Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.1 - EX-99.1 - Aeglea BioTherapeutics, Inc. | agle-ex991_6.htm |
| 8-K - 8-K - Aeglea BioTherapeutics, Inc. | agle-8k_20210318.htm |

Reimagining The Potential Of Human Enzyme Therapeutics Corporate Overview – March 2021 Exhibit 99.2

Forward Looking Statements ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 2 This presentation and the accompanying oral presentation contain “forward-looking” statements that are based on our management’s beliefs and assumptions and on information currently available to management. Forward-looking statements include all statements other than statements of historical fact contained in this presentation, including information concerning our current and future financial performance, business plans and objectives, current and future clinical and preclinical development activities, timing and success of our ongoing and planned clinical trials and related data, the timing of announcements, updates and results of our clinical trials and related data, our ability to obtain and maintain regulatory approval, the potential therapeutic benefits and economic value of our lead product candidate and our other product candidates, potential growth opportunities, financing plans, use and adequacy of financing plans, competitive position, industry environment and potential market opportunities. Forward-looking statements are subject to known and unknown risks, uncertainties, assumptions and other factors including, but not limited to, those related to the success, cost and timing of our product candidate development activities and ongoing and planned clinical trials; our plans to develop and commercialize targeted therapeutics, including our lead product candidate pegzilarginase and our other product candidates for the treatment of homocystinuria and cystinuria; the design, progress of patient enrollment and dosing in our clinical trials, the ability of our product candidates to achieve applicable endpoints in clinical trials, the ability for patients who participate in the Phase 3 PEACE trial to participate in a long-term extension study, the safety profile of our product candidates in clinical trials, the potential for data from our current and future clinical trials to support a marketing application, as well as the timing of these events, the potential for preclinical studies to be predictive of current or future clinical trials, our ability to obtain funding for our operations, development and commercialization of our product candidates; the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on our operations and clinical development activities; the timing of and our ability to obtain and maintain regulatory approvals; the potential for expeditated development and review of pegzilarginase as of a result of its Breakthrough Therapy designation; the potential addressable markets of the our product candidates; the rate and degree of market acceptance and clinical utility of our product candidates; the size and growth potential of the markets for our product candidates, and our ability to serve those markets; our commercialization, marketing and manufacturing capabilities and strategy; future agreements with third parties in connection with the commercialization of our product candidates; our expectations regarding our ability to obtain and maintain intellectual property protection; our dependence on third party manufacturers; our ability to develop our own commercial manufacturing facility; the success of competing therapies that are or may become available; our ability to attract and retain key scientific or management personnel; our ability to identify additional product candidates with significant commercial potential consistent with our commercial objectives; and our estimates regarding expenses, future revenue, capital requirements and needs for additional financing. Moreover, we operate in a very competitive and rapidly changing environment, and new risks may emerge from time to time. It is not possible for our management to predict all risks, nor can we assess the impact of all factors on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements we may make. In light of these risks, uncertainties and assumptions, the forward-looking events and circumstances discussed herein may not occur and actual results could differ materially and adversely from those anticipated or implied in the forward-looking statements. Further information on these and other factors that could affect these forward-looking statements is contained in our most recent Annual Report on Form 10-K filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and other reports filed by the SEC. You should not rely upon forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. Although our management believes that the expectations reflected in our forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee that the future results, levels of activity, performance or events and circumstances described in the forward-looking statements will be achieved or occur. We undertake no obligation to publicly update any forward-looking statements, whether written or oral, that may be made from time to time, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise.

Addressing Metabolic Imbalances to Improve the Lives of Patients ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 3 Delivering Metabolic Harmony Aeglea BioTherapeutics (Nasdaq: AGLE) At Aeglea, we believe that every patient deserves a chance at a better life. We are committed to helping people with rare and devastating metabolic diseases who have limited treatment options because having a rare disease doesn’t mean that you are in the fight alone. [PHOTOS]
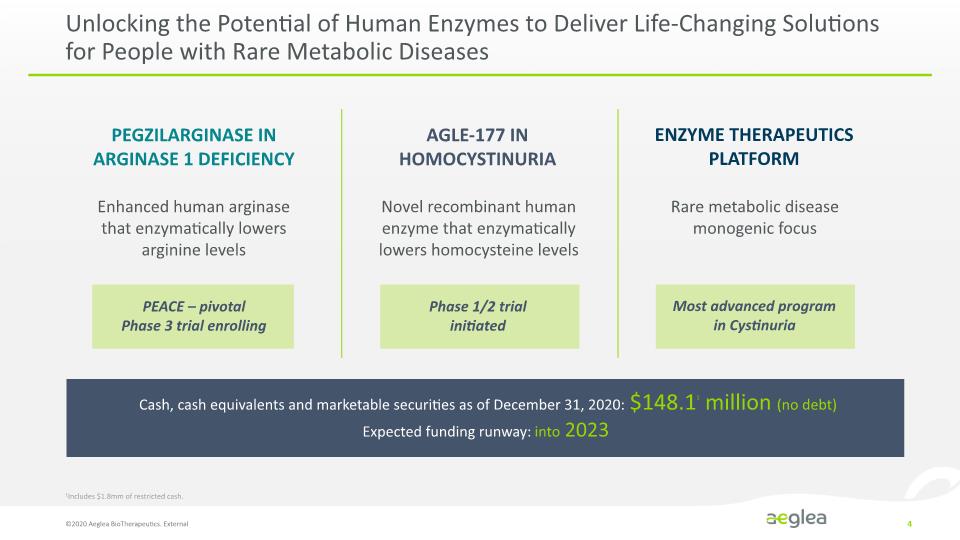
Unlocking the Potential of Human Enzymes to Deliver Life-Changing Solutions for People with Rare Metabolic Diseases ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 4 PEGZILARGINASE IN ARGINASE 1 DEFICIENCY AGLE-177 IN HOMOCYSTINURIA ENZYME THERAPEUTICS PLATFORM Enhanced human arginase that enzymatically lowers arginine levels PEACE – pivotal Phase 3 trial enrolling Novel recombinant human enzyme that enzymatically lowers homocysteine levels Phase 1/2 trial initiated Rare metabolic disease monogenic focus Most advanced program in Cystinuria Cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities as of December 31, 2020: $148.11 million (no debt) Expected funding runway: into 2023 1Includes $1.8mm of restricted cash.
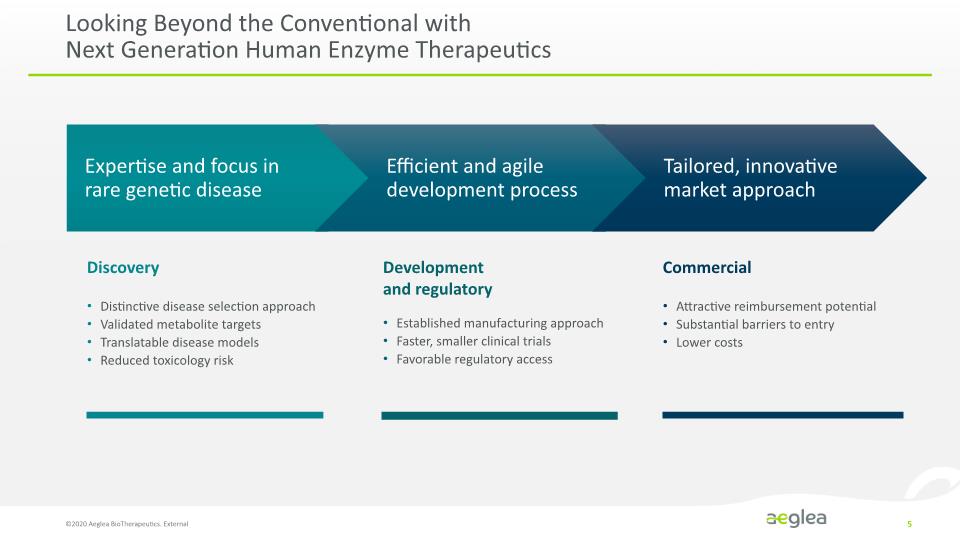
Looking Beyond the Conventional with Next Generation Human Enzyme Therapeutics ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 5 Distinctive disease selection approach Validated metabolite targets Translatable disease models Reduced toxicology risk Established manufacturing approach Faster, smaller clinical trials Favorable regulatory access Attractive reimbursement potential Substantial barriers to entry Lower costs Discovery Development and regulatory Commercial Expertise and focus in rare genetic disease Efficient and agile development process Tailored, innovative market approach
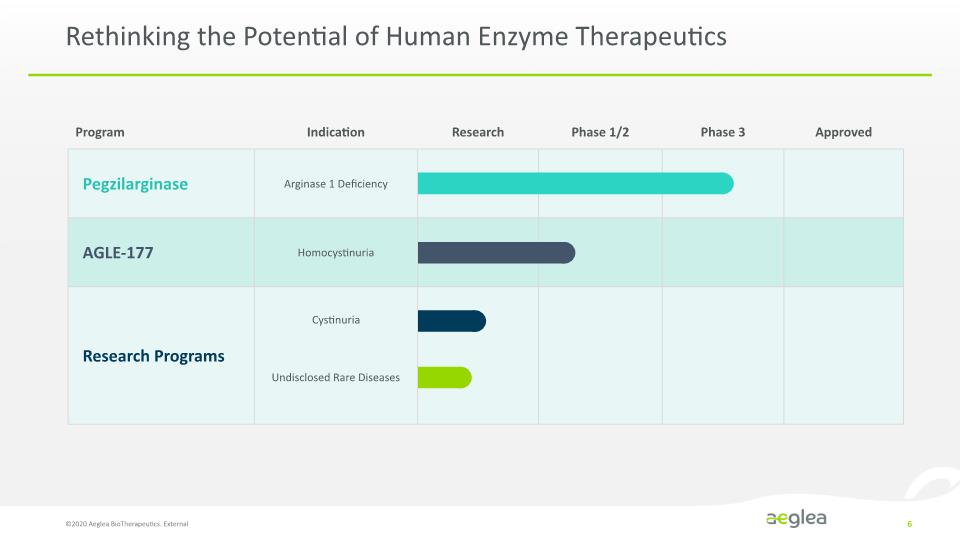
Rethinking the Potential of Human Enzyme Therapeutics ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 6 *[LINE GRAPH] Program Indication Research Phase 1/2 Phase 3 Approval Pegzilarginase Arginase 1 Deficiency AGLE-177 Homocystinuria Research Programs Cystinuria Undisclosed Rare Diseases

Highly Experienced Leadership Team in Drug Discovery & Development Anthony G. Quinn, MD PhD Chief Executive Officer Leslie Sloan, PhD Chief Operating Officer Scott Rowlinson, PhD Vice President of Research Michael C. Hanley, MBA Chief Commercial Officer Eric Bradford, MD MBA Chief Development Officer ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 7 [ANTHONY G. QUINN PHOTO] [LESLIE SLOAN PHOTO] [SCOTT ROWLINSON PHOTO] [MICHAEL C. HANLEY PHOTO] [ERIC BRADFORD PHOTO] [ROCHE LOGO] [LILLY LOGO] [SYNAGEVA LOGO] [GSK LOGO] [ASTRAZENECA LOGO] [IPSEN LOGO] [PFIZER LOGO] [HORIZON LOGO]

Pegzilarginase in Arginase 1 Deficiency
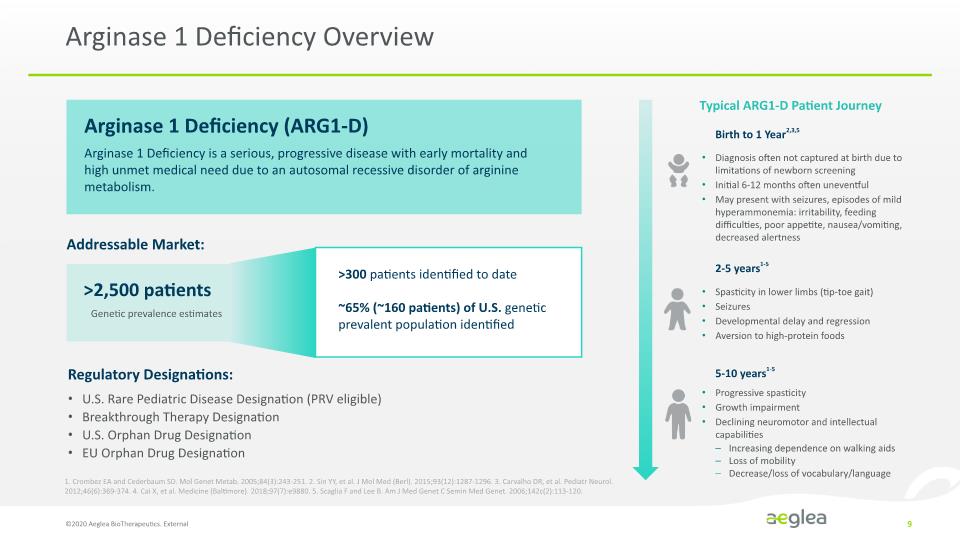
Arginase 1 Deficiency Overview ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 9 Arginase 1 Deficiency (ARG1-D) Arginase 1 Deficiency is a serious, progressive disease with early mortality and high unmet medical need due to an autosomal recessive disorder of arginine metabolism. Addressable Market: >2,500 patients Genetic prevalence estimates U.S. Rare Pediatric Disease Designation (PRV eligible) Breakthrough Therapy Designation U.S. Orphan Drug Designation EU Orphan Drug Designation Regulatory Designations: Typical ARG1-D Patient Journey Birth to 1 Year2,3,5 2-5 years1-5 5-10 years1-5 Diagnosis often not captured at birth due to limitations of newborn screening Initial 6-12 months often uneventful May present with seizures, episodes of mild hyperammonemia: irritability, feeding difficulties, poor appetite, nausea/vomiting, decreased alertness Spasticity in lower limbs (tip-toe gait) Seizures Developmental delay and regression Aversion to high-protein foods Progressive spasticity Growth impairment Declining neuromotor and intellectual capabilities Increasing dependence on walking aids Loss of mobility Decrease/loss of vocabulary/language >300 patients identified to date ~65% (~160 patients) of U.S. genetic prevalent population identified 1. Crombez EA and Cederbaum SD. Mol Genet Metab. 2005;84(3):243-251. 2. Sin YY, et al. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015;93(12):1287-1296. 3. Carvalho DR, et al. Pediatr Neurol. 2012;46(6):369-374. 4. Cai X, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(7):e9880. 5. Scaglia F and Lee B. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2006;142c(2):113-120.
