Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.2 - China Power Equipment, Inc. | ex31-2.htm |
| EX-21.1 - China Power Equipment, Inc. | ex21-1.htm |
| EX-31.1 - China Power Equipment, Inc. | ex31-1.htm |
| EX-32.1 - China Power Equipment, Inc. | ex32-1.htm |
U.S. SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
|
x
|
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
|
|
|
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2009
|
|
o
|
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
|
|
|
For the transition period from ________________ to ________________
|
Commission File Number 000-51379
CHINA POWER EQUIPMENT, INC.
(Name of small business issuer in its charter)
|
Maryland
|
20-5101287
|
|
|
(State or other jurisdiction of
|
(IRS. Employer
|
|
|
incorporation or organization)
|
Identification No.)
|
|
|
Room 602, 6/F, Block B, Science & Technology Park of Xi Dian University,
No. 168 Kechuang Road, Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone
Xi’an, Shaanxi, China 710065
|
||
|
(Address of principal executive offices)
|
||
Issuer’s telephone number, including area code 86-29-8831-0282/8831-0560
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: None.
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None.
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No þ
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was Required to submit and post such files). ¨ Yes o No
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Check one:
Large accelerated filer ¨ Accelerated Filer ¨ Non-accelerated filer ¨ Smaller reporting company þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ¨ No þ
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the registrant (7,586,740 shares) based on the price of $0.51 at which the registrant’s common stock was last sold as of the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second quarter, was $3,734,002. For purposes of this computation, all officers, directors, and 10% beneficial owners of the registrant are deemed to be affiliates. Such determination should not be deemed to be an admission that such officers, directors, or 10% beneficial owners are, in fact, affiliates of the registrant.
As of March 29, 2010, there were outstanding 14,908,313 shares of the registrant’s common stock, par value $.001 per share.
Documents incorporated by reference: None.
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Form 10-K
Table of Contents
|
Page
|
||||
|
PART I
|
||||
|
Item 1.
|
3 | |||
|
Item 1A.
|
12 | |||
|
Item 2.
|
23
|
|||
|
Item 3.
|
23 | |||
|
Item 4.
|
23 | |||
|
PART II
|
||||
|
Item 5.
|
24 | |||
|
Item 7.
|
25 | |||
|
Item 8.
|
35 | |||
|
Item 9.
|
38 | |||
|
Item 9A(T).
|
39 | |||
|
Item 9B.
|
40 | |||
|
PART III
|
||||
|
Item 10.
|
40 | |||
|
Item 11.
|
42 | |||
|
Item 12.
|
45 | |||
|
Item 13.
|
46 | |||
|
Item 14.
|
46 | |||
|
PART IV
|
||||
|
Item 15.
|
47 | |||
| 50 | ||||
PREDICTIVE STATEMENTS AND ASSOCIATED RISK
Certain statements in this Report, and the documents incorporated by reference herein, constitute predictive statements. Such predictive statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors which may cause deviations in actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied. Such factors include, but are not limited to: market and customer acceptance and demand for our products; our ability to market our products; the impact of competitive products and pricing; the ability to develop and launch new products on a timely basis; the regulatory environment, including government regulation in the PRC; our ability to obtain the requisite regulatory approvals to commercialize our products; fluctuations in operating results, including spending for research and development and sales and marketing activities; and other risks detailed from time-to-time in our filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
The words "believe, expect, anticipate, intend and plan" and similar expressions identify predictive statements. These statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that cannot be known or quantified and, consequently, actual results may differ materially from those expressed or implied by such predictive statements. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these predictive statements, which speak only as of the date they are made.
Unless otherwise noted, all currency figures in this filing are in U.S. dollars. References to "RMB" or “yuan” are to the Chinese renminbi (also known as the yuan). According to the currency exchange website www.oanda.com, as of December 31, 2009, US $1.00 = RMB 6.8372.
PART I
ITEM 1.BUSINESS
Corporate History
China Power Equipment, Inc. (“China Power”, the “Company”, or “we”) was incorporated in the State of Maryland on May 17, 2006 for the purpose of acquiring an existing company with continuing operations. China Power formed An Sen (Xi’an) Power Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (“An Sen”) which was granted a license as a wholly-owned foreign enterprise in the city of Xi’an under the laws of the People’s Republic of China (“PRC”) on November 3, 2006. An Sen is a wholly-owned subsidiary of China Power and a limited liability company organized under the laws of the PRC.
On November 8, 2006, An Sen entered into a Management Entrustment Agreement (“the Agreement”) with Xi’an Amorphous Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd. (“Zhongxi”) whereby An Sen assumed financial and operating control over Zhongxi. In exchange for entering into this agreement, shareholders of Zhongxi were issued 9,000,000 shares of China Power common stock, resulting in a change of control of China Power. Zhongxi was founded in Xi’an China under the laws of the PRC on June 29, 2004, and currently manufactures 59 different products, including silicon steel core and amorphous alloy core transformers and cores.
Pursuant to the Agreement, An Sen has the right to manage and control Zhongxi, receive the financial benefits and is exposed to the financial risks of Zhongxi, including, without limitation, the assumption of any risk of loss from Zhongxi’s operations, the obligation to pay the outstanding liabilities of Zhongxi, including debt, if Zhongxi does not have sufficient cash on hand to do so, and any deficiencies if net assets are less than registered capital as a result of any losses. While neither China Power nor An Sen will co-sign Zhongxi contracts, An Sen will continue to be exposed to the financial risks of Zhongxi for its future obligations with third parties through the operation of Management Entrustment Agreement. Mr. Song, the legal representative for Zhongxi and Yarong Feng, the legal representative for An Sen, hold positions as directors and executive officers of each of An Sen and Zhongxi; therefore the Management Entrustment Agreement was not entered into at arm's length because the parties to the agreement were related prior to the transaction and under common control immediately thereafter. Under the Management Entrustment Agreement and pursuant to consent of the shareholders of Zhongxi, Zhongxi and its shareholders entrusted to An Sen its management rights, the rights and powers of its shareholders and board of directors, and the right to receive all of Zhongxi's profits in exchange for An Sen's assumption of the obligation to fund all operating losses and liabilities of Zhongxi. In addition, An Sen has the right to vote as if it holds 100% of the common stock of Zhongxi on all matters that are brought before Zhongxi's shareholders. As a result of entering into the Management Entrustment Agreement, An Sen has functional control over Zhongxi and for purposes of GAAP we can consolidate the financial results of Zhongxi. DeHeng Law Office, our PRC counsel, has advised us that in their opinion the Management Entrustment Agreement is legal and enforceable under PRC law. In the event of a breach of the Management Entrustment Agreement, as set forth in Article 5 of the Amended and Restated Management Entrustment Agreement annexed hereto as Exhibit 1.17, the breaching party is liable for monetary damages and there is no right of termination for breach.
To date, none of Zhongxi’s profits have been paid to An Sen, nor has Zhongxi paid any other fees to An Sen pursuant to the Management Entrustment Agreement as available funds have been used for working capital.
The Management Entrustment Agreement was utilized instead of a direct acquisition of the assets or common stock of Zhongxi, because of the lack of clarity in the implementation of current PRC laws regarding the use of a non-PRC entity’s equity as consideration to acquire a PRC entity’s equity or assets. This makes it highly uncertain, if not impossible, for a non-PRC entity (such as China Power) to use its equity to acquire a PRC entity (such as Zhongxi). While PRC law does allow for the purchase of equity interests in, or assets of a PRC entity by a non-PRC entity for cash, the purchase price must be based on the appraised value of the equity or assets. Because the Company did not have sufficient cash to pay the estimated full value of all of the assets of Zhongxi, the Company, through An Sen, entered into the Management Entrustment Agreement in exchange for the right to exercise functional control over Zhongxi.
Neither China Power nor An Sen have any operations or plan to have any operations in the future other than acting as a holding company and management company for Zhongxi and raising capital for its operations. However, we reserve the right to change our operating plans regarding China Power and An Sen.
Business Overview
China Power Equipment, Inc. (“China Power” or the “Company”) is a holding company. Through its wholly owned subsidiary, An Sen and its affiliated operating company, Zhongxi, it designs, manufactures, and distributes amorphous alloy transformer cores and amorphous alloy core electricity transformers in the People’s Republic of China.
|
The use of amorphous alloy cores creates a new generation of energy saving electrical power transformers that are used to step down voltage in the final phase of electricity distribution – near consumers and companies.
In China, electricity is generated at 6,000 to 10,000 volts and then stepped up to high voltages for long-distance distribution. When the electricity reaches the user’s district, the voltage is stepped down, the electricity is sent onward to the transformer near the users, and then is stepped down again to either 220 volts or 380 volts to make the electricity ready to use.
China Power creates a range of amorphous alloy transformer cores for the transformers that perform this final voltage reduction.
|
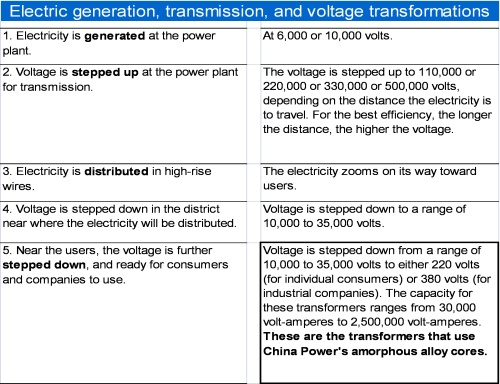 |
A typical amorphous alloy core transformer consumes 77.6 percent less electricity to operate (compared with silicon steel core transformers), leaving more net electricity available for consumers. The typical numbers are 670 watts consumed by a steel core transformer, 150 watts consumed by the amorphous alloy transformer.
Since the amorphous alloy transformer consumes less electricity, it reduces the need to generate electricity. In turn, less coal is burned to provide the same net electricity to the consumers. The result is lower air pollution and more affordable electricity with greater availability.
Products
China Power (through Zhongxi) designs, manufactures, and distributes amorphous alloy cores in the PRC that are the main component in a new generation of energy saving electrical power transformers. Zhongxi also sells amorphous alloy transformers and is expanding its manufacturing of this type of transformers.
China Power has discontinued its legacy silicon steel transformer business, and no longer is a manufacturer or distributor of silicon steel transformers. Traditional steel core transformers were approximately 20 percent of China Power’s sales in 2007 and 6 percent of sales in 2008. Amorphous alloy cores and amorphous alloy transformers constituted almost all of the Company’s sales in 2009.
|
China Power currently manufactures 59 different products, primarily amorphous alloy cores and, to a lesser extent, amorphous alloy core transformers that are subcontracted to other companies.
The amorphous alloy core, on the right, has 3,150 layers of amorphous alloy strip, weighs about 68.3 kilograms (150.6 pounds), and will be used in an electric transformer to step down 10,000 volts to 220 volts. The assembly of the core is done by a combination of computer-controlled cutting and precision alignment of each delicate thin alloy strip, careful shaping by hand to the final form, computer-controlled heat treatment matched to the core’s specific application, then final assurance testing, finishing, and protective packaging. The typical price for this core is about RMB 2,934 (about $428).
China Power outsourced its previous steel core transformer production in 2008 and discontinued distributing steel core transformers made by other companies in 2009.
China Power currently produces the amorphous alloy core series SH15, SBH15, and DH15, as well as the transformer series that use those cores, as shown below. The transformer production is currently subcontracted to other companies but will be taken in-house when China Power’s transformer capacity is established.
|
 |
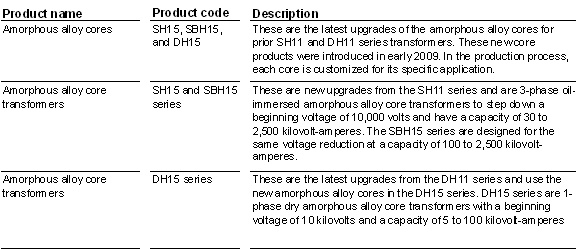
Amorphous Alloy Cores and Transformer Products
Zhongxi uses a patented, innovative production technology for making amorphous alloy transformers cores. The underlying technology relies on the electrical and magnetic properties of amorphous alloy materials. Amorphous alloys exhibit conductivity properties that are far superior to silicon steel that is used in traditional power transformers. As a result, Zhongxi believes that an amorphous alloy transformer can result in energy savings for its customers. In addition, we use technologies that are more environmentally friendly and energy-saving than technologies that are used to make traditional steel cores and transformers.
The amorphous alloy strip, the key raw material used in our manufacturing process, is made by our supplier using flat plate flow liquid state chilling technology to make the molten alloy steel. The molten alloy steel is then put through a super-freezing process where the cooling speeds are up to one million degrees per second. The micro-mechanism of the resulting metal possesses long range unordered glass state features, completely different from traditional metal alloy material. The resulting amorphous metal is characterized by high intensity, high saturation induction density, high magnetic permeability, rigidity, anticorrosion, wearability, resistivity, low coercivity, low loss, good frequency characteristics and temperature characteristic and good tenacity together with improved electromechanical coupling coefficients, thermal conductivity, and surfactivity. These qualities significantly improve the operational efficiencies of electrical power transformers. We believe this new material will replace silicon steel and permalloy, and will be extensively used in transformer, mutual-inductor, reactance unit, and similar products to further electronic product miniaturization, high frequency, high efficiency, environment protection and energy-saving, which is superior when compared with traditional core materials.
A series of Chinese government regulations have encouraged the use of amorphous alloy core transformers since 1998 because of their energy saving properties. These regulations specified new energy codes for the manufacture and sale of transformers, setting stricter regulations regarding a transformer's maximum energy consumption limit. In 1998 the Chinese government confirmed the policy of proposing domestic amorphous alloy materials and transformers. In 2000 the Chinese government listed the amorphous alloy transformer as important environmental protection product. In 2005 the Chinese government listed energy saving transformer as an industry encouraged by the nation. In the “Eleventh Five Year Plan” announced in 2006, the Chinese government set up the goal for all the local governments to reduce energy consumption by 20%.
In 2007, the amorphous alloy industry was considered by the government as one of the industries with significant growing potential. In 2008, the Chinese government launched an “Economic Stimulation Program” that is expected to accelerate the construction of both infrastructure and the electric power grid in rural areas. In 2009, the State Grid Corporation of China entered into a letter of intent for a clean development mechanism program with the World Bank to install high-efficiency amorphous alloy transformers that will gradually replace 166,000 of the most inefficient transformers in China.
Exit Strategy For Silicon Steel Cores and Transformers Business
Zhongxi no longer manufactures, markets, sells, or distributes silicon steel cores or silicon steel transformers, since it exited those product lines in 2009.
Originally, Zhongxi started the business of steel cores and transformers in 2004. On September 10, 2004 Zhongxi leased facilities owned by Xi’an Zhongxi Zhengliu Dianlu Transformer Factory Ltd. (“ZD”), so Zhongxi could manufacture traditional steel core transformers, for an initial lease fee of RMB 30,000 plus RMB 100,000 per year in rent payable after Zhongxi completed certain agreed upon leasehold improvements (the “2004 Lease”). The term of the 2004 Lease runs from the execution date to 2028, with a 10 year option to renew by Zhongxi. The agreement can be terminated by mutual agreement or the parties with provisions that provide that a breaching party will owe a non-breaching party 10% of the lease fee in liquidated damages.
In 2006, Zhongxi outsourced the production of traditional steel core transformers to ZD in order to be able to allocate Zhongxi’s resources to producing amorphous alloy cores and transformers. On March 25, 2006, in order to transform its primary business to the manufacture of amorphous alloy cores and transformers, Zhongxi subleased (the “2006 Sub-Lease”) its manufacturing facilities back to ZD for RMB 500,000 per year for a period of three years ending on March 31, 2009. The Sub-Lease was renewed in 2009 on a month to month basis with a monthly lease payment of RMB 41,666.67 (the “2009 Sub-Lease”).
During term of the 2009 Sub-Lease, no rental payments will be due under the 2004 Lease. Under the terms of the 2009 Sub-Lease, ZD will give priority to the steel core transformers ordered by Zhongxi. ZD is responsible for all of the costs and expenses related to the operation of the manufacturing facility. Upon termination of the 2009 Sub-Lease, ZD has a right of first refusal to release the facilities from Zhongxi and manufacture steel core transformers for Zhongxi upon the same terms and conditions as in the 2006 Sub-Lease in the event that Zhongxi decides to continue to outsource these operations. In the event that ZD does not exercise its right of first refusal, the 2009 Sub-Lease terminates and the provisions of the 2004 Lease continue to apply. This arrangement permitted Zhongxi to continue receiving revenue from sales of steel cores and transformers while Zhongxi built revenues from manufacturing and selling amorphous alloy cores and transformers.
Market For Zhongxi’s Products
China's traditional steel core transformer market is extremely competitive, with several high profile participants. The rising price of raw materials used in steel core transformers has resulted in relatively narrow profit margins for the steel core transformer makers.
The energy-saving performance and environmental improvements that come from amorphous alloy transformers, and China’s national policy guidance that encourages their use, make traditional silicon steel transformers uncompetitive and essentially obsolete. As a result, the demand for high-efficiency amorphous alloy cores and transformers greatly exceeds the current supply. The order backlog continues to grow.
The competitive environment in China for amorphous alloy cores and transformers currently supports prices that are attractively higher than all the costs associated with the amorphous alloy products business.
We made the strategic business decision to focus our manufacturing resources on amorphous alloy cores and amorphous alloy core transformers to gain a larger share of the lucrative amorphous alloy power products market, enjoy the financial benefits of premium pricing, earn an internal rate of return greater than the cost of capital, contribute to improving China’s environment by reducing air and solids pollution and to help China meet its commitment to reduce greenhouse gases, and help improve the quality of life for China’s citizens by increasing the net amount of electricity in both urban and rural regions, at affordable prices.
We believe that our decision to focus on the market for amorphous alloy transformer cores, and later transformers, will enable it to establish a leadership position in the market and to participate in this growth on a broad scale.
China Power’s strategy is designed to establish the Company as a leader in the global amorphous alloy core and transformer market.
China Power has completed the first phase of this transition plan to shift its manufacturing capabilities to amorphous alloy and to build stockpiles of the main material (amorphous alloy strip) used in the core manufacturing process. The Company plans to strengthen its sales and marketing efforts, build relationships with appropriate state and national government agencies, and establish relationships with additional major transformer manufacturers.
China Power intends to continue to develop new products to improve transformer efficiency and meet customer and market demand.
Once China Power secures sufficient manufacturing capacity, it expects to pursue markets outside of China. For example, China Power’s management believes that South Korea presents an opportunity to enter into a new market with a very substantial demand for amorphous transformers due to Korea’s policy that at least 3 percent of all newly-installed power transformers will be amorphous core transformers. China Power’s amorphous alloy transformer has entered and passed the testing phase for the Korean electricity network. Potential customers in other countries, including Turkey, Kenya, and Vietnam, that have voiced interest in the company’s high-efficiency products.
Customers Of Zhongxi
China Power’s direct and indirect customers, include China’s primary electricity generator and supplier, the State Grid Corporation of China, provincial electric suppliers, large suppliers of electrical equipment to the electrical power industry, and other electric power transformers manufacturers.
The State Grid Corporation of China (“State Grid”) builds and operates the electric power grids and provides secure and reliable power supply for the development of the Chinese society. Its service area covers 26 provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities directly under the jurisdiction of the Chinese Central Government, which accounts for 88 percent of the China’s national territory. The State Grid is an entity owned and managed by the Chinese government and is the major buyer of electric power transformers in China.
Marketing And Production Strategy Of Zhongxi
Through Zhongxi, China Power’s strategy for marketing and production consists of the following:
|
·
|
Increase its market share in amorphous alloy transformer cores by effective marketing and direct selling to the transformer makers, and by cooperating with their customers (the Chinese governments and their government agencies).
|
|
·
|
Market to transformer makers by assisting them with the specification, design, engineering, prototyping, and final product performance validation for the amorphous alloy transformers they will need for specific applications. The customers accept China Power’s technical assistance in exchange for the customers’ commitments to purchase all their cores from China Power.
|
|
·
|
Reduce the backlog for cores by obtaining more supply of amorphous alloy core strip (one of its main raw materials), and by creating higher production capacity to increase the production of cores.
|
|
·
|
As the backlog is being eliminated, China Power will prudently expand capacity so that it can deliver all new orders promptly, consistent with the customers’ just-in-time specifications. Customers will then have high assurance that their high-quality cores will arrive at the times and performances specified.
|
|
·
|
Expand its capacity in its production plants in phases to optimize the company’s return on assets.
|
|
·
|
Increase its market share in high-performance electrical transformers that use the company’s amorphous alloy transformer cores by introducing its new line of amorphous alloy transformers and by expanding sales in geographic regions not served by China Power’s current customers that make transformers. About 90 percent of China’s installed electric transformers do not yet have amorphous alloy cores. This is a large market with enough room for both China Power and its customers to supply transformers without significant competitive conflict.
|
|
·
|
Make transformer customers the first priority on its core production. China Power will fill all its customers’ orders for cores at the time specified – before it supplies cores to its own transformer production line. With its anticipated production capacity, the company believes it also will be able to supply all the cores needed for its transformer production lines.
|
Raw Materials And Principal Suppliers Of Zhongxi
Zhongxi’s amorphous alloy cores have three main raw materials: amorphous alloy strip, silicon steel sheet, and epoxy resin. Except for amorphous alloy strip, these materials are currently readily available in its domestic or the international market.
