Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.2 - EX-99.2 - Nabriva Therapeutics plc | a18-13938_1ex99d2.htm |
| 8-K - 8-K - Nabriva Therapeutics plc | a18-13938_18k.htm |
Safe Harbor and Disclaimer This presentation contains forward-looking statements that involve substantial risks and uncertainties. All statements, other than statements of historical facts, contained in this presentation, including statements about our future expectations, plans and prospects, including but not limited to statements about the development of our product candidates, the clinical utility of lefamulin for CABP, our plans for filing of regulatory approvals, efforts to bring lefamulin to market, the development of lefamulin for additional indications, the development of additional formulations of lefamulin, plans to pursue research and development of other product candidates, our plans to enter into arrangements with external collaborators, the sufficiency of our existing cash resources and other statements containing the words “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “plan,” “predict,” “project,” “target,” “potential,” “will,” “would,” “could,” “should,” “continue,” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. We may not actually achieve the plans, intentions or expectations disclosed in our forward-looking statements, and you should not place undue reliance on our forward-looking statements. Actual results may differ materially from those indicated by such forward-looking statements as a result of various important factors, including: the uncertainties inherent in the initiation and conduct of clinical trials, availability and timing of data from clinical trials, whether results of early clinical trials or trials in different disease indications will be indicative of the results of ongoing or future trials, whether results of our Phase 3 clinical trials of lefamulin are indicative of the clinical utility of lefamulin for CABP, uncertainties associated with regulatory review of clinical trials and applications for marketing approvals, the availability or commercial potential of product candidates including lefamulin for use as a first-line empiric monotherapy for the treatment of moderate to severe CABP, the sufficiency of cash resources and need for additional financing and such other important factors as are set forth under the caption "Risk