Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - EMMAUS LIFE SCIENCES, INC. | a16-11274_18k.htm |
Exhibit 99.1
Yutaka Niihara, MD, MPH Chairman and CEO Peter Ludlum, CMA, MBA Co-President and Chief Business Officer Bringing Hope to Patients with Sickle Cell Disease May 2016

Disclaimers This presentation contains forward-looking statements, including, but not limited to, statements related to management’s expectations, hopes, beliefs, intentions or strategies regarding the future. Any statements that refer to projections, forecasts or other characterizations of future events or circumstances, including statements related to future regulatory matters, our future intellectual property and patent positions, new product opportunities or the future financial condition or results of operations of Emmaus, are forward-looking statements. The words “anticipates,” “approaches”, “believes,” “continue,” “could,” “estimates,” “expects,” “intends,” “may,” “might,” “plans,” “possible,” “potential,” “predicts,” “projects,” “seeks,” “should,” “will,” “would” and similar expressions, or the negatives of such terms, may identify forward-looking statements, but the absence of these words does not mean that a statement is not forward-looking. Emmaus' actual results and the timing of events could differ materially from those anticipated in such forward-looking statements as a result of certain risks and uncertainties, which include, without limitation, risks related to the company’s ability to raise additional capital to fund operations; obtaining FDA and other regulatory approval for our drug products, including our L-glutamine treatment for sickle-cell disease; successful completion of our clinical trials; our ability to commercialize our drug products, including our L-glutamine treatment for SCD; our reliance on third party manufacturers for our drug products; market acceptance of our products; our dependence on licenses for certain of our products; our reliance on the expected growth in demand for our products; exposure to intellectual property claims from third parties; the lack of a public trading market for our securities; the cost of complying with current and future governmental regulations and the impact of any changes in the regulations on our operations; our heavy reliance on the services of our founder, Dr. Yutaka Niihara; and the other factors referenced in our Form 10-K and Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), including, without limitation, under the sections entitled “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” and “Business,” and in other documents we file with the SEC. Emmaus undertakes no duty or obligation to update any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation as a result of new information, future events or changes in its expectations. We have prepared this presentation and the information contained herein for informational and discussion purposes only. The information contained herein is qualified in its entirety by reference to our periodic reports filed with the SEC, which are available at www.sec.gov. This presentation does not constitute an offer to sell, or a solicitation of an offer to subscribe for or buy, any of our securities. Certain information, including statistical data and other factual statements, contained in this presentation has been obtained from published sources prepared by other parties considered to be generally reliable. However, we assume no responsibility for the accuracy of such information. There is no representation or warranty, expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, adequateness or completeness of any such information used in this presentation.

Phase 3 trial in sickle cell disease (SCD) completed Cochran-Mantel Henszel (CMH) using “Modified Ridit” analysis, P-value of 0.005 One of the largest trials conducted in sickle cell disease 230 adult and pediatric patients Favorable regulatory environment Orphan Drug Designation (U.S. & E.U.) Fast Track Designation Founded December 2000 Who We Are Sickle Cell Disease is our Focus

Corporate History Approach Based on Academic Findings* Emmaus’ research and development leverages L-glutamine research of Drs. Yutaka Niihara and Charles Zerez L-glutamine studies funded by National Institute of Health (1996) Sought to understand link between glutamine availability in healthy and sickled red blood cell (RBC) Heightened susceptibility to oxidation by sickle RBC Identified nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and its reduced form (NADH) as the primary regulators of oxidation Hypothesized that reduced levels of NADH to be an indicator of increased oxidation Preliminary studies affirmed; Company entered into pilot trial Pilot trial indicated statistically significant increases in NADH levels and redox potential Follow-up dosing study was completed identifying the 20-30g daily dose RBC endothelial adhesion was reduced with pharmaceutical grade L-glutamine therapy (PGLG) treatment Investigational New Drug application submitted May 1997 * From Dr. Niihara’s early work at UCLA and LABioMed.