The current supplier of raw amorphous alloy strip for manufacturing amorphous alloy core is Hitachi Metals Co., Ltd., which is the biggest manufacturer of amorphous alloy strip in the world. Zhongxi has taken steps to build a strong relationship with Hitachi, in order to be able to purchase sufficient amounts of the product to meet its needs. Notwithstanding the fact that the supply of Hitachi's amorphous alloy strip is exceeded by the global demand for its product, we believe our relationship with Hitachi will generally permit us to purchase sufficient amounts of material to keep up with our demand. We expect that a new source of amorphous alloy strip will soon be available from Beijing Advanced Technology & Science Materials Co., Ltd. (“AT&M”). We have signed an agreement with AT&M whereby we have been given priority to purchase amorphous alloy strip products.
In September 2009, AT&M completed their test production of amorphous alloy strip, using their facility that has an annual capacity of 10,000 metric tons. Zhongxi has used some of AT&M’s test strip to manufacture test cores and transformers that are permitting electric power grid organizations and other transformer makers to test and to validate that the cores and transformers using AT&M’s amorphous alloy will perform as expected, are equivalent in quality and performance to production that uses Hitachi’s amorphous alloy, and are qualified for production purchases. Zhongxi believes that this second source for amorphous alloy strip, when approved for production, is likely to help alleviate the raw material constraint that has been a concern in the global transformer industry.
Competition
While many manufacturers are capable of producing traditional transformers, fewer than 20 manufacturers in China have the technology to produce amorphous alloy core transformers and only four are capable of large scale production. For the production of amorphous alloy cores, Zhongxi is one of only three major manufacturers in China. The other two are Shanghai Zhixin Electric Co., Ltd. and Beijing Zhong Ji Lian Gong Co., Ltd.
Comparative data for Zhongxi and its two main competitors in the amorphous alloy and steel core business is shown in the table below.
|
China Power
|
Shanghai Zhixin
Electric Co. Ltd. (1)
|
Beijing Zhong
Ji Lian Gong Co.,
Ltd.
|
||||||||||
|
Year established
|
2004
|
1998
|
2005
|
|||||||||
|
Sales in 2009 in RMB
|
163,266,080
|
1,040,349,497
|
126,000,000
|
|||||||||
|
Sales in 2009 in US $ (2)
|
23,866,239
|
152,077,869
|
18,418,629
|
|||||||||
|
Geographic market coverage
|
National
|
National
|
National
|
|||||||||
|
Annual production capacity, metric
|
1,500 tons
|
20,000 tons
|
5,000 tons
|
|||||||||
(1) 2009 sales for Shanghai Zhixin Electric Co. Ltd. were estimated based on its sales through September 30, 2009 because their audited year 2009 financial statements are not yet available.
(2) US$ amounts were translated using year 2009 average exchange rate of $1 = RMB 6.8409
While Zhongxi’s competitors are larger, we believe Zhongxi has a number of advantages over its competition. Its patented “Consecutive Anneal Stove For Amorphous Metal Distribution Transformer Cores” permits it to produce its cores at a lower cost than its competitors, which we believe will permit it to price its product lower than competitors but keep higher margins. In addition, we believe that its experience as a transformer manufacturer will permit it to offer better service and products that are better designed to meet its customer's needs. Zhongxi’s management also believes that its competitors are totally dependent on imported amorphous alloy strip as raw materials, while Zhongxi has taken steps to learn how to use amorphous alloy strip obtained from domestic sources that should relieve the supply shortage and reduce a constraint to our manufacturing process, which Zhongxi’s management expects will continue to plague its competitors.
Research and Development
Research and development has been and continues to be a chief component of Zhongxi’s strategy, and it has strong independent research and development abilities. Zhongxi has three Chinese national patents: 3-phase oil-immersed amorphous alloy transformer (patent number ZL01212922.4), dry type transformer (patent number ZL98234558.5), and Consecutive Anneal Stove For Amorphous Metal Distribution Transformer Core (patent number ZL200620078995.4). Zhongxi’s use of advanced equipment, the three-stage continuous annealing furnace, improves product quality.
Zhongxi's leading researcher, Mr. Xu Zewei, is one of the forerunners in the research of amorphous alloy core transformers in China. He has extensive research experience in electromagnetism and has initiated and participated in more than 20 research projects and made ground-breaking discoveries. Zhongxi's research team consists of PhDs and graduate students who collectively have decades of experience in transformer design and development. The Company is also dedicated to bringing new talents to the group; the newcomers have successfully served in helping to keep the research team at the leading edge of power transformer research and development.
In 2007, Zhongxi was recognized by the Xi’an municipal government as the only R&D and production technology center for amorphous alloy cores.
In June 2009, Zhongxi invested RMB 1,500,00 to purchase the foil-winding technology for amorphous alloy transformers. The foil-winding technology for amorphous alloy transformers is an improvement compared to the wire-winding technology used to manufacture traditional transformers. This technology allows substituting copper wire with copper foil, which makes it possible to build an amorphous alloy transformer of a smaller size and at a lower cost.
As of December 31, 2009, we had 5 full-time employees and 2 part-time employees engaged in the company-sponsored research and development. Research and development expenses in 2009 were RMB 750,000 (about $109,694) and in 2008 were RMB 550,000 (about $78,997).
Intellectual Property
Trademarks
The Company has no registered trademarks.
Patents
Zhongxi has three Chinese national patents: (i) 3-phase oil-immersed amorphous alloy core transformer, patent number ZL01212922.4, which will expire on January 10, 2011, (ii) dry type transformer, patent number ZL98234558.5, which will expire on June 30, 2012, and (iii) Consecutive Anneal Stove For Amorphous Metal Distribution Transformer Core, patent number ZL200620078995.4, which will expire on May 18, 2016.
Domain Names
Zhongxi owns and operates a website under the internet domain name of http://www.chinapower-equipment.com.
Government Regulation
Zhongxi is not subject to any requirements for governmental permits or approvals or any self regulatory professional associations for the manufacture and sale of amorphous alloy cores or amorphous alloy transformers. Zhongxi is not subject to any significant government regulation of the business or production, or any other government permits or approval requirements, except for the laws and regulations of general applicability for corporations formed under the laws of the PRC.
Compliance With Environmental Laws
To our knowledge, neither the production nor the sale of our products constitute activities or generate materials, in a material manner, which causes Zhongxi’s operations to be subject to the PRC environmental laws.
Risk Of Loss And Product Liability Insurance
Delivery of Zhongxi’s products is arranged by Zhongxi. Usually, Zhongxi delivers its products primarily through independent logistics companies. Its current shipping companies include Shaanxi Haoyuntong Logistic, Ltd. and Xi'an Haina Logistic Company. Its standard shipping agreements require the shipping companies to purchase shipping insurance at their cost and to bear the risk of loss in shipping.
Zhongxi currently does not carry any product liability or other similar insurance, nor does Zhongxi have property insurance covering our plants, manufacturing equipment, and office buildings. While product liability lawsuits in the PRC are rare and Zhongxi has never experienced significant failures of its products, we cannot assure you that Zhongxi would not face liability in the event of any failure of any of its products.
Employees
The table below presents the number of our employees on December 31, 2009 and 2008.
|
Category
|
2009
|
2008
|
||||||
|
Administration
|
22
|
23
|
||||||
|
Manufacturing
|
30
|
28
|
||||||
|
Research & development
|
5
|
5
|
||||||
|
Sales & support
|
4
|
2
|
||||||
|
Total
|
61
|
58
|
||||||
Executive Office
Our principal executive offices are located at: Room 602, 6/F, Block B, Science & Technology Park of Xi Dian University, No. 168 Kechuang Road, Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China 710065. Our telephone number at that address is 86-29-8831-0282.
ITEM 1A.RISK FACTORS
An investment in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider all of the risks described below, together with the other information contained in this report, before making a decision to purchase our common stock. You should only purchase our common stock if you can afford to lose your entire investment.
An Investment In Our Common Stock Involves A High Degree Of Risk. You Should Carefully Consider The Risks Described Below And The Other Information Contained In This Prospectus Before Deciding To Invest In Our Common Stock.
The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only ones we may face. Additional risks and uncertainties not currently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial may also adversely affect our business, financial condition, and or operating results. If any of the following risks, or any other risks not described below, actually occur, it is likely that our business, financial condition, and operating results could be seriously harmed. As a result, the trading price of our common stock could decline, and you could lose part or all of your investment.
We Do Not Have Any Equity Ownership Interest in Zhongxi, Our Operating Business, And Our Executives Are Also Affiliates of Zhongxi and An Sen, The Parties To The Management Entrustment Agreement.
We do not have any equity ownership interest in Zhongxi. We control Zhongxi through a Management Entrustment Agreement between Zhongxi and our wholly owned subsidiary An Sen. Both An Sen and Zhongxi are controlled by affiliates of Zhongxi and Alloy Science, including Mr. Song, our CEO and Chairman who holds approximately 43.8% of the shares of common stock of Zhongxi and 19.8% of our common stock, and by Ms. Yarong Feng and Mr. Gouan Zhang who are affiliates of Zhongxi and An Sen who control approximately 25.5% of our common stock as trustees for the shareholders of Alloy Science. Mr. Song is also the President and CEO of An Sen, acting CEO and President of Alloy Science, and one of the trustees for 93.75% of the Alloy Science shares held by shareholders of Alloy Science. Ms. Feng is a Director of China Power, Director of An Sen, Chief Financial Officer and Director Zhongxi, Secretary to the Board of Directors of Alloy Science, and a Trustee for the shareholders of Alloy Science. Mr. Zhang is a Vice General Manager of China Power, Vice General Manager of An Sen, Vice General Manager and director of Zhongxi, and Trustee under Voting Trust and Escrow Agreement for Alloy Science.
RISKS RELATED TO OUR BUSINESS
Our Limited Operating History May Not Serve As An Adequate Basis To Judge Our Future Prospects And Results Of Operations.
Zhongxi commenced its business operations in 1999. Its limited operating history may not provide a meaningful basis on which to evaluate its business. We cannot assure you that Zhongxi will maintain our profitability or that it will not incur net losses in the future. We expect that the operating expenses of Zhongxi will increase as it expands. Any significant failure to realize anticipated revenue growth could result in significant operating losses. Zhongxi will continue to encounter risks and difficulties frequently experienced by companies at a similar stage of development, including our potential failure to: (a) raise adequate capital for expansion and operations; (b) implement the business model and strategy and adapt and modify them as needed; (c) increase awareness of the brands of Zhongxi, protect its reputation and develop customer loyalty; (d) manage the expanding operations and service offerings of Zhongxi, including the integration of any future acquisitions; (e) maintain adequate control of the expenses of Zhongxi; (f) anticipate and adapt to changing conditions in the transformer and electric power market in which Zhongxi operates as well as the effect of any changes in government regulations, mergers and acquisitions involving our competitors, technological developments, and other significant competitive and market dynamics.
If Zhongxi is not successful in addressing any or all of these risks, our business may be materially and adversely affected.
The Failure Of Zhongxi To Compete Effectively May Adversely Affect Its Ability To Generate Revenue.
Zhongxi competes primarily on the basis of its ability to find purchasers for our transformer cores. There can be no assurance that it will continue to find such purchasers in new areas as we attempt to expand or that its competitors will not negotiate more favorable arrangements.
We expect that we will be required to continue to invest in expansion capacity and research and development efforts in order for Zhongxi to remain competitive. Zhongxi’s contemplated expansion will require large amounts of capital. Zhongxi’s competitors may have better resources and better strategies to raise capital which could have a material adverse effect on its business, results of operations and financial condition.
Zhongxi May Not Be Able To Effectively Control And Manage Its Growth.
If business of Zhongxi and its markets grow and develop, it will be necessary for us to finance and manage expansion in an orderly fashion. Any expansion would increase demands on the existing management, workforce, and facilities of Zhongxi. Failure to satisfy such increased demands could interrupt or adversely affect the operations of Zhongxi, cause delays in production and delivery of amorphous alloy cores and create administrative inefficiencies.
We May Require Additional Financing In The Future And A Failure To Obtain Such Required Financing Will Inhibit The Ability Of Zhongxi To Grow.
The continued growth of the business of Zhongxi may require additional funding from time to time. Funding would be used for general corporate purposes, which could include acquisitions, investments, repayment of debt, capital expenditures, and repurchase of our capital stock, among other things. Obtaining additional funding would be subject to a number of factors, including market conditions, operating performance, and investor sentiment, many of which are outside of our control. These factors could make the timing, amount, and terms and conditions of additional funding unattractive or unavailable to us.
The Terms Of Any Future Financing May Adversely Affect Your Interest As Stockholders.
If we require additional financing in the future, we may be required to incur indebtedness or issue equity securities, the terms of which may adversely affect your interests in us. For example, the issuance of additional indebtedness may be senior in right of payment to your shares upon liquidation of the Company. In addition, indebtedness may be under terms that make the operation of the business of Zhongxi more difficult because the lender's consent could be required before we take certain actions. Similarly the terms of any equity securities we issue may be senior in right of payment of dividends to your common stock and may contain superior rights and other rights as compared to your common stock. Further, any such issuance of equity securities may dilute your interest in us.
The Protection Of Intellectual Property Rights In The PRC Is Not As Effective As In The United States Or Other Countries.
Our success depends, in part, on our ability to protect the proprietary technologies of Zhongxi. As of the date of this annual report, Zhongxi has three patents, two patents for the production technology of amorphous alloy transformers and one patent for equipment for the production of amorphous alloy cores. We intend to apply for three additional patents for the designs of newer upgraded amorphous alloy cores that we have been put in production and are currently selling to our customers.
Protection of intellectual property in the PRC has historically been weak, primarily because of ambiguities in the PRC laws and difficulties in enforcement. Accordingly, intellectual property rights and confidentiality protections in the PRC may not be as effective as they are in the United States and other countries. Policing unauthorized uses of proprietary technology is difficult and expensive, and we might need to resort to litigation to enforce or defend patents issued to us or to determine the enforceability, scope and validity of Zhongxi’s proprietary rights or those of others. Such litigation could require significant expenditure of cash and management efforts and could harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations. An adverse determination in any such litigation would impair our intellectual property rights and could harm our business, competitive position, business prospects, and reputation. There is no guarantee that Zhongxi’s intellectual property is or will be sufficiently protected. Nor is there any guarantee that its current or potential competitors that do not have such technology, will not obtain or develop, similar technology, which could negatively impact our competitive advantage over such companies and our business.
We And Or Zhongxi May Be Exposed To Intellectual Property Infringement And Other Claims By Third Parties, Which, If Successful, Could Cause Us And or Zhongxi To Pay Significant Damage Awards And Incur Other Costs.
Although we believe that the technology Zhongxi uses, including its patented technology and technology for which Zhongxi has applied for patents, is significantly distinguished from other patented technology, and any infringement claim relating to the technology of Zhongxi would be unlikely to succeed, we cannot assure you that our assessment is or will remain correct. In addition, as litigation becomes more common in the PRC in commercial disputes, we face a higher risk of being the subject of intellectual property infringement claims. The validity and scope of claims relating to patents for amorphous core and transformer technology and related devices and machines involve complex technical, legal, and factual questions and analysis and, therefore, may be highly uncertain. The defense and prosecution of intellectual property suits, patent opposition proceedings and related legal and administrative proceedings can be both costly and time consuming and may significantly divert the efforts and resources of our technical and management personnel. An adverse determination in any such litigation or proceeding to which we and or Zhongxi may become a party could subject us and or Zhongxi to significant liability to third parties, including damage awards, and could require Zhongxi to seek licenses from third parties, pay ongoing royalties, or to redesign products or subject Zhongxi to injunctions preventing the manufacture and sale of its products. Protracted litigation could also result in the customers or potential customers of Zhongxi deferring or limiting their purchase or use of its products until resolution of such litigation.
Zhongxi Depends On A Concentration Of Raw Materials Suppliers. Any Significant Fluctuation In Price Of Raw Materials May Have A Material Adverse Effect On The Manufacturing Cost Of The Products Of Zhongxi.
Zhongxi relies on raw materials, especially amorphous alloy strip, silicon steel sheets and epoxy resin, to produce its products. Zhongxi enters into supply contracts for these raw materials. Therefore, the availability of raw materials is subject to risks of contract fulfillment from the counterparties of Zhongxi. The support of government on amorphous alloy transformer industry may increase the demand of amorphous alloy strip, silicon steel sheet and epoxy resin, which will bring the increase of price. For the major material, amorphous alloy strip, the only supplier is Hitachi Metals Co., Ltd. Currently, Hitachi’s amorphous alloy strip global supply falls short of demand. In the event that Hitachi is unable to provide us with the amorphous alloy strip we require, Zhongxi may be unable to find alternate sources, or find alternate sources at reasonable prices. In such event, the business and financial results of Zhongxi would be materially and adversely affected.
Beijing Advanced Technology & Science Materials Co., Ltd. (“AT&M”) may become second supplier for amorphous alloy strip, which is the main material used in our production. Beijing Advanced Technology & Science Materials Co., Ltd. is the company’s English name, while the translation of its Chinese name into English is China An Tai Technology Co., Ltd. The company uses both names. The supply of amorphous alloy strip from AT&M may help relieve the potential shortage of amorphous alloy strip in the future. However, with the increasing demand in both China’s and the world’s market, a shortage for the raw material may still exist in the future. In such event, if our company can not find any alternatives, the business and financial results of Zhongxi would be materially and adversely affected.
While Zhongxi Has Some Long Term Supply Contracts With Its Suppliers Of Raw Materials, Any Significant Fluctuation In Price Of Raw Materials May Have A Material Adverse Effect On Its Manufacturing Costs.
Silicon steel sheet and epoxy resin are two other raw materials that Zhongxi uses, in addition to amorphous alloy strip. The prices of the sheet steel and epoxy resin are subject to market conditions. Our operating company has certain long-term contracts or arrangements with its suppliers; however, the contracts may not be sufficient to cover its needs. While some of these raw materials are generally available, other raw materials for the amorphous cores and transformers produced by Zhongxi have limited suppliers, and we cannot assure you that prices will not rise because of changes in market conditions. An increase in component or raw material costs relative to the product prices of Zhongxi could have a material adverse effect on its gross margins and earnings.
Potential Environmental Liability Could Have A Material Adverse Effect On Operations And The Financial Condition Of Zhongxi.
To the knowledge of our management team, neither the manufacture of transformer cores nor the sale and distribution of transformer cores and transformers requires Zhongxi to comply with PRC environmental laws other than laws of general applicability. Zhongxi has never been the subject of allegations of any environmental regulation; however, there can be no assurance that the PRC government will not amend its current environmental protection laws and regulations. The business and operating results of Zhongxi could be materially and adversely affected if Zhongxi were to increase expenditures to comply with environmental regulations affecting its operations.
We May Engage In Future Acquisitions That Could Dilute The Ownership Interests Of Our Stockholders, Cause Us To Incur Debt, And Assume Contingent Liabilities.
We may review acquisition and strategic investment prospects that we believe would complement our current product offerings, augment our market coverage, or enhance our technical capabilities, or otherwise offer growth opportunities. From time to time we review investments in new businesses, and we expect to make investments in and or to acquire businesses, products, or technologies in the future. In the event of any future acquisitions, we could issue equity securities which would dilute current stockholders' percentage ownership; incur substantial debt; assume contingent liabilities; or expend significant cash.
These actions could have a material adverse effect on our operating results or the price of our common stock. Moreover, even if we do obtain benefits in the form of increased sales and earnings, there may be a lag between the time when the expenses associated with an acquisition are incurred and the time when we recognize such benefits. Acquisitions and investment activities also entail numerous risks, including difficulties in the assimilation of acquired operations, technologies and or products; unanticipated costs associated with the acquisition or investment transaction; the diversion of management's attention from other business concerns; adverse effects on existing business relationships with suppliers and customers; risks associated with entering markets in which we have no or limited prior experience; the potential loss of key employees of acquired organizations; and substantial charges for the amortization of certain purchased intangible assets, deferred stock compensation or similar items. We cannot ensure that we will be able to successfully integrate any businesses, products, technologies, or employees that we might acquire in the future, and our failure to do so could have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results, and financial condition.
