Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EXCEL - IDEA: XBRL DOCUMENT - FHC Holdings Corp | Financial_Report.xls |
| EX-10.24 - EXHIBIT 10.24 - FHC Holdings Corp | v305812_ex10-24.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 - FHC Holdings Corp | v305812_ex23-1.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EXHIBIT 21.1 - FHC Holdings Corp | v305812_ex21-1.htm |
| EX-23.2 - EXHIBIT 23.2 - FHC Holdings Corp | v305812_ex23-2.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - FHC Holdings Corp | v305812_ex31-2.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - FHC Holdings Corp | v305812_ex31-1.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - FHC Holdings Corp | v305812_ex32-1.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D. C. 20549
FORM 10-K
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d)
OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended January 28, 2012
Commission file number 001-35239
FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 20-8874704 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of | (I.R.S. Employer | |
| incorporation or organization) | Identification Number) |
3480 W. 12th Street, Houston, TX 77008
(Address of principal executive offices including ZIP code)
(713) 864-1358
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class |
Name of each exchange on which registered | |
| Common Stock, par value $.01 per share | The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer ¨ | Accelerated filer ¨ |
| Non-accelerated filer x (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company ¨ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act).Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of the registrant’s common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of July 30, 2011 was approximately $376.7 million.
As of March 1, 2012, there were 43,538,592 shares of Common Stock outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held July 10, 2012 are incorporated by reference into Part III of this report.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| PART I. | ||
| Item 1. | Business | 3 |
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors | 12 |
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments | 28 |
| Item 2. | Properties | 28 |
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings | 28 |
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures | 28 |
| PART II. | ||
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities | 29 |
| Item 6. | Selected Financial Data | 31 |
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 34 |
| Item 7a. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk | 54 |
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | 55 |
| Item 9. | Changes and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosures | 77 |
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures | 77 |
| Item 9B. | Other Information | 77 |
| PART III. | ||
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance | 77 |
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation | 77 |
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters | 77 |
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence | 77 |
| Item 14. | Principal Accounting Fees and Services | 78 |
| PART IV. | ||
| Item 15. | Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules | 78 |
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains statements that constitute forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These statements concern our business, operations and financial performance and condition as well as our plans, objectives and expectations for our business operations and financial performance and condition, which are subject to risks and uncertainties. All statements other than statements of historical fact included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are forward-looking statements. These statements may include words such as “aim”, “anticipate”, “assume”, “believe”, “can have”, “could”, “due”, “estimate”, “expect”, “goal”, “intend”, “likely”, “may”, “objective”, “plan”, “potential”, “positioned”, “predict”, “should”, “target”, “will”, “would” and other words and terms of similar meaning in connection with any discussion of the timing or nature of future operating or financial performance or other events or trends. For example, all statements we make relating to our estimated and projected earnings, sales, costs, expenditures, cash flows, growth rates, market share and financial results, our plans and objectives for future operations, growth or initiatives, strategies or the expected outcome or impact of pending or threatened litigation are forward-looking statements.
These forward-looking statements are based on current expectations, estimates, forecasts and projections about our business and the industry in which we operate and our management’s beliefs and assumptions. These statements are not guarantees of future performance or development and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that are in many cases beyond our control. All of our forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that may cause our actual results to differ materially from our expectations. Factors that may cause such differences include, but are not limited to, the risks described under “Risk Factors,” including:
| Ÿ | our ability to identify and respond to new and changing fashion trends, customer preferences and other related factors; |
| Ÿ | our ability to maintain a broad and shallow merchandise assortment; |
| Ÿ | failure to execute successfully our growth strategy; |
| Ÿ | disruptions to our information systems in the ordinary course or as a result of systems upgrades; |
| Ÿ | changes in consumer spending and general economic conditions; |
| Ÿ | increasing cost of raw materials and other inputs used in the production of our merchandise; |
| Ÿ | changes in the competitive environment in our industry and the markets we serve, including increased competition from other retailers; |
| Ÿ | failure of our new boutiques or existing boutiques to achieve sales and operating levels consistent with our expectations; |
| Ÿ | the success of the malls and shopping centers in which our boutiques are located; |
| Ÿ | our dependence on a strong brand image; |
| Ÿ | failure of our e-commerce business to continue to grow consistent with our growth strategy; |
| Ÿ | our dependence upon key senior management or our inability to hire or retain additional personnel; |
| Ÿ | disruptions in our supply chain and distribution facility; |
| Ÿ | our indebtedness and lease obligations; |
| Ÿ | our reliance upon independent third-party transportation providers for all of our merchandise shipments; |
| Ÿ | hurricanes, natural disasters, unusually adverse weather conditions, boycotts and unanticipated events; |
| Ÿ | the seasonality of our business; |
| Ÿ | increases in costs of fuel, or other energy, transportation or utilities costs and in the costs of labor and employment; |
| Ÿ | the impact of governmental laws and regulations and the outcomes of legal proceedings; |
| Ÿ | restrictions imposed by our indebtedness on our current and future operations; |
| Ÿ | our failure to maintain effective internal controls; |
| Ÿ | our inability to protect our trademarks or other intellectual property rights; and |
| Ÿ | increased costs as a result of being a public company. |
| 1 |
The above is not a complete list of factors or events that could cause actual results to differ from our expectations, and it is not possible for us to predict all of them. We derive many of our forward-looking statements from our own operating budgets and forecasts, which are based upon many detailed assumptions. While we believe that our assumptions are reasonable, we caution that it is very difficult to predict the impact of known factors, and it is impossible for us to anticipate all factors that could affect our actual results. Important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from our expectations, or cautionary statements, are disclosed under “Risk Factors”, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. All written and oral forward-looking statements attributable to us, or persons acting on our behalf, are expressly qualified in their entirety by the cautionary statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K as well as other cautionary statements that are made from time to time in our other SEC filings and public communications. You should evaluate all forward-looking statements made in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and otherwise in the context of these risks and uncertainties.
Potential investors and other readers are urged to consider these factors carefully in evaluating the forward-looking statements and are cautioned not to place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements we make. These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Except as required by law, we undertake no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements publicly whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise.
| 2 |
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
General
Francesca’s Holdings Corporation was incorporated in Delaware in 2007. We are a holding company and all of our business operations are conducted through Francesca’s Collections, Inc. our wholly-owned indirect subsidiary, a corporation formed and existing under the laws of the State of Texas. Francesca’s Collections, Inc., is wholly-owned by Francesca’s LLC, a limited liability company formed and existing under the laws of the State of Delaware. Francesca’s LLC is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Francesca’s Holdings Corporation. Our principal executive office is located at 3480 W. 12th Street, Houston, Texas 77008, our telephone number is (713) 864-1358 and our fax number is (713) 426-2751. We maintain a website at www.francescascollections.com. Except where the context otherwise requires or where otherwise indicated, the terms “Francesca’s,” “we,” “us,” “our,” “the company,” and “our business” refer to Holdings and its consolidated subsidiaries as a combined entity.
We operate on a fiscal calendar which, in a given fiscal year, consists of a 52- or 53-week period ending on the Saturday closest to January 31st. The reporting periods contained in our audited consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K contain 52 weeks of operations in fiscal year 2011, which ended January 28, 2012, 52 weeks of operations in fiscal year 2010, which ended January 29, 2011, and 52 weeks of operations in fiscal year 2009, which ended January 30, 2010. Our fiscal year 2008 included 52 weeks of operations, which ended January 31, 2009. For fiscal year 2007, which ended on December 31, 2007, the company operated on a fiscal calendar year ending December 31st.
Our Company
francesca’s collections® is one of the fastest growing specialty retailers in the United States. Our retail locations are designed and merchandised to feel like independently owned, upscale boutiques and provide our customers with an inviting, intimate and differentiated shopping experience. We believe we offer compelling value with a diverse and uniquely balanced mix of high-quality, trend-right apparel, jewelry, accessories and gifts at attractive prices. We tailor our assortment to appeal to our core 18-35 year-old, fashion conscious female customer, although we find that women of all ages are attracted to our eclectic and sophisticated merchandise selection and boutique setting. We carry a broad selection but limited quantities of individual styles and introduce new merchandise to our boutiques five days a week in order to create a sense of scarcity and newness, which helps drive customer shopping frequency and loyalty.
By offering a differentiated shopping experience and high-quality merchandise at a compelling value, our boutiques have been successful across a wide variety of geographic markets and shopping venues. We believe we have an opportunity to continue to grow our boutique base from 283 locations in 41 states as of January 28, 2012 to approximately 900 boutiques in the United States over the next seven to ten years based on our flexible boutique format, the financial characteristics of our boutiques and our ongoing analysis of shopping venues that meet our criteria for new boutiques. Our merchandise is also available through our e-commerce website, www.francescascollections.com.
We believe that through the strength of our business model and our disciplined operating philosophy, we have achieved strong financial performance and growth that is among the best in the specialty retail sector:
| Ÿ | Between fiscal year 2009 and 2011 our net sales increased from $79.4 million to $204.2 million, representing a compound annual growth rate of 60.4%. |
| Ÿ | Our comparable boutique sales (see footnote 6 to the table under “Selected Consolidated Financial and Operating Data”) increased by 10.4% in fiscal year 2011 after a 15.2% increase in fiscal year 2010. |
| Ÿ | Between the end of fiscal year 2009 and 2011 our boutique count increased from 147 to 283, representing a compound annual growth rate of 38.8%. |
| Ÿ | Between fiscal year 2009 and 2011 our income from operations increased from $17.5 million to $43.5 million, representing a compound annual growth rate of 57.8%. |
Our Competitive Strengths
We believe the following strengths differentiate us from our competitors and are key drivers of our success:
| 3 |
| Ÿ | Proven Trend-Right Merchandise Delivered at a Compelling Value. Our boutiques carry a broad but shallow selection of high-quality, trend-right apparel, jewelry, accessories and gifts at attractive prices. Our buyers closely monitor the marketplace to identify and source proven fashion trends that will appeal to our core customers. We primarily offer exclusive items under our proprietary labels, but carry a small selection of third-party, nationally recognized brands that we use opportunistically in certain categories. We offer a broad selection of merchandise, but intentionally purchase small quantities of individual items for each boutique such that we frequently replenish our boutiques with new merchandise, keeping the shopping experience fresh and exciting for our customers. The short lead times of our vendors maximizes our speed to market, as it generally takes only four to twelve weeks from the time an order is placed to the time merchandise is available on the boutique floor. With these short lead times, we are able to make more informed buying decisions to meet customers’ merchandise expectations, and to react quickly to changing fashion trends. This approach, combined with our uniquely balanced product mix of approximately 50% apparel and 50% jewelry, accessories and gifts, is designed to encourage more frequent visits by our customers and reduce the seasonal fluctuations and margin erosion experienced by many other specialty retailers. We believe the expertise of our buyers and our broad base of vendors allows us to quickly identify and respond to emerging fashion trends in apparel, jewelry, accessories and gifts to offer quality merchandise at prices that ‘surprise and delight’ our customers. |
| Ÿ | Differentiated Shopping Experience. Each of our retail locations is uniquely designed and merchandised to feel like an independently owned, upscale boutique. Contemporary music, scented candles, small hand-made signs and vintage yet vibrant fixtures create a warm and inviting environment that showcases our eclectic assortment. Our open floor design enables customers to easily view merchandise and we use a number of body forms to provide full outfit ideas to encourage customers to buy multiple items. Merchandise presentations, including display windows, tables and walls, are refreshed every two to three weeks to keep our boutiques new and exciting. Our passionate boutique managers and associates, with the support of corporate guidelines, are encouraged to infuse each boutique with their personality, which increases their motivation and enhances the shopping experience. We believe these attributes, along with our strategy of carrying a broad selection but limited quantities of individual styles, create a unique “treasure hunt” atmosphere that strongly appeals to our customers and differentiates us in the marketplace. |
| Ÿ | Powerful Boutique Economics and Rigorous Real Estate Selection Process. We have a proven boutique format that works across a wide variety of shopping venues, market sizes, climates and demographics. Our boutiques average approximately 1,400 square feet, which is meaningfully smaller than most specialty retailers. The performance of our boutiques and our flexible real estate format enhance our ability to secure prominent, highly visible locations in regional malls, lifestyle centers, street locations and strip centers. We deploy a rigorous real estate selection process with all new boutique opportunities measured against specific financial and geographic criteria. Over the previous two fiscal years, on average our new boutiques have generated first year cash return on net investment in excess of 150% and paid back our net investment on a pre-tax basis in less than one year, due to our ability to consistently obtain best-in-class locations combined with relatively low capital investment and operating cost requirements, allowing us to fund all of our growth from internally generated cash flow. In our real estate selection process, we assess the viability of potential sites by analyzing the demographics of the trade area and the performance of the shopping venue, including selected relevant and adjacent retailers. Based on this analysis, we believe the financial characteristics of our new boutiques, coupled with our proven ability to operate across different shopping venues and geographies, provide us with a wide scope of new boutique opportunities and enhance our ability to profitably expand our boutique base. |
| Ÿ | Solid and Scalable Infrastructure. We continually invest in systems, controls and human resources to support our growth. In recent years we have made significant improvements to the infrastructure of our finance, buying and planning, real estate and IT departments. For instance, we believe that we have developed an integrated sourcing, distribution and merchandising process that is scalable and will facilitate the continued growth in the number of boutiques we operate. This process starts with our buyers who work closely with an established and diverse group of vendors to identify trend-right, high-quality merchandise for our boutiques. From on-hand inventories or special orders and their international networks of manufacturers, our vendors make frequent deliveries of merchandise consisting of floor-ready, pre-tagged items to our warehouse. We then sort, allocate and distribute the pre-packs to our boutiques five days a week based on current inventory levels and sales trends. Our boutique managers are able to readily merchandise the product and tailor the displays to differentiate their boutiques and reflect local market tastes. As we focus on organic, viral and in-boutique marketing to increase customer loyalty and build our brand image we do not believe that we will require significant investments in traditional marketing and advertising initiatives as we expand our boutique base. |
| Ÿ | Experienced Management Team with a Disciplined Operating Philosophy. Our senior management has extensive experience across a broad range of disciplines in the retail industry, including merchandising, real estate, supply chain and finance. Our highly skilled executive team includes two of our Founders, John De Meritt, our President and Chief Executive Officer, and Kyong Gill, our Executive Vice Chairperson. Together they lead a dynamic team with a strong background at companies such as David’s Bridal, Chico’s, CVS, Banana Republic, Nordstrom and J.C. Penney. Our management team has built a solid operating foundation based on sound retail principles that define our culture. Our disciplined operating philosophy is grounded in a relentless focus on providing great merchandise and a best-in class boutique experience supported by uncompromising site selection and continual enhancements to our infrastructure. |
| 4 |
Our Growth Strategy
We believe we can continue to grow our revenues and earnings by executing on the following strategies:
| Ÿ | Grow Our Boutique Base. We believe there is an opportunity to significantly increase the number of boutiques we operate. Based on our proven ability to open our flexible retail format in various shopping venues in new and existing markets, the financial characteristics of our boutiques and our ongoing analysis of shopping venues that meet our criteria for new boutiques (including a third party research study), we believe we have the potential to grow our base from 283 locations in 41 states as of January 28, 2012 to approximately 900 boutiques over the next seven to ten years in the U.S. We opened 76 new boutiques in fiscal year 2011 and we plan to open approximately 75 new boutiques per year in fiscal years 2012 and 2013 and one outlet store in fiscal year 2012. We have identified a sufficient number of shopping venues that we believe meet our real estate selection criteria. Because these shopping venues possess characteristics similar to those of the shopping venues in which our existing boutiques are located, we expect our new boutiques, on average, to generate first year cash return on net investment of approximately 150% and to pay back our net investment on a pre-tax basis in less than one year. We expect that landlords will continue to pay construction allowances to cover a substantial portion of our construction costs or perform a substantial portion of the construction work to reduce our net investment in each new boutique. While we have recently been able to obtain favorable levels of tenant allowances due in part to national and regional economic conditions and higher vacancy rates, we believe that tenant allowances will continue to be available based on real estate industry practices over the past twenty years under varying economic conditions. Additionally, based on the substantial real estate industry experience of members of our management team, we believe that the amounts of future tenant allowances, while possibly lower than the levels of recent periods, will be consistent with those we have projected in connection with developing our expansion plans, which factor in expected declines in the level of tenant allowances. We believe we have a proven process that allows us to identify boutique locations, secure leases on acceptable terms, construct and merchandise each boutique as well as staff and train boutique employees such that we can successfully open boutiques at the expected pace while maintaining our favorable boutique economics over the next two fiscal years and beyond. In markets where we have opened a significant number of boutiques in close proximity to one another, we have been able to deliver similar first year and ongoing financial results. Therefore, we believe that our long term growth plans of opening multiple boutiques in the same markets should deliver boutique economics in line with our historical performance. |
| Ÿ | Drive Comparable Boutique Sales. Our comparable boutique sales increased 10.4% in fiscal year 2011 after a 15.2% increase in fiscal year 2010. We intend to drive comparable boutique sales by featuring high-quality, trend-right merchandise at a compelling value and refining our distinctive boutique experience. We intend to maintain our broad but shallow merchandising approach, which we believe will result in increased units and dollars per transaction and protect margins. In addition, we are increasing the sophistication of our buying and planning infrastructure, enhancing our buying team with additional category-specific buyers, and augmenting boutique-level management. |
| Ÿ | Expand the Penetration and Presence of Our E-Commerce Business. We complement our boutiques with a growing e-commerce business. We use the same successful business principles deployed in our boutiques by offering limited assortment of individual styles to create a sense of scarcity and newness, which increases the frequency of customer visits to the site. Our e-commerce business not only generates incremental sales and profits but also builds brand awareness and boutique traffic, and helps us access markets where we do not currently have a boutique. Our e-commerce sales grew by 49.5% in fiscal year 2011 and represented 1.4% of our total net sales. We expect e-commerce sales growth to outpace the growth of boutique sales as consumers discover the complementary nature of shopping with us online and through our boutiques. |
| Ÿ | Enhance Operating Margins. Our strong expected boutique growth should permit us to take advantage of economies of scale in sourcing and to also leverage our existing infrastructure, corporate overhead and other fixed costs. In addition, we expect to benefit from the implementation of a new enterprise software platform that we began to introduce in stages in August 2011 and plan to finalize during the first quarter of fiscal year 2013. This will enable us to more efficiently operate and manage our point-of-sale, management reporting, merchandise planning, ordering and allocation, and related inventory management functions. |
| 5 |
Our History
Our company was founded in 1999 by Chong Yi, Kyong Gill, our Executive Vice Chairperson, Insuk Koo and John De Meritt, our President and Chief Executive Officer, (collectively referred to as the “Founders”). We opened our first boutique in Houston, Texas that same year. Initially, we focused on selling fashion jewelry, accessories and selected home décor but as our boutique base grew across the United States we expanded our merchandise offering to include apparel, which has become our largest category and, we believe, a significant driver of growing customer loyalty and return visits. In recent years, we have augmented our strong management team with additional skilled and experienced executives who now lead our buying, merchandise planning, boutique operations, finance, real estate, information technology, e-commerce and corporate support activities. In February 2010, CCMP acquired a controlling interest in the company with the goal of supporting Mr. De Meritt and the management team in accelerating our growth. CCMP purchased approximately 84% of the outstanding shares of common stock of the company from the Founders, trusts controlled by certain Founders, Kal Malik, our Executive Vice President and General Counsel, Bear Growth Capital Partners LP (“BGCP”), and BGCP/Francesca’s Holdings, LP. The acquisition was completed pursuant to two separate stock purchase agreements which included customary representations, warranties, covenants and indemnities among CCMP and the selling stockholders. The company has no material continuing, current, or future rights or obligations under either of the stock purchase agreements. In connection with the CCMP acquisition, the company, CCMP, the Founders (and trusts controlled by certain Founders), Mr. Malik, and certain other stockholders of the company entered into a stockholders’ agreement to provide, among other things, for the terms of the stock ownership in the company. The stockholders’ agreement terminated upon the completion of our initial public offering (“IPO”), described below, provided that certain registration and indemnification rights set forth in the stockholders’ agreement survived the completion of the IPO.
On July 27, 2011, we completed our IPO of 11,500,000 shares of common stock of which 2,941,176 shares were sold by the Company and 8,558,824 shares were sold by the selling stockholders (including 616,109 by members of the Company’s management). In February 2012, certain of our stockholders sold 11,336,476 shares of common stock in a public offering. As of March 1, 2012, CCMP owned approximately 36% of our outstanding common stock.
Our Market
Our distinct boutique environment and carefully selected, trend-right merchandise attract a wide demographic. While our broad assortment appeals to women of varying ages and diverse backgrounds, from value-conscious to the more affluent, our primary customer is a fashion conscious woman between the ages of 18 and 35. She is college educated and has moderate to high disposable income. She enjoys shopping for the latest fashions and is attracted to our upscale boutique shopping environment, compelling value proposition and highly personalized customer service. Our core customer represents a growing segment of the U.S. population and we believe she spends a higher proportion of her income on fashion than the general population. According to the United States Census Bureau’s 2010 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates, approximately 35.5 million women between the ages of 18 to 35 live in the United States.
Our unique merchandise combination of apparel, jewelry, accessories and gifts allows us to participate in a number of large market segments. The apparel and women’s wear segment, which represents approximately 50% of our sales, had a market size of approximately $160 billion in 2010, according to the Womenswear in the United States report, published May 2010 by DataMonitor, an international market research firm (DataMonitor reference code: 0072-2278).
Our Merchandise Offering and Merchandising Strategy
We offer a broad and shallow selection of fashion apparel, jewelry, accessories and gifts targeted to our core customer, who seeks trend-right, high-quality merchandise at attractive prices. We have a well-balanced assortment of product categories with approximately 50% of our fiscal year 2011 sales generated by non-apparel items. Our diverse merchandise contributes to the ‘treasure hunt’ atmosphere in our boutiques and is one which we aim to maintain as we grow. We carry a broad selection but limited quantities of each style and we deliver new merchandise to our boutiques five days a week. This contributes to a sense of scarcity and newness within our boutiques, mitigates fashion risk, reduces the seasonality of the inventory and protects margins.
Our wide range of apparel, jewelry, accessories and gifts fills the various casual and dressy fashion needs of our customers and our selection of gifts ranges from the elegant to the irreverent. Our 1,400 square foot boutiques carry approximately 3,000 SKUs at any one time and we stock about 15,000 different styles during the course of a year. The majority of our merchandise is sold under our proprietary labels and we also sell a select assortment of third-party, nationally recognized brands. Our e-commerce business features an edited selection of our boutique merchandise. The table below shows the breakdown of our fiscal year 2011 net sales by product category:
| 6 |
|
Apparel 51% of Net Sales |
Jewelry 20% of Net Sales |
Accessories 16% of Net Sales |
Gifts 13% of Net Sales | |||
| Dresses, Tops, Denim, Skirts, Pants, Outerwear, Jackets & Coats, Layering Essentials, Intimates | Necklaces, Earrings, Bracelets, Rings | Handbags, Totes, Shoulder-Bags, Clutches, Wallets, Shoes, Belts, Hats, Scarves, Sunglasses, Umbrellas, Watches | Candles, Cards, Stationery, Coasters, Hand Crèmes, Soaps, Magnets, Wall Art, Miscellaneous Items |
Our buying and planning team is responsible for selecting and sourcing our merchandise, managing inventory levels and allocating items to boutiques. Each product category has a set of dedicated buyers with oversight provided by our Chief Merchandising Officer. The buying and planning team holds weekly meetings to review merchandise performance and identify new fashion trends. Our buyers also make regular trips to important industry markets and trade shows and visit Asia several times per year. We have access to the expertise of hundreds of designers employed by our large vendor base who provide us with a large selection of new styles for review each week. Our buyers collaborate with vendors to place special orders and to modify presented styles based on current fashion trends and their in-depth knowledge of our customers’ preferences, which means most of our merchandise is unique to francesca’s collections®. Before placing an order, every item is evaluated for style, quality, fit, value and profitability to ensure it meets standards consistent with our francesca’s collections® brand.
Our Sourcing Strategy
Our ability to quickly make decisions on trend-right items combined with the short production lead times of our vendors maximizes our speed to market. We use vendors based in the United States that source from both domestic and overseas markets and it generally takes only four to twelve weeks from the time an order is placed to the time merchandise is available on the boutique floor. With these short lead times, we are able to make more informed buying decisions in terms of customers’ merchandise expectations, and to quickly react to changing fashion trends. This also supports our merchandise strategy of offering a broad but limited assortment that is infused with new items five days a week. Due to the limited quantity of our buys in any one style, we avoid material inventory positions in individual styles and this enhances our ability to quickly deliver trend-right merchandise and minimizes the risk of fashion misses, which can lead to increased inventory markdowns and diminished gross margins.
We do not own or operate any manufacturing facilities. We have relationships with a diverse base of over 200 vendors and our top 10 vendors sourced approximately 42% of our merchandise in fiscal year 2011, while no single vendor accounted for more than 15% of our purchases. KJK Trading Corporation (“KJK Trading”) was our largest vendor in both fiscal year 2011 and 2010. We are KJK Trading’s sole customer. KJK Trading is owned and operated by Ki Juing Gu. Mr. Gu is the brother-in-law of Ms. Insuk Koo (one of our Founders). Although KJK Trading assists us in the design of apparel items, KJK Trading does not act as our broker or agent in the sourcing of our merchandise. We select merchandise for purchase from KJK Trading after being presented with a variety of new styles identified by KJK Trading. Stony Leather, Inc. (“Stony”) was our second largest vendor in fiscal years 2011 and 2010. In addition to us, Stony has several other customers. Chong Yi and Insuk Koo (two of the four Founders) own and operate Stony. Mr. Yi and Ms. Koo along with their sister Ms. Kyong Gill (our Executive Vice Chairperson and one of the four Founders) are stockholders of Francesca’s. Stony provides the sourcing for jewelry, accessories and gift items. Both KJK Trading and Stony maintain separate offices and employees as third-party vendors. See “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Related Party Transactions”.
We do not enter into exclusive contracts with our vendors and we continue to expand our vendor network. This provides us with access to an even more extensive variety of merchandise from a greater number of vendors at competitive prices. We believe our vendors view us as an important retail partner given our growth and market position. Our vendors utilize a network of domestic and overseas factories, providing them access to significant capacity. We source our inventory primarily from domestic vendors.
Each of our vendors is required to adhere to our vendor standards, which are designed to ensure that our vendors conduct their business in a legal, ethical and responsible manner. This also includes the requirement that all of our vendors comply with the applicable laws and regulations of the United States, those of the respective country of manufacture or exportation and all state and local laws and regulations.
| 7 |
Our Sales Channels
We conduct our business through boutiques and our e-commerce website, www.francescascollections.com. We do not incorporate the information contained on, or accessible through, our website into this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and it should not be considered a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Boutiques
In fiscal year 2011, our boutiques generated net sales of $201.3 million, which represented 98.6% of total net sales. As of January 28, 2012, we operated 283 boutiques under the name francesca’s collections® in 41 states throughout the United States. The following list shows the number of boutiques operated by state as of January 28, 2012, and demonstrates that we have been successful in opening boutiques in a wide range of geographies.
| Number of Boutiques |
Number of Boutiques | |||||
| Alabama | 7 | Mississippi | 2 | |||
| Arizona | 8 | Missouri | 7 | |||
| Arkansas | 3 | Nebraska | 3 | |||
| California | 32 | Nevada | 4 | |||
| Colorado | 4 | New Hampshire | 2 | |||
| Connecticut | 5 | New Jersey | 14 | |||
| Delaware | 1 | New Mexico | 1 | |||
| Florida | 21 | New York | 6 | |||
| Georgia | 10 | North Carolina | 9 | |||
| Idaho | 1 | Ohio | 9 | |||
| Illinois | 16 | Oklahoma | 4 | |||
| Indiana | 5 | Oregon | 1 | |||
| Iowa | 2 | Pennsylvania | 5 | |||
| Kansas | 3 | Rhode Island | 3 | |||
| Kentucky | 4 | South Carolina | 6 | |||
| Louisiana | 6 | Tennessee | 9 | |||
| Maine | 1 | Texas | 29 | |||
| Maryland | 5 | Virginia | 7 | |||
| Massachusetts | 8 | Washington | 4 | |||
| Michigan | 5 | Wisconsin | 6 | |||
| Minnesota | 5 |
Boutique Design and Environment
The differentiated shopping experience offered through our boutiques is central to the francesca’s collections® brand. Our boutiques are designed and merchandised to deliver a warm and inviting atmosphere that creates the sense for our customers that they are shopping in an independently owned, upscale boutique. Although we strive to maintain a relatively consistent look and feel in all of our boutiques, the intricacies of each boutique’s physical properties, geographic market and shopping venue, as well as the autonomy we provide to our boutique managers in visually merchandising the boutiques, make each feel different and in tune with its local clientele.
Our boutiques typically range in size from 1,000 to 1,800 square feet, with an average size of approximately 1,400 square feet. We seek locations that have a boutique front at least 20 feet wide, which we adorn with visually appealing architectural lighting, signage and display window presentations. Inside, we use a warm earth tone color palette and soft lighting. We include rugs, lush fabrics and table cloths to create a sense of depth and richness. Chandeliers and antique displays such as ottomans, dressing room chairs and wall mirrors reinforce the unique ambiance and add to the sense of sophistication and style. All of this provides a dense canvas for our colorful displays of trend-right merchandise. Each boutique’s merchandise presentation, including display windows, tables and walls, is refreshed every two to three weeks to keep our shopping experience new and exciting. We believe by constantly changing our visual merchandising and floor sets, we give our customers a reason to shop our boutiques frequently, building customer loyalty. Our boutique managers also use our intranet website to share best-practices with each other, such as ideas for displays. We believe these grass-root interactions improve the sense of community among our boutique managers and enhance the shopping experience for our customers.
| 8 |
Staffing in our boutiques consists of a salaried boutique manager, an assistant manager and a minimum of four part-time associates. Our compensation structure for non-salaried employees consists of an hourly wage plus a monthly bonus based on performance, paid in cash or gift cards to all associates immediately upon achievement of the stated monthly sales goal. We endeavor to hire boutique personnel that are friendly and customer-service driven individuals. In addition to a comprehensive training program for visual merchandising, customer service and operations, boutique managers benefit from ongoing field-level support and training updates as well as guides and manuals.
