Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.2 - EX-99.2 - CASSAVA SCIENCES INC | sava-20201104xex99_2.htm |
| 8-K - 8-K - CASSAVA SCIENCES INC | sava-20201104x8k.htm |
Exhibit 99.1

Sumifilam Significantly Improves Eleven CSF Biomarkers in a Randomized, Placebo-controlled, One-month Clinical Trial in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients Lindsay BURNS, Hoau-Yan WANG, Zhe PEI, Kuo-Chieh LEE, Yaneicy GONZALEZ-ROJAS, Tamara DOEHNER, John PUENTE, Patrick SCIARA, Brian BECK, Evelyn LOPEZ-BRIGNONI, Boris NIKOLOV, Carrie CROWLEY, Nadav FRIEDMANN November 7, 2020 CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 1

Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. To identify such forward-looking statements, in some cases we use terms such as “predicts, “believes,” “potential,” “estimates,” “anticipates,” “expects,” “plans,” “intends,” “may,” “could,” “might,” “should” or other words that will convey risk or uncertainty of future events or outcomes. All statements other than statements of historical fact contained in this presentation including, but not limited to, statements regarding plans or timing for future Phase 3 clinical studies with sumifilam; the interpretation of prior or current results of our Phase 2 clinical studies, including the measured effects of sumifilam on cognition; plans to publish results in a peer-reviewed journal; potential health benefits, if any, of changes in levels of CSF biomarkers; verbal commentaries made by Cassava Sciences’ employees; and potential benefits, if any, of the Company’s product candidates for Alzheimer’s disease are forward-looking statements. Such statements are based largely on our current expectations and projections about future events. Such statements speak only as of the date of this presentation and are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and assumptions, including, but not limited to, those risks relating to the ability to conduct or complete clinical studies on expected timelines, to demonstrate the specificity, safety, efficacy or potential health benefits of our product candidates, the