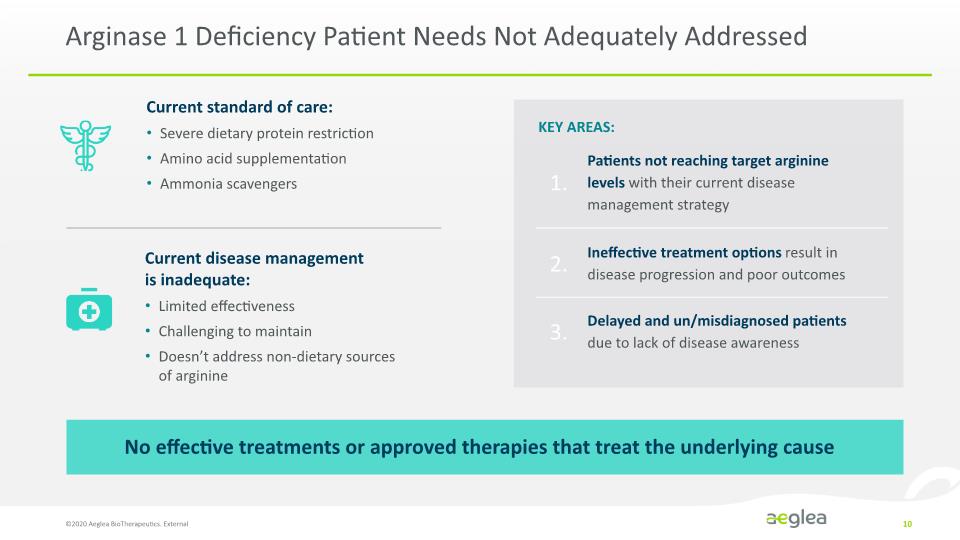
KEY AREAS: Arginase 1 Deficiency Patient Needs Not Adequately Addressed No effective treatments or approved therapies that treat the underlying cause ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 10 Current standard of care: Severe dietary protein restriction Amino acid supplementation Ammonia scavengers Current disease management is inadequate: Limited effectiveness Challenging to maintain Doesn’t address non-dietary sources of arginine Delayed and un/misdiagnosed patients due to lack of disease awareness Patients not reaching target arginine levels with their current disease management strategy Ineffective treatment options result in disease progression and poor outcomes 1. 2. 3.
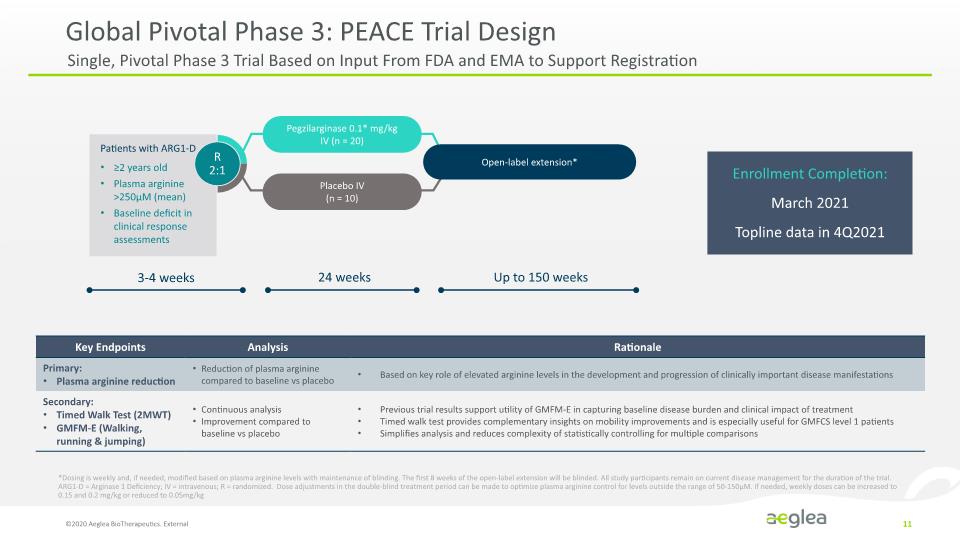
Global Pivotal Phase 3: PEACE Trial Design ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 11 Single, Pivotal Phase 3 Trial Based on Input From FDA and EMA to Support Registration *Dosing is weekly and, if needed, modified based on plasma arginine levels with maintenance of blinding. The first 8 weeks of the open-label extension will be blinded. All study participants remain on current disease management for the duration of the trial. ARG1-D = Arginase 1 Deficiency; IV = intravenous; R = randomized. Dose adjustments in the double-blind treatment period can be made to optimize plasma arginine control for levels outside the range of 50-150µM. If needed, weekly doses can be increased to 0.15 and 0.2 mg/kg or reduced to 0.05mg/kg Enrollment Completion: March 2021 Topline data in 4Q2021 Patients with ARG1-D ≥2 years old Plasma arginine >250 µM (mean) Baseline deficit in clinical response assessments R 2:1 Pegzilarginase 0.1* mg/kg IV (n = 20) IV (n = 20) Open-label extension* 3-4 weeks 24 weeks Up to 150 weeks Key Endpoints Primary: Plasma arginine reduction Secondary: Timed Walk Test (2MWT) GMFM-E (Walking, running & jumping) Analysis Reduction of plasma arginine compared to baseline vs placebo Continuous analysis Improvement compared to baseline vs placebo Rationale Based on key role of elevated arginine levels in the development and progression of clinically important disease manifestations Previous trial results support utility of GMFM-E in capturing baseline disease burden and clinical impact of treatment Timed walk test provides complementary insights on mobility improvements and is especially useful for GMFCS level 1 patients Simplifies analysis and reduces complexity of statistically controlling for multiple comparisons
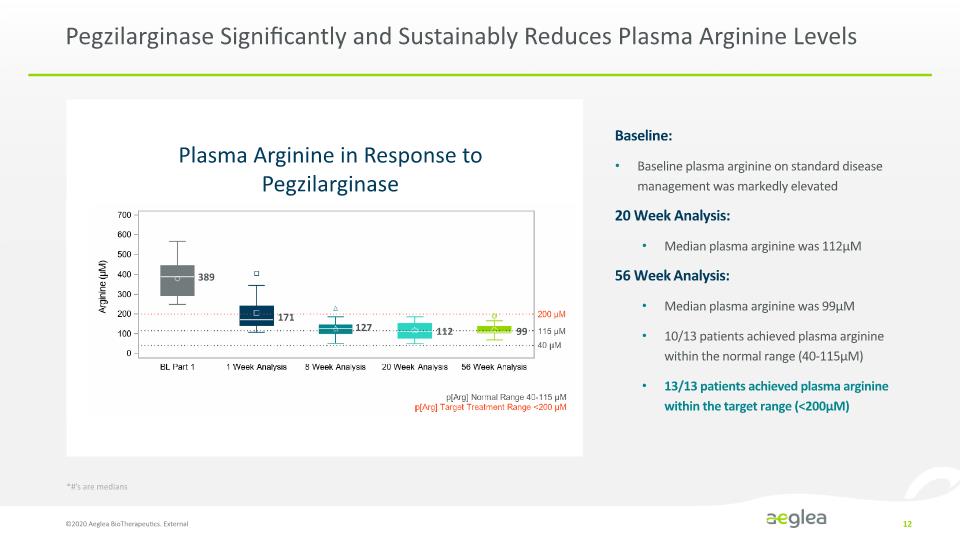
Pegzilarginase Significantly and Sustainably Reduces Plasma Arginine Levels ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 12 Plasma Arginine in Response to Pegzilarginase Baseline: Baseline plasma arginine on standard disease management was markedly elevated 20 Week Analysis: Median plasma arginine was 112µM 56 Week Analysis: Median plasma arginine was 99µM 10/13 patients achieved plasma arginine within the normal range (40-115µM) 13/13 patients achieved plasma arginine within the target range (<200µM) *#’s are medians 389 171 127 112 99 *[BAR CHART] Arginine (µM) 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 BL Part 1 1 Week Analysis 8 Week Analysis 20 Week Analysis 56 Week Analysis 200 µM 115 µM 40 µM p[Arg] Normal Range 40-115 µM p[Arg] Target Treatment Range <200 µM
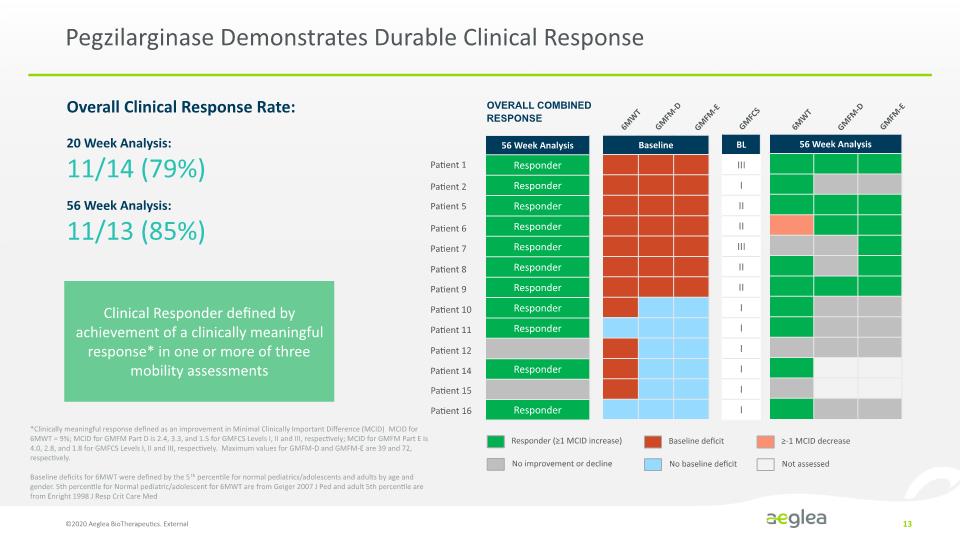
Clinical Responder defined by achievement of a clinically meaningful response* in one or more of three mobility assessments Pegzilarginase Demonstrates Durable Clinical Response ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 13 20 Week Analysis: 11/14 (79%) 56 Week Analysis: 11/13 (85%) *Clinically meaningful response defined as an improvement in Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID) MCID for 6MWT = 9%; MCID for GMFM Part D is 2.4, 3.3, and 1.5 for GMFCS Levels I, II and III, respectively; MCID for GMFM Part E is 4.0, 2.8, and 1.8 for GMFCS Levels I, II and III, respectively. Maximum values for GMFM-D and GMFM-E are 39 and 72, respectively. Baseline deficits for 6MWT were defined by the 5th percentile for normal pediatrics/adolescents and adults by age and gender. 5th percentile for Normal pediatric/adolescent for 6MWT are from Geiger 2007 J Ped and adult 5th percentile are from Enright 1998 J Resp Crit Care Med Overall Clinical Response Rate: *[CLINICAL RESPONSE CHART] Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4 Patient 5 Patient 6 Patient 7 Patient 8 Patient 9 Patient 10 Patient 11 Patient 12 Patient 13 Patient 14 Patient 15 Patient 16 OVERALL COMBINED RESPONSE 56 Week Analysis Responder Responder Responder Responder Responder Responder Responder Responder Responder Responder Responder 6MWT GMFM-D GMFM-E GMFCS Baseline BL III I II II III II II I I I I I I 6MWT GMFM-D GMFM-E 56 Week Analysis Responder (≥1 MCID increase) No improvement or decline Baseline deficit No baseline deficit ≥-1 MCID decrease Not assessed