Factors" in the annual and quarterly reports we file with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission. In addition, the forward-looking statements included in this presentation represent our views as of the date of this presentation. We anticipate that subsequent events and developments will cause our views to change. However, while we may elect to update these forward-looking statements at some point in the future, we specifically disclaims any obligation to do so. These forward-looking statements should not be relied upon as representing our views as of any date subsequent to the date of this presentation. 2
Nabriva: Addressing the Demand for New Antibiotics Lefamulin, the lead molecule of a new class of antibiotics in clinical development for CABP, demonstrated positive topline results in both the LEAP 1 and LEAP 2 Phase 3 trials, with an NDA filing expected in the fourth quarter of 2018 Pre-commercial activities initiated to optimize adoption at launch and long term potential for a large underserved market* Highly experienced management team in place to build a fully integrated anti-infective company Focused on creating value through innovation and business development 3 * Lefamulin is an investigational drug candidate and has not received regulatory approval for any indication. Information provided in this slide is based on research and development performed to date.
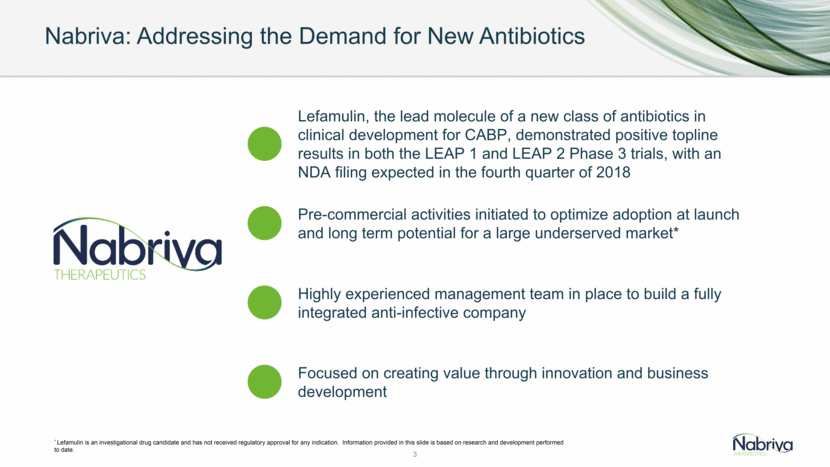
4 Overview of the Lefamulin Clinical Program Extensive PK/PD Characterization and Preclinical Program with 20 Phase I studies Proof-of-Concept Phase 2 ABSSSI LEAP 1: Efficacy and Safety of IV-to-Oral Lefamulin in Adults with CABP LEAP 2: Efficacy and Safety of Oral Lefamulin in Adults with CABP Pediatric Program and Life Cycle Management
LEAP 2 TRIAL DESIGN and DEMOGRAPHICS

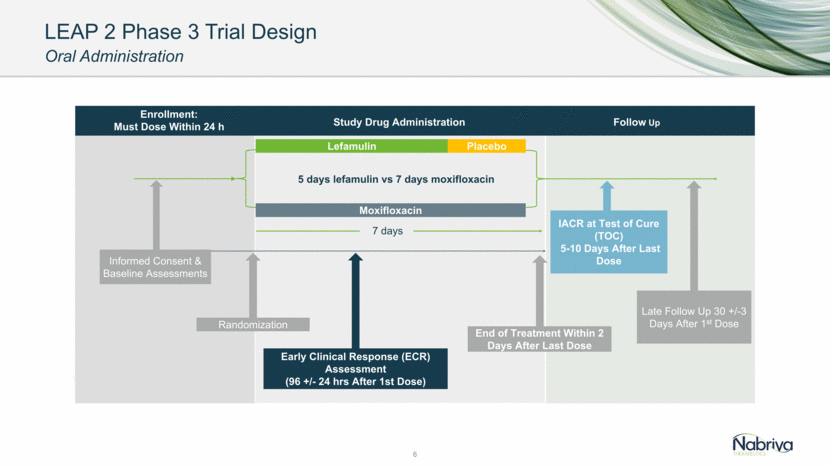
LEAP 2 Phase 3 Trial Design Oral Administration 6 Lefamulin Moxifloxacin Informed Consent & Baseline Assessments Randomization Early Clinical Response (ECR) Assessment (96 +/- 24 hrs After 1st Dose) End of Treatment Within 2 Days After Last Dose Late Follow Up 30 +/-3 Days After 1st Dose 5 days lefamulin vs 7 days moxifloxacin Follow Up Study Drug Administration Enrollment: Must Dose Within 24 h IACR at Test of Cure (TOC) 5-10 Days After Last Dose 7 days *10 days if MRSA confirmed as the causative pathogen Placebo
