Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - MELINTA THERAPEUTICS, INC. /NEW/ | d405551d8k.htm |
 Developing
Well-Differentiated Antibiotics to Meet Medical Needs
Cempra Corporate Presentation
September 2012
Developing Well-Differentiated
Antibiotics to Meet Medical Needs
Exhibit 99.1 |
 Forward Looking
Statement 2
This presentation contains forward-looking statements regarding future events. These
statements are just predictions and are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause
the actual events or results to differ materially. These risks and uncertainties include,
among others: risks related to the costs, timing, regulatory review and results of our
studies and clinical trials; our ability to obtain FDA approval of our product
candidates; our dependence on the success of Solithromycin and Taksta; our need to obtain
additional funding and our ability to obtain future funding on acceptable terms; our
anticipated capital expenditures and our estimates regarding our capital requirements;
the possible impairment of, or inability to obtain, intellectual property rights and the
costs of obtaining such
rights
from
third
parties;
the
unpredictability
of
the
size
of
the
markets
for,
and
market
acceptance
of,
any
of
our
products,
including
Solithromycin
and
Taksta;
our
ability
to produce and sell any approved products and the price we are able to realize for those
products;
our
ability
to
retain
and
hire
necessary
employees
and
to
staff
our
operations
appropriately; our ability to compete in our industry; innovation by our competitors; and
our ability to stay abreast of and comply with new or modified laws and regulations that
currently apply or become applicable to our business. Please refer to the documents that
we file from time to time with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
|
 Lead program,
Solithromycin, has the potential to be the first Oral and IV macrolide approved
since
Zithromax/Z-PAK
-
Oral
Phase
3
trial
in
CABP
is
expected
to
begin
2H
2012
Solithromycin
Phase
2
trial
for
bacterial
urethritis
is
running
-
Results
expected
2H
2012
Antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea is a major global threat and new treatment
options for gonorrhea are urgently needed
Second program, Taksta, is an oral drug that is effective against MRSA, which we are
developing
for
long-term
treatment
of
Prosthetic
Joint
Infections
(PJI)-
Phase
2
trial
expected
to
begin
2H
2012
-
a
potential
orphan
indication
New
FDA
guidance
provides
regulatory
pathway
–
The
GAIN
Act
provides
incentives
for
antibacterial development
Large market opportunity with global antibiotic sales in the multibillions
Significant need for new antibiotics driven by resistance and tolerability issues
Strong management team with extensive, successful experience in antibiotic drug
development and approval -
Azactam, Biaxin, Fidaxomicin, Synercid, Viread
Highlights
3 |
 Significant need
for new treatment driven by:
Resistance
Adverse events/lack of tolerability
Inappropriate spectrum
Lack of IV-oral
Lack of pediatric dosing formulation
Acceptability for long term use
Developing Differentiated Antibiotics to Meet
Significant Needs
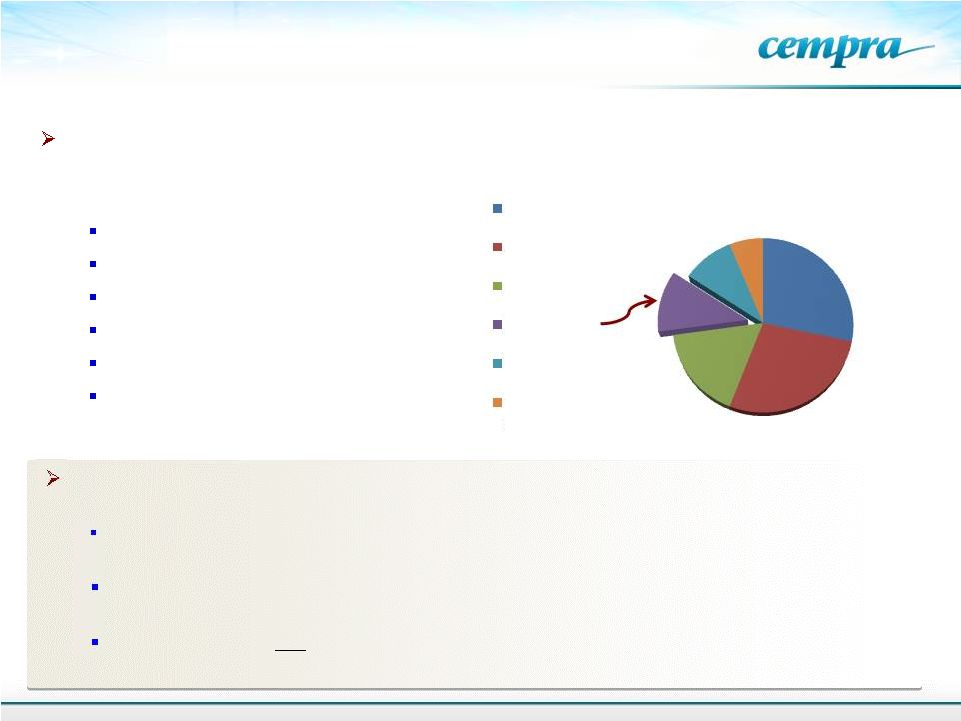
4
Global antibiotic sales in 2009
Total $42B
From B. Hamad, IMS Health
Nature Drug Discovery, 2010, 9:
675-676.
