Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.1 - eWELLNESS HEALTHCARE Corp | ex31-1.htm |
| EX-32.2 - eWELLNESS HEALTHCARE Corp | ex32-2.htm |
| EX-31.2 - eWELLNESS HEALTHCARE Corp | ex31-2.htm |
| EX-32.1 - eWELLNESS HEALTHCARE Corp | ex32-1.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
[X] ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015
[ ] TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
Commission file number 333-181440

eWellness Healthcare Corporation
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Nevada | 90-1073143 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of | (I.R.S. Employer | |
| incorporation or organization) | Identification No.) |
| 11825 Major Street, Culver City, California | 90230 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
(310) 915-6100
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Copies of Communications to:
Louis Taubman, Esq.
Hunter Taubman Fischer
1450 Broadway, Suite 26
New York, NY 10018
(917) 512-0827
Fax (212) 202-6380
Securities registered under Section 12(b) of the Act: None
Securities registered under Section 12(g) of the Act: Common Stock, $0.001 par value
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes [ ] No [X]
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes [ ] No [X]
Indicate by check mark whether the issuer (1) filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes [X] No [ ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
Yes [X] No [ ]
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. [X]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer [ ] | Accelerated filer [ ] |
| Non-accelerated filer [ ] (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company [X] |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act).
Yes [ ] No [X]
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was sold, or the average bid and asked prices of such common equity, as of the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter is $1,688,100.
The number of shares of Common Stock, $0.001 par value, outstanding on March 28, 2016 is 18,847,770 shares.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
None
eWellness Healthcare Corporation
Form 10-K
For the Year Ended December 31, 2015
Table of Contents
| 2 |

THE FIRST PHYSICAL THERAPY TELEMEDICINE COMPANY TO OFFER INSURANCE REIMBURSEABLE REAL-TIME DISTANCE MONITORED TREATMENTS

| 3 |
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This document contains “forward-looking statements”. All statements other than statements of historical fact are “forward-looking statements” for purposes of federal and state securities laws, including, but not limited to, any projections of earnings, revenue or other financial items; any statements of the plans, strategies and objections of management for future operations; any statements concerning proposed new services or developments; any statements regarding future economic conditions or performance; any statements of belief; and any statements of assumptions underlying any of the foregoing.
Forward-looking statements may include the words “may,” “could,” “estimate,” “intend,” “continue,” “believe,” “expect” or “anticipate” or other similar words. These forward-looking statements present our estimates and assumptions only as of the date of this report. Accordingly, readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the dates on which they are made.
Throughout this Annual Report references to “we”, “our”, “us”, “eWellness”, “the Company”, and similar terms refer to eWellness Healthcare Corporation and its wholly owned subsidiary.
eWellness was incorporated in Nevada in May 2013. Following a share exchange we completed in April 2014, pursuant to which eWellness Corporation, a Nevada corporation became our wholly owned subsidiary, we abandoned our prior business plan and we are now pursuing eWellness Corporation’s historical businesses and proposed businesses.
The Company and Nature of Business
Our business model is to license our PHZIO (“PHZIO”) platform to any physical therapy (“PT”) clinic in the U.S. and or have large-scale employers use our PHZIO platform as a fully PT monitored corporate wellness program.
The Company’s initial licensee is Evolution Physical Therapy (“EPT”), which is owned by our CEO, Darwin Fogt, MPT. All treatment revenue for 2015 was reimbursed to EPT, but was not sufficient to generate sales for the Company. The Company is in the process of developing marketing channel partnerships with industry association members, existing software-based telemedicine providers and physical therapy billing and practice management providers. These partnerships, if completed, are anticipated to begin adding third party PT licensee revenue during the second quarter of 2016.
The Company’s PHZIO home physical therapy exercise platform has been designed to disrupt the $30 billion physical therapy and the $8 billion corporate wellness industries. PHZIO re-defines the way physical therapy can be delivered. PHZIO is the first real-time remote monitored 1-to-many physical therapy platform for home use. Due to the real-time patient monitoring feature, the PHZIO platform is insurance reimbursable by payers such as: Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield.
The PHZIO Solution: A New Physical Therapy Delivery System
| ● | SaaS technology platform solution for providers bundling rehabilitation services and employer wellness programs; | |
| ● | First real-time remote monitored 1-to-many physical therapy treatment platform for home use; | |
| ● | Ability for physical therapists to observe multiple patients simultaneously in real-time; | |
| ● | Solves what has been a structural problem and limitation in post-acute care practice growth. | |
| ● | PT practices can experiencing 20% higher adherence & compliance rates versus industry standards; and | |
| ● | Tracking to 30% increase in net income for a PT practice. |
| 4 |
PHZIO Treatment Session
The image below illustrates a typical PHZIO treatment session from a patient’s point of view. There is communication between patients and PT conducted via text / video messaging. The patient is also able to examine her form during the exercise sessions. The monitoring PT is remotely monitoring his patient real-time from his office.

Patient program adherence in 2015 was nearly 85 percent due the real-time patient monitoring and the at-home use of the platform. Now physical therapy practices have a way to scale profitably using a technology platform that can help them grow beyond the limits of the typical brick and mortar PT clinic.
Additional Treatment Protocols: The Company’s initial PHZIO application is a 6-month exercise program for patients with back, knee or hip pain. The next two platforms are anticipated to be released in the second quarter of 2016 include a total knee and hip replacement exercise program. These hip and knee programs have been designed to be integrated into any hospital or medical group's Medicare CMS bundled payment model for post-acute care physical therapy. These two programs are anticipated to be followed by woman's health and geriatric programs by the end of the third quarter of 2016.
Our PHZIO platform enables employees or patients to engage with live or on-demand video based physical therapy telemedicine treatments from their home or office. Following a physicians exam and prescription for physical therapy to treat back, knee or hip pain, a patient can be examined by a physical therapist and if found appropriate inducted in the Company’s PHZIO program that includes a progressive 6-month telemedicine exercise program (including monthly in-clinic check ups). All PHZIO treatments are monitored by a licensed therapist that sees everything the patient is doing while providing their professional guidance and feedback in real-time. This ensures treatment compliance by the patient, maintains the safety and integrity of the prescribed exercises, tracks patient metrics and captures pre and post treatment evaluation data. PHZIO unlocks a host of potential for revolutionizing patient treatment models and directly links back to the established brick and mortar physical therapy clinic. This unique model enables any physical therapy practice to be able to execute more patient care while utilizing their same resources, and creates more value than was ever before possible.
During 2015 our PHZIO platform achieved the following metrics:
| ● | The total (insurance reimbursed) monitored PHZIO visits in 2015: 699 patient visits (239 paid patient visits total). | |
| ● | The average insurance reimbursement per PHZIO session in 2015: $46.87 (excluding co-payments). | |
| ● | The top line wellness goals of our PHZIO program are to graduate at least 80% of inducted patients through our 6-month program. Patients should expect to experience an average of a 20% reduction in BMI, a 4-inch reduction in waist size, weight loss of at least 20 pounds, significant overall improvement in balance, coordination, flexibility, strength, and lumbopelvic stability. Patients also should scored better on Functional Outcomes Scales (Oswestry and LEFS), which indicates improved functional activity levels due to reduced low back, knee and hip pain. |
| 5 |
Our PHZIO platform, including: design, testing, exercise intervention, follow-up, and exercise demonstration, has been developed by accomplished Los Angeles based physical therapist Darwin Fogt. Mr. Fogt has extensive experience and education working with diverse populations from professional athletes to morbidly obese. He understands the most beneficial exercise prescription to achieve optimal results and has had great success in motivating all patient types to stay consistent in working toward their goals. Additionally, his methods have proven effective and safe as he demonstrates exercises with attention to proper form to avoid injury. Mr. Fogt has established himself as a national leader in his field and has successfully implemented progressive solutions to delivering physical therapy: he has consulted with and been published by numerous national publications including Runner’s World, Men’s Health, Men’s Journal, and various Physical Therapy specific magazines; his 13 plus years of experience include rehabilitating the general population, as well as professional athletes, Olympic gold medalists, and celebrities. He has bridged the gap between physical therapy and fitness by opening Evolution Fitness, which uses licensed physical therapists to teach high intensity circuit training fitness classes. He also founded one of the first exclusive prenatal and postnatal physical therapy clinic in the country. Mr. Fogt is a leader in advancing the profession to incorporate research-based methods and focus on, not only rehabilitation but also wellness, functional fitness, performance, and prevention. He is able to recognize that the national healthcare structure (federal and private insurance) is moving toward a model of prevention and that the physical therapy profession will take a larger role in providing wellness services to patients.
Innovators in other industries have solved access, cost and quality inefficiencies through the implementation of technology platforms and business models that deliver products and services on-demand and create new economies by connecting and empowering both consumers and businesses. We have taken the same approach to solving the pervasive access, cost and quality challenges facing the current access to physical therapy clinics.
Our underlying technology platform is complex, deeply integrated and purpose-built over the three years for the evolving physical therapy marketplace. Our PHZIO platform is highly scalable and can support substantial growth of third party licensees. Our PHZIO platform provides for broad interconnectivity between PT practitioners and their patients and, we believe, uniquely positions us as a focal point in the rapidly evolving PT industry to introduce innovative, technology-based solutions, such as remote patient monitoring, post-discharge treatment plan adherence and in-home care.
We plan to generate revenue from third-party PT and corporate wellness licensees on a contractually recurring per PHZIO session fee basis. Our PHZIO platform is anticipated to transform the access, cost and quality dynamics of physical therapy delivery for all of the market participants. We further believe any patient, employer, health plan or healthcare professional interested in a better approach to physical therapy is a potential PHZIO platform user.
Backround on our PHZIO Technology
We have our CTO, Curtis Hollister and 3 program developers and 1 content manager that support of the PHZIO system and all four team members are located in Ottawa Canada. The below noted chart contains information on our PHZIO System.
| 6 |
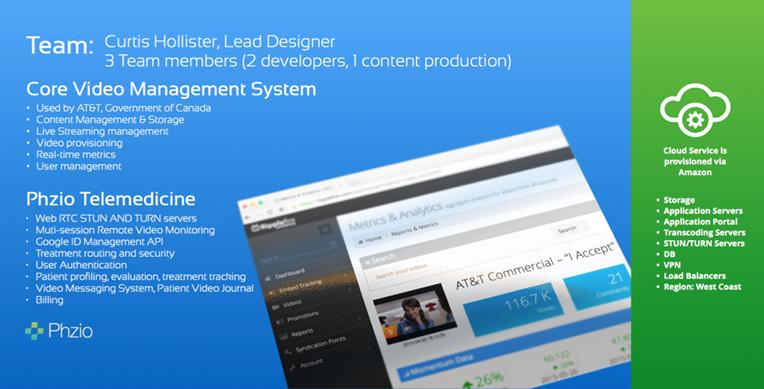
IP and Licensing
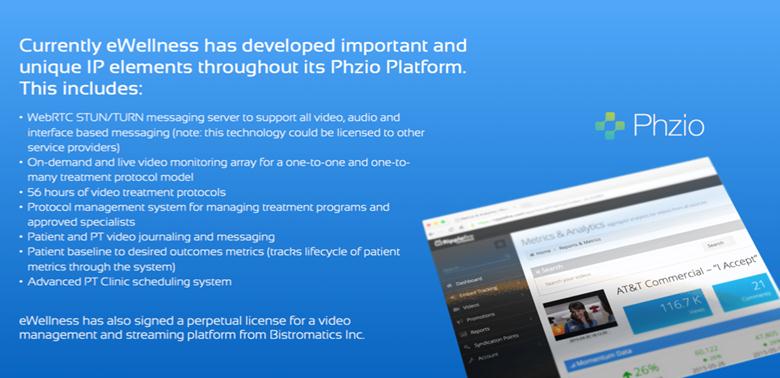
We have licensed our telemedicine platform from Bistromatics Inc. a company owned by our CTO, Curtis Hollister, for perpetuity for any telemedicine application in any market worldwide. The below noted chart highlights what we have built to date.
| 7 |
Our History
We entered into a share exchange agreement (the “Initial Exchange Agreement”) pursuant to which we agreed to issue, 9,200,000 shares of our unregistered common stock, $.001 par value (the “common stock”) to the shareholders of eWellness Corporation, a Nevada corporation (“eWellness” or “Private Co.”). In addition, our former chief executive officer agreed to tender 5,000,000 shares of common stock back to the Company for cancellation and also to assign from his holdings an additional 2,500,000 shares to the shareholders of eWellness Corporation resulting in a total of 11,700,000 shares owned by those shareholders, as well as a further assignment of an additional 2,100,000 shares to other parties as stated therein. There were no warrants, options or other equity instruments issued in connection with the share exchange agreement.
The closing of the Initial Exchange Agreement was conditioned upon certain, limited customary representations and warranties, as well as, among other things, our compliance with Rule 419 (“Rule 419”) of Regulation C under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended and the consent of our shareholders as required under Rule 419. However, Rule 419 required that the share exchange transaction (the “Share Exchange”) contemplated by the Initial Exchange Agreement occur on or before March 18, 2014. Accordingly, after numerous discussions with management and eWellness, the parties entered into an Amended and Restated Share Exchange Agreement (the “Share Exchange Agreement”) to reflect a revised business combination structure, pursuant to which we would: (i) file a registration statement on Form 8-A (“Form 8A”) to register our common stock pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Exchange Act, which we did on May 1, 2014 and (ii) seek to convert the participants of the 419 transaction into participants of a similarly termed private offering (the “Converted Offering”). We also agreed to change our name to eWellness Healthcare Corporation to more accurately reflect our new business and operations after the Share Exchange, which occurred and was effective as of April 25, 2014.
As the parties satisfied all of the closing conditions, on April 30, 2014, pursuant to the terms of the Share Exchange Agreement, we purchased 100% of eWellness’ common stock in exchange for 9,200,000 shares of our then outstanding shares of common stock and the share exchange closed. As a result, eWellness became our wholly owned subsidiary and its shareholders owned approximately 76.97% of our then issued and outstanding common stock, after giving effect to the cancellation of 5,000,000 shares of our common stock held by Andreas A. McRobbie-Johnson, our former chief executive officer and the further assignment of his shares of common stock as described therein.
On July 22, 2015, our wholly owned subsidiary, eWellness Corporation, was merged into the Company and, therefore, no longer exists as a separate entity.
Recent Developments
● On April 1, 2015, we entered into an Operating Agreement with Evolution Physical Therapy , a company owned by our CEO, wherein it is agreed that EPT would be able to operate our PHZIO telemedicine platform and offer it to selected physical therapy patients of EPT. The Company is to receive 75% of the net insurance reimbursements from the patient for use of the platform. The Company will advance capital requested by EPT for costs specifically associated with operating the www.phzio,com platform and associated physical therapy treatments – computer equipment, office or facilities rental payments, physical therapist or physical therapy assistant, administrative staff, patient induction equipment, office supplies, utilities and other associated operating costs. It is anticipated that the operation of the platform by EPT will generate positive cash flow within 90 days from the start of patient induction. On May 7, 2015, EPT inducted the first patient using our platform. All treatment revenue of approximately $13,500 for 2015 was reimbursed to EPT, but was not sufficient to generate sales for the Company. The total (insurance reimbursed) monitored PHZIO visits in 2015: 699 patient visits (267 paid patient visits total). The average insurance reimbursement per PHZIO session in 2015: $51.26 (excluding co-payments). The top line wellness goals of our PHZIO program are to graduate at least 80% of inducted patients through our 6-month program. Patients should expect to experience an average of a 20% reduction in BMI, a 4-inch reduction in waist size, weight loss of at least 20 pounds, significant overall improvement in balance, coordination, flexibility, strength, and lumbopelvic stability. Patients also should score better on Functional Outcomes Scales (Oswestry and LEFS), which indicates improved functional activity levels due to reduced low back, knee and hip pain.
| 8 |
On April 17, 2015, we entered into an agreement with Akash Bajaj, M.D., M.P.H. The agreement is for Dr. Bajaj to serve as a consultant and as the Chairman of the Company’s Clinical Advisory Board. The term of the agreement is for one year with annual renewal as desired. The agreement further sets the hourly rate to be paid at $225 per hour with payment to be at the end of each month. Further, the Company granted Dr. Bajaj a five-year non-statutory option to purchase 100,000 shares of common stock at a price of $.35 per share. The options will vest over a 12 month period at 8,333 per month.
The Physical Therapy Telemedicine Space
One of the most promising and rapidly developing areas of healthcare and rehabilitation is telemedicine – the use of telecommunication technologies to provide health information, assessment, monitoring, and treatment to individuals with chronic conditions from a distance. Increasingly, insurers, healthcare providers, and technology vendors are using telemedicine solutions and services to make medical intervention both more convenient and accessible to patients to raise the quality of care while reducing costs. (Herrick 2007).
Low back pain is second only to upper respiratory problems as a symptom-related reason for visits to a physician. (Andersson 1999 Hart 1995). By 2023, the estimated cost of chronic conditions including low back pain and diabetes including treatment and lost productivity will swell to $4.2 trillion annually. (Deyo 2001). Home-based telemedicine holds promise as an effective method for providing physical therapy exercise programs to these segments of our populations including people with back, hip and knee pain and for those individuals who may be pre-diabetic and/or are obese.
Physical therapy intervention including core muscle strengthening exercise along with lumbar flexibility and gluteus maximus strengthening is an effective rehabilitation technique for all chronic low back pain patients irrespective of different duration (less than one year and more than one year) of their pain. (Kumar 2014). It has also been widely proven that strengthening and aerobic exercises are effective at reducing symptoms and preventing knee pain among patients with osteoarthritis and other painful knee conditions. (Senanik 2012).
Physical therapy intervention is becoming an increasingly accepted mode of intervention delivery and policy recommendations have been made to State Boards of Physical Therapy. (Julian 2014). The PHZIO platform complies and exceeds the recommendations for physical therapy intervention delivered via telemedicine.
The PHZIO platform eliminates the barrier of transportation, offers participants the flexibility of exercising at their preferred time of day, and does not involve as much energy or time necessary to get to an exercise or fitness facility.
Traditionally, physical therapy exercise programs are based upon exercise and education provisioned by physical therapist to patients at a brick and mortar facility using a face-to-face model of care. Over the past three years, we have conceptualized, designed, engineered, tested and deployed our PHZIO platform.
Our PHZIO Platform
Our current PHZIO 6-month 78 session 40-minute on-line distance monitored telemedicine exercise program is a physician prescribed (insurance reimbursable) physical therapy exercise program designed around an exercise kit that includes: an inflatable exercise ball, latex resistance bands, a yoga mat and stretch strap that provides a comprehensive exercise regimen that minimizes stress on the joints while allowing for hundreds of progressive exercises that focus on strength, balance, cardiovascular conditioning, coordination and flexibility.
| ● | Our PHZIO platform is an on-line distance monitored telemedicine exercise program with a 6-month duration, wherein seventy-eight (78) individual 40-minute progressive exercise sessions are watched & interacted with by a patient on their laptop computer. | |
| ● | The patients are inducted into the PHZIO program through a physician prescription and physical therapist evaluation. The PHZIO physical therapy program is designed around an exercise kit that includes: an inflatable exercise ball, latex resistance bands, a yoga mat and stretch strap. |
| 9 |
| ● | The patient follows the PHZIO instructions and performs the specific exercises while being remotely monitored by a physical therapist through the camera located on the laptop computer. The PHZIO program provides a comprehensive exercise regimen that minimizes stress on the joints while allowing for hundreds of progressive exercises that focuses on strength, balance, coordination, and flexibility. | |
| ● | The PHZIO program is designed to be operated in a patient’s home or office in order to increase compliance and eliminate transportation to a fitness center or gym. | |
| ● | Our physical therapists monitor up to 30 patients at a time while these patients are on-line and following along with our PHZIO exercise program. Each patient and physical therapist has real-time text and video conferencing capability when interaction is needed between the patient and our physical therapist. |
When patients are referred to eWellness licensee, a physical therapist and assistant will evaluate patients for the program. The goal is to ensure compliance with the regimen, reduce BMI to a healthy number, help patients lose weight and boost their activity level for the six-month program.
Patients can access a series of progressively difficult workouts in 40- to 45-minute videos from home. They use a unique log-in from an application, which will securely store all their data over a six-month period. When patients log on, it triggers a camera in the physical therapists’ remote office.
Physical therapists will monitor patients to ensure compliance. A remote physical therapist watches in real time while the patient is performing the exercises and guides him through his exercise sessions. The therapist provides constant feedback, instruction and motivation and ensures patients are doing the exercises properly and safely. The supervising therapist can speak to the user or communicate through text message.
Competition
We have identified multiple privately-held telemedicine and exercise platform companies that utilize Avatar/Kinect-based telerehb platforms incuding: Reflexion Health, RespondWell, Physmodo, Jintronx, MotionCare 360 and Five Plus. Additionally, we have identified other video-based physical therapy solutions such as: Bluejay, PT Pal, VitalRock, Physiotech, SimplyTherapy and YouTube. Yet, none of these companies have real-time PT monitoring, one-to-many platform, treatments reimbursable by payors and strong program compliance and adherence by patients.
The PZHIO.COM Exercise Program
A Monitored In-office & Telemedicine Exercise Program: Our 6-month PHZIO exercise program has been designed to provide patients, who are accepted into the program, with traditional one-on-one PT evaluations, re-evaluations (every one to four weeks throughout the PHZIO program depending on type of insurance), and at the conclusion of the program a Physical Performance Test. These PTs are known as Induction & Evaluation Physical Therapists (“IEPTs”). All patient medical data, information and records are retained in the files of the IEPT. The IEPT will also evaluate the progress of the patient’s participation in our PHZIO program.
| ● | Physician Diagnosis: Following a physician’s diagnosis of a patient with non-acute back pain, who is also likely overweight and pre-diabetic, a physician may prescribe the patient to participate in the eWellness PHZIO exercise program. | |
| ● | Enrollment Process: The accepted patients are assessed by a PT, located at a PT Licensee clinic and then enrolled in our PHZIO program by going online to our PHZIO program virtual private network (“VPN”) and creating a login name and password. The patient will then populate their calendar with planned times when they anticipate exercising. They will also be provided with a free exercise ball, resistance stretch bands, stretch strap and yoga mat at induction. |
| 10 |
| ● | Exercising Begins: The day after the patient receives the equipment, the patient will log on to our VPN at least 3 times per week, to watch and follow the prescribed 40 minute on-line exercise program. The PHZIO platform also allows two-way communication (videoconferencing) with one of our licensee’s On-line Physical Therapists (“OLPT’s”), who is responsible for monitoring on-line patients. The OLPT’s are also available to answer patient’s questions. When available the patients exercise sessions are recorded and stored in our system as proof that they completed the prescribed exercises. There are 78 various 40-minute exercise videos that are viewed by our patients in successive order. | |
| ● | Open 6am-9:30am 5 days per week: Our PHZIO system has a calendar function so that patients can schedule when they will login to our PHZIO system. This calendar enables a PT Licensee to better spread the load of patients participating in any forty-minute on-line exercise program during our 15 hours of weekly operations, 6am through 9:30am Monday through Friday. Also, if the patient is not on-line at the planned exercise time, our system can send them an automated reminder, via text, voicemail and or e-mail messaging. |
Trackable Physical Therapy. The exercise PHZIO prescription and instruction will be delivered with a series of on-line videos easily accessed by each patient on the internet. Each video will be 40 minutes in length with exercises, which will specifically address the common impairments associated with diabetes and/or obesity. Exercise programs will be able to be performed within each patient’s own home or work location without requiring standard gym equipment. Each patient will be required to log in to the system with will monitor performance automatically in order to ensure their compliance. Each patient will be required to follow up with their referring physician and PT at designated intervals and metrics such as blood pressure, blood sugars, BMI, etc. will be recorded to ensure success of the program.
Patient Program Goals. On average each patient is targeted to lose 2 pounds per week, totaling up to 48 pounds over the duration of the program to progress toward healthier defined BMI, reduction body fat percentage by at least 8%, reduced reliance on medication for blood glucose regulation and dosage or frequency and a goal of at least a 50% adherence to continuing the PHZIO program independently at conclusion of program.
Trackable Video Exercise Program. The On-Line PHZIO video content includes all aspects of wellness preventative care to ensure the best results: cardiovascular training, resistance training, flexibility, and balance and stabilization; research studies on all such distinct impairments have shown to provide effective treatment results. Each video integrates each of the four components to guarantee a comprehensive approach to the wellness program, but each video will specifically highlight one of the four components. All of our PHZIO video content can be viewed on all desktops, tablets, PC’s and MAC computers.
Specific Video Programs. Each patient will receive a prescription for six months (26 week) of physical therapy and exercise that is provided by viewing on-line programs produced by eWellness where the patient can do these exercises and stretching on their own at least 3 days per week for at least 40 minutes. The PHZIO videos can be watched on a laptop or desktop computer. In order to view the videos the patient would log onto the eWellness web-site and would be directed to watch the appropriate video in sequence. As the patient is logged-in, eWellness will be able to monitor how often and if the entire video session was viewed. This data would be captured and sent weekly to the prescribing physician and eWellness PT for review. At all times, a licensed OLPT/PTA will have access to each patient utilizing the videos and will be able to communicate with a patient via video-conferencing and/or instant messaging. This will help improve adherence to the program as well as the success and safety of the patients’ treatments. A patient will also be instructed to walk or ride a bike at least 30 minutes three days per week in addition to participating in our program.
