Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - GENOCEA BIOSCIENCES, INC. | jan20198k.htm |

Next generation cancer immunotherapies 1

This presentation contains “forward-looking” statements that are within the meaning of federal securities laws and are based on our management’s beliefs and assumptions and on information currently available to management. Forward-looking statements include information concerning our possible or assumed future results of operations, business strategies, clinical trials and pre-clinical studies, regulatory approval of our product candidates, liquidity position and capital needs, financing plans, industry environment, potential growth opportunities, potential market opportunities and the effects of competition. Forward-looking statements include all statements that are not historical facts and can be identified by terms such as “anticipates,” “believes,” “expects,” “could,” “seeks,” “estimates,” “intends,” “may,” “plans,” “potential,” “predicts,” “projects,” “should,” “will,” “would” or similar expressions and the negatives of those terms. Forward-looking statements represent our management’s beliefs and assumptions only as of the date of this presentation. Our operations involve risks and uncertainties, many of which are outside our control, and any one of which, or combination of which, could materially affect our results of operations and whether the forward-looking statements ultimately prove to be correct. Factors that Disclaimer may materially affect our results of operations include, among other things, our ability to progress product candidates in preclinical and clinical trials, the ability of ATLAS™ to identify promising oncology vaccine and immunotherapy product candidates, the scope, rate and progress of our preclinical and clinical trials and other research and development activities, anticipated timing of IND applications and new clinical trials, the amount of funds that we may require to conduct our clinical trials for our product candidates, the timing of, and ability to, obtain and maintain necessary regulatory approvals for our product candidates, and those listed in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2018 and other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”). Except as required by law, we assume no obligation to update these forward-looking statements publicly, or to update the reasons actual results could differ materially from those anticipated in the forward-looking statements, even if new information becomes available in the future. You may get copies of our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q and our other SEC filings for free by visiting EDGAR on the SEC website at http://www.sec.gov. 2

Why Genocea? Revolutionary antigen discovery platform TARGETS MATTER PROPRIETARY PLATFORM GEN-009 GEN-011 Two differentiated, clinical stage programs Neoantigen Neoantigen vaccine cell therapy 2Q 2020 IND Significant near-term, Mid 2020 1H 2021 value-creating initial clinical data milestones initial clinical data 3

CORPORATE OVERVIEW Developing cancer therapies by unlocking the targets that matter most Proprietary platform that selects antigens enabling powerful anti-tumor immune responses Uniquely profiles tumor Avoids potential barriers to efficacy Selects the therapeutically and T cell repertoire + = relevant antigens Clinically validated platform Only platform to identify inhibigens (antigens of inhibitory/pro-tumor T cell responses) TARGETS MATTER Best-in-class clinical stage programs GEN-009: neoantigen vaccine GEN-011: neoantigen T cell therapy Data show unprecedented, broad Potential first-in-class (peripheral blood CD4+ and CD8+ immune responses to lymphocyte-derived, non-engineered) T cell therapy 99% of all immunized antigens for solid tumors Initial clinical data in mid 2020 IND in 2Q 2020 Combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) Initial clinical data in 1H 2021 4

Antigen Selection Drives Next Generation of IO Therapies Lessons from the IO Revolution: • Patient T cells can be unleashed to kill tumors • T cells that kill tumors attack neoantigens (tumor mutations that are often individualized) Opportunities: • ICI: improve response rates by amplifying anti- tumor T cell responses • T cell therapies: enhance target breadth and specificity Next Generation IO Therapy: • Directing T cells to the therapeutically relevant neoantigens 5

Antigen Selection: Our Critical Differentiator Uniquely identifying therapeutically relevant neoantigens Relevant both to tumor and patient immune system (surface-expressed and immunogenic) Groups antigens according to T cell responses (anti-tumor, TARGETS MATTER pro-tumor, or irrelevant) Comprehensive For any patient, any antigen type, any cancer, and both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells Well- protected Issued global patent families protect into 2030s Substantial know-how 6

Profiling Both T cell and Tumor Essential to Antigen Selection ATLAS: Antigens eliciting anti- tumor T cell responses Identifies T cell antigens relevant to Surface peptides recognized by both tumor T cells Relevance T cell receptor and immune Candidate antigen system – by design MHC molecule Surface-expressed peptides Tumor cell Personalized tumor mutations 7

