirement Benefits
The Company recognizes an asset for the overfunded status or a liability for the underfunded status of its pension and post-retirement benefit plans. The funded status is recorded within other long-term liabilities or assets. Changes in the plans’ funded status are recognized in other comprehensive income in the period the change occurs.
Fair Value Measurement
A fair value hierarchy (Level 1, Level 2, or Level 3) is used to categorize fair value amounts based on the quality of inputs used to measure fair value. Accordingly, fair values derived from Level 1 inputs utilize quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. Fair values derived from Level 2 inputs are based on quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, and inputs other than quoted prices that are either directly or indirectly observable for the asset or liability. Level 3 inputs are unobservable inputs for the asset or liability, and include situations where there is little, if any, market activity for the asset or liability.
The Company uses appropriate valuation techniques based on the available inputs to measure the fair values of its applicable assets and liabilities. When available, the Company measures fair value using Level 1 inputs because they generally provide the most reliable evidence of fair value. In some valuations, the inputs may fall into different levels in the hierarchy. In these cases, the asset or liability level within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurements.
Financial Instruments
The estimated fair value of financial instruments has been determined based on the Company’s assessment of available market information and appropriate valuation methodologies. The Company’s non-derivative financial instruments that are included in current assets and current liabilities are recorded at cost in the consolidated balance sheets. The estimated fair value of these financial instruments approximates their carrying value due to their short-term nature. Derivative instruments are recorded at fair value in the consolidated balance sheets.
The Company’s commodity contracts are measured and recorded at fair value using Level 1 inputs based on quoted prices in an active market, Level 2 inputs based on quoted market prices for similar instruments, or Level 3 inputs based on third party sources and other available market based data. The Company’s catalyst lease obligation and derivatives related to the Company’s crude oil and feedstocks and refined product purchase obligations are measured and recorded at fair value using Level 2 inputs on a recurring basis, based on observable market prices for similar instruments.
Derivative Instruments
The Company is exposed to market risk, primarily related to changes in commodity prices for the crude oil and feedstocks used in the refining process as well as the prices of the refined products sold. The accounting treatment for commodity contracts depends on the intended use of the particular contract and on whether or not the contract meets the definition of a derivative.
All derivative instruments, not designated as normal purchases or sales, are recorded in the balance sheet as either assets or liabilities measured at their fair values. Changes in the fair value of derivative instruments that either are not designated or do not qualify for hedge accounting treatment or normal purchase or normal sale accounting are recognized currently in earnings. Contracts qualifying for the normal purchase and sales exemption are accounted for upon settlement. Cash flows related to derivative instruments that are not designated or do not qualify for hedge accounting treatment are included in operating activities.
The Company designates certain derivative instruments as fair value hedges of a particular risk associated with a recognized asset or liability. At the inception of the hedge designation, the Company documents the relationship between the hedging instrument and the hedged item, as well as its risk management objective and strategy for undertaking various hedge transactions. Derivative gains and losses related to these fair value hedges, including hedge ineffectiveness, are recorded in cost of sales along with the change in fair value of the hedged asset or liability
F- 14
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
attributable to the hedged risk. Cash flows related to derivative instruments that are designated as fair value hedges are included in operating activities.
Economic hedges are hedges not designated as fair value or cash flow hedges for accounting purposes that are used to (i) manage price volatility in certain refinery feedstock and refined product inventories, and (ii) manage price volatility in certain forecasted refinery feedstock purchases and refined product sales. These instruments are recorded at fair value and changes in the fair value of the derivative instruments are recognized currently in cost of sales.
Derivative accounting is complex and requires management judgment in the following respects: identification of derivatives and embedded derivatives, determination of the fair value of derivatives, documentation of hedge relationships, assessment and measurement of hedge ineffectiveness and election and designation of the normal purchases and sales exception. All of these judgments, depending upon their timing and effect, can have a significant impact on the Company’s earnings.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2015, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2015-02, "Consolidation (Topic 810): Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis" ("ASU 2015-02"), which changed existing consolidation requirements associated with the analysis a reporting entity must perform to determine whether it should consolidate certain types of legal entities, including limited partnerships and variable interest entities. The Company has adopted this guidance retrospectively. The adoption of this guidance did not have any impact on the Company as it does not have any variable interest entities that would be affected by this ASU.
In August 2015, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2015-14, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Deferral of the Effective Date” (“ASU 2015-14”), which defers the effective date of ASU 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers” (“ASU 2014-09”) for all entities by one year. Additional ASUs have been issued in 2016 that provide certain implementation guidance related to ASU 2014-09 (collectively, the Company refers to ASU 2014-09 and these additional ASUs as the "Updated Revenue Recognition Guidance").The Updated Revenue Recognition Guidance will replace most existing revenue recognition guidance in GAAP when it becomes effective. Under ASU 2015-14, this guidance becomes effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017 and permits the use of either the retrospective or modified retrospective transition method. Under ASU 2015-14, early adoption is permitted only as of annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim reporting periods within that reporting period. The Company has established a working group to assess the Updated Revenue Recognition Guidance, including its impact on our business processes, accounting systems, controls and financial statement disclosures. Our preliminary expectation is that we will adopt this guidance using the modified retrospective method whereby a cumulative effect adjustment is recognized upon adoption and the Updated Revenue Recognition is applied prospectively. It is not anticipated that the Company will early adopt this new guidance. The working group is in the early stages of its implementation plan and continues to evaluate the impact of this new standard on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and related disclosures. Although our analysis of the new standard is still in process and interpretative and industry specific guidance is still developing, the Company currently does not expect the new standard to have a material impact on the amount or timing of revenues recognized for the majority of its revenue arrangements.
In November 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-17 (Topic 740), "Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes" ("ASU 2015-17") which is intended to simplify the presentation of deferred taxes in a classified balance sheet. This guidance states that deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities should be presented as noncurrent in a classified statement of financial position. Under ASU 2015-17, this guidance becomes effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016 and interim periods within those annual periods with early adoption permitted as of the beginning of an annual or interim period after issuance of the ASU. The Company early adopted the new standard in its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures on a prospective basis. The Company did not have any current deferred tax assets or liabilities in the prior year to reclassify from current to non-current.
F- 15
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
In January 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-01, "Financial Instruments - Overall (Subtopic 825-10): Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities" ("ASU 2016-01"), which amends how entities measure equity investments that do not result in consolidation and are not accounted for under the equity method and how they present changes in the fair value of financial liabilities measured under the fair value option that are attributable to their own credit. ASU 2016-01 also changes certain disclosure requirements and other aspects of current US GAAP but does not change the guidance for classifying and measuring investments in debt securities and loans. Under ASU 2016-01, this guidance becomes effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted in certain circumstances. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this new standard on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, "Leases (Topic 842)" ("ASU 2016-02"), to increase the transparency and comparability about leases among entities. The new guidance requires lessees to recognize a lease liability and a corresponding lease asset for virtually all lease contracts. It also requires additional disclosures about leasing arrangements. ASU 2016-02 is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2018, and requires a modified retrospective approach to adoption. Early adoption is permitted. The Company has established a working group to study and lead implementation of the new guidance in ASU 2016-02. This working group was formed during 2016 and has begun the process of compiling a central repository for all leases entered into by the Company and its subsidiaries for further analysis as the implementation project progresses. It is not anticipated that the Company will early adopt this new guidance. The working group continues to evaluate the impact of this new standard on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures. At this time, the Company has identified that the most significant impacts of this new guidance will be to bring nearly all leases on its balance sheet with “right of use assets” and “lease obligation liabilities” as well as accelerating the interest expense component of financing leases.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-06, “Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815): Contingent Put and Call Options in Debt Instruments No. 2016-06 March 2016 a consensus of the FASB Emerging Issues Task Force” (“ASU 2016-06”), to increase consistency in practice in applying guidance on determining if an embedded derivative is clearly and closely related to the economic characteristics of the host contract, specifically for assessing whether call (put) options that can accelerate the repayment of principal on a debt instrument meet the clearly and closely related criterion. The guidance in ASU 2016-06 applies to all entities that are issuers of or investors in debt instruments (or hybrid financial instruments that are determined to have a debt host) with embedded call (put) options. ASU 2016-06 is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and requires a modified retrospective approach to adoption. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this new standard on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-09, “Compensation - Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting” (“ASU 2016-09”) which is intended to simplify certain aspects of the accounting for share-based payments to employees. The guidance in ASU 2016-09 requires all income tax effects of awards to be recognized in the income statement when the awards vest or are settled rather than recording excess tax benefits or deficiencies in additional paid-in capital. The guidance in ASU 2016-09 also allows an employer to repurchase more of an employee’s shares than it can today for tax withholding purposes without triggering liability accounting and to make a policy election to account for forfeitures as they occur. ASU 2016-09 also contains additional guidance for nonpublic entities that do not apply to the Company. ASU 2016-09 is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and requires a modified retrospective approach to adoption. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this new standard on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13, “Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments” (“ASU 2016-13”) which requires credit losses on available-for-sale debt securities to be presented as an allowance rather than as a write-down. ASU 2016-13 is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2019, and requires a modified retrospective approach to adoption.
F- 16
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Early adoption is permitted for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2018. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this new standard on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-15, "Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments" ("ASU 2016-15"), which reduces the existing diversity in practice in how certain cash receipts and cash payments are presented and classified in the statement of cash flows under Topic 230. ASU 2016-15 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted, including adoption in an interim period. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this new standard on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In October 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-16, "Income Taxes (Topic 740): Intra-Entity Transfers of Assets Other Than Inventory" ("ASU 2016-16"), which reduces the existing diversity in practice in how income tax consequences of an intra-entity transfer of an asset other than inventory should be recognized. The amendments in ASU 2016-16 require an entity to recognize such income tax consequences when the intra-entity transfer occurs rather than waiting until such time as the asset has been sold to an outside party. The amendments do not contain any new disclosure requirements but point out that certain existing income tax disclosures might be applicable in the period an intra-entity transfer of an asset other than inventory occurs. ASU 2016-16 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted as of the beginning of an annual reporting period for which interim or annual statements have not been issued. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this new standard on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In October 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-17, "Consolidation (Topic 810): Interests Held through Related Parties That Are under Common Control" ("ASU 2016-2017"), which amends the consolidation guidance on how a reporting entity that is the single decision maker of a variable interest entity (“VIE”) should treat indirect interests in the entity held through related parties that are under common control with the reporting entity when determining whether it is the primary beneficiary of that VIE. The amendments in this ASU do not change the characteristics of a primary beneficiary in current GAAP. The amendments in this ASU require that reporting entity, in determining whether it satisfies the second characteristic of a primary beneficiary, to include all of its direct variable interests in a VIE and, on a proportionate basis, its indirect variable interests in a VIE held through related parties, including related parties that are under common control with the reporting entity. ASU 2016-2017 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted, including adoption in an interim period. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this new standard on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-01, "Business Combinations (Topic 805): Clarifying the Definition of a Business" ("ASU 2017-01"), which provides guidance to assist entities with evaluating when a set of transferred assets and activities is a business. Under ASU 2017-01, it is expected that the definition of a business will be narrowed and more consistently applied. ASU 2017-01 is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those periods. The amendments in this ASU should be applied prospectively on or after the effective date. The Company will apply the provisions of this guidance for determining if it has acquired a business or a set of assets for future acquisitions, if any, after it becomes effective.
3. ACQUISITIONS
Torrance Acquisition
On July 1, 2016, the Company acquired from ExxonMobil Oil Corporation and its subsidiary, Mobil Pacific Pipe Line Company, the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets (collectively, the "Torrance Acquisition"). The Torrance refinery, located in Torrance, California, is a high-conversion, delayed-coking refinery. The facility is strategically positioned in Southern California with advantaged logistics connectivity that offers flexible raw material sourcing and product distribution opportunities primarily in the California, Las Vegas and Phoenix area markets. The Torrance Acquisition provides the Company with a broader more diversified asset base and increases the number of operating refineries from four to five and expands the Company's combined crude oil throughput
F- 17
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
capacity. The acquisition also provides the Company with a presence in the PADD 5 market.
In addition to refining assets, the transaction includes a number of high-quality logistics assets including a sophisticated network of crude and products pipelines, product distribution terminals and refinery crude and product storage facilities. The most significant of the logistics assets is a crude gathering and transportation system which delivers San Joaquin Valley crude oil directly from the field to the refinery. Additionally, included in the transaction are several pipelines which provide access to sources of crude oil including the Ports of Long Beach and Los Angeles, as well as clean product outlets with a direct pipeline supplying jet fuel to the Los Angeles airport.
The aggregate purchase price for the Torrance Acquisition was $521,350 in cash after post-closing purchase price adjustments, plus final working capital of $450,582. In addition, the Company assumed certain pre-existing environmental and regulatory emission credit obligations in connection with the Torrance Acquisition. The transaction was financed through a combination of cash on hand, including proceeds from PBF Energy's October 2015 Equity Offering and the 2023 Senior Secured Notes Offering and borrowings under the asset based revolving credit agreement (the "Revolving Loan").
The Company accounted for the Torrance Acquisition as a business combination under GAAP whereby we recognize assets acquired and liabilities assumed in an acquisition at their estimated fair values as of the date of acquisition. The final purchase valuation was in process as of December 31, 2016 as the purchase price and fair value allocation may be subject to adjustment pending completion of our assessment of the estimated costs and duration of certain assumed pre-existing environmental obligations.
The total purchase consideration and the fair values of the assets and liabilities at the acquisition date, which may be subject to adjustment as noted above, were as follows:
Purchase Price | |||
Gross purchase price | $ | 537,500 | |
Working capital | 450,582 | ||
Post close purchase price adjustments | (16,150 | ) | |
Total consideration | $ | 971,932 | |
The following table summarizes the preliminary amounts recognized for assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the acquisition date.
Fair Value Allocation | |||
Inventories | $ | 404,542 | |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 1,186 | ||
Property, plant and equipment | 703,443 | ||
Deferred charges and other assets, net | 68,053 | ||
Accounts payable | (2,688 | ) | |
Accrued expenses | (64,137 | ) | |
Other long-term liabilities | (138,467 | ) | |
Fair value of net assets acquired | $ | 971,932 | |
The Company’s condensed consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2016, include the results of operations of the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets since July 1, 2016 during which period the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets contributed revenues of $1,977,204 and net income of $86,394. On an unaudited pro forma basis, the revenues and net income of the Company assuming the Torrance Acquisition had occurred on January 1, 2015, are shown below. The unaudited pro forma information does not purport to present what the Company’s actual results would have been had the acquisition occurred on January 1, 2015, nor is the financial information indicative of the results of future operations. The unaudited pro forma financial
F- 18
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
information includes the depreciation and amortization expense attributable to the Torrance Acquisition and interest expense associated with related financing.
Years ended December 31, | |||||||
(Unaudited) | 2016 | 2015 | |||||
Pro forma revenues | $ | 16,987,548 | $ | 16,252,729 | |||
Pro forma net income (loss) attributable to PBF Holding Company LLC | $ | 31,565 | $ | (176,410 | ) | ||
The unaudited amount of revenues and net income above have been calculated after conforming accounting policies of the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets to those of the Company and certain one-time adjustments.
Chalmette Acquisition
On November 1, 2015, the Company acquired from ExxonMobil, Mobil Pipe Line Company and PDV Chalmette, L.L.C., 100% of the ownership interests of Chalmette Refining, which owns the Chalmette refinery and related logistics assets (collectively, the “Chalmette Acquisition”). The Chalmette refinery, located outside of New Orleans, Louisiana, is a dual-train coking refinery and is capable of processing both light and heavy crude oil. Subsequent to the closing of the Chalmette Acquisition, Chalmette Refining is a wholly-owned subsidiary of PBF Holding. Chalmette Refining is strategically positioned on the Gulf Coast with logistics connectivity that offers flexible raw material sourcing and product distribution opportunities, including the potential to export products and provides geographic diversification into PADD 3.
Chalmette Refining owns 100% of the MOEM Pipeline, providing access to the Empire Terminal, as well as the CAM Connection Pipeline, providing access to the Louisiana Offshore Oil Port facility through a third party pipeline. Chalmette Refining also owns 80% of each of the Collins Pipeline Company and T&M Terminal Company, both located in Collins, Mississippi, which provide a clean products outlet for the refinery to the Plantation and Colonial Pipelines. Also included in the acquisition are a marine terminal capable of importing waterborne feedstocks and loading or unloading finished products; a clean products truck rack which provides access to local markets; and a crude and product storage facility.
The aggregate purchase price for the Chalmette Acquisition was $322,000 in cash, plus inventory and final working capital of $245,963. As described below, the valuation of the working capital was finalized in the first quarter of 2016. The transaction was financed through a combination of cash on hand and borrowings under the Company’s Revolving Loan.
The Company accounted for the Chalmette Acquisition as a business combination under US GAAP whereby we recognize assets acquired and liabilities assumed in an acquisition at their estimated fair values as of the date of acquisition. Any excess consideration transferred over the estimated fair values of the identifiable net assets acquired is recorded as goodwill. The final purchase price and fair value allocation were completed as of March 31, 2016. During the measurement period, which ended in March 2016, adjustments were made to the Company's preliminary fair value estimates related primarily to inventories and accounts payable.
