Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - Contango ORE, Inc. | ctgo-20150630x10kxex312.htm |
| EX-99.10 - EXHIBIT 99.10 - Contango ORE, Inc. | exhibit9910-auditedpeakgol.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 UHY LLP CONSENT - Contango ORE, Inc. | uhyconsent-231.htm |
| EX-23.2 - EXHIBIT 23.2 - BDO USA, LLP CONSENT - Contango ORE, Inc. | bdoconsent-232.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - Contango ORE, Inc. | ctgo-20150630x10kxex311.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - Contango ORE, Inc. | ctgo-20150630x10kxex321.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - Contango ORE, Inc. | ctgo-20150630x10kxex322.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
ý | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2015 | |
OR
¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to | |
Commission file number 000-54136
CONTANGO ORE, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Delaware | 27-3431051 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (IRS Employer Identification No.) | |
3700 BUFFALO SPEEDWAY, SUITE 925
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77098
(Address of principal executive offices)
(713) 877-1311
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Common Stock, Par Value $0.01 per share | OTCBB | |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No ý
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No ý
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ý No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ý No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
Large accelerated filer | ¨ | Accelerated filer | ¨ | |||
Non-accelerated filer | ¨ | Smaller reporting company | ý | |||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No ý
As of December 31, 2014 the aggregate market value of the registrant's common stock held by non-affiliates (based upon the closing sale price of such common stock as reported on the OTCBB was $17,301,142. As of October 9, 2015, there were 3,904,540 shares of the registrant’s common stock outstanding.
Documents Incorporated by Reference
Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14 of Part III have been omitted from this report since registrant will file with the Securities and Exchange Commission, not later than 120 days after the close of its fiscal year, a definitive proxy statement, pursuant to Regulation 14A. The information required by Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14 of this report, which will appear in the definitive proxy statement, is incorporated by reference into this Form 10-K.
CONTANGO ORE, INC.
ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K
FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED JUNE 30, 2015
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page | |||
SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA | |||
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK | |||
Item 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION | 28 | |
i
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Some of the statements made in this report may contain “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. The words and phrases “should be”, “will be”, “believe”, “expect”, “anticipate”, “estimate”, “forecast”, “goal” and similar expressions identify forward-looking statements and express expectations about future events. These include such matters as:
• | The Company's financial position |
• | Business strategy, including outsourcing |
• | Meeting Company forecasts and budgets |
• | Anticipated capital expenditures |
• | Prices of gold and associated minerals |
• | Timing and amount of future discoveries (if any) and production of natural resources on our Tetlin Property |
• | Operating costs and other expenses |
• | Cash flow and anticipated liquidity |
• | Prospect development |
• | New governmental laws and regulations |
Although the Company believes the expectations reflected in such forward-looking statements are reasonable, such expectations may not occur. These forward-looking statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause the Company's actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from future results expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. These factors include among others:
• | Ability to raise capital to fund capital expenditures |
• | Operational constraints and delays |
• | The risks associated with exploring in the mining industry |
• | The timing and successful discovery of natural resources |
• | Availability of capital |
• | Declines and variations in the price of gold and associated minerals |
• | Price volatility for natural resources |
• | Availability of operating equipment |
• | Operating hazards attendant to the mining industry |
• | Weather |
• | The ability to find and retain skilled personnel |
• | Restrictions on mining activities |
• | Legislation that may regulate mining activities |
• | Impact of new and potential legislative and regulatory changes on mining operating and safety standards |
• | Uncertainties of any estimates and projections relating to any future production, costs and expenses. |
• | Timely and full receipt of sale proceeds from the sale of mined products (if any) |
• | Stock price and interest rate volatility |
• | Federal and state regulatory developments and approvals |
• | Availability and cost of material and equipment |
• | Actions or inactions of third-parties |
• | Potential mechanical failure or under-performance of facilities and equipment |
• | Environmental risks |
• | Strength and financial resources of competitors |
• | Worldwide economic conditions |
• | Expanded rigorous monitoring and testing requirements |
• | Ability to obtain insurance coverage on commercially reasonable terms |
• | Competition generally and the increasing competitive nature of the mining industry |
You should not unduly rely on these forward-looking statements in this report, as they speak only as of the date of this report. Except as required by law, the Company undertakes no obligation to publicly release any revisions to these forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances occurring after the date of this report or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. See the information under the heading “Risk Factors” in this Form 10-K for some of the important factors that could affect the Company's financial performance or could cause actual results to differ materially from estimates contained in forward-looking statements.
ii
PART I
Item 1. BUSINESS
Overview
The Company is a Houston-based company, whose primary business is the participation in a joint venture to explore in the State of Alaska for gold ore and associated minerals. On January 8, 2015, the Company and Royal Gold, Inc. (“Royal Gold”), through their wholly-owned subsidiaries, consummated the transactions (the “Transactions”) contemplated under the Master Agreement, dated as of September 29, 2014 (the “Master Agreement”), including the formation of a joint venture, Peak Gold, LLC (the "Joint Venture Company"), to advance exploration of the Company’s Tetlin Property, which is prospective for gold and associated minerals. As of June 30, 2015, the Joint Venture Company had leased or had control over State of Alaska properties totaling approximately 774,356 acres for the exploration of gold ore and associated minerals.
Background
Contango Mining Company (“Contango Mining”), a wholly owned subsidiary of Contango Oil & Gas Company (“Contango”), was formed on October 15, 2009 for the purpose of engaging in exploration in the State of Alaska for (i) gold ore and associated minerals and (ii) rare earth elements. Contango Mining initially acquired a 50% interest in properties from Juneau Exploration, L.P., (“JEX”) in exchange for $1 million and a 1.0% overriding royalty interest in the properties under a Joint Exploration Agreement (the “Joint Exploration Agreement”). On September 15, 2010, Contango Mining acquired the remaining 50% interest in the properties by increasing the overriding royalty interest in the properties granted to JEX to 3.0% pursuant to an Amended and Restated Conveyance of Overriding Royalty Interest (the “Amended ORRI Agreement”), and JEX and Contango Mining terminated the Joint Exploration Agreement. JEX assisted the Company in acquiring additional properties in Alaska pursuant to an Advisory Agreement dated September 6, 2012, and the Company granted to JEX a 2% overriding royalty interest in the additional properties acquired. On September 29, 2014, pursuant to a Royalty Purchase Agreement between JEX and Royal Gold (the “Royalty Purchase Agreement”), JEX sold its entire overriding royalty interest in the properties to Royal Gold. On the same date, the Company terminated the Advisory Agreement with JEX.
The Company was formed on September 1, 2010 as a Delaware corporation and on November 29, 2010, Contango Mining assigned all its properties and certain other assets and liabilities to Contango. Contango contributed the properties and $3.5 million of cash to the Company, pursuant to the terms of a Contribution Agreement (the “Contribution Agreement”), in exchange for approximately 1.6 million shares of the Company’s common stock. The transactions occurred between companies under common control. Contango then distributed all of the Company’s common stock to Contango’s stockholders of record as of October 15, 2010, promptly after the effective date of the Company’s Registration Statement Form 10 on the basis of one share of common stock for each ten (10) shares of Contango’s common stock then outstanding.
In connection with the closing of the Transactions with Royal Gold (the “Closing”), the Company formed Peak Gold, LLC and contributed to the Joint Venture Company its Tetlin Property near Tok, Alaska, together with other personal property (the “Contributed Assets”) at an agreed value of $45.7 million (the “Contributed Assets Value”). At the Closing, the Company and Royal Gold, through their wholly-owned subsidiaries, entered into a Limited Liability Company Agreement for the Joint Venture Company (the “Joint Venture Company LLC Agreement”). The audited financial statements of Peak Gold, LLC as of the year ended June 30, 2015 are filed as an exhibit to this Form 10-K.
Upon Closing, Royal Gold initially invested $5 million to fund exploration activity. The initial $5 million did not give Royal Gold an equity stake in the Joint Venture Company. Royal Gold has the option to earn up to a 40% economic interest in the Joint Venture Company by investing up to $30 million (inclusive of the initial $5 million investment) prior to October 2018. On August 31, 2015, the Joint Venture Company approved additional exploration work during the fall of 2015. Royal Gold agreed to make an additional capital contribution of up to approximately $4 million for an aggregate investment of approximately $9 million. Royal Gold may earn up to an approximately 8% economic ownership of the joint venture by contributing the $9 million. The proceeds of Royal Gold’s investment have been and will be used by the Joint Venture Company for additional exploration of the Tetlin Property.
Properties
Since 2009, the Company's primary focus has been the exploration of a mineral lease with the Tetlin Village Council for the exploration of minerals on approximately 675,000 acres near Tok, Alaska (the "Tetlin Lease") and almost all of the Company's resources have been directed to that end. All significant work presently conducted by the Company has been directed at exploration of the Tetlin Lease and increasing understanding of the characteristics of, and economics of, any mineralization. There are no known quantifiable mineral reserves on the Tetlin Lease or any of the Company's other properties as defined by the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC") Industry Guide 7.
1
The Tetlin Lease originally had a ten year term beginning July 2008 with an option to renew 50% of the acreage for an additional ten years. In December 2012, the Tetlin Lease was amended, allowing the Company to renew 100% of the acreage in 2018, in exchange for $200,000, which the Company paid to the Tetlin Village Council. If the properties under the Tetlin Lease are placed into commercial production, the Tetlin Lease will be held throughout production and the Company would be obligated to pay a production royalty to the Native Village of Tetlin, which varies from 2.0% to 5.0%, depending on the type of metal produced and the year of production. In June 2011, the Company paid the Tetlin Village Council $75,000 in exchange for reducing the production royalty payable to them by 0.25%. In July 2011, the Company paid the Tetlin Village Council an additional $150,000 in exchange for further reducing the production royalty by 0.50%. These payments lowered the production royalty to a range of 1.25% to 4.25%, depending on the type of metal produced and the year of production. On or before July 15, 2020, the Tetlin Village Council has the option to increase its production royalty by (i) 0.25% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $150,000, or (ii) 0.50% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $300,000, or (iii) 0.75% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $450,000.
The Joint Venture Company also holds certain state of Alaska unpatented mining claims for the exploration of gold ore and associated minerals. The Company believes that the Joint Venture Company holds good title to its properties, in accordance with standards generally accepted in the mineral industry. As is customary in the mineral industry, the Company conducts only a preliminary title examination at the time it acquires a property. The Joint Venture Company conducted a title examination prior to the assignment of the Tetlin Lease to the Joint Venture Company and performed certain curative title work. Before the Joint Venture Company begins any mine development work, however, the Joint Venture Company is expected to again conduct a full title review and perform curative work on any defects that it deems significant. A significant amount of additional work is likely required in the exploration of the properties before any determination as to the economic feasibility of a mining venture can be made. Due to harsh weather conditions in Alaska, the Joint Venture Company's exploration field work will be normally restricted to May through October.
The following table summarizes the Tetlin Lease and unpatented mining claims (the "Tetlin Property") held by the Joint Venture Company as of June 30, 2015:
Property | Location | Commodities | Claims | Acres | Type | |||||
Tetlin-Tok | Eastern Interior | Gold, Copper | 131 | 10,850 | State Mining Claims | |||||
Eagle | Eastern Interior | Gold, Copper | 428 | 65,946 | State Mining Claims | |||||
Bush | Eastern Interior | Gold, Copper | 48 | 7,680 | State Mining Claims | |||||
West Fork | Eastern Interior | Gold, Copper | 48 | 7,680 | State Mining Claims | |||||
Triple Z | Eastern Interior | Gold, Copper | 45 | 7,200 | State Mining Claims | |||||
Tetlin-Village | Eastern Interior | Gold, Copper | - | 675,000 | Lease | |||||
TOTALS: | 700 | 774,356 | ||||||||
Strategy
Partnering with strategic industry participants to expand future exploration work. In connection with an evaluation of the Company’s strategic options conducted by the Board of Directors and its financial advisor, the Company determined to continue its exploration activities on the Tetlin Property through a joint venture with an experienced industry participant. As a result, the Company formed the Joint Venture Company pursuant to a Joint Venture Company's LLC Agreement with Royal Gold. Under the Joint Venture Company's LLC Agreement, Royal Gold is appointed as the manager of the Joint Venture Company (the “Manager”), initially, with overall management responsibility for operations of the Joint Venture Company through October 31, 2018, and, thereafter, provided Royal Gold earns at least a forty percent (40%) percentage interest by October 31, 2018. Royal Gold may resign as Manager and can be removed as Manager for a material breach of the Joint Venture Company LLC Agreement, a material failure to perform its obligations as the Manager, a failure to conduct the Joint Venture Company operations in accordance with industry standards and applicable laws, and other limited circumstances. The Manager will manage, and direct the operation of the Joint Venture Company, and will discharge its duties, in accordance with approved programs and budgets. The Manager will implement the decisions of the Management Committee of the Joint Venture Company (the “Management Committee”) and will carry out the day-to-day operations of the Joint Venture Company. Except as expressly delegated to the Manager, the Joint Venture Company's LLC Agreement provides that the Management Committee has exclusive authority to determine all management matters related to the Company. Initially, the Management Committee consists of one appointee designated by the Company and two appointees designated by Royal Gold. Each designate on the Management Committee will be entitled to one vote. Except for the list of specific actions set forth in the Joint Venture Company's LLC Agreement, the affirmative vote by a majority of designates will be required for action.
2
Structuring Incentives to Drive Behavior. The Company believes that equity ownership aligns the interests of the Company's executives, employees and directors with those of its stockholders. The Company’s directors, officers and employees do not receive cash compensation for their work for the Company. As of June 30, 2015, the Company's directors, officers, and employees beneficially own approximately 10.7% of the Company's common stock. An additional 21.6% of the Company's common stock is beneficially owned by the Estate of Mr. Kenneth R. Peak, the Company's former Chairman, who passed away on April 19, 2013.
Exploration and Mining Property
Exploration and mining rights in Alaska may be acquired in the following manner: public lands, private fee lands, unpatented Federal or State of Alaska mining claims, patented mining claims, and tribal lands. The primary sources for acquisition of these lands are the United States government, through the Bureau of Land Management and the United States Forest Service, the Alaskan state government, tribal governments, and individuals or entities who currently hold title to or lease government and private lands.
Tribal lands are those lands that are under control by sovereign Native American tribes, such as land constituting the Tetlin Lease or Alaska Native corporations established by the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act of 1971 (ANSCA). Areas that show promise for exploration and mining can be leased or joint ventured with the tribe controlling the land, including land constituting the Tetlin Lease.
The State of Alaska government owns public lands. Mineral resource exploration, development and production are administered primarily by the State Department of Natural Resources. Ownership of the subsurface mineral estate, including alluvial and lode mineral rights, can be acquired by staking a 40 acre or 160 acre mining claim, which right is granted under Alaska Statute Sec. 38.05.185 to 38.05.275, as amended (the “Alaska Mining Law”). The State government continues to own the surface estate, subject to certain rights of ingress and egress owned by the claimant, even though the subsurface can be controlled by a claimant with a right to extract through claim staking. However, the claimant does not own unfettered title to the minerals or the and the mining claim is subject to annual assessment work requirements, the payment of annual rental fees and royalties due to the State of Alaska after commencement of commercial production. Both private fee-land and unpatented mining claims and related rights, including rights to use the surface, are subject to permitting requirements of Federal, State, Tribal and Local governments.
Consulting Services provided by Avalon Development Corporation
Until January 8, 2015, the Company was a party to a Professional Services Agreement (“PSA”) with Avalon to provide certain geological consulting services and exploration activities with respect to the Tetlin Property. Pursuant to the PSA, Avalon provided geological consulting services and exploration activities, including all field work at the Tetlin Lease. The Company paid Avalon on a per diem basis and reimbursed Avalon for its expenses. As additional compensation, the owner of Avalon received restricted shares of common stock and stock options to purchase shares of common stock of the Company.
Avalon is a Fairbanks, Alaska based mineral exploration consulting firm, which has conducted mineral exploration in Alaska since 1985. The President of Avalon is Curtis J. Freeman who graduated from the College of Wooster, Ohio, with a B.A. degree in Geology (1978) and graduated from the University of Alaska with an M.S. degree in Economic Geology (1980). From 1980 to the present Mr. Freeman has been actively employed in various capacities in the mining industry in numerous locations in North America, Central America, South America, New Zealand and Africa. Avalon's team of engineers and geoscientists combined with its geographic information systems (GIS) database allows Avalon to synthesize existing geological, geochemical and geophysical data and identify specific target areas for ground evaluation and/or acquisition. Avalon’s exploration team has identified or conducted discovery drilling on several gold deposits in Alaska and has completed digital GIS compilations of the Tintina Gold Belt, a regional-scale mineral province stretching from southwest Alaska to the southern Yukon Territory. Avalon also has experience exploring for copper, nickel and platinum group elements (“Cu-Ni-PGE”) deposits and also created a comprehensive GIS compilation of Cu-Ni-PGE prospects in Alaska, an internally-owned database that contains data on over 200 PGE occurrences in Alaska.
In connection with the Transactions, the Company terminated the PSA with Avalon, and Avalon is now providing services to the Joint Venture Company.
Services Provided by Tetlin Village Members
Since the start of the term of the Tetlin Lease, the Company, and the Joint Venture Company have worked closely with the Tetlin Village Council to train and employ Tetlin residents during Tetlin project exploration programs. During the 2013 and 2015 exploration programs, there were more than 15 Tetlin residents working on the Tetlin project exploration program, employed on a seasonal basis through Avalon. Their duties included reconnaissance soil, stream sediment and pan concentrate sampling,
3
diamond drill core processing, drill pad construction and related tasks, expediting services, food services, database management, vehicle transportation and maintenance services, reclamation activities, and project management tasks.
On October 15, 2010, the Company entered into a consulting agreement (as amended, the “Consulting Agreement”), with the Chief of the Tetlin Village (the “Consultant”), which was terminated in January 2015, in connection with the Transactions. Under the terms of the Consulting Agreement, the Consultant assisted the Company in negotiations with other native tribes to lease additional properties and assisted the Company with State of Alaska and Federal governmental affairs issues. The Company paid the Consultant $5,000 per month and certain lodging costs while the Consultant was in Fairbanks, Alaska, in exchange for his services.
Community Affairs
In April 2015, the Joint Venture Company entered into a Community Support Agreement with the Tetlin Village for a one year period, renewable by mutual consent of both parties annually. Under the agreement the Joint Venture Company provides payments to the village three times during the year for an aggregate amount of $100,000. The agreement defines agreed uses for the funds and auditing rights regarding use of funds. In addition, the Joint Venture Company supports the Tetlin Village in maintenance of the village access road, which is used by the Company on a daily basis during the exploration season on an as needed basis. Funding through the end of August 2015 has amounted to $95,000.
The Company's activities have increased road traffic and general activity on the Tetlin lands. During the fiscal years ended June 30, 2015 and 2014, the Company expended approximately $30,000 and $434,000, respectively, on road work, snow plowing, flood relief, winter fuel, village repairs and charitable contributions.
In August 2013, the Company advanced $100,000 to the Tetlin Village Council under a Promissory Note (the "Tetlin Note") for road improvements. The terms of the Tetlin Note required the advance be repaid without interest on the earlier of (i) October 1, 2013 or (ii) a date that was within five days following the date the Tetlin Village Council received funds from the State of Alaska for road improvements. The Tetlin Note was repaid on October 4, 2013.
Adverse Climate Conditions
Weather conditions will affect the Joint Venture Company's ability to conduct exploration activities and mine any ore from the Tetlin Property in Alaska. While exploratory drilling and related activities may only be conducted from May to October on the Tetlin Property, the Company believes development work and any subsequent mining may be conducted year-round.
Competition
The Joint Venture Company currently faces strong competition for the acquisition of exploration-stage properties as well as extraction of any minerals in Alaska. Numerous larger mining companies actively seek out and bid for mining prospects as well as for the services of third party providers and supplies, such as mining equipment and transportation equipment. The Joint Venture Company's competitors in the exploration, development, acquisition and mining business include major integrated mining companies as well as numerous smaller mining companies, almost all of which have significantly greater financial resources and in-house technical expertise. In addition, the Joint Venture Company will compete with others in efforts to obtain financing to further explore and develop its mineral properties.
