Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - BeiGene, Ltd. | a17-19943_18k.htm |
| EX-99.3 - EX-99.3 - BeiGene, Ltd. | a17-19943_1ex99d3.htm |
| EX-99.2 - EX-99.2 - BeiGene, Ltd. | a17-19943_1ex99d2.htm |
| EX-99.1 - EX-99.1 - BeiGene, Ltd. | a17-19943_1ex99d1.htm |
Exhibit 99.4
August 2017

2 Disclosures Certain statements contained in this presentation and in the accompanying oral presentation, other than statements of fact that are independently verifiable at the date hereof, may constitute forward-looking statements. Examples of such forward-looking statements include those regarding investigational drug candidates and clinical trials and the status and related results thereto, as well those regarding continuing and further development efforts and transactions with third parties. Such statements, based as they are on the current analysis and expectations of management, inherently involve numerous risks and uncertainties, known and unknown, many of which are beyond BeiGene’s control. Such risks include but are not limited to: the impact of general economic conditions, general conditions in the pharmaceutical industries, changes in the global and regional regulatory environments in the jurisdictions in which BeiGene does business, market volatility, fluctuations in costs and changes to the competitive environment. Consequently, actual future results may differ materially from the anticipated results expressed in the forward-looking statements. In the case of forward-looking statements regarding investigational drug candidates and continuing further development efforts, specific risks which could cause actual results to differ materially from BeiGene’s current analysis and expectations include: failure to demonstrate the safety, tolerability and efficacy of our drug candidates, final and quality controlled verification of data and the related analyses, the expense and uncertainty of obtaining regulatory approval, including from the FDA, CFDA and EMA, and the possibility of having to conduct additional clinical trials. Further, even if regulatory approval is obtained, pharmaceutical products are generally subject to stringent on-going governmental regulation, challenges in gaining market acceptance and competition. These statements are also subject to a number of material risks and uncertainties that are described in BeiGene’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The reader should not place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements included in this presentation or in the accompanying oral presentation. These statements speak only as of the date made, and BeiGene is under no obligation and disavows any obligation to update or revise such statements as a result of any event, circumstances or otherwise, unless required by applicable legislation or regulation. Clinical data in this presentation relating to BeiGene’s investigational drug candidates is from early phase, single-arm trials. When such data are presented in relation to other investigational or marketed drug products, the presentation and discussion are not based on head-to-head trials between BeiGene’s investigational drug candidates and other products. BeiGene is still conducting clinical trials and, as additional patients are enrolled and evaluated, data on BeiGene’s investigational drug candidates may change. This presentation and the accompanying oral presentation contains data and information obtained from third-party studies and internal company analysis of such data and information. BeiGene has not independently verified the data and information obtained from these sources. Forward-looking information obtained from these sources is subject to the same qualifications noted above.

Investment Highlights Global oncology company with four internally developed assets, each with demonstrated proof-of-concept and a potentially differentiated profile Lead asset BGB-3111, a potentially best-in-class BTK inhibitor, is in registrational trials both globally and in China; PD-1 mAb in registrational trials in China and recently partnered with Celgene to expand global development; third asset PARP inhibitor also expected to enter late-stage development Strategic collaboration with Celgene transforms BeiGene into commercial-stage company in China in advance of potential future commercialization of internally developed compounds Structural advantages as a local player in China, the world’s second largest pharma market We believe all of our clinical-stage assets are the first in their classes to be developed under the domestic regulatory pathway in China to enter clinical testing and present data Productive drug discovery engine, expanding global development capabilities, and world-renowned scientific advisory board 3

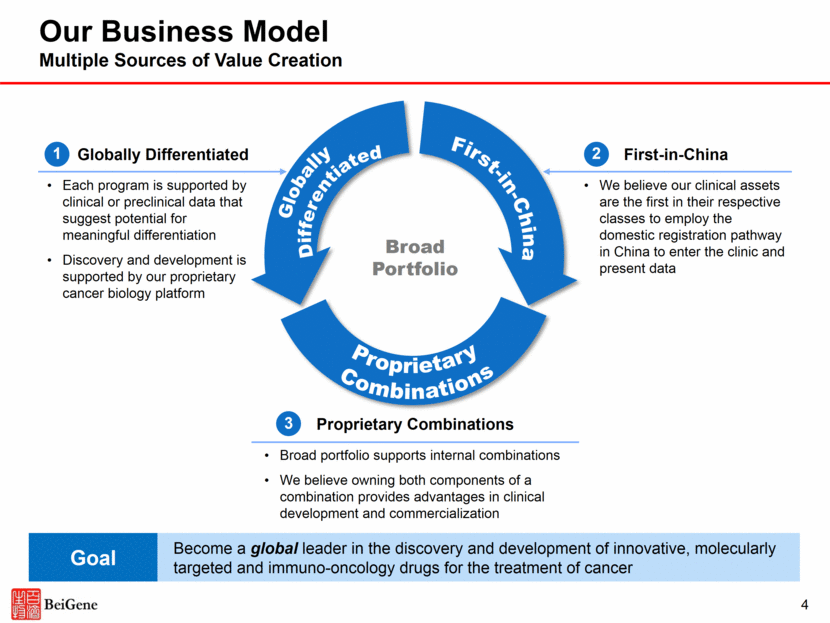
Our Business Model Multiple Sources of Value Creation Broad Portfolio First-in-China Globally Differentiated Proprietary Combinations First-in-China Proprietary Combinations Globally Differentiated 1 2 3 Each program is supported by clinical or preclinical data that suggest potential for meaningful differentiation Discovery and development is supported by our proprietary cancer biology platform We believe our clinical assets are the first in their respective classes to employ the domestic registration pathway in China to enter the clinic and present data Broad portfolio supports internal combinations We believe owning both components of a combination provides advantages in clinical development and commercialization 4 Become a global leader in the discovery and development of innovative, molecularly targeted and immuno-oncology drugs for the treatment of cancer Goal
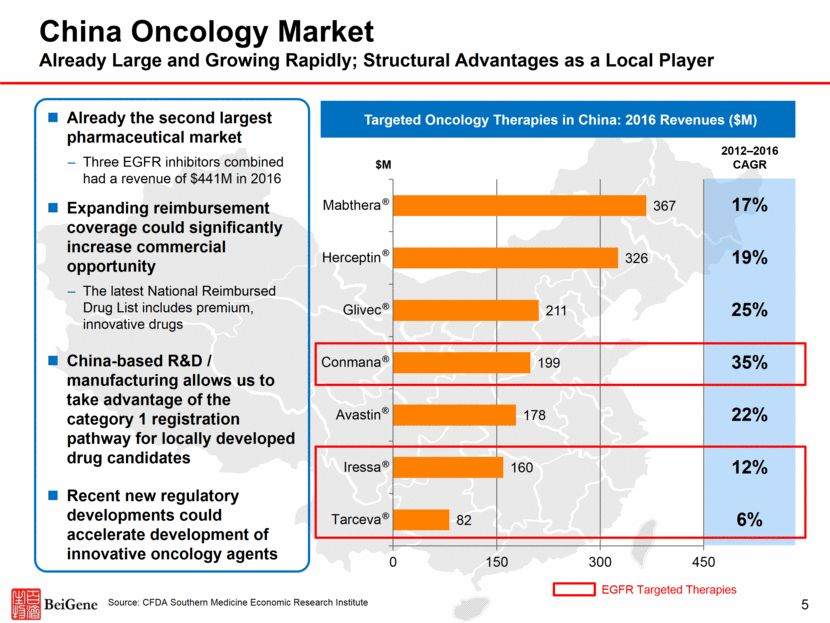
China Oncology Market Already Large and Growing Rapidly; Structural Advantages as a Local Player Already the second largest pharmaceutical market Three EGFR inhibitors combined had a revenue of $441M in 2016 Expanding reimbursement coverage could significantly increase commercial opportunity The latest National Reimbursed Drug List includes premium, innovative drugs China-based R&D / manufacturing allows us to take advantage of the category 1 registration pathway for locally developed drug candidates Recent new regulatory developments could accelerate development of innovative oncology agents Targeted Oncology Therapies in China: 2016 Revenues ($M) $M 2012–2016 CAGR 17% 19% 25% 35% 22% 6% 12% Source: CFDA Southern Medicine Economic Research Institute ® ® ® ® ® ® ® EGFR Targeted Therapies 5
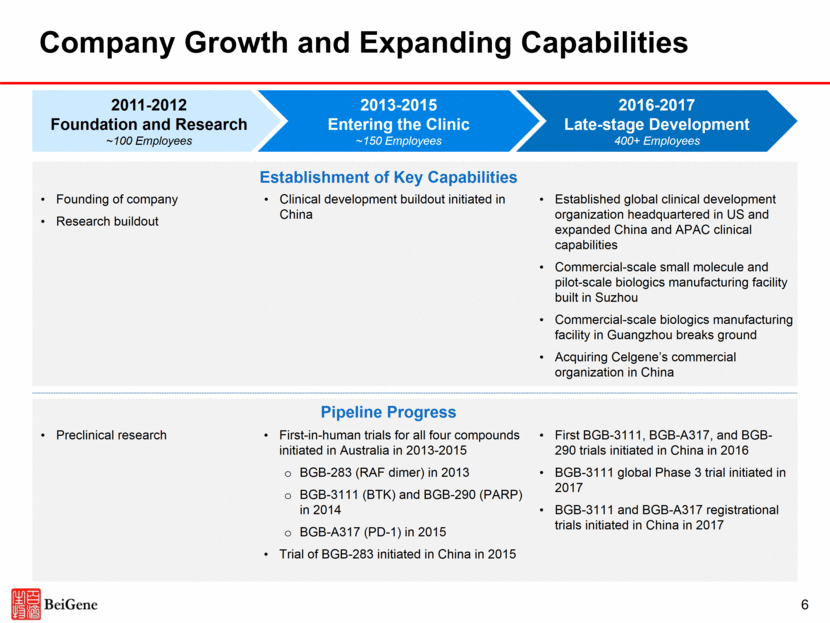
