Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EXCEL - IDEA: XBRL DOCUMENT - WHOLE FOODS MARKET INC | Financial_Report.xls |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - WHOLE FOODS MARKET INC | wfm10-k2014ex311.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - WHOLE FOODS MARKET INC | wfm10-k2014ex312.htm |
| EX-12.1 - EXHIBIT 12.1 - WHOLE FOODS MARKET INC | wfm10-k2014ex121.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - WHOLE FOODS MARKET INC | wfm10-k2014ex322.htm |
| EX-32.3 - EXHIBIT 32.3 - WHOLE FOODS MARKET INC | wfm10-k2014ex323.htm |
| EX-31.3 - EXHIBIT 31.3 - WHOLE FOODS MARKET INC | wfm10-k2014ex313.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - WHOLE FOODS MARKET INC | wfm10-k2014ex321.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EXHIBIT 21.1 - WHOLE FOODS MARKET INC | wfm10-k2014ex211.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 - WHOLE FOODS MARKET INC | wfm10-k2014ex231.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
x | Annual report pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 for the fiscal year ended September 28, 2014; or |
¨ | Transition report pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 for the transition period from ________ to ________ |
Commission File Number: 0-19797

WHOLE FOODS MARKET, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Texas | 74-1989366 | |
(State of incorporation) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
550 Bowie Street, Austin, Texas | 78703 | |
(Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: 512-477-4455
Securities registered pursuant to section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
Common Stock, no par value | NASDAQ Global Select Market | |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer x | Accelerated filer ¨ | Non-accelerated filer ¨ | Smaller reporting company ¨ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of all common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of April 13, 2014 was $18,230,824,706. The number of shares of the registrant’s common stock, no par value, outstanding as of November 18, 2014 was 359,747,100 shares.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
The information required by Part III of this report, to the extent not set forth herein, is incorporated by reference from the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of the Stockholders to be held March 10, 2015.
Whole Foods Market, Inc.
Annual Report on Form 10-K
For the Fiscal Year Ended September 28, 2014
Table of Contents
Page | ||
Disclaimer on Forward-looking Statements
Certain statements in this Report on Form 10-K and from time to time in other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, news releases, reports, and other written and oral communications made by us and our representatives, constitute forward-looking statements within the meaning of the U.S. Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward-looking statements are often identified by words such as “anticipate,” “believe,” “intend,” “estimate,” “expect,” “continue,” “could,” “can,” “may,” “will,” “likely,” “depend,” “would,” “plan,” “project,” “predict,” “goal,” “target,” “sustain,” “seek” and similar expressions, and include references to assumptions and relate to our future prospects, developments and business strategies. Except for the historical information contained herein, the matters discussed in this report are forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties that may cause our actual results to be materially different from such forward-looking statements and could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, operating results and cash flows. These risks and uncertainties include general business conditions, changes in overall economic conditions that impact consumer spending, the impact of competition and other factors which are often beyond the control of the Company, as well other risks listed in Part I, “Item 1A. Risk Factors,” of this report and risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial. We wish to caution you that you should not place undue reliance on such forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date on which they were made. We do not undertake any obligation to update forward-looking statements.
This information should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes included in this report.
Unless otherwise specified, references to “Whole Foods Market,” “Company,” or “we” in this report include Whole Foods Market, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries.
PART I
Item 1. Business.
General
Whole Foods Market is the leading retailer of natural and organic foods, the first national “Certified Organic” grocer, and uniquely positioned as America’s Healthiest Grocery Store™. The Company incorporated in 1978, opened the first Whole Foods Market store in 1980, and is based in Austin, Texas. We completed our initial public offering in January 1992, and our common stock trades on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the symbol “WFM.” Our Company mission is to promote the vitality and well-being of all individuals by supplying the highest quality, most wholesome foods available. Since the purity of our food and the health of our bodies are directly related to the purity and health of our environment, our mission is devoted to the promotion of organically grown foods, healthy eating, and the sustainability of our entire ecosystem. Through our growth, we have had a significant and positive impact on the natural and organic foods movement throughout the United States, helping lead the industry to nationwide acceptance over the last 36 years.
We have one operating segment, natural and organic foods supermarkets. We are the largest retailer of natural and organic foods in the U.S. and the 7th largest public food retailer overall based on 2013 sales rankings from Progressive Grocer. As of September 28, 2014, we operated 399 stores in the United States (“U.S.”), Canada, and the United Kingdom (“U.K.”), averaging over 7.7 million customer visits each week. Our stores average 38,000 square feet in size and are supported by our Austin headquarters, regional offices, distribution centers, bakehouse facilities, commissary kitchens, seafood-processing facilities, meat and produce procurement centers, and a specialty coffee and tea procurement and roasting operation.
The following is a summary of our annual percentage sales and net long-lived assets by geographic area for the fiscal years indicated:
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||
Sales: | ||||||||
United States | 96.7 | % | 96.7 | % | 96.8 | % | ||
Canada and United Kingdom | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.2 | |||||
Total sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||
Long-lived assets, net: | ||||||||
United States | 96.0 | % | 95.7 | % | 95.2 | % | ||
Canada and United Kingdom | 4.0 | 4.3 | 4.8 | |||||
Total long-lived assets, net | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||
1
A five-year summary of certain financial and operating information can be found in Part II, “Item 6. Selected Financial Data,” of this report. See also Part II, “Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Industry Overview
According to Nielsen’s TDLinx and Progressive Grocer, the U.S. supermarket industry, which includes conventional supermarkets, supercenters, warehouse grocery stores, military commissaries and limited-assortment and natural/gourmet-positioned supermarkets, had approximately $620.2 billion in sales in 2013, a 3% increase over the prior year. Within this broader category, natural product sales through retail channels were approximately $89.4 billion, an 11% increase over the prior year, according to Natural Foods Merchandiser, a leading trade publication for the natural foods industry. We believe the growth in sales of natural and organic foods is being driven by numerous factors, including:
• | heightened awareness of the role that healthy eating plays in long-term wellness; |
• | a better-educated and wealthier populace whose median age is increasing each year; |
• | a highly influential younger generation that values health, sustainability, organic, local and ethical trade; |
• | increasing consumer concern over the purity and safety of food; and |
• | environmental concerns. |
Organic foods are foods grown through methods that emphasize the use of renewable resources and the conservation of soil and water to enhance environmental quality. All products labeled as organic and sold within a retail store or used within the production of foods labeled as organic must be verified by an accredited certifying agency. Organic equivalency arrangements between the U.S., Canada, the European Union, Japan, and Korea help protect organic standards, enhance cooperation, and facilitate trade in organic products. Furthermore, all retailers that handle, store and sell organic products must implement measures to protect organic integrity. In the U.S., under the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s (“USDA”) Organic Rule, which was implemented into federal law in 2002, organic food products are produced using:
• | agricultural management practices that promote healthy ecosystems and prohibit the use of genetically modified seeds or crops, sewage sludge, long-lasting pesticides, herbicides or fungicides; |
• | livestock management practices that promote healthy, humanely treated animals by providing organically grown feed, fresh air and outdoor access while using no antibiotics or growth hormones; and |
• | food-processing practices that protect the integrity of the organic product and disallow irradiation, genetically modified organisms (“GMOs”) or synthetic preservatives. |
Our Purpose and Core Values
We believe that much of our success to date is because we remain a uniquely mission-driven company. The purpose of our business is not only to generate profits but to create value for all of our major stakeholders, each of which is linked interdependently. Our Core Values succinctly express this purpose:
• | We sell the highest quality natural and organic products available. |
• | We satisfy, delight and nourish our customers. |
• | We support team member happiness and excellence. |
• | We create wealth through profits and growth. |
• | We serve and support our local and global communities. |
• | We practice and advance environmental stewardship. |
• | We create ongoing win-win partnerships with our suppliers. |
• | We promote the health of our stakeholders through healthy eating education. |
Our Quality Standards and Differentiated Product Offering
We believe our high quality standards differentiate our stores from other supermarkets and enable us to attract and maintain a broad base of loyal customers. Our groundbreaking quality standards ensure the products we sell meet a higher standard – one that bans hundreds of ingredients commonly found in other stores as well as numerous manufacturing, farming, fishing and ranching practices that don’t measure up. Our quality standards are as follows:
• | We carefully evaluate each and every product we sell. |
• | We feature foods that are free of artificial preservatives, colors, flavors, sweeteners and hydrogenated fats. |
• | We are passionate about great tasting food and the pleasure of sharing it with others. |
• | We are committed to foods that are fresh, wholesome and safe to eat. |
• | We seek out and promote organically grown foods. |
• | We provide food and nutritional products that support health and well-being. |
2
We offer the broadest selection of high-quality natural and organic products, with a strong emphasis on perishable foods. An average store carries more than 32,000 SKUs, with some of our larger stores carrying up to 49,000 SKUs. Our product selection includes, but is not limited to: produce and floral, grocery, meat, seafood, bakery, prepared foods and catering, coffee, tea, beer, wine, cheese, nutritional supplements, vitamins, body care, and lifestyle products including books, pet products, and household products. Approximately 30% of our sales, outside of prepared foods and bakery, were organic in fiscal year 2014. The following is a summary of annual percentage sales by product category for the fiscal years indicated:
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||
Perishables: | ||||||||
Prepared foods and bakery | 19.2 | % | 19.0 | % | 18.9 | % | ||
Other perishables | 47.6 | 47.2 | 47.0 | |||||
Total perishables | 66.8 | 66.2 | 65.9 | |||||
Non-perishables | 33.2 | 33.8 | 34.1 | |||||
Total sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||
Exclusive Brands
Our exclusive brands program, which generated approximately $1.8 billion in sales in fiscal year 2014 and currently features approximately 4,400 SKUs, is a key component of our value platform and essential to our product innovation and differentiation strategy. In fiscal year 2014, exclusive brands accounted for approximately 13% of total retail sales and 18% of non-perishable sales. Our 365 Everyday Value® brand accounts for approximately half of our exclusive brand items, and over one-third of our exclusive brand offerings are certified organic. Other brands include, but are not limited to, Allegro Coffee, Engine 2 Plant-Strong, and Whole Foods Market. Successful product launches in fiscal year 2014 included our 365 Everyday Value pre-packed chicken, Whole Paws® pet products, 365 Everyday Value and Whole Foods Market frozen dessert and novelties, and Whole Catch® wild-caught frozen seafood steaks and fillets. In addition to our exclusive brands, we regularly offer more than 400 temporary exclusives, which are branded products that are unique to Whole Foods Market in terms of flavor, size or other attributes.
Health Starts Here®
We believe our Health Starts Here program and our positioning as America’s Healthiest Grocery Store™ are key competitive advantages. Health Starts Here is a mindful approach to healthy eating rooted in four simple principles to build better meals: Focus on Whole Foods, Eat Plant-Strong™, Choose Healthy Fats, and Consider Nutrient Density. Products in our salad and hot bars, prepared meals in our self- and full-serve cases, and all prepared foods venues that meet these guidelines carry our “Health Starts Here” logo. In addition, in fiscal year 2014, several stores piloted our Health Starts Here “Good, Better, Best” rating system. Created by doctors and registered dietitians based on scientific research as well as guidelines proposed by the USDA, U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”), World Health Organization and American Heart Association, this new rating system was designed to help customers find the most health-promoting foods in our stores.
Responsibly Grown
In October 2014, we introduced our Responsibly Grown “Good, Better, Best” rating system for produce and flowers. Using a science-based index, Responsibly Grown measures performance on important sustainable farming topics, including pest management, farm worker welfare, pollinator protection, water conservation and protection, soil health, ecosystems and biodiversity, waste, air, energy and climate. The new ratings provide greater transparency for our shoppers, allowing them to make more informed decisions, and recognize growers for responsible practices that go beyond their organic and local efforts.
Whole Trade® Guarantee
Products with the Whole Trade Guarantee label are sourced from developing countries and meet our high quality standards, provide more money to producers, ensure better wages and working conditions for workers, and utilize sound environmental practices. Nearly 500 products in our stores carry our Whole Trade Guarantee seal, and demand for these products continues to grow. Whole Foods Market donates 1% of sales of these products to Whole Planet Foundation® to help alleviate world poverty.
Commitment to Local
We are committed to buying from local producers whose products meet our high quality standards, particularly those who are dedicated to environmentally friendly, sustainable agriculture. For some stores, “local” is defined as within a certain mile radius, and for others, it means within the metro, state, or tri-state area. Buying local allows us to offer our shoppers the freshest, most flavorful pick of seasonal products; it bolsters local economies by keeping money in the pockets of community growers; and it contributes to responsible land development and the preservation of viable green spaces. Whole Foods Market currently purchases produce from more than 2,000 different farms through various suppliers, and in fiscal year 2014, approximately 24% of the produce sold in our stores came from local farms. Through our Local Producer Loan Program we have budgeted up to $25
3
million to support and promote local production. As of September 28, 2014, we had disbursed approximately $14 million in loans to nearly 200 local producers company-wide under this program.
Animal Welfare
Whole Foods Market is dedicated to promoting animal welfare on farms and ranches. We encourage innovative animal production practices that improve the lives of animals raised for meat and poultry in our stores and have stringent animal welfare standards in place for all species found in our meat departments. Work on our “animal compassionate” standards started in 2003 and subsequently evolved into a tiered standards program that transitioned to the Global Animal Partnership foundation in 2008. Global Animal Partnership’s 5-Step® Animal Welfare Rating Standards program is currently in all of our stores in the U.S. and Canada. All beef, chicken, pork and turkey in our fresh meat cases comes from producers who meet or exceed the requirements of this certification, rated accordingly on a scale from 1 to 5+.
Seafood Sustainability
We continue to collaborate with the Marine Stewardship Council (“MSC”) to offer as much MSC-certified seafood as possible. For wild-caught seafood, we label our products with color-coded seafood sustainability ratings developed by partnering organizations The Safina Center (formerly Blue Ocean Institute) and Monterey Bay Aquarium. Ratings are based on key criteria for sustainable fisheries using science-based, transparent ranking methods. Since April 2012, we have not sold any wild-caught seafood from “red-rated” fisheries. For farmed seafood, our standards continue to be the highest in the industry. The “Responsibly Farmed” logo in our seafood cases indicates that the farms we source from have passed a third-party audit and meet our quality standards. In addition, we launched new quality standards in 2013 for farmed mollusks, including clams, oysters and mussels, and worked with our supplier partners and third-party auditors in 2014 to verify these standards were met.
GMO Transparency
We believe that quality and transparency are inseparable, and providing detailed information about the products we sell is part of our mission. Accordingly, we announced in March 2013 that all food products in our stores in the U.S. and Canada must be labeled by 2018 to indicate whether they contain genetically modified organisms (“GMOs”). We are the first national grocery chain to set a deadline for full GMO transparency. Currently, we have thousands of products within our stores that are certified organic and/or Non-GMO Project™ verified. This includes over 8,000 products carrying the “Non-GMO Project Verified” seal.
Whole Body Standards
We believe the quality of the items and ingredients people apply to their bodies topically is as important as the food they put into their bodies. We encourage our personal care product suppliers to use plant-based and naturally derived ingredients, pure essential oil fragrances, gentle preservatives and non-petroleum ingredients, and we never sell personal care products that have been tested on animals. Currently, there are 50 ingredients common in conventional body care products that are not allowed in the products we sell. Our Premium Body Care™ standards raise the bar even higher, banning over 400 ingredients. This additional tier of standards meets our strictest guidelines for quality sourcing, environmental impact, results and safety and was designed to evolve as new science-based studies and research come to light. In addition, since there are no mandatory government standards for “organic” label claims on body care products, we require all products making an organic claim to be certified to one of two standards: the USDA’s National Organic Program or NSF International’s 305 Standard for Personal Care Products Containing Organic Ingredients.
Eco-Scale™
In 2011, we became the first national retailer to launch its own comprehensive set of green cleaning standards to help shoppers make informed choices for their homes and the planet. Under our Eco-Scale rating system, all household cleaning products in our stores are required to list all ingredients on their packaging, a labeling practice not currently required by the U.S. government. This rating system allows shoppers to easily identify a product’s environmental impact and safety based on a red-orange-yellow-green color scale. We are committed to working with our suppliers to evaluate and independently audit every product in our cleaning category, and all brands in our stores meet our baseline orange standard.
Growth Strategy
We are a Fortune 500 company, ranking number 218 on the 2014 list. Our sales have grown rapidly due to strong comparable store sales growth, acquisitions and new store openings from approximately $93 million in fiscal year 1991, excluding the effect of pooling-of-interests transactions completed since 1991, to approximately $14.2 billion in fiscal year 2014, a 23-year compounded annual growth rate of approximately 24%.
4
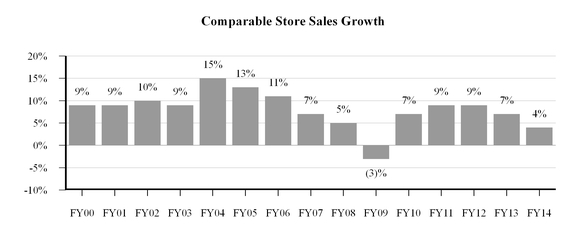
Over the last 15 fiscal years, our comparable store sales growth has averaged 8%, as shown in the following chart. Sales of a store are deemed to be comparable commencing in the fifty-third full week after the store was opened or acquired. Companies may define comparable store sales differently; thus growth rates across companies may not be comparable.
Our growth strategy is to expand primarily through new store openings, and while we may pursue acquisitions of smaller chains that provide access to desirable geographic areas and experienced team members, such acquisitions are not expected to significantly impact our future store growth or financial results. We have a disciplined, opportunistic real estate strategy, opening stores in existing trade areas as well as new areas, including international locations. We typically target premium real estate sites, and while new stores may be as small as 15,000 square feet or as large as 75,000 square feet, the majority fall in the range of 35,000 to 45,000 square feet.
Our historical store growth and sales mix for the fiscal years indicated is summarized below:
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||
Stores at beginning of fiscal year | 362 | 335 | 311 | 299 | 284 | |||||
Stores opened | 34 | 26 | 25 | 18 | 16 | |||||
Acquired stores | 4 | 6 | — | — | 2 | |||||
Relocated stores | (1 | ) | (5 | ) | (1 | ) | (6 | ) | — | |
Divested or closed stores | — | — | — | — | (3 | ) | ||||
Stores at end of fiscal year | 399 | 362 | 335 | 311 | 299 | |||||
Stores with major expansions (1) | — | 2 | 2 | 1 | — | |||||
Total gross square footage at end of fiscal year | 15,162,000 | 13,779,000 | 12,735,000 | 11,832,000 | 11,231,000 | |||||
Year-over-year growth | 10% | 8% | 8% | 5% | 6% | |||||
(1) Defined as square footage increases of greater than 20% completed during the fiscal year.
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||
Sales mix: | ||||||||||
Identical stores (1) | 93.3 | % | 93.5 | % | 93.3 | % | 94.6 | % | 93.2 | % |
New and acquired stores, including relocated stores | 6.2 | 5.6 | 5.4 | 4.5 | 5.9 | |||||
Other retail sales, primarily stores with major expansions | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.2 | |||||
Other sales, primarily non-retail external sales | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.7 | |||||
Total sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % |
(1) Identical store sales do not include sales from new, acquired or relocated stores or stores with major expansions.
Our historical store development pipeline as of the dates indicated is summarized below:
November 5, 2014 | November 6, 2013 | November 7, 2012 | November 2, 2011 | November 3, 2010 | ||||||
Stores in development | 114 | 94 | 79 | 62 | 52 | |||||
Average size (gross square feet) | 41,000 | 38,000 | 37,000 | 35,000 | 39,000 | |||||
Total gross square footage in development | 4,723,000 | 3,605,000 | 2,896,000 | 2,192,000 | 2,052,000 | |||||
As a percentage of existing square footage | 31% | 26% | 22% | 18% | 18% | |||||
5
Store Description
We strive to transform food shopping from a chore into a dynamic experience by designing and operating stores with a lively, inspirational atmosphere, mission-oriented décor and well-trained team members. We offer an exciting product mix that emphasizes our high quality standards and healthy eating, with a range of choices at every price level, ever-changing selections, samples, open kitchens, scratch bakeries, hand-stacked produce, bulk departments and extensive prepared foods stations featuring wood-burning pizza ovens; burrito stations and ethnic foods; juicing and hand-crafted coffee stations; and greens, beans and grains cooking bars, among others. We also incorporate environmentally sustainable aspects into our store design, and many stores have bicycle racks and electric vehicle charging stations. Our stores typically include sit-down eating areas and customer service booths, and some stores offer special services such as chair massage, personal shopping, online ordering and home delivery. Some stores also offer sit-down wine bars and tap rooms featuring local and/or craft beer and wine, creating a destination for customer gathering. We believe our stores play a unique role as a third place, besides the home and office, where people can gather, interact and learn while at the same time discovering the many joys of eating and sharing food.
Our store development work starts early. We conscientiously work to serve our communities through volunteer work, partnerships, and incorporating community feedback throughout the design process. By tailoring our store size, design, product selection and pricing to the particular community, we have been able to move into more segments of the market – urban and suburban, domestic and international. Most of our stores are located in high-traffic shopping areas on premier real estate sites and are either freestanding or in strip centers. We also have a number of urban stores located in high-density, mixed-use developments. In selecting store locations, we use an internally developed model to analyze potential sites based on various criteria such as education levels, population density and income levels within certain drive times. After we have selected a target site, our development group does a comprehensive site study and sales projection and works with our regional teams to develop construction and operating cost estimates. Each project must meet an internal Economic Value Added (“EVA®”) hurdle return, based on our internal weighted average cost of capital, which for new stores generally is expected to be cumulative positive EVA in five years or less. In its simplest definition, EVA is equivalent to net operating profits after taxes minus a charge on the cost of invested capital necessary to generate those profits. Our current internal weighted average cost of capital metric is 8%.
