Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - Theravance Biopharma, Inc. | a17-18737_18k.htm |
| EX-99.1 - EX-99.1 - Theravance Biopharma, Inc. | a17-18737_1ex99d1.htm |
Exhibit 99.2
August 2, 2017 Velusetrag (TD-5108) Top-line Results from Phase 2b Study in Gastroparesis THERAVANCE®, the Cross/Star logo, VIBATIV® and MEDICINES THAT MAKE A DIFFERENCE® are registered
trademarks, and TOURTM is a trademark, of the Theravance Biopharma group of companies.
© 2017 Theravance Biopharma. All rights reserved.
Forward Looking Statements Under the safe harbor provisions of the U.S. Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, the company cautions investors that any forward-looking statements or projections made by the company are subject to risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially from the forward-looking statements or projections. Examples of forward-looking statements in this presentation include statements relating to the company’s business plans and objectives, including financial and operating results, potential partnering transactions and sales targets, the company’s regulatory strategies and timing and results of clinical studies, the potential benefits and mechanisms of action of the company’s product and product candidates (including their potential as components of combination therapies and the timing and use of the net proceeds from the proposed offering). The company’s forward-looking statements are based on the estimates and assumptions of management as of the date of this presentation and are subject to risks and uncertainties that may cause the actual results to be materially different than those projected, such as risks related to delays