LEAP 2: Phase 3 Trial Design 7 FDA Primary Endpoint: Early Clinical Response (ECR) ITT Population EMA Primary Endpoint: Investigator Assessment of Clinical Response (IACR) at Test of Cure (mITT and CE-TOC Population) FDA and EMA Primary Endpoints 72-120 hours after first dose of study drug Improvement in > 2 of 4 CABP signs/symptoms No worsening in any CABP signs/symptoms Alive Did not receive non-study antibacterial therapy for the treatment of CABP Non-inferiority margin 10%, >90% power At 5-10 days after the last dose of study drug: Signs/symptoms of CABP have resolved/improved such that no additional antibacterial therapy is administered for the treatment of CABP Non-inferiority margin 10%, >90% power ITT = Intent to Treat, mITT = Modified Intent to Treat, CE-TOC = Clinically Evaluable at Test of Cure
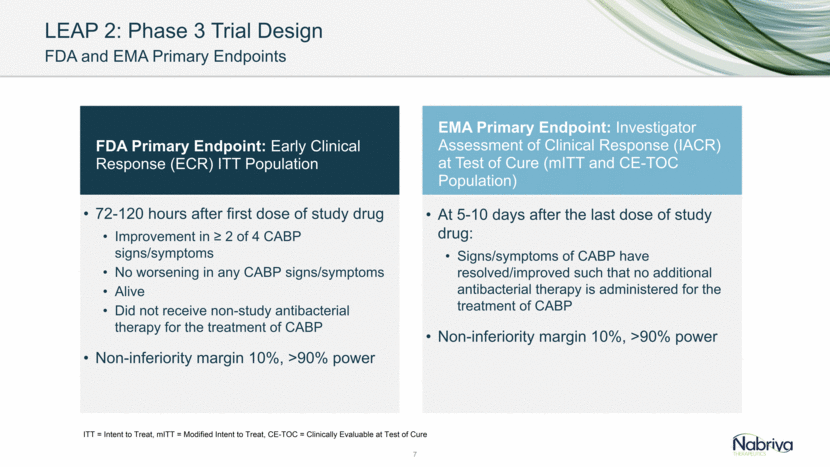
LEAP 2 Phase 3 Trial Design CABP Symptom Assessment for ECR Symptom Absent (0) Mild (1) Moderate (2) Severe (3) Dyspnea Resolution (to pre-CABP baseline) or absence of dyspnea Dyspnea on exertion (e.g., climbing stairs) Dyspnea with normal/routine activities (e.g., walking) Dyspnea at rest or requiring oxygen therapy Cough Resolution (to pre-CABP baseline) or absence of cough Transient, does not interfere with normal activity Frequent, interferes with normal activity or sleep Constant, interferes with most or all activity or sleep Production of purulent sputum Resolution (to pre-CABP baseline) or absence of sputum production Sputum production rarely causes difficulty or distress Sputum production often causes difficulty or distress Constant difficulty with sputum production Chest pain Resolution or absence of chest pain related to CABP Transient, does not interfere with normal activity Frequent, interferes with normal activity or sleep Constant, interferes with most or all activity or sleep 8
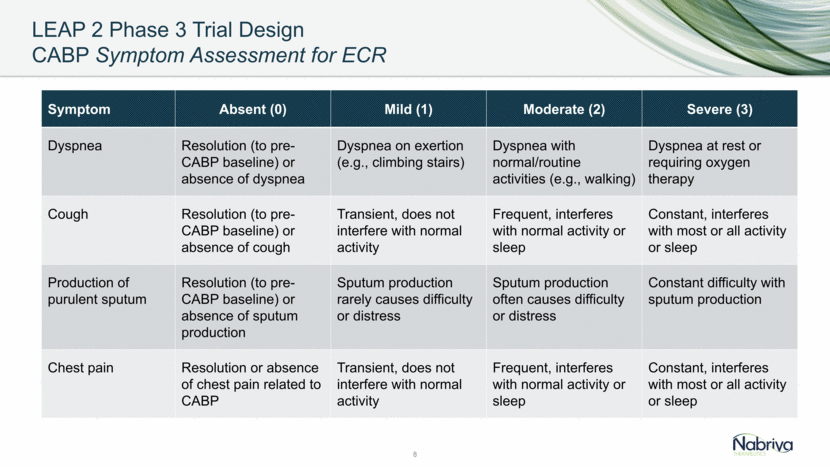
LEAP 2 Phase 3 Trial Populations and Disposition High Patient Completion and Microbiological Isolate Recovery Rates 9 Category Lefamulin n (%) Moxifloxacin n (%) TOTAL n (%) All Randomized (ITT) 370 368 738 Modified ITT (mITT) 368 (99.5%) 368 (100%) 736 (99.7%) Clinically Evaluable-Test of Cure (CE-TOC) 330 (89.2%) 326 (88.6%) 656 (88.9%) Microbiological ITT (microITT) 205 (55.4%) 186 (50.5%) 391 (53.0%) Completed Study 353 (95.4%) 354 (96.2%) 707 (95.8%) Completed ECR Assessment 356 (96.2%) 362 (98.4%) 718 (97.3%) Completed TOC Assessment 355 (95.9%) 354 (96.2%) 709 (96.1%)
