Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.2 - SECTION 906 CERTIFICATION OF THE CFO - Perspecta Inc. | perspecta331202010-kex322.htm |
| EX-32.1 - SECTION 906 CERTIFICATION OF THE CEO - Perspecta Inc. | perspecta331202010-kex321.htm |
| EX-31.2 - SECTION 302 CERTIFICATION OF THE CFO - Perspecta Inc. | perspecta331202010-kex312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - SECTION 302 CERTIFICATION OF THE CEO - Perspecta Inc. | perspecta331202010-kex311.htm |
| EX-23.1 - CONSENT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM - Perspecta Inc. | perspecta331202010-kex231c.htm |
| EX-21.1 - LIST OF SUBSIDIARIES - Perspecta Inc. | perspecta331202010-kex211l.htm |
| EX-4.1 - DESCRIPTION OF THE COMPANY'S SECURITIES - Perspecta Inc. | perspecta331202010-kex41de.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
☑ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020
or
☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from _____________ to ____________
Commission File Number: 001-38033

PERSPECTA INC. | |||
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in Its Charter) | |||
Nevada | 82-3141520 | ||
(State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | ||
15052 Conference Center Drive, Chantilly, Virginia | 20151 | ||
(Address of Principal Executive Offices) | (Zip Code) | ||
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (571) 313-6000 | |||
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: | |||
Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
Common Stock, $0.01 par value per share | PRSP | New York Stock Exchange | |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None | |||
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. ☑ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. ☐ Yes ☑ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. ☑ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). ☑ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer ☑ | Accelerated filer ☐ | Non-accelerated filer ☐ | Smaller reporting company ☐ | Emerging growth company ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). ☐ Yes ☑ No
The aggregate market value of Perspecta’s voting and non-voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter, which was September 30, 2019, was approximately $3.61 billion.
160,584,045 shares of common stock, par value $0.01 per share, were outstanding as of April 30, 2020.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of Perspecta’s Definitive Proxy Statement relating to its 2020 Annual Meeting of Shareholders (the “2020 Proxy Statement”), which will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A within 120 days after the registrant’s fiscal year ended March 31, 2020, are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K where indicated.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Item | Page | ||
1. | |||
1A. | |||
1B. | |||
2. | |||
3. | |||
4. | |||
5. | |||
6. | |||
7. | |||
7A. | |||
8. | |||
9. | |||
9A. | |||
9B. | |||
10. | |||
11. | |||
12. | |||
13. | |||
14. | |||
PART IV | |||
15. | |||
16. | |||
1
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
All statements and assumptions contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K that do not directly and exclusively relate to historical facts could be deemed “forward-looking statements.” Forward-looking statements are often identified by the use of words such as “anticipates,” “believes,” “estimates,” “expects,” “may,” “could,” “should,” “forecast,” “goal,” “intends,” “objective,” “plans,” “projects,” “strategy,” “target” and “will” and similar words and terms or variations of such. These statements represent current expectations and beliefs, and no assurance can be given that the results described in such statements will be achieved.
Forward-looking statements include, among other things, statements with respect to our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows, business strategies, prospects, operating efficiencies or synergies, competitive position, growth opportunities, share repurchases, dividend payments, plans and objectives of management and other matters. Such statements are subject to numerous assumptions, risks, uncertainties and other factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those described in such statements, many of which are outside of our control. Important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those described in forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to:
• | various risks related to health epidemics, pandemics and similar outbreaks, such as the coronavirus disease 2019 (“COVID-19”) pandemic, which may have material adverse effects on our business, financial position, results of operations and/or cash flows; |
• | any issue that compromises our relationships with the U.S. federal government, or any state or local governments, or damages our professional reputation; |
• | changes in the U.S. federal, state and local governments’ spending and mission priorities that shift expenditures away from agencies or programs that we support; |
• | any delay in completion of the U.S. federal government’s budget process; |
• | failure to comply with numerous laws, regulations and rules, including regarding procurement, anti-bribery and organizational conflicts of interest; |
• | failure by us or our employees to obtain and maintain necessary security clearances or certifications; |
• | our ability to compete effectively in the competitive bidding process and delays, contract terminations or cancellations caused by competitors’ protests of major contract awards received by us; |
• | our ability to accurately estimate or otherwise recover expenses, time and resources for our contracts; |
• | problems or delays in the development, delivery and transition of new products and services or the enhancement of existing products and services to meet customer needs and respond to emerging technological trends; |
• | failure of third parties to deliver on commitments under contracts with us; |
• | misconduct or other improper activities from our employees or subcontractors; |
• | delays, terminations or cancellations of our major contract awards, including as a result of our competitors protesting such awards and the impact of the U.S. Navy’s decision not to award us the re-compete of the Next Generation Enterprise Network (“NGEN”) contract, known as the Next Generation Enterprise Network-Re-Compete Service Management, Integration, and Transport (“NGEN-R SMIT”) contract; |
• | failure of our internal control over financial reporting to detect fraud or other issues; |
• | failure or disruptions to our systems, due to cyber-attack, service interruptions or other security threats; |
• | failure to be awarded task orders under our indefinite delivery/indefinite quantity (“ID/IQ”) contracts; |
• | changes in government procurement, contract or other practices or the adoption by the government of new laws, rules and regulations in a manner adverse to us; |
• | uncertainty from the expected discontinuance of the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) and transition to any other interest rate benchmark; and |
• | the other factors described in “Risk Factors” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
There may be other factors that may cause our actual results to differ materially from the forward-looking statements, including factors disclosed under the sections titled “Business,” “Risk Factors,” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” herein and in other information we publicly disclose from time to time. You should evaluate all forward-looking statements made in this Annual Report on Form 10-K in the context of these risks and uncertainties. Our public filings may be accessed through our investor relations website, https://investors.perspecta.com, or through the website maintained by the SEC at https://www.sec.gov.
No assurance can be given that any expectation, goal or plan set forth in any forward-looking statement can or will be achieved, and readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on such statements which speak only as of the date they are made. We do not undertake any obligation to update or release any revisions to any forward-looking statement or to
2
report any events or circumstances after the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events, except as required by law.
Throughout this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we refer to Perspecta Inc., together with our consolidated or combined subsidiaries, as “we,” “us,” “our,” “Perspecta,” or the “Company.” All references to “Vencore” are to our legacy companies Vencore Holding Corp. (“Vencore HC”), KGS Holding Corp. (“KGS HC”) and their respective subsidiaries on a combined basis for the period prior to May 31, 2018, the date they were acquired by Perspecta. The term “Parent” refers to DXC Technology Company (“DXC”) for the period from April 1, 2017 to May 31, 2018. We also refer throughout to (1) the Consolidated Combined Financial Statements as the “Financial Statements,” (2) the Consolidated Combined Statements of Operations as the “Statements of Operations,” (3) the Consolidated Combined Statements of Comprehensive Income as the “Statements of Comprehensive Income,” (4) the Consolidated Balance Sheets as the “Balance Sheets,” (5) the Consolidated Combined Statements of Cash Flows as the “Statements of Cash Flows” and (6) the Consolidated Combined Statements of Changes in Shareholders’ Equity as the “Statements of Changes in Shareholders’ Equity.” In addition, references throughout to numbered “Notes” refer to the numbered Notes to the Consolidated Combined Financial Statements that we include in the Financial Statements and Supplementary Data section of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
Our Company
Perspecta is a leading provider of end-to-end enterprise information technology (“IT”), mission, and operations-related services across the United States (“U.S.”) federal government as well as to certain state and local government agencies.
Perspecta provides government customers with highly differentiated offerings and capabilities, offering compelling scale, a promising financial profile, an extensive intellectual property portfolio, and unparalleled knowledge in areas that are directly aligned with government priorities. Perspecta has evolved from some of the most iconic firms in government services market with a proud legacy of service to customers for more than 50 years.
On May 31, 2018, Perspecta Inc. became an independent company through the consummation of the spin-off of the DXC U.S. Public Sector (“USPS”) business (the “Spin-Off”), and mergers with Vencore HC and KGS HC (the “Mergers”). To effect the Spin-Off, DXC distributed all of the shares of Perspecta common stock on a pro rata basis to the record holders of DXC common stock (the “Distribution”). On June 1, 2018, Perspecta began trading on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol “PRSP.”
On July 31, 2019, Perspecta acquired all of the equity interests of Knight Point Systems, LLC (“Knight Point”). Knight Point delivers end-to-end managed services and solutions focused on modernizing IT systems, protecting critical networks and driving digital transformation to improve customer transparency and operational efficiency. Knight Point leverages a portfolio of intellectual property to solve complex customer challenges in cloud, cybersecurity and agile development and operations (“DevOps”) environments.
Our Offerings
With offerings in mission services, digital transformation and enterprise operations, our team of nearly 14,000 engineers, analysts, investigators and architects create repeatable, differentiated solutions aligned to our customers' goals. Our end-to-end portfolio of service offerings and solutions are supported by a strong engine of innovation in Perspecta Labs Inc. (“Perspecta Labs”), and a broad partner network. Our ten offering families consist of:
• | Application services. We develop, modernize, transform and manage customers’ enterprise application portfolios enabling a shift of IT spend from maintenance and operations to innovation. Our customers experience accelerated time-to-mission benefits by applying agile DevOps frameworks, accelerators, and other reusable components. |
• | Analytics and data services. We offer an analytic services portfolio and robust partner ecosystem which enables our customers to gain rapid insights that accelerate their digital transformation journey and to make critical decisions to enable business and mission outcomes defensible with data-driven analysis. |
3
• | Applied research. We deliver research, engineering, consulting and technology solutions that drive market innovation. Primary research areas include cybersecurity, cloud, quantum computing, network configuration and data analytics capabilities. |
• | Cybersecurity. We bring transformative cyber expertise and mission-enabled solutions to the forefront of operations. Our security solutions predict attacks, proactively respond to threats, ensure compliance and protect data, applications, infrastructure and endpoints. |
• | Cloud computing and infrastructure services. We help customers maximize their private cloud, public cloud and legacy infrastructure, in order to transform, optimize, and secure their hybrid environments. |
• | Digital strategy and transformation. We accelerate customers’ digital transformation and business results through innovative approaches to transforming legacy technologies, processes and applications. |
• | Digital workplace. We provide a user-focused digital workplace environment to enable government organizations to accomplish their missions with secure devices, productivity and collaboration tools, and workplace support. |
• | Integrated Solutions. Our industry-specific solutions enable organizations to quickly integrate technology, transform their operations and develop new ways of doing business. |
• | Investigative services. We provide identification and authentication validation to government organizations through investigative and risk mitigation services. We also help the government identify and eliminate fraud, waste, and abuse through integrated data analysis, medical claims review, and investigation services. |
• | Systems engineering and integration. We help customers design, manage and integrate complex systems throughout the project life cycle to ensure enterprises are successful, affordable and reliable. |
Long Standing Relationships with Industry and Customers
We support the toughest problems throughout the U.S. public sector such as protecting networks from cyber threats, enabling a trusted workforce to handle sensitive information, delivering student financial aid, and ensuring the integrity of government health care payments. Using our market-leading enterprise offerings and solutions, we help our government customers implement modern collaborative workplaces, hybrid cloud platforms and integrated digital systems of engagement with their enterprise management systems. By delivering these modern enterprise solutions, often while ensuring interoperability with mission critical legacy systems, we help our government customers better realize the benefits of technology, which will ultimately enable them to fulfill their mission objectives and achieve business outcomes.
We believe that our sophisticated solutions and proprietary processes and tools, developed over decades-long support of our customers’ missions, promote our longstanding relationships with our customers, some of which span over 50 years.
We categorize our customers into two reporting segments that engage in business activities from which revenue is recognized and expenses are incurred, and for which discrete financial information is available. These operating results are regularly reviewed by our chief operating decision maker, who is our Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”). Our reportable segments are:
• | Defense and Intelligence, which provides services to the Department of Defense (“DoD”), intelligence community, branches of the U.S. Armed Forces, and other DoD agencies; and |
• | Civilian and Health Care, which provides services to the Department of Homeland Security (“DHS”), Department of Justice (“DOJ”), Department of Health and Human Services (“HHS”), as well as other federal civilian and state and local government agencies. |
In fiscal year 2020, 94% of our $4.50 billion in revenue was from the U.S. federal government, and we serve as the prime contractor on 94% of our contracts, as measured by annual revenue. Although rarely exercised, a significant portion of each segment’s contracts are subject to termination at the election of the government.
Defense and Intelligence Segment
We provide a broad array of services for our Defense and Intelligence customers, including enterprise IT for massive DoD networks, model-based systems engineering and integration to support classified missions, applied research and development for defense and intelligence laboratories, and investigative support for personal security clearances. Example customer engagements include:
• | U.S. Navy. We provide the U.S. Navy with innovative solutions to secure its intranet, the largest in the world, by implementing a broad range of integrated security solutions to improve depth and secure posture, and network security and authentication for secure network access across all devices. Through our multifaceted security |
4
solution, the U.S. Navy’s intranet successfully detects over 300 million threats and prevents over 2.5 billion unauthorized intrusion attempts per year.
• | Defense Information Systems Agency (“DISA”). We partnered with DISA to transform key applications and services to drive efficiencies, improve security and capture costs savings. Through the integration of our offerings, DISA is able to provide integrated, interoperable and assured infrastructure capabilities, applications and services to its users across the software development lifecycle, engineering and technical support. |
• | U.S. federal government. We are partnering with a client in the U.S. federal government to develop a DevOps environment, providing IT and engineering services for software residing on the government’s secure version of Amazon Web Services (“AWS”). The program scope includes identifying, prioritizing, integrating, and testing new and modified software and components to satisfy the architectural vision of the enterprise of the software services platform. Through the contract, our government client has enjoyed an exponential growth in the user base and the number of software services offerings to the enterprise community, and as a result, realized savings in project schedules and cost across many contracts within the enterprise. |
Revenue generated from Defense and Intelligence segment customers was $3.10 billion, or approximately 69% of our revenue in fiscal year 2020 as compared to $2.59 billion, or approximately 64% of our revenue in fiscal year 2019. Our key Defense and Intelligence customers include the U.S. Army, U.S. Navy, U.S. Marine Corps, U.S. Air Force, and the Joint Combatant Commands. In fiscal year 2020, customers that generated more than 10% of Defense and Intelligence segment revenue include the U.S. Navy, the National Reconnaissance Office and the Defense Counterintelligence and Security Agency.
Civilian and Health Care Segment
Our work spans the full breadth of civilian and health care agencies across the U.S. federal government as well as selected state and local governments, including homeland security, financial services, law enforcement, education, and enterprise IT. Example customer engagements include:
• | Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (“CMS”). As a result of the implementation of the Affordable Care Act, uninsured Americans were able to purchase health insurance through the Federal Health Insurance Marketplace (healthcare.gov), which we helped CMS and the U.S. government develop. More than 18 million people used the healthcare.gov website from November 1 to December 15, 2017, including 700,000 users on the Spanish-language website. Despite the high usage, website reliability and security were never compromised. |
• | County of San Diego. To help San Diego County probation officers more efficiently manage their caseloads, we developed the Probation Utility and Mobile Applications, which has provided on-demand access to cases and the ability to enter contact notes in the field. We rationalized and modernized hundreds of applications in a heterogeneous applications infrastructure across a distributed management structure, transforming the applications environment to enable the county to achieve its IT vision of “anytime, anywhere” service. |
Revenue generated from Civilian and Health Care segment customers was $1.40 billion, or approximately 31% of our revenue in fiscal year 2020 as compared to $1.44 billion, or approximately 36% of our revenue in fiscal year 2019. In fiscal year 2020, CMS, DHS and the County of San Diego each generated more than 10% of Civilian and Health Care segment revenue.
Business Environment and Competitive Landscape
Market Dynamics
We believe the future of the U.S. public sector is sustained change enabled by new technologies, increased prioritization of research and development and the demand for empowered citizens and employees. Organizations are expected to deliver services that range from simple and flexible citizen-focused solutions that support their daily interactions with state and federal agencies, to complex, enterprise systems and mission solutions that aid in supporting our country’s critical defense and intelligence needs. Organizations must be able to offer advanced research and development initiatives that target evolving technologies and expand the U.S.’ lead in myriad essential capabilities such as cybersecurity and artificial intelligence.
To adapt to these changing needs, government agencies are developing an ecosystem of partners and value-added service providers who can collaborate with industry on new technologies, and creating connected environments through
5
digital platforms. They are also overhauling processes through digital transformation and gaining control over their vast IT estate to become more effective and efficient in supporting programs.
At the center of this shift is a rapid migration from government-owned and developed custom IT systems, to standardized, service-delivered platforms and utilities. In this environment, we believe a limited number of key digital platforms will become dominant, such as Microsoft Azure, Office 365 and Microsoft Dynamics, AWS and ServiceNow, Inc. (“ServiceNow”).
Competitive Landscape
Our market for providing services and solutions to the U.S. public sector is highly competitive and fragmented, favoring companies with innovative capabilities, deep domain expertise, proven delivery and competitive cost structures. The competitive landscape continues to evolve, as many of our competitors are leveraging mergers and acquisitions to create additional scale, add capabilities or gain access to new customers. Simultaneously, we are seeing increased pressure for many customers to utilize small businesses. Despite these challenges, we believe we are well suited to compete given our deep customer insight and the breadth of our enterprise IT and mission-support. Given that we provide services across the U.S. public sector marketplace, we regularly compete and partner with a broad array of companies including:
• | Pure-play U.S. government service providers that are highly specialized firms with exceptional mission knowledge, customer intimacy or specific intellectual property (“IP”) that can make them major competitors in the markets that they serve. Some of our competitors in this category include Leidos Holdings, Inc., Booz Allen Hamilton Inc., CACI International Inc., Science Applications International Corporation and ManTech International Corporation. |
• | IT and professional services arms of large aerospace and defense contractors that are capable of competing across our entire market, possessing the reputation and ability to compete on large deals with any U.S. government agency and the financial strength to manage and execute large-scale programs. Some of the large defense contractors we regularly compete with include Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation, General Dynamics, Raytheon Company, and The Boeing Company. |
• | Diversified commercial consulting, technology and outsourcing service providers that are successful with commercial customers, and leverage those commercial qualifications and references to compete broadly across the public sector market. Some of our competitors in this category include subsidiaries of International Business Machines Corporation, Deloitte LLP, AT&T Inc., Verizon Communications Inc., Dell Inc., Accenture plc, NTT Data Corp, and CGI Group Inc. |
• | Small businesses that generally provide services to the U.S. government pursuant to requirements and socioeconomic incentive programs designed to create entrepreneurial opportunities for small business owners. These can include businesses identified to receive a “fair proportion” of government contracts through the Small Business Act such as small disadvantaged businesses, woman owned small businesses, HUBZone businesses and service disabled veteran owned small businesses. |
• | Commercial IT vendors have recently emerged as players in the U.S. government market. These vendors include AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Inc., Salesforce.com, Inc., ServiceNow and other cloud providers. We typically do not compete directly with these firms. Rather, we often compete with other systems integrators that leverage these vendors as a core part of their solution on a specific business opportunity. |
Our ability to compete successfully in the market is predicated on the combination of deep customer relationships, innovative technical capabilities, a highly skilled workforce and the relentless commitment to solving our customers’ most pressing mission challenges.
Employees
As a service company providing enterprise solutions, our employees are our most valuable and important asset. As of March 31, 2020, we had nearly 14,000 full-time and part-time employees led by an experienced team of senior executives with a long history of supporting the U.S. public sector.
Approximately 19% of our employees are military veterans. Approximately 75% of our employees hold some form of security clearance or background investigation certification. Approximately 25% of our employees hold Top Secret and/or Sensitive Compartmented Information level clearance, which typically requires the completion of a polygraph.
6
Intellectual Property
Our services and solutions are not generally dependent upon patent protection, although we anticipate we will selectively seek certain patent protections, and we own or hold licenses under more than 270 patents and patent applications. Our largely proprietary IP portfolio, comprising products, technical services, consulting, methodologies, and know-how, are protected using non-disclosure agreements and contractual arrangements, as well as one or more of the following: trade secret, patent, copyright or trademark protections.
For our work under U.S. federal government funded contracts and subcontracts, the U.S. federal government obtains certain rights to data, software and related information developed under such contracts or subcontracts. These rights may allow the U.S. federal government to disclose such data, software and related information to third parties.
Intellectual Property Arrangements with DXC
Pursuant to the Separation and Distribution Agreement (the “SDA”) and the Intellectual Property Matters Agreement (“IPMA”) entered into between us and DXC on May 31, 2018, DXC retained ownership of substantially all proprietary IP owned by DXC and USPS at the time of the Distribution and used by us. Pursuant to the IPMA, DXC grants us a perpetual, royalty-free, non-assignable license to certain know-how owned by DXC that we used to run our business prior to the Spin-Off. In addition, DXC grants us a perpetual, royalty-free, non-assignable license to certain software used in the conduct of the Perspecta business (including binaries, APIs, libraries, scripts, patches, configuration files, examples and documentation). Upon termination or expiration of the IPMA, we will only be entitled to access and use the then-current versions of the licensed products in our possession. The foregoing licenses granted to us will be restricted to use solely in connection with U.S. government and certain state and local government customers, and will be exclusive with respect to the federal government market for a period of five years, and non-exclusive with respect to certain U.S. state and local government customers. In addition, any improvements we make to such IP or derivative works of such IP that we develop during the five-year term of the agreement will be assigned to DXC and licensed back to us subject to the same limitations on use. Any additional rights to use other DXC products, improvements or proprietary rights will be negotiated by the parties in good faith on commercially reasonable arm’s-length terms.
Pursuant to the IPMA, we grant to DXC a perpetual, royalty-free, transferrable, assignable license to know-how owned by us as of the Spin-Off. Further, we grant to DXC a perpetual, royalty-free, fully paid-up, non-assignable license to any IP acquired or developed by us within six months following the Spin-Off (other than IP rights acquired from Vencore HC or KGS HC). During the first five years following the Distribution, the foregoing licenses granted by us will be restricted to use solely in connection with private sector customers on an exclusive basis and certain U.S. state and local government customers on a non-exclusive basis.
In addition to the foregoing licenses, we grant DXC a non-transferrable, non-assignable license for the five years following the Distribution to access, use, copy, make improvements and sublicense certain IP we obtained from our acquisition of Vencore HC or KGS HC. The foregoing license is exclusive with respect to DXC’s private sector business and non-exclusive for all other fields. Such license is royalty-free to the extent DXC does not commercially exploit the IP of Vencore HC or KGS HC, and will otherwise be subject to a commercially reasonable royalty, to be negotiated in good faith, for commercial exploitation. Further, we agreed to negotiate in good faith the terms and conditions of a license or services agreement relating to or permitting use by DXC of Perspecta Labs as acquired from Vencore HC and our existing security and digital protection service offerings, in each case on commercially reasonable arm’s-length terms in DXC’s private sector field. Further, during the five years following the Distribution, DXC will have the first right to participate in the event Perspecta Labs wishes to pursue research and development which has potential applicability in the DXC private sector field. Perspecta Labs must notify DXC of such opportunities and DXC has the right to elect to enter a collaborative development and commercialization effort with Perspecta Labs.
All licenses granted to us by DXC will not extend to any acquiring party of our business, and will be limited to the Perspecta entities that are subsidiaries prior to such acquisition. If either we or DXC divest any portion of our businesses or acquire a new business, the licenses granted under the IPMA may follow such divested business or extend to such newly acquired business, provided the licensed party adheres to all restrictions on the relevant license, notably the relevant licensed fields of each party.
DXC will indemnify Perspecta from all losses incurred by Perspecta as a direct result of any third-party claim that Perspecta’s use of any improvements to the products licensed by DXC under the IPMA infringes or misappropriates any U.S. copyright, trademark or trade secret, except to the extent resulting from Perspecta’s modification, adaptation, failure
7
to update, or third-party components. Perspecta will indemnify DXC from all losses incurred by DXC as a direct result of any third-party claim relating to Perspecta’s use of the products licensed by DXC, or arising from DXC’s use of Perspecta’s improvements to the licensed products, except to the extent resulting from DXC’s modification, adaptation, failure to update, or third-party components.
Regulatory Matters
As a U.S. government contractor, Perspecta’s business is heavily regulated and, as a result, our need for compliance awareness and business and employee support is significant. Specifically, Perspecta’s industry is governed by various laws and regulations, including but not limited to laws and regulations relating to: the formation, administration, and performance of contracts; the security and control of information and information systems; international trade compliance; human trafficking; and the mandatory disclosure of “credible evidence” of a violation of certain criminal laws receipt of significant overpayments, or violations of the civil False Claims Act. In addition, U.S. government contractors are generally subject to other federal and state laws and regulations, including:
• | the Federal Acquisition Regulation (“FAR”), agency supplements to the FAR, and related regulations, which regulate the formation, administration, and performance of U.S. federal government contracts; |
• | the False Claims Act, which allows the government and whistleblowers filing on behalf of the government to pursue treble damages, civil penalties and sanctions for the provision of false or fraudulent claims to the U.S. federal government. |
• | the Truth in Negotiations Act, which requires certification and disclosure of cost and pricing data in connection with the negotiation of certain contracts, modifications, or task orders; |
• | the Procurement Integrity Act, which regulates access to competitor bid and proposal information, as well as certain internal government procurement sensitive information, and regulates our ability to provide compensation to certain former government procurement officials; |
• | laws and regulations restricting the ability of employees of the U.S. government to accept gifts or gratuities from a contractor; |
• | post-government employment laws and regulations, which restrict the ability of a contractor to recruit and hire current employees of the U.S. government and deploy former employees of the U.S. government; |
• | laws, regulations, and executive orders requiring the safeguarding of and restricting the use and dissemination of information classified for national security purposes or determined to be “controlled unclassified information,” “covered defense information,” or “for official use only”; |
• | laws and regulations relating to the export of certain products, services, and technical data, including requirements regarding any applicable licensing of our employees involved in such work; |
• | laws, regulations, and executive orders regulating the handling, use, and dissemination of personally identifiable information in the course of performing a U.S. government contract; |
• | laws, regulations, and executive orders governing organizational conflicts of interest that may prevent us from bidding for or restrict our ability to compete for certain U.S. government contracts because of the work that we currently perform for the U.S. government; |
• | laws, regulations, and executive orders that mandate compliance with requirements to protect the government from risks related to our supply chain; |
• | laws, regulations, and mandatory contract provisions providing protections to employees or subcontractors seeking to report alleged fraud, waste, and abuse related to a government contract; |
• | the DoD’s “Contractor Business Systems Rule,” which authorizes DoD agencies to withhold a portion of our payments if we are determined to have a significant deficiency in any of our accounting, cost estimating, purchasing, earned value management, material management and accounting, or property management systems; and |
• | the Cost Accounting Standards and the Cost Principles, which impose accounting requirements that govern our right to reimbursement under certain cost-based U.S. government contracts and require consistency of accounting practices over time. |
We are also subject to oversight by the U.S. Office of Federal Contract Compliance Programs (“OFCCP”) for federal contract and affirmative action compliance, including the following areas:
• | affirmative action plans; |
• | applicant tracking; |
• | compliance training; |
• | customized affirmative action databases and forms; |
8
• | glass ceiling and compensation audits; |
• | desk and on-site audits; |
• | conciliation agreements; |
• | disability accessibility for applicants and employees; |
• | diversity initiatives; |
• | equal employment opportunity compliance; |
• | employment eligibility verification (known as “E-Verify”); |
• | internal affirmative action audits; |
• | internet recruiting and hiring processes; |
• | OFCCP administrative enforcement actions; |
• | record-keeping requirements; and |
• | Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 compliance. |
The U.S. federal government routinely revises its procurement practices and adopts new contract statutes, rules and regulations. In order to anticipate compliance with changes to laws and regulations, we participate in industry-wide associations that represent the industry perspectives on proposed regulations to the government, monitor proposed regulatory changes to adapt our policies and processes to accommodate the changes when they become effective, maintain compliance staff in our corporate departments, and conduct awareness and training for affected employees, such as our contracts staff and government compliance team.
The U.S. federal government has a broad range of tools available to enforce its procurement law and policies. These include debarring or suspending a particular contractor, certain of its operations and/ or individual employees from future government business. Individuals, on behalf of the federal government, may also bring qui tam suits against us for any alleged fraud related to payments under a U.S. federal government contract or program.
Seasonality
The U.S. federal government’s fiscal year ends on September 30th of each year. It is not uncommon for U.S. federal government agencies to award extra tasks or complete other contract actions in the weeks before the end of its fiscal year in order to avoid the loss of unexpended fiscal year funds. We have historically experienced increased bid and proposal costs in the months leading up to the U.S. federal government’s fiscal year end as we pursue new contract opportunities shortly before the U.S. federal government fiscal year end. We also experience some seasonality effects from the timing of the fiscal year end close for state and local governments, which in many instances are different than the U.S. federal government fiscal year end. In general, we tend to experience an increase in revenue in our first and fourth fiscal quarters from our state and local government customers as the first half of the calendar year is when funds are generally allocated to specific projects. Finally, we also tend to generate less revenue and profit from our labor services during our third fiscal quarter as a result of higher leave-taking during the holiday season.
Available Information
We use our corporate website, https://perspecta.com, as a routine channel for distribution of important information, including detailed company information, financial news, Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) filings, Annual Reports, historical stock information and links to webcasts. Perspecta’s Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, all amendments to those reports, and the Proxy Statements for our Annual Meetings of Shareholders will be made available, free of charge, on our corporate website as soon as reasonably practicable after such reports have been filed with or furnished to the SEC.
Our corporate governance guidelines, Board of Directors’ committee charters (including the charters of the Audit Committee, Human Resources and Compensation Committee and Nominating/Corporate Governance Committee) and code of business conduct and ethics entitled “The Standard” are also available on our website. The information on our website is not incorporated by reference into, and is not a part of, this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The SEC maintains a website (https://www.sec.gov) that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC.
9
Information About Our Executive Officers
The following table presents information concerning the individuals who serve as our executive officers, and their titles, including a brief summary of the business experience of each of them.
Name | Age | Year First Appointed as Officer | Position Held With the Registrant as of the Filing Date | |||
Mr. John M. Curtis | 63 | 2018 | President, Chief Executive Officer and Director | |||
Mr. John P. Kavanaugh | 58 | 2018 | Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | |||
Mr. James L. Gallagher | 53 | 2018 | Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary | |||
Ms. Tammy M. Heller | 47 | 2018 | Senior Vice President and Chief Human Resources Officer | |||
Mr. William G. Luebke | 53 | 2018 | Senior Vice President, Principal Accounting Officer and Controller | |||
John M. Curtis has served as our President, Chief Executive Officer and as a Director on our Board of Directors since May 2018. From July 2013 until the completion of the Spin-Off and Mergers, Mr. Curtis was the President and Chief Executive Officer of Vencore, Inc., a private defense contractor.
John P. Kavanaugh has served as our Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer since May 2018. Mr. Kavanaugh was previously the Vice President of Finance for the Americas Region of DXC, a multinational information technology services provider, since April 2017. Mr. Kavanaugh previously served as the Vice President of Finance for the Americas Region of Computer Sciences Corporation (“CSC”), a multinational information technology services and professional services provider, from January 2015 to April 2017.
James L. Gallagher has served as our Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary since May 2018. Mr. Gallagher was previously the Vice President and Deputy General Counsel for the USPS Region of DXC since April 2017. From November 2015 to March 2017, Mr. Gallagher served as Vice President and Associate General Counsel for the U.S. Public Sector business at HPE, a multinational enterprise information technology company, and held that same role at Hewlett-Packard Company, a multinational information technology company, from 2013 to October 2017.
Tammy M. Heller has served as our Senior Vice President and Chief Human Resources Officer since May 2018. From 2014 to March 2018, Ms. Heller was the Vice President of Global Human Resources at CGI Group Inc., a global IT consulting, systems integration, outsourcing, and solutions company.
William G. Luebke has served as our Senior Vice President, Principal Accounting Officer and Controller since May 2018. Mr. Luebke served from December 2015 to March 2018 as Vice President, Controller and Principal Accounting Officer of CSRA Inc., an information technology services government contractor. Mr. Luebke previously served as Head of Global Internal Audit and Enterprise Risk Management at CSC from August 2013 to November 2015.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
This section highlights significant factors, events, and uncertainties that make an investment in our securities risky. The events and consequences discussed in these risk factors could, in circumstances we may not be able to accurately predict, recognize, or control, have a material adverse effect on our business, growth, reputation, prospects, financial condition, operating results, cash flows, liquidity, and stock price. These risk factors do not identify all risks that we face; our operations could also be affected by factors, events, or uncertainties that are not presently known to us or that we currently do not consider to present significant risks to our operations.
Risks Relating to Our Business
We face various risks related to health epidemics, pandemics and similar outbreaks, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, which may have material adverse effects on our business, financial position, results of operations and/or cash flows.
We face various risks related to health epidemics, pandemics and similar outbreaks, including the global outbreak of COVID-19, which the World Health Organization declared as a pandemic in March 2020. The continued spread of COVID-19 has led to disruption and volatility in the global capital markets, which increases the cost of capital and adversely impacts access to capital. If significant portions of our workforce or subcontractors are unable to work
10
effectively, including because of illness, quarantines, shelter-in-place orders, closures of our facilities, closures of our customers’ facilities or other restrictions or government actions in connection with the COVID-19 pandemic, our operations will likely be impacted. We may be unable to perform fully on our contracts and our costs may increase as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. These cost increases may not be fully recoverable or adequately covered by insurance.
It is possible that the continued spread of COVID-19 could also further cause disruption in our operations, cause delay, or limit the ability of, the U.S. government and other customers to perform, including in making timely payments to us, impact our customers’ ability or timeliness to award new business, impact our ability to hire employees necessary to perform our operations, impact investment performance and cause other events that would negatively impact our business that we currently are unable to predict. Additionally, it is possible that customers may cancel our contracts, which would negatively impact our business.
We continue to work with our customers, employees, suppliers, local communities and others to address the global COVID-19 pandemic. We continue to monitor the situation, to assess further possible implications to our operations, supply chain and customers, and to take actions in an effort to mitigate adverse consequences. At this time we cannot predict the future impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, but it could have a material adverse effect on our operating results and cash flows.
We depend heavily on contracts with the U.S. government and its contractors for most of our revenue. If our relationships with such agencies are harmed, our future revenue and operating profits could materially decline.
The government, at the U.S. federal, state and local levels, is our primary customer, with revenue from U.S. government contracts, either as a prime contractor or a subcontractor, accounting for substantially all of our revenue. We believe the performance of our business will continue to depend primarily on our ability to be awarded work under U.S. government contracts, as we expect this will be the primary source of substantially all of our revenue in the foreseeable future.
For this reason, any issue that compromises our relationship with the U.S. government generally or any U.S. government agency that we serve could cause our revenue to materially decline. Among the key factors in maintaining our relationship with U.S. government agencies are our performance on contracts, the strength of our professional reputation, compliance with applicable laws and regulations, and the strength of our relationships with customer personnel. In addition, the failure to maintain adequate protection against security breaches, including from cyber-attack, or the mishandling or perceived mishandling of sensitive information, could harm our relationship with U.S. government agencies. This could include, for example, our failure to maintain the confidentiality of sensitive information associated with the work we perform for our customers, or even disclosure of the existence of our business relationships with certain of our customers, including as a result of misconduct or other improper activities by our employees or subcontractors. Our relationship with the U.S. government could also be damaged as a result of an agency’s dissatisfaction with work performed by us, a subcontractor, or other third parties that provide services or products for a specific project for any reason, including due to perceived or actual deficiencies in the performance or quality of our work. In such case, we may incur additional costs to address any such situation and the profitability of that work might be impaired. In addition, to the extent our performance under a contract does not meet a U.S. government agency’s expectations, such agency customer may seek to terminate the contract prior to its scheduled expiration date, provide a negative assessment of our performance to government-maintained contractor past-performance repositories, fail to award us additional business under existing contracts or otherwise, and direct future business to our competitors. Further, negative publicity concerning government contractors in general or us in particular may harm our reputation with U.S. government contractors. To the extent our reputation or relationships with U.S. government agencies is impaired, our revenue and operating profits could materially decline.