or difficulties in commencing or completing clinical studies, the potential that results from clinical or non-clinical studies indicate product candidates are unsafe or ineffective (including when our product candidates are studied in combination with other compounds), delays or failure to achieve and maintain regulatory approvals for product candidates, risks of collaborating with third parties to discover, develop and commercialize products, risks associated with establishing and maintaining sales, marketing and distribution capabilities, and market conditions that may affect whether the offering will be made or consummated on the proposed terms, if at all. Other risks affecting the company are described under the heading “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in the company’s Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) on May 9,2017, and other periodic reports filed with the SEC.

Gastroparesis Presents a Meaningful Opportunity to Improve Lives of Patients 1 Rey et al., Prevalence of Hidden Gastroparesis in the Community: The Gastroparesis “Iceberg.” J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil., 2012; 18:34-42. Gastroparesis is a severe disease with debilitating symptoms Characterized by delayed gastric emptying Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, postprandial fullness, early satiety, and upper abdominal pain High prevalence1 Estimated 6M patients in US Split between diabetic, idiopathic, and other One approved therapy in 35 years Significant safety concerns limit use A disease in significant need of therapeutic innovation
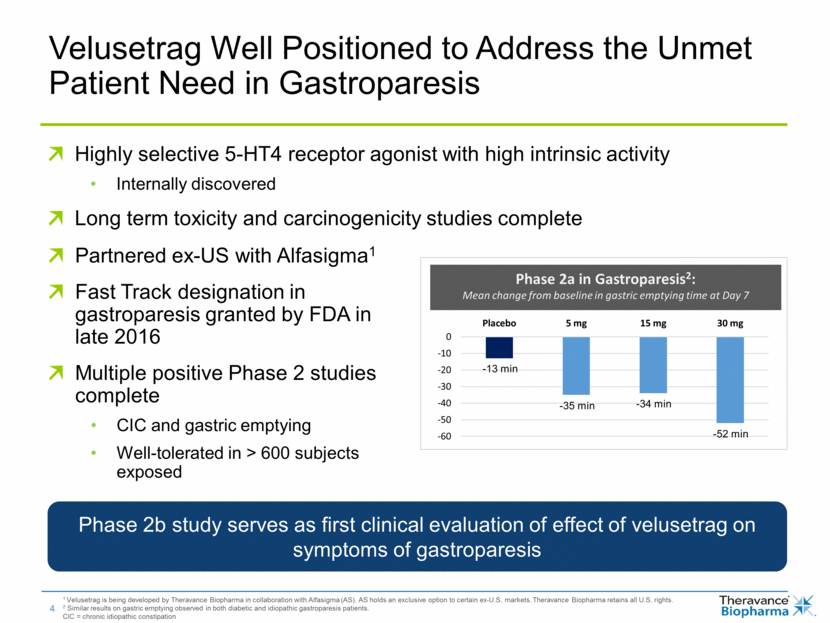