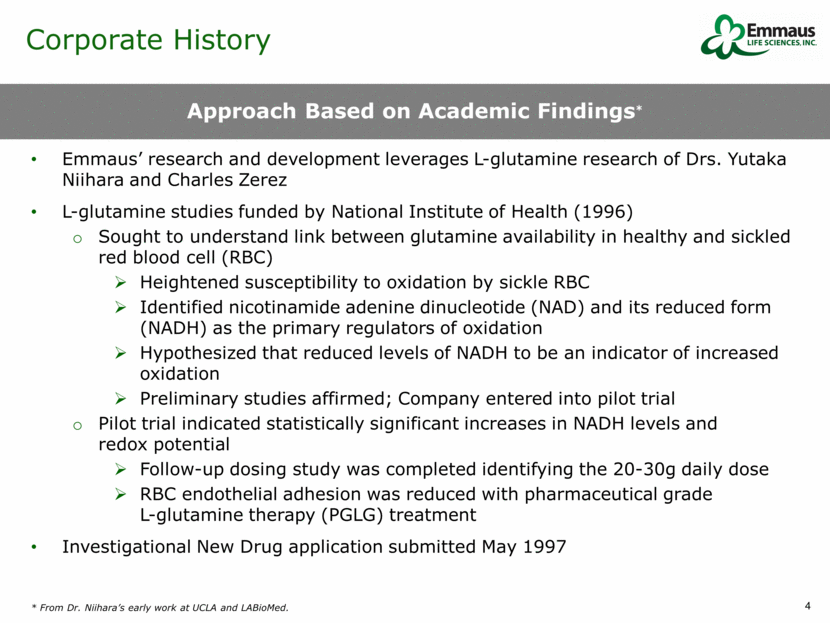
Leadership Name Title Prior Experience Yutaka Niihara, M.D., MPH Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer Willis Lee, MS Vice Chairman and Chief Operating Officer Peter Ludlum, CMA, MBA Co-President and Chief Business Officer Lan Tran, MPH Co-President and Chief Administrative Officer Charles Stark, Pharm.D. Senior V.P. of R&D
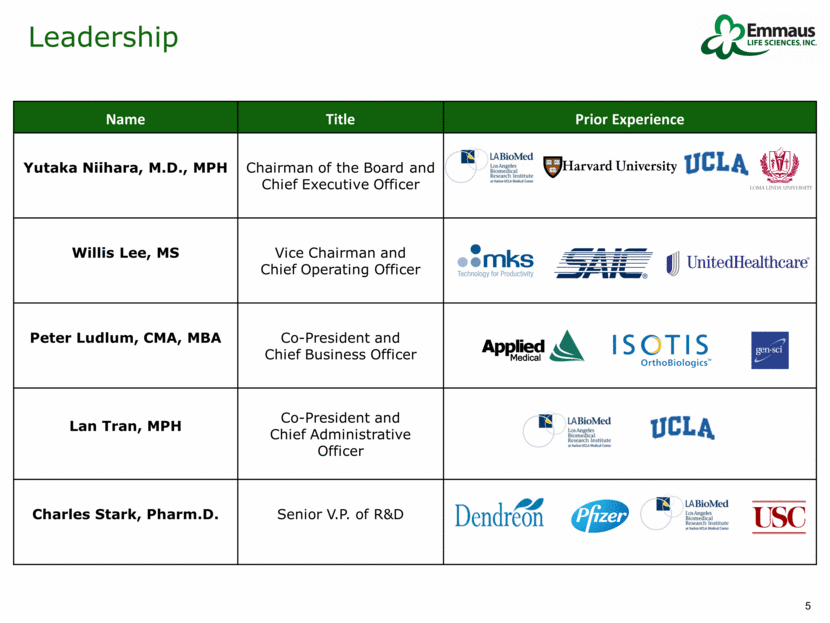
2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 Founded Emmaus Medical, LLC December 2000 FDA grants Fast Track Designation January 2005 FDA grants Orphan Drug Designation August 2001 Phase 2 trial completed October 2008 SME granted to Emmaus Medical Europe February 2012 Clinical portion of Phase 3 trial completed December 2013 Second meeting with FDA October 2014 FDA authorizes Phase 3 trial April 2009 EMA grants Orphan Drug Designation July 2012 First meeting with FDA June 2014 Key Milestones Informed FDA of Intent to Submit New Drug Application in Summer of 2016
SCD Represents a Substantial Unmet Medical Need* 20 to 25 million patients worldwide, primarily in Africa 100,000 patients in U.S. Orphan Drug Designation Fast Track Designation 80,000 patients in E.U. Increasing due to migration Orphan Drug Designation In the U.S. 1:500 newborns of African American origin have SCD 1:1,200 newborns of Hispanic origin have SCD 10% of the African American population has sickle cell trait Estimated at over 1 million in India In Brazil 1:1,800 newborns have SCD A Large Global Market Opportunity * http://www.iasp-pain.org/PublicationsNews/NewsDetail.aspx?ItemNumber=4896&navItemNumber=643
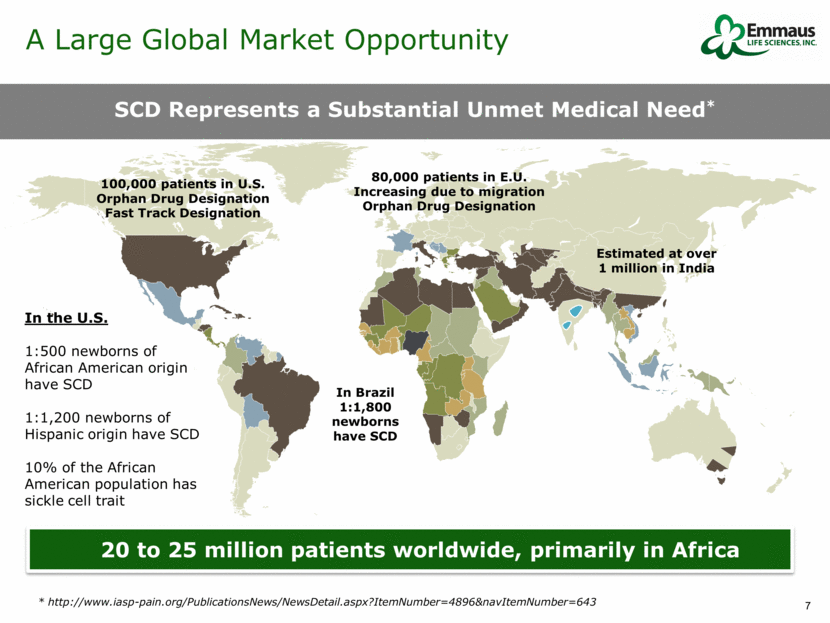
Market Scale Combined Annual Market Potential Approaching $2 Billion, Roughly Equally Distributed Across U.S. and E.U. $1.9 Billion Annual addressable market estimates assume 100,000 patients treated in U.S./per annum at $30/day and 80,000 patients treated in Europe at the same corresponding level Annual Gross Revenues U.S Market E.U. Market
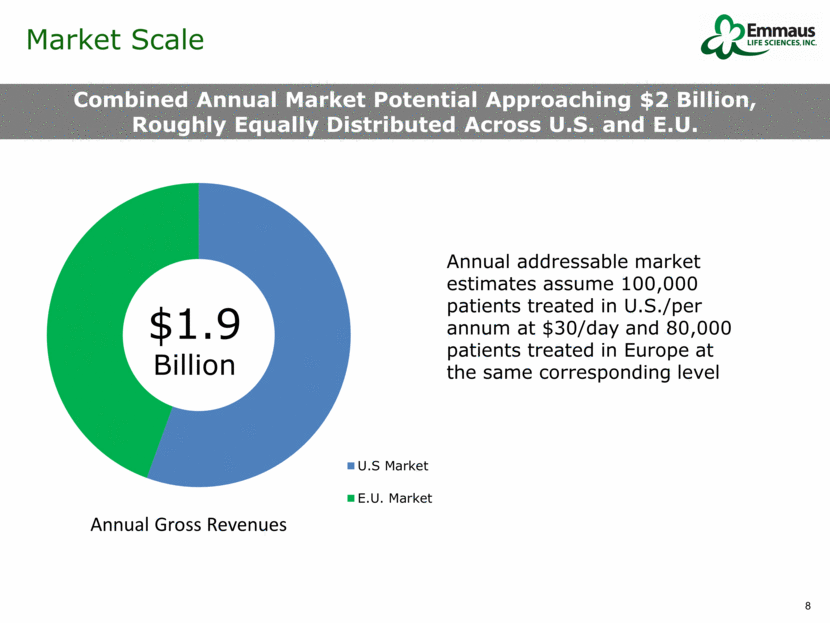
