Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-23.2 - Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. | ex23-2.htm |
| EX-10.114 - Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. | ex10-114.htm |
| EX-5.1 - Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. | ex5-1.htm |
As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on July 14, 2020
Registration No. 333-______
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM S-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
CLEAN ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Nevada | 3990 | 20-2675800 | ||
(State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation) |
(Primary Standard Classification Code) |
(IRS Employer Identification No.) |
2990 Redhill Ave,
Costa Mesa, California 92626
Telephone: (949) 273-4990
(Address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of registrant’s principal executive offices)
Kambiz Mahdi
Chief Executive Officer
Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
2990 Redhill Ave,
Costa Mesa, California 92626
Telephone: (949) 273-4990
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of agent for service)
Copy to:
The Newman Law Firm, PLLC
1872 Pleasantville Road, Suite 177
Briarcliff Manor, NY 10510
Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale to the public:
As soon as practicable after the effective date of this Registration Statement.
If any of the securities being registered on this form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, check the following box. [X]
If this form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. [ ]
If this form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. [ ]
If this form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. [ ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act:
| Large accelerated filer | [ ] | Accelerated filer | [ ] | |
| Non-accelerated filer | [X] | Smaller reporting company | [X] | |
| Emerging growth company | [ ] | |||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided to Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act. [ ]
CALCULATION OF REGISTRATION FEE
| Title of each class of securities to be registered | Amount To Be Registered(1) | Proposed Maximum Offering Price Per Share(2) | Proposed Maximum Aggregate Offering Price | Amount of Registration Fee(3) | ||||||||||||
| Common Stock, $0.001 par value | 74,720,000 | $ | $ | 1,298,633 | $ | 168.56 | ||||||||||
| Total: | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||
| (1) | In accordance with Rule 416(a), this registration statement shall also cover an indeterminate number of shares that may be issued and resold resulting from stock splits, stock dividends or similar transactions. |
| (2) | Estimated pursuant to Rule 457(c) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), based on the average of the closing prices as reported on the OTCQB within 5 business days prior to the date of the filing of this Registration Statement. |
| (3) | The fee is calculated at a rate of $129.80 per million dollars, pursuant to Section 6(b) of the Securities Act of 1933. |
| The registrant hereby amends this registration statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the registrant shall file a further amendment which specifically states that this registration statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933 or until the registration statement shall become effective on such date as the Securities and Exchange Commission, acting pursuant to said section 8(a), may determine. | |
The information in this preliminary prospectus is not complete and may be changed. We may not sell these securities until the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This preliminary prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities and it is not soliciting an offer to buy these securities in any state where the offer or sale is not permitted.
Subject to completion. Dated July 14, 2020. |
PRELIMINARY PROSPECTUS

CLEAN ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
74,720,000 Shares of Common Stock
The selling stockholder identified in this prospectus may offer an indeterminate number of shares of its common stock, which will consist of up to 74,720,000 shares of common stock to be sold by GHS Investments LLC (“GHS”) pursuant to an Equity Financing Agreement (the “Financing Agreement”) dated June 8, 2020. If issued presently, the 74,720,000 shares of common stock registered for resale by GHS would represent 10% of our issued and outstanding shares of common stock as of July 14, 2020. Additionally, the 74,720,000shares of our common stock registered for resale herein would represent approximately 30% of the Company’s public float which would not include 764,562 shares of our common stock currently held by GHS.
The selling stockholder may sell all or a portion of the shares being offered pursuant to this prospectus at fixed prices and prevailing market prices at the time of sale, at varying prices, or at negotiated prices. See the section of this prospectus entitled “Plan of Distribution” for additional information.
We will not receive any proceeds from the sale of the shares of our common stock by GHS. We will sell shares to GHS at a price equal to 80% of the two day average lowest closing price of our common stock during the ten (10) consecutive trading day period beginning on the date on which we deliver a put notice to GHS (the “Market Price”). There will be a minimum of ten (10) trading days between purchases.
GHS is an underwriter within the meaning of the Securities Act of 1933, and any broker-dealers or agents that are involved in selling the shares may be deemed to be “underwriters” within the meaning of the Securities Act of 1933 in connection with such sales. In such event, any commissions received by such broker-dealers or agents and any profit on the resale of the shares purchased by them may be deemed to be underwriting commissions or discounts under the Securities Act of 1933.
Our common stock is traded on OTCQB Markets under the symbol “CETY”. On July 1, 2020, the reported closing price for our common stock was $0.018 per share.
This offering is highly speculative, and these securities involve a high degree of risk and should be considered only by persons who can afford the loss of their entire investment. See “Risk Factors” beginning on page [●]. Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or passed upon the accuracy or adequacy of this prospectus. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
The date of this prospectus is July 14, 2020.
| 2 |
TABLE OF CONTENTS
You may only rely on the information contained in this prospectus or that we have referred you to. We have not authorized any person to give you any supplemental information or to make any representations for us. This prospectus does not constitute an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any securities other than the Common Stock offered by this prospectus. This prospectus does not constitute an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any Common Stock in any circumstances in which such offer or solicitation is unlawful. Neither the delivery of this prospectus nor any sale made in connection with this prospectus shall, under any circumstances, create any implication that there has been no change in our affairs since the date of this prospectus is correct as of any time after its date. You should not rely upon any information about our company that is not contained in this prospectus. Information contained in this prospectus may become stale. You should not assume the information contained in this prospectus or any prospectus supplement is accurate as of any date other than their respective dates, regardless of the time of delivery of this prospectus, any prospectus supplement or of any sale of the shares. Our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects may have changed since those dates. The selling stockholders are offering to sell and seeking offers to buy shares of our common stock only in jurisdictions where offers and sales are permitted.
| 3 |
This summary highlights information contained elsewhere in this prospectus and does not contain all of the information that you should consider in making your investment decision. Before investing in our common stock, you should carefully read this entire prospectus, including our financial statements and the related notes and the information set forth under the headings “Risk Factors” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in each case included elsewhere in this prospectus.
Unless the context otherwise requires, references to “we,” “our,” “us,” or the “Company” in this prospectus mean Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. on a consolidated basis with its wholly-owned subsidiaries.
We design, produce and market clean energy products and integrated solutions focused on energy efficiency and renewables. Our initial principal product is the Clean CycleTM heat generator, offered through our wholly owned subsidiary Heat Recovery Solutions, (HRS). The Clean CycleTM generator captures waste heat from a variety of sources and turns it into electricity. By using our Clean CycleTM generator commercial and industrial heat generators boost their overall energy efficiency and the savings created provide our customers with a fast return on their investment. The Clean CycleTM generator saves fuel, reduces pollution and requires little maintenance. We also use our Clean CycleTM generator to manufacture Biomass Power Plants and Co-generation Distribution Power Plants that produce clean energy.
Industrial facilities, power plants, high rise buildings and waste to energy plants currently waste heat and energy during their production processes. Our Clean Cycle TM generators are used in commercial and industrial heat generators to boost their overall energy efficiency. Our products save fuel, reduce pollution, require little maintenance and provide an attractive return on investment.
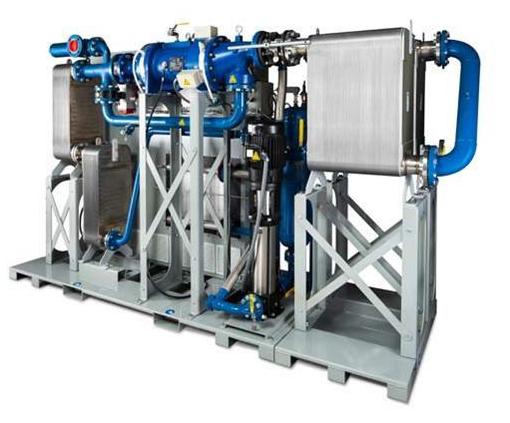 |
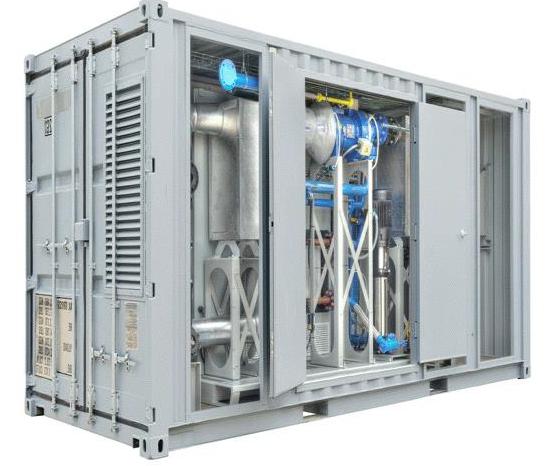 | |
| Clean Cycle II Heat Generator | Containerized Clean Cycle II Heat Generator |
We compete based on efficiency, maintenance and our customer’s return on investment. We have an exclusive license from Calnetix to use their magnetic turbine for heat waste recovery applications. We believe that the magnetic turbine technology is more efficient than our competitor’s turbines which allows our systems to generate more electricity at lower heat ranges. Because our generator is magnetic, it requires far less maintenance than our competitors who use oil, gearbox and rubber seals in their turbines. We have the advantage of selling a system that was originally manufactured and sold by General Electric International so our Clean CycleTM generator has a substantial market base and we believe has a reputation as one of the defacto standards in the market.
| 4 |
Our greatest advantage is that the Clean CycleTM generator is a product that can be delivered on a turnkey basis, not a major project that needs to be designed, manufactured and installed. We believe that this is one of the most distinguishing features of our Clean Cycle™ generator, as it significantly reduces the time our customers spend on installation, improves the speed with which we can deliver our product and reduces startup costs.
Over 123 Clean CycleTM generators are installed to date with 88 units used in biomass/landfill projects, 4 with diesel electric generators, 3 with turbine electric generators and 26 in industrial electric production applications.
The Clean CycleTM generator is delivered on a turnkey basis and does not require major planning for design, manufacturing and installation. In addition to attractive returns on capital investment, we believe that the ease of installation distinguishes our Clean Cycle™ generators by significantly reducing installation time, improving delivery times and lowering costs.
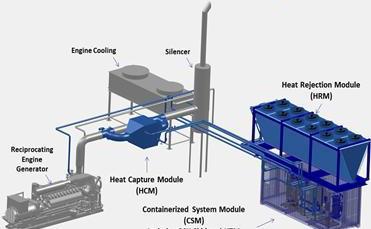
A Complete ORC System
We estimate that one clean system using our Clean CycleTM generator can generate 1 GWh of electricity per year from waste heat and avoid more than 350 metric tons of CO2 per year which we estimate is the annual equivalent of the CO2 emissions of approximately 200 cars.
Our goal is to become a leading provider of renewable and energy efficiency products and solutions by helping commercial companies and municipalities eliminate energy waste, reduce emissions, lower cost and generate incremental revenue.
Company Information and History
We were incorporated in California in July 1995 under the name Probe Manufacturing Industries, Inc. We redomiciled to Nevada in April 2005 under the name Probe Manufacturing, Inc. We manufactured electronics and provided services to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) of industrial, automotive, semiconductor, medical, communication, military, and high technology products. On September 11, 2015 Clean Energy HRS, or “CE HRS”, our wholly owned subsidiary acquired the assets of Heat Recovery Solutions from General Electric International. In November 2015, we changed our name to Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Our principal executive offices are located at 2990 Redhill Avenue, Costa Mesa, CA 92626. Our telephone number is (949) 273-4990. Our common stock is listed on the OTCQB Markets under the symbol “CETY.”
Our internet website address is www.cetyinc.com and our subsidiary’s web site is www.heatrecoverysolutions.com.
The Company has three reportable segments: Clean Energy HRS (HRS), Cety Europe and the legacy electronic contract manufacturing services (Electronic Assembly) division.
| 5 |
Employees
We presently have 12 employees, including production, program management, materials management, engineering, sales, quality, and administrative and management personnel. We have never experienced work stoppages and we are not a party to any collective bargaining agreement. We have one employee that works full time in CETY Europe and 1 full time employee in our Electronics Assembly segment.
GHS Equity Financing Agreement and Registration Rights Agreement
On June 8, 2020, we entered into an Equity Financing Agreement (“Equity Financing Agreement”) and Registration Rights Agreement (“Registration Rights Agreement”) with GHS Investments LLC, a Nevada limited liability company (“GHS”). Under the terms of the Equity Financing Agreement, GHS agreed to provide the Company with up to $2,000,000 upon effectiveness of a registration statement on Form S-1 (the “Registration Statement”) filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “Commission”)
Following effectiveness of the Registration Statement, the Company shall have the discretion to deliver puts (each, a “Put”) to GHS and GHS will be obligated to purchase shares of the Company’s common stock, par value $0.001 per share (the “Common Stock”) based on the investment amount specified in each Put notice. The maximum amount that the Company shall be entitled to put to GHS in each Put notice shall not be less than $10,000 nor exceed two hundred percent (200%) of the average daily trading dollar volume of the Company’s Common Stock during the ten (10) trading days preceding the put, or $400,000. Pursuant to the Equity Financing Agreement, GHS and its affiliates will not be permitted to purchase shares, and the Company may not request Puts from GHS, that would result in GHS’s beneficial ownership equaling more than 4.99% of the Company’s outstanding Common Stock. The price of each share in a Put shall be equal to eighty percent (80%) of the average of the lowest two closing prices for the 10 days prior to the Put notice from the Company (the “Purchase Price”). Puts may be delivered by the Company to GHS until (i) the earlier of thirty-six (36) months after the date of the Equity Financing Agreement, (ii) the date on which GHS has purchased an aggregate of $2,000,000 worth of Common Stock under the terms of the Equity Financing Agreement or (iii) such time the Registration Statement is no longer in effect. In accordance with the Equity Financing Agreement, the Company issued GHS 764,526 shares of its Common Stock which was equal to the Purchase Price as of the execution date of the Equity Financing Agreement and is obligated to issue $5,000 of Common Stock upon delivery of the second and third Puts at the then applicable Purchase Price.
The Registration Rights Agreement provides that the Company shall (i) use its best efforts to file with the Commission the Registration Statement within 30 days of the date of the Registration Rights Agreement; and (ii) use reasonable commercial efforts to have the Registration Statement declared effective by the Commission within 30 days after the date the Registration Statement is filed with the Commission, but in no event more than 90 days after the Registration Statement is filed.
| Shares currently outstanding (1): | 762,895,515 | |
| Shares being offered: | 74,720,000 | |
| Offering Price per share: | The selling stockholders may sell all or a portion of the shares being offered pursuant to this prospectus at fixed prices and prevailing market prices at the time of sale, at varying prices or at negotiated prices. | |
| Use of Proceeds: | We will not receive any proceeds from the sale of the shares of our common stock by the selling stockholder. | |
| Trading Symbol: | CETY | |
| Risk Factors: | See “Risk Factors” beginning on page [●] herein and the other information in this prospectus for a discussion of the factors you should consider before deciding to invest in shares of our common stock. |
(1)
The number of shares of our Common Stock outstanding prior to and to be outstanding immediately after this offering, as set forth in the table above, is based on 762,895,515 shares outstanding as of July 10, 2020, and excluding 74,720,000 shares of Common Stock issuable in this offering
| 6 |
| Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. | ||||||||
| Consolidated Statement of Operations | ||||||||
| for the three months ended March 31, | ||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
| Sales | $ | 858,816 | $ | 224,363 | ||||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 343,277 | 149,177 | ||||||
| Gross Profit | 515,539 | 75,186 | ||||||
| General and Administrative | ||||||||
| General and Administrative expense | 95,720 | 60,642 | ||||||
| Salaries | 209,547 | 203,303 | ||||||
| Travel | 29,158 | 40,117 | ||||||
| Professional Fees | 21,887 | 4,019 | ||||||
| Facility lease and Maintenance | 110,455 | 82,034 | ||||||
| Depreciation and Amortization | 9,443 | 11,763 | ||||||
| Total Expenses | 476,210 | 401,878 | ||||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) From Operations | 39,329 | (326,692 | ) | |||||
| Change in derivative liability | (130,994 | ) | (159,733 | ) | ||||
| Gain / (Loss) on debt settlement’ | 22,221 | - | ||||||
| Interest and Financing fees | (244,130 | ) | (240,352 | ) | ||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) Before Income Taxes | (313,574 | ) | (726,777 | ) | ||||
| Income Tax Expense | - | - | ||||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) | $ | (313,574 | ) | $ | (726,777 | ) | ||
| Per Share Information: | ||||||||
| Basic and diluted weighted average number of common shares outstanding | 758,170,513 | 566,027,100 | ||||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) per common share basic and diluted | $ | (0.00 | ) | $ | (0.00 | ) | ||
The accompanying footnotes are in integral part of these condensed consolidated financial statements.
| 7 |
| Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. | ||||||||
| Consolidated Statement of Operations | ||||||||
| For the years ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Sales | $ | 1,610,008 | $ | 1,331,171 | ||||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 952,782 | 810,489 | ||||||
| Gross Profit | 657,226 | 520,682 | ||||||
| General and Administrative | ||||||||
| General and Administrative expense | 382,871 | 232,571 | ||||||
| Salaries | 802,951 | 740,146 | ||||||
| Professional fees | 130,709 | 142,234 | ||||||
| Travel | 246,078 | 114,534 | ||||||
| Consulting | 73,443 | 79,084 | ||||||
| Bad Debt Expense | 128,463 | 50,000 | ||||||
| Facility lease | 305,883 | 280,239 | ||||||
| Depreciation and Amortization | 41,437 | 52,444 | ||||||
| Share Based Expense | - | 353,140 | ||||||
| Total Expenses | 2,111,835 | 2,044,392 | ||||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) From Operations | (1,454,609 | ) | (1,523,710 | ) | ||||
| Change in derivative liability | 216,269 | 116,259 | ||||||
| Gain / (Loss) on disposition of assets | 2,389 | |||||||
| Interest and Financing fees | (1,317,643 | ) | (1,404,955 | ) | ||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) Before Income Taxes | (2,555,983 | ) | (2,810,017 | ) | ||||
| Income Tax Expense | - | - | ||||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) | $ | (2,555,983 | ) | $ | (2,810,017 | ) | ||
| Per Share Information: | ||||||||
| Basic and diluted weighted average number of common shares outstanding | 641,349,437 | 553,354,983 | ||||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) per common share basic and diluted | $ | (0.00 | ) | $ | (0.01 | ) | ||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| 8 |
Risks About Our Business
OUR INDEPENDENT ACCOUNTANTS HAVE ISSUED A GOING CONCERN OPINION AND IF WE CANNOT OBTAIN ADDITIONAL FINANCING AND/OR REDUCE OUR OPERATING COSTS SUFFICIENTLY, WE MAY HAVE TO CURTAIL OPERATIONS AND MAY ULTIMATELY CEASE TO EXIST.
Going Concern
The financial statements have been prepared on a going concern basis, which contemplates continuity of operations, realization of assets and liquidation of liabilities in the normal course of business. The Company had a total stockholder’s deficit of $5,252,478 and a working capital deficit of $6,785,689 and a net loss of $2,555,983 for the year ended December 31, 2019. The company also had an accumulated deficit of $14,215,718 as of December 31, 2019 and used $2,224,168 in net cash from operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2019. Therefore, there is substantial doubt about the ability of the Company to continue as a going concern. There can be no assurance that the Company will achieve its goals and reach profitable operations and is still dependent upon its ability (1) to obtain sufficient debt and/or equity capital and/or (2) to generate positive cash flow from operations.
WE HAVE AN ACCUMULATED DEFICIT AND MAY INCUR ADDITIONAL LOSSES; THEREFORE, WE MAY NOT BE ABLE TO OBTAIN THE ADDITIONAL FINANCING NEEDED FOR WORKING CAPITAL, CAPITAL EXPENDITURES AND TO MEET OUR DEBT SERVICE OBLIGATIONS.
As of December 31, 2019, we had current liabilities of $8,929,141. Our debt could limit our ability to obtain additional financing for working capital, capital expenditures, debt service requirements, or other purposes in the future, as needed; to plan for, or react to, changes in technology and in our business and competition; and to react in the event of an economic downturn.
We may not be able to meet our debt service obligations. If we are unable to generate sufficient cash flow or obtain funds for required payments, or if we fail to comply with covenants in our revolving lines of credit, we will be in default.
WE ARE IN DEFAULT IN OUR OBLIGATIONS TO OUR MAJOR CREDITORS
We are currently in default on the payment of $1,200,000 and accrued interest of approximately 241,961 as of the date of this filing. This is the balance of the purchase price pursuant to our asset purchase agreement with General Electric International, due to a combination of our inability to raise sufficient capital as expected and our belief that we are entitled to a reduction in purchase price we paid as reflected in the principal amount of the outstanding note. In addition, we are in default in the amount of $972,233 in accrued transitional fees, we may use some of the proceeds to settle this obligation.
We are also in default of $258,325 payments of principal and interest on our notes payable to Cybernaut Zfounder Ventures.
We are in discussions with both General Electric International and Cybernaut Zfounder Ventures.
Our business, results of operations and financial condition may be adversely affected by public health epidemics, including the coronavirus or COVID-19.
Our business, results of operations and financial condition may be adversely affected if a public health epidemic, including the coronavirus or COVID-19 interferes with the ability of us, our employees, workers, contractors, suppliers, customers and other business partners to perform our and their respective responsibilities and obligations relative to the conduct of our business. We maintain offices in HaiXi with employees and workers upon whom we rely to, among other things, identify sources of supply in China, conduct factory inspections, place orders for merchandise, perform factory monitoring with respect to production, quality control and other requirements, and arrange shipping. A public health epidemic, including the coronavirus, poses the risk that we or our employees, workers, contractors, suppliers, customers and other business partners may be prevented from conducting business activities for an indefinite period of time, including due to shutdowns that may be requested or mandated by governmental authorities. We face similar risks if a public health epidemic, including the coronavirus, affects other geographic areas where our employees, workers, contractors, suppliers, customers and other business partners are located.
| 9 |
IF DEMAND FOR THE PRODUCTS AND SERVICES THAT THE COMPANY OFFERS SLOWS, OUR BUSINESS WOULD BE MATERIALLY AFFECTED.
Demand for products which it intends to sell depends on many factors, including:
| ● | the economy, and in periods of rapidly declining economic conditions, customers may defer purchases or may choose alternate products; |
| ● | the cost of oil, gas and solar energy; |
| ● | the competitive environment in the heat to power sectors may force us to reduce prices below our desired pricing level or increase promotional spending; |
| ● | our ability to maintain efficient, timely and cost-effective production and delivery of the products and services; and, |
| ● | All of these factors could result in immediate and longer term declines in the demand for the products and services that we offer, which could adversely affect our sales, cash flows and overall financial condition. |
WE OPERATE IN A HIGHLY COMPETITIVE MARKET. IF WE DO NOT COMPETE EFFECTIVELY, OUR PROSPECTS, OPERATING RESULTS, AND FINANCIAL CONDITION COULD BE ADVERSELY AFFECTED.
The markets for our products and services are highly competitive, with companies offering a variety of competitive products and services. We expect competition in our markets to intensify in the future as new and existing competitors introduce new or enhanced products and services that are potentially more competitive than our products and services. We believe many of our competitors and potential competitors have significant competitive advantages, including longer operating histories, ability to leverage their sales efforts and marketing expenditures across a broader portfolio of products and services, larger and broader customer bases, more established relationships with a larger number of suppliers, contract manufacturers, and channel partners, greater brand recognition, and greater financial, research and development, marketing, distribution, and other resources than we do and the ability to offer financing for projects. Our competitors and potential competitors may also be able to develop products or services that are equal or superior to ours, achieve greater market acceptance of their products and services, and increase sales by utilizing different distribution channels than we do. Some of our competitors may aggressively discount their products and services in order to gain market share, which could result in pricing pressures, reduced profit margins, lost market share, or a failure to grow market share for us. If we are not able to compete effectively against our current or potential competitors, our prospects, operating results, and financial condition could be adversely affected.
WE MAY LOSE OUT TO LARGER AND BETTER-ESTABLISHED COMPETITORS.
The alternative power industry is intensely competitive. Most of our competitors have significantly greater financial, technical, marketing and distribution resources as well as greater experience in the industry than we have. Our products may not be competitive with other technologies, both existing at the current time and in the future. If this happens, our sales and revenues will decline, or fail to develop at all. In addition, our current and potential competitors may establish cooperative relationships with larger companies to gain access to greater development or marketing resources. Competition may result in price reductions, reduced gross margins and loss of market share.
| 10 |
OUR INTERNATIONAL OPERATIONS SUBJECT US TO RISKS, WHICH COULD ADVERSELY AFFECT OUR OPERATING RESULTS.
Our international operations are exposed to the following risks, several of which are out of our control:
political and economic instability, international terrorism and anti-American sentiment, particularly in emerging markets;
| ● | preference for locally branded products, and laws and business practices favoring local competition; | |
| ● | unusual or burdensome foreign laws or regulations, and unexpected changes to those laws or regulations; | |
| ● | |import and export license requirements, tariffs, taxes and other barriers; | |
| ● | costs of customizing products for foreign countries; | |
| ● | increased difficulty in managing inventory; | |
| ● | less effective protection of intellectual property; and | |
| ● | difficulties and costs of staffing and managing foreign operations. |
Any or all of these factors could adversely affect our ability to execute any geographic expansion strategies or have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
OUR PRODUCTS MAY BE DISPLACED BY NEWER TECHNOLOGY.
The alternative power industry is undergoing rapid and significant technological change. Third parties may succeed in developing or marketing technologies and products that are more effective than those developed or marketed by us, or that would make our technology obsolete or non-competitive. Accordingly, our success will depend, in part, on our ability to respond quickly to technological changes. We may not have the resources to do this.
WE MUST HIRE QUALIFIED ENGINEERING, DEVELOPMENT AND PROFESSIONAL SERVICES PERSONNEL.
We cannot be certain that we can attract or retain a sufficient number of highly qualified mechanical engineers, industrial technology and manufacturing process developers and professional services personnel. To deploy our products quickly and efficiently, and effectively maintain and enhance them, we will require an increasing number of technology developers. We expect customers that license our technology will typically engage our professional engineering staff to assist with support, training, consulting and implementation. We believe that growth in sales depends on our ability to provide our customers with these services and to attract and educate third-party consultants to provide similar services. As a result, we plan to hire professional services personnel to meet these needs. New technical and professional services personnel will require training and education and it will take time for them to reach full productivity. To meet our needs for engineers and professional services personnel, we also may use costlier third-party contractors and consultants to supplement our own staff. Competition for qualified personnel is intense, particularly because our technology is specialized and only a limited number of individuals have acquired the needed skills. Additionally, we will rely on third-party implementation providers for these services. Our business may be harmed if we are unable to establish and maintain relationships with third-party implementation providers.
WE MAY BE ADVERSELY AFFECTED BY SHORTAGES OF REQUIRED COMPONENTS. IN ADDITION, WE DEPEND ON A LIMITED NUMBER OF SUPPLIERS TO PROCURE OUR PARTS FOR PRODUCTION WHICH IF AVAILABILITY OF PRODUCTS BECOMES COMPROMISED IT COULD ADD TO OUR COST OF GOODS SOLD AND AFFECT OUR REVENUE GROWTH.
At various times, there have been shortages of some of the components that we use, as a result of strong demand for those components or problems experienced by suppliers. These unanticipated component shortages have resulted in curtailed production or delays in production, which prevented us from making scheduled shipments to customers in the past and may do so in the future. Our inability to make scheduled shipments could cause us to experience a reduction in our sales and an increase in our costs and could adversely affect our relationship with existing customers as well as prospective customers. Component shortages may also increase our cost of goods sold because we may be required to pay higher prices for components in short supply and redesign or reconfigure products to accommodate substitute components.
| 11 |
OUR PRINCIPAL SHAREHOLDERS, DIRECTORS AND EXECUTIVE OFFICERS, IN THE AGGREGATE, BENEFICIALLY OWN MORE THAN 50% OF OUR OUTSTANDING COMMON STOCK AND THESE SHAREHOLDERS, IF ACTING TOGETHER, WILL BE ABLE TO EXERT SUBSTANTIAL INFLUENCE OVER ALL MATTERS REQUIRING APPROVAL OF OUR SHAREHOLDERS.
Our principal shareholders, directors and executive officers in the aggregate, beneficially own more than 50% our outstanding common stock on a fully diluted basis. These shareholders, if acting together, will be able to exert substantial influence over all matters requiring approval of our shareholders, including amendments to our Articles of Incorporation, fundamental corporate transactions such as mergers, acquisitions, the sale of the company, and other matters involving the direction of our business and affairs and specifically the ability to determine the members of our board of directors. (See “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Managements”).
IF WE LOSE KEY SENIOR MANAGEMENT PERSONNEL OUR BUSINESS COULD BE NEGATIVELY AFFECTED. FURTHER, WE WILL NEED TO RECRUIT AND RETAIN ADDITIONAL SKILLED MANAGEMENT PERSONNEL AND IF WE ARE NOT ABLE TO DO SO, OUR BUSINESS AND OUR ABILITY TO CONTINUE TO GROW COULD BE HARMED.
Our success depends to a large extent upon the continued services of our executive officers. We could be seriously harmed by the loss of any of our executive officers. In order to manage our growth, we will need to recruit and retain additional skilled management personnel and if we are not able to do so, our business and our ability to continue to grow could be harmed. We are presently dependent to a great extent upon the experience, abilities and continued services of Kambiz Mahdi, our Chief Executive Officer. The loss of his services would delay our business operations substantially. Although a number of companies in our industry have implemented workforce reductions, there remains substantial competition for highly skilled employees.
WE ARE SUBJECT TO ENVIRONMENTAL COMPLIANCE RISKS AND UNEXPECTED COSTS THAT WE MAY INCUR WITH RESPECT TO ENVIRONMENTAL MATTERS MAY RESULT IN ADDITIONAL LOSS CONTINGENCIES, THE QUANTIFICATION OF WHICH CANNOT BE DETERMINED AT THIS TIME.
We are subject to various federal, state, local and foreign environmental laws and regulations, including those governing the use, storage, discharge and disposal of hazardous substances in the ordinary course of our manufacturing process. If more stringent compliance or cleanup standards under environmental laws or regulations are imposed, or the results of future testing and analyses at our current or former operating facilities indicate that we are responsible for the release of hazardous substances, we may be subject to additional remediation liability. Further, additional environmental matters may arise in the future at sites where no problem is currently known or at sites that we may acquire in the future. Currently unexpected costs that we may incur with respect to environmental matters may result in additional loss contingencies, the quantification of which cannot be determined at this time.
OUR SALES AND CONTRACT FULFILLMENT CYCLES CAN BE LONG, UNPREDICTABLE AND VARY SEASONALLY, WHICH CAN CAUSE SIGNIFICANT VARIATION IN REVENUES AND PROFITABILITY IN A PARTICULAR QUARTER.
The timing of our sales and related customer contract fulfillment is difficult to predict. Many of our customers are large enterprises, whose purchasing decisions, budget cycles and constraints and evaluation processes are unpredictable and out of our control. Further, the timing of our sales is difficult to predict. The length of our sales cycle, from initial evaluation to payment for our products and services, can range from several months to well over a year and can vary substantially from customer to customer. Our sales efforts involve significant investment in resources in field sales, marketing and educating our customers about the use, technical capabilities and benefits of our products and services. Customers often undertake a prolonged evaluation process. As a result, it is difficult to predict exactly when, or even if, we will make a sale to a potential customer or if we can increase sales to our existing customers. Large individual sales have, in some cases, occurred in quarters subsequent to those we anticipated, or have not occurred at all. In addition, the fulfillment of our customer contracts is partially dependent on other factors related to our customers’ businesses that are not in our control. as with the sales cycle, this can also cause revenues and earnings to fluctuate from quarter to quarter. If our sales and/or contract fulfillment cycles lengthen or our substantial upfront investments do not result in sufficient revenue to justify our investments, our operating results could be adversely affected.
We have experienced seasonal and end-of-quarter concentration of our transactions and variations in the number and size of transactions that close in a particular quarter, which impacts our ability to grow revenue over the long term and plan and manage cash flows and other aspects of our business and cost structure. Our transactions vary by quarter, with the fourth quarter typically being our largest. If expectations for our business turn out to be inaccurate, our revenue growth may be adversely affected over time and we may not be able to adjust our cost structure on a timely basis and our cash flows may suffer.
| 12 |
OUR OPERATING MARGINS MAY DECLINE AS A RESULT OF INCREASING PRODUCT COSTS.
Our business is subject to significant pressure on pricing and costs caused by many factors, including competition, the cost of components used in our products, labor costs, constrained sourcing capacity, inflationary pressure, pressure from customers to reduce the prices we charge for our products and services, and changes in consumer demand. Costs for the raw materials used in the manufacture of our products are affected by, among other things, energy prices, consumer demand, fluctuations in commodity prices and currency, and other factors that are generally unpredictable and beyond our control. Increases in the cost of raw materials used to manufacture our products or in the cost of labor and other costs of doing business in the United States and internationally could have an adverse effect on, among other things, the cost of our products, gross margins, operating results, financial condition, and cash flows.
WE MAY NEED TO RAISE ADDITIONAL CAPITAL REQUIRED TO GROW OUR BUSINESS, AND WE MAY NOT BE ABLE TO RAISE CAPITAL ON TERMS ACCEPTABLE TO US OR AT ALL.
Growing and operating our business will require significant cash outlays and capital expenditures and commitments. We have utilized cash on hand and cash generated from operations as sources of liquidity. If cash on hand and cash generated from operations are not sufficient to meet our cash requirements, we will need to seek additional capital, potentially through equity or debt financing, to fund our growth. Our ability to access the credit and capital markets in the future as a source of liquidity, and the borrowing costs associated with such financing, are dependent upon market conditions.