The required cash investment for new stores varies depending on the size of the store, geographic location, degree of landlord incentives and complexity of site development issues. To a significant degree, it also depends on how the project is structured, including costs for elements that often increase or decrease rent, e.g., lease acquisition costs, shell and/or garage costs, and landlord allowances. Because of these differences, the average development cost per square foot may vary significantly from project to project.
Seasonality
The Company’s average weekly sales and gross profit as a percentage of sales are typically highest in the second and third fiscal quarters, and lowest in the fourth fiscal quarter due to seasonally slower sales during the summer months. Gross profit as a percentage of sales is also lower in the first fiscal quarter due to the product mix of holiday sales. For this reason, results in a quarter are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be achieved in other quarters or for the full fiscal year.
Purchasing and Distribution
The majority of our purchasing occurs at the regional and national levels, enabling us to negotiate better volume discounts with major vendors and distributors while allowing our store buyers to focus on local products and the unique product mix necessary to keep the neighborhood market feel in our stores. We also remain committed to buying from local producers who meet our high quality standards.
Our produce procurement center facilitates the procurement and distribution of the majority of the produce we sell. We also operate three seafood processing and distribution facilities, a specialty coffee and tea procurement and roasting operation, and 11 regional distribution centers that focus primarily on perishables distribution to our stores across the U.S., Canada and the U.K. In addition, we have three regional commissary kitchens and five bakehouse facilities, all of which distribute products to our stores. Other products are typically procured through a combination of specialty wholesalers and direct distributors.
United Natural Foods, Inc. (“UNFI”) is our single largest third-party supplier, accounting for approximately 32% of our total purchases in fiscal year 2014. Our long-term relationship with UNFI as our primary supplier of dry grocery and frozen food products extends through 2020.
Store Operations
We strive to promote a strong company culture featuring a team approach to store operations that we believe is distinctly more empowering to team members than that of the traditional supermarket. Whole Foods Market stores each employ between approximately 55 and 680 team members who generally comprise 10 self-managed teams per store, each led by a team leader.
6
Each team within a store is responsible for a different product offering or aspect of store operations such as prepared foods, grocery, or customer service, among others. We also promote a decentralized approach to store operations in which many decisions are made by teams at the individual store level. In this structure, an effective store team leader is critical to the success of the store. The store team leader works closely with one or more associate store team leaders, as well as with all of the department team leaders, to operate the store as efficiently and profitably as possible.
Team members are involved at all levels of our business. We strive to create a company-wide consciousness of “shared fate” by uniting the interests of team members as closely as possible with those of our shareholders. One way we reinforce this concept is through our Gainsharing program. Under Gainsharing, as part of our annual planning process, each team receives a labor budget expressed as a percentage of their team’s sales, with leverage built into the budgets on an overall company basis. When teams come in under budget due either to higher sales or lower labor costs, a portion of the surplus is divided among the team members and paid out every four weeks, and a portion is set aside in a savings pool. When teams are over budget (or in a labor deficit position), no Gainsharing money is paid out. Instead, the overage is taken out of the team’s savings pool or, in the absence of savings, paid back using future surpluses. The savings pool is paid out annually after the end of the fiscal year to all teams with a positive balance. Rewarding our team members for increases in labor productivity – something they can control – gives them a direct stake in the success of our business. We also encourage stock ownership among team members through our broad-based team member stock option plan, stock purchase plan and 401(k) plan.
Team Members
We created more than 8,800 new jobs throughout the Company in fiscal year 2014. As of September 28, 2014, we had approximately 87,200 team members, including approximately 58,100 full-time, 26,100 part-time and 3,000 seasonal team members. Full-time team members accounted for approximately 69% of all permanent positions at the end of fiscal year 2014 and full-time voluntary turnover was approximately 11%. We believe this is very low for the food retailing industry and allows us to better serve our customers.
For the past 17 years, our team members have helped Whole Foods Market become one of FORTUNE magazine’s “100 Best Companies to Work for in America.” We are one of only 13 companies to make the “100 Best” list every year since its inception. All of our team members are non-union, and we consider our team member relations to be very strong.
We believe in empowering our team members to make Whole Foods Market not only a great place to shop but a great place to build a career. Our salary and benefits programs reflect our philosophy of egalitarianism. To ensure they are perceived as fundamentally fair to all stakeholders, our books are open to our team members, including our annual individual compensation report. We also have a salary cap that limits the total cash compensation paid to any team member in a calendar year to 19 times the average annual wage, including bonuses, of all full-time team members. In addition, our co-founder and co-Chief Executive Officer, John Mackey, has voluntarily set his annual salary at $1 and receives no cash bonuses or stock option awards.
All full-time and part-time team members are eligible to receive stock options through annual leadership grants or through service-hour grants once they have accumulated 6,000 service hours (approximately three years of full-time employment). Approximately 94% of the equity awards granted under the Company’s stock plan since its inception in 1992 have been granted to team members who are not executive officers. In fiscal year 2014, approximately 7,000 team members exercised approximately 1.5 million stock options worth approximately $36 million in gains before taxes, or an average of about $5,200 per team member.
As medical costs continue to rise, we periodically restructure how costs are shared between the Company and team members to ensure our health plan remains sustainable. By participating in our company-wide benefits vote every three years, team members can take an active role in choosing the benefits made available by the Company and how they share in the cost; 82% of eligible team members cast a ballot in our most recent vote. Under the current medical plan, Whole Foods Market provides health care coverage at no cost to full-time team members working 30 or more hours per week and having a minimum of 20,000 service hours (approximately 10 years of full-time employment). Full-time team members with 800 to 19,999 service hours pay a premium of $15 per paycheck. In addition, the Company provides personal wellness dollars in the form of either a health reimbursement arrangement (“HRA”) or health savings account (“HSA”). Based on service hours, team members can receive up to $1,800 per year to help cover the cost of deductibles and other allowable out-of-pocket health care expenses not covered by insurance.
Two of the ways we promote the health of our team members are through the Total Health Immersion Program and Healthy Discount Incentive Program. The Total Health Immersion Program provides educational opportunities for team members that are fully paid by the Company. Since launching this program in the fall of 2009, more than 2,800 team members have participated. The Healthy Discount Incentive Program offers additional store discounts of up to 35%, going beyond the standard store discount that all team members receive, based on meeting designated biometric criteria (cholesterol/LDL, BMI or waist-height ratio,
7
blood pressure) and being nicotine-free. In fiscal year 2014, approximately 14,000 team members participated in biometric screenings, with approximately 9,300 receiving higher-level discount cards.
Competition
Food retailing is a large, intensely competitive industry. Our competition includes but is not limited to local, regional, national and international conventional and specialty supermarkets, natural foods stores, warehouse membership clubs, online retailers, smaller specialty stores, farmers’ markets and restaurants, each of which competes with us on the basis of store ambiance and experience, product selection and quality, customer service, price, convenience or a combination of these factors.
Marketing
We generally invest less in paid media and marketing than other supermarkets – approximately 0.4% of our total sales in fiscal year 2014. We allocate our marketing investments among strategic national and regional programs and our individual stores; and we benefit from valuable earned media, social media and word-of-mouth advocacy. Company-wide, we publish roughly 1,200 messages per day across 830 social media channels. Our overall social media footprint on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and Google+ is approximately 9 million, with 4 million Facebook “likes” and 4.5 million Twitter followers. This includes both our global brand accounts and individual store accounts, which enable us to build deeper community ties and connect more directly to the tastes and needs of the local customers we serve. In addition, we have dedicated marketers in every store to develop and execute local events and to create the best possible in-store experience for our customers. We strategically focus our global marketing activity on engaging shoppers and growing their basket with fantastic and unique product selections, choices and in-store experiences; and our marketing investments emphasize community nonprofit partnerships that help grow our business and our communities at the same time.
In October 2014, we launched our first-ever national brand campaign. As a cutting-edge leader in sustainability standards, animal welfare, healthy eating and environmental stewardship, we have been quietly telling our story for decades. This campaign – Values Matter – is our opportunity to raise awareness with a louder voice and engage our customers in dialogue on these commitments. The campaign encompasses national television, print and digital advertising, including a dynamic web experience where customers can explore the values that differentiate us in the marketplace, as well as share what matters most to them.
Value Programs
We remain committed to the highest quality standards and to providing a clear range of choices in every category, both of which are important drivers of sales growth over the long term. In addition to our 365 Everyday Value exclusive products, we competitively price thousands of branded items and have extended value choices to our perishables departments as well. We also regularly promote thousands of products each month, including the widest array of organic and non-GMO sale items available. Our website features budget-friendly recipes and money-saving tips, and we offer in-store value tours and The Whole Deal value guide, which features supplier-sponsored and Whole Foods Market exclusive brand coupons online and in all stores in the U.S. and Canada.
Digital Roadmap
In the digital space, we are innovating and creating seamless and unique experiences that add choices, convenience, information and flexibility to support our customers’ busy lifestyles. In fiscal year 2014, we became the first national Instacart partner to offer both grocery delivery and in-store pickup in select U.S. markets, and we were one of the first merchants to integrate with Apple Pay. We continue to evolve the customer experience online, adding new features, products and merchandising to our eStore; and we recently began piloting an affinity (loyalty) program that will allow us to identify, understand, engage with and extend value to our customers in ways that are most relevant and meaningful to them.
Global Responsibility
We seek to be a deeply responsible company in the communities where we do business around the world, providing ethically sourced, high-quality products and transparent information to our customers, reducing our impact on the environment, and actively participating in our local communities. Each store retains a separate budget for making contributions to a variety of philanthropic and community activities, fostering goodwill and developing a high profile within the community. Our goal is to contribute at least 5% of our after-tax profits annually to nonprofit organizations. In addition, we cover all operating costs for our three foundations, allowing 100% of public donations to be dedicated to program support.
Whole Planet Foundation
Created in 2005, Whole Planet Foundation (www.wholeplanetfoundation.org) is an independent, nonprofit organization whose mission is to empower the poor through microcredit, with a focus on developing-world communities that supply our stores with product. Microcredit is a system pioneered by Professor Muhammad Yunus, founder of the Grameen Bank in Bangladesh and co-recipient of the 2006 Nobel Peace Prize. The philosophy behind microcredit is to provide the poor access to credit without
8
requiring contracts or collateral, enabling them to lift themselves out of poverty by creating or expanding home-based businesses. Program grants are funded in part by the sale of products under the Company’s Whole Trade Guarantee Program, along with support from customers, suppliers and team members. As of September 28, 2014, Whole Planet Foundation has partnered with various microfinance institutions to facilitate approximately $60 million in various donor-funded grants for 116 projects in 61 countries where the Company sources products. Over 800,000 borrower families (89% women) have received loans, which are being used for home-based businesses including poultry and pig farming, agriculture, furniture making, tailoring, and selling handicrafts, homemade and bakery-made foods, clothing and footwear. It is estimated that each woman supports a family of more than five, which means our support is contributing to the prosperity of approximately 4.2 million individuals.
Whole Kids Foundation™
Whole Kids Foundation (www.wholekidsfoundation.org), an independent nonprofit organization founded in 2011, is dedicated to improving children’s nutrition by supporting schools and inspiring families. The foundation provides grants for school gardens and salad bars and offers cooking and nutrition education for teachers and staff. Through the generosity of Whole Foods Market customers, suppliers and community donors, approximately 2,100 schools in the U.S. and Canada have received school garden grants since 2011. In addition, Whole Foods Market and Whole Kids Foundation, in partnership with Let’s Move Salad Bars to Schools, have provided more than 3,500 salad bars to schools around the country. Our team members and customers continue to support these initiatives, recently donating more than $3.5 million during the foundation’s fall 2014 fundraising campaign.
Whole Cities Foundation™
Whole Cities Foundation (www.wholefoodsmarket.com/whole-cities-foundation) is the newest member of the Whole Foods Market family of foundations. Founded in 2014, this independent nonprofit is dedicated to individual and community health through collaborative partnerships, education and broader access to nutritious food in underserved communities. Specifically, Whole Cities Foundation invests in partnerships with grassroots organizations creating innovative solutions to food access and health in their communities. Urban farms that collaborate with nutrition education programs to offer affordable healthy food, cooking classes, and health and wellness information are one example. To date, Whole Cities Foundation has focused its partnerships in New Orleans, LA, Detroit, MI and Jackson, MS, with future partnerships to be established in Englewood, IL and Newark, NJ. Whole Foods Market has committed to providing $1 million in seed money over the next three years to Whole Cities Foundation.
Healthy Eating Education
Our Health Starts Here® program is a mindful approach to healthy eating rooted in simple ways to build better meals. Paired with practical tools and valuable educational resources online and in our stores, the program includes, among other things: in-store healthy eating specialists; healthy eating store tours, classes and networking opportunities; Health Starts Here 28-Day Challenges; and Health Starts Here-labeled foods in our salad and hot bars as well as prepared meals in our self- and full-serve cases. By offering an informed approach to food as a source for improved health and vitality, we hope to play a big part in the solution to the health care crisis in America.
Green Mission®
We are committed to supporting wise environmental practices and being a leader in environmental stewardship. Since 2004, we have purchased over 4.3 billion kilowatt hours of wind-based renewable energy, earning seven Environmental Protection Agency (“EPA”) Green Power awards. We have 17 stores and one distribution center using or hosting rooftop solar systems, four stores with fuel cells, two stores with rooftop farms, and one store with non-HFC refrigeration and a rooftop combined heat and power (CHP) system. We also have installed electric vehicle charging stations at more than 45 U.S. stores. We have made a commitment to reduce energy consumption at all of our stores by 25% per square foot by 2015, and we build our new stores with the environment in mind, using green building innovations whenever possible. Twenty-three of our stores have received Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (“LEED”) certification by the U.S. Green Building Council; 29 stores have earned Green Globes certification from the Green Building Initiative; and 45 stores have received GreenChill Certification awards from the EPA.
We discontinued the use of disposable plastic grocery bags at the checkouts in all of our stores in 2008 and refund at least a nickel per reusable bag at checkout. We also were the first national retailer to provide Forest Stewardship Council certified paper bags originating from 100% post-consumer recycled fiber. Unless located in a community that does not support recycling and composting, all of our stores are involved in a recycling program, and most participate in a composting program where food waste and compostable paper items are regenerated into compost. Additionally, in 2007 we introduced fiber packaging in many of our prepared foods departments as a compostable alternative to traditional petroleum and wood- or tree-based materials. We also are working to eliminate the use of Styrofoam in packing materials shipped to our Company and in product packaging in our stores.
9
Recognitions
Whole Foods Market was recognized on a number of lists in fiscal year 2014, including but not limited to: FORTUNE’s “World’s Most Admired Companies” and “100 Best Companies to Work for in America” lists. We also earned the top spot on Consumer Reports’ list of “Supermarkets with the Best Food in America,” Greenpeace’s “Carting Away the Oceans” report, and we were named “Best Brand on Pinterest” at the 6th Annual Shorty Industry Awards.
Trademarks
Trademarks owned by the Company or its subsidiaries include, but are not limited to: “Whole Foods Market,” the “Whole Foods Market” logo, “365 Everyday Value,” the “365 Everyday Value” logo, “AFA,” “Allegro Coffee Company,” “America’s Healthiest Grocery Store,” “ANDI,” “Awesome Eats,” “Bread & Circus,” “Dark Rye,” “Eco-Scale,” “Fresh & Wild,” “Fresh Fields,” “Grab & Give,” “Greenlife Grocery,” “Green Mission,” “Harry’s Farmers Market,” “Health Starts Here,” the “Health Starts Here” logo, “Ideal Market,” “Improving Lives with Every Purchase,” “Merchant of Vino,” “Mrs. Gooch’s,” the “Responsibly Grown” logo, “Vine Buys,” “Wellspring,” “Whole Baby,” the “Whole Body” logo, “Whole Catch,” “Whole Cities Foundation,” “The Whole Deal,” “Whole Foods, Whole People, Whole Planet,” “Whole Journeys,” “Whole Kids,” “Whole Kids Foundation,” “Whole Paws,” the “Whole Paws” logo, “Whole Planet Foundation,” “Whole Story,” and “Whole Trade.” The Company and its subsidiaries have registered or applied to register numerous trademarks, service marks, stylized logos, and brand names in the U.S. and in many additional countries throughout the world. In addition, the Company licenses certain trademarks, including “ENGINE 2” and “PLANT-STRONG,” which are trademarks owned by Engine 2 for Life, LLC. The Company considers certain of its trademarks to be of material importance and actively defends and enforces such trademarks. The duration of trademark registrations varies from country to country; however, trademarks are generally valid and may be renewed indefinitely as long as they are in use and/or their registrations are properly maintained.
Executive Officers of the Registrant
The following table sets forth the name, age, and position of each of the persons who was serving as an executive officer of the Company as of November 18, 2014:
Name | Age | Position | |
John Mackey | 61 | Co-Chief Executive Officer | |
Walter Robb | 61 | Co-Chief Executive Officer | |
A.C. Gallo | 61 | President and Chief Operating Officer | |
Glenda Flanagan | 61 | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | |
James Sud | 62 | Executive Vice President of Growth and Business Development | |
David Lannon | 48 | Executive Vice President of Operations | |
Kenneth Meyer | 46 | Executive Vice President of Operations | |
John Mackey, co-founder of the Company, has served as co-Chief Executive Officer since May 2010, was the Chief Executive Officer from 1978 to May 2010 and was President from June 2001 to October 2004. Mr. Mackey co-authored Conscious Capitalism: Liberating the Heroic Spirit of Business, a 2013 New York Times and Wall Street Journal best seller. To date, profits from books sold at Whole Foods Market stores, along with 100% of the royalties received by Mr. Mackey, have resulted in donations of more than $160,000 to Whole Planet Foundation.
Walter Robb has served as co-Chief Executive Officer since May 2010. Mr. Robb also served as the co-President and co-Chief Operating Officer from 2004 to May 2010, as Chief Operating Officer from 2001 to September 2004, and as Executive Vice President from 2000 to February 2001. Since joining the Company in 1991, Mr. Robb has also served as Store Team Leader and President of the Northern California Region.
A.C. Gallo has served as President and Chief Operating Officer of the Company since May 2010. Prior to that, he was co-President and co-Chief Operating Officer since September 2004. Mr. Gallo also served as Chief Operating Officer from December 2003 to September 2004. Mr. Gallo has held various positions with the Company and with Bread & Circus, Inc., which was acquired by the Company in October 1992, including Vice President and President of the North Atlantic Region, and Executive Vice President of Operations.
Glenda Flanagan has served as Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of the Company since December 1988.
James Sud has served as Executive Vice President of Growth and Business Development of the Company since February 2001. Mr. Sud joined the Company in May 1997 and served as Vice President and Chief Operating Officer until February 2001. Mr. Sud served as a director of the Company from 1980 to 1997.
10
David Lannon has served as Executive Vice President of Operations of the Company since February 2012. Prior to that, Mr. Lannon had served as President of the Northern California Region since December 2007 and President of the North Atlantic Region from March 2001 to December 2007. Mr. Lannon has held various positions with the Company and with Bread & Circus, Inc., which was acquired by the Company in October 1992, including Store Team Leader, Director of Store Operations and Vice President of the North Atlantic Region.
Kenneth Meyer has served as Executive Vice President of Operations of the Company since February 2012. Mr. Meyer also served as President of the Mid-Atlantic Region from October 2004 to February 2012. Mr. Meyer has held various positions with the Company and with Fresh Fields Market, which was acquired by the Company in August 1996, including Store Team Leader, Vice President of the Southwest Region, and President of the South Region.
Available Information
Our corporate website is www.wholefoodsmarket.com. We make available through the Investor Relations section of this site, free of charge, the Company’s Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) filings, including annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, interactive data, current reports on Form 8-K, proxy statement, Section 16 filings, and all amendments to those reports. We also make available our corporate governance documents, Code of Business Conduct, and Board of Directors committee charters and policies. We have included our website as an inactive textual reference only. Information contained on our website is not incorporated by reference into this Report on Form 10-K.
Item 1A. Risk Factors.
Business and Operating Risks
Our growth depends on increasing sales in comparable stores and on new store openings, and our failure to achieve these goals could negatively impact our results of operations and financial condition.
Our continued growth depends on our ability to increase sales in our comparable stores and open new stores. Our operating results may be materially impacted by fluctuations in our comparable store sales. Our comparable store sales growth could be lower than our historical average for many reasons including the impact of new and acquired stores entering into the comparable store base, the opening of new stores that cannibalize store sales in existing areas, general economic conditions, increased competition, price changes in response to competitive factors, possible supply shortages, and cycling against any year of above-average sales results.
Our growth strategy includes opening new stores in existing and new areas and operating those stores successfully. Successful implementation of this strategy is dependent on finding suitable locations, and we face competition from other retailers for such sites. There can be no assurance that we will continue to grow through new store openings. We may not be able to open new stores timely or operate them successfully. Also, we may not be able to successfully hire and train new team members or integrate those team members into the programs and policies of the Company. We may not be able to adapt our distribution, management information and other operating systems to adequately supply products to new stores at competitive prices so that we can operate the stores in a successful and profitable manner.
