Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.2 - EX-32.2 - BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL INC | d463750dex322.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL INC | d463750dex321.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL INC | d463750dex312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL INC | d463750dex311.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL INC | d463750dex231.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EX-21.1 - BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL INC | d463750dex211.htm |
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(D) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(D) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission file number 001-31361
BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 35-2089858 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| 4131 ParkLake Avenue, Suite #225 Raleigh, NC |
27612 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number: 919-582-9050
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class |
Name of exchange on which registered | |
| Common stock, par value $.001 | Nasdaq Capital Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files) Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, or a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See definition of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer | ☐ | Accelerated filer | ☒ | |||
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | ☐ | |||
| Emerging growth company | ☐ | |||||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates as of June 30, 2017 was approximately $124,774,588 based on the closing sale price of the company’s common stock on such date of $2.80 per share, as reported by the NASDAQ Capital Market.
As of March 13, 2018, there were 58,465,111 shares of company common stock issued and 58,449,620 shares of company common stock outstanding.
Table of Contents
BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc.
Annual Report on Form 10-K
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Unless we have indicated otherwise, or the context otherwise requires, references in this Report to “BDSI,” the “Company,” “we,” “us” and “our” or similar terms refer to BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc., a Delaware corporation and its consolidated subsidiaries.
Table of Contents
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Report and the documents we have filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (which we refer to herein as the SEC) that are incorporated by reference herein contain forward-looking statements, within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), that involve significant risks and uncertainties. Any statements contained, or incorporated by reference, in this Report that are not statements of historical fact may be forward-looking statements. When we use the words “anticipate,” “believe,” “could,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “plan,” “predict,” “project,” “will” and other similar terms and phrases, including references to assumptions, we are identifying forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties which may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from those expressed or implied by forward-looking statements.
A variety of factors, some of which are outside our control, may cause our operating results to fluctuate significantly. They include:
| • | our plans and expectations regarding the timing and outcome of research, development, commercialization, manufacturing, marketing and distribution efforts relating to our BEMA® (as defined below) drug delivery technology platform and any of our approved products or product candidates; |
| • | the domestic and international regulatory process and related laws, rules and regulations governing our technologies and our approved and proposed products and formulations, including: (i) the timing, status and results of our or our commercial partners’ filings with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and its foreign equivalents, (ii) the timing, status and results of non-clinical work and clinical studies, including regulatory review thereof and (ii) the heavily regulated industry in which we operate our business generally; |
| • | our ability to enter into strategic partnerships for the development, commercialization, manufacturing and distribution of our products and product candidates; |
| • | our ability, or the ability of our commercial partners, to actually develop, commercialize, manufacture or distribute our products and product candidates, including for BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®, which we are self-commercializing; |
| • | our ability to generate commercially viable products and the market acceptance of our BEMA® technology platform and our proposed products and product candidates; |
| • | our ability to finance our operations on acceptable terms, either through the raising of capital, the incurrence of convertible or other indebtedness or through strategic financing or commercialization partnerships; |
| • | our expectations about the potential market sizes and market participation potential for our approved or proposed products; |
| • | the protection and control afforded by our patents or other intellectual property, and any interest patents or other intellectual property that we license, of our or our partners’ ability to enforce our rights under such owned or licensed patents or other intellectual property; |
| • | the outcome of ongoing or potential future litigation (and related activities, including inter partes reviews, inter partes reexaminations and “Paragraph IV” litigations) or other claims or disputes relating to our business, technologies, patents, products or processes; |
| • | our expected revenues (including sales, milestone payments and royalty revenues) from our products or product candidates and any related commercial agreements of ours; |
| • | the ability of our manufacturing partners to supply us or our commercial partners with clinical or commercial supplies of our products in a safe, timely and regulatory compliant manner and the ability of such partners to address any regulatory issues that have arisen or may in the future arise; |
| • | our ability to retain members of our management team and our employees; and |
| • | competition existing today or that will likely arise in the future. |
The foregoing does not represent an exhaustive list of risks that may impact the forward-looking statements used herein or in the documents incorporated by reference herein. Please see “Risk Factors” for additional risks which could adversely impact our business and financial performance and related forward-looking statements.
Moreover, new risks regularly emerge and it is not possible for our management to predict all risks, nor can we assess the impact of all risks on our business or the extent to which any risk, or combination of risks, may cause actual results to differ from those contained in any forward-looking statements. All forward-looking statements included in this Report are based on information available to us on the date hereof. Except to the extent required by applicable laws or rules, we undertake no obligation to publicly update or
1
Table of Contents
revise any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. All subsequent written and oral forward-looking statements attributable to us or persons acting on our behalf are expressly qualified in their entirety by the cautionary statements contained throughout this Report and the documents we have filed with the SEC.
| Item 1. | Description of Business. |
Overview
We are a specialty pharmaceutical company with a focus in the areas of pain management and addiction medicine. We have built a portfolio of products utilizing our novel and proprietary BioErodible MucoAdhesive (or BEMA®) drug delivery technology, a small, erodible polymer film for application to the buccal mucosa (the lining inside the cheek), which we currently commercialize in the U.S. utilizing our own sales force while working in partnership with third parties to commercialize our products outside the U.S. We were incorporated in the State of Indiana in 1997 and were reincorporated as a Delaware corporation in 2002.
BELBUCA® (buprenorphine) buccal film incorporates buprenorphine in our BEMA technology and was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) on October 26, 2015, for the management of pain severe enough to require daily, around the clock, long-term opioid treatment for which alternative treatment options are inadequate. BELBUCA® is designated by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency (“DEA”) as a Schedule III product, meaning it has less abuse and addiction potential compared to Schedule II products such as morphine, oxycodone and hydrocodone. BELBUCA® is also commercially available in Canada following market authorization from Health Canada in June 2017 and our subsequent exclusive agreement with Purdue Pharma (Canada) in July 2017 for the licensing and distribution rights of BELBUCA® in Canada.
Along with BELBUCA®, we utilize our sales force to commercialize BUNAVAIL® (buprenorphine and naloxone) buccal film, which was approved by the FDA on June 6, 2014. BUNAVAIL® utilizes our BEMA technology to deliver higher doses of buprenorphine along with the abuse deterrent, naloxone, for the treatment of opioid dependence and as part of a complete treatment plan to include counseling and psychosocial support.
Our third approved product, ONSOLIS® (fentanyl buccal soluble film), is currently marketed outside the U.S. through partnerships, and we are currently assessing strategic options for the reintroduction of ONSOLIS® to the U.S. market following the termination during 2017 of a licensing agreement with Collegium Pharmaceutical, Inc. (or Collegium).
As part of our corporate growth strategy, we have licensed, and will continue to explore opportunities to acquire or license additional drug delivery technologies or drugs utilizing the delivery or other technologies of other companies. As we gain access to such drugs and technologies, we will seek to utilize our development and commercialization experience to, either by ourselves or through partnerships, navigate the resulting products through the regulatory review process and ultimately bring them to the marketplace.
Our clinical and regulatory development strategy has focused primarily on our ability to utilize the FDA’s 505(b)(2) approval process to obtain more timely and efficient approval of new formulations of previously approved, active therapeutics incorporated into our drug delivery technology. Because the 505(b)(2) approval process is designed to address new formulations of previously approved drugs, we believe it has the potential to be more cost efficient and expeditious and have less regulatory approval risk than other FDA approval approaches.
An overview of our approved products and key products in development is set out below:
BELBUCA® (buprenorphine) buccal film for Chronic Pain
BELBUCA® is a partial mu-opioid agonist and a treatment indicated for the management of pain severe enough to require daily, around the clock, long-term opioid treatment for which alternative treatment options are inadequate. As described further below, our former commercial partner, Endo Pharmaceuticals Inc. (or Endo), received approval of the New Drug Application (or NDA) for BELBUCA® on October 23, 2015.
In January 2012, we announced the signing of a worldwide licensing and development agreement for BELBUCA® (which we refer to herein as the Endo Agreement) with Endo under which we granted to Endo the exclusive, worldwide rights to develop and commercialize BELBUCA® for the treatment of chronic pain. The financial terms of our agreement with Endo included: (i) a $30 million upfront, non-refundable license fee, which we received in January 2012; (ii) $95 million in milestone payments based on achievement of pre-defined intellectual property, clinical development and regulatory events (which we have received following receipt of a $50 million milestone payment associated with the FDA approval of BELBUCA®); (iii) $55 million in potential sales threshold payments upon achievement of designated sales levels; and (iv) a tiered, mid- to upper-teen royalty on net sales of BELBUCA® in the United States and a mid- to high-single digit royalty on net sales of BELBUCA® outside the United States.
2
Table of Contents
On January 23, 2014, we announced with Endo positive top-line results from the Phase 3 efficacy study of BELBUCA® in opioid-“naïve” subjects. The trial successfully met its primary efficacy endpoint in demonstrating that BELBUCA® resulted in significantly (p=0.0012) improved chronic pain relief compared to placebo. Additional secondary endpoints were supportive of the efficacy of BELBUCA® compared to placebo. The most commonly reported adverse events in patients treated with BELBUCA® compared to placebo during the double-blind portion of the study were nausea (10% vs. 7%, respectively), vomiting (4% vs. <1%, respectively) and constipation (4% vs. 3%, respectively). The locking of the database for the opioid naïve study triggered a $10 million milestone payment from Endo per the terms of the license agreement, which we received in February 2014.
On July 7, 2014, we announced with Endo positive top-line results from the Phase 3 efficacy study of BELBUCA® in opioid-“experienced” subjects. The trial successfully met its primary efficacy endpoint in demonstrating that BELBUCA® resulted in significantly (p<0.00001) improved chronic pain relief compared to placebo. Additional secondary endpoints were supportive of the efficacy of BELBUCA® compared to placebo. The most commonly reported adverse events in patients treated with BELBUCA® compared to placebo were nausea (7% vs. 7%, respectively), vomiting (5% vs. 2%, respectively) and constipation (3% vs. 1%, respectively). Locking of the database for the opioid experienced study triggered an additional $10 million milestone payment from Endo per the terms of the license agreement, which we received in July 2014.
On December 23, 2014, we and Endo announced the NDA submission for BELBUCA®, which was accepted by FDA in February 2015. Acceptance of the filing of the NDA by FDA triggered and we received an additional $10 million milestone payment from Endo which we subsequently received.
On October 26, 2015, we and Endo announced the FDA approval of BELBUCA® for use in patients with chronic pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment and for which alternative treatment options are inadequate. The approval of BELBUCA® was based on the two double-blind, placebo-controlled, enriched-enrollment Phase 3 studies. A total of 1,559 opioid experienced (study BUP-307) and opioid naïve (BUP-308) patients received study drug. In both studies, BELBUCA® demonstrated a consistent, statistically significant improvement in patient-reported pain relief at every week from baseline to week 12, compared to placebo. BELBUCA® is available in seven dose strengths, allowing for flexible dosing ranging from 75 mcg to 900 mcg every 12 hours. This enables physicians to individualize titration and treatment based on the optimally effective and tolerable dose for each patient. The FDA’s approval of BELBUCA® triggered a milestone payment to us from Endo of $50 million, of which $20 million had been deferred for future revenue recognition but was recognized as revenue in January 2017 upon termination of our agreement with Endo. (See below for Endo Termination).
BELBUCA® became commercially available from Endo in February 2016. Endo reported favorable early healthcare provider feedback and positive patient experience with regard to efficacy, tolerability and the buccal film formulation. Endo also filed a submission for BELBUCA® with Health Canada in the second quarter of 2016.
On December 8, 2016, we announced an agreement with Endo terminating Endo’s licensing of rights for BELBUCA®. This announcement followed a strategic decision made by Endo to discontinue commercial efforts of its branded pain business. On January 6, 2017, we announced the closing of the transaction to reacquire the license to BELBUCA® from Endo. As a result, the worldwide rights to BELBUCA® were transferred back to us. Going forward, we will not be responsible for future royalties or milestone payments to Endo, and Endo will not be obligated to any future milestone payments to us.
Behind a revised commercialized plan that took into consideration the current climate for prescribing opioids for chronic pain, we initially leveraged our existing sales force to capitalize on commercial synergies with BUNAVAIL® for a focused commercial approach targeting identified healthcare providers which we believe creates the potential to incrementally grow BELBUCA® sales without the requirement of significant resources. In mid-January 2017, we completed the expansion and training of our sales force, allowing for promotion of BELBUCA® to commence in late January. As a Schedule III opioid (meaning that buprenorphine, the active ingredient in BELBUCA®, has less abuse and addiction potential compared to Schedule II opioids such as oxycodone, hydrocodone and morphine), BELBUCA® is differentiated from other opioids and has the potential to address some of the most critical issues facing healthcare providers treating chronic pain with prescription opioids – abuse, misuse, addiction and the risk of overdose. These elements are at the center of the opioid crisis in our country and led to the 2017 declaration by the President of a Public Health Emergency. We are working with health care providers as well as various government agencies to provide education on buprenorphine and these key differences. As part of these efforts, we participated in a round table meeting convened in Washington D.C. by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (or HHS) in October 2017 with nine other manufacturers to discuss efforts to advance pain management therapies and the treatment of opioid use disorder in response to the opioid crisis. The meeting provided an opportunity for us to share the work we are doing to use our innovative drug delivery technology and products and make available alternative formulations of buprenorphine based on knowledge that it provides an effective, Schedule III alternative to other more addictive opioids. Based on this and other meetings we will continue to have with government policy makers, we are optimistic about the future role of buprenorphine for chronic pain management.
3
Table of Contents
BELBUCA® total prescriptions in 2017, according to Symphony Health, totaled nearly 86,000, an increase of 84% over 2016. BELBUCA share of total buprenorphine prescriptions (products for the treatment of chronic pain only) for 2017 totaled 12% versus 7% for the prior year. In addition to a steady increase in BELBUCA prescription sales through 2017, there was also an increase in the use of higher doses of BELBUCA as healthcare providers became more comfortable with the use of BELBUCA and awareness of the full range of doses increased. In 2016, 19% of BELBUCA prescriptions were for doses of 450 mcg or greater, compared to 33% in 2017. As such, the average price per prescription increased.
In June 2017, we announced the approval of BELBUCA® by Health Canada and in July our exclusive agreement with Purdue Pharma (Canada) for the licensing, distribution, marketing and sale of BELBUCA® in Canada. According to the Canadian Pain Society, pain is the most common reason for seeking healthcare, with 1 in 5 Canadian adults suffering from chronic pain. We view Purdue as a strong partner for BELBUCA® in Canada given its long history and commitment to pain management as well as its expertise and strong presence in the Canadian pain market. In return for the licensing and distribution rights to BELBUCA® in Canada, BioDelivery Sciences is eligible to receive upfront and potential milestones of up to $4.5 million CAD as well as royalties on net sales. On January 30, 2018, we along with Purdue announced the launch and commercial availability of BELBUCA in Canada.
Additionally, to capitalize on the commercial opportunity for BELBUCA, we increased the size of our sales force in early 2018 from 65 to 85 sales representatives. This increase allows us to reach additional high potential targets that were not covered previously, as well as improve our ability to optimize our reach and frequency among existing targets.
BUNAVAIL® (buprenorphine and naloxone) buccal film
We believe that the widespread use of buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid dependence and the need for improved means of delivery to address existing administration challenges present an important commercial opportunity. Therefore, we developed a BEMA® formulation of buprenorphine and naloxone specifically for the treatment of opioid dependence. The product combines a “high dose” of buprenorphine along with an abuse deterrent agent, naloxone. BUNAVAIL® provides us with an opportunity to compete in the growing opioid dependence market which, according to Symphony Health, exceeded $2.5 billion in sales in the U.S in 2017, an increase of 14% over the prior year.
In September 2012, we announced the positive outcome of the pivotal pharmacokinetic study comparing BUNAVAIL® to Suboxone® sublingual tablets. The study was designed to compare the relative bioavailability of buprenorphine and naloxone between BUNAVAIL® and the reference product, Suboxone® tablets. The results demonstrated that the two key pharmacokinetic parameters, maximum drug plasma concentration (Cmax) and total drug exposure (AUC), for buprenorphine were comparable to Suboxone® sublingual tablet, and that the same parameters for naloxone were similar or less than Suboxone® tablet. This was followed by initiation of the safety study requested by the FDA, assessing the safety and tolerability of BUNAVAIL® in patients converted from a stable dose of Suboxone® (buprenorphine and naloxone) sublingual tablets or films. A total of 249 patients were enrolled in the study, (191 patients completed) which completed in December 2012. Results of the study showed a very favorable safety and tolerability profile along with strong study subject retention and high dose form acceptability ratings. Data showed that over 91% of patients who switched from Suboxone® film or tablets considered the taste of BUNAVAIL® to be very pleasant, pleasant or neutral and over 82% rated the ease of use of BUNAVAIL® as very easy, easy or neutral. The study also showed a decrease in the incidence of constipation symptoms from 41% at baseline, before conversion of patients from Suboxone tablets or films to BUNAVAIL®, to 13% following 12 weeks of treatment with BUNAVAIL®.
On July 31, 2013, we submitted the NDA for BUNAVAIL® to the FDA for review, and On June 6, 2014, we announced the FDA approval of BUNAVAIL® for the maintenance treatment of opioid dependence as part of a complete treatment plan to include counseling and psychosocial support.
Following thorough review and analysis of a variety of commercialization strategies, which included entertaining commercial partnerships, a decision was made to commercialize BUNAVAIL® utilizing both internal and external resources.
On November 3, 2014, we announced the availability of BUNAVAIL® in the U.S. During the year ended 2015, we recognized $4.2 million in BUNAVAIL® sales revenue in its first full year on the market. In 2016, we took several steps to grow sales and profitability of the product including consolidating the sales force to focus on our most productive territories and executing additional managed care contracts. Six such agreements were secured between July and November 2016. BUNAVAIL® sales in 2016 were $8.3 million, representing a 98% increase from the previous year.
In May 2017, we announced that the FDA had approved a Supplemental New Drug Application (known as an sNDA) for BUNAVAIL revising the indication to include the initiation of buprenorphine treatment for opioid dependence. The approval broadened the indication for BUNAVAIL to include induction, or the initial process undertaken when a patient is transitioned from the abused opioid responsible for their addiction to the dose of BUNAVAIL which is intended to provide relief from cravings and withdrawal.
4
Table of Contents
As a result of the reacquisition of BELBUCA® in January 2017 and its market opportunity, our field sales force focus was shifted primarily to BELBUCA®, with BUNAVAIL® efforts limited to existing BUNAVAIL® prescribers and support behind existing BUNAVAIL managed care contracts. Following the transition of our sales force focus to BELBUCA®, total prescriptions of BUNAVAIL® in 2017 declined 20% over the prior year and subsequently leveled off as the year progressed. Given the significantly lower margins associated with BUNAVAIL, we continue to place our primary commercial efforts behind the continued growth of BELBUCA going into 2018. However, we continue to believe opportunity remains for BUNAVAIL growth as efforts to improve access to all treatment options for opioid dependence continues to gain support and government legislation has allowed for an increase in the number of patients that a physician can treat with buprenorphine. In November 2016, HHS also announced that nurse practitioners and physician assistants could begin taking the required training to prescribe buprenorphine for opioid use disorder and that those nurse practitioners and physician assistants who completed the required training could seek a waiver to begin prescribing buprenorphine beginning in early 2017, which further improved access to treatment.
ONSOLIS® (fentanyl buccal soluble film)
On July 16, 2009, we announced the U.S. approval of our first product, ONSOLIS® (fentanyl buccal soluble film). ONSOLIS® is indicated for the treatment of breakthrough pain (i.e., pain that “breaks through” the effects of other medications being used to control persistent pain) in opioid tolerant patients with cancer. In May 2010, regulatory approvals were granted for Canada, and in October 2010, approval was obtained in the European Union (which we refer to herein as E.U.) through the E.U.’s Decentralized Procedure, with Germany acting as the reference member state. ONSOLIS® is marketed in Europe under the trade-name BREAKYL™.
The FDA approval of ONSOLIS®, together with our satisfactory preparation of launch supplies of ONSOLIS®, triggered the payment to us by our commercial partner, Meda AB, a leading international specialty pharmaceutical company based in Sweden that was acquired by Mylan N.V. in 2016 (which we refer to herein as Meda), of approval milestones aggregating $26.8 million. The first national approval of BREAKYL™ in the E.U. resulted in a milestone payment of $2.5 million from Meda. A second milestone payment of $2.5 million was subsequently realized at the time of first commercial sale in the E.U. in October 2012. We began receiving royalties from Meda on net sales of ONSOLIS® in the U.S. following launch and from BREAKYL™ following launch in the E.U. Our royalty revenue from this product remains below original projections due to certain regulatory conditions in the U.S., which are discussed below.
We granted commercialization and distribution rights for ONSOLIS® on a worldwide basis (except in South Korea and Taiwan) to Meda. Meda secured access to additional markets through acquisition of European businesses from Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc.
In 2010, we licensed commercialization rights for ONSOLIS® for the remaining worldwide territories through execution of licensing agreements with KUNWHA Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (or Kunwha), for South Korea and TTY Biopharm Co., Ltd. (or TTY) for Taiwan where the product is marketed as PAINKYL™. The Kunwha License Agreement was terminated on August 31, 2015.
Although we have generated licensing-related and other revenue to date from the commercial sales of ONSOLIS®/BREAKYL™/PAINKYL™, such revenue has been limited to date due to multiple factors, including a highly restrictive Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) imposed by the FDA and certain formulation issues described below. The lack of approved REMS programs for our direct competitors resulted in an un-level playing field, which created an unfavorable selling environment for ONSOLIS® into 2012. In the E.U., BREAKYL™ was launched on a country by country basis starting in the fourth quarter of 2012 and continues to be sold by Meda. TTY launched PAINKYL™ in Taiwan in 2015.
On December 29, 2011, the FDA approved a “class-wide” REMS program covering all transmucosal fentanyl products under a single risk management program. The program, which is referred to as the Transmucosal Immediate Release Fentanyl (TIRF) REMS Access Program, was designed to ensure informed risk-benefit decisions before initiating treatment with a transmucosal fentanyl product, and while patients are on treatment, to ensure appropriate use. The TIRF REMS program was implemented in March 2012. The approved program covers all marketed transmucosal fentanyl products under a single program which will enhance patient safety while limiting the potential administrative burden on prescribers and their patients. One common program also ended the disparity in prescribing requirements for ONSOLIS® compared to similar products and provided ONSOLIS® with the opportunity for retail and inpatient facility access.
On March 12, 2012, we announced the postponement of the U.S. relaunch of ONSOLIS® following the initiation of the class-wide REMS until the product formulation could be modified to address two appearance-related issues. The appearance-related issues involved the formation of microscopic crystals and a fading of the color in the mucoadhesive layer and were raised by the FDA during
5
Table of Contents
an inspection of our North American manufacturing partner for ONSOLIS®, Aveva Drug Delivery Systems, Inc. (or Aveva) which is now a subsidiary of Apotex Inc. (or Apotex). While the appearance issues did not affect the product’s underlying integrity, safety or performance, the FDA believed that the fading of the color in particular may potentially confuse patients, necessitating a modification of the product and its specification before it can be manufactured and distributed. The source of microcrystal formation and the potential for fading of ONSOLIS® was found to be specific to a buffer used in its formulation. We modified the formulation and submitted a prior approval supplement that responded to the FDA questions and led to FDA approval of the new formulation of ONSOLIS® in August 2015.
On January 27, 2015, we announced that we had entered into an assignment and revenue sharing agreement with Meda to return to us the marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® for the U.S. and the right to seek marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® in Canada and Mexico.
On May 11, 2016, we announced the signing of a licensing agreement under which we granted to Collegium the exclusive rights to develop and commercialize ONSOLIS® in the U.S. Under terms of the agreement, Collegium was responsible for the manufacturing, distribution, marketing and sales of ONSOLIS® in the U.S. We collaborated with Collegium on the ongoing transfer of manufacturing to a new contract manufacturer, which includes a planned submission of a Prior Approval Supplement (Supplement) to the FDA. Financial terms of our agreement with Collegium included a $2.5 million upfront non-refundable payment, a $4 million payment upon first commercial sale, $3 million payable to us related to ONSOLIS® patent milestone, up to $17 million in potential payments based on achievement of performance and sales milestones, and upper-teen percent royalties based on various annual U.S. net sales thresholds, with Meda to share in a major portion of the partnership proceeds. Meda continues to commercialize ONSOLIS® under the brand name BREAKYL™ in the E.U.
In December 2017, we announced the reacquisition of U.S. rights to ONSOLIS® from Collegium, which agreement formally terminated March 8, 2018. We are assessing options for U.S. commercialization of ONSOLIS®, including the use of our current sales force, or potentially out-licensing the product.
Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection
In 2014, we entered into an exclusive agreement with Evonik Corporation (or Evonik) to develop and commercialize a proprietary, injectable microparticle formulation of buprenorphine potentially capable of providing 30 days of continuous therapy following a single subcutaneous injection. Microsphere-based, long acting buprenorphine injection has the ability to change the treatment paradigm in opioid dependence. Such a dosage form has the opportunity to improve therapy compliance through continuous delivery of drug for up to 30 days and addresses challenges regarding patient adherence to long-term buprenorphine treatment, which is critical to successfully manage opioid dependence and the potential for misuse and diversion.
While we plan to pursue an indication for the maintenance treatment of opioid dependence, we have also secured the rights and plans to develop a product for the treatment of chronic pain in patients requiring continuous opioid therapy. As part of the agreement, we will have the right to license the product(s) following the attainment of Phase 1 ready formulations. At that point, Evonik could receive downstream payments for milestones related to regulatory filings and subsequent NDA approvals as well as product royalties. Evonik has the exclusive rights to develop the formulation and manufacture the product(s).
In 2015, we completed initial development work and preclinical studies which have resulted in the identification of a formulation we believe is capable of providing 30 days of continuous buprenorphine treatment. During a pre-IND meeting with the FDA in November 2015, the FDA requested an additional study to assess the fate of the polymers used in the formulation. In 2016, we completed this study as well as additional preclinical work and other activities to support a planned Phase 1 clinical study. We submitted an Investigational New Drug application (or IND) for this product candidate to the FDA in December 2016 and as of December 31, 2017, have completed steps necessary to initiate a Phase 1 clinical study.
Clonidine Topical Gel
In March 2013, we announced our entry into a worldwide Exclusive License Agreement (which we refer to as the Arcion Agreement) with privately held Arcion Therapeutics (or Arcion), under which we would develop and commercialize Clonidine Topical Gel (formerly ARC4558) for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy (or PDN) and potentially other indications. Under the terms of the agreement, we made an upfront payment of $2 million to Arcion in the form of unregistered shares of our common stock. Additional financial terms of the licensing agreement include a milestone payment to Arcion of $2.5 million in unregistered shares of our common stock upon acceptance by the FDA of a NDA for Clonidine Topical Gel and a cash payment to Arcion of between $17.5 and $35 million upon NDA approval, depending on certain regulatory and commercial considerations. In addition, the licensing agreement includes sales milestones and low single-digit royalties on net worldwide sales.
6
Table of Contents
In March 2015, we announced that the primary efficacy endpoint in a Phase 3 study of Clonidine Topical Gel compared to placebo did not meet statistical significance, although certain secondary endpoints showed statistically significant improvement over placebo. Final analysis of the study identified a sizeable patient population with a statistically significant improvement (n=158; p<0.02) in pain score vs placebo. Following thorough analysis of the data and identification of the reasons behind the study results, we announced on December 8, 2015 that we had initiated a Phase 2b study. On December 13, 2016, we announced that the Phase 2b study failed to show a statistically significant difference in pain relief between Clonidine Topical Gel and placebo, and as a result we have no further plans for development of Clonidine Topical Gel. Given the perceived lack of efficacy, at least in this dosage form and at this strength, and given the resources to support the product by us, the rights to Clonidine Topical Gel were returned to Arcion in February 2017.
Additional Overview Information
From our inception through December 31, 2017, we have recorded accumulated losses totaling approximately $305.1 million. Our historical operating losses have resulted principally from our research and development activities, including clinical trial activities for our product candidates and general and administrative expenses. Ultimately, if we secure additional approvals from the FDA and other regulatory bodies throughout the world for our product candidates or other products or product candidates that we may acquire or in-license in the future, our goal will be to augment our current sources of revenue and, as applicable, deferred revenue (principally licensing fees), with sales of such products or royalties from such sales, on which we may pay royalties or other fees to our licensors and/or third-party collaborators as applicable.
We intend to finance our research and development, commercialization and distribution efforts and our working capital needs primarily through:
| • | commercializing our approved products such as BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®; |
| • | partnering with other pharmaceutical companies, as we have done with Purdue and Meda, to assist in the distribution and commercialization of our products, for which we would expect to receive an upfront payment, milestones and royalty payments; and |
| • | securing proceeds from public and private financings and other potential strategic transactions. |
We have based our estimates of development costs, market size estimates, peak annual sales projections and similar matters described below and elsewhere in this Report on our market research, third party reports and publicly available information which we consider reliable. However, readers are advised that the projected dates for filing and approval of our INDs or NDAs with the FDA or other regulatory authorities, our estimates of development costs, our projected sales and similar metrics regarding BUNAVAIL®, BELBUCA®, ONSOLIS®, Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection or any other product candidates discussed below and elsewhere in this Report are merely estimates and subject to many factors, many of which may be beyond our control, which will likely cause us to revise such estimates. Readers are also advised that our projected sales figures do not take into account the royalties and other payments we will need to make to our licensors and strategic partners. Our estimates are based upon our management’s reasonable judgments given the information available and their previous experiences, although such estimates may not prove to be accurate.
The BEMA® Drug Delivery Technology
Our BEMA® drug delivery technology consists of a small, bi-layered erodible polymer film for application to the buccal mucosa (the lining inside the cheek). BEMA® films have the capability to deliver a rapid, reliable dose of drug across the buccal mucosa for time-critical conditions such as “breakthrough” cancer pain or in situations where gastrointestinal absorption of an oral drug is not practical or reliable, or in facilitating the administration of drugs with poor oral bioavailability.
We believe that the BEMA® technology permits control of two critical factors allowing for better dose-to-dose reproducibility: (i) the contact area for mucosal drug delivery, and (ii) the time the drug is in contact with that area, known as residence time. In contrast to competing transmucosal delivery systems like lozenges, buccal tablets and matrix-based delivery systems placed under the tongue or sprayed in the oral cavity, BEMA® products are designed to:
| • | adhere to buccal mucosa in seconds and dissolve in minutes; |
| • | permit absorption without patients being required to move the product around in the mouth for absorption, thus avoiding patient intervariability; |
| • | allow for unidirectional drug flow into the mucosa as a result of a backing layer on the side of the BEMA® film facing into the patient’s mouth |
7
Table of Contents
| • | provide a reproducible delivery rate, not susceptible to varying or intermittent contact with oral membranes; and |
| • | dissolve completely, leaving no residual product or waste and avoiding patient removal, and the possibility for diversion or disposal of partially used product. |
We currently own the BEMA® drug delivery technology. We previously licensed the BEMA® drug delivery technology on an exclusive basis from Atrix Laboratories (previously known as QLT USA, Inc., now known as TOLMAR Therapeutics, Inc., which we refer to herein as Tolmar).
Overview of “Specialty Pharmaceuticals” and the 505(b)(2) Regulatory Pathway
Our corporate focus is “specialty pharmaceuticals” with characteristics that provide substantial points of differentiation from existing products. Our product portfolio is based on the application of drug delivery technologies and/or new dosage forms/indications to existing drugs for the creation of novel products. We then seek proprietary protection and FDA approval, and subsequently commercialize these products ourselves or through partners. We believe that research and development efforts focused on novel dose forms of FDA approved drugs is less risky than attempting to discover new drugs, sometimes called new chemical entities (known as NCEs). Our corporate focus came to initial fruition with the FDA’s approval of ONSOLIS® (fentanyl buccal soluble film) in 2009 and was replicated in 2014 with the approval of BUNAVAIL® (buprenorphine and naloxone) buccal film and again in 2015 with the approval of BELBUCA® (buprenorphine) buccal film. It is our goal to replicate this success with our current product candidates, and to identify new product candidates suitable for this development strategy that would add significant commercial value to us.
An important part of our strategy is the utilization of FDA’s 505(b)(2) NDA process for approval. Under the 505(b)(2) process, we are able to seek FDA approval of a new dosage form, dosage regimen or new indication of an FDA approved drug. This regulation enables us to partially rely on the FDA’s previous findings of safety and effectiveness for the drug, including clinical and nonclinical testing, and thereby reduce, although not eliminate, the need to engage in these costly and time-consuming activities. A typical development program for a 505(b)(2) submission will include:
| • | single and multiple dose toxicity studies in a single animal species, |
| • | pharmacokinetic evaluation of the new dosage form in humans, |
| • | stability data on the drug substance, |
| • | description of drug product components and formulation, |
| • | description and validation of manufacturing processes, |
| • | one-year stability data on three commercial scale batches of drug product, and |
| • | depending on the drug product, may include: |
| (i) | one or more placebo controlled clinical studies in humans to establish the efficacy of the product, and/or |
| (ii) | a long term clinical study to establish the safety of the product in the intended patient population. |
This drug development and regulatory approval process is less extensive and lengthy than for a NCE and, as a result, we believe, is a more cost-effective way to bring new product candidates to market.
We have and intend to continue to target markets with unmet needs and new dosage forms of known drugs. As a result of employing well known drugs in novel technologies or new dosage forms/indications, we believe health care providers will be familiar with the drugs and accustomed to prescribing them. As with ONSOLIS®, BELBUCA®, and BUNAVAIL® our drug candidates have been through the regulatory process with safety and efficacy established for an indication, a formulation and a dose range. Consequently, our clinical trials need to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of our products in the chosen patient population.
Endo Licensing Agreement for BELBUCA® and its Termination
On January 6, 2012, we entered into the world-wide licensing and development agreement for BELBUCA® with Endo, which was subsequently terminated as described above. Under terms of the agreement, Endo was responsible for the manufacturing, distribution, marketing and sales of BELBUCA® on a worldwide basis. The agreement called for Endo to commercialize BELBUCA® outside the U.S. through its own efforts or through regional partnerships. In the U.S., we and Endo collaborated on the planning and finalization of the Phase 3 clinical development program and regulatory strategy for BELBUCA® for chronic pain. On October 23, 2015 the FDA approved BELBUCA® for licensing in the United States.
8
Table of Contents
In aggregate, the agreement was worth up to $180 million to us if all milestones or thresholds are met, which includes an upfront non-refundable license fee of $30 million (received January 2012), as well as intellectual property, development, regulatory and commercial milestone and sales threshold payments. We would have received a tiered mid to upper teen royalty on U.S. net sales of BELBUCA® and a tiered mid to upper single-digit royalty on sales outside the U.S. One of the key intellectual property milestones under our Endo Agreement was achieved when, in April 2012, the USPTO granted US Patent No. 8,147,866 (issued from US Patent Application No. 13/184,306), which will extend the exclusivity of the BEMA® drug delivery technology for BELBUCA® (as well as BUNAVAIL® discussed below) from 2020 to 2027. As a result (and included in the aforementioned $180 million if all milestones or thresholds are met), we received a milestone payment in the amount of $15 million in May 2012, and also received an additional milestone payment of $20 million which was paid at the time of approval of a NDA by the FDA for BELBUCA®. The aforementioned $20 million patent-related payment will be earned over the extended patent period from 2020 to 2027. As mentioned above, the obligations of this milestone were extinguished upon the closing of the termination arrangements. Additionally, we achieved another milestone with the locking of the database for our Phase 3 opioid naive clinical study on January 17, 2014. For the achievement of this milestone, per the terms of the agreement, we were due a milestone payment in the amount of $10 million, which was received February 2014 (which is included in the aforementioned $180 million if all milestones or thresholds are met) within thirty (30) days of the database lock. On June 25, 2014, the database for the pivotal Phase 3 efficacy study of BELBUCA® in opioid-experienced patients was locked. The locking of the database triggered a $10 million milestone payment from Endo, which was received July 2014. On December 23, 2014, we and Endo announced the submission of a NDA for BELBUCA® to the FDA, which was accepted February 23, 2015, which triggered a $10 million milestone payment due from Endo to us. As stated above, on October 23, 2015 the FDA approved BELBUCA® for licensing in the United States, which we announced on October 26, 2015. The FDA’s approval of BELBUCA® triggered a milestone payment to us from Endo of $50 million, of which $20 million has been deferred for future revenue recognition as the payment is contingently refundable in the event a generic product is commercially launched during the patent extension period. As mentioned below, the obligations of this milestone were extinguished upon the closing of the termination agreement. This $20 million was recognized as revenue in January 2017.
On December 8, 2016 we announced we had entered into a termination agreement with Endo (the Endo Termination Agreement) terminating Endo’s licensing of rights for BELBUCA® CIII (buprenorphine) buccal film. The transaction terminating Endo’s licensing of rights for BELBUCA® closed on January 6, 2017. This transaction follows a strategic decision announced by Endo in December regarding its U.S. branded pain business. As a result of the agreement, the world-wide rights to BELBUCA® were transferred back to us. We are not responsible for future royalties or milestone payments to Endo and Endo will not be obligated to any future milestone payments to us. The termination agreement with Endo is filed as an exhibit to this Report.
At the closing of the transactions contemplated by the Endo Termination Agreement we purchased from Endo the following assets (which we refer to as the Assets): (i) current BELBUCA® product inventory and work-in-progress, (ii) material manufacturing contracts related to BELBUCA®, (iii) BELBUCA-related domain names and trademarks (including the BELBUCA® trademark), (iv) BELBUCA®-related manufacturing equipment, and (v) all pre-approval regulatory submissions, including any Investigational New Drug Applications and New Drug Applications, regulatory approvals and post-approval regulatory submissions concerning BELBUCA®. The purchase price for the Assets (which we refer to as the Asset Purchase Price) was equal to the sum of: (i) the aggregate book value of the portion of the transferred product inventory forecasted to be used or sold by the Company, (ii) the aggregate book value of work-in-progress inventory, and (iii) the assumption of any assumed liabilities. Upon Closing, we accepted transfer of the Assets and assumed and agreed to discharge when due all applicable liabilities assumed by us, which consisted of post-closing obligations for liabilities and payments associated with the Assets, the assumed contracts related to the Assets and applicable taxes (with the obligation for pre-closing and other certain liabilities resulting from the acts or omissions of Endo being retained by Endo).
The Asset Purchase Price, together with all other payments (including a non-compete covenant payment) due to Endo under the Endo Termination Agreement, are payable to Endo in cash, in four quarterly installments on the last calendar day of each quarter in 2017. Furthermore, we will not be responsible for future royalties or milestone payments to Endo, and Endo will not be obligated to any future milestone payments to us. The Termination Agreement contains customary representations and warranties and mutual releases and indemnification.
At the closing of the Termination Agreement, we and Endo entered into a Transition Services Agreement which governed the post-closing rights and responsibilities of us and Endo in connection with the license termination and the transfer of the Assets to us. Under this agreement, we and Endo agreed to the handling of transition matters such as managing customer contracts, BELBUCA® price reporting, payments, returns and rebates, and customer and managed care relations. In connection therewith, Endo agreed to provide to us an agreed upon number of work hours to be provided by Endo personnel during the transition for certain of these transition services and other assistance with respect to the transition of BELBUCA® to us.
In conjunction with the aforementioned Endo Termination Agreement, on December 7, 2016, we also entered into a distribution agreement (which we refer to as the Distribution Agreement) with Par Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (or Par) for the distribution of an authorized generic BELBUCA® product after the launch of a generic BELBUCA® product by a third party. The Distribution
9
Table of Contents
Agreement covers distribution within the entire United States, has an initial term of three years after the launch of a generic BELBUCA® product by a third party, an initial automatic renewal period of two years, and additional automatic one-year renewal periods thereafter, which will occur unless either party provides written notice of termination an agreed upon period of time prior to the expiration of the initial term or any renewal term. In exchange for distribution rights of the generic product, Par will pay us an agreed upon base purchase price and a deferred purchase price equal to a percentage of profit (as such term is specifically agreed to in the Distribution Agreement) with respect to units of each dosage strength of generic product. During the term of the Distribution Agreement, Par is precluded from manufacturing for sale in the United States, or distributing in the United States, any equivalent product, provided that nothing prohibits Par from continuing or undertaking to develop any equivalent product or selling such equivalent product outside of the U.S. The Distribution Agreement contains customary termination provisions for bankruptcy, withdrawal of product from the market, and regulatory and legislative changes, as well as a termination right for insufficient profits or Par’s acquisition by or of a party challenging our patents with respect to BELBUCA®.
Meda Licensing Agreements for ONSOLIS®
North American Agreement. On September 5, 2007, we entered into a definitive License and Development Agreement with Meda and our subsidiary Arius pursuant to which we and Arius agreed to grant to Meda an exclusive commercial license to market, sell, and, following regulatory approval, continue development of ONSOLIS® in the United States, Mexico and Canada (which we refer to as the Meda North American License).
Pursuant to such license agreement, we have received or will receive:
| • | a $30.0 million milestone payment (received in 2007). |
| • | a $29.8 million milestone payment for the approval of ONSOLIS® by the FDA and provision of commercial supplies of ONSOLIS® in the U.S. (received in 2009). |
| • | a double-digit royalty on net sales of ONSOLIS® in the covered territories, subject to certain third-party royalty payment costs and adjustments, as well as other adjustments in the event of certain specific supply disruptions. The license agreement provides for certain guaranteed minimum annual royalties to us during the second through seventh years following the product’s first commercial sale, which occurred in the fourth quarter of 2009. |
| • | sales milestones equaling an aggregate of $30 million will be payable at: |
| • | $10.0 million when and if annual sales meet or exceed $75.0 million; |
| • | $10.0 million when and if annual sales meet or exceed $125.0 million; and |
| • | $10.0 million when and if annual sales meet or exceed $175.0 million. |
European Agreement. In 2006, we announced collaboration with Meda to develop and commercialize BEMA® Fentanyl (marketed as BREAKYL™ in Europe). Under terms of the agreement, we granted Meda rights to the European development and commercialization of BREAKYL™, in exchange for an upfront fee of $2.5 million and a $2.5 million milestone payment (received in 2008) for completion of Phase 3 clinical trials. We have also received a double-digit royalty on net sales and additional milestone payments of $2.5 million upon approval and $2.5 million upon launch in the first country in the European territory (received in 2012). Meda has managed the regulatory submission in Europe that led to approval in October 2010. Meda will exclusively commercialize BREAKYL™ in Europe.
In 2009, we received a $3 million payment in exchange for amending the European agreement to provide Meda the worldwide rights to ONSOLIS®, except for South Korea and Taiwan. The sales royalties to be received by us will be the same for all territories as agreed to for Europe. In addition, various terms of the European agreements have been modified to reflect the rights and obligations of both us and Meda in recognition of the expansion of the scope of the European agreements.
On January 27, 2015, we announced that we had entered into an assignment and revenue sharing agreement with Meda to return to us the marketing authorization for ONSOLIS® in the U.S. and the right to seek marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® in Canada and Mexico. Following the return of the U.S. marketing authorization from Meda, we submitted a prior approval supplement for the new formulation to the FDA in March 2015, which was approved in August 2016. In connection with the return of the U.S. marketing authorization by Meda to us in January 2015, the remaining U.S.-related deferred revenue of $1.0 million was recorded as contract revenue during the year ended December 31, 2015. There was no remaining U.S.-related contract revenue to record during the year ended December 31, 2016. On February 27, 2016, we entered into an extension of the assignment and revenue sharing agreement to extend the period until December 31, 2016.
10
Table of Contents
Efforts to extend our supply agreement with its ONSOLIS® manufacturer, Aveva, which is now a subsidiary of Apotex, Inc., were unsuccessful and the agreement expired. However, we identified an alternate supplier and requested guidance from the FDA on the specific requirements for obtaining approval to supply product from this new vendor. Based on current estimates, we expect to submit the necessary documentation to the FDA for qualification of the new manufacturer by the first quarter of 2018.
Collegium License and Development Agreement for ONSOLIS® and its Termination
On May 11, 2016, we entered into a definitive License and Development Agreement (which we refer to as the Collegium Agreement) with Collegium under which we granted Collegium the exclusive rights to develop and commercialize ONSOLIS® in the U.S. Under the terms of the Collegium Agreement, Collegium will be responsible for the manufacturing, distribution, marketing and sales of ONSOLIS® in the U.S. We are obligated to use commercially reasonable efforts to continue the transfer of manufacturing to the anticipated manufacturer for ONSOLIS® and to submit a corresponding Prior Approval Supplement (the “Supplement”) to the FDA with respect to the current NDA for ONSOLIS®. Following approval of the Supplement, the NDA and manufacturing responsibility for ONSOLIS® (including the manufacturing relationship with our manufacturer, subject to our entering into an appropriate agreement with such manufacturer that is acceptable and assignable to Collegium) will be transferred to Collegium.
