Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - HALOZYME THERAPEUTICS, INC. | a58046e8vk.htm |
Exhibit 99.1

| Halozyme Therapeutics Matrix Therapies for Life Doug Muchmore, M.D., VP, Endocrinology Clinical Development Robert H. Uhl, Senior Director, Investor Relations Canaccord Cardiovascular, Diabetes & Obesity Conference San Francisco, December 8, 2010 |

| Safe Harbor The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 provides a "safe harbor" for forward-looking statements. All statements made in this presentation that are not statements of historical fact constitute forward-looking statements. The matters referred to in forward-looking statements could be affected by the risks and uncertainties of the Company's business. Such risks inherent to the Company's business will be described in the Company's filings, when they occur, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, as well as in its press releases. The Company's actual results may differ materially from those expressed in or indicated by such forward-looking statements. 2 |

| Halozyme Investment Highlights Strong technology foundation and pipeline of proprietary and partnered programs with significant revenue potential Core technology is rHuPH20 hyaluronidase enzyme ("PH20"): FDA approved, with strong safety profile and IP protection Phase 3 programs - HyQ SC with Baxter and Herceptin(r) SC with Roche Phase 2 ultrafast insulin product with potential best-in-class profile Other Matrix degrading enzymes - PEGPH20 for oncology and HTI-501 for dermatology offer better treatments and patient benefits Solid financial position: Cash of $90 million end of 3Q10, includes equity offering for additional $60 million in September 2010 3 |

| 4 PH20 Core Technology: Targets Hyaluronan (HA) in "Matrix" |
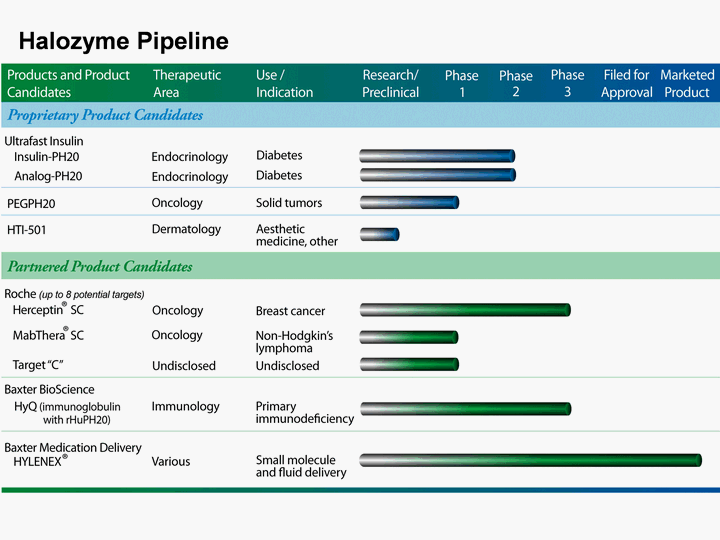
| Halozyme Pipeline |
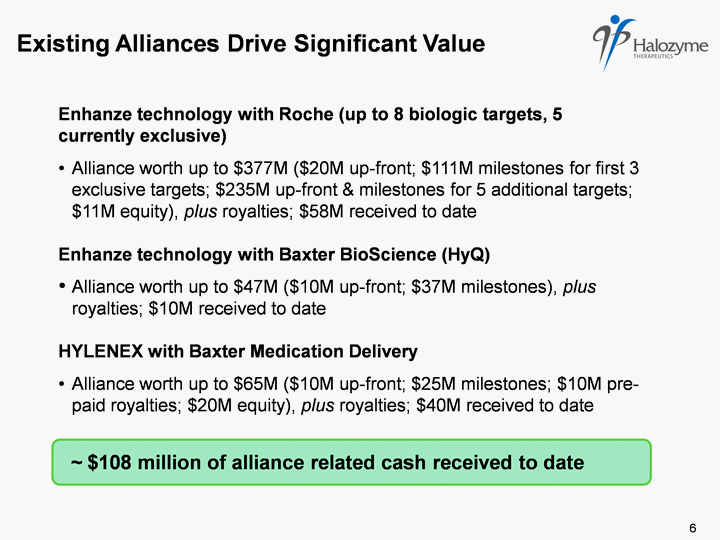
| Existing Alliances Drive Significant Value ~ $108 million of alliance related cash received to date Enhanze technology with Roche (up to 8 biologic targets, 5 currently exclusive) Alliance worth up to $377M ($20M up-front; $111M milestones for first 3 exclusive targets; $235M up-front & milestones for 5 additional targets; $11M equity), plus royalties; $58M received to date Enhanze technology with Baxter BioScience (HyQ) Alliance worth up to $47M ($10M up-front; $37M milestones), plus royalties; $10M received to date HYLENEX with Baxter Medication Delivery Alliance worth up to $65M ($10M up-front; $25M milestones; $10M pre- paid royalties; $20M equity), plus royalties; $40M received to date 6 |
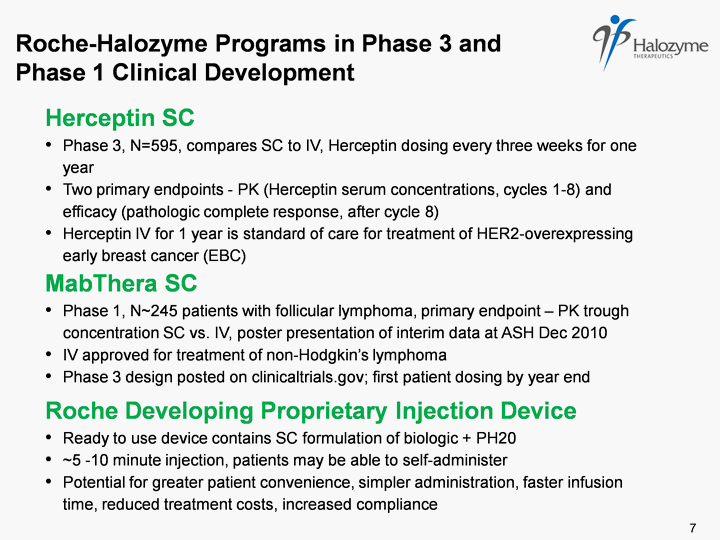