A failure to maintain the privacy and security of customer-related and business information could damage our reputation and business.
We receive, retain, and transmit certain personal information about our customers, team members and suppliers and entrust that information to third party business associates. Our business, which operates primarily in the U.S., Canada and the U.K., heavily depends upon the secure momentary storage of data associated with cashless payments as well as the secure transmission of a significant amount of confidential information over public networks. Additionally, the use of individually identifiable data by our business and our business associates is regulated at the national and local or state level in all of our operating countries. Privacy and information security laws and regulations change, and compliance with updates may result in cost increases due to necessary systems changes and the development of new administrative processes. A compromise of our security systems or those of our business associates that results in our customers’, team members’ or suppliers’ information being obtained by unauthorized persons or a breach of information security laws and regulations could adversely affect our reputation with our customers, team members and others, as well as our operations, results of operations, financial condition and liquidity, and could result in litigation against us or the imposition of penalties. In addition, a security breach could require that we expend significant additional resources related to remediation, including changes in the information security systems, and could result in a disruption of our operations, particularly our online business.
Disruptions in our information systems could harm our ability to run our business.
We rely extensively on information systems for point-of-sale processing in our stores, supply chain, financial reporting, human resources and various other processes and transactions. Our information systems are subject to damage or interruption from
11
power outages, computer and telecommunications failures, computer viruses, security breaches, including breaches of our transaction processing or other systems that could result in the compromise of confidential customer data, catastrophic events, and usage errors by our team members. If our systems are breached, damaged or cease to function properly, we may have to make significant investments to fix or replace them, suffer interruptions in our operations, and face costly litigation, and our reputation with our customers may be harmed. Any material interruption in our information systems may have a material adverse effect on our operating results.
Disruption of significant supplier relationships could negatively affect our business.
United Natural Foods, Inc. (“UNFI”) is our single largest third-party supplier, accounting for approximately 32% of our total purchases in fiscal year 2014. Due to this concentration of purchases from a single third-party supplier, the cancellation of our distribution arrangement or the disruption, delay or inability of UNFI to deliver product to our stores may materially and adversely affect our operating results while we establish alternative distribution channels.
Claims under our self-insurance program may differ from our estimates, which could materially impact our results of operations.
The Company uses a combination of insurance and self-insurance plans to provide for the potential liabilities for workers’ compensation, general liability, property insurance, director and officers’ liability insurance, vehicle liability and team member health care benefits. Liabilities associated with the risks that are retained by the Company are estimated, in part, by considering historical claims experience, demographic factors, severity factors and other actuarial assumptions. Our results could be materially impacted by claims and other expenses related to such plans if future occurrences and claims differ from these assumptions and historical trends.
The loss of key management or difficulties recruiting and retaining qualified team members could negatively affect our business.
We are dependent upon a number of key management and other team members. If we were to lose the services of a significant number of key team members within a short period of time, this could have a material adverse effect on our operations. We do not maintain key person insurance on any team member. Our continued success also is dependent upon our ability to attract and retain qualified team members to meet our future growth needs. We face intense competition for qualified team members, many of whom are subject to offers from competing employers. We may not be able to attract and retain necessary team members to operate our business.
Perishable foods product losses could materially impact our results of operations.
Our stores offer a significant number of perishable products, accounting for approximately 66.8% of our total sales in fiscal year 2014. The Company’s emphasis on perishable products may result in significant product inventory losses in the event of extended power outages, natural disasters or other catastrophic occurrences.
Unions may attempt to organize our team members, which could harm our business.
All of our team members are non-union, and we consider our team member relations to be very strong. From time to time unions have attempted to organize all or part of our team member base at certain stores and non-retail facilities. Responding to such organization attempts is distracting to management and team members and may have a negative financial impact on a store, facility or the Company as a whole.
Market and Other External Risks
Increased competition may adversely affect our revenues and profitability.
Our competitors include but are not limited to local, regional, national and international supermarkets, natural food stores, warehouse membership clubs, online retailers, small specialty stores, farmers’ markets, and restaurants. Their businesses compete with us for products, customers and locations. In addition, some are expanding more aggressively in offering a range of natural and organic foods. Some of these competitors may have been in business longer or may have greater financial or marketing resources than we do and may be able to devote greater resources to sourcing, promoting and selling their products. As competition in certain areas intensifies, our operating results may be negatively impacted through a loss of sales, reduction in margin from competitive price changes, and/or greater operating costs such as marketing.
Economic conditions that adversely impact consumer spending could materially impact our business.
Our operating results may be materially impacted by changes in overall economic conditions that impact consumer confidence and spending, including discretionary spending. Future economic conditions affecting disposable consumer income such as employment levels, business conditions, changes in housing market conditions, the availability of credit, interest rates, tax rates, fuel and energy costs, the impact of natural disasters or acts of terrorism, and other matters could reduce consumer spending or cause consumers to shift their spending to lower-priced competitors. In addition, there can be no assurance that various governmental activities to stimulate the economy will restore consumer confidence or change spending habits.
12
Adverse publicity may reduce our brand value and negatively impact our business.
We believe our Company has built an excellent reputation as a food retailer, socially responsible corporation and employer, and we believe our continued success depends on our ability to preserve, grow and leverage the value of our brand. Brand value is based in large part on perceptions of subjective qualities, and even isolated incidents can erode trust and confidence, particularly if they result in adverse publicity, governmental investigations or litigation, which can negatively impact these perceptions and our business. We believe that many customers choose to shop our stores because of their interest in health, nutrition and food safety and that they hold us to a higher food safety standard than other supermarkets. There is increasing governmental scrutiny of and public awareness regarding food safety. The real or perceived sale of contaminated food products by us could result in government enforcement action, private litigation, product recalls and other liabilities, the settlement or outcome of which might have a material adverse effect on our operating results and brand value.
Changes in the availability of quality natural and organic products could impact our business.
We source our products from a variety of local, regional, national and international suppliers, and we rely on them to meet our quality standards and supply products in a timely and efficient manner. There is, however, no assurance that quality natural and organic products will be available to meet our needs. If other competitors significantly increase their natural and organic product offerings, if new laws require the reformulation of certain products to meet tougher standards, or if natural disasters or other catastrophic events occur, the supply of these products may be constrained.
A widespread health epidemic could materially impact our business.
The Company’s business could be severely impacted by a widespread regional, national or global health epidemic. Our stores are a place where customers come together, interact and learn and at the same time discover the many joys of eating and sharing food. A widespread health epidemic may cause customers to avoid public gathering places or otherwise change their shopping behaviors. Additionally, a widespread health epidemic could also adversely impact our business by disrupting production and delivery of products to our stores and by impacting our ability to appropriately staff our stores.
Our stock price may be volatile and adversely affected by general market factors, including fluctuations in our quarterly results of operations.
In fiscal year 2014, the closing market price per share of our common stock ranged from $36.46 to $65.24. The market price of our common stock could be subject to significant fluctuation in response to various market factors and events, including variations in our sales and earnings results and any failure to meet market expectations. Our quarterly operating results and quarter-to-quarter comparisons could fluctuate for many reasons, including, but not limited to, price changes in response to competitive factors, seasonality, holiday shifts, increases in store operating costs, including commodity costs, possible supply shortages, general economic conditions, extreme weather-related disruptions, and other business costs. In addition, we may be impacted by changes in ratings and earnings estimates by securities analysts; publicity regarding us, our competitors, or the natural products industry generally; new statutes or regulations or changes in the interpretation of existing statutes or regulations affecting the natural products industry specifically; sales of substantial amounts of common stock in the public market or the perception that such sales could occur; broad price fluctuations in the overall stock market and other factors.
Our investments in money market funds and certain other securities are subject to market risks, which may result in losses.
As of September 28, 2014, we had approximately $65 million in short-term investments classified as cash and cash equivalents and approximately $673 million in available-for-sale marketable securities. We have invested these amounts primarily in state and local municipal obligations, government agency securities, corporate commercial paper and bonds, and money market funds meeting certain criteria. These investments are subject to general credit, liquidity, market and interest rate risks, which, if they materialize, could have a negative impact on our results of operations.
Financial Reporting, Legal and Other Regulatory Risks
Pending or future legal proceedings could materially impact our results of operations.
From time to time, we are party to legal proceedings, including matters involving personnel and employment issues, personal injury, product liability, protecting our intellectual property, acquisitions, and other proceedings arising in the ordinary course of business. Our results could be materially impacted by the decisions and expenses related to pending or future proceedings.
Effective tax rate changes and results of examinations by taxing authorities could materially impact our results of operations.
Our future effective tax rates could be adversely affected by the earnings mix being lower than historical results in states or countries where we have lower statutory rates and higher-than-historical results in states or countries where we have higher statutory rates, by changes in the valuation of our deferred tax assets and liabilities, or by changes in tax laws or interpretations thereof. In addition, we are subject to periodic audits and examinations by the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) and other state and local taxing authorities. Our results could be materially impacted by the determinations and expenses related to proceedings
13
by the IRS and other state and local taxing authorities. See Note 9 to the consolidated financial statements, “Income Taxes,” in Part II, “Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data,” of this report.
Changes in accounting standards and estimates could materially impact our results of operations.
Generally accepted accounting principles and related accounting pronouncements, implementation guidelines, and interpretations for many aspects of our business, such as accounting for insurance and self-insurance, inventories, goodwill and intangible assets, store closures, leases, income taxes and share-based payments, are highly complex and involve subjective judgments. Changes in these rules or their interpretation or changes in underlying estimates, assumptions or judgments by our management could significantly change or add significant volatility to our reported earnings without a comparable underlying change in cash flow from operations.
Unfavorable changes in governmental regulation could harm our business.
The Company is subject to various local, state, federal and international laws, regulations and administrative practices affecting our business, and we must comply with provisions regulating health and sanitation standards, food labeling, equal employment, minimum wages, and licensing for the sale of food and, in some stores, alcoholic beverages. Our new store openings could be delayed or prevented or our existing stores could be impacted by difficulties or failures in our ability to obtain or maintain required approvals or licenses. Changes in existing laws or implementation of new laws, regulations and practices (e.g., health care legislation) could have a significant impact on our business.
The USDA’s Organic Rule facilitates interstate commerce and the marketing of organically produced food, and provides assurance to our customers that such products meet consistent, uniform standards. Compliance with this rule could pose a significant burden on some of our suppliers, which may cause a disruption in some of our product offerings.
We cannot predict the nature of future laws, regulations, interpretations or applications, or determine what effect either additional government regulations or administrative orders, when and if promulgated, or disparate local, state, federal and international regulatory schemes would have on our business in the future. They could, however, require the reformulation of certain products to meet new standards, the recall or discontinuance of certain products not able to be reformulated, additional recordkeeping, expanded documentation of the properties of certain products, expanded or different labeling and/or scientific substantiation. Any or all of such requirements could have an adverse effect on our operating results.
The risk associated with doing business in other countries could materially impact our results of operations.
Though only 3.3% of our total sales in fiscal year 2014, the Company’s international operations are subject to certain risks of conducting business abroad, including fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, changes in regulatory requirements, and changes or uncertainties in the economic, social and political conditions in the Company’s geographic areas, among other things.
A failure of our internal control over financial reporting could materially impact our business or stock price.
The Company’s management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. An internal control system, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. Further, the design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints, and the benefits of controls must be considered relative to their costs. Because of the inherent limitations in all internal control systems, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Any failure to maintain an effective system of internal control over financial reporting could limit our ability to report our financial results accurately and timely or to detect and prevent fraud, and could expose us to litigation or adversely affect the market price of our common stock. The Company’s management concluded that its internal control over financial reporting was effective as of September 28, 2014. See Part II, “Item 9A. Controls and Procedures – Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting,” of this report.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
Not applicable.
14
Item 2. Properties.
As of September 28, 2014, we operated 399 stores: 381 stores in 42 U.S. states and the District of Columbia; 9 stores in Canada; and 9 stores in the U.K. We own 15 stores, two distribution facilities and land for one facility in development. We also own three properties leased to third parties; a building on leased land, which is leased to third parties; and a parking facility and one store in development on leased land. All other stores, distribution centers, bakehouses and administrative facilities are leased, and we have options to renew most of our leases in five-year increments. In addition, as of September 28, 2014, we had 25 leased properties and adjacent spaces that are not being utilized in current operations, of which 17 are related to our acquisition of Wild Oats Markets in August 2007. We are actively negotiating to sublease or terminate leases related to these locations.
The following table shows the number of our stores by U.S. state, the District of Columbia, Canada and the U.K. as of September 28, 2014:
Location | Number of stores | Location | Number of stores | Location | Number of stores | |||||
Alabama | 1 | Kansas | 3 | New York | 15 | |||||
Arizona | 11 | Kentucky | 2 | North Carolina | 11 | |||||
Arkansas | 1 | Louisiana | 5 | Ohio | 6 | |||||
California | 76 | Maine | 1 | Oklahoma | 3 | |||||
Canada | 9 | Maryland | 9 | Oregon | 8 | |||||
Colorado | 20 | Massachusetts | 29 | Pennsylvania | 10 | |||||
Connecticut | 9 | Michigan | 6 | Rhode Island | 3 | |||||
District of Columbia | 4 | Minnesota | 6 | South Carolina | 4 | |||||
Florida | 21 | Mississippi | 1 | Tennessee | 4 | |||||
Georgia | 10 | Missouri | 2 | Texas | 25 | |||||
Hawaii | 3 | Nebraska | 2 | United Kingdom | 9 | |||||
Idaho | 1 | Nevada | 5 | Utah | 5 | |||||
Illinois | 19 | New Hampshire | 1 | Virginia | 10 | |||||
Indiana | 3 | New Jersey | 12 | Washington | 7 | |||||
Iowa | 1 | New Mexico | 4 | Wisconsin | 2 | |||||
Item 3. Legal Proceedings.
From time to time we are a party to legal proceedings including matters involving personnel and employment issues, personal injury, product liability, protecting our intellectual property, acquisitions and other proceedings arising in the ordinary course of business which have not resulted in any material losses to date. Although management does not expect that the outcome in these proceedings will have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations, litigation is inherently unpredictable. Therefore, we could incur judgments or enter into settlements of claims that could materially impact our results.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures.
Not applicable.
15
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
Whole Foods Market’s common stock is traded on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the symbol “WFM.”
The Company is a member of the Standard & Poor’s S&P 500 Index and the NASDAQ-100® Index.
On May 7, 2013, the Company’s Board of Directors declared a two-for-one stock split of the Company’s common stock, which was effected through a 100% stock dividend distributed on May 29, 2013 to shareholders of record at the close of business on May 17, 2013. Shareholders received one additional share of Whole Foods Market common stock for each share owned. All shares reserved for issuance pursuant to the Company’s stock option and stock purchase plans were automatically increased by the same proportion. In addition, shares subject to outstanding options or other rights to acquire the Company’s stock and the exercise price for such shares were adjusted proportionately. All references to share or per share amounts in the accompanying consolidated financial statements and applicable disclosures have been adjusted to reflect this two-for-one stock split. This was the Company’s fourth stock split since going public in January 1992. The Company previously effected two-for-one stock splits in the form of a 100% stock dividend on November 29, 1993, June 4, 2001 and December 27, 2005.
The following table sets forth the intra-day quarterly high and low sale prices of the Company’s common stock for fiscal years 2014 and 2013:
High | Low | ||||||
Fiscal year 2014: | |||||||
September 30, 2013 to January 19, 2014 | $ | 65.59 | $ | 52.04 | |||
January 20, 2014 to April 13, 2014 | 56.42 | 48.91 | |||||
April 14, 2014 to July 6, 2014 | 51.33 | 37.02 | |||||
July 7, 2014 to September 28, 2014 | 40.45 | 36.08 | |||||
Fiscal year 2013: | |||||||
October 1, 2012 to January 20, 2013 | $ | 50.93 | $ | 43.43 | |||
January 21, 2013 to April 14, 2013 | 48.47 | 40.70 | |||||
April 15, 2013 to July 7, 2013 | 53.63 | 42.23 | |||||
July 8, 2013 to September 29, 2013 | 59.35 | 51.00 | |||||
As of November 18, 2014, there were 1,345 holders of record of Whole Foods Market’s common stock, and the closing stock price was $47.89.
Dividends
The following table provides a summary of dividends declared per common share during fiscal years 2014 and 2013 (in millions, except per share amounts):
Date of declaration | Dividend per common share | Date of record | Date of payment | Total amount | |||||||
Fiscal year 2014: | |||||||||||
November 1, 2013 | $ | 0.12 | January 17, 2014 | January 28, 2014 | $ | 45 | |||||
February 24, 2014 | 0.12 | April 11, 2014 | April 22, 2014 | 44 | |||||||
June 12, 2014 | 0.12 | July 3, 2014 | July 15, 2014 | 44 | |||||||
September 11, 2014 (1) | 0.12 | September 26, 2014 | October 7, 2014 | 43 | |||||||
Fiscal year 2013: | |||||||||||
November 29, 2012 | $ | 1.00 | December 10, 2012 | December 21, 2012 | $ | 371 | |||||
November 7, 2012 | 0.10 | January 18, 2013 | January 29, 2013 | 37 | |||||||
March 15, 2013 | 0.10 | April 12, 2013 | April 23, 2013 | 37 | |||||||
June 12, 2013 | 0.10 | July 5, 2013 | July 16, 2013 | 37 | |||||||
September 10, 2013 | 0.10 | September 27, 2013 | October 8, 2013 | 37 | |||||||
(1) Dividend accrued at September 28, 2014
16
On November 4, 2014, the Company’s Board of Directors authorized an increase in the Company’s quarterly dividend to $0.13 per common share from $0.12 per common share, payable on January 27, 2015, to shareholders of record at the close of business on January 16, 2015. The Company will pay future dividends at the discretion of the Company’s Board of Directors. The continuation of these payments, the amount of such dividends, and the form in which dividends are paid (cash or stock) depend on many factors, including the results of operations and the financial condition of the Company. Subject to these qualifications, the Company currently expects to pay dividends on a quarterly basis.
Performance Graph
The following graph and accompanying table show the cumulative five-year total return to shareholders of Whole Foods Market, Inc.’s common stock relative to the cumulative total returns of the S&P 500 Index, the NASDAQ Composite Index, and the S&P Food Retail Index. The graph tracks the performance of a $100 investment in our common stock and in each of the indices (with the reinvestment of all dividends) from September 30, 2009 to September 30, 2014. The stock price performance included in this graph is not necessarily indicative of future stock price performance.
9/30/2009 | 9/30/2010 | 9/30/2011 | 9/30/2012 | 9/30/2013 | 9/30/2014 | ||||||||||||
Whole Foods Market, Inc. | 100.00 | 121.71 | 215.66 | 323.74 | 400.67 | 263.85 | |||||||||||
NASDAQ Composite | 100.00 | 112.55 | 116.28 | 153.12 | 189.49 | 227.09 | |||||||||||
S&P 500 | 100.00 | 110.16 | 111.42 | 145.07 | 173.13 | 207.30 | |||||||||||
S&P Food Retail | 100.00 | 107.25 | 115.48 | 141.87 | 216.58 | 219.66 | |||||||||||
Copyright© 2014 S&P, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc. All rights reserved.
17
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The following table provides information about the Company’s share repurchase activity during the twelve weeks ended September 28, 2014.
Period (1) | Total number of shares purchased | Average price paid per share | Total number of shares purchased as part of publicly announced plans or programs (2) | Approximate dollar value of shares that may yet be purchased under the plans or programs (2) | |||||||||
July 7, 2014 - August 3, 2014 | 1,517,916 | $ | 38.04 | 1,517,916 | $ | 942,264,547 | |||||||
August 4, 2014 - August 31, 2014 | 1,109,312 | 38.10 | 1,109,312 | 900,000,009 | |||||||||
September 1, 2014 - September 28, 2014 | — | — | — | 900,000,009 | |||||||||
Total | 2,627,228 | $ | 38.06 | 2,627,228 | |||||||||
(1) | Periodic information is presented by reference to our fiscal periods during the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2014. |
(2) | Effective August 1, 2014, a share repurchase program was authorized pursuant to the authority of the Company’s Board of Directors whereby the Company may make up to $1.0 billion in purchases of outstanding shares of common stock of the Company through August 1, 2016. Under the share repurchase program, purchases can be made from time to time using a variety of methods, which may include open market purchases. The specific timing, price and size of purchases will depend on prevailing stock prices, general economic and market conditions, and other considerations. Purchases may be made through a Rule 10b5-1 plan pursuant to pre-determined metrics set forth in such plan. The Board’s authorization of the share repurchase program does not obligate the Company to acquire any particular amount of common stock, and the program may be suspended or discontinued at any time at the Company’s discretion. |
18
Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
Whole Foods Market, Inc.
Summary Financial Information
(In millions, except per share amounts and operating data)
The following selected financial data are derived from the Company’s consolidated financial statements and should be read in conjunction with “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and “Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this report.
