Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.2 - EX-32.2 - CITIZENS HOLDING CO /MS/ | d798066dex322.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - CITIZENS HOLDING CO /MS/ | d798066dex321.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - CITIZENS HOLDING CO /MS/ | d798066dex312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - CITIZENS HOLDING CO /MS/ | d798066dex311.htm |
| EX-23 - EX-23 - CITIZENS HOLDING CO /MS/ | d798066dex23.htm |
| EX-21 - EX-21 - CITIZENS HOLDING CO /MS/ | d798066dex21.htm |
| 10-K - 10-K - CITIZENS HOLDING CO /MS/ | d798066d10k.htm |
Exhibit 13 – 2019 Annual Report to Shareholders
TO OUR STOCKHOLDERS
I am pleased to present the annual report and a summary of the Company’s accomplishments for 2019. We experienced positive trends in several areas that should enhance the value of your investment. These positive trends include growth, both internally, and externally due to the acquisition of Charter Bank.
During 2019 total loans increased internally by 9.23% while deposits grew by 3.07%. The acquisition brought external growth and increased total assets by another $157.1 million. Due to combined internal growth and the acquisition, the bank ended 2019 with $1.195 billion in total assets and total capital of $110.8 million. I am very pleased with our growth accomplishments for the year.
Along with the already stated asset growth, we added some valuable members to our Gulf Coast team and to the overall bank team. It has been very encouraging to see the interaction of these individuals and the integration of processes that has happened over the last few months. This combination will give the Bank five good branch locations across the Coast. This begins a network of convenience for existing and future customer relationships. The Gulf Coast division is well positioned to be an enhancement in many ways for the Bank. This should enable the Bank to carry our brand of banking further into more Mississippi communities.
In November, we were saddened to learn that Steve Webb passed away. Steve was a former Director, President, CEO and Chairman of Citizens Bank and Citizens Holding Company. During his tenure he oversaw the formation of the Holding Company and growth of the Bank, both geographically and in asset size. I have been a beneficiary of Steve’s work and legacy. The bank and I have had a great foundation to stand on as we grow and prosper, and Steve was an integral part of that foundation. I am thankful to Steve for the lessons he taught and his accomplishments that made us a better company.
I hope it is evident to the owners of this great company that the Board of Directors and staff are continually analyzing any opportunity that would further maximize your investment. As the financial services landscape continues to change, we will continue to evolve in technology, personnel and products in order to remain relevant within the market. But we will do that with the same commitment to integrity, customer service and sound business practices that have been in place since 1908.
As I have stated many times, because we are blessed with great stockholders, great customers and great employees, our Company continues to prosper. I appreciate your continued participation and support in all we do to improve the Company.
It is an honor to be able to serve you and I look forward to what we can accomplish together in 2020.
Sincerely,
Greg McKee
President and CEO
Exhibit 13
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Philadelphia, Mississippi
Consolidated Financial Statements
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018 and for the
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
CONTENTS
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm |
1 – 3 | |
| Management’s Assessment of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
|
4 – 5 | |
| Consolidated Financial Statements |
||
| Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition |
6 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Income |
7 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
8 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Changes in Shareholders’ Equity |
9 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows |
10 – 11 | |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements |
12 – 72 | |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Citizens Holding Company
Opinion on Financial Statement
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of financial condition of Citizens Holding Company and subsidiary (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive (loss) income, changes in shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes to the consolidated financial statements (collectively, referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, are in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (the “PCAOB”), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013, and our report dated March 13, 2020, expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ HORNE LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 1998.
Memphis, Tennessee
March 13, 2020
1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Citizens Holding Company
Opinion on the Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Citizens Holding Company and subsidiary’s (the “Company”) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013. In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria for effective internal control over financial reporting described in the Internal Control – Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (the “PCAOB”), the consolidated statements of financial condition of Citizens Holding Company and subsidiary (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income (loss), changes in shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes to the consolidated financial statements and our report dated March 13, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting in the accompanying Report on Management’s Assessment of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (a) pertain to the
2
maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (b) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (c) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ HORNE LLP
Memphis, Tennessee
March 13, 2020
3
[CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY LETTERHEAD]
Report on Management’s Assessment of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Citizens Holding Company (the “Company”) is responsible for the preparation, integrity and fair presentation of the consolidated financial statements included in this annual report. The consolidated financial statements and notes included in this annual report have been prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States and necessarily include some amounts that are based on management’s best estimates and judgments.
Management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that: (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
The system of internal control over financial reporting as it relates to the financial statements is evaluated for effectiveness by management and tested for reliability through a program of internal audits. Actions are taken to correct potential deficiencies as they are identified. Any system of internal control, no matter how well designed, has inherent limitations, including the possibility that a control can be circumvented or overridden, and misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and not be detected. Also, because of changes in conditions, internal control effectiveness may vary over time. Accordingly, even an effective system of internal control will provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation.
4
Citizens Holding Company
Page Two
Management, with the participation of the Company’s principal executive officer and principal financial officer, conducted an assessment of the effectiveness of the Company’s system of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria for effective internal control over financial reporting described in the “Internal Control – Integrated Framework,” (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this assessment, management has concluded that, as of December 31, 2019, the Company’s system of internal control over financial reporting was effective. HORNE LLP, the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm that has audited the Company’s financial statements included in this annual report, has issued an attestation report on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019 which is included herein.
| /s/ Greg L. McKee |
/s/ Robert T. Smith | |
| Greg L. McKee |
Robert T. Smith | |
| President and Chief Executive Officer |
Treasurer and Chief Financial Officer | |
March 13, 2020
5
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition
December 31, 2019 and 2018
(in thousands, except share data)
| ASSETS |
2019 | 2018 | ||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
$ | 15,937 | $ | 12,592 | ||||
| Interest bearing deposits with other banks |
58,557 | 8,080 | ||||||
| Federal funds sold |
1,600 | — | ||||||
| Securities available for sale, at fair value |
464,383 | 444,746 | ||||||
| Loans, net of allowance for loan losses of $3,755 in 2019 and $3,372 in 2018 |
573,312 | 425,905 | ||||||
| Bank premises, furniture, fixtures and equipment, net |
24,672 | 19,717 | ||||||
| Other real estate owned, net |
3,552 | 3,440 | ||||||
| Accrued interest receivable |
4,181 | 4,166 | ||||||
| Cash surrender value of life insurance |
25,088 | 25,384 | ||||||
| Deferred tax assets |
3,684 | 6,634 | ||||||
| Other assets |
20,468 | 7,966 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total assets |
$ | 1,195,434 | $ | 958,630 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
||||||||
| Deposits |
||||||||
| Non-interest bearing deposits |
$ | 190,406 | $ | 170,030 | ||||
| Interest bearing deposits |
708,590 | 586,192 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total deposits |
898,996 | 756,222 | ||||||
| Securities sold under agreement to repurchase |
170,410 | 107,965 | ||||||
| Accrued interest payable |
1,128 | 471 | ||||||
| Deferred compensation payable |
9,453 | 9,053 | ||||||
| Other liabilities |
2,647 | 1,053 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities |
1,082,634 | 874,764 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Shareholders’ equity |
||||||||
| Common stock, $.20 par value, authorized 22,500,000 shares; 5,578,131 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 and 4,904,530 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2018 |
1,116 | 981 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
17,883 | 4,298 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss, net of tax benefit of ($262) in 2019 and ($4,978) in 2018 |
(789 | ) | (14,975 | ) | ||||
| Retained earnings |
94,590 | 93,562 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total shareholders’ equity |
112,800 | 83,866 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity |
$ | 1,195,434 | $ | 958,630 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these statements.
6
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Consolidated Statements of Income
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018, and 2017
(in thousands, except share and per share data)
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Interest income |
||||||||||||
| Interest and fees on loans |
$ | 24,652 | $ | 20,241 | $ | 18,734 | ||||||
| Interest on securities |
||||||||||||
| Taxable |
7,993 | 8,345 | 8,179 | |||||||||
| Non-taxable |
1,808 | 2,579 | 3,319 | |||||||||
| Other interest |
908 | 193 | 273 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total interest income |
35,361 | 31,358 | 30,505 | |||||||||
| Interest expense |
||||||||||||
| Deposits |
7,719 | 2,811 | 1,922 | |||||||||
| Other borrowed funds |
2,003 | 1,648 | 1,421 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total interest expense |
9,722 | 4,459 | 3,343 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net interest income |
25,639 | 26,899 | 27,162 | |||||||||
| (Provision for) reversal of loan losses |
(573 | ) | (334 | ) | 543 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net interest income after (provision for) reversal of loan losses |
25,066 | 26,565 | 27,705 | |||||||||
| Non-interest income |
||||||||||||
| Service charges on deposit accounts |
4,413 | 4,562 | 4,239 | |||||||||
| Other service charges and fees |
3,129 | 2,879 | 2,638 | |||||||||
| Net gains on sales of securities |
191 | 11 | 105 | |||||||||
| Other income |
2,015 | 1,148 | 1,315 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total non-interest income |
9,748 | 8,600 | 8,297 | |||||||||
| Non-interest expense |
||||||||||||
| Salaries and employee benefits |
14,883 | 14,530 | 14,772 | |||||||||
| Occupancy expense |
2,099 | 2,017 | 2,175 | |||||||||
| Equipment expense |
3,146 | 3,713 | 3,210 | |||||||||
| Other expense |
7,430 | 7,404 | 8,070 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total non-interest expense |
27,558 | 27,664 | 28,227 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income before income taxes |
7,256 | 7,501 | 7,775 | |||||||||
| Income tax expense |
1,354 | 828 | 4,071 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income |
$ | 5,902 | $ | 6,673 | $ | 3,704 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income per share – basic |
$ | 1.17 | $ | 1.36 | $ | 0.76 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income per share – diluted |
$ | 1.17 | $ | 1.36 | $ | 0.76 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
5,063,736 | 4,889,420 | 4,878,691 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted |
5,066,103 | 4,899,218 | 4,895,848 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these statements.
7
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018, and 2017
(in thousands)
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 5,902 | $ | 6,673 | $ | 3,704 | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) |
||||||||||||
| Unrealized holding gains (losses) on available-for-sale securities |
19,093 | (8,982 | ) | 6,241 | ||||||||
| Income tax effect |
(4,764 | ) | 2,240 | (2,080 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net unrealized gains (losses) |
14,329 | (6,742 | ) | 4,161 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Reclassification adjustment for gains included in net income |
(191 | ) | (11 | ) | (105 | ) | ||||||
| Income tax effect |
48 | 3 | 26 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net gains included in net income |
(143 | ) | (8 | ) | (79 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total other comprehensive income (loss) |
14,186 | (6,750 | ) | 4,082 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
$ | 20,088 | $ | (77 | ) | $ | 7,786 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these statements.
8
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Shareholders’ Equity
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018, and 2017
(in thousands, except per share data)
| Accumulated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number | Additional | Other | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| of Shares | Common | Paid-In | Comprehensive | Retained | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Issued | Stock | Capital | Loss | Earnings | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, January 1, 2017 |
4,882,579 | $ | 976 | $ | 3,802 | $ | (10,719 | ) | $ | 91,000 | $ | 85,059 | ||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | — | — | — | 3,704 | 3,704 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid ($0.96 per share) |
— | — | — | — | (4,697 | ) | (4,697 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Options exercised |
4,626 | 1 | 92 | — | — | 93 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock granted |
7,500 | 2 | (2 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Stock compensation expense |
— | — | 211 | — | — | 211 | ||||||||||||||||||
| AOCI reclassification |
— | — | — | (1,588 | ) | 1,588 | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income, net |
— | — | — | 4,082 | — | 4,082 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2017 |
4,894,705 | 979 | 4,103 | (8,225 | ) | 91,595 | 88,452 | |||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | — | — | — | 6,673 | 6,673 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid ($0.96 per share) |
— | — | — | — | (4,706 | ) | (4,706 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Options exercised |
2,325 | — | 27 | — | — | 27 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock granted |
7,500 | 2 | (2 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Stock compensation expense |
— | — | 170 | — | — | 170 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss, net |
— | — | — | (6,750 | ) | — | (6,750 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2018 |
4,904,530 | 981 | 4,298 | (14,975 | ) | 93,562 | 83,866 | |||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | — | — | — | 5,902 | 5,902 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid ($0.96 per share) |
— | — | — | — | (4,874 | ) | (4,874 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Common stock issued in connection with acquisition |
666,101 | 133 | 13,424 | — | — | 13,557 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock granted |
7,500 | 2 | (2 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Stock compensation expense |
— | — | 163 | — | — | 163 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income, net |
— | — | — | 14,186 | — | 14,186 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2019 |
5,578,131 | $ | 1,116 | $ | 17,883 | $ | (789 | ) | $ | 94,590 | $ | 112,800 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
9
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018, and 2017
1 of 2
(in thousands)
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities |
||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 5,902 | $ | 6,673 | $ | 3,704 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities |
||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
912 | 937 | 1,003 | |||||||||
| Amortization of premiums and accretion of discounts on investment securities, net |
5,294 | 3,283 | 3,317 | |||||||||
| Stock compensation expense |
163 | 170 | 211 | |||||||||
| Provision for (reversal of) loan losses |
573 | 334 | (543 | ) | ||||||||
| Gain on sale of securities |
(191 | ) | (11 | ) | (105 | ) | ||||||
| Gain from death benefit proceeds on BOLI |
(371 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Net gain on sale of other real estate owned |
(311 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Deferred income tax expense |
459 | 973 | 3,885 | |||||||||
| Net writedown on other real estate owned |
— | — | 414 | |||||||||
| Decrease in accrued interest receivable |
382 | 285 | 269 | |||||||||
| Increase in cash surrender value life insurance |
(709 | ) | (771 | ) | (722 | ) | ||||||
| Increase (decrease) in accrued interest payable |
166 | 273 | (1 | ) | ||||||||
| Increase in deferred compensation liability |
400 | 432 | 411 | |||||||||
| Net change in other operating assets and liabilities |
(722 | ) | (407 | ) | (1,224 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
11,947 | 12,171 | 10,619 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from calls, paydowns and maturities of securities available-for-sale |
59,189 | 40,964 | 42,390 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from sales of securities available-for-sale |
122,171 | 17,620 | 114,061 | |||||||||
| Purchases of investment securities available-for-sale |
(160,591 | ) | (10,550 | ) | (162,449 | ) | ||||||
| Increase in federal funds sold |
(1,600 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Death benefit proceeds from bank-owned life insurance |
1,549 | — | — | |||||||||
| Purchases of bank premises, furniture, fixtures and equipment |
(1,042 | ) | (346 | ) | (2,911 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from sales of bank premises, furniture, fixtures and equipment |
— | 264 | — | |||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of other real estate owned |
584 | 812 | 138 | |||||||||
| Net (increase) decrease in interest bearing deposits with other banks |
(48,927 | ) | (6,547 | ) | 47,071 | |||||||
| Net cash paid in acquisition of business |
(317 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
10
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018, and 2017
2 of 2
(in thousands)
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Purchases of Federal Home Loan Bank Stock |
— | (476 | ) | (499 | ) | |||||||
| Net increase in loans |
(44,678 | ) | (24,108 | ) | (11,788 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash (used by) provided by investing activities |
(73,662 | ) | 17,633 | 26,013 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities |
||||||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in deposits |
$ | 16,459 | $ | 35,536 | $ | (39,469 | ) | |||||
| Net (decrease) increase in federal funds purchased |
— | (1,500 | ) | 1,500 | ||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in securities sold under agreement to repurchase |
62,444 | (34,532 | ) | (7,785 | ) | |||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options |
— | 27 | 93 | |||||||||
| Dividends paid to shareholders |
(4,874 | ) | (4,706 | ) | (4,697 | ) | ||||||
| Net (decrease) increase in Federal Home |
||||||||||||
| Loan Bank advances |
(8,969 | ) | (30,000 | ) | 10,000 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
65,060 | (35,175 | ) | (40,358 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and due from banks |
3,345 | (5,371 | ) | (3,726 | ) | |||||||
| Cash and due from banks, beginning of year |
12,592 | 17,963 | 21,689 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash and due from banks, end of year |
$ | 15,937 | $ | 12,592 | $ | 17,963 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information |
||||||||||||
| Cash paid for |
||||||||||||
| Interest |
$ | 9,065 | $ | 4,186 | $ | 3,344 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income taxes |
$ | 685 | $ | 410 | $ | 1,782 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Noncash disclosures |
||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for acquisition of business |
$ | 13,557 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Real estate acquired by foreclosure |
$ | 385 | $ | 260 | $ | 89 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
11
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
(in thousands, except share and per share data)
Nature of Business
Citizens Holding Company (referred to herein as the “Company”) owns and operates The Citizens Bank of Philadelphia (the “Bank”). In addition to full service commercial banking, the Bank offers title insurance services through its subsidiary, Title Services LLC. As a state bank, the Bank is subject to regulations of the Mississippi Department of Banking and Consumer Finance and the Federal Deposit Insurance Company. The Company is also subject to the regulations of the Federal Reserve. The area served by the Bank is east central, several southern and northern counties of Mississippi and the surrounding areas. Services are provided at multiple branch offices.
Basis of Financial Statement Presentation
The accounting policies of the Company and its subsidiary conform to generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) in the United States of America and to general practices within the banking industry. The consolidated financial statements of the Company include the accounts of the Bank and its subsidiary (collectively, the “Company”). All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Estimates that are particularly susceptible to significant change relate to the determination of the allowance for loan losses and the valuation of real estate acquired in connection with foreclosures or in satisfaction of loans. In connection with the determination of the allowance for loan losses and valuation of foreclosed real estate, management obtains independent appraisals for significant properties.
While management uses available information to recognize losses on loans and to value foreclosed real estate, future additions to the allowance or adjustments to the valuation may be necessary based on changes in local economic conditions. In addition, regulatory agencies, as an integral part of their examination process, periodically review the Company’s allowance for loan losses and valuations of foreclosed real estate. Such agencies may require the Company to recognize additions to the allowance or to make adjustments to the valuation based on their judgments about information available to them at the time of their examination. Due to these factors, it is reasonably possible that the allowance for loan losses and valuation of foreclosed real estate may change materially in the near term.
12
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Continued
Cash, Due from Banks and Interest Bearing Deposits with Other Banks
For the purpose of reporting cash flows, cash and due from banks includes cash on hand and demand deposits. Cash flows from loans originated by the Company, deposits, and federal funds purchased and sold are reported net in the statement of cash flows. The Company is required to maintain average reserve balances with the Federal Reserve Bank based on a percentage of deposits.
Interest-bearing deposits with other banks mature within one year and are carried at cost.
Investment Securities
In accordance with the investments topic of the Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”), securities are classified as “available-for-sale,” “held-to-maturity” or “trading”. Fair values for securities are based on quoted market prices where available. If quoted market prices are not available, fair values are based on quoted market prices of comparable instruments. Gains or losses on the sale of securities are determined using the specific identification method. Currently, the Company has no trading securities.
Securities Available-for-Sale
Securities that are held for indefinite periods of time or used as part of the Company’s asset/liability management strategy and that may be sold in response to interest rate changes, changes in prepayment risk, the need to increase regulatory capital and other similar factors are classified as available-for-sale (“AFS”). Securities available-for-sale are reported at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses reported, net of related income tax effect, as a separate component of shareholders’ equity.
Securities Held to Maturity
Securities that are held-to-maturity (“HTM”) are those securities that the Company has the positive intent and ability to hold until maturity. These securities cannot be sold in response to the risk factors discussed above for available for sale securities. These securities are reported at book value. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, there were no securities classified as HTM.
13
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Continued
Realized gains or losses, determined on the basis of the cost of specific securities sold, are included in earnings. The amortization of premiums and accretion of discounts are recognized in interest income.
The Company periodically reviews its securities for impairment based upon a number of factors, including but not limited to, length of time and extent to which the fair value has been less than cost, the likelihood of the security’s ability to recover any decline in its fair value, financial condition of the underlying issuer, ability of the issuer to meet contractual obligations and ability to retain the security for a period of time sufficient to allow for recovery in fair value. Impairments on securities are recognized when management, based on its analysis, deems the impairment to be other-than-temporary. Disclosures about unrealized losses in the Company’s securities portfolio that have not been recognized as other-than-temporary impairments are provided in Note 3.
Loans and Allowance for Loan Losses
Loans receivable that management has the intent and ability to hold for the foreseeable future or until maturity or payoff are reported at the principal amount outstanding, net of unearned income and an allowance for loan losses. The Company has no loans held-for-sale.
Unearned income includes deferred fees net of deferred direct incremental loan origination cost. Unearned income attributable to loans held with a maturity of more than one year is recognized as income or expense over the life of the loan.
Unearned discounts on installment loans are recognized as income over the terms of the loans by a method that approximates the interest method. Unearned income and interest on commercial loans are recognized based on the principal amount outstanding. For all other loans, interest is accrued daily on the outstanding balances. For impaired loans, interest is discontinued on a loan when management believes, after considering collection efforts and other factors, that the borrower’s financial condition is such that collection of interest is doubtful. Cash collections on impaired loans are credited to the loan receivable balance, and no interest income is recognized on those loans until the principal balance has been collected. The Company generally discontinues the accrual of interest income when a loan becomes 90 days past due as to principal or interest; however, management may elect to continue the accrual when the estimated net realizable value of collateral is sufficient to cover the principal balance and the accrued interest. Interest income on other nonaccrual loans is recognized only to the extent of interest payments. Upon discontinuance of the accrual of interest on a loan, any previously accrued but unpaid interest is reversed against interest income.
14
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Continued
A loan is impaired when management determines that it is probable the Company will be unable to collect all contractual principal and interest payments due in accordance with the terms of the loan agreement. Impaired loans are measured based on the present value of expected future cash flows discounted at the loan’s effective interest rate or, as a practical expedient, at the loan’s observable market price or the fair value of the collateral if the loan is collateral dependent. The amount of impairment, if any, and any subsequent changes are included in the allowance for loan losses.
Troubled debt restructurings (“TDR”) are those for which concessions have been granted to the borrower due to a deterioration of the borrower’s financial condition. Such concessions may include reduction in interest rates or deferral of interest or principal payments. In evaluating whether to restructure a loan, management analyzes the long-term financial condition of the borrower, including guarantor and collateral support, to determine whether the proposed concessions will increase the likelihood of repayment of principal and interest. TDR are classified as performing, unless they are on nonaccrual status of 90 days or more delinquent, in which case they are considered nonperforming.
The allowance for loan losses is established through a provision for loan losses charged against net income. Loans determined to be uncollectible are charged against the allowance for loan losses, and subsequent recoveries, if any, are credited to the allowance. The allowance represents an amount, which, in management’s judgment, will be adequate to absorb estimated probable losses on existing loans that may become uncollectible. In order to determine an adequate level of allowance, management utilizes a model that calculates the allowance for loan loss by applying an average historical charge-off percentage by loan segment and over a 20 quarter period of time with the most current quarters weighted to show the effect of the most recent chargeoff activity to the current loan balances in the corresponding loan segment. Additionally, for loan balances over $100, specific reserves on an individual loan basis may be applied in addition to the allowance calculated using the model. This specific reserve is determined by an extensive review of the borrower’s credit history, capacity to pay, adequacy of collateral and general economic conditions related to the respective loan. This specific reserve will stay in place until such time that the borrower’s obligation is satisfied or the loan is greatly improved.
Large groups of small-balance homogenous loans are collectively evaluated for impairment. Accordingly, the Company does not separately identify individual consumer and residential loans for impairment disclosures.
15
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Continued
Business Combinations, Accounting for Credit-Deteriorated Purchased Loans and Related Assets
Business combinations are accounted for by applying the acquisition method in accordance with ASC 805, “Business Combinations.” Under the acquisition method, identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed and any non-controlling interest in the acquiree at the acquisition date are measured at their fair values as of that date and are recognized separately from goodwill. Results of operations of the acquired entities are included in the Consolidated Statements of Income from the date of acquisition. Acquisition costs incurred by the Company are expensed as incurred.
Loans purchased in business combinations with evidence of credit deterioration since origination and for which it is probable that all contractually required payments will not be collected are considered to be credit-impaired. Purchased credit deteriorated loans are accounted for in accordance with ASC 310-30, “Loans and Debt Securities Acquired with Deteriorated Credit Quality” (“ASC 310-30”), and initially measured at fair value, which includes estimated future credit losses expected to be incurred over the life of the loans. Increases in expected cash flows to be collected on these loans are recognized as an adjustment of the loan’s yield over its remaining life, while decreases in expected cash flows are recognized as an impairment.
Bank Premises, Furniture, Fixtures and Equipment
The Company’s premises, furniture, fixtures and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation computed by straight-line methods over the estimated useful lives of the assets, which range from three to forty years. Costs of major additions and improvements are capitalized. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred.
