Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corp | hc10009099x1_ex32-2.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corp | hc10009099x1_ex32-1.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corp | hc10009099x1_ex31-2.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corp | hc10009099x1_ex31-1.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 - Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corp | hc10009099x1_ex23-1.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EXHIBIT 21.1 - Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corp | hc10009099x1_ex21-1.htm |
| EX-4.3 - EXHIBIT 4.3 - Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corp | hc10009099x1_ex4-3.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019
OR
| o | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 001-36099
CHERRY HILL MORTGAGE INVESTMENT CORPORATION
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
Maryland
|
46-1315605
|
|
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization)
|
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.)
|
|
|
|
|
1451 Route 34, Suite 303
Farmingdale, New Jersey |
07727
|
|
(Address of principal executive offices)
|
(Zip Code)
|
(877) 870 – 7005
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
Title of Each Class
|
Trading Symbol(s)
|
Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered
|
|
Common Stock, $0.01 par value
8.20% Series A Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock, $0.01 par value |
CHMI
CHMI-PRA |
New York Stock Exchange
New York Stock Exchange |
|
8.250% Series B Fixed-to-Floating Rate Cumulative Redeemable
Preferred Stock, $0.01 par value |
CHMI-PRB
|
New York Stock Exchange
|
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes o No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
Large accelerated filer
|
o
|
Accelerated filer
|
☒
|
|
Non-accelerated filer
|
o
|
Smaller reporting company
|
o
|
|
Emerging growth company
|
o
|
|
|
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No ☒
The aggregate market value of the registrant’s common stock, $0.01 par value per share, at June 28, 2019, held by those persons deemed by the registrant to be non-affiliates (based upon the closing sale price of the common stock on the New York Stock Exchange on June 28, 2019) was approximately $253.2 million. Shares of the registrant’s common stock held by each executive officer and director and by each entity or person that, to the registrant’s knowledge, owned 10% or more of the registrant’s outstanding common stock as of June 28, 2019, have been excluded from this number in that these persons may be deemed affiliates of the registrant. The determination of affiliate status for this purpose is not necessarily a conclusive determination for other purposes.
On February 27, 2020, the registrant had a total of 16,660,655 shares of common stock, $0.01 par value, outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant’s Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A relating to its 2020 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission by no later than April 29, 2020 are incorporated by reference into Part III, Items 10 through 14, inclusive, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K as indicated herein.
GLOSSARY
This glossary defines some of the terms that we use elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is not a complete list of all of the defined terms used herein. In this Annual Report on Form 10-K, unless specifically stated otherwise or the context otherwise indicates, references to “we,” “us,” “our,” the “Company” or “CHMI” refer to Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation, a Maryland corporation, together with its consolidated subsidiaries; references to the “Manager” refer to Cherry Hill Mortgage Management, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company; and references to the “Operating Partnership” refer to Cherry Hill Operating Partnership, LP, a Delaware limited partnership.
“Agency” means a U.S. Government agency, such as Ginnie Mae, or a GSE.
“Agency RMBS” means RMBS issued by an Agency or for which an Agency guarantees payments of principal and interest on the securities.
“ASC” means an Accounting Standards Codification.
“ARM” means an adjustable-rate residential mortgage loan.
“CFTC” means the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission.
“CMO” means a collateralized mortgage obligation. CMOs are either loss share securities issued by a GSE or structured debt instruments representing interests in specified pools of mortgage loans subdivided into multiple classes, or tranches, of securities, with each tranche having different maturities or risk profiles.
“credit enhancement” means techniques to improve the credit ratings of securities, including overcollateralization, creating retained spread, creating subordinated tranches and insurance.
“Excess MSR” means an interest in an MSR, representing a portion of the interest payment collected from a pool of mortgage loans, net of a basic servicing fee paid to the mortgage servicer.
“Fannie Mae” means the Federal National Mortgage Association.
“FHA” means the Federal Housing Administration.
“Freddie Mac” means the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation.
“FRM” means a fixed-rate residential mortgage loan.
“Ginnie Mae” means the Government National Mortgage Association, a wholly-owned corporate instrumentality of the United States of America within HUD.
“GSE” means a government-sponsored enterprise. When we refer to GSEs, we mean Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac.
“HUD” means the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development.
“hybrid ARM” means a residential mortgage loan that has an interest rate that is fixed for a specified period of time (typically three, five, seven or ten years) and thereafter adjusts to an increment over a specified interest rate index.
“inverse IO” means an inverse interest-only security, which is a type of stripped security. These debt securities receive no principal payments and have a coupon rate which has an inverse relationship to its reference index.
“IO” means an interest-only security, which is a type of stripped security. IO strips receive a specified portion of the interest on the underlying assets.
“MBS” means mortgage-backed securities.
“MSR” means a mortgage servicing right. An MSR provides a mortgage servicer with the right to service a mortgage loan or a pool of mortgages in exchange for a portion of the interest payments made on the mortgage or the underlying mortgages. An MSR is made up of two components: a basic servicing fee and an Excess MSR. The basic servicing fee is the amount of compensation for the performance of servicing duties.
“mortgage loan” means a loan secured by real estate together with the right to receive the payment of principal and interest on the loan (including the servicing fee).
i
“non-Agency RMBS” means CMOs that either are loss share securities issued by a GSE or are not issued or guaranteed by an Agency, including investment grade (AAA through BBB rated) and non-investment grade (BB rated through unrated) classes.
“non-conforming loan” means a residential mortgage loan that does not conform to the Agency underwriting guidelines and does not meet the funding criteria of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
“non-QM loan” means a mortgage loan that does not satisfy the requirements for a qualified mortgage.
“prime mortgage loan” means a mortgage loan that generally conforms to GSE underwriting guidelines or is a non-QM loan with a FICO score generally above 700.
“qualified mortgage” means a mortgage that complies with the ability to repay rule and related requirements in Regulation Z.
“REIT” means a real estate investment trust.
“residential mortgage pass-through certificate” is a MBS that represents an interest in a “pool” of mortgage loans secured by residential real property where payments of both interest and principal (including principal prepayments) on the underlying residential mortgage loans are made monthly to holders of the security, in effect “passing through” monthly payments made by the individual borrowers on the mortgage loans that underlie the security, net of fees paid to the issuer/guarantor and servicer.
“RMBS” means a residential Agency MBS or a non-Agency RMBS.
“Servicing Related Assets” means Excess MSRs and MSRs.
“SIFMA” means the Securities Industry and Financial Markets Association.
“stripped security” is an RMBS structured with two or more classes that receives different distributions of principal or interest on a pool of RMBS. Stripped securities include IOs and inverse IOs.
“TBA” means a forward-settling Agency RMBS where the pool is “to-be-announced.” In a TBA, a buyer will agree to purchase, for future delivery, Agency RMBS with certain principal and interest terms and certain types of underlying collateral, but the particular Agency RMBS to be delivered is not identified until shortly before the TBA settlement date.
“TRS” means a taxable REIT subsidiary.
“UPB” means unpaid principal balance.
“U.S. Treasury” means the U.S. Department of Treasury.
“VA” means the Department of Veterans Affairs.
“VA mortgage loan” means a mortgage loan that is partially guaranteed by the VA in accordance with its regulations.
ii
FORWARD-LOOKING INFORMATION
We make forward-looking statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). For these statements, we claim the protections of the safe harbor for forward-looking statements contained in such Sections. Forward-looking statements are subject to substantial risks and uncertainties, many of which are difficult to predict and are generally beyond our control. These forward-looking statements include information about possible or assumed future results of our business, financial condition, liquidity, results of operations, plans and objectives. When we use the words “believe,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “estimate,” “plan,” “continue,” “intend,” “should,” “could,” “would,” “may,” “potential” or the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology, we intend to identify forward-looking statements. Statements regarding the following subjects, among others, may be forward-looking:
| • | the Company’s investment objectives and business strategy; |
| • | the Company’s ability to raise capital through the sale of its equity and debt securities and to invest the net proceeds of any such offering in the target assets, if any, identified at the time of the offering; |
| • | the Company’s ability to obtain future financing arrangements and refinance existing financing arrangements as they mature; |
| • | the Company’s expected leverage; |
| • | the Company’s expected investments and the timing thereof; |
| • | the Company’s ability to acquire Servicing Related Assets and mortgage and real estate-related securities; |
| • | estimates and statements relating to, and the Company’s ability to make, future distributions to holders of the Company’s securities; |
| • | the Company’s ability to compete in the marketplace; |
| • | market, industry and economic trends; |
| • | recent market developments and actions taken and to be taken by the U.S. Government, the U.S. Treasury and the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, Ginnie Mae and the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”); |
| • | mortgage loan modification programs and future legislative actions; |
| • | the Company’s ability to maintain its qualification as a REIT under the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), and limitations on the Company’s business due to compliance with requirements for maintaining its qualification as a REIT under the Code; |
| • | the Company’s ability to maintain its exclusion from regulation as an investment company under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the “Investment Company Act”); |
| • | projected capital and operating expenditures; |
| • | availability of qualified personnel; and |
| • | projected prepayment and/or default rates. |
iii
The Company’s beliefs, assumptions and expectations can change as a result of many possible events or factors, not all of which are known to it or are within its control. If any such change occurs, the Company’s business, financial condition, liquidity and results of operations may vary materially from those expressed in, or implied by, the Company’s forward-looking statements. These risks, along with, among others, the following factors, could cause actual results to vary from the Company’s forward-looking statements:
| • | the factors referenced in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including those set forth under “Item 1. Business” and “Item 1A. Risk Factors”; |
| • | general volatility of the capital markets; |
| • | changes in the Company’s investment objectives and business strategy; |
| • | availability, terms and deployment of capital; |
| • | availability of suitable investment opportunities; |
| • | the Company’s dependence on the Manager and the Company’s ability to find a suitable replacement if the Company or the Manager were to terminate the management agreement the Company has entered into with the Manager; |
| • | changes in the Company’s assets, interest rates or the general economy; |
| • | increased rates of default and/or decreased recovery rates on the Company’s investments, including as a result of the effects of more severe weather and changes in traditional weather patterns; |
| • | changes in interest rates, interest rate spreads, the yield curve, prepayment rates or recapture rates; |
| • | limitations on the Company’s business due to compliance with requirements for maintaining its qualification as a REIT under the Code and its exclusion from regulation as an investment company under the Investment Company Act; |
| • | the degree and nature of the Company’s competition, including competition for the residential mortgage assets in which the Company invests; and |
| • | other risks associated with acquiring, investing in and managing residential mortgage assets. |
Although the Company believes that the expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, it cannot guarantee future results, levels of activity, performance or achievements. These forward-looking statements apply only as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The Company is not obligated, and does not intend, to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. See “Item 1A. Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
iv
| Item 1. | Business |
Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation is a publicly traded residential real estate finance company focused on acquiring, investing in and managing residential mortgage assets in the United States. We were incorporated in Maryland on October 31, 2012, and we commenced operations on October 9, 2013, following the completion of our initial public offering (“IPO”) and a concurrent private placement. Our common stock is listed and traded on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol “CHMI.” We are externally managed by Cherry Hill Mortgage Management, LLC, an SEC-registered investment adviser established by Stanley Middleman. Our Manager is a party to a services agreement with Freedom Mortgage Corporation (“Freedom Mortgage”), which is owned and controlled by Mr. Middleman. Our Manager is owned by a “blind trust” for the benefit of Mr. Middleman.
We operate so as to continue to qualify to be taxed as a REIT under the Code. To qualify as a REIT, we must distribute annually to our stockholders an amount at least equal to 90% of our REIT taxable income, determined without regard to the deduction for dividends paid and excluding any net capital gain. We currently expect to distribute substantially all of our REIT taxable income to our stockholders. We will be subject to income tax on our taxable income that is not distributed and to an excise tax to the extent that certain percentages of our taxable income are not distributed by specified dates. CHMI Solutions, Inc. (“Solutions”), our TRS, and its wholly owned subsidiary, Aurora Financial Group, Inc. (“Aurora”), are subject to regular corporate U.S. federal, state and local income taxes on their taxable income.
Our principal objective is to generate attractive current yields and risk-adjusted total returns for our stockholders over the long term, primarily through dividend distributions and secondarily through capital appreciation. We attempt to attain this objective by selectively constructing and actively managing a portfolio of Servicing Related Assets and RMBS. Subject to market conditions, we may also invest in prime residential mortgage loans and other cash flowing residential mortgage assets.
We operate our business through the following segments: (i) investments in RMBS; (ii) investments in Servicing Related Assets; and (iii) “All Other.” For information regarding the segments in which we operate, see “Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data—Note 3—Segment Reporting.”
Our Targeted Asset Classes
Our primary targeted asset classes currently include:
| • | RMBS, including Agency RMBS, residential mortgage pass-through certificates, CMOs and TBAs; and |
| • | Servicing Related Assets consisting of MSRs and Excess MSRs. |
Our Strategy
Our strategy, which may change due to the availability and terms of capital and as market conditions warrant, involves:
| • | allocating a substantial portion of our equity capital to the acquisition of Servicing Related Assets through bulk and flow purchases; |
| • | the creation of intercompany Excess MSRs from MSRs acquired by our mortgage servicing subsidiary, Aurora; |
| • | acquiring RMBS on a leveraged basis; and |
| • | opportunistically mitigating our prepayment and interest rate and, to a lesser extent, credit risk by using a variety of hedging instruments and, where applicable and available, recapture agreements. |
Servicing Related Asset Strategy. The primary focus of our Servicing Related Asset strategy is the acquisition of MSRs from servicers, which may include Freedom Mortgage, on a bulk and/or flow purchase basis on terms to be negotiated in the future. We currently expect that our investments in Excess MSRs will be through the creation of intercompany Excess MSRs from the MSRs so acquired.
1
Our ability to acquire MSRs is subject to the applicable REIT qualification tests. We have to hold our MSRs through Aurora, which is subject to corporate income tax. In certain cases, we will create Excess MSRs from those MSRs which will be transferred to one of our subsidiaries which function as qualified REIT subsidiaries. These intercompany transfers are eliminated in consolidation for financial statement purposes. The portion of the interest payments represented by the Excess MSRs will not be subject to an entity level tax as long as we comply with the REIT qualification tests. The tax liability of Aurora negatively impacts our returns from the MSRs that it holds. In addition, our investments in MSRs will expose us to default risk and the potential for credit losses.
We do not directly service the mortgage loans underlying the MSRs we acquire; rather, we contract with third-party subservicers to handle servicing functions for the loans underlying the MSRs.
RMBS Strategy. Our RMBS strategy focuses primarily on the acquisition and ownership of Agency RMBS that are whole-pool, residential mortgage pass-through certificates. However, from time to time, we invest in CMOs, including IOs and inverse IOs, primarily to take advantage of particularly attractive prepayment-related or structural opportunities in the RMBS markets. In addition to investing in specific pools of Agency RMBS, we utilize TBAs. Pursuant to these TBA transactions, we agree to purchase or sell, for future delivery, Agency RMBS with certain principal and interest terms and certain types of underlying collateral, but the particular Agency RMBS to be delivered is not identified until shortly before the TBA settlement date. Generally, we do not take delivery of the specified pool but instead enter into an offsetting transaction before the date when we would be required to take delivery. Our ability to engage in TBA transactions is limited by the gross income and asset tests applicable to REITs.
Our RMBS strategy includes selective investments in current issue, private label non-Agency RMBS and GSE risk-sharing securities. GSE risk-sharing securities are general obligations of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac that provide credit protection with respect to defaults on reference pools of loans. We currently expect to expand our participation in that market. However, the extent of our investments in GSE risk-sharing securities is limited by the gross income and asset tests applicable to REITs. We also may invest opportunistically in legacy non-Agency RMBS issued during or after 2010. If and when market conditions permit us to execute our prime mortgage loan acquisition and financing strategy, we expect that we would retain certain bonds collateralized by the prime mortgage loans we securitize. Non-Agency RMBS are subject to risk of default, among other risks, and could result in greater losses.
Prime Mortgage Loans. We believe that the market for non-conforming loans including, in particular, prime non-conforming mortgage loans, will grow. While we remain interested in investing in this asset class, we do not currently anticipate that either market conditions or available long-term financing will allow us to execute this strategy in 2020. The prime mortgage loans may be ARMs, hybrid ARMs or FRMs with original terms to maturity of not more than 30 years and will be either fully amortizing or interest-only for up to ten years, and fully amortizing thereafter. We expect that these loans may include both qualified mortgages and, if and when market conditions permit, non-QM loans.
Our overall strategy, and each category of assets within that strategy, is adaptable to changing market environments, subject to compliance with the income and other tests that we must satisfy to maintain our qualification as a REIT and maintain our exclusion from regulation as an investment company under the Investment Company Act. As a result, our acquisition and management decisions will depend on prevailing market conditions, and our targeted asset classes and strategy may vary over time in response to market conditions.
Our Manager
We are externally managed by our Manager and, with the exception of Aurora, our licensed mortgage servicing subsidiary, which has five leased employees, we have no employees. We have entered into a management agreement with our Manager, pursuant to which our Manager is responsible for our investment strategies and decisions and our day-to-day operations, subject to the supervision and oversight of our board of directors. Our Manager is a Delaware limited liability company originally established by Mr. Middleman. The Manager is party to a services agreement with Freedom Mortgage, which is owned and controlled by Mr. Middleman. The sole member of the Manager is a blind trust for the benefit of Mr. Middleman. We rely on our Manager to provide or obtain on our behalf the personnel and services necessary for us to conduct our business.
2
The principal office and place of business of our Manager is 1451 Route 34, Suite 303, Farmingdale, New Jersey 07727, and the telephone number of our Manager’s executive offices is (877) 870-7005.
We have a Risk Committee to monitor our investment policies, portfolio holdings, financing and hedging strategies and compliance with our investment guidelines. The members of our Risk Committee are Mr. Lown, our President and Chief Executive Officer; Mr. Evans, our Chief Investment Officer; Mr. Hutchby, our Chief Financial Officer, Treasurer and Secretary; our MSR portfolio manager; and our General Counsel.
Our Manager is registered as an investment adviser under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, as amended, and is subject to the regulatory oversight of the Investment Management Division of the SEC.
Our Investment Guidelines
The investment guidelines for our assets and borrowings are as follows:
| • | No investment will be made if it causes us to fail to qualify as a REIT under the Code. |
| • | No investment will be made if it causes us to be regulated as an investment company under the Investment Company Act. |
| • | We will not enter into principal transactions or split price executions with Freedom Mortgage or any of its affiliates unless such transaction is otherwise in accordance with our investment guidelines and the management agreement between us and our Manager and the terms of such transaction are at least as favorable to us as to Freedom Mortgage or its affiliate. |
| • | Any proposed material investment that is outside our targeted asset classes must be approved by at least a majority of our independent directors. |
Our Manager makes the determinations as to the percentage of assets that are invested in each of our targeted asset classes, consistent with our investment guidelines. Our Manager’s acquisition decisions depend on prevailing market conditions and may change over time in response to opportunities available in different interest rate, economic and credit environments. In addition, our investment guidelines may be changed from time to time by our board of directors without the approval of our stockholders. Changes to our investment guidelines may include, without limitation, modification or expansion of the types of assets which we may acquire.
Our board of directors receives a report of our investments each quarter in conjunction with our board’s review of our quarterly results. The nominating and corporate governance committee of our board of directors, which is comprised solely of our independent directors, will review the material terms of any transaction between us and Freedom Mortgage, including the pricing terms, to determine if the terms of those transactions are fair and reasonable. We also retain two independent valuation services to assist our management and our independent directors in making pricing determinations on any Servicing Related Assets we may purchase from Freedom Mortgage.
In 2013 and 2014, we acquired Excess MSRs from Freedom Mortgage and entered into recapture agreements with Freedom Mortgage. For reporting purposes, these Excess MSRs were aggregated into three pools: Excess MSR Pool 1, Excess MSR Pool 2 and Excess MSR Pool 2014. On November 15, 2016, we sold the Excess MSRs in Excess MSR Pool 1 and the Excess MSRs in Excess MSR Pool 2014 to Freedom Mortgage. We sold the Excess MSRs in Excess MSR Pool 2 to Freedom Mortgage on February 1, 2017. In connection with the sale of the Excess MSRs in Excess MSR Pool 2 to Freedom Mortgage, Freedom Mortgage transferred to Aurora Ginnie Mae MSRs on mortgage loans that had an aggregate UPB of approximately $4.5 billion as of January 31, 2017. In connection with these sales, we repaid the outstanding borrowings drawn on our $25 million term loan with NexBank SSB (the “NexBank term loan”). In addition, the Acknowledgment Agreement that we and Freedom Mortgage entered into with Ginnie Mae at the time of our IPO was terminated. In connection with the sale transactions, Freedom Mortgage made 12 monthly yield maintenance payments aggregating $3.0 million to the Company from December 2016 to November 2017. While we no longer own any of these Excess MSRs, this information is presented because the investments are reflected in the audited consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
3
Our Financing Strategies and Use of Leverage
We finance our RMBS with what we believe to be a prudent amount of leverage, which will vary from time to time based upon the particular characteristics of our portfolio, availability of financing and market conditions. Our borrowings for RMBS consist of repurchase transactions under master repurchase agreements. These agreements represent uncommitted financing provided by the counterparties. Our repurchase transactions are collateralized by our RMBS. In a repurchase transaction, we sell an asset to a counterparty at a discounted value, or the loan amount, and simultaneously agree to repurchase the same asset from such counterparty at a price equal to the loan amount plus an interest factor. Despite being legally structured as sales and subsequent repurchases, repurchase transactions are generally accounted for as debt secured by the underlying assets. During the term of a repurchase transaction, we generally receive the income and other payments distributed with respect to the underlying assets. While the proceeds of our repurchase financings often will be used to purchase additional RMBS subject to the same master repurchase agreement, our repurchase financing arrangements do not restrict our ability to use proceeds from these arrangements to support our other liquidity needs. Our master repurchase agreements are documented under the standard form master repurchase agreement published by SIFMA.
We have entered into repurchase agreements with 30 counterparties as of December 31, 2019. From time to time, we expect to negotiate and enter into additional master repurchase agreements with other counterparties that could produce opportunities to acquire certain RMBS that may not be available from our existing counterparties. See “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Aurora has three separate MSR financing facilities: a term loan for $20.0 million and secured by all Ginnie Mae MSRs owned by Aurora, which also includes a $10.0 million revolver to finance advances on the pledged Ginnie Mae MSRs; a revolving loan for up to $200.0 million, $100.0 million of which is committed, and secured by all Fannie Mae MSRs owned by Aurora; and a revolving loan for up to $100.0 million secured by all Freddie Mac MSRs owned by Aurora. See “Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data—Note 12—Notes Payable.” We may utilize other types of borrowings in the future, including corporate debt, securitization, or other more complex financing structures. Additionally, we may take advantage of available borrowings, if any, under new programs established by the U.S. Government to finance our assets. We also may raise capital by issuing unsecured debt or preferred or common stock.
Interest and Financing Risk Hedging
Subject to maintaining our qualification as a REIT and maintaining our exclusion from regulation as an investment company under the Investment Company Act, we use certain derivative financial instruments and other hedging instruments to mitigate interest rate risk and financing pricing risk we expect to arise from our repurchase agreement financings associated with our RMBS and the MSR financing facilities for our MSRs. We also attempt to mitigate duration and basis risk arising from our RMBS portfolio. The hedging instruments that we currently use include: interest rate swaps, TBAs, swaptions and Treasury futures. We may also use financial futures, options, interest rate cap agreements, and forward sales. Our overall hedging strategy reflects the natural but limited hedging effect of our Servicing Related Assets, which tend to increase in value as interest rates rise. See “Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data—Note 2—Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies—Derivatives and Hedging Activities.”
Policies with Respect to Certain Other Activities
If our board of directors determines that additional funding is required, we may raise such funds through additional offerings of equity or debt securities, the retention of cash flow and other funds from debt financing, or a combination of these methods. Our board of directors has the authority, without stockholder approval, to issue additional shares of common stock or preferred stock in any manner and on such terms and for such consideration as it deems appropriate, at any time. We may, in the future, offer equity or debt securities in exchange for assets. We have not in the past and will not in the future underwrite the securities of other companies. Our board of directors may change any of these policies without prior notice to, or a vote of, our stockholders.
4
Competition
We compete with other mortgage REITs, specialty finance companies, savings and loan associations, banks, mortgage bankers, insurance companies, mutual funds, institutional investors, investment banking firms, financial institutions, governmental bodies and other entities for investment opportunities in general. See “Item 1A. Risk Factors—We operate in a highly competitive market.”
Employees
We do not have any employees other than those of our licensed mortgage servicing subsidiary, Aurora, which has five leased employees.
Our Tax Status
We have elected to be taxed as a REIT under the Code. Provided that we maintain our qualification as a REIT, we generally will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax on our REIT taxable income that is currently distributed to our stockholders. REITs are subject to a number of organizational and operational requirements, including a requirement that they currently distribute at least 90% of their annual REIT taxable income excluding net capital gains. We cannot assure you that we will be able to comply with such requirements in the future. Failure to qualify as a REIT in any taxable year would cause us to be subject to U.S. federal income tax on our taxable income at regular corporate rates (and any applicable state and local taxes). Even if we qualify for taxation as a REIT, we may be subject to certain federal, state, local and non-U.S. taxes on our income. For example, the income generated by our TRS and its subsidiary, Aurora, is subject to U.S. federal, state and local income tax. See “Item 1A. Risk Factors—U.S. Federal Income Tax Risks” for additional tax status information.
Our Exclusion from Regulation as an Investment Company
We are organized as a holding company and conduct business primarily through our subsidiaries. We believe we have conducted and intend to conduct our operations so that neither we nor any of our subsidiaries are required to register as an investment company under the Investment Company Act.
Section 3(a)(1)(A) of the Investment Company Act defines an investment company as any issuer that is or holds itself out as being engaged primarily in the business of investing, reinvesting or trading in securities. Section 3(a)(1)(C) of the Investment Company Act defines an investment company as any issuer that is engaged or proposes to engage in the business of investing, reinvesting, owning, holding or trading in securities and owns or proposes to acquire investment securities having a value exceeding 40% of the value of the issuer’s total assets (exclusive of U.S. Government securities and cash items) on an unconsolidated basis, which we refer to as the 40% test. Excluded from the term “investment securities,” among other things, are U.S. Government securities and securities issued by majority-owned subsidiaries that are not themselves investment companies and are not relying on the exclusion from the definition of investment company set forth in Section 3(c)(1) or Section 3(c)(7) of the Investment Company Act.
We believe neither we nor our Operating Partnership is considered an investment company under Section 3(a)(1)(A) of the Investment Company Act because neither we nor our Operating Partnership engage primarily or hold ourselves out as being engaged primarily in the business of investing, reinvesting or trading in securities. Rather, through our Operating Partnership’s wholly-owned or majority-owned subsidiaries, we and our Operating Partnership are primarily engaged in the non-investment company businesses of these subsidiaries, namely the business of purchasing or otherwise acquiring mortgages and other interests in real estate.
We rely upon certain exemptions from registration as an investment company under the Investment Company Act, including, in the case of our subsidiary, Cherry Hill QRS I, LLC, Section 3(c)(5)(C) of the Investment Company Act. Section 3(c)(5)(C), as interpreted by the staff of the SEC, requires an entity to invest at least 55% of its assets in “mortgages and other liens on and interests in real estate,” which we refer to as “qualifying real estate interests,” and at least 80% of its assets in qualifying real estate interests plus “real estate-related assets.” In satisfying the 55% requirement, the entity may treat securities issued with respect to an underlying pool of mortgage loans in which it holds all of the certificates issued by the pool as qualifying real estate interests. We treat the Agency whole-pool pass-through securities in which we have invested as qualifying real estate interests for purposes of the 55% requirement. The Servicing Related Assets and non-Agency RMBS we have acquired are not treated as qualifying real estate interests for purposes of the 55% requirement, but are
5
treated as real estate-related assets that qualify for the 80% test. In addition, Cherry Hill QRS I, LLC will treat its investments in Cherry Hill QRS II, LLC, Cherry Hill QRS III, LLC (“QRS III”), Cherry Hill QRS IV, LLC (“QRS IV”) and Cherry Hill QRS V, LLC (“QRS V”) as real estate-related assets because substantially all of the assets held by those subsidiaries are real estate-related assets.
We monitor our compliance with the 40% test and the holdings of our subsidiaries to ensure that each of our subsidiaries is in compliance with an applicable exemption or exclusion from registration as an investment company under the Investment Company Act. In the event that we or our Operating Partnership were to acquire assets that could make either entity fall within the definition of an investment company under Section 3(a)(1)(A) or Section 3(a)(1)(C) of the Investment Company Act, we believe that we would still qualify for an exclusion from registration pursuant to Section 3(c)(5)(C).
Qualification for exclusion from registration under the Investment Company Act limits our ability to make certain investments. In addition, complying with the tests for exclusion from registration could restrict the time at which we can acquire and sell assets. To the extent that the SEC or its staff provides more specific guidance regarding any of the matters bearing upon such exclusions, we may be required to adjust our strategy accordingly. Any additional guidance from the SEC or its staff could further inhibit our ability to pursue the strategies we have chosen.
Website Access to Reports
We maintain a website at www.chmireit.com. We are providing the address to our website solely for the information of investors. The information on our website is not a part of, nor is it incorporated by reference, into this report. Through our website, we make available, free of charge, our annual proxy statements, annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. The SEC maintains a website that contains these reports at www.sec.gov
Corporate Information
Our principal executive offices are located at 1451 Route 34, Suite 303, Farmingdale, New Jersey 07727. Our telephone number is (877) 870-7005.
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors |
The Company’s business and operations are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties, the occurrence of which could adversely affect its business, financial condition, results of operations and ability to make distributions to stockholders and could cause the value of the Company’s capital stock to decline. Please refer to the section entitled “Forward-Looking Information.”
Risks Related to Our Business
We may not be able to continue to generate sufficient revenue to make or sustain distributions to our stockholders.
We cannot assure you that we will be able to continue to generate sufficient returns to pay our operating expenses and make satisfactory distributions to our stockholders. The results of our operations depend on several factors, including the availability of opportunities for the acquisition of target assets, the level and volatility of interest rates, the availability of adequate short and long-term financing, conditions in the financial markets and general economic conditions.
Difficult conditions in the mortgage and residential real estate markets as well as general market concerns may adversely affect the value of the assets in which we invest, and these conditions may persist for the foreseeable future.
Our business is materially affected by conditions in the residential mortgage market, the residential real estate market, the financial markets and the economy in general. In particular, the residential mortgage market in the United States has experienced a variety of difficulties and changed economic conditions, including defaults,
6
credit losses and liquidity concerns. Certain commercial banks, investment banks and insurance companies incurred extensive losses from exposure to the residential mortgage market as a result of these difficulties and conditions. These factors have impacted investor perception of the risk associated with RMBS, other real estate-related securities and various other asset classes in which we may invest. As a result, values of our target assets have experienced volatility. Deterioration of the mortgage market and investor perception of the risks associated with RMBS and other residential mortgage assets that we acquire could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to make distributions to our stockholders.
We are dependent on mortgage servicers to service the mortgage loans relating to our Servicing Related Assets.
Our investments in Servicing Related Assets are dependent on the entity performing the actual servicing of the mortgage loans, called the mortgage servicer, to perform its servicing obligations. As a result, we could be materially and adversely affected if a mortgage servicer is terminated by the applicable Agency. The duties and obligations of mortgage servicers are defined through contractual agreements, which generally provide for the possibility for termination of the mortgage servicer in the absolute discretion of the applicable Agency. In addition, the termination of a mortgage servicer could take effect across all mortgages being serviced by that mortgage servicer.
We could also be materially and adversely affected if a mortgage servicer is unable to adequately service the underlying mortgage loans due to the following reasons, among others:
| • | its failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations; |
| • | its failure to perform its loss mitigation obligations; |
| • | a downgrade in its servicer rating; |
| • | its failure to perform adequately in its external audits; |
| • | a failure in or poor performance of its operational systems or infrastructure; |
| • | regulatory or legal scrutiny, enforcement proceedings, consent orders or similar actions regarding any aspect of its operations, including, but not limited to, servicing practices and foreclosure processes lengthening foreclosure timelines; or |
| • | the transfer of servicing to another party. |
MSRs are subject to numerous federal, state and local laws and regulations and may be subject to various judicial and administrative decisions imposing various requirements and restrictions on the mortgage servicer’s business. If any mortgage servicer that we use actually or allegedly fails to comply with applicable laws, rules or regulations, that mortgage servicer could be exposed to fines, penalties or other costs, or the mortgage servicer could be terminated by the applicable Agency. If these laws, regulations and decisions change, we could be exposed to similar fines, penalties or costs. In addition, if a mortgage servicer that we use experiences any of the failures or regulatory scrutiny described above, then we could become subject to heightened regulatory or legal scrutiny by virtue of being a counterparty of these entities. Such scrutiny could result in our incurring meaningful additional costs or fines or being subject to material operational requirements or restrictions, each of which could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
In addition, a bankruptcy by any mortgage servicer that services the mortgage loans for us could result in:
| • | payments made by such mortgage servicer to us, or obligations incurred by it, being voided by a court under federal or state preference laws or federal or state fraudulent conveyance laws; or |
| • | any agreement between us and the mortgage servicer being rejected in a bankruptcy proceeding. |
Because we do not and in the future may not have the employees, servicing platforms, or technical resources necessary to service mortgage loans, upon a discontinuance or bankruptcy of any mortgage servicer that we use, we would need to engage an alternate mortgage servicer, which may not be readily available on acceptable terms or at all.
Any of the foregoing events could have a material and adverse effect on us.
7
The performance of loans underlying our MSRs may be adversely affected by the performance of the related mortgage servicer.
The performance of the loans underlying our MSRs is subject to risks associated with inadequate or untimely servicing. If our mortgage servicers commit a material breach of their obligations as a servicer, we may be subject to damages if the breach is not cured within a specified period of time following notice. Poor performance by a mortgage servicer may result in greater than expected delinquencies and foreclosures and losses on the mortgage loans underlying our MSRs. A substantial increase in our delinquency or foreclosure rate or the inability to process claims could adversely affect our ability to access the capital and secondary markets for our financing needs.
Our ability to invest in, and dispose of, our investments in Servicing Related Assets may be subject to the receipt of third-party consents.
The Agencies may require that we submit ourselves to costly or burdensome conditions as a prerequisite to their consent to our investments in Servicing Related Assets. These conditions may diminish or eliminate the investment potential of certain of those assets by making such investments too expensive for us or by severely limiting the potential returns available or otherwise imposing unacceptable conditions. The potential costs, issues or restrictions associated with receiving any such Agency’s consent for any such acquisitions or dispositions by us cannot be determined with any certainty. To the extent we are unable to acquire or dispose of Servicing Related Assets when we determine it would be beneficial to do so, our results of operations may be adversely impacted.
The value of our Servicing Related Assets may vary substantially with changes in interest rates.
The values of Servicing Related Assets are highly sensitive to changes in interest rates. The value of Servicing Related Assets typically increases when interest rates rise and decreases when interest rates decline due to the effect those changes in interest rates have on prepayment estimates. Subject to qualifying and maintaining our qualification as a REIT, we may pursue various hedging strategies to seek to reduce our exposure to adverse changes in interest rates. Our hedging activity will vary in scope based on the level and volatility of interest rates, the type of assets held and other changing market conditions. Interest rate hedging may fail to protect or could adversely affect us. To the extent we do not utilize derivatives to hedge against changes in the fair value of our Servicing Related Assets, our balance sheet, results of operations and cash flows would be susceptible to significant volatility due to changes in the fair value of, or cash flows from, those assets as interest rates change.
If delinquencies increase, the value of our Servicing Related Assets may decline significantly.
Delinquency rates have a significant impact on the value of our Servicing Related Assets. An increase in delinquencies will generally result in lower revenue because, typically, servicers will only collect servicing fees from GSEs or mortgage owners for performing loans. Our expectation of delinquencies is a significant assumption underlying the cash flow projections on the related pools of mortgage loans. If delinquencies are significantly greater than expected, the actual fair value of the Servicing Related Assets could be diminished. As a result, we could suffer a loss.
Prepayment rates can change, adversely affecting the performance of our assets.
The frequency at which prepayments (including voluntary prepayments by borrowers, loan buyouts and liquidations due to defaults and foreclosures) occur on mortgage loans is affected by a variety of factors, including the prevailing level of interest rates as well as economic, demographic, tax, social, legal, and other factors. Generally, borrowers tend to prepay their mortgage loans when prevailing mortgage rates fall below the interest rates on their mortgage loans. If borrowers prepay their mortgage loans at rates that are faster or slower than expected, it may adversely affect our results.
We record our Servicing Related Assets on our balance sheet at fair value, and changes in their fair value are reflected in our consolidated results of operations. The determination of the fair value of Servicing Related Assets requires our management to make numerous estimates and assumptions that could materially differ from actual results. Such estimates and assumptions include, among other things, prepayment rates, as well as estimates of the future cash flows from the Servicing Related Assets, interest rates, delinquencies and foreclosure rates of the underlying mortgage loans. The ultimate realization of the value of the Servicing Related Assets,
8
which are measured at fair value on a recurring basis, may be materially different than the fair values of such assets as may be reflected in our consolidated financial statements as of any particular date. The use of different estimates or assumptions in connection with the valuation of these assets could produce materially different fair values for such assets. Our failure to make accurate assumptions regarding prepayment rates or the other factors examined in determining fair value could cause the fair value of our Servicing Related Assets to vary materially, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations and cash flows. If the fair value of our Servicing Related Assets decreases, we would be required to record a non-cash charge, which would have a negative impact on our financial results. Furthermore, a significant increase in prepayment speeds could materially reduce the ultimate cash flows we receive from the Servicing Related Assets, and we could ultimately receive substantially less than what we paid for such assets.
Prepayment rates also affect the fair values of our RMBS. Voluntary prepayment rates generally increase when interest rates fall and decrease when interest rates rise, but changes in prepayment rates are difficult to predict as changes may occur faster or slower than changes in the market interest rates. Prepayments can also occur when borrowers sell the property and use the sale proceeds to prepay the mortgage as part of a physical relocation or when borrowers default on their mortgages and the mortgages are prepaid from the proceeds of a foreclosure sale of the property. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac will generally purchase mortgages that are 120 days or more delinquent from mortgage-backed securities trusts when the cost of guaranteed payments to security holders, including advances of interest at the security coupon rate, exceeds the cost of holding the nonperforming loans in their portfolios. Ginnie Mae provides the issuer the option to buy loans that are 90 days or more delinquent out of the mortgage-backed securities that it services, which may also contribute to an increase in prepayment rates. Consequently, prepayment rates also may be affected by conditions in the housing and financial markets, which may result in increased delinquencies on mortgage loans. Additionally, changes in the GSEs decisions as to when to repurchase delinquent loans can materially impact prepayment rates.
Interest rate mismatches between our assets and any borrowings used to fund purchases of our assets may reduce our income during periods of changing interest rates.
Some of our assets will be fixed-rate securities or have a fixed rate component (such as RMBS backed by hybrid ARMs). This means that the interest we earn on these assets will not vary over time based upon changes in a short-term interest rate index. Although the interest we would earn on any RMBS backed by ARMs generally will adjust for changing interest rates, such interest rate adjustments may not occur as quickly as the interest rate adjustments to any related borrowings, and such interest rate adjustments will generally be subject to interest rate caps, which potentially could cause such RMBS to acquire many of the characteristics of fixed-rate securities if interest rates were to rise above the cap levels. We generally fund our fixed-rate target assets with short-term borrowings. Therefore, there will be an interest rate mismatch between our assets and liabilities. Although we hedge to minimize interest rate exposure, the use of interest rate hedges also introduces the risk of other interest rate mismatches and exposures. During periods of changing interest rates, these mismatches could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to make distributions to our stockholders.
Ordinarily, short-term interest rates are lower than long-term interest rates. If short-term interest rates rise disproportionately relative to long-term interest rates (a flattening of the yield curve), our borrowing costs may increase more rapidly than the interest income earned on our assets. Because we expect that our investments in RMBS, on average, will bear interest based on longer-term rates than our borrowings, a flattening of the yield curve would tend to decrease our net income and the market value of our assets. Additionally, to the extent cash flows from RMBS are reinvested in new RMBS, the spread between the yields of the new RMBS and available borrowing rates may decline, which could reduce our net interest margin or result in losses. Any one of the foregoing risks could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders. It is also possible that short-term interest rates may exceed long-term interest rates, in which event our borrowing costs may exceed our interest income and we could incur operating losses.
We cannot predict the impact future actions by regulators or U.S. government bodies, including the U.S. Federal Reserve, will have on our business, and any such actions may negatively impact us.
Regulators and U.S. government bodies have a major impact on our business. The U.S. Federal Reserve is a major participant in, and its actions significantly impact, the residential mortgage market. For example, quantitative easing, a program implemented by the U.S. Federal Reserve to keep long-term interest rates low and
9
stimulate the U.S. economy, has had the effect of reducing the difference between short-term and long-term interest rates. As a result of the reduction in long-term interest rates, prepayment speeds increased. The U.S. Federal Reserve’s purchases of Agency RMBS have resulted in a narrowing of the spread earned by Agency RMBS investors. The U.S. Federal Reserve has discontinued quantitative easing and has begun to reduce its balance sheet (quantitative tightening). We cannot predict or control the impact future actions by regulators or U.S. government bodies such as the U.S. Federal Reserve will have on our business. Accordingly, future actions by regulators or U.S. government bodies, including the U.S. Federal Reserve, could have a material and adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Interest rate caps on the ARMs and hybrid ARMs that may back our RMBS may reduce our net interest margin during periods of rising interest rates.
ARMs and hybrid ARMs are typically subject to periodic and lifetime interest rate caps. Periodic interest rate caps limit the amount an interest rate can increase during any given period. Lifetime interest rate caps limit the amount an interest rate can increase through the maturity of the loan. We generally fund our RMBS with borrowings that typically are not subject to similar restrictions. Accordingly, in a period of rapidly increasing interest rates, our financing costs could increase without limitation while caps could limit the interest we earn on the ARMs and hybrid ARMs that will back our RMBS. This problem is magnified for ARMs and hybrid ARMs that are not fully indexed because such periodic interest rate caps prevent the coupon on the security from fully reaching the specified rate in one reset. Further, some ARMs and hybrid ARMs may be subject to periodic payment caps that result in a portion of the interest being deferred and added to the principal outstanding. As a result, we may receive less cash income on RMBS backed by ARMs and hybrid ARMs than necessary to pay interest on our related borrowings. Interest rate caps on RMBS backed by ARMs and hybrid ARMs could reduce our net interest margin if interest rates were to increase beyond the level of the caps, which could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
Our Manager relies on analytical models and other data to analyze potential asset acquisition and disposition opportunities and to manage our portfolio. These models are based on assumptions and actual results may differ significantly from the modeled expectations.
