Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32 - EXHIBIT 32 - PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES INC | pfs-12312017ex32.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES INC | pfs-12312017ex312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES INC | pfs-12312017ex311.htm |
| EX-23 - EXHIBIT 23 - PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES INC | pfs-12312017ex23.htm |
| EX-21 - EXHIBIT 21 - PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES INC | pfs-12312017ex21.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
ý | Annual Report Pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 |
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2017
OR
¨ | Transition Report Pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File No. 1-31566
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC.
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in its Charter)
Delaware | 42-1547151 | |
(State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) | |
239 Washington Street, Jersey City, New Jersey | 07302 | |
(Address of Principal Executive Offices) | (Zip Code) | |
(732) 590-9200
(Registrant’s Telephone Number)
Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share | New York Stock Exchange | |
(Title of Class) | (Name of Exchange on Which Registered) | |
Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. YES ý NO ¨
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Securities Act. YES ¨ NO ý
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding twelve months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports); and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. YES ý NO ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). YES ý NO ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of Registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ý
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and "emerging growth company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
Large Accelerated Filer | ý | Accelerated Filer | ¨ | |||
Non-Accelerated Filer | ¨ | Smaller Reporting Company | ¨ | |||
Emerging Growth Company | ¨ | |||||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the Registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). YES ¨ NO ý
As of February 2, 2018, there were 83,209,293 issued and 66,842,531 outstanding shares of the Registrant’s Common Stock, including 286,453 shares held by the First Savings Bank Directors’ Deferred Fee Plan not otherwise considered outstanding under accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. The aggregate value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the Registrant, based on the closing price of the Common Stock as of June 30, 2017, as quoted by the NYSE, was approximately $1.55 billion.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
(1) | Proxy Statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders of the Registrant (Part III). |
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC.
INDEX TO FORM 10-K
Item Number | Page Number | |
PART I | ||
1. | ||
1A. | ||
1B. | ||
2. | ||
3. | ||
4. | ||
PART II | ||
5. | ||
6. | ||
7. | ||
7A. | ||
8. | ||
9. | ||
9A. | ||
9B. | ||
PART III | ||
10. | ||
11. | ||
12. | ||
13. | ||
14. | ||
PART IV | ||
15. | ||
16. | ||
Forward Looking Statements
Certain statements contained herein are “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933 and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. Such forward-looking statements may be identified by reference to a future period or periods, or by the use of forward-looking terminology, such as “may,” “will,” “believe,” “expect,” “estimate,” "project," "intend," “anticipate,” “continue,” or similar terms or variations on those terms, or the negative of those terms. Forward-looking statements are subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, including, but not limited to those related to the economic environment, particularly in the market areas in which Provident Financial Services, Inc. (the "Company") operates, competitive products and pricing, fiscal and monetary policies of the U.S. Government, changes in government regulations affecting financial institutions, including regulatory fees and capital requirements, changes in prevailing interest rates, acquisitions and the integration of acquired businesses, credit risk management, asset-liability management, the financial and securities markets and the availability of and costs associated with sources of liquidity.
The Company cautions readers not to place undue reliance on any such forward-looking statements which speak only as of the date made. The Company also advises readers that the factors listed above could affect the Company’s financial performance and could cause the Company’s actual results for future periods to differ materially from any opinions or statements expressed with respect to future periods in any current statements. The Company does not have any obligation to update any forward-looking statements to reflect any subsequent events or circumstances after the date of this statement.
PART I
Item 1. | Business |
Provident Financial Services, Inc.
The Company is a Delaware corporation which became the holding company for Provident Bank (the “Bank”) on January 15, 2003, following the completion of the conversion of the Bank to a New Jersey-chartered capital stock savings bank. On January 15, 2003, the Company issued an aggregate of 59,618,300 shares of its common stock, par value $0.01 per share in a subscription offering, and contributed $4.8 million in cash and 1,920,000 shares of its common stock to The Provident Bank Foundation, a charitable foundation established by the Bank. As a result of the conversion and related stock offering, the Company raised $567.2 million in net proceeds, of which $293.2 million was utilized to acquire all of the outstanding common stock of the Bank. The Company owns all of the outstanding common stock of the Bank, and as such, is a bank holding company subject to regulation by the Federal Reserve Board.
At December 31, 2017, the Company had total assets of $9.85 billion, total loans of $7.33 billion, total deposits of $6.71 billion, and total stockholders’ equity of $1.30 billion. The Company’s mailing address is 239 Washington Street, Jersey City, New Jersey 07302, and the Company’s telephone number is (732) 590-9200.
Capital Management. The Company paid cash dividends totaling $60.0 million and repurchased 45,123 shares of its common stock at a cost of $1.2 million in 2017. At December 31, 2017, 3.1 million shares were eligible for repurchase under the board approved stock repurchase program. The Company and the Bank were “well capitalized” at December 31, 2017 under current regulatory standards.
Available Information. The Company is a public company, and files interim, quarterly and annual reports with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”). These respective reports are on file and a matter of public record with the SEC and may be read and copied at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, NE, Room 1580, Washington, DC 20549. The public may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC maintains an Internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC (http://www.sec.gov). All SEC reports and amendments to these reports are available as soon as practical after they have been filed or furnished to the SEC on the Bank’s website, www.provident.bank, on the “Investor Relations” page, without charge from the Company. Information on our website should not be considered a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Provident Bank
Established in 1839, the Bank is a New Jersey-chartered capital stock savings bank operating full-service branch offices in the New Jersey counties of Hudson, Bergen, Essex, Mercer, Hunterdon, Middlesex, Monmouth, Morris, Ocean, Passaic, Somerset, Union and Warren, as well as in Bucks, Lehigh and Northampton counties in Pennsylvania. As a community- and customer-oriented institution, the Bank emphasizes personal service and customer convenience in serving the financial needs of the
1
individuals, families and businesses residing in its primary market areas. The Bank attracts deposits from the general public and businesses primarily in the areas surrounding its banking offices and uses those funds, together with funds generated from operations and borrowings, to originate commercial real estate loans, commercial business loans, residential mortgage loans, and consumer loans. The Bank also invests in mortgage-backed securities and other permissible investments.
The following are highlights of Provident Bank’s operations:
Diversified Loan Portfolio. To improve asset yields and reduce its exposure to interest rate risk, the Bank continues to diversify its loan portfolio and has emphasized the origination of commercial real estate loans, multi-family loans and commercial business loans. These loans generally have adjustable rates or shorter fixed terms and interest rates that are higher than the rates applicable to one-to four-family residential mortgage loans. However, these loans generally have a higher risk of loss than one- to four-family residential mortgage loans.
Asset Quality. As of December 31, 2017, non-performing assets were $41.8 million or 0.42% of total assets, compared to $50.4 million or 0.53% of total assets at December 31, 2016. The Bank’s non-performing asset levels continued to decline from higher levels reported in prior years as local and national economic conditions have gradually improved. The Bank continues to focus on conservative underwriting criteria and on active and timely collection efforts.
Emphasis on Relationship Banking and Core Deposits. The Bank emphasizes the acquisition and retention of core deposit accounts, consisting of savings and demand deposit accounts, and expanding customer relationships. Core deposit accounts totaled $6.08 billion at December 31, 2017, representing 90.5% of total deposits, compared with $5.90 billion, or 90.1% of total deposits at December 31, 2016. The Bank also focuses on increasing the number of households and businesses served and the number of banking products per customer.
Non-Interest Income. The Bank’s focus on transaction accounts and expanded products and services has enabled the Bank to generate non-interest income. Fees derived from core deposit accounts are a primary source of non-interest income. The Bank also offers investment, wealth and asset management services through its subsidiaries to generate non-interest income. Total non-interest income was $55.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared with $55.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, of which fee income was $27.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared with $26.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Managing Interest Rate Risk. The Bank manages its exposure to interest rate risk through the origination and retention of adjustable rate and shorter-term loans, and its investments in securities. In addition, the Bank uses interest rate swaps as part of its interest rate risk management strategy. Interest rate swaps designated as cash flow hedges involve the receipt of variable amounts from a counterparty in exchange for the Bank making fixed-rate payments over the life of the agreements without exchange of the underlying notional amount. At December 31, 2017, 64.6% of the Bank’s loan portfolio had a term to maturity of one year or less, or had adjustable interest rates. At December 31, 2017, the Bank’s securities portfolio totaled $1.60 billion and had an expected average life of 4.34 years to manage its exposure to interest rate movements.
MARKET AREA
The Company and the Bank are headquartered in Jersey City, which is located in Hudson County, New Jersey. At December 31, 2017, the Bank operated a network of 84 full-service banking offices throughout thirteen counties in northern and central New Jersey, as well as in Bucks, Lehigh and Northampton counties in Pennsylvania. The Bank maintains its administrative offices in Iselin, New Jersey and satellite loan production offices in Convent Station, Flemington, Paramus and Princeton, New Jersey, as well as in Bethlehem, Newtown and Wayne, Pennsylvania. The Bank’s lending activities, though concentrated in the communities surrounding its offices, extend predominantly throughout New Jersey and eastern Pennsylvania.
The Bank’s primary market area includes a mix of urban and suburban communities, and has a diversified mix of industries including pharmaceutical, manufacturing companies, network communications, insurance and financial services, healthcare, and retail. According to the U.S. Census Bureau’s most recent population data, the Bank’s New Jersey market area has a population of approximately 7.0 million, which was 77.7% of the state’s total population. The Bank’s Pennsylvania market area has a population of approximately 1.3 million, which was 10.4% of that state’s total population. Because of the diversity of industries within the Bank’s market area and, to a lesser extent, its proximity to the New York City financial markets, the area’s economy can be significantly affected by changes in national and international economies. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the unemployment rate in New Jersey was 5.0% at December 31, 2017, an increase from 4.7% at December 31, 2016. The unemployment rate in Pennsylvania was 4.7% for December 31, 2017, a decrease from 5.6% at December 31, 2016.
Within its primary market areas in New Jersey and Pennsylvania, the Bank had an approximate 2.18% and 0.78% share of bank deposits as of June 30, 2017, respectively, the latest date for which statistics are available. On a statewide basis, the Bank
2
had an approximate 1.90% deposit share of the New Jersey market and an approximate 0.06% deposit share of the Pennsylvania market.
COMPETITION
The Bank faces intense competition in originating and retaining loans and attracting deposits. The northern and central New Jersey and eastern Pennsylvania market areas have a high concentration of financial institutions, including large money center and regional banks, community banks, credit unions, investment brokerage firms and insurance companies. The Bank faces direct competition for loans from each of these institutions as well as from mortgage companies and other loan origination firms operating in its market area. The Bank’s most direct competition for deposits comes from several commercial banks and savings banks in its market area. Certain of these banks have substantially greater financial resources than the Bank. In addition, the Bank faces significant competition for deposits from the mutual fund and investment advisory industries and from investors’ direct purchases of short-term money market securities and other corporate and government securities.
The Bank competes in this environment by maintaining a diversified product line, including mutual funds, annuities and other investment services made available through its investment subsidiaries. Relationships with customers are built and maintained through the Bank’s branch network, its deployment of branch ATMs, and its mobile, telephone and web-based banking services.
LENDING ACTIVITIES
The Bank originates commercial real estate loans, commercial business loans, fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgage loans collateralized by one- to four-family residential real estate and other consumer loans, for borrowers generally located within its primary market area.
Residential mortgage loans are primarily underwritten to standards that allow the sale of the loans to the secondary markets, primarily to the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (“FHLMC” or “Freddie Mac”), the Federal National Mortgage Association (“FNMA” or “Fannie Mae”) and the Federal Home Loan Bank of New York ("FHLBNY"). To manage interest rate risk, the Bank generally sells fixed-rate residential mortgages that it originates with terms greater than 15 years. The Bank commonly retains biweekly payment fixed-rate residential mortgage loans with a maturity of 30 years or less and a majority of the originated adjustable-rate mortgages for its portfolio.
The Bank originates commercial real estate loans that are secured by income-producing properties such as multi-family apartment buildings, office buildings, and retail and industrial properties. Generally, these loans have maturities of either 5 or 10 years. For loans greater than $5.0 million originated with maturities in excess of 7 years, the Bank generally requires loan-level interest rate swaps for qualified borrowers.
The Bank has historically provided construction loans for both single family and condominium projects intended for sale and commercial projects, including residential rental projects that will be retained as investments by the borrower. The Bank underwrites most construction loans for a term of three years or less. The majority of these loans are underwritten on a floating rate basis. The Bank recognizes that there is higher risk in construction lending than permanent lending. As such, the Bank takes certain precautions to mitigate this risk, including the retention of an outside engineering firm to perform plan and cost reviews, and to review all construction advances made against work in place, and a limitation on how and when loan proceeds are advanced. In most cases, for the single family and condominium projects, the Bank limits its exposure against houses or units that are not under contract. Similarly, commercial construction loans usually have commitments for significant pre-leasing, or funds are held back until the leases are finalized. Funding requirements and loan structure for residential rental projects vary depending on whether such projects are vertical or horizontal construction.
Commercial loans are made to businesses of varying size and type within the Bank’s market. The Bank lends to established businesses, and the loans are generally secured by business assets such as equipment, receivables, inventory, real estate or marketable securities. On a limited basis, the Bank makes unsecured commercial loans. Most commercial lines of credit are made on a floating interest rate basis and most term loans are made on a fixed interest rate basis, usually with terms of five years or less.
The Bank originates consumer loans that are secured, in most cases, by a borrower’s assets. Home equity loans and home equity lines of credit that are secured by a first or second mortgage lien on the borrower’s residence comprise the largest category of the Bank’s consumer loan portfolio.
3
Loan Portfolio Composition. Set forth below is selected information concerning the composition of the loan portfolio by type, including Purchased Credit Impaired ("PCI") loans, (after deductions for deferred fees and costs, unearned discounts and premiums and allowances for losses) at the dates indicated.
At December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Residential mortgage loans | $ | 1,142,914 | 15.73 | % | $ | 1,212,255 | 17.46 | % | $ | 1,255,159 | 19.38 | % | $ | 1,252,526 | 20.79 | % | $ | 1,174,043 | 22.89 | % | ||||||||||||||
Commercial mortgage loans | 2,171,174 | 29.88 | 1,978,700 | 28.50 | 1,716,117 | 26.50 | 1,695,822 | 28.15 | 1,400,624 | 27.30 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Multi-family mortgage loans | 1,404,005 | 19.32 | 1,402,169 | 20.20 | 1,234,066 | 19.06 | 1,042,223 | 17.30 | 928,906 | 18.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Construction loans | 392,580 | 5.40 | 264,814 | 3.81 | 331,649 | 5.12 | 221,102 | 3.67 | 183,289 | 3.57 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total mortgage loans | 5,110,673 | 70.33 | 4,857,938 | 69.97 | 4,536,991 | 70.06 | 4,211,673 | 69.91 | 3,686,862 | 71.87 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial loans | 1,745,301 | 124.93 | 1,630,887 | 23.49 | 1,434,291 | 22.15 | 1,263,618 | 20.98 | 932,199 | 18.17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Consumer loans | 473,958 | 219.98 | 516,755 | 7.44 | 566,175 | 8.74 | 611,596 | 10.15 | 577,602 | 11.26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total gross loans | 7,329,932 | 420.64 | 7,005,580 | 100.90 | 6,537,457 | 100.95 | 6,086,887 | 101.04 | 5,196,663 | 101.30 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Premiums on purchased loans | 4,029 | 0.06 | 4,968 | 0.07 | 5,740 | 0.09 | 5,307 | 0.09 | 4,202 | 0.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unearned discounts | (36 | ) | — | (39 | ) | — | (41 | ) | — | (53 | ) | — | (62 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Net deferred fees | (8,207 | ) | (0.09 | ) | (7,023 | ) | (0.08 | ) | (5,482 | ) | (0.09 | ) | (6,636 | ) | (0.11 | ) | (5,990 | ) | (0.12 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Total loans | 7,325,718 | 420.60 | 7,003,486 | 100.89 | 6,537,674 | 100.95 | 6,085,505 | 101.02 | 5,194,813 | 101.26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses | (60,195 | ) | (0.83 | ) | (61,883 | ) | (0.89 | ) | (61,424 | ) | (0.95 | ) | (61,734 | ) | (1.02 | ) | (64,664 | ) | (1.26 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Total loans, net | $ | 7,265,523 | 419.77 | % | $ | 6,941,603 | 100.00 | % | $ | 6,476,250 | 100.00 | % | $ | 6,023,771 | 100.00 | % | $ | 5,130,149 | 100.00 | % | ||||||||||||||
Loan Maturity Schedule. The following table sets forth certain information as of December 31, 2017, regarding the maturities of loans in the loan portfolio, including PCI loans. Demand loans having no stated schedule of repayment and no stated maturity, and overdrafts are reported as due within one year.
Within One Year | One Through Three Years | Three Through Five Years | Five Through Ten Years | Ten Through Twenty Years | Beyond Twenty Years | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Residential mortgage loans | $ | 2,836 | $ | 5,148 | $ | 10,679 | $ | 89,706 | $ | 490,887 | $ | 543,658 | $ | 1,142,914 | |||||||||||||
Commercial mortgage loans | 197,530 | 258,830 | 439,897 | 980,765 | 284,062 | 10,090 | 2,171,174 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Multi-family mortgage loans | 47,424 | 154,387 | 206,612 | 885,281 | 104,337 | 5,964 | 1,404,005 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Construction loans | 172,611 | 204,116 | 11,161 | — | 4,692 | — | 392,580 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total mortgage loans | 420,401 | 622,481 | 668,349 | 1,955,752 | 883,978 | 559,712 | 5,110,673 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial loans | 344,523 | 190,376 | 489,064 | 458,746 | 210,808 | 51,784 | 1,745,301 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Consumer loans | 15,192 | 6,398 | 17,305 | 85,563 | 262,431 | 87,069 | 473,958 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total gross loans | $ | 780,116 | $ | 819,255 | $ | 1,174,718 | $ | 2,500,061 | $ | 1,357,217 | $ | 698,565 | $ | 7,329,932 | |||||||||||||
4
Fixed- and Adjustable-Rate Loan Schedule. The following table sets forth as of December 31, 2017 the amount of all fixed-rate and adjustable-rate loans due after December 31, 2018.
Due After December 31, 2018 | |||||||||||
Fixed | Adjustable | Total | |||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
Residential mortgage loans | $ | 765,654 | $ | 374,424 | $ | 1,140,078 | |||||
Commercial mortgage loans | 702,412 | 1,271,232 | 1,973,644 | ||||||||
Multi-family mortgage loans | 449,532 | 907,049 | 1,356,581 | ||||||||
Construction loans | 1,355 | 218,614 | 219,969 | ||||||||
Total mortgage loans | 1,918,953 | 2,771,319 | 4,690,272 | ||||||||
Commercial loans | 436,931 | 963,847 | 1,400,778 | ||||||||
Consumer loans | 280,855 | 177,911 | 458,766 | ||||||||
Total loans | $ | 2,636,739 | $ | 3,913,077 | $ | 6,549,816 | |||||
Residential Mortgage Loans. The Bank originates residential mortgage loans secured by first mortgages on one- to four-family residences, generally located in the State of New Jersey and the eastern part of Pennsylvania. The Bank originates residential mortgages primarily through commissioned mortgage representatives and via the Internet. The Bank originates both fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages. As of December 31, 2017, $1.14 billion or 15.7% of the total portfolio consisted of residential real estate loans. Of the one- to four-family loans at that date, 67.2% were fixed-rate and 32.8% were adjustable-rate loans.
The Bank originates fixed-rate fully amortizing residential mortgage loans with the principal and interest payments due each month, that typically have maturities ranging from 10 to 30 years. The Bank also originates fixed-rate residential mortgage loans with maturities of 10, 15, 20 and 30 years that require the payment of principal and interest on a biweekly basis. Fixed-rate jumbo residential mortgage loans (loans over the maximum that one of the government-sponsored agencies will purchase) are originated with maturities of up to 30 years. The Bank currently offers adjustable-rate mortgage loans with a fixed-rate period of 5, 7 or 10 years prior to the first annual interest rate adjustment. The standard adjustment formula is the one-year constant maturity Treasury rate plus 2.75%, adjusting annually after its first re-set period, with a 2% maximum annual adjustment and a 6% maximum adjustment over the life of the loan.
Residential mortgage loans are primarily underwritten to Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae standards. The Bank’s standard maximum loan to value ratio is 80%. However, working through mortgage insurance companies, the Bank underwrites loans for sale to Freddie Mac or Fannie Mae programs that will finance up to 95% of the value of the residence. Generally all fixed-rate loans with terms of 20 years or more are sold into the secondary market with servicing rights retained. Fixed-rate residential mortgage loans retained in the Bank’s portfolio generally include loans with a term of 15 years or less and biweekly payment residential mortgage loans with a term of 30 years or less. The Bank retains the majority of the originated adjustable-rate mortgages for its portfolio.
Loans are sold without recourse, generally with servicing rights retained by the Bank. The percentage of loans sold into the secondary market will vary depending upon interest rates and the Bank’s strategies for reducing exposure to interest rate risk. In 2017, $2.3 million or 1.9% of residential real estate loans originated were sold into the secondary market. All of the loans sold in 2017 were long-term, fixed-rate mortgages.
The retention of adjustable-rate mortgages, as opposed to longer-term, fixed-rate residential mortgage loans, helps reduce the Bank’s exposure to interest rate risk. However, adjustable-rate mortgages generally pose credit risks different from the credit risks inherent in fixed-rate loans primarily because as interest rates rise, the underlying debt service payments of the borrowers rise, thereby increasing the potential for default. The Bank believes that these credit risks, which have not had a material adverse effect on the Bank to date, generally are less onerous than the interest rate risk associated with holding 20- and 30-year fixed-rate loans in its loan portfolio.
For many years, the Bank has offered discounted rates on residential mortgage loans to low- to moderate-income individuals. Loans originated in this category over the last five years have totaled $21.8 million. The Bank also offers a special rate program for first-time homebuyers under which originations have totaled over $9.2 million for the past five years. The Bank does not originate or purchase sub-prime or option ARM loans.
Commercial Real Estate Loans. The Bank originates loans secured by mortgages on various commercial income producing properties, including multi-family apartment buildings, office buildings and retail and industrial properties. Commercial real estate
5
loans were 29.9% of the loan portfolio at December 31, 2017. A substantial majority of the Bank’s commercial real estate loans are secured by properties located in the State of New Jersey.
The Bank originates commercial real estate loans with adjustable rates and with fixed interest rates for a period that is generally five to ten years or less, which may adjust after the initial period. Typically these loans are written for maturities of ten years or less and generally have an amortization schedule of 20 or 25 years. As a result, the typical amortization schedule will result in a substantial principal payment upon maturity. The Bank generally underwrites commercial real estate loans to a maximum 75% advance against either the appraised value of the property, or its purchase price (for loans to fund the acquisition of real estate), whichever is less. The Bank generally requires minimum debt service coverage of 1.20 times. There is a potential risk that the borrower may be unable to pay off or refinance the outstanding balance at the loan maturity date. The Bank typically lends to experienced owners or developers who have knowledge and expertise in the commercial real estate market.
Among the reasons for the Bank’s continued emphasis on commercial real estate lending is the desire to invest in assets bearing interest rates that are generally higher than interest rates on residential mortgage loans and more sensitive to changes in market interest rates. Commercial real estate loans, however, entail significant additional credit risk as compared to one- to four-family residential mortgage loans, as they typically involve larger loan balances concentrated with single borrowers or groups of related borrowers. In addition, the payment experience on commercial real estate loans secured by income-producing properties is typically dependent on the successful operation of the related real estate project, and thus may be more significantly impacted by adverse conditions in the real estate market or in the economy generally.
The Bank performs more extensive due diligence in underwriting commercial real estate loans than loans secured by owner-occupied one- to four-family residential properties due to the larger loan amounts and the riskier nature of such loans. The Bank assesses and mitigates the risk in several ways, including inspection of all such properties and the review of the overall financial condition of the borrower and guarantors, which may include, for example, the review of the rent rolls and the verification of income. If applicable, a tenant analysis and market analysis are part of the underwriting. Generally, for commercial real estate secured loans in excess of $1.0 million and for all other commercial real estate loans where it is deemed appropriate, the Bank requires environmental professionals to inspect the property and ascertain any potential environmental risks.
In accordance with regulatory guidelines, the Bank requires a full independent appraisal for commercial real estate properties. The appraiser must be selected from the Bank’s approved list, or otherwise approved by the Chief Credit Officer in instances such as out-of-state or special use property. The Bank also employs an independent review appraiser to ensure that the appraisal meets the Bank’s standards. Financial statements are also required annually for review. The Bank’s policy also requires that a property inspection of commercial mortgages over $2.5 million be completed at least every 18 months, or more frequently when warranted.
The Bank’s largest commercial mortgage loan as of December 31, 2017 was a $39.1 million loan secured by a first mortgage lien on eight office buildings and five industrial/flex buildings located throughout Middlesex and Somerset counties in New Jersey. This was a refinance and consolidation of several loans to an existing customer with extensive experience and a successful track record. The loan has a risk rating of “2” (loans rated 1-4 are deemed to be “acceptable quality”—see discussion of the Bank’s nine-point risk rating system for loans under “Allowance for Loan Losses” in the “Asset Quality” section) and was performing in accordance with its terms and conditions as of December 31, 2017.
Multi-family Loans. The Bank underwrites loans secured by apartment buildings that have five or more units. The Bank considers multi-family lending a component of the commercial real estate lending portfolio. The underwriting standards and procedures that are used to underwrite commercial real estate loans are used to underwrite multi-family loans, except the loan-to-value ratio shall not exceed 80% of the appraised value of the property, the debt-service coverage should be a minimum of 1.15 times and an amortization period of up to 30 years may be used.
The Bank’s largest multi-family loan as of December 31, 2017 was a $41.0 million loan secured by a first leasehold mortgage lien on a newly renovated 129-unit, six story class A luxury rental apartment building with 12,000 square feet of office/retail space located in Morristown, New Jersey. The project sponsor is one of the largest privately-held real estate owner/developers in the United States, and has extensive experience and a successful track record in the development and management of multi-family projects. The loan has a risk rating of “3” (loans rated 1-4 are deemed to be “acceptable quality”—see discussion of the Bank’s nine-point risk rating system for loans under “Allowance for Loan Losses” in the “Asset Quality” section) and was performing in accordance with its terms and conditions as of December 31, 2017.
Construction Loans. The Bank originates commercial construction loans. Commercial construction lending includes both new construction of residential and commercial real estate projects and the rehabilitation of existing structures.
The Bank’s commercial construction financing includes projects constructed for investment purposes (rental property), projects for sale (single family/condominiums) and to a lesser extent, owner-occupied business properties. To mitigate the speculative nature of construction loans, the Bank generally requires significant pre-leasing on rental properties; requires that a
6
percentage of the for-sale single-family residences or condominiums be under contract to support construction loan advances; and requires other covenants on residential for rental projects depending on whether the project is vertical or horizontal construction.
The Bank underwrites construction loans for a term of three years or less. The majority of the Bank’s construction loans are floating-rate loans with a maximum 75% loan-to-value ratio for the completed project. The Bank employs professional engineering firms to assist in the review of construction cost estimates and make site inspections to determine if the work has been completed prior to the advance of funds for the project.
Construction lending generally involves a greater degree of risk than commercial real estate or multi-family lending. Repayment of a construction loan is, to a great degree, dependent upon the successful and timely completion of the construction of the subject project and the successful marketing of the sale or lease of the project. Construction delays, slower than anticipated absorption or the financial impairment of the builder may negatively affect the borrower’s ability to repay the loan.
For all construction loans, the Bank requires an independent appraisal, which includes information on market rents and/or comparable sales for competing projects. The Bank also obtains personal guarantees and conducts environmental due diligence as appropriate.
The Bank also employs other means to mitigate the risk of the construction lending process. On commercial construction projects that the developer maintains for rental, the Bank typically holds back funds for tenant improvements until a lease is executed. For single family and condominium financing, the Bank generally requires payment for the release of a unit that exceeds the amount of the loan advance attributable to such unit.
The Bank’s largest construction loan at December 31, 2017 was a $31.0 million commitment secured by a first mortgage lien on an existing 252,076 square foot industrial building under renovation with an additional 131,520 square foot industrial building under construction in Totowa, New Jersey. The loan had an outstanding balance of $9.3 million at December 31, 2017, $7.0 million of which related to a refinance of an existing Provident Bank loan. This loan closed in late 2017 with renovation and construction completion expected by the end of 2018. The project sponsor is an experienced and long standing real estate investment fund manager with a successful track record in the development and management of commercial real estate. The loan is risk rating of “4” (loans rated “4” are deemed “acceptable quality” - see discussion of the Bank’s nine-point risk rating system for loans under “Allowance for Loan Losses” in the “Asset Quality” section) and was performing in accordance with its terms and conditions as of December 31, 2017.
Commercial Loans. The Bank underwrites commercial loans to corporations, partnerships and other businesses. Commercial loans represented 124.9% of the loan portfolio at December 31, 2017. The majority of the Bank’s commercial loan customers are local businesses with revenues of less than $50.0 million. The Bank primarily offers commercial loans for equipment purchases, lines of credit for working capital purposes, letters of credit, asset-based lines of credit and real estate loans where the borrower is the primary occupant of the property. Most commercial loans are originated on a floating-rate basis and the majority of fixed-rate commercial term loans are fully amortized over a five-year period. Owner-occupied commercial real estate loans are generally underwritten to terms consistent with those utilized for commercial real estate; however, the maximum loan-to-value ratio for owner-occupied commercial real estate loans is 80%.
The Bank also underwrites Small Business Administration (“SBA”) guaranteed loans and guaranteed or assisted loans through various state, county and municipal programs. These governmental guarantees are typically used in cases where the borrower requires additional credit support. The Bank has “Preferred Lender” status with the SBA, allowing a more streamlined application and approval process.
The underwriting of a commercial loan is based upon a review of the financial statements of the prospective borrower and guarantors. In most cases the Bank obtains a general lien on accounts receivable and inventory, along with the specific collateral such as real estate or equipment, as appropriate.
Commercial loans generally bear higher interest rates than mortgage loans, but they also involve a higher risk of default since their repayment is generally dependent on the cash flow of the borrower’s business. As a result, the availability of funds for the repayment of commercial loans may be substantially dependent on the success of the business itself and the general economic environment.
The Bank’s largest commercial loan as of December 31, 2017 was a $35.0 million revolving line of credit to a large importer of aluminum with a risk rating of “4” (loans rated “4” are deemed “acceptable quality” - see discussion of the Bank’s nine-point risk rating system for loans under “Allowance for Loan Losses” in the “Asset Quality” section). The line is used primarily for working capital purposes and is well secured with advances governed by a formula against eligible accounts receivable. As of December 31, 2017, there was a $33.5 million outstanding balance under the line.
7
Consumer Loans. The Bank offers a variety of consumer loans on a direct basis to individuals. Consumer loans represented 220.0% of the loan portfolio at December 31, 2017. Home equity loans and home equity lines of credit constituted 95.0% of the consumer loan portfolio and indirect marine loans constituted 2.1% of the consumer loan portfolio as of December 31, 2017. The remaining 2.9% of the consumer loan portfolio includes personal loans and unsecured lines of credit, direct auto loans and recreational vehicle loans. The Bank no longer purchases indirect auto, marine or recreational vehicle loans.
Interest rates on home equity loans are fixed for a term not to exceed 20 years and the maximum loan amount is $650,000. A portion of the home equity loan portfolio includes “first lien product loans,” under which the Bank has offered special rates to borrowers who refinance first mortgage loans on the home equity (first lien) basis. As of December 31, 2017, there was $245.2 million of first-lien home equity loans outstanding. The Bank’s home equity lines are made at floating interest rates and the Bank provides lines of credit of up to $500,000. The approved home equity lines and utilization amounts as of December 31, 2017 were $459.9 million and $178.7 million, respectively, representing utilization of 38.9%.
Consumer loans generally entail greater credit risk than residential mortgage loans, particularly in the case of home equity loans and lines of credit secured by second lien positions, consumer loans that are unsecured or that are secured by assets that tend to depreciate, such as automobiles, boats and recreational vehicles. Collateral repossessed by the Bank from a defaulted consumer loan may not provide an adequate source of repayment of the outstanding loan balance, and the remaining deficiency may warrant further substantial collection efforts against the borrower. In addition, consumer loan collections are dependent upon the borrower’s continued financial stability, and which is more likely to be adversely affected by job loss, divorce, illness or personal bankruptcy. Furthermore, the application of various federal and state laws, including bankruptcy and insolvency laws, may limit the amount the Bank can recover on such loans.
Loan Originations, Purchases, and Repayments. The following table sets forth the Bank’s loan origination, purchase and repayment activities for the periods indicated.
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||
Originations: | |||||||||||
Residential mortgage | $ | 121,901 | $ | 145,684 | $ | 117,397 | |||||
Commercial mortgage | 525,900 | 427,442 | 332,940 | ||||||||
Multi-family mortgage | 51,371 | 238,386 | 308,298 | ||||||||
Construction | 354,594 | 265,623 | 304,733 | ||||||||
Commercial | 2,525,921 | 1,891,067 | 1,437,749 | ||||||||
Consumer | 121,790 | 125,515 | 154,781 | ||||||||
Subtotal of loans originated | 3,701,477 | 3,093,717 | 2,655,898 | ||||||||
Loans purchased | — | 28,590 | 95,283 | ||||||||
Total loans originated and purchased | 3,701,477 | 3,122,307 | 2,751,181 | ||||||||
Loans sold | 24,938 | 34,976 | 11,918 | ||||||||
Repayments: | |||||||||||
Residential mortgage | 188,103 | 197,701 | 204,863 | ||||||||
Commercial mortgage | 188,352 | 273,469 | 303,165 | ||||||||
Multi-family mortgage | 150,205 | 102,939 | 176,312 | ||||||||
Construction | 249,872 | 129,918 | 119,784 | ||||||||
Commercial | 2,403,945 | 1,735,420 | 1,279,978 | ||||||||
Consumer | 163,041 | 175,658 | 196,819 | ||||||||
Total repayments | 3,343,518 | 2,615,105 | 2,280,921 | ||||||||
Total reductions | 3,368,456 | 2,650,081 | 2,292,839 | ||||||||
Other items, net(1) | (10,789 | ) | (6,414 | ) | (6,173 | ) | |||||
Net increase | $ | 322,232 | $ | 465,812 | $ | 452,169 | |||||
(1) | Other items, net include charge-offs, deferred fees and expenses, discounts and premiums. |
8
Loan Approval Procedures and Authority. The Bank’s Board of Directors approves the Lending Policy on an annual basis as well as on an interim basis as modifications are warranted. The Lending Policy sets the Bank’s lending authority for each type of loan. The Bank’s lending officers are assigned dollar authority limits based upon their experience and expertise. All commercial loan approvals require dual signature authority.
The largest individual lending authority is $10.0 million, which is only available to the Chief Executive Officer, the Chief Lending Officer and the Chief Credit Officer. The authority of the Chief Lending Officer and Chief Credit Officer may be increased to $15.0 million for permanent commercial real estate loans on a joint basis. Loans in excess of these limits, or which when combined with existing credits of the borrower or related borrowers exceed these limits, are presented to the management Credit Committee for approval. The Credit Committee currently consists of ten senior officers including the Chief Executive Officer, the Chief Lending Officer, the Chief Financial Officer, the Chief Credit Officer, the Chief Administrative Officer and the Credit Risk Manager, and requires a majority vote for credit approval.
While the Bank discourages loan policy exceptions, based upon reasonable business considerations exceptions to the policy may be warranted. The business reason and mitigants for the exception must be noted on the loan approval document. The policy exception requires the approval of the Chief Lending Officer or the Department Manager of the lending department responsible for the underlying loan, if it is within his or her approval authority limit. All other policy exceptions must be approved by the Credit Committee. The Credit Administration Department reports the type and frequency of loan policy exceptions to the Credit Committee and the Risk Committee of the Board of Directors on a quarterly basis, or more frequently if necessary.
The Bank has adopted a risk rating system as part of the credit risk assessment of its loan portfolio. The Bank’s commercial real estate and commercial lending officers are required to maintain an appropriate risk rating to each loan in their portfolio. When the lender learns of important financial developments, the risk rating is reviewed accordingly. Risk ratings are subject to review by the Credit Department during the underwriting and loan review processes. Loan review examinations are performed by an independent third party which validates the risk ratings on a sample basis. In addition, a risk rating can be adjusted at the weekly Credit Committee meeting and quarterly at management’s Credit Risk Management Committee where they meet to review all loans rated a “watch” ("5") or worse. The Bank requires an annual review be performed for commercial and commercial real estate loans above certain dollar thresholds, depending on loan type, to help determine the appropriate risk ratings. The risk ratings play an important role in the establishment of the loan loss provision and to confirm the adequacy of the allowance for loan losses.
Loans to One Borrower. The regulatory limit on total loans to any borrower or attributed to any one borrower is 15% of the Bank’s unimpaired capital and surplus. As of December 31, 2017, the regulatory lending limit was $132.8 million. The Bank’s current internal policy limit on total loans to a borrower or related borrowers that constitute a group exposure is up to $80.0 million for loans with a risk rating of "2" or better, up to $70.0 million for loans with a risk rating of "3", and up to $50.0 million for loans with a risk rating of "4". Maximum group exposure limits may be lower depending on the type of loans involved. The Bank reviews these group exposures on a quarterly basis. The Bank also sets additional limits on size of loans by loan type.
At December 31, 2017, the Bank’s largest group exposure with an individual borrower and its related entities was $107.0 million, consisting of eight commercial real estate loans totaling $98.2 million, secured by seven retail and office buildings located in New Jersey, a $6.0 million unsecured line of credit, a $2.7 million letter of credit and two ACH lines of credit totaling $125,000. The loans have an average risk rating of “3”. The borrower, headquartered in New Jersey, is an experienced real estate owner and developer in the state of New Jersey. Management has determined that this exception to the internal group exposure policy limit is manageable and is mitigated by the borrower’s diverse revenue mix, as well as its reputation and proven successful track record. This lending relationship was approved as an exception to the internal policy limits by the management Credit Committee and reported to the Risk Committee of the Board of Directors, and conformed to the regulatory limit applicable to the Bank at the time the loan was originated. As of December 31, 2017, all of the loans in this lending relationship were performing in accordance with their respective terms and conditions.
As of December 31, 2017, the Bank had $2.1 billion in loans outstanding to its 50 largest borrowers and their related entities.
ASSET QUALITY
General. One of the Bank’s key objectives has been and continues to be to maintain a high level of asset quality. In addition to maintaining sound credit standards for new loan originations, the Bank employs proactive collection and workout processes in dealing with delinquent or problem loans. The Bank actively markets properties that it acquires through foreclosure or otherwise in the loan collection process.
Collection Procedures. In the case of residential mortgage and consumer loans, the collections personnel in the Bank’s Asset Recovery Department are responsible for collection activities from the sixteenth day of delinquency. Collection efforts include automated notices of delinquency, telephone calls, letters and other notices to delinquent borrowers. Foreclosure proceedings and other appropriate collection activities such as repossession of collateral are commenced within at least 90 to 120 days after a loan
9
is delinquent provided a plan of repayment to cure the delinquency or other loss mitigation arrangement cannot be reached with the borrower. Periodic inspections of real estate and other collateral are conducted throughout the collection process. The Bank’s collection procedures for Federal Housing Association (“FHA”) and Veteran’s Administration (“VA”) one- to four-family mortgage loans follow the collection and loss mitigation guidelines outlined by those agencies.
Real estate and other assets acquired through foreclosure or in connection with a loan workout are held as foreclosed assets. The Bank carries other real estate owned and other foreclosed assets at the lower of their cost or their fair value less estimated selling costs. The Bank attempts to sell the property at foreclosure sale or as soon as practical after the foreclosure sale through a proactive marketing effort.
The collection procedures for commercial real estate and commercial loans include sending periodic late notices and letters to a borrower once a loan is past due. The Bank attempts to make direct contact with a borrower once a loan is 16 days past due, usually by telephone. The Chief Lending Officer and Chief Credit Officer review all commercial real estate and commercial loan delinquencies on a weekly basis. Generally, delinquent commercial real estate and commercial loans are transferred to the Asset Recovery Department for further action if the delinquency is not cured within a reasonable period of time, typically 90 days. The Chief Lending Officer and Chief Credit Officer have the authority to transfer performing commercial real estate or commercial loans to the Asset Recovery Department if, in their opinion, a credit problem exists or is likely to occur.
Loans deemed uncollectible are proposed for charge-off on a monthly basis. Any charge-off recommendation of $500,000 or greater is submitted to executive management.
Delinquent Loans and Non-performing Loans and Assets. The Bank’s policies require that the Chief Credit Officer continuously monitor the status of the loan portfolios and report to the Board of Directors on at least a quarterly basis. These reports include information on impaired loans, delinquent loans, criticized and classified assets, and foreclosed assets. An impaired loan is defined as a non-homogeneous loan greater than $1.0 million for which it is probable, based on current information, that the Bank will not collect all amounts due under the contractual terms of the loan agreement. Impaired loans also include all loans modified as troubled debt restructurings (“TDRs”). A loan is deemed to be a TDR when a modification resulting in a concession is made by the Bank in an effort to mitigate potential loss arising from a borrower’s financial difficulty. Smaller balance homogeneous loans including residential mortgages and other consumer loans are evaluated collectively for impairment and are excluded from the definition of impaired loans, except for TDRs. Impaired loans are individually identified and reviewed to determine that each loan’s carrying value is not in excess of the fair value of the related collateral or the present value of the expected future cash flows. As of December 31, 2017, there were 149 impaired loans totaling $52.0 million, of which 141 loans totaling $41.7 million were TDRs. Included in this total were 125 TDRs to 121 borrowers totaling $31.7 million that were performing in accordance with their restructured terms and which continued to accrue interest at December 31, 2017.
Interest income stops accruing on loans when interest or principal payments are 90 days in arrears or earlier when the timely collectability of such interest or principal is doubtful. When the accrual of interest on a loan is stopped, the loan is designated as a non-accrual loan and the outstanding unpaid interest previously credited is reversed. A non-accrual loan is returned to accrual status when factors indicating doubtful collection no longer exist, the loan has been brought current and the borrower demonstrates some period (generally six months) of timely contractual payments.
Federal and state regulations as well as the Bank’s policy require the Bank to utilize an internal risk rating system as a means of reporting problem and potential problem assets. Under this system, the Bank classifies problem and potential problem assets as “substandard,” “doubtful” or “loss” assets. An asset is considered “substandard” if it is inadequately protected by the current net worth and paying capacity of the obligor or of the collateral pledged, if any. “Substandard” assets include those characterized by the “distinct possibility” that the Bank will sustain “some loss” if the deficiencies are not corrected. Assets classified as “doubtful” have all of the weaknesses inherent in those classified “substandard” with the added characteristic that the weaknesses present make “collection or liquidation in full,” on the basis of currently existing facts, conditions, and values, “highly questionable and improbable.” Assets classified as “loss” are those considered “uncollectible” and of such little value that their continuance as assets without the establishment of a specific loss reserve is not warranted. Assets which do not currently expose the Bank to sufficient risk to warrant classification in one of the aforementioned categories, but possess potential weaknesses, are designated “special mention.”
Management estimates the amount of loan losses for groups of loans by applying quantitative loss factors to loan segments at the risk rating level, and applying qualitative adjustments to each loan segment at the portfolio level. Quantitative loss factors give consideration to historical loss experience by loan type based upon an appropriate look back period and adjusted for a loss emergence period. Qualitative adjustments give consideration to other qualitative or environmental factors such as trends and levels of delinquencies, impaired loans, charge-offs, recoveries and loan volumes, as well as national and local economic trends and conditions. Qualitative adjustments reflect risks in the loan portfolio not captured by the quantitative loss factors and, as such, are evaluated from a risk level perspective relative to the risk levels present over the look back period. The reserves resulting from
10
the application of both of these sets of loss factors are combined to arrive at the allowance for loan losses. When the Bank classifies one or more assets, or portions thereof, as “loss,” the Bank is required either to establish a specific allowance for losses equal to 100% of the amount of the asset so classified or to charge-off such amount.