If the patient is not viewing the videos, then the prescribing physician and/or the eWellness PT would reach out to the patient by telephone and/or e-mail to encourage the patient to keep up their physical fitness regime. After each series the patient returns for an office visit to the prescribing physician for blood tests, blood pressure and a weight management check- up as well as a follow-up visit with the PT for assessment of the patient’s progress toward established goals.
Exercise Patient Kits. Each patient will receive a home exercise tool kit, which will include: an inflatable exercise ball, a hand pump, a yoga mat, a yoga strap, and varying levels of resistance bands, free of any additional charges. Each of the PHZIO exercise videos will include exercises that incorporate the items in the tool kit. By using a bare minimum of equipment, patients should be able to participate more easily at home or at their workplace. Our estimated cost of the kit is $49, which we pay and factored in to our revenue stream and internal projections.
| 11 |
Our Cloud-based PHZIO System Design. Our CTO, Curtis Hollister, is currently a principal shareholder and operator of two video content platform based businesses in Ottawa Canada that have built and own the intellectual property for various global corporate and governmental projects having similar requirements as ours. Not only will Mr. Hollister’s experience stand to significantly shorten our path to service activation of our own program, but his industry contacts will provide immediate access to valuable resources. Because of this access, initially all system maintenance, updates and upgrades of our PHZIO platform will be made by Mr. Hollister as our Chief Technology Officer and a readily available team of independent freelance consultants in Ottawa. Additionally, through his ownership in these video content platform businesses, the Company was able to enter into an agreement with one of them to secure the rights to intellectual property completing approximately 100% of the Company’s systems requirements at a total cost of $20,000. Our platform was built based on the Zendesk® highly-scalable customer service application platform. Currently, all system maintenance, updates and upgrades will be made by Mr. Hollister’s team in Ottawa.
Insurance/Reimbursement
Thus far in the state of California our initial licensee has successfully gained reimbursement from Blue Cross, Blue Shield and CIGNA insurance companies. The licensee receiver reimbursements that are equivalent to in-clinic patient reimbursements. For PT licensee patients whose insurance companies provide little or no reimbursement for Physical Therapy Telemedicine Reimbursement, they may have higher co-payments for participating in the PHZIO program or be responsible to pay the full cost of such services.
Expansion into other markets where telemedicine has high support. On December 20th 2013, we executed a 25-year licensing agreement with a London, Ontario based telemedicine company Physical Relief Telemedicine Health Care Services (“PRTHCS”), pursuant to which we granted PRTHCS a limited, transferable right to use and promote our PHZIO Program within the province of Ontario; additional Canadian territories may be added at the parties mutual discretion. PRTHCS has a known track-record in the telemedicine industry in Canada. To date PRTHCS has been unsuccessful in licensing our PHZIO platform to any Canadian based PT clinics.
Our Planned Expansion into other States where Telemedicine has high support. The most common path being taken by states is to cover telemedicine services in their Medicaid program. 42 states now provide some form of Medicaid reimbursement for telemedicine services (mostly physician to physician consultations). More importantly 16 states have now expanded their definition of telemedicine to include physical therapy and have also required that state and private insurance plans cover telemedicine services. Those 16 states with the broadest telemedicine policies include: Alaska, Georgia, Hawaii, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Oregon, Texas, Virginia and Vermont.
Company Development Costs As of the date of this Report, we have spent approximately 28 months developing our unique business model and our design for eWellness’s automated website and systems for our PHZIO program. Over the course of the 28-month development phase we expended approximately $2,057,611 in travel expenses, legal, consulting services and miscellaneous expenses.
Initial Program Patient Inclusion Criteria
While eWellness hopes to be able to provide assistance to as many people as possible, we do have some requirements for entrance into our program. Each individual must be:
| ● | Cleared for cardiovascular exercise. | |
| ● | Covered by private health insurance or federal or state insurance and/or pay the partial or full monthly program fee themselves. | |
| ● | Experiencing some level of back pain and be overweight. |
| 12 |
| ● | Screened and identified as pre-diabetic or early-stage Type II (NIDDM) diabetes. | |
| ● | Capable of accessing a smart phone or computer with internet access. | |
| ● | Experiencing no neuropathy. |
Intellectual Property
With adequate funding, we anticipate the development of various Application and Pioneering Methods patent protect and Trademark protection associated with our technology platform and unique physical therapy treatments.
REGULATIONS AND HEALTHCARE REFORM
Numerous federal, state and local regulations regulate healthcare services and those who provide them. Some states into which we may expand have laws requiring facilities employing health professionals and providing health-related services to be licensed and, in some cases, to obtain a certificate of need (that is, demonstrating to a state regulatory authority the need for, and financial feasibility of, new facilities or the commencement of new healthcare services). Only one of the states in which we intend to roll out our services requires a certificate of need for the operation of our physical therapy business functions. Our therapists however, are required to be licensed, as determined by the state in which they provide services. Failure to obtain or maintain any required certificates, approvals or licenses could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
State Legislation
Insurance reimbursement for our PHZIO services is likely to improve in 2016 and beyond based upon current draft legislation in Congress that seeks to significantly expand Medicare’s reimbursement for telemedicine services including for physical therapy. If passed, this legislation would drive private healthcare insurers to also reimburse for physical therapy associated with telemedicine. Also, in early November 2014, we were advised by the California State Board of Physical Therapy (“CSBPT”) that we could operate our PHZIO platform and bill patients insurance within the Association’s rules in the state of California.
Stark Law
Provisions of the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1993 (42 U.S.C. § 1395nn) (the “Stark Law”) prohibit referrals by a physician of “designated health services” which are payable, in whole or in part, by Medicare or Medicaid, to an entity in which the physician or the physician’s immediate family member has an investment interest or other financial relationship, subject to several exceptions. Unlike the Fraud and Abuse Law, the Stark Law is a strict liability statute. Proof of intent to violate the Stark Law is not required. Physical therapy services are among the “designated health services”. Further, the Stark Law has application to the Company’s management contracts with individual physicians and physician groups, as well as, any other financial relationship between us and referring physicians, including any financial transaction resulting from a clinic acquisition. The Stark Law also prohibits billing for services rendered pursuant to a prohibited referral. Several states have enacted laws similar to the Stark Law. These state laws may cover all (not just Medicare and Medicaid) patients. Many federal healthcare reform proposals in the past few years have attempted to expand the Stark Law to cover all patients as well. As with the Fraud and Abuse Law, we consider the Stark Law in planning our clinics, marketing and other activities, and believe that our operations are in compliance with the Stark Law. If we violate the Stark Law, our financial results and operations could be adversely affected. Penalties for violations include denial of payment for the services, significant civil monetary penalties, and exclusion from the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
| 13 |
HIPAA
In an effort to further combat healthcare fraud and protect patient confidentially, Congress included several anti-fraud measures in the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (“HIPAA”). HIPAA created a source of funding for fraud control to coordinate federal, state and local healthcare law enforcement programs, conduct investigations, provide guidance to the healthcare industry concerning fraudulent healthcare practices, and establish a national data bank to receive and report final adverse actions. HIPAA also criminalized certain forms of health fraud against all public and private insurers. Additionally, HIPAA mandates the adoption of standards regarding the exchange of healthcare information in an effort to ensure the privacy and electronic security of patient information and standards relating to the privacy of health information. Sanctions for failing to comply with HIPAA include criminal penalties and civil sanctions. In February of 2009, the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (“ARRA”) was signed into law. Title XIII of ARRA, the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (“HITECH”), provided for substantial Medicare and Medicaid incentives for providers to adopt electronic health records (“EHRs”) and grants for the development of health information exchange (“HIE”). Recognizing that HIE and EHR systems will not be implemented unless the public can be assured that the privacy and security of patient information in such systems is protected, HITECH also significantly expanded the scope of the privacy and security requirements under HIPAA. Most notable are the new mandatory breach notification requirements and a heightened enforcement scheme that includes increased penalties, and which now apply to business associates as well as to covered entities. In addition to HIPAA, a number of states have adopted laws and/or regulations applicable in the use and disclosure of individually identifiable health information that can be more stringent than comparable provisions under HIPAA.
We believe that our current business operations are fully compliant with applicable standards for privacy and security of protected healthcare information. We cannot predict what negative effect, if any, HIPAA/HITECH or any applicable state law or regulation will have on our business.
Other Regulatory Factors
Political, economic and regulatory influences are fundamentally changing the healthcare industry in the United States. Congress, state legislatures and the private sector continue to review and assess alternative healthcare delivery and payment systems. Based upon newly finalized FDA rules, we believe that our PHZIO platform is exempt from Federal Drug Administration (“FDA”) regulation. Yet, in the unlikely event that these rules change in the future, the FDA could then require us to seek 510K approvals for our on-line services that could create delays in provisioning our PHZIO services. (See FDA ruling noted below) Also, potential alternative approaches could include mandated basic healthcare benefits, controls on healthcare spending through limitations on the growth of private health insurance premiums, the creation of large insurance purchasing groups, and price controls. Legislative debate is expected to continue in the future and market forces are expected to demand only modest increases or reduced costs. For instance, managed care entities are demanding lower reimbursement rates from healthcare providers and, in some cases, are requiring or encouraging providers to accept capitated payments that may not allow providers to cover their full costs or realize traditional levels of profitability. We cannot reasonably predict what impact the adoption of any federal or state healthcare reform measures or future private sector reform may have on our business.
FDA Ruling: Examples of Mobile App’s which it Intends to Exclude from Regulation
On September 25, 2013, the FDA issued Finalized Guidance of medical mobile applications (“Apps”). The FDA has issued a ruling on Apps that may meet the definition of a medical device, but they have determined that they will not exercise enforcement on these Apps. The Guidance contains an appendix that provides examples of mobile apps that MAY meet the definition of medical device but for which FDA intends to exercise enforcement discretion. These mobile apps may be intended for use in the diagnosis of disease or other conditions, or in the cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease. Even though these mobile apps may meet the definition of medical device, the FDA intends to exercise enforcement discretion for these mobile apps because they pose lower risk to the public. The FDA understands that there may be other unique and innovative mobile apps that may not be covered in this list that may also constitute healthcare related mobile apps. This list is not exhaustive; it is only intended to provide clarity and assistance in identifying the mobile apps that will not be subject to regulatory requirements at this time. Based on our understanding of the Guidance, although there can be no guarantee, we believe our PHZIO platform will not be subject to regulatory requirements at this time because such services seem to fall within the statutory examples.
| 14 |
Employees
As of December 31, 2015, we had 4 employees and various consultants. We utilize the services of consultants for safety testing, regulatory and legal compliance, and other services.
NOTES REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
The statements contained in this annual report are not purely historical are forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Exchange Act. These include statements about the Company’s expectations, beliefs, intentions or strategies for the future, which are indicated by words or phrases such as “anticipate,” “expect,” “intend,” “plan,” “will,” “the Company believes,” “management believes” and similar words or phrases. The forward-looking statements are based on the Company’s current expectations and are subject to certain risks, uncertainties and assumptions. The Company’s actual results could differ materially from results anticipated in these forward-looking statements. All forward-looking statements included in this document are based on information available to the Company on the date hereof, and the Company assumes no obligation to update any such forward-looking statements.
Investing in our securities involves a great deal of risk. Careful consideration should be made of the following factors as well as other information included in this Annual Report before deciding to purchase our common stock. Our business, financial condition or results of operations could be affected materially and adversely by any or all of these risks.
THE FOLLOWING MATTERS MAY HAVE A MATERIAL ADVERSE EFFECT ON OUR BUSINESS, FINANCIAL CONDITION, LIQUIDITY, RESULTS OF OPERATIONS OR PROSPECTS, FINANCIAL OR OTHERWISE. REFERENCE TO THIS CAUTIONARY STATEMENT IN THE CONTEXT OF A FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENT OR STATEMENTS SHALL BE DEEMED TO BE A STATEMENT THAT ANY ONE OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING FACTORS MAY CAUSE ACTUAL RESULTS TO DIFFER MATERIALLY FROM THOSE IN SUCH FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENT OR STATEMENTS.
Risks Related to our Financial Condition
If we fail to raise additional capital, our ability to implement our business model and strategy could be compromised.
We have limited capital resources and operations. To date, our operations have been funded entirely from the proceeds from equity and debt financings or loans from our management. While we have sufficient funds once the financing is completed to our launch our PHZIO platform in Los Angeles, if we take on any additional markets in the United States, we will likely require substantial additional capital in the near future to develop and market new products, services and technologies. We also hope to reach other markets through our “White Labeling” strategy, but that can not be guaranteed.
We are currently raising up to $2.5 million in new financing that we anticipate closing in the second quarter of 2016. We need at least $400,000 to launch our planned marketing program to the PT industry. Accordingly, if we do not receive such funds, we will likely be unable to carry out our business.. We may not be able to obtain additional financing on terms acceptable to us, or at all. Even if we obtain financing for our near term operations and product development, we may require additional capital beyond the near term. If we are unable to raise capital when needed, our business, financial condition and results of operations would be materially adversely affected, and we could be forced to reduce or discontinue our operations.
eWellness is an early stage company with a short operating history and a relatively new business model in an emerging and rapidly evolving market, which makes it difficult to evaluate its future prospects. eWellness is a pre-revenue, early stage entity and is subject to all of the risks inherent in a young business enterprise, such as, among other things, lack of market recognition and limited banking and financial relationships. As a result, we have little operating history to aid in assessing future prospects. We will encounter risks and difficulties as an early stage company in a new and rapidly evolving market. We may not be able to successfully address these risks and difficulties, which could materially harm our business and operating results.
| 15 |
We may be subject to liability for failure to comply with Rule 419 under the Securities Act.
Prior to our acquisition of eWellness Corporation, we did not technically comply with the requirements of Rule 419 under the Securities Act. If a consummated acquisition meeting the requirements of Rule 419 did not occur by a date 18 months after the September 14, 2012 effective date of the initial registration statement we filed, Rule 419(e)(2)(iv) requires a blank check company to return the funds held in the escrow account to all investors who participated in the offering within five (5) business days[1]. When we did not complete the Share Exchange by March 18, 2014, rather than physically return the funds, we gave the investors who participated in the financing that was initially conducted pursuant to Rule 419, the right to have their funds returned or use their funds to purchase the same shares in a private offering to be conducted pursuant to Rule 506(b) of the Securities Act; all of the investors directed us to use their respective funds for the private placement. Regardless, after various comments and discussions with the SEC’s staff within the division of corporate finance, it seems that such constructive compliance with Rule 419 is not permissible and we should have physically returned the investors’ funds when the Share Exchange was not completed by March 18, 2014. Consequently, the SEC may bring an enforcement action or commence litigation against us for failure to strictly comply with Rule 419. If any claims or actions were to be brought against us relating to our lack of compliance with Rule 419, we could be subject to penalties (including criminal penalties), required to pay fines, make damages payments or settlement payments. In addition, any claims or actions could force us to expend significant financial resources to defend ourselves, could divert the attention of our management from our core business and could harm our reputation.
Risks Related to our Products and Development of our Business
Our telemedicine platform is new and has only limited operation experience.
eWellness’ has developed and tested its unique telemedicine platform www.PHZIO that is a Distance Monitored Physical Therapy Program (“PHZIO program”) to pre-diabetic, cardiac and health challenged patients, through contracted physician practices and healthcare systems specifically designed to help prevent patients that are pre-diabetic from becoming diabetic.
Our success is currently dependent upon our ability to maintain and develop Mr. Fogt’s relationship with other physicians.
Now that we are using our PHZIO platform to generate our success, we are dependent upon our CEO’s ability to maintain his current relationship with other physicians and our collective ability to establish relationships with other physicians. If we cannot generate new relationships or current relationships do not translate into service contracts or license agreements for our PHZIO platform, we may not have alternative streams of revenue and therefore we may need to cease operations until such time as we find an alternative provider or forever.
We depend upon reimbursement by third-party payers.
Substantially all of our revenues are anticipated to be derived from private third-party PT clinics that gain their revenue to pay our licensing fees from insurance payers. Initiatives undertaken by industry and government to contain healthcare costs affect the profitability of our licensee clinics. These payers attempt to control healthcare costs by contracting with healthcare providers to obtain services on a discounted basis. We believe that this trend will continue and may limit reimbursement for healthcare services. If insurers or managed care companies from whom we receive substantial payments were to reduce the amounts paid for services, our profit margins may decline, or we may lose PT licensees if they choose not to renew our contracts with these insurers at lower rates. In addition, in certain geographical areas, our operations may be approved as providers by key health maintenance organizations and preferred provider plans; failure to obtain or maintain these approvals would adversely affect our financial results. Although we created a business plan that will enable us to achieve revenue based on current reimbursement policies, if our belief that the insurance industry is poised for change, to offer more reimbursement for the services we seek to provide is not realized, we may not achieve the success we predict and we may not be able to carry out all the plans we disclose herein related to telemedicine. Ultimately, a shift in thinking and a willingness to adapt to new physical therapy telemedicine services and reimbursement thereof by healthcare providers is needed for the successful integration of our PHZIO telemedicine platform in mainstream healthcare environments.
1Pursuant to Rule 419(b)(2)(vi), a blank check company is entitled to use 10% of the proceed/escrowed funds; therefore, if a return of funds is required, only 90% of the proceed/escrowed funds need be returned. Here, the Company received $100,000 proceeds and used $10,000 as per Rule 419(b)(2)(vi); therefore, only $90,000 was subject to possible return.
| 16 |
Dependence on Key Existing and Future Personnel
Our success will depend, to a large degree, upon the efforts and abilities of our officers and key management employees. The loss of the services of one or more of our key employees could have a material adverse effect on our operations. In addition, as our business model is implemented, we will need to recruit and retain additional management and key employees in virtually all phases of our operations. Key employees will require a strong background in our industry. We cannot assure that we will be able to successfully attract and retain key personnel.
Currently, our management’s participation in our business and operations is limited
To date, we have been unable to offer cash compensation to our officers due to our lack of revenue. Accordingly, each of the Company’s executive officers maintain jobs outside of their position at eWellness. Although each of our executive officers have made preparations to devote their efforts, on a full time basis, towards our objectives once we can afford executive compensation commensurate with that being paid in the marketplace, until such time, our officers will not devote their full time and attention to the operations of the Company. None of our officers have committed a specific portion of their time or an approximate number of hours per week in writing to the objectives of the company and no assurances can be given as to when we will be financially able to engage our officers on a full time basis and therefore, until such time, it is possible that the inability of such persons to devote their full time attention to the Company may result in delays in progress toward implementing our business plan.
We operate in a highly competitive industry
Although we are not aware of any other Distance Monitored Physical Therapy Telemedicine Program precisely like ours, and targeting our specific population, we shall encounter competition from local, regional or national entities, some of which have superior resources or other competitive advantages in the larger physical therapy space. Intense competition may adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations. We may also experience competition from companies in the wellness space. These competitors may be larger and more highly capitalized, with greater name recognition. We will compete with such companies on brand name, quality of services, level of expertise, advertising, product and service innovation and differentiation of product and services. As a result, our ability to secure significant market share may be impeded. Although we believe our PHZIO services will enable us to service more patients than traditional physical therapy providers, if these more established offices or providers start offering similar services to ours, their name recognition or experience may enable them to capture a greater market share.
Limited product testing and operations
We have built out the technology platform and video library necessary to execute our planned business strategy. Of course, there may be other factors that prevent us from successfully marketing a product including, but not limited to, our limited cash resources. Further, our proposed reimbursement plan and the eventual operating results could susceptible to varying interpretations by scientists, medical personnel, regulatory personnel, statisticians and others, which may delay, limit or prevent our executing our proposed business plan.
| 17 |
We face substantial competition, and others may discover, develop, acquire or commercialize products before or more successfully than we do
We operate in a highly competitive environment. Our products compete with other products or treatments for diseases for which our products may be indicated. Other healthcare companies have greater clinical, research, regulatory and marketing resources than us. In addition, some of our competitors may have technical or competitive advantages for the development of technologies and processes. These resources may make it difficult for us to compete with them to successfully discover, develop and market new products.
We depend upon the cultivation and maintenance of relationships with the physicians in our markets
Our success is dependent upon referrals from physicians in the communities that our PT Licensees will service and their ability to maintain good relations with these physicians and other referral sources. Physicians referring patients to their clinics are free to refer their patients to other therapy providers or to their own physician owned therapy practice. If our PT licensees are unable to successfully cultivate and maintain strong relationships with physicians and other referral sources, our business may decrease and our net operating revenues may decline.
We also depend upon our ability to recruit and retain experienced physical therapists
Our future revenue generation is dependent upon referrals from physicians in the communities our clinics serve, and our ability to maintain good relations with these physicians. Our PT licensees are the front line for generating these referrals and we are dependent on their talents and skills to successfully cultivate and maintain strong relationships with these physicians. If they cannot recruit and retain our base of experienced and clinically skilled therapists, our business may decrease and our net operating revenues may decline.
Our revenues may fluctuate due to weather
We anticipate having a significant number of PT licensees in locations in states that normally experience snow and ice during the winter months. Also, a significant number of our clinics may be located in states along the Gulf Coast and Atlantic Coast, which are subject to periodic winter storms, hurricanes and other severe storm systems. Periods of severe weather may cause physical damage to our facilities or prevent our staff or patients from traveling to our clinics, which may cause a decrease in our future net operating revenues.
Certain of our internal controls, particularly as they relate to billings and cash collections, are largely decentralized at our clinic locations
Our future PT licensees operations are largely decentralized and certain of our internal controls, particularly the processing of billings and cash collections, occur at the clinic level. Taken as a whole, we believe our future internal controls for these functions at our PT licensees clinical facilities will be adequate. Our controls for billing and collections largely depend on compliance with our written policies and procedures and separation of functions among clinic personnel. We also intend to maintain corporate level controls, including an audit compliance program, that are intended to mitigate and detect any potential deficiencies in internal controls at the clinic level. The effectiveness of these controls to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or the level of compliance with our policies and procedures deteriorates.
Risks Related to Regulation
Our products may be subject to product liability legal claims, which could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Certain of our products provide applications that relate to patient clinical information. Any failure by our products to provide accurate and timely information concerning patients, their medication, treatment and health status, generally, could result in claims against us which could materially and adversely impact our financial performance, industry reputation and ability to market new system sales. In addition, a court or government agency may take the position that our delivery of health information directly, including through licensed practitioners, or delivery of information by a third party site that a consumer accesses through our websites, exposes us to assertions of malpractice, other personal injury liability, or other liability for wrongful delivery/handling of healthcare services or erroneous health information. We anticipate that in the future we will maintain insurance to protect against claims associated with the use of our products as well as liability limitation language in our end-user license agreements, but there can be no assurance that our insurance coverage or contractual language would adequately cover any claim asserted against us. A successful claim brought against us in excess of or outside of our insurance coverage could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. Even unsuccessful claims could result in our expenditure of funds for litigation and management time and resources.
| 18 |
Certain healthcare professionals who use our Cloud-based products will directly enter health information about their patients including information that constitutes a record under applicable law that we may store on our computer systems. Numerous federal and state laws and regulations, the common law and contractual obligations, govern collection, dissemination, use and confidentiality of patient-identifiable health information, including:
| ● | state and federal privacy and confidentiality laws; | |
| ● | contracts with clients and partners; | |
| ● | state laws regulating healthcare professionals; | |
| ● | Medicaid laws; | |
| ● | the HIPAA and related rules proposed by the Health Care Financing Administration; and | |
| ● | Health Care Financing Administration standards for Internet transmission of health data. |
HIPAA establishes elements including, but not limited to, federal privacy and security standards for the use and protection of Protected Health Information. Any failure by us or by our personnel or partners to comply with applicable requirements may result in a material liability to us.
Although we have systems and policies in place for safeguarding Protected Health Information from unauthorized disclosure, these systems and policies may not preclude claims against us for alleged violations of applicable requirements. Also, third party sites and/or links that consumers may access through our web sites may not maintain adequate systems to safeguard this information, or may circumvent systems and policies we have put in place. In addition, future laws or changes in current laws may necessitate costly adaptations to our policies, procedures, or systems.
There can be no assurance that we will not be subject to product liability claims, that such claims will not result in liability in excess of our insurance coverage, that our insurance will cover such claims or that appropriate insurance will continue to be available to us in the future at commercially reasonable rates. Such product liability claims could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
There is significant uncertainty in the healthcare industry in which we operate, and we are subject to the possibility of changing government regulation, which may adversely impact our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The healthcare industry is subject to changing political, economic and regulatory influences that may affect the procurement processes and operation of healthcare facilities. During the past several years, the healthcare industry has been subject to an increase in governmental regulation of, among other things, reimbursement rates and certain capital expenditures.