Cephalosporins
beta-lactams
Fluoroquinolones
Macrolides
Other antibacterials
Tetracyclines /
aminoglycosides
$11.9B
$11.5B
$7.1B
$4.8B
$4B
$2.6B
At least 30% of pneumococci in the U.S. are resistant to azithromycin (Z-Pak) –
the leading macrolide
Anti-gonorrhea
antibiotics
are
slowly
losing
their
effectiveness.
CDC
has
announced new
guidelines,
removing
Cefixime,
the
last
oral
drug
available
for
treating
gonorrhoea
Growing need for oral
therapies to address chronic staphyloccocal infections (MRSA)
infections –
chronic therapy of prosthetic joint infections
The growing need: |
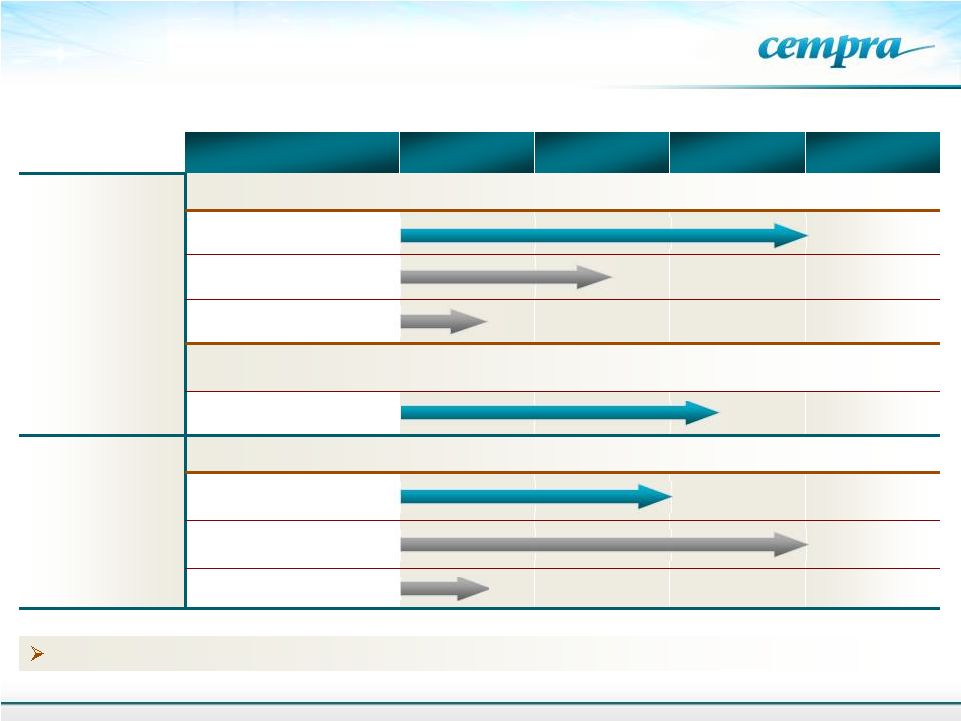 Cempra’s
Portfolio Addresses The Critical Needs
in The Antibiotic Market
Non-Antibiotic Macrolide
Program:
GERD/Diabetic gastroparesis and COPD are in preclinical stage
Product
Formulation
Preclinical
Phase 1
Phase 2
Phase 3
CEM-101
(Solithromycin)
Community Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP)
Oral
Intravenous (IV)
Oral Suspension/Pediatric
Future CEM-101 indications:
Urethritis,
Other respiratory tract infections (RTI’s), chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis (CF), malaria, eye infections, etc.