severity and duration of health care precautions given the international outbreak of an infectious disease and including those described in the section entitled “Risk Factors” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019 and future reports to be filed with the SEC. In light of these risks, uncertainties and assumptions, forward-looking statements and events discussed in this presentation are inherently uncertain and may not occur. Actual results could differ quickly, materially and adversely from those anticipated or implied in the forward-looking statements. Accordingly, you should never rely upon forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. We do not undertake any obligation to update this corporate presentation or any forward-looking statements included therein, except as required by law. The content of this presentation is solely our responsibility and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 2

Disclosures Sumifilam is under clinical development by Cassava Sciences, Inc. L.H. Burns, PhD, N. Friedmann, PhD, MD, and C. Crowley are employees of Cassava Sciences. H-Y. Wang, PhD, is a consultant to Cassava Sciences. H-Y. Wang, PhD, Z. Pei, PhD, and K-C. Lee are employees of City University of New York School of Medicine. Sumifilam benefits from long-term scientific & financial support from the National Institute on Aging (AG050301, AG056166, AG060878, AG065152).
CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 3
Introduction to Sumifilam Sumifilam is a proprietary, small molecule drug candidate to treat Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative diseases. Drug was discovered and developed in-house, 2008 to present. Sumifilam binds a single target, has a dual mechanism of action: Reduces neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. Published preclinical and mechanism of action data support sumifilam’s potential as a disease-modifying drug for AD that may also enhance cognition.
CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 4
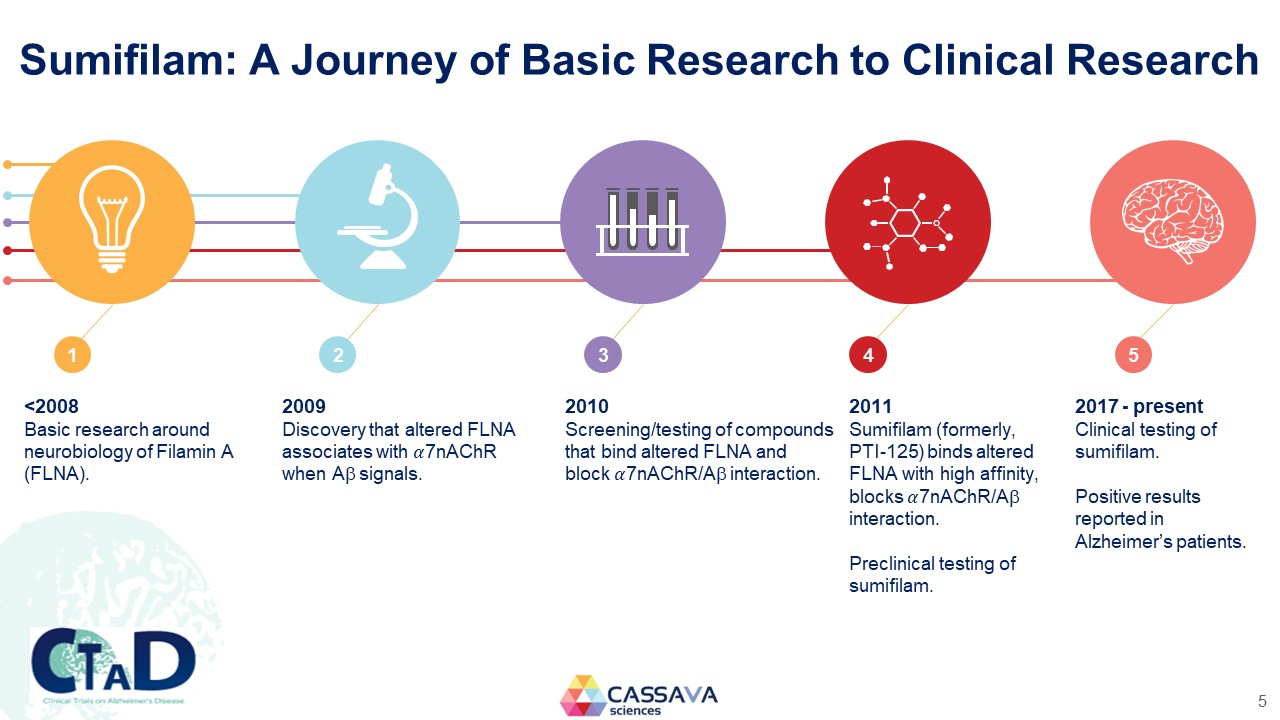
