Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.02 - EXHIBIT 32.02 - VERISIGN INC/CA | vrsn-20161231x10kxex3202.htm |
| EX-32.01 - EXHIBIT 32.01 - VERISIGN INC/CA | vrsn-20161231x10kxex3201.htm |
| EX-31.02 - EXHIBIT 31.02 - VERISIGN INC/CA | vrsn-20161231x10kxex3102.htm |
| EX-31.01 - EXHIBIT 31.01 - VERISIGN INC/CA | vrsn-20161231x10kxex3101.htm |
| EX-23.01 - EXHIBIT 23.01 - VERISIGN INC/CA | vrsn-20161231x10kxex2301.htm |
| EX-21.01 - EXHIBIT 21.01 - VERISIGN INC/CA | vrsn-20161231x10kxex2101.htm |
| EX-3.01 - EXHIBIT 3.01 - VERISIGN INC/CA | vrsn-20161231x10kxex301.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
————————
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
þ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016
OR
o | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 000-23593
————————
VERISIGN, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Delaware | 94-3221585 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
12061 Bluemont Way, Reston, Virginia | 20190 | |
(Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (703) 948-3200
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered |
Common Stock $0.001 Par Value Per Share | NASDAQ Global Select Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
———————
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. YES þ NO o
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. YES o NO þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. YES þ NO o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). YES þ NO o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of the registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer | þ | Accelerated filer | o | ||||
Non-accelerated filer | o | Smaller reporting company | o | ||||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.): YES o NO þ
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity stock held by non-affiliates of the Registrant as of June 30, 2016, was $3.4 billion based upon the last sale price reported for such date on the NASDAQ Global Select Market. For purposes of this disclosure, shares of Common Stock held by persons known to the Registrant (based on information provided by such persons and/or the most recent schedule 13Gs filed by such persons) to beneficially own more than 5% of the Registrant’s Common Stock and shares held by officers and directors of the Registrant have been excluded because such persons may be deemed to be affiliates. This determination is not necessarily a conclusive determination for other purposes.
Number of shares of Common Stock, $0.001 par value, outstanding as of the close of business on February 10, 2017: 102,328,550 shares.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the definitive Proxy Statement to be delivered to stockholders in connection with the 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders are incorporated by reference into Part III
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page | ||
2
For purposes of this Annual Report, the terms “Verisign”, “the Company”, “we”, “us”, and “our” refer to VeriSign, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries.
PART I
ITEM 1. | BUSINESS |
Overview
We are a global provider of domain name registry services and internet security, enabling internet navigation for many of the world’s most recognized domain names and providing protection for websites and enterprises around the world (“Registry Services”). Our Registry Services ensure the security, stability, and resiliency of key internet infrastructure and services, including the .com and .net domains, two of the internet’s root servers, and operation of the root-zone maintainer function for the core of the internet’s Domain Name System (“DNS”). Our product suite also includes Security Services, consisting of Distributed Denial of Service (“DDoS”) Protection Services, Verisign iDefense Security Intelligence Services (“iDefense”) and Managed Domain Name System (“Managed DNS”) Services. On February 9, 2017, we entered into an agreement to sell the iDefense business, subject to customary closing conditions.
We have one reportable segment, which consists of Registry Services and Security Services. We have operations inside as well as outside the United States (“U.S.”). For certain additional information about our segment, including a geographic breakdown of revenues and changes in revenues, see “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in Item 7 and Note 9, “Geographic and Customer Information” of our Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 15 of this Form 10-K.
We were incorporated in Delaware on April 12, 1995. Our principal executive offices are located at 12061 Bluemont Way, Reston, Virginia 20190. Our telephone number at that address is (703) 948-3200. Our common stock is traded on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the ticker symbol VRSN. VERISIGN, the VERISIGN logo, and certain other product or service names are registered or unregistered trademarks in the U.S. and other countries. Other names used in this Form 10-K may be trademarks of their respective owners. Our primary website is Verisign.com. The information available on, or accessible through, this website is not incorporated in this Form 10-K by reference.
Our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), are available, free of charge, on the Investor Relations section of our website as soon as is reasonably practicable after filing such reports with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). The public may read and copy any materials we file with the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, NE, Washington, DC 20549. The public may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC maintains an internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC at sec.gov.
Pursuant to our agreements with the Internet Corporation for Assigned Name and Numbers (“ICANN”), we make available on our website (at www.Verisign.com/zone) files containing all active domain names registered in the .com and .net registries. At the same website address, we make available a summary of the active zone count registered in the .com and .net registries and the number of .com and .net domain names in the domain name base. The domain name base is the active zone plus the number of domain names that are registered but not configured for use in the respective top level domain zone file plus the number of domain names that are in a client or server hold status. These files and the related summary data are updated at least once per day. The update times may vary each day. The number of domain names provided in this Form 10-K are as of midnight of the date reported.
We announce material financial information to our investors using our investor relations website https://investor.Verisign.com, SEC filings, investor events, news and earnings releases, public conference calls and webcasts. We use these channels as well as social media to communicate with our investors and the public about our company, our products and services, and other issues. It is possible that the information we post on social media could be deemed to be material information. Therefore, we encourage investors, the media, and others interested in our Company to review the information we post on the social media channels listed below. This list may be updated from time to time on our investor relations website.
https://www.Facebook.com/Verisign
https://www.Twitter.com/Verisign
https://www.LinkedIn.com/company/Verisign
https://www.YouTube.com/user/Verisign
https://www.Verisign.com
https://blog.Verisign.com
3
The contents of these websites are not intended to be incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10-K or in any other report or document we file, and any references to these websites are intended to be inactive textual references only.
Registry Services
Registry Services operates the authoritative directory of all .com, .net, .cc, .tv, and .name domain names, among others and the back-end systems for all .gov, .jobs, and .edu domain names, among others. Registry Services allows individuals and organizations to establish their online identities, while providing the secure, always-on access they need to communicate and transact reliably with large-scale online audiences.
We are the exclusive registry of domain names within the .com, .net, and .name generic top-level domains (“gTLDs”), among others, under agreements with ICANN and also, with respect to the .com agreement, the U.S. Department of Commerce (“DOC”). We are also the exclusive registry of domain names within certain transliterations of .com and .net in a number of different native languages and scripts (“IDN gTLDs”). As a registry, we maintain the master directory of all second-level domain names in these gTLDs and IDN gTLDs (e.g., johndoe.com and janedoe.net). Our global constellation of domain name servers provides internet protocol (“IP”) address information in response to queries, enabling the use of browsers, email systems, and other systems on the internet. In addition, we own and maintain the shared registration system that allows all registrars to enter new second-level domain names into the master directory and to submit modifications, transfers, re-registrations and deletions for existing second-level domain names (“Shared Registration System”).
Separate from our agreements with ICANN, we have agreements to be the exclusive registry for the .tv and .cc country code top-level domains (“ccTLDs”) for Tuvalu and Cocos (Keeling) Islands, respectively, and to operate the back-end registry systems for the .gov, .jobs, and .edu gTLDs, among others. These TLDs, other than .gov, are also supported by our global constellation of domain name servers and Shared Registration System.
We also provide internationalized domain name (“IDN”) services that enable internet users to access websites in characters representing their local language. Our legacy TLDs and ccTLDs can support registrations in as many as 350 different native languages and scripts.
Domain names can be registered for between one and 10 years, and the fees charged for .com, .net and .name may only be increased according to adjustments prescribed in our agreements with ICANN over the applicable term. With respect to .com, price increases require prior approval by the DOC according to the terms of Amendment 32 of the Cooperative Agreement, as amended, between the DOC and Verisign (“Cooperative Agreement”). Revenues for .cc and .tv domain names and our IDN gTLDs are based on a similar fee system and registration system, though the fees charged are not subject to the same pricing restrictions as those imposed by ICANN on .com, .net and .name. The fees received from operating the .gov registry are based on the terms of Verisign’s agreement with the U.S. General Services Administration. The fees received from operating the .jobs registry infrastructure, and that of others for which Verisign provides such services, are based on the terms of Verisign’s agreements with those respective registry operators. No fees are received from operating the .edu registry infrastructure.
Historically, we have experienced higher domain name growth in the first quarter of the year compared to other quarters. Our quarterly revenue does not reflect these seasonal patterns because the preponderance of our revenue for each quarterly period is provided by the ratable recognition of our deferred revenue balance. The effect of this seasonality has historically resulted in the largest amount of growth in our deferred revenue balance occurring during the first quarter of the year compared to the other quarters. In the second half of 2015 and in the first quarter of 2016, we experienced an increase in the level of new domain name registrations largely through registrars in China. The volume of these new registrations was inconsistent and episodic compared to prior periods, and by the end of the first quarter of 2016, reverted back to a more normalized registration pace. A significant portion of these domain name registrations from the second half of 2015 did not renew during the fourth quarter of 2016.
Security Services
Security Services provides infrastructure assurance to organizations and is comprised of DDoS Protection Services, iDefense, and Managed DNS Services.
DDoS Protection Services supports online business continuity by providing monitoring and mitigation services against DDoS attacks. We help companies stay online without needing to make significant investments in infrastructure or establish internal DDoS expertise. As a cloud-based service, it can be deployed quickly and easily, with no customer premise equipment required. This saves time and money through operational efficiencies, support costs, and economies of scale to provide detection and protection against the largest DDoS attacks. Customers include financial institutions, software-as-a-service providers, e-commerce providers, and media companies. Customers pay a subscription fee that varies depending on the customer’s network requirements.
4
iDefense provides 24 hours a day, every day of the year, access to cyber intelligence related to vulnerabilities, malicious code, and global threats. Our teams enable companies to improve vulnerability management, incident response, fraud mitigation, and proactive mitigation of the particular threats targeting their industry or global operations. Customers include financial institutions, large corporations, and governmental and quasi-governmental organizations. Customers pay a subscription fee for iDefense.
Managed DNS Services is a hosting service that delivers DNS resolution, improving the availability of web-based systems. It provides DNS availability through a globally distributed, securely managed, cloud-based DNS infrastructure, allowing enterprises to save on capital expenses associated with DNS infrastructure deployment and reduce operational costs and complexity associated with DNS management. Managed DNS service provides full support for DNS Security Extensions (“DNSSEC”) compliance features and Geo Location traffic routing capabilities. DNSSEC is designed to protect the DNS infrastructure from man-in-the-middle attacks that corrupt, or poison, DNS data. Geo Location allows website owners to customize responses for end-users based on their physical location or IP address, giving them the ability to deliver location-specific content. Customers include financial institutions, e-commerce, and software-as-a-service providers. Customers pay a subscription fee that varies based on the amount of DNS traffic they receive.
Operations Infrastructure
Our operations infrastructure consists of three secure data centers in Dulles, Virginia; New Castle, Delaware; and Fribourg, Switzerland as well as more than 100 resolution sites around the world. These secure data centers operate 24 hours a day, supporting our business units and services. The performance and scale of our infrastructure are critical for our business, and give us the platform to maintain our leadership position. Key features of our operations infrastructure include:
• | Distributed Servers: We operate a large number of high-speed servers globally to support localized capacity and availability demands. In conjunction with our proprietary software, processes and procedures, this platform offers rapid failover, global and local load balancing, and threshold monitoring on critical servers. |
• | Networking: We deploy and maintain a redundant and diverse global network, maintain high-speed, redundant connections to numerous internet service providers, and maintain peering relationships globally to ensure that our critical services are readily accessible to customers at all times. |
• | Security: We incorporate architectural concepts such as protected domains, restricted nodes and distributed access control in our system architecture. In addition, we employ firewalls and intrusion detection software, as well as proprietary security mechanisms at many points across our infrastructure. We perform recurring internal vulnerability testing and controls audits, and also contract with third-party security consultants who perform periodic penetration tests and security risk assessments on our systems. Verisign has engineered resiliency and diversity into how it hosts classes of products throughout its set of interconnected sites to mitigate unknown vendor defects and zero-hour security vulnerabilities. This includes different physical security silos, which themselves are separated into bulkheads, and in which servers are located. Corporate networks are in their own physical silo. Thus, the corporate networks to which personnel directly connect are separated from the silos that house production services; administration of production gear from corporate systems must go through an internal, fortified intermediary; and account credentials used within the corporate networks are not used within the production silos, nor on the fortified systems. |
• | Data Integrity: Verisign employs both phased and systemic integrity validation operations via a number of proprietary mechanisms on all internal DNS publication operations. |
As part of our operations infrastructure for our Registry Services business, we operate all authoritative domain name servers that answer domain name queries for the .com and .net zones, as well as for the other TLDs for which we are the registry operator. We also administer and operate two of the 13 root zone servers that contain authoritative data for the very top of the DNS hierarchy. Our domain name servers provide the associated authoritative name servers and IP addresses for every .com and .net domain name on the internet and a large number of other TLD queries, resulting in an average of approximately 143 billion transactions per day. These name servers are located in resolution facilities which are in a controlled and monitored environment, incorporating security and system maintenance features. This network of name servers is one of the cornerstones of the internet’s DNS infrastructure.
We have continuously expanded our infrastructure to meet demands to support normal and peak system load and attack volumes based on what we have experienced historically, as well as to address projected internet attack trends.
Call Centers and Help Desk: We provide customer support services through our phone-based call centers, email help desks and web-based self-help systems. Our Virginia call center is staffed 24 hours a day, every day of the year to support our
5
businesses. All call centers have a staff of trained customer support agents and also provide web-based support services utilizing customized automatic response systems to provide self-help recommendations.
Operations Support and Monitoring: Through our network operations centers, we have an extensive monitoring capability that enables us to track the status and performance of our critical database systems and our global resolution systems. Our network operations center is staffed 24 hours a day, every day of the year.
Disaster Recovery Plans: We have disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities that are designed to deal with the loss of entire data centers and other facilities. Our Registry Services business maintains dual mirrored data centers that allow rapid failover with no data loss and no loss of function or capacity, as well as off-continent tertiary Registry Services capabilities. Our critical data services (including domain name registration and global resolution) use advanced storage systems that provide data protection through techniques such as synchronous mirroring and remote replication.
Marketing, Sales and Distribution
We offer promotional marketing programs for our registrars based upon market conditions and the business environment in which the registrars operate. We seek to expand our existing businesses through focused marketing programs that target growth in the .com and .net domain name base, both domestically and in emerging international markets, and by extending our brand and serving new markets through the IDN gTLDs, which we have begun launching. We market our Security Services worldwide through multiple distribution channels, including direct sales and indirect channels. We have marketing and sales offices in several different countries around the world.
Research and Development
We believe that timely development of new and enhanced services, including monitoring and visualization, registry provisioning platforms, navigation and resolution services, data services, value added services, and Security Services, as well as new and enhanced ways to ensure the security, stability, and resiliency of our services, is necessary to remain competitive in the marketplace. During 2016, 2015, and 2014 our research and development expenses were $59.1 million, $63.7 million and $67.8 million, respectively.
Our future success will depend, in large part, on our ability to continue to maintain and enhance our current technologies and services and to develop new ones. We actively investigate and incubate new concepts and evaluate new business ideas through our innovation pipeline. We expect that most of the future enhancements to our existing services and our new services will be the result of internal development efforts in collaboration with suppliers, other vendors, customers, and the technology community. Under certain circumstances, we may also acquire or license technology from third parties.
The markets for our services are dynamic, characterized by rapid technological developments, frequent new product introductions, and evolving industry standards. The constantly changing nature of these markets and their rapid evolution will require us to continually improve the performance, features, and reliability of our services, particularly in response to competitive offerings, and to introduce both new and enhanced services as quickly as possible and prior to our competitors.
Competition
We compete with numerous companies in both the Registry Services and Security Services businesses. The overall number of our competitors may increase and the identity and composition of competitors may change over time.
New technologies and the expansion of existing technologies may increase competitive pressure. In addition, our markets are characterized by announcements of collaborative relationships involving our competitors. The existence or announcement of any such relationships could adversely affect our ability to attract and retain customers.
Competition in Registry Services: We face competition in the domain name registry space from other gTLD and ccTLD registries that are competing for the business of entities and individuals that are seeking to obtain a domain name registration, establish a web presence, as well as other uses of domain names, such as branded email. In addition to the gTLDs and ccTLDs we operate or for which we provide back-end registry services, there are over 1,140 other operational gTLD registries, over 250 Latin script ccTLD registries, more than 50 IDN ccTLD registries, and over 80 IDN gTLDs. Under our agreements with ICANN, we are subject to certain restrictions in the operation of .com, .net and .name on pricing, bundling, marketing, methods of distribution, the introduction of new registry services, and use of registrars that do not apply to ccTLDs and other gTLDs and therefore may create a competitive disadvantage.
To the extent end-users navigate using search engines or social media, as opposed to direct navigation, we may face competition from search engine operators such as Google, Microsoft, and Yahoo!, operators of social networks such as Facebook,
6
and operators of microblogging tools such as Twitter. In addition, we may face competition from these social media businesses to the extent they are used to establish an online presence by end-users instead of through the use of a domain name. Furthermore, to the extent end-users increase the use of web and mobile applications to locate and access content, we may face competition from providers of such web and mobile applications.
We also face competition from service providers that offer outsourced domain name registration, resolution and other DNS services to organizations that require a reliable and scalable infrastructure. Among the competitors are Neustar, Inc., Afilias plc, Donuts Inc., RightSide Group, Ltd., and CentralNic Ltd.
Competition in Security Services: Several of our current and potential competitors have longer operating histories and/or significantly greater financial, technical, marketing, and other resources than we do and therefore may be able to respond more quickly than we can to new or changing opportunities, technologies, standards, and customer requirements. Many of these competitors also have broader and more established distribution channels that may be used to deliver competing products or services directly to customers through bundling or other means. If such competitors were to bundle competing products or services for their customers, we may experience difficulty establishing or increasing demand for our products and services or distributing our products successfully. In addition, it may be difficult to compete against consolidation and partnerships among our competitors which create integrated product suites.
Our Security Services business faces competition from companies such as Akamai Technologies, Inc., Amazon, AT&T Inc., BlueCat Networks, Cloudflare, Cisco OpenDNS, Cyveillance, Inc., Dynamic Network Services, Inc., FireEye, Inc., Imperva, Inc., Infoblox Inc., International Business Machines Corporation, Level 3 Communications, Inc., Neustar, Inc., Nominum, Inc., RiskIQ, Inc., SecureWorks, ThreatConnect, Inc., ThreatStream, Inc., and Verizon Communications Inc.
Industry Regulation
The internet is governed under a multi-stakeholder model comprising civil society, the private sector including for-profit and not-for-profit organizations such as ICANN, governments including the U.S. government, academia, non-governmental organizations, and international organizations. ICANN plays a central coordination role in the multi-stakeholder system. ICANN is mandated through its bylaws to uphold a private sector-led multi-stakeholder approach to internet governance for the public benefit. The multi-stakeholder process has and will continue to create policies, programs, and standards that directly or indirectly impact or affect our business. In addition, country-level regulations, such as those implemented by China, impose additional costs on our Registry Services and can affect the growth or renewal rates of domain name registrations. Similarly, in the European Union, legislative and regulatory bodies responsible for data privacy continue to enhance and modify data privacy protections, which impacts our collection and delivery of personal data as we provide our domain name registry services.
As the exclusive registry of domain names within the .com and .net gTLDs, we have entered into certain agreements with ICANN and, in the case of .com, the DOC under a Cooperative Agreement.
.com Registry Agreement
Following the extension of the .com Registry Agreement on October 20, 2016, the .com Registry Agreement provides that we will continue to be the sole registry operator for domain names in the .com gTLD through November 30, 2024. As part of the extension of the .com Registry Agreement, the Company and ICANN agreed to negotiate in good faith to amend the terms of the .com Registry Agreement: (i) by October 20, 2018, to preserve and enhance the security and stability of the internet or the .com TLD, and (ii) as a result of any changes to, or the termination or expiration of, the Cooperative Agreement. The .com Registry Agreement includes pricing restrictions for .com domain name registrations, which sets a maximum price of $7.85 for a .com domain name registration and is consistent with the terms of the Cooperative Agreement as set forth below. In addition to the maximum price of $7.85, on a quarterly basis, we pay $0.25 to ICANN for each annual increment of a domain name registered or renewed during such quarter. We are required to comply with and implement temporary specifications or policies and consensus policies, as well as other provisions pursuant to the .com Registry Agreement relating to handling of data and other registry operations. The .com Registry Agreement also provides a procedure for Verisign to propose, and ICANN to review and approve, additional registry services.
The .com and .net Registry Agreements with ICANN contain a “presumptive” right of renewal upon the expiration of their current terms. In addition to ICANN’s approval, a renewal of the .com Registry Agreement must be approved by the DOC, which, under certain circumstances, could refuse to grant its approval to the renewal of the .com or .net Registry Agreement on similar terms, or at all. ICANN could terminate or refuse to renew our .com Registry Agreement if, upon proper notice, (i) we fail to cure a fundamental and material breach of certain specified obligations, and (ii) we fail to timely comply with a final decision of an arbitrator or court. See “Risk Factors - Risks arising from our agreements governing our Registry Services business could limit our ability to maintain or grow our business” in Part I, Item 1A of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further information.
7
Our .com and .net Registry Agreements contain obligations to provide access to our systems, restrictions on our ability to market and bundle our products and services, and restrictions on our ability to control our registrar channel or own a registrar.
Cooperative Agreement
The Cooperative Agreement will expire on November 30, 2018, unless the DOC, in its sole discretion, extends the term. The DOC has the right to conduct a public interest review for the sole purpose of determining whether the DOC will exercise its right to extend the term of the Cooperative Agreement. In connection with the aforementioned review, we agreed to cooperate fully and to work in good faith to reach a mutual agreement with the DOC to resolve issues identified in such review and to implement any agreed upon changes as of the expiration of the current term of the Cooperative Agreement.
The Cooperative Agreement provides that the Maximum Price (as defined in the .com Registry Agreement) of a .com domain name shall not exceed $7.85 for the term of the .com Registry Agreement, except that the we are entitled to increase the Maximum Price of a .com domain name due to the imposition of any new Consensus Policy or documented extraordinary expense resulting from an attack or threat of attack on the Security or Stability of the DNS as described in the .com Registry Agreement, provided that we may not exercise such right unless the DOC provides prior written approval that the exercise of such right will serve the public interest, such approval not to be unreasonably withheld. The Cooperative Agreement further provides that we shall be entitled at any time during the term of the .com Registry Agreement to seek to remove the pricing restrictions contained in the .com Registry Agreement if we demonstrate to the DOC that market conditions no longer warrant pricing restrictions in the .com Registry Agreement, as determined by the DOC.
The Cooperative Agreement also provides that the DOC’s approval of the .com Registry Agreement is not intended to confer federal antitrust immunity on us with respect to the .com Registry Agreement. The Cooperative Agreement also provides that any renewal or extension of the .com Registry Agreement is subject to prior written approval by the DOC. The DOC shall approve such renewal if it concludes that approval will serve the public interest in (a) the continued security and stability of the internet DNS and the operation of the .com registry including, in addition to other relevant factors, consideration of Verisign’s compliance with consensus policies and technical specifications, its service level agreements as set forth in the .com Registry Agreement, and the investment associated with improving the security and stability of the DNS, and (b) the provision of Registry Services as defined in the .com Registry Agreement at reasonable prices, terms and conditions. The parties have an expectancy of renewal of the .com Registry Agreement so long as the foregoing public interest standard is met and Verisign is not in breach of the .com Registry Agreement.
.net Registry Agreement
On June 27, 2011, we entered into a renewal of our Registry Agreement with ICANN for the .net gTLD (the “.net Registry Agreement”). The .net Registry Agreement provides that we will continue to be the sole registry operator for domain names in the .net TLD through June 30, 2017.
Root Zone Maintainer Service Agreement
In the fourth quarter of 2016, the United States government completed a transition of the historical role played by the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (“NTIA”) in the coordination of the DNS. As part of the transition, the NTIA discharged us from our obligations under the Cooperative Agreement to perform Root Zone Maintainer functions and we entered into a new agreement with ICANN, the Root Zone Maintainer Service Agreement (“RZMA”) under which we now perform the Root Zone Maintainer functions on behalf of ICANN. The RZMA will expire on October 20, 2024.
The descriptions of the .com Registry Agreement, the Cooperative Agreement, and the .net Registry Agreement are qualified in their entirety by the text of the complete agreements that are incorporated by reference as exhibits in this Form 10-K.
Intellectual Property
We rely on a combination of copyrighted software, trademarks, service marks, patents, trade secrets, know-how, restrictions on disclosure, and other methods to protect our proprietary assets. We also enter into confidentiality and/or invention assignment agreements with our employees, consultants and current and potential affiliates, customers and business partners. We also generally control access to and distribution of proprietary documentation and other confidential information.