Velusetrag Well Positioned to Address the Unmet Patient Need in Gastroparesis 1 Velusetrag is being developed by Theravance Biopharma in collaboration with Alfasigma (AS). AS holds an exclusive option to certain ex-U.S. markets. Theravance Biopharma retains all U.S. rights. 2 Similar results on gastric emptying observed in both diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis patients. CIC = chronic idiopathic constipation Highly selective 5-HT4 receptor agonist with high intrinsic activity Internally discovered Long term toxicity and carcinogenicity studies complete Phase 2b study serves as first clinical evaluation of effect of velusetrag on symptoms of gastroparesis Phase 2a in Gastroparesis2: Mean change from baseline in gastric emptying time at Day 7 -13 min -35 min -34 min -52 min Partnered ex-US with Alfasigma1 Fast Track designation in gastroparesis granted by FDA in late 2016 Multiple positive Phase 2 studies complete CIC and gastric emptying Well-tolerated in > 600 subjects exposed -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 Placebo 5 mg 15 mg 30 mg
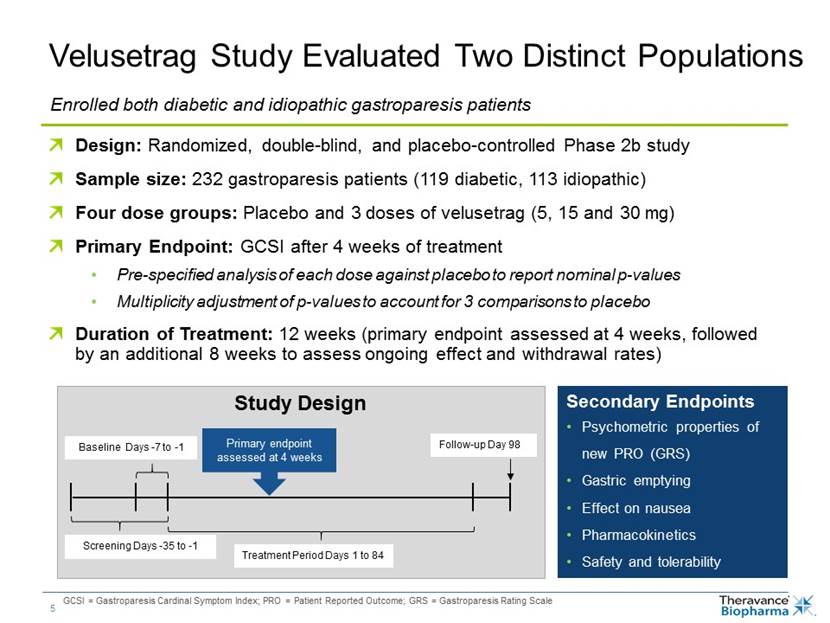
Velusetrag Study Evaluated Two Distinct Populations Enrolled both diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis patients Design: Randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled Phase 2b study Sample size: 232 gastroparesis patients (119 diabetic, 113 idiopathic) Four dose groups: Placebo and 3 doses of velusetrag (5, 15 and 30 mg) Primary Endpoint: GCSI after 4 weeks of treatment Pre-specified analysis of each dose against placebo to report nominal p-values Multiplicity adjustment of p-values to account for 3 comparisons to placebo Duration of Treatment: 12 weeks (primary endpoint assessed at 