Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. | ex322-gahr4x10xk2019xq4.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. | ex321-gahr4x10xk2019xq4.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. | ex312-gahr4x10xk2019xq4.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. | ex311-gahr4x10xk2019xq4.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 - Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. | ex231-gahr4x10xk2019xq4.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EXHIBIT 21.1 - Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. | ex211-gahr4x10xk2019xq4.htm |
| EX-4.2 - EXHIBIT 4.2 - Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. | ex42-gahr4x10xk2019xq4.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019 | |
or
¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to | |
Commission File Number: 000-55775
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Maryland | 47-2887436 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
18191 Von Karman Avenue, Suite 300 Irvine, California | 92612 | |
(Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (949) 270-9200
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered | ||
None | None | None | ||
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
Common stock, $0.01 par value per share
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. ¨ Yes x No
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. ¨ Yes x No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Sections 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. x Yes ¨ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). x Yes ¨ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer | ¨ | Accelerated filer | ¨ |
Non-accelerated filer | x | Smaller reporting company | ¨ |
Emerging growth company | x | ||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). ¨ Yes x No
There is no established market for the registrant’s common stock. On April 4, 2019, the registrant’s board of directors established an updated estimated per share net asset value of the registrant’s common stock of $9.54 as of December 31, 2018. As of the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter, there were approximately 73,217,485 shares of Class T common stock and 5,355,072 shares of Class I common stock held by non-affiliates, excluding shares owned by officers of American Healthcare Investors, LLC, the registrant’s affiliated co-sponsor, for an aggregate market value of $698,495,000 and $51,087,000, respectively, assuming a market value as of that date of $9.54 per share.
As of March 13, 2020, there were 74,891,729 shares of Class T common stock and 5,682,901 shares of Class I common stock of Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. outstanding.
______________________________________
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
The registrant incorporates by reference portions of the Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. definitive proxy statement for the 2020 annual meeting of stockholders (into Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14 of Part III).
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
(A Maryland Corporation)
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page | |
2
PART I
Item 1. Business.
The use of the words “we,” “us” or “our” refers to Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. and its subsidiaries, including Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Holdings, LP, except where otherwise noted.
Company
Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc., a Maryland corporation, was incorporated on January 23, 2015 and therefore we consider that our date of inception. We were initially capitalized on February 6, 2015. We invest in a diversified portfolio of real estate properties, focusing primarily on medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities. We also operate healthcare-related facilities utilizing the structure permitted by the REIT Investment Diversification and Empowerment Act of 2007, which is commonly referred to as a “RIDEA” structure (the provisions of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code, authorizing the RIDEA structure were enacted as part of the Housing and Economic Recovery Act of 2008). We may also originate and acquire secured loans and real estate-related investments on an infrequent and opportunistic basis. We generally seek investments that produce current income. We qualified to be taxed as a real estate investment trust, or REIT, under the Code for federal income tax purposes beginning with our taxable year ended December 31, 2016, and we intend to continue to qualify to be taxed as a REIT.
On February 16, 2016, we commenced our initial public offering, or our initial offering, in which we were initially offering to the public up to $3,150,000,000 in shares of our Class T common stock, consisting of up to $3,000,000,000 in shares of our Class T common stock in the primary portion of our initial offering and up to $150,000,000 in shares of our Class T common stock pursuant to our distribution reinvestment plan, as amended, or the DRIP. Effective June 17, 2016, we reallocated certain of the unsold shares of Class T common stock being offered and began offering shares of Class I common stock, such that we were offering up to approximately $2,800,000,000 in shares of Class T common stock and $200,000,000 in shares of Class I common stock in the primary portion of our initial offering, and up to an aggregate of $150,000,000 in shares of our Class T and Class I common stock pursuant to the DRIP, aggregating up to $3,150,000,000. On February 15, 2019, we terminated our initial offering, and as of such date, we sold 75,639,681 aggregate shares of our Class T and Class I common stock, or approximately $754,118,000, and a total of $31,021,000 in distributions were reinvested that resulted in 3,253,535 shares of our common stock being issued pursuant to the DRIP portion of our initial offering.
On January 18, 2019, we filed a Registration Statement on Form S-3 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Act, to register a maximum of $100,000,000 of additional shares of our common stock to be issued pursuant to the DRIP, or the 2019 DRIP Offering. The Registration Statement on Form S-3 was automatically effective with the SEC upon its filing. We commenced offering shares pursuant to the 2019 DRIP Offering on March 1, 2019, following the termination of our initial offering on February 15, 2019. We collectively refer to the DRIP portion of our initial offering and the 2019 DRIP Offering as our DRIP Offerings. As of December 31, 2019, a total of $21,609,000 in distributions were reinvested that resulted in 2,260,164 shares of our common stock being issued pursuant to the 2019 DRIP Offering.
On April 4, 2019, our board of directors, or our board, at the recommendation of the audit committee of our board, comprised solely of independent directors, unanimously approved and established an updated estimated per share net asset value, or NAV, of our common stock of $9.54. We provide this estimated per share NAV to assist broker-dealers in connection with their obligations under Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, or FINRA, Rule 2231 with respect to customer account statements. The estimated per share NAV is based on the estimated value of our assets less the estimated value of our liabilities, divided by the number of shares outstanding on a fully diluted basis, calculated as of December 31, 2018. This valuation was performed in accordance with the methodology provided in Practice Guideline 2013-01, Valuations of Publicly Registered Non-Listed REITs, issued by the Institute for Portfolio Alternatives, or the IPA, in April 2013, in addition to guidance from the SEC. We intend to continue to publish an updated estimated per share NAV on at least an annual basis. See our Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on April 8, 2019, for more information on the methodologies and assumptions used to determine, and the limitations and risks of, our updated estimated per share NAV.
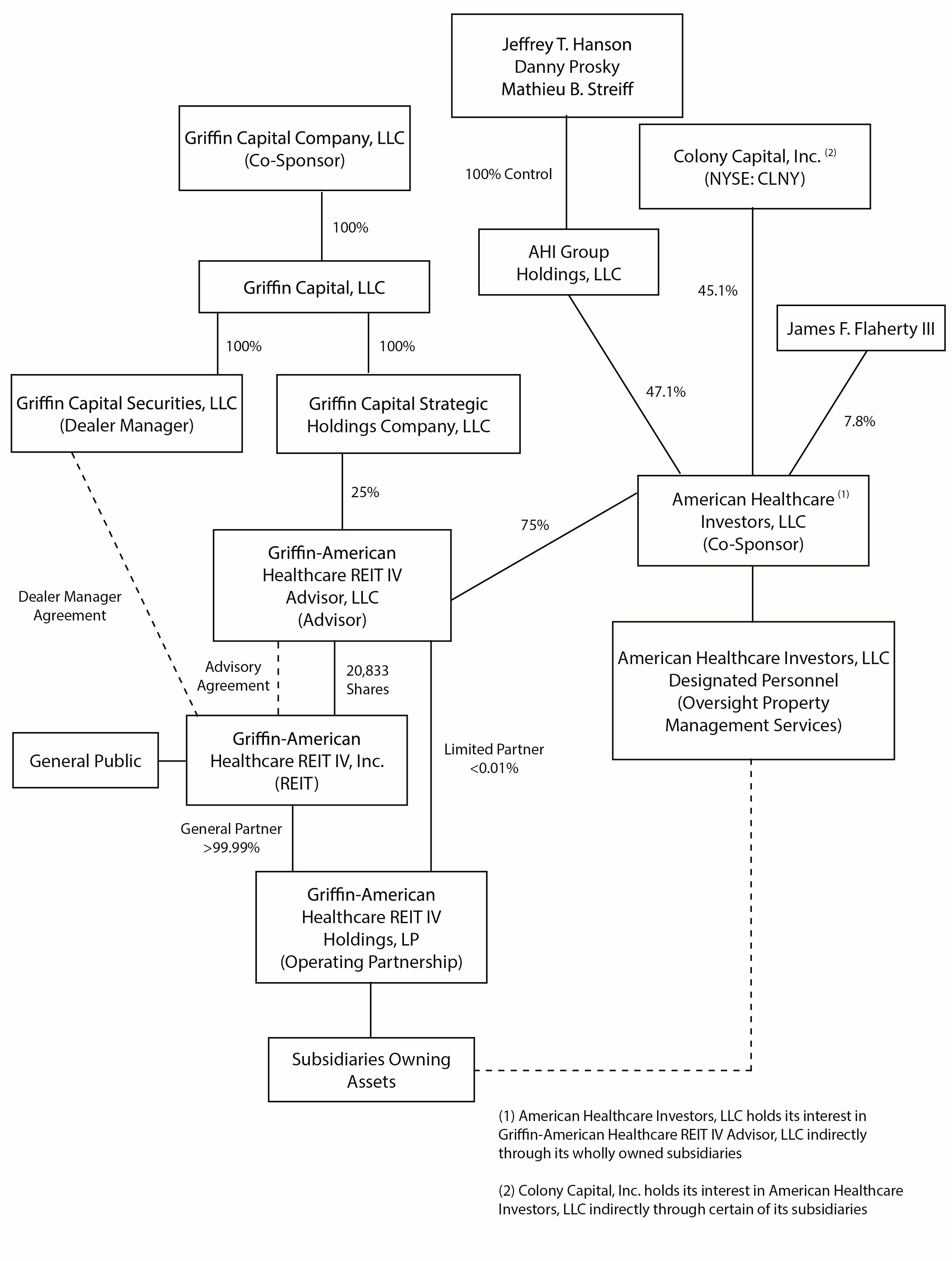
We conduct substantially all of our operations through Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Holdings, LP, or our operating partnership. We are externally advised by Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Advisor, LLC, or our advisor, pursuant to an advisory agreement, or the Advisory Agreement, between us and our advisor. The Advisory Agreement was effective as of February 16, 2016 and had a one-year initial term, subject to successive one-year renewals upon the mutual consent of the parties. The Advisory Agreement was last renewed pursuant to the mutual consent of the parties on February 12, 2020 and expires on February 16, 2021. Our advisor uses its best efforts, subject to the oversight and review of our board, to, among other things, research, identify, review and make investments in and dispositions of properties and securities on our behalf consistent with our investment policies and objectives. Our advisor performs its duties and responsibilities under the Advisory Agreement as our fiduciary. Our advisor is 75.0% owned and managed by wholly owned subsidiaries of American
3
Healthcare Investors, LLC, or American Healthcare Investors, and 25.0% owned by a wholly owned subsidiary of Griffin Capital Company, LLC, or Griffin Capital, or collectively, our co-sponsors. American Healthcare Investors is 47.1% owned by AHI Group Holdings, LLC, or AHI Group Holdings, 45.1% indirectly owned by Colony Capital, Inc. (NYSE: CLNY), or Colony Capital, and 7.8% owned by James F. Flaherty III, a former partner of Colony Capital. We are not affiliated with Griffin Capital, Griffin Capital Securities, LLC, or our dealer manager, Colony Capital or Mr. Flaherty; however, we are affiliated with Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Advisor, LLC, American Healthcare Investors and AHI Group Holdings.
Key developments
• | On April 4, 2019, our board, at the recommendation of the audit committee of our board, comprised solely of independent directors, unanimously approved and established the most recent estimated per share NAV of our common stock of $9.54. |
• | On November 1, 2019, we entered into an amendment to our line of credit and term loans with Bank of America, N.A., KeyBank, National Association and a syndicate of other banks, as lenders. The material terms of such amendment increased the term loan commitment by $45,000,000 and increased the revolving line of credit by $85,000,000, which increased the aggregate borrowing capacity to $530,000,000. See Note 7, Line of Credit and Term Loans, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for a further discussion. |
• | As of March 19, 2020, we had completed 46 property acquisitions whereby we owned 89 properties, comprising 94 buildings, or approximately 4,863,000 square feet of gross leasable area, or GLA, for an aggregate contract purchase price of $1,087,588,000. As of March 19, 2020, we also own a 6.0% interest in a joint venture which owns a portfolio of integrated senior health campuses and ancillary businesses. |
4
Our Structure
The following chart indicates the relationship among us, our advisor and certain of its affiliates as of March 19, 2020:
Our principal executive offices are located at 18191 Von Karman Avenue, Suite 300, Irvine, California 92612, and our telephone number is (949) 270-9200. We maintain a website at http://www.healthcarereitiv.com, at which there is additional information about us and our affiliates. The contents of that site are not incorporated by reference in, or otherwise a part of, this filing. We make our periodic and current reports, and all amendments to those reports, available at http://www.healthcarereitiv.com as soon as reasonably practicable after such materials are electronically filed with the SEC. They also are available for printing by any stockholder upon request. In addition, copies of our filings with the SEC may be obtained from the SEC’s website, http://www.sec.gov. Access to these filings is free of charge.
5
Investment Objectives
Our investment objectives are:
• | to preserve, protect and return our stockholders’ capital contributions; |
• | to pay regular cash distributions; and |
• | to realize growth in the value of our investments upon our ultimate sale of such investments. |
Our board may change our investment objectives if it determines it is advisable and in the best interest of our stockholders.
During the term of the Advisory Agreement, decisions relating to the purchase or sale of investments will be made by our advisor, subject to oversight by our advisor’s investment committee and our board.
Investment Strategy
We have invested, and may continue to invest, in a diversified portfolio of real estate properties, focusing primarily on medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities. On an infrequent and opportunistic basis, we also may originate or acquire real estate-related investments such as mortgage, mezzanine, bridge and other loans, common and preferred stock of, or other interests in, public or private unaffiliated real estate companies, commercial mortgage-backed securities, and certain other securities, including collateralized debt obligations and foreign securities. We have acquired properties and may continue to acquire properties either directly or jointly with third parties. We generally seek investments that produce current income.
We seek to maximize long-term stockholder value by generating sustainable growth in cash flows and portfolio value. In order to achieve these objectives, we may invest using a number of investment structures which may include direct acquisitions, joint ventures, leveraged investments, issuing securities for property and direct and indirect investments in real estate. In order to maintain our exemption from regulation as an investment company under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, or the Investment Company Act, we may be required to limit our investments in certain types of real estate-related investments. See “Investment Company Act Considerations” below for a further discussion.
In addition, when and as determined appropriate by our advisor, our portfolio may also include properties in various stages of development other than those producing current income. These stages would include, without limitation, unimproved land both with and without entitlements and permits, property to be redeveloped and repositioned, newly constructed properties and properties in lease-up or other stabilization, all of which will have limited or no relevant operating histories and no current income. Our advisor will make this determination based upon a variety of factors, including the available risk-adjusted returns for such properties when compared with other available properties, the appropriate diversification of the portfolio, and our objectives of realizing both current income and capital appreciation upon the ultimate sale of properties.
For each of our investments, regardless of property type, we seek to invest in properties with the following attributes:
• | Quality. We seek to acquire properties that are suitable for their intended use with a quality of construction that is capable of sustaining the property’s investment potential for the long-term, assuming funding of budgeted maintenance, repairs and capital improvements. |
• | Location. We seek to acquire properties that are located in established or otherwise appropriate markets for comparable properties, with access and visibility suitable to meet the needs of its occupants. In addition to United States properties, we also seek to acquire international properties that meet our investment criteria. |
• | Market; Supply and Demand. We focus on local or regional markets that have potential for stable and growing property level cash flows over the long-term. These determinations are based in part on an evaluation of local and regional economic, demographic and regulatory factors affecting the property. For instance, we favor markets that indicate a growing population and employment base or markets that exhibit potential limitations on additions to supply, such as barriers to new construction. Barriers to new construction include lack of available land and stringent zoning restrictions. In addition, we generally seek to limit our investments in areas that have limited potential for growth. |
• | Predictable Capital Needs. We seek to acquire properties where the future expected capital needs can be reasonably projected in a manner that would enable us to meet our objectives of growth in cash flows and preservation of capital and stability. |
6
• | Cash Flows. We seek to acquire properties where the current and projected cash flows, including the potential for appreciation in value, would enable us to meet our overall investment objectives. We evaluate cash flows as well as expected growth and the potential for appreciation. |
We have not invested more than 10.0% of the proceeds available for investment from our initial offering in unimproved or non-income producing properties or in other investments relating to unimproved or non-income producing property. A property is considered unimproved or currently non-income producing property for purposes of this limitation if it: (i) is not acquired for the purpose of currently producing rental or other operating income; or (ii) has no development or construction in process at the date of acquisition or planned in good faith to commence within one year of the date of acquisition.
We have not invested more than 10.0% of the proceeds available for investment from our initial offering in commercial mortgage-backed securities. In addition, we have not invested more than 10.0% of the proceeds available for investment from our initial offering in equity securities of public or private real estate companies.
We are not limited as to the geographic areas where we may acquire properties. We are not specifically limited in the number or size of properties we may acquire or on the percentage of our assets that we may invest in a single property or investment. The number and mix of properties and real estate-related investments we will acquire will depend upon real estate and market conditions and other circumstances existing at the time we are acquiring our properties and making our investments and the amount of debt financing available.
Real Estate Investments
We have invested, and may continue to invest, in a diversified portfolio of real estate investments, focusing primarily on medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities. We generally seek investments that produce current income. Our investments may include:
• | medical office buildings; |
• | skilled nursing facilities; |
• | senior housing facilities; |
• | healthcare-related facilities operated utilizing a RIDEA structure; |
• | long-term acute care facilities; |
• | surgery centers; |
• | memory care facilities; |
• | specialty medical and diagnostic service facilities; |
• | laboratories and research facilities; |
• | pharmaceutical and medical supply manufacturing facilities; and |
• | offices leased to tenants in healthcare-related industries. |
Our advisor generally seeks to acquire real estate on our behalf of the types described above that will best enable us to meet our investment objectives, taking into account the diversification of our portfolio at the time, relevant real estate and financial factors, the location, the income-producing capacity, and the prospects for long-range appreciation of a particular property and other considerations. As a result, we may acquire properties other than the types described above. In addition, we may acquire properties that vary from the parameters described above for a particular property type.
The consideration for each real estate investment must be authorized by a majority of our directors or a duly authorized committee of our board, and ordinarily is based on the fair market value of the investment. If the majority of our independent directors or a duly authorized committee of our board so determines, or if the investment is to be acquired from one of our co-sponsors, our advisor, any of our directors or an affiliate thereof, the fair market value determination must be supported by an appraisal obtained from a qualified, independent appraiser selected by a majority of our independent directors.
Our real estate investments generally take the form of holding fee title or long-term leasehold interests. Our investments may be made either directly through our operating partnership or indirectly through investments in joint ventures, limited liability companies, general partnerships or other co-ownership arrangements with the developers of the properties, affiliates of our advisor or other persons. See “Joint Ventures” below for a further discussion.
In addition, we have participated in sale-leaseback transactions in which we purchase real estate investments and lease them back to the sellers of such properties. Our advisor will use its best efforts to structure any such sale-leaseback transaction
7
such that the lease will be characterized as a “true lease” and so that we will be treated as the owner of the property for federal income tax purposes.
Our obligation to close a transaction involving the purchase of real estate is generally conditioned upon the delivery and verification of certain documents from the seller or developer, including, where appropriate:
• | plans and specifications; |
• | environmental reports (generally a minimum of a Phase I investigation); |
• | building condition reports; |
• | surveys; |
• | evidence of marketable title subject to such liens and encumbrances as are acceptable to our advisor; |
• | audited financial statements covering recent operations of real properties having operating histories unless such statements are not required to be filed with the SEC and delivered to stockholders; |
• | title insurance policies; and |
• | liability insurance policies. |
In determining whether to purchase a particular real estate investment, we may, in circumstances in which our advisor deems it appropriate, obtain an option on such property, including land suitable for development. The amount paid for an option is normally surrendered if the real estate is not purchased, and is normally credited against the purchase price if the real estate is purchased. We also may enter into arrangements with the seller or developer of a real estate investment whereby the seller or developer agrees that if, during a stated period, the real estate investment does not generate specified cash flows, the seller or developer will pay us cash in an amount necessary to reach the specified cash flows level, subject in some cases to negotiated dollar limitations.
We will not purchase or lease real estate in which one of our co-sponsors, our advisor, any of our directors or any of their affiliates have an interest without a determination by a majority of our disinterested directors and a majority of our disinterested independent directors that such transaction is fair and reasonable to us and at a price to us no greater than the cost of the real estate investment to the affiliated seller or lessor, unless there is substantial justification for the excess amount and the excess amount is reasonable. In no event will we acquire any such real estate investment at an amount in excess of its current appraised value.
We have obtained, and we intend to continue to obtain, adequate insurance coverage for all real estate investments in which we invest.
We have acquired, and we intend to continue to acquire, leased properties with long-term leases and we generally do not intend to operate any healthcare-related facilities directly. As a REIT, we are prohibited from operating healthcare-related facilities directly; however, from time to time we have leased and may continue to lease a healthcare-related facility that we acquire to a wholly owned taxable REIT subsidiary, or TRS. In such an event, our TRS will engage a third party in the business of operating healthcare-related facilities to manage the property utilizing a RIDEA structure.
Joint Ventures
We have entered into, and we may continue to enter into, joint ventures, general partnerships and other arrangements with one or more institutions or individuals, including real estate developers, operators, owners, investors and others, some of whom may be affiliates of our advisor, for the purpose of acquiring real estate. Such joint ventures may be leveraged with debt financing or unleveraged. We have entered into and may continue to enter into joint ventures to further diversify our investments or to access investments which meet our investment criteria that would otherwise be unavailable to us. In determining whether to invest in a particular joint venture, our advisor will evaluate the real estate that such joint venture owns or is being formed to own under the same criteria described elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the selection of our other properties. However, we will not participate in tenant in common syndications or transactions.
Joint ventures with unaffiliated third parties may be structured such that the investment made by us and the co-venturer are on substantially different terms and conditions. For example, while we and a co-venturer may invest an equal amount of capital in an investment, the investment may be structured such that we have a right to priority distributions of cash flows up to a certain target return while the co-venturer may receive a disproportionately greater share of cash flows than we are to receive once such target return has been achieved. This type of investment structure may result in the co-venturer receiving more of the cash flows, including appreciation, of an investment than we would receive. See Item 1A, Risk Factors — Risks Related to Joint Ventures, for a further discussion.
8
We may invest in general partnerships or joint ventures with other Griffin Capital programs or American Healthcare Investors-sponsored programs or affiliates of our advisor to enable us to increase our equity participation in such ventures, so that ultimately we own a larger equity percentage of the property. Our entering into joint ventures with our advisor or any of its affiliates may result in certain conflicts of interest. See Item 1A, Risk Factors — Risks Related to Conflicts of Interest — We have entered into and may continue to enter into joint ventures with other programs sponsored or advised by one of our co-sponsors or one of their affiliates and may face conflicts of interest or disagreements with our joint venture partners that may not be resolved as quickly or on terms as advantageous to us as would be the case if the joint venture had been negotiated at arm’s-length with an independent joint venture partner, for a further discussion.
We may only enter into joint ventures with other Griffin Capital programs or American Healthcare Investors-sponsored programs, affiliates of our advisor or any of our directors for the acquisition of properties if:
• | a majority of our directors, including a majority of our independent directors, not otherwise interested in such transaction, approves the transaction as being fair and reasonable to us; and |
• | the investment by us and such affiliates are on substantially the same terms and conditions. |
Real Estate-Related Investments
In addition to our acquisition of medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities, on an infrequent and opportunistic basis, we also may invest in real estate-related investments, including loans (mortgage, mezzanine, bridge and other loans) and securities investments (common and preferred stock of or other interests in public or private unaffiliated real estate companies, commercial mortgage-backed securities, and certain other securities, including collateralized debt obligations and foreign securities).
Investing In and Originating Loans
Our criteria for making or investing in loans will be substantially the same as those involved in our investment in properties. We do not intend to make loans to other persons, to underwrite securities of other issuers or to engage in the purchase and sale of any types of investments other than those relating to real estate. We will not make or invest in mortgage loans, including a construction loan, on any one property if the aggregate amount of all mortgage loans outstanding on the property, including our loan, would exceed an amount equal to 85.0% of the appraised value of the property, as determined by an appraiser, unless we find substantial justification due to other underwriting criteria; however, our policy generally will be that the aggregate amount of all mortgage loans outstanding on the property, including our loan, would not exceed 75.0% of the appraised value of the property. We may find such justification in connection with the purchase of loans in cases in which we believe there is a high probability of our foreclosure upon the property in order to acquire the underlying assets and in which the cost of the loan investment does not exceed the fair market value of the underlying property. We will not invest in or make loans unless an appraisal has been obtained concerning the underlying property, except for those loans insured or guaranteed by a government or government agency. In cases in which a majority of our independent directors so determine and in the event the transaction is with one of our co-sponsors, our advisor, any of our directors or any of their respective affiliates, the appraisal will be obtained from a certified independent appraiser to support its determination of fair market value.
We may invest in first and second mortgage loans, mezzanine loans and bridge loans. However, we will not make or invest in any loans that are subordinate to any mortgage or equity interest of our advisor, any of our directors, one of our co-sponsors, or any of our affiliates. We also may invest in participations in mortgage loans. Second mortgage loans are secured by second deeds of trust on real property that is already subject to prior mortgage indebtedness. A mezzanine loan is a loan made in respect of certain real property but is secured by a lien on the ownership interests of the entity that, directly or indirectly, owns the real property. A bridge loan is short term financing, for an individual or business, until permanent or the next stage of financing can be obtained. Mortgage participation investments are investments in partial interests of mortgages of the type described above that are made and administered by third-party mortgage lenders.
In evaluating prospective loan investments, our advisor considers factors such as the following:
• | the ratio of the investment amount to the underlying property’s value; |
• | the property’s potential for capital appreciation; |
• | expected levels of rental and occupancy rates; |
• | the condition and use of the property; |
• | current and projected cash flows of the property; |
• | potential for rent increases; |
• | the degree of liquidity of the investment; |
9
• | the property’s income-producing capacity; |
• | the quality, experience and creditworthiness of the borrower; |
• | general economic conditions in the area where the property is located; |
• | in the case of mezzanine loans, the ability to acquire the underlying real property; and |
• | other factors that our advisor believes are relevant. |
In addition, we will seek to obtain a customary lender’s title insurance policy or commitment as to the priority of the mortgage or condition of the title. Because the factors considered, including the specific weight we place on each factor, will vary for each prospective loan investment, we do not, and are not able to, assign a specific weight or level of importance to any particular factor.
We may purchase existing loans from affiliates, and we may make or invest in loans in which the borrower is an affiliate. Our advisor will evaluate all potential loan investments to determine if the security for the loan and the loan-to-value ratio meets our investment criteria and objectives. Most loans that we will consider for investment would provide for monthly payments of interest and some may also provide for principal amortization, although many loans of the nature that we will consider provide for payments of interest only and a payment of principal in full at the end of the loan term. We will not originate loans with negative amortization provisions.
We are not limited as to the amount of our assets that may be invested in mezzanine loans, bridge loans and second mortgage loans. However, we recognize that these types of loans are riskier than first deeds of trust or first priority mortgages on income-producing, fee-simple properties, and we expect to minimize the amount of these types of loans in our portfolio. Our advisor will evaluate the fact that these types of loans are riskier in determining the rate of interest on the loans. We do not have any policy that limits the amount that we may invest in any single loan or the amount we may invest in loans to any one borrower. We have not established a portfolio turnover policy with respect to loans we may invest in or originate.
Our loan investments may be subject to regulation by federal, state and local authorities and subject to various laws and judicial and administrative decisions imposing various requirements and restrictions, including among other things, regulating credit granting activities, establishing maximum interest rates and finance charges, requiring disclosures to customers, governing secured transactions and setting collection, repossession and claims handling procedures and other trade practices. In addition, certain states have enacted legislation requiring the licensing of mortgage bankers or other lenders and these requirements may affect our ability to effectuate our proposed investments in loans. Commencement of operations in these or other jurisdictions may be dependent upon a finding of our financial responsibility, character and fitness. We may determine not to make loans in any jurisdiction in which the regulatory authority determines that we have not complied in all material respects with applicable requirements.
Investing in Securities
We may invest in the following types of securities: (i) equity securities such as common stocks, preferred stocks and convertible preferred securities of public or private unaffiliated real estate companies (including other REITs, real estate operating companies and other real estate companies); (ii) debt securities such as commercial mortgage-backed securities and debt securities issued by other unaffiliated real estate companies; and (iii) certain other types of securities that may help us reach our diversification and other investment objectives. These other securities may include, but are not limited to, various types of collateralized debt obligations and certain non-United States dollar denominated securities.
Our advisor has substantial discretion with respect to the selection of specific securities investments. Our charter provides that we may not invest in equity securities unless a majority of our directors, including a majority of our independent directors, not otherwise interested in the transaction, approve such investment as being fair, competitive and commercially reasonable. Consistent with such requirements, in determining the types of securities investments to make, our advisor will adhere to a board-approved asset allocation framework consisting primarily of components such as: (i) target mix of securities across a range of risk/reward characteristics; (ii) exposure limits to individual securities; and (iii) exposure limits to securities subclasses (such as common equities, debt securities and foreign securities). Within this framework, our advisor will evaluate specific criteria for each prospective securities investment including, but not limited to:
• | positioning the overall portfolio to achieve an optimal mix of real estate and real estate-related investments; |
• | diversification benefits relative to the rest of the securities assets within our portfolio; |
• | fundamental securities analysis; |
• | quality and sustainability of underlying property cash flows; |
• | broad assessment of macroeconomic data and regional property level supply and demand dynamics; |
10
• | potential for delivering high current income and attractive risk-adjusted total returns; and |
• | additional factors considered important to meeting our investment objectives. |
Commercial mortgage-backed securities are securities that evidence interests in, or are secured by, a single commercial mortgage loan or a pool of commercial mortgage loans. Commercial mortgage-backed securities generally are pass-through certificates that represent beneficial ownership interests in common law trusts whose assets consist of defined portfolios of one or more commercial mortgage loans. They typically are issued in multiple tranches whereby the more senior classes are entitled to priority distributions from the trust’s income. Losses and other shortfalls from expected amounts to be received in the mortgage pool are borne by the most subordinate classes, which receive payments only after the more senior classes have received all principal and/or interest to which they are entitled. Commercial mortgage-backed securities are subject to all of the risks of the underlying mortgage loans. We may invest in investment grade and non-investment grade commercial mortgage-backed securities. However, we have not invested more than 10.0% of the proceeds available for investment from our initial offering in commercial mortgage-backed securities.
We have not invested more than 10.0% of the proceeds available for investment from our initial offering in equity securities of public or private real estate companies. The specific number and mix of securities in which we invest will depend upon real estate market conditions, other circumstances existing at the time we are investing in securities, the amount of any future indebtedness that we may incur and any possible future equity offerings. We will not invest in securities of other issuers for the purpose of exercising control and the first or second mortgages in which we intend to invest will likely not be insured by the Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the Department of Veterans Affairs or otherwise guaranteed or insured. Real estate-related equity securities are generally unsecured and also may be subordinated to other obligations of the issuer. Our investments in real estate-related equity securities will involve special risks relating to the particular issuer of the equity securities, including the financial condition and business outlook of the issuer.
Our Strategies and Policies With Respect to Borrowing
We have used, and intend to continue to use, secured and unsecured debt as a means of providing additional funds for the acquisition of properties and real estate-related investments. Our ability to enhance our investment returns and to increase our diversification by acquiring assets using additional funds provided through borrowing could be adversely impacted if banks and other lending institutions reduce the amount of funds available for the types of loans we seek. When interest rates are high or financing is otherwise unavailable on a timely basis, we may purchase certain assets for cash with the intention of obtaining debt financing at a later time. We have also used, and may continue to use, derivative financial instruments such as fixed interest rate swaps and caps to add stability to interest expense and to manage our exposure to interest rate movements.
We anticipate that our overall leverage will not exceed 50.0% of the combined market value of all of our real estate, real estate-related investments and joint venture interests, as determined at the end of each calendar year. For these purposes, the fair market value of each asset will be equal to the purchase price paid for the asset or, if the asset was appraised subsequent to the date of purchase, then the fair market value will be equal to the value reported in the most recent independent appraisal of the asset. Our borrowing policies do not limit the amount we may borrow with respect to any individual investment. As of December 31, 2019, our aggregate borrowings were 36.3% of the combined market value of all our real estate and joint venture interest.
Our board reviews our aggregate borrowings at least quarterly to ensure that such borrowings are reasonable in relation to our net assets. Our borrowing policies preclude us from borrowing in excess of 300% of our net assets, unless any excess in such borrowing is approved by a majority of our independent directors and is disclosed in our next quarterly report along with justification for such excess. Net assets for purposes of this calculation are defined as our total assets, other than intangibles, valued at cost before deducting depreciation, amortization, bad debt and other similar non-cash reserves, less total liabilities. Generally, the preceding calculation is expected to approximate 75.0% of the aggregate cost of our real estate and real estate-related investments before depreciation, amortization, bad debt and other similar non-cash reserves. However, we may temporarily borrow in excess of these amounts if such excess is approved by a majority of our independent directors and disclosed to stockholders in our next quarterly report, along with justification for such excess. In such event, we will review our debt levels at that time and take action to reduce any such excess as soon as practicable. We may also incur indebtedness to finance improvements to properties and, if necessary, for working capital needs or to meet the distribution requirements applicable to REITs under the federal income tax laws. In addition, if our cash flows from operations are not sufficient to pay the stockholder servicing fee paid with respect to our shares of Class T common stock sold, we will pay the stockholder servicing fee through borrowings in anticipation of future cash flows. As of March 19, 2020 and December 31, 2019, our leverage did not exceed 300% of the value of our net assets.
By operating on a leveraged basis, we have more funds available for our investments. This generally enables us to make more investments than would otherwise be possible, potentially resulting in enhanced investment returns and a more diversified portfolio.
11
Our advisor uses its best efforts to obtain financing on the most favorable terms available to us and refinances assets during the term of a loan only in limited circumstances, such as when a decline in interest rates makes it beneficial to prepay an existing loan, when an existing loan matures or if an attractive investment becomes available and the proceeds from the refinancing can be used to purchase such investment. The benefits of the refinancing may include increased cash flows resulting from reduced debt service requirements, an increase in distributions from proceeds of the refinancing, and an increase in diversification and assets owned if all or a portion of the refinancing proceeds are reinvested.
Our charter restricts us from borrowing money from one of our co-sponsors, our advisor, any of our directors or any of their respective affiliates unless such loan is approved by a majority of our directors, including a majority of our independent directors, not otherwise interested in the transaction, as being fair, competitive and commercially reasonable and no less favorable to us than comparable loans between unaffiliated parties.
When incurring secured debt, we may incur recourse indebtedness, which means that the lenders’ rights upon our default generally will not be limited to foreclosure on the property that secured the obligation. If we incur mortgage indebtedness, we will endeavor to obtain level payment financing, meaning that the amount of debt service payable would be substantially the same each year, although some mortgages are likely to provide for one large payment and we may incur floating or adjustable rate financing when our board determines it to be in our best interest.
Our board controls our strategies with respect to borrowing and may change such strategies at any time without stockholder approval, subject to the maximum borrowing limit of 300% of our net assets described above.
Real Estate Acquisitions
Our advisor evaluates various potential investments on our behalf and engage in discussions and negotiations with real property sellers, developers, brokers, lenders, investment managers and others regarding such potential investments. We expect that this will normally occur upon the signing of a purchase agreement for the acquisition of a specific, significant property or real estate-related investment, but may occur before or after such signing or upon the satisfaction or expiration of major contingencies in any such purchase agreement, depending on the particular circumstances surrounding each potential investment.
Sale or Disposition of Assets
Our advisor and our board will determine whether a particular property or real estate-related investment should be sold or otherwise disposed of after consideration of the relevant factors, including performance or projected performance of the property and market conditions, with a view toward achieving our principal investment objectives.
We intend to hold each property or real estate-related investment we acquire for an extended period. However, circumstances might arise which could result in a shortened holding period for certain investments. A property or real estate-related investment may be sold before the end of the expected holding period if:
• | diversification benefits exist associated with disposing of the investment and rebalancing our investment portfolio; |
• | an opportunity arises to pursue a more attractive investment; |
• | in the judgment of our advisor, the value of the investment might decline; |
• | with respect to properties, a major tenant involuntarily liquidates or is in default under its lease; |
• | the investment was acquired as part of a portfolio acquisition and does not meet our general acquisition criteria; |
• | an opportunity exists to enhance overall investment returns by raising capital through sale of the investment; or |
• | in the judgment of our advisor, the sale of the investment is in the best interest of our stockholders. |
The determination of whether a particular property or real estate-related investment should be sold or otherwise disposed of will be made after consideration of the relevant factors, including prevailing economic conditions, with a view toward maximizing our investment objectives.
Construction and Development Activities
From time to time, we may construct and develop real estate assets or render services in connection with these activities. We may be able to reduce overall purchase costs by constructing and developing property versus purchasing a finished property. We retain and will continue to retain independent contractors to perform the actual construction work on tenant improvements, such as installing heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems.
12
Additionally, we may engage our advisor or its affiliates to provide development-related services for all or some of the properties that we develop or acquire for refurbishment. In those cases, we pay our advisor or its affiliates a development fee that is usual and customary for comparable services rendered for similar projects in the geographic market where the services are provided. However, we do not pay a development fee to our advisor or its affiliates if our advisor or any of its affiliates elect to receive an acquisition fee based on the cost of such development. In the event that our advisor assists with planning and coordinating the construction of any tenant improvements or capital improvements, our advisor may be paid a construction management fee of up to 5.0% of the cost of such improvements.
Terms of Leases
The terms and conditions of any lease we enter into with our tenants may vary substantially from those we describe in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. However, we expect that a majority of our leases will require the tenant to pay or reimburse us for some or all of the operating expenses of the building based on the tenant’s proportionate share of rentable space within the building. Operating expenses typically include, but are not limited to, real estate and other taxes, utilities, insurance and building repairs, and other building operation and management costs. We expect to be responsible for the replacement of specific structural components of a property such as the roof of the building or the parking lot. We expect that many of our leases will have terms of five or more years, some of which may have renewal options.
Board Review of Our Investment Policies and Report of Independent Directors
Our board has established written policies on investments and borrowing. Our board is responsible for monitoring the administrative procedures, investment operations and performance of our company and our advisor to ensure such policies are carried out. Our charter requires that our independent directors review our investment policies at least annually to determine that the policies we are following are in the best interest of our stockholders. Each determination and the basis therefore is required to be set forth in the minutes of the applicable meetings of our directors. Implementation of our investment policies also may vary as new investment techniques are developed. Our investment policies may not be altered by our board without the approval of our stockholders.
As required by our charter, our independent directors have reviewed our policies outlined above and determined that they are in the best interests of our stockholders because: (i) they increase the likelihood that we will be able to acquire a diversified portfolio of income-producing properties, thereby reducing risk in our portfolio; (ii) there are sufficient property acquisition opportunities with the attributes that we seek; (iii) our executive officers, directors and affiliates of our advisor have expertise with the type of real estate investments we seek; and (iv) our borrowings will enable us to purchase assets and earn more real estate revenue earlier than we would otherwise have been able to, thereby increasing our likelihood of generating income for our stockholders and preserving stockholder capital.
Tax Status
We qualified and elected to be taxed as a REIT under the Code beginning with our taxable year ended December 31, 2016. To maintain our qualification as a REIT, we must meet certain organizational and operational requirements, including our requirement to currently distribute at least 90.0% of our annual taxable income, excluding net capital gains, to our stockholders. As a REIT, we generally will not be subject to federal income tax on taxable income that we distribute to our stockholders.
Distribution Policy
In order to maintain our qualification as a REIT for federal income tax purposes, among other things, we are required to distribute at least 90.0% of our annual taxable income, excluding net capital gains, to our stockholders. We cannot predict if we will generate sufficient cash flows to continue to pay cash distributions to our stockholders on an ongoing basis or at all. The amount of any cash distributions is determined by our board and depends on the amount of distributable funds, current and projected cash requirements, tax considerations, any limitations imposed by the terms of indebtedness we may incur and other factors. If our investments produce sufficient cash flows, we expect to continue to pay distributions to our stockholders on a monthly basis. Because our cash available for distribution in any year may be less than 90.0% of our annual taxable income, excluding net capital gains, for the year, we may be required to borrow money, use proceeds from the issuance of securities (in subsequent offerings, if any) or sell assets to pay out enough of our taxable income to satisfy the distribution requirement. These methods of obtaining funds could affect future distributions by increasing operating costs. We did not establish any limit on the amount of net proceeds from our initial offering, and we have not established any limit on the amount of net proceeds from any future offerings, that may be used to fund distributions, except that, in accordance with our organizational documents and Maryland law, we may not make distributions that would: (i) cause us to be unable to pay our debts as they become due in the usual course of business; or (ii) cause our total assets to be less than the sum of our total liabilities plus senior liquidation preferences.
13
To the extent that distributions to our stockholders are paid out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits, such distributions are taxable as ordinary income. To the extent that our distributions exceed our current and accumulated earnings and profits, such amounts constitute a return of capital to our stockholders for federal income tax purposes, to the extent of their basis in their stock and thereafter will constitute capital gain. Any portion of distributions to our stockholders paid from net offering proceeds constitutes a return of capital to our stockholders.
Monthly distributions are calculated with daily record dates so distribution benefits begin to accrue immediately upon becoming a stockholder. However, our board could, at any time, elect to pay distributions quarterly to reduce administrative costs.
The amount of distributions we pay to our stockholders is determined by our board and is dependent on a number of factors, including funds available for the payment of distributions, our financial condition, capital expenditure requirements, annual distribution requirements needed to maintain our status as a REIT under the Code and restrictions imposed by our organizational documents and Maryland Law.
See Part II, Item 5, Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities — Distributions, for a further discussion of distributions approved by our board.
Competition
We compete with many other entities engaged in real estate investment activities for acquisitions of medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities, including international, national, regional and local operators, acquirers and developers of healthcare real estate properties. The competition for healthcare real estate properties may significantly increase the price we must pay for medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities or other assets we seek to acquire, and our competitors may succeed in acquiring those properties or assets themselves. In addition, our potential acquisition targets may find our competitors to be more attractive because they may have greater resources, may be willing to pay more for the properties or may have a more compatible operating philosophy. In particular, larger healthcare REITs may enjoy significant competitive advantages that result from, among other things, a lower cost of capital and enhanced operating efficiencies. Further, the number of entities and the amount of funds competing for suitable investment properties may increase. This competition will result in increased demand for these assets, and therefore, increased prices paid for them. If there is an increased interest in single-property acquisitions among tax-motivated individual purchasers, we may pay higher prices per property if we purchase single properties in comparison with portfolio acquisitions. If we pay higher prices per property for medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing or other healthcare-related facilities, our business, financial condition, results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders may be materially and adversely affected and our stockholders may experience a lower return on their investment.
In addition, income from our investments is dependent on the ability of our tenants and operators to compete with other healthcare operators. These operators compete on a local and regional basis for residents and patients and the operators’ ability to successfully attract and retain residents and patients depends on key factors such as the number of facilities in the local market, the types of services available, the quality of care, reputation, age and appearance of each facility and the cost of care in each locality. Private, federal and state payment programs and the effect of other laws and regulations may also have a significant impact on the ability of our tenants and operators to compete successfully for residents and patients at the properties. For additional information on the risks associated with our business, please see Item 1A, Risk Factors.
Government Regulations
Many laws and governmental regulations are applicable to our properties and changes in these laws and regulations, or their interpretation by agencies and the courts, occur frequently.
Costs of Compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act. Under the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990, as amended, or the ADA, all public accommodations must meet federal requirements for access and use by disabled persons. Although we believe that we are in substantial compliance with present requirements of the ADA, none of our properties have been audited, nor have investigations of our properties been conducted to determine compliance. Additional federal, state and local laws also may require modifications to our properties or restrict our ability to renovate our properties. We cannot predict the cost of compliance with the ADA or other legislation. We may incur substantial costs to comply with the ADA or any other legislation.
Costs of Government Environmental Regulation and Private Litigation. Environmental laws and regulations hold us liable for the costs of removal or remediation of certain hazardous or toxic substances which may be on our properties. These laws could impose liability without regard to whether we are responsible for the presence or release of the hazardous materials. Government investigations and remediation actions may have substantial costs and the presence of hazardous substances on a
14
property could result in personal injury or similar claims by private plaintiffs. Various laws also impose liability on a person who arranges for the disposal or treatment of hazardous or toxic substances and such person often must incur the cost of removal or remediation of hazardous substances at the disposal or treatment facility. These laws often impose liability whether or not the person arranging for the disposal ever owned or operated the disposal facility. As the owner of our properties, we may be deemed to have arranged for the disposal or treatment of hazardous or toxic substances.
Other Federal, State and Local Regulations. Our properties are subject to various federal, state and local regulatory requirements, such as state and local fire and life safety requirements. If we fail to comply with these various requirements, we may incur governmental fines or private damage awards. While we believe that our properties are and will be in substantial compliance with all of these regulatory requirements, we do not know whether existing requirements will change or whether future requirements will require us to make significant unanticipated expenditures that will adversely affect our ability to make distributions to our stockholders. We believe, based in part on engineering reports which are generally obtained at the time we acquire the properties, that all of our properties comply in all material respects with current regulations. However, if we were required to make significant expenditures under applicable regulations, our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to satisfy our debt service obligations and to pay distributions could be adversely affected.
Issuing Securities for Property
Subject to limitations contained in our organizational and governance documents, we may issue, or cause to be issued, shares of our stock or limited partnership units in our operating partnership in any manner (and on such terms and for such consideration) in exchange for real estate. Our existing stockholders have no preemptive rights to purchase such shares of our stock or limited partnership units in any such offering, and any such offering might cause a dilution of a stockholder’s initial investment.
In order to induce the contributors of such properties to accept units in our operating partnership, rather than cash, in exchange for their properties, it may be necessary for us to provide them additional incentives. For instance, our operating partnership’s partnership agreement provides that any holder of units may exchange limited partnership units on a one-for-one basis for shares of our common stock, or, at our option, cash equal to the value of an equivalent number of shares of our common stock. We may, however, enter into additional contractual arrangements with contributors of property under which we would agree to repurchase a contributor’s units for shares of our common stock or cash, at the option of the contributor, at set times. In order to allow a contributor of a property to defer taxable gain on the contribution of property to our operating partnership, we might agree not to sell a contributed property for a defined period of time or until the contributor exchanged the contributor’s units for cash or shares of our common stock. Such an agreement would prevent us from selling those properties, even if market conditions made such a sale favorable to us. Although we may enter into such transactions with other existing or future American Healthcare Investors or Griffin Capital programs, we do not currently intend to do so. If we were to enter into such a transaction with an entity managed by one of our co-sponsors or its affiliates, we would be subject to the risks described in Item 1A, Risk Factors — Risks Related to Conflicts of Interest. We may acquire assets from, or dispose of assets to, affiliates of our advisor, which could result in us entering into transactions on less favorable terms than we would receive from a third party or that negatively affect the public’s perception of us.
Significant Tenants
As of December 31, 2019, we had one tenant that accounted for 10.0% or more of our total property portfolio’s annualized base rent or annualized net operating income, or NOI, as follows:
Tenant | Annualized Base Rent(1) | Percentage of Annualized Base Rent | Acquisition | Reportable Segment | GLA (Sq Ft) | Lease Expiration Date | ||||||||
RC Tier Properties, LLC | $ | 7,782,000 | 10.4% | Missouri SNF Portfolio | Skilled Nursing | 385,000 | 09/30/33 | |||||||
(1) | Annualized base rent is based on contractual base rent from leases in effect as of December 31, 2019, inclusive of our senior housing — RIDEA facilities. The loss of this tenant or its inability to pay rent could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations. |
Geographic Concentration
For a discussion of our geographic information, see Item 2, Properties — Geographic Diversification/Concentration Table, as well as Note 18, Concentration of Credit Risk, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
15
Employees
We have no employees and our executive officers are all employees of one of our co-sponsors of our advisor. Our day-to-day management is performed by our advisor and its affiliates. We cannot determine at this time if or when we might hire any employees, although we do not anticipate hiring any employees during the next twelve months. We do not directly compensate our executive officers for services rendered to us. However, our executive officers, consultants and the executive officers and key employees of our advisor and its affiliates are eligible for awards pursuant to the 2015 Incentive Plan, or our incentive plan. As of December 31, 2019, no awards had been granted to our executive officers, consultants or the executive officers or key employees of our advisor or its affiliates under this plan.
Investment Company Act Considerations
We conduct and intend to continue to conduct our operations, and the operations of our operating partnership and any other subsidiaries, so that no such entity meets the definition of an “investment company” under Section 3(a)(1) of the Investment Company Act. We primarily engage in the business of investing in real estate assets; however, our portfolio may include, to a much lesser extent, other real estate-related investments. We have also acquired and may continue to acquire real estate assets through investments in joint venture entities, including joint venture entities in which we may not own a controlling interest. We anticipate that our assets generally will be held in wholly and majority-owned subsidiaries of the company, each formed to hold a particular asset. We monitor our operations and our assets on an ongoing basis in order to ensure that neither we, nor any of our subsidiaries, meet the definition of “investment company” under Section 3(a)(1) of the Investment Company Act. Among other things, we monitor the proportion of our portfolio that is placed in investments in securities.
Information About Industry Segments
Financial Accounting Standards Board, or FASB, Accounting Standards Codification, or ASC, Topic 280, Segment Reporting, establishes standards for reporting financial and descriptive information about a public entity’s reportable segments. We segregate our operations into reporting segments in order to assess the performance of our business in the same way that management reviews our performance and makes operating decisions. Accordingly, when we acquired our first medical office building in June 2016; senior housing facility in December 2016; senior housing — RIDEA facility in November 2017; and skilled nursing facility in March 2018, we added a new reportable segment at each such time. As of December 31, 2019, we operated through four reportable business segments — medical office buildings, senior housing, senior housing — RIDEA and skilled nursing facilities.
Medical Office Buildings. As of December 31, 2019, we owned 43 medical office buildings, or MOBs. These properties typically contain physicians’ offices and examination rooms and may also include pharmacies, hospital ancillary service space and outpatient services such as diagnostic centers, rehabilitation clinics and day-surgery operating rooms. While these properties are similar to commercial office buildings, they require additional parking spaces as well as plumbing, electrical and mechanical systems to accommodate multiple exam rooms that may require sinks in every room and special equipment such as x-ray machines. In addition, MOBs are often built to accommodate higher structural loads for certain equipment and may contain other specialized construction. Our MOBs are typically multi-tenant properties leased to healthcare providers (hospitals and physician practices) for approximately three to ten years. Based on GLA, approximately 38.5% of our MOBs are located on hospital campuses and 8.4% are affiliated with hospital systems. Our medical office buildings segment accounted for approximately 45.1%, 40.7% and 67.0% of total revenues for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
Senior Housing. As of December 31, 2019, we owned 19 senior housing facilities. Senior housing facilities cater to different segments of the elderly population based upon their personal needs, and include assisted living, memory care, and independent living. Residents of assisted living facilities typically need assistance with eating, bathing, dressing, and/or medications and those services can be provided by staff at the facility. Services provided by our tenants in these facilities are primarily paid for by the residents directly or through private insurance and are less reliant on government reimbursement programs such as Medicaid and Medicare. Our senior housing facilities are leased to single tenants under triple-net lease structures, whereby the tenant is responsible for making rent payments, maintaining the properties and paying taxes and other expenses. Leases are typically 12 to 15 years with fixed annual escalations and required lease coverage ratios. Our senior housing segment accounted for approximately 7.0%, 10.6% and 16.4% of total revenues for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
Senior Housing — RIDEA. As of December 31, 2019, we owned and operated 14 senior housing facilities utilizing a RIDEA structure. Such facilities are of a similar property type as our senior housing segment discussed above; however, we have entered into agreements with healthcare operators to manage the facilities on our behalf utilizing a RIDEA structure. The healthcare operators we engage provide management and operational services at the facility and we retain the net earnings generated by the performance of the facility after payment of the management fee and other operational and maintenance
16
expenses. As a result, under a RIDEA structure we retain the upside from improved operational performance, and similarly the risk of any decline in performance. Substantially all of our leases with residents in the senior housing facilities are for a term of one year or less. Our senior housing — RIDEA segment accounted for approximately 38.2%, 43.6% and 16.6% of total revenues for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
Skilled Nursing Facilities. As of December 31, 2019, we owned 11 skilled nursing facilities, or SNFs. Skilled nursing facility residents are generally higher acuity and need assistance with eating, bathing, dressing, and/or require assistance with medication and also require available 24-hour nursing care. SNFs offer restorative, rehabilitative and custodial nursing care for people not requiring the more extensive and sophisticated treatment available at hospitals. Ancillary revenues and revenues from sub-acute care services are derived from providing services to residents beyond room and board and include occupational, physical, speech, respiratory and intravenous therapy, wound care, oncology treatment, brain injury care, orthopedic therapy and other services. Certain SNFs provide some of the foregoing services on an out-patient basis. Skilled nursing services provided by our tenants in these SNFs are primarily paid for either by private sources or through the Medicare and Medicaid programs. Our SNFs are leased to a single tenant under a triple-net lease structure with approximately 12 to 15 year terms and fixed annual rent escalations. Our skilled nursing facilities segment accounted for approximately 9.7% and 5.1% of total revenues for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. We did not own any SNFs for the year ended December 31, 2017.
For a further discussion of our segment reporting for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, see Note 17, Segment Reporting, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 1A. Risk Factors.
Investment Risks
There is no public market for the shares of our common stock. Therefore, it will be difficult for our stockholders to sell their shares of our common stock and, if our stockholders are able to sell their shares of our common stock, they will likely sell them at a substantial discount.
We commenced a best efforts initial public offering on February 16, 2016 and terminated our initial offering on February 15, 2019. However, there currently is no public market for the shares of our common stock. We do not expect a public market for our stock to develop prior to the listing of the shares of our common stock on a national securities exchange, which we do not expect to occur in the near future and which may not occur at all. Additionally, our charter contains restrictions on the ownership and transfer of shares of our stock, and these restrictions may inhibit our stockholders’ ability to sell their shares of our common stock. Our charter provides that no person may own more than 9.9% in value of our issued and outstanding shares of capital stock or more than 9.9% in value or in number of shares, whichever is more restrictive, of the issued and outstanding shares of our common stock. Any purported transfer of the shares of our common stock that would result in a violation of either of these limits will result in such shares being transferred to a trust for the benefit of a charitable beneficiary or such transfer being declared null and void. We have adopted a share repurchase plan, but it is limited in terms of the amount of shares of our common stock which may be repurchased annually and is subject to our board’s discretion. Our board may also amend, suspend, or terminate our share repurchase plan at any time upon 30 days’ written notice. Therefore, it will be difficult for our stockholders to sell their shares of our common stock promptly or at all. If our stockholders are able to sell their shares of our common stock, our stockholders may only be able to sell them to an unrelated third party at a substantial discount from the price they paid. This may be the result, in part, of the fact that, at the time we made our investments, the amount of funds available for investment were reduced by up to 4.0% of the gross offering proceeds (excluding the 2.0% of the gross offering proceeds portion of the dealer manager fee funded by our advisor), which amounts were used to pay selling commissions and a dealer manager fee. We also were required to use gross offering proceeds to pay acquisition fees, acquisition expenses and asset management fees. Unless our aggregate investments increase in value to compensate for these fees and expenses, which may not occur, it is unlikely that our stockholders will be able to sell their shares of our common stock, whether pursuant to our share repurchase plan or otherwise, without incurring a substantial loss. We cannot assure our stockholders that their shares of our common stock will ever appreciate in value to equal the price our stockholders paid for their shares of our common stock. Therefore, shares of our common stock should be considered illiquid and a long-term investment, and our stockholders must be prepared to hold their shares of our common stock for an indefinite length of time.
The estimated value per share of our common stock may not be an accurate reflection of the fair value of our assets and liabilities and likely will not represent the amount of net proceeds that would result if we were liquidated or dissolved or completed a merger or other sale of our company.
On April 4, 2019, our board, at the recommendation of the audit committee, which is comprised solely of independent directors, unanimously approved and established an updated estimated per share NAV of our common stock of $9.54. We are providing this updated estimated per share NAV to assist broker-dealers in connection with their obligations under FINRA Rule
17
2231 with respect to customer account statements. The valuation was performed in accordance with the methodology provided in Practice Guideline 2013-01, Valuations of Publicly Registered Non-Listed REITs, issued by the IPA in April 2013, in addition to guidance from the SEC.
The updated estimated per share NAV was determined after consultation with our advisor and an independent third-party valuation firm, the engagement of which was approved by the audit committee. FINRA rules provide no guidance on the methodology an issuer must use to determine its estimated per share NAV. As with any valuation methodology, our independent valuation firm’s methodology is based upon a number of estimates and assumptions that may not be accurate or complete. Different parties with different assumptions and estimates could derive a different estimated per share NAV, and these differences could be significant.
