Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.1 - EX-99.1 - Alexza Pharmaceuticals Inc. | d73331exv99w1.htm |
| EX-99.2 - EX-99.2 - Alexza Pharmaceuticals Inc. | d73331exv99w2.htm |
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - Alexza Pharmaceuticals Inc. | d73331e8vk.htm |
Exhibit 99.3

| ABSTRACT Background: AZ-004 (inhaled loxapine) is being developed for the treatment of agitation in patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Loxapine was administered via inhalation using the Staccato(r) system, which delivers thermally-generated drug aerosol to the deep lungs for rapid systemic absorption with IV-like kinetics. Objective: To describe the cardiovascular safety of inhaled loxapine from 2 separate clinical protocols: a Phase 1 study in 32 subjects on chronic antipsychotic medication; and a thorough QT (TQT) study in 48 healthy volunteers. Methods: Consenting male and female adults, 18 to 65 years of age, were enrolled in the studies and randomly assigned to treatment. The Phase 1 study was a double blind, placebo controlled, parallel group investigation of the safety of repeat doses (at time 0, 4 and 8 hours) in subjects on chronic antipsychotic medication. Each cohort received either 5 mg x 3 doses, 10 mg x 3 doses, placebo x 3 doses, or 10 mg followed by two doses of 5 mg. The TQT study was a double-blind, double-dummy, active- and placebo-controlled, 3 period crossover study investigating the effect on QT interval of single doses of 10 mg AZ-004, 400 mg oral moxifloxacin, and placebo. Results: In the Phase 1 study, there were no important changes in vital signs with repeat dosing in subjects on chronic antipsychotic medication. In the highest dose group (10 mg x 3), mean changes from baseline in systolic BP were -1.75, -3.13, and -4.38 mmHg at 10 minutes after the first, second, and third doses, respectively. In the TQT study, AZ-004 did not increase QT intervals, as demonstrated by the upper bound of the one-sided 95% CIs placed on the point estimate of the placebo-subtracted change of QTcI being less than 10 ms at all 11 post-dose time points. Moxifloxacin significantly prolonged QTcI demonstrating assay sensitivity. Conclusions: AZ-004 had no significant hemodynamic effect in subjects on chronic antipsychotic regimens, and did not significantly prolong the QT interval at therapeutic doses. THE CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF INHALED LOXAPINE (AZ-004) Daniel A. Spyker, MD, PhD, Mildred D. Gottwald, PharmD, Robert S. Fishman, MD, James V. Cassella, PhD Alexza Pharmaceuticals, Mountain View, CA INTRODUCTION AZ-004 (inhaled loxapine) is being developed to provide a rapidly acting, noninvasive alternative for the treatment of agitation in patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder Inhaled loxapine is administered via inhalation using the Staccato(r) system, which delivers thermally generated drug aerosol to the lungs for rapid systemic absorption with IV-like kinetics. In separate Phase 3 studies in patients with schizophrenia (n=344) or bipolar disorder (n=314), there was a highly significant reduction in agitation (assessed by Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale - Excited Component [PANSS- EC]) after administration of 5 mg or 10 mg AZ-004, compared with placebo, starting as early as 10 min after dosing. OBJECTIVE To describe the cardiovascular safety of inhaled loxapine from 2 separate clinical protocols A Phase 1 multi-dose study in 32 subjects on chronic antipsychotic medication A thorough QT study in 48 healthy volunteers METHODS Loxapine was delivered by oral inhalation using the Staccato system. The hand-held Staccato system provides rapid, reliable deep lung delivery of a drug using a thermally-generated condensation aerosol. A single inhalation actuates the controlled, rapid heating of a thin layer of excipient-free drug on a metal substrate. The time from breath-activated substrate heating to drug entry into the respiratory tract is less than 1 second. NR6-6 |
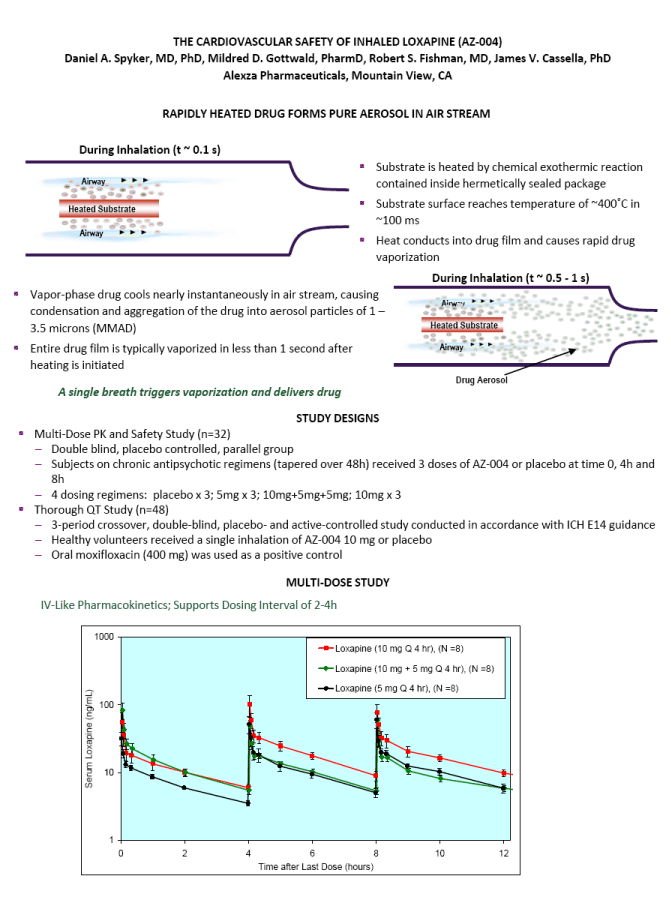
| THE CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF INHALED LOXAPINE (AZ-004) Daniel A. Spyker, MD, PhD, Mildred D. Gottwald, PharmD, Robert S. Fishman, MD, James V. Cassella, PhD Alexza Pharmaceuticals, Mountain View, CA RAPIDLY HEATED DRUG FORMS PURE AEROSOL IN AIR STREAM During Inhalation (t ~ 0.1 s) Heated Substrate Airway Airway Substrate is heated by chemical exothermic reaction contained inside hermetically sealed package Substrate surface reaches temperature of ~400^C in ~100 ms Heat conducts into drug film and causes rapid drug vaporization Vapor-phase drug cools nearly instantaneously in air stream, causing condensation and aggregation of the drug into aerosol particles of 1 - 3.5 microns (MMAD) Entire drug film is typically vaporized in less than 1 second after heating is initiated Heated Substrate Airway Airway Drug Aerosol During Inhalation (t ~ 0.5 - 1 s) A single breath triggers vaporization and delivers drug STUDY DESIGNS Multi-Dose PK and Safety Study (n=32) Double blind, placebo controlled, parallel group Subjects on chronic antipsychotic regimens (tapered over 48h) received 3 doses of AZ-004 or placebo at time 0, 4h and 8h 4 dosing regimens: placebo x 3; 5mg x 3; 10mg+5mg+5mg; 10mg x 3 Thorough QT Study (n=48) 3-period crossover, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled study conducted in accordance with ICH E14 guidance Healthy volunteers received a single inhalation of AZ-004 10 mg or placebo Oral moxifloxacin (400 mg) was used as a positive control MULTI-DOSE STUDY IV-Like Pharmacokinetics; Supports Dosing Interval of 2-4h |
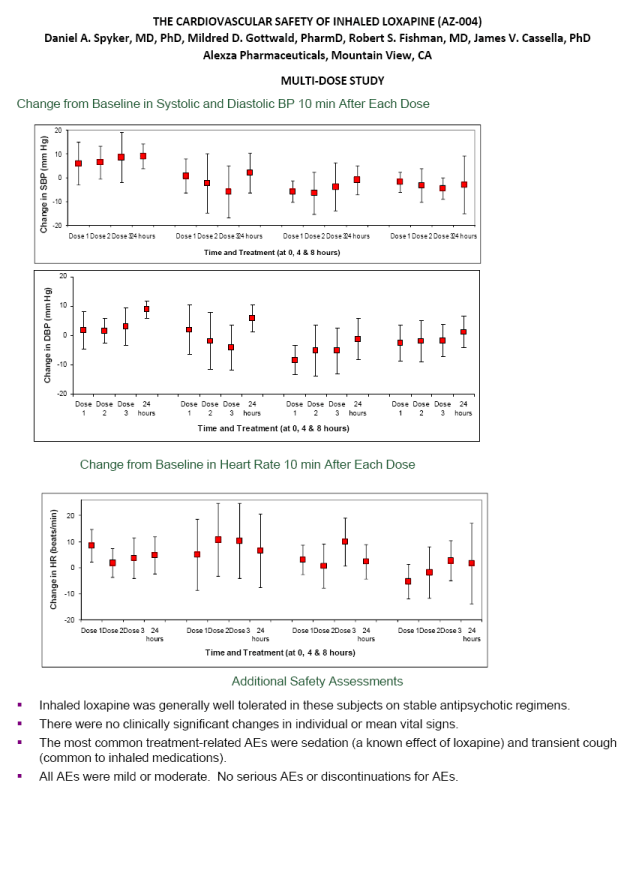
| THE CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF INHALED LOXAPINE (AZ-004) Daniel A. Spyker, MD, PhD, Mildred D. Gottwald, PharmD, Robert S. Fishman, MD, James V. Cassella, PhD Alexza Pharmaceuticals, Mountain View, CA MULTI-DOSE STUDY Change from Baseline in Systolic and Diastolic BP 10 min After Each Dose Change from Baseline in Heart Rate 10 min After Each Dose Additional Safety Assessments Inhaled loxapine was generally well tolerated in these subjects on stable antipsychotic regimens. There were no clinically significant changes in individual or mean vital signs. The most common treatment-related AEs were sedation (a known effect of loxapine) and transient cough (common to inhaled medications). All AEs were mild or moderate. No serious AEs or discontinuations for AEs. |