Sept. 28, 2014 | Sept. 29, 2013 | Sept. 30, 2012 | Sept. 25, 2011 | Sept. 26, 2010 | |||||||||||
Consolidated Statements of Operations Data (1) | |||||||||||||||
Sales | $ | 14,194 | $ | 12,917 | $ | 11,699 | $ | 10,108 | $ | 9,006 | |||||
Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs | 9,150 | 8,288 | 7,543 | 6,571 | 5,870 | ||||||||||
Gross profit | 5,044 | 4,629 | 4,156 | 3,537 | 3,136 | ||||||||||
Direct store expenses | 3,586 | 3,285 | 2,983 | 2,629 | 2,377 | ||||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 446 | 397 | 372 | 311 | 272 | ||||||||||
Pre-opening expenses | 67 | 52 | 47 | 41 | 38 | ||||||||||
Relocation, store closure and lease termination costs | 11 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 11 | ||||||||||
Operating income | 934 | 883 | 744 | 548 | 438 | ||||||||||
Interest expense | — | — | — | (4 | ) | (33 | ) | ||||||||
Investment and other income | 12 | 11 | 8 | 8 | 7 | ||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 946 | 894 | 752 | 552 | 412 | ||||||||||
Provision for income taxes | 367 | 343 | 286 | 209 | 166 | ||||||||||
Net income | 579 | 551 | 466 | 343 | 246 | ||||||||||
Preferred stock dividends | — | — | — | — | 6 | ||||||||||
Income available to common shareholders | $ | 579 | $ | 551 | $ | 466 | $ | 343 | $ | 240 | |||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 1.57 | $ | 1.48 | $ | 1.28 | $ | 0.98 | $ | 0.72 | |||||
Weighted average shares outstanding | 367.8 | 371.2 | 364.8 | 350.5 | 332.5 | ||||||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 1.56 | $ | 1.47 | $ | 1.26 | $ | 0.97 | $ | 0.72 | |||||
Weighted average shares outstanding, diluted basis | 370.5 | 374.5 | 368.9 | 354.6 | 343.4 | ||||||||||
Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.48 | $ | 1.40 | $ | 0.28 | $ | 0.20 | $ | — | |||||
Consolidated Balance Sheets Data | |||||||||||||||
Net working capital | $ | 499 | $ | 892 | $ | 1,126 | $ | 574 | $ | 414 | |||||
Total assets | 5,744 | 5,538 | 5,294 | 4,292 | 3,987 | ||||||||||
Long-term debt (including current maturities) | 62 | 27 | 24 | 18 | 509 | ||||||||||
Shareholders’ equity | 3,813 | 3,878 | 3,802 | 2,991 | 2,373 | ||||||||||
Operating Data | |||||||||||||||
Number of stores at end of fiscal year | 399 | 362 | 335 | 311 | 299 | ||||||||||
Average store size (gross square footage) | 38,000 | 38,000 | 38,000 | 38,000 | 38,000 | ||||||||||
Average weekly sales per store | $ | 722,000 | $ | 711,000 | $ | 682,000 | $ | 636,000 | $ | 588,000 | |||||
Comparable store sales increase (2) | 4.3% | 6.9% | 8.7% | 8.5% | 7.1% | ||||||||||
(1) Fiscal years 2014, 2013, 2011 and 2010 were 52-week years and fiscal year 2012 was a 53-week year.
(2) Sales of a store are deemed to be comparable commencing in the fifty-third full week after the store was opened. Stores acquired in purchase acquisitions enter the comparable store base effective the fifty-third full week following the date of merger. Stores closed for eight or more days are excluded from the comparable store base from the first fiscal week of closure until re-opened for a full fiscal week. Comparable sales growth is calculated on a same-calendar-week to same-calendar-week basis.
19
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
Overview
Whole Foods Market is the leading retailer of natural and organic foods, the first national “Certified Organic” grocer, and uniquely positioned as America’s Healthiest Grocery Store™. Our Company mission is to promote the vitality and well-being of all individuals by supplying the highest quality, most wholesome foods available. Since the purity of our food and the health of our bodies are directly related to the purity and health of our environment, our mission is devoted to the promotion of organically grown foods, healthy eating, and the sustainability of our entire ecosystem. We believe that much of our success to date is because we remain a uniquely mission-driven company. Through our growth, we have had a significant and positive impact on the natural and organic foods movement throughout the United States, helping lead the industry to nationwide acceptance. The Company incorporated in 1978, opened the first Whole Foods Market store in 1980, and as of September 28, 2014, operated 399 stores: 381 stores in 42 U.S. states and the District of Columbia; 9 stores in Canada; and 9 stores in the United Kingdom. We have one operating segment, natural and organic foods supermarkets.
Our continued growth depends on our ability to increase sales in our comparable stores and open new stores. Our growth strategy includes opening new stores in existing and new areas and operating those stores successfully. The Company’s average weekly sales and gross profit as a percentage of sales are typically highest in the second and third fiscal quarters, and lowest in the fourth fiscal quarter due to seasonally slower sales during the summer months. Gross profit as a percentage of sales is also lower in the first fiscal quarter due to the product mix of holiday sales.
Sales of a store are deemed to be comparable commencing in the fifty-third full week after the store was opened or acquired. Stores closed for eight or more days are excluded from the comparable store base from the first fiscal week of closure until re-opened for a full fiscal week. Comparable sales growth is calculated on a same-calendar-week to same-calendar-week basis. The methods used to calculate comparable store sales may differ between companies; thus growth rates across companies may not be comparable.
The Company reports its results of operations on a 52- or 53-week fiscal year ending on the last Sunday in September. Fiscal years 2014 and 2013 were 52-week years and fiscal year 2012 was a 53-week year, with an additional week falling in the fourth fiscal quarter.
Economic and Industry Factors
Food retailing is a large, intensely competitive industry. According to Nielsen’s TDLinx and Progressive Grocer, the U.S. supermarket industry, which includes conventional supermarkets, supercenters, warehouse grocery stores, military commissaries and limited-assortment and natural/gourmet-positioned supermarkets, had approximately $620.2 billion in sales in 2013, a 3% increase over the prior year. Within this broader category, natural product sales through retail channels totaled approximately $89.4 billion, increasing 11% over the prior year, according to Natural Foods Merchandiser. Our competition includes but is not limited to local, regional, national and international conventional and specialty supermarkets, natural foods stores, warehouse membership clubs, online retailers, smaller specialty stores, farmers’ markets and restaurants, each of which competes with us on the basis of store ambiance and experience, product selection and quality, customer service, price, convenience or a combination of these factors.
We offer the broadest selection of high-quality natural and organic products, with a strong emphasis on perishable foods. We believe our high quality standards differentiate our stores from other supermarkets and enable us to attract and maintain a broad base of loyal customers, averaging over 7.7 million customer visits each week. Our groundbreaking quality standards ensure the products we sell meet a higher standard – one that bans hundreds of ingredients commonly found in other stores as well as numerous manufacturing, farming, fishing and ranching practices that don’t measure up.
Highlights for Fiscal Year 2014
• | We achieved record total sales of $14.2 billion, a 9.9% increase over the prior year. |
• | We opened a record 38 new stores including four acquired stores, translating to 10.0% ending square footage growth. |
• | Comparable store sales increased 4.3% on top of 6.9% in the prior year. |
• | Average weekly sales per store were a record $722,000. |
• | Sales per gross square foot reached a record $990. |
• | EBITDA totaled $1.3 billion, or 9.2% of sales. |
• | Operating income totaled $934 million, or 6.6% of sales. |
• | Diluted earnings per share were $1.56, a 6% increase over the prior year. |
• | Return on invested capital totaled 14.6%. |
20
• | Cash flow from operations totaled $1.1 billion, and free cash flow was $378 million. |
• | We returned $170 million in dividends to shareholders. |
• | We repurchased 13.9 million shares of common stock totaling $578 million. |
Targets for Fiscal Year 2015
The Company is focusing on metrics it believes are key to the long-term health of the Company. The Company’s annual targets for fiscal year 2015 are:
• | Sales growth over 9%; |
• | Comparable store sales growth in the low to middle single digits; |
• | Square footage growth of 9% to 10% based on 38 to 42 new stores, including five to six relocations; |
• | EBITDA margin of approximately 9%; and |
• | ROIC greater than 14%. |
The Company expects to continue its value strategy and to make additional investments in areas such as technology, marketing, and new and existing stores. The Company believes this is the right strategy to drive sales growth over the longer term. Reflecting its ongoing value efforts, the Company expects a greater decline in gross margin, excluding LIFO, in fiscal year 2015 than in fiscal year 2014. The Company expects to maintain expense discipline and improve its cost structure, with the biggest savings coming from internal distribution, coordinated purchasing and labor leverage. Results may fluctuate on a quarterly basis, but for fiscal year 2015, the Company expects annual diluted earnings per share growth in line with or slightly higher than sales growth.
The Company expects store openings to be spread fairly evenly throughout the year, with the seven former Dominick’s locations re-opening as Whole Foods Market stores in the last three quarters of the year. The Company also notes that Easter will fall in the second quarter of fiscal year 2015 versus the third quarter of fiscal year 2014, positively impacting comparable store sales growth in the second quarter and negatively impacting comparable store sales growth in the third quarter by an estimated 50 to 60 basis points.
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth the Company’s consolidated statements of operations data expressed as a percentage of sales:
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||
Sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||
Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs | 64.5 | 64.2 | 64.5 | |||||
Gross profit | 35.5 | 35.8 | 35.5 | |||||
Direct store expenses | 25.3 | 25.4 | 25.5 | |||||
General and administrative expenses | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.2 | |||||
Pre-opening expenses | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.4 | |||||
Relocation, store closure and lease termination costs | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |||||
Operating income | 6.6 | 6.8 | 6.4 | |||||
Investment and other income, net of interest expense | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |||||
Income before income taxes | 6.7 | 6.9 | 6.4 | |||||
Provision for income taxes | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.4 | |||||
Net income | 4.1 | % | 4.3 | % | 4.0 | % | ||
Figures may not sum due to rounding.
Sales
Sales totaled approximately $14.2 billion, $12.9 billion and $11.7 billion in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively, representing increases of 9.9%, 10.4% and 15.7% over the previous fiscal years, respectively. Sales increases for all years are due to comparable store sales increases and stores opened or acquired less than one fiscal year. Sales growth percentages reflect an additional week of sales in fiscal year 2012, a 53-week year. Total sales increased 12.6% in fiscal year 2013 over the previous fiscal year on a comparative 52-week basis. Comparable store sales increased 4.3%, 6.9% and 8.7% during fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively, and contributed approximately 94.3%, 94.5% and 95.3% to total sales in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. As of September 28, 2014, there were 360 locations in the comparable store base as compared to 335 locations and 311 locations as of September 29, 2013 and September 30, 2012, respectively.
21
Gross Profit
Gross profit totaled approximately $5.0 billion, $4.6 billion and $4.2 billion in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Gross profit as a percentage of sales decreased 30 basis points in fiscal year 2014 compared to the prior fiscal year. Net LIFO inventory reserves increased approximately $16 million during fiscal year 2014, due primarily to inflation in product costs, as compared to an increase of approximately $2 million in fiscal year 2013, resulting in a negative impact of 10 basis points year over year. Cost of goods increased 18 basis points as a percentage of sales during fiscal year 2014, reflecting the decision not to pass through all product cost increases to customers as part of our value strategy. Gross profit as a percentage of sales increased 31 basis points and 53 basis points in fiscal years 2013 and 2012, respectively, compared to the prior fiscal years. Increases in prior years were driven primarily by improvement in occupancy costs and costs of goods sold. Additionally, the increase in gross profit as a percentage of sales in fiscal year 2012 reflects a 10 basis point improvement in LIFO due to moderation of inflation during the year.
Our gross profit may increase or decrease slightly depending on the mix of sales from new stores, our value strategy, or the impact of commodity costs or a host of other factors, including possible supply shortages and extreme weather-related disruptions. Relative to existing stores, gross profit margins tend to be lower for new stores and increase as stores mature, reflecting lower shrink as volumes increase, as well as increasing experience levels and operational efficiencies of the store teams.
Direct Store Expenses
Direct store expenses totaled approximately $3.6 billion, $3.3 billion and $3.0 billion in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. During fiscal year 2014, the 16 basis point decrease in direct store expenses as a percentage of sales reflects equal leverage in wages and health care costs, while the 7 basis point decrease in direct store expenses as a percentage of sales during fiscal year 2013 reflects leverage in wages. The 51 basis point decrease in direct store expenses as a percentage of sales in fiscal year 2012 primarily reflects leverage of 25 basis points in wages, 16 basis points in depreciation expense and 8 basis points in health care costs.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses totaled approximately $446 million, $397 million and $372 million in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. During fiscal year 2014, general and administrative expenses as a percentage of sales increased seven basis points, primarily due to higher share-based payment expense and additional investments in technology. The improvement in general and administrative expenses as a percentage of sales during fiscal year 2013 of 11 basis points was due primarily to leverage in wages. Higher wages and share-based payment expense, resulting primarily from our higher stock price, drove the 10 basis point increase in general and administrative expenses as a percentage of sales during fiscal year 2012.
Share-based payment expense was included in the following line items on the Consolidated Statements of Operations for the fiscal years indicated (in millions):
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs | $ | 2 | $ | 2 | $ | 2 | |||||
Direct store expenses | 34 | 32 | 22 | ||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 32 | 23 | 18 | ||||||||
Share-based payment expense before income taxes | 68 | 57 | 42 | ||||||||
Income tax benefit | (26 | ) | (22 | ) | (16 | ) | |||||
Net share-based payment expense | $ | 42 | $ | 35 | $ | 26 | |||||
Pre-opening Expenses
Pre-opening expenses totaled approximately $67 million, $52 million and $47 million in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Average pre-opening expense per new store opened, including pre-opening rent, totaled approximately $2 million in each of fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012.
Relocation, Store Closure and Lease Termination Costs
Relocation, store closure and lease termination costs totaled approximately $11 million, $12 million and $10 million in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
The numbers of stores opened, acquired and relocated were as follows:
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||
New and acquired stores | 37 | 27 | 24 | |||||
Relocated stores | 1 | 5 | 1 | |||||
22
Investment and Other Income, net of Interest Expense
Investment and other income, net of interest expense, which includes interest income, investment gains and losses, gift card breakage and other income, totaled approximately $12 million, $11 million and $8 million in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Income Taxes
Income taxes resulted in an effective tax rate of approximately 38.8%, 38.4% and 38.1% in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The higher effective tax rate in fiscal year 2014 primarily reflects a shift in the mix and level of earnings throughout the jurisdictions in which we operate. The lower effective tax rate for fiscal year 2012 reflects the tax effects of a reduction of reserves for uncertain tax positions in fiscal year 2012.
Non-GAAP measures
In addition to reporting financial results in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP, the Company provides information regarding Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation and Amortization (“EBITDA”) margin, free cash flow and Return on Invested Capital (“ROIC”) as additional information about its operating results. These measures are not in accordance with, or an alternative to, GAAP. We believe that these presentations provide useful information to management, analysts and investors regarding certain additional financial and business trends relating to our results of operations and financial condition. In addition, management uses these measures for reviewing the financial results of the Company as well as a component of incentive compensation.
The following is a tabular reconciliation of the non-GAAP financial measure EBITDA margin to GAAP net income, which the Company believes is the most directly comparable GAAP financial measure. EBITDA margin for the fiscal years indicated was as follows (in millions):
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 579 | $ | 551 | $ | 466 | |||||
Provision for income taxes | 367 | 343 | 286 | ||||||||
Investment and other income, net of interest expense | (12 | ) | (11 | ) | (8 | ) | |||||
Operating income | 934 | 883 | 744 | ||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 377 | 339 | 311 | ||||||||
EBITDA | $ | 1,311 | $ | 1,222 | $ | 1,055 | |||||
Sales | $ | 14,194 | $ | 12,917 | $ | 11,699 | |||||
EBITDA margin | 9.2% | 9.5% | 9.0% | ||||||||
The Company defines free cash flow as net cash provided by operating activities less capital expenditures. The following is a tabular reconciliation of the non-GAAP financial measure free cash flow for the fiscal years indicated (in millions):
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 1,088 | $ | 1,009 | $ | 920 | |||||
Development cost of new locations | (447 | ) | (339 | ) | (262 | ) | |||||
Other property and equipment expenditures | (263 | ) | (198 | ) | (194 | ) | |||||
Free cash flow | $ | 378 | $ | 472 | $ | 464 | |||||
23
The Company defines ROIC as annualized adjusted earnings divided by average invested capital. Earnings are annualized on a 52-week basis. Adjustments to earnings are defined in the following tabular reconciliation. Invested capital reflects an average of the trailing four quarters. ROIC for the fiscal years indicated was as follows (in millions):
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 579 | $ | 551 | $ | 466 | |||||
Total rent expense, net of tax (1) | 241 | 222 | 211 | ||||||||
Estimated depreciation on capitalized operating leases, net of tax (2) | (161 | ) | (148 | ) | (141 | ) | |||||
Adjusted earnings, including interest related to operating leases | 659 | 625 | 536 | ||||||||
Annualized adjusted earnings | $ | 579 | $ | 551 | $ | 457 | |||||
Annualized adjusted earnings, including interest related to operating leases | $ | 659 | $ | 625 | $ | 526 | |||||
Average working capital, excluding current portion of long-term debt | $ | 707 | $ | 886 | $ | 956 | |||||
Average property and equipment, net | 2,731 | 2,308 | 2,090 | ||||||||
Average other assets | 1,103 | 1,066 | 955 | ||||||||
Average other liabilities | (580 | ) | (524 | ) | (460 | ) | |||||
Average invested capital | $ | 3,961 | $ | 3,736 | $ | 3,541 | |||||
Average estimated asset base of capitalized operating leases (3) | 3,169 | 2,891 | 2,740 | ||||||||
Average invested capital, adjusted for capitalization of operating leases | $ | 7,130 | $ | 6,627 | $ | 6,281 | |||||
ROIC | 14.6% | 14.7% | 12.9% | ||||||||
ROIC, adjusted for capitalization of operating leases | 9.2% | 9.4% | 8.4% | ||||||||
(1) Total rent includes minimum base rent of all tendered leases
(2) Estimated depreciation equals two-thirds of total rent expense
(3) Estimated asset base equals eight times total annualized rent expense
Liquidity and Capital Resources and Changes in Financial Condition
The following table summarizes the Company’s cash and short-term investments as of the dates indicated (in millions):
September 28, 2014 | September 29, 2013 | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 190 | $ | 290 | |||
Short-term investments - available-for-sale securities | 553 | 733 | |||||
Total | $ | 743 | $ | 1,023 | |||
Additionally, the Company held long-term investments in available-for-sale securities totaling approximately $120 million and $302 million at September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, respectively.
We generated cash flows from operating activities totaling approximately $1.1 billion, $1.0 billion and $920 million in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Cash flows from operating activities resulted primarily from our net income plus non-cash expenses and changes in operating working capital.
Net cash used in investing activities totaled approximately $484 million, $289 million and $1.3 billion for fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Net sales and maturities of available-for-sale securities totaled approximately $334 million and $282 million in fiscal years 2014 and 2013 compared to net purchases totaling approximately $871 million in fiscal year 2012. Our principal historical capital requirements have been the funding of the development or acquisition of new stores and acquisition of property and equipment for existing stores. Net payments for the purchase of acquired entities totaled approximately $73 million in fiscal year 2014 related to the acquisition of certain land and buildings, which have cash flows from existing tenants, and four retail locations. During fiscal year 2013, net payments for the purchase of acquired entities totaled approximately $22 million primarily related to the acquisition of six retail locations. The required cash investment for new stores varies depending on the size of the new store, geographic location, degree of work performed by the landlord and complexity of site development issues. Capital expenditures for fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 totaled approximately $710 million, $537 million and $456 million, respectively, of which approximately $447 million, $339 million and $262 million, respectively, was for new store
24
development and approximately $263 million, $198 million and $194 million, respectively, was for remodels and other property and equipment expenditures.
The following table provides information about the Company’s store growth and development activities:
Stores opened during fiscal year 2013 | Stores opened during fiscal year 2014 | Stores opened during fiscal year 2015 as of Nov. 5, 2014 | Total leases signed as of Nov. 5, 2014 | |||||
Number of stores (including relocations) | 32 | 38 | 3 | 114 | ||||
Number of relocations | 5 | 1 | 1 | 14 | ||||
Percentage in new markets | 31% | 55% | 0% | 17% | ||||
Average store size (gross square feet) | 36,000 | 37,000 | 46,000 | 41,000 | ||||
Total square footage | 1,138,000 | 1,408,000 | 139,000 | 4,723,000 | ||||
Average pre-opening expense per store | $2 million | $2 million | ||||||
Average pre-opening rent per store | $1 million | $1 million | ||||||
We believe we will produce operating cash flows in excess of the capital expenditures needed to open the 114 stores in our current store development pipeline. As of November 5, 2014, the Company operated 401 stores totaling approximately 15.2 million square feet and expects to cross the 500-store mark in fiscal year 2017. Longer term, the Company sees demand for 1,200 Whole Foods Market stores in the United States. We have a disciplined, opportunistic real estate strategy, opening stores in existing trade areas as well as new areas, including international locations. Our growth strategy is to expand primarily through new store openings, and while we may continue to pursue acquisitions of smaller chains that provide access to desirable geographic areas and experienced team members, such acquisitions are not expected to significantly impact our future store growth or financial results.
Net cash used in financing activities totaled approximately $698 million and $517 million in fiscal years 2014 and 2013, respectively. Net cash provided by financing activities totaled approximately $297 million in fiscal year 2012.