Recently enacted public laws reforming the U.S. healthcare system may have an impact on our business. The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (H.R. 3590; Public Law 111-148) (“PPACA”) and The Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 (H.R. 4872) (the “Reconciliation Act”), which amends the PPACA (collectively the “Health Reform Laws”), were signed into law in March 2010. The Health Reform Laws contain various provisions which may impact us and our patients. Some of these provisions may have a positive impact, while others, such as reductions in reimbursement for certain types of providers, may have a negative impact due to fewer available resources. Increases in fraud and abuse penalties may also adversely affect participants in the health care sector, including us.
| 19 |
Various legislators have announced that they intend to examine further proposals to reform certain aspects of the U.S. healthcare system. Healthcare providers may react to these proposals, and the uncertainty surrounding such proposals, by curtailing or deferring investments, including those for our systems and related services. Cost-containment measures instituted by healthcare providers as a result of regulatory reform or otherwise could result in a reduction of the allocation of capital funds. Such a reduction could have an adverse effect on our ability to sell our systems and related services. On the other hand, changes in the regulatory environment have increased and may continue to increase the needs of healthcare organizations for cost-effective data management and thereby enhance the overall market for healthcare management information systems. We cannot predict what effect, if any, such proposals or healthcare reforms might have on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
As existing regulations mature and become better defined, we anticipate that these regulations will continue to directly affect certain of our products and services, but we cannot fully predict the effect at this time. We have taken steps to modify our products, services and internal practices as necessary to facilitate our compliance with the regulations, but there can be no assurance that we will be able to do so in a timely or complete manner. Achieving compliance with these regulations could be costly and distract management’s attention and divert other company resources, and any noncompliance by us could result in civil and criminal penalties.
Developments of additional federal and state regulations and policies have the potential to positively or negatively affect our business. Our software is not anticipated to be considered a medical device by the FDA. Yet, if it were, it could be subject to regulation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) as a medical device. Such regulation could require the registration of the applicable manufacturing facility and software and hardware products, application of detailed record-keeping and manufacturing standards, and FDA approval or clearance prior to marketing. An approval or clearance requirement could create delays in marketing, and the FDA could require supplemental filings or object to certain of these applications, the result of which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We may be subject to false or fraudulent claim laws
There are numerous federal and state laws that forbid submission of false information or the failure to disclose information in connection with submission and payment of physician claims for reimbursement. In some cases, these laws also forbid abuse of existing systems for such submission and payment. Any failure of our services to comply with these laws and regulations could result in substantial liability including, but not limited to, criminal liability, could adversely affect demand for our services and could force us to expend significant capital, research and development and other resources to address the failure. Errors by us or our systems with respect to entry, formatting, preparation or transmission of claim information may be determined or alleged to be in violation of these laws and regulations. Determination by a court or regulatory agency that our services violate these laws could subject us to civil or criminal penalties, invalidate all or portions of some of our client contracts, require us to change or terminate some portions of our business, require us to refund portions of our services fees, cause us to be disqualified from serving clients doing business with government payers and have an adverse effect on our business.
We are subject to the Stark Law, which may result in significant penalties
Provisions of the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1993 (42 U.S.C. § 1395nn) (the “Stark Law”) prohibit referrals by a physician of “designated health services” which are payable, in whole or in part, by Medicare or Medicaid, to an entity in which the physician or the physician’s immediate family member has an investment interest or other financial relationship, subject to several exceptions. Unlike the Fraud and Abuse Law, the Stark Law is a strict liability statute. Proof of intent to violate the Stark Law is not required. Physical therapy services are among the “designated health services”. Further, the Stark Law has application to the Company’s management contracts with individual physicians and physician groups, as well as, any other financial relationship between us and referring physicians, including any financial transaction resulting from a clinic acquisition. The Stark Law also prohibits billing for services rendered pursuant to a prohibited referral. Several states have enacted laws similar to the Stark Law. These state laws may cover all (not just Medicare and Medicaid) patients. Many federal healthcare reform proposals in the past few years have attempted to expand the Stark Law to cover all patients as well. As with the Fraud and Abuse Law, we consider the Stark Law in planning our clinics, marketing and other activities, and believe that our operations are in compliance with the Stark Law. If we violate the Stark Law, our financial results and operations could be adversely affected. Penalties for violations include denial of payment for the services, significant civil monetary penalties, and exclusion from the Medicare and Medicaid programs.
| 20 |
If our products fail to comply with evolving government and industry standards and regulations, we may have difficulty selling our products
We may be subject to additional federal and state statutes and regulations in connection with offering services and products via the Internet. On an increasingly frequent basis, federal and state legislators are proposing laws and regulations that apply to Internet commerce and communications. Areas being affected by these regulations include user privacy, pricing, content, taxation, copyright protection, distribution, and quality of products and services. To the extent that our products and services are subject to these laws and regulations, the sale of our products and services could be harmed.
We incur significant costs as a result of operating as a public company and our management will have to devote substantial time to public company compliance obligations
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, as well as rules subsequently implemented by the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), and the stock exchange, has imposed various requirements on public companies, including requiring changes in corporate governance practices. Our management and other personnel will need to devote a substantial amount of time to these compliance requirements and any new requirements that the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 may impose on public companies. Moreover, these rules and regulations, along with compliance with accounting principles and regulatory interpretations of such principles, have increased and will continue to increase our legal, accounting and financial compliance costs and have made and will continue to make some activities more time-consuming and costly. For example, we expect these rules and regulations to make it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance, and we may be required to accept reduced policy limits and coverage or incur substantial costs to maintain the same or similar coverage. These rules and regulations could also make it more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified persons to serve on our board of directors or our board committees, or as executive officers. We will evaluate the need to hire additional accounting and financial staff with appropriate public company experience and technical accounting and financial knowledge. We estimate the additional costs we expect to be incurred as a result of being a public company to be up to $500,000 annually.
Part of the requirements as a public company will be to document and test our internal control procedures in order to satisfy the requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, which requires annual management assessments of the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting and a report by our independent registered public accounting firm addressing these assessments. The process of designing and implementing effective internal controls is a continuous effort that requires us to anticipate and react to changes in our business and the economic and regulatory environments and to expend significant resources to maintain a system of internal controls that is adequate to satisfy our reporting obligations as a public company.
Effective internal controls are necessary for us to provide reliable financial reports and to effectively prevent fraud. We maintain a system of internal control over financial reporting, which is defined as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by our board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
We cannot assure you that we will not, in the future, identify areas requiring improvement in our internal control over financial reporting. We cannot assure that the measures we will take to remediate any areas in need of improvement will be successful or that we will implement and maintain adequate controls over our financial processes and reporting in the future as we continue our growth. If we are unable to maintain appropriate internal financial reporting controls and procedures, it could cause us to fail to meet our reporting obligations, result in the restatement of our financial statements, harm our operating results, subject us to regulatory scrutiny and sanction, cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information and have a negative effect on the market price for shares of our common stock.
| 21 |
Risks Relating to Our Securities
There is a limited market for our common stock, and there may never be, an active market for our common stock and we cannot assure you that the common stock will remain liquid or that it will continue to be listed on a securities exchange.
Our common stock is listed on the OTCQB exchange and trades under the symbol “EWLL”. An investor may find it difficult to obtain accurate quotations as to the market value of the common stock and trading of our common stock may be extremely sporadic. For example, several days may pass before any shares may be traded. A more active market for the common stock may never develop. In addition, if we fail to meet the criteria set forth in SEC regulations, various requirements would be imposed by law on broker-dealers who sell our securities to persons other than established customers and accredited investors. Consequently, such regulations may deter broker-dealers from recommending or selling the common stock, which may further affect its liquidity. This would also make it more difficult for us to raise additional capital.
Until our common stock is listed on the NASDAQ or another stock exchange, we expect that our common stock will continue to be eligible to trade on the OTC Bulletin Board, another over-the-counter quotation system, or on the “pink sheets,” where our stockholders may find it more difficult to dispose of shares or obtain accurate quotations as to the market value of our common stock.
In addition, after such listing, our securities may be classified as penny stock. The SEC has adopted Rule 15g-9 which establishes the definition of a “penny stock,” for purposes relevant to us, as any equity security that has a market price of less than $5.00 per share or with an exercise price of less than $5.00 per share whose securities are admitted to quotation but do not trade on the Nasdaq Capital Market or on a national securities exchange. For any transaction involving a penny stock, unless exempt, the rules require delivery of a document to investors stating the risks, special suitability inquiry, regular reporting and other requirements. Prices for penny stocks are often not available and investors are often unable to sell this stock. Consequently, such rule may deter broker-dealers from recommending or selling our common stock, which may further affect its liquidity. This would also make it more difficult for us to raise additional capital following a business combination.
Our stock price and ability to finance may be adversely affected by our outstanding convertible securities and warrants.
Sales of the shares of our common stock issuable upon exercise of outstanding warrants and upon conversion of our convertible securities, would likely have a depressive effect on the market price of our common stock. Further, the existence of, and/or potential exercise or conversion of all or a portion of these securities, create a negative and potentially depressive effect on our stock price because investors recognize that they “over hang” the market at this time. As a result, the terms on which we may obtain additional financing during the period any of these warrants or convertible securities remain outstanding may be adversely affected by the existence of such warrants and convertible securities.
Insiders have substantial control over us, and they could delay or prevent a change in our corporate control even if our other stockholders wanted it to occur.
Our executive officers, directors, and principal stockholders beneficially own, in the aggregate, approximately 60% of our outstanding common stock at March 22, 2016. These stockholders are able to control all matters requiring stockholder approval, including the election of directors and approval of significant corporate transactions. This could delay or prevent an outside party from acquiring or merging with us, or other business consolidation even if our other stockholders wanted it to occur; it may also discourage a potential acquirer from making a tender offer for our common stock, which may further affect its liquidity.
| 22 |
We do not intend to pay dividends on our common stock for the foreseeable future.
We currently intend to retain any earnings to support our growth strategy and may begin paying dividends in late 2017, although that is not guaranteed.
We intend to issue more shares to raise capital, which will result in substantial dilution.
Our Certificate of Incorporation authorizes the issuance of a maximum of 100,000,000 shares of common stock and 10,000,000 shares of preferred stock. Any additional financings effected by us may result in the issuance of additional securities without stockholder approval and the substantial dilution in the percentage of common stock held by our then existing stockholders. Moreover, the common stock issued in any such transaction may be valued on an arbitrary or non-arm’s-length basis by our management, resulting in an additional reduction in the percentage of common stock held by our current stockholders. Our board of directors has the power to issue any or all of such authorized but unissued shares without stockholder approval. To the extent that additional shares of common stock or preferred stock are issued in connection with a financing, dilution to the interests of our stockholders will occur and the rights of the holder of common stock might be materially and adversely affected.
Our publicly filed reports are subject to review by the SEC, and any significant changes or amendments required as a result of any such review may result in material liability to us and may have a material adverse impact on the trading price of the Company’s common stock.
The reports of publicly traded companies are subject to review by the SEC from time to time for the purpose of assisting companies in complying with applicable disclosure requirements, and the SEC is required to undertake a comprehensive review of a company’s reports at least once every three years under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. SEC reviews may be initiated at any time. We could be required to modify, amend or reformulate information contained in prior filings as a result of an SEC review. Any modification, amendment or reformulation of information contained in such reports could be significant and result in material liability to us and have a material adverse impact on the trading price of the Company’s common stock.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
As a smaller Reporting Company, we are not required to provide this information; however, in light of its unknown outcome, management determined to disclose the following. As further explained elsewhere in this Report, we did receive comments on the Current Report on Form 8-K that was initially filed on May 6, 2014. Although we responded to all of the comments, the SEC continued to have concerns about the issues it raised and terminated its review of that Form 8-K without clearing all of the comments. See, Risk Factors “We may be subject to liability for failure to comply with Rule 419 under the Securities Act” and Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, “Contingencies.”
Our eWellness Corporate Office is located in Culver City, California. We lease 150 square feet for $500 per month from Evolution Physical Therapy, a company owned by our CEO. (See “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” below).
We are not currently a party to any litigation. However, from time to time, we may become a party to litigation matters involving claims against us. Although we have not received notice that any proceeding or enforcement action has been instituted as of the date of this Report, as further explained elsewhere in this Report, the final comment received from the SEC regarding the Current Report of Form 8-K that we initially filed on May 6, 2014, was that they were terminating their review of that filing because they continued to have concerns about certain of the issues raised, specifically a Rule 419 violation, that they could not resolve and were going to take further steps they deem appropriate. Please refer to the related discussion in Part I, Risk Factors “We may be subject to liability for failure to comply with Rule 419 under the Securities Act” and Part II, Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, “Contingencies.”
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
| 23 |
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market Information. As of March 1, 2016, our common stock is listed on the OTCQB exchange and trades under the symbol “EWLL”. The Company is currently applying for DTC.eligibility.
Holders. As of March 22, 2016, we had 18,847,770 shares of $0.001 par value common stock issued and outstanding held by 104 shareholders of record. There are also 322,500 of restricted common stock that will be issued if debt is converted and 5,746,895 of outstanding warrants to purchase common equity of the Company.
Dividend Policy. We have neither declared nor paid any cash dividends on either preferred or common stock. For the foreseeable future, we intend to retain any earnings to finance the development and expansion of our business and do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our preferred or common stock. Any future determination to pay dividends will be at the discretion of the Board of Directors and will be dependent upon then existing conditions, including its financial condition, results of operations, capital requirements, contractual restrictions, business prospects, and other factors that the Board of Directors considers relevant.
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans. On August 6, 2015, the Board of Directors approved the 2015 Stock Option Plan, pursuant to which certain directors, officers, employees and consultants will be eligible for certain stock options and grants. The Plan is effective as of August 1, 2015 and the maximum number of shares reserved and available for granting awards under the Plan shall be an aggregate of 3,000,000 shares of common stock, provided however that on each January 1, starting with January 1, 2016, an additional number of shares equal to the lesser of (A) 2% of the outstanding number of shares (on a fully-diluted basis) on the immediately preceding December 31 and (B) such lower number of shares as may be determined by the Board or committee charged with administering the plan. This plan may be amended at any time by the Board or appointed plan Committee.
The 2015 Stock Option Plan
On July 31, 2015, our Board of Directors approved the 2015 Stock Option Plan. The following is a brief description of certain important features of the 2015 Plan, the full text of which is attached as Exhibit 10.7. This summary is qualified in its entirety by reference to Exhibit 10.7.
General. The 2015 Plan provides for any option, stock appreciation right, restricted stock, restricted stock unit, performance award, dividend equivalent, or other stock-based award to employees, officers, directors and consultants of the Company and its affiliates.
Administration. The 2015 Plan shall be administered and interpreted by the Board of Directors or by a Committee appointed by the Board of Directors. If the Board of Directors administers the 2015 Plan, references to the “Committee” shall be deemed to refer to the Board of Directors. To the extent permitted by applicable law, the Committee may at any time delegate to one or more officers or directors of the Company some or all of its authority over the administration of the 2015 plan. Such delegation may be revoked at any time.
The Committee has the authority to administer and interpret the 2015 Plan, to determine the employees to whom awards will be made under the 2015 Plan and, subject to the terms of the 2015 Plan, the type and size of each award, the terms and conditions for vesting, cancellation and forfeiture of awards and the other features applicable to each award or type of award. The Committee may accelerate or defer the vesting or payment of awards, cancel or modify outstanding awards, waive any conditions or restrictions imposed with respect to awards of the stock issued pursuant to awards and make any and all other determinations that it deems appropriate with respect to the administration of the 2015 Plan, subject to the minimum vesting requirements of the 2015 Plan, the provisions of Sections 162(m) of the Internal Revenue Code and any applicable laws or exchange rules.
| 24 |
Eligibility. All employees, officers, directors and consultants are eligible to receive awards under the 2015 Plan. The definition of “employee” means any person including officers and directors of the Company or a parent or subsidiary of the Company. Neither service as a Director nor payment of a director’s fee by the Company will be sufficient to constitute “employment” by the Company. Participation is discretionary — awards are subject to approval by the Committee. Pursuant to the 2015 Plan, the Company is permitted to grant nonstatutory stock options, restricted stock, stock appreciation rights, performance shares, restricted stock units and other stock based awards to the employees, directors and consultants. Incentive stock options are not issuable under the 2015 Plan.
Shares Subject to the Plan. The number of Shares available for granting awards under the 2015 Plan shall be (A) 3,000,000, plus (B) additional Shares as follows: As of January 1 of each year, commencing with the January 2, 2016, the aggregate number of Shares available for granting Awards under the Plan shall automatically increase by a number of Shares equal to the lesser of (x) 2% of the total number of Shares then outstanding and (y) such lower number of Shares as may be determined by the Committee, subject to certain adjustment. Shares of Company common stock issued in connection with awards under the 2015 Plan may be shares that are authorized but unissued, or previously issued shares that have been reacquired, or both.
Types of Awards. The following types of awards may be made under the 2015 Plan. All of the awards described below are subject to the conditions, limitations, restrictions, vesting and forfeiture provisions determined by the Committee, in its sole discretion, subject to such limitations as are provided in the plan. The number of shares subject to any award is also determined by the Committee, in its discretion.
Fair Market Value. Fair Market Value shall mean, with respect to any property (including, without limitation, any shares or other securities), the fair market value of such property determined by such methods or procedures as shall be established from time to time by the Board or the Committee.
Option. Option shall mean a non-qualified stock option.
Stock Appreciation Rights. A Stock Appreciation Right granted under the Plan shall confer on the holder thereof a right to receive, upon exercise thereof, the excess of (1) the Fair Market Value of one Share on the date of exercise or, if the Board or the Committee shall so determine in the case of any such right other than one related to any Incentive Stock Option, at any time during a specified period before or after the date of exercise over (2) the grant price of the right as specified by the Board or the Committee. Subject to the terms of the Plan, the grant price, term, methods of exercise, methods of settlement, and any other terms and conditions of any Stock Appreciation Right shall be as determined by the Board or the Committee. The Board and the Committee may impose such conditions or restrictions on the exercise of any Stock Appreciation Right as it may deem appropriate.
Restricted Stock. A restricted stock award is an award of outstanding shares of Company common stock that does not vest until after a specified period of time, or satisfaction of other vesting conditions as determined by the Committee, and which may be forfeited if conditions to vesting are not met. Participants generally receive dividend payments on the shares subject to their award during the vesting period (unless the awards are subject to performance-vesting criteria) and are also generally entitled to indicate a voting preference with respect to the shares underlying their awards. All shares underlying outstanding restricted stock awards are voted proportionately to the restricted shares for which voting instructions are received.
Restricted Stock Units. Restricted Stock Units shall consist of a Restricted Stock, Performance Share or Performance Unit Award that the Administrator in its sole discretion permits to be paid out in installments or on a deferred basis, in accordance with rules and procedures established by the Administrator.
| 25 |
Performance Awards. Performance Awards may be granted to Employees, directors and consultants at any time and from time to time, as will be determined by the Administrator. The Administrator may set performance objectives based upon the achievement of Company-wide, divisional or individual goals, applicable federal or state laws, or any other basis determined by the Administrator in its discretion.
Dividend Equivalents. The Board and the Committee are hereby authorized to grant Awards under which the holders thereof shall be entitled to receive payments equivalent to dividends or interest with respect to a number of Shares determined by the Board or the Committee, and the Board and the Committee may provide that such amounts (if any) shall be deemed to have been reinvested in additional Shares or otherwise reinvested. Subject to the terms of the 2015 Plan, such Awards may have such terms and conditions as the Board or the Committee shall determine.
Other Stock-based Awards. The Board and the Committee are authorized to grant such other Awards that are denominated or payable in, valued in whole or in part by reference to, or otherwise based on or related to, Shares (including, without limitation, securities convertible into Shares), as are deemed by the Board or the Committee to be consistent with the purposes of the Plan, provided, however, that such grants must comply with applicable law. Subject to the terms of the 2015 Plan, the Board or the Committee shall determine the terms and conditions of such Awards.
Duration. The Board may amend, alter, suspend, discontinue, or terminate the Plan, including, without limitation, any amendment, alteration, suspension, discontinuation, or termination that would impair the rights of any Participant, or any other holder or beneficiary of any Award theretofore granted, without the consent of any share owner, participant of the 2015 Plan, other holder or beneficiary of an Award, or other Person. No Award shall be granted under the Plan more than 10 years after August 1, 2015. However, unless otherwise expressly provided in an applicable Award Agreement, any Award theretofore granted may extend beyond such date, and the authority of the Board and the Committee to amend, alter, adjust, suspend, discontinue, or terminate any such Award, or to waive any conditions or rights under any such Award, and the authority of the Board to amend the Plan, shall extend beyond such date.
The following table shows the aggregate amount of securities authorized for issuance under all equity compensation plans as of December 31, 2015:
Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights (a) |
Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights (b) |
Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a)) (c) |
|||||
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders |
- | - | |||||
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders |
$ | - | - | ||||
Total |
$ | - | - | ||||
As of the year ended December 31, 2015, no options had been issued per the stock option plan explained above.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
Information regarding any equity securities we have sold during the period covered by this Report that were not registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, is set forth below. Each such transaction was exempt from the registration requirements of the Securities Act by virtue of Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act or Rule 506 of Regulation D promulgated by the SEC, unless otherwise noted. Unless stated otherwise: (i) the securities were offered and sold only to accredited investors; (ii) there was no general solicitation or general advertising related to the offerings; (iii) each of the persons who received these unregistered securities had knowledge and experience in financial and business matters which allowed them to evaluate the merits and risk of the receipt of these securities, and that they were knowledgeable about our operations and financial condition; (iv) no underwriter participated in, nor did we pay any commissions or fees to any underwriter in connection with the transactions; and, (v) each certificate issued for these unregistered securities contained a legend stating that the securities have not been registered under the Securities Act and setting forth the restrictions on the transferability and the sale of the securities.
| 26 |
On January 24, 2015, we extended the term of an outstanding consulting and service agreement, pursuant to which the Company shall issue 400,000 shares of restricted common stock and 400,000 callable common stock purchase warrants at a strike price of $0.35 per share.
On February 23, 2015, we entered into a one-year agreement with a consultant in connection with certain corporate finance, investor relations and related business matters in exchange for 60,000 shares of restricted common stock.
On April 9, 2015, we issued $270,080 Notes (including an aggregate of $123,980 that was converted from certain other outstanding notes, including accrued interest, and future contractual cash consulting fees) that are initially convertible into 771,657 shares of our common stock, pursuant to a private financing; we sold that same amount of Series A Senior Convertible Redeemable Notes convertible into shares of the Company’s common stock, at $0.35 per share and Series A Warrants, all pursuant to separate Securities Purchase Agreements entered into with each investor. The Warrants are exercisable to purchase up to 771,657 shares of Common Stock.
On May 30, 2015, the Company received $25,000 in exchange for a 90-day promissory note at an interest rate of 5% per annum. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 150,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.35 per share. This note and accrued interest was due on August 28, 2015.
On May 20, 2015, the Company signed an agreement with a firm for financial advisory services for a period of 12 months. As the retainer, the Company issued 250,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock for $.35 per share.
On May 20, 2015, the Company signed an agreement with a firm for strategic advisory services until either party terminates the agreement. As part of the commitment fee, the Company issued 250,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock for $.35 per share.
On July 14, 2015, the Company issued 250,000 shares of common stock for conversion of $87,500 of convertible debt. These shares were issued at $.35 per share.
On July 15, 2015, the Company received $18,000 in exchange for a 90-day promissory note at an interest rate of 5% per annum. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 150,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. This note and accrued interest was due on October 15, 2015.
On August 19, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 96,000 shares for conversion of $33,600 of convertible debt. These shares were issued at $.35 per share.
On August 26, 2015, the Company extended the term of the $25,000 promissory note issued on May 30, 2015 that was originally due on August 28 2015 to October 23, 2015. As consideration for the extension the Company agreed to an annual interest rate of 12% retroactive to the original date of the note and issued 150,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share.
On September 10, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 663,277 shares for conversion of $232,147 of convertible debt. These shares were issued at $.35 per share.
On September 16, 2015, the Company received $2,500 in exchange for a 90-day promissory note at an interest rate of 12% per annum and a risky loan fee of $625. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 50,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. This note, accrued interest and risky loan fee was due on December 14, 2015. The Company paid this note, accrued interest and risky loan fee on December 6, 2015.
On September 16, 2015, the Company received $12,500 in exchange for a 90-day promissory note at an interest rate of 12% per annum and a risky loan fee of $3,125. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 250,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. This note, accrued interest and risky loan fee was due on December 14, 2015. The Company paid this note, accrued interest and risky loan fee on December 6, 2015.
| 27 |
On September 16, 2015, the Company received $22,500 in exchange for a 90-day promissory note at an interest rate of 12% per annum and a risky loan fee of $5,625. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 450,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. This note, accrued interest and risky loan fee was due on December 14, 2015.
On October 1, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 50,273 shares of common stock for the accrued interest on the debt conversions on July 14, 2015, August 19, 2015, and September 10, 2015. The shares were issued at $.35 per share.