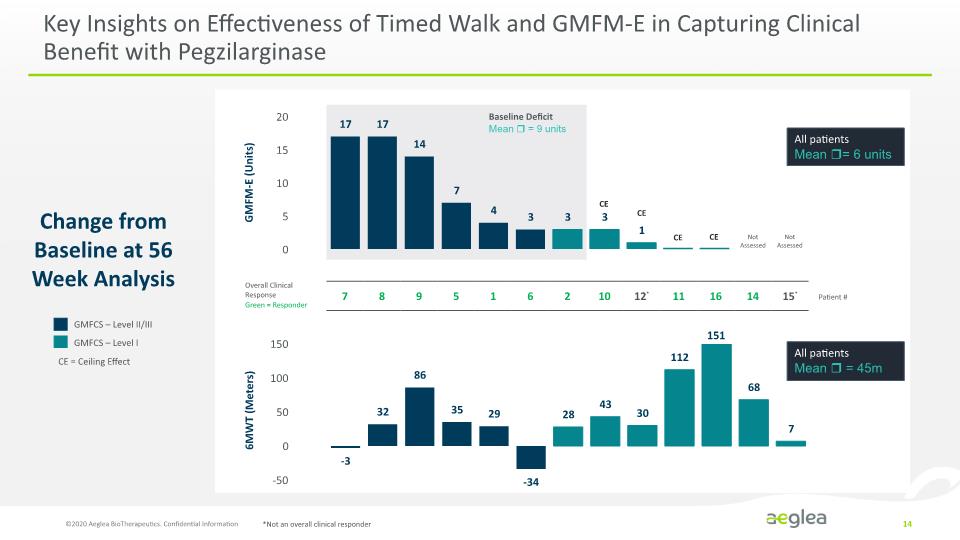
Key Insights on Effectiveness of Timed Walk and GMFM-E in Capturing Clinical Benefit with Pegzilarginase ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. Confidential Information 14 GMFM-E (Units) Change from Baseline at 56 Week Analysis Not Assessed Not Assessed GMFCS – Level II/III GMFCS – Level I 6MWT (Meters) CE CE CE = Ceiling Effect Baseline Deficit Mean = 9 units CE CE 151 *Not an overall clinical responder Overall Clinical Response Green = Responder Patient # All patients Mean = 6 units All patients Mean = 45m [BAR CHART] [BAR CHART] 20 15 10 5 0 17 17 14 7 4 3 3 3 1 7 8 9 5 1 6 2 10 12* 11 16 14 15* 150 100 50 0 -50 -3 32 86 35 29 -34 28 43 30 112 68 7

Safety Summary ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 15 Pegzilarginase was shown to have a favorable safety profile More than 1,3501 doses administered in the Phase 1/2 clinical trial (101A) and Phase 2 OLE study (102A) Approximately 5001 intravenous doses Most treatment-related adverse events were mild The frequency of treatment-related adverse events decreased over time Hypersensitivity and hyperammonemia were the most common treatment-related serious adverse events; expected and manageable 1Dose data as of September 10, 2020 Phase 1/2 Trial and Open Label Extension Study of Pegzilarginase in Arginase 1 Deficiency
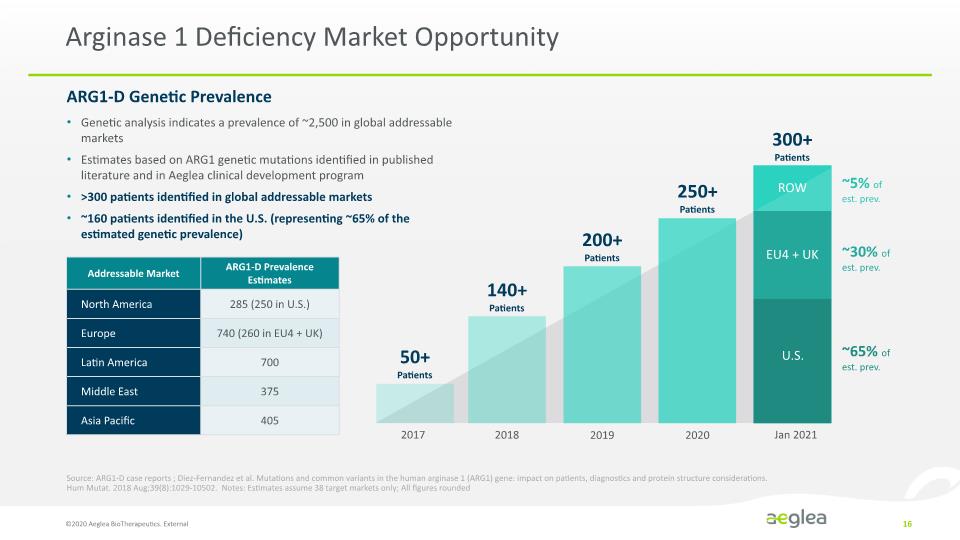
Arginase 1 Deficiency Market Opportunity ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 16 Genetic analysis indicates a prevalence of ~2,500 in global addressable markets Estimates based on ARG1 genetic mutations identified in published literature and in Aeglea clinical development program >300 patients identified in global addressable markets ~160 patients identified in the U.S. (representing ~65% of the estimated genetic prevalence) ARG1-D Genetic Prevalence Source: ARG1-D case reports ; Diez-Fernandez et al. Mutations and common variants in the human arginase 1 (ARG1) gene: impact on patients, diagnostics and protein structure considerations. Hum Mutat. 2018 Aug;39(8):1029-10502. Notes: Estimates assume 38 target markets only; All figures rounded 2017 2018 2019 2020 Jan 2021 50+ Patients 140+ Patients 200+ Patients 250+ Patients 300+ Patients U.S. EU4 + UK ROW ~65% of est. prev. ~5% of est. prev. ~30% of est. prev. Addressable Market North America Europe Latin America Middle East Asia Pacific ARG1-D Prevalence Estimates 285 (250 in U.S.) 740 (260 in EU4 + UK) 700 375 405
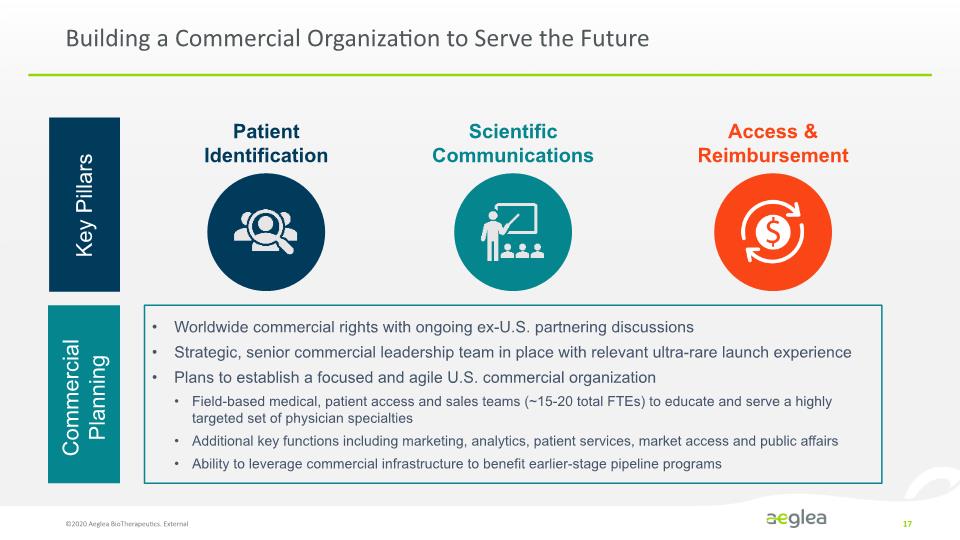
Building a Commercial Organization to Serve the Future Patient Identification Scientific Communications Access & Reimbursement Worldwide commercial rights with ongoing ex-U.S. partnering discussions Strategic, senior commercial leadership team in place with relevant ultra-rare launch experience Plans to establish a focused and agile U.S. commercial organization Field-based medical, patient access and sales teams (~15-20 total FTEs) to educate and serve a highly targeted set of physician specialties Additional key functions including marketing, analytics, patient services, market access and public affairs Ability to leverage commercial infrastructure to benefit earlier-stage pipeline programs Commercial Planning Key Pillars ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 17
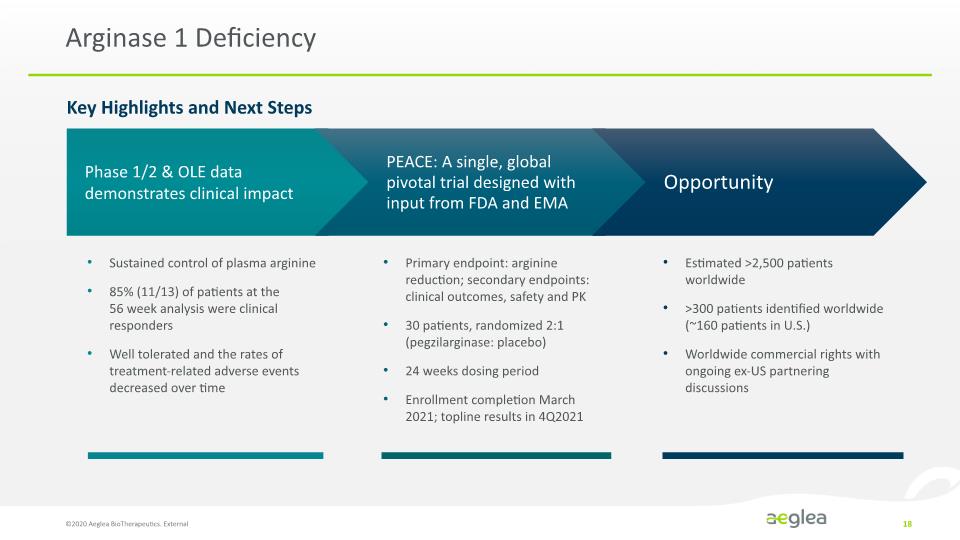
Arginase 1 Deficiency Key Highlights and Next Steps ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 18 Sustained control of plasma arginine 85% (11/13) of patients at the 56 week analysis were clinical responders Well tolerated and the rates of treatment-related adverse events decreased over time Primary endpoint: arginine reduction; secondary endpoints: clinical outcomes, safety and PK 30 patients, randomized 2:1 (pegzilarginase: placebo) 24 weeks dosing period Enrollment completion March 2021; topline results in 4Q2021 Estimated >2,500 patients worldwide >300 patients identified worldwide (~160 patients in U.S.) Worldwide commercial rights with ongoing ex-US partnering discussions Phase 1/2 & OLE data demonstrates clinical impact PEACE: A single, global pivotal trial designed with input from FDA and EMA Opportunity
AGLE-177 in Homocystinuria