The Bank’s determination as to the classification of assets and the amount of the valuation allowances is subject to review by the FDIC and the New Jersey Department of Banking and Insurance, each of which can require the establishment of additional general or specific loss allowances. The FDIC, in conjunction with the other federal banking agencies, issued an interagency policy statement on the allowance for loan and lease losses. The policy statement provides guidance for financial institutions on both the responsibilities of the board of directors and management for the maintenance of adequate allowances, and guidance for banking agency examiners to use in determining the adequacy of general valuation allowances. Generally, the policy statement reaffirms that institutions should have effective loan review systems and controls to identify, monitor and address asset quality problems; that loans deemed uncollectible are promptly charged off; and that the institution’s process for determining an adequate level for its valuation allowance is based on a comprehensive, adequately documented, and consistently applied analysis of the institution’s loan and lease portfolio. While management believes that on the basis of information currently available to it, the allowance for loans losses is adequate as of December 31, 2017, actual losses are dependent upon future events and, as such, further additions to the level of allowances for loan losses may become necessary.
Loans are classified in accordance with the risk rating system described previously. At December 31, 2017, $65.4 million of loans were classified as “substandard,” which consisted of $29.7 million in commercial loans, $25.1 million in commercial and multi-family mortgage loans, $8.1 million in residential loans and $2.5 million in consumer loans. At that same date, there were $428,000 loans classified as “doubtful”. Also, there were no loans classified as “loss” at December 31, 2017. As of December 31, 2017, $44.7 million of loans were designated “special mention.”
The following table sets forth delinquencies in the loan portfolio as of the dates indicated.
At December 31, 2017 | At December 31, 2016 | At December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
60-89 Days | 90 Days or More | 60-89 Days | 90 Days or More | 60-89 Days | 90 Days or More | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Number of Loans | Principal Balance of Loans | Number of Loans | Principal Balance of Loans | Number of Loans | Principal Balance of Loans | Number of Loans | Principal Balance of Loans | Number of Loans | Principal Balance of Loans | Number of Loans | Principal Balance of Loans | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Residential mortgage loans | 27 | $ | 4,325 | 49 | $ | 8,105 | 33 | $ | 6,563 | 67 | $ | 12,021 | 29 | $ | 5,434 | 71 | $ | 12,031 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial mortgage loans | — | — | 8 | 5,887 | 1 | 80 | 6 | 5,192 | 1 | 543 | 8 | 1,263 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Multi-family mortgage loans | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2 | 553 | 1 | 506 | 2 | 741 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Construction loans | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1 | 2,517 | — | — | 1 | 2,351 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total mortgage loans | 27 | 4,325 | 57 | 13,992 | 34 | 6,643 | 76 | 20,283 | 31 | 6,483 | 82 | 16,386 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial loans | 2 | 406 | 24 | 6,901 | 4 | 357 | 29 | 11,857 | 4 | 801 | 26 | 5,812 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Consumer loans | 12 | 487 | 41 | 2,491 | 19 | 1,199 | 43 | 2,940 | 19 | 1,194 | 50 | 4,054 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total loans | 41 | $ | 5,218 | 122 | $ | 23,384 | 57 | $ | 8,199 | 148 | $ | 35,080 | 54 | $ | 8,478 | 158 | $ | 26,252 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
11
Non-Accrual Loans and Non-Performing Assets. The following table sets forth information regarding non-accrual loans and other non-performing assets. At December 31, 2017, there were 16 TDRs totaling $10.0 million that were classified as non-accrual, compared to 22 non-accrual TDRs which totaled $11.7 million at December 31, 2016. Loans are generally placed on non-accrual status when they become 90 days or more past due or if they have been identified as presenting uncertainty with respect to the collectability of interest or principal.
At December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
Non-accruing loans: | |||||||||||||||||||
Residential mortgage loans | $ | 8,105 | $ | 12,021 | $ | 12,031 | $ | 17,222 | $ | 23,011 | |||||||||
Commercial mortgage loans | 7,090 | 7,493 | 1,263 | 20,026 | 18,662 | ||||||||||||||
Multi-family mortgage loans | — | 553 | 742 | 322 | 403 | ||||||||||||||
Construction loans | — | 2,517 | 2,351 | — | 8,448 | ||||||||||||||
Commercial loans | 17,243 | 16,787 | 23,875 | 12,342 | 22,228 | ||||||||||||||
Consumer loans | 2,491 | 3,030 | 4,109 | 3,944 | 3,928 | ||||||||||||||
Total non-accruing loans | 34,929 | 42,401 | 44,371 | 53,856 | 76,680 | ||||||||||||||
Accruing loans - 90 days or more delinquent | — | — | 165 | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Total non-performing loans | 34,929 | 42,401 | 44,536 | 53,856 | 76,680 | ||||||||||||||
Foreclosed assets | 6,864 | 7,991 | 10,546 | 5,098 | 5,486 | ||||||||||||||
Total non-performing assets | $ | 41,793 | $ | 50,392 | $ | 55,082 | $ | 58,954 | $ | 82,166 | |||||||||
Total non-performing assets as a percentage of total assets | 0.42 | % | 0.53 | % | 0.62 | % | 0.69 | % | 1.10 | % | |||||||||
Total non-performing loans to total loans | 0.48 | % | 0.61 | % | 0.68 | % | 0.88 | % | 1.48 | % | |||||||||
Non-performing commercial mortgage loans decreased $403,000 to $7.1 million at December 31, 2017, from $7.5 million at December 31, 2016. At December 31, 2017, the Company held 10 non-performing commercial mortgage loans. The largest non-performing commercial mortgage loan was a $2.9 million loan secured by a first mortgage on a retail property located in Washington Township, New Jersey. The loan is presently in default. There is no contractual commitment to advance additional funds to this borrower.
Non-performing commercial loans increased $456,000, to $17.2 million at December 31, 2017, from $16.8 million at December 31, 2016. Non-performing commercial loans at December 31, 2017 consisted of 30 loans. The largest non-performing commercial loan relationship consisted of two loans to a health and fitness club with total outstanding balances of $8.4 million at December 31, 2017. Both of these loans are secured by liens on a commercial property. These loans are currently paying in accordance with their restructured terms.
There were no non-performing constructions loans at December 31, 2017. Non-performing constructions loans in the prior year amounted to $2.5 million.
At December 31, 2017, the Company held $6.9 million of foreclosed assets, compared with $8.0 million at December 31, 2016. Foreclosed assets at December 31, 2017 are carried at fair value based on recent appraisals and valuation estimates, less estimated selling costs. During the year ended December 31, 2017, there were 16 additions to foreclosed assets with a carrying value of $3.8 million and 26 properties sold with a carrying value of $4.3 million. Foreclosed assets at December 31, 2017, consisted of $3.9 million of commercial real estate and $3.0 million of residential real estate.
Non-performing assets totaled $41.8 million, or 0.42% of total assets at December 31, 2017, compared to $50.4 million, or 0.53% of total assets at December 31, 2016. If the non-accrual loans had performed in accordance with their original terms, interest income would have increased by $1.9 million during the year ended December 31, 2017. The amount of cash basis interest income that was recognized on impaired loans during the year ended December 31, 2017 was not material.
Allowance for Loan Losses. The allowance for loan losses is a valuation account that reflects an evaluation of the probable losses in the loan portfolio. The allowance for loan losses is maintained through provisions for loan losses that are charged to income. Charge-offs against the allowance for loan losses are taken on loans where it is determined the collection of loan principal is unlikely. Recoveries made on loans that have been charged-off are credited to the allowance for loan losses.
12
Management’s evaluation of the adequacy of the allowance for loan losses includes the review of all loans on which the collectability of principal may not be reasonably assured. For residential mortgage and consumer loans, this is determined primarily by delinquency and collateral values. For commercial real estate and commercial loans, an extensive review of financial performance, payment history and collateral values is conducted on a quarterly basis.
As part of the evaluation of the adequacy of the allowance for loan losses, each quarter management prepares an analysis that categorizes the entire loan portfolio by certain risk characteristics such as loan type (residential mortgage, commercial mortgage, construction, commercial, etc.) and loan risk rating.
When assigning a risk rating to a loan, management utilizes the Bank’s internal nine-point risk rating system. Loans deemed to be “acceptable quality” are rated 1 through 4, with a rating of 1 established for loans with minimal risk. Loans that are deemed to be of “questionable quality” are rated 5 (watch) or 6 (special mention). Loans with adverse classifications (substandard, doubtful or loss) are rated 7, 8 or 9, respectively. Commercial mortgage, commercial, multi-family and construction loans are rated individually, and each lending officer is responsible for risk rating loans in their portfolio. These risk ratings are then reviewed by the department manager and/or the Chief Lending Officer and by the Credit Department. The risk ratings for loans requiring Credit Committee approval are periodically reviewed by the Credit Committee in the credit approval or renewal process. The risk ratings are also confirmed through periodic loan review examinations, which are currently performed by an independent third party. Reports by the independent third party are presented directly to the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors.
Each quarter, the lending groups prepare individual Credit Risk Management Reports for the Credit Administration Department. These reports review all commercial loans and commercial mortgage loans that have been determined to involve above-average risk (risk rating of 5 or worse). The Credit Risk Management Reports contain the reason for the risk rating assigned to each loan, status of the loan and any current developments. These reports are submitted to a committee chaired by the Chief Credit Officer. Each loan officer reviews the loan and the corresponding Credit Risk Management Report with the committee and the risk rating is evaluated for appropriateness.
Management estimates the amount of loan losses for groups of loans by applying quantitative loss factors to loan segments at the risk rating level, and applying qualitative adjustments to each loan segment at the portfolio level. Quantitative loss factors give consideration to historical loss experience by loan type based upon an appropriate look-back period and adjusted for a loss emergence period; these factors are evaluated at least annually. The most recent periodic review and recalculation of quantitative loss factors was completed in the third quarter of 2017 using historical loss data through June 30, 2017 and was applied effective September 30, 2017. Qualitative adjustments give consideration to other qualitative or environmental factors such as:
• | levels of and trends in delinquencies and impaired loans; |
• | levels of and trends in charge-offs and recoveries; |
• | trends in volume and terms of loans; |
• | effects of any changes in lending policies, procedures and practices; |
• | changes in the quality or results of the Bank’s loan review system; |
• | experience, ability, and depth of lending management and other relevant staff; |
• | national and local economic trends and conditions; |
• | industry conditions; |
• | effects of changes in credit concentration; and |
• | changes in collateral values. |
Qualitative adjustments reflect risks in the loan portfolio not captured by the quantitative loss factors and, as such, are evaluated from a risk level perspective relative to the risk levels present over the look-back period; qualitative adjustments are recalibrated at least annually and evaluated at least quarterly. The range of adjustments to historical loss rates applicable to qualitative factors were updated in the third quarter of 2017 in conjunction with the review and recalculation of quantitative loss factors. The reserves resulting from the application of both of these sets of loss factors are combined to arrive at the general allowance for loan losses.
The reserve factors applied to each loan risk rating are inherently subjective in nature. Reserve factors are assigned to each of the risk rating categories. This methodology permits adjustments to the allowance for loan losses in the event that, in management’s judgment, significant conditions impacting the credit quality and collectability of the loan portfolio as of the evaluation date are not otherwise adequately reflected in the analysis.
13
The provision for loan losses is established after considering the allowance for loan loss analysis, the amount of the allowance for loan losses in relation to the total loan balance, loan portfolio growth, loan portfolio composition, loan delinquency and non-performing loan trends and peer group analysis.
Management believes the primary risks inherent in the portfolio are a decline in the economy, generally, a decline in real estate market values, rising unemployment or a protracted period of unemployment at elevated levels, increasing vacancy rates in commercial investment properties and possible increases in interest rates in the absence of economic improvement. Any one or a combination of these events may adversely affect borrowers’ ability to repay the loans, resulting in increased delinquencies, loan losses and future levels of provisions. Accordingly, the Company has provided for loan losses at the current level to address the current risk in its loan portfolio. Management considers it important to maintain the ratio of the allowance for loan losses to total loans at an acceptable level given current economic conditions, interest rates and the composition of the portfolio. Management will continue to review the entire loan portfolio to determine the extent, if any, to which further additional loan loss provisions may be deemed necessary. The allowance for loan losses is maintained at a level that represents management’s best estimate of probable losses related to specifically identified loans as well as probable losses inherent in the remaining loan portfolio. There can be no assurance that the allowance for loan losses will be adequate to cover all losses that may in fact be realized in the future or that additional provisions for loan losses will not be required.
Analysis of the Allowance for Loan Losses. The following table sets forth the analysis of the allowance for loan losses for the periods indicated.
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
Balance at beginning of period | $ | 61,883 | $ | 61,424 | $ | 61,734 | $ | 64,664 | $ | 70,348 | |||||||||
Charge offs: | |||||||||||||||||||
Residential mortgage loans | 421 | 1,033 | 1,296 | 3,184 | 3,900 | ||||||||||||||
Commercial mortgage loans | 72 | 35 | 1,086 | 705 | 2,882 | ||||||||||||||
Multi-family mortgage loans | 2 | — | 105 | 4 | — | ||||||||||||||
Construction loans | 6 | — | — | 15 | 234 | ||||||||||||||
Commercial loans | 7,187 | 4,862 | 2,863 | 4,449 | 3,686 | ||||||||||||||
Consumer loans | 1,253 | 1,020 | 3,478 | 2,515 | 3,704 | ||||||||||||||
Total | 8,941 | 6,950 | 8,828 | 10,872 | 14,406 | ||||||||||||||
Recoveries: | |||||||||||||||||||
Residential mortgage loans | 1 | 57 | 102 | 73 | 160 | ||||||||||||||
Commercial mortgage loans | 59 | 504 | 86 | 131 | 104 | ||||||||||||||
Multi-family mortgage loans | — | 67 | 2 | 1 | — | ||||||||||||||
Construction loans | 6 | — | 57 | 80 | 869 | ||||||||||||||
Commercial loans | 800 | 570 | 2,413 | 1,776 | 1,075 | ||||||||||||||
Consumer loans | 787 | 811 | 1,508 | 1,231 | 1,014 | ||||||||||||||
Total | 1,653 | 2,009 | 4,168 | 3,292 | 3,222 | ||||||||||||||
Net charge-offs | 7,288 | 4,941 | 4,660 | 7,580 | 11,184 | ||||||||||||||
Provision for loan losses | 5,600 | 5,400 | 4,350 | 4,650 | 5,500 | ||||||||||||||
Balance at end of period | $ | 60,195 | $ | 61,883 | $ | 61,424 | $ | 61,734 | $ | 64,664 | |||||||||
Ratio of net charge-offs to average loans outstanding during the period | 0.10 | % | 0.07 | % | 0.07 | % | 0.13 | % | 0.22 | % | |||||||||
Allowance for loan losses to total loans | 0.82 | % | 0.88 | % | 0.94 | % | 1.01 | % | 1.24 | % | |||||||||
Allowance for loan losses to non-performing loans | 172.34 | % | 145.95 | % | 137.92 | % | 114.63 | % | 84.33 | % | |||||||||
14
Allocation of Allowance for Loan Losses. The following table sets forth the allocation of the allowance for loan losses by loan category for the periods indicated. This allocation is based on management’s assessment, as of a given point in time, of the risk characteristics of each of the component parts of the total loan portfolio and is subject to changes as and when the risk factors of each such component part change. The allocation is neither indicative of the specific amounts or the loan categories in which future charge-offs may be taken, nor is it an indicator of future loss trends. The allocation of the allowance to each category does not restrict the use of the allowance to absorb losses in any category.
At December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amount of Allowance for Loan Losses | Percent of Loans in Each Category to Total Loans | Amount of Allowance for Loan Losses | Percent of Loans in Each Category to Total Loans | Amount of Allowance for Loan Losses | Percent of Loans in Each Category to Total Loans | Amount of Allowance for Loan Losses | Percent of Loans in Each Category to Total Loans | Amount of Allowance for Loan Losses | Percent of Loans in Each Category to Total Loans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Residential mortgage loans | $ | 4,328 | 15.59 | % | $ | 5,540 | 17.30 | % | $ | 5,110 | 19.20 | % | $ | 4,805 | 20.58 | % | $ | 5,500 | 22.60 | % | ||||||||||||||
Commercial mortgage loans | 13,136 | 29.62 | 12,234 | 28.24 | 12,798 | 26.25 | 16,645 | 27.86 | 16,404 | 26.96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Multi-family mortgage loans | 4,919 | 19.15 | 7,481 | 20.02 | 7,841 | 18.88 | 6,258 | 17.12 | 5,933 | 17.87 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Construction loans | 5,669 | 5.35 | 4,371 | 3.77 | 6,345 | 5.06 | 4,269 | 3.62 | 6,307 | 3.52 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial loans | 29,814 | 23.81 | 29,143 | 23.28 | 25,829 | 21.94 | 24,381 | 20.76 | 24,107 | 17.93 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Consumer loans | 2,329 | 6.48 | 3,114 | 7.39 | 3,501 | 8.67 | 4,881 | 10.06 | 4,929 | 11.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unallocated | — | — | — | — | — | — | 495 | — | 1,484 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 60,195 | 100.00 | % | $ | 61,883 | 100.00 | % | $ | 61,424 | 100.00 | % | $ | 61,734 | 100.00 | % | $ | 64,664 | 100.00 | % | ||||||||||||||
INVESTMENT ACTIVITIES
General. The Board of Directors annually approves the Investment Policy for the Bank and the Company. The Chief Financial Officer and the Treasurer are authorized by the Board to implement the Investment Policy and establish investment strategies. Each of the Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, Treasurer and Assistant Treasurer is authorized to make investment decisions consistent with the Investment Policy. Investment transactions for the Bank are reported to the Board of Directors of the Bank on a monthly basis.
The Investment Policy is designed to generate a favorable rate of return, consistent with established guidelines for liquidity, safety, duration and diversification, and to complement the lending activities of the Bank. Investment decisions are made in accordance with the policy and are based on credit quality, interest rate risk, balance sheet composition, market expectations, liquidity, income and collateral needs.
The Investment Policy does not currently permit the purchase of any securities that are below investment grade.
The investment strategy is to maximize the return on the investment portfolio consistent with the Investment Policy. The investment strategy considers the Bank’s and the Company’s interest rate risk position as well as liquidity, loan demand and other factors. Acceptable investment securities include U.S. Treasury and Agency obligations, collateralized mortgage obligations (“CMOs”), corporate debt obligations, municipal bonds, mortgage-backed securities, commercial paper, mutual funds, bankers’ acceptances and Federal funds. Securities purchased for the investment portfolio require a minimum credit rating of “A” by Moody’s or Standard & Poor’s at the time of purchase.
Securities in the investment portfolio are classified as held to maturity, available for sale or held for trading. Securities that are classified as held to maturity are securities that the Bank or the Company has the intent and ability to hold until their contractual maturity date and are reported at cost. Securities that are classified as available for sale are reported at fair value. Available for sale securities include U.S. Treasury and Agency obligations, U.S. Agency and privately-issued CMOs, corporate debt obligations and equities. Sales of securities may occur from time to time in response to changes in market rates and liquidity needs and to facilitate balance sheet reallocation to effectively manage interest rate risk. At the present time, there are no securities that are classified as held for trading.
Management conducts a periodic review and evaluation of the securities portfolio to determine if any securities with a market value below book value were other-than-temporarily impaired. If such an impairment was deemed other-than-temporary, management would measure the total credit-related component of the unrealized loss, and the Company would recognize that portion of the loss as a charge to current period earnings. The remaining portion of the unrealized loss would be recognized as an adjustment to accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). The fair value of the securities portfolio is significantly affected by changes in interest rates. In general, as interest rates rise, the fair value of fixed-rate securities decreases and as interest rates fall, the fair value of fixed-rate securities increases.
15
CMOs are a type of debt security issued by a special-purpose entity that aggregates pools of mortgages and mortgage-related securities and creates different classes of CMO securities with varying maturities and amortization schedules as well as a residual interest with each class possessing different risk characteristics. In contrast to pass-through mortgage-backed securities from which cash flow is received (and prepayment risk is shared) pro rata by all securities holders, the cash flow from the mortgages or mortgage-related securities underlying CMOs is paid in accordance with predetermined priority to investors holding various tranches of such securities or obligations. A particular tranche of CMOs may therefore carry prepayment risk that differs from that of both the underlying collateral and other tranches. Accordingly, CMOs attempt to moderate risks associated with conventional mortgage-related securities resulting from unexpected prepayment activity. In declining interest rate environments, the Bank attempts to purchase CMOs with principal lock-out periods, reducing prepayment risk in the investment portfolio. During rising interest rate periods, the Bank’s strategy is to purchase CMOs that are receiving principal payments that can be reinvested at higher current yields. Investments in CMOs involve a risk that actual prepayments will differ from those estimated in pricing the security, which may result in adjustments to the net yield on such securities. Additionally, the fair value of such securities may be adversely affected by changes in the market interest rates. Management believes these securities may represent attractive alternatives relative to other investments due to the wide variety of maturity, repayment and interest rate options available.
At December 31, 2017, the Bank held $102,000 in privately-issued CMOs in the investment portfolio. The Bank and the Company do not invest in collateralized debt obligations, mortgage-related securities secured by sub-prime loans, or any preferred equity securities.
Amortized Cost and Fair Value of Securities. The following table sets forth certain information regarding the amortized cost and fair values of the Company’s securities as of the dates indicated.
At December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Amortized Cost | Fair Value | Amortized Cost | Fair Value | Amortized Cost | Fair Value | ||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Held to Maturity: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | $ | 382 | $ | 396 | $ | 893 | $ | 924 | $ | 1,597 | $ | 1,658 | |||||||||||
FHLB obligations | 410 | 403 | 409 | 407 | 500 | 498 | |||||||||||||||||
FHLMC obligations | 1,600 | 1,564 | 1,600 | 1,560 | 500 | 500 | |||||||||||||||||
FNMA obligations | 1,799 | 1,763 | 1,798 | 1,762 | 3,096 | 3,099 | |||||||||||||||||
FFCB obligations | 499 | 491 | 499 | 496 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 462,942 | 470,484 | 473,653 | 474,852 | 458,062 | 472,661 | |||||||||||||||||
Corporate obligations | 10,020 | 9,938 | 9,331 | 9,286 | 9,929 | 9,915 | |||||||||||||||||
Total held-to-maturity | $ | 477,652 | $ | 485,039 | $ | 488,183 | $ | 489,287 | $ | 473,684 | $ | 488,331 | |||||||||||
Available for Sale: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
U.S Treasury obligations | — | — | 7,995 | 8,008 | 8,006 | 8,004 | |||||||||||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 993,548 | 988,367 | 952,992 | 951,861 | 857,430 | 863,861 | |||||||||||||||||
FHLMC obligations | — | — | 10,009 | 10,014 | 20,101 | 20,059 | |||||||||||||||||
FHLB obligations | 19,014 | 19,005 | 25,136 | 25,164 | 30,298 | 30,273 | |||||||||||||||||
FNMA obligations | — | — | 21,978 | 22,010 | 31,997 | 31,998 | |||||||||||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 3,259 | 3,388 | 3,727 | 3,743 | 4,193 | 4,308 | |||||||||||||||||
Corporate obligations | 26,047 | 26,394 | 19,013 | 19,037 | 5,516 | 5,512 | |||||||||||||||||
Equity securities | 417 | 658 | 397 | 549 | 397 | 519 | |||||||||||||||||
Total available for sale | $ | 1,042,285 | $ | 1,037,812 | $ | 1,041,247 | $ | 1,040,386 | $ | 957,938 | $ | 964,534 | |||||||||||
Average expected life of securities(1) | 4.34 years | 4.24 years | 4.40 years | ||||||||||||||||||||
(1) | Average expected life is based on prepayment assumptions utilizing prevailing interest rates as of the reporting dates and excludes equity securities. |
16
The aggregate carrying values and fair values of securities by issuer, where the aggregate book value of such securities exceeds ten percent of stockholders’ equity are as follows (in thousands):
Amortized Cost | Fair Value | ||||||
At December 31, 2017: | |||||||
FNMA | $ | 476,768 | $ | 473,608 | |||
FHLMC | 440,362 | 437,855 | |||||
The following table sets forth certain information regarding the carrying value, weighted average yields and contractual maturities of the Company’s debt securities portfolio as of December 31, 2017. No tax equivalent adjustments were made to the weighted average yields. Amounts are shown at amortized cost for held to maturity securities and at fair value for available for sale securities.
At December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
One Year or Less | More Than One Year to Five Years | More Than Five Years to Ten Years | After Ten Years | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Carrying Value | Weighted Average Yield (1) | Carrying Value | Weighted Average Yield (1) | Carrying Value | Weighted Average Yield (1) | Carrying Value | Weighted Average Yield (1) | Carrying Value | Weighted Average Yield(1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Held to Maturity: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | $ | 110 | 3.49 | % | $ | 272 | 5.37 | % | $ | — | — | % | $ | — | — | % | $ | 382 | 4.83 | % | ||||||||||||||
Agency obligations | 600 | 1.03 | 3,708 | 1.57 | — | — | — | — | 4,308 | 1.49 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Corporate obligations | 1,565 | 1.55 | 8,455 | 2.50 | — | — | — | — | 10,020 | 2.35 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 4,958 | 3.47 | 55,189 | 3.12 | 260,937 | 2.61 | 141,858 | 2.72 | 462,942 | 2.71 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total held to maturity | $ | 7,233 | 2.85 | % | $ | 67,624 | 2.97 | % | $ | 260,937 | 2.61 | % | $ | 141,858 | 2.72 | % | $ | 477,652 | 2.70 | % | ||||||||||||||
Available for Sale: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
State and municipal obligations | $ | 396 | 3.92 | % | $ | — | — | % | $ | 2,992 | 2.78 | % | $ | — | — | % | $ | 3,388 | 2.91 | % | ||||||||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 401 | 3.68 | 25,789 | 1.70 | 205,439 | 2.50 | 756,738 | 2.61 | 988,367 | 2.56 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Agency obligations | 19,005 | 1.15 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 19,005 | 1.15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Corporate obligations | 989 | 2.60 | 3,048 | 2.99 | 22,357 | 4.99 | — | — | 26,394 | 4.67 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total available for sale(2) | $ | 20,791 | 1.32 | % | $ | 28,837 | 1.84 | % | $ | 230,788 | 2.74 | % | $ | 756,738 | 2.61 | % | $ | 1,037,154 | 2.59 | % | ||||||||||||||
(1) | Yields are not tax equivalent. |
(2) | Totals exclude $658,000 of available for sale equity securities at fair value. |
SOURCES OF FUNDS
General. Primary sources of funds consist of principal and interest cash flows received from loans and mortgage-backed securities, contractual maturities on investments, deposits, FHLBNY advances and proceeds from sales of loans and investments. These sources of funds are used for lending, investing and general corporate purposes, including acquisitions and common stock repurchases.
Deposits. The Bank offers a variety of deposits for retail and business accounts. Deposit products include savings accounts, checking accounts, interest-bearing checking accounts, money market deposit accounts and certificate of deposit accounts at varying interest rates and terms. The Bank also offers investment, insurance, IRA and KEOGH products. Business customers are offered several checking account and savings plans, cash management services, remote deposit capture services, payroll origination services, escrow account management and business credit cards. The Bank focuses on relationship banking for retail and business customers to enhance the customer experience. Deposit activity is influenced by state and local economic conditions, changes in interest rates, internal pricing decisions and competition. Deposits are primarily obtained from the areas surrounding the Bank’s branch locations. To attract and retain deposits, the Bank offers competitive rates, quality customer service and a wide variety of products and services that meet customers’ needs, including online and mobile banking.
Deposit pricing strategy is monitored monthly by the management Asset/Liability Committee and Pricing Committee. Deposit pricing is set weekly by the Bank’s Treasury Department. When setting deposit pricing, the Bank considers competitive
17
market rates, FHLBNY advance rates and rates on other sources of funds. Core deposits, defined as savings accounts, interest and non-interest bearing checking accounts and money market deposit accounts, represented 90.5% of total deposits at December 31, 2017 and 90.1% of total deposits at December 31, 2016. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, time deposits maturing in less than one year amounted to $424.4 million and $439.0 million, respectively.
The following table indicates the amount of certificates of deposit by time remaining until maturity as of December 31, 2017.
Maturity | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
3 Months or Less | Over 3 to 6 Months | Over 6 to 12 Months | Over 12 Months | ||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
Certificates of deposit of $100,000 or more | $ | 143,270 | $ | 44,581 | $ | 33,288 | $ | 94,935 | $ | 316,074 | |||||||||
Certificates of deposit less than $100,000 | 75,241 | 62,882 | 65,186 | 115,426 | 318,735 | ||||||||||||||
Total certificates of deposit | $ | 218,511 | $ | 107,463 | $ | 98,474 | $ | 210,361 | $ | 634,809 | |||||||||
Certificates of Deposit Maturities. The following table sets forth certain information regarding certificates of deposit.
Period to Maturity from December 31, 2017 | At December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Less Than One Year | One to Two Years | Two to Three Years | Three to Four Years | Four to Five Years | Five Years or More | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rate: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0.00 to 0.99% | $ | 249,087 | $ | 30,103 | $ | 4,115 | $ | — | $ | 9 | $ | 255 | $ | 283,569 | $ | 421,772 | $ | 497,327 | |||||||||||||||||
1.00 to 2.00% | 175,361 | 65,190 | 49,875 | 24,992 | 23,978 | 3,296 | 342,692 | 228,111 | 226,456 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2.01 to 3.00% | — | 284 | 713 | 155 | 7,392 | — | 8,544 | 950 | 15,081 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3.01 to 4.00% | — | — | — | 4 | — | — | 4 | 4 | 23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4.01 to 5.00% | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 104 | 492 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5.01 to 6.00% | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 200 | 302 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6.01 to 7.00% | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 6 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Over 7.01% | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 36 | 34 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 424,448 | $ | 95,577 | $ | 54,703 | $ | 25,151 | $ | 31,379 | $ | 3,551 | $ | 634,809 | $ | 651,183 | $ | 739,721 | |||||||||||||||||
Borrowed Funds. At December 31, 2017, the Bank had $1.74 billion of borrowed funds. Borrowed funds consist primarily of FHLBNY advances and repurchase agreements. Repurchase agreements are contracts for the sale of securities owned or borrowed by the Bank, with an agreement to repurchase those securities at an agreed-upon price and date. The Bank uses wholesale repurchase agreements, as well as retail repurchase agreements as an investment vehicle for its commercial sweep checking product. Bank policies limit the use of repurchase agreements to collateral consisting of U.S. Treasury obligations, U.S. government agency obligations or mortgage-related securities.
As a member of the FHLBNY, the Bank is eligible to obtain advances upon the security of the FHLBNY common stock owned and certain residential mortgage loans, provided certain standards related to credit-worthiness have been met. FHLBNY advances are available pursuant to several credit programs, each of which has its own interest rate and range of maturities.
18
The following table sets forth the maximum month-end balance and average balance of FHLBNY advances and securities sold under agreements to repurchase for the periods indicated.
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
Maximum Balance: | |||||||||||
FHLBNY advances | $ | 1,288,448 | $ | 1,343,095 | $ | 1,363,122 | |||||
FHLBNY line of credit | 472,000 | 173,000 | 160,000 | ||||||||
Securities sold under agreements to repurchase | 210,702 | 283,233 | 346,361 | ||||||||
Average Balance: | |||||||||||
FHLBNY advances | 1,237,979 | 1,315,278 | 1,249,193 | ||||||||
FHLBNY line of credit | 179,003 | 37,608 | 80,847 | ||||||||
Securities sold under agreements to repurchase | 164,982 | 224,421 | 273,934 | ||||||||
Weighted Average Interest Rate: | |||||||||||
FHLBNY advances | 1.78 | % | 1.76 | % | 1.84 | % | |||||
FHLBNY line of credit | 1.17 | 0.61 | 0.40 | ||||||||
Securities sold under agreements to repurchase | 1.26 | 1.42 | 1.49 | ||||||||
The following table sets forth certain information as to borrowings at the dates indicated.
At December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
FHLBNY advances | 1,127,335 | 1,295,080 | 1,350,282 | ||||||||
FHLBNY line of credit | 472,000 | 161,000 | 96,000 | ||||||||
Securities sold under repurchase agreements | 143,179 | 156,665 | 261,350 | ||||||||
Total borrowed funds | $ | 1,742,514 | $ | 1,612,745 | $ | 1,707,632 | |||||
Weighted average interest rate of FHLBNY advances | 1.74 | % | 1.77 | % | 1.77 | % | |||||
Weighted average interest rate of FHLBNY line of credit | 1.53 | % | 0.79 | % | 0.49 | % | |||||
Weighted average interest rate of securities sold under agreements to repurchase | 1.00 | % | 1.35 | % | 1.47 | % | |||||
WEALTH MANAGEMENT SERVICES
As part of the Company’s strategy to increase fee related income, the Company’s wholly owned subsidiary, Beacon Trust Company (“Beacon”) is engaged in providing wealth management and asset management services. In addition to its trust and estate administration services, Beacon is also a provider of asset management services which are often introduced to existing clients through the Bank’s extensive branch network. Beacon offers a full range of asset management services to individuals, municipalities, non-profits, corporations and pension funds. These services include investment management, asset allocation, trust and fiduciary services, financial and tax planning, family office services, estate settlement services and custody.
Beacon focuses on delivering personalized investment strategies based on each client’s risk profile. These strategies are focused on maximizing clients’ investment returns, while minimizing expenses. Most of the fee income generated by Beacon is based on assets under management.
SUBSIDIARY ACTIVITIES
PFS Insurance Services, Inc., formerly Provident Investment Services, Inc., is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Bank, and a New Jersey licensed insurance producer that sells insurance and investment products, including annuities to customers through a third-party networking arrangement.
Dudley Investment Corporation is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Bank which operates as a New Jersey Investment Company. Dudley Investment Corporation owns all of the outstanding common stock of Gregory Investment Corporation.
19
Gregory Investment Corporation is a wholly owned subsidiary of Dudley Investment Corporation. Gregory Investment Corporation operates as a Delaware Investment Company. Gregory Investment Corporation owns all of the outstanding common stock of PSB Funding Corporation.
PSB Funding Corporation is a majority owned subsidiary of Gregory Investment Corporation. It was established as a New Jersey corporation to engage in the business of a real estate investment trust for the purpose of acquiring mortgage loans and other real estate related assets from the Bank.
Bergen Avenue Realty, LLC, a New Jersey limited liability company is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Bank formed to manage and sell real estate acquired through foreclosure. At December 31, 2017, Bergen Avenue Realty, LLC had total assets of $4.1 million.
Bergen Avenue Realty PA, LLC, a Pennsylvania limited liability company is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Bank formed to manage and sell real estate acquired through foreclosure in Pennsylvania. At December 31, 2017, Bergen Avenue Realty PA, LLC had total assets of $854,000.
Beacon Trust Company, a New Jersey limited purpose trust company, is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Bank.
Beacon Investment Advisory Services, Inc. is a wholly owned subsidiary of Beacon Trust Company, incorporated under Delaware law and is a registered investment advisor.
PERSONNEL
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had 957 full-time and 97 part-time employees. None of the Company’s employees are represented by a collective bargaining group. The Company believes its working relationship with its employees is good.
REGULATION and SUPERVISION
General
As a bank holding company controlling the Bank, the Company is subject to the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, as amended (“BHCA”), and the rules and regulations of the Federal Reserve Board under the BHCA. The Company is also subject to the provisions of the New Jersey Banking Act of 1948 (the “New Jersey Banking Act”) and the regulations of the Commissioner of the New Jersey Department of Banking and Insurance (“Commissioner”) under the New Jersey Banking Act applicable to bank holding companies. The Company and the Bank are required to file reports with, and otherwise comply with the rules and regulations of the Federal Reserve Board and the Commissioner. The Federal Reserve Board and the Commissioner conduct periodic examinations to assess the Company’s compliance with various regulatory requirements. The Company files certain reports with, and otherwise complies with, the rules and regulations of the SEC under the federal securities laws and the listing requirements of the New York Stock Exchange.
The Bank is a New Jersey chartered savings bank, and its deposit accounts are insured up to applicable limits by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”). The Bank is subject to extensive regulation, examination and supervision by the Commissioner as the issuer of its charter, and by the FDIC as its deposit insurer. The Bank files reports with the Commissioner and the FDIC concerning its activities and financial condition, and it must obtain regulatory approval prior to entering into certain transactions, such as mergers with, or acquisitions of, other depository institutions and opening or acquiring branch offices. The Commissioner and the FDIC conduct periodic examinations to assess the Bank’s compliance with various regulatory requirements. This regulation and supervision establishes a comprehensive framework of activities in which a savings bank can engage and is intended primarily for the protection of the deposit insurance fund and depositors. The regulatory structure also gives the regulatory authorities extensive discretion in connection with their supervisory and enforcement activities and examination policies, including policies with respect to the classification of assets and the establishment of adequate loan loss reserves for regulatory purposes.
Any change in applicable laws and regulations, whether by the Commissioner, the FDIC, the Federal Reserve Board or through legislation, could have a material adverse impact on the Company and the Bank and their operations.
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 (the “Dodd-Frank Act”) made extensive changes in the regulation of depository institutions and their holding companies. Certain provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act have impacted, and will continue to impact the Company and the Bank. For example, the Dodd-Frank Act created the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau as an independent bureau of the Federal Reserve Board. The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau has assumed responsibility for the implementation of the federal financial consumer protection and fair lending laws and regulations and has the authority to impose new requirements. However, institutions with less than $10 billion in assets, such as the Bank, continue to be examined for compliance with consumer protection and fair lending laws and regulations by, and are subject to the enforcement
20
authority of their principal regulator, although the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau has back-up authority to examine and enforce consumer protection laws against all institutions, including those with less than $10 billion in assets.
As of December 31, 2017, the Bank had consolidated assets of $9.85 billion. The Dodd-Frank Act established several measures that apply to institutions and holding companies once they reach $10 billion in assets. In addition to Consumer Financial Protection Bureau compliance examinations, as discussed above, limits on debit card interchange fees apply, which will reduce the Bank’s fee income. Certain enhanced prudential standards will also become applicable such as additional risk management requirements, both from a framework and corporate governance perspective. Stress testing requirements and related filing requirements, which involve assessing the potential impact on the Bank and Company of various scenarios prescribed by the federal regulatory agencies, also become applicable. These and other supervisory and regulatory implications of crossing the $10 billion threshold would likely result in increased regulatory costs.
The material laws and regulations applicable to the Company and the Bank are summarized below and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
New Jersey Banking Regulation
Activity Powers. The Bank derives its lending, investment and other activity powers primarily from the applicable provisions of the New Jersey Banking Act and its related regulations. Under these laws and regulations, savings banks, including the Bank, generally may, subject to certain limits, invest in:
(1) | real estate mortgages; |
(2) | consumer and commercial loans; |
(3) | specific types of debt securities, including certain corporate debt securities and obligations of federal, state and local governments and agencies; |
(4) | certain types of corporate equity securities; and |
(5) | certain other assets. |
A savings bank may also invest pursuant to a “leeway” power that permits investments not otherwise permitted by the New Jersey Banking Act, subject to certain restrictions imposed by the FDIC. “Leeway” investments must comply with a number of limitations on the individual and aggregate amounts of such investments. A savings bank may also exercise trust powers upon the approval of the Commissioner. New Jersey savings banks may exercise those powers, rights, benefits or privileges authorized for national banks or out-of-state banks or for federal or out-of-state savings banks or savings associations, provided that before exercising any such power, right, benefit or privilege, prior approval by the Commissioner by regulation or by specific authorization is required. The exercise of these lending, investment and activity powers is limited by federal law and the related regulations. See “Federal Banking Regulation-Activity Restrictions on State-Chartered Bank” below.
Loans-to-One-Borrower Limitations. With certain specified exceptions, a New Jersey chartered savings bank may not make loans or extend credit to a single borrower and to entities related to the borrower in an aggregate amount that would exceed 15% of the bank’s capital funds. A New Jersey chartered savings bank may lend an additional 10% of the bank’s capital funds if secured by collateral meeting the requirements of the New Jersey Banking Act. The Bank currently complies with applicable loans-to-one-borrower limitations.
Dividends. Under the New Jersey Banking Act, a stock savings bank may declare and pay a dividend on its capital stock only to the extent that the payment of the dividend would not impair the capital stock of the savings bank. In addition, a stock savings bank may not pay a dividend unless the savings bank would, after the payment of the dividend, have a surplus of not less than 50% of its capital stock, or the payment of the dividend would not reduce the surplus. Federal law may also limit the amount of dividends that may be paid by the Bank.
Minimum Capital Requirements. Regulations of the Commissioner impose on New Jersey chartered depository institutions, including the Bank, minimum capital requirements similar to those imposed by the FDIC on insured state banks. At December 31, 2017, the Bank was considered “well capitalized” under FDIC guidelines.
Examination and Enforcement. The New Jersey Department of Banking and Insurance may examine the Company and the Bank whenever it deems an examination advisable. The Department examines the Bank at least every two years. The Commissioner may order any savings bank to discontinue any violation of law or unsafe or unsound business practice and may direct any director, officer, attorney or employee of a savings bank engaged in an objectionable activity, after the Commissioner has ordered the activity to be terminated, to show cause at a hearing before the Commissioner why such person should not be removed.
21
Federal Banking Regulation
Capital Requirements. Federal regulations require federally insured depository institutions to meet several minimum capital standards: a common equity Tier 1 capital to risk-based assets ratio of 4.5%, a Tier 1 capital to risk-based assets ratio of 6.0%, a total capital to risk-based assets of 8.0%, and a 4.0% Tier 1 capital to total assets leverage ratio. These capital requirements are the result of a final rule implementing recommendations of the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision and certain requirements of the Dodd-Frank Act, and were effective January 1, 2015.
In determining the amount of risk-weighted assets for purposes of calculating risk-based capital ratios, all assets, including certain off-balance sheet assets (e.g., recourse obligations, direct credit substitutes, residual interests) are multiplied by a risk weight factor assigned by the regulations based on the risks believed inherent in the type of asset. Higher levels of capital are required for asset categories believed to present greater risk. Common equity Tier 1 capital is generally defined as common stockholders’ equity and retained earnings. Tier 1 capital is generally defined as common equity Tier 1 and additional Tier 1 capital. Additional Tier 1 capital includes certain noncumulative perpetual preferred stock and related surplus and minority interests in equity accounts of consolidated subsidiaries. Total capital includes Tier 1 capital (common equity Tier 1 capital plus additional Tier 1 capital) and Tier 2 capital. Tier 2 capital is comprised of capital instruments and related surplus, meeting specified requirements, and may include cumulative preferred stock and long-term perpetual preferred stock, mandatory convertible securities, intermediate preferred stock and subordinated debt. Also included in Tier 2 capital is the allowance for loan and lease losses limited to a maximum of 1.25% of risk-weighted assets and, for institutions that have exercised an opt-out election regarding the treatment of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income, up to 45% of net unrealized gains on available-for-sale equity securities with readily determinable fair market values. Calculation of all types of regulatory capital is subject to deductions and adjustments specified in the regulations. In assessing an institution’s capital adequacy, the FDIC takes into consideration, not only these numeric factors, but qualitative factors as well, and has the authority to establish higher capital requirements for individual institutions where deemed necessary.
In addition to establishing the minimum regulatory capital requirements, the regulations limit capital distributions and certain discretionary bonus payments to management if the institution does not hold a “capital conservation buffer” consisting of 2.5% of common equity Tier 1 capital to risk-weighted asset above the amount necessary to meet its minimum risk-based capital requirements. The capital conservation buffer requirement was effective on January 1, 2016 at 0.625% of risk-weighted assets and will increase each year until fully implemented at 2.5% on January 1, 2019. The capital conservation buffer during the calendar year 2017 was 1.25% and increased to 1.875% on January 1, 2018.
The following table shows the Bank’s Tier 1 leverage ratio, common equity Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio, Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio, and total risk-based capital ratio, at December 31, 2017:
As of December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||
Capital | Percent of Assets(1) | Capital Requirements (1) | Capital Requirements with Capital Conservation Buffer (1) | |||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||
Tier 1 leverage capital | $ | 834,084 | 9.07 | % | 4.00 | % | 4.00 | % | ||||
Common equity Tier 1 risk-based capital | 834,084 | 11.15 | 4.50 | 5.75 | ||||||||
Tier 1 risk-based capital | 834,084 | 11.15 | 6.00 | 7.25 | ||||||||
Total risk-based capital | 894,430 | 11.95 | 8.00 | 9.25 | ||||||||
(1) For purposes of calculating regulatory Tier 1 leverage capital, assets are based on adjusted total leverage assets. In calculating common equity Tier 1 risk-based capital, Tier 1 risk-based capital and total risk-based capital, assets are based on total risk-weighted assets.
As of December 31, 2017, the Bank was considered “well capitalized” under FDIC guidelines.
Activity Restrictions on State-Chartered Banks. Federal law and FDIC regulations generally limit the activities and investments of state-chartered FDIC insured banks and their subsidiaries to those permissible for national banks and their subsidiaries, unless such activities and investments are specifically exempted by law or consented to by the FDIC.