Oral –
Urethritis
Taksta
Fusidic Acid
Acute and Chronic Treatment of Staph (MRSA)
Oral –
Chronic Prosthetic
Joint Infections
Oral –
ABSSSI
Oral Suspension/Pediatric
5
TM |
 6
Solithromycin –
(CEM-101)
A next generation macrolide for respiratory tract infections, including
CABP, entering Phase 3 |
 7
Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia
(CABP)
Pneumococci (80% of cases)
Haemophilus
Staphylococcus
Moraxella
Legionella
Mycoplasma
Chlamydophila
Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia
(HAP)
Pseudomonas
Enteric gram-negatives (E.coli, Klebsiella,
Serratia, etc.)
Staphyloccci, MRSA
Pneumococcus
Haemophilus
Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia
(VAP)
Pseudomonas
Enteric gram-negatives (Klebsiella, Serratia,
etc.)
Acinetobacter
Staphyloccci, MRSA
Burkholderia
Viral Pneumonia
Influenza
Other viruses
All Pneumonias Are Not Created Equal |
 Community-Acquired Bacterial
Pneumonia (CABP)
No. 1 cause of death due to infection
Pneumococcus is the most common
cause of fatal CABP
Most common cause of chronic bronchitis,
sinusitis, meningitis and otitis media
5-6 million cases/year
~1 million hospital admissions/year
~1.6 million fatal cases of pneumococcal
disease worldwide annually
Pneumococcal diseases cause
more deaths per year in U.S. than
breast or prostate cancer
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2010. Active Bacterial Core
Surveillance Report, Emerging Infections Program Network, Streptococcus
pneumoniae, 2009. http://www.cdc.gov/abcs/reports-
findings/survreports/spneu09.pdf. Accessed February 3, 2011.
Xu. et al. Deaths: Final Data for 2007. Natl Vital
Stat Rep. 2010; 58: 1-51
8
Drug Discovery News May 2012. Report forecasts increases in
respiratory disease incidence, market. |
 9
Monotherapy, IV-Oral in CABP -
Currently Possible Only With Fluoroquinolones
Although FQs are approved and used widely for
treatment
of
CABP
–
Adverse
events
are
associated
with
their
use
–
It
is
not
approved
for
use
in
pediatrics
Fluoroquinolones affect bowel flora and select for
CDAD
Far more could be done to stop the deadly bacteria
C. diff By Peter Eisler, USA TODAY August 17, 2012
Tendonitis -
That can lead to spontaneous rupture of multiple
tendons, commonly Achilles, which may occur during
therapy or typically within 12 weeks, but can occur
years after therapy has been discontinued.
Adverse events from FQ treatment increase cost to hospitals, insurance companies and
patients Look, I know its ruptured
doc.. But surely I’ll still be
able
to run in the marathon
next
week… |
 Azithromycin’s long, low blood/tissue
levels favors selection of resistant
bacteria
A new macrolide is needed
Impact of Macrolide Therapy on Mortality in
Severe CABP
Restrepo, MI. et al. Eur Resp J. 2009; 33: 153-159.
Survival of CABP patients treated in accordance
with IDSA/ATS guideline using combinations
with a macrolide or a quinolone
-
macrolide
Martin-Loeches, I. et al. Intensive Care Med. 2010; 36:
612-620.
CONFIDENTIAL
10
IDSA and KOLs recommend a ß-lactam plus
Several reports show that addition of a
macrolide results in better patient outcome
Addition of macrolide decreases mortality by
>50% in patients with highest PORT scores
+ macrolide
a macrolide for CABP |
 Solithromycin
Opportunity 11
Azithromycin (Zithromax/Z-Pak), the
leading macrolide, went generic in 2005
52 million prescriptions and $1.1 billion in
sales in 2010
Widespread azithromycin use has led to
resistance issues
Lack of new macrolides with improved
resistance profiles has led physicians to
turn to fluoroquinolones (Levaquin) despite
side effect concerns
Total
2009
Pneumonia
Oral
Prescriptions
–
By
Class (Branded and Generic)
Source: IMS
Macrolides are the most widely
prescribed treatment for CABP and
other RTIs
Broad spectrum of activity
Good safety
Excellent tissue/intracellular distribution
and anti-inflammatory activity
Pneumococcal
resistance
rate
in
China
–
96.4%
Asian Network Surveillance. AAC. 2012; 56: 1418-1426.
Canadian Bacterial Surveillance Network.
http://microbiology.mtsinai.on.ca/research/cbsn/.