We have been issued numerous patents in the U.S. and abroad, covering a wide range of our technologies. Additionally, we continue to file numerous patent applications with respect to certain of our technologies in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and internationally. Patents may not be awarded with respect to these applications and even if such patents are awarded, such
8
patents may not provide us with sufficient protection. We continue to focus on growing our patent portfolio and consider opportunities for its strategic use.
We have obtained trademark registrations for the VERISIGN mark and VERISIGN logo in the U.S. and certain countries, and have pending trademark applications for the VERISIGN logo in a number of other countries. We have common law rights in other proprietary names. We take steps to enforce and police Verisign’s trademarks. We rely on the strength of our Verisign brand to help differentiate ourselves in the marketing of our products and services.
Our principal intellectual property consists of, and our success is dependent upon, proprietary software used in our Registry Services business and certain methodologies (many of which are patented or for which patent applications are pending) and technical expertise and proprietary know-how we use in both the design and implementation of our current and future registry services. We own our proprietary Shared Registration System through which registrars submit second-level domain name registrations for each of the registries we operate, as well as the ATLAS distributed lookup system which processes billions of queries per day. Some of the software and protocols used in our registry services are in the public domain or are otherwise available to our competitors. Some of the software and protocols used in our business are based on open standards set by organizations such as the Internet Engineering Task Force. To the extent any of our patents are considered “standard essential patents,” we may be required to license such patents to our competitors on reasonable and non-discriminatory terms or otherwise be limited in our ability to assert such patents.
Employees
The following table shows a comparison of our consolidated employee headcount, by function:
As of December 31, | ||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Employee headcount by function: | ||||||||
Cost of revenues | 324 | 314 | 299 | |||||
Sales and marketing | 143 | 183 | 171 | |||||
Research and development | 228 | 253 | 318 | |||||
General and administrative | 295 | 269 | 273 | |||||
Total | 990 | 1,019 | 1,061 | |||||
We have never had a work stoppage, and no U.S.-based employees are represented under collective bargaining agreements. Our ability to achieve our financial and operational objectives depends in large part upon our continued ability to attract, integrate, train, retain, and motivate highly qualified sales, technical and managerial personnel, and upon the continued service of our senior management and key sales and technical personnel. Competition for qualified personnel in our industry and in some of our geographical locations is intense, particularly for software development personnel.
9
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
In addition to other information in this Form 10-K, the following risk factors should be carefully considered in evaluating us and our business because these factors currently have a significant impact or may have a significant impact on our business, operating results or financial condition. Actual results could differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements contained in this Form 10-K as a result of the risk factors discussed below and elsewhere in this Form 10-K and in other filings we make with the SEC.
Risks arising from our agreements governing our Registry Services business could limit our ability to maintain or grow our business.
We are parties to (i) a Cooperative Agreement (as amended) with the DOC with respect to the .com gTLD and (ii) Registry Agreements with ICANN for .com, .net, .name, and other gTLDs including our IDN gTLDs. As substantially all of our revenues are derived from our Registry Services business, limitations and obligations in, or changes or challenges to, these agreements, particularly the agreements that involve .com and .net, could have a material adverse impact on our business. Certain competing registries, such as the ccTLDs, do not face the same limitations or obligations that we face in our agreements.
Modifications or Amendments. In October 2016, the Company and ICANN entered into an amendment to extend the term of the .com Registry Agreement to November 30, 2024 (the “.com Amendment”). As part of the .com Amendment, the Company and ICANN agreed to negotiate in good faith to amend the terms of the .com Registry Agreement: (i) by October 20, 2018, to preserve and enhance the security and stability of the internet or the .com TLD, and (ii) as a result of any changes to, or the termination or expiration of, the Cooperative Agreement. In a related risk, if we have a failure in our operation of the .gov registry, such a failure could call into question our ability to preserve the security and stability of the internet and result in damage to our reputation. We can provide no assurance that any new terms for the .com Registry Agreement that we agree to as a result of the above obligations will not have a material adverse impact on our business, operating results, financial condition, and cash flows.
The DOC approved the .com Amendment under amendment 34 to the Cooperative Agreement. The DOC did not extend the term of the Cooperative Agreement, which will expire on November 30, 2018, unless the DOC, in its sole discretion, extends the term. Under amendment 34, the DOC has the right to conduct a public interest review for the sole purpose of determining whether the DOC will exercise its right to extend the term of the Cooperative Agreement. In connection with the aforementioned review, we agreed to cooperate fully and to work in good faith to reach a mutual agreement with the DOC to resolve issues identified in such review and to implement any agreed upon changes as of the expiration of the current term of the Cooperative Agreement. We can provide no assurance that any changes that we agree to as a result of the above obligations will not have a material adverse impact on our business, operating results, financial condition, and cash flows.
In addition, our Registry Agreements for new gTLDs, including the Registry Agreements for our IDN gTLDs, include ICANN’s right to amend the agreements without our consent, which could impose unfavorable contract obligations on us that could impact our plans and competitive positions with respect to new gTLDs. At the time of renewal of our .com or .net Registry Agreements, ICANN might also attempt to impose this same unilateral right to amend these registry agreements under certain conditions. ICANN has also included new mandatory obligations on new gTLD registry operators, including us, that may increase the risks and potential liabilities associated with operating new gTLDs. ICANN might seek to impose these new mandatory obligations in our other Registry Agreements under certain conditions. We can provide no assurance that any changes to our Registry Agreements as a result of the above obligations will not have a material adverse impact on our business, operating results, financial condition, and cash flows.
Pricing. Under the terms of the Cooperative Agreement with the DOC and the .com Registry Agreement with ICANN, we are restricted during the term of the Registry Agreement from increasing the price of registrations or renewals of .com domain names above $7.85, except that we are entitled to increase the price up to 7%, with the prior approval of the DOC, due to the imposition of any new Consensus Policies, as established and defined under ICANN’s bylaws, or documented extraordinary expense resulting from an attack or threat of attack on the security and stability of the DNS. However, it is uncertain that such circumstances will arise, or if they do, whether we would seek, or the DOC would approve, any request to increase the price for .com domain name registrations. We also have the right under the Cooperative Agreement to seek the removal of these pricing restrictions if we demonstrate that market conditions no longer warrant such restrictions. However, it is uncertain when such circumstances will arise, or when they do, whether the DOC will agree to the removal of these pricing restrictions. In comparison, under the terms of the .net and .name Registry Agreements with ICANN, we are permitted to increase the price of domain name registrations and renewals in these TLDs up to 10% per year. Additionally, ICANN’s registry agreements for the new gTLDs do not contain such pricing restrictions.
Vertical integration. Under the .com, .net, and .name Registry Agreements with ICANN, as well as the Cooperative Agreement with the DOC, we are not permitted to acquire, directly or indirectly, control of, or a greater than 15% ownership
10
interest in, any ICANN-accredited registrar. Historically, all gTLD registry operators were subject to this vertical integration prohibition; however, ICANN has established a process whereby registry operators may seek ICANN’s approval to remove this restriction, and ICANN has approved such removal in some instances. If we were to seek removal of the vertical integration restrictions contained in our agreements, it is uncertain whether ICANN and/or DOC approval would be obtained. Additionally, ICANN’s registry agreement for new gTLDs generally permits such vertical integration, with certain limitations including ICANN’s right, but not the obligation, to refer such vertical integration activities to competition authorities. Furthermore, such vertical integration restrictions do not generally apply to ccTLD registry operators. If registry operators of new or existing gTLDs, or ccTLDs, are able to obtain competitive advantages through such vertical integration, it could materially harm our business.
Renewal and Termination. Our .com, .net, and .name Registry Agreements with ICANN contain “presumptive” rights of renewal upon the expiration of their current terms on November 30, 2024, July 1, 2017 and August 15, 2018 respectively. The Registry Agreements for our new gTLDs including our IDN gTLDs are subject to a 10-year term and contain similar “presumptive” renewal rights. If certain terms in our .com and .net Registry Agreements are not similar to such terms generally in effect in the registry agreements of the five largest gTLDs, then a renewal of these agreements shall be upon terms reasonably necessary to render such terms similar to the registry agreements for those other gTLDs. There can be no assurance that such terms, if they apply, will not have a material adverse impact on our business. A renewal of the .com Registry Agreement must be approved by the DOC, which, under certain circumstances, could refuse to grant its approval to the renewal of the .com Registry Agreement on similar terms, or at all. A failure (i) by ICANN or the DOC to approve the renewal of the .com Registry Agreement prior to the expiration of its current term on November 30, 2024, or (ii) by ICANN to approve the renewal of .net Registry Agreement prior to or upon the expiration of its current term on July 1, 2017, would have, absent an extension, a material adverse effect on our business. ICANN could terminate or refuse to renew our .com or .net Registry Agreements if, upon proper notice, (i) we fail to cure a fundamental and material breach of certain specified obligations, and (ii) we fail to timely comply with a final decision of an arbitrator or court. ICANN’s termination or refusal to renew either the .com or .net Registry Agreement would have a material adverse effect on our business.
Consensus Policies. Our Registry Agreements with ICANN require us to implement Consensus Policies and specifications or policies established on a temporary basis (“Temporary Policies”). ICANN could adopt Consensus Policies or Temporary Policies that are unfavorable to us as the registry operator of .com, .net and our other gTLDs, that are inconsistent with our current or future plans, that impose substantial costs on our business, that subject the Company to additional legal risks or that affect our competitive position. Such Consensus Policies or Temporary Policies could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Legal challenges. Our Registry Agreements have faced, and could continue to face, challenges, including possible legal challenges, resulting from our activities or the activities of ICANN, registrars, registrants, and others, and any adverse outcome from such challenges could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Governmental regulation and the application of new and existing laws in the U.S. and overseas may slow business growth, increase our costs of doing business, create potential liability and have an adverse effect on our business.
Application of new and existing laws and regulations in the U.S. or overseas to the internet and communications industry can be unclear. The costs of complying or failing to comply with these laws and regulations could limit our ability to operate in our current markets, expose us to compliance costs and substantial liability, and result in costly and time-consuming litigation. For example, the government of the People’s Republic of China (“PRC”) has indicated that it will issue new regulations, and has begun to enforce existing regulations, that could impose additional costs on our provision of Registry Services in the PRC and could impact the growth or renewal rates of domain name registrations in the PRC. In addition to registry operators, the regulations will require registrars to obtain a government-issued license for each TLD whose domain name registrations they intend to sell directly to registrants. Their failure to obtain the required licenses could also impact the growth of our business in the PRC.
Foreign, federal or state laws could have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows, and our ability to conduct business in certain foreign countries. For example, laws designed to restrict who can register and who can distribute domain names, the online distribution of certain materials deemed harmful to children, online gambling, counterfeit goods, and cybersquatting; laws designed to require registrants to provide additional documentation or information in connection with domain name registrations; and laws designed to promote cyber security may impose significant additional costs on our business or subject us to additional liabilities. We have contracts pursuant to which we provide services to the U.S. government and they impose compliance costs, including compliance with the Federal Acquisition Regulation, which could be significant to the Company.
Due to the nature of the internet, it is possible that state or foreign governments might attempt to regulate internet transmissions or prosecute us for violations of their laws. We might unintentionally violate such laws, such laws may be modified, and new laws may be enacted in the future. In addition, as we launch our IDN gTLDs and increase our marketing
11
efforts of our other gTLDs in foreign countries, we may raise our profile in certain foreign countries thereby increasing the regulatory and other scrutiny of our operations. Any such developments could increase the costs of regulatory compliance for us, affect our reputation, force us to change our business practices or otherwise materially harm our business. In addition, any such new laws could impede growth of or result in a decline in domain name registrations, as well as impact the demand for our services.
Undetected or unknown defects in our service, security breaches, and DDoS attacks could expose us to liability and harm our business and reputation.
Services as complex as those we offer or develop could contain undetected defects or errors. Despite testing, defects or errors may occur in our existing or new services, which could result in compromised customer data, including DNS data, diversion of development resources, injury to our reputation, tort or contract claims, increased insurance costs or increased service costs, any of which could harm our business. Performance of our services could have unforeseen or unknown adverse effects on the networks over which they are delivered as well as, more broadly, on internet users and consumers, and third-party applications and services that utilize our services, which could result in legal claims against us, harming our business. Our failure to identify, remediate and mitigate security breaches or our inability to meet customer expectations in a timely manner could also result in loss of or delay in revenues, loss of market share, failure to achieve market acceptance, injury to our reputation and increased costs.
In addition to undetected defects or errors, we are also subject to cyber-attacks and attempted security breaches. We retain certain customer and employee information in our data centers and various domain name registration systems. It is critical to our business strategy that our facilities and infrastructure remain secure and are perceived by the marketplace to be secure. The Company, as an operator of critical internet infrastructure, is frequently targeted and experiences a high rate of attacks. These include the most sophisticated forms of attacks, such as advanced persistent threat attacks and zero-hour threats. These forms of attacks involve situations where the threat is not compiled or has been previously unobserved within our observation and threat indicators space until the moment it is launched. In addition, these forms of attacks may target specific unidentified or unresolved vulnerabilities that exist only within the target’s operating environment, making these attacks virtually impossible to anticipate and difficult to defend against. In addition to external threats, we may be subject to insider threats from current, former or contract employees; these threats can be realized from intentional or unintentional actions of such employees. The Shared Registration System, the root zone servers, the Root Zone Management System, the TLD name servers and the TLD zone files that we operate are critical to our Registry Services operations. Despite the significant time and money expended on our security measures, we have been subject to a security breach, as disclosed in our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2011, and our infrastructure may in the future be vulnerable to physical break-ins, outages resulting from destructive malcode, computer viruses, attacks by hackers or nefarious actors or similar disruptive problems, including hacktivism. It is possible that we may have to expend additional financial and other resources to address such problems. Any physical or electronic break-in or other security breach or compromise of the information stored at our data centers or domain name registration systems may cause an outage of or jeopardize the security of information stored on our premises or in the computer systems and networks of our customers. In such an event, we could face significant liability, customers could be reluctant to use our services and we could be at risk for loss of various security and standards-based compliance certifications needed for operation of our businesses, all or any of which could adversely affect our reputation and harm our business. Such an occurrence could also result in adverse publicity and therefore adversely affect the market’s perception of the security of e-commerce and communications over the internet as well as of the security or reliability of our services.
We use externally developed technology, systems and services including both hardware and software, for a variety of purposes, including, without limitation, encryption and authentication, employee email, back-office support, and other functions. While we have developed operational policies and procedures to reduce the impact of a security breach at a vendor where Company data is stored or processed, such measures cannot provide absolute security. Breaches of our vendors’ technology, systems and services could expose us or our customers to a risk of loss or misuse of Company data, including but not limited to personal information.
Additionally, our networks have been, and likely will continue to be, subject to DDoS attacks. Recent attacks against others have demonstrated that DDoS attacks continue to grow in size and sophistication and have an ability to widely disrupt internet services. While we have adopted mitigation techniques, procedures and strategies to defend against such attacks, there can be no assurance that we will be able to defend against every attack, especially as the attacks increase in size and sophistication. Any attack, even if only partially successful, could disrupt our networks, increase response time, negatively impact our ability to meet our contracted service level obligations, and generally hamper our ability to provide reliable service to our Registry Services customers and the broader internet community. Further, we sell DDoS protection services to our Security Services customers. Although we increase our knowledge of and develop new techniques in the identification and mitigation of attacks through the protection of our Security Services customers, the DDoS protection services share some of the infrastructure used in our Registry Services business. Therefore the provision of such services might expose our critical
12
Registry Services infrastructure to temporary degradations or outages caused by DDoS attacks against those customers, in addition to any directed specifically against us and our networks.
Changes to the multi-stakeholder model of internet governance could materially and adversely impact our business.
The internet is governed under a multi-stakeholder model comprising civil society, the private sector including for-profit and not-for-profit organizations such as ICANN, governments including the U.S. government, academia, non-governmental organizations and international organizations.
Role of the U.S. Government. In the fourth quarter of 2016, the United States government completed a transition of the historical role played by NTIA in the coordination of the DNS. Changes arising from this transition to the multi-stakeholder model of internet governance could materially and adversely impact our business. For example, ICANN has adopted bylaws that are designed, in part, to enhance accountability through a new organization called the Empowered Community, which is comprised of a cross section of industry participants. ICANN or the Empowered Community may assert positions that could negatively impact our strategy or our business.
Furthermore, as part of the transition, the NTIA discharged us from our obligations under the Cooperative Agreement to perform Root Zone Maintainer functions and we entered into a new agreement with ICANN, the Root Zone Maintainer Service Agreement (“RZMA”) under which we now perform the Root Zone Maintainer functions on behalf of ICANN. As we perform the Root Zone Maintainer function under the RZMA, we may be subject to claims challenging the agreement or our performance under the agreement, and we may not have immunity from, or sufficient indemnification for, such claims.
By completing the transition discussed above, the U.S. Government through the NTIA has ended its coordination and management of important aspects of the DNS including the IANA functions and the root zone. There can be no assurance that the removal of the U.S. Government oversight of these key functions will not negatively impact our business.
Role of ICANN. ICANN plays a central coordination role in the multi-stakeholder system. ICANN is mandated through its bylaws to uphold a private sector-led multi-stakeholder approach to internet governance for the public benefit. If ICANN or the Empowered Community fails to uphold or significantly redefines the multi-stakeholder model, it could harm our business. Additionally, the Empowered Community could adversely impact ICANN, which could negatively impact its ability to coordinate the multi-stakeholder system of governance, or negatively affect our interests. Also, legal, regulatory or other challenges could be brought challenging the legal authority underlying the roles and actions of ICANN, the Empowered Community or us.
Role of foreign governments. Some governments and members of the multi-stakeholder community have questioned ICANN’s role with respect to internet governance and, as a result, could seek a multilateral oversight body as a replacement. Additionally, the role of ICANN’s Governmental Advisory Committee, which is comprised of representatives of national governments, could change, giving governments more control of internet governance. Some governments and governmental authorities outside the U.S. have in the past disagreed, and may in the future disagree, with the actions, policies or programs of ICANN, the U.S. Government and us relating to the DNS. Changes to the roles that foreign governments play in internet governance could materially and adversely impact our business.
We operate two root zone servers and are contracted to perform the Root Zone Maintainer function. Under ICANN’s New gTLD Program, we face increased risk from these operations.
We operate two of the 13 root zone servers. Root zone servers are name servers that contain authoritative data for the very top of the DNS hierarchy. These servers have the software and DNS configuration data necessary to locate name servers that contain authoritative data for the TLDs. These root zone servers are critical to the functioning of the internet. Under the RZMA, we play a key operational role in support of the IANA function as the Root Zone Maintainer. In this role, we provision and publish the authoritative root zone data and make it available to all root server operators.
Under its New gTLD Program, ICANN has recommended delegations into the root zone of a large number of new gTLDs. In view of our role as the Root Zone Maintainer, and as a root server operator, we face increased risks should ICANN’s delegation of these new gTLDs, which represent unprecedented changes to the root zone in volume and frequency, cause security and stability problems within the DNS and/or for parties who rely on the DNS. Such risks include potential instability of the DNS including potential fragmentation of the DNS should ICANN’s delegations create sufficient instability, and potential claims based on our role in the root zone provisioning and delegation process. These risks, alone or in the aggregate, have the potential to cause serious harm to our Registry Services business. Further, our business could also be harmed through security, stability and resiliency degradation if the delegation of new gTLDs into the root zone causes problems to certain components of the DNS ecosystem or other aspects of the global DNS, or other relying parties are negatively impacted as a result of domain name collisions or other new gTLD security issues, such as exposure or other leakage of private or sensitive information.
13
Additionally, DNSSEC enabled in the root zone and at other levels of the DNS requires new preventative maintenance functions and complex operational practices that did not exist prior to the introduction of DNSSEC. Any failure by us or the IANA functions operator to comply with stated practices, such as those outlined in relevant DNSSEC Practice Statements, introduces risk to DNSSEC relying parties and other internet users and consumers of the DNS, which could have a material adverse impact on our business.
The evolution of internet practices and behaviors and the adoption of substitute technologies may impact the demand for domain names.
Domain names and the domain name system have been used by consumers and businesses to access or disseminate information, conduct e-commerce, and develop an online identity for many years. The growth of technologies such as social media, mobile devices, apps and the dominance of search engines has evolved and changed the internet practices and behaviors of consumers and businesses alike. These changes can impact the demand for domain names by those who purchase domain names for personal, commercial and investment reasons. Factors such as the evolving practices and preferences of internet users and how they navigate the internet as well the motivation of domain name registrants and how they will monetize their investment in domain names can negatively impact our business. Some domain name registrars and registrants seek to purchase and resell domain names following an increase in their value. Adverse changes in the resale value of domain names could result in a decrease in the demand and/or renewal rates for domain names in our TLDs obtained for resale.
Some domain name registrants use a domain name to access or disseminate information, conduct e-commerce, and develop an online identity. Currently, internet users often navigate to a website either by directly typing its domain name into a web browser, the use of an app on their smart phone or mobile device, the use of a voice recognition technology such as Alexa, Cortana, Google Assistant, or Siri, or through the use of a search engine. If (i) web browser or internet search technologies were to change significantly; (ii) internet users’ preferences or practices shift away from recognizing and relying on web addresses for navigation through the use of new and existing technologies; (iii) internet users were to significantly decrease the use of web browsers in favor of applications to locate and access content; or (iv) internet users were to increasingly use third level domains or alternate identifiers, such as social networking and microblogging sites, in each case the demand for domain names in our TLDs could decrease. This may trigger current or prospective customers and parties in our target markets to reevaluate their need for registration or renewal of domain names.
Some domain name registrars and registrants seek to generate revenue through advertising on their websites; changes in the way these registrars and registrants are compensated (including changes in methodologies and metrics) by advertisers and advertisement placement networks, such as Google, Yahoo!, Baidu and Bing, have, and may continue to, adversely affect the market for those domain names favored by such registrars and registrants which has resulted in, and may continue to result in, a decrease in demand and/or the renewal rate for those domain names. For example, according to published reports, Google has in the past changed (and may change in the future) its search algorithm, which may decrease site traffic to certain websites and provide less pay-per-click compensation for certain types of websites. This has made such websites less profitable which has resulted in, and may continue to result in, fewer domain registrations and renewals. In addition, as a result of the general economic environment, spending on online advertising and marketing may not increase or may be reduced, which in turn, may result in a further decline in the demand for those domain names.
If any of the above factors negatively impact the renewal of domain names or the demand for new domain names, we may experience material adverse impacts on our business, operating results, financial condition and cash flows.
Many of our markets are evolving, and if these markets fail to develop or if our products and services are not widely accepted in these markets, our business could be harmed.
We seek to serve many new, developing and emerging markets in foreign countries to grow our business. These markets are rapidly evolving, and may not grow. Even if these markets grow, our services may not be widely used or accepted. Accordingly, the demand for our services in these markets is very uncertain. The factors that may affect market acceptance or adoption of our services in these markets include the following:
• | regional internet infrastructure development, expansion, penetration and adoption; |
• | market acceptance and adoption of products and services based upon technologies other than those we use, which are substitutes for our products and services; |
• | public perception of the security of our technologies and of IP and other networks; |
• | the introduction and consumer acceptance of new generations of mobile devices, and in particular the use of alternative internet navigation mechanisms other than web browsers; |
• | increasing cyber threats and the associated customer need and demand for our Security Services offerings; |
14
• | government regulations affecting internet access and availability, domain name registrations or the provision of registry services, or e-commerce and telecommunications over the internet; |
• | the maturity and depth of the sales channels within developing and emerging markets and their ability and motivation to establish and support sales for domain names; |
• | preference by markets for the use of their own country’s ccTLDs as a substitute or alternative to our TLDs; and |
• | increased acceptance and use of new gTLDs as substitutes for established gTLDs. |
If the market for e-commerce and communications over IP and other networks does not grow or these services are not widely accepted in the market, our business could be materially harmed.
We may face operational and other risks from the introduction of new gTLDs by ICANN and our provision of back-end registry services.
Approximately 1,000 new gTLDs have already been delegated in this initial round of new gTLDs. ICANN plans on offering a second round of new gTLDs after the completion of the initial round, the timing of which is uncertain. As set forth in the Verisign Labs Technical Report #1130007 version 2.2: New gTLD Security and Stability Considerations released on March 28, 2013, and expanded upon in our more recent publications, we continue to believe there are issues regarding the deployment of the new gTLDs that should have been addressed before any new gTLDs were delegated, and despite our and others’ efforts, some of these issues have not been addressed by ICANN sufficiently, if at all. For example, domain name collisions have been reported to ICANN, which have resulted in various network interruptions for enterprises as well as confusion and usability issues that have led to phishing attacks. It is anticipated that as additional new gTLDs are delegated more domain name collisions and associated security issues will occur.