Before making a new investment or engaging in a new activity that is not permissible for a national bank or otherwise permissible under federal law or FDIC regulations, an insured bank must seek approval from the FDIC to make such investment or engage in such activity. The FDIC will not approve the activity unless the bank meets its minimum capital requirements and
22
the FDIC determines that the activity does not present a significant risk to the FDIC insurance fund. Certain activities of subsidiaries that are engaged in activities permitted for national banks only through a “financial subsidiary” are subject to additional restrictions.
Federal law permits a state-chartered savings bank to engage, through financial subsidiaries, in any activity in which a national bank may engage through a financial subsidiary and on substantially the same terms and conditions. In general, the law permits a national bank that is well-capitalized and well-managed to conduct, through a financial subsidiary, any activity permitted for a financial holding company other than insurance underwriting, insurance investments, real estate investment or development or merchant banking. The total assets of all such financial subsidiaries may not exceed the lesser of 45% of the bank’s total assets or $50 billion. The bank must have policies and procedures to assess the financial subsidiary’s risk and protect the bank from such risk and potential liability, must not consolidate the financial subsidiary’s assets with the bank’s and must exclude from its own assets and equity all equity investments, including retained earnings, in the financial subsidiary. The Bank currently meets all conditions necessary to establish and engage in permitted activities through financial subsidiaries.
Federal Home Loan Bank System. The Bank is a member of the FHLB system which consists of twelve regional FHLBs, each subject to supervision and regulation by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (“FHFA”). The FHLB provides a central credit facility primarily for member institutions. As a member of the FHLB of New York, the Bank is required to purchase and hold shares of capital stock in that FHLB in an amount as required by that FHLB’s capital plan and minimum capital requirements. The Bank is in compliance with these requirements. The Bank has received dividends on its FHLBNY stock, although no assurance can be given that these dividends will continue to be paid. For the year ended December 31, 2017, dividends paid by the FHLBNY to the Bank totaled $4.1 million.
Deposit Insurance. As a member institution of the FDIC, deposit accounts at the Bank are generally insured by the FDIC’s Deposit Insurance Fund (“DIF”) up to a maximum of $250,000 for each separately insured depositor.
Under the FDIC’s risk-based assessment system, insured institutions were originally assigned a risk category based on supervisory evaluations, regulatory capital levels and certain other factors. An institution’s assessment rate depended upon the category to which it was assigned, and certain adjustments specified by FDIC regulations. Institutions deemed less risky paid lower assessments. No institution may pay a dividend if it is in default of its federal deposit insurance assessment.
The Dodd-Frank Act required the FDIC to revise its procedures to base its assessments upon each insured institution’s total assets less tangible equity instead of deposits. The FDIC finalized a rule, effective April 1, 2011, that set the assessment range (inclusive of possible adjustments) at 25 to 45 basis points of total assets less tangible equity. However, as described below, there were recent changes to both the FDIC’s assessment range and its risk-based assessment procedures.
The FDIC has established a long range target size for the DIF of 2 percent of insured deposits. The FDIC’s regulations also provided for a lower assessment rate schedule when the DIF reached 1.15% of total insured deposits. The 1.15% ratio was achieved as of June 30, 2016. As a result, effective July 1, 2016, the assessment range (inclusive of possible adjustments) has been lowered to 1.5 to 30 basis points for banks of less than $10 billion in consolidated assets. The Dodd-Frank Act requires banks of greater than $10 billion of assets to pay to increase the DIF reserve ratio from 1.15% to 1.35%. Consequently, also effective July 1, 2016, banks of greater than $10 billion of assets now pay a surcharge of 4.5 basis points on assets above $10 billion until the earlier of the reserve ratio reaching 1.35% or December 31, 2018 (when a short fall assessment would be applied). At the same time, the FDIC eliminated the risk categories. Most institutions are now assessed based on financial ratios derived from statistical models that estimate the probability of a bank’s failure within three years. Banks of greater than $10 billion are assessed based on a rate derived from a scorecard which assesses certain factors such as examination ratings, financial measures related to the bank’s ability to withstand stress and measures of loss severity to the DIF if the bank should fail.
Enforcement. The FDIC has extensive enforcement authority over insured savings banks, including the Bank. This enforcement authority includes, among other things, the ability to assess civil money penalties, to issue cease and desist orders and to remove directors and officers. In general, these enforcement actions may be initiated in response to violations of law and to unsafe or unsound practices.
Transactions with Affiliates. Transactions between an insured bank, such as the Bank, and any of its affiliates are governed by Sections 23A and 23B of the Federal Reserve Act and its implementing regulations. An affiliate of a bank is any company or entity that controls, is controlled by or is under common control with the bank. A subsidiary of a bank that is not also a depository institution, financial subsidiary or other entity defined by the regulation generally is not treated as an affiliate of the bank for purposes of Sections 23A and 23B.
23
Section 23A:
• | limits the extent to which a bank or its subsidiaries may engage in “covered transactions” with any one affiliate to an amount equal to 10% of such bank’s capital stock and retained earnings, and limits all such transactions with all affiliates to an amount equal to 20% of such capital stock and retained earnings; and |
• | requires that all such transactions be on terms that are consistent with safe and sound banking practices. |
The term “covered transaction” includes the making of loans, purchase of assets, issuance of guarantees and other similar types of transactions. Further, most loans by a bank to any of its affiliates must be secured by collateral in amounts ranging from 100 to 130 percent of the loan amounts. In addition, any covered transaction by a bank with an affiliate and any purchase of assets or services by a bank from an affiliate must be on terms that are substantially the same, or at least as favorable to the bank, as those that would be provided to a non-affiliate.
Prohibitions Against Tying Arrangements. Banks are subject to statutory prohibitions on certain tying arrangements. A depository institution is prohibited, subject to certain exceptions, from extending credit to or offering any other service, or fixing or varying the consideration for such extension of credit or service, on the condition that the customer obtain some additional service from the institution or its affiliates or that the customer not obtain services of a competitor of the institution.
Privacy Standards. FDIC regulations require the Company and the Bank to disclose their privacy policies, including identifying with whom they share “non-public personal information” to customers at the time of establishing the customer relationship and annually thereafter.
The FDIC regulations also require the Company and the Bank to provide their customers with initial and annual notices that accurately reflect their privacy policies and practices. In addition, the Company and the Bank are required to provide their customers with the ability to “opt-out” of having the Company and the Bank share their non-public personal information with unaffiliated third parties before they can disclose such information, subject to certain exceptions.
Community Reinvestment Act and Fair Lending Laws. All FDIC insured institutions have a responsibility under the Community Reinvestment Act and related regulations to help meet the credit needs of their entire communities, including low- and moderate-income neighborhoods and borrowers (i.e. assessment(s)). In connection with its examination of a state chartered savings bank, the FDIC is required to assess the institution’s record of compliance with the Community Reinvestment Act. Among other things, the current Community Reinvestment Act regulations rate an institution based upon its actual performance in meeting community needs. In particular, the current examination and evaluation process focuses on three tests:
• | a lending test, to evaluate the institution’s record of making home mortgage, small business, small farm, and consumer loans, if applicable, in its assessment area(s), with consideration given towards, amongst other factors, borrower characteristics and geographic distribution; |
• | an investment test, to evaluate the institution’s record of helping to meet the credit needs of its assessment area(s) through qualified investments characterized as a lawful investment, deposit, membership share, or grant that has as its primary purpose community development; and |
• | a service test, to evaluate the institution’s systems for delivering retail banking services through its branches, ATMs and other offices and access facilities, including the distribution of its branches, ATMs and other offices/access facilities, and the institution’s record of opening and closing branches. |
An institution’s failure to comply with the provisions of the Community Reinvestment Act could, at a minimum, result in regulatory restrictions on its activities, including, but not limited to, engaging in acquisitions and mergers. The Bank received an “Outstanding” Community Reinvestment Act rating in its most recently completed federal examination, which was conducted by the FDIC as of December 2014.
In addition, the Equal Credit Opportunity Act and the Fair Housing Act prohibit lenders from discriminating in their lending practices on the basis of the borrower’s characteristics as specified in those statutes. An institution’s failure to comply with the Equal Credit Opportunity Act and/or the Fair Housing Act could result in enforcement actions by the FDIC, as well as other federal regulatory agencies and the Department of Justice.
Safety and Soundness Standards. Each federal banking agency, including the FDIC, has adopted guidelines establishing general standards relating to internal controls, information and internal audit systems, loan documentation, credit underwriting, interest rate exposure, asset growth, asset quality, earnings, compensation, fees and benefits. In general, the guidelines require, among other things, appropriate systems and practices to identify and manage the risks and exposures specified in the guidelines. The guidelines prohibit excessive compensation as an unsafe and unsound practice and describe compensation as excessive when
24
the amounts paid are unreasonable or disproportionate to the services performed by an executive officer, employee, director, or principal stockholder.
In addition, FDIC regulations require a bank that is given notice by the FDIC that it is not satisfying any of such safety and soundness standards to submit a compliance plan to the FDIC. If, after being so notified, a bank fails to submit an acceptable compliance plan or fails in any material respect to implement an accepted compliance plan, the FDIC may issue an order directing corrective and other actions of the types to which a significantly undercapitalized institution is subject under the “prompt corrective action” provisions discussed below. If a bank fails to comply with such an order, the FDIC may seek to enforce such an order in judicial proceedings and to impose civil monetary penalties.
Prompt Corrective Action. Federal law requires the FDIC and the other federal banking regulators to promptly resolve the problems of undercapitalized institutions. Federal law also establishes five categories, consisting of “well capitalized,” “adequately capitalized,” “undercapitalized,” “significantly undercapitalized” and “critically undercapitalized.” The FDIC’s regulations define the five capital categories as follows:
An institution will be treated as “well capitalized” if:
• | its ratio of total capital to risk-weighted assets is at least 10%; |
• | its ratio of Tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets is at least 8%; |
• | its ratio of common equity Tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets is at least 6.5%; and |
• | its ratio of Tier 1 capital to total assets is at least 5%, and it is not subject to any order or directive by the FDIC to meet a specific capital level. |
An institution will be treated as “adequately capitalized” if:
• | its ratio of total capital to risk-weighted assets is at least 8%; or |
• | its ratio of Tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets is at least 6%; |
• | its ratio of common equity Tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets is at least 4.5%; and |
• | its ratio of Tier 1 capital to total assets is at least 4% and it is not a well-capitalized institution. |
An institution will be treated as “undercapitalized” if:
• | its total risk-based capital is less than 8%; or |
• | its Tier 1 risk-based-capital is less than 6%; |
• | its ratio of common equity Tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets is less than 4.5%; or |
• | its leverage ratio is less than 4% |
An institution will be treated as “significantly undercapitalized” if:
• | its total risk-based capital is less than 6%; |
• | its Tier 1 capital is less than 4%; |
• | its ratio of common equity to risk-weighted assets is less than 3%; or |
• | its leverage ratio is less than 3%. |
An institution that has a tangible capital to total assets ratio equal to or less than 2% would be deemed “critically undercapitalized.” The FDIC is required, with some exceptions, to appoint a receiver or conservator for an insured state bank if that bank is critically undercapitalized. The FDIC may also appoint a conservator or receiver for an insured state bank on the basis of the institution’s financial condition or upon the occurrence of certain events, including:
• | insolvency, or when the assets of the bank are less than its liabilities to depositors and others; |
• | substantial dissipation of assets or earnings through violations of law or unsafe or unsound practices; |
• | existence of an unsafe or unsound condition to transact business; |
• | likelihood that the bank will be unable to meet the demands of its depositors or to pay its obligations in the normal course of business; and |
25
• | insufficient capital, or the incurring or likely incurring of losses that will substantially deplete all of the institution’s capital with no reasonable prospect of replenishment of capital without federal assistance. |
The previously discussed final rule that increased capital requirements effective January 1, 2015 adjusted the prompt action categories as reflected above.
Loans to a Bank’s Insiders
Federal Regulation. A bank’s loans to its executive officers, directors, any owner of 10% or more of its stock (each, an insider) and any of certain entities affiliated with any such person (an insider’s related interest) are subject to the conditions and limitations imposed by Section 22(h) of the Federal Reserve Act and the Federal Reserve Board’s Regulation O. Under these restrictions, the aggregate amount of the loans to any insider and the insider’s related interests may not exceed the loans-to-one-borrower limit applicable to national banks, which is comparable to the loans-to-one-borrower limit applicable to loans by the Bank. All loans by a bank to all insiders and insiders’ related interests in the aggregate may not exceed the bank’s unimpaired capital and unimpaired surplus. With certain exceptions, loans to an executive officer, other than loans for the education of the officer’s children and certain loans secured by the officer’s residence may not exceed at any one time the higher of 2.5% of the bank’s unimpaired capital and unimpaired surplus or $25,000, but in no event more than $100,000. Regulation O also requires that any proposed loan to an insider or a related interest of that insider be approved in advance by a majority of the board of directors of the bank, with any interested directors not participating in the voting, if such loan, when aggregated with any existing loans to that insider and the insider’s related interests, would exceed either (1) $500,000; or (2) the greater of $25,000 or 5% of the bank’s unimpaired capital and surplus.
Generally, loans to insiders must be made on substantially the same terms as, and follow credit underwriting procedures that are not less stringent than, those prevailing at the time for, comparable transactions with other persons, and not involve more than the normal risk of payment or present other unfavorable features. An exception may be made for extensions of credit made pursuant to a benefit or compensation plan of a bank that is widely available to employees of the bank and that does not give any preference to insiders of the bank over other employees of the bank.
In addition, federal law prohibits extensions of credit to a bank’s insiders and their related interests by any other institution that has a correspondent banking relationship with the bank, unless such extension of credit is on substantially the same terms as those prevailing at the time for comparable transactions with other persons and does not involve more than the normal risk of repayment or present other unfavorable features.
The Bank does not, as a matter of policy, make loans to its directors or to their immediate family members and related interests.
New Jersey Regulation. Provisions of the New Jersey Banking Act impose conditions and limitations on the liabilities owed to a savings bank by its directors and executive officers and by corporations and partnerships controlled by such persons that are comparable in many respects to the conditions and limitations imposed on the loans and extensions of credit to insiders and their related interests under Regulation O, as discussed above. The New Jersey Banking Act also provides that a savings bank that is in compliance with Regulation O is deemed to be in compliance with such provisions of the New Jersey Banking Act.
Federal Reserve System
Under Federal Reserve Board regulations, the Bank is required to maintain non-interest earning reserves against its transaction accounts. For 2018, the Federal Reserve Board regulations generally require that reserves of 3% must be maintained against aggregate transaction accounts over $16.0 million and up to $122.3 million, and 10% against that portion of total transaction accounts in excess of up to $122.3 million. The first $16.0 million of otherwise reservable balances are exempted from the reserve requirements. The Bank is in compliance with these requirements. These requirements are adjusted annually by the Federal Reserve Board. Because required reserves must be maintained in the form of either vault cash, a non-interest bearing account at a Federal Reserve Bank or a pass-through account as defined by the Federal Reserve Board, the effect of this reserve requirement is to reduce the Bank’s interest-earning assets. The Bank is authorized to borrow from the Federal Reserve Bank discount window.
Internet Banking
Technological developments continue to significantly alter the ways in which financial institutions and their customers conduct their business. The growth of the Internet has caused banks to adopt and refine alternative distribution and marketing systems. The federal bank regulatory agencies have targeted various aspects of internet banking, including the security and systems. There can be no assurance that the bank regulatory agencies will adopt new regulations that will not materially affect the Bank’s Internet operations or restrict any such further operations.
26
The USA PATRIOT Act
The USA PATRIOT Act gives the federal government powers to address terrorist threats through enhanced domestic security measures, expanded surveillance powers, increased information sharing, and broadened anti-money laundering requirements. By way of amendments to the Bank Secrecy Act, Title III of the USA PATRIOT Act included measures intended to encourage information sharing among bank regulatory agencies and law enforcement bodies. Further, certain provisions of Title III imposed affirmative obligations on a broad range of financial institutions, including banks, thrifts, brokers, dealers, credit unions, money transfer agents and parties registered under the Commodity Exchange Act.
The bank regulatory agencies have increased the regulatory scrutiny of the Bank Secrecy Act and anti-money laundering programs maintained by financial institutions. Significant penalties and fines, as well as other supervisory orders may be imposed on a financial institution for non-compliance with these requirements. In addition, the federal bank regulatory agencies must consider the effectiveness of financial institutions engaging in a merger transaction in combating money laundering activities. The Bank has adopted policies and procedures which are in compliance with these requirements.
Holding Company Regulation
Federal Regulation. The Company is regulated as a bank holding company, and as such, is subject to examination, regulation and periodic reporting under the Bank Holding Company Act, as administered by the Federal Reserve Board.
The Federal Reserve Board has adopted capital adequacy guidelines for bank holding companies on a consolidated basis. The Dodd-Frank Act directed the Federal Reserve Board to issue consolidated capital requirements for depository institution holding companies that are not less stringent, both quantitatively and in terms of components of capital, than those applicable to institutions themselves. The previously discussed final rule regarding regulatory capital requirements implemented the Dodd-Frank Act as to bank holding company capital standards. Consolidated regulatory capital requirements identical to those applicable to the subsidiary banks applied to bank holding companies (with greater than $1 billion of assets) as of January 1, 2015. As is the case with institutions themselves, the capital conservation buffer was effective on January 1, 2016, and will increase each year until fully implemented on January 1, 2019. As of December 31, 2017, the Company’s regulatory capital ratios exceed these minimum capital requirements.
The following table shows the Company’s Tier 1 leverage capital ratio, common equity Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio, Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio and the total risk-based capital ratio as of December 31, 2017.
As of December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||
Capital | Percent of Assets(1) | Capital Requirements (1) | Capital Requirements with Capital Conservation Buffer (1) | |||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||
Tier 1 leverage capital | $ | 887,924 | 9.65 | % | 4.00 | % | 4.00 | % | ||||
Common Equity Tier 1 risk-based capital | 887,924 | 11.87 | 4.50 | 5.75 | ||||||||
Tier 1 risk-based capital | 887,924 | 11.87 | 6.00 | 7.25 | ||||||||
Total risk-based capital | 948,119 | 12.67 | 8.00 | 9.25 | ||||||||
(1) | For purposes of calculating regulatory Tier 1 leverage capital, assets are based on adjusted total leverage assets. In calculating common equity Tier 1 capital, Tier 1 risk-based capital and total risk-based capital, assets are based on total risk-weighted assets. |
As of December 31, 2017, the Company was “well capitalized” under Federal Reserve Board guidelines.
Regulations of the Federal Reserve Board provide that a bank holding company must serve as a source of strength to any of its subsidiary banks and must not conduct its activities in an unsafe or unsound manner. Federal Reserve Board policies generally provide that bank holding companies should pay dividends only out of current earnings and only if the prospective rate of earnings retention in the holding company appears consistent with the organization’s capital needs, asset quality and overall financial condition. Federal Reserve Board guidance sets forth the supervisory expectation that bank holding companies will inform and consult with Federal Reserve Board staff in advance of issuing a dividend that exceeds earnings for the quarter and should inform the Federal Reserve Board and should eliminate, defer or significantly reduce dividends if: (i) net income available to stockholders for the past four quarters, net of dividends previously paid during that period, is not sufficient to fully fund the dividends; (ii) prospective rate of earnings retention is not consistent with the bank holding company’s capital needs and overall current and prospective financial condition; or (iii) the bank holding company will not meet, or is in danger of not meeting, its minimum
27
regulatory capital adequacy ratios. Under the prompt corrective action provisions discussed above, a bank holding company parent of an undercapitalized subsidiary bank would be directed to guarantee, within limitations, the capital restoration plan that is required of such an undercapitalized bank. If the undercapitalized bank fails to file an acceptable capital restoration plan or fails to implement an accepted plan, the Federal Reserve Board may prohibit the bank holding company parent of the undercapitalized bank from paying any dividends or making any other form of capital distribution without the prior approval of the Federal Reserve Board.
As a bank holding company, the Company is required to obtain the prior approval of the Federal Reserve Board to acquire all, or substantially all, of the assets of any bank or bank holding company. Prior Federal Reserve Board approval will be required for the Company to acquire direct or indirect ownership or control of any voting securities of any bank or bank holding company if, after giving effect to such acquisition, it would, directly or indirectly, own or control more than 5% of any class of voting shares of such bank or bank holding company.
A bank holding company is required to give the Federal Reserve Board prior written notice of any purchase or redemption of its outstanding equity securities if the gross consideration for the purchase or redemption, when combined with the net consideration paid for all such purchases or redemptions during the preceding 12 months will be equal to 10% or more of the company’s consolidated net worth. The Federal Reserve Board may disapprove such a purchase or redemption if it determines that the proposal would constitute an unsafe and unsound practice, or would violate any law, regulation, Federal Reserve Board order or directive, or any condition imposed by, or written agreement with, the Federal Reserve Board. Such notice and approval is not required for a bank holding company that would be treated as “well capitalized” under applicable regulations of the Federal Reserve Board, is well-managed, and that is not the subject of any unresolved supervisory issues.
In addition, a bank holding company which does not opt to become a financial holding company under applicable federal law is generally prohibited from engaging in, or acquiring direct or indirect control of any company engaged in non-banking activities. One of the principal exceptions to this prohibition is for activities found by the Federal Reserve Board to be so closely related to banking or managing or controlling banks as to be permissible. Some of the principal activities that the Federal Reserve Board has determined by regulation to be so closely related to banking as to be permissible are:
• | making or servicing loans; |
• | performing certain data processing services; |
• | providing discount brokerage services, or acting as fiduciary, investment or financial advisor; |
• | leasing personal or real property; |
• | making investments in corporations or projects designed primarily to promote community welfare; and |
• | acquiring a savings and loan association. |
Bank holding companies that qualify and opt to become a financial holding company may engage in activities that are financial in nature or incident to activities which are financial in nature. Financial holding companies may engage in a broader array of activities including insurance and investment banking.
Bank holding companies may qualify to become a financial holding company if at the time of the election and on a continuing basis:
• | each of its depository institution subsidiaries is “well capitalized”; |
• | each of its depository institution subsidiaries is “well managed”; and |
• | each of its depository institution subsidiaries has at least a “Satisfactory” Community Reinvestment Act rating at its most recent examination. |
The Company filed an election to qualify as a financial holding company under federal regulations on January 31, 2014 which was deemed effective by the Federal Reserve Board on March 5, 2015.
Under federal law, depository institutions are liable to the FDIC for losses suffered or anticipated by the FDIC in connection with the default of a commonly controlled depository institution or any assistance provided by the FDIC to such an institution in danger of default. This law would potentially be applicable to the Company if it ever acquired as a separate subsidiary, a depository institution in addition to the Bank.
New Jersey Regulation. Under the New Jersey Banking Act, a company owning or controlling a savings bank is regulated as a bank holding company. The New Jersey Banking Act defines the terms “company” and “bank holding company” as such terms are defined under the BHCA. Each bank holding company controlling a New Jersey chartered bank or savings bank must file certain reports with the Commissioner and is subject to examination by the Commissioner.
28
Acquisition of Control. Under federal law and under the New Jersey Banking Act, no person may acquire control of the Company or the Bank without first obtaining approval of such acquisition of control from the Federal Reserve Board and the Commissioner.
Federal Securities Laws. The Company’s common stock is registered with the SEC under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. The Company is subject to the information, proxy solicitation, insider trading restrictions and other requirements under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
Investment Adviser Regulation
Beacon Investment Advisory Services, Inc. is an investment adviser registered with the SEC. As such, it is required to make certain filings with and is subject to periodic examination by, the SEC.
Delaware Corporation Law
The Company is incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware. As a result, the rights of its stockholders are governed by the Delaware General Corporate Law and the Company’s Certificate of Incorporation and Bylaws.
TAXATION
Federal Taxation
General. The Company is subject to federal income taxation in the same general manner as other corporations, with some exceptions discussed below. The following discussion of federal taxation is intended only to summarize certain pertinent federal income tax matters and is not a comprehensive description of the tax rules applicable to the Company.
On December 22, 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act ("Tax Act") was enacted. Included as part of the law, was a permanent reduction in the federal corporate income tax rate from 35% to 21% effective January 1, 2018. Based upon the change in the tax rate, the Company revalued its net deferred tax asset at December 31, 2017 to reflect the reduced rate that will apply in future periods when theses deferred taxes are settled or realized. As a result of the enactment of the Tax Act, the Company recognized an additional tax expense of $3.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2017.
Method of Accounting. For federal income tax purposes, the Company currently reports its income and expenses on the accrual method of accounting and uses a tax year ending December 31 for filing its consolidated federal income tax returns.
Bad Debt Reserves. Prior to the Small Business Protection Act of 1996 (the “1996 Act”), the Bank was permitted to establish a reserve for bad debts and to make annual additions to the reserve. These additions could, within specified formula limits, be deducted in arriving at taxable income. The Bank was required to use the direct charge-off method to compute its bad debt deduction beginning with its 1996 federal income tax return. Savings institutions were required to recapture any excess reserves over those established as of December 31, 1987 (base year reserve).
Taxable Distributions and Recapture. Prior to the 1996 Act, bad debt reserves created prior to January 1, 1988 were subject to recapture into taxable income should the Bank fail to meet certain asset and definitional tests. Federal legislation has eliminated these recapture rules. Retained earnings at December 31, 2017 included approximately $51.8 million for which no provisions for income tax had been made. This amount represents an allocation of income to bad debt deductions for tax purposes only. Events that would result in taxation of these reserves include failure to qualify as a bank for tax purposes, distributions in complete or partial liquidation, stock redemptions and excess distributions to shareholders. At December 31, 2017, the Bank had an unrecognized tax liability of $13.7 million with respect to this reserve.
Corporate Alternative Minimum Tax. The Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), imposes an alternative minimum tax (AMT) at a rate of 20% on a base of regular taxable income plus certain tax preferences (alternative minimum taxable income or AMTI). The AMT is payable to the extent such AMTI is in excess of an exemption amount and the AMT exceeds the regular income tax. Net operating losses can offset no more than 90% of AMTI. Certain payments of alternative minimum tax may be used as credits against regular tax liabilities in future years. The Company has not been subject to the alternative minimum tax and has no such amounts available as credits for carryover. The recently enacted Tax Act repeals the corporate AMT effective for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017.
Net Operating Loss Carryovers. Under the general rule, a financial institution may carry back net operating losses to the preceding two taxable years and forward to the succeeding 20 taxable years. At December 31, 2017, the Company had approximately $1.3 million of Federal Net Operating Losses ("NOLs"). These NOLs were generated by entities the Company acquired in previous years and are subject to an annual Code Section 382 limitation. The Tax Act limits limits the NOL deduction for a given year to 80% of taxable income, effective with respect to losses arising in tax years beginning after December 31, 2017. It also repeals the
29
pre-enactment carryback provision for NOLs and provides for the indefinite carryforward of NOLs arrising in tax years ending after December 31, 2017.
Corporate Dividends-Received Deduction. The Company may exclude from its income 100% of dividends received from the Bank as a member of the same affiliated group of corporations.
State Taxation
New Jersey State Taxation. The Company and the Bank file New Jersey Corporation Business Tax returns. Generally, the income of financial institutions in New Jersey, which is calculated based on federal taxable income subject to certain adjustments, is subject to New Jersey tax. The Company and the Bank are currently subject to the corporation business tax at 9% of apportioned taxable income.
New Jersey tax law does not and has not allowed for a taxpayer to file a tax return on a combined or consolidated basis with another member of the affiliated group where there is common ownership. However, if the taxpayer cannot demonstrate by clear and convincing evidence that the tax filing discloses the true earnings of the taxpayer on its business carried on in the State of New Jersey, the Director of the New Jersey Division of Taxation may, at the director’s discretion, require the taxpayer to file a consolidated return of the entire operations of the affiliated group or controlled group, including its own operations and income.
Pennsylvania State Taxation. The Bank is subject to Pennsylvania Mutual Thrift Institutions Tax. Mutual thrift institutions tax is imposed at the rate of 11.5% on net taxable income of mutual thrift institutions in Pennsylvania, including savings banks without capital stock, building and loan associations, savings and loan associations, and savings institutions having capital stock.
New York State Taxation. In 2014, New York State enacted significant and comprehensive reforms to its corporate tax system that went into effect January 1, 2015. The new legislation resulted in significant changes to the method of calculating income taxes for banks, including changes to future period tax rates, rules relating to the sourcing of income, and the elimination of the banking corporation tax so that banking corporations will now be taxed under New York State’s corporate franchise tax. The corporate franchise tax is based on the combined entire net income of the Company and its affiliates allocable and apportionable to New York State and taxed at a rate of 6.5%. The amount of revenues that are sourced to New York State under the new legislation can be expected to fluctuate over time. In addition, the Company and its affiliates are subject to the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (“MTA”) Surcharge allocable to business activities carried on in the Metropolitan Commuter Transportation District. The MTA surcharge for 2017 was 28.3% of a recomputed New York State franchise tax, calculated using a 6.5% tax rate on allocated and apportioned entire net income. The Bank is currently under audit with respect to its New York State combined franchise tax return for tax years 2015 and 2016.
Item 1A. Risk Factors.
In the ordinary course of operating our business, we are exposed to a variety of risks inherent to the financial services industry. The following discusses the significant risk factors that could affect our business and operations. If any of the following conditions or events actually occur, our business, financial condition or results of operations could be negatively affected, the market price of your investment in the Company’s common stock could decline, and you could lose all or a part of your investment in the Company’s common stock.
Changes in interest rates could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Our financial condition and results of operations are significantly affected by changes in market interest rates, and the degree to which these changes disparately impact short-term and long-term interest rates. Our results of operations substantially depend on our net interest income, which is the difference between the interest income we earn on our interest-earning assets and the interest expense we pay on our interest-bearing liabilities.
The Federal Reserve Board has maintained interest rates at historically low levels through its targeted federal funds rate and recently shifted its strategy to a measured approach of increasing the targeted federal funds rate. If the Federal Reserve Board’s recent policy action to increase short-term rates does not result in a commensurate increase in long-term rates, we may experience a flattening or inverted yield curve that could negatively impact our net interest margin and earnings.
Our interest-bearing liabilities may be subject to repricing or maturing more quickly than our interest-earning assets. If rates increase rapidly, we may have to increase the rates we pay on our deposits and borrowed funds more quickly than we can increase the interest rates we earn on our loans and investments, resulting in a negative effect on interest spreads and net interest income. In addition, the effect of rising rates could be compounded if deposit customers move funds into higher yielding accounts. In the event of a 300 basis point increase in interest rates, whereby rates ramp up evenly over a twelve-month period, and assuming management took no actions to mitigate the effect of such change, we are projecting that our net interest income would decrease 3.8% or $11.2 million. Conversely, should market interest rates fall below current levels, our net interest income could also be
30
negatively affected if competitive pressures keep us from further reducing rates on our deposits, while the yields on our assets decrease through loan prepayments and interest rate adjustments.
Changes in interest rates also affect the value of our interest-earning assets and in particular our securities portfolio. Generally, the value of securities fluctuates inversely with changes in interest rates. At December 31, 2017, our available for sale securities portfolio totaled $1.04 billion. Unrealized gains and losses on securities available for sale are reported as a separate component of stockholders’ equity. Decreases in the fair value of securities available for sale resulting from increases in interest rates therefore could have a temporary adverse effect on stockholders’ equity.
We are also subject to other financial risks related to interest rate movements. Changes in interest rates can affect the average lives of loans and mortgage related securities. Increases in interest rates can result in extending the average lives of our loans and mortgage related securities, thereby reducing the amount of cash flows available to invest in higher-yielding assets. Decreases in interest rates can result in the prepayment or refinancing of loans and loans underlying mortgage related securities, resulting in accelerated cash flows subject to reinvestment at reduced market interest rates and increased premium amortization.
We are subject to liquidity risk.
Liquidity risk is the potential that we will be unable to meet our obligations as they become due or capitalize on growth opportunities as they arise because of an inability to liquidate assets or obtain adequate funding on a timely basis at a reasonable cost. Liquidity is required to fund various obligations, including loan originations and commitments, withdrawals by depositors, repayments of borrowings, operating expenses and capital expenditures. Liquidity is derived primarily from deposit growth and retention; principal and interest payments, sales, maturities, and prepayments of loans and investment securities; net cash provided from operations; and access to other funding sources.
Our access to funding sources in amounts adequate to finance our activities could be impaired by factors specific to us or the financial services industry in general. Factors detrimental to our access to liquidity sources include a decrease in the level of our business activity due to a market downturn, lack of competitiveness, or adverse regulatory action against us. Our ability to borrow could also be impaired by factors that are not specific to us, such as a severe disruption of the financial markets or negative views and expectations about the prospects for the financial services industry.
If our allowance for loan losses is not sufficient to cover actual loan losses, our earnings could decrease.
We make various assumptions and judgments about the collectability of our loan portfolio, including the creditworthiness of our borrowers and the value of the real estate and other assets serving as collateral for the repayment of many of our loans. In determining the amount of the allowance for loan losses, we rely on our loan quality reviews and credit risk ratings, loan portfolio trends, our experience and our evaluation of economic conditions, among other factors. If our assumptions prove to be incorrect, or if delinquencies or non-accrual and non-performing loans increase, the allowance for loan losses may not be sufficient to cover losses inherent in our loan portfolio, resulting in additions to our allowance. Material additions to the allowance would materially decrease our net income.
Bank regulators periodically review our allowance for loan losses and may require us to increase our provision for loan losses or recognize further loan charge-offs. In 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board released an updated standard for determining credit losses, which fundamentally changes how financial institutions calculate their allowance reserves. The new standard, which will become effective for reporting periods effective January 1, 2020, will require us to adopt a “Current Expected Credit Loss” model that measures projected credit losses over the estimated life of the asset. This approach is a significant departure from the current accounting standard, which estimates potential credit losses based on losses considered to be probable and reasonably estimable. When adopted, this new standard may increase our allowance for credit losses, which could materially affect our financial condition and future results of operations. The extent of the increase, if any, will ultimately depend upon the nature and characteristics of our loan portfolio at the adoption date, as well as the macroeconomic assumptions and forecasts used at that date. Therefore, the potential financial impact is currently unknown.
Our commercial real estate, multi-family, and commercial loans expose us to increased lending risks.
A significant portion of our loan portfolio consists of commercial real estate, multi-family, commercial and, to a lesser extent, construction loans. These loans are generally regarded as having a higher risk of default and loss than single-family residential mortgage loans, because repayment of these loans often depends on the successful operation of a business or of the underlying property. In addition, our construction loans, multi-family loans, commercial mortgage loans and commercial loans have significantly larger average loan balances compared to our single-family residential mortgage loans. Also, many of our borrowers of these types of loans have more than one loan outstanding with us. Consequently, any adverse development with respect to one loan or one credit relationship can expose us to a significantly greater risk of loss compared to an adverse development with respect to one single-family residential mortgage loan.
31
We may be adversely affected by recent changes in U.S. tax laws.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which was enacted in December 2017, is likely to have both positive and negative effects on our financial performance. For example, the new legislation will result in a reduction in our federal corporate tax rate from 35% to 21% beginning in 2018, which will have a favorable impact on our earnings and capital generation abilities. However, the new legislation also enacted limitations on certain deductions that will have an impact on the banking industry, borrowers and the market for single-family residential real estate. These limitations include (1) a lower limit on the deductibility of mortgage interest on single-family residential mortgage loans, (2) the elimination of interest deductions for certain home equity loans, (3) a limitation on the deductibility of business interest expense, and (4) a limitation on the deductibility of property taxes and state and local income taxes. As a result of the enactment of this legislation, the Company recognized an additional tax expense of $3.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2017.
The recent changes in the tax laws may have an adverse effect on the market for, and the valuation of, residential properties, and on the demand for such loans in the future, and could make it harder for borrowers to make their loan payments. In addition, these recent changes may also have a disproportionate effect on taxpayers in states with high residential home prices and high state and local taxes, like New Jersey. If home ownership becomes less attractive, demand for mortgage loans could decrease. The value of the properties securing loans in our loan portfolio may be adversely impacted as a result of the changing economics of home ownership, which could require an increase in our provision for loan losses, which would reduce our profitability and could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If bank regulators impose limitations on our commercial real estate lending activities, earnings could be adversely affected.
The FDIC, the OCC and the FRB (collectively, the “Agencies”) have issued joint guidance entitled “Concentrations in Commercial Real Estate Lending, Sound Risk Management Practices” (the “CRE Guidance”). Although the CRE Guidance did not establish specific lending limits, it provides that a bank’s commercial real estate lending exposure may receive increased supervisory scrutiny where total non-owner occupied commercial real estate loans, including loans secured by apartment buildings, investor commercial real estate and construction and land loans (“CRE Loans”), represent 300% or more of an institution’s total risk-based capital and the outstanding balance of the CRE Loan portfolio has increased by 50% or more during the preceding 36 months. While our level of CRE Loans equaled 453% of total risk-based capital at December 31, 2017, our CRE Loan portfolio has not increased by 50% or more during the preceding 36 months.
In December 2015, the Agencies released a new statement on prudent risk management for commercial real estate lending (the “2015 Statement”). In the 2015 Statement, the Agencies express concerns about easing commercial real estate underwriting standards, direct financial institutions to maintain underwriting discipline and exercise risk management practices to identify, measure and monitor lending risks, and indicate that the Agencies will continue “to pay special attention” to commercial real estate lending activities and concentrations going forward. If our regulators were to impose restrictions on the amount of commercial real estate loans we can hold in our loan portfolio, or require higher capital ratios as a result of the level of commercial real estate loans held, our earnings or our ability to engage in certain merger and acquisition activity could be adversely affected.
Our continuing concentration of loans in our primary market area may increase our risk.
Our success is significantly affected by general economic conditions in northern and central New Jersey, and eastern Pennsylvania. Unlike some larger banks that are more geographically diversified, we provide banking and financial services to customers mostly located in our primary markets. Consequently, a downturn in economic conditions in our local markets would have a significant impact on our loan portfolios, the ability of borrowers to meet their loan payment obligations and the value of the collateral securing our loans. Adverse local economic conditions caused by inflation, recession, unemployment or other factors beyond our control would impact these local economic conditions and could negatively affect the financial results of our banking operations. Additionally, because we have a significant amount of real estate loans, depressed real estate values and real estate sales could also have a negative effect on the ability of many of our borrowers to make timely repayments of their loans, which would have an adverse impact on our earnings and overall financial condition.
We target our business development and marketing strategy for loans to serve primarily the banking and financial services needs of small- to medium-sized businesses in northern and central New Jersey and eastern Pennsylvania. These businesses generally have fewer financial resources in terms of capital or borrowing capacity than larger entities. If general economic conditions negatively impact these businesses, our results of operations and financial condition may be adversely affected.
Risks associated with cyber-security could negatively affect our earnings.
The financial services industry continues to experience increasing numbers of severe cyber-attacks aimed at gaining unauthorized access to systems and data, or obstructing access to bank systems as a way to misappropriate assets and sensitive information, corrupt and destroy data, or cause operational disruptions.
We have established policies, processes, and tools to limit the impact of cyber-attacks, but such events may still occur or may not be adequately addressed if they do occur. Although we rely on security safeguards to secure our data, these safeguards may not fully protect our systems from compromises or breaches.
32
We also rely on the integrity and security of a variety of third party processors, payment clearing and settlement systems, as well as the various participants involved in these systems, many of which have no direct relationship with us. Failure by these participants or their systems to protect our customers’ transaction data and maintain operational resiliency may put us at risk for possible losses due to fraud or operational disruption.
Our customers are also the target of cyber-attacks and identity theft. Large scale identity theft could result in customers' accounts being compromised and fraudulent activities being performed in their name. We have implemented safeguards against these types of activities but they may not fully protect us from fraudulent financial losses.
The occurrence of a breach of security involving our customers' information, regardless of its origin, could damage our reputation and result in a loss of customers and business, and subject us to additional regulatory scrutiny, and could expose us to litigation and possible financial liability. Any of these events could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
We operate in a highly regulated environment and may be adversely affected by changes in laws and regulations.
We are subject to extensive regulation, supervision and examination by the New Jersey Department of Banking and Insurance, our chartering authority, and by the FDIC, as insurer of our deposits. As a bank holding company, we are subject to regulation and oversight by the Federal Reserve Board. Such regulation and supervision govern the activities in which a bank and its holding company may engage and are intended primarily for the protection of the insurance fund and depositors. These regulatory authorities have extensive discretion in connection with their supervisory and enforcement activities, including the requirement for additional capital, the imposition of restrictions on our operations, the classification of our assets, the adequacy of our allowance for loan losses, and our management of risks posed by our reliance on third party vendors. Any change in such regulation and oversight, whether in the form of regulatory policy, regulations, or legislation, could have a material impact on our operations.
The potential exists for additional Federal or state laws and regulations regarding capital requirements, lending and funding practices and liquidity standards, and bank regulatory agencies are expected to remain active in responding to concerns and trends identified in examinations, including the potential issuance of formal enforcement orders. Actions taken to date, as well as potential actions, may not have the beneficial effects that are intended. In addition, new laws, regulations, and other regulatory changes could increase our costs of regulatory compliance and of doing business, and otherwise affect our operations. New laws, regulations, and other regulatory changes, may significantly affect the markets in which we do business, the markets for and value of our loans and investments, and our ongoing operations, costs and profitability.
We will be subject to heightened regulatory requirements when we exceed total assets of $10 billion.
Provident's total assets were $9.85 billion at December 31, 2017. Banks with assets in excess of $10 billion are subject to requirements imposed by the Dodd-Frank Act and its implementing regulations including the examination authority of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau to assess our compliance with federal consumer financial laws, imposition of higher FDIC premiums, reduced debit card interchange fees, enhanced risk management frameworks and stress testing, all of which increase operating costs and reduce earnings.
As we approach $10 billion in assets, we are incurring additional costs to prepare for the implementation of these imposed requirements. We may be required to invest more significant management attention and resources to evaluate and continue to make any changes necessary to comply with new statutory and regulatory requirements under the Dodd-Frank Act. Further, federal financial regulators may require us to accelerate our actions and investments to prepare for compliance before we exceed $10 billion in total consolidated assets, and may suspend or delay certain regulatory actions, such as approving a merger agreement, if they deem our preparations to be inadequate. Upon reaching this threshold, we face the risk that we may fail to meet these requirements, which may negatively impact our results of operations and financial condition. While we cannot predict what effect any presently contemplated or future changes in the laws or regulations or their interpretations would have on us, these changes could be materially adverse to our investors.
A general economic slowdown or uncertainty that produces either reduced returns or excessive market volatility could adversely impact our wealth management fee income.
A general economic slowdown could affect the value of the assets under management in our wealth management business resulting in lower fee income. Furthermore, conditions that produce extended market volatility could affect our ability to provide our clients with an adequate return, thereby impacting our ability to attract new clients or causing existing clients to seek more stable investment opportunities with alternative wealth advisors.
Strong competition within our market area may limit our growth and profitability.
Competition in the banking and financial services industry is intense and expanding with entrants into our market providing new and innovative technology-driven financial solutions. Our profitability depends upon our continued ability to successfully compete in our market area. We compete with commercial banks, savings institutions, mortgage banking firms, credit unions, finance companies, investment advisers, wealth managers, mutual funds, insurance companies, online lenders, and brokerage and investment banking firms operating both locally and elsewhere.
33
In particular, over the past decade, our local markets have experienced the effects of substantial banking consolidation, and large out-of-state competitors have grown significantly. Many of these competitors have substantially greater resources and lending limits than we do, and may offer certain deposit and loan pricing, services or credit criteria that we do not or cannot provide. There are also a number of strong locally-based competitors with large capital positions in our market who may deploy aggressive strategies to drive growth, take our customers and win market share.
Furthermore, key components of the financial services value chain have been replicated by digital innovation, commonly referred to as Fintech. The adoption of these Fintech solutions within our market area may cause greater and faster disruption to our business model if we are unable to keep pace with, or invest wisely in, these enabling technologies.
Because the financial services business involves a high volume of transactions, we face significant operational risks.
We operate in diverse market segments and rely on the ability of our employees, systems and third party providers, who are used extensively in support of our operations, to process a high number of transactions. Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from our operations, including but not limited to, the risk of fraud by employees or persons outside our company, the execution of unauthorized transactions by employees, errors relating to transaction processing and technology, breaches of the internal control system and compliance requirements, the occurrence of systems failures and disruptions, and business continuation and disaster recovery. Insurance coverage may not be available for such losses, or where available, such losses may exceed insurance limits. This risk of loss also includes the potential legal actions that could arise as a result of an operational deficiency or as a result of noncompliance with applicable regulatory standards, adverse business decisions or their implementation, and customer attrition due to potential negative publicity. While we maintain a risk management program that is designed to minimize risk, we could suffer losses, face regulatory action, and suffer damage to our reputation as a result of our failure to properly anticipate and manage these risks.