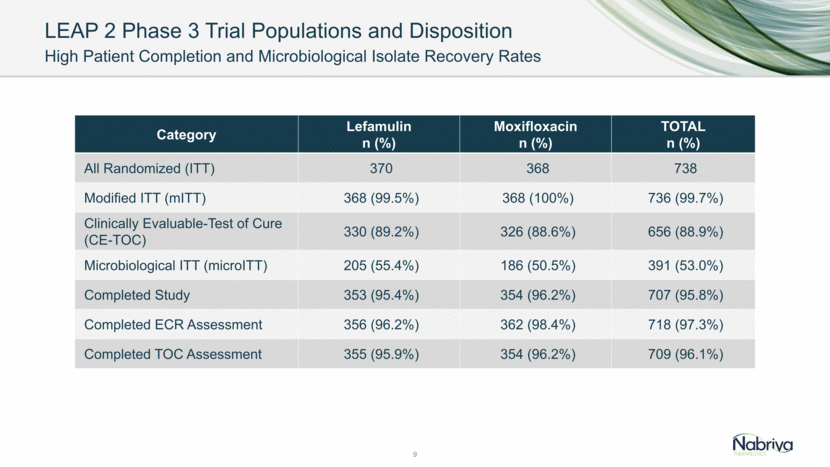
LEAP 2 Phase 3 Trial ITT Population Balanced Baseline Characteristics Between Treatment Groups 10 Category Lefamulin n (%) Moxifloxacin n (%) TOTAL n (%) Age <65 years 234 (63.2%) 227 (61.7%) 461 (62.5%) 65-74 78 (21.1%) 79 (21.5%) 157 (21.3%) >75 58 (15.7%) 62 (16.8%) 120 (16.3%) Demographics Male 207 (55.9%) 180 (48.9%) 387 (52.4%) BMI (kg/m2) (Mean) 26.54 26.48 26.51 Race (White) 274 (74.1%) 270 (73.4%) 544 (73.7%) Renal Status Severe impairment (CrCl <30 ml/min) 4 (1.1%) 3 (0.8%) 7 (0.9%) Moderate impairment (CrCl 30-<60ml/min) 64 (17.3%) 70 (19.0%) 134 (18.2%) Mild impairment (CrCl 60-<90 ml/min) 112 (30.3%) 117 (31.8%) 229 (31.0%) Normal function (CrCl >90 ml/min) 190 (51.4%) 178 (48.4%) 368 (49.9%)
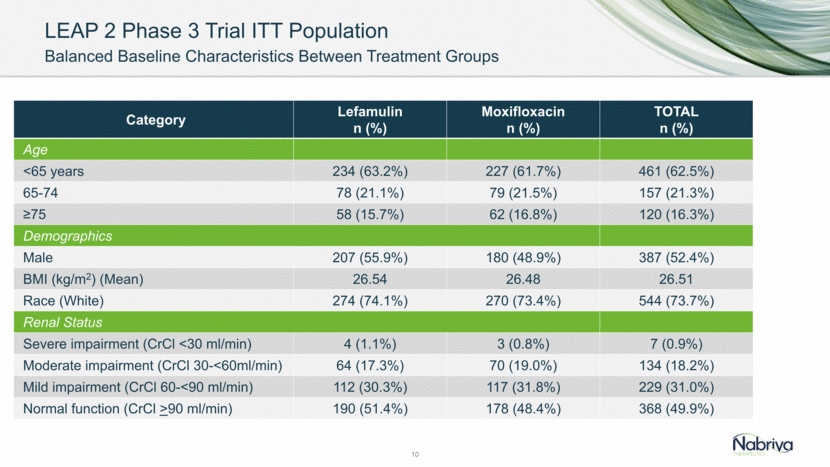
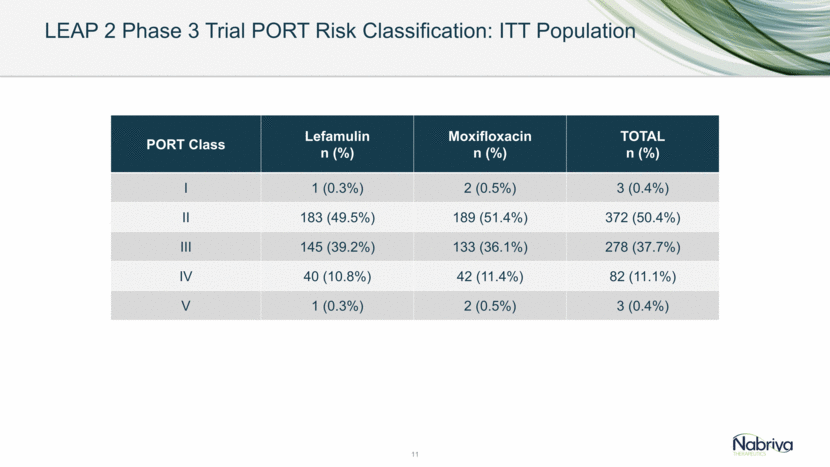
LEAP 2 Phase 3 Trial PORT Risk Classification: ITT Population 11 PORT Class Lefamulin n (%) Moxifloxacin n (%) TOTAL n (%) I 1 (0.3%) 2 (0.5%) 3 (0.4%) II 183 (49.5%) 189 (51.4%) 372 (50.4%) III 145 (39.2%) 133 (36.1%) 278 (37.7%) IV 40 (10.8%) 42 (11.4%) 82 (11.1%) V 1 (0.3%) 2 (0.5%) 3 (0.4%)
LEAP 2 TRIAL EFFICACY RESULTS

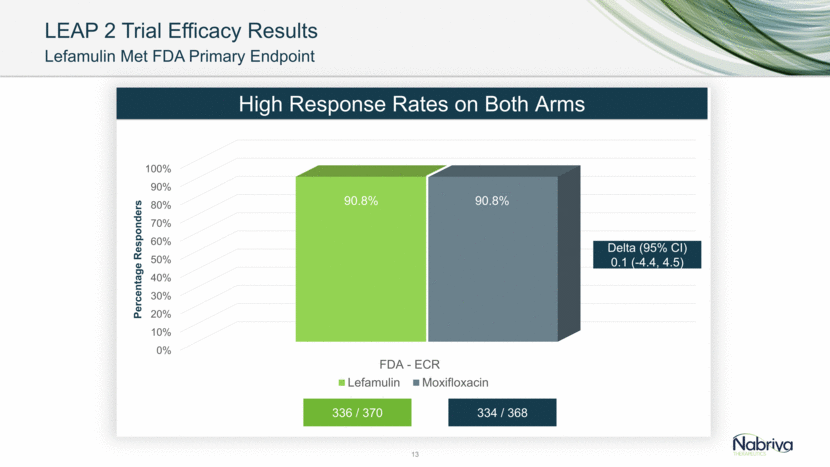
LEAP 2 Trial Efficacy Results 13 Lefamulin Met FDA Primary Endpoint 336 / 370 334 / 368 High Response Rates on Both Arms Delta (95% CI) 0.1 (-4.4, 4.5) 336 / 370 334 / 368
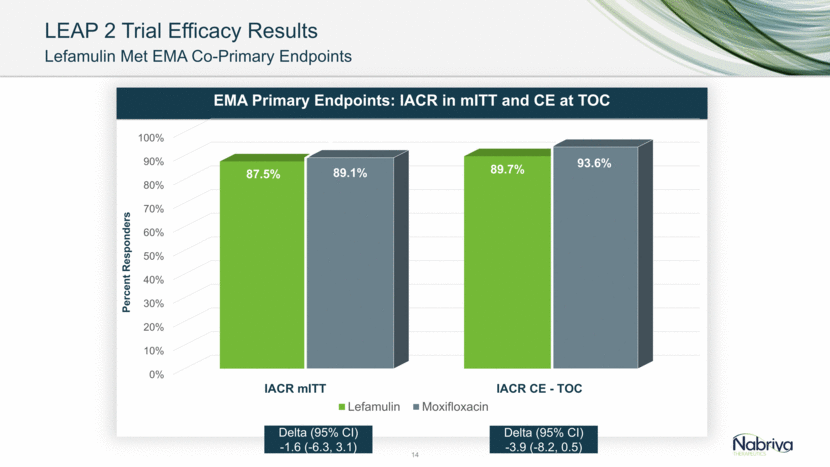
LEAP 2 Trial Efficacy Results Lefamulin Met EMA Co-Primary Endpoints 14 Delta (95% CI) -3.9 (-8.2, 0.5) Delta (95% CI) -1.6 (-6.3, 3.1) 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% IACR mITT IACR CE - TOC 87.5% 89.7% 89.1% 93.6% Percent Responders EMA Primary Endpoints: IACR in mITT and CE at TOC Lefamulin Moxifloxacin
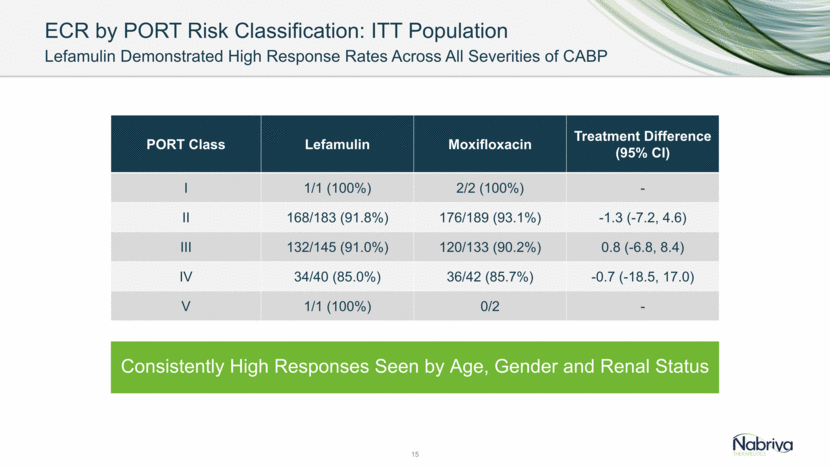
ECR by PORT Risk Classification: ITT Population Lefamulin Demonstrated High Response Rates Across All Severities of CABP 15 PORT Class Lefamulin Moxifloxacin Treatment Difference (95% CI) I 1/1 (100%) 2/2 (100%) - II 168/183 (91.8%) 176/189 (93.1%) -1.3 (-7.2, 4.6) III 132/145 (91.0%) 120/133 (90.2%) 0.8 (-6.8, 8.4) IV 34/40 (85.0%) 36/42 (85.7%) -0.7 (-18.5, 17.0) V 1/1 (100%) 0/2 - Consistently High Responses Seen by Age, Gender and Renal Status
