Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.1 - EXHIBIT 99.1 - WHITE MOUNTAINS INSURANCE GROUP LTD | wtm10ka2019ex991.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - WHITE MOUNTAINS INSURANCE GROUP LTD | wtm10-ka2019ex322.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - WHITE MOUNTAINS INSURANCE GROUP LTD | wtm10-ka2019ex321.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - WHITE MOUNTAINS INSURANCE GROUP LTD | wtm10-ka2019ex312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - WHITE MOUNTAINS INSURANCE GROUP LTD | wtm10-ka2019ex311.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 - WHITE MOUNTAINS INSURANCE GROUP LTD | wtm10-ka2019ex231.htm |
| 10-K/A - 10-K/A - WHITE MOUNTAINS INSURANCE GROUP LTD | wtm10-ka2019ma.htm |

Exhibit 99.2 QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) 1

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) TABLE OF CONTENTS Page Consolidated Financial Statements: Balance Sheets 3 Statements of Operations 4 Statements of Changes in Members’ Equity 5 Statements of Cash Flows 6 Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements 7 – 20 2

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) (THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE AND PER SHARE AMOUNTS) ASSETS December 31 2019 2018 Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents $ 10,028 $ 5,662 Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts 56,012 37,150 Prepaid expenses and other current assets 1,301 1,287 Total current assets 67,341 44,098 Property and equipment, net 755 881 Intangible assets, net 20,397 25,108 Goodwill 18,402 18,402 Total assets $ 106,895 $ 88,489 LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS' EQUITY Current liabilities: Accounts payable $ 40,455 $ 27,014 Accrued expenses 6,532 5,160 Current portion of long-term debt 1,000 3,067 Current portion of deferred rent 40 92 Total current liabilities 48,028 35,333 Long-term debt, net of current portion 96,218 11,183 Deferred rent, net of current portion 330 370 Total liabilities $ 144,576 $ 46,886 Commitments and contingencies (See note 8) Members' equity: Class A common and paid in capital 135,809 73,003 Class B common and paid in capital 14,901 11,718 Dividends in excess of earnings (188,391) (43,118) Total members' equity (37,681) 41,603 Total liabilities and members' equity $ 106,895 $ 88,489 3

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) (THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE AND PER SHARE AMOUNTS) Years Ended December 31, 2019 2018 Net revenues $ 407,902 $ 297,125 Cost of revenues 339,941 244,955 Gross profit 67,961 52,170 Operating expenses 13,560 5,367 Payroll and benefits expense 23,816 26,393 Amortization of intangible assets 4,859 10,286 Income from operations 25,726 10,125 Interest expense 6,800 1,194 Net income (loss) $ 18,926 $ 8,930 ` 4

