Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - Eagle Mountain Corp | v379365_ex31-1.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - Eagle Mountain Corp | v379365_ex32-2.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - Eagle Mountain Corp | v379365_ex32-1.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - Eagle Mountain Corp | v379365_ex31-2.htm |
UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-Q
(Mark One)
| þ | QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the quarterly period ended March 31, 2014
OR
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission file number: 000-50140
USmart Mobile Device Inc.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 16-1642709 | ||||
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
Room 1703, 17/F.,
Tower 1, Enterprise Square, 9 Sheung Yuet Road, Kowloon Bay,
Kowloon, Hong Kong.
(Address of principal executive offices) (Zip code)
011-852-3666-9939
(Registrant’s telephone number including area code)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer | ¨ | Accelerated filer | ¨ |
| Non-accelerated filer | ¨ | Smaller reporting company | þ |
| (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No þ
The Registrant had 39,684,495 shares of common stock outstanding as of May 20, 2014.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| Page | |||||
| PART I | FINANCIAL INFORMATION | ||||
| Item 1. | Financial Statements (Unaudited) | 1 | |||
| Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets (Unaudited) | 1 | ||||
| Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income (Unaudited) | 3 | ||||
| Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows (Unaudited) | 4 | ||||
| Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited) | 6 | ||||
| Item 2. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 25 | |||
| Item 3. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk | 34 | |||
| Item 4. | Controls and Procedures | 35 | |||
| PART II | OTHER INFORMATION | ||||
| Item 1. | Legal Proceedings | 36 | |||
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors | 36 | |||
| Item 2. | Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds | 36 | |||
| Item 3. | Defaults Upon Senior Securities | 36 | |||
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures | 36 | |||
| Item 5. | Other Information | 36 | |||
| Item 6. | Exhibits | 36 | |||
| SIGNATURES | 37 | ||||
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
| Item 1. | Financial Statements |
Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets (Unaudited)
| Notes | As of March 31, 2014 (Unaudited) | As of December 31, 2013 (Audited) | ||||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||||||
| Current assets | ||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | - | $ | 231,119 | ||||||||
| Restricted cash | - | - | ||||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $0 for 2014 and $555,993 for 2013 | - | 1,358,873 | ||||||||||
| Inventories, net | 3 | - | 1,081,511 | |||||||||
| Current assets (liabilities) held for disposal | (12,390,969 | ) | - | |||||||||
| Other current assets | - | 91,618 | ||||||||||
| Total current assets | $ | (12,390,969 | ) | $ | 2,763,121 | |||||||
| Long-term assets: | ||||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 4 | - | 8,212,849 | |||||||||
| Other deposits | - | 138,234 | ||||||||||
| Amounts due from Aristo / Mr. Yang | 7 | - | 931,652 | |||||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | (12,390,969 | ) | $ | 12,045,856 | |||||||
| LIABILITIES | ||||||||||||
| Current liabilities | ||||||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | - | $ | 623,069 | ||||||||
| Accruals | 296,778 | 554,231 | ||||||||||
| Lines of credit and loan facilities | 8 | - | 3,178,580 | |||||||||
| Bank loans | 9 | - | 3,222,113 | |||||||||
| Current portion of loan from a third party | 12 | - | 641,026 | |||||||||
| Current portion of capital lease | 5 | - | 75,917 | |||||||||
| Income tax payable | - | (177,291 | ) | |||||||||
| Due to shareholders for converted pledged collateral | 112,533 | 112,385 | ||||||||||
| Other current liabilities | 10 | 12,444,000 | ||||||||||
| Total current liabilities | $ | 409,311 | $ | 20,674,030 | ||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
| 1 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets (Unaudited)
| Notes | As of March 31, 2014 (Unaudited) | As of December 31, 2013 (Audited) | ||||||||||
| Long-term Liabilities | ||||||||||||
| Loan from a third party, less current portion | $ | - | $ | 6,410,256 | ||||||||
| Capital lease, less current portion | 5 | - | 57,511 | |||||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities | - | 5,569 | ||||||||||
| Total long-term liabilities | - | 6,473,336 | ||||||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | $ | 409,311 | 27,147,366 | |||||||||
| NET ASSETS (LIABILITIES) | $ | (12,800,280 | ) | (15,101,510 | ) | |||||||
| Commitments and contingencies | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||||
| STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||||||
| Preferred stock, 20,000,000 shares authorized; 0 shares issued and outstanding as of March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||||
| Common stock, $0.001 par value; 50,000,000 shares authorized; 39,684,495 and 39,684,495 shares issued and outstanding as of March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 | 39,685 | 39,685 | ||||||||||
| Additional paid in capital | 4,333,723 | 4,333,723 | ||||||||||
| Exchange reserve | (3,327 | ) | (1,810 | ) | ||||||||
| Retained earnings (deficits) | (17,170,361 | ) | (16,879,337 | ) | ||||||||
| (12,800,280 | ) | (12,507,739 | ) | |||||||||
| Non-controlling interest | - | (2,593,771 | ) | |||||||||
| TOTAL STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | (12,800,280 | ) | (15,101,510 | ) | ||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
| 2 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income (Unaudited)
| Notes | Three months ended March 31, 2014 (Unaudited) | Three months ended March 31, 2013 (Unaudited) | ||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 561,870 | $ | 14,460,228 | ||||||||
| Costs of sales | 587,308 | 14,558,743 | ||||||||||
| Gross profit (loss) | $ | (25,438 | ) | $ | (98,515 | ) | ||||||
| Operating expenses | ||||||||||||
| Selling and distribution costs | 87,375 | 32,661 | ||||||||||
| General and administrative expenses | 211,448 | 1,086,856 | ||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations | $ | (324,261 | ) | $ | (1,218,032 | ) | ||||||
| Other expenses (income) | ||||||||||||
| Rental income | - | (44,038 | ) | |||||||||
| Interest expenses | - | 221,469 | ||||||||||
| Management and service income | 31,488 | (42,332 | ) | |||||||||
| Interest income | 3 | (530 | ) | |||||||||
| Loss (profit) on disposals of fixed assets | - | (1,872,724 | ) | |||||||||
| Exchange differences | (3,360 | ) | 2,841 | |||||||||
| Miscellaneous | 5,106 | (52,562 | ) | |||||||||
| Share result of a jointly-controlled entity | - | (318,488 | ) | |||||||||
| Income (loss) before income taxes | $ | (291,024 | ) | $ | 888,332 | |||||||
| Income taxes provision (reversal) | - | - | ||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | (291,024 | ) | $ | 888,332 | |||||||
| Attributable to: | ||||||||||||
| Non-controlling interest | - | (93,830 | ) | |||||||||
| Shareholders of the Company | (291,024 | ) | 982,162 | |||||||||
| $ | (291,024 | ) | $ | 888,332 | ||||||||
| Earnings (loss) per share – basic and diluted | $ | (0.01 | ) | $ | 0.02 | |||||||
| Weighted average number of shares – basic and diluted | 11 | 39,684,495 | 39,474,495 | |||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
| 3 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows (Unaudited)
| Notes | As of March 31, 2014 (Unaudited) | As of March 31, 2013 (Unaudited) | ||||||||||
| Cash flows provided by (used for) operating activities : | ||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | (291,024 | ) | $ | 982,162 | |||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by (used for) operating activities: | ||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | - | - | ||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | - | 119,846 | ||||||||||
| Change in inventory reserve | - | (48,055 | ) | |||||||||
| Loss (gain) on disposal of fixed assets | - | (1,872,724 | ) | |||||||||
| Loss (gain) on investment in a jointly-controlled entity | - | (318,488 | ||||||||||
| Loss (gain) share by non-controlled party | - | (93,830 | ) | |||||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities: | ||||||||||||
| (Increase) decrease in assets | ||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable | 1,358,873 | 241,333 | ||||||||||
| Inventories | 1,081,511 | 400,924 | ||||||||||
| Other current assets | 91,618 | (32,137 | ) | |||||||||
| Current asset held for disposal | 12,390,969 | |||||||||||
| Other assets | 138,234 | 13,963 | ||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in liabilities | ||||||||||||
| Accounts payable | (623,069 | ) | (197,579 | ) | ||||||||
| Accounts payable – related parties | - | (500,000 | ) | |||||||||
| Accrued expenses | (257,453 | ) | (23,962 | ) | ||||||||
| Income tax payable | 171,722 | 0 | ||||||||||
| Other current liabilities | (12,444,000 | ) | 637,282 | |||||||||
| Total adjustments | $ | 1,908,405 | $ | (1,673,427 | ) | |||||||
| Net cash provided by (used for) operating activities | $ | 1,617,381 | $ | (691,265 | ) | |||||||
| Cash flows provided by (used for) investing activities: | ||||||||||||
| Advanced from Aristo / Mr. Yang | $ | 148 | $ | 0 | ||||||||
| Advanced to Aristo / Mr. Yang | 931,652 | (218,814 | ) | |||||||||
| Decrease (increase) of restricted cash | - | (2,484 | ) | |||||||||
| Decrease in Minority Interest | 2,592,254 | - | ||||||||||
| Decrease of Fixed assets | 8,212,849 | 2,531,391 | ||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used for) investing activities | $ | 11,736,903 | $ | 2,310,093 | ||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
| 4 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows (Unaudited) (Continued)
| Notes | As of March 31, 2014 (Unaudited) | As of March 31, 2013 (Unaudited) | ||||||||||
| Cash flows provided by (used for) financing activities: | ||||||||||||
| Net borrowings on lines of credit and loans | $ | (10,229,862 | ) | $ | (1,923,336 | ) | ||||||
| Principal payments to bank | (3,222,113 | ) | (378,858 | ) | ||||||||
| Principal payments under capital lease obligation | (133,428 | ) | (23,981 | ) | ||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used for) financing activities | $ | (13,585,403 | ) | $ | (2,326,175 | ) | ||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | $ | (231,119 | ) | $ | (704,863 | ) | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents–beginning of year | 231,119 | 639,462 | ||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents–end of year | $ | - | $ | (67,885 | ) | |||||||
| Supplementary disclosure of cash flow information: | ||||||||||||
| Interest paid | $ | - | $ | 221,469 | ||||||||
| Income tax paid (reversal) | $ | (177,291 | ) | $ | 0 | |||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
| 5 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 1. | Organization and Principal Activities |
USmart Mobile Device Inc. (“USmart”) and its subsidiaries are referred to herein collectively and on a consolidated basis as the “Company” or “we”, “us” or “our” or similar terminology.
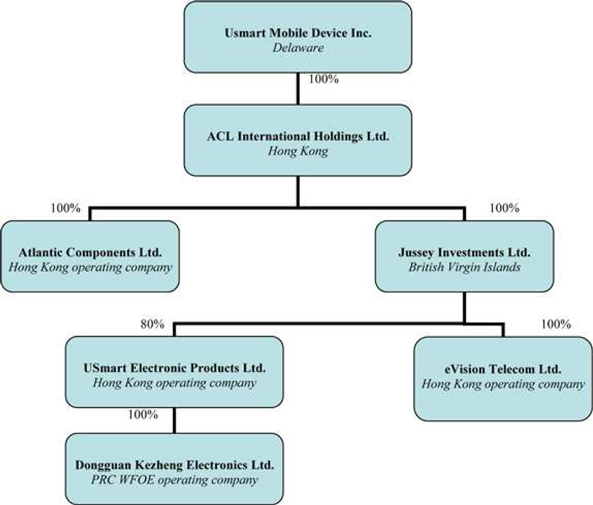
The Company was incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware on September 17, 2002 and previously known as ACL Semiconductors Inc. The Company acquired Atlantic Components Limited, a Hong Kong incorporated company (“Atlantic”) through a reverse-acquisition that was effective September 30, 2003. On September 28, 2012, the Company acquired Jussey Investments Limited, a company incorporated in British Virgin Islands (“Jussey”) (please refer to Note 14 for more information on the acquisition).