| THE CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF INHALED LOXAPINE (AZ-004) Daniel A. Spyker, MD, PhD, Mildred D. Gottwald, PharmD, Robert S. Fishman, MD, James V. Cassella, PhD Alexza Pharmaceuticals, Mountain View, CA THOROUGH QT STUDY QTcI after Loxapine: LSmean Differences from Placebo in Change from Baseline and 90% CI QTcI after Moxifloxacin: LSmean Differences from Placebo in Change from Baseline and 90% CI |
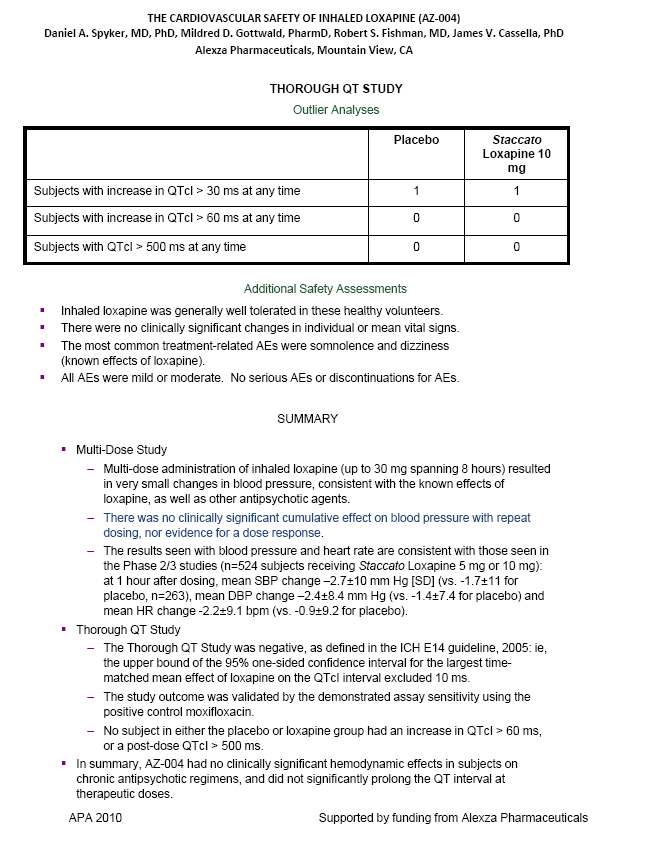
| THE CARDIOVASCULAR SAFETY OF INHALED LOXAPINE (AZ-004) Daniel A. Spyker, MD, PhD, Mildred D. Gottwald, PharmD, Robert S. Fishman, MD, James V. Cassella, PhD Alexza Pharmaceuticals, Mountain View, CA THOROUGH QT STUDY Outlier Analyses Placebo Staccato Loxapine 10 mg Subjects with increase in QTcI > 30 ms at any time 1 1 Subjects with increase in QTcI > 60 ms at any time 0 0 Subjects with QTcI > 500 ms at any time 0 0 Additional Safety Assessments Inhaled loxapine was generally well tolerated in these healthy volunteers. There were no clinically significant changes in individual or mean vital signs. The most common treatment-related AEs were somnolence and dizziness (known effects of loxapine). All AEs were mild or moderate. No serious AEs or discontinuations for AEs. SUMMARY Multi-Dose Study Multi-dose administration of inhaled loxapine (up to 30 mg spanning 8 hours) resulted in very small changes in blood pressure, consistent with the known effects of loxapine, as well as other antipsychotic agents. There was no clinically significant cumulative effect on blood pressure with repeat dosing, nor evidence for a dose response. The results seen with blood pressure and heart rate are consistent with those seen in the Phase 2/3 studies (n=524 subjects receiving Staccato Loxapine 5 mg or 10 mg): at 1 hour after dosing, mean SBP change -2.7+-10 mm Hg [SD] (vs. -1.7+-11 for placebo, n=263), mean DBP change -2.4+-8.4 mm Hg (vs. -1.4+-7.4 for placebo) and mean HR change -2.2+-9.1 bpm (vs. -0.9+-9.2 for placebo). Thorough QT Study The Thorough QT Study was negative, as defined in the ICH E14 guideline, 2005: ie, the upper bound of the 95% one-sided confidence interval for the largest time- matched mean effect of loxapine on the QTcI interval excluded 10 ms. The study outcome was validated by the demonstrated assay sensitivity using the positive control moxifloxacin. No subject in either the placebo or loxapine group had an increase in QTcI > 60 ms, or a post-dose QTcI > 500 ms. In summary, AZ-004 had no clinically significant hemodynamic effects in subjects on chronic antipsychotic regimens, and did not significantly prolong the QT interval at therapeutic doses. APA 2010 Supported by funding from Alexza Pharmaceuticals |