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN MEMBERS’ EQUITY FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) (THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE AND PER SHARE AMOUNTS) Class A Common Class B Common Dividends in Total Units Amount Units Amount excess of Members' earnings Equity Balance as of December 31, 2017 1,136,842 $ 73,003 46,529 $ - $ (36,170) $ 36,834 Class B vesting - - 16,314 - - - Class B forfeited - - - - - - Class A issuances - - - - - - Class B issuances - - - 11,718 - 11,718 Member distributions - - - - (15,879) (15,879) Net Income - - - - 8,930 8,930 Balance as of December 31, 2018 1,136,842 $ 73,003 62,843 $ 11,718 $ (43,118) $ 41,603 Class B vesting - - 13,832 - - - Class B forfeited - - (23,842) - - - Class A issuances - 62,805 - - - 62,805 Class B issuances - - - 3,184 - 3,184 Member distributions - - - - (164,199) (164,199) Net Income - - - - 18,926 18,926 Balance as of December 31, 2019 1,136,842 $ 135,809 52,833 $ 14,901 $ (188,391) $ (37,681) 5
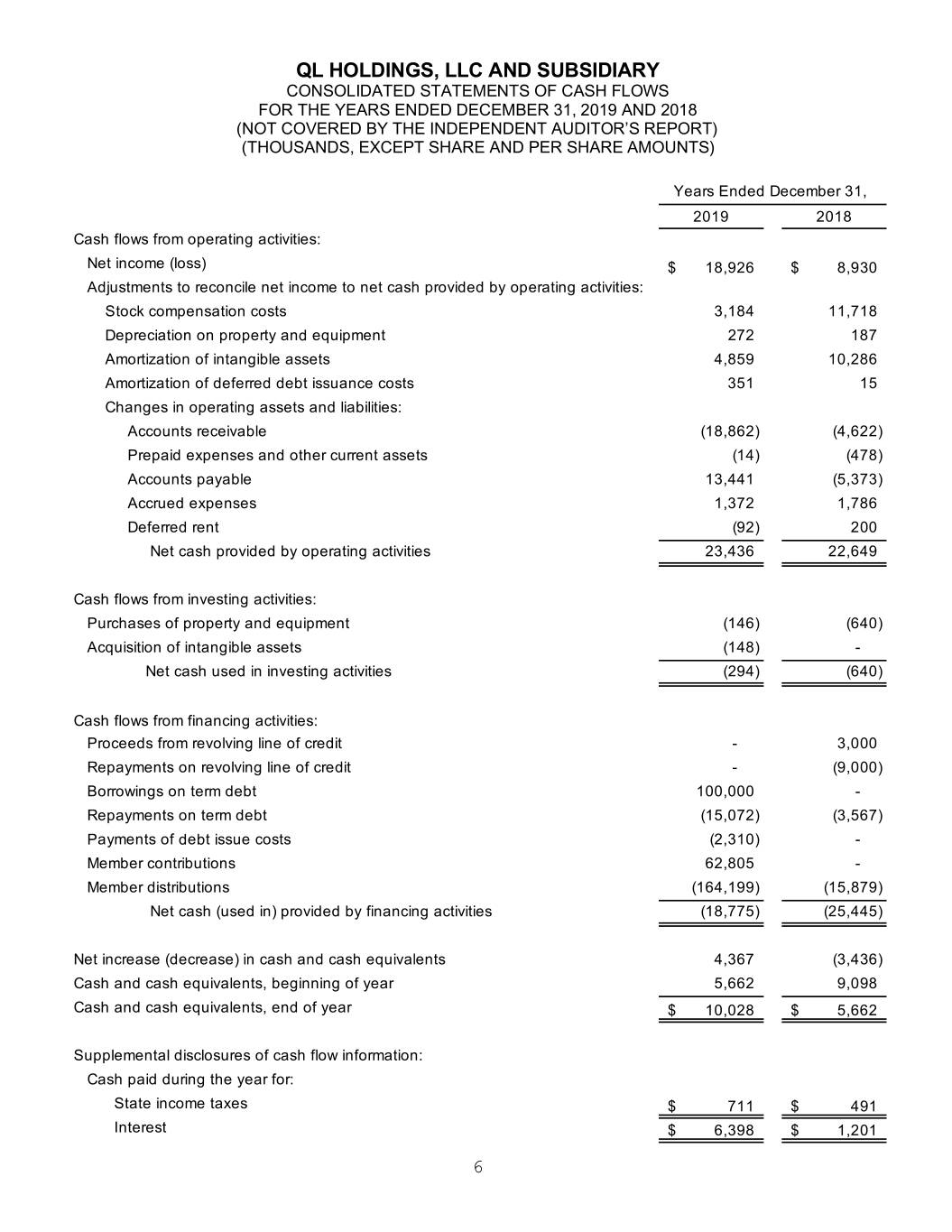
QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) (THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE AND PER SHARE AMOUNTS) Years Ended December 31, 2019 2018 Cash flows from operating activities: Net income (loss) $ 18,926 $ 8,930 Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: Stock compensation costs 3,184 11,718 Depreciation on property and equipment 272 187 Amortization of intangible assets 4,859 10,286 Amortization of deferred debt issuance costs 351 15 Changes in operating assets and liabilities: Accounts receivable (18,862) (4,622) Prepaid expenses and other current assets (14) (478) Accounts payable 13,441 (5,373) Accrued expenses 1,372 1,786 Deferred rent (92) 200 Net cash provided by operating activities 23,436 22,649 Cash flows from investing activities: Purchases of property and equipment (146) (640) Acquisition of intangible assets (148) - Net cash used in investing activities (294) (640) Cash flows from financing activities: Proceeds from revolving line of credit - 3,000 Repayments on revolving line of credit - (9,000) Borrowings on term debt 100,000 - Repayments on term debt (15,072) (3,567) Payments of debt issue costs (2,310) - Member contributions 62,805 - Member distributions (164,199) (15,879) Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities (18,775) (25,445) Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents 4,367 (3,436) Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year 5,662 9,098 Cash and cash equivalents, end of year $ 10,028 $ 5,662 Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: Cash paid during the year for: State income taxes $ 711 $ 491 Interest $ 6,398 $ 1,201 6

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) NOTE 1. ORGANIZATION Formation and Acquisition QL Holdings, LLC (“QLH”), a Delaware limited liability company, was formed on March 7, 2014, for the sole purpose of reorganizing the ownership structure of Quote Lab, Inc. (“QL Inc.”) and MediaAlpha Ventures, LLC (“MAV”) in order to effectuate the purchase of 60% of the membership interests of QLH by White Mountains Capital, Inc. (“WMC”), pursuant to the membership interest purchase agreement effective March 14, 2014 (the “Acquisition” or “Closing”). Concurrent to the Closing, QL Inc. was restructured into QuoteLab, LLC (“QL”), a Delaware limited liability company, and the historical owners (collectively, the “Sellers”) transferred all ownership of QL and MAV to QLH. The Acquisition was accounted for under the acquisition method of accounting in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 805, Business Combinations (“ASC 805”), under which the purchase price was allocated to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on the estimated fair values at the date of the Acquisition. In accordance with ASC 805, QLH and its wholly owned subsidiaries QL and MAV (collectively, the “Company”), elected the option to apply pushdown accounting, and accordingly, recorded goodwill to the extent the purchase price exceeded the fair value of assets acquired, net of liabilities assumed, on the accounting records of QLH. The Company prepared the valuations for all identifiable intangible assets acquired internally. On September 26, 2016, MAV was dissolved to effectuate its merger with QL, pursuant to the Certificate of Merger of Domestic Limited Liability Companies. Nature of Business The Company does business as MediaAlpha. MediaAlpha is a leading marketing technology company that enables the programmatic buying and selling of vertical-specific, performance-based media between advertisers (buyers of advertising inventory) and publishers (sellers of advertising inventory) through cost-per-click, cost-per-call and cost-per-lead pricing models. MediaAlpha’s media buying platform (“MediaAlpha for Advertisers”) enables advertisers to create and automate data-driven bidding strategies designed to improve the efficiency and enhance the overall performance of their customer acquisition spend. MediaAlpha has developed distinctive platform solutions for a range of insurance verticals, including auto, motorcycle, home, renter, health and life, and non-insurance verticals, including travel, education and personal finance. NOTE 2. SIGNIFICANT TRANSACTIONS Healthplans.com Acquisition On October 5, 2017, the Company entered into an agreement with Healthplans.com, LLC to acquire certain assets, including customer relationships and domain names, associated with its life, health, and Medicare business (the “Healthplans.com Acquisition”) for cash consideration. The Healthplans.com acquisition was accounted for as an asset acquisition with the purchase price allocated to the assets acquired based on their relative estimated fair values at the acquisition date. Insignia Capital Group On February 26, 2019, WMC and founders sold 25% of their class A membership units to Insignia Capital Group in connection with a recapitalization transaction. The transaction valued MediaAlpha at approximately $350 million. As part of that transaction, MediaAlpha entered into a new secured credit 7