We Are Responsible For The Indemnification Of Our Officers And Directors.
Our Articles of Incorporation provide for the indemnification and or exculpation of our directors, officers, employees, and agents to the maximum extent provided, and under the terms provided, by the laws and decisions of the courts of the state of Maryland. This indemnification policy could result in substantial expenditures, which we may be unable to recoup, which could adversely affect our business and financial conditions.
We May Have Difficulty Establishing Adequate Management, Legal, And Financial Controls In The PRC.
The PRC historically has not adopted a western style of management and financial reporting concepts and practices, as well as modern banking, computer, and other control systems. Zhongxi may have difficulty in hiring and retaining a sufficient number of qualified employees to work in the PRC. As a result of these factors, it may experience difficulty in establishing management, legal, and financial controls, collecting financial data, and preparing financial statements, books of account and corporate records, and instituting business practices that meet Western standards.
We May Not Have Adequate Internal Accounting Controls. While We Have Certain Internal Procedures In Our Budgeting And Forecasting And In The Management And Allocation Of Funds, Our Internal Controls May Not Be Adequate.
We are constantly striving to improve our internal accounting controls. We hope to develop an adequate internal accounting control to budget, forecast, manage, and allocate our funds and account for them. There is no guarantee that such improvements will be adequate or successful or that such improvements will be carried out on a timely basis. If we do not have adequate internal accounting controls, we may not be able to appropriately budget, forecast, and manage our funds, we may also be unable to prepare accurate accounts on a timely basis to meet our continuing financial reporting obligations and we may not be able to satisfy our obligations under the US securities laws.
Our Internal Controls Over Financial Reporting May Not Be Effective, And Our Independent Auditors May Not Be Able To Certify As To Their Effectiveness, Which Could Have A Significant And Adverse Effect On Our Business.
Rules adopted by the SEC pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 require annual assessment of our internal control over financial reporting, and attestation of this assessment by our company's independent registered public accountants. The SEC extended the compliance dates for "non-accelerated filers," as defined by the SEC. Accordingly, we believe that the attestation requirement of management's assessment by our independent registered public accountants will first apply to our annual report for the year 2010. The standards that must be met for management to assess the internal control over financial reporting as effective are new and complex, and require significant documentation, testing, and possible remediation to meet the detailed standards. Our lack of familiarity with Section 404 may unduly divert management's time and resources in executing the business plan. If, in the future, management identifies one or more material weaknesses, or our external auditors are unable to attest that our management's report is fairly stated or to express an opinion on the effectiveness of our internal controls, this could result in a loss of investor confidence in our financial reports, have an adverse effect on our stock price and or subject us to sanctions or investigation by regulatory authorities.
We Do Not Have Key Man Insurance On Our President And CEO, Mr. Song, On Whom We Rely For The Management Of Zhongxi’s Business.
We depend, to a large extent, on the abilities and participation of our current management team, but have a particular reliance upon Mr. Yongxing Song. The loss of the services of Mr. Song, for any reason, may have a material adverse effect on our business and prospects. We cannot assure you that we will be able to find a suitable replacement for Mr. Song. We do not carry key man life insurance for any of our key employees.
We May Not Be Able To Hire And Retain Qualified Employees To Support The Growth Of Zhongxi And If We Are Unable To Retain Or Hire These Employees In The Future, Our Ability To Improve Our Products And Implement Our Business Objectives Could Be Adversely Affected.
Competition for senior management and employees in the PRC is intense, the pool of qualified candidates in the PRC is very limited, and Zhongxi may not be able to retain the services of its senior executives or senior employees, or attract and retain high-quality senior executives or senior employees in the future. This failure could materially and adversely affect our future growth and financial condition.
Zhongxi Does Not Presently Maintain Fire, Theft, Product Liability, Or Any Other Property Insurance, Which Leaves Us With Exposure In The Event Of Loss Or Damage To Its Properties Or Claims Filed Against Us And or Zhongxi.
Neither we nor Zhongxi maintains fire, theft, product liability, or other insurance of any kind. We bear the economic risk with respect to loss of or damage or destruction to our property and to the interruption of our business as well as liability to third parties for personal injury or damage or destruction to their property that may be caused by our personnel or products. This liability could be substantial and the occurrence of such loss or liability may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and prospects. However product liability lawsuits in the PRC are rare, and Zhongxi has never experienced significant failure of its products.
Neither We Nor Zhongxi Maintains A Reserve Fund For Warranty Or Defective Equipment Claims. Zhongxi’s Costs Could Substantially Increase If We Experience A Significant Number Of Warranty Claims.
Currently, Zhongxi provides a six-month warranty to its customers who have purchased its transformers but it does not plan to continue to do so in the future. The warranties require us to replace defective equipment. As of March 29, 2010, Zhongxi has received no warranty claims for its products. Consequently, the costs associated with its warranty claims have historically been minimal, and we have therefore not established any reserve funds for potential warranty claims. If Zhongxi begins to receive warranty claims, our financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
RISKS RELATED TO OUR INDUSTRY
A Drop In The Retail Price Of The Traditional Transformer Cores In The PRC May Have A Negative Effect On The Business Of Zhongxi.
If the retail price of traditional steel transformer cores is reduced, the purchaser may choose not to purchase the more expensive amorphous alloy transformer cores. Such decrease of demand may lead to a decrease in profits of Zhongxi and us. Although management of Zhongxi believes that current retail amorphous alloy transformer cores prices support a reasonable return on investment for its products, there can be no assurance that future retail pricing will remain at such levels.
Existing Regulations And Changes To Existing Regulations May Significantly Reduce Demand For The Products Of Zhongxi.
The development of the market for amorphous alloy cores and transformers is supported by relevant government regulations. Even though we believe such supporting policies of the government will not change in the near future, there is no guarantee that changes will not happen in the long run. We are responsible for knowing the requirements of individual cities and must design equipment to comply with varying standards. Any new government regulations or utility policies that relate to our amorphous alloy transformer cores products may result in significant additional expenses to us, our resellers, and their customers and, as a result, could cause a significant reduction in demand for our products.
If Amorphous Alloy Technology Is Not Suitable For Widespread Adoption, Or Sufficient Demand For Amorphous Alloy Products Does Not Develop Or Takes Longer To Develop Than We Anticipate, The Sales Of Zhongxi Would Not Significantly Increase And Neither We Nor Zhongxi Would Be Able To Achieve Or Sustain Profitability.
The market for amorphous alloy products is emerging and rapidly evolving, and its future success is uncertain. If amorphous alloy technology proves to be unsuitable for widespread commercial deployment or if demand for amorphous alloy products fails to develop sufficiently, Zhongxi would be unable to generate enough revenues to achieve and sustain profitability. In addition, demand for amorphous alloy products in the markets and geographic regions Zhongxi targets may not develop or may develop more slowly than we anticipate. Many factors will influence the widespread adoption of amorphous alloy technologies and demand for amorphous alloy products, including (i) cost-effectiveness of amorphous alloy technologies as compared with conventional steel transformer technologies; (ii) performance and reliability of amorphous alloy products as compared with conventional steel transformer technologies; and (iii) capital expenditures by customers that tend to decrease if the PRC or global economy slows down.
RISKS RELATED TO DOING BUSINESS IN THE PRC.
Changes In The Policies Of The PRC Government Could Have A Significant Effect On The Business We May Be Able To Conduct In The PRC And The Profitability Of Such Business.
The PRC's economy is in a transition from a planned economy to a market oriented economy, subject to five-year and annual plans adopted by the government that set national economic development goals. Policies of the PRC government can have significant effects on the economic conditions of the PRC. The PRC government has confirmed that economic development will follow the model of a market economy. Under this direction, we believe that the PRC will continue to strengthen its economic and trading relationships with foreign countries and business development in the PRC will follow market forces. While we believe that this trend will continue, there can be no assurance that this will be the case. A change in policies by the PRC government could adversely affect our interests by, among other factors: changes in laws, regulations or the interpretation thereof, confiscatory taxation, restrictions on currency conversion, imports or sources of supplies, or the expropriation or nationalization of private enterprises. Although the PRC government has been pursuing economic reform policies for more than two decades, there is no assurance that the government will continue to pursue such policies or that such policies may not be significantly altered, especially in the event of a change in leadership, social or political disruption, or other circumstances affecting the PRC's political, economic, and social life.
The PRC Laws And Regulations Governing The Current Business Operations Of Zhongxi Are Sometimes Vague And Uncertain. Any Changes In Such PRC Laws And Regulations May Harm The Business Of Zhongxi.
The PRC laws and regulations governing our current business operations are sometimes vague and uncertain. There are substantial uncertainties regarding the interpretation and application of PRC laws and regulations, including the laws and regulations governing the business of Zhongxi, or the enforcement and performance of our arrangements with customers in the event of the imposition of statutory liens, death, bankruptcy, and criminal proceedings. We and any future subsidiaries are considered foreign persons or foreign funded enterprises under PRC laws, and as a result, we are required to comply with PRC laws and regulations. New laws and regulations that affect existing and new businesses may also be applied retroactively. We cannot predict what effect the interpretation of existing or new PRC laws or regulations may have on our businesses.
A Slowdown Or Other Adverse Developments In The PRC Economy May Harm Our Customers And The Demand For Our Services And Our Products.
All of our operations are conducted in the PRC and all of our revenues are currently generated from sales in the PRC. Although the PRC economy has grown significantly in recent years, we cannot assure you that this growth will continue. The amorphous alloy industry in the PRC is relatively new and growing. However, a slowdown in overall economic growth, an economic downturn, a recession, or other adverse economic developments in the PRC could significantly reduce the demand for our products and harm our business.
Inflation In The PRC Could Negatively Affect Our Profitability And Growth.
While the PRC economy has experienced rapid growth, such growth has been uneven among various sectors of the economy and in different geographical areas of the country. Rapid economic growth could lead to growth in the money supply and rising inflation. If prices for the products of Zhongxi rise at a rate that is insufficient to compensate for the rise in the costs of its supplies, it may harm the profitability of Zhongxi. In order to control inflation in the past, the PRC government has imposed controls on bank credit, limits on loans for fixed assets and restrictions on state bank lending. Such an austere policy can lead to a slowing of economic growth. In October 2004, the People's Bank of China, the PRC's central bank, raised interest rates for the first time in nearly a decade and indicated in a statement that the measure was prompted by inflationary concerns in the Chinese economy. Repeated rises in interest rates by the central bank would likely slow economic activity in China which could, in turn, materially increase our costs and also reduce demand for our products.
Governmental Control Of Currency Conversion May Affect The Value Of Your Investment.
The PRC government imposes controls on the convertibility of the renminbi into foreign currencies and, in certain cases, the remittance of currency out of the PRC. We receive substantially all of our revenues in renminbi, which is currently not a freely convertible currency. Shortages in the availability of foreign currency may restrict our ability to remit sufficient foreign currency to pay dividends, or otherwise satisfy foreign currency denominated obligations. Under existing PRC foreign exchange regulations, payments of current account items, including profit distributions, interest payments and expenditures from the transaction, can be made in foreign currencies without prior approval from the PRC State Administration of Foreign Exchange by complying with certain procedural requirements. However, approval from appropriate governmental authorities is required where renminbi is to be converted into foreign currency and remitted out of China to pay capital expenses such as the repayment of bank loans denominated in foreign currencies.
The PRC government may also in the future restrict access to foreign currencies for current account transactions. If the foreign exchange control system prevents us from obtaining sufficient foreign currency to satisfy our currency demands, we may not be able to pay certain of our expenses as they come due.
The Fluctuation Of The Renminbi May Harm Your Investment.
The value of the Chinese renminbi against the U.S. dollar and other currencies may fluctuate and is affected by, among other things, changes in the PRC's political and economic conditions. As we rely entirely on revenues earned in the PRC, any significant revaluation of the renminbi may materially and adversely affect our cash flows, revenues and financial condition. For example, to the extent that we need to convert U.S. dollars we receive from an offering of our securities into renminbi for the operations of Zhongxi, appreciation of the renminbi against the U.S. dollar would diminish the value of the proceeds of the offering and this could harm the business, financial condition, and results of operations for us and Zhongxi. Conversely, if we decide to convert renminbi from Zhongxi into U.S. dollars for the purpose of making payments for dividends on our common shares or for other business purposes and the U.S. dollar appreciates against the renminbi, the U.S. dollar equivalent of the renminbi we convert would be reduced. In addition, the depreciation of significant U.S. dollar denominated assets could result in a charge to our income statement and a reduction in the value of these assets.
On July 21, 2005, the PRC government changed its decade-old policy of pegging the value of the renminbi to the U.S. dollar. Under the new policy, the renminbi is permitted to fluctuate within a narrow and managed band against a basket of certain foreign currencies. This change in policy has resulted in an appreciation of the renminbi against the U.S. dollar. While the international reaction to the renminbi revaluation has generally been positive, there remains significant international pressure on the PRC government to adopt an even more flexible currency policy, which could result in a further and more significant appreciation of the renminbi against the U.S. dollar.
PRC State Administration Of Foreign Exchange ("SAFE") Regulations Regarding Offshore Financing Activities By PRC Residents May Increase The Administrative Burden We Face. The Failure By Our Shareholders Who Are PRC Residents To Make Any Required Applications And Filings Pursuant To Such Regulations May Prevent Us From Being Able To Distribute Profits And Could Expose Us And Our PRC Resident Shareholders To Liability Under PRC Law.
In October 2005, the PRC State Administration of Foreign Exchange (“SAFE”) issued a public notice the Notice on Relevant Issues in the Foreign Exchange Control over Financing and Return Investment Through Special Purpose Companies by Residents Inside China, or the SAFE notice (“SAFE #75”), which requires PRC residents, including both legal persons and natural persons, to register with the competent local SAFE branch before establishing or controlling any company outside of China, referred to as an "offshore special purpose company," for the purpose of overseas equity financing involving onshore assets or equity interests held by them. In addition, any PRC resident that is the shareholder of an offshore special purpose company is required to amend its SAFE registration with the local SAFE branch with respect to that offshore special purpose company in connection with any increase or decrease of capital, transfer of shares, merger, division, equity investment, or creation of any security interest over any assets located in China. Moreover, if the offshore special purpose company was established and owned the onshore assets or equity interests before the implementation date of the SAFE notice, a retroactive SAFE registration is required to have been completed before March 31, 2006. If any PRC shareholder of any offshore special purpose company fails to make the required SAFE registration and amendment, the PRC subsidiaries of that offshore special purpose company may be prohibited from distributing their profits and the proceeds from any reduction in capital, share transfer, or liquidation to the offshore special purpose company. Moreover, failure to comply with the SAFE registration and amendment requirements described above could result in liability under PRC laws for evasion of applicable foreign exchange restrictions.
We believe that our PRC resident controlling shareholder, Mr. Song, has taken all necessary steps as instructed by the local SAFE branch to comply with SAFE #75 by filing a disclosure form regarding his ownership status; however, we cannot assure you that this disclosure document will be sufficient. It is also unclear exactly whether our other PRC resident shareholders must make disclosure to SAFE. While our PRC counsel has advised us that only the PRC resident shareholders who receive ownership of the foreign holding company in exchange for ownership in the PRC operating company are subject to SAFE #75, there can be no assurance that SAFE will not require our other PRC resident shareholders to register and make the applicable disclosure. In addition, SAFE #75 requires that any monies remitted to PRC residents outside of the PRC be returned within 180 days; however, there is no indication of what the penalty will be for failure to comply or if shareholder non-compliance will be considered to be a violation of SAFE #75 by us or otherwise affect us. In the event that the proper procedures are not followed under SAFE #75, we could lose the ability to remit monies outside of the PRC and would therefore be unable to pay dividends or make other distributions. Our PRC resident shareholders could be subject to fines, other sanctions and even criminal liabilities under the PRC Foreign Exchange Administrative Regulations promulgated January 29, 1996, as amended.
The PRC's Legal And Judicial System May Not Adequately Protect The Business And Operations Of Zhongxi And The Rights Of Foreign Investors
The PRC legal and judicial system may negatively affect foreign investors. In 1982, the National People's Congress amended the Constitution of China to authorize foreign investment and guarantee the "lawful rights and interests" of foreign investors in the PRC. However, the PRC's system of laws is not yet comprehensive. The legal and judicial systems in the PRC are still rudimentary, and enforcement of existing laws is inconsistent. Many judges in the PRC lack the depth of legal training and experience that would be expected of a judge in a more developed country. Because the PRC judiciary is relatively inexperienced in enforcing the laws that do exist, anticipation of judicial decision-making is more uncertain than would be expected in a more developed country. It may be impossible to obtain swift and equitable enforcement of laws that do exist, or to obtain enforcement of the judgment of one court by a court of another jurisdiction. The PRC's legal system is based on the civil law regime, that is, it is based on written statutes; a decision by one judge does not set a legal precedent that is required to be followed by judges in other cases. In addition, the interpretation of Chinese laws may be varied to reflect domestic political changes.
The promulgation of new laws, changes to existing laws and the pre-emption of local regulations by national laws may adversely affect foreign investors. However, the trend of legislation over the last 20 years has significantly enhanced the protection of foreign investment and allowed for more control by foreign parties of their investments in Chinese enterprises. There can be no assurance that a change in leadership, social or political disruption, or unforeseen circumstances affecting the PRC's political, economic, or social life, will not affect the PRC government's ability to continue to support and pursue these reforms. Such a shift could have a material adverse effect on our business and prospects.
As a matter of substantive law, the Foreign Invested Enterprise laws provide significant protection from government interference. In addition, these laws guarantee the full enjoyment of the benefits of corporate Articles and contracts to Foreign Invested Enterprise participants. These laws impose standards concerning corporate formation and governance, which are qualitatively different from the general corporation laws of the United States. Similarly, the PRC accounting laws mandate accounting practices, which are not consistent with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. PRC's accounting laws require that an annual "statutory audit" be performed in accordance with PRC accounting standards and that the books of account of Foreign Invested Enterprises are maintained in accordance with Chinese accounting laws. Article 14 of the People's Republic of China Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise Law requires a wholly foreign-owned enterprise to submit certain periodic fiscal reports and statements to designated financial and tax authorities, at the risk of business license revocation. While the enforcement of substantive rights may appear less clear than United States procedures, the Foreign Invested Enterprises and Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprises are Chinese registered companies, which enjoy the same status as other Chinese registered companies in business-to-business dispute resolution. Any award rendered by an arbitration tribunal is enforceable in accordance with the United Nations Convention on the Recognition and Enforcement of Foreign Arbitral Awards (1958). Therefore, as a practical matter, although no assurances can be given, the Chinese legal infrastructure, while different in operation from its United States counterpart, should not present any significant impediment to the operation of Foreign Invested Enterprises
Any Recurrence Of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Or SARS, Or Another Widespread Public Health Problem, Could Harm Our Operations.
A renewed outbreak of SARS or another widespread public health problem (such as bird flu) in the PRC, where all of our revenues are derived, could significantly harm our operations. Our operations may be impacted by a number of health-related factors, including quarantines or closures of some of our offices that would adversely disrupt our operations. Any of the foregoing events or other unforeseen consequences of public health problems could significantly harm our operations.
Because Our Principal Assets Are Located Outside Of The United States And Most Of Our Directors And All Of Our Officers Reside Outside Of The United States, It May Be Difficult For You To Enforce Your Rights Based On U.S. Federal Securities Laws Against Us And Our Officers Or To Enforce U.S. Court Judgment Against Us Or Them In The PRC.
Most of our directors and all of our officers reside outside of the United States. In addition, Zhongxi is located in the PRC and substantially all of its assets are located outside of the United States. It may therefore be difficult for investors in the United States to enforce their legal rights based on the civil liability provisions of the U.S. Federal securities laws against us in the courts of either the U.S. or the PRC and, even if civil judgments are obtained in U.S. courts, to enforce such judgments in PRC courts. Further, it is unclear if extradition treaties now in effect between the United States and the PRC would permit effective enforcement against us or our officers and directors of criminal penalties, under the U.S. Federal securities laws or otherwise.
The Relative Lack Of Public Company Experience Of Our Management Team May Put Us At A Competitive Disadvantage.
Our management team lacks public company experience, which could impair our ability to comply with legal and regulatory requirements such as those imposed by Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. The individuals who now constitute our senior management have never had responsibility for managing a publicly traded company. Such responsibilities include complying with federal securities laws and making required disclosures on a timely basis. Our senior management may not be able to implement programs and policies in an effective and timely manner that adequately responds to such increased legal, regulatory compliance, and reporting requirements. Our failure to comply with all applicable requirements could lead to the imposition of fines and penalties and distract our management from attending to the growth of our business.
RISKS RELATED TO OUR COMMON STOCK.
