Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EXCEL - IDEA: XBRL DOCUMENT - DAVEY TREE EXPERT CO | Financial_Report.xls |
| EX-21 - EXHIBIT 21 - DAVEY TREE EXPERT CO | davey123114ex21.htm |
| EX-23 - EXHIBIT 23 - DAVEY TREE EXPERT CO | davey123114ex23.htm |
| EX-10.8 - EXHIBIT 10.8 - DAVEY TREE EXPERT CO | davey123114ex108.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - DAVEY TREE EXPERT CO | davey123114ex312.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - DAVEY TREE EXPERT CO | davey123114ex322.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - DAVEY TREE EXPERT CO | davey123114ex311.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - DAVEY TREE EXPERT CO | davey123114ex321.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
x ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2014
OR
¨ TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from ______________ to ______________
Commission file number 000-11917

THE DAVEY TREE EXPERT COMPANY
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Ohio | 34-0176110 |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
1500 North Mantua Street
P.O. Box 5193
Kent, Ohio 44240
(Address of principal executive offices) (Zip code)
(330) 673-9511
(Registrant's telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
None
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
Common Shares, $1.00 par value
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer (as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act). Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T(§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
(Check one): Large Accelerated Filer ¨ Accelerated Filer x Non-Accelerated Filer ¨ Smaller Reporting Company ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ¨ No x
There were 13,168,800 Common Shares outstanding as of February 27, 2015. The aggregate market value of the Common Shares held by nonaffiliates of the registrant as of July 1, 2014 was $330,928,487. For purposes of this calculation, it is assumed that the registrant's affiliates include the registrant's Board of Directors and its executive officers.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant's definitive Proxy Statement for the 2015 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, to be held on May 19, 2015, are incorporated by reference into Part III (to be filed within 120 calendar days of the registrant’s fiscal year end).
Page 1
NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This annual report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements (within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995) in "Item 7 - Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," "Item 7A - Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk," and elsewhere. These statements relate to future events or our future financial performance. In some cases, forward-looking statements may be identified by terminology such as "may," "will," "should," "expects," "plans," "anticipates," "believes," "estimates," "predicts," "potential," "continue" or the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology. These statements are only predictions and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause our or our industry's actual results, levels of activity, performance or achievements to differ materially from what is expressed or implied in these forward-looking statements. Some important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those in the forward-looking statements include:
▪ | Our business, other than tree services to utility customers, is highly seasonal and weather dependent. |
▪ | The effects of the uneven economic recovery and the continuing financial and credit uncertainties may adversely impact our customers’ spending and pricing for our services, and impede our collection of accounts receivable. |
▪ | Significant customers, particularly utilities, may experience financial difficulties, resulting in payment delays or delinquencies. |
▪ | The seasonal nature of our business and changes in general and local economic conditions, among other factors, may cause our quarterly results to fluctuate, and our prior performance is not necessarily indicative of future results. |
▪ | The uncertainties in the credit and financial markets may limit our access to capital. |
▪ | Significant increases in fuel prices for extended periods of time will increase our operating expenses. |
▪ | We have significant contracts with our utility, commercial and government customers that include liability risk exposure as part of those contracts. Consequently, we have substantial excess-umbrella liability insurance, and increases in the cost of obtaining adequate insurance, or the inadequacy of our self-insurance accruals or insurance coverages, could negatively impact our liquidity and financial condition. |
▪ | Because no public market exists for our common shares, the ability of shareholders to sell their common shares is limited. |
▪ | We are subject to intense competition. |
▪ | Our failure to comply with environmental laws could result in significant liabilities, fines and/or penalties. |
▪ | The impact of regulations initiated as a response to possible changing climate conditions could have a negative effect on our results of operations or our financial condition. |
▪ | We may encounter difficulties obtaining surety bonds or letters of credit necessary to support our operations. |
▪ | We are dependent, in part, on our reputation of quality, integrity and performance. If our reputation is damaged, we may be adversely affected. |
▪ | We may be unable to attract and retain a sufficient number of qualified employees for our field operations, and we may be unable to attract and retain qualified management personnel. |
▪ | Our facilities could be damaged or our operations could be disrupted, or our customers or vendors may be adversely affected, by events such as natural disasters, pandemics, terrorist attacks or other external events. |
▪ | We are subject to third-party and governmental regulatory claims and litigation that may have an adverse effect on us. |
▪ | We may misjudge a competitive bid and be contractually bound to an unprofitable contract. |
Although we believe that the expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee future results, levels of activity, performance or achievements. We are under no duty to update any of the forward-looking statements after the date of this annual report on Form 10-K to conform these statements to actual future results.
Page 2
THE DAVEY TREE EXPERT COMPANY FORM 10-K For the Year Ended December 31, 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS | |
Page | |
PART I | |
PART II | |
PART III | |
PART IV | |
“We,” “Us,” “Our,” “Davey” and “Davey Tree,” unless the context otherwise requires, means The Davey Tree Expert Company and its subsidiaries.
Page 3
PART I
Item 1. Business.
General
The Davey Tree Expert Company, which was founded in 1880 and incorporated in Ohio in 1909, and its subsidiaries ("we" or "us") provides a wide range of arboriculture, horticulture, environmental and consulting services to our customers throughout the United States and Canada. We have two reportable operating segments organized by type or class of customer: Residential and Commercial, and Utility.
Our Residential and Commercial segment provides services to our residential and commercial customers including: the treatment, preservation, maintenance, removal, planting of trees, shrubs and other plant life; the practice of landscaping, grounds maintenance, tree surgery, tree feeding and tree spraying; the application of fertilizer, herbicides and insecticides; and, natural resource management and consulting, forestry research and development, and environmental planning.
Our Utility segment is principally engaged in providing services to our utility customers--investor-owned, municipal utilities, and rural electric cooperatives--including: the practice of line-clearing and vegetation management around power lines, rights-of-way and chemical brush control; and, natural resource management and consulting, forestry research and development and environmental planning.
We also maintain research, technical support and laboratory diagnostic facilities.
Competition and Customers
Our Residential and Commercial segment is one of the largest national tree care organizations in the United States, and competes with other national and local firms with respect to its services. On a national level, our competition is primarily landscape construction and maintenance companies as well as residential and commercial lawn care companies. At a local and regional level, our competition comes mainly from small, local companies which are engaged primarily in tree care and lawn services. Our Utility segment is the second largest organization in the industry in the United States, and competes principally with one major national competitor, as well as several smaller regional firms.
Principal methods of competition in both operating segments are customer service, marketing, image, performance and reputation. Our program to meet our competition stresses the necessity for our employees to have and project to customers a thorough knowledge of all horticultural services provided, and utilization of modern, well-maintained equipment. Pricing is not always a critical factor in a customer's decision with respect to Residential and Commercial segment; however, pricing is generally the principal method of competition for our Utility segment, although in most instances consideration is given to reputation and past production performance.
We provide a wide range of horticultural services to private companies, public utilities, local, state and federal agencies, and a variety of industrial, commercial and residential customers. During 2014, we had revenues of approximately $66 million, or approximately 8% of total revenues, from Pacific Gas & Electric Company ("PG&E"), one of our largest customers.
Regulation and Environment
Our facilities and operations, in common with those of the industry generally, are subject to governmental regulations designed to protect the environment. This is particularly important with respect to our services regarding insect and disease control, because these services involve to a considerable degree the blending and application of spray materials, which require formal licensing in most areas. Constant changes in environmental conditions, environmental awareness, technology and social attitudes make it necessary for us to maintain a high degree of awareness of the impact such changes have on the market for our services. We believe that we comply in all material respects with existing federal, state and local laws regulating the use of materials in our spraying operations as well as the other aspects of our business that are subject to any such regulation.
Marketing
We solicit business from residential customers principally through referrals, direct mail programs and to a lesser extent through the placement of advertisements in national magazines and trade journals, local newspapers and "yellow pages" telephone directories. We also employ online marketing and lead generation strategies including email marketing campaigns, search engine optimization, search engine marketing, and social media communication. Business from utility and commercial
Page 4
customers is obtained principally through negotiated contracts and competitive bidding. We carry out all of our sales and services through our employees. We generally do not use agents, and do not franchise our name or business.
Seasonality
Our business is seasonal, primarily due to fluctuations in horticultural services provided to Residential and Commercial customers and to a lesser extent by budget constraints imposed on our Utility customers. Because of this seasonality, we have historically incurred losses in the first quarter, while sales and earnings are generally highest in the second and third quarters of the calendar year. Consequently, this has created heavy demands for additional working capital at various times throughout the year. We borrow primarily against bank commitments in the form of a revolving credit facility to provide the necessary funds for our operations. You can find more information about our bank commitments in “Liquidity and Capital Resources” under “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” on pages 24-25 of this report.
Other Factors
Due to rapid changes in equipment technology and intensity of use, we must constantly update our equipment and processes to ensure that we provide competitive services to our customers and continue our compliance with the Occupational Safety and Health Act.
We own several trademarks including "Davey," "Davey and Design," "Arbor Green Pro," "Arbor Green," and "Davey Resource Group." Through substantial advertising and use, we believe that these trademarks have become of value in the identification and acceptance of our products and services.
Employees
We employed approximately 7,600 employees at December 31, 2014. However, employment levels fluctuate due to seasonal factors affecting our business. We consider our employee relations to be good.
Domestic and Foreign Operations
We sell our services to customers in the United States and Canada.
We do not consider the risks attendant to our business with foreign customers, other than currency exchange risks, to be materially different from those attendant to our business with domestic customers.
Financial Information About Segments and Geographic Areas
Certain financial information regarding our operations by segment and geographic area is contained in Note S to our consolidated financial statements, which are included in Part II, Item 8 of this report.
Access to Company Information
Davey Tree’s internet address is http://www.davey.com. Through our internet website, by hyperlink to the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) website (http://www.sec.gov), we make available, free of charge, our Annual Report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and all amendments to those reports. Availability of the reports occurs contemporaneously with the electronic posting to the SEC’s website as the reports are electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC. The information on our website is not a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The following documents are also made available on our website and a copy will be mailed, without charge, upon request to our Corporate Secretary:
▪ | Code of Ethics |
▪ | Code of Ethics for Financial Matters |
Item 1A. Risk Factors.
The factors described below represent the principal risks we face. Except as otherwise indicated, these factors may or may not occur and we are not in a position to express a view on the likelihood of any such factor occurring. Other factors may exist that we do not consider to be significant based on information that is currently available or that we are not currently able to anticipate.
Page 5
Our business is highly seasonal and weather dependent.
Our business, other than tree services to utility customers, is highly seasonal and weather dependent, primarily due to fluctuations in horticultural services provided to Residential and Commercial customers. We have historically incurred losses in the first quarter, while revenue and operating income are generally highest in the second and third quarters of the calendar year. Inclement weather, such as uncharacteristically low or high (drought) temperatures, in the second and third quarters could dampen the demand for our horticultural services, resulting in reduced revenues that would have an adverse effect on our results of operations.
The effects of the unpredictable economic recovery and the continuing financial and credit uncertainties may adversely impact our customers’ future spending as well as pricing and payment for our services, thus negatively impacting our operations and growth.
While the economy has shown signs of improvement, sustainability of economic recovery remains uncertain. A slowing or stoppage in economic recovery may adversely impact the demand for our services and potentially result in depressed prices for our services and the delay or cancellation of projects. This makes it difficult to estimate our customers' requirements for our services and, therefore, adds uncertainty to customer demand. Increased uncertainty about the economy may cause a reduction in our customers' spending for our services and may also impact the ability of our customers to pay amounts owed, which could reduce our cash flow and adversely impact our debt or equity financing. These events could have a material adverse effect on our operations and our ability to grow at historical levels.
Financial difficulties or the bankruptcy of one or more of our major customers could adversely affect our results.
Our ability to collect our accounts receivable and future sales depends, in part, on the financial strength of our customers. We grant credit, generally without collateral, to our customers. Consequently, we are subject to credit risk related to changes in business and economic factors throughout the United States and Canada. In the event customers experience financial difficulty, and particularly if bankruptcy results, our profitability may be adversely impacted by our failure to collect our accounts receivable in excess of our estimated allowance for uncollectible accounts. Additionally, our future revenues could be reduced by the loss of a customer due to bankruptcy. Our failure to collect accounts receivable and/or the loss of one or more major customers could have an adverse effect on our net income and financial condition.
Our business is dependent upon service to our utility customers and we may be affected by developments in the utility industry.
We derive approximately 51% of our total revenues from our Utility segment. Significant adverse developments in the utility industry generally, or specifically for our major utility customers, could result in pressure to reduce costs by utility industry service providers (such as us), delays in payments of our accounts receivable, or increases in uncollectible accounts receivable, among other things. As a result, such developments could have an adverse effect on our results of operations.
Our quarterly results may fluctuate.
We have experienced and expect to continue to experience quarterly variations in revenues and operating income as a result of many factors, including:
▪ | the seasonality of our business; |
▪ | the timing and volume of customers' projects; |
▪ | budgetary spending patterns of customers; |
▪ | the commencement or termination of service agreements; |
▪ | costs incurred to support growth internally or through acquisitions; |
▪ | changes in our mix of customers, contracts and business activities; |
▪ | fluctuations in insurance expense due to changes in claims experience and actuarial assumptions; and |
▪ | general and local economic conditions. |
Accordingly, our operating results in any particular quarter may not be indicative of the results that you can expect for any other quarter or for the entire year.
Page 6
We may not have access to capital in the future due to continuing uncertainties in the financial and credit markets.
We may need new or additional financing in the future to conduct our operations, expand our business or refinance existing indebtedness. Continued weakness in the general economic conditions and/or financial markets in the United States or globally could affect adversely our ability to raise capital on favorable terms or at all. From time-to-time we have relied, and may also rely in the future, on access to financial markets as a source of liquidity for working capital requirements, acquisitions and general corporate purposes. Our access to funds under our revolving credit facility is dependent on the ability of the financial institutions that are parties to the facility to meet their funding commitments. Those financial institutions may not be able to meet their funding commitments if they experience shortages of capital and liquidity or if they experience excessive volumes of borrowing requests within a short period of time. The continuation of economic disruptions and any resulting limitations on future funding, including any restrictions on access to funds under our revolving credit facility, could have a material adverse effect on us.
We are subject to the risk of changes in fuel costs.
The cost of fuel is a major operating expense of our business. Significant increases in fuel prices for extended periods of time will cause our operating expenses to fluctuate. An increase in cost with partial or no corresponding compensation from customers would lead to lower margins that would have an adverse effect on our results of operations.
We could be negatively impacted if our self-insurance accruals or our insurance coverages prove to be inadequate.
We are generally self-insured for losses and liabilities related to workers' compensation, vehicle liability and general liability claims (including any wild fire-related claims, up to certain retained coverage limits). A liability for unpaid claims and associated expenses, including incurred but not reported losses, is actuarially determined and reflected in our consolidated balance sheet as an accrued liability. The determination of such claims and expenses, and the extent of the need for accrued liabilities, are continually reviewed and updated. If we were to experience insurance claims or costs above our estimates and were unable to offset such increases with earnings, our business could be adversely affected. Also, where we self-insure, a deterioration in claims management, whether by our management or by a third-party claims administrator, could lead to delays in settling claims, thereby increasing claim costs, particularly as it relates to workers’ compensation. In addition, catastrophic uninsured claims filed against us or the inability of our insurance carriers to pay otherwise-insured claims would have an adverse effect on our financial condition.
Furthermore, many customers, particularly utilities, prefer to do business with contractors with significant financial resources, who can provide substantial insurance coverage. Should we be unable to renew our excess liability insurance and other commercial insurance policies at competitive rates, this loss would have an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
The unavailability or cancellation of third-party insurance coverage may have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations as well as disrupt our operations.
Any of our existing excess insurance coverage may not be renewed upon the expiration of the coverage period or future coverage may not be available at competitive rates for the required limits. In addition, our third-party insurers could fail, suddenly cancel our coverage or otherwise be unable to provide us with adequate insurance coverage. If any of these events occur, they may have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations as well as disrupt our operations. For example, we have operations in California, which has an environment prone to wildfires. Should our third-party insurers determine to exclude coverage for wildfires in the future, we could be exposed to significant liabilities, having a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations and potentially disrupting our California operations.
Because no public market exists for our common shares, your ability to sell your common shares may be limited.
Our common shares are not traded on any national exchange, market system or over-the-counter bulletin board. Because no public market exists for our common shares, your ability to sell these shares is limited.
Page 7
We are subject to intense competition.
We believe that each aspect of our business is highly competitive. Principal methods of competition in our operating segments are customer service, marketing, image, performance and reputation. Pricing is not always a critical factor in a customer’s decision with respect to Residential and Commercial; however, pricing is generally the principal method of competition for Utility, although in most instances consideration is given to reputation and past production performance. On a national level, our competition is primarily landscape construction and maintenance companies as well as residential and commercial lawn care companies. At a local and regional level, our competition comes mainly from small, local companies which are engaged primarily in tree care and lawn services. Our Utility segment competes principally with one major national competitor, as well as several smaller regional firms. Furthermore, competitors may have lower costs because privately-owned companies operating in a limited geographic area may have significantly lower labor and overhead costs. Our competitors may develop the expertise, experience and resources to provide services that are superior in both price and quality to our services. These strong competitive pressures could inhibit our success in bidding for profitable business and may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our failure to comply with environmental laws could result in significant liabilities.
Our facilities and operations are subject to governmental regulations designed to protect the environment, particularly with respect to our services regarding insect and tree, shrub and lawn disease management, because these services involve to a considerable degree the blending and application of spray materials, which require formal licensing in most areas. Continual changes in environmental laws, regulations and licensing requirements, environmental conditions, environmental awareness, technology and social attitudes make it necessary for us to maintain a high degree of awareness of the impact such changes have on our compliance programs and the market for our services. We are subject to existing federal, state and local laws, regulations and licensing requirements regulating the use of materials in our spraying operations as well as certain other aspects of our business. If we fail to comply with such laws, regulations or licensing requirements, we may become subject to significant liabilities, fines and/or penalties, which could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
We cannot predict the impact that the debate on changing climate conditions, including legal, regulatory and social responses thereto, may have on our business.
Many scientists, environmentalists, international organizations, political activists, regulators and other commentators believe that global climate change has added, and will continue to add, to the unpredictability, frequency and severity of natural disasters in certain parts of the world. In response, a number of legal and regulatory measures and social initiatives have been introduced in an effort to reduce greenhouse gas and other carbon emissions that these parties believe may be contributors to global climate change. These proposals, if enacted, could result in a variety of regulatory programs, including potential new regulations, additional charges and taxes to fund energy efficiency activities, or other regulatory actions. Any of these actions could result in increased costs associated with our operations and impact the prices we charge our customers.
We cannot predict the impact, if any, that changing climate conditions will have on us or our customers. However, it is possible that the legal, regulatory and social responses to real or imagined climate change could have a negative effect on our results of operations or our financial condition.
We may be adversely affected if we are unable to obtain necessary surety bonds or letters of credit.
Surety market conditions are currently difficult as a result of significant losses incurred by many sureties in recent years, both in the construction industry as well as in certain larger corporate bankruptcies. As a result, less bonding capacity is available in the market and terms have become more expensive and restrictive. Further, under standard terms in the surety market, sureties issue or continue bonds on a project-by-project basis and can decline to issue bonds at any time or require the posting of collateral as a condition to issuing or renewing any bonds. If surety providers were to limit or eliminate our access to bonding, we would need to post other forms of collateral for project performance, such as letters of credit or cash. We may be unable to secure sufficient letters of credit on acceptable terms, or at all. Accordingly, if we were to experience an interruption or reduction in the availability of bonding capacity, our liquidity may be adversely affected.
We may be adversely affected if our reputation is damaged.
We are dependent, in part, upon our reputation of quality, integrity and performance. If our reputation were damaged in some way, it may impact our ability to grow or maintain our business.
Page 8
We may be unable to employ a sufficient workforce for our field operations.
Our industry operates in an environment that requires heavy manual labor. We may experience slower growth in the labor force for this type of work than in the past. As a result, we may experience labor shortages or the need to pay more to attract and retain qualified employees.
We may be unable to attract and retain skilled management.
Our success depends, in part, on our ability to attract and retain key managers. Competition for the best people can be intense and we may not be able to promote, hire or retain skilled managers. The loss of services of one or more of our key managers could have a material adverse impact on our business because of the loss of the manager's skills, knowledge of our industry and years of industry experience, and the difficulty of promptly finding qualified replacement personnel.
Natural disasters, pandemics, terrorist attacks and other external events could adversely affect our business.
Natural disasters, pandemics, terrorist attacks and other adverse external events could materially damage our facilities or disrupt our operations, or damage the facilities or disrupt the operations of our customers or vendors. The occurrence of any such event could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We are subject to third-party and governmental regulatory claims and litigation.
From time-to-time, customers, vendors, employees, governmental regulatory authorities and others may make claims and take legal action against us. Whether these claims and legal actions are founded or unfounded, if such claims and legal actions are not resolved in our favor, they may result in significant financial liability. Any such financial liability could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. Any such claims and legal actions may also require significant management attention and may detract from management's focus on our operations.
We may be adversely affected if we enter into a major unprofitable contract.
Our Residential and Commercial segment and our Utility segment frequently operate in a competitive bid contract environment. As a result, we may misjudge a bid and be contractually bound to an unprofitable contract, which could adversely affect our results of operations.
Item 1B. Unresolved SEC Staff Comments.
There are no unresolved comments from the Staff of the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Item 2. Properties.
Our corporate headquarters campus is located in Kent, Ohio which, along with several other properties in the surrounding area, includes The Davey Institute's research, technical support and laboratory diagnostic facilities.
We conduct administrative functions through our headquarters and our offices in Livermore, California (Utility Services). Our Canadian operations’ administrative functions are conducted through properties located in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia. We believe our properties are well maintained, in good condition and suitable for our present operations. A summary of our properties follows:
Segment | Number of Properties | How Held | Square Footage | Number of States or Provinces | ||||
Residential and Commercial | 29 | Owned | 263,231 | 14 | ||||
Utility | 3 | Owned | 36,037 | 3 | ||||
Residential and Commercial, and Utility | 2 | Owned | 12,400 | 2 | ||||
We also rent approximately 135 properties in 29 states and three provinces.
None of our owned or rented properties used by our business segments is individually material to our operations.