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) facility with Monroe Capital Management Advisors, LLC on February 26, 2019 ("Monroe Credit Facility"). See Note 7 for more information. White Mountains remains a significant equity holder in MediaAlpha with a 42% ownership interest on a fully-diluted basis. Insignia capital is a significant minority equity holder in MediaAlpha with a 22% ownership interest on a fully-diluted basis. MediaAlpha's founders continue to lead the business, and each remain a significant equity holder. The Company incurred total transaction expenses of $9.4 million in 2019, including $8.7 million related to the sale of Class A membership units to Insignia Capital Group and the closing of the new secured credit facility with Monroe Capital Management Advisors, LLC. NOTE 3. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES Basis of Presentation The consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“US GAAP”). The Company maintains their accounting records under the accrual method of accounting in conformity with US GAAP, where revenues and expenses are recorded as earned and incurred, respectively. Principles of Consolidation The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of QLH and its wholly owned subsidiary QL. Significant intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated upon consolidation. Use of Estimates The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with US GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of certain assets and liabilities, certain disclosures at the date of the consolidated financial statements, as well as the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Significant estimates affecting the consolidated financial statements have been prepared on the basis of the most current and best available information. However, actual results from the resolution of such estimates and assumptions may vary from those used in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements. Revenue Recognition The Company operates primarily in the insurance and travel verticals and generates revenue by facilitating cost per call, cost per lead, and cost per click media transactions (“Monetization Transactions”). The Monetization Transactions are used for both Company owned and operated (or “O&O”) properties as well as third party providers of online media (or “Publishers”). The price and amount of advertising sold varies, and is a function of a number of market conditions and consumer attributes, including (i) the time of day, (ii) the source of the media and quality of conversion by source, (iii) the demographic classification and geographic location of consumers, (iv) advertiser bids, and (v) advertiser demand and budget. The Monetization Transactions are summarized as follows: • Call revenue is earned and recognized when a consumer transfers to a call advertiser and remains engaged for a requisite duration of time, as specified by each advertiser. 8

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) • Click revenue is recognized on a pay-per-click basis and revenue is earned and recognized when a consumer clicks on a listed advertiser’s link, presented subsequent to a user search (e.g. auto insurance quote search or airfare search). • Lead revenue is recognized when the Company delivers data leads to lead advertisers. Data leads are generated when users complete a full quote request on the O&O properties or by users of Publisher sites who make the data lead available through the MediaAlpha Exchange. Delivery is deemed to have occurred at the time of lead transfer. Revenue related to revenue sharing arrangements with Publishers is recognized based on the Monetization Methods resulting from media generated through Publisher websites. Revenue is recorded at gross amounts and revenue share payments to Publishers are recorded in costs of revenue. Revenue related to the licensing of the Company’s software platform used to serve, track, price, and report on the Monetization Methods is recognized on a net basis as a percentage of the licensee’s gross revenue generated. The Company adopted ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (“ASC 606”), which governs how the Company recognizes revenue derived from the Monetization Transactions. The Company recognizes revenue when the Company transfers promised goods or services to clients in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the Company is entitled. The Company recognizes revenue pursuant to the framework contained in ASC 606: (i) identify the contract with a client; (ii) identify the performance obligations in the contract, including whether they are distinct in the context of the contract; (iii) determine the transaction price, including the constraint on variable consideration; (iv) allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract; and (v) recognize revenue when the Company satisfies the performance obligations. Generally, the Company’s contracts with advertisers specify a period of time covered and a budget governing spend limits. While contracts can specify a term, most of the Company’s contracts can be terminated at any time without penalty. Specific prices for each lead, click, or call delivered are specified in the MediaAlpha platform and determined in real time based on market conditions, at the discretion of the customer. As a result, the transaction price for each Monetization Transaction is determined and recorded in real time and no estimation of variable consideration or future consideration is required. The Company satisfies its performance obligations as services are provided. The Company does not promise to provide any other significant goods or services to its customers after delivery and does not allow returns. Separately from agreements the Company has with its customers, the Company has agreements with Internet search companies and Publishers to generate Monetization Transactions delivered to customers. The Company receives revenue from customers for the Monetization Transactions, and: (i) Pays a fee to the Internet search companies to drive consumers to O&O properties (ii) Pays a revenue share to Publishers, recorded simultaneously with recording of revenue derived from Monetization Transactions. The Company is the principal in the transactions described above. As a result, fees derived from Monetization Transactions are recorded as revenue and fees paid to Internet search companies and Publishers are included in cost of revenue. With respect to private marketplace transactions where Publishers and Advertisers leverage the MediaAlpha platform to execute Monetization Transactions but remain the primarily obligors of the transactions, MediaAlpha charges a licensing fee on the gross media transacted and recognizes the revenue on a net basis. In these relationships, the Advertisers and Publishers contract with one another 9