The Company is currently engaged in the production, manufacturing and distribution of smartphones, electronic products and components in Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (“Hong Kong”) and the People’s Republic of China (“China” or the “PRC”) through its operating subsidiaries and VIE:
| (i) | Atlantic Components Limited, a Hong Kong incorporated company and the Company’s original principle operating subsidiary which is controlled by the Company through its subsidiary, ACL International Holdings Limited (“ACL Holdings”); and |
| (ii) | Aristo Technologies Limited, a Hong Kong incorporated company (“Aristo”), solely owned by Mr. Chung-Lun Yang, the Company’s Chairman of the Board of Directors (“Mr. Yang”); and |
| (iii) | eVision Telecom Limited (“eVision”), a Hong Kong incorporated company which was acquired through an acquisition of its holding company, Jussey; and |
| (iv) | USmart Electronic Products Limited (“UEP”), a Hong Kong incorporated company which was acquired through an acquisition of its holding company, Jussey; and |
| (v) | Dongguan Kezheng Electronics Limited (“Kezheng”), a wholly foreign-owned enterprise (“WFOE”) organized under the laws of the PRC which is acquired through an acquisition of its ultimate holding company, Jussey. |
The Company owns 100% equity interest of ACL International Holdings Limited, a Hong Kong incorporated company, which owns:
| (i) | 100% equity interest of Atlantic (restructured on December 17, 2010); and |
| (ii) | 100% equity interest of Jussey Investments Limited, a company incorporated in British Virgin Islands (acquired by ACL Holdings on September 28, 2012) which owns: |
| a. | 100% equity interest in eVision; and |
| b. | 80% equity interest in UEP, which owns 100% equity interest in Kezheng. |
| 6 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 1. | Organization and Principal Activities (Continued) |
On March 23, 2010, USmart concluded that Aristo, a related company solely owned by Mr. Yang is a variable interest entity under FASB ASC 810-10-25 and is therefore subject to consolidation with USmart beginning fiscal year 2007 under the guidance applicable to variable interest entities.
Business Activity
USmart was incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware on September 17, 2002. The Company has been primarily engaged in the business of distribution of memory products mainly under “Samsung” brand name which principally comprised Dynamic Random Access Memory (“DRAM”), Graphic Random Access Memory (“Graphic RAM”), and Flash memory components for the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (“Hong Kong”) and People’s Republic of China (the “PRC” or “China”) markets formerly through its indirectly wholly owned subsidiary Atlantic Components Limited (“Atlantic”), a Hong Kong incorporated company, and ATMD (Hong Kong) Limited (“ATMD”) after April 1, 2012. The Company, through its wholly owned subsidiary ACL International Holdings Limited (“ACL Holdings”), owns 30% equity interest in ATMD, the joint venture with Tomen Devices Corporation (“Tomen”). ATMD offers a broad range of industry-leading Samsung semiconductor products, and additional components from SAMCO (such as wifi and camera modules) and SMD (smartphone panels). Atlantic integrated around 90% of its business relating to procurement of semiconductors and electronic parts from Samsung to ATMD. Subsequent to the start of the operations of ATMD, the Company’s sales, the cost of sales and operating expenses are expected to evolve in accordance with the transition of the Company’s business as described above. Through the acquisition of Jussey Investments Limited (“Jussey”) on September 28, 2012, the Company has diversified its product portfolio and customer network, obtained design and manufacturing capabilities, and tapped into the blooming telecommunication industry with access to the 3G baseband licenses.
| 7 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 2. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
| (a) | Method of Accounting |
The Company maintains its general ledger and journals with the accrual method accounting for financial reporting purposes. The consolidated financial statements and notes are representations of management. Accounting policies adopted by the Company conform to generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America and have been consistently applied in the presentation of consolidated financial statements.
| (b) | Principles of Consolidation |
The consolidated financial statements are presented in US Dollars and include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiary. All significant inter-company balances and transactions are eliminated in consolidation.
The Company owned its subsidiary soon after its inception and continued to own the equity’s interests through March 31, 2014. The following table depicts the identity of the subsidiary:
| Name of Subsidiary | Place of Incorporation | Attributable Equity Interest % | Registered Capital | |||||||
| ACL International Holdings Limited | Hong Kong | 100 | $ | 0.13 | ||||||
| Alpha Perform Technology Limited | BVI | 100 | $ | 1,000 | ||||||
| Atlantic Components Limited (1) | Hong Kong | 100 | $ | 384,615 | ||||||
| Aristo Technologies Limited (2) | Hong Kong | 100 | $ | 1,282 | ||||||
| Dongguan Kezheng Electronics Limited (3) | PRC | 80 | $ | 580,499 | ||||||
| eVision Telecom Limited (4) | Hong Kong | 100 | $ | 25,641 | ||||||
| Jussey Investments Limited (1) | BVI | 100 | $ | 1 | ||||||
| USmart Electronic Products Limited (4) | Hong Kong | 80 | $ | 1.28 | ||||||
| Note: | (1) Wholly owned subsidiary of ACL International Holdings Limited |
(2) Deemed variable interest entity
(3) Wholly owned subsidiary of USmart Electronic Products Limited
(4) Wholly or partially owned by Jussey Investments Limited
Variable Interest Entities
According to ASC 810-10-25 which codified FASB Interpretation No. 46 (Revised December 2003), Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities – an interpretation of ARB No. 51 (FIN 46R), an entity that has one or more of the three characteristics set forth therein is considered a variable interest entity. One of such characteristics is that the equity investment at risk in the relevant entity is not sufficient to permit the entity to finance its activities without additional subordinated financial support provided by any parties, including the equity holders.
ASC 810-05-08A specifies the two characteristics of a controlling financial interest in a variable interest entity (“VIE”): (1) the power to direct the activities of a VIE that most significantly impact the VIE’s economic performance; and (2) the obligation to absorb losses of the VIE that could potentially be significant to the VIE or the right to receive benefits from the VIE that could potentially be significant to the VIE. The Company is the primary beneficiary of Aristo because the Company can direct the activities of Aristo through the common director and major shareholder. Also, the Company extended substantial accounts receivable to Aristo and created an obligation to absorb loss if Aristo failed. Moreover, ASC 810-25-42 & 43 provides guidance on related parties treatment of VIE and specifies the relationship of de-facto agent and principal. This guidance will help to determine whether the Company will consolidate Aristo.
| 8 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 2. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued) |
| (b) | Principles of consolidation (Continued) |
Owing to the extent of outstanding large amounts of accounts receivable since 2007 together with the nominal amount of paid-up capital contributed by Mr. Yang when Aristo was formed, it has been determined that Aristo cannot finance its operations without subordinated financial support from USmart and accordingly, USmart is considered to be the de facto principal of Aristo, Aristo is considered to be the de facto subsidiary of the Company, and Mr. Yang is considered to be a related party of both the Company and Aristo.
By virtue of the above analysis, it has been determined that the Company is the primary beneficiary of Aristo.
Aristo Technologies Limited
The Company used to sell Samsung memory chips to Aristo and allowed long grace periods for Aristo to repay the open accounts receivable. Being the biggest creditor, the Company did not require Aristo to pledge assets or enter into any agreements to bind Aristo to specific repayment terms. The Company did not experience any bad debt from Aristo. Hence, the Company did not provide any bad debt provision derived from Aristo. Although, the Company was not involved in Aristo’s daily operation, it believes that there will not be significant additional risk derived from the trading relationship and transactions with Aristo.
Aristo is engaged in the marketing, selling and servicing of computer products and accessories including semiconductors, LCD products, mass storage devices, consumer electronics, computer peripherals and electronic components for different generations of computer related products. Aristo carries various brands of products such as Samsung, Hynix, Micron, Elpida, Qimonda, Lexar, Dane-Elec, Elixir, SanDisk and Winbond. Aristo 2012 and 2011 sales were around 2 million and 14 million; it was only a small distributor that accommodated special requirements for specific customers.
Aristo supplies different generations of computer related products. Old generation products will move slowly owing to lower market demand. According to the management experience and estimation on the actual market situation, old products carrying on hand for ten years will have no resell value. Therefore, inventories on hand over ten years will be written-off by Aristo immediately.
The Company sold to Aristo in order to fulfill Aristo’s periodic need for memory products based on prevailing market prices, which Aristo, in turn, sells to its customers. The sales to Aristo during the first quarter of 2014 and 2013 were $Nil. For fiscal year 2013, sales to Aristo were $3,337,735 with account receivable of $4,850,769 as of December 31, 2013. For fiscal year 2012, sales to Aristo were $106,031 with account receivable of $5,323,933 as of December 31, 2012. For fiscal year 2011, sales to Aristo were $7,086,379 with accounts receivable of $16,871,739 as of December 31, 2011.
The Company purchases from Aristo, from time to time, LCD panels, Samsung memory chips, DRAM, Flash memory, central processing units, external hard disks, DVD readers and writers that the Company cannot obtain from Samsung directly due to supply limitations.
Acquisition
The Company uses the acquisition method of accounting for business combinations which requires that the assets acquired and liabilities assumed be recorded at the date of the acquisition at their respective fair values. Assets acquired and liabilities assumed in a business combination that arise from contingencies are recognized at fair value if fair value can reasonably be estimated. If the fair value of an asset acquired or liability assumed that arises from a contingency cannot be determined at the date of acquisition, the asset or liability is recognized if probable and reasonably estimable; if these criteria are not met, no asset or liability is recognized. Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Any excess of the purchase price (consideration transferred) over the estimated fair values of net assets acquired is recorded as goodwill. Transaction costs and costs to restructure the acquired company are expensed as incurred. The operating results of acquired business are reflected in the acquirer’s consolidated financial statements and results of operations after the date of the acquisition.
| 9 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 2. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued) |
| (c) | Jointly-controlled entity |
A jointly-controlled entity is a corporate joint venture that is subject to joint control, resulting in none of the participating parties having unilateral control over the economic activity of the jointly-controlled entity.
The Group’s investment in a jointly-controlled entity is stated in equity method for the consolidated statement of financial position the Group’s shares of the equity of a jointly-controlled entity and the consolidated income statement and consolidated reserves, respectively.
| (d) | Use of estimates |
The preparation of consolidated financial statements that conform with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Management makes these estimates using the best information available at the time, however, actual results could differ materially from those estimates.
| (e) | Economic and political risks |
The Company’s operations are conducted in Hong Kong and China. A large number of customers are located in Southern China. Accordingly, the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations may be influenced by the political, economic and legal environment in Hong Kong and China, and by the general state of the economy in Hong Kong and China.