Changes in U.S. government spending, programs and mission priorities could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations or prospects.
Substantially all of our revenue is generated from contracts with the U.S. government and its agencies, and we depend significantly upon continued U.S. federal government expenditures on intelligence, defense, space and federal civilian programs for which we provide support. These expenditures have not remained constant over time, have been reduced in certain periods and recently have been affected by the U.S. federal government’s efforts to improve efficiency and reduce costs. As a result, our business, financial condition, results of operations or prospects could be adversely affected by several factors, including:
• | budgetary constraints, including Congressionally-mandated automatic spending cuts, that affect U.S. federal government spending generally or specific agencies in particular; |
11
• | changes in available funding or in government programs, including a shift in expenditures away from agencies or programs that we support; |
• | reduced U.S. federal government outsourcing of functions that we are currently contracted to provide, including as a result of increased insourcing by various U.S. federal government agencies due to changes in the definition of “inherently governmental” work, including proposals to limit contractor access to sensitive or classified information and work assignments; |
• | efforts to improve efficiency and reduce costs affecting government programs, including a continuation of recent efforts by the U.S. federal government to decrease spending for management support service contracts; |
• | government agencies awarding contracts on a technically-acceptable/lowest-cost basis to reduce expenditures; |
• | delays in the payment of our invoices by government payment offices; |
• | U.S. government shutdowns due to a failure by elected officials to fully fund the government, such as the partial shutdown in December 2018 and January 2019, and other potential disruption of the appropriations process; |
• | an inability by the U.S federal government to fund its operations as a result of a failure to increase the U.S. federal government’s debt ceiling, a credit downgrade of U.S. government obligations or for any other reason; |
• | elections, particularly that result in a change of the Presidential administration or control of Congress, or other changes in the political climate; and |
• | general economic conditions, including a slowdown of the economy or unstable economic conditions and actions taken in response to such conditions, including emergency spending that may reduce funds available for other government priorities. |
In addition, any disruption in the functioning of U.S. government agencies, including as a result of U.S. government closures and shutdowns, pandemic diseases or viral contagions such as the recent outbreak of COVID-19, terrorism, war, natural disasters and other weather-related events, destruction of or damage to U.S. government facilities, and other potential calamities could have a negative impact on our operations and cause us to lose revenue or incur additional costs due to, among other things, our inability to deploy our staff or our subcontractors to customer locations or facilities as a result of such disruptions.
The U.S. federal government budget deficits, the national debt, and prevailing economic conditions, as well as government actions taken to address them, could negatively affect U.S. federal government expenditures on intelligence, defense, space and federal civilian programs for which we provide support. In particular, the Budget Control Act of 2011, as amended by subsequent legislation, provides for automatic spending cuts (referred to as “sequestration”) totaling approximately $1.2 trillion between 2013 and 2021, including an estimated $500 billion in federal defense spending cuts over this time period. Although Congress acted to prevent the sequestration cuts to discretionary programs for 2019, if further action is not taken, sequestration could occur in the remainder of 2020 or in 2021. We are unable to predict the extent of the impact of budget cuts, including as a result of sequestration, on our business, results of operations and prospects. In addition, in response to an Office of Management and Budget (“OMB”) mandate, U.S. federal government agencies have reduced management support services spending in recent years. If federal awards for management support services decline, our revenue and operating profits may materially decline and further efforts by the OMB to decrease federal awards for management support services could have a material and adverse effect on our business, results of operations and prospects.
These or other factors could cause our intelligence, defense and federal civilian customers to decrease the number or value of new contracts awarded generally and fail to award us new contracts, reduce their purchases under our existing contracts, exercise their right to terminate our contracts, or not exercise options to renew our contracts, any of which could cause a material decline in our revenue.
A delay in the completion of the U.S. federal government’s budget process and statutory debt limit could have a material adverse effect on our revenue and operating results.
On an annual basis, the U.S. Congress must approve budgets that govern spending by each of the federal agencies we support. When the U.S. Congress does not pass the annual budget on a timely basis, it may enact a continuing resolution that allows U.S. federal government agencies to operate at spending levels approved in the previous budget cycle. Under a continuing resolution, funding may not be available for new projects. In addition, when U.S. federal government agencies operate on the basis of a continuing resolution, they may delay funding we expect to receive on contracts we are already performing. Any such delays would likely result in new business initiatives being delayed or canceled and could
12
have a material adverse effect on our revenue, cash flows and operating results. Furthermore, a failure to complete the budget process and fund government operations pursuant to a continuing resolution may result in a U.S. federal government shutdown, such as the partial shutdown in December 2018 and January 2019. A shutdown may result in us incurring substantial costs without reimbursement under our contracts and the delay or cancellation of key programs, which could have a material adverse effect on our revenue, cash flows and operating results.
In August 2019, legislation was enacted that raised spending levels and suspended the debt limit for two years. On August 1, 2021, the debt limit will be reinstated at a level covering all borrowing that occurred during the suspension. When the Treasury Department exhausts all financing options, it will no longer be able to pay for all federal obligations if the debt limit is not suspended or increased again. If the debt limit is exceeded, some federal payments to creditors, vendors, contractors, state and local governments, beneficiaries, and other entities would either be delayed or limited. These delays in payments would, in effect, be borrowings from contractors such as us, and would create a backlog of unpaid bills until the government collects more revenue or other sources of cash than its outlays. In some cases, delaying federal payments incurs interest penalties under some statutes such as the Prompt Payment Act, which directs the government to pay interest penalties to contractors if it does not pay them by the required payment date. Were there to be a delay in paying for all federal obligations, it is expected that this would result in significant economic and financial consequences that may have a lasting impact on federal programs and the U.S. federal government’s ability to borrow in the future. Failure by Congress to address the debt limit could result in delayed or limited payments to creditors, vendors, contractors, state and local governments and other entities, which could have a material adverse effect on our revenue and operating results.
We are subject to extensive and complex laws and regulations relating to award, administration and performance of U.S. government contracts. Our business and reputation could be adversely affected by the application of these laws.
We must comply with and are affected by laws and regulations relating to the award, administration and performance of U.S. government contracts. Government contract laws and regulations affect how we do business with our customers and impose certain risks and costs on our business. U.S. government contractors are subject to a greater risk of investigation, criminal prosecution, civil fraud, whistleblower lawsuits and other legal actions and liabilities than companies with solely commercial customers. A violation of specific laws and regulations, by us, our employees, others working on our behalf, a supplier or a venture partner, could harm our reputation and result in the imposition of fines and penalties, the termination of our contracts, suspension or debarment from bidding on or being awarded contracts, loss of our ability to export products or services, and civil or criminal investigations or proceedings. In some instances, these laws and regulations impose terms or rights that are different from those typically found in commercial transactions.
Our U.S. federal, state and local government contracts may be terminated by such U.S. federal, state or local government customer at any time and may contain other provisions permitting such customer to discontinue contract performance, allow a contract to expire, or that are otherwise unfavorable to us, and if discontinued contracts are not replaced, our operating results may differ materially and adversely from those anticipated.
U.S. federal, state and local government contracts contain provisions and are subject to laws and regulations that provide those government customers with rights and remedies not typically found in commercial contracts. These rights and remedies allow government customers to, among other things:
• | terminate existing contracts, with short notice, for convenience as well as for default; |
• | reduce orders under or otherwise modify contracts; |
• | for contracts subject to the Truth in Negotiations Act, reduce the contract price or cost where it was increased because a contractor or subcontractor furnished cost or pricing data during negotiations that was not complete, accurate, and current; |
• | for some contracts, demand a refund, make a forward price adjustment, or terminate a contract for default if a contractor provided inaccurate or incomplete data during the contract negotiation process and/or reduce the contract price under certain triggering circumstances, including the revision of price lists or other documents upon which the contract award was predicated; |
• | terminate our facility security clearances and thereby prevent us from receiving classified contracts; |
• | cancel multi-year contracts and related orders if funds for contract performance for any subsequent year become unavailable; |
• | decline to exercise an option to renew a multi-year contract or issue task orders in connection with ID/IQ contracts; |
13
• | assert rights in solutions, systems, and technology produced by us during contract performance, and continue to use that work product without continuing to contract for our services, and/or disclose or permit such work product to be used by third parties, including other U.S. government agencies and our competitors, which could harm our competitive position; |
• | prohibit future procurement awards with a particular U.S. federal government agency due to a finding of organizational conflict of interest based upon prior related work performed for the U.S. federal government agency that would give a contractor an unfair advantage over competing contractors, or the existence of conflicting roles that might bias a contractor’s judgment; |
• | suspend or debar us from doing business with the U.S. federal government; |
• | impose fines and penalties on us, and subject us to criminal prosecution; |
• | repurpose funds to address rated orders; |
• | control or prohibit the export of our services; and |
• | impose special handling and control requirements for controlled information. |
Upon termination for convenience of a fixed-price type contract, we normally are entitled to receive the purchase price for delivered items, reimbursement for allowable costs for work-in-process and an allowance for profit on the contract or adjustment for loss if completion of performance would have resulted in a loss.
Upon termination for convenience of a cost-reimbursable contract, we normally are entitled to reimbursement of allowable costs plus a portion of the fee. Allowable costs would include our cost to terminate agreements with our suppliers and subcontractors. The amount of the fee recovered, if any, is related to the portion of the work accomplished prior to termination and is determined by negotiation. We attempt to ensure that adequate funds are available by notifying the customer when its estimated costs, including those associated with a possible termination for convenience, approach levels specified as being allotted to its programs. As funds are typically appropriated on a fiscal-year basis and as the costs of a termination for convenience may exceed the costs of continuing a program in a given fiscal year, occasionally programs do not have sufficient funds appropriated to cover the termination costs were the U.S. federal government to terminate them for convenience. Under such circumstances, the U.S. federal government could assert that it is not required to appropriate additional funding.
A termination arising out of our default may expose us to liability and have a material adverse effect on our ability to compete for future contracts and orders. In addition, on those contracts for which we are teamed with others and are not the prime contractor, the U.S. federal government could terminate a prime contract under which we are a subcontractor, notwithstanding the quality of our services as a subcontractor. In the case of termination for default, the U.S. federal government could make claims to reduce the contract value or recover its procurement costs and could assess other special penalties. However, under such circumstances we have rights and access to remedial actions under laws and the FAR.
Budget cuts, the impact of sequestration or efforts by the OMB to decrease federal awards for management support services may cause U.S. federal government agencies with which we currently have contracts to terminate, reduce the number of task orders under, or fail to renew such contracts. If a government customer were to unexpectedly terminate, cancel, or decline to exercise an option to renew with respect to one or more of our significant contracts, or suspend or debar us from doing business with such government customer, our revenue and operating results could be materially harmed.
Our business is subject to reviews, audits and cost adjustments by the U.S. federal government, which, if resolved unfavorably to us, could adversely affect our profitability, cash flows or growth prospects.
Government audits and reviews may conclude that our practices are not consistent with applicable laws and regulations and result in adjustments to contract costs and mandatory customer refunds. U.S. federal government agencies, including the Defense Contract Audit Agency, the Defense Contract Management Agency (“DCMA”) and various agency Inspectors General, routinely audit and investigate government contractors. These agencies review a contractor’s performance under its contracts, its cost structure, its business systems, and compliance with applicable laws, regulations and standards. A finding of material weaknesses or significant control deficiencies in a contractor’s business systems or a finding of noncompliance with the FAR or Cost Accounting Standards can result in reduced billing rates to U.S. government customers until the material weakness or control deficiencies are corrected and their remediation is accepted by the DCMA. The U.S. federal government has the ability to decrease or withhold certain payments when it deems systems subject to its review to be inadequate. Additionally, any costs found to be misclassified may be subject to repayment. We have unaudited and/or unsettled incurred cost claims related to past years, which places risk on our ability to issue final
14
billings on contracts for which authorized and appropriated funds may be expiring. We may be subject to civil or criminal penalties and administrative sanctions, including reductions of the value of contracts, contract modifications or terminations, forfeiture of profits, suspension of payments, penalties, fines and suspension, or prohibition from doing business with the U.S. government, based on audits or investigations conducted regarding our business and operations. In addition, we could incur significant legal costs and suffer serious reputational harm if allegations of impropriety were made against us. The agencies conducting these audits and reviews have come under increased scrutiny. As a result, audits and reviews have become more rigorous and the standards to which we are held are being more strictly interpreted, which has increased the likelihood of an audit or review resulting in an adverse outcome.
Further, we are in the process of integrating the USPS and Vencore business systems, and as a result, any finding of noncompliance in either legacy company’s business system could result in a negative impact for the combined entity. Such adjustments, whether to USPS, Vencore, or to the combined entity, can be applied retroactively, which could result in significant customer refunds. Receipt of adverse audit findings or the failure to obtain an “approved” determination on our various business systems could significantly and adversely affect our business by, among other things, restricting our ability to bid on new contracts and, for those proposals under evaluation, diminishing our competitive position. A determination of noncompliance in our business systems could also result in the U.S. federal government imposing penalties and sanctions against us, including withholding of payments, suspension of payments and increased government scrutiny. Increased scrutiny could adversely impact our ability to perform on contracts, affect our ability to invoice for work performed, delay the receipt of timely payment on contracts, and weaken our ability to compete for new contracts with the U.S. federal government.
The U.S. government’s organizational conflict of interest rules could limit our ability to successfully compete for new contracts or task orders or may require us to exit or wind down certain existing contracts or task orders, any of which could adversely affect our results of operations and prospects.
Past efforts by the U.S. government to reform its procurement practices have focused, among other areas, on the separation of certain types of work to facilitate objectivity and avoid or mitigate organizational conflicts of interest, and the strengthening of regulations governing organizational conflicts of interest. Organizational conflicts of interest may arise from circumstances in which a contractor has:
• | impaired objectivity during performance; |
• | unfair access to non-public information; or |
• | the ability to set the “ground rules” for another procurement for which the contractor competes. |
A focus on organizational conflicts of interest issues has resulted in legislation and regulations aimed at increasing organizational conflicts of interest requirements, including, among other things, separating sellers of products and providers of advisory services in major defense acquisition programs. These organizational conflicts of interest regulations have led to increased bid protests related to arguments to disqualify or overturn awards based on conflict grounds.
Future legislation and regulations may increase the restrictions in current organizational conflicts of interest regulations and rules. To the extent that organizational conflicts of interest laws, regulations and rules limit our ability to successfully compete for new contracts or task orders with the U.S. government and/or commercial entities, or require us to exit certain existing contracts or task orders or wind down certain existing contracts or task orders, either because of organizational conflicts of interest issues arising from our business or because companies with which we are affiliated or with which we otherwise conduct business create organizational conflicts of interest issues for us, our results of operations and prospects could be materially and adversely affected.
We may fail to obtain and maintain necessary security clearances or certifications, which may adversely affect our ability to perform on certain contracts.
Many U.S. government programs require contractor employees and facilities to have security clearances or certifications. Depending on the level of required clearance, security clearances and certifications can be difficult and time consuming to obtain. Our inability, or that of our employees or prospective employees or facilities, to obtain or retain necessary security clearances or certifications, may prevent us from bidding on, winning or performing new contracts, or effectively competing for expiring contracts, and we may lose existing contracts, which may adversely affect our operating results and inhibit the execution of our growth strategy.
15
We derive a majority of our revenue from contracts awarded through a competitive bidding process, and our revenue and profitability may be materially adversely affected if we are unable to compete effectively in the process.
We derive a majority of our revenue from U.S. government contracts awarded through competitive bidding processes including through competitions for orders under multiple award contracts. We do not expect this to change for the foreseeable future. Our failure to compete effectively in this procurement environment would have a material adverse effect on our revenue and profitability. In addition, our current contracts are re-competed from time to time, and we are not assured of winning these re-competes. In circumstances where we do not win those re-competes, and those lost contracts are not replaced, our operating results may be materially and adversely affected. The full impact of the loss of a significant contract may not be fully reflected in our results, and may be difficult to estimate, for a lengthy period following an adverse decision. For example, in February 2020, the U.S. Navy announced that Perspecta was not awarded the NGEN-R SMIT contract, the re-compete of the NGEN contract currently held by the Company. The NGEN contract is currently set to expire on December 31, 2020. As a result of the U.S. Navy’s decision not to award the NGEN-R SMIT contract to us, our operating results may be materially and adversely affected following expiration of the contract. Additionally, we have a limited history of protesting contract awards, and our ability to successfully protest and overturn a contract award is indeterminate.
The competitive bidding process involves risk and significant costs to businesses operating in this environment, including:
• | the necessity to expend resources, make financial commitments (such as procuring leased premises) and bid on engagements in advance of the completion of their design, which may result in unforeseen difficulties in execution and cost overruns; |
• | the substantial cost and managerial time and effort spent to prepare bids and proposals for contracts that may not be awarded to us; |
• | the ability to accurately estimate the resources and costs that will be required to service any contract we are awarded; |
• | the expense and delay that may arise when our competitors protest or challenge contract awards made to us pursuant to competitive bidding, and the risk that any such protest or challenge could result in the resubmission of bids on modified specifications, or in termination, reduction, or modification of the awarded contract; and |
• | any opportunity costs associated with not bidding and winning other contracts we might otherwise pursue. |
In circumstances where contracts are held by other companies and are scheduled to expire, we may not be provided the opportunity to bid on those contracts if the government extends the existing contract. Our ability to win particular contracts that are awarded through the competitive bidding process may mean that we are not able to operate in the market for services that are provided under those contracts for the duration of those contracts to the extent that there is no additional demand for such services. In addition, when the government elects to use a multiple award ID/IQ contract, government-wide acquisition contract, or other schedule contract (collectively a “contract vehicle”) that we do not hold, we are unable to compete for work under that contract vehicle as a prime contractor. An inability to consistently win new contract awards or compete for work as a prime contractor over any extended period could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and prospects.
Our earnings and profitability may vary based on the mix of our contracts and may be adversely affected by our failure to accurately estimate or otherwise recover the expenses, time, and resources for our contracts.
We enter into several different types of contracts with our government customers for our services including cost-reimbursable, time-and-materials, and fixed-price. Each of these types of contracts, to varying degrees, involves the risk that we could underestimate our cost of fulfilling the contract, which may reduce the profit we earn or lead to a financial loss on the contract and adversely affect our operating results.
Under cost-reimbursable contracts, we are reimbursed for allowable costs up to a ceiling and paid a fee, which may be fixed or performance-based. When our actual costs exceed the contract ceiling or are not allowable under the terms of the contract or applicable regulations, we may not be able to recover those costs. In particular, there is increasing focus by the U.S. government on the extent to which government contractors, including us, are able to receive reimbursement for employee compensation, including rules that substantially limit the level of allowable compensation cost for executive-level and other employees. In addition, there is risk of compensation being deemed unallowable or payments being withheld as a result of government audit, review, or investigation.
16
Under time-and-materials contracts, we are reimbursed for the hours worked using predetermined hourly rates for each labor category, and typically reimbursed for other direct contract costs and expenses at cost. We assume financial risk on time-and-materials contracts because our cost of performance may exceed these negotiated hourly rates.
Under fixed-price contracts, we perform specific tasks for a predetermined price. Compared to time-and-materials and cost-reimbursable contracts, fixed-price contracts generally offer higher margin opportunities because we receive the benefits of any cost savings, but involve greater financial risk because we bear the impact of any cost overruns. Because we assume the risk for cost overruns and contingent losses on fixed-price contracts, an increase in the percentage of fixed-price contracts in our contract mix could increase our risk of suffering losses. In addition, the government procurement policies have focused on requiring disclosure of cost and pricing data in the context of fixed-price contracting, which can impact the profitability of those contracts.
Additionally, our profits could be adversely affected if our costs under any of these contracts exceed the assumptions we used in bidding for the contract. For example, we may miscalculate the costs, resources, or time needed to complete projects or meet contractual milestones as a result of delays on a particular project, including delays in designs, engineering information, or materials provided by the customer or a third party, delays or difficulties in equipment and material delivery, schedule changes, and other factors, some of which are beyond our control.
We have recorded provisions in our consolidated financial statements for losses on our contracts, as required under U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”), but our contract loss provisions may not be adequate to cover all actual losses that we may incur in the future. Actual losses could have an adverse effect on our business and financial results.
We may earn less revenue than projected, or no revenue, under certain of our contracts.
Many of our federal government contracts include multi-year performance periods in which Congress appropriates funds on an annual basis. As a result, many of our contracts are only partially funded at any point during their full performance period and unfunded contract work is subject to future appropriations by Congress. As a result, our backlog may not result in revenue or revenue may be delayed. We calculate our unfunded backlog based on the aggregate contract revenue that we have the potential to realize. Inaccurate backlog estimates or failure to realize estimated backlog amounts as revenue can materially and adversely affect our future operating results and cash flows.
Some of our contracts with our clients are ID/IQ contracts. ID/IQ contracts provide for the issuance by the client of orders for services or products under the contract and often contain multi-year terms and unfunded ceiling amounts, which allow but do not commit the government customer to purchase products and services from contractors. Our ability to generate revenue under each of these types of contracts depends upon our ability to be awarded task orders for specific services by the client. ID/IQ contracts may be awarded to one contractor (single award) or several contractors (multiple award). Multiple contractors must compete under multiple award ID/IQ contracts for task orders to provide particular services, and contractors earn revenue only to the extent that they successfully compete for these task orders. A failure to be awarded task orders under such contracts would have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition. In addition, our ability to maintain our existing business and win new business depends on our ability to maintain our prime and subcontractor positions on our ID/IQ contracts.
Many of our contracts contain provisions that require innovative design capabilities, are technologically complex or are dependent upon factors not wholly within our control. Failure to meet these obligations could adversely affect our revenue and profitability.
We design and develop technologically advanced and innovative products and services applied by our customers in a variety of environments. Problems and delays in development or delivery as a result of issues with respect to design, technology, licensing and patent rights, labor, learning curve assumptions or materials and components could prevent us from achieving contractual requirements.
In addition, our offerings cannot be tested and proven in all situations and are otherwise subject to unforeseen problems that could negatively affect revenue and profitability such as problems with quality and workmanship, country of origin, delivery of subcontractor components or services and unplanned degradation of product performance. Among the factors that may adversely affect revenue and profits could be unforeseen costs and expenses not covered by insurance or indemnification from the customer, diversion of management focus in responding to unforeseen problems, loss of follow-
17
on work, and, in the case of certain contracts, repayment to the U.S. government customer of contract cost and fee payments we previously received.
Failure of third parties to deliver on commitments under contracts and misconduct of employees, subcontractors, agents and business partners could cause us to lose existing contracts or customers and adversely affect our ability to obtain new contracts and customers and could have a significant adverse impact on our business and reputation.
Our contracts are complex and may require us to partner with other parties, including software and hardware vendors, to provide the solutions required by our customers. Our ability to deliver the solutions and provide the services required by our customers depends on our, and our partners’, ability to meet customers’ delivery schedules. Our failure or the failure of our partners to deliver services or products on time can adversely affect our ability to complete performance under our contracts, which may have a material and adverse impact on our revenue and profitability.
Misconduct includes fraud or other improper activities such as falsifying time or other records and violations of laws and regulations, including the Procurement Integrity Act and anti-corruption laws. Other examples include the failure to comply with our code of business conduct and ethics (The Standard), policies and procedures or with U.S. federal, state or local government procurement regulations, rules regarding the use and safeguarding of classified or other protected information, legislation regarding the pricing of labor and other costs in government contracts, laws and regulations relating to environmental, health or safety matters, international trade controls (particularly the International Traffic in Arms Regulations), lobbying or similar activities and any other applicable laws or regulations. Any data loss or information security lapses resulting in the compromise of personal information or the improper use or disclosure of sensitive or classified information could result in claims, remediation costs, regulatory sanctions against us, loss of current and future contracts and serious harm to our reputation. Although we have implemented policies, procedures and controls to prevent and detect these activities, these precautions may not prevent all misconduct and, as a result, we could face unknown risks or losses. Our failure to comply with applicable laws or regulations or misconduct by any of our employees, subcontractors, agents or business partners could damage our reputation and subject us to fines and penalties, restitution or other damages, loss of security clearance, loss of current and future customer contracts and suspension or debarment from contracting with U.S. federal, state or local government agencies, any of which would adversely affect our business and our future results.
Our business could be adversely affected by delays, terminations or cancellations caused by our competitors protesting major contract awards received by us or by adverse protest decisions in contracts awarded to us.
U.S. government contracts are frequently subject to bid protests from unsuccessful bidders on new program awards. Bid protests may result in significant expense to us, and termination or cancellation of an awarded contract as a result of the award being overturned. It can take many months for the relevant U.S. government agency to resolve protests by one or more of our competitors of contract awards we receive. Even if we do not lose the awarded contract, the resulting delay in the startup and funding of the work under these contracts may cause our revenue and profitability to be materially and adversely affected.
The U.S. government may revise its procurement, contract or other practices in a manner materially adverse to us at any time.
Our industry continues to experience significant changes to business practices as a result of an increased focus on affordability, efficiencies and recovery of costs, among other items. Legislation, regulations and initiatives dealing with procurement reform, mitigation of potential organizational conflicts of interest, deterrence of fraud, and environmental responsibility or sustainability could have a material adverse effect on us. Moreover, shifts in the buying practices of government agencies (such as increased usage of fixed-price contracts with disclosure of cost and pricing data, multiple award contracts and small business set-aside contracts) could have material adverse effects on government contractors, including us. The government may:
• | revise its procurement practices or adopt new contract laws, rules, and regulations, such as cost accounting standards, organizational conflicts of interest, and other rules governing inherently governmental functions at any time; |
• | reduce, delay, or cancel procurement programs resulting from government efforts to improve procurement practices and efficiency; |
• | limit the creation of new government-wide or agency-specific multiple award contracts; |
18
• | face restrictions or pressure from government employees and their unions regarding the amount of services the U.S. federal, state or local governments may obtain from private contractors; |
• | award contracts on a technically acceptable/lowest-cost basis to reduce expenditures, and we may not be the lowest-cost provider of services; |
• | adopt new socio-economic requirements, including setting aside procurement opportunities for small, disadvantaged, minority-, women- or veteran-owned businesses; |
• | change the basis upon which it reimburses our compensation and other expenses or otherwise limit such reimbursements; and |
• | at its option, terminate or decline to renew our contracts. |
In addition, any new contracting methods could be costly or administratively difficult for us to implement and could materially adversely affect our future revenue and profit margin. Furthermore, changes to the procurement system could cause delays in the procurement decision-making process. Any such changes to the government’s procurement practices or the adoption of new contracting rules or practices could impair our ability to obtain new or re-compete contracts, and any such changes or increased associated costs could materially and adversely affect our results of operations. Moreover, cost-cutting initiatives announced by the U.S. federal government may significantly change the way the U.S. federal government solicits, negotiates, and manages its contracts, which could result in an increase in competitive pressure and decreased profitability on contracts and have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Failure to collect, or a delay in payment of, our receivables may materially and adversely affect our business and financial condition.
We depend on the timely collection of our receivables to generate cash flow, provide working capital, and continue our business operations. Over the course of a long-term contract, a customer’s financial condition may decline and lower its ability to pay its obligations. This would cause our cash collections to decrease and bad debt expense to increase. While we may resort to alternative methods to pursue claims or collect receivables, these methods are expensive and time consuming, and successful collection is not guaranteed. Failure to collect our receivables or prevail on claims would have an adverse effect on our profitability and cash flows.
U.S. federal, state or local governments may delay or fail to pay invoices for a number of reasons, including lack of appropriated funds, lack of an approved budget, or as a result of audit findings by government regulatory agencies. Some prime contractors, for whom we are a subcontractor, have significantly fewer financial resources than we do, which may increase the risk that we may not be paid in full or that payment may be delayed.
We seek to mitigate these risks and to manage our liquidity by relying on a receivables purchase facility, as amended (the “MARPA Facility”), to provide us with up to $300 million in funding based on the availability of eligible U.S. federal government receivables and certain state government receivables. However, pursuant to the terms of the MARPA Facility, the failure by Congress to pass legislation funding U.S. federal government operations in whole or in part affecting an Approved Obligor (as defined in the MARPA Facility), or the failure of such legislation to become law, constitutes an Approved Obligor Termination Event (as defined in the MARPA Facility) that entitles the MARPA Facility administrative agent to exercise various rights and remedies, including the right to terminate commitments under the MARPA Facility. Such an event could cause either a termination or a suspension of the MARPA Facility. A termination would result in, among other things, the Company having to immediately repurchase all previously sold receivables. A protracted suspension of the commitments under the MARPA Facility would cause the suspension of new receivables sales and result in the MARPA Facility outstanding balance running off over time. Any of these outcomes could materially reduce the Company’s liquidity and increase the Company’s debt and interest expense.
Our business is subject to fluctuations that may cause our operating results to decline.
The U.S. federal government’s fiscal year ends on September 30th of each year. It is not uncommon for U.S. federal government agencies to award extra tasks or complete other contract actions in the weeks before the end of its fiscal year in order to avoid the loss of unexpended fiscal year funds. We have historically experienced increased bid and proposal costs in the months leading up to the U.S. federal government’s fiscal year end as we pursue new contract opportunities shortly before the U.S. federal government fiscal year end. We also experience some seasonality effects from the timing of the fiscal year end close for state and local governments, which in many instances are different than the U.S. federal government fiscal year end. In general, we tend to experience an increase in revenue in our first and fourth fiscal quarters from our state and local government customers as the first half of the calendar year is when funds are generally allocated to specific projects. Finally, we also tend to generate less revenue and profit from our labor services during our third fiscal
19
quarter as a result of higher leave-taking during the holiday season. We may continue to experience this seasonality in future periods, and our results of operations may be affected by it. While not certain, changes in the U.S. federal government’s funding and spending patterns have altered historical seasonality trends, supporting our approach to managing the business on an annual basis. Seasonality is just one of a number of factors, many of which are outside of our control, which may negatively affect our operating results in any period.
Our ability to provide customers with competitive services is dependent on our ability to attract and retain qualified personnel, including our senior management team.
Our ability to grow and provide our customers with competitive services is partially dependent on our ability to attract and retain highly motivated people with the skills necessary to serve our customers. The markets we serve are highly competitive, and competition for skilled employees in the technology outsourcing, consulting, and systems integration and enterprise services markets is intense. Personnel with the requisite skills, qualifications, or security clearance may be in short supply or generally unavailable. The loss of personnel could impair our ability to perform under certain contracts, which could have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations, prospects and cash flows.
Our failure to hire, train, motivate, and effectively utilize employees with the right mix of skills and experience in the right geographic regions and for the right offerings to meet the needs of our customers could adversely affect our financial performance. For example, a low employee utilization rate could adversely affect our profitability and the level of engagement of our employees. Conversely, a high employee utilization rate could adversely affect employee engagement and attrition and the quality of the work performed, as well as our ability to staff projects. Our inability to hire and retain enough employees with the skills or backgrounds needed to meet current demand could lead us to redeploy existing personnel, increase our reliance on subcontractors or increase employee compensation levels, all of which could also negatively affect our profitability. Having more employees than necessary with certain skill sets or in certain geographic areas can also increase our costs or reduce our profitability, and we may need to rebalance our supply of skills and resources with customer demand in those geographic areas. Effective utilization and retention of our employees can be adversely affected by the loss of a significant contract, such as the NGEN contract, and by disruptions in government operations or procurement processes. See “Changes in U.S. government spending, programs and mission priorities could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations or prospects” and “A delay in the completion of the U.S. federal government’s budget process and statutory debt limit could have a material adverse effect on our revenue and operating results.”
In addition to attracting and retaining qualified technical personnel, we depend on continued leadership from our senior management team. Our senior management team is very important to our business because we depend on them to lead projects successfully and because personal reputations and individual business relationships are a critical element of obtaining and maintaining customer engagements in our industry, particularly with agencies performing classified operations. The loss or disruption of any of our senior executives’ leadership could cause us to lose customer relationships or new business opportunities, and could materially and adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Our business and financial results could be negatively affected by cyber-attack, service interruptions or other security threats.
As a provider of IT services to U.S. public sector customers, we store and process large amounts of sensitive information which includes personally identifiable information, protected health information, personnel information, classified information, controlled unclassified information, financial information and other confidential information concerning our business and employees and those of our customers (collectively referred to as “sensitive information”). We are subject to attempted cyber and other information security threats, including computer viruses, malware, insider threats, and attacks by hackers, as are our customers, suppliers and subcontractors. Any electronic or other security breach or compromise may compromise the security of sensitive information stored or transmitted through our IT systems and networks, and could expose us to regulatory scrutiny, actions and penalties, extensive contractual liability litigation, reputational harm, and a loss of customer confidence, which could have a material and adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Computer hackers, or other unauthorized third parties, may penetrate our network security and misappropriate or compromise our sensitive information or that of third parties, create system disruptions or cause shutdowns. Computer hackers also may develop and deploy viruses, worms, and other malicious software programs that attack our products or
20
otherwise exploit any security vulnerabilities of these products. In addition, hardware and operating system software and applications we produce or that we procure from third parties may contain defects in design or manufacture, including “bugs” and other problems that could unexpectedly interfere with the operation of the system. The costs to eliminate or alleviate cyber or other security problems, including bugs, viruses, worms, malicious software programs, and other security vulnerabilities, are significant, and our efforts to address these problems may not be successful and could result in interruptions, delays, cessation of service, and loss of existing or potential customers, which may impede our sales, manufacturing, distribution or other critical functions and materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, in many cases we must rely on the safeguards put in place by our customers, suppliers, subcontractors and other third parties to protect against and report cyber threats. As such, we require our subcontractors supporting or involving covered defense information to maintain certain security standards. We work with other companies in the industry and government participants to share threat intelligence and promote increased awareness and enhanced protections against cybersecurity threats, and we seek to detect and investigate all security events and to prevent their occurrence or recurrence. National security regulations or other confidentiality obligations may prevent us or our counterparties from sharing information regarding threats or attacks when they occur, or ever, which could impair our ability to respond to and effectively counteract such threats. Our failure to detect, prevent or adequately respond to a threat incident or cyber-attack could subject us to liability and reputational damage and have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Increasing data privacy and information security obligations impose regulatory pressures on our customers’ businesses and, indirectly, on our operations.
In response to increasing data privacy and information security obligations, our customers have sought, and may continue to seek, to contractually impose certain strict data privacy and information security obligations on us. Under certain of our customer contracts we are specifically tasked with cybersecurity certification and compliance obligations and are responsible for implementing cybersecurity measures to protect against, detect and mitigate these threats. Some of our customer contracts may not limit our liability for the loss of sensitive information. Our inability to adequately address these concerns could adversely affect our business, results of operations and prospects. Compliance with new privacy and security laws, requirements and regulations, where required or undertaken by us, may result in cost increases due to potential systems changes, the development of additional administrative processes and increased enforcement actions, fines and penalties. While we strive to comply with all applicable data protection laws and regulations as well as internal privacy policies, any failure or perceived failure to comply or any misappropriation, loss or other unauthorized disclosure of sensitive information may result in proceedings or actions against us by government or other entities, private lawsuits against us (including class actions) or the loss of customers, which could potentially have an adverse effect on our business, reputation, results of operations and prospects.
Internal system or service failures could disrupt our business and impair our ability to effectively provide our services and products to our customers, which could damage our reputation and adversely affect our revenues and profitability.