Boutique Economics
We believe that our broad and shallow merchandising strategy and the differentiated shopping experience we offer to our customers contributes to the success of our boutiques, which generate attractive returns. Over the previous two fiscal years, we opened 138 boutiques which averaged approximately 1,400 square feet and, of the locations open 12 or more months, boutique sales averaged approximately $750,000 in the first year. On average, these boutiques delivered first-year, pre-tax cash return on net investment in excess of 150% and paid back our net investment on a pre-tax basis in less than one year. In fiscal year 2011, the cost of build-out with related fixtures and equipment to open our new boutiques was approximately $180,000 per boutique while tenant allowances averaged approximately $81,000 per boutique. We allocated approximately $45,000 of opening inventory per new boutique in fiscal year 2011. While we do not foresee further significant cost increases, there can be no assurance that those costs will not continue to increase. Based on our disciplined, rigorous real estate selection process and similarity of site characteristics, we expect new boutique economics to be consistent with our recent history
Boutique Growth and Site Selection
We have a proven track record of increasing our boutique base at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 38% over the previous five years. The table below indicates certain historical information regarding our boutiques as of the end of each of the periods indicated below:
Fiscal Year 2011 | Fiscal Year 2010 | Fiscal Year 2009 | Fiscal Year 2008 | Calendar Year 2007(3) | ||||||||||||||||
| Mall | 128 | 69 | 25 | 4 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Street Location/Lifestyle Center | 155 | 138 | 122 | 107 | 77 | |||||||||||||||
| Total Boutiques | 283 | 207 | 147 | 111 | 78 | |||||||||||||||
| Boutiques Opened | 76 | 62 | 36 | 31 | 16 | |||||||||||||||
| Boutiques Closed | — | 2 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Total Gross Square Feet (in thousands) | 399 | 296 | 210 | 158 | 110 | |||||||||||||||
| Average Square Feet Per Boutique (in thousands)(1) | 1,409 | 1,428 | 1,428 | 1,419 | 1,408 | |||||||||||||||
| Net Sales Per Average Square Foot(2) | $ | 554 | $ | 508 | $ | 429 | $ | 384 | $ | 401 | ||||||||||
| (1) | Because of our rapid growth, for purposes of providing a sales per square foot measure we use average square feet during the period as opposed to total gross square feet at the end of the period. For periods consisting of more than one fiscal quarter, average square feet is calculated as (a) the sum of the total gross square feet at the beginning of the period and total gross square feet at the end of each fiscal quarter within the period, divided by (b) the number of fiscal quarters within the period plus one (which, for a fiscal year, is five). There may be variations in the way in which some of our competitors and other retailers calculate sales per square foot or similarly titled measures. As a result, data in this report regarding our average square feet and net sales per average square foot for period may not be comparable to similar data made available by other retailers. |
| (2) | Net sales per average square foot are calculated by dividing net sales for the period by the average square feet during the period. |
| (3) | Please see note 1 to the “Selected Consolidated Financial and Operating Data” section. In January 2008, we changed our fiscal year end from December 31st to the Saturday closest to January 31st. We opened two boutiques in the month of January 2008, which is a time period not captured in Calendar Year 2007 nor Fiscal Year 2008. These two boutiques are included in Boutiques Opened in the calendar year ended December 31, 2007, but are not in included in Total Boutiques or calculations of Total Gross Square Feet, Average Gross Square Feet per Boutique or Net Sales Per Average Gross Square Foot in the calendar year ended December 31, 2007. |
Our flexible boutique format has enabled us to successfully open boutiques across a variety of shopping venues, market sizes, climates and demographics. We believe this provides us with a wide scope of real estate opportunities and enhances our ability to profitably expand our boutique base. Based on this flexible boutique format, the financial characteristics of our boutiques and our ongoing analysis of shopping venues that meet our criteria for new boutiques (including a third party research we commissioned with a nationally recognized retail real estate consulting firm), we believe we have the potential to grow our base from 283 locations in 41 states as of January 28, 2012 to approximately 900 boutiques in the United States over the next seven to ten years. We opened 76 new boutiques in fiscal year 2011 and we plan to open approximately 75 new boutiques per year in fiscal years 2012 and 2013 and one outlet store in fiscal year 2012. We believe we can continue to successfully open new boutiques at an annual rate of at least 75 for the next three to five years. Based on our rigorous real estate selection process, our flexible boutique format and the financial characteristics of our boutiques, we believe that the per boutique costs associated with opening new boutiques over the next two years will be similar to our current costs for opening new boutiques. We expect to fund the costs of our boutique growth through cash flow generated by our operations and through our revolving credit facility if necessary. We expect to open boutiques in both new and existing markets and across regional malls, lifestyle centers, street locations and strip centers. In the short term, we see a particular opportunity to open new boutiques with attractive lease terms in regional malls.
| 9 |
Our real estate committee utilizes a disciplined approach to site selection, which analyzes the prospective shopping venue for factors such as overall shopping venue productivity, competitive environment and specific sales of other retailers deemed most relevant as well as the configuration of available space for potential new boutique locations. We seek prominent locations in high-traffic areas of the shopping venue and in close proximity to other retailers targeting similar customers. We also evaluate each new boutique location based on projected sales and determine whether the capital investment and estimated boutique four-wall contribution satisfies our targeted return threshold, occupancy costs, and boutique contribution. As a result of our powerful boutique economics and our rigorous site selection process, we have only closed two boutiques since we began business in 1999.
Boutique locations and related sales and customer traffic may be adversely affected by, among other things, economic conditions in a particular area, competition from nearby retailers selling similar merchandise, changing lifestyle choices of consumers in a particular market and the closing or decline in popularity of other businesses located near our boutiques. Changes in areas around our boutique locations that result in reductions in customer foot traffic or otherwise render the locations unsuitable could cause our sales to be less than expected. Boutiques located in street locations and lifestyle centers may be more susceptible to such changes than boutiques located in malls.
E-Commerce
Our e-commerce business consists of our www.francescascollections.com website. Through our website, our customers are able to purchase individual items or recommended full outfits, shop the latest jewelry, gift or fashion merchandise and special promotions, create a wish list, sign up for our mailing list, connect and follow us on social media sites such as Facebook and Twitter, as well as obtain current information on our boutique locations. This channel enables us to reach customers in all states and further build our brand. We currently obtain and collect customer email information from our boutiques and website and use it to generate marketing programs, such as our weekly ‘Pick of the Week’ email campaign. During fiscal year 2010 we made several improvements to our website to enhance our e-commerce business capabilities and its growth. These improvements have allowed us to support a more dynamic presentation of merchandise, process more orders and enhance our marketing efforts. In fiscal year 2011, our e-commerce sales increased 49.5% relative to fiscal year 2010, but still only represented 1.4 % of total net sales. We believe there is significant potential to expand this channel over time.
Marketing and Advertising
We focus on organic, viral and in-boutique marketing to increase customer loyalty and build our brand image. By locating our boutiques in prominent, high-traffic locations and refraining from traditional television, radio and print advertising, we encourage people to ‘discover’ francesca’s collections®. We believe that many of our customers develop a personal connection with our boutiques and become our ambassadors in the local community by spreading the word about francesca’s collections®. We also use email communications, our website and, increasingly, social networking sites Facebook and Twitter and fashion related blogs to achieve our marketing goals. Our boutique managers are passionate about francesca’s collections® and contribute to our marketing effort by hosting in-boutique activities, such as fashion shows and private parties, and also independently promote their own boutique via blogs, YouTube and social networking sites.
Distribution
We distribute all of our merchandise from our distribution center (located within our corporate headquarters) in Houston, Texas. Our current combined facility occupies approximately 100,000 square feet, consisting of approximately 70,000 square feet of warehouse and distribution space, which services our boutiques and e-commerce business, and approximately 30,000 square feet of office space for our corporate headquarters. Our merchandise are received, inspected, managed, stored and distributed through our distribution warehouse, with the exception of approximately 10% of our merchandise which are drop-shipped by our vendors directly to our boutiques. The majority of our merchandise are currently pre-ticketed and pre-sorted by our vendors, which allows us to efficiently ship from our distribution center directly to our boutiques, thereby reducing labor costs. We use third-party providers to ship new items to our boutiques five days a week, which ensures a steady flow of new styles. Our current distribution center, which is comprised of four separate buildings, can support at least 450 boutiques and is sufficient to support our expected growth plans for the foreseeable future. However, in December 2011, we entered into a lease for space in a single building near our existing headquarters and distribution facility and expect to relocate our headquarters and distribution facility to the new space by no later than November 1, 2012. We believe that the new facility will be sufficient to support our growth plans for several years.
| 10 |
Management Information Systems
Our management information technology systems provide support and timely information to our management team. We believe our current systems provide us with operational efficiencies, scalability, management control and timely reporting that allows us to identify and respond to operating trends in our business. We use a combination of customized and industry-standard software systems to support boutique point-of-sale, merchandise planning and buying, e-commerce, inventory management, financial reporting and administrative functions.
We are in the process of upgrading several of our systems to provide improved support for our current operations and position us for continued growth. This includes the implementation of a fully integrated enterprise software platform from JDA, which we began to introduce in stages in August 2011 and plan to finalize in the first quarter of fiscal year 2013. Throughout the installation and stabilization of JDA, we will continue to run our existing platform to ensure continuity during the conversion. We expect the new JDA system will enhance customer service, improve operational efficiency, enhance management reporting and control and increase synergies between our e-commerce business and our boutiques.
Competition
The women’s apparel, jewelry, accessories and gifts market is large, fragmented and highly competitive. The largest competitors include national and regional department stores, specialty retailers, mass merchants and internet-based retailers. Due to the breadth of our merchandise, it is difficult to identify companies that compete with us in every product category. However, select national, women’s specialty stores chains that we believe are competitors and that we encounter in multiple markets include White House | Black Market, Ann Taylor, Charlotte Russe, Brighton Collectibles and Anthropologie. Our boutiques also compete with individual, often owner-operated specialty shops in each of the markets that we operate as well as broadly merchandised department stores and certain specialty stores in categories such as accessories and footwear. We may face new competitors and increased competition from existing competitors as we expand into new markets and increase our presence in existing markets.
The principal basis upon which we compete is by offering a differentiated shopping experience through high-quality, trend-right merchandise at attractive prices in a warm and inviting boutique environment with excellent customer service. In addition, our manageable boutique size and flexible but disciplined real estate strategy provide us with a competitive advantage that is not easily replicated by our major competitors. Our success also depends in substantial part on our ability to respond quickly to fashion trends so that we can meet the changing demands of our customers.
Intellectual Property
We have registered our trademark francesca’s collections® with the United States Patent and Trademark Office. In addition, we own domain names, including www.francescascollections.com, and we own unregistered copyright rights in our website content. We believe our trademarks have value, and we diligently protect them against infringement. For instance, we have recently filed applications to register our trademark internationally. We will also continue to file new applications as appropriate to protect our intellectual property rights.
Regulation and Legislation
We are subject to labor and employment laws, laws governing advertising and promotions, privacy laws, product and other safety regulations, consumer protection regulations, environmental requirements and other laws that regulate retailers and govern the promotion and sale of merchandise and the operation of boutiques and warehouse facilities. We monitor changes in these laws and believe that we are in compliance with applicable laws in all material respects.
Insurance
We use insurance for a number of risk management activities, including workers’ compensation, general liability, automobile liability and employee-related health care benefits, a portion of which is paid by the employees. We evaluate our insurance requirements on an ongoing basis and believe we maintain adequate levels of coverage.
| 11 |
Our Employees
As of January 28, 2012, we had approximately 1,970 total employees. Of our total employees, approximately 129 were based at our corporate headquarters in Houston, Texas, and approximately 1,841 were boutique employees. We had approximately 605 full-time employees and approximately1,365 part-time employees, who are primarily boutique employees. None of our employees are represented by a labor union, and we have had no labor-related work stoppages as of January 28, 2012. Our relationship with our employees is one of the keys to our success, and we believe that relationship is satisfactory.
Seasonality
Our wide-range of merchandise and our strategy of carrying a broad selection but limited quantities of each item reduces our overall seasonality relative to other specialty retailers. Nevertheless, our business is mildly seasonal in nature and demand is generally the highest in the fourth fiscal quarter due to the year-end holiday season and lowest in the first fiscal quarter. As a result of this seasonality and generally because of variation in consumer spending habits, we experience fluctuations in net sales and working capital requirements during the year. See “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Seasonality” for more information.
Privacy Policy
In the course of our business, we collect information about our customers, including customer data submitted to us in connection with purchases of our merchandise at boutiques as well as from our e-commerce business. We respect the privacy of our customers and take steps to safeguard the confidentiality of the information that they provide to us.
ITEM 1B. RISK FACTORS
If any of the following risks actually occurs, our business, financial condition, results of operation, cash flow and prospects could be materially and adversely affected. As a result, the trading price of our common stock could decline.
Our success depends on our ability to anticipate, identify and respond quickly to new and changing fashion trends, customer preferences and other factors, and our inability to anticipate, identify and respond to these changes and trends could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our core market, apparel, jewelry, accessories and gifts for women from 18 to 35-years old, is subject to rapidly shifting fashion trends, customer tastes and demands. Accordingly, our success is dependent on our ability to anticipate, identify and respond to the latest fashion trends and customer demands, and to translate such trends and demands into appropriate, saleable product offerings in a timely manner. A small number of our employees are primarily responsible for performing this analysis and making product purchase decisions. Our failure to anticipate, identify or react swiftly and appropriately to new and changing styles, trends or desired image preferences or to accurately anticipate and forecast demand for certain product offerings is likely to lead to lower demand for our merchandise, which could cause, among other things, sales declines, excess inventories and a greater number of markdowns. Further, if we are not able to anticipate, identify and respond to changing fashion trends and customer preferences, we may lose customers and market share to those of our competitors who are able to better anticipate, identify and respond to such trends and preferences. In addition, because our success depends on our brand image, our business could be materially adversely affected if new product offerings are not accepted by our customers. Our new product offerings may not be met with the same level of acceptance as our past product offerings and we may not be able to adequately respond to fashion trends in a timely manner or the preferences of our customers. If we do not accurately forecast or analyze fashion trends and sales levels, our business, financial condition and results of operations will be adversely affected.
| 12 |
If we are not able to successfully maintain a broad and shallow merchandise assortment, we may be unable to attract a sufficient number of customers to our boutiques or sell sufficient quantities of our merchandise through our e-commerce business, which could result in excess inventories and markdowns.
We use the term broad and shallow to refer to a diverse merchandise assortment with relatively small inventory of each product. We believe that our strategy to offer our customers a broad and shallow merchandise assortment has contributed significantly to the success of our business. Among other things, we believe that this strategy creates a constant sense of newness and scarcity value, which drives repeat boutique visits and increased sales. In addition, we believe that this strategy helps us reduce markdowns. There can be no assurance that we will be able to continue to adequately stock our boutiques with a sufficiently broad and shallow assortment of merchandise. As we increase order volumes in connection with opening new boutiques and expanding our e-commerce business, it may become increasingly difficult for us to accurately forecast the optimal amount of merchandise to order from our vendors and continue to offer a broad and shallow merchandise assortment at each boutique. If we are unable to offer a broad and shallow merchandise assortment, customers may choose to visit our boutiques less frequently, our brand could be impaired, our market share may decline and our results of operations could deteriorate. Further, any failure to maintain a broad and shallow merchandise assortment could lead to excess inventories which could lead to markdowns.
Our growth strategy depends in large part upon our ability to successfully open and operate new boutiques each year in a timely and cost-effective manner.
Our strategy to grow our business depends in large part on continuing to successfully open a substantial number of new boutiques each year for the foreseeable future. The success of this strategy will depend largely upon our ability to find a sufficient number of suitable locations, our ability to recruit, hire and train qualified personnel to operate our new boutiques and our ability to scale our infrastructure to successfully integrate our new boutiques.
Our ability to successfully open and operate new boutiques depends on many factors that may be outside of our control including, among others, our ability to:
| Ÿ | identify desirable boutique locations, primarily in malls, lifestyle centers, street locations and strip centers, as well as other types of shopping venues and outlet malls, which may be difficult and costly, particularly in an improving real estate environment; |
| Ÿ | negotiate acceptable lease terms, including favorable levels of tenant allowances, which may be difficult, particularly in an improving real estate environment; |
| Ÿ | maintain out-of-pocket, build-out costs in line with our boutique economic model, including by receiving expected levels of tenant allowances for a portion of our construction expenses, and managing these construction expenses at reasonable levels, which may be difficult, particularly in an improving real estate environment; |
| Ÿ | efficiently source and distribute additional merchandise; |
| Ÿ | hire, train and retain a growing workforce of boutique managers, boutique associates and other personnel; |
| Ÿ | successfully integrate new boutiques into our existing control structure and operations, including our information technology systems; |
| Ÿ | efficiently expand the operations of our distribution facility to meet the needs of a growing boutique network; |
| Ÿ | identify and satisfy the merchandise and other preferences of our customers in new geographic areas and markets; and |
| Ÿ | address competitive, merchandising, marketing, distribution and other challenges encountered in connection with expansion into new geographic areas and markets. |
Our near-term expansion plans have us opening new boutiques in or near the areas where we have existing boutiques. To the extent that we open boutiques in markets where we already have existing boutiques, we may experience reduced net sales at those existing boutiques. Also, if we expand into new geographic areas, we will need to successfully identify and satisfy the fashion preferences of customers in those areas. In addition, we will need to address competitive, merchandising, marketing, distribution and other challenges encountered in connection with any expansion and our limited brand recognition in new markets may limit our expansion strategy and cause our business and growth to suffer.
Finally, newly opened boutiques may not be received as well as, or achieve net sales or profitability levels comparable to those of, our existing boutiques in our estimated time periods, or at all. If our boutiques fail to achieve, or are unable to sustain, acceptable net sales and profitability levels, our business may be materially harmed and we may incur significant costs associated with closing or relocating boutiques. In addition, our current expansion plans are only estimates, and the actual number of boutiques we open each year and the actual number of suitable locations for our new boutiques could differ significantly from these estimates. If we fail to successfully open and operate new boutiques and execute our growth plans, the price of our common stock could decline.
| 13 |
We may not be able to efficiently source and distribute the additional merchandise quantities necessary to support our growth.
Our success depends on our ability to source and distribute merchandise efficiently. The sourcing of our merchandise is dependent, in part, on our relationships with our vendors. If we are unable to maintain these relationships we may not be able to continue to source merchandise at competitive prices that appeal to our customers. If we do not succeed in maintaining good relationships with our vendors or if our growth outpaces the ability of our vendors to scale up and the company cannot identify new vendors to meet the demand for additional merchandise production, the company could see its costs go up or the delivery time on its new orders substantially increase.
Increases in the cost of the raw materials or other inputs used in the production of our merchandise could result in the loss of suppliers, increase our cost of goods sold and occupancy costs and adversely affect our financial results.
The success of our business is in part driven by the compelling price-value proposition we offer our customers. If the costs of the raw materials, particularly cotton, leather and synthetics, used in producing our merchandise increase, our vendors would look to pass these cost increases along to us. The price and availability of such raw materials may fluctuate significantly, depending on many factors which are outside of our control, including commodity prices, crop yields and weather patterns. If our vendors attempt to pass any cost increases on to us and we refuse to pay the increases, we could lose certain vendors as suppliers, resulting in the risk that we could not fill our orders in a timely manner or at all. If we pay the increases, we could either attempt to raise retail prices, which could adversely affect our sales and our brand image, or choose not to raise prices, which could adversely affect the profitability of our merchandise sales.
We are planning to replace several core information technology systems, which could disrupt our operations and adversely affect our financial results.
We recently completed the process of upgrading our existing merchandising, warehousing and point-of-sale applications to the latest supported software releases for these applications. The purpose of the upgrade is to allow the company to scale for the boutique growth that occurred in calendar year 2011 and that is planned during calendar year 2012 and over the next several years. Additionally, this upgrade will allow us to continue to operate our business while we are preparing to launch our new enterprise technology platform.
In fiscal year 2011, we replaced our previous merchandise management, allocation and merchandise analytics systems with a new enterprise technology platform. These replacements were completed in the third quarter of fiscal year 2011.
During the third quarter of fiscal year 2012, we plan to begin to replace our boutiques’ point-of-sale software and merchandise planning systems. We expect to complete the implementation of our new enterprise technology platform in the first quarter of fiscal year 2013. Also, our accounting system may need to be upgraded and replaced over time depending on our growth.
The risks associated with the above information technology systems changes, as well as any failure of such systems to operate effectively, could disrupt and adversely impact the promptness and accuracy of our merchandise distribution, transaction processing, financial accounting and reporting, including the implementation of our internal controls over financial reporting, the efficiency of our operations and our ability to properly forecast earnings and cash requirements. We could be required to make significant additional expenditures to remediate any such failures or problems.
We believe that other companies have experienced significant delays and cost overruns in implementing similar systems changes, and we may encounter problems as well. We may not be able to successfully implement these new systems or, if implemented, we may still face unexpected disruptions in the future. Any resulting disruptions could harm our business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
Our current growth plans will place a strain on our existing resources and could cause us to encounter challenges we have not faced before.
As our number of boutiques and our e-commerce sales grow, our operations will become more complex. While we have grown substantially as a company since inception, much of this growth occurred recently in fiscal years 2010 and 2011. As we move forward, we expect our growth to bring new challenges that we have not faced before. Among other difficulties that we may encounter, this growth will place a strain on our existing infrastructure, including our distribution facilities, information technology systems, financial controls, real estate and boutique operations staffs, and may make it more difficult for us to adequately forecast expenditures, such as real estate and construction expenses, budgeting will become more complex, and we may also place increased burdens on our vendors, as we will likely increase the size of our merchandise orders. The increased demands that our growth plans will place on our infrastructure may cause us to operate our business less efficiently, which could cause a deterioration in the performance of our existing boutiques. New order delivery times could lengthen as a result of the strains that growth will place on our existing resources and our growth may make it otherwise difficult for us to respond quickly to changing trends, consumer preferences and other factors. This could impair our ability to continue to offer trend-right merchandise which could result in excess inventory, greater markdowns, loss of market share and decreased sales.
| 14 |
In addition, our planned expansion is expected to place increased demands on our existing operational, managerial, administrative and other resources. Specifically, our inventory management systems and personnel processes may need to be further upgraded to keep pace with our current growth strategy. We cannot anticipate all of the demands that our expanding operations will impose on our business, and our failure to appropriately address these demands could have an adverse effect on us.
Our business is sensitive to consumer spending and economic conditions.
Consumer purchases of discretionary retail items and specialty retail products, which include our apparel, jewelry, accessories and gifts, may be adversely affected by economic conditions such as employment levels, salary and wage levels, the availability of consumer credit, inflation, high interest rates, high tax rates, high fuel prices and consumer confidence with respect to current and future economic conditions. Consumer purchases may decline during recessionary periods or at other times when unemployment is higher or disposable income is lower. These risks may be exacerbated for retailers like us that focus significantly on selling discretionary fashion merchandise. Consumer willingness to make discretionary purchases may decline, may stall or may be slow to increase due to national and regional economic conditions. Our financial performance is particularly susceptible to economic and other conditions in regions or states where we have a significant number of boutiques. There remains considerable uncertainty and volatility in the national and global economy. Further or future slowdowns or disruptions in the economy could adversely affect mall traffic and new mall and shopping center development and could materially and adversely affect us and our growth plans. We may not be able to maintain our recent rate of growth in net sales if there is a decline in consumer spending.
In addition, a deterioration of economic conditions and future recessionary periods may exacerbate the other risks faced by our business, including those risks we encounter as we attempt to execute our growth plans. Such risks could be exacerbated individually or collectively.
We operate in the highly competitive specialty retail apparel and accessories industry and the size and resources of some of our competitors may allow them to compete more effectively than we can, which could adversely impact our growth and market share.
We face intense competition in the specialty retail apparel and accessories industry. We compete on the basis of a combination of factors, including price, breadth, quality and style of merchandise, as well as our in-boutique experience and level of customer service, our brand image and our ability to anticipate, identify and respond to new and changing fashion trends. While we believe that we compete primarily with specialty retailers and internet businesses that specialize in women’s apparel and accessories, we also face competition from department stores, mass merchandisers and value retailers. We believe our primary competitors include specialty apparel and accessories retailers that offer their own private labels, including, among others, White House | Black Market, Ann Taylor Loft, Charlotte Russe and Anthropologie. In addition, our expansion into markets served by our competitors and entry of new competitors or expansion of existing competitors into our markets could have an adverse effect on our business.
We also compete with a wide variety of large and small retailers for customers, vendors, suitable boutique locations and personnel. The competitive landscape we face, particularly among specialty retailers, is subject to rapid change as new competitors emerge and existing competitors change their offerings. We cannot assure you that we will be able to compete successfully and navigate the shifts in our market.
Many of our competitors are, and many of our potential competitors may be, larger and have greater name recognition and access to greater financial, marketing and other resources. Therefore, these competitors may be able to adapt to changes in trends and customer desires more quickly, devote greater resources to the marketing and sale of their products, generate greater brand recognition or adopt more aggressive pricing policies than we can. As a result, we may lose market share, which could reduce our sales and adversely affect our results of operations. Many of our competitors also utilize advertising and marketing media which we do not, including advertising through the use of direct mail, newspapers, magazines, billboards, television and radio, which may provide them with greater brand recognition than we have.
| 15 |
Our competitors may also sell certain products or substantially similar products through the Internet or through outlet centers or discount stores, increasing the competitive pressure for those products. We cannot assure you that we will continue to be able to compete successfully against existing or future competitors. Our expansion into markets served by our competitors and entry of new competitors or expansion of existing competitors into our markets could have a material adverse effect on us. Competitive forces and pressures may intensify as our presence in the retail marketplace grows.
We do not possess exclusive rights to many of the elements that comprise our in-boutique experience and merchandise offerings. Some specialty retailers offer a personalized shopping experience that in certain ways is similar to the one we strive to provide to our customers. Our competitors may seek to emulate facets of our business strategy and in-boutique experience, which could result in a reduction of any competitive advantage or special appeal that we might possess. In addition, some of our merchandise offerings are sold to us on a non-exclusive basis. As a result, our current and future competitors, especially those with greater financial, marketing or other resources, may be able to duplicate or improve upon some or all of the elements of our in-boutique experience or merchandise offerings that we believe are important in differentiating our boutiques and our customers’ shopping experience. If our competitors were to duplicate or improve upon some or all of the elements of our in-boutique experience or product offerings, our competitive position and our business could suffer.
Our inability to maintain or increase our comparable boutique sales could adversely impact our net sales, profitability, cash flow and stock price.
We may not be able to sustain or increase the levels of comparable boutique sales that we have experienced in the recent past. If our future comparable boutique sales decline or fail to meet market expectations, our profitability could be harmed and the price of our common stock could decline. In addition, the aggregate comparable boutique sales levels of our boutiques have fluctuated in the past and can be expected to fluctuate in the future. A variety of factors affect comparable boutique sales, including fashion trends, competition, current national and regional economic conditions, pricing, changes in our merchandise mix, prior period comparable boutique sales levels, inventory shrinkage, the timing and amount of markdowns, the success of our marketing programs, holiday timing and weather conditions. In addition, it may be more challenging for us to sustain high levels of comparable boutique sales growth during and after our planned expansion. These factors may cause our comparable boutique sales results to be materially lower than in recent periods and lower than market expectations, which could harm our business and our earnings and result in a decline in the price of our common stock.
Our inability to maintain or increase our operating margins could adversely affect the price of our common stock.
We intend to continue to increase our operating margins through scale efficiencies, improved systems, continued cost discipline and enhancements to our merchandise offerings. If we are unable to successfully manage the potential difficulties associated with our growth plans, we may not be able to capture the scale efficiencies that we expect from expansion. If we are not able to continue to capture scale efficiencies, improve our systems, continue our cost discipline and enhance our merchandise offerings, we may not be able to achieve our goals with respect to operating margins. In addition, if we do not adequately refine and improve our various ordering, tracking and allocation systems, we may not be able to increase sales and reduce inventory shrinkage. As a result, our operating margins may stagnate or decline, which could adversely affect the price of our common stock.
Our ability to attract customers to our boutiques depends on locating our boutiques in suitable locations. Conditions or changes affecting boutique locations, including any decrease in customer traffic, could cause our sales to be less than expected.
Boutique locations and related sales and customer traffic may be adversely affected by, among other things, economic conditions in a particular area, competition from nearby retailers selling similar merchandise, changing lifestyle choices of consumers in a particular market and the closing or decline in popularity of other businesses located near our boutique. Although we have opened many boutiques in mall locations, our approach to identifying locations for our boutiques has historically favored street locations and lifestyle centers. As a result, many of our boutiques are located outside of malls near other retailers or public venues that we believe are consistent with our customers’ lifestyle choices. Changes in areas around our boutique locations that result in reductions in customer foot traffic or otherwise render the locations unsuitable could cause our sales to be less than expected. Boutiques located in street locations and lifestyle centers may be more susceptible to such changes than boutiques located in malls.
| 16 |
Our business depends on a strong brand image, and if we are not able to maintain and enhance our brand, particularly in new markets where we have limited brand recognition, we may be unable to attract a sufficient number of customers to our boutiques or sell sufficient quantities of our merchandise.
We believe that our brand image and brand awareness has contributed significantly to the success of our business. We also believe that maintaining and enhancing our brand image particularly in new markets where we have limited brand recognition is important to maintaining and expanding our customer base. Maintaining and enhancing our brand image may require us to make substantial investments in areas such as merchandising, marketing, boutique operations, community relations, boutique promotions and employee training. These investments may be substantial and may not ultimately be successful.
We do not use traditional advertising channels and if we fail to adequately continue to connect with our customer base, our business could be adversely affected.
We focus on organic, viral and in-boutique marketing to capture the interest of our customers and drive them to our boutiques and website. We do not use traditional advertising channels, such as newspapers, magazines, billboards, television and radio, which are used by some of our competitors. We expect to increase our use of social media, such as Facebook and Twitter, in the future. If our marketing efforts are not successful, there may be no immediately available or cost effective alternative marketing channel for us to use to build or maintain brand awareness. As we execute our growth strategy, our ability to successfully integrate new boutiques into their surrounding communities or to expand into new markets will be adversely impacted if we fail to connect with our target customers. Failure to successfully connect with our target customers in new and existing markets could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We depend on our senior management personnel and may not be able to retain or replace these individuals or recruit additional personnel, which could harm our business.
Our future success is substantially dependent on the continued service of our senior management, particularly Mr. De Meritt, one of our Founders and our President and Chief Executive Officer and a member of our board of directors, and Ms. Gill, another of our Founders and the Executive Vice Chairperson of our board of directors. These employees have extensive experience both with our company and in our industry and are familiar with our business, systems and processes. The loss of services of one or more of our key employees could impair our ability to manage our business effectively and could have an adverse effect on our business, as we may not be able to find suitable individuals to replace them on a timely basis or at all. In addition, any departures of key personnel could be viewed in a negative light by investors and analysts, which could cause our common stock price to decline. We do not maintain key person insurance on any employee.
In addition to these key employees, we have other employees in positions, including those employees responsible for our merchandising and operations departments that, if vacant, could cause a temporary disruption in our business until such positions are filled.
If we are unable to find, train and retain key personnel, including new boutique employees that reflect our brand image and embody our culture, we may not be able to grow or sustain our operations.
Our success depends in part upon our ability to attract, motivate and retain a sufficient number of boutique employees, including boutique managers, who understand and appreciate our customers, brand and corporate culture, and are able to adequately and effectively represent our culture and establish credibility with our customers. Like most retailers, we experience significant employee turnover rates, particularly among boutique employees. Our planned growth will require us to hire and train even more personnel to manage such growth. If we are unable to hire and retain boutique personnel capable of consistently providing a high level of customer service, as demonstrated by their enthusiasm for our culture, understanding of our customers and knowledge of the merchandise we offer, our ability to open new boutiques may be impaired, the performance of our existing and new boutiques could be materially adversely affected and our brand image may be negatively impacted. There is a high level of competition for experienced, qualified personnel in the retail industry and we compete for personnel with a variety of companies looking to hire for retail positions. Historically, we have prided ourselves on our commitment to employee growth and development and we focus on promoting from within our team. Our growth plans will strain our ability to staff our new boutiques, particularly at the boutique manager level, which could have an adverse effect on our ability to maintain a cohesive and consistently strong team, which in turn could have an adverse impact on our business. If we are unable to attract, train and retain employees in the future, we may not be able to serve our customers effectively, thus reducing our ability to continue our growth and to operate our existing boutiques as profitably as we have in the past
| 17 |
Union attempts to organize our employees could negatively affect our business.
None of our employees are currently subject to a collective bargaining agreement. As we continue to grow and enter different regions, unions may attempt to organize all or part of our employee base at certain boutiques or within certain regions. Responding to such organization attempts may distract management and employees and may have a negative financial impact on individual boutiques, or on our business as a whole.
We have one corporate headquarters and distribution facility and have not yet implemented disaster recovery procedures. Disruptions to the operations at that location could have an adverse effect on our business operations.