Our Manager relies on analytical models and information and data supplied by third parties. These models and data may be used to value assets or potential asset acquisitions and dispositions and to conduct our asset management activities. If these models and data prove to be incorrect, misleading or incomplete, any decisions made in reliance thereon could expose us to potential risks. In addition, models are only as accurate as the assumptions that go into building the models. Our Manager’s use of models and data may induce it to purchase certain assets at prices that are too high, sell certain other assets at prices that are too low or miss favorable opportunities altogether. Similarly, any hedging activities that are based on faulty models and data may prove to be unsuccessful.
Some models, such as prepayment models or mortgage default models, may be predictive in nature. The use of predictive models has inherent risks. For example, such models may incorrectly forecast future behavior, leading to potential losses. In addition, the predictive models used by our Manager may differ substantially from those models used by other market participants, with the result that valuations based on these predictive models may be substantially higher or lower for certain assets than actual market prices. Furthermore, because predictive models are usually constructed based on historical data supplied by third parties, the success of relying on such models may depend heavily on the accuracy and reliability of the supplied historical data, and, in the case of predicting performance in scenarios with little or no historical precedent (such as extreme broad-based declines in home prices, or deep economic recessions or depressions), such models must employ greater degrees of extrapolation, and are therefore more speculative and of more limited reliability.
All valuation models rely on correct market data inputs. If incorrect market data is entered into even a well-founded valuation model, the resulting valuations will be incorrect. However, even if market data is input correctly, “model prices” will often differ substantially from market prices, especially for securities with complex characteristics or whose values are particularly sensitive to various factors. If our market data inputs are incorrect or our model prices differ substantially from market prices, our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to make distributions to our stockholders could be materially adversely affected.
10
Valuations of some of our assets will be inherently uncertain, may be based on estimates, may fluctuate over short periods of time and may differ from the values that would have been used if a ready market for these assets existed.
While in many cases our determination of the fair value of our assets is based on valuations provided by third-party dealers and pricing services, we value assets based upon our judgment, and such valuations may differ from those provided by third-party dealers and pricing services. Valuations of certain assets are often difficult to obtain or unreliable. Depending on the complexity and illiquidity of an asset, valuations of the same asset can vary substantially from one dealer or pricing service to another. The valuation process has been particularly difficult recently because market events have made valuations of certain assets unpredictable, and the disparity of valuations provided by third-party dealers has widened. Our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to make distributions to our stockholders could be materially adversely affected if our fair value determinations of these assets are materially higher than actual market values.
An increase in interest rates may cause a decrease in the volume of certain of our target assets, which could adversely affect our ability to acquire target assets that satisfy our investment objectives and to make distributions to our stockholders.
Rising interest rates generally reduce the demand for mortgage loans due to the higher cost of borrowing. A reduction in the volume of mortgage loans originated may affect the volume of target assets available to us, which could adversely affect our ability to acquire assets that satisfy our investment objectives. Rising interest rates may also cause our target assets that were issued prior to an interest rate increase to provide yields that are below prevailing market interest rates. If rising interest rates cause us to be unable to acquire a sufficient volume of our target assets with a yield that is above our borrowing cost, our ability to satisfy our investment objectives and to make distributions to our stockholders could be materially adversely affected.
We are highly dependent on information systems and third parties, and systems failures or cybersecurity incidents could significantly disrupt our business, which may, in turn, negatively affect the market price of our securities and our ability to operate our business.
Our business is highly dependent on communications and information systems. Any failure or interruption of those systems or cyber-attacks or security breaches of our networks or systems could cause delays or other problems in our securities trading activities, including MBS trading activities. A disruption or breach could also lead to unauthorized access to and release, misuse, loss or destruction of our confidential information or personal or confidential information of third parties, which could lead to regulatory fines, costs associated with remediating the breach, reputational harm, financial losses, litigation. In addition, we also face the risk of operational failure, termination or capacity constraints of any of the third parties with which we do business or that facilitate our business activities, including clearing agents or other financial intermediaries we use to facilitate our securities transactions, if their respective systems experience failure, interruption, cyber-attacks or security breaches. The costs and losses associated with these risks are difficult to predict and quantify, but could have a significant adverse effect on our operating results. Additionally, the legal and regulatory environment surrounding information privacy and security in the U.S. and international jurisdictions is constantly evolving.
Computer malware, viruses, computer hacking and phishing attacks have become more prevalent in our industry. Although we have not detected a material cybersecurity breach to date, other financial services institutions have reported material breaches of their systems, some of which have been significant. Even with all reasonable security efforts, not every breach can be prevented or even detected. There is no assurance that we, or the third parties that facilitate our business activities, have not or will not experience a breach. It is difficult to determine what, if any, negative impact may directly result from any specific interruption or cyber-attacks or security breaches of the networks or systems of third parties that facilitate our business activities but such computer malware, viruses, and computer hacking and phishing attacks may negatively affect our financial condition, results of operations, the market value of our common or preferred stock, and our ability to make distributions to our stockholders.
The lack of liquidity of our assets may adversely affect our business, including our ability to sell our assets.
Mortgage-related assets generally experience periods of illiquidity, including the period of delinquencies and defaults with respect to residential and commercial mortgage loans during the financial crisis. In addition, validating third-party pricing for illiquid assets may be more subjective than with respect to more liquid assets.
11
Any illiquidity of our assets makes it difficult for us to sell such assets if the need or desire arises. In addition, if we are required to liquidate all or a portion of our portfolio quickly, we may realize significantly less than the value at which we previously recorded our assets. Assets that are illiquid are more difficult to finance, and to the extent that we use leverage to finance assets that become illiquid we may lose that leverage or have it reduced. Assets tend to become less liquid during times of financial stress, which is often the time that liquidity is most needed. As a result, our ability to sell assets or vary our portfolio in response to changes in economic and other conditions may be limited by liquidity constraints, which could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
We use leverage in executing our business strategy, which may adversely affect the return on our assets and may reduce cash available for distribution to our stockholders, as well as increase losses when economic conditions are unfavorable.
We use leverage to finance our investments in certain of our target assets and to enhance our financial returns. Our primary source of leverage is short-term borrowings under master repurchase agreements collateralized by our RMBS assets (‘repo financing”). Other sources of leverage include MSR financings and, in the future, may include other credit facilities.
Through the use of leverage, we acquire positions with market exposure significantly greater than the amount of capital committed to the transaction. Although we generally are not required to maintain any particular minimum or maximum target debt-to-equity leverage ratio with respect to our RMBS assets, the amount of leverage we may employ for this asset class will depend upon the availability of particular types of financing and our Manager’s assessment of the credit, liquidity, price volatility, financing counterparty risk and other factors. Our Manager has discretion, without the need for further approval by our board of directors, to change the amount of leverage we utilize for our RMBS. A change in our leverage strategy may increase our exposure to interest rate and real estate market fluctuations or require us to sell a portion of our existing investments, which could result in gains or losses and therefore increase our earnings volatility. Decisions to employ additional leverage in executing our RMBS investment strategies could increase the risk inherent in our RMBS acquisition strategy.
Although we do not have a targeted debt-to-equity ratio for our RMBS, we are subject to margin calls as a result of our financing activity. We use leverage for the primary purpose of financing our RMBS portfolio and not for the purpose of speculating on changes in interest rates. We are restricted in the amount of leverage we may employ by the terms and provisions of some of our financing agreements and the terms of agreements that we may enter into in the future may include limits on leverage.
Our ability to achieve our investment and leverage objectives depends on our ability to borrow money in sufficient amounts and on favorable terms. In particular, our ability to execute on our prime mortgage loan strategy and our ability to build a significant servicing portfolio is dependent on obtaining sufficient financing on attractive terms. In addition, we must be able to renew or replace our maturing borrowings on a continuous basis. In recent years, investors and financial institutions that lend in the securities repurchase market have tightened lending standards in response to the difficulties and changed economic conditions that have materially adversely affected the RMBS market. These market disruptions have been most pronounced in the non-Agency RMBS market, but the impact has also extended to Agency RMBS, which has made the value of these assets unstable and relatively illiquid compared to prior periods. More recently, the repo financing market has experienced a severe liquidity issue resulting in the infusion of additional liquidity by the Federal Reserve. These market disruptions and liquidity issues could potentially increase our financing costs and reduce our liquidity. In addition, because we rely on short-term financing, we are exposed to changes in the availability of financing which may make it more difficult for us to secure continued financing.
Leverage magnifies both the gains and the losses of our positions. Leverage increases our returns as long as we earn a greater return on investments purchased with borrowed funds than our cost of borrowing such funds. However, if we use leverage to acquire an asset and the value of the asset decreases, the leverage may increase our loss. Even if the asset increases in value, if the asset fails to earn a return that equals or exceeds our cost of borrowing, the leverage will decrease our returns.
We are required to post large amounts of cash as collateral or margin to secure our leveraged RMBS positions. In the event of a sudden, precipitous drop in value of our financed assets, we might not be able to liquidate assets quickly enough to repay our borrowings, further magnifying losses. Even a small decrease in the
12
value of a leveraged asset may require us to post additional margin or cash collateral. Our debt service payments and posting of margin or cash collateral will reduce cash flow available for distribution to stockholders. We may not be able to meet our debt service obligations. To the extent that we cannot meet our debt service obligations, we risk the loss of some or all of our assets to sale to satisfy our debt obligations.
To the extent we might be compelled to liquidate qualifying real estate assets to repay debts, our compliance with the REIT rules regarding our assets and our sources of income could be negatively affected, which could jeopardize our qualification as a REIT. Failing to qualify as a REIT would cause us to be subject to U.S. federal income tax (and any applicable state and local taxes) on all of our income and decrease profitability and cash available for distributions to stockholders.
Adverse market developments generally will cause our lenders to require us to pledge cash as additional collateral. If our assets were insufficient to meet these collateral requirements, we might be compelled to liquidate particular assets at inopportune times and at unfavorable prices.
Adverse market developments, including a sharp or prolonged rise in interest rates, a change in prepayment rates or increasing market concern about the value or liquidity of one or more types of our target assets, might reduce the market value of our portfolio, which generally will cause our lenders to initiate margin calls. A margin call means that the lender requires us to pledge cash as additional collateral to re-establish the ratio of the value of the collateral to the amount of the borrowing. If we are unable to satisfy margin calls, our lenders may foreclose on our collateral. The liquidation of collateral may jeopardize our ability to qualify as a REIT. Our failure to qualify as a REIT would cause us to be subject to U.S. federal income tax (and any applicable state and local taxes) on all of our income and decrease profitability and cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
Our use of repurchase transactions gives our lenders greater rights in the event that we file for bankruptcy, which may make it difficult for us to recover our collateral in the event of a bankruptcy filing.
Our borrowings under master repurchase agreements are intended to qualify for special treatment under the bankruptcy code, giving our lenders the ability to void the automatic stay provisions of the bankruptcy code and take possession of and liquidate collateral pledged in our repurchase transactions without delay if we file for bankruptcy. Furthermore, the special treatment of repurchase agreements under the bankruptcy code may make it difficult for us to recover our pledged assets in the event that any of our lenders files for bankruptcy. Thus, the use of repurchase transactions exposes our pledged assets to risk in the event of a bankruptcy filing by either our lenders or us.
If our lenders default on their obligations to resell the RMBS back to us at the end of the repurchase transaction term, the value of the RMBS has declined by the end of the repurchase transaction term or we default on our obligations under the repurchase transaction, we will lose money on these transactions. Any such losses may materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to pay distributions to our stockholders.
When we engage in a repurchase transaction, we initially sell securities to the financial institution in exchange for cash, and our counterparty is obligated to resell the securities to us at the end of the term of the transaction, which is typically from 30 to 180 days, but which may be up to 364 days or more. The cash we receive when we initially sell the securities is less than the value of those securities. This difference is referred to as the haircut. If these haircuts are increased, we will be required to post additional cash collateral for our RMBS. If our counterparty defaults on its obligation to resell the securities to us, we would incur a loss on the transaction equal to the amount of the haircut (assuming there was no change in the value of the securities). See “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources” for information regarding borrowings under the Company’s repurchase agreements.
If we default on one of our obligations under a repurchase transaction, the counterparty can terminate the transaction and cease entering into any other repurchase transactions with us. Such a default also would constitute a default under many of our financing agreements with other counterparties. In that case, there is no assurance we would be able to establish a suitable replacement facility on acceptable terms or at all.
13
Hedging against interest rate changes and other risks may materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to make distributions to our stockholders.
Subject to maintaining our qualification as a REIT and exemption from registration under the Investment Company Act, we pursue various hedging strategies to seek to reduce our exposure to adverse changes in interest rates. Our hedging activity varies in scope based on the level and volatility of interest rates, the types of liabilities and assets held and other changing market conditions. Interest rate hedging may fail to protect or could adversely affect us because, among other things:
| • | interest rate hedging can be expensive, particularly during periods of rising and volatile interest rates; |
| • | available interest rate hedges may not correspond directly with the interest rate risk for which protection is sought; |
| • | the duration of the hedge may not match the duration of the related assets or liabilities being hedged; |
| • | to the extent hedging transactions do not satisfy certain provisions of the Code, and are not made through a TRS, the amount of income that a REIT may earn from hedging transactions to offset interest rate losses is limited by U.S. federal tax provisions governing REITs; |
| • | the value of derivatives used for hedging may be adjusted from time to time in accordance with accounting rules to reflect changes in fair value. Downward adjustments or “mark-to-market losses” would reduce our total stockholders’ equity; |
| • | the credit quality of the hedging counterparty owing money on the hedge may be downgraded to such an extent that it impairs our ability to sell or assign our side of the hedging transaction; and |
| • | the hedging counterparty owing money in the hedging transaction may default on its obligation to pay. |
Our hedging transactions, which are intended to limit losses, may actually adversely affect our earnings, which could reduce our cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
Changes in regulations relating to swaps activities may cause us to limit our swaps activity or subject us and our Manager to additional disclosure, recordkeeping, and other regulatory requirements.
The enforceability of agreements underlying hedging transactions may depend on compliance with applicable statutory and commodity and other regulatory requirements and, depending on the identity of the counterparty, applicable international requirements. Recently, new regulations have been promulgated by U.S. and foreign regulators attempting to strengthen oversight of derivative contracts. Any actions taken by regulators could constrain our strategy and could increase our costs, either of which could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to make distributions to our stockholders. In particular, the Dodd-Frank Act requires most derivatives to be executed on a regulated market and cleared through a central counterparty, which has resulted in increased margin requirements and costs. On December 7, 2012, the CFTC issued a no-action letter that provides mortgage REITs relief from such registration, or the MREIT No-Action Letter, if they meet certain conditions and submit a claim for such no-action relief. We believe we meet the conditions set forth in the MREIT No-Action Letter, and we have filed our claim with the CFTC to perfect the use of the no-action relief from registration. However, if in the future we do not meet the conditions set forth in the MREIT No-Action Letter or the relief provided by the MREIT No-Action Letter becomes unavailable for any other reason, we may need to seek to obtain another exemption from registration or we may be required to register as a “commodity pool operator” with the CFTC. If we are required to register with the CFTC as a commodity pool operator, we would become subject to additional disclosure, recordkeeping and reporting requirements, which may increase our expenses or otherwise limit our ability to conduct our business as contemplated.
We may change our investment strategy, investment guidelines and asset allocation without notice or stockholder consent, which may result in riskier investments. In addition, our charter provides that our board of directors may authorize us to revoke or otherwise terminate our REIT election, without the approval of our stockholders.
Our board of directors has the authority to change our investment strategy or asset allocation at any time without notice to or consent from our stockholders. To the extent that our investment strategy changes in the future, we may make investments that are different from, and possibly riskier than, the investments described in
14
this Annual Report on Form 10-K and the other documents we file with the SEC from time to time. A change in our investment may increase our exposure to interest rate and real estate market fluctuations or require us to sell a portion of our existing investments, which could result in gains or losses and therefore increase our earnings volatility. Furthermore, a change in our asset allocation could result in our allocating assets in a different manner than as described in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
In addition, our charter provides that our board of directors may authorize us to revoke or otherwise terminate our REIT election, without the approval of our stockholders, if it determines that it is no longer in our best interests to qualify as a REIT. These changes could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, the market value of our common or preferred stock, and our ability to make distributions to our stockholders.
We operate in a highly competitive market.
Our profitability depends, in large part, on our ability to acquire targeted assets at favorable prices. We compete with a number of entities when acquiring our targeted assets, including other mortgage REITs, financial companies, public and private funds, commercial and investment banks and residential and commercial finance companies. We may also compete with the U.S. Federal Reserve and the U.S. Treasury to the extent they purchase assets in our targeted asset classes. Many of our competitors are substantially larger and have considerably greater access to capital and other resources than we do. Furthermore, new companies with significant amounts of capital have recently been formed or have raised additional capital, and may continue to be formed and raise additional capital in the future, and these companies may have objectives that overlap with ours, which may create competition for assets we wish to acquire. Some competitors may have a lower cost of funds and access to funding sources that are not available to us. In addition, some of our competitors may have higher risk tolerances or different risk assessments, which could allow them to consider a wider variety of assets to acquire and establish more relationships than us. We also may have different operating constraints from those of our competitors including, among others, (i) tax-driven constraints such as those arising from our qualification as a REIT, (ii) restraints imposed on us by our efforts to comply with certain exclusions or exemptions from the definition of an “investment company” under the Investment Company Act and (iii) restraints and additional costs arising from our status as a public company. Furthermore, competition for assets in our targeted asset classes may lead to the price of such assets increasing, which may further limit our ability to generate desired returns. We cannot assure you that the competitive pressures we face will not have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our ability to make distributions to our stockholders depends on our operating results, our financial condition and other factors, and we may not be able to make regular cash distributions at a fixed rate or at all under certain circumstances.
We intend to continue to distribute to our stockholders all or substantially all of our REIT taxable income in each year (subject to certain adjustments), and may distribute more than our REIT taxable income. This distribution policy will enable us to avoid being subject to U.S. federal income tax on our taxable income that we distribute to our stockholders. However, our ability to make distributions will depend on our earnings, applicable law, our financial condition and such other factors as our board of directors may deem relevant from time to time. We will declare and make distributions to our stockholders only to the extent approved by our board of directors.
Residential whole mortgage loans are subject to increased risks.
We may acquire and manage pools of residential whole mortgage loans. Residential whole mortgage loans are subject to increased risks of loss. Unlike Agency RMBS, whole mortgage loans generally are not guaranteed by the U.S. Government or any GSE, though in some cases they may benefit from private mortgage insurance. Additionally, by directly acquiring whole mortgage loans, we do not receive the structural credit enhancements that benefit senior tranches of CMOs. A whole mortgage loan is directly exposed to losses resulting from default. Therefore, the value of the underlying property, the creditworthiness and financial position of the borrower and the priority and enforceability of the lien will significantly impact the value of such mortgage loan. In the event of a foreclosure, we may assume direct ownership of the underlying real estate. The liquidation proceeds upon sale of such real estate may not be sufficient to recover our cost basis in the loan, and any costs or delays involved in the foreclosure or liquidation process may increase losses.
15
Whole mortgage loans are also subject to “special hazard” risk (property damage caused by hazards, such as earthquakes or environmental hazards, not covered by standard property insurance policies), and to bankruptcy risk (reduction in a borrower’s mortgage debt by a bankruptcy court). The increased severity of weather events such as floods, tornados and hurricanes due to climate change may increase the risk or amount of loss due to property damage. In addition, claims may be assessed against us on account of our position as a mortgage holder or property owner, including assignee liability, responsibility for tax payments, environmental hazards and other liabilities. In some cases, these liabilities may be “recourse liabilities” or may otherwise lead to losses in excess of the purchase price of the related mortgage or property.
Risks Related to Our Relationship with our Manager
We are dependent on our Manager and certain key personnel that are provided to us through our Manager and may not find a suitable replacement if our Manager terminates the management agreement or such key personnel are no longer available to us.
We do not have any employees of our own other than five leased employees of our licensed mortgage servicing subsidiary, Aurora. We are completely reliant on our Manager, which has significant discretion as to the implementation of our operating policies and execution of our business strategies and risk management practices. The departure of any of our senior officers could have a material adverse effect on our ability to achieve our objectives.
We can offer no assurance that our Manager will remain our manager or that we will continue to have access to our senior management. We are subject to the risk that our Manager will terminate the management agreement or that we may deem it necessary to terminate the management agreement or prevent certain individuals from performing services for us and that no suitable replacement will be found to manage us.
If our management agreement is terminated and no suitable replacement is found to manage us or we are unable to find a suitable replacement on a timely basis, we may not be able to continue to execute our business strategy. No assurances can be given that our Manager will act in our best interests with respect to the allocation of personnel, services and resources to our business. The failure of any of the key personnel of our Manager to service our business with the requisite time and dedication could materially and adversely affect our ability to execute our business strategy.
The management fee payable to our Manager is payable regardless of the performance of our portfolio, which may reduce our Manager’s incentive to devote the time and effort to seeking profitable opportunities for our portfolio.
We pay our Manager a management fee, which may be substantial, based on our stockholders’ equity (as defined in the management agreement) regardless of the performance of our portfolio. The management fee takes into account the net issuance proceeds of both common and preferred stock offerings, as well as issuances of equity securities by our Operating Partnership. Our Manager’s entitlement to non-performance-based compensation might reduce its incentive to devote the time and effort of its professionals to seeking profitable opportunities for our portfolio, which could result in a lower performance of our portfolio and materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our investment guidelines are very broad, and our board of directors will not approve each decision to acquire, dispose of, or otherwise manage an asset.
Our Manager is authorized to follow very broad guidelines in pursuing our strategy. Our board of directors will periodically review our portfolio and asset-management decisions. However, it generally will not review all of our proposed acquisitions, dispositions and other management decisions. In addition, in conducting periodic reviews, our board of directors will rely primarily on information provided to it by our Manager. Furthermore, our Manager may arrange for us to use complex strategies or to enter into complex transactions that may be difficult or impossible to unwind by the time they are reviewed by our board of directors. Our Manager has great latitude within the broad guidelines in determining the types of assets it may decide are proper for us to acquire and other decisions with respect to the management of those assets subject to our maintaining our qualification as a REIT. Poor decisions could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to make distributions to our stockholders.
16
There will be conflicts of interest in our relationships with our Manager and Freedom Mortgage, which could result in decisions that are not in the best interests of our stockholders.
Our Manager is a Delaware limited liability company established by Mr. Middleman. The Manager is a party to a services agreement with Freedom Mortgage, which is wholly owned and controlled by Mr. Middleman. The Manager is owned by a “blind trust” for the benefit of Mr. Middleman.
We are dependent on our Manager for our day-to-day management and operations. In turn, the Manager is dependent on the performance of Freedom Mortgage under the services agreement. Various potential and actual conflicts of interest may arise from the activities of Freedom Mortgage and its affiliates by virtue of this relationship. The ability of our Manager’s officers and personnel, with the exception of those officers that are dedicated to us, to engage in other business activities may reduce the time our Manager and certain of its officers and personnel spend managing us.
We may choose not to enforce, or to enforce less vigorously, our rights under our management agreement or our rights as a third party beneficiary to the services agreement between our Manager and Freedom Mortgage because of our desire to maintain ongoing relationships with our Manager and Freedom Mortgage. In the future, Freedom Mortgage may sponsor other vehicles that invest in Servicing Related Assets, prime loans or other residential mortgage assets, and there may be situations where we compete with Freedom Mortgage or its affiliates for opportunities to acquire Servicing Related Assets, prime mortgage loans or other residential mortgage assets. Freedom Mortgage is a separate and distinct company with its own business interests and will be under no obligation to maintain its current business strategy. Freedom Mortgage will be under no obligation to offer Servicing Related Assets or any other residential mortgage assets to us, and Freedom Mortgage may offer those assets to third parties without offering such assets to us.
In addition, there may be conflicts of interest inherent in our relationship with Freedom Mortgage through our Manager to the extent Freedom Mortgage or our Manager invests in or creates new vehicles to invest in assets in which we may invest or whose investment objectives overlap with our investment objectives. Certain investments appropriate for us may also be appropriate for one or more of these other investment vehicles. Members of our board of directors may serve as officers and/or directors of these other entities. In addition, in the future, our Manager or its affiliates may have investments in and/or earn fees from such other investment vehicles that are higher than their economic interests in us and which may therefore create an incentive to allocate investments to such other investment vehicles.
Our management agreement with our Manager generally does not limit or restrict our Manager or its affiliates from engaging in any business or managing other pooled investment vehicles that invest in investments that meet our investment objectives, except that under our management agreement neither our Manager nor any entity controlled by or under common control with our Manager is permitted to raise or sponsor any new pooled investment vehicle whose investment policies, guidelines or plans target as its primary investment category investments in Excess MSRs.
The ability of our Manager and its officers and employees to engage in other business activities, subject to the terms of our management agreement with our Manager, may reduce the amount of time our Manager, its officers or other employees spend managing us. In addition, we may engage (subject to our investment guidelines) in material transactions with Freedom Mortgage or our Manager, including, but not limited to, certain financing arrangements, co-investments in, or purchases of, MSRs or other assets, that present an actual, potential or perceived conflict of interest. It is possible that actual, potential or perceived conflicts could give rise to investor dissatisfaction, litigation or regulatory enforcement actions. Appropriately dealing with conflicts of interest is complex and difficult, and our reputation could be damaged if we fail, or appear to fail, to deal appropriately with one or more potential, actual or perceived conflicts of interest. Regulatory scrutiny of, or litigation in connection with, conflicts of interest could have a material adverse effect on our reputation, which could materially adversely affect our business in a number of ways, including causing an inability to raise additional funds, a reluctance of counterparties to do business with us, a decrease in the prices of our common or preferred securities and a resulting increased risk of litigation and regulatory enforcement actions.
17
The management agreement with our Manager was not negotiated on an arm’s-length basis and may not be as favorable to us as if it had been negotiated with an unaffiliated third party and may be costly and difficult to terminate.
The management agreement with our Manager was negotiated between related parties, and its terms, including fees payable, may not be as favorable to us as if it had been negotiated on an arm’s-length basis with an unrelated third party. Various potential and actual conflicts of interest may arise from the activities of Freedom Mortgage and its affiliates.
Termination of our management agreement without cause is subject to several conditions, which may make such a termination difficult, and a significant termination fee would be payable by us. That fee will increase the effective cost to us of terminating the management agreement, thereby adversely affecting our ability to terminate our Manager without cause.
Pursuant to the management agreement, our Manager will not assume any responsibility other than to render the services called for thereunder and will not be responsible for any action of our board of directors in following or declining to follow the Manager’s advice or recommendations. Under the terms of the management agreement, our Manager, Freedom Mortgage, and their affiliates and each of their officers, directors, trustees, members, stockholders, partners, managers, Investment Committee members, employees, agents, successors and assigns, will not be liable to us for acts or omissions performed in accordance with and pursuant to the management agreement, except because of acts constituting bad faith, willful misconduct, gross negligence, fraud or reckless disregard of their duties under the management agreement. In addition, we will indemnify our Manager, Freedom Mortgage, and their affiliates and each of their officers, directors, trustees, members, stockholders, partners, managers, Investment Committee members, employees, agents, successors and assigns, with respect to all expenses, losses, damages, liabilities, demands, charges and claims arising from acts of our Manager not constituting bad faith, willful misconduct, gross negligence, fraud or reckless disregard of duties, performed in good faith in accordance with and pursuant to the management agreement.
If our Manager ceases to be our Manager pursuant to the management agreement, our lenders and our derivative counterparties may cease doing business with us.
If our Manager ceases to be our Manager, it would constitute an event of default or early termination event under some of our financing and hedging agreements, upon which our counterparties would have the right to terminate their agreements with us. If our Manager ceases to be our Manager for any reason, including upon the non-renewal of our management agreement, and we are unable to obtain financing or enter into or maintain derivative transactions, our business, financial condition and results of operations and our ability to make distributions to our stockholders may be materially adversely affected.
Risks Related to Our Organizational Structure
Maintenance of our exclusion from regulation as an investment company under the Investment Company Act imposes significant limitations on our operations.
We intend to continue to conduct our operations so that neither we nor any of our subsidiaries is required to register as an investment company under the Investment Company Act. We conduct our business primarily through our Operating Partnership and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. The securities issued by our subsidiaries that are excluded from the definition of “investment company” under Section 3(c)(7) of the Investment Company Act, together with other investment securities we may own, cannot exceed 40% of the value of all of our assets (excluding U.S. Government securities and cash) on an unconsolidated basis. This requirement limits the types of businesses in which we may engage and the assets we may hold. Certain of our subsidiaries rely on the exclusion provided by Section 3(c)(5)(C) under the Investment Company Act which is designed for entities primarily engaged in the business of “purchasing or otherwise acquiring mortgages and other liens on and interests in real estate.” This exclusion generally requires that at least 55% of the entity’s assets on an unconsolidated basis consist of qualifying real estate interests and at least 80% of the entity’s assets consist of qualifying real estate interests or real estate-related assets. These requirements limit the assets those subsidiaries can own and the timing of sales and purchases of those assets.
18
To classify the assets held by our subsidiaries as qualifying real estate interests or real estate-related assets, we rely on no-action letters and other guidance published by the SEC staff regarding those kinds of assets, as well as upon our analyses (in consultation with outside counsel) of guidance published with respect to other types of assets. There can be no assurance that the laws and regulations governing the Investment Company Act status of companies similar to ours, or the guidance from the SEC or its staff regarding the treatment of assets as qualifying real estate interests or real estate-related assets, will not change in a manner that adversely affects our operations. To the extent that the SEC staff provides more specific guidance regarding any of the matters bearing upon our exemption from the need to register under the Investment Company Act, we may be required to adjust our strategy accordingly. Any additional guidance from the SEC staff could further inhibit our ability to pursue the strategies that we have chosen. Furthermore, although we intend to monitor the assets of our subsidiaries regularly, there can be no assurance that our subsidiaries will be able to maintain their exclusion from registration. Any of the foregoing could require us to adjust our strategy, which could limit our ability to make certain investments or require us to sell assets in a manner, at a price or at a time that we otherwise would not have chosen. This could negatively affect the value of our common or preferred stock, the sustainability of our business model and our ability to make distributions.
The ownership limits in our charter may discourage a takeover or business combination that may have benefited our stockholders.
To assist us in qualifying as a REIT, among other purposes, our charter generally limits, unless waived by our board of directors, the beneficial or constructive ownership of any class of our stock by any person, other than Mr. Middleman, to no more than 9.0% in value or the number of shares, whichever is more restrictive, of the outstanding shares of any class or series of our stock. This and other restrictions on ownership and transfer of our shares of stock contained in our charter may discourage a change of control of us and may deter individuals or entities from making tender offers for our common stock on terms that might be financially attractive to you or which may cause a change in our management. In addition to deterring potential transactions that may be favorable to our stockholders, these provisions may also decrease your ability to sell our common stock.
Our stockholders’ ability to control our operations is severely limited.
Our board of directors approves our major strategies, including our strategies regarding investments, financing, growth, debt capitalization, REIT qualification and distributions. Our board of directors may amend or revise these and other strategies without a vote of our stockholders.
Certain provisions of Maryland law could inhibit a change in our control.
Certain provisions of the Maryland General Corporation Law, or the MGCL, may have the effect of inhibiting a third party from making a proposal to acquire us or impeding a change of control under circumstances that otherwise could provide our stockholders with the opportunity to realize a premium over the then-prevailing market price of our common stock, including:
| • | “business combination” provisions that, subject to limitations, prohibit certain business combinations between us and an “interested stockholder” (defined generally as any person who beneficially owns 10% or more of the voting power of our outstanding voting stock or an affiliate or associate of ours who, at any time within the two-year period immediately prior to the date in question, was the beneficial owner of 10% or more of the voting power of our then-outstanding stock) or an affiliate of an interested stockholder for five years after the most recent date on which the stockholder became an interested stockholder, and thereafter require two supermajority stockholder votes to approve any such combination; and |
| • | “control share” provisions that provide that a holder of “control shares” of the Company (defined as voting shares of stock which, when aggregated with all other shares of stock owned by the acquiror or in respect of which the acquiror is able to exercise or direct the exercise of voting power (except solely by virtue of a revocable proxy), entitle the acquiror to exercise one of three increasing ranges of voting power in electing directors) acquired in a “control share acquisition” (defined as the direct or indirect acquisition of ownership or control of issued and outstanding “control shares,” subject to certain exceptions) generally has no voting rights with respect to the control shares except to the extent approved by our stockholders by the affirmative vote of two-thirds of all the votes entitled to be cast on the matter, excluding all interested shares. |
19
We have elected to opt-out of these provisions of the MGCL, in the case of the business combination provisions, by resolution of our board of directors exempting any business combination between us and any other person (provided that such business combination is first approved by our board of directors, including a majority of our directors who are not affiliates or associates of such person), and, in the case of the control share provisions, pursuant to a provision in our bylaws. However, our board of directors may by resolution elect to repeal the foregoing opt-out from the business combination provisions of the MGCL, and we may, by amendment to our bylaws, opt in to the control share provisions of the MGCL in the future.
Our authorized but unissued common and preferred stock may prevent a change in our control.
Our charter authorizes us to issue additional authorized but unissued common stock and preferred stock without stockholder approval. In addition, our board of directors may, without stockholder approval, (i) amend our charter to increase or decrease the aggregate number of our shares of stock or the number of shares of any class or series of stock that we have authority to issue, (ii) classify or reclassify any unissued common stock or preferred stock and set the preferences, rights and other terms of the classified or reclassified shares. As a result, among other things, our board may establish a class or series of common stock or preferred stock that could delay or prevent a transaction or a change in our control that might involve a premium price for our common stock or otherwise be in the best interests of our stockholders.
Our rights and the rights of our stockholders to take action against our directors and officers are limited, which could limit your recourse in the event of actions not in your best interest.
Our charter limits the liability of our present and former directors and officers to us and our stockholders for money damages to the maximum extent permitted under Maryland law. Under current Maryland law, our present and former directors and officers will not have any liability to us or our stockholders for money damages other than liability resulting from:
| • | actual receipt of an improper benefit or profit in money, property or services; or |
| • | active and deliberate dishonesty by the director or officer that was established by a final judgment and is material to the cause of action. |
In addition, our charter authorizes us to indemnify our present and former directors and officers for actions taken by them in those and other capacities to the maximum extent permitted by Maryland law, and our bylaws require us to indemnify our present and former directors and officers, to the maximum extent permitted by Maryland law, in the defense of any proceeding to which he or she is made, or threatened to be made, a party by reason of his or her service to us as a director or officer in these and other capacities. In addition, we may be obligated to pay or reimburse the expenses incurred by our present and former directors and officers without requiring a preliminary determination of their ultimate entitlement to indemnification. As a result, we and our stockholders may have more limited rights against our present and former directors and officers than might otherwise exist absent the current provisions in our charter and bylaws or that might exist with other companies, which could limit your recourse in the event of actions not in your best interests.
Our charter contains provisions that make removal of our directors difficult, which could make it difficult for our stockholders to effect changes to our management.
Our charter provides that, subject to the rights of holders of one or more classes or series of preferred stock to elect or remove one or more directors, a director may be removed only for “cause” (as defined in our charter), and then only by the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of the votes entitled to be cast generally in the election of directors. Vacancies may be filled only by a majority of the remaining directors in office, even if less than a quorum, for the full term of the directorship in which the vacancy occurred (other than vacancies among any directors elected by the holder or holders of any class or series of preferred stock, if such right exists). These requirements make it more difficult to change our management by removing and replacing directors and may prevent a change in our control that is in the best interests of our stockholders.
20
Risks Related to Our Common Stock
The market price and trading volume of our common stock may be volatile.
The market price of our common stock may be highly volatile and subject to wide fluctuations. In addition, the trading volume in our common stock may fluctuate and cause significant price variations to occur. The stock market has experienced price and volume fluctuations that have affected the market price of many companies in industries similar or related to ours and that have been unrelated to these companies’ operating performances. If the market price of our common stock declines significantly, you may be unable to resell your shares at a gain. Further, fluctuations in the trading price of our common stock may adversely affect the liquidity of the trading market for our common stock and, in the event that we seek to raise capital through future equity financings, our ability to raise such equity capital.
We cannot assure you that the market price of our common stock will not fluctuate or decline significantly in the future. Some of the factors that could negatively affect our share price or result in fluctuations in the price or trading volume of our common stock include:
| • | actual or anticipated variations in our quarterly operating results; |
| • | increases in market interest rates that lead purchasers of our common stock to demand a higher yield or to seek alternative investments; |
| • | changes in market valuations of similar companies; |
| • | adverse market reaction to any increased indebtedness we incur in the future; |
| • | additions or departures of key personnel; |
| • | actions by stockholders; |
| • | speculation in the press or investment community; |
| • | general market, economic and political conditions and the impact of these conditions on the global credit markets; |
| • | the operating performance of other similar companies; |
| • | changes in accounting principles; and |
| • | passage of legislation or other regulatory developments that adversely affect us or our industry. |
Future sales of our common stock or securities convertible into our common stock could cause the market value of our common stock to decline and could result in dilution of your shares.
Sales of substantial amounts of shares of our common stock or securities convertible into our common stock could cause the market price of our common stock to decrease significantly. We cannot predict the effect, if any, of future sales of our common stock or securities convertible into our common stock, or the availability of shares of our common stock for future sales, on the value of our common stock. Sales of substantial amounts of shares of our common stock or securities convertible into our common stock, or the perception that such sales could occur, may adversely affect prevailing market values for our common stock.
Future offerings of debt securities, which would rank senior to our common stock upon our liquidation, and future offerings of equity securities, which would dilute the common stock holdings of our existing stockholders and may be senior to our common stock for the purposes of dividend and liquidating distributions, may adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
In the future, we may attempt to increase our capital resources by making offerings of debt or additional offerings of equity securities, including commercial paper, medium-term notes, senior or subordinated notes and classes of preferred stock or common stock. Upon liquidation, holders of our debt securities and shares of preferred stock and lenders with respect to other borrowings will receive a distribution of our available assets prior to the holders of our common stock. Additional equity offerings may dilute the holdings of our existing stockholders or reduce the market price of our common stock, or both. Our preferred stock could have a preference on liquidating distributions or a preference on dividend payments that could limit our ability to make a dividend distribution to the holders of our common stock. Because our decision to issue securities in any future
21
offering will depend on market conditions and other factors beyond our control, we cannot predict or estimate the amount, timing or nature of our future offerings. Thus, holders of our common stock bear the risk of our future offerings reducing the market price of our common stock and diluting their stock holdings in us.
Broad market fluctuations could negatively impact the market price of our common stock.
The stock market has experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that have affected the market price of many companies in industries similar or related to ours and that have been unrelated to these companies’ operating performances. These broad market fluctuations could reduce the market price of our common stock. Furthermore, our operating results and prospects may be below the expectations of public market analysts and investors or may be lower than those of companies with comparable market capitalizations, which could lead to a material decline in the market price of our common stock.
We have not established a minimum distribution payment level with respect to our common stock, and we cannot assure you of our ability to make distributions in the future.
We expect to make regular distributions to holders of our common stock and preferred stock in amounts such that we distribute all or substantially all of our REIT taxable income in each year. We have not established a minimum distribution payment level with respect to our common stock, and our ability to make distributions may be adversely affected by a number of factors, including the risk factors described in this report. All distributions will be made at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend on our earnings, our financial condition, debt covenants, maintenance of our REIT qualification, applicable law and other factors as our board of directors may deem relevant from time to time.
No assurance can be given that the level of any distributions we make to our stockholders will achieve a market yield or increase or even be maintained over time, any of which could materially and adversely affect the market price of our common stock. In addition, some of our distributions may include a return of capital, which would reduce the amount of capital available to operate our business.
Distributions that we make to our stockholders will generally be taxable to our stockholders as ordinary income. However, a portion of our distributions may be designated by us as long-term capital gains to the extent that they are attributable to capital gain income recognized by us or may constitute a return of capital to the extent that they exceed our earnings and profits as determined for U.S. federal income tax purposes. A return of capital is not taxable, but has the effect of reducing the tax basis of a stockholder’s investment in our common stock.
Common stock eligible for future sales may depress the market price of our common stock.
We cannot predict the effect, if any, of future sales of shares of our common stock or securities that are convertible into or exchangeable or exercisable for shares of our common stock, or the availability of such securities for future sales, on the value of our common stock. Sales of substantial amounts of our common stock or securities that are convertible into or exchangeable or exercisable for shares of our common stock, or the perception that such sales could occur, may adversely affect prevailing market prices for our common stock.
We have registered for public resale 1,000,000 shares of our common stock held by Mr. Middleman. Mr. Middleman could sell, or indicate an intention to sell, any or all of these shares in the public market. As a result, the trading price of our common stock could decline. In addition, the perception in the market that these sales may occur could also cause the trading price of our common stock to decline.
Risks Related to Our Preferred Stock
Our 8.20% Series A Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock (the “Series A Preferred Stock”) and our 8.250% Series B Fixed-to-Floating Rate Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock (the “Series B Preferred Stock,” and together with the Series A Preferred Stock, the “Preferred Stock”) ranks junior to our existing and future indebtedness and will rank junior to any other class or series of stock we may issue in the future with terms specifically providing that such stock ranks senior to the Preferred Stock with respect to the payment of dividends and the distribution of assets in the event of our liquidation, dissolution or winding up (“Senior Stock”), and your interests could be diluted by the issuance of additional shares of preferred stock and by other transactions.
Our Preferred Stock ranks junior to all of our existing and future indebtedness and any Senior Stock we may issue in the future and to other non-equity claims on us and our assets available to satisfy claims against us,
22
including claims in bankruptcy, liquidation or similar proceedings. In the event of our bankruptcy, liquidation or dissolution or the winding-up of our affairs, our assets will be available to pay obligations on our Preferred Stock only after all of our indebtedness and other liabilities have been paid. In addition, our Preferred Stock would effectively rank junior to all indebtedness and other liabilities of any existing or future subsidiaries. Such subsidiaries are or would be separate legal entities and have or will have no legal obligation to pay any amounts to us in respect of dividends due on our Preferred Stock. If we are forced to liquidate our assets to pay our creditors, we may not have sufficient assets to pay amounts due on any or all of our Preferred Stock then outstanding. We may in the future incur substantial amounts of debt and other obligations that will rank senior to our Preferred Stock.
Our charter currently authorizes the issuance of up to 100,000,000 shares of preferred stock in one or more classes or series. Subject to limitations prescribed by Maryland law and our charter, our board of directors is authorized to issue, from our authorized but unissued shares of stock, preferred stock in such classes or series as our board of directors may determine and to establish from time to time the number of shares of preferred stock to be included in any such class or series. The issuance of additional shares of either series of Preferred Stock or any class or series of stock we may issue in the future with terms specifically providing that such stock ranks on parity with our Preferred Stock with respect to the payment of dividends and the distribution of assets in the event of our liquidation, dissolution or winding up (“Parity Stock”) would dilute the interests of the holders of our Preferred Stock, and the issuance of any Senior Stock or the incurrence of additional indebtedness could affect our ability to pay dividends on, redeem or pay the liquidation preference on our Preferred Stock. Other than the limited conversion rights afforded to holders of our Preferred Stock that may become exercisable in connection with certain changes of control, none of the provisions relating to our Preferred Stock contain any terms relating to or limiting our indebtedness or affording the holders of our Preferred Stock protection in the event of a highly leveraged or other transaction, including a merger or the sale, lease or conveyance of all or substantially all our assets, so long as the rights of the holders of our Preferred Stock are not materially and adversely affected.