Company Growth and Expanding Capabilities 2013-2015 Entering the Clinic ~150 Employees 2011-2012 Foundation and Research ~100 Employees 2016-2017 Late-stage Development 400+ Employees Founding of company Research buildout Clinical development buildout initiated in China Established global clinical development organization headquartered in US and expanded China and APAC clinical capabilities Commercial-scale small molecule and pilot-scale biologics manufacturing facility built in Suzhou Commercial-scale biologics manufacturing facility in Guangzhou breaks ground Acquiring Celgene’s commercial organization in China Establishment of Key Capabilities Preclinical research First-in-human trials for all four compounds initiated in Australia in 2013-2015 BGB-283 (RAF dimer) in 2013 BGB-3111 (BTK) and BGB-290 (PARP) in 2014 BGB-A317 (PD-1) in 2015 Trial of BGB-283 initiated in China in 2015 First BGB-3111, BGB-A317, and BGB-290 trials initiated in China in 2016 BGB-3111 global Phase 3 trial initiated in 2017 BGB-3111 and BGB-A317 registrational trials initiated in China in 2017 Pipeline Progress 6
Strategic Collaboration With Celgene BGNE to Acquire China Commercial Ops; CELG to License A317 in Major Markets ex-China Collaboration transforms BeiGene into commercial-stage company BeiGene to acquire Celgene’s operations in China BeiGene to license and assume commercial responsibility for Celgene’s approved therapies in China (ABRAXANE®, REVLIMID®, and VIDAZA®), and pipeline agent CC-122 Collaboration leverages both companies’ geographical strengths to maximize BGB-A317’s value Celgene to gain exclusive rights to develop and commercialize BGB-A317 for solid tumors in the US, Europe, Japan, and rest of the world outside Asia BeiGene to retain exclusive rights for solid tumors in Asia (ex-Japan), and for hematological malignancies and combinations with its portfolio products globally Initial payments and investments to exceed $400M; potential milestones of nearly $1B Upon closing, BeiGene to receive $263M in upfront licensing fees Celgene to invest $150M in BeiGene by purchasing 32.7 million (5.9%*) of BeiGene’s ordinary shares at $4.58 per share ($59.55 per ADS), a 35% premium** BeiGene eligible for up to $980M in development, regulatory, and sales milestones, as well as royalties Collaboration prepares BeiGene for the potential future commercialization of internally developed compounds in China 7 *Based on the shares outstanding as of July 5, 2017 **Premium calculated relative to an 11-day VWAP of BeiGene’s ADS ending June 30, 2017

Building Manufacturing Capacity Partnership with Guangzhou Development District for Biologics Manufacturing Joint venture (JV), BeiGene Biologics, formed with Guangzhou Development District (GDD) Between BeiGene Hong Kong and Guangzhou GET Technology Development, an affiliate of GDD To build a biologics manufacturing facility located in Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China JV also provides funding for research and clinical development in China Expected direct investments total RMB2.2 billion ($330M) BeiGene HK’s cash contribution totals RMB200 million ($30M) GET contributes RMB1 billion ($150M) including a small equity investment and a shareholder loan to the JV Shareholder loan from GET will have an annual interest rate of 8% and may be convertible to a minority equity interest in the JV subject to conditions and after the conversion GET is expected to remain a small minority holder of the JV Manufacturing factory (a subsidiary of the JV) expected to secure a commercial loan of RMB1 billion ($150M) and will receive an interest subsidy (subject to a certain limit) Provides increased funding for clinical trials BeiGene cash infusion to JV more than offset by clinical trial funding by JV No cash interest payment expected near-term Debt will be held at the subsidiary level of BeiGene with no recourse to the parent company Important strategic asset for the long-term growth of the Company 8

Ron Levy, M.D. Stanford, former Chief of Oncology The BeiGene Team Scientific Advisory Board Charles Sawyers, M.D. Past President of AACR. NCI Board of Scientific Councilors David Schenkein, M.D CEO of Agios; adjunct attending physician in hematology at Tufts Medical Center Neal Rosen, M.D., Ph.D. Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, Member in the Department of Medicine Jedd Wolchok, M.D., Ph.D. Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, Chief, Melanoma and Immunotherapeutics Service Team of 400+ in China, US, and Australia Xiaodong Wang, Ph.D. Founder & Chairman SAB John V. Oyler Founder & CEO Management National Institute of Biological Sciences in Beijing (NIBS) Howard Liang, Ph.D. CFO and Chief Strategy Officer Eric Hedrick, M.D. Chief Advisor Ji Li, Ph.D. Global Head of Business Development Amy Peterson, M.D. Chief Medical Officer, Immuno-oncology Jane Huang, M.D. Chief Medical Officer, Hematology Steve Young, Ph.D. Former Head of Medicinal Chemistry at Merck’s West Point lab 9
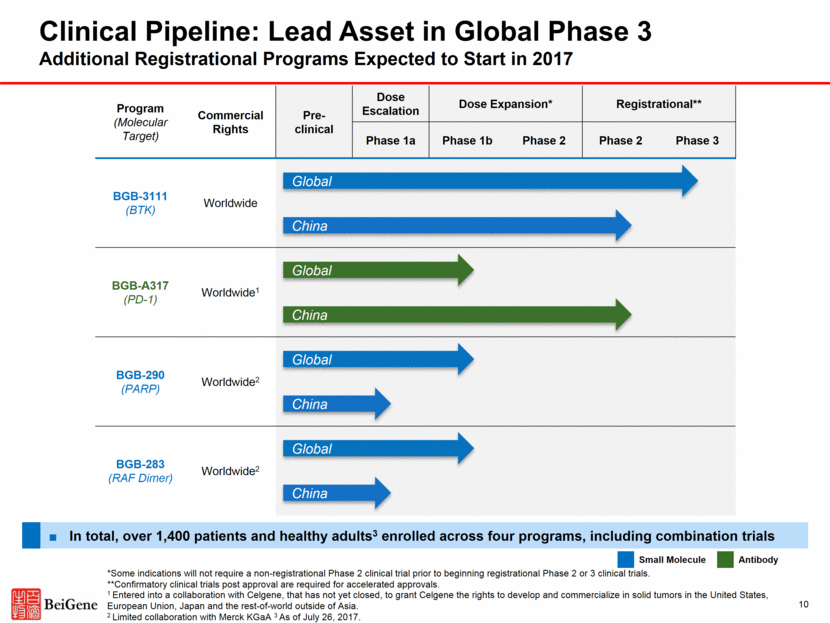
In total, over 1,400 patients and healthy adults3 enrolled across four programs, including combination trials Clinical Pipeline: Lead Asset in Global Phase 3 Additional Registrational Programs Expected to Start in 2017 Program (Molecular Target) Commercial Rights Pre-clinical Dose Escalation Dose Expansion* Registrational** Phase 1a Phase 1b Phase 2 Phase 2 Phase 3 BGB-3111 (BTK) Worldwide BGB-A317 (PD-1) Worldwide1 BGB-290 (PARP) Worldwide2 BGB-283 (RAF Dimer) Worldwide2 Global Global Global Global Small Molecule Antibody 10 1 Entered into a collaboration with Celgene, that has not yet closed, to grant Celgene the rights to develop and commercialize in solid tumors in the United States, European Union, Japan and the rest-of-world outside of Asia. 2 Limited collaboration with Merck KGaA 3 As of July 26, 2017. China China China China *Some indications will not require a non-registrational Phase 2 clinical trial prior to beginning registrational Phase 2 or 3 clinical trials. **Confirmatory clinical trials post approval are required for accelerated approvals.
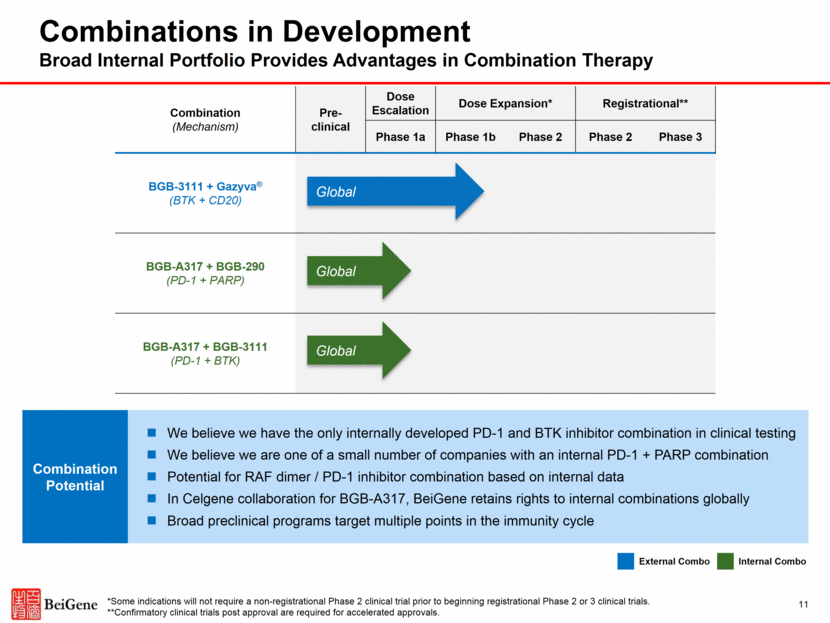
Combination (Mechanism) Pre-clinical Dose Escalation Dose Expansion* Registrational** Phase 1a Phase 1b Phase 2 Phase 2 Phase 3 BGB-3111 + Gazyva® (BTK + CD20) BGB-A317 + BGB-290 (PD-1 + PARP) BGB-A317 + BGB-3111 (PD-1 + BTK) Global Global Global External Combo Internal Combo 11 Combinations in Development Broad Internal Portfolio Provides Advantages in Combination Therapy We believe we have the only internally developed PD-1 and BTK inhibitor combination in clinical testing We believe we are one of a small number of companies with an internal PD-1 + PARP combination Potential for RAF dimer / PD-1 inhibitor combination based on internal data In Celgene collaboration for BGB-A317, BeiGene retains rights to internal combinations globally Broad preclinical programs target multiple points in the immunity cycle Combination Potential *Some indications will not require a non-registrational Phase 2 clinical trial prior to beginning registrational Phase 2 or 3 clinical trials. **Confirmatory clinical trials post approval are required for accelerated approvals.