Financial terms of the License Agreement include;
| • | $2.5 million upfront non-refundable payment, (received in June 2016); |
| • | reimbursement to us for a pre-determined amount of the remaining expenses associated with the ongoing transfer of the manufacturing of ONSOLIS®; |
| • | $4 million payable to us upon first commercial sale of ONSOLIS® in the U.S; |
| • | $3 million payable to us related to ONSOLIS® patent milestone; |
| • | up to $17 million in potential payments to us based on achievement of certain performance and sales milestones; and |
| • | upper-teen percent royalties payable by Collegium to us based on various annual U.S. net sales thresholds, subject to customary adjustments and the royalty sharing arrangements described below. |
The Collegium Agreement also contained customary termination provisions that include a right by either party to terminate upon the other party’s uncured material breach, insolvency or bankruptcy, as well as in the event a certain commercial milestone is not met.
On December 8, 2017, Collegium provided us the required 90-day notice regarding termination of the license and development agreement for ONSOLIS® between us and Collegium. Collegium’s decision to terminate the license involved their execution of a license agreement to commercialize Nucynta® (tapentadol) Immediate Release and Nucynta® ER (tapentadol). The license and development agreement for ONSOLIS® between us and Collegium formally ended on March 8, 2018. We are working with Collegium to transfer the assets back to us and reach final resolution of financial matters.
ONSOLIS® was originally licensed to, and launched in the U.S. by, Meda. In January 2015, we entered into an assignment and revenue sharing agreement (which we refer to as the ARS Agreement) with Meda pursuant to which Meda transferred the marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® in the United States back to us. Under the ARS Agreement, financial terms were established that enable Meda to share a significant portion of the proceeds of milestone and royalty payments received by us from any new North American partnership for ONSOLIS® that may be executed by us. The execution of the Collegium Agreement also required the execution of a definitive termination agreement between us and Meda embodying those royalty-sharing terms, returning ONSOLIS®-related assets and rights in the U.S., Canada, and Mexico to us, and including certain other provisions. In addition, our royalty obligations to CDC IV, LLC (or CDC IV), an entity that originally provided funding for the development of ONSOLIS®, and its assignees will remain in effect. CDC IV provided funding for the development of ONSOLIS® in the past.
Key Collaborative and Supply Relationships
We are and have been a party to collaborative agreements with corporate partners, contractors, universities and government agencies. Research collaboration may result in new inventions which are generally considered joint intellectual property unless invented solely by individuals we employ, or by third party transfer to us by contract. Our collaboration arrangements are intended to provide us with access to greater resources and scientific expertise in addition to our in-house capabilities. We also have supply arrangements with several of the key component producers of our delivery technology. Our collaborative and supply relationships include:
| • | Meda. For a description of our agreements with Meda, please see “Meda Licensing Agreements for ONSOLIS®” above. |
11
Table of Contents
| • | Collegium. For a description of our agreements with Collegium, please see “Collegium License and Development Agreement for ONSOLIS®” above. |
| • | LTS Lohmann Therapie-Systeme AG. Effective December 15, 2006, we entered into a Process Development Agreement with LTS Lohmann Therapie-Systeme AG (which we refer to herein as LTS). Under the agreement, LTS has granted us a license under European Patent No. 0 949 925, regarding BREAKYL™ in the E.U. Our BREAKYL™ agreement is renewable for successive terms of two-year terms and shall continue until terminated under the following conditions: i) bankruptcy/insolvency, ii) intellectual property loss, iii) breach of contract iv) supply failure, and v) mutual agreement. LTS manufactures BREAKYL™ for sale in the E.U. and PAINKYL™ for sale in the Republic of China (Taiwan). |
| • | ARx. Effective July 30, 2014, we entered into an agreement with ARx, LLC. Pursuant to which ARx acts as a supplier of BUNAVAIL® laminate or bulk product for the United States. Our supply agreement with ARx was then amended July 14, 2017 and now the agreement runs until December 31, 2023. The agreement can be further renewed for additional terms by mutual agreement. |
| • | Sharp. Effective March 6, 2014, we entered into an agreement with Sharp Corporation (“Sharp”) to punch or cut the BUNAVAIL® laminate or bulk product into individual dosage units and package them to supply finished BUNAVAIL® film products. Our supply agreement with Sharp ran for an initial term from March 6, 2014 until December 31, 2016 and was extended by mutual agreement for a subsequent one-year term until December 31, 2017, which has been extended to December 31, 2018. Effective January 6, 2017, we assumed Endo’s agreement with Sharp to package the individual dosage units to supply finished BELBUCA® film products, which expires on December 31, 2022. This specific BELBUCA® packaging agreement is being added to our original supply agreement with Sharp so that both BUNAVAIL® and BELBUCA® packaging are governed by the same agreement which can be extended by mutual agreement for subsequent one-year terms. |
| • | Tapemark. Effective January 6, 2017, we assumed Endo’s agreement with The Tapemark Company to punch or cut the BELBUCA® laminate or bulk product into individual dosage units which are then transferred to Sharp for final packaging and supply of finished BELBUCA® film products. Our BELBUCA® agreement runs from the assumption of the agreement on January 6, 2017 and shall continue until terminated under the following conditions: i) at will termination, with 36-months prior written notice, ii) default, with prior written notice, iii) finished product withdrawal, iv) inability to supply, v) bankruptcy/insolvency, and vi) mutual agreement. |
We also have relationships with third party contract research organizations that assist us with the management of our clinical trials.
In pursuing potential commercial opportunities, we intend to seek and rely upon additional collaborative relationships with corporate partners. Such relationships may include initial funding, milestone payments, licensing payments, royalties, access to proprietary drugs or potential applications of our drug delivery technologies or other relationships. Our agreements with Endo and Meda are examples of these types of relationships, and we will continue to seek other similar arrangements.
Relationship with CDC IV, LLC
On July 14, 2005, we entered into a Clinical Development and License Agreement (which we refer to as the “CDLA”), with the predecessor of CDC IV, which provided funds to us for the development of ONSOLIS®. On February 16, 2006, we announced that, as a result of our achievement of certain milestones called for under the CDLA, CDC IV made its initial $2 million payment to us. On May 16, 2006, we issued CDC IV 2 million shares of our common stock in return for accelerating the funding of the $4.2 million balance of $7 million of aggregate commitment under the CDLA and for eliminating the then required $7 million milestone repayment to CDC IV upon the approval by the FDA of ONSOLIS®.
Under the CDLA, as amended, CDC IV is entitled to receive a low-double digit royalty based on net sales of ONSOLIS®. The CDLA includes minimum royalties of $375,000 per quarter beginning in the second full year following commercial launch. The minimum provision came into effect in 2011. The royalty term and minimum payments end upon the latter of expiration of the patent or generic entry into any particular country.
The term of the CDLA lasts until the CDLA is terminated. Either we or CDC IV may terminate the CDLA for uncured breach or upon bankruptcy-like events, in each case following written notice. CDC IV may terminate the CDLA, following applicable cure periods, if we: (i) default on indebtedness in excess of $1 million which was accelerated or for which payment has been demanded, or (ii) fail to satisfy a judgment greater than $500,000.
12
Table of Contents
We and CDC IV entered into a Royalty Purchase and Amendment Agreement, dated September 5, 2007 (or the RPAA) pursuant to which we granted CDC IV a 1% royalty on sales of the next BEMA® product, which is BUNAVAIL®, including an active pharmaceutical ingredient other than fentanyl, to receive FDA approval. In connection with the 1% royalty grant as previously mentioned: (i) CDC IV shall have the option to exchange its royalty rights to BUNAVAIL® in favor of royalty rights to a substitute BEMA® product, (ii) we shall have the right, no earlier than six (6) months prior to the initial commercial launch of BUNAVAIL®, to propose in writing and negotiate the key terms pursuant to which it would repurchase the royalty from CDC IV, (iii) CDC IV’s right to the royalty shall immediately terminate at any time if annual net sales of BUNAVAIL® equal less than $7.5 million in any calendar year following the third (3rd) anniversary of initial launch of the product and CDC IV receives $18,750 in three (3) consecutive quarters as payment for CDC IV’s 1% royalty during such calendar year and (iv) CDC IV shall have certain information rights with respect to BUNAVAIL®. The amount of royalties which we may be required to pay (including estimates of the minimum royalties) is not presently determinable because product sales estimates cannot be reasonably determined and the regulatory approvals of the product for sale is not possible to predict. As such, we expect to record such royalties, if any, as cost of sales.
On November 21, 2016 we entered into an Amended and Restated Clinical Development and License Agreement with CDC IV and Athyrium that did not materially change the rights of the parties under the CDLA, but merely clarified and memorialized in a single agreement the rights and obligations of our company, CDC IV and Athyrium under the CDLA and its various amendments as described above.
Research and Development
Most of our research and development relating to our BEMA® and other technologies is conducted through third parties in collaboration with us.
Research and development expenses include salaries and benefits for personnel involved in our research and development activities and direct and third-party development costs, which include costs relating to the formulation and manufacturing of our product candidates, costs relating to non-clinical studies, including toxicology studies, and clinical trials, and costs relating to compliance with regulatory requirements applicable to the development of our product candidates. For the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, we spent approximately $13.0 million, $18.9 million and $20.6 million, respectively, on research and development, and such expenses represented approximately 18%, 28% and 27%, respectively, of our total operating expenses for such fiscal years.
Endo was responsible for reimbursing us for certain research and development clinical trial expenses that exceed $45 million, as detailed in our License and Development Agreement that was executed on January 5, 2012. For the year ended December 31, 2015, we incurred $0.9 million in such research and development expenses that were reimbursable by Endo to us. There were no reimbursements by Endo in 2017 or 2016 as the program ended in 2015.
Collegium was responsible for reimbursing us for a pre-determined amount of the remaining expenses associated with the ongoing transfer of the manufacturing of ONSOLIS®, as detailed in our definitive License and Development Agreement that was executed on May 11, 2016. For the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, we have incurred $0.8 million and $1.1 million, respectively, in such reimbursements that are reimbursable by Collegium to us. There were no reimbursements by Collegium in 2015.
Market Overview for BELBUCA®, BUNAVAIL®, ONSOLIS® and Our Product Candidate
The following table summarizes the status of our marketed products and our current product candidates:
|
Product/Formulation |
Indication |
Development Status |
Commercial Status | |||
| BELBUCA® |
Management of pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment and for which alternative treatment options are inadequate | Approval: U.S. in October 2015; Canada in June 2017 |
Canada partnership with Purdue (Canada); in-house commercialization in U.S. | |||
13
Table of Contents
|
Product/Formulation |
Indication |
Development Status |
Commercial Status | |||
| BUNAVAIL® |
Treatment of opioid dependence | Approval: U.S. in June 2014 | In-house commercialization in U.S. | |||
| ONSOLIS®/BREAKYL™ /PAINKYL™ (U.S./E.U./Taiwan trade names, respectively) |
Breakthrough cancer pain in opioid tolerant patients | Approval: U.S. in July 2009; Canada in May 2010; E.U. in October 2010 and Taiwan in July 2013 |
Partnership with Meda in all regions except North America, Taiwan and South Korea; partnership with TTY in Taiwan; exploring options for U.S. commercialization | |||
| Buprenorphine ER Injection |
Opioid dependence and chronic pain | IND submitted December 2016 |
Not partnered | |||
The pharmaceutical industry and the therapeutic areas in which we compete are highly competitive and subject to rapid and substantial regulatory and technological changes. Developments by others may render our BEMA® technology, our marketed products and any proposed drug products and formulations under development noncompetitive or obsolete, or we may be unable to keep pace with technological developments or other market factors. Technological competition in the industry from pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, universities, governmental entities and others diversifying into the field is intense and is expected to increase.
Below are some examples of companies seeking to develop potentially competitive technologies, though the examples are not all-inclusive. Many of these entities have significantly greater research and development capabilities than do we, as well as substantially more sales and marketing, manufacturing, financial and managerial resources. These entities represent significant competition for us. In addition, acquisitions of, or investments in, competing pharmaceutical or biotechnology companies by large corporations could increase such competitors’ research, financial, sales and marketing, manufacturing and other resources. Such potential competitive technologies may ultimately prove to be safer, more effective, or less costly than any product candidates that we are currently developing or may be able to develop. Additionally, our competitive position may be materially affected by our ability to develop or successfully commercialize our drugs and technologies. Other external factors may also impact the ability of our products to meet expectations or effectively compete, including pricing pressures, healthcare reform and other government interventions as well as limitations on access that may be placed upon us through managed care organizations or through competitive contracting with payers.
There have been a growing number of companies developing products utilizing various thin film drug delivery technologies. While numerous over-the-counter pharmaceutical products have been brought to market in thin film formulations, few containing prescription products have been introduced in the U.S. Among the products to receive FDA approval are BUNAVAIL®, BELBUCA®, and ONSOLIS® (BDSI), Suboxone® film (Indivior) and Zuplenz® (Midatech Pharma). Companies in the development and manufacture of thin film technologies include LTS, ARx LLC and MonoSol Rx LLC, dba Aquestive Therapeutics (“Aquestive”). In addition, a number of companies are developing improved versions of existing products using oral dissolving, nasal spray, aerosol, sustained release injection and other drug delivery technologies. We believe that potential competitors are seeking to develop and commercialize technologies for buccal, sublingual or mucosal delivery of various therapeutics or groups of therapeutics. While our information concerning these competitors and their development strategy is limited, we believe our technology can be differentiated because the BEMA® technology provides for a rapid and consistent delivery, high drug bioavailability and convenient use based on how the BEMA® technology adheres to the buccal membrane and dissolves. Our clinical trials across a number of BEMA® products have demonstrated that the technology is an effective means of drug delivery that is well tolerated and offers convenience to patients.
BELBUCA® (buprenorphine) buccal film for chronic pain
Chronic pain is often defined as any pain lasting more than 12 weeks. Whereas acute pain is a normal sensation that alerts us to possible injury, chronic pain persists – often for months or even longer. Chronic pain may arise from an initial injury, such as back sprain, or there may be an ongoing cause, such as an illness. Sometimes there is no clear cause. According to the National Institutes of Health, approximately 100 million people in the U.S. are living with chronic pain.
BELBUCA® was approved by the FDA on October 26, 2015 for use in patients with pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment for which alternative options are inadequate. Compared to currently marketed products and products under development, we believe that BELBUCA® is differentiated based on the following features:
| • | strong and durable efficacy in both opioid naïve and opioid experienced patients; |
| • | Schedule III designation by DEA, which indicates less abuse and addiction potential compared Schedule II opioids, which include oxycodone, hydrocodone and morphine; |
14
Table of Contents
| • | at higher doses, published studies have shown that buprenorphine’s physiologic effects reach a plateau, and this ceiling effect may result in a lower risk of overdose related respiratory depression; |
| • | favorable tolerability with a low incidence of constipation and low discontinuation rate; |
| • | flexible dosing options covering up to 160 mg morphine sulfate equivalents (MSE); and |
| • | buccal administration to optimize buprenorphine delivery. |
Because of the safety, tolerability and efficacy benefits associated with this opioid, we believe that BELBUCA® is well suited for patients with pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment for which alternative treatments, such as non-opioids or immediate release opioids, are inadequate.
The pain market is well established, with many pharmaceutical companies marketing new formulations of existing products as well as generic versions of older, non-patent protected products. In 2017, according to data from Symphony Health, the market for extended release opioids in the U.S. totaled nearly $4.5 billion in annual sales with nearly 16 million prescriptions dispensed. However, prescription sales of long acting opioids declined by 10% in 2017 compared to 2016 amidst wide-ranging efforts to curb misuse, abuse and over use of opioids in order to address the current opioid crisis. In March 2017, the President Trump signed an executive order establishing the President’s Commission on Combating Drug Addiction and the Opioid Crisis and in October declared the opioid crisis a national emergency. While governmental and other efforts continue to focus on combating the current opioid epidemic, we remain committed to focusing on responsible opioid prescribing and believe that products such as BELBUCA and BUNAVAIL can help play an important role in addressing the current healthcare crisis in the U.S.
A number of products are competitors to BELBUCA®. One area of focus for us (and previously for Endo) is to position BELBUCA® in patients who are transitioning from short to long acting opioids. Indications for such use include pain associated with lower back and severe arthritis conditions where alternative treatment options have been inadequate, and pain is severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment. Marketed competitors for these indications include Butrans® (buprenorphine transdermal patch) from Purdue and Schedule II opioids such as OxyContin® from Purdue and Nucynta® ER from Depomed/Collegium. Other competition includes multiple generic Schedule II oral opioid formulations, such as morphine, hydrocodone, and fentanyl containing products.
Additionally, “abuse deterrent” formulations of pain products are currently being marketed, in clinical development or under FDA review. These formulations, such as Embeda® from Pfizer, Hysingla® ER from Purdue, Zohydro® ER from Pernix Therapeutics, MorphaBond™ ER from Daiichi Sankyo, Xtampza® ER from Collegium and Arymo™ ER from Egalet, as well as new formulations of OxyContin®, use a variety of technologies that aim to minimize the potential for abuse and misuse. Abuse deterrent products are likely to play an unclear but increasingly important role in prescribing, potentially even replacing the original product.
An advantage of BELBUCA® is that the compound, buprenorphine, may be inherently less likely to cause abuse and addiction given the lower propensity for the product to cause euphoria and is the current basis of its Schedule III classification.
The first buprenorphine formulation for the treatment of chronic pain, Purdue Pharma’s Butrans® (buprenorphine transdermal system), was approved in 2010. Butrans®, like BELBUCA®, is indicated for use in patients with pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment for which alternative options are inadequate. Butrans delivers buprenorphine transdermally (through the skin) over a period of seven days. The approval of Butrans® signaled the interest and approvability of new formulations of buprenorphine. Butrans is available in a range of doses to treat patients on up to 80 mg MSE (morphine sulfate equivalents) compared to 180 mg MSE with BELBUCA®. It is our view that the flexibility of dosing with a BEMA® formulation, wider range of doses and ease of use will make it a preferred formulation for a significant number of patients with chronic pain conditions. Butrans® was launched in early 2011. Sales of Butrans® in 2017 totaled over $239 million, a decrease of 10% over the prior year. The decrease is primarily attributed to the launch of generic buprenorphine transdermal patches in 2017, which in December 2017, accounted for one-third of all buprenorphine transdermal patch prescriptions.
Insys Therapeutics, Inc. (or Insys) is developing sublingual buprenorphine spray for the treatment of pain. Results of a Phase 3 trial of this product were reported in August 2016 and indicated that sublingual buprenorphine spray was well tolerated and led to reduced pain vs. placebo over 48 hours after a bunionectomy procedure. Insys announced in December 2017 that the New Drug Application for its buprenorphine sublingual spray for moderate-to-severe acute pain had been accepted for filing by the FDA. Insys is also considering future studies in chronic pain; however, development of a product for the treatment of chronic pain is more complex with lengthier trials and greater risk, thus sublingual buprenorphine spray for chronic pain is not viewed as a near-term threat to BELBUCA®. While limited information is available, other formulations of buprenorphine may also be in early stages of development for the treatment of pain. Relmada Therapeutics Inc. has in its pipeline an oral, enteric-coated buprenorphine (BuTab) for chronic pain and opioid dependence indications. In December 2015, Relmada announced topline results of a proof-of-concept pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers which showed that the product can be delivered at therapeutic levels through the gastrointestinal route, though the bioavailability remained low. No further development is noted.
15
Table of Contents
In addition to direct competitors, there are other factors that impact the market for pain products in general. The significant pricing pressures and availability of generic products in the U.S. and other regions are likely to have increasing influence on the pharmaceutical market, including pain products. Additionally, opioids continue to garner increased scrutiny based on the growing problem of prescription drug abuse and addiction. It remains unclear what additional steps, if any, the FDA or other government agencies may take to address the problem of opioid abuse and addiction. However, in July 2012 the FDA approved a class-wide REMS program for the extended release and long-acting opioids. The class-wide REMS program consists of a REMS-compliant educational program offered by an accredited provider of continuing medical education, patient counseling materials and a medication guide. BELBUCA® falls within the existing class-wide REMS program. In August 2014, the DEA published in the Federal Register its final ruling moving hydrocodone combination products (such as Vicodin, Lortab, Norco, etc.) from Schedule III to the more-restrictive Schedule II, as recommended by the Assistant Secretary for Health of HHS and as supported by the DEA’s own evaluation of relevant data. As a result of the ruling, hydrocodone containing products are now classified in the same category (Schedule II) as morphine and oxycodone. In addition, HHS’s Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (or the CDC) in March 2016 issued guidelines for prescribing opioids for chronic pain. CDC developed and published the CDC Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain to provide recommendations for the prescribing of opioid pain medication for patients 18 and older in primary care settings. Recommendations focus on the use of opioids in treating chronic pain. The guidelines advocate use of nonpharmacologic therapy and nonopioid pharmacologic therapy as first line therapy for chronic pain. When starting opioid therapy for chronic pain, clinicians are advised to prescribe immediate-release opioids instead of extended-release/long-acting (ER/LA) opioids and to prescribe the lowest effective dosage. The availability of the guidelines has resulted in confusion and cautiousness, particularly among primary care physicians, and a reduced willingness to treat patients for chronic pain. A sharp reduction in prescriptions among Primary Care Physicians and an increase among Pain Specialists are evidence of the shift in prescribing and in the dynamics of pain treatment. Additionally, in June 2017, the FDA requested that Endo Pharmaceuticals remove Opana ER (oxymorphone), from the market based on concerns that the benefits of the drug may no longer outweigh its risks. This is the first time the agency has taken steps to remove a currently marketed opioid pain medication from sale due to the public health consequences of abuse. The FDA’s decision was based on a review of all available postmarketing data, which demonstrated a significant shift in the route of abuse of Opana ER from nasal to injection following the product’s reformulation. It is anticipated that other steps will be taken to further limit the use, duration dose or availability of certain opioids – particularly those with Schedule II designation.
BUNAVAIL®
In June 2014, BUNAVAIL® was approved by the FDA for the maintenance treatment of opioid dependence – and in May 2017 we announced that the BUNAVAIL® indication was expanded to include induction of buprenorphine treatment for opioid dependence. BUNAVAIL® contains the partial opioid agonist buprenorphine, which binds to the same receptors as opiate drugs but has a higher affinity. Naloxone, an opioid antagonist, is included as an abuse deterrent. When used as directed, the naloxone is swallowed and minimally absorbed; however, if misused (i.e., dissolved and injected), the naloxone rapidly precipitates withdrawal symptoms.
Treatment with buprenorphine reduces the typical cravings and withdrawal symptoms associated with coming off opioid prescription painkillers and heroin. This allows the individual suffering from an addiction to opioids –along with counseling and support – to work toward recovery. On average, treatment lasts a couple months, reflecting relatively high dropout rates, but a significant number of people remain on buprenorphine treatment chronically, with nearly one-quarter of patients still on therapy after nine months. BUNAVAIL® provides an alternative treatment utilizing the advanced BEMA® drug delivery technology. BUNAVAIL® provides the highest bioavailability of any buprenorphine-containing product for opioid dependence, allowing for effective treatment with half the dose compared to Suboxone® film. Additionally, BUNAVAIL® offers convenient and discrete buccal administration and avoids the need for patients to avoid talking and swallowing during administration. Data has also demonstrated an excellent tolerability profile with a 68% reduction at the end of 12 weeks in the incidence of constipation in a Phase 3 trial in patients converted from Suboxone® sublingual tablets or film to BUNAVAIL®.
The total U.S. market for buprenorphine containing products for opioid dependence exceeded $25 billion in 2017, an increase of 14% over 2016. The market has grown steadily as a result of the rapidly escalating problem of prescription opioid misuse and abuse, a recent resurgence of heroin use, the growing number of physicians treating opioid dependence, and the inclusion of addiction treatment as an essential benefit in the Affordable Care Act. Additionally, important steps were taken by government agencies in 2015 to expand access to medication assisted treatment (MAT) with buprenorphine for opioid use disorder. In August 2016, based on a new ruling from HHS, the cap on the number of patients eligible to be treated by waivered physicians increased from a maximum of 100 to 275. According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), over 3,900 clinicians applied for and were granted waivers to prescribe buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid dependence at the increased limit by early 2018 with a total of over 46,000 waivered practitioners in total. Subsequently, The Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act (CARA) was signed into law. This was the first major federal addiction legislation in 40 years, and the most comprehensive effort undertaken to address the opioid epidemic. The legislation included expansion of office-based treatment by allowing Nurse Practitioners and Physician Assistants to prescribe buprenorphine for opioid dependence beginning in 2018.
16
Table of Contents
The products currently marketed for this indication include Suboxone®, a sublingual film formulation of buprenorphine and naloxone, a sublingual tablet of buprenorphine and naloxone, (Zubsolv®), and generic formulations of both buprenorphine and buprenorphine/naloxone tablets. Buprenorphine/naloxone combination products make up the majority of the category and represent 82% of total prescriptions. Suboxone® film, the market leader with 70% of total buprenorphine/naloxone prescriptions, achieved sales of over $1.7 billion in the U.S. in 2017. In December 2014, Reckitt Benckiser Group PLC, the manufacturer of Suboxone® sublingual tablets and films, announced that it completed the spin-off of that company’s pharmaceutical business (including the Suboxone® brand) under the name Indivior PLC (or Indivior) in order to allow the consumer goods group to focus on its consumer health and hygiene products. The Indivior business focuses on addiction treatment and closely related areas including opioid overdose, cocaine overdose and alcohol dependence.
Generic buprenorphine/naloxone tablet formulations were launched in early 2013 by Actavis (now known as Teva Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (or Teva) and Amneal Pharmaceuticals and were followed by additional entrants. The impact of generic buprenorphine/naloxone tablets on Suboxone® film and on the overall branded market has been somewhat limited to date, with generic buprenorphine/naloxone tablets accounting for only 23% of total buprenorphine/naloxone product prescriptions. Additional generics may enter the market, though the timing is unclear and the impact is anticipated to be limited.
A sublingual tablet, referred to as Zubsolv® was approved by FDA in July 2013 and subsequently launched in September 2013. Zubsolv® is a sublingual formulation of buprenorphine/naloxone using Orexo’s proprietary sublingual drug delivery technology. Orexo is a specialty pharmaceutical company with headquarters in Sweden. Orexo is developing treatments using its proprietary sublingual drug delivery technology, which includes the marketed product Abstral® that delivers fentanyl for the treatment of breakthrough cancer pain. Zubsolv® is being marketed predominantly based on its claims of improved taste and faster dissolve time compared to Suboxone®. Sales for Zubsolv® in 2017 were relatively flat and totaled approximately $123 million in the U.S. for a prescription market share of 5%.
While limited information is available, a sublingual spray formulation of buprenorphine/naloxone is in development from Insys Therapeutics and is currently in Phase I development studies.
While we anticipate that the market for buprenorphine/naloxone products for the treatment of opioid dependence will get increasingly more competitive, we believe a BEMA® formulation of buprenorphine/naloxone has significant appeal given its buccal administration, enhanced delivery of buprenorphine, tolerability profile, convenience, and lack of taste issues. We also believe that the increased number of companies promoting the use of buprenorphine containing-products for opioid dependence has the potential to create greater awareness and help to further expand what is already a significant and growing market.
ONSOLIS®
According to the National Cancer Institute, there are approximately 14.5 million people in the United States diagnosed with or living with cancer. Cancer patients often suffer from a variety of symptoms including pain as a result of their cancer or cancer treatment. Pain is a widely prevalent symptom in cancer patients, and an estimated 50% to 90% of those with cancer also suffer from what is referred to as breakthrough cancer pain (or BTCP). Following rapid onset that peaks in three to five minutes, BTCP episodes can last several minutes to an hour, and usually occur several times per day. BTCP can be difficult to treat due to its severity, rapid onset and the often unpredictable nature. Physicians typically treat BTCP with a variety of short-acting opioid medications, including morphine and fentanyl. A number of formulations of fentanyl are available employing a variety of drug delivery technologies, all which provide rapid onset and relatively short duration of action to address the fast onset and short duration of BTCP.
For ONSOLIS®, in the breakthrough cancer pain area, the market has become increasingly crowded and more competitive in recent years. The principal competitor had traditionally been Teva Pharmaceutical, which completed its acquisition of Cephalon in October 2011. Teva markets both lozenge (Actiq®) and effervescent buccal tablet (Fentora®) formulations of fentanyl. In recent years, newer product entries, particularly Subsys® (fentanyl sublingual spray) from Insys, have gained significant market share. Additional competitors include the sublingual tablet formulation of fentanyl (Abstral®) and a nasal spray formulation of fentanyl (Lazanda®). In addition, multiple generic formulations of Actiq® are currently available.
On December 29, 2011, the FDA approved a REMS program covering all transmucosal fentanyl products. The program, which is referred to as the Transmucosal Immediate Release Fentanyl (TIRF) REMS Access Program, was designed to ensure informed risk-benefit decisions before initiating treatment with a transmucosal fentanyl product, and while patients are on treatment, to ensure
17
Table of Contents
appropriate use. The approved program covers all marketed transmucosal fentanyl products, including ONSOLIS®, under a single program which is meant to enhance patient safety while limiting the potential administrative burden on prescribers and their patients. One common program ended the disparity in prescribing requirements for ONSOLIS® compared to similar products.
Other potent acute pain products are also in development, including ARX-04 from AcelRx Pharmaceuticals, which is a sublingual tablet drug/device delivery system containing sufentanil for the treatment of acute pain. Following a December 2016 NDA submission, AcelRx received a complete response letter from the FDA in October 2017. While we have limited information regarding ARX-04 and potential other competitors and their development status and strategy, we believe that our technology may be differentiated because unlike these potential competitors, ONSOLIS® has a predefined residence time on the buccal membrane providing for consistent drug delivery from dose to dose. We believe that the competitive formulations of fentanyl will have intra-dose variability, meaning the patient may not get the same response each time the product is administered. In addition, it is our belief that many of the other competitive products may have tolerability issues and a higher level of potential abuse based on how they are delivered.
The chart below lists products that we believe may compete directly with ONSOLIS®.
| Product |
Company |
Description |
Status | |||
|
Actiq® (oral transmucosal fentanyl citrate) |
Teva/Generics | Lozenge | Marketed (generics available) | |||
|
Fentora® (fentanyl buccal tablet) |
Teva Pharmaceutical | Effervescent buccal tablet | Marketed | |||
|
Abstral® (fentanyl sublingual tablet) |
Sentynl Therapeutics | Sublingual tablet | Marketed | |||
|
Lazanda® (fentanyl nasal spray) |
Slan Medicinal | Nasal spray | Marketed | |||
|
Subsys® (fentanyl sublingual spray) |
INSYS Therapeutics | Sublingual spray | Marketed | |||
| NAL1239 |
NAL Pharmaceuticals | Orally dissolving film | Proposed 505(b)(2) NDA | |||
| ARX-04 (sufentanil) |
AcelRx Pharmaceuticals | Sublingual tablet | NDA filed (U.S.) | |||
In Europe, multiple formulations of fentanyl have been approved and launched for the treatment of breakthrough cancer pain, including ONSOLIS® (marketed as BREAKYL™ by Meda/Mylan) as well as Abstral®, Effentora®, and Instanyl® (intranasal fentanyl spray).
Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection
Despite the availability of effective treatments, including BUNAVAIL® buccal film, challenges remain regarding patient adherence to long-term buprenorphine treatment, which is critical to successfully managing opioid dependence. This has led to interest in alternative delivery systems for buprenorphine. One such opportunity is the development of an injectable, long-acting formulation. Microsphere-based, long acting, buprenorphine extended release injection has the ability to change the treatment paradigm in opioid dependence and pain management. Such a dosage form provides improved therapy compliance through continuous delivery of drug for up to 30 days. In 2014, we entered into an exclusive agreement with Evonik to develop and commercialize a proprietary, injectable microparticle formulation of buprenorphine potentially capable of providing 30 days of continuous therapy following a single subcutaneous injection. While we plan to pursue an indication for the maintenance treatment of opioid dependence, we have also secured the rights and are developing a product for the treatment of chronic pain in patients requiring continuous opioid therapy. Significant progress has been made in the development of a formulation to allow for delivery once per month as well as provide advantages over other injectable buprenorphine products. We submitted an IND for Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection in December 2016.
In terms of potential competition for Buprenorphine ER Injection, Probuphine, a subcutaneous implantable rod containing buprenorphine from Braeburn Pharmaceuticals was approved in May 2016. In December 2012, Titan Pharmaceuticals announced the signing of a license agreement with Braeburn Pharmaceuticals. The license granted Braeburn exclusive commercialization rights in the United States and Canada. While limited information is available on current use of Probuphine, given the need for surgical implantation and removal as well as dosing limitations, we do not expect Probuphine to be a significant competitor to our buprenorphine injection.
In November 2017, Indivior announced the FDA approval of Sublocade (buprenorphine extended release) injection for subcutaneous use. Sublocade is the first once-monthly injectable buprenorphine formulation and was approved for the treatment of moderate to severe opioid use disorder in patients who have initiated treatment with a transmucosal buprenorphine-containing product followed by dose adjustment for a minimum of seven days. Sublocade was evaluated in a 24-week, Phase 3 pivotal study in which
18
Table of Contents
patients were randomized to one of two Sublocade regimens or placebo. Both dosage regimens of Sublocade were shown to be superior to placebo in achieving more illicit opioid-free weeks. Sublocade is expected to be made available in the first quarter of 2018 in single dose, pre-filled syringes (100 mg, 300 mg) and will require refrigeration. The product is intended to be administered only by a healthcare provider and will distributed through a restricted distribution system. A second extended release buprenorphine injection, CAM2038, is also in development. In January 2018, Braeburn Pharmaceuticals announced it had received a complete response letter from the FDA for their weekly and monthly injection. The FDA has requested additional information in order to progress the application forward.
Licenses, Intellectual Property and Proprietary Information
Our intellectual property strategy is intended to maximize protection of our proprietary technologies and know-how and to further expand targeted opportunities by extension of our patents, trademarks, license agreements and trade secrets portfolio. In addition, an element of our strategic focus provides for varying specific royalty or other payment obligations by our commercial partners as our applicable intellectual property portfolio changes or business activity reaches certain thresholds.
However, patent positions of biotechnology and pharmaceutical organizations are uncertain and involve complex legal and technical issues. There is considerable uncertainty regarding the breadth of claims in patent cases which results in varied degrees of protection. While we believe that our intellectual property position is sound, it may be that our pending patent applications will not be granted or that our awarded claims may be too narrow to protect the products against competitors. It is also possible that our intellectual property positions will be challenged or that patents issued to others prior to our patent issuance may preclude us from commercializing our products. It is also possible that other parties could have or could obtain patent rights which may cover or block our products or otherwise dominate our patent position.
BEMA® Technology
The drug delivery technology space is congested, although we do not believe that our BEMA® products conflict with, are dominated by, or infringe any external patents and we do not believe that we require licenses under external patents for our BEMA® based products in the United States. It is possible, however, that a court of law in the United States or elsewhere might determine otherwise. If a court were to determine that we were infringing other patents and that those patents were valid, we might be required to seek one or more licenses to commercialize our products or technologies and we may be unable to obtain such licenses from the patent holders. If we were unable to obtain a license, or if the terms of the license were onerous, there may be a material adverse effect upon our business plan to commercialize these products.
This potential exists in our present litigation with Aquestive. Aquestive claimed in a litigation initiated in late 2010 that our confidential and trade secret manufacturing process for ONSOLIS® infringes their patented manufacturing process for thin films. We do not believe that we have infringed these claims. Moreover, we believe that the original claims in Aquestive patents ‘588, ‘292 and ‘891 are invalid or overbroad, and, in connection with inter partes and ex parte reexamination proceedings we have brought before the USPTO, the USPTO has either rejected and cancelled all claims, amended the original claims to make them narrower, or issued narrower, new claims replacing the broader original claims for each of the ‘588, ‘292 and US patent No 7,357,891 (which we refer to as the ’891 Patent), respectively. We also believe that the manufacturing processes for our products, including BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® do not infringe Aquestive’s patents, at least because they do not meet the limitations of the original, amended or new claims of Aquestive’s patents. We maintain our manufacturing processes for our BEMA® products and product candidates as trade secrets. Based on our examination of these patents, we do not believe our manufacturing processes infringe Aquestive’s patents. On March 7, 2012, the court granted our motion to stay the case pending outcome of the reexamination proceedings in the USPTO. On July 3, 2012, the USPTO issued an ex parte reexamination certificate on the ‘891 patent, in which all original claims were amended to make them narrower. On August 26, 2012, the USPTO issued an ex parte reexamination certificate on the United States Patent No 7,425,292 (which we refer to as the ’292 Patent), in which all the original broader claims were replaced with narrower, new claims. As for the United States Patent No. 7,824,588) (which we refer to as the ’588 Patent), after the reexamination proceedings (and its appeals process), on April 17, 2014, the Patent Trial and Appeal Board (“PTAB”) of the USPTO issued a Decision on Appeal affirming the Examiner’s rejection (and confirming the invalidity) of all the claims of the ’588 Patent. Aquestive did not request a rehearing by the May 17, 2014 due date for making such a request and did not further appeal the Decision to the Federal Court of Appeals by the June 17, 2014 due date for making such an appeal. Subsequently, on August 5, 2014, the USPTO issued a Certificate of Reexamination cancelling the ‘588 Patent claims. The litigation resumed and on September 25, 2015 the court granted our motion of Summary Judgement of Intervening Rights and dismissed the case. Aquestive filed an appeal with the Federal Circuit and has subsequently decided to withdraw the appeal. On February 25, 2016, Aquestive filed an Unopposed Motion For Voluntary Dismissal Of Appeal, which was granted by the court on February 26, 2016 and the case dismissed. Thus, the district court’s grant of the Summary Judgement of Intervening Rights will stand.
19
Table of Contents
On March 1, 2011, we were granted a patent extending the exclusivity of the BEMA® drug delivery technology in Canada to 2027. The Canadian Patent No. 2,658,585 provides additional patent protection for ONSOLIS® and BELBUCA®. In April 2012, the USPTO granted US Patent No. 8,147,866, which will extend the exclusivity of the BEMA® drug delivery technology for BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® in the United States from 2020 to 2027. In April 2014, the USPTO granted US Patent No. 8,703,177 (issued from US Patent Application No. 13/590,094), which will extend the exclusivity of the BEMA® drug delivery technology for BUNAVAIL® in the United States to at least 2032. In February 2018, we were granted US Patent No. 9,901,539, which will extend the exclusivity of the BEMA® technology for BELBUCA® in the United States to December 21, 2032.
We own various patents and patent applications relating to the BEMA® technology. US Patent No. 6,159,498 (expiration date October 2016), US Patent No. 7,579,019 (expiration date January 22, 2020), US Patent No. 8,147,866 (expiration date July 23, 2027), US Patent 8,703,177 (expiration date August 20, 2032), US Patent 9,522,188 (expiration date April 24, 2035), US Patent 9,597,288 (expiration date July 23, 2027), US Patent 9,655,843 (expiration date July 23, 2027), US Patent 9,901,539 (expiration date December 21, 2032, Canadian Patent No. 2,658,585 (expiration date July 2027), EP2054031 (expiration date July 2027) and EP 0 973 497 (expiration date October 2017) are of particular value to our business and technology platform relating to the BEMA® delivery technology. On February 16, 2010, we filed a complaint with the United States Federal District Court for the District of Columbia, requesting the USPTO be required to further extend the patent term for US 7,579,019 from 835 days to 1,191 days. In March 2011, we prevailed in this case, and the patent expiration date of US Patent No. 7,579,019 is now extended from January 31, 2019 to January 22, 2020.
On January 22, 2014, Aquestive filed a Petition for Inter Partes Review (or IPR) on US Patent No. 7,579,019 with the USPTO. In the Petition, Aquestive is requesting an inter partes review because it is asserting that the claims of US Patent No. 7,579,019 are alleged to be unpatentable over certain prior art references. The USPTO instituted the IPR on the US Patent No. 7,579,019 (which we refer to as the ’019 Patent).. The USPTO found all claims patentable and Aquestive filed a Request for Rehearing. On December 19, 2016, the PTAB issued a final decision denying Aquestive’s request for rehearing. Aquestive did not appeal this final decision.
With respect to trademarks, “BDSI®,” “BEMA®”, “BELBUCA®” and “BUNAVAIL®” are registered trademarks of BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc. ONSOLIS® and BREAKYL™ are also trademarks owned by BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc. PAINKYL™ is a trademark owned by TTY Biopharm.
Clonidine Topical Gel
On March 26, 2013, we entered into the Arcion Agreement with Arcion pursuant to which Arcion agreed to grant to us an exclusive commercial world-wide license, with rights of sublicense, under certain patent and other intellectual property rights of Arcion to develop, manufacture, market, and sell gel products containing clonidine (or a derivative thereof), alone or in combination with other active ingredients, for topical administration for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy and other indications (the Clonidine Gel Products).
Per the Arcion Agreement, we had exclusive rights to various patents pertaining to the Clonidine Gel Products. US Patent No. 6,147,102 (expiration date October 26, 2019), US Patent No. 6,534,048 (expiration date October 26, 2019), US Patent No. 8,026,266 (expiration date September 30, 2029) and their corresponding patents in other countries (e.g., Australia, Canada, Germany, etc.) which were of value to our business and technology platform relating to the Clonidine Gel Products.
On December 13, 2016, we announced that the Phase 2b study failed to show a statistically significant difference in pain relief between Clonidine Topical Gel and placebo, and as a result we have no further plans for development of Clonidine Topical Gel. Given the perceived lack of efficacy, at least in this dosage form and at this strength, and given the resources to support the product by us, the rights to Clonidine Topical Gel were returned to Arcion in February 2017.
Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection Product Candidate
On October 27, 2014, we entered into a definitive Development and Exclusive License Option Agreement (which we refer to as the Evonik Development Agreement) with Evonik pursuant to which Evonik agreed to grant two exclusive options to acquire exclusive worldwide licenses, with rights of sublicense, to certain patents and other intellectual property rights of Evonik to develop and commercialize certain injectable, extended release products containing buprenorphine (which we refer to as Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection Products). If such options are exercised, such licenses would be memorialized in a definitive license agreement.
Although we do not believe that any Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection Products would conflict with, dominated by, or infringing any external patents and we do not believe that we require licenses under external patents for Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection Products, it is possible, however, that a court of law in the United States or elsewhere might determine otherwise. If a court were to determine that we were infringing other patents and that those patents were valid, we might be required to seek one or more licenses to commercialize our products or technologies. We may be unable to obtain such licenses from the patent holders. If we were unable to obtain a license, or if the terms of the license were onerous, there may be a material adverse effect upon our business plan to commercialize these products.
20
Table of Contents
Manufacturing
We rely on third-party manufacturers, packagers, and analytical testing laboratories to produce commercial product and developmental products for research, product development, and clinical supplies. We are currently party to the following manufacturing arrangements for different companies:
BELBUCA®
Effective January 5, 2012, we entered a license and development agreement with Endo for BELBUCA®. Over the past two years, the technical operations and supply activities have been gradually transitioned from our company to Endo. As a result of the licensing and developmental agreement, all of the commercial supply agreements will be negotiated by and the responsibility of Endo.
On December 8, 2016, we announced the reacquisition of the world-wide rights of BELBUCA® from Endo. This agreement went into effect on January 6, 2017. As a part of the reacquisition rights, we continue to honor the contractual relationships put in place by Endo with the API and excipient manufacturers, contract manufacturing and packaging organizations, and analytical testing facilities.
BUNAVAIL®
Effective July 30, 2014, we entered a Supply Agreement with ARx LLC for manufacturing, and effective March 6, 2014, we entered a Supply Agreement with Sharp for packaging for BUNAVAIL® commercial supplies, respectively. Both companies underwent successful FDA preapproval inspections and will be subject to annual quality audits. Both our contracts are also supported by a quality assurance agreement requiring our counterparties to adhere to product quality standards and cGMP manufacturing and packaging requirements. BUNAVAIL® is currently manufactured by ARx LLC.
ONSOLIS®
Effective October 17, 2005, we entered into an agreement with Aveva to supply ONSOLIS® for clinical trials and commercial sale. Under the terms of this agreement, Aveva was the sole supplier of ONSOLIS® for the United States and Canada. On March 12, 2012, we announced the postponement of the U.S. relaunch of ONSOLIS® following the initiation of the class-wide REMS with two appearance issues raised by FDA during an inspection of Aveva’s manufacturing facility. Specifically, the FDA identified the formation of microscopic crystals and a fading of the color in the mucoadhesive layer during the 24-month shelf life of the product. ONSOLIS® has been subsequently reformulated with 24 months of available stability data on the reformulated product.
On March 30, 2012, Apotex, Inc. announced its acquisition of our contract manufacturing organization Aveva Drug Delivery Systems and issued a notification of termination of the supply agreement for manufacturing of ONSOLIS®. On October 9, 2014, Aveva sent us written notice of their intent not to renew our supply agreement. In February 2015, we re-acquired the rights to the ONSOLIS® NDA from Meda, and we submitted the reformulated product on March 27, 2015 as a prior approval supplement. The reformulated product was approved by the FDA on August 11, 2015. Subsequently, our supply agreement with Aveva expired on October 15, 2015.