Share repurchase activity for fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 was as follows (in millions, except per share amounts):
Number of common shares acquired (1) | Average price per common share acquired | Total cost of common shares acquired | ||||||||
Fiscal year 2014: | ||||||||||
First Quarter | 1.1 | $ | 56.06 | $ | 62 | |||||
Second Quarter | 1.0 | 52.86 | 55 | |||||||
Third Quarter | 9.1 | 39.45 | 361 | |||||||
Fourth Quarter | 2.6 | 38.06 | 100 | |||||||
Total fiscal year 2014 | 13.9 | $ | 41.51 | $ | 578 | |||||
Fiscal year 2013: | ||||||||||
First Quarter | 0.5 | $ | 46.04 | $ | 26 | |||||
Second Quarter | 0.9 | 43.46 | 37 | |||||||
Third Quarter | 0.5 | 51.83 | 25 | |||||||
Fourth Quarter | 0.7 | 55.36 | 37 | |||||||
Total fiscal year 2013 | 2.6 | $ | 48.70 | $ | 125 | |||||
Fiscal year 2012: | ||||||||||
First Quarter | 0.1 | $ | 31.85 | $ | 4 | |||||
Second Quarter | — | — | — | |||||||
Third Quarter | 0.6 | 43.20 | 24 | |||||||
Fourth Quarter | — | — | — | |||||||
Total fiscal year 2012 | 0.7 | $ | 41.34 | $ | 28 | |||||
(1) Number of shares may not sum due to rounding
Share repurchase activity during fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 was pursuant to various share repurchase programs authorized by the Company’s Board of Directors. As of September 28, 2014, one share repurchase program remains in effect, with prior programs having expired or been cancelled.
25
The following table outlines the share repurchase program authorized by the Company’s Board of Directors, and the related repurchase activity as of September 28, 2014 (in millions):
Effective date | Expiration date | Amount authorized | Cost of repurchases | Authorization available | |||||||||
August 1, 2014 | August 1, 2016 | $ | 1,000 | $ | 100 | $ | 900 | ||||||
Under the share repurchase program, purchases can be made from time to time using a variety of methods, which may include open market purchases. The specific timing, price and size of purchases will depend on prevailing stock prices, general economic and market conditions, and other considerations. Purchases may be made through a Rule 10b5-1 plan pursuant to pre-determined metrics set forth in such plan. The Board’s authorization of the share repurchase program does not obligate the Company to acquire any particular amount of common stock, and the program may be suspended or discontinued at any time at the Company’s discretion.
Subsequent to fiscal year end, the Company repurchased approximately 0.9 million shares of the Company’s common stock at an average price per share of $47.39 for a total of approximately $43 million bringing the total current available authorization to approximately $857 million.
During the first quarter of fiscal year 2014, the Company’s Board of Directors declared a 20% increase in the quarterly dividend to $0.12 per common share. The following table provides a summary of dividends declared per common share during fiscal years 2014 and 2013 (in millions, except per share amounts):
Date of declaration | Dividend per common share | Date of record | Date of payment | Total amount | |||||||
Fiscal year 2014: | |||||||||||
November 1, 2013 | $ | 0.12 | January 17, 2014 | January 28, 2014 | $ | 45 | |||||
February 24, 2014 | 0.12 | April 11, 2014 | April 22, 2014 | 44 | |||||||
June 12, 2014 | 0.12 | July 3, 2014 | July 15, 2014 | 44 | |||||||
September 11, 2014 (1) | 0.12 | September 26, 2014 | October 7, 2014 | 43 | |||||||
Fiscal year 2013: | |||||||||||
November 29, 2012 | $ | 1.00 | December 10, 2012 | December 21, 2012 | $ | 371 | |||||
November 7, 2012 | 0.10 | January 18, 2013 | January 29, 2013 | 37 | |||||||
March 15, 2013 | 0.10 | April 12, 2013 | April 23, 2013 | 37 | |||||||
June 12, 2013 | 0.10 | July 5, 2013 | July 16, 2013 | 37 | |||||||
September 10, 2013 | 0.10 | September 27, 2013 | October 8, 2013 | 37 | |||||||
(1) Dividend accrued at September 28, 2014
On November 4, 2014, the Company’s Board of Directors authorized an increase in the Company’s quarterly dividend to $0.13 per common share from $0.12 per common share. The Company will pay future dividends at the discretion of the Company’s Board of Directors. The continuation of these payments, the amount of such dividends, and the form in which dividends are paid (cash or stock) depend on many factors, including the results of operations and the financial condition of the Company. Subject to these qualifications, the Company currently expects to pay dividends on a quarterly basis.
Net proceeds to the Company from the exercise of stock options by team members are driven by a number of factors, including fluctuations in our stock price, and totaled approximately $42 million, $81 million and $370 million in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The Company intends to keep its broad-based stock option program in place, but also intends to limit the number of shares granted in any one year so that annual earnings dilution from share-based payment expense will not exceed 10%. The Company believes this strategy is best aligned with its stakeholder philosophy because it limits future earnings dilution from options and at the same time retains the broad-based stock option plan, which the Company believes is important to team member morale, its unique corporate culture and its success. At September 28, 2014, September 29, 2013 and September 30, 2012 approximately 37.6 million shares, 42.3 million shares and 16.8 million shares of our common stock, respectively, were available for future stock incentive grants.
26
The Company is committed under certain capital leases for rental of certain buildings, land and equipment, and certain operating leases for rental of facilities and equipment. These leases expire or become subject to renewal clauses at various dates through 2054. The following table shows payments due by period on contractual obligations as of September 28, 2014 (in millions):
Total | Less than 1 year | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | More than 5 years | |||||||||||||||
Capital lease obligations (including interest) | $ | 97 | $ | 5 | $ | 10 | $ | 10 | $ | 72 | |||||||||
Operating lease obligations (1) | 8,272 | 401 | 939 | 984 | 5,948 | ||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 8,369 | $ | 406 | $ | 949 | $ | 994 | $ | 6,020 | |||||||||
(1) Amounts exclude taxes, insurance and other related expense
Gross unrecognized tax benefits and related interest and penalties at September 28, 2014 were not material. Although a reasonably reliable estimate of the period of cash settlement with respective taxing authorities cannot be determined due to the high degree of uncertainty regarding the timing of future cash outflows associated with the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits, as of September 28, 2014, the Company does not expect tax audit resolution will reduce its unrecognized tax benefits in the next 12 months.
We periodically make other commitments and become subject to other contractual obligations that we believe to be routine in nature and incidental to the operation of the business. Management believes that such routine commitments and contractual obligations do not have a material impact on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Our principal historical sources of liquidity have included cash generated by operations, available cash and cash equivalents, and short-term investments. Absent any significant change in market conditions, we expect planned expansion and other anticipated working capital and capital expenditure requirements for the next 12 months will be funded by these sources. There can be no assurance, however, that the Company will continue to generate cash flows at or above current levels or that other sources of capital will be available to us in the future.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
Our off-balance sheet arrangements at September 28, 2014 consisted of operating leases disclosed in the above contractual obligations table. Additionally, we enter into forward purchase agreements for certain products in the ordinary course of business. Purchase commitments do not exceed anticipated use within an operating cycle. We have no other off-balance sheet arrangements that have had, or are reasonably likely to have, a material current or future effect on our consolidated financial statements or financial condition.
Critical Accounting Policies
The preparation of our financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses and related disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities. Actual amounts may differ from these estimates. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions and factors that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate the continued appropriateness of our accounting policies and resulting estimates to make adjustments we consider appropriate under the facts and circumstances.
We have chosen accounting policies that we believe are appropriate to report accurately and fairly our operating results and financial position, and we apply those accounting policies in a consistent manner. Our significant accounting policies are summarized in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements in “Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this report. We believe that the following accounting policies are the most critical in the preparation of our financial statements because they involve the most difficult, subjective or complex judgments about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain.
Inventories
The Company values inventories at the lower of cost or market. Cost was determined using the dollar value retail last-in, first-out (“LIFO”) method for approximately 93.5% and 92.8% of inventories in fiscal years 2014 and 2013, respectively. Under the LIFO method, the cost assigned to items sold is based on the cost of the most recent items purchased. As a result, the costs of the first items purchased remain in inventory and are used to value ending inventory. The excess of estimated current costs over LIFO carrying value, or LIFO reserve, was approximately $48 million and $32 million at September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, respectively. Costs for remaining inventories are determined by the first-in, first-out method. Cost before the LIFO adjustment is principally determined using the item cost method, which is calculated by counting each item in inventory, assigning costs to each of these items based on the actual purchase cost (net of vendor allowances) of each item and recording the actual cost of items sold.
27
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Goodwill consists of the excess of cost of acquired enterprises over the sum of the amounts assigned to identifiable assets acquired less liabilities assumed. Goodwill is reviewed for impairment annually at the Company’s fiscal year end, or more frequently if impairment indicators arise, on a reporting unit level. We allocate goodwill to one reporting unit for goodwill impairment testing. A qualitative assessment, based on macroeconomic factors, industry and market conditions and company-specific performance, is performed to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is impaired. If it is more likely than not, we compare our fair value, which is determined utilizing both a market value method and discounted projected future cash flows, to our carrying value for the purpose of identifying impairment. Our annual impairment review requires extensive use of accounting judgment and financial estimates. Application of alternative assumptions and definitions, such as reviewing goodwill for impairment at a different organizational level, could produce significantly different results. Because of the significance of the judgments and estimation processes, it is possible that materially different amounts could be recorded if we used different assumptions or if the underlying circumstances were to change.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets and Long-Lived Assets to be Disposed of
The Company evaluates long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances, such as unplanned negative cash flow, short lease life, or a plan to close is established, indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to future undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are determined to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the fair value of the assets. The fair value, based on hierarchy input Level 3, is determined using management’s best estimate based on a discounted cash flow model based on future store operating results using internal projections or based on a review of the future benefit the Company anticipates receiving from the related assets. Additionally for closing locations, the Company estimates net future cash flows based on its experience and knowledge of the area in which the closed property is located and, when necessary, utilizes local real estate brokers. Assets to be disposed of are reported at the lower of the carrying amount or fair value less costs to sell. Application of alternative assumptions, such as changes in estimates of future cash flows, could produce significantly different results. Because of the significance of the judgments and estimation processes, it is likely that materially different amounts could be recorded if we used different assumptions or if the underlying circumstances were to change.
Insurance and Self-Insurance Liabilities
The Company uses a combination of insurance and self-insurance plans to provide for the potential liabilities for workers’ compensation, general liability, property insurance, director and officers’ liability insurance, vehicle liability, and employee health care benefits. Liabilities associated with the risks that are retained by the Company are estimated, in part, by considering historical claims experience, demographic factors, severity factors and other actuarial assumptions. While we believe that our assumptions are appropriate, the estimated accruals for these liabilities could be significantly affected if future occurrences and claims differ from these assumptions and historical trends.
We have not made any changes in the accounting methodology used to establish our insurance and self-insured liabilities during the past three fiscal years.
Because of the significance of the judgments and estimation processes, it is likely that materially different amounts could be recorded if we used different assumptions or if the underlying circumstances were to change. A 10% change in our insurance and self-insured liabilities at September 28, 2014 would have affected net income by approximately $9 million for fiscal year 2014.
Leases
The Company generally leases stores, non-retail facilities and administrative offices under operating leases. Store lease agreements generally include rent holidays, rent escalation clauses and contingent rent provisions for percentage of sales in excess of specified levels. We recognize rent on a straight-line basis over the expected term of the lease, which includes rent holiday periods and scheduled rent increases. The expected lease term begins with the date the Company has the right to possess the leased space for construction and other purposes. The expected lease term may also include the exercise of renewal options if the exercise of the option is determined to be reasonably assured. The expected lease term is also used in the determination of whether a store is a capital or operating lease. Amortization of land and building under capital lease is included with occupancy costs, while the amortization of equipment under capital lease is included with depreciation expense. Additionally, we review leases for which we are involved in construction to determine whether build-to-suit and sale-leaseback criteria are met. For those leases that trigger specific build-to-suit accounting, developer assets are recorded during the construction period with an offsetting liability. Sale-leaseback transactions are recorded as financing lease obligations. We record tenant improvement allowances and rent holidays as deferred rent liabilities, and amortize the deferred rent over the expected lease term to rent. We record rent
28
liabilities for contingent percentage of sales lease provisions when we determine that it is probable that the specified levels as defined by the lease will be reached.
Reserves for Closed Properties
The Company maintains reserves for retail stores and other properties that are no longer being utilized in current operations. The Company provides for closed property operating lease liabilities using a discount rate to calculate the present value of the remaining noncancelable lease payments and lease termination fees after the closing date, net of estimated subtenant income. The closed property lease liabilities are expected to be paid over the remaining lease terms, which generally range from nine months to 14 years. The reserves for closed properties include management’s estimates for lease subsidies, lease terminations and future payments on exited real estate. The Company estimates subtenant income and future cash flows based on the Company’s experience and knowledge of the area in which the closed property is located, the Company’s previous efforts to dispose of similar assets, existing economic conditions and when necessary utilizes local real estate brokers.
Adjustments to closed property reserves primarily relate to changes in estimated subtenant income or actual exit costs differing from original estimates. Adjustments are made for changes in estimates in the period in which the changes become known.
Because of the significance of the judgments and estimation processes, it is likely that materially different amounts could be recorded if we used different assumptions or if the underlying circumstances were to change. A 10% change in our closed property reserves at September 28, 2014 would not have materially affected net income for fiscal year 2014.
Share-Based Payments
The Company maintains several share-based incentive plans. We grant both options to purchase common stock and restricted common stock under our Whole Foods Market 2009 Stock Incentive Plan. Options outstanding are governed by the original terms and conditions of the grants, unless modified by a subsequent agreement. Options are granted at an option price equal to the market value of the stock at the grant date and generally vest ratably over a four- or nine-year period beginning one year from grant date and have a five, seven or ten year term. The grant date is established once the Company’s Board of Directors approves the grant and all key terms have been determined. Stock option grant terms and conditions are communicated to team members within a relatively short period of time. Our Company generally approves one primary stock option grant annually, occurring during a trading window. Restricted common stock is granted at the market price of the stock on the day of grant and generally vests over a three-, four- or six-year period.
The Company uses the Black-Scholes multiple option pricing model which requires extensive use of accounting judgment and financial estimates, including estimates of the expected term team members will retain their vested stock options before exercising them, the estimated volatility of the Company’s common stock price over the expected term, and the number of options that will be forfeited prior to the completion of their vesting requirements. The related share-based payment expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period. The tax savings resulting from tax deductions in excess of expense reflected in the Company’s financial statements are reflected as a financing cash flow.
The Company intends to keep its broad-based stock option program in place, but also intends to limit the number of shares granted in any one year so that annual earnings per share dilution from share-based payment expense will not exceed 10%.
We do not believe there is a reasonable likelihood that there will be a material change in the future estimates or assumptions we use to determine share-based payment expense. However, if actual results are not consistent with our estimates or assumptions, we may be exposed to changes in share-based payment expense that could be material.
Because of the significance of the judgments and estimation processes, it is likely that materially different amounts could be recorded if we used different assumptions or if the underlying circumstances were to change. A 10% change in our share-based payment expense would not have materially affected net income for fiscal year 2014.
Income Taxes
We recognize deferred income tax assets and liabilities by applying statutory tax rates in effect at the balance sheet date to differences between the book basis and the tax basis of assets and liabilities. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to reverse. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are adjusted to reflect changes in tax laws or rates in the period that includes the enactment date. Significant accounting judgment is required in determining the provision for income taxes and related accruals, deferred tax assets and liabilities. In the ordinary course of business, there are transactions and calculations where the ultimate tax outcome is uncertain. In addition, we are subject to periodic audits and examinations by the Internal Revenue Service and
29
other state and local taxing authorities. Although we believe that our estimates are reasonable, actual results could differ from these estimates.
The Company recognizes the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position only if it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position. The tax benefits recognized in the financial statements from such a position should be measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement.
To the extent we prevail in matters for which reserves have been established, or are required to pay amounts in excess of our reserves, our effective income tax rate in a given financial statement period could be materially affected. An unfavorable tax settlement would require use of our cash and would result in an increase in our effective income tax rate in the period of resolution. A favorable tax settlement would be recognized as a reduction in our effective income tax rate in the period of resolution.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
We are primarily exposed to interest rate changes on our investments. We do not use financial instruments for trading or other speculative purposes. We are also exposed to foreign exchange fluctuations on our foreign subsidiaries.
The analysis presented for each of our market risk sensitive instruments is based on a 10% change in interest or currency exchange rates. These changes are hypothetical scenarios used to calibrate potential risk and do not represent our view of future market changes. As the hypothetical figures discussed below indicate, changes in fair value based on the assumed change in rates generally cannot be extrapolated because the relationship of the change in assumption to the change in fair value may not be linear. The effect of a variation in a particular assumption is calculated without changing any other assumption. In reality, changes in one factor may result in changes in another, which may magnify or counteract the sensitivities.
Interest Rate Risk
We seek to minimize the risks from interest rate fluctuations through ongoing evaluation of the composition of our investments.
The Company holds short-term investments that are classified as cash equivalents. We had cash equivalent investments totaling approximately $65 million and $194 million at September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, respectively. The Company also holds available-for-sale securities generally consisting of state and local municipal obligations and corporate bonds and commercial paper which hold high credit ratings. We had short-term investments totaling approximately $553 million and long-term investments totaling approximately $120 million at September 28, 2014. Short-term investments totaled approximately $733 million and long-term investments totaled approximately $302 million at September 29, 2013.
These investments are recorded at fair value and are generally short term in nature, and therefore changes in interest rates would not have a material impact on the valuation of these investments. During fiscal years 2014 and 2013, a hypothetical 10% increase or decrease in interest rates would not have materially affected interest income earned on these investments.
Foreign Currency Risk
The Company is exposed to foreign currency exchange risk. We own and operate nine stores in Canada and nine stores in the U.K. Sales made from stores in Canada and the U.K. are made in exchange for Canadian dollars and Great Britain pounds sterling, respectively. The Company does not currently hedge against the risk of exchange rate fluctuations.
At September 28, 2014, a hypothetical 10% change in value of the U.S. dollar relative to the Canadian dollar or Great Britain pound sterling would not have materially affected our consolidated financial statements.
30
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
Whole Foods Market, Inc.
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements
Page | |
31
Whole Foods Market, Inc.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders of Whole Foods Market, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Whole Foods Market, Inc. as of September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, shareholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended September 28, 2014. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of Whole Foods Market, Inc. at September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended September 28, 2014, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), Whole Foods Market, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of September 28, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (1992 framework) and our report dated November 21, 2014 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Austin, TX
November 21, 2014
32
Whole Foods Market, Inc.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
The Board of Directors and Shareholders of Whole Foods Market, Inc.
