Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - China TransInfo Technology Corp. | exh312.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - China TransInfo Technology Corp. | exh322.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - China TransInfo Technology Corp. | exh311.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - China TransInfo Technology Corp. | exh321.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 - China TransInfo Technology Corp. | exhibit231.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C.
20549
FORM 10-K/A
(Amendment No.
2)
x ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE
SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended: December 31, 2008
OR
¨ TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 or 15(d) OF THE
SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from __________ to ____________
Commission File Number: 001-34134
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its
charter)
| Nevada | 87-0616524 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
Floor 9, Vision Building,
No. 39 Xueyuanlu,
Haidian District
Beijing, China 100083
(Address of principal
executive office and zip code)
(86 10) 82671299
(Registrant’s
telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Each Class | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered | |
| Common Stock, Par Value $0.001 | NASDAQ Global Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known
seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes ¨
No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to
file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes ¨
No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all
reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange
Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the
registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such
filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes x
No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, or a non-accelerated filer. See definition of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer ¨ | Accelerated filer ¨ | Non-accelerated filer ¨ | Smaller reporting company x |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell
company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act).
Yes ¨
No x
As of June 30, 2008, the aggregate market value of the shares of the Registrant’s common stock held by non-affiliates (based upon the closing price of such shares as reported on the Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board) was approximately $35.9 million. Shares of the Registrant’s common stock held by each executive officer and director and each by each person who owns 10 percent or more of the outstanding common stock have been excluded in that such persons may be deemed to be affiliates of the Registrant. This determination of affiliate status is not necessarily a conclusive determination for other purposes.
As of March 23, 2009, there were 22,187,314 shares of the Registrant’s common stock outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE:
None.
EXPLANATORY NOTE
This Amendment No. 2 on Form 10-K/A (the “Amendment”) hereby amends our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008, previously filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “Commission’) on March 25, 2009, as amended by Amendment No.1 on Form 10-K/A filed with the Commission on December 28, 2009 (the “Original Filing”). This Amendment is being filed mainly to:
1)
revise the disclosures under the heading “ Liquidity and Capital Resources” to reflect the uncertainty with respect to our liquidity as a result of the dividend restrictions in China;
2)
revise the advertising revenue recognition policy to clarify that we recognize advertising revenue ratably over the period in which the advertisement is to be published; and
3)
include the cooperation agreement between Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and Peking University, Earth and Space College in the exhibit list.
This Amendment does not reflect events occurring after the filing of the Original Filing or modify or update those disclosures, including the exhibits to the Original Filing affected by subsequent events.
In addition, as required by Rule 12b-15 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), this Amendment contains new certifications pursuant to Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14 under the Exchange Act and Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
i
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
Overview
We are a leading provider of public transportation information systems technology and related comprehensive technology solutions in China. Our goal is to become the largest transportation information product and related comprehensive technology solutions provider, as well as the largest integrated transportation information platform and commuter traffic media platform builder and operator in China. Substantially all of our operations are conducted through our variable interest entities (the “VIE Entities”) that are companies formed in the People’s Republic of China (“PRC”) and owned principally or completely by our PRC affiliates. Through our VIE Entities, we are involved in developing multiple applications in transportation, digital city, and land and resource filling systems based on Geographic Information Systems (“GIS”) technologies which are used to service the public sector.
Our main focus is on providing transportation solutions. Our major products and services include:
-
Transportation Planning Information System,
-
Pavement Maintenance System,
-
Electronic toll collection (“ETC”),
-
Traffic Information Service System,
-
Taxi Security Monitoring, Commanding and Dispatching Platform,
-
GIS-T (Transportation) Middleware,
-
Traffic Flow Surveying Systems,
-
Intelligent Parking System,
-
Red Light Violation Snapshot System,
-
Intelligent Highway Vehicle Monitoring System,
-
Intelligent Public Transport System,
-
Palmcity Navigation Engine,
-
Comprehensive Location Based Service Platform,
-
Digital City,
-
2-D and 3-D GIS.
We also offer full range solutions for transportation oriented GIS (“GIS-T”) covering transportation planning, design, construction, maintenance and operation.
1
History and Corporate Structure
Corporate History
We were originally incorporated in Nevada on August 3, 1998 under the name R & R Ranching, Inc. to breed bison. On December 10, 2003, we executed an agreement and plan of reorganization (the “Intra-Asia Agreement”) with Intra-Asia Entertainment Corporation, a Delaware corporation (“Intra-Asia Delaware”), whereby Intra-Asia Delaware became our wholly-owned subsidiary and we amended our articles of incorporation to change our name to “Intra-Asia Entertainment Corporation.” From the first half of 2006 until May 14, 2007 when we completed a reverse acquisition transaction with Cabowise International Ltd. (“Cabowise”), a British Virgin Islands (“BVI”) company, we were a blank check company and did not engage in active business operations other than our search for, and evaluation of, potential business opportunities for acquisition or participation.
On May 14, 2007, we acquired Cabowise through a share exchange transaction pursuant to which we issued to the shareholders of Cabowise 10,841,492 shares of our common stock in exchange for all of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Cabowise. Cabowise thereby became our wholly-owned subsidiary and the former shareholders of Cabowise became our controlling stockholders. On the same day, our indirect Chinese subsidiary, Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited (“Oriental Intra-Asia”), acquired eighty-five percent (85%) equity interest in Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. (“PKU”), which commenced its businesses in October 2000. As a result, PKU became a majority-owned subsidiary of Oriental Intra-Asia.
VIE Restructuring
Current Chinese laws restrict companies with foreign ownership to operate in three business segments that we recently entered into: online services, taxi advertising, and security and surveillance related business. In order to comply with the applicable Chinese laws, we determined to restructure our subsidiaries and enter into a series of commercial arrangements to allow the Company to operate in these restricted business segments (“Restructuring”).
On February 3, 2009, as described below, through our indirect Chinese subsidiary, Oriental Intra-Asia and Oriental Intra-Asia’s former subsidiary, PKU, we entered into a series of equity transfer agreements with China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., a company formed under Chinese law (the “Group Company”), pursuant to which we transferred all of our indirect equity interests in PKU and PKU’s subsidiaries to the Group Company. Established in China on May 26, 2008, the Group Company is wholly owned by four Chinese affiliates of the Company, Shudong Xia, our Chairman, CEO and President and the beneficial owner of approximately 43% of the Company’s outstanding capital stock, Zhiping Zhang, the Company’s Vice President of Research and Development, Zhibin Lai, the Company’s Vice President and Wei Gao, the designee of SAIF Partners III L.P., a 11% shareholder of the Company (the “Group Company Shareholders”).
Through Oriental Intra-Asia and PKU, we entered into the following specific agreements to transfer all of its equity interests in its respective Chinese subsidiaries to the Group Company (the “Equity Transfer”):
-
Pursuant to an equity transfer agreement (the “PKU Equity Transfer Agreement”), entered into by and between Oriental Intra-Asia and the Group Company, Oriental Intra-Asia transferred all of its 97% equity interests in PKU to the Group Company;
-
Pursuant to an equity transfer agreement (the “Beijing Tian Hao Equity Transfer Agreement”), entered into by and between PKU and the Group Company, PKU transferred all of its 100% equity interests in Beijing Tian Hao Ding Xin Science and Technology Co., Ltd. to the Group Company;
-
Pursuant to an equity transfer agreement (the “China TranWiseway Equity Transfer Agreement”), entered into by and between PKU and the Group Company, PKU transferred all of its 70% equity interests in China TranWiseway Information Technology Co., Ltd. to the Group Company;
-
Pursuant to an equity transfer agreement (the “Zhangcheng Culture Equity Transfer Agreement”), entered into by and between PKU and the Group Company, PKU transferred all of its 100% equity interests in Zhangcheng Culture and Media Co., Ltd. to the Group Company;
2
-
Pursuant to an equity transfer agreement (the “Zhangcheng Science Equity Transfer Agreement”), entered into by and between PKU and the Group Company, PKU transferred all of the 100% equity interests in Beijing Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd. to the Group Company; and
-
Pursuant to an equity transfer agreement (the “Shanghai Yootu Equity Transfer Agreement”), entered into by and between PKU and the Group Company, PKU transferred all of its 100% equity interests in Shanghai Yootu Information Technology Co., Ltd. to the Group Company.
In connection with the Equity Transfer, on February 3, 2009, the following contractual arrangements were also made among relevant parties, which have given us contractual rights to control and manage the business of the Group Company and the Group Company’s subsidiaries (the “Contractual Arrangement” and together with the Equity Transfer, the “Restructuring”):
-
Pursuant to an exclusive technical consulting and services agreement (the “Service Agreement”), entered into by and among Oriental Intra-Asia, the Group Company and the Group Company’s subsidiaries, Oriental Intra-Asia agreed to provide certain technical and consulting services to the Group Company and the Group Company’s subsidiaries (each a “VIE Entity” and collectively, the “VIE Entities”) in exchange for the payment by each VIE Entity of an annual development and consulting services fee that is to be determined solely by Oriental Intra-Asia;
-
Pursuant to an equity pledge agreement (the “Pledge Agreement”), entered into by and among Oriental Intra-Asia and each of the Group Company Shareholders, the Group Company Shareholders agreed to pledge all of their equity interests in the Group Company (the “Equity Interests”), to Oriental Intra-Asia as collateral security for Oriental Intra-Asia’s collection of the fees under the Service Agreement;
-
Pursuant to an option agreement (the “Option Agreement”), entered into by and among Oriental Intra-Asia and each of the Group Company Shareholders, the Group Company Shareholders agreed to grant to Oriental Intra-Asia an option to purchase, from time to time, all or a part of the Equity Interests, at the exercise price equal to the lowest possible price permitted by Chinese laws;
-
Pursuant to separate powers of attorney (the “Powers of Attorney”), each Group Company Shareholder agreed to grant to Oriental Intra-Asia a power to excise on his or her behalf all voting rights as a shareholder at the shareholders’ meetings of the Group Company that have been given to him or her by law and by the Articles of Association of the Group Company; and
-
Pursuant to an operating agreement, entered into by and among Oriental Intra-Asia, the VIE Entities and the Group Company Shareholders, (a) Oriental Intra-Asia agreed to act as the guarantor for the VIE Entities in the contracts, agreements or transactions in connection with the VIE Entities’ operation between the VIE Entities and any other third parties and to provide full guarantee for the VIE Entities in performing such contracts, agreements or transactions, subject to applicable laws, in exchange for which the VIE Entities agreed to mortgage the receivables of their operation and all of their assets which have not been mortgaged to any third parties to Oriental Intra-Asia, and (b) the VIE Entities and the Group Company Shareholders agreed to accept the provision of the corporate policies and guidance by Oriental Intra-Asia at any time in respect of the appointment and dismissal of the VIE Entities’ employees, the VIE Entities’ daily operation and administration as well as financial administrative systems, including the appointment of senior managers recommended by Oriental Intra-Asia (the “Operating Agreement” and together with the Service Agreement, Pledge Agreement, Option Agreement, Powers of Attorney, the PKU Equity Transfer Agreement, the Beijing Tian Hao Equity Transfer Agreement, the China TranWiseway Equity Transfer Agreement, the Zhangcheng Culture Equity Transfer Agreement, the Zhangcheng Science Equity Transfer Agreement, and the Shanghai Yootu Equity Transfer Agreement, the “Restructuring Documents”).
3
The main purpose of the Restructuring is to allow us to engage in the above three restricted business segments in China. As a result of the Restructuring, we transferred all of our indirect equity interests in PKU and PKU’s subsidiaries to the affiliated Group Company and accordingly, PKU and PKU’s subsidiaries became direct and indirect subsidiaries of the Group Company, which is wholly owned by the Group Company Shareholders who are all Chinese citizens. At the same time, through the Contractual Arrangement, we maintain substantial control over the VIE Entities’ daily operations and financial affairs, election of their senior executives and all matters requiring shareholder approval. Under FASB Interpretation No. 46R “Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities” (“FIN 46R”), we are required to consolidate the VIE Entities into our financial statements because the Contractual Arrangement provides us with the risks and rewards associated with equity ownership, even though we do not own any of the outstanding equity interests in any of the VIE Entities. As a result the Restructuring, we are able to engage in these three restricted business segments through the VIE Entities and derive the economic benefits that we would otherwise have as the owner of VIE Entities while still complying with Chinese laws.
The following chart reflects our organizational structure as of March 23, 2009:
4
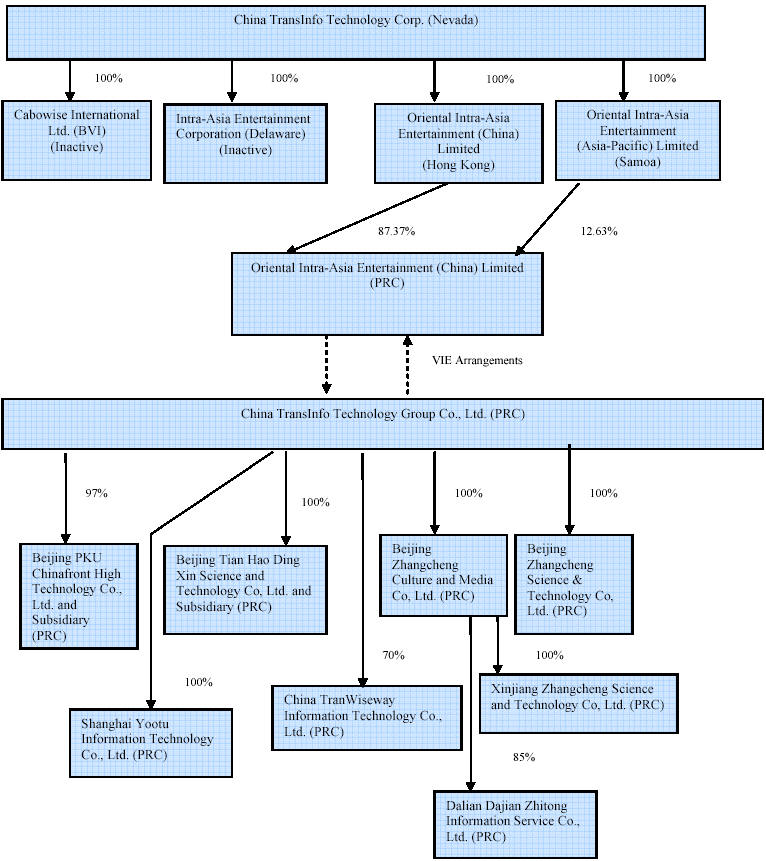
5
Our Industry
Transportation in China
Over the past two decades, China has completed series of large-scale highway infrastructure projects. As a result, according to the Ministry of Communication, China now has the second longest highway network in the world with a total length of approximately 53,800 kilometers at the end of 2007. In addition, China has approximately 70% of the world’s toll highways according to highway management department of the Ministry of Communication. According to the China’s 11th 5-Year Plan, it is estimated that the total mileage of urban rapid transit projects in China will exceed 1,862 kilometers by 2010, with total new investment of nearly $74 billion from 2006 to 2010.
China has a population of about 1.33 billion, which accounts for about 20% of the world’s population and makes it the most populous country in the world. With rapid economic development and urbanization, car ownership has increased dramatically, leading to unprecedented transportation challenges in many cities of China. According to Traffic Management Bureau of Ministry of Public Security, at the end of 2008 China had over 129 million private vehicles. The number is estimated to grow at least 5% over the next several years. Given the current conditions, the Chinese government intends to improve transportation management using advanced information technology solutions. At the same time, motorists are also eager to have access to real time traffic information. This strong demand from the private and public sectors is creating an unprecedented market opportunity for transportation information products and services.
The Ministry of Communication is the country’s highest level transportation regulator. In December 2004, the Ministry of Communication announced a development plan for Chinese national highway system. Under this plan, China will expand its highway network to 65,000 kilometers by 2010, and to 85,000 kilometers by 2020. After its completion, the Chinese national highway network will connect all provincial capitals and cities with populations of at least half-a-million. Under the plan, the total investment in the national highway network will be about $300 billion for the period from 2005 to 2020. From 2005 to 2010, the annual investment in the plan is expected to be approximately $22 billion, with an additional $14.5 billion to be invested annually between 2010 to 2020. Along with the new $584 billion of a new investment included in the recently announced Chinese economy stimulus plan, the Ministry of Communication in November 2008 submitted its new budget to the Chinese central government with the total investments in the transportation sector at about $730 billion for the next 3 to 5 years.
Intelligent Transportation Systems in China
Intelligent Transportation Systems (“ITS”) provide information and data tools for different types of transportation infrastructure by deploying solutions such as communication, monitoring, tolling and planning. The 14th World Congress on ITS, defined ITS as comprehensive systems that integrate and apply advanced information, communication, control, sensor, and computer technology to effectively coordinate people, vehicles, and roads/rails to realize real-time information transfer, as well as on-time, highly efficient, safe, and energy-efficient transportation.
China’s ITS industry is still at its early stage in terms of developments. Although China’s rapid economic growth over the past decade and accelerating urbanization have led to development of its transportation infrastructure, China has also recognized a need to use nationwide transportation networks more efficiently and effectively. China began its ITS efforts in early 1990s with goals to enhance transportation management efficiency, to improve network throughput, and to reduce the negative effect of transportation to the economy and environment. In terms of highways, China has been investing heavily in building up the ITS. However, compared to an average proportion of 7%-10% of ITS investment to total highway investment in developed countries, China has only reached about 1%. Also, almost all highways are toll highways in China, which means ITS is a necessity. Given that China is ranked second in total highway length and first in total toll highway mileage in the world, a larger-scale, more advanced ITS is needed. The increasing urban and highway traffic density also drives continued developments for ITS applications in communication and planning. As increasingly more urban and highway ITS gets deployed, the ITS market will shift towards focusing on specialized information solutions and value-added information services in the future. The urban ITS market is also still at a very initial development stage, comparable to that of the highway ITS market 10 years ago. On the other hand, this is a large but fragmented market with great potential.
6
Despite being at an early stage, the overall ITS market in China is highly attractive due to rapidly developing transportation infrastructure and increasing demand for ITS applications to manage it. The unique characteristics of China’s ITS industry mentioned above and the current low penetration level underline the large market potential. China’s expanding transportation network, along with its need for more effective and efficient transportation networks, has led to the need for better ITS. As a result of this and support provided by recent central government policies, investment in the ITS industry has increased significantly. According to the Chinese government’s 11th 5-year Plan, the Chinese government is estimated to spend approximately $7.3 billion on IT spending in the segments of transportation. Even though there is no current breakdown of IT spending from the new $730 billion budget by the Ministry of Communication, we estimated that it would not go below 5% of the total spending.
Our Growth Strategy
Our objective is to be the largest provider of transportation information products and comprehensive solutions, as well as the largest operator and provider of real time transportation information platform in China. Our strategy for achieving these objectives includes the following key elements:
-
Expand geographic footprint to cover all major markets in China - Based on our successful track record and reputation, management sees significant opportunities to grow revenues from existing clients by winning follow-on contracts for subsequent phases of project implementation, and by capitalizing on our first mover advantage and the high cost of switching to other vendors. In addition to our executive offices in Beijing, we have offices established in Shanghai, Chongqing, Taiyuan (Shanxi Province), Chengdu (Sichuan Province), Hangzhou (Zhejiang Province), Huhhot (Inner Mongolia), Urumqi (Xinjiang) and Dalian (Liaoning Province). We currently provide our products and services in over twenty provinces in China. Our long-term plan is to manage our national operations through different offices and identify potential expansion opportunities.
-
Strengthen R&D capability to enhance and expand core products and further penetrate customer base – We expect to provide additional value-added services and add-ins to our current platform through continuous research and development, enhancement of our product and service offerings and maintenance of our technological leadership position in our core areas of focus. We believe the continuous refinement of our offerings will make the overall platform more attractive to potential customers.
-
Continue to enhance our leadership position in the rapidly growing transportation information technology market – We plan to leverage our strong brand recognition and maintain a high contract bid/win ratio and follow on orders with our transportation information products and services by expanding our sales channels, increasing our product offerings and focusing on customer satisfaction and our other competitive strengths to gain additional market shares.
-
Pursue strategic acquisitions to support strong internal growth – We expect that strategic acquisitions will enable our geographic expansion, enhance our technological capabilities or competitive advantages, enrich product and service lines, provide recurring revenue opportunities and propel our expansion into high growth enterprise class markets.
-
Explore Opportunities in the large China consumer Market – We believe the Chinese consumer represents a large growth opportunity for us. The number of vehicles is expected to continue to grow. As a result, traffic congestion is becoming a serious concern in many Chinese cities. We provide real-time traffic information on our real-time traffic website. Our real-time traffic software for mobile devices, is pre-installed in some cell phones and can also be downloaded from our website. The growth of automobiles in China and 3G build out will enable the Chinese consumer to make more use of its mobile device and applications such as those that provide real time traffic data.
7
Our Products and Services
Our core business is developing the Intelligent Transportation Systems, or ITS, in the transportation sector utilizing GIS application software and technologies. We also develop GIS applications in digital city and land & resource areas. When providing services to customers for GIS application software, some of our customers require us to purchase necessary hardware and provide system integration for them. Our major products and services include:
Transportation Planning Information System
Our transportation planning information system is a software system utilized by traffic management engineers to plan roads and water transportation, safety monitoring and conduct strategic planning. The system facilitates the comprehensive management of different information and data required for traffic planning such as national economic data, road and waterway data and digital mapping data. The system provides planners with information search tools, statistical analysis and models to serve planning and organizing needs. We have been providing this system to the Ministry of Communication of PRC for their nationwide transportation planning and analysis purposes.