Accessed March 2011
62.6%
25.5%
11.9%
Extended Spectrum
Macrolides
Quinolones
Other
Erythromycin-Resistant S. pneumoniae Isolates in
NA |
 History of
Macrolide Development 12
In vitro
activity is similar.
Better PK, acid stable,
fewer GI effects
Resistance is now widespread
More potent than 2
generation macrolides
Active against macrolide-resistant strains, 2 binding
sites, acid stable, good PK, better tissue
distribution
Telithromycin
–
major
adverse
events
Others
have
failed
–
no
other
new
macrolides
More potent than 3 generation macrolides
Active against 1 , 2 and 3 generation
macrolide-resistant strains, 3 ribosomal binding
sites, extended spectrum, good PK and tissue
distribution, intravenous and oral dosing
Effective in Phase 2 oral and well-tolerated
(Solithromycin)
First Generation Macrolide
Second Generation Macrolide
Third Generation Macrolides, “Ketolides”
Fourth Generation Macrolide, Fluoroketolide
nd
rd
st
nd
rd |
 # of
Organisms Solithromycin
Azithromycin
MIC
90
(µg/ml)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
(150)
0.25
>16
Haemophilus influenzae
(100)
2
2
Streptococcus pyogenes
(100)
0.03
>16
Legionella pneumophila
(30)
0.015
2
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
(36)
0.000125
0.0005
Chlamydophila pneumoniae
(10)
0.25
0.125
Solithromycin: Spectrum of Activity
That Addresses CABP Pathogens
Solithromycin (CEM-101) is several fold more potent than azithromycin against S.
pneumoniae, a critical pathogen in CABP and respiratory tract infections
13
Solithromycin has
demonstrated class-leading
potency in vitro against
macrolide-resistant
pneumococcus
CEM-101’s unique chemical structure necessitates mutations at three
distinct
sites
for
resistance
to
develop
–
no
other
macrolide
has
more
than
two |
 Population
Solithromycin
Levofloxacin
Success rate, %
Success rate, %
ITT*
72.3
71.6
MITT
77.8
71.4
Solithromycin: Comparable Efficacy to Standard of
Care
(Levaquin)
-
Oral
Phase
2
Trial
14
Solithromycin
performed
favorably
in
mITT
at
TOC
when
CABP
pathogens
were
isolated
-
key
criteria used by the FDA
Randomized 132 patients received either Solithromycin or Levofloxacin:
* Early
Clinical
Response
defined
as:
Improvement at 72 hours in severity from baseline in at least two of the following
signs/symptoms: cough, dyspnea, chest pain, sputum production
Without worsening in any of the above 4 signs/symptoms -
patient is clinically stable
Proposed
by
FDA,
November
3
rd
2011
for
future
CABP
trial
design
and
defined
by
the
Foundation
for the NIH (FNIH) |
 Solithromycin
demonstrated a favorable safety and tolerability profile, with a lower incidence of AEs
than levofloxacin Fewer treatment emergent AEs (30% vs 46%)
Fewer study subjects with SAEs (2 vs 7 subjects)
Fewer drug discontinuations due to AEs (0 vs 6 subjects)
Fewer GI related AEs (14% vs 24%)
No significant liver safety issues
No QT signals of concern
No bitter after-taste
15
Solithromycin: Favorable Safety and Tolerability –
Oral Phase 2 Trial |
 Community-Acquired Bacterial
Pneumonia (CABP) –
Standard-of-Care
16
Macrolides have kept a large segment of the global antibiotic market in spite of
fluoroquinolones
Macrolide segment not crowded
Mostly
occupied
by
azithromycin
and
clarithromycin
–
rising
incidence
of
resistance
No new macrolides except solithromycin
Solithromycin
is
being
developed
for
monotherapy
for
CABP
–
replacing
current
standard
of
care
-
a
cephalosporin
plus
azithromycin
cost of two drugs
No oral cephalosporin for step down
Side effects of two drugs
Solithromycin has the spectrum of activity that provides coverage for CABP pathogens,
including azithromycin-resistant bacteria
Step down IV to oral therapy could give a pharmacoeconomic advantage over current
treatment options |
 Solithromycin:
Intravenous Development First Injectable Macrolide in 20 Years
17
High plasma levels after IV
administration to address
the most resistant bacteria.
Well tolerated
No QT effects.