Any system or service disruptions, including those caused by ongoing projects to improve our information technology systems and the delivery of services, whether through our shared services organization or outsourced services, that are not anticipated and appropriately mitigated, could have a material adverse effect on our business including, among other things, an adverse effect on our ability to perform on contracts, bill our customers for work performed on our contracts, collect the amounts that have been billed and produce accurate financial statements in a timely manner. We are also subject to systems failures, including network, software or hardware failures, whether caused by us, third-party service providers, cybersecurity threats, malicious insiders, natural disasters, power shortages, terrorist attacks or other events, which could cause loss of data and interruptions or delays in our business, cause us to incur remediation costs, subject us to claims and damage our reputation. In addition, the failure or disruption of our communications could cause us to interrupt or suspend our operations or otherwise adversely affect our business. Our property and business interruption insurance may be inadequate to compensate us for all losses that may occur as a result of any system or operational failure or disruption and, as a result, our future results could be adversely affected.
21
Customer systems failures could damage our reputation and adversely affect our revenues and profitability.
Many of the systems and networks that we develop, install and maintain for our customers involve managing and protecting personal information and information relating to national security and other sensitive government functions. While we have programs designed to comply with relevant privacy and security laws and restrictions, the failure, security breach or service interruption of a system or network that we develop, install or maintain, whether caused by us, third-party service providers, cybersecurity threats or other events, may lead to the loss of revenue, remediation costs or claims for damages or contract termination. Any such event could cause serious harm to our reputation, results of operations or financial condition, and prevent us from having access to or being eligible for further work on such systems and networks. Our errors and omissions liability insurance may be inadequate to compensate us for all of the damages that we may incur and, as a result, our future results could be adversely affected.
Our business and operations expose us to numerous legal and regulatory requirements, and any violation of these requirements could harm our business.
We are subject to numerous federal, state and foreign legal requirements on matters as diverse as data privacy and protection, employment and labor relations, environmental, health and safety, immigration, taxation, anti-corruption, import/export controls, trade restrictions, internal and disclosure control obligations, securities regulation and anti-competition. Compliance with diverse and changing legal requirements is costly, time consuming and requires significant resources. Violations of one or more of these diverse legal requirements in the conduct of our business could result in significant fines and other damages, criminal sanctions against us or our officers, prohibitions on doing business (including suspension or debarment from government contracts or grants) and damage to our reputation. Violations of these regulations or contractual obligations related to regulatory compliance in connection with the performance of customer contracts could also result in liability for significant monetary damages, fines and/or criminal prosecution, unfavorable publicity and other reputational damage, restrictions on our ability to compete for certain work and allegations by our customers that we have not performed our contractual obligations.
We are subject to the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977, as amended (“FCPA”), and similar anti-bribery laws in other jurisdictions. We pursue opportunities in certain parts of the world that experience government corruption and, in certain circumstances, compliance with anti-bribery laws may conflict with local customs and practices. Our internal policies mandate compliance with all applicable anti-bribery laws. We require our employees, partners, subcontractors, agents, and others to comply with the FCPA and other anti-bribery laws. Our policies or procedures may not protect us against liability under the FCPA or other laws for actions taken by our employees and intermediaries. Violations of the FCPA (whether due to our own acts or our omissions, or due to the acts or omissions of others) could cause us to suffer from severe criminal or civil penalties or other sanctions, which could have a material adverse effect on our reputation, business, results of operations or cash flows. In addition, detecting, investigating, and resolving actual or alleged violations of the FCPA or other anti-bribery violations is expensive and could consume significant time and attention of our senior management.
In the course of providing services to customers, we may inadvertently infringe on the IP rights of others and be exposed to claims for damages.
In recent years, there has been significant litigation involving IP rights in technology industries. The solutions we provide to our customers may inadvertently infringe on the IP rights of third parties resulting in claims for damages against us or our customers.
Any infringement, misappropriation or related claims, whether or not meritorious, are time consuming, divert technical and management personnel and are costly to resolve. As a result of any such dispute, we may have to develop non-infringing technology, pay damages, enter into royalty or licensing agreements, cease utilizing certain products or services or take other actions to resolve the claims. These actions, if required, may be costly or unavailable on terms acceptable to us. If we are unable to prevail in the litigation or retain or obtain sufficient rights or develop non-infringing IP or otherwise alter our business practices on a timely or cost-efficient basis, our business and operating results may be adversely affected. Additionally, the publicity resulting from infringing IP rights may damage our reputation and adversely impact our ability to develop new business.
In addition, U.S. government contracts typically contain provisions that allow the U.S. government to claim rights, including IP rights, in products and data developed and/or delivered under such agreements. We may not have the right to prohibit the U.S. government from using or disclosing certain technologies developed by us, and we may not be able to
22
prohibit third party companies, including our competitors, from using those technologies commercially or in providing products and services to the U.S. government. The U.S. government generally takes the position that it has an unlimited right to royalty-free use of technologies that are developed under U.S. government contracts.
Our ability to pursue strategic acquisitions and partnerships may impact our ability to compete in the markets we serve.
Aside from pursuing organic growth, we may explore potential strategic acquisitions that could allow us to expand our operations. However, we may be unable to identify attractive candidates or complete acquisitions on terms favorable to us. In addition, our ability to successfully integrate the operations we acquire and leverage these operations to generate revenue and earnings growth may significantly impact future revenue and earnings as well as investor returns. Integrating acquired operations is a significant challenge, and we may not be able to manage such integrations successfully. Failure to successfully integrate acquired operations may adversely affect our cost structure, thereby reducing our margins and return on investment.
We have also entered into, and expect to seek to enter into, additional strategic partnerships with other industry participants as part of an effort to expand our business. However, we may be unable to identify attractive strategic partnership candidates or complete such partnerships on terms favorable to us. In addition, our inability to successfully implement our partnership strategies or our strategic partners’ failure to fulfill their obligations could adversely affect our investments in such partnerships and our anticipated business expansion.
Our ability to expand our business beyond U.S. federal and certain state and local government customers is subject to restrictions imposed by our agreements with DXC.
We are subject to non-compete provisions pursuant to which we and DXC generally agree to not compete in certain customer, product and service categories through May 2020, subject to certain exceptions. Additionally, we hold a perpetual, royalty-free license to use certain DXC IP, restricted to use solely in connection with U.S. federal and certain state and local government customers, and exclusive with respect to the U.S. federal government market until May 2023, and non-exclusive with respect to certain U.S. state and local government customers. The Non-U.S. Agency Agreement between DXC and us appoints DXC as our exclusive agent outside the U.S. for certain non-U.S. government customers, excepting certain U.S. government contracts, through May 2023. While we have no current plans to expand our existing business in ways that would require us to engage in business beyond the scope of the rights to IP we currently have, we are unable to engage in business activities outside the scope of that license until the expiration of those restrictions unless we develop or acquire new IP. The foregoing restrictions may limit our ability to engage in certain activities, may potentially lead to costly and disruptive disputes, and may materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We face intense competition, which could cause us to lose business, lower prices or suffer employee departures.
Our business operates in a highly competitive industry, and we generally compete with a wide variety of U.S. government contractors, including large defense contractors, diversified service providers and small businesses. There is also a significant industry trend toward consolidation, which may lead to the emergence of companies that are better able to compete against us. Some of our competitors possess greater financial and technical resources than we do and could, among other things:
• | divert sales from us by winning very large-scale government contracts, a risk that is enhanced by the recent trend in government procurement practices to bundle services into larger contracts; |
• | force us to offer lower prices in order to win or maintain contracts; |
• | seek to hire our employees; or |
• | adversely affect our relationships with current clients, including our ability to successfully re-compete on incumbent work. |
If we lose business, are forced to lower our prices or suffer employee departures, our revenue and our operating profits could be adversely affected. In addition, we may face competition from our subcontractors who, from time to time, seek to obtain prime contractor status on contracts for which they currently serve as a subcontractor to us. If one or more of our current subcontractors are awarded prime contractor status on such contracts in the future, it could divert sales from us and could force us to charge lower prices, which could have a material adverse effect on our revenue and profitability.
23
The U.S. federal government may prefer small, disadvantaged, minority-, women- or veteran-owned businesses. As a result, we may have fewer opportunities to bid on new or incumbent work.
As a result of Small Business Administration (“SBA”), U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (“VA”) and other set-aside and preference programs, the U.S. federal government may decide to restrict certain procurements only to bidders that qualify as small, disadvantaged, minority-, women- or veteran-owned. As a result, we would not be eligible to perform as a prime contractor on those programs and would be restricted as to the work we could perform as a subcontractor on those programs. An increase in the amount of procurements under the SBA, VA or other set-aside or preference programs may impact our ability to bid on new procurements as a prime contractor or restrict our ability to re-compete on incumbent work that is placed in the set-aside program.
We have substantial indebtedness and the ability to incur significant additional indebtedness, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We have substantial indebtedness and may increase our indebtedness in the future. As of March 31, 2020, our total indebtedness, including finance leases, was approximately $2.62 billion.
Our level of indebtedness could have important consequences. For example, it could:
• | increase our vulnerability to general adverse economic and industry conditions; |
• | limit our ability to obtain additional financing to fund future working capital, capital expenditures and other general corporate requirements or to carry out other aspects of our business; |
• | increase our cost of borrowing; |
• | require us to dedicate a substantial portion of our cash flow from operations to payments on indebtedness, thereby reducing the availability of such cash flow to fund working capital, capital expenditures and other general corporate requirements or to carry out other aspects of our business; |
• | limit our ability to make material acquisitions or take advantage of business opportunities that may arise, pay cash dividends or repurchase our common stock; |
• | expose us to fluctuations in interest rates, to the extent our borrowings bear variable rates of interest; |
• | limit our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and industry; and |
• | place us at a potential disadvantage compared to our competitors that have less debt. |
Our ability to make scheduled payments on and to refinance our indebtedness will depend on and be subject to our future financial and operating performance, which in turn is affected by general economic, financial, competitive, business and other factors beyond our control, including the availability of financing in the banking and capital markets. Our business may fail to generate sufficient cash flow from operations or to borrow funds in an amount sufficient to enable us to make payments on our debt, to refinance our debt or to fund our other liquidity needs. If we were unable to make payments on or refinance our debt or obtain new financing under these circumstances, we would have to consider other options, such as asset sales, equity issuances or negotiations with our lenders to restructure the applicable debt. The terms of debt agreements that we entered into in connection with the Spin-Off and Mergers and market or business conditions may limit our ability to take some or all of these actions. In addition, if we incur additional debt, the related risks described above could be exacerbated.
The agreements governing our indebtedness contain restrictive covenants, which restrict our operational flexibility.
The agreements governing our indebtedness contain restrictions and limitations affecting our ability to engage in activities that may be in our long-term best interests, including covenants that place limitations on the incurrence of additional indebtedness; the creation of liens; the payment of dividends; sales of assets; fundamental changes, including mergers and acquisitions; loans and investments; negative pledges; transactions with affiliates; restrictions affecting subsidiaries; modification to charter documents in a manner materially adverse to the lenders; and changes in fiscal year and limitations on conduct of business.
In addition, certain agreements governing our indebtedness contain financial maintenance covenants requiring, as of the end of any fiscal quarter, (a) a ratio of consolidated total net debt to consolidated EBITDA (as defined in the debt agreement) not in excess of 4.50:1.00, stepping down to 4.25:1.00 at the end of the quarter ending September 30, 2020, and thereafter stepping up to 4.50:1.00 during the twelve-month period following the consummation of a permitted acquisition that involves consideration with a fair market value in excess of $100 million and (b) a ratio of consolidated
24
EBITDA to interest expense of not less than 3.00:1.00. Perspecta was in compliance with these covenants at March 31, 2020. The agreements governing our indebtedness also contain affirmative covenants and representations and warranties customary for financings of this type.
Events beyond our control could affect our ability to meet these covenants. Our failure to comply with obligations under the agreements governing our indebtedness may result in an event of default under those agreements. A default, if not cured or waived, may permit acceleration of our indebtedness. If our indebtedness is accelerated, we cannot be certain that we will have sufficient funds available to pay the accelerated indebtedness or that we will have the ability to refinance the accelerated indebtedness on terms favorable to us or at all. This could have serious consequences to our financial condition, operating results and business and could cause us to become insolvent or enter bankruptcy proceedings.
Changes in benchmark interest rates could adversely affect our financing costs and profitability.
The U.K. Financial Conduct Authority, which regulates LIBOR, has announced that it will no longer compel banks to contribute data for the calculation of LIBOR after December 31, 2021. It is likely that banks will no longer continue to contribute submissions for the calculation of LIBOR after that date, which creates significant uncertainty around the publication of LIBOR beyond 2021 and whether LIBOR will continue to be viewed as a reliable market benchmark. It remains unclear what rate or rates may develop as accepted alternatives to LIBOR, or what the effect of such changes will be on the markets for LIBOR-based financial instruments. The Secured Overnight Financing Rate (“SOFR”) has been recommended by the Alternative Reference Rates Committee as an alternative for USD LIBOR, but issues and uncertainty remain with respect to its implementation. We have made efforts to ensure that our credit arrangements provide for alternative benchmark rates, but those alternative rates could lead to increased interest rates on our outstanding debt, which would adversely impact interest expense and cash flows.
We may need to raise additional capital, and we cannot be sure that additional financing will be available.
We must fund our ongoing working capital, capital expenditure and financing requirements through cash flows from operations and new sources of capital, including additional financing. Our ability to obtain future financing depends, among other things, on our financial condition and results of operations as well as on the condition of the capital markets or other credit markets at the time we seek financing. Increased volatility and disruptions in the financial markets could make it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain financing. In addition, the adoption of new statutes and regulations, the implementation of recently enacted laws or new interpretations or the enforcement of older laws and regulations applicable to the financial markets or the financial services industry could result in a reduction in the amount of available credit or an increase in the cost of credit. If we do not have sufficient access to the capital markets on terms that we find acceptable, our financial condition, operating results and business could be materially and adversely affected. Additionally, if any of our current credit ratings are lowered or withdrawn by a rating agency, our ability to obtain financing could be adversely impacted, and the cost of financing could increase, which could adversely impact our results of operations and cash flows.
A termination of our defined benefit pension plan would adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
As of March 31, 2020, we had unfunded pension obligations related to Vencore HC’s defined benefit pension plan of approximately $166 million. The Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation (the “PBGC”) has authority under the Employment Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended, to terminate an underfunded defined benefit pension plan under certain circumstances, including when (1) the plan has not met the minimum funding requirements, (2) the plan cannot pay current benefits when due, or (3) the loss to the PBGC is reasonably expected to increase unreasonably over time if the plan is not terminated. If the PBGC were to terminate our U.S. defined benefit pension plan, our obligations with respect to such plan would become due and payable in full. Any such event or the failure by us to pay our pension plan insurance premiums with respect to our U.S. defined benefit pension plan could result in the PBGC obtaining a lien on our assets. Such an event would materially and adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
25
We have identified a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting which could, if not remediated, adversely affect investor confidence in our company, the value of our common shares and our ability to report our financial condition and results of operations in an accurate manner.
We are responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). As discussed in Part II, Item 9A “Controls and Procedures” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we identified a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2020. We identified instances where we did not adequately determine the appropriate number of performance obligations when determining revenue recognition when (or as) we satisfy a performance obligation. Additionally, we identified a deficiency in the operation of control over the review of estimated total costs at completion (“EAC”) as certain risk reserves were not fully supported and certain estimates inappropriately included the full program performance periods. Solely as a result of this material weakness, we concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was not effective as of March 31, 2020, and that our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective as of March 31, 2020.
A material weakness is defined as a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of our annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. The existence of a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting could result in errors in our financial statements that could cause us to fail to meet our reporting obligations and cause shareholders to lose confidence in our reported financial information, all of which could materially and adversely affect us and the market price of our common shares. As discussed in Part II, Item 9A “Controls and Procedures” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we have developed a remediation plan to address the material weakness and have already implemented certain actions from the remediation plan in the first fiscal quarter of fiscal year 2021. We plan to continue to take measures to remedy the material weakness in accordance with the remediation plan.
Our internal control over financial reporting may not be able to detect fraud or other issues.
We are required under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 to include a report of management on our internal control that contains an assessment by management of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. In addition, beginning with the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020, the independent registered public accounting firm auditing our financial statements is required to report on the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of the end of each fiscal year. Effective internal control is necessary for us to provide reliable financial reports and effectively prevent fraud. However, a control system, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. We may not detect all control issues or fraud. In connection with the Mergers, and as we continue to grow our business, our internal control continues to become more complex and require more resources.
We may be unable to realize the anticipated revenue growth or synergies from acquisitions within the anticipated time frame or in the anticipated amounts, or may incur additional and/or unexpected costs in order to realize them.
The revenue growth and synergies with existing operations that we realize may differ materially from our estimates, and we cannot provide assurances that these anticipated benefits will be achieved. In addition, any revenue growth or cost savings that we realize may be offset, in whole or in part, by reductions in other revenue or increases in other expenses.
Assumptions relating to these projections involve subjective decisions and judgments with respect to, among other things, the estimated impact of certain operational adjustments, labor management and other cost and savings adjustments, as well as future economic, competitive, industry and market conditions and future business decisions, all of which are inherently uncertain and may be beyond the control of our management. The internal financial projections used to calculate estimated cost savings also do not take into account any circumstances or events occurring after the date on which they were prepared. These internal financial projections reflect assumptions as to certain business decisions that are subject to change. As a result, actual results may differ materially from those contained in these internal financial projections.
Failure to realize the expected costs savings and synergies related to acquisitions could result in increased costs and have an adverse effect on the combined company’s financial results and prospects.
26
Goodwill and intangible assets represent a significant amount of our total assets and any impairment of these assets would negatively impact our results of operations.
Goodwill and intangible assets are tested for impairment on an annual basis, as of the first day of the second fiscal quarter, and between annual tests if circumstances change, or if an event occurs that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying amount. Factors that could necessitate an interim impairment assessment include, but are not limited to, a sustained decline in our stock price, significant decreases in federal government appropriations or funding for our contracts, the loss of significant business or significant underperformance relative to historical or projected future operating results. For example, we incurred a non-cash, pre-tax impairment charge of approximately $796 million primarily related to goodwill and intangible assets in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2020 as a result of the U.S. Navy’s decision not to award the NGEN-R SMIT to us. Any future impairment of goodwill or other intangible assets would have a negative impact on our profitability and financial results.
Changes in our effective income tax rate could impact our business, results of operations, liquidity, and net income.
An increase in our effective income tax rate could adversely affect our business, results of operations, liquidity, and net income. Various factors influence our effective income tax rate, including changes in tax law and related regulations, interpretation of existing laws, tax treaties, our mix of earnings across jurisdictions, and our ability to sustain our reporting positions on examination. Changes in any of those factors could change our effective tax rate, which could adversely affect our net income.
Our insurance coverage and self-insurance reserves may not provide adequate levels of coverage against claims.
We are self-insured for our employee medical plan and we recognize as a liability our estimated costs of claims incurred but not reported as of the balance sheet date. Given that our self-insurance began on January 1, 2020, our history and experience with claims is short, and if a greater amount of claims are incurred than we have estimated, or if medical costs increase beyond what we expect, our liabilities may not be sufficient and we could recognize additional expense, which could adversely affect our operating results and cash flows.
Risks Relating to the Spin-Off and Mergers
The actions required to integrate the business operations acquired in the Mergers demand significant management time and attention and may require us to incur significant incremental costs.
The actions required to integrate the business operations acquired in the Mergers have demanded, and are expected to continue to demand, significant amounts of management’s time and attention, which is in addition to, and may divert management’s time and attention from, the operation of our remaining businesses and the execution of our other strategic initiatives. Additionally, we have incurred significant costs and may incur future significant costs related to the integration of USPS, Vencore HC and KGS HC.
We could have an indemnification obligation to DXC if the Distribution were determined not to qualify for tax-free treatment, which could materially adversely affect our financial condition.
If, due to any transaction undertaken by us, it was determined that the Distribution was determined not to qualify for tax-free treatment under Section 355 of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986 (the “Code”), DXC would generally be subject to tax as if it sold the DXC common stock in a taxable transaction, which could result in a material tax liability. In addition, each DXC stockholder who received Perspecta common stock in the Distribution would generally be treated as receiving a taxable distribution in an amount equal to the fair market value of the Perspecta common stock received by the stockholder in the Distribution.
In addition, the Distribution would be taxable to DXC (but not to DXC stockholders) pursuant to Section 355(e) of the Code if one or more persons acquire a 50% or greater interest in the stock of DXC or us, directly or indirectly (including through acquisitions of our stock after the Mergers), as part of a plan or series of related transactions that includes the Distribution. In addition, Section 355(e) of the Code generally creates a presumption that any direct or indirect acquisition of stock of DXC or us within two years before or after the Distribution is part of a plan that includes the Distribution, although the parties may be able to rebut that presumption in certain circumstances. The process for determining whether
27
an acquisition is part of a plan under these rules is complex, inherently factual in nature, and subject to a comprehensive analysis of the facts and circumstances of the particular case. If the U.S. Department of Treasury and Internal Revenue Service were to determine that direct or indirect acquisitions of stock of DXC or us, either before or after the Distribution, were part of a plan that includes the Distribution, such determination could cause Section 355(e) of the Code to apply to the Distribution, which could result in a material tax liability.
Under the Tax Matters Agreement, we were required to indemnify DXC against taxes resulting from the Distribution arising as a result of any Prohibited Act (as defined in the Tax Matters Agreement). If we were required to indemnify DXC for taxes resulting from a Prohibited Act, that indemnification obligation would likely be substantial and could materially adversely affect our financial condition.
To address compliance with Section 355(e) of the Code, in the Tax Matters Agreement, we agreed to certain restrictions that may limit our ability to pursue certain strategic transactions or engage in other transactions, including stock issuances, certain asset dispositions, mergers, consolidations and other strategic transactions for a period of time following the Distribution. As a result, we may decide to forgo certain transactions that otherwise could be advantageous.
Under the Tax Matters Agreement, Perspecta is restricted from taking certain actions that could adversely affect the intended U.S. federal income tax treatment of the Spin-Off and such restrictions could significantly impair Perspecta’s ability to implement strategic initiatives that otherwise would be beneficial.
The Tax Matters Agreement generally restricts us from taking certain actions that could adversely affect the intended U.S. federal income tax treatment of the Spin-Off. Failure to adhere to these restrictions, including in certain circumstances that may be outside of our control, could result in tax being imposed on DXC for which we could bear responsibility and for which we could be obligated to indemnify DXC. In addition, even if we are not responsible for tax liabilities of DXC under the Tax Matters Agreement, we nonetheless could be liable under applicable tax law for such liabilities if DXC were to fail to pay such taxes. Because of these provisions in the Tax Matters Agreement, we are restricted from taking certain actions, particularly for the two years following the Spin-Off, including (among other things) the ability to freely issue stock, to make certain acquisitions and to raise additional equity capital. These restrictions could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity and financial condition, and otherwise could impair our ability to implement strategic initiatives. Also, our indemnity obligation to DXC might discourage, delay or prevent a change of control that our shareholders may consider favorable.
We have limited operating history as an independent publicly-traded company, and our historical financial information is not necessarily representative of the results we would have achieved as an independent publicly traded company and may not be a reliable indicator of our future results.
We derived the Perspecta historical financial information through May 31, 2018 included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K from DXC’s combined and consolidated financial statements, and this information does not necessarily reflect the results of operations and financial positions we would have achieved as an independent publicly-traded company during the periods presented or those that we will achieve in the future. This is primarily because of the following factors:
• | Prior to the Spin-Off, we operated as part of DXC’s broader corporate organization and DXC performed various corporate functions for us, including IT, tax administration, treasury activities, technical accounting, benefits administration, procurement, legal and ethics and compliance program administration. Our historical financial information through May 31, 2018 reflects allocations of corporate expenses from DXC for these and similar functions. These allocations may not reflect the costs we incur for similar services as an independent publicly-traded company. |
• | We entered into transactions with DXC that did not exist prior to the Spin-Off, such as DXC’s provision of certain IT services, which has caused us to incur new costs. |
• | Our historical financial information through May 31, 2018 does not reflect changes that have resulted from our separation from DXC, including changes in our cost structure, personnel needs, tax profile, financing and business operations. As part of DXC, we enjoyed certain benefits from DXC’s operating diversity, size, purchasing power, borrowing leverage and available capital for investments, and we lost these benefits after the Spin-Off. As an independent entity, we may be unable to purchase goods, services and technologies, such as insurance and health care benefits and computer software licenses, or access capital markets on terms as favorable to us as those we obtained as part of DXC prior to the Spin-Off. |
28
• | The Mergers resulted in our consolidated operations and the results therefrom being substantially different than USPS’s operations and the results therefrom and as a result, our historical information will not necessarily reflect our results of operations going forward. |
Following the Spin-Off, we are also responsible for the additional costs associated with being an independent publicly-traded company, including costs related to corporate governance, investor and public relations, and public reporting. Therefore, the financial statements through May 31, 2018 may not be indicative of our future performance as an independent publicly-traded company. For additional information about our past financial performance and the basis of presentation of the financial statements, see “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the financial statements and the notes included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Our potential indemnification liabilities pursuant to the SDA could materially and adversely affect us.
The SDA between us and DXC provides for, among other things, the principal corporate transactions required to effect the Spin-Off, certain conditions to the Spin-Off and provisions governing the relationship between us and DXC after the Spin-Off. Among other things, the SDA provides for indemnification obligations designed to make us financially responsible for substantially all liabilities that may exist relating to or arising out of our business. If we are required to indemnify DXC under the circumstances set forth in the SDA, we may be subject to substantial liabilities. For a description of the SDA, see “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence - Agreements with DXC - Separation and Distribution Agreement.”
In connection with the Spin-Off, DXC will indemnify us for certain liabilities. However, these indemnities may not be sufficient to insure us against the full amount of such liabilities, or DXC’s ability to satisfy its indemnification obligation may be impaired in the future.
Pursuant to the SDA and other agreements we entered into in connection with the Spin-Off, DXC has agreed to indemnify us for certain liabilities. However, third parties could seek to hold us responsible for any of the liabilities that DXC will agree to retain pursuant to these agreements, and DXC may not be able to fully satisfy its indemnification obligations under these agreements. Moreover, even if we ultimately succeed in recovering from DXC any amounts for which we are held liable, we may be temporarily required to bear these losses while seeking recovery from DXC.
Risks Relating to our Common Stock and Capital Structure
Our stock price may fluctuate significantly.
The market price of our common stock may fluctuate widely, depending on many factors, some of which may be beyond our control, including:
• | actual or anticipated fluctuations in our operating results due to factors related to our business; |
• | success or failure of our business strategies; |
• | our quarterly or annual earnings, or those of other companies in our industry; |
• | our ability to obtain financing as needed; |
• | announcements by us or our competitors of significant acquisitions or dispositions; |
• | changes in accounting standards, policies, guidance, interpretations or principles; |
• | changes in earnings estimates by securities analysts or our ability to meet those estimates; |
• | the operating and stock price performance of other comparable companies; |
• | investor perception of our company and the IT services industry; |
• | overall market fluctuations; |
• | results from any material litigation or government investigation; |
• | changes in laws and regulations (including tax laws and regulations) affecting our business; |
• | changes in capital gains taxes and taxes on dividends affecting shareholders; and |
• | general economic conditions and other external factors. |
Stock markets in general have experienced volatility that has often been unrelated to the operating performance of a particular company. These broad market fluctuations could adversely affect the trading price of our common stock.
29
We may not pay dividends or repurchase shares of our common stock, and our indebtedness may limit our ability to pay dividends or repurchase shares of our common stock.
The timing, declaration, amount and payment of future dividends to shareholders and the repurchase of shares falls within the discretion of our Board of Directors. Our Board of Directors’ decisions regarding the payment of future dividends and share repurchases will depend on many factors, including our financial condition, earnings, capital requirements of our business and covenants associated with debt obligations, as well as legal requirements, regulatory constraints, industry practice and other factors that our Board of Directors deems relevant. We may not continue to pay dividends or repurchase shares at the current levels.
We have contracts with the U.S. federal government that are classified, which may limit investor insight into portions of our business.
Revenue is derived from classified programs with the U.S. federal government that are subject to security restrictions that preclude the dissemination of information that is classified for national security purposes. We are limited in our ability to provide information about these classified programs, their risks or any disputes or claims relating to such programs. As a result, investors may have less insight into our classified programs than our other programs and therefore less ability to fully evaluate the risks related to our classified business.
Provisions in our Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation and Bylaws and of Nevada law may prevent or delay an acquisition of our company, which could decrease the trading price of our common stock.
Several provisions of our Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation, Bylaws and Nevada law may discourage, delay or prevent a merger or acquisition that shareholders may consider favorable. These include provisions that:
• | permit us to issue blank check preferred stock with conversion and exchange rights that could negatively affect the rights of our common shareholders, and the Board of Directors could take that action without shareholder approval; |
• | preclude shareholders from calling special meetings except where such special meetings are requested by shareholders representing 75% of the capital stock entitled to vote. Our Bylaws prevent shareholder action by written consent for the election of directors and require the written consent of 90% of the capital stock entitled to vote for any other shareholder actions by written consent; |
• | require shareholders to follow certain advance notice and disclosure requirements in order to propose business or nominate directors at an annual or special meeting; and |
• | limit our ability to enter into business combination transactions with certain shareholders. |
These and other provisions of our Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation, Bylaws and Nevada law may discourage, delay or prevent certain types of transactions involving an actual or a threatened acquisition or change in control of Perspecta, including unsolicited takeover attempts, even though the transaction may offer our shareholders the opportunity to sell their shares of our common stock at a price above the prevailing market price.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
As of March 31, 2020, we conducted our operations in approximately 70 leased locations occupying approximately 2.7 million rentable square feet. Our major locations are in Chantilly, Clarksville and Herndon, Virginia, where we occupy approximately 1.1 million square feet, collectively, used primarily for our corporate headquarters, customer service and data centers. We have other significant facilities located in Boise, Idaho, King of Prussia, Pennsylvania, San Diego, California and El Paso, Texas, where we occupy approximately 0.2 million, 0.1 million, 0.1 million and 0.1 million rentable square feet, respectively, used for customer service. We consider our facilities to be well-maintained and adequate to meet our current needs.
30
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
See Note 20 – “Commitments and Contingencies” to the financial statements for information regarding legal proceedings in which we are involved.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
31
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED SHAREHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market Information
Our common stock has been listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol “PRSP” since June 1, 2018. Prior to that time, there was no public market for our stock.
Number of Holders
As of April 30, 2020, there were 37,244 holders of record of our common stock.
Payment of Dividends
The Company expects to pay a quarterly cash dividend at the discretion of, and upon quarterly approval by, its board of directors.
Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities
There were no sales of unregistered equity securities during the year ended March 31, 2020.
Use of Proceeds
Not applicable.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
On June 1, 2018, our Board of Directors authorized up to $400 million for future repurchases of outstanding shares of our common stock. Repurchases may be made at the Company’s discretion from time to time on the open market depending on market conditions. The repurchase program has no time limit, does not obligate the Company to make any repurchases and may be suspended for periods or discontinued at any time. The following table provides information on a monthly basis for the quarter ended March 31, 2020 with respect to the Company’s purchase of equity securities:
Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased | Average Price Paid Per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs (in millions) | ||||||||||
January 1, 2020 to January 31, 2020 | 60,891 | $ | 27.43 | 60,891 | $ | 293 | ||||||||
February 1, 2020 to February 29, 2020 | 225,009 | $ | 24.73 | 225,009 | $ | 288 | ||||||||
March 1, 2020 to March 31, 2020 | 664,465 | $ | 19.53 | 664,465 | $ | 275 | ||||||||
Total | 950,365 | $ | 21.27 | 950,365 | ||||||||||
32
Performance Comparison Graph
The following graph shows a comparison from June 1, 2018 (the date our common stock commenced trading on the New York Stock Exchange) through March 31, 2020 of the cumulative total return for our common stock, with the comparable cumulative total return of the Standard & Poor’s (“S&P”) Midcap 400 Index and the Dow Jones US Computer Services Index. The graph assumes that $100 was invested at the market close on June 1, 2018 in our common stock, the S&P Midcap 400 Index and the Dow Jones US Computer Services Index and that dividends have been reinvested. The stock price performance of the following graph is not necessarily indicative of future stock price performance.
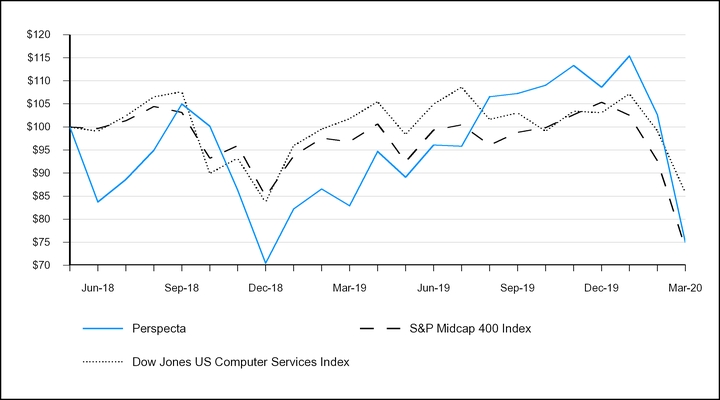
Equity Compensation Plans
See Item 12, contained in Part III of this Annual Report for information regarding our equity compensation plans.
33
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
You should read the selected financial data presented below in conjunction with the information contained under “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the financial statements and accompanying notes included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10‑K.
Statement of Operations Data:
Successor(1) | Predecessor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fiscal Years Ended March 31, | Five Months Ended March 31, 2017 | Fiscal Years Ended October 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 4,504 | $ | 4,030 | $ | 2,819 | $ | 1,073 | $ | 2,732 | $ | 2,585 | |||||||||||||
(Loss) income before taxes | (730 | ) | 112 | 199 | 59 | 129 | (51 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Income tax expense (benefit) | (54 | ) | 40 | (9 | ) | 23 | 49 | (22 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Net (loss) income | (676 | ) | 72 | 208 | 36 | 80 | (29 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
(Loss) earnings per common share (2): | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | (4.17 | ) | 0.44 | 1.46 | 0.25 | 0.56 | (0.20 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Diluted | (4.17 | ) | 0.44 | 1.46 | 0.25 | 0.56 | (0.20 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Dividends declared per common share | 0.24 | 0.20 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
(1) The selected historical financial data prior to June 1, 2018 may not be indicative of our performance, financial conditions or results of operations following the Spin-Off and Mergers. The fiscal years 2020, 2019 and 2018 are not directly comparable to periods ending prior to April 1, 2017, which reflect USPS’s financial results before the HPES Merger (as defined in Note 2 – “Acquisitions”) on April 1, 2017.
(2) Earnings per common share information for the fiscal periods ended March 31, 2018 and prior are computed using the 142.43 million shares of Perspecta common stock resulting from the Distribution as Perspecta did not operate as a stand-alone entity during the period, and therefore, no Perspecta common stock, stock options or other equity awards were outstanding and no dividends were declared or paid by Perspecta.