In May 2016, we engaged in a licensing agreement with Collegium for ONSOLIS® and initiated a facility qualification and manufacturing of registration batches with Tapemark, our contract manufacturing organization for ONSOLIS®. We anticipate submission of the Prior Approval Supplement in the first quarter of 2018 for this new commercial manufacturing and packaging site.
BREAKYL™
Effective December 15, 2006, we entered into a process development agreement and a commercial Supply Agreement on April 26, 2012, both with LTS. Under the terms of this supply agreement, LTS is the exclusive manufacturer of BEMA® Fentanyl for all countries with exception of the United States and Canada. LTS continues to manufacture BREAKYL™ for MEDA since it was first launched in the E.U. in September 2012.
21
Table of Contents
PAINKYL™
We entered a license and commercial supply agreement with TTY in Taiwan on October 4, 2010. In July 2013, Taiwan FDA (TFDA) approved PAINKYL™ for market authorization. LTS manufacture PAINKYL™ for TTY since it was first launched on January 28, 2015.
Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection
Effective October 27, 2014, we entered into an exclusive agreement with Evonik to develop and commercialize a proprietary long acting, sustained release, biodegradable microparticle buprenorphine formulation capable of providing 30 days of continuous therapy following a subcutaneous injection. Through the agreement, we also secured the license to Evonik-owned intellectual property related to products for the maintenance treatment of opioid dependence and for the treatment of chronic pain. This product is currently in development.
Clonidine Topical Gel
Effective October 22, 2014, we entered into a master service agreement with Ei LLC for formulation, analytical and manufacturing services, clinical supplies, packaging and product release for the Clonidine Topical Gel. We have also made similar arrangements with Frontage and Tapemark for bulk manufacture for initial clinical trial supplies and individual dose units packaging, respectively. In December 2016, we announced that our CLO-291 study did not meet its primary end point and as a result, all manufacturing plans for the clonidine gel have been terminated.
Sales and Marketing
Following, and assuming, completion of clinical development and regulatory approval for each candidate product, we will pursue one of several approaches (or a combination thereof) for marketing and selling our products. These include selling the products through our own sales force, licensing the products to appropriate partners so that they can market and distribute the products for us, co-promotions where we would share in the sales promotion, or use of a contract sales organization. We currently employ two of these approaches as we promote BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® through our own sales force and have licensed commercialization rights to Meda and TTY for BREAKYL™/ PAINKYL™ for breakthrough cancer pain.
In 2014, we launched BUNAVAIL® with the creation of an exclusive contract sales force through Quintiles, a contract sales organization. In 2016, we converted the contract sales force into one employed by us to provide a greater sense of belonging and responsibility, to reduce administrative costs and inefficiencies, and to give us greater flexibility to accommodate future strategic options. Using our own sales force provides us with significantly more control over commercialization efforts and makes us capable of selling our own products in specialty pharmaceutical markets while leaving promotional responsibilities for large primary care audiences and ex-U.S. markets with partners.
In January 2017, following the reacquisition of BELBUCA® from Endo, our sales force began selling BELBUCA® in addition to BUNAVAIL®. Given the greater long-term commercial and profitability opportunities with BELBUCA®, we have transitioned our primary commercial emphasis to BELBUCA®. We also expanded the sales force to 65 territories because of the opportunity created by the reacquisition of BELBUCA®.
In January 2018, to further accelerate the growth of BELBUCA® we further expanded the sales force to 85 territories and 9 Regional Sales Managers supporting both BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®.
BELBUCA® (buprenorphine) buccal film for Chronic Pain
We announced the signing of a worldwide licensing and development agreement for BELBUCA® with Endo in January 2012. Under terms of the agreement, Endo was responsible for the manufacturing, distribution, marketing and sales of BELBUCA® on a worldwide basis. On December 8, 2016, we announced that we were reacquiring the worldwide license to BELBUCA® from Endo; the transition went into effect on January 6, 2017. We believe that Endo built a significant foundation for BELBUCA® and that the safety, tolerability and efficacy profile of BELBUCA provides us with a strong opportunity to gain a share of the $10 billion U.S. opioid market.
Given this large market opportunity and the greater profitability of BELBUCA®, we have expanded our sales force and have made BELBUCA® our primary commercial emphasis, while continuing to support BUNAVAIL®. Our sales force is focused on current BELBUCA® prescribers and clinicians we believe have the greatest opportunity to be adopters of BELBUCA®, such as high prescribers of: long-acting opioids, Butrans and/or short acting opioids chronically. In parallel, we are heavily focused on increasing
22
Table of Contents
market access for BELBUCA®. More than half of all long-acting opioid prescriptions are through commercial payers. As of January 2018, BELBUCA® is covered in formulary platforms that represent more than 85% of commercial lives. Approval rates within the commercial channel remain favorable at about 80%. This improved formulary position has also had a positive impact on reversal rates which declined to approximately 6.5% in 2017 as patient cost shares improved. Although we continue to see favorable approval rates for BELBUCA® within the Medicare space, we continue to pursue improved access to make BELBUCA® more accessible to the senior population suffering with chronic pain.
We believe that educating clinicians regarding the safety, tolerability and efficacy benefits of BELBUCA® will also be important to gaining share in the large chronic pain market. As such, we are sponsoring BELBUCA®-focused speaker programs in regions across the U.S. A key goal of these programs is to position BELBUCA® as an alternative to Schedule II opioids for the treatment of moderate to severe chronic pain that is not adequately controlled with commonly prescribed first-line therapies (e.g. short acting opioids).
Canada
On July 12, 2017 we announced the signing of a licensing agreement under which we granted the exclusive rights to distribute, market and sell BELBUCA® in Canada to Purdue Pharma (Canada). Under terms of the agreement, we will receive upfront and potential milestones of up to $4.5 million CAD as well as royalties on net sales from Purdue. In January 2018, BELBUCA® became commercially available in Canada.
Other Regions
For commercialization of BELBUCA® in other regions outside the U.S. and Canada, we are currently seeking partners with commercial reach and experience in pain management in their respective regions.
BUNAVAIL®
During 2013, we engaged in the process of assessing a variety of strategic options for the commercialization of BUNAVAIL® in the U.S. The options we explored included commercial partnerships, co-promotion arrangements, leading commercial efforts internally using contract resources, or a combination of the strategic options. Outside the U.S., we are pursuing partnerships.
Following a thorough assessment of commercialization options for BUNAVAIL®, we identified BUNAVAIL® as an attractive product to build a commercial presence capable of supporting both BUNAVAIL® and our other future products. Additionally, the self-commercialization of BUNAVAIL® supported our longer-term vision to become a fully integrated pharmaceutical company. The dynamics of the opioid dependence market made self-commercialization a feasible and attractive option. In total, approximately 90% of all prescriptions are written by approximately 5,000 physicians – which include primary care physicians, psychiatrists, addiction medicine specialists and pain specialists, with most concentrated in the eastern third of the U.S. and the west coast, allowing for coverage of a majority of the prescriber base with a modest sized sales force. Additionally, the relatively small prescriber base along with the limited number of competitors results in relatively modest marketing expenditures. And finally, the high awareness and physician acceptance of buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid dependence lessens the need for costly educational and promotional programs.
On November 3, 2014, we announced the availability of BUNAVAIL® in the U.S. where it was supported by a 60-person field sales force and a full marketing effort targeting the nearly 5,000 physicians who are responsible for approximately ninety percent of prescriptions for buprenorphine products for the treatment of opioid dependence. The launch was also supported by a full marketing effort aimed at increasing product awareness including advertising and promotion, direct mail and email, a speakers’ program and a number of initiatives, including a copay support program, to minimize access issues. Our managed care efforts continued to progress as we executed six new managed care contracts between July and November 2016 which were beneficial to our sales efforts in 2017.
In August 2015, we announced the appointment of Scott M. Plesha as Senior Vice President of Sales. Mr. Plesha joined us with more than 25 years of sales experience within the pharmaceutical and medical industries. In January 2018, Mr. Plesha was promoted to President of our company.
As noted above, in January 2017 with the reacquisition of BELBUCA®, we transitioned our primary commercial emphasis from BUNAVAIL® to BELBUCA®. Our BUNAVAIL® efforts are now focused on current BUNAVAIL® prescribers and on increasing prescriptions related to current, upcoming and future managed care contracts where BUNAVAIL® is placed in a favorable formulary position. We believe that in this structure, and with the increase in our sales force size in late 2016 and early 2017, we can maintain a competitive share of voice through both personal and non-personal selling efforts. We also believe that BUNAVAIL® offers distinct and important benefits over other products in the opioid dependence market which will allow for sales growth in the long term.
23
Table of Contents
ONSOLIS®/BREAKYL™
Europe
In September 2006, we secured an exclusive licensing and supply agreement with Meda for the commercialization rights for BEMA® Fentanyl in the E.U., which is being marketed in Europe under the trade name BREAKYL™. BREAKYL™ received marketing authorization from the European regulatory authorities in October 2010 and has been launched in over thirteen European countries including Germany, France and the U.K. On January 2, 2009, we entered into amendments to our agreements with Meda to grant Meda worldwide commercialization rights for ONSOLIS®/BREAKYL™ except for Taiwan and South Korea. The sales royalties to be received by us will be the same for all Meda territories as agreed to for Europe.
North America
In September 2007, we secured an exclusive licensing and supply agreement with Meda for the commercialization rights for ONSOLIS®, under which Meda was responsible for the sales, marketing and distribution of ONSOLIS® in the U.S., Canada and Mexico.
ONSOLIS® was commercially launched in the United States in mid-October 2009 following approval by the FDA in July 2009. Under the Meda agreement, ONSOLIS® commercial efforts were supported by a therapeutic specialty sales force assembled by Meda to target oncologists and pain management specialists treating breakthrough cancer pain.
ONSOLIS® was approved by the Canadian regulatory authorities in May 2010 and was the first product approved in Canada for the management of breakthrough cancer pain. Meda Valeant Pharma Canada Inc., a joint venture between Meda and Valeant Canada Limited was responsible for promotion of ONSOLIS® in Canada. ONSOLIS® was launched in Canada in the third quarter of 2011.
On March 12, 2012, we announced the postponement of the U.S. relaunch of ONSOLIS® following the initiation of the class-wide REMS until the product formulation could be modified to address two appearance-related issues. Such appearance-related issues involved the formation of microscopic crystals and a fading of the color in the mucoadhesive layer, raised by the FDA during an inspection of our North American manufacturing partner for ONSOLIS®, Aveva. While the appearance issues do not affect the product’s underlying integrity, safety or performance, the FDA believed that the fading of the color in particular may potentially confuse patients, necessitating a modification of the product and its specification before it can be manufactured and distributed. The source of microcrystal formation and the potential for fading of ONSOLIS® was found to be specific to a buffer used in its formulation.
On January 27, 2015, we announced that we had entered into the Assignment Agreement with Meda to return to us the marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® for the U.S. and the right to seek marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® in Canada and Mexico. We made modifications to the formulation for ONSOLIS®, submitted a prior approval supplement and subsequently received FDA approval in August 2015. On May 11, 2016, we announced the signing of a licensing agreement under which we granted the exclusive rights to develop and commercialize ONSOLIS® in the U.S. to Collegium. Under terms of the agreement, Collegium will be responsible for the manufacturing, distribution, marketing and sales of ONSOLIS® in the U.S. Both companies are collaborating on the ongoing transfer of manufacturing, which includes submission of a Prior Approval Supplement (Supplement) to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
On December 8, 2017, we received a 90-day notice from Collegium regarding the return of the U.S. rights to ONSOLIS® from Collegium; which transition went into effect on March 8, 2018. We are currently evaluating a range of options for commercializing ONSOLIS®, including the potential to market and sell ONSOLIS® via our existing sales force.
Additional Territories
In 2010, licensing agreements were secured in Taiwan and South Korea providing the opportunity for commercialization in all territories globally. In May 2010, we announced a commercial partnership with Kunwha for the exclusive rights to develop and commercialize ONSOLIS® in the Republic of Korea. Those rights were subsequently returned to us due to changes in the market dynamics and the Kunwha License Agreement was terminated on August 31, 2015. In October 2010, a commercial partnership with TTY was announced, providing commercialization rights for Taiwan. This agreement resulted in potential milestone payments of up to $1.3 million (including an upfront payment of $0.3 million) along with royalties based on sales.
In November 2011, we announced that TTY had submitted a NDA for marketing authorization of BEMA® Fentanyl to the Taiwan Food and Drug Administration. This triggered a milestone payment to us of approximately $0.3 million, which was received November 2011. In July 2013, we announced the regulatory approval of BEMA® Fentanyl in Taiwan, where the product is now marketed under the brand name PAINKYL™. The approval in Taiwan resulted in a milestone payment of $0.3 million to us, which was received in the third quarter of 2013. TTY launched PAINKYL™ in Taiwan in 2015.
24
Table of Contents
Government Regulation
The nonclinical and clinical development, manufacturing and marketing of any drug product, is subject to significant regulation by governmental authorities in the United States and other countries. Complying with these regulations involves considerable time, expense and uncertainty.
In the United States, drugs are subject to rigorous federal regulation and, to a lesser extent, state regulation. The Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act, as amended, and the regulations promulgated thereunder, and other federal and state statutes and regulations govern, among other things, the testing, manufacture, safety, efficacy, labeling, storage, record keeping, approval, advertising and promotion of our drugs. Drug development and approval within this regulatory framework is difficult to predict, requires a number of years and involves the expenditure of substantial resources. Moreover, ongoing legislation by Congress and rulemaking by the FDA presents an ever-changing landscape where we could be required to undertake additional activities before any governmental approval to market our products is granted.
The steps required before a pharmaceutical product may be marketed in the United States include:
| 1. | small scale manufacturing of the product; |
| 2. | laboratory and nonclinical tests for safety of the product; |
| 3. | submission of an IND to the FDA for the product which must become effective before human clinical trials can commence; |
| 4. | larger scale manufacturing of the product; |
| 5. | clinical trials to characterize the efficacy and safety of the product in the intended patient population; |
| 6. | submission of an NDA to the FDA; and |
| 7. | approval of the NDA by the FDA. |
In addition to obtaining FDA approval for each product, each product-manufacturing establishment must be registered with, and approved by, the FDA. Manufacturing establishments are subject to biennial inspections by the FDA and must comply with the FDA’s Good Manufacturing Practices and with other federal and local regulations.
Nonclinical Testing
Nonclinical testing includes laboratory evaluations of the active drug substance and formulation, as well as tissue culture and animal studies to assess the safety and potential efficacy of the investigational product. Nonclinical tests must be conducted by laboratories that comply with FDA Good Laboratory Practices regulations. Nonclinical testing is inherently risky and the results can be unpredictable or difficult to interpret. The results of nonclinical testing are submitted to the FDA as part of an IND and are reviewed by the FDA prior to the commencement of clinical trials. Unless the FDA places a clinical hold on an IND, clinical studies may begin thirty (30) days after the IND is submitted.
We have relied and intend to continue to rely on third party contractors to perform nonclinical trials.
Clinical Research
Clinical research involves administration of the investigational product to healthy volunteers and/or to patients under the supervision of a qualified investigator. Clinical trials must be conducted in accordance with Good Clinical Practices following protocols acceptable to FDA that detail the objectives of the study, the parameters to be used to monitor safety and the efficacy and the planned evaluation of results. Each protocol must be submitted to the FDA prior to its conduct. Further, each clinical study must be conducted under the auspices of an independent institutional review board that protects the rights and welfare of the study subjects. The drug product used in clinical trials must be manufactured according to Good Manufacturing Practices.
25
Table of Contents
Clinical research is typically conducted in three sequential phases, but the phases may overlap and not all phases may be necessary when developing investigational products that will utilize the FDA’s 505(b)(2) approval process. Phase 1 studies are typically performed in normal healthy volunteers to assess the safety (adverse side effects), absorption, metabolism, bio-distribution, excretion, and food and drug interactions of the investigational drug product. Additional studies may be performed to assess abuse potential as well as limited measures of pharmacologic effect. Phase 2 is the proof of principle stage and involves studies in a limited number of patients in order to:
| • | assess the potential efficacy of the product for specific, targeted indications; |
| • | identify the range of doses and dose regimens likely to be effective for the indication; and |
| • | identify possible adverse events and safety risks. |
When there is evidence that the product may be effective and has an acceptable safety profile in Phase 2 evaluations, Phase 3 trials are undertaken to establish the clinical efficacy and safety profile of the product within a larger population at geographically dispersed clinical study sites. Phase 3 frequently involves randomized controlled trials and, whenever possible, studies are conducted in a manner so that neither the patient nor the investigator knows what treatment is being administered. We, or the FDA, may suspend clinical trials at any time if it is believed that the individuals participating in such trials are being exposed to unacceptable health risks.
New Drug Application and FDA Approval Process
The results of the pharmaceutical and manufacturing development work, nonclinical studies and clinical studies are submitted to the FDA in the form of an NDA for approval to market and sell the product. The testing and approval process is likely to require substantial time and effort. In addition to the results of nonclinical and clinical testing, the NDA applicant must submit detailed information about chemistry, manufacturing and controls that will describe how the product is made, packaged, labeled, and tested through the manufacturing process. The manufacturing process continues to develop throughout the period of clinical trials such that, at the time of the NDA, it has been demonstrated that there is control of the process and the product can be made consistently at commercial scale.
The NDA review process involves FDA investigation into the details of the manufacturing process, as well as the design and analysis of each of the nonclinical and clinical studies. This review includes inspection of the manufacturing facility, the data recording process for the clinical studies, the record keeping at a sample of clinical trial sites and a thorough review of the results for each nonclinical and clinical study. Through this review, the FDA reaches a decision about the risk-benefit profile of a product candidate. If the benefit outweighs the risk, the FDA begins negotiation with the company on the content of an acceptable package insert and an associated REMS plan if required.
The NDA review process is affected by many factors, including the severity of the disease, the availability of alternative treatments, and the risks and benefits demonstrated in clinical trials. Consequently, there is a risk that approval may not be granted on a timely basis, if at all. The FDA may deny approval of an NDA if applicable regulatory criteria are not satisfied. Moreover, if regulatory approval of a product is granted, such approval may entail limitations on the indicated uses for which it may be marketed, require additional testing or information, or require post-marketing testing (Phase 4) and surveillance to monitor the safety of a company’s product if it does not believe the NDA contains adequate evidence of its safety. Finally, product approvals may be withdrawn if compliance with regulatory standards is not maintained or health problems are identified that would alter the risk-benefit analysis for the product. Post-approval studies may be conducted to explore the use of the product for new indications or populations such as pediatrics.
Among the conditions for NDA approval is the requirement that any prospective manufacturer’s quality control and manufacturing procedures conform to Good Manufacturing Practices and the specifications approved in the NDA. In complying with standards set forth in these regulations, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money and effort in the area of quality control and quality assurance to ensure full technical compliance. Manufacturing establishments, both foreign and domestic, also are subject to inspections by or under the authority of the FDA and by other federal, state or local agencies. Additionally, in the event of non-compliance, the FDA may issue warning letters and/or seek criminal and civil penalties, enjoin manufacture, seize product or revoke approval.
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy
In March 2008, new legislation designated as the Food and Drug Administration Amendments Act of 2007 (the FDAAA) took effect. This legislation strengthened the FDA’s authority over drug safety and directs the FDA to develop systems aimed at managing the risk-benefit ratio of a drug, with a particular focus on post-approval safety. FDAAA authorized the FDA to require and enforce a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy, or REMS, if the FDA determines that it is necessary to ensure that the benefits of a drug outweigh the potential risks. The legislation also provides the FDA with increased authority to require REMS at any point in a drug product’s lifecycle based on new safety information.
26
Table of Contents
A REMS is defined by the FDA as a strategy to manage a known or potential serious risk associated with a drug or biological product. The FDA’s assessment of whether to require a REMS as a condition for approval considers factors such as the size of the population likely to use the drug, the seriousness of the disease or condition that is to be treated by the drug, the expected benefit, and the seriousness of any known or potential adverse events that may be related to the drug. A REMS may be conveyed through the use of a number of tools including a Medication Guide for distribution when the drug is dispensed, a communication plan to physicians to convey potential risks, and elements to ensure safe use. These elements may include provisions that healthcare providers who prescribe the drug and pharmacists who dispense the drug have particular training, experience or special certifications; that the drug be dispensed only in certain healthcare settings; that the drug be dispensed to patients with evidence of safe-use conditions; and/or that patients must be enrolled in a registry. Under the FDAAA, the FDA has also been granted enforcement authority over violations of the REMS provisions. The FDA may impose civil monetary penalties, the drug or biological product can be deemed misbranded, and/or the FDA may obtain injunctive relief against further distribution of the product.
On December 29, 2011, the FDA approved a “class-wide” REMS program covering all transmucosal fentanyl products under a single risk management program. ONSOLIS® is subject to this REMS.
Additionally, FDA has implemented a class-wide REMS covering the extended release and long acting opioid drug products. The class-wide REMS program consists of a REMS-compliant educational program offered by an accredited provider of continuing medical education, patient counseling materials and a medication guide. BELBUCA® is subject to this existing class-wide REMS program. The cost and implementation of the extended release and long-acting opioid REMS is shared among multiple companies in the category.
There also continues to be a REMS in place for buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid dependence. BUNAVAIL® is included in this existing REMS that is far less cumbersome than the ONSOLIS® REMS and includes a medication guide and healthcare professional and patient education.
International Approval
Whether or not FDA approval has been obtained, approval of a product by regulatory authorities in foreign countries must be obtained prior to the commencement of commercial sales of the drug in such countries. The requirements governing the conduct of clinical trials and drug approvals vary widely from country to country, and the time required for approval may be longer or shorter than that required for FDA approval. Although there are some procedures for unified filings for certain European countries, in general, each country at this time has its own procedures and requirements.
Other Regulation
In addition to regulations enforced by the FDA, we are also subject to United States regulation under the Controlled Substances Act, the Occupational Safety and Health Act, the Environmental Protection Act, the Toxic Substances Control Act, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act and other present and potential future federal, state, local or similar foreign regulations. Our research and development may involve the controlled use of hazardous materials, chemicals and radioactive compounds. Although we believe that our safety procedures for handling and disposing of such materials comply with the standards prescribed by state and federal regulations, the risk of accidental contamination or injury from these materials cannot be completely eliminated. In the event of any accident, we could be held liable for any damages that result and any such liability could exceed our resources.
Employees
As of March 13, 2018, we have 115 full-time and 1 part-time employees. Six are involved in our clinical development program and operations, fourteen handle our administration, accounting, and supply chain management, four handle our marketing and managed markets and ninety-two handle our outside sales. Advanced degrees and certifications of our staff include one Ph.D, one M.D, two CPAs, eleven MBAs, four MSs, four MAs, one JD, one MPA, one MEDU, one RAC and one RN. None of our employees are covered by collective bargaining agreements. From time to time, we also employ independent contractors on a consulting basis or to support our administrative functions. We consider relations with all of our employees to be good. Each of our employees has entered into confidentiality, intellectual property assignment and non-competition agreements with us.
Available Information
Our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to reports filed pursuant to Sections 13(a) and 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (which we refer to herein as the Exchange Act), are filed with the SEC. Such reports and other information that we file with the SEC are available free of charge on
27
Table of Contents
our website at http://bdsi.investorroom.com/sec_filings when such reports are available on the SEC website. The public may read and copy any materials that we file with the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, NE, Room 1580, Washington, DC 20549. The public may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC maintains an Internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC at http://www.sec.gov. The contents of these websites are not incorporated into this filing. Further, the foregoing references to the URLs for these websites are intended to be inactive textual references only.
28
Table of Contents
| Item 1A. | RISK FACTORS |
Investing in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. Before purchasing our common stock, you should carefully consider the following risk factors as well as all other information contained in this Report, including our consolidated financial statements and the related notes. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only ones facing us. Additional risks and uncertainties that we are unaware of, or that we currently deem immaterial, also may become important factors that affect us. If any of the following risks occur, our business, financial condition or results of operations could be materially and adversely affected. In that case, the trading price of our common stock could decline, and you may lose some or all of your investment.
Risks Relating to Our Business
We have incurred significant losses since inception, have relatively limited working capital and have only generated minimal revenues from actual products sales. As such, you cannot rely upon our historical operating performance to make an investment decision regarding our company.
From our inception in January 1997 and through December 31, 2017, we have recorded significant losses. Our accumulated deficit at December 31, 2017 was approximately $305.1 million. As of December 31, 2017, we had working capital of approximately $13.6 million, but until our product revenue grows more substantially, we will continue to use our working capital to maintain our operations. Our ability to generate revenue and achieve profitability depends upon our ability, alone or with others, to effectively market and sell our products, secure and maintain payer access, maintain required regulatory approvals, manufacture our products to meet demand and complete the development of our product candidates and product concepts. We may be unable to achieve any or all of these goals.
Although we have generated licensing-related and other revenue to date, we have only recently begun to generate revenue from the commercial sales of our approved products — BELBUCA®, BUNAVAIL® and ONSOLIS®. In the case of BELBUCA®, our approval has generated milestone revenue from our prior commercial partner Endo. However, in January 2017, we obtained the commercialization rights back to BELBUCA® and are utilizing our internal sales force to sell our product. In the case of BUNAVAIL®, sales have been challenging since we commenced the commercial launch of the product in November 2014 and are subject to the risks of launching a new product. There is a risk that we will be unable to generate sustained and predictable revenues from product sales. In the case of ONSOLIS®, sales have been adversely affected by: (i) the lack of a uniform REMS program at the time of the launch of ONSOLIS®, and (ii) certain post-FDA approval appearance issues associated with ONSOLIS® which have led to the temporary suspension of manufacturing and marketing of ONSOLIS® in the US and Canada.
Since our inception, we have engaged primarily in research and development, licensing technology, seeking grants, raising capital and recruiting scientific and management personnel. Since 2005, we have also focused on clinical and commercialization activities, originally relating to ONSOLIS® and more recently with BELBUCA®, BUNAVAIL® and Buprenorphine Sustained Release injection and formerly Clonidine Topical Gel. This relatively limited operating history may not be adequate to enable you to fully assess our ability to develop and commercialize our technologies and proposed formulations or products, obtain FDA approval and achieve market acceptance of our proposed formulations or products and respond to competition. We may be unable to fully develop, obtain regulatory approval for, commercialize, manufacture, market, sell and derive material revenues from our product candidates or product concepts in the timeframes we project, if at all, and our inability to do so would materially and adversely impact our viability as a company.
There are risks and we have experienced challenges associated with our launch of BUNAVAIL®. We thus cannot accurately predict the volume or timing of any future sales of BUNAVAIL®, making the timing of any revenues therefrom difficult to predict.
In 2014, we commenced the commercial launch of BUNAVAIL®, which represented the commencement of the first self-commercialization effort for our company. As such, our ability to establish and increase sales of BUNAVAIL® is important to us, both for the revenue it may generate as well as to demonstrate our capabilities as an integrated specialty pharmaceutical company as opposed to a research and development organization. The commercial launch of any product is subject to significant risks, and particularly so for us given the size and relative inexperience of our company with commercial operations. In addition, we face lengthy customer evaluation and formulary and managed care approval processes associated with the launch of BUNAVAIL®. Consequently, we have and may continue to incur substantial expenses and devote significant management effort and expense in developing customer trial and adoption of BUNAVAIL® which may have an adverse impact on our ability to generate revenue from sales of this product. We must obtain approval for commercial insurance and government reimbursement, and receive and maintain favorable formulary placement, in order to generate sales of BUNAVAIL®, which approval is subject to risk, potential delays and contract terms, and which may not actually occur or may occur with less favorable terms. The sales of BUNAVAIL® are also
29
Table of Contents
dependent on the effectiveness of our selling and promotional efforts as well as influenced by competitive activity and our ability to effectively compete with companies with greater resources, new product approvals, pricing pressure, litigation, regulatory influences, and generic entrants. We have to some extent experienced all of the foregoing in connection with our launch of BUNAVAIL®. As such, we cannot accurately predict the volume or timing of any future sales of BUNAVAIL®, and our inability to commercialize this product would likely have an adverse effect on our results of operations and public stock price.
We have limited experience as a company in self-commercializing pharmaceutical products, which heightens the risks related to our self-commercialization of BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®.
Prior to the launch of BUNAVAIL®, we had only partnered our products with larger pharmaceutical companies, who have taken primary responsibility for development and commercialization activities for such products. We are presently self-commercializing BUNAVAIL® and BELBUCA®. As a company, prior to our commercialization of BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®, we had never been primarily responsible for manufacturing, supply chain, sales and marketing efforts for one of our products, and therefore our efforts with BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® are our initial efforts in this regard. Given this relatively limited experience, there is a risk that we may be unable to adequately execute one or more elements of our commercial plans for BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®. If this were to occur, we may not achieve anticipated revenues from BELBUCA® or BUNAVAIL®, which would have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, cash flow, reputation and stock price.
BUNAVAIL® was the first product that we had elected to commercialize and we began to commercialize BELBUCA® in January 2017. If we are unable to adequately develop, implement, or manage our sales, marketing and distribution capabilities, either on our own or through third parties who perform these functions, our commercialization efforts for BELBUCA® or BUNAVAIL® or any future product we may commercialize would not produce the desired results, which would hurt our revenues and results of operations.
Prior to our decision to commercialize BUNAVAIL®, we had relied on third parties to manage sales and marketing efforts for us, including Meda for ONSOLIS® and Endo for BELBUCA® until January 2017. We therefore have limited experience as a company in commercializing a product, and our sales, marketing and distribution capabilities are new. As such, we may not achieve success in marketing and promoting BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®, or any other products we develop or acquire in the future or products we may commercialize through the exercise of co-promotion rights. Specifically, to optimize the commercial potential of BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®, we must execute upon our commercialization plan effectively and efficiently. In addition, we must continually assess and modify our commercialization plan to adapt to the promotional response. Further, we must continue to focus and refine our marketing campaign to ensure a clear and understandable physician-patient dialogue around BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® as an appropriate therapy. In addition, we must provide our sales force with the highest quality training, support, guidance and oversight for them to effectively promote BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®. If we fail to perform these commercial functions in the highest quality manner, BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® will not achieve its maximum commercial potential or any level of success at all. In addition, sales and marketing efforts could be negatively impacted by the delay or failure to obtain additional supportive clinical trial data for our products. The deterioration or loss of our sales force would materially and adversely impact our ability to generate sales revenue, which would hurt our results of operations. Finally, we are competing and expect to compete with other companies that currently have extensive and well-funded marketing and sales operations, and our marketing and sales efforts may be unable to compete against these other companies, which would also hurt our results of operations.
If our competitors are successful in obtaining approval for Abbreviated New Drug Applications for products that have the same active ingredients as BELBUCA® or BUNAVAIL®, sales of BELBUCA® or BUNAVAIL® may be adversely affected.
Our competitors may submit for approval certain Abbreviated New Drug Applications (“ANDAs”) which provide for the marketing of a drug product that has the same active ingredients in the same strengths and dosage form as a drug product already listed with the FDA, and which has been shown to be bioequivalent to such FDA-listed drug. Drugs approved in this way are commonly referred to as generic versions of a listed drug and can often be substituted by pharmacists under prescriptions written for an original listed drug. Any applicant filing an ANDA is required to certify to the FDA that the new product subject to the ANDA will not infringe an already approved product’s listed patents or that such patents are invalid (otherwise known as a Paragraph IV Certification).
In February 2016, we announced that a generic competitor (Teva) had filed a Paragraph IV Certification challenging certain of our BUNAVAIL®-related patents and we received notices regarding Paragraph IV certifications from Teva in November and December 2016, seeking to find invalid two Orange Book listed patents relating specifically to BELBUCA®. The filing of this certification required us to initiate costly litigation against Teva. In addition, a number of our competitor companies have filed Paragraph IV Certifications challenging the patent for Suboxone® film, the market leader in the field in which we are seeking to generate sales of BUNAVAIL®. To the extent that any company is successful in challenging the validity of certain patents covering
30
Table of Contents
BUNAVAIL® or Suboxone® film under a Paragraph IV Certification, it could result in FDA approval of a drug that is lower in price to BUNAVAIL® or Suboxone® film. Such a new drug could make it more difficult for BUNAVAIL® to gain any significant market share in an increasingly generic marketplace, which would have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, cash flow, reputation and stock price.
In October 2017, we announced that we had entered into a settlement agreement with Teva that resolved our BUNAVAIL® patent litigation against Teva pending in the U.S. District Court for the District of Delaware. As part of the Settlement Agreement, which is subject to review by the U.S. Federal Trade Commission and the U.S. Department of Justice, we entered into a non-exclusive license agreement with Teva that permits Teva to first begin selling its generic version of BUNAVAIL® in the U.S. on July 23, 2028 or earlier under certain circumstances. Other terms of the agreement are confidential.
In February 2018, we announced that we had entered into a Settlement Agreement with Teva that resolves our previously reported BELBUCA®, patent litigation against Teva pending in the United States District Court for the District of Delaware. As part of the settlement agreement, which is subject to review by the U.S. Federal Trade Commission and the U.S. Department of Justice, we entered into a non-exclusive license agreement with Teva that permits Teva to first begin selling its generic version of BELBUCA® in the U.S. on January 23, 2027 or earlier under certain circumstances. Other terms of the agreement are confidential.
As such, we have been and may continue to be subject to ANDA-related litigation, which is costly and distracting and has the potential to impair the long-term value of our products.
Until we can generate recurring and predictable revenues for commercial operations, we will likely need to raise additional capital from time to time to continue our operations or expand our business, and our failure to do so would significantly impair our ability to fund our operations, develop our technologies and product candidates, attract commercial partners, retain key personnel or promote our products.
Historically, our operations have been funded almost entirely by external financing and not from commercial revenues. Such financing has historically come primarily from license and royalty fees, traditional secured loans, the sale of common and preferred stock and convertible debt to third parties, related party loans and, to a lesser degree, from grants. At December 31, 2017, we had cash of approximately $21.2 million. Since revenue from BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® sales and royalty payments from MEDA and TTY have been and may continue to be unpredictable, there is a material risk that we will be unable to fund our company from our own generated revenues.
As such, and given our anticipated cash usage and lack of significant revenues, we will likely need to raise additional capital in the future to fund our anticipated operating expenses and progress our business plans. In fact, we may require significant additional capital to further our planned activities. If additional financing is not available when required or is not available on acceptable terms, we may be unable to fund our operations and planned growth, develop or enhance our technologies, take advantage of business opportunities or respond to competitive market pressures. Any negative impact on our operations may make raising additional capital more difficult or impossible and may also result in a lower price for our shares.
We may have difficulty raising any needed additional capital.
We may have difficulty raising needed capital in the future as a result of, among other factors, our lack of material revenues from sales, as well as the inherent business risks associated with our company and present and future market conditions. Our business currently only generates a limited amount of revenue from product sales and milestone revenues, and such current sources of revenue will likely not be sufficient to meet our present and short-term capital requirements. Therefore, given that we plan to continue to expend substantial funds on commercialization activities (including those relating to BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®) as well as potentially on other strategic initiatives, there is a risk that we will require additional capital to fund these activities. If adequate funds are unavailable, we may be required to delay, reduce the scope of or eliminate one or more of our research, development or commercialization programs, product launches or marketing efforts, any of which may materially harm our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our long-term capital requirements are subject to numerous risks.
Our long-term capital requirements are expected to depend on many factors, including, among others:
| • | the number of potential products we have in development; |
31
Table of Contents
| • | progress and cost of our research and development programs; |
| • | progress with non-clinical studies and clinical trials; |
| • | time and costs involved in obtaining regulatory (including FDA) clearance and addressing regulatory and other issues that may arise post-approval (such as we have experienced with ONSOLIS® and, to a lesser extent, with BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®); |
| • | costs involved in preparing, filing, prosecuting, maintaining and enforcing (through litigation or other means) our patents, trademarks and other intellectual property; |
| • | costs of developing sales, marketing and distribution channels and our ability to sell our products; |
| • | costs involved in establishing manufacturing capabilities for commercial quantities of our products; |
| • | costs we may incur in acquiring new technologies or products; |
| • | competing technological and market developments; |
| • | market acceptance of our products; |
| • | costs for recruiting and retaining employees and consultants; |
| • | costs for training physicians; and |
| • | legal, accounting, insurance and other professional and business-related costs. |
We may consume available resources more rapidly than currently anticipated, resulting in the need for additional funding sooner than anticipated. We may seek to raise any necessary additional funds through equity or debt financings, collaborative arrangements with corporate partners or other sources, which may have a material effect on our current or future business prospects.
Our additional financing requirements could result in dilution to existing stockholders.
The additional financings which we have undertaken and which we will likely in the future require, have and may be obtained through one or more transactions that have diluted or will dilute (either economically or in percentage terms) the ownership interests of our stockholders. Further, we may not be able to secure such additional financing on terms acceptable to us, if at all. We have the authority to issue additional shares of common stock and preferred stock, as well as additional classes or series of ownership interests or debt obligations which may be convertible into any one or more classes or series of ownership interests. We are authorized to issue 75 million shares of common stock and 5 million shares of preferred stock. Such securities may be issued without the approval or other consent of our stockholders.
Our term loan agreement with CRG Servicing LLC (or CRG) and other lenders party thereto contains restrictions that limit our flexibility in operating our business. We may be required to make a prepayment or repay the outstanding indebtedness earlier than we expect under our Credit Agreement if a prepayment event or an event of default occurs, including a material adverse change with respect to us, which could have a materially adverse effect on our business.
In February 2017, we entered into a term loan agreement with CRG. Pursuant to the loan agreement, we borrowed $45.0 million from the lenders as of the closing date and may be eligible to borrow up to an additional $30.0 million in two tranches of $15.0 million each contingent upon achievement of certain minimum net revenue and minimum market capitalization conditions. In December 2017, we were eligible and elected to receive the second draw of the $15.0 million. We utilized approximately $29.4 million of the initial loan proceeds to repay all the amounts owed by us under our existing amended and restated loan and security agreement, dated May 29, 2015, with MidCap Financial Trust (or MidCap).
Our agreement with CRG contains various covenants that limit our ability to engage in specified types of transactions. These covenants limit our ability to, among other things:
| • | incur additional indebtedness; |
| • | enter into a merger, consolidation or certain changing of control events without complying with the terms of the loan agreement; |
| • | change the nature of our business; |
| • | change our organizational structure or type; |
32
Table of Contents
| • | amend, modify or waive any of our material agreements or organizational documents; |
| • | grant certain types of liens on our assets; |
| • | make certain investments; |
| • | pay cash dividends; |
| • | enter into material transactions with affiliates; and |
The restrictive covenants of the term loan agreement could cause us to be unable to pursue business opportunities that we or our stockholders may consider beneficial. A breach of any of these covenants could result in an event of default under the term loan agreement. An event of default will also occur if, among other things, a material adverse change in our business, operations or condition occurs, or a material impairment of the prospect of our repayment of any portion of the amounts we owe under the term loan agreement occurs. In the case of a continuing event of default under the agreement, CRG could elect to declare all amounts outstanding to be immediately due and payable and terminate all commitments to extend further credit, proceed against the collateral in which we granted CRG a security interest under the term loan agreement and related agreements, or otherwise exercise the rights of a secured creditor. Amounts outstanding under the term loan agreement are secured by all of our existing and future assets (excluding certain intellectual property).
We may not have enough available cash or be able to raise additional funds on satisfactory terms, if at all, through equity or debt financings to make any required prepayment or repay such indebtedness at the time any such prepayment event or event of default occurs. In such an event, we may be required to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or commercialization efforts or grant to others rights to develop and market product candidates that we would otherwise prefer to develop and market ourselves. Our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected as a result.
We may not qualify for additional lending under our loan agreement with CRG. If we do not have access to such funds, our cash position could become materially impaired.
Under our loan agreement with CRG, we may qualify for a remaining tranche of $15 million only if we are able to achieve a certain minimum net revenue and market capitalization threshold. There is a risk that we may not achieve one or more of these thresholds for reasons both within and outside of our control, and our inability to meet these conditions would deny us access to additional funding from CRG. If we do not have access to additional CRG funding, and if we are unable to secure other sources of funding (which may be unavailable on desirable terms, and may not be available at all), our cash position could become materially impaired, which in turn could have a material adverse effect on our company and stock price.
Until ONSOLIS® returns to the market in North America, we will not receive additional revenues from ONSOLIS®.
ONSOLIS® was originally licensed to and launched in the U.S. by Meda. In January 2015, we entered into an assignment and revenue sharing agreement with Meda under which Meda transferred the marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® for the U.S. back to us. On May 11, 2016, we and Collegium executed a definitive license and development Agreement under which we have granted the exclusive rights to develop and commercialize ONSOLIS® in the U.S. to Collegium.
On December 8, 2017, we received the required 90-day notice from Collegium regarding termination of the License Agreement and the effective date of termination is March 8, 2018. We are assessing our commercial options for ONSOLIS®.
Social issues around the abuse of opioids, including law enforcement concerns over diversion of opioids and regulatory efforts to combat abuse, misuse and addiction could impact the potential market for BELBUCA®, BUNAVAIL® and our product candidate.
Media stories regarding prescription drug abuse and the diversion of opioids and other controlled substances are commonplace. Law enforcement and regulatory agencies may apply policies and guidelines that seek to limit the availability or use of opioids. Such efforts may inhibit our ability to commercialize BELBUCA®, potentially BUNAVAIL® and our product candidate.
Aggressive enforcement and unfavorable publicity regarding, for example, the use or misuse of oxycodone or other opioid drugs; the limitations of abuse-resistant formulations; the ability of drug abusers to discover previously unknown ways to abuse opioid drugs; public inquiries and investigations into prescription drug abuse; litigation; or regulatory activity regarding sales, marketing, distribution or storage of opioid drugs could have a material adverse effect on our reputation. Such negative publicity could reduce the potential size of the market for BELBUCA®, and possibly BUNAVAIL® and our product candidates and decrease the revenues we are able to generate from their sale. Similarly, to the extent opioid abuse becomes less prevalent or less urgent of a public health issue, regulators and third-party payers may not be willing to pay a premium for abuse-deterrent formulations of opioids or opioids such as BELBUCA® with less abuse and addiction potential compared to Schedule II opioids.
33
Table of Contents
Efforts by the FDA and other regulatory bodies to combat abuse of opioids may negatively impact the market for our product candidates. In February 2016, the FDA released an action plan to address the opioid abuse epidemic and reassess the FDA’s approach to opioid medications. The plan identifies FDA’s focus on implementing policies to reverse the opioid abuse epidemic, while maintaining access to effective treatments. The actions set forth in the FDA’s plan include strengthening post marketing study requirements to evaluate the benefit of long-term opioid use, changing the REMS requirements to provide additional funding for physician education courses, releasing a draft guidance setting forth approval standards for generic-abuse deterrent opioid formulations, and seeking input from the FDA’s Scientific Board to broaden the understanding of the public risks of opioid abuse. The FDA’s Scientific Advisory Board met to address these issues on March 1, 2016. The FDA’s plan is part of a broader initiative led by the HHS to address opioid-related overdose, death and dependence. The HHS initiative’s focus is on improving physician’s use of opioids through education and resources to address opioid over-prescribing, increasing use and development of improved delivery systems for naloxone, which can reverse overdose from both prescription opioids and heroin, to reduce overdose-related deaths, and expanding the use of Medication-Assisted Treatment, which couples counseling and behavioral therapies with medication to address substance abuse. Also, as part of this initiative, the CDC has launched a state grant program to offer state health departments resources to assist with abuse prevention efforts, including efforts to track opioid prescribing through state-run electronic databases. In March 2016, as part of the HHS initiative, the CDC released a new Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain. The guideline is intended to assist primary care providers treating adults for chronic pain in outpatient settings. The guideline provides recommendations to improve communications between doctors and patients about the risks and benefits of opioid therapy for chronic pain, improve the safety and effectiveness of pain treatment, and reduce the risks associated with long-term opioid therapy. The guideline does not specifically address the use of buprenorphine for chronic pain or make treatment recommendations about the use of abuse-deterrent opioids. Many of these changes and others could cause us to expend additional resources in developing and commercializing BELBUCA® and our product candidates to meet additional requirements.
Government agencies may establish and promulgate usage guidelines that could limit the use of our products and drug candidate.
National and state level government agencies, professional and medical societies, and other groups may establish usage guidelines that apply to our products and drug candidate. These guidelines could address such matters as usage and dose, among other factors. Application of such guidelines could limit the clinical use or commercial appeal of our products or drug candidate.
Acceptance of our technologies, product candidates or products in the marketplace is uncertain and failure to achieve market acceptance will prevent or delay our ability to generate material revenues.
Our future financial performance will depend, to a large extent, upon the introduction and physician and patient acceptance of our technologies, product candidates and products. Even if approved for marketing by the necessary regulatory authorities, our technologies, product candidates and products may not achieve market acceptance.