The Company’s operations and customers in Hong Kong and Southern China are subject to special considerations and significant risks not typically associated with companies in North America and Western Europe. These include risks associated with, among others, the political, economic and legal environments, and foreign currency exchange. The Company’s results may be adversely affected by changes in the political and social conditions in Hong Kong and China, and by changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, currency conversion, remittances abroad, and rates and methods of taxation, among other things.
| (f) | Property, plant and equipment |
Property, plant and equipment are carried at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is provided over their estimated useful lives, using the straight-line method.
Estimated useful lives of the plant and equipment are as follows:
| Automobiles | 3 1/3 years |
| Computers | 5 years |
| Leasehold improvement | 5 years |
| Land and buildings | By estimated useful life |
| Office equipment | 5 years |
| Machinery | 10 years |
The cost and related accumulated depreciation of assets sold or otherwise retired are eliminated from the accounts and any gain or loss is included in the statement of income.
| 10 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 2. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued) |
| (g) | Account receivable |
Accounts receivable is carried at the net invoiced value charged to customer. The Company records an allowance for doubtful accounts to cover estimated credit losses. Management reviews and adjusts this allowance periodically based on historical experience and its evaluation of the collectability of outstanding accounts receivable. The Company evaluates the credit risk of its customers utilizing historical data and estimates of future performance.
| (h) | Accounting for impairment of long-lived assets |
The Company periodically evaluates the carrying value of long-lived assets to be held and used, including intangible assets subject to amortization, when events and circumstances warrant such a review, pursuant to the guidelines established in ASC No. 360 (formerly Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 144). The carrying value of a long-lived asset is considered impaired when the anticipated undiscounted cash flow from such asset is separately identifiable and is less than its carrying value. In that event, a loss is recognized based on the amount by which the carrying value exceeds the fair market value of the long-lived asset. Fair market value is determined primarily using the anticipated cash flows discounted at a rate commensurate with the risk involved. Losses on long-lived assets to be disposed of are determined in a similar manner, except that fair market values are reduced for the cost to dispose.
During the reporting years, there was no impairment loss.
| (i) | Cash and cash equivalents |
The Company considers all highly liquid investments purchased with original maturities of three months or less to be cash equivalents. The Company maintains bank accounts in Hong Kong. The Company does not maintain any bank accounts in the United States of America.
| (j) | Inventories |
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market and are comprised of purchased computer technology resale products. Cost is determined using the first-in, first-out method.
| (k) | Lease assets |
Leases that substantially transfer all the benefits and risks of ownership of assets to the company are accounted for as capital leases. At the inception of a capital lease, the asset is recorded together with its long term obligation (excluding interest element) to reflect the purchase and the financing.
Leases which do not transfer substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership to the company are classified as operating leases. Payments made under operating leases are charged to income statement in equal installments over the accounting periods covered by the lease term. Lease incentives received are recognized in income statement as an integral part of the aggregate net lease payments made. Contingent rentals are charged to income statement in the accounting period which they are incurred.
| 11 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 2. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued) |
| (l) | Income taxes |
We are governed by the Internal Revenue Code of the United States, the Hong Kong Inland Revenue Department and the PRC’s Income Tax Laws. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets, including tax loss and credit carry forwards, and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income of the period that includes the enactment date. Deferred income tax expense represents the change during the period in the deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities. The components of the deferred tax assets and liabilities are individually classified as current and non-current based on their characteristics. Realization of the deferred tax asset is dependent on generating sufficient taxable income in future years. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when, in the opinion of management, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
The Company did not have any interest or penalty recognized in the income statements for the period ended March 31, 2014 and March 31, 2013 or the balance sheet, as of March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013. The Company did not have uncertainty tax positions or events leading to uncertainty tax position within the next 12 months. The Company’s 2010, 2011 and 2012 U.S. federal income tax returns are subject to U.S. Internal Revenue Service examination and the Company’s 2006/7, 2007/8, 2008/9, 2009/2010, 2010/11, 2011/12, 2012/13, Hong Kong Company Income Tax filing are subject to Hong Kong Inland Revenue Department examination. The Company’s 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, and 2012 PRC income tax returns are subject to PRC State Administration of Taxation examination.
| (m) | Foreign currency translation |
The accompanying consolidated financial statements are presented in United States dollars (USD). The functional currencies of the Company’s operating business based in Hong Kong and PRC are the Hong Kong Dollar (HKD) and Renminbi (RMB) respectively. The consolidated financial statements are translated into United States dollars from HKD with a ratio of USD1.00=HKD7.80, a fixed exchange rate maintained between Hong Kong and United States derived from the Hong Kong Monetary Authority pegging HKD and USD monetary policy. For our subsidiaries whose functional currency are the RMB, statement of income, balance sheets and cash flows are translated with a ratio of RMB1.00=HKD1.235 an average exchange rate during the period.
Exchange gains or losses arising from foreign currency transactions are included in the determination of net income for the respective periods. All of our revenue transactions are transacted in the functional currencies. We have not entered into any material transactions that are either originated, or to be settled, in currencies other than the HKD, RMB and USD. Accordingly, transaction gains or losses have not had, and are not expected to have a material effect on our results of operations.
The RMB is not freely convertible into any other currencies. In addition, all foreign exchange transactions in the PRC must be conducted through authorized institutions. Accordingly, management cannot provide any assurance that the RMB underlying the consolidated financial statement amounts could have been, or could be, converted into HKD or USD at the exchange rates used to translate the functional currency into the reporting currency.
| 12 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 2. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued) |
| (n) | Revenue recognition |
The Company derives revenues from resale of computer memory products, providing both ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) and OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) services for various electronic products, such as computer and peripherals, flash storage devices and home electronic products. The Company recognizes revenue in accordance with the ASC 605 “Revenue Recognition”. Under ASC 605, revenue is recognized when there is persuasive evidence of an arrangement, delivery has occurred or services are rendered, the sales price is determinable, and collectability is reasonably assured. Revenue typically is recognized at time of shipment. Sales are recorded net of discounts, rebates, and returns, which historically were not material.
| (o) | Advertising |
The Group expensed all advertising costs as incurred. Advertising expenses included in general and administrative expenses were $0 and $86 for the period ended March 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
| (p) | Segment reporting |
The Company’s sales are generated from Hong Kong and the rest of China and substantially all of its assets are located in Hong Kong.
| (q) | Fair value of financial instruments |
The carrying amount of the Company’s cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, lines of credit, convertible debt, accounts payable, accrued expenses, and long-term debt approximates their estimated fair values due to the short-term maturities of those financial instruments.
| (r) | Comprehensive income |
Comprehensive income is defined to include all changes in equity except those resulting from investments by owners and distributions to owners. Among other disclosures, all items that are required to be recognized under current accounting standards as components of comprehensive income are required to be reported in a financial statement that is presented with the same prominence as other consolidated financial statements. The Company has no items that represent other comprehensive income and, therefore, has not included a schedule of comprehensive income in the consolidated financial statements.
| (s) | Basic and diluted earnings (loss) per share |
In accordance with ASC No. 260 (formerly SFAS No. 128), “Earnings Per Share,” the basic earnings (loss) per common share is computed by dividing net earnings (loss) available to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted earnings (loss) per common share is computed similarly to basic earnings (loss) per common share, except that the denominator is increased to include the number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding if the potential common shares had been issued and if the additional common shares were dilutive.
| (t) | Reclassification |
Certain amounts in the prior period have been reclassified to conform to the current consolidated financial statement presentation.
| 13 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 2. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued) |
| (u) | Recently implemented standards |
In January 2013, FASB has issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2013-01, Balance Sheet (Topic 210): Clarifying the Scope of Disclosures about Offsetting Assets and Liabilities. This ASU clarifies that ordinary trade receivables and receivables are not in the scope of ASU No. 2011-11, Balance Sheet (Topic 210): Disclosures about Offsetting Assets and Liabilities. Specifically, ASU 2011-11 applies only to derivatives, repurchase agreements and reverse purchase agreements, and securities borrowing and securities lending transactions that are either offset in accordance with specific criteria contained in the FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ (Codification) or subject to a master netting arrangement or similar agreement. The FASB undertook this clarification project in response to concerns expressed by U.S. stakeholders about the standard’s broad definition of financial instruments. After the standard was finalized, companies realized that many contracts have standard commercial provisions that would equate to a master netting arrangement, significantly increasing the cost of compliance at minimal value to financial statement users. An entity is required to apply the amendments in ASU 2013-01 for fiscal years beginning on or after January 1, 2013, and interim periods within those annual periods. An entity should provide the required disclosures retrospectively for all comparative periods presented. The effective date is the same as the effective date of ASU 2011-11.
In February 2013, FASB has issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2013-02, Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reporting of Amounts Reclassified Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income. This ASU improves the transparency of reporting these reclassifications. Other comprehensive income includes gains and losses that are initially excluded from net income for an accounting period. Those gains and losses are later reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income into net income. The amendments in this ASU do not change the current requirements for reporting net income or other comprehensive income in financial statements. All of the information that this ASU requires already is required to be disclosed elsewhere in the financial statements under U.S. GAAP.
The new amendments will require an organization to:
Present (either on the face of the statement where net income is presented or in the notes) the effects on the line items of net income of significant amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income - but only if the item reclassified is required under U.S. GAAP to be reclassified to net income in its entirety in the same reporting period.
Cross-reference to other disclosures currently required under U.S. GAAP for other reclassification items (that are not required under U.S. GAAP) to be reclassified directly to net income in their entirety in the same reporting period. This would be the case when a portion of the amount reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income is initially transferred to a balance sheet account (e.g., inventory for pension-related amounts) instead of directly to income or expense.
The amendments apply to all public and private companies that report items of other comprehensive income. Public companies are required to comply with these amendments for all reporting periods (interim and annual). A private company is required to meet the reporting requirements of the amended paragraphs about the roll forward of accumulated other comprehensive income for both interim and annual reporting periods. However, private companies are only required to provide the information about the effect of reclassifications on line items of net income for annual reporting periods, not for interim reporting periods. The amendments are effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2012, for public companies and are effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2013, for private companies. Early adoption is permitted.
In February 2013, FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2013-03, Financial Instruments (Topic 825). This ASU clarifies the scope and applicability of a disclosure exemption that resulted from the issuance of Accounting Standards Update No. 2011-04, Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Amendments to Achieve Common Fair Value Measurement and Disclosure Requirements in U.S. GAAP and IFRSs. The amendment clarifies that the requirement to disclose "the level of the fair value hierarchy within which the fair value measurements are categorized in their entirety (Level 1, 2, or 3)" does not apply to nonpublic entities for items that are not measured at fair value in the statement of financial position, but for which fair value is disclosed. This ASU is the final version of Proposed Accounting Standards Update 2013-200—Financial Instruments (Topic 825) which has been deleted. The amendments are effective upon issuance.
| 14 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 2. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued) |
| (u) | Recently implemented standards (Continued) |
In February 2013, FASB has issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2013-04, Liabilities (Topic 405): Obligations Resulting from Joint and Several Liability Arrangements for Which the Total Amount of the Obligation Is Fixed at the Reporting Date. This ASU provides guidance for the recognition, measurement, and disclosure of obligations resulting from joint and several liability arrangements for which the total amount of the obligation within the scope of this ASU is fixed at the reporting date, except for obligations addressed within existing guidance in U.S. GAAP. The guidance requires an entity to measure those obligations as the sum of the amount the reporting entity agreed to pay on the basis of its arrangement among its co-obligors and any additional amount the reporting entity expects to pay on behalf of its co-obligors. The guidance in this ASU also requires an entity to disclose the nature and amount of the obligation as well as other information about those obligations. The amendments in this ASU are effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2013. For nonpublic entities, the amendments are effective for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2014, and interim periods and annual periods thereafter. The amendments in this ASU should be applied retrospectively to all prior periods presented for those obligations resulting from joint and several liability arrangements within the ASU’s scope that exist at the beginning of an entity’s fiscal year of adoption. An entity may elect to use hindsight for the comparative periods (if it changed its accounting as a result of adopting the amendments in this ASU) and should disclose that fact. Early adoption is permitted.