Homocystinuria Overview ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 20 PRV – Priority Review Voucher 1 >30,000 represents estimated prevalence of Classical Homocystinuria (including B6-responsive and B6-non-responsive) in 38 addressable markets based on results of U.S. ICD-10 claims analysis extrapolated to global markets; all figures rounded. Sellos-Moura et al 2020. 2 Mudd et al 1985. 3 Kožich et al, 2020. 4 ~6,000-6,600 represents estimated prevalence of B6-non-responsive Homocystinuria in the U.S (~3,300) and the EU4 plus UK (~3,300) U.S. Orphan Drug Designation EU Orphan Drug Designation U.S. Rare Pediatric Disease Designation (PRV eligible) Regulatory Designations: Homocystinuria (HCU): Cystathionine beta synthase (CBS) deficiency, also known as Classical Homocystinuria, is a serious and progressive metabolic disorder characterized by elevated levels the amino acid homocysteine. Addressable Market: >30,000 patients1 ~15,000 – 18,000 patients B6-non-responsive population 2,3 ~6,000-6,600 estimated B6-non-responsive patients in the U.S. & EU4 + UK4 Serious Disease Complications Eyes Lens dislocation, glaucoma, severe near-sightedness Nervous System Intellectual and developmental delays, behavioral abnormalities, seizures Vascular Life-threatening thrombotic events, heart attack, stroke Skeletal Long bone (Marfanoid) features, skeletal deformities, osteoporosis

Current Homocystinuria Treatments Have Limited Effectiveness and Create a Significant Burden for Patients ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 21 Patients intolerant of available adjunctive therapies due to either safety issues or other adverse reactions Therapy-resistant patients on standard disease management KEY AREAS: Patients who are at high risk of non-compliance which places them at increased risk of severe complications Unmet Need: Therapy that addresses both disease and treatment burden Current standard of care: B6 (pyridoxine) for responsive patients Low-methionine diet + amino acid supplements Betaine Current disease management is inadequate with an inability to control tHcy levels: Limited effectiveness Non-compliance Poor tolerability of amino acid supplementation and Betaine 1. 2. 3. tHcy – Total plasma homocysteine
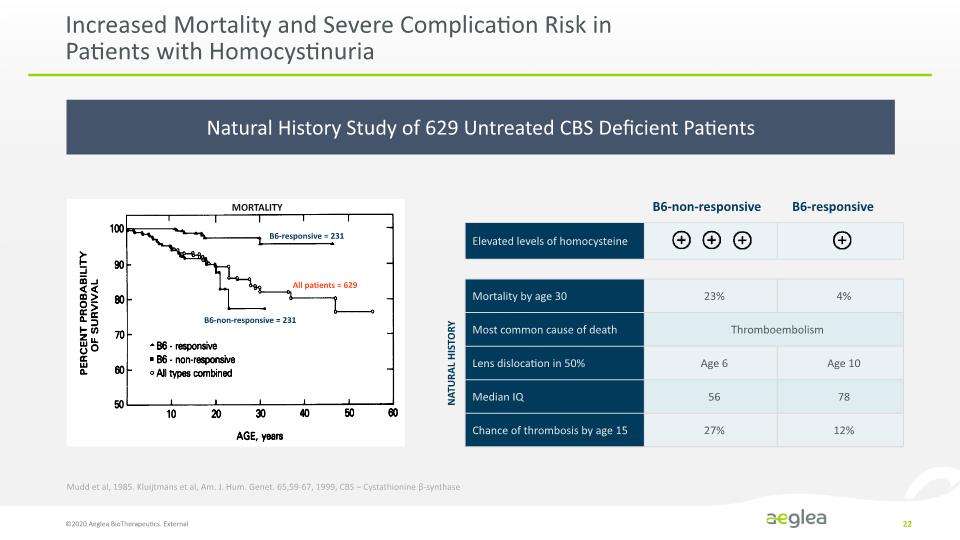
Natural History Study of 629 Untreated CBS Deficient Patients Increased Mortality and Severe Complication Risk in Patients with Homocystinuria ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 22 B6-responsive = 231 All patients = 629 B6-non-responsive = 231 MORTALITY NATURAL HISTORY Mudd et al, 1985. Kluijtmans et al, Am. J. Hum. Genet. 65,59-67, 1999, CBS – Cystathionine β-synthase B6-non-responsive B6-responsive *[LINE CHART] PERCENT PROBABILITY OF SURVIVAL 100 90 80 70 60 50 10 20 30 40 50 60 AGE, years B6 – responsive B6 – non-responsive All types combined Elevate level of homocysteine Mortality by age 30 Most common cause of death Lens dislocation in 50% Median IQ Chance of thrombosis by age 15 B6-non-responsive B6-responsive 23% Thromboembolism Age 6 56 27% 4% Age 10 78 12%
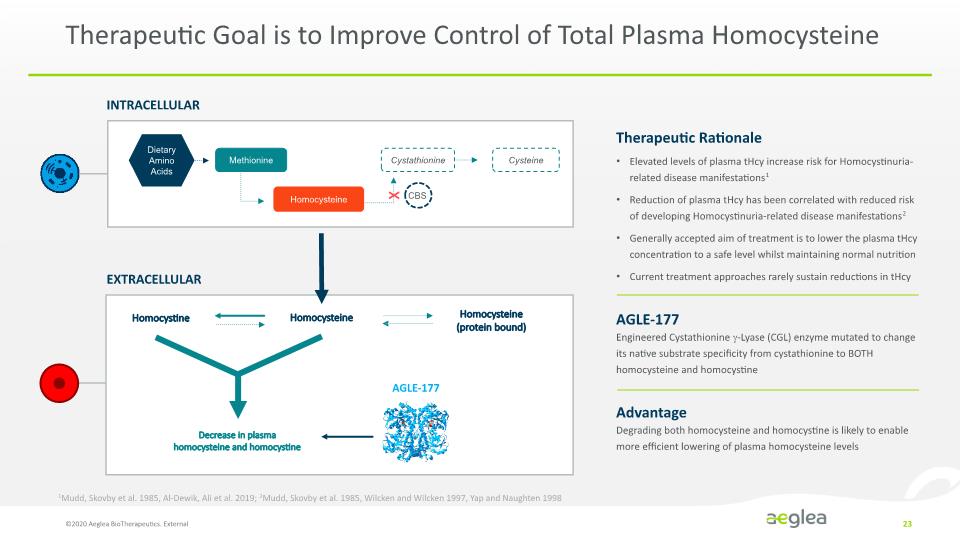
Therapeutic Goal is to Improve Control of Total Plasma Homocysteine ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 23 INTRACELLULAR EXTRACELLULAR Homocysteine Homocystine AGLE-177 Homocysteine (protein bound) Decrease in plasma homocysteine and homocystine X Therapeutic Rationale Elevated levels of plasma tHcy increase risk for Homocystinuria-related disease manifestations1 Reduction of plasma tHcy has been correlated with reduced risk of developing Homocystinuria-related disease manifestations2 Generally accepted aim of treatment is to lower the plasma tHcy concentration to a safe level whilst maintaining normal nutrition Current treatment approaches rarely sustain reductions in tHcy AGLE-177 Engineered Cystathionine -Lyase (CGL) enzyme mutated to change its native substrate specificity from cystathionine to BOTH homocysteine and homocystine Advantage Degrading both homocysteine and homocystine is likely to enable more efficient lowering of plasma homocysteine levels 1Mudd, Skovby et al. 1985, Al-Dewik, Ali et al. 2019; 2Mudd, Skovby et al. 1985, Wilcken and Wilcken 1997, Yap and Naughten 1998 [INTRACELLULAR EXTRACELLULAR CHART] Dietary Amino Acids Methionine Cystathionine CBS Cysteine Homocysteine
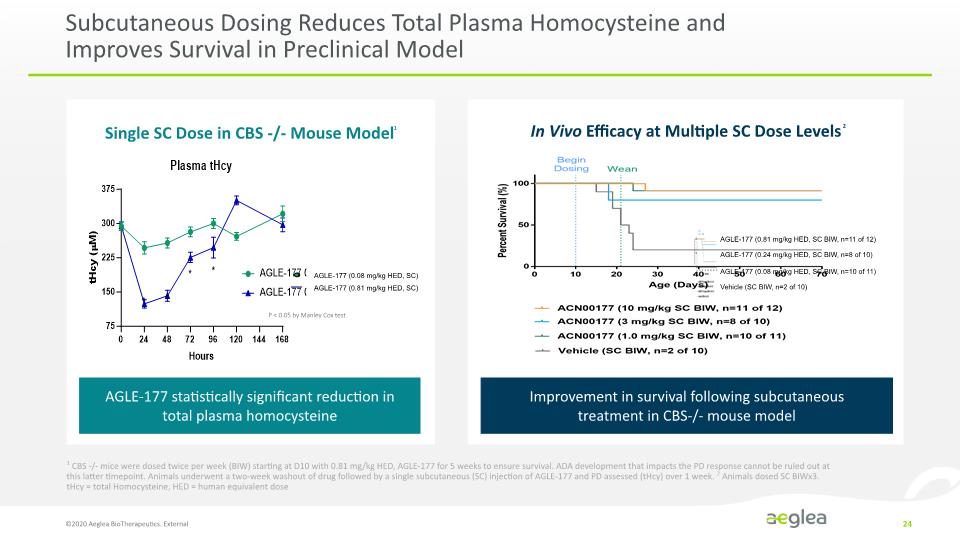