In addition, any equity securities we issue, including any preferred stock, may be on terms that are dilutive or potentially dilutive to our stockholders, and the prices at which new investors would be willing to purchase our securities may be lower than the offering price per share of our Common Stock. The holders of any equity securities we issue, including any preferred stock, may also have rights, preferences or privileges which are senior to those of existing holders of Common Stock. If new sources of financing are required, but are insufficient or unavailable, we will be required to modify our growth and operating plans based on available funding, if any, which would harm our ability to grow our business.
NATURAL DISASTERS AND OTHER CATASTROPHIC EVENTS BEYOND OUR CONTROL COULD ADVERSELY AFFECT OUR BUSINESS OPERATIONS AND FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE.
The occurrence of one or more natural disasters, such as fires, hurricanes, tornados, tsunamis, floods and earthquakes; geo-political events, such as civil unrest in a country in which our suppliers are located or terrorist or military activities disrupting transportation, communication or utility systems; or other highly disruptive events, such as nuclear accidents, pandemics, unusual weather conditions or cyber-attacks, could adversely affect our operations and financial performance. Such events could result, among other things, in operational disruptions, physical damage to or destruction or disruption of one or more of our properties or properties used by third parties in connection with the supply of products or services to us, the lack of an adequate workforce in parts or all of our operations and communications and transportation disruptions. These factors could also cause consumer confidence and spending to decrease or result in increased volatility in the United States and global financial markets and economy. Such occurrences could have a material adverse effect on us and could also have indirect consequences such as increases in the costs of insurance if they result in significant loss of property or other insurable damage.
WE HAVE ISSUED A SUBSTANTIAL AMOUNT OF CONVERTIBLE SECURITIES WHICH IF CONVERTED WILL SUBSTANTIALLY DILUTE ALL OF OUR STOCKHOLDERS.
We have issued a substantial amount of convertible securities which, if converted, would result in substantial dilution to our stockholders. As of the date of this Offing Circular we have outstanding the convertible notes, warrants and preferred stock as set forth below:
| Convertible Notes - and Approximate common share equivalents | 507,650,818 | |||
| Convertible Preferred series D and approximate common share equivalents | 8,739,000 | |||
| Warrants a and Common Stock equivalent’s | 174,250,000 | |||
| Total Convertible Common Stock equivalents | 690,639,818 |
| 13 |
MGW Investments I Limited (“MGWI”) holds two notes, the interest and principal of which may be converted into shares of our common stock at a fixed conversion price of $.003 per share which, at the time of this filing, equal approximately 65,946,000 shares and 391,458,333 shares respectively, or an aggregate of 457,404,333 shares. In addition, MGWI holds a warrant to purchase 168,000,000 shares of our common stock. Calvin Pang, our director, is a beneficial owner of the securities held by MGWI. We have also issued warrants to purchase 6,250,000 shares of our common stock to other investors and convertible notes to other investors convertible into an additional 65,235,485 shares.
OUR ISSUANCE OF ADDITIONAL CAPITAL STOCK IN CONNECTION WITH FINANCINGS, ACQUISITIONS, INVESTMENTS, OUR EQUITY INCENTIVE PLANS, OR OTHERWISE WILL DILUTE ALL OTHER STOCKHOLDERS.
We expect to issue additional capital stock in the future that will result in dilution to all other stockholders. We expect to grant equity awards to employees, directors, and consultants under our equity incentive plans. We may also raise capital through equity financings in the future. As part of our business strategy, we may acquire or make investments in complementary companies, products, or technologies, and issue equity securities to pay for any such acquisition or investment. Any such issuances of additional capital stock may cause stockholders to experience significant dilution of their ownership interests and the per share value of our common stock to decline.
WE MAY MAKE ACQUISITIONS THAT ARE DILUTIVE TO EXISTING STOCKHOLDERS. IN ADDITION, OUR LIMITED EXPERIENCE IN ACQUIRING OTHER BUSINESSES, PRODUCT LINES AND TECHNOLOGIES MAY MAKE IT DIFFICULT FOR US TO OVERCOME PROBLEMS ENCOUNTERED IN CONNECTION WITH ANY ACQUISITIONS WE MAY UNDERTAKE.
We intend to evaluate and explore strategic opportunities as they arise, including business combinations, strategic partnerships, and the purchase, licensing or sale of assets. In connection with any such future transaction, we could issue dilutive equity securities, incur substantial debt, reduce our cash reserves or assume contingent liabilities.
Our experience in acquiring other businesses, product lines and technologies is limited. Our inability to overcome problems encountered in connection with any acquisitions could divert the attention of management, utilize scarce corporate resources and otherwise harm our business. Any potential future acquisitions also involve numerous risks, including:
| ● | problems assimilating the purchased operations, technologies or products; | |
| ● | costs associated with the acquisition; | |
| ● | adverse effects on existing business relationships with suppliers and customers; | |
| ● | risks associated with entering markets in which we have no or limited prior experience; | |
| ● | potential loss of key employees of purchased organizations; and | |
| ● | potential litigation arising from the acquired company’s operations before the acquisition. |
Furthermore, acquisitions may require material charges and could result in adverse tax consequences, substantial depreciation, deferred compensation charges, in-process research and development charges, the amortization of amounts related to deferred compensation and identifiable purchased intangible assets or impairment of goodwill, any of which could negatively affect our results of operations.
| 14 |
WE MAY BE SUBJECT TO GOVERNMENT LAWS AND REGULATIONS PARTICULAR TO OUR OPERATIONS WITH WHICH WE MAY BE UNABLE TO COMPLY.
We may not be able to comply with all current and future government regulations which are applicable to our business. Our business operations are subject to all government regulations normally incident to conducting business (e.g., occupational safety and health acts, workmen’s compensation statutes, unemployment insurance legislation, income tax, and social security laws and regulations, environmental laws and regulations, consumer safety laws and regulations, etc.) as well as to governmental laws and regulations applicable to small public companies and their capital formation efforts. Although we will make every effort to comply with applicable laws and regulations, we can provide no assurance of our ability to do so, nor can we predict the effect of those regulations on our proposed business activities. Our failure to comply with material regulatory requirements would likely have an adverse effect on our ability to conduct our business and could result in our cessation of active business operations.
COMPLIANCE WITH CHANGING REGULATION OF CORPORATE GOVERNANCE AND PUBLIC DISCLOSURE WILL RESULT IN ADDITIONAL EXPENSES.
Changing laws, regulations and standards relating to corporate governance and public disclosure, including the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and related SEC regulations, have created uncertainty for public companies and significantly increased the costs and risks associated with accessing the public markets and public reporting. Our management team will need to invest significant management time and financial resources to comply with both existing and evolving standards for public companies, which will lead to increased general and administrative expenses and a diversion of management time and attention from revenue generating activities to compliance activities.
OUR REVENUE GROWTH RATE DEPENDS PRIMARILY ON OUR ABILITY TO EXECUTE OUR BUSINESS PLAN.
We may not be able to identify and maintain the necessary relationships within our industry. Our ability to execute our business plan also depends on other factors, including the ability to:
1. Negotiate and maintain contracts and agreements with acceptable terms;
2. Hire and train qualified personnel;
3. Maintain marketing and development costs at affordable rates; and,
4. Maintain an affordable labor force.
Risks About Our Stock
OUR COMMON STOCK MAY BE DEEMED A “PENNY STOCK,” WHICH WOULD MAKE IT MORE DIFFICULT FOR OUR INVESTORS TO SELL THEIR SHARES.
Our common stock is currently subject to the “penny stock” rules adopted under Section 15(g) of the Exchange Act. The penny stock rules generally apply to companies whose common stock is not listed on The Nasdaq Stock Market or another national securities exchange and trades at less than $4.00 per share, other than companies that have had average revenues of at least $6,000,000 for the last three years or that have tangible net worth of at least $5,000,000 ($2,000,000 if the company has been operating for three or more years). These rules require, among other things, that brokers who trade penny stock to persons other than “established customers” complete certain documentation, make suitability inquiries of investors and provide investors with certain information concerning trading in the security, including a risk disclosure document and quote information under certain circumstances. Many brokers have decided not to trade penny stocks because of the requirements of the penny stock rules and, as a result, the number of broker-dealers willing to act as market makers in these securities is limited. If we remain subject to the penny stock rules for any significant period, it could have an adverse effect on the market, if any, for our securities. If our securities are subject to the penny stock rules, investors will find it more difficult to dispose of our securities.
WE MAY IN THE FUTURE ISSUE ADDITIONAL SHARES OF OUR COMMON STOCK, WHICH MAY HAVE A DILUTIVE EFFECT ON OUR STOCKHOLDERS.
Our Certificate of Incorporation authorizes the issuance of 2,000,000,000 shares of common stock of which 762,895,515 are issued and outstanding and 20,000,000 shares of preferred stock, of which 7,500 shares are issued and 5,700 shares are outstanding as of July 10, 2020. The future issuance of our common stock may result in substantial dilution in the percentage of our common shares held by our then existing stockholders. We may value any Common Stock issued in the future on an arbitrary basis. The issuance of common stock for future services or acquisitions or other corporate actions may have the effect of diluting the value of the shares held by our investors and might have an adverse effect on any trading market for our common stock.
| 15 |
OUR BOARD OF DIRECTORS HAS AUTHORIZED A REVERSE STOCK SPLIT OF UP TO 50 SHARES OF OUR COMMON STOCK INTO ONE SHARE OF OUR COMMON STOCK WHICH MAY HAVE A DILUTIVE EFFECT ON OUR STOCKHOLDERS.
If implemented by our Board of Directors, a reverse stock split will reduce the number of outstanding shares of our Common Stock without reducing the number of shares of available but unissued Common Stock, which will also have the effect of increasing the number of authorized but unissued shares. The issuance of additional shares of our Common Stock may have a dilutive effect on the ownership of existing shareholders. The liquidity of the shares of our common stock may be adversely affected by a reverse stock split given the reduced number of shares that will be outstanding following a reverse stock split, especially if the market price of our common stock does not increase as a result of the reverse stock split. Although we believe that a higher market price of our common stock may help generate greater or broader investor interest, we cannot assure you that a reverse stock split will result in a share price that will attract new investors.
OUR SECURITIES ARE THINLY TRADED WHICH DOES NOT PROVIDE LIQUIDITY FOR OUR INVESTORS.
Our securities are quoted on the OTCQB Market. The OTCQB Market is an inter-dealer, over-the-counter market that provides significantly less liquidity than the NASDAQ Stock Market or national or regional exchanges. Securities traded on the OTCQB Market are usually thinly traded, highly volatile, have fewer market makers and are not followed by analysts. The Securities and Exchange Commission’s order handling rules, which apply to NASDAQ-listed securities, do not apply to securities quoted on the OTCQB Market. Quotes for stocks included on the OTCQB Market are not listed in newspapers. Therefore, prices for securities traded solely on the OTCQB Market may be difficult to obtain and holders of our securities may be unable to resell their securities at or near their original acquisition price, or at any price.
Investors must contact a broker-dealer to trade on the OTCQB Market. As a result, you may not be able to buy or sell our securities at the times that you may wish. Furthermore, when investors place market orders to buy or sell a specific number of shares at the current market price it is possible for the price of a stock to go up or down significantly during the lapse of time between placing a market order and its execution.
THE MARKET PRICE AND TRADING VOLUME OF SHARES OF OUR COMMON STOCK MAY BE VOLATILE.
The market price of our common stock could fluctuate significantly for many reasons, including for reasons unrelated to our specific performance, such as reports by industry analysts, investor perceptions, or negative announcements by customers, or competitors regarding their own performance, as well as general economic and industry conditions. In addition, when the market price of a company’s shares drops significantly, stockholders could institute securities class action lawsuits against the company. A lawsuit against us could cause us to incur substantial costs and could divert the time and attention of our management and other resources.
IF WE FAIL TO MAINTAIN EFFECTIVE INTERNAL CONTROLS OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING, THE PRICE OF OUR COMMON STOCK MAY BE ADVERSELY AFFECTED.
As a public reporting company, we are required to establish and maintain appropriate internal controls over financial reporting. Failure to establish those controls, or any failure of those controls once established, could adversely impact our public disclosures regarding our business, financial condition or results of operations. Any failure of these controls could also prevent us from maintaining accurate accounting records and discovering accounting errors and financial frauds. Rules adopted by the SEC pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 require annual assessment of our internal control over financial reporting and may require attestation of this assessment by our independent registered public accountants. The standards that must be met for management to assess the internal control over financial reporting as effective are complex, and require significant documentation, testing and possible remediation to meet the detailed standards. We may encounter problems or delays in completing activities necessary to make an assessment of our internal control over financial reporting. In addition, the attestation process by our independent registered public accountants is new and we may encounter problems or delays in completing the implementation of any requested improvements and receiving an attestation of our assessment by our independent registered public accountants.
| 16 |
COMPLIANCE WITH CHANGING REGULATION OF CORPORATE GOVERNANCE AND PUBLIC DISCLOSURE WILL RESULT IN ADDITIONAL EXPENSES.
Changing laws, regulations and standards relating to corporate governance and public disclosure, including the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and related SEC regulations, have significantly increased the costs and risks associated with accessing the public markets and public reporting. Our management team will need to invest significant management time and financial resources to comply with both existing and evolving standards for public companies, which will lead to increased general and administrative expenses and a diversion of management time and attention from revenue generating activities to compliance activities.
WE DO NOT INTEND TO PAY DIVIDENDS IN THE FORESEEABLE FUTURE; THEREFORE, YOU MAY NEVER SEE A RETURN ON YOUR INVESTMENT.
We do not anticipate the payment of cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. We anticipate that any profits from our operations will be devoted to our future operations. Any decision to pay dividends will depend upon our profitability at the time, cash available and other factors
OUR OPERATING RESULTS AND SHARE PRICE MAY BE VOLATILE AND THE MARKET PRICE OF OUR COMMON STOCK AFTER THIS OFFERING MAY DROP BELOW THE PRICE YOU PAY.
Our quarterly operating results have in the past fluctuated and are likely to do so in the future. As a result, the trading price of the shares of our common stock following this offering is likely to be highly volatile and could be subject to wide fluctuations in response to various factors, some of which are beyond our control. In addition to the factors discussed in this “Risk Factors” section and elsewhere in this Prospectus, these factors include:
| ● | the success of competitive products or technologies; |
| ● | actual or anticipated changes in our growth rate relative to our competitors; |
| ● | announcements by us or our competitors of significant acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures, collaborations or capital commitments; |
| ● | regulatory or legal developments in the United States and other countries; |
| ● | the recruitment or departure of key personnel; |
| ● | the level of expenses; |
| ● | changes in our backlog in a given period; |
| ● | actual or anticipated changes in estimates as to financial results, development timelines or recommendations by securities analysts; |
| ● | variations in our financial results or those of companies that are perceived to be similar to us; |
| ● | fluctuations in the valuation of companies perceived by investors to be comparable to us; |
| ● | inconsistent trading volume levels of our shares; |
| ● | announcement or expectation of additional financing efforts; |
| ● | sales of our common stock by us, our insiders or our other stockholders; |
| ● | market conditions in the clean energy sector; and |
| ● | general economic, industry and market conditions. |
These and other factors, many of which are beyond our control, may cause our operating results and the market price and demand for our shares to fluctuate substantially. While we believe that operating results for any particular quarter are not necessarily a meaningful indication of future results, fluctuations in our quarterly operating results could limit or prevent investors from readily selling their shares and may otherwise negatively affect the market price and liquidity of our shares. In addition, the stock market in general, and companies in our markets in particular, have experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that have often been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of these companies. Broad market and industry factors may negatively affect the market price of our common stock, regardless of our actual operating performance. The realization of any of these risks or any of a broad range of other risks, including those described in these “Risk Factors,” could have a dramatic and material adverse impact on the market price of the shares of our common stock.
| 17 |
WE MAY BE SUBJECT TO SECURITIES LITIGATION, WHICH IS EXPENSIVE AND COULD DIVERT MANAGEMENT ATTENTION.
The market price of the shares of our common stock may be volatile, and in the past companies that have experienced volatility in the market price of their securities have been subject to securities class action litigation. We may be the target of this type of litigation in the future. Securities litigation against us could result in substantial costs and divert our management’s attention from other business concerns, which could seriously harm our business.
WE HAVE BROAD DISCRETION IN THE USE OF THE NET PROCEEDS FROM THIS OFFERING AND MAY NOT USE THEM EFFECTIVELY.
Our management will have broad discretion in the application of the net proceeds from this offering and could spend the proceeds in ways that do not improve our results of operations or enhance the value of our common stock. The failure by our management to apply these funds effectively could result in financial losses that could have a material adverse effect on our business and cause the market price of our shares of common stock to decline. Pending their use, we may invest the net proceeds from this offering in a manner that does not produce income or that loses value. If we do not invest the net proceeds from this offering in ways that enhance stockholder value, we may fail to achieve expected financial results, which could cause the price of our shares of common stock to decline.
Risks Related to the Offering
Our existing stockholders may experience significant dilution from the sale of our common stock pursuant to the GHS financing agreement.
The sale of our common stock to GHS Investments LLC in accordance with the Financing Agreement may have a dilutive impact on our shareholders. As a result, the market price of our common stock could decline. In addition, the lower our stock price is at the time we exercise our put options, the more shares of our common stock we will have to issue to GHS in order to exercise a put under the Financing Agreement. If our stock price decreases, then our existing shareholders would experience greater dilution for any given dollar amount raised through the offering.
The perceived risk of dilution may cause our stockholders to sell their shares, which may cause a decline in the price of our common stock. Moreover, the perceived risk of dilution and the resulting downward pressure on our stock price could encourage investors to engage in short sales of our common stock. By increasing the number of shares offered for sale, material amounts of short selling could further contribute to progressive price declines in our common stock.
The issuance of shares pursuant to the GHS financing agreement may have a significant dilutive effect.
Depending on the number of shares we issue pursuant to the GHS Financing Agreement, it could have a significant dilutive effect upon our existing shareholders. Although the number of shares that we may issue pursuant to the Financing Agreement will vary based on our stock price (the higher our stock price, the less shares we have to issue), there may be a potential dilutive effect to our shareholders, based on different potential future stock prices, if the full amount of the Financing Agreement is realized. Dilution is based upon common stock put to GHS and the stock price discounted to GHS’s purchase price of 80% of the lowest trading price during the pricing period.
GHS Investments LLC will pay less than the then-prevailing market price of our common stock which could cause the price of our common stock to decline.
Our common stock to be issued under the GHS Financing Agreement will be purchased at a twenty percent (20%) discount, or eighty percent (80%) of the lowest closing price for the Company’s common stock during the ten (10) consecutive trading days immediately preceding the Purchase Date (as defined in the GHS Financing Agreement).
GHS has a financial incentive to sell our shares immediately upon receiving them to realize the profit between the discounted price and the market price. If GHS sells our shares, the price of our common stock may decrease. If our stock price decreases, GHS may have further incentive to sell such shares. Accordingly, the discounted sales price in the Financing Agreement may cause the price of our common stock to decline.
We may not have access to the full amount under the financing agreement.
The lowest two closing prices for the 10 days ended July 10, 2020 was approximately $0.0166. At that price we would be able to sell shares to GHS under the Financing Agreement at the discounted price of $0.01328. At that discounted price, the 74,720,000 shares would only represent approximately $992,282, which is far below the full amount of the Financing Agreement. In addition, any single drawdown may not exceed two hundred percent (200%) of the average daily trading dollar volume of the Company’s Common Stock during the ten (10) trading days preceding the put, which is approximately $7,162 on the date of this Registration Statement, and cannot exceed $400,000.
| 18 |
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Some of the statements under “Summary”, “Risk Factors”, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations”, “Description of Our Business” and elsewhere in this Prospectus constitute forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements relate to expectations, beliefs, projections, future plans and strategies, anticipated events or trends and similar matters that are not historical facts. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terms such as “anticipate”, “believe”, “could”, “estimate”, “expect”, “intend”, “may”, “plan”, “potential”, “should”, “will” and “would” or the negatives of these terms or other comparable terminology.
You should not place undue reliance on forward looking statements. The cautionary statements set forth in this Prospectus, including in “Risk Factors” and elsewhere, identify important factors which you should consider in evaluating our forward-looking statements. These factors include, among other things:
| ● | Our independent accountants have issued a going concern opinion, | |
| ● | Intense competition, which may reduce our sales, operating profits, or both, | |
| ● | Our ability to obtain future financing, | |
| ● | Our ability to execute our strategic plan, | |
| ● | Dilution due to exercise of Convertible notes | |
| ● | We are in default of our agreements with General Electric and Cybernaut Zfounder Ventures , | |
| ● | Our products may be displaced by newer technology, | |
| ● | Majority ownership by our principal shareholders, directors and executive officers, | |
| ● | Concentration of customers, | |
| ● | We are a Penny Stock and lack of liquidity in trading our common stock, | |
| ● | Failure to maintain effective internal controls, | |
| ● | Our highly competitive market, | |
| ● | Limited human resources and ability manage our growth, and | |
| ● | Dependence on our management, senior professionals and other key personnel. |
Although the forward-looking statements in this Prospectus are based on our beliefs, assumptions and expectations, taking into account all information currently available to us, we cannot guarantee future transactions, results, performance, achievements or outcomes. No assurance can be made to any investor by anyone that the expectations reflected in our forward-looking statements will be attained, or that deviations from them will not be material and adverse. We undertake no obligation, other than as maybe be required by law, to re-issue this Prospectus or otherwise make public statements updating our forward-looking statements.
| 19 |
The selling stockholder identified in this prospectus, GHS, may offer and sell up to 74,720,000 shares of our common stock, which consists of shares of common stock to be initially purchased by GHS pursuant to the Financing Agreement. If issued presently, the shares of common stock registered for resale by GHS would represent approximately 10% of our issued and outstanding shares of common stock, based on the 762,895,515 shares of our issued and outstanding shares as of July 10, 2020. Additionally, the 74,720,000 shares of our common stock registered for resale herein would represent approximately 30% of the Company’s public float which would not include 764,562 shares of our common stock currently held by GHS.
We may require the selling stockholder to suspend the sales of the shares of our common stock being offered pursuant to this prospectus upon the occurrence of any event that makes any statement in this prospectus or the related registration statement untrue in any material respect or that requires the changing of statements in those documents in order to make statements in those documents not misleading.
The selling stockholder identified in the table below may from time to time offer and sell under this prospectus any or all of the shares of common stock described under the column “Shares of Common Stock Being Offered” in the table below.
GHS will be deemed to be an underwriter within the meaning of the Securities Act. Any profits realized by the selling stockholder may be deemed to be underwriting commissions.
We cannot give an estimate as to the number of shares of common stock that will actually be held by the selling stockholder upon termination of this offering, because the selling stockholder may offer some or all of the common stock under the offering contemplated by this prospectus or acquire additional shares of common stock. The total number of shares that may be sold hereunder will not exceed the number of shares offered hereby. Please read the section entitled “Plan of Distribution” in this prospectus.
The manner in which the selling stockholder acquired or will acquire shares of our common stock is discussed below under “The Offering.”
The following table sets forth the name of the selling stockholder, the number of shares of our common stock beneficially owned by such stockholder before this offering, the number of shares to be offered for such stockholder’s account and the number and (if one percent or more) the percentage of the class to be beneficially owned by such stockholder after completion of the offering. The number of shares owned are those beneficially owned, as determined under the rules of the SEC, and such information is not necessarily indicative of beneficial ownership for any other purpose. Under such rules, beneficial ownership includes any shares of our common stock as to which a person has sole or shared voting power or investment power and any shares of common stock which the person has the right to acquire within 60 days of July 10, 2020, through the exercise of any option, warrant or right, through conversion of any security or pursuant to the automatic termination of a power of attorney or revocation of a trust, discretionary account or similar arrangement, and such shares are deemed to be beneficially owned and outstanding for computing the share ownership and percentage of the person holding such options, warrants or other rights, but are not deemed outstanding for computing the percentage of any other person. Beneficial ownership percentages are calculated based on 762,895,515 shares of our common stock outstanding as of July 10, 2020.
Unless otherwise set forth below, (a) the persons and entities named in the table below have sole voting and sole investment power with respect to the shares set forth opposite the selling stockholder’s name, subject to community property laws, where applicable, and (b) no selling stockholder had any position, office or other material relationship within the past three years, with us or with any of our predecessors or affiliates. The number of shares of common stock shown as beneficially owned before the offering is based on information furnished to us or otherwise based on information available to us at the timing of the filing of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part.
| 20 |
| Shares Owned by the Selling Stockholder before the | Shares of Common Stock Being | Number of Shares to be Owned by Selling Stockholder After the Offering and Percent of Total Issued and Outstanding Shares | ||||||||||||||
| Name of Selling Stockholder | Offering (1) | Offered | # of Shares(2) | % of Class (2) | ||||||||||||
| GHS Investments LLC (3) | 764,526 | 74,720,000 | (4) | 764,526 | 0.01 | % | ||||||||||
Notes:
| (1) | The shares currently owned by GHS consist entirely of shares received upon shares issued by the Company to GHS upon execution of the Equity Financing Agreement. |
| (2) | Because the selling stockholder may offer and sell all or only some portion of the 74,720,000 shares of our common stock being offered pursuant to this prospectus and may acquire additional shares of our common stock in the future, we can only estimate the number and percentage of shares of our common stock that the selling stockholder will hold upon termination of the offering based on the shares currently held. |
| (3) | Mark Grober exercises voting and dispositive power with respect to the shares of our common stock that are beneficially owned by GHS. |
| (4) | Consists of up to 74,720,000 shares of common stock to be sold by GHS pursuant to the Financing Agreement. |
The selling stockholder may, from time to time, sell any or all of its shares of Company common stock through the OTC Link or any other stock exchange, quotation board, market or trading facility on which the shares of our common stock are quoted or traded, or in private transactions. These sales may be at fixed prices, prevailing market prices at the time of sale, at varying prices, or at negotiated prices. The selling stockholder may use any one or more of the following methods when selling shares:
| ● | ordinary brokerage transactions and transactions in which the broker-dealer solicits purchasers; |
| ● | block trades in which the broker-dealer will attempt to sell the shares as agent but may position and resell a portion of the block as principal to facilitate the transaction; |
| ● | purchases by a broker-dealer as principal and resale by the broker-dealer for its account; |
| ● | privately negotiated transactions; |
| ● | broker-dealers may agree with the selling stockholders to sell a specified number of such shares at a stipulated price per share; or |
| ● | a combination of any such methods of sale. |
Additionally, broker-dealers engaged by the selling stockholder may arrange for other brokers-dealers to participate in sales. Broker-dealers may receive commissions or discounts from the selling stockholder (or, if any broker-dealer acts as agent for the purchaser of shares, from the purchaser) in amounts to be negotiated, but, except as set forth in a supplement to this prospectus, in the case of an agency transaction not in excess of a customary brokerage commissions in compliance with FINRA Rule 2440; and in the case of a principal transaction, a markup or markdown in compliance with FINRA IM-2440.
GHS is an underwriter within the meaning of the Securities Act of 1933, and any broker-dealers or agents that are involved in selling the shares may be deemed to be “underwriters” within the meaning of the Securities Act of 1933 in connection with such sales. Any commissions received by such broker-dealers or agents, and any profit on the resale of the shares purchased by them, may be deemed to be underwriting commissions or discounts under the Securities Act of 1933. GHS has informed us that it does not have any written or oral agreement or understanding, directly or indirectly, with any person to distribute the Company’s common stock. Pursuant to a requirement by FINRA, the maximum commission or discount to be received by any FINRA member or independent broker-dealer may not be greater than 8% of the gross proceeds received by us for the sale of any securities being registered pursuant to Rule 415 promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933.
| 21 |
Discounts, concessions, commissions and similar selling expenses, if any, attributable to the sale of shares will be borne by the selling stockholder. The selling stockholder may agree to indemnify any agent, dealer, or broker-dealer that participates in transactions involving sales of the shares if liabilities are imposed on that person under the Securities Act of 1933.
We have entered into an agreement with GHS to keep this prospectus effective until GHS (i) has sold all of the common shares purchased by it under the Financing Agreement and (ii) has no further right to acquire any additional shares of common stock under the Financing Agreement.
The resale shares will be sold only through registered or licensed brokers or dealers if required under applicable state securities laws. In addition, in certain states, the resale shares may not be sold unless they have been registered or qualified for sale in the applicable state or an exemption from the registration or qualification requirement is available and is complied with.
Under applicable rules and regulations under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, any person engaged in the distribution of the resale shares may not simultaneously engage in market making activities with respect to the common stock for the applicable restricted period, as defined in Regulation M, prior to the commencement of the distribution. In addition, the selling stockholders will be subject to applicable provisions of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and the rules and regulations thereunder, including Regulation M, which may limit the timing of purchases and sales of shares of the common stock by the selling stockholder or any other person. We will make copies of this prospectus available to the selling stockholder.
We are required to pay certain fees and expenses incurred by us incident to the registration of the shares covered by this prospectus. We have agreed to indemnify the selling stockholder against certain losses, claims, damages and liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act of 1933. We will not receive any proceeds from the resale of any of the shares of our common stock by the selling stockholder. We will receive proceeds from the sale of our common stock to GHS under the Financing Agreement. Neither the Financing Agreement with GHS nor any rights of the parties under the Financing Agreement with GHS may be assigned or delegated to any other person.
| 22 |
PRICE RANGE OF COMMON STOCK AND RELATED MATTERS
Our common stock is quoted on the OTCQB tier of the OTC Markets Group quotation system (www.otcmarkets.com) under the trading ticker “CETY.” The following tables set forth the range of high and low prices for our common stock for the two years ended June 30, 2019 and the three months ended March 31, 2020, as reported on the OTC Market Group’s quotation system. These quotations reflect inter-dealer prices, without retail markup, markdown, or commission and may not necessarily represent actual transactions.
| Fiscal 2020 | High | Low | ||||||
| First Quarter (January 1 – March 31) | $ | 0.30 | $ | 0.10 | ||||
| Fiscal 2019 | High | Low | ||||||
| First Quarter (January 1 – March 31) | $ | 0.30 | $ | 0.10 | ||||
| Second Quarter (April 1 – June 30) | $ | 0.47 | $ | 0.28 | ||||
| Third Quarter (July 1 – September 30) | $ | 0.39 | $ | 0.14 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter (October 1 – December 31) | $ | 0.60 | $ | 0.16 | ||||
| Fiscal 2017 | High | Low | ||||||
| First Quarter (January 1 – March 31) | $ | 0.70 | $ | 0.26 | ||||
| Second Quarter (April 1 – June 30) | $ | 0.50 | $ | 0.25 | ||||
| Third Quarter (July 1 – September 30) | $ | 0.50 | $ | 0.30 | ||||
On July 10, 2020, the last sales price per share of our common stock was $018.
Holders of Common Equity
As of July 10, 2020, there were approximately 1,800 stockholders of record. An additional number of stockholders are beneficial holders of our Common Stock in “street name” through banks, brokers and other financial institutions that are the record holders.
Dividend Information
We have not paid any cash dividends to our shareholders. The declaration of any future cash dividends is at the discretion of our board of directors and depends upon our earnings, if any, our capital requirements and financial position, our general economic conditions, and other pertinent conditions. It is our present intention not to pay any cash dividends in the foreseeable future, but rather to reinvest earnings, if any, in our business operations.
Rule 10B-18 Transactions
During the year ended December 31, 2020, there were no repurchases of the Company’s common stock by the Company.
| 23 |
The Company will use the proceeds from the sale of the shares of common stock sold to GHS, for general corporate and working capital purposes, and continued business operations, or for other purposes that the Board of Directors, in good faith, deems to be in the best interest of the Company.
DETERMINATION OF OFFERING PRICE
We have not set an offering price for the shares registered hereunder, as the only shares being registered are those sold pursuant to the Financing Agreement with GHS. GHS may sell all or a portion of the shares being offered pursuant to this prospectus at fixed prices, at prevailing market prices at the time of sale, at varying prices, or at negotiated prices.
The sale of our common stock to GHS in accordance with the Equity Financing Agreement may have a dilutive impact on our shareholders. As a result, our net income per share could decrease in future periods and the market price of our common stock could decline. In addition, the lower our stock price is at the time we exercise our put option, the more shares of our common stock we will have to issue to GHS. If our stock price decreases, then our existing shareholders would experience greater dilution for any given dollar amount raised through the offering.
The perceived risk of dilution may cause our stockholders to sell their shares, which would contribute to a decline in the price of our common stock. Moreover, the perceived risk of dilution and the resulting downward pressure on our stock price could encourage investors to engage in short sales of our common stock. By increasing the number of shares offered for sale, material amounts of short selling could further contribute to progressive price declines in our common stock.
Dilution represents the difference between the offering price (market price) and the net tangible book value per share immediately after completion of this Offering. Net tangible book value is the amount that results from subtracting total liabilities and intangible assets (product development costs) from total assets. Dilution arises mainly as a result of our arbitrary determination of the Offering price of the shares being offered. Dilution of the value of the shares you purchase is also a result of the lower book value of shares of our common stock held by our existing shareholders.