Sumifilam: A Journey of Basic Research to Clinical Research 1 <2008 Basic research around neurobiology of Filamin A (FLNA). 2 2009 Discovery that altered FLNA associates with ��7nAChR when A signals. 3 2010 Screening/testing of compounds that bind altered FLNA and block ��7nAChR/A interaction. 4 2011 Sumifilam (formerly, PTI-125) binds altered FLNA with high affinity, blocks 7nAChR/A interaction. Preclinical testing of sumifilam. 5 2017 - present Clinical testing of sumifilam. Positive results reported in Alzheimer’s patients. CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 5

Phase 2b Clinical Study of Sumifilam I. Mechanism of Action II. Phase 2b Study Results II. Study Conclusions CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 6
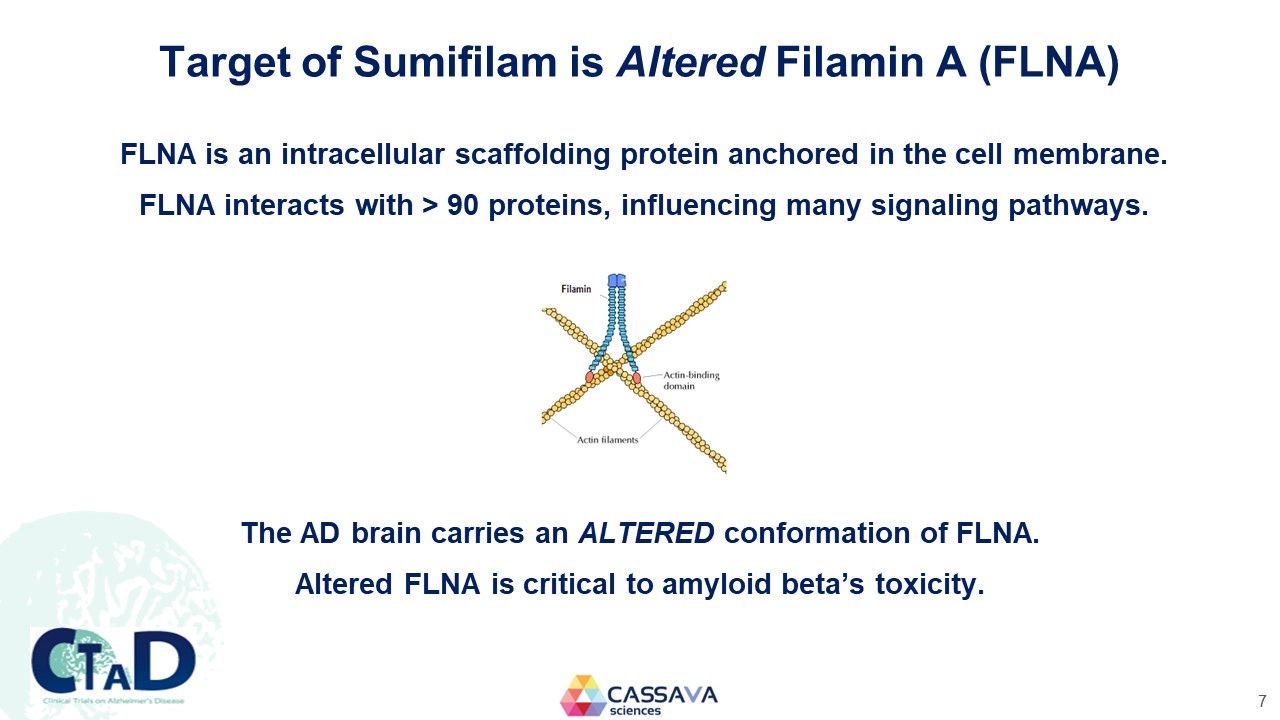
Target of Sumifilam is Altered Filamin A (FLNA) FLNA is an intracellular scaffolding protein anchored in the cell membrane. FLNA interacts with > 90 proteins, influencing many signaling pathways. Filamin Actin-binding domain Actin filaments The AD brain carries an ALTERED conformation of FLNA. Altered FLNA is critical to amyloid beta’s toxicity. CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 7
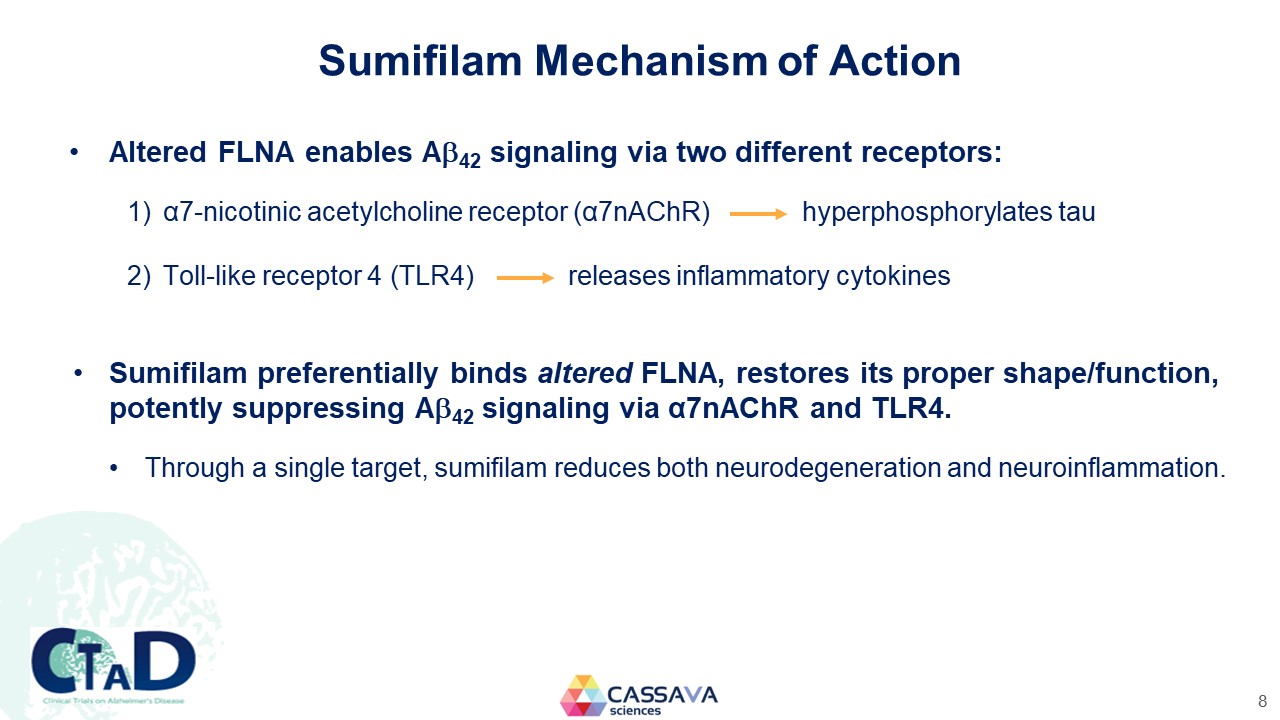
Sumifilam Mechanism of Action Altered FLNA enables A42 signaling via two different receptors: 1) α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR) hyperphosphorylates tau 2) Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) releases inflammatory cytokines Sumifilam preferentially binds altered FLNA, restores its proper shape/function, potently suppressing α42 signaling via α7nAChR and TLR4. Through a single target, sumifilam reduces both neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 8
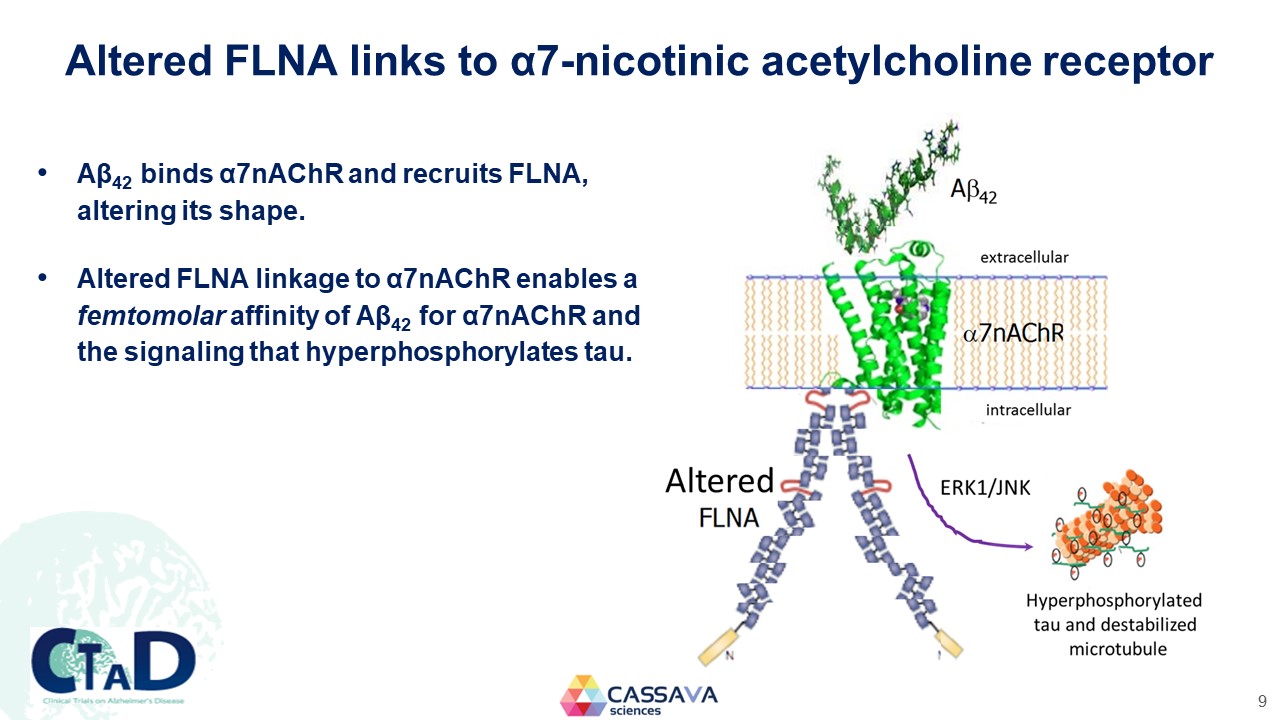
Altered FLNA links to α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor Aβ42 binds α7nAChR and recruits FLNA, altering its shape. Altered FLNA linkage to α7nAChR enables a femtomolar affinity of Aβ42 for α7nAChR and the signaling that hyperphosphorylates tau. Sumifilam binds altered FLNA, restores its normal shape, stops Aβ42 signaling and tau hyperphosphorylation. Aβ42 extracellular α7nAChR intracellular Alterned FLNA RK1/JNK Hyperphosporylated tau and destablized microtubule CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 9
