Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.1 - EX-99.1 - Aeglea BioTherapeutics, Inc. | agle-ex991_6.htm |
| 8-K - 8-K - Aeglea BioTherapeutics, Inc. | agle-8k_20200525.htm |

Dr Ravi M Rao, MD PhD Chief Medical Officer, Aeglea BioTherapeutics On behalf of the 101A/102A Investigators and Research Staff 1 Year Data from First in Human Study of Pegzilarginase for the Treatment of Arginase 1 Deficiency (ARG1-D) Diaz GA1, Bechter MW2, Sloan LS2, Rao RM2, Zori RT3 Exhibit 99.2

Bechter MW, Sloan LS, Rao RM are full time employees of Aeglea BioTherapeutics Diaz GA, Zori RT have performed as consultants and received travel support from Aeglea BioTherapeutics The investigational use of pegzilarginase will be discussed during this presentation Disclosures
Arginase 1 Deficiency (ARG1-D) Autosomal recessive disorder of arginine metabolism due to ARG1 enzyme deficiency Recent genetic prevalence data suggests > 2500 patients worldwide1 >700 patients in Europe >250 patients in US Typically presents at ~2-4 years of age, can be later2,3 Developmental delay with increasing intellectual disability Failure to thrive and short stature Prominent and progressive neurological manifestations4 Impaired mobility due to characteristic spastic diplegia Seizures are a common feature Additional abnormalities due to impairment urea cycle Hyperammonemia but less prominent than other urea cycle disorders Protein aversion, food refusal and