Balance Sheet Data:
Successor(1) | Predecessor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | March 31, 2018 | March 31, 2017 | October 31, 2016 | October 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 5,405 | $ | 6,083 | $ | 3,679 | $ | 1,073 | $ | 1,234 | $ | 1,512 | |||||||||||||
Finance leases | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Current finance lease obligations | 111 | 137 | 160 | 139 | 145 | 127 | |||||||||||||||||||
Non-current finance lease obligations | 136 | 168 | 144 | 155 | 215 | 223 | |||||||||||||||||||
Total finance leases | 247 | 305 | 304 | 294 | 360 | 350 | |||||||||||||||||||
Long-term debt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Current maturities of long-term debt | 89 | 80 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Long-term debt, net of current maturities | 2,283 | 2,297 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Total long-term debt | 2,372 | 2,377 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Total equity | 1,357 | 2,162 | 2,729 | 416 | 338 | 555 | |||||||||||||||||||
(1) The selected historical financial data prior to June 1, 2018 may not be indicative of our performance, financial conditions or results of operations following the Spin-Off and Mergers. The fiscal years 2020, 2019 and 2018 are not directly comparable to periods ending prior to April 1, 2017, which reflect USPS’s financial results before the HPES Merger (as defined in Note 2 – “Acquisitions”) on April 1, 2017.
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion and analysis is intended to help investors understand our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and capital resources. You should read this discussion in conjunction with the financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this document.
The statements in this discussion regarding industry outlook, expectations regarding our future performance, liquidity and capital resources and other non-historical statements are forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements are subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, including, but not limited to, the risks and uncertainties described in “Risk Factors” and “Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.” Actual results may differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements.
34
The financial information, discussed below, reflects our financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows. The financial information discussed below and included in this document, however, may not necessarily reflect what our financial condition, results of operations, or cash flows would have been had we been operated as a separate, independent entity during the periods presented, or what our financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows may be in the future.
Overview
We are a leading provider of end-to-end enterprise IT services to government customers across U.S. federal, state and local markets. Using our market-leading enterprise offerings and solutions, we help our government customers implement modern collaborative workplaces, hybrid cloud platforms and integrated digital systems of engagement with their enterprise management systems. By delivering these modern enterprise solutions, often while ensuring interoperability with mission critical legacy systems, we believe we have helped our government customers better realize the benefits of technology, which will ultimately enable them to fulfill their mission objectives and achieve their desired business outcomes.
In addition to providing substantial benefits through increased efficiencies and capabilities, we believe demand for our services is also driven by the technological advances that already reinvented commercial industries, which are now exerting a similar evolutionary effect on government customers. In response to these pressures, we believe government customers are increasingly turning to outside partners, such as Perspecta, to help guide them through this digital transformation.
We believe our breadth of contracts and customers in the U.S. government, and our longstanding history of having partnered with our public sector customers for more than 50 years via our legacy companies, provides us with a competitive advantage. For example, we have existing contracts with a wide variety of public sector entities including agencies of the DoD, the VA, the U.S. Postal Service, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and large state and local government customers such as the county of San Diego, California. Based on this breadth of experience and our expertise, we believe we are well positioned to help our U.S. government customers continue their ongoing digital transformation journey.
Perspecta was formed on May 31, 2018, when DXC completed the Spin-Off and Mergers. Following the completion of the Spin-Off and Mergers, Perspecta, a Nevada corporation, became a publicly traded company. Perspecta’s common stock began trading under the ticker symbol “PRSP” on the New York Stock Exchange on June 1, 2018. The financial results of Perspecta prior to May 31, 2018, are based upon the historical results of USPS and do not give effect to the Mergers. See Note 1 – “Overview and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” to the financial statements for additional details. On October 29, 2019, the Company filed for arbitration against DXC to resolve certain disputed items related to the Spin-Off. After completion of the Spin-Off, the Company began assessing the respective rights, responsibilities and obligations of DXC and the Company under the SDA and other related Spin-Off agreements. Based on this assessment, and in accordance with the provisions of the agreements, the Company disputed certain transactions that were effected by DXC in connection with the Spin-Off. The Company has been addressing these matters with DXC pursuant to the terms of the SDA, including its confidentiality provisions and dispute resolution provisions that require executive escalation, mediation and binding arbitration. Based on the status of the arbitration, we currently are unable to predict the impact of any resolutions of these matters on the Company.
The purpose of this Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (“MD&A”) is to present information that management believes is relevant to an assessment and understanding of Perspecta’s results of operations and cash flows for the year ended March 31, 2020. This MD&A is provided as a supplement to, and should be read in conjunction with, our financial statements and accompanying notes, as well as the other information included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and our other public filings.
See our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2019, filed with the SEC on June 6, 2019, under Part II, Item 7 “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” for a discussion and analysis comparing our results for the year ended March 31, 2019 to the year ended March 31, 2018.
Segments and Services
Our reportable segments are (1) Defense and Intelligence, which provides services to the DoD, intelligence community, branches of the U.S. Armed Forces, and other DoD agencies, and (2) Civilian and Health Care, which provides services to
35
the DHS, DOJ, HHS, as well as other federal civilian and state and local government agencies. Segment information is included in Note 19 – “Segment Information” to the financial statements. For a discussion of risks associated with our operations, see Part I, Item 1A “Risk Factors.”
Factors and Trends Affecting our Results of Operations
Revenue Generation
Revenue is generated by providing services on a variety of contract types which vary in duration from as little as six months to more than ten years. Factors affecting revenue include, among others, our ability to successfully:
• | bid on and win new contract awards; |
• | satisfy existing customers, obtain add-on business, and win contract re-competes; |
• | compete on services offered, delivery models offered, technical ability and innovation, quality, flexibility, experience, and results created; and |
• | identify and integrate acquisitions and leverage them to generate new revenue. |
Earnings are impacted by the above revenue factors and, among others, our ability to:
• | integrate acquisitions and eliminate redundant costs; |
• | control costs, particularly labor costs, subcontractor expenses, and overhead costs including health care, pension and general and administrative costs; |
• | anticipate talent needs to avoid staff shortages or excesses; and |
• | accurately estimate various factors incorporated in contract bids and proposals. |
Competitive Markets
We believe that we are well positioned to take advantage of the markets in which we operate because of our expertise in providing information technology services to public sector customers. Our ability to effectively manage project engagements, including logistics, client requirements, engineering resources and service levels, will affect our financial performance. Increased competition from other government contractors and market entrants seeking to take advantage of certain industry trends may result in the emergence of companies that are better able to compete against us.
Regulations
Increased audit, review, investigation and general scrutiny by U.S. government agencies of government contractors’ performance under U.S. government contracts and compliance with the terms of those contracts and applicable laws could affect our operating results. Negative publicity and increased scrutiny of government contractors in general, including us, relating to U.S. government expenditures for contractor services; incidents involving the mishandling of sensitive or classified information; and the increasingly complex requirements of the DoD and the intelligence community, including those related to cybersecurity, management of federal health care cost growth, and focus on reforming existing government regulation of various sectors of the economy, such as financial regulation and health care, could impact our ability to perform in the marketplace.
Seasonality
For information on the seasonality of our business see Part I, Item 1 “Business.”
Cash Flows
Cash flows are affected by the above earnings factors and, in addition, by the following factors:
• | the ability to efficiently manage capital resources and expenditures; |
• | timely management of receivables and payables; |
• | investment opportunities available, particularly related to business acquisitions and implementations, dispositions and large outsourcing contracts; and |
• | tax obligations. |
36
Economic and Industry Factors
Our results of operations are impacted by general economic conditions including macroeconomic conditions. We are monitoring current macroeconomic and credit market conditions and levels of business confidence and their potential effect on our customers and on us. A severe and/or prolonged economic downturn could adversely affect our customers’ financial condition and the levels of business activities in the industries and geographies in which we operate. Such a downturn may reduce demand for our services or depress pricing of those services and have a material adverse effect on our new contract bookings and results of operations. Particularly in light of recent economic uncertainty, we continue to monitor costs closely in order to respond to changing conditions and to manage any impact to our results of operations. Our results of operations are also affected by the evolving priorities of the U.S. federal government, as well as by the pace of technological change and the type and level of technology spending by our customers. The ability to identify and capitalize on these markets and technological changes early in their cycles is a key driver of our performance.
Revenue is driven by our ability to secure new contracts and to deliver solutions and services that add value to our customers. Our ability to add value for customers, and therefore generate revenue, depends in part on our ability to deliver market-leading service offerings and to deploy skilled teams of professionals quickly across all government industries and domains. Our market is highly competitive and has characteristics unique to the federal contracting environment. Almost all of our U.S. federal government contracts and subcontracts may be modified, curtailed, or terminated either at the convenience of the government or for default based on factors set forth in the FAR. Upon termination for convenience of a fixed-price type contract, our U.S. federal government contracts normally entitle us to receive the purchase price for delivered items, reimbursement for contractual commitments and allowable costs for work-in-process, and a reasonable allowance for profit, although there can also be financial impact resulting from the negotiated contract settlement. Upon termination for convenience of a U.S. federal government cost reimbursable or time and material contract, we are normally entitled to reimbursement of allowable costs plus a fee. Allowable costs generally include the cost to terminate agreements with suppliers and subcontractors.
The amount of the fee recovered, if any, generally is related to the portion of the work completed prior to termination and is determined by negotiation. See Part I, Item 1A “Risk Factors.” If contracts are lost through the competitive bid process, our operating results may differ materially and adversely from those anticipated. Finally, shifting U.S. federal government priorities can also impact the future of projects. Management monitors U.S. federal government priorities and industry factors through numerous industry and government publications and forecasts, legislative activity, budgeting and appropriation processes, and by participating in industry professional associations in order to anticipate these shifting priorities.
Backlog
Total contract value (“TCV”) backlog is our estimate of the remaining revenue from existing signed contracts, assuming the exercise of all options relating to such contracts and including executed task orders issued under ID/IQ contracts. TCV backlog can include award fees, incentive fees, or other variable consideration estimated at the most likely amount to which the Company is expected to be entitled to the extent that it is probable that a significant reversal of cumulative revenue recognized will not occur. TCV backlog includes both funded and unfunded future revenue under government contracts.
We define funded backlog as estimated future revenue under government contracts and task orders for which funding has been appropriated by Congress and authorized for expenditure by the applicable agency. Funded backlog does not include the full potential value of the Company’s contracts because Congress often appropriates funds to be used by an agency for a particular program of a contract on a yearly or quarterly basis even though the contract may call for performance over a number of years. As a result, contracts typically are only partially funded at any point during their term, and all or some of the work to be performed under the contracts may remain unfunded unless and until Congress makes subsequent appropriation and the procuring agency allocates funding to the contract.
A variety of circumstances or events may cause changes in the amount of our TCV backlog and funded backlog, including the execution of new contracts, the extension of existing contracts, the non-renewal or completion of current contracts, the early termination of contracts, and adjustment to estimates for previously included contracts. Changes in the amount of our funded backlog also are affected by the funding cycles of the government.
37
The estimated value of our TCV backlog as of March 31, 2020 was as follows:
(in millions) | Funded Backlog | Unfunded Backlog | Total TCV Backlog | |||||||||
Defense and Intelligence | $ | 1,092 | $ | 7,250 | $ | 8,342 | ||||||
Civilian and Health Care | 928 | 4,079 | 5,007 | |||||||||
Total backlog | $ | 2,020 | $ | 11,329 | $ | 13,349 | ||||||
The contract awards during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020 were as follows (in millions):
Defense and Intelligence | $ | 3,780 | ||
Civilian and Health Care | 2,306 | |||
Total contract awards | $ | 6,086 | ||
Results of Operations
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The fourth quarter of fiscal year 2020 marked the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. Substantially all of the services we provide to our government customers have been considered essential services, which has allowed them to continue. Due to the mission-critical nature of the majority of our business, the overall impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on our results of operations and liquidity were immaterial in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2020.
We have experienced and expect to continue to experience certain disruptions in our operations and impact to our workforce and subcontractor workforce due to illness, quarantines, shelter-in-place orders, closures of our facilities, closures of our customers’ facilities and other restrictions or government actions in connection with the COVID-19 pandemic. At the outset of the pandemic, we deployed our Crisis and Business Continuity Plan, which provides an integrated and coordinated crisis management and continuity of operations framework for all personnel during a crisis, and we have implemented new protocols including telework or other means of remote work for our employees. With respect to our impacted programs that, by their nature, cannot be supported remotely, we have accommodated those customers who have implemented shiftwork or other mitigation protocols by maintaining our workforce in a “mission ready” state such that the workforce is able to mobilize in a timely manner.
On March 27, 2020, the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security (“CARES”) Act was enacted. The CARES Act is a $2 trillion stimulus package meant to combat the economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. The CARES Act includes a provision under which government contractors can seek reimbursement for amounts related to keeping the employee base in a ready state during disruptions such as closed facilities, reduced work schedules or mandated quarantines to support social distancing. Guidance from our customers continues to evolve regarding what types of costs will be reimbursed; however, we currently anticipate that many of our customers will reimburse costs incurred by Perspecta and our subcontractors. The relevant provision of the CARES Act is in effect until September 30, 2020. We continue to evaluate this and other provisions of the CARES Act, as well as any other legislative or regulatory initiatives that seek to address the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on our business.
For additional discussion of the risks associated with the COVID-19 pandemic, see Part I, Item 1A “Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Fiscal Year 2020 Highlights
Financial highlights for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020 include the following:
• | Revenue was $4.50 billion. |
• | Net loss was $676 million, including the cumulative impact of certain items of $1,176 million, reflecting impairment charges of $796 million, restructuring costs of $17 million, separation, transaction and integration-related costs of $85 million, net actuarial losses on the defined benefit pension plan of $72 million and amortization of acquired intangible assets of $206 million. |
• | We generated $626 million of cash from operations. |
38
Revenue for Years Ended March 31, 2020 and March 31, 2019
Our total revenue for the year ended March 31, 2020 was $4.50 billion, an increase of $474 million as compared to revenue for the year ended March 31, 2019. The revenue growth is primarily driven by a full year of Vencore revenue and net growth on existing contracts and acquisitions, partially offset by decreases in contract completions. Substantially all of the Company’s services have been deemed to be essential by federal, state and local government officials, and the Company has maintained its workforce at near full capacity. Therefore, the COVID-19 pandemic did not have a significant impact on revenue for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020.
Revenue by segment was as follows:
Fiscal Years Ended | Change | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | $ | % | |||||||||||
Defense and Intelligence | $ | 3,101 | $ | 2,587 | $ | 514 | 20 | % | |||||||
% of total revenue | 69 | % | 64 | % | |||||||||||
Civilian and Health Care | 1,403 | 1,443 | (40 | ) | (3 | )% | |||||||||
% of total revenue | 31 | % | 36 | % | |||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 4,504 | $ | 4,030 | $ | 474 | 12 | % | |||||||
Defense and Intelligence Segment
Our Defense and Intelligence segment revenue during the year ended March 31, 2020 was $3.1 billion, or 69% of our total revenue for the period, and represented an increase of $514 million or 20% as compared to the prior year. Including the $230 million of Vencore revenue in April and May of 2018, Defense and Intelligence increased $284 million, or 10%, primarily due to new business wins coupled with additional task orders and volume growth on existing programs. The NGEN contract generated over 25% of revenue in this segment during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020 and 2019. The Company was not awarded the re-compete of this contract, and the existing contract will expire December 31, 2020.
Civilian and Health Care Segment
Our Civilian and Health Care segment revenue during the year ended March 31, 2020 was $1.4 billion, or 31% of our total revenue for the period, and represented a decrease of $40 million or 3% as compared to the prior year. Including the $14 million of Vencore revenue in April and May of 2018, Civilian and Health Care decreased $54 million, or 4%, primarily due to the completion or wind down of certain programs, partially offset by the sale of IT assets and related transition services to NASA ACES in the second quarter of fiscal year 2020.
39
Costs and Expenses for Years Ended March 31, 2020 and March 31, 2019
Fiscal Year Ended | % of Revenue | Fiscal Year Ended | % of Revenue | Change from 2020 to 2019 | |||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | $ | % | |||||||||||||||||
Costs of services | $ | 3,460 | 77 | % | $ | 3,043 | 76 | % | $ | 417 | 14 | % | |||||||||
Selling, general and administrative | 303 | 7 | % | 300 | 7 | % | 3 | 1 | % | ||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 374 | 8 | % | 330 | 8 | % | 44 | 13 | % | ||||||||||||
Impairment charges | 796 | 18 | % | — | — | % | 796 | NM | |||||||||||||
Restructuring costs | 17 | — | % | 10 | — | % | 7 | 70 | % | ||||||||||||
Separation, transaction and integration-related costs | 85 | 2 | % | 106 | 3 | % | (21 | ) | (20 | )% | |||||||||||
Interest expense, net | 137 | 3 | % | 121 | 3 | % | 16 | 13 | % | ||||||||||||
Other expense, net | 62 | 1 | % | 8 | — | % | 54 | 675 | % | ||||||||||||
Total costs and expenses | $ | 5,234 | 116 | % | $ | 3,918 | 97 | % | $ | 1,316 | 34 | % | |||||||||
(Loss) income before taxes | $ | (730 | ) | (16 | )% | $ | 112 | 3 | % | $ | (842 | ) | (752 | )% | |||||||
Income tax expense (benefit) | (54 | ) | (1 | )% | 40 | 1 | % | (94 | ) | (235 | )% | ||||||||||
Net (loss) income | $ | (676 | ) | (15 | )% | $ | 72 | 2 | % | $ | (748 | ) | (1,039 | )% | |||||||
Costs of services
Costs of services for the year ended March 31, 2020 were $3.5 billion and increased by $417 million as compared to cost of services for the year ended March 31, 2019. Costs of services as a percentage of revenue was 77% for the year ended March 31, 2020, as compared to 76% for the same period of the prior year due to continued focus on cost discipline and program management on our fixed-price portfolio. Substantially all of the Company’s services have been deemed to be essential by federal, state and local government officials, and the Company has maintained its workforce near full capacity. Therefore, the COVID-19 pandemic did not have a significant impact on cost of services for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020.
Selling, general and administrative
Selling, general and administrative expenses for the year ended March 31, 2020 was $303 million and increased by $3 million as compared to the year ended March 31, 2019. Selling, general and administrative expenses as a percentage of revenue was 7% for both of the years ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Depreciation and amortization
Depreciation and amortization for the year ended March 31, 2020 was $374 million and represented 8% of revenue, unchanged on a percentage of revenue basis, from the year ended March 31, 2019.
Impairment charges
Impairment charges for the year ended March 31, 2020 were $796 million and represented 18% of revenue, which was due to the loss of the NGEN-R SMIT contract as discussed in Note 8 – “Goodwill” and Note 9 – “Intangible Assets.”
Separation, transaction and integration-related costs
Separation, transaction and integration-related costs for the year ended March 31, 2020 were $85 million and represented 2% of revenue. Separation, transaction and integration-related costs were primarily associated with integration-related expenses incurred in connection with the Spin-Off and Mergers.
Interest expense, net
Interest expense, net for the year ended March 31, 2020 was $137 million, an increase of $16 million as compared to the year ended March 31, 2019, primarily due to the full year of interest for the Credit Facilities (as defined in Note 10 – “Debt” to the financial statements) as compared to ten months of interest in fiscal year 2019.
40
Other expense, net
Other expense, net comprises certain components of the net periodic pension cost for defined benefit pension plans, equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliates and other miscellaneous gains and losses. The $54 million increase in other expense, net for the year ended March 31, 2020 as compared to the prior year was primarily due to a pension remeasurement charge of $72 million in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2020 compared to $35 million in the prior year, and $25 million of expense related to a decrease in an asset corresponding with the release of indemnified pre-Spin-Off liabilities for uncertain tax positions, a portion of which was released as a benefit to income tax expense in the current year. Offsetting the expenses were $33 million of gains on the sale of facilities in fiscal year 2020, compared to a $24 million gain in fiscal year 2019 on the May 2018 sale of a contract to eliminate a potential organizational conflict of interest that resulted from the Mergers.
Income tax expense (benefit)
Our effective tax rate (“ETR”) for the year ended March 31, 2020 was 7%. In fiscal year 2020, the ETR was primarily impacted by the impairment of goodwill related to the NGEN contract and the release of indemnified liabilities for unrecognized tax benefits. Our ETR for the year ended March 31, 2019 was 36%. In fiscal year 2019, the ETR was primarily impacted by discrete items including the revaluation of our state deferred taxes, the posting of a valuation allowance on our Virginia state tax deferred items, and non-deductible transaction costs. A reconciliation of the differences between the U.S. federal statutory rate and the ETR, as well as other information about our income tax provision, is provided in Note 13 – “Income Taxes” to the financial statements.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We pursue a cash management and capital deployment strategy that balances funding our current operating needs with growing our business. Existing cash and cash equivalents and cash generated by operations continue to be our primary sources of liquidity, as well as available borrowings under our Revolving Credit Facility (as defined in Note 10 – “Debt” to the financial statements) and sale of receivables under a U.S. federal government and a certain state government obligor receivables purchase facility established pursuant to the Master Accounts Receivable Purchase Agreement, dated July 14, 2017, by and among PES LLC, our wholly-owned subsidiary, and certain financial institutions (the “MARPA Facility”).
Our primary cash needs will continue to be for working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions, the return of cash to shareholders through share repurchases and dividend payments, and other discretionary investments, as well as to service our outstanding indebtedness, including borrowings under our Credit Facilities. Our ability to fund our future operating needs depends, in part, on our ability to continue to generate positive cash flows from operations and, if necessary, raise cash in the capital markets. Based upon our history of generating strong cash flows, it is our belief that we will be able to meet our short-term liquidity and cash needs, including debt servicing, through the combination of cash flows from operating activities, available cash balances, available borrowings under our Revolving Credit Facility and sales of receivables under our MARPA Facility. If these sources of liquidity need to be augmented, additional cash requirements would likely be financed through the issuance of debt or equity securities, although there can be no assurance that we will able to obtain such financing on acceptable terms (or at all) in the future.
In July 2017, the Financial Conduct Authority (the authority that regulates LIBOR) announced it intends to stop compelling banks to submit rates for the calculation of LIBOR after 2021. The Alternative Reference Rates Committee (“ARRC”) has proposed that the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (“SOFR”) is the rate that represents best practice as the alternative for use in derivatives and other financial contracts that are currently indexed to LIBOR. ARRC has proposed a paced market transition plan to SOFR from LIBOR and organizations are currently working on industry wide and company specific transition plans as it relates to derivatives and cash markets exposed to LIBOR. The Company has material contracts that are indexed to LIBOR and is continuing to monitor this activity and evaluate the related risks.
Our exposure to operational liquidity risk is primarily from long-term contracts which require significant investment of cash during the initial phases of the contracts. The recovery of these investments is over the life of the contract and is dependent upon our performance as well as customer acceptance.
See Note 20 – “Commitments and Contingencies” to the financial statements for discussion of general purpose of guarantees and commitments.
41
The anticipated sources of funds to fulfill such commitments are listed below:
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | |||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 147 | ||
Available borrowings under our Revolving Credit Facility | 700 | |||
Total liquidity | $ | 847 | ||
Cash and Cash Equivalents and Cash Flows
Prior to the Spin-Off and Mergers we reflected transfers of cash to and from Parent’s cash management system as a component of Parent company investment on the balance sheet. The following table summarizes our cash flow activity:
Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | ||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 626 | $ | 462 | ||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (210 | ) | (1,318 | ) | ||||
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (294 | ) | 955 | |||||
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents, including restricted | 122 | 99 | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents, including restricted, at beginning of year | 99 | — | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents, including restricted, at end of year | 221 | 99 | ||||||
Less restricted cash and cash equivalents included in other current assets | 74 | 11 | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 147 | $ | 88 | ||||
Net cash provided by operating activities for the year ended March 31, 2020 was $626 million, as compared to $462 million for the year ended March 31, 2019. The increase of $164 million included increases in net cash of $62 million from movements in working capital assets and liabilities and a $102 million increase in net income adjusted for non-cash items.
Net cash used in investing activities for the year ended March 31, 2020 was $210 million, as compared to $1.32 billion during the year ended March 31, 2019. The decrease of $1.11 billion was primarily due to less cash being used in the current year to invest in the Knight Point acquisition, as compared to more cash being used in the prior year to invest in the larger Spin-Off and Mergers, partially offset by the proceeds from the sale and leaseback transactions.
Net cash used in financing activities for the year ended March 31, 2020 was $294 million, as compared to net cash provided by financing activities of $955 million during the year ended March 31, 2019. The decrease in cash provided by financing activities of $1.25 billion was primarily due to the financing of the Spin-Off and Mergers in the prior year. Routine revolver activity, debt payments and finance lease payments provided a combined $158 million cash flow improvement compared to the prior year. The Company also returned more cash to investors in the current year through increased share repurchase activity and dividend payments, as those activities were newly initiated in the prior year.
Capital Resources
The following table summarizes our total debt:
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | ||||||
Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | 89 | $ | 80 | ||||
Long-term debt, net of current maturities | 2,283 | 2,297 | ||||||
Total debt | $ | 2,372 | $ | 2,377 | ||||
The $5 million decrease in total debt during the year ended March 31, 2020 resulted from the August 2019 restructuring of our senior secured credit facilities, scheduled and discretionary debt payments and debt-financed capital expenditures. At March 31, 2020, $700 million was available under our Revolving Credit Facility, and we were in compliance with all financial covenants associated with our borrowings as of March 31, 2020. For more information on our debt, see Note 10 – “Debt” to the financial statements.
42
The following table summarizes our capitalization ratios:
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | ||||||
Total debt and finance leases | $ | 2,619 | $ | 2,682 | ||||
Cash and cash equivalents | 147 | 88 | ||||||
Net debt(1) | $ | 2,472 | $ | 2,594 | ||||
Total debt and finance leases | $ | 2,619 | $ | 2,682 | ||||
Total shareholders’ equity | 1,357 | 2,162 | ||||||
Total capitalization | $ | 3,976 | $ | 4,844 | ||||
Debt-to-total capitalization | 66 | % | 55 | % | ||||
Net debt-to-total capitalization(1) | 62 | % | 54 | % | ||||
(1) Net debt is total debt less cash and cash equivalents. Net debt and net debt-to-total capitalization are non-GAAP measures used by management to assess our ability to service our debts using only our cash and cash equivalents. We present these non-GAAP measures to assist investors in analyzing our capital structure in a more comprehensive way compared to gross debt based ratios alone.
The decrease in our total capitalization as of March 31, 2020, as compared to March 31, 2019, was primarily driven by the $796 million of impairment charges discussed further in Note 8 – “Goodwill” and Note 9 – “Intangible Assets.”
Interest Rate Swaps
We use interest rate swaps to reduce our exposure to increases in interest rates on our variable rate debt. The interest rate swaps effectively convert our floating interest rate debt into fixed interest rate debt. Each swap agreement is designated as a cash flow hedge. We pay a stream of fixed interest payments for the term of the swap, and in turn, receive variable interest payments based on one-month LIBOR. At March 31, 2020, one-month LIBOR was 0.99%. The net receipt or payment from the interest rate swap agreements is included on the statements of operations as interest expense. As discussed above, sometime after 2021, there is expected to be a transition from LIBOR as an interest rate benchmark. We continue to evaluate the implications of the LIBOR transition for our swap arrangements.
The following table summarizes our interest rate swaps at March 31, 2020:
Inception | Maturity | Notional Amount (in millions) | Weighted Average Interest Rate Paid | ||||||
May 2018 | May 2021 | $ | 400 | 2.57 | % | ||||
May 2018 | May 2022 | 500 | 2.61 | % | |||||
October 2018 | October 2022 | 200 | 2.92 | % | |||||
May 2018 | May 2023 | 500 | 2.68 | % | |||||
Total / Weighted average interest rate | $ | 1,600 | 2.66 | % | |||||
Cash Dividends and Share Repurchase Programs
On May 21, 2020, the company increased the quarterly common stock dividend 17% to $0.07 per common share from $0.06 per common share. The payment of future quarterly dividends is subject to approval by the Board of Directors. See Note 18 – “Shareholders’ Equity” to the financial statements for information on our cash dividends and share repurchase programs.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We are party to a receivables sales arrangement with off-balance sheet risk. See Note 5 – “Receivables” to the financial statements for information about our receivables sales arrangement.
43
Contractual Obligations
Our contractual obligations as of March 31, 2020 were as follows:
(in millions) | Less than 1 year | 2-3 years | 4-5 years | More than 5 years | Total | |||||||||||||||
Debt(1) | $ | 97 | $ | 388 | $ | 1,371 | $ | 533 | $ | 2,389 | ||||||||||
Finance lease obligations(2) | 123 | 124 | 20 | — | 267 | |||||||||||||||
Operating lease obligations | 45 | 65 | 40 | 41 | 191 | |||||||||||||||
Purchase obligations(3) | 51 | 43 | 43 | — | 137 | |||||||||||||||
Interest payments(4) | 106 | 168 | 94 | 7 | 375 | |||||||||||||||
Totals(5)(6) | $ | 422 | $ | 788 | $ | 1,568 | $ | 581 | $ | 3,359 | ||||||||||
(1) Amounts represent scheduled principal cash payments of long-term debt.
(2) Amounts represent scheduled principal cash payments of finance lease obligations.
(3) Includes long-term purchase and separate services agreements with DXC for the purchase of certain hardware, software, and support services as well as the provision of certain outsourced IT services and excludes agreements that are cancelable without penalty. If we cancel the purchase agreements prior to their natural expiration, we will be required to pay to DXC any required shortfall. If we cancel the services agreements for any reason other than for cause, we will have to pay DXC significant termination fees, which will vary, depending on the date and manner of termination. Purchase obligations assumed from DXC will reflect a significant increase as a result of newly executed contracts. Also includes a five-year enterprise software and services agreement with a third-party vendor.
(4) Amounts represent scheduled interest payments on long-term debt and finance lease obligations.
(5) See Note 16 – “Pension and Other Benefit Plans” for the estimated liability related to estimated future benefit payments under our pension and other postretirement plans that have been omitted from this table.
(6) We have excluded obligations for unrecognized tax benefits of $39 million, as the timing of such payments, if any, cannot be reasonably estimated.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The preparation of the financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenue and expenses, as well as the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. In some cases, changes in the accounting estimates are reasonably likely to occur from period to period. Accordingly, actual results could differ materially from our estimates under different assumptions, judgments or conditions. We consider the following policies to be critical because of their complexity and the high degree of judgment involved in implementing them: revenue recognition, acquisition accounting and goodwill, and income taxes.
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s revenue from contracts with customers is derived from its primary service offerings, including technology and business solutions, systems engineering and integration, cybersecurity, applied research and big data analytics, and investigative and risk mitigation services to the U.S. government and its agencies. The Company also serves various state and local governments.
The Company performs under various types of contracts, which include (1) fixed price contracts, such as firm-fixed-price (“FFP”), (2) cost reimbursable contracts such as cost-plus-fixed-fee, cost-plus-award-fee and cost-plus-incentive-fee, and (3) time-and-materials (“T&M”) contracts, including fixed-price-level-of-effort (“FP-LOE”) contracts.
To determine the proper revenue recognition, the Company first evaluates whether it has a duly approved and enforceable contract with a customer, in which the rights of the parties and payment terms are identified, and collectability is probable. The Company also evaluates whether two or more contracts should be combined and accounted for as a single contract, including the task orders issued under an ID/IQ award. In addition, the Company assesses contract modifications to determine whether the changes to existing contracts should be accounted for as part of the original contract or as a separate contract. Contract modifications for the Company may relate to changes in contract specifications and requirements and do not add distinct services, and therefore are accounted for as part of the original contract. If contract modifications add distinct goods or services and increase the contract value by the stand-alone selling price, those modifications are accounted for as separate contracts.
For each contract, the Company assesses if multiple promises should be accounted for as separate performance obligations or combined into a single performance obligation. The Company generally separates multiple promises in a contract as separate performance obligations if those promises are distinct, both individually and in the context of the
44
contract. If multiple promises in a contract are highly interrelated or comprise a series of distinct services performed over time, they are combined and accounted for as a single performance obligation.
The Company’s contracts with the U.S. federal government often contain options to renew existing contracts for an additional period of time (generally a year at a time) under the same terms and conditions as the original contract. The Company accounts for renewal options as separate contracts when they include distinct goods or services at stand-alone selling prices.
Contracts with the U.S. federal government are generally subject to the FAR and priced on an estimated or actual costs of providing the goods or services. The FAR provides guidance on types of costs that are allowable in establishing prices for goods and services provided to the U.S. federal government and its agencies. Each contract is competitively priced and bid separately. Pricing for non-U.S. federal government agencies is based on specific negotiations with each customer. The Company excludes any taxes collected or imposed when determining the transaction price.
Certain of the Company’s contracts contain award fees, incentive fees or other provisions that may either increase or decrease the transaction price. These variable amounts generally are awarded upon achievement of certain performance metrics, program milestones or cost targets and can be based upon customer discretion. The Company estimates variable consideration at the expected value amount to which it expects to be entitled based on the assessment of the contractual variable fee criteria, complexity of work and related risks, extent of customer discretion, amount of variable consideration received historically and the potential of significant reversal of revenue.
The Company allocates the transaction price of a contract to its performance obligations in the proportion of such obligation’s stand-alone selling price. The stand-alone selling prices of the Company’s performance obligations are generally based on an expected cost-plus margin approach. For certain product sales, the Company uses prices from other stand-alone sales. Substantially none of the Company’s contracts contain a significant financing component that would require an adjustment to the transaction price of the contract.
The Company recognizes revenue on our service contracts primarily over time as there is continuous transfer of control to the customer over the duration of the contract as the Company performs the promised services. For U.S. federal government contracts, continuous transfer of control to the customer is evidenced by clauses in the contract that allow the customer to unilaterally terminate the contract for convenience, pay for costs incurred plus a reasonable profit and take control of any work-in-process.
The Company’s IT and business process outsourcing arrangements typically have a single performance obligation that are a series of distinct goods or services that are substantially the same and are provided over a period of time using the same measure of progress. Revenue derived from IT and business process outsourcing arrangements is generally comprised of a series of distinct services, and thus, is recognized over time based upon the level of services delivered in the distinct periods in which they are provided using an input method based on time increments. IT outsourcing arrangements may include nonrefundable upfront fees billed for activities to familiarize us with the client’s operations, take control over their administration and operation, and adapt them to the Company’s solutions. These activities typically do not qualify as separate performance obligations, and the related revenue is allocated to the relevant performance obligation and satisfied over time as the performance obligation is satisfied.
On FFP contracts, revenue recognized over time generally uses a method that measures the extent of progress toward completion of a performance obligation, principally using a cost-input method (referred to as the cost-to-cost method). Under the cost-to-cost method, revenue is recognized based on the proportion of total cost incurred to EAC. The cost-to-cost method best depicts the Company’s performance and transferring control of services promised to the customer. A performance obligation’s EAC includes all direct costs such as materials, labor, subcontract costs, overhead, and a ratable portion of general and administrative costs. In addition, the Company includes in an EAC future losses of a performance obligation estimated to be incurred on onerous contracts, as and when known, and the most likely amount of transaction price (revenue) that the Company expects to receive for unpriced change orders (modifications). On certain other contracts, principally T&M, FP-LOE, and cost-plus-fixed-fee, revenue is recognized using the right-to-invoice practical expedient as we are contractually able to invoice the customer based on the control transferred to the customer.
The Company has contracts to provide services that will be delivered under distinct and individual performance obligations. Revenue for contracts in which control of services provided does not transfer until delivery to the customer is recognized at a point in time.
45
Acquisition Accounting and Goodwill
When we acquire a controlling financial interest through a business combination, we use the acquisition method of accounting to allocate the purchase consideration to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed, which are recorded at fair value. Any excess of purchase consideration over the net fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed is recognized as goodwill.
Acquisition-related costs are recognized separately from the business combination and are expensed as incurred. The results of operations of acquired businesses are included in the financial statements from the acquisition date.