As of March 31, 2020, the net tangible book value of our shares of common stock was (7,460,457), or approximately ($0.01) per share based upon 762,130,989 shares then outstanding. Upon completion of this Offering, if 100% of the shares are sold (74,720,000 shares) at a discounted market price of $0.0144 (80% of $0.018 market price) per share, the net tangible book value of the 836,850,989 shares to be outstanding will be approximately $(6,384,489) or approximately ($.008) per share. Based on these figures, current shareholders will not experience a dilution in terms of net tangible book value per share as a result of this offering.
| 24 |
On June 8, 2020, we entered into an Equity Financing Agreement (the “Financing Agreement”) with GHS Investments LLC (“GHS”) for an equity line. Although we are not required to sell shares under the Financing Agreement, the Financing Agreement gives us the option to sell to GHS up to $2,000,000 worth of our common stock, in increments, beginning on the first trading day after the effective date of this Registration Statement and ending on the earlier of (i) the date GHS has purchased an aggregate of $2,000,000 of our common stock pursuant to the Financing Agreement, (ii) June 8, 2023, thirty-six months from the date of execution of the Financing Agreement, or (iii) the date that this registration statement is no longer in effect (the “Open Period”). $2,000,000 was stated to be the total amount of available funding in the Financing Agreement, because this was the maximum amount that GHS and we agreed to for the funding. There is no assurance the market price of our common stock will increase in the future, or that we will ever sell (i) $2,000,000 of our common stock to GHS, or (ii) all 74,720,000shares being registered hereunder. The number of common shares that remain issuable may not be sufficient, dependent upon the share price, to allow us to access the full amount contemplated under the Financing Agreement. If the closing prices of our common stock remains the same and does not materially increase, we will not be able to place puts for the full commitment amount under the Financing Agreement. The average of lowest two closing prices for the 10 days ended July 10, 2020 was approximately $0.0166. At that price we would be able to sell shares to GHS under the Financing Agreement at the discounted price of $0.01328. At that discounted price, the 74,720,000 shares would only represent approximately $992,282, which is far below the full amount of the Financing Agreement. In addition, any single drawdown may not exceed two hundred percent (200%) of the average daily trading dollar volume of the Company’s Common Stock during the ten (10) trading days preceding the put, which is approximately $7,162 on the date of this Registration Statement, and cannot exceed $400,000. We paid GHS 764,526 shares of our common stock upon the signing of the Financing Agreement and are obligated to pay $5,000 in our common stock upon the delivery of the second and third Put Notices (defined below) at the then applicable purchase price under that Put Notice.
During the Open Period, the Company may, in its sole discretion, deliver a put notice (“Put Notice”) to GHS which shall state the dollar amount requested by the Company (the “Put Amount”) and number of shares intends to sell to GHS on a designated closing date. The purchase price (the “Purchase Price”) of the common stock sold pursuant to a Put Notice will be set at eighty percent (80%) of the average of the two lowest closing prices of the common stock during the ten consecutive trading day period immediately preceding the date on which the Company delivers the Put Notice to GHS. We are obligated to deliver a number of shares to GHS equal to Put Amount divided by the Purchase Price in consideration of the payment of the Put Amount less $1,000 for transaction costs incurred by GHS. For example, if we delivered a put notice to GHS for $20,000, and the average of the lowest two trading days for the past 10 consecutive trading days is $.02, we would be obligated to issue GHS 1,250,000 shares of our common stock at a purchase price of $.016 per share. The 20% price per share discount GHS will receive with each put sale means that GHS will effectively be paying us $20,000, less $1,000 in transaction costs as a Put Amount for $25,000 in our stock that is issued.
In addition, the Financing Agreement (i) imposes an ownership limitation on GHS of 4.99% (i.e., GHS has no obligation to purchase shares if it beneficially owns more than 4.99% of our common stock), (ii) requires a minimum of ten (10) trading days between put notices, (iii) prohibits any single Put Amount from under $10,000 or exceeding $400,000 or exceeding two times the average daily trading dollar volume for the Company’s common stock during the 10 days preceding the Put Notice or (iv) delivering a Put Notice within 10 days prior to the closing of a prior Put Amount. .
In order for the Company to be eligible to deliver put notices to GHS, the following conditions must be met: (i) a registration statement shall be declared effective and remain effective; (ii) at all times during the period beginning on the related put notice date and ending on and including the related closing date of the put, the Company’s common stock shall have been listed or quoted for trading on OTCQB or its equivalent and shall not have been suspended from trading thereon for a period of two (2) consecutive trading days during the open period; (iii) the Company has not defaulted or be in breach of the Financing Agreement or Registration Rights Agreement; (iv) no injunction shall be issued or remain in force in connection with the purchase of the Company’s shares; and (v) the issuance of the shares will not violate any shareholder approval requirements of OTCQB. If any of the events described above occurs during a pricing period, then GHS shall have not obligation to purchase the shares delivered in the Put Notice. Further the terms of the Financing Agreement require that the Company take all commercially reasonable steps necessary to have this registration statement be declared effective no more than 90 days following the date this registration statement was originally filed.
| 25 |
GHS is not permitted to engage in short sales involving our common stock, or to engage in other activities that could manipulate the market for our common stock, during the period commencing June 8, 2020, and continuing through the termination of the Financing Agreement. In accordance with Regulation SHO, however, sales of our common stock by GHS after delivery of a put notice of such number of shares reasonably expected to be purchased by GHS under a put will not be deemed short sales.
In order for the Company’s exercise of a put to be effective, we must deliver the documents, instruments and writings required under the Financing Agreement. GHS is not required to purchase the put shares unless:
| ● | Our registration statement with respect to the resale of the shares of common stock delivered in connection with the applicable put shall have been declared effective; |
| ● | we shall have obtained all material permits and qualifications required by any applicable state for the offer and sale of the registrable securities; and |
| ● | we shall have filed all requisite reports, notices, and other documents with the SEC in a timely manner. |
As we draw down on the equity line of credit reflected in the Financing Agreement, shares of our common stock will be sold into the market by GHS. The sale of these shares could cause our stock price to decline. In turn, if our stock price declines and we issue more puts, more shares will come into the market, which could cause a further drop in our stock price. The Company determines when and whether to issue a put to GHS, so the Company will know precisely both the stock price used as the reference point, and the number of shares issuable to GHS upon such exercise. You should be aware that there is an inverse relationship between the market price of our common stock and the number of shares to be issued under the equity line of credit. We have no obligation to utilize the full amount available under the equity line of credit.
Neither the Financing Agreement nor any of our rights or GHS’s rights thereunder may be assigned to any other person.
There is no assurance the market price of our common stock will increase in the future. The number of common shares that remain issuable may not be sufficient, dependent upon the share price, to allow us to access the full amount contemplated under the Financing Agreement. If the bid/ask spread remains the same we will not be able to place a put for the full commitment under the Financing Agreement. Based on the lowest two day average closing price of our common stock during the ten (10) consecutive trading day period preceding the filing date of this registration statement was approximately $0.0166, the registration statement covers the offer and possible sale of $$992,282 worth of our shares.
We have authorized capital stock consisting of the following. The total number of shares of capital stock which the Corporation shall have authority to issue is: 2,020,000,000. These shares shall be divided into two classes with one billion two hundred million (2,000,000,000) shares designated as common stock at $.001 par value (the “Common Stock”) and twenty million (20,000,000) shares designated as preferred stock at $.001 par value (the “Preferred Stock”).The Preferred Stock of the Corporation shall be issuable by authority of the Board of Director(s) of the Corporation in one or more classes or one or more series within any class and such classes or series shall have such voting powers, full or limited, or no voting powers, and such designations, preferences, limitations or restrictions as the Board of Directors of the Corporation may determine, from time to time. We have 762,895,515 common shares outstanding as of the date of this filing.
Common Stock
Our Articles of Incorporation authorize us to issue 2,000,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.001 per share. As of July 10, 2020, there were 762,895,515 shares of common stock outstanding. All outstanding shares of common stock are, and the common stock to be issued will be, fully paid and non-assessable. Each share of our common stock has identical rights and privileges in every respect. The holders of our common stock are entitled to vote upon all matters submitted to a vote of our shareholders and are entitled to one vote for each share of common stock held. There are no cumulative voting rights.
| 26 |
The holders of our common stock are entitled to share equally in dividends and other distributions that our Board of Directors may declare from time to time out of funds legally available for that purpose, if any, after the satisfaction of any prior rights and preferences of any outstanding preferred stock. If we liquidate, dissolve or wind up, the holders of common stock shares will be entitled to share ratably in the distribution of all of our assets remaining available for distribution after satisfaction of all our liabilities and our obligations to holders of our outstanding preferred stock.
Preferred Stock
Our Articles of Incorporation authorize us to issue 20,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.001 per share. Our Board of Directors has the authority to issue additional shares of preferred stock in one or more series, and fix for each series, the designation of and number of shares to be included in each such series. Our Board of Directors is also authorized to set the powers, privileges, preferences, and relative participating, optional or other rights, if any, of the shares of each such series and the qualifications, limitations or restrictions of the shares of each such series.
Unless our Board of Directors provides otherwise, the shares of all series of preferred stock will rank on parity with respect to the payment of dividends and to the distribution of assets upon liquidation. Any issuance by us of shares of our preferred stock may have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a change of our control or an unsolicited acquisition proposal. The issuance of preferred stock also could decrease the amount of earnings and assets available for distribution to the holders of common stock or could adversely affect the rights and powers, including voting rights, of the holders of common stock.
We previously authorized 440 shares of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock, 20,000 shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock, and 15,000 shares Series C Convertible Preferred Stock. As of August 20, 2006, all series A, B, and C preferred had been converted into common stock.
Effective August 7, 2013, our Board of Directors designated a series of our preferred stock as Series D Preferred Stock, authorizing 15,000 shares. Our Series D Preferred Stock offering terms authorized us to raise up to $1,000,000 with an over-allotment of $500,000 in multiple closings over the course of six months. We received an aggregate of $750,000 in financing in subscription for Series D Preferred Stock, or 7,500 shares.
The following are primary terms of the Series D Preferred Stock. The Series D Preferred holders were initially entitled to be paid a special monthly divided at the rate of 17.5% per annum. Initially, the Series D Preferred Stock was also entitled to be paid special dividends in the event cash dividends were not paid when scheduled. If the Company does not pay the dividend within five (5) business days from the end of the calendar month for which the payment of such dividend to owed, the Company will pay the investor a special dividend of an additional 3.5%. Any unpaid or accrued special dividends will be paid upon a liquidation or redemption. For any other dividends or distributions, the Series D Preferred Stock participates with common stock on an as-converted basis. The Series D Preferred holders may elect to convert the Series D Preferred Stock, in their sole discretion, at any time after a one year (1) year holding period, by sending the Company a notice to convert. The conversion rate is equal to the greater of $0.08 or a 20% discount to the average of the three (3) lowest closing market prices of the common stock during the ten (10) trading day period prior to conversion. The Series D Preferred Stock is redeemable from funds legally available for distribution at the option of the individual holders of the Series D Preferred Stock commencing any time after the one (1) year period from the offering closing at a price equal to the initial purchase price plus all accrued but unpaid dividends, provided, that if the Company gave notice to the investors that it was not in a financial position to redeem the Series D Preferred, the Company and the Series D Preferred holders are obligated to negotiate in good faith for an extension of the redemption period. The Company timely notified the investors that it was not in a financial position to redeem the Series D Preferred and the Company and the investors have engaged in ongoing negotiations to determine an appropriate extension period. The Company may elect to redeem the Series D Preferred Stock any time at a price equal to initial purchase price plus all accrued but unpaid dividends, subject to the investors’ right to convert, by providing written notice about its intent to redeem. Each investor has the right to convert the Series D Preferred Stock at least ten (10) days prior to such redemption by the Company.
| 27 |
In connection with the subscriptions for the Series D Preferred, we issued series F warrants to purchase an aggregate of 375,000 shares of our common stock at $.10 per share and series G warrants to purchase an aggregate of 375,000 shares of our common stock at $.20 per share.
On August 21, 2014, a holder holding 5,000 shares of Preferred Series D Preferred agreed to lower the dividend rate to 13% on its Series D Preferred. In September 2015, all holders of Series D Preferred signed and delivered estoppel agreements, whereby the holders agreed, among other things, that the Series D Preferred was not in default and to reduce (effective as of December 31, 2015) the dividend rate on the Series D Preferred Stock to six percent per annum and to terminate the 3.5% penalty in respect of unpaid dividends accruing on or after such date.
In the first quarter of 2019, we signed agreements to issue 4,000,000 shares of common stock valued at $.015 for a total value of $60,000 for the conversion of 800 preferred series D shares, which were subsequently issued. We also recorded a $60,000 inducement fee to account for the difference in the fair value which we offset to retained earnings. We also reclassed 200 preferred valued at $20,000, which were previously recorded as converted preferred dividends.
Warrants
On May 31, 2019, we entered into a subscription agreement pursuant to which the Company agreed to sell 168,000,000 units (each a “Unit” and together the “Units”) to MGW Investment I Limited MGWI for an aggregate purchase price of $1,999,200, or $.0119 per Unit, with each unit consisting of one share of common stock, par value $.001 per share (the “Common Stock”) and a warrant (the “Warrant”) to purchase one share of common stock. The Common Stock will be issued to MGWI at such time as the Company increases the number of shares of its authorized Common Stock. The Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
On June 10, 2019 we issued 500,000 shares of common stock at $.02 per share to an accredited investor for an aggregate price of $10,000 in a private sale. We also issued 500,000 warrants as part of the transaction. Each Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
On July 18, 2019 we issued 500,000 shares of common stock at $.02 per share to an accredited investor for an aggregate price of $10,000 in a private sale. We also issued 500,000 warrants as part of the transaction. Each Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
On September 19, 2019 we entered into a stock purchase agreement for 250,000 units to an accredited investor a private sale. Each unit consist of one share of common stock and one warrant to purchase one share of common stock exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement. The shares were included in the shares to be issued as of September 30, 2019 and were subsequently issued on October 15, 2019.
On December 5, 2019 we issued 5,000,000 units to an accredited investor a private sale. Each unit consist of one share of common stock and one warrant to purchase one share of common stock exercisable at $.04 per share.
| Warrants - Common Share Equivalents | Weighted Average Exercise price | Warrants exercisable - Common Share Equivalents | Weighted Average Exercise price | ||||||||||||||
| Outstanding December 31, 2019 | - | $ | - | - | $ | - | |||||||||||
| Issued | 174,250,000 | $ | 0.04 | 174,250,000 | $ | 0.04 | |||||||||||
| Exercised | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||
| Expired | - | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| Outstanding June 30, 2020 | 174,250,000 | $ | 0.04 | 174,250,000 | $ | 0.04 | |||||||||||
| 28 |
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
Below is a description of the Company’s compensation plan adopted in 2011.
2011 Plan
The purpose of awards under the 2011 Plan is to attract and retain talented employees and the services of select non-employees, further align employee and stockholder interests and closely link employee compensation with Company performance. Eligible participants under the 2011 Plan will be such full or part-time officers and other employees, directors, consultants and key persons of the Company and any Company subsidiary who are selected from time to time by the Board or committee of the Board authorized to administer the 2011 Plan, as applicable, in its sole discretion.
The Plan provides for the issuance of up to 15,000,000 shares of common stock of the Company through the grant of non-qualified options (the “Non-qualified Options”), incentive options (the “Incentive Options” and together with the Non-qualified Options, the “Options”) and restricted stock (the “Restricted Stock”), unrestricted stock (the “Unrestricted Stock”) and Stock Appreciation Rights (“SARs”) to directors, officers, consultants, attorneys, advisors and employees. The 15,000,000 shares available under the 2011 Plan represent approximately 2% of the Company’s issued and outstanding common stock as of July 10, 2020. There are no outstanding grants under the 2011 Plan.
The 2011 Plan shall be administered by a committee consisting of two or more independent, non-employee and outside directors (the “Committee”). In the absence of such a Committee, the Board shall administer the 2011 Plan. The 2011 Plan is currently being administered by the Board but it is intended for the Compensation Committee to administer the 2011 Plan as soon as practicable.
Options are subject to the following conditions:
(i) The Committee determines the strike price of Incentive Options at the time the Incentive Options are granted. The assigned strike price must be no less than 100% of the Fair Market Value (as defined in the Plan) of the Company’s Common Stock. In the event that the recipient is a Ten Percent Owner (as defined in the Plan), the strike price must be no less than 110% of the Fair Market Value of the Company.
(ii) The strike price of each Non-qualified Option will be at least 100% of the Fair Market Value of such share of the Company’s Common Stock on the date the Non-qualified Option is granted.
(iii) The Committee fixes the term of Options, provided that Options may not be exercisable more than ten years from the date the Option is granted and provided further that Incentive Options granted to a Ten Percent Owner may not be exercisable more than five years from the date the Incentive Option is granted.
(iv) The Committee may designate the vesting period of Options. In the event that the Committee does not designate a vesting period for Options, the Options will vest in equal amounts on each fiscal quarter of the Company through the five (5) year anniversary of the date on which the Options were granted. The vesting period accelerates upon the consummation of a Sale Event (as defined in the Plan).
(v) Options are not transferable, and Options are exercisable only by the Options’ recipient, except upon the recipient’s death.
(vi) Incentive Options may not be issued in an amount or manner where the amount of Incentive Options exercisable in one year entitles the holder to Common Stock of the Company with an aggregate Fair Market value of greater than $100,000.
Awards of Restricted Stock are subject to the following conditions:
(i) The Committee grants Restricted Stock Options and determines the restrictions on each Restricted Stock Award (as defined in the Plan). Upon the grant of a Restricted Stock Award and the payment of any applicable purchase price, grantee is considered the record owner of the Restricted Stock and entitled to vote the Restricted Stock if such Restricted Stock is entitled to voting rights.
(ii) Restricted Stock may not be delivered to the grantee until the Restricted Stock has vested.
| 29 |
(iii) Restricted Stock may not be sold, assigned, transferred, pledged or otherwise encumbered or disposed of except as provided in the Plan or in the Award Agreement (as defined in the Plan).
Stock Options
We currently have no outstanding stock options
Dividend Policy
We have never declared a cash dividend on our common stock and our Board of Directors does not anticipate that we will pay cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Any future determination to pay cash dividends will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend upon our financial condition, operating results, capital requirements, restrictions contained in our agreements and other factors which our Board of Directors deems relevant.
We are obligated to pay dividends to certain holders of our preferred stock which we pay out of legally available funds from time to time or reach arrangements with our holders of preferred stock to convert limited quantities of preferred stock at favorable conversion prices in lieu of dividend payments.
Transfer Agent
The transfer agent for our Common Stock is Colonial Stock Transfer, Inc., 66 Exchange Place, 1st floor, Salt Lake City, UT 84111, (801) 355-5704.
Anti-Takeover Effects of Various Provisions of Nevada Law
Provisions of the Nevada Revised Statutes could make it more difficult to acquire us by means of a tender offer, a proxy contest or otherwise, or to remove incumbent officers and directors. These provisions, summarized below, would be expected to discourage certain types of takeover practices and takeover bids our Board may consider inadequate and to encourage persons seeking to acquire control of us to first negotiate with us. We believe that the benefits of increased protection of our ability to negotiate with the proponent of an unfriendly or unsolicited proposal to acquire or restructure us will outweigh the disadvantages of discouraging takeover or acquisition proposals because, among other things, negotiation of these proposals could result in an improvement of their terms.
Blank Check Preferred
Our articles of incorporation permit our Board to issue preferred stock with voting, conversion and exchange rights that could negatively affect the voting power or other rights of our common stockholders. The issuance of our preferred stock could delay or prevent a change of control of our Company.
Amendments to our Articles of Incorporation and Bylaws
Under the Nevada Revised Statutes, our articles of incorporation may not be amended by stockholder action alone.
Nevada Anti-Takeover Statute
We may be subject to Nevada’s Combination with Interested Stockholders Statute (Nevada Corporation Law Sections 78.411-78.444) which prohibits an “interested stockholder” from entering into a “combination” with the corporation, unless certain conditions are met. An “interested stockholder” is a person who, together with affiliates and associates, beneficially owns (or within the prior two years, did beneficially own) 10% or more of the corporation’s capital stock entitled to vote.
Limitations on Liability and Indemnification of Officers and Directors
The Nevada Revised Statutes limits or eliminates the personal liability of directors to corporations and their stockholders for monetary damages for breaches of directors’ fiduciary duties as directors.
| 30 |
The limitation of liability and indemnification provisions under the Nevada Revised Statues and in our articles of incorporation and bylaws may discourage stockholders from bringing a lawsuit against directors for breach of their fiduciary duties. These provisions may also have the effect of reducing the likelihood of derivative litigation against directors and officers, even though such an action, if successful, might otherwise benefit us and our stockholders. However, these provisions do not limit or eliminate our rights, or those of any stockholder, to seek non-monetary relief such as injunction or rescission in the event of a breach of a director’s fiduciary duties. Moreover, the provisions do not alter the liability of directors under the federal securities laws. In addition, your investment may be adversely affected to the extent that, in a class action or direct suit, we pay the costs of settlement and damage awards against directors and officers pursuant to these indemnification provisions.
Authorized but Unissued Shares
Our authorized but unissued shares of Common Stock and preferred stock will be available for future issuance without stockholder approval, except as may be required under the listing rules of any stock exchange on which our Common Stock is then listed. We may use additional shares for a variety of corporate purposes, including future public offerings to raise additional capital, corporate acquisitions and employee benefit plans. The existence of authorized but unissued shares of Common Stock and preferred stock could render more difficult or discourage an attempt to obtain control of us by means of a proxy contest, tender offer, merger or otherwise.
Penny Stock Regulation
The SEC has adopted regulations which generally define “penny stock” to be any equity security that has a market price (as defined) of less than $5.00 per share or an exercise price of less than $5.00 per share. Such securities are subject to rules that impose additional sales practice requirements on broker-dealers who sell them. For transactions covered by these rules, the broker-dealer must make a special suitability determination for the purchaser of such securities and have received the purchaser’s written consent to the transaction prior to the purchase. Additionally, for any transaction involving a penny stock, unless exempt, the rules require the delivery, prior to the transaction, of a disclosure schedule prepared by the SEC relating to the penny stock market. The broker-dealer also must disclose the commissions payable to both the broker-dealer and the registered representative, current quotations for the securities and, if the broker-dealer is the sole market-maker, the broker-dealer must disclose this fact and the broker-dealer’s presumed control over the market. Finally, among other requirements, monthly statements must be sent disclosing recent price information for the penny stock held in the account and information on the limited market in penny stocks. As the Shares immediately following this Offering will likely be subject to such penny stock rules, purchasers in this Offering will in all likelihood find it more difficult to sell their Shares in the secondary market.
The legality of the issuance of the shares of Common Stock offered by this Prospectus will be passed upon for us by The Newman Law Firm, PLLC, Briarcliff Manor, New York.
The financial statements of Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. as of December 31, 2019, and 2018, which includes an explanatory paragraph relating to its ability to continue as a going concern, included in this Prospectus have been audited by Fruci & Associates II, PLLC, an independent auditor, as stated in their reports appearing herein. Such financial statements have been so included in reliance upon the reports of such firm given its authority as experts in accounting and auditing.
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
We have filed an Prospectus on Form 1-A with the Commission under Regulation A of the Securities Act with respect to the Common Stock offered by this Prospectus. This Prospectus, which constitutes a part of the Prospectus, does not contain all of the information set forth in the Prospectus or the exhibits and schedules filed therewith. For further information with respect to us and our Common Stock, please see the Prospectus and the exhibits and schedules filed with the Prospectus. Statements contained in this Prospectus regarding the contents of any contract or any other document that is filed as an exhibit to the Prospectus are not necessarily complete, and each such statement is qualified in all respects by reference to the full text of such contract or other document filed as an exhibit to the Prospectus.
| 31 |
INFORMATION WITH RESPECT TO THE REGISTRANT
Company Information
We were incorporated in California in July 1995 under the name Probe Manufacturing Industries, Inc. We redomiciled to Nevada in April 2005 under the name Probe Manufacturing, Inc. We manufactured electronics and provided services to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) of industrial, automotive, semiconductor, medical, communication, military, and high technology products. On September 11, 2015 Clean Energy HRS, or “CE HRS”, our wholly owned subsidiary acquired the assets of Heat Recovery Solutions from General Electric International. In November 2015, we changed our name to Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Our principal executive offices are located at 2990 Redhill Avenue, Costa Mesa, CA 92626. Our telephone number is (949) 273-4990. Our common stock is listed on the OTCQB Markets under the symbol “CETY.”
Our internet website address is www.cetyinc.com and our subsidiary’s web site is www.heatrecoverysolutions.com The information contained on our websites are not incorporated by reference into this document, and you should not consider any information contained on, or that can be accessed through, our website as part of this document.
The Company has three reportable segments: Clean Energy HRS (HRS), Cety Europe and the legacy electronic contract manufacturing services (Electronic Assembly) division.
Segments
Clean Energy HRS (HRS)
We design, build and deliver power from industrial heating systems and biomass sources to produce environmentally friendly energy at competitive prices using our Clean CycleTM heat generators acquired from General Electric International. Our initial principal product is the Clean CycleTM heat generator, offered through our wholly owned subsidiary Heat Recovery Solutions, (HRS). The Clean CycleTM generator captures waste heat from a variety of sources and turns it into electricity. By using our Clean CycleTM generator commercial and industrial heat generators boost their overall energy efficiency and the savings created provide our customers with a fast return on their investment. The Clean CycleTM saves fuel, reduces pollution and requires very little maintenance.
Cety Europe
CETY Europe Sales and Service Center is the Sales, warranty and service company for CETY’s Clean Cycle™ Heat Recovery Solutions (HRS) and includes a 24/7 Call Center, support Field Service Personnel, including remote access to the Waste Heat Generators and inventory spare parts to support the currently commissioned 65 Clean CycleTM installations in Europe. The service center also provides support services for new European sales. CETY has identified substantial unmet market needs in many European countries including the United Kingdom, Germany, Italy, Ukraine, Croatia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Austria, Belarus and the Czech Republic. Cety Europe will sell and distribute the Clean CycleTM Waste Heat Generators and replacement parts from the Clean Energy HRS line of products. The CETY Europe Sales and Service Center will be well suited to handle any warranty and/or service issues, as well as sell and distribute the Clean energy HRS line of products. Cety Europe has 1 employee.
| 32 |
Electronic Assembly
The Electronic assembly business was our core legacy business until we acquired the Heat Recovery Solutions technology and business assets from GE. We consolidated the Probe Manufacturing (Electronic Assembly), now named Clean Energy Technologies, Inc with the Clean Energy HRS, LLC. in order to support a few legacy electronics assembly customers and support the electronics manufacturing portion of our newly acquired technology from General Electric by Clean Energy HRS, LLC. Although this is not our core focus nor do we intend to grow this segment, we still derive a revenue stream to help offset a portion of the overhead. This segment provides contract manufacturing services of electronic printed circuit board assemblies to customers in the medical and aerospace industries. The services provided are contract in nature and are built the customers specification. They supply the design and component specifications. We purchase the components and solder the components to the bare printed circuit boards.
Our customers are legacy customers of Probe Manufacturing and we do not conduct any additional sales or marketing activities in this segment. We have many larger and better funded competitors in the United States and Asia that specialize in circuit board manufacturing and our customers may migrate to these competitors since we do not focus on developing any new products or services for this segment. We do not view this segment as being material to the long term growth of the Company.
General Business Overview
We design, produce and market clean energy products and integrated solutions focused on energy efficiency and renewables. Our initial principal product is the Clean CycleTM heat generator, offered through our wholly owned subsidiary Heat Recovery Solutions, (HRS). The Clean CycleTM generator captures waste heat from a variety of sources and turns it into electricity. By using our Clean CycleTM generator commercial and industrial heat generators boost their overall energy efficiency and the savings created provide our customers with a fast return on their investment. The Clean CycleTM generator saves fuel, reduces pollution and requires little maintenance. We also use our Clean CycleTM generator to manufacture Biomass Power Plants and Co-generation Distribution Power Plants that produce clean energy.
 |
 | |
| Clean Cycle II Heat Generator | Containerized Clean Cycle II Heat Generator |
We compete based on efficiency, maintenance and our customer’s return on investment. We have an exclusive license from Calnetix to use their magnetic turbine for heat waste recovery applications. We believe that the magnetic turbine technology is more efficient than our competitor’s turbines which allows our systems to generate more electricity at lower heat ranges. Because our generator is magnetic, it requires far less maintenance than our competitors who use oil, gearbox and rubber seals in their turbines. We have the advantage of selling a system that was originally manufactured and sold by General Electric International so our Clean CycleTM generator has a substantial market base and we believe has a reputation as one of the defacto standards in the market.
Our greatest advantage is that the Clean CycleTM generator is a product that can be delivered on a turnkey basis, not a major project that needs to be designed, manufactured and installed. We believe that this is one of the most distinguishing features of our Clean Cycle™ generator, as it significantly reduces the time our customers spend on installation, improves the speed with which we can deliver our product and reduces startup costs.
Over 123 Clean CycleTM generators are installed to date with 88 units used in biomass/landfill projects, 4 with diesel electric generators, 3 with turbine electric generators and 26 in industrial electric production applications.
| 33 |
We compete based on efficiency, maintenance and our customer’s return on investment. We have a proprietary magnetic bearing technology with several global patents that we acquired from General Electric International. We believe that the magnetic turbine technology is more efficient than our competitor’s turbines which allows our systems to generate more electricity at lower heat ranges. Because our generator is magnetic, it requires less maintenance than our competitors who use oil, gearbox and rubber seals in their turbines. We have the advantage of selling a system that was originally manufactured and sold by General Electric International so our Clean CycleTM generator has a substantial market base and we believe has a reputation as one of the defacto standards in the market.
The Clean CycleTM generator is delivered on a turnkey basis and does not require major planning for design, manufacturing and installation. In addition to attractive returns on capital investment, we believe that the ease of installation distinguishes our Clean Cycle™ generators by significantly reducing installation time, improving delivery times and lowering costs.
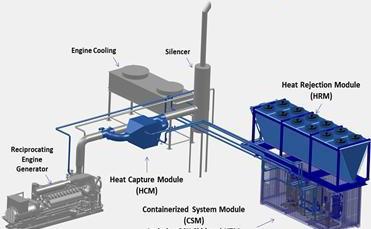
A Complete ORC System
We estimate that one clean system using our Clean CycleTM generator can generate 1 GWh of electricity per year from waste heat and avoid more than 350 metric tons of CO2 per year which we estimate is the annual equivalent of the CO2 emissions of approximately 200 cars.
Our Products

Our Clean CycleTM generator:
| ● | Requires no fuel, | |
| ● | produces no emissions, and | |
| ● | is closed loop, meaning it has feedback control within the system. | |
| ● | Meticulously engineered and improved by General Electric International and | |
| ● | is available in a complete package for indoor, outdoor and remote sites. |
The major components are delivered as a complete turnkey package and include, the Integrated Power Module (“IPM”), our patented the magnetic bearing turbine, the electronics controls with the ancillary mechanical parts, packaged inside a container when used outdoors. The condenser comes as a separate piece which is purchased by either us or our customer through third party manufactures and attaches to the top of the container. Once the condenser is attached to the container all that is left to do is attach the container to the heat source, and it is ready to produce energy.
| 34 |
Due to the low amount of moving parts the IPM is a minimal maintenance solution, that requires no oils, no lubricants, no external rotating seals, and does not require manned operation. The whole package (except condenser) is mounted inside a 20ft shipping container. The Condenser comes as a separate piece and attaches to the top of the container. Once the condenser is attached to the container all that is left to do is attach the container to the heat source, and it is ready to produce energy.

Our Core technology a magnetic bearing turbine called Integrated Power Module (IPM).
| ✓ | Mag lev bearing generator | |
| ✓ | Lower maintenance: no oils, no lubricants | |
| ✓ | Efficient at any output: no gearbox | |
| ✓ | Power electronics – power factor of 1 |
There are also different types of turbines utilized in the ORC systems. The Clean Cycle utilizes an integrated power module which runs on magnetic bearings and its hermetically sealed into a single unit, eliminating the need for gear box, lubrication systems and rotating seals and it’s more efficient than screw expanders.
Packaging
| ✓ | Single part number (85% OF BOP) | |
| ✓ | Product, not a project | |
| ✓ | Same unit used on all heat sources | |
| ✓ | Re-deployable and movable | |
| ✓ | Small footprint |
 |
 |
| 35 |
20ft ISO Containerized Stackable Solution
The Clean Cycle containerized has been meticulously engineered to reliably produce power.
Clean CycleTM generator and the Organic Rankine Cycle
The Organic Rankine Cycle is a thermodynamic process where heat is transferred to a fluid at a constant pressure. The fluid inside the generator is vaporized and then expanded in a vapor turbine that drives a turbine generator, producing electricity. The spent vapor is condensed to liquid and recycled back through the cycle.
Its applications include power generation from solar, geothermal and waste heat sources. According to an article in Distributed Energy, a leading industry magazine, Organic Rankine Cycle systems are most useful for waste heat recovery. Waste heat recovery can be applied to a variety of low- to medium temperature heat streams
Raw Materials/Suppliers
Our products are manufactured primarily from components available from multiple suppliers and to a lesser extend from custom fabricated components available from various sources. We purchase our components from suppliers based on price and availability. Our significant suppliers include Power House, Concise Instrument, and Grainger.
Patents
We currently hold 16 patents in 6 countries and 28 pending applications in 8 countries, which were acquired from General Electric International relating to our magnetic turbine technology.
Intellectual Property
As part of our asset acquisition from General Electric International we acquired an exclusive, irrevocable, sublicensable, limited transferable, royalty free, fully paid, worldwide perpetual license to develop, improve and commercialize Calnetix’s magnetic turbine in any Organic Rankine Cycle based application where heat is sourced from a reciprocating combustion engine of any type, except marine vessels, any gas or steam turbine systems for electrical power generation applications or any type of biomass boiler system.
Our Services
Engineering. Our global engineering team supports the installation and maintenance of our Clean CycleTM generators, supports our technology customers and innovative start-ups with a broad range of electrical, mechanical and software engineering services. CETY has assembled a team of experts from around the globe to assist customers at any point in the design cycle. These services include design processes from electrical, software, mechanical and Industrial design. Utilization of CETY’s design services will enable rapid market entry for our customers and potential equity partners. Our systems have been designed to be more of a product than a project and provide the solution providers greater flexibility.
Supply Chain Management. CETY’s supply chain solution provides maximum flexibility and responsiveness through a collaborative and strategic approach with our customers. CETY can assume supply chain responsibility from component sourcing through delivery of finished product. CETY’s focus on the supply chain allows us to build internal and external systems and better our relationships with our customers, which allows us to capitalize on our expertise to align with our partners and customer’s objectives and integrate with their respective processes.