In March 2013, FASB has issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2013-05, Foreign Currency Matters (Topic 830). This ASU resolve the diversity in practice about whether Subtopic 810-10, Consolidation—Overall, or Subtopic 830-30, Foreign Currency Matters—Translation of Financial Statements, applies to the release of the cumulative translation adjustment into net income when a parent either sells a part or all of its investment in a foreign entity or no longer holds a controlling financial interest in a subsidiary or group of assets that is a nonprofit activity or a business (other than a sale of in substance real estate or conveyance of oil and gas mineral rights)within a foreign entity. In addition, the amendments in this Update resolve the diversity in practice for the treatment of business combinations achieved in stages (sometimes also referred to as step acquisitions) involving a foreign entity. This ASU is the final version of Proposed Accounting Standards Update EITF11Ar—Foreign Currency Matters (Topic 830), which has been deleted. The amendments in this Update are effective prospectively for fiscal years (and interim reporting periods within those years) beginning after December 15, 2013. For nonpublic entities the amendments in this Update are effective prospectively for the first annual period beginning after December 15, 2014, and interim and annual periods thereafter. The amendments should be applied prospectively to derecognition events occurring after the effective date. Prior periods should not be adjusted. Early adoption is permitted. If an entity elects to early adopt the amendments, it should apply them as of the beginning of the entity’s fiscal year of adoption.
| 15 |
The FASB has issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2014-07, Applying Variable Interest Entities Guidance to Common Control Leasing Arrangements. The guidance addresses the consolidation of lessors in certain common control leasing arrangements and is based on a consensus reached by the Private Company Council (PCC). Under current U.S. GAAP, a company is required to consolidate an entity in which it has a controlling financial interest. The assessment of controlling financial interest is performed under either: (a) a voting interest model; or (b) a variable interest entity model. In a variable interest entity model, the company has a controlling financial interest when it has: (a) the power to direct the activities that most significantly affect the economic performance of the entity; and (b) the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits of the entity that could be potentially significant to the entity. To determine which model applies, a company preparing financial statements must first determine whether it has a variable interest in the entity being evaluated for consolidation and whether that entity is a variable interest entity.
The new guidance allows a private company to elect (when certain conditions exist) not to apply the variable interest entity guidance to a lessor under common control. Instead, the private company would make certain disclosures about the lessor and the leasing arrangement. Under the amendments in this ASU, a private company lessee could elect an alternative not to apply variable interest entity guidance to a lessor when:
-The private company lessee and the lessor are under common control;
-The private company lessee has a leasing arrangement with the lessor;
-Substantially all of the activity between the private company lessee and the lessor is related to the leasing activities (including supporting leasing activities) between those two companies, and
-If the private company lessee explicitly guarantees or provides collateral for any obligation of the lessor related to the asset leased by the private company, then the principal amount of the obligation at inception does not exceed the value of the asset leased by the private company from the lessor. If elected, the accounting alternative should be applied to all leasing arrangements meeting the above conditions. The alternative should be applied retrospectively to all periods presented, and is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2014, and interim periods within annual periods beginning after December 15, 2015. Early application is permitted for all financial statements that have not yet been made available for issuance.
The FASB has issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2014-08, Presentation of Financial Statements (Topic 205) and Property, Plant, and Equipment (Topic 360): Reporting Discontinued Operations and Disclosures of Disposals of Components of an Entity. The amendments in the ASU change the criteria for reporting discontinued operations while enhancing disclosures in this area. It also addresses sources of confusion and inconsistent application related to financial reporting of discontinued operations guidance in U.S. GAAP.
Under the new guidance, only disposals representing a strategic shift in operations should be presented as discontinued operations. Those strategic shifts should have a major effect on the organization’s operations and financial results. Examples include a disposal of a major geographic area, a major line of business, or a major equity method investment. In addition, the new guidance requires expanded disclosures about discontinued operations that will provide financial statement users with more information about the assets, liabilities, income, and expenses of discontinued operations.
The new guidance also requires disclosure of the pre-tax income attributable to a disposal of a significant part of an organization that does not qualify for discontinued operations reporting. This disclosure will provide users with information about the ongoing trends in a reporting organization’s results from continuing operations. The amendments in this ASU enhance convergence between U.S. GAAP and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Part of the new definition of discontinued operation is based on elements of the definition of discontinued operations in IFRS 5, Non-Current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations. The amendments in the ASU are effective in the first quarter of 2015 for public organizations with calendar year ends. For most nonpublic organizations, it is effective for annual financial statements with fiscal years beginning on or after December 15, 2014. Early adoption is permitted.
| 16 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 3. | Inventories |
Inventories consisted of the following at March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013:
| March 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | |||||||
| Finished goods | $ | - | $ | 3,044,793 | ||||
| Less allowance for excess and obsolete inventory | - | (1,963,282 | ) | |||||
| Inventory, net | $ | - | $ | 1,081,511 | ||||
The following is a summary of the change in the Company’s inventory valuation allowance:
| March 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | |||||||
| Inventory valuation allowance, beginning of the period | $ | - | $ | 2,625,375 | ||||
| Obsolete inventory sold | - | (662,093 | ) | |||||
| Additional inventory provision | - | 0 | ||||||
| Inventory valuation allowance, end of period | $ | - | $ | 1,963,282 | ||||
| Note 4. | Property, Plant and Equipment, net |
Property, plant and equipment, net consisted of the following at March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013:
| March 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | |||||||
| At cost | ||||||||
| Land and buildings | $ | - | $ | 8,574,682 | ||||
| Automobiles | - | 642,241 | ||||||
| Office equipment | - | 268,863 | ||||||
| Leasehold improvements | - | 543,550 | ||||||
| Furniture and fixtures | - | 57,302 | ||||||
| Machinery | - | 668,185 | ||||||
| $ | - | $ | 10,754,823 | |||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation | - | (2,541,974 | ) | |||||
| $ | - | $ | 8,212,849 | |||||
Depreciation and amortization expense totaled $0 and $119,846 for the three months ended March 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Automobiles include the following amounts under capital leases:
| March 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | |||||||
| Cost | $ | - | $ | 399,473 | ||||
| Less accumulated depreciation | - | (341,876 | ) | |||||
| Total | $ | - | $ | 57,597 | ||||
| 17 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 5. | Capital Lease Obligations |
The Company leases automobiles under four capital leases that expire between July 2013 and December 2015. Aggregate future obligations under the capital leases in effect as of March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 are as follows:
The Company has several non-cancellable capital leases relating to automobiles:
| March 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | |||||||
| Current portion | $ | - | $ | 75,917 | ||||
| Non-current portion | - | 57,511 | ||||||
| $ | - | $ | 133,428 | |||||
At March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, the value of automobiles under capital leases as follows:
| March 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | |||||||
| Cost | $ | - | $ | 399,473 | ||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation | - | (341,876 | ) | |||||
| $ | - | $ | 57,597 | |||||
At March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, the Company had obligations under capital leases repayable as follows:
| March 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | |||||||
| Total minimum lease payments | ||||||||
| - Within one year | $ | - | $ | 81,906 | ||||
| - After one year but within 5 years | - | 60,351 | ||||||
| $ | - | $ | 142,257 | |||||
| Interest expenses relating to future periods | - | (8,829 | ) | |||||
| Present value of the minimum lease payments | $ | - | $ | 133,428 | ||||
Interest expense related to capital leases totaled $Nil and $2,380 for the three months ended March 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
| 18 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 6. | Stock Options |
On March 31, 2006, the Board of Directors adopted the 2006 Equity Incentive Stock Plan (the “Plan”) and the majority stockholder approved the Plan by written consent. The purpose of the Plan is to provide additional incentive to employees, directors and consultants and to promote the success of the Company’s business. The Plan permits the Company to grant both incentive stock options (“Incentive Stock Options” or “ISOs”) within the meaning of Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code (the “Code”), and other options which do not qualify as Incentive Stock Options (the “Non- Qualified Options”) and stock awards.
Unless earlier terminated by the Board of Directors, the Plan (but not outstanding options) terminates on March 31, 2016, after which no further awards may be granted under the Plan. The Plan is administered by the full Board of Directors or, at the Board of Director’s discretion, by a committee of the Board of Directors consisting of at least two persons who are “disinterested persons” defined under Rule 16b-2(c)(ii) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Committee”).
Recipients of options under the Plan (“Optionees”) are selected by the Board of Directors or the Committee. The Board of Directors or Committee determines the terms of each option grant, including (1) the purchase price of shares subject to options, (2) the dates on which options become exercisable and (3) the expiration date of each option (which may not exceed ten years from the date of grant). The minimum per share purchase price of options granted under the Plan for Incentive Stock Options and Non-Qualified Options is the fair market value (as defined in the Plan) on the date the option is granted.
Optionees will have no voting, dividend or other rights as stockholders with respect to shares of Common Stock covered by options prior to becoming the holders of record of such shares. The purchase price upon the exercise of options may be paid in cash, by certified bank or cashier’s check, by tendering stock held by the Optionee, as well as by cashless exercise either through the surrender of other shares subject to the option or through a broker. The total number of shares of Common Stock available under the Plan, and the number of shares and per share exercise price under outstanding options will be appropriately adjusted in the event of any stock dividend, reorganization, merger or recapitalization or similar corporate event.
The Board of Directors may at any time terminate the Plan or from time to time make such modifications or amendments to the Plan as it may deem advisable and the Board of Directors or Committee may adjust, reduce, cancel and re-grant an unexercised option if the fair market value declines below the exercise price except as may be required by any national stock exchange or national market association on which the Common Stock is then listed. In no event may the Board of Directors, without the approval of stockholders, amend the Plan if required by any federal, state, local or foreign laws or regulations or any stock exchange or quotation system on which the Common Stock is listed or quoted and the applicable laws of any other country or jurisdiction where options or stock purchase rights are granted under the Plan.
Subject to limitations set forth in the Plan, the terms of option agreements will be determined by the Board of Directors or Committee, and need not be uniform among Optionees.
As of March 31, 2014, the Company has not granted any options according to the condition set forth in the 2006 Equity Incentive Stock Plan and therefore, there were no options outstanding under this Plan.
| Note 7. | Related Party Transactions |
Related party receivables are payable on demand upon the same terms as receivables from unrelated parties.
Transactions with Aristo Technologies Limited / Mr. Yang
This represented Aristo transactions with various related parties of Mr. Yang.
As of March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, we had an outstanding receivable from Aristo / Mr. Yang, the Chairman of our Board of Directors, totaling $Nil and $931,652, respectively. These advances bear no interest and are payable on demand. The receivable due from Aristo / Mr. Yang to the Company is derived from the consolidation of the financial statements of Aristo, a variable interest entity, with the Company. A repayment plan has been entered with Mr. Yang.
| 19 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 7. | Related Party Transactions (Continued) |
Transactions with Solution Semiconductor (China) Limited
Mr. Yang is a director and the sole beneficial owner of the equity interests of Solution Semiconductor (China) Ltd. (“Solution”).