| Herceptin SC Phase 3, N=595, compares SC to IV, Herceptin dosing every three weeks for one year Two primary endpoints - PK (Herceptin serum concentrations, cycles 1-8) and efficacy (pathologic complete response, after cycle 8) Herceptin IV for 1 year is standard of care for treatment of HER2-overexpressing early breast cancer (EBC) MabThera SC Phase 1, N~245 patients with follicular lymphoma, primary endpoint - PK trough concentration SC vs. IV, poster presentation of interim data at ASH Dec 2010 IV approved for treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma Phase 3 design posted on clinicaltrials.gov; first patient dosing by year end Roche Developing Proprietary Injection Device Ready to use device contains SC formulation of biologic + PH20 ~5 -10 minute injection, patients may be able to self-administer Potential for greater patient convenience, simpler administration, faster infusion time, reduced treatment costs, increased compliance Roche-Halozyme Programs in Phase 3 and Phase 1 Clinical Development 7 |
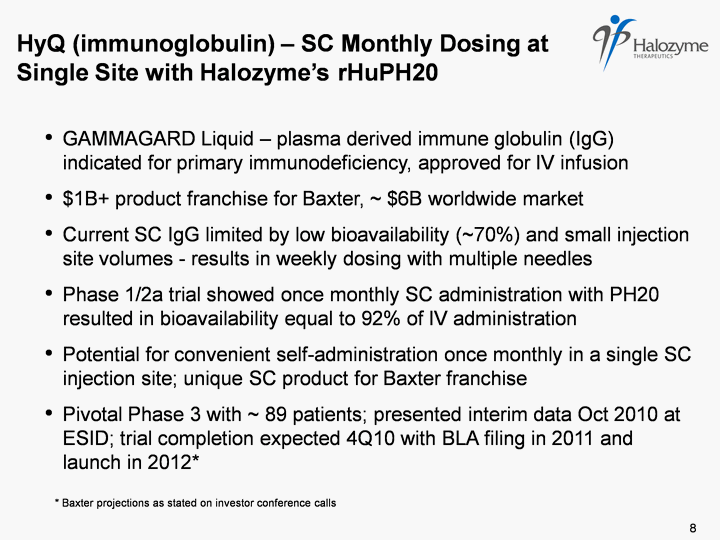
| GAMMAGARD Liquid - plasma derived immune globulin (IgG) indicated for primary immunodeficiency, approved for IV infusion $1B+ product franchise for Baxter, ~ $6B worldwide market Current SC IgG limited by low bioavailability (~70%) and small injection site volumes - results in weekly dosing with multiple needles Phase 1/2a trial showed once monthly SC administration with PH20 resulted in bioavailability equal to 92% of IV administration Potential for convenient self-administration once monthly in a single SC injection site; unique SC product for Baxter franchise Pivotal Phase 3 with ~ 89 patients; presented interim data Oct 2010 at ESID; trial completion expected 4Q10 with BLA filing in 2011 and launch in 2012* HyQ (immunoglobulin) - SC Monthly Dosing at Single Site with Halozyme's rHuPH20 8 * Baxter projections as stated on investor conference calls |

| HYLENEX - For Use in Pediatric Hydration Voluntary product recall announced May 2010 to ensure patient safety; no medical or adverse events reported in conjunction with the manufacturing issues Manufacturing issue unique to HYLENEX, does not impact any other Halozyme development programs Halozyme has completed root cause investigation and has submitted materials to FDA 9 |
| Proprietary Product Candidates Target the Matrix Ultrafast Insulin - PH20 with regular and mealtime analog insulins for diabetes PEGPH20 - Pegylated PH20 targets HA expressing tumors HTI-501 - Novel Matrix remodeling enzyme targets collagen degradation 10 |