Acts of terrorism and other external events could impact our ability to conduct business.
Our business is subject to risk from external events. Financial institutions have been, and continue to be, targets of terrorist threats aimed at compromising their operating and communication systems. The metropolitan New York and Philadelphia areas remain central targets for potential acts of terrorism, including cyber terrorism, which could affect not only our operations but those of our customers. Events such as these may become more common in the future and could cause significant damage such as disrupt power and communication services, impact the stability of our facilities and result in additional expenses, impair the ability of our borrowers to repay their loans, reduce the value of collateral securing the repayment of our loans, which could result in the loss of revenue. While we have established and regularly test disaster recovery procedures, the occurrence of any such event could have a material adverse effect on our business, operations and financial condition.
We hold certain intangible assets that could be classified as impaired in the future. If these assets are considered to be either partially or fully impaired in the future, our earnings could decline.
We record all assets acquired and liabilities assumed by the Company in purchase acquisitions, including goodwill and other intangible assets, at fair value. At December 31, 2017, goodwill totaling $411.6 million was not amortized but remains subject to impairment tests at least annually, or more often if events or circumstances indicate it may be impaired. Other intangible assets are amortized over their estimated useful lives and are subject to impairment tests if events or circumstances indicate a potential inability to realize the carrying amount. The initial recording and subsequent impairment testing of goodwill and other intangible assets requires subjective judgments about the estimates of the fair value of assets acquired.
It is possible that our future impairment testing could result in an impairment of the value of goodwill or other identified intangible assets, or both. If we determine impairment exists at a given point in time, our earnings and the book value of the related intangible asset(s) will be reduced by the amount of the impairment. In any event, the results of impairment testing on goodwill and other identified intangible assets have no impact on our tangible book value or regulatory capital levels.
A State Bank in New Jersey could be disruptive to our overall strategies and potentially reduce the level of public funds held on deposit with us.
We maintain a large and relatively stable level of deposits from local government entities, primarily through relationships we have cultivated with New Jersey municipalities. These moneys are a relatively low-cost source used to fund our loans and investments. The State of New Jersey is considering creating a State Bank, whose purpose would be to promote small businesses, fair educational lending, housing, infrastructure improvements, community development, economic development, commerce, and industry in the State. As currently proposed, it intends to permit State funds, including funds from State institutions and any State public source, to be held by the State Bank. There can be no assurance that legislation to create a State Bank will pass or whether it will pass as currently proposed.
Given the degree of our funding reliance on many New Jersey-based public entities and the potential scope of the proposed State Bank’s lending activities, we are uncertain of the impact this proposal may have on us. If we are unable to retain the current level of public funds on deposit, we may need to increase the costs associated with our funding needs, which could have a negative impact on our net income.
34
Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments |
There are no unresolved comments from the staff of the SEC to report.
Item 2. | Properties |
Property
At December 31, 2017, the Bank conducted business through 84 full-service branch offices located in Hudson, Bergen, Essex, Hunterdon, Mercer, Middlesex, Monmouth, Morris, Ocean, Passaic, Somerset, Union and Warren counties in New Jersey, and in Bucks, Lehigh and Northampton counties in Pennsylvania. The Bank maintains satellite loan production offices in Convent Station, Flemington, Paramus and Princeton, New Jersey, as well as in Bethlehem, Newtown and Wayne, Pennsylvania. The aggregate net book value of premises and equipment was $63.2 million at December 31, 2017.
On December 13, 2017, the Company completed the sale and leaseback of 12 of its New Jersey banking offices, which had a net book value of $14.5 million. Net proceeds from the sale totaled $20.7 million. The transaction did not have a significant immediate impact on the Company’s financial statements as the resultant net gain on sale will be recognized over the 10 year term of the leases as a reduction of rent expense.
The Company’s executive offices are located in a leased facility at 239 Washington Street, Jersey City, New Jersey, which is also the Bank’s Main Office. The Bank’s administrative offices are located in a leased facility at 100 Wood Avenue South, Iselin, New Jersey.
Item 3. | Legal Proceedings |
The Company is involved in various legal actions and claims arising in the normal course of its business. In the opinion of management, these legal actions and claims are not expected to have a material adverse impact on the Company’s financial condition and results of operations.
Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures |
Not applicable.
35
PART II
Item 5. | Market For Registrant’s Common Equity and Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities. |
The Company’s common stock trades on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) under the symbol “PFS.” Trading in the Company’s common stock commenced on January 16, 2003.
As of February 1, 2018, there were 83,209,293 shares of the Company’s common stock issued and 66,842,531 shares outstanding, and approximately 4,935 stockholders of record.
The table below shows the high and low closing prices reported on the NYSE for the Company’s common stock, as well as the cash dividends paid per common share during the periods indicated.
2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
High | Low | Dividend | High | Low | Dividend | ||||||||||||||||||
First Quarter | $ | 28.64 | $ | 24.99 | $ | 0.19 | $ | 20.23 | $ | 17.93 | $ | 0.17 | |||||||||||
Second Quarter | 26.65 | 23.34 | 0.19 | 20.68 | 18.66 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||
Third Quarter | 26.81 | 23.50 | 0.20 | 21.66 | 19.22 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||
Fourth Quarter | 28.75 | 25.83 | 0.35 | 28.70 | 20.86 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||
The $0.35 cash dividend paid per common share in the fourth quarter of 2017 included a $0.15 special cash dividend declared by the Board of Directors on November 16, 2017 and paid on December 22, 2017. On January 26, 2018, the Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.20 per common share, which was paid on February 28, 2018, to common stockholders of record as of the close of business on February 15, 2018. The Company’s Board of Directors intends to review the payment of dividends quarterly and plans to continue to maintain a regular quarterly cash dividend in the future, subject to financial condition, results of operations, tax considerations, industry standards, economic conditions, regulatory restrictions that affect the payment of dividends by the Bank to the Company and other relevant factors.
The Company is subject to the requirements of Delaware law that generally limit dividends to an amount equal to the difference between the amount by which total assets exceed total liabilities and the amount equal to the aggregate par value of the outstanding shares of capital stock. If there is no difference between these amounts, dividends are limited to net income for the current and/or immediately preceding year. In addition, Federal Reserve Board guidance sets forth the supervisory expectation that bank holding companies will inform and consult with Federal Reserve Board staff in advance of issuing a dividend that exceeds earnings for the quarter and should inform the Federal Reserve Board and should eliminate, defer or significantly reduce dividends if: (i) net income available to stockholders for the past four quarters, net of dividends previously paid during that period, is not sufficient to fully fund the dividends; (ii) prospective rate of earnings retention is not consistent with the bank holding company’s capital needs and overall current and prospective financial condition; or (iii) the bank holding company will not meet, or is in danger of not meeting, its minimum regulatory capital adequacy ratios.
36
Stock Performance Graph
Set forth below is a stock performance graph comparing (a) the cumulative total return on the Company’s common stock for the period December 31, 2012 through December 31, 2017, (b) the cumulative total return on stocks included in the Russell 2000 Index over such period, and (c) the cumulative total return of the SNL Thrift Index over such period. The SNL Thrift Index, produced by SNL Financial LC, contains all thrift institutions traded on the NYSE and NASDAQ stock exchange. Cumulative return assumes the reinvestment of dividends and is expressed in dollars based on an assumed investment of $100 on December 31, 2012.
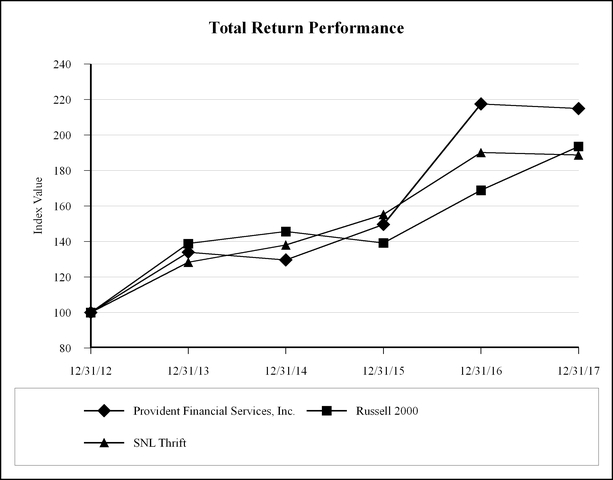
Period Ending | ||||||||||||||||||
Index | 12/31/2012 | 12/31/2013 | 12/31/2014 | 12/31/2015 | 12/31/2016 | 12/31/2017 | ||||||||||||
Provident Financial Services, Inc. | 100.00 | 133.92 | 129.63 | 149.62 | 217.53 | 214.91 | ||||||||||||
Russell 2000 | 100.00 | 138.82 | 145.62 | 139.19 | 168.85 | 193.58 | ||||||||||||
SNL Thrift | 100.00 | 128.33 | 138.02 | 155.20 | 190.11 | 188.72 | ||||||||||||
37
The following table reports information regarding purchases of the Company’s common stock during the fourth quarter of 2017 under the stock repurchase plan approved by the Company’s Board of Directors:
ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Period | (a) Total Number of Shares Purchased | (b) Average Price Paid per Share | (c) Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs(1) | (d) Maximum Number of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs(1)(2) | |||||||||
October 1, 2017 through October 31, 2017 | — | $ | — | — | 3,148,526 | ||||||||
November 1, 2017 through November 30, 2017 | 2,033 | 25.92 | 2,033 | 3,146,493 | |||||||||
December 1, 2017 through December 31, 2017 | — | — | — | 3,146,493 | |||||||||
Total | 2,033 | $ | 25.92 | 2,033 | |||||||||
(1) | On October 24, 2007, the Company’s Board of Directors approved the purchase of up to 3,107,077 shares of its common stock under a seventh general repurchase program which commenced upon completion of the previous repurchase program. The repurchase program has no expiration date. All shares purchased during the fourth quarter of 2017 were repurchased pursuant to the seventh general repurchase program. |
(2) | On December 20, 2012, the Company’s Board of Directors approved the purchase of up to 3,017,770 shares of its common stock under an eighth general repurchase program which will commence upon completion of the seventh repurchase program. The repurchase program has no expiration date. |
All common stock repurchases for the three months ended December 31, 2017 were made in connection with employee income tax withholding on stock-based compensation.
Item 6. | Selected Financial Data |
The summary information presented below at or for each of the periods presented is derived in part from and should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements of the Company presented in Item 8.
At December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
Selected Financial Condition Data: | |||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 9,845,274 | $ | 9,500,465 | $ | 8,911,657 | $ | 8,523,377 | $ | 7,487,328 | |||||||||
Loans, net(1) | 7,265,523 | 6,941,603 | 6,476,250 | 6,023,771 | 5,130,149 | ||||||||||||||
Investment securities held to maturity | 477,652 | 488,183 | 473,684 | 469,528 | 357,500 | ||||||||||||||
Securities available for sale | 1,037,812 | 1,040,386 | 964,534 | 1,074,395 | 1,157,594 | ||||||||||||||
Deposits | 6,714,166 | 6,553,629 | 5,923,987 | 5,792,523 | 5,202,471 | ||||||||||||||
Borrowed funds | 1,742,514 | 1,612,745 | 1,707,632 | 1,509,851 | 1,203,879 | ||||||||||||||
Stockholders’ equity | 1,298,661 | 1,251,781 | 1,196,065 | 1,144,099 | 1,010,753 | ||||||||||||||
38
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
Selected Operations Data: | |||||||||||||||||||
Interest income | $ | 323,846 | $ | 302,315 | $ | 291,781 | $ | 279,361 | $ | 252,777 | |||||||||
Interest expense | 45,644 | 43,748 | 41,901 | 40,472 | 36,767 | ||||||||||||||
Net interest income | 278,202 | 258,567 | 249,880 | 238,889 | 216,010 | ||||||||||||||
Provision for loan losses | 5,600 | 5,400 | 4,350 | 4,650 | 5,500 | ||||||||||||||
Net interest income after provision for loan losses | 272,602 | 253,167 | 245,530 | 234,239 | 210,510 | ||||||||||||||
Non-interest income | 55,697 | 55,393 | 55,222 | 41,168 | 44,153 | ||||||||||||||
Non-interest expense | 187,822 | 183,778 | 180,589 | 169,991 | 148,763 | ||||||||||||||
Income before income tax expense | 140,477 | 124,782 | 120,163 | 105,416 | 105,900 | ||||||||||||||
Income tax expense | 46,528 | 36,980 | 36,441 | 31,785 | 35,366 | ||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 93,949 | $ | 87,802 | $ | 83,722 | $ | 73,631 | $ | 70,534 | |||||||||
Earnings per share: | |||||||||||||||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 1.46 | $ | 1.38 | $ | 1.33 | $ | 1.22 | $ | 1.23 | |||||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 1.45 | $ | 1.38 | $ | 1.33 | $ | 1.22 | $ | 1.23 | |||||||||
(1) | Loans are shown net of allowance for loan losses, deferred fees and unearned discount. |
At or For the Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||
Selected Financial and Other Data(1) | ||||||||||||||
Performance Ratios: | ||||||||||||||
Return on average assets | 0.99 | % | 0.95 | % | 0.96 | % | 0.92 | % | 0.97 | % | ||||
Return on average equity | 7.28 | 7.12 | 7.12 | 6.75 | 7.08 | |||||||||
Average net interest rate spread | 3.07 | 2.98 | 3.07 | 3.18 | 3.19 | |||||||||
Net interest margin(2) | 3.21 | 3.11 | 3.20 | 3.30 | 3.31 | |||||||||
Average interest-earning assets to average interest-bearing liabilities | 1.27 | 1.25 | 1.24 | 1.22 | 1.22 | |||||||||
Non-interest income to average total assets | 0.58 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.51 | 0.61 | |||||||||
Non-interest expenses to average total assets | 1.97 | 1.99 | 2.07 | 2.11 | 2.05 | |||||||||
Efficiency ratio(3) | 56.25 | 58.54 | 59.19 | 60.70 | 57.18 | |||||||||
Asset Quality Ratios: | ||||||||||||||
Non-performing loans to total loans | 0.48 | % | 0.61 | % | 0.68 | % | 0.88 | % | 1.48 | % | ||||
Non-performing assets to total assets | 0.42 | 0.53 | 0.62 | 0.69 | 1.10 | |||||||||
Allowance for loan losses to non-performing loans | 172.34 | 145.95 | 137.92 | 114.63 | 84.32 | |||||||||
Allowance for loan losses to total loans | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 1.01 | 1.24 | |||||||||
Capital Ratios: | ||||||||||||||
Leverage capital(4) | 9.65 | % | 9.25 | % | 9.25 | % | 9.21 | % | 9.42 | % | ||||
Total risk based capital(4) | 12.67 | 12.50 | 12.57 | 13.06 | 12.89 | |||||||||
Average equity to average assets | 13.53 | 13.38 | 13.53 | 13.57 | 14.14 | |||||||||
Other Data: | ||||||||||||||
Number of full-service offices | 84 | 87 | 87 | 86 | 77 | |||||||||
Full time equivalent employees | 1,006 | 1,001 | 1,008 | 967 | 886 | |||||||||
(1) | Averages presented are daily averages. |
(2) | Net interest income divided by average interest earning assets. |
(3) | Represents the ratio of non-interest expense divided by the sum of net interest income and non-interest income. |
39
(4) | Leverage capital ratios are presented as a percentage of quarterly average tangible assets. Risk-based capital ratios are presented as a percentage of risk-weighted assets. |
At December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
Efficiency Ratio Calculation: | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||
Net interest income | $ | 278,202 | $ | 258,567 | $ | 249,880 | $ | 238,889 | $ | 216,010 | ||||||||||
Non-interest income | 55,697 | 55,393 | 55,222 | 41,168 | 44,153 | |||||||||||||||
Total income | $ | 333,899 | $ | 313,960 | $ | 305,102 | $ | 280,057 | $ | 260,163 | ||||||||||
Non-interest expense | $ | 187,822 | $ | 183,778 | $ | 180,589 | $ | 169,991 | $ | 148,763 | ||||||||||
Expense/income | 56.25 | % | 58.54 | % | 59.19 | % | 60.70 | % | 57.18 | % | ||||||||||
Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
General
On January 15, 2003, the Company became the holding company for the Bank, following the completion of the conversion of the Bank to a New Jersey-chartered capital stock savings bank. The Company issued an aggregate of 59,618,300 shares of its common stock in a subscription offering to eligible depositors. Concurrent with the conversion, the Company contributed an additional 1,920,000 shares of its common stock and $4.8 million in cash to The Provident Bank Foundation, a charitable foundation established by the Bank.
The Company conducts business through its subsidiary, the Bank, a community- and customer-oriented bank currently operating full-service branches and loan production offices throughout northern and central New Jersey, as well as Bucks, Lehigh and Northampton counties in Pennsylvania.
Strategy
Established in 1839, the Bank is the oldest New Jersey-chartered bank in the state. The Bank offers a full range of retail and commercial loan and deposit products, and emphasizes personal service and convenience.
The Bank’s strategy is to grow profitably through a commitment to credit quality and expanding market share by acquiring, retaining and expanding customer relationships, while carefully managing interest rate risk.
In recent years, the Bank has focused on commercial mortgage, multi-family, construction and commercial loans as part of its strategy to diversify the loan portfolio and reduce interest rate risk. These types of loans generally have adjustable rates that initially are higher than residential mortgage loans and generally have a higher rate of risk. The Bank’s credit policy focuses on quality underwriting standards and close monitoring of the loan portfolio. At December 31, 2017, these commercial loan types accounted for 77.9% of the loan portfolio and retail loans accounted for 22.1%. The Company intends to continue to focus on commercial mortgage, multi-family, construction and commercial lending relationships.
The Company’s relationship banking strategy focuses on increasing core accounts and expanding relationships through its branch network, mobile banking, online banking and telephone banking touch points. The Company continues to evaluate opportunities to increase market share by expanding within existing and contiguous markets. Core deposits, consisting of savings and demand deposit accounts, are generally a stable, relatively inexpensive source of funds. At December 31, 2017, core deposits were 90.5% of total deposits.
The Company’s results of operations are primarily dependent upon net interest income, the difference between interest earned on interest-earning assets and the interest paid on interest-bearing liabilities. Changes in interest rates could have an adverse effect on net interest income to the extent the Company’s interest-bearing assets and interest-bearing liabilities reprice or mature at different times or relative interest rates. An increase in interest rates generally would result in a decrease in the Company’s average interest rate spread and net interest income, which could have a negative effect on profitability. The Company generates non-interest income such as income from retail and business account fees, loan servicing fees, loan origination fees, loan level swap fees, appreciation in the cash surrender value of Bank-owned life insurance, income from loan or securities sales, fees from wealth management services and investment product sales and other fees. The Company’s operating expenses consist primarily of compensation and benefits expense, occupancy and equipment expense, data processing expense, the amortization of intangible assets, marketing and advertising expense and other general and administrative expenses. The Company’s results of operations are also affected by general economic conditions, changes in market interest rates, changes in asset quality, changes in asset values, actions of regulatory agencies and government policies.
40
Critical Accounting Policies
The Company considers certain accounting policies to be critically important to the fair presentation of its financial condition and results of operations. These policies require management to make complex judgments on matters which by their nature have elements of uncertainty. The sensitivity of the Company’s consolidated financial statements to these critical accounting policies, and the assumptions and estimates applied, could have a significant impact on its financial condition and results of operations. These assumptions, estimates and judgments made by management can be influenced by a number of factors, including the general economic environment. The Company has identified the following as critical accounting policies:
• | Adequacy of the allowance for loan losses |
• | Valuation of securities available for sale and impairment analysis |
• | Valuation of deferred tax assets |
The calculation of the allowance for loan losses is a critical accounting policy of the Company. The allowance for loan losses is a valuation account that reflects management’s evaluation of the probable losses in the loan portfolio. The Company maintains the allowance for loan losses through provisions for loan losses that are charged to income. Charge-offs against the allowance for loan losses are taken on loans where management determines that the collection of loan principal is unlikely. Recoveries made on loans that have been charged-off are credited to the allowance for loan losses.
Management's evaluation of the adequacy of the allowance for loan losses includes a review of all loans on which the collectability of principal may not be reasonably assured. For residential mortgage and consumer loans, this is determined primarily by delinquency status. For commercial mortgage, multi-family, construction and commercial loans, an extensive review of financial performance, payment history and collateral values is conducted on a quarterly basis.
As part of the evaluation of the adequacy of the allowance for loan losses, each quarter management prepares an analysis that categorizes the entire loan portfolio by certain risk characteristics such as loan type (residential mortgage, commercial mortgage, construction, commercial, etc.) and loan risk rating.
When assigning a risk rating to a loan, management utilizes a nine point internal risk rating system. Loans deemed to be “acceptable quality” are rated 1 through 4, with a rating of 1 established for loans with minimal risk. Loans deemed to be of “questionable quality” are rated 5 (watch) or 6 (special mention). Loans with adverse classifications (substandard, doubtful or loss) are rated 7, 8 or 9, respectively. Commercial mortgage, multi-family, construction and commercial loans are rated individually and each lending officer is responsible for risk rating loans in their portfolio. These risk ratings are then reviewed by the department manager and/or the Chief Lending Officer and the Credit Department. The risk ratings are also confirmed through periodic loan review examinations, which are currently performed by an independent third party, and periodically by the Credit Committee in the credit renewal or approval process. In addition, the Bank requires an annual review be performed for commercial and commercial real estate loans above certain dollar thresholds, depending on loan type, to help determine the appropriate risk rating.
Management estimates the amount of loan losses for groups of loans by applying quantitative loss factors to loan segments at the risk rating level, and applying qualitative adjustments to each loan segment at the portfolio level. Quantitative loss factors give consideration to historical loss experience by loan type based upon an appropriate look-back period and adjusted for a loss emergence period. Quantitative loss factors are evaluated at least annually. Management completed its annual evaluation of the quantitative loss factors for the quarter ended September 30, 2017. Qualitative adjustments give consideration to other qualitative or environmental factors such as trends and levels of delinquencies, impaired loans, charge-offs, recoveries and loan volumes, as well as national and local economic trends and conditions. Qualitative adjustments reflect risks in the loan portfolio not captured by the quantitative loss factors and, as such, are evaluated from a risk level perspective relative to the risk levels present over the look-back period. Qualitative adjustments are evaluated at least quarterly. The reserves resulting from the application of both of these sets of loss factors are combined to arrive at the allowance for loan losses.
Management believes the primary risks inherent in the portfolio are a general decline in the economy, a decline in real estate market values, rising unemployment or a protracted period of elevated unemployment, increasing vacancy rates in commercial investment properties and possible increases in interest rates in the absence of economic improvement. Any one or a combination of these events may adversely affect borrowers’ ability to repay the loans, resulting in increased delinquencies, loan losses and future levels of provisions. Accordingly, the Company has provided for loan losses at the current level to address the current risk in its loan portfolio. Management considers it important to maintain the ratio of the allowance for loan losses to total loans at an acceptable level given current economic conditions, interest rates and the composition of the portfolio.
Although management believes that the Company has established and maintained the allowance for loan losses at appropriate levels, additions may be necessary if future economic and other conditions differ substantially from the current operating environment. Management evaluates its estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis giving consideration to historical
41
experience and other factors, including the current economic environment, which management believes to be reasonable under the circumstances. Such estimates and assumptions are adjusted when facts and circumstances dictate. Illiquid credit markets, volatile securities markets, and declines in the housing and commercial real estate markets and the economy generally have combined to increase the uncertainty inherent in such estimates and assumptions. As future events and their effects cannot be determined with precision, actual results could differ significantly from these estimates. Changes in estimates resulting from continuing changes in the economic environment will be reflected in the financial statements in future periods. In addition, various regulatory agencies periodically review the adequacy of the Company’s allowance for loan losses as an integral part of their examination process. Such agencies may require the Company to recognize additions to the allowance or additional write-downs based on their judgments about information available to them at the time of their examination. Although management uses the best information available, the level of the allowance for loan losses remains an estimate that is subject to significant judgment and short-term change.
The Company’s available for sale securities portfolio is carried at estimated fair value, with any unrealized gains or losses, net of taxes, reported as accumulated other comprehensive income or loss in Stockholders’ Equity. Estimated fair values are based on market quotations or matrix pricing as discussed in Note 5 to the consolidated financial statements. Securities which the Company has the positive intent and ability to hold to maturity are classified as held to maturity and carried at amortized cost. Management conducts a periodic review and evaluation of the securities portfolio to determine if any declines in the fair values of securities are other-than-temporary. In this evaluation, if such a decline were deemed other-than-temporary, management would measure the total credit-related component of the unrealized loss, and recognize that portion of the loss as a charge to current period earnings. The remaining portion of the unrealized loss would be recognized as an adjustment to accumulated other comprehensive income. The fair value of the securities portfolio is significantly affected by changes in interest rates. In general, as interest rates rise, the fair value of fixed-rate securities decreases and as interest rates fall, the fair value of fixed-rate securities increases. The Company determines if it has the intent to sell these securities or if it is more likely than not that the Company would be required to sell the securities before the anticipated recovery. If either exists, the entire decline in value is considered other-than-temporary and would be recognized as an expense in the current period. In its evaluations, the Company did not recognize an other-than-temporary impairment charge on securities for the years ended 2017, 2016 and 2015.
The determination of whether deferred tax assets will be realizable is predicated on the reversal of existing deferred tax liabilities and estimates of future taxable income. Such estimates are subject to management’s judgment. A valuation allowance is established when management is unable to conclude that it is more likely than not that it will realize deferred tax assets based on the nature and timing of these items. The Company did not require a valuation allowance at December 31, 2017 and 2016.
42
Analysis of Net Interest Income
Net interest income represents the difference between income on interest-earning assets and expense on interest-bearing liabilities. Net interest income depends on the relative amounts of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities and the rates of interest earned on such assets and paid on such liabilities.
Average Balance Sheet. The following table sets forth certain information for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015. For the periods indicated, the total dollar amount of interest income from average interest-earning assets and the resultant yields, as well as the interest expense on average interest-bearing liabilities is expressed both in dollars and rates. No tax equivalent adjustments were made. Average balances are daily averages.
For the Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Average Outstanding Balance | Interest Earned/ Paid | Average Yield/ Cost | Average Outstanding Balance | Interest Earned/ Paid | Average Yield/ Cost | Average Outstanding Balance | Interest Earned/ Paid | Average Yield/ Cost | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest-earning assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Deposits | $ | 19,670 | $ | 199 | 1.00 | % | $ | 62,704 | $ | 314 | 0.50 | % | $ | 22,663 | $ | 57 | 0.25 | % | ||||||||||||||
Federal funds sold and short-term investments | 51,790 | 1,071 | 2.07 | 13,010 | 184 | 1.42 | 1,431 | 1 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Investment securities(1) | 487,616 | 13,027 | 2.67 | 478,901 | 13,208 | 2.76 | 473,425 | 13,494 | 2.85 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Securities available for sale | 1,044,703 | 22,384 | 2.14 | 1,008,900 | 19,377 | 1.92 | 1,029,249 | 20,323 | 1.97 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Federal Home Loan Bank NY Stock | 73,995 | 4,061 | 5.49 | 72,928 | 3,513 | 4.82 | 73,162 | 3,075 | 4.20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loans(2) | 6,971,512 | 283,104 | 4.06 | 6,669,778 | 265,719 | 3.98 | 6,215,347 | 254,831 | 4.10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total interest-earning assets | 8,649,286 | 323,846 | 3.74 | 8,306,221 | 302,315 | 3.64 | 7,815,277 | 291,781 | 3.73 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Non-interest earning assets | 885,499 | 906,332 | 876,723 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 9,534,785 | $ | 9,212,553 | $ | 8,692,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Savings deposits | $ | 1,101,103 | 12,205 | 0.35 | % | $ | 1,047,061 | 1,709 | 0.16 | % | $ | 984,704 | 1,039 | 0.11 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Demand deposits | 3,477,413 | 2,092 | 0.19 | 3,305,269 | 10,106 | 0.31 | 2,955,133 | 8,045 | 0.27 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Time deposits | 649,195 | 5,144 | 0.79 | 725,802 | 5,132 | 0.71 | 784,242 | 5,437 | 0.69 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Borrowed funds | 1,581,964 | 26,203 | 1.66 | 1,577,307 | 26,801 | 1.70 | 1,603,974 | 27,380 | 1.71 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total interest-bearing liabilities | 6,809,675 | 45,644 | 0.67 | 6,655,439 | 43,748 | 0.66 | 6,328,053 | 41,901 | 0.66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Non-interest bearing liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Non-interest bearing deposits | 1,366,354 | 1,243,224 | 1,117,372 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Non-interest bearing liabilities | 68,783 | 81,044 | 70,976 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total Non-Interest Bearing Liabilities | 1,435,137 | 1,324,268 | 1,188,348 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total liabilities | 8,244,812 | 7,979,707 | 7,516,401 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stockholders’ equity | 1,289,973 | 1,232,846 | 1,175,599 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total liabilities and equity | $ | 9,534,785 | $ | 9,212,553 | $ | 8,692,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest income | $ | 278,202 | $ | 258,567 | $ | 249,880 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest rate spread | 3.07 | % | 2.98 | % | 3.07 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest earning assets | $ | 1,839,611 | $ | 1,650,782 | $ | 1,487,224 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest margin(3) | 3.21 | % | 3.11 | % | 3.20 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ratio of interest-earning assets to total interest-bearing liabilities | 1.27x | 1.25x | 1.24x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1) | Average outstanding balance amounts are at amortized cost. |
(2) | Average outstanding balances are net of the allowance for loan losses, deferred loan fees and expenses, and loan premiums and discounts and include non-accrual loans. |
(3) | Net interest income divided by average interest-earning assets. |
43
Rate/Volume Analysis. The following table presents the extent to which changes in interest rates and changes in the volume of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities have affected interest income and interest expense during the periods indicated. Information is provided in each category with respect to: (i) changes attributable to changes in volume (changes in volume multiplied by prior rate); (ii) changes attributable to changes in rate (changes in rate multiplied by prior volume); and (iii) the net change. The changes attributable to the combined impact of volume and rate have been allocated proportionately to the changes due to volume and the changes due to rate.
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 vs. 2016 | 2016 vs. 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Increase/(Decrease) Due to | Total Increase/ (Decrease) | Increase/(Decrease) Due to | Total Increase/ (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Volume | Rate | Volume | Rate | ||||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest-earning assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Deposits, Federal funds sold and short-term investments | $ | 1 | $ | 771 | $ | 772 | $ | 295 | $ | 145 | $ | 440 | |||||||||||
Investment securities | 238 | (419 | ) | (181 | ) | 155 | (441 | ) | (286 | ) | |||||||||||||
Securities available for sale | 706 | 2,301 | 3,007 | (397 | ) | (549 | ) | (946 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Federal Home Loan Bank Stock | 52 | 496 | 548 | (10 | ) | 448 | 438 | ||||||||||||||||
Loans | 12,185 | 5,200 | 17,385 | 18,252 | (7,364 | ) | 10,888 | ||||||||||||||||
Total interest-earning assets | 13,182 | 8,349 | 21,531 | 18,295 | (7,761 | ) | 10,534 | ||||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Savings deposits | 92 | 292 | 384 | 69 | 601 | 670 | |||||||||||||||||
Demand deposits | 547 | 1,551 | 2,098 | 1,011 | 1,050 | 2,061 | |||||||||||||||||
Time deposits | (572 | ) | 584 | 12 | (411 | ) | 106 | (305 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Borrowed funds | 79 | (677 | ) | (598 | ) | (454 | ) | (125 | ) | (579 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total interest-bearing liabilities | 146 | 1,750 | 1,896 | 215 | 1,632 | 1,847 | |||||||||||||||||
Net interest income | $ | 13,036 | $ | 6,599 | $ | 19,635 | $ | 18,080 | $ | (9,393 | ) | $ | 8,687 | ||||||||||
Comparison of Financial Condition at December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016
Total assets increased $344.8 million, or 3.6%, to $9.85 billion at December 31, 2017, from $9.50 billion at December 31, 2016. The increase in total assets was primarily due to a $322.2 million increase in total loans and a $46.5 million increase in total cash and cash equivalents, partially offset by a $20.9 million decrease in premises and equipment and a $7.6 million decrease in total investments.
Total loans increased $322.2 million, or 4.6%, to $7.33 billion at December 31, 2017, from $7.00 billion at December 31, 2016. For the year ended December 31, 2017, loan originations, including advances on lines of credit, totaling $3.70 billion was partially offset by repayments of $3.34 billion and loan sales of $24.9 million. The loan portfolio had net increases of $192.5 million in commercial mortgage loans, $127.8 million in construction loans, $114.4 million in commercial loans and $1.8 million in multi-family mortgage loans, partially offset by net decreases of $69.3 million in residential mortgage loans and $42.8 million in consumer loans.
Commercial loans, consisting of commercial real estate, multi-family, construction and commercial loans, totaled $5.71 billion, accounting for 77.9% of the loan portfolio at December 31, 2017, compared to $5.28 billion, or 75.3% of the loan portfolio at December 31, 2016. The Company intends to continue to focus on the origination of commercially-oriented loans. Retail loans, which consist of one- to four-family residential mortgage and consumer loans, such as fixed-rate home equity loans and lines of credit, totaled $1.62 billion and accounted for 22.1% of the loan portfolio at December 31, 2017, compared to $1.73 billion, or 24.7%, of the loan portfolio at December 31, 2016.
The Company does not originate or purchase sub-prime or option ARM loans. Prior to September 30, 2008, the Company originated “Alt-A” mortgages in the form of stated income loans with a maximum loan-to-value ratio of 50% on a limited basis.
44
The balance of these “Alt-A” loans at December 31, 2017 was $4.2 million. Of this total, there were no loans that were 90 days or more delinquent.
The Company participates in loans originated by other banks, including participations designated as Shared National Credits (“SNC”). The Company’s gross commitments and outstanding balances as a participant in SNCs were $342.5 million and $223.9 million, respectively, at December 31, 2017. At December 31, 2017, no SNC relationships were classified as substandard.
The Company had outstanding junior lien mortgages totaling $205.1 million at December 31, 2017. Of this total, 24 loans totaling $1.3 million were 90 days or more delinquent, and were allocated total loss reserves of $238,000.
The allowance for loan losses decreased $1.7 million to $60.2 million at December 31, 2017, as a result of net charge-offs of $7.3 million during 2017, partially offset by provisions for loan losses of $5.6 million. The decrease in the allowance for loan losses was a function of the decline in non-performing loans, partially offset by the growth in the loan portfolio. Total non-performing loans at December 31, 2017 were $34.9 million, or 0.48% of total loans, compared with $42.4 million, or 0.61% of total loans at December 31, 2016. At December 31, 2017, impaired loans totaled $52.0 million with related specific reserves of $2.7 million, compared with impaired loans totaling $52.0 million with related specific reserves of $2.3 million at December 31, 2016. Within total impaired loans, there were $31.4 million of loans for which the present value of expected future cash flows or current collateral valuations exceeded the carrying amounts of the loans and for which no specific reserves were required in accordance with GAAP. At December 31, 2017, the Company’s allowance for loan losses was 0.82% of total loans, compared with 0.88% of total loans at December 31, 2016. The decline in the loan coverage ratio from December 31, 2016, resulted from an overall improvement in asset quality.
Non-performing commercial mortgage loans decreased $403,000 to $7.1 million at December 31, 2017, from $7.5 million at December 31, 2016. At December 31, 2017, the Company held 10 non-performing commercial mortgage loans. The largest non-performing commercial mortgage loan was a $2.9 million loan secured by a first mortgage on a retail property located in Washington Township, New Jersey. The loan is presently in default. There is no contractual commitment to advance additional funds to this borrower.
Non-performing commercial loans increased $456,000 to $17.2 million at December 31, 2017, from $16.8 million at December 31, 2016. Non-performing commercial loans at December 31, 2017 consisted of 30 loans. The largest non-performing commercial loan relationship consisted of two loans to a health and fitness club with total outstanding balances of $8.4 million at December 31, 2017. Both of these loans are secured by liens on a commercial property. These loans are currently paying in accordance with their restructured terms.
There were no non-performing constructions loans at December 31, 2017. Non-performing constructions loans at the prior year-end were $2.5 million.
At December 31, 2017, the Company held $6.9 million of foreclosed assets, compared with $8.0 million at December 31, 2016. Foreclosed assets are carried at fair value based on recent appraisals and valuation estimates, less estimated selling costs. During the year ended December 31, 2017, there were 16 additions to foreclosed assets with a carrying value of $3.8 million and 26 properties sold with a carrying value of $4.3 million. Foreclosed assets at December 31, 2017 consisted of $3.9 million of commercial real estate and $3.0 million of residential real estate.
Non-performing assets totaled $41.8 million, or 0.42% of total assets at December 31, 2017, compared to $50.4 million, or 0.53% of total assets at December 31, 2016. If the non-accrual loans had performed in accordance with their original terms, interest income would have increased by $1.9 million during the year ended December 31, 2017. The amount of cash basis interest income that was recognized on impaired loans during the year ended December 31, 2017 was not material.
Total deposits increased $160.5 million, or 2.4%, during the year ended December 31, 2017 to $6.71 billion. Total core deposits, which consist of savings and demand deposit accounts, increased $176.9 million, or 3.0%, to $6.08 billion at December 31, 2017, while time deposits decreased $16.4 million to $634.8 million at December 31, 2017. The increase in core deposits for the year ended December 31, 2017 was largely attributable to a $140.0 million increase in interest bearing demand deposits and a $103.6 million increase in non-interest bearing demand deposits, partially offset by a $50.7 million decrease in money market deposits and a $16.0 million decrease in savings deposits. At December 31, 2017, core deposits represented 90.5% of total deposits compared to 90.1% at December 31, 2016.
Borrowed funds increased $129.8 million, or 8.0%, during the year ended December 31, 2017, to $1.74 billion, as wholesale funds, combined with net deposit inflows, were used to fund the Company's asset growth. Borrowed funds represented 17.7% of total assets at December 31, 2017, an increase from 17.0% at December 31, 2016.
45
Total stockholders’ equity increased $46.9 million, or 3.7%, to $1.30 billion at December 31, 2017, from $1.25 billion at December 31, 2016. This increase resulted from net income earned during the year of $93.9 million, the allocation of shares to stock-based compensation plans of $11.5 million, exercised stock options of $3.0 million, and the reissuance of shares for the dividend reinvestment program of $2.1 million, partially offset by cash dividends paid to stockholders of $60.0 million, a $2.7 million other comprehensive loss and common stock repurchases of $1.2 million. Common stock repurchases for the year ended December 31, 2017, which were made in connection with withholding to cover income taxes on stock-based compensation, totaled 45,123 shares at an average cost of $27.08 per share. At December 31, 2017, approximately 3.1 million shares remained eligible for repurchase under the current authorizations.
Comparison of Operating Results for the Years Ended December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016
General. Net income for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $93.9 million, compared to $87.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. Basic and diluted earnings per share were $1.46 and $1.45 for the year ended December 31, 2017, respectively, compared to basic and diluted earnings per share of $1.38 for 2016.
As a result of the enactment of the Tax Act on December 22, 2017, the Company recognized additional tax expense of $3.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2017. Offsetting the effect of the change in tax law, earnings for the year ended December 31, 2017 were favorably impacted by year-over-year growth in average loans outstanding, growth in both average non-interest bearing and interest bearing core deposits and expansion of the net interest margin. The improvement in the net interest margin was driven by the upward repricing of adjustable rate assets and relatively stable cost of funds.
Net Interest Income. Net interest income increased $19.6 million to $278.2 million for 2017, from $258.6 million for 2016. The average interest rate spread increased nine basis points to 3.07% for 2017, from 2.98% for 2016. The net interest margin increased ten basis points to 3.21% for 2017, compared to 3.11% for 2016. For the year ended December 31, 2017, the increase in net interest income was largely due to growth in average loans outstanding, growth in average core deposits, and expansion in the net interest margin.
Interest income increased $21.5 million, or 7.1%, to $323.8 million for 2017, compared to $302.3 million for 2016. The increase in interest income was attributable to an increase in average earning asset balances and an increase in the yield on average interest-earning assets. Average interest-earning assets increased $343.1 million, or 4.1%, to $8.65 billion for 2017, compared to $8.31 billion for 2016. The average outstanding loan balances increased $301.7 million, or 4.5%, to $6.97 billion for 2017 from $6.67 billion for 2016, the average balance of securities available for sale increased $35.8 million, or 3.5%, to $1.04 billion for 2017, compared to $1.01 billion for 2016, and the average balance of investment securities held to maturity increased $8.7 million, or 1.8%, to $487.6 million for 2017, compared to $478.9 million for 2016. The yield on interest-earning assets increased ten basis points to 3.74% for 2017, from 3.64% for 2016, mainly due to increases in the weighted average yields on total loans, FHLBNY stock and the securities available for sale portfolio.
Interest expense increased $1.9 million, or 4.3%, to $45.6 million for 2017, from $43.7 million for 2016. The increase in interest expense was primarily attributable to an increase in average interest-bearing deposits for the year, which combined with an increase in non-interest bearing deposits largely funded the growth in average interest-earning assets. The increase in interest expense was partially offset by a shift in the funding composition to lower-costing core deposits from time deposits and borrowings. The average rate paid on interest-bearing liabilities increased one basis point to 0.67% for 2017, compared to 2016. The average rate paid on interest-bearing deposits increased four basis points to 0.37% for 2017, from 0.33% for 2016. The average rate paid on borrowings decreased four basis points to 1.66% for 2017, from 1.70% for 2016. The average balance of interest-bearing liabilities increased $154.2 million to $6.81 billion for 2017, compared to $6.66 billion for 2016. Average interest-bearing deposits increased $149.6 million, or 2.9%, to $5.23 billion for 2017, from $5.08 billion for 2016. Within average interest-bearing deposits, average interest-bearing core deposits increased $226.2 million, or 5.2% for 2017, compared with 2016, while average time deposits decreased $76.6 million, or 10.6% for 2017, compared with 2016. Average non-interest bearing demand deposits increased $123.1 million, or 9.9%, to $1.37 billion for 2017, from $1.24 billion for 2016. Average outstanding borrowings decreased $4.7 million, or 0.3%, to $1.58 billion for 2017, compared to 2016.
Provision for Loan Losses. Provisions for loan losses are charged to operations in order to maintain the allowance for loan losses at a level management considers necessary to absorb probable credit losses inherent in the loan portfolio. In determining the level of the allowance for loan losses, management considers past and current loss experience, evaluations of real estate collateral, current economic conditions, volume and type of lending, adverse situations that may affect a borrower’s ability to repay the loan and the levels of non-performing and other classified loans. The amount of the allowance is based on estimates, and the ultimate losses may vary from such estimates as more information becomes available or later events change. Management assesses the adequacy of the allowance for loan losses on a quarterly basis and makes provisions for loan losses, if necessary, in order to maintain the adequacy of the allowance. The Company’s emphasis on continued diversification of the loan portfolio through the origination of commercial loans has been one of the more significant factors management has considered in evaluating
46
the allowance for loan losses and provision for loan losses for the past several years. As the Company looks to further increase the amount of such types of loans in the portfolio, management may determine that additional or increased provisions for loan losses are necessary, which could adversely affect earnings.
The provision for loan losses was $5.6 million in 2017, compared to $5.4 million in 2016. The increase in the provision for loan losses was primarily attributable to year-over-year growth in the loan portfolio. Net charge-offs for 2017 were $7.3 million, compared to $4.9 million for 2016. Total charge-offs for the year ended December 31, 2017 were $8.9 million, compared to $7.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. Recoveries for the year ended December 31, 2017, were $1.7 million, compared to $2.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. The allowance for loan losses at December 31, 2017 was $60.2 million, or 0.82% of total loans, compared to $61.9 million, or 0.88% of total loans, at December 31, 2016. At December 31, 2017, non-performing loans as a percentage of total loans were 0.48%, compared to 0.61% at December 31, 2016. Non-performing assets as a percentage of total assets were 0.42% at December 31, 2017, compared to 0.53% at December 31, 2016. At December 31, 2017, non-performing loans were $34.9 million, compared to $42.4 million at December 31, 2016, and non-performing assets were $41.8 million at December 31, 2017, compared to $50.4 million at December 31, 2016.