During the three months ended March 31, 2014 and 2013, we received service fee of $Nil and $3,846 respectively, from Solution. The service fee was charged for back office support for Solution.
During the three months ended March 31, 2014 and 2013, we sold products of $Nil and $15,833 respectively, to Solution. As of March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, there were no outstanding accounts receivables from Solution.
Two facilities located in Hong Kong owned by Solution were used by the Company as collateral for loans from DBS Bank (Hong Kong) Limited (“DBS Bank”) (formerly Overseas Trust Bank Limited) and The Bank of East Asia, Limited (“BEA Bank”) respectively.
Transactions with Systematic Information Limited
Mr. Yang, the Company’s Chairman of the Board of Directors, is a director and shareholder of Systematic Information Ltd. (“Systematic Information”) with a total of 100% interest.
During the three months ended March 31, 2014 and 2013, we received service fee of $Nil and $1,846 respectively, from Systematic Information. The service fee was charged for back office support for Systematic Information.
During the three months ended March 31, 2014 and 2013, we sold products for $Nil and $327,115 respectively, to Systematic Information. As of March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, there were no outstanding accounts receivables from Systematic Information.
A workshop located in Hong Kong owned by Systematic Information was used by the Company as collateral for loans from BEA Bank.
Transactions with City Royal Limited
Mr. Yang, the Company’s Chairman of the Board of Directors, is a 50% shareholder of City Royal Limited (“City”). The remaining 50% of City is owned by the wife of Mr. Yang. A residential property located in Hong Kong owned by City was used by the Company as collateral for loans from DBS Bank.
Transactions with Aristo Components Limited
Mr. Ben Wong appointed as new Chief Executive Officer on February 1, 2013. He is a 90% shareholder of Aristo Components Ltd. (“Aristo Comp”). The remaining 10% of Aristo Comp is owned by a non-related party.
During the three months ended March 31, 2014 and 2013, we received a service fee of $Nil and $3,077 respectively, from Aristo Comp. The service fee was charged for back office support for Aristo Comp.
Transactions with Atlantic Ocean (HK) Limited
Mr. Yang is a director and 60% shareholder of Atlantic Ocean (HK) Limited (“Ocean”).
During the three months ended March 31, 2014 and 2013, we sold products for $Nil and $7,070 respectively, to Ocean. As of March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, there were no outstanding accounts receivables from Ocean.
| 20 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 8. | Revolving Lines of Credit and Loan Facilities |
The summary of banking facilities at March 31, 2013 is as follows:
| Granted facilities | Utilized facilities | Not Utilized Facilities | ||||||||||
| Lines of credit and loan facilities | ||||||||||||
| Import/Export Loan | $ | 8,653,847 | $ | 6,395,985 | $ | 2,257,862 | ||||||
| Bank Loans | 5,720,451 | (a) | 5,720,451 | 0 | ||||||||
| Revolving Short Term Loan | 1,538,462 | (a) | 1,528,620 | 9,842 | ||||||||
| Overdraft | 474,359 | (b) | 327,252 | 147,107 | ||||||||
| $ | 16,387,119 | $ | 13,972,308 | $ | 2,414,811 | |||||||
(a) The bank loans are combined from the summary of Note 9, total bank loans amount to $7,249,071 with a revolving short term loan of $1,528,620. The revolving short term loan is placed under Other Current Liabilities on the balance sheet. It has a facility limit of $1,538,462, bearing an interest rate of 0.5% below Hong Kong prime rate per annum.
(b) Including in cash and cash equivalents
As of March 31, 2014, the Company decided to dispose the fully owned operating subsidiaries and all the relevant banking facilities are included in the disposal plan.
| 21 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| NOTE 9. | BANK LOANS |
Bank loans were comprised of the following as of March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013
| March 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | |||||||
| Installment loan provided by BEA Bank having a maturity date in July 28, 2014 and carrying an interest rate of Hong Kong dollar Prime Rate at 5.25% as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 +0.25%, payable in monthly installments of $13,291 including interest through December 2013 without any balloon payment requirements | $ | - | $ | 89,744 | ||||
| Installment loan provided by BEA Bank having a maturity date in April 18, 2015 and carrying an interest rate of Hong Kong dollar Prime Rate at 5.25% as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 +0.25%, payable in monthly installments of $46,065 including interest through December 2013 without any balloon payment requirements | - | 683,761 | ||||||
| Installment loan provided by DBS Bank having a maturity date in April 25, 2015 and carrying an interest rate of Hong Kong Prime dollar Rate at 5.25% as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 +0.5%, payable in monthly installments of $55,939 including interest through December 2013 without any balloon payment requirements | - | 859,612 | ||||||
| Installment loan provided by DBS Bank having a maturity date in June 2, 2023 and carrying an interest rate of one month HIBOR at 0.28% as of December 31+2%, it was fully repaid on 23 September, 2013 | - | - | ||||||
| Installment loan provided by DBS Bank having a maturity date in September 15, 2023 and carrying an interest rate of Hong Kong dollar Prime Rate at December 31, 2012 -2.5%, it was fully repaid on 23 September, 2013 | - | - | ||||||
| Installment loan provided by DBS Bank having a maturity date in June 2, 2026 and carrying an interest rate of one month HIBOR at December 31, 2012 +2%, it was fully repaid on 23 September, 2013 | - | - | ||||||
| Installment loan provided by DBS Bank having a maturity date in July 21, 2026 and carrying an interest rate of Hong Kong dollar Prime Rate at 5.25% as of December 31, 2012 -2.4%, it was fully repaid on 23 September, 2013 | - | - | ||||||
| Installment loan having a maturity date in 23 September, 2028 and carrying an interest rate of 2% per annum over one month HIBOR (0.2143% at December 31, 2013) from Fubon Bank payable in monthly installments of $6,283 including interest through December 2013 without any balloon payment requirements | - | 947,971 | ||||||
| Term loan having a maturity due in 23 January, 2014 and carrying an interest rate of 3.88429 per annum from Fubon Bank without any balloon payment requirements | - | 641,025 | ||||||
| $ | - | $ | 3,222,113 | |||||
| 22 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| NOTE 9. | BANK LOANS (CONTINUED) |
An analysis on the repayment of bank loan as of March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 are as follow:
| March 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | |||||||
| Carrying amount that are repayable on demand or within twelve months from | ||||||||
| December 31, 2013 containing a repayable on demand clause: | ||||||||
| Within twelve months | $ | - | $ | 1,937,063 | ||||
| Carrying amount that are not repayable within twelve months from September 30, 2013 containing a repayable on demand clause but shown in current liabilities: | ||||||||
| After 1 year, but within 2 years | $ | - | $ | 505,656 | ||||
| After 2 years, but within 5 years | - | 118,775 | ||||||
| After 5 years | - | 660,619 | ||||||
| $ | - | $ | 1,285,050 | |||||
| $ | - | $ | 3,222,113 | |||||
With respect to all of the debt and credit arrangements referred to in this Note 8 and Note 9, the Company pledged its assets to a bank group in Hong Kong comprised of DBS Bank, BEA Bank and Fubon Bank, as collateral for all current and future borrowings from the bank group by the Company. In addition to the above pledged collateral, the debt is also secured by:
| 1. | Collateral for loans from DBS Bank: |
| (a) | a security interest on a residential property located in Hong Kong owned by City, a related party; |
| (b) | a workshop located in Hong Kong owned by Solution, a related party; and |
| (c) | an unlimited personal guarantee by Mr. Yang |
| 2. | Collateral for loans from BEA Bank: |
| (a) | a workshop located in Hong Kong owned by Systematic Information, a related party; |
| (b) | a workshop located in Hong Kong owned by Solution, a related party; and |
| (c) | an unlimited personal guarantee by Mr. Yang |
| 3. | Collateral for loans from Fubon Bank |
| (a) | a security interest on two residential properties located in Hong Kong owned by Aristo, a company wholly owned by Mr. Yang; and |
| (b) | an unlimited personal guarantee by Mr. Yang |
| 4. | As of March 31, 2014, the Company decided to dispose the fully owned operating subsidiaries and all the relevant banking facilities are included in the disposal plan. |
| Note 10. | Other Current Liabilities |
The other current liabilities consisted the following as of March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013:
| March 31, 2014 | December 31, 2012 | |||||||
| Revolving short term loan | $ | - | $ | 1,538,168 | ||||
| Trade deposit from customers | - | 7,725,475 | ||||||
| Temporary reciepts | - | 2,242,999 | ||||||
| Others | - | 937,358 | ||||||
| $ | - | $ | 12,444,000 | |||||
The trade deposit from customers is deposit received from customers for future orders.
| 23 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 11. | Weighted Average Number of Shares |
The Company has a 2006 Incentive Equity Stock Plan, under which the Company may grant options to its employees for up to 5 million shares of common stock. There was no dilutive effect to the weighted average number of shares for the period ended March 31, 2014 and March 31, 2013 since there were no outstanding options at March 31, 2014 and March 31, 2013 (please refer to Note 6 for more information on the 2006 Equity Incentive Stock Plan).
| Note 12. | Loan from a third party |
On September 26, 2013, Atlantic Components Limited entered into a Loan Agreement with Excel Precise International Limited, an unrelated third party, for a loan facility to the aggregate extent of HKD55 Million (USD7,051,282). The amount HKD55 Million has been drawn down on September 27, 2013. The rate of interest is 1.1% per month and payable on the 26th day of each calendar month.
The Loan is collateral with mortgage over two Properties owned by Atlantic Components Limited and Personal Guaranteed by Wong, Fung Ming and Yang, Chung Lun.
The repayment time schedule contained in the Loan Agreement as at December 31, 2013 as follows:
| Date of Repayment | Amount | |||
| The Last date of the 12-month period from September 27, 2013 | 641,026 | |||
| The Last date of the 24-month period from September 27, 2013 | 1,282,051 | |||
| The Last date of the 36-month period from September 27, 2013 | 5,128,205 | |||
| 7,051,282 | ||||
| Current portion | 641,026 | |||
| Non-current portion | 6,410,256 | |||
| 7,051,282 | ||||
The Loan facility is to provide purpose temporary relief for the Company’s liquidity during the negotiation with new banker for a better term on a new banking facility.
As of March 31, 2014, the Company decided to dispose the fully owned operating subsidiaries and all the loans from third parties are included in the disposal plan.
| Note 13. | Acquisition |
On September 28, 2012, the Company completed its acquisition of 100% equity interest of Jussey Investments Limited (“Jussey”), a company incorporated in British Virgin Islands, for aggregate purchase consideration of approximately US$2,150,000, payable by way of cash or equivalent in favor to the seller within 5 business days after the completion of the acquisition. Jussey owns 100% equity interest in eVision Telecom Limited (“eVision”), a Hong Kong incorporated company, and 80% equity interest in USmart Electronic Products Limited (“UEP”), a Hong Kong incorporated company. Jussey indirectly owns 80% of Dongguan Kezheng Electronics Limited (“Kezheng”), a wholly foreign-owned enterprise (“WFOE”) organized under the laws of the PRC by UEP.
Through the acquisition, the Company has diversified its product portfolio, enhanced its distributor role to a Research and Develop (“R&D”) manufacturer with its own products and brands, entered the telecommunication industry, gained access to the 3G baseband licenses, and design and manufacturing matrix and facility.