Other Real Estate Owned
Other real estate owned (“OREO”) consists of properties repossessed by the Company on foreclosed loans. These assets are stated at fair value at the date acquired less estimated costs to sell. Losses arising from the acquisition of such property are charged against the allowance for loan losses. Declines in value resulting from subsequent revaluation of the property or losses resulting from disposition of such property are expensed as incurred. Revenue and expenses from operations of other real estate owned are reflected as other income (expense).
Cash Surrender Value of Life Insurance
The Company has purchased life insurance contracts on certain employees and directors. Certain of such policies were acquired to fund deferred compensation arrangements with employees and directors. The cash surrender value of the Company owned policies is carried at the actual cash surrender value of the policy at the balance sheet date. Changes in the value of the policies are classified in non-interest income.
16
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Continued
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets include core deposits purchased and goodwill. Core deposit intangibles are amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated economic lives ranging from 5 to 10 years. Goodwill and other intangible assets with indefinite lives are not amortized but are tested at least annually for impairment. Fair values are determined based on market valuation multiples for the Company and comparable businesses based on the assets and cash flow of the Bank, the Company’s only reportable segment. If impairment has occurred, the goodwill or other intangible asset is reduced to its estimated fair value through a charge to expense.
Trust Assets
Assets held by the trust department of the Company in its fiduciary or agency capacities are not assets of the Company and are not included in the consolidated financial statements.
Income Taxes
Provisions for income taxes are based on taxes payable or refundable for the current year and the changes in deferred tax assets and liabilities, excluding components of other comprehensive income. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are included in the financial statements at currently enacted income tax rates applicable to the period in which the deferred tax assets and liabilities are expected to be realized or settled. As changes in tax laws or rates are enacted, deferred tax assets and liabilities are adjusted through the provision for income taxes. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when, in the opinion of management, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Comprehensive income (loss) includes net earnings reported in the consolidated statements of income and changes in unrealized gain (loss) on securities available-for-sale reported as a component of shareholders’ equity. Unrealized gain (loss) on securities available-for-sale, net of related income taxes, was the only component of accumulated other comprehensive income for the Company.
17
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Continued
Net Income Per Share
Net income per share-basic is computed by dividing net income by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the year. Net income per share-diluted is based on the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding for the periods, including the dilutive effect of the Company’s outstanding stock options and restricted stock grants. The effect of the dilutive shares for the years 2019, 2018 and 2017 is illustrated in the following table.
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Basic weighted average shares outstanding |
5,063,736 | 4,889,420 | 4,878,691 | |||||||||
| Dilutive effect of stock options |
2,367 | 9,798 | 17,157 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Dilutive weighted average shares outstanding |
5,066,103 | 4,899,218 | 4,895,848 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income |
$ | 5,902 | $ | 6,673 | $ | 3,704 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income per share-basic |
$ | 1.17 | $ | 1.36 | $ | 0.76 | ||||||
| Net income per share-diluted |
$ | 1.17 | $ | 1.36 | $ | 0.76 | ||||||
Advertising Costs
Advertising costs are charged to expense when incurred. Advertising expense was $551, $640 and $650 for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
Securities Sold Under Agreements to Repurchase
Securities sold under agreements to repurchase are accounted for as collateralized financing transactions and are recorded at the amounts at which the securities were sold. Securities, generally United States Government, federal agency and state county municipal securities, pledged as collateral under these financing arrangements cannot be sold or re-pledged by the secured party.
Reclassifications
Certain information for 2017 and 2018 has been reclassified to conform to the financial presentation for 2019. Such reclassifications had no effect on net income or shareholders’ equity.
18
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Continued
Stock-Based Compensation
At December 31, 2019, the Company had outstanding grants under two stock-based compensation plans, which are the 1999 Directors’ Stock Compensation Plan and the 2013 Incentive Compensation Plan. Compensation expense for option grants and restricted stock awards is determined based on the estimated fair value of the stock options and restricted stock on the applicable grant or award date. The Company has elected to account for forfeitures in compensation cost when they occur as permitted under the guidance in ASC 718, “Compensation—Stock Compensation” (“ASC 718”). Expense associated with the Company’s stock-based compensation is included under the line item “Salaries and benefits” on the Consolidated Statements of Income. The Company recognizes compensation expense for all share-based payments to employees in accordance with ASC 718, “Compensation – Stock Compensation.” See Note 19 for further details regarding the Company’s stock-based compensation.
Subsequent Events
The Company has evaluated, for consideration of recognition or disclosure, subsequent events that have occurred through the date of issuance of its financial statements, and has determined that no significant events occurred after December 31, 2019 but prior to the issuance of these financial statements that would have a material impact on its Consolidated Financial Statements.
Adoption of New Accounting Standards
ASU 2016-02 “Leases” (Topic 842)” (“ASU 2016-02”) requires lessees and lessors recognize lease assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet and disclose key information about leasing arrangements. ASU 2016-02 was effective for the Company on January 1, 2019. ASU 2016-02 provides for a modified retrospective transition approach requiring lessees to recognize and measure leases on the balance sheet at the beginning of either the earliest period presented or as of the beginning of the period of adoption with the option to elect certain practical expedients. The Company has elected to apply ASU 2016-02 as of the beginning of the period of adoption (January 1, 2019) and have not restated comparative periods. Of the optional practical expedients available under ASU 2016-02, all that apply have been adopted.
The Company’s operating leases relate primarily to branch properties and related equipment. As a result of implementing ASU 2016-02, we recognized an operating lease right-of-use (“ROU”) asset of $1,009 and an operating lease liability of $1,009 on January 1, 2019, with no impact on our consolidated statements of income or condensed consolidated statement of cash flows compared to the prior lease accounting model. The ROU asset and liability are recorded in other assets and other liabilities, respectively, in the consolidated statements of financial condition. See Note 8. Premises and Equipment for additional information.
19
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Continued
Newly Issued, But Not Yet Effective Accounting Standards
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, “Financial Instruments – Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments” (“ASU 2016-13”). ASU 2016-13 makes significant changes to the accounting for credit losses on financial instruments and disclosures about them. The new current expected credit loss (CECL) impairment model will require an estimate of expected credit losses, measured over the contractual life of an instrument, which considers reasonable and supportable forecasts of future economic conditions in addition to information about past events and current conditions. The standard provides significant flexibility and requires a high degree of judgment with regards to pooling financial assets with similar risk characteristics, determining the contractual terms of said financial assets and adjusting the relevant historical loss information in order to develop an estimate of expected lifetime losses. In addition, ASU 2016-13 amends the accounting for credit losses on debt securities and purchased financial assets with credit deterioration. The amendments in ASU 2016-13 were originally effective for fiscal years beginning after December 31, 2019, and interim periods within those years for public business entities that are SEC filers. However, in October 2019, the FASB approved deferral of the effective date for ASU 2016-13 for certain companies. The new effective date for the Company is January 1, 2023. ASU 2016-13 permits the use of estimation techniques that are practical and relevant to the Company’s circumstances, as long as they are applied consistently over time and faithfully estimate expected credit losses in accordance with the standard. The ASU lists several common credit loss methods that are acceptable such as a discounted cash flow method, loss-rate method and probability of default/loss given default (PD/LGD) method. Depending on the nature of each identified pool of financial assets with similar risk characteristics, the Company currently plans on implementing a PD/LGD method or a loss-rate method to estimate expected credit losses. The Company expects ASU 2016-13 to have a significant impact on the Company’s accounting policies, internal controls over financial reporting and footnote disclosures. The Company has assessed its data and system needs and has begun designing its financial models to estimate expected credit losses in accordance with the standard. Further development, testing and evaluation of said models is required to determine the impact that adoption of this standard will have on the financial condition and results of operations of the Company.
ASU 2018-13 “Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820) – Changes in the Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurement” (“ASU 2018-13”) removes the requirement to disclose the amount of and reasons for transfers between Level 1 and Level 2 fair value measurement methodologies, the policy for timing of transfers between levels and the valuation processes for Level 3 fair value measurements. It also adds a requirement to disclose changes in unrealized gains and losses for the period included in other comprehensive income for recurring Level 3 fair value measurements held at the end of the reporting period and the range and weighted average of significant unobservable inputs used to develop Level 3 measurements. For certain unobservable inputs, entities may disclose other quantitative information in lieu of the weighted average if the other quantitative information would be a more reasonable and rational method to reflect the distribution of unobservable inputs used to develop Level 3 fair value measurements. ASU 2018-13 is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2019. Management is currently evaluating the impact this ASU will have on the Company’s financial statements.
20
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
In January 2017, FASB issued ASU 2017-04, “Intangibles - Goodwill and Other (Topic 350)” (“ASU 2017-04”). ASU 2017-04 amends and simplifies current goodwill impairment testing by eliminating certain testing under the current provisions. Under the new guidance, an entity should perform the goodwill impairment test by comparing the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying value and recognize an impairment charge for the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the reporting unit’s fair value. An entity still has the option to perform the qualitative assessment for a reporting unit to determine if a quantitative impairment test is necessary. ASU 2017-04 becomes effective for the company for periods beginning after December 15, 2022. Management is currently evaluating the impact this ASU will have on the Company’s financial statements.
In December 2019, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2019-12, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Simplifying the Accounting for Income Taxes to simplify various aspects of the current guidance to promote consistent application of the standard among reporting entities by moving certain exceptions to the general principles. The amendments are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2020, with early adoption permitted. Management is currently evaluating the impact this ASU will have on the Company’s financial statements.
Note 2. Business Combinations
(dollar amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
Acquisition of Charter Bank
Effective October 1, 2019, the Company completed its acquisition of Charter Bank (“Charter”) in a transaction valued at approximately $19,668. The Company issued 666,101 shares of common stock and paid approximately $6,110 to Charter stockholders for 100% voting equity interest in Charter. On October 1, 2019, Charter operated 4 banking locations on the Mississippi Gulf Coast.
The Company recorded approximately $10,719 in intangible assets which consist of goodwill of $9,953 and a core deposit intangible of $766. Goodwill resulted from a combination of revenue enhancements from expansion in existing markets and efficiencies resulting from operational synergies. The fair value of the core deposit intangible is being amortized on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life, currently expected to be 7 years.
The Company recorded approximately $558 in expenses related to the merger in 2019. Merger expenses were expensed as incurred and are included in other expense in the consolidated statements of income.
The following table summarizes the allocation of purchase price to assets and liabilities acquired in connection with the Company’s acquisition of Charter based on their fair values on October 1, 2019.
| Purchase Price: |
||||||||
| Shares issued to common shareholders |
666,101 | |||||||
| Purchase price per share |
$ | 20.35 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Value of stock paid |
$ | 13,555 | ||||||
| Cash consideration paid |
6,110 | |||||||
| Cash paid for fractional shares |
3 | |||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total Purchase Price |
$ | 19,668 | ||||||
| Net Assets Acquired: |
||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity at transaction date |
$ | 11,383 | ||||||
| Increase (decrease) to net assets as a result of fair value adjustments to assets acquired and liabilities assumed: |
||||||||
| Securities |
(237 | ) | ||||||
| Loans, including loans held for sale |
(347 | ) | ||||||
| Premises and equipment |
(1,252 | ) | ||||||
| Intangible assets |
575 | |||||||
| Other assets |
(272 | ) | ||||||
| Deposits |
(135 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Net Assets Acquired |
9,715 | |||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Goodwill resulting from merger |
$ | 9,953 | ||||||
|
|
|
21
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 2. Continued
The following table summarizes the fair value on October 1, 2019 of assets acquired and liabilities assumed at acquisition date in connection with the merger with Charter.
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 7,343 | ||
| Investment securities available for sale |
26,607 | |||
| Loans |
103,665 | |||
| Premises and equipment |
4,813 | |||
| Intangible assets |
10,719 | |||
| Other assets |
3,957 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total assets |
157,104 | |||
| Deposits |
126,316 | |||
| Borrowings |
8,969 | |||
| Other liabilities |
2,151 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total liabilities |
$ | 137,436 | ||
|
|
|
|||
22
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 2. Continued
Supplemental Pro Forma Condensed Consolidated Results of Operations
The following unaudited pro forma condensed consolidated financial information presents the results of operations for the twelve months ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 of the Company as though the Charter merger had been completed as of January 1, 2018. The unaudited estimated pro forma information combines the historical results of Charter with the Company’s historical consolidated results and includes adjustments reflecting the estimated impact of certain fair value adjustments for the periods presented. The pro forma information is not necessarily indicative of what would have occurred had the acquisitions taken place on January 1, 2018. The pro forma information does not include the effect of any cost-saving or revenue-enhancing strategies. Merger expenses are reflected in the period in which they were incurred.
| (Unaudited) | ||||||||
| Year Ended | ||||||||
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Net interest income - pro forma |
$ | 29,237 | $ | 32,206 | ||||
| Noninterest income - pro forma |
$ | 10,090 | $ | 9,014 | ||||
| Noninterest expense - pro forma |
$ | 35,075 | $ | 32,714 | ||||
| Net income - pro forma |
$ | 2,692 | $ | 6,982 | ||||
| Earnings per share - pro forma |
||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.53 | $ | 1.43 | ||||
| Diluted |
$ | 0.53 | $ | 1.43 | ||||
For the three months ended December 31, 2019, Charter, the acquiree, had net interest income of $1,021, non-interest income of $720 and income before income taxes of $1,362 included in the consolidated statements of income for the year ended December 31, 2019.
23
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 3. Investment Securities
(in thousands)
The amortized cost and estimated fair value of securities available-for-sale and the corresponding amounts of gross unrealized gains and losses recognized in accumulated other comprehensive income at December 31, 2019 and 2018 were as follows:
| Gross | Gross | |||||||||||||||
| Amortized | Unrealized | Unrealized | ||||||||||||||
| 2019 |
Cost | Gains | Losses | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
| Securities available-for-sale |
||||||||||||||||
| Obligations of U.S. |
||||||||||||||||
| Government agencies |
$ | 97,400 | $ | — | $ | 289 | $ | 97,111 | ||||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities |
308,310 | 640 | 2,050 | 306,900 | ||||||||||||
| State, County, Municipals |
59,724 | 708 | 60 | 60,372 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | 465,434 | $ | 1,348 | $ | 2,399 | $ | 464,383 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Gross | Gross | |||||||||||||||
| Amortized | Unrealized | Unrealized | ||||||||||||||
| 2018 |
Cost | Gains | Losses | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
| Securities available-for-sale |
||||||||||||||||
| Obligations of U.S. |
||||||||||||||||
| Government agencies |
$ | 99,366 | $ | — | $ | 3,388 | $ | 95,978 | ||||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities |
259,742 | 5 | 12,373 | 247,374 | ||||||||||||
| State, County, Municipals |
105,591 | 67 | 4,264 | 101,394 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | 464,699 | $ | 72 | $ | 20,025 | $ | 444,746 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
24
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 3. Continued
The following tables show the gross unrealized losses and fair value of the Company’s investments classified as AFS investments with unrealized losses that are not deemed to be other-than-temporarily impaired, aggregated by investment category and length of time that individual securities have been in a continuous unrealized loss position, at December 31, 2019 and 2018.
A summary of unrealized loss information for AFS securities, categorized by security type follows:
| December 31, 2019 | Less than 12 months | 12 months or more | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Description of Securities |
Fair Value | Unrealized Losses |
Fair Value | Unrealized Losses |
Fair Value | Unrealized Losses |
||||||||||||||||||
| Obligations of U.S. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government agencies |
$ | 76,682 | 217 | $ | 20,429 | 72 | $ | 97,111 | 289 | |||||||||||||||
| Mortgage backed securities |
101,730 | 871 | 76,630 | 1,179 | 178,360 | 2,050 | ||||||||||||||||||
| State, County, Municipal |
8,280 | 37 | 3,731 | 23 | 12,011 | 60 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 186,692 | 1,125 | $ | 100,790 | 1,274 | $ | 287,482 | 2,399 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018 | Less than 12 months | 12 months or more | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Description of Securities |
Fair Value |
Unrealized Losses |
Fair Value | Unrealized Losses |
Fair Value | Unrealized Losses |
||||||||||||||||||
| Obligations of U.S. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government agencies |
$ | — | — | $ | 95,978 | 3,388 | $ | 95,978 | 3,388 | |||||||||||||||
| Mortgage backed securities |
12,258 | 179 | 234,929 | 12,194 | 247,187 | 12,373 | ||||||||||||||||||
| State, County, Municipal |
12,624 | 285 | 76,536 | 3,979 | 89,160 | 4,264 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 24,882 | 464 | $ | 407,443 | 19,561 | $ | 432,325 | 20,025 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
25
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 3. Continued
The Company’s unrealized losses on its Obligations of United States Government agencies, Mortgage backed securities and State, County and Municipal bonds are the result of an upward trend in interest rates, mainly in the mid-term sector. The Company does not intend to sell any of the securities in an unrealized loss position, and it is not more likely than not that the Company will be required to sell any such security prior to the recovery of its amortized cost basis, which may be at maturity. Furthermore, even though a number of these securities have been in a continuous unrealized loss position for a period greater than twelve months, the Company is collecting principal and interest from the respective issuers as scheduled. None of the unrealized losses disclosed in the previous table are related to credit deterioration. As such, the Company did not record any other-than-temporary impairment for the years ended December 31, 2019 or 2018.
The amortized cost and estimated fair value of securities at December 31, 2019, by contractual maturity, are shown below. Expected maturities will differ from contractual maturities because borrowers may have the right to call or prepay obligations with or without call or prepayment penalties.
| Amortized Cost |
Fair Value | |||||||
| Securities AFS |
||||||||
| Due in one year or less |
$ | 345 | $ | 345 | ||||
| Due after one year through five years |
89,920 | 89,681 | ||||||
| Due after five years through ten years |
18,678 | 18,808 | ||||||
| Due after ten years |
48,181 | 48,649 | ||||||
| Residential mortgage backed securities |
259,309 | 258,415 | ||||||
| Commercial mortgage backed securities |
49,001 | 48,485 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 465,434 | $ | 464,383 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Investment securities with fair values of $413,275 and $357,231 at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively, were pledged as collateral for public deposits and securities sold under agreement to repurchase.
26
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 3. Continued
Gross realized gains and losses are included in net gains on sales of securities. Total gross realized gains and gross realized losses from the sale of investment securities for each of the years ended December 31 were:
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Gross realized gains |
$ | 414 | $ | 171 | $ | 633 | ||||||
| Gross realized losses |
223 | 160 | 528 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net realized gains |
$ | 191 | $ | 11 | $ | 105 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Note 4. Federal Home Loan Bank Stock
(in thousands)
The Company, as a member of the Federal Home Loan Bank of Dallas (“FHLB”) system, owns stock in the organization. No ready market exists for the stock, and it has no quoted market value. The Company’s investment in the FHLB is carried at cost of $3,083 and $2,253 at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively, and is included in other assets. The Company purchased stock in 2019 and 2018 at the par value of $100 per share.
27
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 5. Non Purchased Loans
(In Thousands, Except Number of Loans)
“Purchased” loans are those acquired in any of the Company’s previous acquisitions. “Non purchased” loans include all of the Company’s other loans. For purposes of this Note 5, all references to “loans” mean non purchased loans.
The composition of loans, net at December 31, 2019 and 2018 is as follows:
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Real Estate: |
||||||||
| Land Development and Construction |
$ | 66,428 | $ | 41,134 | ||||
| Farmland |
15,595 | 14,498 | ||||||
| 1-4 Family Mortgages |
87,631 | 88,747 | ||||||
| Commercial Real Estate |
207,604 | 203,595 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Real Estate Loans |
377,258 | 347,974 | ||||||
| Business Loans: |
||||||||
| Commercial and Industrial Loans |
84,611 | 66,421 | ||||||
| Farm Production and Other Farm Loans |
683 | 907 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Business Loans |
85,294 | 67,328 | ||||||
| Consumer Loans: |
||||||||
| Credit Cards |
1,833 | 1,648 | ||||||
| Other Consumer Loans |
12,060 | 12,372 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Consumer Loans |
13,893 | 14,020 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Gross Loans |
476,445 | 429,322 | ||||||
| Unearned Income |
(8 | ) | (45 | ) | ||||
| Allowance for Loan Losses |
(3,755 | ) | (3,372 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Loans, net |
$ | 472,682 | $ | 425,905 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The Company has certain lending policies and procedures in place that are designed to maximize loan income within an acceptable level of risk. Management reviews these policies and procedures and submits them to the Company’s Board of Directors for its approval when needed, but no less frequently than annually. A reporting system supplements the review process by
28
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 5. Continued
providing management with frequent reports related to loan production, loan quality, concentrations of credit, loan delinquencies and non-performing and potential problem loans. Diversification in the loan portfolio is a means of managing risk associated with fluctuations in economic conditions.
The Company maintains an independent loan review department that reviews and validates the credit risk program on a periodic basis. Results of this review are presented to management with quarterly reports made to the board of directors. The loan review process complements and reinforces the risk identification and assessment decisions made by the lenders and credit personnel, as well as the Company’s policies and procedures.
Loans are made principally to customers in the Company’s market. The Company’s lending policy provides that loans collateralized by real estate are normally made with loan-to-value (“LTV”) ratios of 80 percent or less. Commercial loans are typically collateralized by property, equipment, inventories or receivables with LTV ratios from 50 percent to 80 percent. Real estate mortgage loans are collateralized by personal residences with LTV ratios of 80 percent or less. Consumer loans are typically collateralized by real estate, vehicles and other consumer durable goods. Approximately $77,700 and $67,500 of the loans outstanding at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, were variable rate loans.
In the ordinary course of business, the Company has granted loans to certain directors, significant shareholders and their affiliates (collectively referred to as “related parties”). These loans were made on substantially the same terms, including interest rates and collateral, as those prevailing at the time for comparable transactions with other unaffiliated persons and do not involve more than normal risk of collectability. Activity in related party loans during 2019 is presented in the following table.
| Balance outstanding at December 31, 2018 |
$ | 2,941 | ||
| Principal additions |
190 | |||
| Principal reductions |
(2,744 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance outstanding at December 31, 2019 |
$ | 387 | ||
|
|
|
|||
Loans are considered to be past due if the required principal and interest payments have not been received as of the date such payments were due. Loans are placed on non-accrual status, when, in management’s opinion, the borrower may be unable to meet payment obligations as they become due, as well as when required by regulatory provisions. Loans may be placed on non-accrual status regardless of whether such loans are considered past due. When interest accruals are discontinued, all unpaid accrued interest is reversed. Interest income is subsequently recognized only to the extent cash payments are received in excess of principal due. Loans are returned to accrual status when all the principal and interest amounts contractually due are brought current and future payments are reasonably assured.