The total purchase consideration and the fair values of the assets and liabilities at the acquisition date were as follows:
Purchase Price | |||
Net cash | $ | 587,005 | |
Cash acquired | (19,042 | ) | |
Total consideration | $ | 567,963 | |
F- 19
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
The following table summarizes the final amounts recognized for assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the acquisition date:
Fair Value Allocation | |||
Accounts receivable | $ | 1,126 | |
Inventories | 271,434 | ||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 913 | ||
Property, plant and equipment | 356,961 | ||
Deferred charges and other assets | 8,312 | ||
Accounts payable | (4,870 | ) | |
Accrued expenses | (28,371 | ) | |
Deferred tax liability | (25,721 | ) | |
Noncontrolling interest | (11,821 | ) | |
Fair value of net assets acquired | $ | 567,963 | |
In addition, in connection with the acquisition of Chalmette Refining, the Company acquired Collins Pipeline Company and T&M Terminal Company, which are both C-corporations for tax purposes. As a result, the Company recognized a deferred tax liability of $25,721 attributable to the book and tax basis difference in the C-corporation assets, which had a corresponding impact on noncontrolling interest of $5,144.
The Company’s condensed consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2016 include the results of operations of the Chalmette refinery for the full year. The Company’s consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2015 include the results of operations of the Chalmette refinery since November 1, 2015 during which period the Chalmette refinery contributed revenues of $643,267 and net income of $53,539. On an unaudited pro forma basis, the revenues and net income of the Company assuming the acquisition had occurred on January 1, 2014, are shown below. The unaudited pro forma information does not purport to present what the Company’s actual results would have been had the acquisition occurred on January 1, 2014, nor is the financial information indicative of the results of future operations. The unaudited pro forma financial information includes the depreciation and amortization expense related to the acquisition and interest expense associated with the Chalmette acquisition financing.
Year ended December 31, | |||
(Unaudited) | 2015 | ||
Pro forma revenues | $ | 16,811,922 | |
Pro forma net income attributable to PBF Holding Company LLC | 397,108 | ||
The unaudited amount of revenues and net income above have been calculated after conforming Chalmette Refining's accounting policies to those of the Company and certain one-time adjustments.
Acquisition Expenses
The Company incurred acquisition related costs consisting primarily of consulting and legal expenses related to the Chalmette Acquisition, the Torrance Acquisition, and other pending and non-consummated acquisitions of $13,622 and $5,833 in the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. These costs are included in the consolidated income statement in General and administrative expenses.
F- 20
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
4. INVENTORIES
Inventories consisted of the following:
December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||
Titled Inventory | Inventory Supply and Intermediation Arrangements | Total | |||||||||
Crude oil and feedstocks | $ | 1,102,007 | $ | — | $ | 1,102,007 | |||||
Refined products and blendstocks | 915,397 | 352,464 | 1,267,861 | ||||||||
Warehouse stock and other | 89,680 | — | 89,680 | ||||||||
$ | 2,107,084 | $ | 352,464 | $ | 2,459,548 | ||||||
Lower of cost or market adjustment | (492,415 | ) | (103,573 | ) | (595,988 | ) | |||||
Total inventories | $ | 1,614,669 | $ | 248,891 | $ | 1,863,560 | |||||
December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||
Titled Inventory | Inventory Supply and Intermediation Arrangements | Total | |||||||||
Crude oil and feedstocks | $ | 1,137,605 | $ | — | $ | 1,137,605 | |||||
Refined products and blendstocks | 687,389 | 411,357 | 1,098,746 | ||||||||
Warehouse stock and other | 55,257 | — | 55,257 | ||||||||
$ | 1,880,251 | $ | 411,357 | $ | 2,291,608 | ||||||
Lower of cost or market adjustment | (966,564 | ) | (150,772 | ) | (1,117,336 | ) | |||||
Total inventories | $ | 913,687 | $ | 260,585 | $ | 1,174,272 | |||||
Inventory under inventory supply and intermediation arrangements included certain crude oil stored at the Company's Delaware City refinery's storage facilities that the Company was obligated to purchase as it was consumed in connection with its Crude Supply Agreement that expired on December 31, 2015; and light finished products sold to counterparties in connection with the A&R Intermediation Agreements and stored in the Paulsboro and Delaware City refineries' storage facilities.
Due to the lower crude oil and refined product pricing environment beginning at the end of 2014 and continuing throughout 2015 and 2016, the Company recorded adjustments to value its inventories to the lower of cost or market. During the year ended December 31, 2016, the Company recorded an adjustment to value its inventories to the lower of cost or market which increased both operating income and net income by $521,348 reflecting the net change in the lower of cost or market inventory reserve from $1,117,336 at December 31, 2015 to $595,988 at December 31, 2016. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded an adjustment to value its inventories to the lower of cost or market which decreased both operating income and net income by $427,226 reflecting the net change in the lower of cost or market inventory reserve from $690,110 at December 31, 2014 to $1,117,336 at December 31, 2015.
An actual valuation of inventories valued under the LIFO method is made at the end of each year based on inventory levels and costs at that time. We recorded a charge related to a LIFO layer decrement of $11,746 during the year ended December 31, 2016. No such LIFO decrement was recorded in the year ended December 31, 2015.
F- 21
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
5. PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property, plant and equipment consisted of the following:
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||
Land | $ | 253,110 | $ | 91,256 | ||||
Process units, pipelines and equipment | 2,504,008 | 2,209,712 | ||||||
Buildings and leasehold improvements | 49,020 | 34,265 | ||||||
Computers, furniture and fixtures | 81,780 | 72,642 | ||||||
Construction in progress | 289,338 | 150,388 | ||||||
3,177,256 | 2,558,263 | |||||||
Less—Accumulated depreciation | (448,557 | ) | (347,173 | ) | ||||
$ | 2,728,699 | $ | 2,211,090 | |||||
Depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 was $104,293, $88,474 and $113,533, respectively. The Company capitalized $8,333 and $3,529 in interest during 2016 and 2015, respectively, in connection with construction in progress.
For the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company determined that it would abandon a capital project at the Delaware City refinery. The project was related to the construction of a new hydrocracker (the “Hydrocracker Project”). The carrying value for the Hydrocracker Project was $28,508. The total pre-tax impairment charge of $28,508 was recorded in depreciation and amortization expense for the year ended December 31, 2014. No additional cash expenditures were incurred related to the Hydrocracker Project subsequent to the impairment charge.
6. DEFERRED CHARGES AND OTHER ASSETS, NET
Deferred charges and other assets, net consisted of the following:
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | ||||||
Deferred turnaround costs, net | $ | 302,919 | $ | 177,236 | |||
Catalyst | 114,788 | 77,725 | |||||
Linefill | 19,485 | 13,504 | |||||
Restricted cash | — | 1,500 | |||||
Environmental credits | 51,636 | 10,829 | |||||
Intangible assets, net | 577 | 219 | |||||
Other | 14,598 | 9,700 | |||||
Total deferred charges and other assets, net | $ | 504,003 | $ | 290,713 | |||
The Company recorded amortization expense related to deferred turnaround costs, catalyst and intangible assets of $105,547, $102,636 and $65,452 for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The restricted cash consisted primarily of cash held as collateral securing the Rail Facility.
F- 22
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Intangible assets, net was comprised of permits and emission credits as follows:
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||
Gross amount | $ | 3,996 | $ | 3,597 | ||||
Accumulated amortization | (3,419 | ) | (3,378 | ) | ||||
Net amount | $ | 577 | $ | 219 | ||||
7. ACCRUED EXPENSES
Accrued expenses consisted of the following:
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | ||||||
Inventory-related accruals | $ | 810,027 | $ | 548,800 | |||
Inventory intermediation arrangements | 225,524 | 252,380 | |||||
Accrued transportation costs | 89,830 | 91,546 | |||||
Excise and sales tax payable | 86,046 | 34,129 | |||||
Renewable energy credit and emissions obligations | 70,158 | 19,472 | |||||
Accrued utilities | 44,190 | 25,192 | |||||
Accrued interest | 28,934 | 22,313 | |||||
Accrued construction in progress | 33,610 | 7,400 | |||||
Accrued salaries and benefits | 17,466 | 61,011 | |||||
Customer deposits | 9,215 | 20,395 | |||||
Environmental liabilities | 8,882 | 2,178 | |||||
Other | 38,847 | 32,619 | |||||
Total accrued expenses | $ | 1,462,729 | $ | 1,117,435 | |||
The Company has the obligation to repurchase certain intermediates and finished products that are held in the Company’s refinery storage tanks at the Delaware City and Paulsboro refineries in accordance with the A&R Intermediation Agreements with J. Aron. As of December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, a liability is recognized for the inventory supply and intermediation arrangements and is recorded at market price for the J. Aron owned inventory held in the Company's storage tanks under the A&R Intermediation Agreements, with any change in the market price being recorded in cost of sales.
The Company is subject to obligations to purchase Renewable Identification Numbers ("RINs") required to comply with the Renewable Fuels Standard. The Company's overall RINs obligation is based on a percentage of domestic shipments of on-road fuels as established by the Environmental Protection Agency ("EPA"). To the degree the Company is unable to blend the required amount of biofuels to satisfy its RINs obligation, RINs must be purchased on the open market to avoid penalties and fines. The Company records its RINs obligation on a net basis in Accrued expenses when its RINs liability is greater than the amount of RINs earned and purchased in a given period and in Prepaid expenses and other current assets when the amount of RINs earned and purchased is greater than the RINs liability. In addition, the Company is subject to obligations to comply with federal and state legislative and regulatory measures to address environmental compliance and greenhouse gas and other emissions, including AB 32 in California. These requirements include incremental costs to operate and maintain our facilities as well as to implement and manage new emission controls and programs, which have contributed to the increase in accrued environmental liabilities and emission obligations following the Torrance Acquisition.
F- 23
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
8. DELAWARE ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT AUTHORITY LOAN
In June 2010, in connection with the Delaware City acquisition, the Delaware Economic Development Authority (the “Authority”) granted the Company a $20,000 loan to assist with operating costs and the cost of restarting the refinery. The loan converted to a grant in tranches of $4,000 annually over a five-year period, starting at the one-year anniversary of the “certified restart date” as defined in the agreement and certified by the Authority. In December 2016, the Company received confirmation from the Authority that the final tranche had satisfied the conditions necessary to be converted to a grant. Accordingly, there was no outstanding balance under the Delaware Economic Development Authority Loan at December 31, 2016.
9. CREDIT FACILITY AND LONG-TERM DEBT
PBF Holding Revolving Loan
On August 15, 2014, PBF Holding amended and restated the terms of the Revolving Loan to, among other things, increase the commitments from $1,610,000 to $2,500,000, and extend the maturity to August 2019. In addition, the amended and restated agreement reduced the interest rate on advances and the commitment fee paid on the unused portion of the facility. The amended and restated agreement also increased the sublimit for letters of credit from $1,000,000 to $1,500,000 and reduced the combined LC Participation Fee and Fronting Fee paid on each issued and outstanding letter of credit. The LC Participation Fee ranges from 1.25% to 2.0% depending on the Company's senior secured debt rating and the Fronting Fee is equal to 0.25%.
An accordion feature allows for increases in the aggregate commitment of up to $2,750,000. In November and December 2015, PBF Holding increased the maximum availability under the Revolving Loan to $2,600,000 and $2,635,000, respectively. At the option of PBF Holding, advances under the Revolving Loan bear interest either at the Alternate Base Rate plus the Applicable Margin, or the Adjusted LIBOR Rate plus the Applicable Margin, all as defined in the agreement. The Applicable Margin ranges from 1.50% to 2.25% for Adjusted LIBOR Rate Loans and from 0.50% to 1.25% for Alternative Base Rate Loans, depending on the Company's senior secured debt rating. Interest is paid in arrears, either quarterly in the case of Alternate Base Rate Loans or at the maturity of each Adjusted LIBOR Rate Loan.
Advances under the Revolving Loan, plus all issued and outstanding letters of credit may not exceed the lesser of $2,635,000 or the Borrowing Base, as defined in the agreement. The Revolving Loan can be prepaid, without penalty, at any time.
The Revolving Loan contains customary covenants and restrictions on the activities of PBF Holding and its subsidiaries, including, but not limited to, limitations on the incurrence of additional indebtedness; liens, negative pledges, guarantees, investments, loans, asset sales, mergers, acquisitions and prepayment of other debt; distributions, dividends and the repurchase of capital stock; transactions with affiliates; the ability to change the nature of our business or our fiscal year; the ability to amend the terms of the Senior Secured Notes facility documents; and sale and leaseback transactions.
In addition, the Revolving Loan has a financial covenant which requires that if at any time Excess Availability, as defined in the agreement, is less than the greater of (i) 10% of the lesser of the then existing Borrowing Base and the then aggregate Revolving Commitments of the Lenders (the “Financial Covenant Testing Amount”), and (ii) $100,000 and until such time as Excess Availability is greater than the Financial Covenant Testing Amount and $100,000 for a period of 12 or more consecutive days, PBF Holding will not permit the Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio, as defined in the agreement and determined as of the last day of the most recently completed quarter, to be less than 1.1 to 1.0.
PBF Holding's obligations under the Revolving Loan (a) are guaranteed by each of its domestic operating subsidiaries that are not Excluded Subsidiaries (as defined in the agreement) and (b) are secured by a lien on (x) PBF LLC’s equity interests in PBF Holding and (y) certain assets of PBF Holding and the subsidiary guarantors, including all deposit accounts (other than zero balance accounts, cash collateral accounts, trust accounts and/or payroll accounts, all of which are excluded from the collateral); all accounts receivable; all hydrocarbon inventory
F- 24
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
(other than the intermediate and finished products owned by J. Aron pursuant to the Inventory Intermediation Agreements) and to the extent evidencing, governing, securing or otherwise related to the foregoing, all general intangibles, chattel paper, instruments, documents, letter of credit rights and supporting obligations; and all products and proceeds of the foregoing.
The outstanding borrowings under the Revolving Loan as of December 31, 2016 was $350,000. There were no outstanding borrowings under the Revolving Loan as of December 31, 2015. Standby letters of credit were $411,997 and $351,511, as of December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively.
PBF Rail Revolving Credit Facility
Effective March 25, 2014, PBF Rail Logistics Company LLC (“PBF Rail”), an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of PBF Holding, entered into a $250,000 secured revolving credit agreement (the “Rail Facility”) with a consortium of banks, including Credit Agricole Corporate & Investment Bank as Administrative Agent. The primary purpose of the Rail Facility was to fund the acquisition by PBF Rail of coiled and insulated crude tank cars and non-coiled and non-insulated general purpose crude tank cars before December 2015. The Rail was amended on two occasions in 2015 and 2016. On December 22, 2016, the Rail Facility was repaid in full and terminated in connection with the issuance of the PBF Rail Term Loan (defined below).
There was no amount outstanding under the Rail Facility at December 31, 2016. There was $67,491 outstanding under the Rail Facility at December 31, 2015.
PBF Rail Term Loan
On December 22, 2016, PBF Rail entered into a $35,000 term loan (the “PBF Rail Term Loan”) with DVB Bank SE (“DVB”). The PBF Rail Term Loan amortizes monthly over its five year term and bears interest at the one month LIBOR plus 2.0%. As security for the PBF Rail Term Loan, PBF Rail pledged, among other things: (i) certain eligible railcars; (ii) the Debt Service Reserve Account; and (iii) PBF Holding's membership interest in PBF Rail. Additionally, the PBF Rail Term Loan contains customary terms, events of default and covenants for transactions of this nature. PBF Rail may at any time repay the PBF Rail Term Loan without penalty in the event that railcars collateralizing the loan are sold, scrapped or otherwise removed from the collateral pool.
As of December 31, 2016, there was $35,000 outstanding under the PBF Rail Term Loan.
Senior Secured Notes
On February 9, 2012, PBF Holding and PBF Holding's wholly-owned subsidiary, PBF Finance Corporation, completed the offering of $675,500 aggregate principal amount of 8.25% Senior Secured Notes due 2020 (the “2020 Senior Secured Notes”). The net proceeds, after deducting the original issue discount, the initial purchasers’ discounts and commissions, and the fees and expenses of the offering, were used to repay all of the outstanding indebtedness plus accrued interest owed under the Toledo Promissory Note, the Paulsboro Promissory Note, and the Term Loan, as well as to reduce the outstanding balance of the Revolving Loan.
On November 24, 2015, PBF Holding and PBF Holding’s wholly-owned subsidiary, PBF Finance Corporation completed an offering of $500,000 in aggregate principal amount of 7.00% Senior Secured Notes due 2023 (the “2023 Senior Secured Notes”, and together with the 2020 Senior Secured Notes, the “Senior Secured Notes”). The net proceeds from this offering were approximately $490,000 after deducting the initial purchasers’ discount and offering expenses. The Company used the proceeds for general corporate purposes, including to fund a portion of the purchase price for the acquisition of the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets.
The 2023 Senior Secured Notes included a registration payment arrangement whereby the Company agreed to use commercially reasonable efforts to consummate an offer to exchange the 2023 Senior Secured Notes for an issue of registered notes with terms substantially identical to the notes not later than 365 days after the date of the original issuance of the notes. This registration statement was declared effective on December 1, 2016 and the exchange was consummated on January 19, 2017. As the exchange offer was not consummated by November 24, 2016,
F- 25
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
additional interest was added at a rate of 0.25% per annum for the period from November 24, 2016 through the consummation of the exchange. As a result, the Company recognized approximately $127 of additional interest expense in 2016.