| Goal - To develop best-in-class rapid-acting insulin products that surpass current standards of care Proprietary insulin formulations of novel PH20 permeation enhancing excipient with Rapid-acting analog insulin (Humalog(r), NovoLog(r), Apidra(r)) ? "Analog-PH20" Short-acting regular human insulin (Humulin(r) R) ? "Insulin-PH20" Currently in Phase 2, targeting commercialization by 2014, depending on most attractive product candidate (Analog-PH20 vs. regular Insulin-PH20) or a partnership Halozyme's Ultrafast Insulin Program 11 |
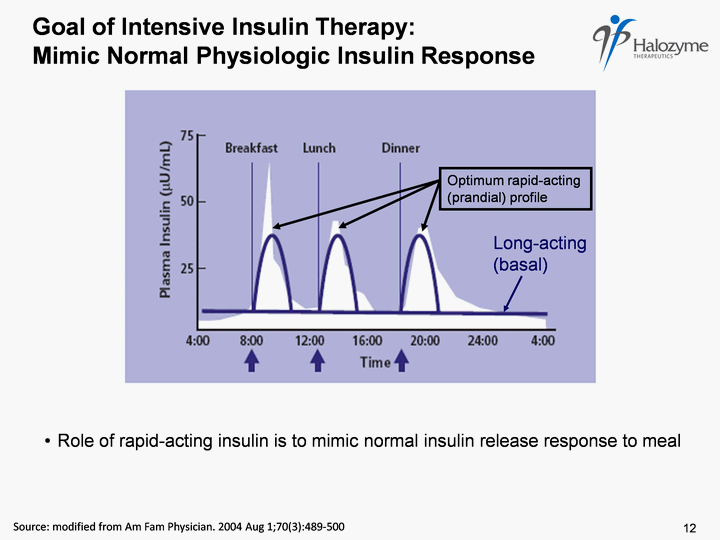
| Goal of Intensive Insulin Therapy: Mimic Normal Physiologic Insulin Response Source: modified from Am Fam Physician. 2004 Aug 1;70(3):489-500 Role of rapid-acting insulin is to mimic normal insulin release response to meal Long-acting (basal) Optimum rapid-acting (prandial) profile 12 |
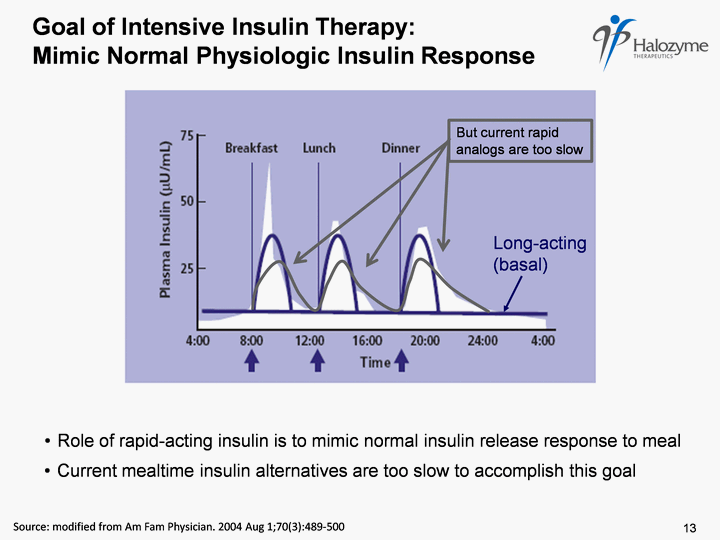
| Goal of Intensive Insulin Therapy: Mimic Normal Physiologic Insulin Response Source: modified from Am Fam Physician. 2004 Aug 1;70(3):489-500 Role of rapid-acting insulin is to mimic normal insulin release response to meal Long-acting (basal) Current mealtime insulin alternatives are too slow to accomplish this goal 13 |
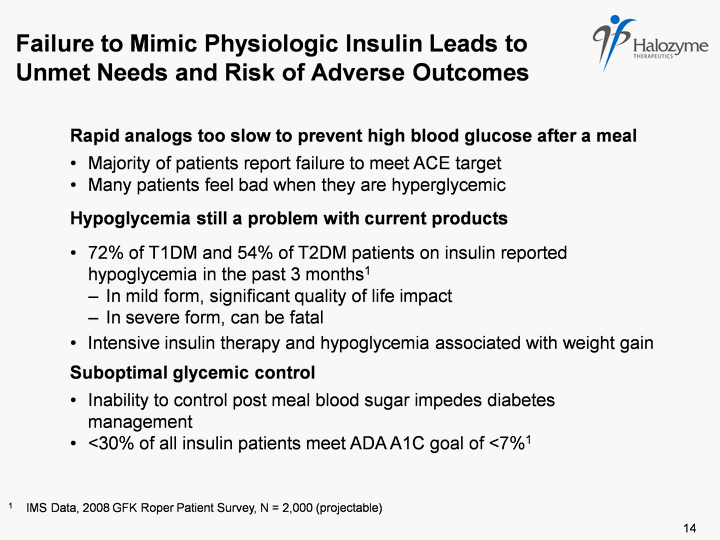
| Failure to Mimic Physiologic Insulin Leads to Unmet Needs and Risk of Adverse Outcomes 1 IMS Data, 2008 GFK Roper Patient Survey, N = 2,000 (projectable) Rapid analogs too slow to prevent high blood glucose after a meal Majority of patients report failure to meet ACE target Many patients feel bad when they are hyperglycemic Hypoglycemia still a problem with current products 72% of T1DM and 54% of T2DM patients on insulin reported hypoglycemia in the past 3 months1 In mild form, significant quality of life impact In severe form, can be fatal Intensive insulin therapy and hypoglycemia associated with weight gain Suboptimal glycemic control Inability to control post meal blood sugar impedes diabetes management <30% of all insulin patients meet ADA A1C goal of <7%1 14 |
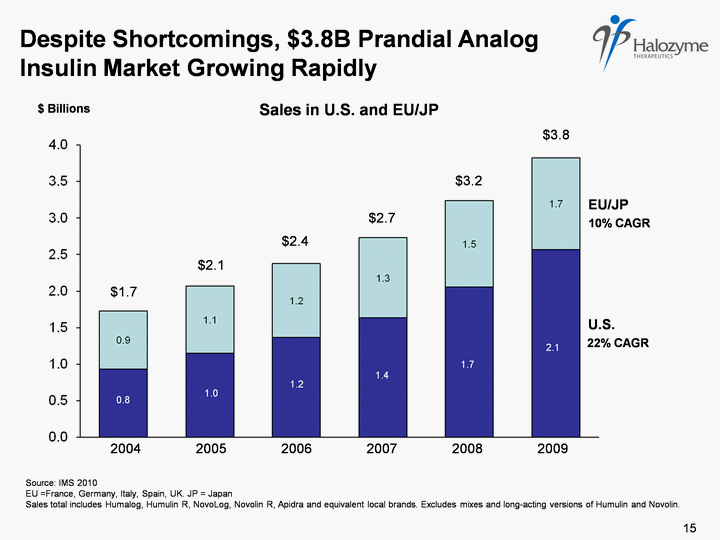
| 1 Source: IMS 2010 EU =France, Germany, Italy, Spain, UK. JP = Japan Sales total includes Humalog, Humulin R, NovoLog, Novolin R, Apidra and equivalent local brands. Excludes mixes and long-acting versions of Humulin and Novolin. Despite Shortcomings, $3.8B Prandial Analog Insulin Market Growing Rapidly 1.0 1.7 2.1 0.8 U.S. 1.2 1.4 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 EU/JP $1.7 $2.1 $2.4 $2.7 $3.2 $3.8 22% CAGR 10% CAGR $ Billions Sales in U.S. and EU/JP 15 |
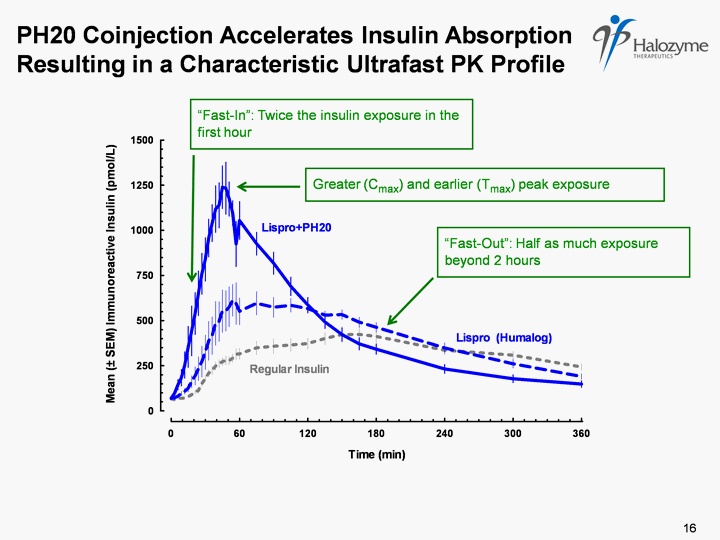
| PH20 Coinjection Accelerates Insulin Absorption Resulting in a Characteristic Ultrafast PK Profile "Fast-In": Twice the insulin exposure in the first hour "Fast-Out": Half as much exposure beyond 2 hours Greater (Cmax) and earlier (Tmax) peak exposure 16 |
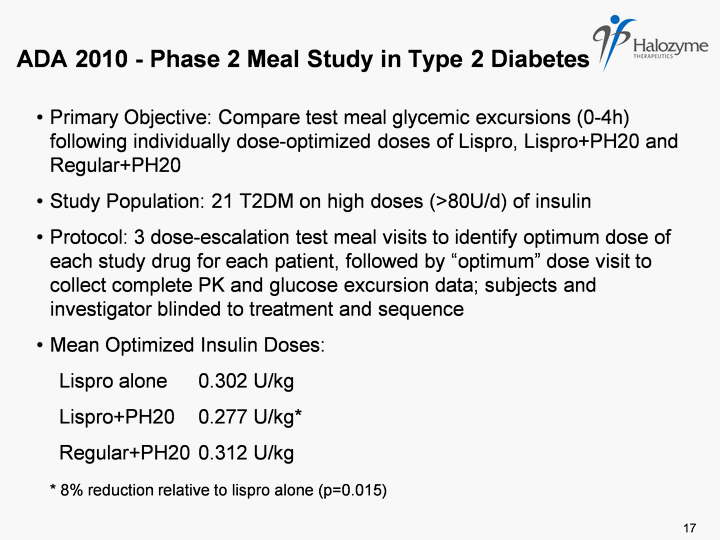