Government Regulation
The Joint Venture Company's mineral exploration activities are generally affected by various laws and regulations, including environmental, conservation, tax and other laws and regulations relating to the exploration of minerals. Various Federal and Alaskan laws and regulations often require permits for exploration activities and also cover extraction of minerals. In addition, the Tetlin Lease is located on land leased from the Tetlin Village Council. Federally recognized Native American tribes are independent governments, with sovereign powers, except as those powers may have been limited by treaty or by the United States Congress. Such tribes maintain their own governmental systems and often their own judicial systems and have the right to tax, and to require licenses and to impose other forms of regulation and regulatory fees, on persons and businesses operating on their lands. As sovereign nations, federally recognized Native American tribes are generally subject only to federal regulation. States do not have the authority to regulate them, unless such authority has been specifically granted by Congress, and state laws generally do not directly apply to them and to activities taking place on their lands, unless they have a specific agreement or compact with the state or federal government allowing for the application of state law. The Joint Venture Company will continue to use its best efforts to ensure that it is in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations but the denial of permits required to explore for or mine ore may prevent it from realizing any revenues arising from the presence of minerals on its properties.
4
Environmental Regulation
The Joint Venture Company believes that it is currently operating in compliance with all environmental regulations. While the Alaska Department of Natural Resources, Office of Project Management and Permitting coordinates the permitting of mine projects on state lands, it has no jurisdiction on Native American land such as the Tetlin Lease. However, the Joint Venture Company has voluntarily elected, with the concurrence of the Chief of Tetlin Village and the Tetlin Village Council, to conduct its mineral exploration activities under the same terms and conditions as required on State of Alaska mining claims.
The Joint Venture Company has been issued Hard Rock Exploration permits and Temporary Water Use Permits covering past and planned activities on the Tetlin Property. These permits were issued to the Company by the Alaska Department of Natural Resources in 2012 and 2013 and assigned to the Joint Venture Company and consist of the following multi-year permits:
1. | Alaska Hard Rock Exploration and Reclamation Permit #2626 covering exploration drilling activities on the Tetlin Lease. This permit extends through December 31, 2015. Each year during the term of the permit, the Company will submit a reclamation statement detailing reclamation actions taken and a letter of intent to do reclamation for the following year. |
2. | Alaska Temporary Water Use Permits F2011-51 and F2012-157, each allowing a seasonal average water use of 21,600 gallons per day during the period May 20 to October 15 during calendar years 2011 through 2016. These water use authorizations are specific to Alaska Hard Rock Exploration permit #2626; |
The above referenced State of Alaska permits were issued to the Company and assigned to the Joint Venture Company to cover its access road, drill pad and core drilling impacts. The Joint Venture Company does not anticipate requiring additional permits from the State of Alaska for the remainder of 2015. Reclamation of surface disturbance, if any, associated with our exploration activities is conducted concurrently where required.
The Joint Venture Company also has received a Nationwide Permit #6, Permit #POA-2013-286, from the U.S. Department of the Army Corps of Engineers with respect to the Joint Venture Company’s intended drilling and access-related disturbances on wetlands within the Tetlin Lease, which is valid through March 18, 2017. However, such lands were classified as wetlands more than 20 years ago and much of the land covered by such permit has since been burned by natural wildfires. As a consequence of the wildfires and natural habitat changes that have taken place since the wildfires, the Tetlin Property may no longer be considered wetlands according to Corps of Engineers guidelines.
The Company began collecting baseline environmental data in 2012 and the Joint Venture Company has continued this process. The Joint Venture Company has not developed a comprehensive environmental permitting strategy as the Company remains in an exploration stage. If and when its exploration work is significantly advanced that additional baseline environmental studies and prefeasibility studies are desirable, the Company will be required to expend considerable funds and resources for an environmental impact statement and related studies to advance any mining project.
Any future mining operations are subject to local, state and federal regulation governing environmental quality and pollution control, including air quality standards, greenhouse gas, waste management, reclamation and restoration of properties, plant and wildlife protection, handling and disposal of radioactive substances, and employee health and safety. Extraction of mineral ore is subject to stringent environmental regulation by state and federal authorities, including the Environmental Protection Agency. Such regulation can increase the cost of planning, designing, installing and operating mining facilities or otherwise delay, limit or prohibit planned operations.
Significant fines and penalties may be imposed for failure to comply with environmental laws. Some environmental laws provide for joint and several strict liability for remediation of releases of hazardous substances. In addition, the Joint Venture Company may be subject to claims alleging personal injury or property damages as a result of alleged exposure to hazardous substances.
The Federal Mine Safety and Health Act of 1977 and regulations promulgated thereunder, as well as, the State of Alaska Department of Labor and Workforce Development impose a variety of health and safety standards on numerous aspects of employee working conditions related to mineral extraction and processing operations, including the training of personnel, operating procedures and operating equipment. In addition, the Joint Venture Company may be subject to additional state and local mining standards. The Company believes that the Joint Venture Company currently is in compliance with applicable mining standards; however, the Company cannot predict whether changes in standards or the interpretation or enforcement thereof will have a material adverse effect on the Joint Venture Company's business, financial condition or otherwise impose restrictions on its ability to conduct mining operations.
A typical time frame for baseline environmental studies and permitting for a gold mine in Alaska may consume a decade or more. There are numerous state and federal permits and authorizations required from many different state and federal agencies.
5
Federal legislation and regulations adopted and administered by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Forest Service, Bureau of Land Management, Fish and Wildlife Service, Mine Safety and Health Administration, and other federal agencies, legislation such as the Federal Clean Water Act, Clean Air Act, National Environmental Policy Act, Endangered Species Act, and Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (“CERCLA”) and various laws and regulations administered by the State of Alaska including the Alaska Department of Fish and Game, the Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation, Alaska Department of Transportation and Public Facilities and the Alaska Department of Natural Resources, have a direct bearing on exploration and mining operations conducted in Alaska. These regulations will make the process for preparing and obtaining approval of a plan of operations much more time-consuming, expensive, and uncertain. The Alaska Department of Natural Resources coordinates the permitting of mining operations in the State of Alaska and has developed a process to integrate federal, state and local government requirements to obtain mine permits, and also provides an opportunity for public comment. Plans of operation will be required to include detailed baseline environmental information and address how detailed reclamation performance standards will be met. In addition, all activities for which plans of operation are required will be subject to a new standard of review by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management, which must make a finding that the conditions, practices or activities do not cause substantial irreparable harm to significant scientific, cultural, or environmental resource values that cannot be effectively mitigated.
CERCLA generally imposes joint and several strict liability for costs of investigation and remediation and for natural resource damages, with respect to the release of hazardous substances (as designated under CERCLA) into the environment. CERCLA also authorizes the EPA, and in some cases, third parties, to take action in response to threats to the public health or the environment and to seek to recover from the potentially responsible parties the costs of such action. The Joint Venture Company's mining operations may generate wastes that fall within CERCLA’s definition of Hazardous Substances.
Employees
The Company has three part-time employees. Of these, two are officers of the Company. Brad Juneau is the Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer of the Company and is responsible for the management of the Company. Leah Gaines is the Vice President, Chief Financial Officer, Chief Accounting Officer, Treasurer and Secretary of the Company and is responsible for the financial and accounting affairs of the Company. Mr. Juneau and Ms. Gaines each devote approximately 10% of their time to the Company’s business. The Company also uses the services of independent consultants and contractors to perform various professional services, including land acquisition, legal, environmental and tax services. In addition, the Joint Venture Company utilizes the services of Avalon to perform geological, exploration and drilling operation services and independent third party engineering firms to evaluate any mineral resources identified.
Directors and Executive Officers
The following table sets forth the names, ages and positions of the Company's directors and executive officers:
Name | Age | Position | ||
Brad Juneau | 55 | Chairman, President, and Chief Executive Officer | ||
Leah Gaines | 39 | Vice President, Chief Financial Officer, Chief Accounting Officer, Treasurer and Secretary | ||
Joseph Compofelice | 66 | Director | ||
Joseph G. Greenberg | 54 | Director | ||
Brad Juneau. Mr. Juneau, the Company's co-founder, was elected President and Chief Executive Officer in December 2012. Mr. Juneau was first appointed President, Acting Chief Executive Officer and director in August 2012 when the Company's Co-founder, Mr. Kenneth R. Peak received a medical leave of absence. Mr. Juneau was appointed Chairman of the Board in April 2013. Mr. Juneau is the sole manager of the general partner of JEX, an oil and gas exploration and production company. Prior to forming JEX in 1998, Mr. Juneau served as Senior Vice President of Exploration for Zilkha Energy Company from 1987 to 1998. Prior to joining Zilkha Energy Company, Mr. Juneau served as Staff Petroleum Engineer with Texas International Company for three years, where his principal responsibilities included reservoir engineering, as well as acquisitions and evaluations. Prior to that, he was a production engineer with Enserch Corporation in Oklahoma City. Mr. Juneau holds a Bachelor of Science degree in Petroleum Engineering from Louisiana State University. Mr. Juneau previously served as a Director of Contango from April 2012 to March 2014.
Leah Gaines. Ms. Gaines was appointed as the Company’s Vice President, Chief Financial Officer, Chief Accounting Officer, Treasurer and Secretary on October 1, 2013. Ms. Gaines has also served as Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of JEX since October 2010. Prior to joining JEX, she served as the Controller for Beryl Oil and Gas, LP and Beryl Resources LP from July 2007 to December 2009. From April 2006 to July 2007, Ms. Gaines held the position of Financial Reporting Manager at SPN Resources, a division of Superior Energy Services. From 2003 to 2006, Ms. Gaines was the Senior Financial Reporting
6
Accountant at Hilcorp Energy. Ms. Gaines was a Principal Accountant at El Paso Corporation in its Power Asset division from 2001 to 2003. Prior to that, Ms. Gaines worked at Deloitte and Touche, LLP for three years as a Senior Auditor. Ms. Gaines graduated Magna Cum Laude from Angelo State University with a Bachelor of Business Administration in Accounting and is a Certified Public Accountant with over seventeen years of experience.
Joseph Compofelice. Mr. Compofelice has been a Director of the Company since its inception. Since January 1, 2014, Mr. Compofelice has been an Operating Partner at White Deer Energy, a private equity firm that targets investments in the energy business. Mr. Compofelice served as Managing Director of Houston Capital Advisors, a boutique financial advisory, mergers and acquisitions investment service from January 2004 to December 2013. Mr. Compofelice served as Chairman of the Board of Trico Marine Service, a provider of marine support vessels serving the international natural gas and oil industry, from 2004 to 2010 and as its Chief Executive Officer from 2007 to 2010. Mr. Compofelice was President and Chief Executive Officer of Aquilex Services Corp., a service and equipment provider to the power generation industry, from October 2001 to October 2003. From February 1998 to October 2000 he was Chairman and CEO of CompX International Inc., a provider of components to the office furniture, computer and transportation industries. From March 1994 to May 1998 he was Chief Financial Officer of NL Industries, a chemical producer, Titanium Metals Corporation, a metal producer and Tremont Corp. Mr. Compofelice received his Bachelor of Science from California State University at Los Angeles and his Masters of Business Administration from Pepperdine University.
Joseph G. Greenberg. Mr. Greenberg has been a Director of the Company since its inception. Mr. Greenberg is Founder and President and CEO of Alta Resources, L.L.C., an oil and gas exploration and production company. Prior to founding Alta Resources in 1999, Mr. Greenberg worked as an exploration geologist for Shell Oil Company and Edge Petroleum Company. Mr. Greenberg received a Bachelor of Science in Geology and Geophysics from Yale University in 1983, and a Masters in Geological Sciences from the University of Texas at Austin in 1986. He has over twenty-eight years of diversified experience in oil and gas exploration and production.
The Board of Directors is responsible for managing the Company, in accordance with the provisions of the Company’s Bylaws and Certificate of Incorporation and applicable law. The number of directors which constitutes the Board of Directors is established by the Board, subject to a minimum of three and a maximum of seven directors. Except, as otherwise provided by the Bylaws for filling vacancies on the Company’s Board of Directors, the Company’s directors are elected at the Company’s annual meeting of stockholders and hold office until their respective successors are elected, or until their earlier resignation or removal. The Company's executive officers are elected annually by the Board and serve until their successors are duly elected and qualified or until their earlier resignation or removal. There are no family relationships between the Company's directors or executive officers.
The Board of Directors elected Mr. Juneau as Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer for a number of reasons. Mr. Juneau is the co-founder of the Company and beneficially owns approximately 9.8% of the Company’s common stock, making him one of the largest shareholders. Mr. Juneau has been an active entrepreneur who founded JEX and built the business into a successful exploration and production company.
Corporate Offices
The Company currently subleases office space from JEX at 3700 Buffalo Speedway, Ste 925, Houston, TX 77098 for approximately $11,000 per quarter.
Code of Ethics
The Company adopted a Code of Ethics for senior management in September 2010. A copy of our Code of Ethics is filed as an Exhibit to this Form 10-K and is also available on the Company's website at www.contangoore.com.
Available Information
You may read and copy all or any portion of this annual report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and current reports on Form 8-K, as well as any amendments and exhibits to those reports, without charge at the office of the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) in Public Reference Room, 100 F Street NE, Washington, DC, 20549. Information regarding the operation of the public reference rooms may be obtained by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. In addition, filings made with the SEC electronically are publicly available through the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov, and at the Company's website at http://www.contangoore.com. This annual report on Form 10-K, including all exhibits and amendments, has been filed electronically with the SEC.
7
Item 1A. RISK FACTORS
In addition to other information set forth elsewhere in this Form 10-K, you should carefully consider the following factors when evaluating the Company. An investment in the Company is subject to risks inherent in the mining business as an exploration stage company. The value of an investment in the Company may decrease, resulting in a complete loss of your investment. The risk factors below are not all inclusive.
Royal Gold will have discretion regarding the use and allocation of funds for further exploration of the Contributed Assets.
Royal Gold is the Manager of the Joint Venture Company and has appointed two designates to the Management Committee of the Joint Venture Company (the “Management Committee”). The Company has appointed one designate to the Management Committee. If, after October 31, 2018, Royal Gold has earned at least a 40% membership interest in the Joint Venture by making the full $30 million investment, Royal Gold will continue to have the right to appoint two designates to the Management Committee and the Company will continue to have the right to appoint one designate, The affirmative vote of a majority of designates will determine most decisions of the Management Committee, including the approval of programs and budgets and the expenditure of Royal Gold’s investments.
The Company must depend upon Royal Gold's management of the Joint Venture Company following termination of the Company's third party consulting agreements.
On September 29, 2014, the Company terminated its advisory agreement with JEX. In addition, the Company terminated its services agreements with Avalon Development Corporation and the Chief of the Tetlin Village in January 2015. Because the Company has historically had part-time employees, none of whom are mineral geoscientists or have experience in the mining industry, the Company has previously depended upon consultants, Avalon Development Corporation and the Chief of the Tetlin Village, for the success of its exploration projects. The Company must depend upon Royal Gold for its expertise in planning work programs, conducting field work, evaluating drilling results and preparing development programs.
There can be no assurance that Royal Gold will continue to fund the Joint Venture Company to continue exploration work.
The Joint Venture Company's LLC Agreement contains earn-in periods where Royal Gold has the option to fund up to $25 million on or before October 31, 2018 after its initial $5 million investment at the Closing of the Master Agreement. There is no requirement that Royal Gold contribute any future amounts to the Joint Venture Company to continue exploration work, and the Company will have limited funds to continue exploration of its Tetlin Property, if Royal Gold fails to contribute additional amounts to the Joint Venture Company.
The Company may retain only a 60% interest in the Joint Venture Company and its interest could be diluted further.
The Company’s only significant asset is its interest in the Joint Venture Company. If Royal Gold makes the full $30 million capital contribution, it will receive a 40% interest in the Joint Venture Company, and the Company will retain a 60% interest in the Joint Venture Company. In addition, once Royal Gold has earned a 40% interest in the Joint Venture Company, it has the option to require the Company to sell an additional 20% of the Company’s interest in the Joint Venture Company in a sale by Royal Gold of its entire 40% interest to a bona fide third party purchaser. Furthermore, if the Company were unable to fund its contributions to the approved programs and budgets for the Joint Venture Company, its interest in the Joint Venture Company would be diluted further.
There can be no assurance that the Company will be capable of raising additional funding required to continue development of the Tetlin Property and meet its funding obligations under the Joint Venture Company's LLC Agreement.
Upon the later of the investment by Royal Gold of $30 million into the Joint Venture Company or October 31, 2018, the Company and Royal Gold will jointly fund the joint venture operations in proportion to their interests in the Joint Venture Company. The capital costs of developing a large gold mining facility could exceed $1 billion. The Company has limited financial resources and the ability of the Company to arrange additional financing in the future will depend, in part, on the prevailing capital market conditions, the exploration results achieved at the Tetlin Property, as well as the market price of metals. There is no assurance that sources of financing will be available to the Company on acceptable terms, if at all. Failure to obtain additional financing on a timely basis will cause the Company’s interest in the Joint Venture Company to be diluted.
Further financing by the Company may include issuances of equity, instruments convertible into equity (such as warrants) or various forms of debt. The Company has issued common stock and other instruments convertible into equity in the past and
8
cannot predict the size or price of any future issuances of common stock or other instruments convertible into equity, and the effect, if any, that such future issuances and sales will have on the market price of the Company’s securities. Any additional issuances of common stock or securities convertible into, or exercisable or exchangeable for, common stock may ultimately result in dilution to the holders of common stock, dilution in any future earnings per share of the Company and may have a material adverse effect upon the market price of the common stock of the Company.
Royal Gold has far greater technical and financial resources than the Company.
Royal Gold is an international precious metals royalty and streaming company with interests in approximately 198 properties on six continents and a market capitalization of approximately $4 billion on June 30, 2015. Because of its vastly superior technical and financial resources, Royal Gold may adopt budgets and work programs for the Joint Venture Company that the Company will be unable to fund in the time frame required, and its interest in the Joint Venture Company may be substantially diluted.
The Joint Venture Company's LLC Agreement restricts the Company’s right to transfer or encumber its interests in the Joint Venture Company.
The Joint Venture Company's LLC Agreement contains certain limitations on transferring or encumbering interests in the Joint Venture Company including any transfer that would cause termination of the Joint Venture Company as a partnership for Federal income tax purposes except none of the restrictions limit the transfer of any capital stock of the Company.
The formation of the Joint Venture Company and appointment of Royal Gold as Manager do not provide assurance that further exploration efforts will be successful.
The formation of the Joint Venture Company and appointment of Royal Gold as Manager do not provide assurance that further exploration of the Tetlin Property will be successful, any additional resource will be discovered or a commercial deposit of gold ore and associated minerals may be located. The results of any further exploration work will be assayed and analyzed to determine if additional work should be performed and additional funds expended.
The probability that an individual prospect will contain commercial grade reserves is extremely remote.
The probability of finding economic mineral reserves on the Tetlin Property is extremely small. It is common to spend millions of dollars on an exploration prospect and complete many phases of exploration and still not obtain mineral reserves that can be economically exploited. Therefore, the possibility that the Tetlin Property will contain commercial mineral reserves and that the Company will recover funds spent on exploration is extremely remote.
The price of gold and the gold mining industry have suffered dramatic declines in the past several years.
With the price of gold declining over the past several years, many large mining companies have announced the closure of existing gold mines and a moratorium on new gold mine development.
The Company's ability to successfully execute its business plan is dependent on its ability to obtain adequate financing.
The Company's business plan, which includes the drilling of the Joint Venture Company’s exploration prospects, will require substantial capital expenditures. The Company's ability to raise capital will depend on many factors, including the status of various capital and industry markets at the time it seeks such capital. Accordingly, the Company cannot be certain that financing will be available to us on acceptable terms, if at all. In the event additional capital resources are unavailable, the Company may be required to cease our exploration and development activities or be forced to sell all or some portion of its interest in the Joint Venture Company in an untimely fashion or on less than favorable terms.
The Company has no revenue to date from the Tetlin Property, which may negatively impact the Company's ability to achieve its business objectives.
Since the acquisition of the Tetlin Property, the Company and the Joint Venture Company have conducted only limited exploration activities and to date have not discovered any commercially viable mineral deposits. The Company's ability to become profitable will be dependent on the receipt of revenues from the extraction of minerals greater than operational expenses. The Company and the Joint Venture Company have carried on their business of exploring the Tetlin Property at a loss since inception and expect that the Company and the Joint Venture Company will continue to incur losses unless and until such time as one of the properties enters into commercial production and generates sufficient revenues to fund its continuing operations. The amounts
9
and timing of expenditures will depend on the progress of ongoing exploration, the results of consultants’ analysis and recommendations, the rate at which operating losses are incurred, and other factors, many of which are beyond control. Whether any mineral deposits discovered would be commercially viable depends on a number of factors, which include, without limitation, the particular attributes of the deposit, market prices for the minerals, and governmental regulations. If the Joint Venture Company cannot discover commercially viable deposits or commence actual mining operations, the Company and the Joint Venture Company may never generate revenues and will never become profitable.
The Company's continued viability depends on the exploration, permitting, development and operation of the Tetlin Lease, which is the only material property of the Joint Venture Company.