self-restriction of protein Low disease awareness leads to delay in diagnosis2 Suspected cases can be diagnosed reliably Plasma Arginine >300µM5 Red Blood Cell Arginase, Genetic testing6 May be initially misdiagnosed as Cerebral Palsy or Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia7 Video by kind permission of Dr D Carvalho 1. Aeglea Data on File 2. Huemer M, et al. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2016;39:331–340 3.Burrage LC, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24:6417–6427 4. Carvalho DR, et al. Pediatr Neurol. 2012;46:369–374 5.Haberle J et al J Inherit Metab Dis, 2019, 6.Diez-Fernandez C, et al. Hum Mutat. 2018;39:1029–1050, 7.Carvalho DR et al. Gene 2012; 509(1): 124-130. Video of patient omitted
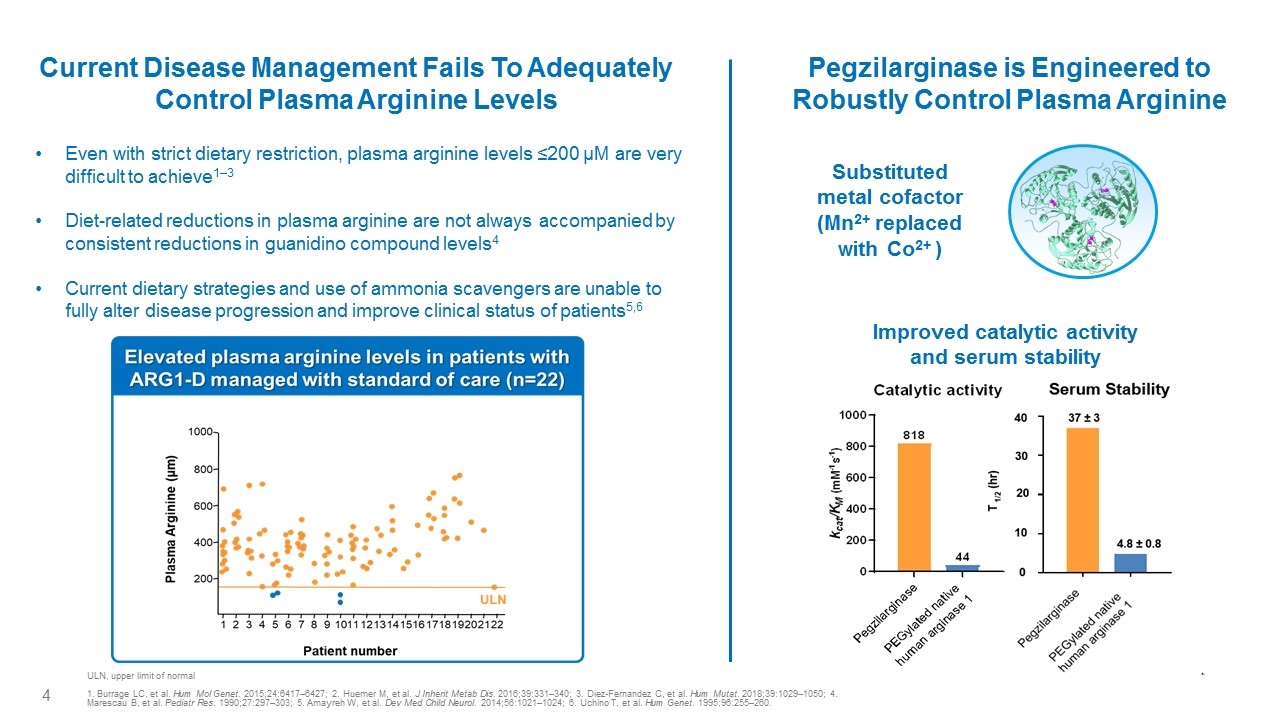
Current Disease Management Fails To Adequately Control Plasma Arginine Levels Improved catalytic activity and serum stability Substituted metal cofactor (Mn2+ replaced with Co2+ ) Pegzilarginase is Engineered to Robustly Control Plasma Arginine Even with strict dietary restriction, plasma arginine levels ≤200 µM are very difficult to achieve1–3 Diet-related reductions in plasma arginine are not always accompanied by consistent reductions in guanidino compound levels4 Current dietary strategies and use of ammonia scavengers are unable to fully alter disease progression and improve clinical status of patients5,6 ULN, upper limit of normal 1. Burrage LC, et al. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24:6417–6427; 2. Huemer M, et al. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2016;39:331–340; 3. Diez-Fernandez C, et al. Hum Mutat. 2018;39:1029–1050; 4. Marescau B, et al. Pediatr Res. 1990;27:297–303; 5. Amayreh W, et al. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2014;56:1021–1024; 6. Uchino T, et al. Hum Genet. 1995;96:255–260. Elevated plasma arginine levels in patients with ARG1-D managed with standard of care (n=22) Plasma Arginine(µm)1000 800 600 400 200 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 ULN Patient number Catalytic activity 1000 800 600 400 200 0 Kcat/KM (mM-1 s-1 818 44 Pegzilarginase Pegylated native human arginase 1 Serum Stability T1/2 (hr) 40 30 20 10 0 37±3 4.8±0.8 Pegzilarginase Pegylated native human arginase 1
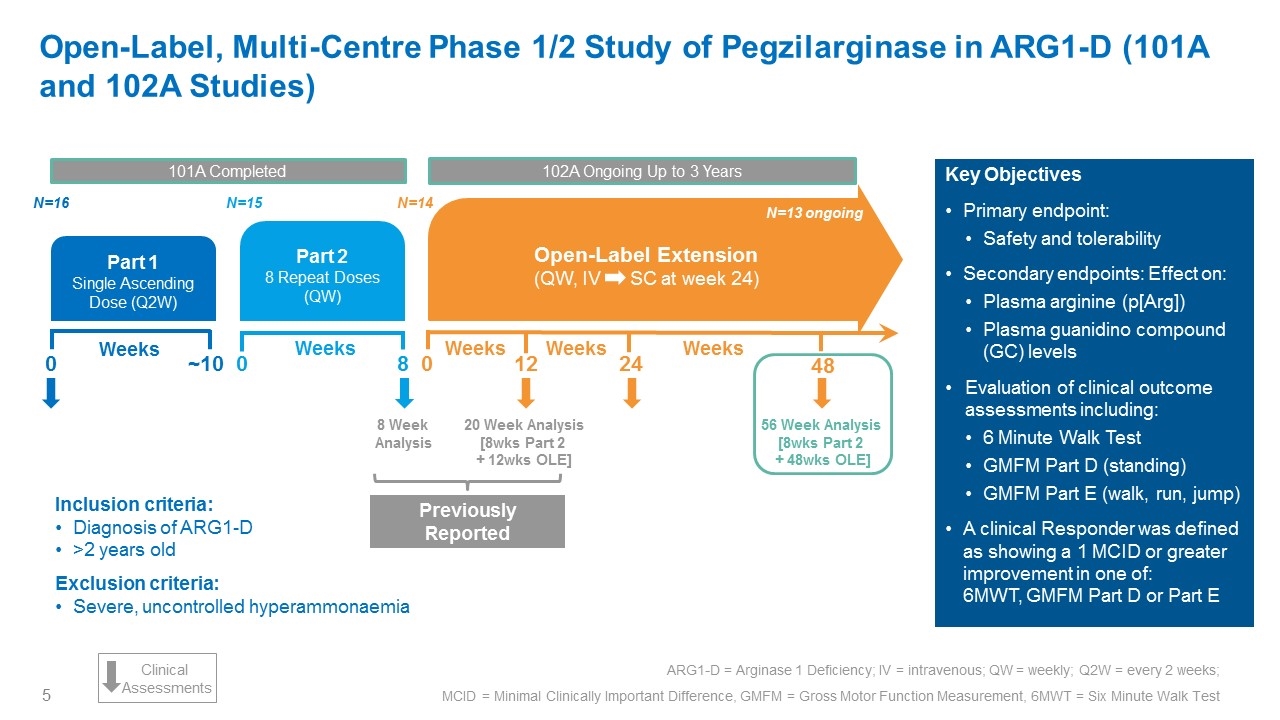
Inclusion criteria: Diagnosis of ARG1-D >2 years old Exclusion criteria: Severe, uncontrolled hyperammonaemia Key Objectives Primary endpoint: Safety and tolerability Secondary endpoints: Effect on: Plasma arginine (p[Arg]) Plasma guanidino compound (GC) levels Evaluation of clinical outcome assessments including: 6 Minute Walk Test GMFM Part D (standing) GMFM Part E (walk, run, jump) A clinical Responder was defined as showing a 1 MCID or greater improvement in one of: 6MWT, GMFM Part D or Part E Open-Label, Multi-Centre Phase 1/2 Study of