Our corporate headquarters and our only distribution facility are co-located in Houston, Texas. Our distribution facility supports both our boutiques and our e-commerce business. A majority of our merchandise is shipped from our vendors to the distribution facility and then packaged and shipped from our distribution facility to our boutiques and our e-commerce customers. The success of our boutiques depends on the timely receipt of merchandise because they must receive merchandise in a timely manner in order to stay current with the fashion preferences of our customers. The efficient flow of our merchandise requires that we have adequate capacity and uninterrupted service in our distribution facility to support both our current level of operations, and the anticipated increased levels that may follow from our growth plans. We believe that our current distribution facility is capable of supporting our growth through approximately 450 boutiques without significant additional capital investment. In order to accommodate future growth beyond approximately 450 boutiques we will either need to expand and upgrade our existing distribution facility or move our distribution operations to a new facility with greater capacity. In December 2011, we entered into a lease for space in a single building near our existing headquarters and distribution facility and expect to relocate our headquarters and distribution facility to the new space by no later than November 1, 2012. We believe that the new facility will be sufficient to support our growth plans for several years.
In addition, if we encounter difficulties associated with our distribution facility or if it were to shut down for any reason, including fire, hurricanes or other natural disaster, we could face inventory shortages resulting in “out-of-stock” conditions in our boutiques, and delays in shipments to our customers, resulting in significantly higher costs and longer lead times associated with distributing our merchandise. See “—The current geographic concentration of our boutiques creates an exposure to local economies, regional downturns and severe weather or other catastrophic occurrences that may materially adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations” below. Also, most of our computer equipment and senior management, including critical resources dedicated to merchandising, financial and administrative functions, are located at our corporate headquarters. Our management and our operations and distribution staff would need to find an alternative location, causing further disruption and expense to our business and operations.
We recognize the need for, and are in the early stages of, developing disaster recovery, business continuity and document retention plans that would allow us to be operational despite casualties or unforeseen events impacting our corporate headquarters or distribution center. Without disaster recovery, business continuity and document retention plans, if we encounter difficulties or disasters with our distribution facility or at our corporate headquarters, our critical systems, operations and information may not be restored in a timely manner, or at all, and this could have an adverse effect on our business.
We will relocate our corporate headquarters and distribution facilities. Any disruption to our operations resulting from the relocation could have an adverse effect on our business.
We will relocate our headquarters and distribution facilities to an existing nearby building. The relocation and consolidation from our current facilities should be completed no later than November 1, 2012. Initially, we will occupy approximately 218,000 square feet, which will house our corporate headquarters, warehouse and distribution facility, including our e-commerce operations, and e-commerce fulfillment. We believe that the new facility will be sufficient to support our growth plans for several years. The lease for the new facilities includes an option to add as much as an additional 122,000 square feet if necessary. The primary lease term of the new facility expires on April 30, 2020; however, we have options to renew the lease for an additional period of up to ten years.
If we encounter difficulties or disruptions associated with our relocation, we could face inventory shortages resulting in “out-of-stock” conditions in our boutiques, delays in shipments to our customers, higher costs and longer lead times, as well as disruptions to our merchandising, financial and administrative functions. Such difficulties or disruptions could have an adverse effect on our business.
| 18 |
Our business requires that we lease substantial amounts of space and we may not be able to continue to lease space on terms as favorable as the leases negotiated in the past.
We do not own any real estate. Instead, we lease all of our boutique locations, as well as our corporate headquarters and distribution facility in Houston, Texas. Our boutiques are leased from third parties, with lease terms of five to ten years. Many of our lease agreements also have additional five-year renewal options. We believe that we have been able to negotiate favorable rental rates and tenant allowances over the last few years due in large part to the state of the economy and higher than usual vacancy rates in a number of regional malls and shopping centers. These trends may not continue, and there is no guarantee that we will be able to continue to negotiate such favorable terms. Many of our leases have early cancellation clauses, which permit the lease to be terminated by us or the landlord if certain sales levels are not met in specific periods or if the shopping venue does not meet specified occupancy standards. In addition to fixed minimum lease payments, most of our boutique leases provide for additional rental payments based on a percentage of sales, or “percentage rent,” if sales at the respective boutiques exceed specified levels, as well as the payment of common area maintenance charges, real property insurance and real estate taxes. Many of our lease agreements have defined escalating rent provisions over the initial term and any extensions. Increases in our already substantial occupancy costs and difficulty in identifying economically suitable new boutique locations could have significant negative consequences, which include:
| · | requiring that a greater portion of our available cash be applied to pay our rental obligations, thus reducing cash available for other purposes and reducing our profitability; | |
| · | increasing our vulnerability to general adverse economic and industry conditions; and | |
| · | limiting our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to changes in, our business or in the industry in which we compete. |
We depend on cash flow from operations to pay our lease expenses and to fulfill our other cash needs. If our business does not generate sufficient cash flow from operating activities to fund these expenses and needs and sufficient funds are not otherwise available to us, we may not be able to service our lease expenses, grow our business, respond to competitive challenges or fund our other liquidity and capital needs, which could harm our business. Additional sites that we lease may be subject to long-term non-cancelable leases if we are unable to negotiate our current standard lease terms. If an existing or future boutique is not profitable, and we decide to close it, we may nonetheless be committed to perform our obligations under the applicable lease including, among other things, paying the base rent for the balance of the lease term. Moreover, even if a lease has an early cancellation clause, we may not satisfy the contractual requirements for early cancellation under that lease. In addition, if we are not able to enter into new leases or renew existing leases on terms acceptable to us, this could have an adverse effect on our results of operations.
Our ability to obtain merchandise on a timely basis at competitive prices could suffer as a result of any deterioration or change in our vendor relationships or events that adversely affect our vendors or their ability to obtain financing for their operations.
We have many important vendor relationships that we believe provide us with a competitive advantage. We do not own or operate any manufacturing facilities. Instead, we purchase all of our merchandise from third-party vendors. Two of our vendors accounted for approximately 19% and 23% of our purchases in fiscal years 2011 and 2010, respectively, with no single vendor accounting for more than 15% of our purchases during either period. One of these vendors is owned and operated by two of our Founders who are the brother and sister of Ms. Kyong Gill, our Executive Vice Chairperson. The other vendor is owned and operated by the brother-in-law of one of our Founders. See “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Related Party Transactions.” Other than the two largest vendors, one additional vendor accounted for more than 5% of our purchases in fiscal year 2011 and no vendor accounted for more than 5% of our purchases during fiscal year 2010. Our business and financial performance depend in large part on our ability to evaluate merchandise quickly for style and then modify any undesirable designs or to improve the quality, look, and fit of the item. We do not have long-term contracts with any of these vendors and we generally operate without any contractual assurances of continued supply, pricing or access to new products. Rather, we receive and review samples almost daily for fit and fashion evaluation. Any of our vendors could discontinue supplying us with desired products in sufficient quantities for a variety of reasons.
The benefits we currently experience from our vendor relationships could be adversely affected if our vendors:
| · | choose to stop providing merchandise samples to us or otherwise discontinue selling merchandise to us; | |
| · | raise the prices they charge us; |
| 19 |
| · | change pricing terms to require us to pay on delivery or upfront, including as a result of changes in the credit relationships some of our vendors have with their various lending institutions; | |
| · | reduce our access to styles, brands and merchandise by entering into broad exclusivity arrangements with our competitors or otherwise in the marketplace; | |
| · | sell similar merchandise to our competitors with similar or better pricing, many of whom already purchase merchandise in significantly greater volume and, in some cases, at lower prices than we do; | |
| · | lengthen their lead times; or | |
| · | initiate or expand sales of apparel and accessories to retail customers directly through their own stores, catalogs or on the internet and compete with us directly. |
We historically have established good working relationships with many small- to mid-size vendors that often have more limited resources, production capacities and operating histories. Market and economic events that adversely impact our vendors could impair our ability to obtain merchandise in sufficient quantities. Such events include difficulties or problems associated with our vendors’ business, finances, labor, ability to import merchandise, costs, production, insurance and reputation. There can be no assurance that we will be able to acquire desired merchandise in sufficient quantities on acceptable terms or at all in the future, especially if we need significantly greater amounts of inventory in connection with the growth of our business. We may need to develop new relationships with larger vendors, as our current vendors may be unable to supply us with needed quantities and we may not be able to find similar merchandise on the same terms from larger vendors. If we are unable to acquire suitable merchandise in sufficient quantities, at acceptable prices with adequate delivery times due to the loss of or a deterioration or change in our relationship with one or more of our key vendors or events harmful to our vendors occur, it may adversely affect our business and results of operations.
A failure in our e-commerce operations could significantly disrupt our business and lead to reduced sales, growth prospects and reputational damage.
While accounting for only 1.4% of our net sales in fiscal years 2011 and 2010, our e-commerce business is rapidly growing and is an important element of our brand and relationship with our customers. Net sales attributable to our e-commerce business increased 49.5% and 85% in fiscal years 2011 and 2010, respectively. Further expanding our e-commerce business is an important part of our growth strategy. In addition to changing consumer preferences, shifting traffic patterns and related customer acquisition costs and buying trends in e-commerce, we are vulnerable to certain additional risks and uncertainties associated with e-commerce sales, including rapid changes in technology, website downtime and other technical failures, security breaches, consumer privacy concerns, changes in state tax regimes and government regulation of internet activities. Our failure to successfully respond to these risks and uncertainties could reduce our e-commerce sales, increase our costs, diminish our growth prospects, and damage our brand, which could negatively impact our results of operations and stock price.
In addition, there is no guarantee that we will be able to further expand our e-commerce business. Many of our competitors already have e-commerce businesses that are substantially larger and more developed than ours, which places us at a competitive disadvantage. If we are unable to further expand our e-commerce business, our growth plans will suffer and the price of our common stock could decline.
System security risk issues, including our failure to protect our customers’ privacy and disruption of our internal operations or information technology systems, could harm our reputation and adversely affect our financial results and stock price.
Experienced computer programmers and hackers, or even internal users, may be able to penetrate or create systems disruptions or cause shutdowns of our network security or that of third-party companies with which we have contracted to provide services. We generally collect and store customer information for marketing purposes and any compromise of customer information could subject us to customer or government litigation and harm our reputation, which could adversely affect our business and growth. Moreover, we could incur significant expenses or disruptions of our operations in connection with system failures or data breaches. An increasing number of websites, including several large internet companies, have recently disclosed breaches of their security, some of which have involved sophisticated and highly targeted attacks on portions of their sites. Because the techniques used to obtain unauthorized access, disable or degrade service or sabotage systems, change frequently and often are not recognized until launched against a target, we may be unable to anticipate these techniques or to implement adequate preventative measures. In addition, sophisticated hardware and operating system software and applications that we buy or license from third-parties may contain defects in design or manufacture, including “bugs” and other problems that could unexpectedly interfere with the security and operation of the systems. The costs to us to eliminate or alleviate security problems, viruses and bugs, or any problems associated with the outsourced services provided to us, could be significant, and efforts to address these problems could result in interruptions, delays or cessation of service that may impede our sales, distribution or other critical functions.
| 20 |
In addition, almost all states have adopted breach of data security statutes or regulations that require notification to consumers if the security of their personal information is breached, and at least one state has adopted regulations requiring every company that maintains or stores personal information to adopt a comprehensive written information security program. Governmental focus on data security may lead to additional legislative action, and the increased emphasis on information security may lead customers to request that we take additional measures to enhance security or restrict the manner in which we collect and use customer information to gather insights into customer behavior and craft our marketing programs. As a result, we may have to modify our business systems and practices with the goal of further improving data security, which would result in reduced net sales, increased expenditures and operating complexity. Any compromise of our security or accidental loss or theft of customer data in our possession could result in a violation of applicable privacy and other laws, significant legal and financial exposure and damage to our reputation, which could adversely impact our business, results of operations and stock price.
The current geographic concentration of our boutiques creates an exposure to local economies, regional downturns and severe weather or other catastrophic occurrences that may materially adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
We operated 32 boutiques in California as of January 28, 2012, making California our largest market, representing approximately 11% of our total boutiques. We also have boutique concentration in Texas and Florida, operating 29 boutiques and 21 boutiques in those states, respectively, as of January 28, 2012. As a result, our business is currently more susceptible to regional conditions than the operations of more geographically diversified competitors, and we are vulnerable to economic downturns in those regions. Any unforeseen events or circumstances that negatively affect these areas could materially adversely affect our sales and profitability. These factors include, among other things, changes in demographics and population.
Further, our corporate headquarters and only distribution center are currently, and following our relocation to our new facilities will be, located at a single facility in Houston, Texas. Our single distribution center receives, stores and distributes merchandise to all of our boutiques and fulfills all sales for our e-commerce business. Most of our computer equipment and senior management, including critical resources dedicated to merchandising and financial and administrative functions, are located at our corporate headquarters. As described elsewhere in the risk factors in this report, we do not have adequate disaster recovery systems and plans at our corporate headquarters and distribution facility. As a result, our business may be more susceptible to regional natural disasters and catastrophes than the operations of more geographically diversified competitors. See “—We have one corporate headquarters and distribution facility and have not yet implemented disaster recovery procedures. Disruptions to the operations at that location could have an adverse effect on our business operations” above.
In addition, a substantial number of our boutiques are located in the southeastern United States. The southeastern United States, Texas and other states along the Gulf Coast, in particular, are prone to severe weather conditions. For example, hurricanes have passed through Texas, Florida and other states along the Gulf Coast causing extensive damage to the region. Adverse weather conditions impacting Texas and other states along the Gulf Coast, and the southeastern United States generally could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition. All of our boutique locations expose us to additional diverse risks, given that natural disasters or other unanticipated catastrophes, such as telecommunications failures, cyber-attacks, fires or terrorist attacks, can occur anywhere and could cause disruptions in our operations. Extensive or multiple disruptions in our operations, whether at our boutiques or our corporate headquarters and distribution center, due to natural disasters or other catastrophes could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and stock price.
Our results may be adversely affected by fluctuations in energy costs.
Energy costs have fluctuated dramatically in the past and may fluctuate in the future. These fluctuations may result in an increase in our transportation costs for distribution, utility costs for our retail boutiques and costs to purchase product from our vendors. A continual rise in energy costs could adversely affect consumer spending and demand for our merchandise and increase our operating costs and we may be unable to pass along to our customers such increased cost, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and stock price.
| 21 |
Our net sales and merchandise fluctuate on a seasonal basis, leaving our operating results susceptible to adverse changes in seasonal shopping patterns, weather and related risks.
Due to the seasonal nature of the retail industry, we have historically experienced and expect to continue to experience some fluctuations in our net sales and net income. Our net sales and earnings are typically highest in the fourth fiscal quarter due to the year-end holiday season. Net sales during this period cannot be used as an accurate indicator of annual results. Likewise, as is the case with many retailers of apparel, jewelry, accessories and gifts, we typically experience lower net sales in the first fiscal quarter relative to other quarters. If for any reason, including for example poor weather conditions, soft economic environments and loss of consumer confidence, our net sales were below seasonal norms or expectations during typically higher-volume time periods, our net sales, inventory levels and results of operations could be adversely affected. In addition, in order to prepare for these periods, we must order and keep in stock significantly more merchandise than we carry during other parts of the year. This inventory build-up may require us to expend cash faster than is generated by our operations during these periods. Any unanticipated decrease in demand for our merchandise during peak shopping periods could result in excess inventory levels which could require us to sell excess inventory at a substantial markdown, which could have an adverse effect on our business, profitability and brand image. In addition, we may experience variability in net sales as a result of a variety of other factors, including the timing of new boutique openings, boutique events, other marketing activities, sales tax holidays and other holidays, which may cause our results of operations to fluctuate on a quarterly basis and relative to corresponding periods in prior years.
If our vendors fail to comply with applicable laws, including a failure to use acceptable labor practices, or if our vendors suffer disruptions in their businesses, we could suffer adverse business consequences.
Our vendors source the merchandise sold in our boutiques from manufacturers both inside and outside of the United States. Although each of our purchase orders is subject to our vendor manuals, which require compliance with labor, immigration, manufacturing and product safety, environmental and other laws, we do not supervise, control or audit our vendors or the manufacturers that produce the merchandise we sell. The violation, or perception of any violation, of any labor, immigration, manufacturing safety or other laws by any of our vendors or their U.S. and non-U.S. manufacturers, such as use of child labor, or the divergence of the labor practices followed by any of our vendors or these manufacturers from those generally accepted in the United States, could damage our brand image or subject us to boycotts by our customers or activist groups.
Any event causing a sudden disruption of manufacturing or imports, including the imposition of additional import restrictions, could interrupt, or otherwise disrupt the shipment of finished products to us by our vendors and materially harm our operations. Political and financial instability outside the United States, strikes, adverse weather conditions or natural disasters that may occur or acts of war or terrorism in the United States or worldwide, may affect the production, shipment or receipt of merchandise. These factors, which are beyond our control, could materially hurt our business, financial condition and results of operations or may require us to modify our current business practices or incur increased costs.
Changes in laws, including employment laws and laws related to our merchandise, could make conducting our business more expensive or otherwise cause us to change the way we do business.
We are subject to numerous regulations, including labor and employment, truth-in-advertising, consumer protection, product safety, environmental and zoning and occupancy laws and ordinances that regulate retailers generally or govern the promotion and sale of merchandise and the operation of boutiques and warehouse facilities. If these regulations were to change or were violated by our management, employees or vendors, the costs of certain goods could increase, or we could experience delays in shipments of our goods, be subject to fines, penalties or other liabilities or suffer reputational harm, which could reduce demand for our merchandise and hurt our business and results of operations.
In addition to increased regulatory compliance requirements, changes in laws could make the ordinary conduct of our business more expensive or require us to change the way we do business. Laws related to employee benefits and treatment of employees, including laws related to limitations on employee hours, immigration laws, child labor laws, supervisory status, leaves of absence, mandated health benefits or overtime pay, could also negatively impact us, such as by increasing compensation and benefits costs for overtime and medical expenses. Moreover, changes in product safety or other consumer protection laws could lead to increased costs to us for some merchandise, or additional labor costs associated with readying merchandise for sale. It is often difficult for us to plan and prepare for potential changes to applicable laws, and future actions or payments related to these changes could be material to us.
| 22 |
We will require significant capital to fund our expanding business, which may not be available to us on satisfactory terms or at all. We plan to use cash from operations to fund our operations and execute our growth strategy. If we are unable to maintain sufficient levels of cash flow, we may not meet our growth expectations or we may require additional financing which could adversely affect our financial health and impose covenants that limit our business activities.
We plan to continue our growth and expansion, including opening a number of new boutiques, remodeling existing boutiques and upgrading our information technology systems and other infrastructure as opportunities arise. Our plans to expand our boutique base may not be successful and the implementation of these plans may not result in expected increases in our net sales even though they increase our costs. To support our expanding business and execute on our growth strategy, we will require significant capital.
We currently primarily depend on cash flow from operations and our revolving credit facility to fund our business and growth plans. If our business does not generate sufficient cash flow from operations to fund these activities, and sufficient funds are not otherwise available to us from our revolving credit facility, we may need additional equity or debt financing. If such financing is not available to us, or is not available on satisfactory terms, our ability to operate and expand our business or respond to competitive pressures would be curtailed and we may need to delay, limit or eliminate planned boutique openings or operations or other elements of our growth strategy. If we raise additional capital by issuing equity securities or securities convertible into equity securities, your ownership would be diluted.
We may incur additional indebtedness in the future, which may require us to use a substantial portion of our cash flow to service debt and limit our financial and operating flexibility in important ways.
We may incur additional indebtedness in the future. Any borrowings under any future debt financing will require interest payments and need to be repaid or refinanced, could require us to divert funds identified for other purposes to debt service and would create additional cash demands and could impair our liquidity position and add financial risk for us. Diverting funds identified for other purposes for debt service may adversely affect our business and growth prospects. If we cannot generate sufficient cash flow from operations to service our debt, we may need to refinance our debt, dispose of assets or issue equity to obtain necessary funds. We do not know whether we would be able to take any of these actions on a timely basis, on terms satisfactory to us, or at all.
Our level of indebtedness has important consequences to you and your investment in our common stock. For example, our level of indebtedness may:
| · | require us to use a substantial portion of our cash flow from operations to pay interest and principal on our debt, which would reduce the funds available to us for working capital, capital expenditures and other general corporate purposes; | |
| · | limit our ability to pay future dividends; | |
| · | limit our ability to obtain additional financing for working capital, capital expenditures, expansion plans and other investments, which may limit our ability to implement our business strategy; | |
| · | heighten our vulnerability to downturns in our business, the specialty apparel and accessories retail industry or in the general economy and limit our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and the specialty apparel and accessories retail industry; or | |
| · | prevent us from taking advantage of business opportunities as they arise or successfully carrying out our plans to expand our boutique base and product offerings. |
Our business may not generate sufficient cash flow from operations and future borrowings may not be available to us in amounts sufficient to enable us to make payments on our indebtedness or to fund our operations.
The terms of our revolving credit facility do, and the terms of any additional debt financing may, restrict our current and future operations, which could adversely affect our ability to manage our operations and respond to changes in our business.
Our revolving credit facility contains, and any additional debt financing we may incur would likely contain, covenants that restrict our operations, including limitations on our ability to grant liens, incur additional debt, pay dividends, redeem our common stock, make certain investments and engage in certain merger, consolidation or asset sale transactions. A failure by us to comply with the covenants or financial ratios contained in our revolving credit facility or any additional debt financing we may incur could result in an event of default, which could adversely affect our ability to respond to changes in our business and manage our operations. Upon the occurrence of an event of default, the lenders could elect to declare all amounts outstanding to be due and payable and exercise other remedies. If the indebtedness under our revolving credit facility or any additional debt financing we may incur were to be accelerated, our future financial condition could be materially adversely affected.
| 23 |
There are claims made against us from time to time that can result in litigation that could distract management from our business activities and result in significant liability or damage to our brand.
As a growing company with expanding operations, we increasingly face the risk of litigation and other claims against us. Litigation and other claims may arise in the ordinary course of our business and include employee claims, commercial disputes, landlord-tenant disputes, intellectual property issues, product-oriented allegations and slip and fall claims. These claims can raise complex factual and legal issues that are subject to risks and uncertainties and could require significant management time. Litigation and other claims against us could result in unexpected expenses and liabilities, which could materially adversely affect our operations and our reputation.
We may be unable to protect our trademarks or other intellectual property rights.
We believe that our trademarks are integral to our boutique design, our e-commerce business and our success in building our brand image and customer loyalty. We rely on trademark registrations and common law trademark rights to protect the distinctiveness of our brand and have registered those trademarks that we believe are important to our business with the United States Patent and Trademark Office. We cannot assure you that these registrations will prevent imitation of our name, merchandising concept, boutique design or private label merchandise, or the infringement of our other intellectual property rights by others. In most cases, the merchandise we sell is purchased on a non-exclusive basis from vendors that also sell to our competitors. While we use our brand name on these items, our competitors may seek to replicate aspects of our business strategy and in-boutique experience, thereby diluting the experience we offer and adversely affecting our brand and competitive position. Imitation of our name, concept, boutique design or merchandise in a manner that projects lesser quality or carries a negative connotation of our brand image could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We are not aware of any claims of infringement upon or challenges to our right to use any of our brand names or trademarks in the United States. Nevertheless, we cannot be certain that the actions we have taken to establish and protect our trademarks will be adequate to prevent imitation of our merchandise by others or to prevent others from seeking to block sales of our merchandise as a violation of the trademarks or proprietary rights of others. Although we cannot currently estimate the likelihood of success of any such lawsuit or ultimate resolution of such a conflict, such a controversy could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. If disputes arise in the future, we may not be able to successfully resolve these types of conflicts to our satisfaction.
We are currently in the process of registering our trademarks in several foreign countries to seek protection outside the United States. However, international protection of our brand image and the use of these marks may be unavailable or could be limited. Also, other entities may have rights to trademarks that contain portions of our marks or may have registered similar or competing marks for merchandise in foreign countries in which our vendors source our merchandise. There may also be other prior registrations of trademarks identical or similar to our trademarks in other foreign countries of which we are not aware. Accordingly, it may be possible for others to prevent the manufacture of our branded goods in certain foreign countries or the sale or exportation of our branded goods from certain foreign countries to the United States. If we were unable to reach a licensing arrangement with these parties, our vendors may be unable to manufacture our merchandise in those countries. Our inability to register our trademarks or purchase or license the right to use our trademarks or logos in these jurisdictions could limit our ability to obtain supplies from less costly markets or penetrate new markets should our business plan change to include selling our merchandise in those foreign jurisdictions.
Litigation may be necessary to protect our trademarks and other intellectual property rights or to enforce these rights. Any litigation or claims brought by us could result in substantial costs and diversion of our resources, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
We may be subject to liability and other risks if we, our vendors or the manufacturers of our merchandise infringe upon the trademarks or other intellectual property rights of third parties, including the risk that we could acquire merchandise from our vendors without the full right to sell it.
We purchase merchandise that may be subject to design copyrights, design patents or otherwise may incorporate protected intellectual property. While we are not involved in the manufacture of any of the merchandise we purchase from our vendors for sale to our customers, we may be subject to liability if our vendors or the manufacturers of our merchandise infringe upon the trademarks or other intellectual property rights of third parties. We do not independently investigate whether our vendors or the manufacturers with whom they do business legally hold intellectual property rights to the merchandise we purchase. Third parties may bring legal claims, or threaten to bring legal claims, against us that their intellectual property rights are being infringed or violated by our use of intellectual property. Litigation or threatened litigation could be costly and distract our senior management from operating our business. If we were to be found liable for any such infringement, we could be required to pay substantial damages and could be subject to injunctions preventing further infringement. In addition, any payments we are required to make and any injunctions with which we are required to comply as a result of infringement claims could be costly and thereby adversely affect our financial results.
| 24 |
If a third party claims to have licensing rights with respect to merchandise we purchased from a vendor, or if we acquire unlicensed merchandise, we may be obligated to remove this merchandise from our boutiques, incur costs associated with this removal if the distributor or vendor is unwilling or unable to reimburse us and be subject to liability under various civil and criminal causes of action, including actions to recover unpaid royalties and other damages and injunctions. Additionally, we will be required to purchase new merchandise to replace any we remove.
We rely upon independent third-party transportation providers for substantially all of our merchandise shipments.
We currently rely upon independent third-party transportation providers for substantially all of our merchandise shipments, including shipments to all of our boutiques and our direct customers. Our use of outside delivery services for shipments is subject to risks, including increases in fuel prices, which would increase our shipping costs, and employee strikes and inclement weather, which may impact a shipper’s ability to provide delivery services that adequately meet our shipping needs. If we change shipping companies, we could face logistical difficulties that could adversely impact deliveries and we would incur costs and expend resources in connection with such change. Moreover, we may not be able to obtain terms as favorable as those received from the independent third-party transportation providers we currently use, which would increase our costs.
Our ability to source our merchandise efficiently and profitably could be hurt if new trade restrictions are imposed or existing trade restrictions become more burdensome.
We currently purchase all our inventory from domestic vendors, who source our merchandise both domestically and internationally. In fiscal years 2011 and 2010, we believe most of the merchandise sourced by our vendors was produced outside the United States. These vendors, to the extent they obtain merchandise from outside of the United States, are subject to trade restrictions, including tariffs, safeguards or quotas, changes to which could increase the cost or reduce the supply of merchandise available to us. Under the World Trade Organization Agreement, effective January 1, 2005, the United States and other World Trade Organization member countries removed quotas on goods from World Trade Organization members, which in certain instances we believe afford our vendors greater flexibility in importing textile and apparel products from World Trade Organization countries from which they source our merchandise. However, as the removal of quotas resulted in an import surge from China, the United States imposed safeguard quotas on a number of categories of goods and apparel from China, and may impose additional quotas in the future. These and other trade restrictions could have a significant impact on our vendors’ sourcing patterns in the future. The extent of this impact, if any, and the possible effect on our purchasing patterns and costs, cannot be determined at this time. We cannot predict whether any of the countries in which our vendors’ merchandise is currently manufactured or may be manufactured in the future will be subject to additional trade restrictions imposed by the United States or foreign governments, nor can we predict the likelihood, type or effect of any restrictions. Trade restrictions, including increased tariffs or quotas, embargoes, safeguards and customs restrictions against items we offer in our boutiques, as well as United States or foreign labor strikes, work stoppages or boycotts, could increase the cost or reduce the supply of merchandise to our vendors, and we would expect the costs to be passed along in increased prices to us, which could hurt our profitability.
We may be subject to sales tax in states where we operate our e-commerce business, which could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Under current state and federal laws, we are not required to collect and remit sales tax in some states where we sell through our e-commerce business. Legislation is pending in some states that may require us to collect and remit sales tax on e-commerce sales or institute use tax reporting. If states pass sales or use tax laws, we may need to collect and remit current and past sales tax and could face greater exposure to income tax and franchise taxes in these states. Any increase in sales tax or use tax reporting on our internet sales could discourage customers from purchasing through our e-commerce business, which could have an adverse effect on growth prospects.
| 25 |
Increases in the minimum wage could have an adverse effect on our financial results.
From time to time, legislative proposals are made to increase the federal minimum wage in the United States, as well as the minimum wage in a number of individual states. Base wage rates for many of our employees are at or slightly above the minimum wage. As federal or state minimum wage rates increase, we may need to increase not only the wage rates of our minimum wage employees, but also the wages paid to our other hourly employees as well. Any increase in the cost of our labor could have an adverse effect on our operating costs, financial condition and results of operations.
As a result of our recent IPO, our costs have increased significantly and our management is required to devote substantial time to complying with public company regulations.
We have historically operated our business as a private company. In July 2011, we completed our IPO. As a result, we are required to incur additional legal, accounting, compliance and other expenses that we did not incur as a private company. We are obligated to file with the SEC annual and quarterly information and other reports that are specified in Section 13 and other sections of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). In addition, we are also subject to other reporting and corporate governance requirements, including certain requirements of The NASDAQ Stock Market, and certain provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (“Sarbanes-Oxley”) and the regulations promulgated thereunder, which impose significant compliance obligations upon us. We must be certain that we have the ability to institute and maintain a comprehensive compliance function; established internal policies; ensure that we have the ability to prepare financial statements that are fully compliant with all SEC reporting requirements on a timely basis; design, establish, evaluate and maintain a system of internal controls over financial reporting in compliance with Sarbanes-Oxley; involve and retain outside counsel and accountants in the above activities and maintain an investor relations function.
Sarbanes-Oxley, as well as rules subsequently implemented by the SEC and The NASDAQ Stock Market, have imposed increased regulation and disclosure and have required enhanced corporate governance practices of public companies. Our efforts to comply with evolving laws, regulations and standards in this regard are likely to result in increased administrative expenses and a diversion of management’s time and attention from revenue-generating activities to compliance activities. These changes require a significant commitment of additional resources. We may not be successful in implementing or maintaining these requirements, any failure of which could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition. In addition, if we fail to implement or maintain the requirements with respect to our internal accounting and audit functions, our ability to continue to report our operating results on a timely and accurate basis could be impaired. If we do not implement or maintain such requirements in a timely manner or with adequate compliance, we might be subject to sanctions or investigation by regulatory authorities, such as the SEC or The NASDAQ Stock Market. Any such action could harm our reputation and the confidence of investors and customers in our company and could materially adversely affect our business and cause our share price to fall.
In the past, a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting had been identified. If material weaknesses or significant deficiencies arise in the future or if we fail to maintain proper and effective internal controls going forward, our ability to produce accurate and timely financial statements could be impaired, which could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
In the past, the company identified a control deficiency that constituted a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting for such period. This material weakness related to accounting for convertible redeemable preferred stock.
A material weakness is a deficiency or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. A significant deficiency is a deficiency, or combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting that is less severe than a material weakness, yet important enough to merit attention by those responsible for oversight of our financial reporting.
