Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.2 - EX-99.2 - Kaleido Biosciences, Inc. | kldo-ex992_131.htm |
| 8-K - 8-K - Kaleido Biosciences, Inc. | kldo-8k_20210114.htm |

Leading a Novel Approach to Targeting the Microbiome NASDAQ: KLDO January 2021 Exhibit 99.1

Forward-Looking Statements This presentation also contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended, including, without limitation, statements regarding our strategy, business plans and focus, including the therapeutic potential of our Microbiome Metabolic Therapy (MMT) candidates, the timing of initiation, completion and reporting of results of our clinical studies and our strategy, business plans and focus. The words “may,” “will,” “could,” “would,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “project,” “potential,” “continue,” “target” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. Any forward-looking statements in this presentation are based on management’s current expectations and beliefs and are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and important factors that may cause actual events or results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation, including, without limitation, those related to planned clinical and preclinical studies and areas of interest, the preclinical and clinical development and safety profile of our MMT candidates and timelines associated with the programs for such MMT candidates, the fact that interim results from KB013 may not accurately predict final results from KB013 and that such final results may not support continued development of KB109, whether and when, if at all, our MMT candidates will receive approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or other applicable regulatory agencies, if any, competition from other biotechnology companies, and other risks identified in our SEC filings, including the most recently filed 10-K. We caution you not to place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date they are made. We disclaim any obligation to update or revise any such statements to reflect any change in expectations or in events, conditions or circumstances on which any such statements may be based, or that may affect the likelihood that actual results will differ from those set forth in the forward-looking statements.
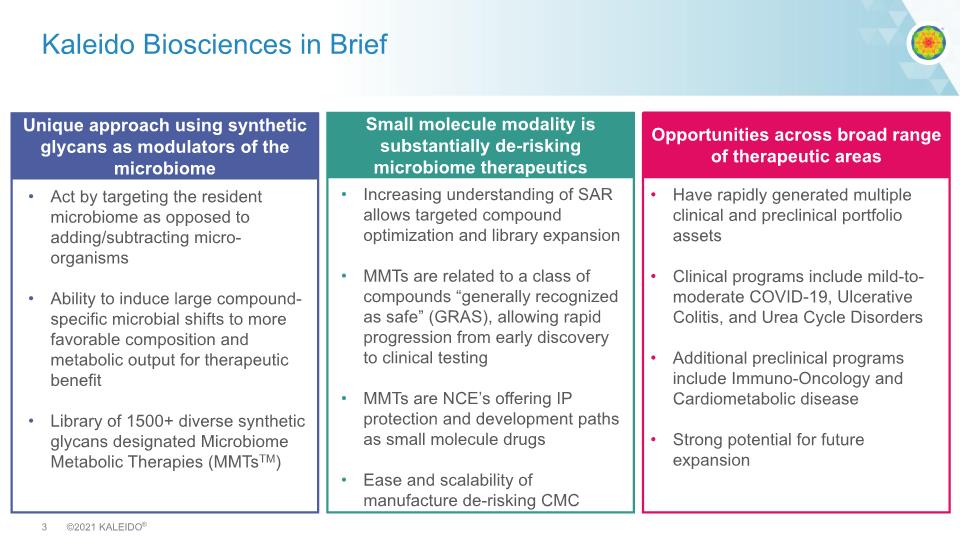
Kaleido Biosciences in Brief Unique approach using synthetic glycans as modulators of the microbiome Act by targeting the resident microbiome as opposed to adding/subtracting micro-organisms Ability to induce large compound-specific microbial shifts to more favorable composition and metabolic output for therapeutic benefit Library of 1500+ diverse synthetic glycans designated Microbiome Metabolic Therapies (MMTsTM) Opportunities across broad range of therapeutic areas Small molecule modality is substantially de-risking microbiome therapeutics Increasing understanding of SAR allows targeted compound optimization and library expansion MMTs are related to a class of compounds “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS), allowing rapid progression from early discovery to clinical testing MMTs are NCE’s offering IP protection and development paths as small molecule drugs Ease and scalability of manufacture de-risking CMC Have rapidly generated multiple clinical and preclinical portfolio assets Clinical programs include mild-to-moderate COVID-19, Ulcerative Colitis, and Urea Cycle Disorders Additional preclinical programs include Immuno-Oncology and Cardiometabolic disease Strong potential for future expansion