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) directly and leverage the MediaAlpha platform to facilitate transparent, real-time transactions utilizing the sophisticated reporting and analytical tools available to them via the Company’s platforms. Cash and Cash Equivalents The Company considers all short-term, highly liquid, unrestricted investments with original maturities of three months or less when purchased, to be cash equivalents. Accounts Receivable Accounts receivables are stated at amounts due from customers. As a general policy, the Company determines an allowance for doubtful accounts by considering a number of factors including the length of time trade accounts receivable are past due, the Company’s previous loss history, the customer’s current ability to pay its obligation to the Company, and the condition of the general economy and the industry as a whole. The Company writes off accounts receivable when they become uncollectible, and payments subsequently received on such receivables are credited to the allowance for doubtful accounts. The Company reported an allowance for doubtful accounts of $0.3 million as of December 31, 2019 and $0.5 million as of December 31, 2018. Financial Instruments and Concentrations of Credit and Business Risk The Company maintains cash balances that can, at times, exceed amounts insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. The Company has not experienced any losses in these accounts and believes it is not exposed to any credit risk in this area based on the financial strength of institutions with which the Company maintains its deposits. The Company’s accounts receivable, which are unsecured, expose the Company to credit risks such as collectability and business risks such as customer concentrations. The Company controls credit risk by investigating the creditworthiness of all customers prior to establishing relationships with them, performing periodic reviews of the credit activities of those customers during the course of the business relationship, regularly analyzing the collectability of accounts receivables, and recording allowances for doubtful accounts when these receivables become uncollectible. Customer concentrations for the years ended December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 consisted of one customer that accounted for approximately $78.8 million, or 19% and $85.6 million or 29% of total net revenues, respectively; the same customer accounted for approximately $4.7 million or 8% of the Company’s total accounts receivable as of December 31, 2019 compared to $4.8 million or 13% as of December 31, 2018. The Company’s accounts payable can expose the Company to business risks such as supplier concentrations. As of December 31, 2019 supplier concentrations consisted of two suppliers that accounted for approximately $84.6 million, or 23%, compared to $58.2 million or 28% of total purchases; the same suppliers accounted for approximately $13.9 million, or 34%, of the Company’s total accounts payable as of December 31, 2019 compared to $8.7 million or 32% as of December 31, 2018. Property and Equipment Property and equipment are stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization expense is calculated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the related assets, which are approximately three years. Leasehold improvements are amortized on a straight-line basis over the shorter of their lease term or the estimated useful life of the leased asset. 10

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) Betterments, renewals, and extraordinary repairs that materially extend the useful lives of assets are capitalized; other repairs and maintenance charges are expensed as incurred. The cost and related accumulated depreciation and amortization applicable to assets retired are removed from the accounts, and the gain or loss on disposition, if any, is recognized in the consolidated statement of operations for the period. Internal-Use Software Development Costs In accordance with FASB ASC Subtopic 350-40, Internal-Use Software, the Company capitalizes certain costs incurred in connection with developing internal use software. The Company expenses all costs that relate to the planning and post-implementation phases of development as operating expenses. Costs incurred in the development phase are capitalized and amortized over the product’s estimated useful life. Costs associated with the repair or maintenance of existing software is included in operating expenses. Amortization expense for capitalized internal-use software development costs is calculated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the software, which is approximately three years. MediaAlpha did not capitalize any software development costs during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018. Goodwill and Other Identifiable Intangible Assets In accordance with FASB ASC Topic 350, Intangibles, Goodwill and Other (“ASC 350”), goodwill and other identifiable intangible assets acquired in a purchase business combination and determined to have an indefinite useful life are not amortized, but instead tested for impairment at least annually and more frequently if events and circumstances indicate that the asset might be impaired. ASC 350 also requires that identifiable intangible assets with estimable useful lives be amortized over their respective estimated useful lives to their estimated residual values and reviewed for impairment in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 360, Property, Plant and Equipment – Impairment or Disposal of Long Lived Assets (“ASC 360”). Impairment of Long-Lived Assets In accordance with ASC 360, long-lived assets such as property and equipment and intangible assets with estimable useful lives are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. An impairment loss is recognized on long- lived assets when indicators of impairment are present and the undiscounted cash flows estimated to be generated by those assets are less than the carrying amount of the assets. In such cases, the carrying value of these assets are adjusted to their estimated fair values and assets held for sale are adjusted to their estimated fair values less selling expenses. Goodwill is not amortized, but rather is evaluated for impairment on an annual basis, or whenever indications of potential impairment exist. In the absence of any indications of potential impairment, the evaluation of goodwill is performed during the fourth quarter of each year. MediaAlpha initially evaluates goodwill using a qualitative approach (step zero) to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of goodwill is greater than its carrying value. If the results of the qualitative evaluation indicate that it is more likely than not that the carrying value of goodwill exceeds its fair value, MediaAlpha performs the two-step quantitative test for impairment. Other intangible assets with finite lives are evaluated for impairment at least annually and when events or changes in circumstances indicate that it is more likely than not that the asset is impaired. For the years 11