Current treatments are toxic and costly Only currently approved drug treatment in the U.S. is a chemotherapy agent with significant warnings of toxic side effects; Not approved for pediatric patients Bone marrow transplant limited by high cost and need for closely matched donors SCD requires ongoing medical attention Encompasses hospitalization, ER and urgent care visits, pain medication Problems with Current Standard of Care No Treatment for SCD Approved by FDA Since 1990s
Oral Daily Maintenance Therapy Reduce oxidant damage to RBC through PGLG PGLG therapy was found to improve NAD Redox Potential thus reducing oxidant stress Up to 30 grams daily as a powder typically dissolved in liquid Our Approach
Emmaus Hydroxyurea Bone Marrow Transplant Acute Treatments Stem Cell Treatments Small Molecule** Availability - Adults Completed Phase 3 Approved since 1998 Limited in use due to lack of closely matched donors Leading candidates in Phase 3 Leading candidates in Phase 1/2 Phase 1/2 Availability - Pediatrics Completed Phase 3 Not approved Limited in use due to lack of closely matched donors Leading candidates in Phase 3 Leading candidates in Phase 1/2 Current trial does not cover pediatrics Ease of Administration Oral Oral Complex surgical procedure Complex surgical procedures Complex surgical procedures Oral Cost Affordable treatment with potential for strong margins Requires blood monitoring High cost Unknown Unknown Unknown Safety Strong safety results from 48-week trial Significant toxicities High risk of complications including graft vs. host disease, infection and death Unknown Unknown Have only done 28-day safety trial Will Treatment Reduce Future Sickle Cell Crises Yes, based on Phase 3 results Unknown Unknown Unknown Unknown Unknown Emmaus’ Advantages* * As of April 2016 / ** Global Blood Therapeutics
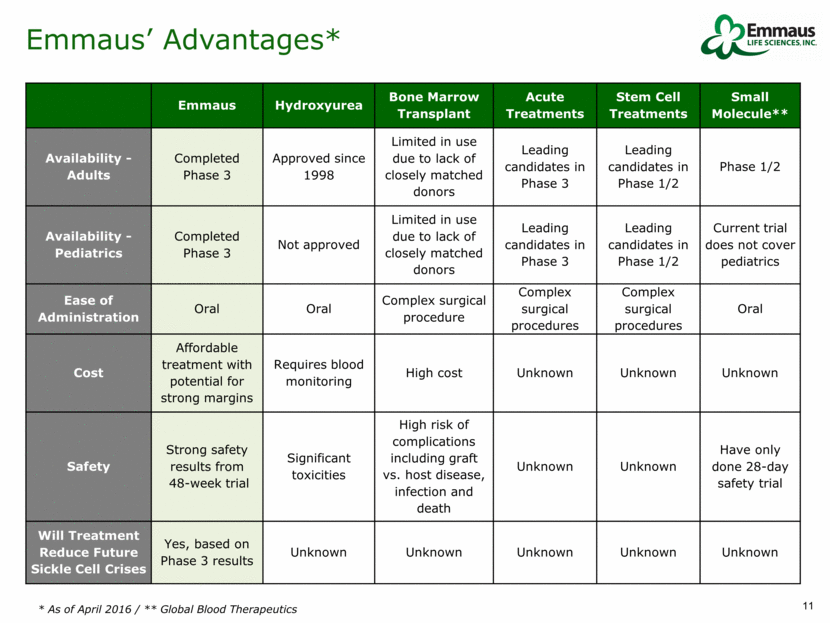
Phase 3 Results Reductions in Frequency and Severity of Crises Median reduction in frequency of crises from 4 to 3* Crises reductions achieved despite 2/3 of patients being on Hydroxyurea therapy Median reduction in frequency of hospitalization from 3 to 2** Decrease in the Severity of Sickle Cell Crises Primary Endpoint Secondary Endpoint Additional