4 weeks, followed by an additional 8 weeks to assess ongoing effect and withdrawal rates) Study Design Baseline Days -7 to -1 Screening Days -35 to -1 Treatment Period Days 1 to 84 Follow-up Day 98 Primary endpoint assessed at 4 weeks Secondary Endpoints Psychometric properties of new PRO2 (GRS) Gastric emptying Effect on nausea Pharmacokinetics Safety and tolerability 1 GCSI = Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index 2 PRO = Patient Reported Outcome
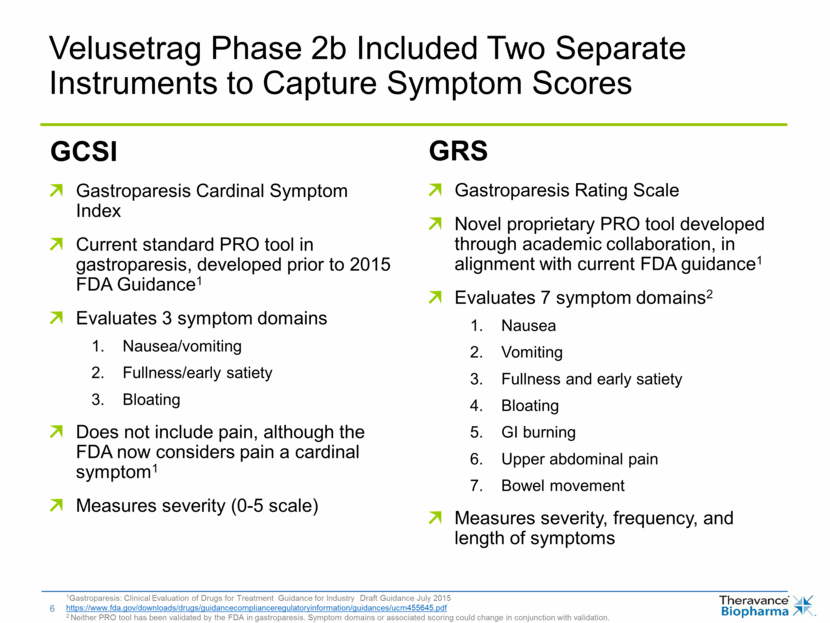
Velusetrag Phase 2b Included Two Separate Instruments to Capture Symptom Scores 1Gastroparesis: Clinical Evaluation of Drugs for Treatment Guidance for Industry Draft Guidance July 2015 https://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformation/guidances/ucm455645.pdf 2 Neither PRO tool has been validated by the FDA in gastroparesis. Symptom domains or associated scoring could change in conjunction with validation. GCSI Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index Current standard PRO tool in gastroparesis, developed prior to 2015 FDA Guidance1 Evaluates 3 symptom domains Nausea/vomiting Fullness/early satiety Bloating Does not include pain, although the FDA now considers pain a cardinal symptom1 Measures severity (0-5 scale) GRS Gastroparesis Rating Scale Novel proprietary PRO tool developed through academic collaboration, in alignment with current FDA guidance1 Evaluates 7 symptom domains2 Nausea Vomiting Fullness and early satiety Bloating GI burning Upper abdominal pain Bowel movement Measures severity, frequency, and length of symptoms
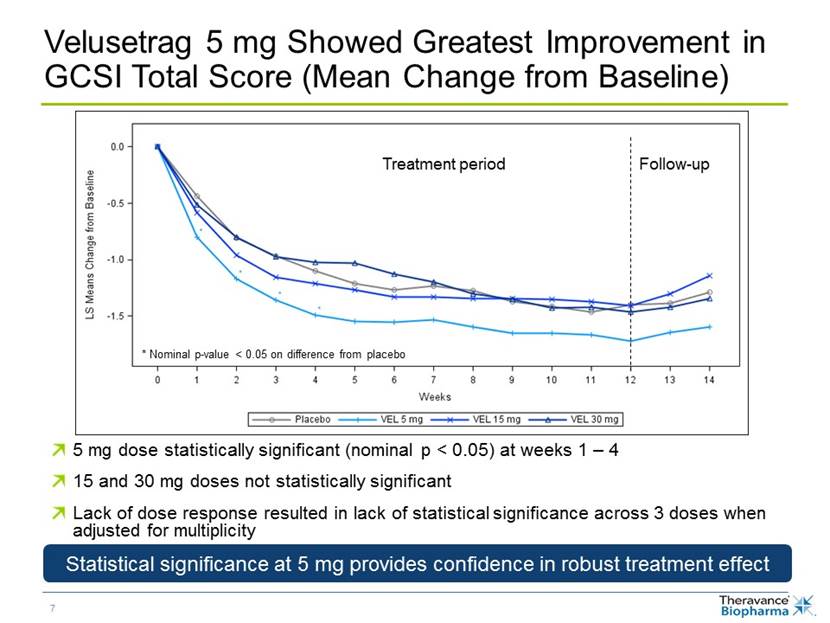