Page 9
Item 3. Legal Proceedings.
We are party to a number of lawsuits, threatened lawsuits and other claims arising out of the normal course of business.
With respect to all such matters, we record an accrual for a loss contingency when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. In addition, narrative information is provided for matters as to which management believes a material loss is reasonably possible.
Management has assessed all such matters, including the matter described below, based on current information and made a judgment concerning their potential outcome, giving due consideration to the nature of the claim, the amount and nature of damages sought and the probability of success. Management's judgment is made subject to the known uncertainty of litigation and management's judgment as to estimates made may prove materially different from actual results.
California Fire Litigation: San Diego County--Davey Tree Surgery Company, a Davey subsidiary, and Davey Resource Group, a Davey division, along with the Company have previously been sued, together with a utility services customer, San Diego Gas & Electric ("SDG&E"), and its parent company, as defendants, and as cross-defendants in cross-complaints filed by SDG&E, in the Superior Court of the State of California in and for the County of San Diego, arising out of a wildfire in San Diego County that started on October 22, 2007, referred to as the Rice Canyon fire.
Numerous lawsuits related to the Rice Canyon fire were filed against SDG&E, its parent company, Sempra Energy, and Davey. The earliest of the lawsuits naming Davey was filed on April 18, 2008. The Court ordered that the lawsuits be organized into four groups based on type of plaintiff, namely insurance subrogation claimants, individual/business claimants, governmental claimants, and plaintiffs seeking class certification. Plaintiffs' motions seeking class certification were denied and the orders denying class certification were affirmed on appeal. SDG&E filed cross-complaints against Davey for contractual indemnity, declaratory relief, and breach of contract.
During the third quarter 2012, Davey entered into a Settlement and Release Agreement (the “Agreement”) among Davey, SDG&E and Davey's insurers.
Under the Agreement (a) Davey paid SDG&E an amount previously expensed and accrued as self-insurance, (b) Davey's insurers paid SDG&E amounts under Davey's insurance policies in effect during the period of the Rice Canyon fire, and (c) SDG&E dismissed its cross-complaints against Davey and agreed to defend and hold harmless Davey from any and all claims that are currently asserted against Davey.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures.
Not applicable.
Page 10
Executive Officers of the Company.
Our executive officers and their present positions and ages as of March 1, 2015 follow:
Name | Position | Age | ||
Karl J. Warnke | Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer | 63 | ||
Patrick M. Covey | President and Chief Operating Officer, U.S. Operations | 51 | ||
Joseph R. Paul, CPA | Chief Financial Officer and Secretary | 53 | ||
Christopher J. Bast, CPA, CTP | Treasurer | 47 | ||
Marjorie L. Conner, Esquire | Assistant Secretary and Counsel | 57 | ||
James E. Doyle | Executive Vice President and General Manager, Davey Tree Expert Co. of Canada, Limited | 46 | ||
Dan A. Joy | Executive Vice President and General Manager, Commercial Landscape Services | 57 | ||
Steven A. Marshall | Executive Vice President, U.S. Utility Operations | 63 | ||
Richard A. Ramsey | Corporate Vice President, Canadian Operations | 65 | ||
Brent R. Repenning | Vice President and General Manager, Davey Resource Group | 43 | ||
Thea R. Sears, CPA | Assistant Controller | 46 | ||
James F. Stief | Executive Vice President, U.S. Residential Operations | 60 | ||
Nicholas R. Sucic, CPA | Vice President and Controller | 68 | ||
Mark J. Vaughn | Vice President and General Manager, Eastern Utility Services | 60 | ||
Mr. Warnke was elected Chairman of the Board, effective May 20, 2009, and continues to serve as President and Chief Executive Officer, having been appointed in January 2007. He was President and Chief Operating Officer from 1999 through December 31, 2006. Prior to that time, he served as Executive Vice President and General Manager - Utility Services, having been appointed in January 1993. Previously, having joined Davey Tree in 1980, Mr. Warnke performed all aspects of tree services and also held various managerial positions, including Operations Manager, Operations Support Services, Equipment and Safety functions and Operations Vice President.
Mr. Covey was elected President and Chief Operating Officer, U.S. Operations effective April 14, 2014 and served as Chief Operating Officer, U.S. Operations having been appointed in February 2012. Prior to that time, Mr. Covey served as Executive Vice President, having been appointed in January 2007, Vice President and General Manager of the Davey Resource Group, having been appointed in March 2005 and was Vice President, Southern Operations, Utility Services, having been appointed in January 2003. Previously, having joined Davey Tree in August 1991, Mr. Covey held various managerial positions, including Manager of Systems and Process Management and Administrative Manager, Utility Services.
Page 11
Mr. Paul was elected Chief Financial Officer and Secretary, effective March 23, 2013, and served as Vice President and Treasurer, having been appointed in May 2011. Mr. Paul joined Davey Tree as Treasurer in December 2005. He is a certified public accountant. Prior to joining us, Mr. Paul served as corporate controller for AccessPoint Openings, LLC, a holding company of distribution and manufacturing companies in the building products industry, having been associated with that firm since 1998. Mr. Paul served in various capacities including director of business expansion and integration at Applied Industrial Technologies, an industrial distributor, from 1993 to 1998. Prior to joining Applied Industrial Technologies, Mr. Paul was an audit manager with Deloitte LLP, having been associated with that firm since 1986.
Mr. Bast was elected Treasurer in April 2013, having joined Davey Tree in March 2013. He is a certified public accountant and a certified treasury professional. Prior to joining us, Mr. Bast served in various management positions from 1994 to 2013 at Diebold, Incorporated, a provider of self-service delivery and security systems, including senior director of North America Finance, a director of investor relations and director of treasury. Prior to joining Diebold, Mr. Bast was an auditor with Deloitte LLP, having been associated with that firm since 1991.
Ms. Conner was elected Assistant Secretary and Counsel in May 1998. Prior to that time, she served as Manager of Legal and Treasury Services.
Mr. Doyle was elected Executive Vice President and General Manager, Davey Tree Expert Co. of Canada, Limited (“Davey Tree Limited”), effective May 21, 2014 and served as Vice President and General Manager, Davey Tree Limited, having been appointed in February 2012. Prior to that time, he served as Vice President and General Manager, Operations, Davey Tree Limited, having been appointed in May 2011 and Vice President, Operations, Davey Tree Limited, having been appointed in January 2006. Previously, having joined Davey Tree in 1989, Mr. Doyle held various managerial positions, including District Manager and Operations Manager.
Mr. Joy was elected Executive Vice President and General Manager, Commercial Landscape Services, effective May 21, 2014 and served as Vice President and General Manager, Commercial Landscape Services, having been appointed in May 2013. Prior to that time, he served as Vice President, Commercial Landscape Services, having been appointed in December 2004 and Operations Manager, Commercial Landscape Services, having been appointed in January 2000. Previously, having joined Davey Tree in 1976, Mr. Joy held various managerial positions, including District Manager and Assistant District Manager.
Mr. Marshall was elected Executive Vice President, U.S. Utility Operations, effective January 1, 2007, and served as Vice President and General Manager of Eastern Utility Services, having been appointed in January 2003. Prior to that time, he served as Vice President, Southern Operations, Utility Services, having been appointed in January 1997. Previously, having joined Davey Tree in 1977, Mr. Marshall held various managerial positions, including Operations Manager, Regional Manager and District Manager.
Mr. Ramsey was elected Corporate Vice President, Canadian Operations, in May 2013 and previously served as Vice President and General Manager, Canadian Operations, since January 2000. Prior to that time, he served as Vice President and General Manager, Commercial Services.
Mr. Repenning was elected Vice President and General Manager, Davey Resource Group, effective June 6, 2010 and served as Vice President, Davey Resource Group, having been appointed in October 2009. Prior to that time, he served as Regional Manager, Davey Resource Group, having been appointed in February 2007. Previously, having joined Davey Tree in 1994, Mr. Repenning held various managerial and operational positions, including Production Manager and Supervisor.
Ms. Sears was elected Assistant Controller in May 2010, and previously served as Manager of Financial Accounting, having been appointed in April 1998. Prior to that time she served as Supervisor of Financial Accounting, having been appointed in September 1995. During her tenure with Davey Tree, Ms. Sears’ responsibilities have included a variety of roles in financial reporting, managerial reporting and operations accounting. She is a certified public accountant.
Mr. Stief was elected Executive Vice President, U.S. Residential Operations, effective February 12, 2012 and previously served as Vice President and General Manager, Residential/Commercial Services, since January 2010. Prior to that time Mr. Stief served as Vice President and General Manager, South, West and Central Residential/Commercial Operations, having been appointed in January 2007 and Vice President South, West and Central Residential/Commercial Operations, having been appointed in January 1997. Previously, having joined Davey Tree in 1978, Mr. Stief held various managerial positions, including Operations Manager and District Manager.
Page 12
Mr. Sucic was elected Vice President and Controller, effective January 1, 2007, and served as Corporate Controller and Chief Accounting Officer since having joined Davey Tree in November 2001. He is a certified public accountant. Prior to joining us, Mr. Sucic served as chief financial officer of Vesper Corporation, a manufacturer of products for industry, from 2000 to 2001; of Advanced Lighting Technologies, Inc., a designer, manufacturer and marketer of metal halide lighting products, from 1996 to 2000; and of various asset management units at The Prudential Investment Corporation, from 1989 to 1996. Prior to joining Prudential, Mr. Sucic was a partner with Ernst & Young LLP, having been associated with that firm since 1970.
Mr. Vaughn was elected Vice President and General Manager, Eastern Utility Services, effective June 6, 2010, and served as Vice President, Eastern Utility Services, having been appointed in December 2007. Prior to that time, he served as Vice President, Northern Operating Group, Utility Services, having been appointed in July 2002. Previously, having joined Davey Tree in 1972, Mr. Vaughn held various managerial positions, including Operations Manager and Regional Manager.
Our officers serve from the date of their election to the next organizational meeting of the Board of Directors and until their respective successors are elected.
Page 13
PART II
Item 5. Market for Company’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
Our common shares are not listed or traded on an established public trading market and market prices are, therefore, not available. Semiannually, for purposes of the Davey 401KSOP and ESOP, the fair market value of our common shares is determined by an independent stock valuation firm, based upon our performance and financial condition, using a peer group of comparable companies selected by that firm. The peer group currently consists of: ABM Industries Incorporated; Comfort Systems USA, Inc.; Dycom Industries, Inc.; FirstService Corporation; MYR Group, Inc.; Quanta Services, Inc.; Rollins, Inc.; and, Scotts Miracle-Gro Company. The semiannual valuations are effective for a period of six months and the per-share price established by those valuations is the price at which our Board of Directors has determined our common shares will be bought and sold during that six-month period in transactions involving Davey Tree or one of its employee benefit or stock purchase plans. Since 1979, we have provided a ready market for all shareholders through our direct purchase of their common shares, although we are under no obligation to do so. These purchases are added to our treasury stock.
Record Holders and Common Shares
On February 27, 2015 we had 3,635 record holders of our common shares.
On February 27, 2015 we had 13,168,800 common shares outstanding and options exercisable to purchase 389,251 common shares, partially-paid subscriptions for 476,197 common shares and purchase rights outstanding for 195,029 common shares.
Dividends
The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the dividends declared per common share (in cents):
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||
Quarter | 2014 | 2013 | ||||
1 | 4.50 | 4.50 | ||||
2 | 4.50 | 4.50 | ||||
3 | 4.50 | 4.50 | ||||
4 | 5.00 | 4.50 | ||||
Total | 18.50 | 18.00 | ||||
We presently expect to pay comparable cash dividends in 2015.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
None.
Page 14
Purchases of Equity Securities
The following table provides information on purchases made by the Company of our common shares during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2014:
Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased | Average Price Paid per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | Maximum Number (or Approximate Dollar Value) of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs | |||||||
Fiscal 2014 | |||||||||||
January 1 to January 25 | 1,318 | $ | 23.90 | n/a | n/a | ||||||
January 26 to February 22 | 332 | 23.90 | n/a | n/a | |||||||
February 23 to March 29 | 87,380 | 26.40 | n/a | n/a | |||||||
Total First Quarter | 89,030 | 26.35 | |||||||||
March 30 to April 26 | 162,903 | 26.40 | n/a | n/a | |||||||
April 27 to May 24 | 97,801 | 26.40 | n/a | n/a | |||||||
May 25 to June 28 | 88,061 | 26.40 | n/a | n/a | |||||||
Total Second Quarter | 348,765 | 26.40 | |||||||||
June 29 to July 26 | 387 | 26.40 | n/a | n/a | |||||||
July 27 to August 23 | 12,142 | 27.80 | n/a | n/a | |||||||
August 24 to September 27 | 48,360 | 27.80 | n/a | n/a | |||||||
Total Third Quarter | 60,889 | 27.79 | |||||||||
September 28 to October 25 | 79,692 | 27.80 | n/a | n/a | |||||||
October 26 to November 29 | 92,991 | 27.80 | n/a | n/a | |||||||
November 30 to December 31 | 56,069 | 27.80 | n/a | n/a | |||||||
Total Fourth Quarter | 228,752 | 27.80 | |||||||||
Total Year to Date | 727,436 | $ | 26.95 | ||||||||
n/a--Not applicable. There are no publicly announced plans or programs to purchase common shares. | |||||||||||
Page 15
Stock Performance Graph
Comparison of five-year cumulative return among The Davey Tree Expert Company, S&P 500 Stock Index and Selected Peer Group Companies Index
The following Performance Graph compares cumulative total shareholder returns for The Davey Tree Expert Company common shares during the last five years to the Standard & Poor’s 500 Stock Index and to an index of selected peer group companies. The peer group, which is the same group used by Davey’s independent stock valuation firm, consists of: ABM Industries Incorporated; Comfort Systems USA, Inc.; Dycom Industries, Inc.; FirstService Corporation; MYR Group, Inc.; Quanta Services, Inc.; Rollins, Inc.; and Scotts Miracle-Gro Company. Each of the three measures of cumulative total return assumes reinvestment of dividends.
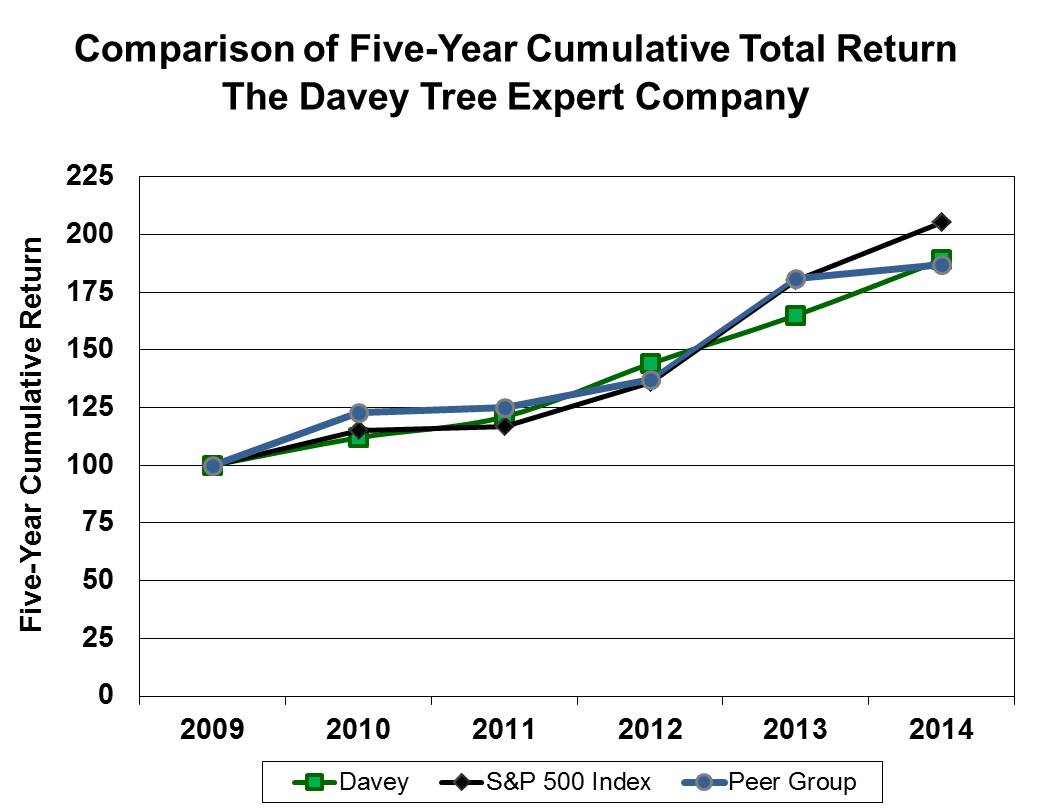
2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | |||||||
Davey Tree | 100 | 112 | 121 | 144 | 165 | 189 | ||||||
S&P 500 Index | 100 | 115 | 117 | 136 | 180 | 205 | ||||||
Peer Group | 100 | 123 | 125 | 137 | 181 | 187 | ||||||
The Performance Graph and related information above shall not be deemed “soliciting material” or be “filed” with the Securities and Exchange Commission, nor shall such information be incorporated by reference into any future filing under the Securities Act of 1933 or Securities Exchange Act of 1934, each as amended, except to the extent that we specifically incorporate it by reference into such filing.
Page 16
Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
Fiscal Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||||||||||||||
(In thousands, except ratio and per share data) | |||||||||||||||||||
Operating Statement Data: | |||||||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 789,911 | $ | 713,848 | $ | 680,153 | $ | 646,034 | $ | 591,732 | |||||||||
Costs and expenses: | |||||||||||||||||||
Operating | 508,677 | 462,646 | 437,332 | 426,626 | 387,272 | ||||||||||||||
Selling | 140,027 | 120,842 | 111,578 | 104,871 | 97,794 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative | 54,970 | 50,654 | 48,171 | 42,793 | 40,170 | ||||||||||||||
Depreciation | 40,970 | 38,231 | 37,365 | 37,818 | 35,530 | ||||||||||||||
Amortization of intangible assets | 2,070 | 1,980 | 1,742 | 1,908 | 1,791 | ||||||||||||||
Gain on sale of assets, net | (806 | ) | (1,294 | ) | (1,802 | ) | (783 | ) | (437 | ) | |||||||||
Income from operations | 44,003 | 40,789 | 45,767 | 32,801 | 29,612 | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense | (2,948 | ) | (2,708 | ) | (2,698 | ) | (3,794 | ) | (2,803 | ) | |||||||||
Interest income | 295 | 311 | 200 | 43 | 46 | ||||||||||||||
Litigation settlement | — | — | — | (2,900 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Other expense | (3,050 | ) | (2,827 | ) | (2,611 | ) | (2,850 | ) | (2,521 | ) | |||||||||
Income before income taxes | 38,300 | 35,565 | 40,658 | 23,300 | 24,334 | ||||||||||||||
Income taxes | 15,131 | 12,712 | 16,063 | 9,235 | 10,281 | ||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 23,169 | $ | 22,853 | $ | 24,595 | $ | 14,065 | $ | 14,053 | |||||||||
Earnings per share--diluted | $ | 1.63 | $ | 1.57 | $ | 1.68 | $ | .97 | $ | .93 | |||||||||
Shares used for computing per share amounts--diluted | 14,238 | 14,602 | 14,609 | 14,537 | 15,031 | ||||||||||||||
Other Financial Data: | |||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | $ | 43,040 | $ | 40,211 | $ | 39,107 | $ | 39,726 | $ | 37,321 | |||||||||
Capital expenditures | 55,731 | 45,205 | 29,734 | 34,701 | 34,753 | ||||||||||||||
Cash flow provided by (used in): | |||||||||||||||||||
Operating activities | 49,279 | 56,310 | 43,936 | 54,422 | 49,275 | ||||||||||||||
Investing activities | (64,060 | ) | (43,205 | ) | (31,179 | ) | (34,128 | ) | (39,304 | ) | |||||||||
Financing activities | 17,335 | (16,891 | ) | (3,377 | ) | (22,044 | ) | (349 | ) | ||||||||||
Cash dividends declared per share | $ | .1850 | $ | .1800 | $ | .1775 | $ | .1700 | $ | .1700 | |||||||||
Page 17
As of December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||||||||||||||
(In thousands, except ratio and per share data) | |||||||||||||||||||
Balance Sheet Data: | |||||||||||||||||||
Working capital | $ | 58,843 | $ | 46,745 | $ | 63,208 | $ | 28,501 | $ | 25,833 | |||||||||
Current ratio | 1.54 | 1.44 | 1.64 | 1.28 | 1.29 | ||||||||||||||
Property and equipment, net | 160,883 | 136,884 | 125,716 | 130,148 | 129,627 | ||||||||||||||
Total assets | 381,004 | 333,378 | 330,932 | 303,734 | 288,307 | ||||||||||||||
Long-term debt | 81,306 | 50,034 | 54,787 | 51,136 | 61,591 | ||||||||||||||
Other long-term liabilities | 54,854 | 46,935 | 59,498 | 49,837 | 38,305 | ||||||||||||||
Shareholders' equity | 136,491 | 131,138 | 118,106 | 100,726 | 98,369 | ||||||||||||||
Common shares: | |||||||||||||||||||
Issued | 21,457 | 21,457 | 21,457 | 21,457 | 21,457 | ||||||||||||||
In treasury | 8,292 | 8,018 | 7,731 | 7,611 | 7,345 | ||||||||||||||
Net outstanding | 13,165 | 13,439 | 13,726 | 13,846 | 14,112 | ||||||||||||||
Stock options: | |||||||||||||||||||
Outstanding | 770 | 662 | 761 | 1,111 | 1,256 | ||||||||||||||
Exercisable | 389 | 342 | 640 | 942 | 945 | ||||||||||||||
ESOT valuation per share | $ | 30.10 | $ | 26.40 | $ | 23.20 | $ | 19.70 | $ | 18.40 | |||||||||
Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
(Amounts in thousands, except share data)
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Results of Operations and Financial Condition (“MD&A”) is provided as a supplement to the accompanying consolidated financial statements and notes to help provide an understanding of our financial condition, cash flows and results of operations. MD&A is organized as follows:
▪ | Overview of 2014 Results; |
▪ | Results of Operations, including fiscal 2014 compared to fiscal 2013, fiscal 2013 compared to fiscal 2012, and liabilities for uncertain income tax positions, and other matters; |
▪ | Liquidity and Capital Resources, including cash flow summary, off-balance sheet arrangements, and capital resources; |
▪ | Recent Accounting Guidance; |
▪ | Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates; and |
▪ | Market Risk Information, including interest rate risk and foreign currency exchange rate risk. |
OVERVIEW OF 2014 RESULTS
General
We provide a wide range of horticultural services to residential, commercial, utility and institutional customers throughout the United States and Canada.