29
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 5. Continued
Year-end non-accrual loans, segregated by class of loans, were as follows:
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Real Estate: |
||||||||
| Land Development and Construction |
$ | 111 | $ | — | ||||
| Farmland |
232 | 200 | ||||||
| 1-4 Family Mortgages |
2,160 | 1,831 | ||||||
| Commercial Real Estate |
9,082 | 7,612 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Real Estate Loans |
11,585 | 9,643 | ||||||
| Business Loans: |
||||||||
| Commercial and Industrial Loans |
338 | 76 | ||||||
| Farm Production and Other Farm Loans |
10 | 31 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Business Loans |
348 | 107 | ||||||
| Consumer Loans: |
||||||||
| Other Consumer Loans |
60 | 89 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Consumer Loans |
60 | 89 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total non-accrual Loans |
$ | 11,993 | $ | 9,839 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
In the event that non-accrual loans had performed in accordance with their original terms, the Company would have recognized additional interest income of approximately $555, $429 and $413 in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
30
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 5. Continued
An age analysis of past due loans, segregated by class of loans, as of December 31, 2019 is as follows:
| Accruing | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans | Loans | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans | 90 or more | 90 or more | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30-89 Days Past Due |
Days Past Due |
Total Past Due Loans |
Current Loans |
Total Loans |
Days Past Due |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Real Estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land Development and Construction |
$ | 736 | $ | — | $ | 736 | $ | 65,692 | $ | 66,428 | $ | — | ||||||||||||
| Farmland |
171 | 39 | 210 | 15,385 | 15,595 | 39 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 Family Mortgages |
3,116 | 777 | 3,893 | 83,738 | 87,631 | 147 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Real Estate |
8,511 | 2,080 | 10,591 | 197,013 | 207,604 | 18 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Real Estate Loans |
12,534 | 2,896 | 15,430 | 361,828 | 377,258 | 204 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Business Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and Industrial Loans |
586 | 312 | 898 | 83,713 | 84,611 | 52 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Farm Production and Other Farm Loans |
17 | — | 17 | 666 | 683 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Business Loans |
603 | 312 | 915 | 84,379 | 85,294 | 52 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Credit Cards |
45 | 18 | 63 | 1,770 | 1,833 | 18 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Consumer Loans |
172 | 42 | 214 | 11,846 | 12,060 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Consumer Loans |
217 | 60 | 277 | 13,616 | 13,893 | 18 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Loans |
$ | 13,354 | $ | 3,268 | $ | 16,622 | $ | 459,823 | $ | 476,445 | $ | 274 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
31
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 5. Continued
An age analysis of past due loans, segregated by class of loans, as of December 31, 2018 is as follows:
| Accruing | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans | Loans | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans | 90 or more | 90 or more | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30-89 Days | Days | Total Past | Current | Total | Days | |||||||||||||||||||
| Past Due | Past Due | Due Loans | Loans | Loans | Past Due | |||||||||||||||||||
| Real Estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land Development and Construction |
$ | 1,494 | $ | 54 | $ | 1,548 | $ | 39,586 | $ | 41,134 | $ | 54 | ||||||||||||
| Farmland |
779 | 29 | 808 | 13,690 | 14,498 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 Family Mortgages |
3,456 | 330 | 3,786 | 84,961 | 88,747 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Real Estate |
1,059 | 2,981 | 4,040 | 199,555 | 203,595 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Real Estate Loans |
6,788 | 3,394 | 10,182 | 337,792 | 347,974 | 54 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Business Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and Industrial Loans |
1,672 | 21 | 1,693 | 64,728 | 66,421 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Farm Production and Other Farm Loans |
9 | — | 9 | 898 | 907 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Business Loans |
1,681 | 21 | 1,702 | 65,626 | 67,328 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Credit Cards |
16 | 4 | 20 | 1,628 | 1,648 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Consumer Loans |
212 | 33 | 245 | 12,127 | 12,372 | 15 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Consumer Loans |
228 | 37 | 265 | 13,755 | 14,020 | 19 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Loans |
$ | 8,697 | $ | 3,452 | $ | 12,149 | $ | 417,173 | $ | 429,322 | $ | 73 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
32
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 5. Continued
Loans are considered impaired when, based on current information and events, it is probable the Company will be unable to collect all the amounts due in accordance with the original contractual terms of the loan agreement, including scheduled principal and interest payments. In determining which loans to evaluate for impairment, management looks at past due loans, bankruptcy filings and any situation that might lend itself to cause a borrower to be unable to repay the loan according to the original contract terms on those loans in excess of $100. If a loan is determined to be impaired and the collateral is deemed to be insufficient to fully repay the loan, a specific reserve will be established. Interest payments on impaired loans are typically applied to principal unless collectability of the principal amount is reasonably assured, in which case interest is recognized on a cash basis. Impaired loans or portions thereof, are charged-off when deemed uncollectible.
Impaired loans as of December 31, by class of loans, are as follows:
| 2019 | Unpaid Principal Balance |
Recorded Investment With No Allowance |
Recorded Investment With Allowance |
Total Recorded Investment |
Related Allowance |
Average Recorded Investment |
||||||||||||||||||
| Real Estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land Development and Construction |
$ | 111 | $ | 58 | $ | 53 | $ | 111 | $ | 16 | $ | 56 | ||||||||||||
| Farmland |
252 | 252 | — | 252 | — | 261 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 Family Mortgages |
839 | 740 | 99 | 839 | 28 | 996 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Real Estate |
11,506 | 5,949 | 3,840 | 9,789 | 566 | 9,337 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Real Estate Loans |
12,708 | 6,999 | 3,992 | 10,991 | 610 | 10,649 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Business: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and Industrial |
144 | — | 144 | 144 | 72 | 72 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Business Loans |
144 | — | 144 | 144 | 72 | 72 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total Loans |
$ | 12,852 | $ | 6,999 | $ | 4,136 | $ | 11,135 | $ | 682 | $ | 10,721 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
33
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 5. Continued
| 2018 | Unpaid Principal Balance |
Recorded Investment With No Allowance |
Recorded Investment With Allowance |
Total Recorded Investment |
Related Allowance |
Average Recorded Investment |
||||||||||||||||||
| Real Estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land Development and Construction |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||
| Farmland |
269 | 269 | — | 269 | — | 135 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 Family Mortgages |
1,153 | 1,062 | 91 | 1,153 | 27 | 728 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Real Estate |
10,601 | 5,209 | 3,675 | 8,884 | 374 | 6,489 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Real Estate Loans |
12,023 | 6,540 | 3,766 | 10,306 | 401 | 7,352 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total Loans |
$ | 12,023 | $ | 6,540 | $ | 3,766 | $ | 10,306 | $ | 401 | $ | 7,352 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
34
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 5. Continued
The following table presents troubled debt restructurings segregated by class:
| December 31, 2019 | Number of Loans |
Pre-Modification Outstanding Recorded Investment |
Post-Modification Outstanding Recorded Investment |
|||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
3 | $ | 4,871 | $ | 2,495 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
3 | $ | 4,871 | $ | 2,495 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| December 31, 2018 | Number of Loans |
Pre-Modification Outstanding Recorded Investment |
Post-Modification Outstanding Recorded Investment |
|||||||||
| Commercial real estate |
3 | $ | 4,871 | $ | 2,782 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
3 | $ | 4,871 | $ | 2,782 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Changes in the Company’s troubled debt restructurings are set forth in the table below:
| Number of Loans |
Recorded Investment |
|||||||
| Total at January 1, 2017 |
3 | $ | 3,288 | |||||
| Reductions due to: |
||||||||
| Principal paydowns |
(241 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total at January 1, 2018 |
3 | 3,047 | ||||||
| Reductions due to: |
||||||||
| Principal paydowns |
(265 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total at January 1, 2019 |
3 | 2,782 | ||||||
| Reductions due to: |
||||||||
| Principal paydowns |
(287 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total at December 31, 2019 |
3 | $ | 2,495 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The allocated allowance for loan losses attributable to restructured loans was $-0- and $174 at December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
The Company had no commitments to lend additional funds on these troubled debt restructurings at December 31, 2019.
35
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 5. Continued
The Company utilizes a risk grading matrix to assign a risk grade to each of its loans when originated and is updated as factors related to the strength of the loan changes. Loans are graded on a scale of 1 to 9. A description of the general characteristics of the 9 risk grades is as follows.
Grade 1. MINIMAL RISK - These loans are without loss exposure to the Company. This classification is reserved for only the best, well secured loans to borrowers with significant capital strength, low leverage, stable earnings and growth and other readily available financing alternatives. This type of loan would also include loans secured by a program of the government.
Grade 2. MODEST RISK - These loans include borrowers with solid credit quality and moderate risk of loss. These loans may be fully secured by certificates of deposit with another reputable financial institution, or secured by readily marketable securities with acceptable margins.
Grade 3. AVERAGE RISK - This is the rating assigned to most of the loans held by the Company. This includes loans with average loss exposure and average overall quality. These loans should liquidate through possessing adequate collateral and adequate earnings of the borrower. In addition, these loans are properly documented and are in accordance with all aspects of the current loan policy.
Grade 4. ACCEPTABLE RISK - Borrower generates sufficient cash flow to fund debt service but most working asset and capital expansion needs are provided from external sources. Profitability and key balance sheet ratios are usually close to peers but one or more may be higher than peers.
Grade 5. MANAGEMENT ATTENTION - Borrower has significant weaknesses resulting from performance trends or management concerns. The financial condition of the borrower has taken a negative turn and may be temporarily strained. Cash flow is weak but cash reserves remain adequate to meet debt service. Management weakness is evident.
Grade 6. OTHER LOANS ESPECIALLY MENTIONED (“OLEM”) - Loans in this category are fundamentally sound but possess some weaknesses. OLEM loans have potential weaknesses, which may, if not checked or corrected, weaken the asset or inadequately protect the Bank’s credit position at some future date. These loans have an identifiable weakness in credit, collateral, or repayment ability but there is no expectation of loss.
Grade 7. SUBSTANDARD ASSETS - Assets classified as substandard are inadequately protected by the current net worth and paying capacity of the obligor or of the collateral pledged, if any. Assets classified as substandard must have a well-defined weakness based upon objective evidence. Assets classified as substandard are characterized by the distinct possibility that the insured institution will sustain some loss if the deficiencies are not corrected. The possibility that liquidation would not be timely requires a substandard classification even if there is little likelihood of total loss.
36
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 5. Continued
Grade 8. DOUBTFUL - A loan classified as doubtful has all the weaknesses of a substandard classification and the added characteristic that the weakness makes collection or liquidation in full, on the basis of currently existing facts, conditions, and values, highly questionable or improbable. The possibility of loss is extremely high, but because of certain important and reasonable specific pending factors that may work to the advantage and strengthening of the asset, its classification as an estimated loss is deferred until its more exact status may be determined. A doubtful classification could reflect the fact that the primary source of repayment is gone and serious doubt exists as to the quality of a secondary source of repayment.
Grade 9. LOSS - Loans classified loss are considered uncollectible and of such little value that their continuance as bankable assets is not warranted. This classification does not mean that the asset has absolutely no recovery or salvage value, but rather it is not practical or desirable to defer writing off this basically worthless asset even though partial recovery may occur in the future. Also included in this classification is the defined loss portion of loans rated substandard assets and doubtful assets.
These internally assigned grades are updated on a continual basis throughout the course of the year and represent management’s most updated judgment regarding grades at December 31, 2019.
37
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 5. Continued
The following table details the amount of gross loans by loan grade and class for the year ended December 31, 2019:
| Satisfactory 1,2,3,4 |
Special Mention 5,6 |
Substandard 7 |
Doubtful 8 |
Loss 9 |
Total Loans |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Real Estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land Development and Construction |
$ | 64,112 | $ | 1,682 | $ | 634 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 66,428 | ||||||||||||
| Farmland |
14,533 | 331 | 731 | — | — | 15,595 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 Family Mortgages |
79,068 | 1,917 | 6,646 | — | — | 87,631 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Real Estate |
169,270 | 21,266 | 17,068 | — | — | 207,604 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Real Estate Loans |
326,983 | 25,196 | 25,079 | — | — | 377,258 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Business Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and Industrial Loans |
80,289 | 128 | 4,194 | — | — | 84,611 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Farm Production and Other Farm Loans |
669 | — | 4 | — | 10 | 683 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Business Loans |
80,958 | 128 | 4,198 | — | 10 | 85,294 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Credit Cards |
1,770 | — | 63 | — | — | 1,833 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Consumer Loans |
11,907 | 59 | 53 | 41 | — | 12,060 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Consumer Loans |
13,677 | 59 | 116 | 41 | — | 13,893 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Loans |
$ | 421,618 | $ | 25,383 | $ | 29,393 | $ | 41 | $ | 10 | $ | 476,445 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
38
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 5. Continued
The following table details the amount of gross loans by loan grade and class for the year ended December 31, 2018:
| Satisfactory 1,2,3,4 |
Special Mention 5,6 |
Substandard 7 |
Doubtful 8 |
Loss 9 |
Total Loans |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Real Estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land Development and Construction |
$ | 39,726 | $ | 840 | $ | 568 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 41,134 | ||||||||||||
| Farmland |
13,248 | 339 | 911 | — | — | 14,498 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 Family Mortgages |
79,659 | 1,751 | 7,337 | — | — | 88,747 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Real Estate |
172,217 | 17,938 | 13,440 | — | — | 203,595 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Real Estate Loans |
304,850 | 20,868 | 22,256 | — | — | 347,974 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Business Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and Industrial Loans |
63,994 | 81 | 2,346 | — | — | 66,421 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Farm Production and Other Farm Loans |
876 | — | 31 | — | — | 907 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Business Loans |
64,870 | 81 | 2,377 | — | — | 67,328 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Credit Cards |
1,628 | — | 20 | — | — | 1,648 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Consumer Loans |
12,181 | 65 | 71 | 55 | — | 12,372 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Consumer Loans |
13,809 | 65 | 91 | 55 | — | 14,020 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Loans |
$ | 383,529 | $ | 21,014 | $ | 24,724 | $ | 55 | $ | — | $ | 429,322 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
39
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 6. Purchased Loans
(In Thousands)
For purposes of this Note 6, all references to “loans” means purchased loans.
The following is a summary of purchased loans at December 31:
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Real Estate: |
||||||||
| Land Development and Construction |
$ | 14,722 | $ | — | ||||
| Farmland |
510 | — | ||||||
| 1-4 Family Mortgages |
35,952 | — | ||||||
| Commercial Real Estate |
32,436 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Real Estate Loans |
83,620 | — | ||||||
| Business Loans: |
||||||||
| Commercial and Industrial Loans |
14,153 | — | ||||||
| Farm Production and Other Farm Loans |
884 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Business Loans |
15,037 | — | ||||||
| Consumer Loans: |
||||||||
| Credit Cards |
— | — | ||||||
| Other Consumer Loans |
1,973 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Consumer Loans |
1,973 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Gross Loans |
100,630 | — | ||||||
| Unearned Income |
— | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Loans, net of unearned income |
$ | 100,630 | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
40
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 6. Continued
An age analysis of past due loans, segregated by class of loans, as of December 31, 2019 is as follows:
| Loans 30-89 Days Past Due |
Loans 90 or more Days Past Due |
Total Past Due Loans |
Current Loans |
Total Loans |
Accruing Loans 90 or more Days Past Due |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Real Estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land Development and Construction |
$ | 528 | $ | — | $ | 528 | $ | 14,194 | $ | 14,722 | $ | — | ||||||||||||
| Farmland |
— | — | — | 510 | 510 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 Family Mortgages |
444 | — | 444 | 35,508 | 35,952 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Real Estate |
603 | — | 603 | 31,833 | 32,436 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Real Estate Loans |
1,576 | — | 965 | 82,044 | 83,620 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Business Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and Industrial Loans |
379 | 3 | 382 | 13,771 | 14,153 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Farm Production and Other Farm Loans |
— | — | — | 884 | 884 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Business Loans |
379 | 3 | 382 | 14,655 | 15,037 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Credit Cards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Consumer Loans |
49 | 8 | 57 | 1,916 | 1,973 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Consumer Loans |
49 | 8 | 57 | 1,916 | 1,973 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Loans |
$ | 2,003 | $ | 11 | $ | 2,014 | $ | 98,615 | $ | 100,630 | $ | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
There were no non credit deteriorated loans that were subsequently impaired and recognized in conformity with ASC 310 as of December 31, 2019.
41
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 6. Continued
The following table details the amount of gross loans by loan grade which are consistent with the Company’s loan grades, and class for the year ended December 31, 2019:
| Special | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Satisfactory | Mention | Substandard | Doubtful | Loss | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1,2,3,4 | 5,6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | Loans | |||||||||||||||||||
| Real Estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land Development and Construction |
$ | 13,890 | $ | 789 | $ | 43 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 14,722 | ||||||||||||
| Farmland |
510 | — | — | — | — | 510 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4 Family Mortgages |
33,737 | 1,535 | 680 | — | — | 35,952 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Real Estate |
30,780 | 1,656 | — | — | — | 32,436 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Real Estate Loans |
78,917 | 3,980 | 723 | — | — | 83,620 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Business Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and Industrial Loans |
13,545 | 608 | — | — | — | 14,153 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Farm Production and Other Farm Loans |
884 | — | — | — | — | 884 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Business Loans |
14,429 | 608 | — | — | — | 15,037 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Credit Cards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Consumer Loans |
1,937 | 36 | — | — | — | 1,973 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Consumer Loans |
1,937 | 36 | — | — | — | 1,973 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Loans |
$ | 95,283 | $ | 4,624 | $ | 723 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 100,630 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
42
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 6. Continued
Loans purchased in business combinations that exhibited, at the date of acquisition, evidence of deterioration of the credit quality since origination, such that it was probable that all contractually required payments would not be collected, were as follows as of December 31, 2019:
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Real Estate: |
||||||||
| Land Development and Construction |
$ | 43 | $ | — | ||||
| Farmland |
— | — | ||||||
| 1-4 Family Mortgages |
706 | — | ||||||
| Commercial Real Estate |
— | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Real Estate Loans |
749 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total PCD Loans |
$ | 749 | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Non-accrual loans of $33 are included in the 1-4 Family Mortgages at December 31, 2019.
The following table presents the fair value of loans determined to be impaired at the time of acquisition:
| Total Purchased Credit Deteriorated Loans | ||||
| Contractually-required principal |
$ | 993 | ||
| Nonaccretable difference |
(68 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Cash flows expected to be collected |
925 | |||
| Accretable yield |
(36 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Fair Value |
$ | 889 | ||
|
|
|
|||
Changes in the accretable yield of loans purchased with deteriorated credit quality were as follows:
| Balance at January 1, 2019 |
$ | — | ||
| Additions through acquisition |
(36 | ) | ||
| Reclasses from nonaccretable difference |
12 | |||
| Accretion |
8 | |||
| Charge-off |
— | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance at December 31, 2019 |
$ | (16 | ) | |
|
|
|
There were no loans classified as TDRs purchased as part of the acquisition of Charter.
43
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 6. Continued
The following table presents the fair value of loans purchased from Charter as of the October 1, 2019 acquisition date:
| October 1, 2019 | ||||
| At acquisition date: |
||||
| Contractually-required principal |
$ | 104,127 | ||
| Nonaccretable difference |
(68 | ) | ||
| Cash flows expected to be collected |
104,059 | |||
| Accretable yield |
(394 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Fair Value |
$ | 103,665 | ||
|
|
|
|||
Note 7. Allowance for Loan Losses
(in thousands)
The allowance for loan losses is a reserve established through a provision for possible loan losses charged to expense, which represents management’s best estimate of probable losses that will occur within the existing portfolio of loans. The allowance, in the judgment of management, is necessary to reserve for estimated loan losses and risks inherent in the loan portfolio.
The allowance on the majority of the loan portfolio is calculated using a historical chargeoff percentage applied to the current loan balances by loan segment. This historical period is the average of the previous five years with the most current years weighted to show the effect of the most recent chargeoff activity. This percentage is also adjusted for economic factors such as unemployment and general business conditions, both local and nationwide.
The group of loans that are considered to be impaired are individually evaluated for possible loss and a specific reserve is established to cover any loss contingency. Loans that are determined to be a loss with no benefit of remaining in the portfolio are charged off to the allowance. These specific reserves are reviewed periodically for continued impairment and adequacy of the specific reserve and adjusted when necessary.
44
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 7. Continued
The following table details activity in the allowance for loan losses by portfolio segment for the years ended December 31:
| Real | Business | |||||||||||||||
| 2019 | Estate | Loans | Consumer | Total | ||||||||||||
| Beginning Balance |
$ | 2,845 | $ | 222 | $ | 305 | $ | 3,372 | ||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
231 | 247 | 95 | 573 | ||||||||||||
| Chargeoffs |
115 | 107 | 138 | 360 | ||||||||||||
| Recoveries |
114 | 9 | 47 | 170 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net chargeoffs |
1 | 98 | 91 | 190 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Ending Balance |
$ | 3,075 | $ | 371 | $ | 309 | $ | 3,755 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Period end allowance allocated to: |
||||||||||||||||
| Loans individually evaluated for impairment |
$ | 610 | $ | 72 | $ | — | $ | 682 | ||||||||
| Loans collectively evaluated for impairment |
2,465 | 299 | 309 | 3,073 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Ending Balance |
$ | 3,075 | $ | 371 | $ | 309 | $ | 3,755 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
45
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 7. Continued
| Real | Business | |||||||||||||||
| 2018 | Estate | Loans | Consumer | Total | ||||||||||||
| Beginning Balance |
$ | 2,151 | $ | 347 | $ | 521 | $ | 3,019 | ||||||||
| Provision for (reversal of) loan losses |
606 | (113 | ) | (159 | ) | 334 | ||||||||||
| Chargeoffs |
223 | 19 | 145 | 387 | ||||||||||||
| Recoveries |
311 | 7 | 88 | 406 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net chargeoffs |
(88 | ) | 12 | 57 | (19 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Ending Balance |
$ | 2,845 | $ | 222 | $ | 305 | $ | 3,372 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Period end allowance allocated to: |
||||||||||||||||
| Loans individually evaluated for impairment |
$ | 401 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 401 | ||||||||
| Loans collectively evaluated for impairment |
2,444 | 222 | 305 | 2,971 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Ending Balance |
$ | 2,845 | $ | 222 | $ | 305 | $ | 3,372 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Real | Business | |||||||||||||||
| 2017 | Estate | Loans | Consumer | Total | ||||||||||||
| Beginning Balance |
$ | 3,117 | $ | 258 | $ | 528 | $ | 3,903 | ||||||||
| Provision for (reversal of) loan losses |
(827 | ) | 254 | 30 | (543 | ) | ||||||||||
| Chargeoffs |
169 | 166 | 102 | 437 | ||||||||||||
| Recoveries |
30 | 1 | 65 | 96 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net chargeoffs |
139 | 165 | 37 | 341 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Ending Balance |
$ | 2,151 | $ | 347 | $ | 521 | $ | 3,019 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Period end allowance allocated to: |
||||||||||||||||
| Loans individually evaluated for impairment |
$ | 442 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 442 | ||||||||
| Loans collectively evaluated for impairment |
1,709 | 347 | 521 | 2,577 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Ending Balance |
$ | 2,151 | $ | 347 | $ | 521 | $ | 3,019 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
46
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 7. Continued
The Company’s recorded investment in loans as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 related to each balance in the allowance for possible loan losses by portfolio segment and disaggregated on the basis of the Company’s impairment methodology was as follows:
| 2019 | Real Estate | Business Loans |
Consumer | Total | ||||||||||||
| Loans individually evaluated for impairment |
$ | 10,991 | $ | 144 | $ | — | $ | 11,135 | ||||||||
| Loans collectively evaluated for impairment |
449,138 | 100,187 | 15,866 | 564,937 | ||||||||||||
| Acquired with deteriorated credit quality |
749 | — | — | 749 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| $ | 460,878 | $ | 100,331 | $ | 15,866 | $ | 577,075 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Real | Business | |||||||||||||||
| 2018 | Estate | Loans | Consumer | Total | ||||||||||||
| Loans individually evaluated for impairment |
$ | 10,306 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 10,306 | ||||||||
| Loans collectively evaluated for impairment |
337,668 | 67,328 | 14,020 | 419,016 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| $ | 347,974 | $ | 67,328 | $ | 14,020 | $ | 429,322 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
47
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 7. Continued
Net chargeoffs (recoveries), segregated by class of loans, were as follows:
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Real Estate: |
||||||||||||
| Land Development and Construction |
$ | (18 | ) | $ | 56 | $ | 98 | |||||
| Farmland |
— | 3 | — | |||||||||
| 1-4 Family Mortgages |
32 | 51 | 41 | |||||||||
| Commercial Real Estate |
(13 | ) | (198 | ) | — | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total Real Estate Loans |
1 | (88 | ) | 139 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Business Loans: |
||||||||||||
| Commercial and Industrial Loans |
98 | 12 | 165 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total Business Loans |
98 | 12 | 165 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Consumer Loans: |
||||||||||||
| Credit Cards |
34 | 36 | (7 | ) | ||||||||
| Other Consumer Loans |
57 | 21 | 44 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total Consumer Loans |
91 | 57 | 37 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total Net Chargeoffs (Recoveries) |
$ | 190 | $ | (19 | ) | $ | 341 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
48
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 8. Bank Premises, Furniture, Fixtures and Equipment
(in thousands)
Bank premises, furniture, fixtures and equipment consist of the following at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018:
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Land and buildings |
$ | 33,791 | $ | 27,052 | ||||
| Furniture, fixtures and equipment |
8,447 | 6,012 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 42,238 | 33,064 | |||||||
| Less accumulated depreciation |
17,566 | 13,347 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 24,672 | $ | 19,717 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively, was $899, $937, and $1,003.
The Company leases certain premises and equipment under operating leases. At December 31, 2019, the Company had lease liabilities and ROU assets totaling $771 related to these leases. Lease liabilities and ROU assets are reflected in other liabilities and other assets, respectively. For the twelve months ended December 31, 2019, the weighted average remaining lease term for operating leases was 1.2 years and the weighted average discount rate used in the measurement of operating lease liabilities was 3.3%.
Lease costs were as follows:
| Twelve Months Ended | ||||
| December 31, 2019 | ||||
| (in thousands) |
||||
| Operating lease cost |
$ | 370 | ||
| Short-term lease cost |
23 | |||
| Variable lease cost |
— | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 393 | |||
|
|
|
|||
There were no sale and leaseback transactions, leverage leases or lease transactions with related parties during the twelve months ended December 31, 2019.