The Company accounted for this acquisition of Jussey and its subsidiaries by acquisition method of accounting. The balance sheet items were stated at fair value. The fair value was accounted upon the issuance of fair value report from an independent valuator engaged for this acquisition.
| 24 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
| Note 14. | Subsequent Events |
In preparing these financial statements, the Company evaluated the events and transactions that occurred from April 1, 2014 through May 20, 2014, the date these financial statements were issued. The Company has decided to dispose the fully owned operating subsidiaries in the way of selling the shareholding of ACL International Holdings Limited. The agreement will be finalized and to be completed in the coming quarter in 2014. Despite mentioned the Company determined that there were no material subsequent events.
| Note 15. | Uncertainty of ability to continue as a going concern |
The Company's financial statements are prepared using the generally accepted accounting principles applicable to a going concern, which contemplates the realization of assets and liquidation of liabilities in the normal course of business. The continuation of the Company as a going concern is dependent upon the ability of the Company to obtain necessary equity financing to continue operations and the attainment of profitable operations. The management will seek to raise funds from shareholders.
For the quarter ended March 31, 2014, the Company has generated revenue of $561,870 and has incurred an accumulated deficit $17,170,361. These financial statements do not include any adjustments relating to the recoverability and classification of recorded asset amounts and classification of liabilities that might be necessary should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern. These factors noted above raise substantial doubts regarding the Company's ability to continue as a going concern.
| Item 2. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
The following discussion highlights the principal factors that have affected our financial condition and results of operations as well as our liquidity and capital resources for the periods described.
The information contained in this Form 10-Q is intended to update the information contained in our annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2012, (the “Form 10-K”), filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), and presumes that readers have access to, and will have read, the “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operation,” our consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto, and other information contained in the Form 10-K. The following discussion and analysis also should be read together with our condensed consolidated financial statements and the notes to the condensed consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto included elsewhere in this Form 10-Q.
Forward-Looking Statements
Information included in this Form 10-Q may contain forward-looking statements. Except for the historical information contained in this discussion of the business and the discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations, the matters discussed herein are forward looking statements. These forward looking statements include but are not limited to the Company’s plans for sales growth and expectations of gross margin, expenses, new product introduction, and the Company’s liquidity and capital needs. This information may involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors which may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by any forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements, which involve assumptions and describe our future plans, strategies and expectations, are generally identifiable by use of the words “may,” “will,” “should,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “estimate,” “believe,” “intend” or “project” or the negative of these words or other variations on these words or comparable terminology. In addition to the risks and uncertainties described in “Risk Factors” contained in the Form 10-K, these risks and uncertainties may include consumer trends, business cycles, scientific developments, changes in governmental policy and regulation, currency fluctuations, economic trends in the U.S. and inflation. Forward-looking statements are based on assumptions that may be incorrect, and there can be no assurance that any projections or other expectations included in any forward-looking statements will come to pass. Our actual results could differ materially from those expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements as a result of various factors. Except as required by applicable laws, we undertake no obligation to update publicly any forward-looking statements for any reason, even if new information becomes available or other events occur in the future.
| 25 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Company Overview and Background
USmart was primarily engaged in the business of distribution of memory products mainly under “Samsung” brand name which principally comprised DRAM, Graphic RAM and Flash for the Hong Kong and PRC markets (“Samsung Business”). After April 1, 2012, the Samsung Business was transferred to ATMD, a joint venture with Tomen. We indirectly own 30% equity interest in ATMD. On September 27, 2013, we sold the entire 30% equity interest of ATMD. Through the acquisition of Jussey on September 28, 2012, we have diversified our product portfolio and customer network, obtained design and manufacturing capabilities, and tapped into the blooming telecommunication industry with access to the 3G baseband licenses acquired by Jussey’s subsidiaries.
ACL International Holdings Limited
ACL Holdings, a holding company incorporated in Hong Kong, is wholly owned by the Company. ACL Holdings owns 100% equity interest of Atlantic, and 100% equity interest of Jussey.
Atlantic Components Limited
Atlantic, a company incorporated in Hong Kong, is indirectly wholly owned by the Company. Atlantic was established in May 1991 by Mr. Chung-Lun Yang, the Company’s Chairman, as a regional distributor of memory products of various manufacturers. In 1993, Samsung Electronics Hong Kong Co., Ltd. (“Samsung”) appointed Atlantic as its authorized distributor and marketer of Samsung’s memory products in Hong Kong and overseas markets. In 2001, Atlantic established a representative office in Shenzhen, China, and began concentrating its distribution and marketing efforts in Southern China.
The Company’s Samsung business was formerly conducted through Atlantic. After April 1, 2012, Atlantic integrated its business relating to procurement of semiconductors and electronic parts directly from Samsung to the joint venture, ATMD, which was finally sold in November 2013. The transition of the business integration has been completed by December 31, 2012. During the transitional period, Atlantic extended its distributor agreement with Samsung to June 30, 2012. After the distributor agreement expired, Atlantic transformed its position from Samsung memory products distributor to a general memory products distributor, and continues its business by providing various brands of memory products to its customers.
Aristo Technologies Limited
On March 23, 2010, the Company concluded that Aristo Technologies Limited (“Aristo”), a related company solely owned by Mr. Yang, is a variable interest entity under FASB ASC 810-10-25 and is therefore subject to consolidation with the Company beginning fiscal year 2007 under the guidance applicable to variable interest entities. Atlantic used to sell Samsung memory chips to Aristo and allows long grace periods for Aristo to repay the open accounts receivable. After the establishment of ATMD, the Company will sell different brands of memory products to Aristo. Being the Company’s biggest creditor, the Company does not require Aristo to pledge assets or enter into any agreements to bind Aristo to specific repayment terms. The Company does not experience any bad debt from Aristo. Hence, the Company does not provide any bad debt provision derived from Aristo. Although, the Company is not involved in Aristo’s daily operation, it believes that there will not be significant additional risk derived from the trading relationship and transactions with Aristo. Aristo is engaged in the marketing, selling and servicing of computer products and accessories including semiconductors, LCD products, mass storage devices, consumer electronics, computer peripherals and electronic components for different generations of computer related products. In addition to Samsung-branded products, Aristo carries various brands of products, such as Hynix, Micron, Qimonda, Lexar, Dane-Elec, Elixir, SanDisk and Winbond. Aristo also provides value-added services to its products and resells it to its customers. Aristo’s 2012 and 2011 sales were around $2 million and $14 million; it was a distributor that accommodated special requirements for specific customers.
Jussey Investments Limited
Jussey, a holding company incorporated in British Virgin Islands, which is wholly owned by the Company, owns 100% equity interest in eVision Telecom Limited (“eVision”), a Hong Kong incorporated company, and 80% equity interest in USmart Electronic Products Limited, a Hong Kong incorporated company, which owns 100% equity interest of Dongguan Kezheng Electronics Limited, a wholly foreign-owned enterprise (“WFOE”) organized under the laws of the PRC (USmart Electronic Products Limited and Dongguan Kezheng Electronics Limited are together referring as “UEP” hereafter). Hence, Jussey indirectly owns 80% of Kezheng.
| 26 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
USmart Electronic Products Limited & Dongguan Kezheng Electronics Limited
UEP was founded in 2006 and it conducts its business through either itself or Kezheng, which has a factory located in Dongguan, PRC. UEP provides Research and Development (“R&D”) and both ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) and OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) services for the three “C” products – Computers, Communications and Consumer electronics devices, such as tablets, portable media players, digital photo frames, and smartphones. UEP has its own R&D and production teams. With the support from eVision, the business of which is described below, UEP is capable of providing its customers with total solutions from design to manufacturing. UEP holds its own brands – USmart and VSmart, which can be used on a broad spectrum of products including memory storage devices, visual and audio products such as digital flat screen television, DAB (Digital Audio Broadcasting) radios, digital photo frames, and other home electronic products. In 2010, UEP began its business development in the telecommunication industry, and successfully obtained the W-CDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access is one of the third-generation (“3G”) wireless standards) license from Intel Mobile Communications GmbH., which offers cellular platforms for global phone makers. W-CDMA baseband is adapted by China Unicom, one of the three major telecommunication carriers in the PRC.
eVision Telecom Limited
Founded in 2011, eVision is a Hong Kong based solution house that specializes in CDMA2000 (also known as Evolution-Data Optimized or “EV-DO”) platform. CDMA2000 is one of the 3G wireless standards. This standard was adapted by China Telecom, one of the three major telecommunication carriers in China. The principal function of eVision is to provide CDMA2000 solutions to UEP. In May 2011, eVision entered into an exclusive R&D servicing agreement (the “Servicing Agreement”) with an independent third party in the PRC (the “R&D House”), a solution house that works closely with South China University of Technology and has a R&D team consisting of members with advanced academic qualifications. On behalf of eVision, the R&D House holds a CDMA2000 software license granted by VIA Telecom Co. Ltd. According to the Servicing Agreement, the R&D House provides R&D services relating to CDMA2000 technology exclusively to eVision, and eVision holds the sole and exclusive right, title and interest to and in the aforementioned license and any R&D results/products obtained or developed by the R&D House during the term of the Servicing Agreement. eVision will also hold all the intellectual property rights that are obtained or developed by the R&D House in the course of such research.
As of March 31, 2014, USmart had decided to dispose the fully owned operating subsidiaries.
| 27 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Corporate Structure
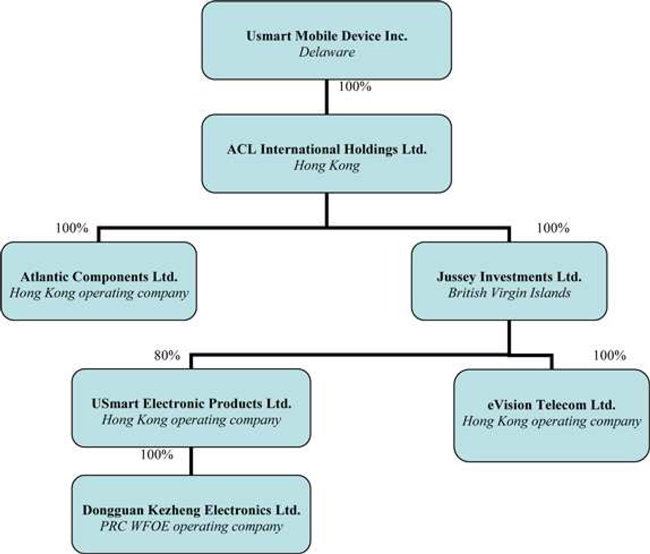
Financial Highlights
The Company has decided to sell all the investment in its fully subsidiary ACL International Limited and the transaction will be completed within a year. Accordingly, the company has put aside all the assets and liabilities of ACL under the current asset held for disposal to reflect the decision.
| · | Net sales for the three months ended March 31, 2014 (“first quarter of 2014”) decreased $13.9 million, or 96.1% to $561,870 compared to the same period in 2013 (“first quarter of 2013”). |
| · | The Company’s gross loss for the first quarter of 2014 reduced by $73,077 or 74.2% to a gross loss of $25,438 compared to the first quarter of 2013. |
| · | Net income for the first quarter of 2014 decreased $1.2 million to a loss $291,024 compared to the net income of 0.9 million for the first quarter of 2013. |
Operating expenses for the first quarter of 2014 decreased by $0.8 million, or 73.3% to $298,823 compared to the first quarter of 2013.