We have taken steps to remediate our internal control deficiencies. However, there are no assurances that the measures we have taken to remediate these internal control weaknesses were completely effective or that similar weaknesses will not recur. We plan to continue to assess our internal controls and procedures and intend to take further action as necessary or appropriate to address any other matters we identify.
No material weaknesses were identified for the fiscal years ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010, and, accordingly, we believe that our remediation efforts were successful. However, we did not perform an assessment of our internal control over financial reporting nor did our auditors perform an audit over our internal control over financial reporting; we therefore cannot assure you that these or other similar issues will not arise in future periods. We anticipate that we will next evaluate our internal control over financial reporting in connection with management’s preparation of our financial statements for the fiscal year ending February 2, 2013.
| 26 |
In addition, if we are unable to conclude that we have effective internal control over financial reporting, our independent auditors are unable to provide us with an unqualified report as required by Section 404 of Sarbanes-Oxley or we are required by Section 404 of Sarbanes-Oxley to restate our financial statements, we may fail to meet our public reporting obligations and investors could lose confidence in our reported financial information, which could have a negative impact on the trading price of our stock.
Certain historical financial information included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K has been derived from unaudited financial statements and, as such, may contain errors that might have been detected in an audit. Accordingly, our reported financial results may not be reflective of our actual results for these prior periods.
Our consolidated financial statements as of and for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2007, as well as our consolidated financial statements as of and for the months ended January 31, 2007 and February 2, 2008, have not been audited. The financial data for those periods included in this report is based on management accounts only and has not been reviewed or audited by an independent registered public accounting firm. Although management believes that these unaudited consolidated financial statements have been prepared on a basis that is consistent with our audited consolidated financial statements, there is a risk that this unaudited financial information may contain errors that might have been detected in an audit and such financial information may not be reflective of our true historical results for those periods. Any differences between the financial information presented for these unaudited periods in this report and our actual historical results may be material. Accordingly, you are cautioned not to place undue reliance on such information.
Concentration of ownership among our existing executive officers, directors and principal stockholders may prevent new investors from influencing significant corporate decisions.
Subsequent to the completion of a secondary offering in February 2012, our executive officers, directors and principal stockholders own, in the aggregate, approximately 41% of our outstanding common stock, or approximately 43% assuming the exercise of outstanding options owned by our executive officers and directors. As a result, these stockholders will be able to exercise significant control over all matters requiring stockholder approval, including the election of directors, amendment of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and approval of significant corporate transactions and will have significant control over our management and policies. This concentration of influence could be disadvantageous to other stockholders with interests different from those of our officers, directors and principal stockholders. Currently, three of the eight members of our board of directors are principals of CCMP, one member is Mr. De Meritt, President and Chief Executive Officer of the company and one member is Ms. Kyong Gill, the Executive Vice Chairperson of our board of directors.
As of March 1, 2012, CCMP holds approximately 36% of our outstanding common stock and the Founders collectively hold approximately 9% of our outstanding common stock. As a result of these ownership positions, these stockholders could take actions that have the effect of delaying or preventing a change-in-control of us or discouraging others from making tender offers for our shares, which could prevent stockholders from receiving a premium for their shares. These actions may be taken even if other stockholders oppose them. The concentration of voting power held by CCMP may have an adverse effect on the price of our common stock. The interests of these stockholders may not be consistent with the interests of other stockholders.
CCMP may have conflicts of interest with us in the future.
CCMP owns a substantial amount of our common stock and representatives of CCMP and its affiliates occupy three seats on our board of directors. CCMP is in the business of making investments in companies and may from time to time acquire and hold interests in businesses that compete directly or indirectly with us. In addition, corporate opportunities may arise in the area of potential acquisitions of competitive businesses that may be attractive to us as well as to CCMP or its affiliates.
CCMP and the members of our board of directors who are affiliated with CCMP, by the terms of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, are not required to offer us any transaction opportunity of which they become aware and could take any such opportunity for themselves or offer it to other companies in which they have an investment, unless such opportunity is expressly offered to them solely in their capacity as our directors. The company, by the terms of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, expressly renounces any interest in any such corporate opportunity to the extent permitted under applicable law, even if the opportunity is one that we would reasonably be deemed to have pursued if given the opportunity to do so. Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation cannot be amended to eliminate the company’s renunciation of any such corporate opportunity arising prior to the date of any such amendment. CCMP or its affiliates may also acquire competing businesses that may not be attractive to us, and have no obligation to refrain from acquiring competing businesses. Any competition could intensify if an affiliate or subsidiary of CCMP were to enter into or acquire a business similar to our specialty retail operations. CCMP or its affiliates may enter into or acquire a competing business in the future.
| 27 |
| ITEM 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
| ITEM 2. | PROPERTIES |
We do not own any real property, but rather lease our properties. Our corporate headquarters, warehouse and distribution center are located in an approximately 100,000 square foot facility in Houston, Texas. The buildings in the facility are leased under agreements expiring in 2013, with options to extend for an additional 5 years. Approximately 70,000 square feet are dedicated to warehouse and distribution space, with the balance used as our corporate offices. In December 2011, we entered into a lease for space in a single building near our existing headquarters and distribution facility and expect to relocate our headquarters and distribution facility to the new space by no later than November 1, 2012. We believe that the new facility will be sufficient to support our growth plans for several years. Initially, we will occupy approximately 218,000 square feet, which will house our corporate headquarters, warehouse and distribution facility, including our e-commerce operations and e-commerce fulfillment. The lease for the new facilities includes an option to add as much as an additional 122,000 square feet if necessary. The primary lease on the new facility expires on April 30, 2020; however, we have options to renew the lease for an additional period of up ten years.
As of January 28, 2012, we had 283 boutiques in 41 states and had executed leases for 61 new boutiques we plan to open in fiscal year 2012. In total we have approximately 398,824 gross square feet across all of our boutiques. Our boutiques are leased from third parties with lease terms of five to ten years and many of our lease agreements have additional five-year renewal options. A majority of our leases have early termination clauses, which permit the lease to be terminated by us if certain sales levels are not met in specific periods or if a shopping center does not meet specified occupancy standards. In addition to fixed minimum lease payments, most of our boutique leases provide for additional rental payments based on a percentage of sales if sales at the respective boutiques exceed specified levels. In addition, a majority of our leases also provide for additional payments associated with common area maintenance, real estate, taxes and insurance. In addition, many of our lease agreements have defined escalating rent provisions over the initial term and extensions.
| ITEM 3. | LEGAL PROCEEDINGS |
We are subject to various legal proceedings and claims, including employment claims, wage and hour claims, intellectual property claims, contractual and commercial disputes and other matters that arise in the ordinary course of our business. While the outcome of these and other claims cannot be predicted with certainty, we do not believe that the outcome of these matters will have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations or financial condition.
| ITEM 4. | MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES |
Not applicable.
| 28 |
PART II
| ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Our common stock has been listed on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the symbol “FRAN” since our IPO. Before then, there was no public market for our common stock. As of January 28, 2012, there were approximately 18 holders of record of our common stock. The number of holders of record is based upon the actual number of holders registered at such date and does not include holders of shares in “street names” or persons, partnerships, associates, corporation or other entities identified in security position listing maintained by depositories.
The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the high and low sales prices of our common stock as reported by the NASDAQ Global Select Market:
| High | Low | |||||||
| Second Quarter of Fiscal Year 2011 (July 22, 2011 to July 30, 2011) | $ | 29.75 | $ | 22.46 | ||||
| Third Quarter of Fiscal Year 2011 (July 31, 2011 to October 29, 2011) | $ | 27.37 | $ | 18.51 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter of Fiscal Year 2011 (October 30, 2011 to January 28, 2012) | $ | 26.58 | $ | 15.36 | ||||
Dividend Policy
We did not declare or pay any dividends on our common stock during fiscal years 2011 and 2009. We declared and paid a dividend of $2.39 per share on our common stock (on a fully diluted basis) during November 2010. We have not declared or paid any dividends since our IPO. We currently expect to retain all available funds and future earnings, if any, for use in the operation and growth of our business and do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Any future determination to pay dividends will be at the discretion of our board of directors, subject to compliance with applicable law and any contractual provisions, including under agreements for indebtedness we may incur, that restrict or limit our ability to pay dividends, and will depend upon, among other factors, our results of operations, financial condition, earnings, capital requirements and other factors that our board of directors deems relevant. Because we are a holding company, our ability to pay dividends depends on our receipt of cash dividends from our operating subsidiaries, which may further restrict our ability to pay dividends as a result of the laws of their jurisdiction of organization, agreements of our subsidiaries or covenants under future indebtedness we may incur.
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
The following table sets forth information regarding equity securities authorized for issuance under our equity compensation plans as of January 28, 2012.
| Plan Category | Number of Securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights (a) | Weighted- average Exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights (b) | Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a)) (c) | |||||||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders (1) | 3,185,112 | $ | 8.68 | 2,283,666 | ||||||||
| Equity plan not approved by security holders | - | - | - | |||||||||
| (1) | Approved before our initial public offering. |
| 29 |
Performance Graph
The following graph compares the cumulative stockholder return on our common stock with the return on the Total Return Index for the NASDAQ Global Select Market and the NASDAQ Retail Trade Stocks. The graph assumes $100 invested on July 22, 2011, in the stock of Francesca’s Holdings Corporation, the NASDAQ Global Stock Market, and the NASDAQ Retail Trade Stocks. It also assumes that all dividends are reinvested.
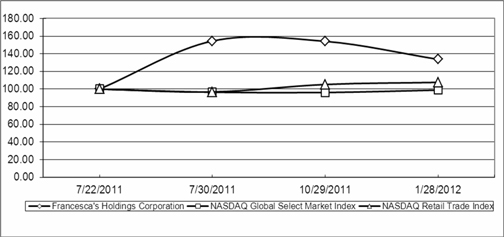
| 7/22/2011 | 7/30/2011 | 10/29/2011 | 1/28/2012 | |||||||||||||
| Francesca's Holdings Corporation | $ | 100.00 | $ | 154.47 | $ | 154.12 | $ | 133.71 | ||||||||
| NASDAQ Global Select Market Index | $ | 100.00 | $ | 96.46 | $ | 96.15 | $ | 98.89 | ||||||||
| NASDAQ Retail Trade Index | $ | 100.00 | $ | 96.82 | $ | 105.26 | $ | 107.62 | ||||||||
The foregoing graph is based on historical data and is not necessarily indicative of future performance.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
Set forth below is information regarding shares of common stock issued by us within the past three years that were not registered under the Securities Act. Also included is the consideration, if any, received by us for such shares and information relating to the section of the Securities Act, or rule of the SEC, under which exemption from registration was claimed.
| (a) | Common Stock |
| · | On February 25, 2010, the Registrant issued 406,000 shares of common stock, as adjusted for the 400-for-1 stock split, to an employee in connection with the exercise of stock options granted pursuant to the Registrant’s 2007 Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| · | On November 11, 2010, the Registrant issued 38,325 shares of common stock to an employee in connection with the exercise of stock options granted pursuant to the Registrant’s 2010 Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| · | On December 16, 2010, the Registrant issued 13,017 shares of common stock to an employee in connection with the exercise of stock options granted pursuant to the Registrant’s 2010 Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| · | On March 29, 2011, the Registrant issued 12,775 shares of common stock to an employee in connection with the exercise of stock options granted pursuant to the Registrant’s 2010 Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| · | On April 1, 2011, the Registrant issued 9,609 shares of common stock to an employee in connection with the exercise of stock options granted pursuant to the Registrant’s 2010 Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| · | On April 5, 2011, the Registrant issued 4,258 shares of common stock to an employee in connection with the exercise of stock options granted pursuant to the Registrant’s 2010 Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| · | On May 9, 2011, the Registrant issued 12,500 shares of common stock to an employee in connection with the exercise of stock options granted pursuant to the Registrant’s 2010 Stock Incentive Plan. |
| 30 |
| · | On May 10, 2011, the Registrant issued 22,259 shares of common stock to certain employees in connection with the exercise of stock options granted pursuant to the Registrant’s 2010 Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| · | On June 1, 2011, the Registrant issued 9,000 shares of common stock to an employee in connection with the exercise of stock options granted pursuant to the Registrant’s 2010 Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| · | On July 21, 2011, the Registrant issued 40,900 shares of common stock to an employee in connection with the exercise of stock options granted pursuant to the Registrant’s 2007 Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| · | On July 21, 2011, the Registrant issued 16,000 shares of common stock to an employee in connection with the exercise of stock options granted pursuant to the Registrant’s 2010 Stock Incentive Plan. |
| (b) | Preferred Stock |
None.
No underwriters were involved in the foregoing issuances of securities. The offers, sales and issuances of the securities described above were deemed to be exempt from registration under the Securities Act in reliance upon Rule 701 of the Securities Act or Section 4(2) of the Securities Act. The offers, sales and issuances of the securities that were deemed to be exempt in reliance on Rule 701 were transactions under compensatory benefit plans and contracts relating to compensation as provided under Rule 701. The offers, sales and issuances of the securities that were deemed to be exempt in reliance upon Section 4(2) were each transactions not involving any public offering, and all recipients of these securities were accredited investors within the meaning of Rule 501 of Regulation D of the Securities Act who were acquiring the applicable securities for investment and not distribution and had represented that they could bear the risks of the investment. Each of the recipients of securities in these transactions had adequate access, through employment, business or other relationships, to information about us.
| ITEM 6. | SELECTED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL AND OPERATING DATA |
The following selected consolidated financial data for each of the years ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010 and the selected consolidated balance sheet data as of January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011 have been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements, which are included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The selected consolidated financial data for the year ended January 31, 2009 and the consolidated balance sheet data as of January 30, 2010 and January 31, 2009 have been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements, which are not included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The selected consolidated financial data and balance sheet for the year ended and as of December 31, 2007 have been derived from our unaudited consolidated financial statements, which are not included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
We operate on a fiscal calendar which, in a given fiscal year, consists of a 52- or 53-week period ending on the Saturday closest to January 31st. The reporting periods contained in our audited consolidated financial statements included in this report contain 52 weeks of operations in fiscal year 2011, which ended January 28, 2012, 52 weeks of operations in fiscal year 2010, which ended January 29, 2011, 52 weeks of operations in fiscal year 2009, which ended January 30, 2010. Our fiscal year 2008 included 52 weeks of operations which ended on January 31, 2009. For fiscal year 2007, which ended on December 31, 2007, the company operated on a fiscal calendar year ending December 31st. The historical results presented below are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for any future period. You should read the selected consolidated financial and operating data for the periods presented in conjunction with “Risk Factors”, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our consolidated financial statements and the related notes, which are included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| 31 |
Consolidated Statements of Operations(1)
| Fiscal Year Ended | Year Ended | |||||||||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | January 31, 2009 | December 31, 2007 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales(2) | $ | 204,158 | $ | 135,176 | $ | 79,367 | $ | 52,290 | $ | 40,210 | ||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs(3) | 97,365 | 65,008 | 37,244 | 25,358 | 19,312 | |||||||||||||||
| Gross profit | 106,793 | 70,168 | 42,123 | 26,932 | 20,898 | |||||||||||||||
| Selling, general, and administrative expense | 63,262 | 40,525 | 24,641 | 19,962 | 14,671 | |||||||||||||||
| Income from operations | 43,531 | 29,643 | 17,482 | 6,970 | 6,227 | |||||||||||||||
| Interest income (expense) | (4,868 | ) | (1,633 | ) | 2 | 4 | 2 | |||||||||||||
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt | (1,591 | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Other income (expense) | 284 | (2 | ) | 38 | 14 | (159 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Income before income tax expense | 37,356 | 28,008 | 17,522 | 6,988 | 6,070 | |||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense | 14,855 | 11,113 | 6,918 | 2,382 | 2,379 | |||||||||||||||
| Net income | 22,501 | 16,895 | 10,604 | 4,606 | 3,691 | |||||||||||||||
| Increase in redemption value of convertible redeemable preferred stock | — | — | (60,271 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Convertible redeemable preferred stock accrued dividends | — | — | (2,022 | ) | (1,641 | ) | (1,703 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to stockholders | $ | 22,501 | $ | 16,895 | $ | (51,689 | ) | $ | 2,965 | $ | 1,988 | |||||||||
| Less: Income attributable to participating securities | — | — | — | (1,038 | ) | (552 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to common stockholders | $ | 22,501 | $ | 16,895 | $ | (51,689 | ) | $ | 1,927 | $ | 1,436 | |||||||||
| Basic earnings (loss) per common share(4) | $ | 0.53 | $ | 0.43 | $ | (1.99 | ) | $ | 0.07 | $ | 0.06 | |||||||||
| Diluted earnings (loss) per common share(4) | $ | 0.52 | $ | 0.41 | $ | (1.99 | ) | $ | 0.07 | $ | 0.06 | |||||||||
| Dividends declared per common share | — | $ | 2.39 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding:(5) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic shares | 42,087 | 39,385 | 26,000 | 26,000 | 26,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Diluted shares | 42,948 | 40,907 | 26,000 | 26,000 | 26,000 | |||||||||||||||
Consolidated Balance Sheet Data(1)
As of Fiscal Year Ended | As of Year Ended | |||||||||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | January 31, 2009 | December 31, 2007 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total current assets | $ | 36,041 | $ | 31,721 | $ | 22,318 | $ | 13,036 | $ | 12,860 | ||||||||||
| Total assets | 72,312 | 59,124 | 31,218 | 16,830 | 14,797 | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt | 22,000 | 87,875 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Total liabilities | 55,410 | 114,592 | 8,242 | 4,556 | 5,107 | |||||||||||||||
| Convertible redeemable preferred stock—series A | — | — | 85,854 | 23,561 | 21,703 | |||||||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) | 16,902 | (55,468 | ) | (62,878 | ) | (11,287 | ) | (12,013 | ) | |||||||||||
| 32 |
Consolidated Balance Sheet Data(1)
As of Fiscal Year Ended | As of Year Ended | |||||||||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | January 31, 2009 | December 31, 2007 | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Comparable boutique sales growth for period(6) | 10.4 | % | 15.2 | % | 9.8 | % | (6.3 | )% | 5.0 | % | ||||||||||
| Number of boutiques open at end of period (not in thousands) | 283 | 207 | 147 | 111 | 78 | |||||||||||||||
| Net sales per average square foot for period (not in thousands)(7) | $ | 554 | $ | 508 | $ | 429 | $ | 384 | $ | 401 | ||||||||||
| Average square feet(8) | 368 | 266 | 185 | 136 | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| Total gross square feet at end of period | 399 | 296 | 210 | 158 | 110 | |||||||||||||||
| (1) | In January 2008, we changed our fiscal year end from December 31st to the Saturday closest to January 31st. The following table presents selected unaudited consolidated financial and other selected data as of and for the months ended February 2, 2008 and January 31, 2007: |
| Month Ended | ||||||||
| February 2, 2008 | January 31, 2007 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Consolidated Statements of Operations Data: | ||||||||
| Net revenues | $ | 2,794 | $ | 1,593 | ||||
| Net loss | (506 | ) | (262 | ) | ||||
| Consolidated Balance Sheet Data: | ||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 14,913 | $ | 8,478 | ||||
| Convertible Redeemable Preferred Stock | $ | 21,920 | $ | — | ||||
| (2) | Net sales plus shipping and handling fees. |
| (3) | Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs includes the direct cost of purchased merchandise, freight costs from our suppliers to our distribution centers and freight costs for merchandise shipped directly from our vendors to our boutiques, allowances for inventory shrinkage and obsolescence, boutique occupancy costs including rent, utilities, common area maintenance, property taxes, depreciation, and boutique repair and maintenance costs and shipping costs related to e-commerce sales. We purchase merchandise from vendors that are considered related party. See note 11 to our consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for more information. |
| (4) | Please see note 2 to our consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for an explanation of per share calculations. |
| (5) | On April 28, 2010, the company authorized a split of its outstanding and authorized common stock in the ratio of four hundred to one. Accordingly, our consolidated financial data included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K have been adjusted to retroactively reflect the effects of the stock split on common shares and per share amounts for all periods presented. |
| (6) | A boutique is included in comparable boutique sales on the first day of the fifteenth full month following the boutique’s opening. When a boutique that is included in comparable boutique sales is relocated, we continue to consider sales from that boutique to be comparable boutique sales. If a boutique is closed for thirty days or longer for a remodel or as a result of weather damage, fire or the like, we no longer consider sales from that boutique to be comparable boutique sales. E-commerce sales are excluded from comparable boutique sales. |
| (7) | Net sales per average square foot are calculated by dividing net sales for the period by the average square feet during the period (see footnote 8 below). |
| (8) | Because of our rapid growth, for purposes of providing sales per square foot measure we use average square feet during the period as opposed to total gross square feet at the end of the period. For periods consisting of more than one fiscal quarter, average square feet is calculated as (a) the sum of the total gross square feet at the beginning of the period and total gross square feet at the end of each fiscal quarter within the period, divided by (b) the number of fiscal quarters within the period plus one (which, for a fiscal year, is five). There may be variations in the way in which some of our competitors and other retailers calculate sales per square foot or similarly titled measures. As a result, data in this report regarding our average square feet and net sales per average square foot for the period may not be comparable to similar data made available by other retailers. |
| 33 |
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations together with “Selected Consolidated Financial and Operating Data” and our consolidated financial statements and the related notes and other financial information and operating data, which are included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Some of the information contained in this discussion and analysis, including information with respect to our plans and strategy for our business, includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. You should review the “Risk Factors” and “Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” sections of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from the results described in or implied by the forward-looking statements contained in the following discussion and analysis.
We operate on a fiscal calendar which, in a given fiscal year, consists of a 52- or 53-week period ending on the Saturday closest to January 31st. The reporting periods contained in our audited consolidated financial statements included in this report contain 52 weeks of operations in fiscal year 2011, which ended January 28, 2012, 52 weeks of operations in fiscal year 2010, which ended January 29, 2011, 52 weeks of operations in fiscal year 2009, which ended January 30, 2010. Our fiscal year 2008 included 52 weeks of operations, which ended on January 31, 2009. For fiscal year 2007, which ended on December 31, 2007, the company operated on a fiscal calendar year ending December 31st. Historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for any future period.
Overview
francesca’s collections® is one of the fastest growing specialty retailers in the United States. Our retail locations are designed and merchandised to feel like independently owned, upscale boutiques and provide our customers with an inviting, intimate and fun shopping experience. We believe we offer compelling value with a diverse and uniquely balanced mix of high-quality, trend-right apparel, jewelry, accessories and gifts at attractive prices. We tailor our assortment to appeal to our core 18-35 year-old, fashion conscious, female customer, although we find that women of all ages are attracted to our eclectic and sophisticated merchandise selection and boutique setting. We carry a broad selection but limited quantities of individual styles and introduce new merchandise to our boutiques five days a week in order to create a sense of scarcity and newness, which helps drive customer shopping frequency and loyalty.
By offering a differentiated shopping experience and high-quality merchandise at a compelling value, our boutiques have been successful across a wide variety of geographic markets and shopping venues. We believe we have an opportunity to continue to grow our boutique base from 283 locations in 41 states as of January 28, 2012 to approximately 900 boutiques in the United States over the next seven to ten years. Our merchandise is also available through our e-commerce website, www.francescascollections.com.
Our company was founded in 1999 by the Founders. We opened our first boutique that same year in Houston, Texas selling fashion jewelry and accessories. In April 2007, the Founders sold a minority ownership interest in the company to BGCP. Early that same year, Mr. De Meritt was appointed the President and Chief Executive Officer of our company. Since 2007, Mr. De Meritt has augmented our strong founding management team with additional highly skilled and deeply experienced executives across key areas of our business. In February 2010, CCMP acquired an approximately 84% controlling interest in the company from the Founders and BGCP (the “CCMP Acquisition”) with the goals of providing liquidity to the Founders and BGCP and supporting Mr. De Meritt and his management team in accelerating our company’s growth. In July 2011, we completed the initial public offering of 11,500,000 shares of our common stock.
Our strong growth and operating results reflect the initiatives taken by our management team which include accelerating the rate of new boutique openings, and further investing in our distribution capability and in our internet site and e-commerce capability, as well as the acceptance of our brand and merchandise as we have expanded into additional regions of the United States. Our net sales increased from $40.2 million in fiscal year 2007 to $204.2 million in fiscal year 2011, a compound annual growth rate of 50.1%. Over the same period, we grew income from operations from $6.2 million to $43.5 million, a compound annual growth rate of 62.6%. While revenue increased at a compound annual growth rate of 50.1%, our total retail square footage growth increased at a compound annual growth rate of 38.1% over that same period, as our boutique sales productivity improved.
Since the beginning of fiscal year 2011, we have increased our boutique base from 207 boutiques to 283 boutiques as of January 28, 2012, an increase of 36.7%. We expect to continue our strong growth in the future. We believe there is a significant opportunity to grow our boutique base to approximately 900 boutiques over the next seven to ten years. We plan to open approximately 75 boutiques per year in fiscal years 2012 and 2013 and one outlet store in fiscal year 2012.
| 34 |
We pursue various initiatives to build brand awareness and create relationships with customers. These initiatives include in-boutique visual merchandising and presentation, periodic promotions including email marketing campaigns, the use of social networks and the building of a customer database.
We continue to invest capital to build the corporate and distribution infrastructure necessary to support our growth. We also continue to invest in our systems infrastructure, including implementation of technology for retail merchandise management, point-of-sale software and software applications to support our e-commerce initiatives. We recently completed the process of upgrading our existing merchandising, warehousing and point-of-sale applications to the latest supported software releases for these applications. During the third quarter of fiscal year 2012, we plan to begin to replace our boutiques’ point-of-sale software and merchandise planning systems. We expect to complete the implementation of our new enterprise technology platform in the first quarter of fiscal year 2013.
In December 2011 we entered into a lease for a space near our existing headquarters and distribution facilities and expect to relocate our headquarters and distribution facilities to the new space by no later than November 1, 2012. We will incur expenses of approximately $0.7 million, or approximately $0.01 per diluted share, in costs for moving, duplicate rent and write-offs of existing leasehold improvements at the existing facilities. Initially, we will occupy approximately 218,000 square feet, which will house our corporate headquarters, warehouse and distribution facility, including our e-commerce operations, and e-commerce fulfillment. The lease for the new facilities includes an option to add as much as an additional 122,000 square feet if necessary. The primary lease term of the new facility expires on April 30, 2020; however, we have options to renew the lease for an additional period of up to ten years. Annual rent expense for the new facility will average approximately $575,000 per year over the primary term of the lease. We believe that the new facility will be sufficient to support the Company’s growth plans for several years.
We are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties many of which are outside of our control and may adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and prospects. These uncertainties and risks include, among others, increases in the cost of raw materials and other inputs used in the production of our merchandise, general economic conditions, the potential lack of success of the malls and other shopping venues in which our boutiques are located, and increased competition as we continue to grow our boutique base. To date, recent increases in the price of cotton, which is used in the production of a portion of our apparel merchandise, have not materially affected our ability to obtain apparel merchandise from our vendors, the prices we pay for such merchandise or the prices we charge our customers for such merchandise. If the price of cotton continues to increase in the future, we may not be able to obtain consistent levels and quality of cotton apparel merchandise or that our sales prices and margins will not be adversely impacted. Any future increases in the price of cotton, or other raw materials used in the production of our merchandise, could materially and adversely impact our results of operations.
How We Assess the Performance of Our Business
In assessing the performance of our business, we consider a variety of performance and financial measures. The key measures for determining how our business is performing are net sales, comparable boutique sales, gross profit, selling, general and administrative expenses and operating income.
Net Sales
Net sales constitute gross sales net of merchandise returns. Net sales consist of sales from comparable boutiques and non-comparable boutiques and sales and shipping revenue from our e-commerce business.
The specialty retail apparel and accessories industry is cyclical, and consequently our net sales are affected by general economic conditions. Purchases of apparel, jewelry, accessories and gift items are sensitive to a number of factors that influence the levels of consumer spending, including economic conditions and the level of disposable consumer income, consumer debt, interest rates and consumer confidence.
Our business is mildly seasonal and as a result, our net sales fluctuate from quarter to quarter. Net sales are usually highest in the fourth fiscal quarter due to the year-end holiday season and lowest in the first fiscal quarter. While December generally experiences the highest level of net sales, January is typically the month with the least net sales. Both months are included in our fourth fiscal quarter.
| 35 |
Comparable Boutique Sales
A boutique is included in comparable boutique sales on the first day of the fifteenth full month following the boutique’s opening, which is when we believe comparability is achieved. When a boutique that is included in comparable boutique sales is relocated, we continue to consider sales from that boutique to be comparable boutique sales. If a boutique is closed for thirty days or longer for a remodel or as a result of weather damage, fire or the like, we no longer consider sales from that boutique to be comparable boutique sales. There may be variations in the way in which some of our competitors and other retailers calculate comparable, “same store” or “same boutique” sales. As a result, data in this report regarding our comparable boutique sales may not be comparable to similar data made available by other retailers. Non-comparable boutique sales is comprised of new boutique sales, e-commerce sales, sales from closed boutiques and other sales not included in comparable boutique sales.
Measuring the change in year-over-year comparable boutique sales allows us to evaluate how our boutique base is performing. Various factors affect comparable boutique sales, including:
| · | consumer preferences, buying trends and overall economic trends; | |
| · | our ability to identify and respond effectively to fashion trends and customer preferences; | |
| · | our ability to provide an assortment of distinctive, high-quality product offerings to generate new and repeat visits to our boutiques; | |
| · | competition; | |
| · | changes in our merchandise mix; | |
| · | changes in pricing and average unit prices; | |
| · | the number of items purchased per transaction or boutique visit; | |
| · | the timing of promotional events and holidays; | |
| · | the timing of introduction of new merchandise and customer acceptance of new merchandise; | |
| · | the level of customer service that we provide in our boutiques; | |
| · | our opening of new boutiques in the vicinity of our existing boutiques; | |
| · | our ability to source and distribute merchandise efficiently; and | |
| · | the number of boutiques we open, close, remodel or relocate in any period. |
Opening new boutiques is an important part of our growth strategy. As we continue to pursue our growth strategy we expect that a significant percentage of our net sales will continue to come from new boutiques not included in comparable boutique sales. Accordingly, comparable boutique sales is only one measure we use to assess the success of our growth strategy. Our rapid pace of new boutique openings may affect the comparability of our results of operations, particularly our comparable boutique sales growth, to similar data made available by other retailers. We also anticipate that sales from our e-commerce business will become a more significant contributor to net sales.
Gross Profit
Gross profit is equal to our net sales less our cost of goods sold and occupancy costs. Gross margin measures gross profit as a percentage of our net sales. Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs includes the direct cost of purchased merchandise, freight costs from our suppliers to our distribution centers and freight costs for merchandise shipped directly from our vendors to our boutiques, allowances for inventory shrinkage and obsolescence, boutique occupancy costs, including rent, utilities, common area maintenance, property taxes, depreciation and boutique repair and maintenance costs, and shipping costs related to e-commerce sales. The components of our cost of goods sold and occupancy costs may not be comparable to the components of cost of goods sold or similar measures of our competitors and other retailers. As a result, data in this report regarding our gross profit and gross margin may not be comparable to similar data made available by our competitors and other retailers.