The Joint Venture Company's only material project at this time is the Tetlin Lease, which is in the exploration stage. The Company's continued viability is based on successfully implementing its strategy, which will require the Joint Venture Company to perform appropriate exploratory and engineering work and evaluate such work, and the permitting and construction of a mine and processing facilities in a reasonable time frame.
The Tetlin Property does not have any proven or probable reserves and the Joint Venture Company may never identify any commercially exploitable mineralization.
None of the Joint Venture Company’s properties have any proven or probable reserves as defined by SEC Industry Guide 7. To date, the Company and the Joint Venture Company have only engaged in material exploration activities on the Tetlin Lease. Accordingly, the Company does not have sufficient information upon which to assess the ultimate success of their exploration efforts. There is no assurance that the Joint Venture Company may ever locate any mineral reserves on the Tetlin Property that may be in economic quantities. Additionally, even if the Joint Venture Company finds minerals in sufficient quantities to warrant recovery, such recovery may not be economically profitable. Mineral exploration is highly speculative in nature, involves many risks and is frequently non-productive. Unusual or unexpected geologic formations and the inability to obtain suitable or adequate machinery, equipment or labor are risks involved in the conduct of exploration programs. If the Joint Venture Company does not establish reserves, it will be required to curtail or suspend our operations, in which case the market value of the Company's common stock will decline, and you may lose all of your investment.
The Tetlin Property is located in the remote regions of Alaska and exploration activities may be limited by weather and limited access and existing infrastructure.
The Joint Venture Company is focused on the exploration of its properties in the State of Alaska. The arctic climate limits most exploration activities to the period from May to October. In addition, the remote location of the properties may limit access and increase exploration expense. Higher costs associated with exploration activities and limitation on the annual periods in which the Joint Venture Company can carry on exploration activities will increase the costs and time associated with our planned exploration activities and could negatively affect the value of the Tetlin Property and the Company's securities.
Concentrating capital investment in the Tetlin Properties in the State of Alaska increases exposure to risk.
The Company and the Joint Venture Company have focused their capital investments in exploring for gold and associated mineral prospects on the Tetlin Property in the State of Alaska. However, the exploration prospects in Alaska may not lead to any revenues or the Joint Venture Company may not be able to drill for mineral deposits at anticipated finding and development costs due to financing, environmental or operating uncertainties. Should the Joint Venture Company be able to make an economic discovery on the Tetlin Property, it would then be solely dependent upon a single mining operation for its revenue and profits.
The Company will rely on the accuracy of the estimates in reports provided to the Company by Royal Gold and the Joint Venture Company’s outside consultants and engineers.
The Company has no in-house mineral engineering capability, and therefore will rely on the accuracy of reports provided to us by Royal Gold, and the Joint Venture Company’s independent third party consultants. If those reports prove to be inaccurate, the Company's financial reports could have material misstatements. Further, the Company will use the reports of Royal Gold and such independent consultants in its financial planning. If the reports prove to be inaccurate, we may also make misjudgments in its financial planning.
10
Exploration activities involve a high degree of risk, and the Joint Venture Company’s exploratory drilling activities may not be successful.
The Company future success will largely depend on the success of the exploration drilling programs of the Joint Venture Company. Participation in exploration drilling activities involves numerous risks, including the significant risk that no commercially marketable minerals will be discovered. The mining of minerals and the manufacture of mineral products involves numerous hazards, including:
• | Ground or slope failures; |
• | Pressure or irregularities in formations affecting ore or wall rock characteristics; |
• | Equipment failures or accidents; |
• | Adverse weather conditions; |
• | Compliance with governmental requirements and laws, present and future; |
• | Shortages or delays in the availability and delivery of equipment; and |
• | Lack of adequate infrastructure, including access to roads, electricity and available housing. |
Poor results from the Joint Venture Company’s drilling activities would materially and adversely affect the Company's future cash flows and results of operations.
The Joint Venture Company has no assurance of title to its properties.
The Joint Venture Company holds 99,356 acres in the form of State of Alaska unpatented mining claims, for gold ore exploration. Unpatented mining claims are unique property interests, in that they are subject to the paramount title of, the State of Alaska and rights of third parties to uses of the surface within their boundaries, and are generally considered to be subject to greater title risk than other real property interests. The rights to deposits of minerals lying within the boundaries of the unpatented state claims are subject to Alaska Statues 38.05.185 - 38.05.280, and are governed by Alaska Administrative Code 11 AAC 86.100 - 86.600. The validity of all State of Alaska unpatented mining claims is dependent upon inherent uncertainties and conditions.
With respect to the Tetlin Lease, the Company retained title lawyers to conduct a preliminary examination of title to the mineral interest prior to executing the Tetlin Lease. The Joint Venture Company conducted a title examination prior to the assignment of the Tetlin Lease to the Joint Venture Company and performed certain curative title work. Prior to conducting any mining activity, however, the Joint Venture Company is expected to again obtain a full title review of the Tetlin Lease to identify more fully any deficiencies in title to the lease and, if there are deficiencies, to identify measures necessary to cure those defects to the extent reasonably possible. However, such deficiencies may not be cured. It does happen, from time to time, that the examination made by title lawyers reveals that the title to properties is defective, having been obtained in error from a person who is not the rightful owner of the mineral interest desired. In these circumstances, the Joint Venture Company may not be able to proceed with exploration of the lease site or may incur costs to remedy a defect. It may also happen, from time to time, that the Joint Venture Company may elect to proceed with mining work despite defects to the title identified in a title opinion.
The Tetlin Lease was executed with a Native American tribe for the exploration of gold ore and associated minerals. The enforcement of contractual rights against Native American tribes with sovereign powers may be difficult.
Federally recognized Native American tribes are independent governments with sovereign powers, except as those powers may have been limited by treaty or the United States Congress. Such tribes maintain their own governmental systems and often their own judicial systems and have the right to tax, and to require licenses and to impose other forms of regulation and regulatory fees, on persons and businesses operating on their lands. As sovereign nations, federally recognized Native American tribes are generally subject only to federal regulation. States do not have the authority to regulate them, unless such authority has been specifically granted by Congress, and state laws generally do not directly apply to them and to activities taking place on their lands, unless they have a specific agreement or compact with the state or Federal government allowing for the application of state law. The Tetlin Lease provides that it will be governed by applicable federal law and the law of the State of Alaska. The Company and the Tetlin Village Council entered into a Stability Agreement, dated October 2, 2014, that was assigned by the Company to the Joint Venture Company. However, no assurance may be given that the choice of law clause in the Tetlin Lease or the agreements with the Tetlin Village Council in the Stability Agreement will be enforceable.
Federally recognized Native American tribes also generally enjoy sovereign immunity from lawsuit similar to that of the states and the United States federal government. In order to sue a Native American tribe (or an agency or instrumentality of a Native American tribe), the Native American tribe must have effectively waived its sovereign immunity with respect to the matter in dispute. Moreover, even if a Native American tribe effectively waives its sovereign immunity, there exists an issue as to the forum in which a lawsuit can be brought against the tribe. Federal courts are courts of limited jurisdiction and generally do not
11
have jurisdiction to hear civil cases relating to matters concerning Native American lands or the internal affairs of Native American governments. Federal courts may have jurisdiction if a federal question is raised by the lawsuit, which is unlikely in a typical contract dispute. Diversity of citizenship, another common basis for federal court jurisdiction, is not generally present in a suit against a tribe because a Native American tribe is not considered a citizen of any state. Accordingly, in most commercial disputes with tribes, the jurisdiction of the federal courts, may be difficult or impossible to obtain. The Tetlin Lease contains a provision in which the Tetlin Village Council expressly waives its sovereign immunity to the limited extent necessary to permit judicial review in the courts in Alaska of certain issues affecting the Tetlin Lease and the Stability Agreement contains, among other things, agreement that any disputes under the Tetlin Lease will be submitted to the jurisdiction of the federal and state courts.
Competition in the mineral exploration industry is intense, and the Joint Venture Company is smaller and has a much more limited operating history than most of its competitors.
The Joint Venture Company will compete with a broad range of mining companies with far greater resources in its exploration activities. Several mining companies concentrate drilling efforts on one type of mineral and thus may enjoy economies of scale and other efficiencies. However, the Joint Venture Company’s drilling strategies currently include exploring for gold ore and associated minerals. As a result, the Joint Venture Company may not be able to compete effectively with such companies. The Joint Venture Company will also compete for the equipment and labor required to operate and to develop its Properties if its exploration activities are successful. Most competitors have substantially greater financial resources than the Joint Venture Company. These competitors may be able to evaluate, bid for and purchase a greater number of properties and prospects than the Joint Venture Company can. In addition, most competitors have been operating for a much longer time than the Joint Venture Company has and have substantially larger staffs. Processing of gold and associated minerals requires complex and sophisticated processing technologies. The Company has no experience in the minerals processing industry.
The Company and the Joint Venture Company have only owned the Tetlin Property since the acquisition by its predecessors of the properties in 2009 and 2010. Furthermore, no member of the Company's management has any technical training or experience in minerals exploration or mining. Because of the Company's limited operating history, the Company has limited insight into trends that may emerge and affect its business. The Company may make errors in predicting and reacting to relevant business trends and will be subject to the risks, uncertainties and difficulties frequently encountered by early-stage companies. Neither the Company nor the Joint Venture Company may be able to compete effectively with more experienced companies or in such a highly competitive environment.
The mining industry is historically a cyclical industry and market fluctuations in the prices of minerals could adversely affect the Company's and Joint Venture Company's business.
Prices for minerals tend to fluctuate significantly in response to factors beyond the Company's control. These factors include:
• | Global economic conditions; |
• | Domestic and foreign tax policy; |
• | The price of gold; |
• | The cost of exploring for, producing and processing gold; |
• | Available transportation capacity; and |
• | The overall supply and demand for gold. |
Changes in gold prices would directly affect revenues and may reduce the amount of funds available to reinvest in exploration activities. Reductions in gold prices not only reduce revenues and profits, but could also reduce the quantities of resources that are commercially recoverable. Declining metal prices may also impact the operations of the Joint Venture Company by requiring a reassessment of the commercial feasibility of any of its mining work.
Because the Company's and Joint Venture Company's sole source of revenue, if its exploration efforts are successful, will be the sale of gold and associated minerals, changes in demand for, and the market price of, gold and associated minerals could significantly affect the Company's Joint Venture Company's profitability. The value and price of the Company's common stock may be significantly affected by declines in the prices of gold minerals and products.
Gold prices fluctuate widely and are affected by numerous factors beyond the Company's control such as interest rates, exchange rates, inflation or deflation, fluctuation in the relative value of the United States dollar against foreign currencies on the world market, global and regional supply and demand for gold, and the political and economic conditions of gold producing countries throughout the world.
12
An increase in the global supply of gold and associated minerals may adversely affect the Company's and Joint Venture Company's business.
The pricing and demand for gold and associated minerals is affected by a number of factors beyond the Joint Venture Company's control, including global economic conditions and the global supply and demand for gold and associated minerals and products. Increases in the amount of gold and associated minerals sold by competitors of the Joint Venture Company may result in price reductions, reduced margins and the Joint Venture Company may not be able to compete effectively against current and future competitors.
The Joint Venture Company is subject to complex laws and regulations, including environmental regulations that can adversely affect the cost, manner or feasibility of doing business.
The Joint Venture Company's exploratory mining operations are subject to numerous laws and regulations governing its operations and the discharge of materials into the environment, including the Federal Clean Water Act, Clean Air Act, Endangered Species Act, and the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act. Federal initiatives are often also administered and enforced through state agencies operating under parallel state statutes and regulations. Failure to comply with such rules and regulations could result in substantial penalties and have an adverse effect on the Joint Venture Company. These laws and regulations may:
• | Require that the Joint Venture Company obtain permits before commencing mining work; |
• | Restrict the substances that can be released into the environment in connection with mining work; |
• | Impose obligations to reclaim land in order to minimize long term effects of land disturbance; |
• | Limit or prohibit mining work on protected areas. |
Under these laws and regulations, the Joint Venture Company could be liable for personal injury and clean-up costs and other environmental and property damages, as well as administrative, civil and criminal penalties. The Company and the Joint Venture Company maintain only limited insurance coverage for sudden and accidental environmental damages. Accordingly, the Joint Venture Company may be subject to liability, or it may be required to cease production from properties in the event of environmental damages. Compliance with environmental laws and regulations and future changes in these laws and regulations may require significant capital outlays, cause material changes or delays in the Joint Venture Company’s current and planned operations and future activities and reduce the profitability of operations. It is possible that future changes in these laws or regulations could increase operating costs or require capital expenditures in order to remain in compliance. Any such, changes could have an adverse effect on the Joint Venture Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
The Joint Venture Company is subject to the Federal Mine Safety and Health Act of 1977 and regulations promulgated thereto, which impose stringent health and safety standards on numerous aspects of its operations.
The Joint Venture Company’s exploration and mining work in Alaska is subject to the Federal Mine Safety and Health Act of 1977, which impose stringent health and safety standards on numerous aspects of mineral extraction and processing operations, including the training of personnel, operating procedures, operating equipment and other matters. The Joint Venture Company’s failure to comply with these standards could have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition or otherwise impose significant restrictions on its ability to conduct mining work.
The Joint Venture Company may be unable to obtain, maintain or renew permits necessary for the exploration, development or operation of any mining activities, which could have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition or results of operation.
The Joint Venture Company must obtain a number of permits that impose strict conditions, requirements and obligations relating to various environmental and health and safety matters in connection with its current and future operations. To obtain certain permits, the Joint Venture Company may be required to conduct environmental studies, collect and present data to governmental authorities and the general public pertaining to the potential impact of its current and future operations upon the environment and take steps to avoid or mitigate the impact. The permitting rules are complex and have tended to become more stringent over time. Accordingly, permits required for mining work may not be issued, maintained or renewed in a timely fashion or at all, or may be conditioned upon restrictions which may impede its ability to operate efficiently. The failure to obtain certain permits or the adoption of more stringent permitting requirements could have a material adverse effect on its business, its plans of operation, and properties in that the Joint Venture Company may not be able to proceed with its exploration, development or mining programs.
13
Anti-takeover provisions of the Company's certificate of incorporation, bylaws and Delaware law could adversely affect a potential acquisition by third parties.
In December 2012, the Board of Directors adopted a shareholder rights plan, which was amended on March 21, 2013, September 29, 2014 and December 18, 2014 (as amended, the "Rights Plan"), pursuant to which one preferred stock purchase right was distributed as a dividend on each share of the Company's common stock held of record. The Rights Plan is scheduled to expire in December 20, 2016. The Rights Plan is designed to deter coercive takeover tactics and to prevent an acquirer from gaining control of the Company without offering a fair price to all of the Company's stockholders. The existence of the Rights Plan, however, could have the effect of making it more difficult for a third party to acquire a majority of Company's outstanding common stock, and thereby adversely affect the market price of the Company's common stock.
In addition, the Company's certificate of incorporation, bylaws and the Delaware General Corporation Law contain provisions that may discourage unsolicited takeover proposals. These provisions could have the effect of inhibiting fluctuations in the market price of the Company's common stock that could result from actual or rumored takeover attempts, preventing changes in the Company's management or limiting the price that investors may be willing to pay for shares of common stock. Among other things, these provisions:
• | Limit the personal liability of directors; |
• | Limit the persons who may call special meetings of stockholders; |
• | Prohibit stockholder action by written consent; |
• | Establish advance notice requirements for nominations for election of the board of directors and for proposing matters to be acted on by stockholders at stockholder meetings; |
• | Require us to indemnify directors and officers to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law; |
• | Impose restrictions on business combinations with some interested parties. |
The Company's common stock is thinly traded.
As of June 30, 2015, there are approximately 3.9 million shares of the Company's common stock outstanding, with directors, and officers and beneficially owning approximately 10.7% of the common stock and the Estate of Mr. Kenneth R. Peak, the Company's former Chairman, beneficially owning approximately 21.6% of our common stock. Since the Company's common stock is thinly traded, the purchase or sale of relatively small common stock positions may result in disproportionately large increases or decreases in the price of the Company's common stock.
The Company does not intend to pay dividends in the foreseeable future.
For the foreseeable future, the Company intends to retain any earnings to finance the development of its business, and the Company does not anticipate paying any cash dividends on its common stock. Any future determination to pay dividends will be at the discretion of the Board of Directors and will be dependent upon then-existing conditions, including our operating results and financial condition, capital requirements, contractual restrictions, business prospects and other factors that the Board of Directors considers relevant. Accordingly, investors must rely on sales of their common stock after any price appreciation, which may never occur, as the only way to realize a return on their investment.
Item 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None
Item 2. PROPERTIES
The Tetlin Property is located in the State of Alaska, and consists of the Tetlin Lease and unpatented mining claims. The Tetlin Property is the only material property of the Joint Venture Company. None of the known prospects on the Tetlin Property are known to host quantifiable mineral reserves as defined by SEC Industry Guide 7.
In connection with the closing of the Transactions with Royal Gold in January 2015 (the "Closing'), the Company formed the Joint Venture Company and contributed to the Joint Venture Company the Tetlin Lease and other related assets. At the Closing, the Company and Royal Gold, through their wholly-owned subsidiaries, entered into the Joint Venture Company LLC Agreement. The Joint Venture Company now holds title to the Tetlin Lease and unpatented mining claims.
The Joint Venture Company believes that it holds good title to its properties in accordance with standards generally accepted in the minerals industry. As is customary in the mining industry, the Company conducted only a preliminary title examination at the time the Company acquired the Tetlin Lease. The Joint Venture Company also conducted a title examination prior to the
14
assignment of the Tetlin Lease to the Joint Venture Company and performed certain curative title work. Before the Joint Venture Company begins any mining activities, however, it is expected to conduct a full title examination and perform curative work on any defects that it deems significant.
Lease with Tetlin Village Council
JEX entered into the Tetlin Lease with the Tetlin Village Council, effective as of July 15, 2008. An undivided 50% leasehold interest was sold to Contango Mining pursuant to the Joint Exploration Agreement dated as of September 29, 2009 in exchange for $1 million and a 1% overriding royalty interest. JEX transferred its remaining 50% leasehold interest to Contango Mining as of September 15, 2010 in exchange for an increased overriding royalty aggregating 3% pursuant to an Amended ORRI Agreement. On September 29, 2014, pursuant to a Royalty Purchase Agreement between JEX and Royal Gold (the “Royalty Purchase Agreement”), JEX sold its entire overriding royalty interest in the Tetlin Lease and unpatented mining claims to Royal Gold .
The Tetlin Lease covers approximately 675,000 acres of land for an initial term of ten years and so long, after such initial term, as the Joint Venture Company continues conducting exploration or mining operations on the Tetlin Lease. The Joint Venture Company is required to spend $350,000 per year annually until July 15, 2018 in exploration costs pursuant to the Tetlin Lease. However, exploration expenditures to date have already satisfied this work commitment requirement for the full lease term through 2018 because exploration funds spent in any year in excess of $350,000 are credited toward future years’ exploration cost requirements. The Tetlin Lease also provides that the Joint Venture Company will pay the Tetlin Village Council a production royalty ranging from 2.0% to 5.0% depending on the type of metal produced and the year of production. As of June 30, 2015, we have paid the Tetlin Village Council $225,000 in exchange for reducing the production royalty payable to them by 0.75%. These payments lowered the production royalty to a range of 1.25% to 4.25% depending on the type of metal produced and the year of production. On or before July 15, 2020, the Tetlin Village Council has the option to increase its production royalty by (i) 0.25% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $150,000, (ii) 0.50% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $300,000, or (iii) 0.75% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $450,000.
Until such time as production royalties begin, the Joint Venture Company will pay the Tetlin Village Council an advance minimum royalty of approximately $75,000 per year, plus an inflation adjustment. As of June 30, 2015, the Joint Venture Company had prepaid $40,000 of the $75,000 advance minimum royalty that is due to the Tetlin Village Council on July 15, 2015. Additionally, the Joint Venture Company will pay Royal Gold a production royalty of 3.0% should it deliver to a purchaser on a commercial basis gold or associated minerals derived from the Tetlin Lease.
Gold Mining Claims
A listing of the Joint Venture Company's State of Alaska unpatented mining claims as of June 30, 2015 for gold and associated minerals are listed in Exhibit 99.1, 99.3, 99.4, 99.5, and 99.6. These mining claims are not known to host quantifiable mineral reserves as defined by SEC Industry Guide 7.
Location of and Access to our Properties
The Tetlin Property is located in the Tetlin Hills and Mentasta Mountains of eastern interior Alaska, 300 kilometers southeast of the city of Fairbanks and 20 kilometers southeast of Tok, Alaska. The Tetlin Lease covers an area measuring approximately 80 kilometers north-south by 60 kilometers east-west in eastern Interior Alaska.