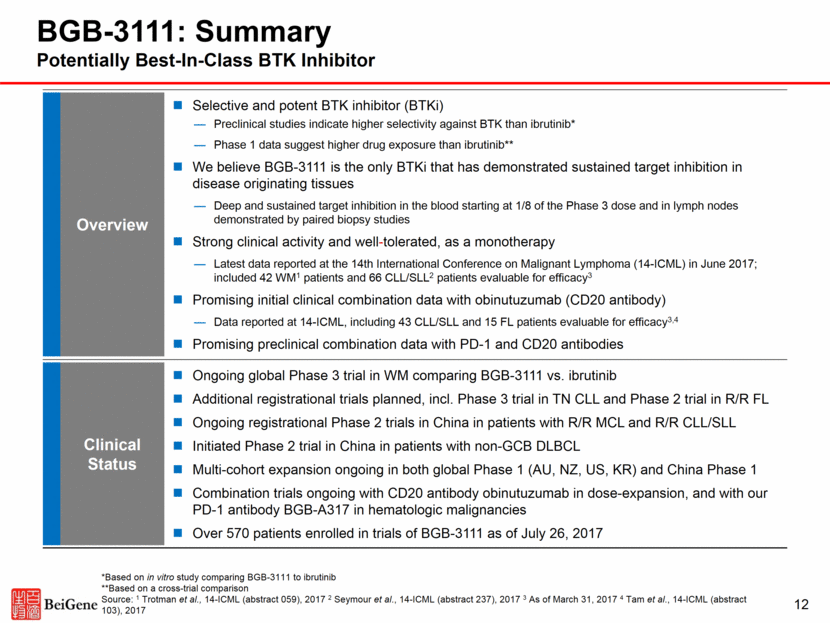
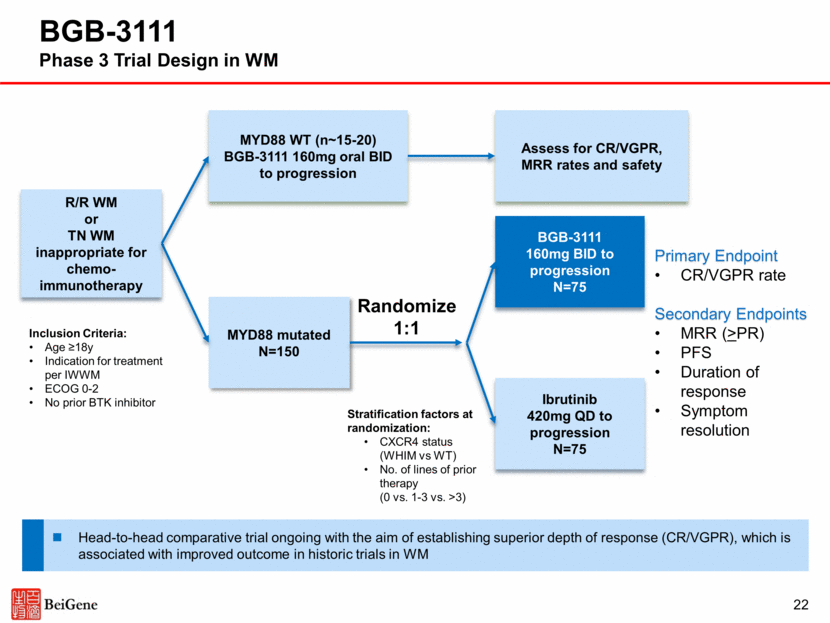
Overview Selective and potent BTK inhibitor (BTKi) Preclinical studies indicate higher selectivity against BTK than ibrutinib* Phase 1 data suggest higher drug exposure than ibrutinib** We believe BGB-3111 is the only BTKi that has demonstrated sustained target inhibition in disease originating tissues Deep and sustained target inhibition in the blood starting at 1/8 of the Phase 3 dose and in lymph nodes demonstrated by paired biopsy studies Strong clinical activity and well-tolerated, as a monotherapy Latest data reported at the 14th International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (14-ICML) in June 2017; included 42 WM1 patients and 66 CLL/SLL2 patients evaluable for efficacy3 Promising initial clinical combination data with obinutuzumab (CD20 antibody) Data reported at 14-ICML, including 43 CLL/SLL and 15 FL patients evaluable for efficacy3,4 Promising preclinical combination data with PD-1 and CD20 antibodies Clinical Status Ongoing global Phase 3 trial in WM comparing BGB-3111 vs. ibrutinib Additional registrational trials planned, incl. Phase 3 trial in TN CLL and Phase 2 trial in R/R FL Ongoing registrational Phase 2 trials in China in patients with R/R MCL and R/R CLL/SLL Initiated Phase 2 trial in China in patients with non-GCB DLBCL Multi-cohort expansion ongoing in both global Phase 1 (AU, NZ, US, KR) and China Phase 1 Combination trials ongoing with CD20 antibody obinutuzumab in dose-expansion, and with our PD-1 antibody BGB-A317 in hematologic malignancies Over 570 patients enrolled in trials of BGB-3111 as of July 26, 2017 12 BGB-3111: Summary Potentially Best-In-Class BTK Inhibitor *Based on in vitro study comparing BGB-3111 to ibrutinib **Based on a cross-trial comparison Source: 1 Trotman et al., 14-ICML (abstract 059), 2017 2 Seymour et al., 14-ICML (abstract 237), 2017 3 As of March 31, 2017 4 Tam et al., 14-ICML (abstract 103), 2017
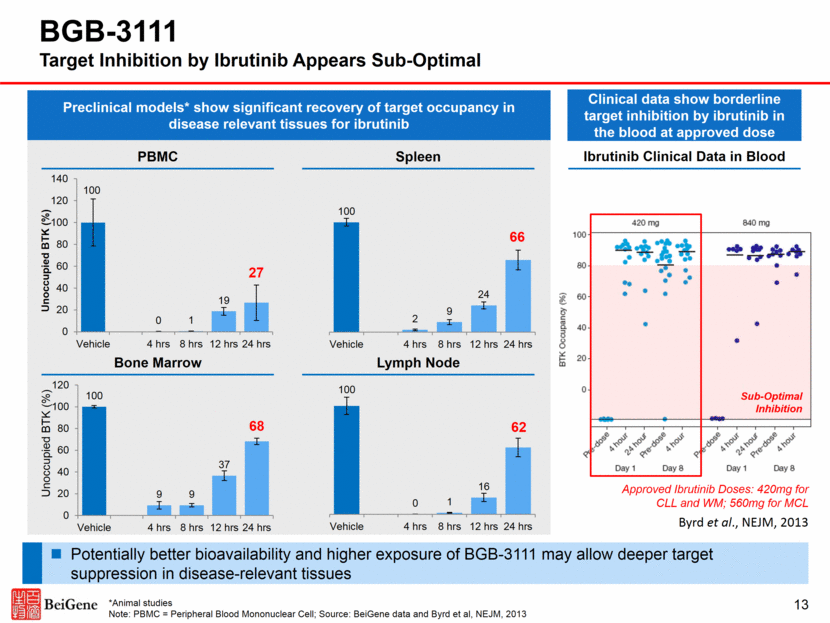
BGB-3111 Target Inhibition by Ibrutinib Appears Sub-Optimal Potentially better bioavailability and higher exposure of BGB-3111 may allow deeper target suppression in disease-relevant tissues *Animal studies Note: PBMC = Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell; Source: BeiGene data and Byrd et al, NEJM, 2013 Ibrutinib Clinical Data in Blood PBMC Spleen Bone Marrow Lymph Node Byrd et al., NEJM, 2013 Approved Ibrutinib Doses: 420mg for CLL and WM; 560mg for MCL Preclinical models* show significant recovery of target occupancy in disease relevant tissues for ibrutinib Clinical data show borderline target inhibition by ibrutinib in the blood at approved dose Sub-Optimal Inhibition 13 100 9 9 37 68 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 Vehicle 4 hrs 8 hrs 12 hrs 24 hrs Unoccupied BTK (%) 100 0 1 19 27 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 Vehicle 4 hrs 8 hrs 12 hrs 24 hrs Unoccupied BTK (%) 100 0 1 16 62 Vehicle 4 hrs 8 hrs 12 hrs 24 hrs 100 2 9 24 66 Vehicle 4 hrs 8 hrs 12 hrs 24 hrs
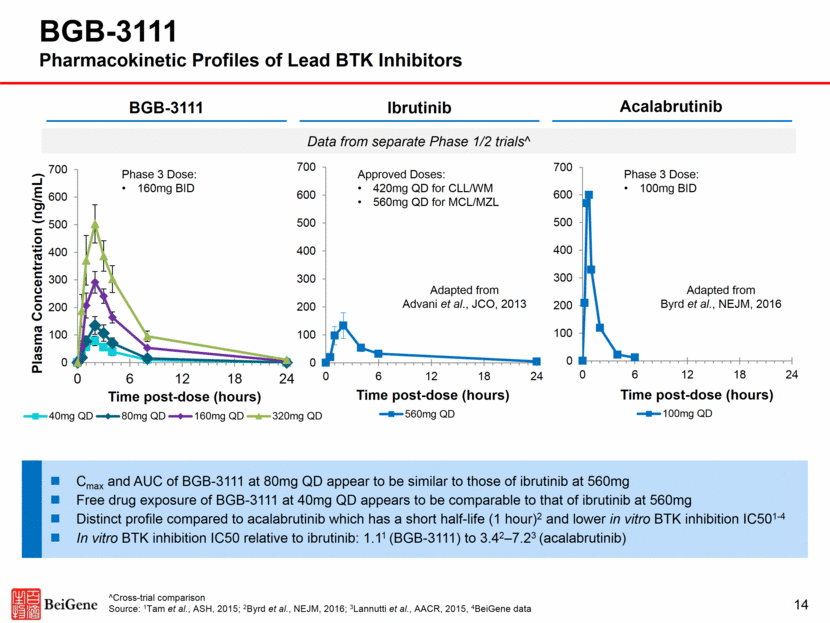
Adapted from Advani et al., JCO, 2013 BGB-3111 Pharmacokinetic Profiles of Lead BTK Inhibitors Cmax and AUC of BGB-3111 at 80mg QD appear to be similar to those of ibrutinib at 560mg Free drug exposure of BGB-3111 at 40mg QD appears to be comparable to that of ibrutinib at 560mg Distinct profile compared to acalabrutinib which has a short half-life (1 hour)2 and lower in vitro BTK inhibition IC501-4 In vitro BTK inhibition IC50 relative to ibrutinib: 1.11 (BGB-3111) to 3.42–7.23 (acalabrutinib) BGB-3111 Ibrutinib Acalabrutinib Adapted from Byrd et al., NEJM, 2016 ^Cross-trial comparison Source: 1Tam et al., ASH, 2015; 2Byrd et al., NEJM, 2016; 3Lannutti et al., AACR, 2015, 4BeiGene data Phase 3 Dose: 160mg BID Phase 3 Dose: 100mg BID Approved Doses: 420mg QD for CLL/WM 560mg QD for MCL/MZL 14 Data from separate Phase 1/2 trials^ 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 0 6 12 18 24 Time post - dose (hours) 560mg QD 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 0 6 12 18 24 Time post - dose (hours) 100mg QD 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 0 6 12 18 24 Plasma Concentration (ng/mL) Time post - dose (hours) 40mg QD 80mg QD 160mg QD 320mg QD
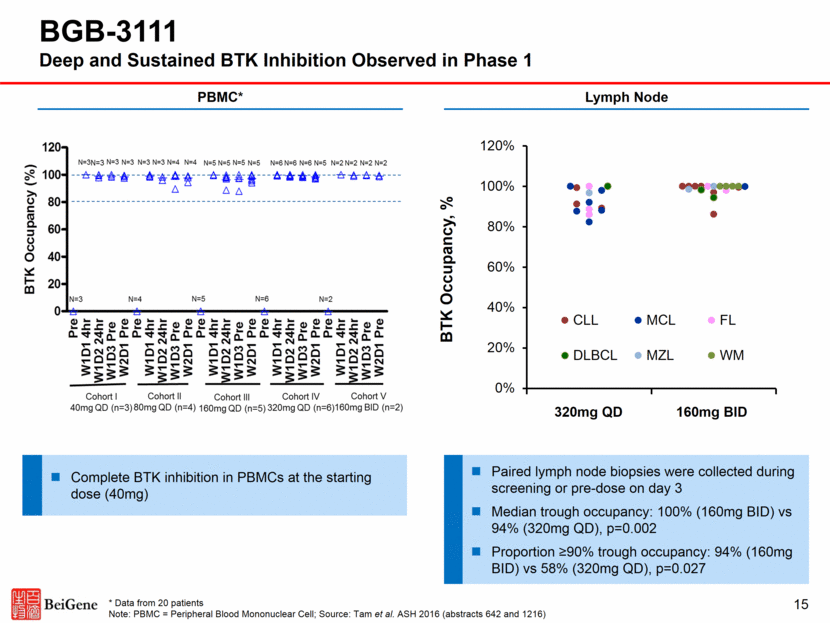
BGB-3111 Deep and Sustained BTK Inhibition Observed in Phase 1 15 PBMC* Lymph Node Complete BTK inhibition in PBMCs at the starting dose (40mg) Paired lymph node biopsies were collected during screening or pre-dose on day 3 Median trough occupancy: 100% (160mg BID) vs 94% (320mg QD), p=0.002 Proportion >90% trough occupancy: 94% (160mg BID) vs 58% (320mg QD), p=0.027 * Data from 20 patients Note: PBMC = Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell; Source: Tam et al. ASH 2016 (abstracts 642 and 1216) 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 120% 0 2 4 BTK Occupancy, % CLL MCL FL DLBCL MZL WM 320mg QD 160mg BID