Sales and Marketing
We utilize both a direct sales force and global distribution group with expertise in heat recovery solutions and clean energy markets.
| 36 |
CETY maintains an online presence through our web portal and social media. Our application engineers assist in converting the opportunities into projects. We provide technical support to our Clean Cycle TM generator clients through providing maintenance and product support.
Our market focus is segmented by the engine heat recovery, biomass & Biogas plants, Landfills, Wastewater treatment plants and boiler applications with excess heat.
Organic Rankine Cycle systems are commonly used to generate power in geothermal, biomass, waste to energy plants, engine heat recovery and more recently, in pipeline compressor heat recovery applications. In these, and other, ORC applications, electric generation efficiencies range from around 8 percent with waste heat sources at 300 ºF, to around 15 percent with waste heat sources near 800 ºF. There are also different types of turbines utilized in the ORC systems. The Clean Cycle utilizes an integrated power module which runs on magnetic bearings and its hermetically sealed into a single unit, eliminating the need for gear box, lubrication systems and rotating seals and it’s more efficient than screw expanders.
Power generation from geothermal brines is the main field of application with 74.8% of all ORC installed capacity in the world, however the total number of plant is relatively low with 337 installations as these applications require large investment and multi-MW plants. As a result, only a few companies (ORMAT, Exergy, TAS and Turboden) have been active in this capital-intensive sector. ORMAT is the indisputable leader in this field with more than 75% of installed capacity and plants, Exergy and TAS are following with around 13% and 6% of the market respectively while Turboden has recently penetrated the geothermal market with about 2% of the installed capacity.
Waste heat recovery is an emerging field for ORC with an interesting potential for all unit sizes. All the big players are active on the markets with medium – large size plants recovering heat from gas turbines, internal combustion engines or industrial processes. Most of the other manufacturers are focused on small waste heat recovery applications with products ranging from 10 to 150 kWel. Waste Heat recovery applications cover 13.9% of the total market.
Biomass applications represent a similar share at 11% and a considerable number of plants, Turboden is the main player on this market.
A total of approximately 800 ORC units have been installed since 2000. Overall the combined ORC systems are estimated to grow at a CAGR of 10% from 2019 to 2023 and the market is expected to grow to approximately $500M, based on a CAGR of 12% from 2019 to 2023.
Our ORC Clean CycleTM II was designed by General Electric International and maintains its history and association with a major brand. Our product is distinguished from its competitors by its magnetic bearing turbine technology offering lower maintenance and higher efficiency of 14% for under 500kW applications with low to medium temperature requirements. We have more than 1,000,000 fleet operating hours and 8 years of history in the field.
Employees
We presently have approximately 12 employees, including production, program management, materials management, engineering, sales, quality, and administrative and management personnel. We have never experienced work stoppages and we are not a party to any collective bargaining agreement. We have one employee that works full time in CETY Europe and 1 full time employee in our Electronics Assembly segment.
Government Regulation
Our operations are subject to certain foreign, federal, state and local regulatory requirements relating to environmental, waste management, and health and safety matters. We believe we operate in substantial compliance with all applicable requirements. However, material costs and liabilities may arise from these requirements or from new, modified or more stringent requirements. Material cost may rise due to additional manufacturing cost of raw or made parts with the application of new regulations. Our liabilities may also increase due to additional regulations imposed by foreign, federal, state and local regulatory requirements relating to environmental, waste management, and health and safety matters. In addition, our past, current and future operations and those of businesses we acquire, may give rise to claims of exposure by employees or the public or to other claims or liabilities relating to environmental, waste management or health and safety concerns.
| 37 |
Our markets can be positively or negatively impacted by the effects of governmental and regulatory matters. We are affected not only by energy policy, laws, regulations and incentives of governments in the markets into which we sell, but also by rules, regulations and costs imposed by utilities. Utility companies or governmental entities could place barriers on the installation of our product or the interconnection of the product with the electric grid. Further, utility companies may charge additional fees to customers who install on-site power generation, thereby reducing the electricity they take from the utility, or for having the capacity to use power from the grid for back-up or standby purposes. These types of restrictions, fees or charges could hamper the ability to install or effectively use our products or increase the cost to our potential customers for using our systems in the future. This could make our systems less desirable, thereby adversely affecting our revenue and profitability potential. In addition, utility rate reductions can make our products less competitive which would have a material adverse effect on our future operations. These costs, incentives and rules are not always the same as those faced by technologies with which we compete. However, rules, regulations, laws and incentives could also provide an advantage to our Heat Recovery Solutions as compared with competing technologies if we are able to achieve required compliance at a lower cost when our Clean Cycle TM generators are commercialized. Additionally, reduced emissions and higher fuel efficiency could help our future customers combat the effects of global warming. Accordingly, we may benefit from increased government regulations that impose tighter emission and fuel efficiency standards.
Research and Development
We had no expenses in Research and Development costs during the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2019.
We operate from a 20,000 sq-ft state of the art facility in Costa Mesa, California USA. We have in-house electro-mechanical assembly and testing capabilities. Our products are compliant with American Society of Mechanical Engineers and are UL and CE approved.
Legal Proceedings.
From time to time we may be party to litigation matters occurring in the ordinary course of our business. As of the date hereof, however, there are no material pending legal or governmental proceedings relating to our Company to which we are a party, and to our knowledge there are no material proceedings to which any of our directors, executive officers or affiliates are a party adverse to us or which have a material interest adverse to us.
Directors, Executive Officers, Promoters and Control Persons
Our officers and directors are the individuals listed below as of December 31, 2019:
| Name | Age | Position | ||
| Kambiz Mahdi | 55 | President, CEO, Director | ||
| John Bennett | 59 | CFO | ||
| Wang Jun | 53 | Director | ||
| Lyu Yongsheng | 67 | Director | ||
| Calvin Pang | 35 | Director |
There are no family relationships among any of the directors or the executive officer.
Biographical Information.
Mr. Kambiz Mahdi, age 55, served as President and Chief Executive Officer of the Company from 1996 until December of 2005 and again from July 2009 until present. Mr. Mahdi also started Billet Electronics a global supply chain provider of products, services and solutions in the technology sector in 2007. Mr. Mahdi has a BS degree in Electrical Engineering from California State University of Northridge. Mr. Mahdi has not served on any other boards of public companies in the past five years.
| 38 |
Our Board of Directors selected Mr. Mahdi to serve as a director because he is our Chief Executive Officer and has served in various executive roles with our company for 14 years, with a focus on electrical design & manufacturing, sales and operations and his insight into the development, marketing, finance, and operations aspects of our company. He has expansive knowledge of engineering and manufacturing industry and relationships with chief executives and other senior management at technology companies. Our Board of Directors believes that Mr. Mahdi brings a unique and valuable perspective to our Board of Directors.
John Bennett, age 55, John Bennett has been with Probe Manufacturing since February 2005, as the Chief Financial Officer. He has been in the Electronic Manufacturing Industry for 22 years. He has held positions as the Controller, Vice President of Finance and Chief Financial Officer, with experience in Contract Manufacturing of Printed Circuit Board Assembly, Cable and Harness Assembly, Box Builds and Battery & Charger assembly. He holds a Bachelor of Science in Accounting from Mesa University and a Master of Science in Finance from the University of Colorado. Mr. Bennett has not served on any other boards of public companies in the past five years.
Mr. Jun Wang, age: 53. Mr. Wang, is the current Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Taiyu (Shenyang) Energy Technology Co., Ltd. and has held those positions since 2002. From 2008 -2012 Mr. Wang served as Chief Executive Officer and director of SmartHeat, Inc. Prior to that, he served as an executive at Beijing HTN Pipeline Equipment Co., Ltd. from 2000 to 2002 and Honeywell from 1996 to 1999. Mr. Wang graduated from Tsinghua University and obtained a master’s degree in engineering. We believe that Mr. Wang is well qualified to serve as a member of our Board of Directors due to his extensive experience in the clean energy business in China and his ability to open potential markets to the company in Asia.
Mr. Yongsheng Lyu. age: 68. Mr. Lyu has acted as an independent project consultant for Taiyu (Shenyang) Energy Technology Co., Ltd. since 2009. From 2003 to 2009, he served as the Executive Director of the Mianyang City Civil Aviation Administration Greening Company. From 1996 to 2003, he was the General Manager of Mianyang Township Enterprise Supply and Marketing Corporation. Mr. Lyu graduated from Jilin University with a bachelor’s degree in engineering. We believe that Mr. Lyu is well qualified to serve as a member of our Board of Directors due to his extensive experience in engineering, sales and marketing and his ability to assist the company in expanding its markets into Asia.
Mr. Calvin Pang. age: 35. Since 2015 Mr. Pang has been the Managing Director of Megawell Capital Limited. From 2007 to 2015, he was a banker at UBS AG managing portfolios of Hong Kong and China based investors. Mr. Pang graduated from the Olin School of Business at Washington University in St. Louis with a bachelor’s degree in business and finance. We believe that Mr. Pang is well qualified to serve as a member of our Board of Directors due to his extensive experience in U.S. and Asian corporate finance and may assist us in developing relationships with financial institutions.
Each director holds office until the earlier of his or her death, resignation, removal from office by the stockholders, or his or her respective successor is duly elected and qualified. There are no arrangements or understandings between any of our nominees or directors and any other person pursuant to which any of our nominees or directors have been selected for their respective positions. No nominee or director is related to any executive officer or any other nominee or director.
Corporate Governance
Director Attendance at Meetings of the Board of Directors
Our Board of Directors held 4 meetings during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019. Each of our incumbent directors attended at least 75.0% of the aggregate total number of meetings of our Board of Directors held during the period for which he served as a director.
| 39 |
Director Attendance at Annual Meetings of the Shareholders
Although we have no policy with regard to attendance by the members of our Board of Directors at our annual meetings, we invite and encourage the members of our Board of Directors to attend our annual meetings to foster communication between Shareholders and our Board of Directors. We did not hold an annual meeting in 2019.
Stockholder Communication with the Board of Directors
Any stockholder who desires to contact members of our Board of Directors, or a specified committee of our Board of Directors, may do so by writing to: Clean Energy Technologies, Inc., Board of Directors, 2990. Redhill Ave, Costa Mesa, California 92626, Attention: Secretary. Communications received will be distributed by our Secretary to such member or members of our Board of Directors as deemed appropriate by our Secretary, depending on the facts and circumstances outlined in the communication received.
Director Independence
We had a four-member Board of Directors in 2019 of which two members are independent directors.
Committees of our Board of Directors
We have no standing committees of our Board of Directors at the current time, which is due to the size of our operations. From time to time, our Board of Directors may establish committees it deems appropriate to address specific areas in more depth than may be possible at a full Board of Directors meeting. As our Company grows, we plan to establish an audit committee, compensation committee and nominating and corporate governance committee. The functions that these committees will perform are currently being performed by our Board of Directors.
Director Nomination Procedures and Diversity
As outlined above, in selecting a qualified nominee, our Board of Directors considers such factors as it deems appropriate, which may include: the current composition of our Board of Directors; the range of talents of a nominee that would best complement those already represented on our Board of Directors; the extent to which a nominee would diversify our Board of Directors; a nominee’s standards of integrity, commitment and independence of thought and judgment; a nominee’s ability to represent the long-term interests of our shareholders as a whole; a nominee’s relevant expertise and experience upon which to be able to offer advice and guidance to management; a nominee who is accomplished in his or her respective field, with superior credentials and recognition; and the need for specialized expertise. While we do not have a formal diversity policy, we believe that the backgrounds and qualifications of our directors, considered as a group, should provide a significant composite mix of experience, knowledge and abilities that will allow our Board of Directors to fulfill its responsibilities. Applying these criteria, our Board of Directors considers candidates for membership on our Board of Directors suggested by its members, as well as by our Shareholders. Members of our Board of Directors annually review our Board of Directors’ composition by evaluating whether our Board of Directors has the right mix of skills, experience and backgrounds.
Our Board of Directors may also consider an assessment of its diversity, in its broadest sense, reflecting, but not limited to, age, geography, gender and ethnicity.
Our Board of Directors identifies nominees by first evaluating the current members of our Board of Directors willing to continue in service. Current members of our Board of Directors with skills and experience relevant to our business and who are willing to continue in service are considered for re-nomination. If any member of our Board of Directors does not wish to continue in service or if our Board of Directors decides not to nominate a member for re-election, our Board of Directors will review the desired skills and experience of a new nominee in light of the criteria set forth above.
Our Board of Directors also considers nominees for our Board of Directors recommended by Shareholders. Notice of proposed stockholder nominations for our Board of Directors must be delivered in accordance with the requirements set forth in our bylaws and SEC Rule 14a-8 promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act. Nominations must include the full name of the proposed nominee, a brief description of the proposed nominee’s business experience for at least the previous five years and a representation that the nominating stockholder is a beneficial or record owner of our common stock. Any such submission must be accompanied by the written consent of the proposed nominee to be named as a nominee and to serve as a director if elected. Nominations should be delivered to: Clean Energy Technologies, Inc., Board of Directors, 2990. Redhill Ave, Costa Mesa, California 92626, Attention: Chief Executive Officer.
| 40 |
Our Board of Directors will recommend the slate of directors to be nominated for election at the annual meeting of shareholders. We have not and do not currently employ or pay a fee to any third party to identify or evaluate, or assist in identifying or evaluating, potential director nominees.
Board of Directors Role in Risk Oversight
Our Board of Directors oversees our shareholders’ interest in the long-term success of our business strategy and our overall financial strength.
Our Board of Directors is actively involved in overseeing risks associated with our business strategies and decisions. It does so, in part, through its approval of all acquisitions and business-related investments and all assumptions of debt, as well as its oversight of our executive officers pursuant to annual reviews. Our Board of Directors is also responsible for overseeing risks related to corporate governance and the selection of nominees to our Board of Directors.
In addition, the Board reviews the potential risks related to our financial reporting. The Board meets with our Chief Financial Officer and communicates with representatives of our independent registered public accounting firm on a quarterly basis to discuss and assess the risks related to our internal controls. Additionally, material violations of our Code of Ethics and related corporate policies are reported to our Board of Directors.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
We have adopted our Code of Ethics, which contains general guidelines for conducting our business and is designed to help our directors, employees and independent consultants resolve ethical issues in an increasingly complex business environment. Our Code of Ethics applies to our Principal Executive Officer, Principal Financial Officer, and persons performing similar functions and all members of our Board of Directors. Our Code of Ethics covers topics including, but not limited to, conflicts of interest, confidentiality of information, and compliance with laws and regulations. Shareholders may request a copy of our Code of Ethics, which will be provided without charge, by writing to: Clean Energy Technologies, Inc., Board of Directors, 2990. Redhill Ave, Costa Mesa, California 92626; Attention: Chief Executive Officer.
Compensation of Directors
The key objective of our non-employee directors’ compensation program is to attract and retain highly qualified directors with the necessary skills, experience and character to oversee our management. We currently use equity-based compensation to compensate our directors due to our restricted cash flow position; however, we may in the future provide cash compensation to our directors. The use of equity-based compensation is designed to recognize the time commitment, expertise and potential liability relating to active Board service, while aligning the interests of our Board of Directors with the long-term interests of our shareholders.
In addition to the compensation provided to our non-employee director, which is detailed below, each non-employee director is reimbursed for any reasonable out-of-pocket expenses incurred in connection with attending in-person meetings of the Board of Directors and Board committees, as well for any fees incurred in attending continuing education courses for directors.
Fiscal Years 2019 and 2018 Annual Cash Compensation
We currently do not provide cash compensation to our directors and as such did not provide any cash compensation during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
Fiscal Years 2019 and 2018 Equity Compensation
Yearly Restricted Share Awards
| 41 |
Under the terms of the discretionary restricted share unit grant provisions of our 2006 Incentive Stock Plan and our 2011 Omnibus Incentive Plan, which we refer to as the 2006 Plan and 2011 Plan, respectively, each non-employee director is eligible to receive grants of restricted common stock share awards at the discretion of our Board of Directors. These yearly restricted share unit awards vest in full on the grant date.
For the year ended December 31, 2019 there were no stock options granted.
Discretionary Grants
Under the terms of the discretionary option grant provisions of the 2006 Plan and the 2011 Plan, non-employee directors are eligible to receive stock options or other stock awards granted at the discretion of the Board of Directors. No director received stock awards pursuant to the discretionary grant program during fiscal year 2019 or 2018.
Director Summary Compensation in Fiscal Years 2018 and 2019
The following table sets forth the fiscal years 2018, and 2019 compensation for our non-employee directors.
| Name | Fees Earned or Paid in Cash ($) (1) | Stock Awards ($) (2) | Total ($) | |||||||||
| Calvin Pang 2018 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||
| Calvin Pang 2019 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||
| Jun Wang 2018 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||
| Jun Wang 2019 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||
| Yongsheng Lyu 2018 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||
| Yongsheng Lyu 2019 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - |
Change of Control and Termination Provisions
None.
Family Relationship
We currently do not have any officers or directors of our Company who are related to each other.
Involvement in Certain Legal Proceedings
During the past ten years no director, executive officer, promoter or control person of the Company has been involved in the following:
| (1) | A petition under the Federal bankruptcy laws or any state insolvency law which was filed by or against, or a receiver, fiscal agent or similar officer was appointed by a court for the business or property of such person, or any partnership in which he was a general partner at or within two years before the time of such filing, or any corporation or business association of which he was an executive officer at or within two years before the time of such filing; |
| (2) | Such person was convicted in a criminal proceeding or is a named subject of a pending criminal proceeding (excluding traffic violations and other minor offenses); |
| 42 |
| (3) | Such person was the subject of any order, judgment, or decree, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any court of competent jurisdiction, permanently or temporarily enjoining him from, or otherwise limiting, the following activities: |
| i. | Acting as a futures commission merchant, introducing broker, commodity trading advisor, commodity pool operator, floor broker, leverage transaction merchant, any other person regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission, or an associated person of any of the foregoing, or as an investment adviser, underwriter, broker or dealer in securities, or as an affiliated person, director or employee of any investment company, bank, savings and loan association or insurance company, or engaging in or continuing any conduct or practice in connection with such activity; |
| ii. | Engaging in any type of business practice; or |
| iii. | Engaging in any activity in connection with the purchase or sale of any security or commodity or in connection with any violation of Federal or State securities laws or Federal commodities laws; |
| (4) | Such person was the subject of any order, judgment or decree, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any Federal or State authority barring, suspending or otherwise limiting for more than 60 days the right of such person to engage in any activity described in paragraph (f)(3)(i) of this section, or to be associated with persons engaged in any such activity; |
| (5) | Such person was found by a court of competent jurisdiction in a civil action or by the Commission to have violated any Federal or State securities law, and the judgment in such civil action or finding by the Commission has not been subsequently reversed, suspended, or vacated; |
| (6) | Such person was found by a court of competent jurisdiction in a civil action or by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission to have violated any Federal commodities law, and the judgment in such civil action or finding by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission has not been subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated; |
| (7) | Such person was the subject of, or a party to, any Federal or State judicial or administrative order, judgment, decree, or finding, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, relating to an alleged violation of: |
| i. | Any Federal or State securities or commodities law or regulation; or |
| ii. | Any law or regulation respecting financial institutions or insurance companies including, but not limited to, a temporary or permanent injunction, order of disgorgement or restitution, civil money penalty or temporary or permanent cease-and-desist order, or removal or prohibition order; or |
| iii. | Any law or regulation prohibiting mail or wire fraud or fraud in connection with any business entity; or |
| (8) | Such person was the subject of, or a party to, any sanction or order, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any self-regulatory organization (as defined in Section 3(a)(26) of the Exchange Act (15 U.S.C. 78c(a)(26))), any registered entity (as defined in Section 1(a)(29) of the Commodity Exchange Act (7 U.S.C. 1(a)(29))), or any equivalent exchange, association, entity or organization that has disciplinary authority over its members or persons associated with a member. |
The following table sets forth the fiscal year 2019 and 2018 compensation for:
| ● | Kambiz Mahdi, our Chief Executive Officer; and |
| ● | John Bennett, our Chief Financial Officer |
The executive officers included in the Summary Compensation Table are referred to in this Form 10K as our named executive officers. A detailed description of the plans and programs under which our named executive officers received the following compensation can be found in the section entitled “Compensation Discussion and Analysis.”
Summary Compensation Table
| Name and Principal | Salary | Bonus | Stock Awards | Option Awards | Non-equity Incentive Plan Compensation | Change in Pension Value and Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Earnings | All Other Compensation | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Position | Year | ($) | ($)(3) | ($)(4) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kambiz Mahdi (1) | 2018 | $ | 275,000 | $ | - | $ | 310,760 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 585,760 | |||||||||||||||||
| Chief Executive Officer | 2019 | $ | 275,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 275,000 | |||||||||||||||||
| John Bennett (2) | 2018 | $ | 140,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 140,000 | |||||||||||||||||
| Chief Financial Officer | 2019 | $ | 171,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 171,000 | |||||||||||||||||
| 43 |
| 1) | On October 18, 2018 we entered into an at will employment agreement with Mr. Mahdi, with an annual salary of $275,000. This agreement may be terminated at any time. In addition as part of the agreement Mr. Mahdi was to be issued 20,000,000 shares of our common stock, as additional compensation. As a result; for the year ended December 31, 2018 we accrued for and subsequently on February 13, 2019, issued 20,000,000 shares at a purchase price of $.0131 per share to Mr. Mahdi in the amount of $262,000. |
| 2) | On May 1, 2019 we entered into an employment agreement with Mr. Bennett, with an annual salary of $175,000. Subsequently on March 9, 2020, John Bennett notified Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. (the “Company”) of his resignation from his position as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer, effective March 9, 2020. Mr. Bennett will remain as a consultant to the Company and assist with maintaining the financial books and records of the Company. |
| 3) | There were no bonuses paid or accrued for any executives for fiscal years 2019 and 2018. |
Outstanding Equity Awards at 2019 Fiscal Year-End
There are no outstanding options or stock awards held by our named executive officers as of December 31, 2019.
Executive Employment Agreements
On October 1, 2015 we entered into a new employment agreement with Mr. Mahdi for 2 years with an annual salary of $275,000. In addition, Mr. Mahdi will receive a severance benefit consisting of a single lump sum cash payment equal the salary that Mr. Mahdi would have been entitled to receive through the remainder or the Employment Period or (1) year, whichever is greater. Mr. Mahdi employment contract expired on October 1, 2018.
On October 18, 2018 we entered into an at-will employment agreement with Mr. Mahdi, with an annual salary of $275,000. This agreement may be terminated at any time. In addition as part of the agreement Mr. Mahdi was to be issued 20,000,000 shares of our common stock, as additional compensation.
Mr. Bennett will receive an annual compensation of $140,000 per year, subject to annual increases based on the greater of the consumer price index or 5.0% to take into account annual cost of living increases and also subject to such increases as may from time to time be determined by the Board of the Directors of the Company. Mr. Bennett will also receive a severance benefit consisting of a single lump sum cash payment equal the salary that Mr. Bennett would have been entitled to receive through the remainder or the Employment Period or two (2) years, whichever is greater. On September 1, 2017 Mr. Bennett’s employment agreement automatically renewed for an additional five years. On May 1, 2019 we entered into an employment agreement with Mr. Bennett, with an annual salary of $175,000. Subsequently on March 9, 2020, John Bennett notified Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. (the “Company”) of his resignation from his position as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer, effective March 9, 2020. Mr. Bennett will remain as a consultant to the Company and assist with maintaining the financial books and records of the Company.
Potential Payments upon Termination or Change of Control
Severance Benefits
Mr. Mahdi will receive a severance benefit consisting of a single lump sum cash payment equal the salary that Mr. Mahdi would have been entitled to receive through the remainder or the Employment Period or One (1) year, whichever is greater.
Mr. Bennett will receive a severance benefit consisting of a single lump sum cash payment equal the salary that Mr. Bennett would have been entitled to receive through the remainder or the Employment Period or two (2) years, whichever is greater. On May 1, 2019 we entered into an employment agreement with Mr. Bennett, with an annual salary of $175,000. Subsequently on March 9, 2020, John Bennett notified Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. (the “Company”) of his resignation from his position as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer, effective March 9, 2020. Mr. Bennett will remain as a consultant to the Company and assist with maintaining the financial books and records of the Company. As a result, Mr. Bennett is not entitled to any severance benefits.
| 44 |
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
The following table shows, as of July 10, 2020 the number of shares of our common stock beneficially owned by (1) any person who is known by us to be the beneficial owner of more than 5.0% of the outstanding shares of our common stock; (2) our directors and former directors; (3) our named executive officers; and (4) all of our directors and executive officers as a group. The percentage of common stock beneficially owned is based on 762,895,515 shares of our common stock outstanding. Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with the rules of the SEC and generally includes securities over which a person has voting or investment power and securities that a person has the right to acquire within 60 days. Unless otherwise provided, the address of each beneficial owner listed is c/o Clean Energy Technologies, Inc., Board of Directors, 2990. Redhill Ave, Costa Mesa, California 92626. We need to footnote how the voting rights are allocated and add them to the number of shares.
| Name of Beneficial Owners (1) | Number of Shares of Common Stock Beneficially Owned | Percentage | ||||||
| 5% Holders | ||||||||
| MGW Investments I Limited | 1,086,476,334 | 78.84 | ||||||
| ETI Partners IV LLC | 57,380,323 | 7.53 | % | |||||
| Cyberfuture One LP (1) | 54,444,170 | 6.89 | ||||||
| Officers and Directors | ||||||||
| Calvin Pang(2) | 1,086,476,334 | 78.84 | % | |||||
| Kambiz Mahdi – Director and CEO (3) | 42,601,618 | 5.59 | % | |||||
| John Bennett – Former Director and CFO | 1,359,200 | 0.18 | % | |||||
| All directors and officers as a group | 1,130,437,152 | 82.03 | % | |||||
1) Conversion to shares of Common Stock is calculated based on 58% of the lowest closing bid price of our common stock for the 15 days ended on April 30, 2020, or $.0148 per share.
2) Calvin Pang has voting and investment power over all of our common stock held by MGW Investment I Limited (“MGWI”). MGWI holds 470,462,668 shares of common stock, convertible promissory notes which can be converted into 448,013,667 shares of Common Stock and warrants to purchase 168,000,000 shares of Common Stock.
3) The shares of common stock are held directly by the Kambiz and Bahareh Mahdi Living Trust and indirectly by Kambiz Mahdi and Bahareh Mahdi as Trustees.
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
Director Independence
The common stock of the Company is currently quoted on the OTCQB, quotation system which currently do not have director independence requirements. On an annual basis, each director and executive officer will be obligated to disclose any transactions with the Company in which a director or executive officer, or any member of his or her immediate family, have a direct or indirect material interest in accordance with Item 407(a) of Regulation S-K. Following completion of these disclosures, the Board will make an annual determination as to the independence of each director using the current standards for “independence” that satisfy the criteria as that term is defined in Rule 5605(a)(2) of the NASDAQ listing standards.
As of March 31, 2019, the Board determined that the following directors are independent under these standards:
Jun Wang
Yongsheng Lyu
| 45 |
Review of Related Person Transactions
Our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics provides guidance for addressing actual or potential conflicts of interests, including those that may arise from transactions and relationships between us and our executive officers or directors, such as:
| ● | Business transaction between the company and any executive are prohibited, unless otherwise approved by the Board; |
| ● | Activities that may interfere with an executive’s performance in carrying out company responsibilities; |
| ● | Activities that call for the use of the company’s influence, resources or facilities; and |
| ● | Activities that may discredit the name or reputation of the company. |
We have various procedures in place to identify potential related person transactions, and the Board of Directors and a separate compliance committee work together in reviewing and considering whether any identified transactions or relationships are covered by the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics.
Transactions with Related Persons
Except as set forth in note 12 in the Notes to the Financial Statements which discusses transactions with related parties and is incorporated by reference herein, none of the Company’s directors or officers, nor any person who beneficially owns, directly or indirectly, shares carrying more than 10% of the voting rights attached to the Company’s shares, nor any relative or spouse of any of the foregoing persons, has had any material interest, direct or indirect, in any transaction to which the Company was a party, and in which the amount involved exceeds the lesser of (i) $120,000 or (ii) one percent of the average of the Company’s total assets at year-end for the last two completed fiscal years..
| 46 |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Summary of Operating Results the three months Ended March 31, 2020 Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2019
Going Concern
The financial statements have been prepared on a going concern basis, which contemplates continuity of operations, realization of assets and liquidation of liabilities in the normal course of business. The Company had a total stockholder’s deficit of $5,407,051 and a working capital deficit of $6,932,492 and a net loss of $313,574 for the three months ended March 31, 2020. The company also had an accumulated deficit of $14,529,292 as of March 31, 2020. Therefore, there is substantial doubt about the ability of the Company to continue as a going concern. There can be no assurance that the Company will achieve its goals and reach profitable operations and is still dependent upon its ability (1) to obtain sufficient debt and/or equity capital and/or (2) to generate positive cash flow from operations.
The three months ended March 31, 2020; we had a net loss of $313,574 compared to a net loss of $726,777 for the same period in 2019. The decrease in the net loss in 2019 was mainly due to the increase in revenue. The three months ended March 31, 2020; our revenue was $858,816 compared to $224,363 for the same period in 2019. For the three months ended March 31, 2020, our gross margin was 60% compared to 34% for the same period in 2019 mainly due to the decrease in material cost for the two-unit sale from the HRS segment. For the three months ended March 31, 2020, our operating expense was $476,210 compared to $401,878 for the same period in 2019. The three months ended March 31, 2020; we had a net gain from operations of $39,329 compared to a net loss from operations of $(326,692) for the same period in 2019.
See note 1 to the notes to the financial statements for a discussion on critical accounting policies
RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
See note 12 to the notes to the financial statements for a discussion on related party transaction
Results the three months Ended March 31, 2020 Compared to the three months ended March 31, 2019
Net Sales
The three months ended March 31, 2020; our total revenue was $858,816, compared to $224,363 for the same period in 2019. The Company has three reportable segments: Clean Energy HRS (HRS), Cety Europe and the legacy engineering and manufacturing services division (Electronic Assembly).
Segment breakdown
The three months ended March 31, 2020, our revenue from Engineering and Manufacturing was $107,567 compared to $151,633 for the same period in 2019. The decrease was due to a drop in orders from one customer in 2020.
The three months ended March 31, 2020, our revenue from HRS was $748,750 compared to $25,448 for the same period in 2018. The increase in revenue from the HRS segment was mainly due to 2 units shipped in 2020 vs. the 0 units shipped in 2019.
The three months ended March 31, 2020, our revenue from Cety Europe was $2,499 compared to $47,282 for the same period in 2019. The decrease in revenue was mainly due to the impact of the Covid 19 virus in Italy.
Gross Profit
The three months ended March 31, 2020; our gross profits increased to $515,539 (60%) from $75,186 (34%) for the same period in 2019. Our gross profits could vary from period to period and is affected by a number of factors, including, production and supply change efficiencies, material costs, and logistics.
| 47 |
Segment breakdown
The three months ended March 31, 2020, our gross profit from Engineering and Manufacturing was $26,606 compared to $25,141 for the same period in 2019. This increase from the Electronic Assembly Segment was mainly due increase in prices with the existing customers.
The three months ended March 31, 2020, our gross profit from HRS was $486,434 compared to $17,835 for the same period in 2019. The increase from the HRS segment was mainly due to 2 units shipped in 2020 vs. the 0 units shipped in 2019 and the lower than normal cost of material due to the inventory that was acquired from GE and the associated purchase price allocation.
The three months ended March 31, 2020, our gross profit from Cety Europe was $2,499 compared to $32,210 for the same period in 2019. The decrease in revenue was mainly due to the impact of the Covid 19 virus in Italy.
Selling, General and Administrative (SG&A) Expenses
The three months ended March 31, 2020; our SG&A expense was $95,720 compared to $60,642 for the same period in 2019. This increase was mainly due to increases in insurance expenses, advertising and promotion, License and permits and additional expenses associated with the commissioning of the Marshal Island installation acquired from GE.
Salaries Expense
The three months ended March 31, 2020; our Salaries expense was $209,547 compared to $203,303 for the same period in 2019.
Travel Expense
The three months ended March 31, 2020; our Salaries expense was $29,158 compared to $40,117 for the same period in 2019. The decrease in revenue was mainly due to the impact of the Covid 19 virus.
Facility Lease and Maintenance Expense
The three months ended March 31, 2020; our Facility Lease expense was $110,455 compared to $82,034 for the same period in 2019. This increase was due to the increase in our lease payments and building maintenance expense in our Costa Mesa facility.
Depreciation and Amortization Expense
The three months ended March 31, 2020, our depreciation and amortization expense was $9,443 compared to $11,763 for the same period in 2019, which remained relatively unchanged.
Professional fees Expense
The three months ended March 31, 2020; our Professional fees expense was $21,887 compared to $4,019 for the same period in 2019. The increase was mainly due to the in our legal and accounting fees related to the Filing of our form 1A and in our audit related fees.
Net Gain (Loss) from operations
The three months ended March 31, 2020, our net gain from operations was $39,329 compared to net loss from operations of $326,692 for the same period in 2019. This increase was primarily due to the higher revenues, higher gross profits discussed above and higher efficiency for the three months ended March 31, 2020.
| 48 |
Change in Derivative Liability
The three months ended March 31, 2020; we had a loss on derivative liability of $130,994 compared to $159,733 for the same period in 2019.
Gain on debt settlement
The three months ended March 31, 2020 we recognized a gain on debt settlement in the amount of $22,221 compared to $0 three months ended March 31, 2019.
Interest and Finance Fees
The three months ended March 31, 2020 interest and finance fees were $244,130 compared to $240,352 for the same period in 2019. The decrease was mainly due to the decrease in the amortization of the debt discount derived from the beneficial conversion features.