The Tetlin Property is accessible via helicopter and via road. The 23-mile long Tetlin Village Road is an all-weather gravel road connecting the village with the town of Tok on the Alaska Highway. The majority of our Tetlin Property is accessible only via helicopter, although many winter trails exist in the Tetlin Hills and Mentasta Mountains in the northern and southwestern parts of the Properties, respectively. Winter trails link Tetlin Village to the village of Old Tetlin and continue south to the Tetlin River airstrip, a 1,500 foot long unmaintained gravel strip located in the Tetlin River Valley. Winter trails also provide access to the Tuck Creek valley from the village of Mentasta on the Tok Cutoff Highway.
Two seasonal dirt roads have been permitted and constructed to allow surface access to the Chief Danny gold-copper-silver prospect in the northern Tetlin Hills. Both of these roads begin along the Tetlin Village Road and extend to the Chief Danny project and access to both roads is controlled by gates at their junction with the Tetlin Village Road.
The paved Alaska Highway passes near the northern edge of the Tetlin Property as does the southern terminus of the Taylor Highway where it joins the Alaska Highway at Tetlin Junction. The 23-mile long Tetlin Village road provides year-round access to the northern Tetlin Hills, linking Tetlin Village to the Alaska Highway. Buried electrical and fiber-optic communications cables follow this road corridor and link Tetlin Village to the Tok power and communications grid. The Tok public electric facility is capable of generating up to 2 megawatts of power, and the nearest high capacity public electric facilities to the Tetlin Property are in Delta Junction, 107 road miles northwest of the Tetlin project and Glennallen, 138 road miles southwest of the Tetlin Property.
15
The Company does not have any plant or equipment at its Tetlin Property, and relies on contractors to perform work. The Company does not believe the Tetlin Property has been previously explored for minerals.
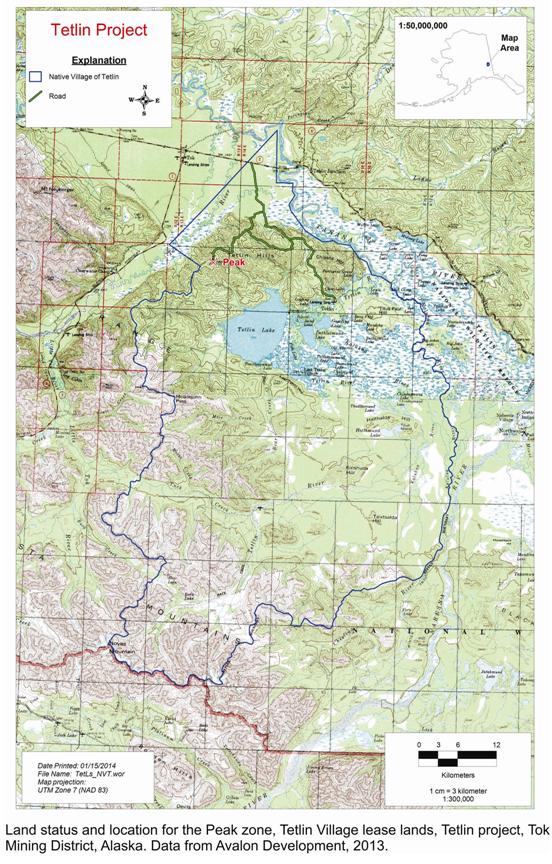
16
Gold Exploration
The Company, through its participation in the Joint Venture Company, controls a total of 774,356 acres consisting of the Tetlin Lease and State of Alaska mining claims for the exploration of gold and associated minerals. To date, our gold exploration has concentrated on the Tetlin Lease, with only a limited amount of work performed on our TOK, Eagle, Bush, AD and Triple Z claims.
The Joint Venture Company initiated a summer of 2015 exploration program on the Tetlin Lease. The work program anticipated spending $5 million with a possible expansion of the work program in early fall if drilling results warranted further work. The drilling program included exploration targets that were helicopter-supported at the Tors, Saddle, North Saddle and Saddle Skarn targets and road-supported work at the Peak Zone area. Most of the initial work program was completed by early August with on-site sample preparation and assay results anticipated by the end of August or early September. On August 31, 2015, the Joint Venture Company approved a budget of up to approximately $4 million for additional exploration work to be completed before the drilling season ends in October.
The exploration effort on the Tetlin Lease has resulted in identifying one mineral deposit (Peak) and several other gold and copper prospects following drilling programs in 2011, 2012, 2013 and 2015. Surface, bedrock, and stream sediment data on the Tetlin Lease as well as on the Eagle and Tok state of Alaska claims adjacent to the Tetlin Lease have been gathered during the summer exploration programs. There was no exploration program 2014. None of the exploration targets are known to host quantifiable commercial mineral reserves and none are near or adjacent to other known significant gold or copper deposits. There has been no recorded past placer or lode mining on Tetlin project, and the Company and the Joint Venture Company are the only entities known to have conducted drilling operations on the Tetlin project.
The majority of the Tetlin Property is hosted within the Yukon-Tanana Terrane (YTT), a regionally extensive package of metamorphic rocks. Rocks of the YTT on the Tetlin Property consist primarily of more deformed, higher temperature metamorphic rocks on the northern third of the project and less deformed, lower temperature metamorphic rocks to the south. Country rocks on the Tetlin Property are intruded by granitic rocks which have not been well mapped.
Large-scale structural features within the Tetlin Property are closely tied to movements along the Tintina-Kaltag and Denali-Farewell fault systems, two continental-scale faults between which are a series of district and prospect-scale northeast, northwest and east-west structures. Limited exposures in the northern half of the property make identification of these structures difficult. Prospect to hand-sample scale folding has been noted throughout the project area.
Although alpine glaciation has affected elevations above 4,500 feet on the southern edge of the Tetlin Property, most of the Tetlin Property escaped Pleistocene continental glaciation. However, due to its proximity to continental glaciers to the north and east, the Tetlin Property was covered by a variable thickness of wind-blown silt ranging up to 10 meters thick. This extremely fine-grained, metal-barren silt effectively masks the geochemical signature of underlying bedrock containing gold-copper-silver mineralization. Following deposition of this silt layer, the Tetlin Property was subject to an extensive period of surface weathering, which now extends 200-300 feet below surface.
From a regional perspective, the Tetlin Property is located in the Tintina Gold Belt in rocks that are highly prospective for gold deposits as well as porphyry copper-molybdenum-gold deposits. These two genetically different types of mineralization overlap in eastern Interior Alaska and the western Yukon Territory and are host to dozens of known prospects, deposits and active mines. In addition, rocks on the southern edge of the Tetlin Property are prospective for nickel-copper-platinum group element deposits. Prior to its discovery in 2009, the style of mineralization discovered on the Chief Danny prospect on the Tetlin Property was unknown in Interior Alaska. Diamond drilling results from 2011 through 2015 have revealed the presence of a distinctive suite of elements and minerals at the Peak and Discovery Zones that do not match the typical characteristics of gold deposits of the Tintina Gold Belt but do share several diagnostic characteristics of gold-copper-silver skarn deposits, possibly as part of a larger porphyry copper-molybdenum-gold system. Skarn is a term that refers to a distinctive class of mineral deposits formed where limestone-bearing rocks are intruded by hot, fluid-bearing granitic rocks. The Peak Zone mineralization most closely resembles the gold-sulfide skarns mined at the Fortitude deposit in the Battle Mountain Mining District of central Nevada.
Chief Danny Prospect
The Chief Danny Prospect currently is the most advanced exploration target on the Tetlin Lease and is comprised of several distinct mineralized areas: the Peak deposit, Discovery Zone, Roadcut Zone and the Saddle Zone. The Chief Danny prospect was discovered during rock, stream sediment and pan concentrate sampling in 2009 and since then has been explored using top of bedrock soil auger sampling, trenching, ground induced polarization (IP) geophysics, airborne magnetic and resistivity surveys and core drilling. Results from this work indicate the presence of a zoned metal-bearing system consisting of a gold-
17
copper-iron enriched core covering six square miles at Chief Danny South (includes Peak, Discovery, Roadcut Zones, North Peak and Blue Moon) and a fault-offset arsenic-gold enriched zone to the north covering three square miles at the Saddle Zone. The Company has conducted extensive drilling on the Peak Zone. The Company has also conducted environmental base line studies on the areas surrounding the Chief Danny prospect, as well as airborne magnetic and resistivity programs. From 2009 through 2015, the Company conducted field-related exploration work at the Chief Danny Prospect, including collecting the following samples:
Year | Program | Core Samples | Rock Samples | Soil Samples | Pan Con Samples | Stream Silt Samples | Core (feet) | IP/Geophysics (kilometers) | Trenching (feet) | |||||||||||||||||
2009 | Chief Danny | — | 958 | 33 | 94 | 11 | — | — | 2,330 | |||||||||||||||||
2010 | Chief Danny | — | 613 | 760 | 668 | 795 | — | 14 | — | |||||||||||||||||
2011 | Chief Danny | 1,267 | 20 | 688 | — | — | 8,057 | 3,957 | — | |||||||||||||||||
2012 | Chief Danny | 5,223 | 82 | 1,029 | — | — | 36,004 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
2013 | Chief Danny | 8,970 | 6 | 1,406 | — | — | 47,079 | 2,524 | — | |||||||||||||||||
2014 | Chief Danny | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
2015 | Chief Danny | 4,287 | 133 | 23,498 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | 19,747 | 1,812 | 3,916 | 762 | 806 | 114,638 | 6,495 | 2,330 | ||||||||||||||||||
2015 Exploration Program. The Joint Venture Company completed 7,162 meters (23,498 ft) of core drilling in 29 core holes during the 2015 Phase 1 drilling program on the Tetlin Property, which was completed August 9, 2015. Drilling targeted seven areas identified through prior geophysical surveys and geochemical sampling outside the Peak Zone in the greater Chief Danny prospect. The Joint Venture Company spent approximately $4.5 million for the 2015 Phase 1 work including drilling, geochemical analyses, landholding fees and other related expenses.
The map below depicts the location of the 29 core holes drilled during the 2015 Phase I drilling program:
2015 PHASE I CORE HOLES DRILLED
18
Significant 2015 Drill Intercepts from the 2015 Phase 1 Program. Sample intervals are calculated using 0.5 grams per ton (gpt) lower cut off for gold with no internal waste less than cutoff grade that is greater than 3 meters in thickness. Intercepts shown are drill intercept lengths. True width of mineralization is unknown. The grade cutoff for gold (Au) is 0.5 gpt; for silver (Ag) is 10 gpt; and for copper (Cu) is 0.1%. The following table summarizes the significant drilling results obtained to date for Phase I of the 2015 Program:
Drill Hole | Zone | From (meters) | To (meters) | Interval (meters) | Au gpt | Au opt | Ag gpt | Cu % |
TET15134 | Saddle | 44.50 | 46.02 | 1.52 | 6.380 | 0.186 | 3.1 | 0.011 |
TET15135 | Saddle | 46.33 | 47.24 | 0.91 | 6.580 | 0.192 | 4.8 | 0.008 |
TET15136 | Saddle | 82.46 | 85.90 | 3.44 | 0.404 | 0.012 | 20.2 | 0.005 |
including | Saddle | 82.91 | 83.46 | 0.55 | 0.362 | 0.011 | 77.3 | 0.004 |
TET15143 | 8 O'clock | 77.78 | 81.38 | 3.60 | 1.742 | 0.051 | 1.0 | 0.171 |
TET15145 | Discovery | 86.26 | 89.31 | 3.05 | 1.385 | 0.040 | 41.0 | 0.010 |
TET15146 | 7 O'clock | 21.79 | 26.82 | 5.03 | 1.075 | 0.031 | 1.4 | 0.151 |
TET15146 | 7 O'clock | 163.98 | 169.77 | 5.79 | 0.788 | 0.023 | 4.9 | 0.115 |
TET15147 | Peak/Peak Deep | 9.39 | 51.28 | 41.89 | 6.072 | 0.177 | 4.6 | 0.198 |
including | Peak/Peak Deep | 22.56 | 26.37 | 3.81 | 16.736 | 0.488 | 4.2 | 0.181 |
and | Peak/Peak Deep | 40.15 | 43.78 | 3.63 | 16.423 | 0.479 | 6.6 | 0.222 |
and | Peak/Peak Deep | 44.29 | 45.61 | 1.32 | 12.700 | 0.370 | 8.7 | 0.293 |
TET15147 | Peak/Peak Deep | 77.26 | 78.94 | 1.68 | 2.170 | 0.063 | 0.5 | 0.016 |
TET15147 | Peak/Peak Deep | 84.58 | 97.73 | 13.15 | 3.687 | 0.108 | 5.6 | 0.238 |
TET15147 | Peak/Peak Deep | 101.70 | 150.12 | 48.42 | 4.980 | 0.145 | 12.0 | 0.338 |
including | Peak/Peak Deep | 130.45 | 132.98 | 2.53 | 11.940 | 0.348 | 37.4 | 1.192 |
and | Peak/Peak Deep | 140.08 | 141.25 | 1.17 | 16.150 | 0.471 | 35.5 | 1.120 |
and | Peak/Peak Deep | 148.74 | 150.12 | 1.38 | 11.700 | 0.341 | 8.8 | 0.356 |
TET15147 | Peak/Peak Deep | 551.13 | 555.10 | 3.97 | 1.055 | 0.031 | 1.1 | 0.086 |
TET15148 | North Peak | 229.60 | 235.45 | 5.85 | 4.630 | 0.135 | 19.1 | 0.012 |
TET15148 | North Peak | 240.84 | 243.84 | 3.00 | 1.843 | 0.054 | 1.6 | 0.034 |
TET15149 | North Peak | 32.92 | 42.69 | 9.77 | 0.552 | 0.016 | 56.0 | 0.013 |
including | North Peak | 39.47 | 40.84 | 1.37 | 0.828 | 0.024 | 189.0 | 0.034 |
TET15149 | North Peak | 56.08 | 57.30 | 1.22 | 6.040 | 0.176 | 17.2 | 0.058 |
TET15149 | North Peak | 173.61 | 182.27 | 8.66 | 1.401 | 0.041 | 16.1 | 0.097 |
TET15151 | North Peak | 11.58 | 14.63 | 3.05 | 1.770 | 0.052 | 1.2 | 0.009 |
TET15151 | North Peak | 31.27 | 39.47 | 8.20 | 0.679 | 0.020 | 1.2 | 0.012 |
TET15153 | North Peak | 10.20 | 32.92 | 22.72 | 9.378 | 0.274 | 1.9 | 0.045 |
including | North Peak | 20.73 | 25.29 | 4.56 | 24.105 | 0.703 | 4.4 | 0.085 |
TET15153 | North Peak | 42.06 | 55.35 | 13.29 | 6.524 | 0.190 | 15.1 | 0.035 |
including | North Peak | 53.80 | 55.35 | 1.55 | 39.900 | 1.164 | 7.0 | 0.085 |
TET15153 | North Peak | 68.07 | 68.70 | 0.63 | 18.700 | 0.545 | 2.9 | 0.063 |
TET15153 | North Peak | 113.61 | 121.63 | 8.02 | 0.744 | 0.022 | 1.5 | 0.058 |
TET15154 | Peak Deep | 132.57 | 153.92 | 21.35 | 0.138 | 0.004 | 22.0 | 0.813 |
including | Peak Deep | 137.31 | 142.87 | 5.56 | 0.281 | 0.008 | 50.1 | 2.253 |
TET15154 | Peak Deep | 21.79 | 48.58 | 26.79 | 0.175 | 0.005 | 53.9 | 0.139 |
including | Peak Deep | 28.92 | 31.44 | 2.52 | 0.932 | 0.027 | 50.4 | 0.143 |
and | Peak Deep | 32.43 | 34.22 | 1.79 | 0.035 | 0.001 | 239.0 | 0.102 |
TET15157 | SW Discovery | 306.08 | 326.33 | 20.25 | 0.016 | 0.000 | 4.5 | 0.142 |
TET15158 | Blue Moon | 25.89 | 31.82 | 5.93 | 0.731 | 0.021 | 0.0 | 0.012 |
TET15158 | Blue Moon | 66.00 | 72.24 | 6.24 | 2.883 | 0.084 | 4.5 | 0.146 |
including | Blue Moon | 69.87 | 70.41 | 0.54 | 21.600 | 0.630 | 17.8 | 0.254 |
19
2014 Exploration Program. No field exploration programs were conducted on the Tetlin project during 2014. Work conducted in previous years was sufficient to satisfy work commitment requirements of the Tetlin Lease and annual work commitment requirements of State of Alaska mining claims that are part of the Tetlin project.
2013 Exploration Program. The Company completed 14,349 meters (47,079 ft) of core drilling in 69 core holes during the 2013 Tetlin project exploration program. Drilling included infill and step-out drilling in the Peak Zone (60 holes, 11,592 meters), and completion of 9 additional core holes on 5 other leads in the greater Chief Danny prospect (2,757 meters). The Company also completed approximately 2,500 line-kilometers of airborne magnetic and electromagnetic geophysics, completed or commenced all of the baseline water quality sampling, cultural resource assessments, wetlands mapping, preliminary metallurgical testing and acid rock drainage testing. The Company spent approximately $9.0 million for this work including drilling, geochemical analyses, airborne geophysics, landholding fees and other related expenses.