The Senior Secured Notes are secured on a first-priority basis by substantially all of the present and future assets of PBF Holding and its subsidiaries (other than assets securing the Revolving Loan). Payment of the Senior Secured Notes is jointly and severally guaranteed by substantially all of PBF Holding’s subsidiaries. PBF Holding has optional redemption rights to repurchase all or a portion of the Senior Secured Notes at varying prices no less than 100% of the principal amounts of the notes plus accrued and unpaid interest. The holders of the Senior Secured Notes have repurchase options exercisable only upon a change in control, certain asset sale transactions, or in event of a default as defined in the indenture agreement.
In addition, the Senior Secured Notes contain customary terms, events of default and covenants for an issuer of non-investment grade debt securities including limitations on PBF Holding's and its restricted subsidiaries’ ability to, among other things, incur additional indebtedness or issue certain preferred stock; make equity distributions, pay dividends on or repurchase capital stock or make other restricted payments; enter into transactions with affiliates; create liens; engage in mergers and consolidations or otherwise sell all or substantially all of our assets; designate subsidiaries as unrestricted subsidiaries; make certain investments; and limit the ability of restricted subsidiaries to make payments to PBF Holding.
At all times after (a) a covenant suspension event (which requires that the Senior Secured Notes have investment grade ratings from both Moody’s Investment Services, Inc. and Standard & Poor’s), or (b) a Collateral Fall-Away Event, as defined in the indenture, the Senior Secured Notes will become unsecured.
Catalyst Leases
Certain subsidiaries of the Company have entered into agreements whereby such subsidiary sold a portion of its precious metals catalyst to a major commercial bank and then leased the catalyst back. The volume of the precious metals catalyst and the lease rate are fixed over the term of each lease, which is generally three years. At the maturity of each lease, the Company must repurchase the precious metals catalyst in question at its then fair market value. The Company believes that there is a substantial market for precious metals catalyst leases and that it will be able to release such catalyst at maturity. The Company treated these transactions as financing arrangements, and the lease payments are recorded as interest expense over the agreements’ terms. The Company has elected the fair value option for accounting for its catalyst lease repurchase obligations as the Company’s liability is directly impacted by the change in value of the underlying catalyst. The fair value of these repurchase obligations as reflected in the fair value of long-term debt outstanding table below is measured using Level 2 inputs.
Details on the catalyst leases at each of the Company's refineries as of December 31, 2016 are included in the following table:
Annual lease fee | Annual interest rate | Expiration date | |||||||
Paulsboro catalyst lease | $ | 140 | 2.20 | % | December 2019 | ||||
Delaware City catalyst lease | $ | 210 | 1.95 | % | October 2019 | ||||
Delaware City catalyst lease - Palladium | $ | 30 | 2.05 | % | October 2019 | ||||
Toledo catalyst lease | $ | 331 | 1.99 | % | June 2017* | ||||
Chalmette catalyst lease | $ | 185 | 3.85 | % | November 2018 | ||||
Chalmette catalyst lease | $ | 171 | 2.20 | % | November 2019 | ||||
Torrance catalyst lease | $ | 143 | 1.78 | % | July 2019 | ||||
F- 26
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
* The Toledo catalyst lease is included in long-term debt as of December 31, 2016 as the Company has the ability and intent to finance this debt through availability under other credit facilities if the catalyst lease is not renewed at maturity.
Long-term debt outstanding consisted of the following:
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||
2020 Senior Secured Notes | $ | 670,867 | $ | 669,644 | ||||
2023 Senior Secured Notes | 500,000 | 500,000 | ||||||
Revolving Loan | 350,000 | — | ||||||
PBF Rail Term Loan | 35,000 | — | ||||||
Rail Facility | — | 67,491 | ||||||
Catalyst leases | 45,969 | 31,802 | ||||||
Unamortized deferred financing costs | (25,277 | ) | (32,217 | ) | ||||
1,576,559 | 1,236,720 | |||||||
Less—Current maturities | — | — | ||||||
Long-term debt | $ | 1,576,559 | $ | 1,236,720 | ||||
Debt Maturities
Debt maturing in the next five years and thereafter is as follows:
Year Ending December 31, | |||
2017 | $ | 9,798 | |
2018 | 4,941 | ||
2019 | 381,230 | ||
2020 | 670,867 | ||
2021 | 35,000 | ||
Thereafter | 500,000 | ||
$ | 1,601,836 | ||
10. AFFILIATE NOTES PAYABLE
During 2013, PBF Holding entered into notes payable with PBF Energy and PBF LLC. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, PBF Holding had outstanding notes payable with PBF Energy and PBF LLC for an aggregate principal amount of $86,298 and $470,047, respectively. The notes have an interest rate of 2.5% and a five-year term but may be prepaid in whole or in part at any time, at the option of PBF Holding, without penalty or premium.
During 2016, PBF LLC converted $379,947 of the outstanding notes payable from PBF Holding to a capital contribution.
F- 27
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
11. OTHER LONG-TERM LIABILITIES
Other long-term liabilities consisted of the following:
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||
Defined benefit pension plan liabilities | $ | 60,007 | $ | 42,509 | ||||
Post-retirement medical plan liabilities | 22,740 | 17,729 | ||||||
Environmental liabilities | 142,935 | 8,189 | ||||||
Other | 429 | 1,397 | ||||||
Total other long-term liabilities | $ | 226,111 | $ | 69,824 | ||||
12. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Transactions and Agreements with PBFX
PBF Holding entered into agreements with PBFX that establish fees for certain general and administrative services, and operational and maintenance services provided by the Company to PBFX. In addition, the Company executed terminal, pipeline and storage services agreements with PBFX under which PBFX provides commercial transportation, terminaling, storage and pipeline services to the Company. These agreements with PBFX include:
Contribution Agreements
Immediately prior to the closing of the contribution agreements, which PBF LLC entered into with PBFX (as defined in the table below, and collectively referred to as the “Contribution Agreements”), PBF Holding contributed certain assets to PBF LLC. PBF LLC in turn contributed those assets to PBFX pursuant to the Contribution Agreements. Certain proceeds received by PBF LLC from PBFX in accordance with the Contribution Agreements were subsequently contributed by PBF LLC to PBF Holding. The Contribution Agreements include the following:
Contribution Agreement | Contribution Date | Assets Contributed | |
Contribution Agreement I | 5/8/2014 | DCR Rail Terminal and the Toledo Truck Terminal | |
Contribution Agreement II | 9/30/2014 | DCR West Rack | |
Contribution Agreement III | 12/11/2014 | Toledo Storage Facility | |
Contribution Agreement IV | 5/5/2015 | Delaware City Products Pipeline and Truck Rack | |
Contribution Agreement V | 8/31/2016 | Torrance Valley Pipeline | |
Pursuant to Contribution Agreement V on August 31, 2016, PBF Holding contributed 50% of the issued and outstanding limited liability company interests of TVPC to PBF LLC. PBFX then acquired 50% of the issued and outstanding limited liability company interests of Torrance Valley Pipeline Company LLC (“TVPC”). TVPC's assets consist of the Torrance Valley Pipeline which include the M55, M1 and M70 pipeline systems, including pipeline stations with storage capacity and truck unloading capability at two of the stations.
PBFX Operating Company LP ("PBFX Op Co"), PBFX’s wholly-owned subsidiary, serves as TVPC's managing member. PBFX, through its ownership of PBFX Op Co, has the sole ability to direct the activities of TVPC that most significantly impact its economic performance. Accordingly, PBFX, and not PBF Holding, is considered to be the primary beneficiary for accounting purposes and as a result PBFX fully consolidates TVPC. Subsequent to the Contribution Agreement V, PBF Holding records an investment in equity method investee on its balance sheet for the 50% of TVPC that it owns. The carrying value of the Company's equity method investment in TVPC was $179,882 and $0 at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The equity investment in TVPC is included in the Non-Guarantor financial position and results of PBF Holding disclosed in "Note 22 - Condensed Consolidating Financial Statements of PBF Holding" as this subsidiary is not a guarantor of the Senior Secured Notes.
F- 28
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Commercial Agreements with PBFX
In connection with the Contribution Agreements described above, PBF Holding entered into long-term, fee-based commercial agreements with PBFX. Under these agreements, PBFX provides various pipeline, rail and truck terminaling and storage services to PBF Holding and PBF Holding has committed to provide PBFX with minimum fees based on minimum monthly throughput volumes. The fees under each of these agreements are supported by contractual fee escalations for inflation adjustments and certain increases in operating costs. PBF Holding believes the terms and conditions under these agreements, as well as the Omnibus Agreement (as defined below) and the Services Agreement (as defined below) each with PBFX, are generally no less favorable to either party than those that could have been negotiated with unaffiliated parties with respect to similar services.
These commercial agreements (as defined in the table below) with PBFX relating to the Contributed Assets include:
Service Agreements | Initiation Date | Initial Term | Renewals (a) | MVC | Force Majeure |
Transportation and Terminaling | |||||
Delaware City Rail Terminaling Services Agreement | 5/8/2014 | 7 years, 8 months | 2 x 5 | 85,000 bpd | PBFX or PBF Holding can declare |
Toledo Truck Unloading & Terminaling Services Agreement | 5/8/2014 | 7 years, 8 months | 2 x 5 | 5,500 bpd | |
Delaware West Ladder Rack Terminaling Services Agreement | 10/1/2014 | 7 years, 3 months | 2 x 5 | 40,000 bpd | |
Toledo Storage Facility Storage and Terminaling Services Agreement- Terminaling Facility (b) | 12/12/2014 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 4,400 bpd | |
Delaware Pipeline Services Agreement | 5/15/2015 | 10 years, 8 months | 2 x 5 | 50,000 bpd | |
Delaware Pipeline Services Agreement- Magellan Connection | 11/1/2016 | 2 years, 5 months | - | 14,500 bpd | |
Delaware City Truck Loading Services Agreement- Gasoline (c) | 5/15/2015 | 10 years, 8 months | 2 x 5 | 30,000 bpd | |
Delaware City Truck Loading Services Agreement- LPGs (c) | 5/15/2015 | 10 years, 8 months | 2 x 5 | 5,000 bpd | |
Torrance Valley Pipeline Transportation Services Agreement- North Pipeline | 8/31/2016 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 50,000 bpd | |
Torrance Valley Pipeline Transportation Services Agreement- South Pipeline | 8/31/2016 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 70,000 bpd | |
Torrance Valley Pipeline Transportation Services Agreement- Midway Storage Tank | 8/31/2016 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 55,000 barrels (d) | |
Torrance Valley Pipeline Transportation Services Agreement- Emido Storage Tank | 8/31/2016 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 900,000 barrels per month | |
Torrance Valley Pipeline Transportation Services Agreement- Belridge Storage Tank | 8/31/2016 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 770,000 barrels per month | |
Storage | |||||
Toledo Storage Facility Storage and Terminaling Services Agreement- Storage Facility (b) | 12/12/2014 | 10 years | 2 x 5 | 3,849,271 barrels (d) | PBFX or PBF Holding can declare |
____________________
(a) | PBF Holding has the option to extend the agreements for up to two additional five-year terms. |
F- 29
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
(b) | The Toledo Storage Facility Storage and Terminaling Services Agreement- Terminaling Facility and the Toledo Storage Facility Storage and Terminaling Services Agreement- Storage Facility are referred to herein collectively as the “Toledo Storage Facility Storage and Terminaling Services Agreement." |
(c) | The Delaware City Truck Loading Services Agreement- Gasoline and the Delaware City Truck Loading Services Agreement- LPGs are referred to herein collectively as the “Delaware City Truck Loading Services Agreement." |
(d) | Reflects the overall capacity of the storage facility. The storage MVC is subject to effective operating capacity of each tank which can be impacted by routine tank maintenance and other factors. |
PBFX Plains Asset Purchase
On April 29, 2016, PBFX's wholly-owed subsidiary, PBF Logistics Products Terminals LLC, purchased four refined products terminals in the greater Philadelphia region (the "East Coast Terminals") from an affiliate of Plains All American Pipeline, L.P. (the "PBFX Plains Asset Purchase"). In connection with the PBFX Plains Asset Purchase, PBFX assumed certain commercial agreements that Plains All American Pipeline, L.P. had previously entered into with PBF Holding and subsequent to the PBFX Plains Asset Purchase on April 29, 2016, PBF Holding entered into additional commercial agreements with PBFX related to the East Coast Terminals. These agreements have initial terms ranging from approximately three months to five years and include:
• | tank lease agreements, under which PBFX provides tank lease services to PBF Holding at the East Coast Terminals, with MVCs of total aggregate shell capacity; and |
• | terminaling service agreements, under which PBFX provides terminaling and other services to PBF Holding at the East Coast Terminals. The terminaling service agreements have no MVCs and are billed based on actual volumes throughput, other than a terminaling services agreement between the East Coast Terminals' Paulsboro, New Jersey location and PBF Holding with a 15,000 bpd MVC. |
Omnibus Agreement
PBF Holding entered into an omnibus agreement by and among PBFX, PBF GP, PBF LLC and PBF Holding at the closing of the PBFX Offering for the provision of executive management services and support for accounting and finance, legal, human resources, information technology, environmental, health and safety, and other administrative functions, as well as (i) PBF LLC’s agreement not to compete with PBFX under certain circumstances, subject to certain exceptions, (ii) PBFX's right of first offer for ten years to acquire certain logistics assets retained by PBF Energy following the PBFX Offering, including certain logistics assets that PBF LLC or its subsidiaries may construct or acquire in the future, subject to certain exceptions, and (iii) a license to use the PBF Logistics trademark and name.
On August 31, 2016, PBF Holding and PBFX entered into the Fourth Amended and Restated Omnibus Agreement (as amended, the "Omnibus Agreement") in connection with the TVPC Acquisition resulting in an increase to the annual administrative fee to $4,000.
Services Agreement
In connection with the PBFX Offering, PBF Holding and certain of its subsidiaries entered into an operation and management services and secondment agreement with PBFX Holding, pursuant to which PBF Holding and its subsidiaries provide PBFX with the personnel necessary for PBFX to perform its obligations under the commercial agreements. PBFX reimburses PBF Holding for the use of such employees and the provision of certain infrastructure-related services to the extent applicable to its operations, including storm water discharge and waste water treatment, steam, potable water, access to certain roads and grounds, sanitary sewer access, electrical power, emergency response, filter press, fuel gas, API solids treatment, fire water and compressed air.
On August 31, 2016, PBF Holding and PBFX entered into the Fourth Amended and Restated Services Agreement (as amended, the "Services Agreement") in connection with the TVPC Acquisition resulting in an increased annual
F- 30
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
fee of approximately $6,386. As noted in "Note 21 - Subsequent Events", the Services Agreement was further amended in 2017.
The Services Agreement will terminate upon the termination of the Omnibus Agreement, provided that PBFX may terminate any service on 30 days’ notice.
Summary of Transactions with PBFX
A summary of revenue and expense transactions with PBFX is as follows:
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
Revenues under affiliate agreements: | ||||||||||||
Services Agreement | $ | 5,121 | $ | 4,533 | $ | 2,298 | ||||||
Omnibus Agreement | 4,805 | 5,297 | 3,600 | |||||||||
Total expenses under affiliate agreements | 175,448 | 142,102 | 59,403 | |||||||||
The total of revenues under affiliate agreements and expenses under affiliate agreements are included in "Revenues" and "Cost of sales, excluding depreciation", respectively, in the Company's statement of operations.
Fuel Strategies International, Inc. Agreement
The Company engaged Fuel Strategies International, Inc, the principal of which is the brother of the former Executive Chairman of the Board of Directors of PBF Energy, to provide consulting services relating to petroleum coke and commercial operations. For the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 there were no charges under this agreement. For the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company incurred charges of $588 under this agreement. This agreement has expired and is no longer in force.
Agreements with the Former Executive Chairman of the Board of Directors
The Company has an agreement with the former Executive Chairman of the Board of Directors of PBF Energy, for the use of an airplane that is owned by a company owned by the former Executive Chairman of PBF Energy. The Company pays a charter rate that is the lowest rate this aircraft is chartered to third-parties. For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, the Company incurred charges of $824, $957 and $1,214, respectively, related to the use of this airplane.
Effective July 1, 2016, PBF Investments LLC entered into a Consulting Services Agreement with the former Executive Chairman of the Board of Directors of PBF Energy for executive consultation with respect to strategic, operational, business and financial matters. Consulting payments made under this agreement were $500 for the year ended December 31, 2016 and payments are expected to be $900 annually through the agreement expiration date of December 31, 2018.
Financial Sponsors
As of December 31, 2013, each of Blackstone and First Reserve, PBF Energy’s financial sponsors, had received the full return of its aggregate amount invested in PBF LLC Series A Units. As a result, pursuant to the amended and restated limited liability company agreement of PBF LLC, the holders of PBF LLC Series B Units are entitled to an interest in the amounts received by Blackstone and First Reserve in excess of their original investment in the form of PBF LLC distributions and from the shares of PBF Energy Class A Common Stock issuable to Blackstone and First Reserve (for their own account and on behalf of the holders of PBF LLC Series B Units) upon an exchange, and the proceeds from the sale of such shares. Such proceeds received by Blackstone and First Reserve are distributed to the holders of the PBF LLC Series B Units in accordance with the distribution percentages specified in the PBF LLC amended and restated limited liability company agreement. The total amount distributed to the PBF LLC
F- 31
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Series B Unit holders for the years ended December 31, 2016 , 2015 and 2014 was $6,152, $19,592, and $130,523 respectively.
13. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Lease and Other Commitments
The Company leases office space, office equipment, refinery facilities and equipment, and railcars under non-cancelable operating leases, with terms ranging from one to twenty years, subject to certain renewal options as applicable. Total rent expense was $129,768, $126,060, and $98,473 for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The Company is party to agreements which provide for the treatment of wastewater and the supply of hydrogen and steam for certain of its refineries. The Company made purchases of $53,364, $36,139 and $40,444 under these supply agreements for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
The fixed and determinable amounts of the obligations under these agreements and total minimum future annual rentals, exclusive of related costs, are approximately:
Year Ending December 31, | |||
2017 | $ | 156,699 | |
2018 | 139,440 | ||
2019 | 115,482 | ||
2020 | 101,503 | ||
2021 | 59,305 | ||
Thereafter | 185,875 | ||
$ | 758,304 | ||
PBF Investments (“PBFI”) has entered into amended and restated employment agreements with members of executive management and certain other key personnel that include automatic annual renewals, unless canceled. Under some of the agreements, certain of the executives would receive a lump sum payment of between one and a half to 2.99 times their base salary and continuation of certain employee benefits for the same period upon termination by the Company “Without Cause”, or by the employee “For Good Reason”, or upon a “Change in Control”, as defined in the agreements. Upon death or disability, certain of the Company’s executives, or their estates, would receive a lump sum payment of at least one half of their base salary.
Environmental Matters
The Company’s refineries, pipelines and related operations are subject to extensive and frequently changing federal, state and local laws and regulations, including, but not limited to, those relating to the discharge of materials into the environment or that otherwise relate to the protection of the environment, waste management and the characteristics and the compositions of fuels. Compliance with existing and anticipated laws and regulations can increase the overall cost of operating the refineries, including remediation, operating costs and capital costs to construct, maintain and upgrade equipment and facilities.
In connection with the Paulsboro refinery acquisition, the Company assumed certain environmental remediation obligations. The Paulsboro environmental liability of $10,792 recorded as of December 31, 2016 ($10,367 as of December 31, 2015) represents the present value of expected future costs discounted at a rate of 8%. At December 31, 2016 the undiscounted liability is $16,655 and the Company expects to make aggregate payments for this liability of $6,591 over the next five years. The current portion of the environmental liability is recorded in Accrued expenses and the non-current portion is recorded in Other long-term liabilities. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, this liability is self-guaranteed by the Company.
F- 32
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
In connection with the acquisition of the Delaware City assets, Valero Energy Corporation (“Valero”) remains responsible for certain pre-acquisition environmental obligations up to $20,000 and the predecessor to Valero in ownership of the refinery retains other historical obligations.
In connection with the acquisition of the Delaware City assets and the Paulsboro refinery, the Company and Valero purchased ten year, $75,000 environmental insurance policies to insure against unknown environmental liabilities at each site. In connection with the Toledo refinery acquisition, Sunoco, Inc. (R&M) ("Sunoco") remains responsible for environmental remediation for conditions that existed on the closing date for twenty years from March 1, 2011, subject to certain limitations.
In connection with the acquisition of the Chalmette refinery, the Company obtained $3,936 in financial assurance (in the form of a surety bond) to cover estimated potential site remediation costs associated with an agreed to Administrative Order of Consent with the EPA. The estimated cost assumes remedial activities will continue for a minimum of thirty years. Further, in connection with the acquisition of the Chalmette refinery, the Company purchased a ten year, $100,000 environmental insurance policy to insure against unknown environmental liabilities at the refinery.
As of November 1, 2015, the Company acquired Chalmette Refining, which was in discussions with the Louisiana Department of Environmental Quality ("LDEQ") to resolve self-reported deviations from refinery operations relating to certain Clean Air Act Title V permit conditions, limits and other requirements. LDEQ commenced an enforcement action against Chalmette Refining on November 14, 2014 by issuing a Consolidated Compliance Order and Notice of Potential Penalty (the "Order") covering deviations from 2009 and 2010. Chalmette Refining and LDEQ subsequently entered into a dispute resolution agreement, the enforcement of which has been suspended while negotiations are ongoing, which may include the resolution of deviations outside the periods covered by the Order. In February 2017, Chalmette Refining and the LDEQ met to resolve the issues under the Order, including the assessment of an administrative penalty against Chalmette Refining. Although a resolution has not been finalized, the administrative penalty is anticipated to be approximately $700, including beneficial environmental projects. To the extent the administrative penalty exceeds such amount, it is not expected to be material to the Company.
On January 24, 2017, in connection with a Clean Air Act inspection in May 2014 by the EPA to determine compliance with 40 CFR Subpart 68 Chemical Accident Prevention Provisions, EPA notified the Chalmette refinery of its intent to bring an enforcement action on two (2) findings from the audit. No settlement or penalty demand has been received to date. It is reasonably possible that EPA will assess penalties in these matters but any such amount is not expected to have a material impact on the Company's financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
On December 23, 2016, the Delaware City refinery received a Notice of Violation (“NOV”) from DNREC concerning a potential violation of the DNREC order authorizing the shipment of crude oil by barge from the Refinery. The NOV alleges that DCR made shipments to locations other than the Paulsboro refinery in violation of the order and requests certain additional information but no penalties have been assessed at this time. On December 28, 2016, DNREC issued a Coastal Zone Act permit (the “Ethanol Permit”) to DCR allowing the utilization of existing tanks and existing marine loading equipment at their existing facilities to enable denatured ethanol to be loaded from storage tanks to marine vessels and shipped to offsite facilities. On January 13, 2017, the issuance of the Ethanol Permit was appealed by two environmental groups. On February 27, 2017, the Coastal Zone Industrial Board held a public hearing and dismissed the appeal, determining that the appellants did not have standing. The release of the Board decision is pending.
On February 3, 2011, EPA sent a request for information pursuant to Section 114 of the Clean Air Act to the Paulsboro refinery with respect to compliance with EPA standards governing flaring. The refinery and EPA have recently engaged in discussions regarding a potential settlement. It is reasonably possible that EPA will assess penalties in these but any such amount is not expected to have a material impact on the Company's financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
F- 33
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
On February 14, 2017, the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (“DNJDEP”) submitted a proposed Administrative Consent Order (“ACO”) which covers air emission violations from 2013 through 2016 and work practice standards that were not subject to an affirmative defense at the Paulsboro refinery (“PRC”). In settlement of the violations, the NJDEP has proposed that PRC pay a civil administrative penalty of $313, which includes $153 for a supplemental environmental project. If the offer is accepted, the remaining $160 shall be remitted by PRC within 30 days of receipt of the offer. This amount is not material to the Company, individually or in the aggregate.
In connection with the acquisition of the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets, the Company assumed certain pre-existing environmental liabilities totaling $142,456 as of December 31, 2016, related to certain environmental remediation obligations to address existing soil and groundwater contamination and monitoring activities, which reflects the current estimated cost of the remediation obligations. The Company expects to make aggregate payments for this liability of $35,677 over the next five years. The current portion of the environmental liability is recorded in Accrued expenses and the non-current portion is recorded in Other long-term liabilities. In addition, in connection with the acquisition of the Torrance refinery and related logistics assets, the Company purchased a ten year, $100,000 environmental insurance policy to insure against unknown environmental liabilities. Furthermore, in connection with the acquisition, the Company assumed responsibility for certain specified environmental matters that occurred prior to the Company’s ownership of the refinery. Specifically, the Company assumed responsibility for specified notices of violation ("NOVs") issued by the Southern California Air Quality Management District ("SCAQMD") in various years before the Company's ownership.
Additionally, subsequent to the acquisition, the Company received further NOVs from the SCAQMD as well as from the City of Torrance and the City of Torrance Fire Department related to alleged operational violations, emission discharges and/or flaring incidents at the refinery. With the exception of one NOV for which a proposed settlement is less than $100, no settlement or penalty demands have been received to date with respect to the other NOVs. As the ultimate outcomes are uncertain, the Company cannot currently estimate the final amount or timing of their resolution. It is reasonably possible that SCAQMD and/or the City of Torrance will assess penalties in these matters but any such amount is not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
On February 17, 2017, in Arnold Goldstein, et al. v. Exxon Mobil Corporation, et al., PBF Energy Inc., PBF Energy Company LLC, the Company and the Company’s subsidiaries, PBF Energy Western Region LLC and Torrance Refining Company LLC, and the manager of the Company’s Torrance refinery along with Exxon Mobil Corporation were named as defendants in a class action and representative action complaint filed on behalf of Arnold Goldstein, John Covas, Gisela Janette La Bella and others similarly situated. The complaint was filed in the Superior Court of the State of California, County of Los Angeles and alleges negligence, strict liability, ultrahazardous activity, a continuing private nuisance, a permanent private nuisance, a continuing public nuisance, a permanent public nuisance and trespass resulting from the February 18, 2015 electrostatic precipitator ("ESP") explosion at the Torrance Refinery which was then owned and operated by Exxon. The operation of the Torrance Refinery by PBF Holding and its affiliated entities subsequent to the Company’s acquisition of the Torrance refinery in July 2016 is also referenced in the complaint. The Company was served with the lawsuit on March 1, 2017 and has not had an opportunity to evaluate the merits of the plaintiffs’ claims. To the extent that plaintiffs’ claims relate to the ESP explosion, Exxon has retained responsibility for any liabilities that would arise from the lawsuit pursuant to the agreement relating to the acquisition of the Torrance Refinery. The Company cannot currently estimate the amount of its potential liability.
The Company's operations and many of the products it manufactures are subject to certain specific requirements of the Clean Air Act (the "CAA") and related state and local regulations. The CAA contains provisions that require capital expenditures for the installation of certain air pollution control devices at the Company's refineries. Subsequent rule making authorized by the CAA or similar laws or new agency interpretations of existing rules, may necessitate additional expenditures in future years.
F- 34
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
In 2010, New York State adopted a Low-Sulfur Heating Oil mandate that, beginning July 1, 2012, requires all heating oil sold in New York State to contain no more than 15 parts per million (“PPM”) sulfur. Since July 1, 2012, other states in the Northeast market began requiring heating oil sold in their state to contain no more than 15 PPM sulfur. Currently, all of the Northeastern states and Washington DC have adopted sulfur controls on heating oil. Most of the Northeastern states will now require heating oil with 15 PPM or less sulfur by July 1, 2018 (except for Pennsylvania and Maryland where 500 PPM sulfur is required). All of the heating oil the Company currently produces meets these specifications. The mandate and other requirements do not currently have a material impact on the Company's financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
The EPA issued the final Tier 3 Gasoline standards on March 3, 2014 under the Clean Air Act. This final rule establishes more stringent vehicle emission standards and further reduces the sulfur content of gasoline starting in January of 2017. The new standard is set at 10 PPM sulfur in gasoline on an annual average basis starting January 1, 2017, with a credit trading program to provide compliance flexibility. The EPA responded to industry comments on the proposed rule and maintained the per gallon sulfur cap on gasoline at the existing 80 PPM cap. The standards set by the new rule are not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
The EPA published the final 2014-2016 standards under the Renewable Fuels Standard ("RFS") late in 2015 and issued final 2017 RFS standards in November 2016. It is not clear that renewable fuel producers will be able to produce the volumes of these fuels required for blending in accordance with the 2017 standards. The final 2017 cellulosic standard is at approximately 135% of the 2016 standard. It is likely that cellulosic RIN production will be lower than needed forcing obligated parties, such as the Company, to purchase cellulosic “waiver credits” to comply in 2017 (the waiver credit option by regulation is only available for the cellulosic standard). The advanced and total renewable RIN requirements were raised (by 7% and 3% respectively) above the original proposed level in May 2016. Production of advanced RINs has been below what is needed for compliance in 2016. Obligated parties, such as the Company, will likely be relying on the nesting feature of the biodiesel RIN to comply with the advanced standard in 2017. While the Company believes that total renewable RIN production will be adequate for 2016 needs, the new 2017 standard will put obligated parties up against the E10 blendwall leaving little flexibility. Compliance in 2017 will likely rely on obligated parties drawing down the supply of excess RINs collectively known as the “RIN bank” and could tighten the RIN market potentially raising RIN prices further. The Company is currently evaluating the final standards, including any possible changes to the program following a new presidential administration, and they may have a material impact on the Company’s cost of compliance with RFS 2.
In addition, on December 1, 2015 the EPA finalized revisions to an existing air regulation concerning Maximum Achievable Control Technologies (“MACT”) for Petroleum Refineries. The regulation requires additional continuous monitoring systems for eligible process safety valves relieving to atmosphere, minimum flare gas heat (Btu) content, and delayed coke drum vent controls to be installed by January 30, 2019. In addition, a program for ambient fence line monitoring for benzene will need to be implemented by January 30, 2018. The Company is currently evaluating the final standards to evaluate the impact of this regulation, and at this time does not anticipate it will have a material impact on the Company's financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
The EPA published a Final Rule to the Clean Water Act (“CWA”) Section 316(b) in August 2014 regarding cooling water intake structures, which includes requirements for petroleum refineries. The purpose of this rule is to prevent fish from being trapped against cooling water intake screens (impingement) and to prevent fish from being drawn through cooling water systems (entrainment). Facilities will be required to implement Best Technology Available (BTA) as soon as possible, but state agencies have the discretion to establish implementation time lines. The Company continues to evaluate the impact of this regulation, and at this time does not anticipate it having a material impact on the Company’s financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
F- 35
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
As a result of the Torrance Acquisition, the Company is subject to greenhouse gas emission control regulations in the state of California pursuant to Assembly Bill 32 (“AB 32”). AB 32 imposes a statewide cap on greenhouse gas emissions, including emissions from transportation fuels, with the aim of returning the state to 1990 emission levels by 2020. AB32 is implemented through two market mechanisms including the Low Carbon Fuel Standard (“LCFS”) and Cap and Trade. The Company is responsible for the AB 32 obligations related to the Torrance refinery beginning on July 1, 2016 and must purchase emission credits to comply with these obligations. Additionally, in September 2016, the state of California enacted Senate Bill 32 (“SB 32”) which further reduces greenhouse gas emissions targets to 40 percent below 1990 levels by 2030.
However, subsequent to the acquisition, the Company is recovering the majority of these costs from its customers, and as such does not expect this obligation to materially impact the Company’s financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. To the degree there are unfavorable changes to AB 32 or SB 32 regulations or the Company is unable to recover such compliance costs from customers, these regulations could have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations, and liquidity.
The Company is subject to obligations to purchase Renewable Identification Numbers (“RINs”) required to comply with the RFS. In late 2015, the EPA initiated enforcement proceedings against companies it believes produced invalid RINs. On October 13, 2016, the Company and its subsidiaries including, Toledo Refining Company LLC and Delaware City Refining Company LLC were notified by the EPA that its records indicated that these entities used potentially invalid RINs. The EPA directed each of the subsidiaries to resubmit reports to remove the potentially invalid RINs and to replace the invalid RINs with valid RINs with the same D Code. The invalid RINs have been retired and the Company does not expect any settlement with the EPA to resolve this matter to be material.
The Company is also currently subject to certain other existing environmental claims and proceedings. The Company believes that there is only a remote possibility that future costs related to any of these other known contingent liability exposures would have a material impact on its financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
PBF LLC Limited Liability Company Agreement
The holders of limited liability company interests in PBF LLC, including PBF Energy, generally have to include for purposes of calculating their U.S. federal, state and local income taxes their share of any taxable income of PBF LLC, regardless of whether such holders receive cash distributions from PBF LLC. PBF Energy ultimately may not receive cash distributions from PBF LLC equal to its share of such taxable income or even equal to the actual tax due with respect to that income. For example, PBF LLC is required to include in taxable income PBF LLC’s allocable share of PBFX’s taxable income and gains (such share to be determined pursuant to the partnership agreement of PBFX), regardless of the amount of cash distributions received by PBF LLC from PBFX, and such taxable income and gains will flow-through to PBF Energy to the extent of its allocable share of the taxable income of PBF LLC. As a result, at certain times, the amount of cash otherwise ultimately available to PBF Energy on account of its indirect interest in PBFX may not be sufficient for PBF Energy to pay the amount of taxes it will owe on account of its indirect interests in PBFX.
Taxable income of PBF LLC generally is allocated to the holders of PBF LLC units (including PBF Energy) pro-rata in accordance with their respective share of the net profits and net losses of PBF LLC. In general, PBF LLC is required to make periodic tax distributions to the members of PBF LLC, including PBF Energy, pro-rata in accordance with their respective percentage interests for such period (as determined under the amended and restated limited liability company agreement of PBF LLC), subject to available cash and applicable law and contractual restrictions (including pursuant to our debt instruments) and based on certain assumptions. Generally, these tax distributions are required to be in an amount equal to our estimate of the taxable income of PBF LLC for the year multiplied by an assumed tax rate equal to the highest effective marginal combined U.S. federal, state and local income tax rate prescribed for an individual or corporate resident in New York, New York (taking into account the nondeductibility of certain expenses). If, with respect to any given calendar year, the aggregate periodic tax distributions were less than the actual taxable income of PBF LLC multiplied by the assumed tax rate, PBF LLC is required to make a “true up” tax distribution, no later than March 15 of the following year, equal to such difference,
F- 36
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
subject to the available cash and borrowings of PBF LLC. PBF LLC obtains funding to pay its tax distributions by causing PBF Holding to distribute cash to PBF LLC and from distributions it receives from PBFX.