Our Business--We have two reportable operating segments organized by type or class of customer: Residential and Commercial, and Utility.
Residential and Commercial--Residential and Commercial provides services to our residential and commercial customers including: the treatment, preservation, maintenance, removal and planting of trees, shrubs and other plant life; the practice of landscaping, grounds maintenance, tree surgery, tree feeding and tree spraying; the application of fertilizer, herbicides and insecticides; and, natural resource management and consulting, forestry research and development, and environmental planning.
Page 18
Utility--Utility is principally engaged in providing services to our utility customers--investor-owned, municipal utilities, and rural electric cooperatives--including: the practice of line-clearing and vegetation management around power lines, rights-of-way and chemical brush control; and, natural resource management and consulting, forestry research and development and environmental planning.
All other operating activities, including research, technical support and laboratory diagnostic facilities, are included in “All Other.”
During the fourth quarter 2013, the Company realigned its reporting to more closely reflect the manner in which performance is assessed and decisions are made in allocating resources to the segments. Our two reportable operating segments are organized by type or class of customer: Residential and Commercial and Utility. The amounts in the table below for 2012 have been conformed to the 2014 and 2013 reporting.
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth our consolidated results of operations as a percentage of revenues and the percentage change in dollar amounts of the results of operations for the periods presented:
Year Ended December 31, | Percentage Change | |||||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2014/2013 | 2013/2012 | ||||||||||
Revenues | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 10.7 | % | 5.0 | % | ||||
Costs and expenses: | ||||||||||||||
Operating | 64.3 | 64.8 | 64.3 | 9.9 | 5.8 | |||||||||
Selling | 17.7 | 16.9 | 16.4 | 15.9 | 8.3 | |||||||||
General and administrative | 7.0 | 7.1 | 7.1 | 8.5 | 5.2 | |||||||||
Depreciation | 5.2 | 5.4 | 5.5 | 7.2 | 2.3 | |||||||||
Amortization of intangible assets | .3 | .3 | .3 | 4.5 | 13.7 | |||||||||
Gain on sale of assets, net | (.1 | ) | (.2 | ) | (.3 | )% | (37.7 | ) | (28.2 | ) | ||||
94.4 | 94.3 | 93.3 | 10.8 | 6.1 | ||||||||||
Income from operations | 5.6 | 5.7 | 6.7 | 7.9 | (10.9 | )% | ||||||||
Other income (expense): | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense | (.4 | ) | (.3 | ) | (.4 | )% | 8.9 | .4 | ||||||
Interest income | — | — | — | nm | nm | |||||||||
Other | (.4 | ) | (.4 | ) | (.3 | )% | nm | nm | ||||||
Income before income taxes | 4.8 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 7.7 | (12.5 | ) | ||||||||
Income taxes | 1.9 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 19.0 | (20.9 | ) | ||||||||
Net income | 2.9 | % | 3.2 | % | 3.6 | % | 1.4 | % | (7.1 | )% | ||||
nm--not meaningful | ||||||||||||||
Revenues of $789,911 were 10.7% higher than last year’s revenues of $713,848. Utility revenues increased 7.4%, and Residential and Commercial increased 15.3%.
Overall, income from operations of $44,003 increased 7.9% from the $40,789 experienced in the prior year. Income from operations was $21,382 in Utility (a 33.1% increase as compared with 2013) and $37,232 for Residential and Commercial (a 10.9% increase as compared with 2013).
Net income of $23,169 was $316 more than the $22,853 earned in 2013. The increase in net income was attributable to higher income from operations.
Operating activities in 2014 provided cash of $49,279 as compared to $56,310 provided in 2013. The $7,031 net decrease was primarily attributable to (i) an increase in net income of $316, (ii) an increase of $2,829 in depreciation and amortization expense, and (iii) $3,859 more cash used from changes in operating assets and liabilities.
Page 19
Investing activities used $64,060 in cash, or $20,855 more than that used in 2013, the result of additional expenditures for purchases of equipment and land and building necessary to support additional business growth and the purchases of businesses.
Financing activities provided $17,335 in cash in 2014, $34,226 more than the $16,891 of cash used in 2013. Our revolving credit facility provided $24,500 in cash in 2014 as compared with the $4,200 used during 2013. Purchases of common shares for treasury of $19,598 were partially offset by net cash received of $10,503 from the sale of common shares and cash received on our common share subscriptions. Dividends paid during 2014 totaled $2,674.
Fiscal 2014 Compared to Fiscal 2013
A comparison of our fiscal year 2014 results to 2013 follows:
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | Change | % Change | |||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 789,911 | $ | 713,848 | $ | 76,063 | 10.7 | % | ||||||
Costs and expenses: | ||||||||||||||
Operating | 508,677 | 462,646 | 46,031 | 9.9 | ||||||||||
Selling | 140,027 | 120,842 | 19,185 | 15.9 | ||||||||||
General and administrative | 54,970 | 50,654 | 4,316 | 8.5 | ||||||||||
Depreciation | 40,970 | 38,231 | 2,739 | 7.2 | ||||||||||
Amortization of intangible assets | 2,070 | 1,980 | 90 | 4.5 | ||||||||||
Gain on sale of assets, net | (806 | ) | (1,294 | ) | 488 | (37.7 | ) | |||||||
745,908 | 673,059 | 72,849 | 10.8 | |||||||||||
Income from operations | 44,003 | 40,789 | 3,214 | 7.9 | ||||||||||
Other income (expense): | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense | (2,948 | ) | (2,708 | ) | (240 | ) | 8.9 | |||||||
Interest income | 295 | 311 | (16 | ) | (5.1 | ) | ||||||||
Other | (3,050 | ) | (2,827 | ) | (223 | ) | 7.9 | |||||||
Income before income taxes | 38,300 | 35,565 | 2,735 | 7.7 | ||||||||||
Income taxes | 15,131 | 12,712 | 2,419 | 19.0 | ||||||||||
Net income | $ | 23,169 | $ | 22,853 | $ | 316 | 1.4 | % | ||||||
nm--not meaningful | ||||||||||||||
Revenues--Revenues of $789,911 increased $76,063 compared with the $713,848 reported in 2013. Utility increased $27,999, or 7.4%, from the prior year. Contract rate increases with one of our largest utility customers, new contracts and increased productivity within our U.S. and Canadian operations account for the increase. Residential and Commercial increased $51,396, or 15.3%, from 2013. Increased snow plowing revenue, added revenues from business acquisitions, additional tree pruning and tree removal revenues and increased production on our liquid service applications account for the increase. Total consolidated revenue of $789,911 includes production incentive revenue, recognized under the completed-performance method, of $4,725 during 2014 as compared with $8,120 during 2013.
Operating Expenses--Operating expenses of $508,677 increased $46,031 from the prior year, and as a percentage of revenues decreased .5% to 64.3%. Utility experienced an increase of $15,596, or 5.5%, from 2013, and as a percentage of revenues decreased 1.3% to 74.5%. Increases in employee labor and benefits expense, equipment repair and maintenance expense, travel expense, fuel expense, subcontractor expense and tool and saw expense were partially offset by decreases in material expense, damage expense and equipment transfer expense. Residential and Commercial increased $30,601, or 17.5%, compared with 2013 and as a percentage of revenue increased .9% to 53.2%. Increased employee labor and benefit expense, repair and maintenance expense, fuel expense, material expense, tool and saw expense, subcontractor expense and disposal expense, were partially offset by a reduction in equipment transfer expense and damage expense.
Page 20
Fuel costs increased in 2014 as compared with fuel costs for 2013 and impacted operating expenses within all segments. During 2014, fuel expense of $35,129 increased $2,201, or 6.7%, from the $32,928 incurred in 2013. Substantially all of the $2,201 increase relates to an increase in volume of fuel.
Selling Expenses--Selling expenses of $140,027 increased $19,185 from 2013 and as a percentage of revenues increased .8% to 17.7%. Utility increased $5,648, or 15.9%, from 2013. Increases in field management wages and incentive expense, field management travel expense, office expense, computer expense, communication expense and employee development expense were partially offset by a reduction in field management auto expense, office rent expense and utilities expense. Residential and Commercial increased $13,415, or 15.2%, from 2013 but as a percentage of revenue remained at 26.3%. Increases in field management wages and incentive expense, field management auto expense, rent expense, computer expense, communication expense, employee development expense, professional services expense and sales and marketing expense were partially offset by a reduction in field management travel expense.
General and Administrative Expenses--General and administrative expenses increased $4,316 to $54,970, a 8.5% increase, from the $50,654 experienced in 2013 and as a percentage of revenues decreased .1% to 7.0%. Pension settlement costs incurred, the result of purchasing annuities related to our defined benefit pension plans, along with increases in salary and incentive expense, office rent and utilities expense, computer expense, office expense and stock compensation expense were partially offset by decreases in management travel expense, communication expense and employee development expense.
Depreciation and Amortization Expense--Depreciation and amortization expense of $43,040 increased $2,829 from the prior year but as a percentage of revenues decreased .2% to 5.4%. The increase is attributable to higher capital expenditures for equipment and an increase in amortization expense related to our purchases of businesses.
Gain on Sale of Assets--Gain on the sale of assets of $806 decreased $488 from the $1,294 experienced in 2013. The decrease is the result of a reduction in the number of equipment units sold in 2014 as compared with 2013.
Interest Expense--Interest expense of $2,948 increased $240 from the $2,708 incurred in 2013. The increase is attributable to higher-average debt levels necessary to fund operations and capital expenditures, partially offset by lower-average interest rates, during the 2014 as compared with 2013.
Other, Net--Other, net of $3,050 increased $223 from the $2,827 experienced in 2013. Other, net, consisted of nonoperating income and expense, including foreign currency losses on the intercompany account balances of our Canadian operations.
Income Taxes--Income taxes for 2014 were $15,131, an effective tax rate of 39.5%, compared with income taxes for 2013 of $12,712, or an effective tax rate of 35.7%. The increase of 3.8% in the effective tax rate of 39.5% for 2014, as compared to 35.7% for 2013, relates primarily to changes in audit settlements and uncertain tax position adjustments.
Net Income--Net income of $23,169 was $316 higher than the $22,853 earned in 2013, the result of higher income from operations.
Page 21
Fiscal 2013 Compared to Fiscal 2012
A comparison of our fiscal year 2013 results to 2012 follows:
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2013 | 2012 | Change | % Change | |||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 713,848 | $ | 680,153 | $ | 33,695 | 5.0 | % | ||||||
Costs and expenses: | ||||||||||||||
Operating | 462,646 | 437,332 | 25,314 | 5.8 | ||||||||||
Selling | 120,842 | 111,578 | 9,264 | 8.3 | ||||||||||
General and administrative | 50,654 | 48,171 | 2,483 | 5.2 | ||||||||||
Depreciation | 38,231 | 37,365 | 866 | 2.3 | ||||||||||
Amortization of intangible assets | 1,980 | 1,742 | 238 | 13.7 | ||||||||||
Gain on sale of assets, net | (1,294 | ) | (1,802 | ) | 508 | (28.2 | ) | |||||||
673,059 | 634,386 | 38,673 | 6.1 | |||||||||||
Income from operations | 40,789 | 45,767 | (4,978 | ) | (10.9 | ) | ||||||||
Other income (expense): | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense | (2,708 | ) | (2,698 | ) | (10 | ) | .4 | |||||||
Interest income | 311 | 200 | 111 | 55.5 | ||||||||||
Other | (2,827 | ) | (2,611 | ) | (216 | ) | 8.3 | |||||||
Income before income taxes | 35,565 | 40,658 | (5,093 | ) | (12.5 | ) | ||||||||
Income taxes | 12,712 | 16,063 | (3,351 | ) | (20.9 | ) | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 22,853 | $ | 24,595 | $ | (1,742 | ) | (7.1 | )% | |||||
nm--not meaningful | ||||||||||||||
Revenues--Revenues of $713,848 increased $33,695 compared with the $680,153 reported in 2012. Utility increased $1,220, or .3%, from the prior year. Additional work obtained on two existing contracts as well as new contracts acquired in our U.S. operations were partially offset by a reduction in revenue on our largest utility account, the result of client-imposed production changes and losses of contracts within both our U.S. and Canadian operations. Residential and Commercial increased $31,458, or 10.4%, from 2012. Despite a slow start in the first quarter of 2013 due to poor weather conditions which delayed our ability to perform liquid service applications, the remainder of the year was strong for our Residential and Commercial operations. Continued contract work with a large customer related to tree damage purportedly caused by one of its products and the addition of a business acquired in the fourth quarter 2012 located in the midwest United States also contributed to the increase. Total consolidated revenue of $713,848 includes production incentive revenue, recognized under the completed-performance method, of $8,120 during 2013 as compared with $5,004 during 2012.
Operating Expenses--Operating expenses of $462,646 increased $25,314 from the prior year, and as a percentage of revenues increased .5% to 64.8%. Utility experienced an increase of $3,801, or 1.3%, from 2012, and as a percentage of revenues increased .7% to 75.8%. Increases in employee labor and benefits expense, equipment repair and maintenance expense, travel expense, fuel expense, tool expense and material expense were partially offset by decreases in subcontractor expense, fuel expense and disposal expense. Residential and Commercial increased $18,531, or 11.9%, compared with 2012 and as a percentage of revenue increased .7% to 52.2%. Increased employee labor and benefit expense, repair and maintenance expense, fuel expense, material expense, tool and saw expense, subcontractor expense and disposal expense, associated with the increased revenue, account for the increase.
Fuel costs increased in 2013 as compared with fuel costs for 2012 and impacted operating expenses within all segments. During 2013, fuel expense of $32,928 increased $639, or 2.0%, from the $32,289 incurred in 2012. Substantially all of the $639 increase relates to an increase in the price of fuel.
Page 22
Selling Expenses--Selling expenses of $120,842 increased $9,264 from 2012 and as a percentage of revenues increased .5% to 16.9%. Utility increased $1,637, or 4.8%, from 2012. Increases in field management wages and incentive expense, office expense and employee development expense were partially offset by a reduction in field management travel expense, computer expense, field management auto expense, professional services expense and communication expense. Residential and Commercial increased $7,024, or 8.6%, from 2012 but as a percentage of revenue decreased .5% to 26.3%. Increases in field management wages and incentive expense, field management auto expense, travel expense, rent expense, computer expense and sales and marketing expense were partially offset by a reduction in communication expense.
General and Administrative Expenses--General and administrative expenses increased $2,483 to $50,654, a 5.2% increase, from the $48,171 experienced in 2012 and as a percentage of revenues remained unchanged from the prior year at 7.1%. Increases in salary and incentive expense, professional services expense, communication expenses and computer expense were partially offset by decreases in pension expense, personal development expense and stock compensation expense.
Depreciation and Amortization Expense--Depreciation and amortization expense of $40,211 increased $1,104 from the prior year but as a percentage of revenues decreased .1% to 5.7%. The increase is attributable to an increase in depreciation expense related to higher capital expenditures for equipment and an increase in amortization expense related to our purchases of businesses.
Gain on Sale of Assets--Gain on the sale of assets of $1,294 decreased $508 from the $1,802 experienced in 2012. Fewer equipment units were sold in 2013 as compared with 2012 which accounts for the decreased gain.
Interest Expense--Interest expense of $2,708 increased $10 from the $2,698 incurred in 2012. The increase is attributable to higher average borrowing levels necessary to fund capital expenditures and operations during the 2013 as compared with 2012.
Other, Net--Other, net of $2,827 increased $216 from the $2,611 experienced in 2012. Other, net, consisted of nonoperating income and expense, including foreign currency losses on the intercompany account balances of our Canadian operations of $146 for 2013 as compared to gains of $11 for 2012.
Income Taxes--Income taxes for 2013 were $12,712, an effective tax rate of 35.7%, compared with income taxes for 2012 of $16,063, or an effective tax rate of 39.5%. The decrease of 3.8% in the effective tax rate of 35.7% for 2013, as compared to 39.5% for 2012, relates primarily to changes in audit settlements and uncertain tax position adjustments.
Net Income--Net income of $22,853 was $1,742 lower than the $24,595 earned in 2012, the result of lower income from operations.
Income Tax—Liabilities for Uncertain Tax Positions
The amount of income taxes we pay is subject to audit by U.S. federal, state and Canadian tax authorities, which may result in proposed assessments. Our estimate for the potential outcome for any uncertain tax issue is highly judgmental. Uncertain tax positions are recognized only if they are more-likely-than-not to be upheld during examination based on their technical merits. The measurement of the uncertain tax position is based on the largest benefit amount that is more-likely-than-not (determined on a cumulative probability basis) to be realized upon settlement of the matter. If payment of these amounts ultimately proves to be unnecessary, the reversal of the liabilities would result in tax benefits being recognized in the period when we determine the liabilities are no longer necessary. If the estimate of tax liabilities proves to be less than the ultimate settlement, a further charge to expense may result.
The Company is routinely under audit by U.S. federal, state, local and Canadian authorities in the area of income tax. These audits include questioning the timing and the amount of income and deductions and the allocation of income and deductions among various tax jurisdictions. During the fourth quarter 2013, the U.S. Internal Revenue Service completed its audit of the Company's U.S. income tax returns for 2010 and 2011 and, during 2010, Canada Revenue Agency completed its audit of the Company's Canadian operations for 2006, 2007 and 2008. With the exception of U.S. state jurisdictions, the Company is no longer subject to examination by tax authorities for the years through 2009. As of December 31, 2014, we believe it is reasonably possible that the total amount of unrecognized tax benefits will not significantly increase or decrease.
Page 23
Goodwill—Impairment Tests
Annually, we perform the impairment tests for goodwill during the fourth quarter. Impairment of goodwill is tested at the reporting-unit level, which for us are also our business segments. Impairment of goodwill is tested by comparing the reporting unit’s carrying value, including goodwill, to the fair value of the reporting unit. The fair values of the reporting units are estimated using discounted projected cash flows. If the carrying value of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value, goodwill is considered impaired and a second step is performed to measure the amount of impairment loss, if any. We conducted our annual impairment tests and determined that no impairment loss was required to be recognized in 2014 or for any prior periods. There were no events or circumstances from the date of our assessment through December 31, 2014 that would impact this conclusion.
The fair values of the reporting units were estimated using discounted projected cash flows for the goodwill impairment tests and analysis that required judgmental assumptions about revenues, operating margins, growth rates, discount rates, and working capital requirements. In determining those judgmental assumptions, we consider data, including--for each reporting unit--its annual budget for the upcoming year, its longer-term performance expectations, anticipated future cash flows and market data. Assumptions were also made for perpetual growth rates for periods beyond the forecast period.
If the fair values of the reporting units were less than the carrying values of the reporting units (including recorded goodwill), determined through the discounted projected cash flow methodology, goodwill impairment may be present. In such an instance, we would measure the goodwill impairment loss, if any, based upon the fair value of the underlying assets and liabilities of the impacted reporting unit, including any unrecognized intangible assets, and estimate the implied fair value of goodwill. An impairment loss would be recognized to the extent that a reporting unit’s recorded goodwill exceeded the implied fair value of goodwill.
The carrying value of the recorded goodwill for all reporting units totaled $28,164 at December 31, 2014. Based upon the goodwill impairment analysis conducted in the fourth quarter 2014, a hypothetical reduction in the fair value of the individual reporting units, ranging from approximately 46% to 63%, would not have resulted in the carrying value of the individual reporting units exceeding the reduced fair value.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Our principal financial requirements are for capital spending, working capital and business acquisitions. Cash generated from operations and our revolving credit facility are our primary sources of capital.
Cash Flow Summary
Our cash flows from operating, investing and financing activities, as reflected in the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flow for the years ended December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, are summarized as follows:
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Cash provided by (used in): | |||||||
Operating activities | $ | 49,279 | $ | 56,310 | |||
Investing activities | (64,060 | ) | (43,205 | ) | |||
Financing activities | 17,335 | (16,891 | ) | ||||
Increase (Decrease) in cash | $ | 2,554 | $ | (3,786 | ) | ||
Net Cash Provided by Operating Activities--Operating activities in 2014 provided cash of $49,279 as compared to $56,310 provided in 2013. The $7,031 net decrease was primarily attributable to (i) an increase in net income of $316, (ii) an increase of $2,829 in depreciation and amortization expense, and (iii) $3,859 more cash used from changes in operating assets and liabilities.
Page 24
Overall, accounts receivable dollars increased $4,489 in 2014 as compared to the $10,307 decrease experienced in 2013. With respect to the change in accounts receivable arising from business levels, the “days-sales-outstanding” in accounts receivable (“DSO”) at the end of 2014 decreased 4 days to 50 days, as compared to 2013. The DSO at December 31, 2013 was 54 days.
Accounts payable and accrued expenses increased $1,206 in 2014, $3,514 more than the decrease of $2,308 experienced in 2013. Increases in trade payables, health insurance expense, professional service accruals, compensated absence accruals and employee compensation accruals were partially offset by a decrease in advance payments from customers and real estate tax accruals.
Self-insurance accruals increased $2,116 in 2014, a change of $7,137 compared to the decrease of $5,021 experienced in 2013. The increase occurred within our general liability and vehicle liability classifications and resulted primarily from an overall increase in deductible amounts under commercial insurance or the self-insured risk retention.
Other assets, net, increased $6,640 in 2014, as compared to the $6,926 increase in 2013. Increases in prepaid expenses, other deposits and operating supplies were partially offset by decreases in tax deposits.
Net Cash Used in Investing Activities--Investing activities used $64,060 in cash, $20,855 more than the $43,205 used in 2013. The increase was primarily the result of additional expenditures for the purchase of equipment and land and building necessary to support additional business growth as well as the purchases of businesses.
Net Cash Used in Financing Activities--Financing activities provided $17,335 in cash in 2014, $34,226 more than the $16,891 of cash used in 2013. Our revolving credit facility provided $24,500 as compared with the $4,200 used during 2013. We use the revolving credit facility primarily for capital expenditures and payments of notes payable, primarily related to acquisitions. Borrowings of long-term debt and capital leases totaled $5,695. Purchases of common shares for treasury of $19,598 were partially offset by net cash received of $10,503 from the sale of common shares and cash received on our common share subscriptions. Dividends paid during 2014 totaled $2,674.