We have entered into agreements to provide back-end registry services to other registry operators and applicants for new gTLDs. We may face risks regarding ICANN requirements for mitigating name collisions in the new gTLDs which we operate or for which we provide back-end registry services. For example, the possibility exists that “controlled interruption” periods may disrupt network services or that privacy or secure communications may be impacted as a result of insufficient preparedness by ICANN and the community for the launch of new gTLDs.
Our agreements with ICANN to provide registry services in connection with our new gTLDs, including our IDN gTLDs, and our agreements to provide back-end registry services directly to other applicants and indirectly through reseller relationships expose us to operational and other risks. For example, the increase in the number of gTLDs for which we provide registry services on a standalone basis or as a back-end service provider could further increase costs or increase the frequency or scope of targeted attacks from nefarious actors.
The business environment is highly competitive and, if we do not compete effectively, we may suffer lower demand for our products, price reductions, reduced gross margins and loss of market share.
The internet and communications network services industries are characterized by rapid technological change and frequent new product and service announcements which require us continually to improve the performance, features and reliability of our services, particularly in response to competitive offerings or alternatives to our products and services. In order to remain competitive and retain our market position, we must continually improve our access to technology and software, support the latest transmission technologies, and adapt our products and services to changing market conditions and our customers’ and internet users’ preferences and practices, or launch entirely new products and services such as new gTLDs in anticipation of, or in response to, market trends. We cannot assure that competing technologies developed by others or the emergence of new industry standards will not adversely affect our competitive position or render our services or technologies noncompetitive or obsolete. In addition, our markets are characterized by announcements of collaborative relationships involving our competitors. The existence or announcement of any such relationships could adversely affect our ability to attract and retain customers. As a result of the foregoing and other factors, we may not be able to compete effectively with current or future competitors, and competitive pressures that we face could materially harm our business.
We face competition in the domain name registry space from other gTLD and ccTLD registries that are competing for the business of entities and individuals that are seeking to obtain a domain name registration and/or establish a web presence. We have applied for new gTLDs including certain IDN gTLDs; however, there is no guarantee that such new gTLDs will be as or more successful than the new gTLDs obtained by our competitors. For example, some of the new gTLDs, including our new gTLDs, may face additional universal acceptance and usability challenges in that current desktop and mobile device software does not ubiquitously recognize these new gTLDs and may be slow to adopt standards or support these gTLDs, even if demand for such products is strong. This is particularly true for IDN gTLDs, but applies to conventional gTLDs as well. As a result of these challenges, it is possible that resolution of domain names within some of these new gTLDs may be blocked within certain
15
state or organizational environments, challenging universal resolvability of these strings and their general acceptance and usability on the internet.
See the “Competition” section in Part I, Item 1 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further information.
We must establish and maintain strong relationships with registrars and their resellers to maintain their focus on marketing our products and services otherwise our Registry Service business could be harmed.
All of our domain name registrations occur through registrars. Registrars and their resellers utilize substantial marketing efforts to increase the demand and/or renewal rates for domain names. Consolidation in the registrar or reseller industry or changes in ownership, management, or strategy among individual registrars or resellers could result in significant changes to their business, operating model and cost structure. Such changes could include reduced marketing efforts or other operational changes that could adversely impact the demand and/or the renewal rates for domain names. With the introduction of new gTLDs, many of our registrars have chosen to, and may continue to choose to, focus their short or long-term marketing efforts on these new offerings and/or reduce the prominence or visibility of our products and services on their e-commerce platforms. Our registrars and resellers sell domain name registrations of other competing registries, and some also sell and support their own services for websites such as email, website hosting, as well as other services. Therefore, our registrars and resellers may be more motivated to sell to registrants to whom they can also market their own services. To the extent that registrars and their resellers focus more on selling and supporting their services and less on the registration and renewal of our TLDs, our revenues could be adversely impacted. Our ability to successfully market our services to, and build and maintain strong relationships with, new and existing registrars or resellers is a factor upon which successful operation of our business is dependent. If we are unable to keep a significant portion of their marketing efforts focused on selling our TLDs as opposed to other competing TLDs or their own services, our business could be harmed.
If we encounter system interruptions or failures, we could be exposed to liability and our reputation and business could suffer.
We depend on the uninterrupted operation of our various systems, secure data centers and other computer and communication networks. Our systems and operations are vulnerable to damage or interruption from:
• | power loss, transmission cable cuts and other telecommunications failures; |
• | damage or interruption caused by fire, earthquake, and other natural disasters; |
• | attacks, including hacktivism, by miscreants or other nefarious actors; |
• | computer viruses or software defects; |
• | physical or electronic break-ins, sabotage, intentional acts of vandalism, terrorist attacks, unintentional mistakes or errors, and other events beyond our control; |
• | risks inherent in or arising from the terms and conditions of our agreements with service providers to operate our networks and data centers; |
• | state suppression of internet operations; and |
• | any failure to implement effective and timely remedial actions in response to any damage or interruption. |
Most of the computing infrastructure for our Shared Registration System is located at, and most of our customer information is stored in, our facilities in New Castle, Delaware; Dulles, Virginia; and Fribourg, Switzerland. To the extent we are unable to partially or completely switch over to our primary alternate or tertiary sites, any damage or failure that causes interruptions in any of these facilities or our other computer and communications systems could materially harm our business. Although we carry insurance for property damage, we do not carry insurance or financial reserves for such interruptions, or for potential losses arising from terrorism.
In addition, our Registry Services business and certain of our other services depend on the efficient operation of the internet connections to and from customers to our Shared Registration System residing in our secure data centers. These connections depend upon the efficient operation of internet service providers and internet backbone service providers, some or all of which have had periodic operational problems or experienced outages in the past beyond our scope of control. In addition, if these service providers do not protect, maintain, improve, and reinvest in their networks or present inconsistent data regarding the DNS through their networks, our business could be harmed.
A failure in the operation or update of the root zone servers, the root zone file, the root zone management system, the TLD name servers, or the TLD zone files that we operate, or other network functions, could result in a DNS resolution or other service outage or degradation; the deletion of one or more TLDs from the internet; the deletion of one or more second-level domain names from the internet for a period of time; or a misdirection of a domain name to a different server. A failure in the
16
operation or update of the supporting cryptographic and other operational infrastructure that we maintain could result in similar consequences. A failure in the operation of our Shared Registration System could result in the inability of one or more registrars to register or maintain domain names for a period of time. In the event that a registrar has not implemented back-up services in conformance with industry best practices, the failure could result in permanent loss of transactions at the registrar during that period. Any of these problems or outages could create potential liability, including liability arising from a failure to meet our service level agreements in our Registry Agreements, and could decrease customer satisfaction, harming our business or resulting in adverse publicity that could adversely affect the market’s perception of the security of e-commerce and communications over the internet as well as of the security or reliability of our services.
Our operating results may be adversely affected as a result of unfavorable market, economic, social and political conditions.
An unstable global economic, social and political environment, including hostilities and conflicts in various regions both inside and outside the U.S., natural disasters, currency fluctuations, and country specific operating regulations may have a negative impact on demand for our services, our business and our foreign operations. The economic, social and political environment has impacted or may negatively impact, among other things:
• | our customers’ continued growth and development of their businesses and our customers’ ability to continue as going concerns or maintain their businesses, which could affect demand for our products and services; |
• | current and future demand for our services, including decreases as a result of reduced spending on information technology and communications by our customers; |
• | price competition for our products and services; |
• | the price of our common stock; |
• | our liquidity and our associated ability to execute on any share repurchase plans; |
• | our ability to service our debt, to obtain financing or assume new debt obligations; and |
• | our ability to obtain payment for outstanding debts owed to us by our customers or other parties with whom we do business. |
In addition, to the extent that the economic, social and political environment impacts specific industry and geographic sectors in which many of our customers are concentrated, that may have a disproportionate negative impact on our business.
Our international operations subject our business to additional economic, legal and political risks that could have an adverse impact on our revenues and business.
A significant portion of our revenues is derived from customers outside the U.S. Doing business in international markets has required and will continue to require significant management attention and resources. We may also need to tailor some of our services for a particular market and to enter into international distribution and operating relationships. We may fail to maintain our ability to conduct business, including potentially material business operations in some international locations, or we may not succeed in expanding our services into new international markets or expand our presence in existing markets. Failure to do so could materially harm our business. Moreover, local laws and customs in many countries differ significantly from those in the U.S. In many foreign countries, particularly in those with developing economies, it is common for others to engage in business practices that are prohibited by our internal policies and procedures or U.S. law or regulations applicable to us. There can be no assurance that our employees, contractors and agents will not take actions in violation of such policies, procedures, laws and/or regulations. Violations of laws, regulations or internal policies and procedures by our employees, contractors or agents could result in financial reporting problems, investigations, fines, penalties, or prohibition on the importation or exportation of our products and services and could have a material adverse effect on our business. In addition, we face risks inherent in doing business on an international basis, including, among others:
• | competition with foreign companies or other domestic companies entering the foreign markets in which we operate, as well as foreign governments actively promoting ccTLDs, which we do not operate; |
• | legal uncertainty regarding liability, enforcing our contracts and compliance with foreign laws; |
• | tariffs and other trade barriers and restrictions; |
• | difficulties in staffing and managing foreign operations; |
• | currency fluctuations; |
• | potential problems associated with adapting our services to technical conditions existing in different countries; |
17
• | difficulty of verifying customer information, including complying with the customer verification requirements of certain countries; |
• | more stringent privacy policies in some foreign countries; |
• | additional vulnerability from terrorist groups targeting U.S. interests abroad; |
• | potentially conflicting or adverse tax consequences; |
• | reliance on third parties in foreign markets in which we only recently started doing business; and |
• | potential concerns of international customers and prospects regarding doing business with U.S. technology companies due to alleged U.S. government data collection policies. |
We rely on our intellectual property rights to protect our proprietary assets, and any failure by us to protect or enforce, or any misappropriation of, our intellectual property could harm our business.
Our success depends in part on our internally developed technologies and related intellectual property. Despite our precautions, it may be possible for an external party to copy or otherwise obtain and use our intellectual property without authorization. Furthermore, the laws of foreign countries may not protect our proprietary rights in those countries to the same extent U.S. law protects these rights in the U.S. In addition, it is possible that others may independently develop substantially equivalent intellectual property. If we do not effectively protect our intellectual property, our business could suffer. Additionally, we have filed patent applications with respect to some of our technology in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and patent offices outside the U.S. Patents may not be awarded with respect to these applications and even if such patents are awarded, third parties may seek to oppose or otherwise challenge our patents, and such patents’ scope may differ significantly from what was requested in the patent applications and may not provide us with sufficient protection of our intellectual property. In the future, we may have to resort to litigation to enforce and protect our intellectual property rights, to protect our trade secrets or to determine the validity and scope of the proprietary rights of others. This type of litigation is inherently unpredictable and, regardless of its outcome, could result in substantial costs and diversion of management attention and technical resources. Some of the software and protocols used in our business are based on standards set by standards setting organizations such as the Internet Engineering Task Force. To the extent any of our patents are considered “standards essential patents,” we may be required to license such patents to our competitors on reasonable and non-discriminatory terms.
We also license externally developed technology that is used in some of our products and services to perform key functions. These externally developed technology licenses may not continue to be available to us on commercially reasonable terms or at all. The loss of or our inability to obtain or maintain any of these technology licenses could hinder or increase the cost of our launching new products and services, entering into new markets and/or otherwise harm our business. Some of the software and protocols used in our Registry Services business are in the public domain or may otherwise become publicly available, which means that such software and protocols are equally available to our competitors.
We rely on the strength of our Verisign brand to help differentiate ourselves in the marketing of our products. Dilution of the strength of our brand could harm our business. We are at risk that we will be unable to fully register, build equity in, or enforce the Verisign logo in all markets where Verisign products and services are sold. In addition, in the U.S. and most other countries’ word marks for TLDs have currently not been successfully registered as trademarks. Accordingly, we may not be able to fully realize or maintain the value of these intellectual property assets.
We could become subject to claims of infringement of intellectual property of others, which could be costly to defend and could harm our business.
We cannot be certain that we do not and will not infringe the intellectual property rights of others. Claims relating to infringement of intellectual property of others or other similar claims have been made against us in the past and could be made against us in the future. It is possible that we could become subject to additional claims for infringement of the intellectual property of other parties. The international use of our logo could present additional potential risks for external party claims of infringement. Any claims, with or without merit, could be time consuming, result in costly litigation and diversion of technical and management personnel attention, cause delays in our business activities generally, or require us to develop a non-infringing logo or technology or enter into royalty or licensing agreements. Royalty or licensing agreements, if required, may not be available on acceptable terms or at all. If a successful claim of infringement were made against us, we could be required to pay damages or have portions of our business enjoined. If we could not identify and adopt an alternative non-infringing logo, develop non-infringing technology or license the infringed or similar technology on a timely and cost-effective basis, our business could be harmed.
An external party could claim that the technology we license from other parties infringes a patent or other proprietary right. Litigation between the licensor and a third party or between us and a third party could lead to royalty obligations for
18
which we are not indemnified or for which indemnification is insufficient, or we may not be able to obtain any additional license on commercially reasonable terms or at all.
In addition, legal standards relating to the validity, enforceability, and scope of protection of intellectual property rights in internet-related businesses, including patents related to software and business methods, are uncertain and evolving. Because of the growth of the internet and internet-related businesses, patent applications are continuously being filed in connection with internet-related technology. There are a significant number of U.S. and foreign patents and patent applications in our areas of interest, and we believe that there has been, and is likely to continue to be, significant litigation in the industry regarding patent and other intellectual property rights.
We could become involved in claims, lawsuits or investigations that may result in adverse outcomes.
In addition to possible intellectual property litigation and infringement claims, we are, and may in the future, become involved in other claims, lawsuits and investigations, including with respect to the RZMA. Such proceedings may initially be viewed as immaterial but could prove to be material. Litigation is inherently unpredictable, and excessive verdicts do occur. Adverse outcomes in lawsuits and investigations could result in significant monetary damages, including indemnification payments, or injunctive relief that could adversely affect our ability to conduct our business and may have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. Given the inherent uncertainties in litigation, even when we are able to reasonably estimate the amount of possible loss or range of loss and therefore record an aggregate litigation accrual for probable and reasonably estimable loss contingencies, the accrual may change in the future due to new developments or changes in approach. In addition, such investigations, claims and lawsuits could involve significant expense and diversion of management’s attention and resources from other matters.
We continue to explore new strategic initiatives, the pursuit of any of which may pose significant risks and could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We explore possible strategic initiatives which may include, among other things, the investment in, and the pursuit of, new revenue streams, services or products, changes to our offerings, initiatives to leverage our patent portfolio, our Security Services business, back-end registry services and IDN gTLDs. In addition, we have evaluated and are pursuing and will continue to evaluate and pursue acquisitions of TLDs that are currently in operation and those that have not yet been awarded as long as they support our growth strategy.
Any such strategic initiative may involve a number of risks, including: the diversion of our management’s attention from our existing business to develop the initiative, related operations and any requisite personnel; possible regulatory scrutiny or third-party claims; possible material adverse effects on our results of operations during and after the development process; our possible inability to achieve the intended objectives of the initiative; as well as damage to our reputation if we are unsuccessful in pursuing a strategic initiative. Such initiatives may result in a reduction of cash or increased costs. We may not be able to successfully or profitably develop, integrate, operate, maintain and manage any such initiative and the related operations or employees in a timely manner or at all. Furthermore, under our agreements with ICANN, we are subject to certain restrictions in the operation of .com, .net, .name and other TLDs, including required ICANN approval of new registry services for such TLDs. If any new initiative requires ICANN review or ICANN determines that such a review is required, we cannot predict whether this process will prevent us from implementing the initiative in a timely manner or at all. Any strategic initiative to leverage our patent portfolio will likely increase litigation risks from potential licensees and we may have to resort to litigation to enforce our intellectual property rights.
We depend on key employees to manage our business effectively, and we may face difficulty attracting and retaining qualified leaders.
We operate in a unique competitive and highly regulated environment and we depend on the knowledge, experience, and performance of our senior management team and other key employees in this regard and otherwise. We periodically experience changes in our management team. If we are unable to attract, integrate, retain and motivate these key individuals and additional highly skilled technical, sales and marketing, and other experienced employees, and implement succession plans for these personnel, our business may suffer. For example, our service products are highly technical and require individuals skilled and knowledgeable in unique platforms and software implementation.
Changes in, or interpretations of, tax rules and regulations or our tax positions may adversely affect our effective tax rates.
We are subject to income taxes in both the U.S. and numerous foreign jurisdictions. Significant judgment is required in determining our worldwide provision for income taxes. In the ordinary course of our business, there are many transactions and calculations where the ultimate tax determination is uncertain. We are subject to audit by various tax authorities. In accordance with U.S. GAAP, we recognize income tax benefits, net of required valuation allowances and accrual for uncertain tax
19
positions. For example, we claimed a worthless stock deduction on our 2013 federal income tax return and recorded a net income tax benefit of $380.1 million. Although we believe our tax estimates are reasonable, the final determination of tax audits and any related litigation could be materially different than that which is reflected in historical income tax provisions and accruals. Should additional taxes be assessed as a result of an audit or litigation, an adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows in the period or periods for which that determination is made could result.
A significant portion of our foreign earnings for the current fiscal year was earned in low tax jurisdictions. Our effective tax rate could fluctuate significantly on a quarterly basis and could be adversely affected to the extent earnings are lower than anticipated in countries where we have lower statutory rates and higher than anticipated in countries where we have higher statutory rates.
Various legislative changes that would reform U.S. corporate tax laws have been or may be proposed by the Trump administration as well as members of Congress, including proposals that would significantly impact how U.S. multinational corporations are taxed on foreign earnings. We are unable to predict whether these or other proposals will be implemented. Although we cannot predict whether or in what form any proposed legislation may pass, if enacted, such legislation could have a material adverse impact on our tax expense or cash flow.
Our foreign earnings, which are indefinitely reinvested offshore, constitute a majority of our cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities, and there is a high cost associated with a change in our indefinite reinvestment assertion or a repatriation of those funds to the U.S.
A majority of our cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities are held by our foreign subsidiaries. Our foreign earnings are indefinitely reinvested offshore and are not available to be used in the U.S. for working capital needs, debt obligations, acquisitions, share repurchases, dividends or other general corporate purposes. In the event that funds from our foreign operations are needed in the U.S. for any purpose, we would be required to accrue and pay additional U.S. taxes in order to repatriate those funds, which could be significant. Further, if we are unable to indefinitely reinvest our foreign earnings our effective tax rate would increase. These could adversely impact our business valuation and stock price.
Our marketable securities portfolio could experience a decline in market value, which could materially and adversely affect our financial results.
As of December 31, 2016, we had $1.8 billion in cash, cash equivalents, marketable securities and restricted cash, of which $1.6 billion was invested in marketable securities. The marketable securities consist primarily of debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury meeting the criteria of our investment policy, which is focused on the preservation of our capital through the investment in investment grade securities. We currently do not use derivative financial instruments to adjust our investment portfolio risk or income profile.
These investments, as well as any cash deposited in bank accounts, are subject to general credit, liquidity, market and interest rate risks, which may be exacerbated by financial market credit and liquidity events. If the global credit or liquidity market deteriorates or other events negatively impact the market for U.S. Treasury securities, our investment portfolio may be impacted and we could determine that some of our investments have experienced an other-than-temporary decline in fair value, requiring an impairment charge which could adversely impact our results of operations and cash flows.
We are subject to the risks of owning real property.
We own the land and building in Reston, Virginia, which constitutes our headquarters facility. Ownership of this property, as well as our data centers in Dulles, Virginia and New Castle, Delaware, may subject us to risks, including:
• | adverse changes in the value of the properties, due to interest rate changes, changes in the commercial property markets, or other factors; |
• | ongoing maintenance expenses and costs of improvements; |
• | the possible need for structural improvements in order to comply with environmental, health and safety, zoning, seismic, disability law, or other requirements; |
• | the possibility of environmental contamination or notices of violation from federal or state environmental agencies; and |
• | possible disputes with neighboring owners, tenants, service providers or others. |
We have anti-takeover protections that may discourage, delay or prevent a change in control that could benefit our stockholders.
20
Our amended and restated Certificate of Incorporation and Bylaws contain provisions that could make it more difficult for an outside party to acquire us without the consent of our Board of Directors (“Board”). These provisions include:
• | our stockholders may take action only at a duly called meeting and not by written consent; |
• | special meetings of our stockholders may be called only by the chairman of the board of directors, the president, our Board, or the secretary (acting as a representative of the stockholders) whenever a stockholder or group of stockholders owning at least thirty-five percent (35%) in the aggregate of the capital stock issued, outstanding and entitled to vote, and who held that amount in a net long position continuously for at least one year, so request in writing; |
• | vacancies on our Board can be filled until the next annual meeting of stockholders by a majority of directors then in office; and |
• | our Board has the ability to designate the terms of and issue new series of preferred stock without stockholder approval. |
In addition, Section 203 of the General Corporation Law of Delaware prohibits a publicly held Delaware corporation from engaging in a business combination with an interested stockholder, generally a person which together with its affiliates owns or within the last three years has owned 15% or more of our voting stock, for a period of three years after the date of the transaction in which the person became an interested stockholder, unless in the same transaction the interested stockholder acquired 85% ownership of our voting stock (excluding certain shares) or the business combination is approved in a prescribed manner. Section 203 therefore may impact the ability of an acquirer to complete an acquisition of us after a successful tender offer and accordingly could discourage, delay or prevent an acquirer from making an unsolicited offer without the approval of our Board.
We have a considerable number of common shares subject to future issuance.
As of December 31, 2016, we had one billion authorized common shares, of which 103.1 million shares were outstanding. In addition, of our authorized common shares, 12.6 million common shares were reserved for issuance pursuant to outstanding equity and employee stock purchase plans (“Equity Plans”), and 36.4 million shares were reserved for issuance upon conversion of our 3.25% Junior Subordinated Convertible Debentures due 2037 (“Subordinated Convertible Debentures”). As a result, we keep substantial amounts of our common stock available for issuance upon exercise or settlement of equity awards outstanding under our Equity Plans and/or the conversion of Subordinated Convertible Debentures into our common stock. Issuance of all or a large portion of such shares would be dilutive to existing security holders, could adversely affect the prevailing market price of our common stock and could impair our ability to raise additional capital through the sale of equity securities.
Our financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected if we do not effectively manage our indebtedness.
We have a significant amount of outstanding debt, and we may incur additional indebtedness in the future. Our substantial indebtedness, including any future indebtedness, requires us to dedicate a significant portion of our cash flow from operations or to arrange alternative liquidity sources to make principal and interest payments, when due, or to repurchase or settle our debt, if triggered, by certain corporate events, certain events of default, or conversion. It could also limit our flexibility in planning for or reacting to changes in our business and our industry, or make required capital expenditures and investments in our business; make it difficult or more expensive to refinance our debt or obtain new debt; trigger an event of default; and increase our vulnerability to adverse changes in general economic and industry conditions. Some of our debt contains covenants which may limit our operating flexibility, including restrictions on share repurchases, dividends, prepayment or repurchase of debt, acquisitions, disposing of assets, if we do not continue to meet certain financial ratios. Any rating assigned to our debt securities could be lowered or withdrawn by a rating agency, which could make it more difficult or more expensive for us to obtain additional debt financing in the future. The settlement amount, contingent interest, and potential recapture of income tax deductions related to our Subordinated Convertible Debentures can be substantial, and can increase significantly based on changes in our stock price. The occurrence of any of the foregoing factors could have a material adverse effect on our business, cash flows, results of operations and financial condition.
ITEM 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
21
ITEM 2. | PROPERTIES |
Our corporate headquarters are located in Reston, Virginia. We have administrative, sales, marketing, research and development and operations facilities located in the U.S., Europe, Asia, and Australia. As of December 31, 2016, we owned approximately 454,000 square feet of space, which includes facilities in Reston and Dulles, Virginia and New Castle, Delaware. As of December 31, 2016, we leased approximately 25,000 square feet of space in Europe, Australia and Asia. These facilities are under lease agreements that expire at various dates through 2019.
We believe that our existing facilities are well maintained and in good operating condition, and are sufficient for our needs for the foreseeable future. The following table lists our major locations and primary use as of December 31, 2016:
Approximate | |||||
Major Locations | Square Footage | Use | |||
United States: | |||||
Reston, Virginia | 221,000 | Corporate Headquarters | |||
New Castle, Delaware | 105,000 | Data Center | |||
Dulles, Virginia | 70,000 | Data Center | |||
Europe: | |||||
Fribourg, Switzerland | 8,000 | Data Center and Corporate Services | |||
The table above does not include approximately 58,000 square feet of space owned by us and leased to third parties.