49
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 8. Continued
A maturity analysis of operating lease liabilities and reconciliation of the undiscounted cash flows to the total operating lease liability is as follows:
| December 31, 2019 | ||||
| Lease payments due: |
||||
| Within one year |
$ | 348 | ||
| After one year but within two years |
312 | |||
| After two years but within three years |
139 | |||
| After three year but within four years |
2 | |||
| After four years but within five years |
— | |||
| After five years |
— | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total undiscounted cash flows |
801 | |||
| Discount on cash flows |
(30 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Total lease liability |
$ | 771 | ||
|
|
|
|||
Note 9. Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
(in thousands)
Changes in the carrying amount of goodwill during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 were as follows:
| Total | ||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 |
$ | 3,150 | ||
| Addition to goodwill from Charter acquisition |
9,953 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance at December 31, 2019 |
$ | 13,103 | ||
|
|
|
|||
The additions to goodwill in 2019 from the Charter acquisition represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed in the relevant transaction. The Company is in the process of completing Charter’s final tax return, core processor conversion and analyzing potential unknown liabilities; as a result, the recorded balance of goodwill attributable to the Charter acquisition is subject to change in future periods.
The following table provides a summary of finite-lived intangible assets as of the dates presented:
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Core deposit intangible |
$ | 766 | $ | — | ||||
| Accumulated amortization |
(27 | ) | — | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total finite-lived intangible assets |
$ | 739 | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
50
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 9. Continued
Core deposit intangible amortization expense for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 was $27, $-0- and $-0-, respectively. The estimated amortization expense of finite-lived intangible assets for the five succeeding fiscal years is summarized as follows:
| Year ending December 31, |
Amount | |||
| 2020 |
$ | 109 | ||
| 2021 |
109 | |||
| 2022 |
109 | |||
| 2023 |
109 | |||
| 2024 |
109 | |||
| Thereafter |
194 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 739 | |||
|
|
|
|||
Note 10. Deposits
(in thousands)
The composition of deposits as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 is as follows:
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Non-interest bearing |
$ | 190,406 | $ | 170,030 | ||||
| NOW and money market accounts |
369,354 | 298,220 | ||||||
| Savings deposits |
83,065 | 76,736 | ||||||
| Time deposits, $250,000 or more |
74,098 | 65,407 | ||||||
| Other time deposits |
182,073 | 145,829 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 898,996 | $ | 756,222 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The scheduled maturities of time deposits at December 31, 2019 are as follows:
| Year Ending December 31, |
Amount | |||
| 2020 |
$ | 137,630 | ||
| 2021 |
59,641 | |||
| 2022 |
27,709 | |||
| 2023 |
15,912 | |||
| 2024 |
15,279 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 256,171 | |||
|
|
|
|||
51
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 11. Federal Home Loan Bank Advances
(in thousands)
Pursuant to collateral agreements with the FHLB, advances are collateralized by all of the Bank’s FHLB stock ($3,083 included in other assets at December 31, 2019) and qualifying first mortgages and other loans. As of December 31, 2019, the balance in qualifying first mortgages and other loans was $177,592.
There were no outstanding FHLB advances at December 31, 2019 or December 31, 2018.
52
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 12. Other Income and Other Expense
(in thousands)
The following is a detail of the major income classifications that are included in other income under non-interest income on the income statement for the year ended December 31:
| Other Income |
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
| BOLI Insurance |
$ | 471 | $ | 495 | $ | 528 | ||||||
| Mortgage Loan Origination Income |
320 | 363 | 340 | |||||||||
| Other Income |
1,224 | 290 | 447 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total Other Income |
$ | 2,015 | $ | 1,148 | $ | 1,315 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The following is a detail of the major expense classifications that comprise the other expense line item in the income statement for the years ended December 31:
| Other Operating Expense |
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||
| Advertising |
$ | 551 | $ | 640 | $ | 650 | ||||||
| Office Supplies |
973 | 975 | 1,009 | |||||||||
| Professional fees |
1,668 | 561 | 515 | |||||||||
| FDIC and State Assessment |
274 | 350 | 417 | |||||||||
| Telephone Expense |
501 | 520 | 530 | |||||||||
| Postage and Freight |
(49 | ) | 567 | 545 | ||||||||
| Loan Collection Expense |
286 | 288 | 472 | |||||||||
| Other Losses |
73 | 243 | 463 | |||||||||
| Debit Card/ATM expense |
551 | 471 | 413 | |||||||||
| Travel and Convention |
200 | 207 | 255 | |||||||||
| Other expenses |
2,402 | 2,582 | 2,801 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total Other Expense |
$ | 7,430 | $ | 7,404 | $ | 8,070 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
53
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 13. Income Taxes
(in thousands)
Income tax expense consists of the following:
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Current payable (benefit) |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
$ | 806 | $ | (181 | ) | $ | 258 | |||||
| State |
89 | 36 | (72 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 895 | (145 | ) | 186 | |||||||||
| Deferred tax expense |
459 | 973 | 3,885 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income tax expense |
$ | 1,354 | $ | 828 | $ | 4,071 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The differences between income taxes calculated at the federal statutory rate and income tax expense were as follows:
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Federal taxes based on statutory rate |
$ | 1,524 | $ | 1,575 | $ | 2,643 | ||||||
| State income taxes, net of federal benefit |
145 | 133 | (48 | ) | ||||||||
| Tax-exempt investment interest |
(309 | ) | (487 | ) | (1,074 | ) | ||||||
| Revaluation of net deferred tax assets as a result of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act |
— | — | 2,559 | |||||||||
| Other, net |
(6 | ) | (394 | ) | (9 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income tax expense |
$ | 1,354 | $ | 828 | $ | 4,071 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Tax Act”), enacted on December 22, 2017, among other things, permanently lowered the statutory federal corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%, effective for tax years including or beginning January 1, 2018. Under the guidance of ASC 740, “Income Taxes” (“ASC 740”), the Company revalued its net deferred tax assets on the date of enactment based on the reduction in the overall future tax benefit expected to be realized at the lower tax rate implemented by the new legislation. After reviewing the Company’s inventory of deferred tax assets and liabilities on the date of enactment and giving consideration to the future impact of the lower corporate tax rates and other provisions of the new legislation, the Company’s revaluation of its net deferred tax assets was $2,559, which was included in “Income tax expense” in the Consolidated Statements of Income for the year ended December 31, 2017.
54
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 13. Continued
At December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, net deferred tax assets consist of the following:
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets |
||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses |
$ | 937 | $ | 841 | ||||
| Deferred compensation liability |
2,488 | 2,419 | ||||||
| Net operating loss carryforward |
1,000 | — | ||||||
| Other real estate owned |
819 | 435 | ||||||
| Acquisition fair value adjustments |
130 | — | ||||||
| Unrealized loss on securities available-for-sale |
262 | 4,978 | ||||||
| Other |
6 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
5,642 | 8,673 | ||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities |
||||||||
| Premises and equipment |
1,603 | 1,856 | ||||||
| Core deposit intangible |
184 | — | ||||||
| Other |
171 | 183 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
1,958 | 2,039 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net deferred tax asset |
$ | 3,684 | $ | 6,634 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The Company has evaluated the need for a valuation allowance related to the above deferred tax assets and, based on the weight of the available evidence, has determined that it is more likely than not that all deferred tax assets will be realized.
As of December 31, 2019, the Company has no unrecognized tax benefits related to federal and state income tax matters. As of December 31, 2019, the Company has not accrued for interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions. It is the Company’s policy to recognize interest or penalties related to income tax matters in income tax expense.
The Company and the Bank file a consolidated United States federal income tax return. The Company is currently open to audit under the statute of limitations by the Internal Revenue Service for the years ended December 31, 2016 through 2018. The Company and Bank’s state income tax returns are open to audit under the statute of limitations for the years ended December 31, 2016 through 2018.
The Company acquired federal net operating losses as part of its Charter acquisition, with varying expiration periods. The federal net operating losses (“NOLs”) acquired were $4,848, including $2,060 created prior to 2018 and $2,788 created during 2019. As part of the Tax Act, the federal NOLs created by Charter during 2019 have an indefinite carryforward period. The federal NOLs created prior to 2018 begin to expire in 2028 and are expected to be fully utilized.
55
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 14. Summarized Financial Information of Citizens Holding Company
(in thousands)
Summarized financial information of Citizens Holding Company, excluding the Bank, at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, and for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, is as follows:
Balance Sheets
December 31, 2019 and 2018
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Assets |
||||||||
| Cash (1) |
$ | 1,736 | $ | 1,596 | ||||
| Investment in bank subsidiary (1) |
110,892 | 82,002 | ||||||
| Other assets (1) |
172 | 268 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total assets |
$ | 112,800 | $ | 83,866 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Liabilities |
||||||||
| Other liabilities |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
| Shareholders’ equity |
112,800 | 83,866 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity |
$ | 112,800 | $ | 83,866 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1) | Fully or partially eliminates in consolidation. |
56
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 14. Continued
Income Statements
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Interest income (1) |
$ | 2 | $ | 2 | $ | 2 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Other income |
||||||||||||
| Dividends from bank subsidiary (1) |
11,242 | 3,990 | 5,472 | |||||||||
| Equity in undistributed earnings (loss) of bank subsidiary (1) |
(4,965 | ) | 3,022 | (1,349 | ) | |||||||
| Other income |
— | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total other income |
6,277 | 7,012 | 4,123 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Other expense |
462 | 446 | 459 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income before income taxes |
5,817 | 6,568 | 3,666 | |||||||||
| Income tax benefit |
(85 | ) | (105 | ) | (38 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income |
$ | 5,902 | $ | 6,673 | $ | 3,704 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (1) | Eliminates in consolidation. |
57
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 14. Continued
Statements of Cash Flows
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities |
||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 5,902 | $ | 6,673 | $ | 3,704 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities |
||||||||||||
| Equity in undistributed loss (earnings) of the Bank |
4,965 | (3,022 | ) | 1,349 | ||||||||
| Stock compensation expense |
163 | 170 | 211 | |||||||||
| Increase in other assets |
97 | 84 | 266 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
11,127 | 3,905 | 5,530 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities |
||||||||||||
| Net cash paid in acquisition activities |
$ | (6,113 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(6,113 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities |
||||||||||||
| Dividends paid to shareholders |
$ | (4,874 | ) | $ | (4,706 | ) | $ | (4,697 | ) | |||
| Proceeds from stock options |
— | 27 | 93 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash used in financing activities |
(4,874 | ) | (4,679 | ) | (4,604 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash |
140 | (774 | ) | 926 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash, beginning of year |
1,596 | 2,370 | 1,444 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash, end of year |
$ | 1,736 | $ | 1,596 | $ | 2,370 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The Bank is required to obtain approval from state regulators before paying dividends.
58
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 15. Related Party Transactions
(in thousands)
The Company had, and may have in the future, banking transactions in the ordinary course of business with directors, significant shareholders, principal officers, their immediate families, and affiliated companies in which they are principal shareholders (commonly referred to as related parties). In management’s opinion, such loans are made on substantially the same terms, including interest rates and collateral, as those prevailing at the time for comparable transactions with unrelated parties, and do not involve more than the normal risk of collectability at the time of the transaction.
Activity in related party loans is detailed in tabular form in Note 5 of the notes to the Financial Statements.
Deposits from related parties at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 approximated $5,406 and $5,606, respectively.
Note 16. Off-Balance Sheet Financial Instruments, Commitments and Contingencies and Concentrations of Risks
(in thousands)
Commitments to Extend Credit
In the ordinary course of business, the Company makes various commitments and incurs certain contingent liabilities to fulfill the financing needs of its customers. These commitments and contingent liabilities include commitments to extend credit and issue standby letters of credit. They involve, to varying degrees, elements of credit risk in excess of the amount recognized in the balance sheets. The Company’s exposure to credit loss in the event of nonperformance by the other party to the financial instrument for commitments to extend credit and standby letters of credit is represented by the contractual amount of those instruments. At December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, commitments related to unused lines of credit were $94,009 and $58,835, respectively, and standby letters of credit were $2,436 and $2,517, respectively. The fair value of such commitments is not materially different than stated values. As some of these commitments are expected to expire without being drawn upon, the total commitment amount does not necessarily represent future cash requirements. The Company applies the same credit policies and standards as it does in the lending process when making these commitments. The collateral obtained is based upon the assessed credit worthiness of the borrower. Collateral held varies, but may include accounts receivable, crops, livestock, inventory, property and equipment, residential real estate and income-producing commercial properties.
59
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 16. Continued
Interest Rate Risk
The Company is principally engaged in providing short-term and medium-term installment, commercial and agricultural loans with interest rates that are fixed or fluctuate with the prime lending rate. These assets are primarily funded through short-term demand deposits and long-term certificates of deposit with variable and fixed rates. Accordingly, the Company is exposed to interest rate risk because in changing interest rate environments interest rate adjustments on assets and liabilities may not occur at the same time or in the same amount. The Company manages the overall rate sensitivity and mix of its asset and liability portfolio and attempts to minimize the effects that interest rate fluctuations will have on its net interest margin.
Legal Proceedings
We are a party to various legal proceedings such as claims and lawsuits arising in the course of our normal business activities. Although the ultimate outcome of all claims and lawsuits outstanding as of December 31, 2019 cannot be ascertained at this time, it is the opinion of management that these matters, when resolved, will not have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations or financial condition.
Concentration of Risk
The Company makes commercial, residential and consumer loans throughout the state of Mississippi. A substantial portion of the customers’ abilities to honor their contracts is dependent on their business and the agricultural economy in the state.
Although the Company’s loan portfolio is diversified, there is a relationship in this state and our operating regions between the agricultural economy and the economic performance of loans made to nonagricultural customers. The Company’s lending policies for agricultural and nonagricultural customers require loans to be well-collateralized and supported by cash flows. Credit losses from loans related to the agricultural economy are consistent with credit losses experienced in the portfolio as a whole. The concentration of credit in the regional agricultural economy is taken into consideration by management in determining the allowance for loan losses. See Note 5 for a summary of loans by type.
60
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 17. Benefit Plans
(in thousands)
The Company provides its employees with a profit sharing and savings plan, which allows employees to direct a percentage of their compensation into a tax deferred retirement account, subject to statutory limitations. To encourage participation, the Company provides a 50 percent matching contribution for up to a maximum of 3 percent of each participant’s compensation, plus discretionary non-matching contributions. Employees are eligible after one year of service. For 2019, 2018 and 2017, the Company’s contributions were $605, $590 and $538, respectively.
In connection with the acquisition of Charter, the Company assumed the Charter Bank 401(k) Plan. The plan was terminated by Charter immediately prior to the acquisition where the Charter employees had the choice to rollover their account balance into the Company’s plan, rollover their account balance into another account or take a distribution. The final distribution of account balances has occurred. There was no impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2019 associated with the plan.
Deferred Compensation Plans
The Company provides a deferred compensation plan covering its directors. Participants in the deferred compensation plan can defer a portion of their compensation for payment after attaining age 70. Life insurance contracts have been purchased which may be used to fund payments under the plan. Expenses related to this plan were $173, $194 and $190 for the plan years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
The Company has also entered into deferred compensation arrangements with certain officers that provide for payments to such officers or their survivors after retirement. Life insurance policies have been purchased that may be used to fund all or a portion of the payments under these arrangements. The obligations of the Company under both the directors and officers deferred compensation arrangements are expensed on a systematic basis over the remaining expected service period of the individual directors and officers. Expenses related to this plan were $586, $535 and $522 for the plan years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
61
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 18. Regulatory Matters
(in thousands)
The Company (on a consolidated basis) and the Bank are subject to various regulatory capital requirements administered by federal banking agencies. Failure to meet the minimum regulatory capital requirements can initiate certain mandatory and possible additional discretionary actions by regulators that, if undertaken, could have a direct material adverse effect on the Company.
Under the regulatory capital adequacy guidelines and the regulatory framework for prompt corrective action, the Company must meet specific capital guidelines involving quantitative measures of the Company’s assets, liabilities and certain off-balance sheet items as calculated under regulatory accounting practices. The Company’s capital amounts and classification under the prompt corrective action guidelines are also subject to qualitative judgments by the regulators about components, risk weightings, and other factors. Quantitative measures established by regulation to ensure capital adequacy require the Company to maintain minimum amounts and ratios of total capital and Tier I capital to risk-weighted assets (as defined in the regulations) and Tier I capital to average assets (as defined in the regulations). Management believes, as of December 31, 2019, that the Company and the Bank meet all capital adequacy requirements to which they are subject.
The FRB, FDIC and other federal banking agencies have established risk-based capital adequacy guidelines. These guidelines are intended to provide a measure of a bank’s capital adequacy that reflects the degree of risk associated with a bank’s operations.
A banking organization’s risk-based capital ratios are obtained by dividing its qualifying capital by its total risk-adjusted assets and off-balance sheet items. Since December 31, 1992, the federal banking agencies have required a minimum ratio of qualifying total capital to risk-adjusted assets and off-balance sheet items of 8%, and a minimum ratio of Tier 1 capital to risk-adjusted assets and off-balance sheet items of 4%.
The Dodd-Frank Act requires the FRB, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (“OCC”) and the FDIC to adopt regulations imposing a continuing “floor” on the risk based capital requirements. In December 2010, the Basel Committee released a final framework for a strengthened set of capital requirements, known as “Basel III”. In July 2013, each of the U.S. federal banking agencies adopted final rules relevant to us: (1) the Basel III regulatory capital reforms; and (2) the “standardized approach of Basel II for non-core banks and bank holding companies, such as the Bank and the Company. The capital framework under Basel III will replace the existing regulatory capital rules for all banks, savings associations and U.S. bank holding companies with greater than $500 million in total assets, and all savings and loan holding companies.
62
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 18. Continued
Beginning January 1, 2015, the Bank began to comply with the Basel III rules, which became effective on January 1, 2019. Among other things, the Basel III rules impact regulatory capital ratios of banking organizations in the following manner:
| • | Create a new requirement to maintain a ratio of common equity Tier 1 capital to total risk-weighted assets of not less than 4.5%; |
| • | Increase the minimum leverage ratio to 4% for all banking organizations (currently 3% for certain banking organizations); |
| • | Increase the minimum Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio from 4% to 6%; and |
| • | Maintain the minimum total risk-based capital ratio at 8%. |
In addition, the Basel III rules will subject a banking organization to certain limitations on capital distributions and discretionary bonus payments to executive officers if the organization did not maintain a capital conservation buffer of common equity Tier 1 capital in an amount greater than 2.5% of its total risk-weighted assets. The capital conservation buffer increases the minimum common equity Tier 1 capital ratio to 7%, the minimum Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio to 8.5% and the minimum total risk-based capital ratio to 10.5% for banking organizations seeking to avoid the limitations on capital distributions and discretionary bonus payments to executive officers.
The Basel III rules also changed the capital categories for insured depository institutions for purposes of prompt corrective action. Under the rules, to be well capitalized, an insured depository institution must maintain a minimum common equity Tier 1 capital ratio of at least 6.5%, a Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio of at least 8%, a total risk-based capital ratio of at least 10.0%, and a leverage capital ratio of at least 5%. In addition, the Basel III rules established more conservative standards for including an instrument in regulatory capital and imposed certain deductions from and adjustments to the measure of common equity Tier 1 capital.
63
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 18. Continued
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the most recent regulatory notification categorized the Bank as well capitalized. There have been no conditions or events that would cause changes to the capital structure of the Company since this notification. To continue to be categorized as well capitalized under the regulatory framework for prompt corrective action, the Company would have to maintain minimum total risk-based, Tier I risk-based, and Tier I leverage ratios as disclosed below, in comparison with actual capital amounts and ratios:
| Minimum Capital | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Capital | Requirement to be | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requirement to be | Adequately | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actual | Well Capitalized | Capitalized | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | |||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Citizens Holding Company |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 leverage ratio |
$ | 98,733 | 8.33 | % | $ | 59,270 | 5.00 | % | $ | 47,416 | 4.00 | % | ||||||||||||
| Common Equity tier 1 capital ratio |
98,733 | 8.33 | % | 77,051 | 6.50 | % | 53,343 | 4.50 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio |
98,733 | 13.86 | % | 56,972 | 8.00 | % | 42,729 | 6.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total risk-based capital ratio |
102,488 | 14.39 | % | 71,215 | 10.00 | % | 56,972 | 8.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
| The Citizens Bank of Philadelphia |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 leverage ratio |
$ | 96,824 | 8.18 | % | $ | 59,206 | 5.00 | % | $ | 47,365 | 4.00 | % | ||||||||||||
| Common Equity tier 1 capital ratio |
96,824 | 8.18 | % | 76,968 | 6.50 | % | 53,285 | 4.50 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio |
96,824 | 13.60 | % | 56,958 | 8.00 | % | 42,719 | 6.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total risk-based capital ratio |
100,579 | 14.13 | % | 71,198 | 10.00 | % | 56,958 | 8.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Citizens Holding Company |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 leverage ratio |
$ | 95,691 | 9.93 | % | $ | 48,191 | 5.00 | % | $ | 38,553 | 4.00 | % | ||||||||||||
| Common Equity tier 1 capital ratio |
95,691 | 9.93 | % | 62,648 | 6.50 | % | 43,372 | 4.50 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio |
95,691 | 17.41 | % | 43,966 | 8.00 | % | 32,974 | 6.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total risk-based capital ratio |
99,063 | 18.03 | % | 54,957 | 10.00 | % | 43,966 | 8.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
| The Citizens Bank of Philadelphia |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 leverage ratio |
$ | 93,827 | 9.74 | % | $ | 48,178 | 5.00 | % | $ | 38,542 | 4.00 | % | ||||||||||||
| Common Equity tier 1 capital ratio |
93,827 | 9.74 | % | 62,631 | 6.50 | % | 43,360 | 4.50 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio |
93,827 | 17.08 | % | 43,944 | 8.00 | % | 32,958 | 6.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total risk-based capital ratio |
97,199 | 17.69 | % | 54,930 | 10.00 | % | 43,944 | 8.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
64
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 19. Fair Values of Financial Instruments
(in thousands)
Under the authoritative guidance on fair value measurements, fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. In determining fair value, the Company uses various methods including market, income and cost approaches. Based on these approaches, the Company often utilizes certain assumptions about risk and or the risks inherent in the inputs to the valuation technique. These inputs can be readily observable, market corroborated, or generally unobservable inputs. The Company utilizes valuation techniques that maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. Based on the observability of the inputs used in the valuation techniques, the Company is required to provide the following information according to the fair value hierarchy. The fair value hierarchy ranks the quality and reliability of the information used to determine fair values. Financial assets and liabilities carried at fair value will be classified and disclosed in one of the three following categories:
| Level 1 |
Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities; | |
| Level 2 |
Quoted prices in active markets for similar assets and liabilities and inputs that are observable for the asset or liability; or | |
| Level 3 |
Unobservable inputs, such as discounted cash flow models or valuations. | |
The determination of where assets and liabilities fall within this hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. The Company used the following methods and assumptions to estimate the fair value of financial instruments that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis:
Investment Securities
The fair values of debt securities available for sale are determined by third party matrix pricing, which is a mathematical technique widely used in the industry to value debt securities without relying exclusively on quoted prices for the specific securities but rather by relying on the securities’ relationship to other benchmark quoted securities (Level 2 inputs).
65
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 19. Continued
The following table presents investment securities that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2019:
| Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets |
Significant Other Observable Inputs |
Significant Unobservable Inputs |
||||||||||||||
| (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | Totals | |||||||||||||
| Securities available for sale |
||||||||||||||||
| Obligations of U.S. |
||||||||||||||||
| Government agencies |
$ | — | $ | 97,111 | $ | — | $ | 97,111 | ||||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities |
— | 306,900 | — | 306,900 | ||||||||||||
| State, County, Municipals |
— | 60,372 | — | 60,372 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| $ | — | $ | 464,383 | $ | — | $ | 464,383 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
The following table presents investment securities that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2018:
| Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets |
Significant Other Observable Inputs |
Significant Unobservable Inputs |
||||||||||||||
| (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | Totals | |||||||||||||
| Securities available for sale |
||||||||||||||||
| Obligations of U.S. |
||||||||||||||||
| Government agencies |
$ | — | $ | 95,978 | $ | — | $ | 95,978 | ||||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities |
— | $ | 247,374 | — | 247,374 | |||||||||||
| State, County, Municipals |
— | $ | 101,394 | — | 101,394 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| $ | — | $ | 444,746 | $ | — | $ | 444,746 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
66
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 19. Continued
Impaired Loans
Loans considered impaired are reserved for at the time the loan is identified as impaired taking into account the fair value of the collateral less estimated selling costs. Collateral may be real estate and/or business assets including but not limited to, equipment, inventory and accounts receivable. The fair value of real estate is determined based on appraisals by qualified licensed appraisers. The fair value of the business assets is generally based on amounts reported on the business’s financial statements. Appraised and reported values may be adjusted based on management’s historical knowledge, changes in market conditions from the time of valuation and management knowledge of the client and the client’s business. Since not all valuation inputs are observable, these nonrecurring fair value determinations are classified Level 3. The unobservable inputs may vary depending on the individual assets with the fair value of real estate based on appraised value being the predominant approach. The Company reviews the certified appraisals for appropriateness and adjusts the value downward to consider selling, closing and liquidation costs, which typically approximates 25% of the appraised value. Impaired loans are reviewed and evaluated on at least a quarterly basis for additional impairment and adjusted accordingly, based on the same factors previously identified.