In accordance with ASC Topic 350, Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets, the Company tests goodwill for impairment on an annual basis, as of the first day of the second fiscal quarter, and between annual tests if circumstances change, or if an event occurs that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying amount. Factors which could necessitate an interim impairment assessment include, but are not limited to, a sustained decline in our stock price, significant decreases in federal government appropriations or funding for our contracts, the loss of significant business or significant underperformance relative to historical or projected future operating results.
Determining the fair value of a reporting unit is judgmental in nature and involves the use of significant estimates and assumptions that we believe are reasonable but inherently uncertain, and actual results may differ from those estimates. The Company engages a third-party valuation specialist to estimate the fair value of the reporting units using both an income approach and a market approach. The income approach incorporates the use of a discounted cash flow method in which the estimated future cash flows and terminal values for each reporting unit are discounted to a present value using a discount rate. Cash flow projections are based on management’s estimates of economic and market conditions, which drive key assumptions of revenue growth rates, operating income, capital expenditures, and working capital requirements. The results of these approaches are used to corroborate the conclusion.
The Company’s annual goodwill impairment analysis, which was performed qualitatively as of July 1, 2019, did not result in an impairment charge. Subsequently, the U.S. Navy announced on February 5, 2020 that Perspecta was not awarded the NGEN-R SMIT contract, the re-compete of the NGEN contract currently held by the Company. We incurred a non-cash, pre-tax impairment charge of approximately $796 million primarily related to goodwill and intangible assets in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2020 as a result of the U.S. Navy’s decision, as discussed further in Note 8 – “Goodwill” and Note 9 – “Intangible Assets.”
Income Taxes
For years ending prior to the Spin-Off and Mergers, our operations were historically included in the tax returns filed by the respective Parent entities of which our businesses have been a part. The Company’s tax balances as of the beginning of the fiscal year, as well as our tax provisions for the pre-merger period contained in the financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, are presented on a separate return basis as if USPS filed its own tax returns. The separate return method applies the accounting guidance for income taxes to the standalone financial statements as if we were a separate taxpayer and a standalone enterprise for the periods presented.
We recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected tax consequences of temporary differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts using enacted tax rates in effect for the year the differences are expected to reverse. We record a valuation allowance to reduce the deferred tax assets to the amount that is more likely than not to be realized.
We record accruals for uncertain tax positions in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification Topic 740, Income Taxes, on the basis of a two-step process in which (1) we determine whether it is more likely than not that the tax positions will be sustained on the basis of the technical merits of the position and (2) for those tax positions that meet the more likely than not recognition threshold, we recognize the largest amount of tax benefit that is more than 50 percent likely to be realized upon ultimate settlement with the related tax authority. We make adjustments to these accruals when facts and circumstances change, such as the closing of a tax audit. The provision for income taxes includes the effects of adjustments for uncertain tax positions, as well as any related interest and penalties.
46
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 1 – “Overview and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” included in our notes to consolidated combined financial statements (under the heading “Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements” and “Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements”).
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
We actively monitor our exposures to potential loss arising from adverse changes in market rates and prices and manage such risks through our regular operating and financing activities or the use of derivative financial instruments.
Our exposure to market risk for changes in interest rates relates primarily to our $2.39 billion of outstanding debt. We present the fair value of our long-term debt using an expected present value technique, which is based on currently observable market inputs, using interest rates currently available to us for instruments with similar terms and remaining maturities. However, the fair value of our debt will generally fluctuate with movements of interest rates, increasing in periods of declining rates of interest and declining in periods of increasing rates of interest. See Note 11 – “Fair Value” to the financial statements for more information. The interest expense associated with our Term Loan A Facilities, Term Loan B Facility, and any loans under our Revolving Credit Facility will vary with market rates.
Our exposure to financial risk from changes in interest rates relates primarily to our $2.29 billion of debt outstanding under our senior secured credit facilities. Pursuant to our interest rate risk management strategies, during the year ended March 31, 2020, we used interest rate cash flow hedges to add stability to our interest expense and to manage our exposure to interest rate increases. The gross notional amount of the Company’s interest rate swaps at March 31, 2020 was $1.60 billion. Net of the benefit from our interest-rate derivatives, a hypothetical 1% increase in interest rates would increase the interest expense incurred under our senior secured loan facilities by approximately $7 million for the next twelve months following March 31, 2020, and likewise decrease our net income and cash flows. We have not entered into any hedging transactions for speculative or trading purposes. Prior to the Spin-Off, DXC managed the risk related to interest rates.
47
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Index to Consolidated Combined Financial Statements | Page |
Notes to Consolidated Combined Financial Statements | |
All financial statement schedules have been omitted since they are either not required, not applicable, or the required information is shown in the financial statements or related notes.
48
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Perspecta Inc.
Chantilly, Virginia
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated combined balance sheets of Perspecta Inc. (the "Company") (formerly the U.S. Public Sector Business of DXC Technology Company) as of March 31, 2020 and March 31, 2019, the related consolidated combined statements of operations, comprehensive income, cash flows, and changes in stockholders’ equity for each of the three years in the period ended March 31, 2020 (collectively referred to as the "financial statements"). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of March 31, 2020 and 2019, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended March 31, 2020, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2020, based on the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated May 22, 2020, expressed an adverse opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting because of a material weakness.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Emphasis of a Matter
As discussed in Note 1 to the financial statements, DXC Technology Company (“DXC”) acquired the Company through the merger of Computer Sciences Corporation and the Enterprise Services Business of Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company (“HPE”) on April 1, 2017. These combined financial statements of the Company were derived from the consolidated and combined financial statements and accounting records of DXC for the period from April 1, 2018 to May 31, 2018 and the fiscal year ended March 31, 2018 as if the Company were operated on a standalone basis during the periods presented. The consolidated combined statements of operations of the Company reflect allocations of general corporate expenses of DXC and HPE. These allocations may not reflect the expense the Company would have incurred as a standalone company for the periods presented.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current-period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
49
Revenue Recognition - Refer to Note 1 to the financial statements
Critical Audit Matter Description
As more fully described in Note 1 to the financial statements, the Company recognizes revenue on service contracts primarily over time as there is continuous transfer of control to the customer over the duration of the contract as the Company performs the promised services. The Company assesses if multiple promises should be accounted for as separate performance obligations or combined into a single performance obligation. The Company generally separates multiple promises in a contract as separate performance obligations if those promises are distinct, both individually and in the context of the contract. If multiple promises in a contract are highly interrelated or comprise a series of distinct services performed over time, they are combined and accounted for as a single performance obligation. The accounting conclusions for contracts involves judgment, particularly as it relates to determining the amount, timing and presentation of revenue that will be recognized for each performance obligation within the contract, and the distinct number of performance obligations represented by the contract.
Given the judgments necessary to determine the amount, timing and presentation of revenue and to understand and differentiate the number of performance obligations contained in the contract, auditing these judgments required extensive audit effort due to the complexity of the underlying programs and a high degree of auditor judgment when performing audit procedures and evaluating the results of those procedures.
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
Our audit procedures related to management’s conclusions on amount, timing and presentation of revenue for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020, included the following, among others:
• | We developed an expectation of revenue based on historical revenue and cost trends and current year costs and compared it to the recorded balance. We tested the accuracy and completeness of costs incurred by selecting a sample of the costs and vouching the costs to invoices or other supporting document(s). |
• | We selected certain long-term contracts for testing and performed the following procedures: |
– | Evaluated the terms and conditions of each contract and the appropriateness of the accounting treatment in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, by: |
▪ | Inspecting the executed contract to evaluate that the facts on which management’s conclusions were reached were consistent with the actual terms and conditions of the contract. |
▪ | Evaluating the contract within the context of the five-step model prescribed by ASC 606 and that management’s conclusions were appropriate by evaluating the nature of the promises within the contract, the interrelationship of the promised services provided, the pattern by which obligations are fulfilled, the number of performance obligations identified, and which party is acting as principal in the fulfillment of the identified performance obligations. |
– | Tested the mathematical accuracy of management’s calculation of revenue for the performance obligation. |
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
McLean, Virginia
May 22, 2020
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2017.
50
PERSPECTA INC.
CONSOLIDATED COMBINED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
CONSOLIDATED COMBINED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(in millions, except per share amounts) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | March 31, 2018 | |||||||||
Revenue | $ | 4,504 | $ | 4,030 | $ | 2,819 | ||||||
Costs of services | 3,460 | 3,043 | 2,155 | |||||||||
Selling, general and administrative | 303 | 300 | 182 | |||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 374 | 330 | 167 | |||||||||
Impairment charges | 796 | — | — | |||||||||
Restructuring costs | 17 | 10 | 14 | |||||||||
Separation, transaction and integration-related costs | 85 | 106 | 90 | |||||||||
Interest expense, net | 137 | 121 | 12 | |||||||||
Other expense, net | 62 | 8 | — | |||||||||
Total costs and expenses | 5,234 | 3,918 | 2,620 | |||||||||
(Loss) income before taxes | (730 | ) | 112 | 199 | ||||||||
Income tax expense (benefit) | (54 | ) | 40 | (9 | ) | |||||||
Net (loss) income | $ | (676 | ) | $ | 72 | $ | 208 | |||||
(Loss) earnings per common share(1): | ||||||||||||
Basic | $ | (4.17 | ) | $ | 0.44 | $ | 1.46 | |||||
Diluted | $ | (4.17 | ) | $ | 0.44 | $ | 1.46 | |||||
(1) Earnings per common share information for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2018 is computed using the 142.43 million shares of Perspecta common stock resulting from the Distribution as Perspecta did not operate as a stand-alone entity during the period, and therefore, no Perspecta common stock, stock options or other equity awards were outstanding and no dividends were declared or paid by Perspecta.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated combined financial statements.
51
PERSPECTA INC.
CONSOLIDATED COMBINED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
CONSOLIDATED COMBINED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | March 31, 2018 | |||||||||
Net (loss) income | $ | (676 | ) | $ | 72 | $ | 208 | |||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of taxes: | ||||||||||||
Actuarial loss on pension plan assets, net of tax benefit of $1, $0 and $0 | (2 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Change in net unrealized gains (losses) on cash flow hedges: | ||||||||||||
Net unrealized losses arising during the period, net of tax effect of $18, $10 and $0 | (52 | ) | (29 | ) | — | |||||||
Net losses reclassified to earnings, net of tax effect of $3, $2 and $0 | 8 | 6 | — | |||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of taxes | (46 | ) | (23 | ) | — | |||||||
Comprehensive (loss) income | $ | (722 | ) | $ | 49 | $ | 208 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated combined financial statements.
52
PERSPECTA INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in millions, except share and per share amounts) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | ||||||
ASSETS | ||||||||
Current assets: | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 147 | $ | 88 | ||||
Receivables, net | 513 | 484 | ||||||
Other receivables | 45 | 92 | ||||||
Prepaid expenses | 81 | 141 | ||||||
Other current assets | 101 | 73 | ||||||
Total current assets | 887 | 878 | ||||||
Property and equipment, net | 307 | 368 | ||||||
Goodwill | 2,671 | 3,179 | ||||||
Intangible assets, net | 1,193 | 1,466 | ||||||
Other assets | 347 | 192 | ||||||
Total assets | $ | 5,405 | $ | 6,083 | ||||
LIABILITIES and SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
Current liabilities: | ||||||||
Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | 89 | $ | 80 | ||||
Current finance lease obligations | 111 | 137 | ||||||
Current operating lease obligations | 39 | — | ||||||
Accounts payable | 218 | 246 | ||||||
Accrued payroll and related costs | 142 | 91 | ||||||
Accrued expenses | 385 | 396 | ||||||
Other current liabilities | 73 | 64 | ||||||
Total current liabilities | 1,057 | 1,014 | ||||||
Long-term debt, net of current maturities | 2,283 | 2,297 | ||||||
Non-current finance lease obligations | 136 | 168 | ||||||
Deferred tax liabilities | 114 | 171 | ||||||
Other long-term liabilities | 458 | 271 | ||||||
Total liabilities | 4,048 | 3,921 | ||||||
Commitments and contingencies | ||||||||
Shareholders’ equity: | ||||||||
Common stock, par value $0.01 per share; authorized 750,000,000 shares; 166,219,561 and 165,844,994 shares issued; 160,583,052 and 163,099,080 shares outstanding | 2 | 2 | ||||||
Additional paid-in capital | 2,266 | 2,242 | ||||||
(Accumulated deficit) retained earnings | (713 | ) | 2 | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (69 | ) | (23 | ) | ||||
Treasury shares at cost, 5,636,509 shares and 2,745,914 shares | (129 | ) | (61 | ) | ||||
Total shareholders’ equity | 1,357 | 2,162 | ||||||
Total liabilities and shareholders' equity | $ | 5,405 | $ | 6,083 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated combined financial statements.
53
PERSPECTA INC.
CONSOLIDATED COMBINED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(in millions, except shares in thousands and per share amounts in ones) | Common Stock | Additional Paid-in Capital | (Accumulated Deficit) Retained Earnings | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss | Treasury Shares | Parent Company Investment | Total Shareholders’ Equity | |||||||||||||||||
Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at April 1, 2017 | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 416 | $ | 416 | |||||||||
Effects of purchase accounting | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2,434 | 2,434 | ||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | — | — | 208 | 208 | ||||||||||||||||
Transfers to Parent, net | — | — | — | — | — | — | (329 | ) | (329 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Balance at March 31, 2018 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2,729 | 2,729 | ||||||||||||||||
Impact of adoption of new accounting standard | — | — | — | — | — | — | 4 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | — | — | 49 | 49 | ||||||||||||||||
Transfers to Parent, net | — | — | — | — | — | — | (145 | ) | (145 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Balance at May 31, 2018 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2,637 | 2,637 | ||||||||||||||||
Dividend to DXC prior to May 31, 2018 | — | — | (984 | ) | — | — | — | — | (984 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Spin-Off activity | 142,426 | 2 | 2,635 | — | — | — | (2,637 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||
Mergers activity | 23,273 | — | 578 | — | — | — | — | 578 | ||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 23 | — | — | — | 23 | ||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | — | — | (23 | ) | — | — | (23 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation | — | — | 9 | — | — | — | — | 9 | ||||||||||||||||
Repurchases of common stock | — | — | — | — | — | (60 | ) | — | (60 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Stock option exercises and other common stock transactions | 146 | — | 2 | — | — | (1 | ) | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||
Dividends declared ($0.20 per common share) | — | — | (12 | ) | (21 | ) | — | — | — | (33 | ) | |||||||||||||
Separation-related tax adjustment | — | — | 14 | — | — | — | — | 14 | ||||||||||||||||
Balance at March 31, 2019 | 165,845 | 2 | 2,242 | 2 | (23 | ) | (61 | ) | — | 2,162 | ||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | (676 | ) | — | — | — | (676 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | — | — | (46 | ) | — | — | (46 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation | — | — | 23 | — | — | — | — | 23 | ||||||||||||||||
Repurchases of common stock | — | — | — | — | — | (66 | ) | — | (66 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Stock option exercises and other common stock transactions | 375 | — | 1 | — | — | (2 | ) | — | (1 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Dividends declared ($0.24 per common share) | — | — | — | (39 | ) | — | — | — | (39 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Balance at March 31, 2020 | 166,220 | $ | 2 | $ | 2,266 | $ | (713 | ) | $ | (69 | ) | $ | (129 | ) | $ | — | $ | 1,357 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated combined financial statements.
54
PERSPECTA INC.
CONSOLIDATED COMBINED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
CONSOLIDATED COMBINED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | March 31, 2018 | |||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Net (loss) income | $ | (676 | ) | $ | 72 | $ | 208 | |||||
Adjustments to reconcile net (loss) income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 374 | 330 | 167 | |||||||||
Impairment charges | 796 | — | — | |||||||||
Net periodic benefit cost | 62 | 26 | — | |||||||||
Share-based compensation | 23 | 11 | 6 | |||||||||
Deferred income taxes | (55 | ) | 8 | (28 | ) | |||||||
Gain on sale or disposal of assets, net | (18 | ) | (25 | ) | — | |||||||
Restructuring charges | 17 | 10 | 14 | |||||||||
Other non-cash charges, net | 12 | 1 | — | |||||||||
Changes in assets and liabilities, net of effects of acquisitions: | ||||||||||||
Receivables, net | 97 | 102 | 49 | |||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 63 | (25 | ) | 20 | ||||||||
Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other current liabilities | 14 | (18 | ) | 113 | ||||||||
Deferred revenue and advanced contract payments | (35 | ) | (11 | ) | (11 | ) | ||||||
Income taxes payable and liability | (46 | ) | (22 | ) | — | |||||||
Accrued restructuring | (1 | ) | (4 | ) | (8 | ) | ||||||
Other assets and liabilities, net | (1 | ) | 7 | — | ||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 626 | 462 | 530 | |||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||||||
Payments for acquisitions, net of cash acquired | (265 | ) | (312 | ) | — | |||||||
Extinguishment of Vencore debt and related costs | — | (994 | ) | — | ||||||||
Proceeds from sale of assets | 77 | 25 | — | |||||||||
Purchases of property, equipment and software | (17 | ) | (26 | ) | (18 | ) | ||||||
Payments for outsourcing contract costs | (5 | ) | (11 | ) | (16 | ) | ||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (210 | ) | (1,318 | ) | (34 | ) | ||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||
Principal payments on long-term debt | (93 | ) | (170 | ) | — | |||||||
Proceeds from debt issuance | — | 2,500 | — | |||||||||
Payments of debt issuance costs | (4 | ) | (46 | ) | — | |||||||
Proceeds from revolving credit facility | 200 | 50 | — | |||||||||
Payments on revolving credit facility | (150 | ) | (50 | ) | — | |||||||
Payments on finance lease obligations | (141 | ) | (172 | ) | (157 | ) | ||||||
Repurchases of common stock | (66 | ) | (59 | ) | — | |||||||
Repurchases of common stock to satisfy tax withholding obligations | (2 | ) | (1 | ) | — | |||||||
Dividend to DXC | — | (984 | ) | — | ||||||||
Dividends paid to Perspecta shareholders | (38 | ) | (25 | ) | — | |||||||
Transfers to Parent, net | — | (88 | ) | (339 | ) | |||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (294 | ) | 955 | (496 | ) | |||||||
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents, including restricted | 122 | 99 | — | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents, including restricted, at beginning of year | 99 | — | — | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents, including restricted, at end of year | 221 | 99 | — | |||||||||
Less restricted cash and cash equivalents included in other current assets | 74 | 11 | — | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 147 | $ | 88 | $ | — | ||||||
Supplemental cash flow disclosures: | ||||||||||||
Interest paid, net | $ | 127 | $ | 115 | $ | 11 | ||||||
Income taxes paid (refunded), net | 32 | 61 | 19 | |||||||||
Supplemental schedule of non-cash investing and financing activities: | ||||||||||||
Leased assets acquired through finance lease obligations | $ | 77 | $ | 180 | $ | 156 | ||||||
Leased assets acquired through operating lease obligations | 100 | — | — | |||||||||
Dividends declared but not yet paid | 10 | 8 | — | |||||||||
Stock issued for the acquisition of Vencore | — | 578 | — | |||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated combined financial statements.
55
PERSPECTA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1 – Overview and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Background
Perspecta is a leading provider of end-to-end enterprise information technology (“IT”), mission, and operations-related services across the United States (“U.S.”) federal government to the Department of Defense (“DoD”), the intelligence community, and homeland security, civilian and health care agencies, as well as to certain state and local government agencies through two reportable segments: (1) Defense and Intelligence, which provides services to the DoD, intelligence community, branches of the U.S. Armed Forces, and other DoD agencies, and (2) Civilian and Health Care, which provides services to the Departments of Homeland Security, Justice, and Health and Human Services, as well as other federal civilian and state and local government agencies.
On May 31, 2018, DXC Technology Company (“DXC”) completed the spin-off of its U.S. Public Sector (“USPS”) business (the “Spin-Off”) and mergers with Vencore Holding Corp (“Vencore HC”) and KGS Holding Corp. (“KGS HC”) (the “Mergers”), which became wholly-owned subsidiaries of Perspecta. As consideration for the Mergers, Perspecta paid affiliates of Veritas Capital Fund Management L.L.C. (“Veritas Capital”) $400 million in cash and approximately 14% of the total number of shares of Perspecta common stock outstanding immediately after the Mergers (on a fully diluted basis, excluding certain unvested equity incentive awards). See Note 2 – “Acquisitions.”
Perspecta’s Amendment No. 3 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (the “Registration Statement”), filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) on April 30, 2018, was declared effective on May 2, 2018. Perspecta’s common stock began regular-way trading on the New York Stock Exchange on June 1, 2018 under the ticker symbol “PRSP.”
The accompanying consolidated combined financial statements and notes present the combined results of operations, financial position, and cash flows of USPS for the periods prior to the completion of the Spin-Off and the combination with Vencore HC and KGS HC. Accordingly, the term “Parent” refers to DXC for the period from April 1, 2017 to May 31, 2018. As used in these Notes, the “Company,” “we,” “us,” and “our” refer to the combined businesses of USPS for the period from April 1, 2017 through May 31, 2018, and to Perspecta and its consolidated subsidiaries beginning June 1, 2018 and for the period from June 1, 2018 through March 31, 2020.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) and pursuant to the rules and regulations of the SEC. In the opinion of management of the Company, the accompanying financial statements of Perspecta and its subsidiaries contain all adjustments, including normal recurring adjustments, necessary to present fairly Perspecta’s financial position as of March 31, 2020 and 2019 and its results of operations and cash flows during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
Prior to the Spin-Off and Mergers, the Parent maintained various benefit and share-based compensation plans at a corporate level and other benefit plans at a subsidiary level. USPS’s employees participate in those programs and a portion of the cost of those plans are allocated and included on the statement of operations. However, the balance sheets do not include any net benefit plan obligations as the pension plans were accounted as multiemployer benefit plans.
After the Spin-Off, DXC does not have any beneficial ownership of Perspecta or USPS. The chairman of the board of directors of Perspecta (the “Board of Directors”) is the former chief executive officer of DXC and served as the chairman of the DXC board of directors until December 31, 2019. Consequently, transactions prior to December 31, 2019 between DXC and Perspecta are reflected as related party transactions pursuant to the disclosure requirements of Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 850, Related Party Disclosures. For additional information about the allocation of expenses from DXC prior to the Spin-Off and certain continuing responsibilities between the Company and DXC, see Note 17 – “Related Party Transactions.”
56
Principles of Consolidation and Combination
The financial statements as of and for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020, and the period from June 1, 2018 to March 31, 2019, reflect the financial position and results of operations of the Company, its consolidated subsidiaries and the joint ventures and partnerships over which the Company has a controlling financial interest. The financial statements as of and for periods prior to the consummation of the Spin-Off reflect the financial position and results of operations of USPS as described above. All intercompany transactions and accounts within the combined businesses of USPS have been eliminated.
Intercompany transactions between USPS and Parent other than leases with Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company’s (“HPE”) wholly-owned leasing subsidiary (“HPE Financial Services”) were considered to be effectively settled in the combined financial statements at the time the transactions were recorded. The total net effect of the settlement of these intercompany transactions is reflected in the combined statements of cash flows within financing activities.
The financial statements for the periods prior to the Spin-Off are prepared on a carved-out and combined basis from the financial statements of DXC. The combined statements of operations of USPS reflect allocations of general corporate expenses from DXC, including, but not limited to, executive management, finance, legal, IT, employee benefits administration, treasury, risk management, procurement and other shared services. These allocations were made on a direct usage basis when identifiable, with the remainder allocated on the basis of revenue, expenses, headcount or other relevant measures. Management of Perspecta considers these allocations to be a reasonable reflection of the utilization of services by, or the benefits provided to, USPS. The allocations may not, however, reflect the expense USPS would have incurred as a stand-alone company for the periods presented. Actual costs that may have been incurred if USPS had been a stand-alone company would depend on a number of factors, including the chosen organizational structure, what functions were outsourced or performed by employees and strategic decisions made in areas such as IT and infrastructure.
Business Segment Information
The Company reports separately information about each of its operating segments that engage in business activities from which revenue is recognized and expenses are incurred, and for which discrete financial information is available. These operating results are regularly reviewed by the Company’s chief operating decision maker, who is the Chief Executive Officer. The two reportable segments are aligned with the Company’s industries:
• | Defense and Intelligence - provides services to the DoD, intelligence community, branches of the U.S. Armed Forces, and other DoD agencies. |
• | Civilian and Health Care - provides services to the Departments of Homeland Security, Justice, and Health and Human Services, as well as other federal civilian and state and local government agencies. |
The segment information for the period prior to the Spin-Off has been recast to reflect the Company’s current reportable segment structure. There is no impact on the Company’s previously reported consolidated combined statements of operations, balance sheets or statements of cash flows resulting from these segment changes.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and accompanying notes.
Amounts subject to significant judgment and/or estimates include, but are not limited to, intangible assets, goodwill, fair value, certain deferred costs, valuation allowances on deferred tax assets, loss accruals for litigation, and inputs used for computing share-based compensation. These estimates are based on management’s best knowledge of historical experience, current events, and various other assumptions that management considers reasonable under the circumstances.
Reclassifications
Certain prior period balances in the accompanying financial statements have been reclassified to conform to the current period presentation. These reclassifications had no impact on total assets, total liabilities, total equity, income before taxes or net income.
57
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s revenue from contracts with customers is derived from its primary service offerings, including technology and business solutions, systems engineering and integration, cybersecurity, applied research and big data analytics, and investigative and risk mitigation services to the U.S. government and its agencies. The Company also serves various state and local governments.
The Company performs under various types of contracts, which include (1) fixed price contracts, such as firm-fixed-price (“FFP”), (2) cost reimbursable contracts such as cost-plus-fixed-fee, cost-plus-award-fee and cost-plus-incentive-fee, and (3) time-and-materials (“T&M”) contracts, including fixed-price-level-of-effort (“FP-LOE”) contracts.
To determine the proper revenue recognition, the Company first evaluates whether it has a duly approved and enforceable contract with a customer, in which the rights of the parties and payment terms are identified, and collectability is probable. The Company also evaluates whether two or more contracts should be combined and accounted for as a single contract, including the task orders issued under an indefinite delivery/indefinite quantity award. In addition, the Company assesses contract modifications to determine whether the changes to existing contracts should be accounted for as part of the original contract or as a separate contract. Contract modifications for the Company may relate to changes in contract specifications and requirements and do not add distinct services, and therefore are accounted for as part of the original contract. If contract modifications add distinct goods or services and increase the contract value by the stand-alone selling price, those modifications are accounted for as separate contracts.
For each contract, the Company assesses if multiple promises should be accounted for as separate performance obligations or combined into a single performance obligation. The Company generally separates multiple promises in a contract as separate performance obligations if those promises are distinct, both individually and in the context of the contract. If multiple promises in a contract are highly interrelated or comprise a series of distinct services performed over time, they are combined and accounted for as a single performance obligation.
The Company’s contracts with the U.S. federal government often contain options to renew existing contracts for an additional period of time (generally a year at a time) under the same terms and conditions as the original contract. The Company accounts for renewal options as separate contracts when they include distinct goods or services at stand-alone selling prices.
Contracts with the U.S. federal government are generally subject to the Federal Acquisition Regulation (“FAR”) and priced on an estimated or actual costs of providing the goods or services. The FAR provides guidance on types of costs that are allowable in establishing prices for goods and services provided to the U.S. federal government and its agencies. Each contract is competitively priced and bid separately. Pricing for non-U.S. federal government agencies is based on specific negotiations with each customer. The Company excludes any taxes collected or imposed when determining the transaction price.
Certain of the Company’s contracts contain award fees, incentive fees or other provisions that may either increase or decrease the transaction price. These variable amounts generally are awarded upon achievement of certain performance metrics, program milestones or cost targets and can be based upon customer discretion. The Company estimates variable consideration at the expected value amount to which it expects to be entitled based on the assessment of the contractual variable fee criteria, complexity of work and related risks, extent of customer discretion, amount of variable consideration received historically and the potential of significant reversal of revenue.
The Company allocates the transaction price of a contract to its performance obligations in the proportion of such obligation’s stand-alone selling price. The stand-alone selling prices of the Company’s performance obligations are generally based on an expected cost-plus margin approach. For certain product sales, the Company uses prices from other stand-alone sales. Substantially none of the Company’s contracts contain a significant financing component that would require an adjustment to the transaction price of the contract.
The Company recognizes revenue on our service contracts primarily over time as there is continuous transfer of control to the customer over the duration of the contract as the Company performs the promised services. For U.S. federal government contracts, continuous transfer of control to the customer is evidenced by clauses in the contract that allow the customer to unilaterally terminate the contract for convenience, pay for costs incurred plus a reasonable profit and take control of any work-in-process.
58
The Company’s IT and business process outsourcing arrangements typically have a single performance obligation that are a series of distinct goods or services that are substantially the same and are provided over a period of time using the same measure of progress. Revenue derived from IT and business process outsourcing arrangements is generally comprised of a series of distinct services, and thus, is recognized over time based upon the level of services delivered in the distinct periods in which they are provided using an input method based on time increments. IT outsourcing arrangements may include nonrefundable upfront fees billed for activities to familiarize us with the client’s operations, take control over their administration and operation, and adapt them to the Company’s solutions. These activities typically do not qualify as separate performance obligations, and the related revenue is allocated to the relevant performance obligation and satisfied over time as the performance obligation is satisfied.
On FFP contracts, revenue recognized over time generally uses a method that measures the extent of progress toward completion of a performance obligation, principally using a cost-input method (referred to as the cost-to-cost method). Under the cost-to-cost method, revenue is recognized based on the proportion of total cost incurred to estimated total costs at completion (“EAC”). The cost-to-cost method best depicts the Company’s performance and transferring control of services promised to the customer. A performance obligation’s EAC includes all direct costs such as materials, labor, subcontract costs, overhead, and a ratable portion of general and administrative costs. In addition, the Company includes in an EAC future losses of a performance obligation estimated to be incurred on onerous contracts, as and when known, and the most likely amount of transaction price (revenue) that the Company expects to receive for unpriced change orders (modifications). On certain other contracts, principally T&M, FP-LOE, and cost-plus-fixed-fee, revenue is recognized using the right-to-invoice practical expedient as we are contractually able to invoice the customer based on the control transferred to the customer.
When a performance obligation is not satisfied over time, the Company recognizes revenue when it satisfies the performance obligation at a point in time. To determine the point in time at which a performance obligation is satisfied, the Company considers indicators of the transfer of control in accordance with ASC Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (“ASC 606”), including delivery of services to the customer, acceptance of services by the customer and having present right to payment.
Billed Receivables
Amounts billed and due from the Company’s customers, primarily the U.S. federal government, are classified as receivables, net of allowance for doubtful accounts on the balance sheets.
Contract Balances
Contract assets consist of unbilled receivables, which result from services provided under contracts when revenue is recognized over time, revenue recognized exceeds the amounts billed to the customer, and right to payment is not just subject to the passage of time. Amounts are invoiced as work progresses in accordance with agreed-upon contractual terms, either at periodic intervals or upon achievement of contractual milestones. Payment to employees and third parties for services provided to customers is generally immediate, while the related billing is generally within 90 days. The portion of the payments retained by the customer until final contract settlement is not considered a significant financing component because the intent is to protect the customer in the event the Company does not perform on our obligations under the contract.
Contract liabilities include advance contract payments and billings in excess of revenue recognized. Under certain contracts, the Company receives advances and milestone payments from its customers that exceed revenue earned to date, resulting in contract liabilities. Advances typically are not considered a significant financing component because it is used to meet working capital demands that can be higher in the early stages of a contract and to protect the Company from the customer failing to adequately complete some or all of its obligations under the contract.
Costs to Obtain a Contract
Certain sales commissions earned by the Company’s sales force are considered incremental and recoverable costs of obtaining a contract with a customer. Sales commissions are deferred and amortized on a straight-line basis over the term of the contract, not to exceed five years. The closing balance of the associated asset and expense was not material as of and during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020.
59
Costs to Fulfill a Contract
Costs incurred to fulfill a contract include costs that are directly related to a contract or an anticipated contract that generate or enhance resources to be used in satisfying performance obligations and are expected to be recovered. These costs are recognized as an asset in accordance with ASC Topic 340, Other Assets and Deferred Costs, and are recognized on a systematic basis that is consistent with the transfer to the customer of the services to which the asset relates. The closing balance of the associated asset and expense was not material as of and during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020.
Share-based Compensation Expense
The Company provides different forms of share-based compensation to its employees and non-employee directors. This includes time-based restricted stock units (“RSUs”), performance-based restricted stock units (“PSUs”), and stock options. The Company accounts for share-based compensation in accordance with ASC Topic 718 Compensation—Stock Compensation, which requires the use of a valuation model to calculate the fair value of certain share-based awards. The fair value of the RSUs and the PSUs awards is determined on the grant date, based on the Company’s closing stock price. Share-based awards generally vest one to three years from the date of grant and are subject to forfeiture if employment terminates prior to the lapse of the restrictions. We expense the fair value of share-based awards on a straight-line basis over the service period during which the restrictions lapse. The Company accounts for forfeitures as they occur.
Income Taxes
The Company recognizes deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected tax consequences of temporary differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts using enacted tax rates in effect for the year the differences are expected to reverse. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
The Company recognizes deferred tax assets to the extent that it believes these assets are more likely than not to be realized. In making such a determination, the Company considers all available positive and negative evidence including future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, projected future taxable income, tax-planning strategies and results of recent operations. If the Company determines that it would not be able to realize the deferred tax assets in the future equal to their net recorded amount, the Company would record a valuation allowance to reduce the deferred tax assets to the amount that is more likely than not to be realized.
The Company records accruals for uncertain tax positions in accordance with ASC Topic 740, Income Taxes, on the basis of a two-step process in which (1) the Company determines whether it is more likely than not that the tax positions will be sustained on the basis of the technical merits of the position and (2) for those tax positions that meet the more likely than not recognition threshold, the Company recognizes the largest amount of tax benefit that is more than 50 percent likely to be realized upon ultimate settlement with the related tax authority. The Company makes adjustments to these accruals when facts and circumstances change, such as the closing of a tax audit. The provision for income taxes includes the effects of adjustments for uncertain tax positions, as well as any related interest and penalties. Interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits are recognized and included in the provision for income taxes on the accompanying statements of operations. Accrued interest and penalties are included in the related tax liability on the balance sheets.
Prior to the Spin-Off and Mergers, the Company's operations were included in the tax returns filed by the respective Parent entities of which USPS’s businesses were a part. Income tax expense and other income tax related information for those periods contained in these financial statements are presented on a separate return basis as if USPS filed its own tax returns. The separate return method applies the accounting guidance for income taxes to the standalone financial statements as if USPS were a separate taxpayer and a standalone enterprise for the periods presented. Current income tax liabilities were assumed to be settled with Parent on the last day of the reporting periods and were relieved through the Parent company investment account and the transfers from (to) Parent, net on the statements of cash flows.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
60
Restricted Cash
The Company accounts for amounts collected associated with its MARPA Facility and unremitted to the Financial Institutions as restricted cash within our other current assets caption on the balance sheet, as well as any other cash balances that are contractually restricted from use in operations. See Note 5 – “Receivables” for additional information and definitions of MARPA Facility and Financial Institutions.
Concentrations of Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to significant concentrations of credit risk consist principally of receivables from trade customers and financing receivables. Perspecta performs ongoing credit evaluations of the financial condition of its customers. The Company’s receivables are primarily with the U.S. federal government, and thus the Company does not have material credit risk exposure.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment, which includes assets under finance lease, are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the asset or the remaining lease term, whichever is shorter.