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) ended December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, there were no impairments recognized for property and equipment, identifiable intangible assets, or goodwill. Deferred Debt Issuance Costs Costs incurred directly as a result from financing transactions are capitalized and amortized to interest expense over the terms of the applicable debt agreements using a method that approximates the effective interest method. These remaining deferred costs are presented as direct deductions from the face amounts of the related long-term debt on the accompanying consolidated balance sheet. Comprehensive Income For the year ended December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company did not have any differences between its net income and comprehensive income. Member Distributions The Company's policy is to record payment of common unit distributions as a reduction to retained earnings, which is in a position of dividends in excess of earnings as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018. Leases The Company categorizes non-cancellable leases at their inception as either operating or capital leases. Costs for operating leases that include incentives such as payment escalations or rent abatements are recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease. Additionally, inducements received from lessors are treated as a reduction of costs over the term of the agreement. Costs for capital leases are capitalized at the present value of the future minimum lease payments, less any taxes and fees, with the corresponding obligation recorded in liabilities. The capital leases are amortized in accordance with the Company’s property and equipment policies and the corresponding obligations are reduced as lease payments are made. Fair Value Measurements The Company accounts for the fair value of its financial instruments in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (“ASC 820”). Non-recurring, nonfinancial assets and liabilities are also accounted for under the provisions of ASC 820. ASC 820 defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value under US GAAP and enhances disclosures about fair value measurements. Fair value is defined under ASC 820 as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value under ASC 820 must maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The standard describes a fair value hierarchy based on three levels of inputs, of which the first two are considered observable and the last unobservable, that may be used to measure fair value. The Company’s management used the following methods and assumptions to estimate the fair value of its intangible assets: • The multi-period-excess-earnings method estimates fair value using the present value of the incremental after-tax cash flows attributable solely to an intangible asset over its remaining life. This 12

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) approach was used to estimate the fair value of intangible assets associated with customer relationships. • The relief-from-royalty method was used to estimate fair value for intangible assets that relate to rights that could be obtained via a license from a third-party owner. Under this method, the fair value is estimated using the present value of license fees avoided by owning rather than leasing the asset. This technique was used to estimate the fair value of domain names. • The with-or-without method estimates the fair value of an intangible asset that provides an incremental benefit. Under this method, the fair value of the intangible asset is calculated by comparing the value of the entity with and without the intangible asset. This approach was used to estimate the fair value of the non-compete agreement. • The cost method estimates the fair value of an intangible asset based on the amount that currently would be required to replace the service capacity of an existing asset (replacement cost). This approach was used to estimate the fair value of the cost to acquire third party publishers. The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of the Company’s financial instruments are financial statement forecasts, annual growth rates, discount rates and weighted average cost of capital. The change in any of those inputs in isolation would result in a significant change of fair value measurement. MediaAlpha records its financial instruments at fair value with the exception of the outstanding debt, which are recorded as debt at face value less unamortized original issue discount and debt issuance costs. The carrying value of the debt as of December 31, 2019 is $97.2 million compared to $14.2 million as of December 31, 2018. During 2019, MediaAlpha also recognized $3.2 million at fair value of stock compensation expense relating to Class B shares compared to $11.7 million during 2018. These equity compensation awards were measured at fair value on a non-recurring basis at the various dates of issuance using a market multiple and discounted cash flows hybrid technique as well as equity transactions with third party investors. Sales Taxes ASC 606-10 provides that the presentation of taxes assessed by a governmental authority, which are directly imposed on revenue-producing transactions (i.e. sales, use, and excise taxes) between a seller and a customer, on a gross basis (included in revenues and costs), or on a net basis (excluded from revenues), is a management decision on accounting policies that should be disclosed. In addition, for any such taxes that are reported on a gross basis, the amounts of those taxes should be disclosed in the consolidated financial statements for each period for which a consolidated statement of operations is presented, if those amounts are significant. Sales taxes for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 are presented on a net basis. Cost of Revenues Cost of revenues is measured based on contract terms and recognized when the related revenue transactions are executed. MediaAlpha’s cost of revenues is comprised primarily of revenue share- based payments to publishers and traffic acquisition costs paid to top tier search engines. Cost of revenue was approximately $339.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 and $245.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The costs consisted primarily of $284.5 million of revenue 13

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) share-based payments and $54.2 million of traffic acquisition costs during 2019 compared to $210.1 million of revenue share-based payments and $34 million of traffic acquisition costs during 2018. Income Taxes QLH and QL are Delaware limited liability companies (or “LLCs”) that have elected to be treated as partnerships for federal income tax purposes and LLCs for Delaware, California, and various other state income tax purposes. Pursuant to these elections, the net income or loss of the Company is included in the tax returns of the members and is not subject to federal income taxes at the partnership level. With few exceptions, the Company is no longer subject to examination by tax authorities for returns filed prior to 2013, and no examinations are currently pending. The Company follows the provisions of uncertain tax positions as addressed in FASB ASC Subtopic 740- 10, Income Taxes, and recognizes interest accrued related to unrecognized tax benefits in operating expenses. The Company did not recognize any liabilities for uncertain tax positions, and has taken no tax positions for which the ultimate deductibility is highly certain but for which there is uncertainty about the timing of such deductibility for tax returns filed through the years-ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The Company had no accruals for interest and penalties and no such interest and penalties were recognized as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, and for the years then ended. Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements Revenue Recognition On January 1, 2018, MediaAlpha adopted ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (ASC 606), which modifies the guidance for revenue recognition. Under ASU 2014-09, revenue is recognized at an amount that reflects the consideration to which an entity expects to be entitled once it fulfills its performance obligations under the terms of its contract with the customer. Adoption of ASU 2014-09 did not have any impact on MediaAlpha's financial statements. Definition of a Business In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-01, Business Combinations: Clarifying the Definition of a Business (ASC 805), which clarifies the definition of a business and affects the determination of whether acquisitions or disposals are accounted for as assets or as a business. Under the new guidance, when substantially all of the fair value of the assets is concentrated in a single identifiable asset or a group of similar identifiable assets, it is not a business. The new guidance is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2018. Adoption of ASU 2017-01 did not have any impact on MediaAlpha’s financial statements. Recently Issued Not Yet Adopted Accounting Pronouncements Leases In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, Leases (ASC 842). The new guidance requires lessees to recognize lease assets and liabilities on the balance sheet for both operating and financing leases, with the exception of leases with an original term of 12 months or less. Under existing guidance recognition of lease assets and liabilities is not required for operating leases. The lease assets and liabilities to be recognized are both measured initially based on the present value of the lease payments. Under the new guidance, a sale-leaseback transaction must meet the recognition criteria under ASC 606, Revenues, in order to be accounted for as sale. The Company is currently in the process of evaluating the potential 14