| ADA 2010 - Phase 2 Meal Study in Type 2 Diabetes Primary Objective: Compare test meal glycemic excursions (0-4h) following individually dose-optimized doses of Lispro, Lispro+PH20 and Regular+PH20 Study Population: 21 T2DM on high doses (>80U/d) of insulin Protocol: 3 dose-escalation test meal visits to identify optimum dose of each study drug for each patient, followed by "optimum" dose visit to collect complete PK and glucose excursion data; subjects and investigator blinded to treatment and sequence Mean Optimized Insulin Doses: Lispro alone 0.302 U/kg Lispro+PH20 0.277 U/kg* Regular+PH20 0.312 U/kg * 8% reduction relative to lispro alone (p=0.015) 17 |
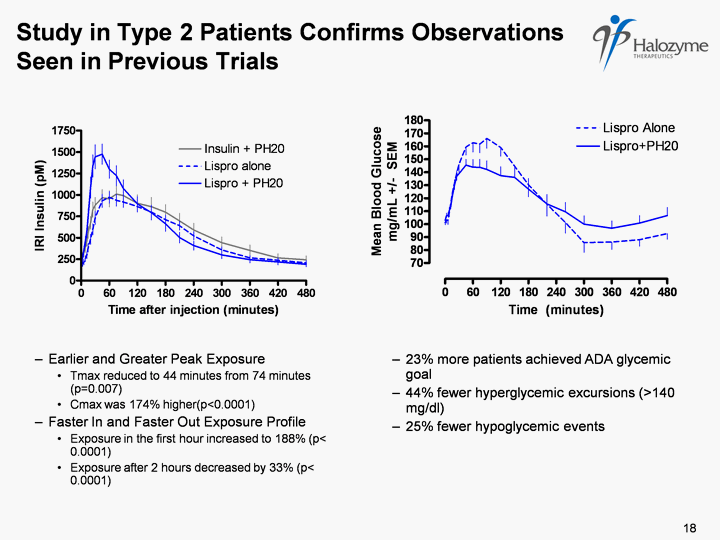
| Study in Type 2 Patients Confirms Observations Seen in Previous Trials Earlier and Greater Peak Exposure Tmax reduced to 44 minutes from 74 minutes (p=0.007) Cmax was 174% higher(p<0.0001) Faster In and Faster Out Exposure Profile Exposure in the first hour increased to 188% (p< 0.0001) Exposure after 2 hours decreased by 33% (p< 0.0001) 18 23% more patients achieved ADA glycemic goal 44% fewer hyperglycemic excursions (>140 mg/dl) 25% fewer hypoglycemic events |
| Recombinant Human Insulin+PH20 - Safe, PK and Efficacy Comparable to Lispro Alone Designed to assess safety of 12 weeks of tid dosing and demonstrate non- inferiority in treatment of patients with T1DM of Insulin-PH20 and lispro Results presented at Diabetes Technology Society November 2010 19 Results- PK for Insulin-PH20 comparable to lispro alone ^ glycemic control comparable to lispro alone as measured by glycemic excursion, A1C, hypoglycemia Overall safety comparable for the two treatments Three times per day take-home study, included over 10,000 doses of insulin with rHuPH20 enzyme, 12 weeks of treatment per study drug Studies underway to demonstrate potential superiority of analog+rHuPH20 to prandial analog alone |
| Two Ongoing Phase 2 Studies - Analogs +- PH20, Part of Intensive TID Insulin Treatment Regime HALO-205, HALO-206, N=110 for each study, 3x/day, 12 weeks crossover Designed to demonstrate meaningful improvement of lispro-PH20 and/or aspart-PH20 vs. Humalog in patients with T1DM or T2DM Results available to Halozyme 3Q11 for presentation in 2012 20 Primary Endpoint Compare Lispro-PH20 or Aspart-PH20 to insulin lispro alone with respect to glycemic control - change in A1C from baseline Secondary Endpoints Compare Lispro-PH20 and Aspart-PH20 results to insulin lispro for - Blood glucose profiles over 3 days, SMBG and CGM Postprandial glucose changes from pre-meal baseline Proportion of patients achieving A1C <7.0%, and A1C ^6.5% Overall rate of hypoglycemia Composite endpoint of proportion of patients achieving A1C goals without unacceptable hypoglycemia |