The updated estimated per share NAV was not audited or reviewed by our independent registered public accounting firm and does not represent the fair value of our assets or liabilities according to accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, or GAAP. Accordingly, with respect to the updated estimated per share NAV, we can give no assurance that:
• | a stockholder would be able to resell his or her shares at our updated estimated per share NAV; |
• | a stockholder would ultimately realize distributions per share equal to our updated estimated per share NAV upon liquidation of our assets and settlement of our liabilities or a sale of the company; |
• | our shares of common stock would trade at our updated estimated per share NAV on a national securities exchange; |
• | an independent third-party appraiser or other third-party valuation firm, other than the third-party valuation firm engaged by our board to assist in its determination of the updated estimated per share NAV, would agree with our estimated per share NAV; or |
• | the methodology used to estimate our updated per share NAV would be acceptable to FINRA or comply with reporting requirements under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, or ERISA, the Code, other applicable law, or the applicable provisions of a retirement plan or individual retirement account, or IRA. |
Further, the updated estimated per share NAV is based on the estimated value of our assets less the estimated value of our liabilities, divided by the number of shares outstanding on a fully diluted basis, calculated as of December 31, 2018. The value of our shares may fluctuate over time in response to developments related to individual assets in the portfolio and the management of those assets and in response to the real estate and finance markets. We intend to continue to engage an independent valuation firm to assist us with publishing an updated estimated per share NAV on at least an annual basis.
For a full description of the methodologies used to value our assets and liabilities in connection with the calculation of the updated estimated per share NAV, see our Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on April 8, 2019.
It may be difficult to accurately reflect recent and material events that may impact our estimated per share NAV between valuations and accordingly, we may be repurchasing shares at too high or too low a price.
Our independent valuation firm will calculate estimates of the market value of our real estate investments, and our board will determine the net value of our real estate investments and liabilities taking into consideration such estimate provided by the independent valuation firm. Our board is ultimately responsible for determining the estimated per share NAV. Since our board will determine our estimated per share NAV at least annually, there may be changes in the value of our assets that are not fully reflected in the most recent estimated per share NAV. As a result, the published estimated per share NAV may not fully reflect changes in value that may have occurred since the prior valuation. Furthermore, our advisor will monitor our portfolio, but it may be difficult to reflect changing market conditions or material events that may impact the value of our portfolio between valuations, or to obtain timely or complete information regarding any such events. Therefore, the estimated per share NAV published before the announcement of an extraordinary event may differ significantly from our actual per share NAV until such time as sufficient information is available and analyzed, the financial impact is fully evaluated, and the appropriate adjustment is made to our estimated per share NAV, as determined by our board. Any resulting disparity may be to the detriment of a stockholder selling shares pursuant to our share repurchase plan.
18
We have experienced losses in the past and we may experience additional losses in the future.
Historically, we have experienced net losses (calculated in accordance with GAAP) and we may not be profitable or realize growth in the value of our investments. Many of our losses can be attributed to start-up costs, general and administrative expenses, depreciation and amortization, as well as acquisition expenses incurred in connection with purchasing properties or making other investments. For a further discussion of our operational history and the factors affecting our losses, see Part II, Item 7, Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations and our Consolidated Financial Statements and the notes thereto.
We have not had sufficient cash available from operations to pay distributions, and therefore, we have paid a portion of distributions from the net proceeds of our initial offering and borrowings, and in the future, may continue to pay distributions from borrowings in anticipation of future cash flows or from other sources. Any such distributions may reduce the amount of capital we ultimately invest in assets, may negatively impact the value of our stockholders’ investment and may cause subsequent investors to experience dilution.
We have used the net proceeds from our initial offering, borrowings and our advisor has waived certain fees payable to it, and in the future, may use borrowed funds or other sources, to pay cash distributions to our stockholders, which may reduce the amount of proceeds available for investment and operations, cause us to incur additional interest expense as a result of borrowed funds or cause subsequent investors to experience dilution. Distributions payable to our stockholders may partially include a return of capital, rather than a return on capital, and we have paid a portion of our distributions from the net proceeds of our initial offering. We have not established any limit on the amount of net proceeds from our initial offering or borrowings that may be used to fund distributions, except that, in accordance with our organizational documents and Maryland law, we may not make distributions that would: (i) cause us to be unable to pay our debts as they become due in the usual course of business; or (ii) cause our total assets to be less than the sum of our total liabilities plus senior liquidation preferences. The actual amount and timing of distributions is determined by our board in its sole discretion and typically depends on the amount of funds available for distribution, which will depend on items such as our financial condition, current and projected capital expenditure requirements, tax considerations and annual distribution requirements needed to maintain our qualification as a REIT. As a result, our distribution rate and payment frequency may vary from time to time. Further, if the aggregate amount of cash distributed in any given year exceeds the amount of our current and accumulated earnings and profits, the excess amount will be deemed a return of capital.
Our board authorized, on a quarterly basis, a daily distribution to our stockholders of record as of the close of business on each day of the period commencing on May 1, 2016 and ending on March 31, 2020. The daily distributions were or will be calculated based on 365 days in the calendar year and are equal to $0.001643836 per share of our Class T and Class I common stock, which is equal to an annualized distribution of $0.60 per share. These distributions were or will be aggregated and paid monthly in arrears in cash or shares of our common stock pursuant to our DRIP Offerings, only from legally available funds.
The distributions paid for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, along with the amount of distributions reinvested pursuant to our DRIP Offerings and the sources of distributions as compared to cash flows from operations were as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||||||||
Distributions paid in cash | $ | 20,905,000 | $ | 13,989,000 | |||||||||
Distributions reinvested | 25,533,000 | 17,612,000 | |||||||||||
$ | 46,438,000 | $ | 31,601,000 | ||||||||||
Sources of distributions: | |||||||||||||
Cash flows from operations | $ | 39,540,000 | 85.1 | % | $ | 15,423,000 | 48.8 | % | |||||
Offering proceeds | 5,396,000 | 11.6 | 16,178,000 | 51.2 | |||||||||
Proceeds from borrowings | 1,502,000 | 3.3 | — | — | |||||||||
$ | 46,438,000 | 100 | % | $ | 31,601,000 | 100 | % | ||||||
As of December 31, 2019, any distributions of amounts in excess of our current and accumulated earnings and profits have resulted in a return of capital to our stockholders, and all or any portion of a distribution to our stockholders may have been paid from net offering proceeds and borrowings. The payment of distributions from our net offering proceeds and borrowings have reduced the amount of capital we ultimately invested in assets and negatively impacted the amount of income available for future distributions.
19
As of December 31, 2019, we had an amount payable of $951,000 to our advisor or its affiliates primarily for asset management fees, which will be paid from cash flows from operations in the future as it becomes due and payable by us in the ordinary course of business consistent with our past practice. See Note 13, Related Party Transactions, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The distributions paid for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, along with the amount of distributions reinvested pursuant to our DRIP Offerings and the sources of our distributions as compared to funds from operations attributable to controlling interest, or FFO, were as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||||||||
Distributions paid in cash | $ | 20,905,000 | $ | 13,989,000 | |||||||||
Distributions reinvested | 25,533,000 | 17,612,000 | |||||||||||
$ | 46,438,000 | $ | 31,601,000 | ||||||||||
Sources of distributions: | |||||||||||||
FFO attributable to controlling interest | $ | 30,109,000 | 64.8 | % | $ | 24,923,000 | 78.9 | % | |||||
Offering proceeds | 13,053,000 | 28.1 | 6,678,000 | 21.1 | |||||||||
Proceeds from borrowings | 3,276,000 | 7.1 | — | — | |||||||||
$ | 46,438,000 | 100 | % | $ | 31,601,000 | 100 | % | ||||||
The payment of distributions from sources other than FFO may reduce the amount of proceeds available for investment and operations or cause us to incur additional interest expense as a result of borrowed funds. For a further discussion of FFO, a non-GAAP financial measure, including a reconciliation of our GAAP net income (loss) to FFO, see Part II, Item 6, Selected Financial Data.
Our stockholders may not be able to adequately evaluate our ability to achieve our investment objectives, and the prior performance of other programs sponsored or co-sponsored by American Healthcare Investors and Griffin Capital may not be an accurate predictor of our future results.
We were formed in January 2015 and did not engage in any material business operations prior to our initial offering. As a result, an investment in shares of our common stock may entail more risks than the shares of common stock of a REIT with a more substantial operating history. In addition, our stockholders should not rely on the past performance of other American Healthcare Investors or Griffin Capital-sponsored or co-sponsored programs to predict our future results. Our stockholders should consider our prospects in light of the risks, uncertainties and difficulties frequently encountered by companies like ours that do not have a substantial operating history, many of which may be beyond our control. For example, due to challenging economic conditions in the past, distributions to stockholders of several private real estate programs sponsored by Griffin Capital were suspended. Therefore, to be successful in this market, we must, among other things:
• | identify and acquire investments that further our investment strategy; |
• | attract, integrate, motivate and retain qualified personnel to manage our day-to-day operations; |
• | respond to competition both for investment opportunities and potential investors’ investment in us; and |
• | build and expand our operational structure to support our business. |
We cannot guarantee that we will succeed in achieving these goals, and our failure to do so could adversely affect our results of operations and cause our stockholders to lose all or a portion of their investment and adversely effect our results of operations.
Our success is dependent on the performance of our co-sponsors. Our co-sponsors and certain of their key personnel will face competing demands relating to their time or fiduciary duties and this may cause our operating results to suffer.
Our ability to achieve our investment objectives and to conduct our operations is dependent upon the performance of our advisor. Our advisor is a joint venture between our two co-sponsors, in which American Healthcare Investors indirectly owns a 75.0% interest and Griffin Capital indirectly owns a 25.0% interest.
Griffin Capital and certain of its key personnel and its respective affiliates serve as key personnel, advisors, managers and sponsors or co-sponsors of 11 other Griffin Capital-sponsored programs, including Griffin-American Healthcare REIT III, Inc., or GA Healthcare REIT III, Griffin Institutional Access Real Estate Fund, or GIA Real Estate, and Griffin Institutional Access Credit Fund, or GIA Credit Fund, and may have other business interests as well. In addition, American Healthcare
20
Investors and its key personnel serve as key personnel and co-sponsor of GA Healthcare REIT III and may sponsor or co-sponsor additional real estate programs in the future. Because these persons have competing demands on their time and resources, they may have conflicts of interest in allocating their time between our business and these other activities. During times of intense activity in other programs and ventures, they may devote less time and fewer resources to our business than is necessary or appropriate. If this occurs, the returns on our stockholders’ investment may suffer. Also, since these individuals owe fiduciary duties to these other entities and their owners, which fiduciary duties may conflict with the duties that they owe to our stockholders and us, their loyalties to these other entities could result in actions or inactions that are detrimental to our business, which could harm the implementation of our investment objectives. Accordingly, competing demands of such key personnel may cause us to be unable to successfully implement our investment objectives or generate cash needed to make distributions to our stockholders, and to maintain or increase the value of our assets.
Additionally, our co-sponsors’ ability to manage our operations successfully is impacted by trends in the general economy, as well as the commercial real estate and credit markets. The current macroeconomic environment may negatively impact the value of commercial real estate assets and contribute to a general slow-down in our industry, which could put downward pressure on our co-sponsors’ revenues and operating results. Since American Healthcare Investors is 47.1% owned by AHI Group Holdings and 45.1% indirectly owned by Colony Capital, our company may not realize the anticipated benefits of the relationship with Colony Capital due to, among other things, the economic and overall conditions of the healthcare real estate industry, conflicts of interests relating to the purchase and leasing of healthcare properties, or American Healthcare Investors and Colony Capital having overlapping interests that could exacerbate other potential conflicts or disputes. To the extent that any of these factors may cause a decline in our co-sponsors’ operating results or revenues, the performance of our advisor may be impacted and in turn, our results of operations and financial condition could also suffer.
Our stockholders may be unable to sell their shares of our common stock because our share repurchase plan is subject to significant restrictions and limitations.
Our share repurchase plan includes significant restrictions and limitations. Except in cases of death or qualifying disability, our stockholders must hold their shares of our common stock for at least one year. Our stockholders must present at least 25.0% of their shares of our common stock for repurchase and until they have held their shares of our common stock for at least four years, repurchases will be made for less than our stockholders paid for their shares of our common stock. Shares of our common stock may be repurchased quarterly, at our discretion, on a pro rata basis, and are limited during any calendar year to 5.0% of the weighted average number of shares of our common stock outstanding during the prior calendar year; provided however, that shares of our common stock subject to a repurchase requested upon the death of a stockholder will not be subject to this cap. Funds for the repurchase of shares of our common stock will come exclusively from the cumulative proceeds we receive from the sale of shares of our common stock pursuant to our DRIP Offerings. In addition, our board may reject share repurchase requests in its sole discretion and reserves the right to amend, suspend or terminate our share repurchase plan at any time upon 30 days’ written notice. Therefore, in making a decision to purchase shares of our common stock, our stockholders should not assume that they will be able to sell any of their shares of our common stock back to us pursuant to our share repurchase plan and our stockholders also should understand that the repurchase price will not necessarily correlate to the value of our real estate holdings or other assets. If our board terminates our share repurchase plan, our stockholders may not be able to sell their shares of our common stock even if our stockholders deem it necessary or desirable to do so.
Our advisor may be entitled to receive significant compensation in the event of our liquidation or in connection with a termination of the Advisory Agreement, even if such termination is the result of poor performance by our advisor.
We are externally advised by our advisor pursuant to the Advisory Agreement between us and our advisor which has a one-year term that expires on February 16, 2021 and is subject to successive one-year renewals upon the mutual consent of us and our advisor. In the event of a partial or full liquidation of our assets, our advisor will be entitled to receive an incentive distribution equal to 15.0% of the net proceeds of the liquidation, after we have received and paid to our stockholders the sum of the gross proceeds from the sale of shares of our common stock, and any shortfall in an annual 6.0% cumulative, non-compounded return to stockholders in the aggregate. In the event of a termination of the Advisory Agreement in connection with the listing of our common stock on a national securities exchange, the partnership agreement provides that our advisor will receive an incentive distribution in redemption of its limited partnership units equal to 15.0% of the amount, if any, by which (i) the market value of our outstanding common stock at listing plus distributions paid by us prior to the listing of the shares of our common stock on a national securities exchange, exceeds (ii) the sum of the gross proceeds from the sale of shares of our common stock (less amounts paid to repurchase shares of our common stock) plus an annual 6.0% cumulative, non-compounded return on the gross proceeds from the sale of shares of our common stock. Upon our advisor’s receipt of the incentive distribution in redemption of its limited partnership units, our advisor will not be entitled to receive any further incentive distributions upon sales of our properties. Further, in connection with the termination or non-renewal of the Advisory Agreement other than due to a listing of the shares of our common stock on a national securities exchange, our advisor shall be entitled to receive a distribution in redemption of its limited partnership units equal to the amount that would be payable as an
21
incentive distribution upon sales of properties, which equals 15.0% of the net proceeds if we liquidated all of our assets at fair market value, after we have received and paid to our stockholders the sum of the gross proceeds from the sale of shares of our common stock and an annual 6.0% cumulative, non-compounded return to our stockholders in the aggregate. Such distribution upon termination of the Advisory Agreement is payable to our advisor even upon termination or non-renewal of the Advisory Agreement as a result of poor performance by our advisor. Upon our advisor’s receipt of this distribution in redemption of its limited partnership units, our advisor will not be entitled to receive any further incentive distributions upon sales of our properties. Any amounts to be paid to our advisor in connection with the termination of the Advisory Agreement cannot be determined at the present time, but such amounts, if paid, will reduce the cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
We may not effect a liquidity event within our targeted time frame of five years after the completion of our offering stage, or at all. If we do not effect a liquidity event, our stockholders may have to hold their investment in shares of our common stock for an indefinite period of time.
On a limited basis, our stockholders may be able to sell shares of our common stock to us through our share repurchase plan. However, in the future we may also consider various forms of liquidity events, including but not limited to: (i) the listing of the shares of our common stock on a national securities exchange; (ii) our sale or merger in a transaction that provides our stockholders with a combination of cash and/or securities of a publicly traded company; and (iii) the sale of all or substantially all of our real estate and real estate-related investments for cash or other consideration. We presently intend to effect a liquidity event within five years after the completion of our offering stage, which we deem to be the completion of our initial offering and any subsequent public offerings, excluding any offerings pursuant to the DRIP or that is limited to any benefit plans. However, we are not obligated, through our charter or otherwise, to effectuate a liquidity event and may not effect a liquidity event within such time or at all. If we do not effect a liquidity event, it will be very difficult for our stockholders to have liquidity for their investment in the shares of our common stock other than limited liquidity through our share repurchase plan.
Our board may change our investment objectives without seeking our stockholders’ approval.
Our board may change our investment objectives without seeking our stockholders’ approval if our directors, in accordance with their fiduciary duties to our stockholders, determine that a change is in their best interest. A change in our investment objectives could reduce our payment of cash distributions to our stockholders or cause a decline in the value of our investments.
Our results of operations, our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders and our ability to dispose of our investments are subject to international, national and local economic factors we cannot control or predict.
Our results of operations are subject to the risks of an international or national economic slowdown or downturn and other changes in international, national and local economic conditions. The following factors may affect income from our properties, our ability to acquire and dispose of properties, and yields from our properties:
• | poor economic times may result in defaults by tenants of our properties due to bankruptcy, lack of liquidity, or operational failures. We may also be required to provide rent concessions, tenant improvement expenditures or reduced rental rates to maintain or increase occupancy levels; |
• | fluctuations in property values as a result of increases or decreases in construction activity, supply and demand, occupancies and rental rates may cause the properties that we acquire to decrease in value. Consequently, we may not be able to recover the carrying amount of our properties, which may require us to recognize an impairment charge or record a loss on sale in earnings; |
• | reduced values of our properties may limit our ability to dispose of assets at attractive prices or to obtain debt financing secured by our properties and may reduce the availability of unsecured loans; |
• | the value and liquidity of our short-term investments and cash deposits could be reduced as a result of a deterioration of the financial condition of the institutions that hold our cash deposits or the institutions or assets in which we have made short-term investments, the dislocation of the markets for our short-term investments, increased volatility in market rates for such investment or other factors; |
• | our lenders under our line of credit and term loans could refuse to fund its financing commitment to us or could fail and we may not be able to replace the financing commitment of such lender on favorable terms, or at all; |
• | increases in index rates and lender spreads or other regulatory or market factors affecting the banking and commercial mortgage-backed securities industries may increase overall borrowing costs; |
• | one or more counterparties to our interest rate swaps could default on their obligations to us or could fail, increasing the risk that we may not realize the benefits of these instruments; |
22
• | increases in supply of competing properties or decreases in demand for our properties may impact our ability to maintain or increase occupancy levels and rents; |
• | constricted access to credit may result in tenant defaults or non-renewals under leases; |
• | job transfers and layoffs may lead to a lower demand for medical services and cause vacancies to increase and a lack of future population and job growth may make it difficult to maintain or increase occupancy levels; |
• | future disruptions in the financial markets, deterioration in economic conditions or a public health crisis, such as coronavirus, may result in lower occupancy in our facilities, increased vacancy rates for commercial real estate due to generally lower demand for rentable space, as well as potential oversupply of rentable space; |
• | governmental actions and initiatives, including risks associated with the impact of a prolonged government shutdown or budgetary reductions or impasses; and |
• | increased insurance premiums, real estate taxes or utilities or other expenses may reduce funds available for distribution or, to the extent such increases are passed through to tenants, may lead to tenant defaults. Also, any such increased expenses may make it difficult to increase rents to tenants on turnover, which may limit our ability to increase our returns. |
The length and severity of any economic slowdown or downturn cannot be predicted. Our results of operations, our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders and our ability to dispose of our investments may be negatively impacted to the extent an economic slowdown or downturn is prolonged or becomes more severe.
We face competition for the acquisition of medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities, which may impede our ability to make acquisitions or may increase the cost of these acquisitions and may reduce our profitability and could cause our stockholders to experience a lower return on our stockholders’ investment.
We compete with many other entities engaged in real estate investment activities for acquisitions of medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities, including international, national, regional and local operators, acquirers and developers of healthcare real estate properties, as well as GA Healthcare REIT III. The competition for healthcare real estate properties may significantly increase the price we must pay for medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities or other assets we seek to acquire, and our competitors may succeed in acquiring those properties or assets themselves. In addition, our potential acquisition targets may find our competitors to be more attractive because they may have greater resources, may be willing to pay more for the properties or may have a more compatible operating philosophy. In particular, larger healthcare REITs may enjoy significant competitive advantages that result from, among other things, a lower cost of capital and enhanced operating efficiencies. Further, the number of entities and the amount of funds competing for suitable investment properties may increase. This competition will result in increased demand for these assets, and therefore, increased prices paid for them. If there is an increased interest in single-property acquisitions among tax-motivated individual purchasers, we may pay higher prices per property if we purchase single properties in comparison with portfolio acquisitions. If we pay higher prices per property for medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing or other healthcare-related facilities, our business, financial condition, results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders may be materially and adversely affected and our stockholders may experience a lower return on their investment.
Risks Related to Our Business
The availability and timing of cash distributions to our stockholders is uncertain. If we fail to pay distributions, their investment in shares of our common stock could suffer.
We expect to continue to pay distributions to our stockholders monthly. However, we bear all expenses incurred in our operations, which are deducted from cash flows generated by operations prior to computing the amount of cash distributions to our stockholders. In addition, our board, in its discretion, may retain any portion of such funds for working capital. We cannot assure our stockholders that sufficient cash will be available to pay monthly distributions to our stockholders or at all. Should we fail for any reason to distribute at least 90.0% of our annual taxable income, excluding net capital gains, we would not qualify for the favorable tax treatment accorded to REITs.
Actual or threatened public health epidemics, pandemics or outbreaks, such as a severe cold and flu season, the coronavirus, or any other widespread illnesses, could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
If an actual or threatened public health epidemic, pandemic, or outbreaks, such as a severe cold and flu season, the coronavirus, or any other widespread illness were to affect the markets in which we or our tenants operate, our business and
23
results of operations could be materially adversely affected. Such a crisis could diminish the public trust in healthcare facilities, especially hospitals or facilities that fail to accurately or timely diagnose, or other facilities such as medical office buildings that are treating (or have treated) patients affected by contagious diseases. If any of our facilities were involved in treating patients for such a contagious disease, other patients might cancel elective procedures or fail to seek needed care from our or our tenants’ facilities. Additionally, our revenues and our operators’ revenues are dependent on occupancy. The occupancy of our senior housing facilities and skilled nursing facilities could significantly decrease in the event of an epidemic or any other widespread illness. Such a decrease could affect the operating income of our senior housing facilities and skilled nursing facilities and the ability of our operators to make payments to us. In addition, a flu pandemic or other widespread illness such as coronavirus could significantly increase the cost burdens faced by our operators, including if they are required to increase staffing and/or implement quarantines for residents. Further, a pandemic might adversely impact our tenants’ and operators’ businesses by causing a temporary shutdown or diversion of patients, by disrupting or delaying production and delivery of materials and products in the supply chain or by causing staffing shortages in those facilities, which could have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations and our ability to pay distributions.
We are uncertain of all of our sources of debt or equity for funding our capital needs. If we cannot obtain funding on acceptable terms, our ability to acquire, and make necessary capital improvements to, properties may be impaired or delayed.
We have not identified all of our sources of debt or equity for funding, and such sources of funding may not be available to us on favorable terms or at all. If we do not have access to sufficient funding in the future, we may not be able to acquire, and make necessary capital improvements to, properties, pay other expenses or expand our business. We anticipate that tenant improvements required at the time of our acquisition of a property will be funded from our net offering proceeds and cash from operations. However, at such time as a tenant of one of our properties does not renew its lease or otherwise vacates its space in one of our buildings, it is likely that, in order to attract new tenants, we will be required to expend substantial funds for tenant improvements and tenant refurbishments to the vacated space. Since we do not anticipate maintaining permanent working capital reserves, we may not have access to funds required in the future for tenant improvements and tenant refurbishments in order to attract new tenants to lease vacated space.
We use mortgage indebtedness and other borrowings, which may increase our business risks, could hinder our ability to pay distributions and could decrease the value of our stockholders’ investment.
We have financed, and will continue to finance, all or a portion of the purchase price of our investments in real estate and real estate-related investments by borrowing funds. We anticipate that our overall leverage will not exceed 50.0% of the combined market value of our real estate and real estate-related investments, as determined at the end of each calendar year. Under our charter, we have a limitation on borrowing that precludes us from borrowing in excess of 300% of our net assets without the approval of a majority of our independent directors. Net assets for purposes of this calculation are defined to be our total assets (other than intangibles), valued at cost prior to deducting depreciation, amortization, bad debt and other non-cash reserves, less total liabilities. Generally speaking, the preceding calculation is expected to approximate 75.0% of the aggregate cost of our real estate and real estate-related investments before depreciation, amortization, bad debt and other similar non-cash reserves. In addition, we may incur mortgage debt and pledge some or all of our real properties as security for that debt to obtain funds to acquire additional real properties or for working capital. We may also borrow funds to satisfy the REIT tax qualification requirement that we distribute at least 90.0% of our annual taxable income, excluding net capital gains, to our stockholders. Furthermore, we may borrow if we otherwise deem it necessary or advisable to ensure that we maintain our qualification as a REIT for federal income tax purposes.
High debt levels may cause us to incur higher interest charges, which would result in higher debt service payments and could be accompanied by restrictive covenants. If there is a shortfall between the cash flows from a property and the cash flows needed to service mortgage debt on that property, then the amount available for distributions to our stockholders may be reduced. In addition, incurring mortgage debt increases the risk of loss since defaults on indebtedness secured by a property may result in lenders initiating foreclosure actions. In that case, we could lose the property securing the loan that is in default, thus reducing the value of their investment. In addition, lenders may have recourse to assets other than those specifically securing the repayment of indebtedness. For tax purposes, a foreclosure on any of our properties will be treated as a sale of the property for a purchase price equal to the outstanding balance of the debt secured by the mortgage. If the outstanding balance of the debt secured by the mortgage exceeds our tax basis in the property, we will recognize taxable income on foreclosure, but we would not receive any cash proceeds. We may give full or partial guarantees to lenders of mortgage debt to the entities that own our properties. When we give a guaranty on behalf of an entity that owns one of our properties, we will be responsible to the lender for satisfaction of the debt if it is not paid by such entity. If any mortgage contains cross-collateralization or cross-default provisions, a default on a single property could affect multiple properties. If any of our properties are foreclosed upon due to a default, our ability to pay cash distributions to our stockholders will be adversely affected.
24
Higher mortgage rates may make it more difficult for us to finance or refinance properties, which could reduce the number of properties we can acquire and the amount of cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
If mortgage debt is unavailable on reasonable terms as a result of increased interest rates or other factors, we may not be able to finance the development or initial purchase of properties. In addition, if we place mortgage debt on properties, we run the risk of being unable to refinance such debt when the loans come due, or of being unable to refinance on favorable terms. If interest rates are higher when we refinance debt, our income could be reduced. We may be unable to refinance debt at appropriate times, which may require us to sell properties on terms that are not advantageous to us, or could result in the foreclosure of such properties. If any of these events occur, our cash flows would be reduced. This, in turn, would reduce cash available for distribution to our stockholders and may hinder our ability to raise more capital by issuing securities or by borrowing more money.
We are dependent on tenants for our revenue, and lease terminations could reduce our distributions to our stockholders.
The successful performance of our real estate investments is materially dependent on the financial stability of our tenants. Lease payment defaults by tenants would cause us to lose the revenue associated with such leases and could cause us to reduce the amount of distributions to our stockholders. If a property is subject to a mortgage, a default by a significant tenant on its lease payments to us may result in a foreclosure on the property if we are unable to find an alternative source of revenue to meet mortgage payments. In the event of a tenant default, we may experience delays in enforcing our rights as landlord and may incur substantial costs in protecting our investment and re-leasing our property. Further, we cannot assure our stockholders that we will be able to re-lease the property for the rent previously received, if at all, or that lease terminations will not cause us to sell the property at a loss.
The senior housing — RIDEA facilities managed by Meridian account for a significant portion of our revenues and/or operating income. Adverse developments in Meridian’s business or financial condition could have a material adverse effect on us.
As of March 19, 2020, Meridian Senior Living, LLC, or Meridian, manages the operations for a majority of our senior housing — RIDEA facilities pursuant to long-term management agreements. These senior housing — RIDEA facilities represent a substantial portion of our portfolio, based on their gross revenues. Although we have various rights as the owner of these senior housing — RIDEA facilities under our management agreements, we rely on Meridian’s personnel, expertise, technical resources and information systems, proprietary information, good faith and judgment to manage our senior housing — RIDEA facilities operations efficiently and effectively, and to identify and manage development opportunities for new senior housing — RIDEA facilities. We also rely on Meridian to provide accurate facility-level financial results for our senior housing — RIDEA facilities in a timely manner and to otherwise operate our senior housing — RIDEA facilities in compliance with the terms of our management agreements and all applicable laws and regulations. We depend on Meridian’s ability to attract and retain skilled personnel to provide these services. A shortage of trained personnel or general inflationary pressures may force Meridian to enhance its pay and benefits package to compete effectively for such personnel, but it may not be able to offset these added costs by increasing the rates charged to residents. As such, any adverse developments in Meridian’s business or financial condition, including its ability to retain key personnel, could impair its ability to manage our senior housing — RIDEA facilities efficiently and effectively and could have a material adverse effect on us. In addition, if Meridian experiences any significant financial, legal, accounting or regulatory difficulties due to a weak economy, industry downturn or otherwise, such difficulties could result in, among other adverse events, impairment of its continued access to capital, the enforcement of default remedies by its counterparties, or the commencement of insolvency proceedings by or against it under the United States, or U.S., Bankruptcy Code. Any one or a combination of these risks could have a material adverse effect on us.
We have rights to terminate our management agreements with third-party operators for our senior housing and senior housing — RIDEA facilities under any circumstances; however, we may be unable to replace such third-party operators effectively, or be able to complete any transition timely, in the event that our management agreements are terminated or not renewed.
We continually monitor and assess our contractual rights and remedies under our management agreements with third-party operators. When determining whether to pursue any existing or future rights or remedies under those agreements, including termination rights, we consider numerous factors, including legal, contractual, regulatory, business and other relevant considerations. We have exercised and in the event that we continue to exercise our rights to terminate management agreements with such third-party operators for any reason or such agreements are not renewed upon expiration of their terms, we have and would attempt to reposition the affected senior housing and/or senior housing — RIDEA facilities with another manager. Although we believe that many qualified national and regional operators would be interested in managing our senior housing and senior housing — RIDEA facilities, we cannot provide any assurance that we have been or would be able to locate another suitable manager or, if we were successful in locating such a manager, that it will or would manage the senior housing and/or senior housing — RIDEA facilities effectively or that any such transition would be completed timely. Any such transition has
25
required and would likely continue to require substantial time, incur additional expenses and result in disruption of the operation of such facilities, including matters relating to staffing and reporting. Moreover, the transition to a replacement manager has required and may continue to require approval by the applicable regulatory authorities and, in most cases, one or more of our lenders including the mortgage lenders for the senior housing and senior housing — RIDEA facilities, and we cannot provide any assurance that such approvals have been or would be granted on a timely basis, if at all. Any inability to replace, or delay in replacing third-party operators as the managers of senior housing and senior housing — RIDEA facilities could have a material adverse effect on us.
If a tenant declares bankruptcy, we may be unable to collect balances due under relevant leases.
Any of our current or future tenants, or any guarantor of one of our current or future tenant’s lease obligations, could be subject to a bankruptcy proceeding pursuant to Title 11 of the bankruptcy laws of the U.S. Such a bankruptcy filing would bar us from attempting to collect pre-bankruptcy debts from the bankrupt tenant or its properties unless we receive an enabling order from the bankruptcy court. Post-bankruptcy debts would be paid currently. If we assume a lease, all pre-bankruptcy balances owing under it must be paid in full. If a lease is rejected by a tenant in bankruptcy, we would have a general unsecured claim for damages. If a lease is rejected, it is unlikely we would receive any payments from the tenant because our claim would be capped at the rent reserved under the lease, without acceleration, for the greater of one year or 15.0% of the remaining term of the lease, but not greater than three years, plus rent already due but unpaid. This claim could be paid only in the event funds were available, and then only in the same percentage as that realized on other unsecured claims.
The bankruptcy of a tenant or lease guarantor could delay our efforts to collect past due balances under the relevant lease, and could ultimately preclude full collection of these sums. Such an event also could cause a decrease or cessation of current rental payments, reducing our cash flows and the amounts available for distributions to our stockholders. In the event a tenant or lease guarantor declares bankruptcy, the tenant or its trustee may not assume our lease or its guaranty. If a given lease or guaranty is not assumed, our cash flows and the amounts available for distributions to our stockholders may be adversely affected.
We face potential adverse consequences of bankruptcy or insolvency by our operators, borrowers, managers and other obligors.
We are exposed to the risk that our operators, borrowers, managers or other obligors may become bankrupt or insolvent. Although our loan, management and other agreements give us the right to exercise certain remedies in the event of default on the obligations owing to us or upon the occurrence of certain insolvency events, federal laws afford certain rights to a party that has filed for bankruptcy or reorganization. For example, if a debtor-manager seeks bankruptcy protection, the automatic stay provisions of the U.S. Bankruptcy Code would preclude us from enforcing our remedies against the manager unless relief is first obtained from the court having jurisdiction over the bankruptcy case. In any of these events, we also may be required to fund certain expenses and obligations, e.g., real estate taxes, debt costs and maintenance expenses, to preserve the value of our properties, avoid the imposition of liens on our properties or transition our properties to a new operator or manager. Furthermore, many of our facilities are leased to healthcare providers who provide long-term custodial care to the elderly. Evicting such operators for failure to pay rent while the facility is occupied may involve specific procedural requirements and may not be successful. Additionally, the financial weakness or other inability of our operators, borrowers or managers to make payments or comply with certain other lease obligations may affect our compliance with certain covenants contained in our debt securities, credit facilities and the mortgages on the properties leased or managed by such operators or managers or otherwise adversely affect our results of operations. Under certain conditions, defaults under the underlying mortgages may result in cross default under our other indebtedness. Although we may be able to secure amendments under the applicable agreements in those circumstances, the bankruptcy of an applicable operator, borrower or manager may potentially result in less favorable borrowing terms than currently available, delays in the availability of funding or other materially adverse consequences.
Long-term leases may not result in fair market lease rates over time; therefore, our income and our distributions could be lower than if we did not enter into long-term leases.
We may enter into long-term leases with tenants of certain of our future properties. Our long-term leases would likely provide for rent to increase over time. However, if we do not accurately judge the potential for increases in market rental rates, we may set the terms of these long-term leases at levels such that even after contractual rental increases, the rent under our long-term leases is less than then-current market rental rates. Further, we may have no ability to terminate those leases or to adjust the rent to then-prevailing market rates. As a result, our income and distributions could be lower than if we did not enter into long-term leases.
26
We may incur additional costs in re-leasing properties, which could adversely affect the cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
We may invest in properties designed or built primarily for a particular tenant of a specific type of use known as a single-user facility. If the tenant fails to renew its lease or defaults on its lease obligations, we may not be able to readily market a single-user facility to a new tenant without making substantial capital improvements or incurring other significant re-leasing costs. We also may incur significant litigation costs in enforcing our rights as a landlord against the defaulting tenant. These consequences could adversely affect our revenues and reduce the cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
Our success is dependent on the performance of our advisor and certain key personnel.
Our ability to achieve our investment objectives and to conduct our operations is dependent upon the performance of our advisor in identifying and acquiring investments, the determination of any financing arrangements, the asset management of our investments and the management of our day-to-day activities. Our advisor has broad discretion over our investment decisions and our stockholders have no opportunity to evaluate the terms of transactions or other economic or financial data concerning our investments that are not described in this annual report or other periodic filings with the SEC. We rely on the management ability of our advisor, subject to the oversight and approval of our board. If our advisor suffers or is distracted by adverse financial or operational problems in connection with their own operations or the operations of American Healthcare Investors or Griffin Capital unrelated to us, our advisor may be unable to allocate time and/or resources to our operations. If our advisor is unable to allocate sufficient resources to oversee and perform our operations for any reason, we may be unable to achieve our investment objectives or to pay distributions to our stockholders. In addition, our success depends to a significant degree upon the continued contributions of our advisor’s officers and certain of the managing directors, officers and employees of American Healthcare Investors, in particular Jeffrey T. Hanson, Danny Prosky and Mathieu B. Streiff, each of whom would be difficult to replace. Messrs. Hanson, Prosky and Streiff currently serve as our executive officers and Mr. Hanson also serves as Chairman of our Board of Directors. We currently do not have an employment agreement with any of Messrs. Hanson, Prosky or Streiff. In the event that Messrs. Hanson, Prosky or Streiff are no longer affiliated with American Healthcare Investors, for any reason, it could have a material adverse effect on our success and American Healthcare Investors may not be able to attract and hire as capable individuals to replace Messrs. Hanson, Prosky and/or Streiff. We do not have key man life insurance on any of our co-sponsors’ key personnel. If our advisor or American Healthcare Investors were to lose the benefit of the experience, efforts and abilities of one or more of these individuals, our operating results could suffer.
Our advisor may terminate the Advisory Agreement, which could require us to pay substantial fees and may require us to find a new advisor.
Either we or our advisor are able to terminate the Advisory Agreement subject to a 60-day transition period with respect to certain provisions of the Advisory Agreement. However, if the Advisory Agreement is terminated in connection with the listing of shares of our common stock on a national securities exchange, the partnership agreement provides that our advisor will receive an incentive distribution in redemption of its limited partnership units equal to 15.0% of the amount, if any, by which (i) the market value of the outstanding shares of our common stock at listing plus distributions paid by us prior to listing, exceeds (ii) the sum of the gross proceeds from the sale of shares of our common stock (less amounts paid to repurchase shares of our common stock) plus an annual 6.0% cumulative, non-compounded return on the gross proceeds from the sale of shares of our common stock. Upon our advisor’s receipt of the incentive distribution in redemption of its limited partnership units, our advisor will not be entitled to receive any further incentive distributions upon sales of our properties. Further, in connection with the termination of the Advisory Agreement other than due to a listing of the shares of our common stock on a national securities exchange, our advisor shall be entitled to receive a distribution in redemption of its limited partnership units equal to the amount that would be payable to our advisor pursuant to the incentive distribution upon sales if we liquidated all of our assets for their fair market value. Upon our advisor’s receipt of this distribution in redemption of its limited partnership units, our advisor will not be entitled to receive any further incentive distributions upon sales of our properties. Any amounts to be paid to our advisor upon termination of the Advisory Agreement cannot be determined at the present time.
If our advisor was to terminate the Advisory Agreement, we would need to find another advisor to provide us with day-to-day management services or have employees to provide these services directly to us. There can be no assurances that we would be able to find new advisors or employees or enter into agreements for such services on acceptable terms.
If we internalize our management functions, we could incur significant costs associated with being self-managed.
Our strategy may involve internalizing our management functions. If we internalize our management functions, we would no longer bear the costs of the various fees and expenses we expect to pay to our advisor under the Advisory Agreement; however, our direct expenses would include general and administrative costs, including legal, accounting, and other expenses related to corporate governance, SEC reporting and compliance. We would also incur the compensation and benefits costs of our officers and other employees and consultants that are now paid by our advisor or its affiliates. In addition, we may issue
27
equity awards to officers, employees and consultants, which awards would decrease net income and FFO, and may further dilute our stockholders’ investment. We cannot reasonably estimate the amount of fees to our advisor we would save and the costs we would incur if we became self-managed. If the expenses we assume as a result of an internalization are higher than the expenses we no longer pay to our advisor, our net income per share and FFO per share may be lower as a result of the internalization than they otherwise would have been, potentially decreasing the amount of funds available to distribute to our stockholders.
As currently organized, we do not directly have any employees. If we elect to internalize our operations, we would employ personnel and would be subject to potential liabilities commonly faced by employers, such as worker’s disability and compensation claims, potential labor disputes and other employee-related liabilities and grievances. Upon any internalization of our advisor, certain key personnel of our advisor or American Healthcare Investors may not be employed by us, but instead may remain employees of our co-sponsors or their affiliates.
If we internalize our management functions, we could have difficulty integrating these functions as a stand-alone entity. Currently, our advisor and its affiliates perform asset management and general and administrative functions, including accounting and financial reporting, for multiple entities. They have a great deal of know-how and can experience economies of scale. We may fail to properly identify the appropriate mix of personnel and capital needs to operate as a stand-alone entity. An inability to manage an internalization transaction effectively could, therefore, result in our incurring additional costs and/or experiencing deficiencies in our disclosure controls and procedures or our internal control over financial reporting. Such deficiencies could cause us to incur additional costs, and our management’s attention could be diverted from most effectively managing our properties.
Because not all REITs calculate MFFO the same way, our use of MFFO may not provide meaningful comparisons with other REITs.
We use modified funds from operations attributable to controlling interest, or MFFO, and the adjustments used to calculate it in order to evaluate our performance against other publicly registered, non-listed REITs, which intend to have limited lives with short and defined acquisition periods and targeted exit strategies shortly thereafter. However, not all REITs calculate MFFO the same way. We define MFFO, a non-GAAP measure, consistent with the IPA’s Practice Guideline 2010-01, Supplemental Performance Measure for Publicly Registered, Non-Listed REITs: Modified Funds from Operations, or the Practice Guideline, issued by the IPA in November 2010. If REITs use different methods of calculating MFFO, it may not be possible for investors to meaningfully compare the performance of certain REITs.
Cybersecurity risks and cyber incidents may adversely affect our business by causing a disruption to our operations, a compromise or corruption of our confidential information, and/or damage to our business relationships, all of which could negatively impact our financial results.
Cyber incidents and cyber-attacks have been occurring globally at a more frequent and severe level and may continue to increase in frequency in the future. A cyber incident is considered to be any adverse event that threatens the confidentiality, integrity or availability of our information resources. These incidents may be an intentional attack or an unintentional event and could involve gaining unauthorized access to our information systems for purposes of misappropriating assets, stealing confidential information, corrupting data or causing operational disruption. The result of these incidents may include disrupted operations, misstated or unreliable financial data, liability for stolen assets or information, increased cybersecurity protection and insurance costs, litigation and damage to our tenant, patient and investor relationships. As our reliance on technology increases, so will the risks posed to our information systems, both internal and those we outsource. There is no guarantee that any processes, procedures and internal controls we have implemented or will implement will prevent cyber intrusions, which could have a negative impact on our financial results, operations, business relationships or confidential information.
A breach of information technology systems on which we rely could materially and adversely impact our business, financial condition, results of operations and reputation.
We and our operators rely on information technology systems, including the Internet and networks and systems maintained and controlled by third-party vendors and other third parties, to process, transmit and store information and to manage or support our business processes. Third-party vendors collect and hold personally identifiable information and other confidential information of our tenants, patients, stockholders and employees. We also maintain confidential financial and business information regarding us and persons and entities with which we do business on our information technology systems. While we and our operators take steps to protect the security of the information maintained in our information technology systems, including the use of commercially available systems, software, tools and monitoring to provide security for processing, transmitting and storing of the information, it is possible that such security measures will not be able to prevent human error or the systems’ improper functioning, or the loss, misappropriation, disclosure or corruption of personally identifiable information or other confidential or sensitive information, including information about our tenants and employees.
28
Cybersecurity breaches, including physical or electronic break-ins, computer viruses, phishing scams, attacks by hackers, breaches due to employee error or misconduct, and similar breaches, can create, and in some instances in the past resulted in, system disruptions, shutdowns or unauthorized access to information maintained on our information technology systems or the information technology systems of our third-party vendors or other third parties or otherwise cause disruption or negative impacts to occur to our business and adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations. While we and most of our operators maintain cyber risk insurance to provide some coverage for certain risks arising out of cybersecurity breaches, there is no assurance that such insurance would cover all or a significant portion of the costs or consequences associated with a cybersecurity breach. As the techniques used to obtain unauthorized access to information technology systems become more varied and sophisticated and the occurrence of such breaches becomes more frequent, we and our third-party vendors and other third parties may be unable to adequately anticipate these techniques or breaches and implement appropriate preventative measures. Any failure to prevent cybersecurity breaches and maintain the proper function, security and availability of our or our third-party vendors’ and other third parties’ information technology systems could interrupt our operations, damage our reputation and brand, damage our competitive position, make it difficult for us to attract and retain tenants, and subject us to liability claims or regulatory penalties, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The expansion of social media platforms presents new risks and challenges.
The inappropriate use of certain social media vehicles could cause brand damage or information leakage or could lead to legal implications from the improper collection and/or dissemination of personally identifiable information or the improper dissemination of material non-public information. In addition, negative posts or comments about us on any social networking website could seriously damage our reputation. Further, the disclosure of non-public company sensitive information through external media channels could lead to information loss as there might not be structured processes in place to secure and protect information. If our non-public sensitive information is disclosed or if our reputation is seriously damaged through social media, it could have a material adverse effect on our business and/or financial condition.
Risks Related to Conflicts of Interest
We are subject to conflicts of interest arising out of relationships among us, our officers, our co-sponsors, our advisor and its affiliates, including the material conflicts discussed below.
Our advisor faces conflicts of interest relating to its compensation structure, including the payment of acquisition fees and asset management fees, which could result in actions that are not necessarily in our stockholders’ long-term best interest.
Under the Advisory Agreement and pursuant to the subordinated participation interest our advisor holds in our operating partnership, our advisor will be entitled to fees and distributions that are structured in a manner intended to provide incentives to our advisor to perform in both our and our stockholders’ long-term best interests. The fees to which our advisor or its affiliates will be entitled include acquisition fees, asset management fees, property management fees, disposition fees and other fees as provided for under the Advisory Agreement and agreement of limited partnership of our operating partnership. The distributions our advisor may become entitled to receive would be payable upon distribution of net sales proceeds to our stockholders, the listing of the shares of our common stock on a national securities exchange, certain merger transactions or the termination of the Advisory Agreement. However, because our advisor will be entitled to receive substantial minimum compensation regardless of our performance, our advisor’s interests may not be wholly aligned with theirs. In that regard, our advisor or its affiliates will receive an asset management fee with respect to the ongoing operation and management of properties based on the amount of our initial investment and capital expenditures and not the performance of those investments, which could result in our advisor not having adequate incentive to manage our portfolio to provide profitable operations during the period we hold our investments. On the other hand, our advisor could be motivated to recommend riskier or more speculative investments in order to increase the fees payable to our advisor or for us to generate the specified levels of performance or net sales proceeds that would entitle our advisor to fees or distributions. Furthermore, our advisor or its affiliates will receive an acquisition fee that is based on the contract purchase price of each property acquired or the origination or acquisition price of any real estate-related investment, rather than the performance of those investments. Therefore, our advisor or its affiliates may have an incentive to recommend investments more quickly or with a higher purchase price or investments that may not produce the maximum risk adjusted returns in order to receive such acquisition fees.
Our advisor may receive economic benefits from its status as a limited partner without bearing any of the investment risk.
Our advisor is a limited partner in our operating partnership. Our advisor is entitled to receive an incentive distribution equal to 15.0% of net sales proceeds of properties after we have received and paid to our stockholders a return of their invested capital and an annual 6.0% cumulative, non-compounded return on the gross proceeds of the sale of shares of our common stock. We bear all of the risk associated with the properties but, as a result of the incentive distributions to our advisor, we are not entitled to all of our operating partnership’s proceeds from property dispositions.
29
The distribution payable to our advisor may influence our decisions about listing the shares of our common stock on a national securities exchange, merging our company with another company and acquisition or disposition of our investments.
Our advisor’s entitlement to fees upon the sale of our assets and to participate in net sales proceeds could result in our advisor recommending sales of our investments at the earliest possible time at which sales of investments would produce the level of return which would entitle our advisor to compensation relating to such sales, even if continued ownership of those investments might be in our stockholders’ long-term best interest. The subordinated participation interest may require our operating partnership to make a distribution to our advisor in redemption of its limited partnership units upon the listing of the shares of our common stock on a national securities exchange or the merger of our company with another company in which our stockholders receive shares that are traded on a national securities exchange if our advisor meets the performance thresholds included in our operating partnership’s limited partnership agreement, even if our advisor is no longer serving as our advisor. To avoid making this distribution, our independent directors may decide against listing the shares of our common stock or merging with another company even if, but for the requirement to make this distribution, such listing or merger would be in our stockholders’ best interest. In addition, the requirement to pay these fees could cause our independent directors to make different investment or disposition decisions than they would otherwise make, in order to satisfy our obligation to our advisor.
We may acquire assets from, or dispose of assets to, affiliates of our advisor, which could result in us entering into transactions on less favorable terms than we would receive from a third party or that negatively affect the public’s perception of us.
We may acquire assets from affiliates of our advisor. Further, we may also dispose of assets to affiliates of our advisor. Affiliates of our advisor may make substantial profits in connection with such transactions and may owe fiduciary and/or other duties to the selling or purchasing entity in these transactions, and conflicts of interest between us and the selling or purchasing entities could exist in such transactions. Because our independent directors would rely on our advisor in identifying and evaluating any such transaction, these conflicts could result in transactions based on terms that are less favorable to us than we would receive from a third party. Also, the existence of conflicts, regardless of how they are resolved, might negatively affect the public’s perception of us.
We have entered into and may continue to enter into joint ventures with other programs sponsored or advised by one of our co-sponsors or one of their affiliates and may face conflicts of interest or disagreements with our joint venture partners that may not be resolved as quickly or on terms as advantageous to us as would be the case if the joint venture had been negotiated at arm’s-length with an independent joint venture partner.
We have entered into and may continue to enter into joint ventures with other programs sponsored or advised by one of our co-sponsors or one of their affiliates and may face certain additional risks and potential conflicts of interest. For example, securities issued by the other Griffin Capital programs or future American Healthcare Investors programs may never have an active trading market. Therefore, if we were to become listed on a national securities exchange, we may no longer have similar goals and objectives with respect to the resale of properties in the future. Joint ventures between us and other Griffin Capital programs, American Healthcare Investors programs or future American Healthcare Investors programs will not have the benefit of arm’s-length negotiation of the type normally conducted between unrelated co-venturers. Under these joint venture agreements, none of the co-venturers may have the power to control the venture, and an impasse could occur regarding matters pertaining to the joint venture, including determining when and whether to buy or sell a particular property and the timing of a liquidation, which might have a negative impact on the joint venture and decrease returns to our stockholders.
Risks Related to Our Organizational Structure
Several potential events could cause our stockholders’ investment in us to be diluted, which may reduce the overall value of their investment.
Our stockholders’ investment in us could be diluted by a number of factors, including:
• | future offerings of our securities, including issuances pursuant to the DRIP and up to 200,000,000 shares of any class or series of preferred stock that our board may authorize; |
• | private issuances of our securities to other investors, including institutional investors; |
• | issuances of our securities pursuant to our incentive plan; or |
• | redemptions of units of limited partnership interest in our operating partnership in exchange for shares of our common stock. |
To the extent we issue additional equity interests, current stockholders’ percentage ownership interest in us will be diluted. In addition, depending upon the terms and pricing of any additional offerings and the value of our real estate and real
30
estate-related investments, our stockholders may also experience dilution in the book value and fair market value of their shares of our common stock.
Our ability to issue preferred stock may include a preference in distributions superior to our common stock and also may deter or prevent a sale of shares of our common stock in which our stockholders could profit.
Our charter authorizes our board to issue up to 200,000,000 shares of preferred stock. Our board has the discretion to establish the preferences and rights, including a preference in distributions superior to our common stockholders, of any issued preferred stock. If we authorize and issue preferred stock with a distribution preference over our common stock, payment of any distribution preferences of outstanding preferred stock would reduce the amount of funds available for the payment of distributions on our common stock. Further, holders of preferred stock are normally entitled to receive a preference payment in the event we liquidate, dissolve or wind up before any payment is made to our common stockholders, likely reducing the amount our common stockholders would otherwise receive upon such an occurrence. In addition, under certain circumstances, the issuance of preferred stock or a separate class or series of common stock may render more difficult or tend to discourage:
• | a merger, tender offer or proxy contest; |
• | assumption of control by a holder of a large block of our securities; or |
• | removal of incumbent management. |
The limit on the percentage of shares of our common stock that any person may own may discourage a takeover or business combination that may have benefited our stockholders.
Our charter restricts the direct or indirect ownership by one person or entity to no more than 9.9% of the value of shares of our then outstanding capital stock (which includes common stock and any preferred stock we may issue) and no more than 9.9% of the value or number of shares, whichever is more restrictive, of our then outstanding common stock. This restriction may discourage a change of control of us and may deter individuals or entities from making tender offers for shares of our stock on terms that might be financially attractive to our stockholders or which may cause a change in our management. This ownership restriction may also prohibit business combinations that would have otherwise been approved by our board and our stockholders. In addition to deterring potential transactions that may be favorable to our stockholders, these provisions may also decrease their ability to sell their shares of our common stock.
Our stockholders’ ability to control our operations is severely limited.
Our board determines our major strategies, including our strategies regarding investments, financing, growth, debt capitalization, REIT qualification and distributions. Our board may amend or revise these and other strategies without a vote of the stockholders. Our charter sets forth the stockholder voting rights required to be set forth therein under the North American Securities Administrators Association. Under our charter and Maryland law, our stockholders have a right to vote only on the following matters:
• | the election or removal of directors; |
• | the amendment of our charter, except that our board may amend our charter without stockholder approval to change our name or the name of other designation or the par value of any class or series of our stock and the aggregate par value of our stock, increase or decrease the aggregate number of shares of stock or the number of shares of stock of any class or series that we have the authority to issue, or effect certain reverse stock splits; |
• | our dissolution; and |
• | certain mergers, consolidations, conversions, statutory share exchanges and sales or other dispositions of all or substantially all of our assets. |
All other matters are subject to the discretion of our board.
Maryland law prohibits certain business combinations, which may make it more difficult for us to be acquired and may limit or delay our stockholders’ ability to dispose of their shares of our common stock.
The Maryland General Corporation Law, or the MGCL, contains many provisions, such as the business combination statute and the control share acquisition statute, that are designed to prevent, or have the effect of preventing, someone from acquiring control of us. Our bylaws exempt us from the control share acquisition statute, which eliminates voting rights for certain levels of shares that could exercise control over us, and our board has adopted a resolution providing that any business combination between us and any other person is exempted from the business combination statute, provided that such business combination is first approved by our board.
31
Under the MGCL, “business combinations” between a Maryland corporation and an interested stockholder or an affiliate of an interested stockholder are prohibited for five years after the most recent date on which the interested stockholder becomes an interested stockholder. These business combinations include a merger, consolidation, share exchange or, in circumstances specified in the statute, an asset transfer or issuance or reclassification of equity securities. An interested stockholder is defined as:
• | any person who beneficially owns, directly or indirectly, 10.0% or more of the voting power of the corporation’s outstanding voting stock; or |
• | an affiliate or associate of the corporation who, at any time within the two-year period prior to the date in question, was the beneficial owner, directly or indirectly, of 10.0% or more of the voting power of the then outstanding stock of the corporation. |
A person is not an interested stockholder under the statute if our board approved in advance the transaction by which he or she otherwise would have become an interested stockholder. However, in approving a transaction, our board may provide that its approval is subject to compliance, at or after the time of approval, with any terms and conditions determined by our board.
After the five-year prohibition, any business combination between the Maryland corporation and an interested stockholder generally must be recommended by the board of the corporation and approved by the affirmative vote of at least:
• | 80.0% of the votes entitled to be cast by holders of outstanding shares of voting stock of the corporation; and |
• | two-thirds of the votes entitled to be cast by holders of voting stock of the corporation other than shares of stock held by the interested stockholder with whom or with whose affiliate the business combination is to be effected or held by an affiliate or associate of the interested stockholder. |
These super-majority vote requirements do not apply if the corporation’s common stockholders receive a minimum price, as defined under the MGCL, for their shares of our common stock in the form of cash or other consideration in the same form as previously paid by the interested stockholder for its shares of our common stock. The business combination statute permits various exemptions from its provisions, including business combinations that are exempted by the board prior to the time that the interested stockholder becomes an interested stockholder.
However, if the bylaw provisions exempting us from the control share acquisition statute or our board resolution opting out of the business combination statute were repealed in whole or in part at any time, these provisions of the MGCL could delay or prevent offers to acquire us and increase the difficulty of consummating any such offers, even if such a transaction would be in our stockholders’ best interest. Furthermore, these limits on ownership and transfer of our equity securities under the MGCL may have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a transaction or a change in control that might involve a premium price for our stockholders’ common stock.