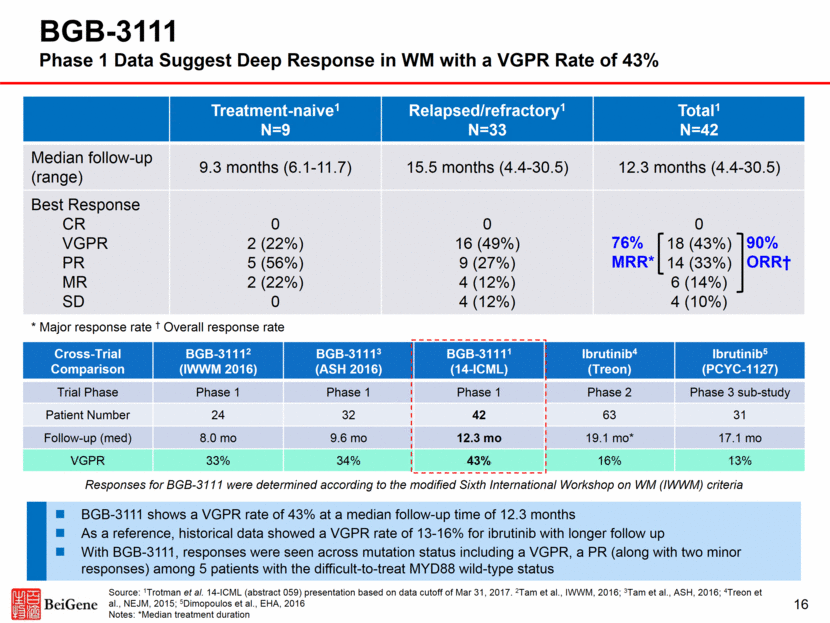
Cross-Trial Comparison BGB-31112 (IWWM 2016) BGB-31113 (ASH 2016) BGB-31111 (14-ICML) Ibrutinib4 (Treon) Ibrutinib5 (PCYC-1127) Trial Phase Phase 1 Phase 1 Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 sub-study Patient Number 24 32 42 63 31 Follow-up (med) 8.0 mo 9.6 mo 12.3 mo 19.1 mo* 17.1 mo VGPR 33% 34% 43% 16% 13% 16 BGB-3111 Phase 1 Data Suggest Deep Response in WM with a VGPR Rate of 43% Treatment-naive1 N=9 Relapsed/refractory1 N=33 Total1 N=42 Median follow-up (range) 9.3 months (6.1-11.7) 15.5 months (4.4-30.5) 12.3 months (4.4-30.5) Best Response CR VGPR PR MR SD 0 2 (22%) 5 (56%) 2 (22%) 0 0 16 (49%) 9 (27%) 4 (12%) 4 (12%) 0 18 (43%) 14 (33%) 6 (14%) 4 (10%) * Major response rate † Overall response rate 76% MRR* 90% ORR† BGB-3111 shows a VGPR rate of 43% at a median follow-up time of 12.3 months As a reference, historical data showed a VGPR rate of 13-16% for ibrutinib with longer follow up With BGB-3111, responses were seen across mutation status including a VGPR, a PR (along with two minor responses) among 5 patients with the difficult-to-treat MYD88 wild-type status Source: 1Trotman et al. 14-ICML (abstract 059) presentation based on data cutoff of Mar 31, 2017. 2Tam et al., IWWM, 2016; 3Tam et al., ASH, 2016; 4Treon et al., NEJM, 2015; 5Dimopoulos et al., EHA, 2016 Notes: *Median treatment duration Responses for BGB-3111 were determined according to the modified Sixth International Workshop on WM (IWWM) criteria
17 Treatment Naive (n = 16) Relapsed/ Refractory (n = 50) Total (n = 66) Median follow-up (range) 7.6 (3.7-11.6) 14.0 (2.2-26.8) 10.5 (2.2-26.8) Best Response ORR CR PR PR-L SD D/C prior to assessment 16 (100%) 1 (6%) 13 (81%) 2 (13%) 0 0 46 (92%) 1 (2%) 41 (82%) 4 (8%) 3 (6%) 1 (2%) 62 (94%) 2 (3%) 54 (82%) 6 (9%) 3 (5%) 1 (2%) BGB-3111 Phase 1 Results Suggest High Activity in CLL/SLL with an ORR of 94% Source: Seymour et al. 14-ICML 2017 (abstract 237) poster based on data cutoff of Mar 31, 2017 Highly active in CLL/SLL with an ORR of 94% at a median follow-up of 10.5 months ORR in patients with del17p and/or 11q- (n=22) was 96%
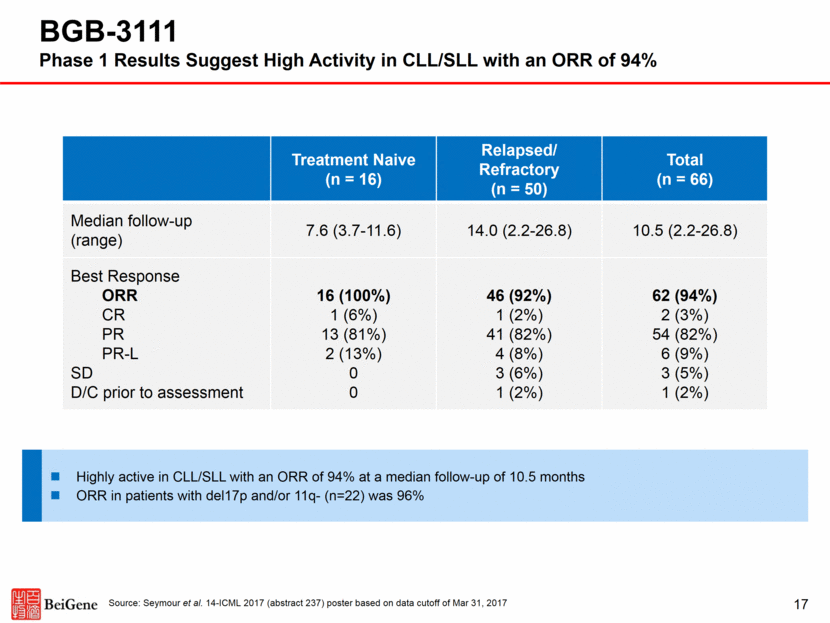
18 BGB-3111 Well-Tolerated in Phase 1 Trials in CLL/SLL and WM: Adverse Events Independent of Causality Most Frequent Adverse Events (>10%) Independent of Causality CLL (n=69)1 WM (n=48)2 AE, n (%) All Grade Grade 3-4 AE, n (%) All Grade Grade 3-4 Petechiae/purpura/contusion 32 (46%) 1 (1%) Petechiae/purpura/contusion 17 (35%) 0 (0%) Fatigue 20 (29%) 0 (0%) Upper respiratory tract infection 15 (31%) 0 (0%) Upper respiratory tract infection 19 (28%) 0 (0%) Constipation 12 (25%) 0 (0%) Cough 16 (23%) 0 (0%) Diarrhea 9 (19%) 1 (2%) Diarrhea 15 (22%) 0 (0%) Epistaxis 9 (19%) 0 (0%) Headache 13 (19%) 0 (0%) Nausea 8 (17%) 0 (0%) Hematuria 10 (15%) 0 (0%) Cough 7 (15%) 0 (0%) Nausea 9 (13%) 0 (0%) Anemia 7 (15%) 4 (8%) Rash 9 (13%) 0 (0%) Headache 7 (15%) 1 (2%) Arthralgia 8 (12%) 0 (0%) Neutropenia 6 (13%) 4 (8%) Muscle spasms 8 (12%) 0 (0%) Rash 6 (13%) 0 (0%) Urinary tract infection 8 (12%) 0 (0%) Sources: 1Seymour et al. 14-ICML 2017 (abstract 237) poster based on data cutoff of Mar 31, 2017; 2Trotman et al. 14-ICML (abstract 059) presentation based on data cutoff of Mar 31, 2017 Very low rate of treatment discontinuation for progression or adverse events In CLL, discontinuation rate for BGB-3111 is 3% (1.5% due to PD, 1.5% due to AE) at mF/U of 10.5 months
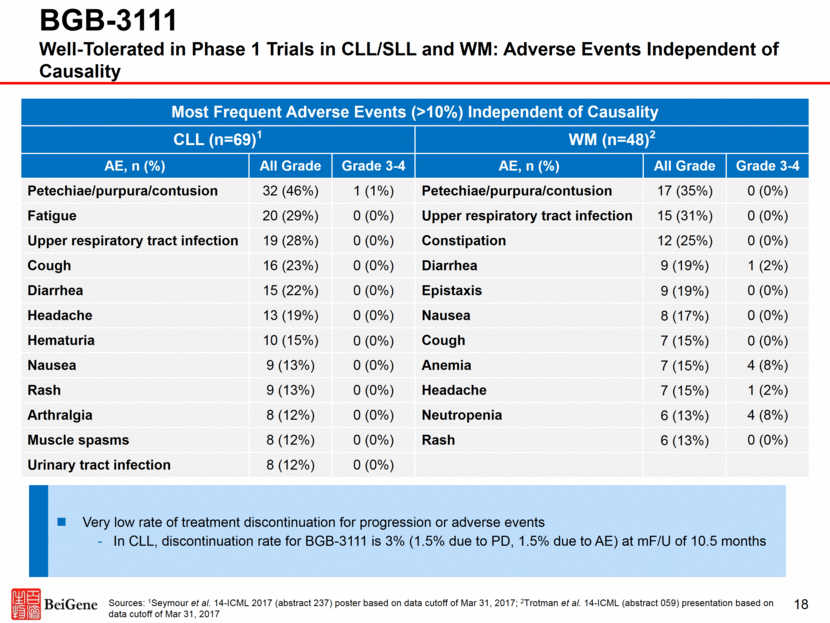
19 BGB-3111 + Obinutuzumab BGB-3111 Does Not Appear to Impair Rituximab-Induced ADCC 1 Data are from preclinical studies Source: Li N, et al. Cancer Res. 2015;75:2597 Published preclinical data suggest that off-target effects of ibrutinib may be detrimental to CD20 mAb-induced ADCC and the activity of the combination In a human MCL xenograft model, the combination of BGB-3111 and CD20 antibody demonstrated improved anti-tumor activity as compared to monotherapies and combination of ibrutinib and CD20 antibody 1
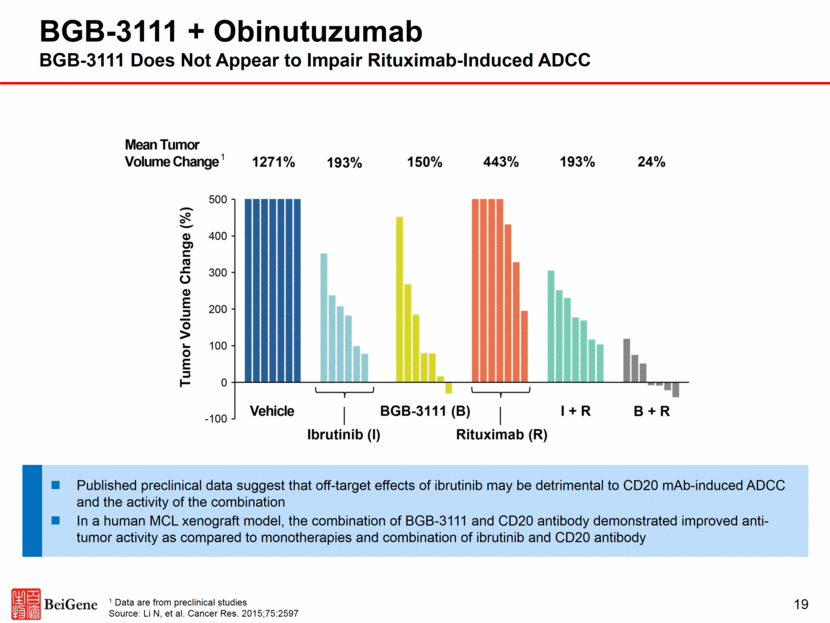
20 BGB-3111 + Obinutuzumab Initial Data Show CRs and High ORR in CLL/SLL and FL After a Short Follow-Up 1Occurred on July 20, 2017 Source: Tam et al., 14-ICML (abstract 103), 2017, presentation based on data cutoff of March 31, 2017 Follow-up and Response TN CLL/SLL (n = 18) R/R CLL/SLL (n = 25) FL (n = 15) Median follow-up, mo. (range) 7.0 (2.8-11.8) 8.0 (3.8-14.0) 6.2 (1.2-10.7) Best Response ORR CR PR PR-L SD PD 16 (89%) 4 (22%) 12 (67%) 0 2 (11%) 0 23 (92%) 4 (16%) 19 (76%) 0 1 (4%) 1 (4%) 11 (73%) 5 (33%) 6 (40%) N/A 2 (13%) 2 (13%) Initial Phase 1 data demonstrate that combination is well tolerated One serious adverse event of grade 3 intracranial bleeding was reported after the data cutoff1 In CLL/SLL, ORR was 89% including CRs in 22% of TN patients, and ORR was 92% with CRs in 16% of R/R patients In FL, ORR was 73% with CRs in 33% of R/R FL patients As of March 31, 2017, all responses (CLL and FL) are ongoing (range 3-23 months)