On October 5, 2015, the Company extended the term of an $18,000 promissory note originally issued on May 15, 2015 that was originally due on October 13, 2015 to December 14, 2015; however, as consideration for the extension, the Company agreed to repay the note, plus interest and the Loan Fee (as hereinafter defined), upon receipt of $100,000 or more in other financing. Interest on the note accrues at the rate of 12% per annum. Unless paid sooner as previously explained, the Company shall pay $4,500 on the maturity date of the note. As additional inducement for the extension, the Company also agreed to issue the lender five-year warrants to purchase up to 150,000 shares of the Company’s common stock at $0.80 per share.
On October 11, 2015, the Company extended the term of an $25,000 promissory note issued on July 15, 2015 that was due on October 23, 2015 to December 14, 2015; however, as a consideration for the extension, the Company agreed to repay the note, plus interest and a risk loan fee of $6,250. As additional inducement for the extension, the Company also agreed to issue the lender five-year warrants to purchase up to 150,000 shares of common stock at $0.80 per share.
On October 11, 2015, the Company received $10,000 in exchange for a 60-day promissory note at an interest rate of 12% per annum and a risky loan fee of $2,500. As an inducement for the promissory note, the Company issued 200,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The note, accrued interest and risky loan fee is due on December 14, 2015.
On November 11, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 179,988 shares of common stock for the conversion of $57,670 of principal and $5,326 of accrued interest. These shares were issued at $.35 per share.
On December 6, 2015, the Company entered into a 90-day Promissory Note for $70,000 at an interest rate of 12% per annum plus a risky loan fee of $17,500 which is being amortized over the term of the loan. As an inducement the Company issued 1,400,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The Company further agreed to repay the loan within three days of the Company receiving $500,000 or more in the current private placement of up to $2,500,000 convertible note with warrants. This Promissory Note resulted from the principal payment to the note holder of $28,222 and the holder cancelling the notes originally signed on May 27, 2015 plus extensions, July 15, 2015 plus extensions, September 16, 2015 and October 11, 2015.
On December 11, 2015, the Company entered into a securities purchase agreement with an accredited investor for (i) a note in the principal amount of $275,000 at a 10% original issue discount , (ii) a warrant to purchase 250,000 shares of the Company’s common stock with an exercise price of $0.80 per share and (iii) 50,000 shares as an additional fee for a value of $5,000.
The securities issued have not been registered under the Securities Act and may not be offered or sold in the United States absent registration or an applicable exemption from registration requirements.
| 28 |
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
Smaller reporting companies are not required to provide this disclosure.
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULT OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and result of operations contains forward-looking statements and involves numerous risks and uncertainties, including, but not limited to, those described in the “Risk Factors” section of the other reports we file with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Actual results may differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terminology such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “potential” or “continue,” the negative of such terms or other comparable terminology. These statements are only predictions.
Although we believe that the expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee future results, levels of activity, performance or achievements. Moreover, neither we, nor any other person, assume responsibility for the accuracy and completeness of the forward-looking statements. We are under no obligation to update any of the forward-looking statements after the filing of this Annual Report to conform such statements to actual results or to changes in our expectations.
The following discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations relates to the operations and financial condition reported in the financial statements of eWellness Healthcare Corporation for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 and should be read in conjunction with such financial statements and related notes included in this report.
Overview
eWellness is in the initial phase of developing a unique telemedicine platform that offers Distance Monitored Physical Therapy Program (“PHZIO program”) to pre-diabetic, cardiac and health challenged patients, through contracted physician practices and healthcare systems specifically designed to help prevent patients that are pre-diabetic from becoming diabetic.
Initially, our focus was on patients with pre-diabetes conditions. However, we have broadened our focus to include overweight patients saddled with lower back pain and knee pain caused by tissue strain and inactivity. We also decided to launch our platform in Los Angeles instead of New York after Blue Shield of California reimbursed our physical therapy telemedicine. We were poised to launch our business in New York through a partnership with Millennium Healthcare, Inc. (“MHI”), but the partnership did not provide the results we were expecting. Additionally, management determined that relocating the Company’s operations closer to where the CEO and Chairman lived made the business more manageable and avoided time and monies lost due to travel. Management believes that by broadening the Company’s focus to include lower back pain and knee pain caused from excess weight, provides additional opportunities for success. The Company remains committed to servicing patients diagnosed as pre-diabetes as well.
As shown in the financial statements accompanying this Annual Report, the Company has had no revenues to date and has incurred only losses since its inception. The Company has had limited operations and has been issued a “going concern” opinion from our accountants, based upon the Company’s reliance upon the sale of our common stock as the sole source of funds for our future operations.
The Company’s operations and corporate offices are located at 11825 Major Street Culver City, CA, 90230, with a telephone number of (310) 915-9700.
| 29 |
The Company’s fiscal year end is December 31.
Plan of Operations
Our business model is to license our PHZIO (“PHZIO”) platform to any physical therapy (“PT”) clinic in the U.S. and or have large-scale employers use our PHZIO platform as a fully PT monitored corporate wellness program.
The Company’s initial licensee is Evolution Physical Therapy (“EPT”), which is owned by our CEO, Darwin Fogt, MPT. All treatment revenue for 2015 was reimbursed to EPT, but was not sufficient to generate sales for the Company. The Company is in the process of developing marketing channel partnerships with industry association members, existing software-based telemedicine providers and physical therapy billing and practice management providers. These partnerships, if completed, are anticipated to begin adding third party PT licensee revenue during the second quarter of 2016.
The Company’s PHZIO home physical therapy exercise platform has been designed to disrupt the $30 billion physical therapy and the $8 billion corporate wellness industries. PHZIO re-defines the way physical therapy can be delivered. PHZIO is the first real-time remote monitored 1-to-many physical therapy platform for home use. Due to the real-time patient monitoring feature, the PHZIO platform is insurance reimbursable by payers such as: Anthem Blue Cross, AETNA and Blue Shield.
The PHZIO Solution: A New Physical Therapy Delivery System
| ● | SaaS technology platform solution for providers bundling rehabilitation services and employer wellness programs; |
| ● | First real-time remote monitored 1-to-many physical therapy treatment platform for home use; |
| ● | Ability for physical therapists to observe multiple patients simultaneously in real-time; |
| ● | Solves what has been a structural problem and limitation in post-acute care practice growth. |
| ● | PT practices can experiencing 20% higher adherence & compliance rates versus industry standards; and |
| ● | Tracking to 30% increase in net income for a PT practice. |
Patient program adherence in 2015 was nearly 85 percent due the real-time patient monitoring and the at-home use of the platform. Now physical therapy practices have a way to scale profitably using a technology platform that can help them grow beyond the limits of the typical brick and mortar PT clinic.
Additional Treatment Protocols: The Company’s initial PHZIO application is a 6-month exercise program for patients with back, knee or hip pain. The next two platforms are anticipated to be released in the second quarter of 2016 include a total knee and hip replacement exercise program. These hip and knee programs have been designed to be integrated into any hospital or medical group's Medicare CMS bundled payment model for post-acute care physical therapy. These two programs are anticipated to be followed by woman's health and geriatric programs by the end of the third quarter of 2016.
Our PHZIO platform enables employees or patients to engage with live or on-demand video based physical therapy telemedicine treatments from their home or office. Following a physician’s exam and prescription for physical therapy to treat back, knee or hip pain, a patient can be examined by a physical therapist and if found appropriate inducted in the Company’s PHZIO program that includes a progressive 6-month telemedicine exercise program (including monthly in-clinic checkups). All PHZIO treatments are monitored by a licensed therapist that sees everything the patient is doing while providing their professional guidance and feedback in real-time. This ensures treatment compliance by the patient, maintains the safety and integrity of the prescribed exercises, tracks patient metrics and captures pre and post treatment evaluation data. PHZIO unlocks a host of potential for revolutionizing patient treatment models and directly links back to the established brick and mortar physical therapy clinic. This unique model enables any physical therapy practice to be able to execute more patient care while utilizing their same resources, and creates more value than was ever before possible.
| 30 |
During 2015 our PHZIO platform achieved the following metrics:
| ● | The total (insurance reimbursed) monitored PHZIO visits in 2015: 699 patient visits (267 paid patient visits total). |
| ● | The average insurance reimbursement per PHZIO session in 2015: $46.87 (excluding co-payments). |
| ● | The top line wellness goals of our PHZIO program are to graduate at least 80% of inducted patients through our 6-month program. Patients should expect to experience an average of a 20% reduction in BMI, a 4-inch reduction in waist size, weight loss of at least 20 pounds, significant overall improvement in balance, coordination, flexibility, strength, and lumbopelvic stability. Patients also should scored better on Functional Outcomes Scales (Oswestry and LEFS), which indicates improved functional activity levels due to reduced low back, knee and hip pain. |
Our PHZIO platform, including: design, testing, exercise intervention, follow-up, and exercise demonstration, has been developed by accomplished Los Angeles based physical therapist Darwin Fogt. Mr. Fogt has extensive experience and education working with diverse populations from professional athletes to morbidly obese. He understands the most beneficial exercise prescription to achieve optimal results and has had great success in motivating all patient types to stay consistent in working toward their goals. Additionally, his methods have proven effective and safe as he demonstrates exercises with attention to proper form to avoid injury. Mr. Fogt has established himself as a national leader in his field and has successfully implemented progressive solutions to delivering physical therapy: he has consulted with and been published by numerous national publications including Runner’s World, Men’s Health, Men’s Journal, and various Physical Therapy specific magazines; his 13 plus years of experience include rehabilitating the general population, as well as professional athletes, Olympic gold medalists, and celebrities. He has bridged the gap between physical therapy and fitness by opening Evolution Fitness, which uses licensed physical therapists to teach high intensity circuit training fitness classes. He also founded one of the first exclusive prenatal and postnatal physical therapy clinic in the country. Mr. Fogt is a leader in advancing the profession to incorporate research-based methods and focus on, not only rehabilitation but also wellness, functional fitness, performance, and prevention. He is able to recognize that the national healthcare structure (federal and private insurance) is moving toward a model of prevention and that the physical therapy profession will take a larger role in providing wellness services to patients.
Innovators in other industries have solved access, cost and quality inefficiencies through the implementation of technology platforms and business models that deliver products and services on-demand and create new economies by connecting and empowering both consumers and businesses. We have taken the same approach to solving the pervasive access, cost and quality challenges facing the current access to physical therapy clinics.
Our underlying technology platform is complex, deeply integrated and purpose-built over the three years for the evolving physical therapy marketplace. Our PHZIO platform is highly scalable and can support substantial growth of third party licensees. Our PHZIO platform provides for broad interconnectivity between PT practitioners and their patients and, we believe, uniquely positions us as a focal point in the rapidly evolving PT industry to introduce innovative, technology-based solutions, such as remote patient monitoring, post-discharge treatment plan adherence and in-home care.
We plan to generate revenue from third-party PT and corporate wellness licensees on a contractually recurring per PHZIO session fee basis. Our PHZIO platform is anticipated to transform the access, cost and quality dynamics of physical therapy delivery for all of the market participants. We further believe any patient, employer, health plan or healthcare professional interested in a better approach to physical therapy is a potential PHZIO platform user.
We have developed various key performance indicators that we anticipate using to assess our business after we on-board third party PT licensees later in the year:
Selling General and Administrative Expenses (SGA). Before even launching, we have received a high indication of interest in our service. We think the demand is warranted, but recognize that in the early stages of our services, we may experience bottlenecks in our ability to meet the demand for same. Under this type of environment it is critical to maintain awareness of the Company’s operational budget goals and how they are being met in our attempts to address demand. Regardless of our growth pace, it is critical to shareholder value that we are mindful of our operational spending.
| 31 |
Cashflow. Because the Company is “early stage” and launching with a minimum of capital, monitoring cashflow on a constant basis will be essential to growth.
During the third quarter of 2015, we pivoted our business model to focus on licensing our PHZIO platform to any physical therapy clinics in the U.S. and or to have large scale employers use our platform as a corporate wellness program. The Physical Therapy industry has remained disconnected and unscalable throughout the technological revolution of the past twenty years. Over 200,000 Physical Therapists are limited to one-on-one patient treatments within a traditional clinic setting. The Physical Therapy industry measures $33 Billion in size with over 270 Million one-on-one treatments delivered annually. This technology gap and market size is the opportunity that the Company is focused on with the recent launch of its PHZIO telemedicine platform.[2]
Our PHZIO platform enables patients to engage with live or on-demand video based physical therapy telemedicine treatments from their home or office. Following a physician’s exam and prescription for physical therapy to treat back, knee or hip pain, a patient can be examined by a physical therapist and if found appropriate inducted in eWellness’ PHZIO program that includes a progressive 6-month telemedicine exercise program (including weekly in-clinic exercise sessions and monthly in-clinic checkups. All PHZIO treatments are monitored by a licensed therapist that sees everything the patient is doing while providing their professional guidance and feedback in real-time. This ensures treatment compliance by the patient, maintains the safety and integrity of the prescribed exercises, tracks patient metrics and captures pre and post treatment evaluation data. PHZIO unlocks a host of potential for revolutionizing patient treatment models and directly links back to the established brick and mortar Physical Therapy clinic. This unique model enables any physical therapy practice to be able to execute more patient care while utilizing their same resources, and creates more value than was ever before possible.
The following video link will provide brief overview about the merits of our PHZIO program. https://ewellnesshealth.com/
Through our Cooperative Operating Agreement with Evolution Physical Therapy (“EPT”) their Marina del Rey, California patient induction office (“PIO”) The Marina del Rey POI is effectively a laboratory for us to support the licensing of our platform to the entire Physical Therapy (“PT”) industry. In April we plan to move this POI to EPT’s Culver City location as we could not extend the lease at that location. Active PT licensing of our PHYSIO platform is anticipated to begin in the second quarter of 2016. We have also developed a separate vertical for our PHZIO platform that focuses on the marketing of our platform as a robust Corporate Wellness program. Active marketing to the large scale employers in the Los Angeles area began in the October 2015 with the expectation of beginning at least pilot program for our Corporate Wellness program during the second quarter of 2016.
We are also actively seeking corporate partnership relationships with other telemedicine companies that if completed, would create a new channel for our corporate wellness PHZIO program. Amid ongoing challenges and changes within the healthcare industry, telemedicine is emerging as an increasingly attractive tool for delivering quality medical & wellness services.
Beginning in early 2016, we began offering our PHZIO program that has been designed to be the most productive physical exercise program available to corporate wellness programs and their employees. We anticipate that employers using our system can significantly improve employee wellness and decrease costs associated with workman’s compensation claims. PHZIO is a comprehensive lifestyle management intervention. Our PHZIO exercise program documents an employee’s success or failure. We can provision highly reliable Return On Investment (“ROI”) metrics displayed on an easy to use HIPAA compliant dashboard for any organization using our PHZIO system.
2 Sources: Harris Williams & Co., Physical Therapy Market Overview, Feb 2014 IBISWorld, Physical Therapists in the US (Report 62134), May 2015
| 32 |
The Current State of Workplace Wellness Programs: Broadly, a workplace wellness program is an employment-based activity or employer-sponsored benefit aimed at promoting health-related behaviors (primary prevention or health promotion) and disease management (secondary prevention). It may include a combination of data collection on employee health risks and population-based strategies paired with individually focused interventions to reduce those risks. A formal and universally accepted definition of a workplace wellness program has yet to emerge, and employers define and manage their programs differently. Programs may be part of a group health plan or be offered outside of that context; they may range from narrow offerings, such as free gym memberships, to comprehensive counseling and lifestyle management interventions4.
Wellness programs have become very common, as 92 percent of employers with 200 or more employees reported offering them in 2009. Survey data indicate that the most frequently targeted behaviors are exercise, addressed by 63 percent of employers with programs; smoking (60 percent); and weight loss (53 percent). In spite of widespread availability, the actual participation of employees in such programs remains limited. While no nationally representative data exist, a 2010 non-representative survey suggests that typically fewer than 20 percent of eligible employees participate in wellness interventions4.
Wellness Program Impact: In industry surveys, employers typically express their conviction that workplace wellness programs are delivering on their promise to improve health and reduce costs. Numerous anecdotal accounts of positive program effects are consistent with this optimistic view. Further, several evaluations of individual programs and summative reviews in the scientific literature provide corroborating evidence for a positive impact4.
In “A Review of the U.S. Workplace Wellness Market “, the most recent scientific literature evaluating the impact of workplace wellness programs on health-related behavior and medical cost outcomes identified 33 peer-reviewed publications that met their standards for methodological rigor. They found, consistent with previous reviews, evidence for positive effects on diet, exercise, smoking, alcohol use, physiologic markers, and health care costs, but limited evidence for effects on absenteeism and mental health. They could not conclusively determine whether or not program intensity was positively correlated with impact. Positive results found in this and other studies should be interpreted with caution, as many of these programs were not evaluated with a rigorous approach, and published results may not be representative of the typical experience of a U.S. employer[3].
The Company intends to close on a private financing of up to $2.5 million by the end of the second quarter of 2016, although there can be no guarantee we will receive any such financing.
Results of Operations of eWellness for the Twelve-month Period Ended December 31, 2015 vs. 2014
REVENUES: eWellness has reported $0 revenues from operations for the years ended December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014. We anticipate the beginning of revenue generation by in the second quarter of 2016.
OPERATING EXPENSES: Total operating expenses increased to $1,400,240 for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $1,325,010 for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase is a result of legal and accounting services expenses.
NET LOSS: The Company incurred a net loss of $1,554,908 for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared with a net loss of $1,339,585 for the year ended December 31, 2014, which reflects an increase of $215,323. The increase is as a result of legal and accounting services expenses.
CONTINGENCIES
The Company may be subject to lawsuits, administrative proceedings, regulatory reviews or investigations associated with its business and other matters arising in the normal conduct of its business. The following is a description of an uncertainty that is considered other than ordinary, routine and incidental to the business.
3 http://www.dol.gov/ebsa/pdf/workplacewellnessmarketreview2012.pdf
| 33 |
The closing of the Initial Exchange Agreement with Private Co. was conditioned upon certain, limited customary representations and warranties, as well as, among other things, our compliance with Rule 419 (“Rule 419”) of Regulation C under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) and the consent of our shareholders as required under Rule 419. Accordingly, we conducted a “Blank Check” offering subject to Rule 419 (the “Rule 419 Offering”) and filed a Registration Statement on Form S-1 to register the shares of such offering; the Registration Statement was declared effective on September 14, 2012. We used 10% of the subscription proceeds as permitted under Rule 419 and the amount remaining in the escrow trust as of the date of the closing of the Share Exchange was $90,000 (the “Trust Account Balance”).
Rule 419 required that the Share Exchange occur on or before March 18, 2014, but due to normal negotiations regarding the transactions and the parties’ efforts to satisfy all of the closing conditions, the Share Exchange did not close on such date. Accordingly, after numerous discussions with management of both parties, they entered into an Amended and Restated Share Exchange Agreement (the “Share Exchange Agreement”) to reflect a revised business combination structure, pursuant to which we would: (i) file a registration statement on Form 8-A (“Form 8A”) to register our common stock pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Exchange Act, which we did on May 1, 2014 and (ii) seek to convert the participants of the Rule 419 Offering into participants of a similarly termed private offering (the “Converted Offering”), to be conducted pursuant to Regulation D, as promulgated under the Securities Act.
Fifty-two persons participated in the Rule 419 Offering and each of them gave the Company his/her/its consent to use his/her/its escrowed funds to purchase shares of the Company’s restricted common stock in the Converted Offering (the “Consent”) rather than have their funds returned. To avoid further administrative work for the investors, we believe that we took reasonable steps to inform investors of the situation and provided them with an appropriate opportunity to maintain their investment in the Company, if they so choose, or have their funds physically returned. Management believed the steps it took constituted a constructive return of the funds and therefore met the requirements of Rule 419.
However, pursuant to Rule 419(e)(2)(iv), “funds held in the escrow or trust account shall be returned by first class mail or equally prompt means to the purchaser within five business days [if the related acquisition transaction does not occur by a date that is 18 months after the effective date of the related registration statement].” As set forth above, rather than physically return the funds, we sought consent from the investors of the Rule 419 Offering to direct their escrowed funds to the Company to instead purchase shares in the Converted Offering. The consent document was given to the investors along with a private placement memorandum describing the Converted Offering and stated that any investor who elected not to participate in the Converted Offering would get 90% of their funds physically returned. Pursuant to Rule 419(b)(2)(vi), a blank check company is entitled to use 10% of the proceed/escrowed funds; therefore, if a return of funds is required, only 90% of the proceed/escrowed funds need be returned. The Company received $100,000 proceeds and used $10,000 as per Rule 419(b)(2)(vi); therefore, only $90,000 was subject to possible return.
As disclosed in the prior amendments to the Initial Form 8-K, we have filed the prior amendments in response to comments from the SEC regarding the Form 8-K and many of those comments pertain to the Company’s potential violation of Rule 419. Although the Company has continued to provide the SEC with information and analysis as to why it believes it did not violate Rule 419, based upon latest communications with the persons reviewing the Form 8-K, they do not agree with the assessments the Company presented to them. Comments and communications indicate that Rule 419 requires a physical return of funds if a 419 offering cannot be completed because a business combination was not consummated within the required time frame; constructive return is not permitted.
As a result of these communications and past comments, we are disclosing that we did not comply with the requirements of Rule 419, which required us to physically return the funds previously submitted to escrow pursuant to the Rule 419 Offering. As a result of our failure to comply with Rule 419, the SEC may bring an enforcement action or commence litigation against us for failure to strictly comply with Rule 419. If any claims or actions were to be brought against us relating to our lack of compliance with Rule 419, we could be subject to penalties (including criminal penalties), required to pay fines, make damages payments or settlement payments. In addition, any claims or actions could force us to expend significant financial resources to defend ourselves, could divert the attention of our management from our core business and could harm our reputation.
| 34 |
Ultimately, the SEC determined to terminate its review of the Initial Form 8-K and related amendments, rather than provide us with additional opportunities to address their concerns and therefore, we did not clear their comments. It is not possible at this time to predict whether or when the SEC may initiate any proceedings, when this issue may be resolved or what, if any, penalties or other remedies may be imposed, and whether any such penalties or remedies would have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. Litigation and enforcement actions are inherently unpredictable, the outcome of any potential lawsuit or action is subject to significant uncertainties and, therefore, determining at this time the likelihood of a loss, any SEC enforcement action and/or the measurement of the amount of any loss is complex. Consequently, we are unable to estimate the range of reasonably possible loss. Our assessment is based on an estimate and assumption that has been deemed reasonable by management, but the assessment process relies heavily on an estimate and assumption that may prove to be incomplete or inaccurate, and unanticipated events and circumstances may occur that might cause us to change that estimate and assumption. In light of the uncertainty of this issue and while Management evaluates the best and most appropriate way to resolve same, management determined to create a reserve on the Company’s Balance Sheet for the $90,000 that was subject to the Consent.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
As of December 31, 2015, we had negative working capital of $1,430,459 compared to negative working capital of $823,585 as of December 31, 2014. Cash flows provided by financing activities were $443,127 and $178,433 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, respectively. The cash balance as of December 31, 2015 was $41,951.
We believe that anticipated cash flows from operations will be insufficient to satisfy our ongoing capital requirements. We are seeking financing in the form of equity capital in order to provide the necessary working capital. Our ability to meet our obligations and continue to operate as a going concern is highly dependent on our ability to obtain additional financing. We cannot predict whether this additional financing will be in the form of equity or debt, or be in another form. We may not be able to obtain the necessary additional capital on a timely basis, on acceptable terms, or at all. In any of these events, we may be unable to implement our current plans which circumstances would have a material adverse effect on our business, prospects, financial conditions and results of operations.
If we are not successful in generating sufficient liquidity from operations or in raising sufficient capital resources, on terms acceptable to us, this could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations liquidity and financial condition.
The independent auditors’ opinion expresses doubt about eWellness’ ability to continue as a going concern. The independent auditors reports on eWellness’ December 31, 2015 and 2014 financial statements included in this Report states that the Company’s recurring losses, lack of revenues and operations and not having any positive operating cash flows since inception, raise substantial doubts about eWellness’ ability to continue as a going concern.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
There are no off-balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our financial condition, changes in financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures or capital resources that is material to investors.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Our significant accounting policies are disclosed in Note 2 of our Financial Statements included elsewhere in this Report.
ITEM 7A: QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Smaller reporting companies are not required to provide this disclosure.