Subcutaneous Dosing Reduces Total Plasma Homocysteine and Improves Survival in Preclinical Model ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 24 AGLE-177 (0.81 mg/kg HED, SC BIW, n=11 of 12) AGLE-177 (0.24 mg/kg HED, SC BIW, n=8 of 10) AGLE-177 (0.08 mg/kg HED, SC BIW, n=10 of 11) Vehicle (SC BIW, n=2 of 10) Single SC Dose in CBS -/- Mouse Model1 In Vivo Efficacy at Multiple SC Dose Levels2 AGLE-177 statistically significant reduction in total plasma homocysteine Improvement in survival following subcutaneous treatment in CBS-/- mouse model 1 CBS -/- mice were dosed twice per week (BIW) starting at D10 with 0.81 mg/kg HED, AGLE-177 for 5 weeks to ensure survival. ADA development that impacts the PD response cannot be ruled out at this latter timepoint. Animals underwent a two-week washout of drug followed by a single subcutaneous (SC) injection of AGLE-177 and PD assessed (tHcy) over 1 week. 2 Animals dosed SC BIWx3. tHcy = total Homocysteine, HED = human equivalent dose P < 0.05 by Manley Cox test AGLE-177 (0.08 mg/kg HED, SC) AGLE-177 (0.81 mg/kg HED, SC) [LINE CHART] [ LINE CHART] Plasma tHcy tHcy (µM) 375 300 225 150 75 0 24 48 72 96 120 144 168 Hours Percent Survival (%) 100 50 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Age (Days) Begin Dosing Wean
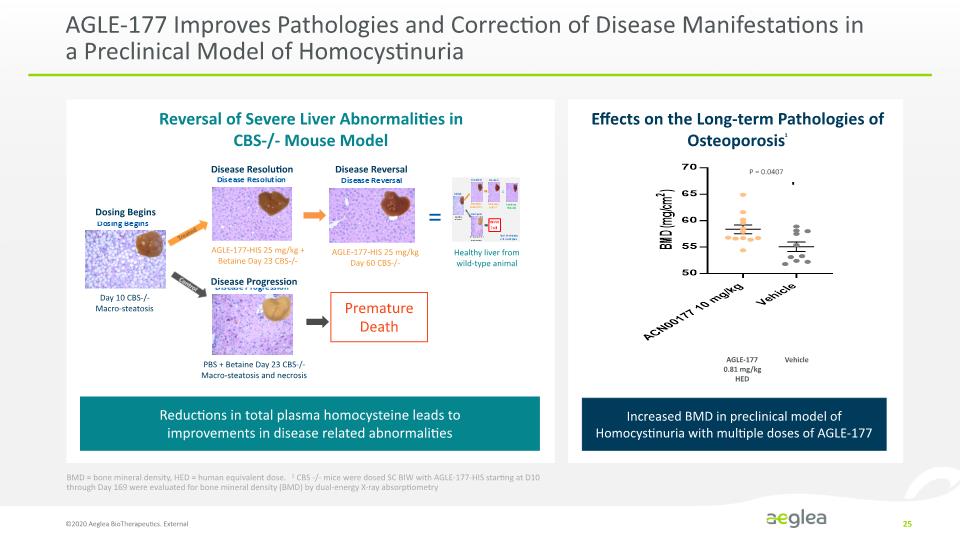
AGLE-177 Improves Pathologies and Correction of Disease Manifestations in a Preclinical Model of Homocystinuria ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 25 Disease Resolution Disease Reversal Dosing Begins Day 10 CBS-/- Macro-steatosis Disease Progression AGLE-177-HIS 25 mg/kg + Betaine Day 23 CBS-/- AGLE-177-HIS 25 mg/kg Day 60 CBS-/- PBS + Betaine Day 23 CBS-/- Macro-steatosis and necrosis Premature Death Healthy liver from wild-type animal Reversal of Severe Liver Abnormalities in CBS-/- Mouse Model Reductions in total plasma homocysteine leads to improvements in disease related abnormalities Effects on the Long-term Pathologies of Osteoporosis1 Increased BMD in preclinical model of Homocystinuria with multiple doses of AGLE-177 BMD = bone mineral density, HED = human equivalent dose. 1 CBS -/- mice were dosed SC BIW with AGLE-177-HIS starting at D10 through Day 169 were evaluated for bone mineral density (BMD) by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry [REVERSAL CHART] [OSTEOPOROSIS CHART] BMD (mg/cm2) 70 65 60 55 50 P = 0.0407 AGLE-177 0.81 mg/kg HED Vehicle
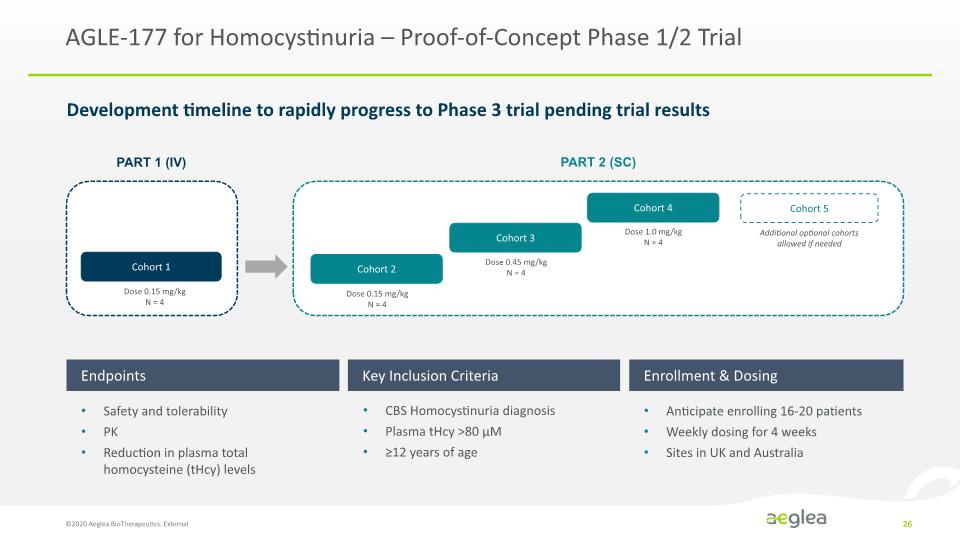
AGLE-177 for Homocystinuria – Proof-of-Concept Phase 1/2 Trial Development timeline to rapidly progress to Phase 3 trial pending trial results ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 26 Endpoints Key Inclusion Criteria Enrollment & Dosing Safety and tolerability PK Reduction in plasma total homocysteine (tHcy) levels CBS Homocystinuria diagnosis Plasma tHcy >80 µM ≥12 years of age Anticipate enrolling 16-20 patients Weekly dosing for 4 weeks Sites in UK and Australia [TIMELINE CHART] PART 1(IV) PART 2 (SC) Cohort 1 Dose 0.15 mg/kg N = 4 Cohort 2 Dose 0.15 mg/kg N = 4 Cohort 3 Dose 0.45 mg/kg N = 4 Cohort 4 Dose 1.0 mg/kg N = 4 Cohort 5 Additional optional cohorts allowed if needed
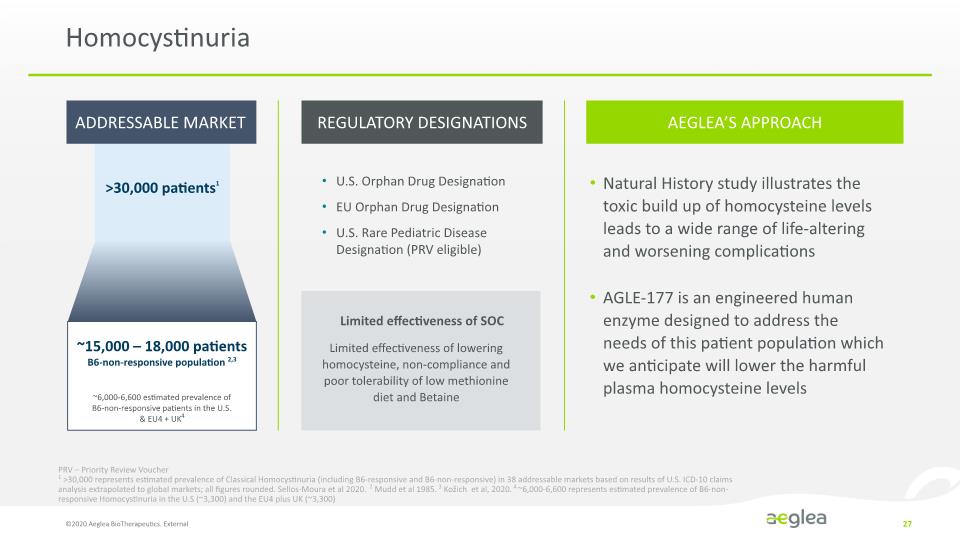
Homocystinuria ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 27 Limited effectiveness of SOC Limited effectiveness of lowering homocysteine, non-compliance and poor tolerability of low methionine diet and Betaine Natural History study illustrates the toxic build up of homocysteine levels leads to a wide range of life-altering and worsening complications AGLE-177 is an engineered human enzyme designed to address the needs of this patient population which we anticipate will lower the harmful plasma homocysteine levels ~15,000 – 18,000 patients B6-non-responsive population 2,3 ~6,000-6,600 estimated prevalence of B6-non-responsive patients in the U.S. & EU4 + UK4 U.S. Orphan Drug Designation EU Orphan Drug Designation U.S. Rare Pediatric Disease Designation (PRV eligible) PRV – Priority Review Voucher 1 >30,000 represents estimated prevalence of Classical Homocystinuria (including B6-responsive and B6-non-responsive) in 38 addressable markets based on results of U.S. ICD-10 claims analysis extrapolated to global markets; all figures rounded. Sellos-Moura et al 2020. 2 Mudd et al 1985. 3 Kožich et al, 2020. 4 ~6,000-6,600 represents estimated prevalence of B6-non-responsive Homocystinuria in the U.S (~3,300) and the EU4 plus UK (~3,300) ADDRESSABLE MARKET REGULATORY DESIGNATIONS AEGLEA’S APPROACH 30,000 patients1

Cystinuria Program
Cystinuria Overview ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 29 Cystinuria: Cystinuria is a metabolic disorder characterized by high levels of amino acid cystine in the urine, leading to the formation of stones in the kidney, ureter and bladder. Persistent stones can result in serious damage to the kidneys, causing an increased risk of hypertension and chronic kidney failure. Addressable Market: Estimated prevalence rate 1:15,000 Based on literature >10,000 Patients in addressable markets Episodes of severe abdominal pain Obstructive syndromes like hydronephrosis Hematuria and infective syndromes like pyelonephritis Chronic pain (opioid addiction risk) Hypertension, chronic kidney disease & reduced life expectancy Cystinuria Impact to Patients Castro Pereira DJ et al 2015, Leslie and Nazzal Renal Calculi (Cystinuria, Cystine Stones) (2018) Reference, Rozanski et al, Mil Med (2005) ), Soucie et al, JM Kidney Int (1994), >10,000 patients in addressable markets represents potential treatable patient population