| 28 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Results of Operations
| Three Months Ended | ||||||||
| March 31, 2014 | March 31, 2013 | |||||||
| (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | |||||||
| Net sales | $ | 561,870 | $ | 14,460,228 | ||||
| Cost of sales | 587,308 | 14,558,743 | ||||||
| Gross profit | (25,438 | ) | (98,515 | ) | ||||
| Operating expenses | ||||||||
| Sales and marketing expenses | 87,375 | 32,661 | ||||||
| General and administrative expenses | 211,448 | 1,086,856 | ||||||
| Profit (loss) from operations | (324,261 | ) | (1,218,032 | ) | ||||
| Other (income) expenses | (33,237 | ) | (2,106,364 | ) | ||||
| (Loss) Income before income taxes provision | (291,024 | ) | 888,332 | |||||
| Income taxes provision | - | - | ||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | (291,024 | ) | $ | 888,332 | |||
| Earnings (loss) per share – basic and diluted | $ | (0.01) | $ | 0.02 | ||||
Unaudited Comparisons for Three Months Ended March 31, 2014 to the Three Months Ended March 31, 2013
Net sales
Net sales consist of product sales, net of returns and allowances and any recoveries from sales of previously written down inventories. Net sales are recognized upon the transfer of legal title of the products to the customers. The quantity of products the Company sells fluctuates with changes in demand from its customers. As the Company decided to sell the operating subsidiaries resulted for the major factors contributed to the significant reduction in the Company’s net sales, down 96.1% to $561,870 for the first quarter of 2014 from $14,460,228 for the first quarter of 2013.
Cost of sales
Cost of sales is comprised of costs of goods purchased from our supplier, costs of manufacturing, assembly and testing of our products, and associated costs related to manufacturing support and quality assurance personnel, as well as provision for excess and obsolete inventories. The Company’s cost of sales, as a percentage of net sales, amounted to approximately 104.5% for the first quarter of 2014 and approximately 100.7% for the first quarter of 2013. Cost of sales decreased by $14.0 million or 96.0%, to $587,308 for the first quarter of 2014 from $14,558,743 for the first quarter of 2013. This decrease was mainly due to a decrease in sales volume.
Gross Profit
Gross profit is net sales less cost of sales and is affected by a number of factors, including competitive pricing, product mix, foundry pricing, cost of test and assembly services, manufacturing yields and provision for excess and obsolete inventories. The Company’s gross profit for the first quarter of 2014 was recorded as a gross loss of $25,438, representing a reduction of $73,077 or 74,2% over a gross loss of $98,515 in the same period of 2013. This result is a consequence of the reduction in sales volume as well as the company’s decision to disposal of the operating subsidiaries in the next quarter.
| 29 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Sales and Marketing Expenses
Sales and marketing expenses consists primarily of associated costs for sales and marketing, commissions, promotional activities, freight shipments, and marine insurance. Sales and marketing expenses increased by $54,714 or 167.5%, to $87,375 for the first quarter of 2014 from $32,661 for the first quarter of 2013. Such decrease was directly attributable to the increase in salaries and compensation paid to the lay-off of employees in the first quarter of 2014.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses consists primarily of compensation (including stock-based compensation) and associated costs for administrative personnel, professional fees including audit and other business registration fee, and director and officer insurance. General and administrative expenses decreased by $875,408 or 80.5%, to $211,448 for the first quarter of 2014 from $1,086,856 for the first quarter of 2013. The decrease was directly attributable to the decision for disposal of operating subsidiaries in the coming quarter.
Income (Loss) from Operations
Loss from operations was $324,261 for the first quarter of 2014 compared to loss of $1,218,032 for the first quarter of 2013. This decrease in loss from operations was mainly due to the decision for disposal of operating subsidiaries in the coming quarter.
Other Expenses (Income)
Other expenses (income) consists primarily of rental income, management and service income, interest income, interest expenses, and profit on disposals of assets. The Company has recorded other income of $33,237 for the first quarter of 2014, a decrease of $2,073,127 from other income of $2,106,364 for the first quarter of 2013. This decrease in other income was mainly due to a net income from disposing of fixed assets of $1,872,724 in the first quarter of 2013.
Interest Expense
Interest expense, including finance charges, relates primarily to our bank borrowings. Interest expense decreased $221,469 or 100%, to $Nil for the first quarter of 2014 from $221,469 for the first quarter of 2013. This change was mainly due to the decision for disposal of operating subsidiaries in the coming quarter.
Net Income (Loss)
As a result of the foregoing, the Company recorded a net loss $291,024 for the first quarter of 2014, decrease of $1,179,356 or 132.8%, from a net income $888,332 for the first quarter of 2013. The result was due the abnormal profit of $1,872,724 from disposals of a fixed asset in the first quarter 2013 and also due to the decision for disposal of operating subsidiaries in the coming quarter.
Critical Accounting Policies
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) recently issued Financial Reporting Release No. 60, “Cautionary Advice Regarding Disclosure About Critical Accounting Policies” (“FRR 60”), suggesting companies provide additional disclosure and commentary on their most critical accounting policies. In FRR 60, the SEC defined the most critical accounting policies as the ones that are most important to the portrayal of a company’s financial condition and operating results, and require management to make its most difficult and subjective judgments, often as a result of the need to make estimates of matters that are inherently uncertain. Based on this definition, our most critical accounting policies include: inventory valuation, which affects cost of sales and gross margin; policies for revenue recognition, allowance for doubtful accounts, and stock-based compensation. The methods, estimates and judgments we use in applying these most critical accounting policies have a significant impact on the results we report in our consolidated financial statements.
| 30 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Revenue Recognition
The Company derives revenues from resale of computer memory products. The Company recognizes revenue in accordance with the ASC 605 “Revenue Recognition”. Under ASC 605, revenue is recognized when there is persuasive evidence of an arrangement, delivery has occurred or services are rendered, the sales price is determinable, and collectability is reasonably assured. Revenue typically is recognized at time of shipment. Sales are recorded net of discounts, rebates, and returns, which historically were not material.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
We account for impairment of property, plant and equipment in accordance with FASB ASC 360. The carrying value of a long-lived asset is considered impaired when the anticipated undiscounted cash flow from such asset is separately identifiable and is less than its carrying value. In that event, a loss is recognized based on the amount by which the carrying value exceeds the fair market value of the long-lived asset. Fair market value is determined primarily using the anticipated cash flows discounted at a rate commensurate with the risk involved. Losses on long-lived assets to be disposed of are determined in a similar manner, except that fair market values are reduced for the cost to dispose. During the reporting years, there was no impairment loss incurred. Competitive pricing pressure and changes in interest rates, could materially and adversely affect our estimates of future net cash flows to be generated by our long-lived assets.
Inventory Valuation
Our policy is to value inventories at the lower of cost or market on a part-by-part basis. In addition, we write down unproven, excess and obsolete inventories to net realizable value. This policy requires us to make a number of estimates and assumptions including market and economic conditions, product lifecycles and forecast demand for our product to value our inventory. To the extent actual results differ from these estimates and assumptions, the balances of reported inventory and cost of products sold will change accordingly. Since Aristo supplies different generations of computer related products, older generation products will sell more slowly owing to lower market demand. According to the management experience and estimation of the actual market situation, old generation products carrying on hand for ten years will have no re-sell value. Therefore, these inventories on hand over ten years will be written off by Aristo immediately.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts.
We maintain an allowance for doubtful accounts for estimated losses resulting from the inability of our customers to make required payments. Our allowance for doubtful accounts is based on our assessment of the collectability of specific customer accounts, the aging of accounts receivable, our history of bad debts, and the general condition of the industry. If a major customer’s credit worthiness deteriorates, or our customers’ actual defaults exceed our historical experience, our estimates could change and impact our reported results.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Our principal sources of liquidity are cash from operations, bank lines of credit and credit terms from suppliers. Our principal uses of cash have been for operations and working capital. We anticipate these uses will continue to be our principal uses of cash in the future.
Our ability to draw down under our various credit and loan facilities is, in each case, subject to the prior consent of the relevant lending institution to make advances at the time of the requested advance and each facility (other than with respect to certain long term mortgage loans) is payable within 90 days of drawdown. Accordingly, on a case by case basis, we may elect to terminate or not renew several of our credit facilities if significant reduction in our available short term borrowings that we do not deem it is commercially reasonable. The Company is seeking to raise $30 million funding in order to pursue certain business expansion. We currently have no commitment for this.
As of March 31, 2014, the Company has total net current liabilities of $12,800,280. This raises substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. We will continue to seek additional sources of available financing on acceptable terms; however, there can be no assurance that we will be able to obtain the necessary additional capital on a timely basis or on acceptable terms, if at all. In addition, if the results are negatively impacted and delayed as a result of political and economic factors beyond management’s control, our capital requirements may increase.
| 31 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
The short-term borrowings from banks to finance the cash flow required to finance the purchase of products from our suppliers must be made a day in advance of the release of goods from suppliers’ warehouse before receiving payments from customers upon physical delivery of such goods in Hong Kong which, in most instances, take approximately two days from the date of such delivery.
The following factors, among others, could have negative impacts on our results of operations and financial position: the termination or change in terms of the banking facilities; pricing pressures in the industry; a continued downturn in the economy in general or in the memory products sector; an unexpected decrease in demand for certain memory products; our ability to attract new customers; an increase in competition in the related markets; and the ability of some of our customers to obtain financing.
Although we believe the expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee future results, levels of activity, performance or achievements. We are under no duty to update any of the forward-looking statements after the date of this report to conform them to actual results or to make changes in our expectations. The establishment of ATMD will not affect our liquidity and capital resources, as pursuant to the joint venture agreement, Tomen will be responsible for the financing of ATMD’s operations.
Net Cash Provided by (Used for) Operating Activities
In the three months ended March 31, 2014, net cash provided by operating activities was $1,617,381 while for the three months ended March 31, 2013, net cash used for operating activities was $691,265, an increase in net cash provided by operating activities of approximately $2.3 million. This increase was primarily due to changes in current assets held for disposal resulted by the decision for disposal of operating subsidiaries as of March 31, 2014.
Net Cash Provided by (Used for) Investing Activities
For the three months ended March 31, 2014, net cash provided by investing activities was $11,736,903 while for the three months ended March 31, 2013 was $2,310,093, an increase of the amount of $9,426,810. This increase was primarily due to changes in fixed assets assigned to current assets hold for disposal resulted by the decision for disposal of operating subsidiaries as of March 31, 2014.
Net Cash Provided by (Used for) Financing Activities
In the three months ended March 31, 2014, net cash used for financing activities was $13,585,403 while for the three months ended March 31, 2013 was $2,326,175, a decrease of the amount of $11,259,228. This decrease was due to the decision for disposal of operating subsidiaries which resulted in the repayment of bank lines of credit and loans payable usage of March 31, 2014.