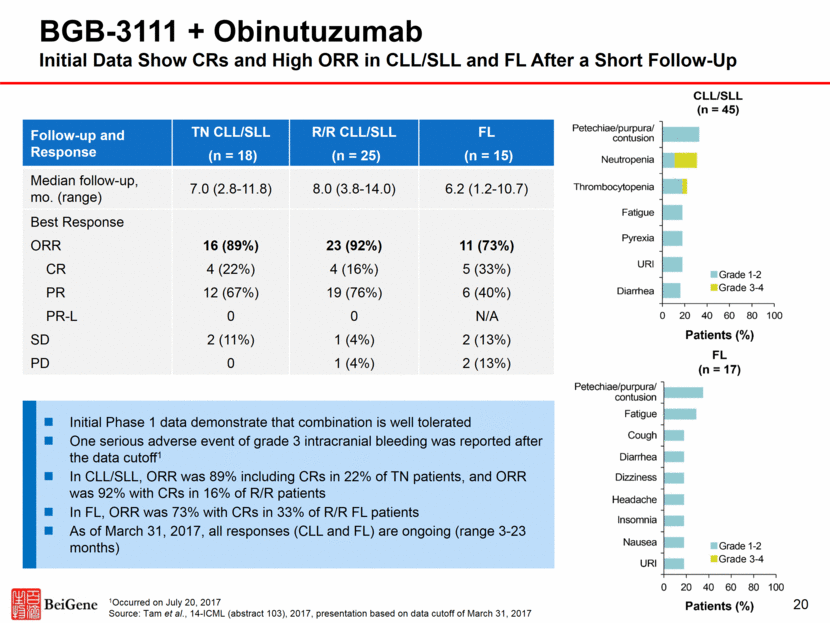
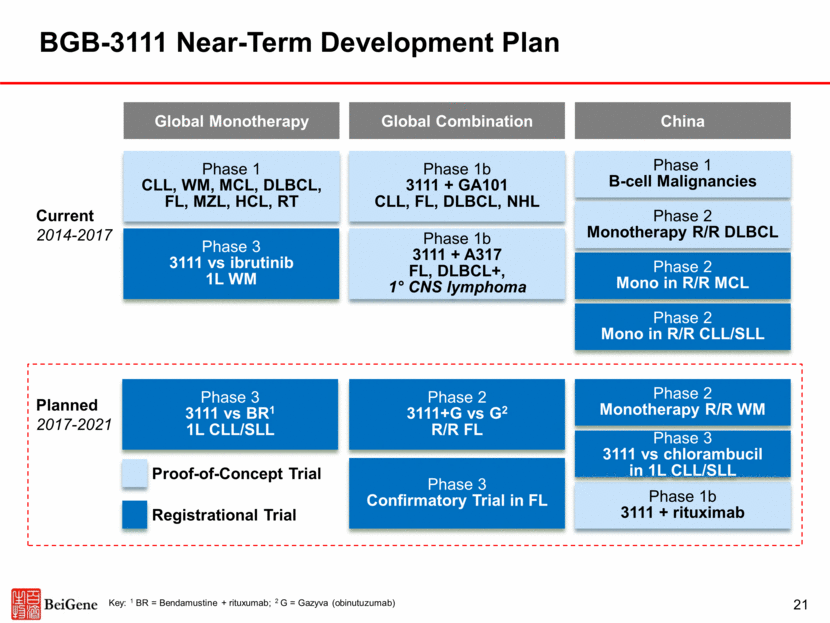
BGB-3111 Near-Term Development Plan Global Monotherapy China Global Combination Phase 1 CLL, WM, MCL, DLBCL, FL, MZL, HCL, RT Phase 1 B-cell Malignancies Phase 1b 3111 + GA101 CLL, FL, DLBCL, NHL Phase 1b 3111 + A317 FL, DLBCL+, 1° CNS lymphoma Phase 2 Mono in R/R MCL Phase 2 Mono in R/R CLL/SLL Phase 3 3111 vs ibrutinib 1L WM Phase 1b 3111 + rituximab Phase 2 Monotherapy R/R WM Phase 2 Monotherapy R/R DLBCL Phase 3 3111 vs chlorambucil in 1L CLL/SLL Phase 3 3111 vs BR1 1L CLL/SLL Phase 2 3111+G vs G2 R/R FL Phase 3 Confirmatory Trial in Earlier-line treatment of FL Current 2014-2017 Proof-of-Concept Trial Registrational Trial Planned 2017-2021 Key: 1 BR = Bendamustine + rituxumab; 2 G = Gazyva (obinutuzumab) 21
Stratification factors at randomization: CXCR4 status (WHIM vs WT) No. of lines of prior therapy (0 vs. 1-3 vs. >3) Inclusion Criteria: Age >18y Indication for treatment per IWWM ECOG 0-2 No prior BTK inhibitor Primary Endpoint CR/VGPR rate Secondary Endpoints MRR (>PR) PFS Duration of response Symptom resolution R/R WM or TN WM inappropriate for chemo-immunotherapy BGB-3111 160mg BID to progression N=75 Ibrutinib 420mg QD to progression N=75 MYD88 mutated N=150 MYD88 WT (n~15-20) BGB-3111 160mg oral BID to progression Assess for CR/VGPR, MRR rates and safety Randomize 1:1 BGB-3111 Phase 3 Trial Design in WM Head-to-head comparative trial ongoing with the aim of establishing superior depth of response (CR/VGPR), which is associated with improved outcome in historic trials 22
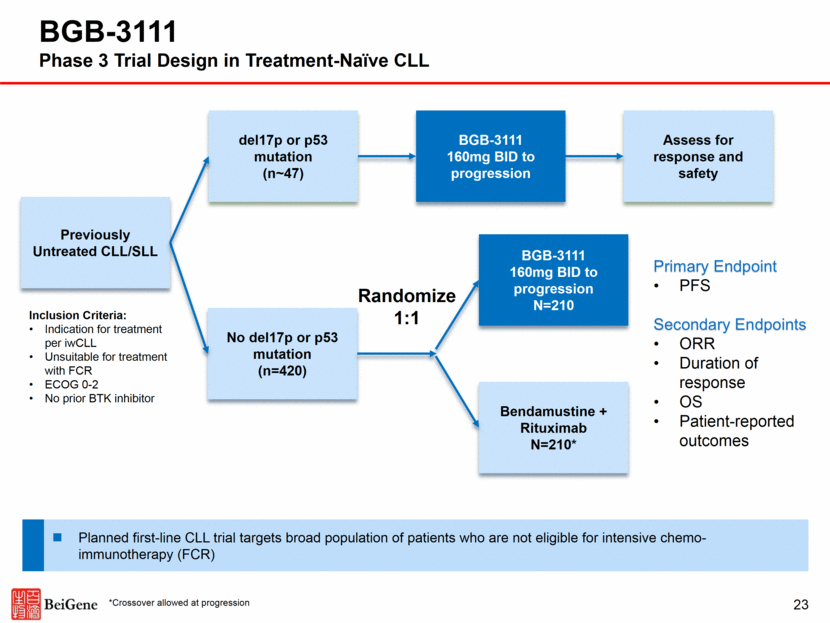
Inclusion Criteria: Indication for treatment per iwCLL Unsuitable for treatment with FCR ECOG 0-2 No prior BTK inhibitor Primary Endpoint PFS Secondary Endpoints ORR Duration of response OS Patient-reported outcomes Previously Untreated CLL/SLL BGB-3111 160mg BID to progression N=210 Bendamustine + Rituximab N=210* No del17p or p53 mutation (n=420) del17p or p53 mutation (n~47) Assess for response and safety Randomize 1:1 BGB-3111 160mg BID to progression Planned first-line CLL trial targets broad population of patients who are not eligible for intensive chemo-immunotherapy (FCR) *Crossover allowed at progression 23 BGB-3111 Phase 3 Trial Design in Treatment-Naïve CLL
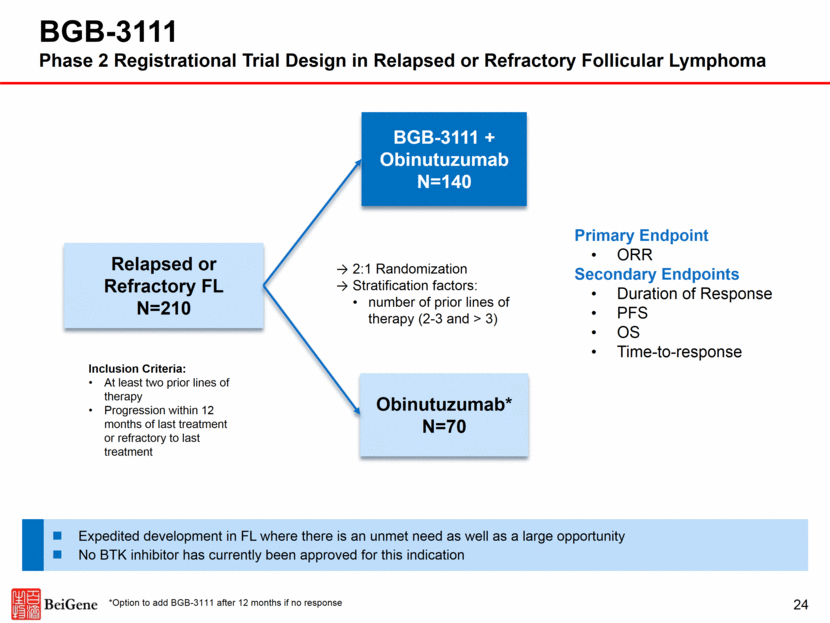
Relapsed or Refractory FL N=210 BGB-3111 + Obinutuzumab N=140 Obinutuzumab* N=70 2:1 Randomization Stratification factors: number of prior lines of therapy (2-3 and > 3) Primary Endpoint ORR Secondary Endpoints Duration of Response PFS OS Time-to-response Expedited development in FL where there is an unmet need as well as a large opportunity No BTK inhibitor has currently been approved for this indication *Option to add BGB-3111 after 12 months if no response 24 BGB-3111 Phase 2 Registrational Trial Design in Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma Inclusion Criteria: At least two prior lines of therapy Progression within 12 months of last treatment or refractory to last treatment
Overview Potential differentiation vs. currently approved PD-1 antibodies Potential cell biology differentiation in lack of Fc receptor binding, which may have a negative effect on the activity of other PD-1 antibodies based on our preclinical data and recent publications1 Superior PD-1 inhibition and functional activities in human immune cells Differentiation in CDR sequences and key binding epitopes on PD-1 Several of the anti-PD-1-responsive tumors, e.g. lung, gastric, liver, and esophageal cancers, are highly prevalent in Asia Over one-third to half of worldwide incidences of these cancers are in China Provides us with trial enrollment and commercial advantages Enabling wholly owned combinations within our portfolio Strong preclinical and biological rationale to combine with BTK, PARP, or RAF dimer inhibitors Strategic collaboration gives Celgene exclusive development and commercial rights for solid tumors in the US, Europe, Japan, and rest of world outside Asia; BeiGene retains exclusive rights for solid tumors in Asia (ex-Japan), and for hematological malignancies and combinations with its portfolio products globally Clinical Status Initiated registrational Phase 2 trials in China in patients with R/R cHL and previously treated, PD-L1-positive UC Initiated a Phase 2 combination trial in China with chemotherapy in first line locally advanced or metastatic esophageal, gastric, or GEJ carcinoma Ongoing global Phase 1 trial in multi-indication expansion and China Phase 1 trial in advanced solid tumors Combination trials are ongoing with each of BGB-290 (PARP) and BGB-3111 (BTK) Nearly 600 patients treated as of July 26, 2017 25 BGB-A317: Summary PD-1 Checkpoint Inhibitor Source: 1 Dahan et al., Cancer Cell, 2015; Arlauckas et al., Sci. Transl. Med., 2017