Our Officers And Directors Control Us Through Their Positions and Stock Ownership And Their Interests May Differ From Other Stockholders.
As of March 29, 2010, there were 14,908,313 shares of our common stock issued and outstanding. Our officers and directors beneficially own approximately 23.6% of our common stock. Mr. Song, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, beneficially owns approximately 19.8% of our common stock. As a result, he is able to influence the outcome of stockholder votes on various matters, including the election of directors and extraordinary corporate transactions including business combinations. Yet Mr. Song's interests may differ from those of other stockholders. Furthermore, ownership of 23.6% of our common stock by our officers and directors reduces the public float and liquidity, and may affect the market price, of our common stock. Mr. Song, Ms. Feng, who is our Director, and Mr. Xu, the Chief Engineer of Zhongxi, each respectively own 35.0%, 3.6%, and 2.3% of Alloy Science, 43.8%, 6.3%, and 5.0% of Zhongxi, and 19.8%, 2.0% and 1.3% of China Power. Mr. Zhang, Vice General Manager for Zhongxi, and Ms. Feng, our Director, hold 25.5% of our common stock as trustees for the shareholders of Alloy Science. In addition, Ms. Feng, our Director, and Mr. Gouang Zhang, our Vice General Manager, hold voting power over approximately 45.08% of the shares of Alloy Science as Trustees for Alloy Science stockholders. Alloy Science is not engaged in any business operations and all of the ownership rights of our officers and directors in Zhongxi are held by An Sen pursuant to the Management Entrustment Agreement.
We Are Not Likely To Pay Cash Dividends In The Foreseeable Future.
We intend to retain any future earnings for use in the operation and expansion of the business of Zhongxi. We do not expect to pay any cash dividends in the foreseeable future but will review this policy as circumstances dictate. Should we decide in the future to do so, as a holding company, our ability to pay dividends and meet other obligations depends upon the receipt of dividends or other payments from our operating subsidiaries. In addition, our operating subsidiaries, from time to time, may be subject to restrictions on their ability to make distributions to us, including restrictions on the conversion of local currency into U.S. dollars or other hard currency and other regulatory restrictions.
Our Common Stock Has Limited Liquidity And Subject To Price Volatility Unrelated To Our Operations.
The market price of our common stock could fluctuate substantially due to a variety of factors, including market perception of our ability to achieve our planned growth, quarterly operating results of other companies in the same industry, trading volume in our common stock, changes in general conditions in the economy and the financial markets, or other developments affecting our competitors or us. In addition, the stock market itself is subject to extreme price and volume fluctuations. This volatility has had a significant effect on the market price of securities issued by many companies for reasons unrelated to their operating performance and could have the same effect on our common stock.
A Large Number Of Shares Will Be Eligible For Future Sale And May Depress Our Stock Price.
We may be required, under terms of future financing arrangements, to offer a large number of common shares to the public, or to register for sale by future private investors a large number of shares sold in private sales to them.
Sales of substantial amounts of common stock, or a perception that such sales could occur, and the existence of options or warrants to purchase shares of common stock at prices that may be below the then-current market price of our common stock, could adversely affect the market price of our common stock and could impair our ability to raise capital through the sale of our equity securities, either of which would decrease the value of any earlier investment in our common stock.
We Are Authorized To Issue "Blank Check" Preferred Stock, Which, If Issued Without Stockholders Approval, May Adversely Affect The Rights Of Holders Of Our Common Stock.
We are authorized to issue 10,000,000 shares of preferred stock, of which 5,000,000 shares have been designated as Series B Preferred Convertible Stock. As of March 29, 2010 there were 4,166,667 shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock issued and outstanding. The Board of Directors is authorized under our Articles of Incorporation, as amended and corrected, to provide for the issuance of additional shares of preferred stock by resolution, and to fix the designation, powers, preferences, and rights of the shares of each such series and the qualifications, limitations, or restrictions thereof without any further vote or action by the stockholders. Any shares of preferred stock so issued are likely to have priority over the common stock with respect to dividend or liquidation rights. In the event of issuance, the preferred stock could be utilized, under certain circumstances, as a method of discouraging, delaying, or preventing a change in control, which could have the effect of discouraging bids for our company and thereby prevent stockholders from receiving the maximum value for their shares. We have no present intention to issue any shares of our preferred stock in order to discourage or delay a change of control. However, there can be no assurance that preferred stock will not be issued at some time in the future.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
All land in the PRC is owned by the government and cannot be sold to any individual or entity. Instead, the government grants landholders a "land use right" after a purchase price for such "land use right" is paid to the government. The "land use right" allows the holder the right to use the land for a specified long-term period of time and enjoys all the ownership incidents to the land. The following are the details regarding our land use rights with regard to the land that Zhongxi uses in its business.
Zhongxi currently maintains two factories: a transformer factory and an amorphous alloy transformer core factory. The transformer factory is in the Xizhang Industrial Park, Daxingxi Road, Xi'an. Its total area is 5,803 square meters, and has more than 50 machines in a manufacturing area of 2,000 square meters. The land use rights of 2,000 square meters of land at Daxinxi Road, Xizhang Industry Village are leased from Xi'an Zhengliu Dianlu Transformer Co., Ltd. for an annual rent of RMB 100,000 yuan ($14,626). The term of the lease is 24 years, which expires in 2028. Zhongxi currently rents the factory built on the 2,000 square meters land to Xi'an Zhongxi Zengliu Dianlu Transformer Factory, Ltd. for an annual rent of RMB 500,000 ($73,129). The lease is currently on a month to month basis with a monthly lease payment of RMB 41,666.67 ($6,094).
The amorphous alloy transformer core factory, with an area of 1,750 square meters is located at Yasen Industry Center, 1st Floor, 1st factory, No. 15 Gao Xin 6th Road, Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone. It has one advanced amorphous transformer core assembly line.
Zhongxi corporate headquarters are now located at: Room 602, 6/F, Block B, Science & Technology Park of Xi Dian University, No. 168 Kechuang Road, Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China 710065, with approximately 460 square meters of usable space.
Zhongxi does not own any land use rights.
ITEM 3.LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
Neither we nor any of our subsidiaries, nor is Zhongxi a party to any pending legal proceedings, nor are we aware of any such proceedings threatened.
ITEM 4.SUBMISSION OF MATTERS TO A VOTE OF SECURITY HOLDERS
None.
PART II
ITEM 5.MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS, AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market Information
Our common stock is quoted on the Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board (“OTCBB”) under the trading symbol “CPQQ.OB”. The table below sets forth the high and low bid price for each quarter since there has been a market for our common stock, as reported by the Yahoo Finance website at http://finance.yahoo.com/q?s=CPQQ.OB. These quotations reflect inter-dealer prices, without retail mark-up, mark-down, or commission and may not represent actual transactions. There were no reported quotations for our common stock during 2008 and the first quarter of 2009 as our common stock was not traded or quoted on any exchange or inter-dealer quotation system until May 2009.
|
High
|
Low
|
|||||||
|
Fourth Quarter 2009
|
$
|
4.05
|
$
|
1.35
|
||||
|
Third Quarter 2009
|
$
|
1.87
|
$
|
0.40
|
||||
|
Second Quarter 2009
|
$
|
0.51
|
$
|
0.25
|
||||
Holders
As of March 29, 2010, there were 14,908,313 shares of our common stock issued and outstanding, and there were approximately 50 holders of record of our outstanding shares of common stock.
Dividends
We have not declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock during either of our two most recent fiscal years. The payment of dividends, if any, is at the discretion of the Board of Directors and is contingent on the Company's revenues and earnings, capital requirements, and financial conditions. We currently intend to retain all earnings, if any, for use in business operations. Accordingly, we do not anticipate declaring any dividends in the near future.
The PRC's national currency, the renminbi, is not a freely convertible currency. Please refer to the risk factors ”Governmental Control Of Currency Conversion May Affect The Value Of Your Investment”, “The Fluctuation Of The Renminbi May Harm Your Investment”, and “PRC State Administration Of Foreign Exchange ("SAFE") Regulations Regarding Offshore Financing Activities By PRC Residents May Increase The Administrative Burden We Face. The Failure By Our Shareholders Who Are PRC Residents To Make Any Required Applications And Filings Pursuant To Such Regulations May Prevent Us From Being Able To Distribute Profits And Could Expose Us And Our PRC Resident Shareholders To Liability Under PRC Law.”
Securities Authorized For Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans.
We do not have any equity compensation plans.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
We have reported all sales of our unregistered equity securities that occurred during 2009 in our Reports on Form 10-Q or Form 8-K, as applicable.
Transfer Agent
The Company's stock transfer agent is OTC Corporate Transfer Service Co., located at 52 Maple Run Drive Jericho, New York 11753. Their telephone number is 516-932-2080, and their facsimile is 516-932-2078.
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and the notes thereto that appear elsewhere in this report. The results shown herein are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected in future periods. This discussion contains forward-looking statements based on current expectations, which involve uncertainties. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by words such as anticipate, believe, continue, could, estimate, expect, intend, likely, may, might, ongoing, plan, potential, predict, should, will, or the negative of these terms or other comparable terms. All forward-looking statements included in this document are based on information available to the management as of the date of this document. Actual results and the timing of events could differ materially from the forward-looking statements as a result of a number of factors. Readers should also carefully review the factors shown in other reports and documents that we file with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Overview
We design, manufacture, and distribute amorphous alloy transformer cores and amorphous alloy transformers in the People's Republic of China (“PRC”) that are used to step down voltage at the final leg of the distribution of electricity to consumers, businesses, and industry. Amorphous alloy cores are contained within the amorphous alloy electric transformers and constitute the main operating component of a new generation of energy saving electrical power transformers. We have ended our legacy distribution of traditional silicon steel transformer cores and transformers, and no longer make, sell, or distribute silicon steel cores or transformers. In 2009, sales of amorphous alloy cores and amorphous alloy transformers products accounted for almost 100% of our revenues. We expect that amorphous alloy cores and amorphous alloy core transformers will be our major products.
Our business is conducted primarily through our operating company, Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi & Technology Co., Ltd. (“Zhongxi”), a PRC company that is controlled through our wholly owned PRC based subsidiary An Sen (Xi'an) Power Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (“An Sen”), which is a “wholly foreign-owned entity” (“WOFE”) under Chinese law.
Critical Accounting Policies, Judgments, and Estimates
Our discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based on our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“GAAP”). The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates, judgments, and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. On an on-going basis, we evaluate our estimates, including those related to receivables from customers, bad debts, inventory, investments, intangible assets, income taxes, financing operations, and contingencies. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions. For further information on our critical accounting policies, please see the discussion in our Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
We believe the following critical accounting policies rely on the significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of our consolidated financial statements.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Our financial instruments consist of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and accrued liabilities. The fair value of these financial instruments approximate their carrying amounts reported in the consolidated balance sheets due to the short-term maturity of these instruments. Significant judgment is required to assess whether the impairment is other-than-temporary. Our judgment of whether an impairment is other-than-temporary is based on an assessment of factors, including severity of the impairment, expected duration of the impairment, and forecasted recovery of fair value.
Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable includes billings for the products delivered. We recognize an allowance for doubtful accounts to ensure accounts receivable are not overstated due to uncollectibility. Bad debt reserves are maintained for all customers based on a variety of factors, including our historical experience regarding the customers’ ability to pay and general economic conditions.
Inventory
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market value. Cost has been determined using the first-in, first-out method. Inventory quantities on hand are regularly reviewed, and where necessary, reserves for excess and unusable inventories are recorded.
Property, plant, and equipment
Property, plant, and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Judgment, experience, and accounting and tax guidelines are used to determine the estimated useful lives of assets. We have determined that our property, plant, and equipment have the following estimated lives:
|
Plant and office buildings
|
20 years
|
|
Plant machinery
|
10 years
|
|
Office equipment
|
5 years
|
Changes in these estimates and assumptions could materially affect our financial position and results of operations.
Intangibles and Other Long-lived Assets
Intangibles and other long-lived assets are stated at cost, less accumulated amortization and impairments. Our intangible assets are being amortized over the expected useful economic life of 10 years.
We review long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may no longer be recoverable. When these events occur, the Company measures impairment by comparing the carrying value of the long-lived assets to the estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to result from the use of the assets and their eventual disposition. If the sum of the expected undiscounted cash flow is less than the carrying amount of the assets, we would recognize an impairment loss based on the fair value of the assets. Changes in these estimates and assumptions could materially affect our financial position and results of operations.
Foreign Currency Translation
Our functional currency and reporting currency is the United States dollar. The functional currency of An Sen and Zhongxi is the renminbi, the currency of the People’s Republic of China.
Our assets and liabilities are translated into United States dollars at the foreign currency exchange rate in effect at the end of the reporting period. Revenues and expenses are translated into dollars using the weighted average foreign exchange rates for the reporting periods. Equity transactions are translated using historical rates. The resulting translation adjustments are recorded as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income within stockholders’ equity.
Income Taxes
We use the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under this method, income tax expense is recognized for the amount of taxes payable or refundable for the current year. In addition, deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the expected future tax consequences of temporary differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities and for operating losses and tax credit carry-forwards. Management must make assumptions, judgments, and estimates to determine our current provision for income taxes and our deferred tax assets and liabilities and any valuation allowance to be recorded against a deferred tax asset. Our judgments, assumptions, and estimates about the current provision for income tax take into account current tax laws, our interpretation of current tax laws, and possible outcomes of current and future audits conducted by foreign and domestic tax authorities. Changes in tax law or our interpretation of tax laws and the resolution of current and future tax audits could significantly affect the amounts provided for income taxes in our consolidated financial statements.
Equity investments
We account for equity investments in entities in which we exercise significant influence but do not own a majority equity interest or control using equity method. We evaluate our equity investments for impairment whenever events and changes in business circumstances indicate the carrying amount of the equity investment may not be fully recoverable. We invested $159,422 (using the exchange rate of RMB 6.8372 to $1.00 as of December 31, 2009) or RMB 1,090,000 in Yan An Amorphous Alloy Transformer Co., Ltd. (“Yan An”) for 20% of its ownership in 2005. We recorded this investment using equity method because of our significant influence over the entity.
Stock-Based Compensation
Our stock-based compensation expense is estimated at the grant date based on the award’s fair value as calculated by the Black-Scholes-Merton (BSM) option-pricing model and is recognized as expense over the requisite service period. The BSM model requires various highly judgmental assumptions including expected volatility and option life. Changes in these assumptions could materially affect our financial position and results of operations.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In June 2009, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (“SFAS”) No. 166, “Accounting for Transfers of Financial Assets, an Amendment of FASB Statement No. 140” (“SFAS No. 166”), expected to be included in the FASB Accounting Standards Codification (“Codification”) as Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC 860”), Transfers and Servicing. This topic improves the comparability of information that a reporting entity provides regarding transfers of financial assets and the effects on its financial statements. This topic is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after November 15, 2009. The Company does not expect the adoption of this topic to have a material effect on its financial statements and related disclosures.
In June 2009, the FASB issued SFAS No. 167, “Amendments to FASB Interpretation No. 46(R)” (“SFAS No. 167”), expected to be included in the Codification as ASC 810, Consolidation. This topic changes the consolidation guidance applicable to a variable interest entity. Among other things, it requires a qualitative analysis to be performed in determining whether an enterprise is the primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity. This topic is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after November 15, 2009. The Company does not expect the adoption of this topic to have a material effect on its financial statements and related disclosures.
In June 2009, the FASB issued SFAS No. 168, “The FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ and the Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles a Replacement of FASB Statement No. 162” (“SFAS No. 168”), included in the Codification as ASC 105, Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. This topic is the source of authoritative accounting principles recognized by the FASB to be applied by nongovernmental entities in the preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. This topic is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after September 15, 2009. On September 30, 2009, the Company adopted this topic, which has no effect on the Company’s financial statements as it is for disclosure purposes only.
In May 2009, the FASB issued SFAS No. 165, “Subsequent Events” (“SFAS No. 165”), included in the Codification as ASC 855, Subsequent Events. This topic establishes the period in which management of a reporting entity should evaluate events and transactions for recognition or disclosure in the financial statements. It also describes the circumstances under which an entity should recognize events or transactions that occur after the balance sheet date. This topic is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009. The Company does not expect the adoption of this topic to have a material effect on its financial statements and related disclosures.
In December 2007, the FASB issued SFAS No. 160, “Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements – an amendment of Accounting Research Bulletin No. 51” (“SFAS 160”), included in the Codification as ASC 810-10-65-1. This topic establishes accounting and reporting standards for ownership interests in subsidiaries held by parties other than the parent, the amount of consolidated net income attributable to the parent and to the noncontrolling interest, changes in a parent’s ownership interest, and the valuation of retained noncontrolling equity investments when a subsidiary is deconsolidated. This topic also establishes disclosure requirements that clearly identify and distinguish between the interests of the parent and the interests of the noncontrolling owners. This topic is effective for fiscal years beginning October 1, 2009. The Company does not expect the effect of the adoption of SFAS 160 to be material.
Results of Operations
Revenues
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
Percent
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Revenues
|
%
|
Revenues
|
%
|
change
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Amorphous alloy cores
|
$ | 16,209,389 | 67.9 | % | $ | 5,365,918 | 57.1 | % | 202.1 | % | ||||||||||
|
Amorphous alloy transformers
|
7,558,544 | 31.7 | % | 3,508,794 | 37.4 | % | 115.4 | % | ||||||||||||
|
Traditional silicon steel cores and transformers
|
98,306 | 0.4 | % | 519,779 | 5.5 | % | -81.1 | % | ||||||||||||
|
Revenues, net
|
$ | 23,866,239 | 100.0 | % | $ | 9,394,491 | 100.0 | % | 154.0 | % | ||||||||||
Net revenues increased $14,471,748 or 154.0% to $23,866,239 in 2009 from $9,394,491 in 2008 primarily due to higher tonnage of amorphous alloy cores and transformers sold, in response to higher orders from existing customers and new customers. To help fulfill the customers’ orders, we subcontracted the manufacturing of some cores and transformers to other companies. The revenues from traditional silicon steel cores and transformers decreased because we are focused on amorphous alloy cores and transformers as our major products and have exited the manufacturing, marketing, and distribution of steel cores and transformers.
Cost of Goods Sold
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
Percent
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
COGS
|
%
|
COGS
|
%
|
change
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Amorphous alloy cores
|
$ | 12,269,445 | 66.5 | % | $ | 4,019,564 | 57.0 | % | 205.2 | % | ||||||||||
|
Amorphous alloy transformers
|
5,806,964 | 32.0 | % | 2,636,708 | 37.4 | % | 120.2 | % | ||||||||||||
|
Traditional silicon steel cores and transformers
|
91,359 | 0.5 | % | 394,467 | 5.6 | % | -76.8 | % | ||||||||||||
|
Cost of goods sold
|
$ | 18,167,768 | 100.0 | % | $ | 7,050,739 | 100.0 | % | 157.7 | % | ||||||||||
Costs of goods sold increased $11,117,029 or 157.7% to $18,167,768 in 2009 from $7,050,739 in 2008 primarily due to higher tonnage of amorphous alloy cores and transformers sold. The price of amorphous alloy strip, the primary raw material for making amorphous alloy cores and transformers, increased in the first quarter of 2009. The price increase also contributed to the increase in the cost of goods sold in 2009 compared with 2008.
Gross Profit and Gross Profit Margin
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Gross profit
|
Gross margin %
|
Gross profit
|
Gross margin %
|
Percent
change
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Amorphous alloy cores
|
$ | 3,939,944 | 24.3 | % | $ | 1,346,354 | 25.1 | % | 192.6 | % | ||||||||||
|
Amorphous alloy transformers
|
1,751,580 | 23.2 | % | 872,086 | 24.9 | % | 100.8 | % | ||||||||||||
|
Traditional silicon steel cores and transformers
|
6,947 | 7.1 | % | 125,312 | 24.1 | % | -94.5 | % | ||||||||||||
|
Gross profit
|
$ | 5,698,471 | 23.9 | % | $ | 2,343,752 | 24.9 | % | 143.1 | % | ||||||||||
Gross profit increased $3,354,719 or 143.1% to $5,698,471 in 2009 from $2,343,752 in 2008 primarily due to higher sales of amorphous alloy cores and transformers.
The gross profit margin (gross profit as a percent of total revenues) decreased 1 percentage point to 23.9% in 2009 from 24.9% in 2008 primarily due to a price increase in the first quarter 2009 for amorphous alloy strip, the primary raw material required to construct amorphous alloy cores and transformers.