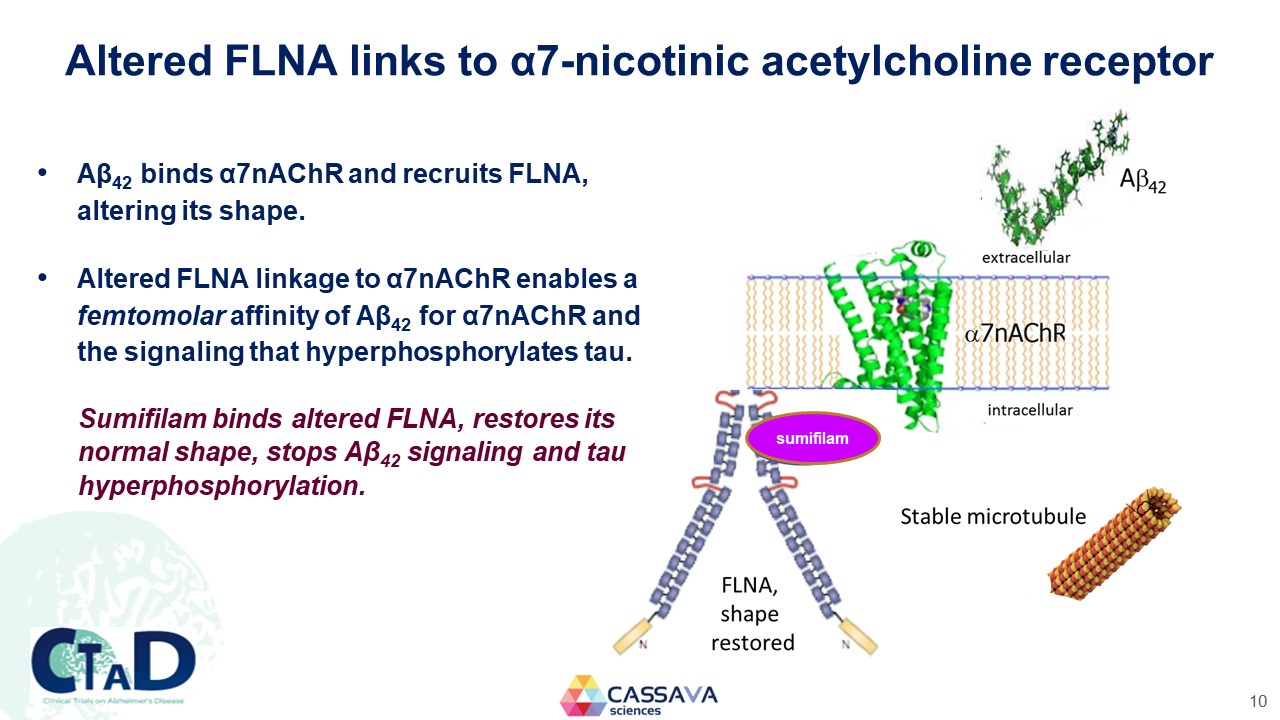
Altered FLNA links to α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor Aβ42 binds α7nAChR and recruits FLNA, altering its shape. Altered FLNA linkage to α7nAChR enables a femtomolar affinity of Aβ42 for α7nAChR and the signaling that hyperphosphorylates tau. Sumifilam binds altered FLNA, restores its normal shape, stops Aβ42 signaling and tau hyperphosphorylation. Aβ42 extracellular α7nAChR intracellular sumifilam FLNA, shape restored Stable microtubule CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 10
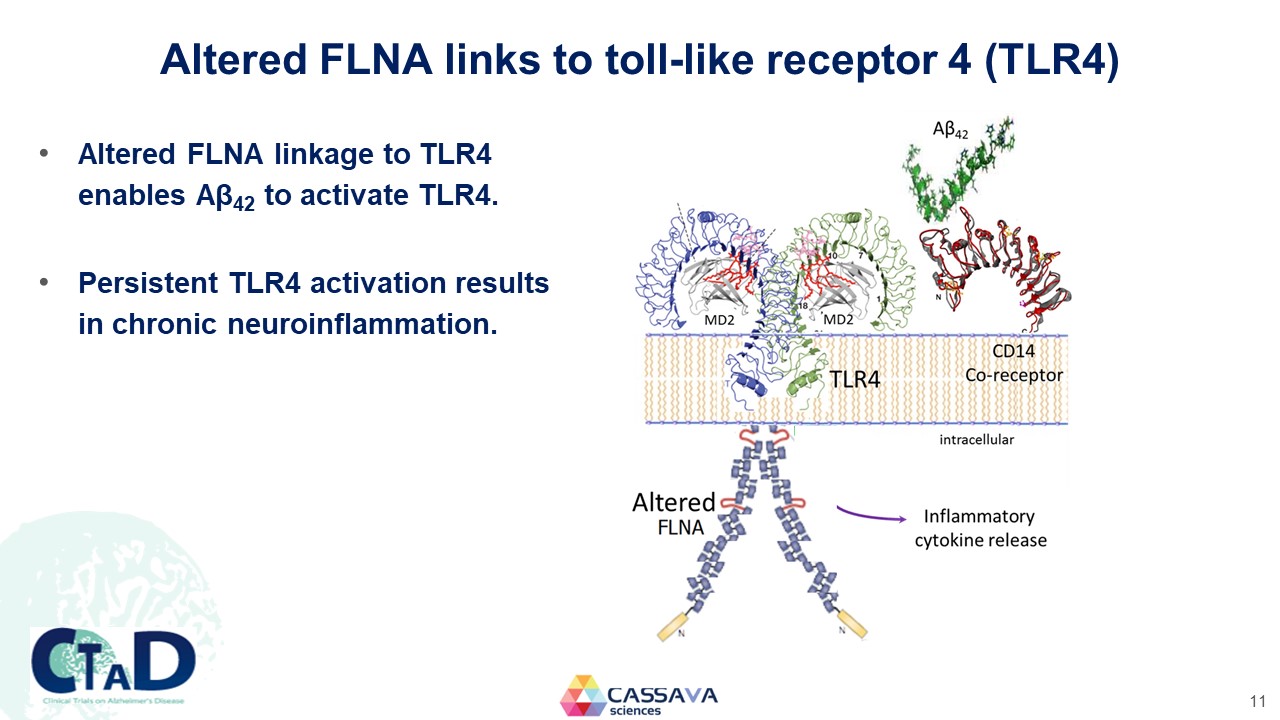
Altered FLNA links to toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) Altered FLNA linkage to TLR4 enables Aβ42 to activate TLR4. Persistent TLR4 activation results in chronic neuroinflammation. MD2 MD2 TLR4 CD14 Co-receptor intraceulluar Alterned FLNA Inflammatory cytokine release CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 11
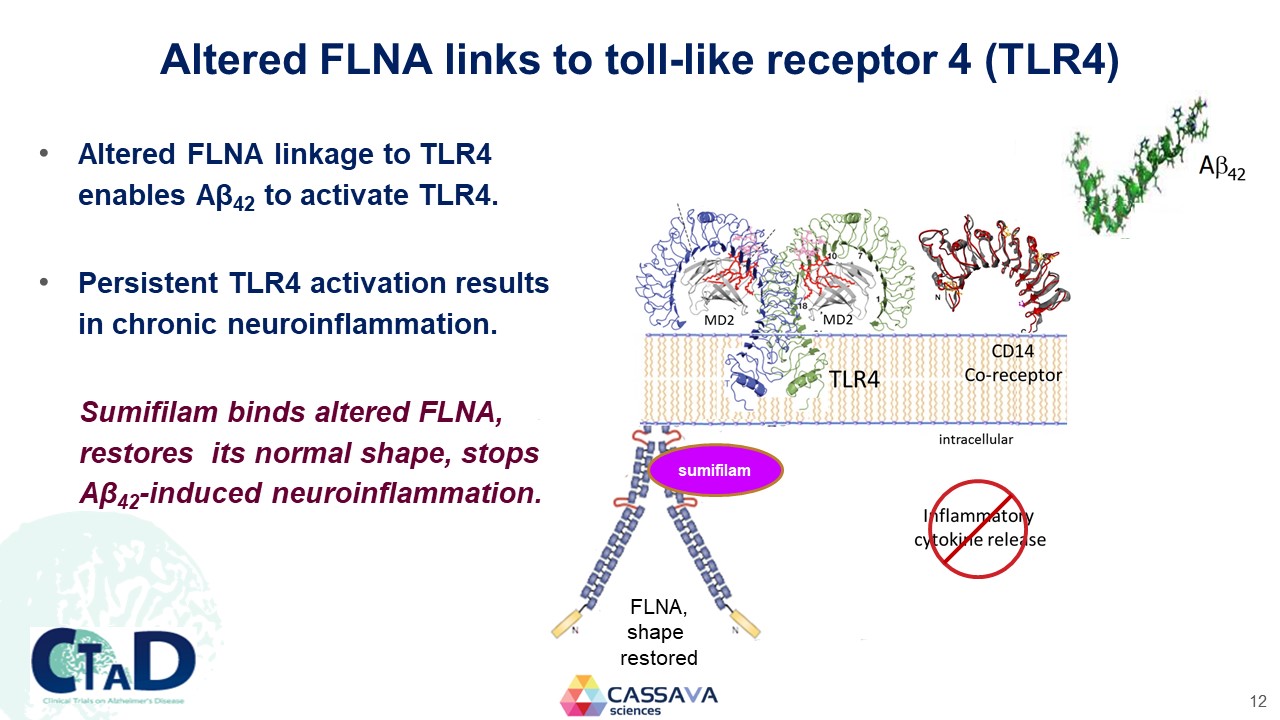
Altered FLNA links to toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) Altered FLNA linkage to TLR4 enables Aβ42 to activate TLR4. Persistent TLR4 activation results in chronic neuroinflammation. Sumifilam binds altered FLNA, restores its normal shape, stops Aβ42-induced neuroinflammation. MD2 MD2 CD14 Co-receptor intracellular TLR4 Aβ42 sumifilam FLNA, shape restored Inflammatory cytokine release CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 12
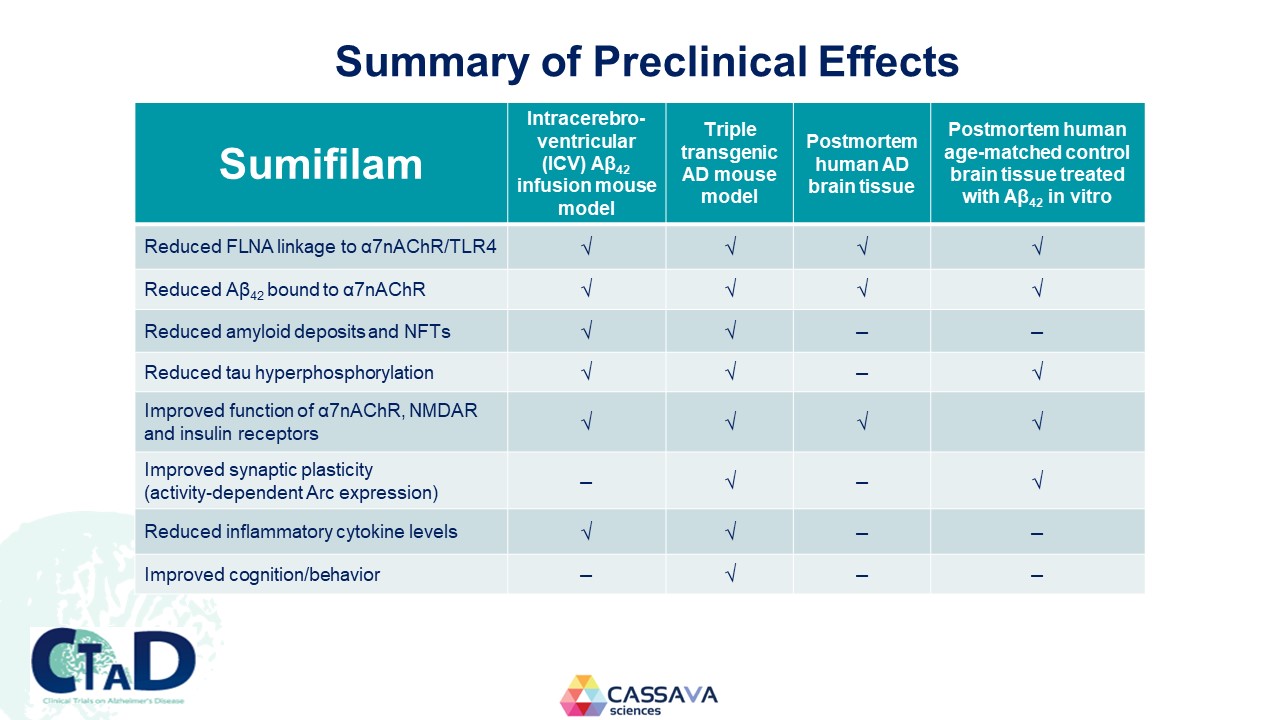
Summary of Preclinical Effects Sumifilam Intracerebro-ventricular (ICV) Aβ42 infusion mouse model Triple transgenic AD mouse model Postmortem human AD brain tissue Postmortem human age-matched control brain tissue treated with Aβ42 in vitro Reduced FLNA linkage to α7nAChR/TLR4 √ √ √ √ Reduced Aβ42 bound to α7nAChR √ √ √ √ Reduced amyloid deposits and NFTs √ √ – – Reduced tau hyperphosphorylation √ √ – √ Improved function of α7nAChR, NMDAR and insulin receptors √ √ √ √ Improved synaptic plasticity (activity-dependent Arc expression) – √ – √ Reduced inflammatory cytokine levels √ √ – – Improved cognition/behavior – √ – – CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 13