Non-Interest Income. For the year ended December 31, 2017, non-interest income totaled $55.7 million, an increase of $304,000, compared to the same period in 2016. Income from Bank-owned life insurance increased $1.2 million to $6.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to the same period in 2016, primarily due to the recognition of death benefit claims. Fee income also increased $1.2 million to $27.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to the same period in 2016, largely due to a $657,000 increase in commercial loan prepayment fee income, a $397,000 increase in deposit related fee income and a $229,000 increase in merchant fee income, partially offset by a $218,000 decrease in income from non-deposit investment products and a $43,000 decrease in debit card revenue. Partially offsetting these increases in non-interest income, other income decreased $2.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared with the same period in 2016, mainly due to a $910,000 decrease in net fees on loan-level interest rate swap transactions, a $583,000 decrease in net gains recognized on loan sales and a $335,000 non-recurring gain recognized on the sale of deposits resulting from a strategic branch divestiture in the prior year.
Non-Interest Expense. Non-interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $187.8 million, an increase of $4.0 million from the year ended December 31, 2016. Compensation and benefits expense increased $3.2 million to $109.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to $106.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. This increase was primarily due to additional salary expense related to annual merit increases, an increase in the accrual for incentive compensation and an increase in stock-based compensation, partially offset by a decrease in retirement benefit costs. Other operating expenses increased $1.2 million to $28.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to $27.6 million for the same period in 2016, largely due to increases in consulting and debit card maintenance expenses, partially offset by a decrease in loan collection expense. Data processing costs increased $694,000 to $13.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared with the same period in 2016, due to increased software maintenance and telecommunication costs. Net occupancy costs increased $437,000, to $25.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to the same period in 2016, resulting from an increase in snow removal costs, combined with an increase in facilities maintenance costs. Partially offsetting these increases in non-interest expense, FDIC insurance expense decreased $1.0 million to $3.9 million for year ended December 31, 2017, compared to $4.9 million for the same period in 2016. This decrease was primarily due to the FDIC's reduction of assessment rates for depository institutions with less than $10.0 billion in assets, which became effective in the quarter ended September 30, 2016. Additionally, amortization of intangibles decreased $721,000 for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared with the same period in 2016, as a result of scheduled reductions in amortization.
Income Tax Expense. For the year ended December 31, 2017, the Company’s income tax expense was $46.5 million, compared with $37.0 million, for the same period in 2016. The Company’s effective tax rate was 33.1% for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared with 29.6% for the year ended December 31, 2016. For the year ended December 31, 2017, the increases in income tax expense and the effective tax rate were a function of growth in pre-tax income and the enactment of the Tax Act, which resulted in additional tax expense of $3.9 million.
Comparison of Operating Results for the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015
General. Net income for the year ended December 31, 2016 was $87.8 million, compared to $83.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. Basic and diluted earnings per share were $1.38 for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to basic and diluted earnings per share of $1.33 for 2015. Net income for the year ended December 31, 2016 was favorably impacted by year-over-year growth in average loans outstanding resulting from organic originations, and increases in both average interest bearing core deposits and average non-interest bearing demand deposits, partially offset by compression in the net interest margin. The growth in average core deposits mitigated the Company's need to utilize higher-cost borrowings to fund loan growth.
47
Net Interest Income. Net interest income increased $8.7 million to $258.6 million for 2016, from $249.9 million for 2015. The average interest rate spread decreased nine basis points to 2.98% for 2016, from 3.07% for 2015. The net interest margin decreased nine basis points to 3.11% for 2016, compared to 3.20% for 2015. For the year ended December 31, 2016, net interest income was favorably impacted by the growth in average loans outstanding and growth in average core deposits, mitigating the effects of compression in the net interest margin.
Interest income increased $10.5 million, or 3.6%, to $302.3 million for 2016, compared to $291.8 million for 2015. The increase in interest income was attributable to an increase in average earning asset balances, partially offset by a decrease in the yield on average interest-earning assets. Average interest-earning assets increased $490.9 million, or 6.3%, to $8.31 billion for 2016, compared to $7.82 billion for 2015. The average outstanding loan balances increased $454.4 million, or 7.3%, to $6.67 billion for 2016 from $6.22 billion for 2015, the average balance of securities available for sale decreased $20.3 million, or 2.0%, to $1.01 billion for 2016, compared to $1.03 billion for 2015, and the average balance of investment securities held to maturity increased $5.5 million, or 1.2%, to $478.9 million for 2016, compared to $473.4 million for 2015. The yield on interest-earning assets decreased nine basis points to 3.64% for 2016, from 3.73% for 2015, due to a reduction in both the weighted average yield on total loans and securities available for sale, partially offset by an increase in the weighted average yield on FHLBNY stock.
Interest expense increased $1.8 million, or 4.4%, to $43.7 million for 2016, from $41.9 million for 2015. The increase in interest expense was primarily attributable to an increase in average interest-bearing deposits for the year, which largely funded the growth in average interest-earning assets. The increase in interest expense was partially offset by a shift in the funding composition to lower-costing core deposits from time deposits and borrowings. The average rate paid on interest-bearing liabilities remained unchanged at 0.66% for 2016, compared to 2015. The average rate paid on interest-bearing deposits increased two basis points to 0.33% for 2016, from 0.31% for 2015. The average rate paid on borrowings decreased one basis point to 1.70% for 2016, from 1.71% for 2015. The average balance of interest-bearing liabilities increased $327.4 million to $6.66 billion for 2016, compared to $6.33 billion for 2015. Average interest-bearing deposits increased $354.1 million, or 7.5%, to $5.08 billion for 2016, from $4.72 billion for 2015. Within average interest-bearing deposits, average interest-bearing core deposits increased $412.5 million, or 10.5%, for 2016, compared with 2015, while average time deposits decreased $58.4 million, or 7.5%, for 2016, compared with 2015. Average non-interest bearing demand deposits increased $125.9 million, or 11.3%, to $1.24 billion for 2016, from $1.12 billion for 2015. Average outstanding borrowings decreased $26.7 million, or 1.7%, to $1.58 billion for 2016, compared with $1.60 billion for 2015.
Provision for Loan Losses. The provision for loan losses was $5.4 million in 2016, compared to $4.4 million in 2015. The increase in the provision for loan losses was primarily attributable to year-over-year growth in the loan portfolio. Net charge-offs for 2016 were $4.9 million, compared to $4.7 million for 2015. Total charge-offs for the year ended December 31, 2016 were $7.0 million, compared to $8.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. Recoveries for the year ended December 31, 2016, were $2.0 million, compared to $4.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The allowance for loan losses at December 31, 2016 was $61.9 million, or 0.88% of total loans, compared to $61.4 million, or 0.94% of total loans, at December 31, 2015. At December 31, 2016, non-performing loans as a percentage of total loans were 0.61%, compared to 0.68% at December 31, 2015. Non-performing assets as a percentage of total assets were 0.53% at December 31, 2016, compared to 0.62% at December 31, 2015. At December 31, 2016, non-performing loans were $42.4 million, compared to $44.5 million at December 31, 2015, and non-performing assets were $50.4 million at December 31, 2016, compared to $55.1 million at December 31, 2015.
Non-Interest Income. For the year ended December 31, 2016, non-interest income totaled $55.4 million, an increase of $171,000, compared to the same period in 2015. Wealth management income increased $718,000 to $17.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, largely due to fees from assets under management acquired in the MDE acquisition, which closed on April 1, 2015. This increase in wealth management income was offset in part by a reduction in income associated with the licensing of indices to exchange traded fund ("ETF") providers, along with a shift in the mix of assets under management which negatively impacted fees earned. Also contributing to the increase in non-interest income, other income increased $153,000 for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with the same period in 2015, primarily due to a $1.2 million increase in net gains recognized on loan sales and a $335,000 gain recognized on the sale of deposits resulting from a strategic branch divestiture, largely offset by a $1.4 million decrease in net fees on loan-level interest rate swap transactions. Partially offsetting these increases in non-interest income, net gains on securities transactions and fee income decreased $590,000 and $235,000, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to the same period in 2015. The decrease in fee income was largely due to a $1.4 million decrease in prepayment fees on commercial loans, partially offset by increases of $708,000 and $529,000 in deposit fees and loan related fee income, respectively.
Non-Interest Expense. Non-interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2016 was $183.8 million, an increase of $3.2 million from the year ended December 31, 2015. Compensation and benefits expense increased $6.5 million to $106.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to $99.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. This increase was primarily due to additional salary expense associated with annual merit increases, an increase in the accrual for annual incentive compensation, increased salary expense associated with new employees from MDE, and an increase in employee medical and
48
retirement benefit costs. Data processing costs increased $530,000 to $13.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with the same period in 2015, principally due to increased software maintenance and core processing costs. Partially offsetting these increases in non-interest expense, net occupancy costs decreased $1.2 million, to $24.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to the same period in 2015, principally due to a decrease in seasonal expenses resulting from a milder winter, combined with decreases in facilities and equipment maintenance expenses. Other operating expenses decreased $1.2 million to $27.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to $28.8 million for the same period in 2015, largely due to $413,000 of non-recurring professional services costs associated with the MDE transaction for the year ended December 31, 2015, combined with decreases in printing expense, business development costs and decreases in foreclosed real estate and non-performing asset-related expenses. The amortization of intangibles decreased $675,000 for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with the same period in 2015, as a result of scheduled reductions in amortization. Additionally, advertising and promotion expenses decreased $541,000 to $3.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to $4.2 million for the same period in 2015, largely due to the Company's shift from higher-costing traditional print advertising to digital media.
Income Tax Expense. For the year ended December 31, 2016, the Company’s income tax expense was $37.0 million, compared with $36.4 million, for the same period in 2015. The Company’s effective tax rate was 29.6% for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with 30.3% for the year ended December 31, 2015. For the year ended December 31, 2016, the increases in income tax expense was a function of growth in pre-tax income. In the third quarter of 2016, the Company adopted Accounting Standards Update ("ASU”) No. 2016-09, "Compensation - Stock Compensation (Topic 718)." The adoption of this ASU resulted in a $158,000 decrease in income tax expense.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Liquidity refers to the Company’s ability to generate adequate amounts of cash to meet financial obligations to its depositors, to fund loans and securities purchases, deposit outflows and operating expenses. Sources of funds include scheduled amortization of loans, loan prepayments, scheduled maturities of investments, cash flows from mortgage-backed securities and the ability to borrow funds from the FHLBNY and approved broker-dealers.
Cash flows from loan payments and maturing investment securities are fairly predictable sources of funds. Changes in interest rates, local economic conditions and the competitive marketplace can influence loan prepayments, prepayments on mortgage-backed securities and deposit flows. For each of the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, loan repayments totaled $3.34 billion and $2.62 billion, respectively.
Commercial real estate loans, multi-family loans, commercial loans, one- to four-family residential loans and consumer loans are the primary investments of the Company. Purchasing securities for the investment portfolio is a secondary use of funds and the investment portfolio is structured to complement and facilitate the Company’s lending activities and ensure adequate liquidity. Loan originations and purchases totaled $3.70 billion for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to $3.12 billion for the year ended December 31, 2016. Purchases for the investment portfolio totaled $276.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to $386.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. At December 31, 2017, the Bank had outstanding loan commitments to borrowers of $1.98 billion, including undisbursed home equity lines and personal credit lines of $270.9 million.
Total deposits increased $160.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2017. Deposit activity is affected by changes in interest rates, competitive pricing and product offerings in the marketplace, local economic conditions, customer confidence and other factors such as stock market volatility. Certificate of deposit accounts that are scheduled to mature within one year totaled $424.4 million at December 31, 2017. Based on its current pricing strategy and customer retention experience, the Bank expects to retain a significant share of these accounts. The Bank manages liquidity on a daily basis and expects to have sufficient cash to meet all of its funding requirements.
As of December 31, 2017, the Bank exceeded all minimum regulatory capital requirements. At December 31, 2017, the Bank’s leverage (Tier 1) capital ratio was 9.07%. FDIC regulations require banks to maintain a minimum leverage ratio of Tier 1 capital to adjusted total assets of 4.00%. At December 31, 2017, the Bank’s total risk-based capital ratio was 11.95%. Under current regulations, the minimum required ratio of total capital to risk-weighted assets is 9.25%. A bank is considered to be well-capitalized if it has a leverage (Tier 1) capital ratio of at least 5.00% and a total risk-based capital ratio of at least 10.00%.
49
Off-Balance Sheet and Contractual Obligations
Off-balance sheet and contractual obligations as of December 31, 2017, are summarized below:
Payments Due by Period | |||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
Total | Less than 1 year | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | More than 5 years | |||||||||||||||
Off-Balance Sheet: | |||||||||||||||||||
Long-term commitments | $ | 1,948,279 | $ | 593,759 | $ | 653,263 | $ | 317,893 | $ | 383,364 | |||||||||
Letters of credit | 27,953 | 25,053 | 2,583 | 317 | — | ||||||||||||||
Total Off-Balance Sheet | 1,976,232 | 618,812 | 655,846 | 318,210 | 383,364 | ||||||||||||||
Contractual Obligations: | |||||||||||||||||||
Operating leases | 45,333 | 8,032 | 14,491 | 8,232 | 14,578 | ||||||||||||||
Certificate of deposits | 634,809 | 424,448 | 150,280 | 56,530 | 3,551 | ||||||||||||||
Total Contractual Obligations | 680,142 | 432,480 | 164,771 | 64,762 | 18,129 | ||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 2,656,374 | $ | 1,051,292 | $ | 820,617 | $ | 382,972 | $ | 401,493 | |||||||||
Off-balance sheet commitments consist of unused commitments to borrowers for term loans, unused lines of credit and outstanding letters of credit. Total off-balance sheet obligations were $1.98 billion at December 31, 2017, an increase of $145.1 million, or 7.9%, from $1.83 billion at December 31, 2016, largely due to an increase in commercial lines of credit.
Contractual obligations consist of operating leases and certificate of deposit liabilities. There were no securities purchases in 2017 and 2016 which will be or were settled in 2018 and 2017, respectively. Total contractual obligations at December 31, 2017 were $680.1 million, a decrease of $4.9 million, or 0.72%, compared to $685.1 million at December 31, 2016. Contractual obligations under operating leases increased $11.4 million, or 33.78%, to $45.3 million at December 31, 2017, from $33.9 million at December 31, 2016, and certificate of deposit accounts decreased $16.4 million, or 2.5%, to $634.8 million at December 31, 2017, from $651.2 million at December 31, 2016.
Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk |
Qualitative Analysis. Interest rate risk is the exposure of a bank’s current and future earnings and capital arising from adverse movements in interest rates. The guidelines of the Company’s interest rate risk policy seek to limit the exposure to changes in interest rates that affect the underlying economic value of assets and liabilities, earnings and capital. To minimize interest rate risk, the Company generally sells all 20- and 30-year fixed-rate mortgage loans at origination. Commercial real estate loans generally have interest rates that reset in five years, and other commercial loans such as construction loans and commercial lines of credit reset with changes in the Prime rate, the Federal Funds rate or LIBOR. Investment securities purchases generally have maturities of five years or less, and mortgage-backed securities have weighted average lives between three and five years.
The Asset/Liability Committee meets on at least a monthly basis to review the impact of interest rate changes on net interest income, net interest margin, net income and the economic value of equity. The Asset/Liability Committee reviews a variety of strategies that project changes in asset or liability mix and the impact of those changes on projected net interest income and net income.
The Company’s strategy for liabilities has been to maintain a stable core-funding base by focusing on core deposit account acquisition and increasing products and services per household. Certificate of deposit accounts as a percentage of total deposits were 9.5% at December 31, 2017, compared to 9.9% at December 31, 2016. Certificate of deposit accounts are generally short-term. As of December 31, 2017, 66.9% of all certificates of deposit had maturities of one year or less compared to 67.4% at December 31, 2016. The Company’s ability to retain maturing time deposit accounts is the result of its strategy to remain competitively priced within its marketplace. The Company’s pricing strategy may vary depending upon current funding needs and the ability of the Company to fund operations through alternative sources, primarily by accessing short-term lines of credit with the FHLBNY during periods of pricing dislocation.
Quantitative Analysis. Current and future sensitivity to changes in interest rates are measured through the use of balance sheet and income simulation models. The analysis captures changes in net interest income using flat rates as a base, a most likely rate forecast and rising and declining interest rate forecasts. Changes in net interest income and net income for the forecast period, generally twelve to twenty-four months, are measured and compared to policy limits for acceptable change. The Company periodically reviews historical deposit re-pricing activity and makes modifications to certain assumptions used in its income
50
simulation model regarding the interest rate sensitivity of deposits without maturity dates. These modifications are made to more closely reflect the most likely results under the various interest rate change scenarios. Since it is inherently difficult to predict the sensitivity of interest bearing deposits to changes in interest rates, the changes in net interest income due to changes in interest rates cannot be precisely predicted. There are a variety of reasons that may cause actual results to vary considerably from the predictions presented below which include, but are not limited to, the timing, magnitude, and frequency of changes in interest rates, interest rate spreads, prepayments, and actions taken in response to such changes. Specific assumptions used in the simulation model include:
• | Parallel yield curve shifts for market rates; |
• | Current asset and liability spreads to market interest rates are fixed; |
• | Traditional savings and interest bearing demand accounts move at 10% of the rate ramp in either direction; |
• | Retail Money Market and Business Money Market accounts move at 25% and 75% of the rate ramp in either direction, respectively; and |
• | Higher-balance demand deposit tiers and promotional demand accounts move at 50% to 75% of the rate ramp in either direction. |
The following table sets forth the results of the twelve month projected net interest income model as of December 31, 2017.
Change in Interest Rates in Basis Points (Rate Ramp) | Net Interest Income | ||||||||
Amount ($) | Change ($) | Change (%) | |||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||
-100 | 293,501 | (1,733 | ) | (0.6 | ) | ||||
Static | 295,234 | — | — | ||||||
+100 | 292,527 | (2,707 | ) | (0.9 | ) | ||||
+200 | 288,748 | (6,486 | ) | (2.2 | ) | ||||
+300 | 284,077 | (11,157 | ) | (3.8 | ) | ||||
The above table indicates that as of December 31, 2017, in the event of a 300 basis point increase in interest rates, whereby rates ramp up evenly over a twelve-month period, the Company would experience a 3.8%, or $11.2 million decrease in net interest income. In the event of a 100 basis point decrease in interest rates, whereby rates ramp down evenly over a twelve-month period, the Company would experience a 0.6%, or $1.7 million decrease in net interest income.
Another measure of interest rate sensitivity is to model changes in economic value of equity through the use of immediate and sustained interest rate shocks. The following table illustrates the economic value of equity model results as of December 31, 2017.
Change in Interest Rates | Present Value of Equity | Present Value of Equity as Percent of Present Value of Assets | ||||||||||||
Dollar Amount | Dollar Change | Percent Change | Present Value Ratio | Percent Change | ||||||||||
(Basis Points) | (Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||
-100 | 1,430,118 | (27,259 | ) | (1.9 | ) | 14.3 | (4.0 | ) | ||||||
Flat | 1,457,377 | — | — | 14.9 | — | |||||||||
+100 | 1,397,108 | (60,269 | ) | (4.1 | ) | 14.7 | (1.7 | ) | ||||||
+200 | 1,328,875 | (128,502 | ) | (8.8 | ) | 14.3 | (4.1 | ) | ||||||
+300 | 1,266,400 | (190,977 | ) | (13.1 | ) | 14.0 | (6.4 | ) | ||||||
The preceding table indicates that as of December 31, 2017, in the event of an immediate and sustained 300 basis point increase in interest rates, the Company would experience a 13.1%, or $191.0 million reduction in the present value of equity. If rates were to decrease 100 basis points, the Company would experience a 1.9%, or $27.3 million decrease in the present value of equity.
Certain shortcomings are inherent in the methodologies used in the above interest rate risk measurements. Modeling changes in net interest income requires the use of certain assumptions regarding prepayment and deposit decay rates, which may or may not reflect the manner in which actual yields and costs respond to changes in market interest rates. While management believes such assumptions are reasonable, there can be no assurance that assumed prepayment rates and decay rates will approximate actual
51
future loan prepayment and deposit withdrawal activity. Moreover, the net interest income table presented assumes that the composition of interest sensitive assets and liabilities existing at the beginning of a period remains constant over the period being measured and also assumes that a particular change in interest rates is reflected uniformly across the yield curve regardless of the duration to maturity or repricing of specific assets and liabilities. Accordingly, although the net interest income table provides an indication of the Company’s interest rate risk exposure at a particular point in time, such measurement is not intended to and does not provide a precise forecast of the effect of changes in market interest rates on the Company’s net interest income and will differ from actual results.
52
Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
The following are included in this item:
(A) | Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm |
(B) | Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting |
(C) | Consolidated Financial Statements: |
(1) | Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 |
(2) | Consolidated Statements of Income for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 |
(3) | Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 |
(4) | Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 |
(5) | Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 |
(6) | Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements |
(D) | Provident Financial Services, Inc., Condensed Financial Statements: |
(1) | Condensed Statement of Financial Condition as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 |
(2) | Condensed Statement of Income for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 |
(3) | Condensed Statement of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 |
The supplementary data required by this Item is provided in Note 19 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
53
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Stockholders and Board of Directors
Provident Financial Services, Inc.:
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of financial condition of Provident Financial Services, Inc. and subsidiary (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, changes in stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three‑year period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes (collectively, the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the three‑year period ended December 31, 2017, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, and our report dated March 1, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ KPMG LLP
We have not been able to determine the specific year that we began serving as the Company’s auditor; however, we are aware that we have served as the Company’s auditor since at least 1997.
Short Hills, New Jersey
March 1, 2018
54
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Stockholders and Board of Directors
Provident Financial Services, Inc.:
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Provident Financial Services, Inc. and subsidiary's (the “Company”) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”), the consolidated statements of financial condition of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, changes in stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes (collectively, the “consolidated financial statements”), and our report dated March 1, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ KPMG LLP
Short Hills, New Jersey
March 1, 2018
55
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition
December 31, 2017 and 2016
(Dollars in Thousands, except share data)
December 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
ASSETS | |||||||
Cash and due from banks | $ | 139,557 | $ | 92,508 | |||
Short-term investments | 51,277 | 51,789 | |||||
Total cash and cash equivalents | 190,834 | 144,297 | |||||
Securities available for sale, at fair value | 1,037,812 | 1,040,386 | |||||
Investment securities held to maturity (fair value of $485,039 and $489,287 at December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively) | 477,652 | 488,183 | |||||
Federal Home Loan Bank Stock | 81,184 | 75,726 | |||||
Loans | 7,325,718 | 7,003,486 | |||||
Less allowance for loan losses | 60,195 | 61,883 | |||||
Net loans | 7,265,523 | 6,941,603 | |||||
Foreclosed assets, net | 6,864 | 7,991 | |||||
Banking premises and equipment, net | 63,185 | 84,092 | |||||
Accrued interest receivable | 29,646 | 27,082 | |||||
Intangible assets | 420,290 | 422,937 | |||||
Bank-owned life insurance | 189,525 | 188,527 | |||||
Other assets | 82,759 | 79,641 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 9,845,274 | $ | 9,500,465 | |||
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||
Deposits: | |||||||
Demand deposits | $ | 4,996,345 | $ | 4,803,426 | |||
Savings deposits | 1,083,012 | 1,099,020 | |||||
Certificates of deposit of $100,000 or more | 316,074 | 290,295 | |||||
Other time deposits | 318,735 | 360,888 | |||||
Total deposits | 6,714,166 | 6,553,629 | |||||
Mortgage escrow deposits | 25,933 | 24,452 | |||||
Borrowed funds | 1,742,514 | 1,612,745 | |||||
Other liabilities | 64,000 | 57,858 | |||||
Total liabilities | 8,546,613 | 8,248,684 | |||||
Stockholders’ Equity: | |||||||
Preferred stock, $0.01 par value, 50,000,000 shares authorized, none issued | — | — | |||||
Common stock, $0.01 par value, 200,000,000 shares authorized, 83,209,293 shares issued and 66,535,017 shares outstanding at December 31, 2017, and 83,209,293 shares issued and 66,082,283 shares outstanding at December 31, 2016, respectively | 832 | 832 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 1,012,908 | 1,005,777 | |||||
Retained earnings | 586,132 | 550,768 | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (7,465 | ) | (3,397 | ) | |||
Treasury stock | (259,907 | ) | (264,221 | ) | |||
Unallocated common stock held by the Employee Stock Ownership Plan | (33,839 | ) | (37,978 | ) | |||
Common stock acquired by the Directors’ Deferred Fee Plan | (5,175 | ) | (5,846 | ) | |||
Deferred compensation—Directors’ Deferred Fee Plan | 5,175 | 5,846 | |||||
Total stockholders’ equity | 1,298,661 | 1,251,781 | |||||
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $ | 9,845,274 | $ | 9,500,465 | |||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
56
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Consolidated Statements of Income
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(Dollars in Thousands, except share data)
Years ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Interest income: | |||||||||||
Real estate secured loans | $ | 189,896 | $ | 180,868 | $ | 176,714 | |||||
Commercial loans | 72,907 | 63,022 | 55,347 | ||||||||
Consumer loans | 20,301 | 21,829 | 22,770 | ||||||||
Securities available for sale and Federal Home Loan Bank stock | 26,445 | 22,890 | 23,398 | ||||||||
Investment securities held to maturity | 13,027 | 13,208 | 13,494 | ||||||||
Deposits, federal funds sold and other short-term investments | 1,270 | 498 | 58 | ||||||||
Total interest income | 323,846 | 302,315 | 291,781 | ||||||||
Interest expense: | |||||||||||
Deposits | 19,441 | 16,947 | 14,521 | ||||||||
Borrowed funds | 26,203 | 26,801 | 27,380 | ||||||||
Total interest expense | 45,644 | 43,748 | 41,901 | ||||||||
Net interest income | 278,202 | 258,567 | 249,880 | ||||||||
Provision for loan losses | 5,600 | 5,400 | 4,350 | ||||||||
Net interest income after provision for loan losses | 272,602 | 253,167 | 245,530 | ||||||||
Non-interest income: | |||||||||||
Fees | 27,218 | 26,047 | 26,282 | ||||||||
Wealth management income | 17,604 | 17,556 | 16,838 | ||||||||
Bank-owned life insurance | 6,693 | 5,470 | 5,345 | ||||||||
Net gain on securities transactions | 57 | 64 | 654 | ||||||||
Other income | 4,125 | 6,256 | 6,103 | ||||||||
Total non-interest income | 55,697 | 55,393 | 55,222 | ||||||||
Non-interest expense: | |||||||||||
Compensation and employee benefits | 109,353 | 106,141 | 99,689 | ||||||||
Net occupancy expense | 25,290 | 24,853 | 26,032 | ||||||||
Data processing expense | 13,922 | 13,228 | 12,698 | ||||||||
FDIC Insurance | 3,887 | 4,887 | 5,036 | ||||||||
Advertising and promotion expense | 3,904 | 3,685 | 4,226 | ||||||||
Amortization of intangibles | 2,670 | 3,391 | 4,066 | ||||||||
Other operating expenses | 28,796 | 27,593 | 28,842 | ||||||||
Total non-interest expenses | 187,822 | 183,778 | 180,589 | ||||||||
Income before income tax expense | 140,477 | 124,782 | 120,163 | ||||||||
Income tax expense | 46,528 | 36,980 | 36,441 | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 93,949 | $ | 87,802 | $ | 83,722 | |||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 1.46 | $ | 1.38 | $ | 1.33 | |||||
Average basic shares outstanding | 64,384,851 | 63,643,622 | 62,945,669 | ||||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 1.45 | $ | 1.38 | $ | 1.33 | |||||
Average diluted shares outstanding | 64,579,222 | 63,851,986 | 63,114,718 | ||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
57
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(Dollars in Thousands)
Years ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 93,949 | $ | 87,802 | $ | 83,722 | |||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax: | |||||||||||
Unrealized gains and losses on securities available for sale: | |||||||||||
Net unrealized losses arising during the period | (2,163 | ) | (4,431 | ) | (3,401 | ) | |||||
Reclassification adjustment for gains included in net income | — | (30 | ) | (391 | ) | ||||||
Total | (2,163 | ) | (4,461 | ) | (3,792 | ) | |||||
Unrealized gains (losses) on derivatives | 379 | 242 | (73 | ) | |||||||
Amortization related to post-retirement obligations | (889 | ) | 3,368 | 1,290 | |||||||
Total other comprehensive loss | (2,673 | ) | (851 | ) | (2,575 | ) | |||||
Total comprehensive income | $ | 91,276 | $ | 86,951 | $ | 81,147 | |||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
58
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Consolidated Statement of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(Dollars in Thousands)
COMMON STOCK | ADDITIONAL PAID-IN CAPITAL | RETAINED EARNINGS | ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE (LOSS) INCOME | TREASURY STOCK | UNALLOCATED ESOP SHARES | COMMON STOCK ACQUIRED BY DDFP | DEFERRED COMPENSATION DDFP | TOTAL STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2014 | $ | 832 | $ | 995,053 | $ | 465,276 | $ | 29 | $ | (271,779 | ) | $ | (45,312 | ) | $ | (7,113 | ) | $ | 7,113 | $ | 1,144,099 | ||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | 83,722 | — | — | — | — | — | 83,722 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | — | (2,575 | ) | — | — | — | — | $ | (2,575 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash dividends paid | — | — | (41,285 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | (41,285 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Distributions from DDFP | — | 85 | — | — | — | — | 596 | (596 | ) | 85 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchases of treasury stock | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase of employee restricted shares to fund statutory tax withholding | — | — | — | — | (1,988 | ) | — | — | — | (1,988 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares issued dividend reinvestment plan | — | 143 | — | — | 1,304 | — | — | — | 1,447 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Option exercises | — | (283 | ) | — | — | 3,449 | — | — | — | 3,166 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allocation of ESOP shares | — | 467 | — | — | — | 3,582 | — | — | 4,049 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allocation of SAP shares | — | 5,073 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 5,073 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allocation of stock options | — | 272 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 272 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2015 | $ | 832 | $ | 1,000,810 | $ | 507,713 | $ | (2,546 | ) | $ | (269,014 | ) | $ | (41,730 | ) | $ | (6,517 | ) | $ | 6,517 | $ | 1,196,065 | |||||||||||||
59
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Consolidated Statement of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 (Continued)
(Dollars in Thousands)
COMMON STOCK | ADDITIONAL PAID-IN CAPITAL | RETAINED EARNINGS | ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE (LOSS) INCOME | TREASURY STOCK | UNALLOCATED ESOP SHARES | COMMON STOCK ACQUIRED BY DDFP | DEFERRED COMPENSATION DDFP | TOTAL STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2015 | $ | 832 | $ | 1,000,810 | $ | 507,713 | $ | (2,546 | ) | $ | (269,014 | ) | $ | (41,730 | ) | $ | (6,517 | ) | $ | 6,517 | $ | 1,196,065 | |||||||||||||
Net income | 87,802 | 87,802 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | — | (851 | ) | — | — | — | — | (851 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash dividends paid | — | — | (45,369 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | (45,369 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Effect of adopting Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2016-09 | — | (622 | ) | 622 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Distributions from DDFP | 131 | 671 | (671 | ) | 131 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchases of treasury stock | — | — | — | — | (1,557 | ) | — | — | — | (1,557 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase of employee restricted shares to fund statutory tax withholding | — | — | — | — | (1,225 | ) | — | — | — | (1,225 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares issued dividend reinvestment plan | — | 356 | — | — | 1,296 | — | — | — | 1,652 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Option exercises | — | (81 | ) | — | — | 6,279 | — | — | — | 6,198 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allocation of ESOP shares | — | 1,199 | — | — | — | 3,752 | — | — | 4,951 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allocation of SAP shares | — | 3,812 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 3,812 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allocation of stock options | — | 172 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 172 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2016 | $ | 832 | $ | 1,005,777 | $ | 550,768 | $ | (3,397 | ) | $ | (264,221 | ) | $ | (37,978 | ) | $ | (5,846 | ) | $ | 5,846 | $ | 1,251,781 | |||||||||||||
60
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Consolidated Statement of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 Continued)
(Dollars in Thousands)
COMMON STOCK | ADDITIONAL PAID-IN CAPITAL | RETAINED EARNINGS | ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE (LOSS) INCOME | TREASURY STOCK | UNALLOCATED ESOP SHARES | COMMON STOCK ACQUIRED BY DDFP | DEFERRED COMPENSATION DDFP | TOTAL STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2016 | $ | 832 | $ | 1,005,777 | $ | 550,768 | $ | (3,397 | ) | $ | (264,221 | ) | $ | (37,978 | ) | $ | (5,846 | ) | $ | 5,846 | $ | 1,251,781 | |||||||||||||
Net income | 93,949 | 93,949 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | — | (2,673 | ) | — | — | — | — | (2,673 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reclassification due to the adoption of ASU No. 2018-02 | — | — | 1,395 | (1,395 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash dividends paid | — | — | (59,980 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | (59,980 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Distributions from DDFP | 232 | 671 | (671 | ) | 232 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchases of treasury stock | — | — | — | — | (443 | ) | — | — | — | (443 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase of employee restricted shares to fund statutory tax withholding | — | — | — | — | (778 | ) | — | — | — | (778 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares issued dividend reinvestment plan | — | 712 | — | — | 1,402 | — | — | — | 2,114 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Option exercises | — | (1,179 | ) | — | — | 4,133 | — | — | — | 2,954 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allocation of ESOP shares | — | 2,200 | — | — | — | 4,139 | — | — | 6,339 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allocation of SAP shares | — | 4,963 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 4,963 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allocation of stock options | — | 203 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 203 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2017 | $ | 832 | $ | 1,012,908 | $ | 586,132 | $ | (7,465 | ) | $ | (259,907 | ) | $ | (33,839 | ) | $ | (5,175 | ) | $ | 5,175 | $ | 1,298,661 | |||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
61
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(Dollars in Thousands)
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | |||||||||||
Net income | $ | 93,949 | $ | 87,802 | $ | 83,722 | |||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization of intangibles | 11,623 | 12,760 | 13,714 | ||||||||
Provision for loan losses | 5,600 | 5,400 | 4,350 | ||||||||
Deferred tax expense | 40,634 | 3,160 | 326 | ||||||||
Income on Bank-owned life insurance | (6,693 | ) | (5,470 | ) | (5,345 | ) | |||||
Net amortization of premiums and discounts on securities | 9,948 | 10,831 | 10,613 | ||||||||
Accretion of net deferred loan fees | (4,655 | ) | (3,408 | ) | (4,624 | ) | |||||
Amortization of premiums on purchased loans, net | 1,021 | 1,311 | 1,100 | ||||||||
Net increase in loans originated for sale | (24,938 | ) | (34,976 | ) | (11,918 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from sales of loans originated for sale | 26,387 | 37,008 | 12,799 | ||||||||
Proceeds from sales and paydowns of foreclosed assets | 5,423 | 6,109 | 4,443 | ||||||||
ESOP expense | 4,600 | 3,706 | 2,997 | ||||||||
Allocation of stock award shares | 4,963 | 3,812 | 4,625 | ||||||||
Allocation of stock options | 203 | 172 | 272 | ||||||||
Net gain on sale of loans | (1,449 | ) | (2,032 | ) | (881 | ) | |||||
Net gain on securities transactions | (57 | ) | (64 | ) | (654 | ) | |||||
Net gain on sale of premises and equipment | (20 | ) | (14 | ) | (4 | ) | |||||
Net gain on sale of foreclosed assets | (819 | ) | (585 | ) | (592 | ) | |||||
Increase in accrued interest receivable | (2,564 | ) | (1,316 | ) | (538 | ) | |||||
(Increase) decrease in other assets | (52,078 | ) | 5,873 | (4,912 | ) | ||||||
Increase (decrease) in other liabilities | 6,142 | (2,770 | ) | 5,373 | |||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 117,220 | 127,309 | 114,866 | ||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | |||||||||||
Proceeds from maturities, calls and paydowns of investment securities held to maturity | 55,720 | 62,975 | 37,271 | ||||||||
Purchases of investment securities held to maturity | (47,894 | ) | (80,349 | ) | (44,254 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from sales of securities | — | 3,401 | 14,005 | ||||||||
Proceeds from maturities, calls and paydowns of securities available for sale | 220,138 | 211,440 | 212,095 | ||||||||
Purchases of securities available for sale | (228,363 | ) | (306,151 | ) | (129,720 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from redemption of Federal Home Loan Bank stock | 130,125 | 56,505 | 87,510 | ||||||||
Purchases of Federal Home Loan Bank stock | (135,583 | ) | (54,050 | ) | (95,902 | ) | |||||
Net cash and cash equivalents paid in acquisition | — | — | (25,855 | ) | |||||||
Death benefit proceeds from bank-owned life insurance | 4,428 | — | 776 | ||||||||
Purchases of loans | — | (28,590 | ) | (95,283 | ) | ||||||
Net increase in loans | (322,443 | ) | (440,999 | ) | (363,436 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from sales of premises and equipment | 20,766 | 14 | 19 | ||||||||
Purchases of premises and equipment | (3,231 | ) | (4,995 | ) | (5,909 | ) | |||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (306,337 | ) | (580,799 | ) | (408,683 | ) | |||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | |||||||||||
Net increase in deposits | 160,537 | 629,642 | 131,464 | ||||||||
Increase in mortgage escrow deposits | 1,481 | 1,107 | 1,696 | ||||||||
Purchase of treasury stock | (443 | ) | (1,557 | ) | — | ||||||
Purchase of employee restricted shares to fund statutory tax withholding | (778 | ) | (1,225 | ) | (1,988 | ) | |||||
Cash dividends paid to stockholders | (59,980 | ) | (45,369 | ) | (41,285 | ) | |||||
Shares issued to dividend reinvestment plan | 2,114 | 1,652 | 1,447 | ||||||||
Stock options exercised | 2,954 | 6,198 | 3,166 | ||||||||
Proceeds from long-term borrowings | 347,000 | 355,000 | 694,937 | ||||||||
Payments on long-term borrowings | (539,745 | ) | (485,202 | ) | (549,935 | ) | |||||
Net increase in short-term borrowings | 322,514 | 35,315 | 52,779 | ||||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | 235,654 | 495,561 | 292,281 | ||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 46,537 | 42,071 | (1,536 | ) | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 144,297 | 102,226 | 103,762 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 190,834 | $ | 144,297 | $ | 102,226 | |||||
Cash paid during the period for: | |||||||||||
Interest on deposits and borrowings | $ | 46,391 | $ | 44,004 | $ | 41,663 | |||||
Income taxes | $ | 40,566 | $ | 33,886 | $ | 40,620 | |||||
Non cash investing activities: | |||||||||||
Transfer of loans receivable to foreclosed assets | $ | 3,845 | $ | 3,631 | $ | 10,074 | |||||
Acquisition: | |||||||||||
Non-cash assets acquired: | |||||||||||
Goodwill and other intangible assets, net | — | — | 25,323 | ||||||||
Other assets | — | — | 1,270 | ||||||||
Total non-cash assets acquired | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 26,593 | |||||
Liabilities assumed: | |||||||||||
Other Liabilities | — | — | 400 | ||||||||
Total liabilities assumed | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 400 | |||||
Common stock issued for acquisitions | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
62
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(1) Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Provident Financial Services, Inc. (the “Company”), Provident Bank (the “Bank”) and their wholly owned subsidiaries. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. Certain reclassifications have been made in the consolidated financial statements to conform with current year classifications.
Business
The Company, through the Bank, provides a full range of banking services to individual and business customers through branch offices in New Jersey and eastern Pennsylvania. The Bank is subject to competition from other financial institutions and to the regulations of certain federal and state agencies, and undergoes periodic examinations by those regulatory authorities.
Basis of Financial Statement Presentation
The consolidated financial statements of the Company have been prepared in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). In preparing the consolidated financial statements, management is required to make estimates and assumptions about future events. These estimates and the underlying assumptions affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures about contingent assets and liabilities as of the dates of the consolidated statements of financial condition, and revenues and expenses for the periods then ended. Such estimates are used in connection with the determination of the allowance for loan losses, evaluation of goodwill for impairment, evaluation of other-than-temporary impairment on securities, evaluation of the need for valuation allowances on deferred tax assets, and determination of liabilities related to retirement and other post-retirement benefits, among others. These estimates and assumptions are based on management’s best estimates and judgment. Management evaluates its estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis using historical experience and other factors, including the current economic environment, which management believes to be reasonable under the circumstances. Such estimates and assumptions are adjusted when facts and circumstances dictate. Illiquid credit markets, volatile securities markets, and declines in the housing market and the economy generally have combined to increase the uncertainty inherent in such estimates and assumptions. As future events and their effects cannot be determined with precision, actual results could differ significantly from these estimates. Changes in estimates resulting from continuing changes in the economic environment will be reflected in the financial statements in future periods.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
For purposes of reporting cash flows, cash and cash equivalents include cash and due from banks, Federal funds sold and commercial paper with original maturity dates less than 90 days.
Securities
Securities include investment securities held to maturity and securities available for sale. The available for sale securities portfolio is carried at estimated fair value, with any unrealized gains or losses, net of taxes, reported as accumulated other comprehensive income or loss in Stockholders’ Equity. Estimated fair values are based on market quotations or matrix pricing. Securities which the Company has the positive intent and ability to hold to maturity are classified as held to maturity and carried at amortized cost. Management conducts a periodic review and evaluation of the securities portfolio to determine if any declines in the fair values of securities are other-than-temporary. In this evaluation, if such a decline were deemed other-than-temporary, management would measure the total credit-related component of the unrealized loss, and recognize that portion of the loss as a charge to current period earnings. The remaining portion of the unrealized loss would be recognized as an adjustment to accumulated other comprehensive income. The fair value of the securities portfolio is significantly affected by changes in interest rates. In general, as interest rates rise, the fair value of fixed-rate securities decreases and as interest rates fall, the fair value of fixed-rate securities increases. The Company determines if it has the intent to sell these securities or if it is more likely than not that the Company would be required to sell the securities before the anticipated recovery. If either exists, the entire decline in value is considered other-than-temporary and would be recognized as an expense in the current period.
Premiums and discounts on securities are amortized and accreted to income using a method that approximates the interest method over the remaining period to contractual maturity, adjusted for anticipated prepayments. Dividend and interest income
63
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
are recognized when earned. Realized gains and losses are recognized when securities are sold or called based on the specific identification method.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
GAAP establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value. The hierarchy gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (level 1 measurements) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (level 3 measurements). A financial instrument’s level within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
Federal Home Loan Bank of New York Stock
The Bank, as a member of the Federal Home Loan Bank of New York (“FHLBNY”), is required to hold shares of capital stock of the FHLBNY at cost based on a specified formula. The Bank carries this investment at cost, which approximates fair value.
Loans
Loans receivable are carried at unpaid principal balances plus unamortized premiums, purchase accounting mark-to-market adjustments, certain deferred direct loan origination costs and deferred loan origination fees and discounts, less the allowance for loan losses.
The Bank defers loan origination fees and certain direct loan origination costs and accretes such amounts as an adjustment to the yield over the expected lives of the related loans using the interest method. Premiums and discounts on loans purchased are amortized or accreted as an adjustment of yield over the contractual lives of the related loans, adjusted for prepayments when applicable, using methodologies which approximate the interest method.
Loans are generally placed on non-accrual status when they are past due 90 days or more as to contractual obligations or when other circumstances indicate that collection is questionable. When a loan is placed on non-accrual status, any interest accrued but not received is reversed against interest income. Payments received on a non-accrual loan are either applied to the outstanding principal balance or recorded as interest income, depending on an assessment of the ability to collect the loan. A non-accrual loan is restored to accrual status when principal and interest payments become less than 90 days past due and its future collectability is reasonably assured.
An impaired loan is defined as a loan for which it is probable, based on current information, that the lender will not collect all amounts due under the contractual terms of the loan agreement. Impaired loans are individually assessed to determine that each loan’s carrying value is not in excess of the fair value of the related collateral or the present value of the expected future cash flows. Residential mortgage and consumer loans are deemed smaller balance homogeneous loans which are evaluated collectively for impairment and are therefore excluded from the population of impaired loans.
Purchased Credit-Impaired (“PCI”) loans, are loans acquired at a discount primarily due to deteriorated credit quality. PCI loans are recorded at fair value at the date of acquisition, with no allowance for loan losses. The difference between the undiscounted cash flows expected at acquisition and the fair value of the PCI loans at acquisition represents the accretable yield and is recognized as interest income over the life of the loans. Contractually required payments for interest and principal that exceed the undiscounted cash flows expected at acquisition represent the non-accretable discount and are not recognized as a yield adjustment or a valuation allowance. Reclassifications of the non-accretable to accretable yield may occur subsequent to the loan acquisition dates due to an increase in expected cash flows of the loans and results in an increase in interest income on a prospective basis.
Allowance for Loan Losses
Losses on loans are charged to the allowance for loan losses. Additions to this allowance are made by recoveries of loans previously charged off and by a provision charged to expense. The determination of the balance of the allowance for loan losses is based on an analysis of the loan portfolio, economic conditions, historical loan loss experience and other factors that warrant recognition in providing for an adequate allowance.