The variable component of our cost of goods sold and occupancy costs is higher in higher volume quarters because the variable component of our cost of goods sold and occupancy costs generally increases as net sales increase. Changes in the mix of our merchandise sold, such as changes in the percentage of apparel sold, may also impact our overall cost of goods sold and occupancy costs. We review our inventory levels on an ongoing basis to identify slow-moving merchandise, and generally use markdowns to clear that merchandise. The timing and level of markdowns are not principally seasonal in nature but are driven by customer acceptance of our merchandise. If we misjudge the market for our merchandise, we may be faced with significant excess inventories for some merchandise and be required to mark down such merchandise in order to sell them. These markdowns may result in selling merchandise below cost. Markdowns have reduced our gross profit in some prior periods and may have a material adverse impact on our earnings for future periods depending on the extent of the markdown discount and the amount of merchandise affected.
| 36 |
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling expense includes boutique payroll, employee benefits, freight from distribution centers to boutiques, boutique pre-opening expense, credit card merchant fees, costs of maintaining our internet presence and operating our e-commerce business while general and administrative expenses includes payroll and benefits for our headquarters and distribution operations, management incentives, professional fees, travel and administration costs and other expenses related to operations at our corporate headquarters, as well as share-based compensation. While selling expense generally varies proportionally with net sales, general and administrative expenses does not generally vary proportionally with net sales. As a result, general and administrative expenses as a percentage of net sales is usually higher in lower volume quarters and lower in higher volume quarters. The components of our selling, general and administrative expenses may not be comparable to those of our competitors and other retailers. We expect that our selling, general and administrative expenses will increase in future periods due to our continuing growth and in part to additional legal, accounting, insurance and other expenses we expect to incur as a result of being a public company. Among other things, we expect that compliance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and related rules and regulations will result in significant legal and accounting costs.
Share-based compensation expense related to stock options was $4.7 million, $2.4 million and $0.1 million for fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Share-based compensation in fiscal year 2011 included a $2.3 million charge related to the accelerated vesting of certain options in connection with our IPO. We granted options to purchase an aggregate of 882,099, 1,994,430 and 406,000 shares of common stock in fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. These and any future stock option grants will increase our share-based compensation expense in fiscal year 2012 and in future fiscal years compared to fiscal year 2011. See “—Critical Accounting Policies”.
Income from Operations
Income from operations is gross profit less selling, general and administrative expenses. We use operating income as an indicator of the productivity of our business and our ability to manage selling, general and administrative expenses. We believe that our operating income, expressed as a percentage of net sales, compares favorably to other specialty retailers.
Results of Operations
The following table summarizes key components of our results of operations for the periods indicated, both in dollars and as a percentage of net sales:
| Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands, except percentages and number of boutiques) | ||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 204,158 | $ | 135,176 | $ | 79,367 | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs | 97,365 | 65,008 | 37,244 | |||||||||
| Gross profit | 106,793 | 70,168 | 42,123 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 63,262 | 40,525 | 24,641 | |||||||||
| Income from operations | 43,531 | 29,643 | 17,482 | |||||||||
| Interest income (expense) | (4,868 | ) | (1,633 | ) | 2 | |||||||
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt | (1,591 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Other income (expense) | 284 | (2 | ) | 38 | ||||||||
| Income before income tax expense | 37,356 | 28,008 | 17,522 | |||||||||
| Income tax expense | 14,855 | 11,113 | 6,918 | |||||||||
| Net income | $ | 22,501 | $ | 16,895 | $ | 10,604 | ||||||
| Percentage of net sales(4): | ||||||||||||
| Net sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs | 47.7 | % | 48.1 | % | 46.9 | % | ||||||
| 37 |
| Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | ||||||||||
| Gross profit | 52.3 | % | 51.9 | % | 53.1 | % | ||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 31.0 | % | 30.0 | % | 31.0 | % | ||||||
| Income from operations | 21.3 | % | 21.9 | % | 22.1 | % | ||||||
| Interest income (expense) | (2.4 | )% | (1.2 | )% | 0.0 | % | ||||||
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt | (0.8 | )% | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | ||||||
| Other income (expense) | 0.2 | % | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | ||||||
| Income before income tax expense | 18.3 | % | 20.7 | % | 22.1 | % | ||||||
| Income tax expense | 7.3 | % | 8.2 | % | 8.7 | % | ||||||
| Net income | 11.0 | % | 12.5 | % | 13.4 | % | ||||||
| Operating data: | ||||||||||||
| Comparable boutique sales growth for period(1) | 10.4 | % | 15.2 | % | 9.8 | % | ||||||
| Number of boutiques open at end of period | 283 | 207 | 147 | |||||||||
| Net sales per average square foot for period (not in thousands)(2) | $ | 554 | $ | 508 | $ | 429 | ||||||
| Average square feet(3) | 368 | 266 | 185 | |||||||||
| Total gross square feet at end of period | 399 | 296 | 210 | |||||||||
| (1) | A boutique is included in comparable boutique sales on the first day of the fifteenth full month following the boutique’s opening. When a boutique that is included in comparable boutique sales is relocated, we continue to consider sales from that boutique to be comparable boutique sales. If a boutique is closed for thirty days or longer for a remodel or as a result of weather damage, fire or the like, we no longer consider sales from that boutique to be comparable boutique sales. E-commerce sales are excluded from comparable boutique sales. |
| (2) | Net sales per average square foot are calculated by dividing net sales for the period by the average square feet during the period (see footnote 3 below). |
| (3) | Because of our rapid growth, for purposes of providing a sales per square foot measure we use average square feet during the period as opposed to total gross square feet at the end of the period. For periods consisting of more than one fiscal quarter, average square feet is calculated as (a) the sum of the total gross square feet at the beginning of the period and total gross square feet at the end of each fiscal quarter within the period, divided by (b) the number of fiscal quarters within the period plus one (which, for a fiscal year, is five). There may be variations in the way in which some of our competitors and other retailers calculate sales per square foot or similarly titled measures. As a result, data in this report regarding our average square feet and net sales per average square foot for the period may not be comparable to similar data made available by other retailers. |
| The following table summarizes the number of boutiques open at the beginning and the end of the periods indicated: |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
January 28, | January 29, | January 30, | ||||||||||
| Number of boutiques open at beginning of period | 207 | 147 | 111 | |||||||||
| Boutiques added | 76 | 62 | 36 | |||||||||
| Boutiques closed | — | (2 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Number of boutiques open at the end of period | 283 | 207 | 147 | |||||||||
We have determined our operating segments on the same basis that we use internally to evaluate performance. Our reporting segments are our boutiques and e-commerce business, which have been aggregated into one reportable financial segment. We aggregate our operating segments because (i) the merchandise offered at our retail locations and through our e-commerce business is largely the same, (ii) we believe that the majority of our e-commerce customers are also customers of our retail locations and (iii) the merchandise margin of both segments is similar.
Fiscal Year 2011 Compared to Fiscal Year 2010
Net sales
Net sales increased 51.0%, or $69.0 million, to $204.2 million in fiscal year 2011 from $135.2 million in fiscal year 2010. This increase resulted primarily from a 42.1% increase in transaction count, which in turn was primarily attributable to the increase in the number of boutiques in operation, and an increase in the average unit retail price. Comparable boutique sales increased 10.4%, or $12.3 million, while non-comparable boutique sales increased $56.7 million in fiscal year 2011 as compared to prior year. There were 202 comparable boutiques and 81 non-comparable boutiques open at January 28, 2012 compared to 137 and 70, respectively, at January 29, 2011.
| 38 |
| Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | Change | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Apparel | $ | 104,666 | $ | 70,326 | $ | 34,340 | ||||||
| Jewelry | 41,802 | 27,911 | 13,891 | |||||||||
| Accessories | 32,084 | 19,567 | 12,517 | |||||||||
| Gift | 25,602 | 17,367 | 8,235 | |||||||||
| Shipping | 220 | 195 | 25 | |||||||||
| 204,374 | 135,366 | 69,008 | ||||||||||
| Allowance for returns | (216 | ) | (190 | ) | (26 | ) | ||||||
| Net sales | $ | 204,158 | $ | 135,176 | $ | 68,982 | ||||||
The preceding table presents sales by merchandise category. As shown in the table, net sales increased in all of our merchandise categories.
Cost of Goods Sold and Occupancy Costs
Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs increased 49.8%, or $32.4 million, to $97.4 million in fiscal year 2011 from $65.0 million in the fiscal year 2010. Cost of merchandise and freight expenses increased by $20.9 million primarily driven by the increased sales volume. Occupancy costs increased by $10.2 million principally due to the increase in the number of boutiques in operation during fiscal year 2011 compared to fiscal year 2010. Allowance for inventory shrinkage increased by $1.3 million primarily due to increased sales. As a percentage of net sales, cost of goods sold and occupancy costs decreased to 47.7% in fiscal year 2011 from 48.1% in fiscal year 2010. This decrease was principally caused by improved merchandise margin as a result of a shift in sales mix to the higher margin merchandise categories as well as a correction to rent expense amounting to $0.7 million recognized in fiscal year 2010 for rent incurred from time of possession to boutique opening for boutiques opened in prior fiscal years.
Gross Profit
Gross profit increased 52.2%, or $36.6 million, to $106.8 million in fiscal year 2011 from $70.2 million in fiscal year 2010. Gross margin increased 40 basis points to 52.3% for fiscal year 2011 from 51.9% for fiscal year 2010 principally due to improved merchandise margin as a result of a shift in sales mix to the higher margin merchandise categories as well as a correction to rent expense amounting to $0.7 million recognized in fiscal year 2010 for rent incurred from time of possession to boutique opening for boutiques opened in prior fiscal years.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses increased 56.1%, or $22.7 million, to $63.3 million in fiscal year 2011 from $40.5 million in fiscal year 2010. Of the total increase, $11.6 million was attributable to the increase in selling expenses, principally caused by the increase in the number of boutiques in operation in fiscal year 2011 compared to prior year. Specifically, payroll and related expenses increased by $9.8 million, credit card merchant fees increased by $0.9 million and boutique and office supplies expense increased by $0.6 million. General and administrative expenses increased by $11.1 million primarily due to additional costs related to adding corporate office and distribution employees to support the larger boutique base and increased net sales as well as additional costs incurred to meet the ongoing requirements for a public company. Specifically, payroll and related expenses increased by $4.6 million, which includes a $2.3 million increase in stock-based compensation associated with the accelerated vesting of certain options in connection with our IPO; professional fees increased by $2.5 million; software and computer services expense increased by $1.6 million, a part of which is related to the new merchandise system conversion; freight expenses increased by $0.6 million; and travel expense increased by $0.5 million. As a percentage of net sales, selling, general and administrative expenses increased to 31.0% in fiscal year 2011 from 30.0% in fiscal year 2010.
Income from Operations
As a result of the foregoing, income from operations increased 46.8%, or $13.9 million, to $43.5 million, or 21.3% of net sales, in fiscal year 2011 from $29.6 million, or 21.9% of net sales, in fiscal year 2010. This increase was principally due to an increase of $36.6 million in gross profit partially offset by an increase of $22.7 million in selling, general and administrative expenses.
| 39 |
Interest Expense
Interest expense increased 198.1%, or $3.2 million, to $4.9 million in fiscal year 2011 from $1.6 million in fiscal year 2010 primarily due to higher average outstanding balance in fiscal year 2011 compared to fiscal year 2010. We entered into our prior senior secured credit facility on November 17, 2010 and therefore interest expense for fiscal year 2010 only reflects approximately ten weeks of interest related to the said facility. On July 27, 2011, net proceeds from our IPO, together with $41.0 million of indebtedness under our revolving credit facility and $6.8 million of cash on hand, were used to repay the $92.0 million (including accrued interest of $0.6 million) outstanding under our prior senior secured credit facility. Our prior senior secured credit facility was then terminated. During the period it was outstanding, our prior senior secured credit facility had an average interest rate of 7.75%. Initial borrowing under our revolving credit facility was $41.0 million and was subsequently reduced to $22.0 million at January 28, 2012. Our revolving credit facility had an average interest rate of 3.80% in fiscal year 2011.
Loss on Early Extinguishment of Debt
Loss on early extinguishment of debt was $1.6 million in fiscal year 2011 due to the write-off of debt issue costs related to early repayment of our prior senior secured credit facility. We did not incur loss on early extinguishment of debt in fiscal year 2010.
Provision for Income Taxes
The increase in provision for income taxes of $3.7 million in fiscal year 2011 compared fiscal year 2010 was primarily due to an increase in pre-tax income. The effective tax rate of 39.8% in fiscal year 2011 was comparable to the effective tax rate of 39.7% in fiscal year 2010.
Net Income
Net income increased 33.2%, or $5.6 million, to $22.5 million in fiscal year 2011 from $16.9 million in fiscal year 2010. This increase was primarily due to a $36.6 million increase in gross profit, but was partially offset by increases in selling, general and administrative expenses of $22.7 million, interest expense of $3.2 million, loss on early extinguishment of debt of $1.6 million and provision for income taxes of $3.7 million.
Fiscal Year 2010 Compared to Fiscal Year 2009
Net Sales
Net sales increased 70.3%, or $55.8 million, to $135.2 million in fiscal year 2010 from $79.4 million in fiscal year 2009. This increase in net sales resulted from an 82% increase in transaction count, which in turn was primarily attributable to the increase in the number of boutiques in operation during fiscal year 2010 as compared to fiscal 2009. In addition, the increase in net sales was partially driven by a strong growth in our accessories and gift categories. Comparable boutique sales increased 15.2% for fiscal year 2010 compared to fiscal year 2009. Comparable boutique sales increased $10.5 million and non-comparable boutique sales increased $45.3 million, with $33.4 million from boutiques that opened in fiscal year 2010. There were 137 comparable boutiques and 70 non-comparable boutiques open at January 29, 2011 compared to 106 and 41, respectively, at January 30, 2010.
Our net e-commerce sales increased to $1.9 million in fiscal year 2010 from $1.0 million in fiscal year 2009. E-commerce sales increased due to our use of a more robust e-commerce technology platform, expanded marketing efforts to a larger customer base and a growing awareness of francesca’s collections® resulting from growth in our boutique base.
| Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | Change | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Apparel | $ | 70,326 | $ | 45,540 | $ | 24,786 | ||||||
| Jewelry | 27,911 | 16,764 | 11,147 | |||||||||
| Accessories | 19,567 | 8,007 | 11,560 | |||||||||
| Gifts | 17,367 | 8,949 | 8,418 | |||||||||
| 40 |
| Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | Change | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Shipping | 195 | 107 | 88 | |||||||||
| 135,366 | 79,367 | 55,999 | ||||||||||
| Allowance for returns | (190 | ) | — | (190 | ) | |||||||
| Net sales | $ | 135,176 | $ | 79,367 | $ | 55,809 | ||||||
The preceding table was prepared from our internal merchandise system and presents sales by merchandise category. As shown in that table, net sales increased in all of our merchandise categories, but growth was particularly high in the accessories and gift categories. We determined that an allowance for returns was not necessary in fiscal year 2009 because our calculation of the return amount for 2009 based on historical returns was not material for that year.
Cost of Goods Sold and Occupancy Costs
Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs increased 74.5%, or $27.8 million, to $65.0 million in fiscal year 2010 from $37.2 million in fiscal year 2009. Cost of merchandise and freight expenses increased by $18.2 million primarily driven by the increased sales volume. Occupancy costs increased by $8.6 million principally due to the increase in the number of boutiques in operation during fiscal year 2010 as compared to fiscal year 2009. This led to higher fixed boutique-level expenses including rent, utilities, depreciation and common area maintenance. Allowance for shrinkage increased by $1.0 million primarily due to increased sales and inventory levels. As a percentage of net sales, cost of goods sold and occupancy costs increased to 48.1% in fiscal year 2010 from 46.9% in fiscal year 2009 which was primarily caused by a decline in merchandise margin resulting from increased sales of markdown merchandise as a percentage of total sales as well as a correction to rent expense of $0.7 million reflecting rent incurred prior to boutique openings in past fiscal years.
Gross Profit
Gross profit increased 66.6%, or $28.0 million, in fiscal year 2010 to $70.2 million from $42.1 million in fiscal year 2009. Gross margin decreased 116 basis points to 51.9% for fiscal year 2010 from 53.1% for fiscal year 2009. This decrease was primarily attributable to a decline in merchandise margin, which decline was primarily due to sales of markdown merchandise accounting for a larger proportion of net sales in fiscal year 2010 as well as a correction to rent expense of $0.7 million, or 50 basis points of gross margin, for rent incurred from time of possession to boutique opening, for boutiques opened in prior fiscal years.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses increased 64.5%, or $15.9 million, to $40.5 million in fiscal year 2010 from $24.6 million in fiscal year 2009. Of the total increase, $8.9 million was attributable to the increase in selling expense, primarily due to an increase in the number of boutiques in operation during fiscal year 2010, compared to fiscal year 2009, which led to higher overall boutique-level labor expenses and other costs to operate our boutiques. Specifically, payroll and related expenses increased by $6.9 million, credit card merchant fee expense increased by $1.1 million and boutique and office supplies expense increased by $0.5 million. Several smaller changes accounted for the $0.4 million remaining increase. General and administrative expenses increased by $7.0 million due to the cost of adding headquarters and distribution employees to manage the larger boutique base and increased net sales as well as increased management incentives. Payroll and related expenses accounted for $5.9 million of the increase, including an increase of $2.3 million in stock compensation expense, and corporate travel expense increased $0.5 million. The remaining increase consisted of smaller year-to-year changes. As a percentage of net sales, selling, general and administrative expenses decreased to 30.0% in fiscal year 2010 from 31.0% in fiscal year 2009, primarily due to lower boutique-level labor expenses as a percentage of sales. The selling expense portion declined as a percentage of net sales to 17.8% in fiscal year 2010 from 19.0% in fiscal year 2009, while the general and administrative portion increased to 12.2% in fiscal year 2010 from 12.0% in fiscal year 2009.
Income from Operations
As a result of the foregoing, income from operations increased $12.2 million, or 69.6%, to $29.6 million in fiscal year 2010 from $17.5 million in fiscal year 2009. Income from operations was 21.9% of net sales in fiscal year 2010 compared to 22.1% in fiscal year 2009.
| 41 |
Interest Expense, Net
Interest expense, net increased by $1.6 million in fiscal year 2010 compared to fiscal year 2009 because the company made initial borrowings under our prior senior secured credit facility during fiscal year 2010.
Provision for Income Taxes
The increase in provision for income taxes of $4.2 million in fiscal year 2010 from fiscal year 2009 was due primarily to a $10.5 million increase in pre-tax income. The effective tax rate of 39.7% in fiscal year 2010 was comparable to the effective tax rate of 39.5% in fiscal year 2009.
Net Income
Net income increased 59.3%, or $6.3 million, to $16.9 million in fiscal year 2010 from $10.6 million in fiscal year 2009. This increase was due primarily to a $28.0 million increase in gross profit, partially offset by increases in selling, general and administrative expenses of $15.9 million, and a higher provision for income taxes of $4.2 million.
Seasonality
Our business is mildly seasonal in nature and demand is generally the highest in the fourth fiscal quarter due to the year-end holiday season and lowest in the first fiscal quarter. In addition, to prepare for these periods, we must order and keep in stock more merchandise than we carry during other parts of the year. We expect inventory levels, along with an increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses, generally to reach their highest levels in anticipation of the increased net sales during these periods. As a result of this seasonality and generally because of variation in consumer spending habits, we experience fluctuations in net sales and working capital requirements during the year.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Our primary sources of liquidity are cash flows from operations and borrowings under our revolving credit facility. Our primary cash needs are for capital expenditures in connection with opening new boutiques and remodeling existing boutiques, investing in improved technology and distribution facility enhancements, funding normal working capital requirements and payments of interest and principal under our revolving credit facility. We also occasionally use cash or our revolving credit facility to issue letters of credit to support merchandise imports or for other corporate purposes. The most significant components of our working capital are cash and cash equivalents, merchandise inventories, accounts payable and other current liabilities. Our working capital position benefits from the fact that we generally collect cash from sales to customers the day of or, in the case of credit or debit card transactions, within several days of the related sales and we typically have up to 30 days to pay our vendors.
While we believe we have sufficient liquidity and capital resources to meet our current operating requirements and expansion plans, we may elect to pursue additional expansion opportunities within the next year which could require additional debt or equity financing. If we are unable to secure additional financing at favorable terms, or if such financing is unavailable due to credit-market conditions, in order to pursue such additional expansion opportunities, our ability to pursue such opportunities could be materially adversely affected.
We were in compliance with all covenants under our (i) prior senior credit facility at the time it was fully paid off on July 27, 2011 and (ii) revolving credit facility as of January 28, 2012. At January 28, 2012, we had $14.0 million of cash and cash equivalents and $43.0 million in borrowing availability under our revolving credit facility. There were no letters of credit outstanding at January 28, 2012.
For the longer term, we expect that our cash flow from operations along with borrowings under our revolving credit facility and tenant allowances for new boutiques will be sufficient to fund capital expenditures, our working capital requirements and to timely meet the principal and interest requirements under our revolving credit facility.
| 42 |
Cash Flow
A summary of our operating, investing and financing activities are shown in the following table.
| Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Provided by operating activities | $ | 46,471 | $ | 21,020 | $ | 13,277 | ||||||
| Used for investing activities | (16,858 | ) | (16,208 | ) | (5,538 | ) | ||||||
| Used for financing activities | (28,083 | ) | (6,063 | ) | — | |||||||
| Net Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 1,530 | $ | (1,251 | ) | $ | 7,739 | |||||
Operating Activities
Operating activities consist primarily of net income adjusted for non-cash items, including depreciation and amortization, deferred taxes, the effect of working capital changes and tenant allowances received from landlords.
| Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
January 28, | January 29, | January 30, 2010 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 22,501 | $ | 16,895 | $ | 10,604 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 4,936 | 2,377 | 1,215 | |||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense | 4,671 | 2,400 | 99 | |||||||||
| Excess tax benefit from stock-based compensation | (449 | ) | (1,757 | ) | — | |||||||
| Loss on sale of assets | 23 | 25 | — | |||||||||
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt | 1,591 | — | — | |||||||||
| Amortization of debt issuance costs | 537 | 158 | — | |||||||||
| Deferred income tax | 721 | (2,685 | ) | (833 | ) | |||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities: | ||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable | 1,898 | (3,557 | ) | (126 | ) | |||||||
| Inventories | (2,729 | ) | (5,581 | ) | (794 | ) | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | (309 | ) | (1,549 | ) | (573 | ) | ||||||
| Accounts payable | 2,481 | 3,443 | 1,434 | |||||||||
| Accrued liabilities | (566 | ) | 3,874 | 1,007 | ||||||||
| Deferred and accrued rents | 6,667 | 5,999 | 1,440 | |||||||||
| Income taxes payable | 4,498 | 978 | (196 | ) | ||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 46,471 | $ | 21,020 | $ | 13,277 | ||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities was $46.5 million and $21.0 million for fiscal years 2011 and 2010, respectively. The increase in cash provided by operating activities in both fiscal years was primarily due to higher net income as a result of our significant sales growth, adjusted for non-cash expenses, including depreciation and amortization, deferred income taxes and stock-based compensation expense in both fiscal years and, in fiscal year 2011, loss on early extinguishment of debt.
Net working capital increased $4.3 million in fiscal year 2011 as merchandise inventory increased in connection with both new as well as existing boutiques; and prepaid assets increased as a result of higher prepaid rent and prepaid insurance. Those working capital increases were partially offset by increases in accounts payable and accrued liabilities in connection with the increase in the number of boutiques in operation as well as a decrease in accounts receivable principally due to collection of tenant allowances. During fiscal year 2010, net working capital decreased $3.1 million primarily as a result of increases in accounts payable and accrued liabilities partially offset by increases in merchandise inventory, accounts receivable, prepaid rent and prepaid insurance. Those changes were principally caused by the increase in the number of boutiques in operation in fiscal year 2010 as compared to fiscal year 2009.
| 43 |
Merchandise inventory increased $2.7 million and $5.6 million in fiscal years 2011 and 2010, respectively, in preparation for new boutique openings, and in anticipation of sales increases in comparable boutiques in the following fiscal year. We estimate inventory levels and capital requirements based on historical boutique sales performance and new boutique opening plans as well as planned merchandise assortment. To the extent that inventory levels substantially increase, we may rely upon various promotional events or pricing strategies to sell through the inventory levels.
Investing Activities
Investing activities consist primarily of capital expenditures for new boutiques, improvements to existing boutiques, as well as investment in information technology and our distribution facility.
| For the Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | ||||||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures for: | ||||||||||||
| New boutiques | $ | 13,267 | $ | 13,176 | $ | 4,872 | ||||||
| Existing boutiques | 748 | 850 | 153 | |||||||||
| Technology | 2,630 | 1,708 | 94 | |||||||||
| Corporate and distribution | 249 | 474 | 419 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of property and equipment | (36 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | $ | 16,858 | $ | 16,208 | $ | 5,538 | ||||||
Our total capital expenditures for fiscal years 2011 and 2010 were $16.9 million and $16.2 million, respectively, with new boutiques accounting for most of our spending at $13.3 million and $13.2 million over the same period. Spending for new boutiques included amounts associated with boutiques that will open within the subsequent fiscal year. The company opened 76 boutiques in fiscal year 2011 compared to 62 boutiques in fiscal year 2010. The average cost of the leasehold improvements, furniture and fixtures, excluding tenant allowances, for new boutiques opened in fiscal year 2011 and 2010 was $180,000 and $170,000, respectively. The increase in the average capital expenditures for new boutiques was primarily due to an increase in the cost of leasehold improvements, signage and technological enhancements. We expect that costs of opening new boutiques will continue to increase in future years. However, we expect that any such increases will not be material and should not adversely impact our expansion plans or pay back and return on our net investment. The average tenant allowance per new boutique was $81,000 and $72,000 in fiscal years 2011 and 2010, respectively while total cash inflows from tenant allowances totaled $7.8 million and $5.0 million over the same period. Tenant allowances are amortized as a reduction in rent expense over the term of the lease. The average collection period for these allowances is approximately six months after boutique opening. As a result, we fund the cost of new boutiques with cash flow from operations, build-out allowances from our landlords, or borrowings under our revolving credit facility. See discussion under “—Revolving Credit Facility”. The remaining capital expenditures of $3.6 million in fiscal year 2011, $3.0 million in fiscal year 2010 and $0.7 million in fiscal year 2009 were primarily for investments in information technology, our corporate offices and for distribution facility enhancements.
Management anticipates that capital expenditures in fiscal year 2012 will be approximately $20.0 million to $22.0 million, including approximately $14.0 million to $16.0 million in connection with new boutique openings. Our technology initiatives are expected to require capital investment of approximately $1.7 million to $2.2 million during fiscal year 2012. We also expect to spend approximately $3.7 million in connection with the relocation of our headquarters and distribution facility to a nearby existing building. The remaining capital expenditures are expected to be used for miscellaneous investments in our existing boutiques, corporate offices and for distribution center enhancements.
We expect that our cash flow from operations along with borrowings under our revolving credit facility and tenant allowances for new boutiques will be sufficient to fund capital expenditures for new boutiques, our technology initiatives including our planned merchandise planning and point-of-sale upgrades, improvements to our corporate offices and distribution facility.
Financing Activities
Financing activities consist principally of borrowings and payments under our prior senior secured credit facility and our revolving credit facility as well as distributions to our stockholders and proceeds from our IPO.
| 44 |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of stock in initial public offering, net of costs | $ | 44,245 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| Proceeds from borrowings under the new revolving credit facility | 41,000 | — | — | |||||||||
| Proceeds from borrowings under the prior senior secured credit facility | — | 95,000 | — | |||||||||
| Repayment of borrowings from under the new revolving credit facility | (19,000 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Repayment of borrowings from under the prior senior secured credit facility | (93,813 | ) | (1,187 | ) | — | |||||||
| Dividends | — | (100,000 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Excess tax benefit from stock-based compensation | 449 | 1,757 | — | |||||||||
| Payment of debt issuance costs | (1,468 | ) | (2,137 | ) | — | |||||||
| Proceeds from the exercise of stock options | 504 | 504 | — | |||||||||
| Net cash (used by) provided by financing activities | $ | (28,083 | ) | $ | (6,063 | ) | $ | — | ||||
Net cash used for financing activities was $28.0 million in fiscal year 2011. On July 27, 2011, we completed our IPO which resulted in net proceeds to us of $44.2 million, after deducting an underwriting discount of $3.5 million and related fees and expenses of $2.3 million. The net proceeds from the offering together with $41.0 million of indebtedness under our revolving credit facility and $6.2 million of cash on hand, were used to repay the $91.4 million principal balance outstanding under the prior senior secured credit facility. Prior to the repayment, we also made the required quarterly principal payment totaling $2.4 million under our prior senior secured credit facility. In connection with our revolving credit facility, we paid $1.5 million of debt issue costs to be amortized over the term of the facility. Subsequent to the completion of our IPO, we made principal payments totaling $19.0 million on our revolving credit facility. Finally, we received cash proceeds of $0.5 million and recorded tax benefit of $0.4 million related to stock option exercises in fiscal year 2011.
During fiscal year 2010, net cash used for financing activities totaled $6.1 million. This included net proceeds of $95.0 million from borrowings under our prior senior secured credit facility, offset by the payment of a $100.0 million cash dividend and the repayment of $1.2 million of indebtedness outstanding under our prior senior secured credit facility.
Revolving Credit Facility
On July 27, 2011, Francesca’s Collections, Inc., our wholly-owned indirect subsidiary, entered into a revolving credit facility in the aggregate amount of $65.0 million that matures on July 27, 2016. The revolving credit facility includes borrowing capacity available for letters of credit. At January 28, 2012, we had $43.0 million in borrowing availability under our revolving credit facility.
All obligations under the revolving credit facility are unconditionally guaranteed by, subject to certain exceptions, Francesca’s LLC, our wholly-owned direct subsidiary and the parent of Francesca’s Collections, Inc., and each of Francesca’s Collections’ existing and future direct and indirect wholly owned domestic subsidiaries. There are currently no subsidiary guarantors for the revolving credit facility because Francesca’s Collections does not currently have any subsidiaries. All obligations under the revolving credit facility, and the guarantees of those obligations (as well as cash management obligations and any interest rate hedging or other swap agreements), are secured by substantially all of Francesca’s Collections’ assets as well as the assets of any subsidiary guarantor.
The borrowings under the revolving credit facility bear interest at a rate equal to an applicable margin plus, at our option, either (a) in the case of base rate borrowings, a rate equal to the highest of (1) the prime rate of Royal Bank of Canada, (2) the federal funds rate plus 1/2 of 1%, and (3) the LIBOR for an interest period of one month plus 1.00%, or (b) in the case of LIBOR borrowings, a rate equal to the higher of (1) 1.50% and (2) the LIBOR for the interest period relevant to such borrowing. The applicable margin for borrowings under the revolving credit facility ranges from 1.25% to 2.25% with respect to base rate borrowings and from 2.25% to 3.25% with respect to LIBOR borrowings, in each case based upon the achievement of specified levels of a ratio of consolidated total debt to consolidated EBITDA. Additionally, we are required to pay a fee to the lenders under the revolving credit facility on the un-borrowed amount at a rate ranging from 0.25% to 0.45%, based on the achievement of specified levels of a ratio of consolidated total debt to consolidated EBITDA. We are also required to pay customary letter of credit fees.
| 45 |
The revolving credit facility contains customary affirmative and negative covenants, including limitations on the ability of Francesca’s Collections and its subsidiaries, to (i) incur additional debt; (ii) create liens; (iii) make certain investments, loans and advances; (iv) sell assets; (v) pay dividends or make distributions or make other restricted payments; (vi) prepay other indebtedness; (vii) engage in mergers or consolidations; (viii) change the business conducted by Francesca’s Collections and its subsidiaries; (ix) engage in certain transactions with affiliates; (x) enter into agreements that restrict dividends from subsidiaries; and (xi) amend certain charter documents and material agreements governing subordinated and junior indebtedness.