The Kaleido Leadership Team
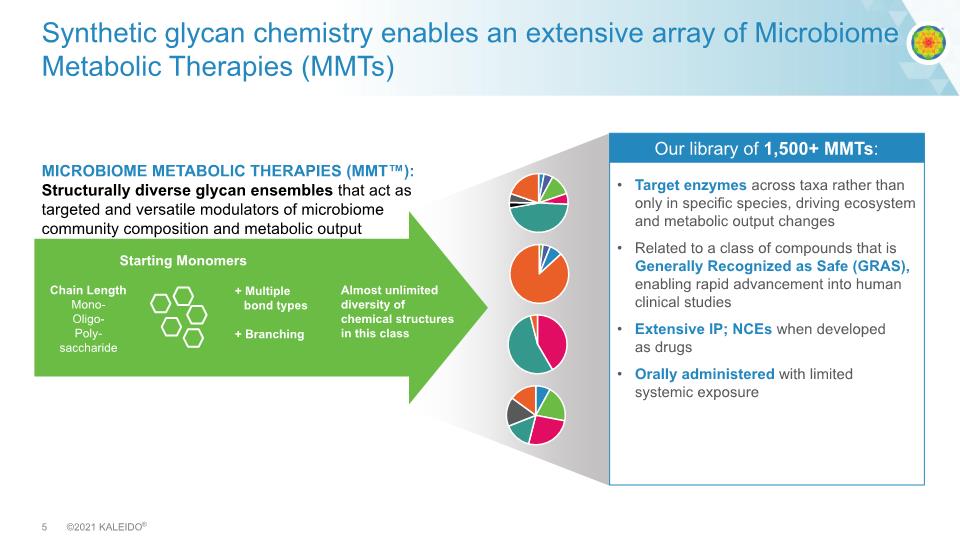
Synthetic glycan chemistry enables an extensive array of Microbiome Metabolic Therapies (MMTs) Target enzymes across taxa rather than only in specific species, driving ecosystem and metabolic output changes Related to a class of compounds that is Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS), enabling rapid advancement into human clinical studies Extensive IP; NCEs when developed as drugs Orally administered with limited systemic exposure MICROBIOME METABOLIC THERAPIES (MMT™): Structurally diverse glycan ensembles that act as targeted and versatile modulators of microbiome community composition and metabolic output Chain Length Mono- Oligo- Poly- saccharide Our library of 1,500+ MMTs: + Multiple bond types + Branching Starting Monomers Almost unlimited diversity of chemical structures in this class
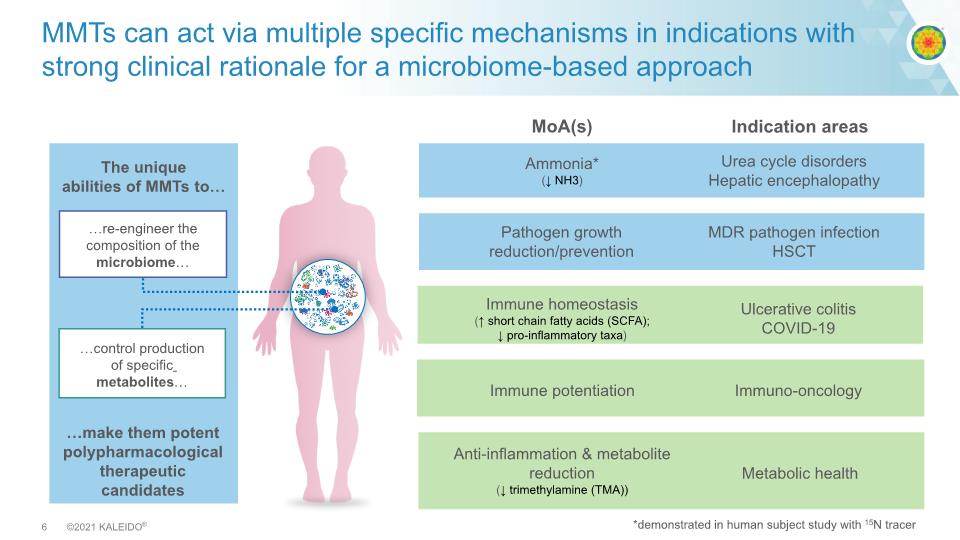
MMTs can act via multiple specific mechanisms in indications with strong clinical rationale for a microbiome-based approach The unique abilities of MMTs to… …make them potent polypharmacological therapeutic candidates Urea cycle disorders Hepatic encephalopathy MDR pathogen infection HSCT Immuno-oncology Ulcerative colitis COVID-19 Metabolic health Ammonia* (↓ NH3) Pathogen growth reduction/prevention Immune potentiation Immune homeostasis (↑ short chain fatty acids (SCFA); ↓ pro-inflammatory taxa) Anti-inflammation & metabolite reduction (↓ trimethylamine (TMA)) Indication areas MoA(s) *demonstrated in human subject study with 15N tracer