Analysis Decrease in the frequency of sickle cell crises Decrease in the frequency of hospitalization Decrease in the cumulative days in hospital Less incidence of acute chest syndrome Delay in the onset of first sickle cell crises Difference between treatment and placebo arms 25% 33% 41% 58% 61% Strong safety and efficacy results represent a compelling risk/benefit profile * Niihara Y., et al. A Phase 3 Study of L-Glutamine Therapy for Sickle Cell Anemia and Sickle ß0-Thalassemia. Blood 2014 124:86; Dec. 5, 2014 * * Niihara Y., et al. Decrease in the Severity of Painful Sickle Cell Crises with Oral Pglg. Blood 2015 126:2175; Dec. 4, 2015
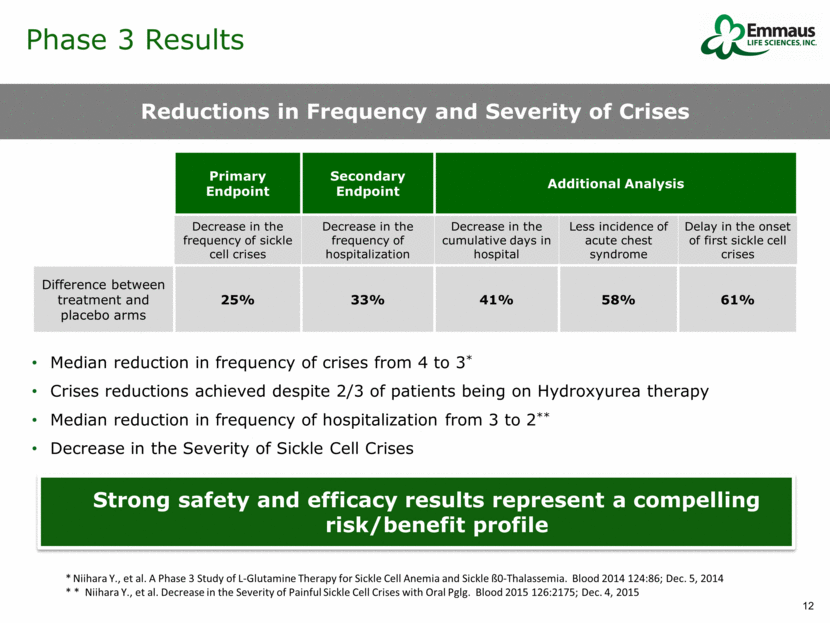
Phase 3 Results Treatment benefited male and female patients Treatment benefited adult and pediatric patients Patients on hydroxyurea showed improvement Serious adverse events were similar between the two groups Subgroups All Show Statistical Significance Phase 3 Subgroups* L-glutamine (n) Placebo (n) P-value* Hydroxyurea use 101 52 < 0.001 No hydroxyurea use 51 26 < 0.001 Male 73 33 < 0.001 Female 79 45 < 0.001 Age < 18 years 75 43 < 0.001 Age > 18 years 77 35 0.001 *P-values are from the Fisher Exact Test * Efficacy analyses of the primary endpoint by key patient subgroups
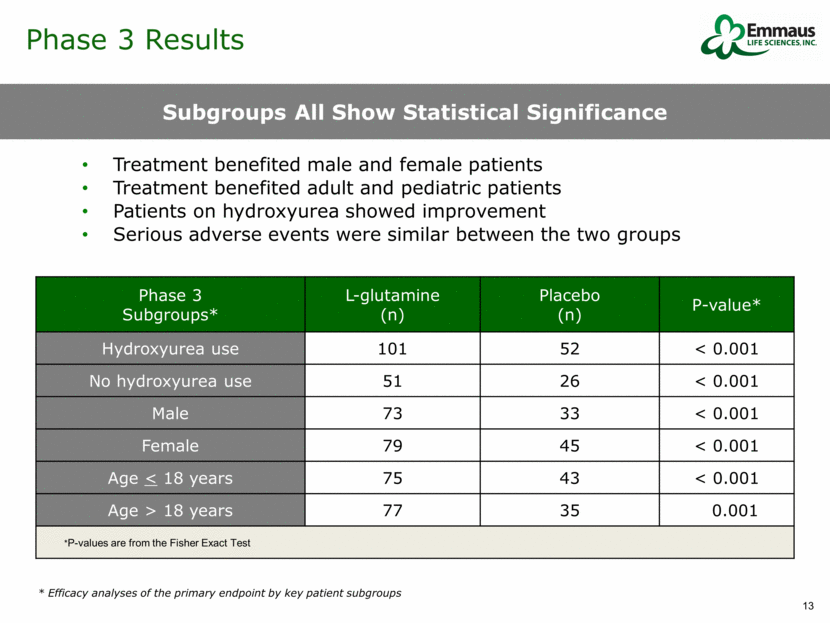
Phase 3 Results Sensitivity Analysis of Number of Sickle Cell Crises and Impact of Ranking Method Primary endpoint for frequency of sickle cell crises was statistically significant Secondary endpoint for frequency of hospitalizations was statistically significant Although Emmaus committed to using Modified Ridit in the end of Phase 2 meetings, the results initially reported to the FDA did not include the Modified Ridit score. A report has been sent to the FDA to correct this. The report was authored by an independent statistician documenting the statistical significance of our data. All P-values above are from the CMH test statistic controlling for hydroxyurea use & region Primary Endpoint P-value Results CMH Statistical Method Used in Test Modified Ridit Ridit Table Rank Number of Sickle Cell Crises p = 0.005 p = 0.005 p = 0.031 p = 0.063