Lefamulin Demonstrated High Response Rate Against All of the Most Common Causes of CABP 16 Lefamulin Moxifloxacin Microbiological ITT (microITT) N = 205 N = 186 Baseline Pathogen ECR (%) ECR (%) Gram Positive S. pneumoniae 110/123 89.4% 115/126 91.3% Penicillin Susceptible 19/25 76.0% 36/38 94.7% Penicillin Resistant 5/5 100% 4/4 100% Multi-Drug Resistant 8/8 100% 10/12 83.3% Macrolide-Resistant 8/9 88.9% 9/11 81.8% S. aureus 13/13 100% 6/6 100% MRSA 2/2 100% 1/1 100% ECR by Baseline Pathogen – Typical Pathogens [micro ITT]
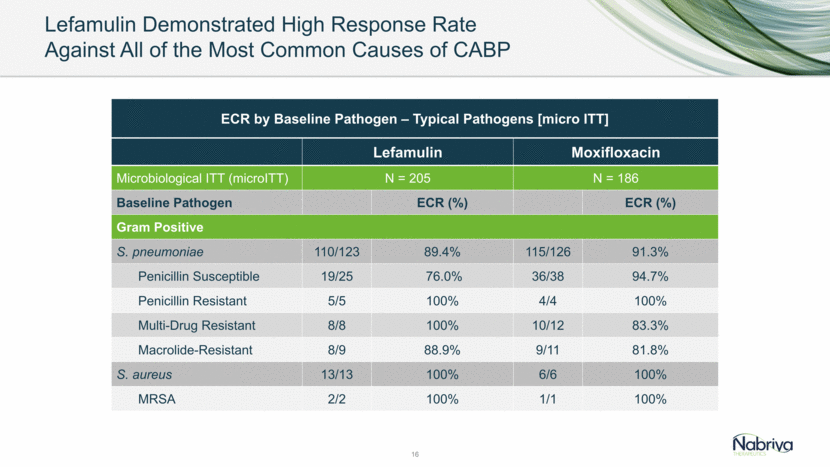
Lefamulin Demonstrated High Response Rate Against All of the Most Common Causes of CABP 17 ECR by Baseline Pathogen – Typical Pathogens [micro ITT] continued Lefamulin Moxifloxacin Baseline Pathogen ECR (%) ECR (%) Gram Negative H. influenzae 50/56 89.3% 44/48 91.7% M. catarrhalis 18/21 85.7% 11/11 100% Atypicals M. pneumoniae 20/20 100% 14/14 100% L. pneumophila 13/16 81.3% 16/17 94.1% C. pneumoniae 15/16 93.8% 12/12 100%
LEAP 2 TRIAL SAFETY and TOLERABILITY DATA

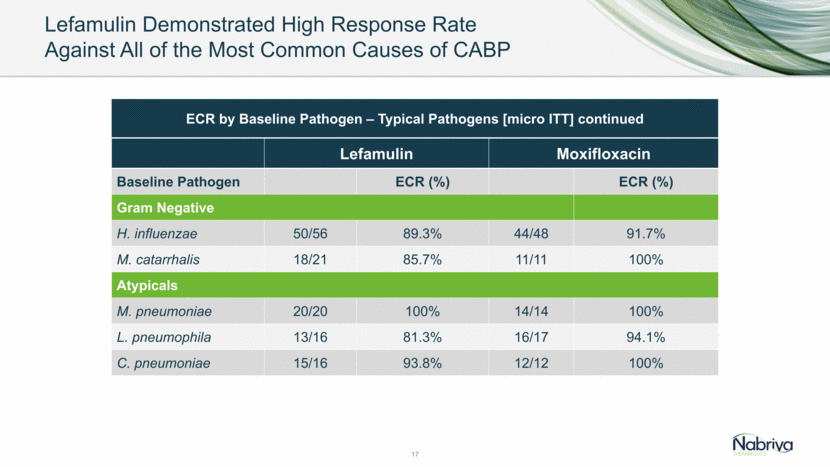
Overview of Adverse Events (mITT) Low Rates of Discontinuation Observed 19 Patients with at Least One Lefamulin (n=368) Moxifloxacin (n=368) Treatment Emergent AE (TEAE) 120 (32.6%) 92 (25.0%) AE Leading to Discontinuation of Study Drug 11 (3.0%) 8 (2.2%) AE Leading to Withdrawal from Study 5 (1.4%) 5 (1.4%) Serious AE (SAE) 17 (4.6%) 18 (4.9%) Treatment Related SAE - 1 (0.3%) Deaths within 30 days 3 (0.8%) 3 (0.8%)
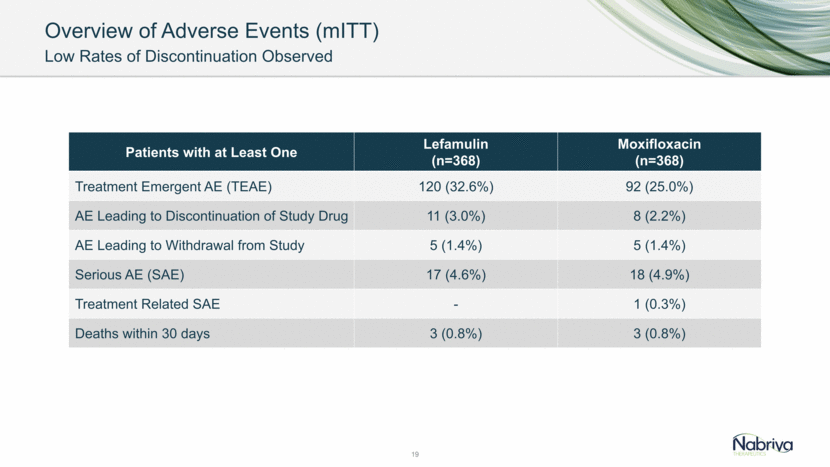
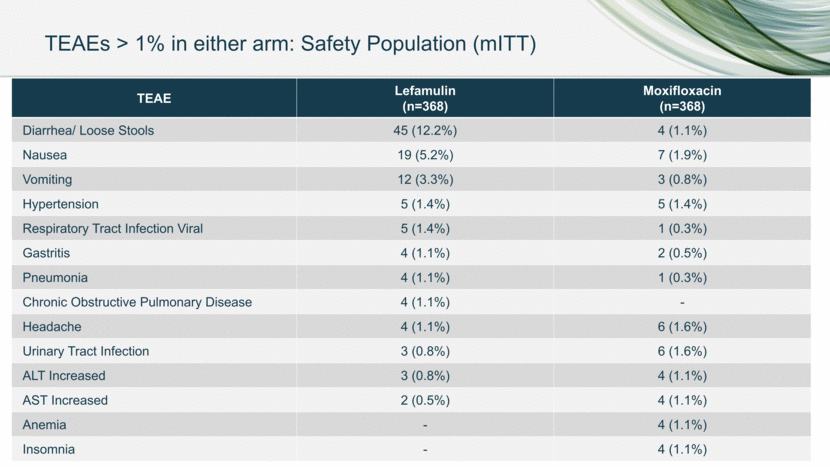
20 TEAE Lefamulin (n=368) Moxifloxacin (n=368) Diarrhea/ Loose Stools 45 (12.2%) 4 (1.1%) Nausea 19 (5.2%) 7 (1.9%) Vomiting 12 (3.3%) 3 (0.8%) Hypertension 5 (1.4%) 5 (1.4%) Respiratory Tract Infection Viral 5 (1.4%) 1 (0.3%) Gastritis 4 (1.1%) 2 (0.5%) Pneumonia 4 (1.1%) 1 (0.3%) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 4 (1.1%) - Headache 4 (1.1%) 6 (1.6%) Urinary Tract Infection 3 (0.8%) 6 (1.6%) ALT Increased 3 (0.8%) 4 (1.1%) AST Increased 2 (0.5%) 4 (1.1%) Anemia - 4 (1.1%) Insomnia - 4 (1.1%) TEAEs > 1% in either arm: Safety Population (mITT)
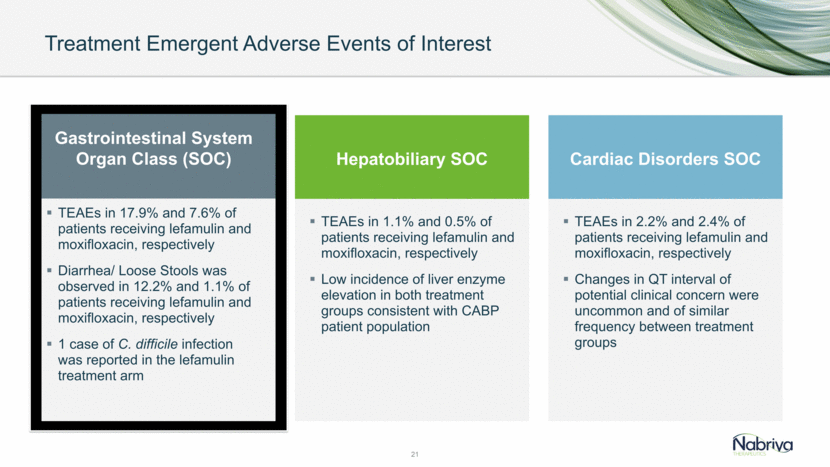
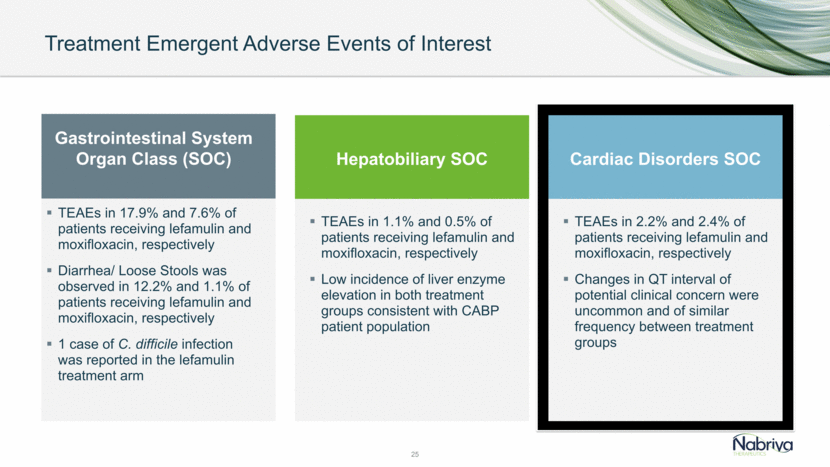