Selling, General, and Administration Expenses
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
Percent
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
$
|
% of Revenue
|
$
|
% of Revenue
|
change
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Selling, general, and administrative expenses
|
$ | 1,170,932 | 4.9 | % | $ | 779,350 | 8.3 | % | 50.2 | % | ||||||||||
Selling, general, and administrative expenses increased $391,582 or 50.2% to $1,170,932 in 2009 from $779,350 in 2008 mainly due to increases in sales tax levy resulting from increases in revenues, higher freight expenses in support of higher sales, higher professional and consulting fees, and higher employee salaries.
Stock-based Compensation
The company incurred an expense of $25,697 in stock-based compensation in 2009 due to stock options granted to an officer in the third quarter 2009. The value of these options is expensed over the term of the respective vesting periods.
Gain on Investment
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
Percent
|
|||||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
change
|
||||||||||
|
Gain on investment
|
$ | 89,755 | $ | 67,505 | 33.0 | % | ||||||
Gain on investment increased $22,250 or 33.0% to $89,755 in 2009 from $67,505 in 2008 primarily due to higher earnings from our 20% equity ownership in Yan An. We invested $159,422 (using the exchange rate of RMB 6.8372 to $1.00 as of December 31, 2009) or RMB 1,090,000 in Yan An for 20% of its ownership in 2005. We recorded this investment using the equity method because of our significant influence on the entity.
The following table summarizes the income statement of Yan An for the year ended December 31, 2009 and 2008.
|
Yan An Amorphous Alloy Transformer Co., Ltd.
|
||||||||
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Exchange rate (RMD to $)
|
6.8372 | 6.9623 | ||||||
|
Sales
|
$ | 4,401,629 | $ | 3,756,878 | ||||
|
Gross profit
|
$ | 743,875 | $ | 687,509 | ||||
|
Income from continuing operations
|
$ | 357,012 | $ | 303,867 | ||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 357,012 | $ | 303,867 | ||||
|
20% investment earnings
|
$ | 71,402 | $ | 60,773 | ||||
|
Dividends received
|
$ | 43,878 | $ | 72,948 | ||||
The following table provides summary balance sheet information for Yan An as of December 31, 2009 and 2008.
|
Yan An Amorphous Alloy Transformer Co., Ltd.
|
||||||||||||||||
|
December 31, 2009
|
December 31, 2008
|
|||||||||||||||
|
RMB
|
$ | RMB | $ | |||||||||||||
|
Total assets
|
26,419,407 | 3,864,068 | 23,948,797 | 3,494,032 | ||||||||||||
|
Total liabilities
|
13,393,299 | 1,958,887 | 11,863,650 | 1,730,858 | ||||||||||||
|
Net assets
|
13,026,108 | 1,905,182 | 12,085,148 | 1,763,174 | ||||||||||||
|
Zhongxi's 20% ownership
|
2,605,222 | 381,036 | 2,417,030 | 352,635 | ||||||||||||
|
Ending balance of investment account
|
1,934,226 | 282,897 | 1,620,222 | 236,384 | ||||||||||||
|
Difference between 20% ownership and ending balance of investment account
|
670,996 | 98,139 | 796,808 | 116,251 | ||||||||||||
The difference of $ 98,139 was mainly due to the discount of RMB 843,672 when we purchased the 20% of ownership in Yan An. Yan An’s net assets were RMB 9,668,360 and we invested RMB 1,090,000 (instead of RMB 1,933,672) to purchase the 20% ownership in Yan An.
Other Income
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
Percent
|
|||||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
change
|
||||||||||
|
Other income
|
$ | 393,224 | $ | 279,436 | 40.7 | % | ||||||
Other income consists primarily of technical support consulting fees, rental income, and government subsidy. During 2009, other income increased $113,788 or 40.7% to $393,224 in 2009 from $279,436 in 2008 primarily due to income generated from providing amorphous alloy transformer technical support in 2009, which we did not offer in 2008.
Interest Expense
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
Percent
|
|||||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
change
|
||||||||||
|
Interest expense
|
$ | 14,268 | $ | 188,110 | -92.4 | % | ||||||
Interest expenses decreased $173,842 or 92.4% to $14,268 in 2009 from $188,110 in 2008 mainly because one major bank loan was paid off in the third quarter of 2008, which ended interest payments for the loan.
Income taxes
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Income taxes
|
$ | 763,455 | $ | 270,559 | ||||
|
Effective tax rate
|
15.3 | % | 15.7 | % | ||||
Our Chinese operating company, Zhongxi, is subject to a 25% standard enterprise income tax in China. However, due to Zhongxi’s high-tech enterprise status, the National Tax Bureau in the Xi’an High-Tech Development Zone granted Zhongxi tax exemptions for 2004 and 2005 and a 50% tax reduction for as long as Zhongxi meets the high-tech enterprise qualification. The increase in the income taxes in 2009 over 2008 was mainly due to the higher net income before income taxes that resulted from higher revenues.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
In a private placement closed on December 2, 2009, we issued an aggregate of 4,166,667 shares of Series B convertible preferred stock with attached warrants to purchase a total of 1,000,000 shares of our common stock in consideration of an aggregate purchase price of $5,000,000. As our Series B convertible preferred stock does not require redemption by us, upon issuance we recorded a one-time deemed dividend of $9,045,005 for the beneficial conversion feature (the "BCF") embedded in the preferred stock.
Between February 13, 2007 and May 30, 2007, we raised $925,000 in a private placement of our Series A Convertible Preferred Stock at a purchase price of $10.00 per share, which we issued together with an aggregate of 4,021,900 warrants to purchase our common stock at a purchase price of $1.00 per share.
On December 18, 2008, the Series A Convertible Preferred Stock shares were converted into 4,021,900 shares of common stock. In connection with the conversion, the Company recorded a deemed dividend of $2,193,483 for the BCF.
Both deemed dividends were charged to retained earnings, which resulted in the accumulated deficit of $5,728,130 and $462,971 as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
We have funded our operations and capital expenditures using cash generated from operations and funds raised from issuing convertible preferred stock. We will continue our investment in the development and enhancement of our production facilities for amorphous alloy cores and transformers. We believe our existing cash and cash equivalents will be sufficient to maintain our operations at the present level for at least the next 12 months.
The following table is the summary of our liquidity and capital resources at the end of the years 2009 and 2008. Working capital is defined as current assets minus current liabilities.
|
December 31, 2009
|
December 31, 2008
|
|||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents
|
$ | 8,883,188 | $ | 1,071,038 | ||||
|
Working capital
|
$ | 9,792,968 | $ | 2,951,991 | ||||
|
Stockholders' equity
|
$ | 17,141,382 | $ | 7,935,218 | ||||
The following table shows the net cash flows that determined our net increase (decrease) in cash for the years 2009 and 2008.
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Net cash provided by operating activities
|
$ | 5,380,655 | $ | 1,135,332 | ||||
|
Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities
|
(2,509,214 | ) | 88,274 | |||||
|
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities
|
4,937,502 | (1,287,089 | ) | |||||
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash
|
3,207 | 60,626 | ||||||
|
Net increase (decrease) in cash
|
$ | 7,812,150 | $ | (2,857 | ) | |||
Operating activities
For the year 2009, net cash provided by operating activities was $5,380,655. This was primarily due to the net income of $4,220,000, adjusted by non-cash related expenses including depreciation and amortization of $249,592 and stock-based compensation of $25,697, and adjusted by a non-cash related gain on investment of $89,755, then increased by a net increase in working capital items of $884,527. The net increase in working capital items was mainly due to the decrease in advances to suppliers of $772,909, a decrease in inventory of $99,416 due to higher demand to our products, and an increase in value added tax and income tax payables of $284,302 that resulted from the increased revenues. The net increase in working capital items was partly offset by the decrease in accounts payable of $163,094 and the decrease in advances from customers of $109,690.
For the year 2008, net cash provided by operating activities was $1,135,332. This was primarily due to the net income of $1,455,793, adjusted by non-cash related expenses including depreciation and amortization of $232,607, provision of bad debts of $40,467, provision for impairment loss of advances to suppliers of $107,885, and a noncash related gain on investment of $67,505, partly offset by a net decrease in working capital items of $633,915. The net decrease in working capital items was mainly due to the increases in accounts receivable of $210,710 and inventory of $92,297, and decreases in accounts payable and accrued expenses and other payables of $482,848. The decrease in working capital items was partly offset by the decrease of $83,518 in advances to suppliers and the increase of $105,293 in income taxes payable.
Investing activities
Net cash used in investing activities was $2,509,214 for the year 2009. The use was primarily attributable to capital expenditures of $1,620,844 for construction in progress for the new plant, $219,270 in intangible assets (amorphous transformer technology), and deposit for the purchase of equipment of $767,445, partly offset by a dividend of $43,854 received from the 20% equity investment and repayment from related parties of $72,913.
Net cash provided by investing activities was $88,274 for the year 2008. It was primarily due to a $65,724 repayment from related parties and a dividend of $71,816 from the 20% equity investment, partly offset by the acquisitions of plant equipment of $49,266.
Financing activities
Net cash provided by financing activities was $4,937,502 for the year 2009 primarily due to the $4,939,450 net proceeds from issuance of Series B convertible preferred stock.
Net cash used in financing activities was $1,287,089 for the year 2008 primarily due to a $1,098,783 repayment of short-term loans and a $186,575 repayment to related parties.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
The following table presents selected financial data for the Company on a consolidated basis for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008.
We derived the selected financial data set forth below from the Company's consolidated audited statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 and the consolidated audited balance sheets as at December 31, 2009 and 2008, each of which is included in this report. You should read the following summary financial data in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" appearing elsewhere in this report.
|
For Year Ended
December 31,
|
||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||
|
Revenues, net
|
$
|
23,866,239
|
$
|
9,394,491
|
||
|
Income from operations
|
$
|
4,501,842
|
$
|
1,564,402
|
||
|
Net income
|
$
|
4,220,000
|
$
|
1,455,793
|
||
|
Total assets
|
$
|
18,881,134
|
$
|
9,675,638
|
||
|
Total liabilities
|
$
|
1,739,752
|
$
|
1,740,420
|
||
|
Stockholders’ equity
|
$
|
17,141,382
|
$
|
7,935,218
|
||
The Company's consolidated audited financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, together with the report of the independent certified public accounting firm thereon and the notes thereto, are presented beginning at page F-1.
|
Page(s)
|
|
|
Consolidated Financial Statements
|
|
|
F-1
|
|
|
F-2
|
|
|
F-3
|
|
|
F-4
|
|
|
F-5
|
ACSBAcquavella, Chiarelli, Shuster, Berkower & Co., LLP
| 517 Route one | 1 Penn Plaza |
| Iselin, New Jersey, 08830 | 36the Floor |
| 732.855.9600 | New York, NY 10119 |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Board of Directors and Stockholders of
China Power Equipment, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of China Power Equipment, Inc. as of December 31, 2009, and the related consolidated statement of income, stockholders’ equity and comprehensive income, and cash flow for the year ended December 31, 2009. China Power Equipment’ management is responsible for these financial statements. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audit included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that out audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of China Power Equipment, Inc. as of December 31, 2009, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2009 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
/s/ Acquavella, Chiarelli, Shuster, Berkower & Co., LLP
Certified Public Accountants
New York, N.Y.
March 25, 2010
MORGENSTERN,SVOBODA & BAER, CPA’s, P.C.
CERTIFIED PUBLIC ACCOUNTANTS
40 Exchange Place, Suite 1820
New York, NY 10005
TEL: (212) 925-9490
FAX: (212) 226-9134
E-Mail: msbcpas@gmail.com
Board of Directors and Stockholders of
China Power Equipment, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of China Power Equipment, Inc. as of December 31, 2008, and the related consolidated statements of income, shareholders’ equity and comprehensive income, and cash flows for the year then ended. China Power Equipment Inc.’s management is responsible for these financial statements. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audit included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of China Power Equipment, Inc. as of December 31, 2008 and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year then ended in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
/s/ Morgenstern, Svoboda & Baer CPA’s P.C.
Certified Public Accountants
New York, NY
March 29, 2009
|
China Power Equipment, Inc.
|
||||||||
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets
|
||||||||
|
December 31,
|
December 31,
|
|||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Assets
|
||||||||
|
Current Assets
|
||||||||
|
Cash
|
$ | 8,883,188 | $ | 1,071,038 | ||||
|
Accounts receivable, net
|
1,949,818 | 2,013,305 | ||||||
|
Advance to suppliers
|
- | 771,407 | ||||||
|
Inventory, net (Note 3)
|
363,312 | 461,634 | ||||||
|
Prepaid expenses and other receivables
|
220,939 | 257,700 | ||||||
|
Total Current Assets
|
11,417,257 | 4,575,084 | ||||||
|
Related party receivables (Note 11)
|
731 | 97,248 | ||||||
|
Property, plant and equipment, net (Note 4)
|
4,593,068 | 3,116,422 | ||||||
|
Intangible assets, net (Note 6)
|
391,513 | 220,742 | ||||||
|
Long-term investment (Note 5)
|
282,897 | 236,384 | ||||||
|
Deposit on contract rights (Note 12)
|
1,316,328 | 1,313,064 | ||||||
|
Deposit for purchase of equipment
|
767,858 | - | ||||||
|
Prepaid capital lease (Note 9)
|
111,482 | 116,694 | ||||||
|
Total Assets
|
$ | 18,881,134 | $ | 9,675,638 | ||||
|
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity
|
||||||||
|
Current Liabilities
|
||||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
$ | 549,065 | $ | 710,480 | ||||
|
Accrued liabilities and other payables
|
395,486 | 409,040 | ||||||
|
Advance from customers
|
32,760 | 142,156 | ||||||
|
Lease payable - current portion (Note 9)
|
2,156 | 1,944 | ||||||
|
Note payable (Note 8)
|
58,503 | 58,358 | ||||||
|
Value-added tax payable
|
219,398 | 64,686 | ||||||
|
Income taxes payable (Note 7)
|
365,751 | 235,262 | ||||||
|
Related party payable (Note 11)
|
1,170 | 1,167 | ||||||
|
Total Current Liabilities
|
1,624,289 | 1,623,093 | ||||||
|
Long-term Liabilities
|
||||||||
|
Lease payable - non current portion (Note 9)
|
115,463 | 117,327 | ||||||
|
Total Long-term Liabilities
|
115,463 | 117,327 | ||||||
|
Stockholders' Equity
|
||||||||
|
Series B convertible preferred stock, $0.001 par value, 5,000,000 shares authorized,
|
||||||||
|
4,166,667 shares and Nil issued and outstanding at December 31, 2009 and 2008
|
4,167 | - | ||||||
|
Common stock: par value $0.001 per share, 100,000,000 shares authorized;
|
||||||||
|
14,908,313 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2009 and 2008
|
14,908 | 14,908 | ||||||
|
Additional paid in capital
|
21,182,026 | 7,176,041 | ||||||
|
Statutory surplus reserve fund (Note 10)
|
642,819 | 202,665 | ||||||
|
Accumulated deficit
|
(5,728,130 | ) | (462,971 | ) | ||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income
|
1,025,592 | 1,004,575 | ||||||
|
Total stockholders' equity
|
17,141,382 | 7,935,218 | ||||||
|
Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity
|
$ | 18,881,134 | $ | 9,675,638 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
|
China Power Equipment, Inc.
|
||||||||
|
Consolidated Statements of Operations
|
||||||||
|
Year Ended,
|
||||||||
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Revenue, net
|
$ | 23,866,239 | $ | 9,394,491 | ||||
|
Cost of goods sold
|
(18,167,768 | ) | (7,050,739 | ) | ||||
|
Gross profit
|
5,698,471 | 2,343,752 | ||||||
|
Operating expenses:
|
||||||||
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses
|
1,170,932 | 779,350 | ||||||
|
Stock-based compensation
|
25,697 | - | ||||||
|
Total operating expenses
|
1,196,629 | 779,350 | ||||||
|
Net income from operations
|
4,501,842 | 1,564,402 | ||||||
|
Other income (expenses)
|
||||||||
|
Gain on investment
|
89,755 | 67,505 | ||||||
|
Other income
|
393,224 | 279,436 | ||||||
|
Interest income
|
12,902 | 3,119 | ||||||
|
Interest expense
|
(14,268 | ) | (188,110 | ) | ||||
|
Total other income
|
481,613 | 161,950 | ||||||
|
Net income before income taxes
|
4,983,455 | 1,726,352 | ||||||
|
Income taxes
|
763,455 | 270,559 | ||||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 4,220,000 | $ | 1,455,793 | ||||
|
Deemed dividend from beneficial conversion feature of preferred stocks
|
(9,045,005 | ) | (2,193,483 | ) | ||||
|
Net loss applicable to common shareholders
|
$ | (4,825,005 | ) | $ | (737,690 | ) | ||
|
Loss per share - basic
|
$ | (0.32 | ) | $ | (0.07 | ) | ||
|
Loss per share - diluted
|
$ | (0.32 | ) | $ | (0.07 | ) | ||
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding:
|
||||||||
|
Basic
|
14,908,313 | 11,036,692 | ||||||
|
Diluted
|
14,908,313 | 11,036,692 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
|
China Power Equipment, Inc.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Consolidated Statements Of Stockholders' Equity
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Retained
|
Accumulated
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Additional
|
Statutory
|
Earnings
|
Other
|
Total
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Preferred Stock
|
Capital Stock
|
Paid-in
|
Surplus
|
(Accumulated
|
Comprehensive
|
Stockholders'
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Shares
|
Amount
|
Shares
|
Amount
|
Capital
|
Reserve
|
deficit)
|
Income
|
Equity
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
BALANCE, JANUARY 1, 2008
|
92,500 | $ | 93 | 10,451,613 | $ | 10,452 | $ | 4,886,921 | $ | 38,629 | $ | 438,755 | $ | 585,381 | $ | 5,960,231 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Conversion of Series A preferred stock
|
(92,500 | ) | (93 | ) | 4,021,900 | 4,022 | (3,929 | ) | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Deemed dividend on preferred stock
|
- | - | - | - | 2,193,483 | - | (2,193,483 | ) | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of common stock
|
- | - | 434,800 | 434 | 99,566 | - | - | - | 100,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Transfer to statutory reserve
|
- | - | - | - | - | 164,036 | (164,036 | ) | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive income:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net income
|
- | - | - | - | - | - | 1,455,793 | - | 1,455,793 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment
|
- | - | - | - | - | - | - | 419,194 | 419,194 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Total comprehensive income
|
1,874,987 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
BALANCE, DECEMBER 31, 2008
|
- | - | 14,908,313 | 14,908 | 7,176,041 | 202,665 | (462,971 | ) | 1,004,575 | 7,935,218 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of preferred stock
|
4,166,667 | 4,167 | - | - | 4,935,283 | - | - | - | 4,939,450 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Deemed dividend on preferred stock
|
- | - | - | - | 9,045,005 | - | (9,045,005 | ) | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-Based Compensation
|
- | - | - | - | 25,697 | - | - | - | 25,697 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Transfer to statutory reserve
|
- | - | - | - | - | 440,154 | (440,154 | ) | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive income:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net income
|
- | - | - | - | - | - | 4,220,000 | - | 4,220,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment
|
- | - | - | - | - | - | - | 21,017 | 21,017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Total comprehensive income
|
4,241,017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
BALANCE, DECEMBER 31, 2009
|
4,166,667 | $ | 4,167 | 14,908,313 | $ | 14,908 | $ | 21,182,026 | $ | 642,819 | $ | (5,728,130 | ) | $ | 1,025,592 | $ | 17,141,382 | |||||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
|
China Power Equipment, Inc.
|
||||||||
|
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
|
||||||||
|
Year Ended,
|
||||||||
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
|
||||||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 4,220,000 | $ | 1,455,793 | ||||
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash:
|
||||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization expense
|
249,592 | 232,607 | ||||||
|
Stock-Based Compensation
|
25,697 | - | ||||||
|
Provision of bad debts
|
90,594 | 40,467 | ||||||
|
Provision of impairment loss of advance to suppliers
|
- | 107,885 | ||||||
|
Gain on investment
|
(89,755 | ) | (67,505 | ) | ||||
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities:
|
||||||||
|
Accounts receivable
|
(22,138 | ) | (210,710 | ) | ||||
|
Advance to suppliers
|
772,909 | 83,518 | ||||||
|
Inventory
|
99,416 | (92,297 | ) | |||||
|
Prepaid expenses and other receivables
|
37,380 | 17,051 | ||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
(163,094 | ) | (442,875 | ) | ||||
|
Accrued expenses and other payables
|
(14,558 | ) | (39,973 | ) | ||||
|
VAT tax payable
|
154,468 | (36,449 | ) | |||||
|
Income taxes payable
|
129,834 | 105,293 | ||||||
|
Advance from customers
|
(109,690 | ) | (17,473 | ) | ||||
|
Net cash provided by operating activities
|
5,380,655 | 1,135,332 | ||||||
|
Cash Flows from Investing Activities
|
||||||||
|
Acquisitions of property, plant and equipment
|
(18,422 | ) | (49,266 | ) | ||||
|
Addition in construction in progress
|
(1,620,844 | ) | - | |||||
|
Acquisitions of intangible assets
|
(219,270 | ) | - | |||||
|
Deposit for purchase of equipment
|
(767,445 | ) | - | |||||
|
Repayment from related parties
|
72,913 | 65,724 | ||||||
|
Dividend from equity interest subsidiary
|
43,854 | 71,816 | ||||||
|
Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities
|
(2,509,214 | ) | 88,274 | |||||
|
Cash Flows from Financing Activities
|
||||||||
|
Principal payments on capital lease
|
(1,948 | ) | (1,731 | ) | ||||
|
Repayment to related parties
|
- | (186,575 | ) | |||||
|
Proceeds from issuing preferred stock
|
4,939,450 | - | ||||||
|
Repayment to short term loans
|
- | (1,098,783 | ) | |||||
|
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities
|
4,937,502 | (1,287,089 | ) | |||||
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents:
|
3,207 | 60,626 | ||||||
|
Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents
|
7,812,150 | (2,857 | ) | |||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period
|
1,071,038 | 1,073,895 | ||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents, end of period
|
$ | 8,883,188 | $ | 1,071,038 | ||||
|
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information
|
||||||||
|
Interest paid in cash
|
$ | 14,268 | $ | 188,110 | ||||
|
Income taxes paid in cash
|
$ | 633,621 | $ | 165,265 | ||||
|
Non-cash investing and financing activities:
|
||||||||
|
Issuance of stocks for advance from investor
|
$ | - | $ | 100,000 | ||||
|
Reclass long-term investment to advance to suppliers
|
$ | - | $ | 706,823 | ||||
|
Conversion of preferred stock to common stock
|
$ | - | $ | 93 | ||||
|
Construction in progress in lieu of repayment from related party
|
$ | 23,794 | $ | - | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
NOTE 1 – ORGANIZATION AND DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
China Power Equipment, Inc. (“China Power”) was incorporated in the State of Maryland on May 17, 2006 for the purpose of acquiring an existing company with continuing operations. China Power formed An Sen (Xi’an) Power Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (“An Sen”) which was granted a license as a wholly-owned foreign enterprise in the city of Xi’an under the laws of the People’s Republic of China (“PRC”) on November 3, 2006. An Sen is a wholly-owned subsidiary of China Power and a limited liability company organized under the laws of the PRC.