Pavement Maintenance System
Our pavement maintenance system is a practical business application system developed specifically for pavement data collection and operations management. Based on field data collected by PDA devices and with the support of a backend data center, the system provides multiple functional modules, such as data acquisition, project management, quality management, equipment management, materials management, assessment analysis, business reports and public travel information inquiries. Our pavement maintenance system can quickly identify pavement issues, efficiently process related data, and maintain information in a scientific manner for timely and accurate support. It solves problems arising from the inefficiency of traditional manual operations by allowing complex information from various sources to be easily processed. By the end of 2008, this application was still under development.
Electronic Toll Collection
Electronic Toll Collection, or ETC, is a technology that allows for electronic payment of tolls. An ETC system is able to determine if a car is registered in a toll payment program, alert enforcers of toll payment violations, and debit the participating account. With ETC, these transactions can be performed without the need for vehicles to stop or slow down. We have been continuously enhancing the functionality of our ETC system, which had not been launched into the market by the end of 2008.
Traffic Information Service System
Our Traffic Information Service System is a software system that provides the public with real time road conditions and related information. The system continuously transmits transportation data gathered from sensory devices and displays the results on an e-map interface. The system also supports web based search and analysis applications. The system has been widely applied and integrated into our solutions provided to various governmental agencies.
Taxi Security Monitoring, Commanding and Dispatching Platform
Our Taxi LED GPS Monitoring and Coordinating System is a highly integrated technological system operated with wireless satellite communication. The system can be used to increase safety and oversight in the taxi industry as well as remote supervision and management of public transportation. The system is composed of a GPS monitoring management center, imbedded GIS, an information transmitting center and onboard monitoring terminal modules. The system platform provides taxi authorities with basic information such as the location of an accident, incident time and images from within a taxi. The system also allows for better coordination with emergency services. The system was used in the cities of Urumqi and Huhhot as of December 31, 2008.
8
GIS-T (Transportation) Middleware
Our GIS-T middleware is based on China’s mainstream traffic GIS platform. The user of our middleware can quickly establish its own application systems without significant customizations. This product has strong applicability in traffic information management, model analysis and visual expression. Our product supports efficient integration of various traffic information models and systems. GIS-T middleware has been widely utilized as technological foundation of many of our transportation information solutions designed for public sector clients.
Traffic Flow Surveying Solutions
We provide transportation management authorities at provincial and municipal levels with traffic flow surveying solutions. These solutions include coil traffic flow detectors, microwave traffic flow detectors and video traffic flow detectors for base stations as well as traffic flow intelligent data centers. We have been providing this solution to multiple provinces in China.
Intelligent Parking System
Our Intelligent Parking System, or IPS, obtains information about available parking spaces, process that information and then presents it to drivers by means of variable message signs. Our system guides drivers in congested areas to the nearest parking facility with available parking spaces and it guides drivers within parking facilities to empty spaces. IPS reduces time and fuel otherwise wasted while searching for empty spaces and helps the parking facilities operate more efficiently. We are one of the first companies in China deploying IPS to serve public and private sector clients.
Red Light Violation Snapshot System
The red light violation snapshot system is used to photograph and record red light violations automatically. The camera captures the violating vehicle, including its license plate number, as it passes through the monitored area. The system also interlinks with a panorama camera to continue photographing the moving vehicle in order to provide comprehensive evidentiary data to authorities. We have been providing this solution to local governmental authorities of transportation.
Intelligent Highway Vehicle Monitoring System
Our highway vehicle monitoring system is used for image snapshot, license plate identification, speed recording, and blacklist database verification of vehicles passing through monitored areas along a given highway. The system consists of a front-end testing unit (camera, video testing module, vehicle tester and LED light) and main control unit (industrial control computer, system management software and communications module). The front-end system uploads images and related data to the command center on real time basis. The central communications server, database server and PC workstation then analyze and manage the uploaded data. The system can be used for automatic vehicle speed testing. The system also assists with traffic flow testing by providing traffic control authorities with relevant traffic data. We have been providing this solution to multiple provinces in China.
Intelligent Traffic Management Platform
Our intelligent traffic management platform is a comprehensive GIS based traffic management platform specially developed for urban traffic command centers. This platform functions as an interface for all ITS subsystems and is the integral element for our intelligent traffic management system. The intelligent traffic management platform allows for the capture of visual images from monitored roads, provides evidence of traffic violations at monitored intersections and records the number of vehicles passing through major urban entrances and exits, among other things. In 2008, we successfully provided real time traffic management solution based on the intelligent traffic management platform to serve the 2008 Olympic Games in Beijing.
9
Dynamic Traffic Information Service Platform
Our dynamic traffic information service platform collects, processes and distributes traffic information. By utilizing arithmetic models based on moving vehicles, the system provides complete dynamic road traffic flow information. The platform also collects, processes and distributes traffic event information. The system can be used to distribute data through several different communication channels, including GPRS, EDGE, CDMA, 3G, RDS-TMC, DAB/DMB, CMMB, Internet and call centers. Our platform captures dynamic traffic information that then can be used for in-car GPS equipment, personal navigation devices (PND), intelligent handsets (Windows Mobile/S60/KJAVA), UMPC, Internet and other terminals. By the end of 2008, we had been continuously enhancing the accuracy rate of current version of the platform and in the process of adding forensic features to the existing version.
Intelligent Public Transport System
Our intelligent bus traffic system inserts information technology into traditional bus traffic systems. Our system optimizes bus traffic routes and helps to improve service levels and management of urban bus traffic. The objective of our intelligent bus system is to realize efficiency in urban public transportation systems and to ensure the safe operation of bus systems while increasing the quality of bus transportation. By the end of 2008, we had been continuously enhancing the functionalities of this system.
Palmcity Navigation Engine
Our PalmCity Explore Navigation Engine is an internet and mobile application based open navigation system, which integrates mapping and navigation into Windows CE (Windows Mobile) and internet applications. By integrating map data, point of interest data storage and management, navigation application development and navigation application framework, PalmCity Explorer Navigation Engine helps navigation application developers and navigation system manufacturers develop unique products and services. We offered our navigation engine in our cell phone real time traffic software mapping add-ons to cell phone manufacturers in 2008.
Comprehensive Location Based Service Platform
Our comprehensive location based service platform is a comprehensive transportation information service platform based on GIS, GPS, ITS and communication technologies. By integrating the latest e-maps of China, highway and city road information, vacant parking spaces, environment and weather information, the system enables real time traffic information, collection, transmission and reporting so as to provide navigation, bus transfers, real time road conditions and location search tools. By the end of 2008, we had been continuously enhancing the functionalities of this system.
Digital City
We provide a full range digital services to many cities in China using a Plan-Construct-Operate model. We analyze different requirements of different regions or cities and design specific information technology systems and digital construction based on a city’s unique requirements. Our typical clients in this segment are local governments, public service departments and enterprises.
2-D and 3-D GIS
We provide software platforms that utilize two-dimensional GIS. Two-dimensional GIS defines and presents special data utilizing an “X” and “Y” axis. Beginning in the 1960s, two-dimensional GIS was widely applied in a variety of sectors, including land management, power, telecommunications and city planning. We also provide software platforms that utilize three-dimensional GIS. Three-dimensional GIS defines and presents special data utilizing an “X”, “Y” and “Z” axis. Compared with two-dimensional GIS, three-dimensional GIS defines special data in a more accurate manner, and can present both the plane and the vertical spatial relation. Moreover, three-dimension GIS can present and analyze more complicated spatial objectives than Computer Aided Design (CAD) and other visualized software. Three-dimensional GIS is better suited for exploration, resource assessment, disaster warning, and production management. It is widely applied in many sectors such as in natural resources (i.e. mineral resources, water resources, etc.) and geology.
10
The Markets for Our Products and Services
We have been marketing and selling our products and services to four main submarkets within the government and regulated sectors in China. These segments are Highway Information Systems; Urban Intelligent Transportation Systems; Digital City, and Land & Resources. Having built a customer base over the years, our strategy is to not only deliver high quality products, but also to provide ongoing value-added services so as to take advantage of any maintenance requirements or technology upgrades that may become necessary in the future. We continue to penetrate these submarkets and believe that we can take advantage of our experience by widening our scope of products and services to include data collection and application service operation.
Highway Information Systems
Our specially designed systems process and store national highway network data and travelers’ information, such as highway information management systems, which perform functions of archiving and retrieving highway data and provide transportation analysis tools. Decision support, predictive information, and performance monitoring are some of ITS applications enabled by highway ITS information management systems. In addition, ITS information management systems can assist in transportation planning, research, and safety management. Our major clients in this segment include the Ministry of Communication, traffic management bureaus, highway management bureaus, and municipal construction committees.
Urban Intelligent Transportation Systems
Key ITS applications for urban traffic management include incident management, signal control, traveler information, and traffic surveillance, intelligent parking indication system. Urban ITS is a combination of basic traffic data, electronic technology, wireless and wire communication technologies, which relies on computer and communication technologies to improve safety and efficiency of urban traffic networks. Traffic surveillance provides monitoring functions in the urban ITS. Most metropolitan areas use loop detectors for traffic surveillance, and many use closed circuit televisions. There are also other types of surveillance tools, such as radar, lasers, or video image processing equipments. The use of vehicles equipped with toll tags or global positioning systems as probes, to determine travel times and locations, is also growing in use. Incident management provides real time incident reporting functions in urban ITS, and it is commonly used by traffic management centers in large metropolitan areas and cities. In some large cities, such as Los Angeles, traffic signal control is also centralized in the traffic management center. In many situations, traffic signal control systems use traffic responsive signals to manage the traffic within urban areas. Such responsive signals can be single signals or a group of interconnected signals. Urban traffic management centers utilize all traffic condition information collected from their ITS to give feedbacks and suggestions to travelers. Such information may be provided directly to the public or to organizations who provide it to users through radio broadcast, internet, or other means. Some major types of traveler information include pre-trip information, en-route driver information, en-route transit information and route guidance.
Digital City
Digital City sector is designed to aid the Chinese government’s initiative to outfit all major cities with broadband, wireless internet access, and information technology infrastructure. Many cities in China, especially in southern China, have experienced rapid economic developments since early 90s. However, the information infrastructures construction in these cities does not match their economy developments. We are one of the pioneers to develop the “Digital City” concept in China . We provide full range digital services to many cities in China with the model of “Planning-Construction-Operation”. We analyze different requirements of different regions or cities and designs specific information technology systems based on unique requirements. Typical clients include local governments, public service departments and enterprises.
11
Land & Resources
The average IT spending in city geographical and land resources managements for each city in China is about RMB 60 million (approximately $8.8 million). Based on China’s 11th 5-year Plan, there are about 100 cities planning to complete GIS construction, which will lead to a RMB6 billion (approximately $880 million) market in China. Land resources systems cover planning, analysis, statistics and construction management for mineral resources. In this business line, we have developed a city geological information analysis system that provides tools to analyze the geological environment based on the integration of a variety of geological information, such as determining the underground structure for city planning and construction. In addition, we have created a disaster forecast system and a mineral resources assessment system that provides a platform to assess the reserves and then help to make decisions regarding the development of the mineral resources by setting up assessment models of mineral resources.
Our Intellectual Property
The following table illustrates the title of different copyrights that we own, their registration numbers, first publication dates, issuance dates, and durations, as well as the significance levels of such copyrights. The significance levels of the copyrights are divided into A, B, C three levels. “A” represents “Frequently Used in our products and services”, “B” represents “Occasionally Used in our products and services”, and “C” represents “Rarely Used in our products and services”.
|
Copyright Title |
Certificate Number | Registration Number | First
Publication Date |
Issue Date |
Expiration Date |
Materiality
Level |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate (JTLWeb V1.0) |
028661 | 2004SR10260 | 09.08.2004 | 10.21.2004 | 12.31.2054 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate ( Land & Resources and House Affairs Information System V1.0) |
027924 | 2004SR09523 | 06.15.2004 | 09.29.2004 | 12.31.2054 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate (GeoPad V1.0) |
002827 | 2002SR2827 | 09.01.2002 | 09.24.2002 | 12.31.2052 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate (Command System of Meeting Urgent Need for Urban Public Emergencies V1.0) |
009303 | 2003SR4212 | 05.10.2003 | 06.9.2003 | 12.31.2053 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate (GeoWeb V1.0) |
006881 | 2003SR1790 | 09.05.2002 | 03.19.2003 | 12.31.2053 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate (EnvMonitor 1.0) |
004358 | 2002SR4358 | 05.18.2002 | 12.6.2002 | 12.31.2052 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate (TranPlan 1.0) V1.0 |
003664 | 2002SR3664 | 06.18.2002 | 11.11.2002 | 12.31.2052 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate ( (e-Gov.Suite 1.0) V 1.0) |
000823 | 2002SR0823 | 05.23.2002 | 07.04.2002 | 12.31.2052 | B |
12
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate (Sm@rtOA 1.0) V 1.0 |
000824 | 2002SR0824 | 09.28.2001 | 07.04.2002 | 12.31.2052 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate (WebMap Engine) V 1.0 |
0009123 | 2001SR2190 | 07.08.2001 | 07.30.2001 | 12.31.2051 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate (Environment Geo V 1.0) |
062877 | 2006SR15211 | 11.30.2005 | 10.31.2006 | 12.31.2056 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate (Environment Protection Emergency Conduct System V 1.0) |
062879 | 2006SR15213 | 11.30.2005 | 10.31.2006 | 12.31.2056 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate (Land and Resources Files’ Collection System V 1.0) |
063008 | 2006SR15342 | 06.30.2006 | 11.02.2006 | 12.31.2056 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Embed-3D-GIS V1.0) |
071603 | 2007SR05608 | 01.30.2007 | 04.17.2007 | 12.31.2057 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Environment Protection Emergency Conduct System V 1.0) |
063509 | 2006SR15843 | 04.30.2006 | 11.13.2006 | 12.31.2056 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Environment Information System V 1.0) |
063510 | 2006SR15844 | 04.30.2006 | 11.13.2006 | 12.31.2056 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Land and Resources Information Management System V 1.0) |
063508 | 2006SR15842 | 06.30.2006 | 11.13.2006 | 12.31.2056 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(GeoWeb For Linux) V1.0 |
086634 | 2007SR20639 | 05.10.2007 | 12.24.2007 | 12.31.2057 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate (Water Carriage Information System) V1.0 |
BJ10658 | 2008SRBJ035 2 | 06.25.2006 | 02.03.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Intelligent Parking Guide System) V1.0 |
BJ10662 | 2008SRBJ035 6 | 06.30.2007 | 02.03.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
13
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Urban Geological Information Management and Services System) V1.0 |
BJ10679 | 2008SRBJ037 3 | 10.10.2007 | 02.03.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Exploiter Navigation Software V1.0) |
BJ10485 | 2008SRBJ017 9 | 11.20.2007 | 01.16.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Location Services Platform System V 1.0) |
088919 | 2008SR01740 | 11.15.2007 | 01.24.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Taxi Security Alarm System Certificate (V1.0) |
BJ16618 | 2008SRBJ631 2 | 11.22.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(City One Card Solution Consumption Real Time Transaction System) V1.0 |
BJ16638 | 2008SRBJ633 2 | 09.12.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Taxi Monitoring Management System v1.0) |
BJ16626 | 2008SRBJ632 0 | 11.18.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Taxi Calling System V1.0) |
BJ16653 | 2008SRBJ634 7 | 09.18.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Advertisement Contract Management System V1.0) |
BJ16612 | 2008SRBJ630 6 | 10.21.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Advertisement Business Information Processing System V1.0) |
BJ16639 | 2008SRBJ633 3 | 09.26.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Media Call Center Business Management System V1.0) |
BJ16620 | 2008SRBJ631 4 | 10.27.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Real Time Information Broadcasting System V1.0) |
BJ16615 | 2008SRBJ630 9 | 09.30.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
14
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Electronic Project Management System V1.0) |
BJ16795 | 2008SRBJ648 9 | 10.20.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Data Collection System V1.0) |
BJ16796 | 2008SRBJ649 0 | 09.18.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | C |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Employee Information Management System V1.0) |
BJ16809 | 2008SRBJ650 3 | 11.20.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | C |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Digitalization Assets Management System V1.0) |
BJ16797 | 2008SRBJ649 1 | 06.10.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | C |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Logistics Information System V1.0) |
BJ16793 | 2008SRBJ648 7 | 01.20.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Students Archive Management System V1.0) |
BJ16808 | 2008SRBJ650 2 | 12.10.2007 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | C |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Product Selling Monitoring System V1.0) |
BJ16792 | 2008SRBJ648 6 | 01.20.2007 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | C |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(E-business Shopping System V1.0) |
BJ16794 | 2008SRBJ648 8 | 08.16.2007 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Expressway ETC System V1.0) |
BJ16694 | 2008SRBJ638 8 | 10.30.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(GIS-T Expressway Equipment Management System V1.0) |
BJ16771 | 2008SRBJ646 5 | 10.21.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Highway Data Collection and Distribution System V1.0) |
BJ16770 | 2008SRBJ646 4 | 10.29.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Highway Transportation Indication System V1.0) |
BJ16769 | 2008SRBJ646 3 | 08.20.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Expressway Emergency Command and Monitoring System V1.0) |
BJ16699 | 2008SRBJ639 3 | 09.10.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
15
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Traffic Information Service System V1.0) |
BJ16751 | 2008SRBJ644 5 | 10.22.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Urban Intelligent Traffic Management System V1.0) |
BJ16906 | 2008SRBJ660 0 | 12.20.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Urban Traffic Information Decision-making and Analysis System V1.0) |
BJ16926 | 2008SRBJ662 0 | 11.18.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Appropriative GIS V1.0) |
BJ16928 | 2008SRBJ662 2 | 12.10.2007 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Highway Information Total Solution and Decision-analysis System V1.0) |
BJ16927 | 2008SRBJ662 1 | 05.18.2007 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Red Light Violation Snapshot System V1.0) |
BJ16905 | 2008SRBJ659 9 | 09.20.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Highway Vehicles Intelligent Testing and Recording System V1.0) |
BJ16876 | 2008SRBJ657 0 | 11.20.2007 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Public Sanitation Quality Monitoring and Alarm System V1.0) |
BJ16457 | 2008SRBJ615 1 | 10.30.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Human Resource Management System V1.0) |
BJ16428 | 2008SRBJ612 2 | 10.20.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Local Sanitation Information Platform V1.0) |
BJ16450 | 2008SRBJ614 4 | 10.10.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Management Competition Imitation Platform V1.0) |
BJ16424 | 2008SRBJ611 8 | 10.14.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
16
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Disabled Association Job Information Management System V1.0) |
BJ16473 | 2008SRBJ616 7 | 09.08.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Message Service Platform V1.0) |
BJ16423 | 2008SRBJ611 7 | 09.30.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Telecom Value-added Service System V1.0) |
BJ16422 | 2008SRBJ611 6 | 10.25.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Emergency Command and Prevention System V1.0) |
BJ16472 | 2008SRBJ616 6 | 10.22.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Palmcity WebGIS Engine V1.0) |
BJ16589 | 2008SRBJ628 3 | 04.10.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Mobile Map Software V1.0) |
BJ16591 | 2008SRBJ628 5 | 05.10.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Multiple-source Traffic Information Integration System V1.0) |
BJ16629 | 2008SRBJ632 3 | 08.26.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Palmcity Traffic information collection System V1.0) |
BJ16605 | 2008SRBJ629 9 | 10.30.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(PalmCity Floating Car Data Processing System V1.0) |
BJ16628 | 2008SRBJ632 2 | 05.30.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(PalmCity Information Exchange Platform V1.0) |
BJ16631 | 2008SRBJ632 5 | 06.21.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(PalmCity In-car PND Comprehensive Information System V1.0) |
BJ16617 | 2008SRBJ631 1 | 10.31.2007 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Super GIS Data Comprehensive Integration System V1.0) |
BJ16604 | 2008SRBJ629 8 | 10.26.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
17
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Water Transportation Flow Investigation VTS System V1.0) |
BJ16641 | 2008SRBJ633 5 | 11.12.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Highway Traffic Flow Investigation Data Center V1.0) |
BJ16507 | 2008SRBJ620 1 | 09.30.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Highway Traffic Flow GIS System V1.0) |
BJ16476 | 2008SRBJ617 0 | 10.27.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Highway Traffic Flow Investigation Equipment Long-distance Monitoring Platform V1.0) |
BJ16557 | 2008SRBJ625 1 | 09.30.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Coil Traffic Flow Data Collection System V1.0) |
BJ16621 | 2008SRBJ631 5 | 10.28.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Video Traffic Flow Data Collection System V1.0) |
BJ16643 | 2008SRBJ633 7 | 11.20.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Video Traffic Flow Investigation - Digital Image Processing System V1.0) |
BJ16622 | 2008SRBJ631 6 | 11.06.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | A |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Video Traffic Flow Investigation Watching-dog System V1.0) |
BJ16627 | 2008SRBJ632 1 | 10.10.2008 | 12.13.2008 | 12.31.2058 | B |
|
|
||||||
|
Computer Software Copyright Registered Certificate(Yootu Real-Time Road Condition Information Processing and Releasing Software V1.0) |
77504 | 2007SL11509 | 05.01.2007 | 08.01.2007 | 12.31.2057 | A |
Research and Development
In 2008 and 2007, our research and development expenses amounted to approximately $2.60 million and $0.96 million, respectively. These expenses were mainly composed of staff costs and research and development equipment purchasing expenses.