We have audited Whole Foods Market, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of September 28, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (1992 framework) (the COSO criteria). Whole Foods Market, Inc.’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Controls over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, Whole Foods Market, Inc. maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of September 28, 2014, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of Whole Foods Market, Inc. as of September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, shareholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended September 28, 2014 of Whole Foods Market, Inc. and our report dated November 21, 2014 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Austin, TX
November 21, 2014
33
Whole Foods Market, Inc.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(In millions)
Assets | September 28, 2014 | September 29, 2013 | |||||
Current assets: | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 190 | $ | 290 | |||
Short-term investments - available-for-sale securities | 553 | 733 | |||||
Restricted cash | 109 | 111 | |||||
Accounts receivable | 198 | 188 | |||||
Merchandise inventories | 441 | 414 | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 97 | 93 | |||||
Deferred income taxes | 168 | 151 | |||||
Total current assets | 1,756 | 1,980 | |||||
Property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation and amortization | 2,923 | 2,428 | |||||
Long-term investments - available-for-sale securities | 120 | 302 | |||||
Goodwill | 708 | 679 | |||||
Intangible assets, net of accumulated amortization | 81 | 65 | |||||
Deferred income taxes | 132 | 72 | |||||
Other assets | 24 | 12 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 5,744 | $ | 5,538 | |||
Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity | |||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||
Current installments of capital lease obligations | $ | 2 | $ | 1 | |||
Accounts payable | 276 | 247 | |||||
Accrued payroll, bonus and other benefits due team members | 379 | 367 | |||||
Dividends payable | 43 | 37 | |||||
Other current liabilities | 557 | 436 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 1,257 | 1,088 | |||||
Long-term capital lease obligations, less current installments | 60 | 26 | |||||
Deferred lease liabilities | 548 | 500 | |||||
Other long-term liabilities | 66 | 46 | |||||
Total liabilities | 1,931 | 1,660 | |||||
Commitments and contingencies | |||||||
Shareholders’ equity: | |||||||
Common stock, no par value, 600.0 shares authorized; 377.1 and 375.7 shares issued; 360.4 and 372.4 shares outstanding at 2014 and 2013, respectively | 2,863 | 2,765 | |||||
Common stock in treasury, at cost, 16.7 and 3.3 shares at 2014 and 2013, respectively | (711 | ) | (153 | ) | |||
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | (7 | ) | 1 | ||||
Retained earnings | 1,668 | 1,265 | |||||
Total shareholders’ equity | 3,813 | 3,878 | |||||
Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | 5,744 | $ | 5,538 | |||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
34
Whole Foods Market, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Operations
Fiscal years ended September 28, 2014, September 29, 2013 and September 30, 2012
(In millions, except per share amounts)
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Sales | $ | 14,194 | $ | 12,917 | $ | 11,699 | |||||
Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs | 9,150 | 8,288 | 7,543 | ||||||||
Gross profit | 5,044 | 4,629 | 4,156 | ||||||||
Direct store expenses | 3,586 | 3,285 | 2,983 | ||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 446 | 397 | 372 | ||||||||
Pre-opening expenses | 67 | 52 | 47 | ||||||||
Relocation, store closure and lease termination costs | 11 | 12 | 10 | ||||||||
Operating income | 934 | 883 | 744 | ||||||||
Investment and other income, net of interest expense | 12 | 11 | 8 | ||||||||
Income before income taxes | 946 | 894 | 752 | ||||||||
Provision for income taxes | 367 | 343 | 286 | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 579 | $ | 551 | $ | 466 | |||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 1.57 | $ | 1.48 | $ | 1.28 | |||||
Weighted average shares outstanding | 367.8 | 371.2 | 364.8 | ||||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 1.56 | $ | 1.47 | $ | 1.26 | |||||
Weighted average shares outstanding, diluted basis | 370.5 | 374.5 | 368.9 | ||||||||
Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.48 | $ | 1.40 | $ | 0.28 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
35
Whole Foods Market, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income
Fiscal years ended September 28, 2014, September 29, 2013 and September 30, 2012
(In millions)
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 579 | $ | 551 | $ | 466 | |||||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | |||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments | (8 | ) | (4 | ) | 5 | ||||||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | (8 | ) | (4 | ) | 5 | ||||||
Comprehensive income | $ | 571 | $ | 547 | $ | 471 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
36
Whole Foods Market, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity
Fiscal years ended September 28, 2014, September 29, 2013 and September 30, 2012
(In millions)
Shares outstanding | Common stock | Common stock in treasury | Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | Retained earnings | Total shareholders’ equity | ||||||||||||
Balances at September 25, 2011 | 357.8 | $ | 2,121 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 870 | $ | 2,991 | ||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | 466 | 466 | |||||||||||
Other comprehensive income, net of tax | — | — | — | 5 | — | 5 | |||||||||||
Dividends ($0.28 per common share) | — | — | — | — | (103 | ) | (103 | ) | |||||||||
Issuance of common stock pursuant to team member stock plans | 13.8 | 366 | — | — | — | 366 | |||||||||||
Purchase of treasury stock | (0.7 | ) | — | (28 | ) | — | — | (28 | ) | ||||||||
Tax benefit related to exercise of team member stock options | — | 63 | — | — | — | 63 | |||||||||||
Share-based payment expense | — | 42 | — | — | — | 42 | |||||||||||
Balances at September 30, 2012 | 370.9 | 2,592 | (28 | ) | 5 | 1,233 | 3,802 | ||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | 551 | 551 | |||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | — | (4 | ) | — | (4 | ) | |||||||||
Dividends ($1.40 per common share) | — | — | — | — | (519 | ) | (519 | ) | |||||||||
Issuance of common stock pursuant to team member stock plans | 4.1 | 81 | — | — | — | 81 | |||||||||||
Purchase of treasury stock | (2.6 | ) | — | (125 | ) | — | — | (125 | ) | ||||||||
Tax benefit related to exercise of team member stock options | — | 36 | — | — | — | 36 | |||||||||||
Share-based payment expense | — | 56 | — | — | — | 56 | |||||||||||
Balances at September 29, 2013 | 372.4 | 2,765 | (153 | ) | 1 | 1,265 | 3,878 | ||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | 579 | 579 | |||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | — | (8 | ) | — | (8 | ) | |||||||||
Dividends ($0.48 per common share) | — | — | — | — | (176 | ) | (176 | ) | |||||||||
Issuance of common stock pursuant to team member stock plans | 1.9 | 21 | 20 | — | — | 41 | |||||||||||
Purchase of treasury stock | (13.9 | ) | — | (578 | ) | — | — | (578 | ) | ||||||||
Tax benefit related to exercise of team member stock options | — | 9 | — | — | — | 9 | |||||||||||
Share-based payment expense | — | 68 | — | — | — | 68 | |||||||||||
Balances at September 28, 2014 | 360.4 | $ | 2,863 | $ | (711 | ) | $ | (7 | ) | $ | 1,668 | $ | 3,813 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
37
Whole Foods Market, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Fiscal years ended September 28, 2014, September 29, 2013 and September 30, 2012
(In millions)
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities | |||||||||||
Net income | $ | 579 | $ | 551 | $ | 466 | |||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 377 | 339 | 311 | ||||||||
Share-based payment expense | 68 | 57 | 42 | ||||||||
LIFO expense | 16 | 2 | — | ||||||||
Deferred income tax benefit | (78 | ) | (51 | ) | (8 | ) | |||||
Excess tax benefit related to exercise of team member stock options | (9 | ) | (37 | ) | (50 | ) | |||||
Accretion of premium/discount on marketable securities | 27 | 31 | 16 | ||||||||
Deferred lease liabilities | 36 | 51 | 77 | ||||||||
Other | 12 | 9 | 1 | ||||||||
Net change in current assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||
Accounts receivable | (14 | ) | 9 | (30 | ) | ||||||
Merchandise inventories | (41 | ) | (42 | ) | (37 | ) | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | (4 | ) | (17 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||
Accounts payable | 30 | — | 10 | ||||||||
Accrued payroll, bonus and other benefits due team members | 12 | 60 | 25 | ||||||||
Other current liabilities | 54 | 51 | 95 | ||||||||
Net change in other long-term liabilities | 23 | (4 | ) | 4 | |||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 1,088 | 1,009 | 920 | ||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities | |||||||||||
Development costs of new locations | (447 | ) | (339 | ) | (262 | ) | |||||
Other property and equipment expenditures | (263 | ) | (198 | ) | (194 | ) | |||||
Purchase of intangible assets | (20 | ) | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||
Purchases of available-for-sale securities | (720 | ) | (1,252 | ) | (3,009 | ) | |||||
Sales and maturities of available-for-sale securities | 1,054 | 1,534 | 2,138 | ||||||||
Decrease (increase) in restricted cash | 2 | (8 | ) | (11 | ) | ||||||
Payment for purchase of acquired entities, net of cash acquired | (73 | ) | (22 | ) | — | ||||||
Other investing activities | (17 | ) | (3 | ) | (1 | ) | |||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (484 | ) | (289 | ) | (1,341 | ) | |||||
Cash flows from financing activities | |||||||||||
Common stock dividends paid | (170 | ) | (508 | ) | (95 | ) | |||||
Issuance of common stock | 42 | 81 | 370 | ||||||||
Purchase of treasury stock | (578 | ) | (125 | ) | (28 | ) | |||||
Excess tax benefit related to exercise of team member stock options | 9 | 37 | 50 | ||||||||
Payments on capital lease obligations | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | — | ||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | (698 | ) | (517 | ) | 297 | ||||||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | (6 | ) | (2 | ) | 1 | ||||||
Net change in cash and cash equivalents | (100 | ) | 201 | (123 | ) | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 290 | 89 | 212 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 190 | $ | 290 | $ | 89 | |||||
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | |||||||||||
Federal and state income taxes paid | $ | 429 | $ | 378 | $ | 202 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
38
Whole Foods Market, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Fiscal years ended September 28, 2014, September 29, 2013 and September 30, 2012
(1) Description of Business
Whole Foods Market is the leading retailer of natural and organic foods. The Company’s mission is to promote the vitality and well-being of all individuals by supplying the highest quality, most wholesome foods available. Through our growth, we have had a significant and positive impact on the natural and organic foods movement throughout the United States, helping lead the industry to nationwide acceptance over the last 36 years. As of September 28, 2014, we operated 399 stores: 381 stores in 42 United States (“U.S.”) states and the District of Columbia; 9 stores in Canada; and 9 stores in the United Kingdom (“U.K.”). The Company has one operating segment and a single reportable segment, natural and organic foods supermarkets.
The following is a summary of annual percentage sales and net long-lived assets by geographic area for the fiscal years indicated:
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||
Sales: | ||||||||
United States | 96.7 | % | 96.7 | % | 96.8 | % | ||
Canada and United Kingdom | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.2 | |||||
Total sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||
Long-lived assets, net: | ||||||||
United States | 96.0 | % | 95.7 | % | 95.2 | % | ||
Canada and United Kingdom | 4.0 | 4.3 | 4.8 | |||||
Total long-lived assets, net | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||
The following is a summary of annual percentage sales by product category for the fiscal years indicated:
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||
Perishables: | ||||||||
Prepared foods and bakery | 19.2 | % | 19.0 | % | 18.9 | % | ||
Other perishables | 47.6 | 47.2 | 47.0 | |||||
Total perishables | 66.8 | 66.2 | 65.9 | |||||
Non-perishables | 33.2 | 33.8 | 34.1 | |||||
Total sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||
(2) Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Definition of Fiscal Year
The Company reports its results of operations on a 52- or 53-week fiscal year ending on the last Sunday in September. Fiscal years 2014 and 2013 were 52-week years and fiscal year 2012 was a 53-week year.
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. All significant majority-owned subsidiaries are consolidated on a line-by-line basis, and all significant intercompany accounts and transactions are eliminated upon consolidation.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We consider all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of 90 days or less to be cash equivalents.
Investments
Available-for-sale investments are recorded at fair value. Unrealized holding gains and losses, net of the related tax effect, on available-for-sale investments are excluded from earnings and are reported as a separate component of shareholders’ equity until realized. A decline in the fair value of any available-for-sale security below cost that is deemed to be other than temporary results in a reduction of the carrying amount to fair value. The impairment is charged to earnings and a new cost basis of the security is established. The Company considers several factors when determining whether an impairment is other than temporary, including the extent and duration of the decline in fair value and whether it is more likely than not that we will be required to sell the security before recovery of its basis. Cost basis is established and maintained utilizing the specific identification method.
The Company also holds certain equity interests accounted for using the cost method of accounting. Equity investments without readily determinable fair values for which we do not have the ability to exercise significant influence are accounted for using
39
the cost method of accounting and classified as “Other assets” on the Consolidated Balance Sheet. Under the cost method, investments are carried at cost and are adjusted only for other-than-temporary declines in fair value, certain distributions, and additional investments. Additionally, the Company holds certain equity interests accounted for using the equity method of accounting. The Company’s share of income and losses from equity method investments is included in “Investment and other income” on the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Restricted Cash
Restricted cash primarily relates to cash held as collateral to support a portion of our projected workers’ compensation obligations. Additionally, the Company holds restricted cash as a rent guarantee on certain operating leases through March 2015.
Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable are shown net of related allowances and consist primarily of credit card receivables, vendor receivables, customer purchases, and occupancy-related receivables. Vendor receivable balances are generally presented on a gross basis separate from any related payable due. Allowance for doubtful accounts is calculated based on historical experience, customer credit risk and application of the specific identification method and was not material in fiscal year 2014 or 2013.
Inventories
The Company values inventories at the lower of cost or market. Cost was determined using the dollar value retail last-in, first-out (“LIFO”) method for approximately 93.5% and 92.8% of inventories in fiscal years 2014 and 2013, respectively. Under the LIFO method, the cost assigned to items sold is based on the cost of the most recent items purchased. As a result, the costs of the first items purchased remain in inventory and are used to value ending inventory. The excess of estimated current costs over LIFO carrying value, or LIFO reserve, was approximately $48 million and $32 million at September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, respectively. Costs for remaining inventories are determined by the first-in, first-out method. Cost before the LIFO adjustment is principally determined using the item cost method, which is calculated by counting each item in inventory, assigning costs to each of these items based on the actual purchase cost (net of vendor allowances) of each item and recording the actual cost of items sold.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation and amortization. The Company provides depreciation of equipment over the estimated useful lives (generally 3 to 15 years) using the straight-line method, and provides amortization of leasehold improvements and real estate assets under capital leases on a straight-line basis over the shorter of the estimated useful lives of the improvements or the expected terms of the related leases. The Company provides depreciation of buildings over the estimated useful lives (generally 20 to 50 years) using the straight-line method. Costs related to a projected site determined to be unsatisfactory and general site selection costs that cannot be identified with a specific store location are charged to operations currently. The Company recognizes a liability for the fair value of a conditional asset retirement obligation when the obligation is incurred. Repair and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred. Upon retirement or disposal of assets, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the balance sheet and any gain or loss is reflected in earnings.
Leases
The Company generally leases stores, non-retail facilities and administrative offices under operating leases. Store lease agreements generally include rent holidays, rent escalation clauses and contingent rent provisions for percentage of sales in excess of specified levels. We recognize rent on a straight-line basis over the expected term of the lease, which includes rent holiday periods and scheduled rent increases. The expected lease term begins with the date the Company has the right to possess the leased space for construction and other purposes. The expected lease term may also include the exercise of renewal options if the exercise of the option is determined to be reasonably assured. The expected lease term is also used in the determination of whether a store is a capital or operating lease. Amortization of land and building under capital lease is included with occupancy costs, while the amortization of equipment under capital lease is included with depreciation expense. Additionally, we review leases for which we are involved in construction to determine whether build-to-suit and sale-leaseback criteria are met. For those leases that trigger specific build-to-suit accounting, developer assets are recorded during the construction period with an offsetting liability. As of September 28, 2014, the Company had developer assets totaling approximately $67 million, with the offsetting liability included in the “Other current liabilities” line item on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Sale-leaseback transactions are recorded as financing lease obligations. We record tenant improvement allowances and rent holidays as deferred rent liabilities, and amortize the deferred rent over the expected lease term to rent. We record rent liabilities for contingent percentage of sales lease provisions when we determine that it is probable that the specified levels as defined by the lease will be reached.
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Goodwill consists of the excess of cost of acquired enterprises over the sum of the amounts assigned to identifiable assets acquired less liabilities assumed. Goodwill is reviewed for impairment annually at the Company’s fiscal year end, or more
40
frequently if impairment indicators arise, on a reporting unit level. We allocate goodwill to one reporting unit for goodwill impairment testing. A qualitative assessment, based on macroeconomic factors, industry and market conditions and company-specific performance, is performed to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is impaired. If it is more likely than not, we compare our fair value, which is determined utilizing both a market value method and discounted projected future cash flows, to our carrying value for the purpose of identifying impairment.
Intangible assets include acquired leasehold rights, favorable lease assets, trade names, brand names, patents, liquor licenses, license agreements, and non-competition agreements. The Company amortizes definite-lived intangible assets on a straight-line basis over the period the intangible asset is expected to generate cash flows, generally the life of the related agreement. Currently, the weighted average life is approximately 17 years for contract-based intangible assets, and approximately 3 years for marketing-related and other identifiable intangible assets. Indefinite-lived intangible assets are reviewed for impairment quarterly, or whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying amount of an intangible asset may not be recoverable.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets and Long-Lived Assets to be Disposed of
The Company evaluates long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances, such as unplanned negative cash flow, short lease life, or a plan to close is established, indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to future undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are determined to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying value of the assets exceeds the fair value of the assets. The fair value, based on hierarchy input Level 3, is determined using management’s best estimate based on a discounted cash flow model based on future store operating results using internal projections or based on a review of the future benefit the Company anticipates receiving from the related assets. Additionally for closing locations, the Company estimates net future cash flows based on its experience and knowledge of the area in which the closed property is located and, when necessary, utilizes local real estate brokers. Assets to be disposed of are reported at the lower of the carrying amount or fair value less costs to sell. When the Company impairs assets related to an operating location, a charge to write down the related assets is included in the “Direct store expenses” or “General and administrative expenses” line item on the Consolidated Statements of Operations. When the Company commits to relocate, close, or dispose of a location, a charge to write down the related assets to their estimated recoverable value is included in the “Relocation, store closure and lease termination costs” line item on the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company records its financial assets and liabilities at fair value in accordance with the framework for measuring fair value in generally accepted accounting principles. This framework establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs used to measure fair value:
• | Level 1: Observable inputs that reflect unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities traded in active markets. |
• | Level 2: Inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. |
• | Level 3: Inputs that are generally unobservable. These inputs may be used with internally developed methodologies that result in management’s best estimate of fair value. |
The Company holds money market fund investments that are classified as cash equivalents that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis based on quoted prices in active markets for identical assets. The Company also holds available-for-sale securities generally consisting of state and local municipal obligations and corporate bonds and commercial paper which hold high credit ratings. These instruments are valued using a series of multi-dimensional relational models and series of matrices with standard inputs obtained from readily available pricing sources and other observable market data, such as benchmark yields and base spread. Investments are stated at fair value with unrealized gains and losses, net of related tax effect, included as a component of shareholders’ equity until realized. Declines in fair value below the Company’s carrying value deemed to be other than temporary are charged against net earnings.
The carrying amounts of accrued payroll, bonuses and other benefits due team members, and other accrued expenses approximate fair value because of their short maturities. Store closure reserves and estimated workers’ compensation claims are recorded at net present value to approximate fair value.
Insurance and Self-Insurance Reserves
The Company uses a combination of insurance and self-insurance plans to provide for the potential liabilities for workers’ compensation, general liability, property insurance, director and officers’ liability insurance, vehicle liability, and employee health care benefits. Liabilities associated with the risks that are retained by the Company are estimated, in part, by considering
41
historical claims experience, demographic factors, severity factors and other actuarial assumptions. The Company had insurance liabilities totaling approximately $152 million and $135 million at September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, respectively, included in the “Other current liabilities” line item on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Reserves for Closed Properties
The Company maintains reserves for retail stores and other properties that are no longer being utilized in current operations. The Company provides for closed property operating lease liabilities using the present value of the remaining noncancelable lease payments and lease termination fees after the closing date, net of estimated subtenant income. The closed property lease liabilities are expected to be paid over the remaining lease terms, which generally range from nine months to 14 years. The Company estimates subtenant income and future cash flows based on the Company’s experience and knowledge of the area in which the closed property is located, the Company’s previous efforts to dispose of similar assets and existing economic conditions. Reserves for closed properties are included in the “Other current liabilities” and “Other long-term liabilities” line items on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
The reserves for closed properties include management’s estimates for lease subsidies, lease terminations and future payments on exited real estate. Adjustments to closed property reserves primarily relate to changes in existing economic conditions, subtenant income or actual exit costs differing from original estimates. Adjustments are made for changes in estimates in the period in which the changes become known.
Revenue Recognition
We recognize revenue for sales of our products at the point of sale. Discounts provided to customers at the point of sale are recognized as a reduction in sales as the products are sold. Sales taxes are not included in revenue.
Cost of Goods Sold and Occupancy Costs
Cost of goods sold includes cost of inventory sold during the period (net of discounts and allowances), distribution and food preparation costs, and shipping and handling costs. The Company receives various rebates from third-party vendors in the form of purchase or sales volume discounts and payments under cooperative advertising agreements. Purchase volume discounts are calculated based on actual purchase volumes. Volume discounts and cooperative advertising discounts in excess of identifiable advertising costs are recognized as a reduction of cost of goods sold when the related merchandise is sold. The Company utilizes forward purchases to limit its exposures to changes in commodity prices. All forward purchase commitments are established at current prices and recorded through cost of goods sold at settlement. Occupancy costs include store rental costs, property taxes, utility costs, repair and maintenance costs, and property insurance. Our largest supplier, United Natural Foods, Inc., accounted for approximately 32%, 32% and 31% of our total purchases in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Direct Store Expenses
Direct store expenses consist of store-level expenses such as salaries and benefits costs, supplies, depreciation, marketing and other store-specific costs. Advertising and marketing expense for fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 was approximately $63 million, $56 million and $51 million, respectively. Advertising costs are charged to expense as incurred, except for certain production costs that are charged to expense when the advertising first takes place.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses consist of salaries and benefits costs, occupancy and other related costs associated with corporate and regional administrative support services.
Pre-opening Expenses
Pre-opening expenses include rent expense incurred during construction of new facilities and costs related to new location openings, including costs associated with hiring and training personnel, smallwares, supplies and other miscellaneous costs. Rent expense is generally incurred approximately nine months prior to a store’s opening date. Other pre-opening expenses are incurred primarily in the 60 days prior to a new store opening. Pre-opening costs are expensed as incurred.
Relocation, Store Closure and Lease Termination Costs
Relocation costs consist of moving costs, estimated remaining net lease payments, accelerated depreciation costs, related asset impairment, and other costs associated with replaced facilities. Store closure costs consist of estimated remaining lease payments, accelerated depreciation costs, related asset impairment, and other costs associated with closed facilities. Lease termination costs consist of estimated remaining net lease payments for terminated leases and idle properties, and associated asset impairments.
42
Share-Based Payments
The Company maintains several share-based incentive plans. We grant both options to purchase common stock and restricted common stock under our Whole Foods Market 2009 Stock Incentive Plan. Options outstanding are governed by the original terms and conditions of the grants, unless modified by a subsequent agreement. Options are granted at an option price equal to the market value of the stock at the grant date and generally vest ratably over a four- or nine-year period beginning one year from grant date and have a five, seven, or ten year term. The grant date is established once the Company’s Board of Directors approves the grant and all key terms have been determined. Stock option grant terms and conditions are communicated to team members within a relatively short period of time. The Company generally approves one primary stock option grant annually, occurring during a trading window. Restricted common stock is granted at the market price of the stock on the day of grant and generally vests over a three-, four- or six-year period.