Other real estate owned
OREO is primarily comprised of real estate acquired in partial or full satisfaction of loans. OREO is recorded at its estimated fair value less estimated selling and closing costs at the date of transfer, with any excess of the related loan balance over the fair value less expected selling costs charged to the ALLL. Subsequent changes in fair value are reported as adjustments to the carrying amount and are recorded against earnings. The Company outsources the valuation of OREO with material balances to third party appraisers. The Company reviews the third-party appraisal for appropriateness and adjusts the value downward to consider selling and closing costs, which typically approximate 25% of the appraised value.
67
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 19. Continued
The following table presents assets measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis during December 31, 2019 and 2018 and were still held at those respective dates:
| Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets |
Significant Other Observable Inputs |
Significant Unobservable Inputs |
||||||||||||||
| (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | Totals | |||||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 |
||||||||||||||||
| Impaired loans |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 4,576 | $ | 4,576 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| $ | — | $ | — | $ | 4,576 | $ | 4,576 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| December 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||||||
| Impaired loans |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 3,365 | $ | 3,365 | ||||||||
| Other real estate owned |
— | — | 189 | 189 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| $ | — | $ | — | $ | 3,554 | $ | 3,554 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Impaired loans with a carrying value of $5,003 and $3,365 had an allocated allowance for loan losses of $427 and $401 at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. The allocated allowance is based on the carrying value of the impaired loan and the fair value of the underlying collateral less estimated costs to sell.
After monitoring the carrying amounts for subsequent declines or impairment after foreclosure, management determined that no fair value adjustments to OREO was necessary or recorded during the year ended December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively.
68
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 19. Continued
The following represents the carrying value and estimated fair value of the Company’s financial instruments at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018:
| Carrying Value | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets |
Significant Other Observable Inputs |
Significant Unobservable Inputs |
Total Fair Value | ||||||||||||||||
| 2019 |
(Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | |||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
$ | 15,937 | $ | 15,937 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 15,937 | ||||||||||
| Interest bearing deposits with banks |
58,557 | 58,557 | — | — | 58,557 | |||||||||||||||
| Federal funds sold |
1,600 | 1,600 | — | — | 1,600 | |||||||||||||||
| Securities available-for-sale |
464,383 | — | 464,383 | — | 464,383 | |||||||||||||||
| Net loans |
573,312 | — | — | 569,640 | 569,640 | |||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits |
$ | 898,996 | $ | 642,825 | $ | 258,100 | $ | — | $ | 900,925 | ||||||||||
| Securities Sold under |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Agreement to Repurchase |
170,410 | 170,410 | — | — | 170,410 | |||||||||||||||
| Carrying Value | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets |
Significant Other Observable Inputs |
Significant Unobservable Inputs |
Total Fair Value | ||||||||||||||||
| 2018 |
(Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | |||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
$ | 12,592 | $ | 12,592 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 12,592 | ||||||||||
| Interest bearing deposits with banks |
8,080 | 8,080 | — | — | 8,080 | |||||||||||||||
| Securities available-for-sale |
444,746 | — | 444,746 | — | 444,746 | |||||||||||||||
| Net loans |
425,905 | — | — | 420,992 | 420,992 | |||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits |
$ | 756,222 | $ | 544,986 | $ | 210,477 | $ | — | $ | 755,463 | ||||||||||
| Securities Sold under |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Agreement to Repurchase |
107,965 | 107,965 | — | — | 107,965 | |||||||||||||||
69
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 20. Stock Based Compensation
(in thousands, except share data)
The Company has a directors’ stock compensation plan and had an employees’ long-term incentive plan. Under the directors’ plan, the Company may grant options for up to 210,000 shares of common stock. The price of each option is equal to the market price determined as of the option grant date. Options granted are exercisable after six months and expire after 10 years. The employee plan expired on April 13, 2009, no options have been granted since this date and all previously granted options either expired or were exercised as of December 31, 2019. The options previously granted under the employee plan expire 10 years from the grant date. The exercise price is equal to the market price of the Company’s stock on the date of grant.
The fair value of each option granted is estimated on the date of the grant using the Black-Sholes option-pricing model. No options were granted in 2019 or 2018, therefore no calculations were required in 2019 or 2018 to determine fair values.
The Company has adopted the 2013 Incentive Compensation Plan (the “2013 Plan”), which the Company has used for all equity grants after the adoption and approval of the 2013 Plan.
During 2019, the Company’s directors received restricted stock grants totaling 7,500 shares of common stock at a then market value of $21.53 per share and in 2018 received 7,500 shares of common stock at a then market value of $22.05 per share. These grants vest over a one-year period during which time the recipients have rights to vote the shares and to receive dividends. The grant date fair value of these shares granted in 2019 was $161 and will be recognized over the one-year restriction period at a cost of $13 per month less deferred taxes of $3 per month. The grant date fair value of the shares granted in 2018 was $165 and was recognized over the one-year restriction period at a cost of $14 per month less deferred taxes of $3 per month.
During 2015, 7,500 shares of restricted stock was granted to the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) that would vest according to a stock performance schedule over the next five years. The stock performance for the Company met the goal for 2016 and the CEO became vested in 20%, or 1,500 shares of the restricted stock at an expense of $32. Again in 2017, the Company met 20% of its goal and the CEO became vested in an additional 1,500 shares of the restricted stock at an expense of $37. The stock performance for the Company did not meet the goal in 2019 or 2018 and no corresponding expense was recorded.
During 2019 and 2018, the Company recorded expense of $163 and $170 and recorded deferred taxes in the amounts of $41 and $42, respectively, related to all of the restricted shares.
At December 31, 2019, there were 12,000 shares non-vested with $54 in unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to the 2013 Plan.
70
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 20. Continued
Following is a summary of the status of the stock options remaining under the plans for the years ending December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017:
| Directors’ Plan | ||||||||
| Number of Shares |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
|||||||
| Outstanding at January 1, 2017 |
78,000 | $ | 21.08 | |||||
| Granted |
— | — | ||||||
| Exercised |
(6,000 | ) | 20.94 | |||||
| Expired |
(9,000 | ) | 22.00 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2017 |
63,000 | $ | 20.96 | |||||
| Granted |
— | — | ||||||
| Exercised |
(6,000 | ) | 18.00 | |||||
| Expired |
(4,500 | ) | 18.00 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2018 |
52,500 | $ | 21.55 | |||||
| Granted |
— | — | ||||||
| Exercised |
— | — | ||||||
| Expired |
(12,000 | ) | 21.75 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2019 |
40,500 | $ | 21.49 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Options exercisable at: |
||||||||
| December 31, 2019 |
40,500 | $ | 21.49 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
71
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 20. Continued
The following table presents the outstanding stock options granted in relation to the option price and the weighted average maturity.
| Options | Weighted | Weighted Average | ||||||||
| Range of Exercise Prices |
Outstanding | Average Price | Life Remaining | |||||||
| $15.01 to $20.00 |
13,500 | 18.76 | 2 years, 4 months | |||||||
| $20.01 to $22.50 |
13,500 | 20.02 | 1 year, 4 months | |||||||
| $22.51 and above |
13,500 | 25.72 | 4 months | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Total |
40,500 | $ | 21.49 | 1 years, 4 months | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
The intrinsic value of options outstanding under the Directors’ Plan at December 31, 2019 was $52. Additionally, the total intrinsic value of options exercised during 2019 and 2018 was $-0- and $24, respectively.
There were no options granted during 2019 under the 2013 Plan.
72
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
as of December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
(in thousands)
OVERVIEW
The following information discusses the financial condition and results of operations of Citizens Holding Company (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017. In this discussion, all references to the activities, operations or financial performance of the Company reflect the Company’s activities, operations and financial performance through its wholly-owned subsidiary, The Citizens Bank of Philadelphia, Mississippi (the “Bank”), unless otherwise specifically noted. The Company’s financial statements and accompanying notes should be read in conjunction with this Management’s Discussion and Analysis.
Over the past three years, the Company has experienced growth in total loans as management has capitalized on opportunities for organic growth within the Company’s market area. Total loans increased over the three-year period by $170,462 or 41.9%. Of the loan growth, $104,127 was purchased in the acquisition of Charter and $66,335, or 16.3%, was organic growth. In the three-year period, net income increased by $2,198 or 59.3%. A large part of this net income growth was due to the tax consequences recorded in the year ended 2017 related to the Tax Act, discussed further in Note 12. Income Taxes. Excluding the impact of the Tax Act of $2,559 in 2017, net income has decreased $361 or 9.7%. As competition for deposits has increased, the cost of deposits has also increased. The yield on earning assets hasn’t increased at the same rate as interest bearing liabilities. Management continues to focus on growing non-interest income while containing costs to the extent possible to help offset shrinking margins. Due to the loan growth over the period, management has increased the provision for loan losses to help manage risks. All of these factors are driving the net income results and continue to be a focus of management moving forward.
During 2019 as compared to 2018, the Company’s total assets increased by $236,804, or 24.7%, loans increased by $147,753, or 34.4%, and total deposits increased by $142,774, or 18.9%. Loans increased in 2019 due to an increased focus on loan production in the Company’s service area coupled with the acquisition of Charter. Certificates of deposit ended 2019 at $256,171, or 21.3% higher than 2018. Demand, NOW, savings and money market accounts increased $97,839, or 12.9% from December 31, 2018 to $642,825 at December 31, 2019.
During 2018 as compared to 2017, the Company’s total assets decreased by $34,465, or 3.5%, loans increased by $23,515, or 5.8%, and total deposits increased by $35,536, or 4.9%. Loans increased in 2018 due to an increased focus on loan production in the Company’s service area, including the loan production office in North Mississippi. Certificates of deposit ended 2018 at $211,236, or 19.0% higher than 2017. Demand, NOW, savings and money market accounts increased $1,863, or 0.3% from December 31, 2017 to $544,986 at December 31, 2018.
In 2019, the Company’s net income after taxes decreased to $5,902, a decrease of $771 from 2018. This decrease was primarily due to a decrease in the Company’s net interest margin caused by an increase in cost funds in excess of the increase in yields on earning assets. An increase in non-interest income coupled with the decrease in non-interest expense helped offset the decrease in net interest income. Net income for 2019 produced, on a fully diluted basis, earnings per share of $1.17 compared to $1.36 for 2018.
73
In 2018, the Company’s net income after taxes increased to $6,673, an increase of $2,930 from 2017. The bulk of this increase was from the Tax Act of 2017 that was signed into law on December 22, 2017 that negatively impacted 2017 earnings. This resulted in an increase in the income tax expense related to this in the amount of $2,559 in 2017. Net interest income after the provision for loan losses decreased in 2018 primarily due to an increase in interest expense on interest bearing liabilities and an increase in the provision for loan losses. An increase in non-interest income coupled with the decrease in non-interest expense helped offset the decrease in net interest income. Net income for 2018 produced, on a fully diluted basis, earnings per share of $1.36 compared to $0.76, after the deferred tax adjustment, for 2017.
The Company’s return on average assets (“ROA”) was 0.51% in 2019, compared to 0.69% in 2018 and 0.37% in 2017. The Company’s return on average equity (“ROE”) was 6.13% in 2019, 7.95% in 2018 and 4.10% in 2017. During these periods, leverage capital ratios (the ratio of equity to average total assets) increased from 9.17% in 2017 to 9.74% in 2018 and decreased to 8.18% in 2019. The ROE in 2019, 2018 and 2017 is a function of the level of net income and equity balances during those years. The changes in ROA were also a result of the Company’s net income in those years and also affected by the increase in total assets during these time periods. The Company set the annual dividend payout rate to approximately 82.05% of 2019 earnings per share, as compared to 70.59% in 2018 and 126.32% in 2017. The leverage capital ratio of 8.18% in 2019 remains above the regulatory requirement of 5% to be considered “well capitalized” under applicable Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (the “FDIC”) guidelines for the Bank.
The Company’s net interest income, non-interest income and income from continuing operations are not directly affected by inflation and changing prices although these factors could influence our customers’ ability to repay loans or cause them to withdraw deposits. The impact of a slowdown in loan repayments could be felt in both liquidity and income. It could affect liquidity by reducing the amount of cash available for new loans and income by increasing the amount of the provision for loan loss expense due to loans that are charged off.
Liquidity is discussed in more detail beginning on page 94 of this report under the heading, Liquidity and Rate Sensitivity. The Company did not have any commitments at December 31, 2019 that would require a material expenditure of capital resources.
The Company is not aware of any developments that would have material impact on its revenues or net income. Interest rate movements are currently projected to be stable for 2020 but it is difficult to know the frequency and size of interest rate movements, if any. A measured increase in interest rates could have the effect of increasing revenues and net income.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
74
Allowance for Loan Losses
The accounting policy most important to the presentation of the Company’s financial statements relates to the allowance for loan loss and the related provision for loan losses. The allowance for loan losses is available to absorb probable credit losses inherent in the entire loan portfolio. The appropriate level of the allowance is based on a monthly analysis of the loan portfolio and represents an amount that management deems adequate to provide for inherent losses, including collective impairment as recognized under ASC Subtopic 450-20, Loss Contingencies. The collective impairment is calculated based on loans grouped by similar risk characteristics. Another component of the allowance is losses on loans assessed as impaired under ASC Subtopic 310-10, Loan Impairments. The balance of these loans determined to be impaired under ASC Subtopic 310-10 and their related allowance is included in management’s estimation and analysis of the allowance for loan losses. For a discussion of other considerations in establishing the allowance for loan losses and the Company’s and the Bank’s loan policies and procedures for addressing credit risk, please refer to the disclosures in this Item under the heading “Provision for Loan Losses and Asset Quality.”
Loans purchased in acquisitions or mergers with evidence of credit deterioration since origination are accounted for under ASC 310-30, “Loans and Debt Securities Acquired with Deteriorated Credit Quality” (“ASC 310-30”). ASC 310-30 prohibits the carryover of an allowance for loan losses for loans purchased in which the acquirer concludes that it will not collect the contractual amount. As a result, these loans are carried at values which represent management’s estimate of the future cash flows of these loans. Increases in expected cash flow to be collected from the contractual cash flows are required to be recognized as an adjustment of the loan’s yield over its remaining life, while decreases in expected cash flows are required to be recognized as an impairment. A more detailed discussion of loans accounted for under ASC 310-30, which were acquired in connection with our mergers, including our acquisitions of Charter, is set forth below under the heading “Provision for Loan Losses and Asset Quality” and in Note 6, “Purchased Loans” in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8, Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
Other Than Temporary Impairment
The Company currently classifies a portion of its debt securities as AFS as they might be sold before maturity. Securities available for sale are carried at fair value, with unrealized holding gains and losses reported in other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax. Interest income includes amortization of purchase premium or discount. Premiums and discounts on securities are amortized on the level-yield method without anticipating prepayments, except for mortgage-backed securities where prepayments are anticipated. Gains and losses on sales are recorded on the trade date and determined using the specific identification method.
75
Management evaluates securities for other-than-temporary impairment (“OTTI”) on at least a quarterly basis, and more frequently when economic or market conditions warrant such an evaluation. For securities in an unrealized loss position, management considers the extent and duration of the unrealized loss, and the financial condition and near-term prospects of the issuer. Management also assesses whether it intends to sell, or it is more likely than not that it will be required to sell, a security in an unrealized loss position before recovery of its amortized cost basis. If either of the criteria regarding intent or requirement to sell is met, the entire difference between amortized cost and fair value is recognized as impairment through earnings. For debt securities that do not meet the aforementioned criteria, the amount of impairment is split into two components as follows: 1) OTTI related to credit loss, which must be recognized in the income statement; and 2) OTTI related to other factors, which is recognized in other comprehensive income. The credit loss is defined as the difference between the present value of the cash flows expected to be collected and the amortized cost basis.
Other Real Estate
Real estate acquired through foreclosure on a loan or by surrender of the real estate in lieu of foreclosure is called “OREO”. OREO is initially recorded at the fair value of the property less estimated costs to sell, which establishes a new cost basis. OREO is subsequently accounted for at the lower of cost or fair value of the property less estimated costs. If fair value declines subsequent to foreclosure, a valuation allowance is recorded through noninterest expense. Fair value is commonly based on recent real estate appraisals. These appraisals may utilize a single valuation approach or a combination of approaches including comparable sales and the income approach. Valuation adjustments are routinely made in the appraisal process by the independent appraisers to adjust for differences between the comparable sales and income data available. Valuation adjustments are also required when the listing price to sell an OREO has had to be reduced below the current carrying value. If there is a decrease in the fair value of the property from the last valuation, the decrease in value is charged to noninterest expense. All income produced from, changes in fair values in, and gains and losses on OREOs is also included in noninterest expense. During the time the property is held, all related operating and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred.
Business Combinations, Accounting for Purchased Loans
The Company accounts for its acquisitions under ASC 805, “Business Combinations,” which requires the use of the acquisition method of accounting. All identifiable assets acquired, including loans, and liabilities assumed are recorded at fair value and recognized separately from goodwill. For a purchased loan, no allowance for loan losses is recorded on the acquisition date because the fair value measurements incorporate assumptions regarding credit risk. This applies even to a purchased loan with evidence of credit deterioration since origination pursuant to ASC 310-30, “Loans and Debt Securities Acquired with Deteriorated Credit Quality” (“ASC 310- 30”). Generally speaking, rather than carry over an allowance for loan losses, as part of the acquisition we establish a “Day 1 Fair Value” of a purchased loan or pools of purchased loans sharing common risk characteristics, which equals the outstanding balance of a purchased loan or 77 pool on the acquisition date less any credit and/or yield discount applied against the purchased loan or pool of loans. In other words, these loans or pools of loans are carried at values which represent our estimate of their future cash flows. After the acquisition date, a purchased loan or pool of loans will either meet or exceed the performance expectations established in determining the Day 1 Fair Values or deteriorate from such expected performance. If the cash flows expected to be collected on a purchased loan or pool of loans decreases from expectations established in determining the Day 1 Fair Values or since our most recent review of such portfolio’s performance, then the decrease is recognized as an impairment, and the Company provides for such loan or pool in the provision for loan losses in its consolidated statement of income; ultimately, the Company may partially or fully charge-off the carrying value thereof. If performance expectations are exceeded such that we increase our expectations of cash flows to be collected on the loan or pool, then the Company reverses any previous provision for such loan or pool and, if it continues to exceed expectations subsequent to the reversal of any previously-established provision, then we adjust the amount of accretable yield recognized on a prospective basis over the loan’s or pool’s remaining life, which has a positive impact on interest income.
Additional detail about our loans acquired in connection with our mergers, including our acquisition of Charter, is set forth below under the heading “Risk Management - Allowance for Loan Losses” and in Note 6, “Purchased Loans” in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8, Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, in this report.
Intangible Assets
Goodwill resulting from business combinations represents the excess of the purchase price over the estimated fair value of the net assets acquired. Goodwill and intangible assets acquired in a business combination and determined to have an indefinite useful life are not amortized, but instead reviewed for impairment when there is evidence to suggest that the estimated fair value of the net assets is lower than the carrying value, or at a minimum of once a year. Intangible assets with definite useful lives are amortized over their estimated useful lives to their estimated residual values. Goodwill was the only intangible asset with an indefinite life on the Company’s balance sheet. Other intangible assets consisted of core deposit intangibles arising from the Company’s acquisition of Charter. These assets are initially measured at fair value and then are amortized on a straight-line method over their estimated useful lives, which were determined to be 7 years.
76
Stock Based Compensation
The Company recognizes stock compensation expenses in accordance with ASC 718, “Compensation—Stock Compensation” (“ASC 718”). The Company sponsors stock plans which most commonly include restricted stock and stock options. The Company accounts for stock based compensation under the fair value recognition provisions whereby compensation cost is measure based on the fair value of the award at the grant date and is recognized in the consolidated financial statements on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period. The fair value of restructured stock is determined based on the closing price of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant. The fair value of stock options is estimated at the date of grant using a Black-Scholes option pricing model. For more information on the Company’s stock options and the assumptions used to calculate the expense of such options, please refer to Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” and Note 20, “Stock Based Compensation” to the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report.
Income Taxes
The Company uses the asset and liability method, which recognizes the future tax consequences attributable to an event or a liability or asset that has been recognized in the consolidated financial statements. Due to tax regulations, several items of income and expense are recognized in different periods for tax return purposes than for financial reporting purposes. These items represent “temporary differences.” Deferred tax assets and liabilities are the expected future tax amounts for the temporary differences between carrying amounts and tax bases of assets and liabilities, computed using enacted tax rates. Deferred tax assets represent future deductions in the Company’s income tax return, while deferred tax liabilities represent future payments to tax authorities. Income tax expense is the total of the current year income tax due or refundable and the change in deferred tax assets and liabilities. A valuation allowance, if needed, reduces deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
A tax position is recognized as a benefit only if it is “more likely than not” that the tax position would be sustained in a tax examination, with a tax examination being presumed to occur. The amount recognized is the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than 50% likely of being realized on examination. For tax positions not meeting the “more likely than not” test, no tax benefit is recorded. The Company recognizes interest and/or penalties related to income tax matters in income tax expense.
Please refer to Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” to the Consolidated Financial Statements of the Company included in this Annual Report for a detailed discussion of other significant accounting policies affecting the Company.
77
DISCLOSURE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
In addition to historical information, this report contains statements that constitute forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, that are based on management’s beliefs, plans, expectations, assumptions and on information currently available to management. The words “may,” “should,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “plan,” “continue,” “believe,” “seek,” “estimate” and similar expressions used in this report that do not relate to historical facts are intended to identify forward-looking statements. These statements appear in a number of places in this report, including, but not limited to, statements found in Item 1, “Business,” and in Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” Citizens Holding Company (the “Company”) notes that a variety of factors could cause its actual results or experience to differ materially from the anticipated results or other expectations described or implied by such forward-looking statements. The risks and uncertainties that may affect the operation, performance, development and results of the business of the Company and the Company’s wholly-owned subsidiary, The Citizens Bank of Philadelphia, Mississippi (the “Bank”), include, but are not limited to, the following:
| • | expectations about the movement of interest rates, including actions that may be taken by the Federal Reserve Board in response to changing economic conditions; |
| • | adverse changes in asset quality and loan demand, the potential insufficiency of the allowance for loan losses and our ability to foreclose on delinquent mortgages; |
| • | the risk of adverse changes in business conditions in the banking industry generally and in the specific markets in which the Company operates; |
| • | extensive regulation, changes in the legislative and regulatory environment that negatively impact the Company and the Bank through increased operating expenses and the potential for regulatory enforcement actions, claims or litigation; |
| • | increased competition from other financial institutions and the risk of failure to achieve our business strategies; |
| • | events affecting our business operations, including the effectiveness of our risk management framework, the accuracy of our estimates, our reliance on third party vendors, the risk of security breaches and potential fraud, and the impact of technological advances; |
| • | our ability to maintain sufficient capital and to raise additional capital when needed; |
| • | our ability to maintain adequate liquidity to conduct business and meet our obligations; |
| • | events affecting our ability to compete effectively and achieve our strategies, such as the risk of failure to achieve the revenue increases expected to result from our acquisitions, branch additions and in new product and service offerings, our ability to control expenses and our ability to attract and retain skilled people; |
| • | events that adversely affect our reputation, and the resulting potential adverse impact on our business operations; |
| • | risks arising from owning our common stock, such as the volatility and trading volume, our ability to pay dividends, the regulatory limitations on stock ownership, and provisions in our governing documents that may make it more difficult for another party to obtain control of us; and |
78
| • | other risks detailed from time-to-time in the Company’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
The Company undertakes no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements subsequent to the date on which they are made.
SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The following selected financial data has been taken from the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements and related notes included in this Annual Report and should be read in conjunction with such consolidated financial statements and related notes. Dollar references in all of the following tables are in thousands except for per share data.
The major components of the Company’s operating results for the past five years are summarized in Table 1—Five Year Financial Summary of Consolidated Statements and Related Statistics.