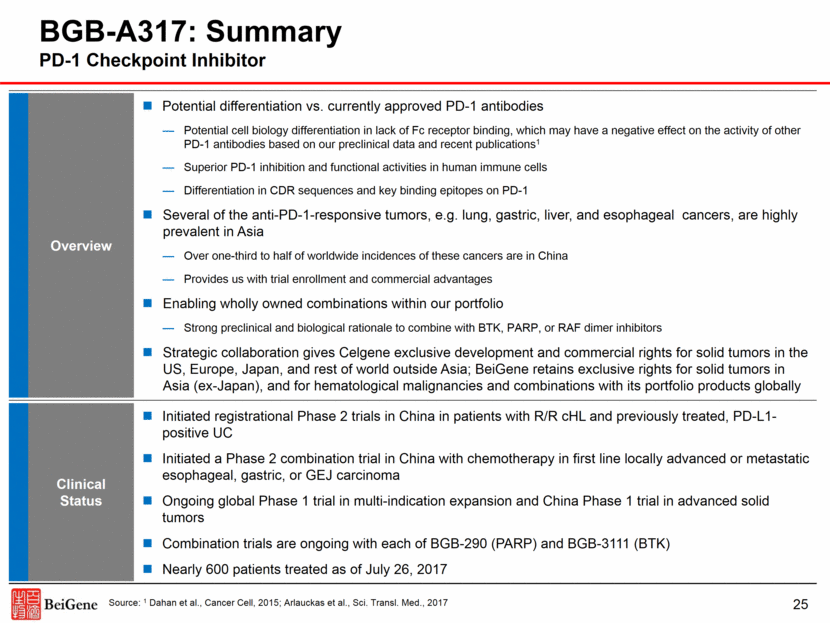
China % of World (2012) Tumor Types That Have Shown Activity to PD-1 Antibodies Are Among the Most Common Cancers in China Source: Data from World Health Organization (2012); Chen et al., CA Cancer J Clin, 2016 Cervix Breast Colon Liver Esophagus 0.25 Gastric Lung All types 22% 36% 43% 49% 51% 19% 11% 12% 2015 New Incidence by Cancer Type in China (million) China has nearly a quarter of the world’s cancer patient population, and one-third to half of cancer patients with certain tumor types are in China, including lung, gastric, esophageal and liver cancers, all of which have shown objective responses to PD-1 antibodies 26 4.29 0.73 0.68 0.48 0.47 0.38 0.27 0.10
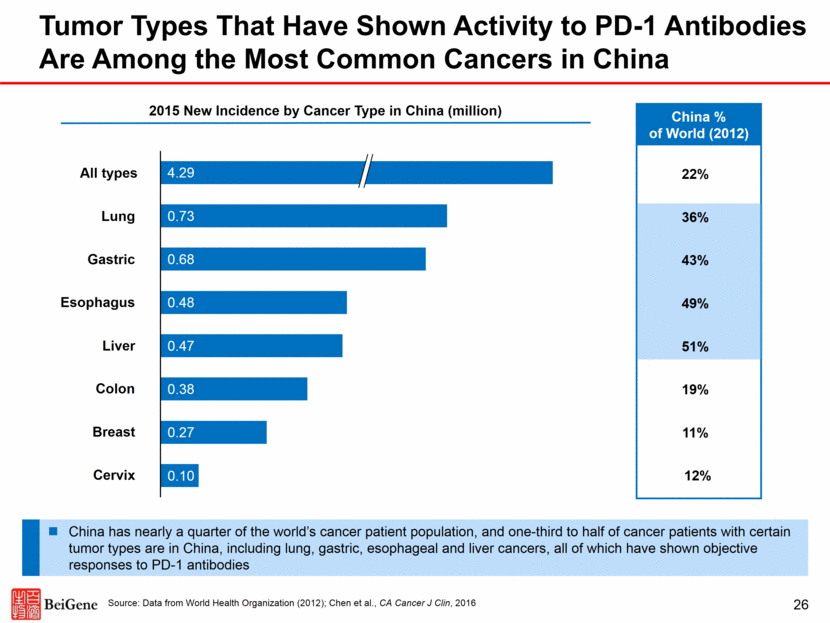
27 BGB-A317 Phase 1 Data Show Proof of Principle and Encouraging Clinical Activity Note: 93 pts included in the chart, the remaining 6 pts were not evaluable for target lesion response based on imaging assessment at the cutoff time Source: 1 Phase 1 data as of September 30, 2016, presented at the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Annual Meeting, 2016 (Desai et al) 2 Phase 1 data as of April 28, 2017, presented at the ESMO World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer (WCGI), 2017 (Yen et al) Duration of Treatment (day): Best Response (%) in Target Lesions + On Treatment The dose escalation data presented at SITC1 represented a mixed population with 27 tumor types which excluded melanoma, NSCLC or head and neck cancer; nearly 15% of the enrolled patients had RCC or urothelial carcinoma (UC) In the SITC1 analysis, 99 patients were evaluable for efficacy as of September 30, 2016, and 15 patients achieved confirmed PRs including 3/9 RCC, 3/6 urothelial carcinoma, 2/4 gastric cancer, 2/2 Merkel cell carcinoma, 1/4 NPC, 1/1 penis squamous cell carcinoma, 1/1 duodenal carcinoma, 1/1 evaluable MSI-h CRC, and 1/1 MSI-h pancreatic cancer patients In early data presented at ESMO WCGI 20172 from hepatocellular carcinoma patients enrolled in dose-escalation and dose-expansion portions of the Phase I trial, there were 3 PRs (1 confirmed, 2 unconfirmed) and 9 cases of SD in 27 efficacy-evaluable patients Phase 1 Data at SITC 20161 Best Objective Response Subject, Treatment status, Cancer Type, Duration of treatment (day) S u m ( B e s t r e s p o n s e ( % o f S L D ) ) 4 3 4 3 2 9 6 4 6 4 9 9 4 2 1 6 4 2 7 0 5 8 4 3 8 5 4 2 2 3 2 9 5 7 7 2 4 3 2 1 1 5 8 8 3 1 1 3 5 1 5 8 2 2 5 8 1 9 2 5 3 9 9 9 9 7 1 8 5 9 9 1 5 6 3 1 6 9 8 4 2 2 2 5 6 7 8 9 8 4 3 1 1 3 1 2 7 1 5 5 5 7 6 4 1 0 8 2 4 8 3 6 6 2 9 1 2 0 2 8 9 2 2 6 9 9 5 5 2 5 4 2 6 1 1 5 3 4 3 7 8 2 2 8 2 4 3 1 2 0 1 9 3 3 2 4 1 5 3 2 2 5 1 6 1 1 2 7 2 5 4 2 4 0 9 9 1 7 2 3 3 1 2 4 7 1 2 7 2 2 6 2 1 6 2 2 1 5 9 1 9 9 3 2 6 2 0 6 1 8 3 2 9 2 2 6 8 3 0 3 3 1 1 2 2 5 3 5 4 3 6 5 M e s o t h e l i o m a C R C C h o l a n g i o c a r c i n o m a O v a r i a n A n a l S C C C e r v i c a l G B M C e r v i c a l O v a r i a n U r o t h e l i a l U r o t h e l i a l O v a r i a n G a s t r i c C h o l a n g i o c a r c i n o m a M e s o t h e l i o m a M e t a s t a s i s u n d i f f e r e n t i a t e d a d e n o c a r c i O v a r i a n O v a r i a n G a l l b l a d d e r C R C O v a r i a n O v a r i a n O v a r i a n O e s o p h a g e a l G a l l b l a d d e r S a r c o m a C e r v i c a l C R C O e s o p h a g e a l C R C C R C C h o l a n g i o c a r c i n o m a C R C C R C M e s o t h e l i o m a E n d o m e t r i a l B r e a s t G a s t r i c A d r e n o c o r t i c o i d c a r c i n o m a A d e n o i d c y s t i c c a r c i n o m a C R C M e s o t h e l i o m a R C C O v a r i a n O v a r i a n R C C P a n c r e a t i c O v a r i a n A d e n o c a r c i n o m a o f m a d i b l e R C C R C C O v a r i a n A n a l S C C O v a r i a n O v a r i a n R C C O v a r i a n m C u S C C H C C O v a r i a n M e s o t h e l i o m a C R C N a s o p h a r y n g e a l E n d o m e t r i a l ( M S I h i g h ) O v a r i a n O v a r i a n S a r c o m a T h y r o i d R C C C e r v i c a l C e r v i c a l R C C R C C O v a r i a n N a s o p h a r y n g e a l P e n i s S C C N a s o p h a r y n g e a l G a s t r i c D u o d e n a l O v a r i a n U r o t h e l i a l M e s o t h e l i o m a M e r k e l c e l l c a r c i n o m a C R C ( M S I h i g h ) G a s t r i c E n d o m e t r i a l P a n c r e a t i c ( M S I h i g h ) N a s o p h a r y n g e a l M e r k e l c e l l c a r c i n o m a U r o t h e l