COVID-19 (KB109)
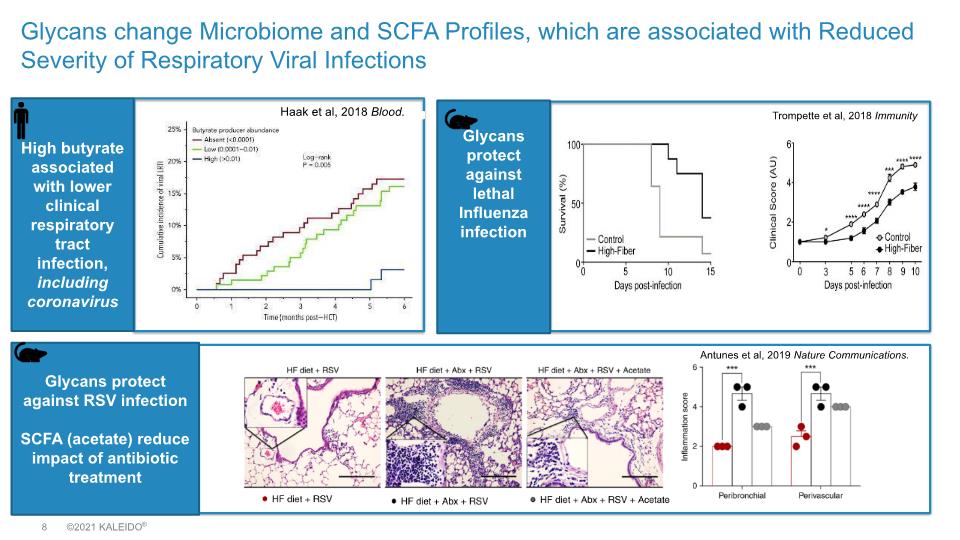
Glycans change Microbiome and SCFA Profiles, which are associated with Reduced Severity of Respiratory Viral Infections High butyrate associated with lower clinical respiratory tract infection, including coronavirus Haak et al, 2018 Blood. Trompette et al, 2018 Immunity Glycans protect against lethal Influenza infection Glycans protect against RSV infection SCFA (acetate) reduce impact of antibiotic treatment Antunes et al, 2019 Nature Communications.
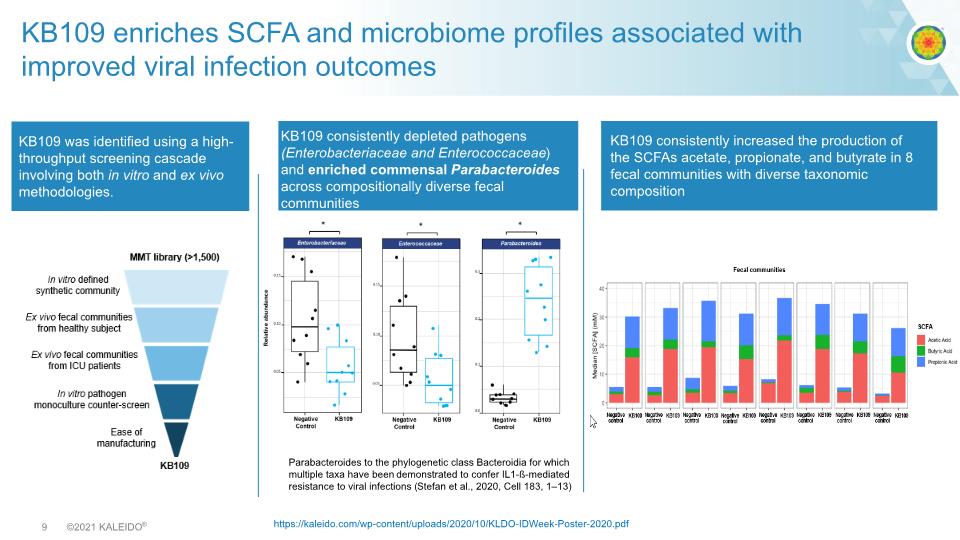
KB109 enriches SCFA and microbiome profiles associated with improved viral infection outcomes KB109 consistently depleted pathogens (Enterobacteriaceae and Enterococcaceae) and enriched commensal Parabacteroides across compositionally diverse fecal communities KB109 consistently increased the production of the SCFAs acetate, propionate, and butyrate in 8 fecal communities with diverse taxonomic composition Parabacteroides to the phylogenetic class Bacteroidia for which multiple taxa have been demonstrated to confer IL1-ß-mediated resistance to viral infections (Stefan et al., 2020, Cell 183, 1–13) KB109 was identified using a high-throughput screening cascade involving both in vitro and ex vivo methodologies. https://kaleido.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/KLDO-IDWeek-Poster-2020.pdf

A Randomized, Open Label, Prospective, Parallel Group Study to Assess the Natural History of COVID-19 and Effects of KB109 in Addition to Supportive Self Care (SSC) Compared to SSC Alone on Measures of Health in Non-hospitalized Patients with Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19
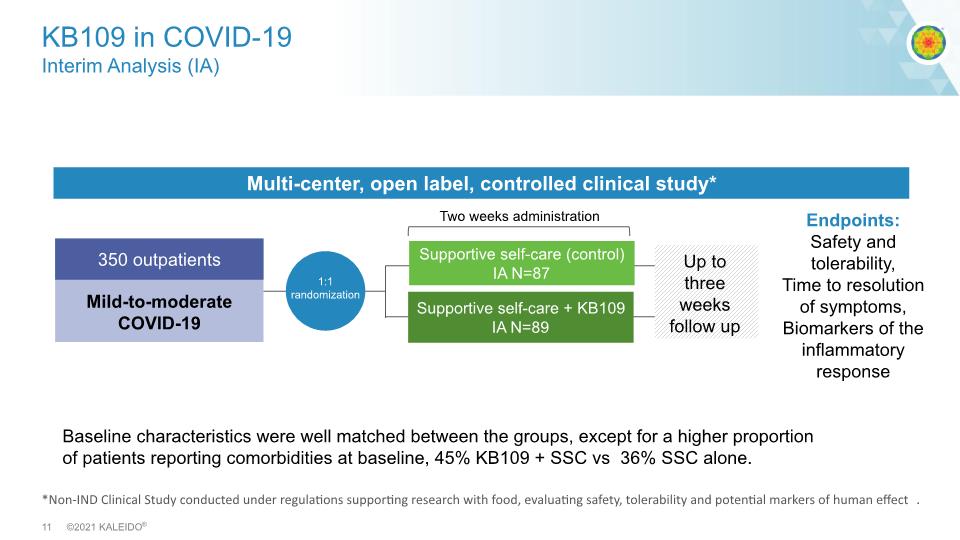
*Non-IND Clinical Study conducted under regulations supporting research with food, evaluating safety, tolerability and potential markers of human effect. KB109 in COVID-19 Interim Analysis (IA) High propionate High acetate Multi-center, open label, controlled clinical study* Mild-to-moderate COVID-19 Two weeks administration Endpoints: Safety and tolerability, Time to resolution of symptoms, Biomarkers of the inflammatory response 350 outpatients Supportive self-care (control) IA N=87 Supportive self-care + KB109 IA N=89 Up to three weeks follow up Baseline characteristics were well matched between the groups, except for a higher proportion of patients reporting comorbidities at baseline, 45% KB109 + SSC vs 36% SSC alone.