The degree of market acceptance for our products and product candidates will depend upon a number of factors, including:
| • | regulatory clearance of marketing claims for the uses that we are developing; |
| • | demonstration of the advantages, safety and efficacy of our products and technologies; |
| • | pricing and reimbursement policies of government and third-party payers such as insurance companies, health maintenance organizations and other health plan administrators; |
| • | ability to attract corporate partners, including pharmaceutical companies, to assist in commercializing our products; |
| • | regulatory programs such as the class-wide REMS for ONSOLIS®, BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® or market (including competitive) forces that may make it more difficult for us to penetrate a particular market segment; and |
| • | ability to timely and effectively manufacture and market our products. |
Physicians, various other health care providers, patients, payers or the medical community in general may be unwilling to accept, utilize or recommend any of our approved products or product candidates. If we are unable to obtain regulatory approval or are unable (either on our own or through third parties) to manufacture, commercialize and market our proposed formulations or products when planned, we may not achieve any market acceptance or generate revenue.
34
Table of Contents
All these risks are particularly true for BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®, which are our two products that we are commercializing ourselves.
If we are unable to convince physicians as to the benefits of our products or product candidates, we may incur delays or additional expense in our attempt to establish market acceptance.
Use of our products and, if approved, our product candidates will require physicians to be informed regarding the intended benefits of our products and product candidates. The time and cost of such an educational process may be substantial. Inability to carry out this physician education process may adversely affect market acceptance of our proposed formulations or products. We may be unable to timely educate physicians regarding our intended pharmaceutical formulations or products in sufficient numbers to achieve our marketing plans or to achieve product acceptance. Any delay in physician education may materially delay or reduce demand for our formulations or products. In addition, we may expend significant funds toward physician education before any acceptance or demand for our products or product candidates are created, if at all. Nonetheless, even with our best efforts, certain physicians may never prescribe our product.
We have been and expect to be significantly dependent on our collaborative agreements for the development and manufacturing of our products and product candidates, which expose us to the risk of reliance on the performance of third parties.
In conducting our operations, we currently rely, and expect to continue to rely, on numerous collaborative agreements with third parties such as manufacturers, contract research organizations, commercial partners, universities, governmental agencies and not-for-profit organizations for both strategic and financial resources. Key among these agreements are our manufacturing agreements with LTS relating to BREAKYL™ and Sharp relating to BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®.
The termination of these relationships, or failure to perform by us or our partners (who are subject to regulatory, competitive and other risks) under their applicable agreements or arrangements with us, or our failure to secure additional agreements for our product candidates, would substantially disrupt or delay our research and development activities, including our in-process and anticipated clinical trials. Any such loss would likely increase our expenses and materially harm our business, financial condition and results of operation.
The risks associated with reliance on key third parties was demonstrated in 2010 when Aveva experienced certain adverse equipment and regulatory issues leading to the temporary stoppage of manufacturing of all products at that site, which left us exposed to delays in our and our partners’ commercial plans. In addition, in March 2012 Meda temporarily suspended distribution of ONSOLIS® following discussions with the FDA regarding issues with the product’s appearance. Specifically, the FDA raised concerns about two cosmetic issues that may have originated from the formulation used in the manufacturing of ONSOLIS® following an inspection of Aveva (now a subsidiary of Apotex), which formerly manufactured ONSOLIS® on our behalf. On March 12, 2012, we announced the postponement of the U.S. and Canadian relaunch of ONSOLIS® until the product formulation can be modified to address these issues. However, on January 27, 2015, we announced that we had entered into an assignment and revenue sharing agreement with Meda to return to us the marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® for the U.S. and the right to seek marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® in Canada and Mexico. Subsequently, on May 11, 2016, we announced the signing of a licensing agreement under which we granted the exclusive rights to develop and commercialize in the U.S. to Collegium.
However, on December 8, 2017, we received the required 90-day notice from Collegium regarding termination of the License Agreement and the effective date of termination was March 8, 2018. We are assessing our commercial options for ONSOLIS®. Any future manufacturing interruptions or related supply issues could have a material adverse effect on our company.
We depend upon key personnel who may terminate their employment with us at any time. Moreover, our former President and Chief Executive Officer retired as of January 2018, and as of the date of this report we have only found a successor for President. We may be unable to fill the key position for Chief Executive Officer with a qualified candidate, which could adversely impact our company.
Our ability to achieve our corporate objectives will depend to a significant degree upon the continued services of key management, technical and scientific personnel, particularly our senior executive officers. Our management and other employees may voluntarily terminate their employment with us at any time. The loss of the services of these or other key personnel, or the inability to attract and retain additional qualified personnel, could result in delays to product development or approval, loss of sales and diversion of management resources. In addition, we depend on our ability to attract and retain other highly skilled personnel, including research scientists. Competition for qualified personnel is intense, and the process of hiring and integrating such qualified personnel is often lengthy. We may be unable to recruit such personnel on a timely basis, if at all, which would negatively impact our development and commercialization programs. Additionally, we do not currently maintain “key person” life insurance on the lives of our executives or any of our employees. This lack of insurance means that we may not have adequate compensation for the loss of the services of these individuals.
35
Table of Contents
In particular, Dr. Sirgo retired as our President and Chief Executive Officer as of January 2018. In December 2017, we promoted Scott Plesha, our Senior Vice President of Sales to President. We are currently conducting a search for a successor to Dr. Sirgo for the position of Chief Executive Officer. Recruiting qualified candidates for such senior executive positions within the specialty pharmaceutical industry is challenging, the timing is uncertain and we may be unsuccessful in filling that key position with a qualified candidate, or even if we do fill that position, that such candidate will perform according to our expectations. In addition, during the transition to a new President and Chief Executive Officer, we may encounter challenges in our operations which could impact our results of operations.
We may be unable to manage our growth effectively.
After focusing our efforts for many years on clinical development of products, our business strategy now contemplates growth and expansion as we continue our evolution into a fully integrated specialty pharmaceutical company. For example, as we in-license or acquire additional product candidates, we will likely have to expand existing operations to conduct additional clinical trials, increase our contract manufacturing capabilities, hire and train new personnel to handle the marketing and sales of our products and assist patients in obtaining reimbursement for the use of our products. We may also need to grow to support our commercial activities for BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® or other approved products. This growth may place significant strain on our management and financial and operational resources. Successful growth is also dependent upon our ability to implement appropriate financial and management controls, systems and procedures. Our ability to effectively manage growth depends on our success in attracting and retaining highly qualified personnel, for which the competition may be intense. If we fail to manage these challenges effectively, our business could be harmed.
We are exposed to product liability, non-clinical and clinical liability risks which could place a substantial financial burden upon us, should lawsuits be filed against us.
Our business exposes us to potential product liability and other liability risks that are inherent in the testing, manufacturing and marketing of pharmaceutical formulations and products. We expect that such claims are likely to be asserted against us at some point. In addition, the use in our clinical trials of pharmaceutical formulations and products and the subsequent sale of these formulations or products by us or our potential collaborators may cause us to bear a portion of or all product liability risks. A successful liability claim or series of claims brought against us could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We currently have a general liability/product liability policy which includes coverage for our clinical trials and our commercially marketed products. Annual aggregate limits include $2 million for general liability, with $1 million for each occurrence; product liability is $15 million for aggregate and $15 million per occurrence with excess liability in the amount of an additional $5 million; umbrella liability is $5 million aggregate and $5 million per occurrence. It is possible that this coverage will be insufficient to protect us from future claims. Under our agreements, our partners are required to carry comprehensive general product liability and tort liability insurance, each in amounts not less than $5 million per incident and $10 million annual aggregate and to name us as an additional insured thereon. However, we or our commercial partners may be unable to obtain or maintain adequate product liability insurance on acceptable terms, if at all, and there is a risk that our insurance will not provide adequate coverage against our potential liabilities. Furthermore, our current and potential partners with whom we have collaborative agreements or our future licensees may not be willing to indemnify us against these types of liabilities and may not themselves be sufficiently insured or have sufficient assets to satisfy any product liability claims. Claims or losses in excess of any product liability insurance coverage that may be obtained by us or our partners could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Moreover, product liability insurance is costly, and due to the nature of the pharmaceutical products underlying BELBUCA®, BUNAVAIL®, ONSOLIS® and our product candidates, we or our partners may not be able to obtain such insurance, or, if obtained, we or our partners may not be able to maintain such insurance on economically feasible terms. If a product or product candidate related action is brought against us, or liability is found against us prior to our obtaining product liability insurance for any product or product candidate, or should we have liability found against us for any other matter in excess of any insurance coverage we may carry, we could face significant difficulty continuing operations.
We are presently a party to lawsuits by third parties who claim that our products, methods of manufacture or methods of use infringe on their intellectual property rights, and we may be exposed to these types of claims in the future.
36
Table of Contents
We are presently, and may continue to be, exposed to litigation by third parties based on claims that our technologies, processes, formulations, methods, or products infringe the intellectual property rights of others or that we have misappropriated the trade secrets of others. This risk is exacerbated by the fact that the validity and breadth of claims covered in pharmaceutical patents is, in most instances, uncertain and highly complex. Any litigation or claims against us, whether or not valid, would result in substantial costs, could place a significant strain on our financial and human resources and could harm our reputation. Such a situation may force us to do one or more of the following:
| • | incur significant costs in legal expenses for defending against an intellectual property infringement suit; |
| • | delay the launch of, or cease selling, making, importing, incorporating or using one or more or all of our technologies and/or formulations or products that incorporate the challenged intellectual property, which would adversely affect our revenue; |
| • | obtain a license from the holder of the infringed intellectual property right, which license may be costly or may not be available on reasonable terms, if at all; or |
| • | redesign our formulations or products, which would be costly and time-consuming. |
With respect to our BEMA® delivery technology, the thin film drug delivery technology space is highly competitive. There is a risk that a court of law in the United States’ or elsewhere could determine that one or more of our BEMA® based products conflicts with or covered by external patents. This risk presently exists in our litigation with Aquestive which was filed by Aquestive in November 2010, wherein Aquestive claims that our and our partner’s trade secret manufacturing process for ONSOLIS® is infringing upon Aquestive patented manufacturing process, as well as a similar litigation with Reckitt Benckiser, Inc., RB Pharmaceuticals Limited, and Aquestive relating to our BUNAVAIL® product which was filed in October 2013. If the courts in these cases were to rule against us and our partner in that case, we could be forced to license technology from Aquestive or otherwise incur liability for damages, which could have a material adverse effect on our ability for us or our partners to market and sell BUNAVAIL® or ONSOLIS®.
We have been granted non-exclusive license rights to European Patent No. 949 925, which is controlled by LTS to market BELBUCA® and ONSOLIS® within the countries of the European Union. We are required to pay a low single digit royalty on sales of products that are covered by this patent in the European Union. We have not conducted freedom to operate searches and analyses for our other proposed products. Moreover, the possibility exists that a patent could issue that would cover one or more of our products, requiring us to defend a patent infringement suit or necessitating a patent validity challenge that would be costly, time consuming and possibly unsuccessful.
Our lawsuits with Aquestive and RB Pharmaceuticals have caused us to incur significant legal costs to defend ourselves, and we would be subject to similar costs if we are a party to similar lawsuits in the future Furthermore, if a court were to determine that we infringe any other patents and that such patents are valid, we might be required to seek one or more licenses to commercialize our BEMA® products. We may be unable to obtain such licenses from the patent holders, which could materially and adversely impact our business.
If we are unable to adequately protect or enforce our rights to intellectual property or secure rights to third-party patents, we may lose valuable rights, experience reduced market share, assuming there is any market share, or incur costly litigation to, enforce, maintain or protect such rights.
Our ability to license, enforce and maintain patents, maintain trade secret protection and operate without infringing the proprietary rights of others will be important to our commercializing any formulations or products under development. The current and future development of our drug delivery technologies is contingent upon whether we are able to maintain licenses and access patented technologies. Without these licenses, the use of technologies would be limited and the sales of our products could be prohibited. Therefore, any disruption in access to the technologies could substantially delay the development and sale of our products.
The patent positions of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, including ours, which involve licensing agreements, are frequently uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions. In addition, the coverage claimed in a patent application can be significantly reduced before the patent is issued. Consequently, our patents, patent applications and licensed rights may not provide protection against competitive technologies or may be held invalid if challenged or could be circumvented. Our competitors may also independently develop drug delivery technologies or products similar to ours or design around or otherwise circumvent patents issued to, or licensed by, us. In addition, the laws of some foreign countries may not protect our proprietary rights to the same extent as U.S. law.
We also rely upon trade secrets, technical know-how and continuing technological innovation to develop and maintain our competitive position. We require our employees, consultants, advisors and collaborators to execute appropriate confidentiality and
37
Table of Contents
assignment-of-inventions agreements with us. These agreements provide that materials and confidential information developed or made known to the individual during the course of the individual’s relationship with us is to be kept confidential and not disclosed to third parties except in specific circumstances and assign the ownership of relevant inventions created during the course of employment to us. These agreements may be breached, and in some instances, we may not have an appropriate remedy available for breach of the agreements. Furthermore, our competitors may independently develop substantially equivalent proprietary information and techniques, reverse engineer, or otherwise gain access to our proprietary technology. We may be unable to meaningfully protect our rights in trade secrets, technical know-how and other non-patented technology.
In addition, we may have to resort to costly and time consuming litigation to protect or enforce our rights under certain intellectual property, or to determine their scope, validity or enforceability. Enforcing or defending our rights could be expensive, could cause significant diversion of our resources and may not prove successful. Any failure to enforce or protect our rights could cause us to lose the ability to exclude others from using our technologies to develop or sell competing products.
We are dependent on third party suppliers for key components of our delivery technologies, products and product candidates.
Key components of our drug delivery technologies, products and product candidates may be provided by sole or limited numbers of suppliers, and supply shortages or loss of these suppliers could result in interruptions in supply or increased costs. Certain components used in our research and development activities, such as the active pharmaceutical component of our products, are currently purchased from a single or a limited number of outside sources. The reliance on a sole or limited number of suppliers could result in:
| • | delays associated with research and development and non-clinical and clinical trials due to an inability to timely obtain a single or limited source component; |
| • | inability to timely obtain an adequate supply of required components; and |
| • | reduced control over pricing, quality and timely delivery. |
Our relationships with our manufacturers and suppliers are particularly important to us and any loss of or material diminution of their capabilities due to factors such as regulatory issues, accidents, acts of God or any other factor would have a material adverse effect on our company. Such risks were demonstrated when certain manufacturing issues were experienced at Aveva in 2010-2011 and when, subsequently and separately, the FDA identified certain product appearance issues with ONSOLIS®, which resulted in the March 2012 postponement of the U.S. and Canadian relaunch of the product. Any loss of or interruption in the supply of components from our suppliers or other third-party suppliers would require us to seek alternative sources of supply or require us to manufacture these components internally, which we are currently not able to do.
If the supply of any components is lost or interrupted, product or components from alternative suppliers may not be available in sufficient quality or in volumes within required time frames, if at all, to meet our or our partners’ needs. This could delay our ability to complete clinical trials, obtain approval for commercialization or commence marketing or cause us to lose sales, force us into breach of other agreements, incur additional costs, delay new product introductions or harm our reputation. Furthermore, product or components from a new supplier may not be identical to those provided by the original supplier. Such differences could have material effects on our overall business plan and timing, could fall outside of regulatory requirements, affect product formulations or the safety and effectiveness of our products that are being developed.
We have limited manufacturing experience and therefore depend on third parties to formulate and manufacture our products. We may not be able to secure or maintain the manufacture of sufficient quantities or at an acceptable cost necessary to successfully commercialize or continue to sell our products.
Our management’s expertise has primarily been in the areas of research and development, formulation development and clinical trial phases of pharmaceutical product development as well as commercial operations. Our management’s experience in the manufacturing of pharmaceutical products is more limited and we have limited equipment and no facilities of our own from which these activities could be performed. Therefore, we are fully dependent on third parties for our formulation development, manufacturing and the packaging of our products. This is particularly true with respect to ARx and Sharp, the primary manufacturers of our approved and commercialized product, BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®. We also rely on LTS, the manufacturer for BREAKYL™ in the E.U. This reliance exposes us to the risk of not being able to directly oversee the production and quality of the manufacturing process and provide ample commercial supplies to formulate sufficient product to conduct clinical trials and maintain adequate supplies to meet market demand for our products.
Furthermore, these third-party contractors, whether foreign or domestic, may experience regulatory compliance difficulty, mechanical shut downs, employee strikes, or any other unforeseeable acts that may delay or limit production, which could leave our commercial partners with inadequate supplies of product to sell, especially when regulatory requirements or customer demand
38
Table of Contents
necessitate the need for additional product supplies. Our inability to adequately establish, supervise and conduct (either ourselves or through third parties) all aspects of the formulation and manufacturing processes, and the inability of third party manufacturers like ARx, Sharp and LTS to consistently supply quality product when required would have a material adverse effect on our ability to commercialize and sell our products. We have faced risks associated with reliance on key third party manufacturers in the past and may be faced with such risks in the future. Any future manufacturing interruptions or related supply issues could have an adverse effect on our company, including loss of sales and royalty revenue and claims by or against us or our partners for breach of contract.
There are risks associated with our reliance on third parties for marketing, sales, managed care and distribution infrastructure and channels.
We expect that we will be required to enter into agreements with commercial partners (such as our agreement with Meda) to engage in sales, marketing and distribution efforts around our products and product candidates. We may be unable to establish or maintain third-party relationships on a commercially reasonable basis, if at all. In addition, these third parties may have similar or more established relationships with our competitors. If we do not enter into relationships with third parties for the sales and marketing of our proposed formulations or products, we will need to develop our own sales and marketing capabilities.
We may be unable to engage qualified distributors. Even if engaged, these distributors may:
| • | fail to satisfy financial or contractual obligations to us; |
| • | fail to adequately market our formulations or products; |
| • | cease operations with little or no notice to us; or |
| • | offer, design, manufacture or promote competing formulations or products. |
If we fail to develop sales, managed care, marketing and distribution channels, we would experience delays in generating sales and incur increased costs, which would harm our financial results.
The class-wide Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) for all transmucosal fentanyl products, and similar programs for other narcotic products, may slow sales and marketing efforts for products that contain narcotics, which could impact our royalty and sales revenue from such products.
Our approved product ONSOLIS® is formulated with the potent narcotic fentanyl. On December 29, 2011, FDA approved a REMS program covering all transmucosal fentanyl products. The program, which is referred to as the Transmucosal Immediate Release Fentanyl (TIRF) REMS Access Program, was designed to ensure informed risk-benefit decisions before initiating treatment with a transmucosal fentanyl product, and while patients are on treatment, to ensure appropriate use. The approved program covers all approved transmucosal fentanyl products under a single program and was implemented in March 2012. Additionally, the FDA has implemented a class-wide REMS covering the extended release and long acting opioid class. The class-wide REMS program consists of a REMS-compliant educational program offered by an accredited provider of continuing medical education, patient counseling materials and a medication guide. BELBUCA® falls within the existing class-wide REMS program. The cost and implementation of the extended release and long-acting opioid REMS is shared among multiple companies in the category.
There also continues to be a REMS in place for buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid dependence referred to as the BTOD (Buprenorphine-containing Transmucosal products for Opioid Dependence) REMS. BUNAVAIL® falls within the existing REMS, which is far less cumbersome and includes a medication guide and healthcare professional and patient education. Given the existence of a REMS in both the extended release and long-acting opioid and opioid dependence markets, we anticipate our products will fit within the existing REMS and will avoid the issues initially encountered with ONSOLIS®, where a REMS program was yet to be developed.
Our business and operations would suffer in the event of system failures.
Despite the implementation of security measures, our internal computer systems and those of our current and any future partners, contractors, and consultants are vulnerable to damage from cyber-attacks, computer viruses, unauthorized access, natural disasters, terrorism, war, and telecommunication and electrical failures. System failures, accidents, or security breaches could cause interruptions in our operations, and could result in a material disruption of our commercialization activities, development programs and our business operations, in addition to possibly requiring substantial expenditures of resources to remedy. The loss of clinical trial data from completed or future clinical trials could result in delays in our regulatory approval efforts and significantly increase our costs to recover or reproduce the data. To the extent that any disruption or security breach were to result in a loss of, or damage to, our data or applications, or inappropriate disclosure of confidential or proprietary information, we could incur liability and the commercialization of any potential product candidate could be delayed.
39
Table of Contents
Risks Related to Our Products in Development and Regulation
We depend in large part on our BEMA® drug delivery technology, and the loss of access to this technology would terminate or delay the further development of our products, injure our reputation or force us to pay higher fees.
We depend, in large part, on our BEMA® drug delivery technology. The loss of this key technology would seriously impair our business and future viability, and could result in delays in developing, introducing or maintaining our products and formulations until equivalent technology, if available, is identified, licensed and integrated. In addition, any defects in the BEMA® technology or other technologies we gain access to in the future could prevent the implementation or impair the functionality of our products or formulations, delay new product or formulation introductions or injure our reputation. If we are required to acquire or enter into license agreements with third parties for replacement technologies, we could be subject to higher fees, milestone or royalty payments, assuming we could access such technologies at all.
Our failure to obtain government approvals, including required FDA approvals, or to comply with ongoing governmental regulations relating to our technologies and proposed products and formulations could delay or limit introduction of our proposed formulations and products and result in failure to achieve revenues or maintain our ongoing business.
Our research and development activities and the manufacture and marketing of our products and product candidates are subject to extensive regulation for safety, efficacy and quality by numerous government authorities in the United States and abroad. Before receiving FDA or foreign regulatory clearance to market our proposed formulations and products, we will have to demonstrate that our formulations and products are safe and effective in the patient population and for the diseases that are to be treated. Clinical trials, manufacturing and marketing of drugs are subject to the rigorous testing and approval process of the FDA and equivalent foreign regulatory authorities. The Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act and other federal, state and foreign statutes and regulations govern and influence the testing, manufacture, labeling, advertising, distribution and promotion of drugs and medical devices. As a result, regulatory approvals can take a number of years or longer to accomplish and require the expenditure of substantial financial, managerial and other resources.
Our failure to complete or meet key milestones relating to the development of our technologies and proposed products and formulations would significantly impair the viability of our company.
In order to be commercially viable, we must research, develop, obtain regulatory approval for, manufacture, introduce, market and distribute formulations or products incorporating our technologies. For each drug that we formulate with our drug delivery technologies, we must meet a number of critical developmental milestones, including:
| • | demonstration of the benefit from delivery of each specific drug through our drug delivery technologies; |
| • | demonstration, through non-clinical and clinical trials, that our drug delivery technologies are safe and effective; and |
| • | establishment of a viable Good Manufacturing Process capable of potential scale-up. |
The estimated required capital and time-frames necessary to achieve these developmental milestones is subject to inherent risks, many of which may be beyond our control. As such, we may not be able to achieve these or similar milestones for any of our proposed product candidates or other product candidates in the future. Our failure to meet these or other critical milestones would adversely affect the viability of our company.
Conducting and completing the clinical trials necessary for FDA approval is costly and subject to intense regulatory scrutiny as well as the risk of failing to meet the primary endpoint of such trials. We will not be able to commercialize and sell our proposed products and formulations without successfully completing such trials.
Clinical testing is expensive and can take many years to complete, and its outcome is inherently uncertain. In order to conduct clinical trials that are necessary to obtain approval by the FDA to market a drug product, the FDA requires the submission of an IND. The FDA has 30 days to review the IND and, unless the FDA raises an issue or concern about the clinical trial plan during that time period, the IND becomes effective at the end of that 30 days and sponsors may proceed with their clinical trial plans. The FDA can suspend or terminate clinical trials at any time due to a number of factors, including for safety or efficacy reasons, because we or our clinical investigators did not comply with the FDA’s requirements for conducting clinical trials, changes in governmental regulations or administrative actions or lack of adequate funding to continue the clinical trial. If the FDA does not permit us to proceed with our
40
Table of Contents
planned clinical trials or the trials are suspended or permanently terminated by us, the FDA or any institutional review boards overseeing the trials, the commercial prospects of our product candidates will be harmed, and our ability to generate product revenues from any of these product candidates will be delayed. In addition, many of the factors that cause, or lead to, a delay in the commencement or completion of clinical trials may also ultimately lead to the denial of regulatory approval of our product candidates.
In addition, it is our stated intention to seek to avail ourselves of the FDA’s 505(b)(2) approval procedure where it is appropriate to do so. Section 505(b)(2) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act permits an applicant to file a NDA where at least some of the information required for approval comes from studies not conducted by or for the applicant and for which the applicant has not obtained a right of reference. The applicant may rely upon published literature and the FDA’s findings of safety and effectiveness based on certain preclinical testing or clinical studies conducted for an approved product. The FDA may also require companies to perform additional studies or measurements to support the change from the approved product. If this approval pathway is not available to us with respect to a particular formulation or product, or at all, the time and cost associated with developing and commercializing such formulations or products may be prohibitive and our business strategy would be materially and adversely affected.
Moreover, we may be required to conduct additional costly and time-consuming clinical studies beyond those that we originally anticipate in the event that our clinical trials fail to meet their primary endpoints or for other reasons, which would render them inadequate to support approval by the FDA. For example, in September 2011, we announced that our Phase 3 clinical trial for BELBUCA® did not meet its primary endpoint and therefore we were required to conduct new and costly trials under our license and development agreement with Endo prior to NDA approval. Additionally, in December 2016, we announced that our Phase 2b clinical study assessing the efficacy and safety of Clonidine Topical Gel failed to show a statistically significant difference in pain relief between Clonidine Topical Gel and placebo. As a result, we discontinued further development of the product. If our trials fail to meet their endpoints and we elect to move forward with clinical development, conducting new clinical trials in accordance with the FDA requirements and with designs that seek to remedy any prior trial deficiencies will require significant additional capital with no assurances of positive outcomes, and will not able to commercialize and sell our any applicable product until we were able to meet our primary endpoints, of which no assurances can be given.
Data obtained from clinical trials are susceptible to varying interpretations, which could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approvals.
Data already obtained, or data we may obtain in the future, from non-clinical studies and clinical trials do not necessarily predict the results that will be obtained from later non-clinical studies and clinical trials. Moreover, non-clinical and clinical data are susceptible to multiple and varying interpretations, which could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. A number of companies in the pharmaceutical industry, including those involved in competing drug delivery technologies, have suffered significant setbacks in advanced clinical trials, even after promising results in earlier trials. The failure to adequately demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of a proposed formulation or product under development could delay or prevent regulatory clearance of the product candidate, resulting in delays to commercialization, and could materially harm our business. In addition, our clinical trials may not demonstrate sufficient levels of safety and efficacy necessary to obtain the requisite regulatory approvals for our drugs, and thus our proposed drugs may not be approved for marketing. Finally, if any of our clinical trials do not meet their primary endpoints, or for a variety of other reasons, we may be required to conduct additional clinical trials in order to progress development of the subject product. These additional trials would be costly and time-consuming and would divert resources from other projects.
The foregoing risks were evidenced by the failure of our Phase 3 trial for BELBUCA® for the treatment of moderate to severe chronic pain to meet its primary endpoint, which we announced September 2011. These risks were further evidenced in that, on March 30, 2015, we announced that the primary efficacy endpoint in the Phase 3 clinical study of Clonidine Topical Gel compared to placebo for the treatment of PDN did not meet statistical significance, although certain secondary endpoints showed statistically significant improvement over placebo. Final analysis of the study identified a sizeable patient population with a statistically significant improvement (n=158; p<0.02) in pain score vs placebo. Following thorough analysis of the data and identification of the reasons behind the study results, we initiated a second study. The study incorporates significant learnings from previously conducted studies and involves tightened and additional inclusion criteria to improve assay sensitivity, reduce bias and ensure compliance with enrollment criteria. In December 2016, we announced that our Phase 2b clinical study assessing the efficacy and safety of Clonidine Topical Gel failed to show a statistically significant difference in pain relief between Clonidine Topical Gel and placebo. As a result, we are discontinuing further development of the product and have returned the rights to Arcion.
41
Table of Contents
If users of our products and product candidates are unable to obtain adequate reimbursement from third-party payers, or if new restrictive legislation is adopted, market acceptance of our proposed formulations or products may be limited and we may not achieve material revenues.
The continuing efforts of government and insurance companies, health maintenance organizations and other payers of healthcare costs to contain or reduce costs of health care may affect our future revenues and profitability, and the future revenues and profitability of our potential customers, suppliers and collaborative partners and the availability of capital. For example, in certain foreign markets, pricing or profitability of prescription pharmaceuticals is subject to government control. In the United States, given recent federal and state government initiatives directed at lowering the total cost of health care, the U.S. Congress and state legislatures will likely continue to focus on health care reform, the cost of prescription pharmaceuticals and on the reform of the Medicare and Medicaid systems. While we cannot predict whether any such legislative or regulatory proposals will be adopted, the announcement or adoption of such proposals and related laws, rules and regulations could materially harm our business, financial conditions, results of operations or stock price. Moreover, the passage of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act in 2010, and efforts to amend or repeal such law, has created significant uncertainty relating to the scope of government regulation of healthcare and related legal and regulatory requirements, which could have an adverse impact on sales of our products.
The ability of our company to commercialize BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®, or any partners with which we have a licensing arrangement to sell ONSOLIS® will depend in part on the extent to which appropriate reimbursement levels for the cost of our proposed formulations and products and related treatments are obtained by governmental authorities, private health insurers and other organizations, such as HMOs. Consumers and third-party payers are increasingly challenging the prices charged for drugs and medical services. Also, the trend toward managed health care in the United States, which could control or significantly influence the purchase of health care services and drugs, as well as legislative proposals to reform health care or reduce government insurance programs, may all result in lower prices for or rejection of our drugs.
We could be exposed to significant drug product liability claims which could be time consuming and costly to defend, divert management attention and adversely impact our ability to obtain and maintain insurance coverage.
The testing, manufacture, marketing and sale of our proposed drug formulations involve an inherent risk that product liability claims will be asserted against us. All of our clinical trials have been, and all of our proposed clinical trials are anticipated to be conducted by collaborators and third-party contractors. We currently have a general liability/product liability policy which includes coverage for our clinical trials and our commercially marketed products. Annual aggregate limits include $2 million for general liability, with $1 million for each occurrence; product liability is $15 million for aggregate and $15 million per occurrence with excess liability in the amount of an additional $5 million; umbrella liability is $5 million aggregate and $5 million per occurrence. It is possible that this coverage will be insufficient to protect us from future claims. Under our agreement, Meda is required to carry comprehensive general product liability and tort liability insurance, each in amounts not less than $5 million per incident and $10 million annual aggregate and to name us as an additional insured thereon.
Should we decide to seek additional insurance against such risks before our product sales commence, there is a risk that such insurance will be unavailable to us, or if it can be obtained at such time, that it will be available at an unaffordable cost. Even if we obtain insurance, it may prove inadequate to cover claims and/or litigation costs, especially in the case of wrongful death claims. Product liability claims or other claims related to our products, regardless of their outcome, could require us to spend significant time and money in litigation or to pay significant settlement amounts or judgments. Any successful product liability or other claim may prevent us from obtaining adequate liability insurance in the future on commercially desirable or reasonable terms. An inability to obtain sufficient insurance coverage at an acceptable cost or otherwise to protect against potential product liability claims could prevent or inhibit the commercialization of our products and product candidates. A product liability claim could also significantly harm our reputation and delay market acceptance of our proposed formulations and products. In addition, although third party partners are required to provide insurance in connection with specific products such partners may face similar insurance related risks.
Our business involves environmental risks related to handling regulated substances which could severely affect our ability to conduct research and development of our drug delivery technology and product candidates.
In connection with our or our partners’ research and clinical development activities, as well as the manufacture of materials and products, we and our partners are subject to federal, state and local laws, rules, regulations and policies governing the use, generation, manufacture, storage, air emission, effluent discharge, handling and disposal of certain materials, biological specimens and wastes. We and our partners may be required to incur significant costs to comply with environmental and health and safety regulations in the future. Our research and clinical development, as well as the activities of our manufacturing and commercial partners, both now and in the future, may involve the controlled use of hazardous materials, including but not limited to certain hazardous chemicals and narcotics. We cannot completely eliminate the risk of accidental contamination or injury from these materials. In the event of such an occurrence, we could be held liable for any damages that result and any such liability could exceed our resources.
42
Table of Contents
Government and other efforts to reform the healthcare industry could have adverse effects on our company, including the inability of users of our current and future approved products to obtain adequate reimbursement from third-party payers, which could lead to diminished market acceptance of, and revenues from, such products.
Our ability to commercialize BELBUCA®, BUNAVAIL® and to sell ONSOLIS® (once it is reformulated and placed back on the market in the U.S. and Canada), alone or with collaborators, will depend in part on the extent to which coverage and reimbursement for the product will be available from:
| • | government and health administration authorities; |
| • | private health maintenance organizations and health insurers; and |
| • | other healthcare payers. |
Significant uncertainty exists as to the reimbursement status of newly approved healthcare products. The regulations that govern marketing approvals, pricing and reimbursement for new drug products vary widely from country to country. In the United States, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Affordability Reconciliation Act of 2010 (“ACA”), is significantly changing the way healthcare is financed by both governmental and private insurers. While we cannot predict what impact on federal reimbursement policies this law or any amendment to it will continue to have in general or specifically on any product that we commercialize, the ACA or any such amendment may result in downward pressure on pharmaceutical reimbursement, which could negatively affect market acceptance of new products. In addition, although the United States Supreme Court has upheld the constitutionality of most of the ACA, several states have not implemented certain sections of the ACA, including 19 that have rejected the expansion of Medicaid eligibility for low income citizens, and some members of the U.S. Congress are still working to repeal the ACA. More recently, President Trump and the Republican majorities in both houses of the U.S. Congress have been seeking to repeal or replace all or portions of the ACA but to date they have been unable to agree on any such legislation.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 includes a provision repealing, effective January 1, 2019, the tax-based shared responsibility payment imposed by the ACA on certain individuals who fail to maintain qualifying health coverage for all or part of a year that is commonly referred to as the “individual mandate”. Additionally, on January 22, 2018, President Trump signed a continuing resolution on appropriations for fiscal year 2018 that delayed the implementation of certain fees mandated by the ACA, including the so-called “Cadillac” tax on certain high cost employer- sponsored insurance plans, the annual fee imposed on certain health insurance providers based on market share, and the medical device excise tax on non-exempt medical devices. Further, the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018, or the BBA, among other things, amends the ACA, effective January 1, 2019, to increase from 50% to 70% the point-of-sale discount that is owed by pharmaceutical manufacturers who participate in Medicare Part D and to close the coverage gap in most Medicare drug plans, commonly referred to as the “donut hole”. Congress may still consider other legislation to repeal and replace elements of the ACA. We expect that the ACA, as currently enacted or as it may be amended or repealed in the future, and other healthcare reform measures that may be adopted in the future, could have a material adverse effect on our industry generally and on our ability to successfully commercialize our products. We cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of government regulation that may arise from future legislation or administrative action, either in the United States or abroad. If we or our collaborators are slow or unable to adapt to changes in existing requirements or the adoption of new requirements or policies, or if we or our collaborators are not able to maintain regulatory compliance, our products may lose any regulatory approval that may have been obtained and we may not achieve or sustain profitability, which would adversely affect our business.
In addition, we are subject to the Federal Drug Supply Chain Security Act of 2013 (“DSCSA”). The U.S. government has enacted DSCSA which requires development of an electronic product tracking and tracing of each prescription drug at the salable unit level through the distribution system, which will be effective incrementally over a 10-year period. Compliance with DSCSA and future U.S. federal or state electronic requirements may increase our operational expenses and impose significant administrative burdens.
43
Table of Contents
We may also be subject to healthcare laws, regulation and enforcement; our failure to comply with those laws could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial conditions.
We may also be subject to several healthcare regulations and enforcement by the federal government and the states and foreign governments in which we conduct our business. The laws that may affect our ability to operate include:
| • | the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (or HIPAA), as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, which governs the conduct of certain electronic healthcare transactions and protects the security and privacy of protected health information; |
| • | the federal healthcare programs’ Anti-Kickback Law, which prohibits, among other things, persons from knowingly and willfully soliciting, receiving, offering or paying remuneration, directly or indirectly, in exchange for or to induce either the referral of an individual for, or the purchase, order or recommendation of, any good or service for which payment may be made under federal healthcare programs such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs; |
| • | federal false claims laws which prohibit, among other things, individuals or entities from knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, claims for payment from Medicare, Medicaid, or other third-party payors that are false or fraudulent; |
| • | federal criminal laws that prohibit executing a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program or making false statements relating to healthcare matters; and |
| • | state law equivalents of each of the above federal laws, such as anti-kickback and false claims laws which may apply to items or services reimbursed by any third-party payor, including commercial insurers. |
If our operations are found to be in violation of any of the laws described above or any other governmental regulations that apply to us, we may be subject to penalties, including civil and criminal penalties, damages, fines, the curtailment or restructuring of our operations, the exclusion from participation in federal and state healthcare programs and imprisonment, any of which could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and our financial results.
Risks Related to Our Common Stock and Series A Non-Voting Convertible Preferred Stock
Our business is subject to increasingly complex corporate governance, public disclosure, and accounting requirements and regulations that could adversely affect our business and financial results and condition.
We are subject to changing rules and regulations of various federal and state governmental authorities as well as the stock exchange on which our common stock is listed. These entities, including the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board, the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) and the Nasdaq Capital Market, have issued a significant number of new and increasingly complex requirements and regulations over the course of the last several years and continue to develop additional requirements and regulations in response to laws enacted by Congress, including the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and, most recently, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Protection Act, or the Dodd-Frank Act.
There are significant corporate governance and executive compensation-related provisions in the Dodd-Frank Act that expressly authorized or required the SEC to adopt additional rules in these areas, such as an advisory shareholder vote to approve of our executives’ compensation (or Say on Pay), proxy access, and an advisory shareholder vote on how often we should include a Say on Pay proposal in our proxy materials for future annual shareholder meetings or any special shareholder meeting for which we must include executive compensation information in the proxy statement for that meeting. Our efforts to comply with these requirements are likely to result in an increase in expenses which is difficult to quantify at this time.
In addition, we are subject to often complex accounting rules and interpretations promulgated by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (including its Emerging Issues Task Force). We have faced challenges of compliance with accounting rules in the past and may face such challenges in the future, and adjustments to or restatements of our financial statements or accounting policies based on such challenges could have a material adverse effect on our public stock price and our reputation.
44
Table of Contents
Our stock price is subject to market factors and market volatility, both generally and with respect to our industry and our company specifically. As such, there is a risk that your investment in our common stock could fluctuate in value.
The overall market for securities in recent years has experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that have particularly affected the market prices of many smaller companies. In particular, the market prices of securities of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies have been extremely volatile and have experienced fluctuations that often have been unrelated or disproportionate to operating performance of these companies. These broad market fluctuations (as well as market reactions to particular developments with our company) have and could continue to result in extreme fluctuations in the price of our common stock, which could cause a decline in the value of your common stock. These fluctuations, as well as general economic and market conditions, may have a material or adverse effect on the market price of our common stock.
If we cannot meet the NASDAQ Capital Market’s continuing listing requirements and NASDAQ rules, NASDAQ may delist our securities, which could negatively affect our company, the price of our securities and your ability to sell our securities.
As of the date of this Report, our shares are listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market. In the future, however, we may not be able to meet the continued listing requirements of the NASDAQ Capital Market and NASDAQ rules, which require, among other things, maintaining a minimum bid price per share of $1.00, minimum stockholders equity of $2.5 million or a minimum market capitalization of $35 million and a majority of “independent” directors on our board of directors. We have been subject to delisting proceedings and comments by NASDAQ in the past, and during 2011 our stock price declined to levels that put us at risk of not being able to maintain the required minimum bid price or market capitalization levels or both. If we are unable to satisfy the NASDAQ criteria for continued listing, especially at our current stock price levels, our securities could again be subject to delisting. Trading, if any, of our securities would thereafter be conducted in the over-the-counter market, in the so-called “pink sheets” or on the OTC Bulletin Board. As a consequence of any such delisting, our stockholders would likely find it more difficult to dispose of, or to obtain accurate quotations as to the prices of our securities.
Our Series A Non-Voting Convertible Preferred Stock ranks senior to our common stock in the event of a bankruptcy, liquidation or winding up of our assets.
As of the date of this Report, we currently have 2,139,000 issued and 2,093,155 outstanding shares of Series A Non-Voting Convertible Preferred Stock, which we issued in connection with our $40 million financing which closed on December 2012. In the event of our bankruptcy, liquidation or winding up, our assets will be available to pay obligations on our Series A Non-Voting Convertible Preferred Stock in preference to the holders of our common stock.
Additional authorized shares of our common stock and preferred stock available for issuance may adversely affect the market for our common stock.
As of March 13, 2018, there are 58,465,111 shares of common stock issued and 58,449,620 shares of common stock outstanding and there were 2,139,000 shares issued and 2,093,155 outstanding of Series A Non-Voting Convertible Preferred Stock issued and outstanding. On July 21, 2011, our stockholders approved an amendment to our certificate of incorporation to increase the number of authorized shares of common stock, par value $.001, of our common stock from 45,000,000 to 75,000,000 shares. This increase in our authorized shares of common stock provides us with the flexibility to issue more shares in the future, which might cause dilution to our stockholders. In addition, the total number of shares of our common stock issued and outstanding does not include shares reserved in anticipation of the exercise of outstanding options or warrants. To the extent such options (including options under our stock incentive plan) or warrants are exercised, the holders of our common stock may experience further dilution.
Moreover, in the event that any future financing should be in the form of, be convertible into or exchangeable for, equity securities, and upon the exercise of options and warrants, investors would experience additional dilution. Finally, in addition to the above referenced shares of common stock which may be issued without stockholder approval, we have 5 million shares of authorized preferred stock, of which 2,139,000 shares have been designated as Series A Non-Voting Convertible Preferred Stock. The remaining 2,290,700 shares of preferred stock remain undesignated shares of preferred stock, the terms of which may be fixed by our board of directors. We have issued preferred stock in the past, and our board of directors has the authority, without stockholder approval, to create and issue one or more additional series of such preferred stock and to determine the voting, dividend and other rights of holders of such preferred stock. The issuance of any of such series of preferred stock may have an adverse effect on the holders of common stock.
Shares eligible for future sale may adversely affect the market for our common stock.
We have a material number of shares of common stock underlying securities of our company, the future sale of which could depress the price of our publicly-traded stock. As of March 13, 2018: (i) 3,042,677 shares of common stock are issuable upon exercise of outstanding stock options at a weighted average exercise price of $3.45 per share, (ii) 3,029,184 restricted stock units eligible to be converted shares of our common stock (iii) 2,093,155 shares of Series A preferred eligible to be converted into shares of our common stock and (iv) 2,136,020 common stock shares underlying outstanding warrants at an average exercise price of $2.60 per share.
45
Table of Contents
In addition, from time to time, certain of our stockholders may be eligible to sell all or some of their shares of common stock by means of ordinary brokerage transactions in the open market pursuant to Rule 144, promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, which we refer to herein as the Securities Act, subject to certain limitations. In general, pursuant to Rule 144, after satisfying a six month holding period: (i) affiliated stockholder (or stockholders whose shares are aggregated) may, under certain circumstances, sell within any three month period a number of securities which does not exceed the greater of 1% of the then outstanding shares of common stock or the average weekly trading volume of the class during the four calendar weeks prior to such sale and (ii) non-affiliated stockholders may sell without such limitations, provided we are current in our public reporting obligations. Rule 144 also permits the sale of securities by non-affiliates that have satisfied a one year holding period without any limitation or restriction. Any substantial sale of our common stock pursuant to Rule 144 or pursuant to any resale report may have a material adverse effect on the market price of our securities.
Furthermore, sales of our common stock by our directors, officers, or employees may occur as a result of sales effected pursuant to predetermined trading plans adopted under the safe-harbor afforded by SEC Rule 10b5-1.
Our certificate of incorporation and bylaws contain provisions that may discourage, delay or prevent a change in our management team that stockholders may consider favorable.
Our certificate of incorporation, as amended, our amended and restated bylaws (which were adopted in 2010) and Delaware law contain provisions that may have the effect of preserving our current management, such as:
| • | providing for a staggered board of directors, which impairs the ability of our stockholders to remove our directors at annual or special meetings of stockholders; |
| • | authorizing the issuance of “blank check” preferred stock without any need for action by stockholders; |
| • | limiting the ability of stockholders to call special meetings of stockholders; |
| • | permitting stockholder action by written consent; |
| • | establishing advance notice requirements for nominations for election to the board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted on by stockholders at stockholder meetings; |
| • | requiring a super-majority vote of our stockholders to remove directors of our company; and |
| • | providing that our stockholders may only remove our directors for “cause” (as defined in our bylaws). |
These provisions affect your rights as a stockholder since they permit our board of directors to make it more difficult for common stockholders to replace members of the board or undertake other significant corporate actions. Because our board of directors is responsible for appointing the members of our management team, these provisions could in turn affect any attempt to replace our current management team.