The Preferred Stock has not been rated.
We have not sought to obtain a rating for our Preferred Stock, and the Preferred Stock may never be rated. It is possible, however, that one or more rating agencies might independently determine to assign a rating to either series of our Preferred Stock or that we may elect to obtain a rating of one or both series of our Preferred Stock in the future. Furthermore, we may elect to issue other securities for which we may seek to obtain a rating. If any ratings are assigned to our Preferred Stock in the future or if we issue other securities with a rating, such ratings, if they are lower than market expectations or are subsequently lowered or withdrawn, could adversely affect the market for or the market value of the Preferred Stock.
Ratings only reflect the views of the issuing rating agency or agencies, and such ratings could at any time be revised downward or withdrawn entirely at the discretion of the issuing rating agency. Further, a rating is not a recommendation to purchase, sell or hold any particular security, including our Preferred Stock. In addition, ratings do not reflect market prices or suitability of a security for a particular investor, and any future rating of our Preferred Stock may not reflect all risks related to the Company and its business, or the structure or market value of our Preferred Stock.
We may not be able to pay dividends or other distributions on the Preferred Stock.
Under Maryland law, no distributions on stock may be made if, after giving effect to the distribution, (i) the corporation would not be able to pay the indebtedness of the corporation as such indebtedness becomes due in the usual course of business or (ii) except in certain limited circumstances when distributions are made from net earnings, the corporation’s total assets would be less than the sum of the corporation’s total liabilities plus, unless the charter provides otherwise (which our charter does, with respect to our Preferred Stock), the amount that would be needed, if the corporation were to be dissolved at the time of the distribution, to satisfy the preferential rights upon dissolution of stockholders whose preferential rights on dissolution are superior to those receiving the distribution. There can be no guarantee that we will have sufficient cash to pay dividends on our Preferred Stock. Our ability to pay dividends may be impaired if any of the risks described in this Annual Report on Form 10-K were to occur. In addition, our ability to pay dividends depends upon our earnings, our financial condition, maintenance of our REIT qualification and other factors as our board of directors may deem relevant from time to time. We cannot assure you that our business will generate sufficient cash flow from operations or that future
23
borrowings will be available to us in an amount sufficient to enable us to make distributions on our Preferred Stock and on our common stock, to pay our indebtedness or to fund our other liquidity needs.
Holders of our Preferred Stock may not be able to exercise conversion rights upon a change of control. If exercisable, the change of control conversion rights applicable to our Preferred Stock may not adequately compensate holders of our Preferred Stock. These change of control conversion rights may also make it more difficult for a party to acquire us or discourage a party from acquiring us.
Upon the occurrence of certain changes of control, each holder of our Preferred Stock will have the right (unless, prior to the Change of Control Conversion Date (as defined below), we have provided notice of our election to redeem some or all of the shares of Preferred Stock held by such holder, in which case such holder will have the right only with respect to shares of Preferred Stock that are not called for redemption) to convert some or all of such holder’s Preferred Stock into shares of our common stock (or, under specified circumstances, certain alternative consideration). Notwithstanding that we generally may not redeem our Series A Preferred Stock prior to August 17, 2022 and our Series B Preferred Stock prior to April 15, 2024, we have a special optional redemption right to redeem our Preferred Stock in the event of certain changes of control, and holders of our Preferred Stock will not have the right to convert any shares that we have elected to redeem prior to the date the Preferred Stock is to be converted, which will be a business day selected by us that is no fewer than 20 days nor more than 35 days after the date on which we provide notice to the holders of Preferred Stock (the “Change of Control Conversion Date”).
If we do not elect to redeem the Preferred Stock prior to the Change of Control Conversion Date, then upon an exercise of the conversion rights provided to the holders of our Preferred Stock, the holders of Preferred Stock will be limited to a maximum number of shares of our common stock (or, if applicable, certain alternative conversion consideration) which may result in a holder receiving shares of common stock (or alternative conversion consideration, as applicable) with a value that is less than the liquidation preference of our Preferred Stock.
In addition, the change of control conversion feature of the Preferred Stock may have the effect of discouraging a third party from making an acquisition proposal for us or of delaying, deferring or preventing a change of control transaction under circumstances that otherwise could provide the holders of Preferred Stock with the opportunity to realize a premium over the then-current market price of such stock or that stockholders may otherwise believe is in their best interests.
Our charter, including the articles supplementary designating the Preferred Stock, contains restrictions upon transfer and ownership of our stock, which may impair the ability of holders to acquire the Preferred Stock or convert Preferred Stock into our common stock.
Our charter, including the articles supplementary designating each series of our Preferred Stock, contains restrictions on transfer and ownership of our stock intended to, among other purposes, assist us in maintaining our qualification as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Our charter provides that generally no person, other than certain exempted holders, may own, or be deemed to own by virtue of the attribution provisions of the Code, more than 9.0% in value or in number of shares, whichever is more restrictive, of the outstanding shares of any class or series of our stock. No holder of our Preferred Stock will be entitled to convert such stock into our common stock to the extent that receipt of shares of our common stock would cause the holder to exceed any of the limitations on ownership and transfer contained in our charter. In addition, these restrictions could have anti-takeover effects and could reduce the possibility that a third party will attempt to acquire control of us, which could adversely affect the market price of our Preferred Stock.
Holders of our Preferred Stock have limited voting rights.
Our common stock is the only class of our securities that carries full voting rights. Holders of our Preferred Stock may vote only (i) to elect two additional directors to our board of directors in the event that six full quarterly dividends (whether or not consecutive) payable on the applicable series of Preferred Stock are in arrears, (ii) on amendments to our charter, including the articles supplementary designating the applicable series of Preferred Stock, that materially and adversely affect the rights of the holders of that series of Preferred Stock or (iii) to authorize, increase or create additional classes or series of Senior Stock. Other than these limited circumstances, holders of our Preferred Stock generally do not have any voting rights.
24
The market price of our Preferred Stock could be substantially affected by various factors.
The market price of our Preferred Stock will depend on many factors, which may change from time to time, including:
| • | prevailing interest rates, increases in which may have an adverse effect on the market price of the Preferred Stock; |
| • | trading prices of common and preferred equity securities issued by REITs and other similar companies; |
| • | the annual yield from distributions on the Preferred Stock as compared to yields on other financial instruments; |
| • | general economic and financial market conditions; |
| • | government action or regulation; |
| • | our financial condition, performance and prospects and those of our competitors; |
| • | changes in financial estimates or recommendations by securities analysts with respect to us, our competitors or our industry; |
| • | our issuance of additional preferred equity securities or the incurrence of debt; and |
| • | actual or anticipated variations in our quarterly operating results and those of our competitors. |
As a result of these and other factors, holders of our Preferred Stock may experience a decrease, which could be substantial and rapid, in the market price of the Preferred Stock, including decreases unrelated to our operating performance or prospects.
Future offerings of debt or equity securities may adversely affect the market price of our Preferred Stock.
Future issuances and sales of Parity Stock, or the perception that such issuances and sales could occur, may cause prevailing market prices for either series of our Preferred Stock and our common stock to decline and may adversely affect our ability to raise additional capital in the financial markets at times and prices favorable to us.
If we decide to issue debt or Senior Stock in the future, it is possible that these securities will be governed by an indenture or other instrument containing covenants or other provisions that will restrict our operating flexibility. Additionally, any convertible or exchangeable securities that we issue in the future may have rights, preferences and privileges more favorable than those of our Preferred Stock and may result in dilution to owners of our Preferred Stock. We and, indirectly, our stockholders, will bear the cost of issuing and servicing such securities. Because our decision to issue debt or equity securities in any future offering will depend on market conditions and other factors beyond our control, we cannot predict or estimate the amount, timing or nature of our future offerings. Thus, holders of our Preferred Stock bear the risk of our future offerings reducing the market price of our Preferred Stock and diluting the value of their holdings in us.
If our common stock is delisted, the ability to transfer or sell shares of our Preferred Stock may be limited and the market value of our Preferred Stock will likely be materially adversely affected.
Other than in connection with certain changes of control, our Preferred Stock does not contain provisions that are intended to protect holders of our Preferred Stock if our common stock is delisted from the New York Stock Exchange (the “NYSE”). Since our Preferred Stock has no stated maturity date, holders of our Preferred Stock may be forced to hold their shares of Preferred Stock and receive stated dividends on the Preferred Stock when, as and if authorized by our board of directors and declared and paid by us with no assurance as to ever receiving the liquidation value thereof. In addition, if our common stock is delisted from the NYSE, it is likely that our Preferred Stock will be delisted from the NYSE as well. Accordingly, if our common stock is delisted from the NYSE, the ability to transfer or sell shares of our Preferred Stock may be limited and the market value of our Preferred Stock will likely be materially adversely affected.
The historical levels of three-month LIBOR are not an indication of the future levels of three-month LIBOR.
From April 15, 2024, the dividend rate for the Series B Preferred Stock will be determined based on three-month LIBOR. In the past, the level of three-month LIBOR has experienced significant fluctuations. Historical levels, fluctuations and trends of three-month LIBOR are not necessarily indicative of future levels.
25
Any historical upward or downward trend in three-month LIBOR is not an indication that three-month LIBOR is more or less likely to increase or decrease at any time during the floating rate period, and holders of the Series B Preferred Stock should not take the historical levels of three-month LIBOR as an indication of its future performance.
Although the actual three-month LIBOR on a dividend payment date or at other times during a dividend period may be higher than the three-month LIBOR on the applicable dividend determination date, only the level of three-month LIBOR on the dividend determination date for such dividend period will be used to establish the dividend rate for that dividend period. As a result, changes in the three-month LIBOR may not result in a comparable change in the market value of the Series B Preferred Stock from April 15, 2024.
Changes in banks’ inter-bank lending rate reporting practices or the method pursuant to which LIBOR is determined may adversely affect the value of the Series B Preferred Stock.
LIBOR and other indices which are deemed “benchmarks” are the subject of recent national, international, and other regulatory guidance and proposals for reform. Some of these reforms are already effective while others are still to be implemented. These reforms may cause such benchmarks to perform differently than in the past, or have other consequences which cannot be predicted. Actions by regulators or law enforcement agencies in the U.K. and elsewhere, as well as actions by the ICE Benchmark Administration (the current administrator of LIBOR), may result in changes to the manner in which LIBOR is determined or the establishment of alternative reference rates. For example, on July 27, 2017, the U.K. Financial Conduct Authority announced that it intends to stop persuading or compelling banks to submit LIBOR rates after 2021.
At this time, it is not possible to predict the effect of any such changes, any establishment of alternative reference rates or any other reforms to LIBOR that may be implemented in the U.K. or elsewhere. Uncertainty as to the nature of such potential changes, alternative reference rates or other reforms may adversely affect the trading market for securities on which the interest or dividend is determined by reference to LIBOR, such as the Series B Preferred Stock. To the extent the Three-Month LIBOR Rate is discontinued or is no longer quoted, the applicable base rate used to calculate dividend payments on the Series B Preferred Stock during the floating rate period will be determined using certain alternative methods. Any of these alternative methods may result in dividend payments that are lower than or that do not otherwise correlate over time with the dividend payments that would have been made on the Series B Preferred Stock during the floating rate period if the three-month LIBOR rate was available in its current form. The final alternative method sets the dividend rate for a dividend period during the floating rate period at the same rate as the immediately preceding dividend period during the floating rate period or, in the case of the first dividend period in the floating rate period, the most recent dividend rate that could have been determined had the floating rate period been applicable prior to the first dividend period in the floating rate period. More generally, any of the above changes or any other consequential changes to LIBOR or any other “benchmark” as a result of international, national or other proposals for reform or other initiatives or investigations, or any further uncertainty in relation to the timing and manner of implementation of such changes, could have a material adverse effect on the value of and return on any securities based on or linked to a “benchmark,” such as the Series B Preferred Stock.
U.S. Federal Income Tax Risks
Our failure to qualify as a REIT would subject us to U.S. federal, state and local income taxes, which could adversely affect the value of our common stock and would substantially reduce the cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
We operate in a manner that is intended to cause us to qualify as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes. However, the U.S. federal income tax laws governing REITs are complex, and interpretations of the U.S. federal income tax laws governing qualification as a REIT are limited. Moreover, our qualification and taxation as a REIT depend upon our ability to meet on a continuing basis, through actual annual operating results, certain qualification tests set forth in the U.S. federal income tax laws. Although we intend to operate so that we continue to qualify as a REIT, given the complex nature of the rules governing REITs, the ongoing importance of factual determinations, including the potential tax treatment of the investments we make, and the possibility of future changes in our circumstances, no assurance can be given that our actual results of operations for any particular taxable year will satisfy such requirements.
26
If we fail to qualify as a REIT in any calendar year, and do not qualify for certain statutory relief provisions, we would be required to pay U.S. federal income tax (and any applicable state and local taxes), including any applicable alternative minimum tax, on our taxable income at regular corporate rates, and dividends paid to our stockholders would not be deductible by us in computing our taxable income. Further, if we fail to qualify as a REIT, we might need to borrow money or sell assets in order to pay any resulting tax. Our payment of income tax would decrease the amount of our income available for distribution to our stockholders. Furthermore, if we fail to qualify or maintain our qualification as a REIT, we no longer would be required under U.S. federal tax laws to distribute substantially all of our REIT taxable income to our stockholders. Unless our failure to qualify as a REIT was subject to relief under U.S. federal tax laws, we could not re-elect to qualify as a REIT until the fifth calendar year following the year in which we failed to qualify.
Complying with REIT requirements may cause us to forego or liquidate otherwise attractive investments.
To qualify as a REIT, we must continually satisfy various tests regarding the sources of our income, the nature and diversification of our assets, the amounts we distribute to our stockholders and the ownership of our common stock. In order to meet these tests, we may be required to forego investments we might otherwise make. We may be required to make distributions to stockholders at disadvantageous times or when we do not have funds readily available for distribution. In addition, we may be unable to pursue investments that would be otherwise advantageous to us in order to satisfy the source of income or asset diversification requirements for qualifying as a REIT. Thus, compliance with the REIT requirements may hinder our investment performance.
Failure to make required distributions would subject us to tax, which would reduce the cash available for distribution to our stockholders.
To qualify as a REIT, we must distribute to our stockholders each calendar year at least 90% of our REIT taxable income (including certain items of non-cash income), determined without regard to the deduction for dividends paid and excluding net capital gain. To the extent that we satisfy the 90% distribution requirement, but distribute less than 100% of our taxable income, we will be subject to U.S. federal corporate income tax on our undistributed income. In addition, we will incur a 4% nondeductible excise tax on the amount, if any, by which our distributions in any calendar year are less than the sum of:
| • | 85% of our REIT ordinary income for that year; |
| • | 95% of our REIT capital gain net income for that year; and |
| • | any undistributed taxable income from prior years. |
We intend to distribute our taxable income to our stockholders in a manner intended to satisfy the 90% distribution requirement and to avoid both corporate income tax and the 4% nondeductible excise tax. However, there is no requirement that TRSs distribute their after tax net income to their parent REIT or its stockholders.
Our taxable income may substantially exceed our net income as determined based on generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”), because, for example, realized capital losses will be deducted in determining our GAAP net income, but may not be deductible in computing our taxable income. In addition, we may invest in assets that generate taxable income in excess of economic income or in advance of the corresponding cash flow from the assets. As a result of the foregoing, we may generate less cash flow than taxable income in a particular year. To the extent that we generate such non-cash taxable income in a taxable year, we may incur corporate income tax and the 4% nondeductible excise tax on that income if we do not distribute such income to stockholders in that year. In that event, we may be required to use cash reserves, incur debt, sell assets, make taxable distributions of our shares or debt securities or liquidate non-cash assets at rates or at times that we regard as unfavorable to satisfy the distribution requirement and to avoid corporate income tax and the 4% nondeductible excise tax in that year.
We may satisfy the 90% distribution test with taxable distributions of our stock or debt securities. The IRS has issued Revenue Procedure 2017-45 authorizing elective cash/stock dividends to be made by publicly held REITs (i.e., REITs that are required to file annual and periodic reports with the SEC under the Exchange Act). Pursuant to Revenue Procedure 2017-45, the IRS will treat the distribution of stock pursuant to an elective cash/stock dividend as a distribution of property under Section 301 of the Code (i.e., a dividend), as long as at
27
least 20% of the total dividend is available in cash and certain other parameters detailed in the Revenue Procedure are satisfied. Although we have no current intention of paying dividends in our own stock, if in the future we choose to pay dividends in our own stock, our stockholders may be required to pay tax in excess of the cash that they receive.
Despite qualification as a REIT, we may face other tax liabilities that reduce our cash flows.
Despite qualification as a REIT, we may be subject to certain U.S. federal, state and local taxes on our income and assets, including taxes on any undistributed income, tax on income from some activities conducted as a result of a foreclosure, and state or local income, property and transfer taxes. In addition, Solutions, Aurora and any other TRSs we form will be subject to regular corporate U.S. federal, state and local taxes. Any of these taxes would decrease cash available for distributions to our stockholders.
We may lose our REIT qualification or be subject to a penalty tax if the U.S. Internal Revenue Service, or IRS, successfully challenges our characterization of our investments in Excess MSRs.
We have created, and may create in the future, Excess MSRs from the MSRs held by Aurora. The IRS has issued two private letter rulings to other REITs holding that Excess MSRs are qualifying assets for purposes of the 75% asset test and produce qualifying income for purposes of the 75% gross income test. Any income that is qualifying income for the 75% gross income test is also qualifying income for the 95% gross income test. A private letter ruling may be relied upon only by the taxpayer to whom it is issued, and the IRS may revoke a private letter ruling. Based on these private letter rulings and other IRS guidance regarding excess mortgage servicing fees, we generally intend to treat our investments in Excess MSRs as qualifying assets for purposes of the 75% asset test and as producing qualifying income for purposes of the 95% and 75% gross income tests. However, we have not sought, and we do not intend to seek, our own private letter ruling. Thus, it is possible that the IRS could successfully take the position that our Excess MSRs are not qualifying assets or do not produce qualifying income, presumably by recharacterizing Excess MSRs as an interest in servicing compensation, in which case we may fail one or more of the income and asset requirements for REIT qualification. If we failed one of those tests, we would either be required to pay a penalty tax, which could be material, to maintain REIT status, or we would fail to qualify as a REIT.
The failure of RMBS subject to a repurchase agreement to qualify as real estate assets would adversely affect our ability to qualify as a REIT.
We have entered into repurchase agreements under which we nominally sell certain of our RMBS to a counterparty and simultaneously agree to repurchase the sold assets. We believe that, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, these transactions will be treated as secured debt and we will be treated as the owner of the RMBS that are the subject of any such repurchase agreement notwithstanding that such agreements may transfer record ownership of such assets to the counterparty during the term of the agreement. It is possible, however, that the IRS could successfully assert that we do not own the RMBS during the term of the repurchase agreement, in which case we could fail to qualify as a REIT.
Our ability to engage in TBA transactions could be limited by the requirements necessary to qualify as a REIT, and we could fail to qualify as a REIT as a result of these investments.
We purchase and sell TBAs for purposes of managing interest related risks associated with our liabilities under repurchase agreements, including duration and basis risks. We generally treat such TBA purchases and sales as hedging transactions that hedge indebtedness incurred to acquire or carry real estate assets, or “qualifying liability hedges” for REIT purposes. From time to time, we also opportunistically engage in TBA transactions because we find them attractive on their own. The law is unclear regarding whether income and gains from TBAs that are not qualifying liability hedges are qualifying income for the 75% gross income test and whether TBAs are qualifying assets for the 75% asset test.
To the extent that we engage in TBA transactions that are not qualifying liability hedges for REIT purposes, unless we receive a favorable private letter ruling from the IRS or we are advised by counsel that income and gains from such TBAs should be treated as qualifying income for purposes of the 75% gross income test, we will limit our income and gains from dispositions of such TBAs and any non-qualifying income to no more than 25% of our gross income for each calendar year. Further, unless we receive a favorable private letter ruling from the IRS or we are advised by counsel that TBAs should be treated as qualifying assets for purposes of the 75%
28
asset test, we will limit our investment in such TBAs and any non-qualifying assets to no more than 25% of our total assets at the end of any calendar quarter and will limit the TBAs held by us that are issued by any one issuer to no more than 5% of our total assets at the end of any calendar quarter. Accordingly, our ability to purchase and sell Agency RMBS through TBAs and to hold or dispose of TBAs, through dollar roll transactions or otherwise, could be limited.
Even if we are advised by counsel that such TBAs should be treated as qualifying assets or that income and gains from such TBAs should be treated as qualifying income, it is possible that the IRS could successfully take the position that such assets are not qualifying assets and such income is not qualifying income. In that event, we could be subject to a penalty tax or we could fail to qualify as a REIT if (i) the value of our TBAs, together with our other non-qualifying assets for the 75% asset test, exceeded 25% of our total assets at the end of any calendar quarter, (ii) the value of our TBAs issued by any one issuer exceeded 5% of our total assets at the end of any calendar quarter, or (iii) our income and gains from our TBAs that are not qualifying liability hedges, together with our non-qualifying income for the 75% gross income test, exceeded 25% of our gross income for any taxable year.
Complying with REIT requirements may limit our ability to hedge effectively.
The REIT provisions of the Code substantially limit our ability to hedge. Our aggregate gross income from non-qualifying hedges, fees, and certain other non-qualifying sources cannot exceed 5% of our annual gross income. As a result, we might have to limit our use of advantageous hedging techniques or implement those hedges through a TRS. Any hedging income earned by a TRS would be subject to U.S. federal, state and local income tax at regular corporate rates. This could increase the cost of our hedging activities or expose us to greater risks associated with interest rate changes or other changes than we would otherwise want to bear.
Our ownership of and relationship with Solutions, Aurora and any future TRSs that we form will be limited and a failure to comply with the limits would jeopardize our REIT status and may result in the application of a 100% excise tax.
A REIT may own up to 100% of the stock of one or more TRSs. A TRS may earn income that would not be qualifying income if earned directly by the parent REIT. Both the subsidiary and the REIT must jointly elect to treat the subsidiary as a TRS. A corporation (other than a REIT) of which a TRS directly or indirectly owns more than 35% of the voting power or value of the stock will automatically be treated as a TRS. Overall, no more than 20% of the value of a REIT’s total assets may consist of stock or securities of one or more TRSs. A domestic TRS will pay U.S. federal, state and local income tax at regular corporate rates on any income that it earns. In addition, if a TRS borrows funds either from us or a third party, it may be unable to deduct all or a portion of the interest paid, resulting in a higher corporate level tax liability. Specifically, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “TCJA”), enacted in 2017, imposes a disallowance of deductions for business interest expense (even if paid to third parties) in excess of the sum of a taxpayer’s business interest income and 30% of the adjusted taxable income of the business, which is its taxable income computed without regard to business interest income or expense, net operating losses or the pass-through income deduction (and for taxable years before 2022, excludes depreciation and amortization). The rules also impose a 100% excise tax on certain transactions between a TRS and its parent REIT that are not conducted on an arm’s-length basis. Solutions, Aurora and any future domestic TRS that we may form will pay U.S. federal, state and local income tax on its taxable income, and its after-tax net income will be available for distribution to us but is not required to be distributed to us unless necessary to maintain our REIT qualification.
Our ownership limitation may restrict change of control or business combination opportunities in which our stockholders might receive a premium for their common stock.
In order for us to qualify as a REIT for each taxable year after 2013, no more than 50% in value of our outstanding shares of stock may be owned, directly or indirectly, by five or fewer individuals during the last half of any calendar year. “Individuals” for this purpose include natural persons, private foundations, some employee benefit plans and trusts, and some charitable trusts. In order to help us qualify as a REIT, among other purposes, our charter generally prohibits any person, other than Mr. Middleman, from beneficially or constructively owning more than 9.0% in value or in number of shares, whichever is more restrictive, of the outstanding shares of any class or series of our stock.
29
The ownership limitation and other restrictions could have the effect of discouraging a takeover or other transaction in which holders of shares of our common stock might receive a premium for their common stock over the then-prevailing market price or which holders might believe to be otherwise in their best interests.
Dividends payable by REITs do not qualify for the reduced tax rates available for some dividends.
The maximum tax rate applicable to “qualified dividend income” payable to U.S. stockholders that are taxed at individual rates is 20% (plus the 3.8% surtax on net investment income, if applicable). Dividends payable by REITs, however, are generally not eligible for the reduced rates on qualified dividend income. Rather, under the TCJA, REIT dividends constitute “qualified business income” and thus a 20% deduction is available to individual taxpayers with respect to such dividends, resulting in a 29.6% maximum federal tax rate (plus the 3.8% surtax on net investment income, if applicable) for individual U.S. stockholders. Without further legislative action, the 20% deduction applicable to REIT dividends will expire on January 1, 2026. The more favorable rates applicable to regular corporate qualified dividends could cause investors who are taxed at individual rates to perceive investments in REITs to be relatively less attractive than investments in the stocks of non-REIT corporations that pay dividends, which could adversely affect the value of the shares of REITs, including our stock.
We may be subject to adverse legislative or regulatory tax changes that could reduce the market price of our common stock.
At any time, the U.S. federal income tax laws or regulations governing REITs or the administrative interpretations of those laws or regulations may be amended. We cannot predict when or if any new U.S. federal income tax law, regulation or administrative interpretation, or any amendment to any existing U.S. federal income tax law, regulation or administrative interpretation, will be adopted, promulgated or become effective and any such law, regulation or interpretation may take effect retroactively. We and our stockholders could be adversely affected by any such change in, or any new, U.S. federal income tax law, regulation or administrative interpretation.
The TCJA made significant changes to the U.S. federal income tax rules for taxation of individuals and corporations. The top corporate income tax rate has been reduced to 21%. In the case of individuals, the tax brackets have been adjusted, the top federal income rate has been reduced to 37%, special rules reduced taxation of certain income earned through passthrough entities and reduced the top effective rate applicable to ordinary dividends from REITs to 29.6% (through a 20% deduction for ordinary REIT dividends received) and various deductions have been eliminated or limited, including limiting the deduction for state and local taxes to $10,000 per year. The TCJA generally requires us to take certain amounts in income no later than the time such amounts are reflected on certain financial statements. The application of this rule may require the accrual of income with respect to our debt instruments, such as original issue discount or market discount, but excluding any accrual of income with respect to our MSRs, earlier than would be the case under the general tax rules, although the precise application of this rule remains unclear at this time. To the extent that this rule requires the accrual of income earlier than under the general tax rules, it could increase our “phantom income,” which may make it more likely that we could be required to borrow funds or take other action to satisfy the REIT distribution requirements for the taxable year in which this “phantom income” is recognized. Most of the changes made by the TCJA and applicable to individuals are temporary and apply only to taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017 and before January 1, 2026. There are only minor changes to the REIT rules (other than the 20% deduction applicable to individuals for ordinary REIT dividends received). The TCJA made numerous other large and small changes to the tax rules that do not affect REITs directly but may affect our stockholders and may indirectly affect us. For example, the TCJA reduced the limit for an individual’s mortgage interest expense to interest on $750,000 of mortgages and does not permit deduction of interest on home equity loans (after grandfathering all existing mortgages). Such change and the reduction in deductions for state and local taxes (including property taxes) may adversely affect the residential mortgage markets in which we invest.
Stockholders are urged to consult with their tax advisors with respect to the status of the TCJA and any other regulatory or administrative developments and proposals and their potential effect on investment in our stock.
30
Our recognition of “phantom” income may reduce a stockholder’s after-tax return on an investment in our common stock.
We may recognize taxable income in excess of our economic income, known as phantom income, in the first years that we hold certain investments, and experience an offsetting excess of economic income over our taxable income in later years. Moreover, under the TCJA, we generally will be required to take certain amounts into income no later than the time such amounts are reflected on certain financial statements. The application of this rule may require the accrual of income with respect to our debt instruments, such as original issue discount or market discount, but excluding any accrual of income with respect to our MSRs, earlier than would be the case under the general tax rules, although the precise application of this rule remains unclear at this time. To the extent that this rule requires the accrual of income earlier than under the general tax rules, it could increase our “phantom income.” As a result, stockholders at times may be required to pay U.S. federal income tax on distributions that economically represent a return of capital rather than a dividend. These distributions would be offset in later years by distributions representing economic income that would be treated as returns of capital for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Taking into account the time value of money, this acceleration of U.S. federal income tax liabilities may reduce a stockholder’s after-tax return on his or her investment to an amount less than the after-tax return on an investment with an identical before-tax rate of return that did not generate phantom income.
Liquidation of our assets may jeopardize our REIT qualification.
To maintain our qualification as a REIT, we must comply with requirements regarding our assets and our sources of income. If we are compelled to liquidate our assets to repay obligations to our lenders or for other reasons, we may be unable to comply with these requirements, thereby jeopardizing our qualification as a REIT, or we may be subject to a 100% tax on any resultant gain if we sell assets that are treated as inventory or property held primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business.
Our qualification as a REIT and exemption from U.S. federal income tax with respect to certain assets may be dependent on the accuracy of legal opinions or advice rendered or given or statements by the issuers of assets that we acquire, and the inaccuracy of any such opinions, advice or statements may adversely affect our REIT qualification and result in significant corporate-level tax.
When purchasing securities, we may rely on opinions or advice of counsel for the issuer of such securities, or statements made in related offering documents, for purposes of determining whether such securities represent debt or equity securities for U.S. federal income tax purposes, the value of such securities, and also to what extent those securities constitute qualified real estate assets for purposes of the REIT asset tests and produce income that qualifies under the 75% gross income test. The inaccuracy of any such opinions, advice or statements may adversely affect our ability to qualify as a REIT and result in significant corporate-level tax.
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments |
None.
| Item 2. | Properties |
Our business is operated from space provided through our Manager located at 1451 Route 34, Suite 303, Farmingdale, New Jersey 07727, telephone (877) 870-7005, and 1270 Avenue of the Americas, Suite 920, New York, New York 10020, telephone (877) 870-7005.
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings |
From time to time, the Company may be involved in various claims and legal actions in the ordinary course of business. As of December 31, 2019, the Company is not aware of any material legal or regulatory claims.
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures |
Not applicable.
31
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
Market Information
Our common stock has been listed and traded on the NYSE under the symbol “CHMI” since October 4, 2013. Prior to October 4, 2013, our common stock was not listed on any exchange or over-the-counter market.
Holders
As of February 27, 2020, we had six holders of record of our common stock. The six holders of record include Cede & Co., which holds shares as nominee for The Depository Trust Company, which itself holds shares on behalf of the beneficial owners of our common stock. Such information was obtained from our registrar and transfer agent.
Stockholder Return Performance
The following graph is a comparison of the cumulative total stockholder return on our common stock, the S&P 500 Index, the Russell 2000 Index and the SNL Finance REIT Index, a peer group index, from December 31, 2014 to December 31, 2019. The graph assumes that $100 was invested on December 31, 2014 in our common stock, the S&P 500 Index, the Russell 2000 Index and the SNL Finance REIT Index and that all dividends were reinvested without the payment of any commissions. There can be no assurance that the performance of our common stock will continue in line with the same or similar trends depicted in the graph below:
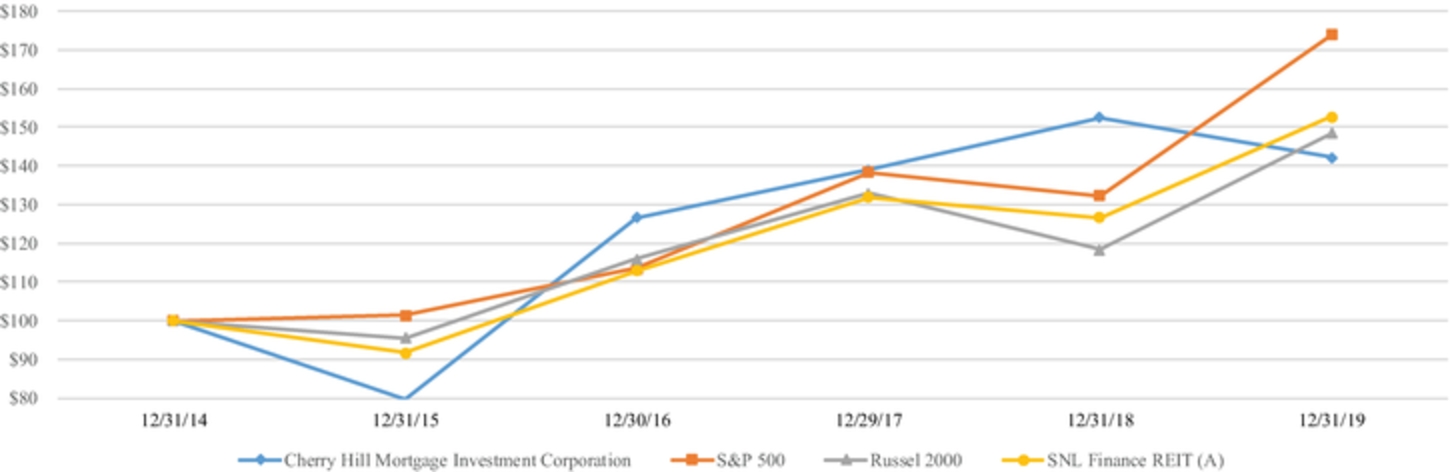
Year Ended |
|||||||||||||||
December 31, 2015 |
December 30, 2016 |
December 29, 2017 |
December 31, 2018 |
December 31, 2019 |
|||||||||||
Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation |
$ | 79.68 | $ | 126.64 | $ | 139.06 | $ | 152.44 | $ | 142 | |||||
Russel 2000 |
$ | 95.59 | $ | 115.95 | $ | 132.94 | $ | 118.30 | $ | 148 | |||||
SNL Finance REIT(A) |
$ | 91.70 | $ | 112.96 | $ | 131.80 | $ | 126.69 | $ | 153 | |||||
S&P 500 |
$ | 101.38 | $ | 113.51 | $ | 138.29 | $ | 132.23 | $ | 174 | |||||
Source: SNL Financial LC
| (A) | In addition to the Company, as of December 31, 2019, the SNL Finance REIT Index comprised the following companies: AG Mortgage Investment Tr Inc., AGNC Investment Corp., American Church Mortgage Co., Annaly Capital Mgmt Inc., Anworth Mortgage Asset Corp., Apollo Commercial Real Estate,Arbor Realty Trust Inc., Ares Commercial RE Corp., Arlington Asset Invt Corp., ARMOUR Residential REIT Inc., Blackstone Mortgage Tr Inc., Broadmark Realty Capital Inc., Capstead Mortgage Corp., Chimera Investment Corp., Colony Credit Real Estate, Inc, CV Holdings Inc., Dynex Capital Inc., Ellington Financial Inc., Ellington Resdl Mrtg REIT, Exantas Capital Corp., Granite Point Mortgage Trust, Great Ajax Corp., Hannon Armstrong Sustainable, Hunt Companies Finance Trust, Invesco Mortgage Capital Inc., Jernigan Capital Inc., KKR Real Estate Finance Trust, Ladder Capital Corp, MFA Financial Inc., New Resdl Invt Corp., New York Mortgage Trust Inc., Orchid Island Capital Inc., PennyMac Mortgage Invt Trust, RAIT Financial Trust, Ready Capital Corp., Redwood Trust Inc., Sachem Capital Corp., Starwood Property Trust Inc., TPG RE Finance Trust Inc, Tremont Mortgage Trust, Two Harbors Investment Corp., United Development Funding IV, and Western Asset Mrtg Cap Corp.. |
32
Securities Authorized For Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
During 2013, the board of directors approved and the Company adopted the Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2013 Plan”). The 2013 Plan provides for the grant of options to purchase shares of the Company’s common stock, stock awards, stock appreciation rights, performance units, incentive awards and other equity-based awards, including long term incentive plan units (“LTIP-OP Units”) of the Operating Partnership. Each LTIP-OP Unit awarded is deemed equivalent to an award of one share of our common stock under the 2013 Plan and reduces the 2013 Plan’s share authorization for other awards on a one-for-one basis.
The following table presents information with respect to the Company’s equity compensation plans as of December 31, 2019:
Equity Incentive Plan Information
As of December 31, 2019
Number of Securities Issued or to be Issued Upon Exercise |
Number of Securities Remaining Available For Future Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans |
|||||
Equity compensation Plans Approved By Shareholders |
1,156,049 | |||||
LTIP-OP Units |
290,275 | |||||
Forfeited LTIP-OP Units |
(916 | ) |
||||
Converted LTIP-OP Units |
(18,917 | ) |
||||
Shares of Common Stock |
76,664 | |||||
Forfeited Shares of Common Stock |
(3,155 | ) |
||||
Equity Compensation Plans Not Approved By Shareholders |
— | |||||
LTIP-OP Units are a special class of partnership interest in the Operating Partnership. LTIP-OP Units may be issued to eligible participants for the performance of services to or for the benefit of the Operating Partnership. Initially, LTIP-OP Units do not have full parity with the Operating Partnership’s common units of limited partnership interest (“OP Units”) with respect to liquidating distributions; however, LTIP-OP Units receive, whether vested or not, the same per-unit distributions as OP Units and are allocated their pro-rata share of the Operating Partnership’s net income or loss. Under the terms of the LTIP-OP Units, the Operating Partnership will revalue its assets upon the occurrence of certain specified events, and any increase in the Operating Partnership’s valuation from the time of grant of the LTIP-OP Units until such event will be allocated first to the holders of LTIP-OP Units to equalize the capital accounts of such holders with the capital accounts of the holders of OP Units. Upon equalization of the capital accounts of the holders of LTIP-OP Units with the other holders of OP Units, the LTIP-OP Units will achieve full parity with OP Units for all purposes, including with respect to liquidating distributions. If such parity is reached, vested LTIP-OP Units may be converted into an equal number of OP Units at any time and, thereafter, enjoy all the rights of OP Units, including redemption rights.
33
| Item 6. | Selected Financial Data |
All currency figures are presented in thousands, except per share amounts or as otherwise noted.
The selected financial data set forth below has been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements.
This information should be read in conjunction with “Item 1. Business,” “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the audited consolidated financial statements and notes thereto included under “Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||
Operating Data: |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
2016 |
2015 |
||||||||||
Income |
|||||||||||||||
Interest income |
$ | 73,338 | $ | 57,715 | $ | 42,049 | $ | 30,722 | $ | 27,712 | |||||
Interest expense |
48,585 | 34,509 | 19,881 | 7,808 | 5,983 | ||||||||||
Net interest income |
24,753 | 23,206 | 22,168 | 22,914 | 21,729 | ||||||||||
Servicing fee income |
73,555 | 50,776 | 24,034 | 7,579 | 1,719 | ||||||||||
Servicing costs |
17,122 | 10,615 | 5,783 | 2,562 | 761 | ||||||||||
Net servicing income |
56,433 | 40,161 | 18,251 | 5,017 | 958 | ||||||||||
Other income (loss) |
|||||||||||||||
Realized gain (loss) on RMBS, available-for-sale, net |
902 | (8,362 | ) |
(503 | ) |
1,399 | 854 | ||||||||
Realized gain on investments in Excess MSRs, net |
— | — | 6,678 | 1,520 | — | ||||||||||
Realized loss on derivatives, net |
(12,362 | ) |
(5,889 | ) |
(5,554 | ) |
(7,963 | ) |
(3,913 | ) |
|||||
Realized gain on acquired assets, net |
26 | — | — | — | 449 | ||||||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives, net |
(10,867 | ) |
3,505 | 6,580 | 12,080 | (59 | ) |
||||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on investments in Excess MSRs |
— | — | — | 249 | (19 | ) |
|||||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on investments in Servicing Related Assets |
(106,772 | ) |
(3,573 | ) |
9,159 | (3,285 | ) |
(1,123 | ) |
||||||
Total Income (Loss) |
(47,887 | ) |
49,048 | 56,779 | 31,931 | 18,876 | |||||||||
Expenses |
|||||||||||||||
General and administrative expense |
4,647 | 3,941 | 3,817 | 3,284 | 3,081 | ||||||||||
Management fee to affiliate |
7,784 | 5,946 | 4,347 | 2,946 | 2,783 | ||||||||||
Total Expenses |
12,431 | 9,887 | 8,164 | 6,230 | 5,864 | ||||||||||
Income (Loss) Before Income Taxes |
(60,318 | ) |
39,161 | 48,615 | 25,701 | 13,012 | |||||||||
Provision for (Benefit from) corporate business taxes |
(16,822 | ) |
1,388 | 601 | 458 | (343 | ) |
||||||||
Net Income (Loss) |
(43,496 | ) |
37,773 | 48,014 | 25,243 | 13,355 | |||||||||
Net (income) loss allocated to noncontrolling interests in Operating Partnership |
703 | (488 | ) |
(655 | ) |
(411 | ) |
(141 | ) |
||||||
Dividends on preferred stock |
9,353 | 5,297 | 1,833 | — | — | ||||||||||
Net Income (Loss) Applicable to Common Stockholders |
$ | (52,146 | ) |
$ | 31,988 | $ | 45,526 | $ | 24,832 | $ | 13,214 | ||||
Net Income (Loss) Per Share of Common Stock |
|||||||||||||||
Basic |
$ | (3.11 | ) |
$ | 2.18 | $ | 3.98 | $ | 3.31 | $ | 1.76 | ||||
Diluted |
$ | (3.11 | ) |
$ | 2.18 | $ | 3.98 | $ | 3.30 | $ | 1.76 | ||||
Weighted Average Number of Shares of Common Stock Outstanding |
|||||||||||||||
Basic |
16,775,113 | 14,649,242 | 11,443,493 | 7,512,444 | 7,509,543 | ||||||||||
Diluted |
16,787,902 | 14,657,498 | 11,450,831 | 7,523,297 | 7,512,444 | ||||||||||
Dividends per share of Common Stock |
$ | 1.78 | $ | 2.11 | $ | 1.96 | $ | 2.11 | $ | 1.98 | |||||
34
Balance Sheet Data: |
December 31, 2019 |
December 31, 2018 |
December 31, 2017 |
December 31, 2016 |
December 31, 2015 |
||||||||||
RMBS, available-for-sale (including pledged assets) |
$ | 2,508,360 | $ | 1,770,110 | $ | 1,840,912 | $ | 671,904 | $ | 508,242 | |||||
Investments in Servicing Related Assets at fair value (including pledged assets) |
291,111 | 294,907 | 122,806 | 61,263 | 97,803 | ||||||||||
Total Assets |
2,956,552 | 2,153,277 | 2,050,685 | 792,878 | 636,340 | ||||||||||
Repurchase agreements |
2,337,638 | 1,598,592 | 1,666,537 | 594,615 | 385,560 | ||||||||||
Federal Home Loan Bank advances |
— | — | — | — | 62,250 | ||||||||||
Derivative liabilities |
12,337 | 3,816 | 344 | 694 | 4,595 | ||||||||||
Notes payable |
166,989 | 157,543 | 39,025 | 22,886 | 24,313 | ||||||||||
Dividends payable |
8,768 | 11,847 | 7,273 | 4,816 | 3,684 | ||||||||||
Total Liabilities |
2,544,909 | 1,789,346 | 1,728,228 | 636,869 | 484,003 | ||||||||||
Total Stockholders’ Equity |
411,643 | 363,931 | 322,457 | 156,009 | 152,337 | ||||||||||
35
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
The following discussion and analysis should be read in conjunction with our audited consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes included in “Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
All currency amounts are presented in thousands, except per share amounts or as otherwise noted.