Tax Receivable Agreement
PBF Energy (the Company's indirect parent) entered into a tax receivable agreement with the PBF LLC Series A and PBF LLC Series B Unit holders (the “Tax Receivable Agreement”) that provides for the payment by PBF Energy to such persons of an amount equal to 85% of the amount of the benefits, if any, that PBF Energy is deemed to realize as a result of (i) increases in tax basis, as described below, and (ii) certain other tax benefits related to entering into the Tax Receivable Agreement, including tax benefits attributable to payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement. For purposes of the Tax Receivable Agreement, the benefits deemed realized by PBF Energy will be computed by comparing the actual income tax liability of PBF Energy (calculated with certain assumptions) to the amount of such taxes that PBF Energy would have been required to pay had there been no increase to the tax basis of the assets of PBF LLC as a result of purchases or exchanges of PBF LLC Series A Units for shares of PBF Energy's Class A common stock and had PBF Energy not entered into the Tax Receivable Agreement. The term of the Tax Receivable Agreement will continue until all such tax benefits have been utilized or expired unless: (i) PBF Energy exercises its right to terminate the Tax Receivable Agreement, (ii) PBF Energy breaches any of its material obligations under the Tax Receivable Agreement or (iii) certain changes of control occur, in which case all obligations under the Tax Receivable Agreement will generally be accelerated and due as calculated under certain assumptions.
The payment obligations under the Tax Receivable Agreement are obligations of PBF Energy and not of PBF LLC or PBF Holding. In general, PBF Energy expects to obtain funding for these annual payments from PBF LLC, primarily through tax distributions, which PBF LLC makes on a pro-rata basis to its owners. Such owners include PBF Energy, which holds a 96.5% and 95.1% interest in PBF LLC as of December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively. PBF LLC obtains funding to pay its tax distributions by causing PBF Holding to distribute cash to PBF LLC and from distributions it receives from PBFX.
14. EQUITY STRUCTURE
PBF Holding has no common stock outstanding. As of December 31, 2016, 100% of the membership interests of PBF Holding were owned by PBF LLC, and PBF Finance had 100 shares of common stock outstanding, all of which were held by PBF Holding. The following sections represent the equity structure of the Company's indirect and direct parents, PBF Energy and PBF LLC, respectively.
Class A Common Stock
Holders of Class A common stock are entitled to receive dividends when and if declared by the Board of Directors of PBF Energy out of funds legally available therefore, subject to any statutory or contractual restrictions on the payment of dividends and to any restrictions on the payment of dividends imposed by the terms of any outstanding preferred stock. Upon PBF Energy's dissolution or liquidation or the sale of all or substantially all of the assets, after payment in full of all amounts required to be paid to creditors and to the holders of preferred stock having liquidation preferences, if any, the holders of shares of Class A common stock will be entitled to receive pro rata remaining assets available for distribution. Holders of shares of Class A common stock do not have preemptive, subscription, redemption or conversion rights.
Class B Common Stock
Holders of shares of Class B common stock are entitled, without regard to the number of shares of Class B common stock held by such holder, to one vote for each PBF LLC Series A Unit beneficially owned by such holder. Accordingly, the members of PBF LLC other than PBF Energy collectively have a number of votes in PBF Energy that is equal to the aggregate number of PBF LLC Series A Units that they hold.
F- 37
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Holders of shares of Class A common stock and Class B common stock vote together as a single class on all matters presented to stockholders for their vote or approval, except as otherwise required by applicable law.
Holders of Class B common stock do not have any right to receive dividends or to receive a distribution upon a liquidation or winding up of PBF Energy.
Preferred Stock
Authorized preferred stock may be issued in one or more series, with designations, powers and preferences as shall be designated by the Board of Directors.
PBF LLC Capital Structure
PBF LLC Series A Units
The allocation of profits and losses and distributions to PBF LLC Series A unit holders is governed by the Limited Liability Company Agreement of PBF LLC. These allocations are made on a pro rata basis with PBF LLC Series C Units. PBF LLC Series A unit holders do not have voting rights.
PBF LLC Series B Units
The PBF LLC Series B Units are intended to be “profit interests” within the meaning of Revenue Procedures 93-27 and 2001-43 of the Internal Revenue Service and have a stated value of zero at issuance. The PBF LLC Series B Units are held by certain of the Company’s current and former officers, have no voting rights and are designed to increase in value only after the Company’s financial sponsors achieve certain levels of return on their investment in PBF LLC Series A Units. Accordingly, the amounts paid to the holders of PBF LLC Series B Units, if any, will reduce only the amounts otherwise payable to the PBF LLC Series A Units held by the Company’s financial sponsors, and will not reduce or otherwise impact any amounts payable to PBF Energy (the holder of PBF LLC Series C Units), the holders of PBF Energy's Class A common stock or any other holder of PBF LLC Series A Units. The maximum number of PBF LLC Series B Units authorized to be issued is 1,000,000.
PBF LLC Series C Units
The PBF LLC Series C Units rank on a parity with the PBF LLC Series A Units as to distribution rights, voting rights and rights upon liquidation, winding up or dissolution. PBF LLC Series C Units are held solely by PBF Energy.
Noncontrolling Interest
Subsequent to the Chalmette Acquisition, PBF Holding recorded noncontrolling interest in two subsidiaries of Chalmette Refining. PBF Holding, through Chalmette Refining, owns an 80% ownership interest in both Collins Pipeline Company and T&M Terminal Company. The Company recorded earnings related to the noncontrolling interest in these subsidiaries of $269 and $274 for the years ended December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively.
F- 38
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
15. STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION
Stock-based compensation expense included in general and administrative expenses consisted of the following:
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
PBF LLC Series A Unit compensatory warrants and options | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 522 | ||||||
PBF Energy options | 11,020 | 7,528 | 4,343 | |||||||||
PBF Energy restricted shares | 7,276 | 1,690 | 1,230 | |||||||||
$ | 18,296 | $ | 9,218 | $ | 6,095 | |||||||
PBF LLC Series A warrants and options
PBF LLC granted compensatory warrants to employees of the Company in connection with their purchase of Series A units in PBF LLC. The warrants grant the holder the right to purchase PBF LLC Series A Units. One-quarter of the PBF LLC Series A compensatory warrants were exercisable at the date of grant and the remaining three-quarters become exercisable over equal annual installments on each of the first three anniversaries of the grant date subject to acceleration in certain circumstances. They are exercisable for ten years from the date of grant. The remaining warrants became fully exercisable in connection with the initial public offering of PBF Energy.
In addition, options to purchase PBF LLC Series A units were granted to certain employees, management and directors. Options vest over equal annual installments on each of the first three anniversaries of the grant date subject to acceleration in certain circumstances. The options are exercisable for ten years from the date of grant.
The Company did not issue PBF LLC Series A Units compensatory warrants or options in 2016, 2015 or 2014.
The following table summarizes activity for PBF LLC Series A compensatory warrants and options for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
Number of PBF LLC Series A Compensatory Warrants and Options | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (in years) | ||||||||
Stock Based Compensation, Outstanding at January 1, 2014 | 841,079 | $ | 10.52 | 7.40 | ||||||
Exercised | (32,934 | ) | 10.00 | — | ||||||
Forfeited | (6,666 | ) | 11.59 | — | ||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2014 | 801,479 | $ | 10.53 | 6.41 | ||||||
Exercised | (160,700 | ) | 10.28 | — | ||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2015 | 640,779 | $ | 10.59 | 5.46 | ||||||
Exercised | (27,833 | ) | 10.00 | — | ||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2016 | 612,946 | $ | 10.62 | 4.47 | ||||||
Exercisable and vested at December 31, 2016 | 612,946 | $ | 10.62 | 4.47 | ||||||
Exercisable and vested at December 31, 2015 | 640,779 | $ | 10.59 | 5.46 | ||||||
Exercisable and vested at December 31, 2014 | 753,985 | $ | 10.41 | 6.34 | ||||||
Expected to vest at December 31, 2016 | 612,946 | $ | 10.62 | 4.47 | ||||||
The total intrinsic value of stock options both outstanding and exercisable at December 31, 2016, was $10,577. The total intrinsic value of stock options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 was $461, $3,452, and $618, respectively.
F- 39
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
There was no unrecognized compensation expense related to PBF LLC Series A warrants and options at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015.
Prior to 2014, members of management of the Company had also purchased an aggregate of 2,740,718 non-compensatory Series A warrants in PBF LLC with an exercise price of $10.00 per unit, all of which were immediately exercisable. There were no non-compensatory warrants exercised during the year ended December 31, 2016 (24,000 non-compensatory warrants were exercised at December 31, 2015). At December 31, 2016 and 2015, there were 32,719 non-compensatory warrants outstanding, respectively.
PBF LLC Series B Units
PBF LLC Series B Units were issued and allocated to certain members of management during the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2010. One-quarter of the PBF LLC Series B Units vested at the time of grant and the remaining three-quarters vested in equal annual installments on each of the first three anniversaries of the grant date, subject to accelerated vesting upon certain events. The Series B Units fully vested during the year ended December 31, 2013. There was no activity in the Series B units for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 or 2014.
PBF Energy options and restricted stock
PBF Energy grants awards of its Class A common stock under the 2012 Equity Incentive Plan which authorizes the granting of various stock and stock-related awards to directors, employees, prospective employees and non-employees. Awards include options to purchase shares of Class A common stock and restricted Class A common stock that vest over a period determined by the plan.
A total of 360,820, 247,720 and 30,348 shares of restricted Class A common stock were granted to certain directors, employees and management of the Company as of December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The PBF Energy options and restricted Class A common stock vest in equal annual installments on each of the first four anniversaries of the grant date subject to acceleration in certain circumstances. The options are exercisable for ten years from the date of grant.
The estimated fair value of PBF Energy options granted during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 was determined using the Black-Scholes pricing model with the following weighted average assumptions:
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||
Expected life (in years) | 6.25 | 6.25 | 6.25 | |||||||||
Expected volatility | 39.7 | % | 38.4 | % | 52.0 | % | ||||||
Dividend yield | 4.73 | % | 3.96 | % | 4.82 | % | ||||||
Risk-free rate of return | 1.42 | % | 1.58 | % | 1.80 | % | ||||||
Exercise price | $ | 26.18 | $ | 30.28 | $ | 24.78 | ||||||
F- 40
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
The following table summarizes activity for PBF Energy options for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014.
Number of PBF Energy Class A Common Stock Options | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (in years) | ||||||||
Stock-based awards, outstanding at January 1, 2014 | 1,320,000 | $ | 26.97 | 9.33 | ||||||
Granted | 1,135,000 | 24.78 | 10.00 | |||||||
Exercised | — | — | — | |||||||
Forfeited | (53,125 | ) | 25.44 | — | ||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2014 | 2,401,875 | $ | 25.97 | 8.67 | ||||||
Granted | 1,899,500 | 30.28 | 10.00 | |||||||
Exercised | (30,000 | ) | 25.79 | — | ||||||
Forfeited | (15,000 | ) | 26.38 | — | ||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2015 | 4,256,375 | $ | 27.89 | 8.32 | ||||||
Granted | 1,792,000 | $ | 26.18 | 10.00 | ||||||
Exercised | (11,250 | ) | 25.86 | — | ||||||
Forfeited | (66,500 | ) | 28.74 | — | ||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2016 | 5,970,625 | $ | 27.37 | 8.02 | ||||||
Exercisable and vested at December 31, 2016 | 2,271,375 | $ | 27.23 | 7.21 | ||||||
Exercisable and vested at December 31, 2015 | 1,136,250 | $ | 26.22 | 7.61 | ||||||
Exercisable and vested at December 31, 2014 | 485,000 | $ | 26.66 | 8.21 | ||||||
Expected to vest at December 31, 2016 | 5,970,625 | $ | 27.37 | 8.02 | ||||||
The total estimated fair value of PBF Energy options granted in 2016 and 2015 was $11,346 and $14,512 and the weighted average per unit fair value was $6.33 and $7.64. The total intrinsic value of stock options outstanding and exercisable at December 31, 2016, was $11,676 and $3,914, respectively. The total intrinsic value of stock options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 was $5 and $133, respectively.
Unrecognized compensation expense related to PBF Energy options at December 31, 2016 was $21,323, which will be recognized from 2017 through 2020.
16. EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS
Defined Contribution Plan
The Company’s defined contribution plan covers all employees. Employees are eligible to participate as of the first day of the month following 30 days of service. Participants can make basic contributions up to 50 percent of their annual salary subject to Internal Revenue Service limits. The Company matches participants’ contributions at the rate of 200 percent of the first 3 percent of each participant’s total basic contribution based on the participant’s total annual salary. The Company’s contribution to the qualified defined contribution plans was $19,746, $12,753 and $11,364 for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Defined Benefit and Post-Retirement Medical Plans
The Company sponsors a noncontributory defined benefit pension plan (the “Qualified Plan”) with a policy to fund pension liabilities in accordance with the limits imposed by the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (“ERISA”) and Federal income tax laws. In addition, the Company sponsors a supplemental pension plan covering certain employees, which provides incremental payments that would have been payable from the Company’s principal pension plan, were it not for limitations imposed by income tax regulations (the “Supplemental
F- 41
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Plan”). The funded status is measured as the difference between plan assets at fair value and the projected benefit obligation which is to be recognized in the balance sheet. The plan assets and benefit obligations are measured as of the balance sheet date.
The non-union Delaware City employees and all Paulsboro, Toledo, Chalmette and Torrance employees became eligible to participate in the Company’s defined benefit plans as of the respective acquisition dates. The union Delaware City employees became eligible to participate in the Company’s defined benefit plans upon commencement of normal operations. The Company did not assume any of the employees’ pension liability accrued prior to the respective acquisitions.
The Company formed the Post-Retirement Medical Plan on December 31, 2010 to provide health care coverage continuation from date of retirement to age 65 for qualifying employees associated with the Paulsboro acquisition. The Company credited the qualifying employees with their prior service under Valero which resulted in the recognition of a liability for the projected benefit obligation. The Post-Retirement Medical Plan was amended during 2013 to include all corporate employees, amended in 2014 to include Delaware City and Toledo employees, amended in 2015 to include Chalmette employees and amended in 2016 to include Torrance employees.
The changes in the benefit obligation, the changes in fair value of plan assets, and the funded status of the Company’s Pension and Post-Retirement Medical Plans as of and for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 were as follows:
Pension Plans | Post-Retirement Medical Plan | |||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||
Change in benefit obligation: | ||||||||||||||||
Benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | 100,011 | $ | 81,098 | $ | 17,729 | $ | 14,740 | ||||||||
Service cost | 36,359 | 24,298 | 1,047 | 967 | ||||||||||||
Interest cost | 3,096 | 2,974 | 528 | 558 | ||||||||||||
Plan amendments | — | — | 2,524 | 1,533 | ||||||||||||
Benefit payments | (3,449 | ) | (2,231 | ) | (575 | ) | (381 | ) | ||||||||
Actuarial loss (gain) | (509 | ) | (6,128 | ) | 1,487 | 312 | ||||||||||
Projected benefit obligation at end of year | $ | 135,508 | $ | 100,011 | $ | 22,740 | $ | 17,729 | ||||||||
Change in plan assets: | ||||||||||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | $ | 57,502 | $ | 40,956 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
Actual return on plan assets | 3,995 | (13 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
Benefits paid | (3,449 | ) | (2,231 | ) | (575 | ) | (381 | ) | ||||||||
Employer contributions | 17,319 | 18,790 | 575 | 381 | ||||||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at end of year | $ | 75,367 | $ | 57,502 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
Reconciliation of funded status: | ||||||||||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at end of year | $ | 75,367 | $ | 57,502 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
Less benefit obligations at end of year | 135,508 | 100,011 | 22,740 | 17,729 | ||||||||||||
Funded status at end of year | $ | (60,141 | ) | $ | (42,509 | ) | $ | (22,740 | ) | $ | (17,729 | ) | ||||
The accumulated benefit obligations for the Company’s Pension Plans exceed the fair value of the assets of those plans at December 31, 2016 and 2015. The accumulated benefit obligation for the defined benefit plans approximated $108,838 and $80,897 at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Benefit payments, which reflect expected future services, that the Company expects to pay are as follows for the years ended December 31:
F- 42
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Pension Benefits | Post-Retirement Medical Plan | |||||||
2017 | $ | 12,307 | $ | 1,202 | ||||
2018 | 8,873 | 1,389 | ||||||
2019 | 11,027 | 1,653 | ||||||
2020 | 13,067 | 1,910 | ||||||
2021 | 16,079 | 2,018 | ||||||
Years 2022-2026 | 114,382 | 10,438 | ||||||
The Company’s funding policy for its defined benefit plans is to contribute amounts sufficient to meet legal funding requirements, plus any additional amounts that may be appropriate considering the funded status of the plans, tax consequences, the cash flow generated by the Company and other factors. The Company plans to contribute approximately $36,300 to the Company’s Pension Plans during 2017.