| Halozyme's Ultrafast Insulin Clinical Studies Euglycemic Clamp Studies in Healthy Volunteers Proof of Concept Study (Vaughn et al. DTT May, 2009) PH20 Dose Selection Study (Posters at IDF and DTS 2009) Variability Study (Poster at DTS 2009) Comprehensive Analog Study (Oral presentation, ADA 2010; poster, EASD 2010) Meal Studies in Patients Type 1 Meal Study (Posters at ADA and EASD 2009) Type 2 Meal Study (President's Poster Session, ADA 2010; oral presentation, EASD 2010) Treatment Studies in Patients Phase 2 Treatment Study,T1DM, Regular-PH20 vs. Lispro alone (Poster at Diabetes Technology Society, November 2010) Phase 2 Treatment Study,T1DM, Analog-PH20 vs. analog alone (in progress) Phase 2 Treatment Study,T2DM, Analog-PH20 vs. analog alone (in progress) 21 |
| Less mealtime hyperglycemia Accelerated insulin action (i.e., fast on) results in early glucose lowering effects and reduced post-meal hyperglycemia More patients meet treatment goals for postprandial hyperglycemia Ultrafast Insulin Could Have Best-in-Class Product Profile vs. Standard of Care Analogs Less hypoglycemia Reduced late insulin action (i.e., fast off) may result in fewer hypoglycemic events Postprandial hyperglycemic excursions may be controlled with lower doses of insulin, further reducing hypoglycemia risk Potential for improved glycemic control Better control of postprandial hyperglycemia should lead to reduced A1C levels Halozyme's ultrafast insulin profile should allow more patients to safely reach A1C goal and better manage their diabetes 22 |
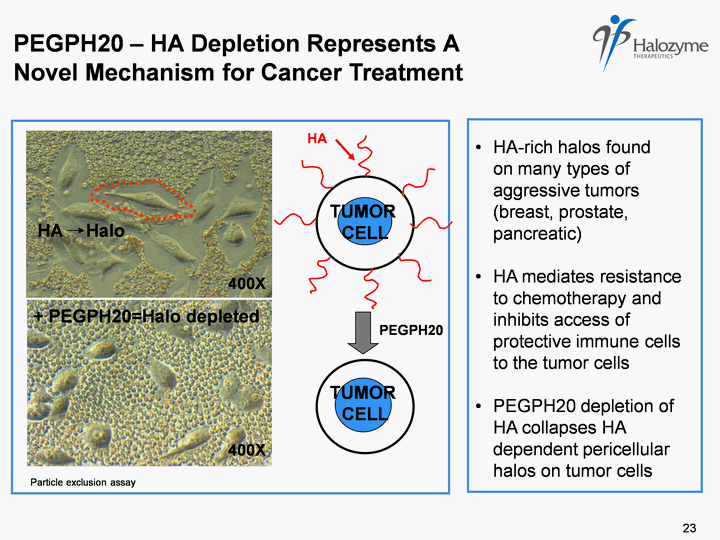
| HA-rich halos found on many types of aggressive tumors (breast, prostate, pancreatic) HA mediates resistance to chemotherapy and inhibits access of protective immune cells to the tumor cells PEGPH20 depletion of HA collapses HA dependent pericellular halos on tumor cells HA TUMOR CELL + PEGPH20=Halo depleted Halo TUMOR CELL PEGPH20 - HA Depletion Represents A Novel Mechanism for Cancer Treatment PEGPH20 HA 400X 400X Particle exclusion assay 23 23 |
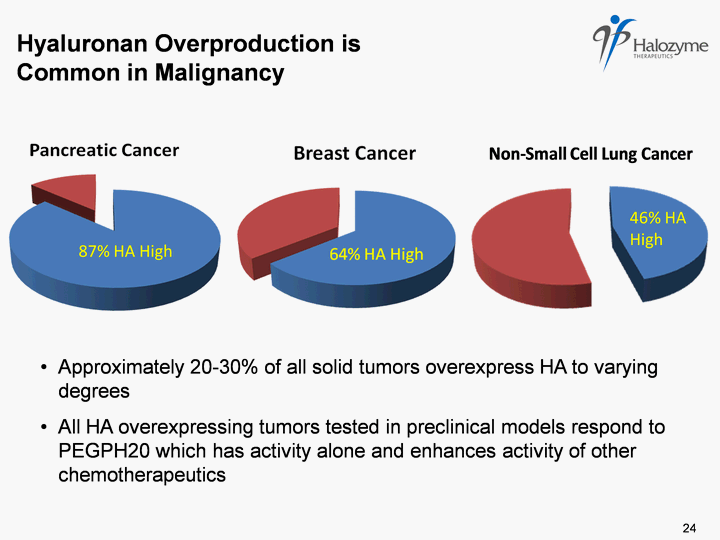
| Hyaluronan Overproduction is Common in Malignancy 87% HA High 46% HA High Approximately 20-30% of all solid tumors overexpress HA to varying degrees All HA overexpressing tumors tested in preclinical models respond to PEGPH20 which has activity alone and enhances activity of other chemotherapeutics 24 |
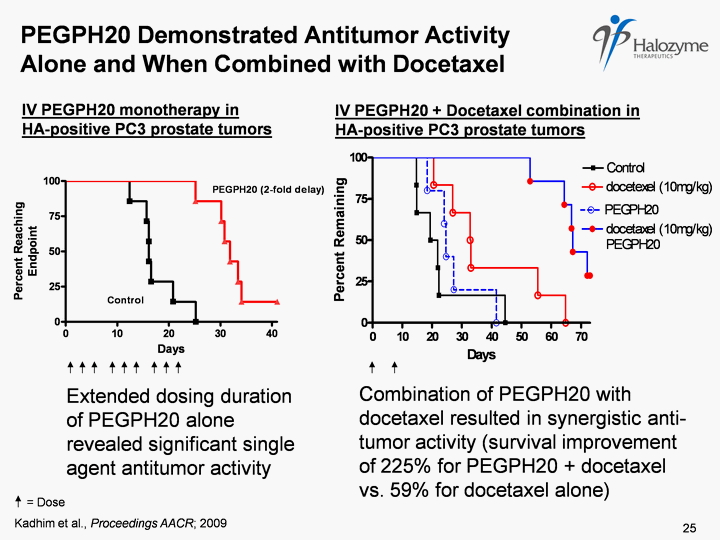