ITEM 3. | LEGAL PROCEEDINGS |
On January 18, 2017, the Company received a Civil Investigative Demand (“CID”) from the Antitrust Division of the United States Department of Justice requesting certain material related to the Company becoming the registry operator for the .web gTLD. We are in the process of responding to the CID. It is not possible at this time to estimate a range of potential financial and non-financial outcomes in connection with this matter.
ITEM 4. | MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES |
Not applicable.
22
EXECUTIVE OFFICERS OF THE REGISTRANT
The following table sets forth information regarding our executive officers as of February 17, 2017:
Name | Age | Position | |||
D. James Bidzos | 61 | Executive Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer | |||
Todd B. Strubbe | 53 | Executive Vice President, Chief Operating Officer | |||
George E. Kilguss, III | 56 | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer | |||
Thomas C. Indelicarto | 53 | Executive Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary | |||
D. James Bidzos has served as Executive Chairman since August 2009 and President and Chief Executive Officer since August 2011. He served as Executive Chairman and Chief Executive Officer on an interim basis from June 2008 to August 2009 and served as President from June 2008 to January 2009. He served as Chairman of the Board since August 2007 and from April 1995 to December 2001. He served as Vice Chairman of the Board from December 2001 to August 2007. Mr. Bidzos served as a director of VeriSign Japan from March 2008 to August 2010 and served as Representative Director of VeriSign Japan from March 2008 to September 2008. Mr. Bidzos served as Vice Chairman of RSA Security Inc., an Internet identity and access management solution provider, from March 1999 to May 2002, and Executive Vice President from July 1996 to February 1999. Prior thereto, he served as President and Chief Executive Officer of RSA Data Security, Inc. from 1986 to February 1999.
Todd B. Strubbe has served as Chief Operating Officer since April 2015. From September 2009 to April 2015, he served as the President of the Unified Communications Business Segment for West Corporation, a provider of technology-driven communications services. Prior to this, he was a co-founder and Managing Partner of Arbor Capital, LLC. He has also served in executive leadership positions at First Data Corporation and CompuBank, N.A. and as an associate and then as an engagement manager with McKinsey & Company, Inc. He also served for five years as an infantry officer with the United States Army. Mr. Strubbe holds an M.B.A. degree from Harvard Business School and a B.S. degree from the United States Military Academy at West Point.
George E. Kilguss, III has served as Chief Financial Officer since May 2012. From April 2008 to May 2012, he was the Chief Financial Officer of Internap Network Services Corporation, an IT infrastructure solutions company. From December 2003 to December 2007, he served as the Chief Financial Officer of Towerstream Corporation, a company that delivers high speed wireless Internet access to businesses. Mr. Kilguss holds an M.B.A. degree from the University of Chicago’s Graduate School of Business and a B.S. degree in Economics and Finance from the University of Hartford.
Thomas C. Indelicarto has served as General Counsel and Secretary since November 2014. From September 2008 to November 2014, he served as Vice President and Associate General Counsel. From January 2006 to September 2008, he served as Litigation Counsel. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Indelicarto was in private practice as an associate at Arnold & Porter LLP and Buchanan Ingersoll (now, Buchanan Ingersoll & Rooney, PC). Mr. Indelicarto also served as a U.S. Army officer for nine years. Mr. Indelicarto holds a J.D. degree from the University of Pittsburgh School of Law and a B.S. degree from Indiana University of Pennsylvania.
23
PART II
ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Price Range of Common Stock
Our common stock is traded on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the symbol “VRSN.” The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the high and low sales prices per share for our common stock as reported by the NASDAQ Global Select Market:
Price Range | ||||||||
High | Low | |||||||
Year ended December 31, 2016: | ||||||||
Fourth Quarter | $ | 86.98 | $ | 74.46 | ||||
Third Quarter | $ | 87.19 | $ | 74.01 | ||||
Second Quarter | $ | 91.99 | $ | 80.47 | ||||
First Quarter | $ | 90.61 | $ | 70.26 | ||||
Year ended December 31, 2015: | ||||||||
Fourth Quarter | $ | 93.94 | $ | 70.21 | ||||
Third Quarter | $ | 71.82 | $ | 61.42 | ||||
Second Quarter | $ | 68.25 | $ | 61.31 | ||||
First Quarter | $ | 67.50 | $ | 53.48 | ||||
On February 10, 2017, there were 470 holders of record of our common stock. We cannot estimate the number of beneficial owners since many brokers and other institutions hold our stock on behalf of stockholders. On February 10, 2017, the reported last sale price of our common stock was $83.14 per share as reported by the NASDAQ Global Select Market.
We have not declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock or any other securities in the last five years. We continually evaluate the overall cash and investing needs of the business and consider the best uses for our cash, including investments in the strengthening of our infrastructure and growth opportunities for our business, as well as potential share repurchases.
For information regarding securities authorized for issuance under our equity compensation plans, see Note 10, “Employee Benefits and Stock-based Compensation,” of our Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 15 of this Form 10-K.
Share Repurchases
The following table presents the share repurchase activity during the three months ended December 31, 2016:
Total Number of Shares Purchased | Average Price Paid per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | Approximate Dollar Value of Shares That May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs (1)(2) | ||||||||||
(Shares in thousands) | |||||||||||||
October 1 – 31, 2016 | 773 | $77.43 | 773 | $ | 529.0 | million | |||||||
November 1 – 30, 2016 | 589 | $80.96 | 589 | $ | 481.4 | million | |||||||
December 1 – 31, 2016 | 662 | $78.85 | 662 | $ | 429.2 | million | |||||||
2,024 | 2,024 | ||||||||||||
(1) | On February 11, 2016, our Board authorized the repurchase of approximately $611.2 million of our common stock, in addition to the $388.8 million of our common stock remaining available for repurchase under the previous share repurchase program, for a total repurchase authorization of up to $1.0 billion of our common stock. |
(2) | Effective February 9, 2017, our Board authorized the repurchase of approximately $640.9 million of our common stock, in addition to the $359.1 million of our common stock remaining available for repurchase under the previous share repurchase program, for a total repurchase authorization of up to $1.0 billion of our common stock. The share repurchase program has no expiration date. Purchases made under the program could be effected through open market transactions, block purchases, accelerated share repurchase agreements or other negotiated transactions. |
24
Performance Graph
The information contained in the Performance Graph shall not be deemed to be “soliciting material” or “filed” with the SEC or subject to the liabilities of Section 18 of the Exchange Act, except to the extent that we specifically incorporate it by reference into a document filed under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), or the Exchange Act.
The following graph compares the cumulative total stockholder return on our common stock, the Standard and Poor’s (“S&P”) 500 Index, and the S&P 500 Information Technology Index. The graph assumes that $100 (and the reinvestment of any dividends thereafter) was invested in our common stock, the S&P 500 Index and the S&P 500 Information Technology Index on December 31, 2011, and calculates the return annually through December 31, 2016. The stock price performance on the following graph is not necessarily indicative of future stock price performance.
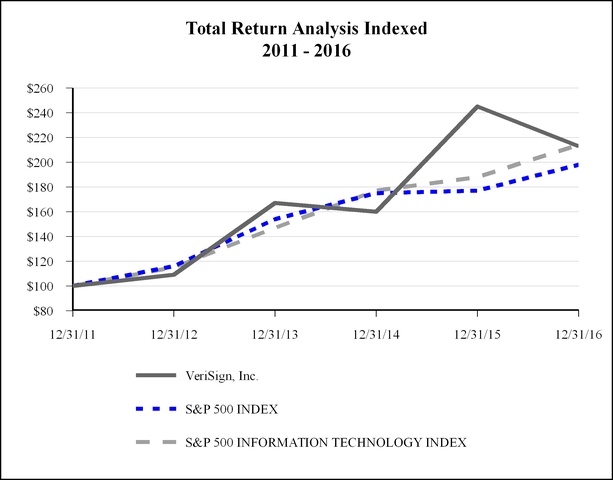
12/31/11 | 12/31/12 | 12/31/13 | 12/31/14 | 12/31/15 | 12/31/16 | |||||||||||||
VeriSign, Inc | $ | 100 | $ | 109 | $ | 167 | $ | 160 | $ | 245 | $ | 213 | ||||||
S&P 500 Index | $ | 100 | $ | 116 | $ | 154 | $ | 175 | $ | 177 | $ | 198 | ||||||
S&P 500 Information Technology Index | $ | 100 | $ | 115 | $ | 147 | $ | 177 | $ | 188 | $ | 214 | ||||||
25
ITEM 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
The following table sets forth selected financial data as of and for the last five fiscal years. The information set forth below is not necessarily indicative of results of future operations, and should be read in conjunction with Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” and our Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 15 of this Form 10-K, to fully understand factors that may affect the comparability of the information presented below.
Selected Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income Data: (in millions, except per share data)
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 (1) | 2012 | |||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 1,142 | $ | 1,059 | $ | 1,010 | $ | 965 | $ | 874 | |||||||||
Operating income | $ | 687 | $ | 606 | $ | 564 | $ | 528 | $ | 457 | |||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 441 | $ | 375 | $ | 355 | $ | 544 | $ | 312 | |||||||||
Income from continuing operations per share: | |||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 4.12 | $ | 3.29 | $ | 2.80 | $ | 3.77 | $ | 1.99 | |||||||||
Diluted | $ | 3.42 | $ | 2.82 | $ | 2.52 | $ | 3.49 | $ | 1.91 | |||||||||
———————
(1) | Income from continuing operations for 2013 includes a $375.3 million income tax benefit related to a worthless stock deduction, net of valuation allowances, and accrual for uncertain tax positions, partially offset by $167.1 million of income tax expense related to the repatriation of cash held by foreign subsidiaries. |
Consolidated Balance Sheet Data: (in millions)
As of December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||
Cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities | $ | 1,798 | $ | 1,915 | $ | 1,425 | $ | 1,723 | $ | 1,556 | |||||||||
Total assets | $ | 2,335 | $ | 2,358 | $ | 1,901 | $ | 2,249 | $ | 2,009 | |||||||||
Deferred revenues | $ | 976 | $ | 961 | $ | 890 | $ | 856 | $ | 813 | |||||||||
Subordinated Convertible Debentures, including contingent interest derivative | $ | 630 | $ | 634 | $ | 621 | $ | 613 | $ | 587 | |||||||||
Long-term debt (1) | $ | 1,237 | $ | 1,235 | $ | 740 | $ | 739 | $ | 100 | |||||||||
——————
(1) | The increase in Long-term debt from 2014 to 2015 was due to the issuance of $500.0 million aggregate principal amount of 5.25% senior unsecured notes due 2025.The increase in Long-term debt from 2012 to 2013 was due to the issuance of $750.0 million aggregate principal amount of 4.625% senior unsecured notes due 2023, offset by the repayment of $100.0 million of outstanding indebtedness under our unsecured credit facility. |
26
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act and Section 21E of the Exchange Act. These forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties, including, among other things, statements regarding our anticipated costs and expenses and revenue mix. Forward-looking statements include, among others, those statements including the words “expects,” “anticipates,” “intends,” “believes” and similar language. Our actual results may differ significantly from those projected in the forward-looking statements. Factors that might cause or contribute to such differences include, but are not limited to, those discussed in the section titled “Risk Factors” in Part I, Item 1A of this Form 10-K. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on the forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date of this Form 10-K. We undertake no obligation to publicly release any revisions to the forward-looking statements or reflect events or circumstances after the date of this document.
Overview
We are a global provider of domain name registry services and internet security, enabling internet navigation for many of the world’s most recognized domain names and providing protection for websites and enterprises around the world. Our Registry Services ensure the security, stability and resiliency of key internet infrastructure and services, including the .com and .net domains, two of the internet’s root servers, and the operation of the root zone maintainer function for the core of the internet’s DNS. Our product suite also includes Security Services, consisting of DDoS Protection Services, iDefense Services, and Managed DNS Services. Revenues from Security Services are not significant in relation to our consolidated revenues. On February 9, 2017, we entered into an agreement to sell the iDefense business, subject to customary closing conditions.
As of December 31, 2016, we had approximately 142.2 million .com and .net registrations in the domain name base. The number of domain names registered is largely driven by continued growth in online advertising, e-commerce, and the number of internet users, which is partially driven by greater availability of internet access, as well as marketing activities carried out by us and third-party registrars. Growth in the number of domain name registrations under our management may be hindered by certain factors, including overall economic conditions, competition from ccTLDs, the introduction of new gTLDs, and ongoing changes in the internet practices and behaviors of consumers and businesses. Factors such as the evolving practices and preferences of internet users, and how they navigate the internet, as well as the motivation of domain name registrants and how they will manage their investment in domain names, can negatively impact our business and the demand for new domain name registrations and renewals.
2016 Business Highlights and Trends
• | We recorded revenues of $1,142.2 million in 2016, which represents an increase of 8% compared to 2015. |
• | We recorded operating income of $686.6 million during 2016, which represents an increase of 13% as compared to 2015. |
• | On October 20, 2016, we announced that the U.S. Department of Commerce approved the extension amendment to the .com Registry Agreement with the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers, pursuant to which Verisign will remain the sole registry operator for the .com registry through November 30, 2024. |
• | We finished 2016 with 142.2 million .com and .net registrations in the domain name base, which represents a 2% increase from December 31, 2015. |
• | The final .com and .net renewal rate for the third quarter of 2016 was 73.0% compared with 71.9% for the same quarter in 2015. The final .com and .net renewal rate for the fourth quarter of 2016 was 67.5% compared with 73.3% for the same quarter in 2015. |
• | We repurchased 7.8 million shares of our common stock for an aggregate cost of $636.5 million in 2016. As of December 31, 2016, there was $429.2 million remaining for future share repurchases under the share repurchase program. |
• | Through February 9, 2017, we repurchased an additional 0.9 million shares for $70.1 million under our share repurchase program. Effective February 9, 2017, our Board authorized the repurchase of approximately $640.9 million of our common stock, in addition to the $359.1 million of our common stock remaining available for repurchase under the previous share repurchase program, for a total repurchase authorization of up to $1.0 billion of our common stock. |
27
• | We generated cash flows from operating activities of $667.9 million in 2016, which represents an increase of 3% as compared to 2015. |
• | On July 28, 2016, we announced an increase in the annual fee for a .net domain name registration from $7.46 to $8.20, which became effective February 1, 2017. |
Critical Accounting Policies and Significant Management Estimates
The discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based upon our Consolidated Financial Statements, which have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. The preparation of these financial statements requires management to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities. On an ongoing basis, management evaluates those estimates. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and on various assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily available from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
An accounting estimate is considered critical if the nature of the estimates or assumptions is material due to the levels of subjectivity and judgment involved, and the impact of changes in the estimates and assumptions would have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements. We believe the following critical accounting estimates and policies have the most significant impact on our consolidated financial statements:
Revenue recognition
We generate revenues by providing services over a period of time. Fees for these services are deferred and recognized as performance occurs. The majority of our revenue transactions contain standard business terms and conditions. However, at times, we enter into non-standard arrangements including multiple-element arrangements. As a result, we must evaluate (1) whether an arrangement exists; (2) how the arrangement consideration should be allocated among the deliverables; (3) when to recognize revenue on the deliverables; and (4) whether all elements of the arrangement have been delivered. Our revenue recognition policy also requires an assessment as to whether collection is reasonably assured, which requires us to evaluate the creditworthiness of our customers.
Fair value of financial instruments
Our Subordinated Convertible Debentures have a contingent interest payment provision that is identified as an embedded derivative. The embedded derivative is accounted for separately at fair value, and is marked to market at the end of each reporting period. We utilize a valuation model based on stock price, bond price, risk free interest rates, volatility, and credit spread observations to estimate the value of the derivative. Several of these inputs to the model are not observable and require management judgment.
Income taxes
Accounting for income taxes requires significant judgments in the development of estimates used in income tax calculations. Such judgments include, but are not limited to, the likelihood we would realize the benefits of net operating loss carryforwards, domestic and/or foreign tax credit carryforwards, the adequacy of valuation allowances, and the rates used to measure transactions with foreign subsidiaries. To the extent recovery of deferred tax assets is not likely, we record a valuation allowance to reduce our deferred tax assets to the amount that is more likely than not to be realized.
Our operations involve dealing with uncertainties and judgments in the application of complex tax regulations in multiple jurisdictions. The final taxes payable are dependent upon many factors, including negotiations with taxing authorities in various jurisdictions and resolution of disputes arising from U.S. federal, state, and international tax audits. We only recognize or continue to only recognize tax positions that are more likely than not to be sustained upon examination. We adjust these amounts in light of changing facts and circumstances; however, due to the complexity of some of these uncertainties, the ultimate resolution may result in a payment that is materially different from our current estimate of the tax liabilities.
Deferred income taxes are not provided for any funds remaining in the foreign subsidiaries because these earnings are intended to be indefinitely reinvested. We consider the following matters, among others, in evaluating our plans for indefinite reinvestment: the forecasts, budgets and financial requirements of the parent and subsidiaries for both the long and short term; the tax consequences of a decision to reinvest; and any U.S. and foreign government programs designed to influence remittances. If factors change and as a result we are unable to indefinitely reinvest the foreign earnings, the income tax expense and payments may differ significantly from the current period and could materially adversely affect our results of operations.
28
Earnings per Share
We use the treasury stock method to calculate the impact of our Subordinated Convertible Debentures on diluted earnings per share. Under this method, only a positive conversion spread related to the Subordinated Convertible Debentures is included in the diluted earnings per share calculations. This is based on our intent and ability to settle the principal amount of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures in cash. A change in our intent and ability would require us to use the if-converted method, which could have a material impact on our diluted earnings per share.
Results of Operations
The following table presents information regarding our results of operations as a percentage of revenues:
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Revenues | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||
Costs and expenses: | ||||||||
Cost of revenues | 17.4 | 18.2 | 18.7 | |||||
Sales and marketing | 7.0 | 8.5 | 9.1 | |||||
Research and development | 5.2 | 6.0 | 6.7 | |||||
General and administrative | 10.3 | 10.1 | 9.6 | |||||
Total costs and expenses | 39.9 | 42.8 | 44.1 | |||||
Operating income | 60.1 | 57.2 | 55.9 | |||||
Interest expense | (10.1 | ) | (10.2 | ) | (8.5 | ) | ||
Non-operating income (loss), net | 0.9 | (1.0 | ) | 0.5 | ||||
Income before income taxes | 50.9 | 46.0 | 47.9 | |||||
Income tax expense | (12.3 | ) | (10.6 | ) | (12.7 | ) | ||
Net income | 38.6 | % | 35.4 | % | 35.2 | % | ||
Revenues
Revenues related to our Registry Services are primarily derived from registrations for domain names in the .com and .net domain name registries. We also derive revenues from operating domain name registries for several other TLDs and from providing back-end registry services to a number of TLD registry operators, all of which are not significant in relation to our consolidated revenues. For domain names registered with the .com and .net registries we receive a fee from registrars per annual registration that is fixed pursuant to our agreements with ICANN. Individual customers, called registrants, contract directly with registrars or their resellers, and the registrars in turn register the domain names with Verisign. Changes in revenues are driven largely by changes in the number of new domain name registrations and the renewal rate for existing registrations as well as the impact of new and prior price increases, to the extent permitted by ICANN and the DOC. New registrations and the renewal rate for existing registrations are impacted by continued growth in online advertising, e-commerce, and the number of internet users, as well as marketing activities carried out by us and our registrars. We increased the annual fee for a .net domain name registration from $6.18 to $6.79 on February 1, 2015, from $6.79 to $7.46 on February 1, 2016, and from $7.46 to $8.20 on February 1, 2017. The annual fee for a .com domain name registration is fixed at $7.85 for the duration of the current .com Registry Agreement through November 30, 2024, except that prices may be raised by up to 7% each year due to the imposition of any new Consensus Policy or documented extraordinary expense resulting from an attack or threat of attack on the Security and Stability (each as defined in the .com Registry Agreement) of the DNS, subject to approval of the DOC. We offer promotional marketing programs for our registrars based upon market conditions and the business environment in which the registrars operate. All fees paid to us for .com and .net registrations are in U.S. dollars. Revenues from Security Services are not significant in relation to our total consolidated revenues.
A comparison of revenues is presented below:
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||
2016 | % Change | 2015 | % Change | 2014 | ||||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 1,142,167 | 8 | % | $ | 1,059,366 | 5 | % | $ | 1,010,117 | ||||||||
29
The following table compares the domain name base for .com and .net managed by our Registry Services business:
December 31, 2016 | % Change | December 31, 2015 | % Change | December 31, 2014 | ||||||||
Domain name base for .com and .net | 142.2 million | 2 | % | 139.8 million | 6 | % | 131.5 million | |||||
2016 compared to 2015: Revenues increased by $82.8 million, primarily due to an increase in the average number of domain names ending in .com and .net and increases in the .net domain name registration fees in February 2015 and 2016. Growth in the domain name base was primarily driven by continued internet growth and marketing activities carried out by us and our registrars. During the second half of 2015 and the first quarter of 2016 we experienced an increased volume of new domain name registrations primarily from our registrars in China. The volume of these new registrations was inconsistent and episodic compared to prior periods, and by the end of the first quarter of 2016, reverted back to a more normalized registration pace. A significant portion of these registrations from the second half of 2015 did not renew in the fourth quarter of 2016, which resulted in a net decrease of 1.9 million domain name registrations during the quarter. Despite the decrease in the domain name base in the fourth quarter, 2016 revenues benefited from this increased volume of registrations in the second half of 2015 and the first quarter of 2016.
2015 compared to 2014: Revenues increased by $49.2 million, primarily due to a 6% increase in the number of domain names ending in .com and .net and increases in the .net domain name registration fees in February 2014 and 2015. Total revenue growth of 5% was slightly less than the 6% growth in the domain name base due to the timing of registrations throughout the year, as a significant portion of new registrations occurred during the third and fourth quarters of 2015.
Ongoing economic uncertainty, competitive pressure from ccTLDs, the introduction of new gTLDs, ongoing changes in internet practices and behaviors of consumers and business, as well as the motivation of existing domain name registrants and how they will manage their investment in domain names, has limited the rate of growth of the domain name base in recent years and may continue to do so in 2017 and beyond.
We expect revenues will remain consistent in 2017, as a result of the increased volume of domain registrations in 2016, continued growth in the domain name base in 2017, and increases in the .net domain name registration fees in February 2016 and 2017, partially offset by the decrease in revenue resulting from the planned divestiture of our iDefense business.
Geographic revenues
We generate revenue in the U.S.; Europe, the Middle East and Africa (“EMEA”); China; and certain other countries, including Canada, Australia and Japan.
The following table presents a comparison of the Company’s geographic revenues:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||
2016 | % Change | 2015 | % Change | 2014 | |||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
U.S | $ | 667,301 | 4 | % | $ | 639,170 | 4 | % | $ | 616,125 | |||||||
EMEA | 207,474 | 7 | % | 193,623 | 6 | % | 182,897 | ||||||||||
China | 127,298 | 53 | % | 83,456 | 27 | % | 65,525 | ||||||||||
Other | 140,094 | (2 | )% | 143,117 | (2 | )% | 145,570 | ||||||||||
Total revenues | $ | 1,142,167 | 8 | % | $ | 1,059,366 | 5 | % | $ | 1,010,117 | |||||||
Revenues for our Registry Services business are attributed to the country of domicile and the respective regions in which our registrars are located, however, this may differ from the regions where the registrars operate or where registrants are located. Revenue growth for each region may be impacted by registrars reincorporating, relocating, or from acquisitions or changes in affiliations of resellers. Revenue growth for each region may also be impacted by registrars domiciled in one region, registering domain names in another region. Although revenues continued to grow in the more mature markets of the U.S. and EMEA during 2016, China saw the highest growth rate due in part to the increased volume of new registrations during the second half of 2015 and the first quarter of 2016.
30
Cost of revenues
Cost of revenues consist primarily of salaries and employee benefits expenses for our personnel who manage the operational systems, depreciation expenses, operational costs associated with the delivery of our services, fees paid to ICANN, customer support and training, consulting and development services, costs of facilities and computer equipment used in these activities, telecommunications expense and allocations of indirect costs such as corporate overhead.
A comparison of cost of revenues is presented below:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||
2016 | % Change | 2015 | % Change | 2014 | |||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
Cost of revenues | $ | 198,242 | 3 | % | $ | 192,788 | 2 | % | $ | 188,425 | |||||||
2016 compared to 2015: Cost of revenues increased by $5.5 million, primarily due to increases in salary and employee benefits expenses, and allocated overhead expenses, partially offset by a decrease in telecommunications expenses. Salary and employee benefits expenses increased by $6.0 million, primarily due to an increase in average headcount and an increase in bonus expenses. Allocated overhead expenses increased by $1.5 million as a result of an increase in average headcount compared to other cost types. Telecommunication expenses decreased by $1.9 million, primarily due to savings on renewals of colocation agreements.