Treatment Emergent Adverse Events of Interest 21 TEAEs in 17.9% and 7.6% of patients receiving lefamulin and moxifloxacin, respectively Diarrhea/ Loose Stools was observed in 12.2% and 1.1% of patients receiving lefamulin and moxifloxacin, respectively 1 case of C. difficile infection was reported in the lefamulin treatment arm TEAEs in 1.1% and 0.5% of patients receiving lefamulin and moxifloxacin, respectively Low incidence of liver enzyme elevation in both treatment groups consistent with CABP patient population Gastrointestinal System Organ Class (SOC) Hepatobiliary SOC Cardiac Disorders SOC TEAEs in 2.2% and 2.4% of patients receiving lefamulin and moxifloxacin, respectively Changes in QT interval of potential clinical concern were uncommon and of similar frequency between treatment groups
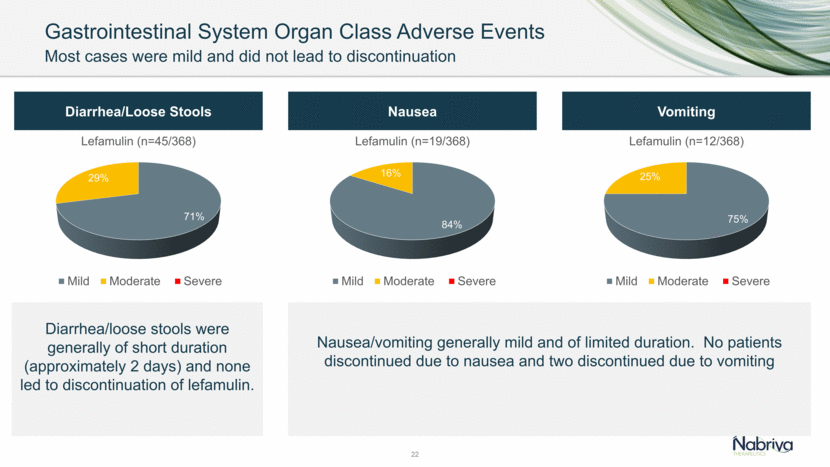
Gastrointestinal System Organ Class Adverse Events 22 Diarrhea/Loose Stools Diarrhea/loose stools were generally of short duration (approximately 2 days) and none led to discontinuation of lefamulin. Nausea Vomiting Nausea/vomiting generally mild and of limited duration. No patients discontinued due to nausea and two discontinued due to vomiting Most cases were mild and did not lead to discontinuation 71% 29% 0% Lefamulin (n=45/368) Mild Moderate Severe 84% 16% 0% Lefamulin (n=19/368) Mild Moderate Severe 75% 25% 0% Lefamulin (n=12/368) Mild Moderate Severe
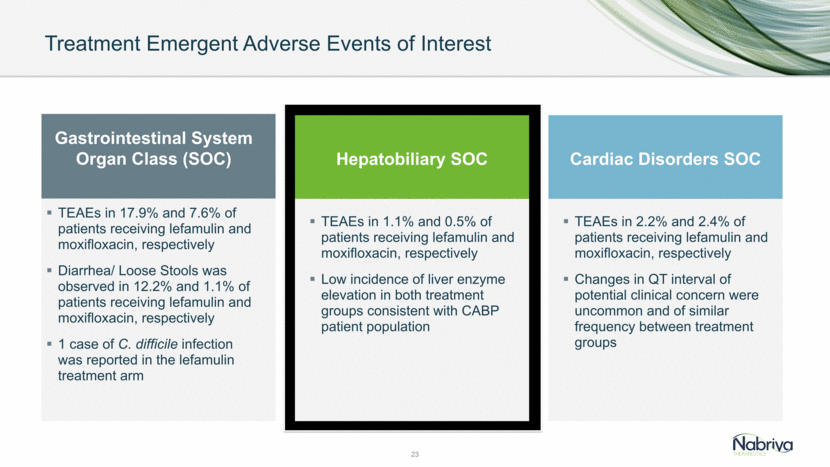
Treatment Emergent Adverse Events of Interest 23 TEAEs in 17.9% and 7.6% of patients receiving lefamulin and moxifloxacin, respectively Diarrhea/ Loose Stools was observed in 12.2% and 1.1% of patients receiving lefamulin and moxifloxacin, respectively 1 case of C. difficile infection was reported in the lefamulin treatment arm TEAEs in 1.1% and 0.5% of patients receiving lefamulin and moxifloxacin, respectively Low incidence of liver enzyme elevation in both treatment groups consistent with CABP patient population Gastrointestinal System Organ Class (SOC) Hepatobiliary SOC Cardiac Disorders SOC TEAEs in 2.2% and 2.4% of patients receiving lefamulin and moxifloxacin, respectively Changes in QT interval of potential clinical concern were uncommon and of similar frequency between treatment groups
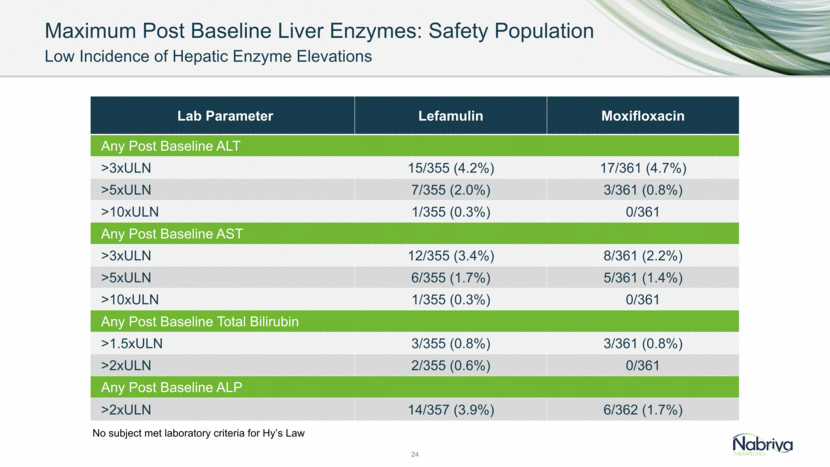
Maximum Post Baseline Liver Enzymes: Safety Population Low Incidence of Hepatic Enzyme Elevations 24 Lab Parameter Lefamulin Moxifloxacin Any Post Baseline ALT >3xULN 15/355 (4.2%) 17/361 (4.7%) >5xULN 7/355 (2.0%) 3/361 (0.8%) >10xULN 1/355 (0.3%) 0/361 Any Post Baseline AST >3xULN 12/355 (3.4%) 8/361 (2.2%) >5xULN 6/355 (1.7%) 5/361 (1.4%) >10xULN 1/355 (0.3%) 0/361 Any Post Baseline Total Bilirubin >1.5xULN 3/355 (0.8%) 3/361 (0.8%) >2xULN 2/355 (0.6%) 0/361 Any Post Baseline ALP >2xULN 14/357 (3.9%) 6/362 (1.7%) No subject met laboratory criteria for Hy’s Law