While management uses available information to recognize losses on loans, future additions to the allowance for loan losses may be necessary based on changes in economic conditions in the Bank’s market area. In addition, various regulatory agencies, as an integral part of their examination process, periodically review the Bank’s allowance for loan losses. Such agencies may
64
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
require the Bank to recognize additions to the allowance or additional write-downs based on their judgments about information available to them at the time of their examination.
Foreclosed Assets
Assets acquired through foreclosure or deed in lieu of foreclosure are carried at the lower of the outstanding loan balance at the time of foreclosure or fair value, less estimated costs to sell. Fair value is generally based on recent appraisals. When an asset is acquired, the excess of the loan balance over fair value, less estimated costs to sell, is charged to the allowance for loan losses. A reserve for foreclosed assets may be established to provide for possible write-downs and selling costs that occur subsequent to foreclosure. Foreclosed assets are carried net of the related reserve. Operating results from real estate owned, including rental income, operating expenses, and gains and losses realized from the sales of real estate owned, are recorded as incurred.
Banking Premises and Equipment
Land is carried at cost. Banking premises, furniture, fixtures and equipment are carried at cost, less accumulated depreciation, computed using the straight-line method based on their estimated useful lives (generally 25 to 40 years for buildings, and 3 to 5 years for furniture and equipment). Leasehold improvements, carried at cost, net of accumulated depreciation, are amortized over the terms of the leases or the estimated useful lives of the assets, whichever are shorter, using the straight-line method. Maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred.
Income Taxes
The Company uses the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in tax expense in the period that includes the enactment date. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are reported as a component of other assets on the consolidated statements of financial condition. The determination of whether deferred tax assets will be realizable is predicated on estimates of future taxable income. Such estimates are subject to management’s judgment. A valuation reserve is established when management is unable to conclude that it is more likely than not that it will realize deferred tax assets based on the nature and timing of these items. The Company recognizes, when applicable, interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in the provision for income taxes.
Trust Assets
Trust assets consisting of securities and other property (other than cash on deposit held by the Bank in fiduciary or agency capacities for customers of the Bank’s wholly owned subsidiary, Beacon Trust Company) are not included in the accompanying consolidated statements of financial condition because such properties are not assets of the Bank.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets of the Bank consist of goodwill, core deposit premiums, customer relationship premium and mortgage servicing rights. Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the estimated fair value of identifiable net assets acquired through purchase acquisitions. In accordance with GAAP, goodwill with an indefinite useful life is not amortized, but is evaluated for impairment on an annual basis, or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate potential impairment between annual measurement dates. Goodwill is analyzed for impairment each year at September 30th. As permitted by GAAP, the Company prepares a qualitative assessment in determining whether goodwill may be impaired. The factors considered in the assessment include macroeconomic conditions, industry and market conditions and overall financial performance of the Company, among others. The Company completed its annual goodwill impairment test as of September 30, 2017. Based upon its qualitative assessment of goodwill, the Company concluded that goodwill was not impaired and no further quantitative analysis was warranted.
Core deposit premiums represent the intangible value of depositor relationships assumed in purchase acquisitions and are amortized on an accelerated basis over 8.8 years. Customer relationship premiums represent the intangible value of customer relationships assumed in the purchase acquisition of Beacon and MDE, and are amortized on an accelerated basis over 12.0 years and 10.4 years, respectively. Mortgage servicing rights are recorded when purchased or when originated mortgage loans are sold, with servicing rights retained. Mortgage servicing rights are amortized on an accelerated method based upon the estimated lives of the related loans, adjusted for prepayments. Mortgage servicing rights are carried at the lower of amortized cost or fair value.
65
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Bank-owned Life Insurance
Bank-owned life insurance is accounted for using the cash surrender value method and is recorded at its realizable value.
Employee Benefit Plans
The Bank maintains a pension plan which covers full-time employees hired prior to April 1, 2003, the date on which the pension plan was frozen. The Bank’s policy is to fund at least the minimum contribution required by the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974. GAAP requires an employer to: (a) recognize in its statement of financial position the over-funded or under-funded status of a defined benefit postretirement plan measured as the difference between the fair value of plan assets and the benefit obligation; (b) measure a plan’s assets and its obligations that determine its funded status at the end of the employer’s fiscal year (with limited exceptions); and (c) recognize as a component of other comprehensive income, net of tax, the actuarial gains and losses and the prior service costs and credits that arise during the period.
The Bank has a 401(k) plan covering substantially all employees of the Bank. The Bank may match a percentage of the first 6% contributed by participants. The Bank’s matching contribution, if any, is determined by the Board of Directors in its sole discretion.
The Bank has an Employee Stock Ownership Plan (“ESOP”). The funds borrowed by the ESOP from the Company to purchase the Company’s common stock are being repaid from the Bank’s contributions and dividends paid on unallocated ESOP shares over a period of up to 30 years. The Company’s common stock not allocated to participants is recorded as a reduction of stockholders’ equity at cost. Compensation expense for the ESOP is based on the average price of the Company’s stock during each quarter and the amount of shares allocated during the quarter.
The Bank has an Equity Plan designed to provide competitive compensation for demonstrated performance and to align the interests of participants directly to increases in shareholder value. The Equity Plan provides for performance-vesting grants as well as time-vesting grants. Time-vesting stock awards, stock options and performance vesting stock awards that are based on a performance condition, such as return on average assets are valued on the closing stock price on the date of grant. Performance vesting stock awards and options that are based on a market condition, such as Total Shareholder Return, would be valued using a generally accepted statistical technique to simulate future stock prices for Provident and the components of the Peer Group which Provident would be measured against.
Expense related to time vesting stock awards and stock options is based on the fair value of the common stock on the date of the grant and on the fair value of the stock options on the date of the grant, respectively, and is recognized ratably over the vesting period of the awards. Performance vesting stock awards and stock options are either dependent upon a market condition or a performance condition. A market condition performance metric is tied to a stock price, either on an absolute basis, or a relative basis against peers, while a performance-condition is based on internal operations, such as earnings per share. The expense related to a market condition performance-vesting stock award or stock option requires an initial Monte Carlo simulation to determine grant date fair value, which will be recognized as a compensation expense regardless of actual payout, assuming that the executive is still employed at the end of the requisite service period. If pre-vesting termination (forfeiture) occurs, then any expense recognized to date can be reversed. The grant date fair value is recognized ratably over the performance period. The expense related to a performance condition stock award or stock option is based on the fair value of the award on the date of grant, adjusted periodically based upon the number of awards or options expected to be earned, recognized over the performance period.
In connection with the First Sentinel acquisition in July 2004, the Company assumed the First Savings Bank Directors’ Deferred Fee Plan (the “DDFP”). The DDFP was frozen prior to the acquisition. The Company recorded a deferred compensation equity instrument and corresponding contra-equity account for the value of the shares held by the DDFP at the July 14, 2004 acquisition date. These accounts will be liquidated as shares are distributed from the DDFP in accordance with the plan document. At December 31, 2017, there were 296,049 shares held by the DDFP.
The Bank maintains a non-qualified plan that provides supplemental benefits to certain executives who are prevented from receiving the full benefits contemplated by the 401(k) Plan’s and the ESOP’s benefit formulas under tax law limits for tax-qualified plans.
Post-retirement Benefits Other Than Pensions
The Bank provides post-retirement health care and life insurance plans to certain of its employees. The life insurance coverage is noncontributory to the participant. Participants contribute to the cost of medical coverage based on the employee’s
66
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
length of service with the Bank. The costs of such benefits are accrued based on actuarial assumptions from the date of hire to the date the employee is fully eligible to receive the benefits. On December 31, 2002, the Bank eliminated postretirement healthcare benefits for employees with less than 10 years of service. GAAP requires an employer to: (a) recognize in its statement of financial position the over-funded or under-funded status of a defined benefit post-retirement plan measured as the difference between the fair value of plan assets and the benefit obligation; (b) measure a plan’s assets and its obligations that determine its funded status as of the end of the employer’s fiscal year (with limited exceptions); and (c) recognize as a component of other comprehensive income, net of tax, the actuarial gains and losses and the prior service costs and credits that arise during the period.
Derivatives
The Company records all derivatives on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition at fair value. The accounting for changes in the fair value of derivatives depends on the intended use of the derivative, whether the Company has elected to designate a derivative in a hedging relationship and apply hedge accounting and whether the hedging relationship has satisfied the criteria necessary to apply hedge accounting. These interest rate derivatives result from a service provided to certain qualifying borrowers in a loan related transaction and, therefore, are not used to manage interest rate risk in the Company’s assets or liabilities. As such, all changes in the fair value of these derivatives are recognized directly in earnings.
The Company also uses interest rate swaps as part of its interest rate risk management strategy. Interest rate swaps designated as cash flow hedges, and which satisfy hedge accounting requirements, involve the receipt of variable amounts from a counterparty in exchange for the Company making fixed-rate payments over the life of the agreements without the exchange of the underlying notional amount. These derivatives were used to hedge the variable cash outflows associated with Federal Home Loan Bank borrowings. The effective portion of changes in the fair value of these derivatives are recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income, and are subsequently reclassified into earnings in the period that the hedged forecasted transaction affects earnings. The ineffective portion of the change in fair value of these derivatives are recognized directly in earnings.
The fair value of the Company's derivatives are determined using discounted cash flow analyses using observable market-based inputs.
Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income is divided into net income and other comprehensive income (loss). Other comprehensive income (loss) includes items previously recorded directly to equity, such as unrealized gains and losses on securities available for sale, unrealized gains and losses on derivatives and amortization related to post-retirement obligations. Comprehensive income is presented in a separate Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income.
Segment Reporting
The Company’s operations are solely in the financial services industry and include providing traditional banking and other financial services to its customers. The Company operates primarily in the geographical regions of northern and central New Jersey and eastern Pennsylvania. Management makes operating decisions and assesses performance based on an ongoing review of the Bank’s consolidated financial results. Therefore, the Company has a single operating segment for financial reporting purposes.
Earnings Per Share
Basic earnings per share is computed by dividing income available to common stockholders by the weighted average number of shares outstanding for the period. Diluted earnings per share reflects the potential dilution that could occur if securities or other contracts to issue common stock (such as stock options) were exercised or resulted in the issuance of common stock. These potentially dilutive shares would then be included in the weighted average number of shares outstanding for the period using the treasury stock method. Shares issued and shares reacquired during the period are weighted for the portion of the period that they were outstanding.
Impact of Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2018, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2018-02, "Income Statement-Reporting Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reclassification of Certain Tax Effects from Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income" to address a narrow-scope financial reporting issue that arose as a consequence of the change in the tax law. On December 22, 2017, the U.S. federal government enacted a tax bill, H.R.1, An Act to Provide for
67
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Reconciliation Pursuant to Titles II and V of the Concurrent Resolution on the Budget for Fiscal Year 2018 (Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017). The ASU permits a reclassification from accumulated other comprehensive income to retained earnings for stranded tax effects resulting from the newly enacted federal corporate income tax rate. The amount of the reclassification would be the difference between the historical corporate income tax rate of 35 percent and the newly enacted 21 percent corporate income tax rate. ASU 2018-02 is effective for all entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within those fiscal years with early adoption permitted, including adoption in any interim period, for (i) public business entities for reporting periods for which financial statements have not yet been issued and (ii) all other entities for reporting periods for which financial statements have not yet been made available for issuance. The changes are required to be applied retrospectively to each period (or periods) in which the effect of the change in the U.S. federal corporate income tax rate in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 is recognized. The Company early adopted ASU 2018-02, which resulted in the reclassification from accumulated other comprehensive income to retained earnings totaling $1.4 million, reflected in the Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders' Equity.
In August 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-12, Derivatives and Hedging: Targeted Improvements to Accounting for Hedging. The purpose of this updated guidance is to better align a company’s financial reporting for hedging activities with the economic objectives of those activities. ASU 2017-12 is effective for public business entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, with early adoption, including adoption in an interim period, permitted. ASU 2017-12 requires a modified retrospective transition method in which the Company will recognize the cumulative effect of the change on the opening balance of each affected component of equity in the statement of financial position as of the date of adoption. The Company is currently assessing the impact that the guidance will have on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In May 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-09, “Compensation-Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Scope of Modification Accounting”. This update provides guidance about changes to terms or conditions of a share-based payment award which would require modification accounting. In particular, an entity is required to account for the effects of a modification if the fair value, vesting condition or the equity/liability classification of the modified award is not the same immediately before and after a change to the terms and conditions of the award. ASU 2017-09 is effective on a prospective basis for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted. The Company's adoption of this guidance is not anticipated to have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In March 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-08, “Receivables - Nonrefundable Fees and Other Costs (Subtopic 310-20): Premium Amortization on Purchased Callable Debt Securities.” This ASU shortens the amortization period for premiums on callable debt securities by requiring that premiums be amortized to the first (or earliest) call date instead of as an adjustment to the yield over the contractual life. This change more closely aligns the accounting with the economics of a callable debt security and the amortization period with expectations that already are included in market pricing on callable debt securities. This ASU does not change the accounting for discounts on callable debt securities, which will continue to be amortized to the maturity date. This guidance includes only instruments that are held at a premium and have explicit call features. It does not include instruments that contain prepayment features, such as mortgage backed securities; nor does it include call options that are contingent upon future events or in which the timing or amount to be paid is not fixed. The effective date for this ASU is fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within the reporting period, with early adoption permitted. Transition is on a modified retrospective basis with an adjustment to retained earnings as of the beginning of the period of adoption. If early adopted in an interim period, adjustments should be reflected as of the beginning of the fiscal year that includes that interim period. The Company is currently assessing the impact this guidance will have on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In March 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-07, "Compensation - Retirement Benefits (Topic 715): Improving the Presentation of Net Periodic Pension Cost and Net Periodic Post-retirement Benefit Cost", which requires that companies disaggregate the service cost component from other components of net benefit cost. This update calls for companies that offer post-retirement benefits to present the service cost, which is the amount an employer has to set aside each quarter or fiscal year to cover the benefits, in the same line item with other current employee compensation costs. Other components of net benefit cost will be presented in the income statement separately from the service cost component and outside the subtotal of income from operations, if one is presented. ASU 2017-07 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company's adoption of this guidance will not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements, or disclosures.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-04, “Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment.” The main objective of this ASU is to simplify the accounting for goodwill impairment by requiring that impairment charges be based upon the first step in the current two-step impairment test under Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 350. Currently, if the fair value of a reporting unit is lower than its carrying amount (Step 1), an entity calculates any impairment charge by comparing the implied
68
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
fair value of goodwill with its carrying amount (Step 2). The implied fair value of goodwill is calculated by deducting the fair value of all assets and liabilities of the reporting unit from the reporting unit’s fair value as determined in Step 1. To determine the implied fair value of goodwill, entities estimate the fair value of any unrecognized intangible assets and any corporate-level assets or liabilities that were included in the determination of the carrying amount and fair value of the reporting unit in Step 1. Under ASU 2017-04, if a reporting unit’s carrying amount exceeds its fair value, an entity will record an impairment charge based on that difference. The impairment charge will be limited to the amount of goodwill allocated to that reporting unit. This standard eliminates the requirement to calculate a goodwill impairment charge using Step 2. ASU 2017-04 does not change the guidance on completing Step 1 of the goodwill impairment test. Under ASU 2017-04, an entity will still be able to perform the current optional qualitative goodwill impairment assessment before determining whether to proceed to Step 1. The standard will be applied prospectively and is effective for annual and interim impairment tests performed in periods beginning after December 15, 2019. Early adoption is permitted for annual and interim goodwill impairment testing dates after January 1, 2017. The Company does not expect ASU 2017-04 to have a significant impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-15, "Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments," a new standard which addresses diversity in practice related to eight specific cash flow issues: debt prepayment or extinguishment costs, settlement of zero-coupon debt instruments or other debt instruments with coupon interest rates that are insignificant in relation to the effective interest rate of the borrowing, contingent consideration payments made after a business combination, proceeds from the settlement of insurance claims, proceeds from the settlement of corporate-owned life insurance policies (including bank-owned life insurance policies), distributions received from equity method investees, beneficial interests in securitization transactions and separately identifiable cash flows and application of the predominance principle. ASU 2016-15 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Entities will apply the standard’s provisions using a retrospective transition method to each period presented. If it is impracticable to apply the amendments retrospectively for some of the issues, the amendments for those issues would be applied prospectively as of the earliest date practicable. The Company's adoption of this guidance is not anticipated to have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, “Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments.” The main objective of this ASU is to provide financial statement users with more decision-useful information about the expected credit losses on financial instruments by a reporting entity at each reporting date. The amendments in this ASU require financial assets measured at amortized cost to be presented at the net amount expected to be collected. The allowance for credit losses would represent a valuation account that would be deducted from the amortized cost basis of the financial asset(s) to present the net carrying value at the amount expected to be collected on the financial asset. The income statement would reflect the measurement of credit losses for newly recognized financial assets, as well as the expected increases or decreases of expected credit losses that have taken place during the period. The measurement of expected credit losses would be based on relevant information about past events, including historical experience, current conditions, and reasonable and supportable forecasts that affect the collectability of the reported amount. An entity will be required to use judgment in determining the relevant information and estimation methods that are appropriate in its circumstances. The amendments in ASU 2016-13 are effective for fiscal years, including interim periods, beginning after December 15, 2019. Early adoption of this ASU is permitted for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact of ASU 2016-13 on the consolidated financial statements. In that regard, the Company has formed a cross-functional working group, under the direction of the Chief Credit Officer, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Risk Officer. The working group is comprised of individuals from various functional areas including credit, risk management, finance and information technology, among others. The Company is currently developing an implementation plan to include assessment of processes, portfolio segmentation, model development, system requirements and the identification of data and resource needs, among other things. Also, the Company is currently evaluating third-party vendor solutions to assist us in the application of the ASU 2016-13. The adoption of the ASU 2016-13 may result in an increase in the allowance for loan losses as a result of changing from an "incurred loss" model, which encompasses allowances for current known and inherent losses within the portfolio, to an "expected loss" model, which encompasses allowances for losses expected to be incurred over the life of the portfolio. Furthermore, ASU 2016-13 will necessitate establishing an allowance for expected credit losses on debt securities. The Company is currently unable to reasonably estimate the impact of adopting ASU 2016-13, it is expected that the impact of adoption will be significantly influenced by the composition, characteristics and quality of our loan and securities portfolios as well as the prevailing economic conditions and forecasts as of the adoption date.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, "Leases (Topic 842).” This ASU requires all lessees to recognize a lease liability and a right-of-use asset, measured at the present value of the future minimum lease payments, at the lease commencement date. Lessor accounting remains largely unchanged under the new guidance. The guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim reporting periods within that reporting period, with early adoption permitted. A
69
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
modified retrospective approach must be applied for leases existing at, or entered into after, the beginning of the earliest comparative period presented in the financial statements. The Company is currently assessing the impact that the guidance will have on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
In January 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-01, "Financial Instruments - Overall: Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Liabilities." This ASU addresses certain aspects of recognition, measurement, presentation, and disclosure of financial instruments. This amendment supersedes the guidance to classify equity securities with readily determinable fair values into different categories, requires equity securities, except equity method investments, to be measured at fair value with changes in the fair value recognized through net income, and simplifies the impairment assessment of equity investments without readily determinable fair values. The amendment requires public business entities that are required to disclose the fair value of financial instruments measured at amortized cost on the balance sheet to measure that fair value using the exit price notion. The amendment requires an entity to present separately in other comprehensive income the portion of the total change in the fair value of a liability resulting from a change in the instrument-specific credit risk when the entity has elected to measure the liability at fair value in accordance with the fair value option. The amendment requires separate presentation of financial assets and financial liabilities by measurement category and form of financial asset on the balance sheet or in the accompanying notes to the financial statements. The amendment reduces diversity in current practice by clarifying that an entity should evaluate the need for a valuation allowance on a deferred tax asset related to available for sale securities in combination with the entity’s other deferred tax assets. This amendment is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Entities should apply the amendment by means of a cumulative-effect adjustment as of the beginning of the fiscal year of adoption, with the exception of the amendment related to equity securities without readily determinable fair values, which should be applied prospectively to equity investments that exist as of the date of adoption. The Company's adoption of this guidance is not anticipated to have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606)." The objective of this amendment is to clarify the principles for recognizing revenue and to develop a common revenue standard for U.S. GAAP and IFRS. This update affects any entity that either enters into contracts with customers to transfer goods or services or enters into contracts for the transfer of nonfinancial assets unless those contracts are in the scope of other standards. The ASU is effective for public business entities for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and early adoption is permitted. Subsequently, the FASB issued the following standards related to ASU 2014-09: ASU 2016-08, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Principal versus Agent Considerations;” ASU 2016-10, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Identifying Performance Obligations and Licensing;” ASU 2016-11, “Revenue Recognition (Topic 605) and Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815): Rescission of SEC Guidance Because of Accounting Standards Updates 2014-09 and 2014-16 Pursuant to Staff Announcements at the March 3, 2016 EITF Meeting;” and ASU 2016-12, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Narrow-Scope Improvements and Practical Expedients.” These amendments are intended to improve and clarify the implementation guidance of ASU 2014-09 and have the same effective date as the original standard. The Company's revenue is comprised of net interest income on interest earning assets and liabilities and non-interest income. The scope of guidance explicitly excludes net interest income as well as other revenues associated with financial assets and liabilities, including loans, leases, securities and derivatives. Accordingly, the majority of the Company's revenues will not be affected. The Company formed a working group to guide implementation efforts including the identification of revenue within the scope of the guidance, as well as the evaluation of revenue contracts and the respective performance obligations within those contracts. The Company has completed its evaluation of this guidance and concluded that there are no material changes related to the timing or amount of revenue recognition. The Company will disaggregate significant categories of revenue within the scope of the guidance and provide the required disclosures starting in the first quarter of 2018. The Company will adopt this guidance in the first quarter of 2018.
(2) Stockholders’ Equity
On January 15, 2003, the Bank completed its plan of conversion, and the Bank became a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company. The Company sold 59.6 million shares of common stock (par value $0.01 per share) at $10.00 per share. The Company received net proceeds in the amount of $567.2 million.
In connection with the Bank’s commitment to its community, the plan of conversion provided for the establishment of a charitable foundation. Provident donated $4.8 million in cash and 1.92 million of authorized but unissued shares of common stock to the foundation, which amounted to $24.0 million in aggregate. The Company recognized an expense, net of income tax benefit, equal to the cash and fair value of the stock during 2003. Conversion costs were deferred and deducted from the proceeds of the shares sold in the offering.
70
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Upon completion of the plan of conversion, a “liquidation account” was established in an amount equal to the total equity of the Bank as of the latest practicable date prior to the conversion. The liquidation account was established to provide a limited priority claim to the assets of the Bank to “eligible account holders” and “supplemental eligible account holders” as defined in the Plan, who continue to maintain deposits in the Bank after the conversion. In the unlikely event of a complete liquidation of the Bank, and only in such event, each eligible account holder and supplemental eligible account holder would receive a liquidation distribution, prior to any payment to the holder of the Bank’s common stock. This distribution would be based upon each eligible account holder’s and supplemental eligible account holder’s proportionate share of the then total remaining qualifying deposits. At December 31, 2017, the liquidation account, which is an off-balance sheet memorandum account, amounted to $11.5 million.
(3) Restrictions on Cash and Due from Banks
Included in cash on hand and due from banks at December 31, 2017 and 2016 was $39.5 million and $36.7 million, respectively, representing reserves required by banking regulations.
(4) Investment Securities Held to Maturity
Investment securities held to maturity at December 31, 2017 and 2016 are summarized as follows (in thousands):
2017 | ||||||||||||
Amortized cost | Gross unrealized gains | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | |||||||||
Agency obligations | $ | 4,308 | — | (87 | ) | 4,221 | ||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 382 | 14 | — | 396 | ||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 462,942 | 9,280 | (1,738 | ) | 470,484 | |||||||
Corporate obligations | 10,020 | 1 | (83 | ) | 9,938 | |||||||
$ | 477,652 | 9,295 | (1,908 | ) | 485,039 | |||||||
2016 | ||||||||||||
Amortized cost | Gross unrealized gains | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | |||||||||
Agency obligations | $ | 4,306 | 2 | (83 | ) | 4,225 | ||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 893 | 31 | — | 924 | ||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 473,653 | 6,635 | (5,436 | ) | 474,852 | |||||||
Corporate obligations | 9,331 | 7 | (52 | ) | 9,286 | |||||||
$ | 488,183 | 6,675 | (5,571 | ) | 489,287 | |||||||
The Company generally purchases securities for long-term investment purposes, and differences between carrying and fair values may fluctuate during the investment period. Investment securities held to maturity having a carrying value of $409.7 million and $384.8 million at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, were pledged to secure other borrowings, securities sold under repurchase agreements and government deposits.
The amortized cost and fair value of investment securities held to maturity at December 31, 2017 by contractual maturity are shown below (in thousands). Expected maturities may differ from contractual maturities due to prepayment or early call privileges of the issuer.
71
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
2017 | ||||||
Amortized cost | Fair value | |||||
Due in one year or less | $ | 7,123 | 7,147 | |||
Due after one year through five years | 67,352 | 67,915 | ||||
Due after five years through ten years | 260,937 | 265,279 | ||||
Due after ten years | 141,858 | 144,302 | ||||
$ | 477,270 | 484,643 | ||||
Mortgage-backed securities totaling $382,000 at amortized cost and $396,000 at fair value are excluded from the table above as their expected lives are expected to be shorter than the contractual maturity date due to principal prepayments.
During 2017, the Company recognized gains of $60,000 and losses of $3,000 related to calls on securities in the held to maturity portfolio, with total proceeds from the calls totaling $32.9 million. There were no sales of securities from the held to maturity portfolio for the year ended December 31, 2017.
For the 2016 period, the Company recognized gains of $15,000 and losses of $1,000 related to calls on securities in the held to maturity portfolio, with total proceeds from the calls totaling $45.9 million. There were no sales of securities from the held to maturity portfolio for the year ended December 31, 2016.
For the 2015 period, the Company recognized gains of $8,000 and no losses related to calls on certain securities in the held to maturity portfolio, with total proceeds from the calls totaling $27.0 million. There were no sales of securities from the held to maturity portfolio for the year ended December 31, 2015.
The following table represents the Company’s disclosure on investment securities held to maturity with temporary impairment (in thousands):
December 31, 2017 Unrealized Losses | ||||||||||||||||||
Less than 12 months | 12 months or longer | Total | ||||||||||||||||
Fair value | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | Gross unrealized losses | |||||||||||||
Agency obligations | $ | 3,821 | (87 | ) | — | — | 3,821 | (87 | ) | |||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 37,317 | (295 | ) | 49,488 | (1,443 | ) | 86,805 | (1,738 | ) | |||||||||
Corporate obligations | 9,662 | (83 | ) | — | 9,662 | (83 | ) | |||||||||||
$ | 50,800 | (465 | ) | 49,488 | (1,443 | ) | 100,288 | (1,908 | ) | |||||||||
December 31, 2016 Unrealized Losses | ||||||||||||||||||
Less than 12 months | 12 months or longer | Total | ||||||||||||||||
Fair value | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | Gross unrealized losses | |||||||||||||
Agency obligations | $ | 3,525 | (83 | ) | — | — | 3,525 | (83 | ) | |||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 172,152 | (5,132 | ) | 6,617 | (304 | ) | 178,769 | (5,436 | ) | |||||||||
Corporate obligations | 4,697 | (52 | ) | — | 4,697 | (52 | ) | |||||||||||
$ | 180,374 | (5,267 | ) | 6,617 | (304 | ) | 186,991 | (5,571 | ) | |||||||||
The Company estimates the loss projections for each non-agency mortgage-backed security by stressing the individual loans collateralizing the security and applying a range of expected default rates, loss severities, and prepayment speeds in conjunction with the underlying credit enhancement for each security. Based on specific assumptions about collateral and vintage, a range of possible cash flows was identified to determine whether other-than-temporary impairment existed during the year ended December 31, 2017. Based on its detailed review of the securities available for sale portfolio, the Company believes that as of December 31, 2017, securities with unrealized loss positions shown above do not represent impairments that are other-than-
72
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
temporary. The Company does not have the intent to sell securities in a temporary loss position at December 31, 2017, nor is it more likely than not that the Company will be required to sell the securities before the anticipated recovery.
The number of securities in an unrealized loss position as of December 31, 2017 totaled 184, compared with 332 at December 31, 2016. All temporarily impaired investment securities were investment grade at December 31, 2017.
(5) Securities Available for Sale
Securities available for sale at December 31, 2017 and 2016 are summarized as follows (in thousands):
2017 | ||||||||||||
Amortized cost | Gross unrealized gains | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | |||||||||
Agency obligations | $ | 19,014 | — | (9 | ) | 19,005 | ||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 993,548 | 4,914 | (10,095 | ) | 988,367 | |||||||
State and municipal obligations | 3,259 | 129 | — | 3,388 | ||||||||
Corporate obligations | 26,047 | 359 | (12 | ) | 26,394 | |||||||
Equity securities | 417 | 241 | — | 658 | ||||||||
$ | 1,042,285 | 5,643 | (10,116 | ) | 1,037,812 | |||||||
2016 | ||||||||||||
Amortized cost | Gross unrealized gains | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | |||||||||
U.S. Treasury obligations | $ | 7,995 | 13 | — | 8,008 | |||||||
Agency obligations | 57,123 | 90 | (25 | ) | 57,188 | |||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 952,992 | 7,249 | (8,380 | ) | 951,861 | |||||||
State and municipal obligations | 3,727 | 19 | (3 | ) | 3,743 | |||||||
Corporate obligations | 19,013 | 35 | (11 | ) | 19,037 | |||||||
Equity securities | 397 | 152 | — | 549 | ||||||||
$ | 1,041,247 | 7,558 | (8,419 | ) | 1,040,386 | |||||||
Securities available for sale having a carrying value of $939.4 million and $720.4 million at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, are pledged to secure other borrowings and securities sold under repurchase agreements.
The amortized cost and fair value of securities available for sale at December 31, 2017, by contractual maturity, are shown below (in thousands). Expected maturities may differ from contractual maturities due to prepayment or early call privileges of the issuer.
2017 | ||||||
Amortized cost | Fair value | |||||
Due in one year or less | $ | 20,406 | 20,390 | |||
Due after one year through five years | 3,009 | 3,048 | ||||
Due after five years through ten years | 24,905 | 25,349 | ||||
$ | 48,320 | 48,787 | ||||
Mortgage-backed securities totaling $993.5 million at amortized cost and $988.4 million at fair value are excluded from the table above as their expected lives are expected to be shorter than the contractual maturity date due to principal prepayments. Also excluded from the table above are equity securities of $417,000 at amortized cost and $658,000 at fair value.
During 2017, there were no sales or calls of securities from the available for sale portfolio. For the 2016 period, proceeds from the sale of securities available for sale were $3.4 million resulting in gross gains of $95,000 and gross losses of $45,000; there were no calls of securities from the available for sale portfolio for the year ended December 31, 2016.
73
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
For the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company did not incur an other-than-temporary impairment charge on securities available for sale.
The following table represents the Company’s disclosure on securities available for sale with temporary impairment (in thousands):
December 31, 2017 Unrealized Losses | ||||||||||||||||||
Less than 12 months | 12 months or longer | Total | ||||||||||||||||
Fair value | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | Gross unrealized losses | |||||||||||||
Agency obligations | $ | 12,006 | (8 | ) | 6,999 | (1 | ) | 19,005 | (9 | ) | ||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 420,746 | (3,936 | ) | 235,056 | (6,159 | ) | 655,802 | (10,095 | ) | |||||||||
Corporate obligations | — | — | 989 | (12 | ) | 989 | (12 | ) | ||||||||||
$ | 432,752 | (3,944 | ) | 243,044 | (6,172 | ) | 675,796 | (10,116 | ) | |||||||||
December 31, 2016 Unrealized Losses | ||||||||||||||||||
Less than 12 months | 12 months or longer | Total | ||||||||||||||||
Fair value | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | Gross unrealized losses | Fair value | Gross unrealized losses | |||||||||||||
Agency obligations | $ | 14,000 | (25 | ) | — | — | 14,000 | (25 | ) | |||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 553,629 | (8,377 | ) | 65 | (3 | ) | 553,694 | (8,380 | ) | |||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 661 | (3 | ) | — | — | 661 | (3 | ) | ||||||||||
Corporate obligations | — | 990 | (11 | ) | 990 | (11 | ) | |||||||||||
$ | 568,290 | (8,405 | ) | 1,055 | (14 | ) | 569,345 | (8,419 | ) | |||||||||
The Company estimates the loss projections for each non-agency mortgage-backed security by stressing the individual loans collateralizing the security and applying a range of expected default rates, loss severities, and prepayment speeds in conjunction with the underlying credit enhancement for each security. Based on specific assumptions about collateral and vintage, a range of possible cash flows was identified to determine whether other-than-temporary impairment existed during the year ended December 31, 2017. Based on its detailed review of the securities available for sale portfolio, the Company believes that as of December 31, 2017, securities with unrealized loss positions shown above do not represent impairments that are other-than-temporary. The Company does not have the intent to sell securities in a temporary loss position at December 31, 2017, nor is it more likely than not that the Company will be required to sell the securities before the anticipated recovery.
The number of securities in an unrealized loss position as of December 31, 2017 totaled 122, compared with 87 at December 31, 2016. There were two private label mortgage-backed securities in an unrealized loss position at December 31, 2017, with an amortized cost of $99,000 and unrealized losses totaling $2,000. Both private label mortgage-backed securities were investment grade at December 31, 2017.
74
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(6) Loans Receivable and Allowance for Loan Losses
Loans receivable at December 31, 2017 and 2016 are summarized as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | |||||
Mortgage loans: | ||||||
Residential | $ | 1,142,347 | 1,211,672 | |||
Commercial | 2,171,056 | 1,978,569 | ||||
Multi-family | 1,403,885 | 1,402,054 | ||||
Construction | 392,580 | 264,814 | ||||
Total mortgage loans | 5,109,868 | 4,857,109 | ||||
Commercial loans | 1,745,138 | 1,630,444 | ||||
Consumer loans | 473,957 | 516,755 | ||||
Total gross loans | 7,328,963 | 7,004,308 | ||||
Purchased credit-impaired ("PCI") loans | 969 | 1,272 | ||||
Premiums on purchased loans | 4,029 | 4,968 | ||||
Unearned discounts | (36 | ) | (39 | ) | ||
Net deferred fees | (8,207 | ) | (7,023 | ) | ||
Total loans | $ | 7,325,718 | 7,003,486 | |||
Premiums and discounts on purchased loans are amortized over the lives of the loans as an adjustment to yield. Required reductions due to loan prepayments are charged against interest income. For the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, $1.0 million, $1.3 million and $1.1 million decreased interest income, respectively, as a result of prepayments and normal amortization.
The following table summarizes the aging of loans receivable by portfolio segment and class of loans, excluding PCI loans (in thousands):
At December 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||
30-59 Days | 60-89 Days | Non-accrual | 90 days or more past due and accruing | Total Past Due | Current | Total Loans Receivable | |||||||||||||||
Mortgage loans: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Residential | $ | 7,809 | 4,325 | 8,105 | — | 20,239 | 1,122,108 | 1,142,347 | |||||||||||||
Commercial | 1,486 | — | 7,090 | — | 8,576 | 2,162,480 | 2,171,056 | ||||||||||||||
Multi-family | — | — | — | — | — | 1,403,885 | 1,403,885 | ||||||||||||||
Construction | — | — | — | — | — | 392,580 | 392,580 | ||||||||||||||
Total mortgage loans | 9,295 | 4,325 | 15,195 | — | 28,815 | 5,081,053 | 5,109,868 | ||||||||||||||
Commercial loans | 551 | 406 | 17,243 | — | 18,200 | 1,726,938 | 1,745,138 | ||||||||||||||
Consumer loans | 2,465 | 487 | 2,491 | — | 5,443 | 468,514 | 473,957 | ||||||||||||||
Total gross loans | $ | 12,311 | 5,218 | 34,929 | — | 52,458 | 7,276,505 | 7,328,963 | |||||||||||||
75
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
At December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||
30-59 Days | 60-89 Days | Non-accrual | 90 days or more past due and accruing | Total Past Due | Current | Total Loans Receivable | |||||||||||||||
Mortgage loans: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Residential | $ | 5,891 | 6,563 | 12,021 | — | 24,475 | 1,187,197 | 1,211,672 | |||||||||||||
Commercial | — | 80 | 7,493 | — | 7,573 | 1,970,996 | 1,978,569 | ||||||||||||||
Multi-family | — | — | 553 | — | 553 | 1,401,501 | 1,402,054 | ||||||||||||||
Construction | — | — | 2,517 | — | 2,517 | 262,297 | 264,814 | ||||||||||||||
Total mortgage loans | 5,891 | 6,643 | 22,584 | — | 35,118 | 4,821,991 | 4,857,109 | ||||||||||||||
Commercial loans | 1,656 | 357 | 16,787 | — | 18,800 | 1,611,644 | 1,630,444 | ||||||||||||||
Consumer loans | 2,561 | 1,199 | 3,030 | — | 6,790 | 509,965 | 516,755 | ||||||||||||||
Total gross loans | $ | 10,108 | 8,199 | 42,401 | — | 60,708 | 6,943,600 | 7,004,308 | |||||||||||||
Included in loans receivable are loans for which the accrual of interest income has been discontinued due to deterioration in the financial condition of the borrowers. The principal amount of these nonaccrual loans was $34.9 million and $42.4 million at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. There were no loans ninety days or greater past due and still accruing interest at December 31, 2017 and 2016.
If the non-accrual loans had performed in accordance with their original terms, interest income would have increased by $1.9 million, $2.2 million and $1.2 million, for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The amount of cash basis interest income that was recognized on impaired loans during the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 was $1.8 million, $1.5 million and $1.9 million respectively.
The Company defines an impaired loan as a non-homogeneous loan greater than $1.0 million for which it is probable, based on current information, that the Bank will not collect all amounts due under the contractual terms of the loan agreement. Impaired loans also include all loans modified as troubled debt restructurings (“TDRs”). A loan is deemed to be a TDR when a loan modification resulting in a concession is made by the Bank in an effort to mitigate potential loss arising from a borrower’s financial difficulty. Smaller balance homogeneous loans including residential mortgages and other consumer loans are evaluated collectively for impairment and are excluded from the definition of impaired loans, unless modified as TDRs. The Company separately calculates the reserve for loan loss on impaired loans. The Company may recognize impairment of a loan based upon: (1) the present value of expected cash flows discounted at the effective interest rate; or (2) if a loan is collateral dependent, the fair value of collateral; or (3) the market price of the loan. Additionally, if impaired loans have risk characteristics in common, those loans may be aggregated and historical statistics may be used as a means of measuring those impaired loans.
The Company uses third-party appraisals to determine the fair value of the underlying collateral in its analysis of collateral dependent impaired loans. A third-party appraisal is generally ordered as soon as a loan is designated as a collateral dependent impaired loan and updated annually, or more frequently if required.
A specific allocation of the allowance for loan losses is established for each impaired loan with a carrying balance greater than the collateral’s fair value, less estimated costs to sell. Charge-offs are generally taken for the amount of the specific allocation when operations associated with the respective property cease and it is determined that collection of amounts due will be derived primarily from the disposition of the collateral. At each fiscal quarter end, if a loan is designated as a collateral dependent impaired loan and the third party appraisal has not yet been received, an evaluation of all available collateral is made using the best information available at the time, including rent rolls, borrower financial statements and tax returns, prior appraisals, management’s knowledge of the market and collateral, and internally prepared collateral valuations based upon market assumptions regarding vacancy and capitalization rates, each as and where applicable. Once the appraisal is received and reviewed, the specific reserves are adjusted to reflect the appraised value. The Company believes there have been no significant time lapses as a result of this process.
At December 31, 2017, there were 149 impaired loans totaling $52.0 million, of which 141 loans totaling $41.7 million were TDRs. Included in this total were 125 TDRs related to 121 borrowers totaling $31.7 million that were performing in accordance with their restructured terms and which continued to accrue interest at December 31, 2017. At December 31, 2016, there were 141 impaired loans totaling $52.0 million, of which 136 loans totaling $41.6 million were TDRs. Included in this total were 114 TDRs related to 110 borrowers totaling $29.9 million that were performing in accordance with their restructured terms and which continued to accrue interest at December 31, 2016.
76
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Loans receivable summarized by portfolio segment and impairment method, excluding PCI loans are as follows (in thousands):
At December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||
Mortgage loans | Commercial loans | Consumer loans | Total Portfolio Segments | |||||||||
Individually evaluated for impairment | $ | 28,459 | 21,223 | 2,359 | 52,041 | |||||||
Collectively evaluated for impairment | 5,081,409 | 1,723,915 | 471,598 | 7,276,922 | ||||||||
Total gross loans | $ | 5,109,868 | 1,745,138 | 473,957 | 7,328,963 | |||||||
At December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
Mortgage loans | Commercial loans | Consumer loans | Total Portfolio Segments | |||||||||
Individually evaluated for impairment | $ | 29,551 | 20,255 | 2,213 | 52,019 | |||||||
Collectively evaluated for impairment | 4,827,558 | 1,610,189 | 514,542 | 6,952,289 | ||||||||
Total gross loans | $ | 4,857,109 | 1,630,444 | 516,755 | 7,004,308 | |||||||
The allowance for loan losses is summarized by portfolio segment and impairment classification, excluding PCI loans as follows (in thousands):
At December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||
Mortgage loans | Commercial loans | Consumer loans | Total Portfolio Segments | Unallocated | Total | |||||||||||||
Individually evaluated for impairment | $ | 1,486 | 1,134 | 70 | 2,690 | — | 2,690 | |||||||||||
Collectively evaluated for impairment | 26,566 | 28,680 | 2,259 | 57,505 | — | 57,505 | ||||||||||||
Total | $ | 28,052 | 29,814 | 2,329 | 60,195 | — | 60,195 | |||||||||||
At December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||
Mortgage loans | Commercial loans | Consumer loans | Total Portfolio Segments | Unallocated | Total | |||||||||||||
Individually evaluated for impairment | $ | 1,986 | 268 | 80 | 2,334 | — | 2,334 | |||||||||||
Collectively evaluated for impairment | 27,640 | 28,875 | 3,034 | 59,549 | — | 59,549 | ||||||||||||
Total | $ | 29,626 | 29,143 | 3,114 | 61,883 | — | 61,883 | |||||||||||
Loan modifications to borrowers experiencing financial difficulties that are considered TDRs primarily involve lowering the monthly payments on such loans through either a reduction in interest rate below a market rate, an extension of the term of the loan without a corresponding adjustment to the risk premium reflected in the interest rate, or a combination of these two methods. These modifications generally do not result in the forgiveness of principal or accrued interest. In addition, the Company attempts to obtain additional collateral or guarantor support when modifying such loans. If the borrower has demonstrated performance under the previous terms and our underwriting process shows the borrower has the capacity to continue to perform under the restructured terms, the loan will continue to accrue interest. Non-accruing restructured loans may be returned to accrual status when there has been a sustained period of repayment performance (generally six consecutive months of payments) and both principal and interest are deemed collectible.
77
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
The following tables present the number of loans modified as TDRs during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 and their balances immediately prior to the modification date and post-modification as of December 31, 2017 and 2016.
Year Ended December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||
Troubled Debt Restructurings | Number of Loans | Pre-Modification Outstanding Recorded Investment | Post-Modification Outstanding Recorded Investment | |||||||
($ in thousands) | ||||||||||
Mortgage loans: | ||||||||||
Residential | 5 | $ | 2,468 | 2,260 | ||||||
Total mortgage loans | 5 | $ | 2,468 | 2,260 | ||||||
Commercial loans | 1 | 874 | 874 | |||||||
Consumer loans | 2 | 262 | 257 | |||||||
Total restructured loans | 8 | $ | 3,604 | 3,391 | ||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||
Troubled Debt Restructurings | Number of Loans | Pre-Modification Outstanding Recorded Investment | Post-Modification Outstanding Recorded Investment | |||||||
($ in thousands) | ||||||||||
Commercial loans | 1 | $ | 1,300 | 1,300 | ||||||
Total restructured loans | 1 | $ | 1,300 | 1,300 | ||||||
All TDRs are impaired loans, which are individually evaluated for impairment, as previously discussed. Estimated collateral values of collateral dependent impaired loans modified during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 exceeded the carrying amounts of such loans. During the year ended December 31, 2017, there were $5.1 million of charge-offs recorded on collateral dependent impaired loans. There were no charge-offs recorded on collateral dependent impaired loans for the same period last year. The allowance for loan losses associated with the TDRs presented in the preceding tables totaled $166,000 and $187,000 at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively and were included in the allowance for loan losses for loans individually evaluated for impairment.