18
Our Research and Development (R&D) Department consists of two departments, one is internal and the other is external, which involves our strategic relationship with the GeoSIS Laboratory at Peking University.
Internal R&D Department
Our internal R&D department consists of 140 researchers with extensive experience in the GIS and transportation information industry. Many of these researchers have worked at multinational corporations.
The primary focus of the internal R&D department is to analyze customer demands and develop application software products, with the use of the most highly advanced software development tools available today.
Our research department is also responsible for monitoring developments in the market for our services so that they can develop new products or improve upon existing products by adopting new technologies and skills.
In addition, the department is responsible for creating training and support manuals and creating new processes for implementation of our software products.
Strategic R&D Partnership with Peking
University
PKU was established in connection with the Peking University’s GeoSIS Laboratory in order to provide university researchers with real life opportunities to test and implement the discoveries created at the University. On August 6, 2005, PKU entered into a cooperation agreement (the “Cooperation Agreement”), with Earth and Space College of Peking University, pursuant to which PKU obtained the access to the university’s GeoSIS Research Lab, which houses over thirty PhDs and researchers to support PKU’s research and development initiatives. Under the Cooperation Agreement, we pay for all R&D expenses of the GeoSIS Laboratory. The Cooperation Agreement has a three-year term that has been automatically renewed for an additional three year.
Our Major Customers
The following table provides information on our most significant clients in fiscal year 2008.
|
TOP TEN CLIENTS IN 2008 |
||||||||
| No. | Name | Description of Client | Sales
(in thousands of US dollars) |
Percentage of | ||||
| 1 | Beijing Zhongjiaokeruan Technology Co., Ltd. | High-tech company in transportation information application development | 3,209 | 10.93% | ||||
| 2 | United Real Estate Development Co., Ltd. | A real estate development company | 1,919 | 6.53% | ||||
| 3 | Transportation Planning & Research Institute | An institute under Ministry of Communication | 1,826 | 6.22% | ||||
| 4 | Beijing Feiwu Technology Co., Ltd. | High-tech company in telecom and electronic products | 1,661 | 5.66% | ||||
| 5 | Beijing Municipal Bureau of Land & Resources | City-level governmental land and resource department | 1,593 | 5.42% | ||||
| 6 | Beijing Xiangxian Technology Co., Ltd. | High-tech company in environmental application development | 1,515 | 5.16% | ||||
19
| 7 | China Construction 1st Division Group Construction & Development Co., Ltd. | A state-owned construction company | 1,489 | 5.07% | ||||
| 8 | Beijing Aoran High-tech Industrial Co., Ltd. | High-tech company in electronic products | 1,338 | 4.55% | ||||
| 9 | Beijing Transportation Information Center | City-level governmental transportation department | 1,282 | 4.36% | ||||
| 10 | Beijing Transportation Committee | City-level governmental transportation department | 1,107 | 3.77% | ||||
| TOTAL | 16,939 | 57.67% |
Regulation
Because our operating VIE entities are located in the PRC, our business are regulated by the national and local laws of the PRC. There are no specific rules or regulations for a company engaged in software development other than mapping which is highly regulated in China.
In addition, we and our PRC subsidiaries are considered foreign persons or foreign-invested enterprises under PRC laws, and therefore subject to foreign ownership restrictions in connection with our online services, advertising in taxies, and security and surveillance related businesses:
Online Service
On December 11, 2001, the State Council of China promulgated the Regulations on the Administration of Foreign Invested Telecommunication Enterprises (the “FITE Regulations”) , which became effective on January 1, 2002. Under the FITE Regulations, a foreign entity is prohibited from owning more than 50% of equity of a provider of value-added telecommunications services in China, which include internet content provision services. In addition, the current Catalogue of Industries for Guiding Foreign Investment (Revised 2007) prohibits a foreign investor from investing in businesses such as news websites and web streaming audio-visual services. As a result, if we or our former Chinese subsidiaries had invested directly in the value-added telecommunications services in China, we would have had at most 50% of the ownership of the business and thus only consolidated no more than 50% of the revenues generated from such business.
Taxi Advertising
For an advertising business involving foreign investment, there have been rigid overseas operation requirements on the foreign investors under the current Chinese laws. Pursuant to the Provisions on Administration of Foreign Invested Advertising Enterprises promulgated by the State Administration for Industry & Commerce and the Ministry of Commerce of China on March 2, 2004, for a wholly foreign owned advertising enterprise, the foreign investors must have at least three years of direct operations in the advertising business outside of China. In case of a joint venture, foreign investors must have at least two years of direct operations in the advertising business outside of China. However, a domestic company without direct foreign investment is not subject to any of these restrictions.
Security and Surveillance Related Business
While there is no Chinese law or regulation specifically prohibiting foreign investment in the security and surveillance related business in China, the nature of this business implies that a vast majority of the customers of this business are governmental entities. Maintaining the confidentiality of sensitive information about national security and other various governmental affairs is one of the most important concerns of these government customers. Therefore, as a practicable matter, governmental entities are more willing to have business relations with purely domestic companies than a company involving foreign investment where confidential governmental information is concerned.
20
In order to comply with these legal restrictions, on February 3, 2009, we conducted the Restructuring and entered into the Contractual Arrangement with the VIE Entities. These arrangements enable us to operate these restricted businesses through these VIE Entities in which we do not hold a direct equity interest. For more information on the regulatory and other risks associated with our contractual agreements related to our VIE Entities, please see the discussion below Item 1A, “Risk Factors.”
We are also subject to PRC’s foreign currency regulations. The PRC government has controlled Renminbi reserves primarily through direct regulation of the conversion of Renminbi into other foreign currencies. Although foreign currencies, which are required for “current account” transactions, can be bought freely at authorized PRC banks, the proper procedural requirements prescribed by PRC law must be met. At the same time, PRC companies are also required to sell their foreign exchange earnings to authorized PRC banks and the purchase of foreign currencies for capital account transactions still requires prior approval of the PRC government.
Our Competition
Competition in China’s transportation information industry is very fragmented and consists of a combination of a few foreign competitors and many domestic transportation information technology companies. Whereas most international competitors seek to provide component software for the industry, our focus is on developing application software and services for the Chinese government and regulated sectors.
We believe that the following competitive strengths enable us to compete effectively in the transportation information industry:
-
Leading-Edge R&D Team - Our research and development team has a strong and extensive technology background and was an early entrant into the three-dimensional Geographic Information System, or GIS, market. The head of our research and development team was the lead engineering architect of the first three-dimensional GIS platform software in China (Chinese Excellence Software Award, 1995).
-
R&D Affiliation with Peking University – Through our early alliance with Peking University, we developed a strong and extensive technology background and we have access to the university’s research labs and PhDs. Under the cooperation agreement between our VIE Entity, PKU and Earth and Space College of Peking University, we have access to the university’s GeoSIS Research Lab and its team of over 30 PhDs and researches who support our R&D initiatives. Peking University is a 3% owner of PKU.
-
Award Winning Technology - Since inception, we have won over nine product awards, including the National Transportation Planning System and Digital City Program award. The awards are indicative of the technological leadership of our Intelligent Transportation System, or ITS and give customers a sense of security that they are purchasing a quality product.
-
Brand Image - We have built a valuable brand image through our track record of successful execution of projects for customers in various sectors. We provide products and services, including value-added services to meet maintenance and technology upgrade requirements, to our governmental and other customers. Our customers include central, provincial and municipal government agencies, construction, real estate development and high-tech companies. We plan to leverage our brand image to obtain new and recurring business.
-
Superior Management - Three members of our executive management team were the first GIS software developers in China. Collectively, they have more than 34 years of experience with GIS, and each has been with PKU since its early days. They are complemented by two executives with extensive finance and corporate financial reporting experience.
21
- Operational and Quality Management - We are ISO9000 certified and conduct internal performance assessments three times per year. Being in close proximity to two of China’s top universities, we have many qualified candidates to choose from for our hiring needs. We subject our potential hires to a rigorous review of their academic and technical skills. We also screen each candidate’s background for potential conflicts of interest and in order to avoid the possible appearance of impropriety in our dealings with government agencies.
We experience competition from both foreign and domestic Chinese competitors. The following is a description of some of our major competitors:
Foreign Competitors
- Image Sensing System, Inc. (ISS) -ISS is headquartered in St. Paul, Minnesota, a technology company focused in infrastructure productivity improvement through the development of software-based detection solutions for the Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) sector and adjacent overlapping markets. ISS’s industry leading computer-enabled detection (CED) products combine embedded software signal processing with sensing technologies for use in transportation, environmental and safety/surveillance management.
With more than 90,000 instances sold in over 60 countries worldwide, its products position to the traffic, security and environmental management markets.
-
Satellic Traffic Management GmbH - Satellic Traffic Management GmbH (Satellic) is a global technology service provider for the setup and operation of progressive toll and traffic management systems. Satellic is a wholly-owned subsidiary of T-Systems, the business customers segment of Deutsche Telekom. The company, which was founded in 2005, has its headquarters in Berlin. Satellic advises governments, companies and associations and is breaking new ground, together with industrial partners on site, in the implementation of traffic infrastructure projects. The company develops new concepts (public private partnership) for financing, traffic management and for emissions protection.
-
Vehicle Information and Communication System Center - Vehicle Information and Communication System Center, founded in 1995 in Tokyo, Japan, is involving of the business of systematical gathering, processing , and editing road traffic information, and managing and operating traffic information system by using communication and broadcasting media, and in turn transmitting accurate traffic information to drivers via in-vehicle navigation devices.
-
Organization for Road System Enhancement - Organization for Road System Enhancement (ORSE), was founded in 1999 in Japan. ORSE’s business is about all hand business of ETC system in Japanese market including disclosing standard for data security in ETC systems, providing processed data for identical ETC systems and developed ETC related technologies.
-
Navteq - Navteq is a world leader in premium-quality digital map data. Its data has been widely applied in-vehicle navigation systems in North America and Europe. Founded in California in 1985, this company has been acquired by Nokia in 2008. Currently, NAVTEQ has more than 4,000 employees worldwide located in 196 offices in 36 countries.
The products offered by our foreign competitors are priced higher than our products. In addition, their software cannot be applied in China without significant modification due to differing industry standards and background. For these reasons, we do not foresee much competition from these international competitors in the area of transportation information application software.
Domestic Chinese Competitors
- Beijing E-Hualu Info Technology Co., Ltd. (E-Hualu) - Founded in 2001, based in Beijing, E-hualu is involved in the business of design and construction of intelligent traffic projects, and the urban traffic command center software development and system integration technology. E-Hualu has developed a series of traffic management application software & hardware systems with independent intellectual property and cooperated with police departments for urban public security and traffic command center constructions.
22
-
Beijing Rhytech Co., Ltd. (Rhytech) - Based in Beijing, Rhytech is focusing on intelligent traffic sector including inter-city intelligent traffic management system, police intelligent traffic management system, railway and tunnel intelligent traffic management system and other value-added intelligent traffic service. Currently, the company has 3 offices throughout China.
-
BOCO Inter-Telecom Holding Co., Ltd. (BOCO Inter-Telecom) - BOCO Inter-Telecom has been listed in Shanghai stock market of A-Share with ticker 600289 since 2000. Affiliated with Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, BOCO Inter-Telecom’s main business includes telecom operation support systems, information security systems and intelligent traffic systems. Its intelligent traffic systems are mainly highway management systems, highway maintenance systems and electronic toll collection systems.
-
Qingdao Hisense TransTech Co., Ltd.( QHNTC) - QHNTC was founded in October 1998. It is a subsidiary of Hisense Co., Ltd. QHNTC engages itself in the development and service of intelligent traffic systems (ITS). Focusing on urban traffic, public transport, logistics and commercial service, the company has developed several proprietary rights in traffic light control systems and urban public security & traffic comprehensive information platforms and other public transportation systems.
-
Beijing Stone Intelligent Transportation System Integration Co., Ltd. - This company focuses on intelligent transportation System, traffic engineering technical system, traffic information system and other serial traffic products.
-
Guangzhou Heartly Teamgo Information System Engineering Co., Ltd. (Heartly Teamgo) - Based in Guanzhou, Guandong Province, founded in 1997, Heartly Teamgo is engaging in intelligent traffic products development, solution and system integration. Mainly dedicated in Guangdong province, this company has developed city intelligent public transportation system, public media information display system, electronic bulletin boards and GPS in-car platform, etc. The company has completed Guangzhou parking systems, public transportation sensor dispatch system and related projects.
-
CenNavi Technologies Co., Ltd (CenNavi) - Founded in 2005, CenNavi collects, processes, distributes and optimizes dynamic traffic information technologies. This company provides real-time traffic information services for vehicle terminals, PND terminals, mobiles phones and internets as well as supports traffic information display and optimal route query to above terminals. Acquired by China's largest navigable e-map manufacturer—NavInfo, this company’s products are mainly sold in vehicle market currently.
-
Shenzhen GENVICT Technologies Co., Ltd. (GENVICT) - GENVICT is a high-tech corporation specialized in developing, designing, manufacturing, supplying and technical services of Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) devices, IC card readers, embedded intelligent terminals and related hardware products. The company is headquartered in Shenzhen, with major customers as expressway, public security, traffic control, finance, urban traffic authorities.
-
NAVINFO - This company is a navigable map and dynamic content service provider in China with over 10-year history in navigation map production. It is the first map producer in China that supports dynamic traffic information release and navigation application.
NavInfo is a leading company in China’s vehicle navigable map market and is an all-round big player in the fields of portable navigation, (location based services) LBS and Internet–based location services and traffic information services. Currently, NavInfo map data have been mainly applied in vehicle navigation market and also applied in portable navigation market, Internet-based location service providers and mobile phone operators in China.
23
Raw Materials
Since we are in the business of developing software applications and providing related services, we do not utilize any significant amount of raw materials. All of the raw materials needed for our business are readily available from several different suppliers and at market driven prices. The company only purchases computers and other software in order to provide its services and software applications to customers.
Our Employees
As of December 31, 2008, we employed a total of 340 full-time employees. The following table sets forth the number of our employees by function as of December 31, 2008.
| Number of | |||
| Department | Employees | ||
| Software Development | 140 | ||
| Quality Control | 34 | ||
| Sales and Marketing | 73 | ||
| Administration | 63 | ||
| Human Resources | 8 | ||
| Finance | 22 | ||
| Total | 340 |
Our employees are not represented by a labor organization or covered by a collective bargaining agreement. We have not experienced any work stoppages. We are required under PRC law to make contributions to the employee benefit plans at specified percentages of the after-tax profit. In addition, we are required by the PRC law to cover employees in China with various types of social insurance. We believe that we are in material compliance with the relevant PRC laws.
We believe that we maintain a satisfactory working relationship with our employees and we have not experienced any significant labor disputes or any difficulty in recruiting staff for our operations.
Seasonality
Our results of operations are not materially affected by seasonality and we do not expect seasonality to cause any material impact on our operations in the future.
24
PART II
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS.
Overview
This subsection of management’s discussion and analysis is an overview of the important factors that management focuses on in evaluating our business, our financial condition our operating performance, our overall business strategy and our earnings for the periods covered.
We are a holding company that only operates through our Chinese VIE Entities, through which we primarily focused on providing transportation information services and products in the Chinese market. We aim to become the largest transportation information products and comprehensive solutions provider, as well as the largest integrated transportation information platform and commuter traffic platform builder and operator in China. In addition, we are developing our transportation system to include electronic toll collection and real time traffic reporting.
Historically, the Company has segmented its services into three specific areas: transportation, land and resources, and digital city. Our transportation solutions track and store a variety of traffic information for various government entities, private sectors clients and individual users. The land and resources segment enables municipal governments to assess the efficiency of land use and the management of natural resources. The digital city sector is designed to aid the Chinese government’s initiative to outfit all major cities with broadband and wireless internet access.
Due to the substantial market demand for transportation information products in China, we have decided to devote more energy and resources to our transportation segment since late 2007, and expects that this segment will become a major driver of our future development. Our transportation products and solutions are targeted for transportation management authorities under the management of the Ministry of Communication and the general public.
Industry Wide Factors that are Relevant to Our
Business
The transportation information industry in China is in the process of rapid and continuous development. We believe that the trend in China’s transportation information industry is the continuous increase of Chinese government’s and public demand for advanced transportation information products and services to support more effective and efficient transportation networks in China. One result of this trend is the growing amount of governmental spending in the sector of transportation. We believe this trend will impact favorably on the demand for our transportation information products and services, and accordingly result in the growth in sales of our transportation products and services.
The development of transportation information products and solutions that are “Made in China” has grown rapidly since 2000. As a leading company in transportation information products and solutions in China, our sales revenues have a high correlation to the high speed growth of the transportation information industry in China generally. Our sales compounded annual growth rate has been at approximately 71% for the past four years and our earnings compounded annual growth rate has also been at about 71% over the same period. Therefore, we believe that our sales over the next five years will grow in close correlation with the rapid growth of China’s transportation information industry.
One main factor that management considers when estimating our future growth is the potential revenue from larger government projects in the transportation sector of the Chinese government based on annual budget reports issued by relevant governmental sectors at both central and local levels. We expect that these potential new projects will create revenues from new transportation information product sales and services. We expect to bid on large projects in the transportation sector going forward.
25
The growing use of GPS and location-based service in China also has a material impact on our industry. We believe that “Made in China” transportation information products and services will have a distinct advantage over similar products and services provided in developed countries, where development costs are generally higher. The Chinese economy is developing at a rapid pace. As a result, there is a growing consumer market that is developing in China. We also believe that the worldwide perception of the quality level of Chinese products is improving.
Results of Operations
For the year ended December 31, 2008, our revenues increased to $29.4 million, an increase of 147.55% over 2007. Gross profit was up 163.96% from the previous year, increasing from $6.25 million to $16.5 million, and operating income reached $11.42 million, an increase of 135.45% . Finally, the Company’s net income for the year increased 150.85% to $11.09 million from $4.42 million in 2007.
As these results show, the Company had a successful year of significant growth in 2008. It was a year of transition for the Company as we evolved from our foundation as a Geo-GIS custom software producer to a comprehensive transportation information solutions provider. As a result, transportation products and solutions have continued to comprise an increasingly large portion of our revenue throughout the year. For 2008, revenue from this area accounted for 62.76%, growing from 39.53% in 2007. Our digital city and land resources urban planning software accounted for the remainder.
In 2008 we continued to provide customized transportation related software solutions to the national government and provincial level governments across China with high bid-win rate of approximately 90%. One of our most high profile contracts was with the Beijing Traffic Management Bureau to build a traffic application system for use during the Olympic Games. Despite its initial intent for the Olympic village area, it was subsequently expanded to cover the entire city. In addition to this, the Company was contracted by the government to provide real time traffic data during the Olympics over personal navigation devices, or PNDs, a restricted access communication device used only in official vehicles. With a high degree of brand recognition and strong governmental relationships, we believe that we will continue to work closely with various governmental agencies to accommodate China’s continued transportation planning needs.
Our consumer-targeted new real time traffic data application business was also successfully launched this year. We have expanded our real time data source network to 10 cities. Our first product related to this was launched in summer of 2008 as the first cell phone-based real time traffic navigation application in China. We expect that more high-end cell phone manufactures will install this function on new handsets to satisfy growing consumer demand for real time traffic data.
Generating comprehensive, accurate data is one of the key goals for our real time data business. As such, we operate our exclusive taxi media platforms to help us collect real time data from moving vehicles. These hardware and software platforms are installed in a city’s fleet of taxis and allow us to generate traffic data based on the speed and location of a taxi. With roof mounted LED screens which are part of the system, we were also able to broadcast advertisements from which we generate revenue. In 2008 we were able to expand our geographic scope for this service area as we began installing our system in Huhhot, the capital city of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region in the beginning of the year. In the fourth quarter of 2008, we added Dalian, a large coastal city in northeastern Liaoning province, as a new market.
A major part of our growth strategy to develop our transportation information products and services in 2008 focused on acquisitions. Early in 2008 we acquired China TransWiseway Information Technology Co., Ltd., a high tech enterprise specializing in highway traffic monitoring projects. Subsequent to this, we acquired Dalian Dajian Zhitong Information Service Co., Ltd., the holder of the rights to Dalian’s taxi advertisements. In the fourth quarter of 2008, we acquired Shanghai Yootu Information Technology Co., Ltd., a Shanghai-based real time traffic data provider. Through these strategic acquisitions we have broadened our geographic range, and acquired new technologies which complement our existing products, enabling us to accelerate the development of new services and product solutions.