In addition, the revolving credit facility requires Francesca’s Collections to comply with the following financial covenants:
| Ÿ | A maximum ratio of (i) lease-adjusted consolidated total debt (as defined in the credit agreement) to (ii) consolidated EBITDA of 4.25 to 1.00. | |
| Ÿ | A minimum ratio of (i) consolidated EBITDA to (ii) interest expense of 4.00 to 1.00. | |
| Ÿ | Maximum capital expenditures of $25.0 million per fiscal year, with any unused portion allowed to be carried over to the next two fiscal years subject to a 50.0% cap. |
We are in compliance with the financial covenants under our revolving credit facility as of January 28, 2012 and our consolidated total lease adjusted leverage ratio and consolidated interest coverage ratio were 1.66 to 1.00 and 9.68 to 1.00, respectively, as of that date. Further, Francesca’s Collections’ ability to pay dividends is subject to restrictions including a maximum secured leverage ratio. If Francesca’s Collections’ debt under the revolving credit facility exceeds that ratio, it is restricted from paying dividends. At January 28, 2012, this ratio was within the required limit, thus, Francesca’s Collections would have been allowed to pay dividends.
The revolving credit facility also contains customary events of default, including: (i) failure to pay principal, interest, fees or other amounts under the revolving credit facility when due taking into account any applicable grace period; (ii) any representation or warranty proving to have been incorrect in any material respect when made; (iii) a cross default with respect to other material indebtedness; (iv) bankruptcy and insolvency events; (v) unsatisfied material final judgments; (vi) a “change of control”; (vii) certain defaults under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974; (viii) the invalidity or impairment of any loan document or any security interest; and (ix) the subordination provisions of any material subordinated debt or junior debt shall cease to be in full force.
Prior Senior Secured Credit Facility
On November 17, 2010, Francesca’s Collections entered into a $100.0 million senior secured credit facility with a syndicate of financial institutions. The prior senior secured credit facility consisted of a $95.0 million term loan facility and a $5.0 million revolving credit facility, each with a scheduled maturity date of November 17, 2013. On July 27, 2011, net proceeds from our IPO, together with $41.0 million of indebtedness under our revolving credit facility and $6.8 million of cash on hand, were used to repay the $92.0 million (including accrued interest of $0.6 million) outstanding under the prior senior secured credit facility. The prior senior secured credit facility was then terminated. We wrote-off the unamortized debt issuance costs of $1.6 million associated with the prior senior secured credit facility and reported a loss on early extinguishment of debt in such amount. During the period amounts were outstanding under the prior senior secured credit facility, it accrued interest at the rate of 7.75%. We were in compliance with the financial covenants under the prior senior secured credit facility.
Critical Accounting Policies
Management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations is based upon our consolidated financial statements which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. The preparation of these financial statements requires estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of our assets, liabilities, net sales and expenses, and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. Management bases estimates on historical experience and other assumptions it believes to be reasonable given the circumstances and evaluates these estimates on an ongoing basis. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
We believe that the following critical accounting policies involve a higher degree of judgment and complexity. See note 1 to our consolidated financial statements which are included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a complete discussion of our significant accounting policies. The following reflect the significant estimates and judgments used in the preparation of our consolidated financial statements.
| 46 |
Revenue Recognition
We recognize revenue upon purchase of merchandise by customers, net of estimated merchandise returns and discounts. Revenue is recognized, for boutique sales, at the point at which the customer receives and pays for the merchandise at the register. For on-line sales, revenue is recognized upon delivery and includes shipping charges. Management estimates future returns on previously sold merchandise based on return history and current sales levels. The estimated sales returns are periodically compared to actual sales returns and adjusted, if appropriate. For fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009, we recognized $0.2 million, $0.2 million and zero, respectively, of allowance for merchandise returns. We do not believe that there is a reasonable likelihood that there will be material changes in future estimates or assumptions we use to calculate our merchandise return reserve. However, if the actual rate of merchandise returns increases significantly, our operating results may be adversely affected.
Gift Cards and Gift Card Breakage
We account for the sale of gift cards as a liability at the time a gift card is sold. The liability is relieved and revenue is recognized upon redemption of the gift card. Our gift cards do not have an expiration date. We will recognize income from the breakage of gift cards when the likelihood of redemption of the gift card is remote based on historical redemption patterns. We have not accumulated adequate historical data to reasonably estimate the amount of gift cards that will never be redeemed. Consequently, we have not recognized gift card breakage income in fiscal years 2011, 2010 or 2009. We do not anticipate recognizing gift card breakage until we accumulate additional data beyond fiscal year 2011.
Inventory Valuation
We value merchandise inventory at the lower of cost or market on a weighted average cost basis. Inventory costs include freight-in. We record merchandise receipts at the time they are delivered to our distribution center or to our boutiques from vendors.
We review our inventory levels to identify slow-moving merchandise and generally use promotional markdowns to clear slow-moving merchandise. Each period we evaluate recent selling trends and the related promotional events or pricing strategies in place to sell through the current inventory levels. Promotional markdowns or additions to the lower of cost or market reserve may occur when inventory exceeds customer demand for reasons of style, seasonal adaptation, changes in customer preference, lack of consumer acceptance of fashion items, competition or if it is determined that the inventory in stock will not sell at its currently ticketed price. Such markdowns may have an adverse impact on earnings, depending on the extent and amount of inventory affected. The anticipated deployment of new merchandise is reflected within the estimated future promotional markdown plan, as such new inventory in certain circumstances will displace merchandise currently on-hand. Additions to the lower of cost or market reserve are recorded as an increase to cost of goods sold and occupancy costs in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
We also estimate an inventory shrinkage reserve for the period of time between the last physical inventory count and the balance sheet date. The estimate for shrinkage reserve can be affected by changes in merchandise mix and changes in actual shrinkage trends.
Impairment of Long-lived Assets
We evaluate long-lived assets held for use and held for sale whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of those assets may not be recoverable. Assets are grouped and evaluated for impairment at the lowest level for which there are identifiable cash flows, which is generally at a boutique level. Boutique assets are reviewed for impairment using factors including, but not limited to, our future operating plans and projected cash flows. The determination of whether an impairment has occurred is based on an estimate of undiscounted future cash flows directly related to that boutique, compared to the carrying value of the assets. We recognize impairment if the sum of the undiscounted future cash flows of a boutique does not exceed the carrying value of the assets. For impaired assets, we recognize a loss equal to the difference between the net book value of the asset and its estimated fair value. Fair value is based on discounted future cash flows of the asset using a discount rate commensurate with the risk. In addition, at the time a decision is made to close a boutique, we accelerate depreciation over the revised useful life of the asset. Based on the analysis performed, there was no impairment for each of the fiscal years ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010.
| 47 |
Income Taxes
We account for income taxes using the liability method. Under this method, the amount of taxes currently payable or refundable is accrued, and deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future tax consequences of temporary differences that currently exist between the tax basis and the financial reporting basis of the company’s assets and liabilities. Valuation allowances are established against deferred tax assets when it is more-likely-than-not that the realization of those deferred tax assets will not occur.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using the enacted tax rates in effect in the years when those temporary differences are expected to reverse. The effect on deferred taxes from a change in tax rate is recognized through continuing operations in the period that includes the enactment date of the change. Changes in tax laws and rates could affect recorded deferred tax assets and liabilities in the future.
A tax benefit from an uncertain tax position may be recognized when it is more-likely-than-not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including resolutions of any related appeals or litigation processes, based on the technical merits. Income tax positions must meet a more-likely-than-not recognition threshold to be recognized.
We recognize tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions and adjust these liabilities when the company’s judgment changes as a result of the evaluation of new information not previously available. Due to the complexity of some of these uncertainties, the ultimate resolution may result in a payment that is materially different from the current estimate of the tax liabilities. These differences will be reflected as increases or decreases to income tax expense and the effective tax rate in the period in which the new information becomes available. Interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits are recognized in income tax expense. There were no uncertain tax positions or related interest or penalties requiring accrual at January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011.
Stock-based Compensation
In connection with our stock based compensation plans, our board of directors considers the estimated fair value of the company’s stock when setting the stock option exercise price as of the date of each grant. Prior to our IPO, because the company was privately held and there was no public market for our common stock, the fair market value of our common stock was determined by our board of directors at the time the option grants were awarded. In determining the fair value of our common stock, the board of directors considered such factors as the company’s actual and projected financial results, the consideration paid by third party investors in the company, including, investments by BGCP and CCMP in arm’s length transactions for their respective investment and controlling investment in the company, the principal amount of the company’s indebtedness, valuations of the company performed by third parties and other factors it believed were material to the valuation process. To the extent financial projections and anticipated boutique openings did not materially change from the date of the BGCP Acquisition or the CCMP Acquisition through date of a stock option grant, our board of directors concluded that the per share price of our common stock related to each of the acquisition transactions represented the most accurate estimate of the fair value of our common stock for purpose of setting the respective option exercise price as of the date of such grant. Additionally, for these grants, in making its determination of fair value our board of directors did not apply control premium or marketability considerations. To timely secure the necessary talent we require to support our growth, our board of directors took into account a number of factors, including utilizing the most recent third-party valuation study available to help establish the exercise price for the applicable grant. Our board of directors did not believe it was necessary to obtain third-party valuation studies as of the date of each option grant; however, for purposes of stock-based compensation expense recognition, we used then-current third-party valuation studies.
Following our IPO, our board of directors determines the exercise price of stock options based on the closing price of our common stock on the grant date.
We account for stock-based compensation in accordance with FASB ASC 718, “Compensation-Stock Compensation”, which establishes accounting for equity instruments exchanged for employee services. Under the provisions of this statement, stock-based compensation cost is measured at the grant date fair value and is recognized as an expense over the employee’s requisite service period (based on the vesting period of the equity grant). As required under this guidance, we estimate forfeitures for options granted which are not expected to vest. Changes in these inputs and assumptions can materially affect the measurement of the estimated fair value of our stock-based compensation expense. We estimate the grant date fair value of stock option awards using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. For fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009, the fair value of stock options was estimated at the grant date using the following assumptions:
| 48 |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
January 28, | January 29, | January 30, | ||||||||||
| Expected volatility | 54.19% – 69.92 | % | 54.21% – 60.59 | % | 85.43 | % | ||||||
| Risk-free interest rate | 1.08% – 2.11 | % | 1.63% – 3.24 | % | 0.90 | % | ||||||
| Weighted average term | 6.00 – 6.50 | 6.27 – 6.50 | 2.00 | |||||||||
| Expected dividend yield | — | — | — | |||||||||
The risk-free interest rate was determined based on the rate of Treasury instruments whose maturities are similar to those of the expected term of the award being valued. The expected dividend yield was based on our expectations of not paying dividends on our common stock for the foreseeable future. The expected volatility incorporates historical volatility of similar entities whose shares prices are publicly available.
Stock-based compensation expense related to stock options was $4.7 million, $2.4 million and $0.1 million for fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Stock-based compensation in fiscal year 2011 included a $2.3 million charge related to the accelerated vesting of certain options in connection with our IPO. We granted options to purchase an aggregate of 882,099, 1,994,430 and 406,000 of shares of our common stock in fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. These grants and any future stock option grants will likely increase our stock-based compensation expense in fiscal year 2012 and in future fiscal years compared to fiscal year 2011.
As of January 28, 2012, we had outstanding vested options to purchase approximately 1,436,392 shares of common stock, at a weighted average exercise price of $4.74 per share and outstanding unvested options to purchase 1,748,720 shares of common stock, at a weighted average exercise price of $11.92 per share. The per share value of each share of common stock underlying the vested and unvested options at the dates of the grant of the options range from $1.43 to $22.69 per share.
2007 Stock Incentive Plan
We granted options to acquire 1,006,000 shares of our common stock under the 2007 plan. The exercise price for options to acquire our common stock granted under the 2007 plan were determined based on, among other factors, the per share enterprise value paid by BGCP for its acquisition of a 35% interest in the company in April 2007 (“BGCP Acquisition”) and third-party valuation reports. The per share price paid in the BGCP Acquisition was negotiated in an arm’s length transaction. Below is a description of the specific grants of options to acquire our common stock in 2008 and 2009 and the factors that were specifically considered at each grant date.
| Ÿ | During April of 2008, we granted options to acquire 100,000 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $1.43 per share. The exercise price for this grant equaled the per share price paid in the BGCP Acquisition in April 2007. Our board used a market based methodology to determine the exercise price per share based on the sale price paid in the BGCP Acquisition. No adjustment was made for lack of marketability discount. A third-party valuation study as of January 31, 2009 obtained for financial accounting purposes concluded that the fair value of the common stock was $0.34 per share which was substantially lower than the exercise price of $1.43 per share we used for this grant. We did not make any adjustment to the original exercise price as a result of the conclusions reached in the third-party valuation study. Nevertheless, the compensation expense recognized in connection with this option grant was computed using the common stock fair value of $0.34 per share and the exercise price of $1.43 per share as of the grant date. |
| Ÿ | On October 5, 2009, we granted options to acquire 406,000 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $0.34 per share. The exercise price for this grant was determined based on a third-party valuation study as of January 31, 2009, which for financial accounting purposes concluded that the fair value of our common stock as of January 31, 2009 was $0.34 per share. The third-party valuation study dated January 31, 2009 was the most recent third-party valuation study available as of the October 5, 2009 grant date. To timely secure the services of the applicable grantee we used this third-party valuation study to set the applicable option exercise price as that was the only third-party valuation study available at such time. After making the October 5, 2009 grant, we received a third-party valuation study as of October 31, 2009, which for financial accounting purposes concluded that the fair value of our common stock as of October 31, 2009 was $3.01 per share. We believe that the increase in per share value was primarily due to boutique openings, increased sales and overall improvement in our performance resulting in increased EBITDA. Additionally, comparable public company business enterprise values to EBITDA multiples used in the valuation increased. We did not make any adjustment to the original option exercise price for the October 5, 2009 option grant after receiving the third-party valuation study as of October 31, 2009. Nevertheless, the compensation expense recognized in connection with the October 5, 2009 option grant was computed using the common stock fair value of $3.01 per share and the exercise price of $0.34 per share as of the grant date. For the two third-party valuation reports as of January 31, 2009 and October 31, 2009, we used a discount of 41% and 44% respectively, for lack of marketability of our common stock in determining the fair value of $0.34 per share and $3.01 per share. |
| 49 |
The following table sets forth all stock option grants to acquire our common stock granted during 2008 and 2009 under the 2007 Stock Incentive Plan.
| Grant Date | Number of Options Granted | Exercise Price Per Share | Common Stock Fair Value per Share at Grant Date | Third-Party Valuation Date | Vesting Period (Years) | Weighted Average Stock Option Fair Value(1) | ||||||||||||||||||
| April 1, 2008 | 100,000 | $ | 1.43 | $ | 0.34 | January 31, 2009 | 5 | $ | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||
| October 5, 2009 | 406,000 | $ | 0.34 | $ | 3.01 | October 31, 2009 | 4 | $ | 2.69 | |||||||||||||||
| (1) | The stock option fair value was determined using a third party valuation study. |
The valuation studies as of January 31, 2009 and October 31, 2009 used the following methodologies to determine the value of our equity: (i) the January 31, 2009 valuation study used a combination of the income approach and the market approach (with each method being assigned a weighting of 50%); and (ii) the October 31, 2009 valuation study used the market approach.
Generally, the income approach focused on the income-producing capability of the company, by calculating the present value of future net cash flows to be generated by us. We developed indications of value by discounting our expected cash flows to the present value at a rate of return that considered the risk related to an investment in the company. The discount rate selected was based on our weighted average cost of capital. Our weighted average cost of capital was calculated by analyzing the cost of our equity and the cost of our debt (with our equity being weighted 98.05% and our debt being weighted 1.95%).
The market approach is a general way of determining the value of a business ownership interest, security or asset by using one or more methods that compare the subject business’ ownership interest, security or asset to similar businesses, ownership interests, securities or assets that have been sold. In the valuation of our equity interests, we applied the market approach by utilizing the guideline public company method.
The guideline public company method compares the subject entity to guideline publicly traded entities (that is, publicly traded entities operating in a generally similar industry to the subject entity). In applying this method, we determined our value based on a multiple of our EBITDA. In determining the appropriate multiple to apply to our EBITDA, we reviewed the business enterprise value to EBITDA multiples of the guideline companies.
In consultation with our valuation consultant we considered factors, such as control vs. minority interest as well as the lack of marketability with respect to our equity in determining the appropriate discount to be applied to the value of our stock. Ultimately, we elected to apply a marketability discount to the value of our stock. The valuation studies as of January 31, 2009 and October 31, 2009 used an option-based methodology in determining the marketability discounts (41% and 44%, respectively). Using the option-based methodology, we determined the appropriate discount based on the value of a put option with respect to the company’s stock (such value being determined based on the Black-Scholes option-pricing model).
During the period between the BGCP Acquisition in April of 2007, and the January 31, 2009 valuation of our stock, our comparable boutique sales were negative. Additionally, during fiscal year 2008 general business conditions affecting the specialty retail industry were negative along with overall economic conditions. Accordingly, the valuation study as of January 31, 2009 reflected a substantial contraction in EBITDA multiples for the retail industry peer group against which we compared our equity valuation during such period.
During the period between the January 31, 2009 valuation of our stock and the October 31, 2009 valuation of our stock, general economic conditions improved and our comparable boutique sales increased. We believe that the increase in per share value during fiscal year 2009 (as reflected in the October 31, 2009 valuation study) was primarily due to new boutique openings, increased sales and overall improvement in our performance, resulting in increased EBITDA. The valuation study as of October 31, 2009 reflected a substantial growth in EBITDA multiples for the retail industry peer group against which we compared our equity valuation during such period. Hence, comparable public company business enterprise values to EBITDA multiples used in the valuation increased.
| 50 |
2010 Stock Incentive Plan
We granted options to acquire 1,994,430 shares of our common stock under the 2010 plan. The exercise price for options granted under the 2010 plan were determined based on, among other factors, the per share enterprise value paid by CCMP for its acquisition of approximately 84% interest in the company in February 2010 (“CCMP Acquisition”) and third-party valuation reports. The per share price paid in the CCMP Acquisition was negotiated in an arm’s length transaction. In establishing the exercise price for options granted during March, May and July 2010, our board of directors concluded that no material change in the financial condition of the company had occurred since the closing of the CCMP Acquisition to warrant an adjustment in the exercise price for these grants. Below is a description of the specific grants of options to acquire our common stock during 2010 and the factors that were specifically considered at each grant date.
| Ÿ | During March of 2010, we granted options to acquire 1,062,400 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $6.13 per share. The exercise price for this grant was equal to the per share price paid in the CCMP Acquisition in February 2010. Our board used a market based methodology to determine the exercise price per share based on the sale price paid in the CCMP Acquisition. Projected sales and anticipated new boutique openings were consistent at March 2010 with sales and growth projections as of February 2010; which validated the use of the CCMP Acquisition price. No adjustment to the exercise price was made for lack of control or lack of marketability discount. |
| Ÿ | During May of 2010, we granted options to acquire 400,000 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $6.13 per share. The exercise price for this grant was equal to the per share price paid in the CCMP Acquisition. Our board used a market based methodology to determine the exercise price per share based on the sale price paid in the CCMP Acquisition. Projected sales and anticipated new boutique openings were consistent at May 2010 with sales and growth projections as of February 2010; which validated the use of the CCMP Acquisition price. No adjustment to exercise price was made for lack of control or lack of marketability discount. |
| Ÿ | During July of 2010, we granted options to acquire 80,000 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $6.13 per share. The exercise price for this grant was equal to the per share price paid in the CCMP Acquisition. Our board used a market based methodology to determine the exercise price per share based on the sale price paid in the CCMP Acquisition. Projected sales and anticipated new boutique openings were consistent at July 2010 with sales and growth projections as of February 2010; which validated the use of the CCMP Acquisition price. No adjustment to exercise price was made for lack of control or lack of marketability discount. |
| Ÿ | During December of 2010, we granted options to acquire 452,030 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $10.19 per share. The exercise price for this grant was determined based on, among other factors, a third-party valuation study of our common stock as described in more detail below. An analysis was performed by the third-party valuation consultant to estimate the fair values of our common stock as of the grant date. The objective of the analysis was to determine the fair market value of the company, its common stock and the fair value of related stock options, as of the valuation date, on a controlling interests basis. The probability-weighted expected return method was used to estimate the fair value of our common stock which, in turn, represented the stock option exercise price on the date of grant. This method was selected based on management’s current expectation of either an initial public offering or a sale or merger of the company in the near future. Three scenarios were incorporated into the valuation: (i) the company being sold to another company (the “M&A Scenario”), (ii) the company engaging in an initial public offering (the “IPO Scenario”), and (iii) the company remaining an independent, privately-held company (the “Private Scenario”). The estimated fair value of our common stock in each scenario was affected by the use of certain assumptions and valuation methodologies. The fair value of the stock was assessed based on the probability weighted potential for each scenario on the date of grant. The estimated fair value under the M&A Scenario considered the projected value of the company upon sale or merger. To arrive at the fair value of our common stock under the M&A Scenario, the discounted value of the cash flow leading up to the date of an assumed merger or sale was added to values from comparable merger and acquisition transactions applying the observed paid-multiples to our financial performance to determine enterprise value. In calculating the fair value of our common stock and the exercise price for the options granted by us in December of 2010, we ascribed a probability weighting of 20% to the M&A Scenario. |
To determine the estimated fair value of our common stock under the IPO Scenario, the public market valuations of other high-growth specialty retailers were reviewed using a variety of methods. For such firms, a number of multiples and ratios such as revenue, earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization, or EBITDA, and net income to enterprise value were calculated. Then those multiples were applied to both our historical and projected financial performance to determine our estimated enterprise value. In calculating the fair value of our common stock and the exercise price for the options granted by us in December of 2010, we ascribed a probability weighting of 70% to the IPO Scenario.
| 51 |
The estimated fair value under the Private Scenario was determined considering valuations based on three different fair value models: (i) an income valuation model that incorporates the calculation of the present value of future cash flows discounted at an appropriate rate applicable given the risks associated with the company and related forecast, (ii) a market valuation model that considers recent sales or offerings of comparable assets between third parties and (iii) the guideline public company method that focuses on comparing the company’s economic performance to guideline publicly traded entities. In calculating the fair value of our common stock and the exercise price for the options granted by us in December of 2010, we ascribed a probability weighting of 10% to the Private Scenario.
We included additional factors in the above scenarios including a significant increase in comparable boutique sales during fiscal year 2010 including a 21.1% comparable boutique sales increase in the third quarter. Additionally, our new boutique openings during fiscal year 2010 exceeded our forecast by a significant percentage. Those accretive factors were partially offset by the impact of the recapitalization of the company in November 2010, whereby we incurred $95.0 million of indebtedness under our prior senior secured credit facility and used the proceeds to declare a $100 million cash dividend.
The following table sets forth all stock option grants to acquire our common stock granted during 2010 under the 2010 Stock Incentive Plan.
| Grant Date | Number of Options Granted | Exercise Price Per Share | Common Stock Fair Value per Share at Grant Date | Third-Party Valuation Date | Vesting Period (Years) | Weighted Average Stock Option Fair Value | ||||||||||||||||||
| March 26, 2010 | 1,062,400 | $ | 6.13 | $ | 6.13 | Not obtained(1) | 4 | $ | 3.93 | |||||||||||||||
| May 1, 2010 | 400,000 | $ | 6.13 | $ | 6.13 | Not obtained(1) | 5 | $ | 3.45 | |||||||||||||||
| July 1, 2010 | 80,000 | $ | 6.13 | $ | 6.13 | Not obtained(1) | 5 | $ | 3.64 | |||||||||||||||
| December 1, 2010 | 452,030 | $ | 10.19 | $ | 10.19 | December 1, 2010 | 5 | $ | 5.83 | (2) | ||||||||||||||
| (1) | Fair value equaled CCMP Acquisition per share price based on our determination that the fair value did not change between the CCMP Acquisition date and option grant date. |
| (2) | The stock option fair value was determined using a third party valuation study. |
During the period between the October 31, 2009 valuation study and the CCMP Acquisition in February of 2010, we experienced growth in sales performance and new boutique openings. We believe that our strong historical financial growth coupled with strong future prospects were the key factors on which CCMP based the price per share it paid in the acquisition.
A portion of the stock options granted to Mr. De Meritt on March 26, 2010 vested in connection with our IPO based on the achievement of certain performance targets. The achievement of such performance targets was measured based on the average trading price of our common stock over the twenty-trading-day period immediately following the completion of our IPO. The recognition of the amount of the approximately $2.3 million compensation expense associated with such vesting was accelerated in the third quarter of fiscal year 2011.
2011 Stock Incentive Plan
We granted options to acquire 882,099 shares of our common stock and 9,600 shares of restricted stock under the 2011 Plan. Since all the grants occurred in conjunction or subsequent to our IPO, the exercise price and fair values were determined using our IPO price or the closing price at the date of grant, as applicable.
The following table sets forth all stock option grants to acquire our common stock granted during 2011 under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan.
Grant Date | Number of | Exercise | Weighted Average Vesting Period (Years) | Weighted Average Stock Option | ||||||||||||
| July 22, 2011 (1) | 767,569 | $ | 17.00 | 5 | $ | 9.24 | ||||||||||
| September 1, 2011 | 10,000 | $ | 22.69 | 5 | $ | 13.19 | ||||||||||
| October 4, 2011 | 94,530 | $ | 20.29 | 3 | $ | 12.64 | ||||||||||
| 52 |
Grant Date | Number of | Exercise | Weighted Average Vesting Period (Years) | Weighted Average Stock Option | ||||||||||||
| December 8, 2011 | 10,000 | $ | 18.82 | 5 | $ | 11.04 | ||||||||||
| (1) | These options were granted in conjunction with the company’s initial public offering. |
Related Party Transactions
Stony Trading Relationship
Stony Leather, Inc. (“Stony”) is one of our inventory vendors. We purchase inventory from Stony on a purchase order basis. Stony sources, wholesales and distributes jewelry, accessories, handbags and gift items. Stony’s customers include retailers, wholesalers, individuals, television shopping networks, and internet-based merchants. We are only one of Stony’s several customers. Stony is based in Houston, Texas with a showroom in New York City, New York. Stony does not own or operate conventional brick and mortar retail outlets.
Chong Yi and Insuk Koo (two of the four Founders) own and operate Stony. Mr. Yi and Ms. Koo are brother and sister. Mr. Yi and Ms. Koo along with their sister Ms. Kyong Gill (our Executive Vice Chairperson and one of the four Founders) are stockholders of Francesca’s. We treat Stony as an independent third-party vendor.
Since the founding of our company, Stony has been a supplier of a variety of our inventory items. Stony has accounted for 7%, 10% and 12% of our total inventory purchases on an annual basis in fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. We negotiate and set the rates for the merchandise and services provided to us by Stony at market rates for such merchandise and services at the time each such transaction is entered into. We often request and receive from Stony merchandise on special order or modify previously ordered merchandise. Generally, Stony provides us a 3% damage allowance to cover the costs of damaged merchandise. The Stony inventory purchases during fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009 were approximately $5.0 million, $5.0 million and $3.1 million, respectively.
KJK Trading Relationship
KJK Trading Corporation (“KJK Trading”) is one of our inventory vendors. We purchase inventory from KJK Trading on a purchase order basis. Although KJK Trading assists us in the design of several items of apparel we sell in our boutiques, KJK Trading does not act as our broker or agent in the sourcing of our merchandise. Beginning in May 2010, we subleased approximately 2,000 square feet of office space to KJK Trading within our headquarters in Houston, Texas. We did not receive any rent payments from KJK Trading in fiscal year 2010. Beginning in January 2011, the rent payment became $1,000 per month. KJK Trading employs several employees to conduct its business. We are the sole customer of KJK Trading. We treat KJK Trading as an independent third-party vendor.
KJK Trading is owned and operated by Ki Juing Gu. Mr. Gu is the brother-in-law of Ms. Insuk Koo (one of our Founders).
KJK Trading has been one of our inventory vendors since 2008. KJK Trading has accounted for 12%, 13% and 11% of our total inventory purchases on an annual basis in fiscal year 2011, fiscal year 2010 and fiscal year 2009, respectively. We negotiate and set the rates for the merchandise and services provided to us by KJK Trading at market rates for such merchandise and services at the time each such transaction is entered into. We often request and receive from KJK Trading merchandise on special order or modify previously ordered merchandise. Generally, KJK Trading provides us a 1% damage allowance to cover the costs of damaged merchandise. The KJK Trading inventory purchases during fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009 were approximately $8.1 million, $6.6 million and $2.8 million, respectively.
BGCP Management Agreement
In April 2007, we entered into a management agreement with BGCP in connection with the BGCP Investment. Prior to the CCMP Acquisition, BGCP was a holder of more than five percent of our voting stock. Under the management agreement, BGCP provided financial advisory and other consulting services to us in exchange for quarterly fees of $62,500. The management agreement was terminated in February 2010 in connection with the CCMP Acquisition. For each of the fiscal years ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010, we incurred fees under the management agreement totaling $0, $0 and $0.3 million, respectively.
| 53 |
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
We are not party to any off balance sheet arrangements.
Contractual Obligations
The following table summarizes our contractual obligations as of January 28, 2012 and the effect such obligations are expected to have on our liquidity and cash flows in future periods.