Net Income / Loss
The three months ended March 31, 2020; our net loss was $313,574 compared to net loss of $726,777 for the same period in 2019. This decrease was primarily due to the higher revenues and gross margins in 2020, higher efficiencies and lower interest expense.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
The three months ended March 31, 2020
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
| Net Cash provided / (Used) In Operating Activities | 39,493 | (332,012 | ) | |||||
| Cash Flows Used In Investing Activities | - | - | ||||||
| Cash Flows Provided / (used) By Financing Activities | 454,560 | 326,588 | ||||||
| Net (Decrease) Increase in Cash and Cash Equivalents | 494,053 | (5,424 | ) | |||||
Capital Requirements for long-term Obligations
Summary of Operating Results for the Year Ended December 31, 2019 Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2018
Going Concern
The financial statements have been prepared on a going concern basis, which contemplates continuity of operations, realization of assets and liquidation of liabilities in the normal course of business. The Company had a total stockholder’s deficit of $5,252,478 and a working capital deficit of $6,785,689 and a net loss of $2,555,983 for the year ended December 31, 2019. The company also had an accumulated deficit of $14,215,718 as of December 31, 2019 and used $2,224,168 in net cash from operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2019. Therefore, there is substantial doubt about the ability of the Company to continue as a going concern. There can be no assurance that the Company will achieve its goals and reach profitable operations and is still dependent upon its ability (1) to obtain sufficient debt and/or equity capital and/or (2) to generate positive cash flow from operations.
| 49 |
For the year ended December 31, 2019, we had a net loss of $2,555,983 compared to a net loss of $2,810,017 for the same period in 2018. The decrease in the net loss in 2019 was mainly due to the decrease in share based expense of interest and financing fees associated with the convertible debt and lines of credit. For the year ended December 31, 2019, our revenue was $1,610,008 compared to $1,331,171 for the same period in 2018. For the year ended December 31, 2019, our cost of goods sold was 59% compared to 61% for the same period in 2018, mainly due to the decrease in material cost. For the twelve months ended December 31, 2019, our gross margin was 41% compared to 39% for the same period in 2018. For the twelve months ended December 31, 2019, our operating expense was $2,111,835 compared to $2,044,392 for the same period in 2018. For the year ended December 31, 2019, we had a net loss from operations of $1,454,609 compared to $1,523,710 for the same period in 2018. Our total stockholder’s equity decreased by $456,784 resulting in shareholder deficit of $5,252,478 as of December 31, 2019. As of December 31, 2019, we had a working capital deficit of $6,785,689 compared to working capital deficit of $6,170,618 as of December 31,2018.
See note 2 to the notes to the financial statements for a discussion on critical accounting policies
RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
See note 12 to the notes to the financial statements for a discussion on related party transaction
Results for the Year Ended December 31, 2019 Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2018
Net Sales
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our total revenue was $1,610,008 compared to $1,331,171 for the same period in 2018. The Company has three reportable segments: Clean Energy HRS (HRS), Cety Europe and the legacy electronic contract manufacturing services division (Electronic Assembly).
Segment breakdown
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our revenue from Engineering and Manufacturing was $513,919 compared to $567,417 for the same period in 2018. The decrease was not material.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our revenue from HRS was $1,012,895 compared to $752,783 for the same period in 2018. The increase in revenue from the HRS segment was mainly due to an increase in the price of the 2 units shipped in 2019 vs. the 2 units shipped in 2018.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our revenue from Cety Europe was $83,194 compared to $10,971 for the same period in 2018. The increase in revenue was mainly due to support of a broader range of customer
Gross Profit
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our gross profits increased to $657,226 (41%) from $520,682 (39%) for the same period in 2018. Our gross profits could vary from period to period and is affected by a number of factors, including, production and supply change efficiencies, material costs, and logistics..
Segment breakdown
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our gross profit from Engineering and Manufacturing was $150,741 compared to $56,231 for the same period in 2018. This increase from the Electronic Assembly Segment was mainly due increase in demand from existing customers.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our gross profit from HRS was $428,445 compared to $457,978 for the same period in 2018. The decrease from the HRS segment was mainly due to lower cost of materials in 2018 as a result of the purchase price allocation of the inventory purchased from GE.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our gross profit from Cety Europe was $78,040 compared to $6,473 for the same period in 2018. The increase was due to the increase in revenue in 2019.
| 50 |
Selling, General and Administrative (SG&A) Expenses
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our SG&A expense was $382,871 compared to $232,571 for the same period in 2018. This increase was mainly due to increase in contractor expense and expenses associated with the commissioning of the Marshal Island installation acquired from GE.
Salaries Expense
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our Salaries expense was $802,951 compared to $740,146 for the same period in 2018.
Facility Lease Expense
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our Facility Lease expense was $305,883 compared to $280,239 for the same period in 2018. This increase was due to the increase in our Costa Mesa facility Lease.
Bad Debt Expense
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our bad debt expense was $128,463 compared to $50,000 for the same period in 2018. This increase was mainly due to increase a bad debt write off $103,463 and an increase in reserve for bad debt of $25,000.
Depreciation and Amortization Expense
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our depreciation and amortization expense was $41,437 compared to $52,444 for the same period in 2018, which remained relatively unchanged.
Professional fees Expense
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our Professional fees expense was $130,709 compared to $142,234 for the same period in 2018. The decrease was mainly due to the decrease in our legal fees related to the transaction with the Confections Ventures Limited and MGW Investments transaction
Consulting Expense
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our Consulting expense was $73,443 compared to $79,084 for the same period in 2018, which remained relatively unchanged.
Share Based Expense
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our share-based expense was $0 compared to $353,140 for the same period in 2018. This was mainly due to the shares granted to Kambiz Mahdi our CEO in the amount of $310,760. Additional shares were issued to others for consulting services in the amount of $42,380.
Net (Loss) from operations
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our net loss from operations was $1,454,609 compared to net loss from operations of $1,523,710 for the same period in 2018. This decrease was primarily due to the higher revenues in 2019 and higher efficiency.
Change in Derivative Liability
For the year ended December 31, 2019, we had a gain on derivative liability of $216,269 compared to $116,259 for the same period in 2018.
| 51 |
Gain on Disposition of Assets
For the year ended December 31, 2019 we recognized a gain on disposition of assets in the amount of $0 compared to $2,389 for the year ended December 31, 2018.
Interest and Finance Fees
For the year ended December 31, 2019 interest and finance fees were $1,317,643 compared to $1,404,955 for the same period in 2018. The decrease was mainly due to the decrease in the amortization of the debt discount derived from the beneficial conversion features.
Net Income / Loss
For the year ended December 31, 2019, our net loss was $2,555,983 compared to net loss of $2,810,017 for the same period in 2018. This decrease was primarily due to the higher revenues in 2019, higher efficiencies and lower interest expense.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
For the years ended December 31,
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Net Cash provided / (Used) In Operating Activities | (2,224,168 | ) | (1,442,899 | ) | ||||
| Cash Flows Used In Investing Activities | (8,000 | ) | - | |||||
| Cash Flows Provided / (used) By Financing Activities | 2,233,118 | 1,439,937 | ||||||
| Net (Decrease) Increase in Cash and Cash Equivalents | 950 | (2,962 | ) | |||||
Audited Financial Statements:
| 52 |
Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Consolidated Balance Sheet
| (Unaudited) | (audited) | |||||||
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Assets | ||||||||
| Current Assets: | ||||||||
| Cash | $ | 501,459 | $ | 7,406 | ||||
| Accounts receivable - net | 1,220,564 | 1,288,258 | ||||||
| Lease receivable asset | 217,584 | 217,584 | ||||||
| Inventory | 523,457 | 630,204 | ||||||
| Total Current Assets | 2,463,064 | 2,143,452 | ||||||
| Property and Equipment - Net | 67,993 | 74,467 | ||||||
| Goodwill | 747,976 | 747,976 | ||||||
| License | 354,322 | 354,322 | ||||||
| Patents | 136,352 | 139,322 | ||||||
| Right of use asset - long term | 771,149 | 822,284 | ||||||
| Other Assets | 25,400 | 25,400 | ||||||
| Total Non Current assets | 2,103,192 | 2,163,771 | ||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 4,566,256 | $ | 4,307,223 | ||||
| Liabilities and Stockholders’ (Deficit) | ||||||||
| Current Liabilities: | ||||||||
| Bank Overdraft | $ | - | $ | 1,480 | ||||
| Accounts payable | 1,703,830 | 1,587,989 | ||||||
| Accrued Expenses | 582,371 | 503,849 | ||||||
| Customer Deposits | 82,730 | 309,230 | ||||||
| Warranty Liability | 100,000 | 100,000 | ||||||
| Deferred Revenue | 33,000 | 47,750 | ||||||
| Derivative Liability | 586,749 | 320,794 | ||||||
| Facility Lease Liability - current | 205,592 | 201,297 | ||||||
| Line of Credit | 1,692,126 | 1,617,086 | ||||||
| Notes payable - GE | 2,400,214 | 2,386,234 | ||||||
| Convertible Notes Payable (net of discount of 156,548 and 80,647 respectively) | 411,362 | 373,249 | ||||||
| Related Party Notes Payable (net of discount of 0 and 29,227 Respectively | 1,597,582 | 1,480,183 | ||||||
| Total Current Liabilities | 9,395,556 | 8,929,141 | ||||||
| Long-Term Debt: | ||||||||
| Facility Lease Liability - long term | 577,751 | 630,560 | ||||||
| Net Long-Term Debt | 577,751 | 630,560 | ||||||
| Total Liabilities | 9,973,307 | 9,559,701 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
| Stockholders’ (Deficit) | ||||||||
| Preferred D stock, stated value $100 per share; 20,000 shares authorized; 7,500 shares and 7,500 shares issued and 5,700 and 6,500 outstanding as of March 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively | 570,000 | 650,000 | ||||||
| Common stock, $.001 par value; 2,000,000,000 shares authorized; 762,130,989 and 753,907,656 shares issued and outstanding as of March 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively | 762,132 | 753,909 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 7,790,109 | 7,559,331 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (14,529,292 | ) | (14,215,718 | ) | ||||
| Total Stockholders’ (Deficit) | (5,407,051 | ) | (5,252,478 | ) | ||||
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Deficit | $ | 4,566,256 | $ | 4,307,223 | ||||
The accompanying footnotes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| F-1 |
Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Consolidated Statement of Operations
for the three months ended March 31,
(Unaudited)
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
| Sales | $ | 858,816 | $ | 224,363 | ||||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 343,277 | 149,177 | ||||||
| Gross Profit | 515,539 | 75,186 | ||||||
| General and Administrative | ||||||||
| General and Administrative expense | 95,720 | 60,642 | ||||||
| Salaries | 209,547 | 203,303 | ||||||
| Travel | 29,158 | 40,117 | ||||||
| Professional Fees | 21,887 | 4,019 | ||||||
| Facility lease and Maintenance | 110,455 | 82,034 | ||||||
| Depreciation and Amortization | 9,443 | 11,763 | ||||||
| Total Expenses | 476,210 | 401,878 | ||||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) From Operations | 39,329 | (326,692 | ) | |||||
| Change in derivative liability | (130,994 | ) | (159,733 | ) | ||||
| Gain / (Loss) on debt settlement’ | 22,221 | - | ||||||
| Interest and Financing fees | (244,130 | ) | (240,352 | ) | ||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) Before Income Taxes | (313,574 | ) | (726,777 | ) | ||||
| Income Tax Expense | - | - | ||||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) | $ | (313,574 | ) | $ | (726,777 | ) | ||
| Per Share Information: | ||||||||
| Basic and diluted weighted average number of common shares outstanding | 758,170,513 | 566,027,100 | ||||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) per common share basic and diluted | $ | (0.00 | ) | $ | (0.00 | ) | ||
The accompanying footnotes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| F-2 |
Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Consolidated Statement of Stockholders Equity
March 31, 2020
(unaudited)
Common Stock .001 Par | Preferred Stock | Common Stock to be issued | Additional Paid in | Accumulated | Stock holders’ Deficit | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Amount | Capital | Deficit | Totals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018 | 555,582,656 | $ | 555,584 | 7,500 | $ | 750,000 | $ | 262,000 | $ | 5,236,457 | $ | (11,599,735 | ) | $ | (4,795,694 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Shares to be issued for compensation | 20,000,000 | 20,000 | (262,000 | ) | 242,000 | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Loss | (726,777 | ) | (726,777 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| March 31, 2019 | 575,582,656 | 575,584 | 7,500 | 750,000 | - | 5,478,457 | (12,326,512 | ) | (5,522,471 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares to be issued | - | - | - | - | 932,680 | 1,066,520 | - | 1,999,200 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares returned from admin. hold | 75,000 | 75 | - | - | - | (75 | ) | - | - | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for cash | 500,000 | 500 | - | - | - | 9,500 | - | 10,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prefered shares reclassed | - | - | (200 | ) | (20,000 | ) | - | 20,000 | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for Preferred stock conversion | 4,000,000 | 4,000 | (800 | ) | (80,000 | ) | - | 136,000 | (60,000 | ) | - | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Loss | (841,795 | ) | (841,795 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| June 30, 2019 | 580,157,656 | 580,159 | 6,500 | 650,000 | 932,680 | 6,710,402 | (13,228,307 | ) | (4,355,066 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares to be issued | 168,000,000 | 168,000 | (932,680 | ) | 764,680 | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for cash | 500,000 | 500 | 9,500 | 10,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subscriptions Received | - | 5,000 | - | 5,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Loss | (658,688 | ) | (658,688 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| September 30, 2019 | 748,657,656 | 748,659 | 6,500 | 650,000 | 5,000 | 7,484,582 | (13,886,995 | ) | (4,998,754 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares to be issued | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for cash | 250,000 | 250 | (5,000 | ) | 4,750 | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subscriptions Received | 5,000,000 | 5,000 | - | 70,000 | 75,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Loss | (328,723 | ) | (328,723 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | 753,907,656 | 753,909 | 6,500 | 650,000 | - | 7,559,332 | (14,215,718 | ) | (5,252,477 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for debt conversion | 1,700,000 | 1,700 | - | 32,300 | 34,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for cash | 4,523,333 | 4,523 | 120,477 | 125,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred conversions | 2,000,000 | 2,000 | (800 | ) | (80,000 | ) | 78,000 | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Loss | (313,574 | ) | (313,574 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| March 31, 2020 | 762,130,989 | $ | 762,132 | 5,700 | $ | 570,000 | $ | - | $ | 7,790,109 | $ | (14,529,292 | ) | $ | (5,407,051 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
The accompanying footnotes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| F-3 |
Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
for the three months ended March 31,
(Unaudited)
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities: | ||||||||
| Net Income / ( Loss ) | $ | (313,574 | ) | $ | (726,777 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash | ||||||||
| used in operating activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 9,443 | 11,763 | ||||||
| Gain on debt settlement | (22,221 | ) | - | |||||
| Financing fees and debt discount | 68,010 | - | ||||||
| Change in derivative liability | 130,994 | 253,576 | ||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
| (Increase) decrease in right of use asset | 51,135 | - | ||||||
| (Increase) decrease in lease liability | (48,514 | ) | - | |||||
| (Increase) decrease in accounts receivable | 67,694 | (54,359 | ) | |||||
| (Increase) decrease in inventory | 106,747 | (32,010 | ) | |||||
| (Increase) decrease in other assets | - | |||||||
| (Decrease) increase in accounts payable | 115,841 | 89,435 | ||||||
| Other (Decrease) increase in accrued expenses | 91,300 | 118,195 | ||||||
| Other (Decrease) increase in accrued expenses related party | 23,889 | |||||||
| Other (Decrease) increase in deferred revenue | (14,750 | ) | 14,750 | |||||
| Other (Decrease) increase in customer deposits | (226,500 | ) | (6,585 | ) | ||||
| Net Cash Provided by (Used In) Operating Activities | 39,493 | (332,012 | ) | |||||
| Cash Flows from Investing Activities | ||||||||
| Purchase property plant and equipment | - | - | ||||||
| Cash Flows Used In Investing Activities | - | - | ||||||
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities | ||||||||
| Bank Overdraft / (Repayment) | (1,480 | ) | 373 | |||||
| Proceeds from notes payable and lines of credit | 271,040 | 326,215 | ||||||
| Proceeds from notes payable related party | 60,000 | |||||||
| Stock issued for cash | 125,000 | - | ||||||
| Cash Flows Provided By Financing Activities | 454,560 | 326,588 | ||||||
| Net (Decrease) Increase in Cash and Cash Equivalents | 494,053 | (5,424 | ) | |||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at Beginning of Period | 7,406 | 6,456 | ||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at End of Period | $ | 501,459 | $ | 1,032 | ||||
| Supplemental Cashflow Information: | ||||||||
| Interest Paid | $ | 75,040 | $ | 106,368 | ||||
| Taxes Paid | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
| Supplemental Non-Cash Disclosure | ||||||||
| Discount on derivatives | $ | 134,961 | $ | 138,000 | ||||
| Shares issued for preferred conversions | $ | 80,000 | $ | - | ||||
| Shares issued for debt conversion conversions | $ | 34,000 | $ | - | ||||
The accompanying footnotes are an integral part of these Consolidated financial statements
| F-4 |
Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
NOTE 1 – BASIS OF PRESENTATION AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES:
These unaudited interim consolidated financial statements as of and for the three months ended March 31, 2020, reflect all adjustments which, in the opinion of management, are necessary to fairly state the Company’s financial position and the results of its operations for the periods presented, in accordance with the accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. All adjustments are of a normal recurring nature.
These unaudited interim consolidated financial statements should be read in conjunction with the Company’s financial statements and notes thereto included in the Company’s fiscal year end December 31, 2019, report. The Company assumes that the users of the interim financial information herein have read, or have access to, the audited financial statements for the preceding period, and that the adequacy of additional disclosure needed for a fair presentation may be determined in that context. The results of operations for the three and three months ended March 31, 2020, are not necessarily indicative of results for the entire year ending December 31, 2020.
The summary of significant accounting policies of Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. is presented to assist in the understanding of the Company’s financial statements. The financial statements and notes are representations of the Company’s management, who is responsible for their integrity and objectivity.
Going Concern
The financial statements have been prepared on a going concern basis, which contemplates continuity of operations, realization of assets and liquidation of liabilities in the normal course of business. The Company had a total stockholder’s deficit of $5,407,051 and a working capital deficit of $6,932,492 and a net loss of $313,574 for the three months ended March 31, 2020. The company also had an accumulated deficit of $14,529,292 as of March 31, 2020. Therefore, there is substantial doubt about the ability of the Company to continue as a going concern. There can be no assurance that the Company will achieve its goals and reach profitable operations and is still dependent upon its ability (1) to obtain sufficient debt and/or equity capital and/or (2) to generate positive cash flow from operations.
Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Such estimates may be materially different from actual financial results. Significant estimates include the recoverability of long-lived assets, the collection of accounts receivable and valuation of inventory and reserves.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We maintain the majority of our cash accounts at a commercial bank. The total cash balance is insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”) up to $250,000 per commercial bank. For purposes of the statement of cash flows we consider all cash and highly liquid investments with initial maturities of one year or less to be cash equivalents.
| F-5 |
Accounts Receivable
We grant credit to our customers and do not require collateral. Our ability to collect receivables is affected by economic fluctuations in the geographic areas and industries served by us. Reserves for un-collectable amounts are provided, based on past experience and a specific analysis of the accounts. Although we expect to collect amounts due, actual collections may differ from the estimated amounts. As of March 31, 2020, and December 31, 2019, we had a reserve for potentially un-collectable accounts of $82,000 and $82,000 respectively. Historically, our bad debt write-offs related to these trade accounts have been insignificant. The three months ended March 31, 2020; our bad debt expense was $0 compared to $0 for the same period in 2019. accounts receivable March 31, 2020.
Lease asset
As of March 31, 2020, and 2019 we had a lease asset that was purchased from General electric with a value of $1,309,527, however due the purchase price allocation, we recognized a value of $217,584. The lease is due to be commissioned in the third quarter of 2020 and will generate approximately $20,000 per month for 120 months. See note 3 for additional information.
Inventory
Inventories are valued at the lower of weighted average cost or market value. Our industry experiences changes in technology, changes in market value and availability of raw materials, as well as changing customer demand. We make provisions for estimated excess and obsolete inventories based on regular audits and cycle counts of our on-hand inventory levels and forecasted customer demands and at times additional provisions are made. Any inventory write offs are charged to the reserve account. As of March 31, 2020, and December 31, 2019, we had a reserve for potentially obsolete inventory of $250,000.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are recorded at cost. Assets held under capital leases are recorded at lease inception at the lower of the present value of the minimum lease payments or the fair market value of the related assets. The cost of ordinary maintenance and repairs is charged to operations. Depreciation and amortization are computed on the straight-line method over the following estimated useful lives of the related assets:
| Furniture and fixtures | 3 to 7 years | |
| Equipment | 7 to 10 years | |
| Leasehold Improvements | 7 years |
Long –Lived Assets
Our management assesses the recoverability of its long-lived assets by determining whether the depreciation and amortization of long-lived assets over their remaining lives can be recovered through projected undiscounted future cash flows. The amount of long-lived asset impairment if any, is measured based on fair value and is charged to operations in the period in which long-lived assets impairment is determined by management. There can be no assurance however, that market conditions will not change or demand for our services will continue, which could result in impairment of long-lived assets in the future.
Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue under ASU No. 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606),” (“ASC 606”).
Performance Obligations Satisfied Over Time
FASB ASC 606-10-25-27 through 25-29, 25-36 through 25-37, 55-5 through 55-10
| F-6 |
An entity transfers control of a good or service over time and satisfies a performance obligation and recognizes revenue over time if one of the following criteria is met:
a. The customer receives and consumes the benefits provided by the entity’s performance as the entity performs (as described in FASB ASC 606-10-55-5 through 55-6).
b. The entity’s performance creates or enhances an asset (for example, work in process) that the customer controls as the asset is created or enhanced (as described in FASB ASC 606-10-55-7).
c. The entity’s performance does not create an asset with an alternative use to the entity (see FASB ASC 606-10-25-28), and the entity has an enforceable right to payment for performance completed to date (as described in FASB ASC 606-10-25-29).
Performance Obligations Satisfied at a Point in Time
FASB ASC 606-10-25-30
If a performance obligation is not satisfied over time, the performance obligation is satisfied at a point in time. To determine the point in time at which a customer obtains control of a promised asset and the entity satisfies a performance obligation, the entity should consider the guidance on control in FASB ASC 606-10-25-23 through 25-26. In addition, it should consider indicators of the transfer of control, which include, but are not limited to, the following:
a. The entity has a present right to payment for the asset
b. The customer has legal title to the asset
c. The entity has transferred physical possession of the asset
d. The customer has the significant risks and rewards of ownership of the asset
e. The customer has accepted the asset
The core principle of the revenue standard is that a company should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. The Company only applies the five-step model to contracts when it is probable that the Company will collect the consideration it is entitled to in exchange for the goods and services transferred to the customer. In Addition a) the company also does not have an alternative use for the asset if the customer were to cancel the contract, and b.) has a fully enforceable right to receive payment for work performed (i.e., customers are required to pay as various milestones and/or timeframes are met)
The following five steps are applied to achieve that core principle for our HRS and Cety Europe Divisions:
| ● | Identify the contract with the customer | |
| ● | Identify the performance obligations in the contract | |
| ● | Determine the transaction price | |
| ● | Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract | |
| ● | Recognize revenue when the company satisfies a performance obligation |
The following steps are applied to our legacy engineering and manufacturing division:
| ● | We generate a quotation | |
| ● | We receive Purchase orders from our customers. | |
| ● | We build the product to their specification | |
| ● | We invoice at the time of shipment | |
| ● | The terms are typically Net 30 days |
Also, from time to time our contracts state that the customer is not obligated to pay a final payment until the units are commissioned, i.e. a final payment of 10%. As of March 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019 we had $33,000 and $47,750 of deferred revenue, which is expected to be recognized in the third quarter of year 2020. There is an additional ~$150,000 to be billed for labor/installation/commissioning services per the customer contracts outstanding as of 12/31/19.
| F-7 |
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Financial Accounting Standards Board issued ASC (Accounting Standards Codification) 820-10 (SFAS No. 157), “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures” for financial assets and liabilities. ASC 820-10 provides a framework for measuring fair value and requires expanded disclosures regarding fair value measurements. FASB ASC 820-10 defines fair value as the price that would be received for an asset or the exit price that would be paid to transfer a liability in the principal or most advantageous market in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. FASB ASC 820-10 also establishes a fair value hierarchy which requires an entity to maximize the use of observable inputs, where available. The following summarizes the three levels of inputs required by the standard that the Company uses to measure fair value:
| ● | Level 1: Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. | |
| ● | Level 2: Observable inputs other than Level 1 prices such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities; quoted prices in markets that are not active or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the related assets or liabilities. | |
| ● | Level 3: Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities. The Company’s derivative liabilities have been valued as Level 3 instruments. We value the derivative liability using a lattice model, with a volatility range of 90% to 112% and using a risk free interest rate of .15% |
The Company’s financial instruments consist of cash, prepaid expenses, inventory, accounts payable, convertible notes payable, advances from related parties, and derivative liabilities. The estimated fair value of cash, prepaid expenses, investments, accounts payable, convertible notes payable and advances from related parties approximate their carrying amounts due to the short-term nature of these instruments.
The carrying amounts of the Company’s financial instruments as of March 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, reflect:
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| Fair value of convertible notes derivative liability – December 31, 2019 | $ | – | $ | – | $ | 320,794 | $ | 320,794 | ||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| Fair value of convertible notes derivative liability – March 31, 2020 | $ | – | $ | – | $ | 586,749 | $ | 586,749 | ||||||||
The carrying amount of accounts payable and accrued expenses are considered to be representative of their respective fair values because of the short-term nature of these financial instruments.
Other Comprehensive Income
We have no material components of other comprehensive income (loss) and accordingly, net loss is equal to comprehensive loss in all periods.
Net Profit (Loss) per Common Share
Basic profit / (loss) per share is computed on the basis of the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. At March 31, 2020, we had outstanding common shares of 762,130,989 used in the calculation of basic earnings per share. Basic Weighted average common shares and equivalents at March 31, 2020 and 2019 were 758,170,513 and 566,027,100, respectively. As of March 31, 2020, we had convertible notes and related party convertible notes, convertible into approximately 498,211,169 of additional common shares, outstanding preferred shares convertible into 8,125,000, calculated @ $.08 of additional common shares and 174,250,000 common stock warrants convertible into an additional. Fully diluted weighted average common shares and equivalents were withheld from the calculation as they were considered anti-dilutive.
| F-8 |
Research and Development
We had no amounts of research and development R&D expense during the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019.
Segment Disclosure
FASB Codification Topic 280, Segment Reporting, establishes standards for reporting financial and descriptive information about an enterprise’s reportable segments. The Company has three reportable segments: Clean Energy HRS (HRS), Cety Europe and the legacy Engineering and Manufacturing services division. The segments are determined based on several factors, including the nature of products and services, the nature of production processes, customer base, delivery channels and similar economic characteristics. Prior to December 31, 2015 we only had one reporting segment.
An operating segment’s performance is evaluated based on its pre-tax operating contribution, or segment income. Segment income is defined as net sales less cost of sales, and segment selling, general and administrative expenses, and does not include amortization of intangibles, stock-based compensation, other charges (income), net and interest and other, net.
Selected Financial Data:
| For the three months ended March 31, | ||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
| Net Sales | ||||||||
| Engineering and Manufacturing | 107,567 | 151,633 | ||||||
| Clean Energy HRS | 748,750 | 25,448 | ||||||
| Cety Europe | 2,499 | 47,282 | ||||||
| Total Sales | 858,816 | 224,363 | ||||||
| Segment income and reconciliation before tax | ||||||||
| Engineering and Manufacturing | 26,606 | 25,141 | ||||||
| Clean Energy HRS | 486,434 | 17,835 | ||||||
| Cety Europe | 2,499 | 32,210 | ||||||
| Total Segment income | 515,539 | 75,186 | ||||||
| Reconciling items | ||||||||
| General and administrative expense | (95,720 | ) | (60,642 | ) | ||||
| Salaries | (209,547 | ) | (203,303 | ) | ||||
| Travel | (29,158 | ) | (40,117 | ) | ||||
| Professional fees | (21,887 | ) | (4,019 | ) | ||||
| Facility lease | (110,455 | ) | (82,034 | ) | ||||
| Depreciation | (9,443 | ) | (11,763 | ) | ||||
| Change in derivative liability | (130,994 | ) | (159,733 | ) | ||||
| Gain debt settlement | 22,221 | - | ||||||
| Interest Expense | (244,130 | ) | (240,352 | ) | ||||
| Net Loss before income tax | (313,574 | ) | (726,777 | ) | ||||
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Total Assets | ||||||||
| Electronics Assembly | 1,851,175 | 1,877,916 | ||||||
| Clean Energy HRS | 2,696,079 | 2,405,628 | ||||||
| Cety Europe | 19,002 | 23,679 | ||||||
| Total Assets | 4,566,256 | 4,307,223 | ||||||
| F-9 |
Share-Based Compensation
The Company has adopted the use of Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 123R, “Share-Based Payment” (SFAS No. 123R) (now contained in FASB Codification Topic 718, Compensation-Stock Compensation), which supersedes APB Opinion No. 25, “Accounting for Stock Issued to Employees,” and its related implementation guidance and eliminates the alternative to use Opinion 25’s intrinsic value method of accounting that was provided in Statement 123 as originally issued. This Statement requires an entity to measure the cost of employee services received in exchange for an award of an equity instruments, which includes grants of stock options and stock warrants, based on the fair value of the award, measured at the grant date (with limited exceptions). Under this standard, the fair value of each award is estimated on the grant date, using an option-pricing model that meets certain requirements. We use the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to estimate the fair value of our equity awards, including stock options and warrants. The Black-Scholes model meets the requirements of SFAS No. 123R; however, the fair values generated may not reflect their actual fair values, as it does not consider certain factors, such as vesting requirements, employee attrition and transferability limitations. The Black-Scholes model valuation is affected by our stock price and a number of assumptions, including expected volatility, expected life, risk-free interest rate and expected dividends. We estimate the expected volatility and estimated life of our stock options at grant date based on historical volatility. For the “risk-free interest rate,” we use the Constant Maturity Treasury rate on 90-day government securities. The term is equal to the time until the option expires. The dividend yield is not applicable, as the Company has not paid any dividends, nor do we anticipate paying them in the foreseeable future. The fair value of our restricted stock is based on the market value of our free trading common stock, on the grant date calculated using a 20-trading-day average. At the time of grant, the share-based compensation expense is recognized in our financial statements based on awards that are ultimately expected to vest using historical employee attrition rates and the expense is reduced accordingly. It is also adjusted to account for the restricted and thinly traded nature of the shares. The expense is reviewed and adjusted in subsequent periods if actual attrition differs from those estimates.
We re-evaluate the assumptions used to value our share-based awards on a quarterly basis and, if changes warrant different assumptions, the share-based compensation expense could vary significantly from the amount expensed in the past. We may be required to adjust any remaining share-based compensation expense, based on any additions, cancellations or adjustments to the share-based awards. The expense is recognized over the period during which an employee is required to provide service in exchange for the award—the requisite service period (usually the vesting period). No compensation cost is recognized for equity instruments for which employees do not render the requisite service. The three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019 we had $0 and $0 respectively, in share-based expense, due to the issuance of common stock. As of March 31, 2020, we had no further non-vested expense to be recognized.
Income Taxes
Federal Income taxes are not currently due since we have had losses since inception.
On December 22, 2018 H.R. 1, originally known as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, (the “Tax Act”) was enacted. Among the significant changes to the U.S. Internal Revenue Code, the Tax Act lowers the U.S. federal corporate income tax rate (“Federal Tax Rate”) from 35% to 21% effective January 1, 2018. The Company will compute its income tax expense the three months ended March 31, 2020 using a Federal Tax Rate of 21%.
Income taxes are provided based upon the liability method of accounting pursuant to ASC 740-10-25 Income Taxes – Recognition. Under this approach, deferred income taxes are recorded to reflect the tax consequences in future years of differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their financial reporting amounts at each year-end. A valuation allowance is recorded against deferred tax assets if management does not believe the Company has met the “more likely than not” standard required by ASC 740-10-25-5.
Deferred income tax amounts reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax reporting purposes.
| F-10 |
As of March 31, 2020, we had a net operating loss carry-forward of approximately $(5,679,574) and a deferred tax asset of $1,192,711 using the statutory rate of 21%. The deferred tax asset may be recognized in future periods, not to exceed 20 years. However, due to the uncertainty of future events we have booked valuation allowance of $(1,192,711). FASB ASC 740 prescribes recognition threshold and measurement attributes for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. FASB ASC 740 also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification, interest and penalties, accounting in interim periods, disclosure and transition. At March 31, 2020 the Company had not taken any tax positions that would require disclosure under FASB ASC 740.
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Deferred Tax Asset | $ | 1,192,711 | $ | 1,126,860 | ||||
| Valuation Allowance | (1,192,711 | ) | (1,126,860 | ) | ||||
| Deferred Tax Asset (Net) | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
On February 13, 2018 , Clean Energy Technologies, Inc., a Nevada corporation (the “Registrant” or “Corporation”) entered into a Common Stock Purchase Agreement (“Stock Purchase Agreement”) by and between MGW Investment I Limited (“MGWI”) and the Corporation. The Corporation received $907,388 in exchange for the issuance of 302,462,667 restricted shares of the Corporation’s common stock, par value $.001 per share (the “Common Stock”).
On February 13, 2018 the Corporation and Confections Ventures Limited. (“CVL”) entered into a Convertible Note Purchase Agreement (the “Convertible Note Purchase Agreement,” together with the Stock Purchase Agreement and the transactions contemplated thereunder, the “Financing”) pursuant to which the Corporation issued to CVL a convertible promissory Note (the “CVL Note”) in the principal amount of $939,500 with an interest rate of 10% per annum interest rate and a maturity date of February 13, 2020. The CVL Note is convertible into shares of Common Stock at $0.003 per share, as adjusted as provided therein. This note was assigned to MGW Investments.