26
Fiscal Year ended December 31, 2008 Compared to Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2007
The following tables set forth key components of our results of operations for the periods indicated, in dollars and percentage of revenues and key components of our revenue for the periods indicated in dollars.
| Years Ended | ||||||
| December 31, | ||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| $ | $ | |||||
| Revenues | 29,370,463 | 11,864,629 | ||||
| Cost of sales | 12,867,258 | 5,612,372 | ||||
| Gross profit | 16,503,205 | 6,252,257 | ||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 5,081,502 | 1,401,169 | ) | |||
| Operating income | 11,421,703 | 4,851,088 | ||||
| Other income and (expenses) | ||||||
| Interest income | 68,782 | 60,289 | ||||
| Interest expenses | (135,120 | ) | (13,968 | ) | ||
| Subsidy income | 530,100 | 146,058 | ||||
| Decrease in fair value of warrant liability | - | 64,359 | ||||
| Other income (expense) | 32,170 | 160,446 | ||||
| Income before income taxes and minority interest | 11,917,634 | 5,268,272 | ||||
| Income taxes | (62,955 | ) | 450,606 | |||
| Minority interest | (764,201 | ) | (396,585 | ) | ||
| Net income | 11,090,477 | 4,421,081 | ||||
| Years Ended | ||||||
| December 31, | ||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| As a percentage of Revenues | ||||||
| Revenues | 100.00 % | 100.00% | ||||
| Cost of sales | 43.81 % | 47.30% | ||||
| Gross profit | 56.19 % | 52.70% | ||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 17.30 % | 11.81% | ||||
| Operating income | 38.89 % | 40.89% | ||||
| Other income and (expenses) | ||||||
| Interest income | 0.23 % | 0.51% | ||||
| Interest expenses | (0.46 % | ) | (0.12 % | ) | ||
| Subsidy income | 1.80 % | 1.23% | ||||
| Decrease in fair value of warrant liability | 0.00 % | 0.54% | ||||
| Other income (expenses) | 0.11 % | 1.35% | ||||
| Income before income taxes and minority interest | 40.57 % | 44.40% | ||||
| Income taxes | 0.21 % | 3.80% | ||||
| Minority interest | (2.60 % | ) | (3.34 % | ) | ||
| Net income | 37.76 % | 37.26% |
27
Revenues. Revenues increased approximately 17.5 million, or 147.55% to approximately $29.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, from approximately $11.9 million in 2007. Approximately 78.50% of this increase is attributable to the increase of our Transportation business in 2008, which had approximately 292.99% increase year over year comparing to 2007. Such an increase mainly resulted from the Company’s major business focus shifting to Transportation business late 2007 and the rapidly developing market opportunities in the transportation information sector in China. Approximately 16.72% of the increase in our 2008 revenue is attributable to the increase in Digital City business, which had about 53.62% increase compared to 2007. Even though we put less focus on Digital City business in 2008, we believe this business is still experiencing healthy growth in China. Land and Resource and Other businesses accounted for the remaining increase of our revenues in 2008. We believe that the overall sales increased also as a result of the growing recognition of our brand name and technology. During 2008, the Company achieved a win rate of approximately 90 percent for project bids and also were able to secure more contracts from recurring clients.
The following table illustrates the revenues from the Chinese government sectors and regulated industries in which we sell our products and services for the periods indicated. The table also provides the percentage of total revenues represented by each listed sector.
| Percentage | ||||||||||||
| Year Ended | of | Year Ended | Percentage of | |||||||||
| December 31, | Total | December 31, | Total | |||||||||
| 2008 | Revenues | 2007 | Revenues | |||||||||
| Transportation | $ | 18,432,187 | 62.76% | $ | 4,690,206 | 39.53% | ||||||
| Digital City | 8,387,422 | 28.56% | 5,459,863 | 46.02% | ||||||||
| Land & Resources | 2,475,023 | 8.42% | 1,321,757 | 11.14% | ||||||||
| Other | 75,831 | 0.26% | 392,803 | 3.31% | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 29,370,463 | 100.00% | $ | 11,864,629 | 100.00% |
As the table above indicates, the Transportation and Digital City sectors accounted for an aggregate of 91.32% and 85.55% of our sales for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. Sales in Land & Resources account for less than 12% of total sales over each of periods indicated above. Our success ratio when bidding on new contracts, was approximately 90% during the year ended December 31, 2008.
Cost of Goods Sold. Our cost of goods sold increased approximately $7.26 million, or 129.27%, to approximately $12.87 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, from approximately $5.61 million in 2007. This increase was mainly due to the increase in sales generally. As a percentage of revenues, the cost of goods sold decreased to 43.81% during the year ended December 31, 2008 from 47.30% in 2007, a result of the execution of higher margin contracts, which resulted in the increase in lower cost software component sales as a percentage of total sales during 2008.
The following table illustrates in detail the items constituting our costs of goods sold.
28
| Year ended | Year ended | |||||
| December | December | |||||
| Cost Item | 31, 2008 | 31, 2007 | ||||
| Salary | $ | 1,311,126 | $ | 771,700 | ||
| Hardware | 5,647,874 | 4,053,972 | ||||
| Software licenses | 1,494,675 | 250,174 | ||||
| Outsourcing | 3,618,116 | 245,743 | ||||
| Others | 795,467 | 290,783 | ||||
| Total | $ | 12,867,258 | $ | 5,612,372 |
Gross Profit. Our gross profit increased approximately $10.25 million, or 163.96%, to approximately $16.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, from approximately $6.25 million in 2007. Gross profit as a percentage of revenues was 56.19% for the year ended December 31, 2008, an increase of 3.49% from 52.70% in 2007. Our gross profit increase was mainly attributable to the increase of sales in 2008 in general. However, our gross profit increase outperformed our revenue increase from 2007 to 2008 by about 11.11%, which was mainly due to the higher increase in sales of Transportation business than that of Digital City business in 2008. Our Transportation business normally has higher margin software components as a percentage of total sales than Digital City business.
Selling Expenses. All of our products are sold into the domestic China market through contracts commissioned by the Chinese government. Various government entities and agencies either invite us to bid for a specific contract or award a contract to us on a no bid basis. This type of procurement process accounts for more than 70% of our total sales. We are often invited to bid on contracts through our professional relationships and are awarded repeat business. As a result, we have not invested heavily in establishing a substantial marketing program. We promote our products by developing relationships through Peking University, professional relationships with various agencies and municipalities within the Chinese government and in participation in industry trade exhibitions. Our marketing expenses therefore are relatively low in comparison to those of our competitors who do not have a record of performance and brand recognition or well-established government contacts.
Selling expenses, including sales representative commissions, promotion fees, salesperson salaries and expenses increased approximately $0.92 million, or 278.79%, to $1.25 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, from $0.33 million in 2007. As a percentage of revenues, selling expenses increased to 4.26% for the year ended December 31, 2008, from 2.74% in 2007. The increase of selling expenses was mainly attributable to our expanded operations and sales volume for the year ended December 31, 2008.
Administrative Expenses. Our administrative expenses were approximately $3.83 million (13.04% of total sales) and approximately $1.07 million (9.07% of total sales) for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. The increase of administrative expenses was mainly attributable to the increased staffing and more expenses associated with being a public company.
Income Taxes . Income Taxes . China TransInfo Technology Corp. is subject to the United States federal income tax at a tax rate of 34%. No provision for income taxes in the United States has been made as China TransInfo Technology Corp. had no United States taxable income in 2008 fiscal year.
Our wholly owned subsidiary Cabowise was incorporated in the BVI and, under the current laws of the BVI, is not subject to income taxes. Our wholly owned subsidiary Intra-Asia Entertainment Corporation (Delaware) was incorporated in Delaware. No provision for state income taxes in Delaware has been made as Intra-Asia Entertainment Corporation (Delaware) had no Delaware taxable income in 2008. Our wholly owned subsidiary Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited (Hong Kong) was incorporated in Hong Kong and, under the current laws of Hong Kong, is not subject to income taxes. Our wholly owned subsidiary Intra-Asia Entertainment (Asia-Pacific) Limited (Samoa) was incorporated in Samoa and, under the current laws of Samoa, is not subject to income taxes.
29
Our former Chinese operating subsidiaries enjoy certain special or preferential tax treatments regarding foreign enterprise income tax in accordance with the “Income Tax Law of the PRC for Enterprises with Foreign Investment and Foreign Enterprises” and its implementing rules. Accordingly, our former Chinese operating subsidiaries have been entitled to tax concessions whereby the profit for its first two financial years beginning with the first profit-making year (after setting off tax losses carried forward from prior years) is exempt from income tax in the PRC and the profit for each of the subsequent three financial years is taxed at 50% of the prevailing tax rates set by the relevant tax authorities. However, on March 16, 2007, the National People’s Congress of China passed the new Enterprise Income Tax Law (“EIT Law”), and on November 28, 2007, the State Council of China passed the Implementing Rules for the EIT Law (“Implementing Rules”), which took effect on January 1, 2008. The EIT Law and Implementing Rules impose a unified EIT of 25.0% on all domestic-invested enterprises and FIEs, unless they qualify under certain limited exceptions. Therefore, nearly all FIEs are subject to the new tax rate alongside other domestic businesses rather than benefiting from the FEIT, and its associated preferential tax treatments, beginning January 1, 2008.
Despite these changes, the EIT Law gives existing FIEs a five-year grandfather period during which they can continue to enjoy their existing preferential tax treatments. We are expecting that the measures to implement the grandfather period will be enacted by the Chinese government in the coming months and will assess what the impact of the new regulations are at that time. The discontinuation of any such special or preferential tax treatment or other incentives would have an adverse affect on any organization’s business, fiscal condition and current operations in China.
In addition to the changes to the current tax structure, under the EIT Law, an enterprise established outside of China with “de facto management bodies” within China is considered a resident enterprise and will normally be subject to an EIT of 25.0% on its global income. The Implementing Rules define the term “de facto management bodies” as “an establishment that exercises, in substance, overall management and control over the production, business, personnel, accounting, etc., of a Chinese enterprise.” If the PRC tax authorities subsequently determine that we should be classified as a resident enterprise, then the organization’s global income will be subject to PRC income tax of 25.0% .
Our VIE Entity, PKU, Zhangcheng Media, Xinjiang Zhangcheng, China TranWiseway, and Dajian Zhitong are subject to Chinese enterprises income tax (“EIT”), at a rate of 25% of the assessable profits. As approved by the local tax authority in the PRC, Beijing Tian Hao and Beijing Zhangcheng are entitled to a two-year exemption from EIT, commencing from the first cumulative profit-making year. Shanghai Yootu is subject to a special EIT at 2.5% of its taxable revenue in 2008. For the year ended December 31, 2007, we recognized income tax expense of $0.45 million while in 2008, we recognized an income tax expense of $0.06 million. All those tax expenses mainly resulted from the decrease in deferred tax assets during 2008.
Net Income . Net income increased approximately $6.67 million, or 150.85%, to $11.09 million in 2008 from approximately $4.42 million in 2007, as a result of the factors described above.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of December 31, 2008, we had cash and cash equivalents (excluding restricted cash) of approximately $16.12 million and restricted cash of approximately $1.21 million. The following table provides detailed information about our net cash flow for all financial statements periods presented in this report.
Cash Flow
| Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||
| December 31, | ||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 2,511,917 | $ | 85,543 | ||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | (10,401,836 | ) | 4,252,311 | |||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 16,870,614 | 1,049,289 | ||||
| Net cash inflow | 9,280,226 | 5,521,074 |
30
Operating Activities:
Net cash provided by operating activities was approximately $2.51 million in fiscal year ended December 31, 2008, which is an increase of approximately $2.42 million from approximately $0.09 million net cash provided by operating activities in fiscal year ended December 31, 2007. Such increase of net cash provided by operating activities was primarily attributable to the increase of our sales and net profit for 2008 compared to 2007. However, we experienced significant increase in cost and estimated earnings in excess of billings on uncompleted contracts in 2008 compared to 2007 mainly due to the fact that our working schedules were ahead of billings based on the payment terms of certain contracts, which negatively affected our cash flows from operations. We also experienced the increase in other receivable, which consists mainly of performance bonds that we put into escrow accounts set up by our customers for contract performance purposes. Such increases were in correlation to the increase of our sales and also negatively impacted our cash from operations. We also had increases in accounts receivable and accounts payable, which were mainly due to the increase of sales and business scale.
Investing Activities:
Our main uses of cash for investing activities are payments relating to the acquisition of property, plant and equipment.
Net cash used in investing activities was approximately $10.4 million in fiscal year 2008, a decrease of $14.65 million from the $4.25 million net cash provided by investing activities in fiscal year 2007. Such decrease of net cash provided by investing activities was primarily attributable to the purchases of GPS and LED screen equipment for our taxi media business as well as the acquisition of China TranWiseway, Dajian Zhitong and Shanghai Yootu during 2008.
Financing Activities
Net cash provided by financing activities for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008 was approximately $16.87 million, while in the same period of 2007 we had approximately $1.05 million net cash provided by financing activities. Such change was mainly attributable to the facts that we raised $15 million in the private placement transaction in July 2008 and borrowed approximately $2.93 million from a bank during 2008.
On June 17, 2008, we entered into a short-term loan agreement with Beijing Bank, Youyi Branch (the “Bank”), pursuant to which the Bank has agreed to loan to us RMB 20,000,000 (approximately $2,934,000) for purchase of its raw materials. The loan has an annual interest rate of 8.964% and the interests must be paid on a quarterly basis commencing September 20, 2008. The loan expires on June 17, 2009 but can be renewed upon the written consent by the Bank. Under the terms of the loan agreement, we are subject to customary affirmative and negative covenants. The loan may be accelerated and the Bank may demand immediate payment of the principal and accrued interests upon the occurrence of an event of default which include, among other things, a failure to make principal or interest payments, a failure to comply with other covenants and certain events of bankruptcy. As of the date of this report, we has an outstanding loan with a principal amount of $2.93 million borrowed from the Bank, which matures on June 17, 2009. There are no financial covenants or ratios under this short-term loan agreement.
On July 17, 2008, we completed a private placement pursuant to which we issued and sold 2,586,207 shares of our common stock to SAIF. As a result of this private placement we raised $15 million in gross proceeds, which left us with approximately $13.21 million in net proceeds after the deduction of offering expenses in the amount of approximately $1.79 million.
We believe that our current cash and cash equivalents and anticipated cash flow from operations will be sufficient to meet our anticipated cash needs, including our cash needs for working capital and capital expenditures for at least the next 12 months. We may, however, require additional cash due to changing business conditions or other future developments, including any investments or acquisitions we may decide to pursue. In addition, because substantially all of our revenues are generated from our indirect PRC subsidiary, Oriental Intra-Asia, after it receives payments from our VIE Entities under various services and other arrangements, the ability of Oriental Intra-Asia to make dividends and other payments to us is subject to the PRC dividend restrictions. Current PRC law permits payments of dividend by Oriental Intra-Asia only out of its accumulated after-tax profits, if any, determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations. Oriental Intra-Asia is also required under PRC laws and regulations to allocate at least 10% of its annual after-tax profits determined in accordance with PRC GAAP to a statutory general reserve fund until the amounts in said fund reaches 50% of Oriental Intra-Asia’s registered capital. Allocations to the statutory reserve fund can only be used for specific purposes and are not transferable to us in the form of loans, advances or cash dividends. As a result, if our existing cash and amount available under existing bank loans insufficient to meet our requirements, we may seek to sell additional equity securities, debt securities or borrow additional funds from lending institutions. We can make no assurances that financing will be available in the amounts we need or on terms acceptable to us, if at all. The sale of additional equity securities, including convertible debt securities, would dilute the interests of our current shareholders. The incurrence of debt would divert cash for working capital and capital expenditures to service debt obligations and could result in operating and financial covenants that restrict our operations and our ability to pay dividends to our shareholders. If we are unable to obtain additional equity or debt financing as required, our business operations and prospects may suffer.
31
Obligations Under Material Contracts
We have entered into a lease agreement with a Chinese individual, Zhao Li, for our rental of space at 07 Floor E-Wing Center, No. 113 Zhichunlu, Haidian District, Beijing, China. Under this lease, we have the right to use 517 square meters of office space in the E-Wing Center. We pay a total monthly rental of RMB 50,000 under this lease agreement (approximately $7,300). This lease expires on December 31, 2010. On June 2, 2007, we entered into a real property purchase agreement with Zhao Li, pursuant to which Mr. Zhao agreed to sell the facility to us for a purchase price of RMB 9,747,000 (approximately $1,429,885). We have paid $1,249,745 to Mr. Zhao as of December 31, 2008.
We also have two other lease agreements for our rental of spaces at the 15th and the 16th floor of E-Wing Center, No. 113 Zhichunlu, Haidian District, Beijing, China. Under these two leases, we have the rights to use 378 square meters of office space at the 15th floor and 609 square meters of office space at the 16th floor in the E-Wing Center, respectively. We pay monthly rentals of RMB 51,011 (approximately $7,447)and RMB 76,783 (approximately $11,209) under these two lease agreements, respectively. The leases expire on August 31, 2010 and March 30, 2011, respectively.
Critical Accounting Policies
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires our management to make assumptions, estimates and judgments that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements, including the notes thereto, and related disclosures of commitments and contingencies, if any. We consider our critical accounting policies to be those that require the more significant judgments and estimates in the preparation of financial statements, including the following:
Principles of Consolidation —The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company, it's wholly owned subsidiaries Intra-Asia Entertainment (Asia Pacific) Limited, Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited and Cabowise International Ltd., its indirectly owned subsidiaries Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited (“Oriental Intra-Asia”), Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. (“PKU”), Beijing Tian Hao Ding Xing Technology Co., Ltd. (“Beijing Tian Hao”), Beijing Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd. (“Beijing Zhangcheng”), Xingjiang Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd. (“Xingjiang Zhangcheng”), Beijing Zhangcheng Culture and Media Co., Ltd. (“Zhangcheng Media”), China TranWiseway Technology Co., Ltd. (“China TranWiseway”), Dalian Dajian Zhitong Information Service Ltd. (“Dajian Zhitong”), Shanghai Yootu Information Technology Co., Ltd. (“Shanghai Yootu”) and its variable interest entity China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd. (“Group Company”). All material intercompany accounts, transactions and profits have been eliminated in consolidation.
On February 3, 2009, the Company, through its indirect Chinese subsidiaries, Oriental Intra-Asia and PKU, entered into a series of equity transfer agreements with China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., or Group Company, a company incorporated under Chinese law, pursuant to which the Company transferred all of its indirect equity interests in PKU and PKU's subsidiaries to the Group Company. The main purpose of the restructuring is to allow the Company to engage in three new business segments, including online services, taxi advertising, and security and surveillance related business in China in which companies with foreign ownership, like the Company and its subsidiaries, are either prohibited or restricted from operating under the current applicable Chinese laws and regulations. Through the contractual or variable interest entity, or VIE, arrangements, the Company maintains substantial control over the VIE Entities' daily operations and financial affairs, election of their senior executives and all matters requiring shareholder approval. Furthermore, as the primary beneficiary of the VIE Entities, the Company is entitled to consolidate the financial results of the VIE Entities in its own consolidated financial statements under FASB Interpretation No. 46R "Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities" ("FIN 46R"). On November 17, 2008, Group Company made a capital contribution of RMB 40,000,000 or $5,868,000 on behalf of Oriental Intra-Asia under nominee agreement to PKU. To follow the Substance-Over-Form principle, all the transactions and events of Group Company’s have been included into the consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2008.
32
Use of Estimates —The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Significant estimates include accrued warranty costs, as well as revenue and costs recorded under the percentage-of-completion method. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash Equivalents —The Company classifies all highly liquid investments purchased with a maturity of three months or less as cash equivalents.
Accounts Receivable —Accounts receivable are carried at original invoice amount less an estimate for doubtful receivables based on a review of all outstanding amounts at year end. Management determines the allowance for doubtful accounts by using historical experience applied to an aging of accounts. Trade receivables are written off when deemed uncollectible. Recoveries of trade receivables previously written off are recorded when received. Allowance for doubtful accounts amounted to $32,439 as of December 31, 2008.
Property and Equipment —Property and equipment are recorded at cost, less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is provided for using straight-line methods over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets, usually three to seven years.
Revenue Recognition —Most of the Company’s revenues are on contracts recognized using the percentage-of-completion method, measured by the ratio of costs incurred to date to estimated total costs for each contract. Contract costs include all direct material and labor costs and those indirect costs related to contract performance, such as supplies and travels. General and administrative costs are charged to expense as incurred. Losses on contracts are recorded in full as they are identified.
We also have very limited system maintenance and technology upgrade services for the systems/platforms we have built for clients. In most cases, such service revenue were secured on separate contracts basis. Such service revenues are recognized ratably over the service periods.
During the year ended December 31, 2008, the Company offered limited taxi media advertising. For taxi media advertising revenue, the Company recognized deferred revenue when cash is received, but the revenue has not yet been earned. The Company recognized taxi media advertising revenue ratably over the period in which the advertising is to be published.
Research and Development —Research and development costs represent the costs of designing, developing and testing products and are expensed as selling, general and administrative expenses as incurred.
Share-Based Payments —The Company adopted Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No 123(R), “Share-Based Payments” (“SFAS No. 123R”) effective January 1, 2006. SFAS No. 123R amends existing accounting pronouncements for share-based payment transactions in which an enterprise receives employee and certain non-employee services in exchange for (a) equity instruments of the enterprise or (b) liabilities that are based on the fair value of the enterprise’s equity instruments or that may be settled by the issuance of such equity instruments. SFAS No.123R generally requires such transactions be accounted for using a fair-value-based method. The Company has never issued any stock options to any employees.
Income Taxes —Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective income tax bases. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. A valuation allowance is established against deferred tax assets if it is more likely than not that all, or some portion, of such assets will not be realized.