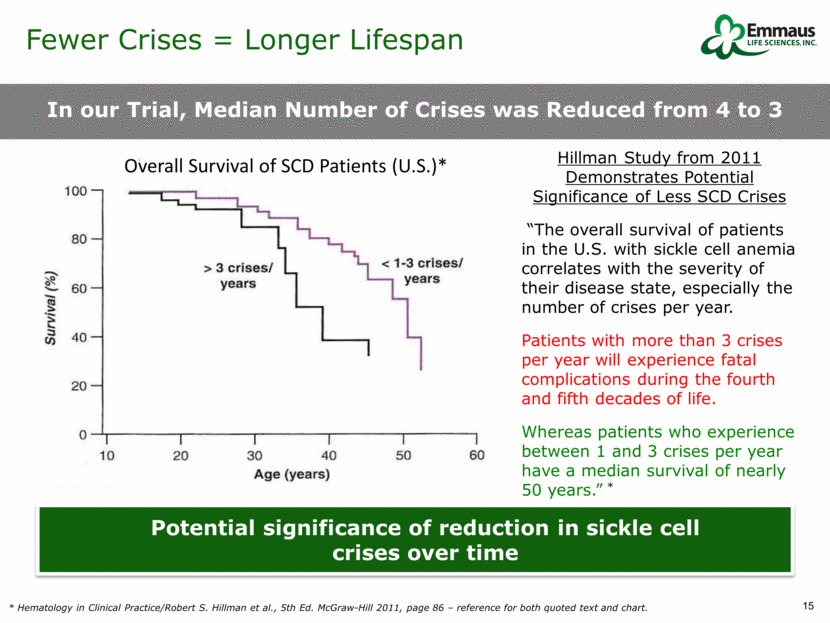
In our Trial, Median Number of Crises was Reduced from 4 to 3 * Hematology in Clinical Practice/Robert S. Hillman et al., 5th Ed. McGraw-Hill 2011, page 86 – reference for both quoted text and chart. Hillman Study from 2011 Demonstrates Potential Significance of Less SCD Crises “The overall survival of patients in the U.S. with sickle cell anemia correlates with the severity of their disease state, especially the number of crises per year. Patients with more than 3 crises per year will experience fatal complications during the fourth and fifth decades of life. Whereas patients who experience between 1 and 3 crises per year have a median survival of nearly 50 years.” * Potential significance of reduction in sickle cell crises over time Fewer Crises = Longer Lifespan Overall Survival of SCD Patients (U.S.)*
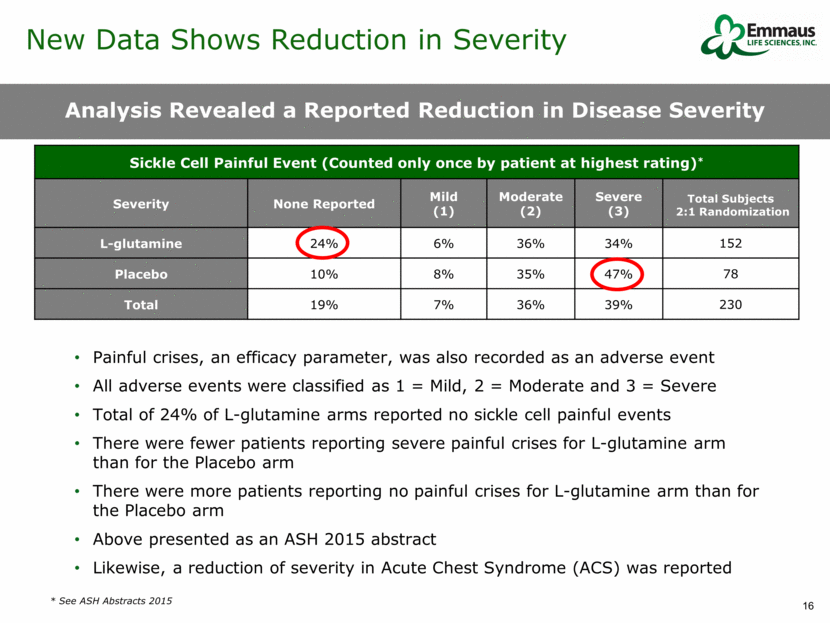
Analysis Revealed a Reported Reduction in Disease Severity * See ASH Abstracts 2015 Sickle Cell Painful Event (Counted only once by patient at highest rating)* Severity None Reported Mild (1) Moderate (2) Severe (3) Total Subjects 2:1 Randomization L-glutamine 24% 6% 36% 34% 152 Placebo 10% 8% 35% 47% 78 Total 19% 7% 36% 39% 230 Painful crises, an efficacy parameter, was also recorded as an adverse event All adverse events were classified as 1 = Mild, 2 = Moderate and 3 = Severe Total of 24% of L-glutamine arms reported no sickle cell painful events There were fewer patients reporting severe painful crises for L-glutamine arm than for the Placebo arm There were more patients reporting no painful crises for L-glutamine arm than for the Placebo arm Above presented as an ASH 2015 abstract Likewise, a reduction of severity in Acute Chest Syndrome (ACS) was reported New Data Shows Reduction in Severity
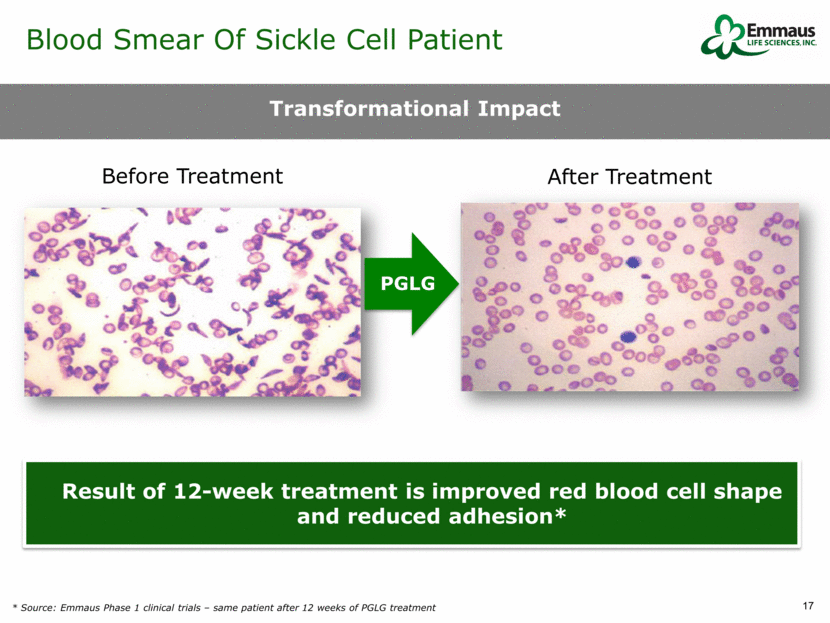
PGLG Result of 12-week treatment is improved red blood cell shape and reduced adhesion* Before Treatment After Treatment Transformational Impact Blood Smear Of Sickle Cell Patient * Source: Emmaus Phase 1 clinical trials – same patient after 12 weeks of PGLG treatment.