New Accounting Pronouncements
In January 2013, FASB has issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2013-01, Balance Sheet (Topic 210): Clarifying the Scope of Disclosures about Offsetting Assets and Liabilities. This ASU clarifies that ordinary trade receivables and receivables are not in the scope of ASU No. 2011-11, Balance Sheet (Topic 210): Disclosures about Offsetting Assets and Liabilities. Specifically, ASU 2011-11 applies only to derivatives, repurchase agreements and reverse purchase agreements, and securities borrowing and securities lending transactions that are either offset in accordance with specific criteria contained in the FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ (Codification) or subject to a master netting arrangement or similar agreement. The FASB undertook this clarification project in response to concerns expressed by U.S. stakeholders about the standard’s broad definition of financial instruments. After the standard was finalized, companies realized that many contracts have standard commercial provisions that would equate to a master netting arrangement, significantly increasing the cost of compliance at minimal value to financial statement users. An entity is required to apply the amendments in ASU 2013-01 for fiscal years beginning on or after January 1, 2013, and interim periods within those annual periods. An entity should provide the required disclosures retrospectively for all comparative periods presented. The effective date is the same as the effective date of ASU 2011-11.
In February 2013, FASB has issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2013-02, Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reporting of Amounts Reclassified Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income. This ASU improves the transparency of reporting these reclassifications. Other comprehensive income includes gains and losses that are initially excluded from net income for an accounting period. Those gains and losses are later reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income into net income. The amendments in this ASU do not change the current requirements for reporting net income or other comprehensive income in financial statements. All of the information that this ASU requires already is required to be disclosed elsewhere in the financial statements under U.S. GAAP.
| 32 |
The FASB has issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2014-07, Applying Variable Interest Entities Guidance to Common Control Leasing Arrangements. The guidance addresses the consolidation of lessors in certain common control leasing arrangements and is based on a consensus reached by the Private Company Council (PCC). Under current U.S. GAAP, a company is required to consolidate an entity in which it has a controlling financial interest. The assessment of controlling financial interest is performed under either: (a) a voting interest model; or (b) a variable interest entity model. In a variable interest entity model, the company has a controlling financial interest when it has: (a) the power to direct the activities that most significantly affect the economic performance of the entity; and (b) the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits of the entity that could be potentially significant to the entity. To determine which model applies, a company preparing financial statements must first determine whether it has a variable interest in the entity being evaluated for consolidation and whether that entity is a variable interest entity.
The new guidance allows a private company to elect (when certain conditions exist) not to apply the variable interest entity guidance to a lessor under common control. Instead, the private company would make certain disclosures about the lessor and the leasing arrangement. Under the amendments in this ASU, a private company lessee could elect an alternative not to apply variable interest entity guidance to a lessor when:
-The private company lessee and the lessor are under common control;
-The private company lessee has a leasing arrangement with the lessor;
-Substantially all of the activity between the private company lessee and the lessor is related to the leasing activities (including supporting leasing activities) between those two companies, and
-If the private company lessee explicitly guarantees or provides collateral for any obligation of the lessor related to the asset leased by the private company, then the principal amount of the obligation at inception does not exceed the value of the asset leased by the private company from the lessor. If elected, the accounting alternative should be applied to all leasing arrangements meeting the above conditions. The alternative should be applied retrospectively to all periods presented, and is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2014, and interim periods within annual periods beginning after December 15, 2015. Early application is permitted for all financial statements that have not yet been made available for issuance.
The FASB has issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2014-08, Presentation of Financial Statements (Topic 205) and Property, Plant, and Equipment (Topic 360): Reporting Discontinued Operations and Disclosures of Disposals of Components of an Entity. The amendments in the ASU change the criteria for reporting discontinued operations while enhancing disclosures in this area. It also addresses sources of confusion and inconsistent application related to financial reporting of discontinued operations guidance in U.S. GAAP.
Under the new guidance, only disposals representing a strategic shift in operations should be presented as discontinued operations. Those strategic shifts should have a major effect on the organization’s operations and financial results. Examples include a disposal of a major geographic area, a major line of business, or a major equity method investment. In addition, the new guidance requires expanded disclosures about discontinued operations that will provide financial statement users with more information about the assets, liabilities, income, and expenses of discontinued operations.
The new guidance also requires disclosure of the pre-tax income attributable to a disposal of a significant part of an organization that does not qualify for discontinued operations reporting. This disclosure will provide users with information about the ongoing trends in a reporting organization’s results from continuing operations. The amendments in this ASU enhance convergence between U.S. GAAP and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Part of the new definition of discontinued operation is based on elements of the definition of discontinued operations in IFRS 5, Non-Current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations. The amendments in the ASU are effective in the first quarter of 2015 for public organizations with calendar year ends. For most nonpublic organizations, it is effective for annual financial statements with fiscal years beginning on or after December 15, 2014. Early adoption is permitted.
| 33 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
The new amendments will require an organization to:
Present (either on the face of the statement where net income is presented or in the notes) the effects on the line items of net income of significant amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income - but only if the item reclassified is required under U.S. GAAP to be reclassified to net income in its entirety in the same reporting period.
Cross-reference to other disclosures currently required under U.S. GAAP for other reclassification items (that are not required under U.S. GAAP) to be reclassified directly to net income in their entirety in the same reporting period. This would be the case when a portion of the amount reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income is initially transferred to a balance sheet account (e.g., inventory for pension-related amounts) instead of directly to income or expense.
The amendments apply to all public and private companies that report items of other comprehensive income. Public companies are required to comply with these amendments for all reporting periods (interim and annual). A private company is required to meet the reporting requirements of the amended paragraphs about the roll forward of accumulated other comprehensive income for both interim and annual reporting periods. However, private companies are only required to provide the information about the effect of reclassifications on line items of net income for annual reporting periods, not for interim reporting periods. The amendments are effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2012, for public companies and are effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2013, for private companies. Early adoption is permitted.
In February 2013, FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2013-03, Financial Instruments (Topic 825). This ASU clarifies the scope and applicability of a disclosure exemption that resulted from the issuance of Accounting Standards Update No. 2011-04, Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Amendments to Achieve Common Fair Value Measurement and Disclosure Requirements in U.S. GAAP and IFRSs. The amendment clarifies that the requirement to disclose "the level of the fair value hierarchy within which the fair value measurements are categorized in their entirety (Level 1, 2, or 3)" does not apply to nonpublic entities for items that are not measured at fair value in the statement of financial position, but for which fair value is disclosed. This ASU is the final version of Proposed Accounting Standards Update 2013-200—Financial Instruments (Topic 825) which has been deleted. The amendments are effective upon issuance.
In February 2013, FASB has issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2013-04, Liabilities (Topic 405): Obligations Resulting from Joint and Several Liability Arrangements for Which the Total Amount of the Obligation Is Fixed at the Reporting Date. This ASU provides guidance for the recognition, measurement, and disclosure of obligations resulting from joint and several liability arrangements for which the total amount of the obligation within the scope of this ASU is fixed at the reporting date, except for obligations addressed within existing guidance in U.S. GAAP. The guidance requires an entity to measure those obligations as the sum of the amount the reporting entity agreed to pay on the basis of its arrangement among its co-obligors and any additional amount the reporting entity expects to pay on behalf of its co-obligors. The guidance in this ASU also requires an entity to disclose the nature and amount of the obligation as well as other information about those obligations. The amendments in this ASU are effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2013. For nonpublic entities, the amendments are effective for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2014, and interim periods and annual periods thereafter. The amendments in this ASU should be applied retrospectively to all prior periods presented for those obligations resulting from joint and several liability arrangements within the ASU’s scope that exist at the beginning of an entity’s fiscal year of adoption. An entity may elect to use hindsight for the comparative periods (if it changed its accounting as a result of adopting the amendments in this ASU) and should disclose that fact. Early adoption is permitted.
In March 2013, FASB has issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2013-05, Foreign Currency Matters (Topic 830). This ASU resolve the diversity in practice about whether Subtopic 810-10, Consolidation—Overall, or Subtopic 830-30, Foreign Currency Matters—Translation of Financial Statements, applies to the release of the cumulative translation adjustment into net income when a parent either sells a part or all of its investment in a foreign entity or no longer holds a controlling financial interest in a subsidiary or group of assets that is a nonprofit activity or a business (other than a sale of in substance real estate or conveyance of oil and gas mineral rights)within a foreign entity. In addition, the amendments in this Update resolve the diversity in practice for the treatment of business combinations achieved in stages (sometimes also referred to as step acquisitions) involving a foreign entity. This ASU is the final version of Proposed Accounting Standards Update EITF11Ar—Foreign Currency Matters (Topic 830), which has been deleted. The amendments in this Update are effective prospectively for fiscal years (and interim reporting periods within those years) beginning after December 15, 2013. For nonpublic entities the amendments in this Update are effective prospectively for the first annual period beginning after December 15, 2014, and interim and annual periods thereafter. The amendments should be applied prospectively to derecognition events occurring after the effective date. Prior periods should not be adjusted. Early adoption is permitted. If an entity elects to early adopt the amendments, it should apply them as of the beginning of the entity’s fiscal year of adoption.
| 34 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
| Item 3. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk |
We are a smaller reporting company as defined by Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act and are not required to provide the information required under this item.
| Item 4. | Controls and Procedures |
(a) Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in reports that we file or submit under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”), as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Limitations on the Effectiveness of Disclosure Controls. In designing and evaluating the Company's disclosure controls and procedures, management recognized that disclosure controls and procedures, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the disclosure controls and procedures are met. Additionally, in designing disclosure controls and procedures, Company management necessarily was required to apply its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible disclosure controls and procedures. The design of any disclosure controls and procedures also is based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures. The Company's CEO and CFO have evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of the Company's disclosure controls and procedures as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) as of May 20, 2014, and based on this evaluation, the Company's principal executive and financial officers have concluded that the Company's disclosure controls and procedures were not effective to ensure that material information is recorded, processed, summarized and reported by management of the Company on a timely basis in order to comply with the Company's disclosure obligations under the Exchange Act and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder. The Company's principal executive and financial officer’s conclusion regarding the Company's disclosure controls and procedures is based on management's conclusion that the Company's internal control over financial reporting are ineffective, as described in our Annual Report on Form 10K as filed with the SEC on April 16, 2014, which included a complete discussion relating to the foregoing evaluation of Disclosures on Controls and Procedures.
(b) Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in our internal control over financial reporting (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act) during the quarter ended March 31, 2014 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
| 35 |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
| Item 1. | Legal Proceedings |
None
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors |
We are a smaller reporting company as defined by Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act and are not required to provide the information required under this item.
| Item 2. | Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds |
None
| Item 3. | Defaults Upon Senior Securities |
None
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures |
Not applicable.
| Item 5. | Other Information |
None
| Item 6. | Exhibits |
Exhibits:
| * 31.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
| * 31.2 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
| * 32.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
| * 32.2 | Certification by Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
| ** 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document. |
| ** 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
| ** 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. |
| ** 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
| ** 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
| ** 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
| * | Filed herewith. |
| ** | Furnished herewith. Pursuant to Rule 406T of Regulation S-T, the Interactive Data Files on Exhibit 101 hereto are deemed not filed or part of any registration statement or prospectus for purposes of Sections 11 or 12 of the Securities Act of 1933, are deemed not filed for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, and otherwise are not subject to liability under those sections. |
| 36 |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| USMART MOBILE DEVICE INC. | ||
| Date: May 20, 2014 | By: | /s/ Ben Wong |
| Ben Wong | ||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||
| Date: May 20, 2014 | By: | /s/ Philip Tsz Fung Lo |
| Philip Tsz Fung Lo | ||
| Chief Financial Officer | ||
| 37 |