| PEGPH20 Demonstrated Antitumor Activity Alone and When Combined with Docetaxel IV PEGPH20 monotherapy in HA-positive PC3 prostate tumors Combination of PEGPH20 with docetaxel resulted in synergistic anti- tumor activity (survival improvement of 225% for PEGPH20 + docetaxel vs. 59% for docetaxel alone) IV PEGPH20 + Docetaxel combination in HA-positive PC3 prostate tumors Extended dosing duration of PEGPH20 alone revealed significant single agent antitumor activity Kadhim et al., Proceedings AACR; 2009 = Dose 25 |
| PEGPH20 - Unique Approach for Treatment of Solid Tumors Hyaluronan is a major component of the tumor matrix PEGPH20 disrupts tumor matrix via unique mechanism of action and may enhance cancer cell sensitivity to chemotherapeutics Two Phase 1 multicenter, open-label, dose evaluation trials of IV administered PEGPH20 +/- dexamethasone in advanced cancer patients underway, interim results presented Oct 2010 Initial dosing regimen resulted in non-inflammatory musculoskeletal pain in patients, muscular events ameliorated by dose reduction or dexamethasone pre-treatment in animal model Planning additional studies to further assess dosing, safety, and antitumor activity of PEGPH20 alone and in combination with other chemotherapeutics 26 |
| HTI-501 (conditionally active recombinant human cathepsin) Disfiguring scars (keloids, hypertrophic scars) and aesthetic applications, such as cellulite, have few viable treatment options rHuCATL - A temporal-spatially controlled recombinant human enzyme, can tightly control the duration and extent of collagen degradation A proof of mechanism study in cellulite has clear safety and pharmacology endpoints Ex-U.S. trial anticipated in 3Q2011 A first-in-class injectable recombinant human enzyme shown preclinically to locally break down the collagen fibrils that can cause disfiguring scars, contractures and cellulite 27 |
| Milestones for 2010 Presentation of PEGPH20 preclinical data, 2Q10 Presentation of Phase 1 three analogs +/- PH20 clamp study at ADA 2Q10 Presentation of Phase 2 standard meal study in T2DM patients at ADA, 2Q10 Expanded PEGPH20 program, start of additional Phase 1 clinical trial, 3Q10 U.S patent issued, rHuPH20 composition of matter, 3Q10 Successful $60 million equity financing completed, 3Q10 Initiation of two Analog-PH20 Phase 2, 3x/day treatment studies, 3Q10 Interim data from PEGPH20 Phase 1 clinical trials, 4Q10 Results of Phase 2 treatment study 3x/day in T1DM patients, regular Insulin- PH20 vs. lispro, 4Q10 Completion of Phase 3 HyQ clinical trial by Baxter in primary immunodeficiency, 4Q10 Potential for additional milestones from the Roche partnership (due to the initiation of clinical trials or other activities) 28 |
| Potential Milestones for 2011 Announcement of top line Phase 3 HyQ results by Baxter, 1H11 Start of PEGPH20 Phase 2 clinical trial in pancreatic cancer, 3Q11 Start of HTI-501 ex-U.S. proof of concept study in aesthetic medicine, 3Q11 Completion of two insulin Analog-PH20 Phase 2, 3x/day treatment studies, 3Q11 Filing of HyQ BLA by Baxter, 2011 Presentation of data from PEGPH20 Phase 1 clinical trial, 2H11 Potential for additional clinical progress from the Roche partnership 29 |