Significant 2013 Drill Intercepts from the Peak Zone. Sample intervals are calculated using a 0.5 grams per ton (gpt) lower cut off for gold with no internal waste that is less than cutoff grade and greater than 3 meters in thickness. Intercepts shown are drill intercept lengths. True width of mineralization is unknown. The grade cutoff for gold (Au) is 0.5 gpt; for silver (Ag) is 10 gpt; and for copper (Cu) is 0.1%. The following table summarizes the significant drilling results released to date for 2013:
Drill Hole | Zone | From (meters) | To (meters) | Interval (meters) | Au gpt | Au_opt | Ag gpt | Cu % |
TET13062 | Peak | 88.90 | 153.70 | 64.80 | 13.101 | 0.382 | 21.0 | 0.482 |
TET13063 | Peak | 131.11 | 171.60 | 40.49 | 16.550 | 0.483 | 36.1 | 0.732 |
TET13064 | Peak | 147.20 | 191.40 | 44.20 | 8.464 | 0.247 | 5.5 | 0.169 |
TET13065 | Peak | 184.45 | 206.93 | 22.48 | 1.160 | 0.034 | 10.5 | 0.403 |
TET13067 | Peak | 114.80 | 125.10 | 10.30 | 0.180 | 0.005 | 18.2 | 0.215 |
TET13068 | Peak | — | 112.80 | 112.80 | 0.196 | 0.006 | 13.5 | 0.267 |
TET13069 | Peak | 54.60 | 162.63 | 108.03 | 0.026 | 0.001 | 11.0 | 0.406 |
TET13070 | Peak | 116.80 | 154.92 | 38.12 | 1.815 | 0.053 | 1.8 | 0.040 |
TET13071 | Peak | 129.90 | 186.50 | 56.60 | 1.182 | 0.034 | 1.9 | 0.048 |
TET13072 | Peak | 170.99 | 199.82 | 28.83 | 1.173 | 0.034 | 6.4 | 0.133 |
TET13073 | Peak | 170.23 | 192.64 | 22.41 | 0.708 | 0.021 | 5.5 | 0.103 |
TET13074 | Peak | 78.90 | 105.80 | 26.90 | 0.079 | 0.002 | 17.9 | 0.336 |
TET13075 | Peak | 83.70 | 134.50 | 50.80 | 0.057 | 0.002 | 8.1 | 0.354 |
TET13076 | Peak | 107.80 | 163.50 | 55.70 | 0.044 | 0.001 | 17.0 | 0.661 |
TET13077 | Peak | 135.48 | 162.12 | 26.64 | 0.022 | 0.001 | 34.6 | 1.110 |
TET13078 | Peak | 77.06 | 105.00 | 27.94 | 2.648 | 0.077 | 3.1 | 0.123 |
TET13079 | Peak | 120.04 | 157.89 | 37.85 | 4.366 | 0.127 | 3.7 | 0.203 |
TET13080 | Peak | 135.41 | 157.38 | 21.97 | 5.378 | 0.157 | 2.7 | 0.070 |
TET13081 | Peak | 146.53 | 179.73 | 33.20 | 2.550 | 0.074 | 52.4 | 0.491 |
TET13082 | Peak | 5.79 | 93.38 | 87.59 | 4.025 | 0.117 | 19.3 | 0.300 |
TET13083 | Peak | 112.46 | 143.65 | 31.19 | 1.350 | 0.039 | 5.5 | 0.163 |
TET13084 | Peak | 134.95 | 160.33 | 25.38 | 5.086 | 0.148 | 9.0 | 0.244 |
TET13085 | Peak | 130.13 | 175.16 | 45.03 | 2.740 | 0.080 | 69.5 | 1.401 |
TET13088 | Peak | 19.18 | 157.20 | 138.02 | 3.626 | 0.106 | 11.4 | 0.113 |
TET13089 | Peak | 2.74 | 101.60 | 98.86 | 2.500 | 0.073 | 3.5 | 0.093 |
TET13090 | Peak | 127.60 | 159.20 | 31.60 | 0.087 | 0.003 | 24.3 | 0.882 |
TET13091 | Peak | 45.11 | 98.78 | 53.67 | 1.111 | 0.032 | 10.5 | 0.249 |
TET13092 | Peak | 77.90 | 87.63 | 9.73 | 0.004 | — | 3.5 | 0.157 |
TET13093 | Peak | 141.70 | 146.56 | 4.86 | 1.184 | 0.035 | 9.7 | 0.092 |
TET13094 | Peak | 129.90 | 153.60 | 23.70 | 0.415 | 0.012 | 106.6 | 0.716 |
TET13095 | Peak | 146.00 | 191.35 | 45.35 | 0.193 | 0.006 | 12.3 | 0.151 |
TET13096 | Peak | 85.04 | 86.70 | 1.66 | 1.968 | 0.057 | 0.9 | 0.013 |
TET13097 | Peak | 171.53 | 196.00 | 24.47 | 0.726 | 0.021 | 8.5 | 0.156 |
20
Drill Hole | Zone | From (meters) | To (meters) | Interval (meters) | Au gpt | Au_opt | Ag gpt | Cu % |
TET13098 | Peak | 9.75 | 94.18 | 84.43 | 4.988 | 0.145 | 16.7 | 0.167 |
TET13100 | Peak | 10.98 | 106.90 | 95.92 | 5.748 | 0.168 | 6.9 | 0.140 |
TET13102 | Peak | 6.35 | 30.90 | 24.55 | 0.758 | 0.022 | 5.9 | 0.223 |
TET13103 | Peak | 150.40 | 186.95 | 36.55 | 0.145 | 0.004 | 88.3 | 0.340 |
TET13104 | Peak | — | 142.60 | 142.60 | 2.529 | 0.074 | 2.4 | 0.082 |
TET13105 | Peak | 50.30 | 52.74 | 2.44 | 1.081 | 0.032 | 1.8 | 0.008 |
TET13106 | Peak | 57.45 | 103.33 | 45.88 | 0.016 | — | 35.1 | 0.070 |
TET13107 | Peak | — | 159.25 | 159.25 | 7.010 | 0.204 | 6.6 | 0.102 |
TET13108 | Peak | 14.33 | 73.25 | 58.92 | 1.058 | 0.031 | 10.8 | 0.130 |
TET13109 | Peak | 81.52 | 114.20 | 32.68 | 0.089 | 0.003 | 3.2 | 0.181 |
TET13110 | Peak | 2.13 | 99.06 | 96.93 | 9.060 | 0.264 | 4.3 | 0.093 |
TET13111 | Peak | 169.77 | 172.82 | 3.05 | 0.175 | 0.005 | 7.6 | 0.232 |
TET13113 | Peak | 82.60 | 97.50 | 14.90 | 0.946 | 0.028 | 66.3 | 0.086 |
TET13117 | Peak | — | 134.82 | 134.82 | 4.848 | 0.141 | 2.9 | 0.084 |
TET13119 | Peak | 6.10 | 80.70 | 74.60 | 1.303 | 0.038 | 2.9 | 0.130 |
TET13120 | Peak | 196.10 | 202.39 | 6.29 | 0.186 | 0.005 | 2.9 | 0.130 |
TET13121 | Peak | 46.70 | 55.26 | 8.56 | 5.671 | 0.165 | 10.8 | 0.121 |
TET13122 | Peak | 81.38 | 84.09 | 2.71 | 2.255 | 0.066 | 3.9 | 0.010 |
TET13124 | Peak | 33.22 | 168.72 | 135.50 | 3.240 | 0.095 | 3.6 | 0.115 |
TET13125 | Peak | 65.17 | 121.92 | 56.75 | 0.284 | 0.008 | 15.3 | 0.523 |
TET13128 | Peak | 116.12 | 119.17 | 3.05 | 0.489 | 0.014 | 2.5 | 0.157 |
TET13129 | Peak | 9.60 | 75.90 | 66.30 | 1.450 | 0.042 | 3.7 | 0.250 |
TET13130 | Peak | 9.14 | 31.39 | 22.25 | 2.348 | 0.068 | 1.1 | 0.082 |
Our 2013 exploration program was designed and supervised by Avalon, the primary geological consultant for the Company. A more complete description of Avalon is set forth in Item 1 - Consulting Services provided by Avalon Development Corporation. The President of Avalon is Curtis J. Freeman who graduated from the College of Wooster, Ohio, with a B.A. degree in Geology (1978) and graduated from the University of Alaska with an M.S. degree in Economic Geology (1980). Mr. Freeman is a member of the American Institute of Professional Geologists, the Society of Economic Geologists, the Geological Society of Nevada, the Alaska Miners Association, the Association for Mineral Exploration of British Columbia and the Prospectors and Developers Association of Canada. From 1980 to the present Mr. Freeman has been actively employed in various capacities in the mining industry in numerous locations in North America, Central America, South America, New Zealand and Africa.
Geochemical Analysis and Security
All original samples submitted in 2013 for geochemical analysis were prepared by two different labs, Acme Analytical Lab and ALS Minerals, at their respective facilities in Fairbanks and analyzed at their respective facilities in Vancouver, British Columbia. Analytical work consisted of gold by fire assay with atomic absorption finish plus multi-element inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrography (ICP-AES) analyses using 4-acid digestion. All samples collected in 2013 were cataloged in the field and shipped via ground transport directly to Acme’s or ALS Minerals’ preparation facility in Fairbanks by an Avalon contractor. Sample reject material from 2012 was submitted as check assays to be prepared by ALS Minerals’ facility in Fairbanks and analyzed at their Vancouver, British Columbia facility. At the conclusion of the 2013 field season, ALS Minerals analyzed 57% of the samples and Acme analyzed 43% of the samples.
All samples submitted for the 2015 Phase 1 program were prepared for assay by ALS Minerals at their facilities in Fairbanks, Alaska and analyzed at their Vancouver, British Columbia facility. Analytical work consisted of gold by fire assay with atomic absorption finish plus multi-element inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrography (ICP-AES) analyses using 4-acid digestion. All samples collected in 2015 were cataloged in the field and shipped via ground transport directly to ALS Minerals’ preparation facility in Fairbanks by an Avalon contractor. Sample reject material from 2012 was submitted as check assays to be prepared by ALS Minerals’ facility in Fairbanks and analyzed at their Vancouver, British Columbia facility.
21
The Company believes the parties working on sampling of the Tetlin Property followed industry accepted procedures for sample preparation, analysis and security.
Sampling, Analysis and Security
During 2013, Avalon personnel inserted 1001 standards and 304 blanks into the flow of soil, rock, and drill core samples prior to shipment to the analytical labs. Blanks consisted of Browns Hill Quarry basalt. Fifteen different commercial standards provided by Analytical Solutions were used during 2013. Values in these standards ranged from 0.514 gpt to 9.25 gpt gold. Six different commercial standards provided by Rock Labs were used during 2013. Values in these standards ranged from 0.084 gpt to 3.562 gpt gold. The quality assurance/quality control procedure was completed on-site at the Avalon warehouse in Tok, Alaska.
To further check the high grade gold and copper values observed in drill holes from the Peak Zone during the 2012 drilling, the rejects from 6 drill holes (666 samples) were resubmitted to ALS Minerals for gold and ICP analyses using identical preparations methods as used for the original Acme samples. Holes that were rich in gold and copper and holes that were rich in silver and copper were selected. The results of these assays continue to show good accuracy and repeatability for all of the elements of interest.
No new geochemical sampling work was conducted on the Tetlin project during 2014. During the Phase 1 2015 program, Avalon personnel inserted 394 standards and 115 blanks into the flow of soil, rock, and drill core samples prior to shipment to the analytical labs. Blanks consisted of Browns Hill Quarry basalt. Fifteen different commercial standards provided by Analytical Solutions were used during 2015. Values in these standards ranged from 0.514 ppm to 9.25 ppm gold. Six different commercial standards provided by Rock Labs were used during 2015. Values in these standards ranged from 0.414 ppm to 1.802 ppm gold. The quality assurance/quality control procedure was completed on-site at the Avalon warehouse in Tok, Alaska.
Rare Earth Elements
While the Company previously acquired state of Alaska and federal unpatented mining claims for the exploration of rare earth elements, the Company abandoned its rare earth element claims to devote more time and resources to its gold exploration.
Acquisition of Other Properties
The Joint Venture Company anticipates from time to time acquiring additional properties in Alaska for exploration, subject to the availability of funds. The acquisitions may include leases or similar rights from Alaska Native corporations or may include filing Federal or State of Alaska mining claims by staking claims for exploration. Acquiring additional properties will likely result in additional expense to the Company for minimum royalties, minimum rents and annual exploratory work requirements.
Item 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
As of the date of this Form 10-K, the Company is not a party to any legal proceedings and the Company is not aware of any proceeding contemplated against the Company.
Item 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
22
PART II
Item 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
The Company's common stock began trading on the Over-The-Counter Bulletin Board (OTCBB) on December 20, 2010 under the symbol “CTGO”. The table below shows the high and low prices of the Company's common stock for the periods indicated.
High | Low | ||||||
Fiscal Year 2014: | |||||||
Quarter ended September 30, 2013 | $ | 12.50 | $ | 8.10 | |||
Quarter ended December 31, 2013 | $ | 11.00 | $ | 9.10 | |||
Quarter ended March 31, 2014 | $ | 14.00 | $ | 9.20 | |||
Quarter ended June 30, 2014 | $ | 13.00 | $ | 10.05 | |||
Fiscal Year 2015: | |||||||
Quarter ended September 30, 2014 | $ | 11.00 | $ | 8.02 | |||
Quarter ended December 31, 2014 | $ | 8.80 | $ | 2.05 | |||
Quarter ended March 31, 2015 | $ | 6.39 | $ | 2.05 | |||
Quarter ended June 30, 2015 | $ | 6.49 | $ | 4.10 | |||
As of June 30, 2015, there were 3,876,206 shares of Contango ORE, Inc. common stock outstanding held by approximately 73 registered shareholders.
The Company does not intend to declare or pay any dividends and currently intends to retain any available funds generated by its operations for the development and growth of its business. It does not currently anticipate paying any cash dividends on its outstanding shares of common stock in the foreseeable future. Any future decision to pay dividends on its common stock will be at the discretion of its Board and will depend on its financial condition, results of operations, capital requirements, and other factors the Board may deem relevant.
The following table sets forth information about the Company's equity compensation plans at June 30, 2015:
Plan Category | Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options | Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options | Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column(b)) | ||||||
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | 445,000 | $ | 10.41 | 299,094 | |||||
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | — | — | — | ||||||
On September 15, 2010, the Company’s Board of Directors (the “Board”) adopted the Contango ORE, Inc. Equity Compensation Plan (the “2010 Plan”), which was approved by the Company’s shareholders. Under the 2010 Plan, the Board may grant restricted stock and option awards to officers, directors, employees or consultants of the Company. Awards made under the 2010 Plan are subject to such restrictions, terms and conditions, including forfeitures, if any, as may be determined by the Board.
In November 2010, the Company's directors, executive officers and technical consultant were granted an aggregate of 93,906 shares of restricted stock. The restricted stock vests over three years, beginning in November 2011, the one year anniversary of the date the shares were granted. In October 2012, the Compensation Committee elected to immediately vest all restricted stock held by Mr. Peak.
23
In December 2013, the Company's directors, executive officers and technical consultant were granted an aggregate of 95,000 shares of restricted stock. The restricted stock vests over two years, beginning with one-third vesting on the date of grant. As of June 30, 2015, there were 21,666 shares of restricted stock that remained unvested.
In November 2014, two employees of the Company were granted an aggregate of 27,000 shares of restricted stock. The restricted stock vests over two years, beginning with one-third vesting on the date of grant. As of June 30, 2015, there were 18,000 shares of such restricted stock that remained unvested.
In January 2015, the Company's non-employee directors were granted an aggregate of 30,000 shares of restricted stock, of which 10,000 shares vested immediately and the remaining 20,000 shares will vest over the next two years. In addition, a former technical consultant was granted an aggregate of 10,000 shares of restricted stock which vested immediately. The Compensation Committee also elected to immediately vest all of the stock options and restricted stock previously issued to the former technical consultant. As of June 30, 2015, there were 20,000 shares of such restricted stock that remained unvested.
As of June 30, 2015, the total compensation cost related to unvested awards not yet recognized was $233,049. The remaining costs will be recognized over the remaining vesting period of the awards.
The option awards listed in the table below have been granted to directors, officers, employees and consultants of the Company:
Option Awards | |||||||
Period Granted | Options Granted | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Vesting Period (7) | Expiration Date | |||
September 2011 (1) | 50,000 | $13.13 | Vests over two years, beginning with one-third on the grant date. | September 2016 | |||
July 2012 (2) | 100,000 | $10.25 | Vests over two years, beginning with one-third on the grant date. | July 2017 | |||
December 2012 (3) | 250,000 | $10.20 | Vests over two years, beginning with one-third on the grant date. | December 2017 | |||
June 2013 (4) | 37,500 | $10.00 | Vested Immediately | June 2018 | |||
July 2013 (5) | 5,000 | $10.00 | Vested Immediately | July 2018 | |||
September 2013 (6) | 37,500 | $10.01 | Vested Immediately | September 2018 | |||
September 2013 (6) | 15,000 | $10.01 | Vests over two years, beginning with one-third on the grant date. | September 2018 | |||
(1) The Company granted 40,000 stock options to its directors and officers and an additional 10,000 stock options to its technical consultant, the owner of Avalon, for services performed during fiscal year 2011.
(2) The Company granted 75,000 stock options to its directors and officers and an additional 25,000 stock options to its technical consultant for services performed during fiscal year 2012.
(3) The Company granted 175,000 stock options to its directors and an additional 75,000 stock options to its technical consultant for services performed during fiscal year 2013.
(4) The Company granted 37,500 stock options to its employees for services performed during fiscal year 2013.
(5) The Company granted 5,000 stock options to an employee of Avalon for services performed during fiscal year 2013.
(6) The Company granted 52,500 stock options to its employees for services performed during the first quarter of fiscal year 2014.
(7) If at any time there occurs a change of control, as defined in the 2010 Plan, any options that are unvested at that time will immediately vest.
On March 22, 2013, the Company completed the issuance and sale of an aggregate of 1,230,999 units (“Units”) at a price of $12.00 per Unit with each Unit consisting of (i) one share of the Company's common stock, par value $0.01 per share and (ii) a five-year warrant to purchase one (1) share of Common Stock at $10.00 per share, in a private placement for total proceeds of approximately $14.1 million, including 83,333 shares that were purchased by Mr. Peak, the Company's then-Chairman and 83,334 shares that were purchased by entities controlled by Mr. Brad Juneau, the Company's Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer. The Units sold were not registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, but the Common Stock issued in the offering and the shares of Common Stock issued upon exercise of the warrants are subject to a Registration Rights Agreement allowing the shares to be registered by the holders at a future date.
24
The 1,230,999 warrants may, at any time on or after the date that is six months following the date of issuance, be exercised in whole or in part for the applicable number of shares. The fair value of each warrant was estimated to be $4.37 as of the date of grant.
Item 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
Not Applicable.
Item 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion and analysis of the Company's financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with the financial statements and the related notes and other information included elsewhere in this report.
Overview
The Company was formed on September 1, 2010 as a Delaware corporation. The Company is Houston-based company, whose primary business is to explore in the state of Alaska for gold ore and associated minerals. The Company has leased or has control over approximately 774,356 acres of State of Alaska properties for the exploration of gold and associated minerals. In connection with the closing of the Transactions with Royal Gold in January 2015, the Company formed the Joint Venture Company and contributed to the Joint Venture Company the Tetlin Lease and other related assets. At the Closing, the Company and Royal Gold, through their wholly-owned subsidiaries, entered into the Joint Venture Company LLC Agreement. The Joint Venture Company now holds title to the Tetlin Lease and unpatented mining claims.
Neither the Company nor the Joint Venture Company has commenced mining or producing commercially marketable minerals. To date, neither the Company nor the Joint Venture Company has not generated any revenue from mineral sales or operations. Neither the Company nor the Joint Venture Company has any recurring source of revenue and other than Royal Gold’s contributions in connection with the Transactions, the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern is dependent on the Company's ability to raise capital to fund future exploration and working capital requirements. In the future, the Joint Venture Company may generate revenue from a combination of mineral sales and other payments resulting from any commercially recoverable minerals from the Tetlin Property. The Company does not expect the Joint Venture Company to generate revenue from mineral sales in the foreseeable future. If the Tetlin Property fails to contain any proven reserves, the Company's ability to generate future revenue, and the Company's results of operations and financial position, would be materially adversely affected. Other potential sources of cash, or relief of demand for cash, include external debt, the sale of shares of the Company's stock, joint ventures, or alternative methods such as mergers or sale of our assets. No assurances can be given, however, that the Company will be able to obtain any of these potential sources of cash. The Company will need to generate significant revenues to achieve profitability and the Company may never do so.
Claim Rentals and Minimum Royalties. Claim rentals and minimum royalties consist of Federal and state of Alaska rental payments, annual labor payments, and minimum royalty payments payable to the Native Village of Tetlin. We recognized claim rental expenses of $129,139 for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2015, compared to $179,394 for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 and $171,439 for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The lower level of claim rentals and minimum royalties the past two years is due to a reduction in minimum labor costs and rentals attributable to the release of 97,280 acres of state of Alaska acreage for the exploration rare earth elements, effective December 1, 2012, and the release of 3,440 of Federal acreage for the exploration of rare earth elements effective September 1, 2014. The Joint Venture Company is responsible for making all future claim rental and minimum royalty payments.
Exploration Expenses. The Company incurred approximately $363,461 of exploration expense for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2015, compared to $7.0 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, and $8.1 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The decrease over the past two years is principally attributable to only minimal exploration expenses in the summer of 2014 and fiscal year 2015. Additionally, since the consummation of the Transactions in January 2015, the Joint Venture Company has incurred all of the exploration expenses for the Company. These 2015 exploration expenses are included within Loss from equity investment in Peak Gold, LLC on the consolidated statement of operations. Components of exploration expense include drilling, permits, fuel, field rentals and field supplies as well as staking, mapping, logging, surveying, plotting and helicopter and other transportation expenses.
Stock-based Compensation Expenses. The Company recognized $0.5 million of stock-based compensation expense for the fiscal period June 30, 2015, related to restricted stock granted officers and directors in December 2013, November 2014, and January 2015 and stock option awards granted officers and directors in December 2012 and September 2013. The Company
25
recognized approximately $0.8 million of stock-based compensation expense for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, related to restricted stock granted to officers and directors in November 2010 and December 2013, and stock option awards to our officers and directors in September 2011, July 2012, December 2012, July 2013, and September 2013. For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013, the Company recognized $1.1 million of stock-based compensation expense related to restricted stock granted to officers and directors in November 2010, and stock option awards granted to officers and directors in September 2011, July 2012, December 2012, and June 2013. All issuances of restricted stock and stock options were made pursuant to the Company’s 2010 Equity Compensation Plan.
General and Administrative Expenses. General and administrative expenses for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2015 were $1.9 million, compared to $1.2 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014. The majority of the fiscal year 2015 costs relate to professional and legal fees associated with the Transactions with Royal Gold which were consummated on January 8, 2015.
General and administrative expenses for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 and 2013 were $1.2 million and $0.7 million, respectively. The year-over-year increase is attributable to increased community affair expenditures and increased legal, accounting and other professional service costs. The Company also began paying office rent in 2014 which contributed to the increase in general and administrative expenses.
The Company's directors and officers currently do not receive cash compensation for their work for the Company. If the Company continues its business activities, and begins paying cash compensation to employees, there could be a significant increase in general and administrative expenses.
Expense Reimbursement. We recognized $750,000 of expense reimbursement for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2015 compared to $0 for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively. This amount relates to an expense reimbursement from Royal Gold to offset the costs associated with the Transactions.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Historically, the Company's primary cash requirements have been for exploration-related expenses and the Company's sources of cash have been from common stock offerings. Cash used in operating expenses for the year ended June 30, 2015 was $1.5 million. The majority of the cash used during the current year was for general and administrative expenses related to the formation of the Joint Venture Company.