2015 compared to 2014: Cost of revenues increased by $4.4 million, primarily due to increases in salary and employee benefits expenses, and registry fee expenses, partially offset by decreases in telecommunications expenses and depreciation expenses. Salary and employee benefits expenses increased by $4.2 million, primarily due to an increase in average headcount and increases in salary, bonus, and allocated benefit expenses. Registry fees due to ICANN increased by $2.7 million resulting from an increase in the volume of .com registrations and renewals. Telecommunication expenses decreased by $1.8 million primarily due to savings on renewals of colocation agreements. Depreciation expenses decreased by $1.6 million due to lower capital spending for equipment replacement in 2014 and 2015.
We expect cost of revenues as a percentage of revenues to remain consistent in 2017 as compared to 2016.
Sales and marketing
Sales and marketing expenses consist primarily of salaries, sales commissions, sales operations and other personnel-related expenses, travel and related expenses, gTLD application costs, trade shows, costs of lead generation, costs of computer and communications equipment and support services, facilities costs, consulting fees, costs of marketing programs, such as online, television, radio, print and direct mail advertising costs, and allocations of indirect costs such as corporate overhead.
A comparison of sales and marketing expenses is presented below:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||
2016 | % Change | 2015 | % Change | 2014 | |||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
Sales and marketing | $ | 80,250 | (11 | )% | $ | 90,184 | (2 | )% | $ | 92,001 | |||||||
2016 compared to 2015: Sales and marketing expenses decreased by $9.9 million, primarily due to decreases in advertising and consulting expenses, salary and employee benefits expenses, stock-based compensation expenses, and allocated overhead expenses. Advertising and consulting expenses decreased by $3.7 million, primarily due to a decrease in marketing activities and advertising agency costs. Salary and employee benefits expenses, including stock-based compensation expenses, decreased by $2.9 million due to a reduction in average headcount. Allocated overhead expenses decreased by $1.4 million due to the decrease in average headcount relative to other cost types.
2015 compared to 2014: Sales and marketing expenses decreased by $1.8 million, primarily due to a decrease in advertising and consulting expenses, partially offset by an increase in salary and employee benefits expenses. Advertising and consulting expenses decreased by $3.2 million, primarily due to a decrease in marketing activities and advertising agency costs. Salary and employee benefits expenses increased by $1.4 million, primarily resulting from an increase in average headcount.
We expect sales and marketing expenses as a percentage of revenues to remain consistent in 2017 as compared to 2016.
31
Research and development
Research and development expenses consist primarily of costs related to research and development personnel, including salaries and other personnel-related expenses, consulting fees, facilities costs, computer and communications equipment, support services used in our service and technology development, and allocations of indirect costs such as corporate overhead.
A comparison of research and development expenses is presented below:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||
2016 | % Change | 2015 | % Change | 2014 | |||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
Research and development | $ | 59,100 | (7 | )% | $ | 63,718 | (6 | )% | $ | 67,777 | |||||||
2016 compared to 2015: Research and development expenses decreased by $4.6 million, primarily due to decreases in salary and employee benefits expenses, and allocated overhead costs, partially offset by a decrease in capitalized labor. Salary and employee benefits expenses, allocated overhead expenses, and capitalized labor decreased by $2.4 million, $1.7 million, and $1.5 million, respectively, due to a reduction in average headcount.
2015 compared to 2014: Research and development expenses decreased by $4.1 million, primarily due to a decrease in salary and employee benefits expenses, including stock-based compensation expenses, contractors and professional services expenses, and allocated overhead costs. Salary and employee benefits expenses, including stock-based compensation expenses decreased by $2.1 million due to a decrease in average headcount. Contract and professional services expenses decreased due to lower consulting costs on various research and development projects. Allocated overhead costs decreased primarily due to a decrease in proportional headcount compared to other cost types.
We expect research and development expenses as a percentage of revenues to remain consistent in 2017 as compared to 2016.
General and administrative
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and other personnel-related expenses for our executive, administrative, legal, finance, information technology and human resources personnel, costs of facilities, computer and communications equipment, management information systems, support services, professional services fees, certain tax and license fees, and bad debt expense, offset by allocations of indirect costs such as facilities and shared services expenses to other cost types.
A comparison of general and administrative expenses is presented below:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||
2016 | % Change | 2015 | % Change | 2014 | |||||||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
General and administrative | $ | 118,003 | 11 | % | $ | 106,730 | 9 | % | $ | 97,487 | |||||||
2016 compared to 2015: General and administrative expenses increased by $11.3 million, primarily due to increases in salary and employee benefits expenses, stock-based compensation expenses, legal expenses, and a decrease in overhead expenses allocated to other cost types, partially offset by a decrease in depreciation expenses and certain non-income related taxes. Salary and employee benefits expenses increased by $8.0 million due to increases in bonus expenses and average headcount. Stock based compensation expenses increased by $4.5 million due to increases in the total value of restricted stock units (“RSUs”) granted in 2015 and 2016 and higher projected achievement levels on certain performance-based RSU grants. Legal expenses increased by $2.6 million primarily due to an increase in services performed by external legal counsel. Overhead expenses allocated to other cost types decreased by $1.6 million due to lower average headcount for other cost types. Depreciation expenses decreased by $2.6 million as a result of a decrease in capital expenditures in recent years. We incurred $2.1 million of certain non-income taxes in 2015, which did not recur in 2016.
32
2015 compared to 2014: General and administrative expenses increased by $9.2 million, primarily due to increases in salary and employee benefits expenses, including stock-based compensation expenses, legal expenses, and miscellaneous expenses, partially offset by a decrease in contract and professional services expenses. Salary and employee benefits expenses, including stock-based compensation, increased by $4.3 million due to annual salary increases and increased expenses related to employee benefits. Stock based compensation expense increased due to an increase in expense related to performance-based RSUs, and the impact of new RSU grants which had a higher grant date fair value due to the increase in our stock price, partially offset by additional expense recognized in 2014 for certain performance-based RSUs which were recorded based on their period-end fair value. Legal expenses increased by $3.3 million primarily due to an increase in services performed by external legal counsel. Miscellaneous expenses increased by $4.0 million primarily due to expenses for certain non-income related taxes in 2015, and certain expense reversals in 2014. Contract and professional services expenses decreased by $2.6 million due to a decrease in consulting costs supporting various corporate functions.
We expect general and administrative expenses as a percentage of revenues to remain consistent in 2017 as compared to 2016.
Interest expense
See Note 6, “Debt and interest expense” of our Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 15 of this Form 10-K. We expect interest expense to remain consistent in 2017 as compared to 2016.
Non-operating income (loss), net
See Note 11, “Non-operating income (loss), net” of our Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 15 of this Form 10-K.
Income tax expense
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
(Dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
Income tax expense | $ | 140,528 | $ | 112,414 | $ | 128,051 | |||||
Effective tax rate | 24 | % | 23 | % | 26 | % | |||||
Our effective tax rate for each year presented was lower than the statutory federal rate of 35% primarily due to benefits from foreign income taxed at lower rates, partially offset by state income taxes. Our effective tax rate for 2014 was also impacted by net income tax expense of $9.8 million related to a reorganization of certain international operations and changes in estimates related to the 2013 worthless stock deduction and the 2014 repatriation of earnings from foreign subsidiaries.
As of December 31, 2016, we had deferred tax assets arising from deductible temporary differences, tax losses, and tax credits of $235.7 million, net of valuation allowances, but before the offset of certain deferred tax liabilities. With the exception of deferred tax assets related to capital loss carryforwards, we believe it is more likely than not that the tax effects of the deferred tax liabilities, together with future taxable income, will be sufficient to fully recover the remaining deferred tax assets. Our deferred tax assets related to net operating loss (“NOL”) carryforwards and tax credit carryforwards decreased in 2016 as a portion of the NOL and tax credit carryforwards were utilized to offset 2016 taxable income.
Beginning in 2015, we qualified for a tax holiday in Switzerland which does not expire, unless the required thresholds are no longer met, or there is a law change which eliminates the holiday. We qualified for another tax holiday in Switzerland which expired on December 31, 2016, but may be renewed if certain criteria are satisfied. An additional tax holiday in Switzerland expired in 2014 and was not extended. The tax holidays provide reduced rates of taxation on certain types of income and also require certain thresholds of foreign source income. These tax holidays increased the Company’s earnings per share by $0.16, $0.14, and $0.50 in 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively.
33
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 231,945 | $ | 228,659 | |||
Marketable securities | 1,565,962 | 1,686,771 | |||||
Total | $ | 1,797,907 | $ | 1,915,430 | |||
As of December 31, 2016, our principal source of liquidity was $231.9 million of cash and cash equivalents and $1.6 billion of marketable securities. The marketable securities consist primarily of debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury meeting the criteria of our investment policy, which is focused on the preservation of our capital through investment in investment grade securities. The cash equivalents consist mainly of amounts invested in money market funds and U.S. Treasury bills purchased with original maturities of less than 90 days. As of December 31, 2016, all of our debt securities have contractual maturities of less than one year. Our cash and cash equivalents are readily accessible. For additional information on our investment portfolio, see Note 2, “Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Marketable Securities,” of our Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 15 of this Form 10-K.
As of December 31, 2016, the amount of cash and cash equivalents and marketable securities held by foreign subsidiaries was $1.4 billion. Our intent remains to indefinitely reinvest these funds outside of the U.S. and accordingly, we have not provided deferred U.S. taxes for these funds. In the event funds from foreign operations are needed to fund operations in the U.S. and if U.S. tax has not already been provided, we would be required to accrue and pay additional U.S. taxes in order to repatriate these funds. As of December 31, 2016, the amount of undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries for which deferred income taxes have not been provided was $926.7 million.
In 2016, we repurchased 7.8 million shares of our common stock at an average stock price of $81.73 for an aggregate cost of $636.5 million under our share repurchase program. In 2015, we repurchased 9.3 million shares of our common stock at an average stock price of $66.59 for an aggregate cost of $621.9 million. In 2014, we repurchased 16.3 million shares of our common stock at an average stock price of $53.15 for an aggregate cost of $867.1million. On February 9, 2017, our Board authorized the repurchase of approximately $640.9 million of our common stock, in addition to the $359.1 million of our common stock remaining available for repurchase under the previous share repurchase program, for a total repurchase authorization of up to $1.0 billion of our common stock.
On March 27, 2015, we issued $500.0 million of 5.25% senior unsecured notes due April 1, 2025. The proceeds were used for general corporate purposes, including, but not limited to, the repurchase of shares under our share repurchase program. As of December 31, 2016, we also had $750.0 million of 4.625% senior unsecured notes outstanding, which are due in May 2023.
On March 31, 2015, we entered into a new $200.0 million unsecured revolving credit facility. This facility will expire in 2020 and replaced our prior unsecured revolving credit facility. As of December 31, 2016, there were no borrowings outstanding under this credit facility.
As of December 31, 2016, we had $1.25 billion principal amount outstanding of our Subordinated Convertible Debentures. The price of our common stock exceeded the conversion price threshold trigger during the fourth quarter of 2016. Accordingly, the Subordinated Convertible Debentures are convertible at the option of each holder through March 31, 2017. We do not expect a material amount of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures to be converted in the near term as the trading price of the debentures exceeds the value that is likely to be received upon conversion. However, we cannot provide any assurance that the trading price of the debentures will continue to exceed the value that would be derived upon conversion or that the holders will not elect to convert the Subordinated Convertible Debentures. If a holder elects to convert its Subordinated Convertible Debentures, we are permitted under the Indenture to pursue an exchange in lieu of conversion or to settle the conversion value (as defined in the Indenture) in cash, stock, or a combination thereof. If we choose not to pursue or cannot complete an exchange in lieu of conversion, we currently have the intent and the ability (based on current facts and circumstances) to settle the principal amount of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures in cash. However, if the principal amount of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures that holders actually elect to convert exceeds our cash on hand and cash from operations, we will need to draw cash from existing financing or pursue additional sources of financing to settle the Subordinated Convertible Debentures in cash. We cannot provide any assurances that we will be able to obtain new sources of financing on terms acceptable to us or at all, nor can we assure that we will be able to obtain such financing in time to settle the Subordinated Convertible Debentures that holders elect to convert. The Subordinated Convertible Debentures continue to generate cash tax benefits while they remain outstanding and they are an important part of our capital structure. Although we
34
will have the right to redeem these debentures under the terms of the indenture starting in August 2017, our intention, based on current conditions, is to not redeem these debentures, which will allow the cash tax benefits to continue to accrue.
We paid contingent interest of $13.4 million in 2016 and $10.8 million in 2015 in addition to the normal coupon interest on the Subordinated Convertible Debentures. On February 16, 2017, we paid contingent interest of $7.7 million and we will pay an additional $7.5 million in August 2017.
During the third quarter of 2016, we paid $143.0 million for the future assignment to us of contractual rights to the .web gTLD, pending resolution of objections by other applicants, regulatory review, and approval from ICANN.
During 2014, we repatriated approximately $740.9 million of cash held by foreign subsidiaries, net of foreign withholding taxes of $28.1 million. We utilized substantially all of the remaining net operating losses generated from the 2013 worthless stock deduction to offset 2014 taxable income including the taxable income recognized in the U.S. as a result of the repatriation.
We believe existing cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities, and funds generated from operations, together with our ability to arrange for additional financing should be sufficient to meet our working capital, capital expenditure requirements, and to service our debt for the next 12 months. We regularly assess our cash management approach and activities in view of our current and potential future needs.
In summary, our cash flows for 2016, 2015, and 2014 were as follows:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 667,949 | $ | 651,482 | $ | 600,949 | |||||
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities | (40,399 | ) | (496,899 | ) | 112,688 | ||||||
Net cash used in financing activities | (623,763 | ) | (117,778 | ) | (859,752 | ) | |||||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | (501 | ) | 246 | (1,500 | ) | ||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 3,286 | $ | 37,051 | $ | (147,615 | ) | ||||
Net cash provided by operating activities
Our largest source of operating cash flows is cash collections from our customers. Our primary uses of cash from operating activities are for personnel related expenditures, and other general operating expenses, as well as payments related to taxes, interest and facilities.
2016 compared to 2015: Cash provided by operating activities increased primarily due to an increase in cash received from customers and a decrease in cash paid for income taxes, partially offset by an increase in cash paid for interest. Cash received from customers increased primarily due to an increase in the number of domain name registration renewals and the increase in .net domain name registration fees in February 2016. Cash paid for income taxes decreased primarily due to income tax payments in 2015 related to the reorganization of certain international operations. Cash paid for interest increased due to the interest paid on the $500.0 million senior notes issued on March 2015, and higher contingent interest related to the Subordinated Convertible Debentures.
2015 compared to 2014: Cash provided by operating activities increased primarily due to an increase in cash received from customers partially offset by increases in cash paid for interest. Cash received from customers increased primarily due to an increase in new and renewed domain name registrations. Cash paid for interest increased as a result of the contingent interest paid to holders of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures and the additional interest paid on the $500.0 million senior notes issued in March 2015.
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities
The changes in cash flows from investing activities primarily relate to purchases, maturities and sales of marketable securities, and purchases of property and equipment and rights to intangible assets.
2016 compared to 2015: The decrease in cash used in investing activities was primarily due to an increase in sales and maturities of marketable securities, net of purchases, and a decrease in purchases of property and equipment and other investing activities, partially offset by the payments made for the future assignment of the rights to the .web gTLD.
35
2015 compared to 2014: The change in cash (used in) provided by investing activities was primarily due to a decrease in proceeds from maturities and sales of marketable securities, partially offset by a decrease in purchases of marketable securities.
Net cash used in financing activities
The changes in cash flows from financing activities primarily relate to share repurchases, proceeds from and repayment of borrowings, stock option exercises, our employee stock purchase plan (“ESPP”), and excess tax benefits from stock-based compensation.
2016 compared to 2015: The increase in net cash used in financing activities was primarily due to an increase in share repurchases, and proceeds from the issuance of senior notes in March 2015, partially offset by an increase in excess tax benefits from stock-based compensation.
2015 compared to 2014: The decrease in net cash used in financing activities was primarily due to the proceeds from the issuance of the senior notes in 2015, a decrease in share repurchases, and higher recognized excess tax benefits associated with stock-based compensation, partially offset by lower proceeds from stock option exercises and ESPP.
Impact of Inflation
We do not believe that inflation has had a significant impact on our operations in any of the periods presented.
Income taxes
We derive significant tax savings from the Subordinated Convertible Debentures. During 2016 and 2015, the interest deduction, for income tax purposes, related to our Subordinated Convertible Debentures, was $183.7 million and $175.0 million, respectively, compared to cash interest paid, including contingent interest, of $54.0 million and $51.4 million in 2016 and 2015, respectively. For income tax purposes, we deduct interest expense on the Subordinated Convertible Debentures calculated at 8.5% of the adjusted issue price, subject to adjustment for actual versus projected contingent interest. The adjusted issue price, and consequently the interest deduction for income tax purposes, grows over the term due to the difference between the interest deduction taken using a comparable yield of 8.5% on the adjusted issue price, and the coupon rate of 3.25% on the principal amount, compounded annually. The interest deduction taken is subject to recapture upon settlement to the extent that the amount paid (in cash or stock) to settle Subordinated Convertible Debentures is less than the adjusted issue price. Interest recognized in accordance with GAAP, which is calculated at 8.39% of the liability component of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures, will also grow over the term, but at a slower rate. This difference will result in a continuing increase in the deferred tax liability on our Consolidated Balance Sheet.
We do not expect to pay significant U.S. federal income taxes during 2017 as a result of the interest deduction on our Subordinated Convertible Debentures, the use of foreign tax credits and other tax attributes. We expect the amount of cash paid for non-U.S. income taxes in 2017 to increase compared to 2016.
Property and Equipment Expenditures
Our planned property and equipment expenditures for 2017 are anticipated to be between $35.0 million and $45.0 million and will primarily be focused on infrastructure upgrades and enhancements to our product portfolio.
Contractual Obligations
See Note 13, “Commitments and Contingencies,” Purchase Obligations and Contractual Agreements, of our Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 15 of this Form 10-K.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
It is not our business practice to enter into off-balance sheet arrangements. As of December 31, 2016, we did not have any significant off-balance sheet arrangements. See Note 13, “Commitments and Contingencies,” Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements, of our Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 15 of this Form 10-K for further information regarding off-balance sheet arrangements.
36
Dilution from Subordinated Convertible Debentures, RSUs and Stock Options
Any conversion of our Subordinated Convertible Debentures may dilute the holdings of existing shareholders due to the potential number of shares that could be required to settle the Subordinated Convertible Debentures. We have the intent and ability to settle the principal amount of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures in cash, but the excess of the conversion value over the principal amount (“the conversion spread”) may be settled in shares of common stock. As of December 31, 2016, there are 36.4 million shares of common stock reserved for issuance upon conversion or repurchase of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures. Based on the if-converted value of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures as of December 31, 2016, the conversion spread could have required us to issue up to 19.9 million shares of common stock.
Grants of stock-based awards are key components of the compensation packages we provide to attract and retain certain of our talented employees and align their interests with the interests of existing stockholders. We recognize that these stock-based awards dilute existing stockholders and have sought to control the number granted while providing competitive compensation packages. As of December 31, 2016, there are a total of 1.8 million unvested RSUs which represent potential dilution of 1.8%. This maximum potential dilution will only result if all outstanding RSUs vest and are settled. In recent years, our stock repurchase program has more than offset the dilutive effect of RSU grants to employees; however, we may reduce the level of our stock repurchases in the future as we may use our available cash for other purposes.
37
ITEM 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
We are exposed to financial market risks, including changes in interest rates, foreign exchange rates and market risks. We have not entered into any market risk sensitive instruments for trading purposes.
Interest rate sensitivity
The fixed income securities in our investment portfolio are subject to interest rate risk. As of December 31, 2016, we had $1.6 billion of fixed income securities, which consisted of U.S. Treasury bills with maturities of less than one year. A hypothetical change in interest rates by 100 basis points would not have a significant impact on the fair value of our investments.
Foreign exchange risk management
We conduct business in several countries and transact in multiple foreign currencies. The functional currency for all of our international subsidiaries is the U.S. Dollar. Our foreign currency risk management program is designed to mitigate foreign exchange risks associated with monetary assets and liabilities of our operations that are denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. The primary objective of this program is to minimize the gains and losses to income resulting from fluctuations in exchange rates. We may choose not to hedge certain foreign exchange exposures due to immateriality, prohibitive economic cost of hedging particular exposures, and limited availability of appropriate hedging instruments. We do not enter into foreign currency transactions for trading or speculative purposes, nor do we hedge foreign currency exposures in a manner that entirely offsets the effects of changes in exchange rates. The program may entail the use of forward or option contracts, which are usually placed and adjusted monthly. These foreign currency forward contracts are derivatives and are recorded at fair market value. We attempt to limit our exposure to credit risk by executing foreign exchange contracts with financial institutions that have investment grade ratings.
As of December 31, 2016, we held foreign currency forward contracts in notional amounts totaling $39.2 million to mitigate the impact of exchange rate fluctuations associated with certain foreign currencies. Gains or losses on the foreign currency forward contracts would be largely offset by the remeasurement of our foreign currency denominated assets and liabilities, resulting in an insignificant net impact to income.
A hypothetical uniform 10% strengthening or weakening in the value of the U.S. dollar relative to the foreign currencies in which our revenues and expenses are denominated would not result in a significant impact to our financial statements.
Market risk management
The fair market values of our Subordinated Convertible Debentures and the senior notes are subject to interest rate risk. Generally, the fair market value of fixed interest rate debt will increase as interest rates fall and decrease as interest rates rise. The Subordinated Convertible Debentures are subject to market risk due to the convertible feature of the debentures. The fair market value will increase as the market price of our common stock increases, and decrease as the market price of our common stock falls. The interest and market value changes affect the fair market value of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures and the senior notes. As of December 31, 2016, the fair value of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures was approximately $2.8 billion and the fair values of the senior notes issued in 2013 and the senior notes issued in 2015 were $764.1 million and $514.1 million, respectively, based on available market information from public data sources.
The fair market value of the contingent interest derivative on Subordinated Convertible Debentures is also subject to market risk and, to a lesser extent, to interest rate risk. Generally, the fair market value of the contingent interest derivative will increase or decrease with the fair market value of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures.
38
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Financial Statements
Verisign’s financial statements required by this Item are set forth as a separate section of this Form 10-K. See Item 15 for a listing of financial statements provided in the section titled “Financial Statements.”
Supplementary Data (Unaudited)
The following tables set forth unaudited supplementary quarterly financial data for the two year period ended December 31, 2016. In management’s opinion, the unaudited data has been prepared on the same basis as the audited information and includes all adjustments (consisting only of normal recurring adjustments) necessary for a fair presentation of the data for the periods presented.
2016 | |||||||||||||||||||
Quarter Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||||||
March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | December 31, | |||||||||||||||
(In thousands, except per share data) | |||||||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 281,876 | $ | 286,466 | $ | 287,554 | $ | 286,271 | $ | 1,142,167 | |||||||||
Gross Profit | $ | 231,294 | $ | 237,713 | $ | 237,747 | $ | 237,171 | $ | 943,925 | |||||||||
Operating Income | $ | 166,767 | $ | 176,267 | $ | 174,776 | $ | 168,762 | $ | 686,572 | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 107,456 | $ | 113,210 | $ | 114,427 | $ | 105,552 | $ | 440,645 | |||||||||
Earnings per share: | |||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.98 | $ | 1.05 | $ | 1.08 | $ | 1.01 | $ | 4.12 | |||||||||
Diluted (1) | $ | 0.82 | $ | 0.87 | $ | 0.90 | $ | 0.84 | $ | 3.42 | |||||||||
——————
(1) | Earnings per share for the year is computed independently and may not equal the sum of the quarterly earnings per share. |
2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
Quarter Ended | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||||||
March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | December 31, | |||||||||||||||
(In thousands, except per share data) | |||||||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 258,422 | $ | 262,539 | $ | 265,780 | $ | 272,625 | $ | 1,059,366 | |||||||||
Gross Profit | $ | 210,069 | $ | 214,318 | $ | 218,562 | $ | 223,629 | $ | 866,578 | |||||||||
Operating Income | $ | 144,237 | $ | 148,965 | $ | 154,462 | $ | 158,282 | $ | 605,946 | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 88,238 | $ | 93,011 | $ | 92,457 | $ | 101,530 | $ | 375,236 | |||||||||
Earnings per share: | |||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.75 | $ | 0.80 | $ | 0.82 | $ | 0.92 | $ | 3.29 | |||||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.66 | $ | 0.70 | $ | 0.70 | $ | 0.76 | $ | 2.82 | |||||||||
——————
Our quarterly revenues and operating results are difficult to forecast. Therefore, we believe that period-to-period comparisons of our operating results will not necessarily be meaningful, and should not be relied upon as an indication of future performance. Also, operating results may fall below our expectations and the expectations of securities analysts or investors in one or more future quarters. If this were to occur, the market price of our common stock would likely decline.