| Halozyme's Programs Target Over $20 Billion in Late Stage Product Opportunities Roche's Herceptin SC in Phase 3 pivotal trial, $5.1B WW product, MabThera(r) SC in Phase 1, $5.9B WW product Baxter BioScience's HyQ with rHuPH20 in pivotal Phase 3, $6B WW market Baxter rollout of FDA approved HYLENEX in pediatric hydration, $200M addressable market Ultrafast Insulin in Phase 2, targeting $3.8B rapid-acting analog insulin market with potential best-in-class profile PEGPH20 in Phase 1 for solid tumors, multi- billion dollar market opportunity 30 Partnered Programs Proprietary Programs |
| Halozyme Therapeutics - Supplementary Slides Investor Presentation December 8, 2010 31 |
| Herceptin(r) - For Treatment of HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women worldwide More than 1M new cases of breast cancer (BC) diagnosed annually worldwide 20-25% of women with breast cancer are HER2-positive Herceptin Humanized monoclonal antibody that targets and blocks the HER2 receptor Approved for adjuvant treatment of HER2-overexpressing BC and metastatic BC Herceptin for 1 year is standard of care in HER2-positive early BC, HERA 2 year results expected in 2012 Herceptin until progression is standard of care in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer Improves response rates, disease-free survival and overall survival as monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy Has been used to treat > 650,000 women with HER2-positive BC worldwide Sources: www.herceptin.com, World Health Organization, http://www.who.int/cancer/detection/breastcancer/en/, Ferlay J, et al., GLOBOCAN 2002. Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide. IARC CancerBase No.5, Version 2.0. IARCPress, Lyon, 2004. 32 |
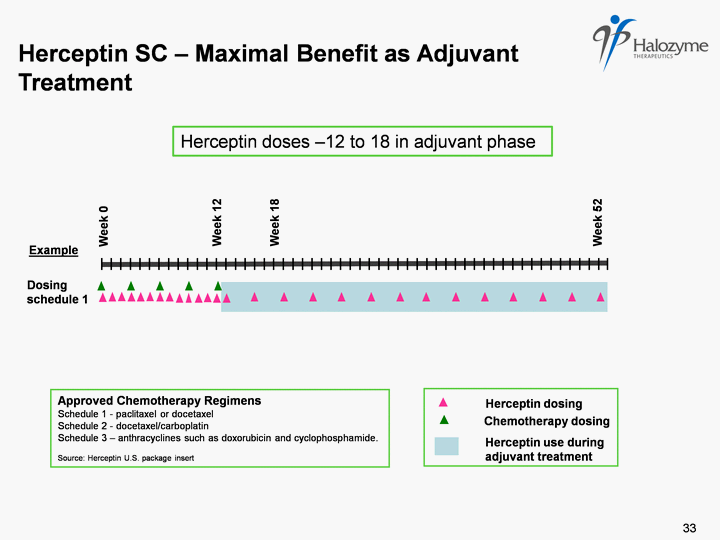
| Herceptin dosing Approved Chemotherapy Regimens Schedule 1 - paclitaxel or docetaxel Schedule 2 - docetaxel/carboplatin Schedule 3 - anthracyclines such as doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide. Source: Herceptin U.S. package insert Chemotherapy dosing Herceptin use during adjuvant treatment Herceptin SC - Maximal Benefit as Adjuvant Treatment Dosing schedule 1 Week 0 Week 18 Week 52 Week 12 Herceptin doses -12 to 18 in adjuvant phase Example 33 |