Results: Favorable Safety and Tolerability Profile Largest study of MMTs conducted so far, leading to most comprehensive safety data set to date Well tolerated with no treatment-related SAEs Hospitalizations: 2 in KB109+SSC vs 3 in SSC alone arm One death due to COVID-19 after withdrawal from study in SSC alone arm More GI-related AEs reported in KB109+SSC arm (18% vs 3%) Similar to that seen in previous studies of MMTs All were mild/moderate None led to study discontinuation There were more GI symptoms reported at baseline in KB109 arm than SSC alone arm (47% vs 33%)

Natural History of Mild to Moderate COVID-19: Time to Resolution of Symptoms
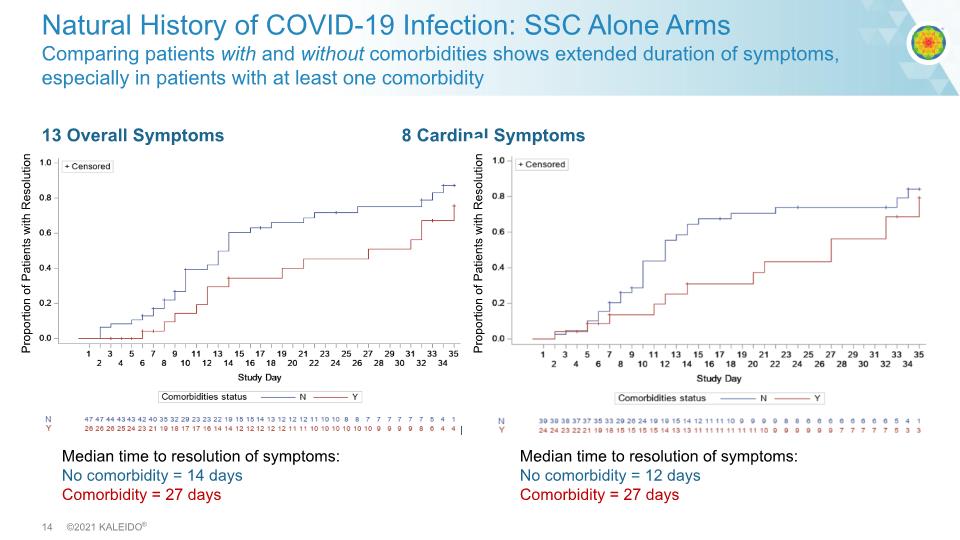
13 Overall Symptoms 8 Cardinal Symptoms Natural History of COVID-19 Infection: SSC Alone Arms Comparing patients with and without comorbidities shows extended duration of symptoms, especially in patients with at least one comorbidity Proportion of Patients with Resolution Proportion of Patients with Resolution Median time to resolution of symptoms: No comorbidity = 14 days Comorbidity = 27 days Median time to resolution of symptoms: No comorbidity = 12 days Comorbidity = 27 days

Time to Resolution of Overall 13 COVID-19 Related Symptoms Cough, chills/repeated shaking with chills, muscle pain, fever, headache, anosmia/ageusia, shortness of breath, sore throat, gastrointestinal disturbance/symptoms, diarrhea, fatigue, nasal congestion, and chest tightness

Kaplan-Meier Curve Intake and Follow-up Period Time to Resolution of Overall 13 Symptoms Primary Analysis

13 Overall Symptoms Full Analysis Set Median time to resolution of symptoms: KB109 + SSC = 18 days SSC alone = 27 days

Time to Resolution of 8 Cardinal COVID-19 Symptoms Cough, chills/repeated shaking with chills, muscle pain, fever, headache, anosmia/ageusia, shortness of breath, and sore throat

Kaplan-Meier curve Intake and Follow-up Period Time to Resolution of 8 Cardinal Symptoms Full analysis set