On and effective as of November 17, 2017, our board adopted our Second Amended and Restated Bylaws (which we refer to as the Second Amended Bylaws). The only material change to the Second Amended Bylaws compared to our previous amended and restated bylaws was a change in the threshold of stockholder vote needed at a duly called meeting of stockholders to remove a member of the board for cause from sixty-six and two-thirds percent (66 2/3%) of the stockholders entitled to vote at such meeting to a majority of the holders of shares entitled to vote at such meeting. This change was made in order for our bylaws to be in conformance with current Delaware law.
The financial and operational projections that we may make from time to time are subject to inherent risks.
The projections that our management may provide from time to time (including, but not limited to, those relating to potential peak sales amounts, product approval, production and supply dates, commercial launch dates, and other financial or operational matters) reflect numerous assumptions made by management, including assumptions with respect to our specific as well as general business, economic, market and financial conditions and other matters, all of which are difficult to predict and many of which are beyond our control. Accordingly, there is a risk that the assumptions made in preparing the projections, or the projections themselves, will prove inaccurate. There will be differences between actual and projected results, and actual results may be materially different from those contained in the projections. The inclusion of the projections in (or incorporated by reference in) this Report should not be regarded as an indication that we or our management or representatives considered or consider the projections to be a reliable prediction of future events, and the projections should not be relied upon as such.
46
Table of Contents
We do not intend to pay dividends on our common stock.
We have never declared or paid any cash dividend on our capital stock. We currently intend to retain any future earnings and do not expect to pay any dividends for the foreseeable future. Therefore, you should not invest in our common stock in the expectation that you will receive dividends.
Our additional financing requirements could result in dilution to existing stockholders.
The additional financings which we have undertaken and which we may in the future require, have and may be obtained through one or more transactions which have diluted or will dilute (either economically or in percentage terms) the ownership interests of our stockholders. Further, we may not be able to secure such additional financing on terms acceptable to us, if at all. We have the authority to issue additional shares of common stock and preferred stock, as well as additional classes or series of ownership interests or debt obligations which may be convertible into any one or more classes or series of ownership interests. We are authorized to issue 75 million shares of common stock and 2,290,700 shares of preferred stock. Such securities may be issued without the approval or other consent of our stockholders.
The common stock’s inclusion in The NASDAQ Stock Market’s “Tick Size Pilot Program” may limit your ability to sell your shares at the volumes, prices or times that you desire.
Effective October 31, 2016, our common stock was selected by The NASDAQ Stock Market based on Market Cap, daily volume and Share Price for inclusion in “Test Group 3” of its “Tick Size Pilot Program”. The program will last for two years and imposes wider minimum quoting and/or trading increments, or “tick sizes”, for certain securities with small market capitalization. Specifically, subject to certain exceptions, the minimum quotation price and minimum trading price for securities in Test Group 3, like the common stock, have been widened to $0.05 per share, which means that the common stock must now be quoted in $0.05 minimum increments and must now trade at $0.05 minimum increments. In addition, securities in Test Group 3 are subject to a “trade-at” requirement that prevents price matching by a trading center that is not displaying a protected bid or protected offer, subject to certain exceptions. As a result, brokerage firms are now required to ensure that your orders with respect to shares of the common stock are priced in nickel increments. This means that the “limit” or “stop” prices that you may place on your order can no longer be in pennies and instead must be in increments of $0.05. We cannot predict the impact, if any, of the common stock’s inclusion in this Tick Size Pilot Program. This program could adversely affect the market for our common stock and could limit your ability to sell your shares at the prices, times and/or volumes that you desire.
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments. |
None.
| Item 2. | Description of Property. |
Our corporate headquarters is located in Raleigh, North Carolina. We moved into our current headquarters in February 2015. The lease for this office, which commenced November 14, 2014 for 89 months, is approximately 12,000 square foot space and has remaining base rent of $1.6 million payable through July 2022. Rent is payable in monthly installments and is subject to yearly price increases and increases for our share of common area maintenance costs. The landlord for this space is HRLP Raleigh, L.P. We believe this space is adequate as our principal executive office location.
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings. |
Readers are advised that the following disclosure regarding our ongoing litigations with MonoSol RX, dba Aquestive Therapeutics and Reckitt Benckiser is intended to provide some background and an update on the matter as required by the rules of the SEC. Additional details regarding the past procedural history of the matter can be found in our previously filed periodic filings with the SEC.
Litigation related to ONSOLIS®
On November 2, 2010, Aquestive filed an action against us and our commercial partners for ONSOLIS® in the Federal District Court of New Jersey (the DNJ) for alleged patent infringement and false marking. We were formally served in this matter on January 19, 2011. Aquestive claimed that our manufacturing process for ONSOLIS®, which has never been disclosed publicly and which we and our partners maintain as a trade secret, infringes on its’588 Patent. Of note, the BEMA® technology itself was not at issue in the case, nor is BELBUCA® or BUNAVAIL®, but rather only the manner in which ONSOLIS®, which incorporates the BEMA® technology, is manufactured. Pursuant to its complaint, Aquestive was seeking an unspecified amount of damages, attorney’s fees and an injunction preventing future infringement of Aquestive’s patents.
47
Table of Contents
We strongly refuted as without merit Aquestive’s assertion of patent infringement, which relates to our confidential, proprietary manufacturing process for ONSOLIS®. On September 12, 2011, we filed a request for inter partes reexamination in the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) of Aquestive’s ’588 Patent demonstrating that all claims of such patent were anticipated by or obvious in the light of prior art references, including several prior art references not previously considered by the USPTO, and thus invalid. On September 16, 2011, we filed a motion for stay pending the outcome of the reexamination proceedings, which subsequently was granted.
In November 2011, the USPTO rejected all 191 claims of Aquestive’s ’588 Patent. On January 20, 2012, we filed requests for reexamination before the USPTO of Aquestive’s ’891 Patent, and’292 Patent, the two additional patents asserted by Aquestive, demonstrating that all claims of those two patents were anticipated by or obvious in the light of prior art references, including prior art references not previously considered by the USPTO, and thus invalid. The USPTO granted the requests for reexamination with respect to Aquestive’s ’292 and ’891 Patents. In its initial office action in each, the USPTO rejected every claim in each patent.
As expected, in the ’891 Patent and ’292 Patent Ex Parte Reexamination proceedings, Aquestive amended the claims several times and made multiple declarations and arguments in an attempt to overcome the rejections made by the USPTO. These amendments, declarations and other statements regarding the claim language significantly narrowed the scope of their claims in these two patents. In the case of the ’891 Patent, not one of the original claims survived reexamination and five separate amendments were filed confirming our position that the patent was invalid. Additionally, we believe that arguments and admissions made by Aquestive prevent it from seeking a broader construction during any subsequent litigation by employing arguments or taking positions that contradict those made during prosecution.
A Reexamination Certificate for Aquestive’s ’891 Patent in its amended form was issued August 21, 2012 (Reexamined Patent No. 7,357,891C1 or the “’891C1 Patent”). A Reexamination Certificate for Aquestive’s ’292 Patent in its amended form was issued on July 3, 2012 (Reexamined Patent No. 7,425,292C1 or the “’292C1 Patent”). These actions by the USPTO confirm the invalidity of the original patents and through the narrowing of the claims in the reissued patents strengthens our original assertion that our products and technologies do not infringe on Aquestive’s original patents.
On June 12, 2013, despite our previously noted success in the prior ex parte reexaminations for the ’292 and ’891 Patents, we filed requests for inter partes reviews (“IPRs”) on the narrowed yet reexamined patents, the ’292 C1 and ’891 C1 Patents, to challenge their validity and continue to strengthen our position. On November 13, 2013, the USPTO decided not to institute the two IPRs for the ’891 C1 and ’292 C1 Patents. The USPTO’s decision was purely on statutory grounds and based on a technicality (in that the IPRs were not filed within what the UPSTO determined to be the statutory period) rather than substantive grounds. Thus, even though the IPRs were not instituted, the USPTO decision preserves our right to raise the same arguments at a later time (e.g., during litigation). Regardless, our assertion that our products and technologies do not infringe the original ’292 and ’891 Patents and, now, the reexamined ’891 C1 and ’292 C1 Patents remains the same.
Importantly, in the case of Aquestive’s ’588 Patent, at the conclusion of the reexamination proceedings (and its appeals process), on April 17, 2014, the PTAB issued a Decision on Appeal affirming the Examiner’s rejection (and confirming the invalidity) of all the claims of the ’588 Patent. Aquestive did not request a rehearing by the May 17, 2014 due date for making such a request and did not further appeal the Decision to the Federal Court of Appeals by the June 17, 2014 due date for making such an appeal. Subsequently, on August 5, 2014, the USPTO issued a Certificate of Reexamination cancelling the ‘588 Patent claims.
Based on our original assertion that our proprietary manufacturing process for ONSOLIS® does not infringe on patents held by Aquestive, and the denial and subsequent narrowing of the claims on the two reissued patents Aquestive has asserted against us while the third has had all claims rejected by the USPTO, we remain confident in our original stated position regarding this matter. Thus far, we have proven that the “original” ’292 and ’891 patents in light of their reissuance with fewer and narrower claims were indeed invalid and the third and final patent, the ’588 patent, was invalid as well with all its claims cancelled. Given the outcomes of the ‘292, ‘891 and ‘588 reexamination proceedings, at a January 22, 2015 status meeting, the Court decided to lift the stay and grant our request for the case to proceed on an expedited basis with a Motion for Summary Judgment to dismiss the action. On September 25, 2015, our motion for summary judgment was ordered and the case was subsequently closed. We were found to be entitled to absolute intervening rights as to both patents in suit, the ‘292 and ‘891 patents and our ONSOLIS® product is not liable for infringing the patents prior to July 3, 2012 and August 21, 2012, respectively. In October 2015, Aquestive appealed the decision of the court to the Federal Circuit. We had no reason to believe the outcome would be different and were prepared to vigorously defend the appeal. Aquestive, however, subsequently decided to withdraw the appeal. On February 25, 2016, Aquestive filed an Unopposed Motion For Voluntary Dismissal Of Appeal, which was granted by the court on February 26, 2016 and the case dismissed. Thus, the district court’s grant of the Summary Judgement of Intervening Rights stands. The possibility exists that Aquestive could file another suit alleging infringement of the ‘292 and ’891 patents. We continue to believe, however, that ONSOLIS® and our other products relying on the BEMA® technology, including BUNAVAIL® and BELBUCA®, do not infringe any amended, reexamined claim from either patent.
48
Table of Contents
Litigation related to BUNAVAIL®
RB and Aquestive Therapeutics (formerly MonoSol Rx)
On October 29, 2013, Reckitt Benckiser, Inc., RB Pharmaceuticals Limited, and Aquestive (collectively, the RB Plaintiffs) filed an action against us relating to our BUNAVAIL® product in the United States District Court for the Eastern District of North Carolina for alleged patent infringement. BUNAVAIL® is a drug approved for the maintenance treatment of opioid dependence. The RB Plaintiffs claim that the formulation for BUNAVAIL®, which has never been disclosed publicly, infringes its patent (United States Patent No. 8,475,832) (the “’832 Patent”).
On May 21, 2014, the Court granted our motion to dismiss. In doing so, the Court dismissed the case in its entirety. The RB Plaintiffs did not appeal the Court Decision by the June 21, 2014 due date and therefore, the dismissal will stand and the RB Plaintiffs lose the ability to challenge the Court Decision in the future. The possibility exists, however, that the RB Plaintiffs could file another suit alleging infringement of the ‘832 Patent. If this occurs, based on our original position that our BUNAVAIL® product does not infringe the ‘832 Patent, we would defend the case vigorously (as we have done so previously), and we anticipate that such claims against us ultimately would be rejected.
On September 20, 2014, based upon our position and belief that our BUNAVAIL® product does not infringe any patents owned by the RB Plaintiffs, we proactively filed a declaratory judgment action in the United States District Court for the Eastern District of North (EDNC) Carolina, requesting the Court to make a determination that our BUNAVAIL® product does not infringe the RB Plaintiffs’ ‘832 Patent, US Patent No. 7,897,080 (the “‘080 Patent”) and US Patent No. 8,652,378 (the “‘378 Patent”). With the declaratory judgment, there is an automatic stay in proceedings. The RB Plaintiffs may request that the stay be lifted, but they have the burden of showing that the stay should be lifted. For the ‘832 Patent, the January 15, 2014 IPR was instituted and in June 2015, all challenged claims were rejected for both anticipation and obviousness. In August 2015, the RB Plaintiffs filed an appeal to the Federal Circuit. The Federal Circuit affirmed the USPTO’s decision, and the RB Plaintiffs then filed a Petition for Panel Rehearing and for Rehearing En Banc, which was denied. A mandate issued on October 25, 2016, pursuant to Rule 41(a) of the Federal Rules of Appellate Procedure, meaning that a petition for certiorari to the Supreme Court is no longer possible for the RB Plaintiffs. The ‘832 IPR was finally resolved with the invalidation of claims 15-19. For the ‘080 Patent, all claims have been rejected in an inter partes reexamination and the rejection of all claims as invalid over the prior art has been affirmed on appeal by the PTAB in a decision dated March 27, 2015. In May 2015, the RB Plaintiffs filed a response after the decision to which we filed comments. In December 2015, the PTAB denied Aquestive’s request to reopen prosecution, but provided Aquestive an opportunity to file a corrected response. Aquestive filed the request in December 2015 and we subsequently filed comments on December 23, 2015. The PTAB issued a communication on July 7, 2016 denying Aquestive’s request to reopen prosecution of the rejections of all claims over the prior art. On January 31, 2017, the PTAB issued a final decision maintaining an additional new ground of rejection in addition to the previous grounds of invalidity. As such, all claims remain finally rejected on multiple grounds. If a request for rehearing is not filed within 30 days, the decision will become final as to the PTAB. Thereafter, if Aquestive does not appeal to the Federal Circuit, the decision will be final and all claims will be cancelled. For the ‘378 Patent, an IPR was filed on June 1, 2014, but an IPR was not instituted. However, in issuing its November 5, 2014 decision not to institute the IPR, the PTAB construed the claims of the ‘378 Patent narrowly. As in prior litigation proceedings, we believe these IPR and the reexamination filings will provide support for maintaining the stay until the IPR and reexamination proceedings conclude. Indeed, given the PTAB’s narrow construction of the claims of the ‘378 Patent, we filed a motion to withdraw the ‘378 Patent from the case on December 12, 2014. In addition, we also filed a joint motion to continue the stay (with RB Plaintiffs) in the proceedings on the same day. Both the motion to withdraw the ‘378 Patent from the proceedings and motion to continue the stay were granted.
On September 22, 2014, the RB Plaintiffs filed an action against us (and our commercial partner) relating to our BUNAVAIL® product in the United States District Court for the District of New Jersey for alleged patent infringement. The RB Plaintiffs claim that BUNAVAIL®, whose formulation and manufacturing processes have never been disclosed publicly, infringes its patent U.S. Patent No. 8,765,167 (the “‘167 Patent”). As with prior actions by the RB Plaintiffs, we believe this is another anticompetitive attempt by the RB Plaintiffs to distract our efforts from commercializing BUNAVAIL®. We strongly refute as without merit the RB Plaintiffs’ assertion of patent infringement and will vigorously defend the lawsuit. On December 12, 2014, we filed a motion to transfer the case from New Jersey to North Carolina and a motion to dismiss the case against our commercial partner. The Court issued an opinion on July 21, 2015 granting our motion to transfer the venue to the Eastern District of North Carolina (“ENDC”) but denying our motion to dismiss the case against our commercial partner as moot. We have also filed a Joint Motion to Stay the case in North Carolina at the end of April 2016, which was granted by the court on May 5, 2016. Thus, the case is now stayed until a final resolution of the ‘167 IPRs in the USPTO. We will continue to vigorously defend this case in the EDNC.
49
Table of Contents
In a related matter, on October 28, 2014, we filed multiple IPR requests on the ’167 Patent demonstrating that certain claims of such patent were anticipated by or obvious in light of prior art references, including prior art references not previously considered by the USPTO, and thus, invalid. The USPTO instituted three of the four IPR requests and we filed a request for rehearing for the non-instituted IPR. The final decisions finding all claims patentable were issued in March 2016 and we filed a Request for Reconsideration in the USPTO in April 2016, which was denied in September 2016 and appealed to Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit (Fed. Cir.) in November 2016. The appeal is currently proceeding in the Federal Circuit with final briefing completed August 7, 2017 and oral argument held February 7, 2018. We anticipate receiving a final decision from the Federal Circuit sometime in 2018.
On January 22, 2014, Aquestive filed a Petition for IPR on the ‘019 Patent. The Petition asserted that the claims of the ‘019 Patent are alleged to be unpatentable over certain prior art references. The IPR was instituted on August 6, 2014. An oral hearing was held in April 2015 and a decision upholding all seven claims was issued August 5, 2015. In September 2015, Aquestive requested that the PTAB rehear the IPR. On December 19, 2016, the PTAB issued a final decision denying Aquestive’s request for rehearing. Aquestive did not file a notice of appeal to the Federal Circuit by February 20, 2017, therefore, PTAB’s decision upholding all claims of our ‘019 patent will be final and unappealable.
On January 13, 2017, Aquestive filed a complaint in the United States District Court for the District of New Jersey alleging BELBUCA® infringes the ‘167 patent. In lieu of answering the complaint, we filed motions to dismiss the complaint and, in the alternative, to transfer the case to the EDNC. Briefing on the motions was completed on June 21, 2017. On July 25, 2017, the Court administratively terminated the case pending the parties submission of a joint stipulation of transfer because the District of New Jersey was an inappropriate venue. This case has been transferred to Delaware District Court. On October 31, 2017 we filed motions to dismiss the complaint and, in the alternative, to transfer the case to the EDNC. Briefing on the motions was completed on December 1, 2017. We anticipate receiving a final decision from the District Court in the 2nd quarter of 2018. We strongly refute as without merit Aquestive’s assertion of patent infringement and will vigorously defend the lawsuit.
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA (formerly Actavis)
On February 8, 2016, we received a notice relating to a Paragraph IV certification from Teva Pharmaceuticals USA (“Teva”) (formerly Actavis) seeking to find invalid three Orange Book listed patents (the “Patents”) relating specifically to BUNAVAIL®. The Paragraph IV certification related to an Abbreviated New Drug Application (the “ANDA”) filed by Teva with the U.S Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) for a generic formulation of BUNAVAIL®. The Patents subject to Teva’s certification were the ’019 Patent, 8,147,866 (the “’866 Patent”) and 8,703,177 (the “’177 Patent”). Under the Food Drug and Cosmetic Act, as amended by the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, as amended (the “Hatch-Waxman Amendments”), after receipt of a valid Paragraph IV notice, we may, and in this case did, bring a patent infringement suit in federal district court against Teva within 45 days from the date of receipt of the certification notice. On March 18, 2016, we filed a complaint in Delaware against Teva, thus entitling us to receive a 30 month stay on the FDA’s ability to give final approval to any proposed products that reference BUNAVAIL®. The 30-month stay was expected to preempt any final approval by the FDA on Teva’s ANDA until at least August of 2018.
We have asserted three different patents against Teva, the ’019 patent, the ‘866 patent, and the ’177 patent. Teva did not raise non-infringement positions with regard to the ’019 and the ’866 patents in its Paragraph IV certification. Teva did raise a non-infringement position on the ’177 patent due to its assertion that the backing layer for its generic product does not have a pH within the claimed range claimed in the patent. We asserted in our complaint that Teva infringed the ‘177 patent either literally or under the doctrine of equivalents.
We believed that Teva was unlikely to prevail on its claims that the ’019, ’866, and ’177 Patents are invalid, and, as we have done in the past, we intend to vigorously defended our intellectual property. Each of the three patents carry the presumption of validity and, the ‘019 Patent has already been the subject of an unrelated IPR before the United States Patent and Trademark Office (“USPTO”) under which we prevailed, and all claims of the ‘019 Patent survived. Teva’s request for rehearing of the final IPR decision regarding the ‘019 Patent was denied by the USPTO on December 19, 2016. Teva did not file a timely appeal at the Federal Circuit.
On December 20, 2016 the USPTO issued U.S. Patent No. 9,522,188 (“the ’188 patent”), and this patent was properly listed in the Orange Book as covering the BUNAVAIL® product. On February 23, 2017 Teva sent a Paragraph IV certification adding the 9,522,188 to its ANDA. An amended Complaint was filed, adding the ’188 patent to the litigation.
On January 31, 2017, we received a notice relating to a Paragraph IV certification from Teva relating to Teva’s ANDA on additional strengths of BUNAVAIL®. On March 16, 2017, we brought suit against Teva and its parent company on these additional strengths within 45 days from the receipt of the notice in Delaware. As in the original case brought by Actavis, we were again entitled to receive a 30 month stay on the FDA’s ability to give final approval to any proposed products that reference the additional strengths of BUNAVAIL®. The 30-month stay was expected to extend until at least August of 2019. On June 20, 2017, the Court entered orders staying both BUNAVAIL® suits at the request of the parties.
50
Table of Contents
On May 23, 2017, the USPTO issued U.S. Patent 9,655,843 (the “’843 Patent”), and this patent was properly listed in the Orange Book as covering the BUNAVAIL® product.
Finally, on October 12, 2017, we announced that we had entered into a settlement agreement with Teva that resolved our BUNAVAIL® patent litigation against Teva pending in the U.S. District Court for the District of Delaware. As part of the Settlement Agreement, which is subject to review by the U.S. Federal Trade Commission and the U.S. Department of Justice, we have entered into a non-exclusive license agreement with Teva that permits Teva to first begin selling its generic version of BUNAVAIL® in the U.S. on July 23, 2028 or earlier under certain circumstances. Other terms of the agreement are confidential.
Litigation related to BELBUCA®
We received notices regarding Paragraph IV certifications from Teva on November 8, 2016, November 10, 2016, and December 22, 2016, seeking to find invalid two Orange Book listed patents (the “Patents”) relating specifically to BELBUCA®. The Paragraph IV certifications relate to three ANDAs filed by Teva with the FDA for a generic formulation of BELBUCA®. The Patents subject to Teva’s certification were the ’019 Patent and the ’866 Patent. Under the Hatch-Waxman Amendments, after receipt of a valid Paragraph IV notice, we may, and in this case did, bring a patent infringement suit in federal district court against Teva USA within 45 days from the date of receipt of the certification notice. We filed complaints in Delaware against Teva on December 22, 2016 and February 3, 2017, thus we were entitled to receive a 30 month stay on the FDA’s ability to give final approval to any proposed products that reference BELBUCA®. The 30-month stay was expected to preempt any final approval by the FDA on Teva’s ANDA Nos. 209704 and 209772 until at least May of 2019 and for Teva’s ANDA No. 209807 until at least June of 2019.
We asserted two different patents against Teva, the ’019 Patent and the ’866 Patent. Teva did not contest infringement of the claims of the ’019 Patent and also did not contest infringement of the claims of the ’866 Patent that cover BELBUCA® in its Paragraph IV certifications.
We believed that Teva was unlikely to prevail on its claims that the ’019 and ’866 Patents are invalid, and, as we have done in the past, we vigorously defended our intellectual property. Both of the patents carry the presumption of validity, and the ’019 Patent has already been the subject of an unrelated IPR before the USPTO under which we prevailed, and all claims of the ‘019 Patent survived. Aquestive’s request for rehearing of the final IPR decision regarding the ’019 Patent was denied by the USPTO on December 19, 2016. Aquestive did not file a timely appeal at the Federal Circuit.
On May 23, 2017, the USPTO issued U.S. Patent 9,655,843 (the “’843 Patent”), and this patent was properly listed in the Orange Book as covering the BELBUCA® product.
On August 28, 2017, the Court entered orders staying both BELBUCA® suits at the request of the parties. On October 18, 2017, the Court entered orders continuing the stay in both BELBUCA® suits at the request of the parties. On December 19, 2017, the Court entered orders continuing the stay in both BELBUCA® suits at the request of the parties.
In February 2018, we announced that we had entered into a settlement agreement with Teva that resolved our BELBUCA® patent litigation against Teva pending in the U.S. District Court for the District of Delaware. As part of the settlement agreement, which is subject to review by the U.S. Federal Trade Commission and the U.S. Department of Justice, we have granted Teva a non-exclusive license (for which we will receive no current or future payments) that permits Teva to first begin selling the generic version of our BELBUCA® product in the U.S. on January 23, 2027 or earlier under certain circumstances (including, for example, upon (i) the delisting of the patents-in-suit from the U.S. FDA Orange Book, (ii) the granting of a license by us to a third party to launch another generic form of BELBUCA® at a date prior to January 23, 2027, or (iii) the occurrence of certain conditions regarding BELBUCA® market share).
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures. |
Not applicable.
51
Table of Contents
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities. |
Our common stock is listed for quotation on the NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol “BDSI”. The range of reported high and reported low sales prices per share for our common stock for each fiscal quarter during 2017 and 2016, as reported by the NASDAQ Capital Market, is set forth below.
Quarterly Common Stock Price Ranges
| Fiscal Year 2017, Quarter Ended: |
High | Low | ||||||
| March 31, 2017 |
$ | 2.15 | $ | 1.65 | ||||
| June 30, 2017 |
$ | 3.05 | $ | 1.55 | ||||
| September 30, 2017 |
$ | 3.60 | $ | 2.30 | ||||
| December 31, 2017 |
$ | 3.10 | $ | 2.05 | ||||
|
Fiscal Year 2016, Quarter Ended: |
High | Low | ||||||
| March 31, 2016 |
$ | 4.90 | $ | 2.53 | ||||
| June 30, 2016 |
$ | 4.00 | $ | 1.86 | ||||
| September 30, 2016 |
$ | 3.10 | $ | 2.23 | ||||
| December 31, 2016 |
$ | 2.70 | $ | 1.50 | ||||
As of March 13, 2018, we had approximately 111 holders of record of our common stock. No cash dividends have been paid on the common stock to date. We currently intend to retain earnings for further business development and do not expect to pay cash dividends in the foreseeable future.
Performance Graph
The following graph shows a comparison of the five-year total cumulative returns of an investment of $100 in cash on December 31, 2012 in (i) our common stock (ii) the Nasdaq Composite Index (iii) the Nasdaq Biotechnology Index and (iv) the NYSE Pharmaceutical Index. All values assume reinvestment of the full amount of all dividends (to date, we have not declared any dividends).
This stock performance graph shall not be deemed “filed” with the SEC or subject to Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act, nor shall it be deemed incorporated by reference in any of our filings under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”). Comparison of cumulative total return on investment since December 31, 2012:
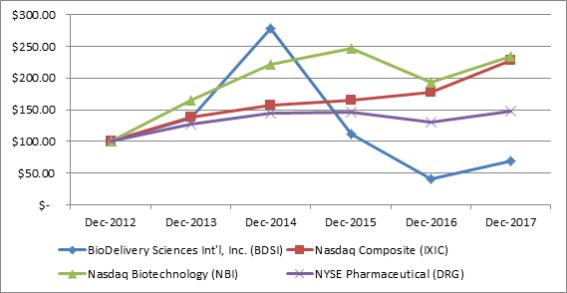
52
Table of Contents
| 12/31/2012 | 12/31/2013 | 12/31/2014 | 12/31/2015 | 12/31/2016 | 12/31/2017 | |||||||||||||||||||
| BioDelivery Sciences Int’l, Inc. |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 136.66 | $ | 278.89 | $ | 111.14 | $ | 40.60 | $ | 68.45 | ||||||||||||
| Nasdaq Composite (U.S. Companies) |
100.00 | 138.32 | 156.85 | 165.84 | 178.28 | 228.63 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Nasdaq Biotechnology |
100.00 | 165.61 | 222.08 | 247.44 | 193.79 | 234.60 | ||||||||||||||||||
| NYSE Pharmaceutical |
100.00 | 126.65 | 144.16 | 146.50 | 130.30 | 147.45 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Item 6. | Selected Financial Data. |
The statements of operations data and statements of cash flows data for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 and the balance sheet data as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 have been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this annual report. The statements of operations data and statements of cash flows data for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 and the balance sheet data as of December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 have been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements not included in this annual report. The following selected financial data should be read in conjunction with our “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and consolidated financial statements and related notes beginning on page F-1 and other financial information included in this Report.
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
| Statements of Operations Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total revenue (1) |
$ | 61,985 | $ | 15,546 | $ | 48,231 | $ | 38,944 | $ | 11,356 | ||||||||||
| Operating loss |
(29,420 | ) | (63,935 | ) | (35,179 | ) | (38,740 | ) | (56,402 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net income (loss) (2) |
5,285 | (67,138 | ) | (37,672 | ) | (54,218 | ) | (57,394 | ) | |||||||||||
| Diluted net income (loss) per share |
0.09 | (1.25 | ) | (0.72 | ) | (1.12 | ) | (1.51 | ) | |||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash, short-term and long-term investments |
$ | 21,195 | $ | 32,019 | $ | 83,560 | $ | 70,472 | $ | 23,176 | ||||||||||
| Total assets (3) |
88,101 | 51,720 | 102,772 | 88,840 | 38,005 | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term liabilities |
53,075 | 50,097 | 42,993 | 4,402 | 12,545 | |||||||||||||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(305,056 | ) | (310,341 | ) | (243,203 | ) | (205,531 | ) | (151,313 | ) | ||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
8,877 | (17,665 | ) | 31,696 | 54,396 | (812 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Statements of Cash Flows Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net cash flows from operating activities |
$ | (32,451 | ) | $ | (53,982 | ) | $ | (3,732 | ) | $ | (28,833 | ) | $ | (60,102 | ) | |||||
| (1) | Total revenue in 2017 includes $20 million in contract revenue from Endo related to a patent extension that was previously recorded as deferred revenue because all or a portion of such $20 million was contingently refundable to Endo if a third party generic product was introduced in the U.S. during the patent extension period from 2020 to 2027. However, due to us and Endo entering into a termination agreement which terminated the BELBUCA® license to Endo effective January 6, 2017, the deferred $20 million was recognized as revenue in January 2017. |
| (2) | Net loss in 2017 includes the bargain purchase gain of the BELBUCA® acquisition from Endo totaling $27.3 million, recorded as income in January 2017. |
| (3) | Total assets for the year ended December 31, 2017 includes the value of the BELBUCA® license and distribution rights intangible asset, net, totaling $40.5 million. |
53
Table of Contents
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations. |
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes appearing elsewhere in this Report. This discussion and analysis contains forward-looking statements that involve risks, uncertainties and assumptions. The actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements as a result of certain factors, including, but not limited to, those which are not within our control.
Overview
Strategy
We are a specialty pharmaceutical company that is developing and commercializing, either on our own or in partnerships with third parties, new applications of approved therapeutics to address important unmet medical needs using both proven and new drug delivery technologies. We have developed and are continuing to develop pharmaceutical products aimed principally in the areas of pain management and addiction.
Our strategy is to:
| • | Focus our commercial and development efforts in the areas of pain management and addiction within the U.S. pharmaceutical marketplace; |
| • | Market our products through specialty sales teams by primarily focusing on high-prescribing U.S. physicians working with patients in the pain and addiction space. |
| • | Identify and acquire rights to products that we believe have potential for near-term regulatory approval through the 505(b)(2) approval process of the U.S Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) or are already FDA approved; |
We believe this strategy will allow us to increase our revenues, improve our margins as we seek profitability and enhance stockholder value.
Background of Our Company
We were incorporated in the State of Indiana in 1997 and were reincorporated as a Delaware corporation and conducted our initial public offering in 2002. In August 2004, we acquired Arius Pharmaceuticals, the then licensee (and now owner) of our BEMA® drug delivery technology, and in July 2006, we licensed commercialization rights in Europe for our lead product; BEMA® based ONSOLIS®, to Meda. In September 2007, we entered into a definitive License and Development Agreement with Meda for ONSOLIS® in the U.S., Canada and Mexico, of which in May 2016, the North American rights to ONSOLIS® were returned to us for marketing authorization. In January 2012, we entered into a definitive License and Development Agreement with Endo for BELBUCA® for chronic pain and in December 2014, we and Endo filed the NDA submission for FDA approval for BELBUCA®, which was accepted February 2015 and later approved by the FDA on October 23, 2015 and commercially launched by Endo in February 2016. On December 8, 2016, we announced that we had entered into a Termination Agreement with Endo terminating Endo’s licensing of rights for BELBUCA®. The closing of the Termination Agreement, and the formal termination of the BELBUCA® license to Endo and closing of the transactions occurred on January 6, 2017. On July 31, 2013, we submitted the NDA for BUNAVAIL® to the FDA for review, and on June 6, 2014, we announced the FDA approval of BUNAVAIL®, which we commercially launched November 3, 2014.
2017 and Beyond Highlights
| • | On January 6, 2017, we announced that we had closed on the Termination Agreement, dated December 7, 2016 (or the Termination Agreement), between us and Endo. The Termination Agreement terminates Endo’s licensing rights and we have simultaneously reacquired our BELBUCA® product. |
| • | On February 21, 2017, we entered into a Term Loan Agreement (or the Loan Agreement) with CRG as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the lenders named in the Loan Agreement (or the Lenders). Pursuant to the Loan Agreement, we borrowed $45.0 million from the Lenders as of the closing date and may be eligible to borrow up to an additional $30.0 million in two tranches of $15.0 million each contingent upon achievement of certain conditions. |
| • | On July 12, 2017, we, along with Purdue Pharma (Canada) announced that we have signed an exclusive agreement for the licensing, distribution, marketing and sale of BELBUCA® in Canada. In return for the licensing and distribution rights to BELBUCA® in Canada, we are eligible to receive upfront and potential milestones of up to CAD 4.5 million as well as royalties on net sales. |
54
Table of Contents
| • | On August 17, 2017, we announced that we would present three posters reviewing the potential impacts of BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® on important issues pertinent to the opioid epidemic, such as safety and diversion, at the PAINWeek 2017 meeting in Las Vegas, NV on September 5 – 9, 2017. |
| • | On September 12, 2017, we announced that Health Canada has granted market authorization to formally transfer the Drug Identification Number (DIN) ownership of BELBUCA® in Canada to our commercial partner, Purdue. This approval triggered a milestone payment to us, which was received October 2017. |
| • | On October 12, 2017, we announced that we had entered into a Settlement Agreement with Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc., Actavis Laboratories UT, Inc. and Teva Pharmaceuticals Industries, Ltd. (collectively, “Teva”) that resolves our previously reported BUNAVAIL® patent litigation against Teva pending in the United States District Court for the District of Delaware. |
| • | On November 27, 2017, we announced that the Ohio Bureau of Workers Compensation had approved a change to its formulary resulting in favorable positioning for our products BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®. BELBUCA® will be added to the formulary as a Tier 1 long-acting opioid without restrictions. |
| • | On December 8, 2017, we received the required 90-day notice from Collegium regarding termination of the previously announced license and development agreement between us and Collegium for our ONSOLIS® product. We are assessing options for commercializing our ONSOLIS® product, including the use of our current sales force or potentially out-licensing the product. |
| • | On December 18, 2017, we announced that the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office had issued a Notice of Allowance of our patent application for U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 13/724,959 (or the ‘959 Patent) that once formally granted, will be listed in the FDA publication “Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations” (known as the “Orange Book”) and will extend the exclusivity of BELBUCA® from July 2027 to December 2032. The ‘959 Patent covers the method of using BEMA® for the treatment of chronic pain. |
| • | On December 20, 2017, we announced the appointment of Scott M. Plesha, formerly our Senior Vice President of Sales and Marketing, to the role of President, effective January 2, 2018. This coincides with the previously announced retirement of Dr. Mark A. Sirgo from his day-to-day role as President and Chief Executive Officer and his continuation as Vice Chairman of the Board of Directors. Besides Mr. Plesha’s new responsibilities as President, Mr. Plesha will continue to directly oversee the sales and marketing functions of our company. |
| • | On December 26, 2017, pursuant to our Term Loan Agreement with CRG, we were eligible and elected, to receive in the Second Draw for gross proceeds of $15.0 million. |
| • | On January 30, 2018, we announced that BELBUCA® is now commercially available in Canada via our exclusive agreement with Purdue (Canada). This milestone triggered a payment in the amount of CAD 1 million, which we received March 2018. |
| • | On February 6, 2018, we announced that we had entered into a Settlement Agreement with Teva that resolves our previously reported BELBUCA® patent litigation against Teva pending in the United States District Court for the District of Delaware. |
Our Products and Related Trends
Our product portfolio currently consists of four products. As of the date of this report, three products are approved by the FDA and one is development. Three of these four products utilize our patented BEMA® thin film drug delivery technology.
| • | BELBUCA® is indicated for the management of chronic pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment and for which alternative treatment options are inadequate. This product was originally licensed on a worldwide basis to Endo. On October 26, 2015, we announced with Endo that the FDA approved BELBUCA®. BELBUCA® was launched by Endo in February 2016. On December 7, 2016, we entered into an agreement with Endo terminating Endo’s licensing of rights for BELBUCA®. This followed a strategic decision made by Endo to discontinue commercial efforts in the branded pain business. On January 6, 2017, we announced the closing of the transaction to reacquire the license to BELBUCA® from Endo. As a result, the worldwide rights to BELBUCA® were transferred back to us. Behind a revised commercialization plan based on market research conducted primarily by Endo that took into consideration the current climate for prescribing opioids for chronic pain, we are leveraging our existing sales force to capitalize on commercial synergies with BUNAVAIL®. This effort is a focused commercial approach targeting identified healthcare providers which we believe create the potential to incrementally grow BELBUCA® sales without the requirement for significant resources. We also will explore other options for longer-term growth for BELBUCA®. In mid-February 2017, we completed the expansion and training of our sales force, allowing for promotion of BELBUCA® |
55
Table of Contents
| to commence in full in late February. We further expanded our sales force beginning of January 2018 to support the commercialization efforts. BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® are currently supported by a field force of approximately eighty-five sales representatives and nine regional sales managers. As previously disclosed, the launch has been more challenging because of the increased scrutiny over the prescribing of opioids that is driven by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines issued in March 2016. The difference that BELBUCA® offers over the Schedule II opioids, such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, morphine, etc., include less addiction and abuse potential along with a ceiling effect on respiratory depression. The approval of BELBUCA® carries a standard post-approval requirement by the FDA to conduct a study to determine the effect of BELBUCA® on QT prolongation (i.e. an abnormal lengthening of the heartbeat). Also required is a study assessing the safety and efficacy of BELBUCA® in pediatric patients and participation in a consortium with other holders of NDAs for long-acting opioids to assess and better understand the risk of abuse, misuse, addiction and overdose with opioids. Prescription sales of BELBUCA have significantly increased since promotion began. |
| • | BUNAVAIL® was approved by the FDA in June 2014 and is indicated for the treatment of opioid dependence. BUNAVAIL® uses our BEMA® technology combined with buprenorphine in tandem with naloxone, an opioid antagonist. We are commercializing BUNAVAIL® ourselves and launched the product during the fourth quarter of 2014. We have been actively engaged in efforts to optimize our commercialization of BUNAVAIL® with particular emphasis in 2016 on better aligning costs with revenue and reducing spending. We will seek to continue to manage our BUNAVAIL® business by focusing sales efforts on those healthcare providers who have been prescribers of BUNAVAIL. And we will continue to use published data evidencing “diversion” (i.e., the illicit use of a legally prescribed controlled substance) associated with the market leader’s product and highlight the other attributes of BUNAVAIL® as we seek to win additional managed care contracts. We also believe there will be an opportunity to introduce more patients to BUNAVAIL® with the lifting of the long-standing limit from 100 to 275 (as outlined in the final ruling by HHS and effective on August 8, 2016), the number of patients per physician that can be treated at any given time with buprenorphine and more recent legislation allowing nurse practitioners and physician assistants to prescribe buprenorphine for opioid dependence. We will continue to closely monitor commercial efforts and seek to increase revenue and profitability, as well as evaluate all options available to preserve the long-term prospects for and maximize the value of BUNAVAIL®. Separately, as with all other buprenorphine containing products for opioid dependence, the approval of BUNAVAIL® carries a standard post-approval requirement by the FDA to conduct a study to determine the effect of BUNAVAIL® on QT prolongation. |
| • | ONSOLIS® is approved in the U.S., the EU (where it is marketed as BREAKYL™) and Taiwan (where it is marketed as PAINKYL™), for the management of breakthrough pain in opioid tolerant adult patients with cancer. ONSOLIS® utilizes our BEMA® thin film drug delivery technology in combination with the narcotic fentanyl. The commercial rights to ONSOLIS® were originally licensed to Meda, a subsidiary of Mylan N.V., in 2006 and 2007 for all territories worldwide except for Taiwan (where it is licensed to TTY). The marketing authorization for ONSOLIS® was returned to us in early 2015 as part of an assignment and revenue sharing agreement with Meda for the United States, Canada and Mexico. Such agreement also facilitated the approval of a new formulation of ONSOLIS® in the U.S. We are currently assessing our commercial options for ONSOLIS®. |
| • | Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection is in development as an injectable, extended release, microparticle formulation of buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid dependence and chronic pain, the rights to which we secured when we entered into a definitive development and exclusive license option agreement from Evonik in October 2014. In 2015, we completed initial development work and preclinical studies which have resulted in the identification of a formulation we believe is capable of providing 30 days of continuous buprenorphine treatment. During a pre-IND meeting with the FDA in November 2015, the FDA requested an additional study to assess the fate of the polymers used in the formulation. In 2016, we completed this study as well as additional preclinical work and other activities to support a planned Phase 1 clinical study. We submitted an Investigational New Drug application (“IND”) for this product candidate to the FDA in December 2016. |
We expect to continue our research and development of pharmaceutical products and related drug delivery technologies, some of which will be funded by our commercialization agreements. We will continue to seek additional license agreements, which may include upfront payments. We anticipate that funding for the next several years will come primarily from earnings from sales of BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®, milestone payments and royalties from Meda and TTY, potential sales of securities and collaborative research agreements, including those with pharmaceutical companies.
We have limited history of commercial operations, having focused the vast majority of our corporate effort on research and development activities. We have, since our founding, received revenue in the form of: (i) product sales from our BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® products, (ii) contract revenue from Endo related to an upfront, non-refundable payment for a license of our BELBUCA® product in 2012, (iii) payment from Endo for certain patent-related milestones (iv) royalty revenue from Meda for sales
56
Table of Contents
of BREAKYL™ and ONSOLIS®, (vi) upfront non-refundable license and milestone payments from Meda in 2007, 2008, 2009 and 2012 (vi) product sales revenue related to BUNAVAIL® sales (vii) contract revenue from Endo related to two full database locks in 2014, (viii) contract revenue from Endo upon FDA acceptance of the filed NDA of our BELBUCA® product in 2015 and subsequent regulatory approval, (ix) and sponsored research revenue from both Endo and Meda. Only the BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® product sales and BREAKYL™ royalty revenues have the potential to be repeating or predictable. Until recurring revenue from product sales (BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® are the foremost opportunity) becomes a larger portion of our total revenue, we anticipate that our quarterly results of operations will fluctuate for the foreseeable future.
Readers are cautioned that period-to-period comparisons of our operating results should not be relied upon as predictive of future performance. Our prospects must be considered in light of the risks, expenses and difficulties normally encountered by companies that are involved in the development and commercialization of their products and related technologies, particularly companies in new and rapidly changing markets such as pharmaceuticals, drug delivery and biotechnology. For the foreseeable future, we must, among other things, invest in non-clinical and clinical trials of, and seek regulatory approval for and commercialization of, our product candidates, the outcomes of which are subject to numerous risks, many of which are beyond our control. We must also maintain our relationships with our key commercial partners and address regulatory, legal and/or commercial issues and risks that relate to our business from time to time, many of which could impact, perhaps negatively, our planned operations. We may not be able to appropriately address these risks and difficulties.
Update on Relaunch Activities in the U.S. for ONSOLIS®
On March 12, 2012, we announced the postponement of the U.S. relaunch of ONSOLIS® following the initiation of the class-wide REMS until the product formulation could be modified to address two appearance-related issues. Such appearance-related issues involved the formation of microscopic crystals and a fading of the color in the mucoadhesive layer, raised by the FDA during an inspection of our North American manufacturing partner for ONSOLIS®, Aveva which is now a subsidiary of Apotex. While the appearance issues did not affect the product’s underlying integrity, safety or performance, the FDA believed that the fading of the color in particular may potentially confuse patients, necessitating a modification of the product and its specification before it can be manufactured and distributed. The source of microcrystal formation and the potential for fading of ONSOLIS® was found to be specific to a buffer used in its formulation. We modified the formulation and submitted a prior approval supplement that responded to FDA questions and led to FDA approval of the new formulation of ONSOLIS® in August 2015.
On January 27, 2015, we announced that we had entered into an assignment and revenue sharing agreement with Meda to return to us the marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® for the U.S. and the right to seek marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® in Canada and Mexico.