General
We are a public residential real estate finance company focused on acquiring, investing in and managing residential mortgage assets in the United States. We were incorporated in Maryland on October 31, 2012, and we commenced operations on or about October 9, 2013 following the completion of our initial public offering and a concurrent private placement. Our common stock, our Series A Preferred Stock and our Series B Preferred Stock are listed and traded on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbols “CHMI,” “CHMI-PRA” and “CHMI-PRB,” respectively. We are externally managed by our Manager, Cherry Hill Mortgage Management, LLC, an SEC-registered investment adviser.
Our principal objective is to generate attractive current yields and risk-adjusted total returns for our stockholders over the long term, primarily through dividend distributions and secondarily through capital appreciation. We attempt to attain this objective by selectively constructing and actively managing a portfolio of Servicing Related Assets and RMBS and, subject to market conditions, other cash flowing residential mortgage assets.
We are subject to the risks involved with real estate and real estate-related debt instruments. These include, among others, the risks normally associated with changes in the general economic climate, changes in the mortgage market, changes in tax laws, interest rate levels, and the availability of financing.
We elected to be taxed as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes commencing with our short taxable year ended December 31, 2013. We operate so as to continue to qualify to be taxed as a REIT. Our asset acquisition strategy focuses on acquiring a diversified portfolio of residential mortgage assets that balances the risk and reward opportunities our Manager observes in the marketplace. Prior to our acquisition of Aurora in May 2015, our Servicing Related Assets consisted of Excess MSRs in three pools: Excess MSR Pool 1, Excess MSR Pool 2 and Excess MSR Pool 2014. The Excess MSRs in these three pools had been previously acquired by the Company from Freedom Mortgage. All of these Excess MSRs were sold back to Freedom Mortgage in November 2016 and February 2017. Aurora has the licenses necessary to service mortgage loans on a nationwide basis and is approved to service loans for Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac and Ginnie Mae.
In addition to Servicing Related Assets, we invest in RMBS, primarily those backed by 30-, 20- and 15-year fixed rate mortgages that offer what we believe to be favorable prepayment and duration characteristics. Our RMBS consist primarily of Agency RMBS on which the payments of principal and interest are guaranteed by an Agency. We have also invested in Agency CMOs consisting of interest only securities (“IOs”) as well as non-Agency RMBS. We finance our RMBS with leverage, the amount of which will vary from time to time depending on the particular characteristics of our portfolio, the availability of financing and market conditions. We do not have a targeted leverage ratio for our RMBS. Our borrowings for RMBS consist of short-term borrowings under master repurchase agreements.
Subject to maintaining our qualification as a REIT, we utilize derivative financial instruments (or hedging instruments) to hedge our exposure to potential interest rate mismatches between the interest we earn on our assets and our borrowing costs caused by fluctuations in short-term interest rates. In utilizing leverage and interest rate hedges, our objectives include, where desirable, locking in, on a long-term basis, a spread between the yield on our assets and the cost of our financing in an effort to improve returns to our stockholders.
We also operate our business in a manner that permits us to maintain our exclusion from registration as an investment company under the Investment Company Act.
On March 29, 2017, we issued and sold 5,175,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.01 per share, raising approximately $81.1 million after underwriting discounts and commissions but before expenses of approximately $229,000. All of the net proceeds were used to invest in RMBS.
36
On August 17, 2017, we issued and sold 2,400,000 shares of our Series A Preferred Stock, raising approximately $58.1 million after underwriting discounts and commissions but before expenses of approximately $193,000. All of the net proceeds from the Series A Preferred Stock offering were also invested in RMBS. See “Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data—Note 6. Equity and Earnings per Common Share—Common and Preferred Stock.”
In April 2018, the Company initiated an at-the-market offering program (the “Preferred Series A ATM Program”) pursuant to which it may offer through one or more sales agents and sell from time to time up to $35 million of its Series A Preferred Stock at prices prevailing at the time, subject to volume and other regulatory limitations. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company issued and sold 63,429 shares of Series A Preferred Stock under the Preferred Series A ATM Program. The shares were sold at a weighted average price of $25.21 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $1.6 million before fees of approximately $26,000. During the year ended December 31, 2018, the Company issued and sold 318,206 shares of Series A Preferred Stock under the Preferred Series A ATM Program. The shares were sold at a weighted average price of $25.37 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $8.1 million before fees of approximately $127,000. The net proceeds were used for general corporate purposes, including investment in RMBS.
On June 4, 2018, the Company issued and sold 2,750,000 shares of its common stock. The underwriters subsequently exercised their option to purchase an additional 338,857 shares for total proceeds of approximately $53.8 million after underwriting discounts and commissions but before expenses of approximately $265,000. All of the net proceeds were invested in RMBS.
In August 2018, the Company initiated an at-the-market offering program (the “Common Stock ATM Program”) pursuant to which it may offer through one or more sales agents and sell from time to time up to $50 million of its common stock at prices prevailing at the time, subject to volume and other regulatory limitations. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company issued and sold 225,646 shares of common stock under the Common Stock ATM Program. The shares were sold at a weighted average price of $17.40 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $3.9 million before fees of approximately $79,000. During the year ended December 31, 2018, the Company issued and sold 833,593 shares of common stock under the Common Stock ATM Program. The shares were sold at a weighted average price of $18.84 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $15.7 million before fees of approximately $314,000. The net proceeds were used for general corporate purposes, including investment in RMBS.
On February 11, 2019, we issued and sold 1,800,000 shares of our Series B Preferred Stock. The underwriters subsequently exercised their option to purchase an additional 200,000 shares for total proceeds of approximately $48.4 million after underwriting discounts and commissions but before expenses of approximately $285,000. The net proceeds from the Series B Preferred Stock offering were invested in RMBS and MSRs.
In September 2019, we initiated a share repurchase program that allows for the repurchase of up to an aggregate of $10.0 million of our common stock. Shares may be repurchased from time to time through privately negotiated transactions or open market transactions, pursuant to a trading plan in accordance with Rules 10b5-1 and 10b-18 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), or by any combination of such methods. The manner, price, number and timing of share repurchases are subject to a variety of factors, including market conditions and applicable SEC rules. The share repurchase program does not require the purchase of any minimum number of shares, and, subject to SEC rules, purchases may be commenced or suspended at any time without prior notice. Unless sooner terminated or extended, the share repurchase program expires on September 3, 2020. In the period from the program’s inception through December 31, 2019, the Company repurchased 235,950 shares of its common stock pursuant to the repurchase program for approximately $3.5 million.
A significant portion of the paydowns of the RMBS acquired as a result of these equity offerings have been or will be deployed into the acquisition of MSRs. The Company may also sell certain of these RMBS and deploy the net proceeds from such sales to the extent necessary to fund the purchase price of MSRs.
This Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Results of Operations and Financial Condition omits discussion and comparison of results of operations and financial condition for the year ended December 31, 2017. That discussion and comparison is included under the heading “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Results of Operations and Financial Condition” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2018.
37
Factors Impacting our Operating Results
Our income is generated primarily by the net spread between the income we earn on our assets and the cost of our financing and hedging activities as well as the amortization of any purchase premiums or the accretion of discounts. Our net income includes the actual interest payments we receive on our RMBS, the net servicing fees we receive on our MSRs and the accretion/amortization of any purchase discounts/premiums. Changes in various factors such as market interest rates, prepayment speeds, estimated future cash flows, servicing costs and credit quality could affect the amount of premium to be amortized or discount to be accreted into interest income for a given period. Prepayment speeds vary according to the type of investment, conditions in the financial markets, competition and other factors, none of which can be predicted with any certainty. Our operating results may also be affected by credit losses in excess of initial anticipations or unanticipated credit events experienced by borrowers whose mortgage loans underlay the MSRs held by Aurora or the non-Agency RMBS held in our portfolio.
Set forth below is the positive gross spread between the yield on RMBS and our costs of funding those assets at the end of each of the quarters indicated below:
Average Net Yield Spread at Period End
Quarter Ended |
Average Asset Yield |
Average Cost of Funds |
Average Net Interest Rate Spread |
||||||
December 31, 2019 |
3.72 | % |
1.84 | % |
1.88 | % |
|||
September 30, 2019 |
3.77 | % |
2.13 | % |
1.64 | % |
|||
June 30, 2019 |
3.83 | % |
2.27 | % |
1.55 | % |
|||
March 31, 2019 |
3.83 | % |
2.21 | % |
1.62 | % |
|||
December 31, 2018 |
3.82 | % |
2.10 | % |
1.72 | % |
|||
September 30, 2018 |
3.77 | % |
2.05 | % |
1.72 | % |
|||
June 30, 2018 |
3.74 | % |
1.83 | % |
1.91 | % |
|||
March 31, 2018 |
3.67 | % |
1.81 | % |
1.86 | % |
|||
December 31, 2017 |
3.66 | % |
1.85 | % |
1.81 | % |
|||
September 30, 2017 |
3.66 | % |
1.85 | % |
1.81 | % |
|||
The Average Cost of Funds also includes the benefits of related swaps.
Changes in the Market Value of Our Assets
We hold our Servicing Related Assets as long-term investments. Our original Excess MSRs were, and our MSRs are, carried at their fair value with changes in their fair value recorded in other income or loss in our consolidated statements of income (loss). Those values may be affected by events or headlines that are outside of our control, such as events impacting the U.S. or global economy generally or the U.S. residential market specifically, and events or headlines impacting the parties with which we do business. See “Item 1A. Risk Factors – Risks Related to Our Business.”
Our RMBS are carried at their fair value, as available-for-sale in accordance with ASC 320, Investments – Debt and Equity Securities, with changes in fair value recorded through accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), a component of stockholders’ equity. As a result, we do not expect that changes in the market value of our RMBS will normally impact our operating results, but such changes will affect our book value. However, at least on a quarterly basis, we assess both our ability and intent to continue to hold our RMBS as long-term investments. As part of this process, we monitor our RMBS for other-than-temporary impairment. A change in our ability and/or intent to continue to hold any of our RMBS could result in our recognizing an impairment charge or realizing losses while holding these assets.
Impact of Changes in Market Interest Rates on Our Assets
The value of our assets may be affected by prepayment rates on mortgage loans. Prepayment speed is the measurement of how quickly borrowers pay down the UPB of their loans or how quickly loans are otherwise liquidated or charged off. Generally, in a declining interest rate environment, prepayment speeds tend to increase. Conversely, in an increasing interest rate environment, prepayment speeds tend to decrease. When we acquire
38
Servicing Related Assets or RMBS, we anticipate that the underlying mortgage loans will prepay at a projected rate generating an expected cash flow (in the case of Servicing Related Assets) and yield. If we purchase assets at a premium to par value and borrowers prepay their mortgage loans faster than expected, the corresponding prepayments on our assets may reduce the expected yield on such assets because we will have to amortize the related premium on an accelerated basis. In addition, we will have to reinvest the greater amounts of prepayments in that lower rate environment, thereby affecting future yields on our assets. If we purchase assets at a discount to par value, and borrowers prepay their mortgage loans slower than expected, the decrease in corresponding prepayments may reduce the expected yield on assets because we will not be able to accrete the related discount as quickly as originally anticipated.
If prepayment speeds are significantly greater than expected, the fair value of the Servicing Related Assets could be less than their fair value as previously reported on our consolidated balance sheets. Such a reduction in the fair value of the Servicing Related Assets would have a negative impact on our book value. Furthermore, a significant increase in prepayment speeds could materially reduce the ultimate cash flows we receive from the Servicing Related Assets, and we could receive substantially less than what we paid for such assets. We do not utilize derivatives to hedge against changes in the fair value of the Servicing Related Assets. Our balance sheet, results of operations and cash flows are susceptible to significant volatility due to changes in the fair value of, or cash flows from, the Servicing Related Assets as interest rates change.
A slower than anticipated rate of prepayment due to an increase in market interest rates also will cause the life of the related RMBS to extend beyond that which was projected. As a result, we would have an asset with a lower yield than current investments for a longer period of time. In addition, if we have hedged our interest rate risk, extension may cause the security to be outstanding longer than the related hedge, thereby reducing the protection intended to be provided by the hedge.
Voluntary and involuntary prepayment rates may be affected by a number of factors including, but not limited to, the availability of mortgage credit, the relative economic vitality of, or natural disasters affecting, the area in which the related properties are located, the servicing of the mortgage loans, possible changes in tax laws, other opportunities for investment, homeowner mobility and other economic, social, geographic, demographic and legal factors, none of which can be predicted with any certainty.
We attempt to reduce the exposure of our MSRs to voluntary prepayments through the structuring of recapture agreements with Aurora’s subservicers. In June 2016, Aurora entered into a joint marketing recapture agreement with Freedom Mortgage. Pursuant to this agreement, Freedom Mortgage attempts to refinance certain mortgage loans underlying Aurora’s MSR portfolio subserviced by Freedom Mortgage. If a loan is refinanced, Aurora will pay Freedom Mortgage a fee for its origination services. Freedom Mortgage will be entitled to sell the loan for its own benefit and will transfer the related MSR to Aurora. The agreement had an initial term of one year, subject to automatic renewals of one year each. See “Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data—Note 7. Transactions with Affiliates and Affiliated Entities.” In the year ended December 31, 2019, Aurora received MSRs with an aggregate UPB of approximately $4.4 million and paid fees of approximately $5,200 to Freedom Mortgage under this joint marketing recapture agreement. In the year ended December 31, 2018, Aurora received MSRs with an aggregate UPB of approximately $21.5 million and paid fees of approximately $32,000 to Freedom Mortgage under this joint marketing recapture agreement.
With respect to our business operations, increases in interest rates, in general, may over time cause:
| • | the interest expense associated with our borrowings to increase; |
| • | the value of our assets to fluctuate; |
| • | coupons on any adjustable-rate and hybrid RMBS we may own to reset, although on a delayed basis, to higher interest rates; |
| • | prepayments on our RMBS to slow, thereby slowing the amortization of our purchase premiums and the accretion of our purchase discounts; and |
| • | an increase in the value of any interest rate swap agreements we may enter into as part of our hedging strategy. |
39
Conversely, decreases in interest rates, in general, may over time cause:
| • | prepayments on our RMBS to increase, thereby accelerating the amortization of our purchase premiums and the accretion of our purchase discounts; |
| • | the interest expense associated with our borrowings to decrease; |
| • | the value of our assets to fluctuate; |
| • | a decrease in the value of any interest rate swap agreements we may enter into as part of our hedging strategy; and |
| • | coupons on any adjustable-rate and hybrid RMBS assets we may own to reset, although on a delayed basis, to lower interest rates. |
Effects of Spreads on our Assets
The spread between the yield on our assets and our funding costs affects the performance of our business. Wider spreads imply greater income on new asset purchases but may have a negative impact on our stated book value. Wider spreads may also negatively impact asset prices. In an environment where spreads are widening, counterparties may require additional collateral to secure borrowings which may require us to reduce leverage by selling assets. Conversely, tighter spreads imply lower income on new asset purchases but may have a positive impact on stated book value of our existing assets. In this case, we may be able to reduce the amount of collateral required to secure borrowings.
Credit Risk
We are subject to varying degrees of credit risk in connection with our assets. Although we expect relatively low credit risk with respect to our portfolios of Agency RMBS, we are subject to the credit risk of borrowers under the loans backing CMOs we own and to the credit enhancements built into the CMO structure. We also are subject to the credit risk of the borrowers under the loans that Aurora services. Through loan level due diligence, we attempt to mitigate this risk by seeking to acquire high quality assets at appropriate prices given anticipated and unanticipated losses. We also conduct ongoing monitoring of acquired MSRs. Nevertheless, unanticipated credit losses could occur which could adversely impact our operating results.
Critical Accounting Policies and Use of Estimates
Our financial statements are prepared in accordance with GAAP, which requires the use of estimates that involve the exercise of judgment and the use of assumptions as to future uncertainties. In accordance with SEC guidance, the following discussion addresses the accounting policies that we apply with respect to our operations. Our most critical accounting policies involve decisions and assessments that could affect our reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, as well as our reported amounts of revenues and expenses. We believe that the decisions and assessments upon which our financial statements are based were reasonable at the time made and based upon information available to us at that time. Our critical accounting policies and accounting estimates may be expanded over time as we diversify our portfolio. The material accounting policies and estimates that we expect to be most critical to an investor’s understanding of our financial results and condition and require complex management judgment are discussed below.
Classification of Investment Securities and Impairment of Financial Instruments
ASC 320, Investments – Debt and Equity Securities, requires that at the time of purchase, we designate a security as either trading, available-for-sale, or held-to-maturity depending on our ability and intent to hold such security to maturity. Securities available-for-sale will be reported at fair value, while securities held-to-maturity will be reported at amortized cost. Although we may hold most of our securities until maturity, we may, from time to time, sell any of our securities as part of our overall management of our asset portfolio. Accordingly, we elect to classify all of our RMBS as available-for-sale. All assets classified as available-for-sale will be reported at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses excluded from earnings and reported as a separate component of stockholders’ equity.
40
When the estimated fair value of a security is less than amortized cost, we consider whether there is an other-than-temporary impairment (“OTTI”) in the value of the security. An impairment is deemed an OTTI if (i) we intend to sell the security, (ii) it is more likely than not that we will be required to sell the security before recovering our cost basis, or (iii) we do not expect to recover the entire amortized cost basis of the security even if we do not intend to sell the security or believe it is more likely than not that we will be required to sell the security before recovering our cost basis. If the impairment is deemed to be an OTTI, the resulting accounting treatment depends on the factors causing the OTTI. If the OTTI has resulted from (i) our intention to sell the security or (ii) our judgment that it is more likely than not that we will be required to sell the security before recovering our cost basis, an impairment loss is recognized in current earnings equal to the difference between our amortized cost basis and fair value. If the OTTI has resulted from our conclusion that we will not recover our cost basis even if we do not intend to sell the security, the credit loss portion of the impairment is recorded in current earnings and the portion of the loss related to other factors, such as changes in interest rates, continues to be recognized in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). Determining whether there is an OTTI may require management to exercise significant judgment and make significant assumptions, including, but not limited to, estimated cash flows, estimated prepayments, expected losses, and expected changes in interest rates. As a result, actual impairment losses could differ from reported amounts. Such judgments and assumptions are based upon a number of factors, including (i) the credit of the issuer or the borrower, (ii) the credit rating of the security, (iii) the key terms of the security, (iv) the performance of the loan or underlying loans, including debt service coverage and loan-to-value ratios, (v) the value of the collateral for the loan or underlying loans, (vi) the effect of local, industry, and broader economic factors, and (vii) the historical and anticipated trends in defaults and loss severities for similar securities.
Fair Valued Assets and Liabilities
ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures, defines fair value as the price that would be received from the sale of an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. ASC 820 clarifies that fair value should be based on the assumptions market participants would use when pricing an asset or liability and establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the information used to develop those assumptions. The fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority to quoted prices available in active markets (i.e., observable inputs) and the lowest priority to data lacking transparency (i.e., unobservable inputs). Additionally, ASC 820 requires an entity to consider all aspects of nonperformance risk, including the entity’s own credit standing, when measuring the fair value of a liability.
ASC 820 establishes a three-level hierarchy to be used when measuring and disclosing fair value. An instrument’s categorization within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of significant input to its valuation. Following is a description of the three levels:
| Level 1 | inputs are quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities as of the measurement date under current market conditions. Additionally, the entity must have the ability to access the active market and the quoted prices cannot be adjusted by the entity. |
| Level 2 | inputs include quoted prices in active markets for similar assets or liabilities; quoted prices in inactive markets for identical or similar assets or liabilities; or inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means for substantially the full-term of the assets or liabilities. |
| Level 3 | unobservable inputs are supported by little or no market activity. The unobservable inputs represent the assumptions that management believes market participants would use to price the assets and liabilities, including risk. Generally, Level 3 assets and liabilities are valued using pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies, or similar techniques that require significant judgment or estimation. |
The level in the fair value hierarchy within which the entirety of a fair value measurement falls is based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety. We have used Level 2 for our RMBSs, our derivative assets and liabilities and Level 3 for our Servicing Related Assets.
When available, we use quoted market prices to determine the fair value of an asset or liability. If quoted market prices are not available, we will consult independent pricing services or third party broker quotes, provided that there is no ongoing material event that affects the issuer of the securities being valued or the
41
market. If there is such an ongoing event, or if quoted market prices are not available, we will determine the fair value of the securities using valuation techniques that use, when possible, current market-based or independently-sourced market parameters, such as interest rates.
Investments in Excess MSRs
Upon acquisition from Freedom Mortgage, we elected to record our investments in Excess MSRs at fair value. We made this election in order to provide the users of our consolidated financial statements with better information regarding the effects of prepayment risk and other market factors on the Excess MSRs. Under this election, we recorded a valuation adjustment on our Excess MSR investments on a quarterly basis to recognize the changes in fair value in net income as described in “–Revenue Recognition on Investments in Excess MSRs” below.
The fair values of those Excess MSRs were determined by projecting net servicing cash flows, which were then discounted to estimate the fair value. The fair values of Excess MSRs are impacted by a variety of factors, including prepayment assumptions, discount rates, delinquency rates, contractually specified servicing fees, and underlying portfolio characteristics. The underlying assumptions and estimated values were corroborated by values received from independent third parties. Changes in fair value of our Excess MSRs were reported in other income or loss in our consolidated statements of income. For additional information on our fair value methodology, see “Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data—Note 9. Fair Value.”
As of December 31, 2019, all of the Excess MSRs originally acquired from Freedom Mortgage have been sold back to Freedom Mortgage.
Revenue Recognition on Investments in Excess MSRs
Investments in Excess MSRs from Freedom Mortgage were aggregated into pools, and each pool of Excess MSRs was accounted for in the aggregate. Income for Excess MSRs was accreted into income on an effective yield or “interest” method, based upon the expected excess servicing amount through the expected life of the underlying mortgages. Changes to expected cash flows resulted in a cumulative retrospective adjustment, which was recorded in the period in which the change in expected cash flows occurred. Under the retrospective method, the income recognized for a reporting period is measured as the difference between the amortized cost basis at the end of the period and the amortized cost basis at the beginning of the period, plus any cash received during the period. The amortized cost basis is calculated as the present value of estimated future cash flows using an effective yield, which is the yield that equates all past actual and current estimated future cash flows to the initial investment. The difference between the fair value of Excess MSRs and their amortized cost basis was recorded as “Unrealized gain (loss) on investments in Excess MSRs” in our consolidated statements of income. Fair value was generally determined by discounting the expected future cash flows using discount rates that incorporated the market risks and liquidity premium specific to the Excess MSRs, and therefore may have differed from their effective yields.
Investments in MSRs
We have elected the fair value option to record our investments in MSRs in order to provide users of our consolidated financial statements with better information regarding the effects of prepayment risk and other market factors on the MSRs. Under this election, we record a valuation adjustment on our investments in MSRs on a quarterly basis to recognize the changes in fair value of our MSRs in net income as described below. Our MSRs represent the right to service mortgage loans. As an owner and manager of MSRs, we may be obligated to fund advances of principal and interest payments due to third-party owners of the loans, but not yet received from the individual borrowers. These advances are reported as servicing advances within the “Receivables and other assets” line item on the consolidated balance sheets. Although transactions in MSRs are observable in the marketplace, the valuation includes unobservable market data inputs (prepayment speeds, delinquency levels, costs to service and discount rates). Changes in the fair value of MSRs as well as servicing fee income and servicing expenses are reported on the consolidated statements of income. In determining the valuation of MSRs, management uses internally developed models that are primarily based on observable market-based inputs but which also include unobservable market data inputs. For additional information on our fair value methodology, see “Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data–Note 9. Fair Value.”
42
Revenue Recognition on Investments in MSRs
Mortgage servicing fee income represents revenue earned for servicing mortgage loans. The servicing fees are based on a contractual percentage of the outstanding principal balance and are recognized as revenue as the related mortgage payments are collected. Corresponding costs to service are charged to expense as incurred. Approximately $16.6 million and $9.9 million in reimbursable servicing advances were receivable at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively, and have been classified within “Receivables and other assets” on the consolidated balance sheets.
Servicing fee income received and servicing expenses incurred are reported on the consolidated statements of income (loss). The difference between the fair value of MSRs and their amortized cost basis is recorded on the consolidated statements of income (loss) as “Unrealized gain (loss) on investments in Servicing Related Assets.” Fair value is generally determined by discounting the expected future cash flows using discount rates that incorporate the market risks and liquidity premium specific to the MSRs and, therefore, may differ from their effective yields.
Revenue Recognition on Securities
Interest income from coupon payments is accrued based on the outstanding principal amount of the RMBS and their contractual terms. Premiums and discounts associated with the purchase of the RMBS are amortized or accreted into interest income over the projected lives of the securities using the effective interest method. Our policy for estimating prepayment speeds for calculating the effective yield is to evaluate historical performance, consensus prepayment speeds, and current market conditions. Adjustments are made for actual prepayment activity.
Repurchase Transactions
We finance the acquisition of our RMBS for our portfolio through repurchase transactions under master repurchase agreements. Repurchase transactions are treated as collateralized financing transactions and are carried at their contractual amounts as specified in the respective transactions. Accrued interest payable is included in “Accrued expenses and other liabilities” on the consolidated balance sheets. Securities financed through repurchase transactions remain on our consolidated balance sheet as an asset and cash received from the purchaser is recorded on our consolidated balance sheet as a liability. Interest paid in accordance with repurchase transactions is recorded in interest expense on the consolidated statements of income (loss).
Income Taxes
We elected to be taxed as a REIT under the Code commencing with our short taxable year ended December 31, 2013. We expect to continue to qualify to be treated as a REIT. U.S. federal income tax law generally requires that a REIT distribute annually at least 90% of its REIT taxable income, without regard to the deduction for dividends paid and excluding net capital gains, and that it pay tax at regular corporate income tax rates to the extent that it annually distributes less than 100% of its taxable income. Our subsidiary TRS, Solutions and its wholly-owned subsidiary, Aurora, are subject to U.S. federal income taxes on their taxable income.
We account for income taxes in accordance with ASC 740, Income Taxes. ASC 740 requires the recording of deferred income taxes that reflect the net tax effect of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of our assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes, including operating loss carry forwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in earnings in the period that includes the enactment date. We assess our tax positions for all open tax years and determines if we have any material unrecognized liabilities in accordance with ASC 740. We record these liabilities to the extent we deem them more-likely-than-not to be incurred. We record interest and penalties related to income taxes within the provision for income taxes in the consolidated statements of income (loss). We have not incurred any interest or penalties.
43
Results of Operations
Presented below is a comparison of the Company’s results of operations for the periods indicated (dollars in thousands):
Results of Operations
Year Ended December 31, |
||||||
2019 |
2018 |
|||||
Income |
||||||
Interest income |
$ | 73,338 | $ | 57,715 | ||
Interest expense |
48,585 | 34,509 | ||||
Net interest income |
24,753 | 23,206 | ||||
Servicing fee income |
73,555 | 50,776 | ||||
Servicing costs |
17,122 | 10,615 | ||||
Net servicing income |
56,433 | 40,161 | ||||
Other income (loss) |
||||||
Realized gain (loss) on RMBS, available-for-sale, net |
902 | (8,362 | ) |
|||
Realized loss on derivatives, net |
(12,362 | ) |
(5,889 | ) |
||
Realized gain on acquired assets, net |
26 | — | ||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives, net |
(10,867 | ) |
3,505 | |||
Unrealized gain (loss) on investments in Servicing Related Assets |
(106,772 | ) |
(3,573 | ) |
||
Total Income (Loss) |
(47,887 | ) |
49,048 | |||
Expenses |
||||||
General and administrative expense |
4,647 | 3,941 | ||||
Management fee to affiliate |
7,784 | 5,946 | ||||
Total Expenses |
12,431 | 9,887 | ||||
Income (Loss) Before Income Taxes |
(60,318 | ) |
39,161 | |||
Provision for (Benefit from) corporate business taxes |
(16,822 | ) |
1,388 | |||
Net Income (Loss) |
(43,496 | ) |
37,773 | |||
Net (income) loss allocated to noncontrolling interests in Operating Partnership |
703 | (488 | ) |
|||
Dividends on preferred stock |
9,353 | 5,297 | ||||
Net Income (Loss) Applicable to Common Stockholders |
$ | (52,146 | ) |
$ | 31,988 | |
44
Presented below is summary financial data on our segments together with a reconciliation to the same data for the Company as a whole, for the periods indicated (dollars in thousands):
Segment Summary Data
For
Servicing Related Assets |
RMBS |
All Other |
Total |
|||||||||
Income Statement |
||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
||||||||||||
Interest income |
$ | 2,820 | $ | 70,518 | $ | — | $ | 73,338 | ||||
Interest expense |
3,669 | 44,916 | — | 48,585 | ||||||||
Net interest income (expense) |
(849 | ) |
25,602 | — | 24,753 | |||||||
Servicing fee income |
73,555 | — | — | 73,555 | ||||||||
Servicing costs |
17,122 | — | — | 17,122 | ||||||||
Net servicing income |
56,433 | — | — | 56,433 | ||||||||
Other expense |
(95,002 | ) |
(34,071 | ) |
— | (129,073 | ) |
|||||
Other operating expenses |
— | — | 12,431 | 12,431 | ||||||||
Benefit from corporate business taxes |
(16,822 | ) |
— | — | (16,822 | ) |
||||||
Net Loss |
$ | (22,596 | ) |
$ | (8,469 | ) |
$ | (12,431 | ) |
$ | (43,496 | ) |
Year Ended December 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||
Interest income |
$ | 99 | $ | 57,616 | $ | — | $ | 57,715 | ||||
Interest expense |
2,314 | 32,193 | 2 | 34,509 | ||||||||
Net interest income (expense) |
(2,215 | ) |
25,423 | (2 | ) |
23,206 | ||||||
Servicing fee income |
50,776 | — | — | 50,776 | ||||||||
Servicing costs |
10,615 | — | — | 10,615 | ||||||||
Net servicing income |
40,161 | — | — | 40,161 | ||||||||
Other expense |
(3,573 | ) |
(10,746 | ) |
— | (14,319 | ) |
|||||
Other operating expenses |
— | — | 9,887 | 9,887 | ||||||||
Provision for corporate business taxes |
1,388 | — | — | 1,388 | ||||||||
Net Income (Loss) |
$ | 32,985 | $ | 14,677 | $ | (9,889 | ) |
$ | 37,773 | |||
Servicing Related Assets |
RMBS |
All Other |
Total |
|||||||||
Balance Sheet |
||||||||||||
December 31, 2019 |
||||||||||||
Investments |
$ | 291,111 | $ | 2,508,360 | $ | — | $ | 2,799,471 | ||||
Other assets |
51,729 | 80,207 | 25,145 | 157,081 | ||||||||
Total assets |
342,840 | 2,588,567 | 25,145 | 2,956,552 | ||||||||
Debt |
166,989 | 2,337,638 | — | 2,504,627 | ||||||||
Other liabilities |
9,762 | 16,503 | 14,017 | 40,282 | ||||||||
Total liabilities |
176,751 | 2,354,141 | 14,017 | 2,544,909 | ||||||||
Book value |
$ | 166,089 | $ | 234,426 | $ | 11,128 | $ | 411,643 | ||||
December 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||
Investments |
$ | 294,907 | $ | 1,770,110 | $ | — | $ | 2,065,017 | ||||
Other assets |
17,817 | 38,165 | 32,278 | 88,260 | ||||||||
Total assets |
312,724 | 1,808,275 | 32,278 | 2,153,277 | ||||||||
Debt |
157,543 | 1,598,592 | — | 1,756,135 | ||||||||
Other liabilities |
7,488 | 10,440 | 15,283 | 33,211 | ||||||||
Total liabilities |
165,031 | 1,609,032 | 15,283 | 1,789,346 | ||||||||
Book value |
$ | 147,693 | $ | 199,243 | $ | 16,995 | $ | 363,931 | ||||
45
Interest Income
Interest income for the year ended December 31, 2019 was $73.3 million as compared to $57.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The $15.6 million increase in interest income for the year ended December 31, 2019 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2018, was comprised of an increase of approximately $2.7 in Servicing Related Assets and an increase of approximately $12.9 million in RMBS primarily resulting from the investment of the net proceeds of the equity offerings that the Company completed during the year ended December 31, 2019.
Interest Expense
Interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2019 was $48.6 million as compared to $34.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The $14.1 million increase for the year ended December 31, 2019 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2018, was comprised of an increase of approximately $1.4 million from Servicing Related Assets and an increase of approximately $12.7 million from RMBS. The changes were primarily due to additional Servicing Related Assets financing, additional repurchase agreement borrowings and an overall increase in repurchase rates offset by a lower swap cost.
Change in Fair Value of Investments in Servicing Related Assets
The fair value of our investments in Servicing Related Assets for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 decreased by approximately $106.8 million and $3.6 million, respectively, primarily due to changes in valuation inputs or assumptions.
Change in Fair Value of Derivatives
The fair value of derivatives for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 decreased by approximately $10.9 million and increased by approximately $3.5 million, respectively, primarily due to changes in interest rates and the composition of our derivatives relative to the prior year.
General and Administrative Expense
General and administrative expense for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 increased by approximately $706,000 and $124,000, respectively, as compared to the prior year. Each increase was primarily due to costs associated with Sarbanes-Oxley compliance and the growth of Aurora.
Management Fees to Affiliate
Management fees for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 increased by approximately $1.8 million and $1.6 million, respectively, from the preceding year-end. Each such increase was due to the sale of our capital stock during the applicable year and the resulting increase in stockholders’ equity, which is the basis for the calculation of the management fee that we pay to the Manager.
Net Income Allocated to Noncontrolling Interests in Operating Partnership
Net income allocated to noncontrolling interests in the Operating Partnership, which are LTIP-OP Units owned by our directors and officers and by certain individuals who provide services to us through the Manager, represented approximately 1.6% and 1.3% of net income for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. Each annual increase relative to the prior year was due primarily to the issuance and sale of additional shares of our capital stock during the applicable year.
46
For the period indicated below, our accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) changed as a result of the indicated gains and losses (dollars in thousands):
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
|||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss, December 31, 2018 |
$ | (38,400 | ) |
Other comprehensive income |
79,814 | ||
Accumulated other comprehensive gain, December 31, 2019 |
$ | 41,414 | |
Year Ended December 31, 2018 |
|||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss, December 31, 2017 |
$ | (2,942 | ) |
Other comprehensive loss |
(35,458 | ) |
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss, December 31, 2018 |
$ | (38,400 | ) |
Our GAAP equity changes as the values of our RMBS are marked to market each quarter, among other factors. The primary causes of mark to market changes are changes in interest rates and credit spreads. During the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, volatility and ultimate decreases in the 10 Year U.S. Treasury rate and widening of credit spreads caused a net unrealized loss on our RMBS in each of those periods, which is recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss).
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
This Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations section contains analysis and discussion of non-GAAP measurements. The non-GAAP measurements include the following:
| • | core earnings; and |
| • | core earnings per average common share. |
Core earnings is a non-GAAP financial measure that we currently define as GAAP net income (loss), excluding realized gain (loss) on RMBS, realized and unrealized gain (loss) on investments in MSRs (net of any estimated MSR amortization), realized and unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives and realized (gain) loss on acquired assets. Core earnings is adjusted to exclude outstanding LTIP-OP Units in our Operating Partnership and dividends paid on preferred stock. Additionally, core earnings excludes any tax (benefit) expense on unrealized gain (loss) on MSRs.
Beginning with the third quarter of 2019, we refined the MSR amortization method utilized in determining the amount of realized and unrealized gain (loss) on investments in MSRs, used to calculate core earnings. MSR amortization refers to the portion of the change in fair value of the MSR that is primarily due to the realization of cashflows or runoff. The new method increased the MSR amortization amount taken into account for the reporting period to better reflect current and expected market conditions and includes an adjustment for any gain or loss on the capital used to purchase the MSR. MSR amortization for periods that ended prior to September 30, 2019 have not been adjusted to reflect our refined MSR amortization method. If the refined MSR amortization method was applied retroactively to the year ended December 31, 2018, we would have reported core earnings attributable to common stockholders per share of $1.97.
Core earnings are provided for purposes of potential comparability to other issuers that invest in residential mortgage-related assets. We believe providing investors with core earnings, in addition to related GAAP financial measures, may provide investors some insight into our ongoing operational performance. However, the concept of core earnings does have significant limitations, including the exclusion of realized and unrealized gains (losses), and given the apparent lack of a consistent methodology among issuers for defining core earnings, it may not be comparable to similarly-titled measures of other issuers, which define core earnings differently from us and each other. As a result, core earnings should not be considered a substitute for our GAAP net income (loss) or as a measure of our liquidity.
47
Core Earnings Summary
Core earnings for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, as compared to the prior year, increased by approximately $780,000 and $7.5 million (a decrease of $0.24 and an increase of $0.03, respectively, per average common share). Each such increase was primarily due to increased invested capital as a result of the sales of our capital stock during the relevant year.
The following table provides GAAP measures of net income (loss) and details with respect to reconciling the aforementioned line items to core earnings and related per average common share amounts, for the periods indicated (dollars in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, |
||||||
2019 |
2018 |
|||||
Net Income (Loss) |
$ | (43,496 | ) |
$ | 37,773 | |
Realized loss (gain) on RMBS, net |
(902 | ) |
8,362 | |||
Realized loss (gain) on derivatives, net |
12,362 | 5,889 | ||||
Realized gain on acquired assets, net |
(26 | ) |
— | |||
Unrealized loss (gain) on derivatives, net |
10,867 | (3,505 | ) |
|||
Unrealized loss (gain) on investments in MSRs, net of estimated MSR amortization |
79,918 | (10,712 | ) |
|||
Tax (benefit) expense on unrealized (loss) gain on MSRs |
(14,878 | ) |
994 | |||
Total core earnings: |
$ | 43,845 | $ | 38,801 | ||
Core earnings attributable to noncontrolling interests in Operating Partnership |
(709 | ) |
(501 | ) |
||
Dividends on preferred stock |
9,353 | 5,297 | ||||
Core Earnings Attributable to Common Stockholders |
$ | 33,783 | $ | 33,003 | ||
Core Earnings Attributable to Common Stockholders, per Diluted Share |
$ | 2.01 | $ | 2.25 | ||
GAAP Net Income (Loss) Per Share of Common Stock, per Diluted Share |
$ | (3.11 | ) |
$ | 2.18 | |
Our Portfolio
MSRs
Aurora’s MSR portfolio of Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac and Ginnie Mae MSRs have an aggregate UPB of approximately $29.1 billion as of December 31, 2019.
The following tables set forth certain characteristics of the mortgage loans underlying those MSRs as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands):
MSR Collateral Characteristics
As of December 31, 2019
Collateral Characteristics |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Current Carrying Amount |
Current Principal Balance |
WA Coupon |
WA Servicing Fee |
WA Maturity (months) |
Weighted Average Loan Age (months) |
ARMs %(A) |
|||||||||||||||
MSRs |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Conventional |
$ | 263,357 | $ | 26,142,780 | 4.27 | % |
0.25 | % |
321 | 23 | 0.2 | % |
|||||||||
Government |
27,754 | 2,925,346 | 3.37 | % |
0.31 | % |
310 | 44 | — | % |
|||||||||||
MSR Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 291,111 | $ | 29,068,126 | 4.18 | % |
0.26 | % |
320 | 25 | 0.2 | % |
|||||||||
48
As of December 31, 2018
Collateral Characteristics |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Current Carrying Amount |
Current Principal Balance |
WA Coupon |
WA Servicing Fee |
WA Maturity (months) |
Weighted Average Loan Age (months) |
ARMs %(A) |
|||||||||||||||
MSRs |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Conventional |
$ | 254,691 | $ | 21,366,980 | 4.37 | % |
0.25 | % |
328 | 17 | 0.3 | % |
|||||||||
Government |
40,216 | 3,480,009 | 3.37 | % |
0.31 | % |
321 | 32 | — | % |
|||||||||||
MSR Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 294,907 | $ | 24,846,989 | 4.23 | % |
0.26 | % |
327 | 19 | 0.2 | % |
|||||||||
| (A) | ARMs % represents the percentage of the total principal balance of the pool that corresponds to ARMs and hybrid ARMs. |
RMBS
The following tables summarize the characteristics of our RMBS portfolio and certain characteristics of the collateral underlying our RMBS as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands):
RMBS Characteristics
As of December 31, 2019
Original Face Value |
Book Value |
Gross Unrealized |
Carrying Value(A) |
Number of Securities |
Weighted Average |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Asset Type |
Gains |
Losses |
Rating |
Coupon |
Yield(C) |
Maturity (Years)(D) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
RMBS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fannie Mae |
$ | 1,878,229 | $ | 1,596,288 | $ | 23,636 | $ | (691 | ) |
$ | 1,619,233 | 198 | (B) |
3.80 | % |
3.65 | % |
27 | ||||||||||||
Freddie Mac |
824,991 | 715,892 | 12,204 | (245 | ) |
727,851 | 88 | (B) |
3.72 | % |
3.59 | % |
28 | |||||||||||||||||
CMOs |
127,229 | 123,053 | 6,030 | — | 129,083 | 30 | (B) |
5.28 | % |
5.26 | % |
11 | ||||||||||||||||||
Private Label MBS |
50,500 | 31,595 | 598 | — | 32,193 | 11 | (B) |
4.06 | % |
4.06 | % |
29 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 2,880,949 | $ | 2,466,828 | $ | 42,468 | $ | (936 | ) |
$ | 2,508,360 | 327 | 3.85 | % |
3.72 | % |
26 | |||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2018
Original Face Value |
Book Value |
Gross Unrealized |
Carrying Value(A) |
Number of Securities |
Weighted Average |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Asset Type |
Gains |
Losses |
Rating |
Coupon |
Yield(C) |
Maturity (Years)(D) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
RMBS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fannie Mae |
$ | 1,362,606 | $ | 1,208,854 | $ | 224 | $ | (30,914 | ) |
$ | 1,178,164 | 154 | (B) |
3.87 | % |
3.70 | % |
25 | ||||||||||||
Freddie Mac |
548,862 | 471,148 | 246 | (12,386 | ) |
459,008 | 63 | (B) |
3.75 | % |
3.60 | % |
27 | |||||||||||||||||
CMOs |
100,129 | 99,023 | 5,060 | (583 | ) |
103,500 | 23 | (B) |
6.30 | % |
6.29 | % |
11 | |||||||||||||||||
Private Label MBS |
30,500 | 29,395 | 76 | (33 | ) |
29,438 | 7 | (B) |
4.10 | % |
4.11 | % |
29 | |||||||||||||||||
Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 2,042,097 | $ | 1,808,420 | $ | 5,606 | $ | (43,916 | ) |
$ | 1,770,110 | 247 | 3.98 | % |
3.82 | % |
25 | |||||||||||||
| (A) | See “Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data—Note 9. Fair Value” regarding the estimation of fair value, which approximates carrying value for all securities. |
| (B) | The Company used an implied AAA rating for the Agency RMBS. Collateralized mortgage obligations (“CMOs”) issued by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac consist of loss share securities, approximately half of which, by unpaid principal balance (“UPB”), are unrated or rated below investment grade at December 31, 2019 by at least one NRSRO. Private label securities are rated investment grade or better by at least one NRSRO as of December 31, 2019. |
49
| (C) | The weighted average yield is based on the most recent gross monthly interest income, which is then annualized and divided by the book value of settled securities. |
| (D) | The weighted average maturity is based on the timing of expected principal reduction on the assets. |
The following table summarizes the net interest spread of our RMBS portfolio as of the dates indicated:
Net Interest Spread
December 31, 2019 |
December 31, 2018 |
|||||
Weighted Average Asset Yield |
2.66 | % |
3.48 | % |
||
Weighted Average Interest Expense |
1.93 | % |
2.17 | % |
||
Net Interest Spread |
0.73 | % |
1.31 | % |
||
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Liquidity is a measurement of our ability to meet potential cash requirements, including ongoing commitments to repay borrowings, fund and maintain investments and other general business needs. Additionally, to maintain our status as a REIT under the Code, we must distribute annually at least 90% of our REIT taxable income. In future years, a portion of this requirement may be able to be met through stock dividends, rather than cash, subject to limitations based on the value of our stock.