The Company uses the Black-Scholes multiple option pricing model which requires extensive use of accounting judgment and financial estimates, including estimates of the expected term team members will retain their vested stock options before exercising them, the estimated volatility of the Company’s common stock price over the expected term, and the number of options that will be forfeited prior to the completion of their vesting requirements. The related share-based payment expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period. The tax savings resulting from tax deductions in excess of expense reflected in the Company’s financial statements are reflected as a financing cash flow.
All full-time team members with a minimum of 400 hours of service may purchase our common stock through payroll deductions under the Company’s Team Member Stock Purchase Plan (“TMSPP”). The TMSPP provides for a 5% discount on the shares’ purchase date market value, which meets the share-based payment “Safe Harbor” provisions, and therefore is non-compensatory. As a result, no compensation expense is recognized for our team member stock purchase plan.
Income Taxes
The Company recognizes deferred income tax assets and liabilities by applying statutory tax rates in effect at the balance sheet date to differences between the book basis and the tax basis of assets and liabilities. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to reverse. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are adjusted to reflect changes in tax laws or rates in the period that includes the enactment date. The Company may recognize the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position if it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained by the taxing authorities based on technical merits of the position. The tax benefits recognized in the financial statements from such a position are measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon settlement. Significant accounting judgment is required in determining the provision for income taxes and related accruals, deferred tax assets and liabilities. The Company believes that its tax positions are consistent with applicable tax law, but certain positions may be challenged by taxing authorities. In the ordinary course of business, there are transactions and calculations where the ultimate tax outcome is uncertain. In addition, we are subject to periodic audits and examinations by the Internal Revenue Service and other state and local taxing authorities. Although we believe that our estimates are reasonable, actual results could differ from these estimates.
Treasury Stock
Under the Company’s stock repurchase program, the Company can repurchase shares of the Company’s common stock on the open market that are held in treasury at cost. Shares held in treasury may be reissued to satisfy exercises of stock options and issuances of restricted stock awards. The Company does not currently intend to retire its treasury shares. The Company’s common stock has no par value.
Earnings per Share
Basic earnings per share are calculated by dividing net income available to common shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the fiscal period. Diluted earnings per share are based on the weighted average number of common shares outstanding plus, where applicable, the additional common shares that would have been outstanding related to dilutive share-based awards using the treasury stock method. Dilutive potential common shares include outstanding stock options and unvested restricted stock awards.
Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income consists of: net income; unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities; and foreign currency translation adjustments, net of income tax, and is reflected in the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income.
Foreign Currency Translation
The Company’s operations in Canada and the U.K. use their local currency as their functional currency. Foreign currency transaction gains and losses related to Canadian intercompany operations are charged to net income in the period incurred.
43
Foreign currency gains and losses were not material in fiscal year 2014, 2013 or 2012. Intercompany transaction gains and losses associated with our U.K. operations are excluded from the determination of net income since these transactions are considered long-term investments in nature. Assets and liabilities are translated at exchange rates in effect at the balance sheet date. Income and expense accounts are translated at the average exchange rates during the fiscal year. Resulting translation adjustments are recorded as a separate component of accumulated other comprehensive income.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and revenues and expenses during the period reported. Actual amounts could differ from those estimates.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers,” which creates a new topic in the Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”), topic 606, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers.” The core principle of the new guidance is that an entity will recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. Additionally, the guidance requires disclosures related to the nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue that is recognized. The amendments are effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2016 and may be applied on either a full or modified retrospective basis. The provisions are effective for the Company’s first quarter of fiscal year ending September 30, 2018. We are currently evaluating the impact that the adoption of these provisions will have on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In April 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-08, “Reporting Discontinued Operations and Disclosures of Disposals of Components of an Entity,” which amends ASC 205, “Presentation of Financial Statements,” and ASC 360, “Property, Plant, and Equipment.” The amendments raise the threshold for reporting discontinued operations to only those disposals that represent a strategic shift or have a major impact on an entity’s financial results and operations. The amendments also expand related disclosure requirements. The amendments are effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2014 and should be applied on prospective basis. The provisions are effective for the Company’s first quarter of fiscal year ending September 25, 2016. We do not expect the adoption of these provisions to have a significant impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In July 2013, the FASB issued ASU No. 2013-11, “Presentation of an Unrecognized Tax Benefit When a Net Operating Loss Carryforward, a Similar Tax Loss, or a Tax Credit Carryforward Exists,” which amends ASC 740, “Income Taxes.” The amendments provide guidance on the financial statement presentation of an unrecognized tax benefit, as either a reduction of a deferred tax asset or as a liability, when a net operating loss carryforward, similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward exists. The amendments are effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2013 and may be applied on either a prospective or retrospective basis. The provisions are effective for the Company’s first quarter of fiscal year ending September 27, 2015. We do not expect the adoption of these provisions to have a significant impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In February 2013, the FASB issued ASU No. 2013-04, “Obligations Resulting from Joint and Several Liability Arrangements for Which the Total Amount of the Obligation Is Fixed at the Reporting Date (a consensus of the FASB Emerging Issues Task Force),” which amends ASC 405, “Liabilities.” The amendments provide guidance on the recognition, measurement, and disclosure of obligations resulting from joint and several liability arrangements, including debt arrangements, other contractual obligations, and settled litigation and judicial rulings, for which the total amount of the obligation is fixed at the reporting date. The amendments are effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2013 and should be applied retrospectively. The provisions are effective for the Company’s first quarter of fiscal year ending September 27, 2015. We do not expect the adoption of these provisions to have a significant impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
44
(3) Fair Value Measurements
Assets Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis
The Company held the following financial assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis based on the hierarchy levels indicated (in millions):
September 28, 2014 | Level 1 Inputs | Level 2 Inputs | Level 3 Inputs | Total | |||||||||||
Cash equivalents: | |||||||||||||||
Money market fund | $ | 46 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 46 | |||||||
Treasury bills | 4 | — | — | 4 | |||||||||||
Commercial paper | — | 15 | — | 15 | |||||||||||
Marketable securities - available-for-sale: | |||||||||||||||
Asset-backed securities | — | 13 | — | 13 | |||||||||||
Commercial paper | — | 33 | — | 33 | |||||||||||
Corporate bonds | — | 97 | — | 97 | |||||||||||
Municipal bonds | — | 530 | — | 530 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 50 | $ | 688 | $ | — | $ | 738 | |||||||
September 29, 2013 | Level 1 Inputs | Level 2 Inputs | Level 3 Inputs | Total | |||||||||||
Cash equivalents: | |||||||||||||||
Money market fund | $ | 73 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 73 | |||||||
Commercial paper | — | 104 | — | 104 | |||||||||||
Municipal bonds | — | 17 | — | 17 | |||||||||||
Marketable securities - available-for-sale: | |||||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | — | 5 | — | 5 | |||||||||||
Municipal bonds | — | 1,010 | — | 1,010 | |||||||||||
Variable rate demand notes | — | 20 | — | 20 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 73 | $ | 1,156 | $ | — | $ | 1,229 | |||||||
Assets Measured at Fair Value on a Nonrecurring Basis
Assets recognized or disclosed at fair value on a nonrecurring basis include items such as property, plant and equipment, intangible assets, and other assets. These assets are measured at fair value if determined to be impaired. Fair value adjustments, based on hierarchy input Level 3, were not material during fiscal year 2014, 2013 or 2012.
(4) Investments
The Company holds investments in marketable securities that are classified as either short- or long-term available-for-sale securities. The Company held the following investments at fair value as of the dates indicated (in millions):
September 28, 2014 | September 29, 2013 | ||||||
Short-term marketable securities - available-for-sale: | |||||||
Asset-backed securities | $ | 9 | $ | — | |||
Commercial paper | 33 | — | |||||
Corporate bonds | 56 | — | |||||
Municipal bonds | 455 | 713 | |||||
Variable rate demand notes | — | 20 | |||||
Total short-term marketable securities | $ | 553 | $ | 733 | |||
Long-term marketable securities - available-for-sale: | |||||||
Asset-backed securities | $ | 4 | $ | — | |||
Corporate bonds | 41 | 5 | |||||
Municipal bonds | 75 | 297 | |||||
Total long-term marketable securities | $ | 120 | $ | 302 | |||
Gross unrealized holding gains and losses were not material at September 28, 2014 or September 29, 2013. Available-for-sale securities totaling approximately $142 million and $252 million were in unrealized loss positions at September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, respectively. The aggregate value of available-for-sale securities in a continuous unrealized loss position for greater than 12 months totaled approximately $3 million and $22 million at September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, respectively. The Company did not recognize any other-than-temporary impairments during the last three fiscal years. At September 28, 2014, the average effective maturity of the Company’s short- and long-term available-for-sale securities was
45
approximately 6 months and 15 months, respectively, compared to approximately 5 months and 16 months, respectively, at September 29, 2013.
At September 28, 2014, the Company held $10 million in equity interest that is accounted for using the cost method of accounting and an ownership interest in a supplier company totaling approximately $4 million at September 28, 2014 which is accounted for using the equity method of accounting. No such equity interests were held as of September 29, 2013.
(5) Property and Equipment
Balances of major classes of property and equipment were as follows (in millions):
September 28, 2014 | September 29, 2013 | ||||||
Land | $ | 139 | $ | 77 | |||
Buildings and leasehold improvements | 2,628 | 2,427 | |||||
Capitalized real estate leases | 81 | 33 | |||||
Fixtures and equipment | 2,099 | 1,706 | |||||
Construction in progress and equipment not yet in service | 362 | 269 | |||||
Property and equipment, gross | 5,309 | 4,512 | |||||
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | (2,386 | ) | (2,084 | ) | |||
Property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation and amortization | $ | 2,923 | $ | 2,428 | |||
Depreciation and amortization expense related to property and equipment totaled approximately $360 million, $324 million and $297 million for fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Property and equipment included accumulated accelerated depreciation and other asset impairments totaling approximately $9 million and $4 million at September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, respectively. Development costs of new locations totaled approximately $447 million, $339 million and $262 million in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Construction accruals related to development sites, remodels, and expansions were included in the “Other current liabilities” line item on the Consolidated Balance Sheets and totaled approximately $116 million and $103 million at September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, respectively.
(6) Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
The Company recorded goodwill totaling approximately $29 million related to the acquisition of four retail locations, and approximately $16 million, primarily related to the acquisition of six retail locations, during fiscal years 2014 and 2013, respectively. There were no impairments of goodwill during fiscal years 2014, 2013 or 2012. The Company acquired definite-lived intangible assets totaling approximately $18 million, primarily related to acquired leasehold rights, and approximately $6 million, primarily favorable lease assets related to the acquisition of six retail locations, during fiscal years 2014 and 2013, respectively. The components of intangible assets as of the dates indicated were as follows (in millions):
September 28, 2014 | September 29, 2013 | ||||||||||||||
Gross carrying amount | Accumulated amortization | Gross carrying amount | Accumulated amortization | ||||||||||||
Definite-lived contract-based | $ | 120 | $ | (45 | ) | $ | 102 | $ | (40 | ) | |||||
Definite-lived marketing-related and other | 1 | (1 | ) | 1 | (1 | ) | |||||||||
Indefinite-lived contract-based | 6 | 3 | |||||||||||||
Total | $ | 127 | $ | (46 | ) | $ | 106 | $ | (41 | ) | |||||
Amortization expense associated with intangible assets totaled approximately $5 million, $5 million and $6 million during fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Future amortization expense associated with the net carrying amount of definite-lived intangible assets is estimated to be as follows (in millions):
Fiscal year 2015 | $ | 6 | |
Fiscal year 2016 | 5 | ||
Fiscal year 2017 | 5 | ||
Fiscal year 2018 | 5 | ||
Fiscal year 2019 | 5 | ||
Future fiscal years | 49 | ||
Total | $ | 75 | |
46
(7) Reserves for Closed Properties
The following table provides a summary of activity in reserves for closed properties during the fiscal years indicated (in millions):
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Beginning balance | $ | 36 | $ | 41 | |||
Additions | 4 | 5 | |||||
Usage | (11 | ) | (11 | ) | |||
Adjustments | 2 | 1 | |||||
Ending balance | $ | 31 | $ | 36 | |||
Additions to store closure reserves primarily relate to the accretion of interest on existing reserves. Additions related to two and eight new closures during fiscal years 2014 and 2013, respectively, were not material. Usage primarily related to ongoing cash rental payments totaled approximately $11 million for each of fiscal years 2014 and 2013.
(8) Leases
The Company is committed under certain capital leases for rental of certain buildings, land and equipment, and certain operating leases for rental of facilities and equipment. These leases expire or become subject to renewal clauses at various dates from 2015 to 2054. The Company had capital lease obligations totaling approximately $62 million and $27 million at September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, respectively.
Rental expense charged to operations under operating leases for fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 totaled approximately $407 million, $374 million and $353 million, respectively, which included contingent rentals totaling approximately $13 million, $13 million and $12 million during those same periods. Sublease rental income totaled approximately $9 million, $8 million and $8 million during fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Minimum rental commitments and sublease rental income required by all noncancelable leases are approximately as follows (in millions):
Capital | Operating | Sublease | |||||||||
Fiscal year 2015 | $ | 5 | $ | 401 | $ | 8 | |||||
Fiscal year 2016 | 5 | 458 | 8 | ||||||||
Fiscal year 2017 | 5 | 481 | 7 | ||||||||
Fiscal year 2018 | 5 | 491 | 6 | ||||||||
Fiscal year 2019 | 5 | 493 | 5 | ||||||||
Future fiscal years | 72 | 5,948 | 10 | ||||||||
97 | $ | 8,272 | $ | 44 | |||||||
Less amounts representing interest | 35 | ||||||||||
Net present value of capital lease obligations | $ | 62 | |||||||||
The present values of future minimum obligations for capital leases shown above are calculated based on interest rates determined at the inception of the lease, or upon acquisition of the original lease.
(9) Income Taxes
Components of income tax expense for the fiscal years indicated were as follows (in millions):
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Current federal income tax | $ | 359 | $ | 321 | $ | 234 | |||||
Current state income tax | 82 | 73 | 53 | ||||||||
Current foreign income tax | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
Total current tax | 443 | 397 | 291 | ||||||||
Deferred federal income tax | (66 | ) | (44 | ) | 1 | ||||||
Deferred state income tax | (10 | ) | (10 | ) | (6 | ) | |||||
Deferred foreign income tax | — | — | — | ||||||||
Total deferred tax | (76 | ) | (54 | ) | (5 | ) | |||||
Total income tax expense | $ | 367 | $ | 343 | $ | 286 | |||||
47
Actual income tax expense for the fiscal years indicated differed from the amount computed by applying statutory corporate income tax rates to income before income taxes as follows (in millions):
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Federal income tax based on statutory rates | $ | 331 | $ | 313 | $ | 263 | |||||
Increase (reduction) in income taxes resulting from: | |||||||||||
Tax-exempt interest | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | |||||
Excess charitable contributions | (8 | ) | (7 | ) | (5 | ) | |||||
Federal income tax credits | (3 | ) | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||
Other, net | 2 | — | 1 | ||||||||
Total federal income taxes | 321 | 303 | 256 | ||||||||
State income taxes, net of federal income tax benefit | 47 | 41 | 31 | ||||||||
Tax impact of foreign operations | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | |||||
Total income tax expense | $ | 367 | $ | 343 | $ | 286 | |||||
Current income taxes receivable totaled approximately $1 million and $7 million at September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, respectively.
The tax effects of temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of the deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities were as follows (in millions):
September 28, 2014 | September 29, 2013 | ||||||
Deferred tax assets: | |||||||
Compensation-related costs | $ | 159 | $ | 122 | |||
Insurance-related costs | 53 | 48 | |||||
Inventories | — | 1 | |||||
Lease and other termination accruals | 13 | 15 | |||||
Rent differential | 156 | 139 | |||||
Tax basis of fixed assets in excess of book basis | 9 | 7 | |||||
Net domestic and international operating loss carryforwards | 20 | 18 | |||||
Other | 8 | 5 | |||||
Gross deferred tax assets | 418 | 355 | |||||
Valuation allowance | (30 | ) | (26 | ) | |||
Deferred tax assets | 388 | 329 | |||||
Deferred tax liabilities: | |||||||
Financial basis of fixed assets in excess of tax basis | (79 | ) | (102 | ) | |||
Inventories | (5 | ) | — | ||||
Capitalized costs expensed for tax purposes | (4 | ) | (4 | ) | |||
Deferred tax liabilities | (88 | ) | (106 | ) | |||
Net deferred tax asset | $ | 300 | $ | 223 | |||
Deferred taxes have been classified on the Consolidated Balance Sheets as follows (in millions):
September 28, 2014 | September 29, 2013 | ||||||
Current assets | $ | 168 | $ | 151 | |||
Noncurrent assets | 132 | 72 | |||||
Net deferred tax asset | $ | 300 | $ | 223 | |||
At September 28, 2014, the Company had international operating loss carryforwards totaling approximately $101 million, all of which have an indefinite life. The Company provided a valuation allowance totaling approximately $30 million for deferred tax assets associated with international operating loss carryforwards, federal credit carryforwards, and deferred tax assets associated with unrecognized tax benefits, for which management has determined it is more likely than not that the deferred tax asset will not be realized. Management believes that it is more likely than not that we will fully realize the remaining domestic deferred tax assets in the form of future tax deductions based on the nature of these deductible temporary differences and a history of profitable operations.
48
The Company intends to utilize earnings in foreign operations for an indefinite period of time, or to repatriate such earnings only when tax-efficient to do so. If these amounts were distributed to the United States, in the form of dividends or otherwise, the Company would be subject to additional U.S. income taxes. Determination of the amount of unrecognized deferred income tax liabilities on these earnings is not practicable because such liability, if any, is dependent on circumstances existing if and when remittance occurs. The Company’s total gross unrecognized tax benefits are classified in the “Other long-term liabilities” line item on the Consolidated Balance Sheets and were not material during the last three fiscal years.
The Company and its domestic subsidiaries file income tax returns with federal, state and local tax authorities within the United States. The Company’s foreign affiliates file income tax returns in Canada and the United Kingdom. The Internal Revenue Service of the United States completed its examination of the Company’s federal tax returns for fiscal year 2012 during the first quarter of fiscal year 2014. With limited exceptions, the Company is no longer subject to federal income tax examinations for fiscal years before 2013 and is no longer subject to state and local income tax examinations for fiscal years before 2008.
(10) Shareholders’ Equity
Common Stock
During fiscal year 2013, the Company’s Board of Directors declared a two-for-one split of the Company’s common stock, which was effected through a stock dividend distributed on May 29, 2013. All references made to share or per share amounts in the accompanying consolidated financial statements and applicable disclosures reflect this two-for-one split.
Dividends per Common Share
The following table provides a summary of dividends declared per common share during fiscal years 2014 and 2013 (in millions, except per share amounts):
Date of declaration | Dividend per common share | Date of record | Date of payment | Total amount | |||||||
Fiscal year 2014: | |||||||||||
November 1, 2013 | $ | 0.12 | January 17, 2014 | January 28, 2014 | $ | 45 | |||||
February 24, 2014 | 0.12 | April 11, 2014 | April 22, 2014 | 44 | |||||||
June 12, 2014 | 0.12 | July 3, 2014 | July 15, 2014 | 44 | |||||||
September 11, 2014 (1) | 0.12 | September 26, 2014 | October 7, 2014 | 43 | |||||||
Fiscal year 2013: | |||||||||||
November 29, 2012 | $ | 1.00 | December 10, 2012 | December 21, 2012 | $ | 371 | |||||
November 7, 2012 | 0.10 | January 18, 2013 | January 29, 2013 | 37 | |||||||
March 15, 2013 | 0.10 | April 12, 2013 | April 23, 2013 | 37 | |||||||
June 12, 2013 | 0.10 | July 5, 2013 | July 16, 2013 | 37 | |||||||
September 10, 2013 | 0.10 | September 27, 2013 | October 8, 2013 | 37 | |||||||
(1) Dividend accrued at September 28, 2014
Treasury Stock
During fiscal year 2014, a new share repurchase program was authorized pursuant to the authority of the Company’s Board of Directors whereby the Company may make up to $1.0 billion in stock purchases of outstanding shares of the common stock of the Company through August 1, 2016. In connection with the new share repurchase program, the $322 million in remaining authorization under the Company’s previous share repurchase program was cancelled. The following table outlines the share repurchase program authorized by the Company’s Board of Directors, and the related repurchase activity as of September 28, 2014 (in millions):
Effective date | Expiration date | Amount authorized | Cost of repurchases | Authorization available | |||||||||
August 1, 2014 | August 1, 2016 | $ | 1,000 | $ | 100 | $ | 900 | ||||||
Under the new share repurchase program, purchases can be made from time to time using a variety of methods, which may include open market purchases. The specific timing, price and size of purchases will depend on prevailing stock prices, general economic and market conditions, and other considerations. Purchases may be made through a Rule 10b5-1 plan pursuant to pre-determined metrics set forth in such plan. The Board’s authorization of the share repurchase program does not obligate the Company to acquire any particular amount of common stock, and the program may be suspended or discontinued at any time at the Company’s discretion.
49
Share repurchase activity for the fiscal years indicated was as follows (in millions, except per share amounts):
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Number of common shares acquired | 13.9 | 2.6 | |||||
Average price per common share acquired | $ | 41.51 | $ | 48.70 | |||
Total cost of common shares acquired | $ | 578 | $ | 125 | |||
Subsequent to fiscal year end, the Company repurchased approximately 0.9 million shares of the Company’s common stock at an average price per share of $47.39 for a total of approximately $43 million bringing the total current available authorization to approximately $857 million.