Intravenous macrolides have not been developed because of safety
and
tolerability issues
FDA
interest
in
IV
dose
-
Allows
enrollment
of
PORT
III –
IV patients
IV toxicology, 28-day in dog and monkey –
well-tolerated
Intravenous and oral formulation allow:
Flexibility for treating severe or moderate pneumonia
Severely ill patients begin treatment in the hospital
and then go home earlier on oral therapy
Pharmacoeconomic advantage
Phase 1 IV clinical trial underway |
 Plan for Phase 3
CABP Studies 18
Phase
3
CABP
trial
design
and
end
points
are
consistent
with
the
proposed
FDA
CABP
guidance Nov 2011
Two phase 3 trials are planned. One oral trial and one IV-to-oral step-down
trial Phase 3 oral planned to begin second half 2012 and complete in 2014
Global study –
<50% PORT II, 50% PORT III and PORT IV
Enroll ~800 patients
Comparator
moxifloxacin
–
a
fluoroquinolone
that
is
used
worldwide
at
same
dose
Enrollment criteria controlled strictly as per FDA guidance
Success criteria: as specified by newly proposed FDA guidance
Primary endpoint: Non-inferiority of early response (at 72 hours) compared to a
fluoroquinolone Secondary endpoints: Safety and pooled mITT at early response
|
 19
Solithromycin for CABP and Multiple
Indications –
Potential Broad Use
Campylobacter
diarrhea
Helicobacter
gastritis
Gonococcal and
non-gonococcal urethritis
Simple Skin Infections
Group B Strep
infections in
pregnancy
Lyme disease and
other tick borne
diseases
Other Diseases:
Ophthalmic Infections
Pediatric Infections
Malaria
prophylaxis
Biodefense
GI Tract Diseases:
Antibacterial and Anti-
inflammatory:
Primary Indication: CABP
Simple RTI’s, Pharyngitis, Sinusitis,
Bronchitis, Acute Exacerbation of Chronic
Bronchitis (AECB)
GU Tract Diseases:
Respiratory Tract Infections (RTI):
COPD
Cystic fibrosis
Panbronchiolitis
Solithromycin-
The Next Generation
Macrolide-
First Fluoroketolide |
 20
Urethral Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates (n= 32,794)
with
elevated
MICs
(>0.25
g/mL)
and
Ceftriaxone
MICs
(>0.125
g/mL).
Gonococcal
Surveillance
project, US. 2006-2011)
Gonococcal Isolate Surveillance Project (Bolan et al.
NEJM 2012. 366:485-487)
D. Gopalrian, et al. WHO Collaborating Center for Gonorrhoea
and other STIs. AAC, 56: 2739-2742, 2012,
MIC
90
(
g/mL)
Range
(
g/mL)
0.25
0.001
-
32
In Vitro Activity of Solithromycin against
256 gonococci
The proportion of N. gonorrhoeae in the US with
elevated
cefixime
MICs
has
increased
17-
fold
between 2006 and the first half of 2011
Last Oral Antibiotic Removed from Recommended
Therapy
for
Gonococcus
-
2
nd
most
common
Communicable Disease |
 21
30 patients with
uncomplicated
gonorrhea
Patient
Population
Gram
stain/culture
NAAT
Clinical
Symptoms
Day 1
Screen and
Diagnosis
Treat with single
dose of
Solithromycin
1200 mg
Day 2
Proven
gonorrhoeae
Test of cure
Symptom
Free
Negative culture
Day 7 (+ 3)
TOC
Uncomplicated
Gonococcal
Urethritis
-
Phase
2
Trial Plan
Current Treatment:
Ceftriaxone
250 mg IM in a single dose OR, IF NOT AN OPTION,
Cefixime
400 mg orally in a single dose
OR
Single
dose
injectable
cephalosporin
regimens
PLUS
Azithromycin
1g
orally
in
a
single
dose
OR
Doxycycline
100 mg orally twice a day for 7 days
Study Design:
Open label, single site, oral treatment of uncomplicated gonorrhea
Success Criteria:
The
primary
outcome
–
bacterial
eradication
at
TOC
(7
day
after
treatment)
Other outcome measures:
Safety and tolerability
th |
 22
TAKSTA™
(Fusidic acid)
An oral antibiotic for MRSA infections
being developed for chronic use in the U.S. |
 23
What is Taksta ?
Taksta is Cempra’s proprietary fusidic acid dosing regimen
Fusidic acid approved in Western Europe, Australia, and other countries
40
years
of
established
safety
and
efficacy
profile
in
acute
and
chronic
use
in
staph
infections ex-U.S.