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) impact of this new accounting guidance, which is effective for the Company for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2020. Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements (Continued) Goodwill In January 2017, the FASB issue ASU 2017-04, Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment (ASC 350), which changes the guidance on goodwill impairment testing. Under the new guidance, the qualitative assessment of the recoverability of goodwill remains the same. However, the second step required under the existing guidance has been eliminated. Goodwill is considered impaired if the carrying value exceeds the estimated fair value. The new guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2021. NOTE 4. Disaggregation of Revenue The following table shows the company’s revenue disaggregated by vertical: Thousands Year Ended December 31, Revenue 2019 2018 Insurance $ 356,559 $ 261,546 Travel 45,249 26,945 Other 6,094 7,034 Total $ 407,902 $ 295,525 NOTE 5. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT Property and equipment consisted of the following as of December 31, Thousands 2019 2018 Leasehold improvements $ 783 $ 877 Furniture and fixtures 302 306 Computers 215 212 Property and equipment, gross $ 1,300 $ 1,395 Less: accumulated depreciation (545) (514) Property and equipment, net $ 755 $ 881 Depreciation expense related to property and equipment amounted to $0.3 million and $0.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018. 15
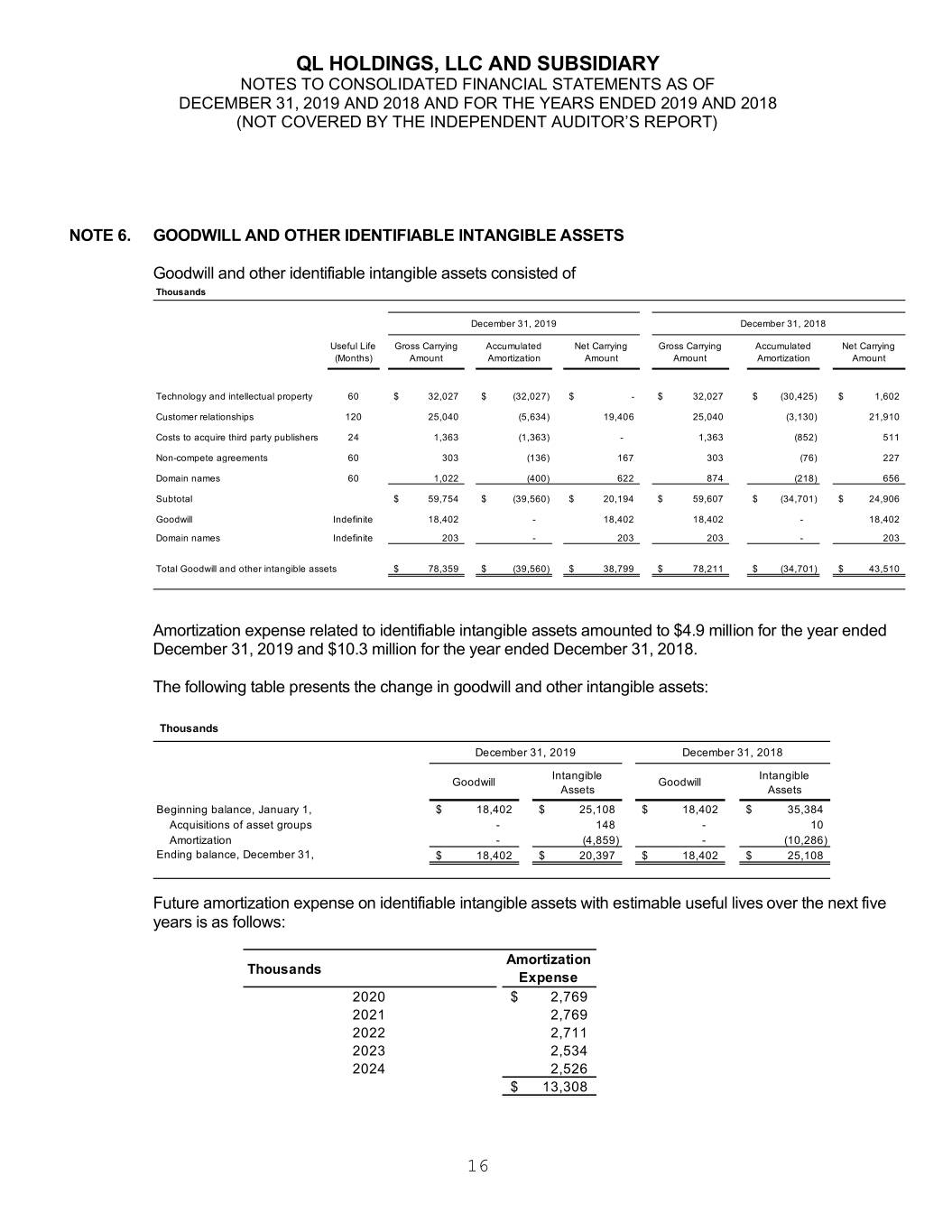
QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) NOTE 6. GOODWILL AND OTHER IDENTIFIABLE INTANGIBLE ASSETS Goodwill and other identifiable intangible assets consisted of Thousands December 31, 2019 December 31, 2018 Useful Life Gross Carrying Accumulated Net Carrying Gross Carrying Accumulated Net Carrying (Months) Amount Amortization Amount Amount Amortization Amount Technology and intellectual property 60 $ 32,027 $ (32,027) $ - $ 32,027 $ (30,425) $ 1,602 Customer relationships 120 25,040 (5,634) 19,406 25,040 (3,130) 21,910 Costs to acquire third party publishers 24 1,363 (1,363) - 1,363 (852) 511 Non-compete agreements 60 303 (136) 167 303 (76) 227 Domain names 60 1,022 (400) 622 874 (218) 656 Subtotal $ 59,754 $ (39,560) $ 20,194 $ 59,607 $ (34,701) $ 24,906 Goodwill Indefinite 18,402 - 18,402 18,402 - 18,402 Domain names Indefinite 203 - 203 203 - 203 Total Goodwill and other intangible assets $ 78,359 $ (39,560) $ 38,799 $ 78,211 $ (34,701) $ 43,510 Amortization expense related to identifiable intangible assets amounted to $4.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 and $10.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The following table presents the change in goodwill and other intangible assets: Thousands December 31, 2019 December 31, 2018 Intangible Intangible Goodwill Goodwill Assets Assets Beginning balance, January 1, $ 18,402 $ 25,108 $ 18,402 $ 35,384 Acquisitions of asset groups - 148 - 10 Amortization - (4,859) - (10,286) Ending balance, December 31, $ 18,402 $ 20,397 $ 18,402 $ 25,108 Future amortization expense on identifiable intangible assets with estimable useful lives over the next five years is as follows: Amortization Thousands Expense 2020 $ 2,769 2021 2,769 2022 2,711 2023 2,534 2024 2,526 $ 13,308 16