This resulted in a change in control, which limited the net operating to that date forward. We are subject to taxation in the U.S. and the states of California. Further, the Company currently has no open tax years’ subject to audit prior to December 31, 2015. The Company is current on its federal and state tax returns.
Reclassification
Certain amounts in the prior period financial statements have been reclassified to conform to the current period presentation. These reclassifications had no effect on reported income, total assets, total liabilities or stockholders’ equity as previously reported. We reclassified accrued interest and other accrued expenses to the respective note’s payable accounts. See Note 8 for the GE liability, convertible notes payable and note 12 regarding the related party disclosure
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
The Company is reviewing the effects of following recent updates. The Company has no expectation that any of these items will have a material effect upon the financial statements.
In June 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2016-13, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses [codified as Accounting Standards Codification Topic (ASC) 326]. ASC 326 adds to US generally accepted accounting principles (US GAAP) the current expected credit loss (CECL) model, a measurement model based on expected losses rather than incurred losses. Under this new guidance, an entity recognizes its estimate of expected credit losses as an allowance, which the FASB believes will result in more timely recognition of such losses. This will become effective in January 2023 and the impact on the company is under evaluation.
| F-11 |
NOTE 2 – ACCOUNTS AND NOTES RECEIVABLE
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Accounts Receivable | $ | 1,302,564 | $ | 1,370,258 | ||||
| Less Reserve for uncollectable accounts | (82,000 | ) | (82,000 | ) | ||||
| Accounts Receivable (Net) | $ | 1,220,564 | $ | 1,288,258 | ||||
Our Accounts Receivable is pledged to Nations Interbanc, our line of credit.
Note 3 – Lease Asset
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Lease asset | $ | 217,584 | $ | 217,584 | ||||
The Company is currently modifying the assets subject to lease to meet the provisions of the agreement, and as of March 31, 2020 any collection on the lease payments was not yet considered probable, resulting in no derecognition of the underlying asset and no net lease investments recognized on the sales-type lease pursuant to ASC 842-30-25-3.
NOTE 4 – INVENTORY
Inventories by major classification were comprised of the following at:
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Raw Material | $ | 745,012 | $ | 848,464 | ||||
| Work in Process | 28,445 | 31,740 | ||||||
| Total | 773,457 | 880,204 | ||||||
| Less reserve for excess or obsolete inventory | (250,000 | ) | (250,000 | ) | ||||
| Inventory | $ | 523,457 | $ | 630,204 | ||||
Our Inventory is pledged to Nations Interbanc, our line of credit.
NOTE 5 – PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
Property and equipment were comprised of the following at:
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Capital Equipment | $ | 1,350,794 | $ | 1,350,794 | ||||
| Leasehold improvements | 75,436 | 75,436 | ||||||
| Accumulated Depreciation | (1,358,237 | ) | (1,351,763 | ) | ||||
| Net Fixed Assets | $ | 67,993 | $ | 74,467 | ||||
| F-12 |
Our Depreciation Expense the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019 was $6,474 and $8,794 respectively.
Our Property Plant and Equipment is pledged to Nations Interbanc, our line of credit.
NOTE 6 – INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Intangible assets were comprised of the following at:
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Goodwill | $ | 747,976 | $ | 747,976 | ||||
| License | 354,322 | 354,322 | ||||||
| Patents | 190,789 | 190,789 | ||||||
| Accumulated Amortization | (54,437 | ) | (51,467 | ) | ||||
| Net Intangible Assets | $ | 1,238,650 | $ | 1,241,620 | ||||
Our Amortization Expense the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019 was $2,969 and $2,969 respectively.
NOTE 7 – ACCRUED EXPENSES
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Accrued Payroll | $ | 261,801 | $ | 192,227 | ||||
| Accrued Interest | 320,570 | 311,620 | ||||||
| Total accrued expenses | $ | 582,371 | $ | 503,847 | ||||
NOTE 8 – NOTES PAYABLE
The Company issued a short-term note payable to an individual, secured by the assets of the Company, dated September 6, 2013 in the amount of $50,000 and fixed fee amount of $3,500. As of March 31, 2020, the outstanding balance was $36,500. Subsequently, on January 30, 2020 we issued 1,700,000 shares of our common stock at a purchase price of $.02 per share, as settlement in full of a note payable of in the amount of $36,500 with accrued interest of 19,721. As a result, we recognized a gain in the amount of $22,221 in the 1st quarter of 2020.
On November 11, 2013, we entered into an accounts receivable financing agreement with American Interbanc (now Nations Interbanc). Amounts outstanding under the agreement bear interest at the rate of 2.5% per month. It is secured by the assets of the Company. In addition, it is personally guaranteed by Kambiz Mahdi, our Chief Executive Officer. As of March 31, 2020, the outstanding balance was $1,692,126 compared to $1,617,086 at December 31, 2019.
On September 11, 2015, our CE HRS subsidiary issued a promissory note in the initial principal amount $1,400,000 and assumed a pension liability of $100,000, for a total liability of $1,500,000, in connection with our acquisition of the heat recovery solutions, or HRS, assets of General Electric International, Inc., a Delaware corporation (“GEII”), including intellectual property, patents, trademarks, machinery, equipment, tooling and fixtures. The note bears interest at the rate of 2.66% per annum. The note is payable on the following schedule: (a) $200,000 in principal on December 31, 2015 and (b) thereafter, the remaining principal amount of $1,200,000, together with interest thereon, payable in equal quarterly installments of principal and interest of $157,609, commencing on December 31, 2016 and continuing until December 31, 2019, at which time the remaining unpaid principal amount of this note and all accrued and unpaid interest thereon shall be due and payable in full.
| F-13 |
Total Liability to GE
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Note payable GE | $ | 1,200,000 | $ | 1,200,000 | ||||
| Accrued transition services | 972,233 | 972,233 | ||||||
| Accrued Interest | 227,981 | 214,001 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 2,400,214 | $ | 2,386,234 | ||||
We are currently in default on the payment of the purchase price pursuant to our asset purchase agreement with General Electric due to a combination of our inability to raise sufficient capital as expected and our belief that we are entitled to a reduction in purchase price we paid. We are in the process of negotiations with General Electric.
Convertible notes
On May 5, 2017 we entered into a nine-month convertible note payable for $78,000, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is not convertible until nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of ninety one percent (61%) of the lowest closing bid price (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. On November 6, 2017 this note was assumed and paid in full at a premium for a total of $116,600 by Cybernaut Zfounder Ventures. An amended term were added to the original note with the interest rate of 14%. This note matured on February 21st of 2018 and is currently in default.
On May 24, 2017 we entered into a nine-month convertible note payable for $32,000, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is not convertible until nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of fifty-five eight percent (58%) of the lowest closing bid price (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. On November 6, 2017 this note was assumed and paid in full at a premium for a total of $95,685, by Cybernaut Zfounder Ventures. An amended term was added to the original note with the interest rate of 14%. This note matured on February 26th, 2018 and is currently in default.
On December 13, 2018 we entered into a convertible note payable for $83,000, with a maturity date of December 13, 2019, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is convertible six months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of fifty-eight percent (65%) of the average of the two lowest trading prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. On May 28, 2019 this note was paid in full.
On February 13, 2019 we entered into a convertible note payable for $138,000, with a maturity date of February 13, 2020, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is not convertible six months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of fifty-eight percent (65%) of the average of the two lowest trading prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. On August 12, 2019 this note was paid in full. The fair value of the convertible feature was $513,829, we recorded a debt discount of $138,000 and an additional loss of $375,828. As of March 31, 2020 the un-amortized debt discount was $0. The total amortized debt discount expense was $138,000.
| F-14 |
On April 9, 2019 we entered into a convertible note payable for $53,000, with a maturity date of April 9, 2020, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is convertible nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of sixty-five percent (65%) of the average of the two lowest closing prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. This note was paid in full on October 10, 2019. The fair value of the convertible feature was $55,604, we recorded a debt discount of $53,000 and an additional loss of $2,604. As of March 31, 2020 the un-amortized debt discount was $0. The total amortized debt discount expense was $53,000.
On October 30, 2019 we entered into a convertible note payable for $103,000, with a maturity date of October 30, 2020, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is convertible nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of sixty-five percent (65%) of the average of the two lowest closing prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. We also entered into a stock purchase agreement for the potential conversion into common stock. Subsequently that note was paid in full on May 1, 2020. The fair value of the convertible feature was $97,471, we recorded a debt discount of $97,471 and an additional loss of $0. As of March 31, 2020, the un-amortized debt discount was $46,821. The total amortized debt discount expense was $33,826 for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and $16,824 for the year ended December 31, 2019
On January 8, 2020 we entered into a convertible note payable for $103,000, with a maturity date of January 8, 2021, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is convertible nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of sixty-five percent (65%) of the average of the two lowest closing prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. We also entered into a stock purchase agreement for the potential conversion into common stock. The fair value of the convertible feature was $87,560, we recorded a debt discount of $87,560. As of March 31, 2020, the un-amortized debt discount was $67,649. The total amortized debt discount expense was $19,910 for the three months ended March 31, 2020.
On February 19, 2020 we entered into a convertible note payable for $53,000, with a maturity date of February 19, 2021, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is convertible nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of sixty-five percent (65%) of the average of the two lowest closing prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. We also entered into a stock purchase agreement for the potential conversion into common stock. The fair value of the convertible feature was $47,401, we recorded a debt discount of $47,401. As of March 31, 2020, the un-amortized debt discount was $42,076. The total amortized debt discount expense was $5,325 for the three months ended March 31, 2020.
Total due to Convertible Notes
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Total convertible notes | $ | 491,285 | $ | 371,785 | ||||
| Accrued Interest | $ | 76,626 | $ | 82,111 | ||||
| Debt Discount | $ | (156,549 | ) | $ | (80,647 | ) | ||
| Total | $ | 411,362 | $ | 373,249 | ||||
| F-15 |
Note 9 – Derivative Liabilities
As a result of the convertible notes we recognized the embedded derivative liability on the date of note issuance. We also revalued the remaining derivative liability on the outstanding note balance on the date of the balance sheet. We value the derivative liability using a binomial lattice model with an expected volatility range of 85% to 92% and a risk-free interest rate range of 1.60% to 1.64%. The remaining derivative liabilities were:
| Derivative Liabilities on Convertible Loans: | ||||
| Derivative Liability December 31, 2019 | $ | 320,794 | ||
| Additions | 134,961 | |||
| Fair market value adjustments | 130,994 | |||
| Derivative Liability March 31, 2020 | 586,749 | |||
NOTE 10 – COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
The company has received an invoice from Oberon Securities for $291,767 which is in dispute. The company believes it has defenses to the claim for compensation and plans to assert appropriate counterclaims and actions as permitted by law. No liability has been recorded for this claim as the Company believes there is a greater than not probability that our Company will prevail in defending against the claim.
Operating Rental Leases
As of May 1, 2017, our corporate headquarters are located at 2990 Redhill Unit A, Costa Mesa, CA. On March 10, 2017, the Company signed a lease agreement for a 18,200-square foot CTU Industrial Building. Lease term is seven years and two months beginning July 1, 2017. In October of 2018 we signed a sublease agreement with our facility in Italy with an indefinite term that may be terminated by either party with a 60 day notice for 1,000 Euro per month. Due to the short termination clause, we are treating this as a month to month lease.
Future minimum lease payments as of March 31, 2020 are:
| Year | Lease Payment | |||
| 2020 | $ | 181,413 | ||
| 2021 | $ | 249,132 | ||
| 2022 | $ | 256,608 | ||
| 2023 | $ | 44,052 | ||
| Imputed Interest | $ | 52,138 | ||
| Net Lease Liability | $ | 783,343 | ||
Our Building expense for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019 was $110,455 and $82,034 respectively.
ASB ASU 2016-02 “Leases (Topic 842)” – In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, which requires lessees to recognize almost all leases on their balance sheet as a right-of-use asset and a lease liability. For income statement purposes, the FASB retained a dual model, requiring leases to be classified as either operating or finance. Classification will be based on criteria that are largely similar to those applied in current lease accounting, but without explicit bright lines. Lessor accounting is similar to the current model, but has been updated to align with certain changes to the lessee model and the new revenue recognition standard. This ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years. We have adopted the above ASU as of January 1, 2019. The right of use asset and lease liability have been recorded at the present value of the future minimum lease payments, utilizing a 5% average borrowing rate and the company is utilizing the transition relief and “running off” on current leases.
| F-16 |
Severance Benefits
Mr. Mahdi will receive a severance benefit consisting of a single lump sum cash payment equal the salary that Mr. Mahdi would have been entitled to receive through the remainder or the Employment Period or One (1) year, whichever is greater.
Mr. Bennett will receive a severance benefit consisting of a single lump sum cash payment equal the salary that Mr. Bennett would have been entitled to receive through the remainder or the Employment Period or One (1) year, whichever is greater. Subsequently on March 9, 2020, John Bennett notified Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. (the “Company”) of his resignation from his position as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer, effective March 9, 2020. Mr. Bennett will remain as a consultant to the Company and assist with maintaining the financial books and records of the Company. As a result, Mr. Bennett is no longer entitled to any severance benefits.
NOTE 11 – CAPITAL STOCK TRANSACTIONS
On April 21, 2005, our Board of Directors and shareholders approved the re-domicile of the Company in the State of Nevada, in connection with which we increased the number of our authorized common shares to 200,000,000 and designated a par value of $.001 per share.
On May 25, 2006, our Board of Directors and shareholders approved an amendment to our Articles of Incorporation to authorize a new series of preferred stock, designated as Series C, and consisting of 15,000 authorized shares.
On June 30, 2017, our Board of Directors and shareholders approved an increase in the number of our authorized common shares to 400,000,000 and in the number of our authorized preferred shares to 10,000,000. The amendment effecting the increase in our authorized capital was filed and effective on July 5, 2017.
On August 28, 2018, our Board of Directors and shareholders approved an increase in the number of our authorized common shares to 800,000,000. The amendment effecting the increase in our authorized capital was filed and effective on August 23, 2018.
On June 10, 2019, our Board of Directors and shareholders approved an increase in the number of our authorized common shares to 2,000,000,000. The amendment effecting the increase in our authorized capital was effective on September 27, 2019.
Common Stock Transactions
In the first quarter of 2019, we signed agreements to issue 4,000,000 shares of common stock valued at $.015 for a total value of $60,000 for the conversion of 800 preferred series D shares, which were subsequently issued.
We also recorded a $60,000 inducement fee (relating to the Preferred series D estoppel agreement and discounted conversion terms) to account for the difference in the fair value which was offset to retained earnings.
On June 10, 2019 we issued 500,000 shares of common stock at $.02 per share to an accredited investor for an aggregate price of $10,000 in a private sale. We also issued 500,000 warrants as part of the transaction. Each Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
On July 19, 2019 we issued 500,000 shares of common stock at $.02 per share to an accredited investor for an aggregate price of $10,000 in a private sale. We also issued 500,000 warrants as part of the transaction. Each Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
| F-17 |
On September 19, 2019 we entered into a stock purchase agreement for 250,000 units at a purchase price of $.02 a unit for an aggregate price of $5,000 to an accredited investor a private sale. Each unit consist of one share of common stock and one warrant to purchase one share of common stock exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement. The shares were included in the shares to be issued as of September 30, 2019 and were subsequently issued on October 15, 2019.
On December 5, 2019 we issued 5,000,000 units at a purchase price of $.015 per unit for an aggregate price of $75,000 to an accredited investor in a private sale. Each unit consist of one share of common stock and one warrant to purchase one share of common stock exercisable at $.04 per share.
On January 21, 2020 our Registration Statement on Form 1-A was qualified with the Securities and Exchange Commission, under which we may offer up to 300,000,000 shares of our common stock at a purchase price of $.03 per share. As of the date hereof, 4,523,333 shares of common stock have been issued thereunder.
On January 30, 2020 we issued 1,700,000 shares of our common stock at a purchase price of $.02 per share, as settlement in full of a note payable of in the amount of $36,500 with accrued interest of 19,721. As a result we recognized a gain in the amount of $22,221 in the 1st quarter of 2020.
On February 3, 2020 we issued 3,690,000 shares of our common stock under our Reg A offering at $.03 per share. These shares are unrestricted and free trading.
On February 4, 2020 we issued 2,000,000 shares of our common stock at a price of $.04 per share, in exchange for the conversion of 800 shares of our Series D Preferred Stock.
On March 17, 2020 we issued 833,333 shares of our common stock under our Reg A offering at $.03 per share. These shares are unrestricted and free trading.
On June 8, 2020, Clean Energy Technology, Inc., a Nevada corporation (the “Company”), entered into an Equity Financing Agreement (“Equity Financing Agreement”) and Registration Rights Agreement (“Registration Rights Agreement”) with GHS Investments LLC, a Nevada limited liability company (“GHS”). Under the terms of the Equity Financing Agreement, GHS agreed to provide the Company with up to $2,000,000 upon effectiveness of a registration statement on Form S-1 (the “Registration Statement”) filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “Commission”) As a result we issued 764,526 Shares of common stock as an inducement fee.
Common Stock
Our Articles of Incorporation authorize us to issue 2,000,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.001 per share. As of March 31, 2020, there were 762,130,989 shares of common stock outstanding. All outstanding shares of common stock are, and the common stock to be issued will be, fully paid and non-assessable. Each share of our common stock has identical rights and privileges in every respect. The holders of our common stock are entitled to vote upon all matters submitted to a vote of our shareholders and are entitled to one vote for each share of common stock held. There are no cumulative voting rights.
The holders of our common stock are entitled to share equally in dividends and other distributions that our Board of Directors may declare from time to time out of funds legally available for that purpose, if any, after the satisfaction of any prior rights and preferences of any outstanding preferred stock. If we liquidate, dissolve or wind up, the holders of common stock shares will be entitled to share ratably in the distribution of all of our assets remaining available for distribution after satisfaction of all our liabilities and our obligations to holders of our outstanding preferred stock.
Preferred Stock
Our Articles of Incorporation authorize us to issue 20,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.001 per share. Our Board of Directors has the authority to issue additional shares of preferred stock in one or more series, and fix for each series, the designation of and number of shares to be included in each such series. Our Board of Directors is also authorized to set the powers, privileges, preferences, and relative participating, optional or other rights, if any, of the shares of each such series and the qualifications, limitations or restrictions of the shares of each such series.
| F-18 |
Unless our Board of Directors provides otherwise, the shares of all series of preferred stock will rank on parity with respect to the payment of dividends and to the distribution of assets upon liquidation. Any issuance by us of shares of our preferred stock may have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a change of our control or an unsolicited acquisition proposal. The issuance of preferred stock also could decrease the amount of earnings and assets available for distribution to the holders of common stock or could adversely affect the rights and powers, including voting rights, of the holders of common stock.
We previously authorized 440 shares of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock, 20,000 shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock, and 15,000 shares Series C Convertible Preferred Stock. As of August 20, 2006, all series A, B, and C preferred had been converted into common stock.
Effective August 7, 2013, our Board of Directors designated a series of our preferred stock as Series D Preferred Stock, authorizing 15,000 shares. Our Series D Preferred Stock offering terms authorized us to raise up to $1,000,000 with an over-allotment of $500,000 in multiple closings over the course of six months. We received an aggregate of $750,000 in financing in subscription for Series D Preferred Stock, or 7,500 shares.
The following are primary terms of the Series D Preferred Stock. The Series D Preferred holders were initially entitled to be paid a special monthly divided at the rate of 17.5% per annum. Initially, the Series D Preferred Stock was also entitled to be paid special dividends in the event cash dividends were not paid when scheduled. If the Company does not pay the dividend within five (5) business days from the end of the calendar month for which the payment of such dividend to owed, the Company will pay the investor a special dividend of an additional 3.5%. Any unpaid or accrued special dividends will be paid upon a liquidation or redemption. For any other dividends or distributions, the Series D Preferred Stock participates with common stock on an as-converted basis. The Series D Preferred holders may elect to convert the Series D Preferred Stock, in their sole discretion, at any time after a one-year (1) year holding period, by sending the Company a notice to convert. The conversion rate is equal to the greater of $0.08 or a 20% discount to the average of the three (3) lowest closing market prices of the common stock during the ten (10) trading day period prior to conversion. The Series D Preferred Stock is redeemable from funds legally available for distribution at the option of the individual holders of the Series D Preferred Stock commencing any time after the one (1) year period from the offering closing at a price equal to the initial purchase price plus all accrued but unpaid dividends, provided, that if the Company gave notice to the investors that it was not in a financial position to redeem the Series D Preferred, the Company and the Series D Preferred holders are obligated to negotiate in good faith for an extension of the redemption period. The Company timely notified the investors that it was not in a financial position to redeem the Series D Preferred and the Company and the investors have engaged in ongoing negotiations to determine an appropriate extension period. The Company may elect to redeem the Series D Preferred Stock any time at a price equal to initial purchase price plus all accrued but unpaid dividends, subject to the investors’ right to convert, by providing written notice about its intent to redeem. Each investor has the right to convert the Series D Preferred Stock at least ten (10) days prior to such redemption by the Company.
In connection with the subscriptions for the Series D Preferred, we issued series F warrants to purchase an aggregate of 375,000 shares of our common stock at $.10 per share and series G warrants to purchase an aggregate of 375,000 shares of our common stock at $.20 per share.
On August 21, 2014, a holder holding 5,000 shares of Preferred Series D Preferred agreed to lower the dividend rate to 13% on its Series D Preferred. In September 2015, all holders of Series D Preferred signed and delivered estoppel agreements, whereby the holders agreed, among other things, that the Series D Preferred was not in default and to reduce (effective as of December 31, 2015) the dividend rate on the Series D Preferred Stock to six percent per annum and to terminate the 3.5% penalty in respect of unpaid dividends accruing on or after such date.
| F-19 |
In the first quarter of 2019, we signed agreements to issue 4,000,000 shares of common stock valued at $.015 for a total value of $60,000 for the conversion of 800 preferred series D shares, which were subsequently issued.
We also recorded a $60,000 inducement fee (in exchange for the “standoff” and estoppel agreement and discounted conversion terms) to account for the difference in the fair value which we offset to retained earnings.
On February 4, 2020 we issued 2,000,000 shares of our common stock at a price of $.04 per share, in exchange for the conversion of 800 shares of our Series D Preferred Stock.
Warrants
A summary of warrant activity for the periods is as follows:
On May 31, 2019, we entered into a subscription agreement pursuant to which the Company agreed to sell 168,000,000 units (each a “Unit” and together the “Units”) to MGW Investment I Limited MGWI for an aggregate purchase price of $1,999,200, or $.0119 per Unit, with each unit consisting of one share of common stock, par value $.001 per share (the “Common Stock”) and a warrant (the “Warrant”) to purchase one share of common stock. The Common Stock will be issued to MGWI at such time as the Company increases the number of shares of its authorized Common Stock. The Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
On June 10, 2019 we issued 500,000 shares of common stock at $.02 per share to an accredited investor for an aggregate price of $10,000 in a private sale. We also issued 500,000 warrants as part of the transaction. Each Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
On July 18, 2019 we issued 500,000 shares of common stock at $.02 per share to an accredited investor for an aggregate price of $10,000 in a private sale. We also issued 500,000 warrants as part of the transaction. Each Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
On September 19, 2019 we entered into a stock purchase agreement for 250,000 units to an accredited investor a private sale. Each unit consist of one share of common stock and one warrant to purchase one share of common stock exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement. The shares were included in the shares to be issued as of September 30, 2019 and were subsequently issued on October 15, 2019.
On December 5, 2019 we issued 5,000,000 units to an accredited investor a private sale. Each unit consist of one share of common stock and one warrant to purchase one share of common stock exercisable at $.04 per share.
| Warrants - Common Share Equivalents | Weighted Average Exercise price | Warrants exercisable - Common Share Equivalents | Weighted Average Exercise price | |||||||||||||
| Outstanding December 31, 2019 | 174,250,000 | $ | 0.04 | 174,250,000 | $ | 0.04 | ||||||||||
| Issued | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Exercised | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| Expired | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Outstanding March 31, 2020 | 174,250,000 | $ | 0.04 | 174,250,000 | $ | 0.04 | ||||||||||
| F-20 |
Stock Options
We currently have no outstanding stock options
NOTE 12 – RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Kambiz Mahdi, our Chief Executive Officer, owns Billet Electronics, which is distributor of electronic components. From time to time, we purchase parts from Billet Electronics. In addition, Billet was a supplier of parts and had dealings with current and former customers of the Company prior to joining the company. Our Board of Directors has approved the transactions between Billet Electronics and the Company.
On September 6, 2016, we entered into a one-year convertible note payable for $87,500, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is not convertible until nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of fifty-five percent (55%) of the lowest closing bid price (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the twenty (20) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. On December 16, 2016 we issued 1,200,000 shares of common stock at $.0031 for a partial conversion of this note in the amount of $3,696. January 4, 2018, we issued 2,300,000 shares of common stock at $.002192 for a partial conversion of this note in the amount of $5,042.
On November 2, 2016, we effected the repayment of the convertible note dated March 15, 2016 for an aggregate amount of $84,000. Concurrently, we entered into an Escrow Funding Agreement with Red Dot Investment, Inc., a California corporation (“Reddot”), pursuant to which Reddot deposited funds into escrow to fund the repayment and we assigned to Reddot our right to acquire the convertible note and Reddot acquired the convertible note. Concurrently, we and Reddot amended the convertible note (a) to have a fixed conversion price of $.005 per share, subject to potential further adjustment in the event of certain Common Stock issuances, (b) to have a fixed interest rate of ten percent (10%) per annum with respect to both the redemption amount and including a financing fee and any costs, expenses, or other fees relating to the convertible note or its enforcement and collection, and any other expense for or on our account (in each case with a minimum 10% yield in the event of payoff or conversion within the first year), such amounts to constitute additional principal under the convertible note, as amended, and (c) as otherwise provided in the Escrow Funding Agreement. The March 2016 convertible note, as so amended, is referred to as the “Master Note.”
Concurrently with the foregoing note repayments, we entered into a Credit Agreement and Promissory Note (the “Credit Agreement”) with Megawell USA Technology Investment Fund I LLC, a Wyoming limited liability company in formation (“MW I”), pursuant to which MW I deposited funds into escrow to fund the repayment of the convertible notes and we assigned to MW I our right to acquire the convertible notes and otherwise agreed that MW I would be subrogated to the rights of each note holder to the extent a note was repaid with funds advanced by MW I. Concurrently, MW I acquired the Master Note and we agreed that all amounts advanced by MG I to or for our benefit would be governed by the terms of the Master Note, including the payment of a financing fees, interest, minimum interest, and convertibility. Reddot is MW I’s agent for purposes of administration of the Credit Agreement and the Master Note and advances thereunder.
On February 13, 2018 the Corporation and Confections Ventures Limited. (“CVL”) entered into a Convertible Note Purchase Agreement (the “Convertible Note Purchase Agreement,” together with the Stock Purchase Agreement and the transactions contemplated thereunder, the “Financing”) pursuant to which the Corporation issued to CVL a convertible promissory Note (the “CVL Note”) in the principal amount of $939,500 with an interest rate of 10% per annum interest rate and a maturity date of February 13, 2020. The CVL Note is convertible into shares of Common Stock at $0.003 per share, as adjusted as provided therein. As a result we recognized a beneficial conversion feature of $532,383, which is amortized over the life of the note. This note was assigned to Mgw Investments and they agreed not to convert the $939,500 note in to shares in excess of the 800,000,000 Authorized limit until we have increased the Authorized shares to the Board approved limit of 2 billion shares.
| F-21 |
On February 8, 2018 the Corporation entered a Convertible Promissory Note in the principal amount of $153,123, due October 8, 2018, with an interest rate of 12% per annum payable to MGWI (the “MGWI Note”). The MGWI Note is convertible into shares of the Corporation’s common stock at the lower of: (i) a 40% discount to the lowest trading price during the previous twenty (20) trading days to the date of a Conversion Notice; or (ii) 0.003. As a result of the closing of the transactions contemplated by the Stock Purchase Agreement and Convertible Note Purchase Agreement, the MGWI Note must be redeemed by the Corporation in an amount that will permit CVL and MGWI and their affiliates to hold 65% of the issued and outstanding Common Stock of the Corporation on a fully diluted basis. The proceeds from the MGWI Note were used to redeem the convertible note of the Corporation to JSJ Investments, Inc. in the principal amount of $103,000 with an interest rate of 12% per annum, due April 25, 2018. At December 31, 2019 the holder of this note beneficially owned 70% of the company and this note is not convertible if the holder holds more than 9.99%, as a result, we did not recognize a derivative liability or a beneficial conversion feature.
On June 21, 2018 the corporation entered into a promissory note with MGW Investment I Limited, for the principal amount of $250,000, with an interest rate of Eight Percent (8%) per annum and a maturity date of June 21, 2019. On May 28, 2019 this note was paid in full.
On September 21, 2018 the corporation entered into a promissory note with MGW Investment I Limited, for the principal amount of $100,000, with an interest rate of Eight Percent (8%) per annum and a maturity date of September 21, 2019. On May 28, 2019 this note was paid in full.
On February 15, 2018 we issued 9,200,000 at a purchase price of .0053 per share as additional compensation in the amount of $48,760.
On October 18, 2018 we entered into an at will employment agreement with Kambiz Mahdi our CEO. This agreement may be terminated at any time. As part of the agreement Mr. Mahdi was to be issued 20,000,000 shares of our common stock, as additional compensation. As a result; the three months ended December 31, 2019 we accrued for and subsequently on February 13, 2019, issued 20,000,000 shares at a purchase price of $.0131 per share to Mr. Mahdi in the amount of $262,000.
On January 10, 2019 the corporation entered into a promissory note with MGW Investment I Limited, for the principal amount of $25,000, with an interest rate of Eight Percent (8%) per annum and a maturity date of January 10, 2020. On May 28, 2019 this note was paid in full.
On May 1, 2019 we entered into an employment agreement with Mr. Bennett, with an annual salary of $175,000.
Subsequently on March 9, 2020, John Bennett notified Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. (the “Company”) of his resignation from his position as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer, effective March 9, 2020. Mr. Bennett will remain as a consultant to the Company and assist with maintaining the financial books and records of the Company.
On May 31, 2019, we entered into a subscription agreement pursuant to which the Company agreed to sell 168,000,000 units (each a “Unit” and together the “Units”) to MGW Investment I Limited MGWI for an aggregate purchase price of $1,999,200, or $.0119 per Unit, with each unit consisting of one share of common stock, par value $.001 per share (the “Common Stock”) and a warrant (the “Warrant”) to purchase one share of common stock. The Common Stock will be issued to MGWI at such time as the Company increases the number of shares of its authorized Common Stock. The Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
In the fourth quarter of 2019 MGW Investment I Limited, advanced $167,950, with no terms or interest rate. In the first quarter of 2020 they advanced an additional $60,000, The outstanding balance on these advances on March 31, 2020 is $227,950.
| F-22 |
Total Related Party Debt
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Total related party notes | $ | 1,320,572 | $ | 1,260,572 | ||||
| Accrued Interest | $ | 277,010 | $ | 248,838 | ||||
| Debt Discount | $ | - | $ | (29,227 | ) | |||
| Total | $ | 1,597,582 | $ | 1,480,183 | ||||
NOTE 13 - WARRANTY LIABILITY
The three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019 there was no change in our warranty liability. Due to the lack of historical warranty cost, any potential change to the warranty accrual is not material.
NOTE 14 – SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
In December 2019, a novel strain of coronavirus (COVID-19) was reported in Wuhan, China and has spread throughout the United States and the rest of the world. The World Health Organization has declared the outbreak to constitute a “Public Health Emergency of International Concern.” This contagious disease outbreak, which has not been contained, and is disrupting supply chains and affecting production and sales across a range of industries in United States and other companies as a result of quarantines, facility closures, and travel and logistics restrictions in connection with the outbreak, as well as the worldwide adverse effect to workforces, economies and financial markets, leading to a global economic downturn. Therefore, the Company expects this matter to negatively impact its operating results. However, the related financial impact and duration cannot be reasonably estimated at this time.
On June 8, 2020, Clean Energy Technology, Inc., a Nevada corporation (the “Company”), entered into an Equity Financing Agreement (“Equity Financing Agreement”) and Registration Rights Agreement (“Registration Rights Agreement”) with GHS Investments LLC, a Nevada limited liability company (“GHS”). Under the terms of the Equity Financing Agreement, GHS agreed to provide the Company with up to $2,000,000 upon effectiveness of a registration statement on Form S-1 (the “Registration Statement”) filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “Commission”)
In accordance with ASC 855, the Company has analyzed its operations subsequent to March 31, 2020 through the date these financial statements were issued, and has determined that it does not have any other material subsequent events to disclose in these financial statements.
| F-23 |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of Clean Energy Technologies Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Clean Energy Technologies Inc. and subsidiaries (“the Company”) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the financial statements). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Going Concern
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the financial statements, the Company has a significant accumulated deficit, net losses, and negative working capital and has utilized significant net cash in operations. These factors raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans in regard to these matters are also described in Note 1. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.

We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2015.