33
Effective January 1, 2007, we adopted Financial Accounting Standard Board (FASB) Interpretation No. 48 (FIN 48), Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes—an interpretation of FASB Statement No. 109 , Accounting for Income Taxes . FIN 48 prescribes a comprehensive model for how companies should recognize, measure, present, and disclose in their financial statements uncertain tax positions taken or expected to be taken on a tax return. Under FIN 48, tax positions are initially recognized in the financial statements when it is more likely than not the position will be sustained upon examination by the tax authorities. Such tax positions are initially and subsequently measured as the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than 50% likely of being realized upon ultimate settlement with the tax authority assuming full knowledge of the position and all relevant facts.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets —The Company adopts SFAS No. 144 "Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets". The Company periodically evaluates long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of an asset may not be recoverable. If the estimated future cash flows (undiscounted and without interest charges) from the use of an asset were less than the carrying value, a write-down would be recorded to reduce the related asset to its estimated fair value.
The assumptions used by management in determining the future cash flows are critical. In the event these expected cash flows are not realized, future impairment losses may be recorded. Management has determined that no impairments of long-lived assets currently exist.
Issuance of Shares by Subsidiaries— Sales of stock by a subsidiary is accounted for in accordance with Staff Accounting Bulletin Topic 5H, “Accounting for Sales of Stock by a Subsidiary.” The Company has adopted the capital transaction method to account for subsidiary stock sales. Accordingly, increases and decreases in the Company’s share of its subsidiary’s net equity resulting from subsidiary stock transactions are recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheets and Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity as increases or decreases to Additional paid-in capital.
Concentrations of Credit Risk —Financial instruments that subject the Company to credit risk consist primarily of accounts receivable, which are concentrated in a small number of customers in the Chinese governments. The Company performs ongoing credit evaluations of its customers. For the year ended December 31, 2008, bad debt expenses totaled RMB 219,012 or $31,571.
Statement of Cash Flows —In accordance with SFAS No. 95, "Statement of Cash Flows", cash flows from the Company's operations are based upon the local currencies. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the statement of cash flows will not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the balance sheet.
Translation Adjustment —The Renminbi ("RMB"), the national currency of the PRC, is the primary currency of the economic environment in which the operations of China IRAE are conducted. The Company uses the United States dollar ("U.S. dollars") for financial reporting purposes.
In accordance with SFAS No. 52, “ Foreign Currency Translation, ” the Company’s results of operations and cash flows are translated at the average exchange rates during the period, assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rates at the balance sheet dates, and equity is translated at the historical exchange rates. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the consolidated statements of cash flows will not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the consolidated balance sheets.
As of December 31, 2008 and 2007, the exchange rates between the RMB (¥) and the USD ($) were ¥ 1=$0.1467 and ¥ 1=$0.1371, respectively. The weighted-average rates of exchange between the RMB and the USD as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 were ¥ 1=$0.14415 and ¥ 1=$0.13167, respectively. Total translation adjustment recognized as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 is $2,499,893 and $887,184, respectively.
34
Comprehensive Income —Comprehensive income includes accumulated foreign currency translation gains and losses. The Company has reported the components of comprehensive income on its statements of stockholders’ equity.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments — The carrying amounts of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, deposits and accounts payable approximate their fair value because of the short maturity of those instruments. The carrying amounts of the Company's long-term debt approximate their fair value because of the short maturity and/or interest rates which are comparable to those currently available to the Company on obligations with similar terms.
Effects of Inflation
Inflation and changing prices have not had a material effect on our business and we do not expect that inflation or changing prices will materially affect our business in the foreseeable future. However, our management will closely monitor the price change and continually maintain effective cost control in operations.
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not have any off balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our financial condition, changes in financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity or capital expenditures or capital resources that is material to an investor in our securities.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In December 2007, the FASB issued SFAS 141R, “ Business Combinations - Revised 2007 ,” which replaces FASB Statement No. 141, “ Business Combinations .” SFAS 141R establishes principles and requirements intending to improve the relevance, representational faithfulness, and comparability of information that a reporting entity provides in its financial reports about a business combination and its effects. This is accomplished through requiring the acquirer to recognize assets acquired and liabilities assumed arising from contractual contingencies as of the acquisition date, measured at their acquisition-date fair values. This includes contractual contingencies only if it is more likely than not that they meet the definition of an asset of a liability in FASB Concepts Statement No. 6, “ Elements of Financial Statements - a replacement of FASB Concepts Statement No. 3. ” This statement also requires the acquirer to recognized goodwill as of the acquisition date, measured as a residual. However, this statement improves the way in which an acquirer’s obligations to make payments conditioned on the outcome of future events are recognized and measured, which in turn improves the measure of goodwill. This statement also defines a bargain purchases as a business combination in which the total acquisition-date fair value of the consideration transferred plus any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree, and it requires the acquirer to recognize that excess in earnings as a gain attributable to the acquirer. This therefore improves the representational faithfulness and completeness of the information provided about both the acquirer’s earnings during the period in which it makes a bargain purchase and the measures of the assets acquired in the bargain purchase. The Company does not expect the adoption of this pronouncement to have a material impact on its financial statements. The adoption of SFAS No. 141(R) changes our accounting treatment for business combinations on a prospective basis effective January 1, 2009. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of SFAS 141(R) on its financial statements.
In December 2007, the FASB issued SFAS No. 160, “ Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Stateme0147nts - an amendment of ARB No. 51, ” which establishes accounting and reporting standards to improve the relevance, comparability, and transparency of financial information in its consolidated financial statements. This is accomplished by requiring all entities, except not-for-profit organizations, that prepare consolidated financial statements to (a) clearly identify, label, and present ownership interests in subsidiaries held by parties other than the parent in the consolidated statement of financial position within equity, but separate from the parent’s equity, (b) clearly identify and present both the parent’s and the noncontrolling interest’s attributable consolidated net income on the face of the consolidated statement of income, (c) consistently account for changes in parent’s ownership interest while the parent retains it controlling financial interest in subsidiary and for all transactions that are economically similar to be accounted for similarly, (d) measure of any gain, loss or retained noncontrolling equity at fair value after a subsidiary is deconsolidated, and (e) provide sufficient disclosures that clearly identify and distinguish between the interests of the parent and the interests of the noncontrolling owners. This Statement also clarifies that a noncontrolling interest in a subsidiary is an ownership interest in the consolidated entity that should be reported as equity in the consolidated financial statements. SFAS No. 160 is effective for us on a prospective basis for business combinations with an acquisition date beginning as of January 1, 2009.
35
In April 2008, FASB issued FASB Staff Position (FSP) FAS 142-3, “Determination of the Useful Life of Intangible Assets,” to provide guidance for determining the useful life of recognized intangible assets and to improve consistency between the period of expected cash flows used to measure the fair value of a recognized intangible asset and the useful life of the intangible asset as determined under Statement 142. The FSP requires that an entity consider its own historical experience in renewing or extending similar arrangements. However, the entity must adjust that experience based on entity-specific factors under FASB Statement 142, Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets. FSP FAS 142-3 is effective January 1, 2009, and will be applied prospectively. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of FSP FAS 142-3 on its financial statements.
In June 2008, FASB ratified a consensus opinion reached by the Emerging Issues Task Force (EITF) on EITF Issue 08-4, “Transition Guidance for Conforming Changes to Issue No. 98-5,” to provide transition guidance for conforming changes made to the abstract for EITF Issue 98-5, “Accounting for Convertible Securities with Beneficial Conversion Features or Contingently Adjustable Conversion Ratios,” relating to EITF Issue 00-27, “Application of Issue No. 98-5 to Certain Convertible Instruments,” and FASB Statement 150, Accounting for Certain Financial Instruments with Characteristics of both Liabilities and Equity.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY FINANCIAL DATA
The full text of our audited consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 begins on page F-1 of this annual report.
36
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENTS SCHEDULES.
| (a) | The following documents are filed as part of this report: |
| (1) | Financial Statement are set forth beginning on page F-1 of the Report |
| • Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | F-2 | |
| • Consolidated Balance Sheets | F-3 – F-4 | |
| • Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income | F-5 | |
| • Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity | F-6 | |
| • Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | F-7 – F-8 | |
| • Notes to Consolidated Statements | F-9 - F-26 |
| (2) |
Financial Statement Schedules: All Schedules are omitted because the information called for is not applicable, is not required, or because the financial information is set forth in the financial statements or notes thereto. | |
| (3) | Exhibits |
Exhibits (including those incorporated by reference).
| Exhibit No. | Description |
| 2.1 |
Share Exchange Agreement, dated May 14, 2007, among the registrant, Cabowise International Ltd., its shareholders, Weicheng International Inc. and Foster Growth Ltd [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 3.1 |
Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of the registrant as filed with the Secretary of State of Nevada on December 19, 2003 [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 10-KSB filed on March 31, 2005]. |
| 3.2 |
Certificate of Amendment to Articles of Incorporation filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada on August 20, 2007. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on August 23, 2007]. |
| 3.3 |
Amended and Restated Bylaws of China TransInfo Technology Corp., adopted May 1, 2008. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008]. |
| 4.1 |
Form of Registration Rights Agreement, dated May 14, 2007 [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 4.2 |
Form of Lock-up Agreement, dated May 14, 2007 [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 4.3 |
Cancellation Agreement, dated May 14, 2007, among the registrant, Weicheng International Inc. and Forster Growth Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007] |
| 4.4 |
Option Agreement, dated April 30, 2007, among Cabowise International Ltd., and certain grantors. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 4.5 |
Registration Rights Agreement, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and SAIF Partners III L.P., dated July 17, 2008. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on July 18, 2008]. |
| 10.1 |
Form of Securities Purchase Agreement, dated May 14, 2007 [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
38
| 10.2 |
Form of Make Good Escrow Agreement, dated May 14, 2007 [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 10.3 |
Closing Escrow Agreement, dated May 14, 2007 , by and among the registrant, certain selling stockholders, Antaeus Capital, Inc. and Thelen Reid Brown Raysman & Steiner LLP [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 10.4 |
Lease Contract of E-Wing Center, dated November 25, 2004,. between Zhao Li and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 10.5 |
Standard Contracts with Employees - Labor Contract between employees and Beijing Jinzhengdong Human Resources Consultant Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 10.6 |
Labor Contract between Xia Shudong and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007].** |
| 10.7 |
Labor Contract between Huang Danxia and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007].** |
| 10.8 |
Labor Contract between Lai Zhibin and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007].** |
| 10.9 |
Labor Contract between Zhang Zhiping and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007].** |
| 10.10 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, dated May 14, 2007, between Xia Shudong, Zhang Zhiping, Lai Zhibin, Yang Chuang and Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.25 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 10.11 |
Real Property Purchase Agreement, dated June 2, 2007, between Mr. Zhao Li and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s quarterly report on Form 10-QSB filed on August 16, 2007]. |
| 10.12 |
Entrust Agreement, dated July 6, 2007, among Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited, Beijing Tiandi Zuobiao Technology Co., Ltd. and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.27 to the registrant’s Registration Statement on Form SB-2 on May 14, 2007.] |
| 10.13 |
Employment Agreement by and between China Trans Info Technology Corp. and Zhihai Mao, dated November 27, 2007. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on December 3, 2007].** |
| 10.14 |
Stock Option Agreement by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Zhihai Mao dated January 7, 2008. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on January 11, 2008].** |
| 10.15 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Independent Director’s Contract, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Jay Trien. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.16 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Independent Director’s Contract, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Zhongsu Chen. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.17 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Independent Director’s Contract, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Dan Liu. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.18 |
Indemnification Agreement, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Jay Trien. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.19 |
Indemnification Agreement, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Zhongsu Chen. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.20 |
Indemnification Agreement, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Dan Liu. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.21 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Stock Option Agreement, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Jay Trien. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
39
| 10.22 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Stock Option Agreement, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Zhongsu Chen. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.23 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, dated May 9, 2008, by and among Xu Wang, Tieying Zhao and PKU. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q filed on May 13, 2008]. |
| 10.24 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, dated May 22, 2008, by and among Beijing Marine Communication & Navigation Company, China TranWiseway Information Technology Co., Ltd. and Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 29, 2008]. |
| 10.25 |
Securities Purchase Agreement, by and among China TransInfo Technology Corp., Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and SAIF Partners III L.P., dated July 17, 2008. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on July 18, 2008]. |
| 10.26 |
Voting Agreement, by among China TransInfo Technology Corp., Karmen Investment Holdings Limited, Leguna Verde Investments Limited and SAIF Partners III L.P., dated July 17, 2008. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on July 18, 2008]. |
| 10.27 |
Loan Agreement, dated June 17, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Beijing Bank, Youyi Branch. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q filed on August 14, 2008]. |
| 10.28 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, dated September 16, 2008, by and among Beijing Zhangcheng Culture and Media Co., Ltd., Sun Jian, Xin Yibo and Zhu Juntao. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on September 19, 2008]. |
| 10.29 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Director Agreement, dated as of September 28, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Brandon Ho-Ping Lin. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 2, 2008].** |
| 10.30 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Director Agreement, dated as of September 28, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Dongyuan Yang. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 2, 2008].** |
| 10.31 |
Indemnification Agreement, dated as of September 28, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Brandon Ho-Ping Lin. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 2, 2008].** |
| 10.32 |
Indemnification Agreement, dated as of September 28, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Dongyuan Yang. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 2, 2008].** |
| 10.33 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Stock Option Agreement, dated as of September 28, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Brandon Ho-Ping Lin. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 2, 2008].** |
| 10.34 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, dated October 1, 2008, by and among Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and Qing Lu, Xiaohong Chen, Hangfei Lin, Gang Li, Jianzhong Zhang and Jieqing Guo. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.35 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, by and between Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited and China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.36 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, by and between Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.37 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, by and between Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.38 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, by and between Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.39 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, by and between Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
40
| 10.40 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, by and between Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.41 |
Exclusive Technical Development and Consulting Agreement, by and among Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited, China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing Tian Hao Ding Xin Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing Zhangcheng Culture and Media Co., Ltd., Beijing Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd., China TranWiseway Information Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai Yootu Information Technology Co., Ltd., Xinjiang Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd., and Dalian Dajian Zhitong Information Service Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.42 |
Equity Pledge Agreement, by and among Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited, Shudong Xia, Zhiping Zhang, Zhibin Lai and Wei Gao, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.43 |
Option Agreement, by and among Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited, Shudong Xia, Zhiping Zhang, Zhibin Lai and Wei Gao, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.44 |
Power of Attorney, signed by Shudong Xia, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.45 |
Power of Attorney, signed by Zhiping Zhang, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.46 |
Power of Attorney, signed by Zhibin Lai, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.47 |
Power of Attorney, signed by Wei Gao, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.48 |
Operating Agreement, by and among Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited, China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing Tian Hao Ding Xin Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing Zhangcheng Culture and Media Co., Ltd., Beijing Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd., China TranWiseway Information Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai Yootu Information Technology Co., Ltd., Xinjiang Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd., and Dalian Dajian Zhitong Information Service Co., Ltd., Shudong Xia, Zhiping Zhang, Zhibin Lai and Wei Gao, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.49 | Cooperation Agreement, dated August 6, 2006, between Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. and Earth and Space College, Peking University. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 14 |
Business Ethics Policy and Code of Conduct [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 14 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 21 |
Subsidiaries of the Company.*** |
| 23.1 |
Consent of Simon & Edwards, LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. * |
| 31.1 | |
| 31.2 | |
| 32.1 | |
| 32.2 |
* Filed herewith.
** Represents management contract or
compensatory plan or arrangement.
*** Previously filed.
41
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Company has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| China TransInfo Technology Corp. | |
| By: | /s/ Shudong Xia |
| Shudong Xia | |
| Chief Executive Officer | |
| Date: February 25, 2010 |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Company in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Capacity | Date | ||
| /s/ Shudong Xia | President and Chief Executive Officer | February 25, 2010 | ||
| Shudong Xia | (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
| /s/ Zhihai Mao | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial | February 25, 2010 | ||
| Zhihai Mao | Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) | |||
| * | Vice President | |||
| Zhibin Lai | ||||
| * | Vice President of Research and Development | |||
| Zhiping Zhang | ||||
| * | Vice President of Finance, Treasurer and | |||
| Danxia Huang | Director | |||
| * | Director | |||
| Jay Trien | ||||
| * | Director | |||
| Zhongsu Chen | ||||
| * | Director | |||
| Dan Liu | ||||
| * | Director | |||
| Brandon Ho-Ping Lin | ||||
| * | Director | |||
| Dongyuan Yang | ||||
| *By: /s/ Shudong Xia | February 25, 2010 | |||
| Attorney-in-fact |
42
EXHIBITS
| Exhibit No. | Description |
| 2.1 |
Share Exchange Agreement, dated May 14, 2007, among the registrant, Cabowise International Ltd., its shareholders, Weicheng International Inc. and Foster Growth Ltd [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 3.1 |
Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of the registrant as filed with the Secretary of State of Nevada on December 19, 2003 [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 10-KSB filed on March 31, 2005]. |
| 3.2 |
Certificate of Amendment to Articles of Incorporation filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Nevada on August 20, 2007. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on August 23, 2007]. |
| 3.3 |
Amended and Restated Bylaws of China TransInfo Technology Corp., adopted May 1, 2008. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008]. |
| 4.1 |
Form of Registration Rights Agreement, dated May 14, 2007 [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 4.2 |
Form of Lock-up Agreement, dated May 14, 2007 [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 4.3 |
Cancellation Agreement, dated May 14, 2007, among the registrant, Weicheng International Inc. and Forster Growth Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007] |
| 4.4 |
Option Agreement, dated April 30, 2007, among Cabowise International Ltd., and certain grantors. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 4.5 |
Registration Rights Agreement, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and SAIF Partners III L.P., dated July 17, 2008. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on July 18, 2008]. |
| 10.1 |
Form of Securities Purchase Agreement, dated May 14, 2007 [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 10.2 |
Form of Make Good Escrow Agreement, dated May 14, 2007 [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 10.3 |
Closing Escrow Agreement, dated May 14, 2007 , by and among the registrant, certain selling stockholders, Antaeus Capital, Inc. and Thelen Reid Brown Raysman & Steiner LLP [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 10.4 |
Lease Contract of E-Wing Center, dated November 25, 2004,. between Zhao Li and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 10.5 |
Standard Contracts with Employees - Labor Contract between employees and Beijing Jinzhengdong Human Resources Consultant Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 10.6 |
Labor Contract between Xia Shudong and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007].** |
| 10.7 |
Labor Contract between Huang Danxia and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007].** |
| 10.8 |
Labor Contract between Lai Zhibin and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007].** |
| 10.9 |
Labor Contract between Zhang Zhiping and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007].** |
43
| 10.10 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, dated May 14, 2007, between Xia Shudong, Zhang Zhiping, Lai Zhibin, Yang Chuang and Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.25 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 10.11 |
Real Property Purchase Agreement, dated June 2, 2007, between Mr. Zhao Li and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s quarterly report on Form 10-QSB filed on August 16, 2007]. |
| 10.12 |
Entrust Agreement, dated July 6, 2007, among Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited, Beijing Tiandi Zuobiao Technology Co., Ltd. and Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.27 to the registrant’s Registration Statement on Form SB-2 on May 14, 2007.] |
| 10.13 |
Employment Agreement by and between China Trans Info Technology Corp. and Zhihai Mao, dated November 27, 2007. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on December 3, 2007].** |
| 10.14 |
Stock Option Agreement by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Zhihai Mao dated January 7, 2008. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on January 11, 2008].** |
| 10.15 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Independent Director’s Contract, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Jay Trien. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.16 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Independent Director’s Contract, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Zhongsu Chen. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.17 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Independent Director’s Contract, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Dan Liu. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.18 |
Indemnification Agreement, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Jay Trien. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.19 |
Indemnification Agreement, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Zhongsu Chen. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.20 |
Indemnification Agreement, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Dan Liu. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.21 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Stock Option Agreement, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Jay Trien. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.22 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Stock Option Agreement, dated as of May 1, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Zhongsu Chen. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2008].** |
| 10.23 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, dated May 9, 2008, by and among Xu Wang, Tieying Zhao and PKU. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q filed on May 13, 2008]. |
| 10.24 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, dated May 22, 2008, by and among Beijing Marine Communication & Navigation Company, China TranWiseway Information Technology Co., Ltd. and Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 29, 2008]. |
| 10.25 |
Securities Purchase Agreement, by and among China TransInfo Technology Corp., Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and SAIF Partners III L.P., dated July 17, 2008. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on July 18, 2008]. |
| 10.26 |
Voting Agreement, by among China TransInfo Technology Corp., Karmen Investment Holdings Limited, Leguna Verde Investments Limited and SAIF Partners III L.P., dated July 17, 2008. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on July 18, 2008]. |
| 10.27 |
Loan Agreement, dated June 17, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Beijing Bank, Youyi Branch. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q filed on August 14, 2008]. |
44
| 10.28 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, dated September 16, 2008, by and among Beijing Zhangcheng Culture and Media Co., Ltd., Sun Jian, Xin Yibo and Zhu Juntao. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on September 19, 2008]. |
| 10.29 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Director Agreement, dated as of September 28, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Brandon Ho-Ping Lin. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 2, 2008].** |
| 10.30 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Director Agreement, dated as of September 28, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Dongyuan Yang. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 2, 2008].** |
| 10.31 |
Indemnification Agreement, dated as of September 28, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Brandon Ho-Ping Lin. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 2, 2008].** |
| 10.32 |
Indemnification Agreement, dated as of September 28, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Dongyuan Yang. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 2, 2008].** |
| 10.33 |
China TransInfo Technology Corp. Stock Option Agreement, dated as of September 28, 2008, by and between China TransInfo Technology Corp. and Brandon Ho-Ping Lin. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 2, 2008].** |
| 10.34 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, dated October 1, 2008, by and among Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and Qing Lu, Xiaohong Chen, Hangfei Lin, Gang Li, Jianzhong Zhang and Jieqing Guo. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.35 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, by and between Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited and China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.36 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, by and between Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.37 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, by and between Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.38 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, by and between Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.39 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, by and between Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.40 |
Equity Transfer Agreement, by and between Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. and China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.41 |
Exclusive Technical Development and Consulting Agreement, by and among Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited, China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing Tian Hao Ding Xin Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing Zhangcheng Culture and Media Co., Ltd., Beijing Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd., China TranWiseway Information Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai Yootu Information Technology Co., Ltd., Xinjiang Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd., and Dalian Dajian Zhitong Information Service Co., Ltd., dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.42 |
Equity Pledge Agreement, by and among Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited, Shudong Xia, Zhiping Zhang, Zhibin Lai and Wei Gao, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.43 |
Option Agreement, by and among Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited, Shudong Xia, Zhiping Zhang, Zhibin Lai and Wei Gao, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.44 |
Power of Attorney, signed by Shudong Xia, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
45
| 10.45 |
Power of Attorney, signed by Zhiping Zhang, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.46 |
Power of Attorney, signed by Zhibin Lai, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.47 |
Power of Attorney, signed by Wei Gao, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.48 |
Operating Agreement, by and among Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited, China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing Tian Hao Ding Xin Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing Zhangcheng Culture and Media Co., Ltd., Beijing Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd., China TranWiseway Information Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai Yootu Information Technology Co., Ltd., Xinjiang Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd., and Dalian Dajian Zhitong Information Service Co., Ltd., Shudong Xia, Zhiping Zhang, Zhibin Lai and Wei Gao, dated February 3, 2009. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on October 7, 2008]. |
| 10.49 | Cooperation Agreement, dated August 6, 2006, between Beijing PKU Chinafront Technology Co., Ltd. and Earth and Space College, Peking University. [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 14 |
Business Ethics Policy and Code of Conduct [Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 14 to the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2007]. |
| 21 |
Subsidiaries of the Company.*** |
| 23.1 |
Consent of Simon & Edwards, LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.* |
| 31.1 | |
| 31.2 | |
| 32.1 | |
| 32.2 |
* Filed herewith
** Represents management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
*** Previously filed.
46
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Page | |
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | F-2 |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets | F-3 – F-4 |
| Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income | F-5 |
| Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity | F-6 |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | F-7-F-8 |
| Notes to Consolidated Statements | F-9-F-26 |
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and
China TransInfo Technology
Corp.