79
TABLE 1 - FIVE YEAR SUMMARY OF CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS AND RELATED
STATISTICS (in thousands, except per share and ratio amounts)
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Summary of Earnings |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Interest Income |
$ | 35,361 | $ | 31,359 | $ | 30,505 | $ | 30,169 | $ | 30,965 | ||||||||||
| Total Interest Expense |
9,722 | 4,459 | 3,343 | 3,098 | 3,077 | |||||||||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
573 | 334 | (543 | ) | (65 | ) | 556 | |||||||||||||
| Non-interest income |
9,748 | 8,599 | 8,296 | 7,692 | 8,327 | |||||||||||||||
| Non-interest expense |
27,558 | 27,665 | 28,227 | 26,480 | 25,591 | |||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
1,354 | 828 | 4,070 | 1,612 | 2,479 | |||||||||||||||
| Net Income |
5,902 | 6,673 | 3,704 | 6,737 | 7,589 | |||||||||||||||
| Per Share Data |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings-basic |
$ | 1.17 | $ | 1.36 | $ | 0.76 | $ | 1.38 | $ | 1.56 | ||||||||||
| Earnings-diluted |
1.17 | 1.36 | 0.76 | 1.38 | 1.56 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends |
0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.93 | |||||||||||||||
| Book value at year end |
20.22 | 17.09 | 18.07 | 17.42 | 17.73 | |||||||||||||||
| Selected Year End Actual Balances |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans, net of unearned income |
$ | 577,067 | $ | 429,277 | $ | 406,605 | $ | 394,051 | $ | 429,582 | ||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses |
3,755 | 3,372 | 3,019 | 3,903 | 6,474 | |||||||||||||||
| Investment Securities |
464,383 | 444,746 | 505,046 | 496,125 | 428,308 | |||||||||||||||
| Earning assets |
1,105,103 | 885,416 | 910,283 | 935,957 | 894,765 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
1,195,434 | 958,630 | 993,096 | 1,025,212 | 973,505 | |||||||||||||||
| Deposits |
898,996 | 756,222 | 720,685 | 760,152 | 753,405 | |||||||||||||||
| Long term borrowings |
6 | 15 | 20,000 | 20,000 | 20,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity |
112,800 | 83,866 | 88,451 | 85,059 | 86,425 | |||||||||||||||
| Selected Year End Average Balances |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans, net of unearned income |
$ | 561,483 | $ | 418,136 | $ | 395,217 | $ | 409,367 | $ | 412,161 | ||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses |
3,667 | 3,002 | 3,586 | 5,051 | 6,637 | |||||||||||||||
| Investment securities |
458,522 | 484,298 | 511,133 | 475,714 | 421,729 | |||||||||||||||
| Earning assets |
1,068,683 | 911,175 | 929,260 | 917,366 | 863,830 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
1,164,570 | 971,893 | 1,013,177 | 996,266 | 945,270 | |||||||||||||||
| Deposits |
929,598 | 760,992 | 762,983 | 766,264 | 725,116 | |||||||||||||||
| Long term borrowings |
10 | 19 | 20,000 | 20,042 | 20,056 | |||||||||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity |
96,295 | 83,907 | 90,230 | 91,766 | 84,250 | |||||||||||||||
80
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Selected Ratios |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Return on average assets |
0.51 | % | 0.69 | % | 0.37 | % | 0.68 | % | 0.80 | % | ||||||||||
| Return on average equity |
6.13 | % | 7.95 | % | 4.10 | % | 7.34 | % | 9.01 | % | ||||||||||
| Dividend payout ratio |
82.05 | % | 70.59 | % | 126.32 | % | 69.57 | % | 59.62 | % | ||||||||||
| Equity to year end assets |
9.44 | % | 8.75 | % | 8.91 | % | 8.30 | % | 8.88 | % | ||||||||||
| Total risk-based capital to risk-adjusted assets |
14.13 | % | 17.69 | % | 18.51 | % | 18.67 | % | 17.54 | % | ||||||||||
| Leverage capital ratio |
8.18 | % | 9.74 | % | 9.17 | % | 9.22 | % | 9.26 | % | ||||||||||
| Efficiency ratio |
77.88 | % | 75.99 | % | 76.35 | % | 71.49 | % | 68.69 | % | ||||||||||
NET INCOME
Net income for 2019 decreased by 11.6% to $5,902 or $1.17 per share-basic and -diluted, from $6,673 or $1.36 per share-basic and -diluted for 2018. The provision for loan losses for 2019 was $573 as compared to $334 in 2018. The increase in the loan loss provision for 2019 was mainly due to the increase in the balance of loans outstanding coupled with management’s assessment of inherent losses in the loan portfolio, including the impact caused by current local and national economic conditions. Non-interest income increased by $1,148, or 13.4%, and non-interest expense decreased by $106 or 0.4%, in 2019. Non-interest income for 2019 increased primarily due to the result of gains from security sales and other real estate coupled with death benefit proceeds from a bank-owned life insurance policy offset by a decrease in mortgage loan origination income. Non-interest expense decreased mainly due to a refund of excess prepaid postage and continued cost containment focus throughout the Company, partially offset by an increase in salaries and benefits related to the Charter acquisition.
Net income for 2018 increased by 0.9% to $6,673 or $1.36 per share-basic and -diluted, from $3,704 or $0.76 per share-basic and -diluted for 2017. The provision for loan losses for 2018 was a positive $334 as compared to negative $543 in 2017. The increase in the loan loss provision for 2018 was mainly due to the increase in the balance of loans outstanding coupled with management’s assessment of inherent losses in the loan portfolio, including the impact caused by current local and national economic conditions. Non-interest income increased by $303, or 3.7%, and non-interest expense decreased by $562 or 2.0%, in 2018. Non-interest income for 2018 increased primarily due to an increase in service charges on deposit accounts and other service charges and fees offset by a decrease in other income. Non-interest expense decreased due to a decrease in salaries and benefits, loan collection expense, other losses and a reduction in other expenses.
Net income for 2017 decreased by 45.0% to $3,704 or $0.76 per share-basic and -diluted, from $6,737 or $1.38 per share-basic and -diluted for 2016. The provision for loan losses for 2017 was a negative $543 as compared to negative $65 in 2016. The increase in the negative loan loss provision for 2017 was mainly due to management’s assessment of inherent losses in the loan portfolio, including the impact caused by current local and national economic conditions and low level of prior years’ loan losses offset by the increase in the balance of loans outstanding. Non-interest income increased by $605, or 7.9%, and non-interest expense increased by $1,748 or 6.6%, in 2017. Non-interest income for 2017 increased primarily due to an increase in other service charges and fees. Non-interest expense increased due to an increase in salaries and benefits, loan collection expense and office supplies.
81
NET INTEREST INCOME
Net interest income is the most significant component of the Company’s earnings. Net interest income is the difference between interest and fees realized on earning assets, primarily loans and securities, and interest paid on deposits and other borrowed funds. The net interest margin is this difference expressed as a percentage of average earning assets. Net interest income is affected by several factors, including the volume of earning assets and liabilities, the mix of earning assets and liabilities, and interest rates. The discussion below is presented on a tax equivalent basis which management believes to be the best way to analyze net interest income.
Net interest income on a tax equivalent basis was $29,897, $27,806 and $28,339 for the years 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. Net interest margin was 2.77%, 3.05% and 3.01% for the same periods. During 2019, the yields on interest earning assets and the rates paid on interest bearing deposits increased. In 2019 as compared to 2018, interest-bearing assets increased by $167,713, or 18.4% and interest-bearing liabilities increased by $145,753, or 20.5%. For the year ended December 31, 2019, the average yield on earnings assets was 3.77%, an increase of 23 basis points compared to the average yield at December 31, 2018. The average rate paid on interest-bearing liabilities was 1.26%, an increase of 64 basis points compared to the average rate at December 31, 2018.
During 2018, the yields on interest earning assets and the rates paid on interest bearing deposits increased. In 2018 as compared to 2017, interest-bearing assets decreased by $24.9 million, or 2.7% and interest-bearing liabilities decreased by $41.2 million, or 5.6%. For the year ended December 31, 2018, the average yield on earnings assets was 3.54%, an increase of 18 basis points compared to the average yield at December 31, 2017. The average rate paid on interest-bearing liabilities was 0.62%, an increase of 18 basis points compared to the average rate at December 31, 2017.
During this three-year period, loans outstanding increased in 2017, 2018 and 2019. Loans generally provide the Company with yields that are greater than the yields on typical investment securities.
Table 2 – Average Balance Sheets and Interest Rates sets forth average balance sheet data, including all major categories of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities, together with the interest earned or interest paid and the average yield or average rate paid on each such category for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017.
82
TABLE 2 – AVERAGE BALANCE SHEETS AND INTEREST RATES
(in thousands)
| Average Balance | Income/Expense | Average Yield/Rate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans, net of unearned(1) |
$ | 560,888 | $ | 417,624 | $ | 394,684 | $ | 29,427 | $ | 20,287 | $ | 18,782 | 5.25 | % | 4.86 | % | 4.76 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Investment Securities |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxable |
388,490 | 376,392 | 392,626 | 7,993 | 8,345 | 8,178 | 2.06 | % | 2.22 | % | 2.08 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax-exempt |
78,843 | 107,906 | 129,709 | 2,423 | 3,445 | 4,448 | 3.07 | % | 3.19 | % | 3.43 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Total Investment Securities |
467,333 | 484,298 | 522,335 | 10,416 | 11,790 | 12,626 | 2.23 | % | 2.43 | % | 2.42 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Federal Funds Sold and Other |
50,666 | 9,253 | 24,999 | 854 | 157 | 274 | 1.69 | % | 1.70 | % | 1.09 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Total Interest Earning Assets(1)(2) |
1,078,887 | 911,175 | 942,018 | 40,697 | 32,234 | 31,682 | 3.77 | % | 3.54 | % | 3.36 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Earning Assets |
85,683 | 69,971 | 71,159 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Assets |
$ | 1,164,570 | $ | 981,146 | $ | 1,013,177 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing Demand |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits (3) |
$ | 381,635 | $ | 325,192 | $ | 347,260 | $ | 3,468 | $ | 1,131 | $ | 806 | 0.91 | % | 0.35 | % | 0.23 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Savings |
79,886 | 79,281 | 74,923 | 130 | 113 | 133 | 0.16 | % | 0.14 | % | 0.14 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time |
274,597 | 191,836 | 189,359 | 5,226 | 1,536 | 983 | 1.90 | % | 0.80 | % | 0.52 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Total Deposits |
736,118 | 596,309 | 611,542 | 8,824 | 2,780 | 1,922 | 1.20 | % | 0.47 | % | 0.31 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Borrowed Funds |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Short-term Borrowings |
121,951 | 116,787 | 130,248 | 1,976 | 1,648 | 907 | 1.62 | % | 1.41 | % | 0.70 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term Borrowings |
— | — | 20,000 | — | — | 514 | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | % | 2.53 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Total Borrowed Funds |
121,951 | 116,787 | 150,248 | 1,976 | 1,648 | 1,421 | 1.62 | % | 1.41 | % | 0.95 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Total Interest-Bearing Liabilities (3) |
858,069 | 713,096 | 761,790 | 10,800 | 4,428 | 3,343 | 1.26 | % | 0.62 | % | 0.44 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Interest Bearing Liabilities |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demand Deposits |
192,672 | 164,682 | 150,689 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other Liabilities |
17,534 | 10,208 | 10,468 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shareholders’ Equity |
96,295 | 83,907 | 90,230 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity |
$ | 1,164,570 | $ | 971,893 | $ | 1,013,177 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest Rate Spread |
2.51 | % | 2.92 | % | 2.92 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Interest Margin |
$ | 29,897 | $ | 27,806 | $ | 28,339 | 2.77 | % | 3.05 | % | 3.01 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Less |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax Equivalent Adjustment |
654 | 906 | 1,177 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Interest Income | $ | 29,243 | $ | 26,900 | $ | 27,162 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
83
| (1) | Overdrafts on demand deposit accounts are not included in the average volume calculation as they are not considered interest earning assets by the Company. They are included in the “Non-Earning Assets” balance above. |
| (2) | Earning Assets in Table 2 does not include the dividend paying stock of the Federal Home Loan Bank. |
| (3) | Demand deposits are not included in the average volume calculation as they are not interest bearing liabilities. They are included within the non-interest bearing liabilities section above. |
Table 3 – Net Average Interest Earning Assets illustrates net interest earning assets and liabilities for 2019, 2018, and 2017.
TABLE 3 – NET AVERAGE INTEREST EARNING ASSETS
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Average interest earning assets |
$ | 1,078,887 | $ | 911,175 | $ | 942,018 | ||||||
| Average interest bearing liabilities |
858,069 | 713,096 | 761,790 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net average interest earning assets |
$ | 220,818 | $ | 198,079 | $ | 180,228 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
84
Table 4 – Volume/Rate Analysis depicts the effect on interest income and interest expense of changes in volume and changes in rate from 2017 through 2019. Variances, which were attributable to both volume and rate, are allocated proportionately between rate and volume using the absolute values of each for a basis for the allocation. Non-accruing loans are included in the average loan balances used in determining the yields. Interest income on tax-exempt securities and loans has been adjusted to a tax equivalent basis using a federal income tax rate of 21% in 2019 and 2018, respectively.
TABLE 4 – VOLUME/RATE ANALYSIS
| (in thousands) 2019 Change from 2018 |
2018 Change from 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Volume | Rate | Total | Volume | Rate | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| INTEREST INCOME |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans |
$ | 6,959 | 2,181 | $ | 9,140 | $ | 1,114 | $ | 391 | $ | 1,505 | |||||||||||||
| Taxable Securities |
268 | (620 | ) | (352 | ) | (360 | ) | 527 | 167 | |||||||||||||||
| Non-Taxable Securities |
(928 | ) | (94 | ) | (1,022 | ) | (696 | ) | (307 | ) | (1,003 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Federal Funds Sold and Other |
703 | (6 | ) | 697 | (267 | ) | 150 | (117 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| TOTAL INTEREST INCOME |
$ | 7,002 | $ | 1,461 | $ | 8,463 | $ | (209 | ) | $ | 761 | $ | 552 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| INTEREST EXPENSE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing demand deposits |
$ | 196 | 2,141 | 2,337 | $ | (77 | ) | $ | 402 | 325 | ||||||||||||||
| Savings Deposits |
1 | 16 | 17 | 6 | (26 | ) | (20 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Time Deposits |
663 | 3,027 | 3,690 | 20 | 533 | 553 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings |
73 | 255 | 328 | (190 | ) | 931 | 741 | |||||||||||||||||
| Long-term borrowings |
— | — | — | — | (514 | ) | (514 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| TOTAL INTEREST EXPENSE |
$ | 933 | $ | 5,439 | 6,372 | $ | (241 | ) | $ | 1,326 | 1,085 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| NET INTEREST INCOME |
$ | 6,070 | $ | (3,979 | ) | $ | 2,091 | $ | 32 | $ | (565 | ) | $ | (533 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
85
LOANS
The loan portfolio constitutes the major earning asset of the Company and, in the opinion of management, offers the best alternative for maximizing net interest margin. The Company’s loan personnel have the authority to extend credit under guidelines established and approved by the Board of Directors. Any aggregate credit that exceeds the authority of the loan officer is forwarded to the Board’s loan committee for approval. The loan committee is composed of certain directors, including the Chairman of the Board of Directors. All aggregate loans that exceed the loan committee’s lending authority are presented to the full Board of Directors for ultimate approval or denial. The loan committee not only acts as an approval body to ensure consistent application of the Company’s loan policy but also provides valuable insight through communication and pooling of knowledge, judgment, and experience of its members.
The Company has stated in its loan policy the following objectives for its loan portfolio:
| • | to make loans after sound and thorough credit analysis; |
| • | to properly document all loans; |
| • | to eliminate loans from the portfolio that are underpriced, high risk or difficult and costly to administer; |
| • | to seek good relationships with the customer; |
| • | to avoid undue concentrations of loans; and |
| • | to keep non-accrual loans to a minimum by aggressive collection policies. |
Loan demand in the Company’s market improved after economic conditions began to show some improvement. Although the Company continues to face intense competition for available loans from other financial institutions and the current economic conditions have improved slightly, the Company was able, in 2018 and 2019, to increase the amount of loans outstanding. Additionally, the acquisition of Charter added a significant amount of loans to the Company’s portfolio in 2019. The overall loan demand in the Company’s operating markets has been robust in certain sectors. Commercial, financial and agricultural has seen the most growth with an increase of 25.3%, or $77,353, in 2019, by 6.6%, or $17,653, in 2018 and by 5.9%, or $14,186, in 2017. Commercial, financial and agricultural loans are the largest segment of the loan portfolio and, by nature, bear a higher degree of risk. Management believes the lending practices, policies and procedures applicable to this loan category are adequate to manage any risk represented by the growth of this loan segment.
Real estate mortgage loans originated by the Company increased by 37.4%, or $33,267 in 2019 and decreased by 7.5%, or $7,177 in 2018, and by 1.9%, or $1,888, in 2017 when compared to the prior years. The increase in mortgage loans in 2019 was mainly driven by the acquisition of Charter coupled with expansion to more metropolitan markets and the decrease in prior years reflects the weakness in some of the Company’s local housing markets coupled with increased competition in the mortgage market.
86
Real estate construction loans increased by $40,063, or 97.4% in 2019 to $81,197 when compared to the $41,134 at December 31, 2018 and by $15,210, or 58.7% when compared to 2017. Real estate construction loans are usually short term in nature and are dependent on construction activity in the Company’s service area. There was a large amount of demand for these types of loans in the Company’s service area during 2019 coupled with the acquisition of Charter.
Consumer loans increased by $2,054 or 14.6% in 2019 and decreased by $1,969 or 12.3% in 2018, and $3,476, or 17.9% in 2017, compared to the prior years. The Company believes that changes in consumer purchasing habits and the increase in loan sources have affected the growth of this segment of loans.
Table 5 – Loans Outstanding reflects outstanding balances by loan type for the past five years. Additional loan information is presented in Note 5, “Loans,” to the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report.
TABLE 5 – LOANS OUTSTANDING
(in thousands)
| AT DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Commercial, financial and agricultural |
$ | 357,789 | $ | 285,420 | $ | 267,767 | $ | 253,581 | $ | 266,464 | ||||||||||
| Real estate - construction |
81,197 | 41,134 | 25,923 | 23,793 | 33,133 | |||||||||||||||
| Real estate - mortgage |
122,014 | 88,747 | 95,925 | 97,812 | 104,046 | |||||||||||||||
| Consumer |
16,075 | 14,021 | 15,990 | 19,466 | 26,625 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| TOTAL LOANS |
$ | 577,075 | $ | 429,322 | $ | 405,605 | $ | 394,652 | $ | 430,268 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Table 6 – Loan Liquidity and Sensitivity to Changes in Interest Rates reflects the maturity schedule or repricing frequency of all loans. Also presented are fixed and variable rate loans maturing after one year.
TABLE 6 – LOAN LIQUIDITY
LOAN MATURITIES AT DECEMBER 31, 2019
| 1 YEAR OR LESS |
1 - 5 YEARS |
OVER 5 YEARS |
Total | |||||||||||||
| Commercial, financial and agricultural |
$ | 66,360 | $ | 228,981 | $ | 62,448 | $ | 357,789 | ||||||||
| Real estate - construction |
26,021 | 48,088 | 7,088 | $ | 81,197 | |||||||||||
| Real estate - mortgage |
22,466 | 73,243 | 26,305 | $ | 122,014 | |||||||||||
| Consumer |
5,973 | 9,167 | 935 | $ | 16,075 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total loans |
$ | 120,820 | $ | 359,463 | $ | 96,776 | $ | 577,059 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
87
SENSITIVITY TO CHANGES IN INTEREST RATES
| 1 - 5 YEARS |
OVER 5 YEARS |
|||||||
| Fixed rates |
$ | 419,139 | $ | 60,129 | ||||
| Variable rates |
57,008 | 37,036 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total loans |
$ | 476,147 | $ | 97,165 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Each loan the Company makes either has a stated maturity as to when the loan is to be repaid or is subject to an agreement between the Company and the customer governing its progressive reduction. The Company’s policy is that every loan is to be repaid by its stated maturity and not carried as a continuing debt. Generally, the Company requires that principal reductions on a loan must have begun prior to the second renewal date of the loan.
PROVISION FOR LOAN LOSSES AND ASSET QUALITY
The allowance for loan losses represents an amount that in management’s judgment will be adequate to absorb estimated probable losses within the existing loan portfolio. Loans that management determines to be uncollectible are charged against the allowance for loan losses, and subsequent recoveries, if any, are credited to the allowance. Management’s judgment in determining the adequacy of the allowance is based on evaluations of the collectability of specific loans and prior loss experience. Other factors considered by management include specific economic events, general economic conditions and trends, and loan portfolio mix and growth. The allowance for loan losses is subject to close regulatory review from the FDIC and the Mississippi Department of Banking and Consumer Finance and is also a factor in each agency’s determination of the Company’s capital adequacy. The estimation of losses in the Company’s loan portfolio is susceptible to changes resulting from changes in the financial condition of individual borrowers and economic conditions in the Company’s market area.
The allowance for loan losses is established through a provision for loan losses charged against net income. This expense is determined by a number of factors, including historical loan losses, assessment of specific credit weaknesses within the portfolio, assessment of the prevailing economic climate, and other factors that may affect the overall condition of the loan portfolio. Management utilized these factors to determine the provision for loan losses for each of 2017, 2018 and 2019. The ratio of net loans charged off to average loans was 0.03% in 2019, 0.00% in 2018 and 0.09% in 2017. Management evaluates the adequacy of the allowance for loan loss on a monthly basis and makes adjustments to the allowance based on this analysis.
The provision for loan losses in 2019 was an expense of $573 compared to an expense of $334 in 2018 and reversal of expense of $543 in 2017. The change in the provision for all three years was mainly due to management’s assessment of inherent losses in the loan portfolio, including the impact caused by current local and national economic conditions. The Company uses a model that takes into account historical charge-offs and recoveries and applies that to certain loan segments of the Company’s portfolio. At the end of 2019, the total allowance for loan losses was $3,755, an amount that management believes to be sufficient to cover estimated probable losses in the loan portfolio.
88
Activity in the allowance for loan losses is reflected in Table 7 – Analysis of Allowance for Loan Losses. The Company’s policy is to charge-off loans when in management’s opinion the loan is deemed uncollectible. Even after it is charged off, however, the Company makes concerted efforts to maximize recovery of such loan.
TABLE 7 – ANALYSIS OF ALLOWANCE FOR LOAN LOSSES
(in thousands except for percentage amounts)
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| BALANCE AT BEGINNING OF YEAR |
$ | 3,372 | $ | 3,019 | $ | 3,903 | $ | 6,474 | $ | 6,542 | ||||||||||
| LOANS CHARGED-OFF |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial, financial and agricultural |
176 | 35 | 166 | 2,397 | 457 | |||||||||||||||
| Real estate - construction |
— | 74 | 112 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Real estate - mortgage |
46 | 133 | 57 | 179 | 201 | |||||||||||||||
| Consumer |
138 | 146 | 102 | 65 | 164 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| TOTAL CHARGE-OFFS |
361 | 388 | 437 | 2,641 | 822 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| CHARGE-OFFS RECOVERED |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial, financial and agricultural |
91 | 219 | 2 | 18 | 45 | |||||||||||||||
| Real estate - construction |
18 | 19 | 14 | 18 | 9 | |||||||||||||||
| Real estate - mortgage |
14 | 81 | 16 | 24 | 52 | |||||||||||||||
| Consumer |
47 | 88 | 64 | 75 | 91 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| TOTAL RECOVERIES |
171 | 407 | 96 | 135 | 197 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net loans charged-off |
190 | (19 | ) | 341 | 2,506 | 625 | ||||||||||||||
| Additions charged to operating expense |
573 | 334 | (543 | ) | (65 | ) | 557 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| BALANCE AT END OF YEAR |
$ | 3,755 | $ | 3,372 | $ | 3,019 | $ | 3,903 | $ | 6,474 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Loans, net of unearned, at year end |
$ | 577,067 | $ | 429,277 | $ | 406,605 | $ | 394,051 | $ | 429,582 | ||||||||||
| Ratio of allowance to loans at year end |
0.65 | % | 0.79 | % | 0.74 | % | 0.99 | % | 1.51 | % | ||||||||||
| Average loans - net of unearned |
$ | 561,483 | $ | 418,136 | $ | 395,217 | $ | 409,367 | $ | 412,161 | ||||||||||
| Ratio of net loans charged-off to average loans |
0.03 | % | 0.00 | % | 0.09 | % | 0.61 | % | 0.15 | % | ||||||||||
89
ALLOCATION OF ALLOWANCE FOR LOAN LOSSES
(in thousands)
| AT DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Commercial, financial and agricultural |
$ | 2,499 | $ | 2,309 | $ | 1,942 | $ | 2,434 | $ | 4,710 | ||||||||||
| Real estate - construction |
375 | 192 | 139 | 120 | 402 | |||||||||||||||
| Real estate - mortgage |
572 | 566 | 417 | 821 | 770 | |||||||||||||||
| Consumer |
309 | 305 | 521 | 528 | 592 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 3,755 | $ | 3,372 | $ | 3,019 | $ | 3,903 | $ | 6,474 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
COMPOSITION OF LOAN PORTFOLIO BY TYPE
| AT DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Commercial, financial and agricultural |
62.00 | % | 66.48 | % | 66.02 | % | 64.25 | % | 61.93 | % | ||||||||||
| Real estate - construction |
14.07 | % | 9.58 | % | 6.39 | % | 6.03 | % | 7.70 | % | ||||||||||
| Real estate - mortgage |
21.14 | % | 20.67 | % | 23.65 | % | 24.79 | % | 24.18 | % | ||||||||||
| Consumer |
2.79 | % | 3.27 | % | 3.94 | % | 4.93 | % | 6.19 | % | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 100.00 | % | 100.00 | % | 100.00 | % | 100.00 | % | 100.00 | % | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Loan balances outstanding, as illustrated in Table 5, increased in 2019 even though the Company maintained tight credit standards and the competition for loans was strong. All loan segments increased during 2019, primarily due to the acquisition of Charter coupled with solid organic growth. In 2018 as compared to 2017, commercial, financial and agricultural along with real estate construction loans increased and real estate mortgage and consumer loans decreased. The allowance for loan losses is allocated to the various categories based on the historical loss percentage for each segment of loan and any specific reserves that might be assigned to those loans.