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) NOTE 7. LONG-TERM DEBT Credit Facility In connection with the Healthplans.com acquisition in October 2017, the Company entered into a Credit Facility with Bridge Bank, providing for a Term Loan of $18.4 million and a Revolver of $6.0 million. The Bridge Bank Credit Facility was collateralized by substantially all of the Company’s assets and contained certain financial covenants, with which the Company was in compliance as of December 31, 2018. At December 31, 2018, the Bridge Bank Term Loan had an outstanding balance of $14.3 million, with no outstanding borrowings under the Revolver. New Revolver and New Term Loan MediaAlpha entered into a new secured credit facility with Monroe Capital management Advisors, LLC on February 26, 2019 ("Monroe Credit Facility"). The new facility provides for a total commitment of $105.0 million, consisting of a $100.0 million Term Loan (“Term Loan”), which was fully drawn at close and a Revolving Credit Facility of $5.0 million (“Revolver”), which was undrawn at close and remains undrawn. Proceeds from the $100.0 million Term Loan were used to (i) pay off the Bridge Bank Term Loan in full, (ii) pay a dividend to class A membership unit holders, (iii) pay transaction expenses, (iv) fund transaction bonuses to employees, and (v) pay profit interests payouts to class B membership unit holders. On June 12, 2019, the Company executed an amendment to the Monroe Credit Facility to bring City National Bank on as a lender. Monroe Capital Management Advisors, LLC assigned $25.0 million of the Term Loan to City National and the $5.0 million Revolver to City National. In connection with the assignment of the Debt, the applicable margin on borrowings was reduced from LIBOR plus 5.50% to LIBOR plus 4.85%. In connection with the amendment, MediaAlpha incurred $0.2 million of legal fees and $0.1 million in an annual administrative agency fee. Given the insignificant change in cash flows, this amendment was accounted for as a modification to the Term Loan. As of December 31, 2019, the Company did not have outstanding borrowings on the Revolver, which allows for maximum borrowings up to $5.0 million. The Term Loan was issued with an original principal balance of $100.0 million. As of December 31, 2019, the balance of the Term Loan outstanding was $97.2 million net of deferred debt issuance costs of $2.0 million. The Monroe Credit Facility is collateralized by substantially all of the Company’s assets and contains certain financial and non-financial covenants, with which the Company was in compliance as of December 31, 2019. The financial covenants include a minimum Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio and a maximum Net Debt to EBITDA ratio. Non-financial covenants include restrictions on permitted equity repurchases, acquisitions, and incurrences of debt. The Revolver and Term Loan mature on February 26, 2025, at which time all outstanding borrowings and accrued interest are due. The Term Loan amortizes at a level rate of $250,000 per quarter, starting June 30, 2019. Additionally, the Term Loan requires a mandatory debt repayment based on an excess cash flow calculation performed annually (“Excess Cash Flow Sweep”). The percentage of excess cash flow to repaid declines based on the Net Debt to EBITDA Ratio. When the Net Debt to EBITDA Ratio is less than 2.00 to 1.00, percentage of excess cash flow will be 25% and 50% otherwise. The Monroe Credit Facility bears interest at a rate equal to LIBOR plus 4.85% on borrowings. 17

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) Future maturities on the term loan are as follows: Thousands December 31, 2019 Due in one year or less $ 1,000 Due in two to three years 2,000 Due in four to five years 2,000 Due after five years 94,250 Total $ 99,250 Less: deferred debt issuance costs, net (2,032) Net of Deferred Debt Issuance Costs $ 97,218 The Company incurred interest expense of $6.8 million during 2019 compared to $1.2 million during 2018. Included in interest expense is $0.4 million of amortization of debt issuance costs during 2019 compared to $0.3 million during 2018. Accrued interest as of December 31, 2019 was $0.02 million compared to $0.01 million for 2018. Deferred Debt Issuance Costs As of December 31, 2019, deferred debt issuance costs, net of accumulated amortization, amounted to $2.0 million compared to $.01 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. Total deferred debt issuance costs amortized to interest expense amounted to $0.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to $0.02 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. Future amortization of deferred debt issuance costs is as follows: Thousands December 31, 2019 2020 $ 426 2021 384 2022 384 2023 384 2024 384 2025 69 $ 2,032 NOTE 8. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES Operating Leases The Company is obligated under certain non-cancellable operating leases for its facilities, which expire on various dates through 2027. Certain facility leases contain predetermined fixed escalation of minimum rents. The Company recognizes rent expense on a straight-line basis for these leases and records the difference between recognized rental expense and the amounts payable under the lease agreement as deferred rent. The deferred rent liability totaled $0.4 million as of December 31, 2019. Total rental expense amounted to $0.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2019, and is included in operating expenses on the accompanying consolidated statement of operations. 18