The TDRs presented in the preceding tables had a weighted average modified interest rate of approximately 4.18% and 5.25%, compared to a yield of 4.19% and 4.25% prior to modification for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
There were no loans modified as TDRs within the previous 12 months from both December 31, 2017 and 2016, which had a payment default (90 days or more past due) during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016.
TDRs that subsequently default are considered collateral dependent impaired loans and are evaluated for impairment based on the estimated fair value of the underlying collateral less expected selling costs.
PCI loans are loans acquired at a discount primarily due to deteriorated credit quality. These loans are accounted for at fair value, based upon the present value of expected future cash flows, with no related allowance for loan losses. At December 31, 2017, PCI loans totaled $1.0 million, compared to $1.3 million at December 31, 2016. The $303,000 decrease from December 31, 2016 was largely due to the full repayment and greater than projected cash flows on certain PCI loans.
78
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
The following table summarizes the changes in the accretable yield for PCI loans for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 (in thousands):
Year ended December 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Beginning balance | $ | 200 | 676 | ||||
Acquisition | — | — | |||||
Accretion | (320 | ) | (1,417 | ) | |||
Reclassification from non-accretable difference | 221 | 941 | |||||
Ending balance | $ | 101 | 200 | ||||
The activity in the allowance for loan losses for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 is as follows (in thousands):
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Balance at beginning of period | $ | 61,883 | 61,424 | 61,734 | |||||
Provision charged to operations | 5,600 | 5,400 | 4,350 | ||||||
Recoveries of loans previously charged off | 1,653 | 2,009 | 4,168 | ||||||
Loans charged off | (8,941 | ) | (6,950 | ) | (8,828 | ) | |||
Balance at end of period | $ | 60,195 | 61,883 | 61,424 | |||||
The activity in the allowance for loan losses by portfolio segment for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 are as follows (in thousands):
For the Year Ended December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||
Mortgage loans | Commercial loans | Consumer loans | Total Portfolio Segments | Unallocated | Total | |||||||||||||
Balance at beginning of period | $ | 29,626 | 29,143 | 3,114 | 61,883 | — | 61,883 | |||||||||||
Provision charged to operations | (1,139 | ) | 7,058 | (319 | ) | 5,600 | — | 5,600 | ||||||||||
Recoveries of loans previously charged off | 66 | 800 | 787 | 1,653 | — | 1,653 | ||||||||||||
Loans charged off | (501 | ) | (7,187 | ) | (1,253 | ) | (8,941 | ) | — | (8,941 | ) | |||||||
Balance at end of period | $ | 28,052 | 29,814 | 2,329 | 60,195 | — | 60,195 | |||||||||||
For the Year Ended December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||
Mortgage loans | Commercial loans | Consumer loans | Total Portfolio Segments | Unallocated | Total | |||||||||||||
Balance at beginning of period | $ | 32,094 | 25,829 | 3,501 | 61,424 | — | 61,424 | |||||||||||
Provision charged to operations | (2,028 | ) | 7,606 | (178 | ) | 5,400 | — | 5,400 | ||||||||||
Recoveries of loans previously charged off | 628 | 570 | 811 | 2,009 | — | 2,009 | ||||||||||||
Loans charged off | (1,068 | ) | (4,862 | ) | (1,020 | ) | (6,950 | ) | — | (6,950 | ) | |||||||
Balance at end of period | $ | 29,626 | 29,143 | 3,114 | 61,883 | — | 61,883 | |||||||||||
79
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Impaired loans receivable by class, excluding PCI loans are summarized as follows (in thousands):
At December 31, 2017 | At December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unpaid Principal Balance | Recorded Investment | Related Allowance | Average Recorded Investment | Interest Income Recognized | Unpaid Principal Balance | Recorded Investment | Related Allowance | Average Recorded Investment | Interest Income Recognized | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Loans with no related allowance | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mortgage loans: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Residential | $ | 13,239 | 10,477 | — | 10,552 | 479 | $ | 10,691 | 7,881 | — | 8,027 | 484 | |||||||||||||||||||
Commercial | 5,037 | 4,908 | — | 5,022 | 12 | 1,556 | 1,556 | — | 1,586 | 40 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Multi-family | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Construction | — | — | — | — | — | 2,553 | 2,517 | — | 2,514 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total | 18,276 | 15,385 | — | 15,574 | 491 | 14,800 | 11,954 | — | 12,127 | 524 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial loans | 19,196 | 14,984 | — | 15,428 | 395 | 21,830 | 18,874 | — | 13,818 | 259 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Consumer loans | 1,582 | 1,041 | — | 1,150 | 69 | 1,493 | 981 | — | 1,026 | 59 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total loans | $ | 39,054 | 31,410 | — | 32,152 | 955 | $ | 38,123 | 31,809 | — | 26,971 | 842 | |||||||||||||||||||
Loans with an allow-ance recorded | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mortgage loans: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Residential | $ | 13,052 | 12,010 | 1,351 | 12,150 | 475 | $ | 14,169 | 13,520 | 1,716 | 13,705 | 519 | |||||||||||||||||||
Commercial | 1,064 | 1,064 | 135 | 1,076 | 54 | 4,138 | 4,077 | 270 | 4,111 | 55 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Multi-family | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Construction | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total | 14,116 | 13,074 | 1,486 | 13,226 | 529 | 18,307 | 17,597 | 1,986 | 17,816 | 574 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial loans | 7,097 | 6,239 | 1,134 | 7,318 | 208 | 1,381 | 1,381 | 268 | 5,956 | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Consumer loans | 1,329 | 1,318 | 70 | 1,349 | 64 | 1,242 | 1,232 | 80 | 1,259 | 66 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total loans | $ | 22,542 | 20,631 | 2,690 | 21,893 | 801 | $ | 20,930 | 20,210 | 2,334 | 25,031 | 644 | |||||||||||||||||||
Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mortgage loans: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Residential | $ | 26,291 | 22,487 | 1,351 | 22,702 | 954 | $ | 24,860 | 21,401 | 1,716 | 21,732 | 1,003 | |||||||||||||||||||
Commercial | 6,101 | 5,972 | 135 | 6,098 | 66 | 5,694 | 5,633 | 270 | 5,697 | 95 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Multi-family | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Construction | — | — | — | — | — | 2,553 | 2,517 | — | 2,514 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total | 32,392 | 28,459 | 1,486 | 28,800 | 1,020 | 33,107 | 29,551 | 1,986 | 29,943 | 1,098 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial loans | 26,293 | 21,223 | 1,134 | 22,746 | 603 | 23,211 | 20,255 | 268 | 19,774 | 263 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Consumer loans | 2,911 | 2,359 | 70 | 2,499 | 133 | 2,735 | 2,213 | 80 | 2,285 | 125 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total loans | $ | 61,596 | 52,041 | 2,690 | 54,045 | 1,756 | $ | 59,053 | 52,019 | 2,334 | 52,002 | 1,486 | |||||||||||||||||||
At December 31, 2017, impaired loans consisted of 149 residential, commercial and commercial mortgage loans totaling $52.0 million, of which 24 loans totaling $20.3 million were included in nonaccrual loans. At December 31, 2016, impaired loans consisted of 141 residential, commercial and commercial mortgage loans totaling $52.0 million, of which 27 loans totaling $22.1 million were included in nonaccrual loans. Specific allocations of the allowance for loan losses attributable to impaired loans totaled $2.7 million and $2.3 million at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. At December 31, 2017 and 2016, impaired loans for which there was no related allowance for loan losses totaled $31.4 million and $31.8 million, respectively. The average balances of impaired loans during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 were $54.0 million and $52.0 million, respectively.
In the normal course of conducting its business, the Bank extends credit to meet the financing needs of its customers through commitments. Commitments and contingent liabilities, such as commitments to extend credit (including loan commitments of $1.71 billion and $1.55 billion, at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, and undisbursed home equity and personal credit lines of $270.9 million and $279.8 million, at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively) exist, which are not reflected in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. These instruments involve elements of credit and interest rate risk in excess of the amount recognized in the consolidated financial statements. The Bank uses the same credit policies and collateral requirements in making commitments and conditional obligations as it does for on-balance sheet loans. Commitments generally have fixed expiration dates or other termination clauses and may require payment of a fee. Since the commitments may expire without being drawn upon, the total commitment amounts do not necessarily represent future cash requirements.
80
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
The Bank evaluates each customer’s creditworthiness on a case-by-case basis. The amount of collateral obtained, if deemed necessary by the Bank upon extension of credit, is based on management’s credit evaluation of the borrower.
The Bank grants residential real estate loans on single- and multi-family dwellings to borrowers primarily in New Jersey. Its borrowers’ abilities to repay their obligations are dependent upon various factors, including the borrowers’ income and net worth, cash flows generated by the underlying collateral, value of the underlying collateral, and priority of the Bank’s lien on the property. Such factors are dependent upon various economic conditions and individual circumstances beyond the Bank’s control; the Bank is therefore subject to risk of loss. The Bank believes that its lending policies and procedures adequately minimize the potential exposure to such risks and that adequate provisions for loan losses are provided for all known and inherent risks. Collateral and/or guarantees are required for virtually all loans.
The Company utilizes an internal nine-point risk rating system to summarize its loan portfolio into categories with similar risk characteristics. Loans deemed to be “acceptable quality” are rated 1 through 4, with a rating of 1 established for loans with minimal risk. Loans that are deemed to be of “questionable quality” are rated 5 (watch) or 6 (special mention). Loans with adverse classifications (substandard, doubtful or loss) are rated 7, 8 or 9, respectively. Commercial mortgage, commercial, multi-family and construction loans are rated individually, and each lending officer is responsible for risk rating loans in their portfolio. These risk ratings are then reviewed by the department manager and/or the Chief Lending Officer and by the Credit Department. The risk ratings are also confirmed through periodic loan review examinations, which are currently performed by an independent third-party. Reports by the independent third-party are presented directly to the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors.
Loans receivable by credit quality risk rating indicator, excluding PCI loans are as follows (in thousands):
At December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Residential | Commercial mortgages | Multi- family | Construction | Total mortgages | Commercial loans | Consumer loans | Total loans | |||||||||||||||||
Special mention | $ | 4,325 | 19,172 | 15 | — | 23,512 | 20,738 | 486 | 44,736 | |||||||||||||||
Substandard | 8,105 | 25,069 | — | — | 33,174 | 29,734 | 2,491 | 65,399 | ||||||||||||||||
Doubtful | — | — | — | — | — | 428 | — | 428 | ||||||||||||||||
Loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Total classified and criticized | 12,430 | 44,241 | 15 | — | 56,686 | 50,900 | 2,977 | 110,563 | ||||||||||||||||
Acceptable/watch | 1,129,917 | 2,126,815 | 1,403,870 | 392,580 | 5,053,182 | 1,694,238 | 470,980 | 7,218,400 | ||||||||||||||||
Total outstanding loans | $ | 1,142,347 | 2,171,056 | 1,403,885 | 392,580 | 5,109,868 | 1,745,138 | 473,957 | 7,328,963 | |||||||||||||||
At December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Residential | Commercial mortgages | Multi- family | Construction | Total mortgages | Commercial loans | Consumer loans | Total loans | |||||||||||||||||
Special mention | $ | 6,563 | 25,329 | 563 | — | 32,455 | 14,840 | 1,242 | 48,537 | |||||||||||||||
Substandard | 12,021 | 23,011 | 553 | 2,517 | 38,102 | 47,255 | 2,940 | 88,297 | ||||||||||||||||
Doubtful | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Total classified and criticized | 18,584 | 48,340 | 1,116 | 2,517 | 70,557 | 62,095 | 4,182 | 136,834 | ||||||||||||||||
Acceptable/watch | 1,193,088 | 1,930,229 | 1,400,938 | 262,297 | 4,786,552 | 1,568,349 | 512,573 | 6,867,474 | ||||||||||||||||
Total outstanding loans | $ | 1,211,672 | 1,978,569 | 1,402,054 | 264,814 | 4,857,109 | 1,630,444 | 516,755 | 7,004,308 | |||||||||||||||
81
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(7) Banking Premises and Equipment
A summary of banking premises and equipment at December 31, 2017 and 2016 is as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | |||||
Land | $ | 12,440 | 17,594 | |||
Banking premises | 58,523 | 81,067 | ||||
Furniture, fixtures and equipment | 45,184 | 43,860 | ||||
Leasehold improvements | 35,240 | 35,455 | ||||
Construction in progress | 1,036 | 1,103 | ||||
152,423 | 179,079 | |||||
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | 89,238 | 94,987 | ||||
Total banking premises and equipment | $ | 63,185 | 84,092 | |||
On December 13, 2017, the Company, completed the sale and leaseback of 12 of its New Jersey banking offices, which had a net book value of $14.5 million. Net proceeds from the sale totaled $20.7 million. The net gain on sale of $6.2 million will be recognized over the 10 year term of the leases as a reduction of rent expense.
Depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 amounted to $9.0 million, $9.4 million and $9.6 million, respectively.
(8) Intangible Assets
Intangible assets at December 31, 2017 and 2016 are summarized as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | |||||
Goodwill | $ | 411,600 | 411,600 | |||
Core deposit premiums | 3,470 | 4,546 | ||||
Customer relationship and other intangibles | 4,483 | 5,957 | ||||
Mortgage servicing rights | 737 | 834 | ||||
Total intangible assets | $ | 420,290 | 422,937 | |||
Amortization expense of intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 is as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Core deposit premiums | $ | 1,076 | 1,300 | 1,757 | |||||
Customer relationship and other intangibles | 1,474 | 1,909 | 2,136 | ||||||
Mortgage servicing rights | 120 | 182 | 173 | ||||||
Total amortization expense of intangible assets | $ | 2,670 | 3,391 | 4,066 | |||||
Scheduled amortization of core deposit and customer relationship intangibles for each of the next five years is as follows (in thousands):
Year ended December 31, | Scheduled Amortization | |||
2018 | $ | 2,004 | ||
2019 | 1,709 | |||
2020 | 1,415 | |||
2021 | 1,120 | |||
2022 | 825 | |||
82
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(9) Deposits
Deposits at December 31, 2017 and 2016 are summarized as follows (in thousands):
2017 | Weighted average interest rate | 2016 | Weighted average interest rate | ||||||||||
Savings deposits | $ | 1,083,012 | 0.17 | % | $ | 1,099,020 | 0.17 | % | |||||
Money market accounts | 1,532,024 | 0.36 | 1,582,750 | 0.31 | |||||||||
NOW accounts | 2,011,334 | 0.46 | 1,871,298 | 0.33 | |||||||||
Non-interest bearing deposits | 1,452,987 | — | 1,349,378 | — | |||||||||
Certificates of deposit | 634,809 | 0.94 | 651,183 | 0.72 | |||||||||
Total deposits | $ | 6,714,166 | $ | 6,553,629 | |||||||||
Scheduled maturities of certificates of deposit accounts at December 31, 2017 and 2016 are as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | |||||
Within one year | $ | 424,448 | 439,035 | |||
One to three years | 150,280 | 134,941 | ||||
Three to five years | 56,529 | 75,751 | ||||
Five years and thereafter | 3,552 | 1,456 | ||||
$ | 634,809 | 651,183 | ||||
Interest expense on deposits for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 is summarized as follows (in thousands):
Years ended December 31, | |||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Savings deposits | $ | 2,092 | 1,709 | 1,039 | |||||
NOW and money market accounts | 12,205 | 10,106 | 8,046 | ||||||
Certificates of deposits | 5,144 | 5,132 | 5,436 | ||||||
$ | 19,441 | 16,947 | 14,521 | ||||||
(10) Borrowed Funds
Borrowed funds at December 31, 2017 and 2016 are summarized as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | |||||
Securities sold under repurchase agreements | $ | 143,179 | 156,665 | |||
FHLB line of credit | 472,000 | 161,000 | ||||
FHLB advances | 1,127,335 | 1,295,080 | ||||
Total borrowed funds | $ | 1,742,514 | 1,612,745 | |||
At December 31, 2017, FHLB advances were at fixed rates and mature between January 2018 and April 2022, and at December 31, 2016, FHLB advances were at fixed rates and mature between January 2017 and April 2022. These advances are secured by loans receivable and investment securities under a blanket collateral agreement.
83
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Scheduled maturities of FHLB advances at December 31, 2017 are as follows (in thousands):
2017 | |||
Due in one year or less | $ | 389,375 | |
Due after one year through two years | 436,551 | ||
Due after two years through three years | 249,169 | ||
Due after three years through four years | 42,240 | ||
Due after four years through five years | 10,000 | ||
Thereafter | — | ||
Total FHLB advances | $ | 1,127,335 | |
Scheduled maturities of securities sold under repurchase agreements at December 31, 2017 are as follows (in thousands):
2017 | |||
Due in one year or less | $ | 108,179 | |
Due after one year through two years | 35,000 | ||
Due after two years through three years | — | ||
Thereafter | — | ||
Total securities sold under repurchase agreements | $ | 143,179 | |
The following tables set forth certain information as to borrowed funds for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 (in thousands):
Maximum balance | Average balance | Weighted average interest rate | |||||||
2017: | |||||||||
Securities sold under repurchase agreements | $ | 210,702 | 164,982 | 1.26 | % | ||||
FHLB line of credit | 472,000 | 179,003 | 1.17 | ||||||
FHLB advances | 1,288,448 | 1,237,979 | 1.78 | ||||||
2016: | |||||||||
Securities sold under repurchase agreements | $ | 283,233 | 224,421 | 1.42 | % | ||||
FHLB line of credit | 173,000 | 37,608 | 0.61 | ||||||
FHLB advances | 1,343,095 | 1,315,278 | 1.76 | ||||||
Securities sold under repurchase agreements include wholesale borrowing arrangements, as well as arrangements with deposit customers of the Bank to sweep funds into short-term borrowings. The Bank uses securities available for sale to pledge as collateral for the repurchase agreements.
(11) Benefit Plans
Pension and Post-retirement Benefits
The Bank has a noncontributory defined benefit pension plan covering its full-time employees who had attained age 21 with at least one year of service as of April 1, 2003. The pension plan was frozen on April 1, 2003. All participants in the pension plan are 100% vested. The pension plan’s assets are invested in investment funds and group annuity contracts currently managed by the Principal Financial Group and Allmerica Financial. Based on the measurement date of December 31, 2017, no contributions will be made to the pension plan in 2018.
In addition to pension benefits, certain health care and life insurance benefits are currently made available to certain of the Bank’s retired employees. The costs of such benefits are accrued based on actuarial assumptions from the date of hire to the date the employee is fully eligible to receive the benefits. Effective January 1, 2003, eligibility for retiree health care benefits was frozen as to new entrants and benefits were eliminated for employees with less than ten years of service as of December 31, 2002. Effective January 1, 2007, eligibility for retiree life insurance benefits was frozen as to new entrants and retiree life insurance benefits were eliminated for employees with less than ten years of service as of December 31, 2006.
84
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
The following table sets forth information regarding the pension plan and post-retirement healthcare and life insurance plans (in thousands):
Pension | Post-retirement | |||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||
Change in benefit obligation: | ||||||||||||||||||
Benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | 29,533 | 28,274 | 28,921 | 20,805 | 25,694 | 28,333 | |||||||||||
Service cost | — | — | — | 105 | 150 | 168 | ||||||||||||
Interest cost | 1,227 | 1,247 | 1,137 | 871 | 1,138 | 1,122 | ||||||||||||
Actuarial loss | — | 70 | 78 | — | — | 122 | ||||||||||||
Benefits paid | (1,590 | ) | (1,247 | ) | (1,179 | ) | (560 | ) | (682 | ) | (644 | ) | ||||||
Change in actuarial assumptions | 2,800 | 1,189 | (683 | ) | 1,536 | (5,495 | ) | (3,407 | ) | |||||||||
Benefit obligation at end of year | $ | 31,970 | 29,533 | 28,274 | 22,757 | 20,805 | 25,694 | |||||||||||
Change in plan assets: | ||||||||||||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | $ | 43,153 | 41,448 | 42,744 | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Actual return on plan assets | 5,307 | 2,952 | (117 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Employer contributions | — | — | — | 560 | 682 | 644 | ||||||||||||
Benefits paid | (1,590 | ) | (1,247 | ) | (1,179 | ) | (560 | ) | (682 | ) | (644 | ) | ||||||
Fair value of plan assets at end of year | $ | 46,870 | 43,153 | 41,448 | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Funded status at end of year | $ | 14,900 | 13,620 | 13,174 | (22,757 | ) | (20,805 | ) | (25,694 | ) | ||||||||
For the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company, in the measurement of its pension plan and post-retirement obligations updated its mortality assumptions to the RP 2014 mortality table with the fully generational projection scale MP 2017 and MP 2016 issued by The Society of Actuaries ("SOA") in October 2017 and 2016, respectively. The prepaid pension benefits of $14.9 million and the unfunded post-retirement healthcare and life insurance benefits of $22.8 million at December 31, 2017 are included in other assets and other liabilities, respectively, in the consolidated statement of financial condition.
The components of accumulated other comprehensive loss (gain) related to the pension plan and other post-retirement benefits, on a pre-tax basis, at December 31, 2017 and 2016 are summarized in the following table (in thousands):
Pension | Post-retirement | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||
Unrecognized prior service cost | $ | — | — | — | — | |||||||
Unrecognized net actuarial loss (gain) | 11,091 | 11,968 | (4,781 | ) | (6,993 | ) | ||||||
Total accumulated other comprehensive loss (gain) | $ | 11,091 | 11,968 | (4,781 | ) | (6,993 | ) | |||||
Net periodic benefit (increase) cost for the years ending December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, included the following components (in thousands):
Pension | Post-retirement | |||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||
Service cost | $ | — | — | — | 105 | 150 | 168 | |||||||||||
Interest cost | 1,227 | 1,247 | 1,137 | 871 | 1,138 | 1,122 | ||||||||||||
Return on plan assets | (2,550 | ) | (2,449 | ) | (2,530 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||
Amortization of: | ||||||||||||||||||
Net gain (loss) | 920 | 943 | 774 | (677 | ) | — | 1 | |||||||||||
Unrecognized prior service cost | — | — | — | — | — | (1 | ) | |||||||||||
Net periodic benefit (increase) cost | $ | (403 | ) | (259 | ) | (619 | ) | 299 | 1,288 | 1,290 | ||||||||
85
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
The weighted average actuarial assumptions used in the plan determinations at December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 were as follows:
Pension | Post-retirement | ||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||
Discount rate | 3.50 | % | 4.25 | % | 4.50 | % | 3.50 | % | 4.25 | % | 4.50 | % | |||||
Rate of compensation increase | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Expected return on plan assets | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Medical and life insurance benefits cost rate of increase | — | — | — | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 | |||||||||||
The Company provides its actuary with certain rate assumptions used in measuring the benefit obligation. The most significant of these is the discount rate used to calculate the period-end present value of the benefit obligations, and the expense to be included in the following year’s financial statements. A lower discount rate will result in a higher benefit obligation and expense, while a higher discount rate will result in a lower benefit obligation and expense. The discount rate assumption was determined based on a cash flow-yield curve model specific to the Company’s pension and post-retirement plans. The Company compares this rate to certain market indices, such as long-term treasury bonds, or the Citigroup pension liability indices, for reasonableness. A discount rate of 3.50% was selected for the December 31, 2017 measurement date.
Assumed health care cost trend rates have a significant effect on the amounts reported for health care plans. A 1% change in the assumed health care cost trend rate would have had the following effects on post-retirement benefits at December 31, 2017 (in thousands):
1% increase | 1% decrease | |||||
Effect on total service cost and interest cost | $ | 170 | 140 | |||
Effect on post-retirement benefits obligation | $ | 4,000 | 3,170 | |||
Estimated future benefit payments, which reflect expected future service, as appropriate for the next five years, are as follows (in thousands):
Pension | Post-retirement | ||||||
2018 | $ | 1,443 | $ | 645 | |||
2019 | 1,496 | 684 | |||||
2020 | 1,538 | 705 | |||||
2021 | 1,593 | 771 | |||||
2022 | 1,635 | 828 | |||||
The weighted-average asset allocation of pension plan assets at December 31, 2017 and 2016 were as follows:
Asset Category | 2017 | 2016 | ||||
Domestic equities | 38 | % | 37 | % | ||
Foreign equities | 11 | % | 11 | % | ||
Fixed income | 49 | % | 50 | % | ||
Real estate | 2 | % | 2 | % | ||
Cash | 0 | % | 0 | % | ||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | ||
The Company’s expected return on pension plan assets assumption is based on historical investment return experience and evaluation of input from the Plan's Investment Consultant and the Company's Benefits Committee which manages the pension plan’s assets. The expected return on pension plan assets is also impacted by the target allocation of assets, which is based on the Company’s goal of earning the highest rate of return while maintaining risk at acceptable levels.
86
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Management strives to have pension plan assets sufficiently diversified so that adverse or unexpected results from one security class will not have a significant detrimental impact on the entire portfolio. The target allocation of assets and acceptable ranges around the targets are as follows:
Asset Category | Target | Allowable Range | ||||
Domestic equities | 37 | % | 30-41% | |||
Foreign equities | 11 | % | 5-13% | |||
Fixed income | 50 | % | 40-65% | |||
Real estate | 2 | % | 0-4% | |||
Cash | 0 | % | 0 | % | ||
Total | 100 | % | ||||
The Company anticipates that the long-term asset allocation on average will approximate the targeted allocation. Actual asset allocations are the result of investment decisions by a third-party investment manager.
The following tables present the assets that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis by level within the U.S. GAAP fair value hierarchy as reported on the statements of net assets available for Plan benefits at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Financial assets and liabilities are classified in their entirety based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
Fair value measurements at December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||
(in thousands) | Total | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | ||||||||
Group annuity contracts | $ | 120 | — | 120 | — | |||||||
Mutual funds: | ||||||||||||
Fixed income | 13,725 | 13,725 | — | — | ||||||||
International equity | 5,110 | 5,110 | — | — | ||||||||
Large U.S. equity | 1,431 | 1,431 | — | — | ||||||||
Small/Mid U.S. equity | 950 | 950 | — | — | ||||||||
Total mutual funds | 21,216 | 21,216 | — | — | ||||||||
Pooled separate accounts | 25,534 | — | 25,534 | — | ||||||||
Total investments | $ | 46,870 | 21,216 | 25,654 | — | |||||||
Fair value measurements at December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
(in thousands) | Total | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | ||||||||
Group annuity contracts | $ | 127 | — | 127 | — | |||||||
Mutual funds: | ||||||||||||
Fixed income | 12,740 | 12,740 | — | — | ||||||||
International equity | 4,659 | 4,659 | — | — | ||||||||
Large U.S. equity | 1,296 | 1,296 | — | — | ||||||||
Small/Mid U.S. equity | 840 | 840 | — | — | ||||||||
Total mutual funds | 19,535 | 19,535 | — | — | ||||||||
Pooled separate accounts | 23,491 | — | 23,491 | — | ||||||||
Total investments | $ | 43,153 | 19,535 | 23,618 | — | |||||||
401(k) Plan
The Bank has a 401(k) plan covering substantially all employees of the Bank. For 2017, 2016 and 2015, the Bank matched 25% of the first 6% contributed by the participants. The contribution percentage is determined by the Board of Directors in its sole discretion. The Bank’s aggregate contributions to the 401(k) Plan for 2017, 2016 and 2015 were $890,000, $850,000 and $770,000, respectively.
87
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan
The Bank maintains a non-qualified supplemental retirement plan for certain senior officers of the Bank. This plan was frozen as of April 1, 2003. The Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, which is unfunded, provides benefits in excess of the benefits permitted to be paid by the pension plan under provisions of the tax law. Amounts expensed under this supplemental retirement plan amounted to $91,000, $96,000 and $93,000 for the years 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. At December 31, 2017 and 2016, $2.0 million and $2.1 million, respectively, were recorded in other liabilities on the consolidated statements of financial condition for this supplemental retirement plan. Decreases of $120,000, $30,000, and $82,000, net of tax, were recorded in other comprehensive income (loss) for 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively, in connection with this supplemental retirement plan.
Retirement Plan for the Board of Directors of Provident Bank
The Bank maintains a Retirement Plan for the Board of Directors of the Bank, a non-qualified plan that provides cash payments for up to 10 years to eligible retired board members based on age and length of service requirements. The maximum payment under this plan to a board member, who terminates service on or after the age of 72 with at least ten years of service on the board, is forty quarterly payments of $1,250. The Bank may suspend payments under this plan if it does not meet Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or New Jersey Department of Banking and Insurance minimum capital requirements. The Bank may terminate this plan at any time although such termination may not reduce or eliminate any benefit previously accrued to a board member without his or her consent. The plan was amended in December 2005 to terminate benefits under this plan for any directors who had less than ten years of service on the board of directors of the Bank as of December 31, 2006.
The plan further provides that, in the event of a change in control (as defined in the plan), the undistributed balance of a director’s accrued benefit will be distributed to him or her within 60 days of the change in control. The Bank paid $13,000, $17,500, and $20,000 to former board members under this plan for each of the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. At December 31, 2017 and 2016, $142,000 and $148,000, respectively, were recorded in other liabilities on the consolidated statements of financial condition for this retirement plan. A decrease of $1,000, a decrease of $3,000, and an increase of $1,800, net of tax, were recorded in other comprehensive income (loss) for 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively, in connection with this plan.
Employee Stock Ownership Plan
The ESOP is a tax-qualified plan designed to invest primarily in the Company’s common stock that provides employees with the opportunity to receive a funded retirement benefit from the Bank, based primarily on the value of the Company’s common stock. The ESOP purchased 4,769,464 shares of the Company’s common stock at an average price of $17.09 per share with the proceeds of a loan from the Company to the ESOP. The outstanding loan principal at December 31, 2017, was $41.4 million. Shares of the Company’s common stock pledged as collateral for the loan are released from the pledge for allocation to participants as loan payments are made.
For the years ending December 31, 2017 and 2016, 242,254 shares and 219,623 shares from the ESOP were released, respectively. Unallocated ESOP shares held in suspense totaled 1,980,536 at December 31, 2017, and had a fair value of $53.4 million. ESOP compensation expense for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 was $4.6 million, $3.7 million and $3.0 million, respectively.
Non-Qualified Supplemental Defined Contribution Plan (“the Supplemental Employee Stock Ownership Plan”)
Effective January 1, 2004, the Bank established a deferred compensation plan for executive management and key employees of the Bank, known as Provident Bank Non-Qualified Supplemental Employee Stock Ownership Plan (the “Supplemental ESOP”). The Supplemental ESOP was amended and restated as the Non-Qualified Supplemental Defined Contribution Plan (the “Supplemental DC Plan”), effective January 1, 2010. The Supplemental DC Plan is a non-qualified plan that provides additional benefits to certain executives whose benefits under the 401(k) Plan and ESOP are limited by tax law limitations applicable to tax-qualified plans. The Supplemental DC Plan requires a contribution by the Bank for each participant who also participates in the 401(k) Plan and ESOP equal to the amount that would have been contributed under the terms of the 401(k) Plan and ESOP but for the tax law limitations, less the amount actually contributed under the 401(k) Plan and ESOP.
The Supplemental DC Plan provides for a phantom stock allocation for qualified contributions that may not be accrued in the qualified ESOP and for matching contributions that may not be accrued in the qualified 401(k) Plan due to tax law limitations. Under the Supplemental 401(k) provision, the estimated expense for the year ending December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 was $17,500, $14,500 and $11,500, respectively, and included the matching contributions plus interest credited at an annual rate equal
88
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
to the ten-year bond-equivalent yield on U.S. Treasury securities. Under the Supplemental ESOP provision, the estimated expense for the year ending December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 was $105,000, $93,000 and $54,000, respectively. The phantom equity is treated as equity awards (expensed at the time of allocation) and not liability awards which would require periodic adjustment to market, as participants do not have an option to take their distribution in cash.
The Amended and Restated Long-Term Incentive Plan
Upon stockholders’ approval of the Amended and Restated Long-Term Incentive Plan on April 4, 2014, shares available for stock awards and stock options under the 2008 Long-Term Equity Incentive Plan were reserved for issuance under the new Amended and Restated Long-Term Incentive Plan. No additional grants of stock awards and stock options will be made under the 2008 Long-Term Equity Incentive Plan. The new plan authorized the issuance of up to 3,686,510 shares of Company common stock with no more than 2,100,000 shares permitted to be issued as stock awards. Shares previously awarded under the 2008 plans that are subsequently forfeited or expire may also be issued under the new plan.
Stock Awards
As a general rule, restricted stock grants are held in escrow for the benefit of the award recipient until vested. Awards outstanding generally vest in three annual installments, commencing one year from the date of the award. Additionally, certain awards are three-year performance vesting awards, which may or may not vest depending upon the attainment of certain corporate financial targets. Expense attributable to stock awards amounted to $5.0 million, $3.8 million and $4.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
A summary status of the granted but unvested stock awards as of December 31, and changes during the year, is presented below:
Restricted Stock Awards | ||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Outstanding at beginning of year | 547,698 | 591,746 | 846,462 | |||||
Granted | 288,519 | 351,836 | 339,936 | |||||
Forfeited | (62,677 | ) | (178,632 | ) | (240,191 | ) | ||
Vested | (112,757 | ) | (217,252 | ) | (354,461 | ) | ||
Outstanding at the end of year | 660,783 | 547,698 | 591,746 | |||||
As of December 31, 2017, unrecognized compensation cost relating to unvested restricted stock totaled $5.7 million. This amount will be recognized over a remaining weighted average period of 1.9 years.
Stock Options
Each stock option granted entitles the holder to purchase one share of the Company’s common stock at an exercise price not less than the fair value of a share of the Company’s common stock at the date of grant. Options generally vest over a five-year period from the date of grant and expire no later than 10 years following the grant date. Additionally, certain options are three-year performance vesting options, which may or may not vest depending upon the attainment of certain corporate financial targets.
A summary of the status of the granted but unexercised stock options as of December 31, and changes during the year is presented below:
89
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||
Number of stock options | Weighted average exercise price | Number of stock options | Weighted average exercise price | Number of stock options | Weighted average exercise price | |||||||||||||||
Outstanding at beginning of year | 703,669 | $ | 14.70 | 1,084,686 | $ | 15.32 | 1,284,321 | $ | 15.32 | |||||||||||
Granted | 42,857 | 26.31 | 76,327 | 18.70 | 65,972 | 16.38 | ||||||||||||||
Exercised | (238,370 | ) | 12.22 | (368,838 | ) | 16.92 | (201,320 | ) | 15.72 | |||||||||||
Forfeited | — | — | (82,006 | ) | 16.42 | (62,287 | ) | 14.93 | ||||||||||||
Expired | (500 | ) | 17.94 | (6,500 | ) | 18.55 | (2,000 | ) | 17.94 | |||||||||||
Outstanding at the end of year | 507,656 | $ | 16.84 | 703,669 | $ | 14.70 | 1,084,686 | $ | 15.32 | |||||||||||
The total fair value of options vesting during 2017, 2016 and 2015 was $168,000, $247,000 and $274,000, respectively.
Compensation expense of approximately $138,000, $70,582 and $10,000 is projected for 2018, 2019 and 2020, respectively, on stock options outstanding at December 31, 2017.
The following table summarizes information about stock options outstanding at December 31, 2017:
Options Outstanding | Options Exercisable | ||||||||||||||
Range of exercise prices | Number of options outstanding | Average remaining contractual life | Weighted average exercise price | Number of options exercisable | Weighted average exercise price | ||||||||||
$10.34-15.23 | 241,740 | 3.4 years | $ | 14.00 | 234,738 | $ | 13.84 | ||||||||
$16.38-26.31 | 265,916 | 7.4 years | $ | 19.13 | 136,183 | $ | 17.45 | ||||||||
The stock options outstanding and stock options exercisable at December 31, 2017 have an aggregate intrinsic value of $5,249,000 and $4,380,000, respectively.
The expense related to stock options is based on the fair value of the options at the date of the grant and is recognized ratably over the vesting period of the options.
Compensation expense related to the Company’s stock option plan totaled $203,000, $172,000 and $272,000 for 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
The estimated fair values were determined on the dates of grant using the Black-Scholes Option pricing model. The fair value of the Company’ stock option awards are expensed on a straight-line basis over the vesting period of the stock option. The risk-free rate is based on the implied yield on a U.S. Treasury bond with a term approximating the expected term of the option. The expected volatility computation is based on historical volatility over a period approximating the expected term of the option. The dividend yield is based on the annual dividend payment per share, divided by the grant date stock price. The expected option term is a function of the option life and the vesting period.
The fair value of the option grants was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following weighted average assumptions:
For the year ended December 31, | ||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Expected dividend yield | 2.89 | % | 3.64 | % | 3.49 | % | ||
Expected volatility | 20.34 | % | 20.71 | % | 21.29 | % | ||
Risk-free interest rate | 2.05 | % | 1.21 | % | 1.58 | % | ||
Expected option life | 8 years | 8 years | 8 years | |||||
The weighted average fair value of options granted during 2017, 2016 and 2015 was $4.20, $2.26 and $2.52 per option, respectively.
90
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(12) Income Taxes
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act ("Tax Act") was signed into law on December 22, 2017. Included as part of the law, was a permanent reduction in the federal corporate income tax rate from 35% to 21% effective January 1, 2018. Based upon the change in the tax rate, the Company revalued its net deferred tax asset at December 31, 2017. As a result of the enactment of the Tax Act, the Company recognized an additional tax expense of $3.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2017.
The current and deferred amounts of income tax expense (benefit) for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 are as follows (in thousands):
Years ended December 31, | |||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Current: | |||||||||
Federal | $ | 4,163 | 32,506 | 33,778 | |||||
State | 1,731 | 1,314 | 2,337 | ||||||
Total current | 5,894 | 33,820 | 36,115 | ||||||
Deferred: | |||||||||
Federal | 39,003 | 2,606 | (525 | ) | |||||
State | 1,631 | 554 | 851 | ||||||
Total deferred | 40,634 | 3,160 | 326 | ||||||
$ | 46,528 | 36,980 | 36,441 | ||||||
The Company recorded deferred tax (benefit) of ($1.4) million, ($3.0) million and ($2.5) million during 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively, related to the unrealized (loss) gain on securities available for sale, which is reported in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax. Additionally, the Company recorded a deferred tax (benefit) expense of ($586,000), $2.3 million and $866,000 in 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively, related to the amortization of post-retirement benefit obligations, which is reported in accumulated other comprehensive income, net of tax.
A reconciliation between the amount of reported total income tax expense and the amount computed by multiplying the applicable statutory income tax rate is as follows (in thousands):
Years ended December 31, | |||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Tax expense at statutory rate of 35% | $ | 49,167 | 43,674 | 42,057 | |||||
Increase (decrease) in taxes resulting from: | |||||||||
State tax, net of federal income tax benefit | 2,185 | 1,215 | 2,072 | ||||||
Tax-exempt interest income | (5,097 | ) | (5,286 | ) | (5,520 | ) | |||
Bank-owned life insurance | (2,343 | ) | (1,915 | ) | (1,871 | ) | |||
Enactment of Tax Act | 3,912 | — | — | ||||||
Other, net | (1,296 | ) | (708 | ) | (297 | ) | |||
$ | 46,528 | 36,980 | 36,441 | ||||||
The net deferred tax asset is included in other assets in the consolidated statements of financial condition. The tax effects of temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of the deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities at December 31, 2017 and 2016 are as follows (in thousands):
91
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
2017 | 2016 | |||||
Deferred tax assets: | ||||||
Allowance for loan losses | $ | 14,884 | 23,852 | |||
Post-retirement benefit | 7,265 | 11,150 | ||||
Deferred compensation | 1,382 | 2,447 | ||||
Purchase accounting adjustments | 1,242 | 1,979 | ||||
Depreciation | 2,284 | 4,025 | ||||
SERP | 651 | 966 | ||||
ESOP | 2,000 | 3,203 | ||||
Stock-based compensation | 4,066 | 5,259 | ||||
Non-accrual interest | 839 | 3,738 | ||||
Unrealized loss on securities | 1,180 | 350 | ||||
State NOL | 18 | 81 | ||||
Federal NOL | 270 | 742 | ||||
Pension liability adjustments | 1,495 | 2,051 | ||||
Other | 2,561 | 1,817 | ||||
Total gross deferred tax assets | 40,137 | 61,660 | ||||
Deferred tax liabilities: | ||||||
Deferred REIT dividend | 22,264 | — | ||||
Pension expense | 6,857 | 10,255 | ||||
Deferred loan costs | 4,043 | 5,477 | ||||
Investment securities, principally due to accretion of discounts | 79 | 167 | ||||
Intangibles | 775 | 548 | ||||
Originated mortgage servicing rights | 184 | 313 | ||||
Total gross deferred tax liabilities | 34,202 | 16,760 | ||||
Net deferred tax asset | $ | 5,935 | 44,900 | |||
Retained earnings at December 31, 2017 includes approximately $51.8 million for which no provision for income tax has been made. This amount represents an allocation of income to bad debt deductions for tax purposes only. Events that would result in taxation of these reserves include the failure to qualify as a bank for tax purposes, distributions in complete or partial liquidation, stock redemptions and excess distributions to stockholders. At December 31, 2017, the Company had an unrecognized tax liability of $13.7 million with respect to this reserve.
As a result of the Beacon Trust acquisition in 2011, the Company acquired federal net operating loss carryforwards. There are approximately $1.3 million of NOL carryforwards available to offset future taxable income as of December 31, 2017. If not utilized, these carryforwards will expire in 2031. Also, the Company's New Jersey NOL carryforwards are approximately $240,000 which are scheduled to expire in 2031. The federal NOLs are subject to a combined annual Code Section 382 limitation in the amount of approximately $840,000. Management has determined that it is more likely than not that it will realize the net deferred tax asset based upon the nature and timing of the items listed above. In order to fully realize the net deferred tax asset, the Company will need to generate future taxable income. Management has projected that the Company will generate sufficient taxable income to utilize the net deferred tax asset; however, there can be no assurance that such levels of taxable income will be generated.
The Company’s policy is to report interest and penalties, if any, related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense. The Company did not have any liabilities for uncertain tax positions or any known unrecognized tax benefits at December 31, 2017 and 2016.
The Company and its subsidiaries file a consolidated U.S. Federal income tax return, separate New Jersey State income tax returns, and a combined New York State income tax return on apportioned and allocated income. The Company, through its bank subsidiary, files a Pennsylvania Mutual Thrift Institution Tax return. The Company's Federal and New York State income tax returns are open for examination from 2015, the New Jersey State income tax returns are open for examination from 2014, and
92
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
the Pennsylvania Mutual Thrift Institutions return is open from 2015. During the fourth quarter of 2017, the Internal Revenue Service completed its examination of the Company's 2014 federal tax return. The completion of the examination did not have an impact on the Company's effective income tax rate. The Company's 2016 and 2015 New York State returns are currently under audit.
(13) Lease Commitments
The approximate future minimum rental commitments, exclusive of taxes and other related charges, for all significant non-cancellable operating leases at December 31, 2017, are summarized as follows (in thousands):
Year ending December 31, | |||
2018 | $ | 8,032 | |
2019 | 7,511 | ||
2020 | 6,980 | ||
2021 | 4,854 | ||
2022 | 3,378 | ||
Thereafter | 14,578 | ||
$ | 45,333 | ||
Rental expense was $8.8 million, $8.7 million and $8.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
(14) Commitments, Contingencies and Concentrations of Credit Risk
In the normal course of business, various commitments and contingent liabilities are outstanding which are not reflected in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. In the opinion of management, the consolidated financial position of the Company will not be materially affected by the outcome of such commitments or contingent liabilities.
The Company is involved in various legal actions and claims arising in the normal course of its business. In the opinion of management, these legal actions and claims are not expected to have a material adverse impact on the Company’s financial condition and results of operations.
A substantial portion of the Bank’s loans are secured by real estate located in New Jersey. Accordingly, the collectability of a substantial portion of the Bank’s loan portfolio and the recovery of a substantial portion of the carrying amount of other real estate owned are susceptible to changes in local real estate market conditions.