ITEM 8: FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
See Index to Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedules appearing on pages F-1 through F-20 of this Form 10-K.
| 35 |
eWELLNESS HEALTHCARE CORPORATION
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND DECEMBER 31, 2014
| F-1 |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors
eWellness Healthcare Corporation
We have audited the accompanying balance sheets of eWellness Healthcare Corporation as of December 31, 2015, and the related statements of operations, stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for the year then ended. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of eWellness Healthcare Corporation as of December 31, 2015, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for the year then ended, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 3 to the financial statements, the Company has a working capital deficit, a deficit in stockholders’ equity and has sustained recurring losses from operations. This raises substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans with regard to these matters are also described in Note 3. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Haynie & Company
Salt Lake City, Utah
March 30, 2016
| F-2 |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors
eWellness Healthcare Corporation
We have audited the accompanying balance sheet of eWellness Healthcare Corporation as of December 31, 2014, and the related statements of operations, stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for the year then ended. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audit included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of eWellness Healthcare Corporation as of December 31, 2014, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for the year then ended, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 3 to the financial statements, the Company has a working capital deficit, a deficit in stockholders’ equity and has sustained recurring losses from operations. This raises substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans with regard to these matters are also described in Note 3. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
HJ Associates & Consultants, LLP
Salt Lake City, Utah
April 7, 2015
| F-3 |
eWELLNESS HEALTHCARE CORPORATION
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| CURRENT ASSETS | ||||||||
| Cash | $ | 41,951 | $ | 900 | ||||
| Advances - related party | - | 7,054 | ||||||
| Prepaid Expenses | 4,053 | 26,274 | ||||||
| Total current assets | 46,004 | 34,228 | ||||||
| Property & equipment, net | 5,964 | 3,231 | ||||||
| Intangible assets, net | 19,862 | 22,816 | ||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 71,830 | $ | 60,275 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) | ||||||||
| CURRENT LIABILITIES | ||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | $ | 248,304 | $ | 174,044 | ||||
| Accounts payable - related party | 43,717 | 56,155 | ||||||
| Accrued expenses - related party | 33,090 | 30,181 | ||||||
| Accrued compensation | 677,000 | 329,000 | ||||||
| Contingent liability | 90,000 | 90,000 | ||||||
| Short term note and liabilities | 71,605 | - | ||||||
| Derivative liability | 2,802 | - | ||||||
| Convertible debt, net of discount | 309,945 | 178,433 | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | 1,476,463 | 857,813 | ||||||
| Total Liabilities | 1,476,463 | 857,813 | ||||||
| STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) | ||||||||
| Preferred stock, authorized, 10,000,000 shares, $.001 value, 0 shares issued and outstanding | - | - | ||||||
| Common stock, authorized 100,000,000 shares, $.001 par value, 18,170,538 and 16,421,000 issued and outstanding, respectively | 18,171 | 16,421 | ||||||
| Additional paid in capital | 2,033,383 | 1,087,320 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (3,456,187 | ) | (1,901,279 | ) | ||||
| Total Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) | (1,404,633 | ) | (797,538 | ) | ||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) | $ | 71,830 | $ | 60,275 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
| F-4 |
eWELLNESS HEALTHCARE CORPORATION
| For Year Ended | ||||||||
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| OPERATING EXPENSES | ||||||||
| Executive compensation | $ | 744,000 | $ | 744,000 | ||||
| General and administrative | 196,354 | 231,124 | ||||||
| Professional fees | 459,886 | 259,856 | ||||||
| Contingent liability expense | - | 90,000 | ||||||
| Research and development - related party | - | 30 | ||||||
| Total Operating Expenses | 1,400,240 | 1,325,010 | ||||||
| Loss from Operations | (1,400,240 | ) | (1,325,010 | ) | ||||
| OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE) | ||||||||
| Gain on extinguishment of debt | 11,323 | 1,200 | ||||||
| Loss on conversion of debt | (31,774 | ) | - | |||||
| Interest income | - | 7 | ||||||
| Interest expense, related parties | (3,920 | ) | (2,708 | ) | ||||
| Interest expense | (129,407 | ) | (13,074 | ) | ||||
| Net Loss before Income Taxes | (1,554,018 | ) | (1,339,585 | ) | ||||
| Income tax expense | (890 | ) | - | |||||
| Net Loss | $ | (1,554,908 | ) | $ | (1,339,585 | ) | ||
| Basic and diluted (loss) per share | $ | (0.09 | ) | $ | (0.10 | ) | ||
| Basic and diluted weighted average shares outstanding | 17,214,861 | 13,698,896 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
| F-5 |
eWELLNESS HEALTHCARE CORPORATION
STATEMENT OF STOCKHOLDERS’ (DEFICIT)
| Preferred Shares | Common Shares | Additional Paid in | Accumulated | Total Stockholders’ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Capital | Deficit | Deficit | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2013 | - | $ | - | 9,200,000 | $ | 9,200 | $ | 561,338 | $ | (561,694 | ) | $ | 8,844 | |||||||||||||||
| Imputed interest-related party | 2,708 | 2,708 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contributed services | 390,000 | 390,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recapitalization at merger | 6,000,000 | 6,000 | (22,509 | ) | (16,509 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for services @ $.10/share | 1,221,000 | 1,221 | 120,879 | 122,100 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Convertible debt discount | 34,904 | 34,904 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | (1,339,585 | ) | (1,339,585 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2014 | - | - | 16,421,000 | 16,421 | 1,087,320 | (1,901,279 | ) | (797,538 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Imputed interest-related party | 3,920 | 3,920 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contributed services and rent | 390,000 | 390,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for services @ $.10/share | 460,000 | 460 | 45,540 | 46,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for debt conversion @ $.35/share | 1,239,538 | 1,240 | 432,599 | 433,839 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued with debt @ $.10/share | 50,000 | 50 | 4,950 | 5,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash conversion feature on debt | 44,189 | 44,189 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrants issued with debt | 7,666 | 7,666 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrants issued for services | 17,199 | 17,199 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | (1,554,908 | ) | (1,554,908 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2015 | - | $ | - | 18,170,538 | $ | 18,171 | $ | 2,033,383 | $ | (3,456,187 | ) | $ | (1,404,633 | ) | ||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
| F-6 |
eWELLNESS HEALTHCARE CORPORATION
| For Year Ended | ||||||||
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities | ||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (1,554,908 | ) | $ | (1,339,585 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 4,428 | 2,797 | ||||||
| Contributed services | 384,000 | 390,000 | ||||||
| Shares issued for consulting services | 45,000 | 122,100 | ||||||
| Imputed interest - related party | 3,920 | 2,708 | ||||||
| Warrants issued for services | 16,640 | - | ||||||
| Debt issued for consulting services | 100,000 | - | ||||||
| Amortization of debt discount to interest expense | 84,462 | 34,904 | ||||||
| Loss on debt conversion | 31,774 | - | ||||||
| Rent contributed by officer | 6,000 | - | ||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities | ||||||||
| Advances - related parties | 7,054 | (7,054 | ) | |||||
| Prepaid expense | 23,780 | (26,274 | ) | |||||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 111,512 | 67,535 | ||||||
| Accounts payable - related party | (12,439 | ) | 56,155 | |||||
| Accrued expenses - related party | 2,908 | 30,181 | ||||||
| Contingent liability | - | 90,000 | ||||||
| Accrued compensation | 348,000 | 329,000 | ||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | (397,869 | ) | (247,533 | ) | ||||
| Cash flows from investing activities | ||||||||
| Intangible asset purchase | - | (20,000 | ) | |||||
| Cash acquired in merger | - | 90,000 | ||||||
| Purchase of equipment | (4,207 | ) | - | |||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (4,207 | ) | 70,000 | |||||
| Cash flows from financing activities | ||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of debt | 104,000 | - | ||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of convertible debt | 386,100 | 178,433 | ||||||
| Payments on debt | (43,223 | ) | - | |||||
| Payments of risky loan fees | (3,750 | ) | - | |||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 443,127 | 178,433 | ||||||
| Net increase in cash | 41,051 | 900 | ||||||
| Cash, beginning of period | 900 | - | ||||||
| Cash, end of period | $ | 41,951 | $ | 900 | ||||
| Supplemental Information: | ||||||||
| Cash paid for: | ||||||||
| Taxes | $ | - | - | |||||
| Interest Expense | $ | 549 | $ | - | ||||
| Non-cash Investing and Financing Activities Prepaid expenses transferred to intangible assets | $ | - | $ | 4,770 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
| F-7 |
eWELLNESS HEALTHCARE CORPORATION
Note 1. The Company
The Company and Nature of Business
eWellness Healthcare Corporation (f/k/a Dignyte, Inc.), (the “Company”, “we”, “us”, “our”) was incorporated in the State of Nevada on April 7, 2011, to engage in any lawful corporate undertaking, including, but not limited to, selected mergers and acquisitions. The Company has generated no revenues to date. Prior to the Share Exchange Agreement discussed below, other than issuing shares to its original shareholder, the Company never commenced any operational activities.
The eWellness strategy as a first-to-market enterprise in the Physical Therapy based telemedicine industry is to deliver a telemedicine physical therapy service augmenting corporate wellness programs and also expand nationally through a Software as a Service (SaaS) business model that enables existing physical therapy practices to extend their offerings via our telemedicine solution. Our objective is to provide Distance Monitored Physical Therapy (PHZIO) Programs to pre diabetic, cardiac and health challenged patients and knee and hip surgery rehabilitation. For corporate wellness program our services are designed to deliver significant healthcare savings to the company while charging a very small relative incremental cost.
Share Exchange Agreement
On April 11, 2014, Digntye, Inc. (“Dignyte”), a publicly held Nevada corporation and eWellness Corporation (“Private Co”), a privately held company incorporated in Nevada, executed a Share Exchange Agreement (or “Initial Exchange Agreement”). Prior to the execution and delivery of the final Amended and Restated Share Exchange Agreement (the “Agreement”), the Board of Directors of Dignyte approved the Agreement and the transactions contemplated thereby. Similarly, the Board of Directors of the Private Co. approved the exchange. On April 25, 2014, immediately prior to the execution and delivery of the Agreement, Dignyte amended its certificate of incorporation to change its corporate name from “Dignyte, Inc.” to “eWellness Healthcare Corporation.”
Pursuant to the Agreement, eWellness Healthcare Corporation issued 9,200,000 shares of unregistered common stock, $.001 par value per share (the “common stock”) to the shareholders of the Private Co. in exchange for all outstanding shares of the Private Co.’s common stock. In addition, our former chief executive officer agreed: (i) to tender 5,000,000 shares of common stock of Dignyte back to the Company for cancellation; (ii) assign from his holdings, an additional 2,500,000 shares of Dignyte to the shareholders of the Private Co. resulting in a total of 11,700,000 shares owned by those shareholders; and, (iii) to a further assignment of an additional 2,100,000 shares of Dignyte to other parties as stated therein (collectively, the “CEO Stock Actions”).
As the parties satisfied all of the closing conditions, on April 30, 2014, we closed the Share Exchange. As a result, the Private Co. shareholders own approximately 76.97% of our issued and outstanding common stock, after giving effect to CEO Stock Actions.
Following the Share Exchange, we abandoned our prior business plan and we are now pursuing the Private Co.’s historical businesses and proposed businesses. The Private Co. is the surviving company under the share exchange and became a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company.
For financial reporting purposes, the Share Exchange represents a “reverse merger” rather than a business combination. Consequently, the transaction is accounted for as a reverse-merger and recapitalization. eWellness Corporation is the acquirer for financial reporting purposes and Dignyte, Inc. is the acquired company. Consequently, the assets and liabilities and the operations that are reflected in the historical financial statements prior to the transactions are those of eWellness Corporation and are recorded at the historical cost basis of eWellness Corporation, and the financial statements after completion of the transaction include the assets, liabilities and operations of eWellness Healthcare Corporation, and eWellness Corporation from the closing date of the transaction. Additionally all historical equity accounts and awards of eWellness Corporation, including par value per share, share and per share numbers, have been adjusted to reflect the number of shares received in the transaction.
| F-8 |
The foregoing description of the Share Exchange Agreement does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the Share Exchange Agreement, a copy of which is attached to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K/A as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on August 6, 2014. At the execution of the Share Exchange Agreement, the number of total shares of common stock outstanding was 15,200,000.
On July 22, 2015, the Company’s wholly owned subsidiary, eWellness Corporation, was merged into the Company and, therefore, no longer exists as a separate entity.
Note 2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared to reflect the financial position, results of operations and cash flows of the Company and have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”).
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ materially from these good faith estimates and judgments.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are recorded at historical cost. Minor additions and renewals are expensed in the year incurred. Major additions and renewals are capitalized and depreciated over their estimated useful lives. Depreciation is recorded over the estimated useful lives of the related assets using the straight-line method for financial statement purposes. The Company uses other depreciation methods (generally accelerated) for tax purposes where appropriate. The estimated useful lives for significant property and equipment categories are as follows:
| Furniture and Fixtures | 5-7 Years | |
| Computer Equipment | 5-7 Years | |
| Software | 3 Years |
The Company regularly evaluates whether events or circumstances have occurred that indicate the carrying value of long-lived assets may not be recoverable. If factors indicate the asset may not be recoverable, we compare the related undiscounted future net cash flows to the carrying value of the asset to determine if impairment exists. If the expected future net cash flows are less than the carrying value, an impairment charge is recognized based on the fair value of the asset. For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, there was no impairment recognized.
Intangible Assets
The Company accounts for assets that are not physical in nature as intangible assets. Intangible assets have either an identifiable or indefinite useful life. Intangible assets with identifiable useful lives are amortized on a straight-line basis over their economic or legal life, whichever is shorter. Intangible assets with indefinite useful lives are reassessed each year for impairment. If an impairment has occurred, then a loss is recognized. An impairment loss is determined by subtracting the asset’s fair value from the asset’s book/carrying value.
| F-9 |
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes under FASB ASC 740-10-30. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are determined based upon differences between the financial reporting and tax basis of assets and liabilities and are measured using the enacted tax rates and laws that will be in effect when the differences are expected to reverse. Accounting standards require the consideration of a valuation allowance for deferred tax assets if it is “more likely than not” that some component or all of the benefits of deferred tax assets will not be realized.
Deferred Offering and Acquisition Costs
The Company defers as other assets the direct incremental costs of raising capital until such time as the offering is completed. At the time of the completion of the offering, the costs will be charged against the capital raised. Should the offering be terminated, the deferred offering costs will be charged to operations during the period in which the offering is terminated. Direct acquisition costs will be expensed as incurred.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company complies with the accounting guidance under Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 820-10, Fair Value Measurements, as well as certain related FASB staff positions. This guidance defines fair value as the price that would be received from selling an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. When determining the fair value measurements for assets and liabilities required to be recorded at fair value, the Company considers the principal or most advantageous market in which it would transact business and considers assumptions that marketplace participants would use when pricing the asset or liability, such as inherent risk, transfer restrictions, and risk of nonperformance.
The guidance also establishes a fair value hierarchy for measurements of fair value as follows:
Level 1 – quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2 – inputs other than Level 1 that are observable, either directly or indirectly, such as quoted prices in active markets for similar assets or liabilities, quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active, or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities.
Level 3 – unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities.
As of December 31, 2015, the Company had the following assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis.
| Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||||||
| Derivative liability | $ | 2,802 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 2,802 | ||||||||
| Total liabilities measure at fair value | $ | 2,802 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 2,802 | ||||||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents includes all cash deposits and highly liquid financial instruments with an original maturity to the Company of three months or less.
| F-10 |
Revenue Recognition
The Company has yet to realize revenues from operations. Once the Company has commenced operations, it will recognize revenues when delivery of goods or completion of services has occurred provided there is persuasive evidence of an agreement, acceptance has been approved by its customers, the fee is fixed or determinable based on the completion of stated terms and conditions, and collection of any related receivable is probable.
Loss per Common Share
The Company follows ASC Topic 260 to account for the loss per share. Basic loss per common share calculations are determined by dividing net loss by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted loss per common share calculations are determined by dividing net loss by the weighted average number of common shares and dilutive common share equivalents outstanding. During periods when common stock equivalents, if any, are anti-dilutive they are not considered in the computation. As the Company has no common stock equivalents and has incurred losses for the period ended December 31, 2015, no dilutive shares are added into the loss per share calculations.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) that are adopted by the Company as of the specified date. As of the period ended December 31, 2015, the Company has elected to the early adoption of ASU 2015-03 that simplifies the presentation of debt issuance costs. The Company had previously used the methodology in this standard and have adopted the pronouncement for current and future debt instruments.
Note 3. Going Concern
For the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company has no revenues and limited operations. The Company has an accumulated loss of $3,456,187. In view of these matters, there is substantive doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. The Company’s ability to continue operations is dependent upon the Company’s ability to raise additional capital and to ultimately achieve sustainable revenues and profitable operations, of which there can be no guarantee. The Company intends to finance its future development activities and its working capital needs largely from the sale of public equity securities with some additional funding from other traditional financing sources, including term notes, until such time that funds provided by operations are sufficient to fund working capital requirements. The financial statements of the Company do not include any adjustments relating to the recoverability and classification of recorded assets, or the amounts and classifications of liabilities that might be necessary should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern.
Note 4. Property and Equipment
Property and equipment consists of computer equipment that is stated at cost $8,421 and $4,214 less accumulated depreciation of $2,457 and $983 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Depreciation expense was $1,474 and $843 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Note 5. Intangible Assets
The Company recognizes the cost of a software license and a license for use of a programming code as intangible assets. The stated cost of these assets were $24,770 and $24,770 less accumulated amortization of $4,908 and $1,954 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, the amortization expense recorded was $2,954 and $1,954, respectively.
| F-11 |
Note 6. Income Taxes
Deferred taxes are provided on a liability method whereby deferred tax assets are recognized for deductible temporary differences and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards and deferred tax liabilities are recognized for taxable temporary differences. Temporary differences are the differences between the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and their tax bases. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when, in the opinion of management, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are adjusted for the effects of changes in tax laws and rates on the date of enactment.
Net deferred tax liabilities consist of the following components as of December 31, 2015 and 2014:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
| NOL Carryover | $ | 436,300 | $ | 314,000 | ||||
| Deferred Rent | 2,300 | |||||||
| Accrued Payroll | 237,000 | 115,200 | ||||||
| Contingent Liability | - | 31,500 | ||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities | ||||||||
| Depreciation | (200 | ) | (300 | ) | ||||
| Valuation allowance | (673,100 | ) | (462,700 | ) | ||||
| Net deferred tax asset | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
The income tax provision differs from the amount of income tax determined by applying the U.S. federal income tax rate to pretax income from continuing operations for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 due to the following:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Book Income | $ | (554.200 | ) | $ | (468,900 | ) | ||
| Depreciation | (300 | ) | (300 | ) | ||||
| Contributed Services | 136,500 | - | ||||||
| Meals & Entertainment | 1,300 | 2,500 | ||||||
| Stock for Expense Accounts | 21,600 | 21,000 | ||||||
| Contributed Interest Expense | 1,400 | 900 | ||||||
| Gain/Loss on settlement of debt through equity | 11,100 | (400 | ) | |||||
| Amortization of debt discount | 19,800 | - | ||||||
| Accrued Payroll | 121,800 | 115,200 | ||||||
| Related Party Interest | 1,400 | - | ||||||
| Contingent Liability | 31,500 | |||||||
| Valuation allowance | 229,600 | 298,500 | ||||||
| $ | - | $ | - | |||||
At December 31, 2015, the Company had net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $1,247,000 that may be offset against future taxable income from the year 2016 through 2035. No tax benefit has been reported in the December 31, 2015 financial statements since the potential tax benefit is offset by a valuation allowance of the same amount.
Due to the change in ownership provisions of the Tax Reform Act of 1986, net operating loss carryforwards for federal income tax reporting purposes are subject to annual limitations. Should a change in ownership occur, net operating loss carryforwards may be limited as to use in future years.
The Company’s policy is to recognize potential interest and penalties accrued related to unrecognized tax benefits within income tax expense. For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company did not recognize any interest or penalties, nor did we have any interest or penalties accrued as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 related to unrecognized benefits.
| F-12 |
The Company has filed for an extension for the federal income tax return in the U.S for the year ended December 31, 2015. The tax years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013 are open for examination for federal income tax purposes and by other major taxing jurisdictions to which we are subject.
Note 7. Related Party Transactions
Through the year ended December 31, 2015, a related party, a company for which the Company’s former Secretary-Treasurer and CFO is also serving as CFO, has paid $91,271 on the Company’s behalf for various operating expenses. The amounts outstanding as of December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014 were $43,717 and $56,155, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded $3,920 imputed interest on the amount owed to the related party based on an interest rate of 8%.
During 2014, the Company entered into a license agreement with a programming company in which one of our directors is Chief Marketing Officer. Through the licensing agreement, we obtained a perpetual license to use the programming code created by a video management platform as a base to develop our telemedicine video service for a license fee of $20,000. The license fee is recorded as an Intangible Asset and Accounts Payable on the Balance Sheet.
On April 1, 2015, the Company entered into an operating agreement with a physical therapy company (“EPT”) which is owned by the Company’s President and Chief Executive Officer. Through the agreement the Company agrees to provide operating capital advances in order for EPT to offer the Company’s PHIZIO platform to physical therapy patients. For accounting and tax purposes, the net profits or losses generated by EPA shall be allocated on a monthly basis. The Company will receive 75% of the net patient insurance reimbursements associated with the operation of the PHIZIO platform.
The Company rents its Culver City, CA office space from a company owned by our CEO. The imputed rent expense of $500 per month is recorded in the Statement of Operations and Additional Paid in Capital in the Balance Sheet.
Throughout the year ended December 31, 2015, the officers of the Company incur business expenses on behalf of the Company. The amounts payable as of the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 were $33,090 and $30,181, respectively.
Note 8. Non-Convertible Notes Payable
On January 27, 2015, the Company issued a promissory note of $20,000 with a shareholder/consultant at an annual interest rate of 12% due and payable on April 23, 2015. On April 9, 2015, as part of the second closing of the convertible debt discussed in Note 8 below, the note for $20,000, together with accrued interest for $3,980 through March 31, 2015 and future consulting fees due and payable through October 2015 of $100,000 were converted to a convertible note of $123,980.11. The consulting fees for future months were booked to prepaid expense and were amortized over the remaining term of the consulting agreement.
On May 30, 2015, the Company received $25,000 in exchange for a 90-day Promissory Note at an interest rate of 5% per annum. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 150,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.35 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $768. On August 26, 2015, the Company entered into an extension of this note for another 90 days to October 23, 2015. As an inducement for this extension, the Company issued 150,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants if $158. On October 11, 2015 the Company entered into a second extension of this note to be due on December 14, 2015. As an inducement for this extension, the Company issued 150,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $300. In addition the interest rate on the note was increased to 12% from the original note date of May 27 plus a risky loan fee of $6,250.
On July 15, 2015, the Company received $18,000 in exchange for a 90-day Promissory Note at an interest rate of 5% per annum. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 150,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $310. On October 5, 2015 the Company entered into an extension of this note to be due on December 14, 2015. As an inducement for this extension, the Company issued 150,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $300. In addition the interest rate on the note was increased to 12% from the original note date of July 15 plus a risky loan fee of $4,500.
| F-13 |
On September 16, 2015, the Company received $22,500 in exchange for a 90-day Promissory Note at an interest rate of 12% per annum plus a risky note fee of $5,625. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 450,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $908.
On September 16, 2015, the Company received $12,500 in exchange for a 90-day Promissory Note at an interest rate of 12% per annum plus a risky loan fee of $3,125 which was amortized over the term of the loan. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 250,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $504. This note, accrued interest and risky loan fee were paid on December 9, 2015.
On September 16, 2015, the Company received $2,500 in exchange for a 90-day Promissory Note at an interest rate of 12% per annum plus a risky loan fee of $625 which was amortized over the term of the loan. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 50,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $101. This note, accrued interest and risky loan fee were paid on December 9, 2015.
On October 11, 2015, the Company received $10,000 in exchange for a Promissory Note which matures on December 14, 2015; however if the Company receives $100,000 or more in its current private placement of up to $2,500,000 convertible note with warrants, the note will be due within three business days of such funds settling in the Company’s account. The note has an interest rate of 12% per annum plus a risky loan fee of $2,500 which was amortized over the term of the loan. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 200,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $385.
On December 6, 2015, the Company entered into a 90-day Promissory Note for $70,000 at an interest rate of 12% per annum plus a risky loan fee of $17,500 which is being amortized over the term of the loan. As an inducement the Company issued 1,400,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $2,800. The Company further agreed to repay the loan within three days of the Company receiving $500,000 or more in the current private placement of up to $2,500,000 convertible note with warrants. This Promissory Note resulted from the principal payment to the note holder of $28,222.94 and the holder cancelling the notes originally signed on May 27, 2015 plus extensions, July 15, 2015 plus extensions, September 16, 2015 and October 11, 2015.