Treatment Emergent Adverse Events of Interest 25 TEAEs in 17.9% and 7.6% of patients receiving lefamulin and moxifloxacin, respectively Diarrhea/ Loose Stools was observed in 12.2% and 1.1% of patients receiving lefamulin and moxifloxacin, respectively 1 case of C. difficile infection was reported in the lefamulin treatment arm TEAEs in 1.1% and 0.5% of patients receiving lefamulin and moxifloxacin, respectively Low incidence of liver enzyme elevation in both treatment groups consistent with CABP patient population Gastrointestinal System Organ Class (SOC) Hepatobiliary SOC Cardiac Disorders SOC TEAEs in 2.2% and 2.4% of patients receiving lefamulin and moxifloxacin, respectively Changes in QT interval of potential clinical concern were uncommon and of similar frequency between treatment groups
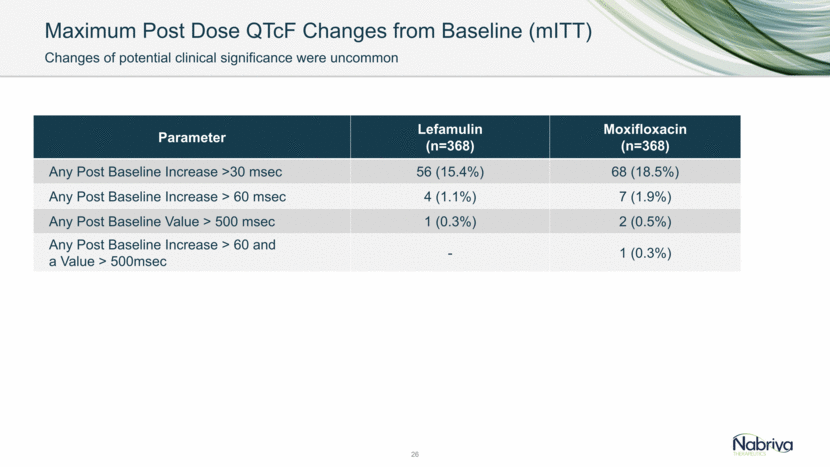
Maximum Post Dose QTcF Changes from Baseline (mITT) 26 Parameter Lefamulin (n=368) Moxifloxacin (n=368) Any Post Baseline Increase >30 msec 56 (15.4%) 68 (18.5%) Any Post Baseline Increase > 60 msec 4 (1.1%) 7 (1.9%) Any Post Baseline Value > 500 msec 1 (0.3%) 2 (0.5%) Any Post Baseline Increase > 60 and a Value > 500msec - 1 (0.3%) Changes of potential clinical significance were uncommon
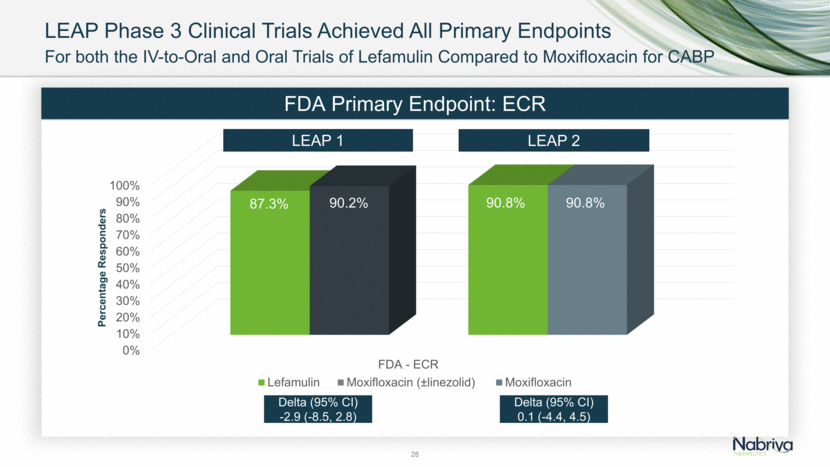
LEAP Phase 3 Clinical Trials Achieved All Primary Endpoints

LEAP Phase 3 Clinical Trials Achieved All Primary Endpoints 28 For both the IV-to-Oral and Oral Trials of Lefamulin Compared to Moxifloxacin for CABP FDA Primary Endpoint: ECR LEAP 1 LEAP 2 Delta (95% CI) 0.1 (-4.4, 4.5) Delta (95% CI) -2.9 (-8.5, 2.8)
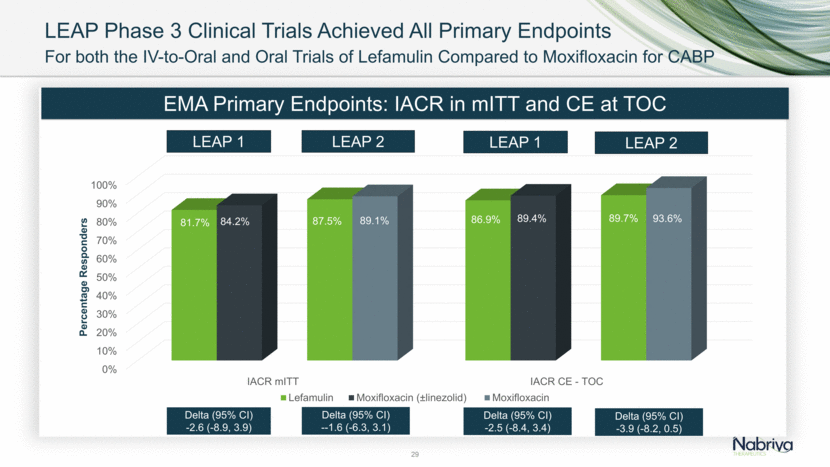
LEAP Phase 3 Clinical Trials Achieved All Primary Endpoints 29 For both the IV-to-Oral and Oral Trials of Lefamulin Compared to Moxifloxacin for CABP EMA Primary Endpoints: IACR in mITT and CE at TOC LEAP 1 LEAP 2 Delta (95% CI) -3.9 (-8.2, 0.5) Delta (95% CI) -2.6 (-8.9, 3.9) Delta (95% CI) --1.6 (-6.3, 3.1) Delta (95% CI) -2.5 (-8.4, 3.4) LEAP 1 LEAP 2
30 % of Patients Discontinuing Study Drug Low Rate of Premature Discontinuations of Study Drug Across Phase 3 Program LEAP 1 IV to Oral LEAP 2 Oral Only