39
ITEM 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
Not applicable.
ITEM 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
a. Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Based on our management’s evaluation, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer (our principal executive officer) and our Chief Financial Officer (our principal financial officer), as of December 31, 2016, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, (the “Exchange Act”)) are effective to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms and is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
b. Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act. Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016 using the criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013 Framework) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”).
Based on our evaluation under the COSO framework, management has concluded that our internal control over financial reporting is effective to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
KPMG LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, has issued a report concerning the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016. See “Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” in Item 15 of this Form 10-K.
c. Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There was no change in our internal control over financial reporting (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act) during the three months ended December 31, 2016 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
d. Inherent Limitations of Disclosure Controls and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Because of their inherent limitations, our disclosure controls and procedures and our internal control over financial reporting may not prevent material errors or fraud. A control system, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. The effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures and our internal control over financial reporting is subject to risks, including that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or that the degree of compliance with our policies or procedures may deteriorate.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
Not applicable.
40
PART III
ITEM 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
The information required by this item relating to our directors and nominees, regarding compliance with Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act, and regarding our Audit Committee, Corporate Governance and Nominating Committee and Compensation Committee will be included under the captions “Proposal No. 1: Election of Directors,” “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management-Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance,” and “Corporate Governance” in our Proxy Statement related to the 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference (“2017 Proxy Statement”).
Pursuant to General Instruction G(3) of Form 10-K, the information required by this item relating to our executive officers is included under the caption “Executive Officers of the Registrant” in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
We have adopted a “Verisign Code of Conduct-2016”, which is posted on our website under “Ethics and Business Conduct” at https://investor.verisign.com/corporate-governance.cfm. The code of conduct applies to all directors, officers and employees, including the principal executive officer, principal financial officer and other senior accounting officers. We have also adopted the “Corporate Governance Principles for the Board of Directors” which provides guidance to our directors on corporate practices that serve the best interests of the Company and its shareholders.
We intend to satisfy any disclosure requirement under Item 5.05 of Form 8-K regarding an amendment to, or waiver from, a provision of the “Verisign Code of Conduct-2016,” to the extent applicable to the principal executive officer, principal financial officer, or other senior accounting officers, by posting such information on our website, on the web page found by clicking through to “Ethics and Business Conduct” as specified above.
ITEM 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
Information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to our 2017 Proxy Statement from the discussions under the captions “Compensation of Directors,” “Non-Employee Director Retainer Fees and Equity Compensation Information” and “Non-Employee Director Compensation Table for Fiscal 2016,” and “Executive Compensation.”
ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
Information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference from the discussions under the captions “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” and “Equity Compensation Plan Information” in our 2017 Proxy Statement.
ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
Information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to our 2017 Proxy Statement from the discussions under the captions “Policies and Procedures with Respect to Transactions with Related Persons,” “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” and “Independence of Directors.”
ITEM 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES |
Information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to our 2017 Proxy Statement from the discussions under the captions “Principal Accountant Fees and Services” and “Policy on Audit Committee Pre-Approval of Audit and Permissible Non-Audit Services of Independent Auditors.”
41
PART IV
ITEM 15. | EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
(a) Documents filed as part of this report
1. Financial statements
• | Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm |
• | Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 |
• | Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the Years Ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 |
• | Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Deficit for the Years Ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 |
• | Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2016, 2015, and 2014 |
• | Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements |
2. Financial statement schedules
Financial statement schedules are omitted because the information called for is not material or is shown either in the consolidated financial statements or the notes thereto. |
3. Exhibits
(a) Index to Exhibits
Pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), the Company has filed certain agreements as exhibits to this Form 10-K. These agreements may contain representations and warranties by the parties thereto. These representations and warranties have been made solely for the benefit of the other party or parties to such agreements and (1) may be intended not as statements of fact, but rather as a way of allocating the risk to one of the parties to such agreements if those statements prove to be inaccurate, (2) may have been qualified by disclosures that were made to such other party or parties and that either have been reflected in the Company’s filings or are not required to be disclosed in those filings, (3) may apply materiality standards different from what may be viewed as material to investors and (4) were made only as of the date of such agreements or such other date(s) as may be specified in such agreements and are subject to more recent developments. Accordingly, these representations and warranties may not describe the Company’s actual state of affairs at the date hereof or at any other time.
Incorporated by Reference | |||||||||||
Exhibit Number | Exhibit Description | Form | Date | Number | Filed Herewith | ||||||
2.01 | Agreement and Plan of Merger dated as of March 6, 2000, by and among the Registrant, Nickel Acquisition Corporation and Network Solutions, Inc. | 8-K | 3/8/00 | 2.1 | |||||||
3.01 | Sixth Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Registrant. | X | |||||||||
3.02 | Amended and Restated Bylaws of VeriSign, Inc. | 10-Q | 7/28/16 | 3.02 | |||||||
4.01 | Indenture dated as of August 20, 2007 between the Registrant and U.S. Bank National Association. | 8-K/A | 9/6/07 | 4.1 | |||||||
4.02 | Indenture, dated as of April 16, 2013, between VeriSign, Inc., each of the subsidiary guarantors party thereto and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee. | 8-K | 4/17/13 | 4.1 | |||||||
4.03 | Indenture dated as of March 27, 2015 between VeriSign, Inc. and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee. | 8-K | 3/30/15 | 4.1 | |||||||
10.01 | Registrant's 2007 Employee Stock Purchase Plan, as adopted August 30, 2007. + | S-1 | 11/5/07 | 10.19 | |||||||
42
Incorporated by Reference | |||||||||||
Exhibit Number | Exhibit Description | Form | Date | Number | Filed Herewith | ||||||
10.02 | Amendment No. Thirty (30) to Cooperative Agreement - Special Awards Conditions NCR-92-18742, between VeriSign and U.S. Department of Commerce managers. | 10-K | 7/12/07 | 10.27 | |||||||
10.03 | VeriSign, Inc. Annual Incentive Compensation Plan. + | 10-K | 2/24/11 | 10.64 | |||||||
10.04 | Registry Agreement between VeriSign, Inc. and the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers, entered into as of June 27, 2011. | 8-K | 6/28/11 | 10.01 | |||||||
10.05 | Form of Amended and Restated Change-in-Control and Retention Agreement. + | 10-Q | 7/29/11 | 10.03 | |||||||
10.06 | Amended and Restated Change-in-Control and Retention Agreement [CEO Form of Agreement]. + | 10-Q | 7/29/11 | 10.04 | |||||||
10.07 | Purchase and Sale Agreement for 12061 Bluemont Way Reston, Virginia between 12061 Bluemont Owner, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, as Seller and VeriSign, Inc., a Delaware corporation, as Purchaser Dated August 18, 2011. | 8-K | 9/7/11 | 10.01 | |||||||
10.08 | Guarantee Agreement, dated as of November 22, 2011, among VeriSign, Inc., the other guarantors identified therein and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent. | 8-K | 11/29/11 | 10.02 | |||||||
10.09 | VeriSign, Inc. 2006 Equity Incentive Plan Form of Non-Employee Director Restricted Stock Unit Agreement. + | 10-Q | 7/27/12 | 10.03 | |||||||
10.10 | Registry Agreement between VeriSign, Inc. and the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers, entered into on November 29, 2012. | 8-K | 11/30/12 | 10.1 | |||||||
10.11 | Amendment Number Thirty-Two (32) to the Cooperative Agreement between VeriSign, Inc. and Department of Commerce, entered into on November 29, 2012. | 8-K | 11/30/12 | 10.2 | |||||||
10.12 | VeriSign, Inc. 2006 Equity Incentive Plan Employee Restricted Stock Unit Agreement. + | 10-Q | 4/25/13 | 10.02 | |||||||
10.13 | VeriSign, Inc. 2006 Equity Incentive Plan Performance-Based Restricted Stock Unit Agreement + | 10-Q | 4/28/16 | 10.01 | |||||||
10.14 | Credit Agreement dated as of March 31, 2015 among VeriSign, Inc., the Lenders as defined therein, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent, and J.P. Morgan Europe Limited, as London Agent. | 8-K | 4/1/15 | 99.1 | |||||||
10.15 | VeriSign, Inc. 2006 Equity Incentive Plan Form of Employee Restricted Stock Unit Agreement + | 10-K | 2/19/16 | 10.70 | |||||||
10.16 | Amendment to the .com Registry Agreement between VeriSign, Inc. and the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers, entered into on October 20, 2016 | 8-K | 10/20/16 | 10.1 | |||||||
10.17 | Amendment Number Thirty-Three (33) to the Cooperative Agreement between VeriSign, Inc. and Department of Commerce, entered into on October 20, 2016 | 8-K | 10/20/16 | 10.2 | |||||||
10.18 | Amendment Number Thirty-Four (34) to the Cooperative Agreement between VeriSign, Inc. and Department of Commerce, entered into on October 20, 2016 | 8-K | 10/20/16 | 10.3 | |||||||
10.19 | Amended and Restated VeriSign, Inc. 2006 Equity Incentive Plan, as amended and restated | DEF 14A | 4/29/16 | Appendix A | |||||||
43
Incorporated by Reference | |||||||||||
Exhibit Number | Exhibit Description | Form | Date | Number | Filed Herewith | ||||||
21.01 | Subsidiaries of the Registrant. | X | |||||||||
23.01 | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. | X | |||||||||
24.01 | Powers of Attorney (Included as part of the signature pages hereto). | X | |||||||||
31.01 | Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rule 13a-14(a). | X | |||||||||
31.02 | Certification of Principal Financial Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rule 13a-14(a). | X | |||||||||
32.01 | Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rule 13a-14(b) and Section 1350 of Chapter 63 of Title 18 of the U.S. Code (18 U.S.C. 1350). * | X | |||||||||
32.02 | Certification of Principal Financial Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rule 13a-14(b) and Section 1350 of Chapter 63 of Title 18 of the U.S. Code (18 U.S.C. 1350). * | X | |||||||||
101.INS | XBRL Instance Document. | X | |||||||||
101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema. | X | |||||||||
101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase. | X | |||||||||
101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase. | X | |||||||||
101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase. | X | |||||||||
101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase. | X | |||||||||
* | As contemplated by SEC Release No. 33-8212, these exhibits are furnished with this Annual Report on Form 10-K and are not deemed filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission and are not incorporated by reference in any filing of VeriSign, Inc. under the Securities Act of 1933 or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, whether made before or after the date hereof and irrespective of any general incorporation language in such filings. |
+ | Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
44
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the City of Reston, Commonwealth of Virginia, on the 17th day of February 2017.
VERISIGN, INC.
By: | /S/ D. JAMES BIDZOS | |
D. James Bidzos | ||
President and Chief Executive Officer | ||
(Principal Executive Officer) | ||
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS that each individual whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints D. James Bidzos, George E. Kilguss, III, and Thomas C. Indelicarto, and each of them, his or her true lawful attorneys-in-fact and agents, with full power of substitution, for him or her and in his or her name, place and stead, in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K and to file the same, with all exhibits thereto and all documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granted unto said attorneys-in-fact and agents, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done in and about the premises, as fully to all intents and purposes as he or she might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents or any of them, or his, her or their substitute or substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities indicated on the 17th day of February 2017.
Signature | Title | |
/S/ D. JAMES BIDZOS | President, Chief Executive Officer, Executive Chairman and Director (Principal Executive Officer) | |
D. JAMES BIDZOS | ||
/S/ GEORGE E. KILGUSS, III | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | |
GEORGE E. KILGUSS, III | ||
/S/ KATHLEEN A. COTE | Director | |
KATHLEEN A. COTE | ||
/S/ THOMAS F. FRIST, III | Director | |
THOMAS F. FRIST, III | ||
/S/ JAMIE S. GORELICK | Director | |
JAMIE S. GORELICK | ||
/S/ ROGER H. MOORE | Director | |
ROGER H. MOORE | ||
/S/ LOUIS A. SIMPSON | Director | |
LOUIS A. SIMPSON | ||
/S/ TIMOTHY TOMLINSON | Director | |
TIMOTHY TOMLINSON | ||
45
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
As required under Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, the consolidated financial statements of Verisign, Inc. are provided in this separate section. The consolidated financial statements included in this section are as follows:
Financial Statement Description | Page |
46
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
VeriSign, Inc.:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of VeriSign, Inc. and subsidiaries (the Company) as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the related consolidated statements of comprehensive income, stockholders’ deficit, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2016. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2016, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), VeriSign, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO), and our report dated February 17, 2017 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of VeriSign, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ KPMG LLP
McLean, Virginia
February 17, 2017
47
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders VeriSign, Inc.:
We have audited VeriSign, Inc.’s (the Company) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting (Item 9A.b). Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of VeriSign, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the related consolidated statements of comprehensive income, stockholders’ deficit, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2016, and our report dated February 17, 2017 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
/s/ KPMG LLP
McLean, Virginia
February 17, 2017
48
VERISIGN, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except par value)
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | ||||||
ASSETS | |||||||
Current assets: | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 231,945 | $ | 228,659 | |||
Marketable securities | 1,565,962 | 1,686,771 | |||||
Accounts receivable, net | 13,051 | 12,638 | |||||
Other current assets | 31,384 | 39,856 | |||||
Total current assets | 1,842,342 | 1,967,924 | |||||
Property and equipment, net | 266,125 | 295,570 | |||||
Goodwill | 52,527 | 52,527 | |||||
Deferred tax assets | 9,385 | 17,361 | |||||
Deposits to acquire intangible assets | 145,000 | 2,000 | |||||
Other long-term assets | 19,193 | 22,355 | |||||
Total long-term assets | 492,230 | 389,813 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 2,334,572 | $ | 2,357,737 | |||
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT | |||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | $ | 203,920 | $ | 188,171 | |||
Deferred revenues | 688,265 | 680,483 | |||||
Subordinated convertible debentures, including contingent interest derivative | 629,764 | 634,326 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 1,521,949 | 1,502,980 | |||||
Long-term deferred revenues | 287,424 | 280,859 | |||||
Senior notes | 1,237,189 | 1,235,354 | |||||
Deferred tax liabilities | 371,433 | 294,194 | |||||
Other long-term tax liabilities | 117,172 | 114,797 | |||||
Total long-term liabilities | 2,013,218 | 1,925,204 | |||||
Total liabilities | 3,535,167 | 3,428,184 | |||||
Commitments and contingencies | |||||||
Stockholders’ deficit: | |||||||
Preferred stock—par value $.001 per share; Authorized shares: 5,000; Issued and outstanding shares: none | — | — | |||||
Common stock—par value $.001 per share; Authorized shares: 1,000,000; Issued shares: 324,118 at December 31, 2016 and 322,990 at December 31, 2015; Outstanding shares: 103,091 at December 31, 2016 and 110,072 at December 31, 2015 | 324 | 323 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 16,987,488 | 17,558,822 | |||||
Accumulated deficit | (18,184,954 | ) | (18,625,599 | ) | |||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (3,453 | ) | (3,993 | ) | |||
Total stockholders’ deficit | (1,200,595 | ) | (1,070,447 | ) | |||
Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit | $ | 2,334,572 | $ | 2,357,737 | |||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
49
VERISIGN, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(In thousands, except per share data)
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
Revenues | $ | 1,142,167 | $ | 1,059,366 | $ | 1,010,117 | |||||
Costs and expenses: | |||||||||||
Cost of revenues | 198,242 | 192,788 | 188,425 | ||||||||
Sales and marketing | 80,250 | 90,184 | 92,001 | ||||||||
Research and development | 59,100 | 63,718 | 67,777 | ||||||||
General and administrative | 118,003 | 106,730 | 97,487 | ||||||||
Total costs and expenses | 455,595 | 453,420 | 445,690 | ||||||||
Operating income | 686,572 | 605,946 | 564,427 | ||||||||
Interest expense | (115,564 | ) | (107,631 | ) | (85,994 | ) | |||||
Non-operating income (loss), net | 10,165 | (10,665 | ) | 4,878 | |||||||
Income before income taxes | 581,173 | 487,650 | 483,311 | ||||||||
Income tax expense | (140,528 | ) | (112,414 | ) | (128,051 | ) | |||||
Net income | 440,645 | 375,236 | 355,260 | ||||||||
Realized foreign currency translation adjustments, included in net income | 85 | (291 | ) | — | |||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on investments | 533 | (519 | ) | 84 | |||||||
Realized (gain) loss on investments, included in net income | (78 | ) | (185 | ) | 3 | ||||||
Other comprehensive income (loss) | 540 | (995 | ) | 87 | |||||||
Comprehensive income | $ | 441,185 | $ | 374,241 | $ | 355,347 | |||||
Earnings per share: | |||||||||||
Basic | $ | 4.12 | $ | 3.29 | $ | 2.80 | |||||
Diluted | $ | 3.42 | $ | 2.82 | $ | 2.52 | |||||
Shares used to compute earnings per share | |||||||||||
Basic | 107,001 | 114,155 | 126,710 | ||||||||
Diluted | 128,833 | 133,031 | 140,895 | ||||||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
50
VERISIGN, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
(In thousands)
Additional Paid-In Capital | Accumulated Deficit | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss | Total Stockholders' Deficit | ||||||||||||||||||||
Common Stock | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2013 | 133,724 | $ | 320 | $ | 18,935,302 | $ | (19,356,095 | ) | $ | (3,085 | ) | $ | (423,558 | ) | |||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 355,260 | — | 355,260 | |||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive income | — | — | — | — | 87 | 87 | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under stock plans | 1,341 | 2 | 17,595 | — | — | 17,597 | |||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | — | 46,728 | — | — | 46,728 | |||||||||||||||||
Net excess income tax benefits associated with stock-based compensation | — | — | 3,823 | — | — | 3,823 | |||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock | (16,613 | ) | — | (883,403 | ) | — | — | (883,403 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2014 | 118,452 | 322 | 18,120,045 | (19,000,835 | ) | (2,998 | ) | (883,466 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 375,236 | — | 375,236 | |||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss | — | — | — | — | (995 | ) | (995 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under stock plans | 1,291 | 1 | 14,689 | — | — | 14,690 | |||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | — | 48,793 | — | — | 48,793 | |||||||||||||||||
Net excess income tax benefits associated with stock-based compensation | — | — | 18,464 | — | — | 18,464 | |||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock | (9,671 | ) | — | (643,169 | ) | — | — | (643,169 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2015 | 110,072 | 323 | 17,558,822 | (18,625,599 | ) | (3,993 | ) | (1,070,447 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 440,645 | — | 440,645 | |||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive income | — | — | — | — | 540 | 540 | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under stock plans | 1,128 | 1 | 13,669 | — | — | 13,670 | |||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | — | 52,430 | — | — | 52,430 | |||||||||||||||||
Net excess income tax benefits associated with stock-based compensation | — | — | 25,058 | — | — | 25,058 | |||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock | (8,109 | ) | — | (662,491 | ) | — | — | (662,491 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2016 | 103,091 | $ | 324 | $ | 16,987,488 | $ | (18,184,954 | ) | $ | (3,453 | ) | $ | (1,200,595 | ) | |||||||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
51
VERISIGN, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In thousands)
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | |||||||||||
Net income | $ | 440,645 | $ | 375,236 | $ | 355,260 | |||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||
Depreciation of property and equipment | 58,167 | 61,491 | 63,690 | ||||||||
Stock-based compensation | 50,044 | 46,075 | 43,977 | ||||||||
Excess tax benefit associated with stock-based compensation | (25,058 | ) | (18,464 | ) | (6,054 | ) | |||||
Unrealized (gain) loss on contingent interest derivative on Subordinated Convertible Debentures | (2,402 | ) | 14,130 | (2,249 | ) | ||||||
Payment of contingent interest | (13,385 | ) | (10,759 | ) | — | ||||||
Amortization of debt discount and issuance costs | 13,411 | 12,292 | 10,878 | ||||||||
Other, net | (3,787 | ) | (1,781 | ) | 480 | ||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities | |||||||||||
Accounts receivable | (871 | ) | 661 | (73 | ) | ||||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets | 8,980 | (1,728 | ) | 11,571 | |||||||
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 40,244 | 21,013 | 45,419 | ||||||||
Deferred revenues | 14,347 | 70,988 | 34,518 | ||||||||
Net deferred income taxes and other long-term tax liabilities | 87,614 | 82,328 | 43,532 | ||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 667,949 | 651,482 | 600,949 | ||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | |||||||||||
Proceeds from maturities and sales of marketable securities and investments | 3,817,899 | 2,767,027 | 3,428,659 | ||||||||
Purchases of marketable securities | (3,691,057 | ) | (3,219,329 | ) | (3,277,096 | ) | |||||
Purchases of property and equipment | (26,574 | ) | (40,656 | ) | (39,327 | ) | |||||
Deposits to acquire intangible assets | (143,000 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Other investing activities | 2,333 | (3,941 | ) | 452 | |||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities | (40,399 | ) | (496,899 | ) | 112,688 | ||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | |||||||||||
Proceeds from issuance of common stock from option exercises and employee stock purchase plans | 13,670 | 14,690 | 17,597 | ||||||||
Repurchases of common stock | (662,491 | ) | (643,169 | ) | (883,403 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from senior notes, net of issuance costs | — | 492,237 | — | ||||||||
Excess tax benefit associated with stock-based compensation | 25,058 | 18,464 | 6,054 | ||||||||
Net cash used in financing activities | (623,763 | ) | (117,778 | ) | (859,752 | ) | |||||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | (501 | ) | 246 | (1,500 | ) | ||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 3,286 | 37,051 | (147,615 | ) | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 228,659 | 191,608 | 339,223 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 231,945 | $ | 228,659 | $ | 191,608 | |||||
Supplemental cash flow disclosures: | |||||||||||
Cash paid for interest | $ | 115,544 | $ | 99,473 | $ | 75,088 | |||||
Cash paid for income taxes, net of refunds received | $ | 14,303 | $ | 39,723 | $ | 35,201 | |||||
52
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
Note 1. Description of Business and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Description of Business
VeriSign, Inc. (“Verisign” or “the Company”) was incorporated in Delaware on April 12, 1995. The Company has one reportable segment, which consists of Registry Services and Security Services. Registry Services ensure the security, stability and resiliency of key internet infrastructure and services, including the .com and .net domains, two of the Internet’s root servers, and operation of the root-zone maintainer functions for the core of the internet’s Domain Name System (“DNS”). Security Services provides infrastructure assurance services consisting of Distributed Denial of Services (“DDoS”) Protection Services, Verisign iDefense Security Intelligence Services (“iDefense”) and Managed DNS Services. On February 9, 2017, the Company entered into an agreement to sell the iDefense business, subject to customary closing conditions.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements of Verisign and its subsidiaries have been prepared in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) in the United States (“U.S.”). All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated.
The preparation of these consolidated financial statements requires management to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
Reclassifications
Certain reclassifications have been made to prior period amounts to conform to current period presentation. Such reclassifications have no effect on net income as previously reported.
Significant Accounting Policies
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Verisign considers all highly-liquid investments purchased with original maturities of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents include certain money market funds, debt securities and various deposit accounts. Verisign maintains its cash and cash equivalents with financial institutions that have investment grade ratings and, as part of its cash management process, performs periodic evaluations of the relative credit standing of these financial institutions.
Marketable Securities
Marketable securities primarily consist of debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury. All marketable securities are classified as available-for-sale and are carried at fair value. Unrealized gains and losses, net of taxes, are reported as a component of Accumulated other comprehensive loss. The specific identification method is used to determine the cost basis of the marketable securities sold. The Company classifies its marketable securities as current based on their nature and availability for use in current operations.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets of 35 to 47 years for buildings, 10 years for building improvements and three to five years for computer equipment, software, office equipment, and furniture and fixtures. Leasehold improvements are amortized using the straight-line method over the lesser of the estimated useful lives of the assets or associated lease terms.
Capitalized Software
Software included in property and equipment includes amounts paid for purchased software and development costs for internally developed software. The following table summarizes such costs capitalized during 2016 and 2015.