Note 9. Convertible Notes Payable
On December 23, 2014 the Company issued $213,337 convertible promissory notes and warrants to purchase shares of common stock to four individual investors. The overall terms of the Notes are as follows:
| ● | Interest rate: 12% per annum. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company had recorded $22,195 of interest expense. | |
| ● | Due date: December 23, 2015. The Company is to pay the principal amount and all accrued and unpaid interest on or before the due date. Two of the convertible notes totaling $72,500 are in default. | |
| ● | Redemption right: Any time the closing price of the Company’s common stock has been at or above $1.50 for 20 consecutive trading days, the Company has the right to redeem all or any part of the principal and accrued interest of the notes, following written notice to the holders of the notes. | |
| ● | Optional Conversion: At the option of the holders, the notes may be converted into shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion price equal to $0.35 per share. | |
| ● | Additionally, if the Company elects to exercise the redemption right, the holders have the opportunity to elect to take the cash payment or to convert all or any portion of the notes into shares of the Company’s common stock. |
| F-14 |
| ● | The conversion price is subject to proportional adjustment in the event of stock splits, stock dividends and similar corporate events. | |
| ● | The notes are senior in rank to any other debt held by our officers, directors or affiliates and may not be subordinated to any other debt issued by the Company without the written consent of the holders. | |
| ● | Warrants: The holders of the notes are granted the right through December 23, 2017 to purchase 625,237 additional shares of common stock at $.35 per share. | |
| ● | During the time that any portion of these Notes are outstanding, if any Event of Default, as defined in the notes, occurs and such Default is not cured by the Company within sixty (60) days of the occurrence of the Event of Default (the “Cure Period”), the amount equal to one hundred fifty percent (150%) of the outstanding principal amount of this Note, together with accrued interest and other amounts owing shall become at the holder’s election, immediately due and payable in cash. The holders at its option have the right, with three (3) business days advance written notice to the Company after the expiration of the Cure Period, to elect to convert the Notes into shares of the Company’s common stock pursuant to the Optional Conversion rights disclosed above. |
| ● | The Company valued the cash conversion feature as the difference in the value of the note at its stated annual interest rate of 12% and the fair value of the note at its discounted value using an expected borrowing rate of 18%. |
On September 10, 2015, a convertible promissory note issued on December 23, 2014 with the principal value of $108,167 was converted to 309,048 shares of common stock at a conversion price of $.35 per share. The warrants associated with this note were not exercised. See Note 10– Equity Transactions below.
On October 1, 2015, 17,513 shares of common stock were issued at $.35 per share for the accrued interest of $6,129 on the note converted on September 10, 2015. See Note 10 – Equity Transactions below.
On November 11, 2015, a convertible promissory note issued on December 23, 2014 with the principal value of $32,670 and accrued interest of $3,517 were converted to 103,393 shares of common stock at a conversion price of $.35 per share. The warrants associated with this note were not exercised. See Note 10 – Equity Transactions below.
The Company’s Balance Sheets report the following related to the December 23, 2014, convertible promissory notes:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||
| Principal amount | $ | 72,500 | ||
| Unamortized debt discount | - | |||
| Net carrying amount | $ | 72,500 | ||
On April 9, 2015, the Company issued $270,080 convertible promissory notes (including an aggregate of $123,980 that was converted from certain other outstanding notes, including accrued interest, and future contractual cash consulting fees) and warrants to purchase shares of common stock to eight individual investors. The overall terms of the notes are as follows:
| ● | Interest rate: 12% per annum. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company had recorded $13,274 of interest expense. | |
| ● | Due date: April 30, 2016. The Company is to pay the principal amount and all accrued and unpaid interest on or before the due date. |
| F-15 |
| ● | Redemption right: Any time the closing price of the Company’s common stock has been at or above $1.50 for 20 consecutive trading days, the Company has the right to redeem all or any part of the principal and accrued interest of the notes, following written notice to the holders of the Notes. | |
| ● | Optional Conversion: At the option of the holders, the notes may be converted into shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion price equal to $0.35 per share. | |
| ● | Additionally, if the Company elects to exercise the redemption right, the holders have the opportunity to elect to take the cash payment or to convert all or any portion of the Notes into shares of the Company’s common stock. | |
| ● | The conversion price is subject to proportional adjustment in the event of stock splits, stock dividends and similar corporate events. | |
|
● | The notes are senior in rank to any other debt held by our officers, directors or affiliates and may not be subordinated to any other debt issued by us without the written consent of the holders. |
| ● | Warrants: The holders of the notes are granted the right through April 30, 2016 to purchase 771,658 additional shares of common stock at $.35 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $1,132. |
| ● | During the time that any portion of these notes are outstanding, if any Event of Default, as defined in the notes, occurs and such Default is not cured by the Company within sixty (60) days of the occurrence of the Event of Default (the “Cure Period”), the amount equal to one hundred fifty percent (150%) of the outstanding principal amount of this Note, together with accrued interest and other amounts owing shall become at the holder’s election, immediately due and payable in cash. The holders at its option have the right, with three (3) business days advance written notice to the Company after the expiration of the Cure Period, to elect to convert the Notes into shares of the Company’s common stock pursuant to the Optional Conversion rights disclosed above. | |
| ● | The Company valued the cash conversion feature as the difference in the value of the note at its stated interest rate of 12% and the fair value of the note at its discounted value using an expected borrowing rate of 18%. The value of the cash conversion feature at inception of the notes was $44,189. |
On July 14, 2015, convertible promissory notes issued on April 9, 2015 with a principal value of $87,500 were converted to 250,000 shares of common stock at $.35 per share. The warrants associated with these notes were not exercised. See Note 10 –Equity Transactions below.
On August 19, 2015, convertible promissory notes issued on April 9, 2015 with a principal value of $33,600 were converted to 96,000 shares of common stock at $.35 per share. The warrants associated with these notes were not exercised. See Note 10 –Equity Transactions below.
On September 10, 2015, a convertible promissory note issued on April 9, 2015 with a principal value of $123,980 was converted to 354,229 shares of common stock at $.35 per share. The warrants associated with this note were not exercised. See Note 10 –Equity Transactions below.
On October 1, 2015, 32,759 shares of common stock were issued at $.35 per share for the accrued interest of $11,466 on the convertible promissory notes converted on July 14, 2015, August 19, 2015, and September 20, 2015. See Note 10 – Equity Transactions below.
On November 11, 2015, a convertible promissory note issued on April 9, 2015, with a principal value of $25,000 plus accrued interest of $1,806 was converted to 76,595 shares of common stock at $.35 per share. The warrants associated with this not were not exercised. See Note 10 – Equity Transactions.
| F-16 |
The Company’s Balance Sheets report the following related to the April 9, 2015 convertible promissory notes:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||
| Principal amount | $ | - | ||
| Unamortized debt discount | - | |||
| Net carrying amount | $ | - |
On December 7, 2015, the Company issued a $275,000 senior convertible promissory note with a 10% original issue discount and warrants to purchase shares of common stock. The overall terms of the notes are as follows:
| ● | Interest rate: 8% per annum. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company had recorded $1,467 of interest expense. The interest rate increases to 15% per annum on any unpaid and overdue principal and interest. | |
| ● | Due date: June 2, 2016. The Company is to pay the principal amount and all accrued and unpaid interest on or before the due date. | |
| ● | Redemption right: With three trading days prior written notice of the Company has the right to redeem all the note equal to the sum of 115% of the principal plus accrued and unpaid interest on the principal amount. | |
| ● | Optional Conversion: At the option of the holder, the note may be converted into shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion price equal to 75% of the lowest per share purchase price, conversion price or exercise price of securities that the Company issues in the next financing transaction. | |
| ● | The note is senior in rank to any other debt of the Company as of the issuance date of the note and to any indebtedness incurred following the issuance date. | |
| ● | Warrants: The holders of the notes are granted the right to purchase 250,000 additional shares of common stock at $.80 per share. | |
| ● | The Company shall be considered to be in Default if the Company fails to obtain a listing of its common stock on at least one of OTCBB, OTCQB, Nasdaq or NYSE within 90 days of the date of the note or fails to maintain the listing of its common stock; the Company fails to comply with the reporting requirements of the 1934 Act and/or ceases to be subject to the reporting requirements of the 1934 Act; the restatement of any financial statements for any date or period from two years prior to the date of the note and until this note is no longer outstanding results in a material adverse effect on the rights of the note holder; the DTC places a “chill” on any of the Company’s securities; the Company’s common stock becomes not eligible for trading through the DTC’s FAST Automated Securities Transfer or Deposit/Withdrawal at Custodian programs; the Company fails to raise at least $1,000,000 in a Primary Offering within 120 days following the list date; the Company fails to appoint VStock Transfer LLC as the transfer agent for its common stock within 30 days of list date. | |
| ● | The Company’s Balance Sheets report the following related to the December 7, 2015, convertible promissory note: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||
| Principal amount | $ | 275,000 | ||
| Unamortized debt discount | (37,555 | ) | ||
| Net carrying amount | $ | 237,445 | ||
Under the guidance of ASC 470-20 Debt With Conversion and Other Options, the common shares of the Company, pending being listed on the OTC, and the net settlement requirements of the warrants will be analyzed at the end of each quarter to determine if the conversion does become readily convertible to cash which would require derivative accounting calculations and recording.
| F-17 |
Note 10. Equity Transactions
Preferred Stock
The total number of shares of preferred stock which the Company shall have authority to issue is 10,000,000 shares with a par value of $0.001 per share. There have been no preferred shares issued as of December 31, 2015.
Common Stock
The total number of shares of common stock which the Company shall have authority to issue is 100,000,000 shares with a par value of $0.001 per share.
On January 24, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 400,000 shares of common stock for consulting services at a value of $40,000. This value was amortized over the life of the contract.
On February 23, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 60,000 shares of common stock for consulting services for a value of $6,000. This value was amortized over the life of the contract
On July 14, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 250,000 shares of common stock for the conversion of convertible debt of $87,500.
On August 19, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 96,000 shares of common stock for conversion of convertible debt of $33,600.
On September 10, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 663,277 shares of common stock for conversion of convertible debt of $232,147.
On October 1, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 50,272 shares of common stock for the accrued interest totaling $17,595 on convertible debt previously converted.
On November 11, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 179,989 shares of common stock for conversion of convertible debt and accrued interest of $62,996.
On December 17, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 50,000 shares of common stock as part of a provision of the convertible debt note payable signed on December 7, 2015. (See Note 9 - Convertible Notes Payable)
As of the period ended December 31, 2015, the Company has 18,170,538 shares of common stock issued and outstanding.
Holders of shares of common stock are entitled to cast one vote for each share held at all stockholders’ meetings for all purposes including the election of directors. The common stock does not have cumulative voting rights.
No holder of shares of stock of any class is entitled as a matter of right to subscribe for or purchase or receive any part of any new or additional issue of shares of stock of any class or of securities convertible into shares of stock of any class, whether now hereafter authorized or whether issued for money, for consideration other than money, or by way of dividend.
On
behalf of the Company, Merriman Capital has filed a Form 211 with FINRA to facilitate trading of our stock in the over-the-counter
market. On February 22, 2016, FINRA issued the Company its trading symbol of EWLL for trading on the over-the-counter market.
The Company is also applying for DTC authorization.
| F-18 |
Warrants
On January 24, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 400,000 warrants that were issued as part of a consulting agreement extension that expired on October 21, 2015. The fair value of the warrants is $11,259 which was recorded as a prepaid expense and amortized over the life of the contract.
On April 9, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 771,658 warrants that were issued as part convertible debt totaling $270,080. The fair value of the warrants is $1,132.
On April 17, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 100,000 warrants that were issued as part of an advisory agreement. The fair value of the warrants was $1,296 which was expensed immediately
On May 20, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 250,000 warrants that were issued as part of an advisory services agreement. The fair value of the warrants is $4,598 and the Company recorded this as consulting expense.
On May 20, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 250,000 warrants that were issued as part of an advisory services agreement. The fair value of the warrants is $1,342 which was recorded as a prepaid expense and amortized over the life of the contract which expires May 20, 2016.
On May 30, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 150,000 warrants that were issued as part of a promissory note. The fair value of the warrants is $768.
On July 15, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 150,000 warrants that were issued as part of a promissory note. The fair value of the warrants is $310.
On August 26, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 150,000 warrants that were issued as part of the extension of a promissory note dated May 26, 2015. The fair value of the warrants is $300.
On September 16, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 750,000 warrants that were issued as part of three promissory notes. The fair value of the warrants is $1,513.
On October 11, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 500,000 warrants that were issued as part of an extension of promissory notes dated May 26, 2015 and July 15, 2015. The fair value of the warrants is $985.
On December 6, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 1,400,000 warrants that were issued as part of a promissory note. The fair value of the warrants is $2,800.
On December 7, 2015, the Company authorized the issuance of 250,000 warrants that were issued as part of a convertible note. The derivative liability for this note is $2,802 associated with these warrants was valued at $2,802. (See Note 12).
| F-19 |
The following is a summary of the status of all of the Company’s warrants as of December 31, 2015 and changes during the period on that end date:
| Weighted | |||||||||
| Number of | Average | ||||||||
| Warrants | Exercise Price | ||||||||
| Outstanding at January 1, 2014 | - | $ | - | ||||||
| Granted | 625,237 | $ | 0.35 | ||||||
| Exercised | - | $ | - | ||||||
| Cancelled | - | $ | - | ||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2014 | 625,237 | $ | 0.35 | ||||||
| Granted | 5,121,658 | $ | 0.63 | ||||||
| Exercised | - | $ | - | ||||||
| Cancelled | - | $ | - | ||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2015 | 5,746,895 | $ | 0.60 | ||||||
For purpose of determining the fair market value of the warrants issued during the year ended December 31, 2015, we used the Black Scholes option valuation model. These valuations were done throughout the year at the date of issuance and not necessarily as of the reporting date. As there is no current market for the Company’s shares, we used $0.10 as the stock price at valuation date to be consistent with prior issuances and the stock prices of comparable companies to determine volatility. The significant assumptions used in the Black Scholes valuation of the date of issuance are as follows:
| Stock price on the valuation date | $ | 0.10 | ||
| Exercise price of warrants | $ | .35 and .80 | ||
| Dividend yield | 0.00 | % | ||
| Years to maturity | 2.5 – 5.0 | |||
| Risk free rate | .75% - 1.93 | % | ||
| Expected volatility | 63% - 88 | % |
Stock Option Plan
On August 6, 2015, the Board of Directors approved the 2015 Stock Option Plan, pursuant to which certain directors, officers, employees and consultants will be eligible for certain stock options and grants. The Plan is effective as of August 1, 2015 and the maximum number of shares reserved and available for granting awards under the Plan shall be an aggregate of 3,000,000 shares of common stock, provided however that on each January 1, starting with January 1, 2016, an additional number of shares equal to the lesser of (A) 2% of the outstanding number of shares (on a fully-diluted basis) on the immediately preceding December 31 and (B) such lower number of shares as may be determined by the Board or committee charged with administering the plan. This plan may be amended at any time by the Board or appointed plan Committee.
Note 11. Commitments, Contingencies
The Company may be subject to lawsuits, administrative proceedings, regulatory reviews or investigations associated with its business and other matters arising in the normal conduct of its business. The following is a description of an uncertainty that is considered other than ordinary, routine and incidental to the business.
The closing of the Initial Exchange Agreement with Private Co. was conditioned upon certain, limited customary representations and warranties, as well as, among other things, our compliance with Rule 419 (“Rule 419”) of Regulation C under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) and the consent of our shareholders as required under Rule 419. Accordingly, we conducted a “Blank Check” offering subject to Rule 419 (the “Rule 419 Offering”) and filed a Registration Statement on Form S-1 to register the shares of such offering; the Registration Statement was declared effective on September 14, 2012. We used 10% of the subscription proceeds as permitted under Rule 419 and the amount remaining in the escrow trust as of the date of the closing of the Share Exchange was $90,000 (the “Trust Account Balance”).
| F-20 |
Rule 419 required that the Share Exchange occur on or before March 18, 2014, but due to normal negotiations regarding the transactions and the parties’ efforts to satisfy all of the closing conditions, the Share Exchange did not close on such date. Accordingly, after numerous discussions with management of both parties, they entered into an Amended and Restated Share Exchange Agreement (the “Share Exchange Agreement”) to reflect a revised business combination structure, pursuant to which we would: (i) file a registration statement on Form 8-A (“Form 8A”) to register our common stock pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Exchange Act, which we did on May 1, 2014 and (ii) seek to convert the participants of the Rule 419 Offering into participants of a similarly termed private offering (the “Converted Offering”), to be conducted pursuant to Regulation D, as promulgated under the Securities Act.
Fifty-two persons participated in the Rule 419 Offering and each of them gave the Company his/her/its consent to use his/her/its escrowed funds to purchase shares of the Company’s restricted common stock in the Converted Offering (the “Consent”) rather than have their funds returned. To avoid further administrative work for the investors, we believe that we took reasonable steps to inform investors of the situation and provided them with an appropriate opportunity to maintain their investment in the Company, if they so choose, or have their funds physically returned. Management believed the steps it took constituted a constructive return of the funds and therefore met the requirements of Rule 419.
However, pursuant to Rule 419(e)(2)(iv), “funds held in the escrow or trust account shall be returned by first class mail or equally prompt means to the purchaser within five business days [if the related acquisition transaction does not occur by a date that is 18 months after the effective date of the related registration statement].” As set forth above, rather than physically return the funds, we sought consent from the investors of the Rule 419 Offering to direct their escrowed funds to the Company to instead purchase shares in the Converted Offering. The consent document (which was essentially a form of rescission) was given to the investors along with a private placement memorandum describing the Converted Offering and stated that any investor who elected not to participate in the Converted Offering would get 90% of their funds physically returned. Pursuant to Rule 419(b)(2)(vi), a blank check company is entitled to use 10% of the proceed/escrowed funds; therefore, if a return of funds is required, only 90% of the proceed/escrowed funds need be returned. The Company received $100,000 proceeds and used $10,000 as per Rule 419(b)(2)(vi); therefore, only $90,000 was subject to possible return.
As disclosed therein, we filed the amendments to the initial Form 8-K in response to comments from the SEC regarding the Form 8-K and many of those comments pertain to an alleged violation of Rule 419. The Company continued to provide the SEC with information and analysis as to why it believes it did not violate Rule 419, but was unable to satisfy the SEC’s concerns. Comments and communications indicate that Rule 419 requires a physical return of funds if a 419 offering cannot be completed because a business combination was not consummated within the required time frame; constructive return is not permitted.
As a result of these communications and past comments, we are disclosing that we did not comply with the requirements of Rule 419, which required us to physically return the funds previously submitted to escrow pursuant to the Rule 419 Offering. As a result of our failure to comply with Rule 419, the SEC may bring an enforcement action or commence litigation against us for failure to strictly comply with Rule 419. If any claims or actions were to be brought against us relating to our lack of compliance with Rule 419, we could be subject to penalties (including criminal penalties), required to pay fines, make damages payments or settlement payments. In addition, any claims or actions could force us to expend significant financial resources to defend ourselves, could divert the attention of our management from our core business and could harm our reputation.
Ultimately, the SEC determined to terminate its review of the Initial Form 8-K and related amendments, rather than provide us with additional opportunities to address their concerns and therefore, we did not clear their comments. It is not possible at this time to predict whether or when the SEC may initiate any proceedings, when this issue may be resolved or what, if any, penalties or other remedies may be imposed, and whether any such penalties or remedies would have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. Litigation and enforcement actions are inherently unpredictable, the outcome of any potential lawsuit or action is subject to significant uncertainties and, therefore, determining at this time the likelihood of a loss, any SEC enforcement action and/or the measurement of the amount of any loss is complex. Consequently, we are unable to estimate the range of reasonably possible loss. Our assessment is based on an estimate and assumption that has been deemed reasonable by management, but the assessment process relies heavily on an estimate and assumption that may prove to be incomplete or inaccurate, and unanticipated events and circumstances may occur that might cause us to change that estimate and assumption. In light of the uncertainty of this issue and while Management evaluates the best and most appropriate way to resolve same, management determined to create a reserve on the Company’s Balance Sheet for the $90,000 that was subject to the Consent.
| F-21 |
On or about June 23, 2014, we entered into a license agreement with Bistromatics Corp., to which one of our directors is Chief Marketing Officer, pursuant to which we obtained a perpetual license to use the programming code created by a video management platform as a base to develop our telemedicine video service for a license fee of $20,000 due by September 30, 2014. The parties entered into an addendum extending the due date of the license fee to December 31, 2014, another addendum extending it to July 1, 2015, another addendum extending it to October 31, 2015 and another addendum extending it to January 31, 2016. Intellectual property developed as a result of this license, will be our property; but Bistromatics will retain the intellectual property for the original code base. We may resell or license the resulting telemedicine platform for an extended license fee of $10,000 for each additional instance the code base will be used. Through this agreement, Bistromatics Corp. built our PHZIO platform; our director purchased the domain name on behalf of the Company and retains no rights to same. This agreement was paid by the year ended December 31, 2015.
The Company rents its Culver City, CA office space from a company owned by our CEO. The rental agreement provides for the value of the rent of $500 per month be recorded as contributed towards the founding eWellness and its operations. During the year ended December 31, 2015, we have recorded this rent payment in the Statements of Operations and Additional Paid in Capital on the Balance Sheet.
In May 2014, the Company signed an Office Service Agreement for office space in New York, New York. A deposit of $17,874 was paid and recorded in prepaid expense. The utilization of the office space began on August 1, 2014 and terminated at December 31, 2014. The Company negotiated a settlement of $5,500 in April, 2015 for the cancellation of the agreement. The settlement resulted in a gain on extinguishment of debt of $11,323.
On January 24, 2015, the Company received $20,000 in consideration for a 90-day Promissory Note at an interest rate of 12% per annum. On April 9, 2015, this note and accrued interest through March 31, 2015 was converted into convertible debt.
On January 24, 2015 the Company extended a previous consulting and service agreement with a consultant from April 21, 2015 to October 20, 2015 for which the Company shall issue 400,000 shares of restricted common stock and 400,000 callable common stock purchase warrants at a strike price of $0.35 per share. These shares were issued on April 9, 2015. Pursuant to this extension agreement, the Company was to pay $10,000 per month consulting fee beginning with February 1, 2015 through the end of the agreement. As discussed in Footnote 7 above, the full $100,000 consulting fees were rolled into a convertible note.
On February 14, 2015, the Company entered into a one-year agreement with BMT, Inc. as a consultant and advisor in connection with certain business development advisory. This agreement is on an at-will basis as determined by the Company in exchange for cash compensation to be invoiced monthly. The total compensation paid as of December 31, 2015 on this agreement is $11,950.
On February 23, 2015, the Company entered into a one-year agreement with a consultant in connection with certain corporate finance, investor relations and related business matters in exchange for 60,000 shares of restricted common stock. These shares were issued on April 14, 2015.
On March 16, 2015, the Company extended a $20,000 licensing fee payment agreement with Bistromatics, Inc. pertaining to intellectual property utilized by the Company until July 1, 2015. The Company made an initial payment of $5,000 with the remaining fees to be to be paid on or before July 1, 2015. On August 11, 2015, the Company signed an addendum to the licensing agreement with Bistromatics to extend the payment of the licensing fee to October 31, 2015. On November 10, 2015, the Company signed an additional addendum to the licensing agreement with Bistromatics to extend the payment of the licensing fee to January 30, 2016. On December 9, 2015, the Company paid the remaining $15,000 due on this licensing agreement.
| F-22 |
On April 1, 2015, the Company entered into an Operating Agreement with Evolution Physical Therapy (“EPT”), a company owned by one of the Company’s officers, wherein it is agreed that EPT would be able to operate the Company’s telemedicine platform www.PHZIO and offer it to selected physical therapy patients of EPT. The Company is to receive 75% of the net insurance reimbursements from the patient for use of the platform. The Company will advance capital requested by EPT for costs specifically associated with operating the www.phzio,com platform and associated physical therapy treatments – computer equipment, office or facilities rental payments, physical therapist or physical therapy assistant, administrative staff, patient induction equipment, office supplies, utilities and other associated operating costs. It is anticipated that the operation of the platform by EPT will generate positive cash flow within 90 days from the start of patient induction.
On April 17, 2015, the Company entered into an agreement with Akash Bajaj, M.D., M.P.H. The agreement is for Dr. Bajaj to serve as a consultant and as the Chairman of the Company’s Clinical Advisory Board. The term of the agreement is for one year with annual renewal as desired. The agreement further sets the hourly rate to be paid at $225 per hour with payment to be at the end of each month. Further, the Company granted Dr. Bajaj a five-year non-statutory option to purchase 100,000 shares of common stock at a price of $.35 per share. The options will vest over a 12 month period at 8,333 per month.
On May 20, 2015, the Company entered into an agreement with Mavericks Capital Securities LLC (“Mavericks”). The term of the contract begins on the effective date and can be terminated within 30 days upon written notice by either party. The Company is to pay Mavericks a monthly retainer fee of $10,000 that is deferred until the Company raises $250,000 in new investor funds from the effective date. In addition, the Company granted Mavericks 250,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.35 per share. On September 28, 2015, the Company and Mavericks entered into an amendment to the consultant agreement pursuat to which Mavericks will also assist the Company in the acquisition of new customers, for which the Company shall pay Mavericks 10% of the revenue received by the Company, net of any pass through costs, from any such customers introduced to the Company by Mavericks; payment shall be made upon the Company’s receipt of such revenues. In the amendment, the parties also further clarified the definition of Customer Acquisition.
On May 20, 2015, the Company entered into a one year agreement with financial advisory company. As the retainer, the Company granted the consultant 250,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.35 per share.
On May 30, 2015, the Company received $25,000 in consideration for a 90-day Promissory Note at an interest rate of 5% per annum. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 150,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.35 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $768. On August 26, 2015, the Company extended the due date of this note for an additional 90 days. As an inducement for the extension, the Company issued 150,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $158. On October 11, 2015, the Company extended a second time the due date of this note for an additional 90 days. As an inducement for the extension, the Company issued 150,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share and a Risky Loan Fee of $6,250. The fair value of the warrants is $300. The Risky Loan Fee was amortized over the term of the second extension. For the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded $1,759 of interest expense for this note. On December 14, 2015, the Company paid the principal of this note to the note holder. The accrued interest was rolled into another note payable dated December 6, 2015. See below.