Velusetrag 5 mg Showed Greatest Improvement in GCSI Total Score (Mean Change from Baseline) * Nominal p-value < 0.05 on difference from placebo 5 mg dose statistically significant (nominal p < 0.05) at weeks 1 – 4 15 and 30 mg doses not statistically significant Lack of dose response resulted in lack of statistical significance across 3 doses when adjusted for multiplicity Follow-up Treatment period
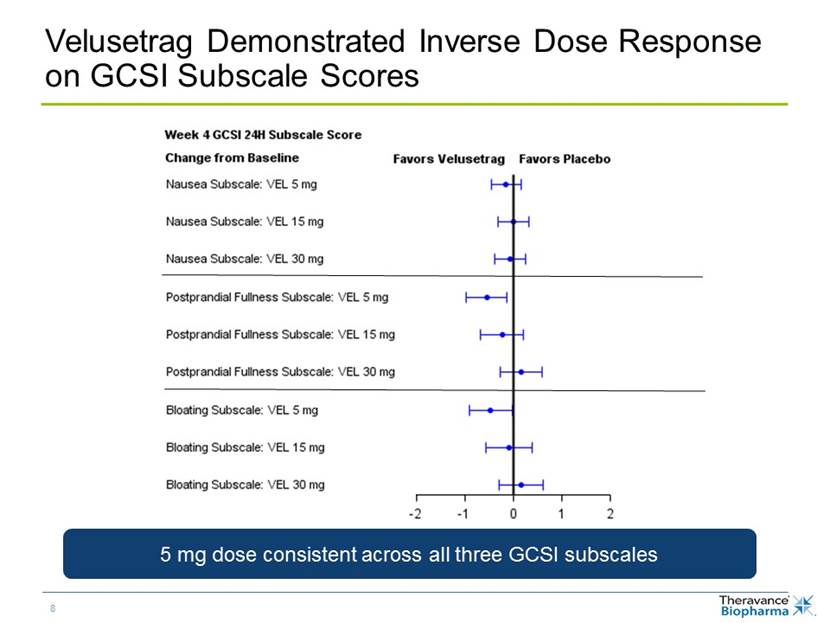
Velusetrag Demonstrated Inverse Dose Response on GCSI Subscale scores 5 mg dose consistent across all three GCSI domains
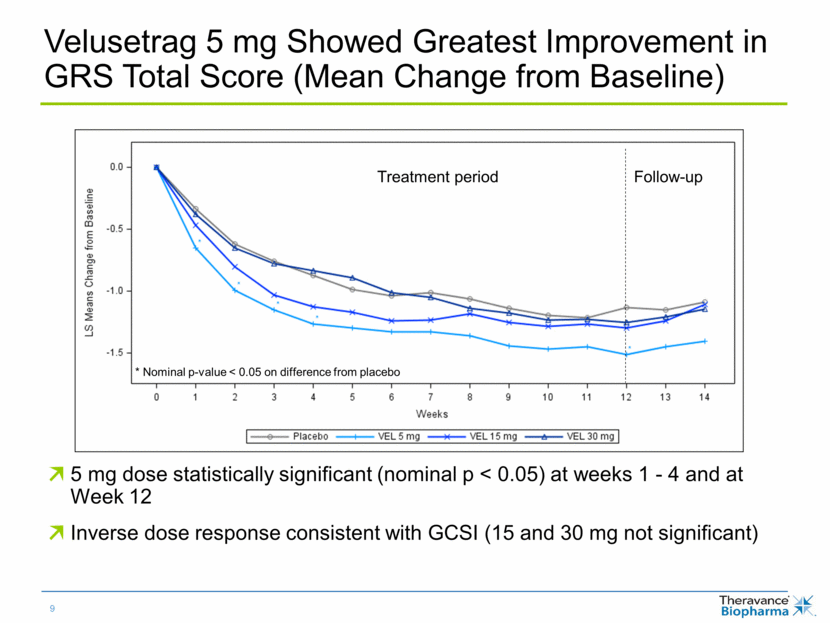
Velusetrag 5 mg Showed Greatest Improvement in GRS Total Score (Mean Change from Baseline) 5 mg dose statistically significant (nominal p < 0.05) at weeks 1 - 4 and at Week 12 Inverse dose response consistent with GCSI (15 and 30 mg not significant) * Nominal p-value < 0.05 on difference from placebo Follow-up Treatment period
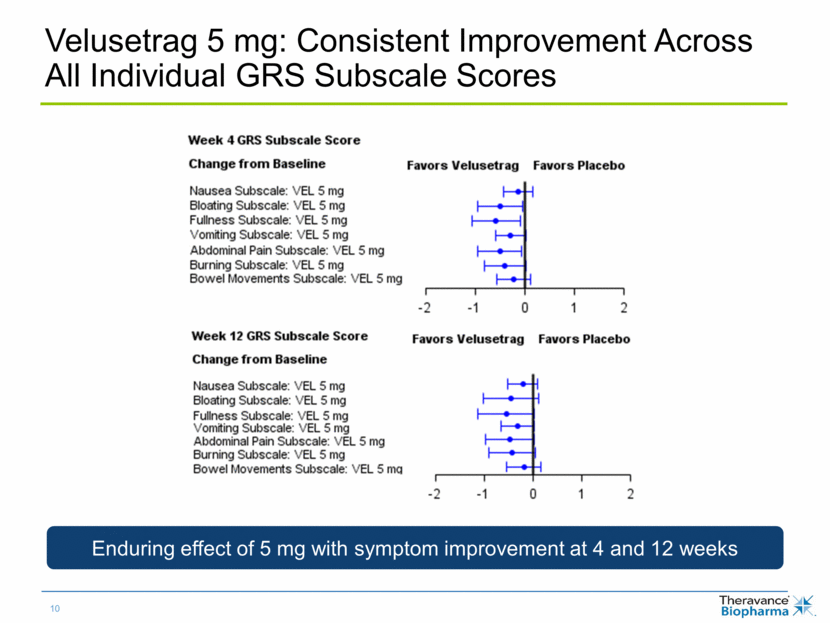
Velusetrag 5 mg: Consistent Improvement Across All Individual GRS Subscale Scores Enduring effect of 5 mg with symptom improvement at 4 and 12 weeks
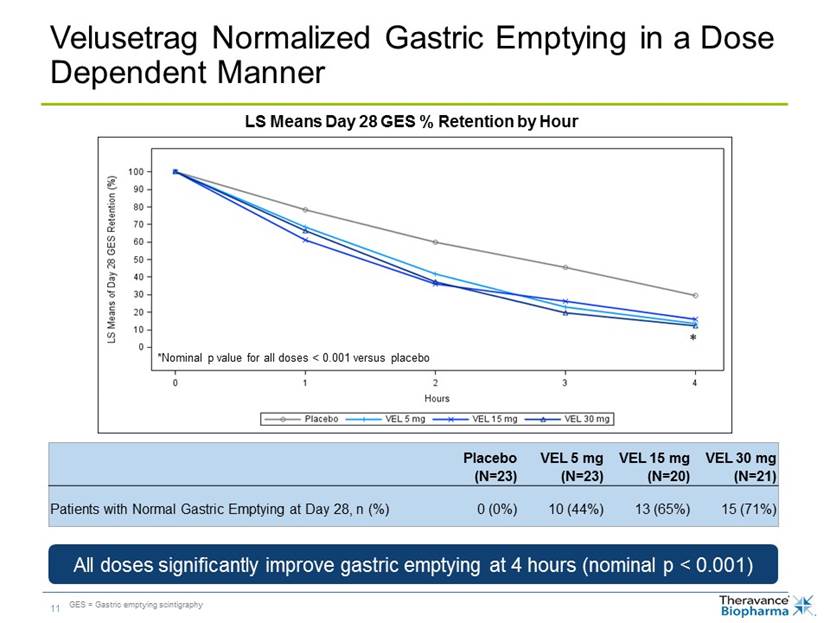
Placebo (N=23) VEL 5 mg (N=23) VEL 15 mg (N=20) VEL 30 mg (N=21) Patients with Normal Gastric Emptying at Day 28, n (%) 0 (0%) 10 (44%) 13 (65%) 15 (71%) Velusetrag Normalized Gastric Emptying in a Dose Dependent Manner LS Means Day 28 GES % Retention by Hour All doses significantly improve gastric emptying at 4 hours (nominal p < 0.001) GES = Gastric emptying scintigraphy *Nominal p value for all doses < 0.001 versus placebo *
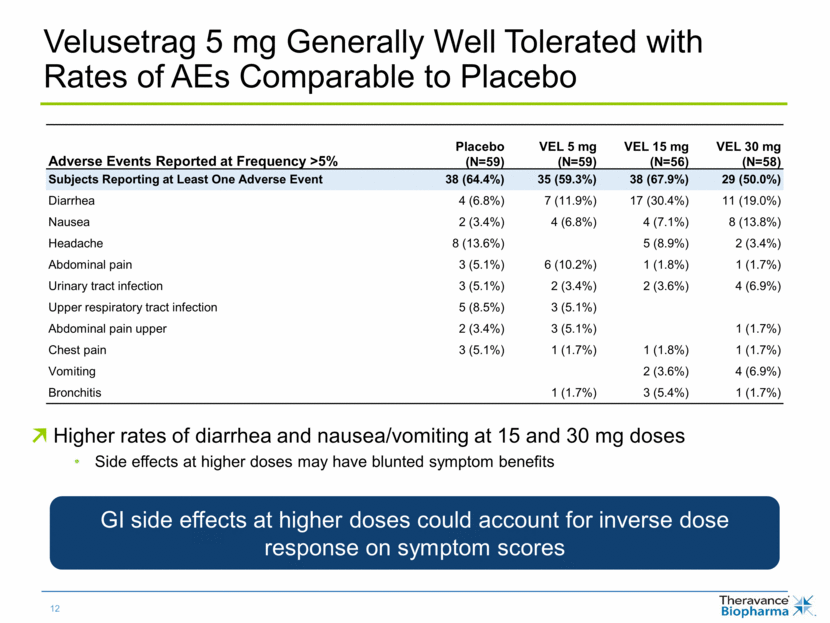