The Tetlin Property is still in the initial stages of exploration, and the longer term liquidity of the Company will be impaired to the extent the Joint Venture Company’s exploration efforts are not successful in generating commercially viable mineral deposits on the Tetlin Property. As of June 30, 2015, the Company has approximately $1.9 million of cash, cash equivalents, and short term investments. Since the Company’s primary business is now the participation in the Joint Venture Company, it expects that its ongoing cash requirements will be related to general and administration expenses. Given this, the Company believes that its current cash balances will be sufficient to meet its working capital requirements for the next twelve months.
On January 8, 2015, Royal Gold invested $5 million to fund exploration activity, and will have the option to earn up to a 40% economic interest in the Joint Venture Company by investing up to $30 million (inclusive of the initial $5 million investment) prior to October 2018. The proceeds of Royal Gold’s investment has been used by the Joint Venture Company for additional exploration of the Tetlin Property. As part of the Closing of the Transactions, Royal Gold paid the Company $750,000 which was utilized to partially reimburse the Company for costs and expenses incurred in the Transactions.
Upon the later of the investment by Royal Gold of $30 million into the Joint Venture Company or October 31, 2018, the Company and Royal Gold will jointly fund the joint venture operations in proportion to their interests in the Joint Venture Company. The capital costs of developing a large gold mining facility could exceed $1 billion. The Company has limited financial resources and the ability of the Company to arrange additional financing in the future will depend, in part, on the prevailing capital market conditions, the exploration results achieved at the Tetlin Property, as well as the market price of metals. There is no assurance that sources of financing will be available to the Company on acceptable terms, if at all. Failure to obtain additional financing on a timely basis will cause the Company’s interest in the Joint Venture Company to be diluted.
Further financing by the Company may include issuances of equity, instruments convertible into equity (such as warrants) or various forms of debt. The Company has issued common stock and other instruments convertible into equity in the past and cannot predict the size or price of any future issuances of common stock or other instruments convertible into equity, and the effect, if any, that such future issuances and sales will have on the market price of the Company’s securities. Any additional issuances of common stock or securities convertible into, or exercisable or exchangeable for, common stock may ultimately result
26
in dilution to the holders of common stock, dilution in any future earnings per share of the Company and may have a material adverse effect upon the market price of the common stock of the Company.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
None
Contractual Obligations
The Tetlin Lease provides for an initial term of ten years and so long after such initial term as the Joint Venture Company continues conducting exploration or mining operations on the Tetlin Lease. The Joint Venture Company is required to spend $350,000 per year annually until July 15, 2018 in exploration costs pursuant to the Tetlin Lease. However, exploration expenditures to date have already satisfied this work commitment requirement for the full lease term, through 2018, because exploration funds spent in any year in excess of $350,000 are credited toward future years’ exploration cost requirements. The Tetlin Lease also provides that the Joint Venture Company will pay the Tetlin Village Council a production royalty ranging from 2.0% to 5.0% depending on the type of metal produced and the year of production. As of June 30, 2015, the Joint Venture Company had paid the Tetlin Village Council $225,000 in exchange for reducing the production royalty payable to them by 0.75%. These payments lowered the production royalty to a range of 1.25% to 4.25% depending on the type of metal produced and the year of production. On or before July 15, 2020, the Tetlin Village Council has the option to increase its production royalty by (i) 0.25% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $150,000, (ii) 0.50% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $300,000, or (iii) 0.75% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $450,000.
Until such time as production royalties begin, the Joint Venture Company will pay the Tetlin Village Council an advance minimum royalty of approximately $75,000 per year, plus an inflation adjustment. As of June 2015, the Joint Venture Company had prepaid $40,000 of the $75,000 advance minimum royalty that is due to the Tetlin Village Council on July 15, 2015. Additionally, the Joint Venture Company will pay Royal Gold a production royalty of 3.0% should it deliver to a purchaser on a commercial basis gold or associated minerals derived from the Tetlin Lease. The Joint Venture Company is obligated to pay claim rentals of $94,815 per year on state of Alaska acreage. Also, if the minimum work requirement is not performed on the property, additional minimum labor payments are due on certain state of Alaska acreage.
Application of Critical Accounting Policies and Management’s Estimates
The discussion and analysis of the Company’s financial condition and results of operations is based upon the consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. The preparation of these consolidated financial statements requires the Company to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses. The Company has identified below the policies that are of particular importance to the portrayal of the Company's financial position and results of operations and which require the application of significant judgment by management. The Company analyzes its estimates, including those related to its mineral reserve estimates, on a periodic basis and bases its estimates on historical experience, independent third party engineers and various other assumptions that management believes to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions. The Company believes the following critical accounting policies affect its more significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of the Company’s consolidated financial statements:
Mineral Property Interests, Exploration Costs: Mineral property interests include interests in the exploration stage mineral properties acquired. The amount capitalized includes costs paid to acquire mineral property interest as well as the costs paid to obtain the lease rights. Exploration costs are expensed as incurred. Development costs are expensed as incurred until the Company obtains proven and probable reserves within its commercially minable properties. Costs of abandoned projects are charged to earnings upon abandonment. Properties determined to be impaired are written-down to the estimated fair value. The Company periodically evaluates whether events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of mineral property interests and related property, plant and equipment may not be recoverable.
Stock-Based Compensation. The Company applies the fair value method of accounting for stock-based compensation. Under this method, the Company measures and recognizes compensation expense for all stock-based payments at fair value at the date of grant and amortizes the amount over the employee’s service period. Management is required to make assumptions including stock price volatility and employee turnover that are utilized to measure compensation expense.
Investment in the Joint Venture Company. The Company’s consolidated financial statements include the investment in Peak Gold, LLC which is accounted for under the equity method. The Company has designated one of the three members of the Management Committee and on June 30, 2015 held a 100% ownership interest in the Company. The Company recorded its
27
investment at the historical cost of the assets contributed. The cumulative losses of the Joint Venture Company exceed the historical cost of the assets contributed to the Joint Venture Company, therefore the Company's investment in Peak Gold, LLC as of June 30, 2015 is zero. The portion of the cumulative loss that exceeds the Company's investment will be suspended and recognized against earnings, if any, from the investment in the Joint Venture Company in future periods. The audited financial statements of Peak Gold, LLC as of the year ended June 30, 2015 are filed as an exhibit to this Form 10-K.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements. See “ Part II. Item 8. “ Financial Statements and Supplementary Data - Note 3 - Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Not applicable.
Item 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
The consolidated financial statements and supplemental information required to be filed under Item 8 of Form 10-K are presented on pages F-1 through F- 18 of this Form 10-K.
Item 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
UHY LLP (“UHY”) served as the “Company’s independent registered public accounting firm to audit the financial statements of the Company for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014. On December 1, 2014, UHY informed the Company that effective on that date, its Texas practice had been acquired by BDO USA, LLP (“BDO”) (the “UHY Transaction”). As a result of the UHY Transaction, UHY resigned as the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm for the fiscal year ending June 30, 2015.
The reports of UHY on the financial statements of the Company as of and for fiscal years ended June 30, 2013 and 2014 did not contain any adverse opinion or disclaimer of opinion and were not qualified or modified as to uncertainty, audit scope or accounting principles.
During the fiscal years ended June 30, 2013 and 2014 and through the effective date of the UHY Transaction, there were no disagreements with UHY on any matter of accounting principles or practices, financial statement disclosure, or auditing scope or procedure, which if not resolved to UHY’s satisfaction would have caused UHY to make reference thereto in connection with its report on the financial statements for such periods. During the fiscal years ended June 30, 2013 and 2014 and through the effective date of the UHY Transaction, there were no reportable events of the types described in Item 304(a)(1)(v) of Regulation S-K.
As a result of the UHY Transaction, the Audit Committee of the Company appointed BDO as the successor independent registered public accounting firm on December 1, 2014. Prior to such appointment, the Company had not consulted with BDO with respect to the application of accounting principles to a specified transaction, either completed or proposed, or the type of audit opinion that might be rendered on the Company’s consolidated financial statements, or any other matter or reportable events listed in Items 304(a)(2)(i) and (iii) of Regulation S-K.
Item 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures. Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our President and Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial and Accounting Officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures, as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act as of June 30, 2015. Based on that evaluation, management concluded that because of certain material weakness in its internal control over financial reporting, as further described below, the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were not effective as of June 30, 2015.
Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Restatement. In connection with preparing the Company’s Form 10-K, the Company reviewed its accounting for the transaction with Royal Gold, Inc. (“Royal Gold”) and the formation of a joint venture, Peak Gold, LLC (the “Joint Venture Company”). At Closing, Royal Gold, as an initial contribution to the Joint Venture Company, contributed $5 million (the “Royal Gold Initial Contribution”) for an option to earn a membership interest with additional contributions. The Royal Gold Initial Contribution did not entitle Royal Gold to a percentage interest in the Joint Venture Company. Royal Gold also had the right, in
28
its sole discretion, to resign from the Company, at any time, prior to the date that Royal Gold contributed in excess of $5 million to the Joint Venture Company. On March 31, 2015 and June 30, 2015, Royal Gold’s percentage interest in the Joint Venture Company was zero. Since inception, Royal Gold has had the right to appoint two of the three members to the Management Committee of the Joint Venture Company. The Joint Venture Company is a variable interest entity since it is dependent on the financial support from its members to continue its exploration activities. The Company is not the primary beneficiary since it does not currently have the power to direct the activities of the Joint Venture Company. The Company previously consolidated the results of Peak Gold, LLC; however, the Company has now concluded that Royal Gold has the ability to initially direct and control operations of the Joint Venture Company and that the Company's position on the Joint Venture Company's Management Committee gives it significant influence but not control; therefore, the Company determined that the Joint Venture Company should be accounted for under the equity method resulting in the restatement of its Form 10-Q filed on May 15, 2015 (the "Original Filing").
In addition, as part of the Closing, Royal Gold paid the Company $750,000 which was utilized to partially reimburse the Company for costs and expenses incurred in the Transactions. This reimbursement was recorded as revenue in the Original Filing and was reclassed to a contra expense account in the Form 10-Q/A to more appropriately reflect the nature of the reimbursement.
For a further discussion of these changes and the impact on our unaudited consolidated financial statements contained in the Original Filing, see “Note 4 - Restatement of Previously Issued Financial Statements” in the notes to unaudited consolidated financial statements in Form 10-Q/A filed on October 9, 2015.
Description of Material Weakness as of June 30, 2015. A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended) such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. As a result of the restatement described above, management, including our President and Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial and Accounting Officer, concluded that, as of June 30, 2015, there was a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting with respect to complex, non-recurring transactions.
Each year, management is required by SEC rules to evaluate the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. That evaluation is conducted under the supervision and with the participation of our President and Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial and Accounting Officer, and is based on the framework in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (1992 framework) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). If we identify any material weakness, the rules do not allow us to conclude that our internal control over financial reporting is effective. Therefore we have concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was not effective as of June 30, 2015.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Other than the material weakness described above, there have been no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the quarter ended June 30, 2015, that have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect our internal control over financial reporting.
This Annual Report on Form 10-K does not include an attestation report from BDO USA, LLP, the Company's independent registered public accounting firm, regarding internal control over financial reporting. Management's report was not subject to attestation by BDO USA, LLP, pursuant to SEC rules that permit the Company to provide only management's report in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
None.
29
PART III
Item 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The information regarding directors, executive officers, promoters and control persons required under Item 10 of Form 10-K will be contained in the Company's Definitive Proxy Statement for the 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (the “Proxy Statement”) under the headings “Election of Directors”, “Executive Compensation”, “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” and “Corporate Governance” and is incorporated herein by reference. The Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC pursuant to Regulation 14A of the Exchange Act, not later than 120 days after June 30, 2015.
Item 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The information required under Item 11 of Form 10-K will be contained in the Proxy Statement under the heading “Executive Compensation” and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The information required under Item 12 of Form 10-K will be contained in the Proxy Statement under the heading “Security Ownership of Certain Other Beneficial Owners and Management” and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
The information required under Item 13 of Form 10-K will be contained in the Proxy Statement under the heading “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence” and “Executive Compensation” and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
The information required under Item 14 of Form 10-K will be contained in the Proxy Statement under the heading “Principal Accountant Fees and Services” and is incorporated herein by reference.
30
PART IV
Item 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a) | Financial Statements and Schedules: |
The consolidated financial statements of the Company are set forth in pages F-1 to F-18 of this Form 10-K. The financial statements of the Company's subsidiary, Peak Gold, LLC, are included as an exhibit to this Form 10-K. No other financial statement schedules have been filed since they are either not required, not applicable, or the information is otherwise included.
(b) | Exhibits: |
The following is a list of exhibits filed as part of this Form 10-K. Where so indicated by a footnote, exhibits, which were previously filed, are incorporated herein by reference.
Exhibit Number | Description | |
3.1 | Certificate of Incorporation of Contango ORE, Inc. (1) | |
3.2 | Bylaws of Contango ORE, Inc. (1) | |
4.1 | Form of Certificate of Contango ORE, Inc. Common Stock (1) | |
4.2 | Certificate of Designation of Series A Junior Preferred Stock of Contango ORE, Inc. (6) | |
4.3 | Rights Agreement, dated as of December 20, 2012, between Contango ORE, Inc. and Computershare Trust Company, N.A., as Rights Agent (6) | |
4.4 | Amendment No. 1 to Rights Agreement, dated as of March 21, 2013, between Contango ORE, Inc. and Computershare Trust Company, N.A.. as Rights Agent (7) | |
4.5 | Amendment No. 2 to Rights Agreement, dated as of September 29, 2014, between Contango ORE, Inc. and Computershare Trust Company,. N.A.. as Rights Agent (11) | |
4.6 | Amendment No. 3 to Rights Agreement, dated as of December 18, 2014, between Contango ORE, Inc and Computershare Trust Company. N.A.. as Rights (12) | |
10.1 | Mineral Lease, effective as of July 15, 2008, between the Native Village of Tetlin and Juneau Exploration Company, d/b/a Juneau Mining Company, as amended by Amendment No. 1 to Mineral Lease, effective as of October 1, 2009. (1) | |
10.2 | Amendment No. 42 to Mineral Lease,effective as of June 1, 2011 (2) | |
10.3 | Amendment No. 3 to Mineral Lease, effective as of July 1, 2011 (2) | |
10.4 | Amendment No. 4 to Mineral Lease, effective as of December 3, 2012 (8) | |
10.5 | Chairman Agreement dated as of November 1, 2010, between Contango ORE, Inc. and Kenneth R. Peak (1) | |
10.6 | Form of 2010 Equity Compensation Plan (1) | |
10.7 | Contribution Agreement, dated as of November 1, 2010, between Contango Oil & Gas Company and Contango ORE, Inc. (1) | |
10.8 | Amended and Restated Professional Services Agreement, dated as of November 1, 2010, between Avalon Development Corporation and Contango ORE, Inc. (1) | |
10.9 | Consulting Agreement, dated as of October 15, 2010, between Mr. Donald Adams and Contango ORE, Inc. (2) | |
10.1 | Revolving Line of Credit Promissory Note dated as of November 10, 2011, between Contango ORE, Inc. and Contango Oil & Gas Company. (3) | |
10.11 | Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of March 22, 2012, between Contango ORE, Inc. and the Purchasers named therein. (4) | |
10.12 | Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of March 22, 2012, between Contango ORE, Inc. and the Purchasers named therein. (4) | |
10.13 | Advisory Agreement, dated as of September 6, 2012, between Contango ORE, Inc. and Juneau Exploration L.P. (9) | |
10.14 | Subscription Agreement, dated as of March 22, 2013, between Contango ORE, Inc. and the Purchasers named therein. (7) | |
10.15 | Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of March 22, 2013, between Contango ORE, Inc. and the Purchasers named therein. (7) | |
31
10.16 | Warrant, dated as of March 22, 2013, issued by Contango ORE, Inc. in favor of the Holders named therein. (7) | |
10.17 | Engagement Letter with Petrie Partners, LLC dated January 23, 2014 (11) | |
10.18 | Master Agreement, by and between Contango ORE, Inc. and Royal Gold, Inc.. dated September 29, 2014 (11) | |
10.19 | Stability Agreement, by and between Contango ORE, Inc. and the Native Village of Tetlin, dated October 2, 2014 (14) | |
14.1 | Code of Ethics (9) | |
23.1 | Consent of UHY LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm† | |
23.2 | Consent of BDO USA, LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm† | |
31.1 | Section 302 CEO Certification † | |
31.2 | Section 302 CFO Certification † | |
32.1 | Section 906 CEO Certification † | |
32.2 | Section 906 CFO Certification † | |
99.1 | Original Schedule of Gold Properties (Excluding Tetlin Lease) (2) | |
99.2 | Original Schedule of REE Properties (2) | |
99.3 | Schedule of Revised TOK Claims (8) | |
99.4 | Schedule of Bush Claims (8) | |
99.5 | Schedule of Revised Eagle Claims (8) | |
99.6 | Schedule of ADC 2 Claims (8) | |
99.7 | 2011 Report of Behre Dolbear & Company (USA) (5) | |
99.8 | Promissory Note from Tetlin Village Council to Contango ORE, Inc. dated August 1, 2013 (10) | |
99.9 | Voting Agreement, dated as September 29, 2014, between Royal Gold, Inc. and the stockholders thereto (11) | |
99.10 | Audited Financial Statements of Peak Gold, LLC as of June 30, 2015† | |
101 | Interactive Data Files † | |
† | Filed herewith |
32
1 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s report on Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form 10, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 26, 2010. |
2 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2011, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 19, 2011. |
3 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s report on Form 10-Q for the three months ended September 30, 2011, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 14, 2011. |
4 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s report on Form 8-K, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on March 27, 2012. |
5 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s report on Form 10-Q for the three months ended December 31, 2011, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on February 6, 2012. |
6 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s report on Form 8-K, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 21, 2012. |
7 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s report on Form 8-K, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on March 25, 2013. |
8 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s report on Form 10-Q for the three months ended March 31, 2013, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on May 15, 2013. |
9 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 11, 2012. |
10 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s report on Form 10-Q for the three months ended September 30, 2013, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 14, 2013. |
11 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s report on Form 8-K, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on January 29, 2014. |
12 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company's report on Form 8-K, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on October 2, 2014. |
13 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company's report on Form 8-K, as with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 18, 2014. |
14 | Filed as an exhibit to the Company's report on Form 10-Q for the six months ended December 31, 2014, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on February 6, 2014. |
33
SIGNATURES
In accordance with Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
CONTANGO ORE, INC. | |||
/s/ BRAD JUNEAU | /s/ Leah Gaines | ||
Brad Juneau President and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | Leah Gaines Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Exchange Act, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Name | Title | Date | ||
/s/ BRAD JUNEAU | Chairman, President, and Chief Executive Officer | October 9, 2015 | ||
BRAD JUNEAU | ||||
/s/ JOSEPH COMPOFELICE | Director | October 9, 2015 | ||
JOSEPH COMPOFELICE | ||||
/s/ JOSEPH G. GREENBERG | Director | October 9, 2015 | ||
JOSEPH G. GREENBERG | ||||
34
CONTANGO ORE, INC.
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Page | |
F-2 | |
Consolidated Balance Sheets | F-4 |
Consolidated Statements of Operations | F-5 |
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | F-6 |
Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity | F-7 |
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements | F-8 |
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
Board of Directors and Shareholders
Contango ORE, Inc.