Non-performing assets and the relative percentages of such assets to loan balances are presented in Table 8 – Non-performing Assets. Non-performing loans include non-accrual loans, loans delinquent 90 days or more based on contractual terms and troubled debt restructurings. Management classifies loans as non-accrual when it believes that collection of interest is doubtful. This typically occurs when payments are past due over 90 days, unless the loans are well secured and in the process of collection. Another measurement of asset quality is OREO, which represents properties acquired by the Company through foreclosure following loan defaults by customers. The percentage of OREO to total loans at December 31, 2019 was 0.62% compared to 0.80% in 2018. OREO increased in 2019 after decreasing in 2018 due to more foreclosures in 2019 partially offset by the sale of several parcels during 2019.
Loans on non-accrual status amounted to $12,026 in 2019 as compared to $9,839 in 2018 and $7,582 in 2017. Interest income forgone on loans classified as non-accrual in 2019 was $555 as compared to $429 in 2018 and $413 in 2017. Upon the classification of a loan as non-accrual, all interest accrued on the loan prior to the time it is classified as non-accrual is reversed and interest accruals are suspended until such time that the loan is in compliance with its terms and deemed collectable.
90
TABLE 8 – NON-PERFORMING ASSETS
(in thousands, except percentages)
| As of December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| PRINCIPAL BALANCE |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-accrual |
$ | 12,026 | $ | 9,839 | $ | 7,582 | $ | 8,879 | $ | 14,423 | ||||||||||
| Accruing loans 90 days or more past due |
274 | 73 | 807 | 206 | 76 | |||||||||||||||
| Troubled debt restructurings |
2,495 | 2,782 | 3,047 | 3,288 | 3,858 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| TOTAL NON-PERFORMING LOANS |
$ | 14,795 | $ | 12,694 | $ | 11,436 | $ | 12,373 | $ | 18,357 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Income on non-accrual loans not recorded |
$ | 555 | $ | 429 | $ | 413 | $ | 652 | $ | 732 | ||||||||||
| Non-performing as a percent of loans |
2.56 | % | 2.96 | % | 2.82 | % | 3.14 | % | 4.26 | % | ||||||||||
| Other real estate owned |
$ | 3,552 | $ | 3,440 | $ | 3,980 | $ | 4,443 | $ | 3,573 | ||||||||||
| OREO as a percent of loans |
0.62 | % | 0.80 | % | 0.98 | % | 1.13 | % | 0.83 | % | ||||||||||
| Allowance as a percent of non-performing loans |
25.38 | % | 26.56 | % | 26.40 | % | 31.54 | % | 35.27 | % | ||||||||||
ASC Subtopic 310-10, Loan Impairments outlines the guidance for evaluating impaired loans. These statements changed the methods of estimating the loan loss allowance for problem loans. In general, when management determines that principal and interest due under the contractual terms of a loan are not fully collectible, management must value the loan using discounted future expected cash flows. Management evaluates the Company’s loans for impairment under ASC Subtopic 310-10. The balances of impaired (including non-accruals) loans for the years 2019, 2018 and 2017 were $11,135, $10,306 and $4,396, respectively.
91
This table details the impaired loans by category for years ending 2019, 2018 and 2017.
| AT DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Commercial, financial and agricultural |
$ | 10,296 | $ | 9,153 | $ | 4,093 | ||||||
| Real estate - mortgage |
839 | 1,152 | 303 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total loans |
$ | 11,135 | $ | 10,305 | $ | 4,396 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Management monitors any loans that are classified under FDIC regulations as loss, doubtful or substandard, even if management has not classified the loans as non-performing or impaired. In addition to loans classified for regulatory purposes, management also designates certain loans for internal monitoring purposes in a “watch” category. Loans may be placed on management’s watch list as a result of delinquent status, management’s concern about the borrower’s financial condition or the value of the collateral securing the loan, a substandard classification during regulatory examinations, or simply as a result of management’s desire to monitor more closely a borrower’s financial condition and performance. Watch category loans may include loans that are still performing and accruing interest and may be current under the terms of the loan agreement but which management has a significant degree of concern about the borrowers’ ability to continue to perform according to the terms of the loan agreement. Watch category loans may also include loans, which, although adequately secured and performing, reflect a past delinquency problem or unfavorable financial trends exhibited by the borrower. Loss exposure on these loans is typically evaluated based primarily upon the estimated liquidation value of the collateral securing the loan.
At December 31, 2019, loans totaling $30,756 were included on the Company’s watch list compared to $26,252 at December 31, 2018. The majority of these loans are real estate loans that, although adequately collateralized, have experienced frequent delinquencies in scheduled payments. The inclusion of loans on this list does not indicate a greater risk of loss; rather it indicates that the loan possesses one of the several characteristics described above warranting increased oversight by management.
SECURITIES
At December 31, 2019, the Company classified all of its securities as AFS. AFS securities are reported at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses included as a separate component of equity, net of tax. The Company does not hold any securities classified as held to maturity or held for trading purposes.
Table 9 – Securities and Securities Maturity Schedule summarizes the amortized cost of securities from 2017 through 2019 and the maturity distribution at December 31, 2019, by classification.
92
TABLE 9 – SECURITIES
(in thousands)
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| SECURITIES AVAILABLE-FOR-SALE |
||||||||||||
| U. S. Government Agencies |
$ | 97,400 | $ | 99,366 | $ | 180,648 | ||||||
| Mortgage Backed Securities |
308,310 | 259,742 | 213,707 | |||||||||
| State, County and Municipal Obligations |
59,724 | 105,591 | 118,786 | |||||||||
| Other Securities |
— | — | 2,865 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| TOTAL SECURITIES AVAILABLE-FOR-SALE |
$ | 465,434 | $ | 464,699 | $ | 516,006 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
SECURITIES MATURITY SCHEDULE
| 1 year or less | 1 to 5 years | 5 to 10 years | over 10 years | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actual Balance |
Average Yield |
Actual Balance |
Average Yield |
Actual Balance |
Average Yield |
Actual Balance |
Average Yield |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AVAILABLE-FOR-SALE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Government Agencies(1) |
$ | — | 0.00 | % | $ | 88,814 | 1.86 | % | $ | 8,586 | 2.32 | % | $ | — | 0.00 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Mortgage Backed Securities |
— | 0.00 | % | 4,849 | 2.19 | % | — | 0.00 | % | 303,461 | 2.31 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
| State, County and Municipal(2) |
345 | 3.13 | % | 1,106 | 1.82 | % | 10,092 | 2.93 | % | 48,181 | 2.67 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| TOTAL AVAILABLE-FOR-SALE |
$ | 345 | 3.13 | % | $ | 94,769 | 1.88 | % | $ | 18,678 | 2.65 | % | $ | 351,642 | 2.36 | % | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| (1) | The maturities for the mortgage backed securities included in this line item are based on final maturity. |
| (2) | Average yields were calculated on tax equivalent basis using a marginal federal income tax rate of 21% and a state tax rate of 5%. |
The change in the carrying value of the AFS portfolio is due to market value fluctuations resulting from the changing interest rate environment during 2018. This change is not used in the Tier 1 capital calculation.
As detailed in Table 9, the security portfolio increased $735 or 0.2% in 2019, decreased $51,307 or 9.9% in 2018 and increased $2,800 or 0.5% in 2017. The Company strives to maximize the yields on its portfolio while balancing pledging needs and managing risk. The Company seeks to invest most of its funds not needed for loan demand or the reduction of other borrowings in higher yielding securities and not in the lower yielding federal funds sold.
DEPOSITS
The Company offers a wide variety of deposit services to individual and commercial customers, such as non-interest-bearing and interest-bearing checking accounts, savings accounts, money market deposit accounts and time deposits. The deposit base is the Company’s major funding source for earning assets. Time deposits increased in 2019 and 2018 due to an increase in rates paid by the Company caused by competition in our operating markets. During this time span, we continue to see an increase in other deposit segments as well, except for Interest-bearing demand in 2018.
93
A three-year schedule of average deposits by type and maturities of time deposits greater than $250 is presented in Table 10 – Deposit Information.
TABLE 10 – DEPOSIT INFORMATION
| (in thousands, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Balance |
Average Rate |
Average Balance |
Average Rate |
Average Balance |
Average Rate |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Noninterest-bearing |
$ | 192,672 | $ | 164,682 | $ | 150,689 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing demand |
381,635 | 0.91 | % | 325,192 | 0.35 | % | 347,260 | 0.23 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Savings |
79,886 | 0.16 | % | 79,281 | 0.14 | % | 74,923 | 0.14 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Time deposits |
274,597 | 1.90 | % | 191,836 | 0.80 | % | 189,359 | 0.52 | % | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| $ | 928,790 | 1.20 | % | $ | 760,991 | 0.47 | % | $ | 762,231 | 0.31 | % | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
MATURITY RANGES OF TIME DEPOSITS
OF $250,000 OR MORE
| AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019 | ||||
| 3 months or less |
$ | 22,392 | ||
| 3 through 12 months |
16,203 | |||
| 1 year to 3 years |
20,856 | |||
| over 3 years |
9,897 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 69,348 | |||
|
|
|
|||
The Company, in its normal course of business, will acquire large time deposits, generally from public entities, with a variety of maturities. These funds are acquired on a bid basis and are considered to be part of the deposit base of the Company.
BORROWINGS
Aside from the core deposit base and large denomination time deposits mentioned above, the remaining funding sources utilized by the Company include short-term and long-term borrowings. Short-term borrowings consist of Federal Funds Purchased from other financial institutions on an overnight basis, short-term advances from the FHLB and securities sold under agreement to repurchase. Long-term borrowings are advances from the FHLB with an initial maturity of greater than one year.
94
TABLE 11 - SHORT-TERM BORROWINGS
(in thousands)
| As of December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings |
||||||||||||
| Year-end balance |
$ | 170,410 | $ | 107,966 | $ | 153,998 | ||||||
| Weighted average rate |
1.05 | % | 1.20 | % | 0.75 | % | ||||||
| Maximum month-end balance |
$ | 181,347 | $ | 140,115 | $ | 201,427 | ||||||
| Year to date average balance |
$ | 121,951 | $ | 116,787 | $ | 130,248 | ||||||
| Weighted average rate |
1.62 | % | 1.41 | % | 0.75 | % | ||||||
The Company borrows funds for short periods from the FHLB as an alternative to Federal Funds Purchased. The Company foresees short-term borrowings to be a continued source of liquidity and likely will continue to use these borrowings as a method to fund short-term needs. At December 31, 2019, the Company had the capacity to borrow up to $222,592 from the FHLB and other financial institutions in the form of Federal Funds Purchased. The Company generally will use these types of borrowings if loan demand is greater than the growth in deposits. At December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company had borrowed $-0- from the FHLB and $-0- in Federal Funds Purchased. In 2019, the balances in Securities Sold Under Agreement to Repurchase increased $62,444, or 57.8% to $170,410. In 2018, these balances decreased to $107,966, a decrease of $46,032, or 29.9%.
At the end of 2019, the Company had long-term debt in the amount of $-0- to the FHLB for advances and $6 payable to the State of Mississippi for advances under the Mississippi Agribusiness Enterprise Loan Program. This program provides interest-free loans to banks to fund loans to qualifying farmers. Farmers that qualify for the program receive 20% of their loan at zero interest. When the loan is repaid, the State of Mississippi receives 20% of the principal payment, which is equal to the amount advanced by the state, and the Company retains the balance of the principal payment.
The remaining maturity schedule of the long-term debt at December 31, 2019 is listed below.
| (in thousands) | ||||
| 2019 | ||||
| Less than one year |
$ | — | ||
| One year to three years |
6 | |||
| Over three years |
— | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total long-term borrowings |
$ | 6 | ||
|
|
|
|||
95
NON-INTEREST INCOME AND EXPENSE
Table 12 - Non-Interest Income and Expense illustrates the Company’s non-interest income and expense from 2017 through 2019 and percentage changes between such years.
TABLE 12 - NON-INTEREST INCOME & EXPENSE
(in thousands)
| % CHANGE | % CHANGE | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | FROM ‘18 | 2018 | FROM ‘17 | 2017 | ||||||||||||||||
| NON-INTEREST INCOME |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Service charges on deposit accounts |
$ | 4,413 | -3.27 | % | $ | 4,562 | 7.62 | % | $ | 4,239 | ||||||||||
| Other operating income |
5,335 | 32.12 | % | 4,038 | -0.49 | % | 4,058 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| TOTAL NON-INTEREST INCOME |
$ | 9,748 | 13.35 | % | $ | 8,600 | 3.65 | % | $ | 8,297 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| NON-INTEREST EXPENSE |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Salaries and employee benefits |
$ | 14,883 | 2.43 | % | $ | 14,530 | -1.64 | % | $ | 14,772 | ||||||||||
| Occupancy expense, including equipment |
5,245 | -8.46 | % | 5,730 | 6.41 | % | 5,385 | |||||||||||||
| Other operating expense |
7,430 | 0.35 | % | 7,404 | -8.25 | % | 8,070 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| TOTAL NON-INTEREST EXPENSE |
$ | 27,558 | -0.38 | % | $ | 27,664 | -1.99 | % | $ | 28,227 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Non-interest income typically consists of service charges on checking accounts, including debit card fees, and other financial services. With continued pressure on interest rates, the Company has sought to increase its non-interest income through the expansion of fee income and the development of new services. Currently, the Company’s main sources of non-interest income are service charges on checking accounts, safe deposit box rentals, credit life insurance premiums and title insurance service fees.
During 2019 as compared to 2018, non-interest income increased by $1,148, or 13.4%, when compared to 2018. An increase in other operating income and net gains on sales of securities was partially offset by a decrease in other income and net gains on sales of securities.
During 2018 as compared to 2017, non-interest income increased by $303, or 3.7%, when compared to 2017. An increase in service charges on deposit accounts and other service charges and fees was partially offset by a decrease in other income and net gains on sales of securities.
Non-interest expenses consist of salaries and benefits, occupancy expense and other overhead expenses incurred by the Company in the transaction of its business. In 2019 as compared to 2018, non-interest expense decreased by $106, or 0.4%, to $27,558. Included in this decrease was a decrease in occupancy expense of $485 or 8.5% partially offset by an increase in salaries and benefits in the amount of $353, or 2.4%, and other expense in the amount of $26, or 0.4%. The decrease in occupancy expense was primarily due to a to a refund of excess prepaid postage and continued cost containment focus throughout the Company. The increase in salaries and benefits was due to the Charter acquisition.
96
In 2018 as compared to 20167 non-interest expense decreased by $562, or 2.0%, to $27,665. Included in this decrease was a decrease in salaries and benefits in the amount of $242, or 1.6%, occupancy expense in the amount of $145, or 6.7%, other expense in the amount of $666, or 8.3%, partially offset by an increase in equipment expense in the amount of $490, or 15.3%. The increase in equipment expense was primarily due to strategic investments in technology over the past few years. The decrease in other expense was in large part due to decreased loan collection expense and other losses attributable to writedowns on other real estate.
In 2019, the Company’s efficiency ratio was 77.88%, compared to 75.99% in 2018 and 76.35% in 2017. The efficiency ratio is calculated to measure the cost of generating one dollar of revenue. The efficiency ratio is calculated by dividing non-interest expense by the sum of net interest income, on a fully tax equivalent basis, and non-interest income.
INCOME TAXES
The Company records a provision for income taxes currently payable, along with a provision for deferred taxes to be realized in the future. Such deferred taxes arise from differences in timing of certain items for financial statement reporting rather than income tax reporting. The deferred tax amount of $3,684 is considered realizable without the use of extraordinary tax planning strategies.
The Company’s effective tax rate was 18.66%, 11.04% and 52.36% in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The major difference between the effective tax rate applied to the Company’s financial statement income and the federal statutory rate of 21%, 21% and 34% in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively, is interest on tax-exempt securities and loans and the impact on deferred tax assets due to tax reform. Further tax information is disclosed in Note 12, “Income Taxes” to the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report.
LIQUIDITY AND RATE SENSITIVITY
Liquidity management is the process by which the Company ensures that adequate liquid funds are available to meet its financial commitments on a timely basis. These commitments include honoring withdrawals by depositors, funding credit obligations to borrowers, servicing long-term obligations, making shareholder dividend payments, paying operating expenses, funding capital expenditures and maintaining reserve requirements.
The Company’s predominant sources of funding include: core deposits (consisting of both commercial and individual deposits); proceeds from maturities of securities; repayments of loan principal and interest; commercial repurchase agreements; Federal Funds Purchased; and short-term and long-term borrowing from the FHLB. In 2019 as compared to 2018, the Company experienced an increase in deposits and repurchase agreements in excess of the increase in loans outstanding. The increase in investment securities is mainly the result of the desire to invest excess funds outside of new loans. The Company relies upon non-core sources of funding, such as commercial repurchase agreements, Federal Funds Purchased and short and long- term borrowings from the FHLB, when deposit growth is not adequate to meet its short-term needs. While the strategy of using these wholesale funding sources is adequate to cover liquidity deficiencies in the short term, the Company’s goal is to increase core deposits as a source of long term funding. Management does not intend to rely on borrowings from the FHLB as the first choice as a source of funds but prefers to increase core deposits through increased competition for available deposits. Management believes that core deposits will increase by offering competitive rates and superior service to the Bank’s customers.
97
The Company had no FHLB advances outstanding at year end as part of our strategy to rely more on core deposits than wholesale funding. However, the Company will continue to use advances if they are needed to maintain the Company’s liquidity position.
The deposit base is diversified between individual and commercial accounts, which the Company believes helps it avoid dependence on large concentrations of funds. The Company does not currently solicit certificates of deposit from brokers. The primary sources of liquidity on the asset side of the balance sheet are securities classified as AFS. All of the $464,383 in the investment securities portfolio is classified in the AFS category, and any securities not pledged are available to be sold, should liquidity needs arise. Management, through its Asset Liability Committee (“ALCO”), and the Board review the Company’s liquidity position on a monthly basis. At December 31, 2019, both the ALCO and the Board of Directors determined that the Company’s liquidity position was adequate.
Table 13 - Funding Uses and Sources details the main components of cash flows for 2019 and 2018.
TABLE 13 - FUNDING USES AND SOURCES
(in thousands)
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average | Increase/(decrease) | Average | Increase/(decrease) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance | Amount | Percent | Balance | Amount | Percent | |||||||||||||||||||
| FUNDING USES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans, net of unearned income |
$ | 560,888 | $ | 142,752 | 34.14 | % | $ | 418,136 | $ | 22,919 | 5.80 | % | ||||||||||||
| Taxable securities |
388,490 | 12,098 | 3.21 | % | 376,392 | (8,329 | ) | -2.16 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Tax-exempt securities |
78,843 | (29,063 | ) | -26.93 | % | 107,906 | (18,506 | ) | -14.64 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Federal funds sold and other |
50,666 | 41,413 | 447.56 | % | 9,253 | (15,746 | ) | -62.99 | % | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| TOTAL USES |
$ | 1,078,887 | $ | 167,200 | 18.34 | % | $ | 911,687 | $ | (19,662 | ) | -2.11 | % | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| FUNDING SOURCES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noninterest-bearing deposits |
$ | 192,672 | $ | 27,990 | 17.00 | % | $ | 164,682 | $ | 13,993 | 9.29 | % | ||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing demand and |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| savings deposits |
461,521 | 57,048 | 14.10 | % | 404,473 | (18,462 | ) | -4.37 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Time deposits |
274,597 | 82,761 | 43.14 | % | 191,836 | 2,477 | 1.31 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings |
1,483 | (19,996 | ) | -93.10 | % | 21,479 | 19,167 | 829.02 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Commercial repo |
124,344 | 29,036 | 30.47 | % | 95,308 | (32,629 | ) | -25.50 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt |
— | — | — | — | (20,029 | ) | -100.00 | % | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| TOTAL SOURCES |
$ | 1,054,617 | $ | 176,839 | 20.15 | % | $ | 877,778 | $ | (35,483 | ) | -3.89 | % | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
The Company’s liquidity depends substantially on the ability of the Bank to transfer funds to the Company in the form of dividends. The information under the heading “Market Price and Dividend Information” in this Annual Report discusses federal and state statutory and regulatory restrictions on the ability of the Bank to transfer funds to the Company in the form of dividends.
98
CAPITAL RESOURCES
The Company and Bank are subject to various regulatory capital guidelines as required by federal and state banking agencies. These guidelines define the various components of core capital and assign risk weights to various categories of assets.
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation Improvement Act of 1991, as amended (“FDICIA”), required federal regulatory agencies to define capital tiers. These tiers are: well capitalized, adequately capitalized, undercapitalized, significantly undercapitalized, and critically undercapitalized. Under FDICIA, a “well-capitalized” institution must achieve a Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio of at least 6.00%, a total capital ratio of at least 10.00%, a leverage ratio of at least 5.00% and not be under a capital directive order. These ratios generally measure the percentage of a bank’s capital to all or certain categories of assets. Failure to meet capital requirements can initiate regulatory action that could have a direct material effect on the Company’s financial statements. If a bank is only adequately capitalized, regulatory approval is required before the bank may accept brokered deposits. If undercapitalized, capital distributions, asset growth, and expansion are limited, and the institution is required to submit a capital restoration plan.
During 2019 as compared to 2018, total capital decreased due to the purchase of Charter, in which the consideration paid was 80% stock and 20% cash partially offset by earnings in excess of dividends paid.
Management believes the Company and the Bank meet all the capital requirements to be well-capitalized under the guidelines established by FDICIA as of December 31, 2019, as noted below in Table 14—Capital Ratios. To be classified as well-capitalized, the Company and Bank must maintain the ratios described above.
99
TABLE 14 – CAPITAL RATIOS
(in thousands, except percentage amounts)
| At December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| Tier 1 capital |
||||||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity |
$ | 112,800 | $ | 83,866 | $ | 88,452 | ||||||
| Less: Intangibles |
(13,856 | ) | (3,150 | ) | (3,150 | ) | ||||||
| Less: DTA related to NOLs |
(1,000 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Add/less: Unrealized loss/(gain) on securities |
789 | 14,975 | 8,225 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| TOTAL TIER 1 CAPITAL |
$ | 98,733 | $ | 95,691 | $ | 93,527 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total capital |
||||||||||||
| Tier 1 capital |
$ | 98,733 | $ | 95,691 | $ | 93,527 | ||||||
| Allowable allowance for loan losses |
3,755 | 3,372 | 3,019 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| TOTAL CAPITAL |
$ | 102,488 | $ | 99,063 | $ | 96,546 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| RISK WEIGHTED ASSETS |
$ | 712,154 | $ | 549,828 | $ | 521,708 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| AVERAGE ASSETS (FOURTH QUARTER) |
$ | 1,185,397 | $ | 963,820 | $ | 1,020,107 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| TIER 1 LEVERAGE RATIO |
8.33 | % | 9.93 | % | 9.17 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| COMMON EQUITY TIER 1 CAPITAL RATIO |
8.33 | % | 9.93 | % | 9.17 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| TIER 1 RISK-BASED CAPITAL RATIO |
13.86 | % | 17.40 | % | 17.93 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| TOTAL RISK-BASED CAPITAL RATIO |
14.39 | % | 18.02 | % | 18.51 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Management’s strategy with respect to capital levels is to maintain a sufficient amount of capital to allow the Company to respond to growth and acquisition opportunities in the Bank’s service area. Over the past three years, the Company has been able to increase the amount of its capital, through retention of earnings, while still maintaining the dividend payout ratio to approximately 70% of earnings per share. The Company does not currently have any commitments for capital expenditures that would require the Company to raise additional capital by means other than retained earnings. The Company does not plan to change this strategy unless needed to support future acquisition activity.