On November 8, 2006, An Sen entered into a Management Entrustment Agreement (“the Agreement”) with Xi’an Amorphous Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd. (“Zhongxi”) whereby An Sen assumed financial and operating control over Zhongxi. In exchange for entering into this agreement, shareholders of Zhongxi were issued 9,000,000 shares of China Power common stock, resulting in a change of control of China Power. As discussed in Principles of Consolidation in Note 2, An Sen has been determined to have a controlling financial interest in Zhongxi as a result of the Agreement, allowing the accounts of Zhongxi to be consolidated with those of An Sen. Applying the rules of SFAS 141, Business Combinations, included in the FASB Accounting Standards Codification (‘Codification’) as Accounting Standards Codification (‘ASC”) 805, Business Combinations, Zhongxi was determined to be the accounting acquirer and the transaction was accounted for as a reverse acquisition resulting in the recapitalization of Zhongxi. Costs and expenses incurred by China Power and An Sen were made in anticipation of the transaction with Zhongxi and have therefore been pushed down and included in the consolidated financial statements.
Zhongxi was founded in Xi’an China under the laws of the PRC on June 29, 2004, and currently manufactures 59 different products, including silicon steel core and amorphous alloy core transformers and cores.
NOTE 2 – SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“US GAAP”) and include the accounts of China Power, its wholly owned subsidiary An Sen, and Zhongxi, a contractually controlled entity (together “the Company”). An Sen controls Zhongxi through the Management Entrustment Agreement dated November 8, 2006.
Under the Management Entrustment Agreement,
1. Zhongxi agrees to irrevocably entrust the right of operation management and the responsibilities and authorities of its shareholders’ meeting and the board of directors to An Sen.
2. The contents of the entrusted operation shall include but not be limited to the following:
1) An Sen shall be in charge of all aspects of Zhongxi’s operations; nominate and replace the members of Zhongxi’s board of directors, engage Zhongxi’s management staff and decide their compensation.
2) An Sen shall manage and control all the funds of Zhongxi. The account of Zhongxi shall be managed and decided solely by An Sen. The seals and signatures for such account shall be the seals and signatures of the personnel appointed and confirmed by An Sen. All the cash of Zhongxi shall be kept in this entrusted account and shall be handled through this account, including but not limited to receipt of all Zhongxi’s business income, current working capital, recovered accounts receivable, etc., and the payment of all accounts payable and operation expenses, employee salaries and asset purchases, etc.
3) All the matters of Zhongxi, including internal financial management, day-to-day operation, external contact execution and performance, tax filing and payment, change of rights and personnel, etc., shall be controlled and managed by An Sen in all aspects.
4) An Sen shall enjoy all the other responsibilities and rights enjoyed by Zhongxi’s shareholders’ meeting in accordance with the Company Law and the articles of association of Zhongxi.
5) An Sen enjoys all the other responsibilities and rights enjoyed by Zhongxi’s board of directors.
As of November 8, 2006, the date the Management Entrustment Agreement became effective, the Company determined to consolidate the results of Zhongxi based on the criteria under Emerging Issues Task Force, or EITF, Issue No. 97-2, included in the Codification as ASC 810, Consolidation. According to that topic, the execution of the Agreement is considered to be a business combination. Accordingly, Zhongxi was determined to be the accounting acquirer and the consolidation with China Power is considered to be a recapitalization of Zhongxi. Periods prior to the combination contain the accounts of Zhongxi and periods subsequent to the combination include the accounts of Zhongxi combined with those of China Power and An Sen. Assets and liabilities are recorded at their historical cost basis and the combination resulted in no gain, loss, or goodwill. All inter-company accounts have been eliminated in consolidation.
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
In concluding that the accounts of Zhongxi should be consolidated, the Company reviewed An Sen’s relationship with Zhongxi under the provisions of the Management Entrustment Agreement and determined that there was a controlling financial interest based on the criteria of ASC 810 relating to the term of the Agreement; An Sen’s ability to exercise control over the operations of Zhongxi and the relationship with its employees and directors; and the fact that An Sen maintains a significant financial interest in Zhongxi.
ASC 810 requires the term of the Agreement be at least the entire remaining life of Zhongxi or a period of 10 years or more. The Company determined that it met the term criteria because termination is prohibited by Zhongxi, making termination within the control of the Company.
In addition, the Company determined that the control criteria under ASC 810 was met because the Agreement assigns to An Sen the charge of normal business operations as well as the ability to nominate and replace the board of directors, hire and fire management staff, and determine compensation.
Finally, the financial interest criteria under ASC 810 require that An Sen be able to control the ability to sell or transfer the operations of Zhongxi and the income generated by Zhongxi. The Agreement specifically gives An Sen the responsibility of formulating plans regarding matters including merger, division, change of corporate form and dissolution of Zhongxi and assigns the income and operations of Zhongxi to An Sen.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company’s financial instruments consist of cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued liabilities. The fair value of these financial instruments approximate their carrying amounts reported in the consolidated balance sheets due to the short term maturity of these instruments.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the Company’s consolidated financial statements in conformity with US GAAP requires management of the Company to make a number of estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the dates of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents consist of cash on hand, cash on deposit with banks, and highly liquid debt investments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased.
Foreign Currency Translation
The functional currency of the Company is the United States dollar. The functional currency of An Sen and Zhongxi is the RMB. The reporting currency of the Company is the United States dollar.
The financial statements of An Sen and Zhongxi are translated into U.S. Dollars (USD) in accordance with Statement of Financial Accounts Standards (SFAS) No. 52, Foreign Currency Translation, included in the Codification as ASC 830, Foreign Currency Matters. According to the topic, all assets and liabilities are translated at the current exchange rate, stockholders equity transactions are translated at the historical rates and income statement items are translated at the average exchange rate for the period. The resulting translation adjustments are reported under other comprehensive income in accordance with SFAS No. 130, Reporting Comprehensive Income as a Component of Shareholders Equity, included in the Codification as ASC 220, Comprehensive Income. Foreign exchange transaction gains and losses are reflected in the income statement. During the year ended December 31, 2009, the foreign currency translation adjustments to the Company’s comprehensive income were $21,017.
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Inventory
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out method) or market value. Cost has been determined using the first-in, first-out method. Inventory quantities on-hand is regularly reviewed, and where necessary, reserves for excess and unusable inventories are recorded.
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is calculated on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets. Depreciation of property and equipment is provided using the straight-line method for substantially all assets with estimated lives as follows:
|
Plant and office building
|
20 years
|
|
Plant machinery
|
10 years
|
|
Automobile
|
10 years
|
|
Office equipment
|
5 years
|
Revenue Recognition
Revenue is recognized when product is shipped to customers and a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and cash collection is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are recorded as advance from customers. The company is subject to value added tax (VAT) withholdings and payments. Sales are recorded net of VAT.
The material terms of the Company’s revenue generating agreements include the following.
Sales contract for Amorphous Metal Distribution Transformer Core:
Payment term: the goods shall be delivered after the payment is received from the buyer.
Responsibility of any breach: if the buyer cannot pay on time, the fine for any breach should be paid by the buyer, the fine is 20% of the part of the contract not executed.
Time for quality guarantee and raising an objection: within 10 days after receiving the goods.
Sales contract for transformer:
Method, time and venue for settlement: complete the payment within one week after tested and qualified.
The ownership of goods: will be transferred upon the shipping of goods.
Seller's obligation related to the quality: warranty for one year from delivery.
Shipping Costs
The Company’s shipping and handling costs are included in Selling, general and administrative expenses. For the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, the shipping costs were $215,822 and $13,676, respectively.
Intangible and Other Long-Lived Assets
Intangibles and other long-lived assets are stated at cost, less accumulated amortization and impairments. The Company’s intangible assets are being amortized over their expected useful economic lives of 10 years.
The Company reviews its long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may no longer be recoverable. When these events occur, the Company measures impairment by comparing the carrying value of the long-lived assets to the estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to result from the use of the assets and their eventual disposition. If the sum of the expected undiscounted cash flow is less than the carrying amount of the assets, the Company would recognize an impairment loss based on the fair value of the assets. There were no impairment write-offs in 2009 and 2008.
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Income Taxes
Deferred income taxes are recognized for temporary differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts in the financial statements, net of operating loss carry forwards and credits, by applying enacted statutory tax rates applicable to future years. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when, in the opinion of management, it is not more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will be realized. Current income taxes are provided for in accordance with the laws of the relevant taxing authorities.
Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable includes billings for the products delivered and services rendered. The Company recognizes an allowance for doubtful accounts to ensure accounts receivable are not overstated due to uncollectibility. Bad debt reserves are maintained for all customers based on a variety of factors, including the length of time the receivables are past due, significant one-time events and historical experience. An allowance for doubtful accounts has been established in amounts of $154,020 and $63,221 at December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company has elected to use the Black-Scholes-Merton (BSM) pricing model to determine the fair value of stock options on the dates of grant. Also, the Company recognizes stock-based compensation using the straight-line method.
In the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, the Company recognized stock-based compensation of $25,697 and $0, respectively.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In June 2009, the FASB issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (“SFAS”) No. 166, “Accounting for Transfers of Financial Assets, an Amendment of FASB Statement No. 140” (“SFAS No. 166”), expected to be included in the FASB Accounting Standards Codification (‘Codification’) as Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC 860”), Transfers and Servicing. This topic improves the comparability of information that a reporting entity provides regarding transfers of financial assets and the effects on its financial statements. This topic is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after November 15, 2009. The Company does not expect the adoption of this topic to have a material effect on its financial statements and related disclosures.
In June 2009, the FASB issued SFAS No. 167, “Amendments to FASB Interpretation No. 46(R)” (“SFAS No. 167”), expected to be included in the Codification as ASC 810, Consolidation. This topic changes the consolidation guidance applicable to a variable interest entity. Among other things, it requires a qualitative analysis to be performed in determining whether an enterprise is the primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity. This topic is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after November 15, 2009. The Company does not expect the adoption of this topic to have a material effect on its financial statements and related disclosures.
In June 2009, the FASB issued SFAS No. 168, “The FASB Accounting Standards Codification ™ and the Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles a Replacement of FASB Statement No. 162” (“SFAS No. 168”), included in the Codification as ASC 105, Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. This topic is the source of authoritative accounting principles recognized by the FASB to be applied by non-governmental entities in the preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. This topic is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after September 15, 2009. On September 30, 2009, the Company adopted this topic, which has no effect on the Company’s financial statements as it is for disclosure purposes only.
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
In May 2009, the FASB issued SFAS No. 165, “Subsequent Events” (“SFAS No. 165”), included in the Codification as ASC 855, Subsequent Events. This topic establishes the period in which management of a reporting entity should evaluate events and transactions for recognition or disclosure in the financial statements. It also describes the circumstances under which an entity should recognize events or transactions that occur after the balance sheet date. This topic is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009.
In December 2007, the FASB issued SFAS No. 160, “Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements—an amendment of Accounting Research Bulletin No. 51” (“SFAS 160”), included in the Codification as ASC 810-10-65-1. This topic establishes accounting and reporting standards for ownership interests in subsidiaries held by parties other than the parent, the amount of consolidated net income attributable to the parent and to the noncontrolling interest, changes in a parent’s ownership interest, and the valuation of retained noncontrolling equity investments when a subsidiary is deconsolidated. This topic also establishes disclosure requirements that clearly identify and distinguish between the interests of the parent and the interests of the noncontrolling owners. This topic is effective for fiscal years beginning October 1, 2009.
NOTE 3– INVENTORY
Inventory consists of:
|
December 31,
|
December 31,
|
|||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Raw materials
|
$ | 261,584 | $ | 424,986 | ||||
|
Work in progress
|
12,180 | 13,349 | ||||||
|
Finished goods
|
89,548 | 23,299 | ||||||
|
Total inventory
|
$ | 363,312 | $ | 461,634 | ||||
NOTE 4 – PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT
Property, plant and equipment consist of:
|
December 31,
|
December 31,
|
|||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Plant and office building
|
$ | 2,389,244 | $ | 2,383,319 | ||||
|
Machinery and production equipment
|
956,564 | 941,347 | ||||||
|
Automobile
|
4,825 | |||||||
|
Office equipment
|
4,530 | 3,789 | ||||||
|
Construction in progress
|
2,232,462 | 585,482 | ||||||
|
Total
|
5,587,625 | 3,913,937 | ||||||
|
Less accumulated depreciation
|
(994,557 | ) | (797,515 | ) | ||||
|
Property, plant and equipment, net
|
$ | 4,593,068 | $ | 3,116,422 | ||||
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
NOTE 5 – INVESTMENT
Investment consists of:
|
December 31,
|
December 31,
|
|||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
20% equity interest
|
$ | 282,897 | $ | 236,384 | ||||
| $ | 282,897 | $ | 236,384 | |||||
In May 2005, Zhongxi made a long-term investment in Shaanxi Yan An Amorphous Alloy Transformer Co., Ltd (“Yan An”) to purchase 20% of equity interest for approximately $159,422 (RMB1,090,000). The equity method has been used for this investment for the yesrs ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. Zhongxi purchased the shares of Shaanxi Yan An Amorphous Alloy Transformer Co., Ltd from Xi'an Amorphous Alloy Science And Technology Co., Ltd. (Alloy Science). The balances for the investment including earnings from the investment as of December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008 were $282,897 and $236,384, respectively. An evaluation had been performed by the company as of December 31, 2009 to ensure that the 20% of the net assets value of Shaanxi Yan An Amorphous Alloy Transformer Co., Ltd was above its investment amount.
The following table summarizes the income statement of Yan An for the year ended December 31, 2009 and 2008:
|
Yan An Amorphous Alloy Transformer Co., Ltd
|
||||||||
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Exchange rate
|
6.8372 | 6.9623 | ||||||
|
Sales
|
$ | 4,401,629 | $ | 3,756,878 | ||||
|
Gross profit
|
$ | 743,875 | $ | 687,509 | ||||
|
Income from continuing operations
|
$ | 357,012 | $ | 303,867 | ||||
|
Net income
|
$ | 357,012 | $ | 303,867 | ||||
|
20% investment earnings
|
$ | 71,402 | $ | 60,773 | ||||
|
Dividends received
|
$ | 43,878 | $ | 72,948 | ||||
The following table provides the summary of balance sheet information for Yan An as of December 31, 2009 and 2008:
|
Yan An Amorphous Alloy Transformer Co., Ltd
|
||||||||||||||||
|
December 31, 2009
|
December 31, 2008
|
|||||||||||||||
|
RMB
|
USD
|
RMB
|
USD
|
|||||||||||||
|
Total assets
|
26,419,407 | 3,864,068 | 23,948,797 | 3,494,032 | ||||||||||||
|
Total liabilities
|
13,393,299 | 1,958,887 | 11,863,650 | 1,730,858 | ||||||||||||
|
Net assets
|
13,026,108 | 1,905,182 | 12,085,148 | 1,763,174 | ||||||||||||
|
Zhongxi's 20% ownership
|
2,605,222 | 381,036 | 2,417,030 | 352,635 | ||||||||||||
|
Ending balance of investment account
|
1,934,226 | 282,897 | 1,620,222 | 236,384 | ||||||||||||
|
Difference
|
670,996 | 98,139 | 796,808 | 116,251 | ||||||||||||
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The difference of $98,139 was mainly due to the discount of RMB843,672 when Alloy Science purchased the 20% of ownership in Yan An. Yan’s net asset was RMB9,668,360 and Alloy Science invested RMB1,090,000 (instead of RMB1,933,672) to purchase the 20% of ownership in Yan An.
The discount is amortized over 10 years, the estimated useful lives of Yan An’s equipment and machinery which are considered the hard to value assets. According to APB 18, paragraph 19 (b) “A difference between the cost of an investment and the amount of underlying equity in net assets of an investee should be accounted for as if the investee were a consolidated subsidiary.”, included in the Codification as ASC 323, Investments—Equity Method and Joint Ventures. When consolidating with Yan An, an entry would be made to reduce the depreciable value of Yan An’s hard to value fixed assets by the discount amount in order to properly allocate the consideration paid to the fair value of assets received and liabilities assumed. The reduction in the book value of the newly acquired fixed assets would result in a lower depreciation expense over the future lives of those fixed assets than that shown on the books of Yan An. Consequently, the Company would recognize income that is slightly higher than its proportionate share of Yan An’s reported income, which exactly is the effect of amortizing the discount into income over the lives of the fixed assets acquired.
The following is the shareholder’s list of Yan An Amorphous Alloy Transformer Co., Ltd as of December 31, 2009:
|
Yan An Amorphous Alloy Transformer Co., Ltd Shareholders’ List
|
|||||||||||
|
Shareholders’ Name
|
# of shares
|
%
|
|||||||||
| 1 |
Mr. Chang Ming
|
4,500,000 | 60.0 | % | |||||||
| 2 |
Zhongxi
|
1,500,000 | 20.0 | % | |||||||
| 3 |
Mr. Yang Shuchen
|
500,000 | 6.7 | % | |||||||
| 4 |
Mr. Zhao Chongxiao
|
500,000 | 6.7 | % | |||||||
| 5 |
Mr. Wang Xinyu
|
500,000 | 6.6 | % | |||||||
|
Total
|
7,500,000 | 100 | % | ||||||||
NOTE 6 – INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Intangible assets, net consists of:
|
December 31,
|
December 31,
|
|||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Technical know-how
|
$ | 219,388 | $ | 218,844 | ||||
|
Amorphous Transformer Technique
|
336,395 | 116,717 | ||||||
|
Total
|
555,783 | 335,561 | ||||||
|
Less: accumulated amortization
|
(164,270 | ) | (114,819 | ) | ||||
|
Intangible assets, net
|
$ | 391,513 | $ | 220,742 | ||||
The intangible assets consist of three patents for the production technology of amorphous alloy transformers in China.
On June 18, 2009, Zhongxi purchased a amorphous transformer aluminum wire technology for $219,388. The technology is being amortized over 10 years based on estimated useful life.
In April 14, 2005, Zhongxi purchased technical know-how from Xi’an Northwest Industry University Gaoshang Science & Technology Co., Ltd for $73,129. The technical know-how is being amortized over 10 years based on useful life estimation.
On September 2, 2004, Zhongxi purchased technical know-how from Alloy Science, which is a related party of the Company, with common owners and directors for $146,259. The technical know-how is being amortized over 10 years based on useful life estimation.