Revolving Credit Facility and 5.09% Senior Unsecured Notes--In November 2013, the Company amended its revolving credit facility. The Amended and Restated Credit Agreement provides for a revolving credit facility with a group of banks under which up to an aggregate of $175,000 is available, with a letter of credit sublimit of $100,000 and a swing line commitment of $15,000 (the previous agreement permitted borrowings up to $140,000 with a letter of credit sublimit of $100,000). Under certain circumstances, the amount available under the revolving credit facility may be increased to $210,000.
The Amended and Restated Credit Agreement extended the term of the revolving credit facility to November 7, 2018 from December 19, 2014. The revolving credit facility contains certain affirmative and negative covenants customary for this type of facility and includes financial covenant ratios with respect to a maximum leverage ratio and a maximum balance sheet leverage ratio. As of December 31, 2014, we were in compliance with all financial covenants contained in our revolving credit facility.
As of December 31, 2014, we had unused commitments under the facility approximating $70,964, and $104,036 committed, which consisted of borrowings of $44,500 and issued letters of credit of $59,536. Borrowings outstanding bear interest, at Davey Tree’s option, of either (a) the base rate or (b) LIBOR plus a margin adjustment ranging from .75% to 1.50%--with the margin adjustments in both instances based on the Company's leverage ratio at the time of borrowing. The base rate is the greater of (i) the agent bank’s prime rate, (ii) LIBOR plus 1.5%, or (iii) the federal funds rate plus .5%. A commitment fee ranging from .10% to .25% is also required based on the average daily unborrowed commitment.
On July 22, 2010, we issued $30,000 of 5.09% Senior Unsecured Notes, Series A, due July 22, 2020 (the "5.09% Senior Notes"). The 5.09% Senior Notes were issued pursuant to a Master Note Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”), between Davey Tree and the purchasers of the 5.09% Senior Notes. The net proceeds of the 5.09% Senior Notes were used in 2010 to pay down borrowings under our revolving credit facility.
The 5.09% Senior Notes are equal in right of payment with our revolving credit facility and all other senior unsecured obligations of the Company. Interest is payable semiannually and five equal, annual principal payments commence on July 22, 2016 (the sixth anniversary of issuance). The Purchase Agreement contains customary events of default and covenants related to limitations on indebtedness and transactions with affiliates and the maintenance of certain financial ratios. As of December 31, 2014, we were in compliance with all financial covenants contained in our revolving credit facility.
Page 25
Contractual Obligations Summary
The following is a summary of our long-term contractual obligations, as at December 31, 2014, to make future payments for the periods indicated:
Contractual Obligations Due -- Year Ending December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description | Total | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | Thereafter | |||||||||||||||||||||
Revolving credit facility | $ | 44,500 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 44,500 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||
Senior unsecured notes | 30,000 | — | 6,000 | 6,000 | 6,000 | 6,000 | 6,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Term loans | 15,087 | 8,281 | 1,234 | 803 | 150 | 159 | 4,460 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Operating lease obligations | 17,231 | 5,813 | 4,470 | 2,918 | 1,764 | 868 | 1,398 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Self-insurance accruals | 57,934 | 23,384 | 13,707 | 8,627 | 4,747 | 2,299 | 5,170 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase obligations | 11,145 | 11,145 | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Other liabilities | 18,968 | 8,022 | 1,076 | 1,143 | 1,144 | 757 | 6,826 | |||||||||||||||||||||
$ | 194,865 | $ | 56,645 | $ | 26,487 | $ | 19,491 | $ | 58,305 | $ | 10,083 | $ | 23,854 | |||||||||||||||
The self-insurance accruals in the summary above reflect the total of the undiscounted amount accrued, for which amounts estimated to be due each year may differ from actual payments required to fund claims. Purchase obligations in the summary above represent open purchase-order amounts we anticipate will become payable within the next year for goods and services we have negotiated for delivery as of December 31, 2014. Other liabilities include estimates of future expected funding requirements related to retirement plans and other sundry items. Because their future cash outflows are uncertain, accrued income tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions, as of December 31, 2014, have not been included in the summary above. Noncurrent deferred taxes and payments related to defined benefit pension plans are also not included in the summary.
As at December 31, 2014, we were contingently liable to our principal banks for letters of credit in the amount of $61,540 of which $59,536 is committed under the revolving credit facility. Substantially all of these letters of credit, which expire within a year, are planned for renewal as appropriate.
Also, as is common with our industry, we have performance obligations that are supported by surety bonds, which expire during 2015 through 2017. We intend to renew the performance bonds where appropriate and as necessary.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
There are no “off-balance sheet arrangements” as that term is defined in Regulation S-K, Item 303(a)(4)(ii) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
Capital Resources
Cash generated from operations and our revolving credit facility are our primary sources of capital.
Cash of $18,415 as of December 31, 2014 included $8,120 in the U.S. and $10,295 in Canada, all of which is subject to U.S. federal income taxes and Canadian taxes if repatriated to the U.S. Currently, we do not expect to repatriate a portion of our 2014 Canadian earnings to satisfy our 2014 U.S. based cash flow needs.
Business seasonality results in higher revenues during the second and third quarters as compared with the first and fourth quarters of the year, while our methods of accounting for fixed costs, such as depreciation and interest expense, are not significantly impacted by business seasonality. Capital resources during these periods are equally affected. We satisfy seasonal working capital needs and other financing requirements with the revolving credit facility and several other short-term lines of credit. We are continually reviewing our existing sources of financing and evaluating alternatives. At December 31, 2014, we had working capital of $58,843, unused short-term lines of credit approximating $7,281, and $70,964 available under our revolving credit facility.
Our sources of capital presently allow us the financial flexibility to meet our capital spending plan and to complete business acquisitions for at least the next twelve months and for the foreseeable future.
Page 26
RECENT ACCOUNTING GUIDANCE
Accounting Standards Update 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606)--In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers ("Topic 606"),” which will replace all current U.S. GAAP guidance on revenue recognition and eliminate all industry-specific guidance.
The new revenue recognition guidance provides a unified model to determine when and how revenue is recognized. The underlying principle is that an entity should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods and services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration for which the entity expects in exchange for those goods and services. The guidance provides a five-step analysis of transactions to determine when and how revenue is recognized. Other major provisions include capitalization of certain contract costs, consideration of the time value of money in the transaction price, and allowing estimates of variable consideration to be recognized before contingencies are resolved in certain circumstances. The guidance also requires enhanced information to be presented in the financial statements regarding the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from an entity’s contracts with customers.
Unless the FASB delays the effective date of the new guidelines, it will be effective for Davey Tree beginning January 1, 2017 and can be applied either retrospectively to each period presented or as a cumulative-effect adjustment as of the date of adoption. Early adoption is not permitted. We are currently evaluating the methods of adoption as well as the impact that it may have, if any, on our consolidated financial statements. The new revenue guidance will supersede existing revenue guidance affecting our Company, and may also affect our business processes and our information technology systems. As a result, our evaluation of the effect of the new revenue guidance will extend over future periods.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND ESTIMATES
Our consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. The preparation of these financial statements requires the use of estimates, judgments and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the periods presented.
On an ongoing basis, we evaluate our estimates and assumptions, including those related to accounts receivable, specifically those receivables under contractual arrangements primarily arising from Utility customers; allowance for doubtful accounts; and self-insurance accruals. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other factors that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results could differ from these estimates.
We believe the following are our “critical accounting policies and estimates”--those most important to the financial presentations and those that require the most difficult, subjective or complex judgments.
Revenue Recognition--Revenues from Residential and Commercial customers are recognized as the services are provided and amounts are determined to be collectible. Revenues from contractual arrangements, primarily with Utility customers, are recognized based on costs incurred to total estimated contract costs. Changes in estimates and assumptions related to total estimated contract costs may have a material effect on the amounts reported as receivables arising from contractual arrangements and the corresponding amounts of revenues and profit.
Utility Customers--We generate a significant portion of revenues and corresponding accounts receivable from our Utility customers in the utility industry. One Utility customer, PG&E, approximated 8% of revenues during 2014, 9% during 2013 and 10% during 2012. Adverse conditions in the utility industry or individual utility customer operations may affect the collectibility of our receivables or our ability to generate ongoing revenues.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts--In determining the allowance for doubtful accounts, we evaluate the collectibility of our accounts receivable based on a combination of factors. In circumstances where we are aware of a specific customer’s inability to meet its financial obligations to us (e.g., bankruptcy filings), we record a specific allowance for doubtful accounts against amounts due to reduce the net recognized receivable to the amount we reasonably believe will be collected. For all other customers, we recognize allowances for doubtful accounts based on the length of time the receivables are past due. If circumstances change (e.g., unexpected material adverse changes in a major customer’s ability to meet its financial obligation to us or higher than expected customer defaults), our estimates of the recoverability of amounts could differ from the actual amounts recovered.
Page 27
Self-Insurance Accruals--We are generally self-insured for losses and liabilities related primarily to workers’ compensation, vehicle liability and general liability claims. We use commercial insurance as a risk-reduction strategy to minimize catastrophic losses. Ultimate losses are accrued based upon estimates of the aggregate liability for claims incurred using certain actuarial assumptions followed in the insurance industry and based on Company-specific experience.
Our self-insurance accruals include claims for which the ultimate losses will develop over a period of years. Accordingly, our estimates of ultimate losses can change as claims mature. Our accruals also are affected by changes in the number of new claims incurred and claim severity. The methods for estimating the ultimate losses and the total cost of claims were determined by third-party consulting actuaries; the resulting accruals are reviewed by management, and any adjustments arising from changes in estimates are reflected in income.
The workers' compensation accruals are discounted as the amount and timing of cash payments related to those accruals are reliably determinable given the nature of workers' compensation benefits and the level of historical claim volume to support the actuarial assumptions and judgments used to derive the expected loss payment pattern. The workers' compensation accruals are discounted using an interest rate that approximates the long-term investment yields over the expected payment pattern of unpaid losses.
Our self-insurance accruals are based on estimates and, while we believe that the amounts accrued are adequate and not excessive, the ultimate claims may be in excess of or less than the amounts provided.
MARKET RISK INFORMATION
In the normal course of business, we are exposed to market risk related to changes in interest rates, changes in foreign currency exchange rates and changes in the price of fuel. We do not hold or issue derivative financial instruments for trading or speculative purposes. We use derivative financial instruments to manage risk, in part, associated with changes in interest rates and changes in fuel prices.
Interest Rate Risk
We are exposed to market risk related to changes in interest rates on long-term debt obligations. We regularly monitor and measure our interest rate risk and, to the extent that we believe we are exposed, from time-to-time we have entered into interest rate swap contracts--derivative financial instruments--with the objective of altering interest rate exposures related to a portion of variable debt.
The following table provides information, as of December 31, 2014, about our debt obligations, including principal cash flows, weighted-average interest rates by expected maturity dates and fair values. Weighted-average interest rates used for variable-rate obligations are based on rates as derived from published spot rates, in effect as at December 31, 2014.
Expected Maturity Date | Fair Value December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | Thereafter | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Liabilities | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Long-term debt: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fixed rate | $ | 7,232 | $ | 6,136 | $ | 6,141 | $ | 6,150 | $ | 6,159 | $ | 10,461 | $ | 42,278 | $ | 36,123 | |||||||||||||||
Average interest rate | 4.7 | % | 5.1 | % | 5.1 | % | 5.1 | % | 5.1 | % | 5.1 | % | |||||||||||||||||||
Variable rate | $ | 45,549 | $ | 1,098 | $ | 662 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 47,309 | $ | 46,259 | |||||||||||||||
Average interest rate | 1.4 | % | 2.0 | % | 2.8 | % | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest rates on the variable-rate debt, as of December 31, 2014, ranged from .9% to 3.3%.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk
We are exposed to market risk related to foreign currency exchange rate risk resulting from our operations in Canada, where we provide a comprehensive range of horticultural services.
Page 28
Our financial results could be affected by factors such as changes in the foreign currency exchange rate or differing economic conditions in the Canadian markets as compared with the markets for our services in the United States. Our earnings are affected by translation exposures from currency fluctuations in the value of the U.S. dollar as compared to the Canadian dollar. Similarly, the Canadian dollar-denominated assets and liabilities may result in financial exposure as to the timing of transactions and the net asset / liability position of our Canadian operations.
For the year ended December 31, 2014, the result of a hypothetical 10% uniform change in the value of the U.S. dollar as compared with the Canadian dollar would not have a material effect on our results of operations or our financial position. Our sensitivity analysis of the effects of changes in foreign currency exchange rates does not factor in a potential change in sales levels or local currency prices. Presently, we do not engage in hedging activities related to our foreign currency exchange rate risk.
Commodity Price Risk
We are subject to market risk from fluctuating prices of fuel--both diesel and gasoline. Beginning in the second quarter 2011, we entered into fuel derivatives as "economic hedges" related to fuel consumed by Davey Tree service vehicles. The objectives of the economic hedges are to fix the price of a portion of our fuel needs and mitigate the earnings and cash flow volatility attributable to the risk of changing prices. As of December 31, 2013, all fuel derivatives previously entered into expired.
Impact of Inflation
The impact of inflation on the results of operations has not been significant in recent years.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
The information set forth in “Market Risk Information” under Item 7. “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
Our consolidated financial statements are attached hereto and listed on page F-1 of this annual report.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures.
(a) Management’s Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
As of the end of the period covered by this Form 10-K, we carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as amended (the “Exchange Act”)). Based on that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures were effective at the reasonable assurance level as of the end of the period covered by this Form 10-K in ensuring that information required to be disclosed in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms and is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
(b) Management’s Discussion of Internal Controls over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Our internal control framework and processes were designed to provide reasonable assurance to management and the Board of Directors that our financial reporting is reliable and that our consolidated financial statements for external purposes have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“U.S. GAAP”).
Page 29
Our management recognizes its responsibility for fostering a strong ethical climate so that our affairs are conducted according to the highest standards of personal and corporate conduct.
Our internal controls over financial reporting include policies and procedures that: (i) provide for the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect our business transactions; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded properly to allow for the preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance that the unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of our assets will be prevented or detected in a timely manner. We maintain a dynamic system of internal controls and processes--including internal controls over financial reporting--designed to ensure reliable financial recordkeeping, transparent financial reporting and protection of physical and intellectual property.
All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
(c) Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we conducted an evaluation as of December 31, 2014, as to the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO 2013”).
As permitted by the Securities and Exchange Commission, our evaluation of, and conclusion on, the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting did not include the internal controls of Wetland Studies and Solutions, Inc., acquired as of the beginning of the second quarter 2014, which is included in our 2014 consolidated financial statements and represented approximately 2% of our total assets as of December 31, 2014 and 1% of our total revenues for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Based on that evaluation, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2014.
Our independent registered public accounting firm has issued an audit report on our internal control over financial reporting, which is included in this report.
/s/ Karl J. Warnke | /s/ Joseph R. Paul | /s/ Nicholas R. Sucic | ||
Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer | Chief Financial Officer and Secretary | Vice President and Controller | ||
Kent, Ohio
March 10, 2015
(d) Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the fourth quarter 2014 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Page 30
(e) Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Report of Ernst & Young, LLP
Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Regarding Internal Control over Financial Reporting
The Board of Directors and Shareholders of
The Davey Tree Expert Company
We have audited The Davey Tree Expert Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 Framework) (the COSO criteria). The Davey Tree Expert Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
As indicated in the accompanying Management's Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting, management's assessment of and conclusion on the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting did not include the internal controls of Wetland Studies and solutions, Inc., which is included in the 2014 consolidated financial statements of The Davey Tree Expert Company and constituted 2% of total assets as of December 31, 2014 and 1% of revenues, for the year then ended. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting of The Davey Tree Expert Company also did not include an evaluation of internal control over financial reporting Wetland Studies and Solutions, Inc.
In our opinion, The Davey Tree Expert Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of The Davey Tree Expert Company as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014 of The Davey Tree Expert Company and our report dated March 10, 2015 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Akron, Ohio
March 10, 2015
Page 31
Item 9B. Other Information.
None.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
Information about our executive officers is included in the section "Executive Officers of the Company,” pursuant to Instruction G of Form 10-K as an unnumbered item to Part I of this report.
Information about our directors is in the section "Election of Directors" of our 2015 Proxy Statement, which is incorporated into this report by reference.
Information about our audit committee and our audit committee financial experts is in the section “Committees of the Board of Directors; Attendance” of our 2015 Proxy Statement, which is incorporated into this report by reference.
Information required by Item 405 of Regulation S-K is in the section “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” of our 2015 Proxy Statement, which is incorporated into this report by reference. See also the section titled "Shareholders Nominations for Director," which is incorporated into this report by reference.
We have adopted a Code of Ethics for Financial Matters that applies to our principal executive officer, principal financial officer and principal accounting officer, or persons performing similar functions. That Code is available on our website or upon request, as described in this report in Item 1. “Business - Access to Company Information.” We intend to disclose, on our website, any amendments to, or waiver of, any provision of that Code that would otherwise be required to be disclosed under the rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
Information about executive and director compensation is in the sections “Compensation Discussion and Analysis,” "Report of the Compensation Committee," "Compensation of Executive Officers" and "Compensation of Directors" of our 2015 Proxy Statement, which are incorporated into this report by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
Information about ownership of our common shares by certain persons is in the section "Ownership of Common Shares" of our 2015 Proxy Statement, which is incorporated into this report by reference. Information about our securities authorized for issuance under equity compensation plans is in the section “Equity Compensation Plans Information” of our 2015 Proxy Statement, which is incorporated into this report by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
Information about certain transactions between us and our affiliates and certain other persons and the independence of directors is in the section “Corporate Governance” of our 2015 Proxy Statement, which is incorporated into this report by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services.
Information about our principal accountant’s fees and services is in the section “Independent Auditors” of our 2015 Proxy Statement, which is incorporated into this report by reference.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules.
(a) (1) and (a) (2) Financial Statements and Schedules.
The response to this portion of Item 15 is set forth on page F-1 of this report.
(b) Exhibits.
The exhibits to this Form 10-K are submitted as a separate section of this report. See Exhibit Index.
Page 32
SIGNATURES |
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized on March 10, 2015. |
THE DAVEY TREE EXPERT COMPANY | ||
By: /s/ Karl J. Warnke | ||
Karl J. Warnke, Chairman, President and | ||
Chief Executive Officer | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities indicated on March 10, 2015. | ||
/s/ Patrick M. Covey | /s/ John E. Warfel | |
Patrick M. Covey, Director | John E. Warfel, Director | |
Chief Operating Officer | ||
/s/ Karl J. Warnke | ||
/s/ J. Dawson Cunningham | Karl J. Warnke, Director, | |
J. Dawson Cunningham, Director | Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer | |
(Principal Executive Officer) | ||
/s/ William J. Ginn | ||
William J. Ginn, Director | /s/ Joseph R. Paul | |
Joseph R. Paul, Chief Financial Officer and Secretary | ||
(Principal Financial Officer) | ||
/s/ Douglas K. Hall | ||
Douglas K. Hall, Director | ||
/s/ Nicholas R. Sucic | ||
Nicholas R. Sucic, Vice President and Controller | ||
(Principal Accounting Officer) | ||
/s/ Sandra W. Harbrecht | ||
Sandra W. Harbrecht, Director | ||
Page 33
EXHIBIT INDEX | ||||
Exhibit No. | Description | |||
3.1 | 2003 Amended Articles of Incorporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 27, 2003). | |||
3.2 | 1987 Amended and Restated Regulations of The Davey Tree Expert Company (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2006). | |||
10.1 | Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement among The Davey Tree Expert Company, as borrower, various lending institutions party thereto, as banks, KeyBank National Association, as lead arranger, syndication agent and administrative agent, and PNC Bank, National Association and Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as co-documentation agents, dated as of November 7, 2013 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant's Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 12, 2013). | |||
10.2 | 2004 Omnibus Stock Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended July 3, 2004). | |||
10.3 | 2004 401KSOP Match Restoration Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended July 3, 2004). | |||
10.4 | Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended July 3, 2004). | |||
10.5 | Retirement Benefit Restoration Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended July 3, 2004). | |||
10.6 | The Davey Tree Expert Company Board of Directors Revised Deferred Compensation Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2013). | |||
10.7 | 2014 Omnibus Stock Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant's Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on May 21, 2014). | |||
10.8 | Stock Subscription Agreement. | Filed Herewith | ||
21 | Subsidiaries of the Registrant. | Filed Herewith | ||
23 | Consent of Ernst & Young LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. | Filed Herewith | ||
31.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | Filed Herewith | ||
31.2 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | Filed Herewith | ||
32.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, 18 U.S.C. Section 1350. | Furnished Herewith | ||
Page 34
Exhibit No. | Description | |||
32.2 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, 18 U.S.C. Section 1350. | Furnished Herewith | ||
101 | The following materials from the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2014, formatted in XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language): (i) the Consolidated Balance Sheets (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Operations, (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income, (iv) the Statements of Consolidated Shareholders' Equity, (v) the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows, and (vi) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. | Filed Herewith | ||
The documents listed as Exhibits 10.2 through 10.8 constitute management contracts or compensatory plans or arrangements.
The Registrant is a party to certain instruments, copies of which will be furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission upon request, defining the rights of holders of long-term debt.