Phase 2b Clinical Study of Sumifilam I. Mechanism of Action II. Phase 2b Study Results III. Study Conclusions CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 14
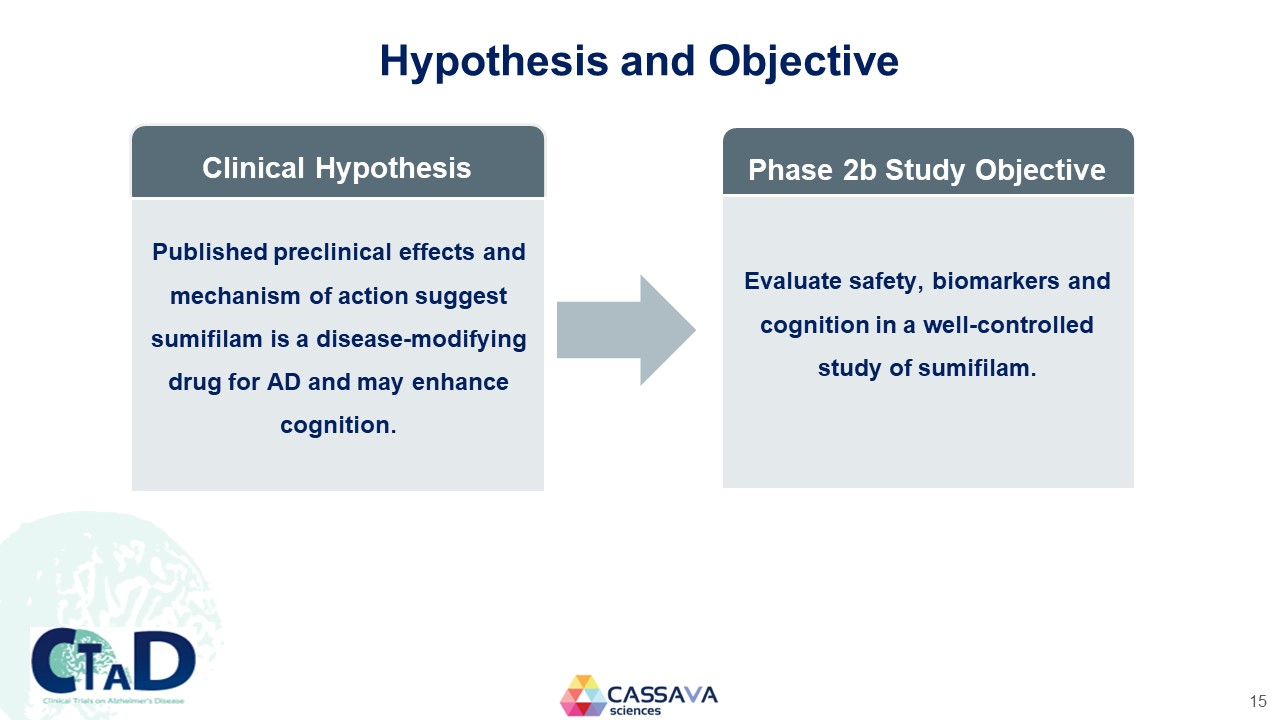
Hypothesis and Objective Clinical Hypothesis Published preclinical effects and mechanism of action suggest sumifilam is a disease-modifying drug for AD and may enhance cognition. Phase 2b Study Objective Evaluate safety, biomarkers and cognition in a well-controlled study of sumifilam. CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 15
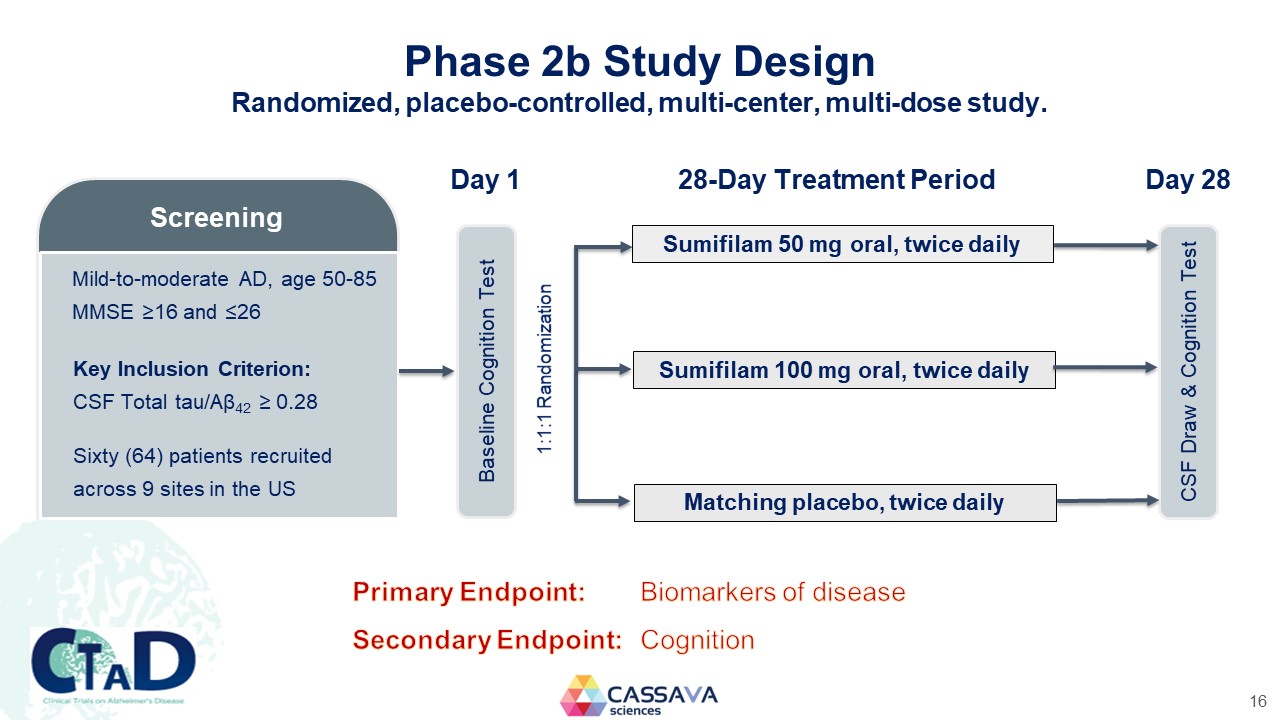
Phase 2b Study Design Randomized, placebo-controlled, multi-center, multi-dose study. Screening Mild-to-moderate AD, age 50-85 MMSE ≥16 and ≤26 Key Inclusion Criterion: CSF Total tau/Aβ42 ≥ 0.28 Sixty (64) patients recruited across 9 sites in the US Day 1 Baseline Cognition Test 1:1:1 Randomization 28-Day Treatment Period Sumifilam 50 mg oral, twice daily Sumifilam 100 mg oral, twice daily Matching placebo, twice daily Day 28 CSF Draw & Cognition Test Primary Endpoint: Biomarkers of disease Secondary Endpoint: Cognition CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 16

Phase 2b – Safety Sumifilam was well-tolerated No serious adverse events No drug-related patient discontinuation No drug-related adverse events Common, non-persistent AEs observed in both placebo & drug groups. CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 17
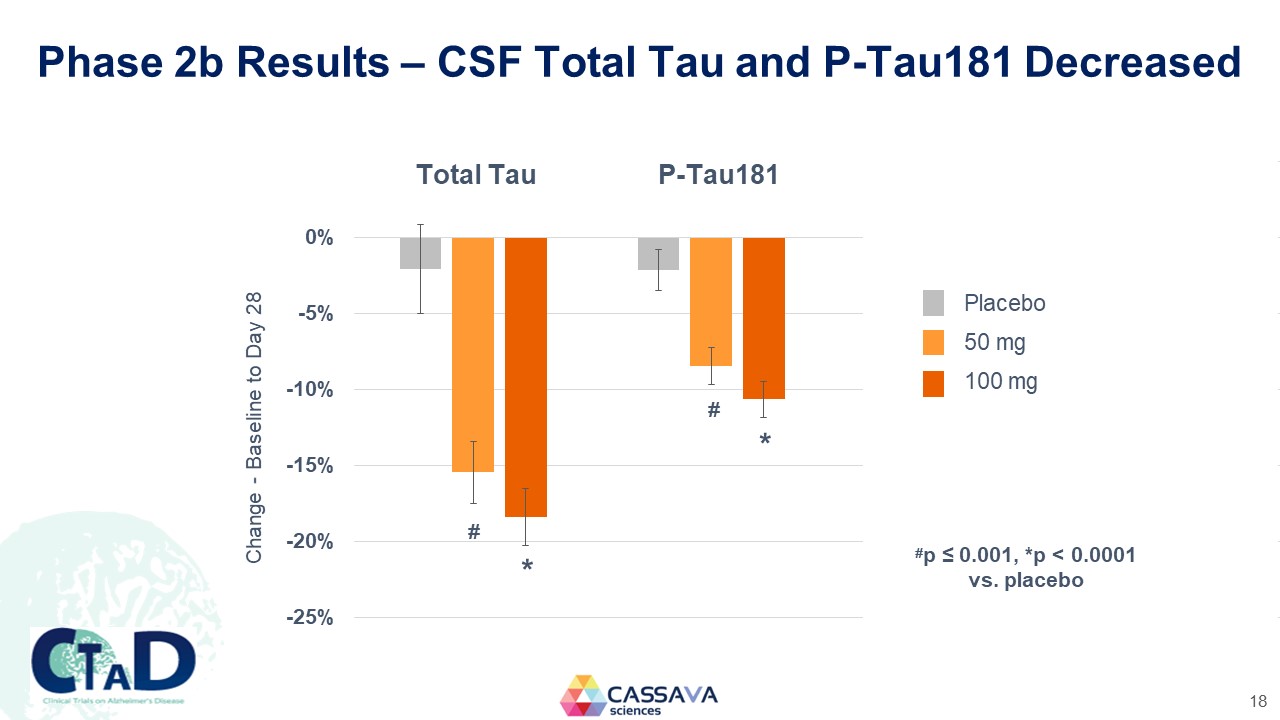
Phase 2b Results – CSF Total Tau and P-Tau181 Decreased Total Tau P-Tau181 Change - Baseline to Day 28 0%-5% -10% -15% -20% -25% * * Placebo 50 mg 100 mg #p ≤ 0.001, *p < 0.0001 vs. placebo CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 18
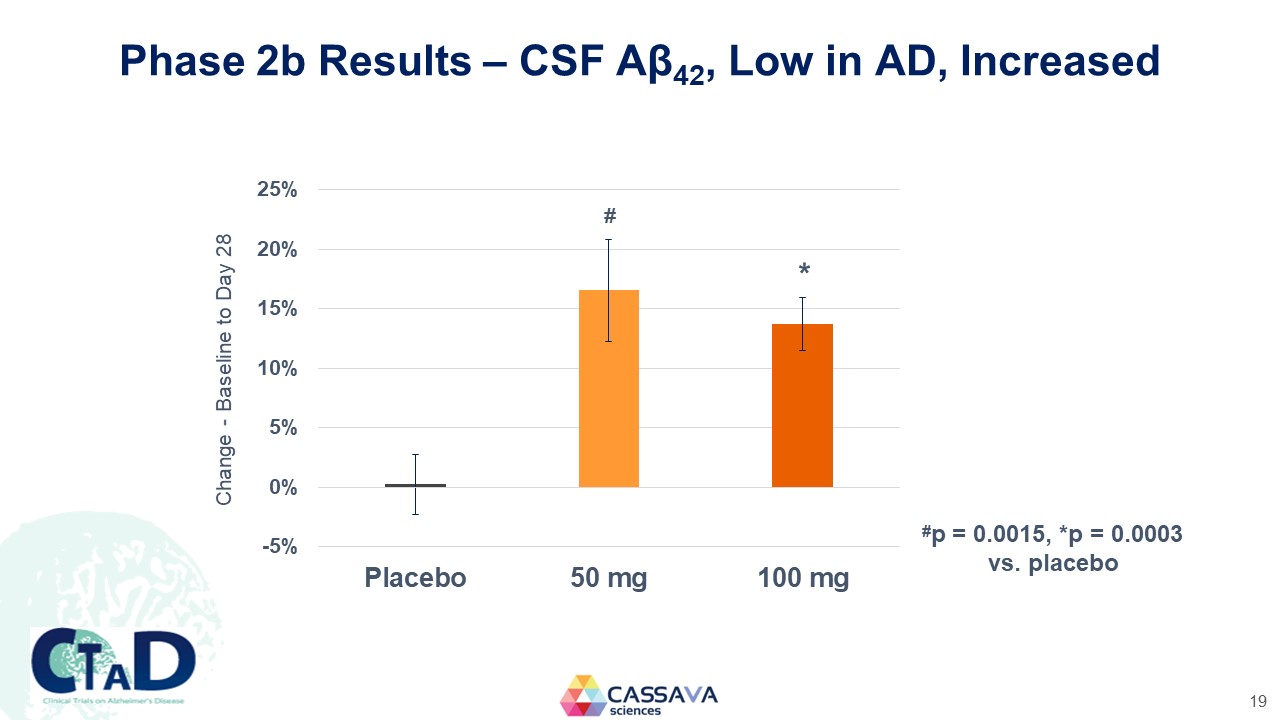