53
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||
Third-party implementation and consulting services | $ | 493 | $ | 426 | |||
Internally developed software | $ | 17,523 | $ | 20,061 | |||
Goodwill and Other Long-lived Assets
Goodwill represents the excess of purchase consideration over fair value of net assets of businesses acquired. Goodwill is not amortized, but instead tested for impairment. All of the Company’s goodwill is included in the Registry Services reporting unit which has a negative carrying value. The Company performs a qualitative analysis at the end of each reporting period to determine if any events have occurred or circumstances exist that would indicate that it is more likely than not that a goodwill impairment exists. The qualitative factors the Company reviews include, but are not limited to: (a) macroeconomic conditions; (b) industry and market considerations such as a deterioration in the environment in which an entity operates; (c) a significant adverse change in legal factors or in the business climate; (d) an adverse action or assessment by a regulator; (e) unanticipated competition; (f) loss of key personnel; (g) a more-likely-than-not expectation of sale or disposal of a reporting unit or a significant portion thereof; or (h) testing for recoverability of a significant asset group within a reporting unit.
Long-lived assets, such as property, plant, and equipment are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset, or asset group, may not be recoverable. Such events or circumstances include, but are not limited to, a significant decrease in the fair value of the underlying business, a significant decrease in the benefits realized from an acquired business, difficulties or delays in integrating the business or a significant change in the operations of an acquired business. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset, or asset group, to estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset, or asset group. An impairment charge is recognized in the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds its fair value.
As of December 31, 2016, the Company’s assets include a deposit related to the purchase of the contractual rights to the .web gTLD, as discussed in Note 4. The amount paid to date has been recorded as a deposit until such time that the contractual rights are transferred to the Company. This asset would be tested for recoverability if the Company were to determine that it is no longer probable that the rights will be transferred. At the time of the transfer of the contractual rights, the Company will record the amount as an indefinite-lived intangible asset subject to review for impairment on an annual basis or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that an impairment is more likely than not.
3.25% Junior Subordinated Convertible Debentures Due 2037 (“Subordinated Convertible Debentures”)
Upon issuance of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures, Verisign separated the liability (debt) and equity (conversion option) components in a manner that reflected the borrowing rate for a similar non-convertible debt. The liability component was recognized based on the fair value of a similar instrument without a conversion feature at issuance. The excess of the principal amount of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures over the liability component at issuance is the equity component or debt discount. Such excess represents the estimated fair value of the conversion feature and is recorded as Additional paid-in capital. The debt discount is amortized using the Company’s effective interest rate over the term of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures as a non-cash charge to interest expense.
The Subordinated Convertible Debentures also have a contingent interest payment provision that requires the Company to pay interest based on certain thresholds, and upon the occurrence of certain events, as outlined in the Indenture governing the Subordinated Convertible Debentures. The contingent interest payment provision has been identified as an embedded derivative, which is accounted for separately at fair value, and is marked to market at the end of each reporting period, with any gains and losses recorded in Non-operating income (loss), net. Contingent interest payments reflect the partial settlement of the embedded derivative. Verisign will have the right to redeem the Subordinated Convertible Debentures under the terms of the indenture, starting August 15, 2017. Therefore, the fair value of the contingent interest embedded derivative for periods after August 15, 2017 is negligible.
Foreign Currency Remeasurement
Verisign conducts business in several different countries and transacts in multiple currencies. The functional currency for all of Verisign’s international subsidiaries is the U.S. Dollar. The Company’s subsidiaries’ financial statements are remeasured
54
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
into U.S. Dollars using a combination of current and historical exchange rates and any remeasurement gains and losses are included in Non-operating income (loss), net. Remeasurement gains or losses in each of the last three years were $1.0 million or less.
Verisign maintains a foreign currency risk management program designed to mitigate foreign exchange risks associated with the monetary assets and liabilities that are denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. The primary objective of this program is to minimize the gains and losses resulting from fluctuations in exchange rates. The Company does not enter into foreign currency transactions for trading or speculative purposes, nor does it hedge foreign currency exposures in a manner that entirely offsets the effects of changes in exchange rates. The program may entail the use of forward or option contracts, which are usually placed and adjusted monthly. These foreign currency forward contracts are derivatives and are recorded at fair market value. The Company records gains and losses on foreign currency forward contracts in Non-operating income (loss), net. The Company recorded gains or losses related to foreign currency forward contracts of less than $1.0 million in each of the last three years.
As of December 31, 2016, Verisign held foreign currency forward contracts in notional amounts totaling $39.2 million to mitigate the impact of exchange rate fluctuations associated with certain assets and liabilities held in foreign currencies.
Revenue Recognition
Verisign recognizes revenues when the following four criteria are met:
• | Persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists: It is the Company’s customary practice to have a written contract, signed by both the customer and Verisign or a service order form from those customers who have previously negotiated a standard master services agreement with Verisign. |
• | Delivery has occurred or services have been rendered: The Company’s services are usually delivered continuously from service activation date through the term of the arrangement. |
• | The fee is fixed or determinable: Substantially all of the Company’s revenue arrangements have fixed or determinable fees. |
• | Collectability is reasonably assured: Collectability is assessed on a customer-by-customer basis. Verisign typically sells to customers for whom there is a history of successful collection. The majority of customers either maintain a deposit with Verisign or provide an irrevocable letter of credit in excess of the amounts owed. New customers are subjected to a credit review process that evaluates the customer’s financial condition and, ultimately, their ability to pay. If Verisign determines from the outset of an arrangement that collectability is not probable based upon its credit review process, revenues are recognized as cash is collected. |
Registry Services
Registry Services revenues primarily arise from fixed fees charged to registrars for the initial registration or renewal of .com, .net, and other domain names. Revenues from the initial registration or renewal of domain names are deferred and recognized ratably over the registration term, generally one year and up to ten years. Fees for renewals and advance extensions to the existing term are deferred until the new incremental period commences. These fees are then recognized ratably over the renewal term.
Verisign also offers promotional marketing programs to its registrars based upon market conditions and the business environment in which the registrars operate. Amounts payable to these registrars for such promotional marketing programs are usually recorded as a reduction of revenue. If Verisign obtains an identifiable benefit separate from the services it provides to the registrars, then amounts payable up to the fair value of the benefit received are recorded as advertising expenses and the excess, if any, is recorded as a reduction of revenue.
Security Services
Following the revenue recognition criteria above, revenues from Security Services are usually deferred and recognized over the service term, generally one to two years.
55
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
Advertising Expenses
Advertising costs are expensed as incurred and are included in Sales and marketing expenses. Advertising expenses, including costs for advertising campaigns conducted jointly with our registrar customers were $17.2 million, $16.0 million, and $20.2 million in 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively.
Income Taxes
Verisign uses the asset and liability method to account for income taxes. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and net operating loss carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. The Company records a valuation allowance to reduce deferred tax assets to an amount whose realization is more likely than not. For every tax-paying component and within each tax jurisdiction, all deferred tax liabilities and assets are offset and presented as a single net noncurrent asset or liability.
The Company’s income taxes payable is reduced by the tax benefits from restricted stock unit (“RSU”) vestings. The Company’s income tax benefit related to RSUs is equal to the fair market value of the stock at the vesting date. If the income tax benefit at exercise or vesting date is greater than the income tax benefit recorded based on the grant date fair value of the stock options or RSUs, such excess tax benefit is recognized as an increase to Additional paid-in capital. If the income tax benefit at exercise or vesting date is less than the income tax benefit recorded based on the grant date fair value of the stock options or RSUs, the shortfall is recognized as a reduction of Additional paid-in capital to the extent of previously recognized excess tax benefits.
Verisign’s global operations involve dealing with uncertainties and judgments in the application of complex tax regulations in multiple jurisdictions. The final taxes payable are dependent upon many factors, including negotiations with taxing authorities in various jurisdictions and resolution of disputes arising from U.S. federal, state, and international tax audits. The Company may only recognize or continue to recognize tax positions that are more likely than not to be sustained upon examination. The Company adjusts these reserves in light of changing facts and circumstances; however, due to the complexity
of some of these uncertainties, the ultimate resolution may result in a payment that is materially different from its current estimate of the tax liabilities.
The Company’s assumptions, judgments and estimates relative to the value of a deferred tax asset take into account predictions of the amount and character of future taxable income, such as income from operations or capital gains income. Actual operating results and the underlying amount and character of income in future years could render the Company’s current assumptions, judgments and estimates of recoverable net deferred taxes inaccurate. Any of the assumptions, judgments and estimates mentioned above could cause the Company’s actual income tax obligations to differ from its estimates, thus materially impacting its financial condition and results of operations.
Stock-based Compensation
The Company’s stock-based compensation is primarily related to RSUs granted to employees and its employee stock purchase plan (“ESPP”). For awards that are expected to vest, after considering estimated forfeitures, stock-based compensation expense is typically recognized ratably over the requisite service period. The Company also grants RSUs which include performance conditions, and in some cases market conditions, to certain executives. The expense for these performance-based RSUs is recognized based on the probable outcome of the performance conditions. The expense recognized for awards with market conditions is based on the grant date fair value of the awards including the impact of the market conditions, using a Monte Carlo simulation model. The Company uses the Black-Scholes option pricing model to determine the fair value of its ESPP offerings. The determination of the fair value of stock-based payment awards using the Monte Carlo simulation model or the Black-Scholes option-pricing model is affected by the Company’s stock price as well as assumptions regarding a number of complex and subjective variables.
56
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
Earnings per Share
The Company computes basic earnings per share by dividing net income by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per share gives effect to dilutive potential common shares, including outstanding stock options, unvested RSUs, ESPP offerings and the conversion spread related to the Subordinated Convertible Debentures using the treasury stock method.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company applies the following fair value hierarchy, which prioritizes the inputs used to measure fair value into three levels and bases the categorization within the hierarchy upon the lowest level of input that is available and significant to the fair value measurement:
• | Level 1: Observable inputs that reflect quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets. |
• | Level 2: Inputs reflect quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in markets that are not active; quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the assets or liabilities; or inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means. |
• | Level 3: Unobservable inputs reflecting the Company’s own assumptions incorporated in valuation techniques used to determine fair value. These assumptions are required to be consistent with market participant assumptions that are reasonably available. |
The Company measures and reports certain financial assets and liabilities at fair value on a recurring basis, including its investments in money market funds classified as Cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities, foreign currency forward contracts, and the contingent interest derivative associated with the Subordinated Convertible Debentures.
Legal Proceedings
Verisign is involved in various investigations, claims and lawsuits arising in the normal conduct of its business, none of which, in its opinion, will have a material adverse effect on its financial condition, results of operations, or cash flows. The Company cannot assure you that it will prevail in any litigation. Regardless of the outcome, any litigation may require the Company to incur significant litigation expense and may result in significant diversion of management attention.
While certain legal proceedings and related indemnification obligations to which the Company is a party specify the amounts claimed, such claims may not represent reasonably possible losses. Given the inherent uncertainties of the litigation, the ultimate outcome of these matters cannot be predicted at this time, nor can the amount of possible loss or range of loss, if any, be reasonably estimated, except in circumstances where an aggregate litigation accrual has been recorded for probable and reasonably estimable loss contingencies. A determination of the amount of accrual required, if any, for these contingencies is made after careful analysis of each matter. The required accrual may change in the future due to new developments in each matter or changes in approach such as a change in settlement strategy in dealing with these matters. The Company does not believe that any such matter currently being reviewed will have a material adverse effect on its financial condition, results of operations, or cash flows.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
On May 28, 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, which requires an entity to recognize the amount of revenue to which it expects to be entitled for the transfer of promised goods or services to customers. The ASU will replace most existing revenue recognition guidance in U.S. GAAP when it becomes effective. The new standard will become effective for the Company on January 1, 2018. The FASB also issued several amendments to the standard, including clarification on accounting for licenses of intellectual property and identifying performance obligations. The Company’s evaluation of the new revenue guidance is substantially complete. The Company does not currently expect the adoption of the new revenue standard to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases. The guidance introduces a lessee model that requires most leases to be reported on the balance sheet. This ASU will become effective for the Company on January 1, 2019 and requires the modified retrospective transition method. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this ASU on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
57
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-09, Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting, which simplifies several aspects of the accounting for share-based payment award transactions, including income tax consequences, classification of awards as either equity or liabilities, and classification on the statement of cash flows. The ASU requires that excess tax benefits and tax deficiencies (the tax effect of the difference between the deduction for tax purposes and the compensation cost recognized for financial reporting purposes) be recognized as income tax expense or benefit in the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income. This change could result in increased volatility in the Company’s effective tax rate in future periods. There are different transition methods for different aspects of the standard. The new standard became effective for the Company on January 1, 2017. Upon adoption of this ASU in the first quarter of 2017, the Company expects to record a deferred tax asset, net of a valuation allowance, for tax credit and tax loss carryforwards related to previously unrecognized excess tax benefits on share-based awards. Additionally, as permitted under the new ASU, the Company has elected to change its policy on accounting for forfeitures and recognize them as they occur. Both of these changes will be adopted using the modified retrospective transition method, which will result in a cumulative-effect adjustment to the January 1, 2017 opening retained earnings balance.
Note 2. Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Marketable Securities
The following table summarizes the Company’s cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities:
As of December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||
Cash | $ | 39,183 | $ | 99,027 | |||
Money market funds | 134,790 | 137,593 | |||||
Time deposits | 4,632 | 4,007 | |||||
Debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury | 1,626,764 | 1,685,882 | |||||
Equity securities of public companies | 2,174 | 890 | |||||
Total | $ | 1,807,543 | $ | 1,927,399 | |||
Included in Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 231,945 | $ | 228,659 | |||
Included in Marketable securities | $ | 1,565,962 | $ | 1,686,771 | |||
Included in Other long-term assets (Restricted cash) | $ | 9,636 | $ | 11,969 | |||
The fair value of the debt securities held as of December 31, 2016 was $1.6 billion, including less than $1.0 million of gross and net unrealized losses. All of the debt securities held as of December 31, 2016 have contractual maturities of less than one year.
58
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
Note 3. Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Assets and Liabilities Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis
The following table summarizes the Company’s financial assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015:
Fair Value Measurement Using | |||||||||||||||
Total Fair Value | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2016: | |||||||||||||||
Assets: | |||||||||||||||
Investments in money market funds | $ | 134,790 | $ | 134,790 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||
Debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury | 1,626,764 | 1,626,764 | — | — | |||||||||||
Equity securities of public companies | 2,174 | 2,174 | — | — | |||||||||||
Foreign currency forward contracts (1) | 242 | — | 242 | — | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 1,763,970 | $ | 1,763,728 | $ | 242 | $ | — | |||||||
Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
Contingent interest derivative on Subordinated Convertible Debentures | $ | 14,339 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 14,339 | |||||||
Foreign currency forward contracts (2) | 87 | — | 87 | — | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 14,426 | $ | — | $ | 87 | $ | 14,339 | |||||||
As of December 31, 2015: | |||||||||||||||
Assets: | |||||||||||||||
Investments in money market funds | $ | 137,593 | $ | 137,593 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||
Debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury | 1,685,882 | 1,685,882 | — | — | |||||||||||
Equity securities of public companies | 890 | 890 | — | — | |||||||||||
Foreign currency forward contracts (1) | 230 | — | 230 | — | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 1,824,595 | $ | 1,824,365 | $ | 230 | $ | — | |||||||
Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
Contingent interest derivative on Subordinated Convertible Debentures | $ | 30,126 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 30,126 | |||||||
Foreign currency forward contracts (2) | 164 | — | 164 | — | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 30,290 | $ | — | $ | 164 | $ | 30,126 | |||||||
(1) | Included in Other current assets |
(2) | Included in Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
The fair value of the Company’s investments in money market funds approximates their face value. Such instruments are classified as Level 1 and are included in Cash and cash equivalents.
The fair value of the debt securities consisting of U.S. Treasury bills is based on their quoted market prices and are classified as Level 1. Debt securities purchased with original maturities in excess of three months are included in Marketable securities. Debt securities purchased with original maturities less than three months are included in Cash and cash equivalents.
The fair value of the equity securities of public companies is based on quoted market prices and are classified as Level 1. Investments in equity securities of public companies are included in marketable securities.
The fair value of the Company’s foreign currency forward contracts is based on foreign currency rates quoted by banks or foreign currency dealers and other public data sources.
The Company utilizes a valuation model to estimate the fair value of the contingent interest derivative on the Subordinated Convertible Debentures. The inputs to the model include stock price, risk free interest rates, volatility, and credit spread observations. As several significant inputs are not observable, the overall fair value measurement of the derivative is
59
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
classified as Level 3. The volatility and credit spread assumptions used in the calculation are the most significant unobservable inputs. As of December 31, 2016, the valuation of the contingent interest derivative assumed a volatility rate of approximately 26% and a credit spread of approximately 4%. The fair value of the contingent interest derivative would not have significantly changed using a volatility rate of either 21% or 31%, or a credit spread of either 3% or 5%.
The following table summarizes the change in the fair value of the Company’s contingent interest derivative on Subordinated Convertible Debentures during the year ended December 31, 2016 and 2015:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||
Beginning balance | $ | 30,126 | $ | 26,755 | |||
Unrealized (gain) loss on contingent interest derivative on Convertible Debentures | (2,402 | ) | 14,130 | ||||
Payment of contingent interest | (13,385 | ) | (10,759 | ) | |||
Ending balance | $ | 14,339 | $ | 30,126 | |||
The contingent interest derivative balance as of December 31, 2016 includes $7.7 million which was paid on February 16, 2017.
As of December 31, 2016, the Company’s other financial instruments include cash, accounts receivable, restricted cash, and accounts payable whose carrying values approximated their fair values. The fair value of the Company’s Subordinated Convertible Debentures was $2.8 billion as of December 31, 2016. The fair values of the Company’s senior notes due 2023 (the “2023 Senior Notes”) and the senior notes due 2025 (the “2025 Senior Notes”) were $764.1 million and $514.1 million, respectively, as of December 31, 2016. The fair values of these debt instruments are based on available market information from public data sources and are classified as Level 2.
Note 4. Deposits to Acquire Intangible Assets
As of December 31, 2016, the Company has paid $145.0 million for the future assignment to the Company of contractual rights to the .web gTLD, pending resolution of objections by other applicants, regulatory review, and approval from ICANN. Upon assignment of the contractual rights, the Company will record the total investment as an indefinite-lived intangible asset.
Note 5. Other Balance Sheet Items
Other Current Assets
Other current assets consist of the following:
As of December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||
Prepaid expenses | $ | 14,385 | $ | 14,823 | |||
Income taxes receivable | 15,328 | 23,098 | |||||
Other | 1,671 | 1,935 | |||||
Total other current assets | $ | 31,384 | $ | 39,856 | |||
60
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
Property and Equipment, Net
The following table presents the detail of property and equipment, net:
As of December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||
Land | $ | 31,141 | $ | 31,141 | |||
Buildings and building improvements | 246,237 | 244,760 | |||||
Computer equipment and software | 441,732 | 432,463 | |||||
Capital work in progress | 4,246 | 5,406 | |||||
Office equipment and furniture | 6,203 | 6,203 | |||||
Leasehold improvements | 1,350 | 1,350 | |||||
Total cost | 730,909 | 721,323 | |||||
Less: accumulated depreciation | (464,784 | ) | (425,753 | ) | |||
Total property and equipment, net | $ | 266,125 | $ | 295,570 | |||
Goodwill
The following table presents the detail of goodwill:
As of December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||
Goodwill, gross | $ | 1,537,843 | $ | 1,537,843 | |||
Accumulated goodwill impairment | (1,485,316 | ) | (1,485,316 | ) | |||
Total goodwill | $ | 52,527 | $ | 52,527 | |||
There was no impairment of goodwill or other long-lived assets recognized in any of the periods presented.
Other Long-Term Assets
Other long-term assets consist of the following:
As of December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||
Long-term restricted cash | 9,636 | 11,969 | |||||
Other taxes receivable | 5,673 | 5,673 | |||||
Long-term prepaid expenses and other assets | 3,884 | 4,713 | |||||
Total other long-term assets | $ | 19,193 | $ | 22,355 | |||
61
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
Accounts Payable and Accrued Liabilities
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities consist of the following:
As of December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 19,455 | $ | 23,298 | |||
Accrued employee compensation | 61,426 | 51,851 | |||||
Customer deposits, net | 52,173 | 48,307 | |||||
Interest Payable | 27,701 | 27,701 | |||||
Taxes payable and other tax liabilities | 23,144 | 16,943 | |||||
Other accrued liabilities | 20,021 | 20,071 | |||||
Total accounts payable and accrued liabilities | $ | 203,920 | $ | 188,171 | |||
Note 6. Debt and Interest Expense
Senior Notes due 2025
On March 27, 2015, the Company issued $500.0 million principal amount of 5.25% senior unsecured notes due April 1, 2025. In connection with the offering the Company incurred $6.5 million of issuance costs which are being amortized to Interest expense over the 10 year term of the notes. The Company pays interest on the notes semi-annually on April 1 and October 1. The Company may redeem the 2025 Senior Notes, in whole or in part, at any time at the Company’s option at specified redemption prices.
Senior Notes due 2023
On April 16, 2013, the Company issued $750.0 million principal amount of 4.625% senior unsecured notes due May 1, 2023. In connection with the offering the Company incurred $12.0 million of issuance costs which are being amortized to Interest expense over the 10 year term of the Senior Notes. The Company pays interest on the notes semi-annually on May 1 and November 1. The Company may redeem the 2023 Senior Notes, in whole or in part, at any time at the Company’s option at specified redemption prices.
The indenture governing the 2023 Senior Notes contains covenants that limit the ability of the Company and/or its restricted subsidiaries, under certain circumstances, to, among other things: (i) pay dividends or make distributions on, or redeem or repurchase, its capital stock; (ii) make certain investments; (iii) create liens on assets; (iv) enter into sale/leaseback transactions and (v) merge or consolidate or sell all or substantially all of its assets. These covenants are subject to a number of important limitations and exceptions. The Indenture also provides for events of default, which, if any of them occurs, may permit or, in certain circumstances, require the principal, premium, if any, accrued and unpaid interest and any other monetary obligations on all the then outstanding Notes to be due and payable immediately.
2015 Credit Facility
On March 31, 2015, the Company entered into a credit agreement for a $200.0 million committed senior unsecured revolving credit facility (the “2015 Credit Facility”). The 2015 Credit Facility includes financial covenants requiring that the Company’s interest coverage ratio not be less than 3.0 to 1.0 for any period of four consecutive quarters and the Company’s leverage ratio not exceed 2.5 to 1.0. As of December 31, 2016, there were no borrowings outstanding under the facility and the Company was in compliance with the financial covenants. The 2015 Credit Facility expires on April 1, 2020 at which time any outstanding borrowings are due. Verisign may from time to time request lenders to agree on a discretionary basis to increase the commitment amount by up to an aggregate of $150.0 million.
62
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
Subordinated Convertible Debentures
In August 2007, Verisign issued $1.25 billion principal amount of 3.25% subordinated convertible debentures due August 15, 2037, in a private offering. The Subordinated Convertible Debentures are initially convertible, subject to certain conditions, into shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion rate of 29.0968 shares of common stock per $1,000 principal amount of Subordinated Convertible Debentures, representing an initial effective conversion price of approximately $34.37 per share of common stock. The conversion rate will be subject to adjustment for certain events as outlined in the Indenture governing the Subordinated Convertible Debentures but will not be adjusted for accrued interest. As of December 31, 2016, approximately 36.4 million shares of common stock were reserved for issuance upon conversion or repurchase of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures.
On or after August 15, 2017, the Company may redeem all or part of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures for the principal amount plus any accrued and unpaid interest if the closing price of the Company’s common stock has been at least 150% of the conversion price then in effect for at least 20 trading days during any 30 consecutive trading-day period prior to the date on which the Company provides notice of redemption.
The Company’s common stock price exceeded the current conversion price threshold trigger of $44.68 during the fourth quarter of 2016. Accordingly, the Subordinated Convertible Debentures were convertible at the option of each holder during the first quarter of 2017. Further, in the event of conversion, the Company intends, and has the ability, to settle the principal amount of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures in cash, and therefore, classified the debt component of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures, net of unamortized debt issuance costs and the embedded contingent interest derivative as a current liability, as of December 31, 2016. The determination of whether or not the Subordinated Convertible Debentures are convertible, and accordingly, the classification as long-term or current, must continue to be performed quarterly. As of December 31, 2016, the if-converted value of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures exceeded its principal amount. Based on the if-converted value of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures as of December 31, 2016, the conversion spread could have required the Company to issue up to an additional 19.9 million shares of common stock.
The Company calculated the carrying value of the liability component at issuance as the present value of its cash flows using a discount rate of 8.5% (borrowing rate for similar non-convertible debt with no contingent payment options), adjusted for the fair value of the contingent interest feature, yielding an effective interest rate of 8.39%. The excess of the principal amount of the debt over the carrying value of the liability component is also referred to as the “debt discount” or “equity component” of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures. The debt discount is being amortized using the Company’s effective interest rate of 8.39% over the term of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures as a non-cash charge included in Interest expense. As of December 31, 2016, the remaining term of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures is 20.6 years. Interest is payable semiannually in arrears on August 15 and February 15.