Our primary sources of funds for liquidity consist of cash provided by operating activities (primarily income from our investments in RMBS and net servicing income from our MSRs), sales or repayments of RMBS and borrowings under repurchase agreements and our MSR financing arrangements.
In the future, sources of funds for liquidity may include additional MSR financing, warehouse agreements, securitizations and the issuance of equity or debt securities, when feasible. During the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2019, we completed underwritten offerings and sales of our capital stock pursuant to our ATM programs which resulted in aggregate net proceeds of approximately $28.8 million. Net proceeds from these offerings and sales are available for general corporate purposes, including investment in RMBS. In the past we have used, and we anticipate that in the future we will use a significant portion of the paydowns of these RMBS to purchase MSRs. We may also sell certain of these RMBS and deploy the net proceeds from such sales to the extent necessary to fund the purchase price of MSRs.
Our primary uses of funds are the payment of interest, management fees, outstanding commitments, other operating expenses, investments in new or replacement assets and the repayment of borrowings, as well as dividends. We may also use capital resources to repurchase additional shares of common stock under our stock repurchase program when we believe such repurchases are appropriate and/or the stock is trading at a significant discount to net asset value. We seek to maintain adequate cash reserves and other sources of available liquidity to meet any margin calls resulting from decreases in value related to a reasonably possible (in the opinion of management) change in interest rates.
As of the date of this filing, we have sufficient liquid assets to satisfy all of our short-term recourse liabilities. With respect to the next twelve months, we expect that our cash on hand combined with the cash flow provided by our operations will be sufficient to satisfy our anticipated liquidity needs with respect to our current investment portfolio, including related financings, potential margin calls and operating expenses. While it is inherently more difficult to forecast beyond the next twelve months, we currently expect to meet our long-term liquidity requirements through our cash on hand and, if needed, additional borrowings, proceeds received from repurchase agreements and similar financings, proceeds from equity offerings and the liquidation or refinancing of our assets.
Our operating cash flow differs from our net income due primarily to: (i) accretion of discount or premium on our RMBS, (ii) unrealized gains or losses on our Servicing Related Assets, and (iii) OTTI on our securities, if any.
Repurchase Agreements
As of December 31, 2019, we had repurchase agreements with 30 counterparties and approximately $2,337.6 million of outstanding repurchase agreement borrowings from 22 of those counterparties, which were used to finance RMBS. As of December 31, 2019, our exposure (defined as the amount of cash and securities
50
pledged as collateral, less the borrowing under the repurchase agreement) to any of the counterparties under the repurchase agreements did not exceed five percent of the Company’s equity. Under these agreements, which are uncommitted facilities, we sell a security to a counterparty and concurrently agree to repurchase the same security at a later date at the same price that we initially sold the security plus the interest charged. The sale price represents financing proceeds and the difference between the sale and repurchase prices represents interest on the financing. The price at which the security is sold generally represents the market value of the security less a discount or “haircut.” The weighted average haircut on our repurchase debt at December 31, 2019 was approximately 4.3%. During the term of the repurchase transaction, which can be as short as a few days, the counterparty holds the security and posts margin as collateral. The counterparty monitors and calculates what it estimates to be the value of the collateral during the term of the transaction. If this value declines by more than a de minimis threshold, the counterparty requires us to post additional collateral (or “margin”) in order to maintain the initial haircut on the collateral. This margin is typically required to be posted in the form of cash and cash equivalents. Furthermore, we are, from time to time, a party to derivative agreements or financing arrangements that may be subject to margin calls based on the value of such instruments.
Set forth below is the average aggregate balance of borrowings under the Company’s repurchase agreements for each of the periods shown and the aggregate balance as of the end of each such period (dollars in thousands):
Repurchase Agreement Average and Maximum Amounts
Quarter Ended |
Average Monthly Amount |
Maximum Month-End Amount |
Quarter Ending Amount |
||||||
December 31, 2019 |
$ | 2,324,976 | $ | 2,337,638 | $ | 2,337,638 | |||
September 30, 2019 |
$ | 2,218,656 | $ | 2,279,448 | $ | 2,266,841 | |||
June 30, 2019 |
$ | 1,882,668 | $ | 1,942,511 | $ | 1,942,511 | |||
March 31, 2019 |
$ | 1,715,842 | $ | 1,785,345 | $ | 1,785,345 | |||
December 31, 2018 |
$ | 1,627,637 | $ | 1,667,553 | $ | 1,598,592 | |||
September 30, 2018 |
$ | 1,690,418 | $ | 1,695,880 | $ | 1,680,394 | |||
June 30, 2018 |
$ | 1,548,441 | $ | 1,693,309 | $ | 1,693,309 | |||
March 31, 2018 |
$ | 1,608,700 | $ | 1,708,338 | $ | 1,500,562 | |||
The increases in the Company’s borrowings under its repurchase agreements were primarily due to the investment of funds in RMBS received from the following sources: amounts borrowed under our MSR financing facilities; and the sales of our capital stock throughout the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
These short-term borrowings were used to finance certain of our investments in RMBS. The RMBS repurchase agreements are guaranteed by the Company. The weighted average difference between the market value of the assets and the face amount of available financing for the RMBS repurchase agreements, or the haircut, was 4.3% and 4.2% as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. The following tables provide additional information regarding borrowings under our repurchase agreements (dollars in thousands):
Repurchase Agreement Characteristics
As of December 31, 2019
RMBS Market Value |
Repurchase Agreements |
Weighted Average Rate |
|||||||
Less than one month |
$ | 955,382 | $ | 928,646 | 2.24 | % |
|||
One to three months |
1,280,854 | 1,231,422 | 1.94 | % |
|||||
Greater than three months |
183,303 | 177,570 | 1.98 | % |
|||||
Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 2,419,539 | $ | 2,337,638 | 2.06 | % |
|||
51
As of December 31, 2018
RMBS Market Value |
Repurchase Agreements |
Weighted Average Rate |
|||||||
Less than one month |
$ | 823,397 | $ | 776,666 | 2.51 | % |
|||
One to three months |
875,291 | 821,926 | 2.56 | % |
|||||
Greater than three months |
— | — | — | % |
|||||
Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 1,698,688 | $ | 1,598,592 | 2.54 | % |
|||
The amount of collateral as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, including cash, was $2,480.9 million and $1,706.9 million, respectively.
The weighted average term to maturity of our borrowings under repurchase agreements as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 was 42 days and 38 days, respectively.
MSR Financing
In September 2016, Aurora and QRS III entered into a loan and security agreement (the “MSR Financing Facility”), pursuant to which Aurora and QRS III pledged their respective rights in all existing and future MSRs for loans owned or securitized by Fannie Mae to secure borrowings up to a maximum of $25.0 million outstanding at any one time. The maximum amount and duration of the revolving period were subsequently increased. This facility was terminated and replaced in September 2019 as a result of which there was no outstanding balance under the MSR Financing Facility at December 31, 2019.
In May 2017, the Company, Aurora and QRS IV obtained a $20.0 million loan (the “MSR Term Facility”) secured by the pledge of Aurora’s Ginnie Mae MSRs and the Company’s ownership interest in QRS IV. The loan bears interest at a fixed rate of 6.18% per annum, amortizes on a ten-year amortization schedule and is due on May 18, 2022. In October 2019, the MSR Term Facility was amended to provide an additional $10 million of borrowing capacity to finance servicing advances on the Ginnie Mae MSRs pledged under the facility. Amounts available to finance servicing advances may be borrowed and reborrowed from time to time and bear interest at a floating rate equal to LIBOR plus a margin. The MSR Term Facility, including the revolving facility for servicing advances, is scheduled to terminate on May 18, 2022.
In July 2018, the Company, Aurora and QRS V (collectively with Aurora and the Company, the “Borrowers”) entered into a $25.0 million revolving credit facility (the “MSR Revolver”) pursuant to which Aurora pledged all of its existing and future MSRs on loans owned or securitized by Freddie Mac. The term of the MSR Revolver is 364 days with the Borrowers’ option for two renewals for similar terms followed by a one-year term out feature with a 24-month amortization schedule. The MSR Revolver was upsized to $45.0 million in September 2018. The Company also has the ability to request up to an additional $5.0 million of borrowings. On April 2, 2019, Aurora and QRS V entered into an amendment that increased the maximum amount of the MSR Revolver to $100.0 million. On June 5, 2019, the term of the MSR Revolver was renewed to July 30, 2020. Amounts borrowed bear interest at an adjustable rate equal to a spread above one-month LIBOR. At December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, approximately $55.5 million and $45.0 million, respectively, was outstanding under the MSR Revolver.
In September 2019, Aurora and QRS III entered into a loan and security agreement (the “Fannie Mae MSR Financing Facility”), to replace the MSR Financing Facility. Under the Fannie Mae MSR Facility, Aurora and QRS III pledged their respective rights in all existing and future MSRs for loans owned or securitized by Fannie Mae to secure borrowings outstanding from time to time. The maximum credit amount outstanding at any one time under the facility is $200 million of which $100 million is committed. Borrowings bear interest at a rate equal to a spread over one-month LIBOR subject to a floor. The term of the facility is 24 months subject to extension for an additional 12 months if the lender agrees beginning in the 20th month. The Company has guaranteed repayment of all indebtedness under the Fannie Mae MSR Financing Facility. Approximately $97.0 million was outstanding under the Fannie Mae MSR Financing Facility at December 31, 2019.
52
Cash Flows
Operating and Investing Activities
Our operating activities provided cash of approximately $69.7 million and $62.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. Our investing activities used cash of approximately $757.1 million and $163.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The cash used for our investing activities resulted from the equity offerings that we completed during the applicable year as well as the execution of our ongoing investment strategy.
Dividends
U.S. federal income tax law generally requires that a REIT distribute annually at least 90% of its REIT taxable income, without regard to the deduction for dividends paid and excluding net capital gains, and that it pay tax at regular corporate rates to the extent that it annually distributes less than 100% of its taxable income. We intend to make regular quarterly distributions of all or substantially all of our REIT taxable income to holders of our common and preferred stock out of assets legally available for this purpose, if and to the extent authorized by our board of directors. Before we pay any dividend, whether for U.S. federal income tax purposes or otherwise, we must first meet both our operating requirements and debt service on our repurchase agreements and other debt payable. If our cash available for distribution is less than our REIT taxable income, we could be required to sell assets or borrow funds to make cash distributions, or, with respect to our common stock, we may make a portion of the required distribution in the form of a taxable stock distribution or distribution of debt securities. We will make distributions only upon the authorization of our board of directors. The amount, timing and frequency of distributions will be authorized by our board of directors based upon a variety of factors, including:
| • | actual results of operations; |
| • | our level of retained cash flows; |
| • | our ability to make additional investments in our target assets; |
| • | restrictions under Maryland law; |
| • | the terms of our preferred stock; |
| • | any debt service requirements; |
| • | our taxable income; |
| • | the annual distribution requirements under the REIT provisions of the Code; and |
| • | other factors that our board of directors may deem relevant. |
Our ability to make distributions to our stockholders will depend upon the performance of our investment portfolio, and, in turn, upon our Manager’s management of our business. Distributions will be made quarterly in cash to the extent that cash is available for distribution. We may not be able to generate sufficient cash available for distribution to pay distributions to our stockholders. In addition, our board of directors may change our distribution policy with respect to our common stock in the future.
We make distributions based on a number of factors, including an estimate of taxable earnings. Dividends distributed and taxable income will typically differ from GAAP earnings due to items such as fair value adjustments, differences in premium amortization and discount accretion, and nondeductible general and administrative expenses. Our common dividend per share may be substantially different than our taxable earnings and GAAP earnings per share. Our GAAP loss and earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 were $3.11 and $2.18, respectively.
53
Off-balance Sheet Arrangements
As of December 31, 2019, we did not have any off-balance sheet arrangements. We did not have any relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, such as entities often referred to as structured investment vehicles, or special purpose or variable interest entities, established to facilitate off-balance sheet arrangements or other contractually narrow or limited purposes. Further, we have not guaranteed any obligations of unconsolidated entities or entered into any commitment or intend to provide additional funding to any such entities.
Contractual Obligations
Our contractual obligations as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 included repurchase agreements, borrowings under our MSR financing arrangements, our Management Agreement with our Manager, our subservicing agreements and our joint marketing recapture agreement with Freedom Mortgage.
The following table summarizes our contractual obligations for borrowed money as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands):
Contractual Obligations Characteristics
As of December 31, 2019
Less than 1 year |
1 to 3 years |
3 to 5 years |
More than 5 years |
Total |
|||||||||||
Repurchase agreements |
|||||||||||||||
Borrowings under repurchase agreements |
$ | 2,337,638 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 2,337,638 | |||||
Interest on repurchase agreement borrowings(A) |
$ | 9,641 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 9,641 | |||||
MSR Term Facility |
|||||||||||||||
Borrowings under MSR Term Facility |
$ | 2,000 | $ | 12,996 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 14,996 | |||||
Interest on MSR Term Facility borrowings |
$ | 885 | $ | 1,063 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,948 | |||||
MSR Revolver |
|||||||||||||||
Borrowings under MSR Revolver |
$ | — | $ | 55,500 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 55,500 | |||||
Interest on MSR Revolver borrowings |
$ | 3,134 | $ | 1,769 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 4,903 | |||||
Fannie Mae MSR Financing Facility |
|||||||||||||||
Borrowings under Fannie Mae MSR Financing Facility |
$ | — | $ | 97,000 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 97,000 | |||||
Interest on Fannie Mae MSR Financing Facility |
$ | 4,170 | $ | 3,481 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 7,651 | |||||
As of December 31, 2018
Less than 1 year |
1 to 3 years |
3 to 5 years |
More than 5 years |
Total |
|||||||||||
Repurchase agreements |
|||||||||||||||
Borrowings under repurchase agreements |
$ | 1,598,592 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,598,592 | |||||
Interest on repurchase agreement borrowings(A) |
$ | 6,624 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,624 | |||||
MSR Term Facility |
|||||||||||||||
Borrowings under MSR Term Facility |
$ | 2,000 | $ | 4,000 | $ | 10,996 | $ | — | $ | 16,996 | |||||
Interest on MSR Term Facility borrowings |
$ | 1,008 | $ | 1,642 | $ | 306 | $ | — | $ | 2,956 | |||||
MSR Financing Facility |
|||||||||||||||
Borrowings under MSR Financing Facility |
$ | — | $ | 96,500 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 96,500 | |||||
Interest on MSR Financing Facility borrowings |
$ | 6,118 | $ | 9,252 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 15,370 | |||||
MSR Revolver |
|||||||||||||||
Borrowings under MSR Revolver |
$ | — | $ | 45,000 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 45,000 | |||||
Interest on MSR Revolver borrowings |
$ | 3,316 | $ | 4,461 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 7,777 | |||||
| (A) | Interest expense is calculated based on the interest rate in effect at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively, and includes all interest expense incurred and expected to be incurred in the future through the contractual maturity of the associated repurchase agreement. |
54
Management Agreement
The Management Agreement with our Manager provides that our Manager is entitled to receive a management fee, the reimbursement of certain expenses and, in certain circumstances, a termination fee. The management fee is an amount equal to 1.5% per annum of our stockholders’ equity, adjusted as set forth in the Management Agreement, and calculated and payable quarterly in arrears. We will also be required to pay a termination fee equal to three times the average annual management fee earned by our Manager during the two four-quarter periods ending as of the end of the most recently completed fiscal quarter prior to the effective date of the termination. Such termination fee will be payable upon termination of the Management Agreement by us without cause or by our Manager if we materially breach the Management Agreement.
We pay all of our direct operating expenses, except those specifically required to be borne by our Manager under the Management Agreement. Our Manager is responsible for all costs incident to the performance of its duties under the Management Agreement. We believe that our Manager uses the proceeds from its management fee in part to pay Freedom Mortgage for services provided under the Services Agreement between the Manager and Freedom Mortgage. The president of Aurora, who also served as our chief financial officer, treasurer and secretary from our inception in October 2012 until June 12, 2019, receives a nominal portion of his overall compensation directly from Aurora for acting as its president. With that exception, our officers receive no cash compensation directly from us. Our Manager provides us with our officers. Our Manager is entitled to be reimbursed for an agreed upon portion of the costs of the wages, salary and other benefits with respect to our chief financial officer, controller and general counsel, originally based on the percentages of their working time and efforts spent on matters related to the Company. The amount of the wages, salary and benefits reimbursed with respect to the officers our Manager provides to us is subject to the approval of the compensation committee of our board of directors.
The term of the Management Agreement will expire on October 22, 2020 and will be automatically renewed for a one-year term on such date and on each anniversary of such date thereafter unless terminated or not renewed as described below. Either we or our Manager may elect not to renew the Management Agreement upon expiration of its initial term or any renewal term by providing written notice of non-renewal at least 180 days, but not more than 270 days, before expiration. In the event we elect not to renew the term, we will be required to pay our Manager the termination fee described above. We may terminate the Management Agreement at any time for cause effective upon 30 days prior written notice of termination from us to our Manager, in which case no termination fee would be due. Our board of directors will review our Manager’s performance prior to the automatic renewal of the Management Agreement and, as a result of such review, upon the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of the members of our board of directors or of the holders of a majority of our outstanding common stock, we may terminate the Management Agreement based upon unsatisfactory performance by our Manager that is materially detrimental to us or a determination by our independent directors that the management fees payable to our Manager are not fair, subject to the right of our Manager to prevent such a termination by agreeing to a reduction of the management fees payable to our Manager. Upon any termination of the Management Agreement based on unsatisfactory performance or unfair management fees, we are required to pay our Manager the termination fee described above. Our Manager may terminate the Management Agreement, without payment of the termination fee, in the event we become regulated as an investment company under the Investment Company Act. Our Manager may also terminate the Management Agreement upon 60 days’ written notice if we default in the performance of any material term of the Management Agreement and the default continues for a period of 30 days after written notice to us, whereupon we would be required to pay our Manager the termination fee described above.
Subservicing Agreements
As of December 31, 2019, Aurora had three subservicing agreements in place, one of which is with Freedom Mortgage. Freedom Mortgage currently is the only sub-servicer for the Ginnie Mae MSRs. Although Freedom Mortgage gave notice of termination of the subservicing agreement without cause, as required by that agreement, Freedom Mortgage has continued to service the Ginnie Mae MSRs pending transfer of the servicing responsibilities, and Aurora has continued to pay for such services. The parties subsequently decided to reinstate the agreement on the terms in effect at the time of the notice of termination, including a three-year term subject to automatic renewal for a similar term unless sooner terminated in accordance with its terms. The agreements have varying initial terms (three years, for Freedom Mortgage and two years for the other two sub-servicers) and are subject to automatic renewal for additional terms equal to the applicable initial term unless either party
55
chooses not to renew. Each agreement may be terminated without cause by either party by giving notice as specified in the agreement. If an agreement is not renewed by the Company or terminated by the Company without cause, market rate de-boarding fees will be due to the sub-servicer. Under each agreement, the sub-servicer agrees to service the applicable mortgage loans in accordance with applicable law and the requirements of the applicable agency and the Company pays customary fees to the applicable subservicer for specified services.
Joint Marketing Recapture Agreement
We attempt to reduce the exposure of our MSRs to voluntary prepayments through the structuring of recapture agreements with Aurora’s subservicers. In June 2016, Aurora entered into a joint marketing recapture agreement with Freedom Mortgage. Pursuant to this agreement, Freedom Mortgage attempts to refinance certain mortgage loans underlying Aurora’s portfolio of MSRs being subserviced by Freedom Mortgage as directed by Aurora. If a loan is refinanced, Aurora will pay Freedom Mortgage a fee for its origination services. Freedom Mortgage will be entitled to sell the loan for its own benefit and will transfer the related MSR to Aurora. The agreement had an initial term of one year, subject to automatic renewals of one year each. This agreement continues in effect since the termination of the subservicing agreement was not, and now will not be, completed by the transfer of the Ginnie Mae MSRs to another subservicer. During the year ended December 31, 2019, MSRs on 19 loans with an aggregate UPB of approximately $4.4 million had been received from Freedom Mortgage which generated approximately $5,200 in fees due to Freedom Mortgage. During the year ended December 31, 2018, MSRs on 98 loans with an aggregate UPB of approximately $21.5 million had been received from Freedom Mortgage which generated approximately $32,000 in fees due to Freedom Mortgage.
Inflation
Virtually all of our assets and liabilities are financial in nature. As a result, interest rates and other factors affect our performance more so than inflation, although inflation rates can often have a meaningful influence over the direction of interest rates. Furthermore, our financial statements are prepared in accordance with GAAP and our distributions are determined by our board of directors primarily based on our REIT taxable income, and, in each case, our activities and balance sheet are measured with reference to historical cost and/or fair market value without considering inflation.
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk |
We seek to manage our risks related to the credit quality of our assets, interest rates, liquidity, prepayment speeds and market value while, at the same time, seeking to provide an opportunity to stockholders to realize attractive risk-adjusted returns through ownership of our capital stock. While we do not seek to avoid risk completely, we believe the risk can be quantified from historical experience and seek to actively manage that risk, to earn sufficient compensation to justify taking those risks and to maintain capital levels consistent with the risks we undertake.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rates are highly sensitive to many factors, including fiscal and monetary policies and domestic and international economic and political considerations, as well as other factors beyond our control. We are subject to interest rate risk in connection with our assets and our related financing obligations. In general, we finance the acquisition of certain of our assets through financings in the form of repurchase agreements and bank facilities. We expect to make use of additional MSR financing, as well as possibly warehouse facilities, securitizations, re-securitizations, and public and private equity and debt issuances in addition to transaction or asset specific funding arrangements. In addition, the values of our Servicing Related Assets are highly sensitive to changes in interest rates, historically increasing when rates rise and decreasing when rates decline. Subject to maintaining our qualification as a REIT, we attempt to mitigate interest rate risk and financing pricing risk through utilization of hedging instruments, primarily interest rate swap agreements and Treasury futures, respectively. We may also use financial futures, options, interest rate cap agreements, and forward sales. These instruments are intended to serve as a hedge against future interest rate or pricing changes on our borrowings.
56
Interest Rate Effect on Net Interest Income
Our operating results depend in large part on differences between the income earned on our assets and our cost of borrowing and hedging activities. The costs of our borrowings are generally based on prevailing market interest rates. During a period of rising interest rates, our borrowing costs generally will increase (1) while the yields earned on our leveraged fixed-rate mortgage assets will remain static and (2) at a faster pace than the yields earned on our leveraged adjustable-rate and hybrid adjustable-rate RMBS, which could result in a decline in our net interest spread and net interest margin. The severity of any such decline would depend on our asset/liability composition at the time as well as the magnitude and duration of the interest rate increase. Further, an increase in short-term interest rates could also have a negative impact on the market value of our assets, other than our Servicing Related Assets. A decrease in interest rates could have a negative impact on the market value of our Servicing Related Assets. If any of these events happen, we could experience a decrease in net income or incur a net loss during these periods, which could adversely affect our liquidity and results of operations.
Hedging techniques are partly based on assumed levels of prepayments of our assets, specifically our RMBS. If prepayments are slower or faster than assumed, the life of the investment will be longer or shorter, which would reduce the effectiveness of any hedging strategies we may use and may cause losses on such transactions. Hedging strategies involving the use of derivatives are highly complex and may produce volatile returns.
Interest Rate Cap Risk
Any adjustable-rate RMBS that we acquire will generally be subject to interest rate caps, which potentially could cause such RMBS to acquire many of the characteristics of fixed-rate securities if interest rates were to rise above the cap levels. This issue will be magnified to the extent we acquire adjustable-rate and hybrid adjustable-rate RMBS that are not based on mortgages which are fully indexed. In addition, adjustable-rate and hybrid adjustable-rate RMBS may be subject to periodic payment caps that result in some portion of the interest being deferred and added to the principal outstanding. This could result in our receipt of less cash income on such assets than we would need to pay the interest cost on our related borrowings. To mitigate interest rate mismatches, we may utilize the hedging strategies discussed above under “—Interest Rate Risk.” Actual economic conditions or implementation of decisions by our Manager may produce results that differ significantly from the estimates and assumptions used in our models.
Prepayment Risk; Extension Risk
The following tables summarize the estimated change in fair value of our interests in our MSRs as of the dates indicated given several parallel shifts in the discount rate and voluntary prepayment rate (dollars in thousands):
MSR Fair Value Changes
As of December 31, 2019
Conventional
(20)% |
(10)% |
—% |
10% |
20% |
|||||||||||
Discount Rate Shift in % |
|||||||||||||||
Estimated FV |
$ | 280,174 | $ | 271,514 | $ | 263,357 | $ | 255,662 | $ | 248,391 | |||||
Change in FV |
$ | 16,817 | $ | 8,157 | $ | — | $ | (7,695 | ) |
$ | (14,966 | ) |
|||
% Change in FV |
6 | % |
3 | % |
— | (3 | )% |
(6 | )% |
||||||
Voluntary Prepayment Rate Shift in % |
|||||||||||||||
Estimated FV |
$ | 298,135 | $ | 279,978 | $ | 263,357 | $ | 248,209 | $ | 234,399 | |||||
Change in FV |
$ | 34,778 | $ | 16,622 | $ | — | $ | (15,148 | ) |
$ | (28,958 | ) |
|||
% Change in FV |
13 | % |
6 | % |
— | (6 | )% |
(11 | )% |
||||||
Servicing Cost Shift in % |
|||||||||||||||
Estimated FV |
$ | 270,584 | $ | 266,970 | $ | 263,357 | $ | 259,743 | $ | 256,130 | |||||
Change in FV |
$ | 7,227 | $ | 3,614 | $ | — | $ | (3,614 | ) |
$ | (7,227 | ) |
|||
% Change in FV |
3 | % |
1 | % |
— | (1 | )% |
(3 | )% |
||||||
57
Government
(20)% |
(10)% |
—% |
10% |
20% |
|||||||||||
Discount Rate Shift in % |
|||||||||||||||
Estimated FV |
$ | 29,841 | $ | 28,760 | $ | 27,754 | $ | 26,817 | $ | 25,942 | |||||
Change in FV |
$ | 2,087 | $ | 1,006 | $ | — | $ | (937 | ) |
$ | (1,812 | ) |
|||
% Change in FV |
8 | % |
4 | % |
— | (3 | )% |
(7 | )% |
||||||
Voluntary Prepayment Rate Shift in % |
|||||||||||||||
Estimated FV |
$ | 31,090 | $ | 29,354 | $ | 27,754 | $ | 26,281 | $ | 24,921 | |||||
Change in FV |
$ | 3,336 | $ | 1,600 | $ | — | $ | (1,474 | ) |
$ | (2,834 | ) |
|||
% Change in FV |
12 | % |
6 | % |
— | (5 | )% |
(10 | )% |
||||||
Servicing Cost Shift in % |
|||||||||||||||
Estimated FV |
$ | 29,132 | $ | 28,443 | $ | 27,754 | $ | 27,066 | $ | 26,377 | |||||
Change in FV |
$ | 1,377 | $ | 689 | $ | — | $ | (689 | ) |
$ | (1,377 | ) |
|||
% Change in FV |
5 | % |
2 | % |
— | (2 | )% |
(5 | )% |
||||||
As of December 31, 2018
Conventional
(20)% |
(10)% |
—% |
10% |
20% |
|||||||||||
Discount Rate Shift in % |
|||||||||||||||
Estimated FV |
$ | 277,424 | $ | 265,607 | $ | 254,692 | $ | 244,585 | $ | 235,204 | |||||
Change in FV |
$ | 22,732 | $ | 10,915 | $ | — | $ | (10,107 | ) |
$ | (19,487 | ) |
|||
% Change in FV |
9 | % |
4 | % |
— | (4 | )% |
(8 | )% |
||||||
Voluntary Prepayment Rate Shift in % |
|||||||||||||||
Estimated FV |
$ | 272,688 | $ | 263,879 | $ | 254,692 | $ | 245,554 | $ | 236,729 | |||||
Change in FV |
$ | 17,996 | $ | 9,187 | $ | — | $ | (9,138 | ) |
$ | (17,963 | ) |
|||
% Change in FV |
7 | % |
4 | % |
— | (4 | )% |
(7 | )% |
||||||
Servicing Cost Shift in % |
|||||||||||||||
Estimated FV |
$ | 261,205 | $ | 257,949 | $ | 254,692 | $ | 251,435 | $ | 248,178 | |||||
Change in FV |
$ | 6,514 | $ | 3,257 | $ | — | $ | (3,257 | ) |
$ | (6,514 | ) |
|||
% Change in FV |
3 | % |
1 | % |
— | (1 | )% |
(3 | )% |
||||||
Government
(20)% |
(10)% |
—% |
10% |
20% |
|||||||||||
Discount Rate Shift in % |
|||||||||||||||
Estimated FV |
$ | 44,591 | $ | 42,299 | $ | 40,216 | $ | 38,314 | $ | 36,572 | |||||
Change in FV |
$ | 4,375 | $ | 2,084 | $ | — | $ | (1,902 | ) |
$ | (3,644 | ) |
|||
% Change in FV |
11 | % |
5 | % |
— | (5 | )% |
(9 | )% |
||||||
Voluntary Prepayment Rate Shift in % |
|||||||||||||||
Estimated FV |
$ | 42,763 | $ | 41,522 | $ | 40,216 | $ | 38,912 | $ | 37,646 | |||||
Change in FV |
$ | 2,547 | $ | 1,306 | $ | — | $ | (1,303 | ) |
$ | (2,569 | ) |
|||
% Change in FV |
6 | % |
3 | % |
— | (3 | )% |
(6 | )% |
||||||
Servicing Cost Shift in % |
|||||||||||||||
Estimated FV |
$ | 41,930 | $ | 41,073 | $ | 40,216 | $ | 39,358 | $ | 38,501 | |||||
Change in FV |
$ | 1,715 | $ | 857 | $ | — | $ | (857 | ) |
$ | (1,715 | ) |
|||
% Change in FV |
4 | % |
2 | % |
— | (2 | )% |
(4 | )% |
||||||
58
The following tables summarize the estimated change in fair value of our RMBS as of the dates indicated given several parallel shifts in interest rates (dollars in thousands):
RMBS Fair Value Changes
As of December 31, 2019
Fair Value Change |
||||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2019 |
+25 Bps |
+50 Bps |
+75 Bps |
+100 Bps |
+150 Bps |
|||||||||||||
RMBS Portfolio |
||||||||||||||||||
RMBS, available-for-sale, net of swaps |
$ | 2,651,237 | ||||||||||||||||
RMBS Total Return (%) |
(0.23 | )% |
(0.59 | )% |
(1.06 | )% |
(1.63 | )% |
(3.06 | )% |
||||||||
RMBS Dollar Return |
$ | (6,210 | ) |
$ | (15,609 | ) |
$ | (28,064 | ) |
$ | (43,321 | ) |
$ | (81,171 | ) |
|||
As of December 31, 2018
Fair Value Change |
||||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2019 |
+25 Bps |
+50 Bps |
+75 Bps |
+100 Bps |
+150 Bps |
|||||||||||||
RMBS Portfolio |
||||||||||||||||||
RMBS, available-for-sale, net of swaps |
$ | 1,822,236 | ||||||||||||||||
RMBS Total Return (%) |
(0.32 | )% |
(0.73 | )% |
(1.22 | )% |
(1.76 | )% |
(3.01 | )% |
||||||||
RMBS Dollar Return |
$ | (5,722 | ) |
$ | (13,181 | ) |
$ | (21,979 | ) |
$ | (31,872 | ) |
$ | (54,308 | ) |
|||
The sensitivity analysis is hypothetical and is presented solely to assist an analysis of the possible effects on the fair value under various scenarios. It is not a prediction of the amount or likelihood of a change in any particular scenario. In particular, the results are calculated by stressing a particular economic assumption independent of changes in any other assumption. In practice, changes in one factor may result in changes in another, which might counteract or amplify the sensitivities. In addition, changes in the fair value based on a 10% variation in an assumption generally may not be extrapolated because the relationship of the change in the assumption to the change in fair value may not be linear.
Counterparty Risk
When we engage in repurchase transactions, we generally sell securities to lenders (i.e., repurchase agreement counterparties) and receive cash from the lenders. The lenders are obligated to resell the same securities back to us at the end of the term of the transaction. Because the cash we receive from the lender when we initially sell the securities to the lender is less than the value of those securities (this difference is the haircut), if the lender defaults on its obligation to resell the same securities back to us we would incur a loss on the transaction equal to the amount of the haircut (assuming there was no change in the value of the securities). As of December 31, 2019, the Company’s exposure (defined as the amount of cash and securities pledged as collateral, less the borrowing under the repurchase agreement) to any of the counterparties under the repurchase agreements did not exceed five percent of the Company’s equity.
Our interest rate swaps and Treasury futures contracts are required to be cleared on an exchange which greatly mitigates, but does not entirely eliminate, counterparty risk.
Our investments in Servicing Related Assets are dependent on the applicable mortgage sub-servicer to perform its sub-servicing obligations. If our sub-servicer fails to perform its obligations and is terminated by one or more Agencies as an approved servicer, the value of the MSRs being subserviced by that sub-servicer may be adversely affected. In addition, when we purchase MSRs from third parties, we rely, to a certain extent, on the ability and willingness of the sellers to perform their contractual obligations to remedy breaches of representations and warranties or to repurchase the affected loan and indemnify us for any losses.
59
Funding Risk
To the extent available on desirable terms, we expect to continue to finance our RMBS with repurchase agreement financing. We also anticipate continuing to finance our MSRs with bank loans secured by a pledge of those MSRs. Over time, as market conditions change, in addition to these financings, we may use other forms of leverage. Weakness in the financial markets, the residential mortgage markets and the economy generally could adversely affect one or more of our potential lenders and could cause one or more of our potential lenders to be unwilling or unable to provide us with financing or to increase the costs of that financing.
Liquidity Risk
Our Servicing Related Assets, as well as some of the assets that may in the future comprise our portfolio, are not publicly traded. A portion of these assets may be subject to legal and other restrictions on resale or will otherwise be less liquid than publicly-traded securities. The illiquidity of these assets may make it difficult for us to sell such assets if the need or desire arises, including in response to changes in economic and other conditions.
Credit Risk
Although we expect relatively low credit risk with respect to our portfolio of Agency RMBS, our investments in CMOs and MSRs expose us to the credit risk of borrowers. To the extent we invest in prime mortgage loans, we expect to encounter credit risk related to these asset classes.
60
| Item 8. | Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data. |
Consolidated Financial Statements
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements
Page |
|||
61
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and subsidiaries (the Company) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of income (loss), comprehensive income (loss), stockholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework), and our report dated February 27, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2012.