(15) Regulatory Capital Requirements
FDIC regulations require banks to maintain minimum levels of regulatory capital. Under the regulations in effect at December 31, 2017, the Bank is required to maintain: (1) a Tier 1 capital to total assets leverage ratio of 4.0%; (2) a common equity Tier 1 capital to risk-based assets ratio of 4.5%; (3) a Tier 1 capital to risk-based assets ratio of 6.0%; and (4) a total capital to risk-based assets ratio of 8.0%. In addition to establishing the minimum regulatory capital requirements, the regulations limit capital distributions and certain discretionary bonus payments to management if the institution does not hold a “capital conservation buffer” consisting of 2.5% of common equity Tier 1 capital to risk-weighted asset above the amount necessary to meet its minimum risk-based capital requirements. The capital conservation buffer requirement was effective on January 1, 2016 at 0.625% of risk-weighted assets and will increase each year until fully implemented at 2.5% on January 1, 2019. The capital conservation buffer during the calendar year 2017 was 1.25% and increased to 1.875% on January 1, 2018.
Under its prompt corrective action regulations, the FDIC is required to take certain supervisory actions (and may take additional discretionary actions) with respect to an undercapitalized institution. Such actions could have a direct material effect on an institution’s financial statements. The regulations establish a framework for the classification of savings institutions into five categories: well capitalized, adequately capitalized, undercapitalized, significantly undercapitalized, and critically undercapitalized. Generally, an institution is considered well capitalized if it has: a leverage (Tier 1) capital ratio of at least 5.00%; a common equity Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio of 6.50%; a Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio of at least 8.00%; and a total risk-based capital ratio of at least 10.00%.
93
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
The foregoing capital ratios are based in part on specific quantitative measures of assets, liabilities and certain off-balance sheet items as calculated under regulatory accounting practices. Capital amounts and classifications are also subject to qualitative judgments by the FDIC about capital components, risk weightings and other factors.
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Bank exceeded all minimum capital adequacy requirements to which it is subject. Further, the most recent FDIC notification categorized the Bank as a well-capitalized institution under the prompt corrective action regulations. There have been no conditions or events since that notification that management believes have changed the Bank’s capital classification.
The Company is regulated as a bank holding company, and as such, is subject to examination, regulation and periodic reporting under the Bank Holding Company Act, as administered by the Federal Reserve Board (“FRB”). The FRB has adopted capital adequacy guidelines for bank holding companies on a consolidated basis substantially similar to those of the FDIC for the Bank. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company was “well capitalized” under FRB guidelines. Regulations of the FRB provide that a bank holding company must serve as a source of strength to any of its subsidiary banks and must not conduct its activities in an unsafe or unsound manner. Under the prompt corrective action provisions discussed above, a bank holding company parent of an undercapitalized subsidiary bank would be directed to guarantee, within limitations, the capital restoration plan that is required of such an undercapitalized bank. If the undercapitalized bank fails to file an acceptable capital restoration plan or fails to implement an accepted plan, the FRB may prohibit the bank holding company parent of the undercapitalized bank from paying any dividend or making any other form of capital distribution without the prior approval of the FRB.
The following table shows the Company’s actual capital amounts and ratios as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, compared to the FRB minimum capital adequacy requirements and the FRB requirements for classification as a well-capitalized institution (dollars in thousands).
Actual capital | FRB minimum capital adequacy requirements | FRB minimum capital adequacy requirements with capital conservation buffer | To be well-capitalized under prompt corrective action provisions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | ||||||||||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 leverage capital | $ | 887,924 | 9.65 | % | $ | 367,999 | 4.00 | % | $ | 367,999 | 4.00 | % | $ | 459,999 | 5.00 | % | |||||||||||
Common equity Tier 1 risk-based capital | 887,924 | 11.87 | 336,736 | 4.50 | % | 430,260 | 5.75 | 486,381 | 6.50 | ||||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 risk-based capital | 887,924 | 11.87 | 448,981 | 6.00 | % | 542,502 | 7.25 | 598,623 | 8.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total risk-based capital | 948,119 | 12.67 | 598,642 | 8.00 | % | 692,157 | 9.25 | 748,278 | 10.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
Actual capital | FRB minimum capital adequacy requirements | FRB minimum capital adequacy requirements with capital conservation buffer | To be well-capitalized under prompt corrective action provisions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | ||||||||||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 leverage capital | $ | 835,282 | 9.25 | % | $ | 361,183 | 4.00 | % | $ | 361,183 | 4.00 | % | $ | 451,479 | 5.00 | % | |||||||||||
Common equity Tier 1 risk-based capital | 835,282 | 11.64 | 323,048 | 4.50 | 367,916 | 5.13 | % | 466,625 | 6.50 | ||||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 risk-based capital | 835,282 | 11.64 | 430,731 | 6.00 | 475,599 | 6.63 | % | 574,308 | 8.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total risk-based capital | 897,165 | 12.50 | 574,308 | 8.00 | 619,176 | 8.63 | % | 717,885 | 10.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
94
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
The following table shows the Bank’s actual capital amounts and ratios as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, compared to the FDIC minimum capital adequacy requirements and the FDIC requirements for classification as a well-capitalized institution (dollars in thousands).
Actual capital | FDIC minimum capital adequacy requirements | FDIC minimum capital adequacy requirements with Capital Conservation buffer | To be well-capitalized under prompt corrective action provisions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | ||||||||||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 leverage capital | $ | 834,084 | 9.07 | % | $ | 367,986 | 4.00 | % | $ | 367,986 | 4.00 | % | $ | 459,983 | 5.00 | % | |||||||||||
Common equity Tier 1 risk-based capital | 834,084 | 11.15 | 336,721 | 4.50 | % | 430,254 | 5.75 | 486,374 | 6.50 | ||||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 risk-based capital | 834,084 | 11.15 | 448,961 | 6.00 | % | 542,494 | 7.25 | 598,615 | 8.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total risk-based capital | 894,430 | 11.95 | 598,615 | 8.00 | % | 692,148 | 9.25 | 748,268 | 10.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
Actual capital | FDIC minimum capital adequacy requirements | FRB minimum capital adequacy requirements with capital conservation buffer | To be well-capitalized under prompt corrective action provisions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | ||||||||||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 leverage capital | $ | 760,708 | 8.42 | % | $ | 361,172 | 4.00 | % | $ | 361,172 | 4.00 | % | $ | 451,465 | 5.00 | % | |||||||||||
Common equity Tier 1 risk-based capital | 760,708 | 10.60 | 323,040 | 4.50 | 367,907 | 5.13 | % | 466,613 | 6.50 | ||||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 risk-based capital | 760,708 | 10.60 | 430,720 | 6.00 | 475,587 | 6.63 | % | 574,293 | 8.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total risk-based capital | 822,743 | 11.46 | 574,293 | 8.00 | 619,160 | 8.63 | % | 717,867 | 10.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
(16) Fair Value Measurements
The Company utilizes fair value measurements to record fair value adjustments to certain assets and liabilities and to determine fair value disclosures. The determination of fair values of financial instruments often requires the use of estimates. Where quoted market values in an active market are not readily available, the Company utilizes various valuation techniques to estimate fair value.
Fair value is an estimate of the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. However, in many instances fair value estimates may not be substantiated by comparison to independent markets and may not be realized in an immediate sale of the financial instrument.
GAAP establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value. The hierarchy gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1 measurements) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3 measurements). The three levels of fair value hierarchy are as follows:
Level 1: | Unadjusted quoted market prices in active markets that are accessible at the measurement date for identical, unrestricted assets or liabilities; |
Level 2: | Quoted prices in markets that are not active, or inputs that are observable either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the asset or liability; and |
Level 3: | Prices or valuation techniques that require inputs that are both significant to the fair value measurement and unobservable (i.e., supported by little or no market activity). |
A financial instrument’s level within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
95
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
The valuation techniques are based upon the unpaid principal balance only, and exclude any accrued interest or dividends at the measurement date. Interest income and expense and dividend income are recorded within the consolidated statements of income depending on the nature of the instrument using the effective interest method based on acquired discount or premium.
Assets Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis
The valuation techniques described below were used to measure fair value of financial instruments in the table below on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016.
Securities Available for Sale
For securities available for sale, fair value was estimated using a market approach. The majority of the Company’s securities are fixed income instruments that are not quoted on an exchange, but are traded in active markets. Prices for these instruments are obtained through third-party data service providers or dealer market participants with which the Company has historically transacted both purchases and sales of securities. Prices obtained from these sources include market quotations and matrix pricing. Matrix pricing, a Level 2 input, is a mathematical technique used principally to value certain securities to benchmark or to comparable securities. The Company evaluates the quality of Level 2 matrix pricing through comparison to similar assets with greater liquidity and evaluation of projected cash flows. As the Company is responsible for the determination of fair value, it performs a quarterly analysis of the prices received from the pricing service to determine whether the prices are reasonable estimates of fair value. Specifically, the Company compares the prices received from the pricing service to a secondary pricing source. Additionally, the Company compares changes in the reported market values and returns to relevant market indices to test the reasonableness of the reported prices. The Company’s internal price verification procedures and review of fair value methodology documentation provided by independent pricing services has not historically resulted in an adjustment in the prices obtained from the pricing service. The Company also may hold equity securities and debt instruments issued by the U.S. government and U.S. government-sponsored agencies that are traded in active markets with readily accessible quoted market prices that are considered Level 1 inputs.
Derivatives
The Company records all derivatives on the statements of financial condition at fair value. The accounting for changes in the fair value of derivatives depends on the intended use of the derivative, whether the Company has elected to designate a derivative in a hedging relationship and apply hedge accounting and whether the hedging relationship has satisfied the criteria necessary to apply hedge accounting. The Company has interest rate derivatives resulting from a service provided to certain qualified borrowers in a loan related transaction and, therefore, are not used to manage interest rate risk in the Company’s assets or liabilities. As such, all changes in fair value of the Company’s derivatives are recognized directly in earnings.
The Company also uses interest rate swaps as part of its interest rate risk management strategy. Interest rate swaps designated as cash flow hedges, and which satisfy hedge accounting requirements, involve the receipt of variable amounts from a counterparty in exchange for the Company making fixed-rate payments over the life of the agreements without the exchange of the underlying notional amount. These derivatives were used to hedge the variable cash outflows associated with FHLBNY borrowings. The effective portion of changes in the fair value of these derivatives are recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income, and are subsequently reclassified into earnings in the period that the hedged forecasted transaction affects earnings. The ineffective portion of the change in fair value of these derivatives are recognized directly in earnings.
The fair value of the Company's derivatives are determined using discounted cash flow analysis using observable market-based inputs, which are considered Level 2 inputs.
Assets Measured at Fair Value on a Non-Recurring Basis
The valuation techniques described below were used to estimate fair value of financial instruments measured on a non-recurring basis as of December 31, 2017 and 2016.
Collateral Dependent Impaired Loans
For loans measured for impairment based on the fair value of the underlying collateral, fair value was estimated using a market approach. The Company measures the fair value of collateral underlying impaired loans primarily through obtaining independent appraisals that rely upon quoted market prices for similar assets in active markets. These appraisals include adjustments, on an individual case-by-case basis, to comparable assets based on the appraisers’ market knowledge and experience, as well as
96
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
adjustments for estimated costs to sell between 5% and 10%. The Company classifies these loans as Level 3 within the fair value hierarchy.
Foreclosed Assets
Assets acquired through foreclosure or deed in lieu of foreclosure are carried at fair value, less estimated costs, which range between 5% and 10%. Fair value is generally based on independent appraisals that rely upon quoted market prices for similar assets in active markets. These appraisals include adjustments, on an individual case basis, to comparable assets based on the appraisers’ market knowledge and experience, and are classified as Level 3. When an asset is acquired, the excess of the loan balance over fair value less estimated selling costs is charged to the allowance for loan losses. A reserve for foreclosed assets may be established to provide for possible write-downs and selling costs that occur subsequent to foreclosure. Foreclosed assets are carried net of the related reserve. Operating results from real estate owned, including rental income, operating expenses, and gains and losses realized from the sales of real estate owned, are recorded as incurred.
There were no changes to the valuation techniques for fair value measurements during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016.
The following tables present the assets and liabilities reported on the consolidated statements of financial condition at their fair value as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, by level within the fair value hierarchy (in thousands).
Fair Value Measurements at Reporting Date Using: | ||||||||||||
December 31, 2017 | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | |||||||||
Measured on a recurring basis: | ||||||||||||
Securities available for sale: | ||||||||||||
Agency obligations | $ | 19,005 | 19,005 | — | — | |||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 988,367 | — | 988,367 | — | ||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 3,388 | — | 3,388 | — | ||||||||
Corporate obligations | 26,394 | — | 26,394 | — | ||||||||
Equities | 658 | 658 | — | — | ||||||||
Total securities available for sale | $ | 1,037,812 | 19,663 | 1,018,149 | — | |||||||
Derivative assets | 7,219 | — | 7,219 | |||||||||
$ | 1,045,031 | 19,663 | 1,025,368 | — | ||||||||
Derivative liabilities | $ | 6,315 | — | 6,315 | — | |||||||
Measured on a non-recurring basis: | ||||||||||||
Loans measured for impairment based on the fair value of the underlying collateral | $ | 6,971 | — | — | 6,971 | |||||||
Foreclosed assets | 6,864 | — | — | 6,864 | ||||||||
$ | 13,835 | — | — | 13,835 | ||||||||
97
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Fair Value Measurements at Reporting Date Using: | ||||||||||||
December 31, 2016 | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | |||||||||
Measured on a recurring basis: | ||||||||||||
Securities available for sale: | ||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury obligations | $ | 8,008 | 8,008 | — | — | |||||||
Agency obligations | 57,188 | 57,188 | — | — | ||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 951,861 | — | 951,861 | — | ||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 3,743 | — | 3,743 | — | ||||||||
Corporate obligations | 19,037 | — | 19,037 | — | ||||||||
Equities | 549 | 549 | — | — | ||||||||
Total securities available for sale | $ | 1,040,386 | 65,745 | 974,641 | — | |||||||
Derivative assets | 7,441 | — | 7,441 | — | ||||||||
$ | 1,047,827 | 65,745 | 982,082 | — | ||||||||
Derivative liabilities | $ | 6,750 | — | 6,750 | — | |||||||
Measured on a non-recurring basis: | ||||||||||||
Loans measured for impairment based on the fair value of the underlying collateral | $ | 11,001 | — | — | 11,001 | |||||||
Foreclosed assets | 7,991 | — | — | 7,991 | ||||||||
$ | 18,992 | — | — | 18,992 | ||||||||
There were no transfers between Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3 during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016.
Other Fair Value Disclosures
The Company is required to disclose estimated fair value of financial instruments, both assets and liabilities on and off the balance sheet, for which it is practicable to estimate fair value. The following is a description of valuation methodologies used for those assets and liabilities.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
For cash and due from banks, federal funds sold and short-term investments, the carrying amount approximates fair value.
Investment Securities Held to Maturity
For investment securities held to maturity, fair value was estimated using a market approach. The majority of the Company’s securities are fixed income instruments that are not quoted on an exchange, but are traded in active markets. Prices for these instruments are obtained through third party data service providers or dealer market participants with which the Company has historically transacted both purchases and sales of securities. Prices obtained from these sources include market quotations and matrix pricing. Matrix pricing, a Level 2 input, is a mathematical technique used principally to value certain securities to benchmark or comparable securities. The Company evaluates the quality of Level 2 matrix pricing through comparison to similar assets with greater liquidity and evaluation of projected cash flows. As the Company is responsible for the determination of fair value, it performs quarterly analysis of the prices received from the pricing service to determine whether the prices are reasonable estimates of fair value. Specifically, the Company compares the prices received from the pricing service to a secondary pricing source. Additionally, the Company compares changes in the reported market values and returns to relevant market indices to test the reasonableness of the reported prices. The Company’s internal price verification procedures and review of fair value methodology documentation provided by independent pricing services has not historically resulted in adjustment in the prices obtained from the pricing service. The Company also holds debt instruments issued by the U.S. government and U.S. government agencies that are traded in active markets with readily accessible quoted market prices that are considered Level 1 within the fair value hierarchy.
98
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
FHLBNY Stock
The carrying value of FHLBNY stock was its cost. The fair value of FHLBNY stock is based on redemption at par value. The Company classifies the estimated fair value as Level 1 within the fair value hierarchy.
Loans
Fair values are estimated for portfolios of loans with similar financial characteristics. Loans are segregated by type such as commercial mortgage, residential mortgage, commercial, construction and consumer. Each loan category is further segmented into fixed and adjustable rate interest terms and into performing and non-performing categories. The fair value of performing loans was estimated using a combination of techniques, including a discounted cash flow model that utilizes a discount rate that reflects the Company’s current pricing for loans with similar characteristics and remaining maturity, adjusted by an amount for estimated credit losses inherent in the portfolio at the balance sheet date. The rates take into account the expected yield curve, as well as an adjustment for prepayment risk, when applicable. The Company classifies the estimated fair value of its loan portfolio as Level 3.
The fair value for significant non-performing loans was based on recent external appraisals of collateral securing such loans, adjusted for the timing of anticipated cash flows. The Company classifies the estimated fair value of its non-performing loan portfolio as Level 3.
Deposits
The fair value of deposits with no stated maturity, such as non-interest bearing demand deposits and savings deposits, was equal to the amount payable on demand and classified as Level 1. The estimated fair value of certificates of deposit was based on the discounted value of contractual cash flows. The discount rate was estimated using the Company’s current rates offered for deposits with similar remaining maturities. The Company classifies the estimated fair value of its certificates of deposit portfolio as Level 2.
Borrowed Funds
The fair value of borrowed funds was estimated by discounting future cash flows using rates available for debt with similar terms and maturities and is classified by the Company as Level 2 within the fair value hierarchy.
Commitments to Extend Credit and Letters of Credit
The fair value of commitments to extend credit and letters of credit was estimated using the fees currently charged to enter into similar agreements, taking into account the remaining terms of the agreements and the present creditworthiness of the counterparties. For fixed rate loan commitments, fair value also considers the difference between current levels of interest rates and the committed rates. The fair value estimates of commitments to extend credit and letters of credit are deemed immaterial.
Limitations
Fair value estimates are made at a specific point in time, based on relevant market information and information about the financial instrument. These estimates do not reflect any premium or discount that could result from offering for sale at one time the Company’s entire holdings of a particular financial instrument. Because no market exists for a significant portion of the Company’s financial instruments, fair value estimates are based on judgments regarding future expected loss experience, current economic conditions, risk characteristics of various financial instruments, and other factors. These estimates are subjective in nature and involve uncertainties and matters of significant judgment and, therefore, cannot be determined with precision. Changes in assumptions could significantly affect the estimates.
Fair value estimates are based on existing on- and off-balance sheet financial instruments without attempting to estimate the value of anticipated future business and the value of assets and liabilities that are not considered financial instruments.
Significant assets and liabilities that are not considered financial assets or liabilities include goodwill and other intangibles, deferred tax assets and premises and equipment. In addition, the tax ramifications related to the realization of the unrealized gains and losses can have a significant effect on fair value estimates and have not been considered in the estimates.
99
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
The following tables present the Company’s financial instruments at their carrying and fair values as of December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016. Fair values are presented by level within the fair value hierarchy.
Fair Value Measurements at December 31, 2017 Using: | |||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Carrying value | Fair value | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | ||||||||||
Financial assets: | |||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 190,834 | 190,834 | 190,834 | — | — | |||||||||
Securities available for sale: | |||||||||||||||
Agency obligations | 19,005 | 19,005 | 19,005 | — | — | ||||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 988,367 | 988,367 | — | 988,367 | — | ||||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 3,388 | 3,388 | — | 3,388 | — | ||||||||||
Corporate obligations | 26,394 | 26,394 | — | 26,394 | — | ||||||||||
Equity securities | 658 | 658 | 658 | — | — | ||||||||||
Total securities available for sale | $ | 1,037,812 | 1,037,812 | 19,663 | 1,018,149 | — | |||||||||
Investment securities held to maturity: | |||||||||||||||
Agency obligations | $ | 4,308 | 4,221 | 4,221 | — | — | |||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 382 | 396 | — | 396 | — | ||||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 462,942 | 470,484 | — | 470,484 | — | ||||||||||
Corporate obligations | 10,020 | 9,938 | — | 9,938 | — | ||||||||||
Total securities held to maturity | $ | 477,652 | 485,039 | 4,221 | 480,818 | — | |||||||||
FHLBNY stock | 81,184 | 81,184 | 81,184 | — | — | ||||||||||
Loans, net of allowance for loan losses | 7,265,523 | 7,217,705 | — | — | 7,217,705 | ||||||||||
Derivative assets | 7,219 | 7,219 | — | 7,219 | — | ||||||||||
Financial liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
Deposits other than certificates of deposits | $ | 6,079,357 | 6,079,357 | 6,079,357 | — | — | |||||||||
Certificates of deposit | 634,809 | 632,744 | — | 632,744 | — | ||||||||||
Total deposits | $ | 6,714,166 | 6,712,101 | 6,079,357 | 632,744 | — | |||||||||
Borrowings | 1,742,514 | 1,739,102 | — | 1,739,102 | — | ||||||||||
Derivative liabilities | 6,315 | 6,315 | — | 6,315 | — | ||||||||||
100
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Fair Value Measurements at December 31, 2016 Using: | |||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | Carrying value | Fair value | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | ||||||||||
Financial assets: | |||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 144,297 | 144,297 | 144,297 | — | — | |||||||||
Securities available for sale: | |||||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury obligations | 8,008 | 8,008 | 8,008 | — | — | ||||||||||
Agency obligations | 57,188 | 57,188 | 57,188 | — | — | ||||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 951,861 | 951,861 | — | 951,861 | — | ||||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 3,743 | 3,743 | — | 3,743 | — | ||||||||||
Corporate obligations | 19,037 | 19,037 | — | 19,037 | — | ||||||||||
Equity securities | 549 | 549 | 549 | — | — | ||||||||||
Total securities available for sale | $ | 1,040,386 | 1,040,386 | 65,745 | 974,641 | — | |||||||||
Investment securities held to maturity: | |||||||||||||||
Agency obligations | $ | 4,306 | 4,225 | 4,225 | — | — | |||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 893 | 924 | — | 924 | — | ||||||||||
State and municipal obligations | 473,653 | 474,852 | — | 474,852 | — | ||||||||||
Corporate obligations | 9,331 | 9,286 | — | 9,286 | — | ||||||||||
Total securities held to maturity | $ | 488,183 | 489,287 | 4,225 | 485,062 | — | |||||||||
FHLBNY stock | 75,726 | 75,726 | 75,726 | — | — | ||||||||||
Loans, net of allowance for loan losses | 6,941,603 | 6,924,440 | — | — | 6,924,440 | ||||||||||
Derivative assets | 7,441 | 7,441 | 7,441 | ||||||||||||
Financial liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
Deposits other than certificates of deposits | $ | 5,902,446 | 5,902,446 | 5,902,446 | — | — | |||||||||
Certificates of deposit | 651,183 | 653,772 | — | 653,772 | — | ||||||||||
Total deposits | $ | 6,553,629 | 6,556,218 | 5,902,446 | 653,772 | — | |||||||||
Borrowings | 1,612,745 | 1,617,023 | — | 1,617,023 | — | ||||||||||
Derivative liabilities | 6,750 | 6,750 | 6,750 | ||||||||||||
101
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(17) Selected Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
The following tables are a summary of certain quarterly financial data for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016.
2017 Quarters Ended | ||||||||||||
March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | |||||||||
(In thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||
Interest income | $ | 77,913 | 80,443 | 81,894 | 83,596 | |||||||
Interest expense | 10,878 | 11,388 | 11,682 | 11,696 | ||||||||
Net interest income | 67,035 | 69,055 | 70,212 | 71,900 | ||||||||
Provision for loan losses | 1,500 | 1,700 | 500 | 1,900 | ||||||||
Net interest income after provision for loan losses | 65,535 | 67,355 | 69,712 | 70,000 | ||||||||
Non-interest income | 12,465 | 14,819 | 15,112 | 13,301 | ||||||||
Non-interest expense | 46,124 | 47,340 | 46,280 | 48,078 | ||||||||
Income before income tax expense | 31,876 | 34,834 | 38,544 | 35,223 | ||||||||
Income tax expense | 8,368 | 10,451 | 11,969 | 15,740 | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 23,508 | 24,383 | 26,575 | 19,483 | |||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.30 | |||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.30 | |||||||
2016 Quarters Ended | ||||||||||||
March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | |||||||||
(In thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||
Interest income | $ | 73,974 | 74,805 | 76,045 | 77,491 | |||||||
Interest expense | 10,905 | 10,895 | 11,074 | 10,874 | ||||||||
Net interest income | 63,069 | 63,910 | 64,971 | 66,617 | ||||||||
Provision for loan losses | 1,500 | 1,700 | 1,000 | 1,200 | ||||||||
Net interest income after provision for loan losses | 61,569 | 62,210 | 63,971 | 65,417 | ||||||||
Non-interest income | 13,018 | 13,824 | 14,066 | 14,485 | ||||||||
Non-interest expense | 44,878 | 45,897 | 45,850 | 47,153 | ||||||||
Income before income tax expense | 29,709 | 30,137 | 32,187 | 32,749 | ||||||||
Income tax expense | 8,736 | 8,781 | 9,281 | 10,182 | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 20,973 | 21,356 | 22,906 | 22,567 | |||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 0.33 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.35 | |||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 0.33 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.35 | |||||||
102
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(18) Earnings Per Share
The following is a reconciliation of the outstanding shares used in the basic and diluted earnings per share calculations.
(Dollars in thousands, except per share data) | For the Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Net income | $ | 93,949 | 87,802 | 83,722 | |||||
Basic weighted average common shares outstanding | 64,384,851 | 63,643,622 | 62,945,669 | ||||||
Plus: | |||||||||
Dilutive shares | 194,371 | 208,364 | 169,049 | ||||||
Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding | 64,579,222 | 63,851,986 | 63,114,718 | ||||||
Earnings per share: | |||||||||
Basic | $ | 1.46 | 1.38 | 1.33 | |||||
Diluted | $ | 1.45 | 1.38 | 1.33 | |||||
Anti-dilutive stock options and awards totaling 369,772 shares, 432,895 shares and 469,018 shares at December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively, were excluded from the earnings per share calculations.
103
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(19) Parent-only Financial Information
The condensed financial statements of Provident Financial Services, Inc. (parent company only) are presented below:
Condensed Statements of Financial Condition
(Dollars in Thousands)
December 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||
Assets | ||||||
Cash and due from banks | $ | 16,921 | 31,851 | |||
Securities available for sale, at fair value | 658 | 549 | ||||
Investment in subsidiary | 1,244,670 | 1,177,110 | ||||
Due from subsidiary—SAP | (4,419 | ) | (3,004 | ) | ||
ESOP loan | 41,419 | 45,971 | ||||
Other assets | (37 | ) | (31 | ) | ||
Total assets | $ | 1,299,212 | 1,252,446 | |||
Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | ||||||
Other liabilities | 551 | 665 | ||||
Total stockholders’ equity | 1,298,661 | 1,251,781 | ||||
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $ | 1,299,212 | 1,252,446 | |||
Condensed Statements of Operations
(Dollars in Thousands)
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Dividends from subsidiary | $ | 59,980 | 45,369 | 41,285 | |||||
Interest income | 1,839 | 1,995 | 2,153 | ||||||
Investment gain | 17 | 15 | 12 | ||||||
Total income | 61,836 | 47,379 | 43,450 | ||||||
Non-interest expense | 1,021 | 902 | 812 | ||||||
Total expense | 1,021 | 902 | 812 | ||||||
Income before income tax expense | 60,815 | 46,477 | 42,638 | ||||||
Income tax expense | 312 | 414 | 505 | ||||||
Income before undistributed net income of subsidiary | 60,503 | 46,063 | 42,133 | ||||||
Earnings in excess of dividends (equity in undistributed net income) of subsidiary | 33,446 | 41,739 | 41,589 | ||||||
Net income | $ | 93,949 | 87,802 | 83,722 | |||||
104
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Condensed Statements of Cash Flows
(Dollars in Thousands)
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 93,949 | 87,802 | 83,722 | |||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities | |||||||||
Earnings in excess of dividends (equity in undistributed net income) of subsidiary | (33,446 | ) | (41,739 | ) | (41,589 | ) | |||
ESOP allocation | 4,600 | 3,706 | 2,997 | ||||||
SAP allocation | 4,963 | 3,812 | 4,625 | ||||||
Stock option allocation | 203 | 172 | 272 | ||||||
Decrease in due from subsidiary—SAP | 1,415 | 465 | 5,333 | ||||||
Increase in other assets | (34,919 | ) | (8,177 | ) | (8,406 | ) | |||
Decrease in other liabilities | (114 | ) | (70 | ) | (55 | ) | |||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 36,651 | 45,971 | 46,899 | ||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | |||||||||
Net decrease in ESOP loan | 4,552 | 3,901 | 3,566 | ||||||
Net cash provided by investing activities | 4,552 | 3,901 | 3,566 | ||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | |||||||||
Purchases of treasury stock | (443 | ) | (1,557 | ) | — | ||||
Purchase of employee restricted shares to fund statutory tax withholding | (778 | ) | (1,225 | ) | (1,988 | ) | |||
Cash dividends paid | (59,980 | ) | (45,369 | ) | (41,285 | ) | |||
Shares issued dividend reinvestment plan | 2,114 | 1,652 | 1,447 | ||||||
Stock options exercised | 2,954 | 6,198 | 3,166 | ||||||
Net cash used in financing activities | (56,133 | ) | (40,301 | ) | (38,660 | ) | |||
Net (decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents | (14,930 | ) | 9,571 | 11,805 | |||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 31,851 | 22,280 | 10,475 | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 16,921 | 31,851 | 22,280 | |||||
105
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(20) Other Comprehensive (Loss) Income
The following table presents the components of other comprehensive (loss) income both gross and net of tax, for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 (in thousands):
For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Before Tax | Tax Effect | After Tax | Before Tax | Tax Effect | After Tax | Before Tax | Tax Effect | After Tax | |||||||||||||||||||
Components of Other Comprehensive (Loss)Income: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized gains and losses on securities available for sale: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net (losses) gains arising during the period | $ | (3,612 | ) | 1,449 | (2,163 | ) | (7,405 | ) | 2,974 | (4,431 | ) | (5,683 | ) | 2,282 | (3,401 | ) | |||||||||||
Reclassification adjustment for gains included in net income | — | — | — | (50 | ) | 20 | (30 | ) | (654 | ) | 263 | (391 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Total | (3,612 | ) | 1,449 | (2,163 | ) | (7,455 | ) | 2,994 | (4,461 | ) | (6,337 | ) | 2,545 | (3,792 | ) | ||||||||||||
Unrealized gains (losses) on derivatives (cash flow hedges) | 633 | (254 | ) | 379 | 404 | (162 | ) | 242 | (122 | ) | 49 | (73 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Amortization related to post retirement obligations | (1,475 | ) | 586 | (889 | ) | 5,628 | (2,260 | ) | 3,368 | 2,156 | (866 | ) | 1,290 | ||||||||||||||
Total other comprehensive (loss) income | $ | (4,454 | ) | 1,781 | (2,673 | ) | (1,423 | ) | 572 | (851 | ) | (4,303 | ) | 1,728 | (2,575 | ) | |||||||||||
The Company, in accordance with ASU No. 2018-02, has elected to reclassify the income tax effects of the Tax Act from accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income to retained earning for the year ended December 31, 2017
The following table presents the changes in the components of accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income, net of tax, for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, including the reclassification of income tax effects due to the adoption of ASU No. 2018-02 for the year ended December 31, 2017 (in thousands):
Changes in Accumulated Other Comprehensive (Loss) Income by Component, net of tax For the Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized Gains on Securities Available for Sale | Post-Retirement Obligations | Unrealized gains (losses) on Derivatives (cash flow hedges) | Accumulated Other Comprehensive (Loss) Income | Unrealized Gains on Securities Available for Sale | Post-Retirement Obligations | Unrealized gains (losses) on Derivatives (cash flow hedges) | Accumulated Other Comprehensive (Loss) Income | ||||||||||||||||||
Balance at the beginning of the period | $ | (510 | ) | (3,056 | ) | 169 | (3,397 | ) | 3,951 | (6,424 | ) | (73 | ) | (2,546 | ) | ||||||||||
Current period change in other comprehensive income (loss) | (2,163 | ) | (889 | ) | 379 | (2,673 | ) | (4,461 | ) | 3,368 | 242 | (851 | ) | ||||||||||||
Reclassification of tax effects due to the adoption of ASU No. 2018-02 | (619 | ) | (901 | ) | 125 | (1,395 | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Balance at the end of the period | $ | (3,292 | ) | (4,846 | ) | 673 | (7,465 | ) | (510 | ) | (3,056 | ) | 169 | (3,397 | ) | ||||||||||
106
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
The following table summarizes the reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 (in thousands):
Reclassifications Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | ||||||||||||||
Amount reclassified from AOCI for the years ended December 31, | Affected line item in the Consolidated Statement of Income | |||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||
Details of AOCI: | ||||||||||||||
Securities available for sale: | ||||||||||||||
Realized net gains on the sale of securities available for sale | $ | — | 50 | 654 | Net gain on securities transactions | |||||||||
— | (20 | ) | (263 | ) | Income tax expense | |||||||||
— | 30 | 391 | Net of tax | |||||||||||
Post-retirement obligations: | ||||||||||||||
Amortization of actuarial losses | 243 | 943 | 774 | Compensation and employee benefits (1) | ||||||||||
(64 | ) | (379 | ) | (311 | ) | Income tax expense | ||||||||
179 | 564 | 463 | Net of tax | |||||||||||
Total reclassifications | $ | 179 | 594 | 854 | Net of tax | |||||||||
(1) This item is included in the computation of net periodic benefit cost. See Note 11. Benefit Plans
107
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Note 21. Derivative and Hedging Activities
The Company is exposed to certain risks arising from both its business operations and economic conditions. The Company principally manages its exposures to a wide variety of business and operational risks through management of its core business activities. The Company manages economic risks, including interest rate, liquidity, and credit risk, primarily by managing the amount, sources, and duration of its assets and liabilities.
Non-designated Hedges. Derivatives not designated in qualifying hedging relationships are not speculative and result from a service the Company provides to certain qualified commercial borrowers in loan related transactions and, therefore, are not used to manage interest rate risk in the Company’s assets or liabilities. The Company executes interest rate swaps with qualified commercial banking customers to facilitate their respective risk management strategies. Those interest rate swaps are simultaneously hedged by offsetting interest rate swaps that the Company executes with a third party, such that the Company minimizes its net risk exposure resulting from such transactions. The interest rate swap agreement which the Company executes with the commercial borrower is collateralized by the borrower's commercial real estate financed by the Company. The collateral exceeds the maximum potential amount of future payments under the credit derivative. As the interest rate swaps associated with this program do not meet the hedge accounting requirements, changes in the fair value of both the customer swaps and the offsetting swaps are recognized directly in earnings. For the years ended December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, the Company had 50 and 36 interest rate swaps with an aggregate notional amount of $734.3 million and $582.2 million, respectively, related to this program. The Company has credit derivatives resulting from participations in interest rate swaps provided to external lenders as part of loan participation arrangements; therefore, they are not used to manage interest rate risk in the Company's assets or liabilities.
Cash flow Hedges of Interest Rate Risk. The Company’s objective in using interest rate derivatives is to add stability to interest expense and to manage its exposure to interest rate movements. To accomplish this objective, the Company primarily uses interest rate swaps as part of its interest rate risk management strategy. Interest rate swaps designated as cash flow hedges involve the receipt of variable amounts from a counterparty in exchange for the Company making fixed-rate payments over the life of the agreements without exchange of the underlying notional amount.
The effective portion of changes in the fair value of derivatives designated and that qualify as cash flow hedges are recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) and are subsequently reclassified into earnings in the period that the hedged forecasted transaction affects earnings. During the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, such derivatives were used to hedge the variable cash outflows associated with Federal Home Loan Bank borrowings. The ineffective portion of the change in fair value of the derivatives is recognized directly in earnings. The Company implemented this program during the quarter ended September 30, 2015. During the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, the Company’s did not record any hedge ineffectiveness.
Amounts reported in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) related to derivatives will be reclassified to interest expense as interest payments are made on the Company’s debt. During the next twelve months, the Company estimates that $127,492 will be reclassified as a decrease to interest expense. As of December 31, 2017, the Company had two outstanding interest rate derivatives with a notional amount of $60.0 million that was designated as a cash flow hedge of interest rate risk.
The table below presents the fair value of the Company’s derivative financial instruments as well as their classification on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 (in thousands):
108
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
As of December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||
Asset Derivatives | Liability Derivatives | |||||||||||
Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition | Fair Value | Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition | Fair Value | |||||||||
Derivatives not designated as a hedging instruments: | ||||||||||||
Interest rate products | Other assets | $ | 6,303 | Other liabilities | $ | 6,315 | ||||||
Credit contracts | Other assets | 1 | — | |||||||||
Total derivatives not designated as hedging instruments | $ | 6,304 | $ | 6,315 | ||||||||
Derivatives designated as a hedging instrument: | ||||||||||||
Interest rate products | Other assets | $ | 915 | Other liabilities | $ | — | ||||||
Total derivatives designated as hedging instruments | $ | 915 | $ | — | ||||||||
As of December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
Asset Derivatives | Liability Derivatives | |||||||||||
Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition | Fair Value | Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition | Fair Value | |||||||||
Derivatives not designated as a hedging instruments: | ||||||||||||
Interest rate products | Other assets | $ | 7,156 | Other liabilities | $ | 6,750 | ||||||
Credit contracts | Other assets | 3 | — | |||||||||
Total derivatives not designated as hedging instruments | $ | 7,159 | $ | 6,750 | ||||||||
Derivatives designated as a hedging instrument: | ||||||||||||
Interest rate products | Other assets | $ | 282 | Other liabilities | $ | — | ||||||
Total derivatives designated as hedging instruments | $ | 282 | $ | — | ||||||||
The tables below present the effect of the Company’s derivative financial instruments on the Consolidated Statements of Income for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 (in thousands).
Gain (loss) recognized in Income on derivatives | ||||||||||||||
For the Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
Consolidated Statements of Income | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||
Derivatives not designated as a hedging instruments: | ||||||||||||||
Interest rate products | Other income | $ | (422 | ) | $ | 186 | $ | 238 | ||||||
Credit contracts | Other income | 2 | 120 | (1 | ) | |||||||||
Total derivatives not designated as hedging instruments | $ | (420 | ) | $ | 306 | $ | 237 | |||||||
Derivatives designated as a hedging instruments: | ||||||||||||||
Interest rate products | Interest expense | (205 | ) | (394 | ) | (122 | ) | |||||||
Total derivatives designated as a hedging instruments | $ | (205 | ) | $ | (394 | ) | $ | (122 | ) | |||||
109
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
The Company has agreements with certain of its derivative counterparties that contain a provision that if the Company defaults on any of its indebtedness, including default where repayment of the indebtedness has not been accelerated by the lender, then the Company could also be declared in default on its derivative obligations.
In addition, the Company has agreements with certain of its derivative counterparties that contain a provision that if the Company fails to maintain its status as a well/adequately capitalized institution, then the counterparty could terminate the derivative positions and the Company would be required to settle its obligations under the agreements.
As of December 31, 2017, the termination value of derivatives in a net liability position, which includes accrued interest, was $352,000. The Company has minimum collateral posting thresholds with certain of its derivative counterparties, and has posted collateral of $250,000 against its obligations under these agreements. If the Company had breached any of these provisions at December 31, 2017, it could have been required to settle its obligations under the agreements at the termination value.
110
Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
None.
Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Christopher Martin, the Company’s Principal Executive Officer, and Thomas M. Lyons, the Company’s Principal Accounting Officer, conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended) as of December 31, 2017. Based upon their evaluation, they each found that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of that date.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. The Company’s internal control system is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance to the Company’s management and board of directors regarding the preparation and fair presentation of published financial statements.
The Company’s internal control over financial reporting includes policies and procedures that pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect transactions and dispositions of assets; provide reasonable assurances that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and the directors of the Company; and provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on its financial statements.
All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017. In making this assessment, we used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013). Based on the assessment management believes that, as of December 31, 2017, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting is effective based on those criteria.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Company’s independent registered public accounting firm that audited the consolidated financial statements has issued an audit report on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017. This report appears on page 55 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
During the last quarter of the year under report, there was no change in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. | Other Information |
None.
111
PART III
Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance |
Information required by this item regarding directors, executive officers and corporate governance is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement to be filed for the Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on April 26, 2018.
Item 11. | Executive Compensation |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement to be filed for the Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on April 26, 2018.
Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement to be filed for the Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on April 26, 2018.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
Set forth below is information as of December 31, 2017 regarding equity compensation plans categorized by those plans that have been approved by the Company's stockholders. There are no plans that have not been approved by the Company's stockholders.
Plan | Number of Securities to be Issued Upon Exercise of Outstanding Options and Rights(1) | Weighted Average Exercise Price(2) | Number of Securities Remaining Available For Issuance Under Plan (3) | ||||||
Equity compensation plans approved by stockholders | 507,656 | $ | 16.84 | 1,820,026 | |||||
Total | 507,656 | $ | 16.84 | 1,820,026 | |||||
________________________
(1) | Consists of outstanding stock options to purchase 507,656 shares of common stock granted under the Company’s stock-based compensation plans. |
(2) | The weighted average exercise price reflects an exercise price of $12.54 for 14,000 stock options granted in 2008; an exercise price of $10.40 for 33,336 stock options granted in 2009; an exercise price of $10.34 for 12,114 stock options granted in 2010; an exercise price of $14.50 for 64,622 stock options granted in 2011; an exercise price of $14.88 for 47,542 stock options and an exercise price of $14.68 for 10,000 stock options granted in 2012; an exercise price of $15.23 for 60,126 stock options granted in 2013; an exercise price of $16.38 for 80,760 stock options granted in 2014; and an exercise price of $18.34 for 65,972 stock options granted in 2015; an exercise price of $18.70 for 76,327 stock options granted in 2016; an exercise price of $26.31 for 42,857 stock options granted in 2017 under the Company’s stock-based compensation plans. |
(3) | Represents the number of available shares that may be granted as stock options and other stock awards under the Company’s stock-based compensation plans. |
Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement to be filed for the Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on April 26, 2018.
Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement to be filed for the Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on April 26, 2018.
112
PART IV
Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
The exhibits and financial statement schedules filed as a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K are as follows:
(a)(1) Financial Statements
Page Number | |
(a)(2) Financial Statement Schedules
No financial statement schedules are filed because the required information is not applicable or is included in the consolidated financial statements or related notes.
(a)(3) Exhibits
3.1 | |
3.2 | |
4.1 | |
10.1 | |
10.2 | |
10.3 | |
10.4 | |
10.5 | |
113
10.6 | |
10.7 | |
10.8 | |
10.9 | |
10.10 | |
10.11 | |
10.12 | |
10.13 | |
21 | |
23 | |
31.1 | |
31.2 | |
32 | |
101 | The following materials from the Company’s Annual Report to Stockholders on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2017, formatted in XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language): (i) the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition, (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Operations, (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income, (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholder’s Equity, (v) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows and (vi) the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
101.INS | XBRL Instance Document |
101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Labels Linkbase Document |
101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
Item 16. | Form 10-K Summary |
Not applicable.
114
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
PROVIDENT FINANCIAL SERVICES, INC. | ||||
Date: | March 1, 2018 | By: | /s/ CHRISTOPHER MARTIN | |
Christopher Martin | ||||
Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer | ||||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
By: | /s/ CHRISTOPHER MARTIN | By: | /s/ THOMAS M. LYONS | |||
Christopher Martin, Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | Thomas M. Lyons, Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) | |||||
Date: | March 1, 2018 | Date: | March 1, 2018 | |||
By: | /s/ FRANK S. MUZIO | |||||
Frank S. Muzio, Senior Vice President and Chief Accounting Officer (Principal Accounting Officer) | ||||||
Date: | March 1, 2018 | |||||
By: | /s/ ROBERT ADAMO | By: | /s/ THOMAS W. BERRY | |||
Robert Adamo, Director | Thomas W. Berry, Director | |||||
Date: | March 1, 2018 | Date: | March 1, 2018 | |||
By: | /s/ LAURA L. BROOKS | By: | /s/ FRANK L. FEKETE | |||
Laura L. Brooks, Director | Frank L. Fekete, Director | |||||
Date: | March 1, 2018 | Date: | March 1, 2018 | |||
By: | /s/ TERENCE GALLAGHER | By: | /s/ MATTHEW K. HARDING | |||
Terence Gallagher, Director | Matthew K. Harding, Director | |||||
Date: | March 1, 2018 | Date: | March 1, 2018 | |||
By: | /s/ CARLOS HERNANDEZ | By: | ||||
Carlos Hernandez, Director | Edward O’Donnell, Director | |||||
Date: | March 1, 2018 | Date: | March 1, 2018 | |||
By: | /s/ JOHN PUGLIESE | |||||
John Pugliese, Director | ||||||
Date: | March 1, 2018 | |||||
115