| Herceptin SC - Phase 3 Clinical Trial Design Registration trial began Oct 2009, full enrollment Dec 2010, N = 595, women with HER2-positive operable or locally advanced breast cancer, HANNAH Pre-operative treatment with 8 cycles of chemotherapy (docetaxel followed by 5-FU/epirubicin/cyclophosphamide) concurrent with IV or SC Herceptin, followed by 10 cycles of Herceptin SC or IV for 10 cycles after surgery, q 3 weeks Surgery between cycles 8 and 9 Follow up for 24 months after last dose of Herceptin Primary endpoints Herceptin serum concentration, comparing SC vs. IV cycles 1-8 Pathologic complete response post-surgery European filing targeted in 2012 (as stated by Roche, March 2010, NY analyst meeting) 34 |
| MabThera(r) SC - Phase 1 Trial Underway Phase 1 began 9/09, N=245 patients with follicular lymphoma, maintenance treatment after response to IV induction therapy Two stages, involves randomization to SC or IV, Stage 1 data presented at ASH, December 5 Primary endpoint - PK trough concentration for SC vs. IV measured at intervals up to day 84 Secondary endpoints PK measures including AUC, Cmax, Tmax, T1/2 up to day 84 Adverse events, laboratory parameters measured at each clinic visit 35 |
| MabThera(r) SC - Phase 3 Trial Design Roche expects to initiate in Q4 2010 Purpose: Investigate the pharmacokinetics, efficacy and safety of MabThera (rituximab) SC versus MabThera IV in patients with previously untreated follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma Patients receive either IV or SC MabThera, with standard chemotherapy (CHOP or CVP) Patients with complete or partial response after 8 treatment cycles receive maintenance treatment for a further maximum number of 12 cycles. Maintenance treatment cycles repeated every 8 weeks Primary endpoints Stage I: Estimate the ratio of trough serum concentrations of MabThera after SC administration to that obtained after IV administration [ Day 21 ] Stage II: Estimate the overall response rate in each treatment arm at the end of induction treatment [ Week 24 (Cycle 8) ] N = ~ 530 patients 36 |
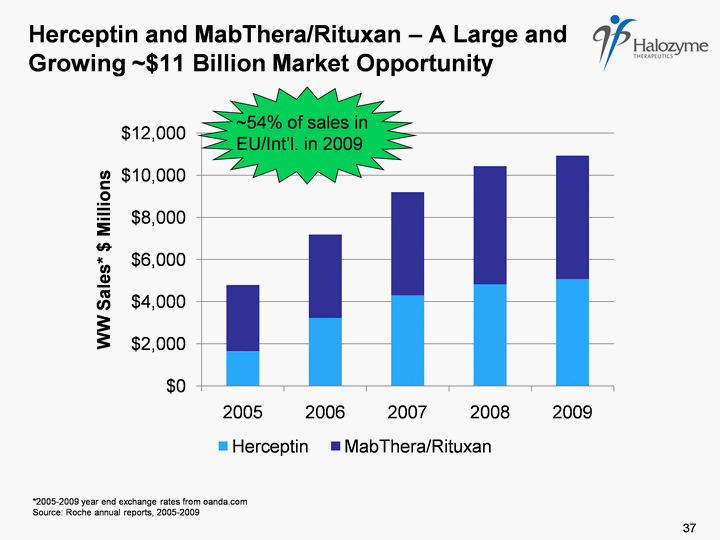
| % Herceptin and MabThera/Rituxan - A Large and Growing ~$11 Billion Market Opportunity *2005-2009 year end exchange rates from oanda.com Source: Roche annual reports, 2005-2009 37 (CHART) ~54% of sales in EU/Int'l. in 2009 |
| Potential Advantages of SC Roche Biologics vs. IV Administration Greater convenience - patients can be treated at physician office, potential for patients to self-administer Roche developing ready-to-use pre-filled administration device, simpler administration, not an infusion-bag prepared by pharmacist Faster infusion time - Herceptin SC expected to be <5 minutes vs. 30-90 minutes for IV Increased compliance - especially important for extended maintenance treatment Reduced treatment costs - outside of hospital and infusion center setting, so more efficient use of healthcare resources 38 |