On May 11, 2016, we announced the signing of a licensing agreement under which we granted the exclusive rights to develop and commercialize in the U.S. to Collegium. Under terms of the agreement, Collegium was responsible for the manufacturing, distribution, marketing and sales of ONSOLIS® in the U.S. Both companies were collaborating on the transfer of manufacturing, which included submission of a Prior Approval Supplement FDA. Upon approval of the Supplement, the NDA and manufacturing responsibility would have been transferred to Collegium. Financial terms of our agreement with Collegium included a $2.5 million upfront non-refundable payment, a $4 million payment upon first commercial sale, $3 million payable to us related to ONSOLIS® patent milestone, up to $17 million in potential payments based on achievement of performance and sales milestones, and upper-teen percent royalties based on various annual U.S. net sales thresholds. Meda was to share in the proceeds of our partnership with Collegium, and the completion of this transaction with Collegium required the execution of a definitive termination agreement between us and Meda embodying those royalty-sharing terms and certain other provisions. Meda continues to commercialize ONSOLIS® under the brand name BREAKYL™ in the E.U. However, on December 8, 2017, Collegium provided us the required 90-day notice regarding termination of the license and development agreement for ONSOLIS® between us and Collegium. The license and development agreement for ONSOLIS® between us and Collegium formally ended on March 8, 2018. We are working with Collegium to transfer the assets back to us and a final resolution of financial matters.
Efforts to extend our supply agreement with our ONSOLIS® manufacturer Aveva have been unsuccessful and the agreement expired. However, we have identified an alternate supplier and requested guidance from the FDA on the specifics required for obtaining approval to supply product from this new vendor. This will in part help us to better determine when ONSOLIS® may be available to the marketplace and help assist us as we seek a new commercial partnership arrangement. Based on our current estimates, we believe that we will submit the necessary documentation to FDA for qualification of the new manufacturer in the first quarter of 2018.
57
Table of Contents
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Impairment Testing
In accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (“GAAP”), goodwill impairment testing is performed at the reporting unit level annually, or more frequently if indicated by events or conditions. We performed an evaluation and determined that there is only one reporting unit. We elected to early adopt ASU Update No. 2017-04 Goodwill and other (Topic 350) “simplifying the Test of Goodwill Impairment” in performing our annual goodwill impairment test in 2017. Under this accounting guidance, the requirements for any reporting unit with a zero or negative carrying amount to perform a qualitative assessment and, if it fails that qualitative test, to perform Step 2 of the goodwill impairment test was eliminated. Therefore, the same impairment assessment under this new accounting standard applies to all reporting units.
Similar to previous guidance, the new standard allows for either a qualitative or a quantitative assessment to be performed. If a qualitative evaluation determines that no impairment exists, then no further analysis is performed. If a qualitative evaluation is unable to determine whether impairment has occurred, a quantitative evaluation is performed. The quantitative impairment test first identifies potential impairments by comparing the fair value of the reporting unit with its carrying value. If the fair value exceeds the carrying amount, goodwill is not impaired. Under ASU 2017-04, if the carrying value exceeds the fair value, an impairment charge is recorded based on that difference, which is different than previous GAAP. Under previous GAAP, if the carrying value exceeds the fair value, an entity was required to calculate the implied fair value of goodwill (Step 2) and record an impairment if the implied fair value is less than the carrying amount.
The determination of goodwill impairment is highly subjective. It considers many factors both internal and external and is subject to significant changes from period to period. No goodwill impairment charges have resulted from this analysis for 2017, 2016 or 2015.
An impairment of a long-lived asset other than goodwill is recognized under GAAP if the carrying value of the asset (or the group of assets of which it is a part) exceeds (i) the future estimated undiscounted cash flow from the use of the asset (or group of assets) and (ii) the fair value of the asset (or asset group). In making this impairment assessment, we predominately use an undiscounted cash flow model derived from internal forecasts. Factors that could change the result of our impairment test include, but are not limited to, different assumptions used to forecast future net sales, expenses, capital expenditures, and working capital requirements used in our cash flow models. If our management determines that the value of intangible assets have become impaired using this approach, we will record an accounting charge for the impairment. No impairment charges have been recorded for other amortizing intangibles in 2017, 2016 or 2015.
The Assigned Value of Acquired Tangible and Intangible Assets and Assumed and Contingent Liabilities Associated with Business Combinations
We account for acquisitions of businesses using the acquisition method of accounting where the cost is allocated to the underlying net tangible and intangible assets acquired, based on their respective estimated fair values. If the estimated fair values of the net assets acquired is more than the purchase price, the excess is immediately recorded in earnings as a bargain purchase gain. Alternatively, if the purchase price is greater than the estimated fair values of the net assets acquired, the excess is recorded as goodwill. Determining the fair value of certain acquired assets and liabilities is subjective in nature and often involves the use of significant estimates and assumptions, including, but not limited to, the selection of appropriate valuation methodology, projected revenue, expenses and cash flows, weighted average cost of capital, discount rates and estimates of terminal values. Business acquisitions are included in our consolidated financial statements as of the date of the acquisition.
Inventory Valuation
We provide inventory write-downs determined primarily by the accumulated cost to manufacture our inventory, which is impacted by component costs and manufacturing yields. The write-down is measured as the difference between the cost of the inventory and net realizable value and charged to cost of sales. At the point of the loss recognition, a new, lower cost basis for that inventory is established, and subsequent changes in facts and circumstances do not result in the restoration or increase in that newly established cost basis.
We provide a reserve for excess and obsolete inventories identified by a lot-by-lot analysis of our finished goods inventory which considers the expiration dates and future demand forecasts. The write-down is measured as the difference between the cost of the inventory on-hand and the expected demand of the inventory. At the point of the loss recognition, a charge to cost of sales is recorded and a reserve is established for that inventory. The inventory reserve is relieved upon the future sale or disposal of that inventory.
58
Table of Contents
Stock-Based Compensation and other Stock-Based Valuation Issues
We account for stock-based awards to employees and non-employees using Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification (FASB)(ASC) FASB ASC Topic 718 — Accounting for Share-Based Payments, which provides for the use of the fair value-based method to determine compensation for all arrangements where shares of stock or equity instruments are issued for compensation. Fair values of equity securities issued are determined by management based predominantly on the trading price of our common stock. The values of these awards are based upon their grant-date fair value. That cost is recognized over the period during which the employee is required to provide service in exchange for the award.
We use the Black-Scholes option pricing model to determine the fair value of stock option and warrant grants. In applying the Black-Scholes option pricing model, assumptions are as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||
| Expected price volatility |
68.76%-78.79% | 62.65%-80.78% | 73.00%-76.78% | |||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.77%-2.05% | 0.56%-1.70% | 1.25%-1.68% | |||
| Weighted average expected life in years |
6 years | 6 years | 6 years | |||
| Dividend yield |
— | — | — |
Revenue Recognition
Endo License, Development and Supply Agreements
In January 2012, we entered into a License and Development Agreement with Endo (which we have recently terminated as described below) pursuant to which we granted Endo an exclusive commercial world-wide license to develop, manufacture, market and sell our BELBUCA® product and to complete U.S. development of such product for purposes of seeking FDA approval (the “Endo Agreement”).
Pursuant to the Endo Agreement, we have received the following recent payments:
| • | $10 million upon FDA acceptance of filing NDA (earned in February 2015); |
| • | $50 million upon regulatory approval, earned in October 2015 and received in November 2015, with the revenue recognition treatment for $20 million of such $50 million payment deferred due to the fact that all or a portion of such $20 million is contingently refundable to Endo based on a third party generic introduction in the U.S. during the patent extension period from 2020 to 2027. However, due to entering into a Termination Agreement with Endo on December 7, 2016 which terminated the BELBUCA® license to Endo effective January 6, 2017, the deferred $20 million was recognized as revenue in January 2017. |
We have assessed our arrangement with Endo and our deliverables thereunder at inception to determine: (i) the separate units of accounting for revenue recognition purposes, (ii) which payments should be allocated to which of those units of accounting and (iii) the appropriate revenue recognition pattern or trigger for each of those payments. The assessment requires subjective analysis and requires management to make judgments, estimates and assumptions about whether deliverables within multiple-element arrangements are separable and, if so, to determine the amount of arrangement consideration to be allocated to each unit of accounting.
At the inception of the Endo arrangement, we determined that the Endo Agreement was a multi-deliverable arrangement with three deliverables: (1) the license rights related to BELBUCA®, (2) services related to obtaining enhanced intellectual property rights through the issuance of a particular patent and (3) clinical development services. We concluded that the license delivered to Endo at the inception of the Endo Agreement has stand-alone value. It was also determined that there was a fourth deliverable, the provision of clinical trial material (or CTM). The amounts involved are, however, immaterial and delivered in essentially the same time frame as the clinical development services. Accordingly, we did not separately account for the CTM deliverable, but consider it part of the clinical development services deliverable.
59
Table of Contents
We were reimbursed by Endo for certain contractor costs when these costs went beyond set thresholds as outlined in the Endo Agreement. Endo reimbursed us for this spending at cost and we received no mark-up or profit. The gross amount of these reimbursed research and development costs were reported as research and development reimbursement revenue. We acted as a principal, had discretion to choose suppliers, bear credit risk and may perform part of the services required in the transactions. Therefore, these reimbursements were treated as revenue to us. The actual expenses creating the reimbursements are reflected as research and development expense. During the year ended December 31, 2015, we recognized $0.9 million, of reimbursable expenses related to the Endo Agreement, which is recorded as research and development reimbursement revenue. There was no research and development reimbursement revenue during the years ended December 31, 2017 or 2016, since the program ended in 2015.
On December 23, 2014, we and Endo announced the submission of a NDA for BELBUCA® to the FDA, which was accepted February 23, 2015. On October 26, 2015, we and Endo announced that the FDA approved BELBUCA® (on October 23, 2015). FDA approval of BELBUCA® triggered a milestone payment to us from Endo of $50 million pursuant to the Endo Agreement, less approximately $6 million of the aforementioned cumulative pre-payments received and recorded in deferred revenue, current. We received payment of such milestone in November 2015. As such, we deferred $20 million of such $50 million payment having been deferred under GAAP due to the fact that all or a portion of such $20 million was contingently refundable to Endo at year ended December 31, 2016. This $20 million was recognized as revenue in January 2017. (See below for Endo Termination). That left $30 million from this $50 million milestone that was recognized as revenue during the year ended December 31, 2015.
On December 7, 2016, we entered into the Termination Agreement with Endo terminating Endo’s licensing of rights for BELBUCA®. The closing of the Termination Agreement, and the formal termination of the BELBUCA® license to Endo and closing of the transaction occurred on January 6, 2017.
Collegium License and Development Agreement
On May 11, 2016, we and Collegium executed a License Agreement under which we granted Collegium the exclusive rights to develop and commercialize ONSOLIS® in the U.S.
60
Table of Contents
Under the terms of the Collegium Agreement, Collegium was responsible for the manufacturing, distribution, marketing and sales of ONSOLIS® in the U.S. We were obligated to use commercially reasonable efforts to continue the transfer of manufacturing to the anticipated manufacturer for ONSOLIS® and to submit a corresponding Prior Approval Supplement (the “Supplement”) to the FDA with respect to the current NDA for ONSOLIS®. Following approval of the Supplement, the NDA and manufacturing responsibility for ONSOLIS® (including the manufacturing relationship with our manufacturer, subject to the company entering into an appropriate agreement with such manufacturer that is acceptable and assignable to Collegium) would have been transferred to Collegium.
On December 8, 2017, we received the required 90-day notice from Collegium regarding termination of the License Agreement and the effective date of termination is March 8, 2018. We are assessing our commercial options for ONSOLIS®.
Pursuant to the Collegium Agreement, we have received the following payments:
| • | a $2.5 million upfront non-refundable payment, payable to us within 30 days of execution of the Collegium Agreement (received June 2016); |
| • | reimbursement to us for a pre-determined amount of the remaining expenses associated with the ongoing transfer of the manufacturing of ONSOLIS®; |
ONSOLIS® was originally licensed to, and launched in the U.S. by, Meda. In January 2015, we entered into an assignment and revenue sharing agreement (the “ARS Agreement”) with Meda pursuant to which Meda transferred the marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® in the United States back to us. Under the ARS Agreement, financial terms were established that enable Meda to share a significant portion of the proceeds of milestone and royalty payments received by us from any new North American partnership for ONSOLIS® that may be executed by us. The execution of the Collegium Agreement also required the execution of a definitive termination agreement between us and Meda embodying those royalty-sharing terms, returning ONSOLIS®-related assets and rights in the U.S., Canada, and Mexico to us, and including certain other provisions. In addition, our royalty obligations to CDC and its assignees will remain in effect. CDC provided funding for the development of ONSOLIS® in the past.
The initial $2.5 million upfront non-refundable payment received June 2016 was recognized as revenue. We have no obligation remaining to Collegium requiring deferral of any recognition of this $2.5 million payment. It was determined that the remaining obligation was inconsequential or perfunctory, thus revenue was recognized upon receipt. The two items in the agreement relate to the transfer of the ONSOLIS® manufacturing process to a third-party vendor and the filing of a Prior Approval Supplement for the ONSOLIS® NDA. Collegium will not receive, nor are they due, a refund if these items are not completed.
All reimbursements from Collegium for expenses related to the manufacturing of ONSOLIS® that were incurred by us were recorded as revenue. We charged Collegium at cost, without markup, for these out-of-pocket expenses incurred by us. In transactions where we act as a principal, with discretion to choose suppliers, bears credit risk and may perform part of the services required in the transactions, revenue is presented at the gross amount of the reimbursement. Additionally, the payment to Meda for their share of the milestone proceeds is recorded as royalty expense.
New Revenue Recognition Standards
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers,” which supersedes the revenue recognition requirements of Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 605, “Revenue Recognition” and most industry-specific guidance on revenue recognition throughout the ASC. The standard’s core principle is that a company will recognize revenue when it transfers promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. In doing so, companies will need to use more judgment and make more estimates than under today’s guidance. In August 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-14, which defers the effective date of ASU 2014-09 for all entities by one year. Accordingly, public business entities should apply the guidance in ASU 2014-09 to annual reporting periods (including interim periods within those periods) beginning after December 15, 2017. The standard may be applied retrospectively to each prior period presented (full retrospective method) or retrospectively with the cumulative effect recognized as of the date of initial application (modified retrospective method).
We used the modified retrospective approach upon adoption of this guidance effective January 1, 2018 using a cumulative effect adjustment to accumulated deficit. We utilized a comprehensive approach to assess the impact of the guidance on our contract portfolio. We reviewed our current accounting policies and practices to identify potential differences resulting from the application of the new requirements to our revenue contracts, including evaluation of performance obligations in the contract, estimating the amount of variable consideration to include in the transaction price, allocating the transaction price to each separate performance obligation and accounting treatment of costs to obtain and fulfill contracts. In addition, we will update certain disclosures, as applicable, included in our financial statements to meet the requirements of the new guidance beginning in January 1, 2018. Under the
61
Table of Contents
new guidance, we are required to evaluate the impact of estimating variable consideration related to our product sales and licensing contracts. We will use the expected value method to estimate the total revenue of the contract, constrained by the probability that there would not be a significant revenue reversal in a future period. We will continue to evaluate the expected value of revenue over the term of the contract and adjust revenue recognition as appropriate. Based on this evaluation, the adoption will not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations, cash flows, accounting policies, business processes, internal controls or disclosures.
Product Royalty Revenues
Product royalty revenue amounts are based on a percentage of net sales revenue of the ONSOLIS® product under our license agreement with Meda. Product royalty revenues are computed on a quarterly basis when revenues are fixed or determinable, collectability is reasonably assured and all other revenue recognition criteria are met. This is shown as product royalty revenues on the accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Meda has the right to reject products that do not comply with product, packaging, or regulatory specifications. Defective product must be identified by Meda within 10 days after inspection at Meda’s distribution site. We bill Meda immediately upon receipt by Meda of product (FOB manufacturer). On a quarterly basis, a reconciliation is prepared that reflects the difference between actual net sales by Meda multiplied by the royalty percentage, and the actual royalty payments made during the quarter (which is based on a “transfer price” at the time we invoice Meda). The parties “true-up” the differences within 45 days of each quarter-end.
Product Sales
Product sales amounts relate to sales of BELBUCA® which we reacquired in January 2017 and BUNAVAIL® which was launched in November 2014. These sales are recognized as revenue when sold to the wholesaler, and when it is realized and earned. This is shown as product sales on the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Revenue is realized or realizable and earned when all the following criteria are met: (a) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; (b) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; (c) our price to the buyer is fixed or determinable; and (d) collectability is reasonably assured. We sell our products primarily to large national wholesalers, which have the right to return the products they purchase. We recognize revenue from sales transactions where the buyer has the right to return the product at the time of sale only if (1) Our price to the buyer is substantially fixed or determinable at the date of sale, (2) the buyer has paid us, or the buyer is obligated to pay us and the obligation is not contingent on resale of the product, (3) the buyer’s obligation to us would not be changed in the event of theft or physical destruction or damage of the product, (4) the buyer acquiring the product for resale has economic substance apart from any provided by us, (5) we do not have significant obligations for future performance to directly bring about resale of the product by the buyer, and (6) the amount of future returns can be reasonably estimated. We recognize product sales net of estimated allowances for rebates, price adjustments, returns, chargebacks and prompt payment discounts. Given the sufficient experience with BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®, we can reasonably estimate the amount of future product returns, and therefore, the risk of estimating product returns has been substantially eliminated. The effect in income from operations and on net income is that the we can recognize revenue earlier on the sell-in method, net of a provision for estimated returns, since we can record revenue once sold to the wholesaler rather than waiting until the product is sold to the end user on a sell-through basis.
We established allowances for estimated rebates, chargebacks and product returns based on numerous qualitative and quantitative factors, including:
| • | the number of and specific contractual terms of agreements with customers; |
| • | estimated levels of inventory in the distribution channel; |
| • | historical rebates, chargebacks and returns of products; |
| • | direct communication with customers; |
| • | anticipated introduction of competitive products or generics; |
| • | anticipated pricing strategy changes by us and/or our competitors; |
| • | analysis of prescription data gathered by a third-party prescription data provider; |
| • | the impact of changes in state and federal regulations; and |
| • | the estimated remaining shelf life of products. |
In our analyses, we use prescription data purchased from a third-party data provider to develop estimates of historical inventory channel sell-through. We utilize an internal analysis to compare historical net product shipments to estimated historical prescriptions written. Based on that analysis, management develops an estimate of the quantity of product in the channel which may be subject to various rebate, chargeback and product return exposures. To estimate months of ending inventory in our distribution channel, we
62
Table of Contents
divide estimated ending inventory in the distribution channel by our recent prescription data, not considering any future anticipated demand growth beyond the succeeding quarter. Monthly for each product line, we prepare an internal estimate of ending inventory units in the distribution channel by adding estimated inventory in the channel at the beginning of the period, plus net product shipments for the period, less estimated prescriptions written for the period. This is done for each product line by applying a rate of historical activity for rebates, chargebacks and product returns, adjusted for relevant quantitative and qualitative factors discussed above, to the potential exposed product estimated to be in the distribution channel.
Cost of Sales
Cost of sales includes direct costs attributable to the production of BELBUCA®, BUNAVAIL®, BREAKYL™ and PAINKYL™. Cost of sales also includes royalty expenses owed to third parties.
For BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®, cost of sales includes raw materials, production costs at our contract manufacturing sites, quality testing directly related to the product, lower of cost of market and depreciation on equipment that we have purchased to produce BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®. It also includes any batches not meeting specifications and raw material yield loss. Deferred cost of sales during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2016 was $1.7 million, respectively. Beginning January 1, 2017, cost of sales for BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® are recognized when sold to the wholesaler from our distribution center. There was no deferred cost of sales for the year ended December 31, 2017. Yield losses and batches not meeting specifications are expensed as incurred.
For BREAKYL™ and PAINKYL™, we do not take ownership of the subject product as we do not have inventory. Accordingly, raw material product is transferred to Meda, in the case of BREAKYL™ and TTY in the case of PAINKYL™, immediately in accordance with the terms of our contractual arrangements with Meda and TTY. LTS manufactures both products for us. Meda’s and TTY’s royalty payments to us include an amount related to cost of sales. Ownership and title to the product, including insurance risk, belong to LTS from raw material through completion and inventory of the subject product, and then to Meda and TTY upon shipment of such subject product. This is in accordance with our contracts with LTS and Meda and TTY, which identify the subject product as FOB manufacturer.
Gross To Net Accruals
A significant majority of our gross to net adjustments to gross product revenues are the result of accruals for our voucher program and Medicaid rebates, with most of those programs having an accrual to payment cycle of anywhere from one to three months. In addition to this relatively short accrual to payment cycle, we receive daily information from the wholesalers regarding their sales of our products and actual on hand inventory levels of its products. This enables us to execute accurate provisioning procedures. Consistent with the pharmaceutical industry, the accrual to payment cycle for returns is longer and can take several years depending on the expiration of the related products.
Prior to January 2017, we were recording sales when prescriptions were filled. However, beginning in the first quarter of 2017, we have begun recording revenue based on a sell-in method, as we now have achieved the ability to record sales ex-factory.
Income taxes
On December 22, 2017, the United States enacted major tax reform legislation, Public Law No. 115-97, commonly referred to as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (or 2017 Tax Act). The 2017 Tax Act, among other changes, lowers the general corporate income tax rate to 21% for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, transitions U.S. international taxation from a worldwide tax system to a territorial system, and provides for a one-time transition tax on the mandatory deemed repatriation of cumulative foreign earnings as of December 31, 2017, which is not applicable to us. We have calculated our best estimate of the impact of the 2017 Tax Act in our income tax provision during the year ended December 31, 2017, in accordance with its understanding of the 2017 Tax Act and guidance available as of the date of this filing and do not believe it will be material to our results of operations. The provisional amount related to the remeasurement of certain deferred tax assets and liabilities is based on the tax rates at which they are expected to reverse in the future. The estimated amount recorded related to the remeasurement of these balances was an income tax benefit of $33.1 million, offset entirely by the reduction in our valuation allowance.
On December 22, 2017, Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 118 (“SAB 118”) was issued to address the application of US GAAP in situations when a registrant does not have the necessary information available, prepared, or analyzed (including computations) in reasonable detail to complete the accounting for certain income tax effects of the 2017 Tax Act. In accordance with SAB 118, we have determined that the $33.1 million of the deferred tax income offset by the reduction in valuation allowance recorded in connection with the re-measurement of certain deferred tax assets and liabilities and the expectation the transition tax is immaterial are reasonable estimates at December 31, 2017.
In addition, North Carolina reduced its corporate income tax rate from 4% to 3% in 2017. This resulted in a tax benefit of $1.7 million, offset by a reduction in our valuation allowance.
We recorded an income tax benefit of $16.0 million in 2017. This benefit was associated with the release of our valuation allowance triggered by the recognition of deferred tax liabilities recorded as part of the Endo BELBUCA® transaction. We did not record income tax expense or pay any income tax in 2016 as we had incurred a net operating loss. We have recognized valuation allowances for all deferred tax assets for years ending 2017 and 2016.
We are required to reduce any deferred tax asset by a valuation allowance if, based on an assessment of positive and negative evidence, including estimates of future taxable income necessary to realize future deductible amounts, it is more likely than not (a likelihood of more than 50 percent) that some portion or all the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The valuation allowance should be sufficient to reduce the deferred tax asset to the amount which is more likely than not to be realized. As a result, we recorded a valuation allowance with respect to all our deferred tax assets. The change in the valuation allowance for the year ended December 31, 2017 independent of the impact of the 2017 Tax Act was $(4.4 million). In addition to the remeasurement of the net deferred tax assets due to the 2017 Tax Act, the valuation allowance decreased in 2017 due primarily to changes in the intangible assets and deferred revenue offset partially by stock compensation and an increase in our net operating loss carryforwards.
Research and Development Expenses
Overview
Our research and development expenses consist (and have historically consisted) primarily of expenses incurred in identifying, developing, testing, manufacturing and seeking regulatory approval of our product candidates, including:
| • | expenses associated with regulatory submissions, clinical trials and manufacturing, including additional expenses to prepare for commercial manufacture prior to FDA approval; |
| • | fees paid to third-party contract research organizations, contract laboratories and independent contractors; |
| • | payments made to consultants who perform research and development on our behalf and assist us in the preparation of regulatory filings; |
| • | personnel related expenses, such as salaries, benefits, travel and other related expenses, including stock-based compensation for personnel directly involved in product development activities; |
| • | payments made to third-party investigators who perform research and development on our behalf and clinical sites where such research and development is conducted; and |
63
Table of Contents
| • | other related expenses. |
Clinical trial expenses for our product candidates are a significant component of our research and development expenses. Product candidates in later stage clinical development generally have higher research and development expenses than those in earlier stages of development, primarily due to the increased size and duration of the clinical trials. We coordinate clinical trials through a number of contracted investigational sites, and the associated expense is based on a number of factors, including actual subject enrollment and visits, direct pass-through costs and other clinical site fees.
Product development expenses are expensed as incurred and reflect costs directly attributable to product candidates in development during the applicable period. Additionally, product development expenses include the cost of qualifying new, current Good Manufacturing Practice (known as cGMP) third-party manufacturing for our product candidates, including expenses associated with any related technology transfer.
Results of Operations
For the Year Ended December 31, 2017 Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2016
Product Sales. We recognized $34.9 million and $8.3 million in product sales during the years ended 2017 and 2016, respectively, from our products BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®. The increase in 2017 over 2016 is a result of the reacquisition of BELBUCA® in January 2017.
Product Royalty Revenues. We recognized $5.1 million and $3.6 million in product royalty revenue during the years ended 2017 and 2016, respectively. The increase in product royalty revenues in 2017 can be attributed to increased BREAKYL™ sales from Meda and PAINKYL™ sales from TTY.
Research and Development Reimbursements. We recognized $0.8 million and $1.1 million of reimbursable revenue during the years ended 2017 and 2016, respectively, which relates to our license agreement with Collegium and composed of reimbursement to us for a pre-determined amount of the remaining expenses associated with the ongoing transfer of the manufacturing of ONSOLIS®.
Contract Revenues. We recognized $21.2 million and $2.5 million in contract revenue during the years ended 2017 and 2016, respectively. Contract revenue in 2017 includes $20 million from Endo related to a patent extension that was previously recorded as deferred revenue because all or a portion of such $20 million was contingently refundable to Endo if a third party generic product was introduced in the U.S. during the patent extension period from 2020 to 2027. However, due to us and Endo entering into a termination agreement on December 7, 2016 which terminated the BELBUCA® license to Endo effective January 6, 2017, the deferred $20 million was recognized as revenue in January 2017. The remaining $1.2 million in contract revenues during 2017 was related to our license agreement with Purdue Canada.
Cost of Sales. We incurred $19.5 million and $11.3 million in cost of sales during the years ended 2017 and 2016, respectively. In 2017, we had minimum $1.5 million contractual royalty due to CDC related to our ONSOLIS® and BREAKYL™ product. Also, in 2017, we incurred $15.8 million in cost of sales for BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® plus $0.6 million related depreciation of manufacturing equipment and $0.2 million in immediate expensing of certain production that did not meet specifications during product validation and batch size scale up and yield losses. Also included in 2017 was $1.0 million in cost of sales for BREAKYL™ in Europe, $0.3 million in cost of sales for PAINKYL™ and $0.1 million cost of sales related to ONSOLIS®. In 2016, we had $1.9 million contractual royalty due to Meda related to our ONSOLIS® licensing arrangement with Collegium and a standard, minimum $1.5 million contractual royalty due to CDC related to our ONSOLIS® and BREAKYL™ product. Also, in 2016, we incurred $6.3 million in cost of sales for BUNAVAIL® plus $0.6 million related depreciation of manufacturing equipment and $0.2 million in immediate expensing of certain production that did not meet specifications during product validation and batch size scale up. Also included in 2016 was $0.7 million in cost of sales for BREAKYL™ in Europe and $0.1 million cost of sales related to BELBUCA®.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses. During the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, selling, general and administrative expenses totaled $58.9 million and $49.3 million, respectively. Selling, general and administrative costs include BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® sales, marketing, and commercial expenses. These costs also include legal expenses for patent defense, professional fees, wages and stock-based compensation expense. The increase in selling, general and administrative expenses in 2017 can be attributed to the increased marketing related to our 2017 reacquisition of BELBUCA® and expansion of our sales force as a result.
64
Table of Contents
Interest Expense, Net. During the year ended December 31, 2017, we had net interest expense of $8.6 million, consisting of $4.4 million of scheduled interest payments and $1.0 million of related amortization of discount and loan costs and $0.6 million of warrant interest expense all related to the February 2017 CRG Term Loan Agreement. In addition, we had remaining $0.9 million of scheduled interest payments and $1.4 million of related amortization of discount, loan costs and loan pay off and $0.2 million of warrant interest expense all related to the July 2013 secured loan facility from MidCap, which was paid off with the CRG term loan. During the year ended December 31, 2016 we had net interest expense of $3.3 million, consisting of $2.9 million of scheduled interest payments and $0.4 million of related amortization of discount and loan costs associated with the July 2015 secured loan facility from MidCap.
Bargain Purchase Gain. During the year ended December 31, 2017, we recorded the value of the bargain purchase gain of the BELBUCA® acquisition from Endo totaling $27.3 million to income. There was no such amount recorded during the year ended December 31, 2016.
Income Tax Expense and Tax Net Operating Loss Carryforwards. We had federal and state net operating loss carryforwards (or NOLs) of approximately $263 million and $292 million, respectively at December 31, 2017 as compared to federal and state NOLs of $225 million and $258 million, respectively as of December 31, 2016. These loss carryforwards expire principally beginning in 2020 through 2035 for federal and 2030 for state purposes, respectively. In accordance with GAAP, it is required that a deferred tax asset be reduced by a valuation allowance if, based on an assessment of positive and negative evidence, including estimates of future taxable income necessary to realize future deductible amounts, it is more likely than not (a likelihood of more than 50 percent) that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The valuation allowance should be sufficient to reduce the deferred tax asset to the amount which is more likely than not to be realized. As a result, we recorded a valuation allowance with respect to all of our deferred tax assets. Under Section 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code, if an ownership change occurs with respect to a “loss corporation” (as defined in the Internal Revenue Code), there are annual limitations on the amount of the net operating loss and other deductions which are available to us.
Expenditures for Research and Development Programs (2017 vs. 2016)
Our research and development expenditures for our approved products and product candidates are as follows in thousands:
| Year Ended December 31, |
Cumulative through December 31, |
|||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | ||||||||||
| BELBUCA® |
$ | 8,497 | $ | 31 | $ | 122,697 | ||||||
| BUNAVAIL® |
2,185 | 5,161 | 40,885 | |||||||||
| ONSOLIS® |
1,254 | 1,487 | 3,054 | |||||||||
| Buprenorphine ER Injection |
885 | 5,674 | 9,785 | |||||||||
| Clonidine Topical Gel* |
219 | 6,525 | 27,519 | |||||||||
| * | Clonidine Topical Gel product candidate was discontinued in December 2016. Minimal expenses in 2017 consist of the winding down of the product candidate which includes allocated wages and compensation. |
Results of Operations
For the Year Ended December 31, 2016 Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2015
Product Sales. We recognized $8.3 million and $4.2 million in product sales during the years ended 2016 and 2015, respectively, from our product BUNAVAIL®. The increase in 2016 over 2015 is a result of a full year of BUNAVAIL® sales revenue recorded on a pull-through basis with an increase in prescription sales.
Product Royalty Revenues. We recognized $3.6 million and $1.4 million in product royalty revenue during the years ended 2016 and 2015, respectively, under our license agreement with Endo for BELBUCA® in 2016 and Meda for BREAKYL™ in Europe during 2016 and 2015. The increase in product royalty revenues in 2016 can be attributed to the 2016 launch of BELBUCA® and increased BREAKYL™ sales.
Research and Development Reimbursements. We recognized $1.1 million of reimbursable revenue during the year ended 2016, which relates to our license agreement with Collegium composed of reimbursement to us for a pre-determined amount of the remaining expenses associated with the ongoing transfer of the manufacturing of ONSOLIS®. We also recognized $0.9 million of
65
Table of Contents
reimbursable revenue related to our agreement with Endo during the year ended 2015. Our 2012 license agreement with Endo included an obligation for Endo to reimburse us for certain trial expenses that exceeded a maximum threshold. In the last quarter of 2013, these thresholds were exceeded. The clinical trial program ended during the first half of 2015.
Contract Revenues. We recognized $2.5 million and $41.8 million in contract revenue during the years ended 2016 and 2015, respectively. Contract revenue in 2016 related to the upfront payment from Collegium for the ONSOLIS® license. Contract revenue in 2015 primarily consisted of recognizing as revenue $40.4 million in two milestone payments from Endo associated with submission and subsequent approval by the FDA of the NDA for BELBUCA®. Also included in 2015 was $1.1 million in contract revenue under our license agreement with Meda. Additionally, we received $0.3 million under our license agreement with Kunwha.
Cost of Sales. We incurred $11.3 million and $8.1 million in cost of sales during the years ended 2016 and 2015, respectively. In 2016, we had $1.9 million contractual royalty due to Meda related to our ONSOLIS® licensing arrangement with Collegium and a standard, minimum $1.5 million contractual royalty due to CDC related to our ONSOLIS® and BREAKYL™ product. Also in 2016, we incurred $6.3 million in cost of sales for BUNAVAIL® plus $0.6 million BUNAVAIL® related depreciation of manufacturing equipment and $0.2 million in immediate expensing of certain production that did not meet specifications during product validation and batch size scale up. Also included in 2016 was $0.7 million in cost of sales for BREAKYL™ in Europe and $0.1 million cost of sales related to BELBUCA®. In 2015, we recorded a standard, minimum $1.5 million contractual royalty to CDC related to our ONSOLIS® and BREAKYL™ product. Also, in 2015 we incurred $5.9 million in cost of sales for BUNAVAIL®. The remaining $0.7 million in 2015 represents cost of sales for BREAKYL™ in Europe.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses. During the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, selling, general and administrative expenses totaled $49.3 million and $54.7 million, respectively. Selling, general and administrative costs include BUNAVAIL® sales, marketing, and commercial expenses. These costs also include legal and professional fees, wages, and stock-based compensation expense. The decrease in selling, general and administrative expenses in 2016 can be attributed to the conversion of the contract sales force into one employed by us, which reduced administrative costs and inefficiencies.
Interest Expense, Net. During the year ended December 31, 2016 we had net interest expense of $3.3 million, consisting of $2.9 million of scheduled interest payments and $0.4 million of related amortization of discount and loan costs associated with the July 2015 secured loan facility from MidCap. During the year ended December 31, 2015 we had net interest expense of $2.5 million, consisting of $2.0 million of scheduled interest payments and $0.5 million of related amortization of discount and loan costs associated with the July 2015 secured loan facility from MidCap.
Income Tax Expense and Tax Net Operating Loss Carryforwards. We had federal and state net operating loss carryforwards (NOLs of approximately $225 million and $258 million, respectively at December 31, 2016 as compared to federal and state NOLs of $168 million and $178 million, respectively as of December 31, 2015. These loss carryforwards expire principally beginning in 2020 through 2035 for federal and 2030 for state purposes, respectively. In accordance with GAAP, it is required that a deferred tax asset be reduced by a valuation allowance if, based on the weight of available evidence it is more likely than not (a likelihood of more than 50 percent) that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The valuation allowance should be sufficient to reduce the deferred tax asset to the amount which is more likely than not to be realized. As a result, we recorded a valuation allowance with respect to all of our deferred tax assets. Under Section 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code, if an ownership change occurs with respect to a “loss corporation” (as defined in the Internal Revenue Code), there are annual limitations on the amount of the net operating loss and other deductions which are available to us.
Expenditures for Research and Development Programs (2016 vs. 2015)
Our research and development expenditures for our approved products and product candidates are as follows in thousands:
| Year Ended December 31, |
Cumulative through December 31, |
|||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| BELBUCA® |
$ | 31 | $ | 2,774 | $ | 114,200 | ||||||
| BUNAVAIL® |
5,161 | 6,228 | 38,700 | |||||||||
| ONSOLIS® |
1,487 | 333 | 1,800 | |||||||||
| Buprenorphine ER Injection |
5,674 | 2,788 | 8,900 | |||||||||
| Clonidine Topical Gel* |
6,525 | 8,501 | 27,300 | |||||||||
| * | Clonidine Topical Gel product candidate was discontinued in December 2016. |
66
Table of Contents
Revenues
The following table summarizes net product sales for the years ended December 31 in thousands:
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| BELBUCA® |
$ | 26,980 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| % of net product sales |
77 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | ||||||
| BUNAVAIL® |
7,942 | 8,266 | 4,157 | |||||||||
| % of net product sales |
23 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net product sales |
$ | 34,922 | $ | 8,266 | $ | 4,157 | ||||||
Major Research and Development Projects
In 2017, our research and development resources were focused on:
| • | Continuing a Medical Affairs effort to support efforts behind the commercialization of BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® |
| • | Transitioning post-marketing initiatives for BELBUCA® to us from Endo including BELBUCA® post approval study commitments and engagement in the Opioid Post-Marketing Requirements (PMR) Consortium |
| • | Collaborating with Collegium on the transfer of ONSOLIS® manufacturing to support the submission of a Prior Approval Supplement to the FDA |
| • | Preparing for potential future clinical development of Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection |
The projected dates for IND and NDA submissions, and FDA approval of NDAs, our estimates of development costs and our projected sales associated with each of our product candidates discussed below and elsewhere in this Report are merely estimates and subject to multiple factors, many of which are, or may be beyond our control, including those detailed in the Risk Factors section of this Report. These factors and risks could cause delays, cost overruns or otherwise cause us to not achieve these estimates. Readers are also advised that our projected sales figures do not take into account the royalties and other payments we will need to make to our licensors and strategic partners. Our estimates are based upon our market research and management’s reasonable judgments, but readers are advised that such estimates may prove to be inaccurate.
The following is a summary of our current major research and development initiatives at December 31, 2017 and the risks related to such initiatives:
BELBUCA ® (buprenorphine) buccal film. BELBUCA® was approved in October 2015 and launched in February 2016. Phase 3 studies to evaluate the efficacy and safety of BELBUCA® in the treatment of opioid naïve and experienced patients with chronic pain were completed in 2014. The BELBUCA® NDA was submitted on December 23, 2014, accepted February 23, 2015 and approved on October 23, 2015. We supported Endo in responding to FDA questions, scale-up of manufacturing and publishing the results of the clinical trials. Following the transfer of BELBUCA® to us in January 2017, we are now leading clinical and medical affairs support behind BELBUCA®. We have assumed responsibility for the conduct of post approval commitments specified by FDA in the approval of BELBUCA®, which include a thorough QT study and a pediatric study. In September 2013, the U.S. FDA announced that it will require all companies holding new drug applications (NDAs) for extended-release/long-acting (ER/LA) opioid analgesic drug products to conduct four post-marketing studies regarding risks associated with their long-term use and one clinical trial to estimate risk of hyperalgesia. The FDA replaced the original requirements with new post-marketing requirements in February 2016. The Opioid PMR Consortium was formed with representatives from each of the member companies providing an opportunity for one set of studies to be completed to satisfy the FDA requirements and distributing the associated costs across all member companies. Each member company pays an equal share of the program costs and new members are required to pay equal share of the costs to date upon program entry and of future costs going forward. We joined the Opioid PMR Consortium in October 2017 and our initial share of the program cost was paid in late 2017. To date, six of eleven studies have been completed and the program is expected to continue into 2020.
The risks to our company associated with BELBUCA® include: (i) inability to manufacture adequate supplies for commercial use; (ii) unexpected product safety issues; (iii) failure of our sales force to effectively sell the product and, (iv) inadequate reimbursement. A technical or commercial failure of BELBUCA® would have a material adverse effect on our future revenue potential and would negatively affect investor confidence in our company and our public stock price.
67
Table of Contents
BUNAVAIL®. The NDA for BUNAVAIL® was approved in June 2014 and BUNAVAIL® was launched in November 2014. Research and development activities in 2017 have included work to support a label expansion of BUNAVAIL® for the induction (conversion to buprenorphine) of opioid dependent subjects, performance of FDA post-marketing study requirements and improvements in commercial manufacturing. In May 2017, we announced that the FDA expanded the BUNAVAIL® label to include induction of opioid dependent patients.
The risks to our company associated with BUNAVAIL® include: (i) unexpected product safety issues; (ii) inability to continue to supply product in adequate quantities to meet the commercial demand; (iii) inability to continue to reduce BUNAVAIL® manufacturing costs; (iv) failure of our sales force to effectively sell the product and, (v) inadequate reimbursement.
ONSOLIS®. We have been collaborating with our U.S. partner Collegium on the ongoing transfer of manufacturing (including the production of registration batches) toward the submission of a Prior Approval Supplement to the FDA. In December 2017, we announced the termination of our U.S. ONSOLIS® agreement with Collegium, and we are currently exploring U.S. commercialization options, including the use of our current sales force, or potentially out-licensing the product.
The risks to our company associated with ONSOLIS® include: (i) inability to manufacture adequate supplies for commercial use; (ii) unexpected product safety issues; (iii) failure to secure a partner to commercialize ONSOLIS in the U.S. or the ability of our sales force to be able to take on commercialization responsibility or effectively sell the product; (iv) inability to successfully transfer manufacturing, file a Prior Approval Supplement, and receive FDA approval of the product, and (v) the inability to reach a mutually beneficial agreement with Meda allowing for the transfer of commercialization rights for ONSOLIS to us .
Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection. In 2014, we entered into an agreement with Evonik to develop and commercialize a long-acting buprenorphine injection capable of providing 30 days of continuous buprenorphine blood concentrations following a single monthly injection. In 2015, we completed initial development work and preclinical studies which have resulted in the identification of a formulation we believe is capable of providing 30 days of continuous buprenorphine treatment. During a pre-IND meeting with FDA in November 2015, the FDA requested an additional study to assess the fate of the polymers used in the formulation. We completed this study and submitted an IND for this product candidate to FDA in December 2016. The risks to our company associated with the Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection program include: (i) inability to manufacture the formulation at adequate scale for clinical development and commercial purposes; (ii) failure of the product to perform in the clinic; (iii) slow patient enrollment in clinical trials; (iv) product safety issues; (v) failure of or delay by the FDA to approve our NDA; (vi) failure of a commercial partner or us to effectively launch and sell the product; and (vii) lack of funding to advance the program.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Since inception, we have financed our operations principally from the sale of equity securities, proceeds from short-term borrowings or convertible notes, funded research arrangements, revenue generated as a result of our worldwide license and development agreement with Meda regarding ONSOLIS®, revenue generated as a result of our January 2012 agreement with Endo regarding our BELBUCA® product and most recently, earnings from the commercialization of our BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® products. We intend to finance our commercialization and working capital needs from existing cash, earnings from the commercialization of BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®, royalty revenue, new sources of debt and equity financing, existing and new licensing and commercial partnership agreements and, potentially, through the exercise of outstanding common stock options and warrants to purchase common stock.
In March 2015, we received a $10 million milestone from Endo upon FDA acceptance of filing our BELBUCA® NDA.
On May 29, 2015, we entered into a $30 million secured loan facility with MidCap. The agreement for this facility was a restatement, amendment and modification of a prior credit and security agreement, dated as of July 5, 2013 among us and a predecessor to MidCap, and certain lenders thereto. We received net loan proceeds in the aggregate amount of approximately $20.1 million and will use the loan proceeds for general corporate purposes or other activities permitted under the credit agreement.
On July 2, 2015, we filed a shelf registration statement which registered up to $150 million of our securities for potential future issuance, and such registration statement was declared effective on July 13, 2015. Concurrent with the filing of such registration statement, we established an “at-the-market” offering program utilizing the universal shelf registration for up to $40 million of Common Stock. Due to our late filing of certain financing information related to its reacquisition of BELBUCA®, we are unable to utilize our universal shelf registration statement and associated at-the-market offering program until April 2018.
68
Table of Contents
On October 26, 2015, we and Endo announced that the FDA approved BELBUCA® for use in patients with chronic pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment for which alternative treatment options are inadequate. FDA approval of BELBUCA® triggered a milestone payment to us from Endo of $50 million pursuant to the Endo Agreement, less approximately $6 million of cumulative pre-payments received. We received payment of such milestone in November 2015. We deferred $20 million of the $50 million payment due to the fact that all or a portion of such $20 million was contingently refundable to Endo at year ended December 31, 2016. This $20 million was recognized as revenue in January 2017.
On May 11, 2016, we and Collegium executed a definitive License and Development Agreement under which we have granted to Collegium the exclusive rights to develop and commercialize ONSOLIS® in the U.S, resulting in a milestone of $2.5 million paid to us in June 2016.
During 2016, we received cumulative payments totaling $1.3 million which related to royalties based on product purchased in Europe by Meda of BREAKYL™.
During 2016, we received cumulative payments totaling $0.9 which related to royalties based on product purchased in Taiwan by TTY of PAINKYL™.
On December 8, 2016, we announced that we had entered into an agreement Endo terminating Endo’s licensing of rights for BELBUCA®. The closing of the Termination Agreement, and the formal termination of the BELBUCA® license to Endo and closing of the transactions occurred on January 6, 2017.