The estimated useful lives of the Company’s property and equipment are as follows:
Property and Equipment | Estimated Useful Lives | |
Buildings | Up to 40 years | |
Computers and related equipment | 4 to 5 years | |
Furniture and other equipment | 2 to 15 years | |
Land | Not a depreciable asset | |
Leasehold improvements | Shorter of lease term or useful life | |
Leases
The Company leases certain real and personal property under non-cancelable operating leases. Lease assets under finance leases are comprised primarily of computers and related equipment. Finance lease obligations primarily consist of contractual arrangements with HPE Financial Services.
Under ASC 842, an arrangement is determined to be a lease at inception if it conveys the right to control the use of an identified asset for a period of time in exchange for consideration. At inception, we determine whether the contract is or contains a lease and, if so, whether the lease should be classified as an operating or a finance lease. The Company recognizes a right-of-use (“ROU”) asset and a lease liability based on the present value of the future minimum lease payments over the lease term at the commencement date, adjusted for any lease incentives, initial direct costs, and potential impairment. At the commencement date, a single discount rate is applied to a group of leases with the same durations. The rate is updated quarterly for new leases that commence during the period, unless a triggering event occurs requiring more frequent reassessment. We define the initial lease term to include renewal options determined to be reasonably certain. Lease assets are evaluated for impairment in a manner consistent with the treatment of other long-lived assets.
Certain leases require us to pay property taxes, insurance and routine maintenance, which are included in variable lease expense. At March 31, 2020, the Company did not have any lease agreements with residual value guarantees or material restrictions or covenants. The Company's lessor arrangements with its customers are immaterial to the results of operations and cash flows.
The Company includes both the amortization of operating lease assets and changes in the lease liabilities in changes in other assets and liabilities, net on the statement of cash flows.
Acquisition Accounting and Goodwill
When the Company acquires a controlling financial interest through a business combination, it uses the acquisition method of accounting to allocate the purchase consideration to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed, which are
61
recorded at fair value as measured on the date of acquisition. Any excess of purchase consideration over the fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed is recognized as goodwill.
Acquisition-related costs are recognized separately from the business combination and are expensed as incurred. The results of operations of acquired businesses are included in the financial statements from the acquisition date.
In accordance with ASC Topic 350, Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets, the Company tests goodwill for impairment on an annual basis, as of the first day of the second fiscal quarter, and between annual tests if circumstances change, or if an event occurs that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying amount. Factors which could necessitate an interim impairment assessment include, but are not limited to, a sustained decline in our stock price, significant decreases in federal government appropriations or funding for our contracts, the loss of significant business or significant underperformance relative to historical or projected future operating results.
Determining the fair value of a reporting unit is judgmental in nature and involves the use of significant estimates and assumptions that we believe are reasonable but inherently uncertain, and actual results may differ from those estimates. The Company engages a third-party valuation specialist to estimate the fair value of the reporting units using both an income approach and a market approach. The income approach incorporates the use of a discounted cash flow method in which the estimated future cash flows and terminal values for each reporting unit are discounted to a present value using a discount rate. Cash flow projections are based on management’s estimates of economic and market conditions, which drive key assumptions of revenue growth rates, operating income, capital expenditures, and working capital requirements. The results of these approaches are used to corroborate the conclusion.
The Company’s annual goodwill impairment analysis, which was performed qualitatively as of July 1, 2019, did not result in an impairment charge. Subsequently, the U.S. Navy announced on February 5, 2020 that Perspecta was not awarded the NGEN-R SMIT contract. The Company performed an interim impairment assessment in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2020, resulting in the impairment charge discussed further in Note 8 – “Goodwill,” as well as impairment charges discussed further in Note 9 – “Intangible Assets.”
Intangible Assets
The estimated useful lives for finite-lived intangible assets are shown below:
Intangible Assets | Estimated Useful Lives | |
Acquired backlog | 1 year | |
Software | 2 to 10 years | |
Developed technology | 6 to 7 years | |
Program assets | 4 to 14 years | |
Outsourcing contract costs | Contract life, excluding option years | |
Acquired backlog intangible assets represent the funded economic value of predominantly long-term contracts, less the amount of revenue already recognized on those contracts. Acquired backlog was valued using the excess earnings approach, amortized over a one year period. Software is amortized predominantly using the straight-line method. Developed technology intangible assets represent acquired intellectual property and were valued using the relief from royalty method. Program assets are acquired customer relationships and are amortized in proportion to the estimated undiscounted cash flows projected over the estimated life of the asset or on a straight-line basis if such cash flows cannot be reliably estimated. Costs of outsourcing contracts, including costs incurred for bid and proposal activities, are generally expensed as incurred. However, certain costs incurred upon initiation of an outsourcing contract are deferred and expensed on a straight-line basis over the contract life, excluding option years. These costs represent incremental external costs or certain specific internal costs primarily associated with assuming control over customer IT operations and transforming them consistent with contract specifications.
62
Long-Lived Asset Impairment
The Company reviews intangible assets with finite lives and long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. The Company assesses the recoverability of assets based on the estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to result from the use and eventual disposition of the asset. If the undiscounted future cash flows are less than the carrying amount, the asset is impaired. We measure the amount of impairment loss, if any, as the difference between the carrying amount of the asset and its fair value using an income approach or, when available and appropriate, using a market approach.
Fair Value
The Company accounts for recurring and non‑recurring fair value measurements in accordance with ASC Topic 820, Fair Value Measurement (“ASC 820”). ASC 820 defines fair value, establishes a fair value hierarchy for assets and liabilities measured at fair value and requires expanded disclosures about fair value measurements. The ASC 820 hierarchy ranks the quality of reliability of inputs, or assumptions, used in the determination of fair value and requires assets and liabilities carried at fair value to be classified and disclosed in one of the following three categories:
Level 1 - Fair value is determined by using unadjusted quoted prices that are available in active markets for identical assets and liabilities.
Level 2 - Fair value is determined by using inputs other than Level 1 quoted prices that are directly or indirectly observable. Inputs can include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets or quoted prices for identical assets and liabilities in inactive markets. Related inputs can also include those used in valuation or other pricing models, such as interest rates and yield curves that can be corroborated by observable market data.
Level 3 - Fair value is determined by inputs that are unobservable and not corroborated by market data. Use of these inputs involves significant and subjective judgments to be made by a reporting entity - e.g., determining an appropriate adjustment to a discount factor for illiquidity associated with a given security. If a change in Level 3 inputs occurs, the resulting amount might result in a significantly higher or lower fair value measurement.
The Company evaluates financial assets and liabilities subject to fair value measurements on a recurring basis to determine the appropriate level at which to classify them each reporting period. This determination requires the Company to make subjective judgments as to the significance of inputs used in determining fair value and where such inputs lie within the ASC 820 hierarchy.
Derivative Instruments
In the normal course of business, the Company is exposed to interest rate fluctuations. As part of its risk management strategy, the Company uses derivative instruments, primarily interest rate swaps, to hedge certain interest rate exposures. The Company’s objective is to add stability to interest expense and to manage its exposure to movements in market interest rates. The Company does not use derivative instruments for trading or any speculative purpose.
The Company uses interest rate swap agreements designated as cash flow hedges to mitigate its exposure to interest rate risk associated with the variability of cash outflows for interest payments on certain floating interest rate debt, which effectively converted the debt into fixed interest rate debt. The Company initially accounted for all changes in fair value of its interest rate swaps on the statements of operations until designation as a cash flow hedge of interest rate risk on June 22, 2018. As a result, the Company recorded a gain of $5 million included in interest expense, net on the statement of operations for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2019.
Following the June 22, 2018 cash flow hedge designation, all changes in the hedging instruments’ fair value are recorded in accumulated other comprehensive loss (“AOCL”) and subsequently reclassified into earnings in the period during which the hedged transactions are recognized in earnings. The effective portion of changes in the fair value of derivatives designated that qualify as cash flow hedges is recorded in AOCL, net of taxes, and is subsequently reclassified into earnings in the period that the hedged forecasted transaction affects earnings along with the related tax effects. The ineffective portion of the change in fair value of the derivatives is recognized directly in earnings. Amounts reported in AOCL related to derivatives will be reclassified to interest expense as interest payments are made on the Company’s variable-rate debt.
63
For the year ended March 31, 2020, the Company performed both retrospective and prospective hedge effectiveness analyses for the interest rate swaps designated as cash flow hedges. The Company applied the long-haul method outlined in ASC Topic 815, Derivatives and Hedging, to assess retrospective and prospective effectiveness of the interest rate swaps. A quantitative effectiveness analysis assessment of the hedging relationship was performed using regression analysis. As of March 31, 2020, the Company determined that the hedging relationship was highly effective.
Pension and Other Benefit Plans
The Company accounts for its pension, other postretirement employee benefit (“OPEB”), defined contribution and deferred compensation plans using the guidance of ASC Topic 710, Compensation—General, and ASC Topic 715, Compensation—Retirement Benefits. The Company recognizes actuarial gains and losses and changes in fair value of plan assets in earnings at the time of plan remeasurement as a component of net periodic benefit cost, included in other expense, net on our statements of operations. Plan remeasurement typically occurs on the last day of each fiscal year. The remaining components of net periodic benefit cost, primarily current period interest costs and expected return on plan assets, are recorded on a monthly basis.
Inherent in the application of the actuarial methods are key assumptions including, but not limited to, discount rates, expected long-term rates of return on plan assets, mortality rates, rates of compensation increases, and medical cost trend rates. Company management evaluates these assumptions annually and updates assumptions as necessary. The fair value of plan assets is determined based on the prevailing market prices or estimated fair value of investments when quoted prices are not available.
We recognize on a plan-by-plan basis the funded status of our postretirement benefit plans under GAAP as either an asset recorded within other non-current assets or a liability recorded within non-current liabilities on our consolidated balance sheets. The GAAP funded status is measured as the difference between the fair value of the plan’s assets and the projected benefit obligation of the plan. The funded status under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended by the Pension Protection Act of 2006, is calculated on a different basis than under GAAP.
Parent Company Investment
Parent company investment on the statements of changes in equity represented Parent’s historical investment in the Company, the net effect of transactions with and allocations from Parent and our accumulated earnings through the date of the Spin-Off and Mergers.
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842) Section A—Leases (“ASU 2016-02”). ASU 2016-02, along with related amendments (“ASC 842”), requires lessees to record, at lease inception, a lease liability for the obligation to make lease payments and a ROU asset for the right to use the underlying asset for the lease term on their balance sheets. Management developed a detailed implementation plan, which included, among other things, implementation of a new lease accounting system, an update to our policies, development of disclosures, evaluation of our controls, and application of the guidance across our contract population. The Company adopted the standard on April 1, 2019 using the optional transition method. Under this method, the Company applied the standard through a cumulative-effect adjustment in the period of adoption. In addition, the Company has elected to adopt additional practical expedients to all classes of leased assets, including combining lease and non-lease components, applying the discount rate to a portfolio of leases with similar lease durations based on the original lease duration, and maintaining prior lease classification upon adoption. The adoption of ASC 842 resulted in the recognition of $114 million and $130 million of ROU assets and lease liabilities, respectively, on our balance sheet related to operating leases. The adoption did not have a material impact on our statements of operations, changes in shareholders’ equity or cash flows. See Note 7 – “Leases” for further details.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments (“ASU 2016-13”). The guidance, along with related amendments, changes the impairment model for most financial assets. The new model uses a forward-looking expected loss method, which requires consideration of a broader range of reasonable and supportable information to inform credit loss estimates. ASU 2016-13 is effective April 1, 2020 for Perspecta. The Company has determined that ASU 2016-13 will not have a material effect on
64
Perspecta’s financial statements upon adoption on April 1, 2020, given the concentration of receivables with the U.S. government.
In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-15, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other—Internal-Use Software (Subtopic 350- 40): Customer’s Accounting for Implementation Costs Incurred in a Cloud Computing Arrangement That Is a Service Contract (“ASU 2018-15”). ASU 2018-15 provides guidance for determining when a cloud computing arrangement includes a software license and makes changes to the requirements for capitalizing implementation costs incurred in a hosting arrangement that is as a service contract. The Company adopted ASU 2018-15 on April 1, 2020 and will apply it to implementation costs incurred after the date of adoption. The impact on the Company’s financial statements and disclosures will depend on the volume of cloud-based solutions implemented.
In March 2020, the FASB issued ASU 2020-04, Reference Rate Reform (Topic 848): Facilitation of the Effects of Reference Rate Reform on Financial Reporting, which provides companies with optional expedients and exceptions to ease the potential accounting burden associated with transitioning away from reference rates that are expected to be discontinued. The optional expedients may be applied to contracts, hedging relationships and other transactions that reference LIBOR or another reference rate expected to be discontinued because of the reference rate reform. The amendments in this update are effective for all entities as of March 12, 2020 and may be adopted using a prospective approach through December 31, 2022. We are currently evaluating the impact of the reference rate reform on the Company’s financial statements and related disclosures.
Other recently issued ASUs effective after March 31, 2020 are not expected to have a material effect on Perspecta’s financial statements.
Note 2 – Acquisitions
Knight Point Systems, LLC
On July 31, 2019, Perspecta acquired all of the equity interests of Knight Point Systems, LLC (“Knight Point”) for $250 million plus customary purchase price adjustments, initially estimated at a total of $265 million and currently estimated at $264 million. Knight Point delivers end-to-end managed services and solutions focused on modernizing IT systems, protecting critical networks and driving digital transformation to improve customer transparency and operational efficiency. Knight Point leverages a portfolio of intellectual property to solve complex customer challenges in cloud, cybersecurity and agile development and operations (“DevOps”) environments.
The Company recognized preliminary fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed and allocated $116 million to goodwill and $125 million to intangible assets. The goodwill is largely attributable to the assembled workforce of Knight Point and expected synergies between the Company and Knight Point. The Company’s preliminary allocation of goodwill to Perspecta’s reportable segments was as follows: $22 million allocated to Defense and Intelligence and $94 million allocated to Civilian and Health Care. The intangible assets consist primarily of program assets of $102 million, developed technology of $18 million and backlog of $5 million. The estimated fair value attributed to intangible assets is being amortized on an accelerated basis over a range of 10 to 12 years for program assets, seven years for developed technology and one year for backlog. The fair value attributed to the intangible assets acquired was based on preliminary estimates, assumptions, and other information compiled by management, including independent valuations that utilized established valuation techniques. All of the value attributed to goodwill and intangible assets is deductible for income tax purposes. The fair values of assets acquired and liabilities assumed are preliminary and based on a valuation using estimates and assumptions that are subject to change, which could result in material changes to the purchase price allocation. The final purchase price allocation is expected to be completed by the first quarter of fiscal year 2021, pending analysis of certain tax adjustments.
The results of operations of Knight Point have been included in the statements of operations beginning August 1, 2019. Pro forma results of operations for this acquisition have not been presented as it is not material to the consolidated results of operations. The acquisition was considered an asset purchase for tax purposes.
Acquisition Subsequent to Period End
On May 1, 2020, Perspecta acquired certain assets of DHPC Technologies, a U.S. developer of electronic warfare technologies. The purchase consideration was approximately $53 million in cash, subject to customary purchase price adjustments. The fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed and the results of operations are not material to the operations of Perspecta. The final purchase price allocation is expected to be completed during fiscal year 2021.
65
Fiscal 2019 Spin-Off and Mergers
On May 31, 2018, immediately following the consummation of the Spin-Off, the Company completed the Mergers. As defined in the Merger Agreement, Perspecta issued shares of Perspecta common stock to Veritas Capital and its affiliates, including 18,877,244 shares to The SI Organization Holdings LLC (the “Vencore HC Stockholder”) and 4,396,097 shares to KGS Holding LLC (the “KeyPoint Stockholder,” and, together with the Vencore HC Stockholder, the “Vencore Stockholders”), representing in the aggregate approximately 14% of the outstanding shares of Perspecta common stock immediately following the Mergers. As a result of these transactions, Vencore HC and KGS HC became wholly-owned subsidiaries of Perspecta.
The Spin-Off and Mergers were structured as a “Reverse Morris Trust” transaction, in which Perspecta was deemed the accounting acquirer of Vencore HC and KGS HC and their respective subsidiaries. Purchase consideration transferred in a business combination is typically measured by reference to the fair value of equity issued or other assets transferred by the accounting acquirer. Accordingly, the fair value of the purchase consideration transferred was measured based on the fair value of approximately 14% of shares of the combined business, $400 million cash transferred by Perspecta to the Vencore Stockholders, and approximately $994 million paid to extinguish certain existing Vencore indebtedness.
Under the acquisition method of accounting, total consideration exchanged was:
(in millions) | Amount | |||
Preliminary fair value of equity purchase consideration received by Vencore Stockholders(1) | $ | 578 | ||
Preliminary fair value of cash purchase consideration received by Vencore Stockholders | 400 | |||
Preliminary fair value of cash consideration paid by USPS to extinguish certain existing Vencore indebtedness | 994 | |||
Consideration transferred | $ | 1,972 | ||
(1) | Represents the fair value of consideration received by the Vencore HC Stockholder and the KeyPoint Stockholder for approximately 14% ownership in the combined company. The fair value of the purchase consideration transferred was based on 18,877,244 shares of Perspecta common stock distributed to Vencore HC Stockholder and 4,396,097 shares of Perspecta common stock distributed to the KeyPoint Stockholder as of the close of business on the record date for the Mergers, at the closing price of $24.86 per share on May 31, 2018. |
The information presented below represents the allocation of Vencore’s purchase price to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed, including acquiree-related transaction costs of $38 million, as of the acquisition date, May 31, 2018. As of March 31, 2019, the Company finalized the accounting for the Mergers. The major classes of assets and liabilities to which the purchase price was allocated were as follows:
(in millions) | Fair Value | |||
Current assets | $ | 333 | ||
Property and equipment | 35 | |||
Intangible assets | 753 | |||
Other assets | 40 | |||
Accounts payable, accrued payroll, accrued expenses, and other current liabilities | (194 | ) | ||
Deferred revenue | (12 | ) | ||
Deferred tax liabilities | (10 | ) | ||
Other liabilities | (119 | ) | ||
Net identifiable assets acquired | 826 | |||
Goodwill | 1,146 | |||
Consideration transferred | $ | 1,972 | ||
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the closing date of the Mergers, and is attributable to the intellectual capital, the acquired assembled work force and expected cost synergies, none of which qualify for recognition as a separate intangible asset. The goodwill discussed above includes approximately $195 million of goodwill that is deductible for tax purposes. Goodwill arising from the Mergers has been allocated to Perspecta’s reporting units based on the relative fair value of assets acquired, with $1.07 billion allocated to the Defense and Intelligence segment and $77 million allocated to the Civilian and Health Care segment.
66
Intangible assets acquired were as follows:
(in millions, except years) | Weighted-average Amortization Period (in years) | Fair Value | ||||
Program assets | 13 | $ | 625 | |||
Developed technology | 6 | 105 | ||||
Backlog | 1 | 22 | ||||
Favorable leases | 4 | 1 | ||||
Total intangible assets | 12 | $ | 753 | |||
Unaudited Pro Forma Financial Information
The following unaudited pro forma financial information presents results as if the Spin-Off and the Mergers and the related financing had occurred on April 1, 2017. The historical consolidated financial information of Perspecta has been adjusted in the pro forma information to give effect to the events that are (1) directly attributable to the transactions, (2) factually supportable and (3) expected to have a continuing impact on the combined results. The effects of the Spin-Off are primarily attributable to interest expense associated with the incurrence of debt in connection with the Spin-Off. The effects of the Mergers primarily relate to amortization of acquired intangible assets. The consolidated financial information of Perspecta includes merger and integration-related costs that are not expected to recur and impact the combined results over the long-term. The unaudited pro forma results do not reflect future events that have occurred or may occur after the transactions, including but not limited to, the impact of any actual or anticipated synergies expected to result from the Mergers. Accordingly, the unaudited pro forma financial information is not necessarily indicative of the results of operations as they would have been had the transactions been effected on April 1, 2017, nor is it necessarily an indication of future operating results.
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2019 Historical Perspecta (1) | Period from April 1, 2018 to May 31, 2018 Historical Vencore | Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||
(in millions, except per share amounts) | Effects of the Spin-Off | Effects of the Mergers | Pro Forma Combined for the Spin-Off and Mergers | |||||||||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 4,030 | $ | 244 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 4,274 | ||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 72 | $ | (57 | ) | $ | (7 | ) | $ | 20 | $ | 28 | ||||||||
Earnings per common share(2): | ||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.44 | $ | 0.17 | ||||||||||||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.44 | $ | 0.17 | ||||||||||||||||
(1) Revenue and pre-tax income includes $1.27 billion and $185 million, respectively, associated with Vencore HC and KGS HC for the period of June 1, 2018 through March 31, 2019. The pre-tax income excludes amortization of acquired intangible assets, acquisition financing and the allocation of certain corporate overhead costs.
(2) Historical and pro forma combined earnings per common share information is computed based on 164.56 million basic weighted average shares and 164.82 million diluted shares. See Note 4 – “(Loss) Earnings Per Share.”
67
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions, except per share amounts) | Historical Perspecta | Historical Vencore | Effects of the Spin-Off | Effects of the Mergers | Pro Forma Combined for the Spin-Off and Mergers | |||||||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 2,819 | $ | 1,384 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 4,203 | ||||||||||
Net income | $ | 208 | $ | 33 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (112 | ) | $ | 128 | ||||||||
Earnings per common share(3): | ||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 1.46 | $ | 0.77 | ||||||||||||||||
Diluted | $ | 1.46 | $ | 0.77 | ||||||||||||||||
(3) Historical earnings per common share information for the year ended March 31, 2018 is computed using the 142.43 million shares of Perspecta common stock resulting from the Distribution. See Note 4 – “(Loss) Earnings Per Share.” Pro forma combined earnings per common share includes the shares issued by Perspecta in connection with the Mergers on May 31, 2018. As a result, both basic and diluted; pro forma combined earnings per common share information is computed based on 165.70 million shares of Perspecta common stock as Perspecta did not operate as a stand-alone entity during the period, and therefore, no Perspecta common stock, stock options or other equity awards were outstanding and no dividends were declared or paid by Perspecta.
Fiscal 2018 HPES Merger
On April 1, 2017, Computer Sciences Corporation (“CSC”), HPE, Everett SpinCo, Inc. (“Everett”), and New Everett Merger Sub Inc., a wholly-owned subsidiary of Everett (“Merger Sub”), completed the strategic combination of CSC with the HPE Enterprise Services business (“HPES”) to form DXC (the “HPES Merger”). At the time of the HPES Merger, Everett was renamed DXC, and as a result of the HPES Merger, CSC became a direct wholly owned subsidiary of DXC. The transaction was determined to be a reverse merger and CSC was determined to be the accounting acquirer of DXC. Therefore, for accounting purposes DXC, and in turn USPS, was subject to purchase price allocation adjustments as of April 1, 2017.
The information presented represents allocation of USPS’s purchase price to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the acquisition date, April 1, 2017. The total fair value of consideration transferred for USPS was approximately $2.85 billion. The purchase price was determined based on the enterprise value of USPS estimated as part of the purchase price allocation related to the HPES Merger compared to the total value of all shares issued by DXC.
68
The allocation of purchase price was completed as of March 31, 2018. The major classes of assets and liabilities to which the purchase price was allocated were as follows:
(in millions) | Fair Value | |||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | — | ||
Accounts receivable | 403 | |||
Prepaid expenses | 86 | |||
Other current assets | 22 | |||
Total current assets | 511 | |||
Property and equipment | 183 | |||
Intangible assets | 976 | |||
Other assets | 28 | |||
Total assets acquired | 1,698 | |||
Current finance lease obligations, accounts payable, accrued payroll, accrued expenses, and other current liabilities | 418 | |||
Deferred revenue | 71 | |||
Non-current finance lease obligations | 162 | |||
Deferred tax liabilities | 204 | |||
Other liabilities | 15 | |||
Total liabilities assumed | 870 | |||
Net identifiable assets acquired | 828 | |||
Goodwill | 2,022 | |||
Total estimated consideration transferred | $ | 2,850 | ||
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed. The goodwill is not deductible for tax purposes. Goodwill arising from the HPES Merger has been allocated to Perspecta’s reporting units based on the relative fair value of assets acquired, with $977 million allocated to the Defense and Intelligence segment and $1.05 billion allocated to the Civilian and Health Care segment.
Note 3 – Revenue
We disaggregate our revenue from contracts with customers by contract-type, whether the Company performs on the contract as the prime contractor or subcontractor, and customer-type for each of our segments, as we believe it best depicts how the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of our revenue and cash flows are affected by economic factors.
Revenue by contract type was as follows:
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2020 | Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Defense and Intelligence | Civilian and Health Care | Total | Defense and Intelligence | Civilian and Health Care | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
Cost-reimbursable | $ | 1,100 | $ | 107 | $ | 1,207 | $ | 830 | $ | 90 | $ | 920 | ||||||||||||
Fixed-price | 1,602 | 837 | 2,439 | 1,365 | 916 | 2,281 | ||||||||||||||||||
Time-and-materials | 399 | 459 | 858 | 392 | 437 | 829 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 3,101 | $ | 1,403 | $ | 4,504 | $ | 2,587 | $ | 1,443 | $ | 4,030 | ||||||||||||
Revenue by prime or subcontractor was as follows:
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2020 | Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Defense and Intelligence | Civilian and Health Care | Total | Defense and Intelligence | Civilian and Health Care | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
Prime contractor | $ | 2,915 | $ | 1,300 | $ | 4,215 | $ | 2,431 | $ | 1,343 | $ | 3,774 | ||||||||||||
Subcontractor | 186 | 103 | 289 | 156 | 100 | 256 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 3,101 | $ | 1,403 | $ | 4,504 | $ | 2,587 | $ | 1,443 | $ | 4,030 | ||||||||||||
69
Revenue by customer type was as follows:
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2020 | Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Defense and Intelligence | Civilian and Health Care | Total | Defense and Intelligence | Civilian and Health Care | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
U.S. federal government, including independent agencies | $ | 3,084 | $ | 1,141 | $ | 4,225 | $ | 2,574 | $ | 1,185 | $ | 3,759 | ||||||||||||
Non-federal (state, local and other) | 17 | 262 | 279 | 13 | 258 | 271 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 3,101 | $ | 1,403 | $ | 4,504 | $ | 2,587 | $ | 1,443 | $ | 4,030 | ||||||||||||
Performance Obligations
As of March 31, 2020, approximately $3.84 billion of revenue is expected to be recognized from remaining unsatisfied performance obligations on executed contracts. The Company expects to recognize approximately 79% of these remaining performance obligations as revenue within one year and approximately 89% within two years, with the remainder recognized thereafter.
Contract Balances
Contract assets and contract liabilities consisted of the following:
(in millions) | Balance Sheets Line Item | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | |||||||
Contract assets: | ||||||||||
Unbilled receivables | Receivables, net | $ | 341 | $ | 301 | |||||
Contract liabilities: | ||||||||||
Current portion of deferred revenue and advance contract payments | Other current liabilities | $ | 25 | $ | 33 | |||||
Non-current portion of deferred revenue and advance contract payments | Other long-term liabilities | 2 | 12 | |||||||
Contract assets increased $40 million during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020, primarily due to the timing of billings and the acquisition of Knight Point. Contract assets were net of $12 million and $31 million of advance contract payments as of March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. There were no significant impairment losses related to the Company’s contract assets during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020.
Contract liabilities decreased $18 million during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020, primarily due to revenue recognized in excess of payments received. During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020, the Company recognized $32 million of the deferred revenue and advance contract payments at March 31, 2019 as revenue. During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2019, the Company recognized $25 million of the deferred revenue and advance contract payments at April 1, 2018 as revenue.
Note 4 – (Loss) Earnings Per Share
Basic (loss) earnings per common share (“EPS”) for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020 is computed using the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding. Diluted EPS reflects the incremental shares issuable upon the assumed exercise of stock options and vesting of other equity awards. EPS for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2019 is computed using the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding between the date of the Distribution and the end of the period. EPS for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2018 is computed using the shares of Perspecta common stock resulting from the Distribution, as we did not operate as a stand-alone entity and therefore, no common stock, stock options or other equity awards were outstanding. Diluted loss per common share for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020 did not include the impact of potentially dilutive stock awards because the result would have been anti-dilutive. The aggregate number of anti-dilutive equity awards excluded from the calculation of EPS for each of the fiscal years ended March 31, 2019 and 2018 was insignificant.
70
The following table reflects the calculation of basic and diluted EPS:
Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(in millions, except per share amounts) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | March 31, 2018 | |||||||||
Net (loss) income | $ | (676 | ) | $ | 72 | $ | 208 | |||||
Common share information: | ||||||||||||
Basic weighted average common shares outstanding | 161.99 | 164.56 | 142.43 | |||||||||
Dilutive effect of equity awards | — | 0.26 | — | |||||||||
Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding | 161.99 | 164.82 | 142.43 | |||||||||
(Loss) earnings per common share: | ||||||||||||
Basic | $ | (4.17 | ) | $ | 0.44 | $ | 1.46 | |||||
Diluted | $ | (4.17 | ) | $ | 0.44 | $ | 1.46 | |||||
Note 5 – Receivables
Receivables, net consisted of the following:
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | ||||||
Billed trade receivables | $ | 173 | $ | 183 | ||||
Unbilled receivables | 341 | 301 | ||||||
Receivables, gross | 514 | 484 | ||||||
Allowance for doubtful accounts | (1 | ) | — | |||||
Receivables, net | $ | 513 | $ | 484 | ||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | ||||||
U.S. federal government, including independent agencies | $ | 468 | $ | 430 | ||||
Non-federal (state, local and other) | 45 | 54 | ||||||
Receivables, net | $ | 513 | $ | 484 | ||||
Receivables Sales Facility
On July 14, 2017, Enterprise Services LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company, which has since been renamed Perspecta Enterprise Solutions LLC (“PES LLC”), entered into a Master Accounts Receivable Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with certain financial institutions (the “Financial Institutions”). The Purchase Agreement established a U.S. federal government obligor receivables purchase facility (the “MARPA Facility”), which is an off-balance sheet facility. Concurrently, Parent entered into a guaranty made in favor of the Financial Institutions, that guarantees the obligations of the sellers and servicers of receivables under the Purchase Agreement. The guaranty does not cover any credit losses under the receivables. In connection with the Spin-Off of USPS, Parent entered into certain amendments to the guaranty whereby Parent can request to terminate its guaranty at the time of the separation of USPS from DXC. On May 31, 2018, the Parent’s guaranty was terminated and Perspecta entered into a new guaranty of PES LLC’s obligations under the Purchase Agreement.
In accordance with the terms of the Purchase Agreement, on January 23, 2018, the Purchase Agreement was amended to increase the aggregate facility limit from $200 million to $300 million (the first amendment), and on May 31, 2018, the Purchase Agreement was amended to increase the aggregate facility limit to $450 million (the second amendment). Effective October 31, 2018, the Company completed the third amendment to the MARPA Facility, reducing the aggregate facility limit to $300 million. Effective October 31, 2019, the Company completed the fourth amendment to the MARPA Facility to extend the term of the MARPA Facility through October 31, 2020.
Under the MARPA Facility, the Company sells eligible U.S. federal government and certain state government obligor receivables, including both billed and certain unbilled receivables. The MARPA Facility has a one-year term, but the Purchase Agreement provides for optional extensions, if agreed to by the Financial Institutions, in each case for an additional six month duration.
71
The Company accounts for these receivable transfers as sales and removes the sold receivables from its balance sheets. The fair value of the sold receivables approximated their book value due to their short-term nature. The Company estimated that its servicing fee was at fair value and therefore, no servicing asset or liability related to these services was recognized as of March 31, 2020. Sold receivables are presented as a change in receivables within operating activities on the statements of cash flows.
During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020, the Company sold $3.42 billion of billed and unbilled receivables, as compared to $2.71 billion during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2019. Collections on sold receivables were $3.31 billion and $2.75 billion during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The amounts outstanding as of March 31, 2020 and 2019 were $255 million and $146 million, respectively. As of March 31, 2020 and 2019, there were $63 million and $11 million, respectively, of cash collected by the Company, but not remitted to the Financial Institutions, which represents restricted cash recorded by the Company within the other current assets caption on the accompanying balance sheets.
Note 6 – Property and Equipment
Property and equipment, net consisted of the following:
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | ||||||
Land, buildings and leasehold improvements | $ | 32 | $ | 58 | ||||
Computers and related equipment | 412 | 409 | ||||||
Furniture and other equipment | 56 | 49 | ||||||
Total property and equipment, gross | 500 | 516 | ||||||
Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization | (193 | ) | (148 | ) | ||||
Property and equipment, net | $ | 307 | $ | 368 | ||||
Depreciation expense was as follows:
Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | March 31, 2018 | |||||||||
Depreciation expense for owned property and equipment | $ | 23 | $ | 9 | $ | 12 | ||||||
Amortization expense for property and equipment under finance lease | 122 | 117 | 57 | |||||||||
Total depreciation and amortization expense for property and equipment | $ | 145 | $ | 126 | $ | 69 | ||||||
Note 7 – Leases
As described in Note 1 – “Overview and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” under the heading “Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements,” effective April 1, 2019, we adopted ASC 842 using the optional transition method. In accordance with the optional transition method, we did not recast the prior period financial statements, and all prior period amounts and disclosures are presented under ASC 840.
The components of lease expense were as follows:
(in millions) | Statement of Operations Line Item(s) | Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2020 | ||||
Finance lease expense | ||||||
Amortization of leased assets | Depreciation and amortization | $ | 122 | |||
Interest on lease obligations | Interest expense, net | 17 | ||||
Total finance lease expense | 139 | |||||
Operating lease expense | Cost of services and selling, general and administrative | 54 | ||||
Variable lease expense | Cost of services and selling, general and administrative | 11 | ||||
Sublease income | Cost of services and selling, general and administrative | (4 | ) | |||
Total lease expense, net | $ | 200 | ||||
72
Under ASC 840, rental expense was approximately $56 million and $44 million during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. Also under ASC 840, net interest expense on finance lease obligations was $20 million and $12 million for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Supplemental balance sheet information related to leases was as follows:
(in millions) | Balance Sheet Line Item | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | |||||||
Assets | ||||||||||
Finance lease assets, gross | Property and equipment, net | $ | 395 | $ | 377 | |||||
Accumulated depreciation | Property and equipment, net | (168 | ) | (130 | ) | |||||
Finance lease assets, net | Property and equipment, net | 227 | 247 | |||||||
Operating lease assets | Other assets | 157 | — | |||||||
Total lease assets | $ | 384 | $ | 247 | ||||||
Liabilities | ||||||||||
Current | ||||||||||
Finance leases | Current finance lease obligations | $ | 111 | $ | 137 | |||||
Operating leases | Other current liabilities | 39 | — | |||||||
Non-current | ||||||||||
Finance leases | Non-current finance lease obligations | 136 | 168 | |||||||
Operating leases | Other long-term liabilities | 129 | — | |||||||
Total lease liabilities | $ | 415 | $ | 305 | ||||||
Supplemental cash flow information related to leases was as follows:
(in millions) | Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2020 | |||
Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease obligations: | ||||
Operating cash flows from operating leases | $ | 51 | ||
Operating cash flows from finance leases | 18 | |||
Financing cash flows from finance leases | 141 | |||
The Company includes both the amortization of operating lease assets and changes in the lease liabilities in changes in other assets and liabilities, net on the statement of cash flows.