Phase 2b Results – CSF Aβ42, Low in AD, Increased Change - Baseline to Day 28 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 0% -5% Placebo 50 mg 100 mg #p = 0.0015, *p = 0.0003 vs. placebo CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 19
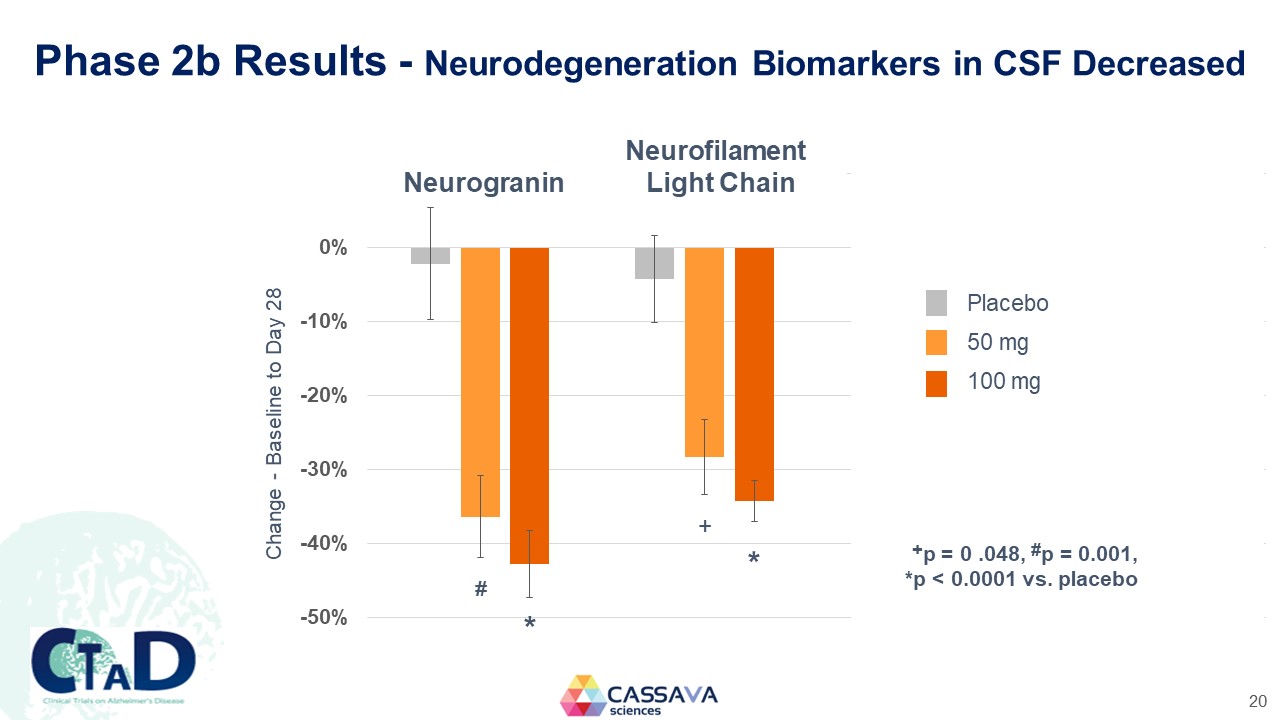
Phase 2b Results - Neurodegeneration Biomarkers in CSF Decreased Neurofilament Neurogranin Light Chain Change - Baseline to Day 28 0% -10% -20% -30% -40% -50% * + * Placebo 50 mg 100 mg +p = 0 .048, #p = 0.001, *p < 0.0001 vs. placebo CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 20
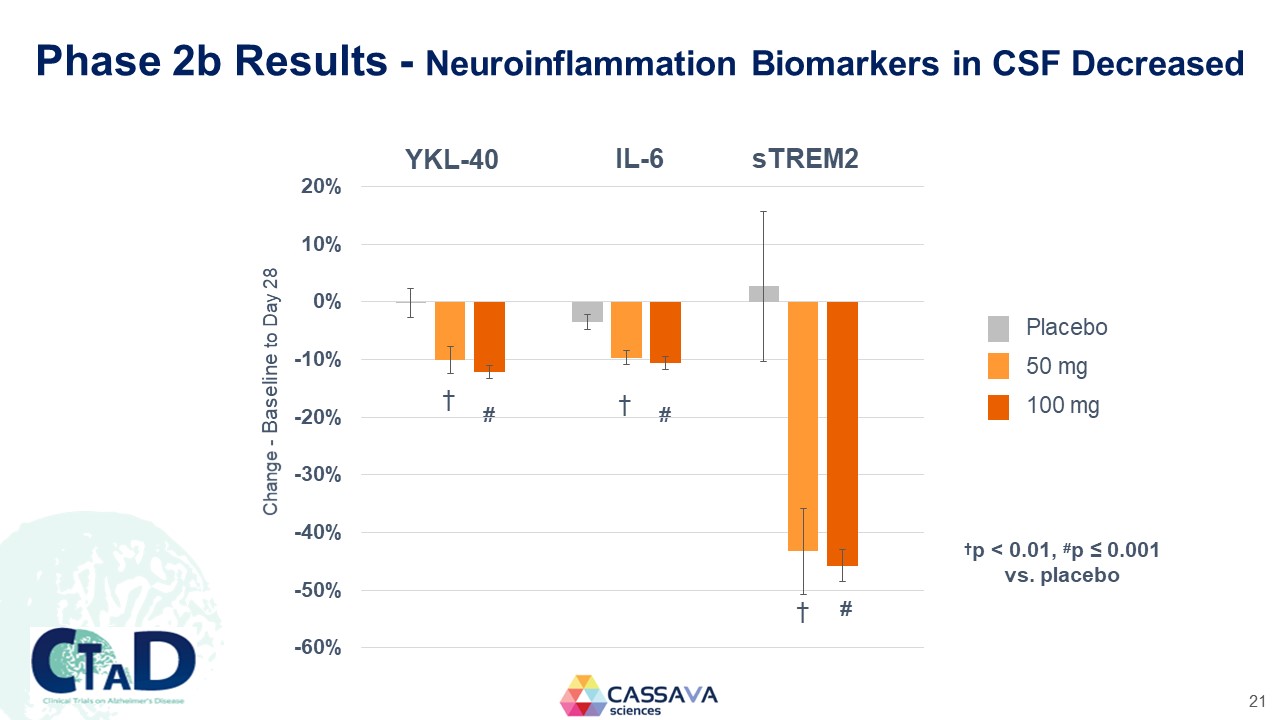
Phase 2b Results - Neuroinflammation Biomarkers in CSF Decreased Change - Baseline to Day 28 YKL-40 IL-6 sTREM2 20% 10% 0% -10% -20% -30% -40% -50% -60% † † # Placebo 50 mg 100 mg †p < 0.01, #p ≤ 0.001 vs. placebo CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 21
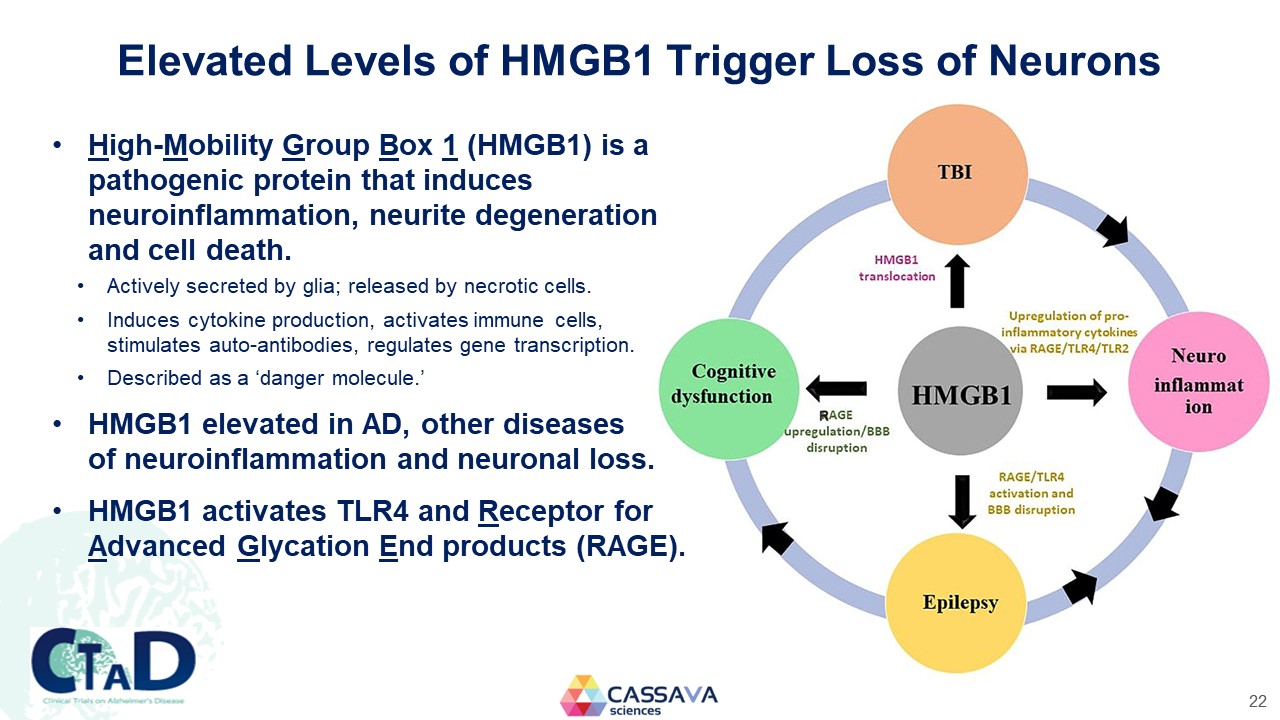
Elevated Levels of HMGB1 Trigger Loss of Neurons High-Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) is a pathogenic protein that induces neuroinflammation, neurite degeneration and cell death. Actively secreted by glia; released by necrotic cells. Induces cytokine production, activates immune cells, stimulates auto-antibodies, regulates gene transcription. Described as a ‘danger molecule.’ HMGB1 elevated in AD, other diseases of neuroinflammation and neuronal loss. HMGB1 activates TLR4 and Receptor for Advanced Glycation End products (RAGE). TBI neuro inflammation Epilepsy Cognitive dysfunction HMGB1 translocation Upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines ia RAGE?TLR4/TLR2 RAGE/TLR4 actiation and BBB disruption RAGE upregulation/BBB disruption CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 22
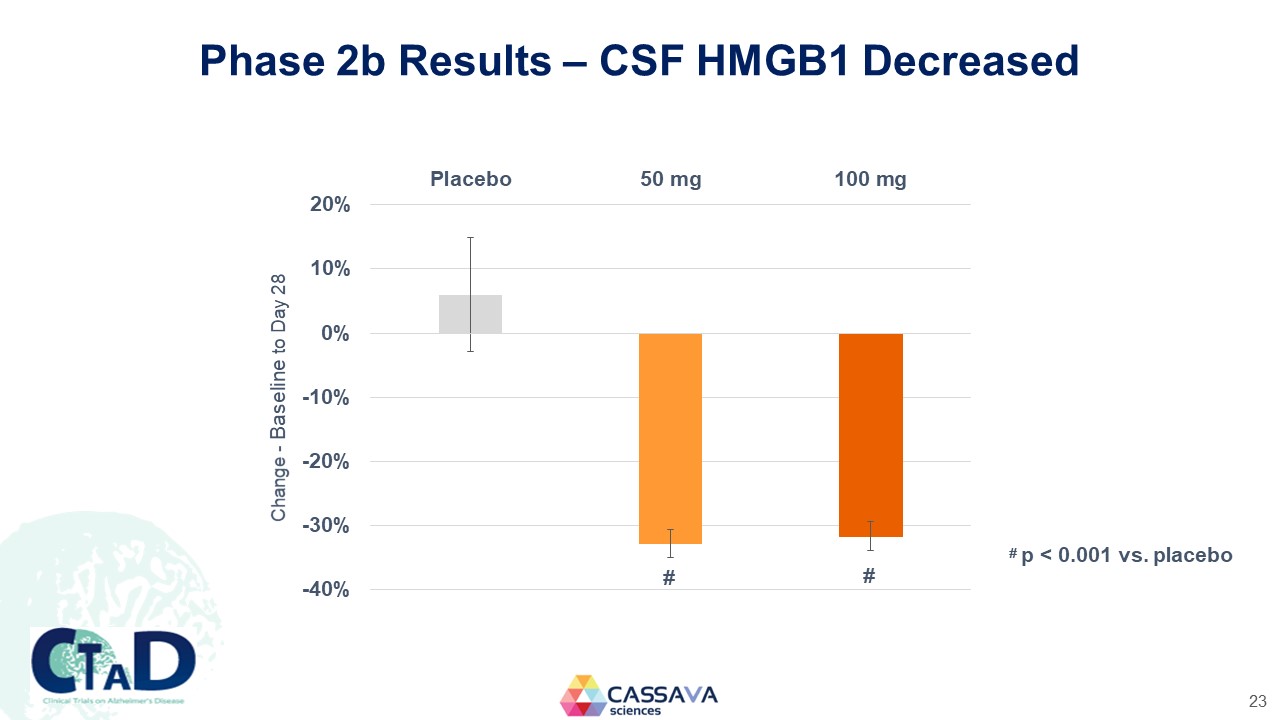
Phase 2b Results – CSF HMGB1 Decreased Placebo 50 mg 100 mg Change - Baseline to Day 28 20% 10% 0% -10% -20% -30% -40% # # # p < 0.001 vs. placebo CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 23
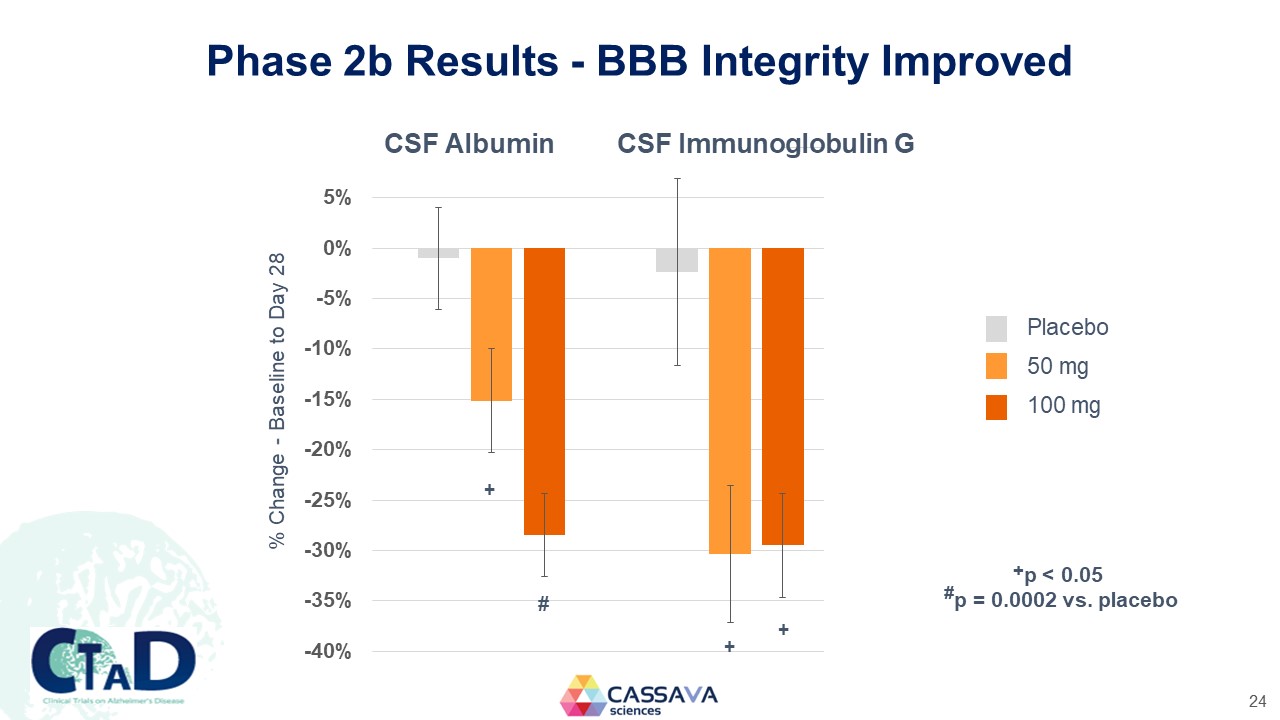
Phase 2b Results - BBB Integrity Improved CSF Albumin CSF Immunoglobulin G % Change - Baseline to Day 28 5% 0% -5% -10% -15% -20% -25% -30% -35% -40% CSF Albumin CSF Immunoglobulin G Placebo 50 mg 100 mg +p < 0.05 #p = 0.0002 vs. placebo CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 24