8 Cardinal Symptoms Full Analysis Set Median time to resolution of symptoms: KB109 + SSC= 15 days SSC alone = 27 days
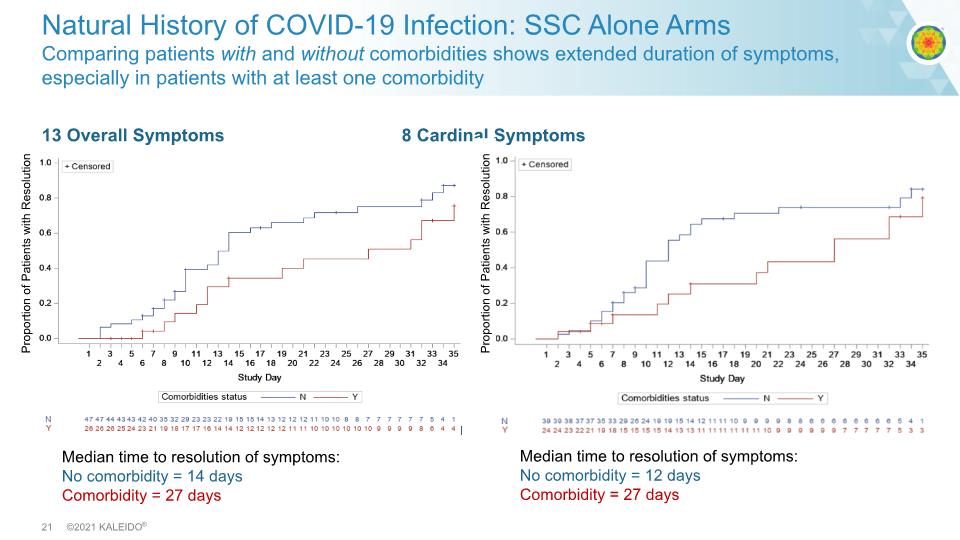
13 Overall Symptoms 8 Cardinal Symptoms Natural History of COVID-19 Infection: SSC Alone Arms Comparing patients with and without comorbidities shows extended duration of symptoms, especially in patients with at least one comorbidity Proportion of Patients with Resolution Median time to resolution of symptoms: No comorbidity = 14 days Comorbidity = 27 days Median time to resolution of symptoms: No comorbidity = 12 days Comorbidity = 27 days Proportion of Patients with Resolution
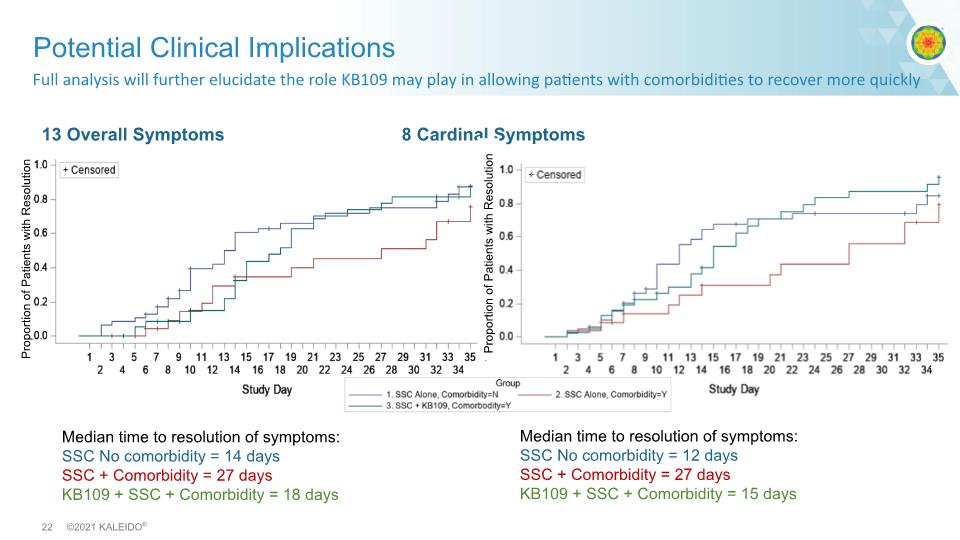
Full analysis will further elucidate the role KB109 may play in allowing patients with comorbidities to recover more quickly Potential Clinical Implications 13 Overall Symptoms 8 Cardinal Symptoms Median time to resolution of symptoms: SSC No comorbidity = 14 days SSC + Comorbidity = 27 days KB109 + SSC + Comorbidity = 18 days Median time to resolution of symptoms: SSC No comorbidity = 12 days SSC + Comorbidity = 27 days KB109 + SSC + Comorbidity = 15 days Proportion of Patients with Resolution Proportion of Patients with Resolution
Preliminary Results from Interim Analysis Requires confirmation from full dataset Study is now fully enrolled with topline data expected for the full study in Q1 Favorable safety and tolerability profile with no new safety signals in the largest study of MMT No differences seen between KB109+SSC and SSC alone arms in patients who did not report a comorbidity at baseline First study to show protracted time to resolution of symptoms in mild to moderate COVID-19, particularly in patients with comorbidities Promising data showing reduction in time to resolution of symptoms in patients who report at least one comorbidity at baseline