Spokane, Washington
May 27, 2020
| F-24 |
Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
| (audited) | (audited) | |||||||
| December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||
| Assets | ||||||||
| Current Assets: | ||||||||
| Cash | $ | 7,406 | $ | 6,456 | ||||
| Accounts receivable - net | 1,288,258 | 507,261 | ||||||
| Lease asset | 217,584 | 217,584 | ||||||
| Inventory | 630,204 | 711,894 | ||||||
| Total Current Assets | 2,143,452 | 1,443,195 | ||||||
| Property and Equipment - Net | 74,467 | 96 ,027 | ||||||
| Goodwill | 747,976 | 747,976 | ||||||
| License | 354,322 | 354,322 | ||||||
| Patents | 139,322 | 151,199 | ||||||
| Right of use asset - long term | 822,284 | - | ||||||
| Other Assets | 25,400 | 25,400 | ||||||
| Total Non Current assets | 2,163,711 | 1,374,924 | ||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 4,307,223 | $ | 2,818,119 | ||||
| Liabilities and Stockholders’ (Deficit) | ||||||||
| Current Liabilities: | ||||||||
| Bank Overdraft | $ | 1,480 | $ | 5,850 | ||||
| Accounts payable - trade | 1,464,363 | 1,033,375 | ||||||
| Accrued Expenses | 1,822,113 | 1,786,796 | ||||||
| Accrued Expenses Related party | 322,545 | 123,394 | ||||||
| Customer Deposits | 309,230 | 365,815 | ||||||
| Warranty Liability | 100,000 | 100,000 | ||||||
| Deferred Revenue | 47,750 | 33,000 | ||||||
| Derivative Liability | 320,794 | 245,988 | ||||||
| Lease Liability - current | 201,297 | - | ||||||
| Notes
Payable - Current (net of note discount of 80,647 and 78.907 respectively) | 3,133,199 | 2,775,090 | ||||||
| Notes
Payable - Current - Related Party (net of note discount of 29,227 and respectively 298,116 | 1,206,370 | 1,144,505 | ||||||
| Total Current Liabilities | 8,929,141 | 7,613,813 | ||||||
| Long-Term Liabilities: | ||||||||
| Lease Liability - long term | 630,560 | - | ||||||
| Net Long-Term Liabilities | 630,560 | - | ||||||
| Total Liabilities | 9,559,701 | 7,613,813 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
| Stockholders’ (Deficit) | ||||||||
| Preferred D stock, stated value $100 per share; 20,000 shares authorized; 6,500 and 7,500 outstanding respectively | 650,000 | 750,000 | ||||||
| Common stock, $.001 par value; 2,000,000,000 shares authorized; 753,907,656 and 555,582,656 shares issued and outstanding respectively | 753,909 | 555,585 | ||||||
| Shares to be issued | - | 262,000 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 7,559,331 | 5,236,456 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (14,215,718 | ) | (11,599,735 | ) | ||||
| Total Stockholders’ (Deficit) | (5,252,478 | ) | (4,795,694 | ) | ||||
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Deficit | $ | 4,307,223 | $ | 2,818,119 | ||||
The accompanying footnotes are an integral part of these financial statements
| F-25 |
Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Consolidated Statement of Operations
For the years ended December 31,
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Sales | $ | 1,610,008 | $ | 1,331,171 | ||||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 952,782 | 810,489 | ||||||
| Gross Profit | 657,226 | 520,682 | ||||||
| General and Administrative | ||||||||
| General and Administrative expense | 382,871 | 232,571 | ||||||
| Salaries | 802,951 | 740,146 | ||||||
| Professional fees | 130,709 | 142,234 | ||||||
| Travel | 246,078 | 114,534 | ||||||
| Consulting | 73,443 | 79,084 | ||||||
| Bad Debt Expense | 128,463 | 50,000 | ||||||
| Facility lease | 305,883 | 280,239 | ||||||
| Depreciation | 41,437 | 52,444 | ||||||
| Share Based Expense | - | 353,140 | ||||||
| Total Expenses | 2,111,835 | 2,044,392 | ||||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) From Operations | (1,454,609 | ) | (1,523,710 | ) | ||||
| Change in derivative liability | 216,269 | 116,259 | ||||||
| Gain / (Loss) on disposition of assets | 2,389 | |||||||
| Interest and Financing fees | (1,317,643 | ) | (1,404,955 | ) | ||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) Before Income Taxes | (2,555,983 | ) | (2,810,017 | ) | ||||
| Income Tax Expense | - | - | ||||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) | $ | (2,555,983 | ) | $ | (2,810,017 | ) | ||
| Per Share Information: | ||||||||
| Basic and diluted weighted average number of common shares outstanding | 641,349,437 | 553,354,983 | ||||||
| Net Profit / (Loss) per common share basic and diluted | $ | (0.00 | ) | $ | (0.01 | ) | ||
The accompanying footnotes are an integral part of these financial statements
| F-26 |
Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Consolidated Statement of Stockholders Equity
December 31, 2019
| Common
Stock .001 Par | Preferred Stock | Common
Stock to be issued | Additional Paid in | Accumulated | Stockholders’ Deficit | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Amount | Capital | Deficit | Totals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2017 | 210,881,122 | $ | 210,883 | $ | 7,500 | $ | 750,000 | $ | 58,000 | $ | 3,657,653 | $ | (8,789,718 | ) | $ | (4,113,182 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Shares to be issued | 4,000,000 | 4,000 | - | - | (58,000 | ) | 54,000 | - | - | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares Issued for Note conversion | 22,938,867 | 22,939 | - | - | - | 184,064 | - | 207,003 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for Services | 13,800,000 | 13,800 | - | - | - | 59,340 | - | 73,140 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for cash | 302,462,667 | 302,463 | - | - | - | 604,914 | - | 907,377 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BCF on notes payable | - | - | - | - | - | 659,985 | - | 659,985 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for services | 1,500,000 | 1,500 | - | - | - | 16,500 | - | 18,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares to be issued for compensation | - | - | - | - | 262,000 | - | - | 262,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Loss | - | - | - | - | - | - | (2,810,017 | ) | (2,810,017 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018 | 555,582,656 | $ | 555,585 | $ | 7,500 | $ | 750,000 | $ | 262,000 | $ | 5,236,456 | $ | (11,599,735 | ) | $ | (4,795,694 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for compensation | 20,000,000 | 20,000 | (262,000 | ) | 242,000 | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares returned from admin. hold | 75,000 | 75 | - | - | - | (75 | ) | - | - | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prefered shares reclassed | - | - | (200 | ) | (20,000 | ) | - | 20,000 | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for Preferred stock conversion | 4,000,000 | 4,000 | (800 | ) | (80,000 | ) | - | 136,000 | (60,000 | ) | - | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued for cash | 174,250,000 | 174,249 | - | - | 1,924,950 | - | 2,099,199 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Loss | (2,555,983 | ) | (2,555,983 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | 753,907,656 | 753,909 | 6,500 | 650,000 | - | 7,559,331 | (14,215,718 | ) | (5,252,478 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
The accompanying footnotes are an integral part of these financial statements
| F-27 |
Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
For the years ended December 31,
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities: | ||||||||
| Net Income / ( Loss ) | $ | (2,555,983 | ) | $ | (2,810,017 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 41,437 | 52,444 | ||||||
| Share based compensation | - | 353,140 | ||||||
| Bad debt expense | 128,463 | 50,000 | ||||||
| Gain on disposal of fixed assets | - | (2,389 | ) | |||||
| Financing fees and debt discount | 86,756 | 447,672 | ||||||
| Change in derivative liability | 269,732 | 116,259 | ||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
| (Increase) decrease in right of use asset | (822,284 | ) | - | |||||
| (Increase) decrease in lease liability | 831,857 | - | ||||||
| (Increase) decrease in accounts receivable | (909,460 | ) | (297,764 | ) | ||||
| (Increase) decrease in inventory | 81,690 | 142,653 | ||||||
| (Increase) decrease in other assets | (1,171 | ) | ||||||
| (Decrease) increase in accounts payable | 430,988 | 36,901 | ||||||
| Other (Decrease) increase in accrued expenses | 35,320 | 169,152 | ||||||
| Other (Decrease) increase in accrued expenses related party | 199,151 | |||||||
| Other (Decrease) increase in deferred revenue | 14,750 | 33,000 | ||||||
| Other (Decrease) increase in customer deposits | (56,585 | ) | 267,221 | |||||
| Net Cash Used In Operating Activities | (2,224,168 | ) | (1,442,899 | ) | ||||
| Cash Flows from Investing Activities | ||||||||
| Purchase property plant and equipment | (8,000 | ) | - | |||||
| Cash Flows Used In Investing Activities | (8,000 | ) | - | |||||
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities | ||||||||
| Bank Overdraft / (Repayment) | (4,370 | ) | (5,013 | ) | ||||
| Payments on notes payable | (277,685 | ) | (218,295 | ) | ||||
| Payments on notes payable related party | (375,000 | ) | - | |||||
| Proceeds from notes payable and lines of credit | 598,024 | 755,868 | ||||||
| Proceeds from notes payable related party | 192,950 | |||||||
| Stock issued for cash | 2,099,199 | 907,377 | ||||||
| Cash Flows Provided By Financing Activities | 2,233,118 | 1,439,937 | ||||||
| Net (Decrease) Increase in Cash and Cash Equivalents | 950 | (2,962 | ) | |||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at Beginning of Period | 6,456 | 9,418 | ||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at End of Period | $ | 7,406 | $ | 6,456 | ||||
| Supplemental Cashflow Information: | ||||||||
| Interest Paid | $ | 543,220 | $ | 328,862 | ||||
| Taxes Paid | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
| Supplemental Non-Cash Disclosure | ||||||||
| Shares issued for Services | $ | - | $ | 353,140 | ||||
| Shares issued for Accounts payable paid in shares | $ | - | $ | 35,368 | ||||
| Shares issued for preferred conversions | $ | 80,000 | $ | - | ||||
| Shares issued for note conversions | $ | - | $ | 171,635 | ||||
The accompanying footnotes are an integral part of these financial statements
| F-28 |
Clean Energy Technologies, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Notes 1- GENERAL
Corporate History
With the vision to combat climate change and creating a better, cleaner and environmentally sustainable future Clean Energy HRS LLC a wholly owned subsidiary of Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. acquired the assets of Heat Recovery Solutions from General Electric International on September 11, 2015. The GE HRS asset acquisition and related financing transactions resulted in a change of control of the Company according to FASB No. 2014-17 Business Combinations (Topic 805). As a result, the transactions qualify as a business combination. In accordance with Topic 805, the Company elected to apply pushdown accounting, using the valuation date of December 31, 2015. As a result we recognized $747,976 in goodwill.
General Electric acquired the rights and 16 global patents to the magnetic bearing technology from Calnetix in October of 2010 and further developed the next generation of the waste heat generators, which was ultimately acquired by Clean Energy Technologies from GE. We completed our production facility post the acquisition in October of 2016. We consolidated our legacy and HRS operations and began our production in early 2017. In early 2018 we engaged with a large institutional equity partner and closed our first round of funding. We are successfully executing on our business strategy by increasing our market presence and broadening our product portfolio in the heat to power markets. We’re continuing to design, build and ship products to Europe, US, Canada, South East Pacific regions and planned expansion into Asia. We are continuing to build a strong back log and pipeline of opportunities while developing the next disruptive heat to power generators with the support of our new equity partners.
Going Concern
The financial statements have been prepared on a going concern basis, which contemplates continuity of operations, realization of assets and liquidation of liabilities in the normal course of business. The Company had a total stockholder’s deficit of $5,252,478 and a working capital deficit of $6,785,689 and a net loss of $2,555,983 for the year ended December 31, 2019. The company also had an accumulated deficit of $14,215,718 as of December 31, 2019 and used $2,224,168 in net cash from operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2019. Therefore, there is substantial doubt about the ability of the Company to continue as a going concern. There can be no assurance that the Company will achieve its goals and reach profitable operations and is still dependent upon its ability (1) to obtain sufficient debt and/or equity capital and/or (2) to generate positive cash flow from operations.
Plan of Operation
Our marketing approach is to position CETY as a worldwide leader in the heat to power & energy efficiency markets by targeting industries that have wasted heat which could potentially turn into electricity.
We are leveraging our proprietary magnetic bearing turbine technology and over 100 installation with 1 million fleet operating to increase our market share in low to medium temperature waste heat recovery markets.
We utilize both a direct sales force and global distribution group with expertise in heat recovery solutions and clean energy markets. We have also established relationships with integrators, consultant and project developers and integrated solution providers.
We plan to leverage our core expertise to identify, acquire and develop leading clean energy and clean technology solutions and products. We will continue to utilize our relationships and expertise to expand in clean and renewable energy sector through new in-house development of disruptive heat to power technologies, acquisitions, cogeneration, and licensing agreements.
CETY maintains an online presence through our web portal and social media. Our application engineers assist in converting the opportunities into projects. We provide technical support to our Clean Cycle TM generator clients through providing maintenance and product support.
The sales of our products are related to the global prices for oil, gas, coal and solar energy. As prices increase our products produce a better return on investment for our customers. They are also dependent on regulatory drivers and financial incentives.
CETY has implemented a new Enterprise Resource planning software by Microsoft providing accurate and timely information to support a more robust and efficient supply chain. The operational leadership is continually working on lowering the cost of manufacturing and identifying lower cost regions to support higher margins of our products.
NOTE 2 – BASIS OF PRESENTATION AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES:
The summary of significant accounting policies of Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. (formerly Probe Manufacturing, Inc.) is presented to assist in the understanding of the Company’s financial statements. The financial statements and notes are representations of the Company’s management, who is responsible for their integrity and objectivity.
The consolidated financial statements and related notes have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“US GAAP”) and include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All material intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Such estimates may be materially different from actual financial results. Significant estimates include the recoverability of long-lived assets, the collection of accounts receivable and valuation of inventory and reserves.
| F-29 |
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We maintain the majority of our cash accounts at a commercial bank. The total cash balance is insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”) up to $250,000 per commercial bank. For purposes of the statement of cash flows we consider all cash and highly liquid investments with initial maturities of one year or less to be cash equivalents.
Accounts Receivable
We grant credit to our customers located within the United States of America; and do not require collateral. Our ability to collect receivables is affected by economic fluctuations in the geographic areas and industries served by us. Reserves for un-collectable amounts are provided, based on past experience and a specific analysis of the accounts. Although we expect to collect amounts due, actual collections may differ from the estimated amounts. As of December 31, 2019, and December 31, 2018, we had a reserve for potentially un-collectable accounts of $82,000 and $57,000. Five (5) customers accounted for approximately 98% of accounts receivable at December 31, 2019. Our trade accounts primarily represent unsecured receivables. Historically, our bad debt write-offs related to these trade accounts have been insignificant. For the year ended December 31, 2019, our bad debt expense was $128,463 compared to $50,000 for the same period in 2018. This increase was mainly due to increase a bad debt write off $103,463 and an increase in reserve for bad debt of $25,000. We also had one customer that accounted for 74% and 2 customers that accounted for 92% of our accounts receivable December 31, 2019. We also had one customer that accounted for 59% of our revenue for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Lease asset
As of December 31, 2019, and 2018 we had a lease asset that was purchased from General electric with a value of $1,309,527, however due the the purchase price allocation, we recognized a value of $217,584. The lease is due to be commissioned in the third quarter of 2020 and will generate approximately $20,000 per month for 120 months. See note 3 for additional information.
Inventory
Inventories are valued at the lower of weighted average cost or market value. Our industry experiences changes in technology, changes in market value and availability of raw materials, as well as changing customer demand. We make provisions for estimated excess and obsolete inventories based on regular audits and cycle counts of our on-hand inventory levels and forecasted customer demands and at times additional provisions are made. Any inventory write offs are charged to the reserve account. As of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, we had a reserve for potentially obsolete inventory of $250,000.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are recorded at cost. Assets held under capital leases are recorded at lease inception at the lower of the present value of the minimum lease payments or the fair market value of the related assets. The cost of ordinary maintenance and repairs is charged to operations. Depreciation and amortization are computed on the straight-line method over the following estimated useful lives of the related assets:
| Furniture and fixtures | 3 to 7 years | |
| Equipment | 7 to 10 years | |
| Leasehold Improvements | 7 years |
| F-30 |
Long –Lived Assets
Our management assesses the recoverability of its long-lived assets by determining whether the depreciation and amortization of long lived assets over their remaining lives can be recovered through projected undiscounted future cash flows. The amount of long-lived asset impairment if any, is measured based on fair value and is charged to operations in the period in which long-lived assets impairment is determined by management. There can be no assurance however, that market conditions will not change or demand for our services will continue, which could result in impairment of long-lived assets in the future.
Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue under ASU No. 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606),” (“ASC 606”).
Performance Obligations Satisfied Over Time
FASB ASC 606-10-25-27 through 25-29, 25-36 through 25-37, 55-5 through 55-10
An entity transfers control of a good or service over time and satisfies a performance obligation and recognizes revenue over time if one of the following criteria is met:
a. The customer receives and consumes the benefits provided by the entity’s performance as the entity performs (as described in FASB ASC 606-10-55-5 through 55-6).
b. The entity’s performance creates or enhances an asset (for example, work in process) that the customer controls as the asset is created or enhanced (as described in FASB ASC 606-10-55-7).
c. The entity’s performance does not create an asset with an alternative use to the entity (see FASB ASC 606-10-25-28), and the entity has an enforceable right to payment for performance completed to date (as described in FASB ASC 606-10-25-29).
Performance Obligations Satisfied at a Point in Time
FASB ASC 606-10-25-30
If a performance obligation is not satisfied over time, the performance obligation is satisfied at a point in time. To determine the point in time at which a customer obtains control of a promised asset and the entity satisfies a performance obligation, the entity should consider the guidance on control in FASB ASC 606-10-25-23 through 25-26. In addition, it should consider indicators of the transfer of control, which include, but are not limited to, the following:
a. The entity has a present right to payment for the asset
b. The customer has legal title to the asset
c. The entity has transferred physical possession of the asset
d. The customer has the significant risks and rewards of ownership of the asset
e. The customer has accepted the asset
The core principle of the revenue standard is that a company should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. The Company only applies the five-step model to contracts when it is probable that the Company will collect the consideration it is entitled to in exchange for the goods and services transferred to the customer. In Addition a) the company also does not have an alternative use for the asset if the customer were to cancel the contract, and b.) has a fully enforceable right to receive payment for work performed (i.e., customers are required to pay as various milestones and/or timeframes are met)
The following five steps are applied to achieve that core principle for our HRS and Cety Europe Divisions:
| ● | Identify the contract with the customer |
| ● | Identify the performance obligations in the contract |
| F-31 |
| ● | Determine the transaction price |
| ● | Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract |
| ● | Recognize revenue when the company satisfies a performance obligation |
The following steps are applied to our legacy engineering and manufacturing division:
| ● | We generate a quotation |
| ● | We receive Purchase orders from our customers. |
| ● | We build the product to their specification |
| ● | We invoice at the time of shipment |
| ● | The terms are typically Net 30 days |
Also, from time to time our contracts state that the customer is not obligated to pay a final payment until the units are commissioned, i.e. a final payment of 10%. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018 we had $47,750 and 33,000 of deferred revenue, which is expected to be recognized in the third quarter of year 2020. There is an additional ~$150,000 to be billed for labor/installation/commissioning services per the customer contracts outstanding as of 12/31/19.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Financial Accounting Standards Board issued ASC (Accounting Standards Codification) 820-10 (SFAS No. 157), “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures” for financial assets and liabilities. ASC 820-10 provides a framework for measuring fair value and requires expanded disclosures regarding fair value measurements. FASB ASC 820-10 defines fair value as the price that would be received for an asset or the exit price that would be paid to transfer a liability in the principal or most advantageous market in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. FASB ASC 820-10 also establishes a fair value hierarchy which requires an entity to maximize the use of observable inputs, where available. The following summarizes the three levels of inputs required by the standard that the Company uses to measure fair value:
| ● | Level 1: Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| ● | Level 2: Observable inputs other than Level 1 prices such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities; quoted prices in markets that are not active or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the related assets or liabilities. |
| ● | Level 3: Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities. The Company’s derivative liabilities have been valued as Level 3 instruments. We value the derivative liability using a lattice model, with a volatility of 112% and using a risk free interest rate of 2.54% |
The Company’s financial instruments consist of cash, prepaid expenses, inventory, accounts payable, convertible notes payable, advances from related parties, and derivative liabilities. The estimated fair value of cash, prepaid expenses, investments, accounts payable, convertible notes payable and advances from related parties approximate their carrying amounts due to the short-term nature of these instruments.
The carrying amounts of the Company’s financial instruments as of December 31 2018 and 2019, reflect:
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| Fair value of convertible notes derivative liability – December 31, 2018 | $ | – | $ | – | $ | 245,988 | $ | 245,988 | ||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| Fair value of convertible notes derivative liability – December 31, 2019 | $ | – | $ | – | $ | 320,794 | $ | 320,794 | ||||||||
The carrying amount of accounts payable and accrued expenses are considered to be representative of their respective fair values because of the short-term nature of these financial instruments.
| F-32 |
Other Comprehensive Income
We have no material components of other comprehensive income (loss) and accordingly, net loss is equal to comprehensive loss in all periods.
Net Profit (Loss) per Common Share
Basic profit / (loss) per share is computed on the basis of the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. At December 31, 2019, we had outstanding common shares of 753,907,656 used in the calculation of basic earnings per share. Basic Weighted average common shares and equivalents at December 31, 2019 and 2018 were 641,349,437 and 553,354,983, respectively. As of December 31, 2019, we had convertible notes, convertible into approximately 411,446,077 of additional common shares, outstanding preferred shares convertible into 8,125,000, calculated @ $.08 of additional common shares and 174,250,000 common stock warrants convertible into an additional. Fully diluted weighted average common shares and equivalents were withheld from the calculation as they were considered anti-dilutive.
Research and Development
We had no amounts of research and development R&D expense during the year ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
Segment Disclosure
FASB Codification Topic 280, Segment Reporting, establishes standards for reporting financial and descriptive information about an enterprise’s reportable segments. The Company has three reportable segments: Clean Energy HRS (HRS), Cety Europe and the legacy electronic manufacturing services division. The segments are determined based on several factors, including the nature of products and services, the nature of production processes, customer base, delivery channels and similar economic characteristics. Refer to note 1 for a description of the various product categories manufactured under each of these segments. Prior to March 31, 2017 we only had one reporting segment.
An operating segment’s performance is evaluated based on its pre-tax operating contribution, or segment income. Segment income is defined as net sales less cost of sales, and segment selling, general and administrative expenses, and does not include amortization of intangibles, stock-based compensation, other charges (income), net and interest and other, net.
Selected Financial Data:
| Years ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Net Sales | ||||||||
| Engineering and Manufacturing | 513,919 | 567,417 | ||||||
| Clean Energy HRS | 1,012,895 | 752,783 | ||||||
| CETY Europe | 83,194 | 10,971 | ||||||
| Total Sales | 1,610,008 | 1,331,171 | ||||||
| Segment income and reconciliation before tax | ||||||||
| Engineering and Manufacturing | 150,741 | 56,231 | ||||||
| Clean Energy HRS | 428,445 | 457,978 | ||||||
| CCETY Europe | 78,040 | 6,473 | ||||||
| Total Segment income | 657,226 | 520,682 | ||||||
| Reconciling items | ||||||||
| General and Administrative expense | (382,871 | ) | (232,571 | ) | ||||
| Salaries | (802,951 | ) | (740,146 | ) | ||||
| Professional fees | (130,709 | ) | (142,234 | ) | ||||
| Travel | (246,078 | ) | (114,534 | ) | ||||
| Consulting | (73,443 | ) | (79,084 | ) | ||||
| Bad debt expense | (128,463 | (50,000 | ) | |||||
| Facility lease | (305,883 | ) | (280,239 | ) | ||||
| Depreciation | (41,437 | ) | (52,444 | ) | ||||
| Share Based Expense | - | (353,140 | ) | |||||
| Change in derivative liability | 216,269 | 116,259 | ||||||
| Gain / (Loss) on disposition of assets | - | 2,389 | ||||||
| Interest Expense | (1,317,643 | ) | (1,404,955 | ) | ||||
| Net Loss before income tax | (2,555,983 | ) | (2,810,017 | ) | ||||
| December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||
| Total Assets | ||||||||
| Electronics Assembly | 1,877,916 | 1,029,129 | ||||||
| Clean Energy HRS | 2,405,628 | 1,777,354 | ||||||
| Cety Europe | 23,679 | 11,636 | ||||||
| Total Assets | 4,307,223 | 2,818,119 | ||||||
| F-33 |
Share-Based Compensation
The Company has adopted the use of Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 123R, “Share-Based Payment” (SFAS No. 123R) (now contained in FASB Codification Topic 718, Compensation-Stock Compensation), which supersedes APB Opinion No. 25, “Accounting for Stock Issued to Employees,” and its related implementation guidance and eliminates the alternative to use Opinion 25’s intrinsic value method of accounting that was provided in Statement 123 as originally issued. This Statement requires an entity to measure the cost of employee services received in exchange for an award of an equity instruments, which includes grants of stock options and stock warrants, based on the fair value of the award, measured at the grant date (with limited exceptions). Under this standard, the fair value of each award is estimated on the grant date, using an option-pricing model that meets certain requirements. We use the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to estimate the fair value of our equity awards, including stock options and warrants. The Black-Scholes model meets the requirements of SFAS No. 123R; however, the fair values generated may not reflect their actual fair values, as it does not consider certain factors, such as vesting requirements, employee attrition and transferability limitations. The Black-Scholes model valuation is affected by our stock price and a number of assumptions, including expected volatility, expected life, risk-free interest rate and expected dividends. We estimate the expected volatility and estimated life of our stock options at grant date based on historical volatility. For the “risk-free interest rate,” we use the Constant Maturity Treasury rate on 90-day government securities. The term is equal to the time until the option expires. The dividend yield is not applicable, as the Company has not paid any dividends, nor do we anticipate paying them in the foreseeable future. The fair value of our restricted stock is based on the market value of our free trading common stock, on the grant date calculated using a 20-trading-day average. At the time of grant, the share-based compensation expense is recognized in our financial statements based on awards that are ultimately expected to vest using historical employee attrition rates and the expense is reduced accordingly. It is also adjusted to account for the restricted and thinly traded nature of the shares. The expense is reviewed and adjusted in subsequent periods if actual attrition differs from those estimates.
We re-evaluate the assumptions used to value our share-based awards on a quarterly basis and, if changes warrant different assumptions, the share-based compensation expense could vary significantly from the amount expensed in the past. We may be required to adjust any remaining share-based compensation expense, based on any additions, cancellations or adjustments to the share-based awards. The expense is recognized over the period during which an employee is required to provide service in exchange for the award—the requisite service period (usually the vesting period). No compensation cost is recognized for equity instruments for which employees do not render the requisite service. For the year ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 we had $0 and $353,140 respectively, in share-based expense, due to the issuance of common stock. As of December 31, 2019, we had no further non-vested expense to be recognized.
| F-34 |
Income Taxes
Federal Income taxes are not currently due since we have had losses since inception.
On December 22, 2018 H.R. 1, originally known as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, (the “Tax Act”) was enacted. Among the significant changes to the U.S. Internal Revenue Code, the Tax Act lowers the U.S. federal corporate income tax rate (“Federal Tax Rate”) from 35% to 21% effective January 1, 2018. The Company will compute its income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2019 using a Federal Tax Rate of 21%.
Income taxes are provided based upon the liability method of accounting pursuant to ASC 740-10-25 Income Taxes – Recognition. Under this approach, deferred income taxes are recorded to reflect the tax consequences in future years of differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their financial reporting amounts at each year-end. A valuation allowance is recorded against deferred tax assets if management does not believe the Company has met the “more likely than not” standard required by ASC 740-10-25-5.
Deferred income tax amounts reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax reporting purposes.
As of December 31, 2019, we had a net operating loss carry-forward of approximately $(5,366,000) and a deferred tax asset of $1,126,860 using the statutory rate of 21%. The deferred tax asset may be recognized in future periods, not to exceed 20 years. However, due to the uncertainty of future events we have booked valuation allowance of $(1,126,860). FASB ASC 740 prescribes recognition threshold and measurement attributes for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. FASB ASC 740 also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification, interest and penalties, accounting in interim periods, disclosure and transition. At December 31, 2019 the Company had not taken any tax positions that would require disclosure under FASB ASC 740.
| December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||
| Deferred Tax Asset | $ | 1,126,860 | $ | 515,944 | ||||
| Valuation Allowance | (1,126,860 | ) | (515,944 | ) | ||||
| Deferred Tax Asset (Net) | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
On February 13, 2018 , Clean Energy Technologies, Inc., a Nevada corporation (the “Registrant” or “Corporation”) entered into a Common Stock Purchase Agreement (“Stock Purchase Agreement”) by and between MGW Investment I Limited (“MGWI”) and the Corporation. The Corporation received $907,388 in exchange for the issuance of 302,462,667 restricted shares of the Corporation’s common stock, par value $.001 per share (the “Common Stock”).
On February 13, 2018 the Corporation and Confections Ventures Limited. (“CVL”) entered into a Convertible Note Purchase Agreement (the “Convertible Note Purchase Agreement,” together with the Stock Purchase Agreement and the transactions contemplated thereunder, the “Financing”) pursuant to which the Corporation issued to CVL a convertible promissory Note (the “CVL Note”) in the principal amount of $939,500 with an interest rate of 10% per annum interest rate and a maturity date of February 13, 2020. The CVL Note is convertible into shares of Common Stock at $0.003 per share, as adjusted as provided therein. This note was assigned to MGW Investments.
This resulted in a change in control, which limited the net operating to that date forward. We are subject to taxation in the U.S. and the states of California. Further, the Company currently has no open tax years’ subject to audit prior to December 31, 2015. The Company is current on its federal and state tax returns.
Reclassification
Certain amounts in the prior period financial statements have been reclassified to conform to the current period presentation. These reclassifications had no effect on reported income, total assets, or stockholders’ equity as previously reported.
| F-35 |
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
The Company is reviewing the effects of following recent updates. The Company has no expectation that any of these items will have a material effect upon the financial statements.
In June 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2016-13, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses [codified as Accounting Standards Codification Topic (ASC) 326]. ASC 326 adds to US generally accepted accounting principles (US GAAP) the current expected credit loss (CECL) model, a measurement model based on expected losses rather than incurred losses. Under this new guidance, an entity recognizes its estimate of expected credit losses as an allowance, which the FASB believes will result in more timely recognition of such losses. This will become effective in January 2023 and will have minimal impact on the company.
NOTE 3 – ACCOUNTS AND NOTES RECEIVABLE
| December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2017 | |||||||
| Accounts Receivable | $ | 1,370,258 | $ | 564,261 | ||||
| Less Reserve for uncollectable accounts | (82,000 | ) | (57,000 | ) | ||||
| Accounts Receivable (Net) | $ | 1,288,258 | $ | 507,261 | ||||
Our Accounts Receivable is pledged to Nations Interbanc, our line of credit.
| December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2017 | |||||||
| Lease asset | $ | 217,584 | $ | 217,584 | ||||
The Company is currently modifying the assets subject to lease to meet the provisions of the agreement, and as of December 31, 2019 any collection on the lease payments was not yet considered probable, resulting in no derecognition of the underlying asset and no net lease investments recognized on the sales-type lease pursuant to ASC 842-30-25-3.
| F-36 |
NOTE 4 – INVENTORY
Inventories by major classification were comprised of the following at:
| December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||
| Raw Material | $ | 848,464 | $ | 952,214 | ||||
| Work in Process | 31,740 | 9,680 | ||||||
| Total | 880,204 | 961,894 | ||||||
| Less reserve for excess or obsolete inventory | (250,000 | ) | (250,000 | ) | ||||
| Inventory | $ | 630,204 | $ | 711,894 | ||||
Our Inventory is pledged to Nations Interbanc, our line of credit.
NOTE 5 – PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
Property and equipment were comprised of the following at:
| December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||
| Capital Equipment | $ | 1,350,794 | $ | 1,342,794 | ||||
| Leasehold improvements | 75,436 | 75,436 | ||||||
| Accumulated Depreciation | (1,351,763 | ) | (1,322,203 | ) | ||||
| Net Fixed Assets | $ | 74,467 | $ | 96,027 | ||||
Our Depreciation Expense for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 was $29,560 and $40,567 respectively.
Our Property Plant and Equipment is pledged to Nations Interbanc, our line of credit.
NOTE 6 – INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Intangible assets were comprised of the following at:
| December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||
| Goodwill | $ | 747,976 | $ | 747,976 | ||||
| License | 354,322 | 354,322 | ||||||
| Patents | 190,789 | 190,789 | ||||||
| Accumulated Amortization | (51,467 | ) | (39,590 | ) | ||||
| Net Intangible Assets | $ | 1,241,620 | $ | 1,253,497 | ||||
Our Amortization Expense for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 was $11,877 and 11,877 respectively.
| F-37 |
NOTE 7 – ACCRUED EXPENSES
| December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||
| Accrued Wages | $ | 192,227 | $ | 224,514 | ||||
| Accrued Interest | 607,736 | 466,425 | ||||||
| Accrued Interest Related party | 248,838 | 123,394 | ||||||
| Customer Deposits | 309,230 | 365,815 | ||||||
| Accrued Payable to GE - TSA | 972,231 | 972,231 | ||||||
| Accrued Rents and Moving Expenses | 123,626 | 123,626 | ||||||
| $ | 2,453,888 | $ | 2,276,005 | |||||
NOTE 8 – NOTES PAYABLE
The Company issued a short-term note payable to an individual, secured by the assets of the Company, dated September 6, 2013 in the amount of $50,000 and fixed fee amount of $3,500. As of December 31, 2019 the outstanding balance was $36,500. Subsequently, on January 30, 2020 we issued 1,700,000 shares of our common stock at a purchase price of $.02 per share, as settlement in full of a note payable of in the amount of $36,500 with accrued interest of 19,721. As a result we recognized a gain in the amount of $22,221 in the 1st quarter of 2020.
On November 11, 2013, we entered in to an accounts receivable financing agreement with American Interbanc (now Nations Interbanc). Amounts outstanding under the agreement bear interest at the rate of 2.5% per month. It is secured by the assets of the Company. In addition, it is personally guaranteed by Kambiz Mahdi, our Chief Executive Officer. As of December 31, 2019, the outstanding balance was $1,602,549 compared to $1,170,462 at December 31, 2018.