The weighted average remaining lease terms and discount rates were as follows:
March 31, 2020 | |||
Weighted average remaining lease term (in years): | |||
Finance leases | 2.8 | ||
Operating leases | 5.6 | ||
Weighted average discount rate: | |||
Finance leases | 6.26 | % | |
Operating leases | 4.32 | % | |
73
As of March 31, 2020, future minimum lease payments required to be made under leases were as follows:
Fiscal Year (in millions) | Operating Leases | Finance Leases | ||||||
2021 | $ | 45 | $ | 123 | ||||
2022 | 35 | 82 | ||||||
2023 | 30 | 42 | ||||||
2024 | 22 | 16 | ||||||
2025 | 18 | 4 | ||||||
Thereafter | 41 | — | ||||||
Total minimum lease payments | 191 | 267 | ||||||
Less: Amount representing interest | (23 | ) | (20 | ) | ||||
Present value of net minimum lease payments | $ | 168 | $ | 247 | ||||
As of March 31, 2020, the Company had aggregate rent obligations of $27 million for operating leases and $5 million for finance leases, for leases that have not commenced, with terms ranging from less than one to eight years.
On October 4, 2019, we completed a sale and leaseback transaction of our Herndon, Virginia facility. The land and buildings sold had a carrying value of $23 million, which was included in other current assets on our balance sheet as of March 31, 2019. We recognized a pre-tax gain on sale of assets of $33 million included in other (income) expense, net on the statements of operations for the year ended March 31, 2020. The leaseback period will facilitate the Company’s exit from the facility.
On December 13, 2019, we completed a sale and leaseback transaction of our Clarksville, Virginia facility. The land and building sold had a carrying value of $26 million, which was included in property and equipment, net on our balance sheet as of March 31, 2019. We recognized an insignificant gain on the sale. The future minimum lease payments required to be made under the leaseback are approximately $15 million over seven years.
Note 8 – Goodwill
The changes in the carrying amount of goodwill by segment were as follows:
(in millions) | Defense and Intelligence | Civilian and Health Care | Total | |||||||||
Balance as of March 31, 2018 | $ | 977 | $ | 1,045 | $ | 2,022 | ||||||
Additions | 1,074 | 83 | 1,157 | |||||||||
Balance as of March 31, 2019 | 2,051 | 1,128 | 3,179 | |||||||||
Additions | 22 | 94 | 116 | |||||||||
Impairment charges | (624 | ) | — | (624 | ) | |||||||
Balance as of March 31, 2020 | $ | 1,449 | $ | 1,222 | $ | 2,671 | ||||||
Goodwill is stated net of accumulated impairment losses of $624 million at March 31, 2020. The additions to goodwill were primarily due to the Mergers described in Note 2 – “Acquisitions.”
The U.S. Navy announced on February 5, 2020 that Perspecta was not awarded the NGEN-R SMIT contract, the re-compete of the NGEN contract currently held by the Company. The NGEN contract was scheduled to expire on September 30, 2020, but three one-month options were exercised by the U.S. Navy, extending the contract through December 31, 2020. In connection with the April 1, 2017 merger of CSC with HPES to form DXC, the reporting unit with the NGEN contract was allocated $624 million of goodwill. As a result of the U.S. Navy’s decision not to award the NGEN-R SMIT contract to us, we tested this goodwill for impairment in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2020 and deemed it fully impaired.
74
Note 9 – Intangible Assets
Intangible assets were as follows:
March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Gross Carrying Value | Accumulated Amortization | Net Carrying Value | Gross Carrying Value | Accumulated Amortization | Net Carrying Value | ||||||||||||||||||
Program assets | $ | 1,458 | $ | (367 | ) | $ | 1,091 | $ | 1,525 | $ | (194 | ) | $ | 1,331 | ||||||||||
Software | 73 | (62 | ) | 11 | 87 | (58 | ) | 29 | ||||||||||||||||
Developed technology | 123 | (48 | ) | 75 | 105 | (22 | ) | 83 | ||||||||||||||||
Backlog | 28 | (26 | ) | 2 | 22 | (18 | ) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||
Outsourcing contract costs | 26 | (12 | ) | 14 | 25 | (7 | ) | 18 | ||||||||||||||||
Favorable leases | — | — | — | 1 | — | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total intangible assets | $ | 1,708 | $ | (515 | ) | $ | 1,193 | $ | 1,765 | $ | (299 | ) | $ | 1,466 | ||||||||||
In connection with the April 1, 2017 merger of CSC with HPES to form DXC, the reporting unit with the NGEN contract was allocated $299 million of intangible assets. We incurred a non-cash, pre-tax impairment charge of approximately $172 million in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2020, primarily related to program assets and outsourcing contract costs that are reflected in accumulated amortization in the table above, as a result of the U.S. Navy’s decision not to award the NGEN-R SMIT contract to us, as discussed further in Note 8 – “Goodwill.”
Amortization expense during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 was $229 million, $204 million and $98 million, respectively.
Estimated future amortization related to intangible assets as of March 31, 2020 was as follows:
Fiscal Year | (in millions) | |||
2021 | $ | 230 | ||
2022 | 151 | |||
2023 | 137 | |||
2024 | 123 | |||
2025 | 104 | |||
Thereafter | 448 | |||
Total future amortization | $ | 1,193 | ||
75
Note 10 – Debt
The Company’s outstanding debt as of March 31, 2020 and 2019 consisted of the following:
(in millions) | Interest Rates | Maturities | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | ||||||||
Revolving Credit Facility | LIBOR + 1.50% | August 2024 | $ | 50 | $ | — | ||||||
Term Loan A Facilities (Tranche 1) | LIBOR + 1.375% | August 2022 | 200 | 246 | ||||||||
Term Loan A Facilities (Tranche 2) | LIBOR + 1.50% | August 2024 | 1,552 | 1,588 | ||||||||
Term Loan B Facility | LIBOR + 2.25% | May 2025 | 491 | 497 | ||||||||
Subtotal senior secured credit facilities | 2,293 | 2,331 | ||||||||||
Other secured borrowings | Various | Various | 12 | — | ||||||||
Total secured debt | 2,305 | 2,331 | ||||||||||
Other unsecured borrowings | Various | Various | 18 | — | ||||||||
Senior unsecured EDS Notes | 7.45% | October 2029 | 66 | 66 | ||||||||
Total debt | 2,389 | 2,397 | ||||||||||
Less: current maturities of long-term debt, net (1) | (89 | ) | (80 | ) | ||||||||
Less: unamortized debt issuance costs and premiums, net (2) | (17 | ) | (20 | ) | ||||||||
Total long-term debt, net of current maturities | $ | 2,283 | $ | 2,297 | ||||||||
(1) Current maturities of long-term debt are presented net of $6 million and $8 million of debt issuance costs as of March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, associated with the Term Loan A Facilities and Term Loan B Facility.
(2) Includes $11 million and $12 million of unamortized premiums as of March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, on the assumed Electronic Data Systems Corporation (“EDS”) Notes.
Term Loan Facilities and Revolving Credit Facility
The Company has secured credit facilities at March 31, 2020 consisting of (1) senior secured term loan credit facilities with an aggregate principal amount of $1.75 billion (the “Term Loan A Facilities”) and $491 million (the “Term Loan B Facility”), net of $27 million of debt issuance costs and (2) a senior secured revolving credit facility in an available principal amount of $750 million (the “Revolving Credit Facility,” and, together with the Term Loan A Facilities and Term Loan B Facility, the “Credit Facilities”), net of $7 million of original debt issuance costs. As of March 31, 2020, $700 million of available credit remained undrawn under the Revolving Credit Facility.
The Credit Facilities contain negative covenants customary for financings of this type, including covenants that place limitations on the incurrence of additional indebtedness; the creation of liens; the payment of dividends or other restricted payments such as share repurchases; sales of assets; fundamental changes, including mergers and acquisitions; loans and investments; negative pledges; transactions with affiliates; restrictions affecting subsidiaries; modification to charter documents in a manner materially adverse to the lenders; changes in fiscal year and limitations on conduct of business. The Credit Facilities also contain affirmative covenants and representations and warranties customary for financings of this type. Perspecta was in compliance with all applicable covenants as of March 31, 2020.
In addition, the Revolving Credit Facility and Term Loan A Facilities contain financial maintenance covenants requiring, as of the end of any fiscal quarter, (a) a ratio of consolidated total net debt to consolidated EBITDA (as defined in the debt agreement) not in excess of 4.50:1.00, stepping down to 4.25:1.00 at the end of the quarter ending September 30, 2020, and thereafter stepping up to 4.50:1.00 during the twelve-month period following the consummation of a permitted acquisition that involves consideration with a fair market value in excess of $100 million and (b) a ratio of consolidated EBITDA to interest expense of not less than 3.00:1.00. Perspecta was in compliance with these covenants at March 31, 2020.
In addition, on May 31, 2018, Perspecta and each of the other grantors party thereto (the “Grantors”) entered into a Collateral Agreement (the “Collateral Agreement”) with MUFG Bank, Ltd. (“MUFG”), in its capacity as administrative agent, and MUFG Union Bank, N.A., in its capacity as collateral agent. Pursuant to the terms of the Collateral Agreement, each of the Grantors granted a perfected first priority security interest in substantially all of its assets to secure its obligations under the Credit Agreement and related documents to which it is a party, subject to certain customary exceptions.
Interest on the Company’s term loans is payable monthly or quarterly in arrears. The Company fully and unconditionally guaranteed term loans issued by its 100% owned subsidiaries. Interest on the Company’s senior notes is payable semi-
76
annually in arrears. Generally, the Company’s notes are redeemable at the Company’s discretion at the then-applicable redemption prices plus accrued interest.
Expected maturities of long-term debt as of March 31, 2020 are as follows:
Fiscal Year | (in millions) | |||
2021 | $ | 97 | ||
2022 | 95 | |||
2023 | 293 | |||
2024 | 92 | |||
2025 | 1,279 | |||
Thereafter | 533 | |||
Total | $ | 2,389 | ||
Note 11 – Fair Value
The Company estimates the fair value of its long-term debt primarily using an expected present value technique, which is based on observable market inputs, using interest rates currently available to the Company for instruments with similar terms and remaining maturities. The estimated fair value of the Company’s long-term debt, excluding finance leases and unamortized debt issuance costs, was $2.18 billion and $2.35 billion as of March 31, 2020 and 2019, as compared with the gross carrying value of $2.39 billion and $2.40 billion, respectively. If measured at fair value, long-term debt, excluding finance lease obligations, would be classified in Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy.
Non-financial assets such as goodwill, tangible assets, intangible assets and other contract related long-lived assets are reduced to fair value in the period an impairment charge is recognized. The fair value measurements, in such instances, would be classified in Level 3. There were no significant impairments recorded during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020 or 2019.
Note 12 – Derivative Instruments
The Company entered into $1.40 billion of notional interest rate swap agreements concurrently with its Credit Facilities (as defined under Note 10 – “Debt”), on May 31, 2018, and $200 million of notional interest rate swap agreements in October 2018. As of March 31, 2020, the Company had interest rate swap agreements with a total notional amount of $1.60 billion.
The pre-tax impact of loss on derivatives designated for hedge accounting recognized in other comprehensive income (loss) was $59 million ($44 million, net of tax) and $31 million ($23 million, net of tax) during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. We reclassified $11 million ($8 million, net of tax) and $8 million ($6 million, net of tax) from AOCL into earnings during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. As of March 31, 2020, we expect amounts of approximately $39 million pertaining to cash flow hedges to be reclassified from AOCL into earnings over the next 12 months.
Fair Value of Derivative Instruments
All derivatives are recorded at fair value on a recurring basis. The Company’s accounting treatment for these derivative instruments is based on its hedge designation. The fair value of interest rate swaps is estimated based on valuation models that use interest rate yield curves as Level 2 inputs. The gross fair value of our derivative liabilities in interest rate swaps designated for hedge accounting were as follows:
(in millions) | Balance Sheets Line Item | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | |||||||
Derivative liabilities: | ||||||||||
Interest rate swaps | Other current liabilities | $ | 37 | $ | 4 | |||||
Interest rate swaps | Other liabilities | 50 | 22 | |||||||
Total derivative liabilities | $ | 87 | $ | 26 | ||||||
Other risks
The Company is exposed to the risk of losses in the event of non-performance by counter parties to its derivative contracts. To mitigate counter party credit risk, the Company regularly reviews its credit exposure and the creditworthiness
77
of counter parties. The Company also enters into enforceable master netting arrangements with some of its counter parties. However, for financial reporting purposes, it is Company policy not to offset derivative assets and liabilities despite the existence of enforceable master netting arrangements with some of its counter parties.
Note 13 – Income Taxes
The provision (benefit) for taxes were as follows:
Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | March 31, 2018 | |||||||||
U.S. federal taxes: | ||||||||||||
Current | $ | (14 | ) | $ | 13 | $ | 16 | |||||
Deferred | (30 | ) | 8 | (38 | ) | |||||||
State taxes: | ||||||||||||
Current | 15 | 19 | 3 | |||||||||
Deferred | (25 | ) | — | 10 | ||||||||
Total income tax expense (benefit) | $ | (54 | ) | $ | 40 | $ | (9 | ) | ||||
Our effective tax rate was 7%, 36% and (5)% for fiscal years ended March 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The Company’s effective tax rate for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020 differs from the U.S. federal statutory rate primarily due to the impairment of non-deductible goodwill and intangibles related to the loss of the NGEN re-compete and the release of indemnified liabilities for unrecognized tax benefits. The differences between the U.S. federal statutory income tax rate and our effective tax rate were as follows:
Fiscal Years Ended | |||||||||
March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | March 31, 2018 | |||||||
U.S. federal statutory rate | 21 | % | 21 | % | 32 | % | |||
State income taxes, net of federal impact | 1 | % | 5 | % | 4 | % | |||
Non-deductible transaction costs | — | % | 3 | % | 4 | % | |||
Goodwill impairment | (18 | )% | — | % | — | % | |||
Remeasurement of state deferred income tax items | — | % | 5 | % | — | % | |||
State valuation allowance | — | % | 3 | % | — | % | |||
Research and development credit | — | % | (3 | )% | — | % | |||
Unrecognized tax benefits | 4 | % | 1 | % | — | % | |||
Interest on federal tax refund, net of tax expense | — | % | (2 | )% | — | % | |||
Impact of Tax Act | — | % | 1 | % | (44 | )% | |||
Other items, net | (1 | )% | 2 | % | (1 | )% | |||
Effective tax rate | 7 | % | 36 | % | (5 | )% | |||
On December 22, 2017, the President of the United States signed into law comprehensive tax legislation commonly referred to as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Tax Act”). As a fiscal year taxpayer with an October 31 tax year-end, the Company was not subject to many of the tax law provisions until fiscal year 2019; however, GAAP principles required the Company to revalue its deferred tax assets and liabilities with resulting tax effects accounted for in the reporting period of enactment including retroactive effects during fiscal year 2018. Perspecta’s fiscal year ended March 31, 2019 contained multiple tax years, one of which began prior to the enactment of the Tax Act and ended upon the Spin-Off on May 31, 2018 and, therefore, the Company was required to blend its federal tax rate to take into account a differing applicable federal tax rate for the portion of the fiscal year preceding the Spin-Off and the portion thereafter. The Company’s net income before taxes for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2019 relating to the period prior to the Spin-Off was subject to federal tax on DXC’s tax return at an applicable federal tax rate of 23.3% under Section 15 of the Code. The Company computed a weighted federal tax rate based upon the number of days that the Company’s fiscal year would be taxed at 23.3% and the number of days that the Company’s federal tax rate was reduced to 21%. For fiscal year 2019, the Company had an estimated blended corporate U.S. federal income tax rate of approximately 21.4%.
The Tax Matters Agreement entered into with DXC in connection with the Spin-Off (the “TMA”) states each company’s rights and responsibilities with respect to payment of taxes, tax return filings and control of tax examinations. For certain of our tax years ending prior to the Spin-Off, we may have joint and several liability with DXC, HPE and/or HP Inc. to the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) for the consolidated U.S. federal income taxes of DXC or predecessor consolidated
78
groups relating to the taxable periods in which we were part of that group. However, the TMA specifies the portion, if any, of this tax liability for which we would bear responsibility, and DXC agrees to indemnify us against any amounts for which we are not responsible. Except for Vencore HC and KGS HC, the Company is generally only responsible for tax assessments, penalties and interest allocable to periods (or portions of periods) beginning after the Spin-Off and Mergers. The TMA also provides special rules for allocating tax liabilities in the event the Spin-Off is determined not to be tax-free. Though valid as between the parties, the TMA is not binding on the IRS.
The Company had receivables for income tax refunds from the IRS and various state tax authorities of approximately $70 million at March 31, 2020, for which it must remit to DXC under the TMA and has a corresponding payable. The receivable is included in other receivables and other assets and the payable is included in accrued expenses on our balance sheets.
Deferred Income Taxes
Deferred income taxes result from temporary differences between the amount of assets and liabilities recognized for financial reporting and tax purposes. The significant components of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities were as follows:
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | ||||||
Deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
Loss carryovers | $ | 83 | $ | 91 | ||||
Employee and retiree benefits | 105 | 54 | ||||||
Accrued liabilities | 15 | 22 | ||||||
Finance lease obligations | 2 | 16 | ||||||
Operating lease obligations | 45 | — | ||||||
Interest expense carryforward | 11 | 11 | ||||||
Other | 1 | 4 | ||||||
Deferred tax assets, gross | 262 | 198 | ||||||
Valuation allowance | (18 | ) | (13 | ) | ||||
Deferred tax assets, net of valuation allowance | 244 | 185 | ||||||
Deferred tax liabilities: | ||||||||
Purchased intangible assets | 233 | 312 | ||||||
Fixed assets | 53 | 30 | ||||||
Operating lease assets | 42 | — | ||||||
Other | 3 | 1 | ||||||
Deferred tax liabilities | 331 | 343 | ||||||
Net deferred tax liabilities | $ | 87 | $ | 158 | ||||
As of March 31, 2020 and 2019, deferred tax assets in the aggregate amount of $27 million and $13 million are included in other assets on the accompanying balance sheets related to individual tax jurisdictions with net deferred tax assets.
The Company has federal net operating loss (“NOL”) carryforwards of $260 million, $55 million net of tax, which will begin to expire in 2033 and state NOL carryforwards of $28 million which will begin to expire in 2024. There is no valuation allowance against the federal NOL.
Unrecognized Tax Benefits
The following table summarizes the activity related to the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits (excluding interest and penalties and related tax attributes), included in other long-term liabilities on the accompanying balance sheets:
Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | March 31, 2018 | |||||||||
Balance at beginning of year | $ | 52 | $ | 8 | $ | 8 | ||||||
Decrease for prior-year tax positions | (25 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Decrease for transfers to Parent | — | (2 | ) | — | ||||||||
Increase for prior-year tax positions | 12 | 45 | — | |||||||||
Increase for current year tax positions | — | 1 | — | |||||||||
Balance at end of year | $ | 39 | $ | 52 | $ | 8 | ||||||
79
Up to $39 million, $52 million and $8 million of the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits as of March 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively, would affect our effective tax rate if realized. During the year ended March 31, 2020, $25 million of indemnified pre-Spin-Off uncertain tax positions were considered effectively settled per Company policy and released as a benefit to income tax expense in the current year.
The Company believes it is reasonably possible that certain liabilities for unrecognized tax benefits, all of which were transferred from Parent, may decrease by approximately $5 million during next year resulting from the settlement of appeals in fiscal year 2008 and 2012 related to the USPS entities. Any amounts that would be recognized are offset by changes to indemnification assets.
The Company accrues interest related to uncertain tax positions and penalties as a component of income tax expense. Interest related to open tax exam years before the Spin-Off is fully indemnified under the TMA. The company recognized interest of approximately $8 million, $9 million and $1 million for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 (carve-out basis), respectively.
For the periods prior to the Spin-Off, the unrecognized tax benefits reflected in the financial statements were determined using the separate return method. As a result of the Spin-Off, the Company recognized $52 million of liabilities for unrecognized tax benefits determined on an asset and liability method that stay with the legal entities included in the Spin-Off of the USPS business from DXC, which were recorded through Parent company investment, net of corresponding indemnification assets.
The Company engages in continuous discussion and negotiation with taxing authorities regarding tax matters in various jurisdictions. The Company is subject to income tax in the U.S. at the federal and state level and is subject to routine corporate income tax audits in these jurisdictions. The Company’s entities included in the Spin-Off are currently under examination or in appeals in several tax jurisdictions. The calendar year 2008 and fiscal year 2012 remain open under applicable statutes of limitations and are currently under review by the IRS and other taxing authorities. The IRS is not currently examining Vencore HC or KGS HC for any open years, but entities related to these businesses are open to examination in various state and local jurisdictions.
The Company believes it has provided adequate reserves for all tax deficiencies or reductions in tax benefits that could result from federal and state tax audits. We regularly assess the likely outcomes of these audits in consultation with the indemnifying parties to determine the appropriateness of unrecognized tax benefits. We adjust our unrecognized tax benefits to reflect the impact of negotiations, settlements, rulings, advice of legal counsel and other information and events pertaining to a specific audit. Income tax audits, however, are inherently unpredictable and the Company may not accurately predict the outcome of these audits. The amounts ultimately paid on resolution of an audit could be materially different from the amounts previously included in the provision (benefit) for taxes on the statements of operations and therefore the resolution of one or more of these uncertainties in any particular period could have a material impact on net income or cash flows.
Note 14 – Share-based Compensation
In May 2018, prior to the Spin-Off and Mergers, the Board of Directors approved the Perspecta Inc. 2018 Omnibus Incentive Plan (the “2018 Employee Equity Plan”) and 2018 Non-employee Director Incentive Plan (the “2018 Director Equity Plan”). Both plans will continue in effect for 10 years. The terms of the 2018 Employee Equity Plan and 2018 Director Equity Plan are substantially similar to the terms of DXC equity plans.
The 2018 Employee Equity Plan allows the Company to grant an aggregate of 9,500,000 shares of its common stock, which includes any shares resulting from the adjustment of the DXC outstanding equity awards. All Perspecta employees are eligible to participate under this plan. The Human Resources and Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors has the broad authority to grant awards and administer the plan. The Board of Directors has the authority to amend the plan, subject to shareholders’ approval for material modifications. The 2018 Employee Equity Plan allows the Company to grant restricted stock awards, RSUs, PSUs, stock options, stock appreciation rights (“SARs”) and other share-based awards. At March 31, 2020, the Company had approximately 6,126,834 shares available to grant based on the number of target equity awards outstanding under the 2018 Employee Equity Plan.
The 2018 Director Equity Plan provides for granting restricted stock and RSUs to non-employee directors. Any non-employee director is eligible to participate. The maximum aggregate number of shares that may be issued under the 2018
80
Director Equity Plan is 310,000. The plan is administered by the Board of Directors or in the Board of Directors’ discretion, the Human Resources and Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors. As of March 31, 2020, the Company had approximately 203,400 shares available to grant under the 2018 Director Equity Plan.
Equity awards generally vest one to three years from the date of grant and are subject to forfeiture if employment terminates prior to the lapse of the restrictions. During the vesting period, ownership of the award cannot be transferred. RSUs and PSUs do not have the voting rights of common stock and the underlying shares are not considered issued and outstanding upon grant. RSUs and PSUs have forfeitable dividend equivalent rights equal to the dividend paid on common stock, which are paid upon vesting. Perspecta does not offer an employee stock purchase plan (“ESPP”).
Parent’s Share-based Incentive Compensation Plans
Prior to the Spin-Off and Mergers, certain of USPS’s employees participated in share-based compensation plans sponsored by Parent. Parent’s share-based compensation plans included incentive compensation plans and an ESPP. All awards granted under the plans were based on Parent’s common shares and, as such, are not reflected on the statements of equity. Share-based compensation expense included expense attributable to USPS based on the awards and terms previously granted under the incentive compensation plan to USPS’s employees and an allocation of Parent’s corporate and shared functional employee expenses. Accordingly, the amounts presented are not necessarily indicative of future awards and do not necessarily reflect the results that USPS would have experienced as an independent company for the periods presented.
Parent’s share-based incentive compensation plans included equity plans adopted in 2017, 2015, 2004 and 2000, as amended (“Principal Equity Plans”). Share-based awards granted from the Principal Equity Plans included restricted stock awards, stock options, and performance-based awards. Employees who meet certain employment qualifications were eligible to receive share-based awards. The outstanding stock options and unvested RSUs and PSUs granted under the Principal Equity Plans were converted upon the Spin-Off and Mergers into economically equivalent Perspecta stock options, RSUs and PSUs, with terms and conditions substantially similar to the terms of such awards prior to the Spin-Off and Mergers. There was no incremental share-based compensation expense recognized as a result of this modification of the awards. Restricted stock awards were accounted for the same as under the 2018 Employee Equity Plan.
Stock options granted under the Principal Equity Plans were generally non-qualified stock options, but the Principal Equity Plans permitted certain options granted to qualify as incentive stock options under the U.S. Internal Revenue Code. Stock options generally vested over three to four years from the date of grant. The exercise price of a stock option was equal to the closing price of Parent’s stock on the option grant date.
Share-based Compensation Expense
Share-based compensation expense and the resulting tax benefits recognized were as follows:
Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | March 31, 2018 | |||||||||
Share-based compensation expense | $ | 23 | $ | 11 | $ | 6 | ||||||
Income tax benefit | 5 | 3 | 2 | |||||||||
Share-based compensation expense, net of tax | $ | 18 | $ | 8 | $ | 4 | ||||||
Time-based Restricted Stock Units
Perspecta grants RSUs to its employees and non-employee directors. RSUs generally vest one to three years from the date of grant and are subject to forfeiture if employees or non-employee directors terminate prior to the lapse of the restrictions. One RSU represents the right to receive one share of Perspecta common stock upon vesting, plus any dividend equivalents accrued during the vesting period.
81
A summary of RSU activity is presented below:
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2020 | |||||||
(in thousands, except per share amounts) | Shares | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value Per Share | |||||
Outstanding at beginning of year | 1,343 | $ | 23 | ||||
Granted | 628 | 23 | |||||
Vested | (318 | ) | 24 | ||||
Forfeited | (164 | ) | 23 | ||||
Outstanding at end of year | 1,489 | $ | 23 | ||||
Unrecognized compensation expense for RSUs as of March 31, 2020 was $22 million, expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.7 years. The total vesting date fair value of RSUs vested for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020 and 2019 was $8 million and $3 million, respectively. The total grant date fair value of restricted stock unit awards vested for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 was $8 million, $1 million and $3 million, respectively.
Performance-based Restricted Stock Units
The Company grants PSUs under the 2018 Employee Equity Plan. The number of PSUs that the employees will receive depends on the Company’s achievement of two performance goals during the three year performance periods. The performance goals under the Program are based on (i) the Company’s adjusted EPS at the end of the performance period, and (ii) the Company’s cumulative adjusted free cash flow for the performance period. The PSUs will only be eligible to vest following the expiration of the three-year performance period. Actual shares vested will be subject to both continued employment by the Company (barring certain exceptions allowing for partial performance periods) and actual financial measures achieved. The actual number of shares of common stock that will be issued to each participant at the end of the applicable performance period will be determined and are subject to a minimum and maximum performance level. The performance period for PSUs granted during fiscal year 2018 ended on March 31, 2020. Performance achievements were measured against pre-determined performance goals resulting in the vesting of 187% of the target fiscal year 2018 award in the first quarter of fiscal year 2021, as certified by the Compensation Committee on May 20, 2020. As of March 31, 2020, shares granted during fiscal years 2020 and 2019 are within year one and year two of the performance period, respectively, and therefore have not vested.
A summary of PSU activity is presented below:
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2020 | |||||||
(in thousands, except per share amounts) | Shares | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value Per Share | |||||
Outstanding at beginning of year | 558 | $ | 24 | ||||
Granted | 923 | 23 | |||||
Forfeited | (114 | ) | 24 | ||||
Outstanding at end of year | 1,367 | $ | 24 | ||||
Unrecognized compensation expense for PSUs as of March 31, 2020 was $13 million, expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.6 years. No PSUs vested for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020.
82
Stock Options
All remaining outstanding stock options were issued by Parent prior to the Spin-Off and Mergers, upon which they were converted to options to purchase Perspecta stock.
A summary of stock option activity is presented below:
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||
(in millions, except shares in thousands and per share amounts in ones) | Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price Per Share | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term in Years | Intrinsic Value | |||||||||
Outstanding at beginning of year | 162 | $ | 12 | ||||||||||
Exercised | (57 | ) | 10 | ||||||||||
Forfeited | (3 | ) | 11 | ||||||||||
Outstanding, vested and exercisable at end of year | 102 | $ | 13 | 2.7 | $ | 520 | |||||||
The aggregate intrinsic value in the table above represents the total pre-tax intrinsic value that certain option holders would have realized had all option holders exercised their options on the last trading day of fiscal year ended March 31, 2020. The aggregate intrinsic value is the difference between Perspecta’s closing share price on the last trading day of the fiscal year and the exercise price, multiplied by the number of in-the-money options. The total intrinsic value of options exercised by certain employees during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 was $1 million, less than $1 million and $3 million, respectively.
Cash received from option exercises was less than $1 million during both fiscal years ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. Cash received from option exercises and purchases under Parent’s ESPP by USPS employees was $3 million during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2018. The net effect of this transaction is reflected within transfers to Parent, net on the statement of cash flows for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2018.
Note 15 – Restructuring
Restructuring charges of $17 million, $10 million and $14 million have been recorded by the Company during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively, based on restructuring activities impacting certain employees and infrastructure. We recorded restructuring charges based on estimated employee terminations and site closure and consolidation plans. We accrued for severance and other employee separation costs under these actions when it was probable that benefits would be paid and the amount was reasonably estimable. The rates used in determining severance accruals were based on existing plans, historical experiences and negotiated settlements.
Fiscal 2020 Restructuring Plan
In connection with the corporate systems integration and rationalization, management approved a restructuring plan (the “2020 Plan”) in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2020 to reduce our operating cost structure, improve competitiveness and facilitate the achievement of acceptable and sustainable profitability. The restructuring initiatives include consolidation of infrastructure to achieve operating efficiencies, optimize utilization of facilities and infrastructure, and strengthen the Company’s competitiveness. The 2020 Plan also focuses on transitioning the Company’s leveraged legacy delivery model to a customer-focused model that will facilitate a more effective decision-making process tailored to our customer needs. There were no related liabilities for this plan at March 31, 2020.
Acquired Restructuring Plan
As a result of the Mergers, the Company acquired deferred costs of $7 million associated with restructuring initiatives from prior years that were reimbursable as agreed upon by the Defense Contract Management Agency. During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2019, these remaining costs were recognized as restructuring expense.
83
Fiscal 2019 Restructuring Plan
In connection with the Spin-Off and Mergers, management approved a restructuring plan (the “2019 Plan”) in November 2018 to better align Perspecta to its mission and business objectives. The restructuring initiatives included a reduction in workforce as well as consolidation of infrastructure to achieve operating efficiencies, optimize utilization of facilities, and strengthen the Company’s competitiveness. The 2019 Plan also focused on transitioning the Company’s legacy delivery model from a centralized, services-focused model to a decentralized, customer-focused model that facilitated a more effective decision-making process tailored to our customer needs. During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2019, expenses of $3 million were recognized and paid under this plan.
Fiscal 2018 Restructuring Plan
On June 30, 2017, Parent approved a restructuring plan (the “2018 Plan”). The restructuring initiatives were intended to reduce Parent’s cost structure and related operating costs, improve its competitiveness, and facilitate the achievement of acceptable and sustainable profitability. The 2018 Plan focuses mainly on optimizing specific aspects of workforce and re-balancing the pyramid structure. Additionally, this plan included facility restructuring.
Note 16 – Pension and Other Benefit Plans
The Company offers a defined benefit pension plan, a retiree medical plan, life insurance benefits, deferred compensation plans and defined contribution plans. The Company’s defined benefit pension and retiree medical plans are not admitting new participants; therefore, changes to pension and OPEB liabilities are primarily due to market fluctuations of investments, actuarial assumptions for the measurement of liabilities and changes in interest rates.
Defined Benefit Plans
As a result of the Mergers, the Company sponsors defined benefit pension and retiree medical plans for the benefit of eligible employees acquired in the Mergers. At the date of the Mergers, the net projected benefit obligations and assets were $489 million and $419 million, respectively, of which $7 million was recorded in other assets and $77 million in other long-term liabilities. The Company did not contribute to the defined benefit pension and other postretirement benefit plans during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020 and 2019.
The following table provides a reconciliation of the Company’s benefit obligation, plan assets and funded status:
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2020 | Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Defined Benefit Pension Plan | Retiree Medical Plan | Defined Benefit Pension Plan | Retiree Medical Plan | ||||||||||||
Projected benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | 491 | $ | 7 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
Benefit obligation assumed as a result of the Mergers | — | — | 482 | 7 | ||||||||||||
Service cost | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
Interest cost | 18 | — | 16 | — | ||||||||||||
Actuarial loss | 35 | — | 13 | 1 | ||||||||||||
Plan participant contributions | — | — | — | 1 | ||||||||||||
Benefits paid | (21 | ) | — | (20 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||||||
Projected benefit obligation at end of year | 523 | 7 | 491 | 7 | ||||||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | 388 | 13 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Assets assumed as a result of the Mergers | — | — | 405 | 14 | ||||||||||||
Actual return on plan assets | (8 | ) | (1 | ) | 3 | — | ||||||||||
Plan participant contributions | — | — | — | 1 | ||||||||||||
Expenses paid | (2 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Benefits paid | (21 | ) | — | (20 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at end of year | 357 | 12 | 388 | 13 | ||||||||||||
(Unfunded) funded status at end of year | $ | (166 | ) | $ | 5 | $ | (103 | ) | $ | 6 | ||||||
84
The following table provides amounts recognized on our balance sheet for the funded status:
March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Defined Benefit Pension Plan | Retiree Medical Plan | Defined Benefit Pension Plan | Retiree Medical Plan | ||||||||||||
Other assets | $ | — | $ | 5 | $ | — | $ | 6 | ||||||||
Other long-term liabilities | 166 | — | 103 | — | ||||||||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | — | 3 | — | — | ||||||||||||
The components of net periodic benefit cost recognized in other expense, net on our statement of operations consisted of the following:
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2020 | Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Defined Benefit Pension Plan | Retiree Medical Plan | Defined Benefit Pension Plan | Retiree Medical Plan | ||||||||||||
Service cost | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
Interest cost | 18 | — | 16 | — | ||||||||||||
Expected return on plan assets | (28 | ) | — | (24 | ) | (1 | ) | |||||||||
Recognition of net actuarial loss | 72 | — | 35 | — | ||||||||||||
Net periodic benefit cost (benefit) | $ | 62 | $ | — | $ | 27 | $ | (1 | ) | |||||||
The weighted-average rates used to determine the benefit obligation at March 31, 2020 and net periodic benefit cost for the subsequent year were as follows:
March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||
Defined Benefit Pension Plan | Retiree Medical Plan | Defined Benefit Pension Plan | Retiree Medical Plan | |||||||||
Discount rate | 3.7 | % | 3.5 | % | 4.1 | % | 4.0 | % | ||||
Expected long-term rate of return on assets | 7.4 | % | 6.2 | % | 7.8 | % | 6.7 | % | ||||
Plan Asset Allocations
The Company has the fiduciary responsibility for making investment decisions related to the assets of our postretirement benefit plans. The objectives for the assets of the defined benefit pension and retiree medical plans are (1) to minimize the net present value of expected funding contributions; (2) to ensure there is a high probability that each plan meets or exceeds our actuarial long‑term rate of return assumptions; and (3) to diversify assets to minimize the risk of large losses. The nature and duration of benefit obligations, along with assumptions concerning asset class returns and return correlations, are considered when determining an appropriate asset allocation to achieve the investment objectives. Investment policies and strategies governing the assets of the plans are designed to achieve investment objectives within prudent risk parameters. Risk management practices include the use of external investment managers; the maintenance of a portfolio diversified by asset class, investment approach, and security holdings; and the maintenance of sufficient liquidity to meet benefit obligations as they come due.