Pegzilarginase in ARG1-D (101A and 102A Studies) ARG1-D = arginase 1 deficiency; IV = intravenous; QW = weekly; Q2W = every 2 weeks ARG1-D = Arginase 1 Deficiency; IV = intravenous; QW = weekly; Q2W = every 2 weeks; MCID = Minimal Clinically Important Difference, GMFM = Gross Motor Function Measurement, 6MWT = Six Minute Walk Test Part 1 Single Ascending Dose (Q2W) N=16 0 ~10 Weeks 101A Completed Part 2 8 Repeat Doses (QW) 0 8 Weeks N=14 N=15 20 Week Analysis [8wks Part 2 + 12wks OLE] 56 Week Analysis [8wks Part 2 + 48wks OLE] 24 48 0 Weeks Weeks Open-Label Extension (QW, IV SC at week 24) 12 N=13 ongoing 102A Ongoing Up to 3 Years Previously Reported Clinical Assessments Weeks 8 Week Analysis
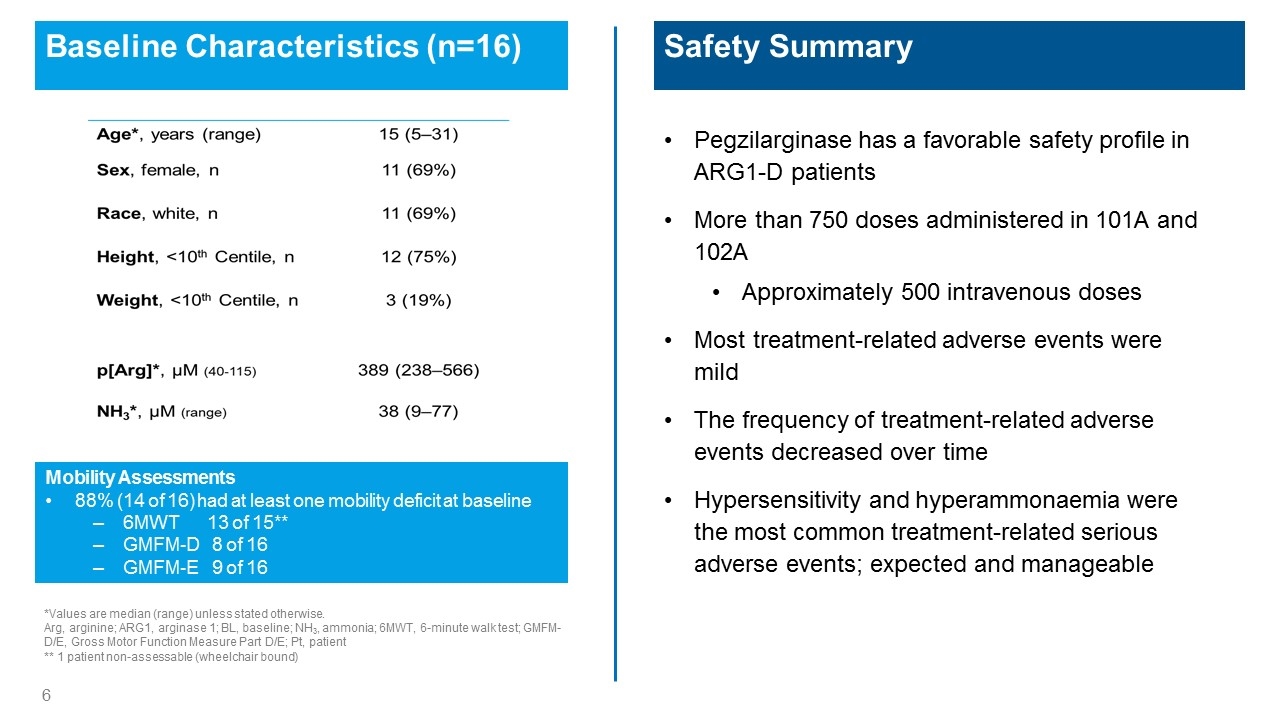
Baseline Characteristics (n=16) *Values are median (range) unless stated otherwise. Arg, arginine; ARG1, arginase 1; BL, baseline; NH3, ammonia; 6MWT, 6-minute walk test; GMFM-D/E, Gross Motor Function Measure Part D/E; Pt, patient ** 1 patient non-assessable (wheelchair bound) Safety Summary Pegzilarginase has a favorable safety profile in ARG1-D patients More than 750 doses administered in 101A and 102A Approximately 500 intravenous doses Most treatment-related adverse events were mild The frequency of treatment-related adverse events decreased over time Hypersensitivity and hyperammonaemia were the most common treatment-related serious adverse events; expected and manageable Mobility