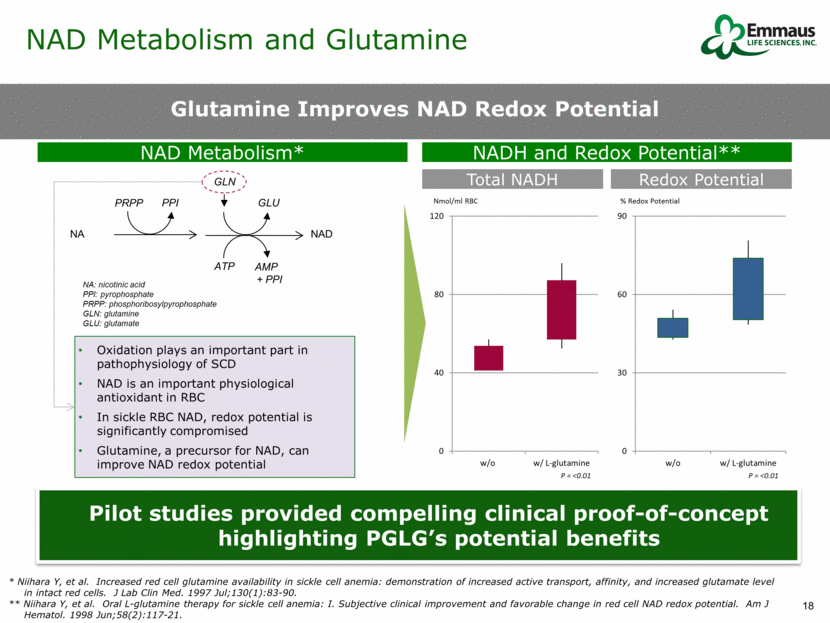
Glutamine Improves NAD Redox Potential NA PRPP PPI GLU GLN ATP AMP + PPI NAD NA: nicotinic acid PPI: pyrophosphate PRPP: phosphoribosylpyrophosphate GLN: glutamine GLU: glutamate NADH and Redox Potential** Oxidation plays an important part in pathophysiology of SCD NAD is an important physiological antioxidant in RBC In sickle RBC NAD, redox potential is significantly compromised Glutamine, a precursor for NAD, can improve NAD redox potential NAD Metabolism* Total NADH Redox Potential Nmol/ml RBC % Redox Potential P = <0.01 Pilot studies provided compelling clinical proof-of-concept highlighting PGLG’s potential benefits P = <0.01 NAD Metabolism and Glutamine * Niihara Y, et al. Increased red cell glutamine availability in sickle cell anemia: demonstration of increased active transport, affinity, and increased glutamate level in intact red cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1997 Jul;130(1):83-90. ** Niihara Y, et al. Oral L-glutamine therapy for sickle cell anemia: I. Subjective clinical improvement and favorable change in red cell NAD redox potential. Am J Hematol. 1998 Jun;58(2):117-21. 0 30 60 90 w/o w/ L-glutamine 0 40 80 120 w/o w/ L-glutamine
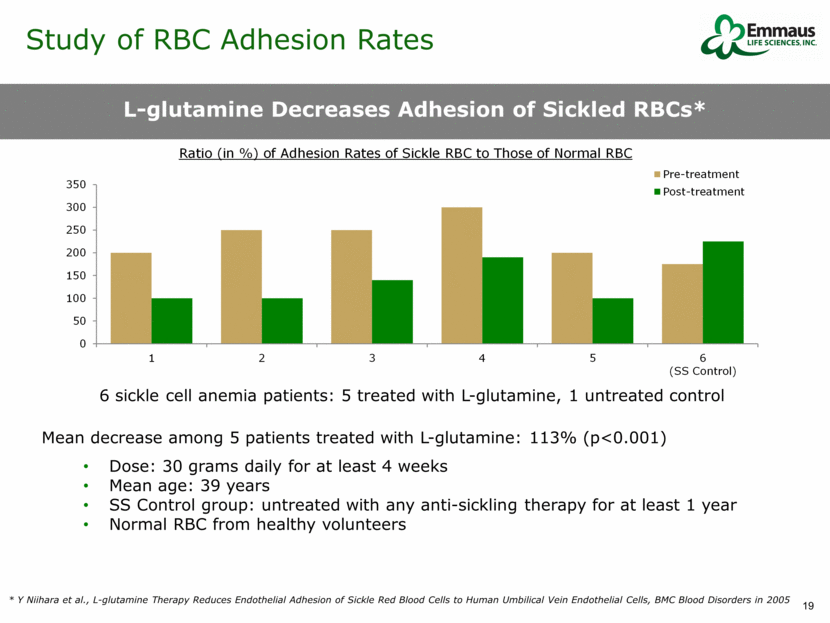
L-glutamine Decreases Adhesion of Sickled RBCs* Mean decrease among 5 patients treated with L-glutamine: 113% (p<0.001) Dose: 30 grams daily for at least 4 weeks Mean age: 39 years SS Control group: untreated with any anti-sickling therapy for at least 1 year Normal RBC from healthy volunteers 6 sickle cell anemia patients: 5 treated with L-glutamine, 1 untreated control * Y Niihara et al., L-glutamine Therapy Reduces Endothelial Adhesion of Sickle Red Blood Cells to Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells, BMC Blood Disorders in 2005 Study of RBC Adhesion Rates 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 1 2 3 4 5 6 (SS Control) Ratio (in %) of Adhesion Rates of Sickle RBC to Those of Normal RBC Pre-treatment Post-treatment