On July 15, 2015, the Company received $18,000 in consideration for a 90-day Promissory Note at an interest rate of 5% per annum. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 150,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $310. On October 5, 2015, the Company extended the payment due date of this note for 90 days. As an inducement for this extension, the Company issued 150,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share and a Risky Loan Fee of $4,500. The fair value of the warrants is $300. The Risky Loan Fee was amortized over the term of the extension. For the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded $1,003 of interest expense for this note. On December 14, 2015, the Company paid $3,822 of the principal to the note holder. The remaining principal and accrued interest was rolled into another note payable dated December 6, 2015. See below.
| F-23 |
On August 6, 2015, the Board of Directors appointed Ms. Rochelle Pleskow as the seventh member of the Board of Directors, effective immediately. Ms. Pleskow is the current head of Healthcare Informatics at HP, and the Board is confident that Ms. Pleskow can add value to the Company’s PHZIO platform through helping to create better patient outcome data. The Company agreed to pay Ms. Pleskow $2,000 per month fees, which shall accrue as of July 1, 2015 and be paid upon the first closing of our next financing. She shall also be eligible to receive any other benefits that are offered to other directors.
On September 16, 2015, the Company received $22,500 in consideration for a 90-day Promissory Note at an interest rate of 12% per annum plus a risky note fee of $5,625 which is being amortized over the term of the loan. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 450,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $908. For the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded $823 of interest expense. The remaining principal and accrued interest was rolled into another note payable dated December 6, 2016, See below.
On September 16, 2015, the Company received $12,500 in exchange for a 90-day Promissory Note at an interest rate of 12% per annum plus a Risky Note Fee of $3,125 which is being amortized over the term of the loan. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 250,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $504. For the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded $457 of interest expense for this note. The principal and accrued interest on this note was paid on December 14, 2015.
On September 16, 2015, the Company received $2,500 in consideration for a 90-day Promissory Note at an interest rate of 12% per annum plus a risky loan fee of $625 which is being amortized over the term of the loan. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 50,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants is $101. For the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded $91 of interest expense for this note. The principal and accrued interest on this note was paid on December 14, 2015.
On December 6, 2015, the Company entered into a 90-day Promissory Note at an interest rate of 12% per annum. This note is from the unpaid principal and accrued interest on the promissory notes dated May 27, 2015, July 15, 2015, September 16, 2015, and October 11, 2015. The Company had paid the note holder $28,223 for principal on these notes. The note is payable within three days of the Company receiving $500,000 or more from its current Private Placement. As an inducement for this promissory note, the Company issued 1,400,000 warrants to purchase Company common stock at $.80 per share and a risky loan fee of $17,500. The risky loan fee is to be amortized over the term of the loan. The fair value of the warrants is $2,800. For the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded $715 of interest expense for this note.
On December 11, 2015 the Company entered into a convertible note with Firstfire Global Opportunities Fund, LLC for $275,000 in principal amount with a 10% original issue discount, and a 5 year warrant to purchase 250,000 shares of common stock of the Company with an exercise price of $0.80 per share. The note matures on June 2, 2016 and shall carry an interest of 8% per annum on the unpaid balance and overdue interest or principal balances shall carry an interest of 15% per annum until paid. It is an unsecured note with priority over existing and future debt. The note is convertible into common stock at the buyer’s discretion at 75% of the lowest per share financing transaction following the closing date. nder the terms of the note the Company shall be considered in default if the Company fails to obtain a listing of its Common Stock on at least one of OTCBB, OTCQB, Nasdaq or NYSE within 90 days of the note date or fails to maintain the listing of its Common Stock; the Company fails to comply with the reporting requirements of the 1934 Act and/or ceases to be subject to the reporting requirements of the 1934 Act; the restatement of any financial statements for any date or period from 2 years prior to the date of the note and until this note is no longer outstanding resulting in a material adverse effect on the rights of the note holder; the DTC places a “chill” on any of the Company’s securities; the Company’s common stock becomes not eligible for trading through the DTC’s FAST Automated Securities Transfer or Deposit/Withdrawal at Custodian programs; the Company fails to raise at least $1,000,000 in a Primary Offering within 120 days following the List Date; the Company fails to appoint VStock Transfer LLC as the transfer agent for its common stock within 30 days of Listing Date. For the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded $1,467 of interest expense on this note.
| F-24 |
From time to time the Company may become a party to litigation matters involving claims against the Company. Except as may be outlined above, management believes that there are no current matters that would have a material effect on the Company’s financial position or results of operations.
Note 12. Derivative Valuation
The warrants granted with the $275,000 senior convertible promissory note (the “Note”) issued on December 7, 2015 (described in Note 7) have a Most Favored Nation clause resulting in the exercise price of the warrants not being fixed. Therefore, this feature has been characterized as a derivate liability to be re-measured at the end of every reporting period with the change in value reported in the statement of operations. At December 31, 2015, the outstanding fair value of the warrants accounted for as a derivative liability amounted to $2,802. As of December 31, 2015. no gain or loss was recognized in the statement of operations as the change in valuation from inception was clearly trivial to the financial statements.
For purposes of determining the fair market value of the derivative liability for the warrants, the Company used Black Scholes option valuation model. The significant assumptions used in the Black Scholes valuation of the derivative are as follows:
| Stock price at valuation date | $ | .10 | ||
| Exercise price of warrants | $ | .80 | ||
| Risk free interest rate | 1.67 | % | ||
| Stock volatility factor | 62.82 | % | ||
| Years to Maturity | 5 | |||
| Expected dividend yield | None |
Note 13. Supplemental Cash Flow Information
During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company had the following non-cash investing and financing activities:
| ● | Accrued interest of $3,848 and $3,980 was rolled into short-term notes and convertible debt, respectively. | |
| ● | $20,000 of short-term notes was transferred to convertible debt. | |
| ● | Issued 4,121,658 warrants valued at $7,666 as incentive for lenders to enter debt agreements. | |
| ● | Increased derivative liability and debt discount by $2,802 for warrant issued debt. | |
| ● | Increased debt discount by $44,189 for the value of the cash conversion feature on debt. | |
| ● | Increased debt discount by $25,000 for an Original Issue Discount on debt. | |
| ● | Increased debt discount by $10,000 for debt issuance costs. | |
| ● | Issued $5,000 of stock as incentive for a lender to enter a debt agreement. | |
| ● | Agreed to pay $40,125 and $5,000 in risky loan fees on short-term notes and convertible debt, respectively. | |
| ● | Transferred $6,500 from account payable to short term notes. | |
| ● | Issued 1,239,538 shares of common stock valued at $433,839 for the extinguishment of $410,917 worth of debt and $22,922 worth of accrued interest. | |
| ● | Issued 540,000 warrants for services valued at $17,199, of which $599 was recorded as a prepaid and $61,640 was recorded as warrants for services. | |
| ● | Issued 460,000 shares of common stock valued at $45,540, of which $1,000 was recorded as a prepaid and $45,000 was recorded as stock for services. |
Note 14. Segment Reporting
The Company has one operating segment, which was identified based upon the availability of discrete financial information and the chief operating decision makers’ regular review of financial information.
Note 15. Subsequent Events
On January 25, 2016, HJ Associates & Consultants, LLP, doing business as HJ & Associates, LLC (“HJ”), associated with an asset acquisition by Haynie & Company, resigned as the independent registered public accounting firm for eWellness Healthcare Corporation (the “Company”). On January 26, 2016, the Company engaged Haynie & Company (“Haynie”), Salt Lake City, Utah, as its new independent registered public accounting firm. The change of the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm from HJ to Haynie was approved unanimously by our board of directors.
On February 26, 2016, the Board of the Directors approved termination with First American Stock Transfer (“First American”), the transfer agent for our common stock. On February 29, 2016, we sent a termination notice to First American.
On February 26, 2016, the Board of Directors approved engagement with VStock Transfer, LLC (“VStock”) as new transfer agent for our common stock, effectively immediately. The common stock records were transferred to VStock on March 9, 2016.
On February 29, 2016, a convertible promissory note issued on December 24, 2015, with a principal value of $69,500 plus accrued interest of $10,031 was converted to 227,232 shares of common stock at $.35 per share.
On March 18, 2016, the Board of Directors approved three separate consulting agreements with three separate consulting firms that were signed on January 20, March 3, and March 11, 2016. The agreements included the issuance authorization of a total 450,000 shares.
| F-25 |
ITEM 9: CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
During the past two years, there was no disagreement of the type described in paragraph (a)(1)(iv) or any reportable event as described in paragraph (a)(1)(v) of Item 304 of Regulation S-K that is required to be disclosed under this Item 9. However, in January 2015, we did change auditors as disclosed below
On January 26, 2015 (“Resignation Date”), Mantyla McReynolds, LLC (“Mantyla”) resigned as our independent registered public accounting firm and the Company accepted the resignation. On January 26, 2015, the Company engaged HJ Associates & Consultants, LLP (“HJ Associates”) to replace Mantyla as our independent registered public accounting firm. The engagement of HJ Associates was approved by the Company’s board of directors.
Mantyla’s audit reports on the financial statements of the Company for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 contained no adverse opinion or disclaimer of opinion, nor were they qualified or modified as to uncertainty, audit scope or accounting principles, except that the audited financial statements contained in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the years ended December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2012 contained a going concern qualification.
There were no disagreements between the Company and Mantyla, for the two most recent years and any subsequent interim period through Resignation Date on any matter of accounting principles or practices, financial statement disclosure, or auditing scope or procedure, which, if not resolved to the satisfaction of Mantyla, would have caused them to make reference to the subject matter of the disagreement in connection with its report. Further, Mantyla has not advised the Company that:
1) During the year ended December 31, 2013 and through the Resignation Date, there were any reportable events, as defined in Item 304(a)(1)(v) of Regulation S-K, with the exception of material weaknesses identified in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting; or
2) information has come to the attention of Mantyla which made it unwilling to rely upon management’s representations, or made it unwilling to be associated with the financial statements prepared by management; or
3) the scope of the audit should be expanded significantly, or information has come to the attention of Mantyla that they have concluded will, or if further investigated, might materially impact the fairness or reliability of a previously issued audit report or the underlying financial statements, or the financial statements issued or to be issued covering the year ended December 31, 2014.
On January 26, 2015, we engaged HJ Associates as our principal accountant to audit our financial statements as successor to Mantyla. During our two most recent fiscal years or subsequent interim periods, we have not consulted with HJ Associates regarding the application of accounting principles to a specific transaction, either completed or proposed, or the type of audit opinion that might be rendered on our financial statements, nor did HJ Associates provide advice to our company, either written or oral, that was an important factor considered by our company in reaching a decision as to the accounting, auditing or financial reporting issue.
On January 25, 2016 (“Resignation Date”), HJ & Associates (“HJ”) resigned as our independent registered public accounting firm associated with an asset acquisition with Haynie and Company (“Haynie”) On January 26, 2015, the Company engaged Haynie to replace HJ as our independent registered public accounting firm. The engagement of Haynie was approved by the Company’s board of directors.
There were no disagreements between the Company and HJ on any matter of accounting principles or practices, financial statement disclosure, or auditing scope or procedure, which, if not resolved to the satisfaction of HJ, would have caused them to make reference to the subject matter of the disagreement in connection with its report.
| 36 |
ITEM 9A: CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures designed to provide reasonable assurance that material information required to be disclosed by us in the reports we file or submit under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that the information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
We performed an evaluation (“Evaluation”), under the supervision and with the participation of our management including our Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”), of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures (“Disclosure Controls”) as of the end of the period covered by this Report pursuant to Rule 13a-15 of the Exchange Act. Based on this evaluation and the existence of the material weaknesses discussed below in “Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting,” our management, including our CEO and CFO, concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective at the reasonable assurance level as of the end of the period covered by this report.
We do not expect that our disclosure controls and procedures will prevent all errors and all instances of fraud. Disclosure controls and procedures, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the disclosure controls and procedures are met. Further, the design of disclosure controls and procedures must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints, and the benefits must be considered relative to their costs. Because of the inherent limitations in all disclosure controls and procedures, no evaluation of disclosure controls and procedures can provide absolute assurance that we have detected all our control deficiencies and instances of fraud, if any. The design of disclosure controls and procedures also is based partly on certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, our principal executive and principal financial officers and effected by our Board, management and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and includes those policies and procedures that:
| ● | pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; |
| ● | provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and directors; and |
| ● | provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. |
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Additionally, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risks that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
| 37 |
Management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013). Based on this assessment, management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was not effective as of December 31, 2015, due to the existence of the material weaknesses discussed below. A material weakness is a control deficiency (within the meaning of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (“PCAOB”) Auditing Standard No. 5), or combination of control deficiencies, that results in more than a remote likelihood that a material misstatement of the annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected.
Management identified the following material weaknesses that have caused management to conclude that as of December 31, 2015, our internal control over financial reporting was not effective:
| ● | Our size has prevented us from being able to employ sufficient resources to enable us to have an adequate level of supervision and segregation of duties within our internal control system. Specifically, there is limited review of financial reporting and policies and procedures have not yet been implemented to analyze, document, monitor and report on non-routine and complex transactions that require management estimation or judgment. | |
| ● | The Company does not have adequate controls and procedures or an internal audit function to detect errors in accounting for certain of its financing transactions. | |
| ● | The lack of sufficient controls in place to ensure that all disclosures required were addressed in our financial statements, which may result in ineffective oversight in the establishment and monitoring of required internal controls and procedures. | |
| ● | Management determined that the Company does not have a sufficient complement of personnel with appropriate training and experience in U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) and lacks certain subject matter expertise related to accounting for income taxes, complex debt and equity transactions, and disclosures. |
This Annual Report on Form 10-K does not include an attestation report of the Company’s registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting due to permanent exemptions for smaller reporting companies. Management’s report was not subject to such attestation pursuant to rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission that permits us to provide only management’s report in this Annual Report.
Remediation Plan for Material Weaknesses
While management believes that the Company’s financial statements previously filed in the Company’s SEC reports have been properly recorded and disclosed in accordance with GAAP, based on the control deficiencies identified above, we have begun taking steps and plan to take additional measures to remediate the underlying causes of the material weakness, primarily through the development and implementation of formal policies, improved processes and documented procedures, as well as the hiring of additional finance personnel. Management believes that the appointment of additional management personnel will lead to increased oversight over the accounting and reporting function. As soon as we can raise sufficient capital or our operations generate sufficient cash flow, we will hire additional personnel to handle our accounting and reporting functions. We also plan to supply enhanced training and education on principles related to accounting for financing transactions, when funds allow.
Management has reviewed the financial statements and underlying information included herein in detail and believes the procedures performed are adequate to fairly present our financial position, results of operations and cash flows for the periods presented in all material respects.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Other than as described above, there have been no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the fourth quarter of 2015 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
| 38 |
Because of its inherent limitations, a system of internal control over financial reporting can provide only reasonable assurance and may not prevent or detect misstatements. Further, because of changes in conditions, effectiveness of internal controls over financial reporting may vary over time. Our system contains self-monitoring mechanisms, and actions are taken to correct deficiencies as they are identified.
None.
ITEM 10: DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS, AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The following table and text set forth the names and ages of all directors and executive officers as of March 18, 2016.
Pursuant to the Share Exchange Agreement, Mr. McRobbie-Johnson resigned as our sole director and from all offices he held prior to the Share Exchange and Donna S. Moore resigned from all of her positions with the Company, i.e. Secretary, Treasurer and CFO. Also pursuant to the Share Exchange Agreement, the following individuals were appointed as our directors, effective immediately after the close of the Share Exchange: Douglas MacLellan (Chairman), Darwin Fogt, Curtis Hollister and David Markowski (collectively, the “New Directors”); and the following individuals were appointed to the following positions: Mr. Fogt as our President and Chief Executive Officer, David Markowski as our Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and Treasurer, and Curtis Hollister as our Chief Technology Officer (collectively, the “New Officers”).
There are no family relationships among our directors and executive officers. Each director is elected at our annual meeting of shareholders and holds office until the next annual meeting of shareholders, or until his successor is elected and qualified. Also provided herein are brief descriptions of the business experience of each director, executive officer and advisor during the past five years and an indication of directorships held by each director in other companies subject to the reporting requirements under the Federal securities laws. None of our officers or directors is a party adverse to us or has a material interest adverse to us.
| Name | Age | Position(s) | ||
| Darwin Fogt | 41 | President, Chief Executive Officer and Member of the Board of Directors | ||
| David Markowski | 55 | Chief Financial Officer and Member of the Board of Directors | ||
| Douglas MacLellan | 60 | Chairman and Secretary | ||
| Curtis Hollister | 42 | Chief Technology Officer and Member of the Board of Directors | ||
| Douglas Cole | 59 | Member of the Board of Directors | ||
| Brandon Rowberry | 41 | Member of the Board of Directors | ||
| Rochelle Pleskow | 55 | Member of the Board of Directors |
Darwin Fogt, President, CEO & Director. Mr. Fogt has been CEO of eWellness Corporation since May 2013. Since 2001, he has been founder, President and practicing therapist of Evolution Physical Therapy, Inc., a privately held company in Los Angeles, CA providing sports and orthopedic physical therapy services. From 2008 to present, Mr. Fogt has also been founder and President of Bebe PT, a physical therapy practice specializing in perinatal rehabilitation and wellness. Additionally, from 2012 to present Mr. Fogt has been founder and President of Evolution Fitness, a primarily cash-based fitness and rehabilitation center serving high level athletes and clients in Culver City, CA. Mr. Fogt has consulted with and been published by numerous national publications including Runner’s World, Men’s Health, Men’s Journal, and various Physical Therapy specific magazines; his 13 plus years of experience include rehabilitating the general population, as well as professional athletes, Olympic gold medalists, and celebrities. Mr. Fogt earned his B.S. in Exercise Science from the University of Southern California in 1996 and his MPT (Master’s of Physical Therapy) from California State University: Long Beach in 2001. He is currently working toward earning his DPT (Doctorate of Physical Therapy) degree.
| 39 |
David Markowski, Chief Financial Officer & Director. Mr. Markowski has been CFO of eWellness Corporation since May 2013. From October 1997 to October 2002 he was CEO and Co-Founder of GFNN, Inc. From 2002 to 2013 Mr. Markowski has maintained various active roles within GFNN’s subsidiaries including Founder, Director and CEO positions. From October 2009 to December 2011, he was the Director of Corporate Development for Visualant, Inc. From June 2003 to 2010 he was President of Angel Systems, Inc. an independent consulting firm with competencies in strategic marketing and business development. From January 1998 to October 1998, Mr. Markowski served as the Vice President of Finance for Medcom USA, a NASDAQ listed company. Prior to that, he had a decade of investment banking experience on Wall Street involved in financing start-ups and public offerings. He is a business development specialist with accolades in INC Magazine and others. Mr. Markowski obtained a BA degree in Marketing from Florida State University in 1982.
Curtis Hollister, Chief Technology Officer & Director. Mr. Hollister has been a founder and CTO of eWellness since May 2013. From November 2008 to present he has been the founder and President of Social Pixels, a privately held Canadian company focused on helping companies apply online media and digital campaigning. From November 2008 to present he has been the founder and President of Ripplefire, a privately held Canadian company also specializing in the digital campaigning space. He is a global entrepreneur and innovator known for his ability to identify and capitalize on industry trends. His high profile projects include such clients as Government of Canada, AT&T, Bell Canada, Microsoft, Nokia, Conversant IP and TD Bank. From 1998 to 2002 Mr. Hollister founded and operated TeamCast.com, a technology spin-off focusing on peer-to-peer networking. From 1997 to 2002 Mr. Hollister founded and operated Intrasoft Technologies, a technology start-up to capitalize on the emerging Intranet application market. From 1995 to 1997 Mr. Hollister founded and operated Intranet Technologies, the first successful Internet service provider in Ottawa, Canada’s capital city. Mr. Hollister graduated from Center Hastings Secondary in 1991 and from 1991 to 1995 attended Carleton University with a special focus on Economics.
Douglas MacLellan, Chairman of the Board. Mr. MacLellan currently serves as Chairman of the Board of eWellness Corporation since May 2013. From November 2009 to present Mr. MacLellan has been an independent director of ChinaNet Online Holdings, Inc. (NASDAQ: CNET) a media development, advertising and communications company. From June 2011 to present Mr. MacLellan has been Chairman of Innovare Products, Inc., a privately held company that develops innovative consumer products. In May 2014, Mr. MacLellan join the Board as an independent director of Jameson Stanford Resources Corporation (OTCBB: JMSN) an early stage mining company. Until April 2014, Mr. MacLellan was Chairman and chief executive officer at Radient Pharmaceuticals Corporation. (OTCQB: RXPC.PK), a vertically integrated specialty pharmaceutical company. He also continues to serve as president and chief executive officer for the MacLellan Group, an international financial advisory firm since 1992. From August 2005 to May 2009, Mr. MacLellan was co-founder and vice chairman at Ocean Smart, Inc., a Canadian based aquaculture company. From February 2002 to September 2006, Mr. MacLellan served as chairman and cofounder at Broadband Access MarketSpace, Ltd., a China based IT advisory firm, and was also co-founder at Datalex Corp., a software and IT company specializing in mainframe applications, from February 1997 to May 2002. Mr. MacLellan was educated at the University of Southern California in economics and international relations.
Douglas Cole, Director. Mr. Cole has been a Director of the company since May 2014. From 2005 to the present Mr. Cole has been a Partner overseeing all ongoing deal activities with Objective Equity LLC, a boutique investment bank focused on the clean tech, mining and mineral sectors. From 2002 to 2005 Mr. Cole has played various executive roles as Executive Vice Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and President of TWL Corporation (TWLP.OB). From May 2000 to September 2005, he was also the Director of Lair of the Bear, The University of California Family Camp located in Pinecrest, California. During the period between 1991 and 1998 he was the CEO of HealthSoft and he also founded and operated Great Bear Technology, which acquired Sony Image Soft and Starpress, then went public and eventually sold to Graphix Zone. In 1995 Mr. Cole was honored by NEA, a leading venture capital firm, as CEO of the year for his work in the Starpress integration. Since 1982 he has been very active with the University of California, Berkeley mentoring early-stage technology companies. Mr. Cole obtained his BA in Social Sciences from UC Berkeley in 1978.
Brandon Rowberry, Director. Mr Rowberry has been a Director since June 2014. He is a well-known healthcare innovation executive. From 2010 to 2014 he drove enterprise-wide Innovation/Venturing for United Health Group where in 2012 they were awarded the prestigious PDMA Outstanding Corporate Innovation Award. From 2012 to present he has also been Managing Director of 7R Ventures an investment and advisory firm. From 2005 to 2009, he was Director of Strategy & Innovation at Circuit City. From 2001 to 2005, he was a Sr. Corporate Consultant focusing on Organizational Development and Innovation at Hallmark. From 2000 to 2001, he was a Manager of Organizational Development & Innovation at Honeywell. Mr. Rowberry has also been a frequent corporate innovation guest speaker on NBC, FOX, ABC. Mr. Rowberry obtained his Masters of Organizational Behavior from Marriott School of Business, BYU in 2000.
| 40 |
Rochelle Pleskow, Director. From 2010 through 2014, Ms. Pleskow served as the Chief Healthcare Information Officer for Hewlett Packard. She developed the framework of healthcare analytics platform, which encompasses quality improvement, outcomes analysis, patient safety, operational analytics, clinical informatics, physician performance, and regulatory compliance monitoring for health plans, hospitals and physicians. From 2008 through 2010, she acted as a senior consultant to various companies on healthcare policy and procedures including acting as an advisor for ASP model start-up, whose business included a HIPAA/HL7 and PCI compliant processing tool, which verifies a patient’s insurance coverage, accurately calculates out-of-pocket costs, and processes payments in one system and at the time of service. This model improves revenue cycle management as it accelerates the collection of patient payments. From 2007 through 2008, she was Director of business Architecture for Blue Shield of California, where she developed the business framework and core elements of a large scale IT systems implementation to increase competitive advantage for Blue Shield of California. Re-engineered core business processes in Health Services Division in order to modernize the technology.
Director Qualifications
We seek directors with established strong professional reputations and experience in areas relevant to the strategy and operations of our businesses. We also seek directors who possess the qualities of integrity and candor, who have strong analytical skills and who are willing to engage management and each other in a constructive and collaborative fashion, in addition to the ability and commitment to devote time and energy to service on the Board and its committees, as necessary. We believe that all of our directors meet the foregoing qualifications.
The Board believes that the leadership skills and other experience of the Board members described below, in addition to each person’s experience set forth above in their respective biographies, provide the Company with a range of perspectives and judgment necessary to guide our strategies and monitor our executives business execution.
Darwin Fogt. Mr. Fogt is a co-founder of the Company and has been serving as a physical therapist for over 12 years and has built three successful physical therapy practices. Mr. Fogt has contributed to the Board’s strong leadership and vision for the development of the Company’s innovative business model.
Douglas MacLellan. Mr. MacLellan is a co-founder of the Company and has been serving as an officer and/or director of various advance technology and high growth companies over the past 20 years. Mr. MacLellan has contributed to the Board’s strong leadership and vision for the development of the Company’s innovative business model.