New York, New York
February 27, 2020
62
Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(in thousands — except share data)
December 31, 2019 |
December 31, 2018 |
|||||
Assets |
||||||
RMBS, available-for-sale (including pledged assets of $2,419,539 and $1,698,688, respectively) |
$ | 2,508,360 | $ | 1,770,110 | ||
Investments in Servicing Related Assets at fair value (including pledged assets of $291,111 and $294,907, respectively) |
291,111 | 294,907 | ||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
24,671 | 31,834 | ||||
Restricted cash |
67,037 | 8,185 | ||||
Derivative assets |
18,289 | 24,258 | ||||
Receivables and other assets |
47,084 | 23,983 | ||||
Total Assets |
$ | 2,956,552 | $ | 2,153,277 | ||
Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity |
||||||
Liabilities |
||||||
Repurchase agreements |
$ | 2,337,638 | $ | 1,598,592 | ||
Derivative liabilities |
12,337 | 3,816 | ||||
Notes payable |
166,989 | 157,543 | ||||
Dividends payable |
8,768 | 11,847 | ||||
Due to affiliates |
3,589 | 2,003 | ||||
Accrued expenses and other liabilities |
15,588 | 15,545 | ||||
Total Liabilities |
$ | 2,544,909 | $ | 1,789,346 | ||
Stockholders’ Equity |
||||||
Series A Preferred stock, $0.01 par value per share, 100,000,000 shares authorized and 2,781,635 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2019 and 100,000,000 shares authorized and 2,718,206 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2018, liquidation preference of $69,541 as of December 31, 2019 and liquidation preference of $67,955 as of December 31, 2018 |
$ | 67,213 | $ | 65,639 | ||
Series B Preferred stock, $0.01 par value per share, 100,000,000 shares authorized and 2,000,000 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2019 and 100,000,000 shares authorized and 0 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2018, liquidation preference of $50,000 as of December 31, 2019 and liquidation preference of $0 as of December 31, 2018 |
48,068 | — | ||||
Common stock, $0.01 par value per share, 500,000,000 shares authorized and 16,660,655 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2019 and 500,000,000 shares authorized and 16,652,170 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2018 |
170 | 167 | ||||
Additional paid-in capital |
302,723 | 298,614 | ||||
(Deficit) Retained earnings |
(47,367 | ) |
34,653 | |||
Treasury stock at cost, 235,950 shares at $14.59 as of December 31, 2019 and 0 shares at $0.00 as of December 31, 2018 |
(3,543 | ) |
— | |||
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
41,414 | (38,400 | ) |
|||
Total Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation Stockholders’ Equity |
$ | 408,678 | $ | 360,673 | ||
Non-controlling interests in Operating Partnership |
2,965 | 3,258 | ||||
Total Stockholders’ Equity |
$ | 411,643 | $ | 363,931 | ||
Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity |
$ | 2,956,552 | $ | 2,153,277 | ||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
63
Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Income (Loss)
(in thousands — except per share data)
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
|||||||
Income |
|||||||||
Interest income |
$ | 73,338 | $ | 57,715 | $ | 42,049 | |||
Interest expense |
48,585 | 34,509 | 19,881 | ||||||
Net interest income |
24,753 | 23,206 | 22,168 | ||||||
Servicing fee income |
73,555 | 50,776 | 24,034 | ||||||
Servicing costs |
17,122 | 10,615 | 5,783 | ||||||
Net servicing income |
56,433 | 40,161 | 18,251 | ||||||
Other income (loss) |
|||||||||
Realized gain (loss) on RMBS, available-for-sale, net |
902 | (8,362 | ) |
(503 | ) |
||||
Realized gain on investments in Excess MSRs, net |
— | — | 6,678 | ||||||
Realized loss on derivatives, net |
(12,362 | ) |
(5,889 | ) |
(5,554 | ) |
|||
Realized gain on acquired assets, net |
26 | — | — | ||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives, net |
(10,867 | ) |
3,505 | 6,580 | |||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on investments in Servicing Related Assets |
(106,772 | ) |
(3,573 | ) |
9,159 | ||||
Total Income (Loss) |
(47,887 | ) |
49,048 | 56,779 | |||||
Expenses |
|||||||||
General and administrative expense |
4,647 | 3,941 | 3,817 | ||||||
Management fee to affiliate |
7,784 | 5,946 | 4,347 | ||||||
Total Expenses |
12,431 | 9,887 | 8,164 | ||||||
Income (Loss) Before Income Taxes |
(60,318 | ) |
39,161 | 48,615 | |||||
Provision for (Benefit from) corporate business taxes |
(16,822 | ) |
1,388 | 601 | |||||
Net Income (Loss) |
(43,496 | ) |
37,773 | 48,014 | |||||
Net (income) loss allocated to noncontrolling interests in Operating Partnership |
703 | (488 | ) |
(655 | ) |
||||
Dividends on preferred stock |
9,353 | 5,297 | 1,833 | ||||||
Net Income (Loss) Applicable to Common Stockholders |
$ | (52,146 | ) |
$ | 31,988 | $ | 45,526 | ||
Net Income (Loss) Per Share of Common Stock |
|||||||||
Basic |
$ | (3.11 | ) |
$ | 2.18 | $ | 3.98 | ||
Diluted |
$ | (3.11 | ) |
$ | 2.18 | $ | 3.98 | ||
Weighted Average Number of Shares of Common Stock Outstanding |
|||||||||
Basic |
16,775,113 | 14,649,242 | 11,443,493 | ||||||
Diluted |
16,787,902 | 14,657,498 | 11,450,831 | ||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
64
Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(in thousands)
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
|||||||
Net income (loss) |
$ | (43,496 | ) |
$ | 37,773 | $ | 48,014 | ||
Other comprehensive income (loss): |
|||||||||
Net unrealized gain (loss) on RMBS |
80,716 | (43,820 | ) |
2,948 | |||||
Reclassification of net realized gain (loss) on RMBS included in earnings |
(902 | ) |
8,362 | 503 | |||||
Other comprehensive income (loss) |
79,814 | (35,458 | ) |
3,451 | |||||
Comprehensive income |
$ | 36,318 | $ | 2,315 | $ | 51,465 | |||
Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests in Operating Partnership |
587 | 30 | 702 | ||||||
Dividends on preferred stock |
9,353 | 5,297 | 1,833 | ||||||
Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to common stockholders |
$ | 26,378 | $ | (3,012 | ) |
$ | 48,930 | ||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
65
Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity
(in thousands — except share data)
Common Stock Shares |
Common Stock Amount |
Preferred Stock Shares |
Preferred Stock Amount |
Additional Paid-in Capital |
Treasury Stock at Cost |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
Retained Earnings (Deficit) |
Non-Controlling Interest in Operating Partnership |
Total Stockholders’ Equity |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2016 |
7,525,348 | $ | 75 | — | $ | — | $ | 148,457 | $ | — | $ | (6,393 | ) |
$ | 12,093 | $ | 1,777 | $ | 156,009 | |||||||||||
Issuance of common stock |
5,175,000 | 52 | — | — | 80,863 | — | — | — | — | 80,915 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net Income (Loss) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 22,178 | 409 | 22,587 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Other Comprehensive Income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 1,672 | — | — | 1,672 | ||||||||||||||||||||
LTIP-OP Unit awards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 135 | 135 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution paid on LTIP-OP Units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (91 | ) |
(91 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Common dividends declared, $0.49 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (3,687 | ) |
— | (3,687 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Balance, March 31, 2017 |
12,700,348 | $ | 127 | — | $ | — | $ | 229,320 | $ | — | $ | (4,721 | ) |
$ | 30,584 | $ | 2,230 | $ | 257,540 | |||||||||||
Issuance of common stock |
8,199 | — | — | — | 25 | — | — | — | — | 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,549 | ) |
(116 | ) |
(1,665 | ) |
|||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 5,887 | — | — | 5,887 | ||||||||||||||||||||
LTIP-OP Unit awards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 146 | 146 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution paid on LTIP-OP Units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (78 | ) |
(78 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Common dividends declared, $0.49 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (6,228 | ) |
— | (6,228 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Balance, June 30, 2017 |
12,708,547 | $ | 127 | — | $ | — | $ | 229,345 | $ | — | $ | 1,166 | $ | 22,807 | $ | 2,182 | $ | 255,627 | ||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock |
12,917 | — | — | — | 238 | — | — | — | — | 238 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of preferred stock |
— | — | 2,400,000 | 57,917 | — | — | — | — | — | 57,917 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of OP units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (238 | ) |
(238 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Net Income before dividends on preferred stock |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 6,766 | 93 | 6,859 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Other Comprehensive Income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 3,574 | — | — | 3,574 | ||||||||||||||||||||
LTIP-OP Unit awards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 194 | 194 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution paid on LTIP-OP Units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (87 | ) |
(87 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Common dividends declared, $0.49 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (6,227 | ) |
— | (6,227 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series A dividends declared, $0.3303 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (593 | ) |
— | (593 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Balance, September 30, 2017 |
12,721,464 | $ | 127 | 2,400,000 | $ | 57,917 | $ | 229,583 | $ | — | $ | 4,740 | $ | 22,753 | $ | 2,144 | $ | 317,264 | ||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock |
— | — | — | — | 59 | — | — | — | — | 59 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net Income before dividends on preferred stock |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 19,964 | 269 | 20,233 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Other Comprehensive Income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (7,682 | ) |
— | — | (7,682 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
LTIP-OP Unit awards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 143 | 143 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution paid on LTIP-OP Units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (81 | ) |
(81 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Common dividends declared, $0.49 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (6,239 | ) |
— | (6,239 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series A dividends declared, $0.5125 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,240 | ) |
— | (1,240 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2017 |
12,721,464 | $ | 127 | 2,400,000 | $ | 57,917 | $ | 229,642 | $ | — | $ | (2,942 | ) |
$ | 35,238 | $ | 2,475 | $ | 322,457 | |||||||||||
Issuance of common stock |
— | — | — | — | 37 | — | — | — | — | 37 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net Income before dividends on preferred stock |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 34,783 | 456 | 35,239 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Other Comprehensive (Loss) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (31,043 | ) |
— | — | (31,043 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
LTIP-OP Unit awards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 138 | 138 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution paid on LTIP-OP Units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (83 | ) |
(83 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Common dividends declared, $0.49 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (6,235 | ) |
— | (6,235 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series A dividends declared, $0.5125 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,213 | ) |
— | (1,213 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Balance, March 31, 2018 |
12,721,464 | $ | 127 | 2,400,000 | $ | 57,917 | $ | 229,679 | $ | — | $ | (33,985 | ) |
$ | 62,573 | $ | 2,986 | $ | 319,297 | |||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
66
Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity (continued)
(in thousands — except share data)
Common Stock Shares |
Common Stock Amount |
Preferred Stock Shares |
Preferred Stock Amount |
Additional Paid-in Capital |
Treasury Stock at Cost |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
Retained Earnings (Deficit) |
Non-Controlling Interest in Operating Partnership |
Total Stockholders’ Equity |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock |
3,097,113 | 31 | — | — | 53,551 | — | — | — | — | 53,582 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of preferred stock |
— | — | 168,212 | 3,981 | — | — | — | — | — | 3,981 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net Income before dividends on preferred stock |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 13,672 | 173 | 13,845 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Other Comprehensive (Loss) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (7,981 | ) |
— | — | (7,981 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
LTIP-OP Unit awards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 162 | 162 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution paid on LTIP-OP Units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (72 | ) |
(72 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Common dividends declared, $0.49 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (7,759 | ) |
— | (7,759 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series A dividends declared, $0.5125 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,317 | ) |
— | (1,317 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Balance, June 30, 2018 |
15,818,577 | $ | 158 | 2,568,212 | $ | 61,898 | $ | 283,230 | $ | — | $ | (41,966 | ) |
$ | 67,169 | $ | 3,249 | $ | 373,738 | |||||||||||
Issuance of common stock |
371,041 | 4 | — | — | 6,751 | — | — | — | — | 6,755 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of preferred stock |
— | — | 103,570 | 2,612 | — | — | — | — | — | 2,612 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net Income before dividends on preferred stock |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 27,135 | 364 | 27,499 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Other Comprehensive Income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (13,228 | ) |
— | — | (13,228 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
LTIP-OP Unit awards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 194 | 194 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution paid on LTIP-OP Units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (109 | ) |
(109 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Common dividends declared, $0.49 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (7,920 | ) |
— | (7,920 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series A dividends declared, $0.5125 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,372 | ) |
— | (1,372 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Balance, September 30, 2018 |
16,189,618 | $ | 162 | 2,671,782 | $ | 64,510 | $ | 289,981 | $ | — | $ | (55,194 | ) |
$ | 85,012 | $ | 3,698 | $ | 388,169 | |||||||||||
Issuance of common stock |
462,552 | 5 | — | — | 8,633 | — | — | — | — | 8,638 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of preferred stock |
— | — | 46,424 | 1,129 | — | — | — | — | — | 1,129 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net Income before dividends on preferred stock |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (38,305 | ) |
(505 | ) |
(38,810 | ) |
|||||||||||||||||
Other Comprehensive Income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 16,794 | — | — | 16,794 | ||||||||||||||||||||
LTIP-OP Unit awards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 168 | 168 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution paid on LTIP-OP Units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (103 | ) |
(103 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Common dividends declared, $0.49 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (10,659 | ) |
— | (10,659 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series A dividends declared, $0.5125 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,395 | ) |
— | (1,395 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2018 |
16,652,170 | $ | 167 | 2,718,206 | $ | 65,639 | $ | 298,614 | $ | — | $ | (38,400 | ) |
$ | 34,653 | $ | 3,258 | $ | 363,931 | |||||||||||
Issuance of common stock |
6,000 | — | — | — | 132 | — | — | — | — | 132 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of preferred stock |
— | — | 2,049,480 | 49,360 | — | — | — | — | — | 49,360 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of OP units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (103 | ) |
(103 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Net (Loss) before dividends on preferred stock |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (20,789 | ) |
(349 | ) |
(21,138 | ) |
|||||||||||||||||
Other Comprehensive Income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 31,981 | — | — | 31,981 | ||||||||||||||||||||
LTIP-OP Unit awards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 266 | 266 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution paid on LTIP-OP Units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (134 | ) |
(134 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Common dividends declared, $0.49 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (8,156 | ) |
— | (8,156 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series A dividends declared, $0.5125 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,419 | ) |
— | (1,419 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series B dividends declared, $0.3667 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (422 | ) |
— | (422 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Balance, March 31, 2019 |
16,658,170 | $ | 167 | 4,767,686 | $ | 114,999 | $ | 298,746 | $ | — | $ | (6,419 | ) |
$ | 3,867 | $ | 2,938 | $ | 414,298 | |||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
67
Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity (continued)
(in thousands — except share data)
Common Stock Shares |
Common Stock Amount |
Preferred Stock Shares |
Preferred Stock Amount |
Additional Paid-in Capital |
Treasury Stock at Cost |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
Retained Earnings (Deficit) |
Non-Controlling Interest in Operating Partnership |
Total Stockholders’ Equity |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock |
238,435 | 3 | — | — | 3,885 | — | — | — | — | 3,888 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of preferred stock |
— | — | 13,949 | 282 | — | — | — | — | — | 282 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net (Loss) before dividends on preferred stock |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (26,720 | ) |
(438 | ) |
(27,158 | ) |
|||||||||||||||||
Other Comprehensive Income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 25,536 | — | — | 25,536 | ||||||||||||||||||||
LTIP-OP Unit awards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 250 | 250 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution paid on LTIP-OP Units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (135 | ) |
(135 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Common dividends declared, $0.49 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (8,289 | ) |
— | (8,289 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series A dividends declared, $0.5125 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,428 | ) |
— | (1,428 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series B dividends declared, $0.5156 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,164 | ) |
— | (1,164 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Balance, June 30, 2019 |
16,896,605 | $ | 170 | 4,781,635 | $ | 115,281 | $ | 302,631 | $ | — | $ | 19,117 | $ | (33,734 | ) |
$ | 2,615 | $ | 406,080 | |||||||||||
Issuance of common stock |
— | — | — | — | 53 | — | — | — | — | 53 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net Income before dividends on preferred stock |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (2,908 | ) |
(43 | ) |
(2,951 | ) |
|||||||||||||||||
Other Comprehensive Income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 15,551 | — | — | 15,551 | ||||||||||||||||||||
LTIP-OP Unit awards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 225 | 225 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution paid on LTIP-OP Units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (133 | ) |
(133 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Common dividends declared, $0.40 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (6,759 | ) |
— | (6,759 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series A dividends declared, $0.5125 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,428 | ) |
— | (1,428 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series B dividends declared, $0.5156 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,031 | ) |
— | (1,031 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Balance, September 30, 2019 |
16,896,605 | $ | 170 | 4,781,635 | $ | 115,281 | $ | 302,684 | $ | — | $ | 34,668 | $ | (45,860 | ) |
$ | 2,664 | $ | 409,607 | |||||||||||
Issuance of common stock |
— | — | — | — | 39 | — | — | — | — | 39 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock |
(235,950 | ) |
— | — | — | — | (3,543 | ) |
— | — | — | (3,543 | ) |
|||||||||||||||||
Net Income before dividends on preferred stock |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 7,624 | 127 | 7,751 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Other Comprehensive Income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 6,746 | — | — | 6,746 | ||||||||||||||||||||
LTIP-OP Unit awards |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 282 | 282 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution paid on LTIP-OP Units |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (108 | ) |
(108 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Common dividends declared, $0.40 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (6,672 | ) |
— | (6,672 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series A dividends declared, $0.5125 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,428 | ) |
— | (1,428 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Preferred Series B dividends declared, $0.5156 per share |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,031 | ) |
— | (1,031 | ) |
||||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2019 |
16,660,655 | $ | 170 | 4,781,635 | $ | 115,281 | $ | 302,723 | $ | (3,543 | ) |
$ | 41,414 | $ | (47,367 | ) |
$ | 2,965 | $ | 411,643 | ||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
68
Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(in thousands)
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
|||||||
Cash Flows From Operating Activities |
|||||||||
Net income (loss) |
$ | (43,496 | ) |
$ | 37,773 | $ | 48,014 | ||
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: |
|||||||||
Realized (gain) loss on RMBS, available-for-sale, net |
(902 | ) |
8,362 | 503 | |||||
Unrealized (gain) loss on investments in Servicing Related Assets |
106,772 | 3,573 | (9,159 | ) |
|||||
Realized gain on investments in Excess MSRs, net |
— | — | (6,678 | ) |
|||||
Realized gain on acquired assets, net |
(26 | ) |
— | — | |||||
Realized loss on derivatives, net |
12,362 | 5,889 | 5,554 | ||||||
Unrealized (gain) loss on derivatives, net |
10,867 | (3,505 | ) |
(6,580 | ) |
||||
Realized (gain) on TBA dollar rolls, net |
(1,667 | ) |
(1,089 | ) |
(379 | ) |
|||
Amortization of premiums on RMBS, available-for-sale |
14,485 | 12,036 | 8,676 | ||||||
Amortization of deferred financing costs |
652 | 205 | 79 | ||||||
LTIP-OP Unit awards |
1,023 | 662 | 607 | ||||||
Changes in: |
|||||||||
Receivables and other assets |
(23,075 | ) |
(7,341 | ) |
(4,345 | ) |
|||
Due to affiliates |
1,586 | (1,032 | ) |
1,141 | |||||
Payables for unsettled trades |
— | — | (6,202 | ) |
|||||
Accrued interest on derivatives |
(5,861 | ) |
(1,686 | ) |
3,875 | ||||
Dividends payable |
(3,079 | ) |
4,574 | — | |||||
Accrued expenses and other liabilities |
43 | 3,531 | 8,709 | ||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities |
$ | 69,684 | $ | 61,952 | $ | 43,815 | |||
Cash Flows From Investing Activities |
|||||||||
Purchase of RMBS |
(1,088,758 | ) |
(410,886 | ) |
(1,348,134 | ) |
|||
Principal paydown of RMBS |
275,086 | 170,740 | 110,409 | ||||||
Proceeds from sale of RMBS |
141,653 | 255,092 | 62,989 | ||||||
Proceeds from sale of Excess MSRs |
— | — | 35,905 | ||||||
Acquisition of MSRs |
(102,976 | ) |
(175,674 | ) |
(81,611 | ) |
|||
Purchase of derivatives |
(913 | ) |
(3,097 | ) |
(2,642 | ) |
|||
Proceeds from sale of derivatives |
18,793 | 1 | 163 | ||||||
Net cash used in investing activities |
$ | (757,115 | ) |
$ | (163,824 | ) |
$ | (1,222,921 | ) |
Cash Flows From Financing Activities |
|||||||||
Borrowings under repurchase agreements |
7,969,930 | 6,721,379 | 4,610,000 | ||||||
Repayments of repurchase agreements |
(7,230,884 | ) |
(6,789,324 | ) |
(3,538,078 | ) |
|||
Proceeds from derivative financing |
(19,090 | ) |
(3,469 | ) |
(5,050 | ) |
|||
Proceeds from bank loans |
121,143 | 120,317 | 26,921 | ||||||
Principal paydown of bank loans |
(112,350 | ) |
(2,004 | ) |
(10,861 | ) |
|||
Dividends paid |
(39,227 | ) |
(37,870 | ) |
(24,214 | ) |
|||
LTIP-OP Units distributions paid |
(510 | ) |
(367 | ) |
(326 | ) |
|||
Conversion of OP units |
(103 | ) |
— | (238 | ) |
||||
Issuance of common stock, net of offering costs |
4,112 | 69,012 | 81,237 | ||||||
Issuance of preferred stock, net of offering costs |
49,642 | 7,722 | 57,917 | ||||||
Repurchase of common stock |
(3,543 | ) |
— | — | |||||
Net cash provided by financing activities |
$ | 739,120 | $ | 85,396 | $ | 1,197,308 | |||
Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash, Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash |
$ | 51,689 | $ | (16,476 | ) |
$ | 18,202 | ||
Cash, Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash, Beginning of Period |
40,019 | 56,495 | 38,293 | ||||||
Cash, Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash, End of Period |
$ | 91,708 | $ | 40,019 | $ | 56,495 | |||
Supplemental Disclosure of Cash Flow Information |
|||||||||
Cash paid during the period for interest expense |
$ | 46,533 | $ | 29,821 | $ | 14,409 | |||
Cash paid during the period for income taxes |
$ | 256 | $ | 53 | $ | 65 | |||
Supplemental Schedule of Non-Cash Investing and Financing Activities |
|||||||||
Dividends declared but not paid |
$ | 8,768 | $ | 11,847 | $ | 7,273 | |||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
69
Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Note 1 — Organization and Operations
Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation (together with its consolidated subsidiaries, the “Company”) was organized in the state of Maryland on October 31, 2012 to invest in residential mortgage assets in the United States. Under the Company’s charter, the Company is authorized to issue up to 500,000,000 shares of common stock and 100,000,000 shares of preferred stock, each with a par value of $0.01 per share.
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company’s subsidiaries, Cherry Hill Operating Partnership, LP (the “Operating Partnership”), CHMI Sub-REIT, Inc. (the “CHMI Sub-REIT”), Cherry Hill QRS I, LLC, Cherry Hill QRS II, LLC, Cherry Hill QRS III, LLC (“QRS III”), Cherry Hill QRS IV, LLC (“QRS IV”), Cherry Hill QRS V, LLC (“QRS V”), CHMI Solutions, Inc. (“CHMI Solutions”) and Aurora Financial Group, Inc. (“Aurora”).
The Company is party to a management agreement (the “Management Agreement”) with Cherry Hill Mortgage Management, LLC (the “Manager”), a Delaware limited liability company established by Mr. Stanley Middleman. The Manager is a party to a Services Agreement with Freedom Mortgage Corporation (“Freedom Mortgage”), which is owned and controlled by Mr. Middleman. The Manager is owned by a “blind trust” for the benefit of Mr. Middleman. For a further discussion of the Management Agreement, see Note 7.
The Company has elected to be taxed as a real estate investment trust (“REIT”), as defined under the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), commencing with its short taxable year ended December 31, 2013. As long as the Company continues to comply with a number of requirements under federal tax law and maintains its qualification as a REIT, the Company generally will not be subject to U.S. federal income taxes to the extent that the Company distributes its taxable income to its stockholders on an annual basis and does not engage in prohibited transactions. However, certain activities that the Company may perform may cause it to earn income that will not be qualifying income for REIT purposes.
Note 2 — Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Accounting
The accompanying consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its consolidated subsidiaries. All significant intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated. The Company consolidates those entities in which it has an investment of 50% or more and has control over significant operating, financial and investing decisions of the entity.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make a number of significant estimates and assumptions. These include estimates of: mortgage servicing rights (“MSRs” or “Servicing Related Assets”); residential mortgage-backed securities (“RMBS” or “securities”) and derivatives; credit losses, including the period of time during which the Company anticipates an increase in the fair values of RMBS sufficient to recover unrealized losses on those RMBS; and other estimates that affect the reported amounts of certain assets, revenues, liabilities and expenses as of the date of, and for the periods covered by, the consolidated financial statements. It is likely that changes in these estimates will occur in the near term. The Company’s estimates are inherently subjective in nature. Actual results could differ from the Company’s estimates, and the differences may be material.
Risks and Uncertainties
In the normal course of business, the Company encounters primarily two significant types of economic risk: credit and market. Credit risk is the risk of default on the Company’s investments in RMBS, Servicing Related Assets and derivatives that results from a borrower’s or derivative counterparty’s inability or unwillingness to make contractually required payments. Market risk reflects changes in the value of investments in RMBS, Servicing Related Assets and derivatives due to changes in interest rates, spreads or other market factors, including prepayment speeds on the Company’s RMBS and Servicing Related Assets. The Company is subject to
70
the risks involved with real estate and real estate-related debt instruments. These include, among others, the risks normally associated with changes in the general economic climate, changes in the mortgage market, changes in tax laws, interest rate levels, and the availability of financing.
The Company also is subject to certain risks relating to its status as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes. If the Company were to fail to qualify as a REIT in any taxable year, the Company would be subject to U.S. federal income tax on its REIT income, which could be material. Unless entitled to relief under certain statutory provisions, the Company would also be disqualified from treatment as a REIT for the four taxable years following the year during which qualification is lost.
Investments in RMBS
Classification – The Company classifies its investments in RMBS as securities available for sale. Although the Company generally intends to hold most of its securities until maturity, it may, from time to time, sell any of its securities as part of its overall management of its portfolio. Securities available for sale are carried at fair value with the net unrealized gains or losses reported as a separate component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), to the extent impairment losses, if any, are considered temporary. Unrealized losses on securities are charged to earnings if they reflect a decline in value that is other-than-temporary, as described below.
Fair value is determined under the guidance of Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (“ASC 820”). Management’s judgment is used to arrive at the fair value of the Company’s RMBS investments, taking into account prices obtained from third-party pricing providers and other applicable market data. The third-party pricing providers use pricing models that generally incorporate such factors as coupons, primary and secondary mortgage rates, rate reset periods, issuer, prepayment speeds, credit enhancements and expected life of the security. The Company’s application of ASC 820 guidance is discussed in further detail in Note 9.
Investment securities transactions are recorded on the trade date. At disposition, the net realized gain or loss is determined on the basis of the cost of the specific investment and is included in earnings. All RMBS purchased and sold in the year ended December 31, 2019 were settled prior to period-end. All RMBS purchased and sold in the year ended December 31, 2018 were settled prior to year-end.
Revenue Recognition – Interest income from coupon payments is accrued based on the outstanding principal amount of the RMBS and their contractual terms. Premiums and discounts associated with the purchase of the RMBS are amortized and accreted, respectively, into interest income over the projected lives of the securities using the effective interest method. The Company’s policy for estimating prepayment speeds for calculating the effective yield is to evaluate historical performance, consensus on prepayment speeds, and current market conditions. Adjustments are made for actual prepayment activity. Approximately $7.7 million and $5.7 million in interest income was receivable at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. Interest income receivable has been classified within “Receivables and other assets” on the consolidated balance sheets. For further discussion of Receivables and other assets, see Note 13.
Impairment – The Company evaluates its RMBS on a quarterly basis to assess whether a decline in the fair value below the amortized cost basis is an other-than-temporary impairment (“OTTI”). The presence of OTTI is based upon a fair value decline below a security’s amortized cost basis and a corresponding adverse change in expected cash flows due to credit related factors as well as non-credit factors, such as changes in interest rates and market spreads. Impairment is considered other-than-temporary if the Company (i) intends to sell the security, (ii) will more likely than not be required to sell the security before recovering its cost basis, or (iii) does not expect to recover the security’s entire amortized cost basis, even if the Company does not intend to sell the security, or the Company believes it is more likely than not that it will be required to sell the security before recovering its cost basis. Under these scenarios, the impairment is other-than-temporary and the full amount of impairment is recognized currently in earnings and the cost basis of the security is adjusted. However, if the Company does not intend to sell the impaired security and it is more likely than not that it will not be required to sell before recovery, the OTTI is separated into (i) the estimated amount relating to credit loss, or the credit component, and (ii) the amount relating to all other factors, or the non-credit component. Only the estimated credit loss amount is recognized currently in earnings, with the remainder of the loss recognized in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). The difference between the new amortized cost basis and the cash flows expected to be collected is accreted into interest income in accordance with the effective interest method. OTTI
71
has been classified within “Realized loss on RMBS, available-for-sale, net” on the consolidated statements of income (loss). For further discussion of OTTI, see Note 4.
Investments in MSRs
Classification – The Company’s MSRs represent the contractual right to service mortgage loans. The Company has elected the fair value option to record its investments in MSRs in order to provide users of the consolidated financial statements with better information regarding the effects of prepayment risk and other market factors on the MSRs. Under this election, the Company records a valuation adjustment on its investments in MSRs on a quarterly basis to recognize the changes in fair value of its MSRs in net income as described below. Fair value is generally determined by discounting the expected future cash flows using discount rates that incorporate the market risks and liquidity premium specific to the MSRs and, therefore, may differ from their effective yields.
Although transactions in MSRs are observable in the marketplace, the valuation includes unobservable market data inputs (prepayment speeds, delinquency levels, costs to service and discount rates). Changes in the fair value of MSRs as well as servicing fee income and servicing expenses are reported on the consolidated statements of income (loss). Fluctuations in the fair value of MSRs is recorded on the consolidated statements of income (loss) as “Unrealized gain (loss) on investments in Servicing Related Assets.” In determining the valuation of MSRs in accordance with ASC 820, management uses internally developed models that are primarily based on observable market-based inputs but which also include unobservable market data inputs. The Company’s application of ASC 820 guidance is discussed in further detail in Note 9. For reporting purposes, conventional conforming loans are aggregated into one category and government conforming loans are aggregated into a separate category.
Revenue Recognition – Mortgage servicing fee income represents revenue earned for servicing mortgage loans. The servicing fees are based on a contractual percentage of the outstanding principal balance and are recognized as revenue as the related mortgage payments are collected. Corresponding costs to service are charged to expense as incurred.
As an owner and manager of MSRs, the Company may be obligated to fund advances of principal and interest payments due to third-party owners of the loans, but not yet received from the individual borrowers. These advances are reported as servicing advances within the “Receivables and other assets” line item on the consolidated balance sheets. Reimbursable servicing advances, other than principal and interest advances, also have been classified within “Receivables and other assets” on the consolidated balance sheets. Although advances on Federal National Mortgage Association (“Fannie Mae”) and Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (“Freddie Mac”) MSRs made in accordance with the relevant guidelines are generally recoverable, the recoverability of similar advances made on Government National Mortgage Association (“Ginnie Mae”) MSRs may be limited under the rules and regulations of the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development, the Department of Veterans Affairs (the “VA”) and the Federal Housing Administration (“FHA”). The Company expects to recover advances on its Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac MSRs. In addition, unrecoverable losses on the loans underlying the Ginnie Mae MSRs have not been significant to date. As a result, the Company has determined that no reserves for unrecoverable advances for the related underlying loans are necessary at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018. For further discussion on the Company’s receivables and other assets, including the Company’s servicing advances, see Note 13.
Servicing fee income received and servicing expenses incurred are reported on the consolidated statements of income. The difference between the fair value of MSRs and their amortized cost basis is recorded on the consolidated statements of income as “Unrealized gain (loss) on investments in MSRs.” Fair value is generally determined by discounting the expected future cash flows using discount rates that incorporate the market risks and liquidity premium specific to the MSRs and, therefore, may differ from their effective yields.
As a result of the Company’s investments in MSRs, it is obligated from time to time to repurchase an underlying loan from the applicable agency for which it is being serviced due to an alleged breach of a representation or warranty. Loans acquired in this manner are recorded at the purchase price less any principal recoveries and are then offered for sale in the scratch and dent market. Loans also may be acquired from pools backing Ginnie Mae securities in order to modify the loan. Those loans typically are re-pooled into other Ginnie Mae securities at fair value. Any loans acquired by the Company for either reason are accounted for as loans held for sale and are recorded in “Other Assets” in the consolidated balance sheets.
72
Derivatives and Hedging Activities
Derivative transactions include swaps, swaptions, Treasury futures and “to-be-announced” securities (“TBAs”). Swaps and swaptions are entered into by the Company solely for interest rate risk management purposes. TBAs and Treasury futures are used to manage duration risk as well as basis risk and pricing risk on the Company’s financing facilities for MSRs. The decision as to whether or not a given transaction/position (or portion thereof) is economically hedged is made on a case-by-case basis, based on the risks involved and other factors as determined by senior management, including restrictions imposed by the Code on REITs. In determining whether to economically hedge a risk, the Company may consider whether other assets, liabilities, firm commitments and anticipated transactions already offset or reduce the risk. All transactions undertaken as economic hedges are entered into with a view towards minimizing the potential for economic losses that could be incurred by the Company. Generally, derivatives entered into are not intended to qualify as hedges under GAAP, unless specifically stated otherwise.
The Company’s bi-lateral derivative financial instruments contain credit risk to the extent that its counterparties may be unable to meet the terms of the agreements. The Company reduces such risk by limiting its exposure to any one counterparty. In addition, the potential risk of loss with any one party resulting from this type of credit risk is monitored. The Company’s interest rate swaps and Treasury futures are required to be cleared on an exchange, which further mitigates, but does not eliminate, credit risk. Management does not expect any material losses as a result of default by other parties to its derivative financial instruments.
Classification – All derivatives are recognized as either assets or liabilities on the consolidated balance sheets and measured at fair value. Due to the nature of these instruments, they may be in a receivable/asset position or a payable/liability position at the end of an accounting period. Derivative amounts payable to, and receivable from, the same party under a contract may be offset as long as the following conditions are met: (i) each of the two parties owes the other determinable amounts; (ii) the reporting party has the right to offset the amount owed with the amount owed by the other party; (iii) the reporting party intends to offset; and (iv) the right to offset is enforceable by law. The Company reports the fair value of derivative instruments gross of cash paid or received pursuant to credit support agreements, and fair value may be reflected on a net counterparty basis when the Company believes a legal right of offset exists under an enforceable master netting agreement. For further discussion on offsetting assets and liabilities, see Note 8.
Revenue Recognition – With respect to derivatives that have not been designated as hedges, any payments under, or fluctuations in the fair value of, such derivatives have been recognized currently in “Realized and unrealized gains (losses) on derivatives, net” in the consolidated statements of income (loss).
Cash and Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash
The Company considers all highly liquid short-term investments with maturities of 90 days or less when purchased to be cash equivalents. Substantially all amounts on deposit with major financial institutions exceed insured limits. Restricted cash represents the Company’s cash held by counterparties (i) as collateral against the Company’s derivatives (approximately $5.7 million and $687,000 at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively) and (ii) as collateral for borrowings under its repurchase agreements (approximately $61.3 million and $7.5 million at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively).
The Company’s centrally cleared interest rate swaps require that the Company post an “initial margin” amount determined by the clearing exchange, which is generally intended to be set at a level sufficient to protect the exchange from the interest rate swap’s maximum estimated single-day price movement. The Company also exchanges “variation margin” based upon daily changes in fair value, as measured by the exchange. As a result of amendments to rules governing certain central clearing activities, the exchange of variation margin is a settlement of the interest rate swap, as opposed to pledged collateral. Accordingly, beginning in the first quarter of 2018 and in subsequent periods, the Company has accounted for the receipt or payment of variation margin on interest rate swaps as a direct reduction or increase to the carrying value of the interest rate swap asset or liability. At December 31, 2019, $1.1 million of variation margin was reported as a decrease to the interest rate swap asset, at fair value. At December 31, 2018, $3.2 million of variation margin was reported as a decrease to the interest rate swap liability, at fair value.
73
Due to Affiliate
The sum under “Due to affiliates” on the consolidated balance sheets represents amounts due to the Manager pursuant to the Management Agreement. For further information on the Management Agreement, see Note 7.
Income Taxes
The Company elected to be taxed as a REIT under Code Sections 856 through 860 beginning with its short taxable year ended December 31, 2013. U.S. federal income tax law generally requires that a REIT distribute annually at least 90% of its REIT taxable income, without regard to the deduction for dividends paid and excluding net capital gains, and that it pay tax at regular corporate income tax rates to the extent that it annually distributes less than 100% of its taxable income. The Company’s taxable REIT subsidiary (“TRS”), CHMI Solutions, as well as CHMI Solutions’s wholly-owned subsidiary, Aurora, are subject to U.S. federal income taxes on their taxable income. To maintain qualification as a REIT, the Company must distribute at least 90% of its annual REIT taxable income to its stockholders and meet certain other requirements such as assets it may hold, income it may generate and its stockholder composition.
The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with ASC 740, Income Taxes. ASC 740 requires the recording of deferred income taxes that reflect the net tax effect of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of the Company’s assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes, including operating loss carry forwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in earnings in the period that includes the enactment date. The Company assesses its tax positions for all open tax years and determines if it has any material unrecognized liabilities in accordance with ASC 740. The Company records these liabilities to the extent it deems them more-likely-than-not to be incurred. The Company records interest and penalties related to income taxes within the provision for income taxes in the consolidated statements of income (loss). The Company has not incurred any interest or penalties.
Realized and Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Investments, Net
The following table presents gains and losses on sales of the specified categories of investments for the periods indicated (dollars in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
|||||||
Realized gain (loss) on RMBS, net |
|||||||||
Gain on RMBS |
$ | 1,285 | $ | 104 | $ | 213 | |||
Loss on RMBS |
(383 | ) |
(8,466 | ) |
(716 | ) |
|||
Net realized gain (loss) on RMBS |
902 | (8,362 | ) |
(503 | ) |
||||
Realized loss on derivatives, net |
(12,362 | ) |
(5,889 | ) |
(5,554 | ) |
|||
Unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives, net |
(10,867 | ) |
3,505 | 6,580 | |||||
Realized gain on Excess MSRs, net |
— | — | 6,678 | ||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on investments in Servicing Related Assets |
(106,772 | ) |
(3,573 | ) |
9,159 | ||||
Realized gain on acquired assets, net |
26 | — | — | ||||||
Total |
$ | (129,073 | ) |
$ | (14,319 | ) |
$ | 16,360 | |
Repurchase Agreements and Interest Expense
The Company finances its investments in RMBS with short-term borrowings under master repurchase agreements. Borrowings under the repurchase agreements are generally short-term debt due within one year. These borrowings generally bear interest rates offered by the “lending” counterparty from time to time for the term of the proposed repurchase transaction (e.g., 30 days, 60 days etc.) of a specified margin over one-month LIBOR. The repurchase agreements represent uncommitted financing. Borrowings under these agreements are treated as collateralized financing transactions and are carried at their contractual amounts, as specified in the respective agreements. Interest is recorded at the contractual amount on an accrual basis.
74
Dividends Payable
Because the Company is organized as a REIT under the Code, it is required by law to distribute annually at least 90% of its REIT taxable income, which it does in the form of quarterly dividend payments. The Company accrues the dividend payable on outstanding shares, excluding treasury shares, on the accounting date, which causes an offsetting reduction in retained earnings.
Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income is defined as the change in equity of a business enterprise during a period resulting from transactions and other events and circumstances, excluding those resulting from investments by and distributions to owners. For the Company’s purposes, comprehensive income represents net income (loss), as presented in the consolidated statements of income (loss), adjusted for unrealized gains or losses on RMBS, which are designated as available for sale.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Leases – In February 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2016-02, Leases, which requires lessees to recognize on their balance sheets both a lease liability for the obligation to make lease payments and a right-of-use asset for the right to use the underlying asset for the lease term. Although the ASU is effective as of January 1, 2019, the Company has not adopted the ASU because it did not have any leases during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
Credit Losses − In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses, which changes the impairment model for most financial assets and certain other instruments. The new model requires the estimation of lifetime expected credit losses and corresponding recognition of allowance for losses on trade and other receivables, held-to-maturity debt securities, loans, and other instruments held at amortized cost. Additionally, allowances for credit losses on Available-for-Sale debt securities will be recognized, rather than direct reductions in the amortized cost of the investments. ASU 2016-13 is effective for the Company in the first quarter of 2020.
The Current Expected Credit Losses model replaces the idea of incurred losses with expected losses for all financial assets, with a few exceptions, not measured at fair value. Expected losses are estimated based on historical experience, current and future economic conditions and forecasting models. Key implementation efforts have included development of internal controls and retrospective analysis of credit related losses. Credit related impairments have not been material in the past, and no current or foreseeable economic factors were identified that would cause a significant impact, partly due to the indemnification language included in our subservicer agreements and the recoverability of servicing advances under agency guides for Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. As a result, the Company has determined that the allowance would not be significant. This determination will be re-evaluated on a quarterly basis.
Upon adoption, the Company will continue to assess for credit losses on available for sale securities consistent with its existing accounting policy with the exclusion of length of time a security has been in an unrealized loss position. The Company will establish an account for the allowance for credit losses on available for sale securities rather than reducing the amortized cost basis as done previously. This is not expected to have a significant impact to the Company’s RMBS portfolio.
Fair Value Measurement - In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-13, Disclosure Framework - Changes to the Disclosure Requirements of Fair Value Measurement, which amends the guidance on the disclosure requirements on fair value measurements in ASC 820. This guidance is effective for annual reporting periods, and interim periods within those annual periods, beginning after December 15, 2019, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the effect that this guidance will have on its consolidated financial statements. The adoption of this ASU is not expected to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
Changes in Presentation
Certain prior period amounts have been reclassified to conform to current period presentation.
75
Note 3 — Segment Reporting
The Company conducts its business through the following segments: (i) investments in RMBS; (ii) investments in Servicing Related Assets; and (iii) “All Other,” which consists primarily of general and administrative expenses, including fees paid to the Company’s directors and management fees and reimbursements paid to the Manager pursuant to the Management Agreement (See Note 7). For segment reporting purposes, the Company does not allocate interest income on short-term investments or general and administrative expenses.
Summary financial data with respect to the Company’s segments is given below, together with a reconciliation to the same data for the Company as a whole (dollars in thousands):
Servicing Related Assets |
RMBS |
All Other |
Total |
|||||||||
Income Statement |
||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
||||||||||||
Interest income |
$ | 2,820 | $ | 70,518 | $ | — | $ | 73,338 | ||||
Interest expense |
3,669 | 44,916 | — | 48,585 | ||||||||
Net interest income (expense) |
(849 | ) |
25,602 | — | 24,753 | |||||||
Servicing fee income |
73,555 | — | — | 73,555 | ||||||||
Servicing costs |
17,122 | — | — | 17,122 | ||||||||
Net servicing income |
56,433 | — | — | 56,433 | ||||||||
Other expense |
(95,002 | ) |
(34,071 | ) |
— | (129,073 | ) |
|||||
Other operating expenses |
— | — | 12,431 | 12,431 | ||||||||
Benefit from corporate business taxes |
(16,822 | ) |
— | — | (16,822 | ) |
||||||
Net Loss |
$ | (22,596 | ) |
$ | (8,469 | ) |
$ | (12,431 | ) |
$ | (43,496 | ) |
Year Ended December 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||
Interest income |
$ | 99 | $ | 57,616 | $ | — | $ | 57,715 | ||||
Interest expense |
2,314 | 32,193 | 2 | 34,509 | ||||||||
Net interest income (expense) |
(2,215 | ) |
25,423 | (2 | ) |
23,206 | ||||||
Servicing fee income |
50,776 | — | — | 50,776 | ||||||||
Servicing costs |
10,615 | — | — | 10,615 | ||||||||
Net servicing income |
40,161 | — | — | 40,161 | ||||||||
Other expense |
(3,573 | ) |
(10,746 | ) |
— | (14,319 | ) |
|||||
Other operating expenses |
— | — | 9,887 | 9,887 | ||||||||
Provision for corporate business taxes |
1,388 | — | — | 1,388 | ||||||||
Net Income (Loss) |
$ | 32,985 | $ | 14,677 | $ | (9,889 | ) |
$ | 37,773 | |||
Year Ended December 31, 2017 |
||||||||||||
Interest income |
$ | 523 | $ | 41,526 | $ | — | $ | 42,049 | ||||
Interest expense |
506 | 19,375 | — | 19,881 | ||||||||
Net interest income |
17 | 22,151 | — | 22,168 | ||||||||
Servicing fee income |
24,034 | — | — | 24,034 | ||||||||
Servicing costs |
5,783 | — | — | 5,783 | ||||||||
Net servicing income |
18,251 | — | — | 18,251 | ||||||||
Other income |
15,837 | 523 | — | 16,360 | ||||||||
Other operating expenses |
— | — | 8,164 | 8,164 | ||||||||
Provision for corporate business taxes |
601 | — | — | 601 | ||||||||
Net Income (Loss) |
$ | 33,504 | $ | 22,674 | $ | (8,164 | ) |
$ | 48,014 | |||
76
Servicing Related Assets |
RMBS |
All Other |
Total |
|||||||||
Balance Sheet |
||||||||||||
December 31, 2019 |
||||||||||||
Investments |
$ | 291,111 | $ | 2,508,360 | $ | — | $ | 2,799,471 | ||||
Other assets |
51,729 | 80,207 | 25,145 | 157,081 | ||||||||
Total assets |
342,840 | 2,588,567 | 25,145 | 2,956,552 | ||||||||
Debt |
166,989 | 2,337,638 | — | 2,504,627 | ||||||||
Other liabilities |
9,762 | 16,503 | 14,017 | 40,282 | ||||||||
Total liabilities |
176,751 | 2,354,141 | 14,017 | 2,544,909 | ||||||||
Book value |
$ | 166,089 | $ | 234,426 | $ | 11,128 | $ | 411,643 | ||||
December 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||
Investments |
$ | 294,907 | $ | 1,770,110 | $ | — | $ | 2,065,017 | ||||
Other assets |
17,817 | 38,165 | 32,278 | 88,260 | ||||||||
Total assets |
312,724 | 1,808,275 | 32,278 | 2,153,277 | ||||||||
Debt |
157,543 | 1,598,592 | — | 1,756,135 | ||||||||
Other liabilities |
7,488 | 10,440 | 15,283 | 33,211 | ||||||||
Total liabilities |
165,031 | 1,609,032 | 15,283 | 1,789,346 | ||||||||
Book value |
$ | 147,693 | $ | 199,243 | $ | 16,995 | $ | 363,931 | ||||
December 31, 2017 |
||||||||||||
Investments |
$ | 122,806 | $ | 1,840,912 | $ | — | $ | 1,963,718 | ||||
Other assets |
8,281 | 48,631 | 30,055 | 86,967 | ||||||||
Total assets |
131,087 | 1,889,543 | 30,055 | 2,050,685 | ||||||||
Debt |
39,025 | 1,666,537 | — | 1,705,562 | ||||||||
Other liabilities |
6,575 | 4,385 | 11,706 | 22,666 | ||||||||
Total liabilities |
45,600 | 1,670,922 | 11,706 | 1,728,228 | ||||||||
Book value |
$ | 85,487 | $ | 218,621 | $ | 18,349 | $ | 322,457 | ||||
Note 4 — Investments in RMBS
RMBS on which the payment of principal and interest is guaranteed by a U.S. government agency or a U.S. government sponsored enterprise are referred to as “Agency RMBS.” RMBS also includes collateralized mortgage obligations (“CMOs”) which are either loss share securities issued by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac or non-Agency RMBS, sometimes called “private label MBS,” which are structured debt instruments representing interests in specified pools of mortgage loans subdivided into multiple classes, or tranches, of securities, with each tranche having different maturities or risk profiles and different ratings by one or more nationally recognized statistical rating organizations (“NRSRO”). All of the Company’s RMBS are classified as available for sale and are, therefore, reported at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in other comprehensive income (loss) except for securities that are OTTI (dollars in thousands):
Summary of RMBS Assets
As of December 31, 2019
Original Face Value |
Book Value |
Gross Unrealized |
Carrying Value(A) |
Number of Securities |
Weighted Average |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Asset Type |
Gains |
Losses |
Rating |
Coupon |
Yield(C) |
Maturity (Years)(D) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
RMBS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fannie Mae |
$ | 1,878,229 | $ | 1,596,288 | $ | 23,636 | $ | (691 | ) |
$ | 1,619,233 | 198 | (B) |
3.80 | % |
3.65 | % |
27 | ||||||||||||
Freddie Mac |
824,991 | 715,892 | 12,204 | (245 | ) |
727,851 | 88 | (B) |
3.72 | % |
3.59 | % |
28 | |||||||||||||||||
CMOs |
127,229 | 123,053 | 6,030 | — | 129,083 | 30 | (B) |
5.28 | % |
5.26 | % |
11 | ||||||||||||||||||
Private Label MBS |
50,500 | 31,595 | 598 | — | 32,193 | 11 | (B) |
4.06 | % |
4.06 | % |
29 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 2,880,949 | $ | 2,466,828 | $ | 42,468 | $ | (936 | ) |
$ | 2,508,360 | 327 | 3.85 | % |
3.72 | % |
26 | |||||||||||||
77
As of December 31, 2018
Original Face Value |
Book Value |
Gross Unrealized |
Carrying Value(A) |
Number of Securities |
Weighted Average |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Asset Type |
Gains |
Losses |
Rating |
Coupon |
Yield(C) |
Maturity (Years)(D) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
RMBS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fannie Mae |
$ | 1,362,606 | $ | 1,208,854 | $ | 224 | $ | (30,914 | ) |
$ | 1,178,164 | 154 | (B) |
3.87 | % |
3.70 | % |
25 | ||||||||||||
Freddie Mac |
548,862 | 471,148 | 246 | (12,386 | ) |
459,008 | 63 | (B) |
3.75 | % |
3.60 | % |
27 | |||||||||||||||||
CMOs |
100,129 | 99,023 | 5,060 | (583 | ) |
103,500 | 23 | (B) |
6.30 | % |
6.29 | % |
11 | |||||||||||||||||
Private Label MBS |
30,500 | 29,395 | 76 | (33 | ) |
29,438 | 7 | (B) |
4.10 | % |
4.11 | % |
29 | |||||||||||||||||
Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 2,042,097 | $ | 1,808,420 | $ | 5,606 | $ | (43,916 | ) |
$ | 1,770,110 | 247 | 3.98 | % |
3.82 | % |
25 | |||||||||||||
| (A) | See Note 9 regarding the estimation of fair value, which approximates carrying value for all securities. |
| (B) | The Company used an implied AAA rating for the Agency RMBS. Collateralized mortgage obligations (“CMOs”) issued by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac consist of loss share securities, approximately half of which, by unpaid principal balance (“UPB”), are unrated or rated below investment grade at December 31, 2019 by at least one NRSRO. Private label securities are rated investment grade or better by at least one NRSRO as of December 31, 2019. |
| (C) | The weighted average yield is based on the most recent gross monthly interest income, which is then annualized and divided by the book value of settled securities. |
| (D) | The weighted average maturity is based on the timing of expected principal reduction on the assets. |
Summary of RMBS Assets by Maturity
As of December 31, 2019
Original Face Value |
Book Value |
Gross Unrealized |
Carrying Value(A) |
Number of Securities |
Weighted Average |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Years to Maturity |
Gains |
Losses |
Rating |
Coupon |
Yield(C) |
Maturity (Years)(D) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1-5 Years |
$ | 1,500 | 895 | 64 | — | 959 | 1 | (B) |
6.34 | % |
6.34 | % |
04 | |||||||||||||||||
5-10 Years |
64,579 | 61,935 | 4,153 | — | 66,088 | 13 | (B) |
5.85 | % |
5.81 | % |
09 | ||||||||||||||||||
Over 10 Years |
2,814,870 | 2,403,998 | 38,251 | (936 | ) |
2,441,313 | 313 | (B) |
3.80 | % |
3.66 | % |
27 | |||||||||||||||||
Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 2,880,949 | $ | 2,466,828 | $ | 42,468 | $ | (936 | ) |
$ | 2,508,360 | 327 | 3.85 | % |
3.72 | % |
26 | |||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2018
Original Face Value |
Book Value |
Gross Unrealized |
Carrying Value(A) |
Number of Securities |
Weighted Average |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Years to Maturity |
Gains |
Losses |
Rating |
Coupon |
Yield(C) |
Maturity (Years)(D) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
5-10 Years |
$ | 24,377 | $ | 15,100 | $ | 731 | $ | (134 | ) |
$ | 15,697 | 7 | (B) |
4.97 | % |
4.93 | % |
09 | ||||||||||||
Over 10 Years |
2,017,720 | 1,793,320 | 4,875 | (43,782 | ) |
1,754,413 | 240 | (B) |
3.97 | % |
3.81 | % |
25 | |||||||||||||||||
Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 2,042,097 | $ | 1,808,420 | $ | 5,606 | $ | (43,916 | ) |
$ | 1,770,110 | 247 | 3.98 | % |
3.82 | % |
25 | |||||||||||||
| (A) | See Note 9 regarding the estimation of fair value, which approximates carrying value for all securities. |
| (B) | The Company used an implied AAA rating for the Agency RMBS. CMOs issued by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac consist of loss share securities, approximately half of which, by UPB, are unrated or rated below investment grade at December 31, 2019 by at least one NRSRO. Private label securities are rated investment grade or better by at least one NRSRO as of December 31, 2019. |
| (C) | The weighted average yield is based on the most recent gross monthly interest income, which is then annualized and divided by the book value of settled securities. |
| (D) | The weighted average maturity is based on the timing of expected principal reduction on the assets. |
At December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company pledged Agency RMBS with a carrying value of approximately $2,419.5 million and $1,698.7 million, respectively, as collateral for borrowings under repurchase agreements. At December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company did not have any securities purchased from and financed with the same counterparty that did not meet the conditions of ASC 860, Transfers and Servicing, to be considered linked transactions and, therefore, classified as derivatives.