Gentlemen:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of China TransInfo Technology Corp. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2008 and December 31, 2007. These consolidated consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of China TransInfo Technology Corp. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2008 and December 31, 2007 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
/s/ Simon & Edward, LLP
Simon & Edward, LLP
City of Industry, California
March 14, 2009
F-2
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| December 31, | ||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Current Assets: | ||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 16,122,464 | $ | 6,842,238 | ||
|
Restricted cash |
1,209,542 | 243,852 | ||||
|
Accounts receivable, net |
7,735,742 | 4,246,805 | ||||
|
Inventory |
23,775 | - | ||||
|
Cost and estimated earnings in excess of billings on uncompleted contracts |
11,912,285 | 2,659,969 | ||||
|
Prepayments |
3,647,731 | 2,328,289 | ||||
|
Other receivable |
2,940,404 | 1,038,329 | ||||
|
Deferred tax assets |
211,708 | 250,668 | ||||
|
Total current assets |
43,803,651 | 17,610,150 | ||||
| Long-term investment | 278,730 | 260,490 | ||||
| Property and equipment, net | 9,874,005 | 3,574,722 | ||||
| Intangible assets, net | 1,490,807 | - | ||||
| Goodwill | 3,095,017 | - | ||||
| Other non-current assets | 147,607 | - | ||||
| Total assets | $ | 58,689,817 | $ | 21,445,362 | ||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the financial statements.
F-3
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| December 31, | ||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY | ||||||
| Current Liabilities: | ||||||
|
Accounts payable |
$ | 5,518,402 | $ | 446,143 | ||
|
Notes payable |
2,934,000 | - | ||||
|
Due to related parties |
528,485 | - | ||||
|
Billings in excess of costs and estimated earnings on uncompleted contracts |
846,971 | 258,265 | ||||
|
Deferred revenue |
214,256 | - | ||||
|
Other payable and accrued liabilities |
1,030,766 | 389,432 | ||||
|
Total current liabilities |
11,072,880 | 1,093,840 | ||||
| Minority interest | 1,465,743 | 655,876 | ||||
| Stockholders' equity : | ||||||
|
Preferred stock, par value $0.001 per share, 10,000,000 shares authorized and 0 shares issued and outstanding |
- | - | ||||
|
Common stock, par value $0.001 per share, 150,000,000 shares authorized , 22,187,314 and 19,601,107 shares issued and outstanding, respectively |
22,187 | 19,601 | ||||
|
Additional paid-in capital |
24,654,890 | 10,905,114 | ||||
|
Retained earnings |
18,974,224 | 7,883,747 | ||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive gain - translation adjustments |
2,499,893 | 887,184 | ||||
| Total stockholders' equity | 46,151,194 | 19,695,646 | ||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $ | 58,689,817 | $ | 21,445,362 | ||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the financial statements.
F-4
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF
OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE
INCOME
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| Revenues | $ | 29,370,463 | $ | 11,864,629 | ||
| Cost of revenues | 12,867,258 | 5,612,372 | ||||
| Gross profit | 16,503,205 | 6,252,257 | ||||
| Operating Expenses: | 5,081,502 | 1,401,169 | ||||
| Income from operations | 11,421,703 | 4,851,088 | ||||
| Other income (expense): | ||||||
|
Interest income |
68,782 | 60,289 | ||||
|
Interest expense |
(135,120 | ) | (13,968 | ) | ||
|
Subsidy income |
530,100 | 146,058 | ||||
|
Decrease in fair value of warrant liability |
- | 64,359 | ||||
|
Other income - net |
32,170 | 160,446 | ||||
|
Total other income (expense) |
495,931 | 417,184 | ||||
| Net income before income taxes and minority interest | 11,917,634 | 5,268,272 | ||||
| Income tax expenses: | ||||||
|
Current |
5,201 | - | ||||
|
Deferred |
57,754 | 450,606 | ||||
|
Total income tax expense |
62,955 | 450,606 | ||||
| Minority interest | (764,201 | ) | (396,585 | ) | ||
| Net income | $ | 11,090,477 | $ | 4,421,080 | ||
|
Weighted average shares of outstanding - basic |
20,678,693 | 15,520,661 | ||||
|
|
||||||
|
Weighted average shares of outstanding- diluted |
20,883,951 | 15,698,439 | ||||
|
Income per share - |
||||||
|
basic |
$ | 0.54 | $ | 0.28 | ||
|
diluted |
$ | 0.53 | $ | 0.28 | ||
| Comprehensive income | ||||||
|
Net income |
$ | 11,090,477 | $ | 4,421,080 | ||
|
Translation adjustments |
1,612,709 | 672,414 | ||||
| Comprehensive income | $ | 12,703,186 | $ | 5,093,494 |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the financial statements.
F-5
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES
IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
| Common Stock | Additional Paid-In | Retained | Accumulated | Total | ||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Capital | Earnings | Gain | Equity | |||||||||||||
| Balance, January 1, 2006 | - | $ | - | $ | 2,416,000 | $ | 475,776 | $ | 52,484 | $ | 2,944,260 | |||||||
| Translation adjustments | 162,286 | 162,286 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net income for the year | 2,986,890 | 2,986,890 | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance, January 1, 2007 | - | - | 2,416,000 | 3,462,666 | 214,770 | 6,093,436 | ||||||||||||
| Conversion of convertible notes | 12,769 | 13 | 26,802 | 26,815 | ||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common shares for warrant converted cashlessly | 239,023 | 239 | (239 | ) | - | |||||||||||||
| Issuance of common shares to former directors | 40,000 | 40 | (40 | ) | - | |||||||||||||
| Cancelled 2,043,783 shares of common stock | (2,043,784 | ) | (2,044 | ) | 2,044 | - | ||||||||||||
| Recapitalization on reverse acquisition | 19,561,432 | 19,561 | 6,295,707 | 6,315,268 | ||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common shares | 1,777,778 | 1,778 | 3,198,222 | 3,200,000 | ||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common shares for services in connection with reverse merger | 13,889 | 14 | (14 | ) | - | |||||||||||||
| Issuance of warrant for services in connection with reverse merger | (1,104,166 | ) | (1,104,166 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Paid Transaction Cost debit to APIC | (1,492,361 | ) | (1,492,361 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Effect of subsidiary equity transactions | 323,247 | 323,247 | ||||||||||||||||
| Warrants issued for services valued at $5.0 per share | 200,105 | 200,105 | ||||||||||||||||
| Reclassification of warrant liability | 1,039,807 | 1,039,807 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net income for the year | 4,421,081 | 4,421,081 | ||||||||||||||||
| Translation adjustments | 672,414 | 672,414 | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance, January 1, 2008 | 19,601,107 | 19,601 | 10,905,114 | 7,883,747 | 887,184 | 19,695,646 | ||||||||||||
| Issuances of Common Stock | 2,586,207 | 2,586 | 14,997,414 | 15,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
| Paid Transaction Cost debit to APIC | (1,794,660 | ) | (1,794,660 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | 217,756 | 217,756 | ||||||||||||||||
| Effect of subsidiary equity transactions | 329,266 | 329,266 | ||||||||||||||||
| Translation adjustments | 1,612,709 | 1,612,709 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net income for the year | 11,090,477 | 11,090,477 | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2008 | 22,187,314 | $ | 22,187 | $ | 24,654,890 | $ | 18,974,224 | $ | 2,499,893 | $ | 46,151,194 | |||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the financial statements.
F-6
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||
| Net income | $ | 11,090,477 | $ | 4,421,081 | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization expenses | 200,746 | 41,915 | ||||
| Bad debt | 31,571 | - | ||||
|
Deferred income tax |
55,531 | 450,606 | ||||
|
Minority interest |
764,201 | 396,585 | ||||
|
Warrants issued for service |
- | 200,105 | ||||
|
Stock-based compensation |
217,756 | - | ||||
|
Loss on disposal of fixed assets |
11,747 | - | ||||
|
Change in fair value of warrant liability |
(64,359 | ) | ||||
|
(Increase) Decrease in assets: |
||||||
|
Restricted cash |
(932,126 | ) | (102,524 | ) | ||
|
Accounts receivable |
(2,634,838 | ) | (1,247,452 | ) | ||
|
Prepayments |
(1,035,964 | ) | (1,089,273 | ) | ||
|
Other receivable |
(1,852,411 | ) | (577,078 | ) | ||
|
Cost and estimated earnings in excess of billings on uncompleted contracts |
(8,088,233 | ) | (1,913,123 | ) | ||
|
Inventory |
185,993 | |||||
|
Other current assets |
234,892 | (129,788 | ) | |||
|
Decrease (Increase) in liabilities: |
||||||
|
Accounts (notes) payable |
4,471,898 | 261,572 | ||||
|
Billings in excess of costs and estimated earnings on uncompleted contracts |
(613,988 | ) | (96,324 | ) | ||
|
Customer deposits |
66,382 | - | ||||
|
Other payable and accrued liabilities |
338,283 | (466,400 | ) | |||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 2,511,917 | 85,543 |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the financial statements.
F-7
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||
|
Cash from acquisitions |
$ | 294,872 | $ | 9,199,660 | ||
|
(Increase) Decrease in loan to others |
- | 277,297 | ||||
|
Payment of cash to the shareholders of the accounting acquirer |
- | (2,000,000 | ) | |||
|
(Increase) Decrease in other non-current assets |
(147,489 | ) | 12,018 | |||
|
Proceeds from disposal of fixed assets |
26,072 | - | ||||
|
Purchases of fixed assets |
(6,037,957 | ) | (3,236,664 | ) | ||
|
Purchases of intangible assets and goodwill |
(4,537,334 | ) | - | |||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | (10,401,836 | ) | 4,252,311 | |||
| Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||
|
Increase in due to related parties |
441,737 | - | ||||
|
Proceeds from (payments of) short-term borrowings |
2,883,000 | (658,350 | ) | |||
|
Net change in minority interests |
300,775 | - | ||||
|
Payable for acquiring subsidiary |
86,490 | - | ||||
|
Payments to related parties |
(190,878 | ) | - | |||
|
Increase in customer deposit |
144,150 | - | ||||
|
Merger (issuance) costs to be charged directly to equity |
(1,794,660 | ) | (1,492,361 | ) | ||
|
Proceeds from issuing shares |
15,000,000 | 3,200,000 | ||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 16,870,614 | 1,049,289 | ||||
| Effect of foreign currency exchange translation | 299,531 | 133,931 | ||||
| Net increase in cash | 9,280,226 | 5,521,074 | ||||
| Cash - beginning | 6,842,238 | 1,321,164 | ||||
| Cash - ending | $ | 16,122,464 | $ | 6,842,238 | ||
| Supplemental disclosures: | ||||||
|
Interest paid |
$ | 135,120 | $ | 13,986 | ||
|
|
||||||
|
Income taxes paid |
$ | 847 | $ | - |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the financial statements.
F-8
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER
31, 2008
1. GENERAL AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Organization and Description of Business —China TransInfo Technology Corp. (the “Company”) was originally incorporated in Nevada on August 3, 1998, under the name R & R Ranching, Inc. to breed bison. In about March 2003, R & R Ranching Inc. sold its bison to Blue Sky Bison Ranch, Ltd.
The Company has experienced several corporate name changes: GloTech Industries, Inc. in March 2003, Intra-Asia Entertainment Corporation in December 2003, China TransInfo Technology Corp. in August 2007.
On May 14, 2007, the Company entered into a share exchange agreement with Cabowise International Ltd. (“Cabowise”), a British Virgin Islands company, the stockholders of Cabowise, Weicheng International Inc. and Foster Growth Ltd. Pursuant to the share exchange agreement, the Company, among other things, agreed to issue to the stockholders of Cabowise an aggregate of 10,841,491 shares of its common stock in exchange for all of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Cabowise. In addition, Cabowise agreed to assign its option to purchase a majority equity interest in Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd (“PKU”) to the Company’s indirect Chinese subsidiary Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited (“Oriental Intra-Asia”).
Cabowise does not have any subsidiaries nor is it engaged in any business. Cabowise’s sole asset was its option to purchase an eighty-five percent (85%) interest in PKU (the “PKU Option”). Pursuant to the share exchange agreement, Cabowise agreed to assign the PKU Option to Oriental Intra-Asia. On May 14, 2007, Cabowise, the Company and Oriental Intra-Asia entered into an assignment and assumption agreement whereby Cabowise assigned the PKU Option to Oriental Intra-Asia. On May 14, 2007, Oriental Intra-Asia exercised the PKU Option, and Oriental Intra-Asia became the owner of an eighty-five percent (85%) equity interest in PKU.
The exchange of shares has been accounted for as a reverse acquisition under the purchase method of accounting since the shareholders of the PKU obtained control of the consolidated entity. Accordingly, the merger of the two companies has been recorded as a recapitalization of PKU, with PKU being treated as the continuing entity. The historical financial statements presented are those of PKU. The continuing company has retained December 31 as its fiscal year end.
During August 2007, the Company completed a 1-for-7.5 reverse split of all issued and outstanding shares of common stock. The capital stock accounts and all share data in this report give effect to the reverse split, applied retroactively, for all periods presented.
PKU is in the business of providing Geography Information System (GIS) application services to the Chinese governments in the sectors of Transportation, Land and Resources, and D igital City. PKU offers GIS application services that cover GIS system planning, deployment, system construction, data testing, system audit and optimization, user’s manual and customer training, through self-developed GIS platform software products applicable for two-dimension and three-dimension system models. PKU was incorporated in Beijing, China on October 30, 2000.
Beijing Tian Hao Ding Xing Technology Co., Ltd. (“Beijing Tian Hao”) is engaged in the business of GIS application research and development. Beijing Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd. (“Beijing Zhangcheng”) was established on October 12, 2007 with registered capital of RMB 10 million. Beijing Zhangcheng Science is engaged in the business of GIS application development for real time traffic information reporting. Beijing Zhangcheng Culture and Media Co., Ltd. (“Zhangcheng Media”) was set up on June 3, 2008 with registered capital of RMB 5 million ,Beijing Zhangcheng Media is mainly engaged in taxi media advertising business. Shanghai Yootu Information Technology Co., Ltd. (“Shanghai Yootu”) was established on February 6, 2007 with registered capital of RMB 2 million, Yootu is engaged in the business of real time traffic data application research and development. Xingjiang Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd. (“Xingjiang Zhangcheng”) was established on January 25, 2008 with registered capital of RMB 10 million.
F-9
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER
31, 2008
1. GENERAL AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES – continued
Xinjiang Zhangcheng is mainly engaged in taxi media advertising business. China TranWiseway Technology Co., Ltd. (“China TranWiseway”) was established on June 28, 2004 with registered capital of RMB 10 million. China TranWiseway is engaged in the business of traffic surveying technology applications. Dalian Dajian Zhitong Infomration Service Ltd. (“Dajian Zhitong”) was established on June 9, 2006 with registered capital of RMB 10 million. Dajian Zhitong is mainly engaged in taxi media advertising business.
Principles of Consolidation —The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company, it's wholly owned subsidiaries Intra-Asia Entertainment (Asia Pacific) Limited, Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited and Cabowise International Ltd., its indirectly owned subsidiaries Oriental Intra-Asia Entertainment (China) Limited (“Oriental Intra-Asia”), Beijing PKU Chinafront High Technology Co., Ltd. (“PKU”), Beijing Tian Hao Ding Xing Technology Co., Ltd. (“Beijing Tian Hao”), Beijing Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd. (“Beijing Zhangcheng”), Xingjiang Zhangcheng Science and Technology Co., Ltd. (“Xingjiang Zhangcheng”), Beijing Zhangcheng Culture and Media Co., Ltd. (“Zhangcheng Media”), China TranWiseway Technology Co., Ltd. (“China TranWiseway”), Dalian Dajian Zhitong Information Service Ltd. (“Dajian Zhitong”), Shanghai Yootu Information Technology Co., Ltd. (“Shanghai Yootu”) and its variable interest entity China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd. (“Group Company”). All material intercompany accounts, transactions and profits have been eliminated in consolidation.
On February 3, 2009, the Company, through its indirect Chinese subsidiaries, Oriental Intra-Asia and PKU, entered into a series of equity transfer agreements with China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., or Group Company, a company incorporated under Chinese law, pursuant to which the Company transferred all of its indirect equity interests in PKU and PKU's subsidiaries to the Group Company. The main purpose of the restructuring is to allow the Company to engage in three new business segments, including online services, taxi advertising, and security and surveillance related business in China in which companies with foreign ownership, like the Company and its subsidiaries, are either prohibited or restricted from operating under the current applicable Chinese laws and regulations. Through the contractual or variable interest entity, or VIE, arrangements, the Company maintains substantial control over the VIE Entities' daily operations and financial affairs, election of their senior executives and all matters requiring shareholder approval. Furthermore, as the primary beneficiary of the VIE Entities, the Company is entitled to consolidate the financial results of the VIE Entities in its own consolidated financial statements under FASB Interpretation No. 46R "Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities" ("FIN 46R"). On November 17, 2008, Group Company made a capital contribution of RMB 40,000,000 or $5,868,000 on behalf of Oriental Intra-Asia under nominee agreement to PKU. To follow the Substance-Over-Form principle, all the transactions and events of Group Company’s have been consolidated to the consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2008.
Use of Estimates —The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Significant estimates include accrued warranty costs, as well as revenue and costs recorded under the percentage-of-completion method. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash Equivalents —The Company classifies all highly liquid investments purchased with a maturity of three months or less as cash equivalents.
Accounts Receivable —Accounts receivable are carried at original invoice amount less an estimate for doubtful receivables based on a review of all outstanding amounts at year end. Management determines the allowance for doubtful accounts by using historical experience applied to an aging of accounts. Trade receivables are written off when deemed uncollectible. Recoveries of trade receivables previously written off are recorded when received. Allowance for doubtful accounts amounted to $32,439 as of December 31, 2008.
Property and Equipment —Property and equipment are recorded at cost, less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is provided for using straight-line methods over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets, usually three to seven years.
F-10
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER
31, 2008
1. GENERAL AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES - continued
Revenue Recognition —Most of the Company’s revenues are on contracts recognized using the percentage-of-completion method, measured by the ratio of costs incurred to date to estimated total costs for each contract. Contract costs include all direct material and labor costs and those indirect costs related to contract performance, such as supplies and travels. General and administrative costs are charged to expense as incurred. Losses on contracts are recorded in full as they are identified.
We also have very limited system maintenance and technology upgrade services for the systems/platforms we have built for clients. In most cases, such service revenue were secured on separate contracts basis. Such service revenues are recognized ratably over the service periods.