Pursuant to the investment policies established, the following target asset allocations have been established and will be utilized for the qualified defined benefit pension plan assets as of March 31, 2020:
Asset Category | Defined Benefit Pension Plan | Retiree Medical Plan | ||||
Cash | 2.5 | % | 5.0 | % | ||
Equity funds | 37.5 | % | 50.0 | % | ||
Fixed income | 17.5 | % | 45.0 | % | ||
Real estate funds | 10.0 | % | — | % | ||
Other | 32.5 | % | — | % | ||
85
Fair Value of Plan Assets
The rules related to accounting for postretirement benefit plans under GAAP require certain fair value disclosures related to postretirement benefit plan assets, even though those assets are not included on our balance sheets. The following table presents the fair value of our defined benefit pension plan and retiree medical plan assets at March 31, 2019 by asset category and their level within the fair value hierarchy, which has three levels based on the uncertainty of the inputs used to determine fair value. Level 1 refers to fair values determined based on quoted prices in active markets for identical assets, Level 2 refers to fair values estimated using significant other observable inputs and Level 3 includes fair values estimated using significant unobservable inputs. Certain other investments are measured at fair value using their net asset value (“NAV”) per share and do not have readily determined values and are thus not subject to leveling in the fair value hierarchy. The NAV is the total value of the fund divided by the number of shares outstanding.
March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investments measured at fair value: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | — | $ | 6 | $ | — | $ | 6 | $ | — | $ | 12 | $ | — | $ | 12 | ||||||||||||||||
Equity funds | 17 | 43 | — | 60 | 18 | 104 | — | 122 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fixed income | 29 | 6 | — | 35 | — | 35 | — | 35 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Real estate funds | — | — | 46 | 46 | — | — | 53 | 53 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Hedge funds | — | — | 8 | 8 | — | — | 25 | 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total investments measured at fair value | $ | 46 | $ | 55 | $ | 54 | 155 | $ | 18 | $ | 151 | $ | 78 | 247 | ||||||||||||||||||
Investments measured at NAV: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity funds | 116 | 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fixed income | 15 | 32 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Hedge funds | 83 | 102 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total investments measured at NAV | 214 | 154 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total investments | $ | 369 | $ | 401 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Changes in fair value measurements of level 3 investments for the defined benefit plans were as follows:
(in millions) | Real Estate Funds | Hedge Funds | Total | |||||||||
Balance at April 1, 2018 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
Assets assumed as a result of the Mergers | 49 | 28 | 77 | |||||||||
Actual return on plan assets held at the reporting date | 5 | (3 | ) | 2 | ||||||||
Purchases, sales and settlements | (1 | ) | — | (1 | ) | |||||||
Balance at March 31, 2019 | 53 | 25 | 78 | |||||||||
Actual return on plan assets held at the reporting date | 2 | (1 | ) | 1 | ||||||||
Purchases, sales and settlements | (9 | ) | (16 | ) | (25 | ) | ||||||
Balance at March 31, 2020 | $ | 46 | $ | 8 | $ | 54 | ||||||
Valuation Techniques
Cash equivalents are mostly comprised of short‑term money‑market instruments and are valued at cost, which approximates fair value.
Equity funds are categorized as Level 1 if the securities trade on national or international exchanges and are valued at their last reported closing price. Equity assets in commingled funds reporting a NAV are categorized as Level 2 and valued using published quotes of securities with similar characteristics. Certain commingled equity funds, consisting of equity mutual funds, are valued using the NAV.
Fixed income funds are categorized as Level 2 if investments in corporate bonds are primarily investment grade bonds, generally priced using model-based pricing methods that use observable market data as inputs. Broker dealer bids or quotes of securities with similar characteristics may also be used. Certain fixed income commingled funds, consisting of emerging market bonds, are valued using NAV.
86
The real estate and hedge funds categorized as Level 3 are valued using nominal methods based on valuation models that include significant unobservable inputs and cannot be corroborated using verifiable observable market data. Use of these inputs involves significant and subjective judgments to be made by a reporting entity. If a change in Level 3 inputs occur, the resulting amount might result in a significantly higher or lower fair value measurement. Valuations for hedge funds are valued by independent administrators. Certain hedge funds are valued using NAV and are generally based on the valuation of the underlying investments. Investments in hedge funds have no discernible concentration in nature of risk.
Expected Future Contributions and Benefit Payments
Fiscal Year (in millions) | Defined Benefit Pension Plan | Retiree Medical Plan | ||||||
Employer contributions: | ||||||||
2021 | $ | 7 | $ | — | ||||
Benefit payments: | ||||||||
2021 | $ | 26 | $ | 1 | ||||
2022 | 25 | — | ||||||
2023 | 26 | 1 | ||||||
2024 | 26 | — | ||||||
2025 | 27 | 1 | ||||||
2025 - 2029 | 144 | 2 | ||||||
Total | $ | 274 | $ | 5 | ||||
Defined Contribution Plans
The Company offers various defined contribution plans for employees. We match most employees’ eligible contributions at rates specified in the plan documents. Our defined contribution expense was $44 million, $33 million and $15 million during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively. In April 2019, the Company terminated two acquired defined contribution plans and transferred the employees and their related assets into the legacy USPS 401(k). That plan was subsequently amended and is now the primary defined contribution plan, aligning benefits across Perspecta. Subsequent to the amendment, the Company’s matching contributions are deposited in a participant’s account twice per year based on each participant’s contributions during the preceding period. The Company matches 100% of the participant’s contributions up to the first 3% of the participant’s annual salary, and 50% on the next 2% of the participant’s annual salary, subject to statutory limitations.
Deferred Compensation Plans
On October 9, 2018, Perspecta’s Board of Directors, upon the recommendation of its Human Resources and Compensation Committee, adopted a framework for a new, Company-sponsored non-qualified deferred compensation plan (the “Plan”), to replace the existing deferred compensation plans. The Plan was effective January 1, 2019.
The Plan is an unfunded, non-qualified deferred compensation plan maintained for the benefit of a select group of management or highly compensated employees of the Company, including the Company’s principal executive officer, principal financial officer and other “named executive officers.” Non-employee directors of the Company are also eligible to participate and defer their cash fees under the Plan.
The Plan is an account-based plan that allows participants to defer voluntarily the payment of current compensation to future years. The Plan permits each participant to defer cash compensation up to any limits set forth in the Plan, which amounts are credited to a bookkeeping account established for the participant under the Plan. The amounts credited to a participant’s account are fully vested. The Plan does not provide for any employer contributions.
Amounts credited to a participant’s account are indexed to one or more deemed investment alternatives chosen by the participant from a range of alternatives available under the Plan. Each participant’s account is adjusted to reflect gains and losses based on the performance of the selected investment alternatives. None of the deemed investment options provide for an above-market or preferential rate of return.
87
A participant may receive distributions from the Plan upon separation from service or on in-service dates specified by the participant, in the form of distribution elected by the participant available under the Plan. There will be a six-month delay for commencement of payment upon termination of employment to any “specified employee” as defined under Internal Revenue Code Section 409A. The Human Resources and Compensation Committee (or its authorized delegate) will be the administrator of the Plan.
Under the deferred compensation plans described above, certain management and highly compensated employees are eligible to defer up to 75% of their regular salary that exceeds the limitation set forth in the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 (the “Code”) Section 401(a)(17) and all or a portion of their incentive compensation. Non-employee directors are eligible to defer up to 100% of their cash compensation. As of March 31, 2020 and 2019, a deferred compensation liability of $12 million and $13 million, respectively, was included in other long-term liabilities on the accompanying balance sheets.
Note 17 – Related Party Transactions
Allocation of Corporate Expenses
The statements of operations include an allocation of general corporate expenses from Parent, recorded within costs of services and selling, general and administrative, for certain management and support functions which were provided on a centralized basis within Parent. These allocations were $24 million and $158 million for the period from April 1, 2018 to May 31, 2018 and the fiscal year ended March 31, 2018, respectively.
Management of the Company and Parent consider these allocations to be a reasonable reflection of the utilization of services by, or the benefits provided to, USPS. These allocations may not, however, reflect the expense USPS would have incurred as a standalone company for the periods presented. Actual costs that may have been incurred if USPS had been a standalone company would depend on a number of factors, including the chosen organizational structure, what functions were outsourced or performed by employees and strategic decisions made in areas such as IT and infrastructure.
Transfers to Parent, net
Transfers to Parent, net are included within Parent company investment. The components of the transfers to Parent, net on the statements of changes in equity for periods presented prior to the Spin-Off and Mergers were as follows:
(in millions) | Two Months Ended May 31, 2018 | Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2018 | ||||||
Cash pooling and general financing activities | $ | (176 | ) | $ | (506 | ) | ||
Corporate allocations | 24 | 158 | ||||||
Income taxes | 7 | 19 | ||||||
Transfers to Parent, net | $ | (145 | ) | $ | (329 | ) | ||
Related Party Transactions
For the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, the Company recognized related party revenue from DXC of $12 million and $13 million, respectively, and incurred related party obligations to DXC of $113 million and $74 million, respectively.
See Note 13 – “Income Taxes” for a description of the TMA between Perspecta and DXC.
Note 18 – Shareholders’ Equity
Description of Capital Stock
The Company has authorized share capital consisting of 750 million shares of common stock, par value $0.01 per share, and 1 million shares of preferred stock, par value $0.01 per share.
Each share of common stock is equal in all respects to every other share of common stock of the Company. Each share of common stock is entitled to one vote per share at each annual or special meeting of shareholders for the election of
88
directors and upon any other matter coming before such meeting. Subject to all the rights of the preferred stock, dividends may be paid to holders of common stock as and when declared by the Board of Directors.
Cash Dividends
During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2020, the Board of Directors declared cash dividends to our shareholders of approximately $39 million in the aggregate, of which approximately $30 million had been paid as of March 31, 2020 and approximately $10 million of which was paid on April 15, 2020. During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2019, the Board of Directors declared cash dividends to our shareholders of approximately $33 million in the aggregate, of which $25 million had been paid as of March 31, 2019 and $8 million of which was paid on April 16, 2019.
On May 21, 2020, the Board of Directors declared a dividend of $0.07 per common share payable on July 15, 2020 to common shareholders of record at the close of business on June 11, 2020.
Share Repurchase Program
On June 1, 2018, the Board of Directors authorized up to $400 million for future repurchases of outstanding shares of Perspecta’s common stock. Repurchases may be made at the Company’s discretion from time to time on the open market depending on market conditions. The repurchase program has no time limit, does not obligate the Company to make any repurchases and may be suspended for periods or discontinued at any time. During the fiscal years ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, the Company repurchased 2.8 million and 2.7 million shares, respectively, of its common stock for aggregate consideration of $65 million and $60 million, respectively. The shares are reported as treasury shares at cost on the accompanying balance sheets. The total remaining authorization for future common share repurchases under the share repurchase program was $275 million as of March 31, 2020.
Note 19 – Segment Information
The Company’s chief operating decision maker, the Chief Executive Officer, evaluates Perspecta’s consolidated operations based on two reportable segments: (1) Defense and Intelligence, and (2) Civilian and Health Care. Reportable segments and their respective operations are defined as follows:
Defense and Intelligence
Through its Defense and Intelligence business, Perspecta provides cybersecurity, data analytics, digital transformation, information technology modernization, and agile software development, as well as technology to support intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance services to the DoD, intelligence community, branches of the U.S. Armed Forces, and other DoD agencies.
Key competitive differentiators for the Defense and Intelligence segment include global scale, solution objectivity, depth of industry expertise, strong partnerships, vendor and product independence and end-to-end solutions and capabilities. Evolving business demands such as globalization, fast-developing economies, government regulation and growing concerns around risk, security, and compliance drive demand for these offerings.
Civilian and Health Care
Through its Civilian and Health Care business, Perspecta provides enterprise IT transformation and modernization, application development and modernization, enterprise security, risk decision support, operations and sustainment, systems engineering, applied research, cyber services, and cloud transformation to the Departments of Homeland Security, Justice, and Health and Human Services, as well as other federal civilian and state and local government agencies.
In the following tables, certain corporate activity is reported separately to reconcile the Company’s segment information to the statements of operations. The accounting policies of the reportable segments are the same as those described herein in Note 1 – “Overview and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies.”
Segment Measures
The following tables summarize operating results regularly provided to the chief operating decision maker by reportable segment and a reconciliation of those reporting results to the statements of operations for the relevant periods.
89
Revenue
Our revenue by reportable segment was as follows:
Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | March 31, 2018 | |||||||||
Defense and Intelligence | $ | 3,101 | $ | 2,587 | $ | 1,416 | ||||||
Civilian and Health Care | 1,403 | 1,443 | 1,403 | |||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 4,504 | $ | 4,030 | $ | 2,819 | ||||||
Segment Profit
The Company’s management uses segment profit as the measure for assessing performance of its segments. Segment profit is defined as segment revenue less segment cost of services, selling, general and administrative and depreciation and amortization, excluding certain operating expenses managed at the corporate level. These unallocated costs include certain corporate function costs, share-based compensation expense, amortization of acquired intangible assets, impairment charges, certain nonrecoverable restructuring costs, separation, transaction and integration-related costs, net periodic benefit cost and gain or loss on sale of assets.
Our segment profit by reportable segment was as follows:
Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | March 31, 2018 | |||||||||
Defense and Intelligence | $ | 444 | $ | 331 | $ | 168 | ||||||
Civilian and Health Care | 152 | 196 | 222 | |||||||||
Total segment profit | 596 | 527 | 390 | |||||||||
Not allocated to segments: | ||||||||||||
Share-based compensation | (23 | ) | (11 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||
Amortization of acquired intangible assets | (206 | ) | (165 | ) | (69 | ) | ||||||
Impairment charges | (796 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Restructuring costs | (17 | ) | (4 | ) | (14 | ) | ||||||
Separation, transaction and integration-related costs | (85 | ) | (106 | ) | (90 | ) | ||||||
Interest expense, net | (137 | ) | (121 | ) | (12 | ) | ||||||
Other unallocated, net | (62 | ) | (8 | ) | — | |||||||
(Loss) income before taxes | $ | (730 | ) | $ | 112 | $ | 199 | |||||
We incurred non-cash, pre-tax impairment charges of approximately $796 million in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2020 as a result of the loss of the NGEN re-compete discussed further in Note 8 – “Goodwill” and Note 9 – “Intangible Assets.” These charges were recognized at a corporate level and were not allocated to the segments.
Total Assets by Segment
Management does not use total assets by segment to evaluate segment performance or allocate resources. As a result, assets are not tracked by segment and therefore, total assets by segment is not disclosed.
90
Depreciation and Amortization
Our depreciation and amortization expense by reportable segment was as follows:
Fiscal Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | March 31, 2020 | March 31, 2019 | March 31, 2018 | |||||||||
Defense and Intelligence | $ | 66 | $ | 74 | $ | 34 | ||||||
Civilian and Health Care | 102 | 91 | 64 | |||||||||
Amortization of acquired intangible assets | 206 | 165 | 69 | |||||||||
Total depreciation and amortization | $ | 374 | $ | 330 | $ | 167 | ||||||
Note 20 – Commitments and Contingencies
The Company is a party to or has responsibility under various lawsuits, claims, investigations and proceedings involving disputes or potential disputes related to commercial, employment and regulatory matters that arise in the ordinary course of business. The Separation and Distribution Agreement between Perspecta and DXC (“SDA”) includes provisions that allocate liability and financial responsibility for litigation involving DXC and the Company and that provide for cross-indemnification of the parties for liabilities a party may incur that are allocated to the other party under the SDA. In addition, under the SDA, DXC and the Company have agreed to cooperate with each other in managing litigation that relates to both parties’ businesses. The SDA also contains provisions that allocate liability and financial responsibility for such litigation. The Company records a liability when it believes that it is both probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. Significant judgment is required to determine both the probability of having incurred a liability and the estimated amount of the liability. The Company reviews these matters at least quarterly and adjusts these liabilities to reflect the impact of negotiations, settlements, rulings, advice of legal counsel and other updated information and events pertaining to a particular matter. Litigation is inherently unpredictable. However, the Company believes it has valid defenses with respect to legal matters pending against it. Nevertheless, cash flows or results of operations could be materially affected in any particular period by the resolution of one or more of these contingencies. The Company believes it has recorded adequate provisions for any such matters and, as of March 31, 2020, it was not reasonably possible that a material loss had been incurred in connection with such matters in excess of the amounts recognized in its financial statements.
Litigation, Proceedings and Investigations
Forsyth, et al. v. HP Inc. and Hewlett Packard Enterprise: This purported class and collective action was filed on August 18, 2016 in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California, against HP Inc. and HPE alleging violations of the Federal Age Discrimination in Employment Act (“ADEA”), the California Fair Employment and Housing Act, California public policy and the California Business and Professions Code. Plaintiffs filed an amended complaint on December 19, 2016. Plaintiffs seek to certify a nationwide class action under the ADEA comprised of all U.S. residents employed by defendants who had their employment terminated pursuant to a work force reduction (“WFR”) plan on or after December 9, 2014 (deferral states) and April 8, 2015 (non-deferral states), and who were 40 years of age or older at the time of termination. Plaintiffs also seek to represent a Rule 23 class under California law comprised of all persons 40 years or older employed by defendants in the state of California and terminated pursuant to a WFR plan on or after August 18, 2012. The case has remained stayed while the parties have engaged in mediation with opt-in plaintiffs who are subject to mandatory, individual arbitration agreements. Two mediation sessions have taken place. In October 2018, a settlement was reached with 16 named and opt-in plaintiffs; that settlement has been completed. On June 26-27, 2019, a second mediation was held, involving 145 opt-in plaintiffs. On December 23, 2019, a settlement was reached with 142 of the 145 opt-in plaintiffs. Former business units of HPE now owned by the Company will be liable in this matter for any recovery by plaintiffs previously associated with the USPS business of HPE.
In addition to the matter noted above, the Company is currently subject in the normal course of business to various claims and contingencies arising from, among other things, disputes with customers, vendors, employees, contract counter parties and other parties, and inquiries and investigations by regulatory authorities and government agencies. Some of these disputes involve or may involve litigation. The financial statements reflect the treatment of claims and contingencies based on management’s view of the expected outcome. The Company consults with outside legal counsel on issues related to litigation and regulatory compliance and seeks input from other experts and advisors with respect to matters in the ordinary course of business. Although the outcome of these and other matters cannot be predicted with certainty, and the impact of the final resolution of these and other matters on the Company’s results of operations in a particular subsequent reporting period could be material and adverse, management does not believe, based on information
91
currently available to the Company, that the resolution of any of the matters currently pending against the Company will have a material adverse effect on the financial position of the Company or the ability of the Company to meet its financial obligations as they become due. Unless otherwise noted, the Company is unable to determine at this time a reasonable estimate of a possible loss or range of losses associated with the foregoing disclosed contingent matters.
Commitments
In connection with the Spin-Off, the Company is obligated to purchase or license from DXC a specified amount of products and services each year for a two-year period ending July 31, 2020 (“Annual Minimum Purchase Amounts”). The Company is in the second and final year of that purchase obligation and continues to make purchases of products and services. If the Company, however, has not met or exceeded the Annual Minimum Purchase Amounts by that date, it must pay DXC the amount of the shortfall. In October 2019, the Company submitted a demand for arbitration claiming, among other things, that DXC breached its obligations under the relevant Spin-Off agreements by failing to properly apply credit against the Annual Minimum Purchase Amounts for eligible items purchased by the Company. The relevant agreements require such disagreements to be treated in a confidential manner through executive escalation, mediation and binding arbitration. Based on the status of the arbitration, we currently are unable to predict the impact of any resolution of this matter. Notwithstanding the arbitration claims, the Company would be obligated to pay DXC any amount of shortfall not addressed in or otherwise subject to the arbitration or covered by other possible defenses.
Guarantees
In the ordinary course of business, the Company may issue performance guarantees to certain of its clients, customers and other parties pursuant to which it has guaranteed the performance obligations of third parties. Some of those guarantees may be backed by standby letters of credit or surety bonds. In general, the Company would be obligated to perform over the term of the guarantee if a specified triggering event occurs as defined by the guarantee. The Company believes the likelihood of having to perform under a material guarantee is remote.
The Company has entered into service contracts with certain of its clients that are supported by financing arrangements. If a service contract is terminated as a result of the Company’s non-performance under the contract or failure to comply with the terms of the financing arrangement, the Company could, under certain circumstances, be required to acquire certain assets related to the service contract. The Company believes the likelihood of having to acquire a material amount of assets under these arrangements is remote.
The Company uses stand-by letters of credit, in lieu of cash, to support various risk management insurance policies, which are cash collateralized. These letters of credit represent a contingent liability and the Company would only be liable if it defaults on its payment obligations on these policies. The Company’s stand-by letters of credit outstanding were less than $1 million as of March 31, 2020. As of March 31, 2020, the Company had $40 million in outstanding surety bonds, of which less than $7 million expire in fiscal year 2021, and $33 million expire in fiscal year 2022.
Indemnifications
In the ordinary course of business, the Company enters into contractual arrangements under which it may agree to indemnify a third party to such arrangement from any losses incurred relating to the services they perform on behalf of the Company or for losses arising from certain events as defined within the particular contract, which may include, for example, litigation or claims relating to past performance. The Company also provides indemnifications to certain vendors and customers against claims of intellectual property infringement made by third parties arising from the use by such vendors and customers of the Company’s software products and services and certain other matters. Some indemnifications may not be subject to maximum loss clauses. Historically, payments made related to these indemnifications have been immaterial.
Note 21 – Subsequent Events
On May 21, 2020, the Company’s board of directors approved a change in the Company’s fiscal year end from March 31 to the Friday nearest March 31 of each year. As a result, fiscal year 2021 will contain 52 weeks and three days beginning April 1, 2020 and ending April 2, 2021. Future fiscal quarters will generally have 13 weeks, each ending on the Friday nearest the end of calendar months June, September, December and March.
92
Supplementary Data – Selected Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 1st Quarter | 2nd Quarter | 3rd Quarter | 4th Quarter | ||||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 1,107 | $ | 1,172 | $ | 1,126 | $ | 1,099 | ||||||||
Costs of services | 836 | 908 | 863 | 853 | ||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative | 72 | 81 | 77 | 73 | ||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 101 | 90 | 92 | 91 | ||||||||||||
Impairment charges (1) | — | — | — | 796 | ||||||||||||
Restructuring costs | 2 | 2 | — | 13 | ||||||||||||
Separation, transaction and integration-related costs | 19 | 20 | 20 | 26 | ||||||||||||
Interest expense, net | 35 | 36 | 34 | 32 | ||||||||||||
Other (income) expense, net | — | (2 | ) | (35 | ) | 99 | ||||||||||
Total costs and expenses | 1,065 | 1,135 | 1,051 | 1,983 | ||||||||||||
Income (loss) before taxes | 42 | 37 | 75 | (884 | ) | |||||||||||
Income tax expense | 11 | 8 | 22 | (95 | ) | |||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 31 | $ | 29 | $ | 53 | $ | (789 | ) | |||||||
Earnings (loss) per common share(2): | ||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.19 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.33 | $ | (4.89 | ) | |||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.19 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.33 | $ | (4.89 | ) | |||||||
Cash dividends per common share | $ | 0.06 | $ | 0.06 | $ | 0.06 | $ | 0.06 | ||||||||
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 1st Quarter | 2nd Quarter | 3rd Quarter | 4th Quarter | ||||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 793 | $ | 1,068 | $ | 1,075 | $ | 1,094 | ||||||||
Costs of services | 597 | 813 | 816 | 817 | ||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative | 61 | 89 | 76 | 74 | ||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 64 | 74 | 76 | 116 | ||||||||||||
Restructuring costs | — | 2 | 1 | 7 | ||||||||||||
Separation, transaction and integration-related costs | 44 | 21 | 19 | 22 | ||||||||||||
Interest expense, net | 10 | 37 | 37 | 37 | ||||||||||||
Other (income) expense, net | (24 | ) | (4 | ) | 2 | 34 | ||||||||||
Total costs and expenses | 752 | 1,032 | 1,027 | 1,107 | ||||||||||||
Income (loss) before taxes | 41 | 36 | 48 | (13 | ) | |||||||||||
Income tax expense | 12 | 12 | 10 | 6 | ||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 29 | $ | 24 | $ | 38 | $ | (19 | ) | |||||||
Earnings (loss) per common share(2): | ||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.15 | $ | 0.23 | $ | (0.12 | ) | |||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.17 | $ | 0.14 | $ | 0.23 | $ | (0.12 | ) | |||||||
Cash dividends per common share | $ | 0.05 | $ | 0.05 | $ | 0.05 | $ | 0.05 | ||||||||
(1) Impairment charges of $796 million were incurred during the quarter ended March 31, 2020 due to the loss of the NGEN re-compete as discussed in Note 8 – “Goodwill” and Note 9 – “Intangible Assets.”
(2) Earnings per common share are computed independently for each of the quarters presented and therefore may not sum to the totals for fiscal years 2020 and 2019 included on our statements of operations.
93
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our CEO and Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”), has evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) as of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K. In designing and evaluating the disclosure controls and procedures, management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives. We maintain disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods required by the Securities and Exchange Commission, or the SEC, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to management, including our CEO and CFO, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Based on and as of the date of such evaluation, our CEO and CFO concluded that the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective due to a material weakness in Perspecta’s internal control over financial reporting, as described below. Notwithstanding the material weakness discussed below, the company’s management, including the CEO and CFO, has concluded that the company's financial statements included in this Form 10-K present fairly, in all material respects, the company's financial position, results of operations and cash flows for the periods presented in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management, with the participation of our CEO and CFO, is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Our internal control system is designed to provide reasonable assurance to our management and Board of Directors regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes.
Our management conducted an assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2020. This assessment was based on the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013 framework). Based on this assessment, management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was not effective as of March 31, 2020 because of the material weakness described below.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that a reasonable possibility exists that a material misstatement of our annual or interim financial statements would not be prevented or detected on a timely basis.
Discussion of Material Weakness
Due to the aggregation of certain control deficiencies, as of March 31, 2020, management identified a material weakness in its internal control over financial reporting related to revenue recognition. None of the control deficiencies resulted in any adjustments to our 2020 annual or interim consolidated financial statements or restatements of financial statements from prior reporting periods. We identified instances where we did not adequately determine the appropriate number of performance obligations when determining revenue recognition when (or as) we satisfy a performance obligation. Additionally, we identified a deficiency in the operation of control over the review of EAC as certain risk reserves were not fully supported and certain estimates inappropriately included the full program performance periods.
94
Remediation Activities
We are currently in the process of remediating the material weakness and have taken and will continue to take steps that we believe will address the underlying causes of the material weakness. The remediation plan includes (i) utilization of the new enterprise resource planning (“ERP”) system implemented in April 2020, as discussed further below, (ii) supplementing existing staff and enhancing controls over the revenue recognition checklist process, and (iii) improving the process and precision around the EAC review, some of which have already been implemented in the first quarter of fiscal year 2021. The material weakness cannot be considered remediated until the remediated controls operate effectively for a sufficient period of time and management has concluded, through testing, that these controls are operating effectively.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have evaluated the changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the quarter ended March 31, 2020 and concluded that there have been two changes in our internal control over financial reporting (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act) that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting, in addition to the remediation activities associated with the material weakness identified above.
Effective January 1, 2020, the Company implemented a new third-party payroll system, which resulted in an update to our payroll related controls and procedures. Additionally, effective January 31, 2020, we implemented a lease accounting system and related controls and procedures with respect to our lease accounting under ASC 842, which was adopted effective April 1, 2019. In addition, in connection with our initiative to integrate and enhance our consolidated information technology systems and business processes, we completed the implementation of a new ERP system, which replaced our existing core financial systems, in April 2020. The new ERP system is designed to enhance the accuracy in maintaining the Company’s financial records, enhance the flow of financial information, improve data management and enhance the timeliness in providing information to our management team. As a result of this implementation, we modified certain existing internal controls over financial reporting and implemented new controls and procedures related to the new ERP system.
There have been no other changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred in the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2020 that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Inherent Limitations of Internal Controls
Our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, does not expect that our disclosure controls and procedures or our internal control over financial reporting will prevent all errors and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within the Company have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision-making can be faulty, and that breakdowns can occur because of a simple error or mistake. Additionally, controls can be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people, or by management override of the control. The design of any system of controls also is based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions. Over time, controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. Because of the inherent limitations in a cost-effective control system, misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and may not be detected.
Our independent registered public accounting firm has issued a report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting, which is included in this Item 9A.
95
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Perspecta Inc.
Chantilly, Virginia
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Perspecta Inc. (the “Company”) (formerly the U.S. Public Sector Business of DXC Technology Company) as of March 31, 2020, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). In our opinion, because of the effect of the material weakness identified below on the achievement of the objectives of the control criteria, the Company has not maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2020, based on the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”), the consolidated combined financial statements as of and for the year ended March 31, 2020 of the Company and our report dated May 22, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements and included an emphasis-of-matter paragraph relating to the allocations inherent in the preparation of the consolidated combined financial statements.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
96
Material Weakness
A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. The following material weakness has been identified and included in management's assessment:
Control Activities - The Company did not design and implement effective control activities based on the criteria established in the COSO Framework. Effective controls over the establishment of revenue recognition methods and the estimated total costs at completion (“EAC”) process were not designed and maintained. These control deficiencies relating to the Company’s revenue recognition methodology for certain contracts constitute a material weakness in the aggregate.
This material weakness was considered in determining the nature, timing, and extent of audit tests applied in our audit of the consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended March 31, 2020, of the Company, and this report does not affect our report on such financial statements.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
McLean, Virginia
May 22, 2020
97
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
On May 21, 2020, the Company’s board of directors approved a change in the Company’s fiscal year end from March 31 to the Friday nearest March 31 of each year. As a result, fiscal year 2021 will contain 52 weeks and three days beginning April 1, 2020 and ending April 2, 2021. Future fiscal quarters will generally have 13 weeks, each ending on the Friday nearest the end of calendar months June, September, December and March.
98
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Information relating to our executive officers appears in Part I, Item 1 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K under the heading “Information About Our Executive Officers.”
Other information required by this item will appear under the headings “Proposal 1 – Election of Directors,” “Delinquent Section 16(a) Reports,” “Corporate Governance,” and “Additional Information – Business for 2021 Annual Meeting” in our 2020 Proxy Statement, which will be filed with the SEC pursuant to Regulation 14A not later than 120 days after March 31, 2020, and such information is incorporated herein by reference.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and Corporate Governance Guidelines
We have adopted a written code of business conduct and ethics that applies to all of our directors, officers and employees, including our CEO, CFO and Principal Accounting Officer. Our code of business conduct and ethics is entitled “The Standard” and is available on our website, https://perspecta.com, under the heading “About Us/Ethics and Social Responsibility.” We intend to disclose future amendments to certain provisions of our code of business conduct and ethics, and waivers of our code of business conduct and ethics granted to executive officers and directors, on the website within four business days following the date of the amendment or waiver.
Our corporate governance guidelines are available on our website, https://perspecta.com, under the heading “About Us/Leadership and governance/Guidelines and policies.”
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
Information required by this item will appear in our 2020 Proxy Statement under the headings “Executive Compensation” and “Corporate Governance” and are incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED SHAREHOLDER MATTERS
The following table gives information about our common stock that may be issued under Perspecta’s equity compensation plans as of March 31, 2020. See Note 14 – “Share-based Compensation” to the financial statements included herein for information regarding the material features of these plans.
Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights | Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights | Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans excluding securities reflected in column (a) | ||||||||
Plan Category | (a) (1) | (b) | (c) | |||||||
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | 2,958,730 | $ | 13.10 | 6,330,234 | ||||||
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | — | — | — | |||||||
Total | 2,958,730 | $ | 13.10 | 6,330,234 | ||||||
(1) Column (a) includes: 2,856,516 shares that have been granted as restricted stock units, including RSUs and PSUs (at the target number of shares), and 102,214 shares granted as options under our equity compensation plans. The weighted average price in column (b) does not take into account shares issued pursuant to restricted stock units.
Other information required by this Item will appear in our 2020 Proxy Statement under the heading “Security Ownership,” which section is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
Information required by this item will appear in our 2020 Proxy Statement under the heading “Corporate Governance” and is incorporated herein by reference.
99
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
Information required by this item will appear in our 2020 Proxy Statement under the heading “Proposal 2 – Ratification of the appointment of Deloitte & Touche as our independent registered public accounting firm for the fiscal year ending April 2, 2021” and is incorporated herein by reference.
100
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a) List of Documents Filed as a Part of this Report
(1) Financial Statements
The financial statements are included under Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
(2) Financial Statement Schedules
All schedules have been omitted because the required information is included in the financial statements included under Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K or the notes thereto, or because it is not required.
(3) Exhibits
See exhibits listed under Part (b) below.
(b) Exhibits
The following exhibits are filed herewith unless otherwise indicated.
Exhibit Number | Description of Exhibit |
2.1 | |
2.2 | |
2.3 | |
2.4 | |
2.5 | |
2.6 | |
2.7 | |
2.8 | |
3.1 | |
3.2 | |
4.1 | |
10.1 | |
10.2 | |
10.3* | |
101
10.4* | |
10.5* | |
10.6* | |
10.7* | |
10.8 | |
10.9 | |
10.10 | |
10.11 | |
10.12 | |
10.13 | |
10.14 | |
10.15 | |
10.16 | |
10.17 | |
10.18 | |
10.19* | |
10.20* | |
10.21* | |
10.22* | |
10.23* | |
10.24* | |
102
10.25* | |
21.1 | |
23.1 | |
31.1 | |
31.2 | |
32.1 | |
32.2 | |
101.INS | XBRL Instance |
101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema |
101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation |
101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition |
101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Labels |
101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation |
*Management contract or compensatory plan or agreement
ITEM 16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY
None.
103
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
PERSPECTA INC. | |||
Dated: | May 22, 2020 | By: | /s/ John P. Kavanaugh |
Name: | John P. Kavanaugh | ||
Title: | Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | ||
104
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated:
Signature | Title | Date | ||
/s/ John M. Curtis | President, Chief Executive Officer and Director | May 22, 2020 | ||
John M. Curtis | (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
/s/ John P. Kavanaugh | Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | May 22, 2020 | ||
John P. Kavanaugh | (Principal Financial Officer) | |||
/s/ William G. Luebke | Senior Vice President and Corporate Controller | May 22, 2020 | ||
William G. Luebke | (Principal Accounting Officer) | |||
/s/ J. Michael Lawrie | Chairman | May 22, 2020 | ||
J. Michael Lawrie | ||||
/s/ Sanju K. Bansal | Director | May 22, 2020 | ||
Sanju K. Bansal | ||||
/s/ Sondra L. Barbour | Director | May 22, 2020 | ||
Sondra L. Barbour | ||||
/s/ Lisa S. Disbrow | Director | May 22, 2020 | ||
Lisa S. Disbrow | ||||
/s/ Glenn A. Eisenberg | Director | May 22, 2020 | ||
Glenn A. Eisenberg | ||||
/s/ Pamela O. Kimmet | Director | May 22, 2020 | ||
Pamela O. Kimmet | ||||
/s/ Ramzi M. Musallam | Director | May 22, 2020 | ||
Ramzi M. Musallam | ||||
/s/ Philip O. Nolan | Director | May 22, 2020 | ||
Philip O. Nolan | ||||
/s/ Betty J. Sapp | Director | May 22, 2020 | ||
Betty J. Sapp | ||||
/s/ Michael E. Ventling | Director | May 22, 2020 | ||
Michael E. Ventling | ||||
105