Based on management’s analysis of the Company’s securities, the performance of the underlying loans and changes in market factors, management determined that unrealized losses as of the balance sheet date on the Company’s securities were primarily the result of changes in market factors, rather than issuer-specific credit impairment, and such losses were considered temporary. The Company performed analyses in relation to such
78
securities, using management’s best estimate of their cash flows, which support its belief that the carrying values of such securities were fully recoverable over their expected holding periods. Such market factors include changes in market interest rates and credit spreads and certain macroeconomic events, none of which will directly impact the Company’s ability to collect amounts contractually due. Management continually evaluates the credit status of each of the Company’s securities and the collateral supporting those securities. This evaluation includes a review of the credit of the issuer of the security (if applicable), the credit rating of the security (if applicable), the key terms of the security (including credit support), debt service coverage and loan to value ratios, the performance of the pool of underlying loans and the estimated value of the collateral supporting such loans, including the effect of local, industry and broader economic trends and factors. Significant judgment is required in this analysis. In connection with the above, the Company weighs the fact that a substantial majority of its investments in RMBS are guaranteed by U.S. government agencies or U.S. government sponsored enterprises.
Unrealized losses that are considered other than temporary are recognized in earnings. The Company did not record any OTTI charges during the year ended December 31, 2019 and recorded approximately $45,000 of OTTI charges during the year ended December 31, 2018.
The following tables summarize the Company’s securities in an unrealized loss position as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands):
RMBS Unrealized Loss Positions
As of December 31, 2019
Duration in Loss Position |
Original Face Value |
Book Value |
Gross Unrealized Losses |
Carrying Value(A) |
Number of Securities |
Weighted Average |
|||||||||||||||||||
Rating |
Coupon |
Yield(C) |
Maturity (Years)(D) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Less than Twelve Months |
$ | 55,588 | $ | 55,429 | $ | (105 | ) |
$ | 55,324 | 5 | (B) |
3.70 | % |
3.53 | % |
29 | |||||||||
Twelve or More Months |
169,346 | 131,540 | (831 | ) |
130,709 | 23 | (B) |
3.76 | % |
3.54 | % |
25 | |||||||||||||
Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 224,934 | $ | 186,969 | $ | (936 | ) |
$ | 186,033 | 28 | 3.74 | % |
3.54 | % |
26 | ||||||||||
As of December 31, 2018
Duration in Loss Position |
Original Face Value |
Book Value |
Gross Unrealized Losses |
Carrying Value(A) |
Number of Securities |
Weighted Average |
|||||||||||||||||||
Rating |
Coupon |
Yield(C) |
Maturity (Years)(D) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
Less than Twelve Months |
$ | 256,937 | $ | 224,617 | $ | (1,563 | ) |
$ | 223,054 | 28 | (B) |
4.26 | % |
4.14 | % |
24 | |||||||||
Twelve or More Months |
1,512,169 | 1,321,115 | (42,353 | ) |
1,278,762 | 181 | (B) |
3.78 | % |
3.60 | % |
25 | |||||||||||||
Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 1,769,106 | $ | 1,545,732 | $ | (43,916 | ) |
$ | 1,501,816 | 209 | 3.85 | % |
3.68 | % |
25 | ||||||||||
| (A) | See Note 9 regarding the estimation of fair value, which approximates carrying value for all securities. |
| (B) | The Company used an implied AAA rating for the Agency RMBS. CMOs issued by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac consist of loss share securities, approximately half of which, by UPB, are unrated or rated below investment grade at December 31, 2019 by at least one NRSRO. Private label securities are rated investment grade or better by at least one NRSRO as of December 31, 2019. |
| (C) | The weighted average yield is based on the most recent gross monthly interest income, which is then annualized and divided by the book value of settled securities. |
| (D) | The weighted average maturity is based on the timing of expected principal reduction on the assets. Except for the security for which the Company has recognized OTTI, the Company does not intend to sell the investments and it is not more likely than not that the Company will be required to sell the investments before recovery of their amortized cost bases which may be maturity. |
79
Note 5 — Investments in Servicing Related Assets
MSRs
Aurora’s MSR portfolio of Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac and Ginnie Mae MSRs have an aggregate UPB of approximately $29.1 billion as of December 31, 2019. The following is a summary of the Company’s Servicing Related Assets as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands):
Servicing Related Assets Summary
As of December 31, 2019
Unpaid Principal Balance |
Cost Basis |
Carrying Value(A) |
Weighted Average Coupon |
Weighted Average Maturity (Years)(B) |
Changes in Fair Value Recorded in Other Income (Loss) |
|||||||||||||
MSRs |
||||||||||||||||||
Conventional |
$ | 26,142,780 | $ | 357,667 | (C) |
$ | 263,357 | 4.27 | % |
26.8 | $ | (94,310 | ) |
|||||
Government |
2,925,346 | 40,216 | (C) |
27,754 | 3.37 | % |
25.8 | (12,462 | ) |
|||||||||
MSR Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 29,068,126 | $ | 397,883 | $ | 291,111 | 4.18 | % |
26.7 | $ | (106,772 | ) |
||||||
As of December 31, 2018
Unpaid Principal Balance |
Cost Basis |
Carrying Value(A) |
Weighted Average Coupon |
Weighted Average Maturity (Years)(B) |
Changes in Fair Value Recorded in Other Income (Loss) |
|||||||||||||
MSRs |
||||||||||||||||||
Conventional |
$ | 21,366,980 | $ | 258,070 | (C) |
$ | 254,691 | 4.37 | % |
27.3 | $ | (3,379 | ) |
|||||
Government |
3,480,009 | 40,410 | (C) |
40,216 | 3.37 | % |
26.8 | (194 | ) |
|||||||||
MSR Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 24,846,989 | $ | 298,480 | $ | 294,907 | 4.23 | % |
27.2 | $ | (3,573 | ) |
||||||
| (A) | Carrying value approximates the fair value of the pools (see Note 9). |
| (B) | The weighted average maturity represents the weighted average expected timing of the receipt of cash flows of each investment. |
| (C) | MSR cost basis consists of the carrying value of the prior period, adjusted for any purchases, sales and principal paydowns of the underlying mortgage loans. |
The tables below summarize the geographic distribution for the states representing 5% or greater of the aggregate UPB of the residential mortgage loans underlying the Servicing Related Assets as of the dates indicated:
Geographic Concentration of Servicing Related Assets
As of December 31, 2019
Percentage of Total Outstanding Unpaid Principal Balance |
|||
California |
13.4 | % |
|
Texas |
6.2 | % |
|
Maryland |
5.6 | % |
|
New York |
5.1 | % |
|
Virginia |
5.1 | % |
|
All other |
64.6 | % |
|
Total |
100.0 | % |
|
80
As of December 31, 2018
Percentage of Total Outstanding Unpaid Principal Balance |
|||
California |
12.7 | % |
|
Texas |
6.4 | % |
|
Florida |
5.1 | % |
|
All other |
75.8 | % |
|
Total |
100.0 | % |
|
Geographic concentrations of investments expose the Company to the risk of economic downturns within the relevant states. Any such downturn in a state where the Company holds significant investments could affect the underlying borrower’s ability to make the mortgage payment and, therefore, could have a meaningful, negative impact on the Company’s Servicing Related Assets.
Note 6 — Equity and Earnings per Common Share
Common and Preferred Stock
On October 9, 2013, the Company completed an initial public offering (the “IPO”) and a concurrent private placement of its common stock. The Company did not conduct any activity prior to the IPO and the concurrent private placement.
The Company’s 8.2% Series A Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock, par value $0.01 per share (the “Series A Preferred Stock”) ranks senior to the Company’s common stock with respect to rights to the payment of dividends and the distribution of assets upon the Company’s liquidation, dissolution or winding up. The Series A Preferred Stock has no stated maturity, is not subject to any sinking fund or mandatory redemption and will remain outstanding indefinitely unless repurchased or redeemed by the Company or converted by the holders of the Series A Preferred Stock into the Company’s common stock in connection with certain changes of control. The Series A Preferred Stock is not redeemable by the Company prior to August 17, 2022, except under circumstances intended to preserve the Company’s qualification as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes and except upon the occurrence of certain changes of control. On and after August 17, 2022, the Company may, at its option, redeem the Series A Preferred Stock, in whole or in part, at any time or from time to time, for cash at a redemption price equal to $25.00 per share, plus any accumulated and unpaid dividends to, but not including, the date fixed for redemption. If the Company does not exercise its rights to redeem the Series A Preferred Stock upon certain changes in control, the holders of the Series A Preferred Stock have the right to convert some or all of their shares of Series A Preferred Stock into a number of shares of the Company’s common stock based on a defined formula, subject to a share cap, or alternative consideration. The share cap on each share of Series A Preferred Stock is 2.62881 shares of common stock, subject to certain adjustments. The Company pays cumulative cash dividends at the rate of 8.2% per annum of the $25.00 per share liquidation preference (equivalent to $2.05 per annum per share) on the Series A Preferred Stock, in arrears, on or about the 15th day of January, April, July and October of each year.
On June 4, 2018, the Company issued and sold 2,750,000 shares of its common stock, par value $0.01 per share. The underwriters subsequently exercised their option to purchase an additional 338,857 shares for total proceeds of approximately $53.8 million after underwriting discounts and commissions but before expenses of approximately $265,000. All of the net proceeds were invested in RMBS.
On February 11, 2019, the Company completed an offering of 1,800,000 shares of the Company’s 8.3% Series B Fixed-to-Floating Rate Cumulative Redeemable Stock, par value $0.01 per share (the “Series B Preferred Stock”). The underwriters subsequently exercised their option to purchase an additional 200,000 shares for total proceeds of approximately $48.4 million after underwriting discounts and commissions but before expenses of approximately $285,000. The net proceeds were invested in RMBS and MSRs.
The Series B Preferred Stock ranks senior to the Company’s common stock with respect to rights to the payment of dividends and the distribution of assets upon the Company’s liquidation, dissolution or winding up, and on parity with the Company’s Series A Preferred Stock with respect to rights to the payment of dividends and the distribution of assets upon the Company’s liquidation, dissolution or winding up. The Series B Preferred Stock has no stated maturity, is not subject to any sinking fund or mandatory redemption and will remain
81
outstanding indefinitely unless repurchased or redeemed by the Company or converted by the holders of the Series B Preferred Stock into the Company’s common stock in connection with certain changes of control. The Series B Preferred Stock is not redeemable by the Company prior to April 15, 2024, except under circumstances intended to preserve the Company’s qualification as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes and except upon the occurrence of certain changes of control. On and after April 15, 2024, the Company may, at its option, redeem the Series B Preferred Stock, in whole or in part, at any time or from time to time, for cash at a redemption price equal to $25.00 per share, plus any accumulated and unpaid dividends to, but not including, the date fixed for redemption. If the Company does not exercise its rights to redeem the Series B Preferred Stock upon certain changes in control, the holders of the Series B Preferred Stock have the right to convert some or all of their shares of Series B Preferred Stock into a number of shares of the Company’s common stock based on a defined formula, subject to a share cap, or alternative consideration. The share cap on each share of Series B Preferred Stock is 2.68962 shares of common stock, subject to certain adjustments. Holders of Series B Preferred Stock will be entitled to receive cumulative cash dividends (i) from and including February 11, 2019 to, but excluding, April 15, 2024 at a fixed rate equal to 8.250% per annum of the $25.00 per share liquidation preference (equivalent to $2.0625 per annum per share) and (ii) from and including April 15, 2024, at a floating rate equal to three-month LIBOR plus a spread of 5.631% per annum. Dividends are payable quarterly in arrears on the 15th day of each January, April, July and October, when and as authorized by the Company’s board of directors and declared by the Company.
A significant portion of the paydowns of the RMBS acquired with offering proceeds have been or will be deployed into the acquisition of MSRs. The Company may also sell certain of these RMBS and deploy the net proceeds from such sales to the extent necessary to fund the purchase price of MSRs.
Common Stock ATM Program
In August 2018, the Company instituted an at-the-market offering (the “Common Stock ATM Program”) of up to $50,000,000 of its common stock. Under the Common Stock ATM Program, the Company may, but is not obligated to, sell shares of common stock from time to time through one or more selling agents. The Common Stock ATM Program has no set expiration date and may be renewed or terminated by the Company at any time. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company issued and sold 225,646 shares of common stock under the Common Stock ATM Program. The shares were sold at a weighted average price of $17.40 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $3.9 million before fees of approximately $79,000. During the year ended December 31, 2018, the Company issued and sold 833,593 shares of common stock under the Common Stock ATM Program. The shares were sold at a weighted average price of $18.84 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $15.7 million before fees of approximately $314,000.
Preferred Stock ATM Program
In April 2018, the Company instituted an at-the-market offering (the “Preferred Series A ATM Program”) of up to $35,000,000 of its Series A Preferred Stock. Under the Preferred Series A ATM Program, the Company may, but is not obligated to, sell shares of Series A Preferred Stock from time to time through one or more selling agents. The Preferred Series A ATM Program has no set expiration date and may be renewed or terminated by the Company at any time. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company issued and sold 63,429 shares of Series A Preferred Stock under the Preferred Series A ATM Program. The shares were sold at a weighted average price of $25.21 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $1.6 million before fees of approximately $26,000. During the year ended December 31, 2018, the Company issued and sold 318,206 shares of Series A Preferred Stock under the Preferred Series A ATM Program. The shares were sold at a weighted average price of $25.37 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $8.1 million before fees of approximately $127,000.
Share Repurchase Program
In September 2019, the Company instituted a share repurchase program that allows for the repurchase of up to an aggregate of $10,000,000 of the Company’s common stock. Shares may be repurchased from time to time through privately negotiated transactions or open market transactions, pursuant to a trading plan in accordance with Rules 10b5-1 and 10b-18 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act, or by any combination of such methods. The manner, price, number and timing of share repurchases are subject to a variety of factors, including market conditions and applicable SEC rules. The share repurchase program does not
82
require the purchase of any minimum number of shares, and, subject to SEC rules, purchases may be commenced or suspended at any time without prior notice. Unless sooner terminated or extended, the share repurchase program expires on September 3, 2020. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company repurchased 235,950 shares of its common stock at a weighted average purchase price of $14.59 per share and paid brokers commissions of approximately $7,000 on such repurchases.
Common Stock Purchase Information
As of December 31, 2019
Fiscal Period |
Total Number of Shares Purchased |
Average Price Paid per Share |
Total Number of Shares Purchased as part of Publicaly Announced Plans or Programs |
Maximum Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs |
||||||||
October 1, 2019 to October 31, 2019 |
— | — | — | $ | 10,000,000 | |||||||
November 1, 2019 to November 30, 2019 |
163,800 | $ | 14.52 | 163,800 | 7,621,091 | |||||||
December 1, 2019 to December 31, 2019 |
72,150 | 14.75 | 72,150 | 6,556,956 | ||||||||
Totals / Averages |
235,950 | $ | 14.59 | 235,950 | $ | 6,556,956 | ||||||
Equity Incentive Plan
During 2013, the board of directors approved and the Company adopted the Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2013 Plan”). The 2013 Plan provides for the grant of options to purchase shares of the Company’s common stock, stock awards, stock appreciation rights, performance units, incentive awards and other equity-based awards, including long term incentive plan units (“LTIP-OP Units”) of the Operating Partnership.
LTIP-OP Units are a special class of partnership interest in the Operating Partnership. LTIP-OP Units may be issued to eligible participants for the performance of services to or for the benefit of the Operating Partnership. Initially, LTIP-OP Units do not have full parity with the Operating Partnership’s common units of limited partnership interest (“OP Units”) with respect to liquidating distributions; however, LTIP-OP Units receive, whether vested or not, the same per-unit distributions as OP Units and are allocated their pro-rata share of the Operating Partnership’s net income or loss. Under the terms of the LTIP-OP Units, the Operating Partnership will revalue its assets upon the occurrence of certain specified events, and any increase in the Operating Partnership’s valuation from the time of grant of the LTIP-OP Units until such event will be allocated first to the holders of LTIP-OP Units to equalize the capital accounts of such holders with the capital accounts of the holders of OP Units. Upon equalization of the capital accounts of the holders of LTIP-OP Units with the other holders of OP Units, the LTIP-OP Units will achieve full parity with OP Units for all purposes, including with respect to liquidating distributions. If such parity is reached, vested LTIP-OP Units may be converted into an equal number of OP Units at any time and, thereafter, enjoy all the rights of OP Units, including redemption rights. Each LTIP-OP Unit awarded is deemed equivalent to an award of one share of the Company’s common stock under the 2013 Plan and reduces the 2013 Plan’s share authorization for other awards on a one-for-one basis.
An LTIP-OP Unit and a share of common stock of the Company have substantially the same economic characteristics in as much as they effectively share equally in the net income or loss of the Operating Partnership. Holders of LTIP-OP Units that have reached parity with OP Units have the right to redeem their LTIP-OP Units, subject to certain restrictions. The redemption is required to be satisfied in cash, or at the Company’s option, the Company may purchase the OP Units for common stock, calculated as follows: one share of the Company’s common stock, or cash equal to the fair value of a share of the Company’s common stock at the time of redemption, for each LTIP-OP Unit. When an LTIP-OP Unit holder redeems an OP Unit (as described above), non-controlling interest in the Operating Partnership is reduced and the Company’s equity is increased.
83
LTIP-OP Units vest ratably over the first three annual anniversaries of the grant date. The fair value of each LTIP-OP Unit was determined based on the closing price of the Company’s common stock on the applicable grant date in all other cases.
The following table sets forth the number of shares of the Company’s common stock and the values thereof (based on the closing prices on the respective dates of grant) granted under the 2013 Plan. Except as otherwise indicated, all shares are fully vested.
The following tables present certain information about the 2013 Plan as of the dates indicated:
Equity Incentive Plan Information
LTIP-OP Units |
Shares of Common Stock |
Number of Securities Remaining Available For Future Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans |
Weighted Average Issuance Price |
||||||||||||||||||
Issued |
Forfeited |
Converted |
Issued |
Forfeited |
|||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2017 |
(178,500 | ) |
916 | 12,917 | (49,619 | ) |
3,155 | 1,288,869 | |||||||||||||
Number of securities issued or to be issued upon exercise |
(45,400 | )(A) |
— | — | (8,256 | )(B) |
— | (53,656 | ) |
$ | 18.17 | ||||||||||
December 31, 2018 |
(223,900 | ) |
916 | 12,917 | (57,875 | ) |
3,155 | 1,235,213 | |||||||||||||
Number of securities issued or to be issued upon exercise |
(66,375 | )(C) |
— | 6,000 | (18,789 | )(D) |
— | (79,164 | ) |
$ | 16.68 | ||||||||||
December 31, 2019 |
(290,275 | ) |
916 | 18,917 | (76,664 | ) |
3,155 | 1,156,049 | |||||||||||||
| (A) | Subject to forfeiture in certain circumstances prior to June 13, 2021. |
| (B) | Subject to forfeiture in certain circumstances prior to June 13, 2019. |
| (C) | Subject to forfeiture in certain circumstances prior to January 2, 2022. |
| (D) | Subject to forfeiture in certain circumstances prior to June 13, 2020. |
The Company recognized approximately $1.0 million and $662,000 in share-based compensation expense in the years ended December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. There was approximately $1.2 million of total unrecognized share-based compensation expense as of December 31, 2019, all of which was related to unvested LTIP-OP Units. This unrecognized share-based compensation expense is expected to be recognized ratably over the remaining vesting period of up to three years. The aggregate expense related to the LTIP-OP Unit grants is presented as “General and administrative expense” in the Company’s consolidated statements of income.
Non-Controlling Interests in Operating Partnership
Non-controlling interests in the Operating Partnership in the accompanying consolidated financial statements relate to LTIP-OP Units and OP Units issued upon conversion of LTIP-OP Units, in either case, held by parties other than the Company.
As of December 31, 2019, the non-controlling interest holders in the Operating Partnership owned 270,442 LTIP-OP Units, or approximately 1.6% of the units of the Operating Partnership. Pursuant to ASC 810, Consolidation, changes in a parent’s ownership interest (and transactions with non-controlling interest unit holders in the Operating Partnership) while the parent retains its controlling interest in its subsidiary should be accounted for as equity transactions. The carrying amount of the non-controlling interest will be adjusted to reflect the change in its ownership interest in the subsidiary, with the offset to equity attributable to the Company.
Earnings per Common Share
The Company is required to present both basic and diluted earnings per common share (“EPS”). Basic EPS is calculated by dividing net income applicable to common stockholders by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during each period. Diluted EPS is calculated by dividing net income applicable to common stockholders by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding plus
84
the additional dilutive effect of common stock equivalents during each period. In accordance with ASC 260, Earnings Per Share, if there is a loss from continuing operations, the common stock equivalents are deemed anti-dilutive and earnings (loss) per share is calculated excluding the potential common shares.
The following table presents basic and diluted earnings per share of common stock for the periods indicated (dollars in thousands, except per share data):
Earnings per Common Share Information
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
|||||||
Numerator: |
|||||||||
Net income (loss) |
$ | (43,496 | ) |
$ | 37,773 | $ | 48,014 | ||
Net (income) loss allocated to noncontrolling interests in Operating Partnership |
703 | (488 | ) |
(655 | ) |
||||
Dividends on preferred stock |
9,353 | 5,297 | 1,833 | ||||||
Net income (loss) applicable to common stockholders |
$ | (52,146 | ) |
$ | 31,988 | $ | 45,526 | ||
Denominator: |
|||||||||
Weighted average common shares outstanding |
16,775,113 | 14,649,242 | 11,443,493 | ||||||
Weighted average diluted shares outstanding |
16,787,902 | 14,657,498 | 11,450,831 | ||||||
Basic and Diluted EPS: |
|||||||||
Basic |
$ | (3.11 | ) |
$ | 2.18 | $ | 3.98 | ||
Diluted |
$ | (3.11 | ) |
$ | 2.18 | $ | 3.98 | ||
There were no participating securities or equity instruments outstanding that were anti-dilutive for purposes of calculating earnings per share for the periods presented.
Note 7 — Transactions with Affiliates and Affiliated Entities
Manager
The Company has entered into the Management Agreement with the Manager, pursuant to which the Manager provides for the day-to-day management of the Company’s operations. The Management Agreement requires the Manager to manage the Company’s business affairs in conformity with the policies that are approved and monitored by the Company’s board of directors. Pursuant to the Management Agreement, the Manager, under the supervision of the Company’s board of directors, formulates investment strategies, arranges for the acquisition of assets, arranges for financing, monitors the performance of the Company’s assets and provides certain advisory, administrative and managerial services in connection with the operations of the Company. For performing these services, the Company pays the Manager the management fee which is payable in cash quarterly in arrears, in an amount equal to 1.5% per annum of the Company’s stockholders’ equity (as defined in the Management Agreement). The term of the Management Agreement will expire on October 22, 2020 and will be automatically renewed for a one-year term on such date and on each anniversary of such date thereafter unless terminated or not renewed as described below. Either we or our Manager may elect not to renew the Management Agreement upon expiration of its initial term or any renewal term by providing written notice of non-renewal at least 180 days, but not more than 270 days, before expiration. In the event we elect not to renew the term, we will be required to pay our Manager a termination fee equal to three times the average annual management fee amount earned by the Manager during the two four-quarter periods ending as of the end of the most recently completed fiscal quarter prior to the non-renewal. We may terminate the Management Agreement at any time for cause effective upon 30 days prior written notice of termination from us to our Manager, in which case no termination fee would be due. Our board of directors will review our Manager’s performance prior to the automatic renewal thereof and, as a result of such review, upon the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of the members of our board of directors or of the holders of a majority of our outstanding common stock, we may terminate the Management Agreement based upon unsatisfactory performance by our Manager that is materially detrimental to us or a determination by our independent directors that the management fees payable to our Manager are not fair, subject to the right of our Manager to prevent such a termination by agreeing to a reduction of the management fees payable to our Manager. Upon any termination of the Management Agreement based on unsatisfactory performance or unfair management fees, we are required to pay
85
our Manager the termination fee described above. Our Manager may terminate the Management Agreement in the event the Company becomes regulated as an investment company under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, in which case the Company would not be required to pay the termination fee described above. Our Manager may also terminate the Management Agreement upon 60 days’ written notice if we default in the performance of any material term of the Management Agreement and the default continues for a period of 30 days after written notice to us, whereupon we would be required to pay our Manager the termination fee described above.
The Manager is a party to a services agreement (the “Services Agreement”) with Freedom Mortgage, pursuant to which Freedom Mortgage provides to the Manager the personnel, services and resources needed by the Manager to carry out its obligations and responsibilities under the Management Agreement. The Company is a named third-party beneficiary to the Services Agreement and, as a result, has, as a non-exclusive remedy, a direct right of action against Freedom Mortgage in the event of any breach by the Manager of any of its duties, obligations or agreements under the Management Agreement that arise out of or result from any breach by Freedom Mortgage of its obligations under the Services Agreement. The Services Agreement will terminate upon the termination of the Management Agreement. Pursuant to the Services Agreement, the Manager will make certain payments to Freedom Mortgage in connection with the services provided. The Management Agreement between the Company and the Manager was negotiated between related parties, and the terms, including fees payable, may not be as favorable to the Company as if it had been negotiated with an unaffiliated third party. At the time the Management Agreement was negotiated, both the Manager and Freedom Mortgage were controlled by Mr. Stanley Middleman, who is also a shareholder of the Company. In 2016, ownership of the Manager was transferred to CHMM Blind Trust, a grantor trust for the benefit of Mr. Middleman.
The Management Agreement provides that the Company will reimburse the Manager for (i) various expenses incurred by the Manager or its officers, and agents on the Company’s behalf, including costs of software, legal, accounting, tax, administrative and other similar services rendered for the Company by providers retained by the Manager and (ii) the allocable portion of the compensation paid to specified officers dedicated to the Company. The amounts under “Due to affiliates” on the consolidated balance sheets consisted of the following for the periods indicated (dollars in thousands):
Management Fees and Compensation Reimbursement to Affiliate
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
|||||||
Management fees |
$ | 6,832 | $ | 5,088 | $ | 3,583 | |||
Compensation reimbursement |
952 | 858 | 764 | ||||||
Total |
$ | 7,784 | $ | 5,946 | $ | 4,347 | |||
Subservicing Agreement
Freedom Mortgage is directly servicing the Company’s portfolio of Ginnie Mae MSRs pursuant to a subservicing agreement entered into on June 10, 2015. Although Freedom Mortgage gave notice of termination of the subservicing agreement without cause during the third quarter of 2018, as required by that agreement, Freedom Mortgage has continued to service the Ginnie Mae MSRs pending transfer of the servicing responsibilities, and Aurora has continued to pay for such services. The parties subsequently decided to reinstate the agreement on the terms in effect at the time of the notice of termination, including a three-year term subject to automatic renewal for a similar term unless sooner terminated in accordance with its terms.
Joint Marketing Recapture Agreement
In June 2016, Aurora entered into a joint marketing recapture agreement with Freedom Mortgage. Pursuant to this agreement, Freedom Mortgage attempts to refinance certain mortgage loans underlying Aurora’s MSR portfolio subserviced by Freedom Mortgage as directed by Aurora. If a loan is refinanced, Aurora will pay Freedom Mortgage a fee for its origination services. Freedom Mortgage will be entitled to sell the loan for its own benefit and will transfer the related MSR to Aurora. The agreement had an initial term of one year, subject to automatic renewals of one year each. This agreement continues in effect since the termination of the subservicing agreement was not, and now will not be, completed by the transfer of the Ginnie Mae MSRs to
86
another subservicer. During the year ended December 31, 2019, MSRs on 19 loans with an aggregate UPB of approximately $4.4 million had been received from Freedom Mortgage which generated approximately $5,200 in fees due to Freedom Mortgage. During the year ended December 31, 2018, MSRs on 98 loans with an aggregate UPB of approximately $21.5 million had been received from Freedom Mortgage which generated approximately $32,000 in fees due to Freedom Mortgage.
Sale of Excess MSRs
On November 15, 2016, the Company sold a portion of the Excess MSRs back to Freedom Mortgage for cash. The Company sold the remaining Excess MSRs back to Freedom Mortgage on February 1, 2017. In connection with this sale of Excess MSRs, Freedom Mortgage transferred to Aurora Ginnie Mae MSRs with a UPB of approximately $4.5 billion and a weighted average servicing fee of approximately 30 basis points at the time of acquisition. The sale has been classified within “Realized gain on investments in Excess MSRs, net” on the consolidated statements of income (loss).
Other Transactions with Affiliated Persons
Aurora leases five employees from Freedom Mortgage and reimburses Freedom Mortgage on a monthly basis.
The Company entered into a loan servicing purchase and sale agreement with Freedom Mortgage on December 15, 2016. The amount of holdback remaining under this agreement was approximately $757,000 as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 and has been classified within “Accrued expenses and other liabilities” on the consolidated balance sheets.
The Company incurred losses of approximately $382,000 on loans repurchased from Ginnie Mae during the year ended December 31, 2019. During the year ended December 31, 2018, there were no such losses since the losses were offset against the holdback amount under the agreement. Under the terms of the agreement with Freedom Mortgage, $326,000 of these foreclosure related losses were on VA loans repurchased from Ginnie Mae and are recoverable from Freedom Mortgage and have been classified within “Receivables and other assets” on the consolidated balance sheets. The remaining $56,000 foreclosure related losses are not reimbursable.
Note 8 — Derivative Instruments
Interest Rate Swap Agreements, Swaptions, TBAs and Treasury Futures
In order to help mitigate exposure to higher short-term interest rates in connection with borrowings under its repurchase agreements, the Company enters into interest rate swap agreements and swaption agreements. Interest rate swap agreements establish an economic fixed rate on related borrowings because the variable-rate payments received on the interest rate swap agreements largely offset interest accruing on the related borrowings, leaving the fixed-rate payments to be paid on the interest rate swap agreements as the Company’s effective borrowing rate, subject to certain adjustments including changes in spreads between variable rates on the interest rate swap agreements and actual borrowing rates. A swaption is an option granting its owner the right but not the obligation to enter into an underlying swap. The Company’s interest rate swap agreements and swaptions have not been designated as qualifying hedging instruments for GAAP purposes.
In order to help mitigate duration risk and manage basis risk and the pricing risk under the Company’s financing facilities, the Company utilizes Treasury futures and forward-settling purchases and sales of RMBS where the underlying pools of mortgage loans are TBAs. Pursuant to these TBA transactions, the Company agrees to purchase or sell, for future delivery, Agency RMBS with certain principal and interest terms and certain types of underlying collateral, but the particular Agency RMBS to be delivered is not identified until shortly before the TBA settlement date. Unless otherwise indicated, references to Treasury futures include options on Treasury futures.
87
The following table summarizes the outstanding notional amounts of derivative instruments as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands):
Derivatives |
December 31, 2019 |
December 31, 2018 |
||||
Notional amount of interest rate swaps |
$ | 2,355,850 | $ | 1,380,000 | ||
Notional amount of swaptions |
40,000 | 110,000 | ||||
Notional amount of TBAs, net |
140,300 | 35,000 | ||||
Notional amount of Treasury futures |
310,300 | 80,000 | ||||
Total notional amount |
$ | 2,846,450 | $ | 1,605,000 | ||
The following table presents information about the Company’s interest rate swap agreements as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands):
Notional Amount |
Weighted Average Pay Rate |
Weighted Average Receive Rate |
Weighted Average Years to Maturity |
|||||||||
December 31, 2019 |
$ | 2,355,850 | 1.70 | % |
1.92 | % |
5.3 | |||||
December 31, 2018 |
$ | 1,380,000 | 2.18 | % |
2.61 | % |
5.1 | |||||
The following table presents information about the Company’s interest rate swaption agreements as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands):
Notional Amount |
Weighted Average Pay Rate |
Weighted Average Receive Rate(A) |
Weighted Average Years to Maturity |
|||||||||
December 31, 2019 |
$ | 40,000 | 2.38 | % |
LIBOR-BBA | % |
10.7 | |||||
December 31, 2018 |
$ | 110,000 | 3.25 | % |
LIBOR-BBA | % |
10.0 | |||||
| (A) | Floats in accordance with LIBOR. |
The following table presents information about realized gain (loss) on derivatives, which is included on the consolidated statements of income for the periods indicated (dollars in thousands):
Consolidated Statements of Income (Loss) Location |
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
Derivatives |
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
|||||||
Interest rate swaps |
Realized (loss) on derivatives, net |
$ | (27,950 | ) |
$ | (2,149 | ) |
$ | (1,573 | ) |
Swaptions |
Realized (loss) on derivatives, net |
(1,544 | ) |
(1,451 | ) |
(680 | ) |
|||
TBAs |
Realized gain (loss) on derivatives, net |
2,251 | (2,315 | ) |
(1,339 | ) |
||||
Treasury futures |
Realized gain (loss) on derivatives, net |
14,881 | 26 | (1,962 | ) |
|||||
Total |
$ | (12,362 | ) |
$ | (5,889 | ) |
$ | (5,554 | ) |
|
Offsetting Assets and Liabilities
The Company has netting arrangements in place with all of its derivative counterparties pursuant to standard documentation developed by the International Swaps and Derivatives Association. Under GAAP, if the Company has a valid right of offset, it may offset the related asset and liability and report the net amount. The Company presents interest rate swaps, swaptions and Treasury futures assets and liabilities on a gross basis in its consolidated balance sheets, but in the case of interest rate swaps beginning in 2018, net of variation margin. The Company presents TBA assets and liabilities on a net basis in its consolidated balance sheets. The Company presents repurchase agreements in this section even though they are not derivatives because they are subject to master netting arrangements. However, repurchase agreements are presented on a gross basis. Additionally, the Company does not offset financial assets and liabilities with the associated cash collateral on the consolidated balance sheets.
88
The following tables present information about the Company’s assets and liabilities that are subject to master netting arrangements or similar agreements and can potentially be offset on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands):
Offsetting Assets and Liabilities
As of December 31, 2019
Gross Amounts of Recognized Assets or Liabilities |
Gross Amounts Offset in the Consolidated Balance Sheet |
Net Amounts of Assets and Liabilities Presented in the Consolidated Balance Sheet |
Gross Amounts Not Offset in the Consolidated Balance Sheet |
Net Amount |
||||||||||||||
Financial Instruments |
Cash Collateral Received (Pledged) |
|||||||||||||||||
Assets |
||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate swaps |
$ | 17,921 | $ | — | $ | 17,921 | $ | (17,921 | ) |
$ | — | $ | — | |||||
Interest rate swaptions |
368 | — | 368 | (368 | ) |
— | — | |||||||||||
TBAs |
2,297 | (2,297 | ) |
— | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Total Assets |
$ | 20,586 | $ | (2,297 | ) |
$ | 18,289 | $ | (18,289 | ) |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
Liabilities |
||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase agreements |
$ | 2,337,638 | $ | — | $ | 2,337,638 | $ | (2,276,251 | ) |
$ | (61,387 | ) |
$ | — | ||||
Interest rate swaps |
10,140 | — | 10,140 | (10,140 | ) |
— | — | |||||||||||
TBAs |
2,720 | (2,297 | ) |
423 | (423 | ) |
— | — | ||||||||||
Treasury futures |
1,774 | — | 1,774 | 3,876 | (5,650 | ) |
— | |||||||||||
Total Liabilities |
$ | 2,352,272 | $ | (2,297 | ) |
$ | 2,349,975 | $ | (2,282,938 | ) |
$ | (67,037 | ) |
$ | — | |||
As of December 31, 2018
Gross Amounts of Recognized Assets or Liabilities |
Gross Amounts Offset in the Consolidated Balance Sheet |
Net Amounts of Assets and Liabilities Presented in the Consolidated Balance Sheet |
Gross Amounts Not Offset in the Consolidated Balance Sheet |
Net Amount |
||||||||||||||
Financial Instruments |
Cash Collateral Received (Pledged) |
|||||||||||||||||
Assets |
||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate swaps |
$ | 23,176 | $ | — | $ | 23,176 | $ | (23,176 | ) |
$ | — | $ | — | |||||
Interest rate swaptions |
170 | — | 170 | (170 | ) |
— | — | |||||||||||
TBAs |
349 | (181 | ) |
168 | (168 | ) |
— | — | ||||||||||
Treasury futures |
744 | — | 744 | (57 | ) |
(687 | ) |
— | ||||||||||
Total Assets |
$ | 24,439 | $ | (181 | ) |
$ | 24,258 | $ | (23,571 | ) |
$ | (687 | ) |
$ | — | |||
Liabilities |
||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase agreements |
$ | 1,598,592 | $ | — | $ | 1,598,592 | $ | (1,591,094 | ) |
$ | (7,498 | ) |
$ | — | ||||
Interest rate swaps |
3,816 | — | 3,816 | (3,816 | ) |
— | — | |||||||||||
TBAs |
181 | (181 | ) |
— | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Treasury futures |
— | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
Total Liabilities |
$ | 1,602,589 | $ | (181 | ) |
$ | 1,602,408 | $ | (1,594,910 | ) |
$ | (7,498 | ) |
$ | — | |||
89
Note 9 – Fair Value
Fair Value Measurements
ASC 820 defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. ASC 820 clarifies that fair value should be based on the assumptions market participants would use when pricing an asset or liability and establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the information used to develop those assumptions. The fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority to quoted prices available in active markets (i.e., observable inputs) and the lowest priority to data lacking transparency (i.e., unobservable inputs). Additionally, ASC 820 requires an entity to consider all aspects of nonperformance risk, including the entity’s own credit standing, when measuring the fair value of a liability.