Proceeds upon issuance of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures were as follows (in thousands):
Principal value of Subordinated Convertible Debentures | $ | 1,250,000 | ||
Less: Issuance costs | (25,777 | ) | ||
Net proceeds, Subordinated Convertible Debentures | $ | 1,224,223 | ||
Amounts recognized at issuance: | ||||
Subordinated Convertible Debentures, including contingent interest derivative (net of issuance costs of $11,328) | $ | 546,915 | ||
Additional paid-in capital | 418,996 | |||
Long-term deferred tax liabilities | 267,225 | |||
Non-operating loss | (8,913 | ) | ||
Net proceeds, Subordinated Convertible Debentures | $ | 1,224,223 | ||
63
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
The table below presents the carrying amounts of the liability and equity components:
As of December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||
Debt discount upon issuance (net of issuance costs of $14,449) | $ | 686,221 | $ | 686,221 | |||
Deferred taxes associated with the debt discount upon issuance | (267,225 | ) | (267,225 | ) | |||
Carrying amount of equity component | $ | 418,996 | $ | 418,996 | |||
Principal amount of Subordinated Convertible Debentures | $ | 1,250,000 | $ | 1,250,000 | |||
Unamortized discount of liability component | (624,315 | ) | (635,378 | ) | |||
Unamortized debt issuance costs associated with the liability component | (10,260 | ) | (10,422 | ) | |||
Carrying amount of liability component | 615,425 | 604,200 | |||||
Contingent interest derivative | 14,339 | 30,126 | |||||
Subordinated Convertible Debentures, including contingent interest derivative | $ | 629,764 | $ | 634,326 | |||
The following table presents the components of the Company’s interest expense:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||
Contractual interest on Subordinated Convertible Debentures | $ | 40,625 | $ | 40,625 | $ | 40,625 | |||||
Contractual interest on Senior Notes | 60,938 | 54,667 | 34,688 | ||||||||
Amortization of debt discount on the Subordinated Convertible Debentures | 11,094 | 10,218 | 9,412 | ||||||||
Credit facility and other interest expense | 2,907 | 2,121 | 1,269 | ||||||||
Total interest expense | $ | 115,564 | $ | 107,631 | $ | 85,994 | |||||
64
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
Note 7. Stockholders’ Deficit
Treasury Stock
Treasury stock is accounted for under the cost method. Treasury stock includes shares repurchased under Stock Repurchase Programs and shares withheld in lieu of minimum tax withholdings due upon vesting of RSUs.
On February 11, 2016, the Company’s Board of Directors (“Board”) authorized the repurchase of approximately $611.2 million of its common stock, in addition to the $388.8 million of its common stock remaining available for repurchase under the previous share repurchase program, for a total repurchase authorization of up to $1.0 billion of its common stock. The share repurchase program has no expiration date. Purchases made under the program could be effected through open market transactions, block purchases, accelerated share repurchase agreements or other negotiated transactions. As of December 31, 2016 there was approximately $429.2 million remaining available for repurchases under the share repurchase program.
Effective February 9, 2017, the Company’s Board authorized the repurchase of approximately $640.9 million of its common stock, in addition to the $359.1 million of its common stock remaining available for repurchase under the previous share repurchase program, for a total repurchase authorization of up to $1.0 billion of its common stock.
The summary of the Company’s common stock repurchases for 2016, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Average Price | Shares | Average Price | Shares | Average Price | ||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands, except average price amounts) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total repurchases under the repurchase plans | 7,789 | $ | 81.73 | 9,338 | $ | 66.59 | 16,316 | $ | 53.15 | ||||||||||||||
Total repurchases for tax withholdings | 320 | $ | 80.74 | 333 | $ | 64.03 | 297 | $ | 54.73 | ||||||||||||||
Total repurchases | 8,109 | $ | 81.70 | 9,671 | $ | 66.50 | 16,613 | $ | 53.18 | ||||||||||||||
Total costs | $ | 662,491 | $ | 643,169 | $ | 883,403 | |||||||||||||||||
Since inception, the Company has repurchased 221.0 million shares of its common stock for an aggregate cost of $8.2 billion, which is recorded as a reduction of Additional paid-in capital.
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss
The following table summarizes the changes in the components of Accumulated other comprehensive loss for 2016 and 2015:
Foreign Currency Translation Adjustments Loss | Unrealized Gain (Loss) On Investments | Total Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss | |||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2014 | $ | (3,160 | ) | $ | 162 | $ | (2,998 | ) | |||
Changes | (291 | ) | (704 | ) | (995 | ) | |||||
Balance, December 31, 2015 | (3,451 | ) | (542 | ) | (3,993 | ) | |||||
Changes | 85 | 455 | 540 | ||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2016 | $ | (3,366 | ) | $ | (87 | ) | $ | (3,453 | ) | ||
65
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
Note 8. Calculation of Earnings per Share
The following table presents the computation of weighted-average shares used in the calculation of basic and diluted earnings per share:
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
(In thousands) | ||||||||
Weighted-average shares of common stock outstanding | 107,001 | 114,155 | 126,710 | |||||
Weighted-average potential shares of common stock outstanding: | ||||||||
Conversion spread related to Subordinated Convertible Debentures | 21,074 | 18,047 | 13,384 | |||||
Unvested RSUs, stock options, and ESPP | 758 | 829 | 801 | |||||
Shares used to compute diluted earnings per share | 128,833 | 133,031 | 140,895 | |||||
The calculation of diluted weighted average shares outstanding, excludes potentially dilutive securities, the effect of which would have been anti-dilutive, as well as performance based RSUs granted by the Company for which the relevant performance criteria have not been achieved. The number of potential shares excluded from the calculation was not significant in any period presented.
Note 9. Geographic and Customer Information
The Company generates revenue in the U.S.; Europe, the Middle East and Africa (“EMEA”); China; and certain other countries, including Canada, Australia and Japan.
The following table presents a comparison of the Company’s geographic revenues:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||
U.S | $ | 667,301 | $ | 639,170 | $ | 616,125 | |||||
EMEA | 207,474 | 193,623 | 182,897 | ||||||||
China | 127,298 | 83,456 | 65,525 | ||||||||
Other | 140,094 | 143,117 | 145,570 | ||||||||
Total revenues | $ | 1,142,167 | $ | 1,059,366 | $ | 1,010,117 | |||||
Revenues for our Registry Services business are generally attributed to the country of domicile and the respective regions in which the Company’s registrars are located, however, this may differ from the regions where the registrars operate or where registrants are located. Revenue growth for each region may be impacted by registrars reincorporating, relocating, or from acquisitions or changes in affiliations of resellers. Revenue growth for each region may also be impacted by registrars domiciled in one region, registering domain names in another region.
The following table presents a comparison of property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation, by geographic region:
As of December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||
U.S. | $ | 261,837 | $ | 287,986 | |||
Other | 4,288 | 7,584 | |||||
Total property and equipment, net | $ | 266,125 | $ | 295,570 | |||
66
VERISIGN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (Continued)
DECEMBER 31, 2016, 2015 AND 2014
Major Customers
One customer accounted for approximately 30% of revenues in 2016 and approximately 31% of revenues in 2015 and 2014. The Company does not believe that the loss of this customer would have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business because, in that event, end-users of this customer would transfer to the Company’s other existing customers.
Note 10. Employee Benefits and Stock-based Compensation
401(k) Plan
The Company maintains a defined contribution 401(k) plan (the “401(k) Plan”) for substantially all of its U.S. employees. Under the 401(k) Plan, eligible employees may contribute up to 50% of their pre-tax salary, subject to the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) annual contribution limits. The Company matches 50% of up to the first 6% of the employee’s annual salary contributed to the plan. The Company contributed $3.8 million in 2016, $3.7 million in 2015, and $3.4 million in 2014 under the 401(k) Plan. The Company can terminate matching contributions at its discretion at any time.
Equity Incentive Plan
The majority of Verisign’s stock-based compensation relates to RSUs. As of December 31, 2016, a total of 11.4 million shares of common stock were reserved for issuance upon the vesting of RSUs and for the future grant of equity awards.
On May 26, 2006, the stockholders of Verisign approved the 2006 Equity Incentive Plan, which was amended and restated on June 9, 2016 (the “2006 Plan”). The 2006 Plan authorizes the award of incentive stock options to employees and non-qualified stock options, restricted stock awards, RSUs, stock bonus awards, stock appreciation rights and performance shares to eligible employees, officers, directors, consultants, independent contractors and advisers. The 2006 Plan is administered by the Compensation Committee which may delegate to a committee of one or more members of the Board or Verisign’s officers the ability to grant certain awards and take certain other actions with respect to participants who are not executive officers or non-employee directors. RSUs are awards covering a specified number of shares of Verisign common stock that may be settled by issuance of those shares (which may be restricted shares). RSUs generally vest over four years. Certain performance-based RSUs, granted to the Company’s executives, vest over either three or four year terms. Additionally, the Company has granted fully vested RSUs to members of its Board in each of the last three years. The Compensation Committee may authorize grants with a different vesting schedule in the future. A total of 27.0 million common shares were authorized and reserved for issuance under the 2006 Plan.
2007 Employee Stock Purchase Plan
On August 30, 2007, the Company’s stockholders approved the 2007 Employee Stock Purchase Plan. A total of 6.0 million common shares were authorized and reserved for issuance under the ESPP. Eligible employees may purchase common stock through payroll deductions by electing to have between 2% and 25% of their compensation withheld to cover the purchase price. Each participant is granted an option to purchase common stock on the first day of each 24-month offering period and this option is automatically exercised on the last day of each six-month purchase period during the offering period. The purchase price for the common stock under the ESPP is 85% of the lesser of the fair market value of the common stock on the first day of the applicable offering period or the last day of the applicable purchase period. Offering periods begin on the first business day of February and August of each year. As of December 31, 2016, 1.2 million shares of the Company’s common stock are reserved for issuance under this plan.
67
Stock-based Compensation
Stock-based compensation is classified in the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income in the same expense line items as cash compensation. The following table presents the classification of stock-based compensation:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||
Stock-based compensation: | |||||||||||
Cost of revenues | $ | 7,253 | $ | 7,009 | $ | 6,400 | |||||
Sales and marketing | 5,738 | 6,763 | 8,023 | ||||||||
Research and development | 6,739 | 6,488 | 7,018 | ||||||||
General and administrative | 30,314 | 25,815 | 22,536 | ||||||||
Total stock-based compensation | $ | 50,044 | $ | 46,075 | $ | 43,977 | |||||
The following table presents the nature of the Company’s total stock-based compensation:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||
RSUs | $ | 37,325 | $ | 36,664 | $ | 32,304 | |||||
Performance-based RSUs | 11,512 | 8,078 | 10,232 | ||||||||
ESPP | 3,593 | 4,051 | 4,192 | ||||||||
Capitalization (Included in Property and equipment, net) | (2,386 | ) | (2,718 | ) | (2,751 | ) | |||||
Total stock-based compensation expense | $ | 50,044 | $ | 46,075 | $ | 43,977 | |||||
The income tax benefit recognized on stock-based compensation within Income tax expense for 2016, 2015, and 2014 was $17.7 million, $16.0 million, and $15.1 million, respectively.
RSUs Information
The following table summarizes unvested RSUs activity:
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Weighted-Average Grant-Date Fair Value | Shares | Weighted-Average Grant-Date Fair Value | Shares | Weighted-Average Grant-Date Fair Value | |||||||||||||||
(Shares in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Unvested at beginning of period | 2,110 | $ | 54.77 | 2,179 | $ | 46.36 | 2,442 | $ | 38.00 | |||||||||||
Granted | 760 | 78.58 | 1,075 | 61.74 | 909 | 55.05 | ||||||||||||||
Vested and settled | (873 | ) | 49.95 | (932 | ) | 43.92 | (878 | ) | 35.99 | |||||||||||
Forfeited | (151 | ) | 61.57 | (212 | ) | 51.47 | (294 | ) | 44.00 | |||||||||||
1,846 | $ | 66.30 | 2,110 | $ | 54.77 | 2,179 | $ | 46.36 | ||||||||||||
The RSUs in the table above include certain RSUs granted to the Company’s executives that are subject to performance conditions, and in some cases, market conditions. The unvested RSUs as of December 31, 2016 include approximately 0.4 million RSUs subject to performance and/or market conditions. The number of RSUs, subject to these performance and market conditions, that ultimately vest may range from zero to a maximum of 0.8 million RSUs depending on the level of performance achieved and whether any market conditions are satisfied.
68
The closing price of Verisign’s stock was $76.07 on December 31, 2016. As of December 31, 2016, the aggregate market value of unvested RSUs was $140.7 million. The fair values of RSUs that vested during 2016, 2015, and 2014 were $70.5 million, $59.8 million, and $47.9 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2016, total unrecognized compensation cost related to unvested RSUs was $67.7 million which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 2.3 years.
Note 11. Non-operating Income (Loss), Net
The following table presents the components of Non-operating income (loss), net:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on contingent interest derivative on Subordinated Convertible Debentures | 2,402 | (14,130 | ) | 2,249 | |||||||
Interest income | 6,191 | 2,128 | 922 | ||||||||
Other, net | 1,572 | 1,337 | 1,707 | ||||||||
Total non-operating income (loss), net | $ | 10,165 | $ | (10,665 | ) | $ | 4,878 | ||||
The unrealized gains and losses on the contingent interest derivative on the Subordinated Convertible Debentures reflects the change in value of the derivative that results primarily from the changes in the Company’s stock price. Interest income is earned principally from the Company’s surplus cash balances and marketable securities.
69
Note 12. Income Taxes
Income before income taxes is categorized geographically as follows:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||
United States | $ | 299,304 | $ | 248,932 | $ | 270,373 | |||||
Foreign | 281,869 | 238,718 | 212,938 | ||||||||
Total income before income taxes | $ | 581,173 | $ | 487,650 | $ | 483,311 | |||||
The provision for income taxes consisted of the following:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||
Current expense (benefit): | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | 34,842 | $ | 13,601 | $ | 4,643 | |||||
State | 240 | 156 | (14 | ) | |||||||
Foreign, including withholding tax | 19,268 | 17,241 | 69,614 | ||||||||
54,350 | 30,998 | 74,243 | |||||||||
Deferred expense (benefit): | |||||||||||
Federal | 64,301 | 65,168 | 76,614 | ||||||||
State | 21,492 | 15,767 | 15,402 | ||||||||
Foreign | 385 | 481 | (38,208 | ) | |||||||
86,178 | 81,416 | 53,808 | |||||||||
Total income tax expense | $ | 140,528 | $ | 112,414 | $ | 128,051 | |||||
The difference between income tax expense and the amount resulting from applying the federal statutory rate of 35% to Income before income taxes is attributable to the following:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||
Income tax expense at federal statutory rate | $ | 203,410 | $ | 170,677 | $ | 169,159 | |||||
State taxes, net of federal benefit | 14,517 | 9,616 | 11,308 | ||||||||
Differences between statutory rate and foreign effective tax rate | (79,087 | ) | (66,238 | ) | (57,876 | ) | |||||
Reorganization of certain non-U.S. operations | — | — | 14,474 | ||||||||
Changes in estimates related to worthless stock deduction | — | — | 14,497 | ||||||||
Change in valuation allowance | (511 | ) | 434 | (41,700 | ) | ||||||
Accrual for uncertain tax positions | 963 | 706 | 22,719 | ||||||||
Other | 1,236 | (2,781 | ) | (4,530 | ) | ||||||
Total income tax expense | $ | 140,528 | $ | 112,414 | $ | 128,051 | |||||
During 2014 the Company repatriated $740.9 million of cash held by foreign subsidiaries, net of $28.1 million of foreign withholding taxes which were accrued during 2013. During 2014, the Company recognized a net income tax benefit of $8.6 million, resulting from the completion of the repatriation and changes to estimates related to the 2013 worthless stock deduction. The components of this net benefit are included in the table above for changes in valuation allowances, adjustments to the benefit from the worthless stock deduction, changes to the accrual for uncertain tax positions and other.
70
Deferred income taxes have not been provided on the undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries because these earnings are intended to be indefinitely reinvested. As of December 31, 2016, the amount of such earnings was $926.7 million. The amount of unrecognized deferred tax liability related to undistributed foreign earnings is estimated to be $264.1 million.
Beginning in 2015, the Company qualified for a tax holiday in Switzerland which does not expire, unless the required thresholds are no longer met, or there is a law change which eliminates the holiday. The Company qualified for another tax holiday in Switzerland which expired on December 31, 2016, but may be renewed if certain criteria are satisfied. An additional tax holiday in Switzerland expired in 2014 and was not extended. The tax holidays provide reduced rates of taxation on certain types of income and also require certain thresholds of foreign source income. These tax holidays increased the Company’s earnings per share by $0.16, $0.14, and $0.50 in 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively. In the fourth quarter of 2014, the Company incurred a charge of $14.5 million in non-US income taxes as a result of a reorganization of certain international operations.
The tax effects of temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows:
As of December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||
Deferred tax assets: | |||||||
Net operating loss carryforwards | $ | 46,879 | $ | 56,108 | |||
Deductible goodwill and intangible assets | 10,473 | 21,044 | |||||
Tax credit carryforwards | 59,337 | 86,951 | |||||
Deferred revenue, accruals and reserves | 114,548 | 106,572 | |||||
Capital loss carryforwards and book impairment of investments | 1,161,772 | 1,162,320 | |||||
Other | 4,791 | 5,039 | |||||
Total deferred tax assets | 1,397,800 | 1,438,034 | |||||
Valuation allowance | (1,162,101 | ) | (1,162,604 | ) | |||
Net deferred tax assets | 235,699 | 275,430 | |||||
Deferred tax liabilities: | |||||||
Property and equipment | (4,212 | ) | (10,787 | ) | |||
Subordinated Convertible debentures | (590,921 | ) | (538,098 | ) | |||
Other | (2,614 | ) | (3,378 | ) | |||
Total deferred tax liabilities | (597,747 | ) | (552,263 | ) | |||
Total net deferred tax liabilities | $ | (362,048 | ) | $ | (276,833 | ) | |
With the exception of deferred tax assets related to capital loss carryforwards, management believes it is more likely than not that the tax effects of the deferred tax liabilities together with future taxable income, will be sufficient to fully recover the remaining deferred tax assets.
As of December 31, 2016, the Company had federal, state and foreign net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $6.8 million, $1.4 billion and $ 16.5 million, respectively, before applying tax rates for the respective jurisdictions. As of December 31, 2016, the Company had federal and state research tax credits of $13.5 million and $2.9 million, respectively, and alternative minimum tax credits of $17.6 million available for future years. Certain net operating loss carryforwards and credits are subject to an annual limitation under Internal Revenue Code Section 382, but are expected to be fully realized. The amount of excess tax benefits from stock-based compensation that have not been recognized as of December 31, 2016, because they did not reduce income taxes payable, was $52.1 million. The federal and state net operating loss and federal tax credit carryforwards expire in various years from 2017 through 2034. The foreign net operating loss can be carried forward indefinitely. As of December 31, 2016, the Company had federal and state capital loss carryforwards of $3.0 billion and $3.1 billion, respectively, before applying tax rates for the respective jurisdictions. The capital loss carryforwards expire in 2018 and are also subject to annual limitations under Internal Revenue Code Section 382. The Company does not expect to realize any tax benefits from the capital loss carryforwards and accordingly has reserved the entire amount through valuation allowance
71
and accrual for uncertain tax positions. As of December 31, 2016, the Company has foreign tax credit carryforwards of $143.9 million. The majority of these foreign tax credits will expire in 2024.
The deferred tax liability related to the Subordinated Convertible Debentures is driven by the excess of the tax deduction taken for interest expense over the amount of interest expense recognized in the consolidated financial statements. The interest expense deducted for tax purposes is based on the adjusted issue price of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures, while the interest expense recognized in accordance with GAAP is based only on the liability portion of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures. The adjusted issue price of the Subordinated Convertible Debentures grows over the term due to the difference between the interest deduction taken for income tax, using a comparable yield of 8.5%, and the coupon rate of 3.25%, compounded annually, adjusted for actual versus projected contingent interest payments
The Company maintains liabilities for uncertain tax positions. These liabilities involve considerable judgment and estimation and are continuously monitored by management based on the best information available including changes in tax regulations and other information. A reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances of the total amounts of gross unrecognized tax benefits is as follows:
As of December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||
Gross unrecognized tax benefits at January 1 | $ | 220,280 | $ | 219,908 | |||
Increases in tax positions for prior years | 119 | — | |||||
Decreases in tax positions for prior years | (71 | ) | — | ||||
Increases in tax positions for current year | 354 | 372 | |||||
Gross unrecognized tax benefits at December 31 | $ | 220,682 | $ | 220,280 | |||
As of December 31, 2016, approximately $212.0 million of unrecognized tax benefits, including penalties and interest, could affect the Company’s tax provision and effective tax rate. It is reasonably possible that during the next twelve months, the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits may change by a significant amount as a result of IRS audits. However the timing of completion and ultimate outcome of the audits remains uncertain. Therefore, the Company cannot currently estimate the impact on the balance of unrecognized tax benefits.
In accordance with its accounting policy, the Company recognizes accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as a component of tax expense. These accruals were not material in any period presented.
The Company’s major taxing jurisdictions are the U.S., the state of Virginia, and Switzerland. The Company’s U.S. federal income tax returns are currently under examination by the IRS for 2010 through 2014. The Company’s other tax returns are not currently under examination by their respective taxing jurisdictions. Because the Company uses historic net operating loss carryforwards and other tax attributes to offset its taxable income in current and future years’ income tax returns for the U.S. and Virginia, such attributes can be adjusted by these taxing authorities until the statute closes on the year in which such attributes were utilized. The open years in Switzerland are the 2012 tax year and forward.
72
Note 13. Commitments and Contingencies
Purchase Obligations and Contractual Agreements
The following table represents the minimum payments required by Verisign under certain purchase obligations, leases, the .tv Agreement with the Government of Tuvalu, and the interest payments and principal on the Subordinated Convertible Debentures and the Senior Notes:
Purchase Obligations | .tv Agreement | Senior Notes | Subordinated Convertible Debentures | Total | |||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
2017 | $ | 30,946 | $ | 5,000 | $ | 60,938 | $ | 48,344 | $ | 145,228 | |||||||||
2018 | 5,265 | 5,000 | 60,938 | 40,625 | 111,828 | ||||||||||||||
2019 | 619 | 5,000 | 60,938 | 40,625 | 107,182 | ||||||||||||||
2020 | — | 5,000 | 60,938 | 40,625 | 106,563 | ||||||||||||||
2021 | — | 5,000 | 60,938 | 40,625 | 106,563 | ||||||||||||||
Thereafter | — | — | 1,411,250 | 1,884,766 | 3,296,016 | ||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 36,830 | $ | 25,000 | $ | 1,715,940 | $ | 2,095,610 | $ | 3,873,380 | |||||||||
The amounts in the table above exclude $212.0 million of income tax related uncertain tax positions, as the Company is unable to reasonably estimate the ultimate amount or time of settlement of those liabilities.
Verisign enters into certain purchase obligations with various vendors. The Company’s significant purchase obligations include firm commitments with telecommunication carriers and other service providers. The Company does not have any significant purchase obligations beyond 2019.
The Company has an agreement with Internet Corporation for Assigned Name and Numbers (“ICANN”) to be the sole registry operator for domain names in the .com registry through November 30, 2024. Under this agreement, the Company pays ICANN on a quarterly basis, $0.25 for each annual increment of a domain name registered or renewed during such quarter. As of December 31, 2016, there were 126.9 million domain names in the .com registry. However, the number of domain names registered and renewed each quarter may vary significantly. The Company incurred registry fees for the .com registry of $31.5 million in 2016, $30.9 million in 2015, and $28.4 million in 2014. Registry fees for other top-level domains that we operate have been excluded from the table above because the amounts are variable or passed through to registrars.
The Company has an agreement with the Government of Tuvalu to be the sole registry operator for .tv domain names through December 31, 2021. Registry fees were $5.0 million in 2016 and 2015, and $4.5 million in 2014.
Verisign leases a small portion of its facilities under operating leases that extend into 2020. Rental expenses under operating leases were not material in any period presented. Future rental expenses under existing operating leases are not material.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company did not have any relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, such as entities often referred to as structured finance or special purpose entities, which would have been established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements or other contractually narrow or limited purposes. As such, the Company is not exposed to any financing, liquidity, market or credit risk that could arise if the Company had engaged in such relationships.
It is not the Company’s business practice to enter into off-balance sheet arrangements. However, in the normal course of business, the Company does enter into contracts in which it makes representations and warranties that guarantee the performance of the Company’s products and services. Historically, there have been no significant losses related to such guarantees.
73
ITEM 16. | 10-K SUMMARY |
None.
74