Page 35
ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K
ITEM 8, ITEM 15(a)(1) and (2)
LIST OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
CERTAIN EXHIBITS
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS SCHEDULES
YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2014
THE DAVEY TREE EXPERT COMPANY
KENT, OHIO
Page 36
LIST OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES | |
FORM 10-K - ITEM 15(a)(1) AND (2) | |
THE DAVEY TREE EXPERT COMPANY | |
The following consolidated financial statements of The Davey Tree Expert Company are included in Item 8: | |
Audited Consolidated Financial Statements: | Page |
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements -- December 31, 2014 | |
Financial Statement Schedules: | |
None. | |
All schedules for which provision is made in the applicable accounting regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission are not required under the related instructions or are inapplicable and therefore have been omitted. | |
F-1
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders of
The Davey Tree Expert Company
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of The Davey Tree Expert Company as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, shareholders' equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of The Davey Tree Expert Company at December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), The Davey Tree Expert Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 Framework) and our report dated March 10, 2015 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Akron, Ohio
March 10, 2015
F-2
THE DAVEY TREE EXPERT COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except per share dollar amounts)
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Assets | |||||||
Current assets: | |||||||
Cash | $ | 18,415 | $ | 15,861 | |||
Accounts receivable, net | 111,598 | 105,256 | |||||
Operating supplies | 6,968 | 5,661 | |||||
Prepaid expenses | 14,088 | 11,393 | |||||
Other current assets | 16,127 | 13,845 | |||||
Total current assets | 167,196 | 152,016 | |||||
Property and equipment: | |||||||
Land and land improvements | 16,553 | 13,904 | |||||
Buildings and leasehold improvements | 33,644 | 27,364 | |||||
Equipment | 482,752 | 442,882 | |||||
532,949 | 484,150 | ||||||
Less accumulated depreciation | 372,066 | 347,266 | |||||
160,883 | 136,884 | ||||||
Other assets | 18,862 | 16,917 | |||||
Identified intangible assets and goodwill, net | 34,063 | 27,561 | |||||
$ | 381,004 | $ | 333,378 | ||||
Liabilities and shareholders' equity | |||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||
Short-term debt | $ | 8,281 | $ | 8,434 | |||
Accounts payable | 42,140 | 37,922 | |||||
Accrued expenses | 34,925 | 36,858 | |||||
Self-insurance accruals | 23,007 | 22,057 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 108,353 | 105,271 | |||||
Long-term debt | 51,306 | 20,034 | |||||
Senior unsecured notes | 30,000 | 30,000 | |||||
Self-insurance accruals | 35,886 | 34,655 | |||||
Other liabilities | 18,968 | 12,280 | |||||
244,513 | 202,240 | ||||||
Common shareholders' equity: | |||||||
Common shares, $1.00 par value, per share; 24,000 shares authorized; 21,457 shares issued and outstanding before treasury shares as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 | 21,457 | 21,457 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 9,461 | 5,008 | |||||
Common shares subscribed | 9,381 | 10,467 | |||||
Retained earnings | 251,470 | 230,975 | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (11,523 | ) | (4,393 | ) | |||
280,246 | 263,514 | ||||||
Less: Cost of Common shares held in treasury; 8,292 shares in 2014 and 8,018 in 2013 | 138,155 | 125,034 | |||||
Common shares subscription receivable | 5,600 | 7,342 | |||||
136,491 | 131,138 | ||||||
$ | 381,004 | $ | 333,378 | ||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements. | |||||||
F-3
THE DAVEY TREE EXPERT COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(In thousands, except per share dollar amounts)
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Revenues | $ | 789,911 | $ | 713,848 | $ | 680,153 | |||||
Costs and expenses: | |||||||||||
Operating | 508,677 | 462,646 | 437,332 | ||||||||
Selling | 140,027 | 120,842 | 111,578 | ||||||||
General and administrative | 54,970 | 50,654 | 48,171 | ||||||||
Depreciation | 40,970 | 38,231 | 37,365 | ||||||||
Amortization of intangible assets | 2,070 | 1,980 | 1,742 | ||||||||
Gain on sale of assets, net | (806 | ) | (1,294 | ) | (1,802 | ) | |||||
745,908 | 673,059 | 634,386 | |||||||||
Income from operations | 44,003 | 40,789 | 45,767 | ||||||||
Other income (expense): | |||||||||||
Interest expense | (2,948 | ) | (2,708 | ) | (2,698 | ) | |||||
Interest income | 295 | 311 | 200 | ||||||||
Other | (3,050 | ) | (2,827 | ) | (2,611 | ) | |||||
Income before income taxes | 38,300 | 35,565 | 40,658 | ||||||||
Income taxes | 15,131 | 12,712 | 16,063 | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 23,169 | $ | 22,853 | $ | 24,595 | |||||
Share data: | |||||||||||
Earnings per share--basic: | $ | 1.68 | $ | 1.61 | $ | 1.74 | |||||
Earnings per share--diluted: | $ | 1.63 | $ | 1.57 | $ | 1.68 | |||||
Weighted-average shares outstanding: | |||||||||||
Basic | 13,821 | 14,171 | 14,102 | ||||||||
Diluted | 14,238 | 14,602 | 14,609 | ||||||||
Dividends declared per share | $ | .1850 | $ | .1800 | $ | .1775 | |||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements. | |||||||||||
F-4
THE DAVEY TREE EXPERT COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(In thousands)
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 23,169 | $ | 22,853 | $ | 24,595 | |||||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | |||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments (losses)/gains | (2,798 | ) | (1,864 | ) | 561 | ||||||
Change in deferred gains on cash flow hedges | — | — | 77 | ||||||||
Defined benefit pension plans: | |||||||||||
Net (loss)/gain arising during the year | (6,023 | ) | 3,717 | (2,170 | ) | ||||||
Reclassification to results of operations: | |||||||||||
Amortization of defined benefit pension items: | |||||||||||
Net actuarial loss | 1,682 | 861 | 752 | ||||||||
Prior service cost | 9 | 8 | 9 | ||||||||
1,691 | 869 | 761 | |||||||||
Defined benefit pension plan adjustments | (4,332 | ) | 4,586 | (1,409 | ) | ||||||
Total other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | (7,130 | ) | 2,722 | (771 | ) | ||||||
Comprehensive income | $ | 16,039 | $ | 25,575 | $ | 23,824 | |||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements. | |||||||||||
F-5
THE DAVEY TREE EXPERT COMPANY
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY
(In thousands, except per share data)
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||
Common shares | ||||||||||||||||||||
At beginning and end of year | 21,457 | $ | 21,457 | 21,457 | $ | 21,457 | 21,457 | $ | 21,457 | |||||||||||
Additional paid-in capital | ||||||||||||||||||||
At beginning of year | 5,008 | 3,431 | 1,721 | |||||||||||||||||
Shares sold to employees | 3,417 | 2,745 | 1,742 | |||||||||||||||||
Options exercised | (273 | ) | (2,273 | ) | (2,100 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Subscription shares, issued | 184 | 98 | 428 | |||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | 1,125 | 1,007 | 1,640 | |||||||||||||||||
At end of year | 9,461 | 5,008 | 3,431 | |||||||||||||||||
Common shares subscribed, unissued | ||||||||||||||||||||
At beginning of year | 531 | 10,467 | 561 | 11,055 | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Common shares, subscribed | — | — | — | — | 638 | 12,563 | ||||||||||||||
Common shares, issued | (39 | ) | (758 | ) | (21 | ) | (409 | ) | (77 | ) | (1,508 | ) | ||||||||
Cancellations | (16 | ) | (328 | ) | (9 | ) | (179 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
At end of year | 476 | 9,381 | 531 | 10,467 | 561 | 11,055 | ||||||||||||||
Retained earnings | ||||||||||||||||||||
At beginning of year | 230,975 | 210,652 | 188,613 | |||||||||||||||||
Net income | 23,169 | 22,853 | 24,595 | |||||||||||||||||
Dividends, $ .1850 per share | (2,674 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Dividends, $ .1800 per share | — | (2,530 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||
Dividends, $ .1775 per share | — | — | (2,556 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
At end of year | 251,470 | 230,975 | 210,652 | |||||||||||||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | ||||||||||||||||||||
At beginning of year | (4,393 | ) | (7,115 | ) | (6,344 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Currency translation adjustments | (2,798 | ) | (1,864 | ) | 561 | |||||||||||||||
Net gain on interest rate contracts | — | — | 77 | |||||||||||||||||
Defined benefit pension plans | (4,332 | ) | 4,586 | (1,409 | ) | |||||||||||||||
At end of year | (11,523 | ) | (4,393 | ) | (7,115 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Common shares held in treasury | ||||||||||||||||||||
At beginning of year | 8,018 | (125,034 | ) | 7,731 | (112,159 | ) | 7,611 | (104,721 | ) | |||||||||||
Shares purchased | 727 | (19,598 | ) | 931 | (21,887 | ) | 892 | (18,103 | ) | |||||||||||
Shares sold to employees | (287 | ) | 3,822 | (299 | ) | 3,853 | (327 | ) | 4,390 | |||||||||||
Options exercised | (116 | ) | 1,861 | (319 | ) | 4,776 | (368 | ) | 5,197 | |||||||||||
Subscription shares, issued | (50 | ) | 794 | (26 | ) | 383 | (77 | ) | 1,078 | |||||||||||
At end of year | 8,292 | (138,155 | ) | 8,018 | (125,034 | ) | 7,731 | (112,159 | ) | |||||||||||
Common shares subscription receivable | ||||||||||||||||||||
At beginning of year | (531 | ) | (7,342 | ) | (561 | ) | (9,215 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
Shares subscribed | — | — | — | — | (638 | ) | (9,732 | ) | ||||||||||||
Payments | 39 | 1,543 | 21 | 1,728 | 77 | 517 | ||||||||||||||
Cancellations | 16 | 199 | 9 | 145 | — | — | ||||||||||||||
At end of year | (476 | ) | (5,600 | ) | (531 | ) | (7,342 | ) | (561 | ) | (9,215 | ) | ||||||||
Common Shareholders' Equity at December 31 | 13,165 | $ | 136,491 | 13,439 | $ | 131,138 | 13,726 | $ | 118,106 | |||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements. | ||||||||||||||||||||
F-6
THE DAVEY TREE EXPERT COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In thousands)
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
Operating activities | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 23,169 | $ | 22,853 | $ | 24,595 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Depreciation | 40,970 | 38,231 | 37,365 | |||||||||
Amortization | 2,070 | 1,980 | 1,742 | |||||||||
Gain on sale of assets | (806 | ) | (1,294 | ) | (1,802 | ) | ||||||
Deferred income taxes | (2,679 | ) | 1,716 | (3,607 | ) | |||||||
Other | (5,638 | ) | (3,228 | ) | 3,493 | |||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||||||
Accounts receivable | (4,489 | ) | 10,307 | (24,294 | ) | |||||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 1,206 | (2,308 | ) | (1,145 | ) | |||||||
Self-insurance accruals | 2,116 | (5,021 | ) | 4,468 | ||||||||
Other assets, net | (6,640 | ) | (6,926 | ) | 3,121 | |||||||
26,110 | 33,457 | 19,341 | ||||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 49,279 | 56,310 | 43,936 | |||||||||
Investing activities | ||||||||||||
Capital expenditures: | ||||||||||||
Equipment | (46,228 | ) | (42,462 | ) | (29,294 | ) | ||||||
Land and buildings | (9,503 | ) | (2,743 | ) | (440 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from sales of property and equipment | 1,366 | 2,080 | 2,955 | |||||||||
Purchases of businesses | (9,695 | ) | (80 | ) | (4,400 | ) | ||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (64,060 | ) | (43,205 | ) | (31,179 | ) | ||||||
Financing activities | ||||||||||||
Revolving credit facility borrowings/(payments), net | 24,500 | (4,200 | ) | 4,200 | ||||||||
Borrowings/(payments) of notes payable | (1,091 | ) | 1,442 | 1,155 | ||||||||
Borrowings/(payments) of long-term debt and capital leases | 5,695 | (583 | ) | (649 | ) | |||||||
Purchase of common shares for treasury | (19,598 | ) | (21,887 | ) | (18,103 | ) | ||||||
Sale of common shares from treasury | 8,762 | 9,582 | 10,735 | |||||||||
Cash received on common-share subscriptions | 1,741 | 1,285 | 1,841 | |||||||||
Dividends | (2,674 | ) | (2,530 | ) | (2,556 | ) | ||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 17,335 | (16,891 | ) | (3,377 | ) | |||||||
Increase (Decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 2,554 | (3,786 | ) | 9,380 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year | 15,861 | 19,647 | 10,267 | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents, end of year | $ | 18,415 | $ | 15,861 | $ | 19,647 | ||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements. | ||||||||||||
F-7
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
A. | Our Business |
We provide a wide range of arboriculture, horticulture, environmental and consulting services to residential, utility, commercial and government entities throughout the United States and Canada. We have two reportable operating segments organized by type or class of customer: Residential and Commercial, and Utility.
Residential and Commercial--Residential and Commercial provides services to our residential and commercial customers including: the treatment, preservation, maintenance, removal, planting of trees, shrubs and other plant life; the practice of landscaping, grounds maintenance, tree surgery, tree feeding and tree spraying; the application of fertilizer, herbicides and insecticides; and, natural resource management and consulting, forestry research and development, and environmental planning.
Utility--Utility is principally engaged in providing services to our utility customers--investor-owned, municipal utilities, and rural electric cooperatives--including: the practice of line-clearing and vegetation management around power lines, rights-of-way and chemical brush control; and, natural resource management and consulting, forestry research and development and environmental planning.
We also maintain research, technical support and laboratory diagnostic facilities.
When we refer to “we,” “us,” “our,” “Davey Tree,” and the “Company,” we mean The Davey Tree Expert Company, unless the context indicates otherwise.
B. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
Principles of Consolidation and Basis of Presentation--The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Davey Tree and our wholly-owned subsidiaries and were prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”) as codified in the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC"). Intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates in Financial Statement Preparation--The preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect reported amounts. Estimates are used for, but not limited to, accounts receivable valuation, depreciable lives of fixed assets, self-insurance accruals, and revenue recognition. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Property and Equipment--Property and equipment are stated at cost. Repair and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred. Depreciation is computed for financial reporting purposes by the straight-line method for land improvements, building and leasehold improvements and by the declining-balance method for equipment, based on the estimated useful lives of the assets, as follows:
Land improvements | 5 to 20 years |
Buildings | 5 to 20 years |
Equipment | 3 to 10 years |
Leasehold improvements | Shorter of lease term or estimated useful life; ranging from 5-to-20 years |
Intangible Assets--Intangible assets with finite lives, primarily customer lists, noncompete agreements and tradenames, are amortized by the straight-line method based on their estimated useful lives, ranging from one-to-ten years.
Long-Lived Assets--We assess potential impairment to our long-lived assets, other than goodwill, when there is evidence that events or changes in circumstances have made recovery of the asset’s carrying value unlikely and the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the estimated future undiscounted cash flow. In the event the assessment indicates that the carrying amounts
F-8
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
B. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued) |
may not be recoverable, an impairment loss would be recognized to reduce the asset’s carrying amount to its estimated fair value based on the present value of the estimated future cash flows.
Goodwill--Goodwill is recorded when the cost of acquired businesses exceeds the fair value of the identified net assets acquired. Goodwill is not amortized, but tested for impairment annually or when events or circumstances indicate that impairment may have occurred. Annually, we perform the impairment tests for goodwill during the fourth quarter. Impairment of goodwill is tested at the reporting-unit level, which for us are also our business segments. Impairment of goodwill is tested by comparing the reporting unit’s carrying value, including goodwill, to the fair value of the reporting unit. The fair values of the reporting units are estimated using discounted projected cash flows. If the carrying value of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value, goodwill is considered impaired and a second step is performed to measure the amount of impairment loss, if any. We conducted our annual impairment tests and determined that no impairment loss was required to be recognized in 2014 or for any prior periods. There were no events or circumstances from the date of our assessment through December 31, 2014 that would impact this conclusion.
Self-Insurance Accruals--We are generally self-insured for losses and liabilities related primarily to workers’ compensation, vehicle liability and general liability claims. We use commercial insurance as a risk-reduction strategy to minimize catastrophic losses. Ultimate losses are accrued based upon estimates of the aggregate liability for claims incurred using certain actuarial assumptions followed in the insurance industry and based on Company-specific experience.
Our self-insurance accruals include claims for which the ultimate losses will develop over a period of years. Accordingly, our estimates of ultimate losses can change as claims mature. Our accruals also are affected by changes in the number of new claims incurred and claim severity. The methods for estimating the ultimate losses and the total cost of claims were determined by third-party consulting actuaries; the resulting accruals are reviewed by management, and any adjustments arising from changes in estimates are reflected in income.
The workers' compensation accruals are discounted as the amount and timing of cash payments related to those accruals are reliably determinable given the nature of workers' compensation benefits and the level of historical claim volume to support the actuarial assumptions and judgments used to derive the expected loss payment pattern. The workers' compensation accruals are discounted using an interest rate that approximates the long-term investment yields over the expected payment pattern of unpaid losses.
Our self-insurance accruals are based on estimates and, while we believe that the amounts accrued are adequate and not excessive, the ultimate claims may be in excess of or less than the amounts provided.
Stock-Based Compensation--Stock-based compensation cost for all share-based payment plans is measured at fair value on the date of grant and recognized over the employee service period on the straight-line recognition method for awards expected to vest. The fair value of all stock-based payment plans—stock option plans, stock-settled stock appreciation rights, and performance-based restricted stock units as well as our Employee Stock Purchase Plan—is determined by the number of awards granted and the price of our common stock. The fair value of each award is estimated on the date of grant using a binomial option-pricing model. The binomial model considers a range of assumptions related to volatility, risk-free interest rate and employee exercise behavior. Expected volatilities utilized in the binomial model are based on historical volatility of our share prices and other factors. Similarly, the dividend yield is based on historical experience and expected future changes. The binomial model also incorporates exercise and forfeiture assumptions based on an analysis of historical data. The expected life of the stock-based awards is derived from the output of the binomial model and represents the period of time that awards granted are expected to be outstanding.
Defined Benefit Pension Plans--We record annual expenses relating to our defined benefit pension plans based on calculations that include various actuarial assumptions, including discount rates and expected long-term rates of return on plan assets. Actuarial assumptions are reviewed annually with modifications made to the assumptions, if necessary, based on current rates and trends. The effects of the actuarial gains or losses are amortized over future service periods. The funded status (that is, the projected benefit obligation less the fair value of plan assets) for each plan is reported in our balance sheet
F-9
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
B. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued) |
using a December 31 measurement date. Changes in the funded status of the plans are recognized in the year in which the changes occur and reported in comprehensive income (loss).
Income Taxes--We compute taxes on income in accordance with the tax rules and regulations where the income is earned. The income tax rates imposed by these taxing authorities vary. Taxable income may differ from pretax income for financial reporting purposes. We compute and recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of temporary differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax bases of our assets and liabilities. Changes in tax rates and laws are reflected in income in the period when such changes are enacted. We account for uncertain tax positions by recognizing the financial statement effects of a tax position only when, based upon the technical merits, it is more-likely-than-not that the position will be sustained upon examination.
Earnings Per Share--Basic earnings per share is determined by dividing the income available to common shareholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted earnings per share is computed similarly to basic earnings per share except that the weighted-average number of shares is increased to include the effect of stock awards that were granted and outstanding during the period.
Revenue Recognition--Revenues from residential and commercial services are recognized as the services are provided and amounts are determined to be collectible. Revenues from contractual arrangements, primarily with utility services customers, are recognized based on costs incurred to total estimated contract costs. During the performance of such contracts, estimated final contract prices and costs are periodically reviewed and revisions are made, as required, to the revenue recognized. On cost-plus-fee contracts, revenue is recognized to the extent of costs incurred plus a proportionate amount of fees earned, and on time-and-material contracts, revenue is recognized to the extent of billable rates times hours worked, plus material and other reimbursable costs incurred. Revisions arise in the normal course of providing services to utility services customers and generally relate to changes in contract specifications and cost allowability. Such revisions are recorded when realization is probable and can be reliably estimated.
Concentration of Credit Risk--Credit risk represents the accounting loss that would be recognized if the counterparties failed to perform as contracted. The principal financial instruments subject to credit risk follow:
Cash--To limit our exposure, we transact our business and maintain banking relationships and our derivative contracts with high credit-quality financial institutions.
Accounts Receivable--Our residential and commercial customers are located geographically throughout the United States and Canada and, as to commercial customers, within differing industries; thus, minimizing credit risk. The credit exposure of utility services customers is directly affected by conditions within the utility industries as well as the financial condition of individual customers. One utility customer approximated 8% of revenues during 2014, 9% in 2013 and 10% in 2012. To reduce credit risk, we evaluate the credit of customers, but generally do not require advance payments or collateral. Exposure to losses on receivables is principally dependent on each customer’s financial condition.
Currency Translation Adjustments--All assets and liabilities of our Canadian operations are translated into United States dollars at year-end exchange rates while revenues and expenses are translated at weighted-average exchange rates in effect during the year. Translation adjustments are recorded as accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in shareholders’ equity.
Interest Rate Risk Management--We have entered into interest rate contracts, from time-to-time, with the objective of altering interest rate exposures related to variable rate debt. In the interest rate contracts, we have agreed with a financial institution to exchange, at specified intervals, the difference between fixed and floating interest amounts calculated on an agreed-upon notional principal amount.
Comprehensive Income (Loss)--Comprehensive income (loss) includes net income and other comprehensive income or loss. Other comprehensive income (loss) refers to revenues, expenses, gains and losses that under U.S. GAAP are included in
F-10
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
B. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued) |
comprehensive income but are excluded from net income as these amounts are recorded directly as an adjustment to shareholders’ equity, net of tax.
C. | Recent Accounting Guidance |
Accounting Standards Update 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606)--In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers ("Topic 606"),” which will replace all current U.S. GAAP guidance on revenue recognition and eliminate all industry-specific guidance.
The new revenue recognition guidance provides a unified model to determine when and how revenue is recognized. The underlying principle is that an entity should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods and services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration for which the entity expects in exchange for those goods and services. The guidance provides a five-step analysis of transactions to determine when and how revenue is recognized. Other major provisions include capitalization of certain contract costs, consideration of the time value of money in the transaction price, and allowing estimates of variable consideration to be recognized before contingencies are resolved in certain circumstances. The guidance also requires enhanced information to be presented in the financial statements regarding the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from an entity’s contracts with customers.
Unless the FASB delays the effective date of the new guidelines, it will be effective for Davey Tree beginning January 1, 2017 and can be applied either retrospectively to each period presented or as a cumulative-effect adjustment as of the date of adoption. Early adoption is not permitted. We are currently evaluating the methods of adoption as well as the impact that it may have, if any, on our consolidated financial statements. The new revenue guidance will supersede existing revenue guidance affecting our Company, and may also affect our business processes and our information technology systems. As a result, our evaluation of the effect of the new revenue guidance will extend over future periods.