Profiles Patients’ Tumor-specific T cell Repertoire For every candidate antigen: Tumor NGS analysis Unique Bacterial vectors sample plasmids expressing each Autologous candidate antigen dendritic cell • Multiplexed cytokine readout • Identifies CD4+ and CD8+ T cell Activation/ RESPONSE responses Suppression separately • ComparedANTIGEN with Autologous background T cell responses to irrelevant antigens Blood sample ATLAS Process 8

ATLAS Selects for Neoantigens that Drive Clinically Relevant Immune Responses Example: NSCLC patient; 52 mutations identified and profiled; IFNγ responses depicted CD8+ T cells CD4+ T cells Neoantigens – selected for therapy Not neoantigens – background-like responses Inhibitory neoantigens (inhibigens) – excluded from therapy Individual mutations Individual mutations • Neoantigens are ideal immunotherapy targets: surface-expressed and immunogenic, by definition • Inhibigens should not be included 9

IMPORTANT POTENTIAL IMPLICATIONS OF INHIBITORY RESPONSES Inclusion of Inhibigens Can Reverse Efficacy of a Protective Therapy Therapeutic vaccination with the Therapeutic vaccination with a The presence of inhibigens in an ATLAS-identified S10 neoantigen pool of ATLAS-identified otherwise protective vaccine is more protective than the inhibigens drives tumor completely abrogates protection published M27 neoantigen hyperprogression 3000 Vehicle (PBS) 1,600 (S10 + M30 + Trp2) Adjuvant only 1,000 M30 + Trp2 + adjuvant 1,400 (M27 + M30 + Trp2) 2500 ) ) ) Adjuvant only 3 (In01 + M30 + Trp2) + Adjuvant 3 M27 + M30 + Trp2 + adjuvant S10 + M30 + Trp2 + adjuvant 3 800 Inhib PoolIn01-04 + Adjuvant 1,200 (M30 + Trp2) 2000 1,000 Saline 600 1500 800 ** 600 1000 400 Tumor volume (mm 400 * Tumor volume(mm 500 Tumor volume (mm 200 **** 200 *** 0 0 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 0 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Day Immunization (D3, D10, D17) Day Day Vaccine Typical s.c. endpoint >3000mm3 D0 D3 D10 D17 B16F10 s.c. 10

IMPORTANT POTENTIAL IMPLICATIONS OF INHIBITORY RESPONSES Clinical Data Suggest ICI Failure May Be Influenced by Inhibigens 70% 60% 50% Non-responder Responder 40% Circle size represents tumor 30% mutational burden (TMB) % Stimulatory % 20% 10% 0% 0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% % Inhibitory Pre-treatment ATLAS screening of T cells from cancer patients identified the proportion of stimulatory (anti-tumor) and inhibitory neoantigen-specific T cell responses 11

ATLAS Enables Next Generation Immunotherapies Tailored to tumor and immune system • Neoantigens must be expressed by tumor and be immunogenic Next Generation IO Drive anti-tumor responses • Include neoantigens of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell • GEN-009: neoantigen responses vaccine • Rule out inhibigens • GEN-011: neoantigen T cell therapy Address important unmet patient needs • Other ATLAS-enabled • Potential to ensure more patients benefit from programs immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy and/or treat those who cannot respond to ICI • Potential predictive tool to select optimal therapy for patients 12

Drives Emerging Immunotherapy Pipeline Discovery Pre- IND Phase 1/2a Pivotal Status & Anticipated Milestones GEN-009 - Neoantigen vaccine • Pioneering immunogenicity: ASCO 2019 Top 10 IO study • Initial clinical data in mid 2020 GEN-011 - Neoantigen T cell therapy • IND in 2Q 2020 • Initial clinical data in 1H 2021 Toolbox of novel assets to enable additional programs GEN- 010 Shared neoantigens Novel TAAs Viral antigens 13

GEN- 009 Generating unprecedented Neoantigen immune responses Vaccine 14

GEN- 009 Optimized Neoantigen Vaccine 15

GEN- 009 Phase 1/2a Trial Part A • Vaccine monotherapy • Patient cohort: no evidence of disease • Multiple tumor types with ICI approval • Objectives: safety, immunogenicity • Status: all patients in follow-up • Vaccine well-tolerated • No disease progression in vaccinated patients • Highly immunogenic

Enables Unparalleled Vaccine Immune Responses Frequency % neoantigens with immune responses 60% 99% Potential Patient Benefits Response breadth to prevent tumor escape Best Peer Results1 GEN-0092 Achieved in Monotherapy combination with ICI 1 Sahin, et al., Nature 2017 (N=8); Ott, et al., Nature 2017 (N=8); Gritstone ESMO Immuno-Oncology Congress Presentation 2019 2 N=8 • Results shown represent highest neoantigen vaccine percentage responses in peer publications • No comparison or head-to-head studies were performed between GEN-009 and the other product candidates noted above. Clinical trial criteria, including, without limitation, number of patients, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and primary endpoints were not necessarily the same. 17