The MGCL and our organizational documents limit our stockholders’ right to bring claims against our officers and directors.
The MGCL provides that a director will not have any liability as a director so long as he or she performs his or her duties in good faith, in a manner he or she reasonably believes to be in our best interest, and with the care that an ordinarily prudent person in a like position would use under similar circumstances. In addition, our charter provides that, subject to the applicable limitations set forth therein or under the MGCL, no director or officer will be liable to us or our stockholders for monetary damages. Our charter also provides that we will generally indemnify our directors, our officers, our advisor and its affiliates for losses they may incur by reason of their service in those capacities unless: (i) their act or omission was material to the matter giving rise to the proceeding and was committed in bad faith or was the result of active and deliberate dishonesty; (ii) they actually received an improper personal benefit in money, property or services; or (iii) in the case of any criminal proceeding, they had reasonable cause to believe the act or omission was unlawful. Moreover, we have entered into separate indemnification agreements with each of our directors and executive officers and intend to enter into indemnification agreements with each of our future directors and executive officers. As a result, we and our stockholders may have more limited rights against these persons than might otherwise exist under common law. In addition, we may be obligated to fund the defense costs incurred by these persons in some cases. However, our charter also provides that we may not indemnify our directors, our advisor and its affiliates for any loss or liability suffered by them or hold them harmless for any loss or liability suffered by us unless they have determined that the course of conduct that caused the loss or liability was in our best interest, they were acting on our behalf or performing services for us, the liability was not the result of negligence or misconduct by our non-independent directors, our advisor and its affiliates or gross negligence or willful misconduct by our independent directors, and the indemnification is recoverable only out of our net assets or the proceeds of insurance and not from our stockholders.
32
Our charter includes a provision that may discourage a stockholder from launching a tender offer for shares of our common stock.
Our charter requires that any tender offer made by a person, including any “mini-tender” offer, must comply with most of the provisions of Regulation 14D of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. The offeror must provide us notice of the tender offer at least ten business days before initiating the tender offer. If the offeror does not comply with these requirements, we will have the first right to purchase the shares of our stock at the tender offer price offered in such non-compliant tender offer. In addition, the non-complying offeror shall be responsible for all of our expenses in connection with that stockholder’s noncompliance. This provision of our charter may discourage a person from initiating a tender offer for shares of our common stock and prevent our stockholders from receiving a premium price for their shares of our common stock in such a transaction.
Our stockholders’ investment return may be reduced if we are required to register as an investment company under the Investment Company Act. To avoid registration as an investment company, we may not be able to operate our business successfully. If we become subject to registration under the Investment Company Act, we may not be able to continue our business.
We conduct and intend to continue to conduct our operations, and the operations of our operating partnership and any other subsidiaries, so that no such entity meets the definition of an “investment company” under Section 3(a)(1) of the Investment Company Act. Under the Investment Company Act, in relevant part, a company is an “investment company” if:
• | pursuant to Section 3(a)(1)(A), it is, or holds itself out as being, engaged primarily, or proposes to engage primarily, in the business of investing, reinvesting or trading in securities; or |
• | pursuant to Section 3(a)(1)(C), it is engaged, or proposes to engage, in the business of investing, reinvesting, owning, holding or trading in securities and owns or proposes to acquire “investment securities” having a value exceeding 40.0% of the value of its total assets (exclusive of U.S. government securities and cash items) on an unconsolidated basis, or the 40.0% test. “Investment securities” excludes U.S. government securities and securities of majority-owned subsidiaries that are not themselves investment companies and are not relying on the exception from the definition of investment company under Section 3(c)(1) or Section 3(c)(7) of the Investment Company Act. |
We monitor our operations and our assets on an ongoing basis in order to ensure that neither we, nor any of our subsidiaries, meet the definition of “investment company” under Section 3(a)(1) of the Investment Company Act. If we were obligated to register as an investment company, we would have to comply with a variety of substantive requirements under the Investment Company Act imposing, among other things:
• | limitations on capital structure; |
• | restrictions on specified investments; |
• | prohibitions on transactions with affiliates; |
• | compliance with reporting, record keeping, voting, proxy disclosure and other rules and regulations that would significantly change our operations; and |
• | potentially, compliance with daily valuation requirements. |
To avoid meeting the definition of an “investment company” under Section 3(a)(1) of the Investment Company Act, we may be unable to sell assets we would otherwise want to sell and may need to sell assets we would otherwise wish to retain. Similarly, we may have to acquire additional income- or loss-generating assets that we might not otherwise have acquired or may have to forgo opportunities to acquire interests in companies that we would otherwise want to acquire and would be important to our investment strategy. Accordingly, our board may not be able to change our investment policies as our board may deem appropriate if such change would cause us to meet the definition of an “investment company.” In addition, a change in the value of any of our assets could negatively affect our ability to avoid being required to register as an investment company. If we were required to register as an investment company but failed to do so, we would be prohibited from engaging in our business, and criminal and civil actions could be brought against us. In addition, our contracts would be unenforceable unless a court were to require enforcement, and a court could appoint a receiver to take control of us and liquidate our business.
As part of our advisor’s obligations under the Advisory Agreement, our advisor agrees to refrain from taking any action which, in its sole judgment made in good faith, would subject us to regulation under the Investment Company Act. Failure to maintain an exclusion from registration under the Investment Company Act would require us to significantly restructure our business plan. For example, because affiliate transactions generally are prohibited under the Investment Company Act, we would not be able to enter into transactions with any of our affiliates if we are required to register as an investment company,
33
and we may be required to terminate the Advisory Agreement and any other agreements with affiliates, which could have a material adverse effect on our ability to operate our business and pay distributions.
We are an “emerging growth company” under the federal securities laws and will be subject to reduced public company reporting requirements.
In April 2012, President Obama signed into law the JOBS Act. We are an “emerging growth company,” as defined in the JOBS Act, and are eligible to take advantage of certain exemptions from, or reduced disclosure obligations relating to, various reporting requirements that are normally applicable to public companies.
We could remain an “emerging growth company” for up to five fiscal years after our initial public offering, or until the earliest of (i) the last day of the first fiscal year in which we have total annual gross revenue of $1.07 billion or more, (ii) December 31 of the fiscal year that we become a “large accelerated filer,” as defined in Rule 12b-2 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (which would occur if the market value of our common stock held by non-affiliates exceeds $700 million, measured as of the last business day of our most recently completed second fiscal quarter, and we have been publicly reporting for at least 12 months), or (iii) the date on which we have issued more than $1 billion in non-convertible debt during the preceding three-year period.
Under the JOBS Act, emerging growth companies are not required to (i) provide an auditor’s attestation report on management’s assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, (ii) comply with new requirements adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board, or PCAOB, which may require a supplement to the auditor’s report in which the auditor must provide additional information about the audit and the issuer’s financial statements, (iii) comply with new audit rules adopted by the PCAOB after April 5, 2012 (unless the SEC determines otherwise), (iv) provide certain disclosures relating to executive compensation generally required for larger public companies, or (v) hold stockholder advisory votes on executive compensation. Other than as set forth in the following paragraph, we have not yet made a decision as to whether to take advantage of any or all of the JOBS Act exemptions that are applicable to us. If we do take advantage of any of the remaining exemptions, we do not know if some investors will find our common stock less attractive as a result.
Additionally, the JOBS Act provides that an “emerging growth company” may take advantage of an extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards that have different effective dates for public and private companies. This means that an “emerging growth company” can delay adopting certain accounting standards until such standards are otherwise applicable to private companies. However, we elected to “opt out” of such extended transition period, and will therefore comply with new or revised accounting standards on the applicable dates on which the adoption of such standards is required for non-emerging growth companies. Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that our decision to opt out of such extended transition period for compliance with new or revised accounting standards is irrevocable.
Risks Related to Investments in Real Estate
If we acquire real estate at a time when the real estate market is experiencing substantial influxes of capital investment and competition for income-producing properties, such real estate investments may not appreciate or may decrease in value.
The real estate market may experience a substantial influx of capital from investors. Any substantial flow of capital, combined with significant competition for income producing real estate, may result in inflated purchase prices for such assets. To the extent we purchase real estate in such an environment in the future, we will be subject to the risk that the value of such investments may not appreciate or may decrease significantly below the amount we paid for such investment.
Acquiring or attempting to acquire multiple properties in a single transaction may adversely affect our operations.
From time to time, we have acquired and may continue to attempt to acquire multiple properties in a single transaction. Portfolio acquisitions are more complex and expensive than single property acquisitions, and the risk that a multiple-property acquisition does not close may be greater than in a single-property acquisition. Portfolio acquisitions may also result in us owning investments in geographically dispersed markets, placing additional demands on our ability to manage the properties in the portfolio. In addition, a seller may require that a group of properties be purchased as a package even though we may not want to purchase one or more properties in the portfolio. In these situations, if we are unable to identify another person or entity to acquire the unwanted properties, we may be required to operate or attempt to dispose of these properties. To acquire multiple properties in a single transaction, we may be required to accumulate a large amount of cash. We would expect the returns that we earn on such cash to be less than the ultimate returns on real property; therefore, accumulating such cash could reduce our funds available for distributions to our stockholders. Any of the foregoing events may have an adverse effect on our operations.
34
Uninsured losses relating to real estate and lender requirements to obtain insurance may reduce our stockholders’ returns.
There are types of losses relating to real estate, generally catastrophic in nature, such as losses due to wars, acts of terrorism, earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, pollution or environmental matters, for which we do not intend to obtain insurance unless we are required to do so by mortgage lenders. If any of our properties incurs a casualty loss that is not fully covered by insurance, the value of our assets will be reduced by any such uninsured loss. In addition, other than any reserves we may establish, we have no source of funding to repair or reconstruct any uninsured damaged property, and we cannot assure our stockholders that any such sources of funding will be available to us for such purposes in the future. Also, to the extent we must pay unexpectedly large amounts for uninsured losses, we could suffer reduced earnings that would result in less cash to be distributed to our stockholders. In cases where we are required by mortgage lenders to obtain casualty loss insurance for catastrophic events or terrorism, such insurance may not be available, or may not be available at a reasonable cost, which could inhibit our ability to finance or refinance our properties. Additionally, if we obtain such insurance, the costs associated with owning a property would increase and could have a material adverse effect on the net income from the property, and, thus, the cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
A significant portion of our annual base rent may be concentrated in a small number of tenants. Therefore, non-renewals, terminations or lease defaults by any of these significant tenants could reduce our net income and have a negative effect on our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
The success of our investments materially depends upon the financial stability of the tenants leasing the properties we own. Therefore, a non-renewal after the expiration of a lease term, termination, default or other failure to meet rental obligations by a significant tenant would significantly lower our net income. Any of these events could have a negative effect on our results of operations, our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders or on our ability to cover distributions with cash flows from operations. As of March 19, 2020, no single tenant accounted for more than 10.0% of our annualized base rent or annualized NOI of our total property portfolio.
A high concentration of our properties in a particular geographic area would magnify the effects of downturns in that geographic area.
We have a concentration of properties in particular geographic areas; therefore, any adverse situation that disproportionately effects one of those areas would have a magnified adverse effect on our portfolio. As of March 19, 2020, our properties located in Missouri accounted for approximately 10.8% of our total property portfolio’s annualized base rent or annualized NOI. Accordingly, there is a geographic concentration of risk subject to fluctuations in such state’s economy.
Terrorist attacks, acts of violence or war or public health crises may affect the markets in which we operate and have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Terrorist attacks, acts of war and public health crises (including the recent coronavirus outbreak) may negatively affect our operations and our stockholders’ investments. We may acquire real estate assets located in areas that are susceptible to terrorist attacks, acts of war, or public health crises. These events may directly impact the value of our assets through damage, destruction, loss or increased security costs. Although we may obtain terrorism insurance, we may not be able to obtain sufficient coverage to fund any losses we may incur. Risks associated with potential acts of terrorism could sharply increase the premiums we pay for coverage against property and casualty claims. Further, certain losses resulting from these types of events are uninsurable or not insurable at reasonable costs.
More generally, any terrorist attack, other act of violence or war, or public health crisis (such as the coronavirus outbreak) could result in increased volatility in, or damage to, the U.S. and worldwide financial markets and economy, all of which could adversely affect our tenants’ ability to pay rent on their leases or our ability to borrow money or issue capital stock at acceptable prices, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Dramatic increases in insurance rates could adversely affect our cash flows and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
We may not be able to obtain insurance coverage at reasonable rates due to high premium and/or deductible amounts. As a result, our cash flows could be adversely impacted due to these higher costs, which would adversely affect our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Delays in the acquisition, development and construction of real properties may have adverse effects on our results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Delays we encounter in the selection, acquisition and development of real properties could adversely affect our stockholders’ returns. Where properties are acquired prior to the start of construction or during the early stages of construction,
35
it will typically take several months to complete construction and rent available space. If we engage in development or construction projects, we will be subject to uncertainties associated with re-zoning for development, environmental concerns of governmental entities and/or community groups, and our builder’s ability to build in conformity with plans, specifications, budgeted costs, and timetables. If a builder fails to perform, we may resort to legal action to rescind the purchase or the construction contract or to compel performance. A builder’s performance may also be affected or delayed by conditions beyond the builder’s control. Therefore, our stockholders could suffer delays in the receipt of cash distributions attributable to those particular real properties. Delays in completion of construction could give tenants the right to terminate preconstruction leases for space at a newly developed project. We may incur additional risks if we make periodic progress payments or other advances to builders prior to completion of construction. These and other such factors can result in increased costs of a project or loss of our investment. In addition, we will be subject to normal lease-up risks relating to newly constructed projects. We also must rely on rental income and expense projections and estimates of the fair market value of property upon completion of construction when agreeing upon a price at the time we acquire the property. If our projections are inaccurate, we may pay too much for a property, and our return on our investment could suffer.
We are permitted to invest in a limited amount of unimproved real property. Returns from development of unimproved properties are also subject to risks associated with re-zoning the land for development and environmental concerns of governmental entities and/or community groups. If we invest in unimproved real property that we intend to develop, our stockholders’ investment would be subject to the risks associated with investments in unimproved real property.
Uncertain market conditions relating to the future disposition of properties could cause us to sell our properties at a loss in the future.
Our advisor, subject to the oversight and approval of our board, may exercise its discretion as to whether and when to sell a property, and we will have no obligation to sell properties at any particular time. We cannot predict with any certainty the various market conditions affecting real estate investments that will exist at any particular time in the future. Because of the uncertainty of market conditions that may affect the future disposition of our properties, we cannot assure our stockholders that we will be able to sell our properties at a profit in the future. Additionally, we may incur prepayment penalties in the event we sell a property subject to a mortgage earlier than we otherwise had planned. Accordingly, the extent to which our stockholders will receive cash distributions and realize potential appreciation on our real estate investments will, among other things, be dependent upon fluctuating market conditions.
Our inability to sell a property when we desire to do so could adversely impact our ability to pay cash distributions to our stockholders.
The real estate market is affected by many factors, such as general economic conditions, availability of financing, interest rates, supply and demand, and other factors that are beyond our control. We cannot predict whether we will be able to sell any property for the price or on the terms set by us, or whether any price or other terms offered by a prospective purchaser would be acceptable to us. We may be required to expend funds to correct defects or to make improvements before a property can be sold. We may not have adequate funds available to correct such defects or to make such improvements. Moreover, in acquiring a property, we may agree to restrictions that prohibit the sale of that property for a period of time or impose other restrictions, such as a limitation on the amount of debt that can be placed or repaid on that property. We cannot predict the length of time needed to find a willing purchaser and to close the sale of a property. Our inability to sell a property when we desire to do so may cause us to reduce our selling price for the property. Any delay in our receipt of proceeds, or diminishment of proceeds, from the sale of a property could adversely impact our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Our stockholders may not receive any profits resulting from the sale of our properties, or receive such profits in a timely manner, because we may provide financing to the purchaser of such property.
If we decide to sell one of our properties in a forced or voluntary liquidation, we may sell our properties either subject to or upon the assumption of any then outstanding mortgage debt or, alternatively, may provide financing to purchasers. We may take a purchase money obligation secured by a mortgage as partial payment. We do not have any limitations or restrictions on our taking such purchase money obligations. When we provide financing to purchasers, we will bear the risk that the purchaser may default on its obligations under the financing, which could negatively impact cash flows from operations. Even in the absence of a purchaser default, the distribution of sale proceeds, or their reinvestment in other assets, will be delayed until the promissory notes or other property we may accept upon the sale are actually paid, sold, refinanced or otherwise disposed of. In some cases, we may receive initial down payments in cash and other property in the year of sale in an amount less than the selling price, and subsequent payments will be spread over a number of years. Therefore, our stockholders may experience a delay in the distribution to our stockholders of the proceeds of a sale until such time. Additionally, if any purchaser defaults under a financing arrangement with us, it could negatively impact our ability to pay cash distributions to our stockholders.
36
We face possible liability for environmental cleanup costs and damages for contamination related to properties we acquire, which could substantially increase our costs and reduce our liquidity and cash distributions to our stockholders.
Because we own and operate real estate, we are subject to various federal, state and local environmental laws, ordinances and regulations. Under these laws, ordinances and regulations, a current or previous owner or operator of real estate may be liable for the cost of removal or remediation of hazardous or toxic substances on, under or in such property. The costs of removal or remediation could be substantial. Such laws often impose liability whether or not the owner or operator knew of, or was responsible for, the presence of such hazardous or toxic substances. Environmental laws also may impose restrictions on the manner in which property may be used or businesses may be operated, and these restrictions may require substantial expenditures. Environmental laws provide for sanctions in the event of noncompliance and may be enforced by governmental agencies or, in certain circumstances, by private parties. Certain environmental laws and common law principles could be used to impose liability for release of and exposure to hazardous substances, including the release of asbestos-containing materials into the air, and third parties may seek recovery from owners or operators of real estate for personal injury or property damage associated with exposure to released hazardous substances. In addition, new or more stringent laws or stricter interpretations of existing laws could change the cost of compliance or liabilities and restrictions arising out of such laws. The cost of defending against these claims, complying with environmental regulatory requirements, conducting remediation of any contaminated property, or of paying personal injury claims could be substantial, which would reduce our liquidity and cash available for distribution to our stockholders. In addition, the presence of hazardous substances on a property or the failure to meet environmental regulatory requirements may materially impair our ability to use, lease or sell a property, or to use the property as collateral for borrowing.
Our real estate investments may be concentrated in medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing or other healthcare-related facilities, making us potentially more vulnerable economically than if our investments were diversified.
As a REIT, we invest primarily in real estate. Within the real estate industry, we have acquired and intend to continue to acquire or selectively develop and own medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities. We are subject to risks inherent in concentrating investments in real estate. These risks resulting from a lack of diversification become even greater as a result of our business strategy to invest to a substantial degree in healthcare-related facilities.
A downturn in the commercial real estate industry generally could significantly adversely affect the value of our properties. A downturn in the healthcare industry could negatively affect our lessees’ ability to make lease payments to us and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders. These adverse effects could be more pronounced than if we diversified our investments outside of real estate or if our portfolio did not include a substantial concentration in medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities.
Certain of our properties may not have efficient alternative uses, so the loss of a tenant may cause us not to be able to find a replacement or cause us to spend considerable capital to adapt the property to an alternative use.
Some of the properties we have acquired and will seek to acquire are healthcare properties that may only be suitable for similar healthcare-related tenants. If we or our tenants terminate the leases for these properties or our tenants lose their regulatory authority to operate such properties, we may not be able to locate suitable replacement tenants to lease the properties for their specialized uses. Alternatively, we may be required to spend substantial amounts to adapt the properties to other uses. Any loss of revenues or additional capital expenditures required as a result may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Our current and future medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities and tenants may be unable to compete successfully, which could result in lower rent payments, reduce our cash flows from operations and amount available for distributions.
Our current and future medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities often will face competition from nearby medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities that provide comparable services. Some of those competing facilities are owned by governmental agencies and supported by tax revenues, and others are owned by nonprofit corporations and may be supported to a large extent by endowments and charitable contributions. These types of support are not available to our buildings.
Similarly, our tenants face competition from other medical practices in nearby hospitals and other medical facilities. Our tenants’ failure to compete successfully with these other practices could adversely affect their ability to make rental payments, which could adversely affect our rental revenues. Further, from time to time and for reasons beyond our control, referral sources, including physicians and managed care organizations, may change their lists of hospitals or physicians to which they
37
refer patients or that are permitted to participate in the payer program. This could adversely affect our tenants’ ability to make rental payments, which could adversely affect our rental revenues.
Any reduction in rental revenues resulting from the inability of our medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities and our tenants to compete successfully may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
The change in accounting standards in the U.S. for leases could reduce the overall demand to lease our properties.
Prior to January 1, 2019, the existing accounting standards for leases required lessees to classify their leases as either capital or operating leases. Under a capital lease, both the leased asset, which represented the tenant’s right to use the property, and the contractual lease obligation were recorded on the tenant’s balance sheet if one of the following criteria are met: (i) the lease transferred ownership of the property to the lessee by the end of the lease term; (ii) the lease contained a bargain purchase option; (iii) the non-cancelable lease term was more than 75.0% of the useful life of the asset; or (iv) if the present value of the minimum lease payments equaled 90.0% or more of the leased property’s fair value. If the terms of the lease did not meet these criteria, the lease was considered an operating lease, and no leased asset or contractual lease obligation was recorded by the tenant.
In order to address concerns raised by the SEC regarding the transparency of contractual lease obligations under the existing accounting standards for operating leases, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update, or ASU, 2016-02, Leases, or ASU 2016-02, in February 2016, which substantially changed the current lease accounting standards, primarily by eliminating the concept of operating lease accounting. As a result, a lease asset and obligation is recorded on the tenant’s balance sheet for all lease arrangements. In addition, ASU 2016-02 and its amendments impact the method in which contractual lease payments are recorded. In order to mitigate the effect of the lease accounting, tenants may seek to negotiate certain terms within new lease arrangements or modify terms in existing lease arrangements, such as shorter lease terms or fewer extension options, which would generally have less impact on tenant balance sheets. Also, tenants may reassess their lease-versus-buy strategies. This could result in a greater renewal risk or shorter lease terms, which may negatively impact our operations and ability to pay distributions. On January 1, 2019, we adopted ASU 2016-02 and its amendments. See Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies — Leases, and Note 16, Leases, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for a further discussion.
We cannot assure our stockholders that our goal to maximize our investment objectives will be realized.
Our advisor and our board determine whether a particular property or real estate-related investment should be sold or otherwise disposed of after consideration of the relevant factors, including prevailing economic conditions, with a view toward maximizing our investment objectives. We cannot assure our stockholders that this objective will be realized. The selling price of a property which is net leased will be determined in large part by the amount of rent payable under the lease(s) for such property. If a tenant has a repurchase option at a formula price, we may be limited in realizing any appreciation. In connection with our sales of properties, we may lend the purchaser all or a portion of the purchase price. In these instances, our taxable income may exceed the cash received in the sale.
Representations and warranties made by us in connection with sales of our properties may subject us to liability that could result in losses and could harm our operating results and, therefore distributions we make to our stockholders.
When we sell a property, we may be required to make representations and warranties regarding the property and other customary items. In the event of a breach of such representations or warranties, the purchaser of the property may have claims for damages against us, rights to indemnification from us or otherwise have remedies against us. In any such case, we may incur liabilities that could result in losses and could harm our operating results and, therefore distributions we make to our stockholders.
Risks Related to the Healthcare Industry
The healthcare industry is heavily regulated and new laws or regulations, changes to existing laws or regulations, loss of licensure or failure to obtain licensure could result in the inability of our tenants to make rent payments to us.
The healthcare industry is heavily regulated by federal, state and local governmental bodies. The tenants in our healthcare properties generally will be subject to laws and regulations covering, among other things, licensure, certification for participation in government programs, and relationships with physicians and other referral sources. Changes in these laws and regulations or our tenants’ failure to comply with these laws and regulations could negatively affect the ability of our tenants to make lease payments to us and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Many of our healthcare properties and their tenants may require a license or certificate of need, or CON, to operate. Failure to obtain a license or CON, or loss of a required license or CON, would prevent a facility from operating in the manner
38
intended by the tenant. These events could materially adversely affect our tenants’ ability to make rent payments to us. State and local laws also may regulate expansion, including the addition of new beds or services or acquisition of medical equipment, and the construction of healthcare-related facilities, by requiring a CON or other similar approval. State CON laws and other similar laws are not uniform throughout the U.S. and are subject to change; therefore, this may adversely impact our tenants’ ability to provide services in different states. We cannot predict the impact of state CON laws or similar laws on our development of facilities or the operations of our tenants.
In addition, state CON laws often materially impact the ability of competitors to enter into the marketplace of our facilities. The repeal of CON laws could allow competitors to freely operate in previously closed markets. This could negatively affect our tenants’ abilities to make rent payments to us.
In limited circumstances, loss of state licensure or certification or closure of a facility could ultimately result in loss of authority to operate the facility or provide services at the facility and require new CON authorization licensure and/or authorization or potential authorization from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services to re-institute operations. As a result, a portion of the value of the facility may be reduced, which would adversely impact our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Reductions in reimbursement from third-party payors, including Medicare and Medicaid, could adversely affect the profitability of our tenants and hinder their ability to make rental payments to us, and comprehensive healthcare reform legislation could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Sources of revenue for our tenants may include the federal Medicare program, state Medicaid programs, private insurance carriers and health maintenance organizations, among others. Efforts by such payors to reduce healthcare costs will likely continue, which may result in reductions or slower growth in reimbursement for certain services provided by some of our tenants. In addition, the healthcare billing rules and regulations are complex, and the failure of any of our tenants to comply with various laws and regulations could jeopardize their ability to continue participating in Medicare, Medicaid and other government sponsored payment programs. Moreover, the state and federal governmental healthcare programs are subject to reductions by state and federal legislative actions. The American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 prevented the reduction in physician reimbursement of Medicare from being implemented in 2013. The Protecting Access to Medicare Act of 2014 prevented the reduction of 24.4% in the physician fee schedule by replacing the scheduled reduction with a 0.5% increase to the physician fee schedule through December 31, 2014, and no increase from January 1, 2015 through March 31, 2015. The potential 21.0% cut in reimbursement that was to be effective April 1, 2015 was removed by the Medicare Access & CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015, or MACRA, and replaced with two new methodologies that will focus upon payment based upon quality outcomes. The first model is the Merit-Based Incentive Payment System, or MIPS, which combines the Physician Quality Reporting System, or PQRS, and Meaningful Use program with the Value Based Modifier program to provide for one payment model based upon (i) quality, (ii) resource use, (iii) clinical practice improvement and (iv) advancing care information through the use of certified Electronic Health Record, or EHR, technology. The second model is the Advanced Alternative Payment Models, or APM, which requires the physician to participate in a risk share arrangement for reimbursement related to his or her patients while utilizing a certified health record and reporting on specific quality metrics. There are a number of physicians that will not qualify for the APM payment method. Therefore, this change in reimbursement models may impact our tenants’ payments and create uncertainty in the tenants’ financial condition.
In 2019, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, or CMS, announced the CMS Primary Cares Initiative, a new set of payment models for primary care physicians. CMS stated that the goal of some of these models is to reduce hospital utilization and the total cost of patient care. These new models may have an effect on the financial condition of our tenants.
CMS has also implemented a value-based program specific to skilled nursing facilities. Under the SNF VBP Program, CMS withholds 2% of fee-for-service payments. The withheld amount is redistributed based upon certain performance measures. The withholding of payments may affect the financial condition and ability to pay of our skilled nursing facility tenants.
The healthcare industry continues to face various challenges, including increased government and private payor pressure on healthcare providers to control or reduce costs. It is possible that our tenants will continue to experience a shift in payor mix away from fee-for-service payors, resulting in an increase in the percentage of revenues attributable to reimbursement based upon value-based principles and quality driven managed care programs, and general industry trends that include pressures to control healthcare costs. The federal government’s goal is to move approximately 90.0% of its reimbursement for providers to be based upon quality outcome models. Pressures to control healthcare costs and a shift away from traditional health insurance reimbursement based upon a fee for service payment to payment based upon quality outcomes have increased the uncertainty of payments.
39
In addition, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010, or the Healthcare Reform Act, is intended to reduce the number of individuals in the U.S. without health insurance and effect significant other changes to the ways in which healthcare is organized, delivered and reimbursed. Included within the legislation is a limitation on physician-owned hospitals from expanding, unless the facility satisfies very narrow federal exceptions to this limitation. Therefore, if our tenants are physicians that own and refer to a hospital, the hospital would be limited in its operations and expansion potential, which may limit the hospital’s services and resulting revenues and may impact the owner’s ability to make rental payments.
Furthermore, the healthcare legislation passed in 2010 included new payment models with new shared savings programs and demonstration programs that include bundled payment models and payments contingent upon reporting on satisfaction of quality benchmarks. The new payment models will likely change how physicians are paid for services. These changes could have a material adverse effect on the financial condition of some of our tenants. Also, on December 22, 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 was signed into law and repeals the individual mandate portion of the Healthcare Reform Act beginning in 2019. With the elimination of the individual mandate, several states brought suit seeking to invalidate the entire Affordable Care Act, and, in December 2018, a federal district court in Texas ruled in favor of these states, finding the entire Affordable Care Act unconstitutional. The district court’s ruling was appealed to the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals, which agreed that the individual mandate is unconstitutional and sent the case back to the district court for further analysis and consideration. Certain states have filed petitions requesting that the U.S. Supreme Court review the Fifth Circuit’s decision. If the entire Affordable Care Act, including the individual mandate, is eventually ruled unconstitutional, our tenants may have more patients who do not have insurance coverage, which may adversely impact the tenants’ collections and revenues. The financial impact on our tenants could restrict their ability to make rent payments to us, which would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to stockholders.
In 2019, CMS implemented changes to its outpatient prospective payment system, or OPPS, which resulted in reduced reimbursement for certain outpatient services furnished by “provider-based” clinicians. The OPPS payment reductions are intended to equalize amounts that the government pays for similar clinical services, regardless of the clinical setting in which they are provided. Healthcare providers and certain provider organizations, including the American Hospital Association, challenged these payment reductions in a lawsuit filed in federal court. A federal judge ruled that the government’s payment reductions for the 2019 OPPS were illegal, a decision which the government has appealed. Despite the court ruling with respect to the 2019 OPPS, CMS continued its reduced payment policy in the 2020 OPPS, a move that the American Hospital Association and other health care organizations have once again challenged. If the government ultimately prevails with respect to the OPPS payment reductions, the payments adjustments may impact the amount of reimbursement our tenants receive for the medical services they provide.
In 2014, state insurance exchanges were implemented, which provide a new mechanism for individuals to obtain insurance. At this time, the number of payors that are participating in the state insurance exchanges varies, and in some regions there are very limited insurance plans available for individuals to choose from when purchasing insurance. In addition, not all healthcare providers will maintain participation agreements with the payors that are participating in the state health insurance exchange. Therefore, it is possible that our tenants may incur a change in their reimbursement if the tenant does not have a participation agreement with the state insurance exchange payors and a large number of individuals elect to purchase insurance from the state insurance exchange. Further, the rates of reimbursement from the state insurance exchange payors to healthcare providers will vary greatly. The rates of reimbursement will be subject to negotiation between the healthcare provider and the payor, which may vary based upon the market, the healthcare provider’s quality metrics, the number of providers participating in the area and the patient population, among other factors. Therefore, it is uncertain whether healthcare providers will incur a decrease in reimbursement from the state insurance exchange, which may impact a tenant’s ability to pay rent.
The insurance plans that participated on the health insurance exchanges created by the Healthcare Reform Act were expecting to receive risk corridor payments to address the high risk claims that they paid through the exchange product. The federal government currently owes the insurance companies approximately $12.3 billion under the risk corridor payment program that is currently disputed by the federal government. Multiple lawsuits have been brought by qualified health plans, or QHPs, to recover the prior risk corridor payments that were anticipated to be paid as part of the health insurance exchange program. In June 2018, the Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit issued an opinion in Moda Health Plan v. United States, concluding that the government does not have to pay health insurers that offered QHPs the full amount owed to them in risk corridors payments. Several insurers sought review of the decision by the U.S. Supreme Court, and the U.S. Supreme Court heard oral arguments on the matter in December 2019. If the U.S. Supreme Court determines that risk corridor payments are not required to be paid to the QHPs offering insurance coverage on the health insurance exchange program, the insurance companies may cease offering the Health Insurance Exchange product to the current beneficiaries and may refuse to participate in future collaborations with the federal government that would increase the number of patients with insurance coverage. Therefore, our tenants may have an increase of self-pay patients and collections may decline, adversely impacting the tenants’ ability to pay rent.
40
The federal government also ceased to provide the cost-share subsidies to the insurance companies that offered the silver plan benefits on the Health Information Exchange. The termination of the cost-share subsidies would impact the subsidy payments due in 2017 and will likely adversely impact the insurance companies, causing an increase in the premium payments for the individual beneficiaries in 2018. Nineteen State Attorneys General filed suit to force the Trump Administration to reinstate the cost share subsidy payments. On October 25, 2017, a California Judge ruled in favor of the Trump Administration and found that the federal government was not required to immediately reinstate payment for the cost shares subsidy. The injunction sought by the Attorneys’ General lawsuit was denied. Subsequently, several insurers filed suit in the U.S. Court of Federal Claims to recover cost-share reduction payments, and in several of the matters, the Court of Federal Claims ruled in favor of the insurers. Nevertheless, because of the government’s refusal to make cost-share reduction payments, our tenants will likely see an increase in individuals who are self-pay or have a lower health benefit plan due to the increase in the premium payments. Our tenants’ collections and revenues may be adversely impacted by the change in the payor mix of their patients and it may adversely impact the tenants’ ability to make rent payments.
In 2017, Congressional activities to attempt to repeal the Healthcare Reform Act failed. However, President Trump signed several Executive Orders that address different aspects of the Healthcare Reform Act. First, on January 20, 2017 an Executive Order was signed to “ease the burden of Obamacare.” Furthermore, on October 12, 2017, President Trump signed an Executive Order the purpose of which was to, among other things, (i) cut healthcare cost-sharing reduction subsidies, (ii) allow more small businesses to join together to purchase insurance coverage, (iii) extend short-term coverage policies, and (iv) expand employers’ ability to provide workers cash to buy coverage elsewhere. The Executive Order required the government agencies to draft regulations for consideration related to Associated Health Plans (AHP), short term limited duration insurance (STLDI) and health reimbursement arrangements (HRA). If the Healthcare Reform Act is modified through Executive Orders, the healthcare industry will continue to change and new regulations may further modify payment models, jeopardizing our tenants’ ability to remit the rental payments.
On January 11, 2018, CMS issued guidance to support state efforts to improve Medicaid enrollee health outcomes by incentivizing community engagement among able-bodied, working-age Medicaid beneficiaries. The policy excludes individuals eligible for Medicaid due to a disability, elderly beneficiaries, children and pregnant women. Thus far, CMS has received proposals from several states seeking requirements for able bodied Medicaid beneficiaries to engage in employment and community engagement initiatives. Kentucky, Indiana, Arkansas, New Hampshire, Arizona, Michigan, Ohio, Utah, South Carolina and Wisconsin have been granted waivers for their programs that require Medicaid beneficiaries to work or get ready for employment, and work requirement waiver requests from other states are currently pending before CMS. However, the states of Kentucky, Arkansas and New Hampshire have had their approvals vacated by courts. In response to CMS’s willingness to entertain Medicaid program waivers, states are seeking waivers to impose other Medicaid eligibility requirements, such as drug testing and eligibility time limits. If the “work requirement” and other eligibility requirements expand to the states’ Medicaid programs, it may decrease the number of patients eligible for Medicaid. The patients that are no longer eligible for Medicaid may become self-pay patients, which may adversely impact our tenant’s ability to receive reimbursement. If our tenants’ patient payor mix becomes more self-pay patients, it may impact our tenants’ ability to collect revenues and pay rent.
Beginning in 2018, CMS cut funding to the 340B Program, which is intended to lower drug costs for certain healthcare providers. A federal court ruled the cuts to the 340B Program reimbursement were unlawful and ordered CMS to develop remedial measures to address the reimbursement cuts. Despite this ruling, CMS finalized plans to implement cuts to 340B Program reimbursement again in 2020. The cuts in the 340B Program may result in some of our tenants having less money available to cover operational costs.
In February of 2018, Congress passed the Bipartisan Balanced Budget Act of 2018. Some of the most notable provisions of the Bipartisan Balanced Budget Act include: (i) the permanent extension of Medicare Special Needs Plans, or SNPs, which provide tailored care for certain qualifying Medicare beneficiaries; (ii) guaranteed funding for the Children’s Health Insurance Program, or CHIP, through 2027; (iii) expansion of Medicare coverage for tele-medicine services; and (iv) expanded testing of certain value-based care models. The extension of SNPs and funding for CHIP secure coverage for patients of our tenants and may reduce the number of uninsured patients treated by our tenants. The expansion of coverage for tele-medicine services could impact the demand for medical properties. If more patients can be treated remotely, providers may have less demand for real property.
The current trend for seniors to delay moving to senior housing facilities until they require greater care or to forgo moving to senior housing facilities altogether could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Seniors have been increasingly delaying their moves to senior housing facilities, including to our leased and managed senior housing facilities, until they require greater care, and increasingly forgoing moving to senior housing facilities altogether. Further, rehabilitation therapy and other services are increasingly being provided to seniors on an outpatient basis or
41
in seniors’ personal residences in response to market demand and government regulation, which may increase the trend for seniors to delay moving to senior housing facilities. Such delays may cause decreases in occupancy rates and increases in resident turnover rates at our senior housing facilities. Moreover, seniors may have greater care needs and require higher acuity services, which may increase our tenants’ and managers’ cost of business, expose our tenants and managers to additional liability or result in lost business and shorter stays at our leased and managed senior housing facilities if our tenants and managers are not able to provide the requisite care services or fail to adequately provide those services. These trends may negatively impact the occupancy rates, revenues, and cash flows at our leased and managed senior housing facilities and our results of operations. Further, if any of our tenants or managers are unable to offset lost revenues from these trends by providing and growing other revenue sources, such as new or increased service offerings to seniors, our senior housing facilities may be unprofitable and we may receive lower returns and rent, and the value of our senior housing facilities may decline.
Events that adversely affect the ability of seniors and their families to afford resident fees at our senior housing facilities could cause our occupancy rates, resident fee revenues and results of operations to decline.
Costs to seniors associated with independent and assisted living services are generally not reimbursable under government reimbursement programs such as Medicare and Medicaid. Only seniors with income or assets meeting or exceeding the comparable median in the regions where our facilities are located typically will be able to afford to pay the entrance fees and monthly resident fees, and a weak economy, depressed housing market or changes in demographics could adversely affect their continued ability to do so. If our tenants and operators are unable to retain and attract seniors with sufficient income, assets or other resources required to pay the fees associated with independent and assisted living services and other services provided by our tenants and operators at our healthcare facilities, our occupancy rates and resident fee revenues could decline, which could, in turn, materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition and our ability to make distributions to stockholders.
Some tenants of our current and future medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities will be subject to fraud and abuse laws, the violation of which by a tenant may jeopardize the tenant’s ability to make rent payments to us.
There are various federal and state laws prohibiting fraudulent and abusive business practices by healthcare providers who participate in, receive payments from or are in a position to make referrals in connection with government-sponsored healthcare programs, including the Medicare and Medicaid programs. Our lease arrangements with certain current and future tenants may also be subject to these fraud and abuse laws. In order to support compliance with the fraud and abuse laws, our lease agreements may be required to satisfy individual state law requirements that vary from state to state, such as the Stark Law exception and the Anti-Kickback Statute safe harbor for lease arrangements, which impacts the terms and conditions that may be negotiated in the lease arrangements.
These federal laws include:
• | the Federal Anti-Kickback Statute, which prohibits, among other things, the offer, payment, solicitation or receipt of any form of remuneration in return for, or to induce, the referral of any item or service reimbursed by state or federal healthcare programs; |
• | the Federal Physician Self-Referral Prohibition, which, subject to specific exceptions, restricts physicians from making referrals for specifically designated health services for which payment may be made under federal healthcare programs to an entity with which the physician, or an immediate family member, has a financial relationship; |
• | the False Claims Act, which prohibits any person from knowingly presenting false or fraudulent claims for payment to the federal government, including claims paid by the Medicare and Medicaid programs; |
• | the Civil Monetary Penalties Law, which authorizes the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to impose monetary penalties or exclusion from participating in state or federal healthcare programs for certain fraudulent acts; |
• | the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, as amended, or HIPAA, Fraud Statute, which makes it a federal crime to defraud any health benefit plan, including private payers; and |
• | the Exclusions Law, which authorizes the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to exclude someone from participating in state or federal healthcare programs for certain fraudulent acts. |
Each of these laws includes criminal and/or civil penalties for violations that range from punitive sanctions, damage assessments, penalties, imprisonment, denial of Medicare and Medicaid payments and/or exclusion from the Medicare and Medicaid programs. Monetary penalties associated with violations of these laws have been increased in recent years. Certain laws, such as the False Claims Act, allow for individuals to bring whistleblower actions on behalf of the government for
42
violations thereof. Additionally, states in which the facilities are located may have similar fraud and abuse laws. Investigation by a federal or state governmental body for violation of fraud and abuse laws or imposition of any of these penalties upon one of our tenants could jeopardize that tenant’s ability to operate or to make rent payments, which may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Adverse trends in healthcare provider operations may negatively affect our lease revenues and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
The healthcare industry is currently experiencing:
• | changes in the demand for and methods of delivering healthcare services; |
• | changes in third-party reimbursement policies; |
• | significant unused capacity in certain areas, which has created substantial competition for patients among healthcare providers in those areas; |
• | increased expense for uninsured patients; |
• | increased competition among healthcare providers; |
• | increased liability insurance expense; |
• | continued pressure by private and governmental payers to reduce payments to providers of services; |
• | increased scrutiny of billing, referral and other practices by federal and state authorities; |
• | changes in federal and state healthcare program payment models; |
• | increased emphasis on compliance with privacy and security requirements related to personal health information; and |
• | increased instability in the Health Insurance Exchange market and lack of access to insurance plans participating in the exchange. |
Moreover, the fines and penalties of HIPAA privacy and security rules increased in 2013. If a tenant breaches a patient’s protected health information and is fined by the federal government, the tenant’s ability to operate and pay rent may be adversely impacted.
These factors may adversely affect the economic performance of some or all of our tenants and, in turn, our lease revenues and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Operators/managers of healthcare properties that we own, or may acquire, may be affected by the financial deterioration, insolvency and/or bankruptcy of other significant operators/managers in the healthcare industry.
Certain companies in the healthcare industry, including some key senior housing operators/managers, are experiencing considerable financial, legal and/or regulatory difficulties which have resulted or may result in financial deterioration and, in some cases, insolvency and/or bankruptcy. The adverse effects on these companies could have a significant impact on the industry as a whole, including but not limited to negative public perception by investors, lenders and consumers. As a result, lessees of healthcare facilities that we own, or may acquire, could experience the damaging financial effects of a weakened industry sector driven by negative headlines, ultimately making them unable to meet their obligations to us, and our business could be adversely affected.
Our healthcare-related tenants may be subject to significant legal actions that could subject them to increased operating costs and substantial uninsured liabilities, which may affect their ability to pay their rent payments to us.
As is typical in the healthcare industry, our healthcare-related tenants may often become subject to claims that their services have resulted in patient injury or other adverse effects. Many of these tenants may have experienced an increasing trend in the frequency and severity of professional liability and general liability insurance claims and litigation asserted against them. The insurance coverage maintained by these tenants may not cover all claims made against them nor continue to be available at a reasonable cost, if at all. In some states, insurance coverage for the risk of punitive damages arising from professional liability and general liability claims and/or litigation may not, in certain cases, be available to these tenants due to state law prohibitions or limitations of availability. As a result, these types of tenants of our medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities operating in these states may be liable for punitive damage awards that are either not covered or are in excess of their insurance policy limits. We also believe that there has been, and will continue to be, an increase in governmental investigations of certain healthcare providers, particularly in the area of Medicare/Medicaid false claims, as well as an increase in enforcement actions resulting from these investigations. Insurance
43
may not always be available to cover such losses. Any adverse determination in a legal proceeding or governmental investigation, whether currently asserted or arising in the future, could have a material adverse effect on a tenant’s financial condition. If a tenant is unable to obtain or maintain insurance coverage, if judgments are obtained in excess of the insurance coverage, if a tenant is required to pay uninsured punitive damages, or if a tenant is subject to an uninsurable government enforcement action, the tenant could be exposed to substantial additional liabilities, which may affect the tenant’s ability to pay rent, which in turn could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
We, our tenants and our operators for our skilled nursing and senior housing facilities may be subject to various government reviews, audits and investigations that could adversely affect our business, including an obligation to refund amounts previously paid to us, potential criminal charges, the imposition of fines, and/or the loss of the right to participate in Medicare and Medicaid programs.
As a result of our tenants’ participation in the Medicaid and Medicare programs, we, our tenants and our operators for our skilled nursing and senior housing facilities are subject to various governmental reviews, audits and investigations to verify compliance with these programs and applicable laws and regulations. We, our tenants and our operators for our skilled nursing and senior housing facilities are also subject to audits under various government programs, including Recovery Audit Contractors, Zone Program Integrity Contractors, Program Safeguard Contractors, Medicaid Integrity Contractors and Unified Program Integrity Contractor programs, in which third-party firms engaged by CMS conduct extensive reviews of claims data and medical and other records to identify potential improper payments under the Medicare and Medicaid programs. Private pay sources also reserve the right to conduct audits. Billing and reimbursement errors and disagreements occur in the healthcare industry. We, our tenants and our operators for our skilled nursing and senior housing facilities may be engaged in reviews, audits and appeals of claims for reimbursement due to the subjectivities inherent in the process related to patient diagnosis and care, record keeping, claims processing and other aspects of the patient service and reimbursement processes, and the errors and disagreements those subjectivities can produce. An adverse review, audit or investigation could result in:
• | an obligation to refund amounts previously paid to us, our tenants or our operators pursuant to the Medicare or Medicaid programs or from private payors, in amounts that could be material to our business; |
• | state or federal agencies imposing fines, penalties and other sanctions on us, our tenants or our operators; |
• | loss of our right, our tenants’ right or our operators’ right to participate in the Medicare or Medicaid programs or one or more private payor networks; |
• | an increase in private litigation against us, our tenants or our operators; and |
• | damage to our reputation in various markets. |
While we, our tenants and our operators for our skilled nursing and senior housing facilities have always been subject to post-payment audits and reviews, more intensive “probe reviews” appear to be a permanent procedure with our fiscal intermediaries. Generally, findings of overpayment from CMS contractors are eligible for appeal through the CMS defined continuum, but there may be rare instances that are not eligible for appeal. We, our tenants and our operators for our skilled nursing and senior housing facilities utilize all defenses at our disposal to demonstrate that the services provided meet all clinical and regulatory requirements for reimbursement.
If the government or a court were to conclude that such errors, deficiencies or disagreements constituted criminal violations, or were to conclude that such errors, deficiencies or disagreements resulted in the submission of false claims to federal healthcare programs, or if the government were to discover other problems in addition to the ones identified by the probe reviews that rose to actionable levels, we and certain of our officers, and our tenants and operators for our skilled nursing and senior housing facilities and certain of their officers, might face potential criminal charges and/or civil claims, administrative sanctions and penalties for amounts that could be material to our business, results of operations and financial condition. In addition, we and/or some of the key personnel of our operating subsidiaries, or those of our tenants and operators for our skilled nursing and senior housing facilities, could be temporarily or permanently excluded from future participation in state and federal healthcare reimbursement programs such as Medicaid and Medicare. In any event, it is likely that a governmental investigation alone, regardless of its outcome, would divert material time, resources and attention from our management team and our staff, or those of our tenants and our operators for our skilled nursing and senior housing facilities and could have a materially detrimental impact on our results of operations during and after any such investigation or proceedings.
In cases where claim and documentation review by any CMS contractor results in repeated poor performance, a facility can be subjected to protracted oversight. This oversight may include repeat education and re-probe, extended pre-payment review, referral to recovery audit or integrity contractors, or extrapolation of an error rate to other reimbursement outside of
44
specifically reviewed claims. Sustained failure to demonstrate improvement towards meeting all claim filing and documentation requirements could ultimately lead to Medicare and Medicaid decertification, which could have a materially detrimental impact on our results of operations. Adverse actions by CMS may also cause third-party payer or licensure authorities to audit our tenants. These additional audits could result in termination of third-party payer agreements or licensure of the facility, which would also adversely impact our operations.
The Healthcare Reform Law imposes additional requirements on skilled nursing facilities regarding compliance and disclosure.
The Health Care and Education and Reconciliation Act of 2010, or the Healthcare Reform Law, requires skilled nursing facilities to have a compliance and ethics program that is effective in preventing and detecting criminal, civil and administrative violations and in promoting quality of care. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services included in the final rule published on October 4, 2016 the requirement for operators to implement a compliance and ethics program as a condition of participation in Medicare and Medicaid. Long-term care facilities, including skilled nursing facilities, had until November 28, 2019 to comply. If our operators fall short in their compliance and ethics programs and quality assurance and performance improvement programs, if and when required, their reputations and ability to attract residents could be adversely affected.
Risks Related to Debt Financing
Increases in interest rates could increase the amount of our debt payments, and therefore, negatively impact our operating results.
Interest we pay on our debt obligations will reduce cash available for distributions. Whenever we incur variable rate debt, increases in interest rates would increase our interest costs, which would reduce our cash flows and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders. If we need to repay existing debt during periods of rising interest rates, we could be required to liquidate one or more of our investments in properties at times which may not permit realization of the maximum return on such investments.
In addition, our variable-rate debt instruments use London Interbank Offering Rate, or LIBOR, as a benchmark for establishing the interest rate. In July 2017, the Financial Conduct Authority, or FCA, that regulates LIBOR announced it intends to stop compelling banks to submit rates for the calculation of LIBOR after 2021. As a result, the Federal Reserve Board and the Federal Reserve Bank of New York organized the Alternative Reference Rates Committee which identified the Secured Overnight Financing Rate, or SOFR, as its preferred alternative to U.S. dollar LIBOR in derivatives and other financial contracts. We are not able to predict when LIBOR will cease to be available or when there will be sufficient liquidity in the SOFR markets. Any changes adopted by FCA or other governing bodies in the method used for determining LIBOR may result in a sudden or prolonged increase or decrease in reported LIBOR. In addition, uncertainty about the extent and manner of future changes may result in interest rates and/or payments that are higher or lower than if LIBOR were to remain available in its current form. The consequences of these developments are uncertain, but could include an increase in the cost of our variable-rate debt instruments. If LIBOR is no longer widely available, or otherwise at our option, we may need to renegotiate with our lenders that utilize LIBOR as a factor in determining the interest rate to replace LIBOR with the new standard that is established. As such, the potential phase-out of LIBOR may have a material adverse effect on the interest rates on our current and future borrowings.
To the extent we borrow at fixed rates or enter into fixed interest rate swaps, we will not benefit from reduced interest expense if interest rates decrease.
We are exposed to the effects of interest rate changes primarily as a result of borrowings we have used to maintain liquidity and fund expansion and refinancing of our real estate investment portfolio and operations. To limit the impact of interest rate changes on earnings, prepayment penalties and cash flows and to lower overall borrowing costs while taking into account variable interest rate risk, we have borrowed and may continue to borrow at fixed rates or variable rates depending upon prevailing market conditions. We have and may also continue to enter into derivative financial instruments such as interest rate swaps and caps in order to mitigate our interest rate risk on a related financial instrument. Therefore, to the extent we borrow at fixed rates or enter into fixed interest rate swaps, we will not benefit from reduced interest expense if interest rates decrease.
Hedging activity may expose us to risks.
We have used and may continue to use derivative financial instruments to hedge our exposure to changes in exchange rates and interest rates on loans secured by our assets. If we use derivative financial instruments to hedge against interest rate fluctuations, we will be exposed to credit risk and legal enforceability risks. In this context, credit risk is the failure of the counterparty to perform under the terms of the derivative contract. If the fair value of a derivative contract is positive, the counterparty owes us, which creates credit risk for us. Legal enforceability risks encompass general contractual risks, including
45
the risk that the counterparty will breach the terms of, or fail to perform its obligations under, the derivative contract. These derivative instruments are speculative in nature and there is no guarantee that they will be effective. If we are unable to manage these risks effectively, our results of operations, financial condition and ability to pay distributions to our stockholders will be adversely affected.
Lenders may require us to enter into restrictive covenants relating to our operations, which could limit our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
When providing financing, a lender may impose restrictions on us that affect our ability to incur additional debt and affect our distribution and operating strategies. We may enter into loan documents that contain covenants that limit our ability to further mortgage the property, discontinue insurance coverage, or replace our advisor. These or other limitations may adversely affect our flexibility and our ability to achieve our investment objectives.
Interest-only indebtedness may increase our risk of default, adversely affect our ability to refinance or sell properties and ultimately may reduce our funds available for distribution to our stockholders.
We may finance or refinance our properties using interest-only mortgage indebtedness. During the interest-only period, the amount of each scheduled payment will be less than that of a traditional amortizing mortgage loan. The principal balance of the mortgage loan will not be reduced (except in the case of prepayments) because there are no scheduled monthly payments of principal during this period. After the interest-only period, we will be required either to make scheduled payments of amortized principal and interest or to make a lump-sum or “balloon” payment at maturity. At the time such a balloon payment is due, we may or may not be able to refinance the balloon payment on terms as favorable as the original loan or sell the particular property at a price sufficient to make the balloon payment. Furthermore, these required principal or balloon payments will increase the amount of our scheduled payments and may increase our risk of default under the related mortgage loan. If the mortgage loan has an adjustable interest rate, the amount of our scheduled payments also may increase at a time of rising interest rates. In addition, payments of principal and interest made to service our debts, including balloon payments, may leave us with insufficient cash to pay the distributions that we are required to pay to maintain our qualification as a REIT. Any of these results would have a significant, negative impact on our stockholders’ investment.
If we are required to make payments under any “bad boy” carve-out guaranties that we may provide in connection with certain mortgages and related loans, our business and financial results could be materially adversely affected.
In obtaining certain nonrecourse loans, we may provide standard carve-out guaranties. These guaranties are only applicable if and when the borrower directly, or indirectly through agreement with an affiliate, joint venture partner or other third party, voluntarily files a bankruptcy or similar liquidation or reorganization action or takes other actions that are fraudulent or improper (commonly referred to as “bad boy” guaranties). Although we believe that “bad boy” carve-out guaranties are not guaranties of payment in the event of foreclosure or other actions of the foreclosing lender that are beyond the borrower’s control, some lenders in the real estate industry have recently sought to make claims for payment under such guaranties. In the event such a claim were made against us under a “bad boy” carve-out guaranty following foreclosure on mortgages or related loan, and such claim were successful, our business and financial results could be materially adversely affected.
Risks Related to Real Estate-Related Investments
The real estate-related investments in which we may invest and the loans underlying such real estate-related investments may be impacted by unfavorable real estate market conditions, which could decrease their value.
If we acquire investments in mortgage or mezzanine loans, or mortgage-backed securities, such investments will involve special risks relating to the particular borrower or issuer of the loans or mortgage-backed securities and we will be at risk of loss on those investments, including losses as a result of defaults on the underlying mortgage loans. Additionally, if we invest in the common and preferred stock of both publicly traded and private unaffiliated real estate companies, such equity securities involve a higher degree of risk than debt securities due to a variety of factors, including the fact that such investments are subordinate to creditors and are not secured by the issuer’s property.
The losses on such real estate-related investments may be caused by many conditions beyond our control, including economic conditions affecting real estate values, tenant defaults and lease expirations, interest rate levels, the financial condition and business outlook of the securities issuer and the other economic and liability risks associated with real estate, including risks relating to rising interest rates. We do not know whether the values of the property securing any of our real estate-related investments, including the value of any real estate-related equity securities, will remain at the levels existing on the dates we initially make the related investment. If the values of the underlying properties drop, our risk will increase and the values of our interests in such real estate-related investments may decrease.
46
We expect a portion of our real estate-related investments to be illiquid and we may not be able to adjust our portfolio in response to changes in economic and other conditions.