Houston, Texas
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of Contango ORE, Inc. (the “Company”) as of June 30, 2015, and the related consolidated statements of operations, shareholders’ equity and cash flows for the year ended June 30, 2015. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audit included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above presents fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Contango ORE, Inc. as of June 30, 2015 and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year ended June 30, 2015 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
/s/ BDO USA, LLP
Houston, Texas
October 9, 2015
F-2
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
Board of Directors and Shareholders
Contango ORE, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of Contango ORE, Inc. (an exploration stage company) (the “Company”) as of June 30, 2014, and the related consolidated statements of operations, shareholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended June 30, 2014. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Contango ORE, Inc. as of June 30, 2014, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended June 30, 2014, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
/s/ UHY LLP
Houston, Texas
August 27, 2014
F-3
CONTANGO ORE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
June 30, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
ASSETS | |||||||
CURRENT ASSETS: | |||||||
Cash | $ | 1,947,046 | $ | 3,448,501 | |||
Prepaid expenses | 67,384 | 98,906 | |||||
Total current assets | 2,014,430 | 3,547,407 | |||||
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT: | |||||||
Mineral properties | — | 1,208,886 | |||||
Accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization | — | — | |||||
Total property and equipment, net | — | 1,208,886 | |||||
OTHER ASSETS: | |||||||
Investment in Peak Gold, LLC (NOTE 10) | — | — | |||||
Other | — | 225,000 | |||||
TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 2,014,430 | $ | 4,981,293 | |||
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||
CURRENT LIABILITIES: | |||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 24,876 | $ | 140,133 | |||
Accrued liabilities | 78,104 | 46,500 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 102,980 | 186,633 | |||||
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (NOTE 12) | |||||||
SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY: | |||||||
Preferred Stock, 15,000,000 shares authorized | — | — | |||||
Common Stock, $0.01 par value, 30,000,000 shares authorized; 3,876,206 shares issued and outstanding at June 30, 2015; 3,805,539 shares issued and outstanding at June 30, 2014 | 38,762 | 38,055 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 32,928,038 | 32,204,002 | |||||
Accumulated deficit | (31,055,350 | ) | (27,447,397 | ) | |||
SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | 1,911,450 | 4,794,660 | |||||
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | $ | 2,014,430 | $ | 4,981,293 | |||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-4
CONTANGO ORE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
Year Ended June 30, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
EXPENSES: | |||||||||||
Claim rentals and minimum royalties | 129,139 | 179,394 | 171,439 | ||||||||
Exploration expense | 363,461 | 6,999,624 | 8,065,936 | ||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 483,080 | 812,698 | 1,133,168 | ||||||||
General and administrative expense | 1,948,387 | 1,206,506 | 662,140 | ||||||||
Expense reimbursement | (750,000 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Total expenses | 2,174,067 | 9,198,222 | 10,032,683 | ||||||||
OTHER (INCOME)/EXPENSE | |||||||||||
Loss from equity investment in Peak Gold, LLC | 1,433,886 | — | — | ||||||||
LOSS BEFORE INCOME TAXES | $ | 3,607,953 | $ | 9,198,222 | $ | 10,032,683 | |||||
Benefit (provision) for income taxes | — | — | — | ||||||||
NET LOSS | $ | 3,607,953 | $ | 9,198,222 | $ | 10,032,683 | |||||
LOSS PER SHARE | |||||||||||
Basic and diluted | $ | 0.94 | $ | 2.43 | $ | 3.54 | |||||
WEIGHTED AVERAGE COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING | |||||||||||
Basic and diluted | 3,842,909 | 3,782,061 | 2,837,523 | ||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-5
CONTANGO ORE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Year Ended June 30, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||
Net loss | $ | (3,607,953 | ) | $ | (9,198,222 | ) | $ | (10,032,683 | ) | ||
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | |||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | 724,743 | 1,178,893 | 1,483,021 | ||||||||
Loss from equity investment in Peak Gold, LLC | 1,433,886 | — | — | ||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||
Decrease in prepaid expenses | 31,522 | 3,626 | 35,497 | ||||||||
Decrease in accounts payable and other accrued liabilities | (83,653 | ) | (1,563,728 | ) | (51,303 | ) | |||||
Net cash used in operating activities | (1,501,455 | ) | (9,579,431 | ) | (8,565,468 | ) | |||||
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||
Note receivable from Tetlin Village | — | (100,000 | ) | — | |||||||
Repayment of note receivable by Tetlin Village | — | 100,000 | — | ||||||||
Acquisition of properties | — | — | (200,000 | ) | |||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | — | — | (200,000 | ) | |||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||
Common stock and warrant issuance, net | — | — | 14,028,135 | ||||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | — | — | 14,028,135 | ||||||||
NET (DECREASE) INCREASE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | (1,501,455 | ) | (9,579,431 | ) | 5,262,667 | ||||||
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING OF PERIOD | 3,448,501 | 13,027,932 | 7,765,265 | ||||||||
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, END OF PERIOD | $ | 1,947,046 | $ | 3,448,501 | $ | 13,027,932 | |||||
NON-CASH INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||
Assets contributed to Peak Gold, LLC | $ | 1,433,886 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-6
CONTANGO ORE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Common Stock | Additional Paid-in Capital | Accumulated Deficit | Total Shareholders’ Equity | |||||||||||||||
Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||
Balance at June 30, 2012 | 2,480,269 | $ | 24,803 | $ | 15,527,205 | $ | (8,216,492 | ) | $ | 7,335,516 | ||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | — | 1,483,021 | — | 1,483,021 | |||||||||||||
Shares vested | 39,126 | 391 | (391 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock, net | 1,230,999 | 12,310 | 9,931,445 | — | 9,943,755 | |||||||||||||
Warrants | — | — | 4,828,245 | — | 4,828,245 | |||||||||||||
Cost of stock and warrant issuance | — | — | (743,865 | ) | — | (743,865 | ) | |||||||||||
Net loss for the period | — | — | — | (10,032,683 | ) | (10,032,683 | ) | |||||||||||
Balance at June 30, 2013 | 3,750,394 | 37,504 | 31,025,660 | (18,249,175 | ) | 12,813,989 | ||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | — | 1,178,893 | — | 1,178,893 | |||||||||||||
Shares vested | 55,145 | 551 | (551 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||
Net loss for the period | — | — | — | (9,198,222 | ) | (9,198,222 | ) | |||||||||||
Balance at June 30, 2014 | 3,805,539 | 38,055 | 32,204,002 | (27,447,397 | ) | 4,794,660 | ||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | — | 724,743 | — | 724,743 | |||||||||||||
Shares vested | 70,667 | 707 | (707 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||
Net loss for the period | — | — | — | (3,607,953 | ) | (3,607,953 | ) | |||||||||||
Balance at June 30, 2015 | 3,876,206 | $ | 38,762 | $ | 32,928,038 | $ | (31,055,350 | ) | $ | 1,911,450 | ||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-7
CONTANGO ORE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Organization and Business
Contango ORE, Inc. (“CORE” or the “Company”) is a Houston-based company that engages in the exploration in Alaska for gold and associated minerals through a joint venture company, Peak Gold, LLC. The Company was formed on September 1, 2010 as a Delaware corporation for the purpose of engaging in the exploration in the State of Alaska for gold ore and associated minerals.
On November 29, 2010, Contango Mining Company (“Contango Mining”), a wholly owned subsidiary of Contango Oil & Gas Company (“Contango”), assigned its the properties and certain other assets and liabilities to Contango. Contango contributed the properties and $3.5 million of cash to the Company, in exchange for approximately 1.6 million shares of the Company’s common stock. The above transactions occurred among companies under common control and was accounted for as transactions among entities under common control, in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") 805, "Business Combinations" whereby the acquired assets and liabilities were recognized in the financial statements at their carrying amounts.
Since the Company is still in an exploration stage an investment in the Company involves a high degree of risk and uncertainty. The Company’s fiscal year end is June 30.
The properties contributed by Contango included: i) a 100% leasehold interest in approximately 675,000 acres (the “Tetlin Lease”) from the Tetlin Village Council, the council formed by the governing body for the Native Village of Tetlin, an Alaska Native Tribe (the "Tetlin Village Council"); ii) approximately 18,021 acres in unpatented mining claims from the state of Alaska for the exploration of gold ore and associated minerals. If any of the properties are placed into commercial production, the Company would be obligated to pay a 3.0% production royalty to Juneau Exploration L.P. (“JEX”). On September 29, 2014, JEX sold its 3.0% production royalty to Royal Gold, Inc. ("Royal Gold"). See Note 14 - Related Party Transactions.
In September 2012, the Company and JEX entered into an Advisory Agreement in which JEX assisted the Company in acquiring 474 unpatented state of Alaska mining claims consisting of 71,896 acres for the exploration of gold and associated minerals in exchange for a 2.0% production royalty on properties acquired after July 1, 2012. If any of such properties are placed into commercial production, the Company would be obligated to pay JEX a 2.0% production royalty under the Advisory Agreement. On September 29, 2014, JEX sold its 2.0% production royalty to Royal Gold and the Company terminated its Advisory Agreement with JEX. See Note 14 - Related Party Transactions.
On September 29, 2014, the Company entered into a Master Agreement (the “Master Agreement”) with Royal Gold, pursuant to which the parties agreed, subject to the satisfaction of various closing conditions, to form a joint venture to advance exploration of the Tetlin Property (as defined below), prospective for gold and associated minerals (the “Transactions”). The Transactions closed on January 8, 2015 (the "Closing").
In connection with the Closing, the Company contributed its Tetlin Lease and state of Alaska mining claims near Tok, Alaska (the "Tetlin Property"), together with other property, to Peak Gold, LLC, a newly formed limited liability company (the “Joint Venture Company”). The Joint Venture Company is managed according to a Limited Liability Company Agreement between subsidiaries of Royal Gold and the Company . At the Closing, Royal Gold made an initial investment of $5 million to fund exploration activity. The initial $5 million does not give Royal Gold an equity stake in the Joint Venture Company. Royal Gold will have the option to obtain up to 40% economic interest in the joint venture by investing up to $30 million (inclusive of the initial $5 million investment) prior to October 2018. Therefore, at Closing, Royal Gold's percentage interest in the Joint Venture Company equaled 0% and the Company's percentage interest in the Joint Venture Company equaled 100%. The proceeds of Royal Gold’s investment will be used by the Joint Venture Company for additional exploration of the Tetlin Property. Royal Gold will initially serve as the Manager of the Joint Venture Company and will manage, direct, and control operations of the Joint Venture Company.
The Company has completed five years of exploration efforts on the Tetlin Property, which has resulted in the discovery of the Peak Zone mineralization within the Chief Danny prospect area on the Tetlin Lease. The Joint Venture Company initiated a Summer 2015 exploration program and anticipates spending approximately $5 million in exploration work on the Tetlin Property. Additionally, the Joint Venture Company acquired 59 new state of Alaska claims consisting of 9,439 acres in the Eagle claim area.
2. Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”).
F-8
These financial statements have been prepared on a going concern basis, which contemplates the realization of assets and the discharge of liabilities in the normal course of business for the foreseeable future. Since the Company’s primary business is now the investment in and management of the Joint Venture Company, it expects that its ongoing cash requirements will only be related to general and administration expenses. Given this, the Company believes that its current cash balances will be sufficient to meet its working capital requirements for the next twelve months.
3. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
The Company’s significant accounting policies are described below.
Principles of Consolidation. The accompanying consolidated fincnial statements include the accounts of Contango ORE, Inc. and its subsidiary after elimination of intercompany balances and transactions.
Management Estimates. The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash Equivalents. Cash equivalents are considered to be highly liquid securities having an original maturity of 90 days or less at the date of acquisition.
Mineral Properties. The amount capitalized includes costs paid to acquire mineral property interests as well as the costs paid for federal and state of Alaska unpatented mining claims. Exploration costs are expensed as incurred. Development costs are expensed as incurred until the Company obtains proven and probable reserves within its commercially minable properties. Costs of abandoned projects are charged to earnings upon abandonment. Any properties determined to be impaired are written-down to their estimated fair value. The Company periodically evaluates whether events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of mineral property interests and any related property, plant and equipment may not be recoverable.
Stock-Based Compensation. The Company applies the fair value method of accounting for stock-based compensation. Under this method, compensation cost is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award and is recognized over the award vesting period. The Company classifies the benefits of tax deductions in excess of the compensation cost recognized for the options (excess tax benefit) as financing cash flows. The fair value of each award is estimated as of the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model.
Income Taxes. The Company follows the liability method of accounting for income taxes under which deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences of (i) temporary differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts in the consolidated financial statements and (ii) operating loss and tax credit carry-forwards for tax purposes. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when, based upon management’s estimates, it is more likely than not that a portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized in a future period. The Company recognized a full valuation allowance as of June 30, 2015 and June 30, 2014 and has not recognized any tax provision or benefit for any of the periods. The Company reviews its tax positions quarterly for tax uncertainties. The Company did not have any uncertain tax positions as of June 30, 2015 or June 30, 2014. The Company files income tax returns in the United States and certain state jurisdictions. The Company's tax returns through fiscal year 2015 remain open for examination by taxing authorities in the respective jurisdictions where those returns are filed.
Investment in the Joint Venture Company. The Company’s consolidated financial statements include the investment in Peak Gold, LLC which is accounted for under the equity method. The Company has designated one of the three members of the Management Committee and on June 30, 2015 held a 100% ownership interest in Peak Gold. Royal Gold will initially serve as the Manager of the Joint Venture Company and will manage, direct, and control operations of the Joint Venture Company. The Company recorded its investment at the historical cost of the assets contributed. The cumulative losses of the Joint Venture Company exceed the historical cost of the assets contributed to the Joint Venture Company; therefore the Company's investment in Peak Gold, LLC as of June 30, 2015 is zero. The portion of the cumulative loss that exceeds the Company's investment will be suspended and recognized against earnings, if any, from the investment in the Joint Venture Company in future periods.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements. In June 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2014-10, “Development Stage Entities.” ASU 2014-10 removes the financial reporting distinction between development stage entities and other reporting entities in United States Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. The amendment therefore eliminates the requirements for development stage entities to (1) present inception-to-date information in the statements of income, cash flows, and shareholder equity, (2) label the financial statements as those of a
F-9
development stage entity, (3) disclose a description of the development stage activities in which the entity is engaged, and (4) disclose in the first year in which the entity is no longer a development stage entity that in prior years it had been in the development stage. The Company early adopted ASU 2014-10 retrospectively during the year ended June 30, 2015; while the adoption of this standard impacted financial statement presentation and disclosure, it did not have a material impact on the financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
The FASB has issued ASU No. 2015-03, Interest - Imputation of Interest (Subtopic 835-30): Simplifying the Presentation of Debt Issuance Costs. The amendments in this ASU require that debt issuance costs related to a recognized debt liability be presented in the balance sheet as a direct deduction from the carrying amount of that debt liability, consistent with debt discounts. The recognition and measurement guidance for debt issuance costs are not affected by the amendments in this ASU. The amendments are effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2015, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption of this ASU is permitted for financial statements that have not been previously issued.
The FASB has issued ASU No. 2015-02, Consolidation (Topic 810): Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis, which is intended to improve targeted areas of consolidation guidance for legal entities such as limited partnerships, limited liability corporations, and securitization structures (collateralized debt obligations, collateralized loan obligations, and mortgage-backed security transactions). The ASU focuses on the consolidation evaluation for reporting organizations (public and private companies and not-for-profit organizations) that are required to evaluate whether they should consolidate certain legal entities. The ASU will be effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2015; and for interim periods, within those fiscal years. Early adoption of this ASU is permitted for financial statements that have not been previously issued.
The FASB has issued ASU No. 2015-01, Income Statement - Extraordinary and Unusual Items (Subtopic 225-20): Simplifying Income Statement Presentation by Eliminating the Concept of Extraordinary Items. This ASU eliminates from U.S. GAAP the concept of extraordinary items. Subtopic 225-20, Income Statement - Extraordinary and Unusual Items, required that an entity separately classify, present, and disclose extraordinary events and transactions. The amendments in this ASU are effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2015. Early adoption of this ASU is permitted for financial statements that have not been previously issued.
4. Costs Incurred
Costs to acquire and explore the Tetlin Property were as follows:
Year Ended June 30, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Acquisition of mineral interests | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 200,000 | |||||
Exploration costs and claim rentals | 492,600 | 7,179,018 | 8,237,375 | ||||||||
Total costs incurred | $ | 492,600 | $ | 7,179,018 | $ | 8,437,375 | |||||
The Tetlin Lease has a ten year term beginning July 2008 with an option to renew for an additional ten years, or so long as the Joint Venture Company continues conducting exploration and mining operations on the Tetlin Lease. The Joint Venture Company may renew the Tetlin lease, consisting of 675,000, acres in 2018.
5. Prepaid Expenses
The Company’s prepaid expenses of $67,384 and $98,906 as of June 30, 2015 and 2014, respectively, relate to prepaid insurance costs, XBRL filing costs and claim rentals.
6. Other Assets
If the Tetlin Lease is placed into commercial production, the Joint Venture Company would be obligated to pay a production royalty to the Tetlin Village of Council, which varies from 2% to 5%, depending on the type of metal produced and the year of production. In June 2011, the Company paid the Tetlin Village Council $75,000 in exchange for reducing the production royalty payable to them by 0.25%. In July 2011, the Company paid the Tetlin Village Council $150,000 in exchange for further reducing the production royalty by 0.50%. These payments lowered the production royalty payable to a range of 1.25% to 4.25%, depending on the type of metal produced and the year of production. On or before July 15, 2020, the Tetlin Village Council has the option to increase its production royalty, if any, by (i) 0.25% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $150,000, or (ii) 0.50% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $300,000, or (iii) 0.75% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $450,000. The Company has made total payments of $225,000 to reduce the Tetlin Village production royalty. This asset was included in the assets contributed to the Joint Venture Company upon consummation of the Transactions.
F-10
7. Loss Per Share
A reconciliation of the components of basic and diluted net loss per share of common stock is presented in the tables below:
Year Ended June 30, 2015 | ||||||||||
Loss | Weighted Average Shares | Loss Per Share | ||||||||
Basic and Diluted Loss per Share: | ||||||||||
Net loss attributable to common stock | $ | 3,607,953 | 3,842,909 | $ | 0.94 | |||||
Year Ended June 30, 2014 | ||||||||||
Loss | Weighted Average Shares | Loss Per Share | ||||||||
Basic and Diluted Loss per Share: | ||||||||||
Net loss attributable to common stock | $ | 9,198,222 | 3,782,061 | $ | 2.43 | |||||
Year Ended June 30, 2013 | ||||||||||
Loss | Weighted Average Shares | Loss Per Share | ||||||||
Basic Loss per Share: | ||||||||||
Net loss attributable to common stock | $ | 10,032,683 | 2,837,523 | $ | 3.54 | |||||
Options and warrants to purchase 1,675,999, 1,675,999, and 1,635,166, shares of common stock were outstanding as of June 30, 2015, 2014, and 2013 respectively. These options and warrants were not included in the computation of diluted earnings per share for the applicable fiscal year, due to being anti-dilutive as a result of the Company’s net loss for all periods presented.
8. Shareholders’ Equity
The Company’s authorized capital stock consists of 30,000,000 shares of common stock and 15,000,000 shares of preferred stock. As of June 30, 2015, the Company had 3,876,206 shares of common stock outstanding. The Company also had an additional 59,666 shares of unvested restricted stock and 1,675,999 options and warrants to purchase shares of common stock outstanding. No shares of preferred stock have been issued. The remaining restricted stock outstanding will vest over the next two years.
2013 Private Placement
On March 22, 2013, the Company completed the issuance and sale of an aggregate of 1,230,999 units (“Units”) at a price of $12.00 per Unit with each Unit consisting of (i) one share of the Company's common stock, par value $0.01 per share and (ii) a five-year warrant to purchase one (1) share of Common Stock at $10.00 per share, in a private placement for total proceeds of approximately $14.1 million, including 83,333 shares that were purchased by Mr. Peak, the Company's then-Chairman and 83,334 shares that were purchased by entities controlled by Mr. Brad Juneau, the Company's President and Chief Executive Officer. The total transaction costs were approximately $0.7 million, including $0.6 million paid to the placement agent. The Company used these proceeds to fund its 2013 exploration program in Alaska and for general corporate purposes. The Units sold were not registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, but the Common Stock issued in the offering and the shares of Common Stock issued upon exercise of the warrants are subject to a Registration Rights Agreement allowing the shares to be registered by the holders at a future date.
The 1,230,999 warrants may, at any time on or after the date that is six months following the date of issuance, be exercised in whole or in part for the applicable number of shares. These warrants expire on March 22, 2018. The fair value of each warrant was estimated to be $4.37 as of the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following weighted average assumptions used: (i) risk-free interest rate of 0.39%; (ii) expected life of 2.8 years; (iii) expected volatility of 82.34%; and (iv) expected dividend yield of 0%.
Rights Plan
F-11
On December 19, 2012, the Company adopted a Rights Plan which was amended on March 21, 2013, September 29, 2014 and December 18, 2014. Under the terms of the amended Rights Plan, each right (a "Right") will entitle the holder to buy 1/100 of a share of Series A Junior Preferred Stock of the Company (the “Preferred Stock”) at an exercise price of $80.00 per share. The Rights will be exercisable and will trade separately from the shares of common stock only if a person or group, other than the Estate of Mr. Kenneth R. Peak, acquires beneficial ownership of 20% or more of the Company's common stock.
Under the terms of the Rights Plan, Rights have been distributed as a dividend at the rate of one Right for each share of common stock held of record or issued by the Company on December 20, 2012. Stockholders will not receive certificates for the Rights, but the Rights will become part of each share of common stock. The Rights may only be exercised prior to their scheduled expiration date of December 19, 2016.
9. Formation of Joint Venture Company
On January 8, 2015, the Company and Royal Gold, through their wholly-owned subsidiary, consummated the Transactions contemplated under the Master Agreement, including the formation of a joint venture to advance exploration of the Company’s Tetlin Property, for gold and associated minerals prospects.