On September 11, 2015, our CE HRS subsidiary issued a promissory note in the initial principal amount $1,400,000 and assumed a pension liability of $100,000, for a total liability of $1,500,000, in connection with our acquisition of the heat recovery solutions, or HRS, assets of General Electric International, Inc., a Delaware corporation (“GEII”), including intellectual property, patents, trademarks, machinery, equipment, tooling and fixtures. The note bears interest at the rate of 2.66% per annum. The note is payable on the following schedule: (a) $200,000 in principal on December 31, 2015 and (b) thereafter, the remaining principal amount of $1,200,000, together with interest thereon, payable in equal quarterly installments of principal and interest of $157,609, commencing on December 31, 2016 and continuing until December 31, 2018, at which time the remaining unpaid principal amount of this note and all accrued and unpaid interest thereon shall be due and payable in full
We are currently in default on the payment of the purchase price pursuant to our asset purchase agreement with General Electric due to a combination of our inability to raise sufficient capital as expected and our belief that we are entitled to a reduction in purchase price we paid. We are in the process of negotiations with General Electric.
Convertible notes
On May 5, 2017 we entered into a nine-month convertible note payable for $78,000, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is not convertible until nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of sixty one percent (61%) of the lowest closing bid price (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. On November 6, 2017 this note was assumed and paid in full at a premium for a total of $116,600 by Cybernaut Zfounder Ventures. An amended term were added to the original note with the interest rate of 14%. This note matured on February 21st of 2018 and is currently in default.
| F-38 |
On May 24, 2017 we entered into a nine-month convertible note payable for $32,000, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is not convertible until nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of fifty-five eight percent (58%) of the lowest closing bid price (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. On November 6, 2017 this note was assumed and paid in full at a premium for a total of $95,685, by Cybernaut Zfounder Ventures. An amended term was added to the original note with the interest rate of 14%. This note matured on February 26th, 2018 and is currently in default.
On September 13, 2017 we entered into a nine-month convertible note payable for $110,000, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is not convertible until nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of fifty-five percent (55%) of the lowest closing bid price (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the twenty-five (25) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. This note was partially converted into common stock and the balance was paid in full on February 14, 2018
On August 17, 2017 we entered into a convertible note payable for $68,000, with a maturity date of May 30, 2018, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is not convertible until nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of fifty-eight percent (58%) of the average of the two lowest trading prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. This note was paid in full on February 15, 2018
On July 25, 2017 we entered into a convertible note payable for $103,000, with a maturity date of April 25, 2018, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is not convertible until nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of ninety percent (60%) of the average of the two lowest trading prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the twenty (20) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. This note was paid in full on February 15, 2018
On December 13, 2018 we entered into a convertible note payable for $83,000, with a maturity date of December 13, 2019, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is convertible six months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of fifty-eight percent (65%) of the average of the two lowest trading prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. On May 28, 2019 this note was paid in full.
February 13, 2019 we entered into a convertible note payable for $138,000, with a maturity date of February 13, 2020, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is not convertible six months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of fifty-eight percent (65%) of the average of the two lowest trading prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. On August 12, 2019 this note was paid in full. The fair value of the convertible feature was $513,829, we recorded a debt discount of $138,000 and an additional loss of $375,828. As of December 31, 2019 the un-amortized debt discount was $0. The total amortized debt discount expense was $138,000.
On April 9, 2019 we entered into a convertible note payable for $53,000, with a maturity date of April 9, 2020, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is convertible nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of sixty-five percent (65%) of the average of the two lowest closing prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. This note was paid in full on October 10, 2019. The fair value of the convertible feature was $55,604, we recorded a debt discount of $53,000 and an additional loss of $2,604. As of December 31, 2019 the un-amortized debt discount was $0. The total amortized debt discount expense was $53,000.
| F-39 |
On October 30, 2019 we entered into a convertible note payable for $103,000, with a maturity date of October 30, 2020, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is convertible nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of sixty-five percent (65%) of the average of the two lowest closing prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. We also entered into a stock purchase agreement for the potential conversion into common stock. Subsequently that note was paid in full on May 1, 2020. The fair value of the convertible feature was $97,471, we recorded a debt discount of $97,471 and an additional loss of $0. As of December 31, 2019 the un-amortized debt discount was $80,647. The total amortized debt discount expense was $16,824.
Note 9 – Derivative Liabilities
As a result of the convertible notes we recognized the embedded derivative liability on the date of note issuance. We also revalued the remaining derivative liability on the outstanding note balance on the date of the balance sheet. We value the derivative liability using a binomial lattice model with an expected volatility range of 85% to 92% and a risk-free interest rate range of 1.60% to 1.64%. The remaining derivative liabilities were:
| December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | |||||||
| Derivative Liabilities on Convertible Loans: | ||||||||
| Outstanding Balance | $ | 320,794 | $ | 245,988 | ||||
| Derivative Liability December 31, 2018 | $ | 245,988 | ||
| Additions | 666,904 | |||
| Fair market value adjustments | (592,098 | ) | ||
| Derivative Liability December 31, 2019 | 320,794 |
NOTE 10 – COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
The company has received an invoice from Oberon Securities for $291,767 which is in dispute. The company believes it has defenses to the claim for compensation and plans to assert appropriate counterclaims and actions as permitted by law. No liability has been recorded for this claim as the Company believes there is a greater than not probability that our Company will prevail in defending against the claim.
Operating Rental Leases
As of May 1, 2017, our corporate headquarters are located at 2990 Redhill Unit A, Costa Mesa, CA. On March 10, 2017, the Company signed a lease agreement for a 18,200-square foot CTU Industrial Building. Lease term is seven years and two months beginning July 1, 2017. Future minimum lease payments for the years ending December 31, are: In October of 2018 we signed a sublease agreement with our facility in Italy with an indefinite term that may be terminated by either party with a 60 day notice for 1,000 Euro per month. Due to the short termination clause, we are treating this as a month to month lease.
| Year | Lease Payment | |||
| 2020 | $ | 241,884 | ||
| 2021 | $ | 249,132 | ||
| 2022 | $ | 256,608 | ||
| 2023 | $ | 44,052 | ||
| Imputed Interest | $ | 40,181 | ||
| Net Lease Liability | $ | 831,857 | ||
| F-40 |
Our lease expense for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 was $305,883 and $280,239 respectively.
ASB ASU 2016-02 “Leases (Topic 842)” – In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, which requires lessees to recognize almost all leases on their balance sheet as a right-of-use asset and a lease liability. For income statement purposes, the FASB retained a dual model, requiring leases to be classified as either operating or finance. Classification will be based on criteria that are largely similar to those applied in current lease accounting, but without explicit bright lines. Lessor accounting is similar to the current model, but has been updated to align with certain changes to the lessee model and the new revenue recognition standard. This ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years. We have adopted the above ASU as of January 1, 2019. The right of use asset and lease liability have been recorded at the present value of the future minimum lease payments, utilizing a 5% average borrowing rate and the company is utilizing the transition relief and “running off” on current leases.
Severance Benefits
Mr. Mahdi will receive a severance benefit consisting of a single lump sum cash payment equal the salary that Mr. Mahdi would have been entitled to receive through the remainder or the Employment Period or One (1) year, whichever is greater.
Mr. Bennett will receive a severance benefit consisting of a single lump sum cash payment equal the salary that Mr. Bennett would have been entitled to receive through the remainder or the Employment Period or One (1) year, whichever is greater. Subsequently on March 9, 2020, John Bennett notified Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. (the “Company”) of his resignation from his position as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer, effective March 9, 2020. Mr. Bennett will remain as a consultant to the Company and assist with maintaining the financial books and records of the Company. As a result, Mr. Bennett is no longer entitled to any severance benefits.
NOTE 11 – CAPITAL STOCK TRANSACTIONS
On April 21, 2005, our Board of Directors and shareholders approved the re-domicile of the Company in the State of Nevada, in connection with which we increased the number of our authorized common shares to 200,000,000 and designated a par value of $.001 per share.
On May 25, 2006, our Board of Directors and shareholders approved an amendment to our Articles of Incorporation to authorize a new series of preferred stock, designated as Series C, and consisting of 15,000 authorized shares.
On June 30, 2017, our Board of Directors and shareholders approved an increase in the number of our authorized common shares to 400,000,000 and in the number of our authorized preferred shares to 10,000,000. The amendment effecting the increase in our authorized capital was filed and effective on July 5, 2017.
On August 28, 2018, our Board of Directors and shareholders approved an increase in the number of our authorized common shares to 800,000,000. The amendment effecting the increase in our authorized capital was filed and effective on August 23, 2018.
On June 10, 2019, our Board of Directors and shareholders approved an increase in the number of our authorized common shares to 2,000,000,000. The amendment effecting the increase in our authorized capital was effective on September 27, 2019.
Common Stock Transactions
On February 13, 2018, Clean Energy Technologies, Inc., a Nevada corporation (the “Registrant” or “Corporation”) entered into a Common Stock Purchase Agreement (“Stock Purchase Agreement”) by and between MGW Investment I Limited (“MGWI”) and the Corporation. The Corporation received $907,377 in exchange for the issuance of 302,462,667 restricted shares of the Corporation’s common stock, par value $.001 per share (the “Common Stock”), as disclosed on form 8K on February 15, 2018.
From January 1 through September 30, 2018 we issued 26,054,672 for partial conversions of our convertible notes. We also issued 13,800,000 shares for additional compensation and 1,500,000 for consulting services.
On October 9, 2018 we issued 884,195 shares at a purchase price of .04 per share for payment of an accounts payable in the amount of $35,367.
February 13, 2019, we issued 20,000,000 at a purchase price of $.0131 per share to Kambiz Mahdi our CEO as additional compensation accrued for in 2018 in the amount of $262,000.
In the first quarter of 2019, we signed agreements to issue 4,000,000 shares of common stock valued at $.015 for a total value of $60,000 for the conversion of 800 preferred series D shares, which were subsequently issued.
We also recorded a $60,000 inducement fee (relating to the Preferred series D estoppel agreement and discounted conversion terms) to account for the difference in the fair value which was offset to retained earnings.
| F-41 |
On June 10, 2019 we issued 500,000 shares of common stock at $.02 per share to an accredited investor for an aggregate price of $10,000 in a private sale. We also issued 500,000 warrants as part of the transaction. Each Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
On July 19, 2019 we issued 500,000 shares of common stock at $.02 per share to an accredited investor for an aggregate price of $10,000 in a private sale. We also issued 500,000 warrants as part of the transaction. Each Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
On September 19, 2019 we entered into a stock purchase agreement for 250,000 units at a purchase price of $.02 a unit for an aggregate price of $5,000 to an accredited investor a private sale. Each unit consist of one share of common stock and one warrant to purchase one share of common stock exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement. The shares were included in the shares to be issued as of September 30, 2019 and were subsequently issued on October 15, 2019.
On December 5, 2019 we issued 5,000,000 units at a purchase price of $.015 per unit for an aggregate price of $75,000 to an accredited investor in a private sale. Each unit consist of one share of common stock and one warrant to purchase one share of common stock exercisable at $.04 per share.
On January 21, 2020 our Registration Statement on Form 1-A was qualified with the Securities and Exchange Commission, under which we may offer up to 300,000,000 shares of our common stock at a purchase price of $.03 per share. As of the date hereof, 4,523,333 shares of common stock have been issued thereunder.
Subsequently on January 30, 2020 we issued 1,700,000 shares of our common stock at a purchase price of $.02 per share, as settlement in full of a note payable of in the amount of $36,500 with accrued interest of 19,721. As a result we recognized a gain in the amount of $22,221 in the 1st quarter of 2020.
Subsequently on February 4, 2020 we issued 2,000,000 shares of our common stock at a price of $.04 per share, in exchange for the conversion of 800 shares of our Series D Preferred Stock.
Common Stock
Our Articles of Incorporation authorize us to issue 2,000,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.001 per share. As of December 31, 2019 there were 753,907,656 shares of common stock outstanding. All outstanding shares of common stock are, and the common stock to be issued will be, fully paid and non-assessable. Each share of our common stock has identical rights and privileges in every respect. The holders of our common stock are entitled to vote upon all matters submitted to a vote of our shareholders and are entitled to one vote for each share of common stock held. There are no cumulative voting rights.
The holders of our common stock are entitled to share equally in dividends and other distributions that our Board of Directors may declare from time to time out of funds legally available for that purpose, if any, after the satisfaction of any prior rights and preferences of any outstanding preferred stock. If we liquidate, dissolve or wind up, the holders of common stock shares will be entitled to share ratably in the distribution of all of our assets remaining available for distribution after satisfaction of all our liabilities and our obligations to holders of our outstanding preferred stock.
Preferred Stock
Our Articles of Incorporation authorize us to issue 20,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.001 per share. Our Board of Directors has the authority to issue additional shares of preferred stock in one or more series, and fix for each series, the designation of and number of shares to be included in each such series. Our Board of Directors is also authorized to set the powers, privileges, preferences, and relative participating, optional or other rights, if any, of the shares of each such series and the qualifications, limitations or restrictions of the shares of each such series.
| F-42 |
Unless our Board of Directors provides otherwise, the shares of all series of preferred stock will rank on parity with respect to the payment of dividends and to the distribution of assets upon liquidation. Any issuance by us of shares of our preferred stock may have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a change of our control or an unsolicited acquisition proposal. The issuance of preferred stock also could decrease the amount of earnings and assets available for distribution to the holders of common stock or could adversely affect the rights and powers, including voting rights, of the holders of common stock.
We previously authorized 440 shares of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock, 20,000 shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock, and 15,000 shares Series C Convertible Preferred Stock. As of August 20, 2006, all series A, B, and C preferred had been converted into common stock.
Effective August 7, 2013, our Board of Directors designated a series of our preferred stock as Series D Preferred Stock, authorizing 15,000 shares. Our Series D Preferred Stock offering terms authorized us to raise up to $1,000,000 with an over-allotment of $500,000 in multiple closings over the course of six months. We received an aggregate of $750,000 in financing in subscription for Series D Preferred Stock, or 7,500 shares.
The following are primary terms of the Series D Preferred Stock. The Series D Preferred holders were initially entitled to be paid a special monthly divided at the rate of 17.5% per annum. Initially, the Series D Preferred Stock was also entitled to be paid special dividends in the event cash dividends were not paid when scheduled. If the Company does not pay the dividend within five (5) business days from the end of the calendar month for which the payment of such dividend to owed, the Company will pay the investor a special dividend of an additional 3.5%. Any unpaid or accrued special dividends will be paid upon a liquidation or redemption. For any other dividends or distributions, the Series D Preferred Stock participates with common stock on an as-converted basis. The Series D Preferred holders may elect to convert the Series D Preferred Stock, in their sole discretion, at any time after a one year (1) year holding period, by sending the Company a notice to convert. The conversion rate is equal to the greater of $0.08 or a 20% discount to the average of the three (3) lowest closing market prices of the common stock during the ten (10) trading day period prior to conversion. The Series D Preferred Stock is redeemable from funds legally available for distribution at the option of the individual holders of the Series D Preferred Stock commencing any time after the one (1) year period from the offering closing at a price equal to the initial purchase price plus all accrued but unpaid dividends, provided, that if the Company gave notice to the investors that it was not in a financial position to redeem the Series D Preferred, the Company and the Series D Preferred holders are obligated to negotiate in good faith for an extension of the redemption period. The Company timely notified the investors that it was not in a financial position to redeem the Series D Preferred and the Company and the investors have engaged in ongoing negotiations to determine an appropriate extension period. The Company may elect to redeem the Series D Preferred Stock any time at a price equal to initial purchase price plus all accrued but unpaid dividends, subject to the investors’ right to convert, by providing written notice about its intent to redeem. Each investor has the right to convert the Series D Preferred Stock at least ten (10) days prior to such redemption by the Company.
In connection with the subscriptions for the Series D Preferred, we issued series F warrants to purchase an aggregate of 375,000 shares of our common stock at $.10 per share and series G warrants to purchase an aggregate of 375,000 shares of our common stock at $.20 per share.
On August 21, 2014, a holder holding 5,000 shares of Preferred Series D Preferred agreed to lower the dividend rate to 13% on its Series D Preferred. In September 2015, all holders of Series D Preferred signed and delivered estoppel agreements, whereby the holders agreed, among other things, that the Series D Preferred was not in default and to reduce (effective as of December 31, 2015) the dividend rate on the Series D Preferred Stock to six percent per annum and to terminate the 3.5% penalty in respect of unpaid dividends accruing on or after such date.
In the first quarter of 2019, we signed agreements to issue 4,000,000 shares of common stock valued at $.015 for a total value of $60,000 for the conversion of 800 preferred series D shares, which were subsequently issued.
We also recorded a $60,000 inducement fee (in exchange for the “standoff” and estoppel agreement and discounted conversion terms) to account for the difference in the fair value which we offset to retained earnings.
Subsequently on February 4, 2020 we issued 2,000,000 shares of our common stock at a price of $.04 per share, in exchange for the conversion of 800 shares of our Series D Preferred Stock.
| F-43 |
Warrants
A summary of warrant activity for the periods is as follows:
On May 31, 2019, we entered into a subscription agreement pursuant to which the Company agreed to sell 168,000,000 units (each a “Unit” and together the “Units”) to MGW Investment I Limited MGWI for an aggregate purchase price of $1,999,200, or $.0119 per Unit, with each unit consisting of one share of common stock, par value $.001 per share (the “Common Stock”) and a warrant (the “Warrant”) to purchase one share of common stock. The Common Stock will be issued to MGWI at such time as the Company increases the number of shares of its authorized Common Stock. The Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
On June 10, 2019 we issued 500,000 shares of common stock at $.02 per share to an accredited investor for an aggregate price of $10,000 in a private sale. We also issued 500,000 warrants as part of the transaction. Each Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
On July 18, 2019 we issued 500,000 shares of common stock at $.02 per share to an accredited investor for an aggregate price of $10,000 in a private sale. We also issued 500,000 warrants as part of the transaction. Each Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
On September 19, 2019 we entered into a stock purchase agreement for 250,000 units to an accredited investor a private sale. Each unit consist of one share of common stock and one warrant to purchase one share of common stock exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement. The shares were included in the shares to be issued as of September 30, 2019 and were subsequently issued on October 15, 2019.
On December 5, 2019 we issued 5,000,000 units to an accredited investor a private sale. Each unit consist of one share of common stock and one warrant to purchase one share of common stock exercisable at $.04 per share.
| Warrants - Common Share Equivalents | Weighted Average Exercise price | Warrants exercisable - Common Share Equivalents | Weighted Average Exercise price | |||||||||||||
| Outstanding December 31, 2018 | - | $ | - | - | $ | - | ||||||||||
| Issued | 174,250,000 | $ | 0.04 | 174,250,000 | $ | 0.04 | ||||||||||
| Exercised | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| Expired | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Outstanding December 31, 2019 | 174,250,000 | $ | 0.04 | 174,250,000 | $ | 0.04 | ||||||||||
Stock Options
We currently have no outstanding stock options
NOTE 12 – RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Kambiz Mahdi, our Chief Executive Officer, owns Billet Electronics, which is distributor of electronic components. From time to time, we purchase parts from Billet Electronics. In addition, Billet was a supplier of parts and had dealings with current and former customers of the Company prior to joining the company. Our Board of Directors has approved the transactions between Billet Electronics and the Company.
On June 15, 2017 Meddy Sahebi Chairman of our Board of Directors advanced the Company $5,000. There were no specified terms for repayment of this loan other than that it was to be repaid within a reasonable time. As of December 31, 2017, the outstanding balance was $5,000. Mr. Sahebi resigned from the board of directors on February 8, 2018 .
| F-44 |
Pursuant to our 2017 Stock Compensation Program, effective July 1, 2017, we made the following stock option grants to members of our Board of Directors: (a) we issued to each of our non-employee members of our Board of Directors first joining the Board in October 2015 and who had not received any compensation for serving as directors of the Company (five persons) options to purchase 150,000 shares of our common stock with an exercise price of $.03 per share, the last sale price of our common stock on June 29, 2017 and (b) we issued to each of our non-employee members of our Board of Directors currently serving on the Board (six persons) options to purchase 300,000 shares of our common stock with an exercise price of $.03 per share. On the non-employee board members resigned, as disclosed in our 8K filed on February 15, 2018. As a result, all remaining stock options were cancelled.
On September 6, 2016, we entered into a one-year convertible note payable for $87,500, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is not convertible until nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of fifty-five percent (55%) of the lowest closing bid price (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the twenty (20) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. On December 16, 2016 we issued 1,200,000 shares of common stock at $.0031 for a partial conversion of this note in the amount of $3,696. January 4, 2018, we issued 2,300,000 shares of common stock at $.002192 for a partial conversion of this note in the amount of $5,042.
On November 2, 2016, we effected the repayment of the convertible note dated March 15, 2016 for an aggregate amount of $84,000. Concurrently, we entered into an Escrow Funding Agreement with Red Dot Investment, Inc., a California corporation (“Reddot”), pursuant to which Reddot deposited funds into escrow to fund the repayment and we assigned to Reddot our right to acquire the convertible note and Reddot acquired the convertible note. Concurrently, we and Reddot amended the convertible note (a) to have a fixed conversion price of $.005 per share, subject to potential further adjustment in the event of certain Common Stock issuances, (b) to have a fixed interest rate of ten percent (10%) per annum with respect to both the redemption amount and including a financing fee and any costs, expenses, or other fees relating to the convertible note or its enforcement and collection, and any other expense for or on our account (in each case with a minimum 10% yield in the event of payoff or conversion within the first year), such amounts to constitute additional principal under the convertible note, as amended, and (c) as otherwise provided in the Escrow Funding Agreement. The March 2016 convertible note, as so amended, is referred to as the “Master Note.”
Concurrently with the foregoing note repayments, we entered into a Credit Agreement and Promissory Note (the “Credit Agreement”) with Megawell USA Technology Investment Fund I LLC, a Wyoming limited liability company in formation (“MW I”), pursuant to which MW I deposited funds into escrow to fund the repayment of the convertible notes and we assigned to MW I our right to acquire the convertible notes and otherwise agreed that MW I would be subrogated to the rights of each note holder to the extent a note was repaid with funds advanced by MW I. Concurrently, MW I acquired the Master Note and we agreed that all amounts advanced by MG I to or for our benefit would be governed by the terms of the Master Note, including the payment of a financing fees, interest, minimum interest, and convertibility. Reddot is MW I’s agent for purposes of administration of the Credit Agreement and the Master Note and advances thereunder.
On February 13, 2018 the Corporation and Confections Ventures Limited. (“CVL”) entered into a Convertible Note Purchase Agreement (the “Convertible Note Purchase Agreement,” together with the Stock Purchase Agreement and the transactions contemplated thereunder, the “Financing”) pursuant to which the Corporation issued to CVL a convertible promissory Note (the “CVL Note”) in the principal amount of $939,500 with an interest rate of 10% per annum interest rate and a maturity date of February 13, 2020. The CVL Note is convertible into shares of Common Stock at $0.003 per share, as adjusted as provided therein. As a result we recognized a beneficial conversion feature of $532,383, which is amortized over the life of the note. This note was assigned to Mgw Investments and they agreed not to convert the $939,500 note in to shares in excess of the 800,000,000 Authorized limit until we have increased the Authorized shares to the Board approved limit of 2 billion shares.
On February 8, 2018 the Corporation entered a Convertible Promissory Note in the principal amount of $153,123, due October 8, 2018, with an interest rate of 12% per annum payable to MGWI (the “MGWI Note”). The MGWI Note is convertible into shares of the Corporation’s common stock at the lower of: (i) a 40% discount to the lowest trading price during the previous twenty (20) trading days to the date of a Conversion Notice; or (ii) 0.003. As a result of the closing of the transactions contemplated by the Stock Purchase Agreement and Convertible Note Purchase Agreement, the MGWI Note must be redeemed by the Corporation in an amount that will permit CVL and MGWI and their affiliates to hold 65% of the issued and outstanding Common Stock of the Corporation on a fully diluted basis. The proceeds from the MGWI Note were used to redeem the convertible note of the Corporation to JSJ Investments, Inc. in the principal amount of $103,000 with an interest rate of 12% per annum, due April 25, 2018. At December 31, 2018 the holder of this note beneficially owned 70% of the company and this note is not convertible if the holder holds more than 9.99%, as a result, we did not recognize a derivative liability or a beneficial conversion feature.
| F-45 |
On June 21, 2018 the corporation entered into a promissory note with MGW Investment I Limited, for the principal amount of $250,000, with an interest rate of Eight Percent (8%) per annum and a maturity date of June 21, 2019. On May 28, 2019 this note was paid in full.
On September 21, 2018 the corporation entered into a promissory note with MGW Investment I Limited, for the principal amount of $100,000, with an interest rate of Eight Percent (8%) per annum and a maturity date of September 21, 2019. On May 28, 2019 this note was paid in full.
On February 15, 2018 we issued 9,200,000 at a purchase price of .0053 per share as additional compensation in the amount of $48,760.
On October 18, 2018 we entered into an at will employment agreement with Kambiz Mahdi our CEO. This agreement may be terminated at any time. As part of the agreement Mr. Mahdi was to be issued 20,000,000 shares of our common stock, as additional compensation. As a result; for the year ended December 31, 2018 we accrued for and subsequently on February 13, 2019, issued 20,000,000 shares at a purchase price of $.0131 per share to Mr. Mahdi in the amount of $262,000.
On January 10, 2019 the corporation entered into a promissory note with MGW Investment I Limited, for the principal amount of $25,000, with an interest rate of Eight Percent (8%) per annum and a maturity date of January 10, 2020. On May 28, 2019 this note was paid in full.
On May 1, 2019 we entered into an employment agreement with Mr. Bennett, with an annual salary of $175,000.
Subsequently on March 9, 2020, John Bennett notified Clean Energy Technologies, Inc. (the “Company”) of his resignation from his position as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer, effective March 9, 2020. Mr. Bennett will remain as a consultant to the Company and assist with maintaining the financial books and records of the Company.
On May 31, 2019, we entered into a subscription agreement pursuant to which the Company agreed to sell 168,000,000 units (each a “Unit” and together the “Units”) to MGW Investment I Limited MGWI for an aggregate purchase price of $1,999,200, or $.0119 per Unit, with each unit consisting of one share of common stock, par value $.001 per share (the “Common Stock”) and a warrant (the “Warrant”) to purchase one share of common stock. The Common Stock will be issued to MGWI at such time as the Company increases the number of shares of its authorized Common Stock. The Warrant is exercisable at $.04 per share of Common Stock and expires one year from the date of the Agreement.
In the fourth quarter of 2019 MGW Investment I Limited, advanced $167,950, with no terms or interest rate. The outstanding balance on this advance on December 31, 2019 is $169,950.
NOTE 13 - WARRANTY LIABILITY
For the year ended December 31, 2018 and 2019 there was no change in our warranty liability.
NOTE 14 – SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
In December 2019, a novel strain of coronavirus (COVID-19) was reported in Wuhan, China and has spread throughout the United States and the rest of the world. The World Health Organization has declared the outbreak to constitute a “Public Health Emergency of International Concern.” This contagious disease outbreak, which has not been contained, and is disrupting supply chains and affecting production and sales across a range of industries in United States and other companies as a result of quarantines, facility closures, and travel and logistics restrictions in connection with the outbreak, as well as the worldwide adverse effect to workforces, economies and financial markets, leading to a global economic downturn. Therefore, the Company expects this matter to negatively impact its operating results. However, the related financial impact and duration cannot be reasonably estimated at this time.
On January 8, 2020 we entered into a convertible note payable for $103,000, with a maturity date of January 8, 2021, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is convertible nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of sixty-five percent (65%) of the average of the two lowest closing prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. We also entered into a stock purchase agreement for the potential conversion into common stock.
On January 21, 2020, we received our “Notice of Qualification” for our form 1-A.
| F-46 |
On January 30, 2020 we issued 1,700,000 shares of our common stock at a purchase price of $.02 per share, as settlement in full of a note payable of in the amount of $36,500 with accrued interest of 19,721. As a result we recognized a gain in the amount of $22,221 in the 1st quarter of 2020.
On February 3, 2020 we issued 3,690,000 shares of our common stock under our Reg A offering at $.03 per share. These shares are unrestricted and free trading.
On February 4, 2020 we issued 2,000,000 shares of our common stock at a price of $.04 per share, in exchange for the conversion of 800 shares of our Series D Preferred Stock.
On February 19, 2020 we entered into a convertible note payable for $53,000, with a maturity date of February 19, 2021, which accrues interest at the rate of 12% per annum. It is convertible nine months after its issuance and has a conversion rate of sixty-five percent (65%) of the average of the two lowest closing prices (as reported by Bloomberg LP) of our common stock for the fifteen (15) Trading Days immediately preceding the date of conversion. We also entered into a stock purchase agreement for the potential conversion into common stock.
On March 17, 2020 we issued 833,333 shares of our common stock under our Reg A offering at $.03 per share. These shares are unrestricted and free trading.
In accordance with ASC 855, the Company has analyzed its operations subsequent to December 31, 2019 through the date these financial statements were issued, and has determined that it does not have any other material subsequent events to disclose in these financial statements.
| F-47 |
WHERE YOU CAN GET ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
We file annual, quarterly and current reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC. You may read and copy our reports or other filings made with the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room, located at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, DC 20549. You can obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. You can also access these reports and other filings electronically on the SEC’s web site, www.sec.gov.
| 52 |
| 53 |
| 54 |
| 55 |
| 56 |
| 57 |
| 58 |
| 59 |
* Filed herewith
| 60 |
The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes:
1. To file, during any period in which offers or sales are being made, a post-effective amendment to this registration statement:
i. To include any Prospectus required by section 10(a)(3) of the Securities Act of 1933;
ii. To reflect in the Prospectus any facts or events arising after the effective date of the registration statement (or the most recent post-effective amendment thereof) which, individually or in the aggregate, represent a fundamental change in the information set forth in the registration statement. Notwithstanding the foregoing, any increase or decrease in volume of securities offered (if the total dollar value of securities offered would not exceed that which was registered) and any deviation from the low or high end of the estimated maximum offering range may be reflected in the form of Prospectus filed with the Commission pursuant to Rule 424(b) if, in the aggregate, the changes in volume and price represent no more than 20% change in the maximum aggregate offering price set forth in the “Calculation of Registration Fee” table in the effective registration statement.
iii. To include any material information with respect to the plan of distribution not previously disclosed in the registration statement or any material change to such information in the registration statement;
2. That, for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each such post-effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
3. To remove from registration by means of a post-effective amendment any of the securities being registered which remain unsold at the termination of the offering.
4. That, for the purpose of determining liability of the registrant under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser in the initial distribution of the securities: The undersigned registrant undertakes that in a primary offering of securities of the undersigned registrant pursuant to this registration statement, regardless of the underwriting method used to sell the securities to the purchaser, if the securities are offered or sold to such purchaser by means of any of the following communications, the undersigned registrant will be a seller to the purchaser and will be considered to offer or sell such securities to such purchaser:
i. Any Preliminary Prospectus or Prospectus of the undersigned registrant relating to the offering required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424;
ii. Any free writing Prospectus relating to the offering prepared by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant or used or referred to by the undersigned registrant;
iii. The portion of any other free writing Prospectus relating to the offering containing material information about the undersigned registrant or its securities provided by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant; and
iv. Any other communication that is an offer in the offering made by the undersigned registrant to the purchaser.
5. That, for the purpose of determining liability under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser: Each Prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b) as part of a registration statement relating to an offering, other than registration statements relying on Rule 430B or other than Prospectuses filed in reliance on Rule 430A, shall be deemed to be part of and included in the registration statement as of the date it is first used after effectiveness. Provided, however, that no statement made in a registration statement or Prospectus that is part of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into the registration statement or Prospectus that is part of the registration statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract of sale prior to such first use, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or Prospectus that was part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately prior to such date of first use.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act of 1933 may be permitted to our directors, officers and controlling persons, we have been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission, such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act of 1933 and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by us of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the corporation in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, we will, unless in the opinion of our counsel the matter has been settled by a controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question of whether such indemnification by us is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and will be governed by the final adjudication of such case.
| 61 |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, the Registrant has duly caused this registration statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the in Costa Mesa, California on July 14, 2020.
CLEAN ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
| By: | /s/ Kambiz Mahdi | |
| Kambiz Mahdi | ||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||
| Date: | July 14, 2020 |
CLEAN ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
| By: | /s/ Calvin Pangt | |
| Chief Financial Officer | ||
| Date: | July 14, 2020, |
POWERS OF ATTORNEY
Each of the undersigned officers and directors of Clean Energy Technologies, Inc, a Nevada corporation, hereby constitutes and appoints Kambiz Mahdi and Calvin Pang and each of them, severally, as his or her attorney-in-fact and agent, with full power of substitution and resubstitution, in his or her name and on his or her behalf, to sign in any and all capacities this registration statement and any and all amendments (including post-effective amendments) and exhibits to this registration statement and any and all applications and other documents relating thereto, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, with full power and authority to perform and do any and all acts and things whatsoever which any such attorney or substitute may deem necessary or advisable to be performed or done in connection with any or all of the above described matters, as fully as each of the undersigned could do if personally present and acting, hereby ratifying and approving all acts of any such attorney or substitute.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this registration statement has been signed by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| By: | /s/ Kambiz Mahdi | |
| Kambiz Mahdi, Director | ||
| Date: | July 14, 2020 |
| By: | /s/ Calvin Pang | |
| Calvin Pang, Director | ||
| Date: | July 14, 2020 |
| By: | /s/ Jun Wang | |
| Jun Wang, Director | ||
| Date: | July 14, 2020 |
| By: | /s/ Yongsheng Lyu | |
| Yongsheng Lyu, Director | ||
| Date: | July 14, 2020 |
| 62 |