On July 12, 2017, we, along with Purdue Pharma (Canada) announced that we have signed an exclusive agreement for the licensing, distribution, marketing and sale of BELBUCA® in Canada. In return for the licensing and distribution rights to BELBUCA® in Canada, we are eligible to receive upfront and potential milestones of up to CAD 4.5 million as well as royalties on net sales, including approximately CAD 1.5 million (0.5 million CAD and 1.0 million CAD received August 2017 and October 2017, respectfully).
During 2017, we received cumulative payments totaling $2.2 million which related to royalties based on product purchased in Europe by Meda of BREAKYL™.
During 2017, we received cumulative payments totaling $1.2 million which related to royalties based on product purchased in Taiwan by TTY of PAINKYL™.
CRG Term Loan Agreement
On February 21, 2017 we and our principal subsidiaries entered into the Loan Agreement with CRG, as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the Lenders.
Pursuant to the Loan Agreement, we borrowed $45.0 million from the Lenders as of the initial closing sate, and may be eligible to borrow up to an additional $30.0 million in two tranches of $15.0 million each (contingent upon achievement of certain conditions, including: (i) in the case of the first tranche, representing the second potential draw under the Loan Agreement (or the Second Draw), satisfying both (a) certain minimum net revenue thresholds on or before September 30, 2017 or December 31, 2017, and (b) a certain minimum market capitalization threshold for a period of time prior to the funding of the Second Draw (provided, that if we do not achieve the minimum net revenue thresholds necessary for the Second Draw but does achieve a certain minimum market capitalization threshold for a period of time prior to December 31, 2017, we would be eligible for a Second Draw funding in the amount of $5.0 million); and (ii) in the case of the second tranche, representing the third potential draw under the Loan Agreement (or the Third Draw), satisfying both (a) certain minimum net revenue thresholds on or before June 30, 2018 or September 30, 2018 and (b) a certain minimum market capitalization threshold for a period of time prior to the funding of the Third Draw. In December 2017, we were eligible for and elected to receive the Second Draw of $15.0 million.
We utilized approximately $29.4 million of the initial loan proceeds to repay all the amounts owed by us under our then existing Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement, dated May 29, 2015, with MidCap (the MidCap Agreement). Upon the repayment of all amounts owed by us under the MidCap Agreement, all commitments under the MidCap Agreement have been terminated and all security interests granted by us and our subsidiaries to the lenders under the MidCap Agreement have been released. We are using the remainder of the initial loan proceeds (after deducting loan origination costs and broker and other fees) of approximately $14.0 million, plus any additional amounts that may be borrowed in the future, for general corporate purposes and working capital.
69
Table of Contents
The Loan Agreement with CRG has a six-year term with the first three years of interest-only payments (which can be extended to four years if we achieve certain net revenue and market capitalization thresholds prior to December 31, 2019), after which quarterly principal and interest payments will be due through the December 31, 2022 maturity date. Interest on the amounts borrowed under the Loan Agreement accrues at an annual fixed rate of 12.50%, 3.5% of which (i.e., a resultant 9.0% rate) may be deferred during the interest-only period by adding such amount to the aggregate principal loan amount. On each borrowing date (including the initial closing we are required to pay CRG a financing fee based on the loan drawn on that date. We are also required to pay the Lenders a final payment fee upon repayment of the Loans in full, in addition to prepayment amounts described below.
We may prepay all or a portion of the outstanding principal and accrued unpaid interest under the Loan Agreement at any time upon prior notice to the Lenders subject to a certain prepayment fees during the first five years of the term (which fees are lowered over time) and no prepayment fee thereafter. In certain circumstances, including a change of control and certain asset sales or licensing transactions, we are required to prepay all or a portion of the loan, including the applicable prepayment premium of on the amount of the outstanding principal to be prepaid.
As security for our obligations under the Loan Agreement, on the funding date of the initial borrowing, we and our subsidiaries entered into a security agreement with CRG whereby we granted to CRG, as collateral agent for the Lenders, a lien on substantially all our assets including intellectual property (subject to certain exceptions). The Loan Agreement requires us to maintain an agreed to minimum cash and cash equivalents balance and, each year through the end of 2022, to meet a minimum net annual revenue threshold. In the event that we do not meet the minimum net annual revenue threshold, then we can satisfy the requirement for that year by raising two (2) times the shortfall by way of raising equity or subordinated debt.
The Loan Agreement also contains customary affirmative and negative covenants for a credit facility of this size and type, including covenants that limit or restrict our ability to, among other things (but subject in each case to negotiated exceptions), incur indebtedness, grant liens, merge or consolidate, dispose of assets, make investments, make acquisitions, enter into transactions with affiliates, pay dividends or make distributions, license intellectual property rights on an exclusive basis or repurchase stock.
The Loan Agreement includes customary events of default that include, among other things, non-payment, inaccuracy of representations and warranties, covenant breaches, a material adverse change (as defined in the Loan Agreement), cross default to material indebtedness or material agreements, bankruptcy and insolvency, material judgments and a change of control. The occurrence and continuance of an event of default could result in the acceleration of the obligations under the Loan Agreement. Under certain circumstances, a default interest rate of an additional 4.00% per annum will apply on all outstanding obligations during the existence of an event of default under the Loan Agreement.
In connection with the initial borrowing made under the Loan Agreement on February 21, 2017, we issued to CRG and certain of its affiliates five separate warrants to purchase an aggregate of 1,701,582 shares of our Common Stock (or the CRG Warrants). The CRG Warrants are exercisable any time prior to February 21, 2027 at a price of $2.38 per share, with typical provisions for cashless exercise and stock-based anti-dilution protection. The exercise of the CRG Warrants could have a dilutive effect to our Common Stock to the extent that the market price per share of the Common Stock, as measured under the terms of the CRG Warrants, exceeds the exercise price of the CRG Warrants. CRG is also entitled to receive a smaller amount of similar warrants concurrently with the funding, if applicable, of the Third Draw.
In connection with the Second Draw, we issued to CRG and certain of its affiliates warrants to purchase an aggregate of 349,452 shares of our Common Stock (or the CRG Second Draw Warrants). The CRG Second Draw Warrants are exercisable any time prior to December 26, 2027, at a price of $3.42 per share, with typical provisions for cashless exercise and stock-based anti-dilution protection. The exercise of the CRG Second Draw Warrants could have a dilutive effect to our Common Stock to the extent that the market price per share of our Common Stock, as measured under the terms of the CRG Second Draw Warrants, exceeds the exercise price of the CRG Warrants.
At December 31, 2017, we had cash and cash equivalents of approximately $21.2 million. We used $32.5 million of cash in operations during the twelve months ended December 31, 2017 and had stockholders’ equity of $8.9 million, versus stockholders’ deficit of $17.7 million at December 31, 2016. We expect that we have sufficient cash to manage our business as currently planned into the second quarter of 2019, which includes access to additional capital from the CRG loan of $15 million if we satisfy the third draw requirements as well as equity markets if we choose or a combination of both that would provide sufficient capital necessary to support the commercialization of BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®. This estimation assumes that we do not otherwise face unexpected events, costs or contingencies, any of which could affect our cash requirements. As a result of our late filing of certain financing information related to its reacquisition of BELBUCA®, we are unable to utilize our universal shelf registration statement and associated at-the-market offering program until April 2018.
70
Table of Contents
Additional capital will be required to support the continued commercialization of our BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® products, the reformulation project for and the anticipated commercial relaunch of ONSOLIS®, the potential continued development of Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection or other products which may be acquired or licensed by us, and for general working capital requirements. Based on product development timelines and agreements with our development partners, the ability to scale up or reduce personnel and associated costs are factors considered throughout the product development life cycle. Available resources may be consumed more rapidly than currently anticipated, potentially resulting in the need for additional funding. Additional funding, capital or loans (including, without limitation, milestone or other payments from commercialization agreements) may be unavailable on favorable terms, if at all.
Also, product development timelines and agreements with our development partners, the ability to scale up or reduce personnel and associated costs are factors considered throughout the product development life cycle. Available resources may be consumed more rapidly than currently anticipated, resulting in the need for additional funding.
Accordingly, we anticipate that we will be required to raise additional capital, which may be available to us through a variety of sources, including:
| • | public equity markets; |
| • | private equity financings; |
| • | commercialization agreements and collaborative arrangements; |
| • | sale of product royalty; |
| • | grants and new license revenues; |
| • | bank loans; |
| • | equipment financing; |
| • | public or private debt; and |
| • | exercise of existing warrants and options. |
Readers are cautioned that additional funding, capital or loans (including, without limitation, milestone or other payments from commercialization agreements) may be unavailable on favorable terms, if at all. If adequate funds are not available, we may be required to significantly reduce or refocus our operations or to obtain funds through arrangements that may require us to relinquish rights to certain technologies and drug formulations or potential markets, either of which could have a material adverse effect on us, our financial condition and our results of operations in 2018 and beyond. To the extent that additional capital is raised through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the issuance of such securities would result in ownership dilution to existing stockholders.
Contractual Obligations and Commercial Commitments
Our non-cancellable contractual obligations as of December 31, 2017 are as follows (in thousands):
| Total | Less than 1 year |
1-3 years | 3-5 years | More than 5 years |
||||||||||||||||
| Operating lease obligations |
$ | 1,641 | $ | 341 | $ | 711 | $ | 589 | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Secured loan facility |
60,162 | — | 20,054 | 40,108 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Interest on secured loan facility |
27,642 | 7,625 | 14,311 | 5,706 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Minimum royalty expenses* |
3,000 | 1,500 | 1,500 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total contractual cash obligations |
$ | 92,445 | $ | 9,466 | $ | 36,576 | $ | 46,403 | $ | — | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| * | Minimum royalty expenses represent a contractual floor that we are obligated to pay CDC and Athyrium regardless of actual sales. |
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
We are not a party to any off balance sheet arrangements.
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk. |
Interest rate risk
71
Table of Contents
Our cash includes all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less. Because of the short-term maturities of our cash, we do not believe that an increase in market rates would have a significant impact on the realized value of our investments. We place our cash on deposit with financial institutions in the United States. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation covers $0.25 million for substantially all depository accounts. As of December 31, 2017, we had approximately $21.2 million, which exceeded these insured limits.
Foreign currency exchange risk
We currently have limited, but may in the future have increased, clinical and commercial manufacturing agreements which are denominated in Euros, CAD or other foreign currencies. As a result, our financial results could be affected by factors such as a change in the foreign currency exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the Euro, CAD or other applicable currencies, or by weak economic conditions in Europe, Canada or elsewhere in the world. We are not currently engaged in any foreign currency hedging activities.
Market indexed security risk
We have issued warrants to various holders underlying shares of our common stock. These warrant investments were measured at their fair value at date of issuance and recorded as warrant expense in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations. We use the Black-Scholes model for valuation of the warrants.
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data. |
Our Consolidated Financial Statements and Notes thereto and the report of Cherry Bekaert LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm, are set forth on pages F-1 through F-45 of this Report.
| Item 9. | Changes In and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure. |
None.
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures. |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our President and our Chief Financial Officer, we carried out an evaluation of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act. Based on that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, at December 31, 2017, such disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
Disclosure controls and procedures are controls and other procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our reports filed or submitted under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified by the SEC. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our reports filed or submitted under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to management, including our President and Chief Financial Officer, or persons performing similar functions, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Limitations on the Effectiveness of Controls
Our disclosure controls and procedures are designed to provide reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of our disclosure control system are met. Because of inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues, if any, within a company have been detected. Our President and Chief Financial Officer have concluded, based on their evaluation as of the end of the period covered by this Report that our disclosure controls and procedures were sufficiently effective to provide reasonable assurance that the objectives of our disclosure control system were met.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the year ended December 31, 2017 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
72
Table of Contents
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
As required by the SEC rules and regulations for the implementation of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Our internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of our consolidated financial statements for external reporting purposes in accordance with GAAP. Our internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that:
| (1) | pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of our company, |
| (2) | provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP, and that our receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and directors, and |
| (3) | provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements. |
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect errors or misstatements in our consolidated financial statements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree or compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. Management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting at December 31, 2017. In making these assessments, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 Framework) (COSO). Based on our assessments and those criteria, management determined that we maintained effective internal control over financial reporting at December 31, 2017.
| Item 9B. | Other Information. |
None.
73
Table of Contents
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance. |
Our directors and executive officers and their ages as of March 13, 2018 are as follows:
| Name |
Age |
Position(s) Held | ||||
| Frank E. O’Donnell, Jr., M.D. |
68 | Chairman of the Board | ||||
| Mark A. Sirgo, Pharm.D. |
64 | Vice Chairman | ||||
| Scott M. Plesha |
53 | President | ||||
| Ernest R. De Paolantonio |
64 | Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and Treasurer | ||||
| Samuel P. Sears, Jr |
74 | Director | ||||
| Thomas W. D’Alonzo |
74 | Director | ||||
| Barry I. Feinberg |
63 | Director | ||||
| Timothy C. Tyson |
65 | Director | ||||
| William M. Watson |
67 | Director | ||||
There are no arrangements between our directors and any other person pursuant to which our directors were nominated or elected for their positions. There are no family relationships between any of our directors or executive officers.
Frank E. O’Donnell, Jr., M.D., age 68, has been our Chairman of the Board and a Director since March 29, 2002. He currently serves as Chairman. Dr. O’Donnell has previously served as our President and Chief Executive Officer. In January 2005, he relinquished the title of President and in August 2005 he relinquished the title of Chief Executive Officer. Until November 2016, Dr. O’Donnell previously served as a Manager of The Hopkins Capital Group, an affiliation of limited liability companies which engage in private equity and venture capital investing in disruptive technologies in healthcare. Dr. O’Donnell is Chairman of Defender Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a privately-held company developing pharmaceuticals for national defense. Until November 2016, Dr. O’Donnell was also Chairman of the Board of Directors of Hedgepath Pharmaceuticals, Inc., which is developing oncology drugs for an orphan indication. Dr. O’Donnell is qualified to serve on our board of directors because of his long history with our company and his extensive experience in managing and investing in biopharmaceutical companies. Dr. O’Donnell is a graduate of The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and received his residency training at the Wilmer Ophthalmological Institute, Johns Hopkins Hospital. Dr. O’Donnell is a former professor and Chairman of the Department of Ophthalmology, St. Louis University School of Medicine. He is a trustee of St. Louis University.
Mark A. Sirgo, Pharm.D., age 64, has been our Director since August 2005 and Vice Chairman since October 2016. He was formerly our President since January 2005 and Chief Executive Officer since August of 2005. He joined our company in August 2004 as Senior Vice President of Commercialization and Corporate Development upon our acquisition of Arius Pharmaceuticals, of which he was a co-founder and Chief Executive Officer. He has also served as our Executive Vice President, Corporate and Commercial Development and our Chief Operating Officer. Dr. Sirgo has over 30 years of experience in the pharmaceutical industry, including 16 years in clinical drug development, 7 years in marketing, sales, and business development and 12 years in executive management positions. Prior to his involvement with Arius Pharmaceuticals from 2003 to 2004, he spent 16 years in a variety of positions of increasing responsibility in both clinical development and marketing at Glaxo, Glaxo Wellcome, and GlaxoSmithKline, including Vice President of International OTC Development and Vice President of New Product Marketing. Dr. Sirgo was responsible for managing the development and FDA approval of Zantac 75 while at Glaxo Wellcome, among other accomplishments. From 1996 to 1999, Dr. Sirgo was Senior Vice President of Global Sales and Marketing at Pharmaceutical Product Development, Inc., a leading contract service provider to the pharmaceutical industry. Dr. Sirgo served on the Board of Directors and as Chairman of the Compensation Committee of Salix Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (NASDAQ:SLXP), a specialty pharmaceutical company specializing in gastrointestinal products since 2008 until its sale in 2015. Dr. Sirgo was added to the Board of Directors of Biomerica, Inc. (NASDAQ: BMRA), a diagnostics and therapeutic company in July of 2016. Dr. Sirgo is qualified to serve on our board of directors because of his extensive and broad based experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Dr. Sirgo received his BS in Pharmacy from The Ohio State University and his Doctorate from Philadelphia College of Pharmacy and Science.
Scott M. Plesha, age 53, joined the company in August 2015 as our Senior Vice President, Sales, with more than 26 years of sales experience and over 18 years of sales management experience within the pharmaceutical and medical industries. Mr. Plesha assumed the additional responsibility of leading our Marketing department in December 2015. In January 2018, Mr. Plesha was appointed to the role of President of our company. Mr. Plesha leads our Specialty Sales Force, Marketing, and Training departments. Prior to joining the company, Mr. Plesha was Senior Vice President, GI Sales Force & Training at Salix Pharmaceuticals, where since 2002 he led Salix’s top rated gastrointestinal (GI) sales forces, the sales training department as well as many other sales operations functions. During Mr. Plesha’s tenure at Salix he was responsible for launching or growing product sales as well as optimizing and
74
Table of Contents
expanding the sales force to accommodate the multiple companies and products that Salix acquired. Prior to joining Salix, Mr. Plesha was a Regional Sales Manager for the O’Classen Dermatologics division of Watson Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Mr. Plesha began his pharmaceutical sales career with Solvay Pharmaceuticals where he was a field as well institutional sales representative. Mr. Plesha received a Bachelor of Arts in Pre-Medical Studies from DePauw University.
Ernest R. De Paolantonio, CPA, MBA, age 64, has been our Chief Financial Officer and Secretary since October of 2013 and has over 35 years of varied financial and business experience in the pharmaceutical industry. Mr. De Paolantonio also became our Treasurer in January 2015. Prior to joining the company, he served as the Chief Financial Officer of CorePharma LLC, a private specialty generic company, and was directly involved in the financial and commercial strategy to establish Core’s proprietary labeled portfolio of products. In addition, he previously served in finance and controllership positions in roles of increasing responsibility at Colombia Laboratories, where he was also responsible for business development and logistics, including supply chain management for the company’s first commercial product launch. Mr. De Paolantonio has served in various financial positions in senior management at Taro Pharmaceuticals where he was the Corporate Controller, Watson Pharmaceuticals where he was Executive Director of Finance, Group Controller and responsible for managing the Corporation’s supply chain of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, and GlaxoSmithKline where he began his career in finance and spent over 17 years in areas of increasing responsibility including; Manufacturing, Corporate Finance, R&D and U.S. Pharmaceuticals where he was Group Controller. Mr. De Paolantonio received his Bachelor of Arts Degree from Lycoming College; his MBA in Finance at Saint Joseph’s University and is a licensed CPA.
Samuel P. Sears, Jr., age 74, was appointed as a member of our board of directors in October, 2011 and since 2013 serves as Chairman of the Compensation Committee. Mr. Sears has extensive experience in the biopharmaceutical, nutraceutical and biotechnology industries. Since 2006, Mr. Sears has been a partner at the law firm of Cetrulo LLP, where he currently serves as managing partner, and from 2000 to 2006, he provided private consulting and legal advisory services to start-up and early stage development companies. From 2013 to December 2016, Mr. Sears served as Director of HedgePath Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (OTCBB: HPPI), a clinical stage biopharmaceutical company which is developing therapeutics for cancer patients. From 2000 to 2013, Mr. Sears served as Director, Chairman of the Audit Committee, Chairman of the Executive Committee, and Member of the Compensation Committee of Commonwealth Biotechnologies, Inc., a research and development support services company. From 1998 to 2000, Mr. Sears served as Vice Chairman and treasurer of American Prescription Providers, Inc., a specialty pharmacy network offering prescriptions and nutraceuticals to patients with chronic diseases. From 1994 through May 1998, Mr. Sears was Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of Star Scientific, Inc. (NASDAQ: CIGX). From 1968 to 1993, Mr. Sears was in private law practice. Mr. Sears is qualified to serve on our board of directors because of his extensive legal and business experience, including in the pharmaceutical industry. Mr. Sears is a graduate of Harvard College and Boston College Law School.
Thomas W. D’Alonzo, age 74, has served as a member of our board since April 23, 2013. Prior to joining our company, Mr. D’Alonzo served as a member of the board of directors of Salix Pharmaceuticals, Ltd. until May 2015 and the Chairman of the Board since from June 2010 to May 2015. Mr. D’Alonzo also served as the Interim Chief Executive Officer of Salix from January 2015 to May 2015. From March 2007 to February 2009, Mr. D’Alonzo served as the Chief Executive Officer and a director of MiMedx Group, Inc. From May 2006 to April 2007, Mr. D’Alonzo was Chief Executive Officer of DARA BioSciences, Inc., now known as DARA Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and he served on its board of directors from September 2005 to December 2008. From 2006 to 2008, he also served on our board of directors. From 2000 to 2007, Mr. D’Alonzo acted as an independent consultant. Prior to that, from 1996 to 1999, Mr. D’Alonzo served as President and Chief Operating Officer of Pharmaceutical Product Development (PPD), a global provider of discovery and development services to pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. Before joining PPD, from 1993 to 1996, he served as President and Chief Executive Officer of GenVec, Inc., a clinical-stage, biopharmaceutical company. From 1983 to 1993, Mr. D’Alonzo held positions of increasing responsibility within Glaxo, Inc., the U.S. division of GSK, including President. Mr. D’Alonzo is qualified to serve on our board of directors because of his extensive experience in working with and managing biopharmaceutical companies. Mr. D’Alonzo received his B.S. in Business Administration from the University of Delaware, and his J.D. from the University of Denver College of Law.
Barry I. Feinberg, M.D., age 63, has served as a member of our board since July 17, 2014. Dr. Feinberg is an expert in the area of pain management and has served as adjunct faculty member of the Department of Anesthesia at Saint Louis University since November 2013. Since 2008, he has also served as a member of the Board of Directors and Medical Executive Committee of the Frontenac Surgery and Spine Care Center, where he maintains his private practice under the name Injury Specialists. From 2003 to 2011, Dr. Feinberg served as a member of the Board of Directors of Professional Imaging, LLC. He has served as a staff member of the Department of Anesthesia at the Missouri Baptist Medical Center in St. Louis, Missouri since August 2004 and as an associated staff member of the Department of Anesthesia at the DePaul Health Center in Bridgeton, Missouri, since June 1995. From 1988 to 1994, Dr. Feinberg served as Director of the Physicians’ Pain Management Center in Bridgeton, Missouri, and the Chairman of the Department of Anesthesia at DePaul Heath Center in Bridgeton from 1986 to 1994. He has also served as Assistant Professor at the Department of Anesthesia at Mount Sinai Medical Center from 1984 to 1986 and staff member at the Intensive Care Unit of the Deborah Heart and Lung Center in Browns Mill, New Jersey, from 1983 to 1984. Dr. Feinberg is qualified to serve on our board of
75
Table of Contents
directors because of his medical degree and his specialty in the field of pain management. Dr. Feinberg received a Bachelor of Science in Biology from the State University of New York, Binghamton and a Doctor of Medicine from State University of New York Downstate Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York. Dr. Feinberg completed a residency in Anesthesiology at University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine. He also received a Juris Doctorate degree from the Washington University School of Law, St. Louis, Missouri.
Timothy C. Tyson, age 65 joined our board as an independent member in October 2016. His corporate career spans over 30 years in the pharmaceutical industry, having in that time held senior executive level leadership positions as well as positions of responsibility overseeing key functional areas such as sales and marketing, manufacturing and supply, and research and development. Mr. Tyson is currently Chairman and CEO of Avara Pharmaceutical Services and Chairman at Icagen Inc. and recently served as Chairman and CEO of Aptuit LLC. From 2002 to 2008, Mr. Tyson served as Chief Operating Officer, President, and Chief Executive Officer of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International. Prior to joining Valeant, Mr. Tyson ran multiple divisions of GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) and was a member of the corporate executive team. During his fourteen-year tenure at GSK, he was President, Global Manufacturing and Supply, and ran Glaxo Dermatology and Cerenex Pharmaceuticals. He was also responsible for managing all sales and marketing for GlaxoWellcome’s U.S. operations, where he launched 32 new products, eight of which reached sales of greater than $1 billion. Mr. Tyson also held positions at Bristol Myers and Proctor & Gamble and served on active duty as an officer in the U.S. Army. Mr. Tyson is a graduate of the United States Military Academy at West Point.
William Mark Watson, CPA, age 67, joined our board as an independent member in December 2017 and is Chairman of the Audit Committee of our board of directors. Mr. Watson is a Certified Public Accountant with over 40 years of experience in public accounting and auditing, having spent his entire career from January 1973 to June 2013 at Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu and its predecessor, most recently as Central Florida Marketplace Leader. Among other industries, he has a particular expertise in the health and life sciences sector, having played a significant role in the development of Deloitte’s audit approach for health and life sciences companies and leading its national healthcare regulatory and compliance practice. He has served as lead audit partner and advisory partner on the accounts of many public companies ranging from middle market firms to Fortune 500 enterprises. Mr. Watson is a member of American Institute of Certified Public Accountants and the Florida Institute of Certified Public Accountants. Mr. Watson is a member of the board of directors and Chairman of the Audit Committee of Hedgepath Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (OTCQX:HPPI). Mr. Watson is qualified to serve on our board due to his expertise in public accounting and his experience with pharmaceutical companies. He received his undergraduate degree in Accounting from Marquette University.
Key Employees
Below are the biographies of certain key non-executive officer employees of our company:
Albert J. Medwar, M.B.A. joined our company in April 2007 and is our Senior Vice President of Corporate and Business Development. Mr. Medwar will be retiring from our company effective April 1, 2018 and will consult with us thereafter for a period of up to 6 months. He will also receive a retirement benefits package. Mr. Medwar has over 25 years of experience in marketing, sales, investor/public relations and business development. Prior to joining our company, Mr. Medwar was the Head of Oncology Marketing at EMD Pharmaceuticals, the U.S. subsidiary of Merck KGaA, where he was responsible for developing the global market for a pipeline of oncology products. Mr. Medwar was also the Marketing Director for Triangle Pharmaceuticals, a start-up company focusing on the development and commercialization of compounds for HIV and hepatitis. Mr. Medwar’s pharmaceutical career began in sales at Burroughs Wellcome, which later became Glaxo Wellcome. After six years of sales experience, he took on marketing research responsibilities, and then played an important role in the launch of a short acting opioid analgesic, remifentanil, and held increasing marketing responsibility for a number of products including a portfolio of anesthetic/analgesic agents, Zofran, and Wellbutrin SR. Mr. Medwar received a Bachelor of Science degree from Cornell University and a Masters of Business Administration from Bentley University.
Michael Bullock has been our National Director, Managed Markets since joining the company in June 2015, with more than 26 years of sales and 18 years of managed markets experience within the pharmaceutical and medical space. Mr. Bullock heads our Managed Markets department and is responsible for developing and implementing market access strategies and managing consultant relationships relating to managed markets, lobbying and government affairs. Prior to joining the company, Mr. Bullock was a Director, Managed Markets for Salix Pharmaceuticals, a GI pharmaceutical and medical device company, where he led a team of National and Regional Account Managers. While at Salix, Mr. Bullock was responsible for implementing market access strategies across various payer channels including commercial, Medicaid, Medicare, GPO, institutional, long term care and employer group customers, as well as developing medical policy for devices. Prior to joining Salix, Mr. Bullock held managed markets positions with UCB, Celltech Pharmaceuticals and Medeva Pharmaceuticals and was a sales representative with Adams Laboratories. Mr. Bullock received his Bachelor of Science in Agricultural Economics from The Ohio State University.
76
Table of Contents
Joseph Lockhart was promoted to Senior Vice President of Operations for our company in January 2018 after having served as our Vice President of Manufacturing and Supply Chain since joining the company in November 2015. Drawing upon over 30 years of experience in the pharmaceutical industry with specific focus in the areas of manufacturing, supply chain, product development, CMC (Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls) and quality, Mr. Lockhart now provides senior-level management to our company’s overall Operations, including Clinical, Quality, Regulatory, and Manufacturing/Supply Chain. Prior to joining our company, Mr. Lockhart served as Vice President, Pharmaceutical Development and Manufacturing at Salix Pharmaceuticals, where since 2001 he established the Pharmaceutical Development and Manufacturing team and contributed to multiple NDA submissions, as well as multiple product acquisitions and launches. During Mr. Lockhart’s tenure at Salix he held positions of increasing responsibility and was responsible for managing Manufacturing, Technical Operations, Formulation Development, and Clinical Trial Material Operations. From 1986 thru 2001 Mr. Lockhart served in various pharmaceutical CMC-related roles and responsibilities at both the Manager and the Director levels of management. Mr. Lockhart received a Master of Business Administration degree from the University of North Carolina at Charlotte as well as a Bachelor of Arts degree in Chemistry from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
James D. Darnley, Jr. joined the company May 2017 and is our Vice President, General Counsel, and Commercial Compliance Officer. Mr. Darnley brings over 30 years of global experience as an attorney and over 23 years of experience in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industry to the company. Prior to joining our company, Mr. Darnley was Head of Intellectual Property at Moderna Therapeutics, a mRNA therapy company. He was also Vice President and Chief Intellectual Property Counsel for Millennium Pharmaceuticals/Takeda Pharmaceuticals International from 2007 to 2015 where he was responsible for global IP support for Oncology research, development and commercial activities as well as general IP support for on-site research and development. Prior to that he worked for BiogenIDEC as a licensing attorney for 4 years and Pharmacia for 9 years where he held positions of increasing responsibility and ultimately became the Site Head of the Pharmacia Intellectual Property Group at its Kalamazoo, Michigan Research & Development Center. Mr. Darnley has worked on a number of complex legal issues over the years including multiple Hatch-Waxman Paragraph IV and 505(b)(2) litigations for VELCADE (bortezomib) and INTEGRILIN (eptifibatide), corporate mergers, acquisitions and divestments (e.g., Sugen, BioVitrum, Asgrow, Conforma, Intellikine, Millennium), the in-licensing and out-licensing of products, research programs and technologies and the creation and implementation of worldwide patent procurement strategies. Mr. Darnley received a bachelor’s degree with honors in biology as well as a law degree from Indiana University, Bloomington, Indiana. During law school, Mr. Darnley was a member of the Indiana Law Journal.
Position of Executive Chairman
On January 20, 2012, our board of directors, upon the recommendation of the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee of the board, created the office of Executive Chairman and appointed Dr. Frank O’Donnell, then our Chairman of the Board, as Executive Chairman of our company. In taking such action, our board was intending to formally memorialize the role that Dr. O’Donnell has played with our company over the years.
As Executive Chairman of our company, Dr. O’Donnell acted as an officer and employee and, as such, performed his duties subject in all instances to the oversight of our board of directors and the power of our board of directors to approve all applicable corporation actions (which powers shall not be vested in the office of Executive Chairman). The Executive Chairman was not an “executive officer” (as defined in SEC Rule 3b-7) of our company as the role of the Executive Chairman by design was not an officer who performs a policy making function for our company. Rather, the Executive Chairman served as a conduit between our board and our executive management team and was available to act as an advisor and consultant to our executive management team, with ultimate responsibility for development and implementation of our corporate policies being vested in our executive officers (Dr. Sirgo, Dr. Vasisht and Mr. De Paolantonio) under the supervision of our board of directors.
Given the maturation of our company and business over the past 5 years during Dr. O’Donnell’s tenure as Executive Chairman, it was determined by the board and Dr. O’Donnell that this level of involvement was no longer required and as such, Dr. O’Donnell and the board agreed to redesignate Dr. O’Donnell’s position as Chairman of the Board effective October 2017 and, effective in May 2017, his base cash compensation was reduced (with the review and approval of the Compensation Committee) to $80,000 annually. Therefore, in 2017, Dr. O’Donnell received the following cumulative compensation for his service as Executive Chairman and Chairman: $181,250 in cash compensation, $132,000 bonus, $342,540 in stock awards and $18,432 in benefits paid in 2017. We do not have a written employment or similar agreement with Dr. O’Donnell relating to his service as our Chairman.
Director Independence
We believe that Samuel P. Sears, Jr., Thomas W. D’Alonzo, Barry I. Feinberg, Timothy C. Tyson and William M. Watson qualify as independent directors for NASDAQ Stock Market purposes. This means that our board of directors is composed of a majority of independent directors as required by NASDAQ Stock Market rules.
77
Table of Contents
Meetings of the Board of Directors and Stockholders
Our board of directors met in person and telephonically eighteen times during 2017 and also acted by unanimous written consent. Each member of our board of directors was present at least 75% of the board of directors meetings held. It is our policy that all directors must attend all stockholder meetings, barring extenuating circumstances. All directors were present at the 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, either in person or telephonically.
Board Committees
Our board of directors has established three standing committees: Audit, Compensation, and Nominating and Corporate Governance. Historically, all independent directors have been members of each board committee. In October 2013, our committees reorganized, and subsequently there were changes to the committee composition. All standing committees (as well as our former Lead Director) operate under a charter that has been approved by the board. Our board of directors has also, from time to time, appointed non-standing committees to assist the board in its duties to our company. The charters for each of our board committees are available at http://www.bdsi.com/Corporate_Governance.aspx.
Audit Committee
Our board of directors has an Audit Committee, composed of William M. Watson, Thomas W. D’Alonzo and Barry I. Feinberg, all of whom are independent directors as defined in accordance with section 3(a)(58)(A) of the Exchange Act and the rules of NASDAQ. Mr. Watson serves as chairman of the committee. The board of directors has determined that Mr. Watson is an “audit committee financial expert” as defined in Item 407(d)(5)(ii) of Regulation S-K. The Audit Committee met five times during 2017. Each member of the Audit Committee was present at 100% of the Audit Committee meetings held during such director’s tenure as a member of the Audit Committee.
Our Audit Committee oversees our corporate accounting, financial reporting practices and the audits and reviews of financial statements. For this purpose, the Audit Committee has a charter (which is reviewed annually). As summarized below, the Audit Committee:
| • | evaluates the independence and performance of, and assesses the qualifications of, our independent auditor and engages such independent auditor; |
| • | approves the plan and fees for the annual audit, quarterly reviews, tax and other audit-related services and approves in advance any non-audit service and fees therefor to be provided by the independent auditor; |
| • | monitors the independence of the independent auditor and the rotation of partners of the independent auditor on our engagement team as required by law; |
| • | reviews the financial statements to be included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K and Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q and reviews with management and the independent auditors the results of the annual audit and reviews of our quarterly financial statements; |
| • | oversees all aspects of our systems of internal accounting and financial reporting control; and |
| • | provides oversight in connection with legal, ethical and risk management compliance programs established by management and the board, including compliance with requirements of Sarbanes-Oxley and makes recommendations to the board of directors regarding corporate governance issues and policy decisions. |
Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee
Our board of directors has a Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee composed of Thomas W. D’Alonzo, Samuel P. Sears and Barry I. Feinberg. Mr. D’Alonzo serves as the chairman of the committee. The Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee is charged with the responsibility of reviewing our corporate governance policies and with proposing potential director nominees to the board of directors for consideration. The Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee met four times in 2017 and has a charter which is reviewed annually. All members of the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee are independent directors as defined by the rules of the NASDAQ Stock Market. The Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee will consider director nominees recommended by security holders. To recommend a nominee please write to the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee c/o Ernest R. De Paolantonio, BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc, 4131 ParkLake Avenue. Suite #225, Raleigh, NC. 27612. The Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee has established nomination criteria by which board candidates are to be evaluated. The Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee will assess all director nominees using the same criteria. During 2017, we did not pay any fees to any third parties to assist in the identification of nominees. During 2017, we did not receive any director nominee suggestions from stockholders.
78
Table of Contents
In 2010, the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee adopted a set of criteria by which it will seek to evaluate candidates to serve on our board of directors. The evaluation methodology includes a scored system based on criteria including items such as experience in the biotechnology sector, experience with public companies, executive managerial experience, operations and commercial experience, fundraising experience and contacts in the investment banking industry, personal and skill set compatibility with current board members, industry reputation, knowledge of our company generally, independence and ethnic and gender diversity. While diversity is considered as a board qualification criteria, it would not be weighted any more or less in an evaluation process than any other criteria. The established criteria do not distinguish board candidates based on whether the candidate is recommended by a stockholder of our company.
Compensation Committee
Our board of directors also has a Compensation Committee, which reviews or recommends the compensation arrangements for our management and employees and also assists the board of directors in reviewing and approving matters such as company benefit and insurance plans, including monitoring the performance thereof. The Compensation Committee has a charter (which is reviewed annually) and is composed of three members: Samuel P. Sears, Jr., Barry I. Feinberg and William M. Watson. Mr. Sears serves as chairman of this committee. The Compensation Committee met five times during 2017.
The Compensation Committee has the authority to directly engage, at our expense, any compensation consultants or other advisers as it deems necessary to carry out its responsibilities in determining the amount and form of employee, executive and director compensation. In 2017, the Compensation Committee engaged Radford, an AON Consulting Company, to obtain market data against which it has measured the competitiveness of our compensation programs. In determining the amount and form of employee, executive and director compensation, the Compensation Committee has reviewed and discussed historical salary information as well as salaries for similar positions at comparable companies. We paid consultant fees to Radford of $0.04 million in 2017.
Lead Director
On July 26, 2007, our board of directors created the position of Lead Director. Our board of directors previously designated William B. Stone, a former director, as our Lead Director. Mr. Stone retired from his position on our board and as the Lead Director for personal reasons effective December 7, 2017. Pursuant to the charter of the Lead Director, the Lead Director shall be an independent, non-employee director designated by our Board who shall serve in a lead capacity to coordinate the activities of the other non-employee directors, interface with and advise management, and perform such other duties as are specified in the charter or as our board may determine. Given the change in the composition of the board arising out of the retirements of Messrs. Stone and Bramlage and the election to the board on December 7, 2017 of Mr. Watson, the board will evaluate early 2018 whether it will designate a new director to serve as Lead Director.
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
Section 16(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, requires that our directors and executive officers and persons who beneficially own more than 10% of our common stock (referred to herein as the “reporting persons”) file with the SEC various reports as to their ownership of and activities relating to our common stock. Such reporting persons are required by the SEC regulations to furnish us with copies of all Section 16(a) reports they file.
Based solely upon a review of copies of Section 16(a) reports and representations received by us from reporting persons, and without conducting any independent investigation of our own, in fiscal year 2017, all Forms 3, 4 and 5 were timely filed with the SEC by such reporting persons, with exception of Niraj Vasisht, who filed a Form 4, which was due February 1, 2017 on February 8, 2017, Francis E. O’Donnell, Jr., who filed a Form 4, which was due on February 17, 2017 on February 24, 2017, Ernest De Paolantonio and Niraj Vasisht, who filed Form 4s, which were due on February 24, 2017 on March 3, 2017 and Mark A. Sirgo, who filed a Form 4, which was due March 17, 2017 on March 31, 2017 and another form 4, which was due September 18, 2017 on September 22, 2017.
Code of Ethics
We have adopted a code of ethics that applies to all employees, as well as each member of our board. Our code of ethics is posted on our website, and we intend to satisfy any disclosure requirement under Item 5.05 of Form 8-K regarding an amendment to, or waiver from, a provision of our code of ethics by posting such information on our website, www.bdsi.com. A copy of our code of ethics is also available in print, without charge, upon written request to 4131 ParkLake Avenue, Suite #225, Raleigh, NC 27612. Attn: Ernest R. De Paolantonio.
79
Table of Contents
Involvement in Certain Legal Proceedings
None
Compensation Discussion and Analysis
The Compensation Committee of our board of directors has the responsibility to review, determine and approve the compensation for our executive officers. Further, the Compensation Committee oversees our overall compensation strategy, including compensation policies, plans and programs that cover all employees.
We employed three executive officers, each of whom served as a “Named Executive Officer” (or NEO) for purposes of SEC reporting as of December 31, 2017: (1) Mark A. Sirgo, Pharm.D., our former President and Chief Executive Officer who retired on January 2, 2018 and who continues to serve as Vice Chairman of our board of directors (see “Sirgo Retirement Agreement” below and who we refer to in this Compensation Discussion and Analysis as our CEO); (2) Ernest R. De Paolantonio, CPA, MBA, our Secretary, Treasurer and Chief Financial Officer; and (3) Niraj Vasisht, Ph.D., our former Senior Vice President and Chief Technology Officer who retired on February 4, 2018 (see “Vasisht Retirement Agreement ” below.)
This Compensation Discussion and Analysis sets forth a discussion of the compensation for our NEOs as of December 31, 2017 as well as a discussion of our philosophies underlying the compensation for our NEOs and our employees generally.
Objectives of Our Compensation Program
The Compensation Committee’s philosophy seeks to align the interests of our stockholders, officers and employees by tying compensation to individual performance and the Company’s performance, both directly in the form of salary and annual cash bonus payments, and indirectly in the form of incentive equity awards. The objectives of our compensation program enhance our ability to:
| • | attract and retain qualified and talented individuals; and |
| • | provide reasonable and appropriate incentives and rewards to our team for building long-term value within our company, in each case in a manner comparable to companies similar to ours. |
In addition, we strive to be competitive with other similarly situated companies in our industry. The process of developing and commercializing pharmaceutical products is a long-term proposition and outcomes may not be measurable for several years. Therefore, to build long-term value for our stockholders, and to achieve our business objectives, we believe that we must compensate our officers and employees in a competitive and fair manner that reflects our current activities but also reflects contributions to building long-term value.
We utilize the services of the Radford Group, an AON consulting company (which we refer to herein as Radford) to review compensation programs of peer companies to assist the Compensation Committee in determining the compensation levels for our NEOs, as well as for other employees of ours. Radford is a recognized independent consulting company and services clients throughout the United States.
The companies that comprise our peer group are selected and reviewed no less frequently than biennially. The current peer group used to evaluate compensation for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 was approved by the Compensation Committee in September 2017 and includes the following companies:
| Company |
Location | |
| AcelRx Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
Redwood City, CA | |
| Alimera Sciences, Inc. |
Alpharetta, GA | |
| Antares Pharma, Inc. |
Ewing, NJ | |
| Aralez Pharmaceuticals Inc. |
Mississauga, ON | |
| Arena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
San Diego, CA | |
| BioCryst Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
Durham, NC | |
| CTI BioPharma Corp. |
Seattle, WA | |
| Cumberland Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
Nashville, TN | |
| DURECT Corporation |
Cupertino, CA | |
| Egalet Corporation |
Wayne, PA |
80
Table of Contents
| Company |
Location | |
| ImmunoGen, Inc. |
Waltham, MA | |
| Neos Therapeutics, Inc. |
Grand Prairie, TX | |
| Osiris Therapeutics, Inc. |
Columbia, MD | |
| Orexigen Therapeutics, Inc. |
La Jolla, CA | |
| Strongbridge BioPharma plc |
Trevose, PA | |
| Sucampo Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
Bethesda, MD | |
| Vericel Corporation |
Cambridge, MA | |
| Vivus, Inc. |
Campbell, CA |
With respect to our employees and non-senior management, we will also take into consideration regional market data in determining appropriate compensation packages, and we have in the past relied on Radford to provide us with such data.
Elements of Our Compensation Program and Why We Chose Each
Main Compensation Components
Our company-wide compensation program, including for our NEOs, is broken down into three main components: base salary, performance cash bonuses and potential long-term compensation in the form of stock options or restricted stock units (or RSUs). We believe these three components constitute the minimum essential elements of a competitive compensation package in our industry. We also have a Performance Long Term Incentive Plan (which we refer to herein as the LTIP) for our NEOs and selected senior officers, which compensates such employees with RSUs based on our achievement of certain pre-determined revenue performance goals.
Salary
Base salary is used to recognize the experience, skills, knowledge and responsibilities required of our NEOs as well as recognizing the competitive nature of the biopharmaceutical industry. This is determined partially by evaluating our peer companies as well as the degree of responsibility and experience levels of our NEOs and their overall contributions to our company. Base salary is one component of the compensation package for NEOs; the other components being cash bonuses, annual equity grants, a long-term incentive plan and our benefit programs. Base salary is determined in advance whereas the other components of compensation are awarded in varying degrees following an assessment of the performance of a NEO. This approach to compensation reflects the philosophy of our board of directors and its Compensation Committee to emphasize and reward, on an annual basis, performance levels achieved by our NEOs, and to provide appropriate retention incentives based on future performance.
Performance Cash Bonus Plan
We have a performance cash bonus plan under which bonuses are paid to our NEOs based on achievement of our performance goals and objectives established by the Compensation Committee and/or our board of directors as well as on individual performance. The bonus program is discretionary and is intended to: (i) strengthen the connection between individual compensation and our achievements; (ii) encourage teamwork among all disciplines within our company; (iii) reinforce our pay-for-performance philosophy by awarding higher bonuses to higher performing employees; and (iv) help ensure that our cash compensation is competitive. Depending on our company’s cash position, the Compensation Committee and our board of directors have the discretion after consulting with our NEOs to not pay (or pay more limited) cash bonuses in order that we may conserve cash and support ongoing development programs and commercialization efforts. Regardless of our cash position, we consistently grant annual merit-based stock options (and, more recently in the case of senior executives, RSUs) to continue incentivizing both our senior management and our employees.