ASC 820 establishes a three level hierarchy to be used when measuring and disclosing fair value. An instrument’s categorization within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of significant input to its valuation. Following is a description of the three levels:
| Level 1 | inputs are quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities as of the measurement date under current market conditions. Additionally, the entity must have the ability to access the active market and the quoted prices cannot be adjusted by the entity. |
| Level 2 | inputs include quoted prices in active markets for similar assets or liabilities; quoted prices in inactive markets for identical or similar assets or liabilities; or inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means for substantially the full-term of the assets or liabilities. |
| Level 3 | unobservable inputs are supported by little or no market activity. The unobservable inputs represent the assumptions that management believes market participants would use to price the assets and liabilities, including risk. Generally, Level 3 assets and liabilities are valued using pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies, or similar techniques that require significant judgment or estimation. |
Recurring Fair Value Measurements
The following is a description of the methods used to estimate the fair values of the Company’s assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis, as well as the basis for classifying these assets and liabilities as Level 2 or 3 within the fair value hierarchy. The Company’s valuations consider assumptions that it believes a market participant would consider in valuing the assets and liabilities, the most significant of which are disclosed below. The Company reassesses and periodically adjusts the underlying inputs and assumptions used in the valuations for recent historical experience, as well as for current and expected relevant market conditions.
RMBS
The Company holds a portfolio of RMBS that are classified as available for sale and are carried at fair value in the consolidated balance sheets. The Company determines the fair value of its RMBS based upon prices obtained from third-party pricing providers. The third-party pricing providers use pricing models that generally incorporate such factors as coupons, primary and secondary mortgage rates, rate reset period, issuer, prepayment speeds, credit enhancements and expected life of the security. As a result, the Company classified 100% of its RMBS as Level 2 fair value assets at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018.
MSRs
The Company, through its subsidiary Aurora, holds a portfolio of MSRs that are reported at fair value in the consolidated balance sheets. The Company uses a discounted cash flow model to estimate the fair value of these assets. Although MSR transactions are observable in the marketplace, the valuation includes unobservable market data inputs (prepayment speeds, delinquency levels, costs to service and discount rates). As a result, the Company classified 100% of its MSRs as Level 3 fair value assets at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018.
90
Derivative Instruments
The Company enters into a variety of derivative instruments as part of its economic hedging strategies. The Company executes interest rate swaps, swaptions, TBAs and treasury futures. The Company utilizes third-party pricing providers to value its derivative instruments. As a result, the Company classified 100% of its derivative instruments as Level 2 fair value assets and liabilities at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018.
Both the Company and the derivative counterparties under their netting arrangements are required to post cash collateral based upon the net underlying market value of the Company’s open positions with the counterparties. Posting of cash collateral typically occurs daily, subject to certain dollar thresholds. Due to the existence of netting arrangements, as well as frequent cash collateral posting at low posting thresholds, credit exposure to the Company and/or counterparties is considered materially mitigated. The Company’s interest rate swaps and Treasury futures contracts are required to be cleared on an exchange, which further mitigates, but does not eliminate, credit risk. Based on the Company’s assessment, there is no requirement for any additional adjustment to derivative valuations specifically for credit.
The following tables present the Company’s assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands).
Recurring Fair Value Measurements
As of December 31, 2019
Level 1 |
Level 2 |
Level 3 |
Carrying Value |
|||||||||
Assets |
||||||||||||
RMBS |
||||||||||||
Fannie Mae |
$ | — | $ | 1,619,233 | $ | — | $ | 1,619,233 | ||||
Freddie Mac |
— | 727,851 | — | 727,851 | ||||||||
CMOs |
— | 129,083 | — | 129,083 | ||||||||
Private Label MBS |
— | 32,193 | — | 32,193 | ||||||||
RMBS total |
— | 2,508,360 | — | 2,508,360 | ||||||||
Derivative assets |
||||||||||||
Interest rate swaps |
— | 17,921 | — | 17,921 | ||||||||
Interest rate swaptions |
— | 368 | — | 368 | ||||||||
Derivative assets total |
— | 18,289 | — | 18,289 | ||||||||
Servicing related assets |
— | — | 291,111 | 291,111 | ||||||||
Total Assets |
$ | — | $ | 2,526,649 | $ | 291,111 | $ | 2,817,760 | ||||
Liabilities |
||||||||||||
Derivative liabilities |
||||||||||||
Interest rate swaps |
— | 10,140 | — | 10,140 | ||||||||
TBAs |
— | 423 | — | 423 | ||||||||
Treasury futures |
— | 1,774 | — | 1,774 | ||||||||
Derivative liabilities total |
— | 12,337 | — | 12,337 | ||||||||
Total Liabilities |
$ | — | $ | 12,337 | $ | — | $ | 12,337 | ||||
91
As of December 31, 2018
Level 1 |
Level 2 |
Level 3 |
Carrying Value |
|||||||||
Assets |
||||||||||||
RMBS |
||||||||||||
Fannie Mae |
$ | — | $ | 1,178,164 | $ | — | $ | 1,178,164 | ||||
Freddie Mac |
— | 459,008 | — | 459,008 | ||||||||
CMOs |
— | 103,500 | — | 103,500 | ||||||||
Private Label MBS |
— | 29,438 | — | 29,438 | ||||||||
RMBS total |
— | 1,770,110 | — | 1,770,110 | ||||||||
Derivative assets |
||||||||||||
Interest rate swaps |
— | 23,176 | — | 23,176 | ||||||||
Interest rate swaptions |
— | 170 | — | 170 | ||||||||
TBAs |
— | 168 | — | 168 | ||||||||
Treasury futures |
— | 744 | — | 744 | ||||||||
Derivative assets total |
— | 24,258 | — | 24,258 | ||||||||
Servicing related assets |
— | — | 294,907 | 294,907 | ||||||||
Total Assets |
$ | — | $ | 1,794,368 | $ | 294,907 | $ | 2,089,275 | ||||
Liabilities |
||||||||||||
Derivative liabilities |
||||||||||||
Interest rate swaps |
— | 3,816 | — | 3,816 | ||||||||
Derivative liabilities total |
— | 3,816 | — | 3,816 | ||||||||
Total Liabilities |
$ | — | $ | 3,816 | $ | — | $ | 3,816 | ||||
The Company may be required to measure certain assets or liabilities at fair value from time to time. These periodic fair value measures typically result from application of certain impairment measures under GAAP. These items would constitute nonrecurring fair value measures under ASC 820. As of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company did not have any assets or liabilities measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis in the periods presented.
Level 3 Assets and Liabilities
The valuation of Level 3 assets and liabilities requires significant judgment by management. The Company estimates the fair value of its Servicing Related Assets based on internal pricing models rather than quotations, and compares the results of these internal models against the results from models generated by third-party pricing providers. The third-party pricing providers and management rely on inputs such as market price quotations from market makers (either market or indicative levels), original transaction price, recent transactions in the same or similar instruments, and changes in financial ratios or cash flows to determine fair value. Level 3 instruments may also be discounted to reflect illiquidity and/or non-transferability, with the amount of such discount estimated by third-party pricing providers and management in the absence of market information. Assumptions used by third-party pricing providers and management due to lack of observable inputs may significantly impact the resulting fair value and, therefore, the Company’s consolidated financial statements.The Company’s management reviews all valuations that are based on pricing information received from third-party pricing providers. As part of this review, prices are compared against other pricing or input data points in the marketplace, along with internal valuation expertise, to ensure the pricing is reasonable.
Changes in market conditions, as well as changes in the assumptions or methodology used to determine fair value, could result in a significant change to estimated fair values. The determination of estimated cash flows used in pricing models is inherently subjective and imprecise. It should be noted that minor changes in assumptions or estimation methodologies can have a material effect on these derived or estimated fair values, and that the fair values reflected below are indicative of the interest rate and credit spread environments as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 and do not take into consideration the effects of subsequent changes in market or other factors.
92
The tables below present the reconciliation for the Company’s Level 3 assets (Servicing Related Assets) measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands):
Level 3 Fair Value Measurements
As of December 31, 2019
Level 3(A) |
|||
MSRs |
|||
Balance at December 31, 2018 |
$ | 294,907 | |
Purchases, sales and principal paydowns: |
|||
Purchases |
104,969 | ||
Other changes(B) |
(1,993 | ) |
|
Purchases, sales and principal paydowns: |
$ | 102,976 | |
Changes in Fair Value due to: |
|||
Changes in valuation inputs or assumptions used in valuation model |
(43,737 | ) |
|
Other changes in fair value(C) |
(63,035 | ) |
|
Unrealized gain (loss) included in Net Income |
$ | (106,772 | ) |
Balance at December 31, 2019 |
$ | 291,111 | |
As of December 31, 2018
Level 3(A) |
|||
MSRs |
|||
Balance at December 31, 2017 |
$ | 122,806 | |
Purchases, sales and principal paydowns: |
|||
Purchases |
178,192 | ||
Other changes(B) |
(2,518 | ) |
|
Purchases, sales and principal paydowns: |
$ | 175,674 | |
Changes in Fair Value due to: |
|||
Changes in valuation inputs or assumptions used in valuation model |
14,648 | ||
Other changes in fair value(C) |
(18,221 | ) |
|
Unrealized gain (loss) included in Net Income |
$ | (3,573 | ) |
Balance at December 31, 2018 |
$ | 294,907 | |
| (A) | Includes the recapture agreement for each respective pool. |
| (B) | Represents purchase price adjustments, principally contractual prepayment protection, and changes due to the Company’s repurchase of the underlying collateral. |
| (C) | Represents changes due to realization of expected cash flows and estimated MSR runoff. |
93
The tables below present information about the significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of the Company’s Servicing Related Assets classified as Level 3 fair value assets as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands):
Fair Value Measurements
As of December 31, 2019
Fair Value |
Valuation Technique |
Unobservable Input(A) |
Range |
Weighted Average |
|||||||||||
MSRs |
|||||||||||||||
Conventional |
$ | 263,357 | Discounted cash flow |
Constant prepayment speed |
7.8% - 21.1% |
13.2 | % |
||||||||
Uncollected payments |
0.4% - 0.8% |
0.7 | % |
||||||||||||
Discount rate |
7.3 | % |
|||||||||||||
Annual cost to service, per loan |
$ | 73 | |||||||||||||
Government |
$ | 27,754 | Discounted cash flow |
Constant prepayment speed |
6.5% - 19.5% |
13.6 | % |
||||||||
Uncollected payments |
2.2% - 9.0% |
2.8 | % |
||||||||||||
Discount rate |
9.4 | % |
|||||||||||||
Annual cost to service, per loan |
$ | 112 | |||||||||||||
TOTAL |
$ | 291,111 | |||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2018
Fair Value |
Valuation Technique |
Unobservable Input(A) |
Range |
Weighted Average |
|||||||||||
MSRs |
|||||||||||||||
Conventional |
$ | 254,691 | Discounted cash flow |
Constant prepayment speed |
4.5% - 20.6% |
9.1 | % |
||||||||
Uncollected payments |
0.5% - 11.7% |
0.9 | % |
||||||||||||
Discount rate |
9.3 | % |
|||||||||||||
Annual cost to service, per loan |
$ | 70 | |||||||||||||
Government |
$ | 40,216 | Discounted cash flow |
Constant prepayment speed |
6.3% - 17.9% |
8.9 | % |
||||||||
Uncollected payments |
3.1% - 12.4% |
4.2 | % |
||||||||||||
Discount rate |
12.0 | % |
|||||||||||||
Annual cost to service, per loan |
$ | 111 | |||||||||||||
TOTAL |
$ | 294,907 | |||||||||||||
| (A) | Significant increases (decreases) in any of the inputs in isolation may result in significantly lower (higher) fair value measurements. A change in the assumption used for discount rates may be accompanied by a directionally similar change in the assumption used for the probability of uncollected payments and a directionally opposite change in the assumption used for prepayment rates. |
Fair Value of Financial Assets and Liabilities
In accordance with ASC 820, the Company is required to disclose the fair value of financial instruments, both assets and liabilities recognized and not recognized in the consolidated balance sheets, for which fair value can be estimated. The following describes the Company’s methods for estimating the fair value for financial instruments.
| • | RMBS available for sale securities, Servicing Related Assets, derivative assets and derivative liabilities are recurring fair value measurements; carrying value equals fair value. See discussion of valuation methods and assumptions within the “Fair Value Measurements” section of this footnote. |
| • | Cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash have a carrying value which approximates fair value because of the short maturities of these instruments. |
| • | The carrying value of repurchase agreements and corporate debt that mature in less than one year generally approximates fair value due to the short maturities. The Company does not hold any repurchase agreements that are considered long-term. |
94
Corporate debt that matures in more than one year consists solely of financing secured by Aurora’s Servicing Related Assets. Approximately ninety percent of the debt is revolving and bears interest at adjustable rates, while the remaining portion is amortizing and bears interest at a fixed rate. Due to the amount of the fixed debt relative to that of all of the corporate debt, the Company considers that the amount of the corporate debt generally approximates fair value.
Repurchased loans held for sale consist primarily of Ginnie Mae buyouts that the Company has purchased at par plus accrued interest. These loans are held for sale and valued at the lower of cost or fair market value. Carrying value of the loans approximates fair value since substantially all such loans are promptly resold for a price that approximates the amount for which they were repurchased by the Company, net of any amortization.
Note 10 — Commitments and Contingencies
The commitments and contingencies of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 are described below.
Management Agreement
The Company pays the Manager a quarterly management fee, calculated and payable quarterly in arrears, equal to the product of one quarter of the 1.5% management fee annual rate and the stockholders’ equity, adjusted as set forth in the Management Agreement as of the end of such fiscal quarter. The Manager relies on resources of Freedom Mortgage to provide the Manager with the necessary resources to conduct the Company’s operations. For further discussion regarding the management fee, see Note 7.
Legal and Regulatory
From time to time, the Company may be subject to potential liability under laws and government regulations and various claims and legal actions arising in the ordinary course of business. Liabilities are established for legal claims when payments associated with the claims become probable and the costs can be reasonably estimated. The actual costs of resolving legal claims may be substantially higher or lower than the amounts established for those claims. Based on information currently available, management is not aware of any legal or regulatory claims that would have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements, and, therefore, no accrual is required as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018.
Commitments to Purchase/Sell RMBS
As of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company held forward TBA purchase and sale commitments, respectively, with counterparties, which are forward Agency RMBS trades, whereby the Company committed to purchasing or selling a pool of securities at a particular interest rate. As of the date of the trade, the mortgage-backed securities underlying the pool that will be delivered to fulfill a TBA trade are not yet designated. The securities are typically “to be announced” 48 hours prior to the established trade settlement date.
As of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company was not obligated to purchase or sell any Agency RMBS securities.
Acknowledgment Agreements
In connection with the Fannie Mae MSR Financing Facility (as defined below) entered into by Aurora and QRS III, those parties also entered into an acknowledgment agreement with Fannie Mae. Pursuant to that agreement, Fannie Mae consented to the pledge by Aurora and QRS III of their respective interests in MSRs for loans owned or securitized by Fannie Mae, and acknowledged the security interest of the lender in those MSRs. See Note 12—Notes Payable for a description of the Fannie Mae MSR Financing Facility and the financing facility it replaced.
In connection with the MSR Revolver (as defined below), Aurora, QRS V, and the lender, with a limited joinder by the Company, entered into an acknowledgement agreement with Freddie Mac pursuant to which Freddie Mac consented to the pledge of the Freddie Mac MSRs securing the MSR Revolver. Aurora and the lender also entered into a consent agreement with Freddie Mac pursuant to which Freddie Mac consented to the pledge of Aurora’s rights to reimbursement for advances on the underlying loans. See Note 12—Notes Payable for a description of the MSR Revolver.
95
Note 11 – Repurchase Agreements
The Company had outstanding approximately $2,337.6 million and $1,598.6 million of borrowings under its repurchase agreements as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. The Company’s obligations under these agreements had weighted average remaining maturities of 42 days and 38 days as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. RMBS and cash have been pledged as collateral under these repurchase agreements (see Note 4).
The repurchase agreements had the following remaining maturities and weighted average rates as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands):
Repurchase Agreements Characteristics
As of December 31, 2019
Repurchase Agreements |
Weighted Average Rate |
|||||
Less than one month |
$ | 928,646 | 2.24 | % |
||
One to three months |
1,231,422 | 1.94 | % |
|||
Greater than three months |
177,570 | 1.98 | % |
|||
Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 2,337,638 | 2.06 | % |
||
As of December 31, 2018
Repurchase Agreements |
Weighted Average Rate |
|||||
Less than one month |
$ | 776,666 | 2.51 | % |
||
One to three months |
821,926 | 2.56 | % |
|||
Greater than three months |
— | — | % |
|||
Total/Weighted Average |
$ | 1,598,592 | 2.54 | % |
||
There were no overnight or demand securities as of December 31, 2019 or December 31, 2018.
Note 12 – Notes Payable
In September 2016, Aurora and QRS III entered into a loan and security agreement (the “MSR Financing Facility”), pursuant to which Aurora and QRS III pledged their respective rights in all existing and future MSRs for loans owned or securitized by Fannie Mae to secure borrowings up to a maximum of $25.0 million outstanding at any one time, subsequently amended to $100 million with the revolving period extended to December 20, 2020. During the revolving period, borrowings bear interest at a rate equal to a spread over one-month LIBOR subject to a floor. At the end of the revolving period, the outstanding amount will be converted to a three-year term loan that will bear interest at a rate calculated at a spread over the rate for one-year interest rate swaps. The revolving period may be further extended by agreement. The Company has previously guaranteed repayment of all indebtedness under the MSR Financing Facility. Approximately $96.5 million was outstanding under the MSR Financing Facility at December 31, 2018. There was no outstanding balance under the MSR Financing Facility at December 31, 2019 because the MSR Financing Facility and the related acknowledgement agreement with Fannie Mae were terminated and replaced in September 2019.
In May 2017, the Company, Aurora and QRS IV obtained a $20.0 million loan (the “MSR Term Facility”) secured by the pledge of Aurora’s Ginnie Mae MSRs and the Company’s ownership interest in QRS IV. The loan bears interest at a fixed rate of 6.18% per annum, amortizes on a ten-year amortization schedule and is due on May 18, 2022. In October 2019, the MSR Term Facility was amended to provide an additional $10 million of borrowing capacity to finance servicing advances on the Ginnie Mae MSRs pledged under the facility. Amounts available to finance servicing advances may be borrowed and reborrowed from time to time and bear interest at a floating rate equal to LIBOR plus a margin. The MSR Term Facility, including the revolving facility for servicing advances, is scheduled to terminate on May 18, 2022.
In July 2018, the Company, Aurora and QRS V (collectively with Aurora and the Company, the “Borrowers”) entered into a $25.0 million revolving credit facility (the “MSR Revolver”) pursuant to which
96
Aurora pledged all of its existing and future MSRs on loans owned or securitized by Freddie Mac. The term of the MSR Revolver is 364 days with the Borrowers’ option for two renewals for similar terms followed by a one-year term out feature with a 24-month amortization schedule. The MSR Revolver was upsized to $45.0 million in September 2018. The Company also has the ability to request up to an additional $5.0 million of borrowings. On April 2, 2019, the Borrowers entered into an amendment that increased the maximum amount of the MSR Revolver to $100.0 million. On June 5, 2019, the term of the MSR Revolver was renewed to July 30, 2020. Amounts borrowed bear interest at an adjustable rate equal to a spread above one-month LIBOR. Approximately $55.5 million and $45.0 million was outstanding under the MSR Revolver at December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively.
In September 2019, Aurora and QRS III entered into a loan and security agreement (the “Fannie Mae MSR Financing Facility”), to replace the MSR Financing Facility. Under the Fannie Mae MSR Facility, Aurora and QRS III pledged their respective rights in all existing and future MSRs for loans owned or securitized by Fannie Mae to secure borrowings outstanding from time to time. The maximum credit amount outstanding at any one time under the facility is $200.0 million of which $100.0 million is committed. Borrowings bear interest at a rate equal to a spread over one-month LIBOR subject to a floor. The term of the facility is 24 months subject to extension for an additional 12 months if the lender agrees beginning in the 20th month. The Company has guaranteed repayment of all indebtedness under the Fannie Mae MSR Financing Facility. Approximately $97.0 million was outstanding under the Fannie Mae MSR Financing Facility at December 31, 2019.
The outstanding long-term borrowings had the following remaining maturities as of the dates indicated (dollars in thousands):
Long-Term Borrowings Repayment Characteristics
As of December 31, 2019
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
2023 |
2024 |
Total |
|||||||||||||
MSR Term Facility |
||||||||||||||||||
Borrowings under MSR Term Facility |
$ | 2,000 | $ | 2,000 | $ | 10,996 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 14,996 | ||||||
MSR Revolver |
||||||||||||||||||
Borrowings under MSR Revolver Facility |
$ | — | $ | 55,500 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 55,500 | ||||||
Fannie Mae MSR Financing Facility |
||||||||||||||||||
Borrowings under Fannie Mae MSR Financing Facility |
$ | — | $ | 97,000 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 97,000 | ||||||
Total |
$ | 2,000 | $ | 154,500 | $ | 10,996 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 167,496 | ||||||
As of December 31, 2018
2019 |
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
2023 |
Total |
|||||||||||||
MSR Term Facility |
||||||||||||||||||
Borrowings under MSR Term Facility |
$ | 2,000 | $ | 2,000 | $ | 2,000 | $ | 10,996 | $ | — | $ | 16,996 | ||||||
MSR Financing Facility |
||||||||||||||||||
Borrowings under MSR Financing Facility |
$ | — | $ | 6,195 | $ | 90,305 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 96,500 | ||||||
MSR Revolver |
||||||||||||||||||
Borrowings under MSR Revolver Facility |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 45,000 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 45,000 | ||||||
Total |
$ | 2,000 | $ | 8,195 | $ | 137,305 | $ | 10,996 | $ | — | $ | 158,496 | ||||||
97
Note 13 – Receivables and Other Assets
The assets comprising “Receivables and other assets” as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 are summarized in the following table (dollars in thousands):
Receivables and Other Assets
December 31, 2019 |
December 31, 2018 |
|||||
Servicing advances |
$ | 16,647 | $ | 9,942 | ||
Interest receivable |
8,222 | 6,540 | ||||
Deferred tax receivable |
14,744 | — | ||||
Repurchased loans held for sale |
3,839 | 2,814 | ||||
Other receivables |
3,632 | 4,687 | ||||
Total other assets |
$ | 47,084 | $ | 23,983 | ||
The Company only records as an asset those servicing advances that the Company deems recoverable.
Note 14 – Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities
The liabilities comprising “Accrued expenses and other liabilities” as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 are summarized in the following table (dollars in thousands):
Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities
December 31, 2019 |
December 31, 2018 |
|||||
Accrued interest payable |
$ | 10,779 | $ | 8,056 | ||
Net current tax payable |
— | 152 | ||||
Net deferred tax payable |
— | 2,078 | ||||
Accrued expenses |
4,809 | 5,259 | ||||
Total accrued expenses and other liabilities |
$ | 15,588 | $ | 15,545 | ||
Note 15 – Summarized Quarterly Results (Unaudited)
The following tables present information about the Company’s quarterly operating results for the periods indicated below (dollars in thousands):
Summarized Quarterly Results
2019 |
||||||||||||
December 31, |
September 30, |
June 30, |
March 31, |
|||||||||
Income |
||||||||||||
Interest income |
$ | 19,770 | $ | 19,383 | $ | 17,216 | $ | 16,969 | ||||
Interest expense |
13,499 | 12,635 | 11,707 | 10,744 | ||||||||
Net interest income |
6,271 | 6,748 | 5,509 | 6,225 | ||||||||
Servicing fee income |
19,318 | 18,687 | 18,362 | 17,188 | ||||||||
Servicing costs |
5,096 | 4,102 | 4,103 | 3,821 | ||||||||
Net servicing income |
14,222 | 14,585 | 14,259 | 13,367 | ||||||||
Other income (loss) |
||||||||||||
Realized gain (loss) on RMBS, available-for-sale, net |
627 | 275 | — | — | ||||||||
Realized loss on derivatives, net |
(17,148 | ) |
12,627 | (365 | ) |
(7,476 | ) |
|||||
Realized gain (loss) on acquired assets, net |
(28 | ) |
54 | — | — | |||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives, net |
3,357 | (2,133 | ) |
(3,819 | ) |
(8,272 | ) |
|||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on investments in Servicing Related Assets |
1,959 | (37,514 | ) |
(44,042 | ) |
(27,175 | ) |
|||||
Total Income (Loss) |
9,260 | (5,358 | ) |
(28,458 | ) |
(23,331 | ) |
|||||
98
2019 |
||||||||||||
December 31, |
September 30, |
June 30, |
March 31, |
|||||||||
Expenses |
||||||||||||
General and administrative expense |
1,352 | 1,194 | 1,138 | 963 | ||||||||
Management fee to affiliate |
1,999 | 2,042 | 1,934 | 1,809 | ||||||||
Total Expenses |
3,351 | 3,236 | 3,072 | 2,772 | ||||||||
Income (Loss) Before Income Taxes |
5,909 | (8,594 | ) |
(31,530 | ) |
(26,103 | ) |
|||||
Provision for (Benefit from) corporate business taxes |
(1,842 | ) |
(5,643 | ) |
(4,372 | ) |
(4,965 | ) |
||||
Net Income (Loss) |
7,751 | (2,951 | ) |
(27,158 | ) |
(21,138 | ) |
|||||
Net (income) loss allocated to noncontrolling interests in Operating Partnership |
(127 | ) |
43 | 438 | 349 | |||||||
Dividends on preferred stock |
2,460 | 2,459 | 2,593 | 1,841 | ||||||||
Net Income (Loss) Applicable to Common Stockholders |
$ | 5,164 | $ | (5,367 | ) |
$ | (29,313 | ) |
$ | (22,630 | ) |
|
Net Income (Loss) Per Share of Common Stock |
||||||||||||
Basic |
$ | 0.31 | $ | (0.32 | ) |
$ | (1.75 | ) |
$ | (1.36 | ) |
|
Diluted |
$ | 0.31 | $ | (0.32 | ) |
$ | (1.75 | ) |
$ | (1.36 | ) |
|
Weighted Average Number of Shares of Common Stock Outstanding |
||||||||||||
Basic |
16,797,523 | 16,883,816 | 16,776,472 | 16,646,114 | ||||||||
Diluted |
16,810,312 | 16,896,605 | 16,789,261 | 16,654,370 | ||||||||
2018 |
||||||||||||
December 31, |
September 30, |
June 30, |
March 31, |
|||||||||
Income |
||||||||||||
Interest income |
$ | 16,958 | $ | 15,323 | $ | 12,019 | $ | 13,415 | ||||
Interest expense |
10,385 | 9,257 | 7,324 | 7,543 | ||||||||
Net interest income |
6,573 | 6,066 | 4,695 | 5,872 | ||||||||
Servicing fee income |
16,574 | 14,017 | 11,535 | 8,650 | ||||||||
Servicing costs |
3,528 | 2,981 | 2,394 | 1,712 | ||||||||
Net servicing income |
13,046 | 11,036 | 9,141 | 6,938 | ||||||||
Other income (loss) |
||||||||||||
Realized loss on RMBS, net |
(2,932 | ) |
(428 | ) |
(121 | ) |
(4,881 | ) |
||||
Realized gain (loss) on derivatives, net |
(3,162 | ) |
(707 | ) |
(2,033 | ) |
13 | |||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives, net |
(30,937 | ) |
8,807 | 6,009 | 19,626 | |||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on investments in MSRs |
(21,924 | ) |
6,218 | (365 | ) |
12,498 | ||||||
Total Income (Loss) |
(39,336 | ) |
30,992 | 17,326 | 40,066 | |||||||
Expenses |
||||||||||||
General and administrative expense |
962 | 1,165 | 937 | 877 | ||||||||
Management fee to affiliate |
1,649 | 1,599 | 1,383 | 1,315 | ||||||||
Total Expenses |
2,611 | 2,764 | 2,320 | 2,192 | ||||||||
Income Before Income Taxes |
(41,947 | ) |
28,228 | 15,006 | 37,874 | |||||||
(Benefit from) provision for corporate business taxes |
(3,137 | ) |
729 | 1,161 | 2,635 | |||||||
Net Income (Loss) |
(38,810 | ) |
27,499 | 13,845 | 35,239 | |||||||
Net income (loss) allocated to noncontrolling interests in Operating Partnership |
505 | (364 | ) |
(173 | ) |
(456 | ) |
|||||
Dividends on preferred stock |
1,395 | 1,372 | 1,317 | 1,213 | ||||||||
99
2018 |
||||||||||||
December 31, |
September 30, |
June 30, |
March 31, |
|||||||||
Net Income (Loss) Applicable to Common Stockholders |
$ | (39,700 | ) |
$ | 25,763 | $ | 12,355 | $ | 33,570 | |||
Net Income (Loss) Per Share of Common Stock |
— | — | — | — | ||||||||
Basic |
$ | (2.42 | ) |
$ | 1.62 | $ | 0.91 | $ | 2.64 | |||
Diluted |
$ | (2.42 | ) |
$ | 1.62 | $ | 0.91 | $ | 2.64 | |||
Weighted Average Number of Shares of Common Stock Outstanding |
||||||||||||
Basic |
16,382,914 | 15,864,774 | 13,616,461 | 12,713,265 | ||||||||
Diluted |
16,391,170 | 15,873,030 | 13,624,676 | 12,721,464 | ||||||||
Basic and diluted net income (loss) per share of common stock are computed independently based on the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during each period. Accordingly, the sum of the quarterly net income (loss) per share amounts may not agree to the total for the year.
Note 16 – Income Taxes
The Company elected to be taxed as a REIT under Code Sections 856 through 860 beginning with its short taxable year ended December 31, 2013. As a REIT, the Company generally will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax to the extent that it distributes its taxable income to its stockholders. To maintain qualification as a REIT, the Company must distribute at least 90% of its annual REIT taxable income to its stockholders and meet certain other requirements such as assets it may hold, income it may generate and its stockholder composition. It is the Company’s policy to distribute all or substantially all of its REIT taxable income. To the extent there is any undistributed REIT taxable income at the end of a year, the Company can elect to distribute such shortfall within the next year as permitted by the Code.
Effective January 1, 2014, CHMI Solutions elected to be taxed as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes; prior to this date, CHMI Solutions was a disregarded entity for U.S. federal income tax purposes. CHMI Solutions has jointly elected with the Company, the ultimate beneficial owner of CHMI Solutions, to be treated as a TRS of the Company, and all activities conducted through CHMI Solutions and its wholly-owned subsidiary, Aurora, are subject to federal and state income taxes. CHMI Solutions files a consolidated tax return with Aurora and is fully taxed as a U.S. C-Corporation.
The state and local tax jurisdictions for which the Company is subject to tax filing obligations recognize the Company’s status as a REIT, and therefore, the Company generally does not pay income tax in such jurisdictions. CHMI Solutions and Aurora are subject to U.S. federal, state and local income taxes.
The components of the Company’s income tax expense (benefit) are as follows for the periods indicated below (dollars in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
|||||||
Current federal income tax expense (benefit) |
$ | — | $ | 116 | $ | (575 | ) |
||
Current state income tax expense (benefit) |
— | 35 | (62 | ) |
|||||
Deferred federal income tax expense (benefit) |
(15,360 | ) |
1,009 | 1,046 | |||||
Deferred state income tax expense (benefit) |
(1,462 | ) |
228 | 192 | |||||
Provision for (Benefit from) Corporate Business Taxes |
$ | (16,822 | ) |
$ | 1,388 | $ | 601 | ||
100
The following is a reconciliation of the statutory federal rate to the effective rate, for the periods indicated below (dollars in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, |
||||||||||||||||||
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
||||||||||||||||
Computed income tax (benefit) expense at federal rate |
$ | (12,665 | ) |
21.0 | % |
$ | 8,225 | 21.0 | % |
$ | 17,015 | 35.0 | % |
|||||
State taxes (benefit), net of federal tax, if applicable |
(1,213 | ) |
2.0 | % |
222 | 0.6 | % |
115 | 0.2 | % |
||||||||
Tax benefit due to federal rate change |
— | — | % |
— | — | % |
(431 | ) |
(0.9 | )% |
||||||||
Tax provision due to State tax rate change |
(249 | ) |
0.4 | % |
— | — | % |
— | — | % |
||||||||
Provision to return adjustment |
5 | (0.0 | )% |
181 | 0.5 | % |
(117 | ) |
(0.2 | )% |
||||||||
REIT income not subject to tax (benefit) |
(2,700 | ) |
4.5 | % |
(7,240 | ) |
(18.6 | )% |
(15,981 | ) |
(32.9 | )% |
||||||
Provision for (Benefit from) Corporate Business Taxes/Effective Tax Rate(A) |
$ | (16,822 | ) |
27.9 | % |
$ | 1,388 | 3.5 | % |
$ | 601 | 1.2 | % |
|||||
| (A) | The provision for income taxes is recorded at the TRS level. |
The Company’s consolidated balance sheets, at December 31, 2019, December 31, 2018 and December 31, 2017, contain the following current and deferred tax liabilities and assets, which are recorded at the TRS level (dollars in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
2019 |
2018 |
2017 |
|||||||
Income taxes payable |
|||||||||
Federal income taxes payable |
$ | — | $ | 116 | $ | — | |||
State and local income taxes payable |
— | 35 | — | ||||||
Income taxes payable |
$ | — | $ | 151 | $ | — | |||
December 31, 2019 |
December 31, 2018 |
December 31, 2017 |
|||||||
Deferred tax (assets) liabilities |
|||||||||
Deferred tax - organizational expenses |
$ | — | $ | (4 | ) |
$ | (10 | ) |
|
Deferred tax - mortgage servicing rights |
(13,045 | ) |
2,082 | 909 | |||||
Deferred tax - net operating loss |
(1,699 | ) |
— | (56 | ) |
||||
Total net deferred tax (assets) liabilities |
$ | (14,744 | ) |
$ | 2,078 | $ | 843 | ||
The deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2019, deferred tax liabilities as of December 31, 2018 and deferred tax liabilities as of December 31, 2017 were each primarily related to MSRs. No valuation allowance has been established at December 31, 2019, December 31, 2018 or December 31, 2017. As of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, deferred tax liabilities are included in “Accrued expenses and other liabilities” in the consolidated balance sheets.
On December 22, 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “TCJA”) was signed into law. The TCJA includes a number of significant changes to existing U.S. corporate income tax laws, most notably a reduction of the U.S. corporate income tax rate from 35 percent to 21 percent, effective January 1, 2018. The Company measures deferred tax assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates that will apply in the years in which the temporary differences are expected to be recovered or paid. Accordingly, the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities were remeasured to reflect the reduction in the U.S. corporate income tax rate, resulting in a $459,000 decrease in income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2017 and a corresponding decrease of the same amount in the Company’s deferred tax liabilities as of December 31, 2017.
Based on the Company’s evaluation, the Company has concluded that there are no significant uncertain tax positions requiring recognition in the Company’s consolidated financial statements. Additionally, there were no amounts accrued for penalties or interest as of or during the periods presented in these consolidated financial statements.
The Company’s 2018, 2017, 2016, 2015, 2014, 2013 and 2012 federal, state and local income tax returns remain open for examination by the relevant authorities.
Note 17 – Subsequent Events
Events subsequent to December 31, 2019 were evaluated and no additional events were identified requiring further disclosure in the consolidated financial statements.
101
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
None.
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures |
Disclosure Controls and Procedures. The Company’s President and Chief Executive Officer and the Company’s Chief Financial Officer have evaluated the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d -15(e) under the Exchange Act) as of the end of the period covered by this report. The Company’s disclosure controls and procedures are designed to provide reasonable assurance that information is recorded, processed, summarized and reported accurately and on a timely basis. Based on such evaluation, the Company’s President and Chief Executive Officer and the Company’s Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, as of the end of such period, the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures are effective.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. There have been no changes in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act) during the most recently completed fiscal quarter that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the Company’s principal executive and principal financial officers and effected by the Company’s board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with GAAP and includes those policies and procedures that:
| • | pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; |
| • | provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and |
| • | provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. |
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control - Integrated Framework, issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on our evaluation under the framework in the 2013 Internal Control-Integrated Framework, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2019.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect all misstatements. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risks that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Ernst & Young LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, has audited the financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and issued its report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, which is included herein.
102
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and subsidiaries’ internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and subsidiaries (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of income (loss), comprehensive income (loss), stockholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes and our report dated February 27, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
New York, New York
February 27, 2020
| Item 9B. | Other Information |
None
103
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Company’s Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A relating to its annual meeting of stockholders (the “Proxy Statement”), to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after December 31, 2019.
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after December 31, 2019.
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after December 31, 2019.
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after December 31, 2019.
| Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after December 31, 2019.
104
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
Documents filed as part of the report
The following documents are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K:
| 1. | Financial Statements. |
The consolidated financial statements of the Company, together with the independent registered public accounting firm’s report thereon, are set forth in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and are incorporated herein by reference. See “Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data,” filed herewith, for a list of financial statements.
| 2. | Financial Statement Schedule. |
All financial statement schedules have been omitted because the required information is not applicable or deemed not material, or the required information is presented in the consolidated financial statements and/or in the notes to the consolidated financial statements filed in response to Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| 3. | Exhibits. |
|
Exhibit
Number |
Description
|
|
Articles of Amendment and Restatement of Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to Amendment No. 2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-11 (Registration No. 333-188214) filed with the SEC on June 10, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amended and Restated Bylaws of Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to Amendment No. 2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-11 (Registration No. 333-188214) filed with the SEC on June 10, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Articles Supplementary designating the Company’s 8.20% Series A Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 8-A (File No. 001-36099) filed with the SEC on August 16, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Articles Supplementary classifying and designating 1,270,000 additional shares of the Company’s 8.20% Series A Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36099) filed with the SEC on April 5, 2018).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Articles Supplementary designating the Company’s 8.250% Series B Fixed-to-Floating Rate Cumulative Redeemable Preferred Stock (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 8-A (File No. 001-36099) filed with the SEC on February 8, 2019).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Specimen Common Stock Certificate (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Amendment No. 1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-11 (Registration No. 333-188214) filed with the SEC on May 29, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Registration Rights Agreement between Stanley Middleman and Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Schedule 13D filed with the SEC by Stanley Middleman on October 11, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Description of Registrant’s Securities.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Flow and Bulk Excess MSR Acquisition Agreement, dated October 9, 2013, by and between Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and Freedom Mortgage Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed with the SEC on October 15, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
105
|
Exhibit
Number |
Description
|
|
Pool 1 Excess MSR Acquisition and Recapture Agreement, dated October 9, 2013, by and between Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and Freedom Mortgage Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed with the SEC on October 15, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pool 2 Excess MSR Acquisition and Recapture Agreement, dated October 9, 2013, by and between Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and Freedom Mortgage Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed with the SEC on October 15, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amended and Restated Management Agreement, entered into as of September 24, 2013, by and among Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and its consolidated subsidiaries and Cherry Hill Mortgage Management, LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to Amendment No. 4 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-11 (Registration No. 333-188214) filed with the SEC on September 26, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amendment No. 1, entered into as of October 22, 2015, to Amended and Restated Management Agreement, entered into as of September 24, 2013, by and among Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and its consolidated subsidiaries and Cherry Hill Mortgage Management, LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36099) filed with the SEC on October 23, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Services Agreement, dated May 1, 2013, between Cherry Hill Mortgage Management, LLC and Freedom Mortgage Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to Amendment No. 1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-11 (Registration No. 333-188214) filed with the SEC on May 29, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form of Indemnification Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to Amendment No. 1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-11 (Registration No. 333-188214) filed with the SEC on May 29, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to Amendment No. 2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-11 (Registration No. 333-188214) filed with the SEC on June 10, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Agreement of Limited Partnership of Cherry Hill Operating Partnership, LP, dated as of April 25, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to Amendment No. 1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-11 (Registration No. 333-188214) filed with the SEC on May 29, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
First Amendment to Agreement of Limited Partnership of Cherry Hill Operating Partnership, LP, dated August 16, 2017 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36099) filed with the SEC on August 16, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Second Amendment to Agreement of Limited Partnership of Cherry Hill Operating Partnership, LP, dated April 5, 2018 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36099) filed with the SEC on April 5, 2018).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Third Amendment to Agreement of Limited Partnership of Cherry Hill Operating Partnership, LP, dated February 8, 2019 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36099) filed with the SEC on February 8, 2019).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form of LTIP Unit Vesting Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to Amendment No. 2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-11 (Registration No. 333-188214) filed with the SEC on June 10, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
106
|
Exhibit
Number |
Description
|
|
Form of Unrestricted Non-Employee Director Stock Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36099) filed with the SEC on January 27, 2014).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form of Restricted Non-Employee Director Stock Award Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36099) filed with the SEC on January 27, 2014).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Letter agreement, dated November 1, 2016, between Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and Freedom Mortgage Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-36099) filed with the SEC on March 16, 2018).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amendment, dated January 9, 2016, to the letter agreement, dated November 1, 2016, between Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation and Freedom Mortgage Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-36099) filed with the SEC on March 16, 2018).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Subsidiaries of Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consent of Ernst & Young LLP.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Certification of Principal Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (furnished herewith).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (furnished herewith).
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.INS*
|
XBRL Instance Document
|
|
|
|
|
101.SCH*
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema
|
|
|
|
|
101.CAL*
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase
|
|
|
|
|
101.DEF*
|
XBRL Taxonomy Definition Linkbase
|
|
|
|
|
101.LAB*
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase
|
|
|
|
|
101.PRE*
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase
|
| * | Filed herewith. |
| + | This document has been identified as a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
107
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
Cherry Hill Mortgage Investment Corporation
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date: February 27, 2020
|
By:
|
/s/ Jeffrey Lown II
|
|
|
|
Jeffrey Lown II
|
|
|
|
President and Chief Executive Officer
(Principal Executive Officer) |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
Date: February 27, 2020
|
By:
|
/s/ Jeffrey Lown II
|
|
|
|
Jeffrey Lown II
|
|
|
|
President and Chief Executive Officer
(Principal Executive Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
Date: February 27, 2020
|
By:
|
/s/ Michael Hutchby
|
|
|
|
Michael Hutchby
|
|
|
|
Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and Treasurer
|
|
|
|
(Principal Financial and Accounting Officer)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date: February 27, 2020
|
By:
|
/s/ Joseph Murin
|
|
|
|
Joseph Murin
|
|
|
|
Director
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date: February 27, 2020
|
By:
|
/s/ Regina M. Lowrie
|
|
|
|
Regina M. Lowrie
|
|
|
|
Director
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date: February 27, 2020
|
By:
|
/s/ Robert C. Mercer, Jr.
|
|
|
|
Robert C. Mercer, Jr.
|
|
|
|
Director
|