The components of net periodic benefit cost were as follows for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
Pension Benefits | Post-Retirement Medical Plan | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||
Components of net period benefit cost: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Service cost | $ | 36,359 | $ | 24,298 | $ | 19,407 | $ | 1,047 | $ | 967 | $ | 1,099 | ||||||||||||
Interest cost | 3,096 | 2,974 | 2,404 | 528 | 558 | 520 | ||||||||||||||||||
Expected return on plan assets | (4,681 | ) | (3,422 | ) | (2,156 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Amortization of prior service cost | 53 | 53 | 39 | 541 | 326 | 258 | ||||||||||||||||||
Amortization of actuarial loss (gain) | 1,043 | 1,228 | 1,033 | — | — | (4 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Net periodic benefit cost | $ | 35,870 | $ | 25,131 | $ | 20,727 | $ | 2,116 | $ | 1,851 | $ | 1,873 | ||||||||||||
The pre-tax amounts recognized in other comprehensive income (loss) for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 were as follows:
Pension Benefits | Post-Retirement Medical Plan | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||
Prior service costs (credits) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 529 | $ | 2,524 | $ | 1,533 | $ | 3,911 | ||||||||||||
Net actuarial loss (gain) | 176 | (2,220 | ) | 8,151 | 1,487 | 312 | 1,201 | |||||||||||||||||
Amortization of losses and prior service cost | (1,096 | ) | (1,281 | ) | (1,072 | ) | (541 | ) | (326 | ) | (255 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total changes in other comprehensive loss (income) | $ | (920 | ) | $ | (3,501 | ) | $ | 7,608 | $ | 3,470 | $ | 1,519 | $ | 4,857 | ||||||||||
The pre-tax amounts in accumulated other comprehensive loss as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 that have not yet been recognized as components of net periodic costs were as follows:
F- 43
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Pension Benefits | Post-Retirement Medical Plan | |||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||
Prior service (costs) credits | $ | (476 | ) | $ | (529 | ) | $ | (5,983 | ) | $ | (3,999 | ) | ||||
Net actuarial (loss) gain | (18,975 | ) | (19,841 | ) | (1,878 | ) | (391 | ) | ||||||||
Total | $ | (19,451 | ) | $ | (20,370 | ) | $ | (7,861 | ) | $ | (4,390 | ) | ||||
The following pre-tax amounts included in accumulated other comprehensive loss as of December 31, 2016 are expected to be recognized as components of net period benefit cost during the year ended December 31, 2017:
Pension Benefits | Post-Retirement Medical Plan | |||||||
Amortization of prior service (costs) credits | $ | (53 | ) | $ | (646 | ) | ||
Amortization of net actuarial (loss) gain | (452 | ) | — | |||||
Total | $ | (505 | ) | $ | (646 | ) | ||
The weighted average assumptions used to determine the benefit obligations as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 were as follows:
Qualified Plan | Supplemental Plan | Post-Retirement Medical Plan | ||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||
Discount rate - benefit obligations | 4.07 | % | 4.17 | % | 4.08 | % | 4.22 | % | 3.68 | % | 3.76 | % | ||||||
Rate of compensation increase | 4.81 | % | 4.81 | % | 5.50 | % | 5.50 | % | — | — | ||||||||
The weighted average assumptions used to determine the net periodic benefit costs for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 were as follows:
Qualified Plan | Supplemental Plan | Post-Retirement Medical Plan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||
Discount rates: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Effective rate for service cost | 4.15 | % | 4.25 | % | 4.55 | % | 4.17 | % | 4.30 | % | 4.55 | % | 4.10 | % | 4.32 | % | 4.55 | % | |||||||||
Effective rate for interest cost | 3.38 | % | 3.31 | % | 4.55 | % | 3.20 | % | 3.16 | % | 4.55 | % | 3.11 | % | 3.09 | % | 4.55 | % | |||||||||
Effective rate for interest on service cost | 3.59 | % | 3.51 | % | 4.55 | % | 3.63 | % | 3.37 | % | 4.55 | % | 3.84 | % | 4.04 | % | 4.55 | % | |||||||||
Expected long-term rate of return on plan assets | 7.00 | % | 7.00 | % | 6.70 | % | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Rate of compensation increase | 4.81 | % | 4.81 | % | 4.64 | % | 5.50 | % | 5.50 | % | 4.64 | % | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
The assumed health care cost trend rates as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 were as follows:
Post-Retirement Medical Plan | ||||||
2016 | 2015 | |||||
Health care cost trend rate assumed for next year | 6.1 | % | 6.1 | % | ||
Rate to which the cost trend rate was assumed to decline (the ultimate trend rate) | 4.5 | % | 4.5 | % | ||
Year that the rate reached the ultimate trend rate | 2038 | 2038 | ||||
F- 44
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Assumed health care costs trend rates have a significant effect on the amounts reported for retiree health care plans. A one percentage-point change in assumed health care costs trend rates would have the following effects on the medical post-retirement benefits:
1% Increase | 1% Decrease | |||||||
Effect on total of service and interest cost components | $ | 14 | $ | (13 | ) | |||
Effect on accumulated post-retirement benefit obligation | 388 | (367 | ) | |||||
The table below presents the fair values of the assets of the Company’s Qualified Plan as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 by level of fair value hierarchy. Assets categorized in Level 2 of the hierarchy consist of collective trusts and are measured at fair value based on the closing net asset value ("NAV") as determined by the fund manager and reported daily. As noted above, the Company’s post retirement medical plan is funded on a pay-as-you-go basis and has no assets.
Fair Value Measurements Using NAV as Practical Expedient (Level 2) | ||||||||
December 31, | ||||||||
2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Equities: | ||||||||
Domestic equities | $ | 23,451 | $ | 17,660 | ||||
Developed international equities | 10,736 | 8,320 | ||||||
Emerging market equities | 5,164 | 4,017 | ||||||
Global low volatility equities | 6,360 | 4,930 | ||||||
Fixed-income | 29,576 | 22,495 | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | 80 | 80 | ||||||
Total | $ | 75,367 | $ | 57,502 | ||||
The Company’s investment strategy for its Qualified Plan is to achieve a reasonable return on assets that supports the plan’s interest credit rating, subject to a moderate level of portfolio risk that provides liquidity. Consistent with these financial objectives as of December 31, 2016, the plan's target allocations for plan assets are 60% invested in equity securities and 40% fixed income investments. Equity securities include international stocks and a blend of U.S. growth and value stocks of various sizes of capitalization. Fixed income securities include bonds and notes issued by the U.S. government and its agencies, corporate bonds, and mortgage-backed securities. The aggregate asset allocation is reviewed on an annual basis.
The overall expected long-term rate of return on plan assets for the Qualified Plan is based on the Company’s view of long-term expectations and asset mix.
F- 45
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
17. REVENUES
The following table provides information relating to the Company’s revenues from external customers for each product or group of similar products for the periods:
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
Gasoline and distillates | $ | 14,017,350 | $ | 11,553,716 | $ | 17,050,096 | ||||||
Asphalt and blackoils | 699,966 | 536,496 | 706,494 | |||||||||
Chemicals | 554,392 | 452,304 | 739,096 | |||||||||
Feedstocks and other | 376,471 | 315,042 | 922,003 | |||||||||
Lubricants | 260,358 | 266,371 | 410,466 | |||||||||
Total Revenues | $ | 15,908,537 | $ | 13,123,929 | $ | 19,828,155 | ||||||
18. INCOME TAXES
PBF Holding is a limited liability company treated as a "flow-through" entity for income tax purposes. Accordingly, there is generally no benefit or provision for federal or state income tax in the PBF Holding financial statements apart from the income tax attributable to two subsidiaries acquired in connection with the acquisition of Chalmette Refining in the fourth quarter of 2015 and its wholly-owned Canadian subsidiary, PBF Energy Limited ("PBF Ltd."). The two subsidiaries acquired in connection with the Chalmette Acquisition are treated as C-Corporations for income tax purposes.
The two acquired subsidiaries incurred $1,378 and $648 of income tax expense for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015. For the year ended December 31, 2016, PBF Holding incurred an income tax benefit in its income statement of $8,412, attributable to PBF Ltd. During the preparation of the financial statements for the first quarter of 2016, management determined that the deferred income tax liabilities for PBF Ltd. were understated for prior periods. As of and for the three months ended March 31, 2016, the Company incurred $30,602 of deferred tax expense and $121 of current tax expense relating to a correction of prior periods which increased the recorded deferred and current tax liabilities by $30,602 and $121, respectively. This correction of prior periods did not impact the results for the fourth quarter of 2016.
19. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
The tables below present information about the Company's financial assets and liabilities measured and recorded at fair value on a recurring basis and indicate the fair value hierarchy of the inputs utilized to determine the fair values as of December 31, 2016 and 2015.
We have elected to offset the fair value amounts recognized for multiple derivative contracts executed with the same counterparty; however, fair value amounts by hierarchy level are presented on a gross basis in the tables below. We have posted cash margin with various counterparties to support hedging and trading activities. The cash
margin posted is required by counterparties as collateral deposits and cannot be offset against the fair value of open
contracts except in the event of default. We have no derivative contracts that are subject to master netting arrangements that are reflected gross on the balance sheet.
F- 46
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
As of December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Fair Value Hierarchy | |||||||||||||||||||||
Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total Gross Fair Value | Effect of Counter-party Netting | Net Carrying Value on Balance Sheet | ||||||||||||||||
Assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Money market funds | $ | 342,837 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 342,837 | N/A | $ | 342,837 | ||||||||||
Commodity contracts | 948 | 35 | — | 983 | (983 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
Derivatives included with inventory intermediation agreement obligations | — | 6,058 | — | 6,058 | — | 6,058 | |||||||||||||||
Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Commodity contracts | 859 | 3,548 | 84 | 4,491 | (983 | ) | 3,508 | ||||||||||||||
Catalyst lease obligations | — | 45,969 | — | 45,969 | — | 45,969 | |||||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total Gross Fair Value | Effect of Counter-party Netting | Net Carrying Value on Balance Sheet | ||||||||||||||||
Assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Money market funds | $ | 631,280 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 631,280 | N/A | $ | 631,280 | ||||||||||
Commodity contracts | 63,810 | 31,256 | 3,543 | 98,609 | (52,482 | ) | 46,127 | ||||||||||||||
Derivatives included with inventory intermediation arrangement | — | 35,511 | — | 35,511 | — | 35,511 | |||||||||||||||
Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Commodity contracts | 49,960 | 2,522 | — | 52,482 | (52,482 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
Catalyst lease obligations | — | 31,802 | — | 31,802 | — | 31,802 | |||||||||||||||
F- 47
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
The valuation methods used to measure financial instruments at fair value are as follows:
• | Money market funds categorized in Level 1 of the fair value hierarchy are measured at fair value based on quoted market prices and included within cash and cash equivalents. |
• | The commodity contracts categorized in Level 1 of the fair value hierarchy are measured at fair value based on quoted prices in an active market. The commodity contracts categorized in Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy are measured at fair value using a market approach based upon future commodity prices for similar instruments quoted in active markets. |
• | The commodity contracts categorized in Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy consist of commodity price swap contracts that relate to forecasted purchases of crude oil for which quoted forward market prices are not readily available due to market illiquidity. The forward price used to value these swaps was derived using broker quotes, prices from other third party sources and other available market based data. |
• | The derivatives included with inventory supply arrangement obligations, derivatives included with inventory intermediation agreement obligations and the catalyst lease obligations are categorized in Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy and are measured at fair value using a market approach based upon commodity prices for similar instruments quoted in active markets. |
Non-qualified pension plan assets are measured at fair value using a market approach based on published net asset values of mutual funds as a practical expedient. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, $9,440 and $9,325, respectively, were included within Deferred charges and other assets, net for these non-qualified pension plan assets.
The table below summarizes the changes in fair value measurements of commodity contracts categorized in Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Balance at beginning of period | $ | 3,543 | $ | 1,521 | |||
Purchases | — | — | |||||
Settlements | (1,149 | ) | (15,222 | ) | |||
Unrealized (gain) loss included in earnings | (2,478 | ) | 17,244 | ||||
Transfers into Level 3 | — | — | |||||
Transfers out of Level 3 | — | — | |||||
Balance at end of period | $ | (84 | ) | $ | 3,543 | ||
There were no transfers between levels during the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
F- 48
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Fair value of debt
The table below summarizes the fair value and carrying value as of December 31, 2016 and 2015.
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||
Carrying value | Fair value | Carrying value | Fair value | ||||||||||||
Senior Secured Notes due 2020 (a) | $ | 670,867 | $ | 696,098 | $ | 669,644 | $ | 706,246 | |||||||
Senior Secured Notes due 2023 (a) | 500,000 | 498,801 | 500,000 | 492,452 | |||||||||||
Revolving Loan (b) | 350,000 | 350,000 | — | — | |||||||||||
PBF Rail Term Loan (b) | 35,000 | 35,000 | — | — | |||||||||||
Rail Facility (b) | — | — | 67,491 | 67,491 | |||||||||||
Catalyst leases (c) | 45,969 | 45,969 | 31,802 | 31,802 | |||||||||||
1,601,836 | 1,625,868 | 1,268,937 | 1,297,991 | ||||||||||||
Less - Current maturities | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Less - Unamortized deferred financing costs | $ | 25,277 | n/a | $ | 32,217 | n/a | |||||||||
Long-term debt | $ | 1,576,559 | $ | 1,625,868 | $ | 1,236,720 | $ | 1,297,991 | |||||||
(a) The estimated fair value, categorized as a Level 2 measurement, was calculated based on the present value of future expected payments utilizing implied current market interest rates based on quoted prices of the Senior Secured Notes.
(b) The estimated fair value approximates carrying value, categorized as a Level 2 measurement, as these borrowings bear interest based upon short-term floating market interest rates.
(c) Catalyst leases are valued using a market approach based upon commodity prices for similar instruments quoted in active markets and are categorized as a Level 2 measurement. The Company has elected the fair value option for accounting for its catalyst lease repurchase obligations as the Company's liability is directly impacted by the change in fair value of the underlying catalyst.
20. DERIVATIVES
The Company uses derivative instruments to mitigate certain exposures to commodity price risk. The Company’s expired crude supply agreements contained purchase obligations for certain volumes of crude oil and other feedstocks. In addition, the Company entered into Inventory Intermediation Agreements that contain purchase obligations for certain volumes of intermediates and refined products. The purchase obligations related to crude oil, feedstocks, intermediates and refined products under these agreements are derivative instruments that have been designated as fair value hedges in order to hedge the commodity price volatility of certain refinery inventory. The fair value of these purchase obligation derivatives is based on market prices of the underlying crude oil and refined products. The level of activity for these derivatives is based on the level of operating inventories.
As of December 31, 2016, there were no barrels (no barrels at December 31, 2015) of crude oil and feedstocks outstanding under these derivative instruments designated as fair value hedges and no barrels (no barrels at December 31, 2015) outstanding under these derivative instruments not designated as hedges. As of December 31, 2016, there were 2,942,348 barrels of intermediates and refined products (3,776,011 barrels at December 31, 2015) outstanding under these derivative instruments designated as fair value hedges and no barrels (no barrels at December 31, 2015) outstanding under these derivative instruments not designated as hedges. These volumes represent the notional value of the contract.
F- 49
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
The Company also enters into economic hedges primarily consisting of commodity derivative contracts that are not designated as hedges and are used to manage price volatility in certain crude oil and feedstock inventories as well as crude oil, feedstock, and refined product sales or purchases. The objective in entering into economic hedges is consistent with the objectives discussed above for fair value hedges. As of December 31, 2016, there were 5,950,000 barrels of crude oil and 2,831,000 barrels of refined products (39,577,000 and 4,599,136, respectively, as of December 31, 2015), outstanding under short and long term commodity derivative contracts not designated as hedges representing the notional value of the contracts.
The following tables provide information about the fair values of these derivative instruments as of December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015 and the line items in the consolidated balance sheet in which the fair values are reflected.
Description | Balance Sheet Location | Fair Value Asset/(Liability) | ||
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: | ||||
December 31, 2016: | ||||
Derivatives included with the inventory intermediation agreement obligations | Accrued expenses | $ | 6,058 | |
December 31, 2015: | ||||
Derivatives included with the inventory intermediation agreement obligations | Accrued expenses | $ | 35,511 | |
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: | ||||
December 31, 2016: | ||||
Commodity contracts | Accrued expenses | $ | 3,508 | |
December 31, 2015: | ||||
Commodity contracts | Accounts receivable | $ | 46,127 | |
The following tables provide information about the gains or losses recognized in income on these derivative instruments and the line items in the consolidated financial statements in which such gains and losses are reflected.
F- 50
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
Description | Location of Gain or (Loss) Recognized in Income on Derivatives | Gain or (Loss) Recognized in Income on Derivatives | ||
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: | ||||
For the year ended December 31, 2016: | ||||
Derivatives included with inventory supply arrangement obligations | Cost of sales | $ | — | |
Derivatives included with the inventory intermediation agreement obligations | Cost of sales | $ | (29,453 | ) |
For the year ended December 31, 2015: | ||||
Derivatives included with inventory supply arrangement obligations | Cost of sales | $ | (4,251 | ) |
Derivatives included with the inventory intermediation agreement obligations | Cost of sales | $ | (59,323 | ) |
For the year ended December 31, 2014 | ||||
Derivatives included with inventory supply arrangement obligations | Cost of sales | $ | 4,428 | |
Derivatives included with the inventory intermediation agreement obligations | Cost of sales | $ | 88,818 | |
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: | ||||
For the year ended December 31, 2016: | ||||
Commodity contracts | Cost of sales | $ | (55,557 | ) |
For the year ended December 31, 2015: | ||||
Commodity contracts | Cost of sales | $ | 32,416 | |
For the year ended December 31, 2014 | ||||
Commodity contracts | Cost of sales | $ | 146,016 | |
Hedged items designated in fair value hedges: | ||||
For the year ended December 31, 2016: | ||||
Crude oil and feedstock inventory | Cost of sales | $ | — | |
Intermediate and refined product inventory | Cost of sales | $ | 29,453 | |
For the year ended December 31, 2015: | ||||
Crude oil and feedstock inventory | Cost of sales | $ | 4,251 | |
Intermediate and refined product inventory | Cost of sales | $ | 59,323 | |
For the year ended December 31, 2014 | ||||
Crude oil and feedstock inventory | Cost of sales | $ | (4,428 | ) |
Intermediate and refined product inventory | Cost of sales | $ | (88,818 | ) |
The Company had no ineffectiveness related to the fair value hedges as of December 31, 2016, 2015, 2014.