Enables Unparalleled Vaccine Immune Responses Effector function Central memory response (ex vivo assay) (IVS assay) CD4+ CD8+ CD4+ CD8+ 87% 51% Best peer 41% results 1 57% 57% 23% GEN-0092 17% 0% Potential Patient Benefits Potential Patient Benefits Rapid tumor killing Durable efficacy 1 As monotherapy: Sahin, et al., Nature 2017 (N=8); Ott, et al., Nature 2017 (N=8) 2 N=8 • Results shown represent highest neoantigen vaccine percentage responses in peer publications • No comparison or head-to-head studies were performed between GEN-009 and the other product candidates noted above. Clinical trial criteria, including, without limitation, number of patients, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and primary endpoints were not necessarily the same. 18

GEN- 009 Phase 1/2a Trial Designed to Showcase Vaccine Benefits in ICI Patients Part B • Combination of GEN-009 and standard-of-care PD-1 based regimen intended in cohorts of patients with advanced disease • Vaccination contribution to be determined after ICI response established • Objectives: safety, immunogenicity, efficacy (initial efficacy: 3 months post-vaccination) • Tumor types: Melanoma, NSCLC, SCCHN, Urothelial, RCC • Initial clinical data expected mid 2020

GEN- 011 Potential first-in-class solid Neoantigen tumor T cell therapy T cell Therapy 20

TIL Therapy Has Changed the Narrative for Solid Tumor T cell Therapy Tumor infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) therapy has delivered durable efficacy in hard-to- treat solid tumor patients • 44% ORR in late-stage cervical cancer patients • Similar benefits in heavily pretreated metastatic melanoma patients • These data have enabled an accelerated path to approval 21

Lessons Learned from TIL Therapy Multiple CD4+ and CD8+ neoantigen targets T cells • Attacks tumor • CD4+ T cells support heterogeneity, limits activity and CD4+ CD8+ tumor escape persistence of CD8+ T cells and both can directly kill tumor cells Diversity of TCRs per Patient safety target neoantigen • Autologous, non- • Multiple “shots on engineered T cell safety goal” for every • Avoid toxicity observed neoantigen with CAR-T and TCR-T approaches 22

Still Significant Opportunities to Enhance T cell Therapy for Solid Tumors Approaches to Address Increase target breadth & specificity TILs only target a limited proportion of neoantigens Neoantigen selection via Avoid deleterious T cell responses Inhibitory, pro- tumor responses to neoantigens should be avoided in a therapeutic context Improve T cell activity & proliferative potential Peripheral blood TILs typically exhausted and expansion protocols exacerbate condition lymphocytes (PBLs) Broaden addressable tumor types TILs must be sterilely extracted from resectable ‘hot’ tumors 23

GEN- 011 ATLAS-Enabled T cell Therapy for Solid Tumors Autologous T cell therapy T cells expanded from peripheral blood: • Both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells with validated antigen responses • Multiple specificities for broader coverage, reduced potential for metastatic escape • HLA agnostic • Ability to address a range of tumor types 24