Inflammatory Bowel Disease (KB295)
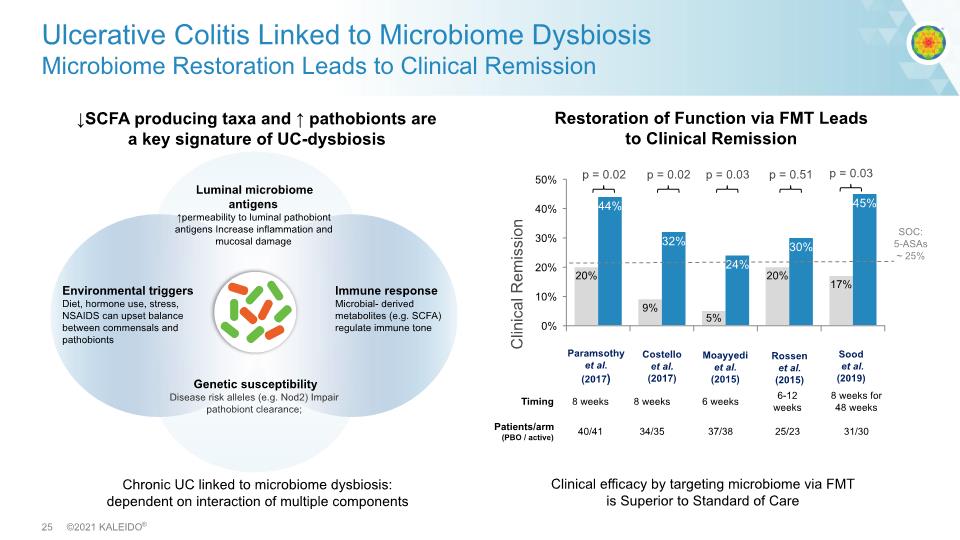
↓SCFA producing taxa and ↑ pathobionts are a key signature of UC-dysbiosis Ulcerative Colitis Linked to Microbiome Dysbiosis Microbiome Restoration Leads to Clinical Remission Clinical efficacy by targeting microbiome via FMT is Superior to Standard of Care p = 0.02 p = 0.02 p = 0.03 p = 0.51 Clinical Remission Paramsothy et al. (2017) Costello et al. (2017) Moayyedi et al. (2015) Rossen et al. (2015) SOC: 5-ASAs ~ 25% Chronic UC linked to microbiome dysbiosis: dependent on interaction of multiple components Sood et al. (2019) p = 0.03 Restoration of Function via FMT Leads to Clinical Remission Luminal microbiome antigens ↑permeability to luminal pathobiont antigens Increase inflammation and mucosal damage Genetic susceptibility Disease risk alleles (e.g. Nod2) Impair pathobiont clearance; Environmental triggers Diet, hormone use, stress, NSAIDS can upset balance between commensals and pathobionts Immune response Microbial- derived metabolites (e.g. SCFA) regulate immune tone
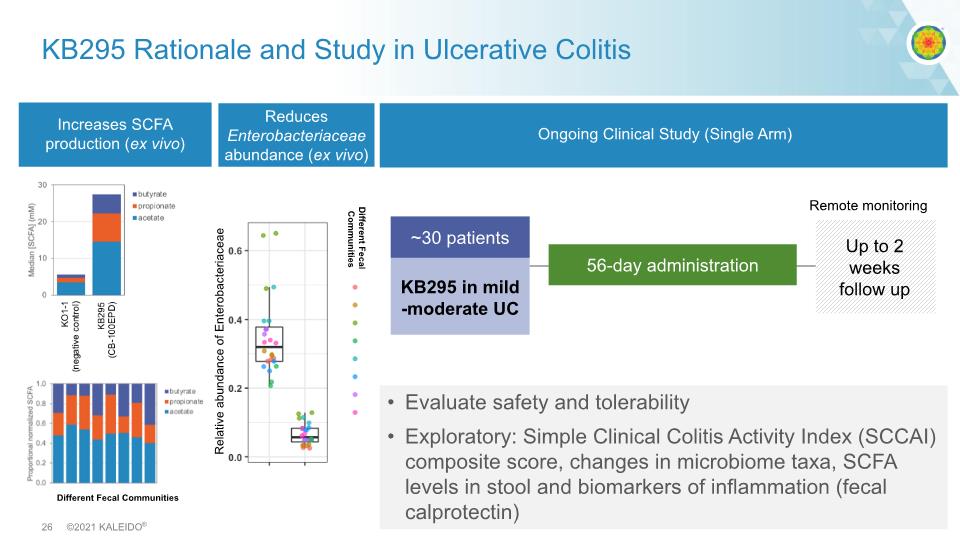
KB295 Rationale and Study in Ulcerative Colitis Increases SCFA production (ex vivo) Ongoing Clinical Study (Single Arm) Evaluate safety and tolerability Exploratory: Simple Clinical Colitis Activity Index (SCCAI) composite score, changes in microbiome taxa, SCFA levels in stool and biomarkers of inflammation (fecal calprotectin) Different Fecal Communities High propionate KB295 in mild-moderate UC ~30 patients 56-day administration Up to 2 weeks follow up Remote monitoring Reduces Enterobacteriaceae abundance (ex vivo) Relative abundance of Enterobacteriaceae

Key Expected Upcoming Milestones – by mid-2021 2020 COVID-19 (K031) study – Q1’2021 COVID-19 (K032) study – Q1’2021 Ulcerative Colitis (K030) study – mid-2021 Clinical Results* *Non-IND clinical studies

Pre-Clinical Programs Intellectual Property Financials

Advancing Our MMTs for Lead Identification Poised to Deliver Multiple Clinical-Ready Programs in 2021 Jeffrey Gordon, MD Glycan chemistry & utilization Gnotobiotic preclinical models combined with computational methods to further identify molecular pathways of how MMTs can modify functional configuration of the gut microbiome and its metabolic outputs