i a l U r o t h e l i a l E n d o m e t r i a l R C C o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o n t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o f f t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o f f t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o f f t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o f f t r e a o n t r e a o f f t r e a o n t r e a o f f t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o f f t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o n t r e a o f f t r e a 0 2 - 0 1 6 0 1 - 0 1 6 0 5 - 0 0 5 0 5 - 0 2 0 0 1 - 0 2 0 0 3 - 0 0 2 0 4 - 0 0 2 0 3 - 0 0 3 0 2 - 0 0 8 0 3 - 0 1 4 0 6 - 0 0 7 0 1 - 0 1 1 0 4 - 0 1 4 0 3 - 0 1 1 0 5 - 0 0 8 0 3 - 0 1 5 0 2 - 0 1 2 0 4 - 0 1 5 0 6 - 0 0 9 0 1 - 0 0 8 0 2 - 0 1 5 0 1 - 0 1 7 0 5 - 0 0 6 0 6 - 0 0 4 0 4 - 0 0 3 0 1 - 0 0 9 0 3 - 0 0 6 0 5 - 0 1 1 0 4 - 0 1 7 0 1 - 0 0 5 0 3 - 0 0 4 0 5 - 0 1 9 0 2 - 0 1 4 0 1 - 0 0 3 0 1 - 0 0 4 0 6 - 0 0 6 0 5 - 0 1 6 0 4 - 0 0 9 0 3 - 0 2 4 0 4 - 0 1 6 0 5 - 0 0 9 0 2 - 0 1 7 0 5 - 0 0 2 0 2 - 0 0 7 0 3 - 0 1 8 0 1 - 0 0 1 0 1 - 0 0 2 0 2 - 0 2 2 0 3 - 0 1 7 0 1 - 0 1 8 0 5 - 0 0 7 0 5 - 0 0 3 0 1 - 0 0 7 0 5 - 0 1 4 0 2 - 0 1 9 0 3 - 0 0 5 0 3 - 0 0 7 0 3 - 0 1 6 0 5 - 0 1 7 0 2 - 0 0 4 0 2 - 0 0 9 0 3 - 0 1 0 0 3 - 0 1 9 0 2 - 0 1 8 0 2 - 0 2 1 0 6 - 0 1 1 0 3 - 0 0 9 0 2 - 0 0 3 0 1 - 0 0 6 0 2 - 0 0 5 0 2 - 0 0 1 0 6 - 0 0 5 0 5 - 0 1 8 0 2 - 0 0 2 0 3 - 0 2 3 0 5 - 0 1 0 0 4 - 0 1 8 0 2 - 0 1 0 0 4 - 0 2 0 0 4 - 0 0 8 0 3 - 0 2 0 0 4 - 0 2 2 0 3 - 0 2 1 0 1 - 0 1 0 0 1 - 0 1 9 0 3 - 0 2 2 0 1 - 0 1 3 0 4 - 0 0 1 0 3 - 0 1 3 0 6 - 0 0 1 0 4 - 0 1 9 0 3 - 0 0 8 0 5 - 0 0 1 140 % 100 % 60 % 20 % -20 % -60 % -100 %
Overview Highly selective PARP1 and PARP2 inhibitor with strong PARP trapping activity Significant brain penetration in preclinical studies, potential for treating brain tumors and metastases Well-tolerated in monotherapy dose escalation data1 with significant anti-tumor activity: Few AEs of myelosuppression, few drug-related grade 3/4 adverse events Most common AEs were grade 1 and 2 nausea (38%) and fatigue (28%) Drug-related SAEs were 3 cases of grade 3 anemia and 1 case of shortness of breath in 29 enrolled patients2 Wide therapeutic window with partial response observed at lowest tested dose of 2.5mg (compared to MTD of 80mg) Among 14 evaluable ovarian cancer patients, 7 had an objective response (6 PR and 1 CR) Of the 10 ovarian cancer patients with germ-line BRCA mutation, 5 had an objective response; of the 3 ovarian cancer patients with germ-line BRCA wild-type, 2 had an objective response Wholly owned combination with BGB-A317 with strong rationale Tolerability profile of BGB-290 supports combination use BRCA-mutated tumors sensitive to PARP inhibition are likely to be immunogenic and PD-1/PD-L1 antibody responsive Platinum sensitivity in ovarian cancer is associated with better response to anti-PD-1 therapy Clinical Status Initiated a global Phase 1b/2 trial in combination with radiation therapy and/or temozolomide (TMZ) in glioblastoma Initiated a global Phase 1 trial in combination with TMZ in locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors Ongoing global Phase 1 multi-indication dose-expansion trial and China Phase 1 trial in patients with ovarian, breast, prostate and other cancers Combination trial with PD-1 antibody BGB-A317 ongoing Over 130 patients treated as of July 26, 2017 28 BGB-290: Summary Highly Selective Inhibitor of PARP1 and PARP2 Source: 1 Dose escalation data as of June 30, 2015, presented at AACR-NCI-EORTC 2015 meeting (Lickliter et al) 2 As of January 19, 2016

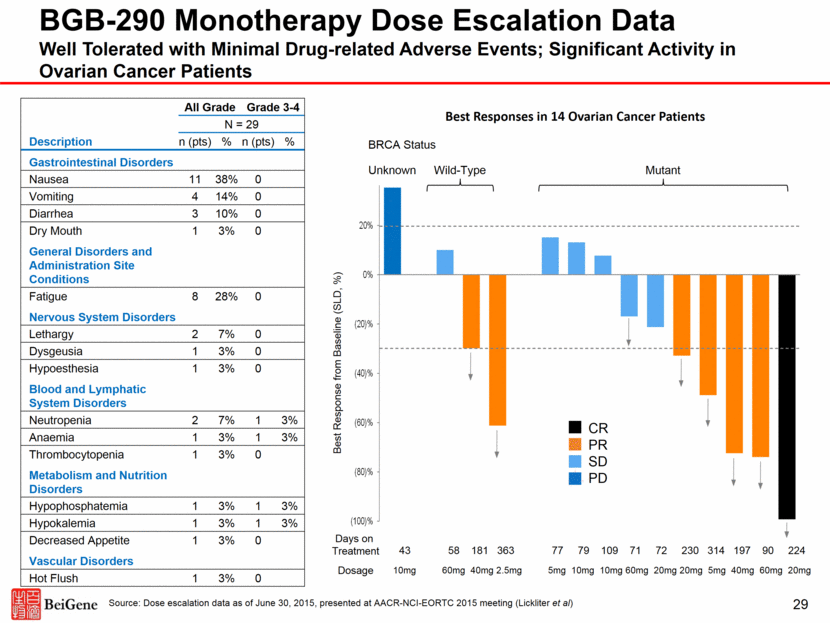
All Grade Grade 3-4 N = 29 Description n (pts) % n (pts) % Gastrointestinal Disorders Nausea 11 38% 0 Vomiting 4 14% 0 Diarrhea 3 10% 0 Dry Mouth 1 3% 0 General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Fatigue 8 28% 0 Nervous System Disorders Lethargy 2 7% 0 Dysgeusia 1 3% 0 Hypoesthesia 1 3% 0 Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders Neutropenia 2 7% 1 3% Anaemia 1 3% 1 3% Thrombocytopenia 1 3% 0 Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders Hypophosphatemia 1 3% 1 3% Hypokalemia 1 3% 1 3% Decreased Appetite 1 3% 0 Vascular Disorders Hot Flush 1 3% 0 29 BGB-290 Monotherapy Dose Escalation Data Well Tolerated with Minimal Drug-related Adverse Events; Significant Activity in Ovarian Cancer Patients Source: Dose escalation data as of June 30, 2015, presented at AACR-NCI-EORTC 2015 meeting (Lickliter et al) Best Response from Baseline (SLD, %) BRCA Status Unknown Wild-Type Mutant Days on Treatment Dosage 43 58 181 363 77 79 109 71 72 230 314 197 90 224 10mg 60mg 40mg 2.5mg 5mg 10mg 10mg 60mg 20mg 20mg 5mg 40mg 60mg 20mg Best Responses in 14 Ovarian Cancer Patients CR PR SD PD