F- 51
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
21. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
Dividend Declared
On February 16, 2017, PBF Energy, PBF Holding's indirect parent, announced a dividend of $0.30 per share on outstanding Class A common stock. The dividend is payable on March 13, 2017 to Class A common stockholders of record at the close of business on February 27, 2017.
Contribution Agreement
On February 15, 2017, PBF LLC entered into a contribution agreement with PBFX pursuant to which PBF LLC has agreed to contribute to PBFX all of the issued and outstanding limited liability company interests of Paulsboro Natural Gas Pipeline Company LLC ("PNGPC"), a wholly-owned subsidiary of PBF Holding. PNGPC owns and operates an existing interstate natural gas pipeline that originates in Delaware County, Pennsylvania, and terminates at the delivery point to PBF Holding's Paulsboro Refinery. PNGPC has Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (“FERC”) approval for, and is in the process of constructing, a new 24” pipeline (the “New Pipeline”) to replace the existing pipeline, which will be abandoned. In consideration for the PNGPC limited liability company interests, at closing, PBFX delivered (i) an intercompany promissory note in an amount to be determined based on the amounts expended through the closing date with respect to the New Pipeline and the abandonment of the existing line, (ii) an expansion rights and right of first refusal agreement in favor of PBF LLC with respect to the New Pipeline and (iii) an assignment and assumption agreement with respect to certain outstanding litigation involving PNGPC and the existing pipeline. The transaction closed on February 28, 2017.
Storage Services Agreement
On February 15, 2017, the Company entered into a ten-year storage services agreement (the “Chalmette Storage Agreement”) with PBFX’s wholly-owned subsidiary, PBFX Operating Company ("PBFX Op Co"), under which PBFX, through PBFX Op Co, will provide storage services to the Company upon the earlier of November 1, 2017 and the completion of construction of a new tank at the Company's Chalmette refinery. PBFX Op Co and Chalmette Refining have entered into a twenty-year lease for the premises upon which the tank will be located and a project management agreement pursuant to which Chalmette Refining will manage the construction of the tank.
Services Agreement
On February 28, 2017, PBFX entered into the Fifth Amended and Restated Services Agreement (as amended, the "Services Agreement") with the Company and certain of its subsidiaries in connection with PNGPC contribution agreement and the Chalmette Storage Agreement. The Services Agreement incorporates the PNGPC natural gas pipeline and the Chalmette storage tank into its provisions and increases the annual fee to be paid to PBF Holding from $6,386 to $6,700 and includes an interim monthly fee with respect to PNGPC's existing pipeline. All annual fees to be paid pursuant to the Services Agreement are indexed for inflation.
F- 52
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
22. CONSOLIDATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF PBF HOLDING
PBF Services Company, Delaware City Refining Company LLC, PBF Power Marketing LLC, Paulsboro Refining Company LLC, Paulsboro Natural Gas Pipeline Company LLC, Toledo Refining Company LLC, Chalmette Refining, L.L.C., PBF Western Region LLC, Torrance Refining Company LLC, Torrance Logistics Company LLC and PBF Investments LLC are 100% owned subsidiaries of PBF Holding and serve as guarantors of the obligations under the Senior Secured Notes. These guarantees are full and unconditional and joint and several. For purposes of the following footnote, PBF Holding is referred to as “Issuer”. The indentures dated February 9, 2012 and November 24, 2015, among PBF Holding, PBF Finance, the guarantors party thereto and Wilmington Trust, National Association, governs subsidiaries designated as “Guarantor Subsidiaries”. PBF Energy Limited, PBF Transportation Company LLC, PBF Rail Logistics Company LLC, MOEM Pipeline LLC, Collins Pipeline Company, T&M Terminal Company, TVP Holding Company LLC ("TVP Holding"), Torrance Basin Pipeline Company LLC and Torrance Pipeline Company LLC are consolidated subsidiaries of the Company that are not guarantors of the Senior Secured Notes. Additionally, our 50% equity investment in Torrance Valley Pipeline Company, held by TVP Holding is included in our Non-Guarantor financial position and results of operations and cash flows as TVP Holding is not a guarantor of the Senior Secured Notes.
The Senior Secured Notes were co-issued by PBF Finance. For purposes of the following footnote, PBF Finance is referred to as “Co-Issuer.” The Co-Issuer has no independent assets or operations.
The following supplemental combining and condensed consolidating financial information reflects the Issuer’s separate accounts, the combined accounts of the Guarantor Subsidiaries and the Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries, the combining and consolidating adjustments and eliminations and the Issuer’s consolidated accounts for the dates and periods indicated. For purposes of the following combining and consolidating information, the Issuer’s investment in its subsidiaries and the Guarantor subsidiaries' investments in their subsidiaries are accounted for under the equity method of accounting.
F- 53
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
22. CONSOLIDATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF PBF HOLDING
CONSOLIDATING BALANCE SHEET
December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||
Issuer | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries | Combining and Consolidating Adjustments | Total | |||||||||||||||
ASSETS | |||||||||||||||||||
Current assets: | |||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 530,085 | $ | 56,717 | $ | 41,366 | $ | (1,463 | ) | $ | 626,705 | ||||||||
Accounts receivable | 599,147 | 7,999 | 8,735 | — | 615,881 | ||||||||||||||
Accounts receivable - affiliate | 2,432 | 4,504 | 695 | — | 7,631 | ||||||||||||||
Inventories | 1,680,058 | — | 183,502 | — | 1,863,560 | ||||||||||||||
Prepaid expense and other current assets | 27,443 | 12,933 | 160 | — | 40,536 | ||||||||||||||
Due from related parties | 24,141,120 | 21,883,569 | 4,692,799 | (50,717,488 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Total current assets | 26,980,285 | 21,965,722 | 4,927,257 | (50,718,951 | ) | 3,154,313 | |||||||||||||
Property, plant and equipment, net | 33,772 | 2,452,877 | 242,050 | — | 2,728,699 | ||||||||||||||
Investment in subsidiaries | 705,034 | 440,377 | — | (1,145,411 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Investment in equity method investee | — | — | 179,882 | — | 179,882 | ||||||||||||||
Deferred charges and other assets, net | 12,317 | 491,673 | 13 | — | 504,003 | ||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 27,731,408 | $ | 25,350,649 | $ | 5,349,202 | $ | (51,864,362 | ) | $ | 6,566,897 | ||||||||
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | |||||||||||||||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 360,260 | $ | 157,277 | $ | 14,291 | $ | (1,463 | ) | $ | 530,365 | ||||||||
Accounts payable - affiliate | 37,077 | 786 | — | — | 37,863 | ||||||||||||||
Accrued expenses | 1,094,581 | 201,935 | 166,213 | — | 1,462,729 | ||||||||||||||
Deferred revenue | 10,901 | 1,438 | 1 | — | 12,340 | ||||||||||||||
Due to related parties | 22,027,065 | 24,031,520 | 4,658,903 | (50,717,488 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Total current liabilities | 23,529,884 | 24,392,956 | 4,839,408 | (50,718,951 | ) | 2,043,297 | |||||||||||||
Delaware Economic Development Authority loan | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Long-term debt | 1,496,085 | 45,908 | 34,566 | — | 1,576,559 | ||||||||||||||
Affiliate notes payable | 86,298 | — | — | — | 86,298 | ||||||||||||||
Deferred tax liabilities | — | — | 45,699 | — | 45,699 | ||||||||||||||
Other long-term liabilities | 30,208 | 192,204 | 3,699 | — | 226,111 | ||||||||||||||
Due to related party - long term | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Total liabilities | 25,142,475 | 24,631,068 | 4,923,372 | (50,718,951 | ) | 3,977,964 | |||||||||||||
Commitments and contingencies | |||||||||||||||||||
Equity: | |||||||||||||||||||
Member's equity | 2,155,863 | 1,714,997 | 374,067 | (2,089,064 | ) | 2,155,863 | |||||||||||||
Retained earnings | 446,519 | (999,693 | ) | 51,763 | 947,930 | 446,519 | |||||||||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (25,962 | ) | (8,236 | ) | — | 8,236 | (25,962 | ) | |||||||||||
Total PBF Holding Company LLC equity | 2,576,420 | 707,068 | 425,830 | (1,132,898 | ) | 2,576,420 | |||||||||||||
Noncontrolling interest | 12,513 | 12,513 | — | (12,513 | ) | $ | 12,513 | ||||||||||||
Total equity | 2,588,933 | 719,581 | 425,830 | (1,145,411 | ) | 2,588,933 | |||||||||||||
Total liabilities and equity | $ | 27,731,408 | $ | 25,350,649 | $ | 5,349,202 | $ | (51,864,362 | ) | $ | 6,566,897 | ||||||||
F- 54
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
22. CONSOLIDATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF PBF HOLDING
CONSOLIDATING BALANCE SHEET
December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
Issuer | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries | Combining and Consolidating Adjustments | Total | |||||||||||||||
ASSETS | |||||||||||||||||||
Current assets: | |||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 882,820 | $ | 6,236 | $ | 28,968 | $ | (3,275 | ) | $ | 914,749 | ||||||||
Accounts receivable | 430,809 | 11,057 | 12,893 | — | 454,759 | ||||||||||||||
Accounts receivable - affiliate | 917 | 2,521 | — | — | 3,438 | ||||||||||||||
Inventories | 608,646 | 363,151 | 202,475 | — | 1,174,272 | ||||||||||||||
Prepaid expense and other current assets | 24,243 | 9,074 | 384 | — | 33,701 | ||||||||||||||
Due from related parties | 20,236,649 | 20,547,503 | 3,262,382 | (44,046,534 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Total current assets | 22,184,084 | 20,939,542 | 3,507,102 | (44,049,809 | ) | 2,580,919 | |||||||||||||
Property, plant and equipment, net | 25,240 | 1,960,066 | 225,784 | — | 2,211,090 | ||||||||||||||
Investment in subsidiaries | 1,740,111 | 143,349 | — | (1,883,460 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Deferred charges and other assets, net | 23,973 | 265,240 | 1,500 | — | 290,713 | ||||||||||||||
Due from related party - long term | — | — | 20,577 | (20,577 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 23,973,408 | $ | 23,308,197 | $ | 3,754,963 | $ | (45,953,846 | ) | $ | 5,082,722 | ||||||||
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | |||||||||||||||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 196,988 | $ | 113,564 | $ | 7,566 | $ | (3,275 | ) | $ | 314,843 | ||||||||
Accounts payable - affiliate | 23,949 | — | — | — | 23,949 | ||||||||||||||
Accrued expenses | 503,179 | 495,842 | 118,414 | — | 1,117,435 | ||||||||||||||
Deferred revenue | 4,043 | — | — | — | 4,043 | ||||||||||||||
Due to related parties | 19,787,807 | 21,026,310 | 3,232,417 | (44,046,534 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Total current liabilities | 20,515,966 | 21,635,716 | 3,358,397 | (44,049,809 | ) | 1,460,270 | |||||||||||||
Delaware Economic Development Authority loan | — | 4,000 | — | — | 4,000 | ||||||||||||||
Long-term debt | 1,137,980 | 31,717 | 67,023 | — | 1,236,720 | ||||||||||||||
Affiliate notes payable | 470,047 | — | — | — | 470,047 | ||||||||||||||
Deferred tax liabilities | — | — | 20,577 | — | 20,577 | ||||||||||||||
Other long-term liabilities | 28,131 | 41,693 | — | — | 69,824 | ||||||||||||||
Due to related party - long term | — | 20,577 | — | (20,577 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Total liabilities | 22,152,124 | 21,733,703 | 3,445,997 | (44,070,386 | ) | 3,261,438 | |||||||||||||
Commitments and contingencies | |||||||||||||||||||
Equity: | |||||||||||||||||||
Member's equity | 1,479,175 | 1,062,717 | 182,696 | (1,245,413 | ) | 1,479,175 | |||||||||||||
Retained earnings | 349,654 | 502,788 | 126,270 | (629,058 | ) | 349,654 | |||||||||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (24,770 | ) | (8,236 | ) | — | 8,236 | (24,770 | ) | |||||||||||
Total PBF Holding Company LLC equity | 1,804,059 | 1,557,269 | 308,966 | (1,866,235 | ) | 1,804,059 | |||||||||||||
Noncontrolling interest | 17,225 | 17,225 | — | (17,225 | ) | 17,225 | |||||||||||||
Total equity | 1,821,284 | 1,574,494 | 308,966 | (1,883,460 | ) | 1,821,284 | |||||||||||||
Total liabilities and equity | $ | 23,973,408 | $ | 23,308,197 | $ | 3,754,963 | $ | (45,953,846 | ) | $ | 5,082,722 | ||||||||
F- 55
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
22. CONSOLIDATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF PBF HOLDING
CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
Year Ended December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||
Issuer | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries | Combining and Consolidating Adjustments | Total | |||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 15,808,556 | $ | 800,647 | $ | 1,524,691 | $ | (2,225,357 | ) | $ | 15,908,537 | ||||||||
Costs, expenses and other | |||||||||||||||||||
Cost of sales, excluding depreciation | 13,813,293 | 649,242 | 1,527,910 | (2,225,357 | ) | 13,765,088 | |||||||||||||
Operating expenses, excluding depreciation | 41 | 1,356,572 | 33,969 | — | 1,390,582 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 123,150 | 27,602 | (1,109 | ) | — | 149,643 | |||||||||||||
Equity income in investee | — | — | (5,679 | ) | — | (5,679 | ) | ||||||||||||
Gain on sale of asset | 2,392 | 150 | 8,832 | — | 11,374 | ||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization expense | 5,836 | 194,701 | 9,303 | — | 209,840 | ||||||||||||||
Total costs, expenses and other | 13,944,712 | 2,228,267 | 1,573,226 | (2,225,357 | ) | 15,520,848 | |||||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 1,863,844 | (1,427,620 | ) | (48,535 | ) | — | 387,689 | ||||||||||||
Other income (expense) | |||||||||||||||||||
Equity in earnings of subsidiaries | (1,502,243 | ) | (74,507 | ) | — | 1,576,750 | — | ||||||||||||
Change in fair value of catalyst lease | — | 1,422 | — | — | 1,422 | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense, net | (125,715 | ) | (1,538 | ) | (2,283 | ) | — | (129,536 | ) | ||||||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes | 235,886 | (1,502,243 | ) | (50,818 | ) | 1,576,750 | 259,575 | ||||||||||||
Income tax expense | — | — | 23,689 | — | 23,689 | ||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | 235,886 | (1,502,243 | ) | (74,507 | ) | 1,576,750 | 235,886 | ||||||||||||
Less income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 269 | 269 | — | (269 | ) | 269 | |||||||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to PBF Holding Company LLC | $ | 235,617 | $ | (1,502,512 | ) | $ | (74,507 | ) | $ | 1,577,019 | $ | 235,617 | |||||||
Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to PBF Holding Company LLC | $ | 233,025 | $ | (1,502,512 | ) | $ | (74,507 | ) | $ | 1,577,019 | $ | 233,025 | |||||||
F- 56
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
22. CONSOLIDATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF PBF HOLDING
CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
Year Ended December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
Issuer | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries | Combining and Consolidating Adjustments | Total | |||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 13,085,122 | $ | 884,930 | $ | 1,633,818 | $ | (2,479,941 | ) | $ | 13,123,929 | ||||||||
Costs, expenses and other | |||||||||||||||||||
Cost of sales, excluding depreciation | 11,514,115 | 1,026,846 | 1,550,579 | (2,479,941 | ) | 11,611,599 | |||||||||||||
Operating expenses, excluding depreciation | (3,683 | ) | 891,534 | 1,517 | — | 889,368 | |||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 143,580 | 21,016 | 2,308 | — | 166,904 | ||||||||||||||
Gain on sale of asset | (249 | ) | (105 | ) | (650 | ) | — | (1,004 | ) | ||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization expense | 9,687 | 178,578 | 2,845 | — | 191,110 | ||||||||||||||
Total costs, expenses and other | 11,663,450 | 2,117,869 | 1,556,599 | (2,479,941 | ) | 12,857,977 | |||||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 1,421,672 | (1,232,939 | ) | 77,219 | — | 265,952 | |||||||||||||
Other income (expense) | |||||||||||||||||||
Equity in earnings of subsidiaries | (1,154,420 | ) | — | — | 1,154,420 | — | |||||||||||||
Change in fair value of catalyst lease | — | 10,184 | — | — | 10,184 | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense, net | (79,310 | ) | (5,876 | ) | (3,008 | ) | — | (88,194 | ) | ||||||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes | 187,942 | (1,228,631 | ) | 74,211 | 1,154,420 | 187,942 | |||||||||||||
Income tax expense | — | — | 648 | — | 648 | ||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | 187,942 | (1,228,631 | ) | 73,563 | 1,154,420 | 187,294 | |||||||||||||
Less income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 274 | 274 | — | (274 | ) | 274 | |||||||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to PBF Holding Company LLC | $ | 187,668 | $ | (1,228,905 | ) | $ | 73,563 | $ | 1,154,694 | $ | 187,020 | ||||||||
Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to PBF Holding Company LLC | $ | 189,774 | $ | (1,228,905 | ) | $ | 73,563 | $ | 1,154,694 | $ | 189,126 | ||||||||