Payments Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | Less than 1 year | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | More than 5 years | ||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt obligations | $ | 22,000 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 22,000 | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Estimated interest on long-term debt obligations(1) | 4,202 | 947 | 1,860 | 1,395 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Operating lease obligations(2) | 157,071 | 19,923 | 38,251 | 34,497 | 64,400 | |||||||||||||||
| Merchandise purchase commitments | 17,197 | 17,197 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Contracts for software application implementation | 2,792 | 752 | 1,489 | 551 | — | |||||||||||||||
| (1) | For purposes of this table, we estimated interest expense to be paid during the remaining term of the revolving credit facility using the interest rate in effect as of January 28, 2012 of 3.75%. |
| (2) | Excludes common area maintenance charges, real estate taxes and certain other expenses which amounted to approximately 38.3% of minimum lease obligations in fiscal year 2011. We expect this percentage to be relatively consistent for the next three years. |
Impact of Inflation
Our results of operations and financial condition are presented based on historical cost. While it is difficult to accurately measure the impact of inflation due to the imprecise nature of the estimates required, we believe the effects of inflation, if any, on our results of operations and financial condition have been immaterial. We cannot assure you, however, that our results of operations and financial condition will not be materially impacted by inflation in the future.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
For a description of a complete list of recent accounting pronouncements, see the notes to our consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this report, which is incorporated herein.
item 7a. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Our principal exposure to market risk relates to changes in interest rates. Our revolving credit facility carries floating interest rates that are tied to LIBOR, the federal funds rate and the prime rate, and therefore, our statements of operations and our cash flows will be exposed to changes in interest rates to the extent that we do not have effective hedging arrangements in place. We historically have not used interest rate swap agreements to hedge the variable cash flows associated with the interest on our credit facilities. At January 28, 2012, the interest rate on our borrowings under the revolving credit facility was 3.75%. Based on a sensitivity analysis at January 28, 2012, assuming the loan balance would be outstanding for a full fiscal year, a 100 basis point increase in interest rates would increase our annual interest by approximately $0.2 million. We do not use derivative financial instruments for speculative or trading purposes; however, this does not preclude our adoption of specific hedging strategies in the future.
| 54 |
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders of
Francesca’s Holdings Corporation:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Francesca’s Holdings Corporation (the “Company”) as of January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011, and the related consolidated statements of operations, changes in convertible redeemable preferred stock and shareholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended January 28, 2012. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. We were not engaged to perform an audit of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of Francesca’s Holdings Corporation at January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended January 28, 2012, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
| /s/ Ernst & Young LLP | |
| March 21, 2012 | |
| Dallas, Texas |
| 55 |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Board of Directors
Francesca’s Holdings Corporation
Houston, Texas
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of operations, changes in convertible redeemable preferred stock and shareholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows of Francesca’s Holdings Corporation (the “Company”) for the year ended January 30, 2010. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audit included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the results of operations and cash flows of Francesca’s Holdings Corporation for the year ended January 30, 2010, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
| /s/ BDO USA, LLP | |
| (formerly known as | |
| BDO Seidman, LLP) |
Houston, Texas
June 22, 2010, except for
footnotes 2 and 9, which
are as of April 15, 2011
| 56 |
Francesca’s Holdings Corporation
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(In thousands)
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current assets: | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 14,046 | $ | 12,516 | ||||
| Accounts receivable | 2,156 | 4,054 | ||||||
| Inventories | 14,688 | 11,959 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 2,352 | 1,321 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 2,799 | 1,871 | ||||||
| Total current assets | 36,041 | 31,721 | ||||||
| Property and equipment, net | 33,199 | 21,300 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 952 | 2,704 | ||||||
| Other assets, net | 2,120 | 3,399 | ||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 72,312 | $ | 59,124 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) | ||||||||
| Current liabilities: | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 8,627 | $ | 6,146 | ||||
| Accrued liabilities | 9,893 | 6,410 | ||||||
| Current portion of long-term debt | — | 5,938 | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | 18,520 | 18,494 | ||||||
| Deferred and accrued rents | 14,890 | 8,223 | ||||||
| Long-term debt | 22,000 | 87,875 | ||||||
| Total liabilities | 55,410 | 114,592 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies | ||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity (deficit): | ||||||||
| Common stock—$.01 par value, 80.0 million shares authorized, 43.5 million and 40.5 million shares issued and outstanding at January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011, respectively | 435 | 405 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 77,071 | 27,232 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (60,604 | ) | (83,105 | ) | ||||
| Total shareholders’ equity (deficit) | 16,902 | (55,468 | ) | |||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) | $ | 72,312 | $ | 59,124 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
| 57 |
Francesca’s Holdings Corporation
Consolidated Statements of operations
(In thousands, except per share data)
| Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | ||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 204,158 | $ | 135,176 | $ | 79,367 | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs | 97,365 | 65,008 | 37,244 | |||||||||
| Gross profit | 106,793 | 70,168 | 42,123 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 63,262 | 40,525 | 24,641 | |||||||||
| Income from operations | 43,531 | 29,643 | 17,482 | |||||||||
| Interest income (expense) | (4,868 | ) | (1,633 | ) | 2 | |||||||
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt | (1,591 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Other income (expense) | 284 | (2 | ) | 38 | ||||||||
| Income before income tax expense | 37,356 | 28,008 | 17,522 | |||||||||
| Income tax expense | 14,855 | 11,113 | 6,918 | |||||||||
| Net income | 22,501 | 16,895 | 10,604 | |||||||||
| Increase in redemption value of convertible redeemable preferred stock | — | — | (60,271 | ) | ||||||||
| Convertible redeemable preferred stock accrued dividends | — | — | (2,022 | ) | ||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to shareholders | $ | 22,501 | $ | 16,895 | $ | (51,689 | ) | |||||
| Less: Income attributable to participating securities | — | — | — | |||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to common shareholders | $ | 22,501 | $ | 16,895 | $ | (51,689 | ) | |||||
| Basic earnings (loss) per common share | $ | 0.53 | $ | 0.43 | $ | (1.99 | ) | |||||
| Diluted earnings (loss) per common share | $ | 0.52 | $ | 0.41 | $ | (1.99 | ) | |||||
| Dividends declared per common share | — | $ | 2.39 | — | ||||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding: | ||||||||||||
| Basic shares | 42,087 | 39,385 | 26,000 | |||||||||
| Diluted shares | 42,948 | 40,907 | 26,000 | |||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
| 58 |
Francesca’s Holdings Corporation
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Convertible Redeemable
Preferred Stock and Shareholders’ EQUITY (Deficit)
(In thousands)
| Additional | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Convertible | Paid-in | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Redeemable Preferred | Capital | Retained | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock—Series A | Common Stock | (Distributions | Earnings | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Shares | Par | in Excess of | (Accumulated | Shareholders’ | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding | Amount | Outstanding | Value | Capital) | Deficit) | Deficit | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, January 31, 2009 | 35 | $ | 23,561 | 26,000 | $ | 260 | $ | (13,124 | ) | $ | 1,576 | $ | (11,288 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Net income | — | — | 10,604 | 10,604 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | — | — | — | — | — | 99 | 99 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Increase in redemption value of Preferred Stock—Series A | — | 60,271 | — | — | (50,014 | ) | (10,257 | ) | (60,271 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Accrued dividends for Preferred Stock—Series A | — | 2,022 | — | — | — | (2,022 | ) | (2,022 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, January 30, 2010 | 35 | 85,854 | 26,000 | 260 | (63,138 | ) | — | (62,878 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 16,895 | 16,895 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conversion of Preferred Stock—Series A to common stock | (35 | ) | (85,854 | ) | 14,000 | 140 | 85,714 | — | 85,854 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | — | — | — | — | 2,400 | — | 2,400 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared and related tax benefit | — | — | — | — | 1,220 | (100,000 | ) | (98,780 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exercised and related tax benefit | — | — | 457 | 5 | 1,036 | — | 1,041 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, January 29, 2011 | — | — | 40,457 | $ | 405 | $ | 27,232 | $ | (83,105 | ) | $ | (55,468 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 22,501 | 22,501 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of stock in initial public offering, net of costs | — | — | 2,941 | 29 | 44,216 | — | 44,245 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | — | — | — | — | 4,671 | — | 4,671 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exercised and related tax benefit | — | — | 140 | 1 | 952 | — | 953 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, January 28, 2012 | — | $ | — | 43,538 | $ | 435 | $ | 77,071 | $ | (60,604 | ) | $ | 16,902 | |||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
| 59 |
Francesca’s Holdings Corporation
Consolidated Statements of Cash flows
(In thousands)
| For the Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | ||||||||||
| Cash Flows Provided by Operating Activities: | ||||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 22,501 | $ | 16,895 | $ | 10,604 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 4,936 | 2,377 | 1,215 | |||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense | 4,671 | 2,400 | 99 | |||||||||
| Excess tax benefit from stock-based compensation | (449 | ) | (1,757 | ) | — | |||||||
| Loss on sale of assets | 23 | 25 | — | |||||||||
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt | 1,591 | — | — | |||||||||
| Amortization of debt issuance costs | 537 | 158 | — | |||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 721 | (2,685 | ) | (833 | ) | |||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities: | ||||||||||||
| Accounts receivables | 1,898 | (3,557 | ) | (126 | ) | |||||||
| Inventories | (2,729 | ) | (5,581 | ) | (794 | ) | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | (309 | ) | (1,549 | ) | (573 | ) | ||||||
| Accounts payable | 2,481 | 3,443 | 1,434 | |||||||||
| Accrued liabilities | (566 | ) | 3,874 | 1,007 | ||||||||
| Deferred and accrued rents | 6,667 | 5,999 | 1,440 | |||||||||
| Income tax payable | 4,498 | 978 | (196 | ) | ||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 46,471 | 21,020 | 13,277 | |||||||||
| Cash Flows Used in Investing Activities: | ||||||||||||
| Purchase of property and equipment | (16,894 | ) | (16,208 | ) | (5,538 | ) | ||||||
| Other | 36 | — | — | |||||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (16,858 | ) | (16,208 | ) | (5,538 | ) | ||||||
| Cash Flows Used in Financing Activities: | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of stock in initial public offering, net of costs | 44,245 | — | — | |||||||||
| Proceeds from borrowings under the new revolving credit facility | 41,000 | — | — | |||||||||
| Proceeds from borrowings under the prior senior secured credit facility | — | 95,000 | — | |||||||||
| Repayment of borrowings under the new revolving credit facility | (19,000 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Repayment of borrowings under the prior senior secured credit facility | (93,813 | ) | (1,187 | ) | — | |||||||
| Dividends | — | (100,000 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Excess tax benefit from stock-based compensation | 449 | 1,757 | — | |||||||||
| Payment of debt issuance costs | (1,468 | ) | (2,137 | ) | — | |||||||
| Proceeds from the exercise of stock options | 504 | 504 | — | |||||||||
| Net cash used in financing activities | (28,083 | ) | (6,063 | ) | — | |||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 1,530 | (1,251 | ) | 7,739 | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year | 12,516 | 13,767 | 6,028 | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of year | $ | 14,046 | $ | 12,516 | $ | 13,767 | ||||||
| Supplemental Disclosures of Cash Flow Information: | ||||||||||||
| Cash paid for income taxes | 8,971 | 13,509 | 7,946 | |||||||||
| Interest paid | 5,569 | 163 | — | |||||||||
| Supplemental Non-Cash Financing Activities: | ||||||||||||
| Accrual of dividends on Preferred Stock – Series A | — | — | 2,022 | |||||||||
| Increase in redemption value of Preferred Stock Series A | — | — | 60,271 | |||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Financial Statements.
| 60 |
FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Nature of Business
Francesca’s Holdings Corporation (the “Company”) is a holding company incorporated in 2007 under the laws of Delaware. The Company’s business operations are conducted through its wholly-owned indirect subsidiary Francesca’s Collections, Inc., a corporation formed and existing under the laws of the State of Texas. Francesca’s Collections, Inc. is wholly-owned by Francesca’s LLC (the “Parent”), a limited liability company formed and existing under the laws of Delaware. Parent is a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company.
The Company operates a national chain of retail boutiques designed and merchandised to feel like independently owned, upscale boutiques and provide its customers with an inviting, intimate and fun shopping experience. The Company offers a diverse and balanced mix of apparel, jewelry, accessories and gifts at attractive prices. At January 28, 2012, the Company operated 283 boutiques, which are located in 41 states throughout the United States, and its e-commerce website.
In February 2010, two affiliates of CCMP Capital Advisors, LLC (“CCMP”), acquired approximately 84% of the Company’s outstanding shares (the “CCMP Acquisition”) from the founders of the Company and Bear Growth Capital Partners, LP (“BGCP”). The Company considered the application of push-down accounting to the Company’s financial statements and determined that, given the percentage of equity interest acquired in the acquisition, push-down accounting treatment was not required. The Company elected not to apply push-down accounting treatment as a result of the acquisition. In connection with the CCMP Acquisition, the Convertible Redeemable Preferred Stock- Series A (“Preferred Stock”) was converted to common stock. In addition, the outstanding stock options became fully vested and the management agreement with the holders of the Preferred Stock was terminated. See Notes 6 and 10 for more information. The Company incurred zero, $0.2 million and $0.7 million of transaction costs which are included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations for the fiscal years ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010, respectively.
On April 28, 2010, the Company authorized a split of its issued and outstanding stock in the ratio of four hundred to one (400-1). Accordingly, the accompanying consolidated financial statements have been retroactively adjusted to reflect the effects of the stock split on common shares and per share amounts.
On July 27, 2011, the Company completed an initial public offering (the “IPO”) of 11,500,000 shares of common stock at a price to the public of $17 per share, of which 2,941,176 shares were sold by the Company and 8,558,824 shares were sold by the selling shareholders (including 616,109 by members of the Company’s management). Upon completion of the offering, the Company received net proceeds of approximately $44.2 million, after deducting the underwriting discount of $3.5 million and related fees and expenses of $2.3 million. On July 27, 2011, net proceeds from the offering, together with $41.0 million of indebtedness under a new revolving credit facility and $6.8 million of cash on hand, were used to repay the $92.0 million (including accrued interest of $0.6 million) outstanding under the senior secured credit facility. The senior secured credit facility was then terminated. See Note 5 for more information.
Fiscal Year
The Company maintains its accounts on a 52- to 53- week year ending on the Saturday closest to January 31. All references herein to fiscal year “2011”, “2010” and “2009” represent the 52-week periods ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010, respectively.
Principles of Consolidation and Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and all its subsidiaries. All significant inter-company balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Management Estimates and Assumptions
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues, net of estimated sales return, and expenses during the reporting periods. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
| 61 |
FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. Assets and liabilities measured at fair value are classified using the following hierarchy, which is based upon the transparency of inputs to the valuation at the measurement date:
| Ÿ | Level 1—Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| Ÿ | Level 2—Inputs, other than the quoted prices in active markets, that are observable either directly or indirectly. |
| Ÿ | Level 3—Unobservable inputs based on the Company’s own assumptions. |
The classification of fair value measurements within the hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the measurement.
Financial assets and liabilities with carrying amounts approximating fair value include cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued liabilities. The carrying amount of these financial assets and liabilities approximates fair value because of their short maturities. The carrying amount of the Company’s debt approximates its fair value due to proximity of the debt issue date and the latest balance sheet date and the variable component of the interest on the debt.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all interest-bearing deposits and investments purchased with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. The Company maintains cash balances at financial institutions that may from time to time exceed the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation’s insurance limits. The Company mitigates this concentration of credit risk by monitoring the credit worthiness of the financial institutions.
Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable consist of amounts due from credit card companies, tenant allowances due from landlords and income tax receivable. The Company’s management has reviewed accounts receivable for collectibility and has determined an allowance for doubtful accounts is not necessary at January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011.
Inventory
The Company values merchandise inventory at the lower of cost or market on a weighted-average cost basis. Inventory costs include freight-in. The Company records merchandise receipts at the time they are delivered to the distribution center or to its boutiques from vendors.
The Company reviews its inventory levels to identify slow-moving merchandise and generally uses promotional markdowns to clear slow-moving merchandise. Each period, the Company evaluates recent selling trends and the related promotional events or pricing strategies in place to sell through the current inventory levels.
The Company also estimates a shrinkage reserve for the period of time between the last physical count and the balance sheet date. The estimate for shrinkage reserve can be affected by changes in merchandise mix and changes in actual shrinkage trends.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost. Depreciation of property and equipment is provided on a straight-line basis for financial reporting purposes using the following useful lives:
| Assets | Estimated Useful Lives | |
| Equipment | 3 - 5 years | |
| Furniture and fixtures | 5 years |
| 62 |
FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Assets | Estimated Useful Lives | |
| Software | 3 years | |
| Signage and leasehold improvements | the lesser of 5 - 10 years or lease term |
Assets under construction are not depreciated until the asset is placed in service and ready for use.
Maintenance and repairs of property and equipment are expensed as incurred, and major improvements are capitalized. Upon retirement, sale or other disposition of property and equipment, the cost and accumulated depreciation are eliminated from the accounts, and any gain or loss is reflected in current earnings.
Impairment of Long-lived Assets
The Company evaluates long-lived assets held for use and held for sale whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of those assets may not be recoverable. Assets are grouped and evaluated for impairment at the lowest level for which there are identifiable cash flows, which is generally at a boutique level. Boutique assets are reviewed for impairment using factors including, but not limited to, the Company’s future operating plans and projected cash flows. The determination of whether an impairment has occurred is based on an estimate of undiscounted future cash flows directly related to that boutique, compared to the carrying value of the assets. The Company recognizes impairment if the sum of the undiscounted future cash flows of a boutique does not exceed the carrying value of the assets. For impaired assets, the Company recognizes a loss equal to the difference between the net book value of the asset and its estimated fair value. Fair value is based on discounted future cash flows of the asset using a discount rate commensurate with the risk. In addition, at the time a decision is made to close a boutique, the Company accelerates depreciation over the revised useful life of the asset. Based on the analysis performed, there was no impairment for each of the fiscal years ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010.
Operating Leases
The Company leases boutiques and distribution center and office space under operating leases. The majority of the Company’s lease agreements provide for tenant improvement allowances, rent escalation clauses and/or contingent rent provisions.
The Company records tenant improvement allowances and other landlord incentives as a component of deferred rent which is amortized on a straight-line basis over the lease term as a reduction of rent expense. The unamortized portion of deferred rent totaled $10.9 million and $5.9 million at January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011, respectively, and is included in deferred and accrued rents in the consolidated balance sheets.
The Company records straight-line rent expense beginning on the earlier of taking possession of the boutique (pre-opening or construction period) or the commencement date of the lease. In fiscal 2010, the Company determined that its policy had historically been inconsistently applied. The Company corrected the deferred rent expense account, resulting in a non-cash $0.7 million cumulative adjustment to record additional rent expense during the first quarter of fiscal 2010. That adjustment was included in the cost of goods sold and occupancy cost in the consolidated statements of operations. The adjustment did not impact historical cash flows and will not impact future net cash flows or the timing of the payments under the related leases. Prior years’ financial statements were not restated as the impact of these issues was immaterial to previously reported results for any individual prior year.
Certain leases provide for contingent rents, in addition to a basic fixed rent, which are determined as a percentage of gross sales in excess of specified levels. The Company records a contingent rent liability and the corresponding rent expense when specified levels have been achieved or when management determines that achieving the specified levels during the fiscal year is probable.
Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue upon purchase of merchandise by customers, net of estimated merchandise returns. Revenue is recognized for boutique sales at the point at which the customer receives and pays for the merchandise at the register. For on-line sales, revenue is recognized upon delivery and includes shipping charges. Management estimates future returns on previously sold merchandise based on return history and current sales levels. The estimated sales returns are periodically compared to actual sales returns and adjusted, if appropriate.
| 63 |
FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Gift Cards and Gift Card Breakage
The Company accounts for the sale of gift cards as a liability at the time a gift card is sold. The liability is relieved and revenue is recognized upon redemption of the gift card. The Company’s gift cards do not have an expiration date. We will recognize income from the breakage of gift cards when the likelihood of redemption of the gift card is remote based on historical redemption patterns. The Company has not accumulated adequate historical data to reasonably estimate the amount of gift cards that will never be redeemed. Consequently, the Company has not recognized gift card breakage income in fiscal years 2011, 2010 or 2009. The Company does not anticipate recognizing gift card breakage until it accumulates additional data beyond fiscal year 2011.
Sales Taxes
The Company excludes all taxes assessed by a government authority directly imposed on revenue producing transactions between a seller and a customer from revenue.
Cost of Goods Sold and Occupancy Costs
Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs include the direct cost of purchased merchandise, freight costs from the Company’s suppliers to its distribution centers and freight costs for merchandise shipped directly from its vendors to its boutiques, allowances for inventory shrinkage and obsolescence, boutique occupancy costs including rent, utilities, common area maintenance, property taxes, depreciation and boutique repair and maintenance costs, and shipping costs related to e-commerce sales.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses include boutique and headquarters payroll, employee benefits, freight from distribution centers to boutiques, boutique pre-opening expense, credit card merchant fees, costs of maintaining and operating the Company’s e-commerce business, travel and administration costs and other expenses related to operations at the corporate headquarters, as well as share-based compensation. Pre-opening expenses (including boutique set-up and training expenses) incurred prior to the opening of new boutiques are expensed as incurred and are included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Freight costs included in selling, general and administrative expenses amounted to $1.3 million, $0.8 million and $0.5 million for the fiscal years ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010, respectively.
Advertising
Costs associated with advertising are charged to expense as incurred. For the years ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010, advertising costs were minimal.
Stock-Based Compensation
In connection with the Company’s stock based compensation plans, the Board of Directors considers the estimated fair value of the Company’s stock when setting the stock option exercise price as of the date of each grant. Prior to the IPO, because the Company was privately held and there was no public market for its common stock, the fair market value of its common stock was determined by the Board of Directors at the time the option grants were awarded. In determining the fair value of the common stock, the Board of Directors considered such factors as the Company’s actual and projected financial results, the consideration paid by third party investors in the Company, including investments by BGCP and CCMP in arm’s length transactions for their respective investment and controlling investment in the Company (as described in Notes 1 and 10), the principal amount of the Company’s indebtedness, valuations of the Company performed by third parties and other factors the Board of Directors believed were material to the valuation process. To the extent financial projections and anticipated boutique openings did not materially change from the date of the BGCP Acquisition or the CCMP Acquisition through the date of a stock option grant, the Board of Directors concluded that the per share price of the common stock related to each of the acquisition transactions represented the most accurate estimate of the fair value of the common stock for purpose of setting the respective option exercise price as of the date of each grant. Additionally, for these grants, in making its determination of fair value, the Board of Directors did not apply control premium or marketability considerations. To timely secure the necessary talent the Company requires to support its growth, the Board of Directors took into account a number of factors, including utilizing the most recent third-party valuation study available to help establish the exercise price for the applicable grant.
| 64 |
FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Following the IPO, the Board of Directors determines the exercise price of stock options based on the closing price of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. See Note 6 for further information.
Stock-based compensation cost is measured at the grant date fair value using the Black Scholes option pricing model and is recognized as an expense on a straight-line basis over the employee’s requisite service period (generally the vesting period of the equity grant). The Company estimates forfeitures for options granted that are not expected to vest. Changes in these inputs and assumptions can materially affect the measurement of the estimated fair value of the stock-based compensation expense.
Debt Issuance Costs
Costs incurred in connection with the Company’s borrowings are capitalized and included in other assets in the consolidated balance sheets. These costs are amortized to interest expense using the effective interest method over the term of the loan. In fiscal year 2011, the Company wrote-off the unamortized balance of debt issuance costs amounting to $1.6 million related to the prior senior secured credit in facility due to its termination, as discussed in Note 1. This write-off was presented as loss on early extinguishment debt in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations. In connection with the new revolving credit facility, the Company incurred $1.5 million of costs that will be amortized over the term of loan. See Note 5 for further information. At January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011, debt issuance costs totaled $1.3 million and $2.0 million, respectively. Amortization expense amounted to $0.5 million, $0.2 million and $0 for the fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes using the liability method. Under this method, the amount of taxes currently payable or refundable is accrued, and deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future tax consequences of temporary differences that currently exist between the tax basis and the financial reporting basis of the Company’s assets and liabilities. Valuation allowances are established against deferred tax assets when it is more-likely-than-not that the realization of those deferred tax assets will not occur.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using the enacted tax rates in effect in the years when those temporary differences are expected to reverse. The effect on deferred taxes from a change in tax rate is recognized through continuing operations in the period that includes the enactment date of the change. Changes in tax laws and rates could affect recorded deferred tax assets and liabilities in the future.
A tax benefit from an uncertain tax position may be recognized when it is more-likely-than-not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including resolutions of any related appeals or litigation processes, based on the technical merits. Income tax positions must meet a more-likely-than-not recognition threshold to be recognized. The Company recognizes tax liabilities for uncertain tax positions and adjusts these liabilities when the Company’s judgment changes as a result of the evaluation of new information not previously available. Due to the complexity of some of these uncertainties, the ultimate resolution may result in a payment that is materially different from the current estimate of the tax liabilities. These differences will be reflected as increases or decreases to income tax expense and the effective tax rate in the period in which the new information becomes available. Interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits are recognized in income tax expense. The Company has no uncertain tax positions or related interest or penalties requiring accrual at January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2011, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2011-04, “Amendments to Achieve Common Fair Value Measurement and Disclosure Requirements in GAAP and International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”).” This pronouncement was issued to provide a consistent definition of fair value and ensure that the fair value measurement and disclosure requirements are similar between U.S. GAAP and IFRS. ASU 2011-04 changes certain fair value measurement principles and enhances the disclosure requirements particularly for level 3 fair value measurements. This pronouncement is effective for reporting periods beginning on or after December 15, 2011. The Company does not expect the adoption of ASU 2011-04 to have a significant impact to the consolidated financial position or results of operations.
| 65 |
FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
In December 2011, the FASB issued ASU 2011-11, Balance Sheet (Topic 210): Disclosures about Offsetting Assets and Liabilities (ASU 2011-11). This newly issued accounting standard requires an entity to disclose both gross and net information about instruments and transactions eligible for offset in the statement of financial position as well as instruments and transactions executed under a master netting or similar arrangement and was issued to enable users of financial statements to understand the effects or potential effects of those arrangements on its financial position. This ASU is required to be applied retrospectively and is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning on or after January 1, 2013. As this accounting standard only requires enhanced disclosure, the adoption of this standard is not expected to have an impact on the Company’s consolidated financial position or results of operations.
2. Earnings (Loss) per Share
Basic earnings (loss) per common share amounts are calculated using the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted earnings (loss) per common share amounts are calculated using the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding for the period and include the dilutive impact of Preferred Stock, while outstanding, and stock options using the if-converted and treasury stock method, respectively.
In the years the Preferred Stock was outstanding, the two-class method was used to calculate basic and diluted earnings (loss) per common share since it is a participating security under ASC 260 Earnings per Share. The two-class method is an earnings allocation formula that determines earnings per share for each class of common stock and participating security according to dividends declared (or accumulated) and participation rights in undistributed earnings. Under the two-class method, basic earnings (loss) per common share is computed by dividing net earnings (loss) attributable to common share after allocation of earnings to participating securities by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the year. Diluted earnings (loss) per common share is computed using the more dilutive of the two-class method or the if-converted method. In periods of net loss, no effect is given to participating securities since they do not contractually participate in the losses of the Company. The following table summarizes the dilutive impact of Preferred Stock for the year it was outstanding and the potential dilution that could occur if options to acquire common stock were exercised or if restricted stocks have fully vested, and reconciles the weighted-average common shares outstanding used in the computation of basic and diluted earnings per share.
| For the Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | ||||||||||
| (In thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||
| Numerator: | ||||||||||||
| Net Income | $ | 22,501 | $ | 16,895 | $ | 10,604 | ||||||
| Less: Increase in redemption value of Preferred Stock | — | — | (60,271 | ) | ||||||||
| Less: Preferred Stock dividends | — | — | (2,022 | ) | ||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to shareholders | 22,501 | 16,895 | (51,689 | ) | ||||||||
| Less: Income attributable to participating securities | — | — | — | |||||||||
| Net income (loss) available to common shareholders | $ | 22,501 | $ | 16,895 | $ | (51,689 | ) | |||||
| Denominator: | ||||||||||||
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding—basic | 42,087 | 39,385 | 26,000 | |||||||||
| Options and other dilutive securities | 861 | 1,522 | — | |||||||||
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding—diluted | 42,948 | 40,907 | 26,000 | |||||||||
| Per common share: | ||||||||||||
| Basic earnings (loss) per common share | $ | 0.53 | $ | 0.43 | $ | (1.99 | ) | |||||
| Diluted earnings (loss) per common share | $ | 0.52 | $ | 0.41 | $ | (1.99 | ) | |||||
Stock options to purchase 0.9 million, 0 and 1.0 million shares of common stock for the fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively, were outstanding but not included in the computation of diluted earnings per shares due to its anti-dilutive effect.
| 66 |
FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
In fiscal year 2009, dividends accrued on the Preferred Stock and the adjustment to record the increase in the redemption value of the Preferred Stock reduced undistributed earnings, to be allocated between common shares and participating securities, to zero for purposes of calculating earnings per share using the two-class method. As such, net losses were solely attributable to common shareholders. Accordingly, the Preferred Stock was not included in the computation of diluted earnings per share as the effect of doing so would have been anti-dilutive. See Note 10 for more information regarding Preferred Stock.
3. Detail of Certain Balance Sheet Accounts
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Accounts and other receivables: | ||||||||
| Credit card receivables | $ | 1,315 | $ | 825 | ||||
| Tenant allowances | 841 | 2,574 | ||||||
| Income tax receivable | — | 655 | ||||||
| $ | 2,156 | $ | 4,054 | |||||
| Property and equipment, net: | ||||||||
| Equipment | $ | 2,329 | $ | 1,798 | ||||
| Furniture and fixtures | 6,650 | 4,475 | ||||||
| Signage and leasehold improvements | 26,324 | 14,829 | ||||||
| Construction in progress | 5,750 | 5,799 | ||||||
| Software | 2,821 | 191 | ||||||
| 43,874 | 27,092 | |||||||
| Less accumulated depreciation | (10,675 | ) | (5,792 | ) | ||||
| $ | 33,199 | $ | 21,300 | |||||
| Accrued liabilities: | ||||||||
| Gift cards and store credits outstanding | $ | 3,140 | $ | 2,110 | ||||
| Accrued payroll, benefits and bonuses | 2,013 | 2,573 | ||||||
| Accrued interest | 69 | 1,308 | ||||||
| Accrued sales tax | 622 | 419 | ||||||
| Income tax payable | 4,049 | — | ||||||
| $ | 9,893 | $ | 6,410 | |||||
| Deferred and accrued rents: | ||||||||
| Deferred rent | $ | 10,889 | $ | 5,880 | ||||
| Accrued rent | 4,001 | 2,343 | ||||||
| $ | 14,890 | $ | 8,223 | |||||
4. Income Taxes
The provision for income tax expense for fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009 is as follows:
| For Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Current: | ||||||||||||
| Federal | $ | 11,009 | $ | 11,778 | $ | 6,667 | ||||||
| State | 3,125 | 2,020 | 1,084 | |||||||||
| Total | 14,134 | 13,798 | 7,751 | |||||||||
| 67 |
FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| For Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Deferred: | ||||||||||||
| Federal | 1,446 | (2,275 | ) | (724 | ) | |||||||
| State | (725 | ) | (410 | ) | (109 | ) | ||||||
| Total | 721 | (2,685 | ) | (833 | ) | |||||||
| Income tax expense | $ | 14,855 | $ | 11,113 | $ | 6,918 | ||||||
A reconciliation of the statutory federal income tax rate to the effective tax rate follows:
| For Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | January 30, 2010 | ||||||||||
| Income tax expense at statutory rate | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||||||
| Nondeductible expenses | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.9 | |||||||||
| State tax, net of federal benefit | 4.2 | 3.7 | 4.0 | |||||||||
| Other | (0.1 | ) | 0.5 | (0.4 | ) | |||||||
| Effective tax rate | 39.8 | % | 39.7 | % | 39.5 | % | ||||||
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recorded due to different carrying amounts for financial and income tax reporting purposes arising from cumulative temporary differences as measured by enacted tax rates, which will be in effect when these temporary differences reverse. These differences consist of the following at January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011:
| January 28, 2012 | January 29, 2011 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
| Inventories | $ | 717 | $ | 502 | ||||
| Accrued liabilities | 1,635 | 819 | ||||||
| Deferred and accrued rents | 5,511 | 2,618 | ||||||
| Equity based compensation | 2,182 | 358 | ||||||
| Total deferred tax assets | 10,045 | 4,297 | ||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities | ||||||||
| Property and equipment | (6,741 | ) | 272 | |||||
| Total deferred tax liabilities | (6,741 | ) | 272 | |||||
| Net deferred tax assets | $ | 3,304 | $ | 4,025 | ||||
The Company’s tax years are subject to examination by federal authorities from 2008 forward, and by state taxing authorities from 2007 forward.
5. Credit Facility
New Revolving Credit Facility
On July 27, 2011, Francesca’s Collections, Inc., a wholly-owned indirect subsidiary of the Company, (the “Borrower”) entered into an Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (the “new revolving credit facility”) with Royal Bank of Canada, as Administrative Agent, and KeyBank National Association, as Syndication Agent, which provides a $65.0 million of revolving credit facility (including borrowing capacity available for letters of credit). The new revolving credit facility is scheduled to terminate on July 27, 2016. As described in Note 1, on July 27, 2011, net proceeds from the Company’s initial public offering, together with $41.0 million of indebtedness under the new revolving credit facility and $6.8 million of cash on hand, were used to repay the $92.0 million (including accrued interest of $0.6 million) outstanding under the prior senior secured credit facility. The prior senior secured credit facility was then terminated. In addition, in connection with the new revolving credit facility, the Company recorded $1.5 million of debt issue costs that is being amortized over the term of the new revolving credit facility. At January 28, 2012, $43.0 million was available under the new revolving credit facility for future borrowings.
| 68 |
FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
All obligations under the new revolving credit facility are unconditionally guaranteed by, subject to certain exceptions, Parent and each of Borrower’s existing and future direct and indirect wholly owned domestic subsidiaries. All obligations under the new revolving credit facility, and the guarantees of those obligations (as well as cash management obligations and any interest rate hedging or other swap agreements), are secured by substantially all of the Borrower’s assets as well as the assets of any subsidiary guarantor.