We may acquire real estate-related investments in connection with privately negotiated transactions which are not registered under the relevant securities laws, resulting in a prohibition against their transfer, sale, pledge or other disposition except in a transaction that is exempt from the registration requirements of, or is otherwise in accordance with, those laws. As a result, our ability to vary our portfolio in response to changes in economic and other conditions may be relatively limited. The mezzanine and bridge loans we may purchase will be particularly illiquid investments due to their short life, their unsuitability for securitization and the greater difficulty of recoupment in the event of a borrower’s default.
If we liquidate prior to the maturity of our real estate-related investments, we may be forced to sell those investments on unfavorable terms or at a loss.
Our board may choose to effect a liquidity event in which we liquidate our assets, including our real estate-related investments. If we liquidate those investments prior to their maturity, we may be forced to sell those investments on unfavorable terms or at a loss. For instance, if we are required to liquidate mortgage loans at a time when prevailing interest rates are higher than the interest rates of such mortgage loans, we would likely sell such loans at a discount to their stated principal values.
Risks Related to Joint Ventures
Property ownership through joint ventures could limit our control of those investments and restrict our ability to operate the property on our term.
In connection with the purchase of real estate, we have and may continue to enter into joint ventures with third parties, including affiliates of our advisor. We may also purchase or develop properties in co-ownership arrangements with the sellers of the properties, developers or other persons. We own operating properties through both consolidated and unconsolidated joint ventures. These structures involve participation in the investment by other parties whose interests and rights may not be the same as ours. Our joint ventures, and joint ventures we may enter into in the future, may involve risks not present with respect to our wholly owned properties, including the following:
• | we may share decision-making authority with our joint venture partners regarding certain major decisions affecting the ownership or operation of the joint venture and the joint venture property, such as, but not limited to, (i) additional capital contribution requirements, (ii) obtaining, refinancing or paying off debt and (iii) obtaining consent prior to the sale or transfer of our interest in the joint venture to a third party, which may prevent us from taking actions that are opposed by our joint venture partners; |
• | our joint venture partners might become bankrupt and such proceedings could have an adverse impact on the operation of the partnership or joint venture; and |
• | the activities of a joint venture could adversely affect our ability to maintain our qualification as a REIT. |
We may structure our joint venture relationships in a manner which may limit the amount we participate in the cash flows or appreciation of an investment.
We have and may continue to enter into joint venture agreements, the economic terms of which may provide for the distribution of income to us otherwise than in direct proportion to our ownership interest in the joint venture. For example, while we and a co-venturer may invest an equal amount of capital in an investment, the investment may be structured such that we have a right to priority distributions of cash flows up to a certain target return while the co-venturer may receive a disproportionately greater share of cash flows than we are to receive once such target return has been achieved. This type of investment structure may result in the co-venturer receiving more of the cash flows, including appreciation, of an investment than we would receive. If we do not accurately judge the appreciation prospects of a particular investment or structure the venture appropriately, we may incur losses on joint venture investments or have limited participation in the profits of a joint venture investment, either of which could reduce our ability to pay cash distributions to our stockholders.
Federal Income Tax Risks
Failure to maintain our qualification as a REIT for federal income tax purposes would subject us to federal income tax on our taxable income at regular corporate rates, which would substantially reduce our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
We qualified and elected to be taxed as a REIT under the Code beginning with our taxable year ended December 31, 2016. To continue to maintain our qualification as a REIT, we must meet various requirements set forth in the Code concerning,
47
among other things, the ownership of our outstanding common stock, the nature of our assets, the sources of our income and the amount of our distributions to our stockholders. The REIT qualification requirements are extremely complex, and interpretations of the federal income tax laws governing qualification as a REIT are limited. Accordingly, we cannot be certain that we will be successful in operating so as to maintain our qualification as a REIT. At any time, new laws, interpretations or court decisions may change the federal tax laws relating to, or the federal income tax consequences of, qualification as a REIT. It is possible that future economic, market, legal, tax or other considerations may cause our board to determine that it is not in our best interest to maintain our qualification as a REIT, and to revoke our REIT election, which it may do without stockholder approval.
If we fail to maintain our qualification as a REIT for any taxable year, we will be subject to federal income tax on our taxable income at corporate rates. In addition, we would generally be disqualified from treatment as a REIT for the four taxable years following the year of losing our REIT status unless the Internal Revenue Service, or IRS, grants us relief under certain statutory provisions. Losing our REIT status would reduce our net earnings available for investment or distribution to our stockholders because of the additional tax liability. In addition, distributions would no longer qualify for the distributions paid deduction, and we would no longer be required to pay distributions. If this occurs, we might be required to borrow funds or liquidate some investments in order to pay the applicable tax.
As a result of all these factors, our failure to maintain our qualification as a REIT could impair our ability to expand our business and raise capital, and would substantially reduce our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Our investment strategy may cause us to incur penalty taxes, lose our REIT status or own and sell properties through TRSs, each of which would diminish the return to our stockholders.
In light of our investment strategy, it is possible that one or more sales of our properties may be “prohibited transactions” under provisions of the Code. If we are deemed to have engaged in a “prohibited transaction” (i.e., we sell a property held by us primarily for sale in the ordinary course of our trade or business), all income that we derive from such sale would be subject to a 100% tax. The Code sets forth a safe harbor for REITs that wish to sell property without risking the imposition of the 100% tax. A principal requirement of the safe harbor is that the REIT must hold the applicable property for not less than two years prior to its sale. Given our investment strategy, it is entirely possible, if not likely, that the sale of one or more of our properties will not fall within the prohibited transaction safe harbor.
If we desire to sell a property pursuant to a transaction that does not fall within the safe harbor, we may be able to avoid the 100% penalty tax if we acquired the property through a TRS or acquired the property and transferred it to a TRS for a non-tax business purpose prior to the sale (i.e., for a reason other than the avoidance of taxes). However, there may be circumstances that prevent us from using a TRS in a transaction that does not qualify for the safe harbor. Additionally, even if it is possible to effect a property disposition through a TRS, we may decide to forego the use of a TRS in a transaction that does not meet the safe harbor based on our own internal analysis, the opinion of counsel or the opinion of other tax advisors that the disposition will not be subject to the 100% penalty tax. In cases where a property disposition is not effected through a TRS, the IRS could successfully assert that the disposition constitutes a prohibited transaction, in which event all of the net income from the sale of such property will be payable as a tax and none of the proceeds from such sale will be distributable by us to our stockholders or available for investment by us.
If we acquire a property that we anticipate will not fall within the safe harbor from the 100% penalty tax upon disposition, then we may acquire such property through a TRS in order to avoid the possibility that the sale of such property will be a prohibited transaction and subject to the 100% penalty tax. If we already own such a property directly or indirectly through an entity other than a TRS, we may contribute the property to a TRS if there is another, non-tax-related business purpose for the contribution of such property to the TRS. Following the transfer of the property to a TRS, the TRS will operate the property and may sell such property and distribute the net proceeds from such sale to us, and we may distribute the net proceeds distributed to us by the TRS to our stockholders. Though a sale of the property by a TRS likely would eliminate the danger of the application of the 100% penalty tax, the TRS itself would be subject to a tax at the federal level, and potentially at the state and local levels, on the gain realized by it from the sale of the property as well as on the income earned while the property is operated by the TRS. This tax obligation would diminish the amount of the proceeds from the sale of such property that would be distributable to our stockholders. As a result, the amount available for distribution to our stockholders would be substantially less than if the REIT had operated and sold such property directly and such transaction was not characterized as a prohibited transaction. The maximum federal corporate income tax rate is currently 21.0%. Federal, state and local corporate income tax rates may be increased in the future, and any such increase would reduce the amount of the net proceeds available for distribution by us to our stockholders from the sale of property through a TRS after the effective date of any increase in such tax rates.
If we own too many properties through one or more of our TRSs, then we may lose our status as a REIT. If we fail to maintain our qualification as a REIT for any taxable year, we will be subject to federal income tax on our taxable income at
48
corporate rates. In addition, we would generally be disqualified from treatment as a REIT for the four taxable years following the year of losing our REIT status. Losing our REIT status would reduce our net earnings available for investment or distribution to stockholders because of the additional tax liability. In addition, distributions to stockholders would no longer qualify for the distributions paid deduction, and we would no longer be required to pay distributions. If this occurs, we might be required to borrow funds or liquidate some investments in order to pay the applicable tax. As a REIT, the value of the securities we hold in all of our TRSs may not exceed 20.0% of the value of all of our assets at the end of any calendar quarter. If the IRS were to determine that the value of our interests in all of our TRSs exceeded 20.0% of the value of total assets at the end of any calendar quarter, then we would fail to maintain our qualification as a REIT. If we determine it to be in our best interest to own a substantial number of our properties through one or more TRSs, then it is possible that the IRS may conclude that the value of our interests in our TRSs exceeds 20.0% of the value of our total assets at the end of any calendar quarter, and therefore, cause us to fail to maintain our qualification as a REIT. Additionally, as a REIT, no more than 25.0% of our gross income with respect to any year may be from sources other than real estate. Distributions paid to us from a TRS are considered to be non-real estate income. Therefore, we may fail to maintain our qualification as a REIT if distributions from all of our TRSs, when aggregated with all other non-real estate income with respect to any one year, are more than 25.0% of our gross income with respect to such year. We will use all reasonable efforts to structure our activities in a manner intended to satisfy the requirements for our qualification as a REIT. Our failure to maintain our qualification as a REIT would adversely affect our stockholders’ return on their investment.
Our stockholders may have a current tax liability on distributions they elect to reinvest in shares of our common stock.
If our stockholders participate in the DRIP, they will be deemed to have received, and for U.S. federal income tax purposes will be taxed on, the amount reinvested in shares of our common stock to the extent the amount reinvested was not a tax-free return of capital. In addition, our stockholders may be treated, for U.S. federal tax purposes, as having received an additional distribution to the extent the shares are purchased at a discount from fair market value. As a result, unless our stockholders are a tax-exempt entity, our stockholders may have to use funds from other sources to pay their tax liability on the value of the shares of common stock received.
We may be subject to adverse legislative or regulatory tax changes that could increase our tax liability or reduce our operating flexibility, including the recently passed Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.
In recent years, numerous legislative, judicial and administrative changes have been made in the provisions of federal and state income tax laws applicable to investments similar to an investment in shares of our common stock. Additional changes to the tax laws are likely to continue to occur, and we cannot assure our stockholders that any such changes will not adversely affect our taxation and our ability to continue to qualify as a REIT or the taxation of a stockholder. Any such changes could have an adverse effect on an investment in shares of our common stock or on the market value or the resale potential of our assets. Our stockholders are urged to consult with their tax advisor with respect to the impact of recent legislation on their investment in our stock and the status of legislative, regulatory or administrative developments and proposals and their potential effect on an investment in shares of our common stock.
Although REITs generally receive better tax treatment than entities taxed as regular corporations, it is possible that future legislation would result in a REIT having fewer tax advantages, and it could become more advantageous for a company that invests in real estate to elect to be treated for U.S. federal income tax purposes as a regular corporation. As a result, our charter provides our board with the power, under certain circumstances, to revoke or otherwise terminate our REIT election and cause us to be taxed as a regular corporation, without the vote of our stockholders. Our board has fiduciary duties to us and our stockholders and could only cause such changes in our tax treatment if it determines in good faith that such changes are in the best interests of our stockholders.
In addition, on December 22, 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act was signed into law. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act made significant changes to the U.S. federal income tax rules for taxation of individuals and businesses, generally effective for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017. In addition to reducing corporate and individual tax rates, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act eliminates or restricts various deductions. Most of the changes applicable to individuals are temporary and apply only to taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017 and before January 1, 2026. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act made numerous large and small changes to the tax rules that do not affect the REIT qualification rules directly but may otherwise affect us or our stockholders.
While the changes in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act generally appear to be favorable with respect to REITs, the extensive changes to non-REIT provisions in the Code may have unanticipated effects on us or our stockholders. Moreover, Congressional leaders have recognized that the process of adopting extensive tax legislation in a short amount of time without hearings and substantial time for review is likely to have led to drafting errors, issues needing clarification and unintended consequences that will have to be revisited in subsequent tax legislation. At this point, it is not clear if or when Congress will address these issues or when the IRS will issue administrative guidance on the changes made in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.
49
We urge our stockholders to consult with their own tax advisor with respect to the status of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act and other legislative, regulatory or administrative developments and proposals and their potential effect on an investment in shares of our common stock.
If we fail to invest a sufficient amount of the net proceeds from selling our common stock in real estate assets within one year from the receipt of the proceeds, we could fail to maintain our qualification as a REIT.
Temporary investment of the net proceeds from sales of our common stock in short-term securities and income from such investment generally will allow us to satisfy various REIT income and asset requirements, but only during the one-year period beginning on the date we receive the net proceeds. If we are unable to invest a sufficient amount of the net proceeds from sales of our common stock in qualifying real estate assets within such one-year period, we could fail to satisfy one or more of the gross income or asset tests and/or we could be limited to investing all or a portion of any remaining funds in cash or cash equivalents. If we fail to satisfy any such income or asset test, unless we are entitled to relief under certain provisions of the Code, we could fail to maintain our qualification as a REIT.
In certain circumstances, we may be subject to federal and state income taxes even if we maintain our qualification as a REIT, which would reduce our cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
Even if we maintain our qualification as a REIT, we may be subject to federal income taxes or state taxes. For example, net income from a “prohibited transaction” will be subject to a 100% tax. We may not be able to make sufficient distributions to avoid excise taxes applicable to REITs. We may also decide to retain capital gains we earn from the sale or other disposition of our property and pay income tax directly on such income. In that event, our stockholders would be treated as if they earned that income and paid the tax on it directly. However, our stockholders that are tax-exempt, such as charities or qualified pension plans, would have no benefit from their deemed payment of such tax liability. We may also be subject to state and local taxes on our income or property, either directly or at the level of the companies through which we indirectly own our assets. Any federal or state taxes we pay will reduce our cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
Dividends payable by REITs generally do not qualify for the reduced tax rates on dividend income as compared to regular corporations, which could adversely affect the value of our shares.
The maximum U.S. federal income tax rate for certain qualified dividends payable to domestic stockholders that are individuals, trusts and estates is 20%. Dividends payable by REITs, however, are generally not eligible for these reduced rates for qualified dividends. For taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017 and before January 1, 2026, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act permits a deduction for certain pass-through business income, including “qualified REIT dividends” (generally, dividends received by a REIT stockholder that are not designated as capital gain dividends or qualified dividend income), which allows U.S. individuals, trusts, and estates to deduct up to 20% of such amounts, subject to certain limitations, resulting in an effective maximum U.S. federal income tax rate of 29.6% on such qualified REIT dividends. Although the reduced U.S. federal income tax rate applicable to dividend income from regular corporate dividends does not adversely affect the taxation of REITs or dividends paid by REITs, the more favorable rates applicable to qualified dividends from C corporations could cause investors who are individuals, trusts and estates to perceive investments in REITs to be relatively less attractive than investments in the stocks of non-REIT corporations that pay dividends, which could adversely affect the value of the shares of REITs, including our shares.
Distributions to tax-exempt stockholders may be classified as UBTI.
Neither ordinary nor capital gain distributions with respect to the shares of our common stock nor gain from the sale of the shares of our common stock should generally constitute unrelated business taxable income, or UBTI, to a tax-exempt stockholder. However, there are certain exceptions to this rule. In particular:
• | part of the income and gain recognized by certain qualified employee pension trusts with respect to our common stock may be treated as UBTI if the shares of our common stock are predominately held by qualified employee pension trusts, and we are required to rely on a special look-through rule for purposes of meeting one of the REIT share ownership tests, and we are not operated in a manner to avoid treatment of such income or gain as UBTI; |
• | part of the income and gain recognized by a tax exempt stockholder with respect to the shares of our common stock would constitute UBTI if the stockholder incurs debt in order to acquire the shares of our common stock; and |
• | part or all of the income or gain recognized with respect to the shares of our common stock by social clubs, voluntary employee benefit associations, supplemental unemployment benefit trusts and qualified group legal services plans which are exempt from federal income taxation under Sections 501(c)(7), (9), (17) or (20) of the Code may be treated as UBTI. |
50
Characterization of our sale-leaseback transactions may be challenged.
We have and may continue to participate in sale-leaseback transactions in which we purchase real estate investments and lease them back to the sellers of such properties. Our advisor will use its best efforts to structure any of our sale-leaseback transactions such that the lease will be characterized as a “true lease” and so that we will be treated as the owner of the property for federal income tax purposes. However, we cannot assure our stockholders that the IRS will not challenge such characterization. In the event that any such sale-leaseback transaction is re-characterized as a financing transaction for federal income tax purposes, deductions for depreciation and cost recovery relating to such real estate investment would be disallowed or significantly reduced. If a sale-leaseback transaction is so recharacterized, we might fail to satisfy the REIT asset tests or income tests and, consequently, lose our REIT status.
Complying with the REIT requirements may cause us to forego otherwise attractive opportunities.
To maintain our qualification as a REIT for federal income tax purposes, we must continually satisfy tests concerning, among other things, the sources of our income, the nature and diversification of our assets, the amounts we distribute to our stockholders and the ownership of shares of our common stock. We may be required to pay distributions to our stockholders at disadvantageous times or when we do not have funds readily available for distribution, or we may be required to liquidate otherwise attractive investments in order to comply with the REIT tests. Thus, compliance with the REIT requirements may hinder our ability to operate solely on the basis of maximizing profits.
If our operating partnership fails to maintain its status as a disregarded entity or as a partnership, its income may be subject to taxation, which would reduce the cash available for distribution to stockholders and likely result in a loss of our REIT status.
We intend to maintain the status of the operating partnership as a disregarded entity or as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes. However, if the IRS were to successfully challenge the status of the operating partnership as a disregarded entity or as a partnership for such purposes, it would be taxable as a corporation. In such event, this would reduce the amount of distributions that the operating partnership could make to us. This would also likely result in our losing REIT status, and, if so, becoming subject to a corporate level tax on our own income. This would substantially reduce any cash available to pay distributions. In addition, if any of the partnerships or limited liability companies through which the operating partnership owns its properties, in whole or in part, loses its characterization as a partnership and is otherwise not disregarded for U.S. federal income tax purposes, it would be subject to taxation as a corporation, thereby reducing distributions to the operating partnership. Such a recharacterization of an underlying property owner could also threaten our ability to maintain our status as a REIT.
Foreign purchasers of shares of our common stock may be subject to FIRPTA tax upon the sale of their shares of our common stock.
A foreign person disposing of a U.S. real property interest, including shares of stock of a U.S. corporation whose assets consist principally of U.S. real property interests, is generally subject to the Foreign Investment in Real Property Tax Act of 1980, as amended, or FIRPTA, on the amount received from the disposition. However, foreign pension plans and certain foreign publicly traded entities are exempt from FIRPTA withholding. Further, such FIRPTA tax does not apply to the disposition of stock in a REIT if the REIT is “domestically controlled.” A REIT is “domestically controlled” if less than 50.0% of the REIT’s stock, by value, has been owned directly or indirectly by persons who are not qualifying U.S. persons during a continuous five-year period ending on the date of disposition or, if shorter, during the entire period of the REIT’s existence. We cannot assure our stockholders that we will qualify as a “domestically controlled” REIT. If we were to fail to so qualify, amounts received by foreign investors on a sale of shares of our common stock would be subject to FIRPTA tax, unless the shares of our common stock were traded on an established securities market and the foreign investor did not at any time during a specified period directly or indirectly own more than 10.0% of the value of our outstanding common stock. However, these rules do not apply to foreign pension plans and certain publicly traded entities.
Foreign stockholders may be subject to FIRPTA tax upon the payment of a capital gains dividend.
A foreign stockholder will likely be subject to FIRPTA upon the payment of any capital gain dividends by us if such gain is attributable to gain from sales or exchanges of U.S. real property interests. However, these rules do not apply to foreign pension plans and certain publicly traded entities.
51
Employee Benefit Plan, IRA, and Other Tax-Exempt Investor Risks
We, and our stockholders that are employee benefit plans, IRAs, annuities described in Sections 403(a) or (b) of the Code, Archer Medical Savings Accounts, health savings accounts, Coverdell education savings accounts, and other arrangements that are subject to ERISA or Section 4975 of the Code (referred to generally as “Benefit Plans and IRAs”) will be subject to risks relating specifically to our having such Benefit Plan and IRA stockholders, which risks are discussed below.
If a stockholder that is a Benefit Plan or IRA fails to meet the fiduciary and other standards under ERISA or the Code as a result of an investment in shares of our common stock, such stockholder could be subject to civil and criminal, if the failure is willful, penalties.
There are special considerations that apply to Benefit Plans and IRAs investing in shares of our common stock. Stockholders that are Benefit Plans and IRAs should consider:
• | whether their investment is consistent with the applicable provisions of ERISA and the Code, or any other applicable governing authority in the case of a plan not subject to ERISA or the Code; |
• | whether their investment is made in accordance with the documents and instruments governing the Benefit Plan or IRA, including any investment policy; |
• | whether their investment satisfies the prudence, diversification and other requirements of Sections 404(a)(1)(B) and 404(a)(1)(C) of ERISA or any similar rule under other applicable laws or regulations; |
• | whether their investment will impair the liquidity needs, the minimum and other distribution requirements, or the tax withholding requirements that may be applicable to such Benefit Plan or IRA; |
• | whether their investment will constitute a prohibited transaction under Section 406 of ERISA or Section 4975 of the Code or any similar rule under other applicable laws or regulations; |
• | whether their investment will produce or result in UBTI, as defined in Sections 511 through 514 of the Code, to the Benefit Plan or IRA; |
• | whether their investment will impair the Benefit Plan’s or IRA’s need to value its assets annually (or more frequently) in accordance with ERISA, the Code and the applicable provisions of the Benefit Plan or IRA; and |
• | whether their investment will cause our assets to be treated as “plan assets” of the Benefit Plan or IRA. |
Failure to satisfy the fiduciary standards of conduct and other applicable requirements of ERISA, the Code, or other applicable statutory or common law may result in the imposition of civil and criminal (if the violation is willful) penalties, and can subject the fiduciary to equitable remedies. In addition, if an investment in our common stock constitutes a prohibited transaction under ERISA or the Code, the “party-in-interest” (within the meaning of ERISA) or “disqualified person” (within the meaning of the Code) who authorized or directed the investment may have to compensate the plan for any losses the plan suffered as a result of the transaction or restore to the plan any profits made by such person as a result of the transaction, or may be subject to excise taxes with respect to the amount involved. In the case of a prohibited transaction involving an IRA, the IRA may be disqualified and all of the assets of the IRA may be deemed distributed and subject to tax.
In addition to considering their fiduciary responsibilities under ERISA and the prohibited transaction rules of ERISA and the Code, stockholders that are Benefit Plans and IRAs should consider the effect of the plan assets regulation, U.S. Department of Labor Regulation Section 2510.3-101, as modified by ERISA Section 3(42). To avoid our assets from being considered “plan assets” under the plan assets regulation, our charter prohibits “benefit plan investors” from owning 25% or more of the shares of our common stock prior to the time that the common stock qualifies as a class of publicly-offered securities, within the meaning of the plan assets regulation. However, we cannot assure our stockholders that those provisions in our charter will be effective in limiting benefit plan investors’ ownership to less than the 25% limit. For example, the limit could be unintentionally exceeded if a benefit plan investor misrepresents its status as a benefit plan investor. If our underlying assets were to be considered “plan assets” of a benefit plan investor subject to ERISA, (i) we would be an ERISA fiduciary and subject to certain fiduciary requirements of ERISA with which it would be difficult for us to comply and (ii) we could be restricted from entering into favorable transactions if the transaction, absent an exemption, would constitute a prohibited transaction under ERISA or the Code. Even if our assets are not considered to be “plan assets,” a prohibited transaction could occur if we or any of our affiliates is a fiduciary (within the meaning of ERISA) of a Benefit Plan or IRA stockholder.
Due to the complexity of these rules and the potential penalties that may be imposed, it is important that stockholders that are Benefit Plans and IRAs consult with their own advisors regarding the potential applicability of ERISA, the Code and any similar applicable law.
52
Stockholders that are Benefit Plans and IRAs may be limited in their ability to withdraw required minimum distributions as a result of an investment in shares of our common stock.
If Benefit Plans or IRAs invest in our common stock, the Code may require such plan or IRA to withdraw required minimum distributions in the future. Our stock will be highly illiquid, and our share repurchase plan only offers limited liquidity. If a Benefit Plan or IRA requires liquidity, it may generally sell its shares, but such sale may be at a price less than the price at which such plan or IRA initially purchased its shares of our common stock. If a Benefit Plan or IRA fails to make required minimum distributions, it may be subject to certain taxes and tax penalties.
Specific rules apply to foreign, governmental and church plans.
As a general rule, certain employee benefit plans, including foreign pension plans, governmental plans established or maintained in the U.S. (as defined in Section 3(32) of ERISA), and certain church plans (as defined in Section 3(33) of ERISA), are not subject to ERISA’s requirements and are not “benefit plan investors” within the meaning of the plan assets regulation. Any such plan that is qualified and exempt from taxation under Sections 401(a) and 501(a) of the Code may nonetheless be subject to the prohibited transaction rules set forth in Section 503 of the Code and, under certain circumstances in the case of church plans, Section 4975 of the Code. Also, some foreign plans and governmental plans may be subject to foreign, state, or local laws which are, to a material extent, similar to the provisions of ERISA or Section 4975 of the Code. Each fiduciary of a plan subject to any such similar law should make its own determination as to the need for, and the availability of, any exemption relief.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
Not applicable.
Item 2. Properties.
As of December 31, 2019, our principal executive offices are located at 18191 Von Karman Avenue, Suite 300, Irvine, California 92612. We do not have an address separate from our advisor or our co-sponsors. Since we pay our advisor fees for their services, we do not pay rent for the use of their space.
As of December 31, 2019, we operated through four reportable business segments comprised of 87 buildings, or approximately 4,522,000 square feet of GLA, acquired for an aggregate contract purchase price of $1,022,889,000. These properties consisted of: 43 medical office buildings, 19 senior housing facilities, 14 senior housing — RIDEA facilities and 11 skilled nursing facilities.
53
The following table presents certain additional information about our properties as of December 31, 2019:
Acquisition(1) | Location | Reportable Segment | GLA (Sq Ft) | % of GLA | Date Acquired | Contract Purchase Price | Annualized Base Rent/ NOI(2) | % of Annualized Base Rent | Leased Percentage(3) | Average Annual Rent Per Leased Sq Ft(4) | |||||||||||||||||||
Auburn MOB | Auburn, CA | Medical Office | 19,000 | 0.4 | % | 06/28/16 | $ | 5,450,000 | $ | 466,000 | 0.6 | % | 100 | % | $ | 25.17 | |||||||||||||
Pottsville MOB | Pottsville, PA | Medical Office | 36,000 | 0.8 | 09/16/16 | 9,150,000 | 788,000 | 1.1 | 100 | % | $ | 21.91 | |||||||||||||||||
Charlottesville MOB | Charlottesville, VA | Medical Office | 74,000 | 1.6 | 09/22/16 | 20,120,000 | 1,990,000 | 2.7 | 100 | % | $ | 26.90 | |||||||||||||||||
Rochester Hills MOB | Rochester Hills, MI | Medical Office | 30,000 | 0.7 | 09/29/16 | 8,300,000 | 664,000 | 0.9 | 87.1 | % | $ | 25.09 | |||||||||||||||||
Cullman MOB III | Cullman, AL | Medical Office | 52,000 | 1.1 | 09/30/16 | 16,650,000 | 1,535,000 | 2.1 | 100 | % | $ | 29.44 | |||||||||||||||||
Iron MOB Portfolio | Cullman and Sylacauga, AL | Medical Office | 208,000 | 4.6 | 10/13/16 | 31,000,000 | 2,789,000 | 3.7 | 85.9 | % | $ | 15.61 | |||||||||||||||||
Mint Hill MOB | Mint Hill, NC | Medical Office | 58,000 | 1.3 | 11/14/16 | 21,000,000 | 1,586,000 | 2.1 | 100 | % | $ | 27.55 | |||||||||||||||||
Lafayette Assisted Living Portfolio | Lafayette, LA | Senior Housing —RIDEA | 80,000 | 1.8 | 12/01/16 | 16,750,000 | 304,000 | 0.4 | 86.8 | % | $ | 3,275.72 | |||||||||||||||||
Evendale MOB | Evendale, OH | Medical Office | 66,000 | 1.5 | 12/13/16 | 10,400,000 | 828,000 | 1.1 | 73.1 | % | $ | 17.23 | |||||||||||||||||
Battle Creek MOB | Battle Creek, MI | Medical Office | 46,000 | 1.0 | 03/10/17 | 7,300,000 | 525,000 | 0.7 | 84.2 | % | $ | 13.51 | |||||||||||||||||
Reno MOB | Reno, NV | Medical Office | 191,000 | 4.2 | 03/13/17 | 66,250,000 | 4,672,000 | 6.3 | 90.4 | % | $ | 27.09 | |||||||||||||||||
Athens MOB Portfolio | Athens, GA | Medical Office | 61,000 | 1.3 | 05/18/17 | 16,800,000 | 1,263,000 | 1.7 | 98.5 | % | $ | 20.97 | |||||||||||||||||
SW Illinois Senior Housing Portfolio | Columbia, Millstadt, Red Bud and Waterloo, IL | Senior Housing | 190,000 | 4.2 | 05/22/17 | 31,800,000 | 2,359,000 | 3.2 | 100 | % | $ | 12.39 | |||||||||||||||||
Lawrenceville MOB | Lawrenceville, GA | Medical Office | 31,000 | 0.7 | 06/12/17 | 11,275,000 | 819,000 | 1.1 | 100 | % | $ | 26.84 | |||||||||||||||||
Northern California Senior Housing Portfolio | Belmont, Fairfield, Menlo Park and Sacramento, CA | Senior Housing | 135,000 | 3.0 | 06/28/17 | 45,800,000 | 3,219,000 | 4.3 | 100 | % | $ | 23.94 | |||||||||||||||||
Roseburg MOB | Roseburg, OR | Medical Office | 62,000 | 1.4 | 06/29/17 | 23,200,000 | 1,602,000 | 2.1 | 100 | % | $ | 25.74 | |||||||||||||||||
Fairfield County MOB Portfolio | Stratford and Trumbull, CT | Medical Office | 80,000 | 1.8 | 09/29/17 | 15,395,000 | 1,953,000 | 2.6 | 94.0 | % | $ | 26.05 | |||||||||||||||||
Central Florida Senior Housing Portfolio(5) | Bradenton, Brooksville, Lake Placid, Lakeland, Pinellas Park, Sanford, Spring Hill and Winter Haven, FL | Senior Housing — RIDEA | 899,000 | 19.9 | 11/01/17 | 109,500,000 | 4,979,000 | 6.7 | 82.4 | % | $ | 5,107.58 | |||||||||||||||||
Central Wisconsin Senior Care Portfolio | Sun Prairie and Waunakee, WI | Skilled Nursing | 236,000 | 5.1 | 03/01/18 | 22,600,000 | 1,798,000 | 2.4 | 100 | % | $ | 7.62 | |||||||||||||||||
Sauk Prairie MOB | Prairie du Sac, WI | Medical Office | 55,000 | 1.2 | 04/09/18 | 19,500,000 | 1,276,000 | 1.7 | 100 | % | $ | 23.18 | |||||||||||||||||
Surprise MOB | Surprise, AZ | Medical Office | 34,000 | 0.8 | 04/27/18 | 11,650,000 | 820,000 | 1.1 | 89.5 | % | $ | 26.93 | |||||||||||||||||
Southfield MOB | Southfield, MI | Medical Office | 85,000 | 1.9 | 05/11/18 | 16,200,000 | 1,123,000 | 1.5 | 77.0 | % | $ | 17.13 | |||||||||||||||||
Pinnacle Beaumont ALF(5) | Beaumont, TX | Senior Housing —RIDEA | 61,000 | 1.3 | 07/01/18 | 19,500,000 | 1,689,000 | 2.3 | 84.2 | % | $ | 24,761.65 | |||||||||||||||||
Grand Junction MOB | Grand Junction, CO | Medical Office | 83,000 | 1.8 | 07/06/18 | 31,500,000 | 2,158,000 | 2.9 | 100 | % | $ | 26.13 | |||||||||||||||||
Edmonds MOB | Edmonds, WA | Medical Office | 55,000 | 1.2 | 07/30/18 | 23,500,000 | 1,477,000 | 2.0 | 96.9 | % | $ | 27.52 | |||||||||||||||||
Pinnacle Warrenton ALF(5) | Warrenton, MO | Senior Housing —RIDEA | 34,000 | 0.8 | 08/01/18 | 8,100,000 | 744,000 | 1.0 | 92.6 | % | $ | 15,292.67 | |||||||||||||||||
54
Acquisition(1) | Location | Reportable Segment | GLA (Sq Ft) | % of GLA | Date Acquired | Contract Purchase Price | Annualized Base Rent/ NOI(2) | % of Annualized Base Rent | Leased Percentage(3) | Average Annual Rent Per Leased Sq Ft(4) | |||||||||||||||||||
Glendale MOB | Glendale, WI | Medical Office | 43,000 | 1.0 | % | 08/13/18 | $ | 7,600,000 | $ | 634,000 | 0.9 | % | 80.3 | % | $ | 18.32 | |||||||||||||
Missouri SNF Portfolio | Florissant, Kansas City, Milan, Moberly, Salisbury, Sedalia, St. Elizabeth and Trenton, MO | Skilled Nursing | 385,000 | 8.4 | 09/28/18 | 88,200,000 | 7,782,000 | 10.4 | 100 | % | $ | 20.19 | |||||||||||||||||
Flemington MOB Portfolio | Flemington, NJ | Medical Office | 49,000 | 1.1 | 11/29/18 | 16,950,000 | 1,214,000 | 1.6 | 98.9 | % | $ | 24.93 | |||||||||||||||||
Lawrenceville MOB II | Lawrenceville, GA | Medical Office | 45,000 | 1.0 | 12/19/18 | 9,999,000 | 1,096,000 | 1.5 | 100 | % | $ | 24.16 | |||||||||||||||||
Mill Creek MOB | Mill Creek, WA | Medical Office | 22,000 | 0.5 | 12/21/18 | 8,250,000 | 560,000 | 0.8 | 100 | % | $ | 25.38 | |||||||||||||||||
Modesto MOB | Modesto, CA | Medical Office | 58,000 | 1.3 | 12/28/18 | 16,000,000 | 1,482,000 | 2.0 | 100 | % | $ | 25.76 | |||||||||||||||||
Michigan ALF Portfolio | Grand Rapids, Holland, Howell, Lansing and Wyoming, MI | Senior Housing | 328,000 | 7.3 | 12/28/18 and 05/01/19 | 70,000,000 | 4,795,000 | 6.4 | 100 | % | $ | 14.62 | |||||||||||||||||
Lithonia MOB | Lithonia, GA | Medical Office | 40,000 | 0.9 | 03/05/19 | 10,600,000 | 703,000 | 0.9 | 84.1 | % | $ | 20.66 | |||||||||||||||||
West Des Moines SNF | West Des Moines, IA | Skilled Nursing | 39,000 | 0.9 | 03/24/19 | 7,000,000 | 546,000 | 0.7 | 100 | % | $ | 14.18 | |||||||||||||||||
Great Nord MOB Portfolio | Tinley Park, IL; Chesterton and Crown Point, IN; and Plymouth, MN | Medical Office | 143,000 | 3.2 | 04/08/19 | 44,000,000 | 3,473,000 | 4.6 | 95.3 | % | $ | 25.44 | |||||||||||||||||
Overland Park MOB | Overland Park, KS | Medical Office | 76,000 | 1.7 | 08/05/19 | 28,350,000 | 2,132,000 | 2.9 | 92.9 | % | $ | 30.08 | |||||||||||||||||
Blue Badger MOB | Marysville, OH | Medical Office | 34,000 | 0.8 | 08/09/19 | 13,650,000 | 857,000 | 1.2 | 100 | % | $ | 24.94 | |||||||||||||||||
Bloomington MOB | Bloomington, IL | Medical Office | 45,000 | 1.0 | 08/13/19 | 18,200,000 | 1,127,000 | 1.5 | 100 | % | $ | 24.97 | |||||||||||||||||
Memphis MOB | Memphis, TN | Medical Office | 27,000 | 0.6 | 08/15/19 | 8,700,000 | 590,000 | 0.8 | 100 | % | $ | 21.93 | |||||||||||||||||
Haverhill MOB | Haverhill, MA | Medical Office | 64,000 | 1.4 | 08/27/19 | 15,500,000 | 1,254,000 | 1.7 | 100 | % | $ | 19.74 | |||||||||||||||||
Fresno MOB | Fresno, CA | Medical Office | 32,000 | 0.7 | 10/30/19 | 10,000,000 | 692,000 | 0.9 | 92.7 | % | $ | 23.16 | |||||||||||||||||
Colorado Foothills MOB Portfolio | Arvada, Centennial and Colorado Springs, CO | Medical Office | 131,000 | 2.8 | 11/19/19 | 31,200,000 | 2,149,000 | 2.9 | 93.0 | % | $ | 17.65 | |||||||||||||||||
Total/weighted average(6) | 4,522,000 | 100 | % | $ | 1,022,889,000 | $ | 74,512,000 | 100 | % | 95.8 | % | $ | 20.23 | ||||||||||||||||
_______
(1) | We own 100% of our properties acquired as of December 31, 2019, with the exception of Central Florida Senior Housing Portfolio, Pinnacle Beaumont ALF and Pinnacle Warrenton ALF. |
(2) | With the exception of our senior housing — RIDEA facilities, annualized base rent is based on contractual base rent from leases in effect as of December 31, 2019. Annualized base rent for our senior housing — RIDEA facilities is based on annualized NOI, a non-GAAP financial measure. See Part II, Item 6, Selected Financial Data, for a further discussion. |
(3) | Leased percentage includes all leased space of the respective acquisition including master leases, except for our senior housing — RIDEA facilities where leased percentage represents resident occupancy on the available units of the RIDEA facilities. |
(4) | Average annual rent per leased square foot is based on leases in effect as of December 31, 2019, except for our senior housing — RIDEA facilities where average annual rent per unit is based on NOI divided by the average occupied units of the senior housing — RIDEA facilities. |
(5) | Acquisition was completed pursuant to a joint venture with an affiliate of Meridian, an unaffiliated third party. Our ownership of the joint venture is approximately 98.0%. |
55
(6) | Weighted average annual rent per leased square foot excludes our senior housing — RIDEA facilities. |
We own fee simple interests in all of our buildings except for nine buildings for which we own fee simple interests in the building and improvements of such properties subject to the respective ground leases.
The following information generally applies to our properties:
• | we believe all of our properties are adequately covered by insurance and are suitable for their intended purposes; |
• | we have no plans for any material renovations, improvements or development with respect to any of our properties, except in accordance with planned budgets; |
• | our properties are located in markets where we are subject to competition for attracting new tenants and retaining current tenants; and |
• | depreciation is provided on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the buildings, up to 39 years, and over the shorter of the lease term or useful lives of the tenant improvements, up to 16 years. Furniture, fixtures and equipment is depreciated over the estimated useful life, up to 20 years. |
For additional information regarding our real estate investments, see Schedule III, Real Estate and Accumulated Depreciation, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Lease Expirations
The following table presents the sensitivity of our annual base rent due to lease expirations for the next 10 years and thereafter at our properties other than our senior housing — RIDEA facilities, by number, total square feet, percentage of leased area, annual base rent and percentage of total annual base rent of expiring leases as of December 31, 2019:
Year | Number of Expiring Leases | Total Square Feet of Expiring Leases | % of Leased Area Represented by Expiring Leases | Annual Base Rent of Expiring Leases | % of Total Annual Base Rent Represented by Expiring Leases(1) | |||||||||
2020 | 46 | 258,000 | 7.8 | % | $ | 6,025,000 | 8.0 | % | ||||||
2021 | 31 | 131,000 | 4.0 | 2,801,000 | 3.7 | |||||||||
2022 | 39 | 239,000 | 7.2 | 5,916,000 | 7.9 | |||||||||
2023 | 33 | 236,000 | 7.2 | 5,939,000 | 8.0 | |||||||||
2024 | 32 | 245,000 | 7.5 | 5,854,000 | 7.8 | |||||||||
2025 | 21 | 232,000 | 7.1 | 5,741,000 | 7.6 | |||||||||
2026 | 12 | 51,000 | 1.5 | 1,370,000 | 1.8 | |||||||||
2027 | 14 | 103,000 | 3.1 | 2,865,000 | 3.8 | |||||||||
2028 | 17 | 178,000 | 5.4 | 4,546,000 | 6.0 | |||||||||
2029 | 16 | 184,000 | 5.6 | 5,516,000 | 7.3 | |||||||||
Thereafter | 49 | 1,437,000 | 43.6 | 28,724,000 | 38.1 | |||||||||
Total | 310 | 3,294,000 | 100 | % | $ | 75,297,000 | 100 | % | ||||||
(1) | The annual base rent percentage is based on the total annual contractual base rent expiring in the applicable year, based on leases in effect as of December 31, 2019. |
56
Geographic Diversification/Concentration Table
The following table lists the states in which our properties are located and provides certain information regarding our portfolio’s geographic diversification/concentration as of December 31, 2019:
State | Number of Buildings | GLA (Sq Ft) | % of GLA | Annualized Base Rent/NOI(1) | % of Annualized Base Rent/NOI | |||||||||
Alabama | 4 | 260,000 | 5.7 | % | $ | 4,324,000 | 5.8 | % | ||||||
Arizona | 1 | 34,000 | 0.8 | 820,000 | 1.1 | |||||||||
California | 8 | 243,000 | 5.4 | 5,858,000 | 7.9 | |||||||||
Colorado | 4 | 214,000 | 4.7 | 4,307,000 | 5.8 | |||||||||
Connecticut | 2 | 80,000 | 1.8 | 1,953,000 | 2.6 | |||||||||
Florida | 10 | 899,000 | 19.9 | 4,979,000 | 6.7 | |||||||||
Georgia | 5 | 177,000 | 3.9 | 3,881,000 | 5.2 | |||||||||
Illinois | 7 | 288,000 | 6.3 | 4,755,000 | 6.4 | |||||||||
Indiana | 2 | 44,000 | 1.0 | 1,176,000 | 1.5 | |||||||||
Iowa | 1 | 39,000 | 0.9 | 546,000 | 0.7 | |||||||||
Kansas | 1 | 76,000 | 1.7 | 2,132,000 | 2.9 | |||||||||
Louisiana | 2 | 80,000 | 1.8 | 304,000 | 0.4 | |||||||||
Massachusetts | 1 | 64,000 | 1.4 | 1,254,000 | 1.7 | |||||||||
Michigan | 12 | 490,000 | 10.8 | 7,108,000 | 9.5 | |||||||||
Minnesota | 1 | 46,000 | 1.0 | 1,028,000 | 1.4 | |||||||||
Missouri | 9 | 419,000 | 9.3 | 8,525,000 | 11.4 | |||||||||
Nevada | 1 | 191,000 | 4.2 | 4,672,000 | 6.3 | |||||||||
New Jersey | 2 | 49,000 | 1.1 | 1,214,000 | 1.6 | |||||||||
North Carolina | 1 | 58,000 | 1.3 | 1,586,000 | 2.1 | |||||||||
Ohio | 2 | 100,000 | 2.2 | 1,685,000 | 2.3 | |||||||||
Oregon | 1 | 62,000 | 1.4 | 1,602,000 | 2.1 | |||||||||
Pennsylvania | 1 | 36,000 | 0.8 | 788,000 | 1.1 | |||||||||
Tennessee | 1 | 27,000 | 0.6 | 590,000 | 0.8 | |||||||||
Texas | 1 | 61,000 | 1.3 | 1,689,000 | 2.3 | |||||||||
Virginia | 1 | 74,000 | 1.6 | 1,990,000 | 2.7 | |||||||||
Washington | 2 | 77,000 | 1.7 | 2,037,000 | 2.7 | |||||||||
Wisconsin | 4 | 334,000 | 7.4 | 3,709,000 | 5.0 | |||||||||
Total | 87 | 4,522,000 | 100 | % | $ | 74,512,000 | 100 | % | ||||||
_______
(1) | Annualized base rent is based on contractual base rent from leases in effect as of December 31, 2019, with the exception of our senior housing — RIDEA facilities, which is based on annualized NOI. |
Indebtedness
For a discussion of our indebtedness, see Note 6, Mortgage Loans Payable, Net, and Note 7, Line of Credit and Term Loans, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings.
None.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures.
Not applicable.
57
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
Market Information
There is no established public trading market for shares of our common stock.
To assist the members of FINRA and their associated persons, pursuant to FINRA Conduct Rule 5110, we disclose in each annual report distributed to stockholders a per share estimated value of the shares, the method by which it was developed, and the date of the data used to develop the estimated value. In addition, we prepare annual statements of the estimated share value to assist fiduciaries of Benefit Plans and IRAs subject to the annual reporting requirements of ERISA in the preparation of their reports relating to an investment in shares of our common stock. For these purposes, our estimated per share NAV is $9.54 as of December 31, 2018, which estimated per share NAV was approved and established by our board on April 4, 2019 based on the estimated value of our assets less the estimated value of our liabilities, divided by the number of shares outstanding on a fully diluted basis, calculated as of December 31, 2018. However, there is no established public trading market for the shares of our common stock at this time, and there can be no assurance that stockholders could receive $9.54 per share if such a market did exist and they sold their shares of our common stock or that they would be able to receive such amount for their shares of our common stock in the future.
Pursuant to FINRA rules, we disclose an estimated per share NAV of our shares based on a valuation performed at least annually, and we disclose the resulting estimated per share NAV in our Annual Reports on Form 10-K distributed to stockholders. When determining the estimated per share NAV, there are currently no SEC, federal and state rules that establish requirements specifying the methodology to employ in determining an estimated per share NAV; provided, however, that the determination of the estimated per share NAV must be conducted by, or with the material assistance or confirmation of, a third-party valuation expert or service and must be derived from a methodology that conforms to standard industry practice. In determining the estimated per share NAV of our shares, our board considered information and analysis, including valuation materials that were provided by an independent third-party valuation firm, information provided by our advisor and the estimated per share NAV recommendation made by the audit committee of our board, which committee is comprised entirely of independent directors. See our Current Report on Form 8-K, filed with the SEC on April 8, 2019, for additional information regarding our independent third-party valuation firm, its valuation materials and the methodology used to determine the estimated per share NAV.
FINRA rules require subsequent valuations to be performed at least annually. The valuations are estimates and consequently should not be viewed as an accurate reflection of the amount of net proceeds that would result from an immediate sale of our assets.
Stockholders
As of March 13, 2020, we had approximately 14,032 stockholders of record.
Distributions
Our board authorized, on a quarterly basis, a daily distribution to our stockholders of record as of the close of business on each day of the period commencing on May 1, 2016 and ending on March 31, 2020. The daily distributions were or will be calculated based on 365 days in the calendar year and are equal to $0.001643836 per share of our Class T and Class I common stock, which is equal to an annualized distribution of $0.60 per share. These distributions were or will be aggregated and paid monthly in arrears in cash or shares of our common stock pursuant to our DRIP Offerings, only from legally available funds.
The amount of distributions paid to our stockholders is determined quarterly by our board and is dependent on a number of factors, including funds available for payment of distributions, our financial condition, capital expenditure requirements and annual distribution requirements needed to maintain our qualification as a REIT under the Code. We have not established any limit on the amount of offering proceeds that may be used to fund distributions, except that, in accordance with our organizational documents and Maryland law, we may not make distributions that would: (i) cause us to be unable to pay our debts as they become due in the usual course of business; or (ii) cause our total assets to be less than the sum of our total liabilities plus senior liquidation preferences.
58
The distributions paid for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, along with the amount of distributions reinvested pursuant to our DRIP Offerings and the sources of distributions as compared to cash flows from operations were as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||||||||
Distributions paid in cash | $ | 20,905,000 | $ | 13,989,000 | |||||||||
Distributions reinvested | 25,533,000 | 17,612,000 | |||||||||||
$ | 46,438,000 | $ | 31,601,000 | ||||||||||
Sources of distributions: | |||||||||||||
Cash flows from operations | $ | 39,540,000 | 85.1 | % | $ | 15,423,000 | 48.8 | % | |||||
Offering proceeds | 5,396,000 | 11.6 | 16,178,000 | 51.2 | |||||||||
Proceeds from borrowings | 1,502,000 | 3.3 | — | — | |||||||||
$ | 46,438,000 | 100 | % | $ | 31,601,000 | 100 | % | ||||||
As of December 31, 2019, any distributions of amounts in excess of our current and accumulated earnings and profits have resulted in a return of capital to our stockholders, and all or any portion of a distribution to our stockholders may have been paid from net offering proceeds and borrowings. The payment of distributions from our net offering proceeds and borrowings have reduced the amount of capital we ultimately invested in assets and negatively impacted the amount of income available for future distributions.
As of December 31, 2019, we had an amount payable of $951,000 to our advisor or its affiliates primarily for asset management fees, which will be paid from cash flows from operations in the future as it becomes due and payable by us in the ordinary course of business consistent with our past practice. See Note 13, Related Party Transactions, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The distributions paid for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, along with the amount of distributions reinvested pursuant to our DRIP Offerings and the sources of our distributions as compared to FFO were as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||||||||
Distributions paid in cash | $ | 20,905,000 | $ | 13,989,000 | |||||||||
Distributions reinvested | 25,533,000 | 17,612,000 | |||||||||||
$ | 46,438,000 | $ | 31,601,000 | ||||||||||
Sources of distributions: | |||||||||||||
FFO attributable to controlling interest | $ | 30,109,000 | 64.8 | % | $ | 24,923,000 | 78.9 | % | |||||
Offering proceeds | 13,053,000 | 28.1 | 6,678,000 | 21.1 | |||||||||
Proceeds from borrowings | 3,276,000 | 7.1 | — | — | |||||||||
$ | 46,438,000 | 100 | % | $ | 31,601,000 | 100 | % | ||||||
The payment of distributions from sources other than FFO may reduce the amount of proceeds available for investment and operations or cause us to incur additional interest expense as a result of borrowed funds. For a further discussion of FFO, a non-GAAP financial measure, including a reconciliation of our GAAP net income (loss) to FFO, see Item 6, Selected Financial Data.
59
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
We adopted our incentive plan, pursuant to which our board or a committee of our independent directors may make grants of options, restricted shares of common stock, stock purchase rights, stock appreciation rights or other awards to our independent directors, employees and consultants. The maximum number of shares of our common stock that may be issued pursuant to our incentive plan is 4,000,000. For a further discussion of our incentive plan, see Note 12, Equity — 2015 Incentive Plan, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The following table provides information regarding our incentive plan as of December 31, 2019:
Plan Category | Number of Securities to be Issued upon Exercise of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights | Weighted Average Exercise Price of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights | Number of Securities Remaining Available for Future Issuance | ||||||
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders(1) | — | — | 3,917,500 | ||||||
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | — | — | — | ||||||
Total | — | 3,917,500 | |||||||
________
(1) | Through December 31, 2019, we granted an aggregate of 12,500 shares of our restricted Class T common stock, as defined in our incentive plan, to each of our independent directors in connection with their initial election and re-election to our board, of which 20.0% vested on the grant date and 20.0% will vest on each of the first four anniversaries of the date of grant. In addition, through December 31, 2019, we granted an aggregate of 15,000 shares of our restricted Class T common stock, as defined in our incentive plan, to each of our independent directors in consideration for their past services rendered. These shares of restricted Class T common stock vest under the same period described above. Prior to April 5, 2019, the fair value of each share at the date of grant was based on the then most recent price paid to acquire one share of our Class T common stock in our initial offering; effective April 5, 2019, the fair value of each share at the date of grant was estimated at the most recent estimated per share NAV approved and established by our board; and with respect to the initial 20.0% of shares of our restricted Class T common stock that vested on the date of grant, expensed as compensation immediately, and with respect to the remaining shares of our restricted Class T common stock, amortized over the period from the service inception date to the vesting date for each vesting tranche (i.e., on a tranche by tranche basis) using the accelerated attribution method. Shares of our restricted Class T common stock may not be sold, transferred, exchanged, assigned, pledged, hypothecated or otherwise encumbered. Such restrictions expire upon vesting. Shares of our restricted Class T common stock have full voting rights and rights to distributions. Such shares are not shown in the chart above as they are deemed outstanding shares of our common stock; however, such grants reduce the number of securities remaining available for future issuance. |
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
None.
Purchase of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchasers
Our share repurchase plan allows for repurchases of shares of our common stock by us when certain criteria are met. Share repurchases will be made at the sole discretion of our board. All share repurchases are subject to a one-year holding period, except for repurchases made in connection with a stockholder’s death or “qualifying disability,” as defined in our share repurchase plan. Subject to funds being available, we will limit the number of shares of our common stock repurchased during any calendar year to 5.0% of the weighted average number of shares of our common stock outstanding during the prior calendar year; provided however, shares of our common stock subject to a repurchase requested upon the death of a stockholder will not be subject to this cap. Funds for the repurchase of shares of our common stock will come exclusively from the cumulative proceeds we receive from the sale of shares of our common stock pursuant to our DRIP Offerings.
The price per share at which we will repurchase shares of our common stock will range from 92.5% to 100% of each stockholder’s repurchase amount depending on the period of time their shares have been held. During our initial offering and with respect to shares repurchased for the quarter ending March 31, 2019, the repurchase amount for shares repurchased under our share repurchase plan was equal to the lesser of (i) the amount per share that a stockholder paid for their shares of our common stock, or (ii) the per share offering price in our initial offering. Commencing with shares repurchased for the quarter ending June 30, 2019, the repurchase amount for shares repurchased under our share repurchase plan is the lesser of the amount per share the stockholder paid for its shares of common stock or the most recent estimated value of one share of the applicable class of common stock as determined by our board. However, if shares of our common stock are to be repurchased in
60
connection with a stockholder’s death or qualifying disability, the repurchase price will be no less than 100% of the price paid to acquire the shares of our common stock from us.
During the three months ended December 31, 2019, we repurchased shares of our common stock as follows:
Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased | Average Price Paid per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased As Part of Publicly Announced Plan or Program | Maximum Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs | |||||||||
October 1, 2019 to October 31, 2019 | — | $ | — | — | (1 | ) | |||||||
November 1, 2019 to November 30, 2019 | — | $ | — | — | (1 | ) | |||||||
December 1, 2019 to December 31, 2019 | 260,029 | $ | 9.29 | 260,029 | (1 | ) | |||||||
Total | 260,029 | $ | 9.29 | 260,029 | |||||||||
___________
(1) | A description of the maximum number of shares that may be purchased under our share repurchase plan is included in the narrative preceding this table. |
61
Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
The following should be read with Part I, Item 1A, Risk Factors, and Item 7, Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, and our accompanying consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of results for any future period.
We had no results of operations for the period from January 23, 2015 (Date of Inception) through December 31, 2015, and therefore, our results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018, 2017 and 2016 are not comparable to the period from January 23, 2015 (Date of Inception) through December 31, 2015. In addition, on January 1, 2019, we adopted ASC Topic 842, Leases, using the modified retrospective approach whereby the cumulative effect of adoption was recognized on the adoption date and prior periods were not restated. As such, with respect to our leases as both lessees and lessors, certain financial information below is presented pursuant to ASC Topic 842 for the year ended December 31, 2019, and pursuant to the lease accounting standard then in effect for the prior years. Therefore, our results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019 may not be comparable to the prior years presented below. See Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies — Leases, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for a further discussion of ASC Topic 842.