Lefamulin: A Promising Potential Treatment Option for CABP Lefamulin met all primary FDA and EMA endpoints in both LEAP 1 and LEAP 2 trials 31 Complete Spectrum of Coverage of Main CABP Pathogens Monotherapy shown to provide the appropriate coverage with a low risk of C. difficile infection Generally Well Tolerated Profile Low rates of discontinuations due to adverse events New Class New Mechanism of Action Overcomes existing mechanism of resistance in vitro and low propensity for development of bacterial resistance Convenient for Patients in Hospital, Transition of Care and the Community Flexible IV and Oral formulations and short course of monotherapy Excellent PK-PD Profile No loading dose; no dose adjustment expected for renal or hepatic insufficiency; mild food interaction potential
Acknowledgments 32 We are grateful for the participation and contributions of the following in the LEAP Program: Anita Das, Ph. D. Gary Moore, M.Sc. The Nabriva Therapeutics team Patients and families Clinical investigators and their staff Collaborating research organizations
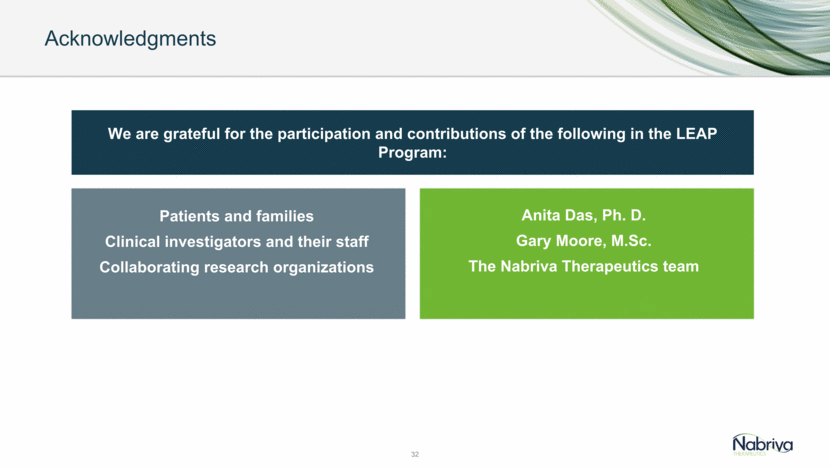
May 2018 Topline data from LEAP 2 Phase 3 trial for CABP Recent and Anticipated Lefamulin Milestones 33 Sept 2017 Topline data from LEAP 1 Phase 3 trial for CABP Mid 2018 Pediatric Study Initiation Q4 2018 Regulatory filing in US (priority review request to FDA) for CABP
34 Gram Negative or MRSA Products Broad Spectrum Products CABP Focus with MRSA Coverage 34 CABP: Underserved by Anti-Infective Portfolios of Other Companies A Potentially Significant Opportunity for Lefamulin

Nabriva: Addressing the Demand for New Antibiotics Lefamulin, the lead molecule of a new class of antibiotics in clinical development for CABP, demonstrated positive topline results in both the LEAP 1 and LEAP 2 Phase 3 trials, with an NDA filing expected in the fourth quarter of 2018 Pre-commercial activities initiated to optimize adoption at launch and long term potential for a large underserved market* Highly experienced management team in place to build a fully integrated anti-infective company Focused on creating value through innovation and business development 35 * Lefamulin is an investigational drug candidate and has not received regulatory approval for any indication. Information provided in this slide is based on research and development performed to date.
Questions?