NCE in the US, Hatch Waxman exclusivity, 5 years obtained by Cempra, dosing regimen
patent,
supply
agreement
of
drug
substance
-
a
fermentation
product
GAIN
Act
adds
an
additional
5
years
of
data
exclusivity
-
A
minimum
of
10
years
of
data
exclusivity
Unique structure, no cross resistance with any other antibiotic
Orally bioavailable
Targeted
against
gram-positive
pathogens,
including
MRSA
-
a
pathogen
of
great
concern
that causes bone and joint infections requiring long-term treatment
TM |
 Tetracyclines
and
Bactrim
(TMP/SMX)
have
significant
limitations
for
oral,
outpatient
use
Linezolid is the only oral antibiotic approved for MRSA but is not recommended for long term
use
TAKSTA has Excellent Activity Against
S.
aureus
in
the
U.S.
(1,710
U.S.
strains)
24
Taksta is highly effective against S. aureus strains found in the U.S.
Antimicrobial
agents
MIC (µg/ml)
90%
% susceptible
Fusidic acid
0.12
99.6
Clindamycin
>2
69.7
Erythromycin
>4
11.2
Levofloxacin
>4
30.2
Linezolid
1
99.9
Tetracycline
1
95.8
TMP/SMX
97.9
Compared with other Oral Agents
Almost all staph
and MRSA
in the U.S.
are susceptible
0.5 |
 25
Osteomyelitis/Prosthetic Joint Infection is a
Significant Opportunity
Growing
need
for
oral
therapies
to
address
MRSA
infections
Physicians cite staph (MRSA) as top pathogen of
concern in prosthetic joint infections and
osteomyelitis
Prosthetic joint replacement is increasing
Risk of life-long bacterial infection of implant
Minimum duration of treatment is 4-6 weeks, with
many patients requiring life-long treatment
Leading drugs for prosthetic joint infections and
osteomyelitis are the same as those for ABSSSI:
vancomycin, daptomycin and linezolid
Total prosthetic-joint infections 1990-2004 (Kurtz et. al)
N Engl J Med. 2009; 361: 787-794
Total arthroplasties performed from 1990-2006 (CDC) |
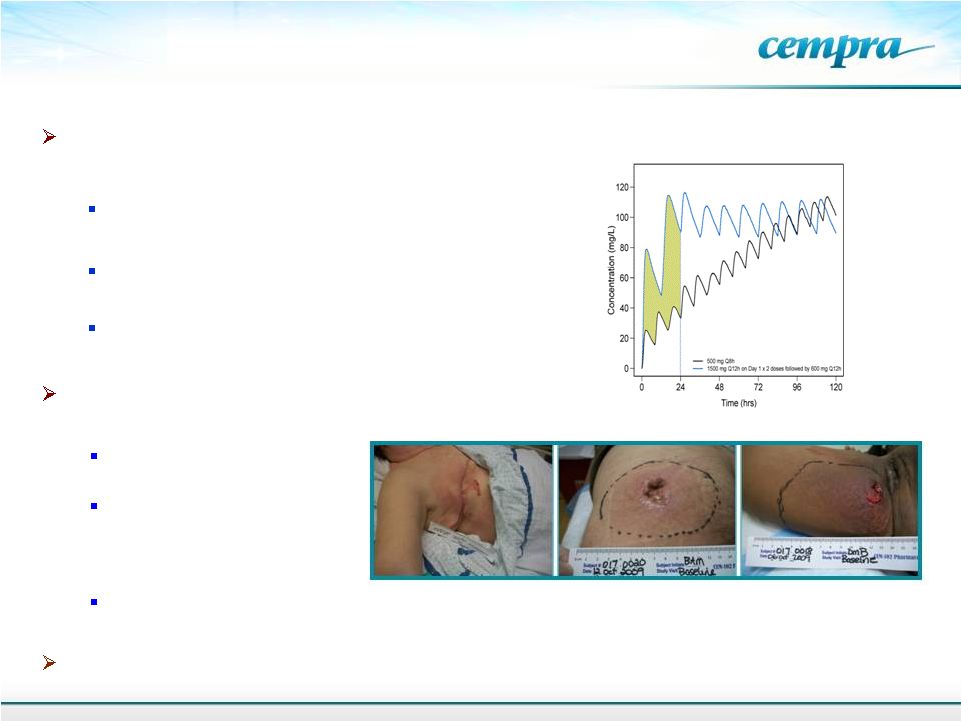 European
dosing Cempra’s loading dose
1500 mg BID loading dose followed by 600 mg BID
maintenance
dose
–
minimizes
resistance
development
Loading
dose
regimen
validated
–
resistance
not
noted
in Phase 2 study
Patent pending
Cempra’s Proprietary TAKSTA Loading Dose
Validated -
Phase 2 Study With MRSA Infections
Cempra developed a proprietary loading dose regimen to prevent resistance to fusidic acid
that has occurred outside the U.S.