The following selected financial data is derived from our consolidated financial statements in Part IV, Item 15, Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules that is a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
Selected Financial Data | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
BALANCE SHEET DATA: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 1,068,327,000 | $ | 896,372,000 | $ | 480,153,000 | $ | 142,758,000 | $ | 202,000 | ||||||||||
Mortgage loans payable, net | $ | 26,070,000 | $ | 16,892,000 | $ | 11,567,000 | $ | 3,965,000 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Line of credit and term loans | $ | 396,800,000 | $ | 275,000,000 | $ | 84,100,000 | $ | 33,900,000 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Stockholders’ equity | $ | 590,079,000 | $ | 557,672,000 | $ | 353,224,000 | $ | 92,255,000 | $ | 200,000 | ||||||||||
Years Ended December 31, | Period from January 23, 2015 (Date of Inception) through | |||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS DATA: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total revenues | $ | 120,770,000 | $ | 84,456,000 | $ | 33,333,000 | $ | 3,156,000 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Net (loss) income | $ | (18,851,000 | ) | $ | (8,586,000 | ) | $ | 508,000 | $ | (5,474,000 | ) | $ | — | |||||||
Net (loss) income attributable to controlling interest | $ | (18,769,000 | ) | $ | (8,354,000 | ) | $ | 541,000 | $ | (5,474,000 | ) | $ | — | |||||||
Net (loss) income per Class T and Class I common share attributable to controlling interest — basic and diluted(1) | $ | (0.24 | ) | $ | (0.15 | ) | $ | 0.02 | $ | (1.75 | ) | $ | — | |||||||
STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS DATA: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 39,540,000 | $ | 15,423,000 | $ | 12,404,000 | $ | (3,621,000 | ) | $ | — | |||||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | $ | (199,934,000 | ) | $ | (411,554,000 | ) | $ | (330,688,000 | ) | $ | (133,322,000 | ) | $ | — | ||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | $ | 161,650,000 | $ | 403,618,000 | $ | 323,150,000 | $ | 138,978,000 | $ | 202,000 | ||||||||||
OTHER DATA: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distributions declared | $ | 47,065,000 | $ | 32,943,000 | $ | 16,672,000 | $ | 1,877,000 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Distributions declared per Class T and Class I common share | $ | 0.60 | $ | 0.60 | $ | 0.60 | $ | 0.40 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Funds from operations attributable to controlling interest(2) | $ | 30,109,000 | $ | 24,923,000 | $ | 14,134,000 | $ | (4,222,000 | ) | $ | — | |||||||||
Modified funds from operations attributable to controlling interest(2) | $ | 33,822,000 | $ | 24,623,000 | $ | 12,941,000 | $ | 287,000 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Net operating income(3) | $ | 64,110,000 | $ | 42,934,000 | $ | 21,838,000 | $ | 2,258,000 | $ | — | ||||||||||
62
_________
(1) | Net income (loss) per Class T and Class I common share is based upon the weighted average number of shares of our common stock outstanding. Distributions by us of our current and accumulated earnings and profits for federal income tax purposes are taxable to stockholders as ordinary income. Distributions in excess of these earnings and profits generally are treated as a non-taxable reduction of the stockholders’ basis in the shares of our common stock to the extent thereof (a return of capital for tax purposes) and, thereafter, as taxable gain. These distributions in excess of earnings and profits will have the effect of deferring taxation of the distributions until the sale of the stockholders’ common stock. |
(2) | Funds from Operations and Modified Funds from Operations: |
Due to certain unique operating characteristics of real estate companies, the National Association of Real Estate Investment Trusts, or NAREIT, an industry trade group, has promulgated a measure known as funds from operations, a non-GAAP measure, which we believe to be an appropriate supplemental performance measure to reflect the operating performance of a REIT. The use of funds from operations is recommended by the REIT industry as a supplemental performance measure, and our management uses FFO to evaluate our performance over time. FFO is not equivalent to our net income (loss) as determined under GAAP.
We define FFO, a non-GAAP measure, consistent with the standards established by the White Paper on funds from operations approved by the Board of Governors of NAREIT, or the White Paper. The White Paper defines funds from operations as net income (loss) computed in accordance with GAAP, excluding gains or losses from sales of certain real estate assets and impairment writedowns of certain real estate assets and investments, plus depreciation and amortization related to real estate, and after adjustments for unconsolidated partnerships and joint ventures. While impairment charges are excluded from the calculation of FFO as described above, investors are cautioned that due to the fact that impairments are based on estimated future undiscounted cash flows and that we intend to have a relatively limited term of our operations, it could be difficult to recover any impairment charges through the eventual sale of the property. Adjustments for unconsolidated partnerships and joint ventures are calculated to reflect funds from operations. Our FFO calculation complies with NAREIT’s policy described above.
Historical accounting for real estate involves the use of GAAP. Any other method of accounting for real estate such as the fair value method cannot be construed to be any more accurate or relevant than the comparable methodologies of real estate valuation found in GAAP. Nevertheless, we believe that the use of FFO, which excludes the impact of real estate-related depreciation and amortization and impairments, provides a further understanding of our performance to investors and to our management, and when compared year over year, reflects the impact on our operations from trends in occupancy rates, rental rates, operating costs, general and administrative expenses and interest costs, which may not be immediately apparent from net income (loss).
However, FFO and MFFO, as described below, should not be construed to be more relevant or accurate than the current GAAP methodology in calculating net income (loss) or in its applicability in evaluating our operating performance. The method utilized to evaluate the value and performance of real estate under GAAP should be construed as a more relevant measure of operational performance and considered more prominently than the non-GAAP FFO and MFFO measures and the adjustments to GAAP in calculating FFO and MFFO.
The IPA, an industry trade group, has standardized a measure known as modified funds from operations, which the IPA has recommended as a supplemental performance measure for publicly registered, non-listed REITs and which we believe to be another appropriate supplemental performance measure to reflect the operating performance of a publicly registered, non-listed REIT having the characteristics described above. MFFO is not equivalent to our net income (loss) as determined under GAAP, and MFFO may not be a useful measure of the impact of long-term operating performance on value if we do not continue to operate with a limited life and targeted exit strategy, as currently intended. We believe that, because MFFO excludes expensed acquisition fees and expenses that affect our operations only in periods in which properties are acquired and that we consider more reflective of investing activities, as well as other non-operating items included in FFO, MFFO can provide, on a going forward basis, an indication of the sustainability (that is, the capacity to continue to be maintained) of our operating performance after the period in which we are acquiring our properties and once our portfolio is in place. By providing MFFO, we believe we are presenting useful information that assists investors and analysts to better assess the sustainability of our operating performance after our initial offering stage has been completed and our properties have been acquired. We also believe that MFFO is a recognized measure of sustainable operating performance by the publicly registered, non-listed REIT industry. Further, we believe MFFO is useful in comparing the sustainability of our operating performance after our initial offering stage and acquisitions are completed with the sustainability of the operating performance of other real estate companies that are not as involved in acquisition activities. Investors are cautioned that MFFO should only be used to assess the sustainability of our operating performance after our initial offering stage has been completed and properties have been acquired, as it excludes
63
expensed acquisition fees and expenses that have a negative effect on our operating performance during the periods in which properties are acquired.
We define MFFO, a non-GAAP measure, consistent with Practice Guideline issued by the IPA in November 2010. The Practice Guideline defines modified funds from operations as funds from operations further adjusted for the following items included in the determination of GAAP net income (loss): acquisition fees and expenses; amounts relating to deferred rent and amortization of above- and below-market leases and liabilities (which are adjusted in order to reflect such payments from a GAAP accrual basis to closer to an expected to be received cash basis of disclosing the rent and lease payments); accretion of discounts and amortization of premiums on debt investments; mark-to-market adjustments included in net income (loss); gains or losses included in net income (loss) from the extinguishment or sale of debt, hedges, foreign exchange, derivatives or securities holdings where trading of such holdings is not a fundamental attribute of the business plan; unrealized gains or losses resulting from consolidation from, or deconsolidation to, equity accounting; and after adjustments for consolidated and unconsolidated partnerships and joint ventures, with such adjustments calculated to reflect modified funds from operations on the same basis. The accretion of discounts and amortization of premiums on debt investments, unrealized gains and losses on hedges, foreign exchange, derivatives or securities holdings, unrealized gains and losses resulting from consolidations, as well as other listed cash flow adjustments are adjustments made to net income (loss) in calculating cash flows from operations and, in some cases, reflect gains or losses which are unrealized and may not ultimately be realized. We are responsible for managing interest rate, hedge and foreign exchange risk, and we do not rely on another party to manage such risk. In as much as interest rate hedges will not be a fundamental part of our operations, we believe it is appropriate to exclude such gains and losses in calculating MFFO, as such gains and losses are based on market fluctuations and may not be directly related or attributable to our operations.
Our MFFO calculation complies with the IPA’s Practice Guideline described above. In calculating MFFO, we exclude acquisition related expenses, amortization of above- and below-market leases, change in deferred rent, fair value adjustments of derivative financial instruments and the adjustments of such items related to our investment in an unconsolidated entity and redeemable noncontrolling interests. The other adjustments included in the IPA’s Practice Guideline are not applicable to us for the periods presented in the table below.
Further, under GAAP, certain contemplated non-cash fair value and other non-cash adjustments are considered operating non-cash adjustments to net income (loss) in determining cash flows from operations. We view fair value adjustments of derivatives and gains and losses from dispositions of assets as items which are unrealized and may not ultimately be realized or as items which are not reflective of on-going operations and are therefore typically adjusted for when assessing operating performance. By excluding such charges that may reflect anticipated and unrealized gains or losses, we believe MFFO provides useful supplemental information.
Our management uses MFFO and the adjustments used to calculate it in order to evaluate our performance against other publicly registered, non-listed REITs which intend to have limited lives with short and defined acquisition periods and targeted exit strategies shortly thereafter. As noted above, MFFO may not be a useful measure of the impact of long-term operating performance if we do not continue to operate in this manner. We believe that our use of MFFO and the adjustments used to calculate it allow us to present our performance in a manner that reflects certain characteristics that are unique to publicly registered, non-listed REITs, such as their limited life, limited and defined acquisition period and targeted exit strategy, and hence, that the use of such measures may be useful to investors.
Presentation of this information is intended to provide useful information to investors as they compare the operating performance of different REITs, although it should be noted that not all REITs calculate funds from operations and modified funds from operations the same way, so comparisons with other REITs may not be meaningful. Furthermore, FFO and MFFO are not necessarily indicative of cash flow available to fund cash needs and should not be considered as an alternative to net income (loss) as an indication of our performance, as an alternative to cash flows from operations, which is an indication of our liquidity, or indicative of funds available to fund our cash needs including our ability to make distributions to our stockholders. FFO and MFFO should be reviewed in conjunction with other measurements as an indication of our performance. MFFO may be useful in assisting management and investors in assessing the sustainability of operating performance in future operating periods, and in particular, after the offering and acquisition stages are complete. FFO and MFFO are not useful measures in evaluating net asset value because impairments are taken into account in determining net asset value but not in determining FFO and MFFO.
Neither the SEC, NAREIT nor any other regulatory body has passed judgment on the acceptability of the adjustments that we use to calculate FFO or MFFO. In the future, the SEC, NAREIT or another regulatory body may decide to standardize the allowable adjustments across the publicly registered, non-listed REIT industry and we would have to adjust our calculation and characterization of FFO or MFFO.
64
The following is a reconciliation of net income (loss), which is the most directly comparable GAAP financial measure, to FFO and MFFO for the periods presented below:
Years Ended December 31, | Period from January 23, 2015 (Date of Inception) through | ||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||
Net (loss) income | $ | (18,851,000 | ) | $ | (8,586,000 | ) | $ | 508,000 | $ | (5,474,000 | ) | $ | — | ||||||
Add: | |||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization related to real estate — consolidated properties | 45,626,000 | 32,658,000 | 13,639,000 | 1,252,000 | — | ||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization related to real estate — unconsolidated entity | 3,365,000 | 891,000 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Net loss attributable to redeemable noncontrolling interests | 82,000 | 232,000 | 33,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Less: | |||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization related to redeemable noncontrolling interests | (113,000 | ) | (272,000 | ) | (46,000 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
FFO attributable to controlling interest | $ | 30,109,000 | $ | 24,923,000 | $ | 14,134,000 | $ | (4,222,000 | ) | $ | — | ||||||||
Acquisition related expenses(a) | $ | 1,974,000 | $ | 2,795,000 | $ | 655,000 | $ | 4,745,000 | $ | — | |||||||||
Amortization of above- and below-market leases(b) | (207,000 | ) | (165,000 | ) | (143,000 | ) | (29,000 | ) | — | ||||||||||
Change in deferred rent(c) | (2,925,000 | ) | (3,029,000 | ) | (1,705,000 | ) | (207,000 | ) | — | ||||||||||
Loss in fair value of derivative financial instruments(d) | 4,385,000 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Adjustments for unconsolidated entity(e) | 486,000 | 99,000 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Adjustments for redeemable noncontrolling interests(e) | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
MFFO attributable to controlling interest | $ | 33,822,000 | $ | 24,623,000 | $ | 12,941,000 | $ | 287,000 | $ | — | |||||||||
Weighted average Class T and Class I common shares outstanding — basic and diluted | 78,396,077 | 54,847,197 | 27,754,701 | 3,131,466 | 20,833 | ||||||||||||||
Net (loss) income per Class T and Class I common share — basic and diluted | $ | (0.24 | ) | $ | (0.16 | ) | $ | 0.02 | $ | (1.75 | ) | $ | — | ||||||
FFO attributable to controlling interest per Class T and Class I common share — basic and diluted | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.45 | $ | 0.51 | $ | (1.35 | ) | $ | — | ||||||||
MFFO attributable to controlling interest per Class T and Class I common share — basic and diluted | $ | 0.43 | $ | 0.45 | $ | 0.47 | $ | 0.09 | $ | — | |||||||||
_________
(a) | In evaluating investments in real estate, we differentiate the costs to acquire the investment from the operations derived from the investment. Such information would be comparable only for publicly registered, non-listed REITs that have completed their acquisition activity and have other similar operating characteristics. By excluding expensed acquisition related expenses, we believe MFFO provides useful supplemental information that is comparable for each type of real estate investment and is consistent with management’s analysis of the investing and operating performance of our properties. Acquisition fees and expenses include payments to our advisor or its affiliates and third parties. |
65
(b) | Under GAAP, above- and below-market leases are assumed to diminish predictably in value over time and amortized, similar to depreciation and amortization of other real estate-related assets that are excluded from FFO. However, because real estate values and market lease rates historically rise or fall with market conditions, including inflation, interest rates, the business cycle, unemployment and consumer spending, we believe that by excluding charges relating to the amortization of above- and below-market leases, MFFO may provide useful supplemental information on the performance of the real estate. |
(c) | Under GAAP, as a lessor, rental revenue is recognized on a straight-line basis over the terms of the related lease (including rent holidays). As a lessee, we record amortization of right-of-use assets and accretion of lease liabilities for our operating leases. This may result in income or expense recognition that is significantly different than the underlying contract terms. By adjusting for such amounts, MFFO may provide useful supplemental information on the realized economic impact of lease terms, providing insight on the expected contractual cash flows of such lease terms, and aligns results with management’s analysis of operating performance. |
(d) | Under GAAP, we are required to include changes in fair value of our derivative financial instruments in the determination of net income or loss. We believe that adjusting for the change in fair value of our derivative financial instruments to arrive at MFFO is appropriate because such adjustments may not be reflective of on-going operations and reflect unrealized impacts on value based only on then current market conditions, although they may be based upon general market conditions. The need to reflect the change in fair value of our derivative financial instruments is a continuous process and is analyzed on a quarterly basis in accordance with GAAP. |
(e) | Includes all adjustments to eliminate the unconsolidated entity’s share or redeemable noncontrolling interests’ share, as applicable, of the adjustments described in notes (a) – (d) above to convert our FFO to MFFO. |
(3) | Net Operating Income: |
NOI is a non-GAAP financial measure that is defined as net income (loss), computed in accordance with GAAP, generated from properties before general and administrative expenses, acquisition related expenses, depreciation and amortization, interest expense, income or loss from unconsolidated entity, other income and income tax benefit or expense. NOI is not equivalent to our net income (loss) as determined under GAAP and may not be a useful measure in measuring operational income or cash flows. Furthermore, NOI is not necessarily indicative of cash flow available to fund cash needs and should not be considered as an alternative to net income (loss) as an indication of our performance, as an alternative to cash flows from operations, as an indication of our liquidity, or indicative of funds available to fund our cash needs including our ability to make distributions to our stockholders. NOI should not be construed to be more relevant or accurate than the current GAAP methodology in calculating net income (loss) or in its applicability in evaluating our operating performance. Investors are also cautioned that NOI should only be used to assess our operational performance in periods in which we have not incurred or accrued any acquisition related expenses.
We believe that NOI is an appropriate supplemental performance measure to reflect the operating performance of our operating assets because NOI excludes certain items that are not associated with the management of the properties. We believe that NOI is a widely accepted measure of comparative operating performance in the real estate community. However, our use of the term NOI may not be comparable to that of other real estate companies as they may have different methodologies for computing this amount.
66
To facilitate understanding of this financial measure, the following is a reconciliation of net income (loss), which is the most directly comparable GAAP financial measure, to net operating income for the periods presented below:
Years Ended December 31, | Period from January 23, 2015 (Date of Inception) through | ||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||
Net (loss) income | $ | (18,851,000 | ) | $ | (8,586,000 | ) | $ | 508,000 | $ | (5,474,000 | ) | $ | — | ||||||
General and administrative | 15,235,000 | 9,172,000 | 4,338,000 | 1,221,000 | — | ||||||||||||||
Acquisition related expenses | 1,974,000 | 2,795,000 | 655,000 | 4,745,000 | — | ||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 45,626,000 | 32,658,000 | 13,639,000 | 1,252,000 | — | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense | 20,576,000 | 6,788,000 | 2,699,000 | 514,000 | — | ||||||||||||||
(Income) loss from unconsolidated entity | (267,000 | ) | 110,000 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
Other income | (175,000 | ) | (11,000 | ) | (1,000 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
Income tax (benefit) expense | (8,000 | ) | 8,000 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
Net operating income | $ | 64,110,000 | $ | 42,934,000 | $ | 21,838,000 | $ | 2,258,000 | $ | — | |||||||||
67
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
The use of the words “we,” “us” or “our” refers to Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. and its subsidiaries, including Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Holdings, LP, except where the context otherwise requires.
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with our accompanying consolidated financial statements and notes thereto appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Such consolidated financial statements and information have been prepared to reflect our financial position as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, together with our results of operations and cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017.
Forward-Looking Statements
Historical results and trends should not be taken as indicative of future operations. Our statements contained in this report that are not historical facts are forward-looking. Actual results may differ materially from those included in the forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements, which are based on certain assumptions and describe future plans, strategies and expectations, are generally identifiable by use of the words “expect,” “project,” “may,” “will,” “should,” “could,” “would,” “intend,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “estimate,” “believe,” “continue,” “predict,” “potential,” “seek” and any other comparable and derivative terms or the negatives thereof. Our ability to predict results or the actual effect of future plans or strategies is inherently uncertain. Factors which could have a material adverse effect on our operations and future investments on a consolidated basis include, but are not limited to: changes in economic conditions generally and the real estate market specifically; legislative and regulatory changes, including changes to laws governing the taxation of real estate investment trusts, or REITs; the availability of capital; changes in interest rates; competition in the real estate industry; the supply and demand for operating properties in our proposed market areas; changes in accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, or GAAP, policies and guidelines applicable to REITs; the success of our investment strategy; the availability of properties to acquire; the availability of financing; and our ongoing relationship with American Healthcare Investors, LLC, or American Healthcare Investors, and Griffin Capital Company, LLC, or Griffin Capital, or collectively, our co-sponsors, and their affiliates. These risks and uncertainties should be considered in evaluating forward-looking statements and undue reliance should not be placed on such statements. Additional information concerning us and our business, including additional factors that could materially affect our financial results, is included herein and in our other filings with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission, or the SEC.
Overview and Background
Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc., a Maryland corporation, was incorporated on January 23, 2015 and therefore we consider that our date of inception. We were initially capitalized on February 6, 2015. We invest in a diversified portfolio of real estate properties, focusing primarily on medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities. We also operate healthcare-related facilities utilizing the structure permitted by the REIT Investment Diversification and Empowerment Act of 2007, which is commonly referred to as a “RIDEA” structure (the provisions of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code, authorizing the RIDEA structure were enacted as part of the Housing and Economic Recovery Act of 2008). We may also originate and acquire secured loans and real estate-related investments on an infrequent and opportunistic basis. We generally seek investments that produce current income. We qualified to be taxed as a REIT under the Code for federal income tax purposes beginning with our taxable year ended December 31, 2016, and we intend to continue to qualify to be taxed as a REIT.
On February 16, 2016, we commenced our initial public offering, or our initial offering, in which we were initially offering to the public up to $3,150,000,000 in shares of our Class T common stock, consisting of up to $3,000,000,000 in shares of our Class T common stock in the primary portion of our initial offering and up to $150,000,000 in shares of our Class T common stock pursuant to our distribution reinvestment plan, as amended, or the DRIP. Effective June 17, 2016, we reallocated certain of the unsold shares of Class T common stock being offered and began offering shares of Class I common stock, such that we were offering up to approximately $2,800,000,000 in shares of Class T common stock and $200,000,000 in shares of Class I common stock in the primary portion of our initial offering, and up to an aggregate of $150,000,000 in shares of our Class T and Class I common stock pursuant to the DRIP, aggregating up to $3,150,000,000. On February 15, 2019, we terminated our initial offering, and as of such date, we sold 75,639,681 aggregate shares of our Class T and Class I common stock, or approximately $754,118,000, and a total of $31,021,000 in distributions were reinvested that resulted in 3,253,535 shares of our common stock being issued pursuant to the DRIP portion of our initial offering. See Note 12, Equity — Common Stock, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for a further discussion.
On January 18, 2019, we filed a Registration Statement on Form S-3 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Act, to register a maximum of $100,000,000 of additional shares of our common stock to be issued pursuant to the DRIP, or the 2019 DRIP Offering. The Registration Statement on Form S-3 was automatically effective with the the SEC upon its filing. We commenced offering shares pursuant to the 2019 DRIP Offering on March 1, 2019, following the
68
termination of our initial offering on February 15, 2019. See Note 12, Equity — Distribution Reinvestment Plan, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for a further discussion. We collectively refer to the DRIP portion of our initial offering and the 2019 DRIP Offering as our DRIP Offerings. As of December 31, 2019, a total of $21,609,000 in distributions were reinvested that resulted in 2,260,164 shares of our common stock being issued pursuant to the 2019 DRIP Offering.
On April 4, 2019, our board of directors, or our board, at the recommendation of the audit committee of our board, comprised solely of independent directors, unanimously approved and established an updated estimated per share net asset value, or NAV, of our common stock of $9.54. We provide this estimated per share NAV to assist broker-dealers in connection with their obligations under Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, or FINRA, Rule 2231 with respect to customer account statements. The estimated per share NAV is based on the estimated value of our assets less the estimated value of our liabilities, divided by the number of shares outstanding on a fully diluted basis, calculated as of December 31, 2018. This valuation was performed in accordance with the methodology provided in Practice Guideline 2013-01, Valuations of Publicly Registered Non-Listed REITs, issued by the Institute for Portfolio Alternatives, or the IPA, in April 2013, in addition to guidance from the SEC. We intend to continue to publish an updated estimated per share NAV on at least an annual basis. See our Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on April 8, 2019, for more information on the methodologies and assumptions used to determine, and the limitations and risks of, our updated estimated per share NAV.
We conduct substantially all of our operations through Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Holdings, LP, or our operating partnership. We are externally advised by Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Advisor, LLC, or our advisor, pursuant to an advisory agreement, or the Advisory Agreement, between us and our advisor. The Advisory Agreement was effective as of February 16, 2016 and had a one-year initial term, subject to successive one-year renewals upon the mutual consent of the parties. The Advisory Agreement was last renewed pursuant to the mutual consent of the parties on February 12, 2020 and expires on February 16, 2021. Our advisor uses its best efforts, subject to the oversight and review of our board, to, among other things, research, identify, review and make investments in and dispositions of properties and securities on our behalf consistent with our investment policies and objectives. Our advisor performs its duties and responsibilities under the Advisory Agreement as our fiduciary. Our advisor is 75.0% owned and managed by wholly owned subsidiaries of American Healthcare Investors and 25.0% owned by a wholly owned subsidiary of Griffin Capital Company. American Healthcare Investors is 47.1% owned by AHI Group Holdings, LLC, or AHI Group Holdings, 45.1% indirectly owned by Colony Capital, Inc. (NYSE: CLNY), or Colony Capital, and 7.8% owned by James F. Flaherty III, a former partner of Colony Capital. We are not affiliated with Griffin Capital, Griffin Capital Securities, LLC, or our dealer manager, Colony Capital or Mr. Flaherty; however, we are affiliated with Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Advisor, LLC, American Healthcare Investors and AHI Group Holdings.
We currently operate through four reportable business segments: medical office buildings, senior housing, senior housing — RIDEA and skilled nursing facilities. As of December 31, 2019, we had completed 43 property acquisitions whereby we owned 82 properties, comprising 87 buildings, or approximately 4,522,000 square feet of gross leasable area, or GLA, for an aggregate contract purchase price of $1,022,889,000. As of December 31, 2019, we also own a 6.0% interest in a joint venture which owns a portfolio of integrated senior health campuses and ancillary businesses.
Critical Accounting Policies
We believe that our critical accounting policies are those that require significant judgments and estimates such as those related to revenue recognition, tenant and resident receivables and allowance for uncollectible accounts, accounting for property acquisitions, capitalization of expenditures and depreciation of assets, impairment of long-lived and intangible assets, properties held for sale and qualification as a REIT. These estimates are made and evaluated on an on-going basis using information that is available as well as various other assumptions believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. However, if our judgment or interpretation of the facts and circumstances relating to various transactions or other matters had been different, we may have applied a different accounting treatment, resulting in a different presentation of our financial statements. We believe that our critical accounting policies affect our more significant estimates and judgments used in the preparation of our financial statements. A summary of our critical accounting policies is included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019, in Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies. There have been no significant changes to our critical accounting policies during 2019 other than those resulting from new accounting standards.
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
For a discussion of recently adopted accounting pronouncements, see Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies — Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
69
Acquisitions in 2020, 2019, 2018 and 2017
For a discussion of our property acquisitions in 2020, 2019, 2018 and 2017, see Note 3, Real Estate Investments, Net and Note 21, Subsequent Events — Property Acquisitions, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Factors Which May Influence Results of Operations
We are not aware of any material trends or uncertainties, other than national economic conditions affecting real estate generally, that may reasonably be expected to have a material impact, favorable or unfavorable, on revenues or income from the acquisition, management and operation of properties other than those listed in Part I, Item 1A, Risk Factors, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. However, due to the recent outbreak of the coronavirus in the U.S. and globally, our residents, tenants and operating partners may be impacted. The impact of the coronavirus on our future results could be significant and will largely depend on future developments, which are highly uncertain and cannot be predicted, including new information which may emerge concerning the severity of the coronavirus, the success of actions taken to contain or treat the coronavirus, and reactions by consumers, companies, governmental entities and capital markets.
Scheduled Lease Expirations
Excluding our senior housing — RIDEA facilities, as of December 31, 2019, our properties were 95.8% leased and during 2020, 7.8% of the leased GLA is scheduled to expire. Our leasing strategy focuses on negotiating renewals for leases scheduled to expire during the next 12 months. In the future, if we are unable to negotiate renewals, we will try to identify new tenants or collaborate with existing tenants who are seeking additional space to occupy. As of December 31, 2019, our remaining weighted average lease term was 8.6 years, excluding our senior housing —RIDEA facilities.
Our senior housing— RIDEA facilities were 83.2% leased for the year ended December 31, 2019 and substantially all of our leases with residents at such properties are for a term of one year or less.
Results of Operations
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
Our operating results are primarily comprised of income derived from our portfolio of properties and expenses in connection with the acquisition and operation of such properties. In general, we expect amounts related to our portfolio of operating properties to increase in the future based on a full year of operations of newly acquired properties as well as any additional real estate and real estate-related investments we may acquire.
We segregate our operations into reporting segments in order to assess the performance of our business in the same way that management reviews our performance and makes operating decisions. Accordingly, when we acquired our first medical office building in June 2016; senior housing facility in December 2016; senior housing — RIDEA facility in November 2017; and skilled nursing facility in March 2018, we added a new reporting segment at each such time. As of December 31, 2019, we operated through four reportable business segments, with activities related to investing in medical office buildings, senior housing, senior housing — RIDEA and skilled nursing facilities.
70
Changes in our operating results are primarily due to owning 87 buildings as of December 31, 2019, as compared to 69 buildings as of December 31, 2018 and as compared to 40 buildings as of December 31, 2017. In addition, the changes in our operating results were due to transitioning the operations of two senior housing facilities within Lafayette Assisted Living Portfolio to a RIDEA structure in February 2019. As of December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we owned the following types of properties:
December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Number of Buildings | Aggregate Contract Purchase Price | Leased % | Number of Buildings | Aggregate Contract Purchase Price | Leased % | Number of Buildings | Aggregate Contract Purchase Price | Leased % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Medical office buildings | 43 | $ | 603,639,000 | 93.1 | % | 29 | $ | 423,439,000 | 93.5 | % | 18 | $ | 262,290,000 | 93.3 | % | ||||||||||||||
Senior housing | 19 | 147,600,000 | 100 | % | 18 | 150,350,000 | 100 | % | 12 | 94,350,000 | 100 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Senior housing — RIDEA | 14 | 153,850,000 | (1 | ) | 12 | 137,100,000 | (1 | ) | 10 | 109,500,000 | (1 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Skilled nursing facilities | 11 | 117,800,000 | 100 | % | 10 | 110,800,000 | 100 | % | — | — | — | % | |||||||||||||||||
Total/weighted average(2) | 87 | $ | 1,022,889,000 | 95.8 | % | 69 | $ | 821,689,000 | 96.4 | % | 40 | $ | 466,140,000 | 95.2 | % | ||||||||||||||
___________
(1) | For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, the leased percentage for the resident units of our senior housing RIDEA facilities was 83.2%, 77.7% and 76.0%, respectively, based on daily average occupancy of licensed beds/units. |
(2) | Leased percentage excludes our senior housing — RIDEA facilities. |
Revenues
Our primary sources of revenue include rent and resident fees and services from our properties. Revenue by reportable segment consisted of the following for the periods then ended:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Real Estate Revenue | |||||||||||
Medical office buildings | $ | 54,508,000 | $ | 34,339,000 | $ | 22,320,000 | |||||
Skilled nursing facilities | 11,681,000 | 4,266,000 | — | ||||||||
Senior housing | 8,421,000 | 8,994,000 | 5,450,000 | ||||||||
Total real estate revenue | 74,610,000 | 47,599,000 | 27,770,000 | ||||||||
Resident Fees and Services | |||||||||||
Senior housing — RIDEA | 46,160,000 | 36,857,000 | 5,563,000 | ||||||||
Total resident fees and services | 46,160,000 | 36,857,000 | 5,563,000 | ||||||||
Total revenues | $ | 120,770,000 | $ | 84,456,000 | $ | 33,333,000 | |||||
71
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, real estate revenue primarily comprised of base rent of $56,373,000, $35,340,000 and $20,705,000, respectively, and expense recoveries of $14,453,000, $8,933,000 and $5,162,000, respectively.
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, resident fees and services consisted of rental fees related to resident leases and extended health care fees. The increase in resident fees and services for the year ended December 31, 2019, compared to the year ended December 31, 2018, was primarily due to a full year of operations during 2019 for two senior housing — RIDEA facilities acquired during the year ended December 31, 2018. The increase in resident fees and services for the year ended December 31, 2018, compared to the year ended December 31, 2017, was primarily due to a full year of operations during 2018 for 10 senior housing — RIDEA facilities acquired during the year ended December 31, 2017. The amount of revenue generated by our properties depends principally on our ability to maintain the occupancy rates of currently leased space and to lease available space at the then existing market rates.
Rental Expenses and Property Operating Expenses
Rental expenses and rental expenses as a percentage of real estate revenue, as well as property operating expenses and property operating expenses as a percentage of resident fees and services, by reportable segment consisted of the following for the periods then ended:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||
Rental Expenses | |||||||||||||||||||||
Medical office buildings | $ | 17,528,000 | 32.2 | % | $ | 9,934,000 | 28.9 | % | $ | 6,694,000 | 30.0 | % | |||||||||
Senior housing | 1,142,000 | 13.6 | % | 1,214,000 | 13.5 | % | 598,000 | 11.0 | % | ||||||||||||
Skilled nursing facilities | 556,000 | 4.8 | % | 351,000 | 8.2 | % | — | — | % | ||||||||||||
Total rental expenses | $ | 19,226,000 | 25.8 | % | $ | 11,499,000 | 24.2 | % | $ | 7,292,000 | 26.3 | % | |||||||||
Property Operating Expenses | |||||||||||||||||||||
Senior housing — RIDEA | $ | 37,434,000 | 81.1 | % | $ | 30,023,000 | 81.5 | % | $ | 4,203,000 | 75.6 | % | |||||||||
Total property operating expenses | $ | 37,434,000 | 81.1 | % | $ | 30,023,000 | 81.5 | % | $ | 4,203,000 | 75.6 | % | |||||||||
Senior housing — RIDEA facilities typically have a higher percentage of direct operating expenses to revenue than medical office buildings, senior housing facilities and skilled nursing facilities due to the nature of RIDEA facilities where we conduct day-to-day operations.
General and Administrative
General and administrative expenses consisted of the following for the periods then ended:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Asset management fees — affiliates | $ | 8,276,000 | $ | 4,975,000 | $ | 2,344,000 | |||||
Professional and legal fees | 3,664,000 | 1,436,000 | 878,000 | ||||||||
Bad debt expense, net | 1,482,000 | 1,274,000 | 83,000 | ||||||||
Transfer agent services | 524,000 | 362,000 | 213,000 | ||||||||
Bank charges | 268,000 | 240,000 | 39,000 | ||||||||
Board of directors fees | 255,000 | 253,000 | 216,000 | ||||||||
Directors’ and officers’ liability insurance | 244,000 | 212,000 | 213,000 | ||||||||
Restricted stock compensation | 207,000 | 185,000 | 131,000 | ||||||||
Franchise taxes | 129,000 | 100,000 | 146,000 | ||||||||
Other | 186,000 | 135,000 | 75,000 | ||||||||
Total | $ | 15,235,000 | $ | 9,172,000 | $ | 4,338,000 | |||||
72
The increase in general and administrative expenses in 2019 as compared to 2018 was primarily due to the purchase of additional properties in 2018 and 2019 and thus incurring higher asset management fees to our advisor or its affiliates and higher professional and legal fees. General and administrative expenses increased by $1,731,000 for the year ended December 31, 2019 in connection with transitioning the operations of two senior housing facilities within Lafayette Assisted Living Portfolio and Northern California Senior Housing Portfolio to a RIDEA structure. The increase in general and administrative expenses in 2018 as compared to 2017 was primarily due to the purchase of additional properties in 2017 and 2018 and thus incurring higher asset management fees to our advisor or its affiliates and higher professional and legal fees. In addition, we incurred higher transfer agent service fees for 2018 as compared to 2017, due to an increase in the number of investors in connection with the increased equity raise pursuant to our offering throughout 2017 and 2018. We expect general and administrative expenses to continue to increase in 2020 as we acquire additional properties and complete the transition of operations of our above mentioned facilities to a RIDEA structure.
Acquisition Related Expenses
For the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2017, acquisition related expenses were $1,974,000 and $655,000, respectively, which primarily related to costs incurred in pursuit of properties that did not result in an acquisition. For the year ended December 31, 2018, acquisition related expenses were $2,795,000, which were related primarily to the acquisition fee paid upon the purchase of 6.0% of the total membership interests in Trilogy REIT Holdings, LLC on October 1, 2018, as well as expenses incurred in pursuit of properties that did not result in an acquisition.
Depreciation and Amortization
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, depreciation and amortization was $45,626,000, $32,658,000 and $13,639,000, respectively, and consisted primarily of depreciation on our operating properties of $27,435,000, $16,723,000 and $8,137,000, respectively, and amortization on our identified intangible assets of $18,074,000, $15,874,000 and $5,493,000, respectively. Included during the year ended December 31, 2019 is $6,226,000 of amortization expense and $1,013,000 of depreciation expense related to the write-off of lease commissions and tenant improvements, respectively, in connection with the termination of a management services agreement with an operator in February 2019.
Interest Expense
Interest expense, including gain or loss in fair value of derivative financial instruments, consisted of the following for the periods then ended:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Interest expense: | |||||||||||
Line of credit and term loans and derivative financial instruments | $ | 13,014,000 | $ | 4,984,000 | $ | 1,819,000 | |||||
Mortgage loans payable | 1,030,000 | 715,000 | 413,000 | ||||||||
Amortization of deferred financing costs: | |||||||||||
Line of credit and term loans | 2,028,000 | 1,000,000 | 442,000 | ||||||||
Mortgage loans payable | 78,000 | 76,000 | 38,000 | ||||||||
Loss in fair value of derivative financial instruments | 4,385,000 | — | — | ||||||||
Amortization of debt discount/premium | 41,000 | 13,000 | (13,000 | ) | |||||||
Total | $ | 20,576,000 | $ | 6,788,000 | $ | 2,699,000 | |||||
The increase in interest expense in 2019 as compared to 2018 and 2017 was primarily related to the increase in debt balances on our line of credit and term loans, as well as interest expense and loss in fair value recognized on our derivative financial instruments we entered into in February 2019. See Note 6, Mortgage Loans Payable, Net, Note 7, Line of Credit and Term Loans and Note 8, Derivative Financial Instruments, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for a further discussion.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Our sources of funds primarily consist of operating cash flows and borrowings. In the normal course of business, our principal demands for funds are for acquisitions of real estate, payment of operating expenses, capital improvement expenditures, interest on our indebtedness and distributions to our stockholders.
Our total capacity to pay operating expenses, capital improvement expenditures, interest and distributions and acquire real estate and real estate-related investments is a function of our current cash position, our borrowing capacity on our line of
73
credit, as well as any future indebtedness that we may incur. As of December 31, 2019, our cash on hand was $15,290,000 and we had $133,200,000 available on our line of credit and term loans. We believe that these resources will be sufficient to satisfy our cash requirements for the foreseeable future, and we do not anticipate a need to raise funds from other sources within the next 12 months.
We estimate that we will require approximately $14,864,000 to pay interest on our outstanding indebtedness in 2020, based on interest rates in effect as of December 31, 2019, and that we will require $8,317,000 to pay down principal on our outstanding indebtedness in 2020. We also require resources to make certain payments to our advisor and its affiliates. See Note 13, Related Party Transactions, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for a further discussion of our payments to our advisor and its affiliates. Generally, cash needs for such items will be met from operations and borrowings.
Our advisor evaluates potential investments and engages in negotiations with real estate sellers, developers, brokers, investment managers, lenders and others on our behalf. When we acquire a property, our advisor prepares a capital plan that contemplates the estimated capital needs of that investment. In addition to operating expenses, capital needs may also include costs of refurbishment, tenant improvements or other major capital expenditures. The capital plan will also set forth the anticipated sources of the necessary capital, which may include a line of credit or other loan established with respect to the investment, other borrowings, operating cash generated by the investment, additional equity investments from us or joint venture partners or, when necessary, capital reserves. In some cases, a lender may require us to establish capital reserves for a particular investment. The capital plan for each investment will be adjusted through ongoing, regular reviews of our portfolio or as necessary to respond to unanticipated additional capital needs.
Based on the budget for the properties we own as of December 31, 2019, we estimate that our discretionary expenditures for capital and tenant improvements could require up to $13,009,000 within the next 12 months. As of December 31, 2019, we had $358,000 of restricted cash in reserve accounts to fund a portion of such capital expenditures. We cannot provide assurance, however, that we will not exceed these estimated expenditures or be able to obtain additional sources of financing on commercially favorable terms or at all.
Other Liquidity Needs
In the event that there is a shortfall in net cash available due to various factors, including, without limitation, the timing of distributions or the timing of the collection of receivables, we may seek to obtain capital to pay distributions by means of secured or unsecured debt financing through one or more third parties, or our advisor or its affiliates. There are currently no limits or restrictions on the use of proceeds from our advisor or its affiliates which would prohibit us from making the proceeds available for distribution. We may also pay distributions from cash from capital transactions, including, without limitation, the sale of one or more of our properties.
In addition, we are continuing to monitor the outbreak of the coronavirus and its impact on residents in our senior housing and skilled nursing facilities, our tenants, operating partners and the healthcare industry as a whole. The magnitude and duration of the pandemic and its impact on our operations and liquidity is uncertain as of the filing date of our report as this continues to evolve globally. However, if the outbreak continues on its current trajectory, such impacts could grow and become material. To the extent that our residents, tenants and operating partners continue to be impacted by the coronavirus outbreak, or by the other risks disclosed in our report, this could materially disrupt our business operations.
Cash Flows
The following table sets forth changes in cash flows:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash — beginning of period | $ | 14,590,000 | $ | 7,103,000 | $ | 2,237,000 | |||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 39,540,000 | 15,423,000 | 12,404,000 | ||||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (199,934,000 | ) | (411,554,000 | ) | (330,688,000 | ) | |||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | 161,650,000 | 403,618,000 | 323,150,000 | ||||||||
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash — end of period | $ | 15,846,000 | $ | 14,590,000 | $ | 7,103,000 | |||||
The following summary discussion of our changes in our cash flows is based on our consolidated statements of cash flows appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is not meant to be an all-inclusive discussion of the changes in our cash flows for the periods presented below.
74
Operating Activities
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, cash flows provided by operating activities primarily related to the cash flows provided by our property operations, offset by payments of general and administrative expenses. See the “Results of Operations” section above for a further discussion. We anticipate cash flows from operating activities to increase in 2020 as we recognize a full year of operations for the properties acquired during 2019 and purchase additional real estate investments in the first quarter of 2020.
Investing Activities
For the year ended December 31, 2019, cash flows used in investing activities related primarily to our 2019 property acquisitions in the amount of $195,249,000 and the payment of $6,497,000 for capital expenditures. For the year ended December 31, 2018, cash flows used in investing activities related primarily to our 2018 acquisitions in the amount of $355,070,000, our investment in an unconsolidated entity for $48,000,000 and the payment of $4,257,000 for capital expenditures. For the year ended December 31, 2017, cash flows used in investing activities related primarily to our 2017 acquisitions in the amount of $328,933,000 and the payment of $1,121,000 for capital expenditures. We generally anticipate that cash flows used in investing activities will decrease due to fewer anticipated acquisitions as a result of the termination of our initial offering in February 2019.
Financing Activities
For the year ended December 31, 2019, cash flows provided by financing activities related primarily to net borrowings on our line of credit and term loans of $121,800,000 as well as funds raised from investors in our initial offering in the amount of $90,438,000, partially offset by $20,905,000 in distributions to our common stockholders, the payment of offering costs of$19,136,000 in connection with our initial offering and 2019 DRIP Offering and $8,609,000 in share repurchases. For the year ended December 31, 2018, cash flows provided by financing activities related primarily to funds raised from investors in our initial offering in the amount of $254,017,000 and net borrowings on our line of credit and term loans of $190,900,000, partially offset by the payment of offering costs of $19,817,000 in connection with our initial offering, distributions to our common stockholders of $13,989,000, the payment of deferred financing costs of $4,092,000 in connection with our line of credit and term loans and mortgage loans payable and $3,312,000 in repurchases of common stock. For the year ended December 31, 2017, cash flows provided by financing activities related primarily to funds raised from investors in our initial offering in the amount of $298,639,000 and net borrowings on our line of credit and term loans of $50,200,000, partially offset by the payment of offering costs of $18,072,000 in connection with our initial offering, distributions to our common stockholders of $6,398,000 and the payment of deferred financing costs of $1,115,000 in connection with our line of credit and term loans and mortgage loans payable.
Distributions
The income tax treatment for distributions reportable for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 was as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||
Ordinary income | $ | 10,099,000 | 21.8 | % | $ | 11,909,000 | 37.7 | % | $ | 6,021,000 | 39.9 | % | ||||||||
Capital gain | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Return of capital | 36,317,000 | 78.2 | 19,673,000 | 62.3 | 9,055,000 | 60.1 | ||||||||||||||
$ | 46,416,000 | 100 | % | $ | 31,582,000 | 100 | % | $ | 15,076,000 | 100 | % | |||||||||
Amounts listed above do not include distributions paid on nonvested shares of our restricted common stock, which have been separately reported.
See Item 5, Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities — Distributions, for a further discussion of our distributions.
75
Financing
We intend to continue to finance all or a portion of the purchase price of our investments in real estate by borrowing funds. We anticipate that our overall leverage will not exceed 50.0% of the combined market value of all of our properties and other real estate-related investments, as determined at the end of each calendar year. For these purposes, the fair market value of each asset will be equal to the purchase price paid for the asset or, if the asset was appraised subsequent to the date of purchase, then the fair market value will be equal to the value reported in the most recent independent appraisal of the asset. Our policies do not limit the amount we may borrow with respect to any individual investment. As of December 31, 2019, our aggregate borrowings were 36.3% of the combined market value of all of our real estate investments.
Under our charter, we have a limitation on borrowing that precludes us from borrowing in excess of 300% of our net assets without the approval of a majority of our independent directors. Net assets for purposes of this calculation are defined to be our total assets (other than intangibles), valued at cost prior to deducting depreciation, amortization, bad debt and other non-cash reserves, less total liabilities. Generally, the preceding calculation is expected to approximate 75.0% of the aggregate cost of our real estate and real estate-related investments before depreciation, amortization, bad debt and other similar non-cash reserves. In addition, we may incur mortgage debt and pledge some or all of our real properties as security for that debt to obtain funds to acquire additional real estate or for working capital. We may also borrow funds to satisfy the REIT tax qualification requirement that we distribute at least 90.0% of our annual taxable income, excluding net capital gains, to our stockholders. Furthermore, we may borrow if we otherwise deem it necessary or advisable to ensure that we maintain our qualification as a REIT for federal income tax purposes. As of March 19, 2020 and December 31, 2019, our leverage did not exceed 300% of the value of our net assets.
Mortgage Loans Payable, Net
For a discussion of our mortgage loans payable, net, see Note 6, Mortgage Loans Payable, Net, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Line of Credit and Term Loans
For a discussion of our line of credit and term loans, see Note 7, Line of Credit and Term Loans, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
REIT Requirements
In order to maintain our qualification as a REIT for federal income tax purposes, we are required to make distributions to our stockholders of at least 90.0% of our annual taxable income, excluding net capital gains. In the event that there is a shortfall in net cash available due to factors including, without limitation, the timing of such distributions or the timing of the collection of receivables, we may seek to obtain capital to pay distributions by means of secured and unsecured debt financing through one or more unaffiliated third parties. We may also pay distributions from cash from capital transactions including, without limitation, the sale of one or more of our properties.
Commitments and Contingencies
For a discussion of our commitments and contingencies, see Note 10, Commitments and Contingencies, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Debt Service Requirements
A significant liquidity need is the payment of principal and interest on our outstanding indebtedness. As of December 31, 2019, we had $27,099,000 ($26,070,000, net of discount/premium and deferred financing costs) of fixed-rate mortgage loans payable outstanding secured by four of our properties. As of December 31, 2019, we had $396,800,000 outstanding, and $133,200,000 remained available under our line of credit and term loans. See Note 6, Mortgage Loans Payable, Net, and Note 7, Line of Credit and Term Loans, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
We are required by the terms of certain loan documents to meet certain covenants, such as leverage ratios, net worth ratios, debt service coverage ratios, fixed charge coverage ratios and reporting requirements. As of December 31, 2019, we were in compliance with all such covenants and requirements on our mortgage loans payable and our line of credit and term loans. As of December 31, 2019, the weighted average effective interest rate on our outstanding debt, factoring in our fixed-rate interest rate swaps, was 4.00% per annum.
76
Contractual Obligations
The following table provides information with respect to: (i) the maturity and scheduled principal repayment of our secured mortgage loans payable and our line of credit and term loans; (ii) interest payments on our mortgage loans payable and our line of credit and term loans; and (iii) ground lease obligations as of December 31, 2019:
Payments Due by Period | |||||||||||||||||||
2020 | 2021-2022 | 2023-2024 | Thereafter | Total | |||||||||||||||
Principal payments — fixed-rate debt | $ | 8,317,000 | $ | 1,273,000 | $ | 1,392,000 | $ | 16,117,000 | $ | 27,099,000 | |||||||||
Interest payments — fixed-rate debt | 757,000 | 1,429,000 | 1,309,000 | 5,443,000 | 8,938,000 | ||||||||||||||
Principal payments — variable-rate debt | — | 396,800,000 | — | — | 396,800,000 | ||||||||||||||
Interest payments — variable-rate debt (based on rates in effect as of December 31, 2019) | 14,107,000 | 12,912,000 | — | — | 27,019,000 | ||||||||||||||
Ground lease obligations | 519,000 | 1,049,000 | 1,064,000 | 47,103,000 | 49,735,000 | ||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 23,700,000 | $ | 413,463,000 | $ | 3,765,000 | $ | 68,663,000 | $ | 509,591,000 | |||||||||
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of December 31, 2019, we had no off-balance sheet transactions, nor do we currently have any such arrangements or obligations.
Inflation
During the year ended December 31, 2019, inflation has not significantly affected our operations because of the moderate inflation rate; however, we expect to be exposed to inflation risk as income from future long-term leases will be the primary source of our cash flows from operations. There are provisions in the majority of our tenant leases that will protect us from the impact of inflation. These provisions include negotiated rental increases, reimbursement billings for operating expense pass-through charges, and real estate tax and insurance reimbursements. However, due to the long-term nature of the anticipated leases, among other factors, the leases may not re-set frequently enough to cover inflation.
Related Party Transactions
For a discussion of related party transactions, see Note 13, Related Party Transactions, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Subsequent Events
For a discussion of subsequent events, see Note 21, Subsequent Events, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
Market risk includes risks that arise from changes in interest rates, commodity prices, equity prices and other market changes that affect market sensitive instruments. In pursuing our business plan, we expect that the primary market risk to which we will be exposed is interest rate risk. There were no material changes in our market risk exposures between the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017.
Interest Rate Risk
We are exposed to the effects of interest rate changes primarily as a result of long-term debt used to acquire properties and make loans and other permitted investments. Our interest rate risk is monitored using a variety of techniques. Our interest rate risk management objectives are to limit the impact of interest rate changes on earnings, prepayment penalties and cash flows and to lower overall borrowing costs while taking into account variable interest rate risk. To achieve our objectives, we may borrow at fixed or variable rates.
We have entered into and may continue to enter into derivative financial instruments such as interest rate swaps in order to mitigate our interest rate risk on a related financial instrument. We do not apply hedge accounting treatment to these derivatives, therefore changes in the fair value of interest rate derivative financial instruments are recorded as a component of interest expense in gain or loss in fair value of derivative financial instruments in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations. As of December 31, 2019, our interest rate swap liabilities are recorded in our accompanying consolidated balance
77
sheets at their aggregate fair value of $4,385,000. We will not enter into derivatives or interest rate transactions for speculative purposes.
As of December 31, 2019, the table below presents the principal amounts and weighted average interest rates by year of expected maturity to evaluate the expected cash flows and sensitivity to interest rate changes.
Expected Maturity Date | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | Thereafter | Total | Fair Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fixed-rate debt — principal payments | $ | 8,317,000 | $ | 622,000 | $ | 651,000 | $ | 681,000 | $ | 711,000 | $ | 16,117,000 | $ | 27,099,000 | $ | 26,677,000 | |||||||||||||||
Weighted average interest rate on maturing fixed-rate debt | 4.75 | % | 4.48 | % | 4.49 | % | 4.49 | % | 4.50 | % | 3.84 | % | 4.18 | % | — | ||||||||||||||||
Variable-rate debt — principal payments | $ | — | $ | 396,800,000 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 396,800,000 | $ | 396,891,000 | |||||||||||||||
Weighted average interest rate on maturing variable-rate debt (based on rates in effect as of December 31, 2019) | — | % | 3.50 | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | 3.50 | % | — | ||||||||||||||||
Mortgage Loans Payable, Net and Line of Credit and Term Loans
Mortgage loans payable was $27,099,000 ($26,070,000, net of discount/premium and deferred financing costs) as of December 31, 2019. As of December 31, 2019, we had four fixed-rate mortgage loans payable with interest rates ranging from 3.67% to 5.25% per annum. In addition, as of December 31, 2019, we had $396,800,000 outstanding under our line of credit and term loans at a weighted-average interest rate of 3.50% per annum.
As of December 31, 2019, the weighted average effective interest rate on our outstanding debt, factoring in our fixed-rate interest rate swaps, was 4.00% per annum. An increase in the variable interest rate on our variable-rate line of credit and term loans constitutes a market risk. As of December 31, 2019, a 0.50% increase in the market rates of interest would have increased our overall annualized interest expense on our variable-rate line of credit and term loans by $744,000, or 5.30% of total annualized interest expense on our mortgage loans payable and our line of credit and term loans. See Note 6, Mortgage Loans Payable, Net, and Note 7, Line of Credit and Term Loans, to the Consolidated Financial Statements that are a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for a further discussion.
Other Market Risk
In addition to changes in interest rates, the value of our future investments is subject to fluctuations based on changes in local and regional economic conditions and changes in the creditworthiness of tenants, which may affect our ability to refinance our debt if necessary.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
See the index at Part IV, Item 15, Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures.
(a) Evaluation of disclosure controls and procedures. We maintain disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our reports under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to us, including our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating the disclosure controls and procedures, we recognize that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives, as ours are designed to do, and we necessarily were required to apply our judgment in evaluating whether the benefits of the controls and procedures that we adopt outweigh their costs.
78
As required by Rules 13a-15(b) and 15d-15(b) of the Exchange Act, an evaluation as of December 31, 2019 was conducted under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act). Based on this evaluation, our chief executive officer and chief financial officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures, as of December 31, 2019, were effective at the reasonable assurance level.
(b) Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over our financial reporting, as such term is defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f). Under the supervision, and with the participation, of our management, including our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued in 2013 by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
Based on our evaluation under the Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued in 2013, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2019.
(c) Changes in internal control over financial reporting. There were no changes in internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the fiscal quarter ended December 31, 2019 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information.
None.
79
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to our definitive proxy statement to be filed with respect to our 2020 annual meeting of stockholders.
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to our definitive proxy statement to be filed with respect to our 2020 annual meeting of stockholders.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to our definitive proxy statement to be filed with respect to our 2020 annual meeting of stockholders.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to our definitive proxy statement to be filed with respect to our 2020 annual meeting of stockholders.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services.
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to our definitive proxy statement to be filed with respect to our 2020 annual meeting of stockholders.
80
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.
(a)(1) Financial Statements:
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Page | |
(a)(2) Financial Statement Schedule:
The following financial statement schedule for the year ended December 31, 2019 is submitted herewith:
All schedules other than the one listed above have been omitted as the required information is inapplicable or the information is presented in our consolidated financial statements or related notes.
(a)(3) Exhibits:
(b) Exhibits:
See Item 15(a)(3) above.
(c) Financial Statement Schedule:
See Item 15(a)(2) above.
81
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of operations, equity and cash flows, for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes and the schedule listed in the Index at Item 15 (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Change in Accounting Principle
As discussed in Note 2 to the financial statements, effective January 1, 2019, the Company adopted FASB ASC Topic 842, Leases, using the modified retrospective approach.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Costa Mesa, California
March 19, 2020
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2015.