Looking Forward 3Q16 1Q17 NDA Filing Summer 2016 Potential Product Approval as Early as 2017 4Q16 2Q17 Planning for a U.S. commercial launch in 2017; Currently exploring partnership opportunities outside U.S. We plan to submit an NDA based on Phase 2 and Phase 3 results If approved, we anticipate: First FDA approved treatment ever for pediatric patients with SCD First new FDA approved treatment for adults with SCD in nearly 20 years NDA and Commercial Launch

Cross Over Product Successes Lovaza (pharmaceutical grade fish oil) Launched in late 2005 by Reliant Pharmaceuticals in the U.S. Nine months ended September 2007, net sales were $206 million GSK acquired Reliant in December 2007 for $1.65 billion GSK had over $1 billion in Lovaza sales last year Niaspan (pharmaceutical grade niacin – vitamin B3) Developed and commercialized by Kos Pharmaceuticals Approved for sale in 1997 Abbott acquired Kos in 2006 for $3.4 billion Between 1997 - 2012 Niaspan generated over $5 billion in sales Carnitor (pharmaceutical grade L-carnitine) Approved by FDA & launched in 1989 by Sigma-Tau Additional follow-on FDA approvals in 1999, 2007 A Strong Precedent Exists for Crossover Pharmaceuticals

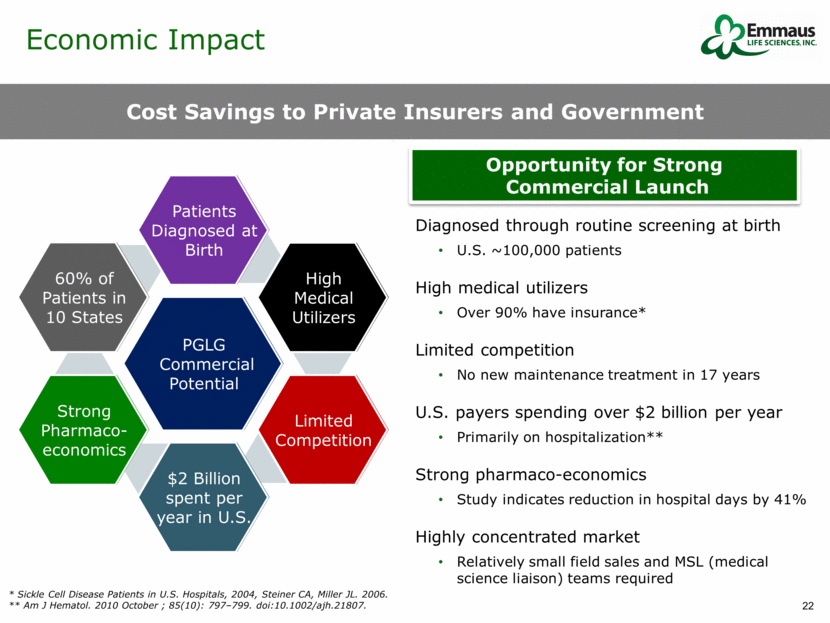
Economic Impact Cost Savings to Private Insurers and Government Diagnosed through routine screening at birth U.S. ~100,000 patients High medical utilizers Over 90% have insurance* Limited competition No new maintenance treatment in 17 years U.S. payers spending over $2 billion per year Primarily on hospitalization** Strong pharmaco-economics Study indicates reduction in hospital days by 41% Highly concentrated market Relatively small field sales and MSL (medical science liaison) teams required PGLG Commercial Potential Patients Diagnosed at Birth High Medical Utilizers Limited Competition $2 Billion spent per year in U.S. Strong Pharmaco- economics 60% of Patients in 10 States Opportunity for Strong Commercial Launch * Sickle Cell Disease Patients in U.S. Hospitals, 2004, Steiner CA, Miller JL. 2006. ** Am J Hematol. 2010 October ; 85(10): 797–799. doi:10.1002/ajh.21807.