26
Data from 155-patient Phase 2 trial demonstrates
efficacy and safety in ABSSSI
Comparable efficacy
to Zyvox (linezolid)
Proprietary loading dose
regimen was well
tolerated and overcame
resistance
Comparable safety to linezolid, despite trial design excluding patients for whom linezolid is
contra- indicated (e.g., those on SSRIs)
End of Phase 2 meeting for ABSSSI with FDA completed |
 Use In
Prosthetic Joint Infections 27
Used outside the U.S. in Osteomyelitis/PJI
Significant physician interest for chronic use in the U.S.
Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010; 29: 171-180
Several reports from ex-USA that PJI
can be successfully treated by
adding FA to the standard of care
Taksta
could
address
the
need
for
a
safe,
oral
product
for
acute
and
chronic
treatment in prosthetic joint infections |
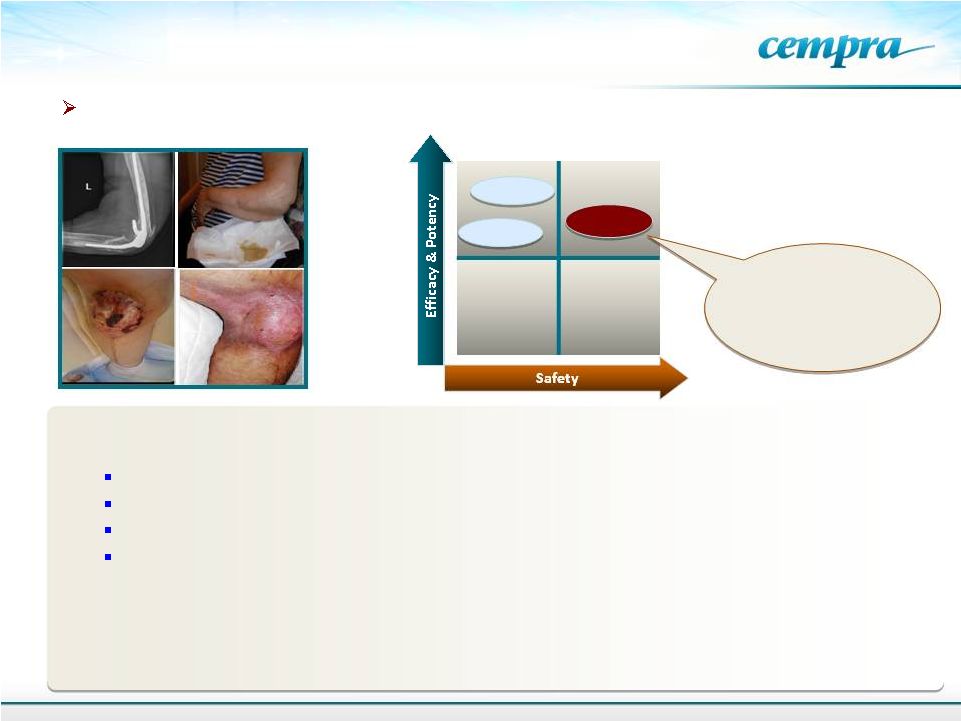 28
Two compassionate use cases of bone/prosthesis infections in North America
Efficacy is
comparable to linezolid but has
better
safety
–
useful
for
oral
chronic use in all
patient populations
PJI Facts:
200,000 Hip Replacements; 550,000 Knee Replacements in 2007
Surgeries increase by 3% per year
1% of hips and 2% of knees develop PJI's
Chronic daily therapy
Total
Joint
and
Hardware
Procedures
-
3,286,000/year
a,b
Potential use in osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, diabetic foot
Potential of Taksta for Chronic Use in
Prosthetic Joint Device Infections
Tedizolid
Linezolid
Taksta
a
Life Science Intelligence market research report. U.S. Markets for Large Replacement
Technologies in 2012. March, 2012.