82
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018
December 31, | |||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||
ASSETS | |||||||
Real estate investments, net | $ | 895,060,000 | $ | 731,676,000 | |||
Cash and cash equivalents | 15,290,000 | 14,388,000 | |||||
Accounts and other receivables, net | 4,608,000 | 11,249,000 | |||||
Restricted cash | 556,000 | 202,000 | |||||
Real estate deposits | 1,915,000 | 3,900,000 | |||||
Identified intangible assets, net | 74,023,000 | 74,723,000 | |||||
Operating lease right-of-use assets, net | 14,255,000 | — | |||||
Other assets, net | 62,620,000 | 60,234,000 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 1,068,327,000 | $ | 896,372,000 | |||
LIABILITIES, REDEEMABLE NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||
Liabilities: | |||||||
Mortgage loans payable, net(1) | $ | 26,070,000 | $ | 16,892,000 | |||
Line of credit and term loans(1) | 396,800,000 | 275,000,000 | |||||
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities(1) | 32,033,000 | 32,395,000 | |||||
Accounts payable due to affiliates(1) | 1,016,000 | 8,588,000 | |||||
Identified intangible liabilities, net | 1,601,000 | 1,627,000 | |||||
Operating lease liabilities(1) | 9,858,000 | — | |||||
Security deposits, prepaid rent and other liabilities(1) | 9,408,000 | 2,827,000 | |||||
Total liabilities | 476,786,000 | 337,329,000 | |||||
Commitments and contingencies (Note 10) | |||||||
Redeemable noncontrolling interests (Note 11) | 1,462,000 | 1,371,000 | |||||
Stockholders’ equity: | |||||||
Preferred stock, $0.01 par value per share; 200,000,000 shares authorized; none issued and outstanding | — | — | |||||
Class T common stock, $0.01 par value per share; 900,000,000 shares authorized; 74,244,823 and 64,996,843 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively | 742,000 | 650,000 | |||||
Class I common stock, $0.01 par value per share; 100,000,000 shares authorized; 5,655,051 and 4,258,128 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively | 56,000 | 42,000 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 719,894,000 | 621,759,000 | |||||
Accumulated deficit | (130,613,000 | ) | (64,779,000 | ) | |||
Total stockholders’ equity | 590,079,000 | 557,672,000 | |||||
Total liabilities, redeemable noncontrolling interests and stockholders’ equity | $ | 1,068,327,000 | $ | 896,372,000 | |||
83
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS — (Continued)
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018
___________
(1) | Such liabilities of Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 represented liabilities of Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Holdings, LP or its consolidated subsidiaries. Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Holdings, LP is a variable interest entity, or VIE, and a consolidated subsidiary of Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. The creditors of Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Holdings, LP or its consolidated subsidiaries do not have recourse against Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc., except for the 2018 Credit Facility, as defined in Note 7, held by Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Holdings, LP in the amount of $396,800,000 and $275,000,000 as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, which is guaranteed by Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
84
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
Revenues: | |||||||||||
Real estate revenue | $ | 74,610,000 | $ | 47,599,000 | $ | 27,770,000 | |||||
Resident fees and services | 46,160,000 | 36,857,000 | 5,563,000 | ||||||||
Total revenues | 120,770,000 | 84,456,000 | 33,333,000 | ||||||||
Expenses: | |||||||||||
Rental expenses | 19,226,000 | 11,499,000 | 7,292,000 | ||||||||
Property operating expenses | 37,434,000 | 30,023,000 | 4,203,000 | ||||||||
General and administrative | 15,235,000 | 9,172,000 | 4,338,000 | ||||||||
Acquisition related expenses | 1,974,000 | 2,795,000 | 655,000 | ||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 45,626,000 | 32,658,000 | 13,639,000 | ||||||||
Total expenses | 119,495,000 | 86,147,000 | 30,127,000 | ||||||||
Other income (expense): | |||||||||||
Interest expense: | |||||||||||
Interest expense (including amortization of deferred financing costs and debt discount/premium) | (16,191,000 | ) | (6,788,000 | ) | (2,699,000 | ) | |||||
Loss in fair value of derivative financial instruments | (4,385,000 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Income (loss) from unconsolidated entity | 267,000 | (110,000 | ) | — | |||||||
Other income | 175,000 | 11,000 | 1,000 | ||||||||
(Loss) income before income taxes | (18,859,000 | ) | (8,578,000 | ) | 508,000 | ||||||
Income tax benefit (expense) | 8,000 | (8,000 | ) | — | |||||||
Net (loss) income | (18,851,000 | ) | (8,586,000 | ) | 508,000 | ||||||
Less: net loss attributable to redeemable noncontrolling interests | 82,000 | 232,000 | 33,000 | ||||||||
Net (loss) income attributable to controlling interest | $ | (18,769,000 | ) | $ | (8,354,000 | ) | $ | 541,000 | |||
Net (loss) income per Class T and Class I common share attributable to controlling interest — basic and diluted | $ | (0.24 | ) | $ | (0.15 | ) | $ | 0.02 | |||
Weighted average number of Class T and Class I common shares outstanding — basic and diluted | 78,396,077 | 54,847,197 | 27,754,701 | ||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
85
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EQUITY
For the Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
Stockholders’ Equity | |||||||||||||||||||
Class T and Class I Common Stock | |||||||||||||||||||
Number of Shares | Amount | Additional Paid-In Capital | Accumulated Deficit | Total Stockholders’ Equity | |||||||||||||||
BALANCE — December 31, 2016 | 11,377,439 | $ | 114,000 | $ | 99,492,000 | $ | (7,351,000 | ) | $ | 92,255,000 | |||||||||
Issuance of common stock | 29,960,609 | 300,000 | 297,776,000 | — | 298,076,000 | ||||||||||||||
Offering costs — common stock | — | — | (29,028,000 | ) | — | (29,028,000 | ) | ||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under the DRIP | 924,358 | 9,000 | 8,680,000 | — | 8,689,000 | ||||||||||||||
Issuance of vested and nonvested restricted common stock | 22,500 | — | 45,000 | — | 45,000 | ||||||||||||||
Amortization of nonvested common stock compensation | — | — | 86,000 | — | 86,000 | ||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock | (77,746 | ) | (1,000 | ) | (734,000 | ) | — | (735,000 | ) | ||||||||||
Fair value adjustment to redeemable noncontrolling interests | — | — | (33,000 | ) | — | (33,000 | ) | ||||||||||||
Distributions declared ($0.60 per share) | — | — | — | (16,672,000 | ) | (16,672,000 | ) | ||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 541,000 | 541,000 | (1) | |||||||||||||
BALANCE — December 31, 2017 | 42,207,160 | $ | 422,000 | $ | 376,284,000 | $ | (23,482,000 | ) | $ | 353,224,000 | |||||||||
Issuance of common stock | 25,537,018 | 256,000 | 254,996,000 | — | 255,252,000 | ||||||||||||||
Offering costs — common stock | — | — | (23,760,000 | ) | — | (23,760,000 | ) | ||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under the DRIP | 1,838,711 | 18,000 | 17,594,000 | — | 17,612,000 | ||||||||||||||
Issuance of vested and nonvested restricted common stock | 22,500 | — | 45,000 | — | 45,000 | ||||||||||||||
Amortization of nonvested common stock compensation | — | — | 140,000 | — | 140,000 | ||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock | (350,418 | ) | (4,000 | ) | (3,308,000 | ) | — | (3,312,000 | ) | ||||||||||
Fair value adjustment to redeemable noncontrolling interests | — | — | (232,000 | ) | — | (232,000 | ) | ||||||||||||
Distributions declared ($0.60 per share) | — | — | — | (32,943,000 | ) | (32,943,000 | ) | ||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | (8,354,000 | ) | (8,354,000 | ) | (1) | |||||||||||
BALANCE — December 31, 2018 | 69,254,971 | $ | 692,000 | $ | 621,759,000 | $ | (64,779,000 | ) | $ | 557,672,000 | |||||||||
Issuance of common stock | 8,884,165 | 89,000 | 88,626,000 | — | 88,715,000 | ||||||||||||||
Offering costs — common stock | — | — | (7,432,000 | ) | — | (7,432,000 | ) | ||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under the DRIP | 2,666,913 | 26,000 | 25,507,000 | — | 25,533,000 | ||||||||||||||
Issuance of vested and nonvested restricted common stock | 22,500 | — | 43,000 | — | 43,000 | ||||||||||||||
Amortization of nonvested common stock compensation | — | — | 164,000 | — | 164,000 | ||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock | (928,675 | ) | (9,000 | ) | (8,600,000 | ) | — | (8,609,000 | ) | ||||||||||
Fair value adjustment to redeemable noncontrolling interests | — | — | (173,000 | ) | — | (173,000 | ) | ||||||||||||
Distributions declared ($0.60 per share) | — | — | — | (47,065,000 | ) | (47,065,000 | ) | ||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | (18,769,000 | ) | (18,769,000 | ) | (1) | |||||||||||
BALANCE — December 31, 2019 | 79,899,874 | $ | 798,000 | $ | 719,894,000 | $ | (130,613,000 | ) | $ | 590,079,000 | |||||||||
___________
(1) | Amount excludes $82,000, $232,000 and $33,000 for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively, of net loss attributable to redeemable noncontrolling interests. See Note 11, Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests, for a further discussion. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
86
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | |||||||||||
Net (loss) income | $ | (18,851,000 | ) | $ | (8,586,000 | ) | $ | 508,000 | |||
Adjustments to reconcile net (loss) income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 45,626,000 | 32,658,000 | 13,639,000 | ||||||||
Other amortization | 3,251,000 | 1,015,000 | 415,000 | ||||||||
Deferred rent | (3,076,000 | ) | (3,029,000 | ) | (1,705,000 | ) | |||||
Stock based compensation | 207,000 | 185,000 | 131,000 | ||||||||
(Income) loss from unconsolidated entity | (267,000 | ) | 110,000 | — | |||||||
Distributions of earnings from unconsolidated entity | 157,000 | — | — | ||||||||
Bad debt expense | 1,482,000 | 1,274,000 | 83,000 | ||||||||
Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments | 4,385,000 | — | — | ||||||||
Share discounts | — | — | 3,000 | ||||||||
Deferred income taxes | (8,000 | ) | 8,000 | — | |||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||
Accounts and other receivables | 3,489,000 | (7,413,000 | ) | (2,166,000 | ) | ||||||
Other assets | (113,000 | ) | (336,000 | ) | (905,000 | ) | |||||
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 2,999,000 | 224,000 | 2,436,000 | ||||||||
Accounts payable due to affiliates | 224,000 | 338,000 | 239,000 | ||||||||
Security deposits, prepaid rent, operating lease and other liabilities | 35,000 | (1,025,000 | ) | (274,000 | ) | ||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 39,540,000 | 15,423,000 | 12,404,000 | ||||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES | |||||||||||
Acquisitions of real estate investments | (195,249,000 | ) | (355,070,000 | ) | (328,933,000 | ) | |||||
Investment in unconsolidated entity | (600,000 | ) | (48,000,000 | ) | — | ||||||
Distributions in excess of earnings from unconsolidated entity | 1,294,000 | 290,000 | — | ||||||||
Capital expenditures | (6,497,000 | ) | (4,257,000 | ) | (1,121,000 | ) | |||||
Real estate deposits | 1,385,000 | (3,400,000 | ) | (300,000 | ) | ||||||
Pre-acquisition expenses | (267,000 | ) | (1,117,000 | ) | (334,000 | ) | |||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (199,934,000 | ) | (411,554,000 | ) | (330,688,000 | ) | |||||
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES | |||||||||||
Payments on mortgage loans payable | (650,000 | ) | (449,000 | ) | (273,000 | ) | |||||
Borrowings under the line of credit and term loans | 257,900,000 | 771,200,000 | 308,600,000 | ||||||||
Payments on the line of credit and term loans | (136,100,000 | ) | (580,300,000 | ) | (258,400,000 | ) | |||||
Deferred financing costs | (1,192,000 | ) | (4,092,000 | ) | (1,115,000 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from issuance of common stock | 90,438,000 | 254,017,000 | 298,639,000 | ||||||||
Contributions from redeemable noncontrolling interests | 151,000 | 369,000 | 1,000,000 | ||||||||
Distributions to redeemable noncontrolling interests | (151,000 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Repurchase of common stock | (8,609,000 | ) | (3,312,000 | ) | (735,000 | ) | |||||
Payment of offering costs | (19,136,000 | ) | (19,817,000 | ) | (18,072,000 | ) | |||||
Security deposits | (96,000 | ) | (9,000 | ) | (96,000 | ) | |||||
Distributions paid | (20,905,000 | ) | (13,989,000 | ) | (6,398,000 | ) | |||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | 161,650,000 | 403,618,000 | 323,150,000 | ||||||||
NET CHANGE IN CASH, CASH EQUIVALENTS AND RESTRICTED CASH | 1,256,000 | 7,487,000 | 4,866,000 | ||||||||
CASH, CASH EQUIVALENTS AND RESTRICTED CASH — Beginning of period | 14,590,000 | 7,103,000 | 2,237,000 | ||||||||
CASH, CASH EQUIVALENTS AND RESTRICTED CASH — End of period | $ | 15,846,000 | $ | 14,590,000 | $ | 7,103,000 | |||||
87
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS — (Continued)
For the Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
RECONCILIATION OF CASH, CASH EQUIVALENTS AND RESTRICTED CASH | |||||||||||
Beginning of period: | |||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 14,388,000 | $ | 7,087,000 | $ | 2,237,000 | |||||
Restricted cash | 202,000 | 16,000 | — | ||||||||
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | $ | 14,590,000 | $ | 7,103,000 | $ | 2,237,000 | |||||
End of period: | |||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 15,290,000 | $ | 14,388,000 | $ | 7,087,000 | |||||
Restricted cash | 556,000 | 202,000 | 16,000 | ||||||||
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | $ | 15,846,000 | $ | 14,590,000 | $ | 7,103,000 | |||||
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION | |||||||||||
Cash paid for: | |||||||||||
Interest | $ | 13,506,000 | $ | 5,194,000 | $ | 2,052,000 | |||||
Income taxes | $ | 30,000 | $ | 14,000 | $ | 7,000 | |||||
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF NONCASH ACTIVITIES | |||||||||||
Investing Activities: | |||||||||||
Accrued capital expenditures | $ | 2,580,000 | $ | 5,391,000 | $ | 1,355,000 | |||||
Accrued pre-acquisition expenses | $ | 412,000 | $ | 154,000 | $ | 75,000 | |||||
Tenant improvement overage | $ | 195,000 | $ | 692,000 | $ | — | |||||
The following represents the increase in certain assets and liabilities in connection with our acquisitions of real estate investments: | |||||||||||
Right-of-use asset | $ | 3,133,000 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Other assets | $ | 112,000 | $ | 225,000 | $ | 236,000 | |||||
Mortgage loans payable, net | $ | 9,735,000 | $ | 5,808,000 | $ | 8,000,000 | |||||
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | $ | 1,146,000 | $ | 3,415,000 | $ | 1,731,000 | |||||
Operating lease liability | $ | 4,489,000 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Security deposits and prepaid rent | $ | 1,601,000 | $ | 2,193,000 | $ | 728,000 | |||||
Financing Activities: | |||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under the DRIP | $ | 25,533,000 | $ | 17,612,000 | $ | 8,689,000 | |||||
Distributions declared but not paid | $ | 4,086,000 | $ | 3,459,000 | $ | 2,117,000 | |||||
Accrued Contingent Advisor Payment | $ | — | $ | 7,866,000 | $ | 7,744,000 | |||||
Accrued stockholder servicing fee | $ | 12,610,000 | $ | 16,395,000 | $ | 12,611,000 | |||||
Receivable from transfer agent | $ | — | $ | 1,670,000 | $ | 471,000 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
88
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
The use of the words “we,” “us” or “our” refers to Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. and its subsidiaries, including Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Holdings, LP, except where otherwise noted.
1. Organization and Description of Business
Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc., a Maryland corporation, was incorporated on January 23, 2015 and therefore we consider that our date of inception. We were initially capitalized on February 6, 2015. We invest in a diversified portfolio of real estate properties, focusing primarily on medical office buildings, skilled nursing facilities, senior housing and other healthcare-related facilities. We also operate healthcare-related facilities utilizing the structure permitted by the REIT Investment Diversification and Empowerment Act of 2007, which is commonly referred to as a “RIDEA” structure (the provisions of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code, authorizing the RIDEA structure were enacted as part of the Housing and Economic Recovery Act of 2008). We may also originate and acquire secured loans and real estate-related investments on an infrequent and opportunistic basis. We generally seek investments that produce current income. We qualified to be taxed as a real estate investment trust, or REIT, under the Code for federal income tax purposes beginning with our taxable year ended December 31, 2016, and we intend to continue to qualify to be taxed as a REIT.
On February 16, 2016, we commenced our initial public offering, or our initial offering, in which we were initially offering to the public up to $3,150,000,000 in shares of our Class T common stock, consisting of up to $3,000,000,000 in shares of our Class T common stock in the primary portion of our initial offering and up to $150,000,000 in shares of our Class T common stock pursuant to our distribution reinvestment plan, as amended, or the DRIP. Effective June 17, 2016, we reallocated certain of the unsold shares of Class T common stock being offered and began offering shares of Class I common stock, such that we were offering up to approximately $2,800,000,000 in shares of Class T common stock and $200,000,000 in shares of Class I common stock in the primary portion of our initial offering, and up to an aggregate of $150,000,000 in shares of our Class T and Class I common stock pursuant to the DRIP, aggregating up to $3,150,000,000. On February 15, 2019, we terminated our initial offering, and as of such date, we sold 75,639,681 aggregate shares of our Class T and Class I common stock, or approximately $754,118,000, and a total of $31,021,000 in distributions were reinvested that resulted in 3,253,535 shares of our common stock being issued pursuant to the DRIP portion of our initial offering. See Note 12, Equity — Common Stock, for a further discussion.
On January 18, 2019, we filed a Registration Statement on Form S-3 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Act, to register a maximum of $100,000,000 of additional shares of our common stock to be issued pursuant to the DRIP, or the 2019 DRIP Offering. The Registration Statement on Form S-3 was automatically effective with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission, or the SEC, upon its filing. We commenced offering shares pursuant to the 2019 DRIP Offering on March 1, 2019, following the termination of our initial offering on February 15, 2019. See Note 12, Equity — Distribution Reinvestment Plan, for a further discussion. We collectively refer to the DRIP portion of our initial offering and the 2019 DRIP Offering as our DRIP Offerings. As of December 31, 2019, a total of $21,609,000 in distributions were reinvested that resulted in 2,260,164 shares of our common stock being issued pursuant to the 2019 DRIP Offering.
We conduct substantially all of our operations through Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Holdings, LP, or our operating partnership. We are externally advised by Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Advisor, LLC, or our advisor, pursuant to an advisory agreement, or the Advisory Agreement, between us and our advisor. The Advisory Agreement was effective as of February 16, 2016 and had a one-year initial term, subject to successive one-year renewals upon the mutual consent of the parties. The Advisory Agreement was last renewed pursuant to the mutual consent of the parties on February 12, 2020 and expires on February 16, 2021. Our advisor uses its best efforts, subject to the oversight and review of our board of directors, or our board, to, among other things, research, identify, review and make investments in and dispositions of properties and securities on our behalf consistent with our investment policies and objectives. Our advisor performs its duties and responsibilities under the Advisory Agreement as our fiduciary. Our advisor is 75.0% owned and managed by wholly owned subsidiaries of American Healthcare Investors, LLC, or American Healthcare Investors, and 25.0% owned by a wholly owned subsidiary of Griffin Capital Company, LLC, or Griffin Capital, or collectively, our co-sponsors. American Healthcare Investors is 47.1% owned by AHI Group Holdings, LLC, or AHI Group Holdings, 45.1% indirectly owned by Colony Capital, Inc. (NYSE: CLNY), or Colony Capital, and 7.8% owned by James F. Flaherty III, a former partner of Colony Capital. We are not affiliated with Griffin Capital, Griffin Capital Securities, LLC, or our dealer manager, Colony Capital or Mr. Flaherty; however, we are affiliated with Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV Advisor, LLC, American Healthcare Investors and AHI Group Holdings.
89
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
We currently operate through four reportable business segments: medical office buildings, senior housing, senior housing — RIDEA and skilled nursing facilities. As of December 31, 2019, we had completed 43 property acquisitions whereby we owned 82 properties, comprising 87 buildings, or approximately 4,522,000 square feet of gross leasable area, or GLA, for an aggregate contract purchase price of $1,022,889,000. As of December 31, 2019, we also own a 6.0% interest in a joint venture which owns a portfolio of integrated senior health campuses and ancillary businesses.
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
The summary of significant accounting policies presented below is designed to assist in understanding our accompanying consolidated financial statements. Such consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes thereto are the representations of our management, who are responsible for their integrity and objectivity. These accounting policies conform to accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, or GAAP, in all material respects, and have been consistently applied in preparing our accompanying consolidated financial statements.
Basis of Presentation
Our accompanying consolidated financial statements include our accounts and those of our operating partnership and the wholly owned subsidiaries of our operating partnership, as well as any VIEs in which we are the primary beneficiary. We evaluate our ability to control an entity, and whether the entity is a VIE and we are the primary beneficiary, by considering substantive terms of the arrangement and identifying which enterprise has the power to direct the activities of the entity that most significantly impacts the entity’s economic performance.
We operate and intend to continue to operate in an umbrella partnership REIT structure in which our operating partnership, or wholly owned subsidiaries of our operating partnership, will own substantially all of the interests in properties acquired on our behalf. We are the sole general partner of our operating partnership, and as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we owned greater than a 99.99% general partnership interest therein. Our advisor is a limited partner, and as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, owned less than a 0.01% noncontrolling limited partnership interest in our operating partnership.
Because we are the sole general partner of our operating partnership and have unilateral control over its management and major operating decisions (even if additional limited partners are admitted to our operating partnership), the accounts of our operating partnership are consolidated in our accompanying consolidated financial statements. All intercompany accounts and transactions are eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of our accompanying consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, as well as the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, at the date of our consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Significant items subject to such estimates and assumptions include, but are not limited to, the initial and recurring valuation of certain assets acquired and liabilities assumed through property acquisitions, allowance for uncollectible accounts, impairment of long-lived assets and contingencies. These estimates are made and evaluated on an on-going basis using information that is currently available as well as various other assumptions believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results could differ from those estimates, perhaps in material adverse ways, and those estimates could be different under different assumptions or conditions.
Cash, Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash
Cash and cash equivalents consist of all highly liquid investments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased. Restricted cash primarily comprises lender required accounts for property taxes, tenant improvements, capital improvements and insurance, which are restricted as to use or withdrawal.
Leases
On January 1, 2019, we adopted Financial Accounting Standards Board, or FASB, Accounting Standards Codification, or ASC, Topic 842, Leases, or ASC Topic 842. ASC Topic 842 supersedes ASC Topic 840, Leases, or ASC Topic 840. We adopted ASC Topic 842 using the modified retrospective approach whereby the cumulative effect of adoption was recognized on the adoption date and prior periods were not restated. There was no net cumulative effect adjustment to retained earnings as of January 1, 2019 as a result of this adoption. Therefore, with respect to our leases as both lessees and lessors, information is presented under ASC Topic 842 for the year ended December 31, 2019, and under ASC Topic 840 for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017. In addition, ASC Topic 842 provides a practical expedient package that allows an entity to not
90
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
reassess the following upon adoption (must be elected as a group): (i) whether an expired or existing contract contains a lease arrangement; (ii) the lease classification related to expired or existing lease arrangements; or (iii) whether costs incurred on expired or existing leases qualify as initial direct costs. We elected such practical expedient package upon our adoption of ASC Topic 842 on January 1, 2019. We determine if a contract is a lease upon inception of the lease. We maintain a distinction between finance and operating leases, which is substantially similar to the classification criteria for distinguishing between capital leases and operating leases in the previous lease guidance.
Lessee: Pursuant to ASC Topic 842, lessees are required to recognize the following for all leases with terms greater than 12 months at the commencement date: (i) a lease liability, which is a lessee’s obligation to make lease payments arising from a lease; and (ii) a right-of-use asset, which is an asset that represents the lessee’s right to use, or control the use of, a specified asset for the lease term. The lease liability is calculated by using either the implicit rate of the lease or the incremental borrowing rate. As a result of the adoption of ASC Topic 842 on January 1, 2019, we recognized an initial amount of operating lease liabilities of $5,334,000 in our consolidated balance sheet for all of our ground leases. In addition, we recorded corresponding right-of-use assets of $11,239,000, which represent the lease liabilities, net of the existing accrued straight-line rent liabilities and adjusted for unamortized above/below market ground lease intangibles. The accretion of lease liabilities and amortization expense on right-of-use assets for our operating leases are included in rental expenses in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Operating lease liabilities are calculated using our incremental borrowing rate based on the information available as of the lease commencement date.
Lessor: Pursuant to ASC Topic 842, lessors bifurcate lease revenues into lease components and non-lease components and separately recognize and disclose non-lease components that are executory in nature. Lease components continue to be recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term and certain non-lease components may be accounted for under the new revenue recognition guidance in ASC Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, or ASC Topic 606. See the “Revenue Recognition” section below. ASC Topic 842 also provides for a practical expedient package that permits lessors to not separate non-lease components from the associated lease component if certain conditions are met. Such practical expedient is limited to circumstances in which: (i) the timing and pattern of transfer are the same for the non-lease component and the related lease component; and (ii) the lease component, if accounted for separately, would be classified as an operating lease. In addition, such practical expedient causes an entity to assess whether a contract is predominately lease or service based, and recognize the revenue from the entire contract under the relevant accounting guidance. Effective upon our adoption of ASC Topic 842 on January 1, 2019, we continue to recognize revenue for our medical office buildings, senior housing and skilled nursing facilities segments under ASC Topic 842 as real estate revenue. Minimum annual rental revenue is recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the related lease (including rent holidays). Differences between real estate revenue recognized and cash amounts contractually due from tenants under the lease agreements are recorded to deferred rent receivable, which is included in other assets, net in our accompanying consolidated balance sheet. Tenant reimbursement revenue, which comprises additional amounts recoverable from tenants for common area maintenance expenses and certain other recoverable expenses, are considered non-lease components and variable lease payments. We qualified for and elected the practical expedient as outlined above to combine the non-lease component with the lease component, which is the predominant component, and therefore the non-lease component is recognized as part of real estate revenue. In addition, as lessors, we exclude certain lessor costs (i.e., property taxes and insurance) paid directly by a lessee to third parties on our behalf from our measurement of variable lease revenue and associated expense (i.e., no gross up of revenue and expense for these costs); and include lessor costs that we paid and are reimbursed by the lessee in our measurement of variable lease revenue and associated expense (i.e., gross up revenue and expense for these costs). Therefore, we no longer record revenue or expense when the lessee pays the property taxes and insurance directly to a third party.
Our senior housing — RIDEA facilities offer residents room and board (lease component), standard meals and healthcare services (non-lease component), and certain ancillary services that are not contemplated in the lease with each resident (i.e., laundry, guest meals, etc.). For our senior housing — RIDEA facilities, we recognize revenue under ASC Topic 606 as resident fees and services, based on our predominance assessment from electing the practical expedient outlined above. See the “Revenue Recognition” section below.
See Note 16, Leases, for a further discussion.
Revenue Recognition
Prior to January 1, 2018, we recognized revenue in accordance with ASC Topic 605, Revenue Recognition, or ASC Topic 605. ASC Topic 605 requires that all four of the following basic criteria be met before revenue is realized or realizable and earned: (i) there is persuasive evidence that an arrangement exists; (ii) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; (iii) the seller’s price to the buyer is fixed or determinable; and (iv) collectability is reasonably assured.
91
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
On January 1, 2018, we adopted ASC Topic 606, applying the modified retrospective method. Results for reporting periods beginning after January 1, 2018 are presented under ASC Topic 606, while prior period amounts are not adjusted and continue to be reported under the accounting standards in effect for the prior period. The adoption of ASC Topic 606 did not have a material impact on the measurement nor on the recognition of revenue as of January 1, 2018; therefore, no cumulative adjustment was made to the opening balance of retained earnings at the beginning of 2018.
Real Estate Revenue
Prior to January 1, 2019, minimum annual rental revenue was recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the related lease (including rent holidays) in accordance with ASC Topic 840. Differences between real estate revenue recognized and cash amounts contractually due from tenants under the lease agreements were recorded to deferred rent receivable. Tenant reimbursement revenue, which comprises additional amounts recoverable from tenants for common area maintenance expenses and certain other recoverable expenses, was recognized as revenue in the period in which the related expenses were incurred. Tenant reimbursements were recognized and presented in accordance with ASC Subtopic 606-10-55-36, Revenue Recognition — Principal Versus Agent Consideration, or ASC Subtopic 606. ASC Subtopic 606 requires that these reimbursements be recorded on a gross basis as we are generally primarily responsible to fulfill the promise to provide specified goods and services. We recognized lease termination fees at such time when there was a signed termination letter agreement, all of the conditions of such agreement had been met and the tenant was no longer occupying the property.
Effective January 1, 2019, we recognize real estate revenue in accordance with ASC Topic 842. See the “Leases” section above.
Resident Fees and Services Revenue
A significant portion of resident fees and services revenue represents healthcare service revenue that is reported at the amount that we expect to be entitled to in exchange for providing patient care. These amounts are due from patients, third-party payors (including health insurers and government programs), other healthcare facilities, and others and includes variable consideration for retroactive revenue adjustments due to settlement of audits, reviews, and investigations. Generally, we bill the patients, third-party payors and other healthcare facilities several days after the services are performed. Revenue is recognized as performance obligations are satisfied.
Performance obligations are determined based on the nature of the services provided by us. Revenue for performance obligations satisfied over time is recognized based on actual charges incurred in relation to total expected (or actual) charges. This method provides a depiction of the transfer of services over the term of the performance obligation based on the inputs needed to satisfy the obligation. Generally, performance obligations satisfied over time relate to patients receiving long-term healthcare services, including rehabilitation services. We measure the performance obligation from admission into the facility to the point when we are no longer required to provide services to that patient. Revenue for performance obligations satisfied at a point in time is recognized when goods or services are provided and we do not believe we are required to provide additional goods or services to the patient.
Because all of its performance obligations relate to contracts with a duration of less than one year, we have elected to apply the optional exemption provided in FASB ASC 606-10-50-14(a) and, therefore, are not required to disclose the aggregate amount of the transaction price allocated to performance obligations that are unsatisfied or partially unsatisfied at the end of the reporting period. The performance obligations for these contracts are generally completed within months of the end of the reporting period.
Disaggregation of Resident Fees and Services Revenue
We disaggregate revenue from contracts with customers according to lines of business and payor classes. The transfer of goods and services may occur at a point in time or over time; in other words, revenue may be recognized over the course of the underlying contract, or may occur at a single point in time based upon a single transfer of control. This distinction is discussed in further detail below. We determine that disaggregating revenue into these categories achieves the disclosure objective to depict how the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows are affected by economic factors.
Resident fees and services revenue includes fees for basic housing and assisted living care. We record revenue when services are rendered at amounts billable to individual residents. Residency agreements are generally for a term of 30 days, with resident fees billed monthly in advance. For patients under reimbursement arrangements with Medicaid, revenue is recorded based on contractually agreed-upon amounts or rates on a per resident, daily basis or as services are rendered.
92
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The following tables disaggregate our resident fees and services revenue by line of business, according to whether such revenue is recognized at a point in time or over time:
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Point in Time | Over Time | Total | Point in Time | Over Time | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
Senior housing — RIDEA | $ | 715,000 | $ | 45,445,000 | $ | 46,160,000 | $ | 847,000 | $ | 36,010,000 | $ | 36,857,000 | ||||||||||||
The following tables disaggregate our resident fees and services revenue by payor class:
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||
2019 | 2018 | |||||||
Medicaid | $ | 6,020,000 | $ | 6,082,000 | ||||
Private and other payors | 40,140,000 | 30,775,000 | ||||||
Total resident fees and services | $ | 46,160,000 | $ | 36,857,000 | ||||
Accounts Receivable, Net — Resident Fees and Services
The beginning and ending balances of accounts receivable, net — resident fees and services are as follows:
Medicaid | Private and Other Payors | Total | ||||||||||
Beginning balance — January 1, 2019 | $ | 6,098,000 | $ | 644,000 | $ | 6,742,000 | ||||||
Ending balance — December 31, 2019 | 3,154,000 | 650,000 | 3,804,000 | |||||||||
(Decrease)/increase | $ | (2,944,000 | ) | $ | 6,000 | $ | (2,938,000 | ) | ||||
Financing Component
We have elected the practical expedient allowed under ASC Topic 606-10-32-18 and, therefore, we do not adjust the promised amount of consideration from patients and third-party payors for the effects of a significant financing component due to our expectation that the period between the time the service is provided to a patient and the time that the patient or a third-party payor pays for that service will be one year or less.
Contract Costs
We have applied the practical expedient provided by ASC Topic 340-40-25-4 and, therefore, all incremental customer contract acquisition costs are expensed as they are incurred since the amortization period of the asset that we otherwise would have recognized is one year or less in duration.
Tenant and Resident Receivables and Allowances
Resident receivables are carried net of an allowance for uncollectible amounts. An allowance is maintained for estimated losses resulting from the inability of residents and payors to meet the contractual obligations under their lease or service agreements. Upon our adoption of ASC Topic 606, substantially all of such allowances are recorded as direct reductions of resident fees and services revenue as contractual adjustments provided to third-party payors or implicit price concessions in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Our determination of the adequacy of these allowances is based primarily upon evaluations of historical loss experience, the residents’ financial condition, security deposits, cash collection patterns by payor and by state, current economic conditions and other relevant factors.
Prior to our adoption of ASC Topic 842, tenant receivables and unbilled deferred rent receivables were reduced for uncollectible amounts. Such amounts were charged to bad debt expense, which was included in general and administrative in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Effective upon our adoption of ASC Topic 842 on January 1, 2019, such amounts are recognized as direct reductions of real estate revenue in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
93
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we had $902,000 and $1,321,000, respectively, in allowances, which was determined necessary to reduce receivables to our estimate of the amount collectible. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we increased allowances by $2,301,000, $1,790,000 and $124,000, respectively, and reduced allowances for collections or adjustments by $1,758,000, $531,000 and $41,000, respectively. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we did not write off any of our receivables directly to bad debt expense or as direct adjustments to revenue. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, $962,000, $21,000 and $0, respectively, of our receivables were written off against the related allowances.
Property Acquisitions
In accordance with ASC Topic 805, Business Combinations, or ASC Topic 805, and ASU 2017-01, Clarifying the Definition of a Business, or ASU 2017-01, we determine whether a transaction is a business combination, which requires that the assets acquired and liabilities assumed constitute a business. If the assets acquired and liabilities assumed are not a business, we account for the transaction as an asset acquisition. Under both methods, we recognize the identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed; however, for a transaction accounted for as an asset acquisition, we allocate the purchase price to the identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their relative fair values. We immediately expense acquisition related expenses associated with a business combination and capitalize acquisition related expenses directly associated with an asset acquisition. As a result of our early adoption of ASU 2017-01 on January 1, 2017, we accounted for the property acquisitions we completed for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 as asset acquisitions rather than business combinations. See Note 3, Real Estate Investments, Net, for a further discussion.
We, with assistance from independent valuation specialists, measure the fair value of tangible and identified intangible assets and liabilities, as applicable, based on their respective fair values for acquired properties. Our method for allocating the purchase price to acquired investments in real estate requires us to make subjective assessments for determining fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed. This includes determining the value of the buildings, land, leasehold interests, furniture, fixtures and equipment, above- or below-market rent, in-place leases, master leases, above- or below-market debt assumed and derivative financial instruments assumed. These estimates require significant judgment and in some cases involve complex calculations. These allocation assessments directly impact our results of operations, as amounts allocated to certain assets and liabilities have different depreciation or amortization lives. In addition, we amortize the value assigned to above- or below-market rent as a component of revenue, unlike in-place leases and other intangibles, which we include in depreciation and amortization in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
The determination of the fair value of land is based upon comparable sales data. In cases where a leasehold interest in the land is acquired, only the above/below market consideration is necessary where the value of the leasehold interest is determined by discounting the difference between the contract ground lease payments and a market ground lease payment back to a present value as of the acquisition date. The fair value of buildings is based upon our determination of the value under two methods: one, as if it were to be replaced and vacant using cost data and, two, also using a residual technique based on discounted cash flow models, as vacant. Factors considered by us include an estimate of carrying costs during the expected lease-up periods considering current market conditions and costs to execute similar leases. We also recognize the fair value of furniture, fixtures and equipment on the premises, as well as the above- or below-market rent, the value of in-place leases, master leases, above- or below-market debt and derivative financial instruments assumed.
The value of the above- or below-market component of the acquired in-place leases is determined based upon the present value (using a discount rate that reflects the risks associated with the acquired leases) of the difference between: (i) the level payment equivalent of the contract rent paid pursuant to the lease; and (ii) our estimate of market rent payments taking into account rent steps throughout the lease. In the case of leases with options, a case-by-case analysis is performed based on all facts and circumstances of the specific lease to determine whether the option will be assumed to be exercised. The amounts related to above-market leases are included in identified intangible assets, net in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets and are amortized against real estate revenue over the remaining non-cancelable lease term of the acquired leases with each property. The amounts related to below-market leases are included in identified intangible liabilities, net in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets and are amortized to real estate revenue over the remaining non-cancelable lease term plus any below-market renewal options of the acquired leases with each property.
The value of in-place lease costs are based on management’s evaluation of the specific characteristics of the tenant’s lease and our overall relationship with the tenants. Characteristics considered by us in allocating these values include the nature and extent of the credit quality and expectations of lease renewals, among other factors. The in-place lease intangible represents the value related to the economic benefit for acquiring a property with in-place leases as opposed to a vacant property, which is evaluated based on a review of comparable leases for a similar property, terms and conditions for marketing and executing new
94
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
leases, and implied in the difference between the value of the whole property “as is” and “as vacant.” The net amounts related to in-place lease costs are included in identified intangible assets, net in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets and are amortized to depreciation and amortization expense over the average downtime of the acquired leases with each property. The net amounts related to the value of tenant relationships, if any, are included in identified intangible assets, net in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets and are amortized to depreciation and amortization expense over the average remaining non-cancelable lease term of the acquired leases plus the market renewal lease term. The value of a master lease, if any, in which a previous owner or a tenant is relieved of specific rental obligations as additional space is leased, is determined by discounting the expected real estate revenue associated with the master lease space over the assumed lease-up period.
The value of above- or below-market debt is determined based upon the present value of the difference between the cash flow stream of the assumed mortgage and the cash flow stream of a market rate mortgage at the time of assumption. The net value of above- or below-market debt is included in mortgage loans payable, net in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets and is amortized to interest expense over the remaining term of the assumed mortgage.
The value of derivative financial instruments, if any, is determined in accordance with ASC Topic 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures, or ASC Topic 820, and is included in other assets or other liabilities in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
The values of contingent consideration assets and liabilities, if any, are analyzed at the time of acquisition. For contingent purchase options, the fair market value of the acquired asset is compared to the specified option price at the exercise date. If the option price is below market, it is assumed to be exercised and the difference between the fair market value and the option price is discounted to the present value at the time of acquisition.
Real Estate Investments, Net
We carry our operating properties at our historical cost less accumulated depreciation. The cost of operating properties includes the cost of land and completed buildings and related improvements. Expenditures that increase the service life of properties are capitalized and the cost of maintenance and repairs is charged to expense as incurred. The cost of buildings and capital improvements is depreciated on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the buildings and capital improvements, up to 39 years, and the cost for tenant improvements is depreciated over the shorter of the lease term or useful life, up to 16 years. The cost of furniture, fixtures and equipment is depreciated over the estimated useful life, up to 20 years. When depreciable property is retired, replaced or disposed of, the related cost and accumulated depreciation is removed from the accounts and any gain or loss is reflected in earnings.
As part of the leasing process, we may provide the lessee with an allowance for the construction of leasehold improvements. These leasehold improvements are capitalized and recorded as tenant improvements and depreciated over the shorter of the useful life of the improvements or the lease term. If the allowance represents a payment for a purpose other than funding leasehold improvements, or in the event we are not considered the owner of the improvements, the allowance is considered to be a lease inducement and is included in other assets, net in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Lease inducement is recognized over the lease term as a reduction of real estate revenue on a straight-line basis. Factors considered during this evaluation include, among other things, who holds legal title to the improvements as well as other controlling rights provided by the lease agreement and provisions for substantiation of such costs, e.g., unilateral control of the tenant space during the build-out process. Determination of the appropriate accounting for the payment of a tenant allowance is made on a lease-by-lease basis, considering the facts and circumstances of the individual tenant lease. Recognition of lease revenue commences when the lessee is given possession of the leased space upon completion of tenant improvements when we are the owner of the leasehold improvements. However, when the leasehold improvements are owned by the tenant, the lease inception date (and the date on which recognition of lease revenue commences) is the date the tenant obtains possession of the leased space for purposes of constructing its leasehold improvements.
Impairment of Long-Lived and Intangible Assets
We periodically evaluate our long-lived assets, primarily consisting of investments in real estate that we carry at our historical cost less accumulated depreciation, for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that its carrying value may not be recoverable. Indicators we consider important and that we believe could trigger an impairment review include, among others, the following:
• | significant negative industry or economic trends; |
• | a significant underperformance relative to historical or projected future operating results; and |
95
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
• | a significant change in the extent or manner in which the asset is used or significant physical change in the asset. |
If indicators of impairment of our long-lived assets are present, we evaluate the carrying value of the related real estate investments in relation to the future undiscounted cash flows of the underlying operations. In performing this evaluation, we consider market conditions and our current intentions with respect to holding or disposing of the asset. We adjust the net book value of leased properties and other long-lived assets to fair value if the sum of the expected future undiscounted cash flows, including sales proceeds, is less than carrying value. We recognize an impairment loss at the time we make any such determination.
If impairment indicators arise with respect to intangible assets with finite useful lives, we evaluate impairment by comparing the carrying amount of the asset to the estimated future undiscounted net cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the estimated future undiscounted net cash flows are less than the carrying amount of the asset, then we estimate the fair value of the asset and compare the estimated fair value to the intangible asset’s carrying value. For all of our reporting units, we recognize any shortfall from carrying value as an impairment loss in the current period.
We test other indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment at least annually, and more frequently if indicators arise. We first assess qualitative factors to determine the likelihood that the fair value of the reporting group is less than its carrying value. If the carrying amount of an indefinite-lived intangible asset exceeds its fair value, an impairment loss is recognized. Fair values of other indefinite-lived intangible assets are usually determined based on discounted cash flows or appraised values, as appropriate.
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we did not incur any impairment losses.
Properties Held for Sale
We will account for our properties held for sale in accordance with ASC Topic 360, Property, Plant, and Equipment, or ASC Topic 360, which addresses financial accounting and reporting for the impairment or disposal of long-lived assets. ASC Topic 360 requires that a property or a group of properties is required to be reported in discontinued operations in the statements of operations for current and prior periods if the disposal represents a strategic shift that has (or will have) a major effect on an entity’s operations and financial results when either (i) the component has been disposed of; or (ii) is classified as held for sale.
In accordance with ASC Topic 360, at such time as a property is held for sale, such property is carried at the lower of (i) its carrying amount or (ii) fair value less costs to sell. In addition, a property being held for sale ceases to be depreciated. We will classify operating properties as property held for sale in the period in which all of the following criteria are met:
• | management, having the authority to approve the action, commits to a plan to sell the asset; |
• | the asset is available for immediate sale in its present condition subject only to terms that are usual and customary for sales of such assets; |
• | an active program to locate a buyer or buyers and other actions required to complete the plan to sell the asset has been initiated; |
• | the sale of the asset is probable and the transfer of the asset is expected to qualify for recognition as a completed sale within one year; |
• | the asset is being actively marketed for sale at a price that is reasonable in relation to its current fair value; and |
• | given the actions required to complete the plan to sell the asset, it is unlikely that significant changes to the plan would be made or that the plan would be withdrawn. |
No properties were held for sale as of December 31, 2019 and 2018.
96
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Derivative Financial Instruments
We are exposed to the effect of interest rate changes in the normal course of business. We seek to mitigate these risks by following established risk management policies and procedures, which include the occasional use of derivatives. Our primary strategy in entering into derivative contracts, such as fixed interest rate swaps, is to add stability to interest expense and to manage our exposure to interest rate movements by effectively converting a portion of our variable-rate debt to fixed-rate debt. We do not enter into derivative instruments for speculative purposes.
Derivatives are recognized as either other assets or other liabilities in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets and are measured at fair value in accordance with ASC Topic 815, Derivatives and Hedging, or ASC Topic 815. ASC Topic 815 establishes accounting and reporting standards for derivative instruments, including certain derivative instruments embedded in other contracts and for hedging activities. Since our derivative instruments are not designated as hedge instruments, they do not qualify for hedge accounting under ASC Topic 815. Changes in the fair value of derivative financial instruments are recorded as a component of interest expense in gain or loss in fair value of derivative financial instruments in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
See Note 8, Derivative Financial Instruments, and Note 14, Fair Value Measurements, for a further discussion of our derivative financial instruments.
Fair Value Measurements
We follow ASC Topic 820 to account for the fair value of certain assets and liabilities. ASC Topic 820 defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. ASC Topic 820 emphasizes that fair value is a market-based measurement, not an entity-specific measurement. Therefore, a fair value measurement should be determined based on the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability. As a basis for considering market participant assumptions in fair value measurements, ASC Topic 820 establishes a fair value hierarchy that distinguishes between market participant assumptions based on market data obtained from sources independent of the reporting entity (observable inputs that are classified within Levels 1 and 2 of the hierarchy) and the reporting entity’s own assumptions about market participant assumptions (unobservable inputs classified within Level 3 of the hierarchy).
Level 1 inputs are quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that we have the ability to access. An active market is defined as a market in which transactions for the assets or liabilities occur with sufficient frequency and volume to provide pricing information on an ongoing basis. Level 2 inputs are inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. Level 2 inputs may include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, as well as inputs that are observable for the asset or liability (other than quoted prices), such as interest rates, foreign exchange rates and yield curves that are observable at commonly quoted intervals. Level 3 inputs are unobservable inputs for the asset or liability, which are typically based on an entity’s own assumptions, as there is little, if any, related market activity. In instances where the determination of the fair value measurement is based on inputs from different levels of the fair value hierarchy, the level in the fair value hierarchy within which the entire fair value measurement falls is based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety. Our assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement in its entirety requires judgment and considers factors specific to the asset or liability.
See Note 14, Fair Value Measurements, for a further discussion.
Real Estate Deposits
Real estate deposits may include refundable and non-refundable funds held by escrow agents and others to be applied towards the acquisition of real estate investments, and such future investments are subject to substantial conditions to closing.
Other Assets, Net
Other assets, net consist of our investment in an unconsolidated entity, deferred financing costs on our line of credit and term loans, prepaid expenses and deposits, lease commissions and deferred rent receivables. Deferred financing costs on our line of credit and term loans include amounts paid to lenders and others to obtain financing. Such costs are amortized using the straight-line method over the term of the related line of credit and term loans, which approximates the effective interest rate method. Amortization of deferred financing costs on our line of credit and term loans are included in interest expense in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Prepaid expenses are amortized over the related contract periods. Lease commissions are amortized using the straight-line method over the term of the related lease.
97
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
We report investments in unconsolidated entities using the equity method of accounting when we have the ability to exercise significant influence over the operating and financial policies. Under the equity method, our share of the investee’s earnings or losses is included in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations. To the extent that our cost basis is different from the basis reflected at the entity level, the basis difference is generally amortized over the lives of the related assets and liabilities, and such amortization is included in our share of equity in earnings of the entity. The initial carrying value of investments in unconsolidated entities is based on the amount paid to purchase the entity interest or the estimated fair value of the assets prior to the sale of interests in the entity. We have elected to follow the cumulative earnings approach when classifying distributions received from equity method investments in our consolidated statements of cash flows, whereby any distributions received up to the amount of cumulative equity earnings would be considered a return on investment and classified in operating activities and any excess distributions would be considered a return of investment and classified in investing activities. We evaluate our equity method investments for impairment based upon a comparison of the estimated fair value of the equity method investment to its carrying value. When we determine a decline in the estimated fair value of such an investment below its carrying value is other-than-temporary, an impairment is recorded. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we did not incur any impairment losses from unconsolidated entities.
See Note 5, Other Assets, Net, for a further discussion.
Stock Compensation
We follow ASC Topic 718, Compensation — Stock Compensation, or ASC Topic 718, to account for our stock compensation pursuant to the 2015 Incentive Plan, or our incentive plan. See Note 12, Equity — 2015 Incentive Plan, for a further discussion of grants under such plan.
Income Taxes
We qualified, and elected to be taxed, as a REIT under the Code for federal income tax purposes beginning with our taxable year ended December 31, 2016, and we intend to continue to qualify to be taxed as a REIT. To maintain our qualification as a REIT, we must meet certain organizational and operational requirements, including a requirement to currently distribute at least 90.0% of our annual taxable income, excluding net capital gains, to our stockholders. As a REIT, we generally will not be subject to federal income tax on taxable income that we distribute to our stockholders.
If we fail to maintain our qualification as a REIT in any taxable year, we will then be subject to federal income taxes on our taxable income at regular corporate rates and will not be permitted to qualify for treatment as a REIT for federal income tax purposes for four years following the year during which qualification is lost unless the Internal Revenue Service, or the IRS, grants us relief under certain statutory provisions. Such an event could have a material adverse effect on our net income and net cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
We may be subject to certain state and local income taxes on our income, property or net worth in some jurisdictions, and in certain circumstances we may also be subject to federal excise taxes on undistributed income. In addition, certain activities that we undertake are conducted by subsidiaries, which we elected to be treated as taxable REIT subsidiaries, or TRSs, to allow us to provide services that would otherwise be considered impermissible for REITs. Accordingly, we recognize income tax benefit (expense) for the federal, state and local income taxes incurred by our TRSs.
We follow ASC Topic 740, Income Taxes, or ASC Topic 740, to recognize, measure, present and disclose in our accompanying consolidated financial statements uncertain tax positions that we have taken or expect to take on a tax return. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we did not have any tax benefits nor liabilities for uncertain tax positions that we believe should be recognized in our accompanying consolidated financial statements.
We account for deferred income taxes using the asset and liability method and recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in our financial statements or tax returns. Under this method, we determine deferred tax assets and liabilities based on the temporary differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. Deferred tax assets reflect the impact of the future deductibility of operating loss carryforwards. A valuation allowance is provided if we believe it is more likely than not that all or some portion of the deferred tax asset will not be realized. Any increase or decrease in the valuation allowance that results from a change in circumstances, and that causes us to change our judgment about the realizability of the related deferred tax asset, is included in income tax benefit or expense in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations when such changes occur. Any increase or decrease in the deferred tax liability that results from a change in circumstances, and that causes us to change our
98
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
judgment about expected future tax consequences of events, is recorded in income tax benefit or expense in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Deferred tax assets are included in other assets, net, and deferred tax liabilities are included in security deposits, prepaid rent and other liabilities, in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
See Note 15, Income Taxes, for a further discussion.
Segment Disclosure
ASC Topic 280, Segment Reporting, establishes standards for reporting financial and descriptive information about a public entity’s reportable segments. We segregate our operations into reporting segments in order to assess the performance of our business in the same way that management reviews our performance and makes operating decisions. Accordingly, when we acquired our first medical office building in June 2016; senior housing facility in December 2016; senior housing — RIDEA facility in November 2017; and skilled nursing facility in March 2018, we added a new reportable segment at each such time. As of December 31, 2019, we have determined that we operate through four reportable business segments, with activities related to investing in medical office buildings, senior housing, senior housing — RIDEA and skilled nursing facilities.
See Note 17, Segment Reporting, for a further discussion.
GLA and Other Measures
GLA and other measures used to describe real estate investments included in our accompanying consolidated financial statements are presented on an unaudited basis.
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
In June 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update, or ASU, 2016-13, Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments, or ASU 2016-13, which introduces a new approach to estimate credit losses on certain types of financial instruments based on expected losses. It also modifies the impairment model for available-for-sale debt securities and provides for a simplified accounting model for purchased financial assets with credit deterioration since their origination. Subsequently, in November 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-19, Codification Improvements to Topic 326, Financial Instruments — Credit Losses, or ASU 2018-19, which amended the scope of ASU 2016-13 to clarify that operating lease receivables should be accounted for under the new leasing standard ASC Topic 842. In April 2019, the FASB issued ASU 2019-04, Codification Improvements to Topic 326, Financial Instruments — Credit Losses, Topic 815, Derivatives and Hedging, and Topic 825, Financial Instruments, or ASU 2019-04, to increase stakeholders’ awareness of the amendments and to expedite improvements to the ASC. In May 2019, the FASB issued ASU 2019-05, Targeted Transition Relief, or ASU 2019-05, to address certain stakeholders’ concerns by providing an option to irrevocably elect the fair value option for certain financial assets previously measured at amortized cost basis. In November 2019, the FASB issued ASU 2019-10, Financial Instruments — Credit Losses (Topic 326), Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815), and Leases (Topic 842),or ASU 2019-10, which provides a framework to stagger effective dates for future major accounting standards and amends the effective dates for certain major new accounting standards to give implementation relief to certain types of entities. ASU 2016-13 and its related amendments are effective for fiscal years and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2019. Early adoption was permitted. We adopted such accounting pronouncements on January 1, 2020, which did not have a material impact to our consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-13, Changes to the Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurement, or ASU 2018-13, which modifies the disclosure requirements in ASC Topic 820 by removing certain disclosure requirements related to the fair value hierarchy, modifying existing disclosure requirements related to measurement uncertainty and adding new disclosure requirements, such as disclosing the changes in unrealized gains and losses for the period included in other comprehensive income for recurring Level 3 fair value measurements held at the end of the reporting period and disclosing the range and weighted average of significant unobservable inputs used to develop Level 3 measurements. ASU 2018-13 is effective for fiscal years and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2019. Early adoption was permitted for any removed or modified disclosures. We adopted ASU 2018-13 on January 1, 2020, which did not have a material impact to our consolidated financial statement disclosures.
99
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
3. Real Estate Investments, Net
Our real estate investments, net consisted of the following as of December 31, 2019 and 2018:
December 31, | |||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Building and improvements | $ | 836,091,000 | $ | 668,814,000 | |||
Land | 103,371,000 | 83,084,000 | |||||
Furniture, fixtures and equipment | 6,656,000 | 5,090,000 | |||||
946,118,000 | 756,988,000 | ||||||
Less: accumulated depreciation | (51,058,000 | ) | (25,312,000 | ) | |||
Total | $ | 895,060,000 | $ | 731,676,000 | |||
Depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 was $27,435,000, $16,723,000 and $8,137,000, respectively. In addition to the acquisitions discussed below, for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we incurred capital expenditures of $4,537,000, $3,643,000 and $1,649,000, respectively, for our medical office buildings, $2,505,000, $5,342,000 and $5,000, respectively, for our senior housing — RIDEA facilities and $75,000, $0 and $822,000, respectively, for our senior housing facilities. We did not incur any capital expenditures for our skilled nursing facilities for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017.