On July 24, 2004, Zhongxi purchased amorphous transformer core manufacturing technology from Beijing Antai Science & Technology Co. Ltd for $117,007. The technology is being amortized over 10 years based on useful life estimation.
Estimated annual amortization expense for each of the next five years is $55,575.
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
NOTE 7 – INCOME TAXES
United States
The Company was incorporated in the United States of America and is subject to U.S. tax law. No provisions for income taxes have been made as the Company has no taxable income for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. The applicable income tax rates for the Company for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 are 34%.
PRC
The Company’s China operation is subject to a PRC 25% standard enterprise income tax based on its taxable net profit. However, due to its high technology products status, the National Tax Bureau in Xi’an High-Tech Development Zone granted Zhongxi the annual tax exemptions for the years ended December 31, 2005 and 2004 and a 50% tax reduction for as long as Zhongxi meets the high-tech enterprise qualification.
The Company uses the asset and liability method, where deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the expected future tax consequences of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial and income tax reporting purposes. There are no material timing differences and therefore no deferred tax asset or liability at December 31, 2009 and 2008.
The provision for income taxes consists of the following:
|
Years Ended December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Current tax
|
||||||||
|
- PRC
|
$ | 763,455 | $ | 270,559 | ||||
|
Total
|
$ | 763,455 | $ | 270,559 | ||||
NOTE 8 – NOTE PAYABLE
On December 28, 2006, the Company signed a loan agreement with Xi’an New City District Science & Technology Bureau to borrow approximately $58,503 (RMB400,000) at 4% stated annual interest rate. The agreement commenced on December 28, 2006 and expired on December 27, 2009. The company extended this loan for one year until December 27, 2010.
Future minimum principal payments are as follows:
|
For the Year Ended December 31:
|
||||
|
2009
|
$ | 58,503 | ||
|
Total
|
$ | 58,503 | ||
NOTE 9– CAPITAL LEASES
The Company is currently leasing a factory from Zhongxi Zhengliu Dianlu Transformer Co., Ltd. The term of the lease runs for a period of 24 years beginning January 1, 2005. The lease agreement contains ownership transfer terms at the end of the lease and calls for annual rent payments in the amount of approximately $1,949 for the year ended December 31, 2009 and annual rent payments are expected to increase every year by at least 10% until the expiration of the agreement.
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
As the result, approximately $138,991 (RMB950,308) was recorded as leased assets on January 1, 2005 when the lease commenced based on the 10% of discounted factor. The lease was classified as a finance lease since a majority of the useful life would be used by the Company and the lease agreement contained a bargain purchase option. The net leased asset account was $111,482 and $116,694 as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
Future minimum lease payments are as follows based on the 10% of discounted factor:
|
For the Year Ended December 31:
|
||||
|
2010
|
$ | 2,156 | ||
|
2011
|
2,384 | |||
|
2012
|
2,637 | |||
|
2013
|
2,917 | |||
|
2014
|
3,226 | |||
|
Thereafter
|
104,299 | |||
|
Less Current Portion
|
(2,156 | ) | ||
|
Long Term Portion
|
$ | 115,463 | ||
NOTE 10 – STATUTORY SURPLUS RESERVE AND STATUTORY COMMON WELFARE FUND
As stipulated by the new Corporate Law of the PRC effective on January 1, 2006, net income after taxation can only be distributed as dividends after appropriation has been made for the following:
|
i.
|
making up cumulative prior years’ losses, if any;
|
|
ii.
|
allocations to the “Statutory surplus reserve” of at least 10% of income after tax, as determined under PRC accounting rules and regulations, until the fund amounts to 50% of the Company’s registered capital;
|
|
iii.
|
allocations to the discretionary surplus reserve, if approved in the stockholders’ general meeting.
|
The Company has appropriated $642,819 and $202,665 as reserve for the statutory surplus reserve requirement as of December 31, 2009 and 2008.
In the Company’s consolidated retained earnings, the amounts representing undistributed earnings of its equity method investment, Yan An Amorphous Alloy Transformer Co., Ltd were $219,617 and $129,862 as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
NOTE 11 – RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Related Party Balance as of December 31, 2009
As of December 31, 2009, the Company was owed $731 from one shareholder of the Company. The advances were non interest bearing and are payable on demand.
As of December 31, 2009, the Company owed $1,170 to one shareholder of the Company. The advance was non interest bearing and are payable on demand.
Related Party Balance as of December 31, 2008
As of December 31, 2008, the Company was owed $48,698 from two of the Company’s shareholders and directors, and $48,550 from one affiliated company in the process of setting up. The advances were non interest bearing and are payable on demand.
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
As of December 31, 2008, the Company owed $1,167 to one shareholder of the Company. The advance was non interest bearing and are payable on demand.
|
Names and relationship of related parties
|
Existing relationships with the Company
|
|
|
Shaanxi Amorphous Alloy Power Co., Ltd. (temporary name)
|
Intend to establish company
|
|
|
Mr. Song Yongxing
|
A shareholder and officer of the company
|
|
|
Ms. Feng Yarong
|
A shareholder of the company
|
On November 8, 2006, An Sen and Zhongxi entered into a Management Entrustment Agreement with Zhongxi granting An Sen the right to manage and control Zhongxi, receive the financial benefits and be exposed to the financial risks of Zhongxi. An Sen and Zhongxi share common officers and directors. As a result, the Management Entrustment Agreement was not entered into at an arm’s length basis because the parties to the agreement are under common control.
NOTE 12 – CONTRACT RIGHTS DEPOSIT
The contract right was purchased from Beijing Antai Science & Technology Co., Ltd for $1,316,328 (RMB9,000,000) to guarantee the supply of amorphous raw material for 3 years starting from the first date of supplying raw material in 2010. The company conducted the evaluation for the impairment of the asset and there is no impairment needed to be recorded as of the date of evaluation. The contract rights deposit expected to be amortized in 3 years starting from the date of purchasing of raw materials from Beijing Antai Science & Technology Co., Ltd.
NOTE 13 – RECLASSIFICATION
Certain amounts in the prior year have been reclassified to conform to the current year’s presentation.
NOTE 14 – STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Preferred Stock
Series B Convertible Preferred Stock
In a private placement closed on December 2, 2009, the Company issued an aggregate of 4,166,667 shares of its series B convertible preferred stock, par value $0.001 per share (the “Series B Preferred Stock”), with attached warrants (the “Warrants”) to purchase a total of 1,000,000 shares of its common stock, par value $0.001 per share (the “Common Stock”) to a number of accredited investors (the “Buyers”), in consideration of an aggregate purchase price of $5,000,000 (the “Private Placement”). The Series B Preferred Stock is convertible into 4,166,667 shares of Common Stock.
The Series B Preferred Stock does not pay annual dividends and shall not have any voting rights except as required by law. In case of the liquidation, the holders of shares of Series B Preferred Stock then outstanding are entitled to receive $1.20 per share (out of available assets) before any distribution or payment can be made to the holders of any junior securities.
As the series B Preferred Stock does not require redemption by the Company, upon issuance, the Company recorded a one-time deemed dividend and as an increase in additional paid-in capital, the intrinsic value of the beneficial conversion feature (the "BCF") of $9,045,005. The intrinsic value of the BCF is the difference between the fair value of the common stock underlying the series B Preferred Stock at issuance and the amount of proceeds to be allocated to the preferred stock. The proceeds of $5,000,000 were allocated to the preferred stock and warrants based on their relative fair values. The warrants were valued using the BSM model and recorded in additional paid-in capital.
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Series A Convertible Preferred Stock
In a private placement completed on May 30, 2007, the Company raised $925,000 through the issuance of its Series A Convertible Preferred Stock, par value $0.001 per share (the “Series A Preferred Stock”), at a purchase price of $10.00 per share which were issued together with an aggregate of 4,021,900 warrants to purchase the common stock at a exercise price of $1.00 per share.
The Series A Preferred Stock was not entitled to any dividends. In case of the liquidation, the holders of shares of Series A Preferred Stock are entitled to receive $10 per share (out of available assets) before any distribution or payment can be made to the holders of any junior securities.
Each share of Series A Preferred Stock is convertible into shares of common stock at the option of the holder at a conversion price of $.23 per share. The aggregate number of shares of common stock which may be issued upon conversion of the Series A Preferred Stock shall be no more than 4,021,900 shares.
On December 18, 2008, the 92,500 shares of Series A Preferred Stock issued and outstanding on that date were converted into 4,021,900 shares of common shares. In connection with the conversion, the Company recorded a deemed dividend of $2,193,483 for the BCF embedded in the Series A Preferred Stock. The proceeds of $925,000 received from the Series A Preferred Stock were allocated to the preferred stock and warrants based on their relative fair values. The warrants were valued using the BSM model and recorded in additional paid-in capital.
Common Stock
At December 31, 2009 the Company has 100,000,000 shares of common stock authorized and 14,908,313 shares issued and outstanding at par value $0.001 per share.
In connection with the Private Placement of the Series B Preferred Stock, the Company also entered into a Make Good Escrow Agreement dated as of November 30, 2009 with the Buyers and Escrow, LLC (the “Escrow Agent”), where the Company committed to place 2,080,000 shares of Common Stock into escrow to be delivered to the Buyers if the Company fails to achieve certain operating income targets.
The 2,080,000 shares of Common Stock held in escrow are not treated as outstanding at December 31, 2009 because the delivery of shares is contingent upon certain events, and any shares not delivered will be returned to the Company for cancellation.
Warrants
The Company has issued warrants in the Series A Preferred Stock private placement to purchase its common stock. The warrants are exercisable for three years at an exercise price of $1.00.
The warrants issued in conjunction with the January 2008 common stock issuance are exercisable for three years at an exercise price of $1.00.
The Warrants issued in connection with the Series B Preferred Stock Private Placement are exercisable for a period of three years from the date of issuance at an initial exercise price of $2.40. The Company has the right, on at least ten (10) day written notice, to require that the holders of the Warrants exercise the Warrants in full and in the event the holders fail to do so, to redeem the outstanding Warrants at a price of one cent ($.01) per share, provided that the market price of the Company’s Common Stock shall equal or exceed $3.50 on each trading day for the consecutive twenty (20) trading days.
The warrants are equity classified and amounts attributable to the warrants are classified within additional paid-in capital.
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The following table summarizes the activities for the warrants for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008.
|
Weighted
|
||||||||
|
Number of
|
Average
|
|||||||
|
Shares
|
Exercise Price
|
|||||||
|
Warrants outstanding, January 1, 2008
|
4,021,900 | $ | 1.00 | |||||
|
Issued
|
434,800 | $ | 1.00 | |||||
|
Warrants outstanding, December 31, 2008
|
4,456,700 | $ | 1.00 | |||||
|
Issued
|
1,000,000 | $ | 2.40 | |||||
|
Warrants outstanding, December 31, 2009
|
5,456,700 | $ | 1.26 | |||||
|
Exercisable as of December 31, 2009
|
5,456,700 | $ | 1.26 | |||||
Stock Options
On July 1, 2009, the Company granted 100,000 stock options to one of its officers. 25,000 stock options vest upon issuance and 37,500 each vest at the beginning of subsequent two quarters.
The following table presents the weighted-average assumptions used to estimate the fair values of the stock options granted in the period presented:
|
2009
|
||||
|
Risk-free interest rate (%)
|
1.6 | % | ||
|
Expected dividend yield (%)
|
- | |||
|
Expected option life (years)
|
3.0 | |||
|
Expected volatility (%)
|
138.3 | % | ||
|
Weighted average grant date fair value
|
$ | 0.41 | ||
The following table summarizes the activities for the Company’s options for the year ended December 31, 2009:
|
Options Outstanding
|
||||||||||||
|
Number of Shares
|
Weighted-Average Exercise Price
|
Weighted-Average Remaining Life (in years)
|
||||||||||
|
Balance at January 1, 2009
|
- | |||||||||||
|
Options granted
|
100,000 | $ | 0.44 | |||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2009
|
100,000 | $ | 0.44 | 4.5 | ||||||||
|
Vested and exercisable as of December 31, 2009
|
62,500 | $ | 0.40 | 4.5 | ||||||||
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
The following table summarizes additional information regarding outstanding, and exercisable and vested stock options at December 31, 2009:
|
Exercise Price
|
Options Outstanding
|
Weighted-Average Remaining Life (in years)
|
Options Exercisable and Vested
|
||||||||||
| $ | 0.23 | 25,000 | 4.5 | 25,000 | |||||||||
| $ | 0.51 | 75,000 | 4.5 | 37,500 | |||||||||
| 100,000 | 62,500 | ||||||||||||
At December 31, 2009, the Company recognized stock-based compensation expense of $25,697 related to these options.
NOTE 15 - LOSS PER SHARE
The following table sets forth the computation of basic loss per share of common stock:
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Basic loss per share:
|
||||||||
|
Numerator:
|
||||||||
|
Net income used in computing basic earnings per share
|
$ | 4,220,000 | $ | 1,455,793 | ||||
|
Deemed dividend from beneficial conversion feature of preferred stock
|
(9,045,005 | ) | (2,193,483 | ) | ||||
|
Net (loss) applicable to common shareholders
|
$ | (4,825,005 | ) | $ | (737,690 | ) | ||
|
Denominator:
|
||||||||
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding
|
14,908,313 | 11,036,692 | ||||||
|
Basic loss per share
|
$ | (0.32 | ) | $ | (0.07 | ) | ||
Diluted loss per share is the same as basic loss per share as the dilutive securities are having an anti-dilutive effect on diluted loss per share.
China Power Equipment, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
Balance of related after-tax components comprising accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) included in stockholders’ equity at December 31, 2009 and 2008 were as follows:
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income, beginning of period
|
$ | 1,004,575 | $ | 585,381 | ||||
|
Change in cumulative translation adjustment
|
21,017 | 419,194 | ||||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income, end of period
|
$ | 1,025,592 | $ | 1,004,575 | ||||
NOTE 17 – SUBSEQUENT EVENT
For the year ended December 31, 2009, the Company has evaluated subsequent event for potential recognition and disclosure through March 25, 2010, the date of financial statement issuance.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A(T). CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
As required by Rule 13a-15 under the Exchange Act, our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2009.
Disclosure controls and procedures refer to controls and other procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the reports we file or submit under the Securities Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the rules and forms of the SEC and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating our disclosure controls and procedures, management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives, and management is required to apply its judgment in evaluating and implementing possible controls and procedures.
Management conducted an evaluation, with the participation and under the supervision of our Chief Executive Officer, Mr. Yongxing Song, and our Chief Financial Officer, Ms. Elaine Lanfeng Zhao, assessing the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2008. Based on its assessment, management concluded that, as of December 31, 2009, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over our financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) or 15d-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, a company’s principal executive and principal financial officers and effected by a company’s board of directors, management and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles and includes those policies and procedures that:
|
•
|
pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of a company;
|
|
|
•
|
provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles and that receipts and expenditures of a company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of a company; and
|
|
|
•
|
provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of a company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
|
Our internal control system was designed to provide reasonable assurance to our management and board of directors regarding the preparation and fair presentation of published financial statements. All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations which may not prevent or detect misstatements. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Our management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control-Integrated Framework. Based on this assessment, management concluded that, as of December 31, 2009, our internal control over financial reporting was effective based on those criteria.
This annual report does not include an attestation report of the company's registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting. Management's report was not subject to attestation by the company's registered public accounting firm pursuant to temporary rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission that permit the company to provide only management's report in this annual report.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal controls over financial reporting during the fourth fiscal quarter of the year 2009 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
None.
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The following are our officers and directors as of the date of this report. Some of our officers and directors are residents of the PRC and, therefore, it may be difficult for investors to effect service of process within the U.S. upon them or to enforce judgments against them obtained from the U.S. courts.
Directors and Executive Officers of China Power:
|
Name
|
Position
|
Age
|
||
|
Yongxing Song
|
Chairman of Board, President, CEO
|
46
|
||
|
Elaine Lanfeng Zhao
|
Chief Financial Officer
|
35
|
||
|
Michael Segal
|
Director
|
66
|
||
|
Yarong Feng
|
Director
|
30
|
||
|
Sue Kuen Leung
|
Director
|
48
|
||
|
Junyi Li
|
Director
|
56
|
The directors will serve until our next annual meeting, or until their successors are duly elected and qualified. The officers serve at the pleasure of the Board.
Mr. Michael Segal, Mr. Sue Kuen Leung, and Mr. Junyi Li are "independent directors" under the Rules of NASDAQ, Marketplace Rule 4200(a)(15).
Mr. Yongxing Song was appointed as our Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer on November 1, 2007. Mr Song has been Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Zhongxi since its inception in June 2004. Mr. Song served as the Chairman of Director for Alloy Science from 1999 to 2004 and remains as acting CEO and President of Alloy Science. Prior to joining us, Mr. Song served as the vice general manager at Xi'an Xianglong Co., Ltd. from 1996 to 1999. Prior to that, Mr. Song served from 1982 to 1996 as a manufacturing planner and manufacturing manager in Qing'an Aviation Electronic Equipment Co., Ltd., which was a subsidiary of Qing'an Group. Mr. Song obtained a master degree in International Trade from University of International Business and Economics in 2003. He graduated from Shaanxi Aviation Profession University in 1988.
Ms. Elaine Zhao has been our Chief Financial Officer since June 1, 2008. In 2005, she founded ELZ Accountancy Corp., a Los Angeles based accounting and financial advisory firm, and she has served as its president since that time. Ms. Zhao continues to work for ELZ. In her work with ELZ, Ms. Zhao has served clients including privately owned and publicly traded company in various industries and has worked with banks in financing small businesses. Ms. Zhao has held Series 7 and 66 licenses as a broker at a national brokerage firm and is an independent financial advisor. From October 2000 to October 2005, Ms. Zhao worked as accountant and auditor at Liang & Company Accountancy Corp. in Los Angeles. Ms. Zhao is a co-founder of the Southern California Chinese Professional Association. She holds an MS in Finance from the Kelley School of Business at Indiana University and is a Certified Public Accountant.
Mr. Michael Segal has been our director since June 8, 2006 and was our President from June 9, 2006 until November 6, 2007. Since 2001, he has been President of Segal Cirone Services Inc., a financial consulting company that advises institutions, banks and high net worth individuals. He has been a Principal, Options Compliance Principal and Branch Office Manager of Whitaker Securities LLC, a member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) since October 23, 2006. Prior to that, Mr. Segal had served as President of Alexander Westcott & Co., Inc., a Broker/Dealer registered with NASD and Secretary of the board of directors of its parent company, President of the Financial Commerce Network Inc., a public company, President of Lamborn Securities Inc. a Broker/Dealer registered with NASD, Branch Manager of Geldermann Securities Inc., President of Greentree Commodities, a Branch Manager at REFCO, Inc., a Senior Vice President at Shearson American Express and a Branch Manager at Investors Overseas Services (Bangkok, Thailand). He is also individually registered as an Introducing Broker with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission and a member of the National Futures Association and a founding member of the Managed Funds Association. Mr. Segal received a B.B.A. in marketing and economics from the University of Miami in Florida. Mr. Segal sits on the board of directors of China Agri Business Inc. (CHBU.OB) and BioStar Pharmaceuticals Inc. (BSPM.OB), public companies traded on the Over-The-Counter Bulletin Board. Additionally Mr. Segal sits on the board of directors of the following privately held companies: Jiali Pharmaceuticals Inc., and Asia Nutracueticals Consulting Co. Ltd.
Ms. Yarong Feng was appointed as the Chief Financial Officer of Zhongxi on June 5, 2007 and our director on November 6, 2007. On November 21, 2006, Ms. Feng was appointed as a trustee for certain stockholders of China Power who were former stockholders of Alloy Science. From 2002, Ms. Feng served as the Secretary to the board of Alloy Science, being mainly responsible for the management of shareholders and coordination for public affairs of the company. From 2001 to 2002, she served as a cashier and later the assistant to Financial Controller with Xi'an Jin Ruan Science and Technology Development Co., Ltd, which was the largest software development enterprise for house fund in Xi'an city. She was awarded "Excellent Secretary to Board of Directors" by Xi'an Hi-tech Industrious Development Zone in 2003. Ms. Feng graduated from Xi'an Finance and Economics Institute in 2001 and majored in finance management.
Mr. Sue Kuen Leung has been our director since March 10, 2010. He also serves as a director of Everpride Biopharmaceutical Company Limited, a company listed on the GEM board of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, since November 2009. He was an executive director of China Golden Development Holdings Limited, a company listed on the main board of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, from April 2007 to December 2008. From June 2006 to January 2007, Mr. Leung was the financial controller of Dragon Hill Holdings Ltd. From August 2004 to August 2005, he was the financial controller of Kader Industrial Co. Ltd. Mr. Leung received a Master’s degree in business administration and a Bachelor of Science (economics) degree from the Hong Kong Polytehnic (currently known as The Hong Kong Polytechnic University). He is a member of the Hong Kong Institute of Certified Public Accountants and an associate of the Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (U.K.). Mr. Leung has over 20 years of experience in accounting and finance.