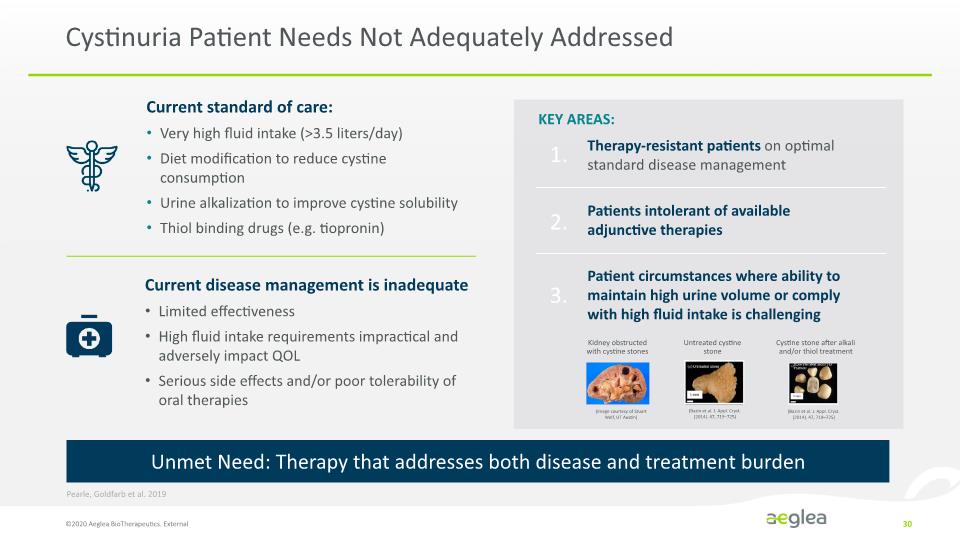
Cystinuria Patient Needs Not Adequately Addressed ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 30 Pearle, Goldfarb et al. 2019 Patient circumstances where ability to maintain high urine volume or comply with high fluid intake is challenging Therapy-resistant patients on optimal standard disease management KEY AREAS: Patients intolerant of available adjunctive therapies 1. 2. 3. Current standard of care: Very high fluid intake (>3.5 liters/day) Diet modification to reduce cystine consumption Urine alkalization to improve cystine solubility Thiol binding drugs (e.g. tiopronin) Current disease management is inadequate Limited effectiveness High fluid intake requirements impractical and adversely impact QOL Serious side effects and/or poor tolerability of oral therapies Unmet Need: Therapy that addresses both disease and treatment burden Kidney obstructed with cystine stones Untreated cystine stone Cystine stone after alkali and/or thiol treatment (Image courtesy of Stuart Wolf, UT Austin) (Bazin et al. J. Appl. Cryst. (2014). 47, 719–725) (Bazin et al. J. Appl. Cryst. (2014). 47, 719–725)
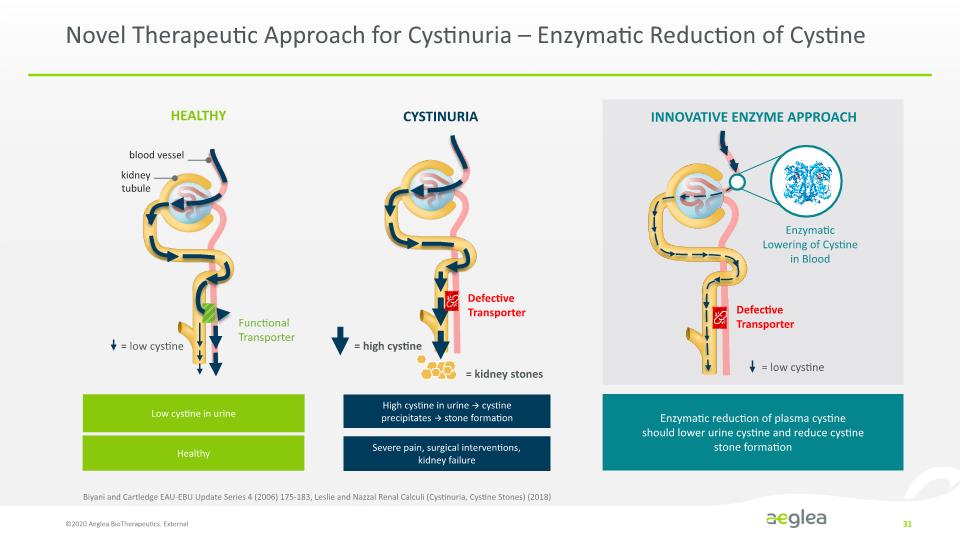
Novel Therapeutic Approach for Cystinuria – Enzymatic Reduction of Cystine ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 31 HEALTHY Low cystine in urine Healthy Functional Transporter INNOVATIVE ENZYME APPROACH Enzymatic reduction of plasma cystine should lower urine cystine and reduce cystine stone formation Biyani and Cartledge EAU-EBU Update Series 4 (2006) 175-183, Leslie and Nazzal Renal Calculi (Cystinuria, Cystine Stones) (2018) [HEALTHY DIAGRAM] [CYSTINURIA DIAGRAM] [INNOVATIVE ENZYME APPROACH DIAGRAM] CYSTINURIA blood vessel kidney tubule = low cystine Defective Transporter = high cystine = kidney stones Enzymatic Lowering of Cystine in Blood Defective Transporter = low cystine High cystine in urine > cystine precipitates > stone formation Severe pain, surgical interventions, kidney failure
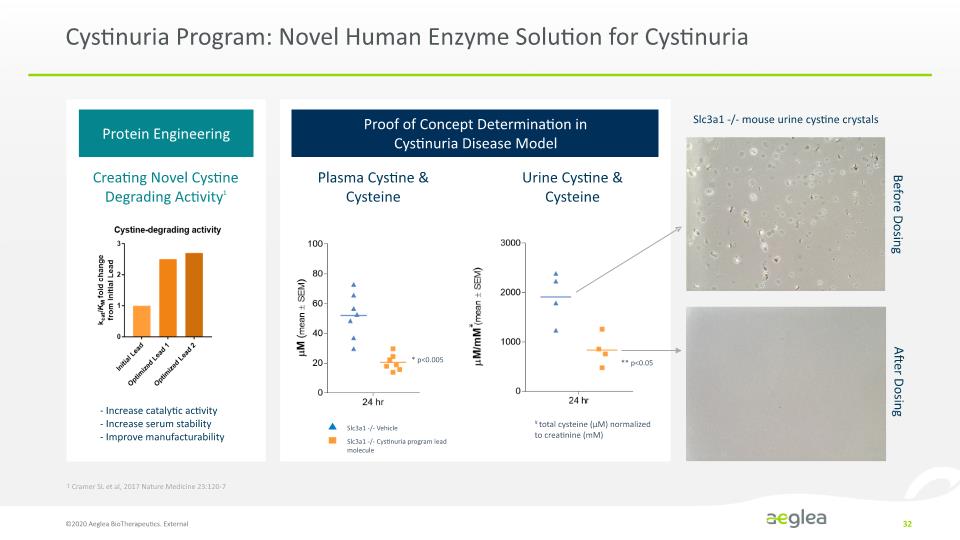
Cystinuria Program: Novel Human Enzyme Solution for Cystinuria ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 32 Before Dosing After Dosing Creating Novel Cystine Degrading Activity1 - Increase catalytic activity - Increase serum stability - Improve manufacturability Slc3a1 -/- mouse urine cystine crystals 1 Cramer SL et al, 2017 Nature Medicine 23:120-7 Cystine-degrading activity kcat/KM fold change from Initial Lead 0 1 2 3 Initial Lead Optimized Lead 1 Optimized Lead 2 Plasma Cystine & Cysteine Urine Cystine & Cysteine µM (mean ± SEM) 24 hr * p< 0.005 Slc3a1 -/- Vehicle Slc3a1 -/- Cystinuria program lead molecule µM/mM¥ (mean ± SEM) 3000 2000 1000 0 24 hr ** p<0.05 ¥ total cysteine (µM) normalize to creatinine (mM)
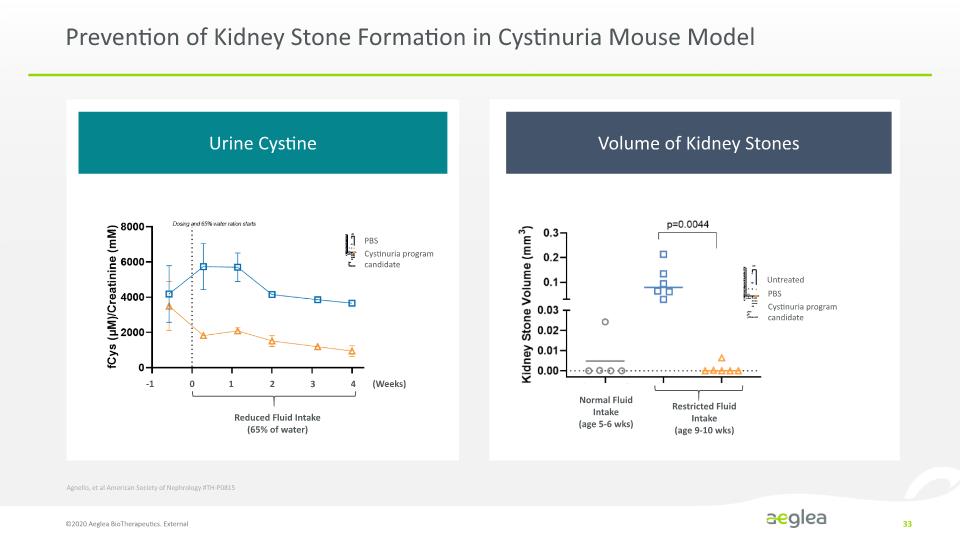
Prevention of Kidney Stone Formation in Cystinuria Mouse Model ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 33 0 1 2 3 4 -1 (Weeks) Reduced Fluid Intake (65% of water) Normal Fluid Intake (age 5-6 wks) Restricted Fluid Intake (age 9-10 wks) Agnello, et al American Society of Nephrology #TH-P0815 [LINE CHART] [PLOT CHART] Urine Cystine Volume of Kidney Stones fCys (µM)/Creatine (mM) 8000 6000 4000 2000 0 Dosing and 65% water ration starts PBS Cystinuria program candidate Kidney Stone Colume (mm3) 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.00 p=0.0044 Untreated PBS Cystinuria program candidate

Human Enzyme Platform

Leveraging Aeglea’s Next Generation Human Enzyme Platform ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 35 High activity human pegylated investigational enzyme Degrades key accumulating metabolite Results in restorative phenotypic improvements in genetically engineered mouse model PROOF OF CONCEPT Vehicle Control Therapeutic Enzyme Therapeutic Approach Unmet Medical Need Patient Population (Addressable Markets) Diagnosis Pegylated enhanced human enzyme Enzymatic control of high levels of a metabolite considered important in disease pathogenesis Very high - no effective therapy Early mortality and serious complications with continued disease progression >5,000 patients Plasma metabolite levels and mutation analysis