Curtis Hollister. Mr. Hollister is a co-founder of the Company and has been serving in senior management positions in various advance technology, software and video content business over the past 20 years. He holds a wealth of experience in software development, video content management and network technology.
David Markowski. Mr. Markowski is a co-founder of the Company and has been serving in senior management positions in various companies over the past 20 years, with an emphasis on corporate finance, accounting, audit, financial modeling and marketing. He holds a wealth of experience in company management skills.
Doug Cole. Mr. Cole is an international business executive with over 20 years of active management and board roles in various software, educational and technology public and private companies.
Brandon Rowberry. Mr. Rowberry has held over 15 years in senior management positions as an innovation expert in various advance technology and healthcare industries. He is anticipated to greatly expand our industry relationships within healthcare insurers and the telemedicine industry.
Rochelle Pleskow. Ms. Pleskow holds a vast knowledge base on healthcare informatics and the scaling of various technology implementations at selected large scale technology and healthcare companies and is anticipated to be a good addition to its board of directors as the Company implements its anticipated white label program to physical therapy clinics through the U.S. marketplace.
| 41 |
Involvement in Certain Legal Proceedings
To the best of the Company’s knowledge, none of the following events occurred during the past ten years that are material to an evaluation of the ability or integrity of any of our executive officers, directors or promoters:
(1) A petition under the Federal bankruptcy laws or any state insolvency law was filed by or against, or a receiver, fiscal agent or similar officer was appointed by a court for the business or property of such person, or any partnership in which he was a general partner at or within two years before the time of such filing, or any corporation or business association of which he was an executive officer at or within two years before the time of such filing;
(2) Convicted in a criminal proceeding or is a named subject of a pending criminal proceeding (excluding traffic violations and other minor offenses);
(3) Subject of any order, judgment, or decree, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any court of competent jurisdiction, permanently or temporarily enjoining him from, or otherwise limiting, the following activities:
(i) Acting as a futures commission merchant, introducing broker, commodity trading advisor, commodity pool operator, floor broker, leverage transaction merchant, any other person regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission, or an associated person of any of the foregoing, or as an investment adviser, underwriter, broker or dealer in securities, or as an affiliated person, director or employee of any investment company, bank, savings and loan association or insurance company, or engaging in or continuing any conduct or practice in connection with such activity;
(ii) Engaging in any type of business practice; or
(iii) Engaging in any activity in connection with the purchase or sale of any security or commodity or in connection with any violation of Federal or State securities laws or Federal commodities laws;
(4) Subject of any order, judgment or decree, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any Federal or State authority barring, suspending or otherwise limiting for more than 60 days the right of such person to engage in any activity described in paragraph (3)(i) above, or to be associated with persons engaged in any such activity;
(5) Found by a court of competent jurisdiction in a civil action or by the Commission to have violated any Federal or State securities law, and the judgment in such civil action or finding by the Commission has not been subsequently reversed, suspended, or vacated;
(6) Found by a court of competent jurisdiction in a civil action or by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission to have violated any Federal commodities law, and the judgment in such civil action or finding by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission has not been subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated;
(7) Subject of, or a party to, any Federal or State judicial or administrative order, judgment, decree, or finding, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, relating to an alleged violation of:
(i) Any Federal or State securities or commodities law or regulation; or
(ii) Any law or regulation respecting financial institutions or insurance companies including, but not limited to, a temporary or permanent injunction, order of disgorgement or restitution, civil money penalty or temporary or permanent cease-and-desist order, or removal or prohibition order; or
(iii) Any law or regulation prohibiting mail or wire fraud or fraud in connection with any business entity; or
| 42 |
(8) Subject of, or a party to, any sanction or order, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any self-regulatory organization, any registered entity (as defined in Section 1(a)(29) of the Commodity Exchange Act (7 U.S.C. 1(a)(29))), or any equivalent exchange, association, entity or organization that has disciplinary authority over its members or persons associated with a member.
Promoters and Certain Control Persons
In light of the efforts and services they provided to the Private Co. prior to the Share Exchange, we believe that Douglas MacLellan and Darwin Fogt may be deemed “promoters” (within the meaning of Rule 405 under the Securities Act), since they took the initiative in the formation of our business and received 10% of our equity securities in exchange for the contribution of property or services, during the last five years. In addition, Gregg C. E. Johnson may be deemed a “promoter” of the Company as a result of his receipt of shares of our common stock at the time of completion of the Share Exchange.
Corporate Governance and Director Independence
Presently, we are not currently listed on a national securities exchange or in an inter-dealer quotation system and therefore are not required to comply with the director independence requirements of any securities exchange. In determining whether our directors are independent, however, we intend to comply with the rules of NASDAQ. The board of directors will also consult with counsel to ensure that the boards of director’s determinations are consistent with those rules and all relevant securities and other laws and regulations regarding the independence of directors, including those adopted under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 with respect to the independence of audit committee members. Nasdaq Listing Rule 5605(a)(2) defines an “independent director” generally as a person other than an Executive Officer or employee of the Company or any other individual having a relationship which, in the opinion of the Company’s board of directors, would interfere with the exercise of independent judgment in carrying out the responsibilities of a director. Our Board of Directors has determined that Douglas Cole, Mr. Rowberry and Ms. Pleskow would qualify as “independent” as that term is defined by Nasdaq Listing Rule 5605(a)(2). Further, Mr. Cole qualifies as “independent” under Nasdaq Listing Rules applicable to board committees.
Due to our lack of operations and size prior to the Share Exchange, we did not have an Audit Committee. For these same reasons, we did not have any other separate committees prior to the Share Exchange; all functions of a nominating committee, audit committee and compensation committee were performed by our sole director. Although, as stated above, we are not the subject of any listing requirements, in connection with the Share Exchange, our Board of Directors established several committees to assist it in carrying out its duties. In particular, committees shall work on key issues in greater detail than would be practical at a meeting of all the members of the Board of Directors; each committee reviews the results of its deliberations with the full Board of Directors.
The standing committees of the Board of Directors currently consist of the Audit Committee, the Compensation Committee and the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee. Current copies of the charters for the Audit Committee, the Compensation Committee, and the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee, as well as our Corporate Governance Guidelines, Code of Ethics and Business Conduct, may be found on our website at www.ewellnesshealth.com, under the heading “Corporate Information—Governance Documents.” Printed versions also are available to any stockholder who requests them by writing to our corporate Secretary at our corporate address. Our Board of Directors may, from time to time, establish certain other committees to facilitate our management.
The Board will consider appointing members to each of the Committees at such time as a sufficient number of independent directors are appointed to the Board or as otherwise determined by the Board. Until such time, the full board of directors will undertake the duties of the audit committee, compensation committee and nominating committee.
A copy of our Code of Ethics is attached as Exhibit 14.1 which is incorporated herein by reference.
| 43 |
Compliance with Section 16(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934
Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act, as amended, requires that our directors, executive officers and persons who own more than 10% of a class of our equity securities that are registered under the Exchange Act to file with the SEC initial reports of ownership and reports of changes of ownership of such registered securities.
Based solely upon a review of information furnished to the Company, to the Company’s knowledge, during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015, all such forms were filed [confirm].
ITEM 11: EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
For the two fiscal years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, we did not pay any compensation to our executive officers, nor did any other person receive a total annual salary and bonus exceeding $100,000. Prior to the Share Exchange, which closed in April 2014, we did not pay our sole officer any compensation nor did we have an employment agreement.
Following the Share Exchange, we do not currently have any formal employment salary arrangement with any of or new officers. However, the Board determined that the following salaries shall be recorded and accrued on a monthly basis as contributed capital and compensation for the following individuals for the services they provide to us:
After 1-1-14, but before profitability
| Monthly | Recognized | Contributed | Compensated | |||||||||
| Douglas MacLellan, Chairman | $ | 20,000 | $ | 11,000 | $ | 9,000 | ||||||
| Darwin Fogt, CEO/President | $ | 14,000 | $ | 7,000 | $ | 7,000 | ||||||
| David Markowski, CFO | $ | 14,000 | $ | 7,000 | $ | 7,000 | ||||||
| Curtis Hollister, CTO | $ | 14,000 | $ | 7,000 | $ | 7,000 | ||||||
At profitability and after
| Monthly | Recognized | Contributed | Compensated | |||||||||
| Douglas MacLellan, Chairman | $ | 20,000 | $ | 0 | $ | 20,000 | ||||||
| Darwin Fogt, CEO/President | $ | 14,000 | $ | 0 | $ | 14,000 | ||||||
| David Markowski, CFO | $ | 14,000 | $ | 0 | $ | 14,000 | ||||||
| Curtis Hollister, CTO | $ | 14,000 | $ | 0 | $ | 14,000 | ||||||
All of our current officers have agreed to defer their compensation until such time as we are cash flow positive; therefore, none of our officers have received any compensation as of the date of this Report. No retirement, pension, profit sharing, stock option or insurance programs or other similar programs have been adopted by the Company for the benefit of the Company’s employees.
Director’s Compensation
We shall continue to maintain the policy regarding director compensation that existed prior to the Share Exchange, pursuant to which directors are not entitled to receive compensation for service rendered to us or for meeting(s) attended except for reimbursement of out-of-pocket expenses. There is no formal or informal arrangements or agreements to compensate employee directors for service provided as a director; however, compensation for new non-employee directors is determined on an ad hoc basis by the existing members of the board of directors at the time a director is elected.
Upon the appointment of Ms. Pleskow (a non-employee director) in August 2015, we agreed to pay her $2,000 per month, which shall accrue as of July 1, 2015 and be paid upon the first closing of our next financing. She shall also be eligible to receive any other benefits that are offered to other directors.
| 44 |
Compensation Policies and Practices as They Relate to the Company’s Risk Management
We believe that our compensation policies and practices for all employees, including executive officers, do not create risks that are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on us.
Employment Contracts
We do not have any formal employment agreement with any of the New Officers. Any future compensation will be determined by the Board of Directors, and, as appropriate, an employment agreement will be executed. We do not currently have plans to pay any compensation until such time as the Company maintains a positive cash flow.
Outstanding Equity Awards
There were no equity awards outstanding as of the end the year ended December 31, 2015.
ITEM 12: SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The following table sets forth certain information regarding beneficial ownership of our common stock as of March 28, 2016 by (i) each person (or group of affiliated persons) who is known by us to own more than five percent (5%) of the outstanding shares of our common stock, (ii) each director, executive officer and director nominee, and (iii) all of our directors, executive officers and director nominees as a group.
Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with SEC rules and generally includes voting or investment power with respect to securities. For purposes of this table, a person or group of persons is deemed to have “beneficial ownership” of any shares of common stock that such person has the right to acquire within 60 days of the date of the respective table. For purposes of computing the percentage of outstanding shares of our common stock held by each person or group of persons named above, any shares that such person or persons has the right to acquire within 60 days of the date of the respective table is deemed to be outstanding for such person, but is not deemed to be outstanding for the purpose of computing the percentage ownership of any other person. The inclusion herein of any shares listed as beneficially owned does not constitute an admission of beneficial ownership.
The business address of each beneficial owner listed is in care of 11825 Major Street, Culver City, California, 90230 unless otherwise noted. Except as otherwise indicated, the persons listed below have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of our common stock owned by them, except to the extent that power may be shared with a spouse.
As of March 28, 2016, we had 18,847,770 shares of common stock issued and outstanding.
| Name of Beneficial Owner | Amount
and Nature of Beneficial Ownership | Percent of Class | ||||||
| Darwin Fogt | 3,750,000 | (1) | 19.9 | % | ||||
| David Markowski | 1,100,000 | 5.8 | % | |||||
| Douglas MacLellan | 3,750,000 | 19.9 | % | |||||
| Curtis Hollister | 1,950,000 | 10.3 | % | |||||
| Douglas Cole | 200,000 | 1.1 | % | |||||
| Brandon Rowberry | 200,000 | 1.1 | % | |||||
| Rochelle Pleskow | 0 | 0 | % | |||||
| All officers and directors as a group (6 persons) | 10,950,000 | 58.1 | % | |||||
| J.F.S. Investments, Inc. (2) | 950,000 | 5.0 | % | |||||
| Evolution Physical Therapy, Inc. (3) | 1,000,000 | (1) | 5.3 | % | ||||
| Summit Capital USA, Inc. (4) | 1,579,002 | (5) | 8.4 | % | ||||
| 45 |
| (1) | This includes 1,000,000 shares held by Evolution Physical Therapy, Inc., which is owned by Mr. Fogt. | |
| (2) | Joseph Salvani is the President and the sole indirect owner of, and controls, J.F.S. Investments, Inc. | |
| (3) | Darwin Fogt is the President and the sole indirect owner of, and controls, Evolution Physical Therapy, Inc. | |
| (4) | This amount includes: (i) 1,274,002 shares held by Summit Capital USA, Inc. (“Summit USA”), which is beneficially owned as follows: 50% owned by Summit Capital Corp. (“Summit Corp.”), 2 Anthony Henday Center, 4914-55 St., Red Deer, AB, Canada T4N 2J4 (Summit Corp. is beneficially owned by Gregg C.E. Johnson and Cheryl L. McRobbie-Johnson); 50% owned by Gregg C.E. Johnson. Mr. Johnson has voting and dispositive control over the securities held by Summit Capital USA, Inc. Mr. Johnson disclaims beneficial ownership of our common stock owned by Summit Capital USA, Inc. except to the extent of his pecuniary interest in such company; (ii) and, (iii) 305,000 shares Mr. Johnson owns directly. |
Changes in Control
As a result of the Share Exchange, eWellness became our wholly owned subsidiary and the officers and directors appointed as of the closing of such transaction own approximately 66.7% of the shares of the Company outstanding post-exchange common stock. As a result, the newly appointed board members control the board.
ITEM 13: CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS
Other than the relationships and transactions discussed below, we are not a party to, nor are we proposed to be a party, to any transaction during the last fiscal year involving an amount exceeding $120,000 and in which a related person, as such term is defined by Item 404 of Regulation S-K, had or will have a direct or indirect material interest.
Related Party Debt: Prior to the closing of the Share Exchange through the year ended December 31, 2015, a related party, a company in which our former Secretary-Treasurer and CFO also served as CFO, paid $91,271 on behalf of the Company. The amount outstanding as of December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014 were $43,717 and $56,156, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded $3,921 imputed interest on the amount owed to the related party. The debt remains a Company liability, which is to be repaid when the Company has sufficient capital to do so and there is no specific time frame within which such repayment must be made.
Share Transfers: Pursuant to the Share Exchange Agreement, Mr. McRobbie (our former CEO and sole director) transferred an aggregate of 2,100,000 shares to the following parties: 1,500,000 to Summit Capital USA, Inc. (“Summit”), over which our former CFO serves as CFO; 300,000 to an unrelated third party; and, 300,000 to Gregg Johnson, who, together with his wife beneficially owns Summit Capital Corp., which is a 50% owner of Summit; all of these shares were issued as compensation for a variety of business consulting services each such named party performed on behalf of the Company pursuant to oral agreements between each party and Mr. McRobbie. The services provided included identifying, evaluating, structuring and providing advice in connection with potential acquisitions, mergers or combinations with potential acquisitions, performance of due diligence, coordination of accounting and legal due diligence, familiarization with the business, operations, properties, financial condition, management and prospects of potential target companies and the coordination of the preparation of all required documentation to complete the acquisition and the filing of all required public disclosures to complete such transaction. These services also included the evaluation of several different business opportunities, including the transaction with eWellness Corporation that was ultimately consummated. Based on the oral agreements with Mr. McRobbie, the fee for these services was earned and due upon the closing of the Share Exchange. The transfer of the 2,100,000 shares was a private transaction between the named individuals and was not a Company issuance.
| 46 |
Programming Agreement: On or about June 23, 2014, we entered into a license agreement with Bistromatics Corp., to which one of our directors, Curtis Hollister, is Chief Marketing Officer, pursuant to which we obtained a perpetual license to use the programming code created by a video management platform as a base to develop our telemedicine video service for a license fee of $20,000; $2,000 of which was due upon execution, $5,000 of which is due on August 1, 2014 and the $13,000 balance is due by September 15, 2014. The parties entered into an addendum extending the due date of the $20,000 license fee to December 31, 2014 and another addendum extending it to July 1, 2015, another addendum extending it to October 31, 2015 and another addendum extending it to January 31, 2016 . Intellectual property developed as a result of this license, will be our property; but Bistromatics will retain the intellectual property for the original code base. We may resell or license the resulting telemedicine platform for an extended license fee of $10,000 for each additional instance the code base will be used. Through this agreement, Bistromatics Corp. built our PHZIO platform; Mr. Hollister purchased the domain name on behalf of the Company and retains no rights to same. This agreement was paid by the year ended December 31, 2015.
Operating Agreement: On April 1, 2015, we entered into an Operating Agreement with EPT (a company owned by our CEO), wherein we agreed that EPT would be able to operate our telemedicine platform www.PHZIO and offer it to selected physical therapy patients of EPT. We shall receive 75% of the net insurance reimbursements from the patient for use of the platform. We will advance capital requested by EPT for costs specifically associated with operating the www.phzio,com platform and associated physical therapy treatments – computer equipment, office or facilities rental payments, physical therapist or physical therapy assistant, administrative staff, patient induction equipment, office supplies, utilities and other associated operating costs. It is anticipated that the operation of the platform by EPT will generate positive cash flow within 90 days from the start of patient induction.
Office Space: The Company rents its Culver City, CA office space from Evolution Physical Therapy (“Evolution”), a company owned by our CEO. Evolution has agreed contribute the annual rent for the year ended December 31, 2015 towards founding eWellness and its operations; the market value of such rent is $500 per month. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded rent expense in the Statement of Operations and Additional Paid in Capital in the Balance Sheet.
Research and Development: The officers of the Company from time to time charge the Company for research and development services. During the years ended December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, the expenses for these service were $0 and $30, respectively.
Review, Approval and Ratification of Related Party Transactions
Our Board of Directors conducts an appropriate review of and oversees all related-party transactions. We have not yet adopted formal standards in respect of the review and approval or ratification of related-party transactions; however, our board has conformed to the following standards: (i) all related-party transactions must be fair and reasonable to us and on terms comparable to those reasonably expected to be agreed to with independent third parties for the same goods and/or services at the time authorized by the board; and (ii) all related-party transactions must be authorized, approved or ratified by the affirmative vote of a majority of the directors who have no interest, either directly or indirectly, in any such related party transaction.
ITEM 14: PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
The following table shows the fees that were billed for the audit and other services provided by Haynie and Company and HJ Associates & Consultants, LLP for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014.
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Audit Fees | $ | 74,000 | $ | 31,000 | ||||
| Audit-Related Fees | 10,000 | - | ||||||
| Tax Fees | - | - | ||||||
| All Other Fees | - | - | ||||||
| Total | $ | [ ] | $ | [ ] |
Audit Fees — This category includes the audit of our annual financial statements, review of financial statements included in our Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q and services that are normally provided by the independent registered public accounting firm in connection with engagements for those fiscal years. This category also includes advice on audit and accounting matters that arose during, or as a result of, the audit or the review of interim financial statements.
| 47 |
Audit-Related Fees — This category consists of assurance and related services by the independent registered public accounting firm that are reasonably related to the performance of the audit or review of our financial statements and are not reported above under “Audit Fees.” The services for the fees disclosed under this category include consultation regarding our correspondence with the Securities and Exchange Commission and other accounting consulting.
Tax Fees — This category consists of professional services rendered by our independent registered public accounting firm for tax compliance and tax advice. The services for the fees disclosed under this category include tax return preparation and technical tax advice.
All Other Fees — This category consists of fees for other miscellaneous items.
Change in Auditor
On January 25, 2016 (“Resignation Date”), HJ Associates & Consultants, LLP, doing business as HJ & Associates, LLC (“HJ”), associated with an asset acquisition by Haynie & Company, resigned as the independent registered public accounting firm for the Company. On January 26, 2016, the Company engaged Haynie & Company (“Haynie”), Salt Lake City, Utah, as its new independent registered public accounting firm. The change of the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm from HJ to Haynie was approved unanimously by our board of directors.
The reports of HJ on the Company’s financial statements for the two most recent fiscal years did not contain an adverse or disclaimer of opinion and were not qualified or modified as to uncertainty, audit scope, or accounting principles.
During the two most recent fiscal years and through the Resignation Date, there were (i) no disagreements between the Company and HJ on any matter of accounting principles or practices, financial statement disclosure, or auditing scope or procedures, which disagreement, if not resolved to the satisfaction of HJ, would have caused HJ to make reference thereto in their reports on the financial statements for such years, and (ii) no “reportable events” as that term is defined in Item 304(a)(1)(v) of Regulation S-K.
During the Company’s two most recent fiscal years and in the subsequent interim period through the Resignation Date, the Company has not consulted with Haynie regarding either (i) the application of accounting principles to a specified transaction, either completed or proposed, or the type of audit opinion that might be rendered on the Company’s financial statements, and neither a written report nor oral advice was provided to the Company that Haynie concluded was an important factor considered by the Company in reaching a decision as to the accounting, auditing or financial reporting issue; or (ii) any matter that was either the subject of a disagreement (as defined in Item 304(a)(1)(iv) of Regulation S-K and the related instructions) or a reportable event (as described in Item 304(a)(1)(v) of Regulation S-K).
Preapproval Policy
Our Board of Directors reviews and approves audit and permissible non-audit services performed by its independent accountants, as well as the fees charged for such services. In its review of non-audit service fees and its appointment of Haynie & Company as our independent accountants, the Board of Directors considered whether the provision of such services is compatible with maintaining independence.
| 48 |
ITEM 15: EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a)
| 1. | The financial statements listed in the “Index to Financial Statements” at page F-1 are filed as part of this report. | |
| 2. | Financial statement schedules are omitted because they are not applicable or the required information is shown in the financial statements or notes thereto. | |
| 3. | Exhibits included or incorporated herein: See index to Exhibits. |
(b) Exhibits
| Exhibit No. | Name/Identification of Exhibit | |
| 3.1(a) | Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Form 8-K/A filed on August 6, 2014) | |
| 3.2 | Bylaws (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3(b) to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed on May 15, 2012) | |
| 10.1 | Amended and Restated Share Exchange Agreement among eWellness Healthcare Corporation (f/k/a Dignyte, Inc.), Andreas A. McRobbie-Johnson, eWellness Corporation and its shareholders dated April 30, 2014. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2014) | |
| 10.2 | Promissory Note (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Form 8-K filed on October 2, 2014) | |
| 10.3 | Supply and Distribution agreement with Millennium Healthcare, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Form 8-K/A filed on June 25, 2014) | |
| 10.4 | Licensing Agreement between the Company and Physical Relief Telemedicine and Technology Healthcare Solutions, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Form 8-K/A filed on June 25, 2014) | |
| 10.5 | License Agreement between the Company and Bistromatics Corp. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Form 8-K/A filed on June 25, 2014) | |
| 10.6 | Securities Purchase Agreement dated December 23, 2014 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Form 8-K filed on January 6, 2015) | |
| 10.7 | Form of 12% Senior Convertible Promissory Note (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Form 8-K filed on January 6, 2015) | |
| 10.8 | Form of Series A Warrant Agreement(Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Form 8-K filed on January 6, 2015) | |
| 10.9 | Form of Registration Rights Agreement(Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Form 8-K filed on January 6, 2015) | |
| 10.10 | Form of Security Agreement(Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Form 8-K filed on January 6, 2015) | |
| 10.11 | 2015 Stock Option Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Form 8-K filed on August 6, 2015) | |
| 14.1 | Code of Ethics Conduct (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 14.1 to the Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2014) | |
| 31.1** | Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350 as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 31.2** | Certification of Principal Financial and Accounting Officer, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350 as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 32.1** | Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(b) of the Exchange Act and Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 32.2** | Certification of Principal Financial and Accounting Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(b) of the Exchange Act and Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 101.INS ** | XBRL Instance Document | |
| 101.SCH ** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | |
| 101.CAL ** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | |
| 101.DEF ** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | |
| 101.LAB ** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | |
| 101.PRE ** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
** Filed herewith.
| 49 |
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| eWellness Healthcare Corporation | ||
| (Registrant) | ||
| By: | /s/ Darwin Fogt | Date: March 30, 2016 |
| Darwin Fogt | ||
| President, CEO | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Darwin Fogt | Chief Executive Officer and Director | March 30, 2016 | ||
| Darin Fogt | (principal executive officer) | |||
| /s/ David Markowski | Chief Financial Officer | March 30, 2016 | ||
| David Markwoski | (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | |||
| /s/ Brandon Rowberry | Director | March 30, 2016 | ||
| Brandon Rowberry | ||||
| /s/ Douglas Cole | Director | March 30, 2016 | ||
| Douglas Cole | ||||
| /s/ Curtis Hollister | Director | March 30, 2016 | ||
| Curtis Hollister | ||||
| /s/ Douglas MacLellan | Director | March 30, 2016 | ||
| Douglas MacLellan | ||||
| /s/ Rochelle Pleskow | Director | March 30, 2016 | ||
| Rochelle Pleskow |
| 50 |