Assessments 88% (14 of 16) had at least one mobility deficit at baseline 6MWT 13 of 15** GMFM-D 8 of 16 GMFM-E 9 of 16 Age*, years (range) 15 (5-31) Sex, female, n 11 (69%) Race white, n 11 (69%) Height, <10th Centile, n 12 (75%) Weight, <10th Centile n 3 (19%) p[Arg]*, µM (40-115) 389 (238-566) NH3*, µM (range) 38 (9-77)
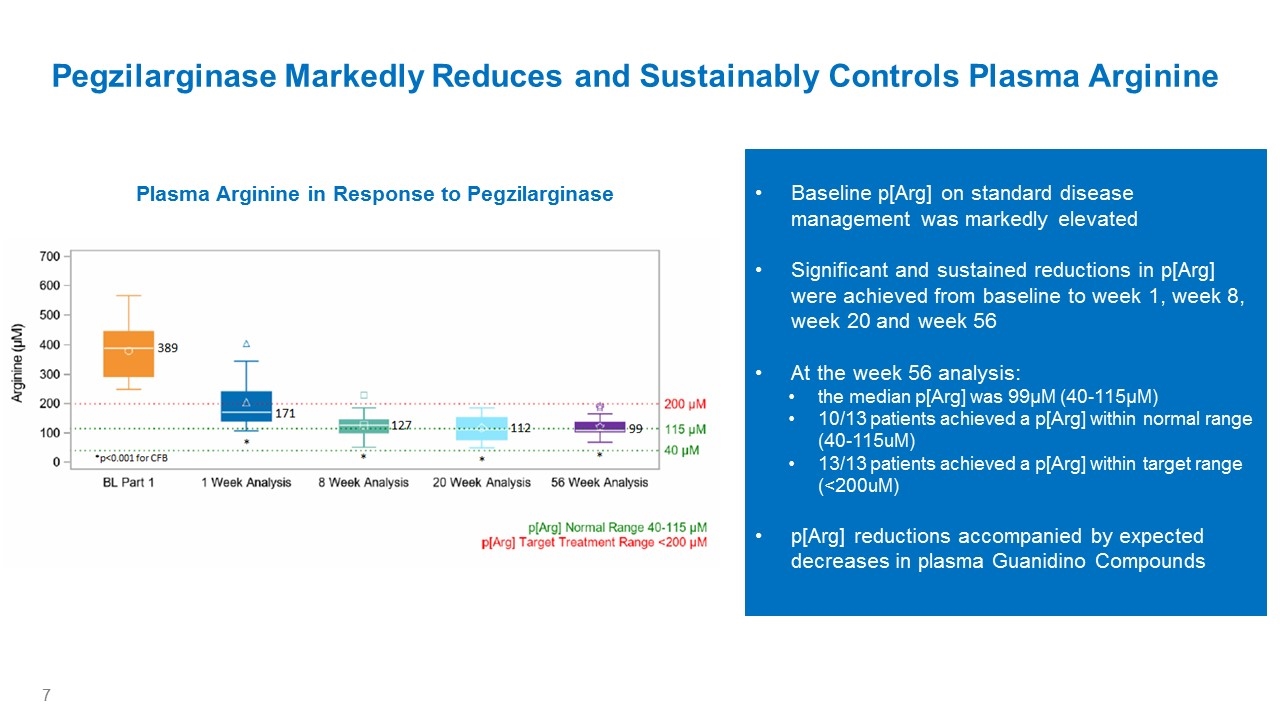
Baseline p[Arg] on standard disease management was markedly elevated Significant and sustained reductions in p[Arg] were achieved from baseline to week 1, week 8, week 20 and week 56 At the week 56 analysis: the median p[Arg] was 99µM (40-115µM) 10/13 patients achieved a p[Arg] within normal range (40-115uM) 13/13 patients achieved a p[Arg] within target range (<200uM) p[Arg] reductions accompanied by expected decreases in plasma Guanidino Compounds Pegzilarginase Markedly Reduces and Sustainably Controls Plasma Arginine Plasma Arginine in Response to Pegzilarginase Arginine (µM) 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 389 *p<0.001 for CFB 171 127 112 99 BL Part 1 1 Week Analysis 8 Week Analysis 20 Week Analysis 56 Week Analysis 200 µM 115 µM 40 µM p[Arg] Normal Range 40-115 µM p[Arg] Target Treatment Range <200 µM
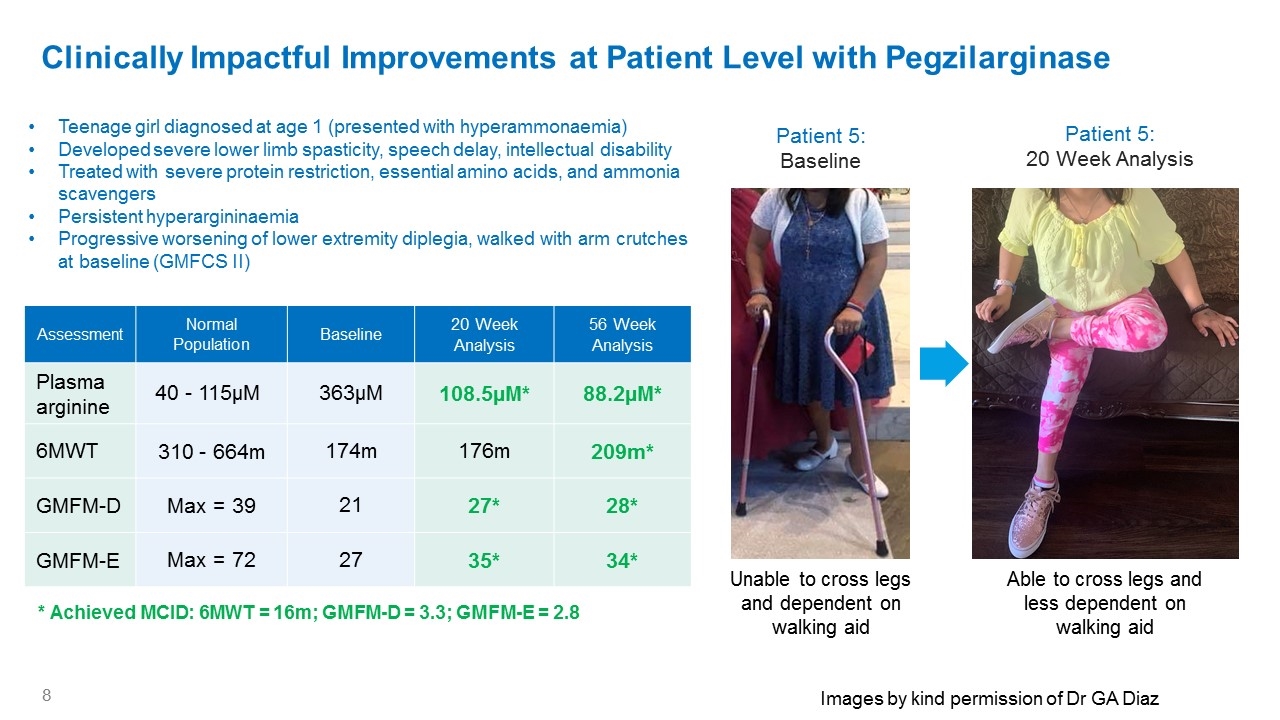