During the year ended December 31, 2008, the Company offered limited taxi media advertising. For taxi media advertising revenue, the Company recognized deferred revenue when cash is received, but the revenue has not yet been earned. The Company recognized taxi media advertising revenue ratably over the period in which the advertising is to be published.
Research and Development —Research and development costs represent the costs of designing, developing and testing products and are expensed as selling, general and administrative expenses as incurred.
Share-Based Payments —The Company adopted Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No 123(R), “Share-Based Payments” (“SFAS No. 123R”) effective January 1, 2006. SFAS No. 123R amends existing accounting pronouncements for share-based payment transactions in which an enterprise receives employee and certain non-employee services in exchange for (a) equity instruments of the enterprise or (b) liabilities that are based on the fair value of the enterprise’s equity instruments or that may be settled by the issuance of such equity instruments. SFAS No.123R generally requires such transactions be accounted for using a fair-value-based method. The Company has never issued any stock options to any employees.
Income Taxes —Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective income tax bases. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. A valuation allowance is established against deferred tax assets if it is more likely than not that all, or some portion, of such assets will not be realized.
Effective January 1, 2007, we adopted Financial Accounting Standard Board (FASB) Interpretation No. 48 (FIN 48), Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes—an interpretation of FASB Statement No. 109 ,
Accounting for Income Taxes . FIN 48 prescribes a comprehensive model for how companies should recognize, measure, present, and disclose in their financial statements uncertain tax positions taken or expected to be taken on a tax return. Under FIN 48, tax positions are initially recognized in the financial statements when it is more likely than not the position will be sustained upon examination by the tax authorities. Such tax positions are initially and subsequently measured as the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than 50% likely of being realized upon ultimate settlement with the tax authority assuming full knowledge of the position and all relevant facts.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets —The Company adopts SFAS No. 144 "Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets". The Company periodically evaluates long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of an asset may not be recoverable. If the estimated future cash flows (undiscounted and without interest charges) from the use of an asset were less than the carrying value, a write-down would be recorded to reduce the related asset to its estimated fair value.
The assumptions used by management in determining the future cash flows are critical. In the event these expected cash flows are not realized, future impairment losses may be recorded. Management has determined that no impairments of long-lived assets currently exist.
F-11
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER
31, 2008
1. GENERAL AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES – continued
Issuance of Shares by Subsidiaries— Sales of stock by a subsidiary is accounted for in accordance with Staff Accounting Bulletin Topic 5H, “Accounting for Sales of Stock by a Subsidiary.” The Company has adopted the capital transaction method to account for subsidiary stock sales. Accordingly, increases and decreases in the Company’s share of its subsidiary’s net equity resulting from subsidiary stock transactions are recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheets and Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity as increases or decreases to Additional paid-in capital.
Concentrations of Credit Risk —Financial instruments that subject the Company to credit risk consist primarily of accounts receivable, which are concentrated in a small number of customers in the Chinese governments. The Company performs ongoing credit evaluations of its customers. For the year ended December 31, 2008, bad debt expenses totaled RMB 219,012 or $31,571.
Statement of Cash Flows —In accordance with SFAS No. 95, "Statement of Cash Flows", cash flows from the Company's operations are based upon the local currencies. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the statement of cash flows will not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the balance sheet.
Translation Adjustment —The Renminbi ("RMB"), the national currency of the PRC, is the primary currency of the economic environment in which the operations of China IRAE are conducted. The Company uses the United States dollar ("U.S. dollars") for financial reporting purposes.
In accordance with SFAS No. 52, “ Foreign Currency Translation, ” the Company’s results of operations and cash flows are translated at the average exchange rates during the period, assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rates at the balance sheet dates, and equity is translated at the historical exchange rates. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the consolidated statements of cash flows will not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the consolidated balance sheets.
As of December 31, 2008 and 2007, the exchange rates between the RMB ( ¥ ) and the USD ($) were ¥ 1=$0.1467 and ¥ 1=$0.1371, respectively. The weighted-average rates of exchange between the RMB and the USD as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 were ¥ 1=$0.14415 and ¥ 1=$0.13167, respectively. Total translation adjustment recognized as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 is $2,499,893 and $887,184, respectively.
Comprehensive Income —Comprehensive income includes accumulated foreign currency translation gains and losses. The Company has reported the components of comprehensive income on its statements of stockholders’ equity.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments — The carrying amounts of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, deposits and accounts payable approximate their fair value because of the short maturity of those instruments.
The carrying amounts of the Company's long-term debt approximate their fair value because of the short maturity and/or interest rates which are comparable to those currently available to the Company on obligations with similar terms.
F-12
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER
31, 2008
1. GENERAL AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES – continued
New Accounting Pronouncements
In December 2007, the FASB issued SFAS 141R, “ Business Combinations - Revised 2007 ,” which replaces FASB Statement No. 141, “ Business Combinations .” SFAS 141R establishes principles and requirements intending to improve the relevance, representational faithfulness, and comparability of information that a reporting entity provides in its financial reports about a business combination and its effects. This is accomplished through requiring the acquirer to recognize assets acquired and liabilities assumed arising from contractual contingencies as of the acquisition date, measured at their acquisition-date fair values. This includes contractual contingencies only if it is more likely than not that they meet the definition of an asset of a liability in FASB Concepts Statement No. 6, “ Elements of Financial Statements - a replacement of FASB Concepts Statement No. 3. ” This statement also requires the acquirer to recognized goodwill as of the acquisition date, measured as a residual. However, this statement improves the way in which an acquirer’s obligations to make payments conditioned on the outcome of future events are recognized and measured, which in turn improves the measure of goodwill. This statement also defines a bargain purchases as a business combination in which the total acquisition-date fair value of the consideration transferred plus any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree, and it requires the acquirer to recognize that excess in earnings as a gain attributable to the acquirer. This therefore improves the representational faithfulness and completeness of the information provided about both the acquirer’s earnings during the period in which it makes a bargain purchase and the measures of the assets acquired in the bargain purchase. The Company does not expect the adoption of this pronouncement to have a material impact on its financial statements. The adoption of SFAS No. 141(R) changes our accounting treatment for business combinations on a prospective basis effective January 1, 2009.
In December 2007, the FASB issued SFAS No. 160, “ Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Stateme0147nts - an amendment of ARB No. 51, ” which establishes accounting and reporting standards to improve the relevance, comparability, and transparency of financial information in its consolidated financial statements. This is accomplished by requiring all entities, except not-for-profit organizations, that prepare consolidated financial statements to (a) clearly identify, label, and present ownership interests in subsidiaries held by parties other than the parent in the consolidated statement of financial position within equity, but separate from the parent’s equity, (b) clearly identify and present both the parent’s and the noncontrolling interest’s attributable consolidated net income on the face of the consolidated statement of income, (c) consistently account for changes in parent’s ownership interest while the parent retains it controlling financial interest in subsidiary and for all transactions that are economically similar to be accounted for similarly, (d) measure of any gain, loss or retained noncontrolling equity at fair value after a subsidiary is deconsolidated, and (e) provide sufficient disclosures that clearly identify and distinguish between the interests of the parent and the interests of the noncontrolling owners. This Statement also clarifies that a noncontrolling interest in a subsidiary is an ownership interest in the consolidated entity that should be reported as equity in the consolidated financial statements. SFAS No. 160 is effective for annual and interim periods beginning on or after December 15, 2008. The statement is to be applied prospectively. However, if comparative statements are issued, the presentation and disclosures should be presented retrospectively for all periods presented only after the adoption of the standard.
In April 2008, FASB issued FASB Staff Position (FSP) FAS 142-3, “Determination of the Useful Life of Intangible Assets,” to provide guidance for determining the useful life of recognized intangible assets and to improve consistency between the period of expected cash flows used to measure the fair value of a recognized intangible asset and the useful life of the intangible asset as determined under Statement 142. The FSP requires that an entity consider its own historical experience in renewing or extending similar arrangements. However, the entity must adjust that experience based on entity-specific factors under FASB Statement 142, Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets. FSP FAS 142-3 is effective January 1, 2009, and will be applied prospectively. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of FSP FAS 142-3 on its financial statements.
In June 2008, FASB ratified a consensus opinion reached by the Emerging Issues Task Force (EITF) on EITF Issue 08-4, “Transition Guidance for Conforming Changes to Issue No. 98-5,” to provide transition guidance for conforming changes made to the abstract for EITF Issue 98-5, “Accounting for Convertible Securities with Beneficial Conversion Features or Contingently Adjustable Conversion Ratios,” relating to EITF Issue 00-27, “Application of Issue No. 98-5 to Certain Convertible Instruments,” and FASB Statement 150, Accounting for Certain Financial Instruments with Characteristics of both Liabilities and Equity.
F-13
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2008
2. RESTRICTED CASH
The Company’s restricted cash balances at December 31, 2008 and 2007 were as follows:
| Exchange | ||||||||||||
| Entity | RMB | Rate | USD | Restriction | ||||||||
| December 31, 2007: | ||||||||||||
| PKU | ¥ | 1,778,640 | 0.1371 | $ | 243,852 | To facilitate Fund Verification Letters | ||||||
| Total | ¥ | 1,778,640 | $ | 243,852 | ||||||||
| December 31, 2008: | ||||||||||||
| PKU | ¥ | 1,245,000 | 0.1467 | $ | 182,642 | To facilitate Banker's Acceptances | ||||||
| China TranWiseway | 7,000,000 | 0.1467 | 1,026,900 | To facilitate Capital Verification | ||||||||
| Total | ¥ | 8,245,000 | $ | 1,209,542 |
During the fourth quarter of 2008, PKU deposited ¥ 1,245,000, or $182,642 in one of its banks to facilitate bank acceptance letters issued by the bank to the Company’s customers. Such letters are a contractual term requested by the customers and are valid for 3 months. During the same quarter, China TranWiseway deposited with ¥ 7,000,000, or $1,026,900 in one its bank to facilitate its capital verification for contributed capital increase purpose required by local authority. The restriction is expected to expire during the first quarter of 2009.
3. COSTS AND ESTIMATED EARNINGS ON UNCOMPLETED CONTRACTS The costs and estimated earnings on uncompleted contracts were as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| Costs incurred on uncompleted contracts | $ | 16,464,203 | $ | 4,147,244 | ||
| Estimated earnings on uncompleted contracts | 20,749,561 | 7,500,636 | ||||
| 37,213,764 | 11,647,880 | |||||
| Less: billings to date | 26,148,450 | 9,246,176 | ||||
| Total | $ | 11,065,314 | $ | 2,401,704 | ||
The costs and estimated earnings on uncompleted contracts are included in the accompanying balance sheets under the following captions:
F-14
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER
31, 2008
3. COSTS AND ESTIMATED EARNINGS ON UNCOMPLETED CONTRACTS - continued
| December 31, | ||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| Costs and estimated earnings in excess of billings on uncompleted contracts | $ | 11,912,285 | $ | 2,659,969 | ||
| Billings in excess of costs and estimated earnings on uncompleted contracts | -846,971 | -258,265 | ||||
| Total | $ | 11,065,314 | $ | 2,401,704 | ||
4. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
The following is a summary of the Company’s property and equipment:
| December 31, | ||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| Automobiles | $ | 454,659 | $ | 125,929 | ||
| Machinery and equipments | 5,640,958 | 422,056 | ||||
| Furniture and fixtures | 147,957 | 40,939 | ||||
| Prepayment for building | 1,249,745 | 864,285 | ||||
| Work-in-progress | 2,676,864 | 2,279,616 | ||||
| 10,170,183 | 3,732,825 | |||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation | (296,178 | ) | -158,103 | |||
| Property and equipment, net | $ | 9,874,005 | $ | 3,574,722 | ||
On June 2, 2007, the Company entered into an agreement to purchase an office building for approximately $1,336,000. As of December 31, 2008 and 2007, the Company’s prepayments totaled $1,249,745 and $864,285, respectively.
The Company entered an agreement with Taxi Association of City of Urumqi for installation of a global positioning system ("GPS") control system. Pursuant to the agreement, the Company will install GPS Control Terminals on the 5,220 rental and taxi cars in the city of Urumqi in exchange for rights of interior or exterior advertisements on each taxi’s rear window, top light (LED display) and interior. According to the agreement, the Company began to operate the system on October 1, 2007 for a period of 15 years. Costs incurred for installed terminals that have been inspected and accepted were recorded as Machinery and Equipment and depreciated over a 7-year period. Costs incurred for uninstalled terminals and installed terminals that have not been inspected and accepted as work-in-progress.
F-15
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2008
4. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT - Continued
In addition, on March 31, 2008, the Company signed the "Agreement for Installation of Taxi GPS Monitoring System" with the Urumqi City Transportation Bureau (the “Transportation Bureau”), which is the higher management authority of the Taxi Association of City of Urumqi. The agreement reconfirmed the Company’s responsibility for providing to the Transportation Bureau's Passenger Transport Office with equipment for LED-based GPS monitoring, network hardware, GPS monitoring platform, and LED-based information release platform and software in exchange for the 15 years’ taxi advertising rights. The Transportation Bureau further guarantees that the Company will be its exclusive cooperation partner for a period of 15 years. No changes related to this guaranty will be made during the 15-year period.
The Company signed a contract jointly with the Huhhot Comprehensive Traffic Information Center and the Huhhot Department of Transportation Administration on January 28, 2008 to exclusively invest in and construct the LED stripe screen advertisement broadcasting system for taxis (LSABS) in the city of Huhhot. The contract is for a period of 15 years, and the Company will provide funding for LED strip screens and taxi rooftop light alterations to construct the city’s Taxi Advertising and Information Release System. Costs incurred for installed terminals that have been inspected and accepted were recorded as Machinery and Equipment and depreciated over a 7-year period. Costs incurred for uninstalled terminals and installed terminals that have not been inspected and accepted were recorded as Work-in-progress.
Depreciation and amortization expenses during fiscal 2008 and 2007 were $200,746 (of which $22,651 was related to intangible assets), and $41,915, respectively.
5. INTANGIBLE ASSETS
The Company’s intangible assets as of December 31, 2008 are summarized as follows:
| Existing technology | $ | 174,573 | |
| Core technology | 1,339,061 | ||
| Less: accumulated amortization | (22,827 | ) | |
| Total | $ | 1,490,807 |
(1) Existing Technology
China TranWiseway, the Company’s indirect 70% owned subsidiary, internally developed the Traffic Volume Long-Distance Monitoring and Data Center Platform technology. The useful life of the technology is estimated at 10 years.
(2) Core Technology
In 2008, the Company purchased software from a third party for total cash consideration of $752,669. This software was integrated into an Electrical Toll collection (“ETC”) non-stop toll system. The Company plans to distribute fully integrated ETC systems with both hardware and software included. Amortization of the ETC technology started during the fourth quarter of 2008 when the ETC system was ready for commercial applications. The useful life of the technology is estimated at 10 years.
In 2008, Beijing Zhangcheng capitalized research and development costs of $586,392 after establishing technical feasibilities for its real time traffic information application software. Amortization of the real time traffic information technology will not start until the application is completely developed, which is expected during the first quarter of 2009.
F-16
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER
31, 2008
6. GOODWILL
The Company has recorded approximately ¥ 6,703,104, or $983,345, ¥ 1,293,441, or $189,748, and ¥ 13,101,047 or $1,921,924 in goodwill in connection with its acquisitions (see Note 9) of equity of China TranWiseway, Dajian Zhitong, and Shanghai Yootu, respectively.
In accordance with the provisions of SFAS No. 142, "Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets", the Company performed the goodwill impairment tests. The results of the tests indicated that no impairment loss was probable because the implied fair value of goodwill related to the equity purchased exceeded the book value of the goodwill. The Company performs its annual impairment test as of the last day of the fiscal year. These impairment tests must be performed more frequently if there are triggering events.
7. NOTE PAYABLE
On June 17, 2008, the Company entered a loan agreement with a commercial bank in the amount of RMB 20,000,000, or $2,934,000. The loan bears an interest rate of 8.964% per annum. The agreement expires on June 17, 2009. For the year ended December 31, 2008, interest expense on the loan totaled RMB 937,359, or $135,120.
8. ACQUISITIONS OF SUBSIDIARIES
(1) China TranWiseway
In May 2008, PKU entered into equity transfer agreements with shareholders of China TranWiseway, pursuant to which, PKU acquired 70% ownership of China TranWiseway for a cash price of RMB 6,500,000 (approximately $953,550). China TranWiseway is a high-tech company specializing in transportation information system and application developments. On May 22, 2008, PKU entered into an agreement supplemental to the aforementioned equity transfer agreements. Pursuant to the supplemental agreement, PKU will make an additional capital contribution of RMB 7,000,000 (approximately $1,026,900) to China TranWiseway to increase the total registered capital to RMB 10,000,000 (approximately $1,467,000), and PKU’s ownership remains at 70%. The purchase price of the 70% ownership in China TranWiseway therefore was RMB 8,600,000, or $1,261,620. As of December 31, 2008, the RMB 7,000,000 has been remitted to China TranWiseway.
In accordance with SFAS No. 141, Business Combinations (“SFAS No. 141”), the acquisition was accounted for under the purchase method of accounting. Accordingly, the results of China TranWiseway have been included in the accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements since the date of acquisition. The purchase price has been allocated to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based upon their estimated fair values and the price was allocated as follows:
| Currency | |||||||||
| Exchange | |||||||||
| In RMB | Rate | In USD | |||||||
| Net tangible assets | ¥ | 706,896 | 0.1467 | $ | 103,702 | ||||
| Existing technology | 1,190,000 | 0.1467 | 174,573 | ||||||
| Goodwill | 6,703,104 | 0.1467 | 983,345 | ||||||
| Total consideration paid | ¥ | 8,600,000 | $ | 1,261,620 |
No supplemental pro forma information is presented for the acquisition due to the immaterial effect of the acquisition on the Company’s results of operations.
F-17
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2008
8. ACQUISITIONS OF SUBSIDIARIES – Continued
(2) Dajian Zhitong
On September 16, 2008, Zhangcheng Media, the Company’s indirectly-owned subsidiary, entered into equity transfer agreements with shareholders of Dajian Zhitong. Pursuant to the agreements, Zhangcheng Media acquired 85% ownership of Dajian Zhitong from three of the shareholders for a cash price of RMB 1,980,000 (approximately $290,000). Included in the price was assumption of Dajian Zhitong's liabilities totaling RMB 1,639,518.
On October 13, 2008, a supplemental agreement to the aforementioned agreements was entered between Zhangcheng Media and the three shareholders of Dajian Zhitong. Pursuant to the agreement, Zhangchang Media will not pay the RMB 1,980,000 to the three shareholders nor assume Dajian Zhitong’s liabilities. Instead, it will make a cash contribution of RMB 9,000,000 directly to Dajian Zhitong. Other terms in the original equity transfer agreements were unaffected. Zhangcheng Media’s ownership in Dajian Zhitong remains at 85%. As a result of the supplemental agreement, the actual acquisition price of the 85% ownership of Dalian Zhitong was RMB 1,350,000=RMB 9,000,000 x (1-85%), (approximately $198,045). As of December 31, 2008, RMB 4,000,000 has been remitted to Dajian Zhitong.
In accordance with SFAS No. 141, the acquisition was accounted for under the purchase method of accounting. Accordingly, the results of Dajian Zhitong have been included in the accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements since the date of acquisition. The purchase price has been allocated to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based upon their estimated fair values and the price was allocated as follows:
| Currency | |||||||||
| In RMB | Exchange Rate | In USD | |||||||
| Net tangible assets | ¥ | 56,559 | 0.1467 | $ | 9,315 | ||||
| Goodwill | 1,293,441 | 0.1467 | 189,748 | ||||||
| Total consideration paid | ¥ | 1,350,000 | $ | 198,883 |
(3) Shanghai Yootu
On October 1, 2008, PKU, the Company’s indirectly-owned subsidiary, entered into an equity transfer agreements with shareholders of Shanghai Yootu. Pursuant to the agreement, PKU acquired 100% ownership of Shanghai Yootu from six individual shareholders. Under the terms of the Equity Transfer Agreement, PKU will make the payments in three installments to the Transferors. The initial cash payment of RMB 8.8 million (approximately $1,290,960) will be paid to the Transferors within five (5) business days after the date of execution of the Equity Transfer Agreement. The remaining two installments will be conditional upon Shanghai Yootu’s results of operations in the next two years (see Note 18)
In accordance with SFAS No. 141, the acquisition was accounted for under the purchase method of accounting. Accordingly, the results of Shanghai Yootu have been included in the accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements since the date of acquisition. The purchase price has been allocated to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based upon their estimated fair values and the price was allocated as follows:
| Currency | |||||||||
| Exchange | |||||||||
| In RMB | Rate | In USD | |||||||
| Net tangible assets | ¥ | (4,301,047 | ) | 0.1467 | $ | (630,964 | ) | ||
| Goodwill | 13,101,047 | 0.1467 | 1,921,924 | ||||||
| Total consideration paid | ¥ | 8,800,000 | $ | 1,290,960 |
No supplemental pro forma information is presented for the acquisitions due to the immaterial effect of the acquisition on the Company’s results of operations.