100
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Acquisitions in 2019
For the year ended December 31, 2019, using net proceeds from our initial offering and debt financing, we completed the acquisition of 18 buildings from unaffiliated third parties. The following is a summary of our property acquisitions for the year ended December 31, 2019:
Acquisition(1) | Location | Type | Date Acquired | Contract Purchase Price | Mortgage Loan Payable(2) | Line of Credit(3) | Total Acquisition Fee(4) | |||||||||||||||
Lithonia MOB | Lithonia, GA | Medical Office | 03/05/19 | $ | 10,600,000 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 477,000 | |||||||||||
West Des Moines SNF | West Des Moines, IA | Skilled Nursing | 03/24/19 | 7,000,000 | — | — | 315,000 | |||||||||||||||
Great Nord MOB Portfolio | Tinley Park, IL; Chesterton and Crown Point, IN; and Plymouth, MN | Medical Office | 04/08/19 | 44,000,000 | — | 15,000,000 | 1,011,000 | |||||||||||||||
Michigan ALF Portfolio(5) | Grand Rapids, MI | Senior Housing | 05/01/19 | 14,000,000 | 10,493,000 | 3,500,000 | 315,000 | |||||||||||||||
Overland Park MOB | Overland Park, KS | Medical Office | 08/05/19 | 28,350,000 | — | 28,700,000 | 638,000 | |||||||||||||||
Blue Badger MOB | Marysville, OH | Medical Office | 08/09/19 | 13,650,000 | — | 12,000,000 | 307,000 | |||||||||||||||
Bloomington MOB | Bloomington, IL | Medical Office | 08/13/19 | 18,200,000 | — | 17,400,000 | 409,000 | |||||||||||||||
Memphis MOB | Memphis, TN | Medical Office | 08/15/19 | 8,700,000 | — | 8,600,000 | 196,000 | |||||||||||||||
Haverhill MOB | Haverhill, MA | Medical Office | 08/27/19 | 15,500,000 | — | 15,450,000 | 349,000 | |||||||||||||||
Fresno MOB | Fresno, CA | Medical Office | 10/30/19 | 10,000,000 | — | 9,950,000 | 225,000 | |||||||||||||||
Colorado Foothills MOB Portfolio | Arvada, Centennial and Colorado Springs, CO | Medical Office | 11/19/19 | 31,200,000 | — | 30,500,000 | 702,000 | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 201,200,000 | $ | 10,493,000 | $ | 141,100,000 | $ | 4,944,000 | ||||||||||||||
___________
(1) | We own 100% of our properties acquired for the year ended December 31, 2019. |
(2) | Represents the principal balance of the mortgage loan payable assumed by us at the time of acquisition. |
(3) | Represents a borrowing under the 2018 Credit Facility, as defined in Note 7, Line of Credit and Term Loans, at the time of acquisition. |
(4) | Our advisor was paid, as compensation for services rendered in connection with the investigation, selection and acquisition of our properties, a base acquisition fee of 2.25% of the contract purchase price paid by us. In addition, the total acquisition fee may include a Contingent Advisor Payment, as defined in Note 13, Related Party Transactions, up to 2.25% of the contract purchase price paid by us. See Note 13, Related Party Transactions — Acquisition and Development Stage — Acquisition Fee, for a further discussion. |
(5) | We added three buildings to our existing Michigan ALF Portfolio. The other six buildings in the Michigan ALF Portfolio were acquired in December 2018. |
101
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
We accounted for our property acquisitions completed during the year ended December 31, 2019 as asset acquisitions. We incurred and capitalized base acquisition fees and direct acquisition related expenses of $6,427,000. In addition, we incurred Contingent Advisor Payments of $418,000 to our advisor for certain property acquisitions. The following table summarizes the purchase price of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the time of acquisition from our property acquisitions in 2019 based on their relative fair values:
2019 Acquisitions | ||||
Building and improvements | $ | 164,084,000 | ||
Land | 20,286,000 | |||
In-place leases | 21,393,000 | |||
Above-market leases | 2,578,000 | |||
Right-of-use asset | 3,133,000 | |||
Total assets acquired | 211,474,000 | |||
Mortgage loan payable (including debt discount of $758,000) | (9,735,000 | ) | ||
Below-market leases | (874,000 | ) | ||
Operating lease liability | (4,489,000 | ) | ||
Total liabilities assumed | (15,098,000 | ) | ||
Net assets acquired | $ | 196,376,000 | ||
102
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Acquisitions in 2018
For the year ended December 31, 2018, using net proceeds from our initial offering and debt financing, we completed the acquisition of 29 buildings from unaffiliated third parties. The following is a summary of our property acquisitions for the year ended December 31, 2018:
Acquisition(1) | Location | Type | Date Acquired | Contract Purchase Price | Mortgage Loan Payable(2) | Line of Credit(3) | Total Acquisition Fee(4) | |||||||||||||||
Central Wisconsin Senior Care Portfolio | Sun Prairie and Waunakee, WI | Skilled Nursing | 03/01/18 | $ | 22,600,000 | $ | — | $ | 22,600,000 | $ | 1,018,000 | |||||||||||
Sauk Prairie MOB | Prairie du Sac, WI | Medical Office | 04/09/18 | 19,500,000 | — | 19,500,000 | 878,000 | |||||||||||||||
Surprise MOB | Surprise, AZ | Medical Office | 04/27/18 | 11,650,000 | — | 8,000,000 | 524,000 | |||||||||||||||
Southfield MOB | Southfield, MI | Medical Office | 05/11/18 | 16,200,000 | 6,071,000 | 10,000,000 | 728,000 | |||||||||||||||
Pinnacle Beaumont ALF(5) | Beaumont, TX | Senior Housing — RIDEA | 07/01/18 | 19,500,000 | — | 19,400,000 | 868,000 | |||||||||||||||
Grand Junction MOB | Grand Junction, CO | Medical Office | 07/06/18 | 31,500,000 | — | 31,400,000 | 1,418,000 | |||||||||||||||
Edmonds MOB | Edmonds, WA | Medical Office | 07/30/18 | 23,500,000 | — | 22,000,000 | 1,058,000 | |||||||||||||||
Pinnacle Warrenton ALF(5) | Warrenton, MO | Senior Housing — RIDEA | 08/01/18 | 8,100,000 | — | 8,100,000 | 360,000 | |||||||||||||||
Glendale MOB | Glendale, WI | Medical Office | 08/13/18 | 7,600,000 | — | 7,000,000 | 342,000 | |||||||||||||||
Missouri SNF Portfolio | Florissant, Kansas City, Milan, Moberly, Salisbury, Sedalia, St. Elizabeth and Trenton, MO | Skilled Nursing | 09/28/18 | 88,200,000 | — | 87,000,000 | 3,970,000 | |||||||||||||||
Flemington MOB Portfolio | Flemington, NJ | Medical Office | 11/29/18 | 16,950,000 | — | 15,500,000 | 763,000 | |||||||||||||||
Lawrenceville MOB II | Lawrenceville, GA | Medical Office | 12/19/18 | 9,999,000 | — | 10,100,000 | 450,000 | |||||||||||||||
Mill Creek MOB | Mill Creek, WA | Medical Office | 12/21/18 | 8,250,000 | — | 6,200,000 | 371,000 | |||||||||||||||
Modesto MOB | Modesto, CA | Medical Office | 12/28/18 | 16,000,000 | — | 15,400,000 | 720,000 | |||||||||||||||
Michigan ALF Portfolio | Grand Rapids, Holland, Howell, Lansing and Wyoming, MI | Senior Housing | 12/28/18 | 56,000,000 | — | 53,400,000 | 2,520,000 | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 355,549,000 | $ | 6,071,000 | $ | 335,600,000 | $ | 15,988,000 | ||||||||||||||
___________
(1) | We own 100% of our properties acquired in 2018, with the exception of Pinnacle Beaumont ALF and Pinnacle Warrenton ALF. |
(2) | Represents the principal balance of the mortgage loan payable assumed by us at the time of acquisition. |
(3) | Represents a borrowing under the 2017 Credit Facility or 2018 Credit Facility, as defined in Note 7, Line of Credit and Term Loans, at the time of acquisition. |
103
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
(4) | Our advisor was paid, as compensation for services rendered in connection with the investigation, selection and acquisition of our properties, a base acquisition fee of 2.25% of the portion of the aggregate contract purchase price paid by us. In addition, the total acquisition fee includes a Contingent Advisor Payment, as defined in Note 13, Related Party Transactions, in the amount of 2.25% of the portion of the aggregate contract purchase price paid by us. See Note 13, Related Party Transactions — Acquisition and Development Stage — Acquisition Fee, for a further discussion. |
(5) | On July 1, 2018 and August 1, 2018, we completed the acquisitions of Pinnacle Beaumont ALF and Pinnacle Warrenton ALF, respectively, pursuant to a joint venture with an affiliate of Meridian Senior Living, LLC, or Meridian, an unaffiliated third party. Our ownership of the joint venture is approximately 98.0%. |
We accounted for our property acquisitions completed during the year ended December 31, 2018 as asset acquisitions. We incurred and capitalized base acquisition fees and direct acquisition related expenses of $13,021,000. In addition, we incurred Contingent Advisor Payments of $7,994,000 to our advisor for such property acquisitions. The following table summarizes the purchase price of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the time of acquisition from our property acquisitions in 2018 based on their relative fair values:
2018 Acquisitions | ||||
Building and improvements | $ | 289,830,000 | ||
Land | 30,878,000 | |||
Furniture, fixtures and equipment | 79,000 | |||
In-place leases | 45,439,000 | |||
Certificates of need | 348,000 | |||
Leasehold interests | 93,000 | |||
Above-market leases | 200,000 | |||
Total assets acquired | 366,867,000 | |||
Mortgage loan payable (including debt discount of $263,000) | (5,808,000 | ) | ||
Below-market leases | (269,000 | ) | ||
Total liabilities assumed | (6,077,000 | ) | ||
Net assets acquired | $ | 360,790,000 | ||
104
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Acquisitions in 2017
For the year ended December 31, 2017, using net proceeds from our initial offering and debt financing, we completed the acquisition of 28 buildings from unaffiliated third parties. The following is a summary of our property acquisitions for the year ended December 31, 2017:
___________
Acquisition(1) | Location | Type | Date Acquired | Contract Purchase Price | Mortgage Loan Payable(2) | Line of Credit(3) | Total Acquisition Fee(4) | |||||||||||||||
Battle Creek MOB | Battle Creek, MI | Medical Office | 03/10/17 | $ | 7,300,000 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 328,000 | |||||||||||
Reno MOB | Reno, NV | Medical Office | 03/13/17 | 66,250,000 | — | 60,000,000 | 2,982,000 | |||||||||||||||
Athens MOB Portfolio | Athens, GA | Medical Office | 05/18/17 | 16,800,000 | — | 7,800,000 | 756,000 | |||||||||||||||
SW Illinois Senior Housing Portfolio | Columbia, Millstadt, Red Bud and Waterloo, IL | Senior Housing | 05/22/17 | 31,800,000 | — | 31,700,000 | 1,431,000 | |||||||||||||||
Lawrenceville MOB | Lawrenceville, GA | Medical Office | 06/12/17 | 11,275,000 | 8,000,000 | 3,000,000 | 507,000 | |||||||||||||||
Northern California Senior Housing Portfolio | Belmont, Fairfield, Menlo Park and Sacramento, CA | Senior Housing | 06/28/17 | 45,800,000 | — | 21,600,000 | 2,061,000 | |||||||||||||||
Roseburg MOB | Roseburg, OR | Medical Office | 06/29/17 | 23,200,000 | — | 23,000,000 | 1,044,000 | |||||||||||||||
Fairfield County MOB Portfolio | Stratford and Trumbull, CT | Medical Office | 09/29/17 | 15,395,000 | — | 15,500,000 | 693,000 | |||||||||||||||
Central Florida Senior Housing Portfolio(5) | Bradenton, Brooksville, Lake Placid, Lakeland, Pinellas Park, Sanford, Spring Hill and Winter Haven, FL | Senior Housing — RIDEA | 11/01/17 | 109,500,000 | — | 112,000,000 | 4,882,000 | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 327,320,000 | $ | 8,000,000 | $ | 274,600,000 | $ | 14,684,000 | ||||||||||||||
(1) | We own 100% of our properties acquired in 2017, with the exception of Central Florida Senior Housing Portfolio. |
(2) | Represents the principal balance of the mortgage loan payable assumed by us at the time of acquisition. |
(3) | Represents a borrowing under the 2016 Line of Credit or 2017 Credit Facility, as defined in Note 7, Line of Credit and Term Loans, at the time of acquisition. |
(4) | Our advisor was paid, as compensation for services rendered in connection with the investigation, selection and acquisition of our properties, a base acquisition fee of 2.25% of the portion of the aggregate contract purchase price paid by us. In addition, the total acquisition fee includes a Contingent Advisor Payment, as defined in Note 13, Related Party Transactions, in the amount of 2.25% of the portion of the aggregate contract purchase price paid by us. See Note 13, Related Party Transactions — Acquisition and Development Stage — Acquisition Fee, for a further discussion. |
(5) | On November 1, 2017, we completed the acquisition of Central Florida Senior Housing Portfolio pursuant to a joint venture with an affiliate of Meridian. Our ownership of the joint venture is approximately 98.0%. |
105
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
We accounted for our property acquisitions completed during the year ended December 31, 2017 as asset acquisitions. We incurred base acquisition fees and direct acquisition related expenses of $11,019,000. In addition, we incurred Contingent Advisor Payments of $7,342,000 to our advisor for such property acquisitions. The following table summarizes the purchase price of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the time of acquisition from our property acquisitions in 2017 based on their relative fair values:
2017 Acquisitions | ||||
Building and improvements | $ | 263,052,000 | ||
Land | 39,879,000 | |||
Furniture, fixtures and equipment | 4,453,000 | |||
In-place leases | 30,754,000 | |||
Above-market leases | 127,000 | |||
Total assets acquired | 338,265,000 | |||
Mortgage loan payable | (8,000,000 | ) | ||
Below-market leases | (571,000 | ) | ||
Above-market leasehold interests | (395,000 | ) | ||
Total liabilities assumed | (8,966,000 | ) | ||
Net assets acquired | $ | 329,299,000 | ||
4. Identified Intangible Assets, Net
Identified intangible assets, net consisted of the following as of December 31, 2019 and 2018:
December 31, | |||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Amortized intangible assets: | |||||||
In-place leases, net of accumulated amortization of $18,273,000 and $11,299,000 as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively (with a weighted average remaining life of 9.5 years and 10.3 years as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively) | $ | 70,650,000 | $ | 67,332,000 | |||
Above-market leases, net of accumulated amortization of $609,000 and $323,000 as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively (with a weighted average remaining life of 9.5 years and 4.5 years as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively) | 3,025,000 | 755,000 | |||||
Leasehold interests, net of accumulated amortization of $217,000 as of December 31, 2018 (with a weighted average remaining life of 69.1 years as of December 31, 2018)(1) | — | 6,288,000 | |||||
Unamortized intangible assets: | |||||||
Certificates of need | 348,000 | 348,000 | |||||
Total | $ | 74,023,000 | $ | 74,723,000 | |||
___________
(1) | Such amount related to our ownership of fee simple interests in the building and improvements of eight of our buildings that are subject to respective ground leases. Upon our adoption of ASC Topic 842 on January 1, 2019, such amount was reclassed to operating lease right-of-use assets, net in our accompanying consolidated balance sheet. See Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies — Leases, and Note 16, Leases, for a further discussion. |
Amortization expense on identified intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 was $18,384,000, $16,180,000 and $5,732,000, respectively, which included $310,000, $208,000 and $142,000, respectively, of amortization recorded against real estate revenue for above-market leases and $0, $98,000 and $97,000, respectively, of amortization recorded to rental expenses for leasehold interests in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
106
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The aggregate weighted average remaining life of the identified intangible assets was 9.5 years and 15.3 years as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. As of December 31, 2019, estimated amortization expense on the identified intangible assets for each of the next five years ending December 31 and thereafter was as follows:
Year | Amount | |||
2020 | $ | 11,696,000 | ||
2021 | 10,088,000 | |||
2022 | 8,674,000 | |||
2023 | 7,410,000 | |||
2024 | 6,161,000 | |||
Thereafter | 29,646,000 | |||
Total | $ | 73,675,000 | ||
5. Other Assets, Net
Other assets, net consisted of the following as of December 31, 2019 and 2018:
December 31, | |||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Investment in unconsolidated entity | $ | 47,016,000 | $ | 47,600,000 | |||
Deferred rent receivables | 8,018,000 | 4,941,000 | |||||
Deferred financing costs, net of accumulated amortization of $1,517,000 and $1,554,000 as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively(1) | 3,583,000 | 4,447,000 | |||||
Prepaid expenses and deposits | 2,380,000 | 2,682,000 | |||||
Lease commissions, net of accumulated amortization of $174,000 and $64,000 as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively | 1,623,000 | 564,000 | |||||
Total | $ | 62,620,000 | $ | 60,234,000 | |||
___________
(1) | Deferred financing costs only include costs related to our line of credit and term loans. See Note 7, Line of Credit and Term Loans, for a further discussion. |
Amortization expense on deferred financing costs of our line of credit and term loans for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 was $2,028,000, $1,000,000 and $442,000, respectively. Amortization expense on lease commissions for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 was $117,000, $61,000 and $9,000, respectively.
Investment in unconsolidated entity represents our purchase of 6.0% of the total membership interests of Trilogy REIT Holdings, LLC, or the Trilogy Joint Venture, from unaffiliated third parties on October 1, 2018 for $48,000,000 in cash, based on an estimated gross enterprise value of $93,154,000 consisting of our equity investment and a calculated share of the debt of the Trilogy Joint Venture based on our ownership interest. The Trilogy Joint Venture, through an approximately 96.7% owned subsidiary, owns and operates purpose-built integrated senior health campuses, including skilled nursing facilities and assisted living facilities, located across several states, as well as certain ancillary businesses. In addition to our membership interests, the Trilogy Joint Venture is 70.0% indirectly owned by Griffin-American Healthcare REIT III, Inc., or GAHR III, and the remaining 24.0% is indirectly owned by NorthStar Healthcare Income, Inc. GAHR III, through a wholly owned subsidiary, serves as the manager of the Trilogy Joint Venture and both GAHR III and us are sponsored by American Healthcare Investors. In connection with the purchase of the Trilogy Joint Venture membership interests, we paid to our advisor a base acquisition fee of approximately $2,096,000, or 2.25% of the estimated gross enterprise value of the Trilogy Joint Venture membership interests acquired by us. Additionally, we paid a Contingent Advisor Payment of approximately $2,096,000, or 2.25% of the estimated gross enterprise value of the Trilogy Joint Venture membership interests acquired by us.
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the unamortized basis difference of our joint venture investment of $17,248,000 and $17,704,000, respectively, is primarily attributable to the difference between the amount for which we purchased our interest in the entity, including transaction costs, and the historical carrying value of the net assets of the entity. This difference is being amortized over the remaining useful life of the related assets and included in income or loss from unconsolidated entity in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
107
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
6. Mortgage Loans Payable, Net
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, mortgage loans payable were $27,099,000 ($26,070,000, net of discount/premium and deferred financing costs) and $17,256,000 ($16,892,000, net of discount/premium and deferred financing costs), respectively. As of December 31, 2019, we had four fixed-rate mortgage loans with interest rates ranging from 3.67% to 5.25% per annum, maturity dates ranging from April 1, 2020 to February 1, 2051 and a weighted average effective interest rate of 4.18%. As of December 31, 2018, we had three fixed-rate mortgage loans with interest rates ranging from 3.75% to 5.25% per annum, maturity dates ranging from April 1, 2020 to August 1, 2029 and a weighted average effective interest rate of 4.51%.
The following table reflects the changes in the carrying amount of mortgage loans payable, net for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018:
December 31, | |||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Beginning balance | $ | 16,892,000 | $ | 11,567,000 | |||
Additions: | |||||||
Assumption of mortgage loans payable, net | 9,735,000 | 5,808,000 | |||||
Amortization of deferred financing costs | 78,000 | 76,000 | |||||
Amortization of discount/premium on mortgage loans payable | 41,000 | 13,000 | |||||
Deductions: | |||||||
Deferred financing costs | (26,000 | ) | (123,000 | ) | |||
Scheduled principal payments on mortgage loans payable | (650,000 | ) | (449,000 | ) | |||
Ending balance | $ | 26,070,000 | $ | 16,892,000 | |||
As of December 31, 2019, the principal payments due on our mortgage loans payable for each of the next five years ending December 31 and thereafter were as follows:
Year | Amount | |||
2020 | $ | 8,317,000 | ||
2021 | 622,000 | |||
2022 | 651,000 | |||
2023 | 681,000 | |||
2024 | 711,000 | |||
Thereafter | 16,117,000 | |||
Total | $ | 27,099,000 | ||
7. Line of Credit and Term Loans
On August 25, 2016, we, through our operating partnership, as borrower, and certain of our subsidiaries, or the subsidiary guarantors, and us, collectively as guarantors, entered into a credit agreement, or the 2016 Credit Agreement, with Bank of America, N.A., or Bank of America, as administrative agent, swing line lender and letters of credit issuer; and KeyBank, National Association, or KeyBank, as syndication agent and letters of credit issuer, to obtain a revolving line of credit with an aggregate maximum principal amount of $100,000,000, or the 2016 Line of Credit, subject to certain terms and conditions.
On August 25, 2016, we also entered into separate revolving notes, or the Revolving Notes, with each of Bank of America and KeyBank, whereby we promised to pay the principal amount of each revolving loan and accrued interest to the respective lender or its registered assigns, in accordance with the terms and conditions of the 2016 Credit Agreement.
On October 31, 2017, we entered into an amendment to the 2016 Credit Agreement, or the Amendment, with Bank of America, as administrative agent, and the subsidiary guarantors and lenders named therein. The material terms of the Amendment provided for: (i) a $50,000,000 increase in the revolving line of credit from an aggregate principal amount of $100,000,000 to $150,000,000; (ii) a term loan with an aggregate maximum principal amount of $50,000,000, that would have
108
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
matured on August 25, 2019; (iii) our right, upon at least five business days’ prior written notice to Bank of America, to increase the 2016 Line of Credit or term loan provided that the aggregate principal amount of all such increases and additions would not have exceeded $300,000,000; (iv) a revision to the definition of Threshold Amount, as defined in the 2016 Credit Agreement, to reflect an increase in such amount for any Recourse Indebtedness, as defined in the 2016 Credit Agreement, to $20,000,000, and an increase in such amount for any Non-Recourse Indebtedness, as defined in the 2016 Credit Agreement, to $50,000,000; (v) the revision of certain Unencumbered Property Pool Criteria, as defined in the 2016 Credit Agreement; and (vi) an increase in the maximum Consolidated Secured Leverage Ratio, as defined in the 2016 Credit Agreement, to be equal to or less than 40.0%. As a result of the Amendment, our aggregate borrowing capacity under the 2016 Line of Credit and the term loan, or collectively, the 2017 Credit Facility, was $200,000,000.
On September 28, 2018, we entered into a second amendment to the 2016 Credit Agreement, or the Second Amendment, with Bank of America, as administrative agent, and the subsidiary guarantors and lenders named therein. The material terms of the Second Amendment provided for an increase in the term loan commitment by an aggregate amount equal to $150,000,000. As a result of the Second Amendment, the aggregate borrowing capacity under the 2017 Credit Facility was $350,000,000. Except as modified by the Second Amendment, the material terms of the 2016 Credit Agreement, as amended, remained in full force and effect.
On November 20, 2018, we, through our operating partnership, terminated the 2016 Credit Agreement, as amended, and related separate revolving notes with each of Bank of America and KeyBank and entered into the 2018 Credit Agreement as described below. We currently do not have any obligations under the 2016 Credit Agreement, as amended, and related separate revolving notes.
On November 20, 2018, we, through our operating partnership as borrower, and certain of our subsidiaries, or the subsidiary guarantors, and us, collectively as guarantors, entered into a credit agreement, or the 2018 Credit Agreement, with Bank of America, as administrative agent, swing line lender and letters of credit issuer; KeyBank, as syndication agent and letters of credit issuer; Citizens Bank, National Association, as syndication agent, joint lead arranger and joint bookrunner; Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as joint lead arranger and joint bookrunner; KeyBanc Capital Markets, as joint lead arranger and joint bookrunner; and the lenders named therein, to obtain a credit facility with an aggregate maximum principal amount of $400,000,000, or the 2018 Credit Facility. The 2018 Credit Facility consisted of a senior unsecured revolving credit facility in the initial aggregate amount of $150,000,000 and a senior unsecured term loan facility in the initial aggregate amount of $250,000,000, which consisted of: (i) a $200,000,000 term loan made on November 20, 2018 and (ii) an up to $50,000,000 delayed-draw term loan made one additional time during the Term Loan Delayed Draw Commitment Period, as defined in the 2018 Credit Agreement. Such delayed draw was made on January 18, 2019. The proceeds of loans made under the 2018 Credit Facility may be used for refinancing existing indebtedness and for general corporate purposes including for working capital, capital expenditures and other corporate purposes not inconsistent with obligations under the 2018 Credit Agreement. We may obtain up to $20,000,000 in the form of standby letters of credit and up to $50,000,000 in the form of swing line loans. The 2018 Credit Facility matures on November 19, 2021 and may be extended for one 12-month period during the term of the 2018 Credit Agreement subject to satisfaction of certain conditions, including payment of an extension fee.
On November 1, 2019, we entered into an amendment to the 2018 Credit Agreement, or the 2019 Amendment, with Bank of America, KeyBank and a syndicate of other banks, as lenders. The material terms of the 2019 Amendment provided for an increase in the term loan commitment by $45,000,000 and an increase in the revolving credit facility by $85,000,000. As a result of the 2019 Amendment, the aggregate borrowing capacity under the 2018 Credit Facility was $530,000,000. Except as modified by the 2019 Amendment, the material terms of the 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended, remain in full force and effect.
The maximum principal amount of the 2018 Credit Facility may be increased by up to $120,000,000, for a total principal amount of $650,000,000, subject to: (i) the terms of the 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended; and (ii) at least five business days prior written notice to Bank of America.
At our option, the 2018 Credit Facility bears interest at per annum rates equal to (a)(i) the Eurodollar Rate, as defined in the 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended, plus (ii) a margin ranging from 1.70% to 2.20% based on our Consolidated Leverage Ratio, as defined in the 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended, or (b)(i) the greater of: (1) the prime rate publicly announced by Bank of America, (2) the Federal Funds Rate, as defined in the 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended, plus 0.50%, (3) the one-month Eurodollar Rate plus 1.00%, and (4) 0.00%, plus (ii) a margin ranging from 0.70% to 1.20% based on our Consolidated Leverage Ratio. Accrued interest on the 2018 Credit Facility is payable monthly. The loans may be repaid in whole or in part without prepayment premium or penalty, subject to certain conditions.
109
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
We are required to pay a fee on the unused portion of the lenders’ commitments under the 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended, at a per annum rate equal to 0.20% if the average daily used amount is greater than 50.00% of the commitments and 0.25% if the average daily used amount is less than or equal to 50.00% of the commitments, which fee shall be measured and payable on a quarterly basis.
The 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended, contains various affirmative and negative covenants that are customary for credit facilities and transactions of this type, including limitations on the incurrence of debt by our operating partnership and its subsidiaries and limitations on secured recourse indebtedness. The 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended, also imposes certain financial covenants based on the following criteria, which are specifically defined in the 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended: (a) Consolidated Leverage Ratio; (b) Consolidated Secured Leverage Ratio; (c) Consolidated Tangible Net Worth; (d) Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio; (e) Secured Recourse Indebtedness; (f) Consolidated Unencumbered Leverage Ratio; (g) Consolidated Unencumbered Interest Coverage Ratio; and (h) Unencumbered Indebtedness Yield.
In the event of default, Bank of America has the right to terminate the commitment of each Lender, as defined in the 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended, to make Loans, as defined in the 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended, and any obligation of the L/C Issuer, as defined in the 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended, to make L/C Credit Extensions, as defined in the 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended, under the 2018 Credit Agreement, as amended, and to accelerate the payment on any unpaid principal amount of all outstanding loans and interest thereon.
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, our aggregate borrowing capacity under the 2018 Credit Facility was $530,000,000 and $400,000,000, respectively. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, borrowings outstanding totaled $396,800,000 and $275,000,000, respectively, and the weighted average interest rate on such borrowings outstanding was 3.50% and 4.25%, respectively, per annum.
8. Derivative Financial Instruments
We record derivative financial instruments in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets as either an asset or a liability measured at fair value. We did not have any derivative financial instruments as of December 31, 2018. The following table lists the derivative financial instruments held by us as of December 31, 2019, which are included in security deposits, prepaid rent and other liabilities in our accompanying consolidated balance sheet:
Instrument | Notional Amount | Index | Interest Rate | Maturity Date | Fair Value | |||||||||
Swap | $ | 139,500,000 | one month LIBOR | 2.49% | 11/19/21 | $ | 2,441,000 | |||||||
Swap | 58,800,000 | one month LIBOR | 2.49% | 11/19/21 | 1,029,000 | |||||||||
Swap | 36,700,000 | one month LIBOR | 2.49% | 11/19/21 | 642,000 | |||||||||
Swap | 15,000,000 | one month LIBOR | 2.53% | 11/19/21 | 273,000 | |||||||||
$ | 250,000,000 | $ | 4,385,000 | |||||||||||
ASC Topic 815 permits special hedge accounting if certain requirements are met. Hedge accounting allows for gains and losses on derivatives designated as hedges to be offset by the change in value of the hedged item or items or to be deferred in other comprehensive income (loss). As of December 31, 2019, none of our derivative financial instruments were designated as hedges. Derivative financial instruments not designated as hedges are not speculative and are used to manage our exposure to interest rate movements, but do not meet the strict hedge accounting requirements of ASC Topic 815. For the year ended December 31, 2018, we did not have any derivative financial instruments. For the year ended December 31, 2019, we recorded $4,385,000 as an increase to interest expense in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations related to the change in the fair value of our derivative financial instruments.
See Note 14, Fair Value Measurements, for a further discussion of the fair value of our derivative financial instruments.
110
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
9. Identified Intangible Liabilities, Net
Identified intangible liabilities, net consisted of the following as of December 31, 2019 and 2018:
___________
December 31, | |||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Below-market leases, net of accumulated amortization of $702,000 and $678,000 as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively (with a weighted average remaining life of 11.3 years and 5.7 years as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively) | $ | 1,601,000 | $ | 1,245,000 | |||
Above-market leasehold interests, net of accumulated amortization of $13,000 as of December 31, 2018 (with a weighted average remaining life of 51.2 years as of December 31, 2018)(1) | — | 382,000 | |||||
Total | $ | 1,601,000 | $ | 1,627,000 | |||
(1) | Such amount related to our ownership of fee simple interests in the building and improvements of eight of our buildings that are subject to respective ground leases. Upon our adoption of ASC Topic 842 on January 1, 2019, such amount was reclassed to operating lease right-of-use assets, net in our accompanying consolidated balance sheet. See Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies — Leases, and Note 16, Leases, for a further discussion. |
Amortization expense on identified intangible liabilities for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 was$517,000, $380,000 and $291,000, respectively, which included $517,000, $373,000 and $285,000, respectively, of amortization recorded to real estate revenue for below-market leases and $0, $7,000 and $6,000, respectively, of amortization recorded against real estate revenue for above-market leasehold interests in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
The aggregate weighted average remaining life of the identified intangible liabilities was 11.3 years and 16.4 years as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. As of December 31, 2019, estimated amortization expense on the identified intangible liabilities for each of the next five years ending December 31 and thereafter was as follows:
Year | Amount | |||
2020 | $ | 299,000 | ||
2021 | 243,000 | |||
2022 | 217,000 | |||
2023 | 207,000 | |||
2024 | 161,000 | |||
Thereafter | 474,000 | |||
Total | $ | 1,601,000 | ||
10. Commitments and Contingencies
Litigation
We are not presently subject to any material litigation nor, to our knowledge, is any material litigation threatened against us, which if determined unfavorably to us, would have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Environmental Matters
We follow a policy of monitoring our properties for the presence of hazardous or toxic substances. While there can be no assurance that a material environmental liability does not exist at our properties, we are not currently aware of any environmental liability with respect to our properties that would have a material effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows. Further, we are not aware of any material environmental liability or any unasserted claim or assessment with respect to an environmental liability that we believe would require additional disclosure or the recording of a loss contingency.
111
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Other
Our other commitments and contingencies include the usual obligations of real estate owners and operators in the normal course of business, which include calls/puts to sell/acquire properties. In our view, these matters are not expected to have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
11. Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, our advisor owned all of our 208 partnership units outstanding in our operating partnership. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we owned greater than a 99.99% general partnership interest in our operating partnership, and our advisor owned less than a 0.01% limited partnership interest in our operating partnership. The noncontrolling interest of our advisor in our operating partnership, which has redemption features outside of our control, is accounted for as a redeemable noncontrolling interest and is presented outside of permanent equity in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets. See Note 13, Related Party Transactions — Liquidity Stage — Subordinated Participation Interest — Subordinated Distribution Upon Listing, and Note 13, Related Party Transactions — Subordinated Distribution Upon Termination, for a further discussion of the redemption features of the limited partnership units.
In connection with our acquisitions of Central Florida Senior Housing Portfolio, Pinnacle Beaumont ALF and Pinnacle Warrenton ALF, we own approximately 98.0% of the joint ventures with an affiliate of Meridian. The noncontrolling interests held by Meridian have redemption features outside of our control and are accounted for as redeemable noncontrolling interests in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
We record the carrying amount of redeemable noncontrolling interests at the greater of: (i) the initial carrying amount, increased or decreased for the noncontrolling interests’ share of net income or loss and distributions; or (ii) the redemption value. The changes in the carrying amount of redeemable noncontrolling interests consisted of the following for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018:
December 31, | ||||||||
2019 | 2018 | |||||||
Beginning balance | $ | 1,371,000 | $ | 1,002,000 | ||||
Additions | 151,000 | 369,000 | ||||||
Distributions | (151,000 | ) | — | |||||
Fair value adjustment to redemption value | 173,000 | 232,000 | ||||||
Net loss attributable to redeemable noncontrolling interests | (82,000 | ) | (232,000 | ) | ||||
Ending balance | $ | 1,462,000 | $ | 1,371,000 | ||||
12. Equity
Preferred Stock
Our charter authorizes us to issue 200,000,000 shares of our preferred stock, par value $0.01 per share. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, no shares of our preferred stock were issued and outstanding.
Common Stock
Our charter authorizes us to issue 1,000,000,000 shares of our common stock, par value $0.01 per share. On February 6, 2015, our advisor acquired shares of our Class T common stock for total cash consideration of $200,000 and was admitted as our initial stockholder. We used the proceeds from the sale of shares of our Class T common stock to our advisor to make an initial capital contribution to our operating partnership. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, our advisor owned 20,833 shares of our Class T common stock. We commenced our initial offering of shares of our common stock on February 16, 2016, and as of such date we were initially offering to the public up to $3,150,000,000 in shares of our Class T common stock, consisting of up to $3,000,000,000 in shares of our Class T common stock at a price of $10.00 per share in the primary portion of our initial offering and up to $150,000,000 in shares of our Class T common stock for $9.50 per share pursuant to the DRIP. Effective June 17, 2016, we reallocated certain of the unsold shares of our Class T common stock being offered and began offering shares of our Class I common stock, such that we were offering up to approximately $2,800,000,000 in shares of Class T common stock and $200,000,000 in shares of Class I common stock in the primary portion of our initial offering, and up to an aggregate of $150,000,000 in shares of our Class T and Class I common stock pursuant to the DRIP. Subsequent to the reallocation, of the
112
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
1,000,000,000 shares of common stock authorized pursuant to our charter, 900,000,000 shares are classified as Class T common stock and 100,000,000 shares are classified as Class I common stock.
The shares of our Class T common stock in the primary portion of our initial offering were being offered at a price of $10.00 per share prior to April 11, 2018. The shares of our Class I common stock in the primary portion of our initial offering were being offered at a price of $9.30 per share prior to March 1, 2017 and $9.21 per share from March 1, 2017 to April 10, 2018. The shares of our Class T and Class I common stock issued pursuant to the DRIP were sold at a price of $9.50 per share prior to January 1, 2017 and $9.40 per share from January 1, 2017 to April 10, 2018. On April 6, 2018, our board, at the recommendation of the audit committee of our board, comprised solely of independent directors, unanimously approved and established an estimated per share net asset value, or NAV, of our common stock of $9.65. As a result, on April 6, 2018, our board unanimously approved revised offering prices for each class of shares of our common stock to be sold in our initial offering based on the estimated per share NAV of our Class T and Class I common stock of $9.65 plus any applicable per share up-front selling commissions and dealer manager fees funded by us, effective April 11, 2018. Accordingly, the revised offering price for shares of our Class T common stock and Class I common stock sold pursuant to the primary portion of our initial offering on or after April 11, 2018 was $10.05 per share and $9.65 per share, respectively. On February 15, 2019, we terminated our initial offering. We continue to offer shares of our common stock pursuant to the 2019 DRIP Offering. See the “Distribution Reinvestment Plan” section below for a further discussion.
Each share of our common stock, regardless of class, will be entitled to one vote per share on matters presented to the common stockholders for approval; provided, however, that stockholders of one share class shall have exclusive voting rights on any amendment to our charter that would alter only the contract rights of that share class, and no stockholders of another share class shall be entitled to vote thereon.
Through December 31, 2019, we had issued 75,639,681 aggregate shares of our Class T and Class I common stock in connection with the primary portion of our initial offering and 5,513,699 aggregate shares of our Class T and Class I common stock pursuant to our DRIP Offerings. We also granted an aggregate of 82,500 shares of our restricted Class T common stock to our independent directors and repurchased 1,356,839 shares of our common stock under our share repurchase plan through December 31, 2019. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we had 79,899,874 and 69,254,971 aggregate shares of our Class T and Class I common stock, respectively, issued and outstanding.
Distribution Reinvestment Plan
We had registered and reserved $150,000,000 in shares of our common stock for sale pursuant to the DRIP in our initial offering. The DRIP allows stockholders to purchase additional Class T shares and Class I shares of our common stock through the reinvestment of distributions during our initial offering. Pursuant to the DRIP, distributions with respect to Class T shares are reinvested in Class T shares and distributions with respect to Class I shares are reinvested in Class I shares. On February 15, 2019, we terminated our initial offering. We continue to offer up to $100,000,000 in shares of our common stock pursuant to the 2019 DRIP Offering.
Since April 6, 2018, our board has approved and established an estimated per share NAV on at least an annual basis. Commencing with the distribution payment to stockholders paid in the month following such board approval, shares of our common stock issued pursuant the DRIP were or will be issued at the current estimated per share NAV until such time as our board determines an updated estimated per share NAV. The following is a summary of our historical and current estimated per share NAV of our Class T and Class I common stock:
Approval Date by our Board | Established Per Share NAV (Unaudited) | |||
04/06/18 | $ | 9.65 | ||
04/04/19 | $ | 9.54 | ||
113
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, $25,533,000, $17,612,000 and $8,689,000, respectively, in distributions were reinvested and 2,666,913, 1,838,711 and 924,358 shares of our common stock, respectively, were issued pursuant to our DRIP Offerings. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, a total of $52,630,000 and $27,097,000, respectively, in distributions were reinvested that resulted in 5,513,699 and 2,846,786 shares of our common stock, respectively, being issued pursuant to our DRIP Offerings.
Share Repurchase Plan
In February 2016, our board approved a share repurchase plan. The share repurchase plan allows for repurchases of shares of our common stock by us when certain criteria are met. Share repurchases will be made at the sole discretion of our board. Subject to the availability of the funds for share repurchases, we will limit the number of shares of our common stock repurchased during any calendar year to 5.0% of the weighted average number of shares of our common stock outstanding during the prior calendar year; provided, however, that shares subject to a repurchase requested upon the death of a stockholder will not be subject to this cap. Funds for the repurchase of shares of our common stock come exclusively from the cumulative proceeds we receive from the sale of shares of our common stock pursuant to our DRIP Offerings.
All repurchases of our shares of common stock are subject to a one-year holding period, except for repurchases made in connection with a stockholder’s death or “qualifying disability,” as defined in our share repurchase plan. Further, all share repurchases are repurchased following a one-year holding period at a price between 92.5% to 100% of each stockholder’s repurchase amount depending on the period of time their shares have been held. During our initial offering and with respect to shares repurchased for the quarter ending March 31, 2019, the repurchase amount for shares repurchased under our share repurchase plan was equal to the lesser of (i) the amount per share that a stockholder paid for their shares of our common stock, or (ii) the per share offering price in our initial offering. Commencing with shares repurchased for the quarter ending June 30, 2019, the repurchase amount for shares repurchased under our share repurchase plan is the lesser of (i) the amount per share the stockholder paid for their shares of our common stock, or (ii) the most recent estimated value of one share of the applicable class of common stock as determined by our board. See the summary of our historical and current estimated per share NAV in the “Distribution Reinvestment Plan” section above. However, if shares of our common stock are repurchased in connection with a stockholder’s death or qualifying disability, the repurchase price will be no less than 100% of the price paid to acquire the shares of our common stock from us. Furthermore, our share repurchase plan provides that if there are insufficient funds to honor all repurchase requests, pending requests will be honored among all requests for repurchase in any given repurchase period, as follows: first, pro rata as to repurchases sought upon a stockholder’s death; next, pro rata as to repurchases sought by stockholders with a qualifying disability; and, finally, pro rata as to other repurchase requests.
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we received share repurchase requests and repurchased 928,675, 350,418 and 77,746 shares of our common stock, respectively, for an aggregate of $8,609,000, $3,312,000 and $735,000, respectively, at an average repurchase price of $9.27, $9.45 and $9.45 per share, respectively. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we received share repurchase requests and repurchased 1,356,839 and 428,164 shares of our common stock, respectively, for an aggregate of $12,656,000 and $4,047,000, respectively, at an average repurchase price of $9.33 and $9.45 per share, respectively. All shares were repurchased using the cumulative proceeds we received from the sale of shares of our common stock pursuant to our DRIP Offerings.
2015 Incentive Plan
We adopted our incentive plan pursuant to which our board, or a committee of our independent directors, may make grants of options, restricted shares of common stock, stock purchase rights, stock appreciation rights or other awards to our independent directors, employees and consultants. The maximum number of shares of our common stock that may be issued pursuant to our incentive plan is 4,000,000 shares. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we granted an aggregate of 22,500 shares of our restricted Class T common stock at a weighted average grant date fair value of $9.54, $9.65 and $10.00 per share, respectively, to our independent directors in connection with their re-election to our board or in consideration for their past services rendered. Such shares vested 20.0% immediately on the grant date and 20.0% will vest on each of the first four anniversaries of the grant date. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we recognized stock compensation expense of $207,000, $185,000 and $131,000, respectively, which is included in general and administrative in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
114
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Offering Costs
Selling Commissions
We generally paid our dealer manager selling commissions of up to 3.0% of the gross offering proceeds from the sale of Class T shares of our common stock pursuant to the primary portion of our initial offering. Our dealer manager was permitted to enter into participating dealer agreements with participating dealers that provided for a reduction or waiver of selling commissions. To the extent that selling commissions were less than 3.0% of the gross offering proceeds for any Class T shares sold, such reduction in selling commissions was accompanied by a corresponding reduction in the applicable per share purchase price for purchases of such shares. No selling commissions were payable on Class I shares or shares of our common stock sold pursuant to our DRIP Offerings. Our dealer manager was permitted to re-allow all or a portion of these fees to participating broker-dealers. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we incurred $2,241,000, $6,983,000 and $8,329,000, respectively, in selling commissions to our dealer manager. Such commissions were charged to stockholders’ equity as such amounts were paid to our dealer manager from the gross proceeds of our initial offering.
Dealer Manager Fee
With respect to shares of our Class T common stock, our dealer manager generally received a dealer manager fee of up to 3.0% of the gross offering proceeds from the sale of Class T shares of our common stock pursuant to our initial offering, of which 1.0% of the gross offering proceeds was funded by us and up to an amount equal to 2.0% of the gross offering proceeds was funded by our advisor. With respect to shares of our Class I common stock, prior to March 1, 2017, our dealer manager generally received a dealer manager fee up to 3.0% of the gross offering proceeds from the sale of Class I shares of our common stock pursuant to the primary portion of our initial offering, of which 1.0% of the gross offering proceeds was funded by us and an amount equal to 2.0% of the gross offering proceeds was funded by our advisor. Effective March 1, 2017, our dealer manager generally received a dealer manager fee up to an amount equal to 1.5% of the gross offering proceeds from the sale of Class I shares pursuant the primary portion of our initial offering, all of which was funded by our advisor. Our dealer manager was permitted to enter into participating dealer agreements with participating dealers that provided for a reduction or waiver of dealer manager fees. To the extent that the dealer manager fee was less than 3.0% of the gross offering proceeds for any Class T shares sold and less than 1.5% of the gross offering proceeds for any Class I shares sold, such reduction was applied first to the portion of the dealer manager fee funded by our advisor. To the extent that any reduction in dealer manager fee exceeded the portion of the dealer manager fee funded by our advisor, such excess reduction was accompanied by a corresponding reduction in the applicable per share purchase price for purchases of such shares. No dealer manager fee was payable on shares of our common stock sold pursuant to our DRIP Offerings. Our dealer manager was permitted to re-allow all or a portion of these fees to participating broker-dealers.
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we incurred $759,000, $2,364,000 and $2,844,000, respectively, in dealer manager fees to our dealer manager. Such fees were charged to stockholders’ equity as such amounts were paid to our dealer manager or its affiliates from the gross proceeds of our initial offering. See Note 13, Related Party Transactions — Offering Stage — Dealer Manager Fee, for a further discussion of the dealer manager fee funded by our advisor.
Stockholder Servicing Fee
We pay our dealer manager a quarterly stockholder servicing fee with respect to our Class T shares sold as additional compensation to the dealer manager and participating broker-dealers. No stockholder servicing fee is paid with respect to Class I shares or shares of our common stock sold pursuant to our DRIP Offerings. The stockholder servicing fee accrues daily in an amount equal to 1/365th of 1.0% of the purchase price per share of our Class T shares sold in the primary portion of our initial offering and, in the aggregate will not exceed an amount equal to 4.0% of the gross proceeds from the sale of Class T shares in the primary portion of our initial offering. We will cease paying the stockholder servicing fee with respect to our Class T shares sold in the primary portion of our initial offering upon the occurrence of certain defined events. Our dealer manager may re-allow to participating broker-dealers all or a portion of the stockholder servicing fee for services that such participating broker-dealers perform in connection with the shares of our Class T common stock. By agreement with participating broker-dealers, such stockholder servicing fee may be reduced or limited.
115
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Following the termination of our initial offering on February 15, 2019, we no longer incur additional stockholder servicing fees. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we incurred $2,573,000, $8,069,000 and $10,421,000, respectively, in stockholder servicing fees to our dealer manager. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we accrued $12,610,000 and $16,395,000, respectively, in connection with the stockholder servicing fee payable, which is included in accounts payable and accrued liabilities with a corresponding offset to stockholders’ equity in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
13. Related Party Transactions
Fees and Expenses Paid to Affiliates
All of our executive officers and one of our non-independent directors are also executive officers and employees and/or holders of a direct or indirect interest in our advisor, one of our co-sponsors or other affiliated entities. We are affiliated with our advisor, American Healthcare Investors and AHI Group Holdings; however, we are not affiliated with Griffin Capital, our dealer manager, Colony Capital or Mr. Flaherty. We entered into the Advisory Agreement, which entitles our advisor and its affiliates to specified compensation for certain services, as well as reimbursement of certain expenses. Our board, including a majority of our independent directors, has reviewed the material transactions between our affiliates and us during the year ended December 31, 2019. Set forth below is a description of the transactions with affiliates. We believe that we have executed all of the transactions set forth below on terms that are fair and reasonable to us and on terms no less favorable to us than those available from unaffiliated third parties. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we incurred $16,296,000, $22,355,000 and $17,650,000, respectively, in fees and expenses to our affiliates as detailed below.
Offering Stage
Dealer Manager Fee
With respect to shares of our Class T common stock, our dealer manager generally received a dealer manager fee of up to 3.0% of the gross offering proceeds from the sale of Class T shares of our common stock pursuant to the primary portion of our initial offering, of which 1.0% of the gross offering proceeds was funded by us and up to an amount equal to 2.0% of the gross offering proceeds was funded by our advisor. With respect to shares of our Class I common stock, prior to March 1, 2017, our dealer manager generally received a dealer manager fee up to 3.0% of the gross offering proceeds from the sale of Class I shares of our common stock pursuant to the primary portion of our initial offering, of which 1.0% of the gross offering proceeds was funded by us and an amount equal to 2.0% of the gross offering proceeds was funded by our advisor. Effective March 1, 2017, our dealer manager generally received a dealer manager fee up to an amount equal to 1.5% of the gross offering proceeds from the sale of Class I shares pursuant to the primary portion of our initial offering, all of which was funded by our advisor. Our dealer manager was permitted to enter into participating dealer agreements with participating dealers that provided for a reduction or waiver of dealer manager fees. To the extent that the dealer manager fee was less than 3.0% of the gross offering proceeds for any Class T shares sold and less than 1.5% of the gross offering proceeds for any Class I shares sold, such reduction was applied first to the portion of the dealer manager fee funded by our advisor. To the extent that any reduction in dealer manager fee exceeded the portion of the dealer manager fee funded by our advisor, such excess reduction was accompanied by a corresponding reduction in the applicable per share purchase price for purchases of such shares. No dealer manager fee was payable on shares of our common stock sold pursuant to our DRIP Offerings. Our advisor recouped the portion of the dealer manager fee it funded through the receipt of the Contingent Advisor Payment from us, as described below, through the payment of acquisition fees.
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we incurred $1,687,000, $4,878,000 and $5,851,000, respectively, payable to our advisor as part of the Contingent Advisor Payment in connection with the dealer manager fee that our advisor had incurred. Such fee was charged to stockholders’ equity as incurred with a corresponding offset to accounts payable due to affiliates in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets. See Note 12, Equity — Offering Costs — Dealer Manager Fee, for a further discussion of the dealer manager fee funded by us.
Other Organizational and Offering Expenses
Our other organizational and offering expenses incurred in connection with the primary portion of our initial offering (other than selling commissions, the dealer manager fee and the stockholder servicing fee) were funded by our advisor. Our advisor recouped such expenses it funded through the receipt of the Contingent Advisor Payment from us, as described below, through the payment of acquisition fees. No other organizational and offering expenses were paid with respect to shares of our common stock sold pursuant to our DRIP Offerings.
116
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we incurred $114,000, $1,465,000 and $1,583,000, respectively, payable to our advisor as part of the Contingent Advisor Payment in connection with the other organizational and offering expenses that our advisor had incurred. Such expenses were charged to stockholders’ equity as incurred with a corresponding offset to accounts payable due to affiliates in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Acquisition and Development Stage
Acquisition Fee
We pay our advisor or its affiliates an acquisition fee of up to 4.50% of the contract purchase price, including any contingent or earn-out payments that may be paid, of each property we acquire or, with respect to any real estate-related investment we originate or acquire, up to 4.25% of the origination or acquisition price, including any contingent or earn-out payments that may be paid. The 4.50% or 4.25% acquisition fees consist of a 2.25% or 2.00% base acquisition fee, or the base acquisition fee, for real estate and real estate-related acquisitions, respectively, and an additional 2.25% contingent advisor payment, or the Contingent Advisor Payment, as applicable. The Contingent Advisor Payment allowed our advisor to recoup the portion of the dealer manager fee and other organizational and offering expenses funded by our advisor. Therefore, the amount of the Contingent Advisor Payment paid upon the closing of an acquisition did not exceed the then outstanding amounts paid by our advisor for dealer manager fees and other organizational and offering expenses at the time of such closing. For these purposes, the amounts paid by our advisor and considered as “outstanding” were reduced by the amount of the Contingent Advisor Payment previously paid. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the initial $7,500,000 of amounts paid by our advisor to fund the dealer manager fee and other organizational and offering expenses, or the Contingent Advisor Payment Holdback, was retained by us until February 2019, the termination of our initial offering and the third anniversary of the commencement date of our initial offering, at which time such amount was paid to our advisor. Our advisor or its affiliates are entitled to receive these acquisition fees for properties and real estate-related investments acquired with funds raised in our initial offering, including acquisitions completed after the termination of the Advisory Agreement (including imputed leverage of 50.0% on funds raised in our initial offering), or funded with net proceeds from the sale of a property or real estate-related investment, subject to certain conditions. Our advisor may waive or defer all or a portion of the acquisition fee at any time and from time to time, in our advisor’s sole discretion.
The base acquisition fee in connection with the acquisition of real estate investments accounted for as business combinations is expensed as incurred and included in acquisition related expenses in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations. The base acquisition fee in connection with the acquisition of properties accounted for as asset acquisitions or the acquisition of real estate-related investments is capitalized as part of the associated investment in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we paid base acquisition fees of $4,595,000, $10,096,000 and $7,342,000, respectively, to our advisor. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we recorded $0 and $7,866,000, respectively, as part of the Contingent Advisor Payment, which was included in accounts payable due to affiliates with a corresponding offset to stockholders’ equity in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we paid $20,982,000 and $11,316,000, respectively, in Contingent Advisor Payments to our advisor. For a further discussion of amounts paid in connection with the Contingent Advisor Payment, see “Dealer Manager Fee” and “Other Organizational and Offering Expenses,” above. In addition, see Note 3, Real Estate Investments, Net and Note 21, Subsequent Events, for a further discussion.
Development Fee
In the event our advisor or its affiliates provide development-related services, we pay our advisor or its affiliates a development fee in an amount that is usual and customary for comparable services rendered for similar projects in the geographic market where the services are provided; however, we will not pay a development fee to our advisor or its affiliates if our advisor or its affiliates elect to receive an acquisition fee based on the cost of such development.
For the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, we incurred development fees of $34,000 and $6,000, respectively, to our advisor, which was expensed as incurred and included in acquisition related expenses in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations. For the year ended December 31, 2017, we did not incur any development fees to our advisor or its affiliates.
Reimbursement of Acquisition Expenses
We reimburse our advisor or its affiliates for acquisition expenses related to selecting, evaluating and acquiring assets, which are reimbursed regardless of whether an asset is acquired. The reimbursement of acquisition expenses, acquisition fees, total development costs and real estate commissions paid to unaffiliated third parties will not exceed, in the aggregate, 6.0% of
117
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
the contract purchase price of the property or real estate-related investments, unless fees in excess of such limits are approved by a majority of our directors, including a majority of our independent directors, not otherwise interested in the transaction. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, such fees and expenses paid did not exceed 6.0% of the contract purchase price of our property acquisitions, except with respect to our acquisitions of Auburn MOB, Pottsville MOB, Lafayette Assisted Living Portfolio, Athens MOB Portfolio, Northern California Senior Housing Portfolio, Pinnacle Warrenton ALF, Glendale MOB, Missouri SNF Portfolio, Flemington MOB Portfolio and West Des Moines SNF, which excess fees and expenses were approved by our directors as set forth above.
Reimbursements of acquisition expenses in connection with the acquisition of real estate investments accounted for as business combinations are expensed as incurred and included in acquisition related expenses in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Reimbursements of acquisition expenses in connection with the acquisition of properties accounted for as asset acquisitions or the acquisition of real estate-related investments are capitalized as part of the associated investment in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets. For each of the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we incurred $0, $2,000 and $2,000, respectively, in acquisition expenses to our advisor or its affiliates.
Operational Stage
Asset Management Fee
We pay our advisor or its affiliates a monthly fee for services rendered in connection with the management of our assets equal to one-twelfth of 0.80% of average invested assets. For such purposes, average invested assets means the average of the aggregate book value of our assets invested in real estate investments and real estate-related investments, before deducting depreciation, amortization, bad debt and other similar non-cash reserves, computed by taking the average of such values at the end of each month during the period of calculation.
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we incurred $8,276,000, $4,975,000 and $2,344,000, respectively, in asset management fees to our advisor, which are included in general and administrative in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Property Management Fee
American Healthcare Investors or its designated personnel may provide property management services with respect to our properties or may sub-contract these duties to any third party and provide oversight of such third-party property manager. We pay American Healthcare Investors a monthly management fee equal to a percentage of the gross monthly cash receipts of such property as follows: (i) a property management oversight fee of 1.0% of the gross monthly cash receipts of any stand-alone, single-tenant, net leased property, except for such properties operated utilizing a RIDEA structure, for which we pay a property management oversight fee of 1.5% of the gross monthly cash receipts with respect to such property; (ii) a property management oversight fee of 1.5% of the gross monthly cash receipts of any property that is not a stand-alone, single-tenant, net leased property and for which American Healthcare Investors or its designated personnel provide oversight of a third party that performs the duties of a property manager with respect to such property; or (iii) a fair and reasonable property management fee that is approved by a majority of our directors, including a majority of our independent directors, that is not less favorable to us than terms available from unaffiliated third parties for any property that is not a stand-alone, single-tenant, net leased property and for which American Healthcare Investors or its designated personnel directly serve as the property manager without sub-contracting such duties to a third party.
Property management fees are included in property operating expenses and rental expenses in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we incurred property management fees of $1,220,000, $746,000 and $381,000, respectively, to American Healthcare Investors.
Lease Fees
We pay our advisor or its affiliates a separate fee for any leasing activities in an amount not to exceed the fee customarily charged in arm’s-length transactions by others rendering similar services in the same geographic area for similar properties as determined by a survey of brokers and agents in such area. Such fee is generally expected to range from 3.0% to 6.0% of the gross revenues generated during the initial term of the lease.
118
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Lease fees are capitalized as lease commissions, which are included in other assets, net in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets, and amortized over the term of the lease. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we incurred lease fees of $83,000, $94,000 and $64,000, respectively.
Construction Management Fee
In the event that our advisor or its affiliates assist with planning and coordinating the construction of any capital or tenant improvements, we pay our advisor or its affiliates a construction management fee of up to 5.0% of the cost of such improvements. Construction management fees are capitalized as part of the associated asset and included in real estate investments, net in our accompanying consolidated balance sheets or are expensed and included in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations, as applicable. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we incurred construction management fees of $155,000, $28,000 and $1,000, respectively.
Operating Expenses
We reimburse our advisor or its affiliates for operating expenses incurred in rendering services to us, subject to certain limitations. However, we cannot reimburse our advisor or its affiliates at the end of any fiscal quarter for total operating expenses that, in the four consecutive fiscal quarters then ended, exceed the greater of: (i) 2.0% of our average invested assets, as defined in the Advisory Agreement; or (ii) 25.0% of our net income, as defined in the Advisory Agreement, unless our independent directors determined that such excess expenses were justified based on unusual and nonrecurring factors which they deem sufficient.
The following table reflects our operating expenses as a percentage of average invested assets and as a percentage of net income for the 12 month periods then ended:
12 months ended December 31, | ||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||
Operating expenses as a percentage of average invested assets | 1.2 | % | 1.2 | % | 1.3 | % | ||
Operating expenses as a percentage of net income | 37.2 | % | 28.3 | % | 27.9 | % | ||
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, our operating expenses did not exceed the aforementioned limitations as 2.0% of our average invested assets was greater than 25.0% of our net income. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, our advisor incurred operating expenses on our behalf of $132,000, $65,000 and $82,000, respectively. Operating expenses are generally included in general and administrative in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Compensation for Additional Services
We pay our advisor and its affiliates for services performed for us other than those required to be rendered by our advisor or its affiliates under the Advisory Agreement. The rate of compensation for these services has to be approved by a majority of our board, including a majority of our independent directors, and cannot exceed an amount that would be paid to unaffiliated parties for similar services. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, our advisor and its affiliates were not compensated for any additional services.