Strong Momentum with Near-Term Catalysts ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 36 ACCOMPLISHMENTS TARGETED MILESTONES Pegzilarginase: ARG1-D Completion of enrollment: March 2021 Topline pivotal Phase 3 data: 4Q2021 Pegzilarginase: ARG1-D Phase 1/2 & OLE efficacy data at 56 week analysis: Statistically significant arginine reduction vs baseline (p<0.001) Durable high clinical responder rate, 85% First patient dosed in pivotal Phase 3 PEACE trial Breakthrough Therapy Designation (BTD) PRV eligible: Rare Pediatric Disease Designation (RPD) Subcutaneous dosing; all eligible patients in OLE AGLE-177: Homocystinuria Phase 1/2 trial initiated in June 2020 U.S. and EU Orphan Designations PRV eligible: Rare Pediatric Disease Designation (RPD) Preclinical proof of concept: Plasma homocysteine levels reduction improves disease-related abnormalities Natural history study shows clear link between reductions in homocysteine levels and improvement Cystinuria Program Novel human enzyme based solution for disease management Proof of concept: Lowering of plasma cystine lowers urine cystine levels and reduces kidney stone formation in a preclinical disease model
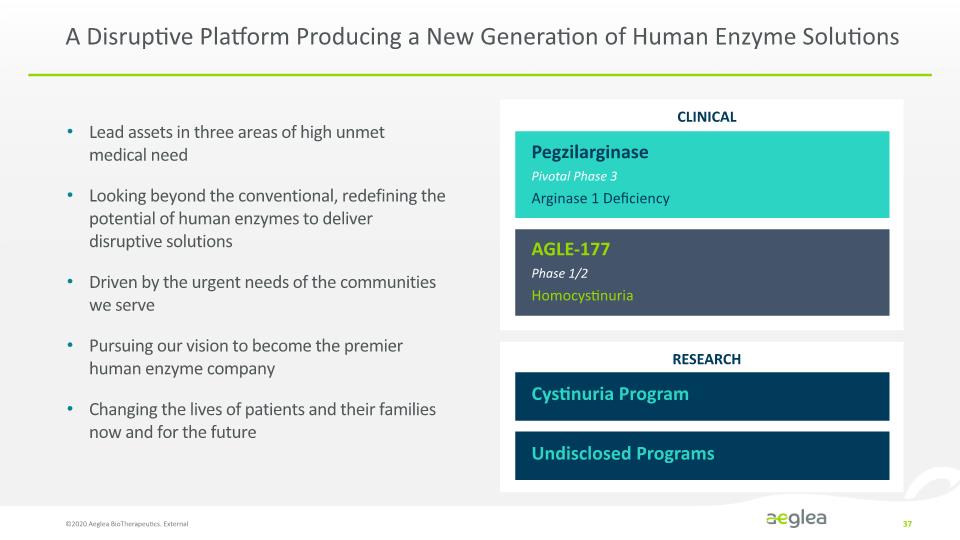
A Disruptive Platform Producing a New Generation of Human Enzyme Solutions ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 37 Lead assets in three areas of high unmet medical need Looking beyond the conventional, redefining the potential of human enzymes to deliver disruptive solutions Driven by the urgent needs of the communities we serve Pursuing our vision to become the premier human enzyme company Changing the lives of patients and their families now and for the future CLINICAL RESEARCH Pegzilarginase Pivotal Phase 3 Arginase 1 Deficiency AGLE-177 Phase 1/2 Homocystinuria Cystinuria Program Undisclosed Programs

Financial Summary ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 38 Cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities as of December 31, 2020: $148.1 million1 (no debt) As of March 12, 2021, 65.6 million2 common shares and pre-funded warrants outstanding Expected funding runway: into 2023 1Includes $1.8mm of restricted cash. 2Includes 48.0 million common shares outstanding and 17.6 million pre-funded warrants $ Millions Three Months Ended 12/31/20 Twelve Months Ended 12/31/20 R&D Expense G&A Expense Net Loss $15.8 $7.0 $22.7 $59.6 $21.8 $80.9

805 Las Cimas Parkway Suite 100 Austin, TX 78746 aeglea.com
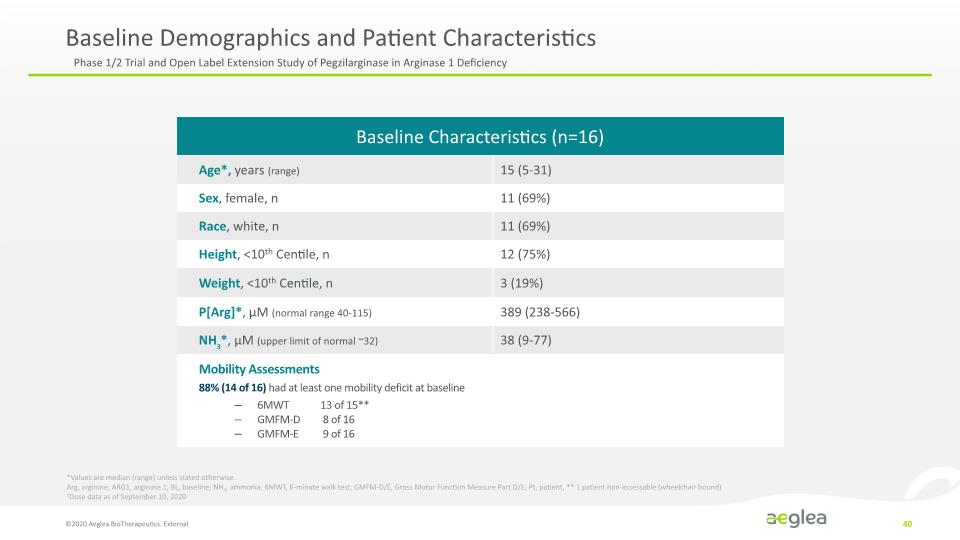
Baseline Demographics and Patient Characteristics ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 40 *Values are median (range) unless stated otherwise. Arg, arginine; ARG1, arginase 1; BL, baseline; NH3, ammonia; 6MWT, 6-minute walk test; GMFM-D/E, Gross Motor Function Measure Part D/E; Pt, patient, ** 1 patient non-assessable (wheelchair bound) 1Dose data as of September 10, 2020 Phase 1/2 Trial and Open Label Extension Study of Pegzilarginase in Arginase 1 Deficiency Baseline Characteristics (n=16) Age*, years (range) Sex, female, n Race, white, n Height, <10th Centile, n Weight, <10th Centile, n P[Arg]*, µM (normal range 40-115) NH3*, µM (upper limit of normal ~32) 15 (5-31) 11 (69%) 11 (69%) (75%) 3 (19%) 389 (238-566) 38 (9-77) Mobility Assessments 88% (14 of 16) had at least one mobility deficit at baseline 6MWT 13 of 15** GMFM-D 8 of 16 GMFM-E 9 of 16
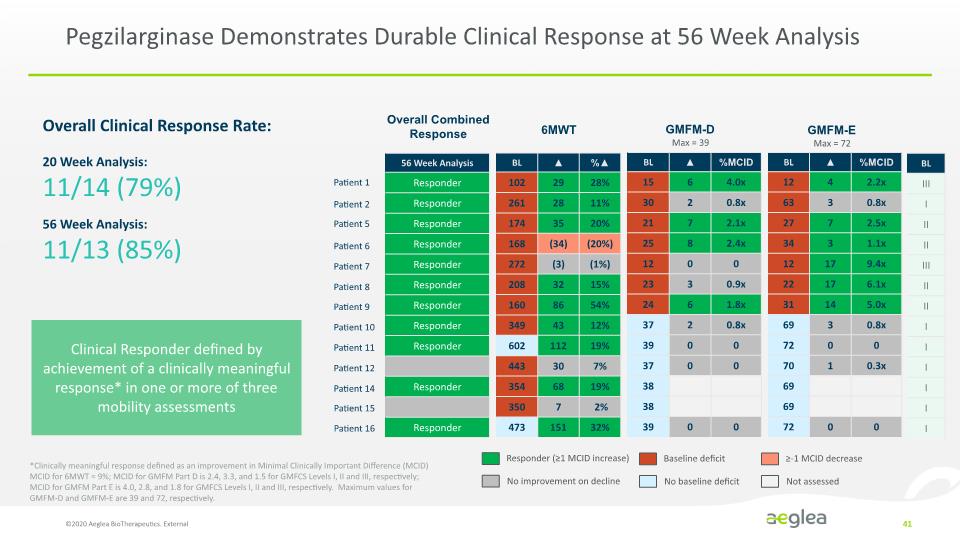
Pegzilarginase Demonstrates Durable Clinical Response at 56 Week Analysis Overall Combined Response Responder (≥1 MCID increase) No improvement on decline Baseline deficit No baseline deficit ≥-1 MCID decrease Not assessed Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 5 Patient 6 Patient 7 Patient 8 Patient 9 Patient 10 Patient 11 Patient 12 Patient 14 Patient 15 Patient 16 6MWT GMFM-D Max = 39 GMFM-E Max = 72 ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 41 Clinical Responder defined by achievement of a clinically meaningful response* in one or more of three mobility assessments 20 Week Analysis: 11/14 (79%) 56 Week Analysis: 11/13 (85%) Overall Clinical Response Rate: *Clinically meaningful response defined as an improvement in Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID) MCID for 6MWT = 9%; MCID for GMFM Part D is 2.4, 3.3, and 1.5 for GMFCS Levels I, II and III, respectively; MCID for GMFM Part E is 4.0, 2.8, and 1.8 for GMFCS Levels I, II and III, respectively. Maximum values for GMFM-D and GMFM-E are 39 and 72, respectively. [56 WEEK ANALYSIS CHART] 56 Week Analysis Responder Responder Responder Responder Responder Responder Responder Responder Responder Responder BL 102 261 174 168 272 208 160 349 602 443 354 350 473 29 28 35 (34) (3) 32 86 43 112 30 68 7 151 % 28% 11% 20% (20%) (1%) 15% 54% 12% 19% 7% 19% 2% 32% BL 15 30 21 25 12 23 24 37 39 37 38 38 39 6 2 7 8 0 3 6 2 0 0 0 %MCID 4.0x 0.8x 2.1x 2.4x 0 0.9x 1.8x 0.8x 0 0 0 BL12 63 27 34 12 22 31 69 72 70 69 69 72 4 3 7 3 17 17 14 3 0 1 0 %MCID 2.2x 0.8x 2.5x 1.1x 9.4x 6.1x 5.0x 0.8x 0 0.3x 0 BL III I II II III II II I I I I I I