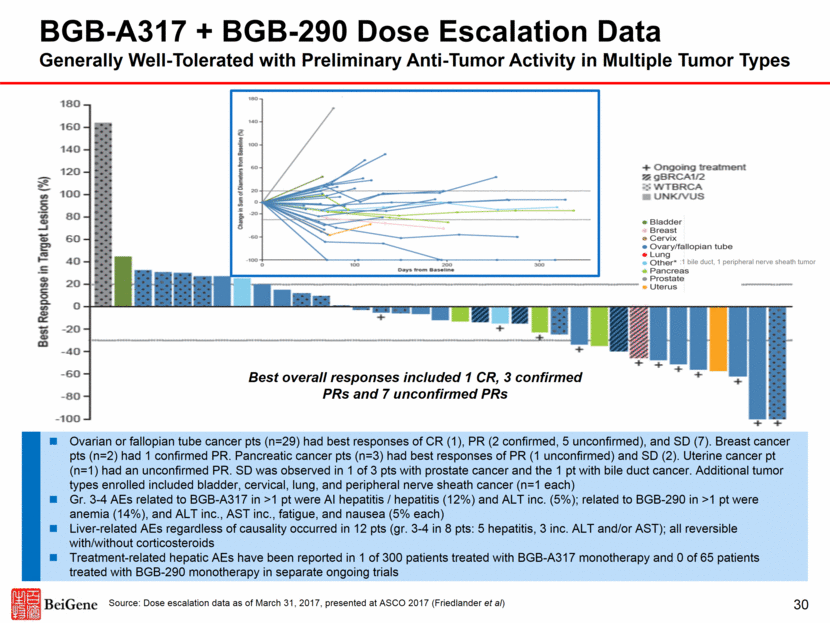
A. Change in Tumor Volume by Baseline Tumor Type BGB-A317 + BGB-290 Dose Escalation Data Generally Well-Tolerated with Preliminary Anti-Tumor Activity in Multiple Tumor Types :1 bile duct, 1 peripheral nerve sheath tumor Best overall responses included 1 CR, 3 confirmed PRs and 7 unconfirmed PRs Ovarian or fallopian tube cancer pts (n=29) had best responses of CR (1), PR (2 confirmed, 5 unconfirmed), and SD (7). Breast cancer pts (n=2) had 1 confirmed PR. Pancreatic cancer pts (n=3) had best responses of PR (1 unconfirmed) and SD (2). Uterine cancer pt (n=1) had an unconfirmed PR. SD was observed in 1 of 3 pts with prostate cancer and the 1 pt with bile duct cancer. Additional tumor types enrolled included bladder, cervical, lung, and peripheral nerve sheath cancer (n=1 each) Gr. 3-4 AEs related to BGB-A317 in >1 pt were AI hepatitis / hepatitis (12%) and ALT inc. (5%); related to BGB-290 in >1 pt were anemia (14%), and ALT inc., AST inc., fatigue, and nausea (5% each) Liver-related AEs regardless of causality occurred in 12 pts (gr. 3-4 in 8 pts: 5 hepatitis, 3 inc. ALT and/or AST); all reversible with/without corticosteroids Treatment-related hepatic AEs have been reported in 1 of 300 patients treated with BGB-A317 monotherapy and 0 of 65 patients treated with BGB-290 monotherapy in separate ongoing trials 30 Source: Dose escalation data as of March 31, 2017, presented at ASCO 2017 (Friedlander et al)
31 Overview Potential to be a first-in-class RAF dimer inhibitor globally Vemurafenib and dabrafenib are only active against the BRAF monomer Potentially addresses several limitations of current BRAF inhibitors, including: Large unmet need in RAS-mutated tumors Rapid development of resistance Proof-of-concept established from dose escalation1 and dose expansion2 trials with durable complete and partial responses in patients with KRAS or BRAF mutations Dose-expansion demonstrated good tolerability profile Most common drug-related AEs (>10%) of any grade were fatigue, dysphonia, decreased appetite, palmar-plantar erythrodysaesthesia syndrome, thrombocytopenia, dermatitis acneiform, diarrhea, rash, nausea, hypertension, and glossodynia Combination potential with PD-1 antibody as an inhibitor of the MAPK pathway Combination with BGB-A317 supported by preclinical data3 Clinical Status Nearly 180 patients treated in Australia, New Zealand, and China Dose-escalation completed; completed dose-expansion enrollment in patients with solid tumors with KRAS, NRAS, or BRAF mutations in Australia and New Zealand in April 2016 Clinical trial in China initiated More frequent observations of grade 3/4 thrombocytopenia in China trial (7 out of 24 patients) compared to the AU/NZ trial (8 out of 105 patients) Trial ongoing to evaluate pharmacokinetics, safety and efficacy BGB-283: Summary Potentially First-in-Class RAF Dimer Inhibitor Source: 1Dose escalation data as of January 31, 2016, presented at AACR 2016 (Desai et al); 2Dose expansion data as of September 2016, presented at AACR 2017 (Desai et al); 3BeiGene data on file
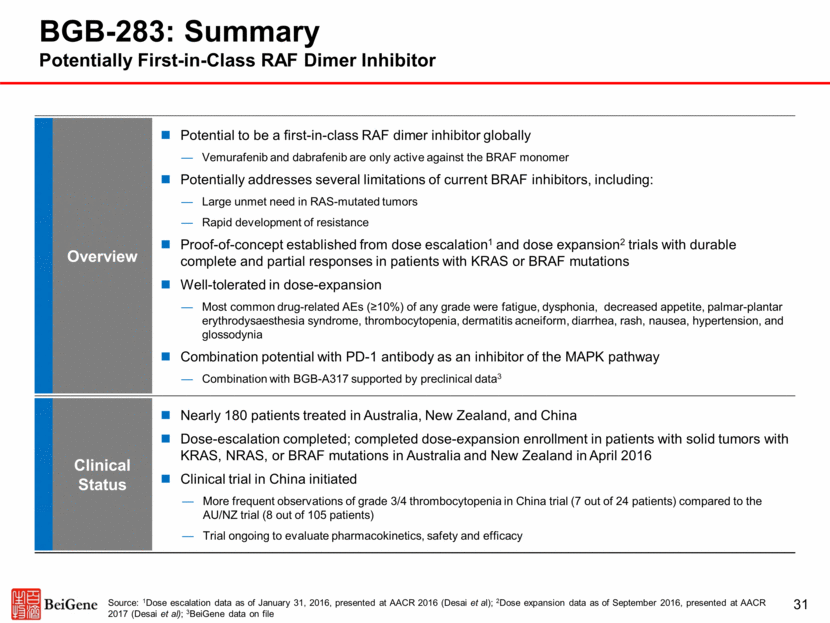
Best Response in Target Lesions * Duration of Treatment (day) BGB-283 Phase 1a/1b: Durable Responses in K-RAS-Mutated Cancers * On Treatment Source: Dose escalation / expansion data as of September 17, 2016, presented at AACR 2017 (Desai et al) 32
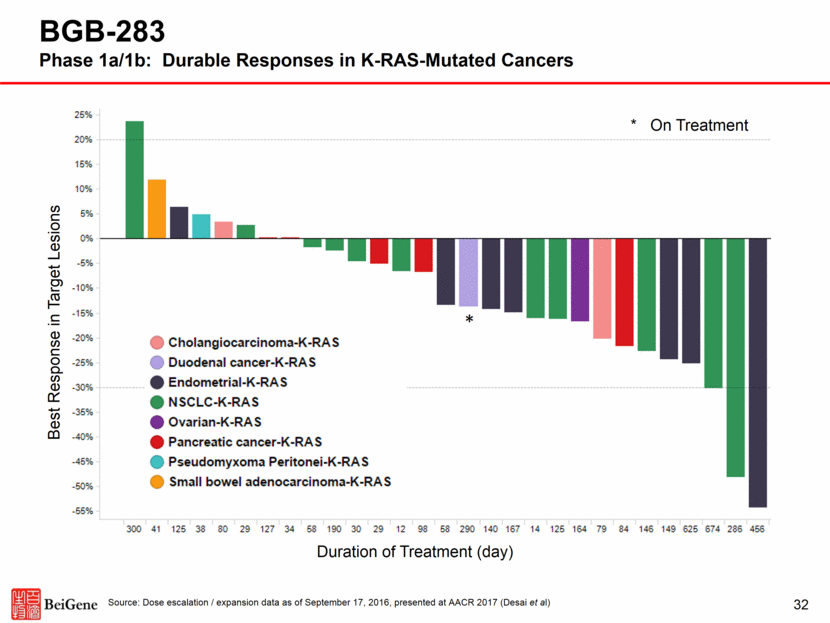
33 Financial Position and Investor Base Strong Balance Sheet Position Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Short-term Investments (6/30/2017) $407M (Unaudited) Stable and Established Investor Base Private Round Investors Investor Base Established Through Private and Subsequent Public Offerings Select New Public Investors Baker Brothers Celgene Transaction Expected to Provide $413M in Cash
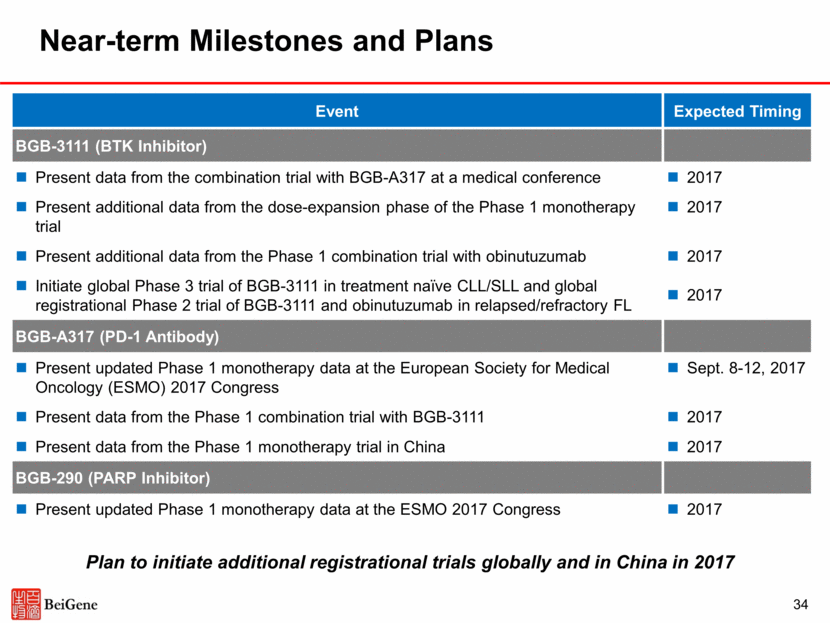
34 Near-term Milestones and Plans Event Expected Timing BGB-3111 (BTK Inhibitor) Present data from the combination trial with BGB-A317 at a medical conference Present additional data from the dose-expansion phase of the Phase 1 monotherapy trial Present additional data from the Phase 1 combination trial with obinutuzumab Initiate global Phase 3 trial of BGB-3111 in treatment naïve CLL/SLL and global registrational Phase 2 trial of BGB-3111 and obinutuzumab in relapsed/refractory FL 2017 2017 2017 2017 BGB-A317 (PD-1 Antibody) Present updated Phase 1 monotherapy data at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2017 Congress Present data from the Phase 1 combination trial with BGB-3111 Present data from the Phase 1 monotherapy trial in China Sept. 8-12, 2017 2017 2017 BGB-290 (PARP Inhibitor) Present updated Phase 1 monotherapy data at the ESMO 2017 Congress 2017 Plan to initiate additional registrational trials globally and in China in 2017