The borrowings under the new revolving credit facility bear interest at a rate equal to an applicable margin plus, at the Company’s option, either (a) in the case of base rate borrowings, a rate equal to the highest of (i) the prime rate of Royal Bank of Canada, (ii) the federal funds rate plus 1/2 of 1% and (iii) the LIBOR for an interest period of one month plus 1.00%; or (b) in the case of LIBOR borrowings, a rate equal to the higher of (1) 1.50% and (2) the LIBOR for the interest period relevant to such borrowing. The applicable margin for borrowings under the new revolving credit facility will range from 1.25% to 2.25% with respect to base rate borrowings and from 2.25% to 3.25% with respect to LIBOR borrowings, in each case based upon the achievement of specified levels of the ratio of consolidated total debt to consolidated EBITDA. Additionally, the Borrower will be required to pay a fee to the lenders under the new revolving credit facility on the unused amount at a rate ranging from 0.25% to 0.45%, based on the achievement of specified levels of the ratio of consolidated total debt to consolidated EBITDA. The Borrower is also required to pay customary letter of credit fees. The average interest rate for the LIBOR borrowings was 3.8% in fiscal year 2011.
The new revolving credit facility requires the Borrower to maintain a maximum consolidated total lease adjusted leverage ratio and a minimum consolidated interest coverage ratio, in each case, on the last day of any fiscal quarter and includes a maximum capital expenditure in any fiscal year. The Borrower’s ability to pay dividends to Holdings is subject to restrictions including a maximum secured leverage ratio. If the Borrower’s debt under the new revolving credit facility exceeds that ratio, it is restricted from paying dividends. At January 28, 2012, this ratio was within the required limit, thus, the Borrower could pay dividends.
The Borrower is in compliance with the debt covenants of its new revolving credit facility as of January 28, 2012.
Senior Secured Credit Facility
On November 17, 2010, the Borrower entered into a senior secured credit facility (the “prior senior secured credit facility”) with a syndicate of financial institutions, which provided financing of up to $100.0 million consisting of a $95.0 million term loan facility and a $5.0 million revolving credit facility each with a maturity date of November 17, 2013. As described in Note 1, on July 27, 2011, the prior senior secured credit facility was terminated. In connection with the termination, the Company wrote-off the unamortized debt issuance costs of $1.6 million associated with the prior senior secured credit facility and included as loss on early extinguishment of debt in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
All obligations under the prior senior secured credit facility were unconditionally guaranteed by, subject to certain exceptions, Parent and each of the Borrower’s existing and future direct and indirect wholly-owned domestic subsidiaries. All obligations under the prior senior secured credit facility, and the guarantees of those obligations (as well as cash management obligations and any interest hedging or other swap agreements), were secured by substantially all of the Borrower’s assets as well as those of the subsidiary guarantor. The borrowings under the prior senior secured credit facility bore interest at a rate equal to an applicable margin plus the base rate or LIBOR rate, at the Borrower’s option. The loans were LIBOR-based and had an interest rate of 7.75% from the time of issuance through termination on July 27, 2011. The Company was in compliance with the debt covenants of the prior senior secured credit facility during the period it was outstanding.
Debt maturities
Borrowings under the new revolving facility, which had aggregate principal balance of $22.0 million at January 28, 2012, are due on July 27, 2016.
| 69 |
FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
6. Stock-Based Compensation
2007 Stock Incentive Plan
In 2007, the Company adopted the Francesca’s Holdings Corporation 2007 Stock Incentive Plan (the “2007 Plan”), to be administered by Board of Directors or a committee designated by its Board of Directors (the “Committee”). Under the 2007 Plan, awards may be in the form of stock options, restricted stock or phantom shares and may be granted to any employee, director or consultant of the Company. With respect to incentive stock options granted, the share exercise price shall not be less than the fair market price on the date of grant. For non-qualified stock options granted, the share exercise price of each option is determined by the compensation committee of the Board of Directors, which considers the estimated fair value of the Company’s stock when setting stock option price as of the date of each grant. The awards generally vest evenly over four to five years and have a ten year contractual term.
The CCMP Acquisition triggered a “Change of Control” that resulted in the acceleration of vesting, in accordance with the provisions of the 2007 Plan, of the 906,000 stock options issued and outstanding. Accordingly, the Company recognized compensation expense of $1.0 million included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statements of operations for the fiscal year ended January 29, 2011 related to the accelerated vesting.
On April 28, 2010, the plan was amended to adjust the number of shares available for issuance to account for a 400-for-1 stock split. Accordingly, the number of shares authorized to be issued under the 2007 Plan increased to 2,105,200 shares. As of April 28, 2010, the Company can no longer grant awards under the 2007 Plan.
2010 Stock Incentive Plan
On February 27, 2010, the Company adopted the Francesca’s Holdings Corporation 2010 Stock Incentive Plan (the “2010 Plan”) to be administered by the Board of Directors or a Committee. Under the 2010 Plan, awards may be in the form of stock options, stock or restricted stock and may be granted to any officers, directors, eligible employees and consultants of the Company. Exercise prices shall not be less than the fair market value of the Company’s common stock at the date of grant as determined by the Board of Directors. The awards generally vest over four to five years and have a ten year contractual term.
On April 28, 2010, the plan was amended to adjust the number of shares available for issuance to account for a 400-for-1 stock split. Accordingly, the number of shares authorized to be issued under the 2010 Plan increased to 2,020,400 shares. As of July 14, 2011 the Company can no longer grant awards under the 2010 Plan.
On August 18, 2011, the vesting period for the options to purchase 545,333 shares of common stock granted on March 26, 2010 to our Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) accelerated due to the performance targets achieved by CCMP and certain of their affiliates. The Company recognized compensation expense in the amount of $2.3 million in the third quarter of fiscal year 2011 as a result of the accelerated vesting of these options.
2011 Stock Incentive Plan
On July 14, 2011, the 2011 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2011 Plan”) was approved by the stockholders and became immediately effective. Under the 2011 Plan, awards may be in the form of nonqualified stock options, stock appreciation rights, stock bonuses, restricted stock, performance stock and other stock-based awards which can be granted to any officers, directors, employees and consultants of the Company. A total of 3,175,365 shares of common stock are authorized for issuance under the 2011 Plan. Awards granted under the 2011 Plan generally vest over three to five years and have a ten-year contractual life. As of January 28, 2012, there were 2,283,666 awards remaining that can be granted under the 2011 Plan.
Stock Option Award Modification
In November 2010, the Board of Directors authorized and paid a cash dividend equal to $2.39 per share on its common stock following the issuance of a senior secured credit facility (see Note 5). In accordance with applicable plan documents, stock option holders are entitled to an equitable adjustment to their stock option awards upon, among other events, a recapitalization of the Company. As a result, the Board of Directors approved the reduction of the exercise price of certain outstanding options (724,000 total options) in an amount equal to the per share cash dividend effective on December 12, 2010 to reduce the dilution effect of the cash dividend. No incremental compensation expense was recognized because the fair value of the awards did not increase as a result of the modification. Additionally, the Board of Directors allowed certain stock option holders (1,318,000 total options) to participate in the cash dividend in lieu of stock price adjustment. The Company recognized incremental compensation expense of $0.3 million in fiscal year 2010 related to vested options for which the option holders received a cash dividend in lieu of the decrease in exercise price.
| 70 |
FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Stock Options
The following table presents stock options granted, vested and expired and aggregate intrinsic value under the existing share-based compensation plans. The intrinsic value of the stock options was calculated based the closing price of the Company’s common stock on the last trading day closest to January 28, 2012.
| Number of Options | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | |||||||||||||
| (Per share data) | (in Years) | (In thousands) | ||||||||||||||
| Outstanding as of January 29, 2011 | 2,443,088 | $ | 5.23 | 8 | ||||||||||||
| Options granted | 882,099 | $ | 17.44 | 10 | ||||||||||||
| Options exercised | (140,075 | ) | $ | 3.60 | 8 | $ | — | |||||||||
| Options forfeited or expired | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Outstanding as of January 28, 2012 | 3,185,112 | $ | 8.68 | 8 | $ | 44,751 | ||||||||||
| Exercisable at January 28, 2012 | 1,436,392 | $ | 4.74 | 7 | $ | 25,846 | ||||||||||
During fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009, 882,099, 1,994,430 and 406,000 stock options, respectively, were granted at a weighted-average grant date fair value of $9.67, $3.99 and $2.77, respectively. In fiscal year 2011, proceeds from stock option exercises amounted to $0.5 million while the intrinsic value amounted to $1.7 million.
The fair value of stock options was estimated on the date of grant using Black Scholes option pricing model using the following assumptions:
| 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | ||||||||||
| Expected volatility | 54.2 % - 69.9% | 54.2 % - 60.6% | 85.4% | |||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate | 1.1% - 2.11% | 1.6% - 3.2% | 0.9% | |||||||||
| Weighted average term | 6.0 - 6.5 | 6.27 - 6.5 | 2.00 | |||||||||
| Expected dividend yield | — | — | — | |||||||||
The risk-free interest rate was determined based on the rate of Treasury instruments with maturities similar to those of the expected term of the award being valued. The expected dividend yield was based on the Company’s expectations of not paying dividends on its common stock for the foreseeable future. The expected volatility incorporates historical and implied volatility of similar entities whose share prices are publicly available.
| 71 |
FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Stock-based compensation expense for the fiscal years ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 28, 2010 totaled approximately $4.7 million, $2.4 million and $0.1 million, respectively.
The following table summarizes information regarding non-vested outstanding stock options as of and for the fiscal year ended January 28, 2012:
| Options | Weighted Average Fair Value at Grant Date | |||||||
| Non-vested as of January 29, 2011 | 1,757,748 | $ | 4.27 | |||||
| Granted | 882,099 | $ | 9.67 | |||||
| Vested | 891,127 | $ | 4.15 | |||||
| Cancelled | — | — | ||||||
| Non-vested as of January 28, 2012 | 1,748,720 | $ | 7.06 | |||||
As of January 28, 2012, there was approximately $11.2 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested stock option awards that is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 4 years. The total fair value of options vested during the fiscal years ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010 was $3.7 million, $2.0 million and less than $0.1 million, respectively.
Restricted Stock Awards
On August 5, 2011, the Company granted 9,600 restricted stock awards, with an aggregate fair value of $0.2 million, to certain employees under the 2011 Plan. These restricted stock awards vest in three equal annual installments on each anniversary from the grant date subject to continuous employment of the grantee. The Company determined the fair value of the award based on the closing price of the Company’s stock on the grant date.
7. Employee Benefits
In October 2009, the Company adopted a Profit Sharing and 401(k) Plan (the “Plan”) under which full-time and part-time employees become eligible to participate following twelve consecutive months of employment. Eligible employees may elect to contribute a percentage of their earnings to the 401(k) component of the Plan, and the Company makes a discretionary contribution to the Plan based on the contribution of the employees. The Profit Sharing component of the Plan is entirely funded by the Company at its sole discretion. Effective January 1, 2011, the 401(k) component of the Plan was amended whereby the Company will make matching contributions equal to 100% of the first 3% of employee contributions and 50% of the next 2% of employee contributions. For the fiscal years ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010, the Company’s matching contributions were $0.2 million, $0.1 million and less than $0.1 million, respectively.
8. Commitments and Contingencies
Operating leases
The Company leases boutique space and office space under operating leases expiring in various years through the fiscal year ending 2023. Certain of the leases provide that the Company may cancel the lease, with penalties as defined in the lease, if the Company’s boutique sales at that location fall below an established level. Certain leases provide for additional rent payments to be made when sales exceed a base amount. Certain operating leases provide for renewal options for periods from three to five years at the market rate at the time of renewal.
| 72 |
Francesca’s Holdings Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Minimum future rental payments under non-cancellable operating leases as of January 28, 2012, are approximately as follows:
| Fiscal Year | Amount | |||
| (in thousands) | ||||
| 2012 | $ | 19,923 | ||
| 2013 | 19,678 | |||
| 2014 | 18,573 | |||
| 2015 | 17,710 | |||
| 2016 | 16,787 | |||
| Thereafter | 64,400 | |||
| $ | 157,071 | |||
For the years ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010, rent expense totaled $17.1 million, $12.2 million and $7.2 million, respectively. For the fiscal years ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010, common area maintenance and other rental charges totaled $6.3 million, $3.9 million and $2.3 million, respectively.
On December 27, 2011, the Company entered into a lease for a new headquarters and distribution facility. Initially, the Company will occupy approximately 218,000 square feet, which will house its corporate headquarters, warehouse and distribution facility which includes its ecommerce operations and ecommerce fulfillment. The lease for the new facilities includes an option to add as much as an additional 122,000 square feet if necessary. The primary term of the lease expires on April 30, 2020; however, the Company has an option to renew the lease for an additional period of up to ten years. Annual rent expense for the new facility will average approximately $575,000 per year over the term of the primary term of the lease.
Legal Proceedings
From time to time, the Company is subject to various claims and legal proceedings arising in the ordinary course of business. While the outcome of any such claim cannot be predicted with certainty, in the opinion of management, the outcome of these matters will not have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, results of operations or financial conditions.
9. Segment Reporting and Concentration of Risk
The Company determined its operating segments on the same basis used internally to evaluate performance. The Company’s reporting segments are the operation of boutiques and the e-commerce website, which have been aggregated into one reportable financial segment. The Company aggregates its operating segments because (i) the merchandise offered at retail locations and through the e-commerce business is largely the same, (ii) management believes that the majority of its e-commerce customers are also customers of retail locations and (iii) the merchandise margin of both segments is similar. All of the Company’s identifiable assets are located in the United States.
The following is net sales information regarding the Company’s major product classes:
| For Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 |
January 29, 2011 |
January 30, 2010 |
||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Apparel | $ | 104,666 | $ | 70,326 | $ | 45,540 | ||||||
| Jewelry | 41,802 | 27,911 | 16,764 | |||||||||
| Accessories | 32,084 | 19,567 | 8,007 | |||||||||
| Gifts | 25,602 | 17,367 | 8,949 | |||||||||
| Shipping | 220 | 195 | 107 | |||||||||
| 204,374 | 135,366 | 79,367 | ||||||||||
| 73 |
Francesca’s Holdings Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
| For Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
| January 28, 2012 |
January 29, 2011 |
January 30, 2010 |
||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Allowance for sales returns | (216 | ) | (190 | ) | — | |||||||
| Net sales | $ | 204,158 | $ | 135,176 | $ | 79,367 | ||||||
For fiscal year 2011, 2010 and 2009, two of the Company’s vendors accounted for approximately 19%, 23% and 23% of its purchases, with no single vendor accounting for more than 15% of purchases. Those vendors are related parties. See Note 11. Other than those mentioned, no vendor accounted for more than 10% of the Company’s purchases during the fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009. The Company believes that there are other vendors that could replace these vendors and therefore loss of one or both would not result in a material disruption to its business.
10. Convertible Redeemable Preferred Stock—Series A
Under its Certificate of Incorporation, the Company is authorized to issue 45,000 shares of undesignated Preferred Stock. In April 2007, the Board of Directors designated 35,000 preferred shares as Convertible Redeemable Preferred Stock—Series A, par value $0.01 per share, all of which were outstanding through February 25, 2010. The recipients of the Preferred Stock simultaneously purchased a portion of the Company’s common stock directly from the common shareholders and then exchanged such common stock for Preferred Stock. Accordingly, to properly record the redemption amount of the Preferred Stock (“Face Amount”) at that time, a distribution in excess of capital was recorded. Distributions in excess of capital primarily represent deemed dividends recorded to properly reflect the redemption value of Preferred Stock. Distributions in excess of capital was charged with these deemed dividends as the Company did not have sufficient retained earnings or additional paid in capital at the time of issuance. Upon conversion of the Preferred Stock to common stock, the redemption value of Preferred Stock was treated as contributed capital, which eliminated the distributions in excess of capital and establish additional paid in capital.
The Convertible Redeemable Preferred Stock—Series A had the following rights and privileges:
| Ÿ | Dividend—The Preferred Stock accrued cash dividends effective each January 1, whether declared or not, at a rate of 12% per year of the original issue price of the Preferred Stock. In the event that certain earnings before income tax, depreciation and amortization (“EBITDA”) thresholds were met in the calendar year 2007, the dividend rate was to be substituted by 15% or 10%, as appropriate in accordance with the Certificate of Designation governing the Preferred Stock. The Company accrued the required dividends, at the dividend rate of 10% having met the conditions under the Certificate of Designation to use such rate, throughout the year and had considered it when estimating the redemption value of the Preferred Stock at each reporting period in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The Preferred Stock could also participate in dividends on common stock, if declared. |
| Ÿ | Voting—The holders of the Preferred Stock voted on an as-converted basis together with the holders of the Company’s common stock as a single class, except with respect to any increase or decrease in the authorized shares of common stock, as to which the holders of the Preferred Stock had no right to vote. |
| Ÿ | Liquidation—Upon any liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company, whether voluntary or involuntary, or the consummation of any Change of Control Transaction (as defined in the Certificate of Designations governing the Preferred Stock) each holder of outstanding shares of Preferred Stock was entitled to receive an amount equal to the greater of (i) $571.43 per share plus all accumulated but unpaid dividends and (ii) the amount that would be distributed or payable in respect of the number of shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Preferred Stock if such conversion occurred immediately prior to such liquidation event or change of control transaction. |
| 74 |
Francesca’s Holdings Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
| Ÿ | Conversion and redemption feature—The Preferred Stock is convertible into equal number of shares of common stock (adjusted for any stock split) or was mandatorily convertible into common stock upon a Qualified IPO as defined in the Certificate of Designation governing the Preferred Stock. Given that the redemption feature was outside the Company’s control, the Preferred Stock was reflected in the consolidated balance sheets as temporary equity for the period it was outstanding. Upon voluntary or mandatory conversion of the Preferred Stock to common stock all accrued and unpaid dividends were to be deemed automatically satisfied and extinguished without any adjustment to the conversion price or any increase in the number of shares of common stock into which the Preferred Stock was convertible in respect of such accrued but unpaid dividends. The redemption price was the greater of the face amount of the Preferred Stock plus all accrued and unpaid dividends (“Base Amount”) or the fair market value of the Preferred Stock. The Company was required to record the Preferred Stock at its estimated fair market value if determined that the fair market value exceeded the Base Amount. For accounting purposes, the Company has elected to adjust the carrying value of Preferred Stock to equal the redemption value at the end of each reporting period. The increase in redemption value was recorded as a reduction to retained earnings or, in the absence of retained earnings, paid in capital. |
The fair value of the Company’s Preferred Stock was estimated using Level 3 inputs. At January 30, 2010, the estimated fair value totaled $85.9 million, exceeding the Base Amount. The fair value was based on the purchase price paid by CCMP upon purchase of approximately 84% of the underlying common shares (into which the shares of Preferred Stock were converted to in February 2010), as further supported by an independent valuation. Accordingly, the Preferred Stock was recorded at its estimated redemption value of $85.9 million, which took into consideration the accrued dividends of $5.6 million. At January 31, 2009, the estimated fair market value of the Preferred Stock, based on an independent valuation, was determined to be less than the Base Amount. Accordingly, the face amount of the Preferred Stock of $20.0 million plus the accrued dividends of $3.6 million appropriately reflected the redemption value of the Preferred Stock at January 31, 2009.
On February 26, 2010, the holders of Preferred Stock exercised their right to convert all of the outstanding Preferred Stock into 14.0 million shares of common stock in connection with the acquisition by CCMP of approximately 84% of the Company’s outstanding shares. Thus, there were no outstanding shares of Preferred Stock subsequent to February 26, 2010.
11. Related Party Transactions
Stony Leather, Inc. (“Stony”) and KJK Trading Corporation (“KJK”) are two of the Company’s vendors that supply apparel, jewelry, accessories and gifts. Stony is owned and operated by certain shareholders of the Company while KJK is owned by the brother-in-law of one of the Company’s founders. During the fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009, purchases from KJK totaled $8.1 million, $6.6 million and $2.8 million, respectively, while purchases from Stony totaled $5.0 million, $5.0 million and $3.1 million, respectively. Purchases from Stony and KJK accounted for 7%, 10% and 12%, respectively, and 12%, 13% and 11%, respectively, of total purchases for the fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Accounts payable due to related parties for inventory purchases was not material at January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011.
The Company entered into a management agreement with the holder of the Preferred Stock where such holder would provide consulting services in exchange for quarterly fees of $62,500. Upon the conversion of the Preferred Stock, the management agreement was terminated. For the fiscal years 2011, 2010 and 2009, the Company incurred management fees totaling zero, zero and $0.3 million, respectively, which are included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statements of operations.
12. Subsequent Events
In February 2012, certain of our stockholders sold 11,336,476 shares of common stock in a public offering. The Company did not receive any proceeds from the offering and incurred $0.6 million of expenses in fiscal year 2011 relating to this offering, which is included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Subsequent to January 28, 2012, the Borrower made principal payments in the aggregate amount of $6.0 million on the new revolving credit facility, bringing the principal balance to $16.0 million.
| 75 |
Francesca’s Holdings Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
13. Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
| Fiscal Year 2011 | ||||||||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter |
Third Quarter |
Second Quarter |
First Quarter |
|||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 61,652 | $ | 50,020 | $ | 51,221 | $ | 41,265 | ||||||||
| Gross profit | $ | 32,335 | $ | 25,833 | $ | 27,001 | $ | 21,624 | ||||||||
| Income from operations | $ | 14,460 | $ | 8,044 | $ | 12,607 | $ | 8,419 | ||||||||
| Net income | $ | 8,353 | $ | 4,744 | $ | 5,485 | $ | 3,918 | ||||||||
| Basic earnings per common share | $ | 0.19 | $ | 0.11 | $ | 0.13 | $ | 0.10 | ||||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 0.19 | $ | 0.11 | $ | 0.13 | $ | 0.10 | ||||||||
| Fiscal Year 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter |
Third Quarter |
Second Quarter |
First Quarter |
|||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 39,882 | $ | 35,073 | $ | 34,804 | $ | 25,417 | ||||||||
| Gross profit | $ | 20,592 | $ | 18,149 | $ | 18,782 | $ | 12,645 | ||||||||
| Income from operations | $ | 8,912 | $ | 8,401 | $ | 9,709 | $ | 2,621 | ||||||||
| Net income | $ | 4,328 | $ | 5,115 | $ | 5,861 | $ | 1,591 | ||||||||
| Basic earnings per common share | $ | 0.11 | $ | 0.13 | $ | 0.15 | $ | 0.04 | ||||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 0.11 | $ | 0.13 | $ | 0.14 | $ | 0.04 | ||||||||
| 76 |
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL
DISCLOSURE
None.
| ITEM 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial and Administrative Officer, we evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures, as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and Rule 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based on that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial and Administrative Officer have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures as of January 28, 2012, were effective to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms and the information required to be disclosed by us is accumulated and communicated to our management to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
This Annual Report on Form 10-K does not include a report of management’s assessment regarding internal control over financial reporting or an attestation report of the Company’s registered public accounting firm, due to a transition period established by the rules of the SEC for newly public companies.
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended January 28, 2012 that have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect our internal control over financial reporting.
| ITEM 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION |
None.
PART III
| ITEM 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference from our Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting to be held on July 10, 2012.
We have adopted a written code of conduct and ethics, which applies to all of our directors, officers and employees, including our principal executive officer and our principal financial and accounting officer. Our Code of Conduct and Ethics is available on our website www.francescascollections.com under the heading “Corporate Governance.” The information contained on our website is not incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| ITEM 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference from our Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting to be held on July 10, 2012.
| ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference from our Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting to be held on July 10, 2012.
| ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference from our Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting to be held on July 10, 2012.
| 77 |
| ITEM 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference from our Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting to be held on July 10, 2012.
PART IV
| ITEM 15. | EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
| (a) | 1. Financial Statements |
The following consolidated financial statements of the Company are included in Part II, Item 8:
| Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of January 28, 2012 and January 29, 2011 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Operations for the Fiscal Years Ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Changes in Convertible Redeemable Preferred Stock and Shareholders’ Equity (Deficit) for the Fiscal years Ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Fiscal Years Ended January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010 | |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements |
| 2. Financial Statements Schedules |
All schedules are omitted because they are not applicable or because the required information is either not material or is included in the Consolidated Financial Statements or Notes thereto.
3. Exhibits
|
Exhibit No. |
Description | |
| 3.1 | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Francesca’s Holdings Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 of Amendment No. 5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 14, 2011). | |
| 3.2 | Amended and Restated Bylaws of Francesca’s Holdings Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.4 of Amendment No. 5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 14, 2011). | |
| 4.1 | Form of Specimen Common Stock of Francesca’s Holdings Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 of Amendment No. 4 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 13, 2011). | |
| 4.2 | Stockholders’ Agreement, dated as of February 26, 2010, among Francesca’s Holdings Corporation, CCMP Capital Investors II, L.P., CCMP Capital Investors (Cayman) II, L.P., Francesca’s Collections, Inc., the Management Stockholders signatory thereto and any other Persons signatory thereto from time to time (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10-1 of the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on April 19, 2011). | |
| 10.1 | Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of July 27, 2011, among Borrower, Parent, the Guarantors, the lenders party thereto, Royal Bank of Canada, as Administrative Agent and as Collateral Agent and KeyBank National Association, as Syndication Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Current Report on Form 8-K filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 29, 2011). | |
| 10.2 | Guaranty and Security Agreement, dated as of November 17, 2010, among Francesca’s Collections, Inc., the other guarantors party thereto, and Royal Bank of Canada, as administrative agent and collateral agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.3 | Form of Indemnification Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 of Amendment No. 5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 14, 2011). | |
| 78 |
| 10.4 ┼ | Francesca’s Holdings Corporation 2007 Stock Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.5 ┼ | Employee Stock Option Agreement for Theresa Backes, dated as of December 1, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.6 ┼ | Francesca’s Holdings Corporation 2010 Stock Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.7 ┼ | Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement for John De Meritt, dated as of March 31, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.8 ┼ | Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement for Khalid M. Malik, dated as of March 31, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.9 ┼ | Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement for Cynthia Thomassee, dated as of May 1, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.10 ┼ | Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement for Gene Morphis, dated as of December 14, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.11 ┼ | Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement for Richard J. Emmett, dated as of March 31, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.12 ┼ | Francesca’s Holdings Corporation 2011 Equity Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 of Amendment No. 5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 14, 2011). | |
| 10.13 ┼ | Francesca’s Holdings Corporation 2011 Equity Incentive Plan - Form of Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 of Amendment No. 5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 14, 2011). | |
| 10.14 ┼ | Francesca’s Holdings Corporation 2011 Equity Incentive Plan - Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 of Amendment No. 5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 14, 2011). | |
| 10.15 ┼ | Francesca’s Holdings Corporation 2011 Executive Bonus Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16 of Amendment No. 5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 14, 2011). | |
| 10.16 ┼ | Employment Agreement between Francesca’s Holdings Corporation, Francesca’s Collections, Inc. and John De Meritt, dated as of February 26, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.17 ┼ | Employment Letter Agreement between Francesca’s Holdings Corporation and Gene Morphis, dated as of September 9, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.18 ┼ | Employment Letter Agreement between Francesca’s Holdings Corporation and Theresa Backes (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.19 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.19 ┼ | Employment Agreement between Francesca’s Holdings Corporation, Francesca’s Collections, Inc. and Kyong Yi Gill, dated as of February 26, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). |
| 79 |
| 10.20 ┼ | Employment Letter Agreement between Francesca’s Holdings Corporation and Khalid M. Malik, dated as of November 12, 2009 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.21 ┼ | Agreement and First Amendment to Employment Letter Agreement between Francesca’s Holdings Corporation and Khalid M. Malik, dated as of February 26, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.22 ┼ | Letter Agreement between Francesca’s Holdings Corporation and Richard J. Emmett, dated as of November 12, 2009 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on June 14, 2011). | |
| 10.23 ┼ | Amendment to Letter Agreement between Francesca’s Holdings Corporation and Richard J. Emmett, dated as of February 26, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24 of Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on May 24, 2011). | |
| 10.24 | Form of Lock-up Agreement (filed herewith) | |
| 10.25 ┼ | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between Francesca’s Holdings Corporation, Francesca’s Collections, Inc. and John De Meritt, dated as of July 14, 2011 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.27 of Amendment No. 5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 14, 2011). | |
| 10.26 ┼ | Amendment to Employment Letter Agreement between Francesca’s Holdings Corporation and Gene Morphis, dated as of July 14, 2011 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.28 of Amendment No. 5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 14, 2011). | |
| 10.27 ┼ | Employment Letter Agreement between Francesca’s Collections, Inc. and Theresa Backes, dated as of July 14, 2011 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.29 of Amendment No. 5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 14, 2011). | |
| 10.28 ┼ | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between Francesca’s Holdings Corporation, Francesca’s Collections, Inc. and Kyong Yi Gill, dated as of July 14, 2011 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.30 of Amendment No. 5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 14, 2011). | |
| 10.29 ┼ | Employment Letter Agreement between Francesca’s Holdings Corporation, Francesca’s Collections, Inc. and Khalid M. Malik, dated as of July 14, 2011 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.31 of Amendment No. 5 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-173581) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on July 14, 2011). | |
| 10.30 | Commercial Park Lease, dated as of December 27, 2011 between Francesca’s Collections, Inc. and Weingarten / Lufkin, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.32 of the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-179069) filed by Francesca’s Holdings Corporation on January 18, 2012). | |
| 21.1 | Subsidiaries of Francesca’s Holdings Corporation (filed herewith) | |
| 23.1 | Consent of Ernst & Young, independent registered public accountants (filed herewith) | |
| 23.2 | Consent of BDO USA LLP, independent registered public accountants (formerly known as BDO Seidman, LLP) (filed herewith) | |
| 31.1 | Certification of the Annual Report Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 by the Chief Executive Officer (filed herewith) | |
| 31.2 | Certification of the Annual Report Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 by the Chief Financial Officer (filed herewith) | |
| 32.1 | Certification of Annual Report Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 by the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer (filed herewith) | |
| 101.1 | The following financial information from Francesca’s Holdings Corporation’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 28, 2012, formatted in XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language) and furnished electronically herewith: (i) the Consolidated Balance Sheets; (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Operations; (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Changes in Convertible Redeemable Preferred Stock and Stockholder’s Equity (Deficit); (iv) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows; and (v) the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, tagged as blocks of texts. |
┼ Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
| 80 |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized on the 21st day of March, 2012.
| FRANCESCA’S HOLDINGS CORPORATION | ||
| By: | /s/ John De Meritt | |
|
Name: John De Meritt Title: President, Chief Executive Officer | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed by the following persons in the capacities held on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ John De Meritt | President, Chief Executive Officer | March 21, 2012 | ||
| John De Meritt | and Director | |||
| (Principal Executive Officer) | ||||
| /s/ Gene Morphis | Chief Financial Officer | March 21, 2012 | ||
| Gene Morphis | (Principal Financial and | |||
| Accounting Officer) | ||||
| /s/ Greg Brenneman | Director, Non-Executive Chairman | March 21, 2012 | ||
| Greg Brenneman | ||||
| /s/ Kyong Gill | Director, Executive Vice Chairperson | March 21, 2012 | ||
| Kyong Gill | ||||
| /s/ Patricia A. Bender | Director | March 21, 2012 | ||
| Patricia A. Bender | ||||
| /s/ Neill Davis | Director | March 21, 2012 | ||
| Neill Davis | ||||
| /s/ Richard Emmett | Director | March 21, 2012 | ||
| Richard Emmett | ||||
| /s/ Joseph Scharfenberger | Director | March 21, 2012 | ||
| Joseph Scharfenberger | ||||
| /s/ Richard Zannino | Director | March 21, 2012 | ||
| Richard Zannino |
| 81 |