F-18
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2008
9. SHARE-BASED PAYMENTS
“ Accounting for Derivative Financial Instruments Indexed to and Potentially Settled in, a Company ’ s Own Stock” (“EITF 00-19”), provides criteria for determining whether freestanding contracts that are settled in a company’s own stock, including common stock warrants, should be designated as either an equity instrument, an asset or as a liability under SFAS No. 133. Under the provisions of EITF 00-19, a contract designated as an asset or a liability must be carried at fair value on a company’s balance sheet, with any changes in fair value recorded in a company’s results of operations. It was determined that the Company's warrants qualify for accounting treatment under EITF 00-19, " Accounting for Derivative Financial Instruments Indexed to, and Potentially Settled in, A Company's Own Stock ". Under the terms of the warrant agreements, if the Company fails to deliver the required number of Warrant Shares, the Company will be obligated to pay cash to settle the warrant claims. As a result, the Company must assume that it could be required to settle the warrants on a net-cash basis, thereby necessitating the treatment of the potential settlement obligation as a liability. The fair values of the warrants are presented on the accompanying consolidated balance sheet as “Accrued Warrant Liability” and the changes in the values of these warrants are shown in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations as “Decrease in fair value of warrants liability.” Such gains and losses are non-operating and have no effect on cash flows from operating activities.
(1) Warrants
Effective January 1, 2006, the Company adopted the fair value recognition provisions of SFAS No. 123R. The Company recognized the share-based compensation cost based on the grant-date fair value estimated in accordance with the new provisions of SFAS No. 123R. The Company issued warrants to Anteaus Capital, Inc., in aggregate, to purchase 277,778 shares of the Company’s common stock in connection with merger related services on May 14, 2007, with an exercise price of $1.80 per share. These warrants will expire on May 13, 2014 pursuant to the common stock purchase warrant agreement. The Company used the Black-Scholes option pricing model to determine the fair value of the stock warrants on May 14, 2007. On May 14, 2007, the fair value was as at $3.97 per share, resulting in a share-based compensation totaling $1,104,166. On November 29, 2007, the Company and Anteaus Capital, Inc. entered an amendment to the Company’s common stock purchase warrants. The amendment eliminated the clause subject to which if the Company fails to deliver the required number of Warrant Shares, the Company will be obligated to pay cash to settle the warrant claims. The 277,778 warrants issued to Antaeus Capital, Inc. have been re-valued at $1,039,807, and reclassified to Additional Paid-in Capital from Accrued Warrant Liability. Other income of $64,359 was recorded to account for the warrants at fair value.
The fair value for the share-based awards was estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the assumptions listed below:
| MAY 14, 2007 | NOVEMBER 29, 2007 | |||||
| Expected volatility | 203% | 148% | ||||
| Expected life (years) | 7 | 6.46 | ||||
| Risk free interest rate | 4.6% | 3.72% |
On November 30, 2007, the Company issued warrants to CCG Investor Relations Partners LLC, in aggregate, to purchase 50,000 shares of the Company’s common stock in connection with investor relations services, with an exercise price of $5.00 per share. These warrants will expire on November 29, 2010 pursuant to the common stock purchase warrant agreement. The fair market value of these stock warrants was $200,105 and was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model in accordance with SFAS No. 123R using the following weighted-average assumptions: expected dividend yield 0%; risk-free interest rate of 3.08%; volatility of 148% and an expected term of three years.
The expected volatilities are based on the historical volatility of the Company’s stock. The observations were made in a 52-week period. The expected terms of stock warrants are based on the remaining contractual life of stock warrants outstanding as these stock warrants vested immediately.
F-19
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER
31, 2008
9. SHARE-BASED PAYMENTS - Continued
A summary of stock warrants for the year ended December 31, 2008 is as follows:
| Weighted-Average | |||||||||
| Weighted- | Remaining | ||||||||
| Average | Contractual Term | ||||||||
| Stock Warrants | Shares | Exercise Price | (Months) | ||||||
| Outstanding at January 1, 2007 | 436,187 | $ | 2.63 | 30.77 | |||||
| Granted | 277,778 | 1.80 | - | ||||||
| 50,000 | 5.00 | ||||||||
| Exercised or converted | (239,023 | ) | 2.63 | - | |||||
| Forfeited or expired | (197,164 | ) | 2.63 | - | |||||
| Outstanding at January 1, 2008 | 327,778 | 2.29 | 70.11 | ||||||
| Granted | - | - | - | ||||||
| Exercised or converted | - | - | - | ||||||
| Forfeited or expired | - | - | - | ||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2008 | 327,778 | 2.29 | 58.08 | ||||||
| Exercisable at December 31, 2008 | 327,778 | $ | 2.29 | 58.08 |
(2) Stock Options
On January 7, 2008, the Company and Mr. Zhihai Mao, the Chief Financial Officer of the Company, entered into a stock option agreement. Pursuant to the terms of the stock option agreement, Mr. Mao was granted a non-qualified option on January 7, 2008 to purchase 200,000 shares of common stock of the Company at an exercise price of $6.70 per share, which was the closing price per share of the Company’s common stock as reported on the OTC Bulletin Board on such date. The option has a term of ten years and expires on January 7, 2018. The option vests in equal installments on a quarterly basis over a three-year period beginning on January 7, 2008. The Company recorded compensation expense of $181,000 during the year ended December 31, 2008 in connection with the stock options.
On May 1, 2008, the Company entered into separate Stock Option Agreements with each of Mr. Trien and Dr. Chen. Under the terms of the Stock Option Agreements, the Company agreed to grant a stock option to each of Mr. Trien and Dr. Chen for the purchase of 30,000 shares of common stock of the Company at an exercise price of $6.50 per share, which was the closing price per share of the Company’s common stock as reported on the OTC Bulletin Board on such date. The option has a term of five years and expires on May 1, 2013. The option vests in equal installments on a quarterly basis over a three-year period except for 2,500 options vested immediately on May 1 for Mr. Trien. The Company recorded compensation expense of $35,306 during the year ended December 31, 2008 in connection with the stock options.
On September 28, 2008, the Company entered into separate Stock Option Agreements with Mr. Ho-Ping Lin. Under the terms of the Stock Option Agreement, the Company agreed to grant a stock option to Mr. Lin for the purchase of 30,000 shares of common stock of the Company at an exercise price of $6.50 per share. The option has a term of five years and expires on September 28, 2013. The option vests in equal installments on a quarterly basis over a three-year period. The Company recorded compensation expense of $1,450 during the year ended December 31, 2008 in connection with the stock options.
F-20
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER
31, 2008
9. SHARE-BASED PAYMENTS – Continued
The Company estimates the fair value of stock options using a Black-Scholes option pricing valuation model, consistent with the provisions of SFAS 123(R) and SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 107 (SAB "107"). Key inputs and assumptions used to estimate the fair value of stock options include the grant price of the award, the expected option term, volatility of the Company’s stock, the risk-free rate and the Company’s dividend yield. Estimates of fair value are not intended to predict actual future events or the value ultimately realized by grantees, and subsequent events are not indicative of the reasonableness of the original estimates of fair value made by the Company.
The fair value of each stock option is estimated on the date of the grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. No dividends were assumed due to the nature of the Company’s current business strategy. The following table presents the assumptions used for options granted:
| September 30, 2008 | June 30, 2008 | March 31, 2008 | |||||||
| Number of options | 30,000 | 60,000 | 200,000 | ||||||
| Risk free interest rate | 2.37% | 2.53 % | 3.00% | ||||||
| Expected life (year) | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | ||||||
| Expected volatility | 30% | 53 % | 53% | ||||||
| Weighted average fair value per option | $ | 0.56 $ | 2.64 $ | 2.76 |
No options were exercised during the year ended December 31, 2008.
As of December 31, 2008, total unrecognized compensation costs related to unvested stock options was $508,621. Unvested stock options are expected to be recognized over a period of 2.17 years.
A summary of options transactions during the year ended December 31, 2008 is as follows:
| Weighted | ||||||
| Number of | Average | |||||
| Options | Exercise Price | |||||
| Outstanding at January 1, 2008 | - | $ | - | |||
| Granted | 290,000 | $ | 6.6 | |||
| Exercised | - | $ | - | |||
| Cancelled | - | $ | - | |||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2008 | 290,000 | $ | 6.6 | |||
| Nonvested as of December 31, 2008 | 225,000 | $ | 6.6 | |||
| Option exercisable as of December 31, 2008: | 65,000 | $ | 6.6 |
10. EQUITY TRANSACTIONS
In April 2007, per the request of the note holders, $21,000 of convertible promissory notes and $5,815 of accrued interest totaled $26,815 were converted into 12,769 shares of the Company’s common stock at $0.28 per share.
In April 2007, 239,023 common shares converted from warrants and issued to the warrant holders cashlessly.
Pursuant to the agreement entered into between the Company and the former directors in April 2007, the Company directly issued 40,000 common shares to the former directors as compensation. The related expense $166,230 was recorded based on the average stock price during the period from February to April 2007.
On May 14, 2007, the Company entered into a cancellation agreement with Weicheng International Inc. and Foster Growth Ltd. Pursuant to the agreement, Weicheng International Inc. agreed to the cancellation of 2,043,784 shares of the Company’s common stock owned by Weicheng International Inc.
F-21
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2008
10. EQUITY TRANSACTIONS - Continued
On May 14, 2007, the Company completed the reverse acquisition transaction with Cabowise whereby the Company issued to the shareholders of Cabowise 10,841,492 shares of the Company’s common stock in exchange for all of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Cabowise. Cabowise thereby became the Company’s wholly-owned subsidiary and the former shareholders of Cabowise became the Company’s controlling stockholders. The exchange of shares was accounted for as a reverse acquisition under the purchase method of accounting since the former shareholders of PKU obtained control of the consolidated entity. Accordingly, the merger of the two companies has been recorded as a recapitalization of PKU, with PKU being treated as the continuing entity.
On May 14, 2007, the Company issued and sold 1,777,778 shares to certain accredited investors for a cash price of $1.80 per share and a total amount of $3,200,000 pursuant to a private placement completed by the Company.
On May 14, 2007, the Company issued 13,889 shares of its common stock (approximately $25,000) to Thelen Reid Brown Raysman & Steiner LLP for their legal services in connection with the share exchange and private placement transaction.
On May 14, 2007, the Company issued to the placement agent, Antaeus Capital, Inc., a seven-year warrant to purchase 277,778 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $1.80. The Company used Black-Scholes option pricing model to determine the fair value of the stock warrants on the grant date. The fair value was at $3.98 per share resulting in a share-based compensation totaling $1,104,166.
Total transaction costs of $1,492,361, including legal, accounting and investment banking fees, etc., were charged directly to equity as a reduction from the cash consideration received for the newly-issued common stock.
Effect of subsidiary equity transactions was calculated under the provisions of the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) Staff Accounting Bulletin Topic 5H (“SAB Topic 5H”) and relates to the issuance of securities of a non-wholly owned subsidiary. The difference between the Company’s book value investment in PKU immediately prior to the transaction and its book value investment in PKU immediately following the transaction for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 amounted to $329,266 and $323,247, respectively.
On July 17, 2008, the Company issued and sold 2,586,207 shares to certain accredited investors for a cash price of $5.80 per share and a total amount of $15,000,000 pursuant to a private placement completed by the Company.
11. INCOME TAXES
The Company adopted the provisions of FASB Interpretation No. 48, Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes, on January 1, 2007. As a result of the implementation of Interpretation 48, the Company recognized no increases or decreases in the total amounts of previously unrecognized tax benefits. The Company had no unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2007 or December 31, 2008. The Company did not incur any interest and penalties related to potential underpaid income tax expenses and also believed that the adoption of FIN 48 does not have a significant impact on the unrecognized tax benefits during the year ended December 31, 2008.
The Company, through its subsidiaries, is governed by the Income Tax Laws of the PRC. Operations in the United States of America have incurred net accumulated operating losses of $3,300,000 as of December 31, 2008 for income tax purposes. However, a hundred percent allowance has been created on the deferred tax asset of $1,500,000 due to uncertainty of its realization.
F-22
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2008
11. INCOME TAXES - Continued
For the year ended December 31, 2008, income tax expenses were as follows:
Years Ended December 31,
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||||||||
| Domestic | Foreign | Domestic | Foreign | |||||||||||||||
| Federal | State | China | Federal | State | China | |||||||||||||
| Current | $ | 5,201 | $ | - | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred | 57,745 | 450,606 | ||||||||||||||||
| $ | 62,946 | $ | 450,606 | |||||||||||||||
PKU, Zhangcheng Media, Xinjiang Zhangcheng, China TranWiseway, and Dajian Zhitong are charged at the tax rate at 25% on the net income for PRC income tax purpose under the new Enterprise Tax Law in 2008. Beijing Tian Hao and Beijing Zhangcheng qualify as “new or high-technology enterprise” located in High-Tech Zones in Beijing, and are entitled to tax exemptions or preferential tax rates on the net income for PRC income tax purposes in 2008. Shanghai Yootu is subject to a special rate at 2.5% of its taxable revenue in 2008.
The Company recognizes deferred tax assets and liabilities for temporary differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of its assets and liabilities. Deferred assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when deemed appropriate.
The tax effects of existing temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of deferred tax assets at December 31, 2008 and 2007 were as follows:
| Deferred Tax Assets | |||||||||
| Net operating loss | Valuation | Net deferred tax | |||||||
| carryforwards | allowance | assets | |||||||
| December 31, 2008 | |||||||||
| Foreign: | |||||||||
| In RMB | ¥ | 1,443,132 | ¥ | - | ¥ | 1,443,132 | |||
| Exchange rate | 0.1467 | 0.1467 | |||||||
| In USD | $ | 211,708 | $ | 211,708 | |||||
| Domestic : | |||||||||
| In USD | $ | 1,500,000 | $ | (1,500,000 | ) | $ | - | ||
| December 31, 2007 | |||||||||
| Foreign: | |||||||||
| In RMB | ¥ | 1,828,361 | ¥ | - | ¥ | 1,828,361 | |||
| Exchange rate | 0.1371 | 0.1371 | |||||||
| In USD | $ | 250,668 | $ | 250,668 | |||||
| Domestic : | |||||||||
| In USD | $ | 1,300,000 | $ | (1,300,000 | ) | $ | - | ||
F-23
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2008
12. INCOME PER SHARE
The Company calculates its basic and diluted earnings per share in accordance with SFAS No. 128, “Earnings Per Share”. Basic earnings per share is calculated by dividing net income by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted earnings per share is calculated by adjusting the weighted average outstanding shares to assume conversion of all potentially dilutive warrants and options include nonvested stock granted to employees. The Company uses the treasury stock method to reflect the potential dilutive effect of the unvested stock options and unexercised warrants. In calculating the number of dilutive shares outstanding, the shares of common stock underlying unvested stock options are assumed to have been delivered on the grant date.
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| Net income, as reported | $ | 11,090,477 | $ | 4,421,081 | ||
| Basic earnings per share: | ||||||
| Basic weighted average share outstanding | 20,678,693 | 15,520,661 | ||||
| Basic earnings per common share | $ | 0.54 | $ | 0.28 | ||
| Diluted earnings per share: | ||||||
| Basic weighted average share outstanding | 20,678,693 | 15,520,661 | ||||
| Effect of dilutive stock options and warrants | 205,258 | 177,778 | ||||
| Diluted weighted average shares outstanding | 20,883,951 | 15,698,439 | ||||
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 0.53 | $ | 0.28 | ||
13. COMPENSATED ABSENCES
Employees earn annual vacation leave at the rate of seven (7) days per year for the first year. Upon completion of the first year of employment, employees earn one (1) additional day for each additional year. At termination, employees are paid for any accumulated annual vacation leave. As of December 31, 2008, vacation liability existed in the amount of $0.
14. RELATED-PARTY TRANSACTIONS Due to Related Parties
During 2008, China TranWiseway had an outstanding loan in the amount of RMB 1,000,000, or $146,700, from its shareholder Beijing Marine Communication & Navigation Company for general working capital needs. The loan has been paid off as of December 31, 2008.
During 2008, Shanghai Yootu borrowed from its former shareholder in the aggregated amount of RMB 3,064,424, or $449,551 for general working capital needs. The borrowings do not bear interest and are payable on demand.
During 2008, Dajian Zhitong borrowed from two of its individual shareholders in the aggregated amount of RMB 538,065, or $78,934 for general working capital needs. The borrowings do not bear interest and are payable on demand.
F-24
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2008
15. CONCENTRATION
a. Cash
The Company maintains cash in two commercial banks located in California. Up to $250,000 of the balance in each bank was insured by the U.S. Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). As of December 31, 2008, uninsured balances totaled $1,422,809.
b. Major Customers
The Company had 1 and 2 major customers that accounted for the following accounts receivable and sales during the fiscal years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively:
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| Revenue: | ||||||
| -Customer A | $ | 3,044,547 | $ | 1,114,932 | ||
| -Customer B | 1,693,276 | |||||
| -Customer C | 1,337,042 | |||||
| Accounts Receivable: | ||||||
| -Customer A | $ | - | 499,603 | |||
| -Customer B | - | |||||
| -Customer C | 428,633 | |||||
16. OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
Balances of related after-tax components comprising accumulated other comprehensive income, included in stockholders' equity, at December 31, 2008 was as follows:
| Foreign Currency | Accumulated Other | |||||
| Translation Adjustment | Comprehensive Income | |||||
| Balance at January 1, 2007 | $ | 214,770 | $ | 214,770 | ||
| Change for the year ended December 31, 2007 | 672,414 | 672,414 | ||||
| Balance at January 1, 2008 | 887,184 | 887,184 | ||||
| Change for the year ended December 31, 2008 | 1,612,709 | 1,612,709 | ||||
| Balance at December 31, 2008 | $ | 2,499,893 | $ | 2,499,893 |
17. SEGMENT INFORMATION
SFAS 131, “ Disclosures about Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information” requires companies to report information about operating segment in interim and annual financial statements. It also requires segment disclosures about products and services geographic and major customers. The Company has determined that it does not have any separately reportable operating segment.
F-25
CHINA TRANSINFO TECHNOLOGY CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER
31, 2008
18. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
(1) Operating Lease
PKU and its subsidiaries rent offices under several operating leases. Rent expenses for these offices totaled $269,011 for the year ended December 31, 2008. The aggregate future minimum payments under these lease agreements over one year are as follows:
| Year ending December 31, | Lease Commitments | ||
| 2009 | $ | 346,616 | |
| 2010 | 297,180 | ||
| 2011 | 28,082 | ||
| Total | $ | 671,878 |
(2) Acquisition of Dajian Zhitong
On September 16, 2008, Zhangcheng Media, the Company’s indirectly-owned subsidiary, entered into equity transfer agreements with shareholders of Dajian Zhitong. Pursuant to the agreements, Zhangcheng Media acquired 85% ownership of Dajian Zhitong from three of the shareholders for a cash price of RMB 1,980,000 (approximately $290,000). Included in the price was assumption of Dajian Zhitong's liabilities totaling RMB 1,639,518. On October 13, a supplemental agreement to the aforementioned agreements was entered. Pursuant to the agreement, Zhangcheng Media will not pay the RMB 1,980,000 to the three shareholders nor assume Dajian Zhitong’s liabilities. Instead, it will make a cash contribution of RMB 9,000,000 directly to Dajian Zhitong. Other terms in the original equity transfer agreements were unaffected. As of December 31, 2008, RMB 4,000,000 of the RMB 9,000,000 contractual capital contribution has been remitted to Dajian Zhitong.
(3) Acquisition of Shanghai Yootu
On October 1, 2008, PKU, the Company’s indirectly-owned subsidiary, entered into equity transfer agreements with shareholders of Shanghai Yootu. Pursuant to the agreement, PKU acquired 100% ownership of Shanghai Yootu from six individual shareholders. Under the terms of the Equity Transfer Agreement, PKU will make the payments in three installments to the Transferors. The initial cash payment of RMB 8.8 million (approximately $1,300,000) was made in 2008. The second payment, consisting of 50% in cash and 50% in the Company’s common stock aggregately equal to twice Shanghai Yootu’s 2009 net income, will be made by the later of (1) January 1, 2010 or (2) the completion of the audit of financial statements of Shanghai Yootu for the year ended December 31, 2009. The final payment, consisting of 50% in cash and 50% in the Company’s common stock aggregately equal to three times Shanghai Yootu’s 2010 net income, will be made by the later of (1) January 1, 2011 or (2) the completion of the audit of financial statements of Shanghai Yootu for the year ended December 31, 2010.
19. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On February 3, 2009, the Company, through its indirect Chinese subsidiaries, Oriental Intra-Asia and PKU, entered into a series of equity transfer agreements with China TransInfo Technology Group Co., Ltd., or Group Company, a company incorporated under Chinese law, pursuant to which the Company transferred all of its indirect equity interests in PKU and PKU's subsidiaries to the Group Company. The main purpose of the restructuring is to allow the Company to engage in three new business segments, including online services, taxi advertising, and security and surveillance related business in China in which companies with foreign ownership, like the Company and its subsidiaries, are either prohibited or restricted from operating under the current applicable Chinese laws and regulations. Through the contractual or variable interest entity, or VIE arrangements, the Company maintains substantial control over the VIE Entities' daily operations and financial affairs, election of their senior executives and all matters requiring shareholder approval. Furthermore, as the primary beneficiary of the VIE Entities, the Company is entitled to consolidate the financial results of the VIE Entities in its own consolidated financial statements under FASB Interpretation No. 46R "Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities" ("FIN 46R").
F-26