D. | Business Combinations |
Our investments in businesses were: (a) $12,853 in 2014, including $1,078 liabilities assumed and debt issued of $2,080; (b) $110 in 2013, including no liabilities assumed and $30 debt issued; and (c) $6,368 in 2012, including liabilities assumed of $1,868 and $100 debt issued.
The net assets of the businesses acquired are accounted for under the acquisition method and were recorded at their fair values at the dates of acquisition. The excess of the purchase price over the estimated fair values of the net assets acquired was recorded as an increase in goodwill of approximately $4,624 in 2014 (all of which is deductible for tax purposes), no goodwill in 2013 and $1,820 in 2012 (of which $258 is deductible for tax purposes).
The results of operations of acquired businesses have been included in the consolidated statements of operations beginning as of the effective dates of acquisition. The effect of these acquisitions on our consolidated revenues and results of operations, either individually or in the aggregate, for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 or 2012 was not significant.
E. | Accounts Receivable, Net and Supplemental Balance Sheet Information |
Accounts receivable, net, consisted of the following:
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Accounts receivable | $ | 98,657 | $ | 93,156 | |||
Receivables under contractual arrangements | 15,362 | 14,309 | |||||
114,019 | 107,465 | ||||||
Less allowances for doubtful accounts | 2,421 | 2,209 | |||||
$ | 111,598 | $ | 105,256 | ||||
Receivables under contractual arrangements consist of work-in-process in accordance with the terms of contracts, primarily, with utility services customers.
The following items comprise the amounts included in the balance sheets:
December 31, | |||||||
Other current assets | 2014 | 2013 | |||||
Refundable income taxes | $ | 2,122 | $ | 5,317 | |||
Deferred income taxes | 8,927 | 7,715 | |||||
Note receivable | 4,319 | — | |||||
Other | 759 | 813 | |||||
Total | $ | 16,127 | $ | 13,845 | |||
December 31, | |||||||
Other assets, noncurrent | 2014 | 2013 | |||||
Assets invested for self-insurance | $ | 13,684 | $ | 12,716 | |||
Investment--cost-method affiliate | 1,168 | 1,168 | |||||
Deferred income taxes | 1,705 | — | |||||
Other | 2,305 | 3,033 | |||||
Total | $ | 18,862 | $ | 16,917 | |||
F-11
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
E. | Accounts Receivable, Net and Supplemental Balance Sheet Information (continued) |
December 31, | |||||||
Accrued expenses | 2014 | 2013 | |||||
Employee compensation | $ | 19,195 | $ | 18,578 | |||
Accrued compensated absences | 8,034 | 6,953 | |||||
Self-insured medical claims | 2,722 | 2,503 | |||||
Customer advances, deposits | 2,030 | 2,191 | |||||
Taxes, other than income | 2,054 | 5,730 | |||||
Other | 890 | 903 | |||||
Total | $ | 34,925 | $ | 36,858 | |||
December 31, | |||||||
Other liabilities, noncurrent | 2014 | 2013 | |||||
Pension and retirement plans | $ | 16,311 | $ | 7,760 | |||
Deferred income taxes | — | 2,564 | |||||
Other | 2,657 | 1,956 | |||||
Total | $ | 18,968 | $ | 12,280 | |||
F. | Supplemental Operating Information |
Other Nonoperating Income (Expense), Net
Other nonoperating (expense) income, net, included in the statements of operations follows:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Other nonoperating expense, net | $ | (3,050 | ) | $ | (2,827 | ) | $ | (2,611 | ) | ||
Other nonoperating (expense) income, net, includes foreign currency (i) losses of $235 for 2014, (ii) losses of $146 for 2013, and (iii) gains of $11 for 2012 on the intercompany balances of our Canadian operations.
F-12
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
G. | Supplemental Cash Flow Information |
Supplemental cash flow information follows:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
Supplemental cash flow information | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
Interest paid | $ | 2,948 | $ | 2,732 | $ | 2,683 | |||||
Income taxes paid, net | 13,577 | 20,133 | 11,131 | ||||||||
Noncash transactions: | |||||||||||
Debt issued for purchases of businesses | $ | 2,080 | $ | 30 | $ | 100 | |||||
Detail of acquisitions: | |||||||||||
Assets acquired: | |||||||||||
Receivables | $ | 1,852 | $ | — | $ | 474 | |||||
Operating supplies | 61 | — | 209 | ||||||||
Prepaid expense | 213 | — | 47 | ||||||||
Equipment | 1,726 | — | 1,826 | ||||||||
Deposits and other | 558 | — | — | ||||||||
Intangibles | 8,443 | 110 | 3,812 | ||||||||
Liabilities assumed | (1,078 | ) | — | (1,868 | ) | ||||||
Debt issued for purchases of businesses | (2,080 | ) | (30 | ) | (100 | ) | |||||
Cash paid | $ | 9,695 | $ | 80 | $ | 4,400 | |||||
H. | Identified Intangible Assets and Goodwill, Net |
The carrying amount of the identified intangibles and goodwill acquired in connection with our investments in businesses were as follows:
Weighted-Average Amortization Period (Years) | December 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | |||||||||||||||
Amortized intangible assets: | ||||||||||||||||||
Customer lists/relationships | 2.5 | years | $ | 16,076 | $ | 12,560 | $ | 14,429 | $ | 11,398 | ||||||||
Employment-related | 2.8 | years | 7,026 | 5,776 | 5,631 | 5,474 | ||||||||||||
Tradenames | 3.3 | years | 5,286 | 4,153 | 4,525 | 3,754 | ||||||||||||
Total | 28,388 | $ | 22,489 | 24,585 | $ | 20,626 | ||||||||||||
Less accumulated amortization | 22,489 | 20,626 | ||||||||||||||||
Identified intangibles, net | 5,899 | 3,959 | ||||||||||||||||
Unamortized intangible assets: | ||||||||||||||||||
Goodwill | Not amortized | 28,164 | 23,602 | |||||||||||||||
$ | 34,063 | $ | 27,561 | |||||||||||||||
F-13
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
H. | Identified Intangible Assets and Goodwill, Net (continued) |
The changes in the carrying amounts of goodwill, by segment, for the year ended December 31, 2014 follow:
Balance at January 1, 2014 | Acquisitions | Translation and Other Adjustments | Balance at December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||
Utility | $ | 3,064 | $ | 360 | $ | — | $ | 3,424 | |||||||
Residential and Commercial | 20,538 | 4,264 | (62 | ) | 24,740 | ||||||||||
Total | $ | 23,602 | $ | 4,624 | $ | (62 | ) | $ | 28,164 | ||||||
Estimated future aggregate amortization expense of intangible assets--The estimated aggregate amortization expense of intangible assets, as of December 31, 2014, in each of the next five years follows:
Estimated Future Amortization Expense | ||||
Year ending December 31, 2015 | $ | 1,876 | ||
2016 | 1,670 | |||
2017 | 1,210 | |||
2018 | 473 | |||
2019 | 338 | |||
I. | Short-Term and Long-Term Debt |
Short-term debt consisted of the following:
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Current portion of long-term debt | $ | 8,281 | $ | 8,434 | |||
At December 31, 2014, we also had unused short-term lines of credit with several banks totaling $7,281, generally at the banks' prime rate or LIBOR plus a margin adjustment of .75% to 1.50%. Long-term debt consisted of the following:
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Revolving credit facility | |||||||
Swing-line borrowings | $ | 7,500 | $ | — | |||
LIBOR borrowings | 37,000 | 20,000 | |||||
44,500 | 20,000 | ||||||
Senior unsecured notes | 30,000 | 30,000 | |||||
Term loans | 15,087 | 8,468 | |||||
89,587 | 58,468 | ||||||
Less current portion | 8,281 | 8,434 | |||||
$ | 81,306 | $ | 50,034 | ||||
Revolving Credit Facility and 5.09% Senior Unsecured Notes--In November 2013, the Company amended its revolving credit facility. The amended and restated credit agreement, which expires in November 2018, permits borrowings as defined up to $175,000 including a letter of credit sublimit of $100,000 and a swing-line commitment of $15,000 (the previous
F-14
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
I. | Short-Term and Long-Term Debt (continued) |
agreement permitted borrowings up to $140,000 with a letter of credit sublimit of $100,000). Under certain circumstances, the amount available under the revolving credit facility may be increased to $210,000. The revolving credit facility contains certain affirmative and negative covenants customary for this type of facility and includes financial covenant ratios with respect to a maximum leverage ratio and a maximum balance sheet leverage ratio.
On July 22, 2010, we issued $30,000 of 5.09% Senior Unsecured Notes, Series A, due July 22, 2020 (the "5.09% Senior Notes"). The 5.09% Senior Notes were issued pursuant to a Master Note Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”), between the Company and the purchasers of the 5.09% Senior Notes. The net proceeds of the 5.09% Senior Notes were used to pay down borrowings under our revolving credit facility.
The 5.09% Senior Notes are equal in right of payment with our revolving credit facility and all other senior unsecured obligations of the Company. Interest is payable semiannually and five equal, annual principal payments commence on July 22, 2016 (the sixth anniversary of issuance). The Purchase Agreement contains customary events of default and covenants related to limitations on indebtedness and transactions with affiliates and the maintenance of certain financial ratios.
As of December 31, 2014, we had unused commitments under the facility approximating $70,964, and $104,036 committed, which consisted of borrowings of $44,500 and issued letters of credit of $59,536. Borrowings outstanding bear interest, at Davey Tree’s option, of either (a) the base rate or (b) LIBOR plus a margin adjustment ranging from .75% to 1.50%--with the margin adjustments in both instances based on the Company's leverage ratio at the time of borrowing. The base rate is the greater of (i) the agent bank’s prime rate, (ii) LIBOR plus 1.5%, or (iii) the federal funds rate plus .5%. A commitment fee ranging from .10% to .25% is also required based on the average daily unborrowed commitment.
Term Loans, Weighted-Average Interest Rate--The weighted-average interest on the term loans approximated 3.03% at December 31, 2014 and 2.04% at December 31, 2013.
Aggregate Maturities of Long-Term Debt--Aggregate maturities of long-term debt for the five years subsequent to December 31, 2014 were as follows: 2015--$8,281; 2016--$7,234; 2017--$6,803; 2018--$6,150; and, 2019--$6,159.
J. | Self-Insurance Accruals |
Components of our self-insurance accruals for workers’ compensation, vehicle liability and general liability follow:
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Workers' compensation | $ | 32,982 | $ | 35,199 | |||
Present value discount | 1,658 | 1,796 | |||||
31,324 | 33,403 | ||||||
Vehicle liability | 4,940 | 4,885 | |||||
General liability | 22,629 | 18,424 | |||||
Total | 58,893 | 56,712 | |||||
Less current portion | 23,007 | 22,057 | |||||
Noncurrent portion | $ | 35,886 | $ | 34,655 | |||
F-15
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
J. | Self-Insurance Accruals (continued) |
The changes in our self-insurance accruals and the discount rate used for the workers’ compensation accrual are summarized in the table below.
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Balance, beginning of year | $ | 56,712 | $ | 61,733 | |||
Provision for claims | 30,340 | 27,084 | |||||
Payment of claims | 28,159 | 32,105 | |||||
Balance, end of year | $ | 58,893 | $ | 56,712 | |||
Workers' compensation discount rate | 2.00 | % | 2.00 | % | |||
K. | Operating Lease Obligations |
We lease facilities under noncancelable operating leases, which are used for district office and warehouse operations. These leases extend for varying periods of time up to five years and, in some cases, contain renewal options. Minimum rental commitments under noncancelable operating leases, as of December 31, 2014 were as follows:
Minimum lease obligations | Operating Lease Obligations | |||
Year ending December 31, 2015 | $ | 5,813 | ||
2016 | 4,470 | |||
2017 | 2,918 | |||
2018 | 1,764 | |||
2019 | 868 | |||
2020 and after | 1,398 | |||
Total minimum lease payments | $ | 17,231 | ||
Total rent expense under all operating leases was $6,554 in 2014, $6,167 in 2013 and $5,860 in 2012.
L. | Common Shares and Preferred Shares |
Preferred Shares--We have authorized a class of 4,000,000 preferred shares, no par value, of which none were issued.
Common Shares--The number of common shares authorized is 24,000,000, par value $1.00. The number of common shares issued during each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014 was 21,456,880. The number of shares in the treasury for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014 was as follows: 2014--8,291,947; 2013--$8,018,269; and 2012--$7,730,878.
Our common shares are not listed or traded on an established public trading market, and market prices are, therefore, not available. Semiannually, an independent stock valuation firm determines the fair market value of our common shares based upon our performance and financial condition. Since 1979, we have provided a ready market for all shareholders through our direct purchase of their common shares, although we are under no obligation to do so. During 2014, purchases of common shares totaled 727,436 shares for $19,598 in cash; we also had direct sales to directors and employees of 13,061 shares for $346, excluding those shares issued through either the exercise of options or the Employee Stock Purchase Plan. We also sold 53,857 shares to our 401(k) plan for $1,444 and issued 105,589 shares to participant accounts to satisfy our liability for the
F-16
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
L. | Common Shares and Preferred Shares (continued) |
2013 employer match in the amount of $2,788. The liability accrued at December 31, 2014 for the 2014 employer match was $2,922. There were also 115,029 shares purchased during 2014 under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan.
Common Shares Outstanding--The table below reconciles the activity of the common shares outstanding:
December 31, | |||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||
Shares outstanding, beginning of year | 13,438,611 | 13,726,002 | |||
Shares purchased | (727,436 | ) | (931,078 | ) | |
Shares sold | 287,536 | 299,330 | |||
Stock subscription offering, employee cash purchases | 49,940 | 25,837 | |||
Options exercised | 116,282 | 318,520 | |||
(273,678 | ) | (287,391 | ) | ||
Shares outstanding, end of year | 13,164,933 | 13,438,611 | |||
On December 31, 2014, we had 13,164,933 common shares outstanding, employee and director options exercisable to purchase 388,851 common shares, partially-paid subscription for 476,197 common shares and purchase rights outstanding for 195,029 common shares.
Stock Subscription Offering--Beginning May 2012, the Company offered to eligible employees and nonemployee directors the right to subscribe to common shares of the Company at $19.70 per share in accordance with the provisions of The Davey Tree Expert Company 2004 Omnibus Stock Plan and the rules of the Compensation Committee of the Company's Board of Directors (collectively, the "plan"). The offering period ended on August 1, 2012 and resulted in the subscription of 637,714 common shares for $12,563 at $19.70 per share.
Under the plan, a participant in the offering purchasing common shares for an aggregate purchase price of less than $5 had to pay with cash. All participants (excluding Company directors and officers) purchasing $5 or more of the common shares had an option to finance their purchase through a down-payment of at least 10% of the total purchase price and a seven-year promissory note for the balance due with interest at 2%. Payments on the promissory note can be made either by payroll deductions or annual lump-sum payments of both principal and interest.
Common shares purchased under the plan have been pledged as security for the payment of the promissory note and the common shares will not be issued until the promissory note is paid-in-full. Dividends will be paid on all subscribed shares, subject to forfeiture to the extent that payment is not ultimately made for the shares.
All participants in the offering purchasing in excess of $5 of common shares were granted a "right" to purchase one additional common share at a price of $19.70 per share for every three common shares purchased under the plan. As a result of the stock subscription, employees were granted rights to purchase 211,800 common shares. Each right may be exercised at the rate of one-seventh per year and will expire seven years after the date that the right was granted. Employees may not exercise a right should they cease to be employed by the Company.
M. | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
Comprehensive income (loss) is comprised of net income and other adjustments that relate to foreign currency translation adjustments, changes in the fair value of interest rate contracts qualifying as cash flow hedges, and defined benefit pension plan adjustments. We do not provide income taxes on currency translation adjustments, as the earnings of our Canadian operations are considered to be indefinitely reinvested.
F-17
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
M. | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) (continued) |
The following summarizes the components of other comprehensive income (loss) accumulated in shareholders’ equity:
Foreign Currency Translation Adjustments | Interest Rate Cash Flow Hedges | Defined Benefit Pension Plans | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income/(Loss) | |||||||||||||
Balance at January 1, 2012 | $ | 2,950 | $ | (77 | ) | $ | (9,217 | ) | $ | (6,344 | ) | |||||
Unrealized gains (losses) | 561 | — | — | 561 | ||||||||||||
Unrealized gains in fair value | — | 123 | — | 123 | ||||||||||||
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | — | — | 1,268 | 1,268 | ||||||||||||
Tax effect | — | — | (507 | ) | (507 | ) | ||||||||||
Unrecognized amounts from defined benefit pension plans | — | — | (3,712 | ) | (3,712 | ) | ||||||||||
Tax effect | — | (46 | ) | 1,542 | 1,496 | |||||||||||
Net of tax amount | 561 | 77 | (1,409 | ) | (771 | ) | ||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2012 | $ | 3,511 | $ | — | $ | (10,626 | ) | $ | (7,115 | ) | ||||||
Unrealized gains (losses) | (1,864 | ) | — | — | (1,864 | ) | ||||||||||
Unrealized gains in fair value | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | — | — | 1,401 | 1,401 | ||||||||||||
Tax effect | — | — | (532 | ) | (532 | ) | ||||||||||
Unrecognized amounts from defined benefit pension plans | — | — | 6,306 | 6,306 | ||||||||||||
Tax effect | — | — | (2,589 | ) | (2,589 | ) | ||||||||||
Net of tax amount | (1,864 | ) | — | 4,586 | 2,722 | |||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2013 | $ | 1,647 | $ | — | $ | (6,040 | ) | $ | (4,393 | ) | ||||||
Unrealized gains (losses) | (2,798 | ) | — | — | (2,798 | ) | ||||||||||
Unrealized gains in fair value | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | — | — | 2,786 | 2,786 | ||||||||||||
Tax effect | — | — | (1,095 | ) | (1,095 | ) | ||||||||||
Unrecognized amounts from defined benefit pension plans | — | — | (9,923 | ) | (9,923 | ) | ||||||||||
Tax effect | — | — | 3,900 | 3,900 | ||||||||||||
Net of tax amount | (2,798 | ) | — | (4,332 | ) | (7,130 | ) | |||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2014 | $ | (1,151 | ) | $ | — | $ | (10,372 | ) | $ | (11,523 | ) | |||||
The amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) related to defined benefit pension plans for 2014, 2013 and 2012 are included in net periodic pension expense and classified in the statement of operations as costs and expenses, general and administrative.
N. | The Davey 401KSOP and Employee Stock Ownership Plan |
On March 15, 1979, we consummated a plan, which transferred control of the Company to our employees. As a part of this plan, we initially sold 120,000 common shares (presently, 11,520,000 common shares adjusted for stock splits) to our Employee Stock Ownership Trust (“ESOT”) for $2,700. The Employee Stock Ownership Plan (“ESOP”), in conjunction with the related ESOT, provided for the grant to certain employees of certain ownership rights in, but not possession of, the common shares held by the trustee of the ESOT. Annual allocations of shares have been made to individual accounts established for the benefit of the participants.
F-18
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
N. | The Davey 401KSOP and Employee Stock Ownership Plan (continued) |
Defined Contribution and Savings Plans--Most employees are eligible to participate in The Davey 401KSOP and ESOP. Effective January 1, 1997, the plan commenced operations and retained the existing ESOP participant accounts and incorporated a deferred savings plan (a "401(k) plan") feature. Participants in the 401(k) plan are allowed to make before-tax contributions, within Internal Revenue Service established limits, through payroll deductions. Effective January 1, 2009 we match, in either cash or our common shares, 100% of the first one percent and 50% of the next three percent of each participant's before-tax contribution, limited to the first four percent of the employee's compensation deferred each year. All nonbargaining domestic employees who attained age 21 and completed one year of service are eligible to participate. In May 2004, we adopted the 401K Match Restoration Plan, a defined contribution plan that supplements the retirement benefits of certain employees that participate in the savings plan feature of The Davey 401KSOP and ESOP Plan, but are limited in contributions because of tax rules and regulations.
Total compensation for these plans, consisting primarily of the employer match, was $2,922 in 2014, $2,788 in 2013, and $2,643 in 2012.
O. | Stock-Based Compensation |
Our shareholders approved the 2014 Omnibus Stock Plan (the “2014 Stock Plan”) at our annual meeting of shareholders on May 20, 2014. The 2014 Stock Plan replaced the expired 2004 Omnibus Stock Plan (the “2004 plan”) previously approved by the shareholders in 2004. The 2014 Stock Plan is administered by the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors and will remain in effect for ten years. All directors of the Company and employees of the Company and its subsidiaries are eligible to participate in the 2014 Stock Plan. The 2014 Stock Plan (similar to the 2004 plan) continues the maintenance of the Employee Stock Purchase Plan, as well as provisions for the grant of stock options and other stock-based incentives. The 2014 Stock Plan provides for the grant of five percent of the number of the Company’s common shares outstanding as of the first day of each fiscal year plus the number of common shares that were available for grant of awards, but not granted, in prior years. In no event, however, may the number of common shares available for the grant of awards in any fiscal year exceed ten percent of the common shares outstanding as of the first day of that fiscal year. Common shares subject to an award that is forfeited, terminated, or canceled without having been exercised are generally added back to the number of shares available for grant under the 2014 Stock Plan.
Stock-based compensation expense under all share-based payment plans—our Employee Stock Purchase Plan, stock option plans, stock-settled stock appreciation rights, and performance-based restricted stock units—included in the results of operations follows:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Compensation expense, all share-based payment plans | $ | 1,860 | $ | 1,411 | $ | 1,508 | |||||
Income tax benefit | 549 | 348 | 383 | ||||||||
Stock-based compensation consisted of the following:
F-19
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
O. | Stock-Based Compensation (continued) |
Employee Stock Purchase Plan--Under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan, all full-time employees with one year of service are eligible to purchase, through payroll deduction, common shares. Employee purchases under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan are at 85% of the fair market value of the common shares--a 15% discount. Purchases under the plan, at 85% of the fair market value of the common shares, have been as follows:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Number of employees participating | 1,684 | 1,500 | 1,157 | ||||||||
Shares purchased during the year | 115,029 | 118,444 | 136,947 | ||||||||
Weighted-average per share purchase price paid | $ | 23.07 | $ | 20.01 | $ | 17.20 | |||||
Cumulative shares purchased since 1982 | 8,751,255 | 8,636,226 | 8,517,782 | ||||||||
Compensation costs are recognized as payroll deductions are made. The 15% discount of total shares purchased under the plan resulted in compensation cost recognized of $463 in 2014, $417 in 2013 and $415 in 2012.