(11) Earnings per Share
The computation of basic earnings per share is based on the number of weighted average common shares outstanding during the period. The computation of diluted earnings per share includes the dilutive effect of common stock equivalents consisting of incremental common shares deemed outstanding from the assumed exercise of stock options and the dilutive effect of restricted stock awards.
A reconciliation of the numerators and denominators of the basic and diluted earnings per share calculations follows (in millions, except per share amounts):
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Net income (numerator for basic and diluted earnings per share) | $ | 579 | $ | 551 | $ | 466 | |||||
Weighted average common shares outstanding (denominator for basic earnings per share) | 367.8 | 371.2 | 364.8 | ||||||||
Incremental common shares attributable to dilutive effect of share-based awards | 2.7 | 3.3 | 4.1 | ||||||||
Weighted average common shares outstanding and potential additional common shares outstanding(denominator for diluted earnings per share) | 370.5 | 374.5 | 368.9 | ||||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 1.57 | $ | 1.48 | $ | 1.28 | |||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 1.56 | $ | 1.47 | $ | 1.26 | |||||
The computation of diluted earnings per share for fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 does not include share-based awards to purchase approximately 9.1 million shares, 7.1 million shares and 0.8 million shares of common stock, respectively, due to their antidilutive effect.
(12) Share-Based Payments
Share-based payment expense before income taxes recognized during fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 totaled approximately $68 million, $57 million and $42 million, respectively. Share-based payment expense was included in the following line items on the Consolidated Statements of Operations for the fiscal years indicated (in millions):
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||
Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs | $ | 2 | $ | 2 | $ | 2 | |||||
Direct store expenses | 34 | 32 | 22 | ||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 32 | 23 | 18 | ||||||||
Share-based payment expense before income taxes | 68 | 57 | 42 | ||||||||
Income tax benefit | (26 | ) | (22 | ) | (16 | ) | |||||
Net share-based payment expense | $ | 42 | $ | 35 | $ | 26 | |||||
At September 28, 2014, September 29, 2013 and September 30, 2012 approximately 37.6 million shares, 42.3 million shares and 16.8 million shares of the Company’s common stock, respectively, were available for future stock incentive grants.
50
Stock Options
The following table summarizes stock option activity (in millions, except per share amounts and contractual lives in years):
Number of options outstanding | Weighted average exercise price | Weighted average remaining contractual life | Aggregate intrinsic value | |||||||||
Outstanding options at September 25, 2011 | 27.3 | $ | 24.50 | |||||||||
Options granted | 7.2 | 44.23 | ||||||||||
Options exercised | (13.7 | ) | 26.44 | |||||||||
Options expired | (0.1 | ) | 25.10 | |||||||||
Options forfeited | (0.7 | ) | 28.32 | |||||||||
Outstanding options at September 30, 2012 | 20.0 | $ | 30.17 | |||||||||
Options granted | 4.3 | 51.33 | ||||||||||
Options exercised | (4.1 | ) | 20.52 | |||||||||
Options expired | (0.1 | ) | 18.86 | |||||||||
Options forfeited | (0.9 | ) | 37.20 | |||||||||
Outstanding options at September 29, 2013 | 19.2 | $ | 36.90 | |||||||||
Options granted | 5.3 | 40.25 | ||||||||||
Options exercised | (1.5 | ) | 24.13 | |||||||||
Options expired | (0.1 | ) | 36.10 | |||||||||
Options forfeited | (0.6 | ) | 42.32 | |||||||||
Outstanding options at September 28, 2014 | 22.3 | $ | 38.37 | 4.81 | $ | 93 | ||||||
Vested/expected to vest at September 28, 2014 | 21.2 | $ | 38.15 | 4.53 | $ | 92 | ||||||
Exercisable options at September 28, 2014 | 9.3 | $ | 32.70 | 3.75 | $ | 78 | ||||||
The weighted average grant date fair value of options granted during fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 was $9.67, $12.36 and $13.68, respectively. The aggregate intrinsic value of stock options at exercise, represented in the table above, was approximately $36 million, $125 million and $201 million during fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The Company realized a tax benefit from stock options exercised during fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 totaling approximately $36 million, $123 million and $198 million, respectively. The total fair value of shares vested during fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 was approximately $192 million, $246 million and $186 million, respectively, including the value of vested options exercised during those same periods. As of the end of fiscal years 2014 and 2013, there was approximately $108 million and $130 million of unrecognized share-based payment expense, respectively, related to unvested stock options, net of estimated forfeitures, related to approximately 11.9 million shares and 12.4 million shares, respectively. The Company anticipates this expense to be recognized over a weighted average period of 2.9 years.
A summary of stock options outstanding and exercisable at September 28, 2014 follows (share amounts in millions):
Range of Exercise Prices | Options Outstanding | Options Exercisable | ||||||||||||||||||||
From | To | Number of options outstanding | Weighted average exercise price | Weighted average remaining life (in years) | Number of options exercisable | Weighted average exercise price | ||||||||||||||||
$ | 9.45 | $ | 18.49 | 1.0 | $ | 9.59 | 1.65 | 1.0 | $ | 9.56 | ||||||||||||
20.42 | 28.50 | 2.4 | 20.43 | 3.30 | 2.1 | 20.42 | ||||||||||||||||
31.25 | 38.50 | 8.1 | 34.81 | 5.22 | 2.4 | 31.25 | ||||||||||||||||
40.81 | 46.28 | 6.2 | 44.29 | 4.62 | 2.8 | 44.26 | ||||||||||||||||
51.25 | 59.15 | 4.6 | 51.93 | 5.79 | 1.0 | 51.86 | ||||||||||||||||
22.3 | $ | 38.37 | 4.81 | 9.3 | $ | 32.70 | ||||||||||||||||
Share-based payment expense related to vesting stock options recognized during fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012 totaled approximately $63 million, $56 million and $42 million, respectively.
51
The fair value of stock option grants has been estimated at the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following weighted average assumptions:
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||
Expected dividend yield | 0.950 | % | 0.880 | % | 0.800 | % | ||
Risk-free interest rate | 1.18 | % | 0.77 | % | 0.58 | % | ||
Expected volatility | 30.96 | % | 31.25 | % | 40.89 | % | ||
Expected life, in years | 4.04 | 3.96 | 4.14 | |||||
Risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve on the date of the grant for the time period equal to the expected term of the grant. Expected volatility is calculated using a ratio of implied volatility based on the Newton-Raphson method of bisection, and four or six year historical volatilities based on the expected life of each tranche of options. The Company determined the use of both implied volatility and historical volatility represents a more accurate calculation of option fair value. Expected life is calculated in two tranches based on weighted average percentage of unexpired options and exercise-after-vesting information over the last five or seven years. Unvested options are included in the term calculation using the “mid-point scenario” which assumes that unvested options will be exercised halfway between vest and expiration date. The assumptions used to calculate the fair value of options granted are evaluated and revised, as necessary, to reflect market conditions and experience. In addition to the above valuation assumptions, the Company estimates an annual forfeiture rate for unvested options and adjusts fair value expense accordingly. The Company monitors actual forfeiture experience and adjusts the rate from time to time as necessary.
Restricted Stock
During fiscal years 2014 and 2013, the Company awarded approximately 0.2 million shares and 0.1 million shares of restricted common stock, respectively, pursuant to the Whole Foods Market 2009 Stock Incentive Plan. Fair value of the restricted share issuances on grant date for fiscal years 2014 and 2013 totaled approximately $11 million and $4 million, respectively.
Total share-based payment expense related to restricted shares during fiscal year 2014 totaled approximately $5 million and is included in the “General and administrative expenses” line item on the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Share-based payment expense related to restricted shares was not material during fiscal year 2013. At September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013, there was approximately $10 million and $3 million of unrecognized share-based payment expense, respectively, related to unvested restricted stock. The Company anticipates this expense to be recognized over a weighted average period of 3.9 years. The number of shares, grant date fair value, and share-based payment expense related to the issuance of restricted common stock were not material during fiscal year 2012.
Team Member Stock Purchase Plan
Under the Team Member Stock Purchase Plan, the Company issued approximately 135,000 shares, 80,000 shares and 120,000 shares of common stock in fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. At September 28, 2014, September 29, 2013 and September 30, 2012, approximately 405,000 shares, 540,000 shares and 620,000 shares of our common stock, respectively, were available for future issuance.
(13) Team Member 401(k) Plan
The Company offers a team member 401(k) plan to all team members with a minimum of 1,000 service hours in one year. In fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, the Company made cash contributions to the plan of approximately $6 million, $6 million and $5 million, respectively.
(14) Quarterly Results (unaudited)
The Company’s first fiscal quarter consists of 16 weeks, the second and third fiscal quarters each are 12 weeks, and the fourth fiscal quarter is 12 or 13 weeks. Fiscal years 2014 and 2013 were 52-week years with twelve weeks in the fourth quarter. Because the first fiscal quarter is longer than the remaining quarters, it typically represents a larger share of the Company’s annual sales from existing stores. Quarter-to-quarter comparisons of results of operations have been and may be materially impacted by the timing of new store openings. The Company believes that the following information reflects all adjustments, consisting of normal recurring accruals, necessary for a fair presentation. The operating results for any quarter are not necessarily indicative of results for any future period.
52
The following tables set forth selected unaudited quarterly Consolidated Statements of Operations information for the fiscal years ended September 28, 2014 and September 29, 2013 (in millions, except per share amounts):
First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | ||||||||||||
Fiscal Year 2014 | |||||||||||||||
Sales | $ | 4,239 | $ | 3,322 | $ | 3,377 | $ | 3,256 | |||||||
Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs | 2,754 | 2,131 | 2,163 | 2,102 | |||||||||||
Gross profit | 1,485 | 1,191 | 1,214 | 1,154 | |||||||||||
Direct store expenses | 1,077 | 840 | 849 | 820 | |||||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 132 | 107 | 102 | 105 | |||||||||||
Pre-opening expenses | 16 | 11 | 18 | 22 | |||||||||||
Relocation, store closure and lease termination costs | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||
Operating income | 255 | 231 | 243 | 205 | |||||||||||
Investment and other income, net of interest expense | 4 | 2 | 4 | 2 | |||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 259 | 233 | 247 | 207 | |||||||||||
Provision for income taxes | 101 | 91 | 96 | 79 | |||||||||||
Net income | $ | 158 | $ | 142 | $ | 151 | $ | 128 | |||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 0.42 | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.41 | $ | 0.35 | |||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 0.42 | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.41 | $ | 0.35 | |||||||
Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.12 | $ | 0.12 | $ | 0.12 | $ | 0.12 | |||||||
First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | ||||||||||||
Fiscal Year 2013 | |||||||||||||||
Sales | $ | 3,856 | $ | 3,027 | $ | 3,058 | $ | 2,976 | |||||||
Cost of goods sold and occupancy costs | 2,508 | 1,926 | 1,939 | 1,915 | |||||||||||
Gross profit | 1,348 | 1,101 | 1,119 | 1,061 | |||||||||||
Direct store expenses | 979 | 769 | 781 | 756 | |||||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 116 | 91 | 95 | 95 | |||||||||||
Pre-opening expenses | 14 | 10 | 13 | 15 | |||||||||||
Relocation, store closure and lease termination costs | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 | |||||||||||
Operating income | 235 | 228 | 228 | 192 | |||||||||||
Investment and other income, net of interest expense | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | |||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 238 | 231 | 230 | 195 | |||||||||||
Provision for income taxes | 92 | 89 | 88 | 74 | |||||||||||
Net income | $ | 146 | $ | 142 | $ | 142 | $ | 121 | |||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 0.39 | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.33 | |||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 0.39 | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.32 | |||||||
Dividends declared per common share | $ | 1.10 | $ | 0.10 | $ | 0.10 | $ | 0.10 | |||||||
Per share amounts are computed independently for each of the quarters presented and the sum of the quarters may not equal the total year amount.
(15) Commitments and Contingencies
The Company is exposed to claims and litigation matters arising in the ordinary course of business and uses various methods to resolve these matters in a manner that we believe best serves the interests of our stakeholders. Our primary contingencies are associated with insurance and self-insurance obligations and litigation matters. Additionally, the Company has retention agreements with certain members of Company management which provide for payments under certain circumstances including change of control. Estimation of our insurance and self-insurance liabilities requires significant judgments, and actual claim settlements and associated expenses may differ from our current provisions for loss. We have exposures to loss contingencies arising from pending or threatened litigation for which assessing and estimating the outcomes of these matters involve substantial uncertainties.
The Company evaluates contingencies on an ongoing basis and has established loss provisions for matters in which losses are probable and the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. Insurance and legal settlement liabilities are included in the “Other
53
current liabilities” line item on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. We believe the recorded reserves in our consolidated financial statements are adequate in light of the probable and estimable liabilities.
(16) Related Party Transactions
The Company provides ongoing support to three independent nonprofit organizations: Whole Planet Foundation, Whole Kids Foundation, and Whole Cities Foundation (the “Foundations”). Whole Planet Foundation’s mission is to empower the poor through microcredit, with a focus on developing-world communities that supply the Company’s stores with product. Whole Kids Foundation is dedicated to improving children’s nutrition through partnerships with schools, educators, and other organizations. Whole Cities Foundation is dedicated to supporting efforts to increase access to nutritious, fresh food and health education in underserved communities. The board of directors of each of the Foundations is principally comprised of members of the Company’s management. Additionally, the Company provides administrative support and covers all operating costs of the Foundations.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company’s management, with the participation of the Company’s co-Chief Executive Officers and Chief Financial Officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”)) as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based on such evaluation, the Company’s co-Chief Executive Officers and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, as of the end of such period, the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of the end of the period covered by this report.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act) during the most recently completed fiscal quarter that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
The Company’s management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s management, including our principal executive officers and principal financial officer, the Company conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting based on criteria established in the framework in Internal Control – Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (1992 framework). Based on this evaluation, the Company’s management concluded that its internal control over financial reporting was effective as of September 28, 2014.
The Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, Ernst & Young LLP, audited the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. Ernst & Young LLP has issued their attestation report which is included in “Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this Report on Form 10-K.
Item 9B. Other Information.
Not applicable.
54
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
The information required by this item about our Company’s Executive Officers is included in Part I, “Item 1. Business” of this Report on Form 10-K under the caption “Executive Officers of the Registrant.” All other information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference from the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held March 10, 2015 to be filed with the Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A (“Proxy Statement”).
The Company has adopted a Code of Business Conduct (the “Code”) for all team members and directors pursuant to section 406 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. A copy of the Code is publicly available on our Whole Foods Market website at http://www.wholefoodsmarket.com/sites/default/files/media/Global/Company%20Info/PDFs/CodeofBusinessConduct2013.pdf and the Company will provide disclosure of future updates, amendments or waivers by posting them to our website. The Code applies to the Company’s principal executive officers, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer, controller and other persons who perform similar functions for the Company, in addition to the corporate directors and employees of the Company. The information contained on our website is not incorporated by reference into this Report on Form 10-K.
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference from the registrant’s Proxy Statement.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
The following table summarizes information about the Company’s equity compensation plans by type as of September 28, 2014 (in millions, except per share amounts):
Plan category | Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options | Weighted average exercise price of outstanding options | Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a)) | ||||||
(a) | (b) | (c) | |||||||
Approved by security holders | 22.3 | $ | 38.37 | 37.6 | |||||
Not approved by security holders | — | — | — | ||||||
Total | 22.3 | $ | 38.37 | 37.6 | |||||
All other information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference from the registrant’s Proxy Statement.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference from the registrant’s Proxy Statement.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services.
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference from the registrant’s Proxy Statement.
55
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.
(a) | The following documents are filed as part of this report: |
(1) Consolidated Financial Statements: See Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data. | |
(2) Financial statement schedules: No schedules are required. | |
(3) Exhibits are incorporated herein by reference or are filed with this report as indicated below. | |
(b) | Exhibits: |
3.1 | Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of the Registrant, dated March 9, 2012 (6) |
3.2 | Amended and Restated By-laws of the Registrant adopted September 6, 2012 (3) |
10.1 | 2009 Stock Incentive Plan (1) |
10.2 | 2007 Team Member Stock Purchase Plan (12) |
10.3 | Form of Executive Retention Plan and Non-Compete Arrangement by and between the executive leadership team of the Registrant and the Registrant (11) |
10.4 | Form of Director & Officer Indemnification Agreement (2) |
10.5 | Agreement for Distribution of Products by and between Whole Foods Market Distribution, Inc. and United Natural Foods, Inc. (Portions of this agreement have been omitted pursuant to a request for confidential treatment filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission) (10) |
10.6 | First Amendment, dated June 2, 2010, to the Agreement for Distribution of Products by and between Whole Foods Market Distribution, Inc. and United Natural Foods, Inc. (Portions of this agreement have been omitted pursuant to a request for Confidential Treatment filed with the Securities Exchange Commission) (4) |
10.7 | Second Amendment, dated October 11, 2010, to the Agreement for Distribution of Products by and between Whole Foods Market Distribution, Inc. and United Natural Foods, Inc. (Portions of this agreement have been omitted pursuant to a request for Confidential Treatment filed with the Securities Exchange Commission) (5) |
10.8 | Third Amendment, effective February 20, 2014, to the Agreement for Distribution of Products by and between Whole Foods Market Distribution, Inc. and United Natural Foods, Inc. (8) |
10.9 | Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement for WFLN and Directors under the 2009 Stock Incentive Plan (7) |
10.10 | Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement for U.S. WFLN and Directors under the 2009 Stock Incentive Plan (9) |
10.11 | Form of Restricted Share Award Agreement under the 2009 Stock Incentive Plan (12) |
12.1 | Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges (13) |
21.1 | Subsidiaries of the Registrant (13) |
23.1 | Consent of Ernst & Young LLP (13) |
31.1 | Certification by Co-Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 17 CFR 240.13a-14(a) (13) |
31.2 | Certification by Co-Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 17 CFR 240.13a-14(a) (13) |
31.3 | Certification by Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 17 CFR 240.13a-14(a) (13) |
32.1 | Certification by Co-Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350 (14) |
32.2 | Certification by Co-Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350 (14) |
32.3 | Certification by Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350 (14) |
101 | The following financial information from the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K, for the period ended September 28, 2014, formatted in eXtensible Business Reporting Language: (i) Consolidated Balance Sheets, (ii) Consolidated Statements of Operations, (iii) Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income, (iv) Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity, (v) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, (vi) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (13) |
56
(1) | Filed as an exhibit to Registrant’s Form S-8 filed May 31, 2013 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
(2) | Filed as an exhibit to Registrant’s Form 8-K filed April 16, 2009 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
(3) | Filed as an exhibit to Registrant’s Form 8-K filed September 7, 2012 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
(4) | Filed as an exhibit to Registrant’s Form 10-Q for the period ended July 4, 2010 filed August 13, 2010 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
(5) | Filed as an exhibit to Registrant’s Form 10-Q for the period ended January 16, 2011 filed February 25, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
(6) | Filed as an exhibit to Registrant’s Form 10-Q for the period ended April 8, 2012 filed May 17, 2012 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
(7) | Filed as an exhibit to Registrant’s Form 10-Q for the period ended July 7, 2013 filed August 9, 2013 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
(8) | Filed as an exhibit to Registrant’s Form 10-Q for the period ended April 13, 2014 filed May 16, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
(9) | Filed as an exhibit to Registrant’s Form 10-Q for the period ended July 6, 2014 filed August 8, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
(10) | Filed as an exhibit to Registrant’s Form 10-K for the period ended September 24, 2006 filed December 8, 2006 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
(11) | Filed as an exhibit to Registrant’s Form 10-K for the period ended September 30, 2012 filed November 21, 2012 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
(12) | Filed as an exhibit to Registrant’s Form 10-K for the period ended September 29, 2013 filed November 22, 2013 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
(13) | Filed herewith. | |
(14) | Furnished herewith. | |
57
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
WHOLE FOODS MARKET, INC.
Date: | November 21, 2014 | By: | /s/ Glenda Flanagan |
Glenda Flanagan | |||
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | |||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities indicated on November 21, 2014.
Name | Title | |
/s/ John Mackey | Co-Chief Executive Officer and Director | |
John Mackey | (Principal Executive Officer) | |
/s/ Walter Robb | Co-Chief Executive Officer and Director | |
Walter Robb | (Principal Executive Officer) | |
/s/ Glenda Flanagan | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | |
Glenda Flanagan | (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | |
/s/ Dr. John B. Elstrott | Chairman of the Board | |
Dr. John B. Elstrott | ||
/s/ Shahid M. Hassan | Director | |
Shahid M. Hassan | ||
/s/ Stephanie Kugelman | Director | |
Stephanie Kugelman | ||
/s/ Jonathan A. Seiffer | Director | |
Jonathan A. Seiffer | ||
/s/ Morris J. Siegel | Director | |
Morris J. Siegel | ||
/s/ Jonathan D. Sokoloff | Director | |
Jonathan D. Sokoloff | ||
/s/ Dr. Ralph Z. Sorenson | Director | |
Dr. Ralph Z. Sorenson | ||
/s/ Gabrielle Greene-Sulzberger | Director | |
Gabrielle Greene-Sulzberger | ||
/s/ William A. Tindell | Director | |
William A. Tindell | ||
58