Clinically Impactful Improvements at Patient Level with Pegzilarginase Assessment Normal Population Baseline 20 Week Analysis 56 Week Analysis Plasma arginine 40 - 115µM 363µM 108.5µM* 88.2µM* 6MWT 310 - 664m 174m 176m 209m* GMFM-D Max = 39 21 27* 28* GMFM-E Max = 72 27 35* 34* Teenage girl diagnosed at age 1 (presented with hyperammonaemia) Developed severe lower limb spasticity, speech delay, intellectual disability Treated with severe protein restriction, essential amino acids, and ammonia scavengers Persistent hyperargininaemia Progressive worsening of lower extremity diplegia, walked with arm crutches at baseline (GMFCS II) Patient 5: Baseline Patient 5: 20 Week Analysis Unable to cross legs and dependent on walking aid Able to cross legs and less dependent on walking aid * Achieved MCID: 6MWT = 16m; GMFM-D = 3.3; GMFM-E = 2.8 Images by kind permission of Dr GA Diaz
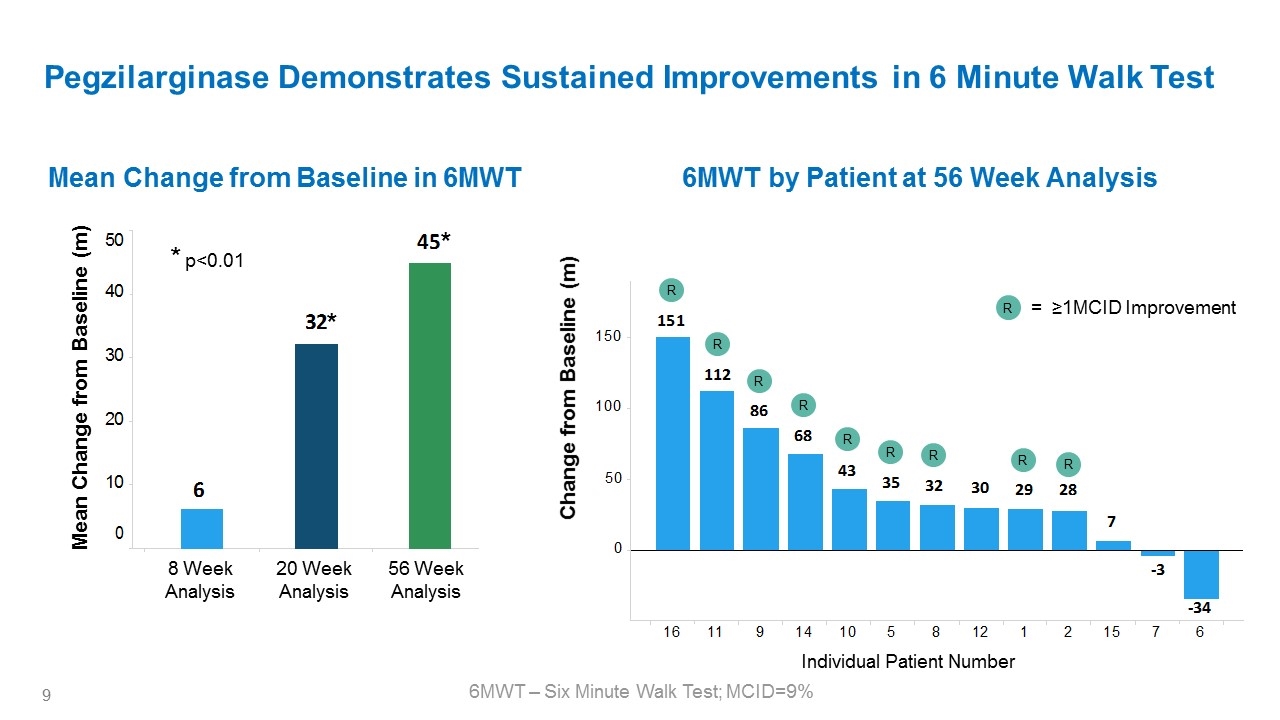
Pegzilarginase Demonstrates Sustained Improvements in 6 Minute Walk Test 6MWT by Patient at 56 Week Analysis Mean Change from Baseline in 6MWT Change from Baseline (m) 6MWT – Six Minute Walk Test; MCID=9% 8 Week Analysis Mean Change from Baseline (m) 20 Week Analysis 56 Week Analysis Individual Patient Number R R R R R R R R R * * * p<0.01 R = ≥1MCID Improvement 50 40 30 20 10 0 6 32* 45* 150 100 50 0 151 112 86 68 43 35 32 30 29 28 7 -3 -34 16 11 9 14 10 5 8 12 1 2 15 7 6
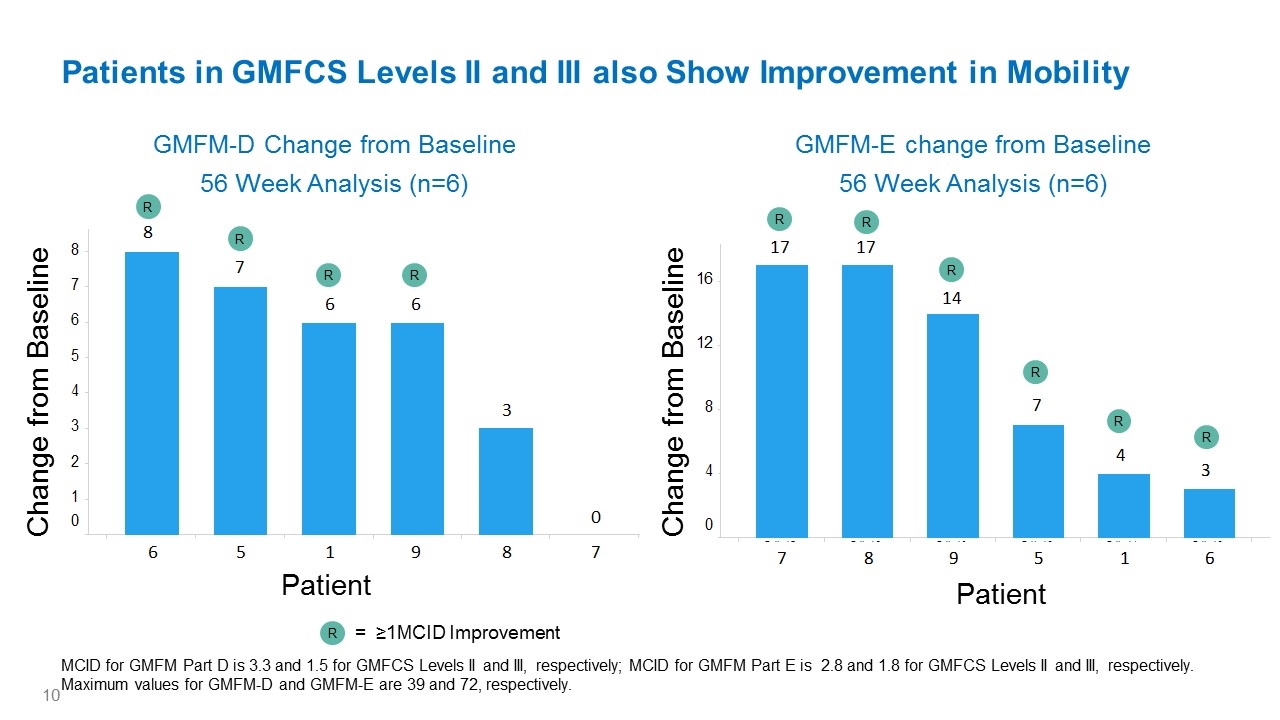