b
Life Science Intelligence market research report. U.S. Markets for Small Joint
Implants and Hardware for the Extremities. January,
2012. |
 Current
Treatment: Debride
and
treat
intravenously
and
orally
for
months
–
replace
prosthesis
if
possible,
Study Design:
Success
Criteria:
The
primary
outcome
–
retention
of
a
functional
prosthesis
at the end of 3 months
Other outcome measures: longer term safety and tolerability, joint & mobility
function
Cempra
will
confirm
trial
design
with
the
FDA
–
Orphan
indication
potential
29
50 patients with
Knee or Hip PJI
Patient
Population
IV vancomycin
+ Taksta
+ rifampin
Discontinue
vancomycin at
7-28 days
Add Taksta to
Current Standard
of Care
Continue with
Taksta +
rifampin
for 3 months
Continue for
3 Months
Taksta as oral
monotherapy
beyond 3
months
Long-Term
Therapy
Prosthetic
Joint
Infection
Phase
2
Trial
Plan
–
Chronic
Oral Treatment of MRSA
may not be possible in older patients |
 2012
Milestones 2H 12: CEM-101 Initiation of dosing of Phase 3 Oral Global Trial for
CABP 2H 12: CEM-101 Completion of Phase 1 IV
4Q 12: Taksta Initiation of dosing of Phase 2 Prosthetic Joint Infection Trial
4Q 12 Solithromycin top line data of Phase 2 Gonococcal Urethritis Study
2013 Milestones
1H 13: CEM-101 Initiation of Phase 3 IV-to-Oral CABP Trial (Financing
TBD) 4Q 13: Taksta top line Prosthetic Joint Infection results
2014 Milestones
1H 14: Taksta Phase 2 Prosthetic Joint Study Results
1H 14: CEM-101 Phase 3 Oral CABP Top line data
30
Clinical Development Plan and
Estimated Milestones |
 31
Capitalization
Cash & Equivalents (at 6/30/12)
$ 57.8M
Long-Term Debt (at 6/30/12)
$ 9.6M
Shares Outstanding
21.0M
Market Capitalization (at 8/30/12)
$167.0M
Cash Runway *
1H 2014
* Includes initiation of CEM-101 P3 oral trial and Taksta P2 PJI trial;
Does not include any potential partnerships. |
 Kenneth Touw,
PhD EVP Regulatory
Carl Foster
EVP Business Development
Mark Hahn, CPA
CFO
David Oldach, MD
SVP Clinical
GILEAD
Prabhavathi Fernandes, PhD
President & CEO
Proven Management Team
David Pereira, PhD
SVP Chemistry
•
Azactam
(aztreonam)
•
Biaxin
(clarithromycin)
•
Dificid
(fidaxomicin)
•
Plenaxis
(abarelix)
•
Zavesca
(miglustat)
•
OncoVax
•
Prilosec
(omeprazole)
•
IPO and M&A
•
Athenix-Bayer CropScience
•
Charles & Colvard (CTHR)
•
E&Y
•
Viread
•
GS-9190
•
Combinations against HCV
•
Synercid
(quinupristin/
dalfopristin)
•
Altace
(ramipril)
•
Embeda
(morphine
and
naltrexone)
•
Acurox
•
Injectable Penicillins
•
Dobutamine HCl Injection
•
Ranitidine Injection
32
(oxycodone) |
 Highlights
33
Lead program, Solithromycin, has the potential to be the first Oral and IV macrolide
approved
since
Zithromax/Z-PAK
-
Oral
Phase
3
trial
in
CABP
is
expected
to
begin
2H
2012
Solithromycin
Phase
2
trial
for
bacterial
urethritis
is
running
-
Results
expected
2H
2012
Antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea is a major global threat and new treatment options for
gonorrhea are urgently needed
Second program, Taksta, is an oral drug that is effective against MRSA, which we are
developing
for
long-term
treatment
of
Prosthetic
Joint
Infections
(PJI)-
Phase
2
trial
expected to begin 2H 2012 -
a potential orphan indication
New
FDA
guidance
provides
regulatory
pathway
–
The
GAIN
Act
provides
incentives
for
antibacterial development
Large market opportunity with global antibiotic sales in the multibillions
Significant need for new antibiotics driven by resistance and tolerability issues
Strong management team with extensive, successful experience in antibiotic drug
development
and
approval
-
Azactam,
Biaxin,
Fidaxomicin,
Synercid,
Viread |