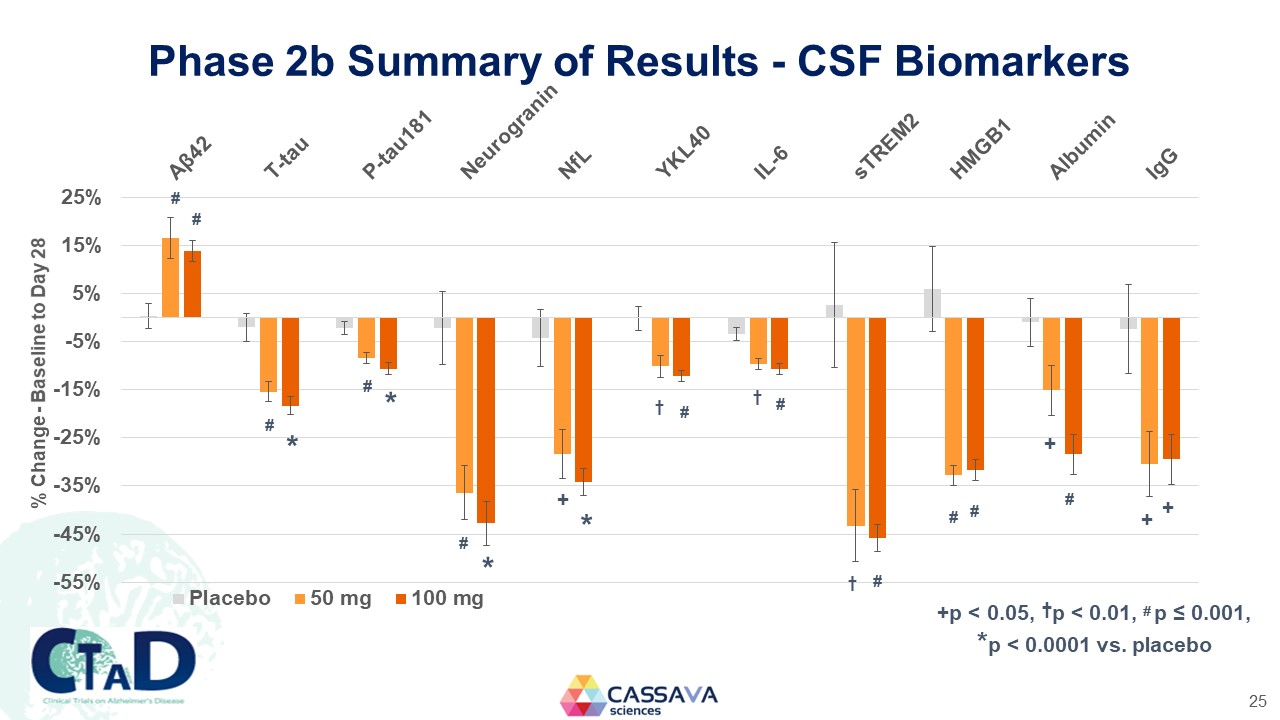
Phase 2b Summary of Results - CSF Biomarkers % Change - Baseline to Day 28 Aβ42 T-tau P-tau151 Neurogranin NfL YKL40 IL-6 sTREM2 HMGB1 Albumin lgG * * * + * t # t t # + # + + Placebo 50 mg 100 mg +p < 0.05, †p < 0.01, # p ≤ 0.001, *p < 0.0001 vs. placebo CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 25

Cognition CANTAB (Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery) is a widely used, computer-based battery of memory tests sensitive to subtle changes in cognition. Tests are independent of language skills, speed, gender or education. Cognitive assessments were made on Day 1 (pre-dose) and again on Day 28. Patients were tested on ‘Episodic Memory’ and ‘Spatial Working Memory’. Patients advance through progressively more difficult levels. Outcome measure = total errors, with errors imputed for more difficult levels not reached, so……. Lower score is better! CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 26
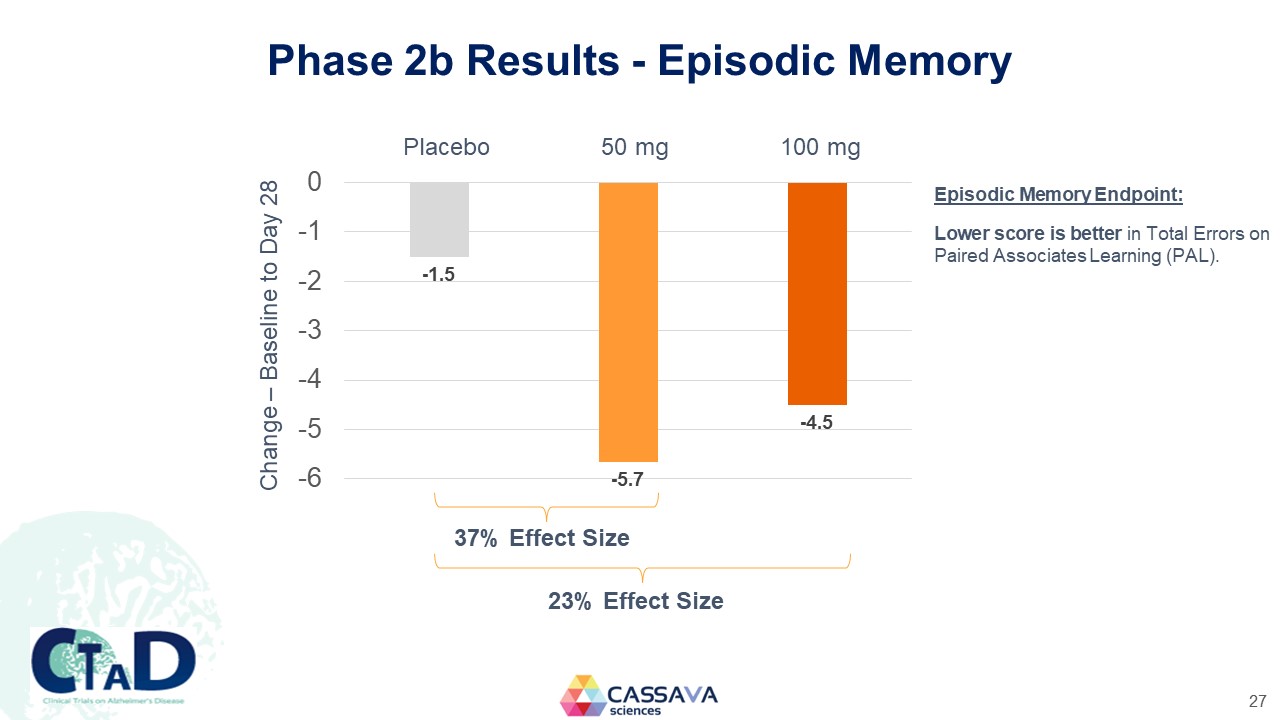
Phase 2b Results - Episodic Memory Change – Baseline to Day 28 Placebo 50 mg 100 mg 0 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -1.5 -5.7 -4.5 7% EffectSize 23% Effect Size Episodic Memory Endpoint: Lower score is better in Total Errors on Paired Associates Learning (PAL). CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 27
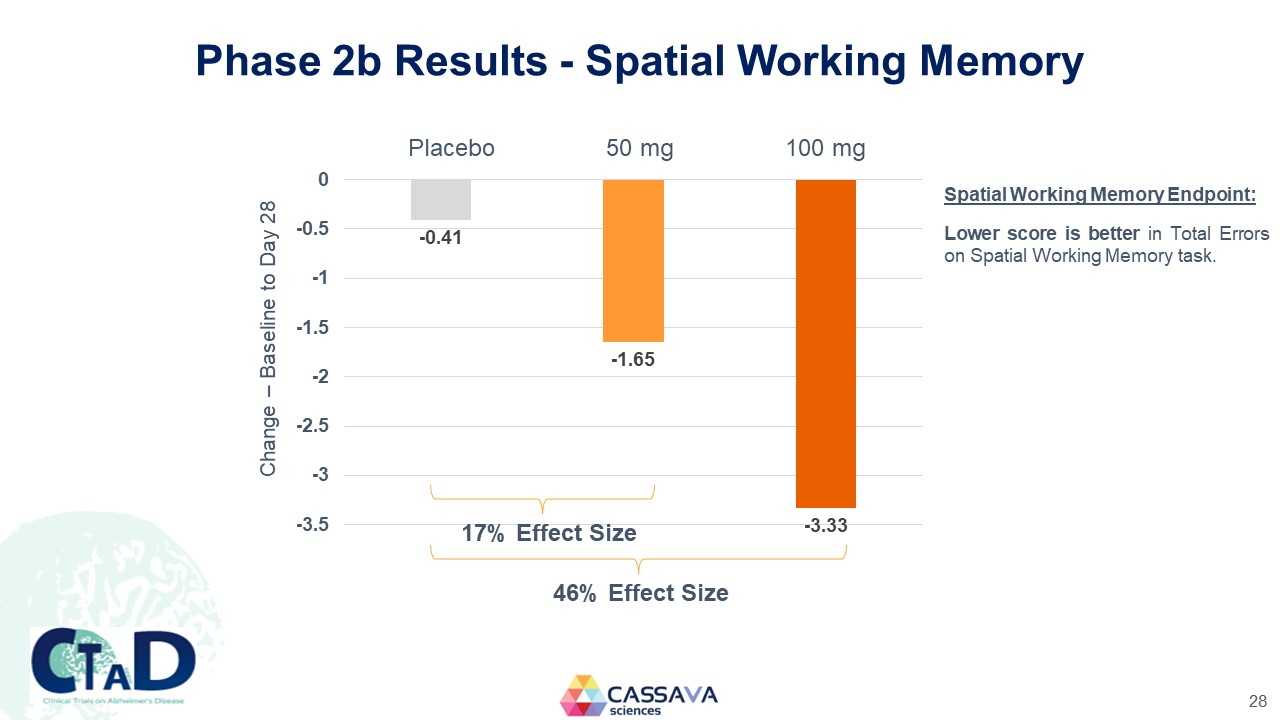
Phase 2b Results - Spatial Working Memory Change – Baseline to Day 28 Placebo 50 mg 100 mg 0 -0.5 -1 -1.5 -2 -2.5 -3 -3.5 -0.41 -1.65 -3.33 17% Effect Size 46% Effect Size Spatial Working Memory Endpoint: Lower score is better in Total Errors on Spatial Working Memory task. CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 28
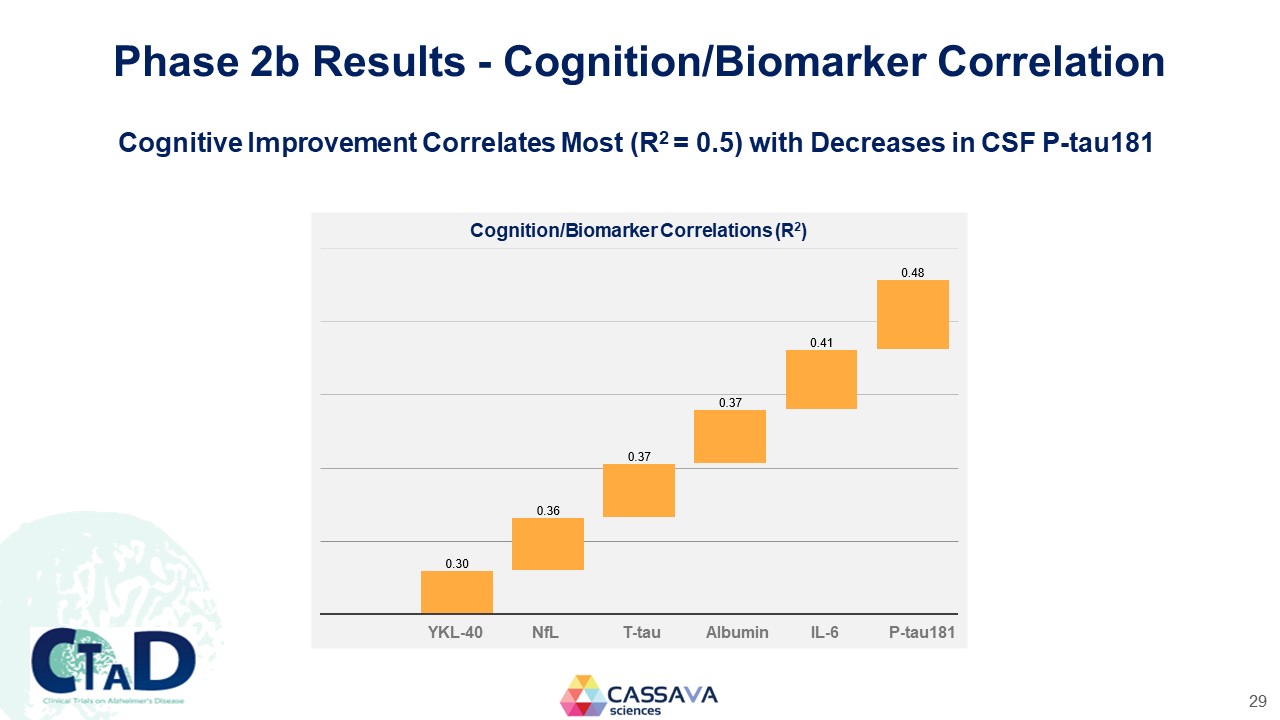
Phase 2b Results - Cognition/Biomarker Correlation Cognitive Improvement Correlates Most (R2 = 0.5) with Decreases in CSF P-tau181 Cognition/Biomarker Correlations (R2) 0.30 0.36 0.37 0.37 0.41 0.48 YKL-40 NfL T-tau Albumin IL-6 P-tau181 CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 29