GMFM-D Change from Baseline 56 Week Analysis (n=6) GMFM-E change from Baseline 56 Week Analysis (n=6) Patients in GMFCS Levels II and III also Show Improvement in Mobility MCID for GMFM Part D is 3.3 and 1.5 for GMFCS Levels II and III, respectively; MCID for GMFM Part E is 2.8 and 1.8 for GMFCS Levels II and III, respectively. Maximum values for GMFM-D and GMFM-E are 39 and 72, respectively. R = ≥1MCID Improvement Patient Change from Baseline Patient Change from Baseline R R R R R R R R R R 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 6 5 1 9 8 7 8 7 6 6 3 0 16 12 8 4 0 7 8 9 5 1 6 17 17 14 7 4 3
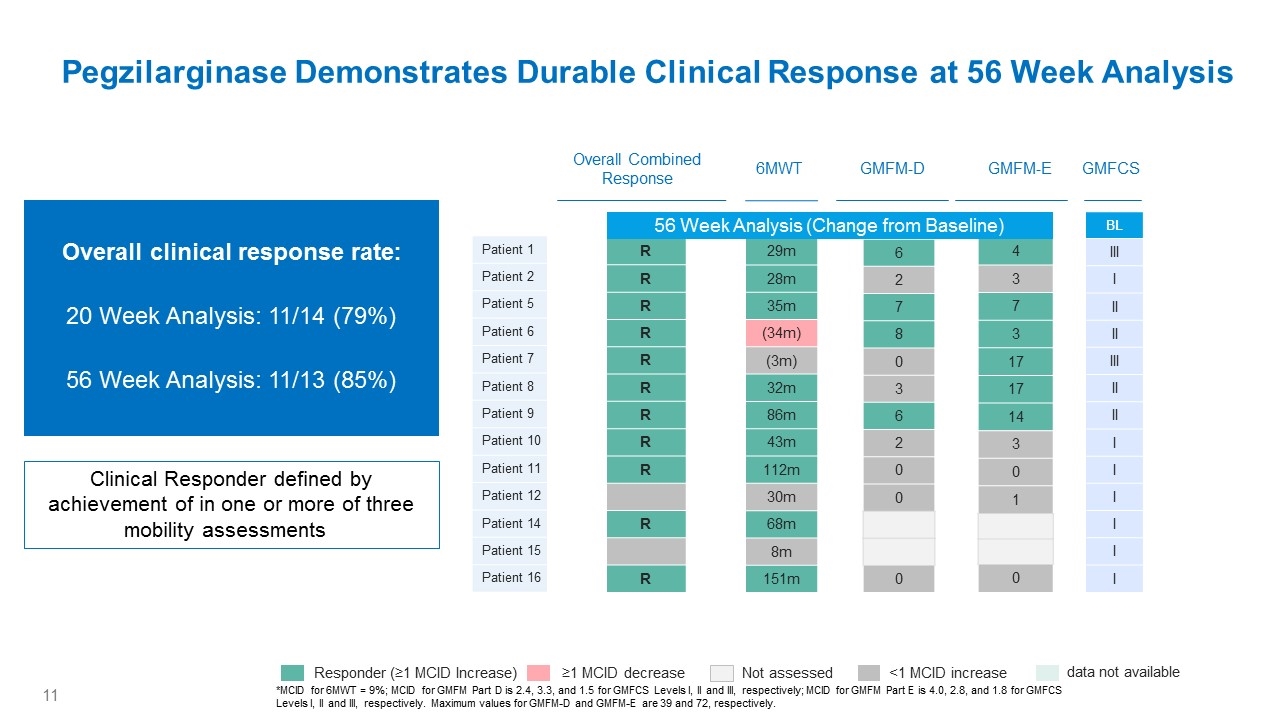
Pegzilarginase Demonstrates Durable Clinical Response at 56 Week Analysis *MCID for 6MWT = 9%; MCID for GMFM Part D is 2.4, 3.3, and 1.5 for GMFCS Levels I, II and III, respectively; MCID for GMFM Part E is 4.0, 2.8, and 1.8 for GMFCS Levels I, II and III, respectively. Maximum values for GMFM-D and GMFM-E are 39 and 72, respectively. Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 5 Patient 6 Patient 7 Patient 8 Patient 9 Patient 10 Patient 11 Patient 12 Patient 14 Patient 15 Patient 16 Overall Combined Response 29m 28m 35m (34m) (3m) 32m 86m 43m 112m 30m 68m 8m 151m 6MWT Week 48 6 2 7 8 0 3 6 2 0 0 0 Week 48 4 3 7 3 17 17 14 3 0 1 0 GMFM-D GMFM-E Week 48 R R R R R R R R R R R BL III I II II III II II I I I I I I GMFCS Not assessed <1 MCID increase Responder (≥1 MCID Increase) ≥1 MCID decrease data not available Clinical Responder defined by achievement of in one or more of three mobility assessments Overall clinical response rate: 20 Week Analysis: 11/14 (79%) 56 Week Analysis: 11/13 (85%) 56 Week Analysis (Change from Baseline)

Conclusions Arginase 1 Deficiency (ARG1-D) is a debilitating, progressive, inherited, metabolic disease driven by the accumulation of arginine and its metabolites, which results in prominent neurological manifestations including progressive spastic diplegia and early mortality Delays in diagnosis are common with some cases initially diagnosed as Cerebral Palsy or Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Pegzilarginase was highly effective in sustainably lowering plasma arginine levels with a favorable safety profile and is now being further evaluated in an active Phase 3 study. Plasma arginine reduction was accompanied by improvements in disease manifestations within 8 weeks and a durable clinical response rate of 85% at 56 Week Analysis These marked improvements in important disease-related manifestations with pegzilarginase on a background of standard treatment suggests the potential for a substantial clinical improvement over current management of patients with ARG1-D

The 101A/102A Investigators and Research Staff wish to acknowledge and thank the Patients, their Families, and Caregivers for their dedication to these studies Acknowledgements Information on the ongoing Phase 3 Pegzilarginase Effect on Arginase 1 Deficiency Clinical Endpoints (PEACE) Study for patients with Arginase 1 Deficiency is available at ARG1Dstudy@aegleabio.com