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) Future minimum lease payments under the non-cancellable leases are as follows: Thousands Years Ending Rent Rent Payments Deferred Rent December 31, Expense 2020 $ 489 $ 449 $ 40 2021 540 466 74 2022 555 501 55 2023 532 503 29 2024 599 531 68 Total $ 2,715 $ 2,449 $ 265 The Deferred Rent balance as of December 31, 2018 was $0.5 million. Rental expense of $0.4 million and $0.2 million was included during 2018. Litigation The Company is subject to certain legal proceedings and claims that arise in the normal course of business. The Company does not believe that the amount of liability, if any, as a result of these proceedings and claims will have a materially adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated financial position, results of operations, and cash flows. NOTE 9. MEMBERS’ EQUITY Authorized, Issued, and Outstanding Units As of December 31, 2019, there are 1,136,842 units of class A membership units authorized, issued, and outstanding, and 169,943 units of class B membership units authorized with 163,800 units issued, of which 52,833 are vested and outstanding. Member Distributions Member distributions generally represent reimbursement of the tax liability passed through to the Company's members as a result of the taxable income generated by the Company. Class A Common Units Class A common units are entitled to: one vote for each class A common unit; distributions from normal operations, approved by the board of directors (“BOD”), in the proportion of units held to the total common units issued and outstanding; and liquidating distributions, approved by the BOD, in the proportion of units held to the total common units issued and outstanding. On October 5, 2017, in connection with the Healthplans.com Acquisition transaction, 136,842 units of class A membership units were issued to the Company’s existing members in exchange for $13.0 million cash. As a result of the contribution, WMC’s membership interest in the Company increased from 60% as of December 31, 2016 to 64% as of December 31, 2017. On February 26, 2019, MediaAlpha closed a transaction whereby WMC and founders sold 25% of their class A membership units, or 284,211 units, to Insignia Capital Group in connection with a recapitalization transaction. The transaction valued MediaAlpha at approximately $350.0 million. Class B Common Units 19

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) Class B common units are non-voting and will participate in the same normal distributions and liquidating distributions as the class A common units, provided that cumulative distributions up to the Participation Threshold, as defined in the amended and restated LLC agreement, have already been paid to the class A common units (the “performance condition”). Class B common units are reserved for issuance to directors, officers, employees, consultants, service providers, and advisors of the Company, upon BOD’s approvals. Class B common units can be redeemed at fair value by the Company upon the occurrence of a Termination Event, as defined in the amended and restated LLC agreement, at the Company’s discretion. In accordance with FASB ASC Subtopic 718-10, Compensation – Stock Compensation, the class B common units’ fair value estimated at the grant date should factor in whether the performance condition is probable. As of December 31, 2019, the company recorded stock compensation expense of $3.2 million for grants of the Class B shares issued between March 2014 and March 2018 compared to $11.7 million in 2018. The remaining class B common units have no fair value based on their grant date and will not be re-valued until achievement of the performance condition is determined to be probable. The following is a summary of the class B common units issued and outstanding as of December 31, Current Year: 2019 Vested Non-Vested Total Total outstanding, beginning of year 62,843 40,247 103,090 Issued - 97,738 97,738 Vested 13,832 (13,832) - Redeemed (23,842) (8,510) (32,352) Forfeited - (4,676) (4,676) Total outstanding, end of year 52,833 110,967 163,800 Prior Year: 2018 Vested Non-Vested Total Total outstanding, beginning of year 46,529 35,061 81,590 Issued - 24,000 24,000 Vested 16,314 (16,314) - Forfeited - (2,500) (2,500) Total outstanding, end of year 62,843 40,247 103,090 NOTE 10. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS The Company has evaluated subsequent events that have occurred from January 1, 2020 to March 30, 2020, which is the date that the consolidated financial statements were available to be issued and determined that there were no subsequent events or transactions that required recognition in the consolidated financial statements, other than the matter described below. On February 28, 2020, MediaAlpha amended the Monroe Credit Facility providing for incremental borrowing term loan capacity of up to $5.0 million (“Delayed Draw Term Loan”). The Delayed Draw Term Loan was undrawn prior to March 30, 2020. If and when drawn, the Delayed Draw Term Loan will carry interest at the same rate as the Monroe Credit Facility and will amortize over the same term as the Term Loan, with no material changes to covenants, seniority, or security. In connection with the 20

QL HOLDINGS, LLC AND SUBSIDIARY NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 AND 2018 AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED 2019 AND 2018 (NOT COVERED BY THE INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT) amendment, on February 28, 2020 MediaAlpha drew down $2.5 million on the Revolver to provide increased liquidity for a contemplated minority investment. The COVID-19 (Coronavirus) outbreak is currently impacting the United States and many countries around the world. Due to the recent and rapidly evolving nature of these events, the Company is unable to estimate the full impact at this time. However, at this time, the Company does not believe the situation will materially impact the Company’s liquidity or capital position. 21