Mr. Junyi Li has been our director since March 10, 2010. He has been active in the amorphous alloy industry for more than 30 years and has served as Vice President of Advanced Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (Public, SHE: 000969) since 2004. Mr. Li previously served as the Executive Deputy Chief of National Amorphous and Nano-Crystalline Engineering Center, and General Manager of the Amorphous Division. As a senior engineer in the industry, Mr. Li was named as an “Advanced Individual” of the “Ninth Five-Year National Key Science and Technology Research Programs” and awarded a special government allowance for scientists. He was also awarded the Second Prize of National Science and Technology Progress and the First Prize of Metallurgical Science and Technology Progress. Mr. Li has a Bachelor’s degree from the Northeastern University and serves as an instructor at the university.
There are no family relationships among our directors or officers.
Code of Ethics
We have not yet adopted a Code of Ethics for our executive officers. We intend to adopt a Code of Ethics applying to our executive officers during the year 2010.
ITEM 11.EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The following table shows the compensation paid to our principal executive officer. None of our executive officers earned more than $100,000 in any of the previous two years.
|
Name and
Principal
Position
|
Year
|
Salary
($)
|
Bonus
($)
|
Stock
Awards
($)
|
Option
Awards
($)
|
Non-Equity
Incentive
Plan
Compen-sation
($)
|
Non-
Qualified
Deferred
Compen-sation
Earnings
($)
|
All
Other
Compen-sation
($)
|
Total
($)
|
||||||||||||
|
Yongxing Song
|
2009
|
6,876
|
10,308
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
17,184
|
||||||||||||
|
CEO, President
|
2008
|
6,876
|
10,308
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
17,184
|
||||||||||||
Compensation Discussion and Analysis
We intend to provide our named executive officers (as defined in Item 402 of Regulation S-K) with a competitive base salary that is in line with their roles and responsibilities when compared to peer companies of comparable size in similar locations.
It is not uncommon for PRC private companies to have base salaries as the sole form of compensation. The base salary level is established and reviewed based on the level of responsibilities, the experience and tenure of the individual, and the current and potential contributions of the individual. The base salary is compared to the list of similar positions within comparable peer companies and consideration is given to the executive’s relative experience in his or her position. Base salaries are reviewed periodically and at the time of promotion or other changes in responsibilities.
We plan to implement a more comprehensive compensation program, which takes into account other elements of compensation, including, without limitation, short- and long-term compensation, cash and non-cash, and other equity-based compensation such as stock options. We expect that this compensation program will be comparable to the programs of our peer companies and aimed to retain and attract talented individuals.
We will also consider forming a compensation committee to oversee the compensation of our named executive officers. The majority of the members of the compensation committee would be independent directors.
Employment Agreements
Pursuant to an employment agreement between Zhongxi and Mr. Yonxing Song dated July 1, 2004, Mr. Song is employed by Zhongxi as its Chief Executive Officer. The term of the agreement is from July 1, 2004 to June 30, 2014. The agreement provides for a salary of RMB 4,000 (US$ 573) per month with a performance bonus of RMB 6,000 (US$ 859) per month. The employment agreement follows the PRC labor laws which include the provision of labor-related insurance, the ability of either party to terminate for cause, termination on 30 days’ notice, termination without notice and the provision by Zhongxi of labor-related benefits.
Pursuant to an employment agreement between Zhongxi and Mr. Zewei Xu dated July 1, 2004, Mr. Xu is employed by Zhongxi as its Chief Engineer. The term of the agreement is from July 1, 2004 to December 31, 2009. The agreement provides for a salary of RMB 2,000 (US$ 286) per month with a performance bonus of up to RMB 3,000 (US$ 429) per month. The employment agreement follows the PRC labor laws which include the provision of labor-related insurance, the ability of either party to terminate for cause, termination on 30 days’ notice, termination without notice and the provision by Zhongxi of labor-related benefits.
Pursuant to an employment agreement between Zhongxi and Mr. Guoan Zhang dated May 1, 2007, Mr. Zhang is employed by Zhongxi as its Vice General Manager. The term of the agreement is from May 1, 2007 to April 30, 2012. The agreement provides for a salary of RMB 2,000 (US$ 286) per month with a performance bonus of up to 3,000 (US$ 429) per month. The employment agreement follows the PRC labor laws which include the provision of labor-related insurance, the ability of either party to terminate for cause, termination on 30 days’ notice, termination without notice and the provision by Zhongxi of labor-related benefits.
Pursuant to an employment agreement between Zhongxi and Ms. Yaron Feng dated July 1, 2004, Ms. Feng is employed by Zhongxi as its Chief Financial Officer. The term of the agreement is from July 1, 2004 to December 31, 2009. The agreement provides for a salary of RMB 2,000 (US$ 286) per month with a performance bonus of up to RMB 3,000 (US$ 429) per month. The employment agreement follows the PRC labor laws which include the provision of labor-related insurance, the ability of either party to terminate for cause, termination on 30 days’ notice, termination without notice and the provision by Zhongxi of labor-related benefits.
According to a Financial Service Contract entered into on May 14, 2008 between us and Elaine Zhao, Elaine Zhao provides financial service to us in consideration for the payment of $45,000 per year. According to an amended stock option agreement, Ms. Zhao has the right to purchase 25,000 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $0.23 per share vested upon grant and 75,000 share of our common stock at an exercise price of $0.51 per share with 37,500 shares vested on October 1, 2009 and the balance of 37,500 shares vested on January 1, 2010. All options expire five years from the date of grant. The agreement may be terminated by either party with four weeks notice.
Outstanding Equity Awards at 2009 Fiscal Year-End
The following table reflects the unexercised options, stock that has not vested and equity incentive plan awards for each named executive officer outstanding as of the end of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2009:
|
Option Awards
|
Stock Awards
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Name
|
Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options
(#)
Exerciseable
|
Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options
(#)
Unexerciseable
|
Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Unearned Options
(#)
|
Option Exercise Price
($)
|
Option Expiration Date
|
Number of Shares or Units of Stock That Have Not Vested
(#)
|
Market Value of Shares of Units of Stock that Have Not Vested
($)
|
Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Number of Unearned Shares, Units or Other Rights That Have Not Vested
(#)
|
Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Market or Payout Value of Unearned Shares, Units or Other Rights That Have Not Vested
($)
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Elaine Zhao
|
25,000
|
(1)
|
—
|
—
|
$
|
0.23
|
7/1/2014
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
37,500
|
(2)
|
37,500
|
(3)
|
—
|
$
|
0.51
|
7/1/2014
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
||||||||||||||||
|
(1)
|
The vesting date of these options was July 1, 2009.
|
|
|
(2)
|
The vesting date of these options was October 1, 2009.
|
|
| (3) |
The vesting date of these options was January 1, 2010.
|
Director Compensation
The following table reflects the compensation of directors for the year ended December 31, 2009:
|
Name of Director
|
Fees
Earned
or Paid in
Cash
($)
|
Stock
Awards
($)
|
Option
Awards
($)
|
Non-Equity
Incentive Plan
Compensation
($)
|
Change in
Pension value
and
Nonqualified
Deferred
Compensation
Earnings
|
All Other
Compensation
($)
|
Total
($)
|
||||||||||||
|
Michael Segal
|
24,000
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
24,000
|
||||||||||||
|
Yarong Feng
|
8,776
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
8,776
|
||||||||||||
On March 10, 2010, Messrs. Leung and Li were appointed as directors of the Company. Each of Messrs Leung and Li entered into an Independent Director Agreement with the Company. A summary of the compensation for the directorship of each of Messrs. Leung and Li is set forth as follows:
|
1.
|
An annual salary of RMB 60,000.00 (approximately $8,800) payable in arrears in equal installments on the last day of each quarter;
|
|
|
2.
|
Reimbursement of pre-approved business-related expenses incurred in the performance of the director’s duties.
|
ITEM 12.SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The following table sets forth certain information with respect to the beneficial ownership of our common stock as of March 29, 2010 by (i) any person or group with more than 5% of our voting securities, (ii) each director, (iii) each executive officer and (iv) all executive officers and directors as a group. Barron Partners LP owns series B convertible preferred stock and warrants which, if fully converted, would result in the ownership of more than 5% of our outstanding common stock. However, the series B preferred stock may not be converted and the warrants may not be exercised if such conversion would result in Barron Partners LP and its affiliates owning more than 4.9% of our outstanding common stock. This limitation may not be waived. As a result, Barron Partners is not deemed to be a 5% stockholder.
|
Amount
and
|
|||||||
|
Name and
Address of
|
Nature of
Beneficial
|
Percent of
|
|||||
|
Title of Class
|
Beneficial Owner
|
Owner
|
Class (1)
|
||||
|
Common Stock
|
Yongxin Song, Chairman of Board, President, CEO
Room 602, 6/F, Block B, Science & Technology Park of Xi Dian University,
No. 168 Kechuang Road, Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone, Xi’an,
Shaanxi, China 710065
|
2,953,125
|
19.8
|
%
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Common Stock
|
Michael Segal, Director
11 East 86th Street, Suite 19B
New York, NY 10028
|
65,323
|
0.4
|
%
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Common Stock
|
Elaine Zhao, CFO
20955 Pathfinder Road, Suite 100
Diamond Bar, CA 91765
|
0
|
-
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Common Stock
|
Yarong Feng, Director
Room 602, 6/F, Block B, Science & Technology Park of Xi Dian University,
No. 168 Kechuang Road, Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone, Xi’an,
Shaanxi, China 710065
|
195,750
|
1.3
|
%
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Common Stock
|
ZeWei Xu, Chief Engineer
Room 602, 6/F, Block B, Science & Technology Park of Xi Dian University,
No. 168 Kechuang Road, Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone, Xi’an,
Shaanxi, China 710065
|
303,750
|
2.0
|
%
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Common Stock
|
Guoan Zhang, Vice General Manager
Room 602, 6/F, Block B, Science & Technology Park of Xi Dian University,
No. 168 Kechuang Road, Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone, Xi’an,
Shaanxi, China 710065
|
0
|
-
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Common Stock
|
All Directors and Officers of the Company as a group
|
3,517,948
|
23.6
|
%
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Common Stock
|
Trustees for Alloy Science Shareholders (2)
|
3,803,625
|
25.5
|
%
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Common Stock & Warrants
|
KWCB Investments, Ltd.
Room B-2403, Yihe Bldg Hanguang Road,
Xi'An. Shaanxi Province 710065. (3)
|
3,043,600
|
17.0
|
%
|
(1) As of March 29, 2010 we had 14,908,313 outstanding shares of common stock. In determining the percent of common stock owned by a stockholder on March 29, 2010, (a) the numerator is the number of shares of common stock beneficially owned by such stockholder, including shares the beneficial ownership of which may be acquired, within 60 days upon the conversion of convertible securities or the exercise of warrants held by such stockholder, and (b) the denominator is the sum of (i) 14,908,313, the number of shares outstanding on March 29, 2010, and (ii) the total number of shares underlying the warrants, which each of the stockholders has the right to acquire within 60 days following March 29, 2010.
(2) The trustees for the trust holding 3,803,625 shares of our common stock are: Ms. Yarong Feng and Mr. Guoan Zhang pursuant to the terms of the Voting Trust and Escrow Agreement by and among the members of the board of Zhongxi and the shareholders of China Power and Equipment who were parties thereto, dated November 21, 2006 (the “Voting Agreement”). Any holder may terminate the voting trust relationship upon written notice to the trustees at any time after November 21, 2008. The Voting Agreement gives the Trustees the right to vote on all matters brought before the shareholders holding our common stock. Ms. Feng and Mr. Zhang’s addresses are Room 602, 6/F, Block B, Science & Technology Park of Xi Dian University, No. 168 Kechuang Road, Hi-tech Industrial Development Zone, Xi'an, Shaanxi, China, 710065.
(3) Consists of 3,043,600 shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of the warrants. Jin Wu has voting and investment control for KWCB Investments, Ltd.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
On November 8, 2006 An Sen and Zhongxi entered into a Management Entrustment Agreement with An Sen granting An Sen the right to manage and control Zhongxi, receive the financial benefits and be exposed to the financial risks of Zhongxi. An Sen and Zhongxi share common officers and directors. As a result, the Management Entrustment Agreement was not entered into at an arm’s length basis because the parties to the agreement were related prior to the transaction and were under common control immediately thereafter.
As previously described in this report under “Description of Business” our board of directors has the right to appoint the board of directors of Zhongxi and its officers and directors.
As of December 31, 2009, the Company was owed $731 from one shareholder of the Company. The advances were non interest bearing and are payable on demand.
As of December 31, 2009, the Company owed $1,170 to one shareholder of the Company. The advance was non interest bearing and are payable on demand.
In May 2005, Zhongxi made a long-term investment in Shaanxi Yan An Amorphous Alloy Transformer Co., Ltd (“Yan An”) to purchase 20% of equity interest for approximately $159,422 (RMB 1,090,000). The equity method has been used for this investment. Zhongxi purchased the shares of Yan An from Alloy Science which is a related party of the Company.
ITEM 14.PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
The following lists fees paid or accrued by us for the audit and other services provided or to be provided by ACSB and Morgenstern for the years ended December 31, 2009 and CVWB for the years ended December 31, 2008:
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Audit Fees
|
$ | 78,900 | $ | 64,000 | ||||
|
Audit Related Fees
|
- | - | ||||||
|
Tax Fees
|
- | - | ||||||
|
All Other Fees
|
- | 20,248 | ||||||
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS
|
Number
|
Description
|
|
3.1
|
Articles of Incorporation filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Maryland on May 17, 2006. (1)
|
|
3.2
|
Articles of Amendment. filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Maryland on August 2, 2007.(1)
|
|
3.3
|
Articles of Amendment filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Maryland on September 14, 2007.(1)
|
|
3.4
|
Articles of Amendment filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Maryland on November 13, 2007.(1)
|
|
3.5
|
Bylaws of the Company.(1)
|
|
3.6
|
Articles of Amendment filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Maryland on February 29, 2008.(2)
|
|
3.7
|
Xi'an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd. Articles of Association.(3)
|
|
3.8
|
Articles Supplementary to the Articles of Incorporation of China Power Equipment, Inc. designating the Series B Convertible Preferred Stock. (6)
|
|
4.1
|
Form of $1.00 Common Stock Warrant.(1)
|
|
4.2
|
Form of $2.40 Common Stock Warrant. (6)
|
|
9.1
|
Voting Trust and Escrow Agreement, dated, November 21, 2006, by and among Zhongxi Shareholders and their trustees.(2)
|
|
10.1
|
Management Entrustment Agreement, dated November 8, 2006, entered into by and between An Sen and Zhongxi.(1)
|
|
10.2
|
Form of Preferred Stock and Warrant Purchase Agreement between the Company and the purchasers of the Series A Convertible Preferred Stock. (2)
|
|
10.3
|
Form of Amendment No. 1 to the Preferred Stock and Warrant Purchase Agreement between the Company and the purchasers of the Series A Convertible Preferred Stock. (1)
|
|
10.4
|
Investment Trust Agreement by and among Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Song Yongxing, Mao Junming, Xu Zewei, Dai Tao, Wang Yuefeng, Lin Yuan, Zhang Wei, Feng Yarong, Shi Sujun, Yu Xinzheng dated October 28, 2006.(2)
|
|
10.5
|
Common Stock and Warrant Purchase Agreement by and among China Power Equipment, Inc. and Seaside Capital II. LLC, dated January 4, 2008. (2)
|
|
10.6
|
Restated Warrant to Purchase common stock (Exhibit A to the Form of Amendment No. 1 to the Preferred Stock and Warrant Purchase Agreement between the Company and the purchasers of the Series A Convertible Preferred Stock filed as Exhibit 10.3 to this Registration Statement). (3)
|
|
10.7
|
Lease Contract for Workshop, Land and Affiliated Equipment, dated September 10, 2004, between Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd, and Xi’an Zhongxi Zhengliu Dianlu Transformer Factory. (3)
|
|
10.8
|
Contract to Sublease Workshop to Xi’an Zhongxi Zhengliu Dianlu Transformer Factory, dated March 25, 2006, between Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd, and Xi’an Zhongxi Zhengliu Dianlu Transformer Factory. (3)
|
|
10.9
|
Cooperation Agreement, dated May 27, 2005, between An Tai Science & Technology Co., Ltd. and Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd. (3)
|
|
10.10
|
Yongchun Science & Technology Inducstry Center Agreement, dated August 20, 2005, between Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd. and Xi’An Yongchun Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (3)
|
|
10.11
|
Termination Agreement, dated October 25, 2007, between Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd. and Xi’An Yongchun Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (3)
|
|
10.12
|
Cooperative Manufacturing Agreement, dated November 11, 2007, by and among Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd, Xi’An Yongchun Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Zhejing Lvneng Electric Co., Ltd. and Xinzhi Chai. (3)
|
|
10.13
|
Employment Agreement, dated July 1, 2004, between Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd. and Yongxing Song. (3)
|
|
10.14
|
Employment Agreement, dated July 1, 2004, between Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd. and Yaong Feng. (3)
|
|
10.15
|
Employment Agreement, dated May 1, 2007, between Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd. and Gou’an Zhang. (3)
|
|
10.16
|
Employment Agreement, dated July 1, 2004, between Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd. and Zewei Xu. (3)
|
|
10.17
|
Amended and Restated Management Entrustment Agreement between An Sen and Zhongxi. (3)
|
|
10.18
|
Share Holding Transfer Agreement, dated May 10, 2005, between Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Science & Technology Co., Ltd. and Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd. (4)
|
|
10.19
|
Technology Transfer Agreement, dated September 2, 2004, between Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Science & Technology Co., Ltd. and Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd. (4)
|
|
10.20
|
Technology Development (Entrust) Contract, dated April 14, 2005, between Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd. and Xi’an Northwest Industry University Gaoshang Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (4)
|
|
10.21
|
Termination Agreement, dated June 25, 2008, by and among Xi’an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd, Xi’An Yongchun Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Zhejing Lvneng Electric Co., Ltd. and Xinzhi Chai. (4)
|
|
10.22
|
Preliminary Financial Service Agreement, dated May 14, 2008, between ELZ Accountancy Corp., and China Power Equipment, Inc. (4)
|
|
10.23
|
Transfer of Offering The Capital, dated July 11, 2007, between Xi’an Zhongxi Zhengliu Dianlu Transformer Factory and Zhejing Lvneng Electric Co., Ltd. (4)
|
|
10.24
|
Agreement, dated September 25, 2008, by and among Xi'an Amorphous Alloy Zhongxi Transformer Co., Ltd., An Sen (Xi'an) Power Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Zhejiang Lvneng Electric Co.Ltd. and Xi'an Zhongxi Zhengliu Dianlu Transformer Factory, Ltd. (5)
|
|
10.25
|
Form of Securities Purchase Agreement dated November 30, 2009, by and among the Company and the Buyers named therein. (6)
|
|
10.26
|
Form of Make Good Escrow Agreement dated November 30, 2009, by and among the Company, Escrow, LLC and the Buyers named therein. (6)
|
|
10.27
|
Form of Independent Director Agreement. (7)
|
Footnotes:
(1) Previously filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form SB-2 (File No. 333-147349) filed with the SEC on November 13, 2007.
(2) Previously filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1/A (File No. 333-147394) on February 29, 2008.
(3) Previously filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1/A (File No. 333-147394) on April 30, 2008.
(4) Previously filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1/A (File No. 333-147394) on August 5, 2008.
(5) Previously filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1/A (File No. 333-147394) on September 25, 2008.
(6) Previously filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K on December 4, 2009.
(7) Previously filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K on March 17, 2010.
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this Report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
CHINA POWER EQUIPMENT, INC
|
||
|
Date: March 30, 2010
|
By:
|
/s/ Yongxing Song
|
|
Yongxing Song
|
||
|
Chief Executive Officer,
President and Director
(principal executive officer)
|
||
|
By:
|
/s/ Elaine Zhao
|
|
|
Elaine Zhao
|
||
|
Chief Financial Officer
(principal financial officer and principal accounting officer)
|
||
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this Report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant in the indicated capacities on March 30, 2010.
|
/s/ Yongxing Song
|
|||
|
Yongxing Song, Director
|
|||
|
/s/ Yarong Feng
|
|||
|
Yarong Feng, Director
|
| /s/ Michael Segal | |||
|
Michael Segal, Director
|
| /s/ Sue Kuen Leung | |||
|
Sue Kuen Leung, Director
|
| /s/ Junyi Li | |||
|
Junyi Li, Director
|