Robust Global IP Portfolio 14 U.S. and European Patents Issued and 150+ Pending Applications Worldwide 12 U.S. Patents + 2 EPO Patents: Glycan pharmaceutical compositions (U.S. and Europe) Methods to treat cancer (U.S.) Methods to treat pathogen infection (U.S.) Methods to treat obesity (U.S.) Methods to treat dysbiosis (U.S.) Methods to reduce ammonia (U.S.) Methods to treat diarrhea (U.S.) Catalyst compositions (U.S. and Europe) 150+ Non-Provisional Applications Pending, Worldwide in 20+ Regions/Countries Glycan compositions Methods of making glycans Methods to modulate short chain fatty acids Continued IP Expansion by Filing Patent Applications Directed to Pharmaceutical Compositions, Methods of Treatment and Methods of Manufacture
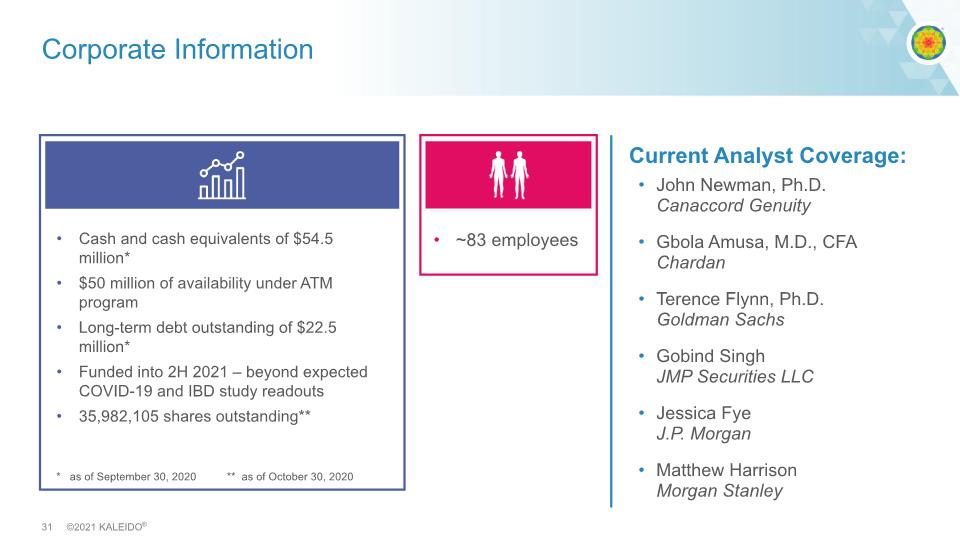
Corporate Information John Newman, Ph.D. Canaccord Genuity Gbola Amusa, M.D., CFA Chardan Terence Flynn, Ph.D. Goldman Sachs Gobind Singh JMP Securities LLC Jessica Fye J.P. Morgan Matthew Harrison Morgan Stanley Current Analyst Coverage: Cash and cash equivalents of $54.5 million* $50 million of availability under ATM program Long-term debt outstanding of $22.5 million* Funded into 2H 2021 – beyond expected COVID-19 and IBD study readouts 35,982,105 shares outstanding** * as of September 30, 2020 ** as of October 30, 2020 ~83 employees
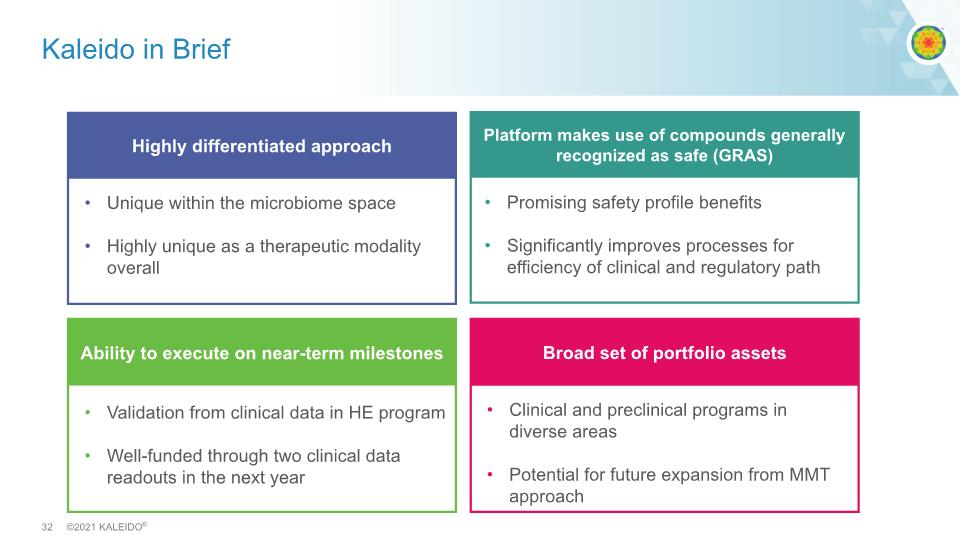
Kaleido in Brief Highly differentiated approach Unique within the microbiome space Highly unique as a therapeutic modality overall Broad set of portfolio assets Platform makes use of compounds generally recognized as safe (GRAS) Ability to execute on near-term milestones Promising safety profile benefits Significantly improves processes for efficiency of clinical and regulatory path Clinical and preclinical programs in diverse areas Potential for future expansion from MMT approach Validation from clinical data in HE program Well-funded through two clinical data readouts in the next year