Stock Option Plans-The stock options outstanding were awarded under a graded vesting schedule, measured at fair value, and have a term of ten years. Compensation costs for stock options are recognized over the requisite service period on the straight-line recognition method. Compensation cost recognized for stock options was $398 in 2014, $234 in 2013 and $166 in 2012.
Stock-Settled Stock Appreciation Rights--During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors awarded 127,050 Stock-Settled Stock Appreciation Rights (“SSARs”) to certain management employees and nonemployee directors, which vest ratably over five years. A stock-settled stock appreciation right is an award that allows the recipient to receive common stock equal to the appreciation in the fair market value of our common stock between the date the award was granted and the conversion date of the shares vested.
The following table summarizes the SSARs as of December 31, 2014:
Stock-Settled Stock Appreciation Rights | Number of Rights | Weighted- Average Award Date Value | Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Life | Unrecognized Compensation Cost | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | ||||||||||||
Unvested, January 1, 2014 | 283,453 | $ | 3.15 | ||||||||||||||
Granted | 127,050 | 4.88 | |||||||||||||||
Forfeited | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Vested | (107,232 | ) | 3.26 | ||||||||||||||
Unvested, December 31, 2014 | 303,271 | $ | 3.84 | 2.0 years | $ | 865 | $ | 8,431 | |||||||||
Employee SSARs | 286,294 | $ | 3.92 | 2.0 years | $ | 838 | $ | 7,959 | |||||||||
Nonemployee Director SSARs | 16,977 | $ | 2.29 | 1.8 years | $ | 27 | $ | 472 | |||||||||
Compensation costs for stock appreciation rights are determined using a fair-value method and amortized over the requisite service period. Compensation expense for stock appreciation rights totaled $384 in 2014, $315 in 2013 and $185 in 2012.
F-20
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
O. | Stock-Based Compensation (continued) |
Performance-Based Restricted Stock Units--During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors awarded 39,476 Performance-Based Restricted Stock Units ("PRSUs") to certain management employees.
Similar awards were made in prior periods. The awards vest over specified periods. The following table summarizes
Performance-Based Restricted Stock Units as of December 31, 2014:
Performance-Based Restricted Stock Units | Number of Stock Units | Weighted- Average Grant Date Value | Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Life | Unrecognized Compensation Cost | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | ||||||||||||
Unvested, January 1, 2014 | 95,558 | $ | 19.03 | ||||||||||||||
Granted | 39,476 | 24.64 | |||||||||||||||
Forfeited | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Vested | (17,325 | ) | 17.48 | ||||||||||||||
Unvested, December 31, 2014 | 117,709 | $ | 21.14 | 2.7 years | $ | 1,456 | $ | 3,272 | |||||||||
Employee PRSUs | 103,139 | $ | 20.78 | 2.9 years | $ | 1,236 | $ | 2,867 | |||||||||
Nonemployee Director PRSUs | 14,570 | $ | 23.61 | 1.8 years | $ | 220 | $ | 405 | |||||||||
Compensation cost for awards is determined using a fair-value method, amortized over the requisite service period. “Intrinsic value” is defined as the amount by which the fair market value of a common share of stock exceeds the exercise price of a performance-based restricted stock unit. Compensation expense on restricted stock awards totaled $615 in 2014, $445 in 2013 and $644 in 2012.
The fair value of each award was estimated on the date of grant using a binomial option-pricing model. The binomial model considers a range of assumptions related to volatility, risk-free interest rate and employee exercise behavior. Expected volatilities utilized in the binomial model are based on historical volatility of our share prices and other factors. Similarly, the dividend yield is based on historical experience and expected future changes. The binomial model also incorporates exercise and forfeiture assumptions based on an analysis of historical data. The expected life of the stock-based awards is derived from the output of the binomial model and represents the period of time that awards granted are expected to be outstanding.
The fair values of stock-based awards granted were estimated at the dates of grant with the following weighted-average assumptions:
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||
Volatility rate | 11.2 | % | 11.3 | % | 11.7 | % | ||
Risk-free interest rate | 2.6 | % | 2.1 | % | 1.6 | % | ||
Expected dividend yield | 1.1 | % | 1.5 | % | 1.5 | % | ||
Expected life of awards (years) | 9.4 | 9.4 | 9.1 | |||||
F-21
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
O. | Stock-Based Compensation (continued) |
General Stock Option Information--The following table summarizes activity under the stock option plans for the year ended December 31, 2014:
Stock Options | Number of Options Outstanding | Weighted- Average Exercise Price | Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Life | Unrecognized Compensation Cost | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | ||||||||||||
Outstanding, January 1, 2014 | 662,246 | $ | 16.68 | ||||||||||||||
Granted | 183,500 | 26.40 | |||||||||||||||
Exercised | (74,715 | ) | 13.11 | ||||||||||||||
Forfeited | (900 | ) | 24.98 | ||||||||||||||
Outstanding, December 31, 2014 | 770,131 | $ | 19.33 | 6.3 years | $ | 1,509 | $ | 6,523 | |||||||||
Exercisable, December 31, 2014 | 388,851 | $ | 14.70 | 3.9 years | $ | 5,094 | |||||||||||
“Intrinsic value” is defined as the amount by which the market price of a common share of stock exceeds the exercise price of an option. Information regarding the stock options outstanding at December 31, 2014 is summarized below:
Stock Options Exercise Price | Number Outstanding | Weighted-Average Remaining Contractual Life | Weighted- Average Exercise Price | Number Exercisable | Weighted- Average Exercise Price | ||||||||||||
Employee options: | |||||||||||||||||
$ 11.25 | 170,047 | 1.4 years | $ | 11.25 | 170,047 | $ | 11.25 | ||||||||||
16.00 | 113,234 | 4.8 years | 16.00 | 113,234 | 16.00 | ||||||||||||
16.60 | 108,900 | 5.8 years | 16.60 | 69,420 | 16.60 | ||||||||||||
23.20 | 194,950 | 8.5 years | 23.20 | 36,150 | 23.20 | ||||||||||||
26.40 | 183,000 | 9.5 years | 26.40 | — | 26.40 | ||||||||||||
770,131 | 6.3 years | $ | 19.33 | 388,851 | $ | 14.70 | |||||||||||
We issue common shares from treasury upon the exercise of stock options, stock-settled stock appreciation rights, performance-based restricted stock units or purchases under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan.
Tax Benefits of Stock-Based Compensation--Our total income tax benefit from share-based awards--as recognized in our consolidated statement of operations--for the last three years was: $549 in 2014, $348 in 2013, and $383 in 2012.
Tax benefits for share-based awards are accrued as stock compensation expense and recognized in our consolidated statement of operations. Tax benefits on share-based awards are realized when: (a) stock-settled stock appreciation rights are exercised; (b) performance-based restricted stock units vest; and, (c) stock options are exercised.
When actual tax benefits realized exceed the tax benefits accrued for share-based awards, we realize an excess tax benefit. We report the excess tax benefit as financing cash inflows rather than operating cash inflows. We had excess tax benefits of: $354 in 2014, $242 in 2013, and $402 in 2012.
F-22
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
P. | Defined Benefit Pension Plans |
We have defined benefit pension plans covering certain current and retired U.S. employees. Plans include: (i) the Employee Retirement Plan (“ERP”) for employees hired prior to January 1, 2009; (ii) a plan for bargaining employees not covered by union pension plans (the “SPP”) for which future benefit accruals were frozen effective December 31, 2013; (iii) a Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (“SERP”); and, (iv) a Benefit Restoration Pension Plan (“Restoration Plan”) for certain key employees hired prior to January 1, 2009.
Both the SERP and the Restoration Plan are defined benefit plans under which nonqualifed supplemental pension benefits will be paid in addition to amounts paid under our qualified retirement defined benefit pension plans, which are subject to Internal Revenue Service limitations on covered compensation.
Effective December 31, 2008, enhanced benefits were implemented to our defined contribution savings plan--The Davey 401KSOP and ESOP--at which time, the Board of Directors approved an amendment to freeze the ERP and the Restoration Plan. The ERP was closed to new participants after December 2008. In connection with the freeze of the ERP and Restoration Plan, (i) benefits currently being paid to retirees continue and (ii) benefits accrued through December 31, 2008 for employees covered by the ERP were not affected. All ERP and Restoration Plan balances remain intact and participant account balances, as well as service credits for vesting and retirement eligibility, remain intact and continue in accordance with the terms of the plans. The 2008 freeze of the ERP and Restoration Plan eliminated future accruals only as did the December 31, 2013 freeze of the SPP.
The change in benefit obligations and the fair value of plans assets follows:
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Change in benefit obligation | |||||||
Projected benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | 31,888 | $ | 36,045 | |||
Service cost | 51 | 222 | |||||
Interest cost | 1,618 | 1,515 | |||||
Actuarial (gains)/losses | 4,838 | (4,272 | ) | ||||
New longevity assumptions | 3,229 | — | |||||
Settlements | (4,319 | ) | — | ||||
Benefits paid | (1,429 | ) | (1,622 | ) | |||
Projected benefit obligation at end of year | $ | 35,876 | $ | 31,888 | |||
Accumulated benefit obligation at end of year | $ | 35,475 | $ | 31,599 | |||
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Change in fair value of plan assets | |||||||
Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | $ | 25,754 | $ | 22,957 | |||
Actual return on plan assets, net of expenses | 136 | 3,793 | |||||
Employer contributions | 1,425 | 626 | |||||
Settlements | (4,319 | ) | — | ||||
Benefits paid | (1,429 | ) | (1,622 | ) | |||
Fair value of plan assets at end of year | $ | 21,567 | $ | 25,754 | |||
F-23
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
P. | Defined Benefit Pension Plans (continued) |
The settlements in the change in benefit obligation and in the change in fair value of plan assets, arise from the purchase, during the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2014, of a guaranteed group annuity contract from a third-party insurance company which unconditionally and irrevocably guarantees the full payment of all annuity payments to the participants that were receiving payments from the ERP plan, with the third-party insurance company having assumed all investment risk associated with funding participant payments.
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Funded status of the plans | |||||||
Fair value of plan assets | $ | 21,567 | $ | 25,754 | |||
Projected benefit obligation | 35,876 | 31,888 | |||||
Funded status of the plans | $ | (14,309 | ) | $ | (6,134 | ) | |
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Amounts reported in the consolidated balance sheets | |||||||
Current liability | $ | (38 | ) | $ | (37 | ) | |
Noncurrent liability | (14,271 | ) | (6,097 | ) | |||
Funded status of the plans | $ | (14,309 | ) | $ | (6,134 | ) | |
The change in funded status of the plans and accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) related to our defined benefit pension plans as at December 31, 2014, is primarily a result of lower discount rate and having implemented a new set of mortality and mortality improvement tables. During the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2014, the Society of Actuaries (“SOA”) issued new mortality and mortality improvement tables that reflect longer life expectancies and thereby indicate the amount of estimated aggregate benefit payments to plan participants is increasing. We have incorporated the new SOA tables--new longevity assumptions--into our December 31, 2014 measurement of pension plans’ benefit obligations.
Amounts included in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), related to our defined benefit pension plans follow:
At December 31, 2014 | At December 31, 2013 | ||||||||||||||
Pretax | Net of Tax | Pretax | Net of Tax | ||||||||||||
Amounts reported in accumulated other comprehensive income | |||||||||||||||
Unrecognized net actuarial loss | $ | 17,093 | $ | 10,339 | $ | 9,942 | $ | 5,995 | |||||||
Unrecognized prior service cost | 55 | 33 | 69 | 45 | |||||||||||
$ | 17,148 | $ | 10,372 | $ | 10,011 | $ | 6,040 | ||||||||
To the extent actuarial losses exceed the greater of 10% of the projected benefit obligation or market-related value of plan assets, the unrecognized actuarial losses will be amortized straight-line on a plan-by-plan basis, over the remaining expected future working lifetime of active participants. The total amount of unrecognized prior service cost is also amortized straight-line on a plan-by-plan basis. The total amortization associated with these amounts that is expected to be recognized in net periodic benefit expense for 2015 follows:
F-24
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
P. | Defined Benefit Pension Plans (continued) |
Year ending December 31, 2015 | |||||||
Pretax | Net of Tax | ||||||
Amortization of Costs Expected to be Recognized Next Year | |||||||
Unrecognized net actuarial loss | $ | 1,546 | $ | 928 | |||
Unrecognized prior service cost | 14 | 8 | |||||
$ | 1,560 | $ | 936 | ||||
The aggregate projected benefit obligation, accumulated benefit obligation and fair value of plan assets for plans in which the fair value of plan assets is less than either the projected benefit obligation or accumulated benefit obligation follow:
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
For pension plans with accumulated benefit obligations in excess of plan assets | |||||||
Projected benefit obligation | $ | 35,876 | $ | 31,888 | |||
Accumulated benefit obligation | 35,475 | 31,599 | |||||
Fair value of plan assets | 21,567 | 25,754 | |||||
The actuarial assumptions follow. The discount rates were used to measure the year-end benefit obligation and compute pension expense for the subsequent year.
December 31, | ||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||
Actuarial assumptions | ||||||||
Discount rate | 4.30 | % | 5.20 | % | 4.25 | % | ||
Expected long-term rate of return on plan assets | 7.50 | 7.75 | 7.75 | |||||
Net periodic benefit expense (income) associated with the defined benefit pension plans included the following components:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Components of pension expense (income) | |||||||||||
Service costs--increase in benefit obligation earned | $ | 51 | $ | 222 | $ | 185 | |||||
Interest cost on projected benefit obligation | 1,618 | 1,515 | 1,657 | ||||||||
Expected return on plan assets | (1,993 | ) | (1,760 | ) | (1,701 | ) | |||||
Settlement loss | 2,065 | — | 219 | ||||||||
Amortization of net actuarial loss | 708 | 1,388 | 1,041 | ||||||||
Amortization of prior service cost | 14 | 14 | 14 | ||||||||
Net pension expense of defined benefit pension plans | $ | 2,463 | $ | 1,379 | $ | 1,415 | |||||
Investment Strategy and Risk Management for Plan Assets--Our investment strategy is to manage the plan assets in order to pay retirement benefits to plan participants while minimizing our cash contributions over the life of the plans. This is accomplished by preserving capital through diversification in high-quality investments through the use of investment
F-25
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
P. | Defined Benefit Pension Plans (continued) |
managers and mutual funds. Performance of all investment managers and mutual funds is monitored quarterly and evaluated over rolling three-to-five year periods.
The plan assets are divided into asset classes that include equity, fixed income, and alternative investments and allocated among target allocations to include: (a) equities of a minimum 55% to a maximum of 65%; (b) fixed income and cash of a minimum 20% to a maximum of 30%; and, (c) alternative investments of a minimum of zero to a maximum of 15%. The purpose of the equity asset class is to provide a total return that simultaneously provides for growth in principal and current income while at the same time preserving the purchasing power of the plan assets, even though assets invested in equities have greater market volatility and risk. The purpose of the fixed income asset class is to provide a deflation hedge, to reduce the overall volatility of plan assets and to produce current income in support of the needs of the plan. The purpose of alternative investments is the diversification benefit of alternative strategies.
Equity assets are to be allocated within certain ranges among the asset categories of large cap growth and value; small/midcap growth and value; and international growth and value. Each of the equity asset categories are assigned to an appropriate asset manager or mutual fund. Fixed income assets are allocated within a certain range to mutual funds of fixed income securities. Alternative investment assets are allocated within a certain range to mutual funds and may include the use of leverage. Short-selling, securities lending, financial futures, margins, options, and derivatives are not used. Investments in nonmarketable securities, commodities, or direct ownership of real estate are prohibited.
Rate-of-return-on-assets assumptions are made by major category of plan assets according to historical analysis, tempered for an assessment of possible future influences that could cause the returns to exceed or trail long-term patterns. The overall expected long-term rate-of-return-on-plan assets net of investment manager fees as at December 31, 2014, was 7.50%.
Plan Assets--The fair values of our pension plan assets at December 31, 2014 by asset category, using the three-level hierarchy of fair value inputs, were as follows:
Fair Value Measurements at December 31, 2014 Using: | ||||||||||||||||
Description | Total Carrying Value at December 31, 2014 | Quoted prices in active markets (Level 1) | Significant other observable inputs (Level 2) | Significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) | ||||||||||||
Asset Category | ||||||||||||||||
Money market funds | $ | 2,442 | $ | — | $ | 2,442 | $ | — | ||||||||
U.S. large-cap equities | ||||||||||||||||
Growth | 2,625 | 2,625 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Value | 2,088 | 2,088 | — | — | ||||||||||||
U.S. small/mid-cap equities | ||||||||||||||||
Growth | 1,623 | 1,623 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Value | 1,844 | 1,844 | — | — | ||||||||||||
International equities | ||||||||||||||||
Growth | 2,128 | 2,128 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Value | 2,124 | 2,124 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Fixed income | 3,747 | 3,747 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Multiclass world-allocation mutual funds | 2,946 | 2,946 | — | — | ||||||||||||
$ | 21,567 | $ | 19,125 | $ | 2,442 | $ | — | |||||||||
The fair values of our pension plan assets at December 31, 2013 by asset category, using the three-level hierarchy of fair value inputs, were as follows:
F-26
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
P. | Defined Benefit Pension Plans (continued) |
Fair Value Measurements at December 31, 2013 Using: | ||||||||||||||||
Description | Total Carrying Value at December 31, 2013 | Quoted prices in active markets (Level 1) | Significant other observable inputs (Level 2) | Significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) | ||||||||||||
Asset Category | ||||||||||||||||
Money market funds | $ | 1,726 | $ | — | $ | 1,726 | $ | — | ||||||||
U.S. large-cap equities | ||||||||||||||||
Growth | 3,639 | 3,639 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Value | 2,971 | 2,971 | — | — | ||||||||||||
U.S. small/mid-cap equities | ||||||||||||||||
Growth | 1,813 | 1,813 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Value | 1,959 | 1,959 | — | — | ||||||||||||
International equities | ||||||||||||||||
Growth | 2,718 | 2,718 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Value | 2,622 | 2,622 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Fixed income | 4,423 | 4,423 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Multiclass world-allocation mutual funds | 3,883 | 3,883 | — | — | ||||||||||||
$ | 25,754 | $ | 24,028 | $ | 1,726 | $ | — | |||||||||
Within the pension plan asset categories, the Level 1 investments are publicly traded in active markets and are valued using the net asset value or closing price of the investment at the measurement date. Securities held by a money market fund are generally high quality and liquid; however, they are reflected as Level 2 because the inputs used to determine fair value are not quoted prices in an active market.
Expected Benefit Plan Contributions--We expect, as of December 31, 2014, to make defined-benefit contributions totaling $1,038 before December 31, 2015.
Expected Benefit Plan Payments--The benefits, as of December 31, 2014, expected to be paid to defined-benefit plan participants in each of the next five years, and in the aggregate for the five years thereafter, follow:
Participants Benefits | ||||
Estimated future payments | ||||
Year ending December 31, 2015 | $ | 1,117 | ||
2016 | 1,268 | |||
2017 | 1,454 | |||
2018 | 1,529 | |||
2019 | 1,618 | |||
Years 2020 to 2024 | 9,233 | |||
Multiemployer Defined Benefit Pension Plans--In providing services to our Utility Services customers, we contribute to multiemployer defined benefit pension plans under the terms of collective-bargaining agreements that cover certain of our union-represented employees.
These plans generally provide retirement benefits to participants based on their service to contributing employers. We do not administer these multiemployer plans. In general, these plans are managed by a board of trustees with the unions appointing certain trustees and other contributing employers of the plan appointing certain members. We generally are not represented on the board of trustees.
F-27
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
P. | Defined Benefit Pension Plans (continued) |
The risks of participating in these multiemployer plans are different from single-employer plans in that: (a) assets contributed to the multiemployer plan by one employer may be used to provide benefits to employees of other participating employers; (b) if a participating employer stops contributing to the plan, the unfunded obligations of the plan may be assumed by the remaining participating employers; and, (c) if we choose to stop participating in a multiemployer plan, we may be required to pay the plan an amount based on the underfunded status of the plan, referred to as a withdrawal liability.
Our participation in the multiemployer defined benefit pension plans is summarized in the table below. The “EIN/Pension Plan Number” column provides the Employer Identification Number (“EIN”) and the three-digit plan number. The most recent Pension Protection Act of 2006 (the “PPA”) zone status is from the Form 5500, “Annual Return/Report of Employee Benefit Plan,” filed by the plan and certified by the plan's actuary. The PPA zone status describes plans that are underfunded. Among other factors, plans in the “critical” red zone are generally less than 65% funded; plans in the “endangered” yellow zone are less than 80% funded; and, plans in the “safe” green zone are at least 80% funded.
Pension Fund | EIN/Pension Plan Number | Pension Protection Act Zone Status | FIB/RP Status Pending Implemented | Davey Tree Contributions | Surcharge Imposed | Expiration Dates of Bargaining Agreement | ||||||||||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||||
National Electric Benefit Fund | 53-0181657/001 | Green | Green | No | $ | 743 | $ | 755 | $ | 417 | No | Ranging from December 31, 2014 to December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||
Eighth District Electrical Pension Fund | 84-6100393/001 | Green | Green | No | 105 | 100 | 75 | No | December 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||
$ | 848 | $ | 855 | $ | 492 | |||||||||||||||||||
We were not listed in the Form 5500 for either plan as having provided more than 5% of the total contributions.
Both the National Electric Benefit Fund and the Eighth District Electrical Pension Fund are green zone status--safe--which represents at least 80% funded and does not require a “financial improvement plan” (“FIP”) or a “rehabilitation plan” (“RP”).
We are party to eight collective-bargaining agreements with the National Electric Benefit Fund, with expiration dates ranging from December 31, 2014 (currently in negotiations) to December 31, 2017 and one collective-bargaining agreement with Eighth District Electrical Pension Fund with an expiration date of December 31, 2017.