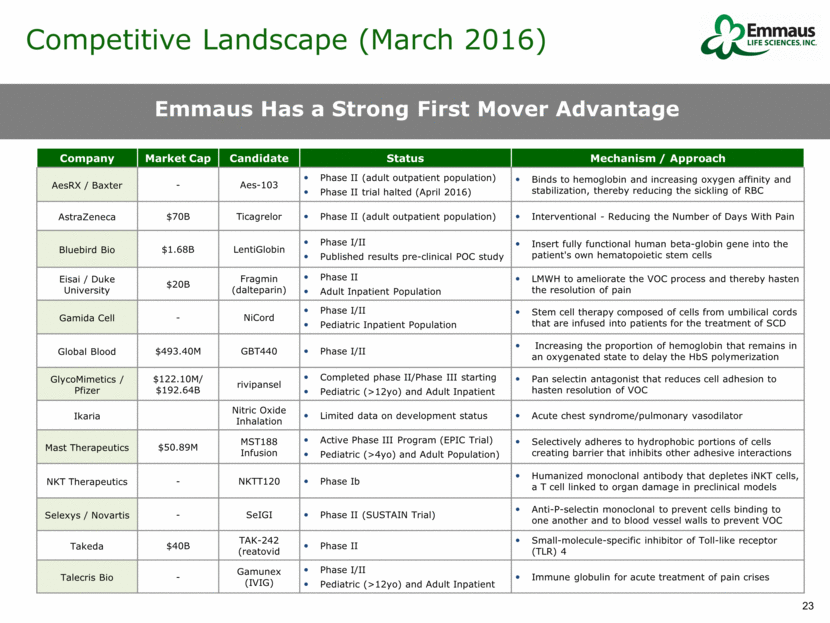
Competitive Landscape (March 2016) Company Market Cap Candidate Status Mechanism / Approach AesRX / Baxter - Aes-103 Phase II (adult outpatient population) Phase II trial halted (April 2016) Binds to hemoglobin and increasing oxygen affinity and stabilization, thereby reducing the sickling of RBC AstraZeneca $70B Ticagrelor Phase II (adult outpatient population) Interventional - Reducing the Number of Days With Pain Bluebird Bio $1.68B LentiGlobin Phase I/II Published results pre-clinical POC study Insert fully functional human beta-globin gene into the patient's own hematopoietic stem cells Eisai / Duke University $20B Fragmin (dalteparin) Phase II Adult Inpatient Population LMWH to ameliorate the VOC process and thereby hasten the resolution of pain Gamida Cell - NiCord Phase I/II Pediatric Inpatient Population Stem cell therapy composed of cells from umbilical cords that are infused into patients for the treatment of SCD Global Blood $493.40M GBT440 Phase I/II Increasing the proportion of hemoglobin that remains in an oxygenated state to delay the HbS polymerization GlycoMimetics / Pfizer $122.10M/ $192.64B rivipansel Completed phase II/Phase III starting Pediatric (>12yo) and Adult Inpatient Pan selectin antagonist that reduces cell adhesion to hasten resolution of VOC Ikaria Nitric Oxide Inhalation Limited data on development status Acute chest syndrome/pulmonary vasodilator Mast Therapeutics $50.89M MST188 Infusion Active Phase III Program (EPIC Trial) Pediatric (>4yo) and Adult Population) Selectively adheres to hydrophobic portions of cells creating barrier that inhibits other adhesive interactions NKT Therapeutics - NKTT120 Phase Ib Humanized monoclonal antibody that depletes iNKT cells, a T cell linked to organ damage in preclinical models Selexys / Novartis - SeIGI Phase II (SUSTAIN Trial) Anti-P-selectin monoclonal to prevent cells binding to one another and to blood vessel walls to prevent VOC Takeda $40B TAK-242 (reatovid Phase II Small-molecule-specific inhibitor of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 Talecris Bio - Gamunex (IVIG) Phase I/II Pediatric (>12yo) and Adult Inpatient Immune globulin for acute treatment of pain crises Emmaus Has a Strong First Mover Advantage
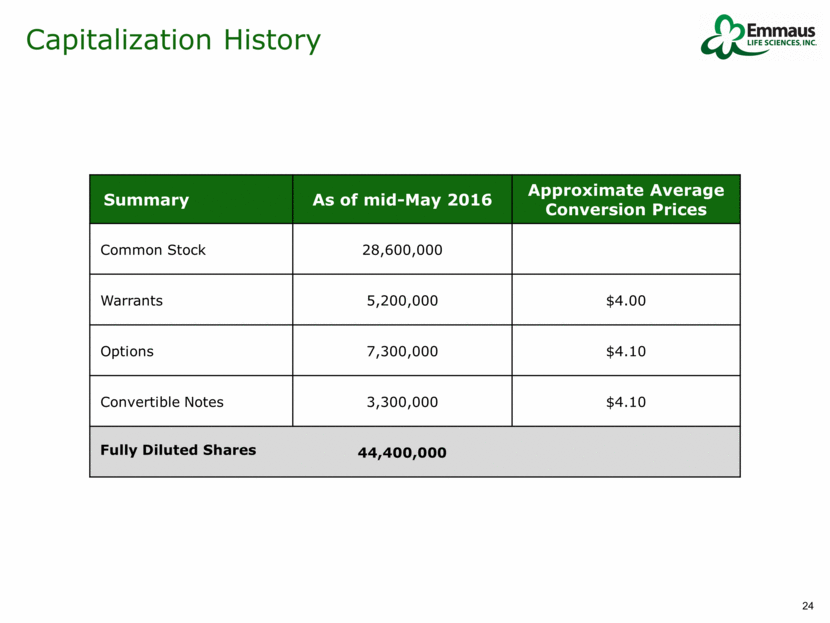
Summary As of mid-May 2016 Approximate Average Conversion Prices Common Stock 28,600,000 Warrants 5,200,000 $4.00 Options 7,300,000 $4.10 Convertible Notes 3,300,000 $4.10 Fully Diluted Shares 44,400,000 Capitalization History