Appendix: COVID-19 Interim Analysis (KB109)
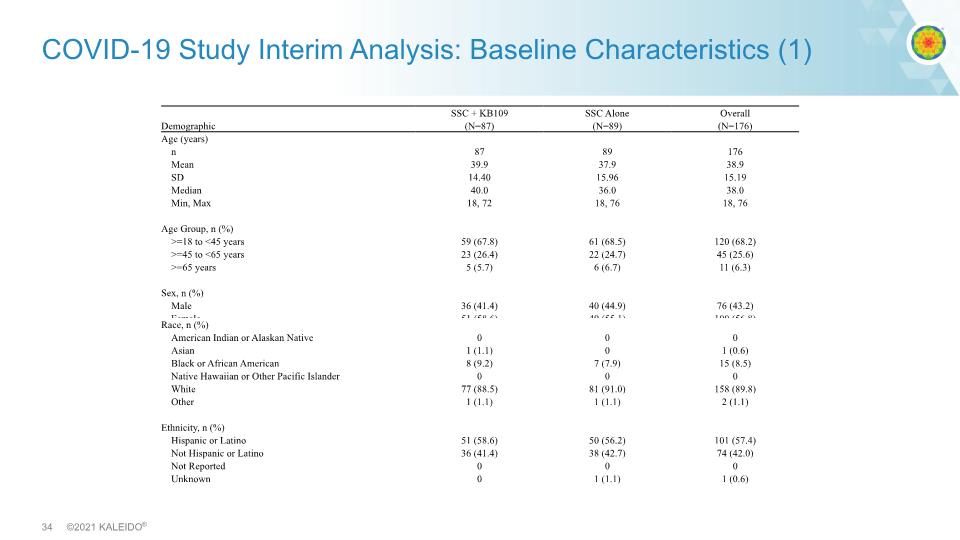
COVID-19 Study Interim Analysis: Baseline Characteristics (1)
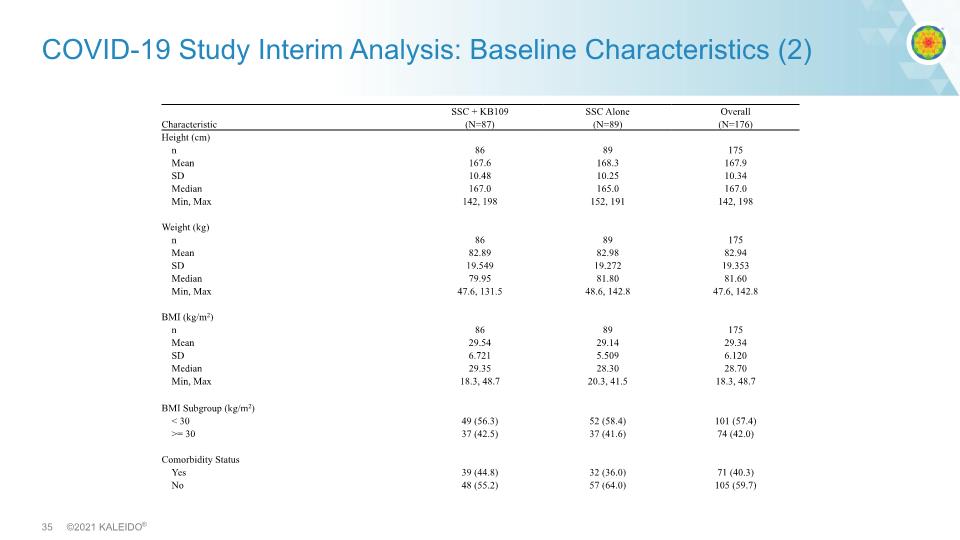
COVID-19 Study Interim Analysis: Baseline Characteristics (2)
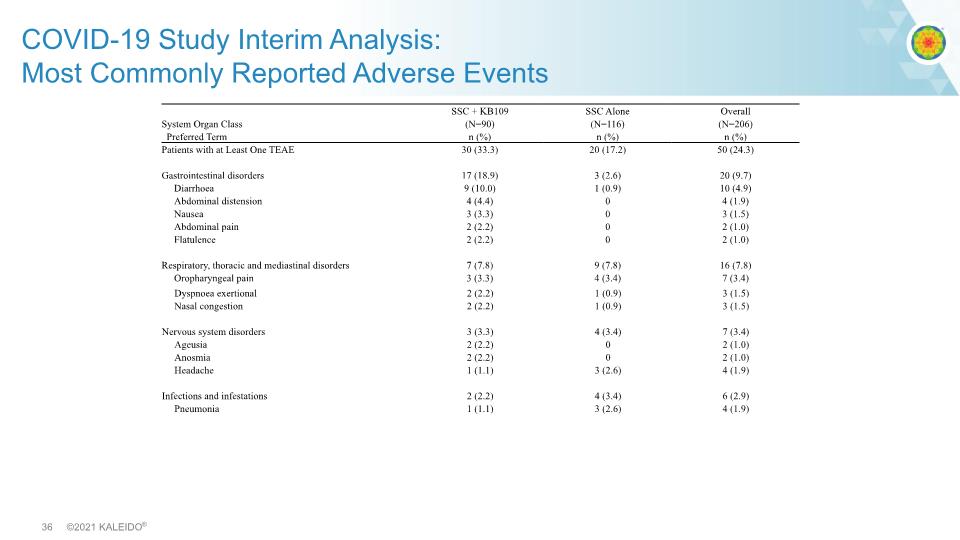
COVID-19 Study Interim Analysis: Most Commonly Reported Adverse Events

COVID-19 Study Interim Analysis: Most Common Symptoms at Baseline
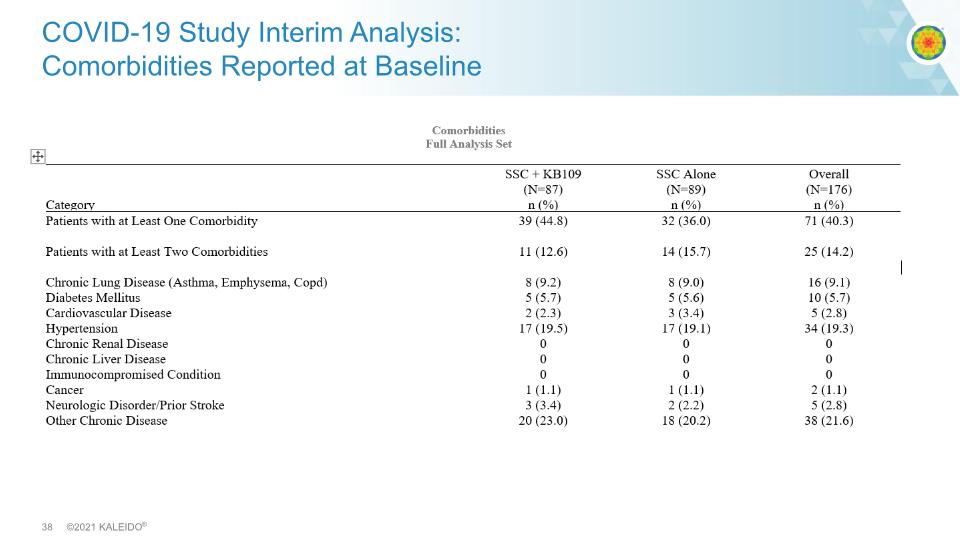
COVID-19 Study Interim Analysis: Comorbidities Reported at Baseline