Velusetrag 5 mg Generally Well Tolerated with Rates of AEs Comparable to Placebo Higher rates of diarrhea and nausea/vomiting at 15 and 30 mg doses Side effects at higher doses may have blunted symptom benefits Adverse Events Reported at Frequency >5% Placebo (N=59) VEL 5 mg (N=59) VEL 15 mg (N=56) VEL 30 mg (N=58) Subjects Reporting at Least One Adverse Event 38 (64.4%) 35 (59.3%) 38 (67.9%) 29 (50.0%) Diarrhea 4 (6.8%) 7 (11.9%) 17 (30.4%) 11 (19.0%) Nausea 2 (3.4%) 4 (6.8%) 4 (7.1%) 8 (13.8%) Headache 8 (13.6%) 5 (8.9%) 2 (3.4%) Abdominal pain 3 (5.1%) 6 (10.2%) 1 (1.8%) 1 (1.7%) Urinary tract infection 3 (5.1%) 2 (3.4%) 2 (3.6%) 4 (6.9%) Upper respiratory tract infection 5 (8.5%) 3 (5.1%) Abdominal pain upper 2 (3.4%) 3 (5.1%) 1 (1.7%) Chest pain 3 (5.1%) 1 (1.7%) 1 (1.8%) 1 (1.7%) Vomiting 2 (3.6%) 4 (6.9%) Bronchitis 1 (1.7%) 3 (5.4%) 1 (1.7%) GI side effects at higher doses could account for inverse dose response on symptom scores
Velusetrag Phase 2b Study Summary Results 5 mg demonstrated statistically significant improvements in gastroparesis symptoms compared to placebo Both PROs: GCSI at 4 weeks and GRS at 4 and 12 weeks1 Both patient sub-types: idiopathic and diabetic gastroparesis Consistent effects in individual symptom domains compared to placebo Inverse dose response observed As dose increased, symptom effect decreased2 Meaningful improvements in gastric emptying at all doses Generally well tolerated: Rates of AEs and SAEs for 5mg comparable to placebo Next Steps: Prepare to meet with regulators to discuss validation of the GRS PRO and next phase of development for velusetrag 1 Nominal p-value < 0.05 at each time point. GCSI-24H at 12 weeks did not demonstrate statistical significance; PRO = Patient Reported Outcome 2 15 and 30 mg velusetrag dose groups did not demonstrate statistical significance