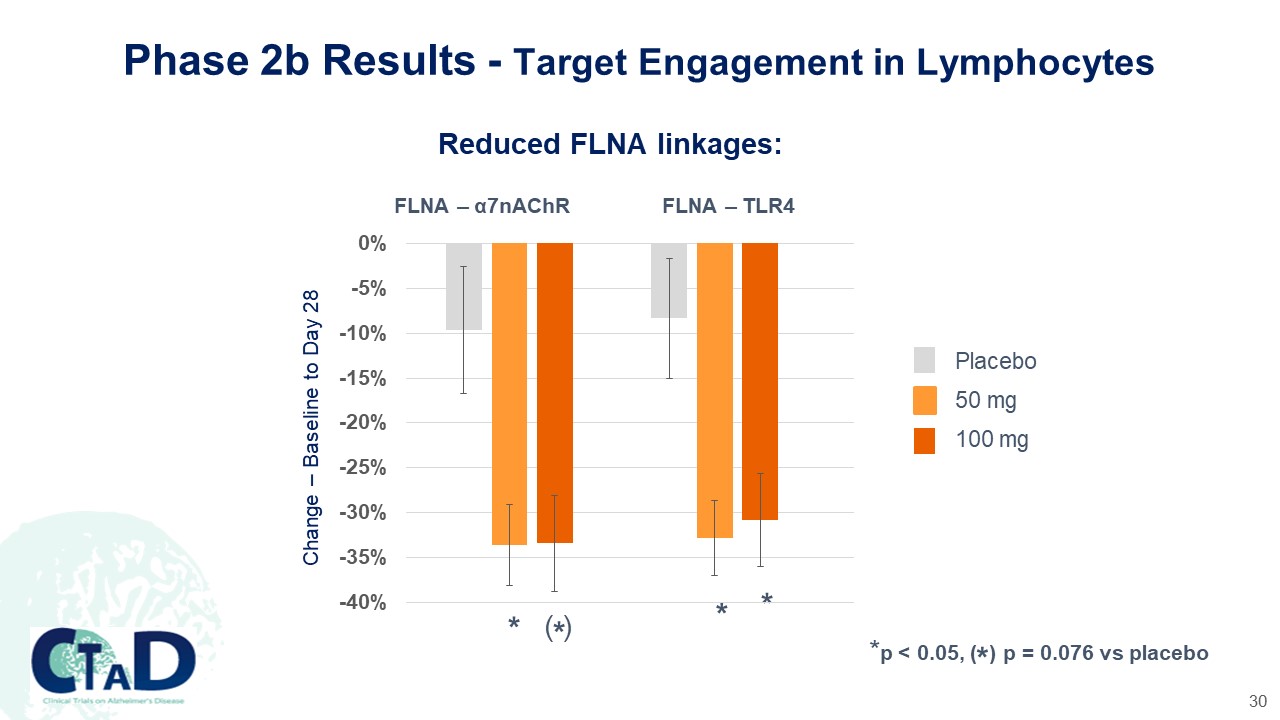
Phase 2b Results - Target Engagement in Lymphocytes Reduced FLNA linkages: FLNA – α7nAChR FLNA – TLR4 Change – Baseline to Day 28 0% -5% -10% -15% -20% -25% -30% -35% -40% * (*) * * Placebo 50 mg 100 mg *p < 0.05, ( ) p = 0.076 vs placebo CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 30

Phase 2b Results - Summary of Drug Effects 98% of patients treated with sumifilam 50 mg or 100 mg b.i.d. for 28 days showed improvements in validated biomarkers of AD pathology; neuroinflammation; and neurodegeneration; with no safety issues. Sumifilam appears to enhance cognition. 37% and 23% effect sizes in Episodic Memory vs. placebo 17% and 46% effect sizes in Spatial Working Memory vs. placebo Improved cognition correlated most strongly with reduction in levels of P-tau181 (R2 = 0.5) Target engagement and mechanism of action were demonstrated in this Phase 2b and in prior clinical and pre-clinical studies. CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 31

Phase 2b Clinical Study of Sumifilam I. Mechanism of Action II. Phase 2b Study Results III. Study Conclusions CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 32
Study Conclusions A well-controlled study of sumifilam showed promising treatment effects in mild-to-moderate AD patients. Sumifilam improved an entire panel of validated biomarkers of disease, neuroinflammation, and BBB integrity, and appeared to enhance cognition. Phase 2b treatment effects replicate prior clinical results and are consistent with published preclinical data and the drug’s mechanism of action. These data highlight sumifilam’s potential as a disease-modifying treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 33

Next Steps On-going: One-year, open-label safety study of sumifilam Enrolling 100 patients with mild-to-moderate AD, including ADAS-Cog assessments. Planned for 2021: Large-scale safety & efficacy study of sumifilam THANK YOU! CTAD Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease CASSAVA sciences 33