Liquidity Stage
Disposition Fees
For services relating to the sale of one or more properties, we pay our advisor or its affiliates a disposition fee up to the lesser of 2.0% of the contract sales price or 50.0% of a customary competitive real estate commission given the circumstances surrounding the sale, in each case as determined by our board, including a majority of our independent directors, upon the provision of a substantial amount of the services in the sales effort. The amount of disposition fees paid, when added to the real estate commissions paid to unaffiliated parties, will not exceed the lesser of the customary competitive real estate commission or an amount equal to 6.0% of the contract sales price. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we did not incur any disposition fees to our advisor or its affiliates.
119
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Subordinated Participation Interest
Subordinated Distribution of Net Sales Proceeds
In the event of liquidation, we will pay our advisor a subordinated distribution of net sales proceeds. The distribution will be equal to 15.0% of the remaining net proceeds from the sales of properties, after distributions to our stockholders, in the aggregate, of: (i) a full return of capital raised from stockholders (less amounts paid to repurchase shares of our common stock pursuant to our share repurchase plan); plus (ii) an annual 6.0% cumulative, non-compounded return on the gross proceeds from the sale of shares of our common stock, as adjusted for distributions of net sales proceeds. Actual amounts to be received depend on the sale prices of properties upon liquidation. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we did not pay any such distributions to our advisor.
Subordinated Distribution Upon Listing
Upon the listing of shares of our common stock on a national securities exchange, in redemption of our advisor’s limited partnership units, we will pay our advisor a distribution equal to 15.0% of the amount by which: (i) the market value of our outstanding common stock at listing plus distributions paid prior to listing exceeds (ii) the sum of the total amount of capital raised from stockholders (less amounts paid to repurchase shares of our common stock pursuant to our share repurchase plan) and the amount of cash equal to an annual 6.0% cumulative, non-compounded return on the gross proceeds from the sale of shares of our common stock through the date of listing. Actual amounts to be received depend upon the market value of our outstanding stock at the time of listing, among other factors. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we did not pay any such distributions to our advisor.
Subordinated Distribution Upon Termination
Pursuant to the Agreement of Limited Partnership, as amended, of our operating partnership upon termination or non-renewal of the Advisory Agreement, our advisor will also be entitled to a subordinated distribution in redemption of its limited partnership units from our operating partnership equal to 15.0% of the amount, if any, by which: (i) the appraised value of our assets on the termination date, less any indebtedness secured by such assets, plus total distributions paid through the termination date, exceeds (ii) the sum of the total amount of capital raised from stockholders (less amounts paid to repurchase shares of our common stock pursuant to our share repurchase plan) and the total amount of cash equal to an annual 6.0% cumulative, non-compounded return on the gross proceeds from the sale of shares of our common stock through the termination date. In addition, our advisor may elect to defer its right to receive a subordinated distribution upon termination until either a listing or other liquidity event, including a liquidation, sale of substantially all of our assets or merger in which our stockholders receive in exchange for their shares of our common stock, shares of a company that are traded on a national securities exchange.
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we did not have any liability related to the subordinated distribution upon termination.
Stock Purchase Plans
On February 29, 2016, our Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors, Jeffrey T. Hanson, our President and Chief Operating Officer, Danny Prosky, and our Executive Vice President and General Counsel, Mathieu B. Streiff, each executed stock purchase plans, or the 2016 Stock Purchase Plans, whereby they each irrevocably agreed to invest 100% of their net after-tax base salary and cash bonus compensation earned as employees of American Healthcare Investors directly into our company by purchasing shares of our Class T common stock. In addition, on February 29, 2016, three Executive Vice Presidents of American Healthcare Investors, including our Executive Vice President of Acquisitions, Stefan K.L. Oh, each executed similar 2016 Stock Purchase Plans whereby they each irrevocably agreed to invest a portion of their net after-tax base salary or a portion of their net after-tax base salary and cash bonus compensation, ranging from 10.0% to 15.0%, as employees of American Healthcare Investors directly into our company by purchasing shares of our Class T common stock. The 2016 Stock Purchase Plans terminated on December 31, 2016.
Purchases of shares of our Class T common stock pursuant to the 2016 Stock Purchase Plans commenced after the initial release from escrow of the minimum offering amount, beginning with the officers’ regularly scheduled payroll payment on April 13, 2016. The shares of Class T common stock were purchased at a price of $9.60 per share, reflecting the purchase price of the shares in our initial offering, exclusive of selling commissions and the dealer manager fee.
120
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
On December 30, 2016, Messrs. Hanson, Prosky and Streiff each executed stock purchase plans for the purchase of shares of our Class I common stock, or the 2017 Stock Purchase Plans, on terms similar to their 2016 Stock Purchase Plans. In addition, on December 30, 2016, Mr. Oh, as well as Wendie Newman and Christopher M. Belford, both of whom were appointed as our Vice Presidents of Asset Management as of June 2017, each executed similar 2017 Stock Purchase Plans whereby they each irrevocably agreed to invest a portion of their net after-tax base salary or a portion of their net after-tax base salary and cash bonus compensation, ranging from 5.0% to 15.0%, earned as employees of American Healthcare Investors directly into our company by purchasing shares of our Class I common stock. The 2017 Stock Purchase Plans terminated on December 31, 2017.
Purchases of shares of our Class I common stock pursuant to the 2017 Stock Purchase Plans commenced beginning with the officers’ regularly scheduled payroll payment on January 23, 2017. The shares of Class I common stock were purchased pursuant to the 2017 Stock Purchase Plans at a price of $9.21 per share, reflecting the purchase price of shares of Class I common stock offered to the public reduced by the dealer manager fees funded by us. No selling commissions, dealer manager fees (including the portion of such dealer manager fees funded by our advisor) or stockholder servicing fees were paid with respect to such sales of our Class I common stock pursuant to the 2017 Stock Purchase Plans.
On December 31, 2017, Messrs. Hanson, Prosky, and Streiff each executed stock purchase plans for the purchase of shares of our Class I common stock, or the 2018 Stock Purchase Plans, on terms similar to their 2017 Stock Purchase Plans. In addition, on December 31, 2017, four Executive Vice Presidents of American Healthcare Investors, including Messrs. Oh and Belford, Ms. Newman and Brian S. Peay, our Chief Financial Officer, each executed similar 2018 Stock Purchase Plans whereby they each irrevocably agreed to invest a portion of their net after-tax base salary or a portion of their net after-tax base salary and cash bonus compensation, ranging from 5.0% to 15.0%, earned on or after January 1, 2018 as employees of American Healthcare Investors directly into shares of our Class I common stock. The 2018 Stock Purchase Plans terminated on December 31, 2018.
Purchases of shares of our Class I common stock pursuant to the 2018 Stock Purchase Plans commenced beginning with the first regularly scheduled payroll payment on January 22, 2018. The shares of Class I common stock were purchased pursuant to the 2018 Stock Purchase Plans at a per share purchase price equal to the per share purchase price of our Class I common stock, which was $9.21 per share prior to April 11, 2018 and $9.65 per share effective as of April 11, 2018. No selling commissions, dealer manager fees (including the portion of such dealer manager fees funded by our advisor) or stockholder servicing fees were paid with respect to such sales of our Class I common stock pursuant to the 2018 Stock Purchase Plans.
For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, our officers invested the following amounts and we issued the following shares of our Class T and Class I common stock pursuant to the applicable stock purchase plan:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Officer’s Name | Title | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | ||||||||||||||||
Jeffrey T. Hanson | Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors | $ | 10,000 | 995 | $ | 329,000 | 34,690 | $ | 263,000 | 28,464 | |||||||||||||
Danny Prosky | President and Chief Operating Officer | 11,000 | 1,103 | 352,000 | 37,111 | 272,000 | 29,480 | ||||||||||||||||
Mathieu B. Streiff | Executive Vice President and General Counsel | 10,000 | 999 | 324,000 | 34,262 | 263,000 | 28,462 | ||||||||||||||||
Brian S. Peay | Chief Financial Officer | 1,000 | 88 | 30,000 | 3,143 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Stefan K.L. Oh | Executive Vice President of Acquisitions | 1,000 | 127 | 34,000 | 3,534 | 32,000 | 3,416 | ||||||||||||||||
Christopher M. Belford | Vice President of Asset Management | 1,000 | 102 | 55,000 | 5,866 | 65,000 | 7,014 | ||||||||||||||||
Wendie Newman | Vice President of Asset Management | 1,000 | 34 | 9,000 | 918 | 8,000 | 828 | ||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 35,000 | 3,448 | $ | 1,133,000 | 119,524 | $ | 903,000 | 97,664 | ||||||||||||||
121
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Accounts Payable Due to Affiliates
The following amounts were outstanding to our affiliates as of December 31, 2019 and 2018:
December 31, | ||||||||
Fee | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Asset management fees | $ | 768,000 | $ | 595,000 | ||||
Property management fees | 145,000 | 97,000 | ||||||
Construction management fees | 65,000 | 18,000 | ||||||
Lease commissions | 21,000 | — | ||||||
Operating expenses | 12,000 | 6,000 | ||||||
Development fees | 4,000 | 6,000 | ||||||
Acquisition fees | 1,000 | — | ||||||
Contingent Advisor Payment | — | 7,866,000 | ||||||
Total | $ | 1,016,000 | $ | 8,588,000 | ||||
14. Fair Value Measurements
Assets and Liabilities Reported at Fair Value
The table below presents our assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2019, aggregated by the level in the fair value hierarchy within which those measurements fall. We did not have any assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2018.
Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets and Liabilities (Level 1) | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | Total | ||||||||||||
Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
Derivative financial instruments | $ | — | $ | 4,385,000 | $ | — | $ | 4,385,000 | |||||||
There were no transfers into or out of fair value measurement levels during the year ended December 31, 2019.
Derivative Financial Instruments
We use interest rate swaps to manage interest rate risk associated with variable-rate debt. The valuation of these instruments is determined using widely accepted valuation techniques including a discounted cash flow analysis on the expected cash flows of each derivative. This analysis reflects the contractual terms of the derivatives, including the period to maturity, and uses observable market-based inputs, including interest rate curves, as well as option volatility. The fair values of interest rate swaps are determined by netting the discounted future fixed cash payments and the discounted expected variable cash receipts. The variable cash receipts are based on an expectation of future interest rates derived from observable market interest rate curves.
We incorporate credit valuation adjustments to appropriately reflect both our own nonperformance risk and the respective counterparty’s nonperformance risk in the fair value measurements. In adjusting the fair value of our derivative contracts for the effect of nonperformance risk, we have considered the impact of netting and any applicable credit enhancements, such as collateral postings, thresholds, mutual puts and guarantees.
Although we have determined that the majority of the inputs used to value our derivative financial instruments fall within Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy, the credit valuation adjustments associated with these instruments utilize Level 3 inputs, such as estimates of current credit spreads, to evaluate the likelihood of default by us and our counterparty. However, as of December 31, 2019, we have assessed the significance of the impact of the credit valuation adjustments on the overall valuation of our derivative positions and have determined that the credit valuation adjustments are not significant to the overall valuation of our derivatives. As a result, we have determined that our derivative valuations in their entirety are classified in Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy.
122
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Financial Instruments Disclosed at Fair Value
Our accompanying consolidated balance sheets include the following financial instruments: cash and cash equivalents, accounts and other receivables, restricted cash, real estate deposits, accounts payable and accrued liabilities, accounts payable due to affiliates, mortgage loans payable and borrowings under the 2018 Credit Facility.
We consider the carrying values of cash and cash equivalents, accounts and other receivables, restricted cash, real estate deposits and accounts payable and accrued liabilities to approximate the fair values for these financial instruments based upon the short period of time between origination of the instruments and their expected realization. The fair value of accounts payable due to affiliates is not determinable due to the related party nature of the accounts payable. These financial assets and liabilities are measured at fair value on a recurring basis based on quoted prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities, and therefore are classified as Level 1 in the fair value hierarchy.
The fair value of our mortgage loans payable and the 2018 Credit Facility is estimated using a discounted cash flow analysis using borrowing rates available to us for debt instruments with similar terms and maturities. We have determined that our mortgage loans payable and the 2018 Credit Facility are classified in Level 2 within the fair value hierarchy as reliance is placed on inputs other than quoted prices that are observable, such as interest rates and yield curves. The carrying amounts and estimated fair values of such financial instruments as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 were as follows:
December 31, | |||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||||||||||
Carrying Amount(1) | Fair Value | Carrying Amount(1) | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
Financial Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
Mortgage loans payable | $ | 26,070,000 | $ | 26,677,000 | $ | 16,892,000 | $ | 16,920,000 | |||||||
Line of credit and term loans | $ | 393,217,000 | $ | 396,891,000 | $ | 270,553,000 | $ | 275,124,000 | |||||||
___________
(1) | Carrying amount is net of any discount/premium and deferred financing costs. |
15. Income Taxes
As a REIT, we generally will not be subject to federal income tax on taxable income that we distribute to our stockholders. We have elected to treat certain of our consolidated subsidiaries as wholly owned taxable REIT subsidiaries, or TRS, pursuant to the Code. TRS may participate in services that would otherwise be considered impermissible for REITs and are subject to federal and state income tax at regular corporate tax rates.
On December 22, 2017, the U.S. government enacted comprehensive tax legislation pursuant to the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, or the Tax Act. The Tax Act makes broad and complex changes to the U.S. tax code, including, but not limited to, reducing the U.S. federal corporate tax rate to 21.0%, eliminating the corporate alternative minimum tax and changing rules related to uses and limitations of net operating loss carryforwards created in tax years beginning after December 31, 2017.
The Tax Act is still unclear in some respects and could be subject to potential amendments and technical corrections. The federal income tax rules dealing with U.S. federal income taxation and REITs are constantly under review by persons involved in the legislative process, the IRS and the U.S. Treasury Department, which results in statutory changes as well as frequent revisions to regulations and interpretations. As a result, the long-term impact of the Tax Act on the overall economy, government revenues, our tenants, us, and the real estate industry cannot be reliably predicted at this time. We continue to work with our tax advisors to determine the full impact that the recent tax legislation as a whole will have on us.
123
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
We did not incur income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2017. The components of income tax (benefit) expense for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 were as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Federal deferred | $ | (1,087,000 | ) | $ | (2,593,000 | ) | |
State deferred | (100,000 | ) | (675,000 | ) | |||
State current | (8,000 | ) | 8,000 | ||||
Valuation allowance | 1,187,000 | 3,268,000 | |||||
Total income tax (benefit) expense | $ | (8,000 | ) | $ | 8,000 | ||
Current Income Tax
Federal and state income taxes are generally a function of the level of income recognized by our TRSs.
Deferred Taxes
Deferred income tax is generally a function of the period’s temporary differences (primarily basis differences between tax and financial reporting for real estate assets and equity investments) and generation of tax net operating losses that may be realized in future periods depending on sufficient taxable income.
We recognize the financial statement effects of an uncertain tax position when it is more likely than not, based on the technical merits of the tax position, that such a position will be sustained upon examination by the relevant tax authorities. If the tax benefit meets the “more likely than not” threshold, the measurement of the tax benefit will be based on our estimate of the ultimate tax benefit to be sustained if audited by the taxing authority. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we did not have any tax benefits or liabilities for uncertain tax positions that we believe should be recognized in our accompanying consolidated financial statements.
We assess the available positive and negative evidence to estimate if sufficient future taxable income will be generated to use the existing deferred tax assets. A valuation allowance is established if we believe it is more likely than not that all or a portion of the deferred tax assets are not realizable. As of December 31, 2019, our valuation allowance fully reserves the net deferred tax asset due to inherent uncertainty of future income. We will continue to monitor industry and economic conditions, and our ability to generate taxable income based on our business plan and available tax planning strategies, which would allow us to utilize the tax benefits of the net deferred tax assets and thereby allow us to reverse all, or a portion of, our valuation allowance in the future.
Any increases or decreases to the deferred income tax assets or liabilities are reflected in income tax benefit or expense in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations. The components of deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 was as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Deferred income tax assets: | |||||||
Fixed assets and intangibles | $ | 2,455,000 | $ | 2,484,000 | |||
Expense accruals and other | 620,000 | 469,000 | |||||
Net operating loss | 1,856,000 | 791,000 | |||||
Valuation allowances | (4,931,000 | ) | (3,744,000 | ) | |||
Total deferred income tax assets | $ | — | $ | — | |||
124
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
At December 31, 2019 and 2018, we had a net operating loss, or NOL, carryforward of $7,179,000 and $2,983,000, respectively, related to the TRSs. These amounts can be used to offset future taxable income, if any. The NOL carryforwards that were incurred before January 1, 2018 begin to expire in 2037 with respect to the TRSs. The NOL carryforwards incurred after December 31, 2017 will be carried forward indefinitely.
Tax Treatment of Distributions
For federal income tax purposes, distributions to stockholders are characterized as ordinary income, capital gain distributions or nontaxable distributions. Nontaxable distributions will reduce U.S. stockholders’ basis (but not below zero) in their shares. The income tax treatment for distributions reportable for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 was as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||
Ordinary income | $ | 10,099,000 | 21.8 | % | $ | 11,909,000 | 37.7 | % | $ | 6,021,000 | 39.9 | % | ||||||||
Capital gain | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Return of capital | 36,317,000 | 78.2 | 19,673,000 | 62.3 | 9,055,000 | 60.1 | ||||||||||||||
$ | 46,416,000 | 100 | % | $ | 31,582,000 | 100 | % | $ | 15,076,000 | 100 | % | |||||||||
Amounts listed above do not include distributions paid on nonvested shares of our restricted common stock which have been separately reported.
16. Leases
Lessor
We have operating leases with tenants that expire at various dates through 2040. For the year ended December 31, 2019, we recognized $74,610,000 of real estate revenue related to operating lease payments, of which $14,878,000 was for variable lease payments. As of December 31, 2019, the following table sets forth the undiscounted cash flows for future minimum base rents due under operating leases for each of the next five years ending December 31 and thereafter for the properties that we wholly own:
Year | Amount | |||
2020 | $ | 62,946,000 | ||
2021 | 61,205,000 | |||
2022 | 58,288,000 | |||
2023 | 53,719,000 | |||
2024 | 48,420,000 | |||
Thereafter | 302,820,000 | |||
Total | $ | 587,398,000 | ||
Future minimum base rents due under operating leases as of December 31, 2018 for each of the next five years ending December 31 and thereafter was as follows:
Year | Amount | |||
2019 | $ | 52,764,000 | ||
2020 | 52,207,000 | |||
2021 | 50,886,000 | |||
2022 | 48,249,000 | |||
2023 | 44,397,000 | |||
Thereafter | 290,103,000 | |||
Total | $ | 538,606,000 | ||
125
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Lessee
We have ground lease obligations that generally require fixed annual rental payments and may also include escalation clauses and renewal options. These leases expire at various dates through 2107, excluding extension options. Certain of our lease agreements include rental payments that are adjusted periodically based on the Consumer Price Index, and may include other variable lease costs (i.e., common area maintenance, property taxes and insurance). Our lease agreements do not contain any material residual value guarantees or material restrictive covenants.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, operating lease costs were $735,000, which are included in rental expenses in our accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Such costs include short-term leases and variable lease costs, which are immaterial. Additional information related to our operating leases as of and for the year ended December 31, 2019 was as follows:
Amount | ||||
Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for new operating lease liabilities | $ | 4,489,000 | ||
Weighted average remaining lease term (in years) | 80.4 | |||
Weighted average discount rate | 5.74 | % | ||
Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of operating lease liabilities: | ||||
Operating cash outflows related to operating leases | $ | 458,000 | ||
As of December 31, 2019, the following table sets forth the undiscounted cash flows of our scheduled obligations for future minimum payments for each of the next five years ending December 31 and thereafter, as well as the reconciliation of those cash flows to operating lease liabilities on the accompanying consolidated balance sheet:
Year | Amount | |||
2020 | $ | 519,000 | ||
2021 | 523,000 | |||
2022 | 526,000 | |||
2023 | 530,000 | |||
2024 | 534,000 | |||
Thereafter | 47,103,000 | |||
Total operating lease payments | 49,735,000 | |||
Less: interest | 39,877,000 | |||
Present value of operating lease liabilities | $ | 9,858,000 | ||
Future minimum operating lease obligations under non-cancelable ground lease obligations as of December 31, 2018 for each of the next five years ending December 31 and thereafter was as follows:
Year | Amount | |||
2019 | $ | 307,000 | ||
2020 | 307,000 | |||
2021 | 307,000 | |||
2022 | 307,000 | |||
2023 | 307,000 | |||
Thereafter | 11,978,000 | |||
Total | $ | 13,513,000 | ||
17. Segment Reporting
As of December 31, 2019, we evaluated our business and made resource allocations based on four reportable business segments — medical office buildings, senior housing, senior housing — RIDEA and skilled nursing facilities.
126
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Our medical office buildings are typically leased to multiple tenants under separate leases, thus requiring active management and responsibility for many of the associated operating expenses (much of which are, or can effectively be, passed through to the tenants). Our senior housing facilities and skilled nursing facilities are primarily single-tenant properties for which we lease the facilities to unaffiliated tenants under triple-net and generally master leases that transfer the obligation for all facility operating costs (including maintenance, repairs, taxes, insurance and capital expenditures) to the tenant. Our senior housing — RIDEA properties include senior housing facilities that are owned and operated utilizing a RIDEA structure.
We evaluate performance based upon segment net operating income. We define segment net operating income as total revenues, less rental expenses and property operating expenses, which excludes depreciation and amortization, general and administrative expenses, acquisition related expenses, interest expense, income or loss from unconsolidated entity, other income and income tax benefit or expense for each segment. We believe that net income (loss), as defined by GAAP, is the most appropriate earnings measurement. However, we believe that segment net operating income serves as an appropriate supplemental performance measure to net income (loss) because it allows investors and our management to measure unlevered property-level operating results and to compare our operating results to the operating results of other real estate companies and between periods on a consistent basis.
Interest expense, depreciation and amortization and other expenses not attributable to individual properties are not allocated to individual segments for purposes of assessing segment performance.
Non-segment assets primarily consist of corporate assets including our investment in unconsolidated entity, cash and cash equivalents, other receivables, real estate deposits and other assets not attributable to individual properties.
Summary information for the reportable segments during the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 was as follows:
Medical Office Buildings | Senior Housing — RIDEA | Senior Housing | Skilled Nursing Facilities | Year Ended December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||
Revenues: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Real estate revenue | $ | 54,508,000 | $ | — | $ | 8,421,000 | $ | 11,681,000 | $ | 74,610,000 | ||||||||||
Resident fees and services | — | 46,160,000 | — | — | 46,160,000 | |||||||||||||||
Total revenues | 54,508,000 | 46,160,000 | 8,421,000 | 11,681,000 | 120,770,000 | |||||||||||||||
Expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Rental expenses | 17,528,000 | — | 1,142,000 | 556,000 | 19,226,000 | |||||||||||||||
Property operating expenses | — | 37,434,000 | — | — | 37,434,000 | |||||||||||||||
Segment net operating income | $ | 36,980,000 | $ | 8,726,000 | $ | 7,279,000 | $ | 11,125,000 | $ | 64,110,000 | ||||||||||
Expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||
General and administrative | $ | 15,235,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
Acquisition related expenses | 1,974,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 45,626,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
Other income (expense): | ||||||||||||||||||||
Interest expense: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Interest expense (including amortization of deferred financing costs and debt discount/premium) | (16,191,000 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Loss in fair value derivative financial instruments | (4,385,000 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Income from unconsolidated entity | 267,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
Other income | 175,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
Loss before income taxes | (18,859,000 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Income tax benefit | 8,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | $ | (18,851,000 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
127
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Medical Office Buildings | Senior Housing — RIDEA | Senior Housing | Skilled Nursing Facilities | Year Ended December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||
Revenues: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Real estate revenue | $ | 34,339,000 | $ | — | $ | 8,994,000 | $ | 4,266,000 | $ | 47,599,000 | ||||||||||
Resident fees and services | — | 36,857,000 | — | — | 36,857,000 | |||||||||||||||
Total revenues | 34,339,000 | 36,857,000 | 8,994,000 | 4,266,000 | 84,456,000 | |||||||||||||||
Expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Rental expenses | 9,934,000 | — | 1,214,000 | 351,000 | 11,499,000 | |||||||||||||||
Property operating expenses | — | 30,023,000 | — | — | 30,023,000 | |||||||||||||||
Segment net operating income | $ | 24,405,000 | $ | 6,834,000 | $ | 7,780,000 | $ | 3,915,000 | $ | 42,934,000 | ||||||||||
Expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||
General and administrative | $ | 9,172,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
Acquisition related expenses | 2,795,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 32,658,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
Other income (expense): | ||||||||||||||||||||
Interest expense (including amortization of deferred financing costs and debt discount/premium) | (6,788,000 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Loss from unconsolidated entity | (110,000 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Other income | 11,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
Loss before income taxes | (8,578,000 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Income tax expense | (8,000 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | $ | (8,586,000 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Medical Office Buildings | Senior Housing — RIDEA | Senior Housing | Year Ended December 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||
Revenues: | ||||||||||||||||
Real estate revenue | $ | 22,320,000 | $ | — | $ | 5,450,000 | $ | 27,770,000 | ||||||||
Resident fees and services | — | 5,563,000 | — | 5,563,000 | ||||||||||||
Total revenues | 22,320,000 | 5,563,000 | 5,450,000 | 33,333,000 | ||||||||||||
Expenses: | ||||||||||||||||
Rental expenses | 6,694,000 | — | 598,000 | 7,292,000 | ||||||||||||
Property operating expenses | — | 4,203,000 | — | 4,203,000 | ||||||||||||
Segment net operating income | $ | 15,626,000 | $ | 1,360,000 | $ | 4,852,000 | $ | 21,838,000 | ||||||||
Expenses: | ||||||||||||||||
General and administrative | $ | 4,338,000 | ||||||||||||||
Acquisition related expenses | 655,000 | |||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 13,639,000 | |||||||||||||||
Other income (expense): | ||||||||||||||||
Interest expense (including amortization of deferred financing costs and debt premium) | (2,699,000 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Other income | 1,000 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 508,000 | ||||||||||||||
128
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Assets by reportable segment as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 were as follows:
December 31, | |||||||
2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Medical office buildings | $ | 600,048,000 | $ | 417,708,000 | |||
Senior housing — RIDEA | 149,055,000 | 146,965,000 | |||||
Senior housing | 142,982,000 | 154,716,000 | |||||
Skilled nursing | 121,749,000 | 115,657,000 | |||||
Other | 54,493,000 | 61,326,000 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 1,068,327,000 | $ | 896,372,000 | |||
18. Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject us to a concentration of credit risk are primarily cash and cash equivalents, accounts and other receivables, restricted cash and real estate deposits. Cash and cash equivalents are generally invested in investment-grade, short-term instruments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased. We have cash and cash equivalents in financial institutions that are insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, or FDIC. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we had cash and cash equivalents in excess of FDIC insured limits. We believe this risk is not significant. Concentration of credit risk with respect to accounts receivable from tenants is limited. In general, we perform credit evaluations of prospective tenants and security deposits are obtained at the time of property acquisition and upon lease execution.
Based on leases in effect as of December 31, 2019, one state in the United States accounted for 10.0% or more of our total property portfolio’s annualized base rent or annualized net operating income. Our properties located in Missouri accounted for approximately 11.4% of our total property portfolio’s annualized base rent or annualized net operating income. Accordingly, there is a geographic concentration of risk subject to fluctuations in such state’s economy.
Based on leases in effect as of December 31, 2019, our four reportable business segments, medical office buildings, senior housing, skilled nursing facilities and senior housing — RIDEA accounted for 62.1%, 13.9%, 13.6% and 10.4%, respectively, of our total property portfolio’s annualized base rent or annualized net operating income.
As of December 31, 2019, we had one tenant that accounted for 10.0% or more of our total property portfolio’s annualized base rent or annualized net operating income, as follows:
Tenant | Annualized Base Rent(1) | Percentage of Annualized Base Rent | Acquisition | Reportable Segment | GLA (Sq Ft) | Lease Expiration Date | ||||||||
RC Tier Properties, LLC | $ | 7,782,000 | 10.4% | Missouri SNF Portfolio | Skilled Nursing | 385,000 | 09/30/33 | |||||||
(1) | Annualized base rent is based on contractual base rent from leases in effect as of December 31, 2019, inclusive of our senior housing — RIDEA facilities. The loss of this tenant or its inability to pay rent could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations. |
129
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
19. Per Share Data
Basic earnings (loss) per share for all periods presented are computed by dividing net income (loss) applicable to common stock by the weighted average number of shares of our common stock outstanding during the period. Net income (loss) applicable to common stock is calculated as net income (loss) attributable to controlling interest less distributions allocated to participating securities of $24,000, $19,000 and $12,000 for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. Diluted earnings (loss) per share are computed based on the weighted average number of shares of our common stock and all potentially dilutive securities, if any. Nonvested shares of our restricted common stock and redeemable limited partnership units of our operating partnership are participating securities and give rise to potentially dilutive shares of our common stock. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, there were 43,500 and 37,500 nonvested shares, respectively, of our restricted common stock outstanding, but such shares were excluded from the computation of diluted earnings per share because such shares were anti-dilutive during these periods. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, there were 208 units of redeemable limited partnership units of our operating partnership outstanding, but such units were excluded from the computation of diluted earnings per share because such units were anti-dilutive during these periods.
20. Selected Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
Set forth below is the unaudited selected quarterly financial data. We believe that all necessary adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments, have been included in the amounts stated below to present fairly, and in accordance with GAAP, the unaudited selected quarterly financial data when read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements.
Quarters Ended | |||||||||||||||
December 31, 2019 | September 30, 2019 | June 30, 2019 | March 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 33,437,000 | $ | 31,118,000 | $ | 30,373,000 | $ | 25,842,000 | |||||||
Expenses | (28,597,000 | ) | (28,421,000 | ) | (29,645,000 | ) | (32,832,000 | ) | |||||||
Other expense | (3,548,000 | ) | (4,608,000 | ) | (6,610,000 | ) | (5,368,000 | ) | |||||||
Income tax benefit (expense) | 25,000 | (7,000 | ) | (7,000 | ) | (3,000 | ) | ||||||||
Net income (loss) | 1,317,000 | (1,918,000 | ) | (5,889,000 | ) | (12,361,000 | ) | ||||||||
Less: net loss attributable to redeemable noncontrolling interests | 6,000 | 19,000 | 32,000 | 25,000 | |||||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to controlling interest | $ | 1,323,000 | $ | (1,899,000 | ) | $ | (5,857,000 | ) | $ | (12,336,000 | ) | ||||
Net income (loss) per Class T and Class I common share attributable to controlling interest — basic and diluted | $ | 0.02 | $ | (0.02 | ) | $ | (0.07 | ) | $ | (0.16 | ) | ||||
Weighted average number of Class T and Class I common shares outstanding — basic and diluted | 79,884,966 | 79,502,193 | 79,026,999 | 75,105,471 | |||||||||||
Quarters Ended | |||||||||||||||
December 31, 2018 | September 30, 2018 | June 30, 2018 | March 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 25,323,000 | $ | 22,281,000 | $ | 19,010,000 | $ | 17,842,000 | |||||||
Expenses | (25,961,000 | ) | (22,384,000 | ) | (18,808,000 | ) | (18,994,000 | ) | |||||||
Other expense | (3,047,000 | ) | (1,596,000 | ) | (1,160,000 | ) | (1,084,000 | ) | |||||||
Income tax expense | (4,000 | ) | (4,000 | ) | — | — | |||||||||
Net loss | (3,689,000 | ) | (1,703,000 | ) | (958,000 | ) | (2,236,000 | ) | |||||||
Less: net loss attributable to redeemable noncontrolling interests | 35,000 | 72,000 | 58,000 | 67,000 | |||||||||||
Net loss attributable to controlling interest | $ | (3,654,000 | ) | $ | (1,631,000 | ) | $ | (900,000 | ) | $ | (2,169,000 | ) | |||
Net loss per Class T and Class I common share attributable to controlling interest — basic and diluted | $ | (0.06 | ) | $ | (0.03 | ) | $ | (0.02 | ) | $ | (0.05 | ) | |||
Weighted average number of Class T and Class I common shares outstanding — basic and diluted | 64,954,525 | 57,769,964 | 51,277,753 | 45,136,647 | |||||||||||
130
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
21. Subsequent Events
Property Acquisitions
Subsequent to December 31, 2019, we completed the acquisition of seven buildings from unaffiliated third parties. The following is a summary of our property acquisitions subsequent to December 31, 2019:
Acquisition | Location | Type | Date Acquired | Contract Purchase Price | Line of Credit(1) | Total Acquisition Fee(2) | ||||||||||||
Catalina West Haven ALF(3) | West Haven, UT | Senior Housing — RIDEA | 01/01/20 | $ | 12,799,000 | $ | 12,700,000 | $ | 278,000 | |||||||||
Louisiana Senior Housing Portfolio(4) | Gonzales, Monroe, New Iberia, Shreveport, Slidell, LA | Senior Housing — RIDEA | 01/03/20 | 34,000,000 | 32,700,000 | 737,000 | ||||||||||||
Catalina Madera ALF(3) | Madera, CA | Senior Housing — RIDEA | 01/31/20 | 17,900,000 | 17,300,000 | 389,000 | ||||||||||||
$ | 64,699,000 | $ | 62,700,000 | $ | 1,404,000 | |||||||||||||
___________
(1) | Represents a borrowing under the 2018 Credit Facility, as defined in Note 7, Line of Credit and Term Loans, at the time of acquisition |
(2) | Our advisor was paid, as compensation for services rendered in connection with the investigation, selection and acquisition of our property, a base acquisition fee of 2.25% of the portion of the contract purchase price paid by us. See Note 13, Related Party Transactions — Acquisition and Development Stage — Acquisition Fee, for a further discussion. |
(3) | On January 1, 2020 and January 31, 2020, we completed the acquisitions of Catalina West Haven ALF and Catalina Madera ALF, respectively, pursuant to a joint venture with an affiliate of Avalon Health Care, Inc., an unaffiliated third party. Our ownership of the joint venture is approximately 90%. |
(4) | On January 3, 2020, we completed the acquisition of Louisiana Senior Housing Portfolio, pursuant to a joint venture with an affiliate of Senior Solutions Management Group, an unaffiliated third party. Our ownership of the joint venture is approximately 90%. |
131
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
SCHEDULE III — REAL ESTATE AND
ACCUMULATED DEPRECIATION
December 31, 2019
Initial Cost to Company | Gross Amount of Which Carried at Close of Period(d) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description(a) | Encumbrances | Land | Buildings and Improvements | Cost Capitalized Subsequent to Acquisition(b) | Land | Buildings and Improvements | Total(c) | Accumulated Depreciation (e)(f) | Date of Construction | Date Acquired | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Auburn MOB (Medical Office) | Auburn, CA | $ | — | $ | 406,000 | $ | 4,600,000 | $ | 72,000 | $ | 406,000 | $ | 4,672,000 | $ | 5,078,000 | $ | (582,000 | ) | 1997 | 06/28/16 | |||||||||||||||||
Pottsville MOB (Medical Office) | Pottsville, PA | — | 1,493,000 | 7,050,000 | 102,000 | 1,493,000 | 7,152,000 | 8,645,000 | (929,000 | ) | 2004 | 09/16/16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Charlottesville MOB (Medical Office) | Charlottesville, VA | — | 4,768,000 | 13,330,000 | 63,000 | 4,768,000 | 13,393,000 | 18,161,000 | (1,599,000 | ) | 2001 | 09/22/16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rochester Hills MOB (Medical Office) | Rochester Hills, MI | 3,103,000 | 1,727,000 | 5,763,000 | 220,000 | 1,727,000 | 5,983,000 | 7,710,000 | (770,000 | ) | 1990 | 09/29/16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cullman MOB III (Medical Office) | Cullman, AL | — | — | 13,989,000 | 75,000 | — | 14,064,000 | 14,064,000 | (1,357,000 | ) | 2010 | 09/30/16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Iron MOB Portfolio (Medical Office) | Cullman, AL | — | — | 10,237,000 | 665,000 | — | 10,902,000 | 10,902,000 | (1,283,000 | ) | 1994 | 10/13/16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cullman, AL | — | — | 6,906,000 | 959,000 | — | 7,865,000 | 7,865,000 | (935,000 | ) | 1998 | 10/13/16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sylacauga, AL | — | — | 7,907,000 | 63,000 | — | 7,970,000 | 7,970,000 | (740,000 | ) | 1997 | 10/13/16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mint Hill MOB (Medical Office) | Mint Hill, NC | — | — | 16,585,000 | 1,118,000 | — | 17,703,000 | 17,703,000 | (2,196,000 | ) | 2007 | 11/14/16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lafayette Assisted Living Portfolio (Senior Housing — RIDEA) | Lafayette, LA | — | 1,327,000 | 8,225,000 | 4,000 | 1,327,000 | 8,229,000 | 9,556,000 | (710,000 | ) | 1996 | 12/01/16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lafayette, LA | — | 980,000 | 4,244,000 | (130,000 | ) | 980,000 | 4,114,000 | 5,094,000 | (385,000 | ) | 2014 | 12/01/16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Evendale MOB (Medical Office) | Evendale, OH | — | 1,620,000 | 7,583,000 | 742,000 | 1,620,000 | 8,325,000 | 9,945,000 | (1,041,000 | ) | 1988 | 12/13/16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Battle Creek MOB (Medical Office) | Battle Creek, MI | — | 960,000 | 5,717,000 | 373,000 | 960,000 | 6,090,000 | 7,050,000 | (788,000 | ) | 1996 | 03/10/17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reno MOB (Medical Office) | Reno, NV | — | — | 64,718,000 | 815,000 | — | 65,533,000 | 65,533,000 | (5,276,000 | ) | 2005 | 03/13/17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Athens MOB Portfolio (Medical Office) | Athens, GA | — | 809,000 | 5,227,000 | 422,000 | 809,000 | 5,649,000 | 6,458,000 | (543,000 | ) | 2006 | 05/18/17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Athens, GA | — | 1,084,000 | 8,772,000 | 109,000 | 1,084,000 | 8,881,000 | 9,965,000 | (777,000 | ) | 2006 | 05/18/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SW Illinois Senior Housing Portfolio (Senior Housing) | Columbia, IL | — | 1,086,000 | 9,651,000 | 3,000 | 1,086,000 | 9,654,000 | 10,740,000 | (883,000 | ) | 2007 | 05/22/17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Columbia, IL | — | 121,000 | 1,656,000 | — | 121,000 | 1,656,000 | 1,777,000 | (135,000 | ) | 1999 | 05/22/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Millstadt, IL | — | 203,000 | 3,827,000 | — | 203,000 | 3,827,000 | 4,030,000 | (302,000 | ) | 2004 | 05/22/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Red Bud, IL | — | 198,000 | 3,553,000 | 51,000 | 198,000 | 3,604,000 | 3,802,000 | (292,000 | ) | 2006 | 05/22/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Waterloo, IL | — | 470,000 | 8,369,000 | — | 470,000 | 8,369,000 | 8,839,000 | (636,000 | ) | 2012 | 05/22/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lawrenceville MOB (Medical Office) | Lawrenceville, GA | 7,738,000 | 1,363,000 | 9,099,000 | 5,000 | 1,363,000 | 9,104,000 | 10,467,000 | (878,000 | ) | 2005 | 06/12/17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Northern California Senior Housing Portfolio (Senior Housing) | Belmont, CA | — | 10,760,000 | 13,631,000 | (293,000 | ) | 10,760,000 | 13,338,000 | 24,098,000 | (956,000 | ) | 1958/2000 | 06/28/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fairfield, CA | — | 317,000 | 6,584,000 | (74,000 | ) | 317,000 | 6,510,000 | 6,827,000 | (483,000 | ) | 1974 | 06/28/17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Menlo Park, CA | — | 5,188,000 | 2,177,000 | (63,000 | ) | 5,188,000 | 2,114,000 | 7,302,000 | (147,000 | ) | 1945 | 06/28/17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sacramento, CA | — | 1,266,000 | 2,818,000 | (245,000 | ) | 1,266,000 | 2,573,000 | 3,839,000 | (210,000 | ) | 1978 | 06/28/17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Roseburg MOB (Medical Office) | Roseburg, OR | — | — | 20,925,000 | 34,000 | — | 20,959,000 | 20,959,000 | (1,651,000 | ) | 2003 | 06/29/17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
132
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
SCHEDULE III — REAL ESTATE AND
ACCUMULATED DEPRECIATION — (Continued)
December 31, 2019
Initial Cost to Company | Gross Amount of Which Carried at Close of Period(d) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description(a) | Encumbrances | Land | Buildings and Improvements | Cost Capitalized Subsequent to Acquisition(b) | Land | Buildings and Improvements | Total(c) | Accumulated Depreciation (e)(f) | Date of Construction | Date Acquired | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fairfield County MOB Portfolio (Medical Office) | Stratford, CT | $ | — | $ | 1,011,000 | $ | 3,538,000 | $ | 319,000 | $ | 1,011,000 | $ | 3,857,000 | $ | 4,868,000 | $ | (475,000 | ) | 1963 | 09/29/17 | |||||||||||||||||
Trumbull, CT | — | 2,250,000 | 6,879,000 | 466,000 | 2,250,000 | 7,345,000 | 9,595,000 | (703,000 | ) | 1987 | 09/29/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Central Florida Senior Housing Portfolio (Senior Housing — RIDEA) | Bradenton, FL | — | 1,058,000 | 5,118,000 | 626,000 | 1,058,000 | 5,744,000 | 6,802,000 | (474,000 | ) | 1973/1983 | 11/01/17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Brooksville, FL | — | 1,378,000 | 10,217,000 | 496,000 | 1,378,000 | 10,713,000 | 12,091,000 | (995,000 | ) | 1960/2007 | 11/01/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Brooksville, FL | — | 934,000 | 6,550,000 | 310,000 | 934,000 | 6,860,000 | 7,794,000 | (533,000 | ) | 2008 | 11/01/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lake Placid, FL | — | 950,000 | 3,476,000 | 267,000 | 950,000 | 3,743,000 | 4,693,000 | (340,000 | ) | 2008 | 11/01/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lakeland, FL | — | 529,000 | 17,541,000 | 841,000 | 529,000 | 18,382,000 | 18,911,000 | (1,146,000 | ) | 1985 | 11/01/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pinellas Park, FL | — | 1,118,000 | 9,005,000 | 833,000 | 1,118,000 | 9,838,000 | 10,956,000 | (803,000 | ) | 2016 | 11/01/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sanford, FL | — | 2,783,000 | 10,019,000 | 661,000 | 2,783,000 | 10,680,000 | 13,463,000 | (810,000 | ) | 1984 | 11/01/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Spring Hill, FL | — | 930,000 | 6,241,000 | 518,000 | 930,000 | 6,759,000 | 7,689,000 | (512,000 | ) | 1988 | 11/01/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Winter Haven, FL | — | 3,119,000 | 21,973,000 | 1,652,000 | 3,119,000 | 23,625,000 | 26,744,000 | (2,031,000 | ) | 1984 | 11/01/17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Central Wisconsin Senior Care Portfolio (Skilled Nursing) | Sun Prairie, WI | — | 587,000 | 3,487,000 | 2,000 | 587,000 | 3,489,000 | 4,076,000 | (224,000 | ) | 1960/2006 | 03/01/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Waunakee, WI | — | 1,930,000 | 14,352,000 | 3,000 | 1,930,000 | 14,355,000 | 16,285,000 | (927,000 | ) | 1974/2005 | 03/01/18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sauk Prairie MOB (Medical Office) | Prairie du Sac, WI | — | 2,154,000 | 15,194,000 | — | 2,154,000 | 15,194,000 | 17,348,000 | (1,033,000 | ) | 2014 | 04/09/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Surprise MOB (Medical Office) | Surprise, AZ | — | 1,759,000 | 9,037,000 | 148,000 | 1,759,000 | 9,185,000 | 10,944,000 | (563,000 | ) | 2012 | 04/27/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Southfield MOB (Medical Office) | Southfield, MI | 5,897,000 | 1,639,000 | 12,907,000 | 22,000 | 1,639,000 | 12,929,000 | 14,568,000 | (900,000 | ) | 1975/2014 | 05/11/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pinnacle Beaumont ALF (Senior Housing — RIDEA) | Beaumont, TX | — | 1,586,000 | 17,483,000 | 61,000 | 1,586,000 | 17,544,000 | 19,130,000 | (745,000 | ) | 2012 | 07/01/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Grand Junction MOB (Medical Office) | Grand Junction, CO | — | 1,315,000 | 27,528,000 | 27,000 | 1,315,000 | 27,555,000 | 28,870,000 | (1,301,000 | ) | 2013 | 07/06/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Edmonds MOB (Medical Office) | Edmonds, WA | — | 4,167,000 | 16,770,000 | 46,000 | 4,167,000 | 16,816,000 | 20,983,000 | (758,000 | ) | 1991/2008 | 07/30/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pinnacle Warrenton ALF (Senior Housing — RIDEA) | Warrenton, MO | — | 462,000 | 7,125,000 | 428,000 | 462,000 | 7,553,000 | 8,015,000 | (333,000 | ) | 1986 | 08/01/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Glendale MOB (Medical Office) | Glendale, WI | — | 794,000 | 5,541,000 | 563,000 | 794,000 | 6,104,000 | 6,898,000 | (417,000 | ) | 2004 | 08/13/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Missouri SNF Portfolio (Skilled Nursing) | Florissant, MO | — | 1,064,000 | 9,301,000 | — | 1,064,000 | 9,301,000 | 10,365,000 | (387,000 | ) | 1987 | 09/28/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Kansas City, MO | — | 1,710,000 | 10,699,000 | — | 1,710,000 | 10,699,000 | 12,409,000 | (485,000 | ) | 1974 | 09/28/18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Milan, MO | — | 181,000 | 5,972,000 | — | 181,000 | 5,972,000 | 6,153,000 | (241,000 | ) | 1980 | 09/28/18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Missouri, MO | — | 473,000 | 9,856,000 | — | 473,000 | 9,856,000 | 10,329,000 | (389,000 | ) | 1963 | 09/28/18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Salisbury, MO | — | 252,000 | 7,581,000 | — | 252,000 | 7,581,000 | 7,833,000 | (305,000 | ) | 1970 | 09/28/18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sedalia, MO | — | 266,000 | 22,397,000 | — | 266,000 | 22,397,000 | 22,663,000 | (794,000 | ) | 1975 | 09/28/18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
St. Elizabeth, MO | — | 329,000 | 4,282,000 | — | 329,000 | 4,282,000 | 4,611,000 | (178,000 | ) | 1981 | 09/28/18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
133
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
SCHEDULE III — REAL ESTATE AND
ACCUMULATED DEPRECIATION — (Continued)
December 31, 2019
Initial Cost to Company | Gross Amount of Which Carried at Close of Period(d) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description(a) | Encumbrances | Land | Buildings and Improvements | Cost Capitalized Subsequent to Acquisition(b) | Land | Buildings and Improvements | Total(c) | Accumulated Depreciation (e)(f) | Date of Construction | Date Acquired | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Trenton, MO | $ | — | $ | 122,000 | $ | 4,507,000 | $ | — | $ | 122,000 | $ | 4,507,000 | $ | 4,629,000 | $ | (177,000 | ) | 1967 | 09/28/18 | ||||||||||||||||||
Flemington MOB Portfolio (Medical Office) | Flemington, NJ | — | 1,473,000 | 10,728,000 | 72,000 | 1,473,000 | 10,800,000 | 12,273,000 | (429,000 | ) | 2002 | 11/29/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Flemington, NJ | — | 586,000 | 2,949,000 | 47,000 | 586,000 | 2,996,000 | 3,582,000 | (133,000 | ) | 1993 | 11/29/18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lawrenceville MOB II (Medical Office) | Lawrenceville, GA | — | 1,000,000 | 7,737,000 | 128,000 | 1,000,000 | 7,865,000 | 8,865,000 | (353,000 | ) | 1990 | 12/19/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mill Creek MOB (Medical Office) | Mill Creek, WA | — | 1,453,000 | 5,935,000 | 8,000 | 1,453,000 | 5,943,000 | 7,396,000 | (198,000 | ) | 1991 | 12/21/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Modesto MOB (Medical Office) | Modesto, CA | — | — | 12,789,000 | 15,000 | — | 12,804,000 | 12,804,000 | (444,000 | ) | 1991/2016 | 12/28/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Michigan ALF Portfolio (Senior Housing) | Grand Rapids, MI | — | 1,334,000 | 8,422,000 | 1,000 | 1,334,000 | 8,423,000 | 9,757,000 | (248,000 | ) | 1953/2016 | 12/28/18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Grand Rapids, MI | 10,361,000 | 1,382,000 | 10,740,000 | 1,000 | 1,382,000 | 10,741,000 | 12,123,000 | (235,000 | ) | 1989 | 05/01/19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Holland, MI | — | 799,000 | 6,984,000 | 3,000 | 799,000 | 6,987,000 | 7,786,000 | (238,000 | ) | 2007/2017 | 12/28/18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Howell, MI | — | 728,000 | 5,404,000 | 1,000 | 728,000 | 5,405,000 | 6,133,000 | (163,000 | ) | 2003 | 12/28/18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lansing, MI | — | 1,175,000 | 12,052,000 | 2,000 | 1,175,000 | 12,054,000 | 13,229,000 | (345,000 | ) | 1988/2015 | 12/28/18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Wyoming, MI | — | 1,542,000 | 12,873,000 | 2,000 | 1,542,000 | 12,875,000 | 14,417,000 | (373,000 | ) | 1964/2016 | 12/28/18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lithonia MOB (Medical Office) | Lithonia, GA | — | 1,129,000 | 8,842,000 | — | 1,129,000 | 8,842,000 | 9,971,000 | (303,000 | ) | 2015 | 03/05/19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
West Des Moines SNF (Skilled Nursing) | West Des Moines, IA | — | 672,000 | 5,753,000 | — | 672,000 | 5,753,000 | 6,425,000 | (136,000 | ) | 2004 | 03/24/19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Great Nord MOB Portfolio (Medical Office) | Tinley Park, IL | — | — | 12,976,000 | — | — | 12,976,000 | 12,976,000 | (376,000 | ) | 2002 | 04/08/19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chesterton, IN | — | 539,000 | 8,937,000 | — | 539,000 | 8,937,000 | 9,476,000 | (238,000 | ) | 2007 | 04/08/19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Crown Point, IN | — | 283,000 | 4,882,000 | — | 283,000 | 4,882,000 | 5,165,000 | (124,000 | ) | 2005 | 04/08/19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Plymouth, MN | — | 1,452,000 | 11,126,000 | — | 1,452,000 | 11,126,000 | 12,578,000 | (265,000 | ) | 2014 | 04/08/19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Overland Park MOB (Medical Office) | Overland Park, KS | — | 2,437,000 | 23,169,000 | 1,366,000 | 2,437,000 | 24,534,000 | 26,971,000 | (304,000 | ) | 2017 | 08/05/19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Blue Badger MOB (Medical Office) | Marysville, OH | — | 1,838,000 | 10,646,000 | — | 1,838,000 | 10,647,000 | 12,485,000 | (141,000 | ) | 2014 | 08/09/19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Bloomington MOB (Medical Office) | Bloomington, IL | — | 3,178,000 | 13,547,000 | — | 3,178,000 | 13,547,000 | 16,725,000 | (170,000 | ) | 1990 | 08/13/19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Memphis MOB (Medical Office) | Memphis, TN | — | 1,210,000 | 6,775,000 | — | 1,210,000 | 6,775,000 | 7,985,000 | (92,000 | ) | 1984 | 08/15/19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Haverhill MOB (Medical Office) | Haverhill, MA | — | 1,620,000 | 12,537,000 | — | 1,620,000 | 12,537,000 | 14,157,000 | (131,000 | ) | 1987 | 08/27/19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fresno MOB (Medical Office) | Fresno, CA | — | 1,412,000 | 8,155,000 | — | 1,412,000 | 8,155,000 | 9,567,000 | (59,000 | ) | 2007 | 10/30/19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Colorado Foothills MOB Portfolio (Medical Office) | Arvada, CO | — | 720,000 | 4,615,000 | — | 720,000 | 4,615,000 | 5,335,000 | (20,000 | ) | 1979 | 11/19/19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Centennial, CO | — | 970,000 | 10,307,000 | — | 970,000 | 10,307,000 | 11,277,000 | (35,000 | ) | 1979 | 11/19/19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Colorado Springs, CO | — | 1,443,000 | 11,123,000 | — | 1,443,000 | 11,123,000 | 12,566,000 | (42,000 | ) | 1999 | 11/19/19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
$ | 27,099,000 | $ | 103,371,000 | $ | 827,722,000 | $ | 15,025,000 | $ | 103,371,000 | $ | 842,747,000 | $ | 946,118,000 | $ | (51,058,000 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
134
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
SCHEDULE III — REAL ESTATE AND
ACCUMULATED DEPRECIATION — (Continued)
December 31, 2019
________________
(a) | We own 100% of our properties as of December 31, 2019, with the exception of Central Florida Senior Housing Portfolio, Pinnacle Beaumont ALF and Pinnacle Warrenton ALF. |
(b) | The cost capitalized subsequent to acquisition is shown net of dispositions. |
135
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
SCHEDULE III — REAL ESTATE AND
ACCUMULATED DEPRECIATION — (Continued)
December 31, 2019
(c) | The changes in total real estate for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 are as follows: |
Amount | |||
Balance — December 31, 2016 | $ | 118,764,000 | |
Acquisitions | 307,384,000 | ||
Additions | 2,476,000 | ||
Dispositions | (74,000 | ) | |
Balance — December 31, 2017 | $ | 428,550,000 | |
Acquisitions | $ | 320,822,000 | |
Additions | 8,985,000 | ||
Dispositions | (1,369,000 | ) | |
Balance — December 31, 2018 | $ | 756,988,000 | |
Acquisitions | $ | 184,402,000 | |
Additions | 7,117,000 | ||
Dispositions | (2,389,000 | ) | |
Balance — December 31, 2019 | $ | 946,118,000 | |
(d) | As of December 31, 2019, for federal income tax purposes, the aggregate cost of our properties is $1,055,615,000. |
(e) | The changes in accumulated depreciation for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 are as follows: |
Amount | |||
Balance — December 31, 2016 | $ | 822,000 | |
Additions | 8,090,000 | ||
Dispositions | (27,000 | ) | |
Balance — December 31, 2017 | $ | 8,885,000 | |
Additions | $ | 16,672,000 | |
Dispositions | (245,000 | ) | |
Balance — December 31, 2018 | $ | 25,312,000 | |
Additions | $ | 27,435,000 | |
Dispositions | (1,689,000 | ) | |
Balance — December 31, 2019 | $ | 51,058,000 | |
(f) | The cost of buildings and capital improvements is depreciated on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the buildings and capital improvements, up to 39 years, and the cost for tenant improvements is depreciated over the shorter of the lease term or useful life, up to 16 years. Furniture, fixtures and equipment is depreciated over the estimated useful life, up to 20 years. |
136
The following exhibits are included, or incorporated by reference, in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2019 (and are numbered in accordance with Item 601 of Regulation S-K).
137
GRIFFIN-AMERICAN HEALTHCARE REIT IV, INC.
EXHIBITS LIST — (Continued)
December 31, 2019
101.INS* | XBRL Instance Document |
101.SCH* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
101.CAL* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
101.LAB* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
101.PRE* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
101.DEF* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
_________
* | Filed herewith. |
** | Furnished herewith. In accordance with Item 601(b)(32) of Regulation S-K, this Exhibit is not deemed “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act or otherwise subject to the liabilities of that section. Such certifications will not be deemed incorporated by reference into any filing under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, except to the extent that the registrant specifically incorporates it by reference. |
138
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary.
None.
139
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
Griffin-American Healthcare REIT IV, Inc. (Registrant) | ||||
By | /s/ JEFFREY T. HANSON | Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors | ||
Jeffrey T. Hanson | ||||
Date: March 19, 2020 | ||||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
By | /s/ JEFFREY T. HANSON | Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors | ||
Jeffrey T. Hanson | (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
Date: March 19, 2020 | ||||
By | /s/ BRIAN S. PEAY | Chief Financial Officer | ||
Brian S. Peay | (Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) | |||
Date: March 19, 2020 | ||||
By | /s/ RICHARD S. WELCH | Director | ||
Richard S. Welch | ||||
Date: March 19, 2020 | ||||
By | /s/ BRIAN J. FLORNES | Independent Director | ||
Brian J. Flornes | ||||
Date: March 19, 2020 | ||||
By | /s/ DIANNE HURLEY | Independent Director | ||
Dianne Hurley | ||||
Date: March 19, 2020 | ||||
By | /s/ WILBUR H. SMITH III | Independent Director | ||
Wilbur H. Smith III | ||||
Date: March 19, 2020 | ||||
140