OFF-BALANCE SHEET ARRANGEMENTS
In the ordinary course of business, the Company makes various commitments and incurs certain contingent liabilities to fulfill the financing needs of its customers. These commitments and contingent liabilities include commitments to extend credit and issue standby letters of credit. These off-balance sheet arrangements are further detailed in Note 14, “Off-Balance Sheet Financial Instruments, Commitments and Contingencies and Concentrations of Risks,” in the notes to the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report.
100
CONTRACTUAL OBLIGATIONS
The following table summarizes the contractual obligations, excluding deposits and securities sold under agreement to repurchase, of the Company as of December 31, 2019.
| Payments Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Less than | 1-3 | 3 - 5 | Over 5 | |||||||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligations | Total | 1 year | Years | Years | Years | |||||||||||||||
| Operating Leases |
$ | 801 | $ | 348 | $ | 451 | $ | 2 | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Other Long-term Liabilities |
6 | — | 6 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 807 | $ | 348 | $ | 457 | $ | 2 | $ | — | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Long-term debt obligations represent borrowings from the FHLB that have an original maturity in excess of one year. Operating leases are primarily for the lease of ATM machines and other leases for mailing equipment. The equipment leases are for various terms. The other long-term liabilities are those obligations of the Company under the Agribusiness Enterprise Loan Program of the State of Mississippi.
101
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
OVERVIEW
The definition of market risk is the possibility of loss that could result from adverse changes in market prices or interest rates. The Company has taken steps to assess the amount of risk that is associated with its asset and liability structure. The Company measures the potential risk on a regular basis and makes changes to its strategies to manage these risks. The Board of Directors reviews important policy limits each month, with a more detailed risk analysis completed on a quarterly basis. These measurement tools are important in allowing the Company to manage market risk and to plan effective strategies to respond to any adverse changes in risk. The Company does not participate in some of the financial instruments that are inherently subject to substantial market risk. All of the financial instruments entered into by the Company are for purposes other than trading. All information presented in this report are denominated in U.S. dollars.
MARKET/INTEREST RATE RISK MANAGEMENT
Interest rate risk is the primary market risk that management must address. Interest rate risk is the exposure of Company earnings and capital to changes in interest rates. All financial institutions assume interest rate risk as an integral part of normal operations.
The primary purpose in managing interest rate risk is to effectively invest capital and preserve the value created by the core banking business of the Company. The Company utilizes an investment portfolio to manage the interest rate risk naturally created through its business activities. The process of managing interest rate risk generally involves both reducing the exposure of the Company’s net interest margin to swings in interest rates and concurrently ensuring that there is sufficient capital and liquidity to support balance sheet growth. The Company uses a quarterly interest rate risk report to evaluate its exposure to interest rate risk, project earnings and manage the composition of the balance sheet and its growth.
In addition to the quarterly interest rate risk report, the Company employs a number of tools to measure interest rate risk. One tool is static gap analysis, which matches assets with specified maturities to liabilities with corresponding maturities. Although management believes that this does not provide a complete picture of the Company’s exposure to interest rate risk, it does highlight significant short-term repricing volume mismatches. The following table presents the Company’s rate sensitivity static gap analysis at December 31, 2019 ($ in thousands):
| Interest Sensitive Within | ||||||||
| 90 days | One year | |||||||
| Total rate sensitive assets |
$ | 193,301 | $ | 180,773 | ||||
| Total rate sensitive liabilities |
265,622 | 92,671 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net gap |
$ | (72,321 | ) | $ | 88,102 | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
102
The analysis shows a negative gap position over the next three-month period, which indicates that the Company would benefit somewhat from a decrease in market interest rates in the very short term. Although rate increases would be detrimental to the interest rate risk of the Company, management believes there is adequate flexibility to alter the overall rate sensitivity structure as necessary to minimize exposure to these changes.
Management believes that static gap analysis does not fully capture the impact of interest rate movements on interest sensitive assets and liabilities. Thus, the Company also measures interest rate risk by analyzing interest rate sensitivity and the rate sensitivity gap. Table 15—Interest Rate Sensitivity provides additional information about the financial instruments that are sensitive to changes in interest rates. This tabular disclosure is limited by its failure to depict accurately the effect on assumptions of significant changes in the economy or interest rates or changes in management’s expectations or intentions relating to the Company’s financial statements. The information in the interest rate sensitivity table below reflects contractual interest rate pricing dates and contractual maturity dates. For indeterminate maturity deposit products (money market, NOW and savings accounts), the tables present principal cash flows in the shortest term. Although these deposits may not reprice within this time frame, the depositors of such funds have the ability to reprice. Weighted average floating rates are based on the rate for that product as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018.
103
TABLE 15 - INTEREST RATE SENSITIVITY AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2019
(in thousands)
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | Thereafter | Carrying Value |
Fair Value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed Rate |
$ | 90,909 | $ | 85,660 | $ | 48,416 | $ | 110,943 | $ | 83,211 | $ | 60,129 | $ | 479,268 | $ | 475,595 | ||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
4.95 | % | 4.77 | % | 4.87 | % | 5.00 | % | 5.25 | % | 4.33 | % | 4.90 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Floating Rate |
$ | 25,758 | $ | 14,582 | $ | 3,049 | $ | 3,274 | $ | 10,345 | $ | 37,036 | $ | 94,044 | $ | 94,044 | ||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
5.30 | % | 3.99 | % | 4.97 | % | 4.90 | % | 4.91 | % | 5.47 | % | 5.10 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Investment securities |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed Rate |
$ | 345 | $ | 10,000 | $ | 53,481 | $ | 25,566 | $ | 5,722 | $ | 370,320 | $ | 465,434 | $ | 464,383 | ||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
3.13 | % | 1.75 | % | 1.92 | % | 1.80 | % | 2.08 | % | 2.41 | % | 2.30 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Floating Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other earning assets |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Floating Rate |
$ | 60,157 | $ | 60,157 | $ | 60,157 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
1.58 | % | 1.58 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing deposits |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed Rate |
$ | 591,785 | $ | 59,641 | $ | 27,709 | $ | 15,912 | $ | 15,279 | $ | 710,326 | $ | 710,195 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
0.93 | % | 1.99 | % | 2.61 | % | 2.37 | % | 2.74 | % | 1.16 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Floating Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other int-bearing liabilities |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Floating Rate |
$ | 170,410 | $ | 170,410 | $ | 170,410 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
1.10 | % | 1.10 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
104
AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2018
(in thousands)
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | Thereafter | Carrying Value |
Fair Value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed Rate |
$ | 81,808 | $ | 54,416 | $ | 70,950 | $ | 32,780 | $ | 83,478 | $ | 34,948 | $ | 358,380 | $ | 353,467 | ||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
4.89 | % | 4.80 | % | 4.49 | % | 4.72 | % | 4.96 | % | 3.58 | % | 4.67 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Floating Rate |
$ | 6,408 | $ | 18,742 | $ | 8,564 | $ | 589 | $ | 1,210 | $ | 32,012 | $ | 67,525 | $ | 67,525 | ||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
5.54 | % | 5.84 | % | 4.99 | % | 6.50 | % | 6.05 | % | 5.78 | % | 5.68 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Investment securities |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed Rate |
$ | 1,875 | $ | 2,440 | $ | 11,648 | $ | 56,074 | $ | 26,738 | $ | 365,924 | $ | 464,699 | $ | 444,746 | ||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
4.28 | % | 3.55 | % | 2.07 | % | 1.97 | % | 1.90 | % | 2.52 | % | 2.42 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Floating Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other earning assets |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed Rate |
$ | 8,080 | $ | 8,080 | $ | 8,080 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
1.69 | % | 1.69 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Floating Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing deposits |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed Rate |
$ | 503,446 | $ | 36,890 | $ | 28,376 | $ | 2,865 | $ | 14,615 | $ | 586,192 | $ | 585,433 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
0.55 | % | 1.41 | % | 2.88 | % | 2.23 | % | 2.75 | % | 0.78 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Floating Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other int-bearing liabilities |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Floating Rate |
$ | 107,966 | $ | 107,966 | $ | 107,966 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Int Rate |
1.20 | % | 1.20 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rate sensitivity gap analysis is another tool management uses to measure interest rate risk. The rate sensitivity gap is the difference between the repricing of interest-earning assets and the repricing of interest-bearing liabilities within certain defined time frames. The Company’s interest rate sensitivity position is influenced by the distribution of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities among the maturity categories. Table 16—Rate Sensitivity Gap reflects interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities by maturity distribution as of December 31, 2018. Product lines repricing in time periods predetermined by contractual agreements are included in the respective maturity categories.
105
TABLE 16 - RATE SENSITIVITY GAP AT DECEMBER 31, 2019
(in thousands, except percentage amounts)
| 1 - 90 Days |
91 - 365 Days |
1 - 5 Years |
Over 5 years |
Total | ||||||||||||||||
| INTEREST EARNING ASSETS |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans |
$ | 83,881 | $ | 103,548 | $ | 346,914 | $ | 28,410 | $ | 562,753 | ||||||||||
| Investment securities |
49,563 | 77,225 | 180,110 | 162,491 | 469,389 | |||||||||||||||
| Interest Bearing Due From Bank Accounts |
58,257 | — | — | — | 58,257 | |||||||||||||||
| Federal funds sold |
1,600 | — | — | — | 1,600 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| TOTAL INTEREST BEARING ASSETS |
$ | 193,301 | $ | 180,773 | $ | 527,024 | $ | 190,901 | $ | 1,091,999 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| INTEREST BEARING LIABILITIES |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest bearing demand deposits |
$ | 32,616 | $ | 20,161 | $ | 107,525 | $ | 26,881 | $ | 187,183 | ||||||||||
| Savings and Money Market deposits |
150,845 | — | 155,369 | 147,943 | 454,157 | |||||||||||||||
| Time deposits |
65,120 | 72,510 | 118,410 | — | 256,040 | |||||||||||||||
| Short term borrowings |
17,041 | — | 102,247 | 51,123 | 170,411 | |||||||||||||||
| Long term borrowings |
— | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| TOTAL INTEREST BEARING LIABILITIES |
$ | 265,622 | $ | 92,671 | $ | 483,551 | $ | 225,947 | $ | 1,067,791 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Rate sensitive gap |
$ | (72,321 | ) | $ | 88,102 | $ | 43,473 | $ | (35,046 | ) | $ | 24,208 | ||||||||
| Rate sensitive cumulative gap |
(72,321 | ) | 15,781 | 59,254 | 24,208 | — | ||||||||||||||
| Cumulative gap as a percentage of total earning assets |
-6.62 | % | 1.45 | % | 5.43 | % | 2.22 | % | ||||||||||||
The purpose of the above table is to measure interest rate risk utilizing the repricing intervals of interest sensitive assets and liabilities. Rate sensitive gaps constantly change as funds are acquired and invested and as rates change. Rising interest rates are likely to increase net interest income in a positive gap position while falling interest rates are beneficial in a negative gap position.
The above rate sensitivity analysis places interest-bearing demand and savings deposits in the shortest maturity category because these liabilities do not have defined maturities. If these deposits were placed in a maturity distribution representative of the Company’s deposit base history, the shortfall of the negative rate sensitive gap position would be reduced in the 1-to-90 day time frame. It is the goal of the Company to achieve a cumulative gap ratio of plus or minus 15% for all periods under one year, with maximum acceptable limits of plus or minus 20%. Quarterly, management discusses with the ALCO and the board of directors the gap position in relation to the established goals, highlights any reasons for variances from the goals and suggests changes to better align the Company’s position with the established goals. When reviewing the Company’s position, impacting factors and suggested changes, the board of directors also considers other corporate objectives, including increasing core deposits and increasing profitability, before implementing changes intended to align the Company’s position with the established goals. While the board of directors continues to closely monitor the Company’s negative gap position, at this time, management does not anticipate making any significant changes to the Company’s operating practices in order to mitigate the negative gap position.
106
The rate sensitivity gap table illustrates that the Company had a large negative cumulative gap position for the 1 to 90-day period as of December 31, 2019. This negative gap position was mainly due to: (1) a large amount of investment securities that have call dates within that period; (2) a significant amount of non-maturity deposits classified within that period; (3) approximately 25.4% of certificates of deposit maturing during that period; and (4) 82.8% of the Company’s loans maturing after that period.
The interest rate sensitivity and rate sensitivity gap tables, taken together, indicate that the Company to be in an asset sensitive position when evaluating the maturities of interest-bearing items. Thus, an increase in the interest rate environment would enhance earnings, while a decrease in interest rates would have the opposite effect on the Company’s earnings. The Company has attempted to mitigate the impact of its interest rate position by increasing the amount of its variable rate loans and also by structuring deposit rates to entice customers to lengthen the maturities of their time deposits. The effect of any changes in interest rates on the Company would be mitigated by the fact that interest-bearing demand and savings deposits may not be immediately affected by changes in general interest rates.
Short term interest rates remained historically low in 2017, but started increasing in 2017 and all of 2018 but then starting decreasing in the second half of 2019 in connection with the target Federal Funds rate by the Federal Reserve Bank. The movement in the short term interest rates impact the Company’s decisions in regards to pricing the Company’s products and services. The short term interest rates have had impact on the Company’s earnings as we positioned our balance sheet for rising rates in 2018 and that was halted in mid-2019. Therefore, this caused an increase in our deposit costs without the corresponding increase in earning asset yields. The Company is focused on positioning the balance sheet to remain more neutral to interest rates during these uncertain times. In 2018, the Company was significantly liability sensitive and has been able to turn the balance sheet to asset sensitive over foreseeable future with a focus on getting closer to neutral through investing the Company’s excess funds into longer-term loans and investment securities. The Company’s net interest margin in 2019 was 2.77% and in 2018 was 3.05% due to the aforementioned facts.
107
Quarterly Financial Trends
| (in thousands, except per share
amounts) 2019 |
||||||||||||||||
| First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | |||||||||||||
| Interest Income |
$ | 8,383 | $ | 8,651 | $ | 8,444 | $ | 9,883 | ||||||||
| Interest Expense |
2,174 | 2,444 | 2,525 | 2,578 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net Interest Income |
6,209 | 6,207 | 5,919 | 7,305 | ||||||||||||
| Provision for Loan Losses |
195 | 265 | 12 | 101 | ||||||||||||
| Non-interest Income |
2,047 | 2,072 | 2,506 | 3,122 | ||||||||||||
| Non-interest Expense |
6,639 | 6,323 | 6,868 | 7,728 | ||||||||||||
| Income Taxes |
195 | 320 | 212 | 627 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net Income |
$ | 1,227 | $ | 1,371 | $ | 1,333 | $ | 1,971 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Per common share: |
||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.25 | $ | 0.28 | $ | 0.27 | $ | 0.35 | ||||||||
| Diluted |
$ | 0.25 | $ | 0.28 | $ | 0.27 | $ | 0.35 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Cash Dividends |
$ | 0.24 | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.24 | ||||||||
| 2018 | ||||||||||||||||
| First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | |||||||||||||
| Interest Income |
$ | 7,600 | $ | 7,778 | $ | 7,888 | $ | 8,093 | ||||||||
| Interest Expense |
795 | 826 | 1,169 | 1,669 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net Interest Income |
6,805 | 6,952 | 6,719 | 6,424 | ||||||||||||
| Provision for Loan Losses |
(237 | ) | 89 | 289 | 193 | |||||||||||
| Non-interest Income |
2,100 | 2,078 | 2,221 | 2,200 | ||||||||||||
| Non-interest Expense |
7,048 | 6,946 | 6,895 | 6,776 | ||||||||||||
| Income Taxes |
322 | 306 | 260 | (60 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net Income |
$ | 1,772 | $ | 1,689 | $ | 1,496 | $ | 1,715 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Per common share: |
||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.36 | $ | 0.35 | $ | 0.31 | $ | 0.35 | ||||||||
| Diluted |
$ | 0.36 | $ | 0.35 | $ | 0.31 | $ | 0.35 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Cash Dividends |
$ | 0.24 | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.24 | ||||||||
Amounts of income tax expense recorded during the fourth quarter of 2017 include a $2,559 charge to income tax expense for the revaluation of the net deferred tax asset as a result of the Tax Cut and Jobs Act. The reduction of income tax expense in the fourth quarter of 2018 is to adjust income taxes to the actual annual effective rate.
108
Market Price and Dividend Information
MARKET PRICE INFORMATION
The Company’s common stock trades on the NASDAQ Global Market (“NASDAQ”) under the symbol “CIZN”. On March 3, 2020, the common stock’s closing price on NASDAQ was $20.56.
On March 3, 2020, shares of the Company’s common stock were held of record by approximately 490 shareholders.
DIVIDENDS
Dividends totaled $0.96 per share for 2019 and 2018.
If funds are available, the Board of Directors of the Company typically declares dividends on a quarterly basis in March, June, September and December with payment following at the end of the month in which the dividend was declared. Funds for the payment by the Company of cash dividends are obtained from dividends, loans or advances received by the Company from the Bank. Accordingly, the declaration and payment of dividends by the Company depend upon the Bank’s earnings and financial condition, general economic conditions, compliance with regulatory requirements, and other factors. The Bank must also receive the approval of the Mississippi Department of Banking and Consumer Finance prior to the payment of a dividend.
109
STOCK PERFORMANCE GRAPH
The following performance graph compares the performance of the Company’s common stock to the NASDAQ Composite Index and the Morningstar Regional Bank index (a peer group of other regional bank holding companies) for the Company’s reporting period. The graph assumes that the value of the investment in the Company’s common stock and each index was $100 at December 31, 2014 and that all dividends were reinvested.
Performance Graph
December 31, 2014 - December 31, 2019
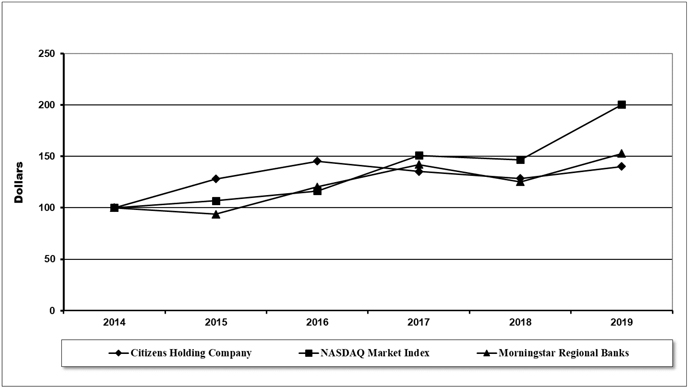
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Citizens Holding Company |
100.00 | 128.03 | 145.40 | 135.29 | 128.51 | 140.28 | ||||||||||||||||||
| NASDAQ Market Index |
100.00 | 106.96 | 116.45 | 150.96 | 146.67 | 200.49 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Morningstar Regional Banks |
100.00 | 93.77 | 120.37 | 142.21 | 125.41 | 152.82 | ||||||||||||||||||
There can be no assurance that the Company’s common stock performance will continue in the future with the same or similar trends depicted in the performance graph above. The Company does not and will not make or endorse any predictions as to future stock performance.
110
THE CITIZENS BANK OFFICERS
111
112
BOARD OF DIRECTORS
| Don Fulton Retired W. G. Yates and Sons Construction Co.
Donald L. Kilgore Special Assistant Attorney General State of Mississippi
David A. King Proprietor Philadelphia Motor Company
Herbert A. King Civil Engineer King Engineering Associates, Inc.
Adam Mars Business Manager Mars, Mars & Mars
Gregory E. Cronin Gulf Coast President Citizens Holding Company and The Citizens Bank |
Craig Dungan, MD Physician Meridian Gastroenterology PLLC
Greg L. McKee President & Chief Executive Officer Citizens Holding Company and The Citizens Bank
David P. Webb Attorney Baker, Donelson, Bearman, Caldwell & Berkowitz, PC
A. T. Williams Certified Public Accountant A. T. Williams, CPA
Terrell E. Winstead Chief Financial Officer Molpus Woodlands Group |
CITIZENS HOLDING COMPANY OFFICERS
Herbert A. King
Chairman
Greg L. McKee
President and Chief Executive Officer
Mark Taylor
Secretary
Robert T. Smith
Treasurer and Chief Financial Officer
Gregory E. Cronin
Gulf Coast President
113
BANKING LOCATIONS
| Philadelphia Main Office |
Collinsville Branch |
Decatur Branch | ||
| 521 Main Street |
9065 Collinsville Road |
15330 Hwy 15 South | ||
| Philadelphia, MS 39350 |
Collinsville, MS 39325 |
Decatur, MS 39327 | ||
| 601.656.4692 |
601.626.7608 |
601.635.2321 | ||
| Westside Branch |
Flowood Branch |
Forest Branch | ||
| 912 West Beacon Street |
5419 Hwy 25 Ste. Q |
247 Woodland Drive North | ||
| Philadelphia, MS 39350 |
Flowood, MS 39232 |
Forest, MS 39074 | ||
| 601.656.4692 |
601.992.7688 |
601.469.3424 | ||
| Northside Branch |
Sebastopol Branch |
Louisville-Main Branch | ||
| 802 Pecan Avenue |
24 Pine Street |
l00 East Main Street | ||
| Philadelphia, MS 39350 |
Sebastopol, MS 39359 |
Louisville, MS 39339 | ||
| 601.656.4692 |
601.625.7447 |
662.773.6261 | ||
| Eastside Branch |
DeKalb Branch |
Noxapater Branch | ||
| 599 East Main Street |
176 Main Avenue |
45 East Main Street | ||
| Philadelphia, MS 39350 |
DeKalb, MS 39328 |
Noxapater, MS 39346 | ||
| 601.656.4692 |
601.743.2115 |
662.724.4261 | ||
| Union Branch |
Kosciusko Branch |
Louisville-Industrial Branch | ||
| 502 Bank Street |
775 North Jackson Street |
803 South Church Street | ||
| Union, MS 39365 |
Kosciusko, MS 39090 |
Louisville, MS 39339 | ||
| 601.774.9231 |
662.289.4356 |
662.773.6261 | ||
| Starkville Branch |
Scooba Branch |
Biloxi Lemoyne Boulevard | ||
| 201 Highway 12 West |
27597 Highway 16 East |
15309 Lemoyne Boulevard | ||
| Starkville, MS 39759 |
Scooba, MS 39358 |
Biloxi, MS 39532 | ||
| 662.323.1420 |
662.476.8431 |
228.207.2343 | ||
| Carthage Main Office |
Meridian Eastgate |
Meridian Broadmoor | ||
| 301 West Main Street |
1825 Hwy 39 North |
5015 Highway 493 | ||
| Carthage, MS 39051 |
Meridian, MS 39301 |
Meridian. MS 39305 | ||
| 601.257.4525 |
601.693.8367 |
601.581.1541 | ||
| Biloxi Cedar Lakes |
Hattiesburg Branch |
Flowood Branch | ||
| 1830 Popps Ferry Road |
6222 Highway 98 |
5419 Highway 25, Suite Q | ||
| Biloxi, MS 39532 |
Hattiesburg, MS 39402 |
Flowood, MS 39232 | ||
| 228.594.6913 |
601.264.4425 |
601.992.7688 | ||
| Oxford Loan Production |
Biloxi Medical Branch |
Gulfport Branch | ||
| 304 Enterprise Dr., Ste A |
1721 Medical Park Dr. |
12008 Hwy 49 | ||
| Oxford, MS 38655 | Biloxi, MS 39532 |
Gulfport, MS 39503 | ||
114
BANKING LOCATIONS - Continued
| Pascagoula Branch |
Ocean Springs Branch |
Phone Teller | ||
| 1519 Jackson Ave |
2702 Bienville Blvd |
1.800.397.0344 | ||
| Pascagoula, MS 39567 |
Ocean Springs, MS 39564 |
Internet and Mobile Banking
http.//www.thecitizensbankphila.com
115
FINANCIAL INFORMATION
CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS
521 Main Street
P.O. Box 209
Philadelphia, MS 39350
601.656.4692
ANNUAL SHAREHOLDER MEETING
The Annual Shareholder meeting of the Citizens Holding Company, Inc. will be held Tuesday, April 28, 2020, at 4:30 P.M. in the lobby of the main office of The Citizens Bank, 521 Main Street, Philadelphia, Mississippi.
STOCK REGISTRAR AND TRANSFER AGENT
American Stock Transfer & Trust Company
59 Maiden Lane
New York, NY 10038
FORM 10-K
The Company’s most recent Annual Report on Form 10-K, filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, is available without charge to shareholders upon request to the Treasurer of the Citizens Holding Company.
FINANCIAL CONTACT
Robert T. Smith
Treasurer and Chief Financial Officer
P.O. 209
Philadelphia, Mississippi 39350
Additional information can be obtained from the Company’s website at www.citizensholdingcompany.com.
116