GEN- 011 Next Generation Neoantigen Adoptive Cell Therapy Collect tumor and ATLAS to select Expand and sort Administer GEN-011 blood samples, neoantigens of pre- neoantigen-specific to patient sequence exome existing CD4+ and T cells CD8+ T cell responses Exclude inhibigens 25
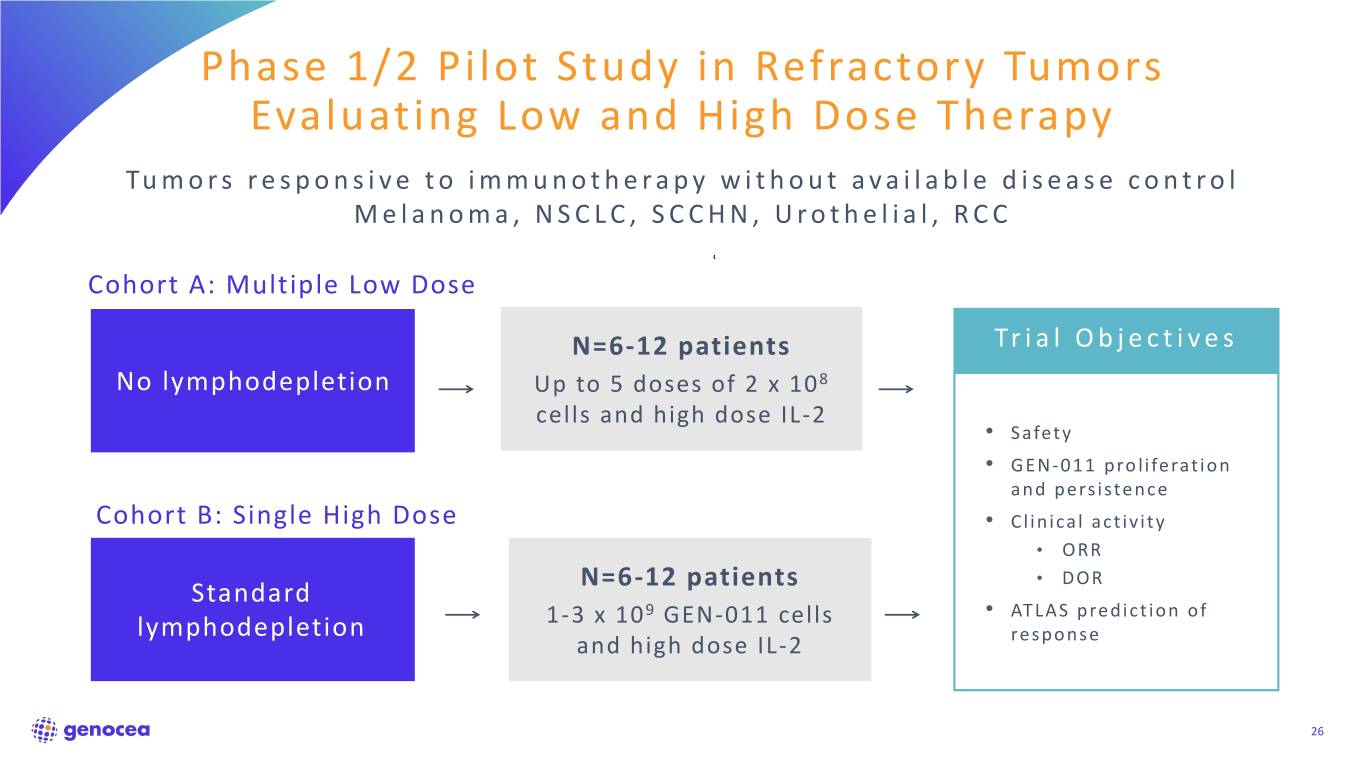
Phase 1/2 Pilot Study in Refractory Tumors Evaluating Low and High Dose Therapy Tumors responsive to immunotherapy without available disease control Melanoma, NSCLC, SCCHN, Urothelial, RCC Cohort A: Multiple Low Dose N=6-12 patients Trial Objectives No lymphodepletion Up to 5 doses of 2 x 108 cells and high dose IL-2 • Safety • GEN-011 proliferation and persistence Cohort B: Single High DoseN= 6-12 Patients • Clinical activity • ORR N=6-12 patients • DOR Standard 9 • ATLAS prediction of lymphodepletion 1-3 x 10 GEN-011 cells and high dose IL-2 response 26

In Scale Development Runs, the GEN-011 Product has Desired Functional Properties Most T cells in the final product are specific for Cells are functionally cytolytic in ATLAS-defined neoantigens an in vitro killing assay Control Antigen-specific 100 Specific Neoantigens 70% 80 5% Unpulsed Control 60 40 % Cytotoxicity 20 0 16:1 8:1 4:1 2:1 1:1 0.5:1 Activation Marker 1 Marker Activation Activation Marker 2 Effector: Target Ratio Production process using 28 patient-specific neoantigens yielded product with 70% neoantigen specific T cells. High neoantigen specificity achieved across key T cell subsets with 60% of CD4+ and 75% of CD8+ neoantigen-specific T cells. Product contained T cells immunogenic against >75% of intended neoantigen targets 27

Why Genocea? Revolutionary antigen discovery platform TARGETS MATTER PROPRIETARY PLATFORM GEN-009 GEN-011 Two differentiated, clinical stage programs Neoantigen Neoantigen vaccine cell therapy 2Q 2020 IND Significant near-term, Mid 2020 1H 2021 value-creating initial clinical data milestones initial clinical data 28
NASDAQ: GNCA 100 Acorn Park Drive Cambridge, MA 02140 USA +1 617.876.8191 www.genocea.com29