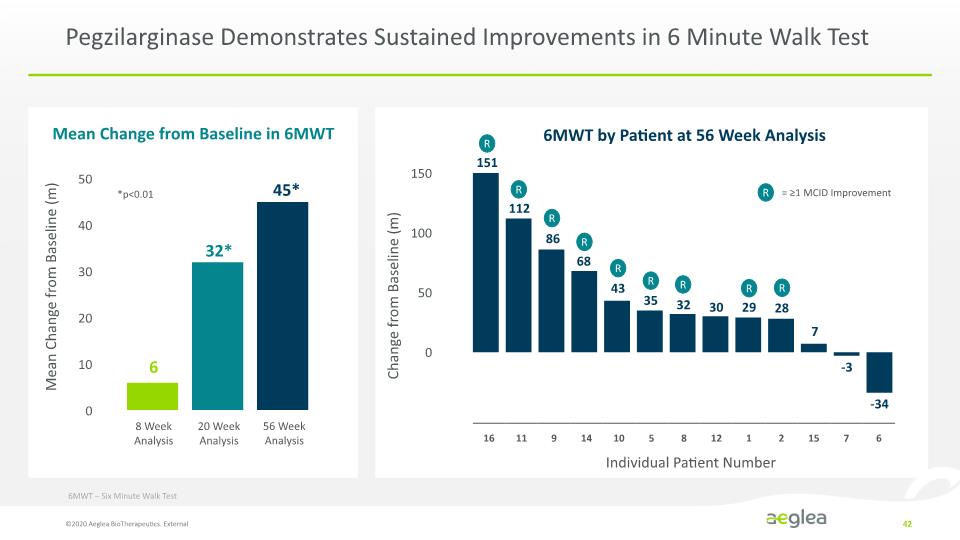
Pegzilarginase Demonstrates Sustained Improvements in 6 Minute Walk Test 6MWT – Six Minute Walk Test Mean Change from Baseline (m) 8 Week Analysis 20 Week Analysis 56 Week Analysis 6 32* 45* *p<0.01 Mean Change from Baseline in 6MWT 151 112 86 68 43 35 32 30 29 28 7 -3 -34 6MWT by Patient at 56 Week Analysis Individual Patient Number Change from Baseline (m) R R R R R R R R R R = ≥1 MCID Improvement 6MWT – Six Minute Walk Test ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 42 [BAR CHART] [BAR CHART] 50 40 30 20 10 0 150 100 50 0 16 11 9 14 10 5 8 12 1 2 15 7 6
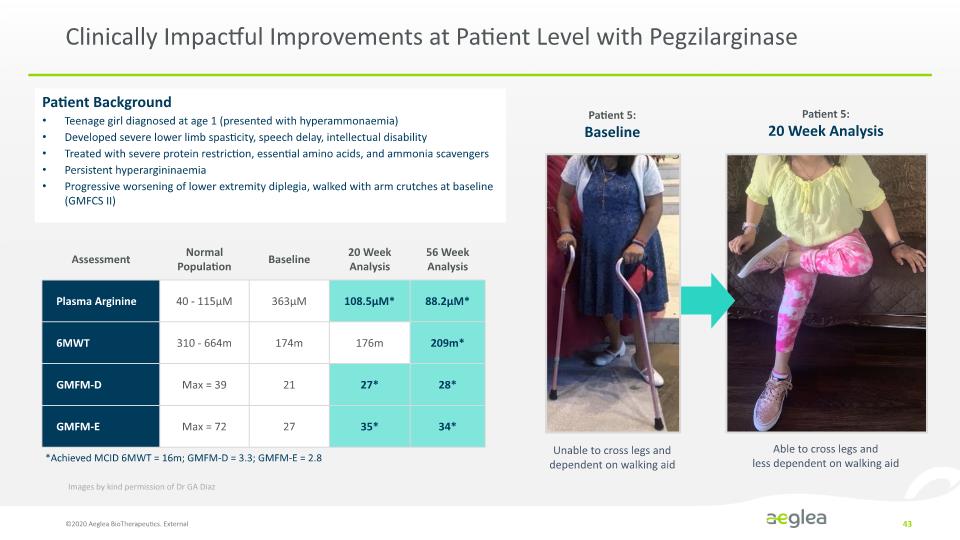
Clinically Impactful Improvements at Patient Level with Pegzilarginase ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 43 Images by kind permission of Dr GA Diaz Patient Background Teenage girl diagnosed at age 1 (presented with hyperammonaemia) Developed severe lower limb spasticity, speech delay, intellectual disability Treated with severe protein restriction, essential amino acids, and ammonia scavengers Persistent hyperargininaemia Progressive worsening of lower extremity diplegia, walked with arm crutches at baseline (GMFCS II) Patient 5: Baseline Patient 5: 20 Week Analysis *Achieved MCID 6MWT = 16m; GMFM-D = 3.3; GMFM-E = 2.8 Unable to cross legs and dependent on walking aid Able to cross legs and less dependent on walking aid Assessment Plasma Arginine 6MWT GMFM-D GMFM-E Normal Population 40 - 115µM 310 - 664m Max = 39 Max = 72 Baseline 363µM 174m 21 27 20 Week Analysis 108.5µM* 176m 27* 35* 56 Week Analysis 88.2µM* 209m* 28* 34*
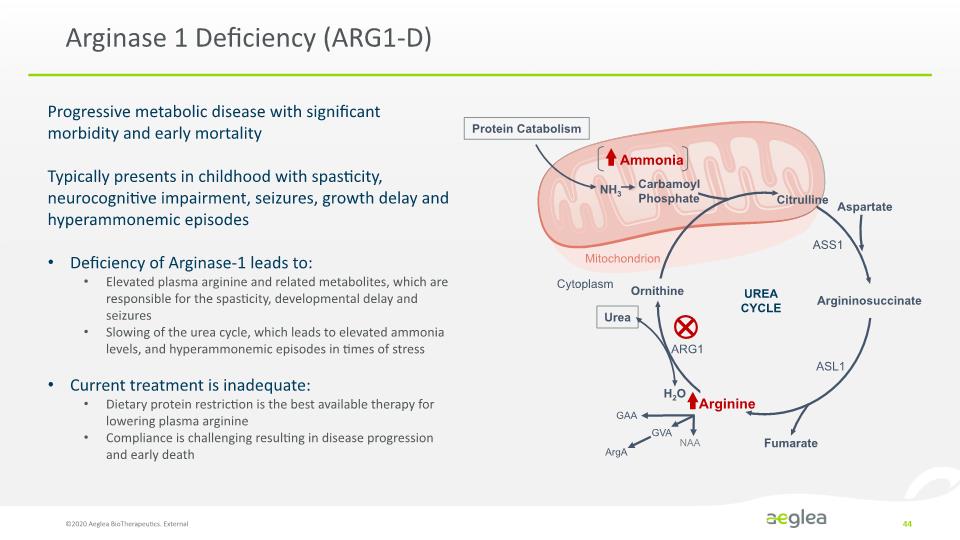
Arginase 1 Deficiency (ARG1-D) ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 44 Progressive metabolic disease with significant morbidity and early mortality Typically presents in childhood with spasticity, neurocognitive impairment, seizures, growth delay and hyperammonemic episodes Deficiency of Arginase-1 leads to: Elevated plasma arginine and related metabolites, which are responsible for the spasticity, developmental delay and seizures Slowing of the urea cycle, which leads to elevated ammonia levels, and hyperammonemic episodes in times of stress Current treatment is inadequate: Dietary protein restriction is the best available therapy for lowering plasma arginine Compliance is challenging resulting in disease progression and early death [UREA CYCLE DIAGRAM] Protein Catabolism Ammonia NH3 Carbamoyl Phosphate Citrulline Aspartate ASS1 Argininosuccinate ASL1 Fumarate Arginine NAA ArgA GVA GAA H2O ARG1 Urea Cytoplasm Mitochondrion UREA CYCLE Ornithine
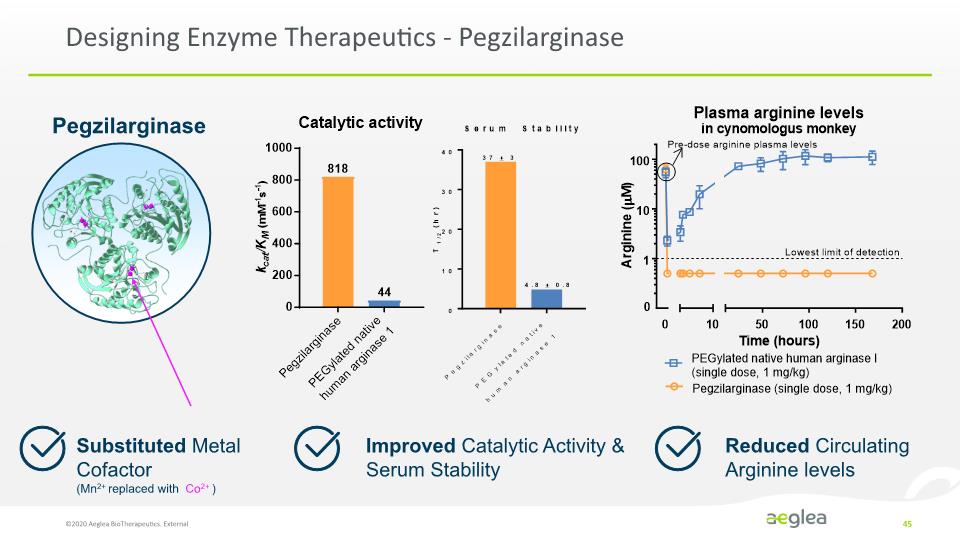
Designing Enzyme Therapeutics - Pegzilarginase ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 45 Improved Catalytic Activity & Serum Stability Reduced Circulating Arginine levels Substituted Metal Cofactor (Mn2+ replaced with Co2+ ) Pegzilarginase [PEGZILARGINASE DIAGRAM] [BAR CHART] [BAR CHART] Catalytic activity kcat/KM(mM-1s-1) 1000 800 600 400 200 0 818 44 Pegzilarginase PEGylated native human arginase 1 Serum Stability T1/2 (hr) 40 30 20 10 0 37 ± 3 4.8 ± 0.8 Plasma arginine levels in cynomologus monkey Pre-dose arginine plasma levels Arginine (µM) 100 10 1 0 0 10 50 100 150 200 Lowest limit of detection PEGylated native human arginase 1 (single dose, 1 mg/kg) Pegzilarginase (single dose, 1mg/kg)
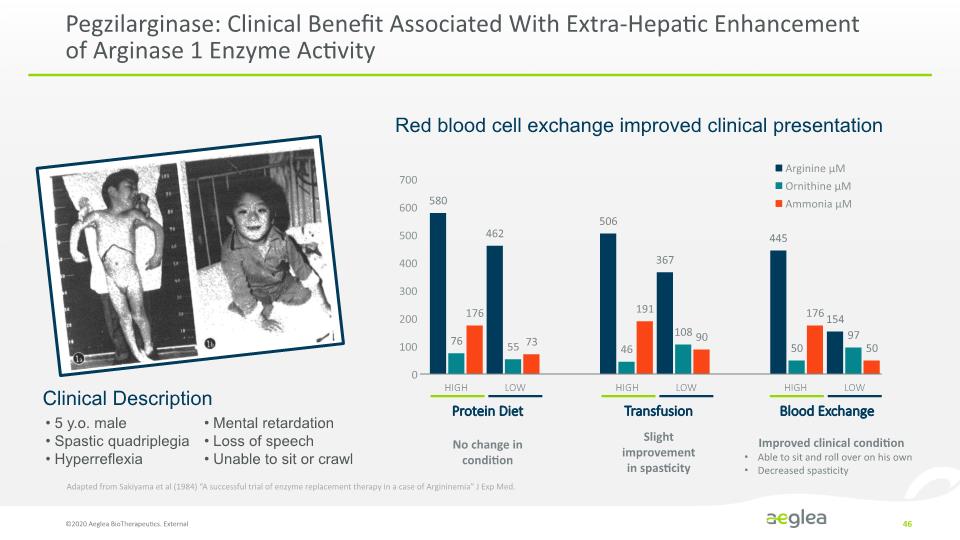
Pegzilarginase: Clinical Benefit Associated With Extra-Hepatic Enhancement of Arginase 1 Enzyme Activity ©2020 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 46 Slight improvement in spasticity Transfusion HIGH LOW Blood Exchange HIGH LOW Improved clinical condition Able to sit and roll over on his own Decreased spasticity Red blood cell exchange improved clinical presentation Adapted from Sakiyama et al (1984) “A successful trial of enzyme replacement therapy in a case of Argininemia” J Exp Med. Clinical Description 5 y.o. male Spastic quadriplegia Hyperreflexia Mental retardation Loss of speech Unable to sit or crawl [BAR CHART] [BAR CHART] HIGH LOW Protein Diet No change in condition 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 580 76 176 462 55 73 506 46 191 367 108 90 445 50 176 154 97 50 Arginine µM Ornithine µM Ammonia µM