Q. | Income Taxes |
Income before income taxes was attributable to the following sources:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
United States | $ | 30,380 | $ | 29,203 | $ | 35,414 | |||||
Canada | 7,920 | 6,362 | 5,244 | ||||||||
Total | $ | 38,300 | $ | 35,565 | $ | 40,658 | |||||
F-28
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
Q. | Income Taxes (continued) |
The provision for income taxes follows:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Currently payable: | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | 13,159 | $ | 7,089 | $ | 15,853 | |||||
State | 2,524 | 2,183 | 2,239 | ||||||||
Canadian | 2,127 | 1,724 | 1,578 | ||||||||
Total current | 17,810 | 10,996 | 19,670 | ||||||||
Deferred taxes | (2,679 | ) | 1,716 | (3,607 | ) | ||||||
Total taxes on income | $ | 15,131 | $ | 12,712 | $ | 16,063 | |||||
A reconciliation of the expected statutory U.S. federal rate to our actual effective income tax rate follows:
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||
Statutory U.S. federal tax rate | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||
State income taxes, net of federal benefit | 3.9 | 3.6 | 3.9 | |||||
Effect of Canadian income taxes | (1.7 | ) | (1.6 | ) | (1.0 | ) | ||
Nondeductible expenses | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.4 | |||||
ESOP dividend deduction | (.7 | ) | (.8 | ) | (.7 | ) | ||
Audit settlements and uncertain tax adjustments | 1.6 | (2.2 | ) | 1.8 | ||||
All other, net | (.5 | ) | (.2 | ) | (.9 | ) | ||
Effective income tax rate | 39.5 | % | 35.7 | % | 39.5 | % | ||
Deferred income taxes reflect the tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amount of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. A valuation allowance is recorded when it is more-likely-than-not that an income tax benefit will not be realized.
Significant components of our current net deferred tax assets and liabilities at December 31, were as follows:
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Deferred tax assets: | |||||||
Accrued compensation obligations | $ | 3,090 | $ | 1,883 | |||
Self-insurance accruals | 8,107 | 7,693 | |||||
Prepaid expenses | (3,160 | ) | (2,565 | ) | |||
Other, net | 1,102 | 908 | |||||
9,139 | 7,919 | ||||||
Less deferred tax asset valuation allowance | 212 | 204 | |||||
Net deferred income tax assets--current | $ | 8,927 | $ | 7,715 | |||
F-29
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
Q. | Income Taxes (continued) |
Significant components of our noncurrent net deferred tax assets and liabilities at December 31, were as follows:
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Deferred tax assets: | |||||||
Self-insurance accruals | $ | 12,554 | $ | 12,129 | |||
Accrued expenses and other liabilities | 1,388 | 895 | |||||
Accrued stock compensation | 1,642 | 1,550 | |||||
Defined benefit pension plans | 4,573 | 1,873 | |||||
Foreign tax credit carryforward | 768 | 768 | |||||
Other future deductible amounts, net | 2,030 | 1,737 | |||||
22,955 | 18,952 | ||||||
Less deferred tax asset valuation allowance | 556 | 564 | |||||
22,399 | 18,388 | ||||||
Deferred tax liabilities: | |||||||
Intangibles | 269 | 234 | |||||
Property and equipment | 20,425 | 20,718 | |||||
20,694 | 20,952 | ||||||
Net deferred tax assets--noncurrent | $ | 1,705 | |||||
Net deferred tax liabilities--noncurrent | $ | 2,564 | |||||
We treat all of our Canadian subsidiary earnings through December 31, 2014 as permanently reinvested and have not provided any U.S. federal or state tax thereon. As of December 31, 2014, approximately $30,459 of undistributed earnings attributable to our Canadian operations was considered to be indefinitely invested. Presently, our intention is to reinvest the earnings permanently.
If, in the future, these earnings are distributed to the U.S. in the form of dividends or otherwise, or if the Company determines such earnings will be remitted in the foreseeable future, the Company would be subject to U.S. income taxes and Canadian withholding taxes. It is not practicable to estimate the amount of taxes that would be payable upon remittance of these earnings given the various tax planning alternatives that we could employ should we decide to repatriate those earnings.
A deferred tax asset has been recorded for the portion of the foreign tax credit that is unavailable in the current year--the foreign tax credit carryforward arising in 2010--wherein we repatriated earnings of our Canadian operations due to capital in Canada in excess of current and future projected needs. As a result, we recognized and recorded in 2010 additional U.S. federal and state taxes that were payable as a result of the repatriation of the previously undistributed earnings. A valuation allowance is required when it is more-likely-than-not that all or a portion of a deferred tax asset will not be realized. Because of the uncertainty regarding realization, a valuation allowance equal to the U.S. tax benefit of the foreign tax credit carryforward is recorded--$768 at December 31, 2014--which is subject to expiration in 2020, if not utilized.
F-30
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
Q. | Income Taxes (continued) |
The amount of income taxes we pay is subject to audit by U.S. federal, state, local and Canadian tax authorities, which may result in proposed assessments. Our estimate for the potential outcome for any uncertain tax issue is highly judgmental. Uncertain tax positions are recognized only if they are more-likely-than-not to be upheld during examination based on their technical merits. The measurement of the uncertain tax position is based on the largest benefit amount that is more-likely-than-not (determined on a cumulative probability basis) to be realized upon settlement of the matter. If payment of these amounts ultimately proves to be unnecessary, the reversal of the liabilities would result in tax benefits being recognized in the period when we determine the liabilities are no longer necessary. If the estimate of tax liabilities proves to be less than the ultimate settlement, a further charge to expense may result.
The balance of unrecognized benefits and the amount of related interest and penalties at December 31, were as follows:
December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Unrecognized tax benefits | $ | 1,949 | $ | 1,221 | |||
Portion, if recognized, would reduce tax expense and effective tax rate | 1,512 | 942 | |||||
Accrued interest on unrecognized tax benefits | 77 | 41 | |||||
Accrued penalties on unrecognized benefits | — | — | |||||
We recognize interest accrued related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense. Penalties, if incurred, would be recognized as a component of income tax expense.
The Company is routinely under audit by U.S. federal, state, local and Canadian authorities in the area of income tax. These audits include questioning the timing and the amount of income and deductions and the allocation of income and deductions among various tax jurisdictions. During the fourth quarter 2013, the U.S. Internal Revenue Service completed its audit of the Company's U.S. income tax returns for 2010 and 2011 and, during 2010, Canada Revenue Agency completed its audit of the Company's Canadian operations for 2006, 2007 and 2008. With the exception of U.S. state jurisdictions, the Company is no longer subject to examination by tax authorities for the years through 2009. As of December 31, 2014, we believe it is reasonably possible that the total amount of unrecognized tax benefits will not significantly increase or decrease.
The changes in our unrecognized tax benefits are summarized in the table below:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Balance, beginning of year | $ | 1,221 | $ | 2,638 | $ | 1,825 | |||||
Additions based on tax positions related to the current year | 587 | 370 | 667 | ||||||||
Additions for tax positions of prior years | 234 | 133 | 149 | ||||||||
Reductions for tax positions of prior years | (79 | ) | (1,155 | ) | (3 | ) | |||||
Reductions related to settlements with taxing authorities | — | (460 | ) | — | |||||||
Lapses in statutes of limitations | (14 | ) | (305 | ) | — | ||||||
Balance, end of year | $ | 1,949 | $ | 1,221 | $ | 2,638 | |||||
F-31
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
R. | Earnings Per Share Information |
Earnings per share is computed as follows:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Income available to common shareholders: | |||||||||||
Net income | $ | 23,169 | $ | 22,853 | $ | 24,595 | |||||
Weighted-average shares: | |||||||||||
Basic: | |||||||||||
Outstanding | 13,337,198 | 13,639,356 | 13,867,771 | ||||||||
Partially-paid share subscriptions | 484,025 | 531,325 | 234,595 | ||||||||
Basic weighted-average shares | 13,821,223 | 14,170,681 | 14,102,366 | ||||||||
Diluted: | |||||||||||
Basic from above | 13,821,223 | 14,170,681 | 14,102,366 | ||||||||
Incremental shares from assumed: | |||||||||||
Exercise of stock subscription purchase rights | 54,824 | 34,273 | 5,750 | ||||||||
Exercise of stock options and awards | 362,229 | 397,478 | 500,741 | ||||||||
Diluted weighted-average shares | 14,238,276 | 14,602,432 | 14,608,857 | ||||||||
Share data: | |||||||||||
Earnings per share--basic | $ | 1.68 | $ | 1.61 | $ | 1.74 | |||||
Earnings per share--diluted | $ | 1.63 | $ | 1.57 | $ | 1.68 | |||||
S. | Operations by Business Segment and Geographic Information |
We provide a wide range of arboriculture, horticulture, environmental and consulting services to residential, utility, commercial and government entities throughout the United States and Canada. We have two reportable operating segments organized by type or class of customer: Residential and Commercial, and Utility.
Residential and Commercial--Residential and Commercial provides services to our residential and commercial customers including: the treatment, preservation, maintenance, removal, planting of trees, shrubs and other plant life; the practice of landscaping, grounds maintenance, tree surgery, tree feeding and tree spraying; the application of fertilizer, herbicides and insecticides; and, natural resource management and consulting, forestry research and development, and environmental planning.
Utility--Utility is principally engaged in providing services to our utility customers--investor-owned, municipal utilities, and rural electric cooperatives--including: the practice of line-clearing and vegetation management around power lines, rights-of-way and chemical brush control; and, natural resource management and consulting, forestry research and development and environmental planning.
All other operating activities, including research, technical support and laboratory diagnostic facilities, are included in “All Other.”
Measurement of Segment Profit and Loss and Segment Assets--We evaluate performance and allocate resources based primarily on operating income and also actively manage business unit operating assets. The accounting policies of the reportable segments are the same as those described in the summary of significant accounting policies except that (a) we compute and recognize depreciation expense for our segments only by the straight-line method and (b) state income taxes are allocated to the segments. Corporate expenses are substantially allocated among the operating segments, but the nature of expenses allocated may differ from year-to-year. There are no intersegment revenues.
F-32
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
S. Operations by Business Segment and Geographic Information (continued)
Segment assets are those generated or directly used by each segment, and include accounts receivable, operating supplies, and property and equipment.
F-33
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
Information on reportable segments and reconciliation to the consolidated financial statements follows:
Utility Services | Residential Commercial Services | All Other | Reconciling Adjustments | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||
Fiscal Year 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 404,519 | $ | 386,274 | $ | (882 | ) | $ | — | $ | 789,911 | ||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 21,382 | 37,232 | (6,037 | ) | (8,574 | ) | (a) | 44,003 | |||||||||||
Interest expense | (2,948 | ) | (2,948 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Interest income | 295 | 295 | |||||||||||||||||
Other income (expense), net | (3,050 | ) | (3,050 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | $ | 38,300 | |||||||||||||||||
Depreciation | $ | 23,225 | $ | 14,544 | $ | — | $ | 3,201 | (b) | $ | 40,970 | ||||||||
Amortization | 174 | 1,896 | — | — | 2,070 | ||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | 25,994 | 17,490 | — | 12,247 | 55,731 | ||||||||||||||
Segment assets, total | 150,002 | 144,413 | — | 86,589 | (c) | 381,004 | |||||||||||||
Fiscal Year 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 376,520 | $ | 334,878 | $ | 2,450 | $ | — | $ | 713,848 | |||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 16,070 | 33,566 | (2,869 | ) | (5,978 | ) | (a) | 40,789 | |||||||||||
Interest expense | (2,708 | ) | (2,708 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Interest income | 311 | 311 | |||||||||||||||||
Other income (expense), net | (2,827 | ) | (2,827 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | $ | 35,565 | |||||||||||||||||
Depreciation | $ | 22,261 | $ | 13,286 | $ | — | $ | 2,684 | (b) | $ | 38,231 | ||||||||
Amortization | 359 | 1,440 | — | 181 | 1,980 | ||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | 21,642 | 17,577 | — | 5,986 | 45,205 | ||||||||||||||
Segment assets, total | 145,021 | 122,542 | — | 65,815 | (c) | 333,378 | |||||||||||||
Fiscal Year 2012 | |||||||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 375,300 | $ | 303,420 | $ | 1,433 | $ | — | $ | 680,153 | |||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 20,107 | 30,787 | (1,366 | ) | (3,761 | ) | (a) | 45,767 | |||||||||||
Interest expense | (2,698 | ) | (2,698 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Interest income | 200 | 200 | |||||||||||||||||
Other income (expense), net | (2,611 | ) | (2,611 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | $ | 40,658 | |||||||||||||||||
Depreciation | $ | 22,844 | $ | 12,236 | $ | — | $ | 2,285 | (b) | $ | 37,365 | ||||||||
Amortization | 465 | 1,058 | — | 219 | 1,742 | ||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | 15,737 | 10,266 | — | 3,731 | 29,734 | ||||||||||||||
Segment assets, total | 150,294 | 122,298 | — | 58,340 | (c) | 330,932 | |||||||||||||
F-34
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
S. | Operations by Business Segment and Geographic Information (continued) |
Reconciling adjustments from segment reporting to consolidated external financial reporting include unallocated corporate items:
(a) | Reconciling adjustments from segment reporting to consolidated external financial reporting include reclassification of depreciation expense and allocation of corporate expenses. |
(b) | Adjustments to declining-balance method depreciation expense from straight-line method and depreciation and amortization of corporate assets. |
(c) | Corporate assets include cash, prepaid expenses, corporate facilities, enterprise-wide information systems and other nonoperating assets. |
Geographic Information--The following presents revenues and long-lived assets by geographic territory:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Revenues | |||||||||||
United States | $ | 706,145 | $ | 637,524 | $ | 607,339 | |||||
Canada | 83,766 | 76,324 | 72,814 | ||||||||
$ | 789,911 | $ | 713,848 | $ | 680,153 | ||||||
December 31, | |||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Long-lived assets, net | |||||||||||
United States | $ | 196,116 | $ | 166,598 | $ | 153,946 | |||||
Canada | 17,692 | 14,764 | 15,237 | ||||||||
$ | 213,808 | $ | 181,362 | $ | 169,183 | ||||||
T. | Fair Value Measurements and Financial Instruments |
Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standard Codification 820, “Fair Value of Measurements and Disclosures (“Topic 820”)” defines fair value based on the price that would be received to sell an asset or the exit price that would be paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. Market participants are defined as buyers or sellers in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability that are independent of the reporting entity, knowledgeable and able and willing to transact for the asset or liability.
Valuation Hierarchy--Topic 820 establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes observable and unobservable inputs used to measure fair value. The hierarchy prioritizes the inputs into three broad levels:
Level 1 inputs are quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the entity has the ability to access.
Level 2 inputs are observable inputs other than prices included in Level 1, such as quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar assets and liabilities in markets that are not active; or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated with observable market data.
Level 3 inputs are unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets and liabilities. This includes certain pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies and similar techniques that use significant unobservable inputs.
T. | Fair Value Measurements and Financial Instruments (continued) |
Our assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis at December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, were as follows:
Fair Value Measurements at December 31, 2014 Using: | ||||||||||||||||
Total Carrying Value at | Quoted prices in active markets | Significant other observable inputs | Significant unobservable inputs | |||||||||||||
Description | December 31, 2014 | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | ||||||||||||
Assets: | ||||||||||||||||
Assets invested for self-insurance, classified as other assets, noncurrent | $ | 13,684 | $ | 13,684 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
Defined benefit pension plan assets | 21,567 | 19,125 | 2,442 | — | ||||||||||||
Liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||
Deferred compensation | $ | 1,423 | $ | — | $ | 1,423 | $ | — | ||||||||
Fair Value Measurements at December 31, 2013 Using: | ||||||||||||||||
Total Carrying Value at | Quoted prices in active markets | Significant other observable inputs | Significant unobservable inputs | |||||||||||||
Description | December 31, 2013 | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | ||||||||||||
Assets: | ||||||||||||||||
Assets invested for self-insurance, classified as other assets, noncurrent | $ | 12,716 | $ | 12,716 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
Defined benefit pension plan assets | 25,754 | 24,028 | 1,726 | — | ||||||||||||
Liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||
Deferred compensation | $ | 1,144 | $ | — | $ | 1,144 | $ | — | ||||||||
The estimated fair value of the deferred compensation--classified as Level 2--is based on the value of the Company's common shares, determined by independent valuation.
F-35
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
T. | Fair Value Measurements and Financial Instruments (continued) |
Fair Value of Financial Instruments--The fair values of our current financial assets and current liabilities, including cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and accrued expenses among others, approximate their reported carrying values because of their short-term nature. The assets invested for self-insurance are money market funds--classified as Level 1--based on quoted market prices of the identical underlying securities in active markets. The estimated fair value of our derivative instruments are calculated based on market rates to settle the instruments, as discussed below, representing the amount we would receive upon sale or pay upon transfer. Financial instruments classified as noncurrent liabilities and their carrying values and fair values were as follows:
December 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | ||||||||||||||
Carrying Value | Fair Value | Carrying Value | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
Revolving credit facility, noncurrent | $ | 44,500 | $ | 44,500 | $ | 20,000 | $ | 20,000 | |||||||
Senior unsecured notes | 30,000 | 30,688 | 30,000 | 28,219 | |||||||||||
Term loans, noncurrent | 6,806 | 7,195 | 34 | 34 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 81,306 | $ | 82,383 | $ | 50,034 | $ | 48,253 | |||||||
The carrying value of our revolving credit facility approximates fair value--classified as Level 2--as the interest rates on the amounts outstanding are variable. The fair value of our senior unsecured notes and term loans--classified as Level 2--is determined based on expected future weighted-average interest rates with the same remaining maturities.
Market Risk--In the normal course of business, we are exposed to market risk related to changes in foreign currency exchange rates, changes in interest rates and changes in fuel prices. We do not hold or issue derivative financial instruments for trading or speculative purposes. In prior years, we have used derivative financial instruments to manage risk, in part, associated with changes in interest rates and changes in fuel prices. Presently, we are not engaged in any hedging or derivative activities.
U. | Commitments and Contingencies |
Letters of Credit
At December 31, 2014, we were contingently liable to our principal banks in the amount of $61,540 for letters of credit outstanding primarily related to insurance coverage.
Surety Bonds
In certain circumstances, we have performance obligations that are supported by surety bonds in connection with our contractual commitments.
Litigation
We are party to a number of lawsuits, threatened lawsuits and other claims arising out of the normal course of business.
With respect to all such matters, we record an accrual for a loss contingency when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. In addition, narrative information is provided for matters as to which management believes a material loss is reasonably possible.
Management has assessed all such matters, including the matter described below, based on current information and made a judgment concerning their potential outcome, giving due consideration to the nature of the claim, the amount and nature of damages sought and the probability of success. Management's judgment is made subject to the known uncertainty of litigation and management's judgment as to estimates made may prove materially different from actual results.
F-36
The Davey Tree Expert Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements--(Continued)
December 31, 2014
(In thousands, except share data)
U. | Commitments and Contingencies (continued) |
California Fire Litigation: San Diego County--Davey Tree Surgery Company, a Davey subsidiary, and Davey Resource Group, a Davey division, along with the Company have previously been sued, together with a utility services customer, San Diego Gas & Electric ("SDG&E"), and its parent company, as defendants, and as cross-defendants in cross-complaints filed by SDG&E, in the Superior Court of the State of California in and for the County of San Diego, arising out of a wildfire in San Diego County that started on October 22, 2007, referred to as the Rice Canyon fire.
Numerous lawsuits related to the Rice Canyon fire were filed against SDG&E, its parent company, Sempra Energy, and Davey. The earliest of the lawsuits naming Davey was filed on April 18, 2008. The Court ordered that the lawsuits be organized into four groups based on type of plaintiff, namely insurance subrogation claimants, individual/business claimants, governmental claimants, and plaintiffs seeking class certification. Plaintiffs' motions seeking class certification were denied and the orders denying class certification were affirmed on appeal. SDG&E filed cross-complaints against Davey for contractual indemnity, declaratory relief, and breach of contract.
During the third quarter 2012, Davey entered into a Settlement and Release Agreement (the “Agreement”) among Davey, SDG&E and Davey's insurers.
Under the Agreement (a) Davey paid SDG&E an amount previously expensed and accrued as self-insurance, (b) Davey's insurers paid SDG&E amounts under Davey's insurance policies in effect during the period of the Rice Canyon fire, and (c) SDG&E dismissed its cross-complaints against Davey and agreed to defend and hold harmless Davey from any and all claims that are currently asserted against Davey.
V. | Quarterly Results of Operations (Unaudited) |
The following is a summary of the results of operations for each quarter of 2014 and 2013.
Fiscal 2014, Three Months Ended | |||||||||||||||
Mar 29 | Jun 29 | Sept 27 | Dec 31 | ||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 157,387 | $ | 213,183 | $ | 216,604 | $ | 202,737 | |||||||
Gross profit (revenues less costs and expenses, operating) | 48,156 | 82,900 | 77,613 | 72,565 | |||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | (4,725 | ) | 23,815 | 17,144 | 7,769 | ||||||||||
Net income (loss) | (6,180 | ) | 14,046 | 9,657 | 5,646 | ||||||||||
Net income (loss) per share--Basic | $ | (.29 | ) | $ | 1.04 | $ | .72 | $ | .21 | ||||||
Net income (loss) per share -- Diluted: | $ | (.29 | ) | $ | 1.01 | $ | .69 | $ | .22 | ||||||
ESOT Valuation per share | $ | 26.40 | $ | 26.40 | $ | 27.80 | $ | 30.10 | |||||||
Fiscal 2013, Three Months Ended | |||||||||||||||
Mar 30 | Jun 29 | Sept 28 | Dec 31 | ||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 143,265 | $ | 195,638 | $ | 194,772 | $ | 180,173 | |||||||
Gross profit (revenues less costs and expenses, operating) | 42,205 | 76,046 | 69,114 | 63,837 | |||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | (6,009 | ) | 23,230 | 14,881 | 8,687 | ||||||||||
Net income (loss) | (4,612 | ) | 13,436 | 8,644 | 5,385 | ||||||||||
Net income (loss) per share -- Basic | $ | (.33 | ) | $ | .97 | $ | .63 | $ | .34 | ||||||
Net income (loss) per share -- Diluted | $ | (.33 | ) | $ | .94 | $ | .61 | $ | .35 | ||||||
ESOT Valuation per share | $ | 23.20 | $ | 23.20 | $ | 23.90 | $ | 26.40 | |||||||
Fourth quarters 2014 and 2013 include a decrease in casualty insurance expense that had the effect of increasing the fourth quarter gross profit for 2014 and 2013 by approximately $3,875 and $3,951, respectively. | |||||||||||||||
F-37