In connection with the Closing of the Transactions, the Company formed the Joint Venture Company. The Company contributed to the Joint Venture Company its Tetlin Property, together with other property (the “Contributed Assets”) at an agreed value of $45.7 million (the “Contributed Assets Value”). At the Closing, the Company and Royal Gold, through their wholly-owned subsidiary, entered into a Limited Liability Company Agreement for the Joint Venture Company (the “Joint Venture Company LLC Agreement”).
Royal Gold will serve as the Manager of the Joint Venture Company ("the Manager") and will initially manage, direct, and control the operation of the Joint Venture Company.
As a condition to the Closing, the Company and the Tetlin Village Council entered into a Stability Agreement dated October 2, 2014, pursuant to which the Company and the Tetlin Village Council, among other things, acknowledged the continued validity of the Tetlin Lease and all its terms notwithstanding any future change in the status of the Tetlin Village Council or the property subject to the Tetlin Lease.
At Closing, Royal Gold, as an initial contribution to the Joint Venture Company, contributed $5 million in restricted cash (the “Royal Gold Initial Contribution”). The Royal Gold Initial Contribution does not entitle Royal Gold to an economic interest in the Joint Venture Company. Therefore, at Closing, Royal Gold’s economic interest in the Joint Venture Company equaled 0% and the Company’s economic interest in the Joint Venture Company equaled 100%. In addition, as part of the Closing, Royal Gold paid the Company $750,000 which was utilized to partially reimburse the Company for costs and expenses incurred in the Transactions and is included as an expense reimbursement on the Company's consolidated statements of operations.
The Joint Venture Company's LLC Agreement provides Royal Gold with the right, but not the obligation, to obtain an economic interest in the Joint Venture Company (up to a maximum of 40%) by making additional contributions of capital to the Joint Venture Company in an aggregate amount equal to $30 million (inclusive of the Royal Gold Initial Contribution of $5 million) during the period beginning on the Closing and ending on October 31, 2018. If Royal Gold makes the full $30 million capital contribution by October 31, 2018, it will receive a 40% economic interest in the Joint Venture Company, and the Company will retain a 60% economic interest in the Joint Venture Company.
The proceeds of Royal Gold’s contributions to the Joint Venture Company (including the Royal Gold Initial Contribution) will be used by the Joint Venture Company to fund further exploration activities on the Tetlin Property included in the Contributed Assets.
Other than the Royal Gold's Initial Contribution, Royal Gold is not under any obligation to make capital contributions, to the Joint Venture Company by October 31, 2018 or thereafter. If Royal Gold does not make any additional capital contributions to the Joint Venture Company by October 31, 2018, and assuming there are no other new investors in the Joint Venture Company, the Company’s economic interest in the Joint Venture Company would continue to be 100% and Royal Gold will be deemed to have resigned as a member of the Joint Venture Company effective as of October 31, 2018.
Both the Company and Royal Gold will have the right to transfer each of their respective percentage interests in the Joint Venture Company to a third party, subject to certain terms and conditions set forth in the Joint Venture Company's LLC Agreement. If either member intends to transfer all or part of its percentage interest to a bona fide third party, the other member will have the right to require the transferring member to include in the intended transfer the other member’s proportionate share of its percentage interests at the same purchase price and terms and conditions. Once Royal Gold has obtained a 40% economic interest in the Joint Venture Company, it will have the additional right to require the Company to sell up to 20% of the Company’s economic interest
F-12
in the Joint Venture Company in a sale of Royal Gold’s entire 40% economic interest to a bona fide third party purchaser. If Royal Gold exercises this right, the Company will be obligated to sell the relevant portion of its percentage interest to a bona fide third party on the same terms and conditions as the interest being sold by Royal Gold.
After October 31, 2018, or such earlier time as Royal Gold has obtained a 40% economic interest in the Joint Venture Company, the members will contribute funds to approved programs and budgets in proportion to their respective economic interests in the Joint Venture Company. If a member elects not to contribute to an approved program and budget or elects to contribute less than its proportionate interest, its economic interest will be recalculated by dividing (i) the sum of (a) the value of its initial contribution plus (b) the total of all of its capital contributions plus (c) the amount of the capital contribution it elects to fund, by (ii) the sum of (a), (b) and (c) above for both members multiplied by 100.
The Joint Venture Company is a variable interest entity since it is dependent on the financial support from its members to continue its exploration activities. The Company is not the primary beneficiary since it does not currently have the power to direct the activities of the Joint Venture Company. This investment is therefore accounted under the equity method.
On August 31, 2015 Royal Gold committed to make an additional capital contribution of approximately $4 million to the Joint Venture Company. By making the additional capital contribution, Royal Gold will earn an economic interest in the Joint Venture Company.
10. Investment in Peak Gold, LLC
The Company recorded its investment at the historical cost of the assets contributed which was approximately $1.4 million. As of June 30, 2015 the Company holds a 100% economic interest in the Joint Venture Company.
The following table is a roll-forward of our investment in the Joint Venture Company from January 8, 2015 (inception) to June 30, 2015:
Inception to | |||
June 30, 2015 | |||
Investment in Peak Gold, LLC at formation | $ | 1,433,886 | |
Loss from equity investment in Peak Gold, LLC | (1,433,886 | ) | |
Investment balance | $ | — | |
The following table presents the condensed balance sheet for Peak Gold, LLC as of June 30, 2015:
June 30, 2015 | |||
ASSETS | |||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 4,757,194 | |
Mineral properties | 1,433,886 | ||
TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 6,191,080 | |
LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS' EQUITY | |||
Accounts payable and other liabilities | $ | 2,060,476 | |
TOTAL LIABILITIES | $ | 2,060,476 | |
MEMBERS' EQUITY | 4,130,604 | ||
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS' EQUITY | $ | 6,191,080 | |
The Company's share in the results of operations for the year ended June 30, 2015 was a loss of $2.3 million. The Peak Gold, LLC loss does not include any provisions related to income taxes as Peak Gold, LLC is treated as a partnership for income tax purposes. As of June 30, 2015 the Joint Venture Company's inception-to-date cumulative loss of $2.3 million, exceeds the historical cost of our investment in Peak Gold, LLC, of $1.4 million. Therefore the investment in Peak Gold, LLC has a balance of zero as of June 30, 2015. The Company is not obligated to make additional capital contributions to the Joint Venture Company and therefore only records losses up to the point of the initial investment which was $1.4 million. The portion of the cumulative loss that exceeds the Company's investment will be suspended and recognized against earnings, if any, from the investment in the
F-13
Joint Venture Company in future periods. The suspended losses for the period from inception to June 30, 2015 are $0.9 million. The following table presents the condensed results of operations for Peak Gold, LLC from inception to the period ended June 30, 2015:
Period Ended | |||
June 30, 2015 | |||
EXPENSES: | |||
Exploration expense | $ | 1,818,318 | |
General and administrative | 484,964 | ||
Total expenses | 2,303,282 | ||
NET LOSS | $ | 2,303,282 | |
11. Stock Based Compensation
On September 15, 2010, the Company’s Board of Directors (the “Board”) adopted the Contango ORE, Inc. Equity Compensation Plan (the “2010 Plan”), which was approved by shareholders on December 8, 2011. Under the 2010 Plan, the Board may issue up to 1,000,000 shares of common stock and options to officers, directors, employees or consultants of the Company. The maximum aggregate number of shares of common stock of the Company with respect to which grants may be made to any individual is 100,000 shares during any calendar year. Awards made under the 2010 Plan are subject to such restrictions, terms and conditions, including forfeitures, if any, as may be determined by the Board.
Under the 2010 Plan, options granted must have an exercise price equal to or greater than the market price of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant. The Company may grant key employees both incentive stock options intended to qualify under Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and stock options that are not qualified as incentive stock options. Stock option grants to non-employees, such as directors and consultants, may only be stock options that are not qualified as incentive stock options. Options generally expire after five years. Upon option exercise the Company's policy is to issue new shares to option holders.
The Company applies the fair value method to account for stock option expense. Under this method, cash flows from the exercise of stock options resulting from tax benefits in excess of recognized cumulative compensation cost (excess tax benefits) are classified as financing cash flows. See Note 3—“Summary of Significant Accounting Policies”. All employee stock option grants are expensed over the stock option’s vesting period based on the fair value at the date the options are granted. The fair value of each option is estimated as of the date of grant using the Black-Scholes options-pricing model. Expected volatilities are based on the historical weekly volatility of the Company's stock with a look back period equal to the expected term of the options. The expected dividend yield is zero as the Company has never declared and to do not anticipate declaring dividends on its common stock. The expected term of the options granted represent the period of time that the options are expected to be outstanding. The simplified method is used for estimating the expected term, due to the lack of historical stock option exercise activity. The risk-free interest rate is based on U.S. Treasury bills with a duration equal to or close to the expected term of the options at the time of grant. The total fair value of stock options vested in fiscal year 2015, 2014, and 2013 was approximately $438,000, $622,000, and $1.0 million, respectively. As of June 30, 2015, the total unrecognized compensation cost related to nonvested stock options was $4,998. As of June 30, 2015 the stock options had a weighted average remaining life of 2.4 years.
F-14
A summary of the status of stock options granted under the 2010 Plan as of June 30, 2015, 2014 and 2013, and changes during the fiscal years then ended, is presented in the table below:
Year Ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Weighted | Weighted | Weighted | |||||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Average | Shares | Average | Shares | Average | ||||||||||||||||||
Under | Exercise | Under | Exercise | Under | Exercise | ||||||||||||||||||
Options | Price | Options | Price | Options | Price | ||||||||||||||||||
Outstanding, beginning of year | 445,000 | $ | 10.41 | 404,167 | $ | 10.49 | 50,000 | $ | 13.13 | ||||||||||||||
Granted | — | 57,500 | $ | 10.01 | 387,500 | $ | 10.19 | ||||||||||||||||
Exercised | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
Forfeited | — | (16,667 | ) | $ | 11.00 | (33,333 | ) | $ | 11.00 | ||||||||||||||
Cancelled | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
Outstanding, end of year | 445,000 | $ | 10.41 | 445,000 | $ | 10.41 | 404,167 | $ | 10.49 | ||||||||||||||
Aggregate intrinsic value | $ | — | $ | 262,175 | $ | — | |||||||||||||||||
Exercisable, end of year | 440,000 | $ | 10.41 | 353,333 | $ | 10.52 | 234,165 | $ | 10.77 | ||||||||||||||
Aggregate intrinsic value | $ | — | $ | 197,191 | $ | — | |||||||||||||||||
Available for grant, end of year | 299,094 | 366,094 | 501,927 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Weighted average fair value of options granted during the year (1) | $ | — | $ | 3.92 | $ | 5.09 | |||||||||||||||||
_______________
(1) There were no options granted during the year ended June 30, 2015. The fair value of each option is estimated as of the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following weighted-average assumptions used for grants during the years ended June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively: (i) risk-free interest rate of 0.51 percent, and 0.44 percent; (ii) expected lives of 2.63 and 2.6 years; (iii) expected volatility of 64.3 percent and 90.1 percent; and (iv) expected dividend yield of zero percent.
The following table summarizes information regarding stock options granted under the Company's 2010 Plan that were outstanding at June 30, 2015:
Options Outstanding | Options Exercisable | |||||||||||||||||
Number of | Weighted | Number of | Weighted | |||||||||||||||
Shares | Average | Weighted | Shares | Average | Weighted | |||||||||||||
Under | Remaining | Average | Under | Remaining | Average | |||||||||||||
Outstanding | Contractual | Exercise | Outstanding | Contractual | Exercise | |||||||||||||
Range of Exercise Price | Options | Life | Price | Options | Life | Price | ||||||||||||
$10.00 - $10.99 | 370,000 | 2.5 | $ | 10.00 | 365,000 | 2.5 | $ | 10.00 | ||||||||||
$11.00 - $11.99 | 25,000 | 2.0 | $ | 11.00 | 25,000 | 2.0 | $ | 11.00 | ||||||||||
$12.00 - $12.99 | 35,000 | 1.2 | $ | 12.75 | 35,000 | 1.2 | $ | 12.75 | ||||||||||
$14.00 - $14.99 | 15,000 | 1.2 | $ | 14.03 | 15,000 | 1.2 | $ | 14.03 | ||||||||||
445,000 | 2.4 | $ | 10.41 | 440,000 | 2.3 | $ | 10.41 | |||||||||||
F-15
Restricted Stock. In November 2010, the Company granted 70,429 restricted shares of common stock to its officers and directors and an additional 23,477 restricted shares to its former technical consultant, the owner of Avalon. All of the restricted stock from this grant was fully vested as of June 30, 2015. In December 2013, the Company's directors, executive officers and technical consultant were granted an aggregate of 95,000 shares of restricted stock. In November 2014, the Company granted 27,000 restricted shares of common stock to its employees. In January 2015, the Company granted an aggregate of 30,000 restricted shares of common stock to two of its non-employee directors. For each grant the restricted stock vests over two years, beginning with one-third vesting on the date of grant. In addition, the Company granted 10,000 restricted shares of common stock to a former technical consultant which vested immediately. The Compensation Committee also elected to immediately vest all of the restricted stock previously issued to the former technical consultant. As of June 30, 2015, there were 59,666 shares of such restricted stock that remained unvested.
A summary of the Company’s restricted stock as of June 30, 2015 and June 30, 2014 and the change during the years then ended, is as follows:
Number of Shares | Weighted Average Fair Value Per Share | |||||
Nonvested balance at June 30, 2013 | 23,478 | $ | 4.65 | |||
Granted | 95,000 | $ | 10.00 | |||
Vested | (55,145 | ) | $ | 7.72 | ||
Forfeited | — | $ | — | |||
Nonvested balance at June 30, 2014 | 63,333 | $ | 10.00 | |||
Granted | 67,000 | $ | 5.05 | |||
Vested | (70,667 | ) | $ | 7.91 | ||
Forfeited | — | $ | — | |||
Nonvested balance at June 30, 2015 | 59,666 | $ | 6.92 | |||
As of June 30, 2015, the total compensation cost related to nonvested restricted share awards not yet recognized was $233,048. The remaining costs are expected to be recognized over the next eighteen months.
Stock-based compensation expense for the periods reflected was as follows:
Year Ended June 30, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Stock-based compensation included in: | |||||||||||
Exploration expenses (1) | $ | 241,663 | $ | 366,195 | $ | 349,853 | |||||
Stock-based compensation expense (2) | 483,080 | 812,698 | 1,133,168 | ||||||||
Total stock-based compensation expense | $ | 724,743 | $ | 1,178,893 | $ | 1,483,021 | |||||
(1) Related to restricted stock and stock option awards to the Company's technical consultant
(2) Related to the restricted stock and stock option awards to the Company's directors and employees.
12. Commitments and Contingencies
Tetlin Lease. The Tetlin Lease has a ten year term beginning July 2008 with an option to renew for an additional ten years, or so long as we the Joint Venture Company continues conducting mining operations on the Tetlin Lease. The Joint Venture Company may renew the Tetlin Lease consisting of 675,000 acres in 2018. The Tetlin Lease has been contributed to the Joint Venture Company (See Note 9).
Pursuant to the terms of the Tetlin Lease, the Joint Venture Company is required to spend $350,000 per year until July 15, 2018 in exploration costs. However, the Company's exploration expenditures through the 2011 exploration program have satisfied this requirement because exploration funds spent in any year in excess of $350,000 are credited toward future years’ exploration cost requirements. Additionally, should the Joint Venture Company derive revenues from the properties covered under the Tetlin Lease, the Company is required to pay the Tetlin Village Council a production royalty ranging from 2.0% to 5.0%, depending on the type of metal produced and the year of production. As of June 30, 2012, the Company had paid the Tetlin Village Council $225,000 in exchange for reducing the production royalty payable to them by 0.75%. These payments lowered the production royalty to a range of 1.25% to 4.25%. On or before July 15, 2020, the Tetlin Village Council has the option to increase their
F-16
production royalty by (i) 0.25% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $150,000, (ii) 0.50% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $300,000, or (iii) 0.75% by payment to the Joint Venture Company of $450,000. Until such time as production royalties begin, the Joint Venture Company must pay the Tetlin Village Council an advance minimum royalty of $50,000 per year. On July 15, 2012, the advance minimum royalty increased to $75,000 per year, and subsequent years are escalated by an inflation adjustment.
Gold Exploration. The Company’s Triple Z, TOK/Tetlin, Eagle, Bush and ADC 2 claims are all located on state of Alaska lands. The annual claim rentals on these projects total $94,815 per year, and are due and payable in full by November 30 of each year. The Company has met the annual labor requirements for the state of Alaska acreage for the next four years, which is the maximum time allowable by Alaska law.
Royal Gold Royalties. Pursuant to the Royalty Purchase Agreement, the Joint Venture Company will pay Royal Gold an overriding royalty of 3.0% should the Joint Venture Company derive revenues from the Tetlin Lease and certain other properties and an overriding royalty of 2.0% should the Joint Venture Company derive revenues from any additional properties.
13. Income Taxes
Year Ended June 30, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Income tax benefit at statutory tax rate | $ | (1,262,783 | ) | $ | (3,219,378 | ) | $ | (3,511,439 | ) | ||
State tax benefit | (220,170 | ) | (547,814 | ) | (1,112,760 | ) | |||||
Permanent differences | 1,580 | 46,876 | 39,823 | ||||||||
Provision to return adjustment | — | 29,544 | (82,070 | ) | |||||||
Valuation allowance | 1,481,373 | 3,690,772 | 4,666,446 | ||||||||
Income tax provision | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
The benefit for income taxes for the periods indicated below are comprised of the following:
Year Ended June 30, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Current: | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
State | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Deferred: | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
State | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
The net deferred tax asset is comprised of the following:
Year Ended June 30, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Deferred tax asset: | |||||||
Capitalized exploration expenses | $ | 8,490,624 | $ | 7,972,994 | |||
State deferred tax assets | 1,880,745 | 1,660,574 | |||||
Stock option expenses | 509,015 | 389,708 | |||||
Net operating losses | 1,773,857 | 1,149,592 | |||||
Valuation allowance | (12,654,241 | ) | (11,172,868 | ) | |||
Net deferred tax assets | $ | — | $ | — | |||
F-17
During fiscal year 2015, we had a change in our valuation allowance of approximately $1.5 million. At June 30, 2015, we have U.S. federal tax loss carry-forwards of approximately $5.1 million. These net operating loss carry-forwards ("NOL")will begin expiring in 2031. Use of NOLs, however, may be limited if we undergo an ownership change. Generally, an ownership change occurs if certain persons or groups, increase their aggregate ownership in us by more than 50 percentage points looking back over a rolling three-year period. If an ownership change occurs, our ability to use our NOLs to reduce income taxes is limited to an annual amount, or the Section 382 limitation, equal to the fair market value of our common stock immediately prior to the ownership change multiplied by the long term tax-exempt interest rate, which is published monthly by the Internal Revenue Service. In the event of an ownership change, NOLs can be used to offset taxable income for years within a carry-forward period subject to the Section 382 limitation. The Company is in the process of evaluating if any of our NOLs may be subject to these limitations.
14. Related Party Transactions
Mr. Brad Juneau, the Company's Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer, is also the sole manager of JEX, a private company involved in the exploration and production of oil and natural gas. JEX was responsible for securing and negotiating the Tetlin Lease and assisting in obtaining the other Tetlin Properties and initially engaged Avalon to conduct mineral exploration activities on the Tetlin Lease. In agreeing to transfer its interests in such properties to Contango Mining, a predecessor of the Company, JEX retained a 3.0% overriding royalty interest in the Tetlin Lease and other Tetlin Property transferred.
In September 2012, the Company and JEX entered into an Advisory Agreement in which JEX continued to provide assistance in acquiring additional properties in Alaska in exchange for a production royalty of 2.0% on properties acquired after July 1, 2012.
On September 29, 2014, pursuant to a Royalty Purchase Agreement between JEX and Royal Gold (the “Royalty Purchase Agreement”), JEX sold its entire overriding royalty interest in the Original Properties and the Additional Properties to Royal Gold. On the same date, the Company terminated its Advisory Agreement with JEX.
The Company currently subleases office space from JEX at 3700 Buffalo Speedway, Ste 925, Houston, TX 77098 for approximately $11,000 per quarter. The lease expires in February 2016. The rent commitment for fiscal year 2016 is approximately $29,000.
15. Subsequent Events
On August 31, 2015, Royal Gold, Inc. agreed to make an additional contribution of capital of up to approximately $4 million to the Joint Venture Company to fund additional drilling and exploration of the Tetlin Property. By making the additional capital contribution, Royal Gold will obtain up to an approximately 8% economic interest in the Joint Venture Company.
Additionally, in August 2015, three employees of the Company were granted an aggregate of 85,000 shares of restricted stock in lieu of cash compensation from the Company. The restricted stock vest over two years, beginning with one-third vesting on the date of grant.
F-18