F- 57
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
22. CONSOLIDATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF PBF HOLDING
CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
Year Ended December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||
Issuer | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries | Combining and Consolidating Adjustments | Total | |||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 19,847,045 | $ | 1,402,253 | $ | 1,007,407 | $ | (2,428,550 | ) | $ | 19,828,155 | ||||||||
Costs, expenses and other | |||||||||||||||||||
Cost of sales, excluding depreciation | 18,467,533 | 1,522,901 | 952,170 | (2,428,550 | ) | 18,514,054 | |||||||||||||
Operating expenses, excluding depreciation | 218 | 880,339 | 144 | — | 880,701 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 123,692 | 16,259 | 199 | — | 140,150 | ||||||||||||||
Gain on sale of assets | (277 | ) | — | (618 | ) | — | (895 | ) | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization expense | 13,583 | 164,525 | 888 | — | 178,996 | ||||||||||||||
Total costs, expenses and other | 18,604,749 | 2,584,024 | 952,783 | (2,428,550 | ) | 19,713,006 | |||||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 1,242,296 | (1,181,771 | ) | 54,624 | — | 115,149 | |||||||||||||
Other income (expense) | |||||||||||||||||||
Equity in earnings of subsidiaries | (1,131,321 | ) | — | — | 1,131,321 | — | |||||||||||||
Change in fair value of catalyst lease | — | 3,969 | — | — | 3,969 | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense, net | (89,858 | ) | (6,225 | ) | (1,918 | ) | — | (98,001 | ) | ||||||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes | 21,117 | (1,184,027 | ) | 52,706 | 1,131,321 | 21,117 | |||||||||||||
Income tax expense | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | 21,117 | (1,184,027 | ) | 52,706 | 1,131,321 | 21,117 | |||||||||||||
Less net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to PBF Holding Company LLC | $ | 21,117 | $ | (1,184,027 | ) | $ | 52,706 | $ | 1,131,321 | $ | 21,117 | ||||||||
Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to PBF Holding Company LLC | $ | 8,779 | $ | (1,194,031 | ) | $ | 52,706 | $ | 1,141,325 | $ | 8,779 | ||||||||
F- 58
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
22. CONSOLIDATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF PBF HOLDING
CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF CASH FLOW
Year Ended December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||
Issuer | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries | Combining and Consolidating Adjustments | Total | |||||||||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 235,886 | $ | (1,502,243 | ) | $ | (74,507 | ) | $ | 1,576,750 | $ | 235,886 | |||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 14,874 | 194,722 | 9,337 | — | 218,933 | ||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | 18,296 | — | — | 18,296 | ||||||||||||||
Change in fair value of catalyst lease obligation | — | (1,422 | ) | — | — | (1,422 | ) | ||||||||||||
Deferred income taxes | — | — | 19,802 | — | 19,802 | ||||||||||||||
Non-cash change in inventory repurchase obligations | 29,453 | — | — | — | 29,453 | ||||||||||||||
Non-cash lower of cost or market inventory adjustment | (521,348 | ) | — | — | — | (521,348 | ) | ||||||||||||
Pension and other post retirement benefit costs | 7,139 | 30,848 | — | — | 37,987 | ||||||||||||||
Equity (income) loss in investee | — | — | (5,679 | ) | — | (5,679 | ) | ||||||||||||
Loss (gain) on sale of assets | 2,392 | 150 | 8,832 | — | 11,374 | ||||||||||||||
Equity in earnings of subsidiaries | 1,502,243 | 74,507 | — | (1,576,750 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Accounts receivable | (168,338 | ) | 3,058 | 4,158 | — | (161,122 | ) | ||||||||||||
Due to/from affiliates | (2,031,933 | ) | 2,046,280 | (4,626 | ) | — | 9,721 | ||||||||||||
Inventories | 217,629 | — | 18,973 | — | 236,602 | ||||||||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | (3,200 | ) | (2,675 | ) | 92 | — | (5,783 | ) | |||||||||||
Accounts payable | 163,272 | 41,025 | 7,405 | 1,812 | 213,514 | ||||||||||||||
Accrued expenses | 531,613 | (353,591 | ) | 49,964 | — | 227,986 | |||||||||||||
Deferred revenue | 6,858 | 1,438 | 1 | — | 8,297 | ||||||||||||||
Other assets and liabilities | (5,833 | ) | (16,238 | ) | 1,193 | — | (20,878 | ) | |||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | (19,293 | ) | 534,155 | 34,945 | 1,812 | 551,619 | |||||||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Acquisition of Torrance refinery and related logistics assets | (971,932 | ) | — | — | — | (971,932 | ) | ||||||||||||
Acquisition of Chalmette refinery, net of cash acquired | — | (2,659 | ) | — | — | (2,659 | ) | ||||||||||||
Expenditures for property, plant and equipment | (21,563 | ) | (255,434 | ) | (5,433 | ) | — | (282,430 | ) | ||||||||||
Expenditures for refinery turnarounds costs | — | (198,664 | ) | — | — | (198,664 | ) | ||||||||||||
Expenditures for other assets | — | (42,506 | ) | — | — | (42,506 | ) | ||||||||||||
Return on investment in subsidiaries | 12,800 | — | — | (12,800 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Capital contributions to subsidiaries | (8,287 | ) | — | — | 8,287 | — | |||||||||||||
Proceeds from sale of assets | 4,802 | — | 19,890 | — | 24,692 | ||||||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities | (984,180 | ) | (499,263 | ) | 14,457 | (4,513 | ) | (1,473,499 | ) | ||||||||||
F- 59
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
22. CONSOLIDATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF PBF HOLDING CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF CASH FLOW (Continued)
Cash flows from financing activities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Proceeds from parent's capital contributions | — | — | 8,287 | (8,287 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Contributions from PBF LLC | 450,300 | — | — | — | 450,300 | ||||||||||||||
Distribution to parent | — | — | (12,800 | ) | 12,800 | — | |||||||||||||
Distributions to members | (139,434 | ) | — | — | — | (139,434 | ) | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from affiliate notes payable | 43,396 | — | — | — | 43,396 | ||||||||||||||
Repayments of affiliate notes payable | (53,524 | ) | — | — | — | (53,524 | ) | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from revolver borrowings | 550,000 | — | — | — | 550,000 | ||||||||||||||
Repayments of revolver borrowings | (200,000 | ) | — | — | — | (200,000 | ) | ||||||||||||
Repayments of Rail Facility revolver borrowings | — | — | (67,491 | ) | — | (67,491 | ) | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from PBF Rail Term Loan | — | — | 35,000 | — | 35,000 | ||||||||||||||
Additional catalyst lease | — | 15,589 | — | — | 15,589 | ||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | 650,738 | 15,589 | (37,004 | ) | 4,513 | 633,836 | |||||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | (352,735 | ) | 50,481 | 12,398 | 1,812 | (288,044 | ) | ||||||||||||
Cash and equivalents, beginning of period | 882,820 | 6,236 | 28,968 | (3,275 | ) | 914,749 | |||||||||||||
Cash and equivalents, end of period | $ | 530,085 | $ | 56,717 | $ | 41,366 | $ | (1,463 | ) | $ | 626,705 | ||||||||
F- 60
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
22. CONSOLIDATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF PBF HOLDING
CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF CASH FLOW
Year Ended December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
Issuer | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries | Combining and Consolidating Adjustments | Total | |||||||||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 187,942 | $ | (1,228,631 | ) | $ | 73,563 | $ | 1,154,420 | $ | 187,294 | ||||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 17,063 | 178,601 | 3,719 | — | 199,383 | ||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | 9,218 | — | — | 9,218 | ||||||||||||||
Change in fair value of catalyst lease obligation | — | (10,184 | ) | — | — | (10,184 | ) | ||||||||||||
Non-cash change in inventory repurchase obligations | — | 63,389 | — | — | 63,389 | ||||||||||||||
Non-cash lower of cost or market inventory adjustment | 279,785 | 147,441 | — | — | 427,226 | ||||||||||||||
Pension and other post retirement benefit cost | 7,576 | 19,406 | — | — | 26,982 | ||||||||||||||
Gain on sale of assets | (249 | ) | (105 | ) | (650 | ) | — | (1,004 | ) | ||||||||||
Equity in earnings of subsidiaries | 1,154,420 | — | — | (1,154,420 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Accounts receivable | 87,689 | 16,124 | (6,177 | ) | — | 97,636 | |||||||||||||
Due to/from affiliates | (1,018,176 | ) | 1,133,364 | (103,084 | ) | — | 12,104 | ||||||||||||
Inventories | (108,751 | ) | (116,074 | ) | (47,067 | ) | — | (271,892 | ) | ||||||||||
Prepaid expense and other current assets | 2,721 | (2,999 | ) | (353 | ) | — | (631 | ) | |||||||||||
Accounts payable | (38,609 | ) | 15,710 | (857 | ) | (1,259 | ) | (25,015 | ) | ||||||||||
Accrued expenses | 27,925 | 8,172 | (73,834 | ) | — | (37,737 | ) | ||||||||||||
Deferred revenue | 2,816 | — | — | — | 2,816 | ||||||||||||||
Other assets and liabilities | (423 | ) | (26,769 | ) | 10 | — | (27,182 | ) | |||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | 601,729 | 206,663 | (154,730 | ) | (1,259 | ) | 652,403 | ||||||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Acquisition of Chalmette refinery, net of cash acquired | (601,311 | ) | 19,042 | 16,965 | — | (565,304 | ) | ||||||||||||
Expenditures for property, plant and equipment | (193,898 | ) | (158,361 | ) | (106 | ) | — | (352,365 | ) | ||||||||||
Expenditures for refinery turnarounds costs | — | (53,576 | ) | — | — | (53,576 | ) | ||||||||||||
Expenditures for other assets | — | (8,236 | ) | — | — | (8,236 | ) | ||||||||||||
Investment in subsidiaries | 10,000 | — | — | (10,000 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Capital contributions to subsidiaries | (5,000 | ) | — | — | 5,000 | — | |||||||||||||
Proceeds from sale of assets | 60,902 | — | 107,368 | — | 168,270 | ||||||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities | (729,307 | ) | (201,131 | ) | 124,227 | (5,000 | ) | (811,211 | ) | ||||||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Proceeds from member's capital contributions | 345,000 | — | 5,000 | (5,000 | ) | 345,000 | |||||||||||||
Distribution to parent | — | — | (10,000 | ) | 10,000 | — | |||||||||||||
Distributions to members | (350,658 | ) | — | — | — | (350,658 | ) | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from intercompany notes payable | 347,783 | — | — | — | 347,783 | ||||||||||||||
Proceeds from revolver borrowings | 170,000 | — | — | — | 170,000 | ||||||||||||||
Repayments of revolver borrowings | (170,000 | ) | — | — | — | (170,000 | ) | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from Rail Facility revolver borrowings | — | — | 102,075 | — | 102,075 | ||||||||||||||
Repayments of Rail Facility revolver borrowings | — | — | (71,938 | ) | — | (71,938 | ) | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from Senior Secured Notes | 500,000 | — | — | — | 500,000 | ||||||||||||||
Deferred financing costs and other | (17,108 | ) | — | — | — | (17,108 | ) | ||||||||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | 825,017 | — | 25,137 | 5,000 | 855,154 | ||||||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 697,439 | 5,532 | (5,366 | ) | (1,259 | ) | 696,346 | ||||||||||||
Cash and equivalents, beginning of period | 185,381 | 704 | 34,334 | (2,016 | ) | 218,403 | |||||||||||||
Cash and equivalents, end of period | $ | 882,820 | $ | 6,236 | $ | 28,968 | $ | (3,275 | ) | $ | 914,749 | ||||||||
F- 61
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE, UNIT, PER SHARE, PER UNIT AND BARREL DATA)
22. CONSOLIDATING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF PBF HOLDING
CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF CASH FLOW
Year Ended December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||
Issuer | Guarantors Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantors Subsidiaries | Combining and Consolidated Adjustments | Total | |||||||||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 21,117 | $ | (1,184,027 | ) | $ | 52,706 | $ | 1,131,321 | $ | 21,117 | ||||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash | |||||||||||||||||||
provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 20,334 | 164,550 | 1,528 | — | 186,412 | ||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | 6,095 | — | — | 6,095 | ||||||||||||||
Change in fair value of catalyst lease obligation | — | (3,969 | ) | — | — | (3,969 | ) | ||||||||||||
Non-cash change in inventory repurchase obligations | — | (93,246 | ) | — | — | (93,246 | ) | ||||||||||||
Non-cash lower of cost or market inventory adjustment | 566,412 | 123,698 | — | — | 690,110 | ||||||||||||||
Pension and other post retirement benefit costs | 6,426 | 16,174 | — | — | 22,600 | ||||||||||||||
Gain on sale of assets | (277 | ) | — | (618 | ) | — | (895 | ) | |||||||||||
Equity in earnings of subsidiaries | 1,131,321 | — | — | (1,131,321 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Accounts receivable | 69,887 | (17,976 | ) | (6,533 | ) | — | 45,378 | ||||||||||||
Due to/from affiliates | (1,227,851 | ) | 1,328,439 | (92,181 | ) | — | 8,407 | ||||||||||||
Inventories | (259,352 | ) | 20,711 | (155,390 | ) | — | (394,031 | ) | |||||||||||
Prepaid expense and other current assets | 22,287 | 1,399 | — | — | 23,686 | ||||||||||||||
Accounts payable | (71,821 | ) | (1,697 | ) | 8,423 | (2,016 | ) | (67,111 | ) | ||||||||||
Accrued expenses | (131,903 | ) | 471 | 191,331 | — | 59,899 | |||||||||||||
Deferred revenue | (6,539 | ) | — | — | — | (6,539 | ) | ||||||||||||
Other assets and liabilities | (1,966 | ) | (258 | ) | (1 | ) | — | (2,225 | ) | ||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | 138,075 | 360,364 | (735 | ) | (2,016 | ) | 495,688 | ||||||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Expenditures for property, plant and equipment | (152,814 | ) | (205,508 | ) | (112,138 | ) | — | (470,460 | ) | ||||||||||
Expenditures for deferred turnaround costs | — | (137,688 | ) | — | — | (137,688 | ) | ||||||||||||
Expenditures for other assets | — | (17,255 | ) | — | — | (17,255 | ) | ||||||||||||
Capital contributions to subsidiaries | (44,346 | ) | — | — | 44,346 | — | |||||||||||||
Proceeds from sale of assets | 133,845 | — | 68,809 | — | 202,654 | ||||||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities | (63,315 | ) | (360,451 | ) | (43,329 | ) | 44,346 | (422,749 | ) | ||||||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Contributions from PBF LLC | 328,664 | — | 44,346 | (44,346 | ) | 328,664 | |||||||||||||
Distributions to members | (361,352 | ) | — | — | — | (361,352 | ) | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from affiliate notes payable | 90,631 | — | — | — | 90,631 | ||||||||||||||
Proceeds from revolver borrowings | 395,000 | — | — | — | 395,000 | ||||||||||||||
Repayments of revolver borrowings | (410,000 | ) | — | — | — | (410,000 | ) | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from Rail Facility revolver borrowings | — | — | 83,095 | — | 83,095 | ||||||||||||||
Repayment of Rail Facility revolver borrowings | — | — | (45,825 | ) | — | (45,825 | ) | ||||||||||||
Deferred financing costs and other | (8,501 | ) | — | (3,218 | ) | — | (11,719 | ) | |||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 34,442 | — | 78,398 | (44,346 | ) | 68,494 | |||||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 109,202 | (87 | ) | 34,334 | (2,016 | ) | 141,433 | ||||||||||||
Cash and equivalents, beginning of period | 76,179 | 791 | — | — | 76,970 | ||||||||||||||
Cash and equivalents, end of period | $ | 185,381 | $ | 704 | $ | 34,334 | $ | (2,016 | ) | $ | 218,403 | ||||||||
F- 62
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
PBF HOLDING COMPANY LLC (Registrant) | ||
By: | /s/ Thomas J. Nimbley | |
(Thomas J. Nimbley) | ||
Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | ||
Date: March 8, 2017
POWER OF ATTORNEY
Each of the officers and directors of PBF Holding Company LLC, whose signature appears below, in so signing, also makes, constitutes and appoints each of Erik Young, Matthew Lucey and Trecia Canty, and each of them, his true and lawful attorneys-in-fact, with full power and substitution, for him in any and all capacities, to execute and cause to be filed with the SEC any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, with exhibits thereto and other documents connected therewith and to perform any acts necessary to be done in order to file such documents, and hereby ratifies and confirms all that said attorneys-in-fact or their substitute or substitutes may do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature | Title | Date | ||
/s/ Thomas J. Nimbley | Chief Executive Officer and Director | March 8, 2017 | ||
(Thomas J. Nimbley) | (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
/s/ Erik Young | Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer | March 8, 2017 | ||
(Erik Young) | (Principal Financial Officer) | |||
/s/ John Barone | Chief Accounting Officer | March 8, 2017 | ||
(John Barone) | (Principal Accounting Officer) | |||
/s/ Trecia Canty | Director | March 8, 2017 | ||
(Trecia Canty) | ||||
/s/ Matthew C. Lucey | Director | March 8, 2017 | ||
(Matthew C. Lucey) | ||||