Based on their employment agreements, each NEO is assigned a target payout under the performance cash bonus plan, expressed as a percentage of base salary for the year. Actual payouts under the performance cash bonus plan are based on the achievement of corporate performance goals and an assessment of individual performance, each of which is separately weighted as a component of such officer’s target payout. For the NEOs, the corporate goals receive the highest weighting to ensure that the bonus system for our management team is closely tied to our corporate performance. Each employee also has specific individual goals and objectives as well that are tied to the overall corporate goals. For employees, mid-year and end-of-year progress is reviewed with the employees’ managers.
81
Table of Contents
Equity Incentive Compensation
We view long-term compensation, currently in the form of stock options and RSUs, which generally vest in annual increments over three years (other than awards under our LTIP, which vest immediately if awarded, and performance based awards as described below), as a tool to align the interests of our NEOs and employees generally with the creation of stockholder value, to motivate our employees to achieve and exceed corporate and individual objectives and to encourage them to remain employed by us. While cash compensation is a significant component of employees’ overall compensation, the Compensation Committee and our board of directors (as well as our NEOs) believe that the driving force of any employee working in a small biotechnology company should be strong equity participation. We believe that this not only creates the potential for substantial longer term corporate value but also serves to motivate employees and retain their loyalty and commitment with appropriate personal compensation over a longer period of time. Our equity awards are granted under our 2011 Equity Incentive Plan (as the same may be amended, supplemented or superseded from time to time, which we refer to herein as the Plan).
Since January 2017, it is our policy to grant equity incentive awards with two types of vesting: time-based and performance-based.
Time-based vesting. The Compensation Committee believes that because time-vested stock options and RSUs have a three-year vesting schedule that begins one year after the date of the award, the equity grants constitute a significant retention incentive and a tool to foster continuity of management, an important factor for a company with a relatively low number of employees.
Performance-based vesting. Based on the Compensation Committee’s review in 2017 of current market practices, pronouncements by corporate governance advisory services and discussions with our institutional investors, beginning with the annual equity awards granted to senior executives (including our NEOs) in February 2017, one-half of the RSUs granted are performance based and vest over a three-year period based on the level of achievement of specified predetermined net revenue and operating income targets, with the remaining one-half being time vested as described above. In March 2018, the Compensation Committee determined that the 2017 performance-based RSU 1/3rd grant would vest at a rate of 85.5% according to the achievement of the aforementioned targets. Such RSUs will vest on the first open window after the filing of our Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Performance Long Term Incentive Plan
In December 2012, in anticipation of the commencement of revenue generating operations by our company by means of product commercialization, the Compensation Committee approved our LTIP. The LTIP is designed as an incentive for our senior management (including our NEOs) to generate revenue for us.
The LTIP consists of RSUs (which, for purposes of the Plan, are defined as and considered (and which we refer to herein as Performance RSUs), which are rights to acquire shares of our common stock. All Performance RSUs granted under the LTIP will be granted under the Plan as “Performance Compensation Awards” under such plan. The participants in the LTIP are either NEOs or senior officers of ours.
The term of the LTIP began with our fiscal year ended December 31, 2012 and lasts through our fiscal year ended December 31, 2019. The total number of Performance RSUs covered by the LTIP is 1,078,000, of which an aggregate of 978,000 were awarded in 2012 (and an aggregate of 35,000 in 2015). The Performance RSUs under the LTIP did not vest upon granting, but instead are subject to potential vesting each year over the eight-year term of the LTIP depending on the achievement of revenue by us, as reported in our Annual Report on Form 10-K. During 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 and 2017, an aggregate of 8,986, 4,447, 21,356, 13,347 and 33,811 Performance RSUs vested, respectively. Performance RSUs will be valued on the day of issuance and will vest annually on the last day preceding the first open trading window after filing our Annual Report on Form 10-K based on the revenue achieved during the prior fiscal year as a proportion of the total cumulative revenue target for the entire term of the LTIP (which we call the Predefined Cumulative Revenue). Predefined Cumulative Revenue is a predefined aggregate revenue target for the entire term of the LTIP that was determined by the Compensation Committee in conjunction with our executive management. The Predefined Cumulative Revenue may be adjusted by the Compensation Committee upon the occurrence of extraordinary corporate events during the term of the LTIP (such as acquisitions by us of revenue generating businesses or assets).
Other Compensation
In addition to the main components of compensation outlined above, we also provide contractual severance and/or change in control benefits to the NEOs as well as to Scott Plesha, who was appointed as our President as of January 2, 2018, (see “Appointment of President” below), Albert J. Medwar, our Senior Vice President, Corporate and Business Development (who will retire from our company as of April 1, 2018 and receive a retirement benefits package that includes equity features), to Joseph Lockhart, our Senior
82
Table of Contents
Vice President Operations, and to James Darnley, our Vice President, General Counsel and Commercial Compliance Officer. The change in control benefits for all applicable persons has a “double trigger.” A double-trigger means that the executive officers will receive the change in control benefits described in the agreements only if there is both (1) a Change in Control of our company (as defined in the agreements) and (2) a termination by us of the applicable person’s employment “without cause” or a resignation by the applicable persons for “good reason” (as defined in the agreements) within a specified time period prior to or following the Change in Control. We believe this double trigger requirement creates the potential to maximize stockholder value because it prevents an unintended windfall to management as no benefits are triggered solely in the event of a Change in Control while providing appropriate incentives to act in furtherance of a change in control that may be in the best interests of the stockholders. We believe these severances or change in control benefits are important elements of our compensation program that assist us in retaining talented individuals at the executive and senior managerial levels and that these arrangements help to promote stability and continuity of our executives and senior management team. We also believe that the interests of our stockholders will be best served if the interests of these members of our management are aligned with theirs. Furthermore, we believe that providing change in control benefits lessens or eliminates any potential reluctance of members of our management to pursue potential change in control transactions that may be in the best interests of the stockholders. Finally, we believe that it is important to provide severance benefits to members of our management to promote stability and to focus on the job at hand.
We also provide benefits to the executive officers that are generally available to all regular full-time employees of ours, including our medical and dental insurance, life insurance and a 401(k) match for all individuals who participate in the 401(k) plan. Currently, we do not provide any perquisites to any of our NEOs. Further, we do not have pension arrangements or post-retirement health coverage for our executive officers or employees. We also do not have deferred compensation plans other than allowing (beginning with respect to RSU awards granted at the beginning of 2017) senior executive recipients of RSUs to defer payment of RSUs that may vest in future years, subject to compliance with Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code (or the Code) and related rules.
All of our employees not specifically under contract are “at-will” employees, which mean that their employment can be terminated at any time for any reason by either us or the employee. Our NEOs (as well as certain of our senior managers) have employment agreements that provide lump sum compensation in the event of their termination without cause or, under certain circumstances, upon a Change of Control.
Determination of Compensation Amounts
Many factors impact the determination of compensation amounts for our NEOs, including the individual’s role in our company and individual performance, length of service with us, competition for talent, individual compensation package, assessments of internal pay equity and industry data. Stock price performance has generally not been a significant factor in determining annual compensation because the price of our common stock is subject to a variety of factors outside of our control.
Industry Survey Data
In collaboration with Radford, each year our Compensation Committee establishes a list of peer companies to best ensure that we are compensating our executives on a fair and reasonable basis, as set forth above under the heading “Objectives of our Compensation Program.” We also utilize Radford-prepared data for below-executive level personnel, which data focuses on similarly-sized life science companies in the Southeastern region of the United States. The availability of peer data is used by the Compensation Committee strictly as a guide in determining compensation levels regarding salaries, cash bonuses and annual equity grants to all employees. However, the availability of this data does not imply that the Compensation Committee is under any obligation to exactly follow peer companies in compensation matters.
Determination of Base Salaries
As a guideline for NEO base salary, we perform formal benchmarking against respective comparable positions in our established peer group. Our guideline is to set targeted NEO salary ranges between the 25th and 50th percentile for comparable positions within our peer group. We then adjust salaries based on our assessment of our NEOs’ levels of responsibility, experience, overall compensation structure and individual performance. The Compensation Committee has the discretion if it believes circumstances warrant, to go above the 50th percentile of the peer group. The Compensation Committee is not obliged to raise salaries purely on the availability of data. Merit-based increases to salaries of executive officers are based on our assessment of individual performance and the relationship to applicable salary ranges. Cost of living adjustments may also be a part of that assessment. The Compensation Committee, in recent years, has tended to maintain cash compensation levels at or near the 50th percentile but to exceed that level in determining equity compensation. The emphasis on equity compensation reflects the Committee’s objective, given that we have only recently engaged in revenue generating operations, to incentivize personnel and to preserve cash in a prudent manner and yet reward personnel for outstanding performance.
83
Table of Contents
Performance Cash Bonus Plan
Concurrently with the beginning of each calendar year, preliminary corporate goals that reflect our business priorities for the coming year are prepared by our NEOs with input from other officers. The draft goals are presented to the Compensation Committee and our full board at the beginning of each year and discussed, revised as necessary, and then approved by our board of directors. The Compensation Committee then reviews the final goals to determine and confirm their appropriateness for use as performance measurements for purposes of the bonus program. The goals may be re-visited during the year and potentially restated in the event of significant changes in corporate strategy or the occurrence of significant corporate events. Following the agreement of our board of directors on the corporate objectives, the goals are then shared with all employees in a formal meeting(s), and are reviewed periodically throughout the year at monthly staff meetings and quarterly board of director meetings.
The performance cash bonus plan for our executive officers and employees in 2017 was adopted by the Compensation Committee in February 2017. The plan sets forth target bonus opportunities, as a percentage of salary, based on the level of responsibility of the position, ranging up to 60% of salary for Dr. Sirgo, who served as CEO in 2017, up to 40% of salary for our NEOs and up to 30% of salary for certain other officers. In setting these percentages, the Compensation Committee determined that the above percentages were reasonable and in line with our peer group. Each employee has the opportunity to achieve up to 100% of his targeted amount, depending on how corporate goals and objectives are achieved, with variances on an “employee by employee” basis to be determined by our Compensation Committee in consultation with senior executives and employees’ direct reports.
Determination of Equity Incentive Compensation
To assist us in assessing the reasonableness of our equity grant amounts, historically we have reviewed Radford supplied information and, prior to Radford, we used information supplied by Equilar, Inc. Such information included equity data from a cross-section of the companies in the above-mentioned surveys. Initially, on-hire stock option grant amounts have generally been targeted at the 25th to 50th percentile for that position or similar industry position, adjusted for internal equity, experience level of the individual and the individual’s total mix of compensation and benefits provided in his or her offer package. Initial on-hire grants typically vest over three years.
In granting equity awards in 2015 as well as prior years, the Compensation Committee utilized a methodology that computed the financial value of the equity granted, applying as a general guideline, a peer group percentile ranging from the 50th to the 75th percentile. At that time, however, the Committee made an exception to the general policy by approving special equity awards to five senior executives (including Dr. Sirgo) in recognition of long-standing contributions to achieving strategic objectives first established more than 10 years earlier.
Beginning in January 2016, the Compensation Committee expanded its criteria for equity awards, considering not only the financial value of awards, but also the “burn rate” (meaning the number of shares awarded as a percentage of total outstanding shares). These two criteria (i.e. financial value and burn rate) often result in disparate computations when contrasted to peer group criteria. Accordingly, the Compensation Committee has attempted to equitably balance those two factors to achieve appropriate equity awards.
In early 2017, with respect to equity awards to senior executives, including NEOs, one-half of the RSUs were awarded in the form of time-based RSUs, as have been exclusively awarded to those executives in recent years, and for the first time, one-half of the RSUs were in the form of performance-based RSUs as described above. This same formula was again used in February 2018.
For a discussion of equity awards made in early 2018, see “Equity Awards in February 2018” under “Compensation Decisions For Performance in 2017” below.
Equity Grant Practices
All stock options and/or RSUs granted to the NEOs and other executives are approved by the Compensation Committee. Exercise prices for options are set using a 30-day volume weighted average price method, which we define as the closing price of our common stock on the Nasdaq Capital Market on the trading day of the date of grant and the 30 trading days preceding that date. RSU grants are valued on the day of issuance and are vested (in the case of either time-based or performance-based vesting), if earned on the last day preceding an open trading window after filing our Annual Report on Form 10-K. Grants are generally made: (i) on the employee’s start date and (ii) at board of director meetings held each January or February and following annual performance reviews. However, grants have been made at other times during the year. The size of year-end grants for each NEO is assessed against our
84
Table of Contents
internal equity guidelines. Current market conditions for grants for comparable positions and internal equity may also be assessed. Also, grants may be made relating to promotions or job- related changes in responsibilities. In addition, on occasion, the Compensation Committee may make special awards for extraordinary individual or our company performance and, as was the case in early 2015, of achievement over an extended period of time.
Compensation Setting Process
At the first of the year, meetings of our board of directors and the Compensation Committee, overall corporate performance and relative achievement of the corporate goals for the prior year are assessed. The relative achievement of each goal is assessed and the summation of the individual components results in an overall corporate goal rating, expressed as a percentage. The Compensation Committee then approves the final disbursement of salary increases, cash bonuses and option or RSU grants, giving an 80% weight factor to the corporate goal rating, and a 20% weight factor for such other performance criteria the Committee may in its discretion deem relevant at the time of the granting awards.
Also near the end of the year, the CEO evaluates the individual performance of each NEO (other than himself) and provides the Compensation Committee with an assessment of the performance of such NEO. In determining the individual performance ratings of the NEOs, we assess performance against many factors, including each NEO’s relative contributions to our corporate goals, demonstrated career growth, level of performance in the face of available resources and other challenges, and the respective officer’s department’s overall performance. This assessment is conducted in a holistic fashion, in contrast to the summation of individual components as is done to arrive at the corporate goal rating.
Following a qualitative assessment of each individual NEO’s performance, our policies provide guidelines for translating this performance assessment into a numerical rating. Both the initial qualitative assessment and the translation into a numerical rating are made by the Compensation Committee on a discretionary basis. We believe that conducting a discretionary assessment for the individual component of the NEOs’ performance provides for flexibility in the evaluation of our NEOs and their adaptability to addressing potential changes in our priorities throughout the year.
The Compensation Committee looks to the CEO’s performance assessments of the other NEOs and his recommendations regarding a performance rating for each, as well as input from the other members of our board of directors. These recommendations may be adjusted by the Compensation Committee prior to finalization. For the CEO, the Compensation Committee evaluates his performance, taking into consideration input from the other members of our board of directors, and considers the achievement of overall corporate objectives by both the CEO specifically and our company generally. The CEO is not present during the Compensation Committee’s deliberations regarding his compensation.
The CEO may also present any recommended changes to base salary and recommendations for annual equity grant amounts for NEOs and other senior executives.
The Compensation Committee has the authority to directly engage, at our expense, any compensation consultants or other advisors (such as Radford) that it deems necessary to determine the amount and form of employee, executive and director compensation. In determining the amount and form of employee, executive and director compensation, the Compensation Committee has reviewed and discussed historical salary information as well as salaries for similar positions at comparable companies. However, the availability of this data does not imply that the Compensation Committee is under any obligation to exactly follow peer companies’ compensation practices.
We paid consultant fees to Radford of $0.04 million in 2017. NEOs may have indirect input in the compensation results for other executive officers by virtue of their participation in the performance review and feedback process for the other executive officers.
Compensation Decisions for Performance in 2017
General Assessment of Management Performance in 2017
The Compensation Committee and our board of directors conducted the performance and compensation review for 2017 in February 2018. The Compensation Committee compared performance as elaborated below.
The corporate objectives for 2017 included the following: (1) for BELBUCA®; to complete the transition of sales, marketing and certain production functions from our former licensee, Endo Pharmaceuticals, to us and to achieve targeted sales revenue; to enter into additional pharmacy benefit management (or PBM) and other payer agreements and to enhance formulary positions; and to enter
85
Table of Contents
into out-licenses agreements in foreign regions; (2) for BUNAVAIL®, to add an additional FDA-approved dosage, to achieve targeted sales revenue, to reduce cost of goods and improve production and inventory efficiencies; and to enter into out-license agreements in foreign regions; and (3) specified objectives in the areas of finance, continued success in ongoing and prospective litigation with respect to our intellectual property and patent portfolio, and the further development of new product candidates and/or the in-licensing of products to complement our existing products.
With respect to BELBUCA®, the transition of commercial functions from Endo to us was smoothly executed and sales goals for 2017 were achieved. There were several notable achievements in 2017 by the addition of new PBM and other payer agreements in a markedly difficult market that favors entrenched legacy products. Regarding out-licensing in foreign regions, we entered into an agreement for Canada but were not successful in any other region during 2017.
With respect to BUNAVAIL®, results for 2017 were generally disappointing. Sales objectives were not met and we decided not to pursue an additional dosage. We did achieve stated goals in reducing cost of goods and in significantly improving production and inventory efficiencies. We were not successful in entering into any out-licensing agreements in foreign regions during 2017.
We successfully executed a new loan agreement for the financing of our operations for the year and into 2018. We continued our success in the areas of intellectual property litigation. We were not able, however, to augment our product line by in-licensing or to further the development of new products.
2017 Cash Bonus Calculations
After reviewing the achievement of the corporate goals and objectives for 2017 as noted above, the Compensation Committee determined that all NEOs should be awarded a cash bonus at 70% of their target. A cash bonus pool, equal to 70% of the aggregate of individual bonus opportunities of all other employees, plus $72,500, was established with our executives having the authority to award individual bonuses from that pool with respect to these employees who reported to them. The cost of all such cash bonuses for 2017 performance (but paid in March 2018) was approximately $0.4 million for NEOs and approximately $0.7 million for employees.
Equity Awards in February 2018
In making annual equity awards in February, 2018, the Compensation Committee continued, with respect to senior executives including our NEOs, a policy first initiated in the prior year, specifically the inclusion of a meaningful element of performance benchmarks to is equity awards. Consequently, equity awards to these executives in February, 2018, are in the form of RSUs, one-half of which are time-based and one-half of which are performance-based, all of which vest over a three-year period beginning in the first year after the date of grant. The performance-based RSUs provide for vesting if specified net revenue and operating income goals are achieved with respect to the three annual fiscal years beginning with the year in which an award was made.
At the beginning of 2018, the total amount of the RSUs awarded to our NEOs and senior executives for 2017 performance (after adjusting pursuant to applicable retirement agreements) was 870,306 RSUs having an approximate value on the date preceding the grant of $1.8 million based on a share price of $2.10.
All other employees of ours (excluding only certain recently-hired persons) were granted stock options priced at the 30-day volume weighted average price of our common stock as of the close the market on February 16, 2018. All options vest annually in one-third equal increments beginning one year after the date of grant. The total amount of options awarded was 400,000 having an approximate Black Scholes value of $0.5 million.
All RSUs and stock options awarded in February, 2018 were granted pursuant to the Plan, as amended.
Individual Performance and Compensation of Dr. Sirgo, our President and CEO During 2017
Dr. Sirgo’s base salary in 2017 was $590,000 per year, an increase of $40,000 per year from his base salary in both 2016 and 2015. Those salary levels were approximately at the 50% percentile of our peer group and therefore consistent with our compensation philosophy.
Dr. Sirgo was awarded a cash bonus for 2017 in the amount of $247,800, which is 70% of his target bonus of 60% of his base salary in 2017, a calculation consistent with our cash bonus policy as well as Dr. Sirgo’s retirement agreement.
Dr. Sirgo was also granted for 2017 a “gross” award of 360,000 RSUs, which Dr. Sirgo has deferred and the board of directors has approved the deferral of this grant until March 15, 2018. The RSU grant will be adjusted to a “net” amount of RSUs in accordance with the terms of the Sirgo Retirement Agreement (see below) of which will vest immediately into shares of our common stock.
86
Table of Contents
The Compensation Committee award of equity compensation to Dr. Sirgo for 2017 is primarily a reflection of his leadership of the transition from Endo Pharmaceuticals to our company of the commercialization of BELBUCA® and the attainment of revenue, manufacturing and supply objectives. In addition, under Dr. Sirgo’s management, we continued to have success in ongoing litigation with respect to our intellectual property and patent portfolio and we successfully negotiated a loan agreement providing sufficient financing for our operations throughout the year. Offsetting factors were disappointing revenue results with respect to BUNAVAIL®, the failure to develop and/or in-license complementary products and somewhat mixed results with respect to entering into additional payer and pharmacy benefit manager agreements.
Individual Performance and Compensation of the Chief Financial Officer
Mr. De Paolantonio’s base salary in 2017 of $350,000 was slightly above the 25th percentile of our peer group and therefore was consistent with our compensation philosophy. His salary for 2018 was increased to $360,000 per year, which is at the 50th percentile and therefore remains consistent with our compensation philosophy.
Mr. De Paolantonio was also granted 140,000 RSUs for 2017 performance, half of which are subject to time-based vesting and half of which are subject to performance-based vesting.
Mr. De Paolantonio continues to effectively guide the financial functions of our company, maintaining the full confidence of our board of directors and its Audit Committee. He has successfully transitioned the accounting and budget functions of our company from a predominately research and development enterprise to one with complex manufacturing, inventory, valuation, cost of goods analysis and revenue recognition issues. Mr. De Paolantonio continues to maintain a proper and harmonious relationship with our independent auditors.
Individual Performance and Compensation of the Senior Vice President and Chief Technology Officer
Dr. Vasisht’s base salary in 2017 of $330,000 was below the 50% percentile of our peer group and therefore is consistent with our compensation philosophy.
Dr. Vasisht was also granted for 2017 a “gross” award of 250,000 RSUs, which has been adjusted to a “net” amount of 198,129 RSUs in accordance with the terms of the Vasisht Retirement Agreement (see below) and which accordingly vested immediately into shares of our common stock.
Dr. Vasisht, first joined our company in 2005, and first became a NEO in 2016. He has been instrumental in the development of BELBUCA®, BUNAVAIL® and ONSOLIS®, in the supervision of our research and development activities, including our analysis of new drug opportunities, and he has played a significant role in the protection of our intellectual property.
Appointment of President
On December 20, 2017, our company appointed Scott M. Plesha, previously our company’s Senior Vice President of Sales and Marketing, to the role of President, effective January 2, 2018. Besides Mr. Plesha’s new responsibilities as President, he will continue to directly oversee the Sales and Marketing functions of our company.
In approving the appointment, our board of directors determined and approved that the person fulfilling the role of President should be a NEO of our company and, as a result, Mr. Plesha became a NEO effective January 2, 2018.
Mr. Plesha and our company are parties to a Letter of Employment, dated December 20, 2017, (which we refer to as the Plesha Letter of Employment) which is subject to successive, automatic one-year extensions unless either party gives notice of non-extension to the other party at least 30 days prior to the end of the applicable term. The Plesha Letter of Employment includes a base salary (which was subject to modification with the approval of the Compensation Committee and is set at three hundred sixty-five thousand dollars ($365,000) for 2018), a target bonus equal to a percentage of his base salary (also subject to modification with the approval of the Compensation Committee and is now set at forty-five percent (45%)), and other employee benefits.
Mr. Plesha was also granted 125,000 RSUs for 2017 performance, half of which are subject to time-based vesting and half of which are subject to performance-based vesting.
87
Table of Contents
We may terminate the Plesha Letter of Employment without cause and Mr. Plesha may resign upon 30 days advance written notice. We may immediately terminate the Plesha Letter of Employment for Cause (as defined in the Plesha Letter of Employment). Upon the termination of Mr. Plesha’s employment for any reason, Mr. Plesha will continue to receive payment of any base salary earned but unpaid through the date of termination and any other payment or benefit to which he is entitled under the applicable terms of any applicable company arrangements. If Mr. Plesha is terminated during the term of the Plesha Letter of Employment other than for Cause, Mr. Plesha is entitled to a lump sum severance payment equal to his full year’s base salary and a pro-rata bonus based on his bonus target; otherwise, Mr. Plesha will be entitled to a one-time cash severance payment equal 50% of his full year’s base salary. In the event that such termination is within six (6) months following a Change of Control (as defined in the Plesha Letter of Employment), the lump sum paid to Mr. Plesha will equal a one-time cash severance payment equal to the amount of his then current annual base salary.
In addition, the Plesha Letter of Employment will terminate prior to its scheduled expiration date in the event of Mr. Plesha’s death or disability. The Plesha Letter of Employment also includes a two-year non-competition and non-solicitation and confidentiality covenants on terms identical to Mr. Plesha’s existing employment arrangement with our company. Under the terms of the Plesha Letter of Employment, Mr. Plesha is also entitled to the following benefits: health insurance, dental insurance, basic life & accidental death & dismemberment insurance, long and short-term disability insurance, 401(k) Plan with employer match, and an employee stock options plan.
Sirgo Retirement Agreement
On August 23, 2017, Dr. Sirgo, our former President and Chief Executive Officer and current Vice Chairman, executed a retirement agreement (which we refer to as the Sirgo Retirement Agreement) memorializing the terms of Dr. Sirgo’s voluntary retirement from our company, which was effective January 2, 2018 (which we refer to as the Sirgo Retirement Date, with the period from August 23, 2017 to the Sirgo Retirement Date being referred to herein as the Sirgo Transition Period). During the Sirgo Transition Period and following the Sirgo Retirement Date, Dr. Sirgo served and will continue to serve as Vice Chairman of our board of directors.
Pursuant to the Sirgo Retirement Agreement, Dr. Sirgo served as our President and Chief Executive Officer during the Sirgo Transition Period. By entering into the Sirgo Retirement Agreement, we and Dr. Sirgo agreed to terminate Dr. Sirgo’s employment agreement with us, dated August 24, 2004, as amended by that First Amendment thereto (collectively with the related confidentiality agreement between our company and Sirgo, the Sirgo Employment Agreement) as of the Sirgo Retirement Date, subject to those provisions of the Sirgo Employment Agreement which survive termination (as the same were modified by the Sirgo Retirement Agreement), including provisions related to confidentiality, non-solicitation and non-competition.
In connection with his retirement from our company, and in consideration of his many years of service to our company (and in lieu of any similar benefits provided for in the Sirgo Employment Agreement), Dr. Sirgo has received or will receive the following benefits pursuant to the Sirgo Retirement Agreement:
| (i) | a cash payment of $0.8 million (less applicable withholdings) which was paid in September 2017; and |
| (ii) | an additional cash payment equal to $0.8 million (less applicable withholdings) which was paid in January 2018. |
In addition, pursuant to the Sirgo Retirement Agreement:
| (i) | as of the Sirgo Retirement Date, all previously vested options held by Sirgo to purchase shares of Common Stock will continue for the life of such options (as opposed to such options terminating on the 90 th day following the Sirgo Retirement Date, as provided for in the Plan; |
| (ii) | Dr. Sirgo will be entitled to receive his ordinary year end equity bonus award (in the form of RSUs) for his service as an officer during 2017, as determined by the Compensation Committee of the Board (or the Sirgo 2017 Equity Award); provided, however, that (A) with respect to RSUs which by their terms would vest with the passage of time (or Time Vesting RSUs), Dr. Sirgo shall receive a number of shares of Common Stock equal to (1) the Net Present Value (as defined in the Sirgo Retirement Agreement) of the Time Vesting RSUs that would have been issued to Dr. Sirgo for the Sirgo 2017 Equity Award had he not retired divided by (2) the 30-day volume weighted average price of the Common Stock (or the 30-day VWAP) as of the date of issuance of the Sirgo 2017 Equity Bonus; and (B) with respect to RSUs which by their terms would vest based on future performance (or Performance Vesting RSUs), Dr. Sirgo shall receive a number of shares of Common Stock determined by multiplying the number of Performance Vesting RSUs that would have been issued to Dr. Sirgo for the Sirgo 2017 Equity Award had he not retired by 0.66; |
88
Table of Contents
| (iii) | as of the Sirgo Retirement Date, all previously granted Time Vesting RSUs issued to Dr. Sirgo pursuant to the Plan that are unvested as of the Sirgo Retirement Date shall terminate and, in lieu thereof, Dr. Sirgo shall receive a one-time issuance of fully vested shares of Common Stock under the Plan, the number of which will be determined with reference to the Time Vesting RSUs being terminated by dividing (A) the Net Present Value of such Time Vesting RSUs by (B) the 30-day VWAP as of the Sirgo Retirement Date, which resulted in the issuance of 795,730 shares that were issued to Dr. Sirgo in January 2018, and all previously granted RSUs issued to Sirgo pursuant to the Plan which vest due to achievement of future performance milestones that are unvested as of the Sirgo Retirement Date shall terminate and, in lieu thereof, Dr. Sirgo shall receive a one-time issuance of 250,000 fully vested shares of Common Stock under the Plan, which were issued to Sirgo in January 2018; and |
| (iv) | Dr. Sirgo will continue to be entitled to receive (if applicable) one hundred percent (100%) of his regular award of vested Common Stock (or the LTIP Stock) under the LTIP, with the amount of such LTIP Stock to be determined and issued in accordance with the terms and provisions of the LTIP. The issuance of the LTIP Stock to Dr. Sirgo as provided for above shall occur, if applicable, concurrently with the issuance of LTIP Stock to our company’s officers, but no later than March 15, 2018. Should Dr. Sirgo voluntarily resign from the Board, in each case prior to payment of any amount of LTIP Stock, Dr. Sirgo’s right to receive LTIP Stock from and after that time shall terminate. In the event a Change in Control (as defined in the Sirgo Retirement Agreement) occurs on or within twelve (12) months following the Retirement Date with a company with whom Dr. Sirgo had contact about a potential transaction in his capacity as an employee of our company prior to the Sirgo Retirement Date, then we shall issue to Dr. Sirgo, as an additional retirement benefit, fully vested shares of Common Stock in an amount equal to the number of shares Dr. Sirgo would have received pursuant to the LTIP had he remained employed with us through the Change in Control. |
For purposes of the Sirgo Retirement Agreement, the term “Change of Control” means the occurrence of any one or more of the following events (it being agreed that, with respect to paragraphs (i) and (iii) of this definition below, a “Change of Control” shall not be deemed to have occurred if the applicable third party acquiring party is an “affiliate” of the Company within the meaning of Rule 405 promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended):
| (i) | an acquisition (whether directly from the Company or otherwise) of any voting securities of the Company (or the Voting Securities) by any “Person” (as the term person is used for purposes of Section 13(d) or 14(d) of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (or the 1934 Act)), immediately after which such Person has “Beneficial Ownership” (within the meaning of Rule 13d-3 promulgated under the 1934 Act) of forty percent (40%) or more of the combined voting power of the Company’s then outstanding Voting Securities. |
| (ii) | (ii) the individuals who, as of the date hereof, are members of our board of directors cease, by reason of a financing, merger, combination, acquisition, takeover or other non-ordinary course transaction affecting our company, to constitute at least fifty-one percent (51%) of the members of our board of directors; or |
| (iii) | (iii) approval by our board of directors and, if required, our stockholders, or execution by us of any definitive agreement with respect to, or the consummation of (it being understood that the mere execution of a term sheet, memorandum of understanding or other non-binding document shall not constitute a Change of Control): |
(A) a merger, consolidation or reorganization involving our company, where either or both of the events described in clauses (i) or (ii) above would be the result;
(B) a liquidation or dissolution of or appointment of a receiver, rehabilitator, conservator or similar person for, or the filing by a third party of an involuntary bankruptcy against, our company; or
(C) an agreement for the sale or other disposition of all or substantially all of the assets of the Company to any Person (other than a transfer to a subsidiary of our company).”
The Sirgo Retirement Agreement also contains other customary provisions, including provisions for Dr. Sirgo’s continuing participation in certain company employee benefit plans, mutual releases of claims by us and Dr. Sirgo (subject to certain exceptions) and a covenant of cooperation.
89
Table of Contents
Vasisht Retirement Agreement
On January 12, 2018, Niraj Vasisht, our former Senior Vice President and Chief Technology Officer, executed a Retirement Agreement (which we refer to as the Vasisht Retirement Agreement) memorializing the terms of Dr. Vasisht’s voluntary retirement from our company, which was effective February 4, 2018 (which we refer to as the Vasisht Retirement Date, with the period from January 12, 2018, to the Vasisht Retirement Date being referred to herein as the Vasisht Transition Period).
Pursuant to the Vasisht Retirement Agreement, Dr. Vasisht continued to serve as our Senior Vice President and Chief Technology Officer during the Vasisht Transition Period. By entering into the Vasisht Retirement Agreement, we and Dr. Vasisht agreed to terminate Vasisht’s employment agreement with us, dated October 8, 2008 (collectively with the related confidentiality agreement between the Company and Vasisht, the Vasisht Employment Agreement) as of the Vasisht Retirement Date, subject to those provisions of the Vasisht Employment Agreement which survive termination (as the same were modified by the Vasisht Retirement Agreement), including provisions related to confidentiality, non-solicitation and non-competition.
In connection with his retirement from our company, and in consideration of his service to our company (and in lieu of any similar benefits provided for in the Vasisht Employment Agreement), Dr. Vasisht received or will receive the following benefits pursuant to the Vasisht Retirement Agreement:
| (i) | a cash separation payment of $0.33 million (less applicable withholdings), in two equal payments of $0.165 million each: the first payment paid January 19, 2018, the second payment to be paid on April 1, 2018; |
| (ii) | an additional cash payment equal to $0.02 million (less applicable withholdings) paid on January 19, 2018, in consideration for a previously deferred raise in Dr. Vasisht’s base salary; |
| (iii) | if a Change of Control (as defined in the Vasisht Employment Agreement) occurs before July 1, 2018, Dr. Vasisht will be entitled to the cash payments provided for in Paragraph 4(d) of the Vasisht Employment Agreement (namely, a cash payment equal to: (A) Dr. Vasisht’s annual base salary plus an amount equal to fifty percent (50%) of his such salary multiplied by (B) 1.5), but less the separation payments made under the Vasisht Retirement Agreement; and |
| (iv) | for a period of 12 months from the Vasisht Retirement Date, Dr. Vasisht will serve as a consultant to our company as requested from time to time during such period with respect to our research and development operations at the rate of $200 per hour. |
In addition, pursuant to the Vasisht Retirement Agreement:
| (i) | as of the Vasisht Retirement Date, all previously vested options held by Dr. Vasisht to purchase shares of Common Stock will continue for the life of such options (as opposed to such options terminating on the 90th day following the Vasisht Retirement Date, as provided for in the Plan; |
| (ii) | Vasisht will be entitled to receive his ordinary year end equity bonus award (in the form of RSUs) for his service as an officer of the Company during 2017, as determined by the Compensation Committee (or the Vasisht 2017 Equity Award); provided, however, that (A) with respect to Time Vesting RSUs, Dr. Vasisht shall receive a number of shares of Common Stock equal to (1) the Net Present Value (as defined in the Vasisht Retirement Agreement) of the Time Vesting RSUs that would have been issued to Dr. Vasisht for the Vasisht 2017 Equity Award had he not retired divided by (2) the 30-day VWAP as of the date of issuance of the Vasisht 2017 Equity Bonus; and (B) with respect to Performance Vesting RSUs, Vasisht shall receive a number of shares of Common Stock determined by multiplying the number of Performance Vesting RSUs that would have been issued to Dr. Vasisht for the 2017 Equity Award had he not retired by 0.66, which calculation resulted in a net issuance of 198,129 shares of Common Stock, which were issued to Dr. Vasisht February 2018; |
| (iii) | Dr. Vasisht shall receive one hundred percent (100%) of his regular award of vested LTIP Stock under the LTIP, with the amount of such LTIP Stock to be determined and issued in accordance with the terms and provisions of the LTIP, in consideration for his work in 2017, and Dr. Vasisht shall also be considered for a bonus in consideration for his work in 2017 in accordance with the normal procedures and conditions for award of a bonus; and |
90
Table of Contents
| (iv) | as of the Vasisht Retirement Date, all previously granted Time Vesting RSUs issued to Dr. Vasisht pursuant to the Plan that are unvested as of the Vasisht Retirement Date shall terminate and, in lieu thereof, Vasisht shall receive a one-time issuance of fully vested shares of Common Stock under the Plan, the number of which will be determined with reference to the Time Vesting RSUs being terminated by dividing (A) the Net Present Value of such Time Vesting RSUs by (B) the 30-day VWAP as of the Vasisht Retirement Date which resulted in the issuance of 309,162 shares that were issued to Dr. Vasisht in February 2018 All previously granted Performance Vesting RSUs that are unvested as of the Vasisht Retirement Date will continue to vest until December 31, 2018, at which time 60% of the unvested Performance RSUs shall vest and 40% of the unvested Performance RSUs shall be deemed forfeited. |
The Vasisht Retirement Agreement also contains other customary provisions, including provisions for Dr. Vasisht’s continuing participation in certain company benefit plans, mutual releases of claims by us and Dr. Vasisht (subject to certain exceptions) and a non-disparagement covenant.
Accounting and Tax Considerations
ASC 718. On January 1, 2006, we began accounting for share-based payments in accordance with the requirements of Accounting Standards Codification 718 (ASC 718), Share-Based Payments. To date, the adoption of ASC 718 has not impacted our stock option granting practices.
Internal Revenue Code Section 162(m). Beginning with our fiscal year ending December 31, 2014, we began to consider the limitations on the deductibility of base salary or bonus amounts as required under Section 162(m) of the Code as the aggregate salary and bonus payments for certain of our NEOS were above the $1,000,000 deductibility limitation. These limitations did not, however, impact the Compensation Committee’s compensation analysis in 2017.
Section 409A. Section 409A of the Code generally changed the tax rules that affect most forms of deferred compensation that were not earned and vested prior to 2005. Under Section 409A, deferred compensation is defined broadly and may potentially cover compensation arrangements such as severance or change in control pay outs and the extension of the post-termination exercise periods of stock options. We take Code Section 409A into account, where applicable, in determining the timing of compensation paid to our executive officers.
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation. |
The following table sets forth all compensation paid to our named executive officers at the end of the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015. Individuals we refer to as our “named executive officers” include our Vice Chairman (formerly served as our Chief Executive Officer) and our most highly compensated executive officers whose salary and bonus for services rendered in all capacities exceeded $100,000 during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017.
| Name and principal position |
Year | Salary ($) |
Bonus ($) |
Stock Awards ($) (24) |
Option Awards ($) |
Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation ($) |
Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Earnings ($) |
All Other Compensation ($) |
Total ($) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mark A. Sirgo, |
|
2017 2016 2015 |
|
|
590,000 571,154 550,000 |
|
|
264,000 165,000 143,700 |
(2)
|
|
703,802 1,072,804 11,770,904 |
(3) (5) (7) |
|
— — — |
|
|
— — — |
|
|
— — — |
|
|
847,714 21,323 21,323 |
(4) (6) (8) |
|
2,405,516 1,828,443 12,485,927 |
| |||||||||
| Ernest R. De Paolantonio, |
|
2017 2016 2015 |
|
|
350,000 363,461 350,000 |
|
|
112,000 61,250 52,500 |
(9)
|
|
176,688 345,544 1,509,450 |
(10) (12) (14) |
|
— — — |
|
|
— — — |
|
|
— — — |
|
|
32,632 33,269 34,704 |
(11) (13) (15) |
|
671,320 803,524 1,946,654 |
| |||||||||
| Niraj Vasisht, Ph.D. |
|
2017 2016 2015 |
|
|
310,000 321,923 310,000 |
|
|
99,200 62,000 57,490 |
(16)
|
|
303,573 570,000 2,945,624 |
(17) (19) (21) |
|
— — — |
|
|
— — — |
|
|
— — — |
|
|
32,508 32,435 33,633 |
(18) (20) (22) |
|
745,281 3,346,657 3,346,657 |
| |||||||||
91
Table of Contents
| (1) | Mark A. Sirgo served as our President, Chief Executive Officer, Director and Vice Chairman until his retirement date of January 2, 2018. Upon retirement, Dr. Sirgo now serves as a Director and Vice Chairman. |
| (2) | The bonus disclosed in this item of $264,000 relates to 2016, but was contingent upon board approval, which occurred March 2017. |
| (3) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of 375,000 unvested executive RSU grants during 2017 with a fair market value (“FMV”) of $1.85, which will vest in equal amounts over three years and 5,026 vested RSUs with a FMV of $2.00 as issued from the LTIP. Pursuant to Dr. Sirgo’s retirement agreement, on January 2, 2018 all unvested time-vesting RSUs terminated and Dr. Sirgo received a one-time issuance of RSUs subject to VWAP calculations. (See Compensation Discussion and Analysis for details on Dr. Sirgo’s retirement agreement.) |
| (4) | Includes: $787,000, gross, retirement payment (See Compensation Discussion and Analysis for detail on Dr. Sirgo’s retirement agreement), $40,000 of legal expenses paid in connection with execution of retirement agreement, $7,214 of health insurance premiums paid and 401(k) matching of $13,500 paid in 2017. |
| (5) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of 275,000 unvested executive RSU grants during 2016 with a FMV of $3.80, which will vest in equal amounts over three years and 15,888 unvested RSUs with a FMV of $1.75 from the LTIP which were earned in 2016 but deferred until 2017. |
| (6) | Includes: $6,235 of health insurance premiums paid and 401(k) matching of $13,250 paid in 2016. |
| (7) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of 800,000 unvested executive RSU grants during 2015 with a FMV of $14.63, which will vest in equal amounts over three years, and 8,189 vested RSUs FMV of $8.17 as issued during 2015 from the LTIP. |
| (8) | Includes: $8,073 of health insurance premiums paid and 401(k) matching of $13,250 paid in 2015. |
| (9) | The bonus disclosed in this item of $112,000 relates to 2016, but was contingent upon board approval, which occurred March 2017. |
| (10) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of 95,000 unvested executive RSU grants during 2017 with a FMV of $1.85, which will vest in equal amounts over three years and 469 vested RSUs with a FMV of $2.00 as issued from the LTIP. |
| (11) | Includes: $19,132 of health insurance premiums paid and 401(k) matching of $13,500 paid in 2017. |
| (12) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of 90,000 unvested executive RSU grants during 2016 with a FMV of $3.80, which will vest in equal amounts over three years and 1,483 vested RSUs with a FMV of $2.39 as issued during 2016 from the LTIP. |
| (13) | Includes: $20,019 of health insurance premiums paid and 401(k) matching of $13,250 paid in 2016. |
| (14) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of 103,175 unvested executive RSU grants during 2015 with a FMV of $14.63, which will vest in equal amounts over three years. |
| (15) | Includes: $21,454 of health insurance premiums paid and 401(k) matching of $13,250 paid in 2015. |
| (16) | The bonus disclosed in this item of $99,200 relates to 2016, but was contingent upon board approval, which occurred March 2017. |
| (17) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of 162,500 unvested executive RSU grants during 2017 with a FMV of $1.85, which will vest in equal amounts over three years and 1,474 vested RSUs with a FMV of $2.00 as issued from the LTIP. Pursuant to Dr. Vasisht’s retirement agreement, on February 4, 2018 all unvested time-vesting RSUs terminated and Dr. Vasisht received a one-time issuance of RSUs subject to VWAP calculations. (See Compensation Discussion and Analysis for details on Dr. Vasisht’s retirement agreement.) |
| (18) | The bonus disclosed in this item of $62,000 relates to 2015, but was contingent upon board approval, which occurred January 2016. |
| (19) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of 150,000 unvested executive RSU grants during 2016 with a FMV of $3.80, which will vest in equal amounts over three years, and 4,661 vested RSUs FMV of $2.39 as issued during 2016 from the LTIP. |
| (20) | Includes: $19,185 of health insurance premiums paid and 401(k) matching of $13,250 paid in 2016. |
| (21) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of 200,000 unvested executive RSU grants during 2015 with a FMV of $14.63, which will vest in equal amounts over three years, and 2,402 vested RSUs with a FMV of $8.17 as issued during 2015 from the LTIP. |
| (22) | Includes: $20,383 of health insurance premiums paid and 401(k) matching of $13,250 paid in 2015. |
| (23) | Niraj Vasisht served as our Senior Vice President and Chief Technology Officer until his retirement date of February 5, 2018. |
| (24) | The reported amounts represent the aggregate grant date fair value of the awards computed in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board Account Standards Codification Topic 718, Stock Compensation, as modified or supplemented, or FASB ASC Topic 718. |
Narrative Disclosure to Summary Compensation Table
Employment Agreements
Except as set forth below, we currently have no written employment agreements with any of our officers, directors, or key employees. All directors and officers have executed confidentiality and noncompetition agreements with us.
92
Table of Contents
The following is a description of our current executive employment agreements:
Mark A. Sirgo, Pharm.D., Vice Chairman, former President and Chief Executive Officer - Dr. Sirgo’s prior employment agreement, dated February 22, 2007, as amended, was subject to successive, automatic one-year extensions unless either party provided notice of non-extension to the other party of at least 30 days prior to the end of the applicable term. The agreement included a base salary, target bonus of up to 50% of his base salary (which was subject to modification with the approval of our Compensation Committee and is now 60%), and other employee benefits. Under the terms of his agreement, Dr. Sirgo received base salary in 2017 of $590,000 per year and a bonus of $264,000, which related to 2016 performance.
Dr. Sirgo’s employment agreement also included a 2-year non-competition and non-solicitation and confidentiality covenants on terms identical to the existing employment agreement. Under the terms of this agreement, he was also entitled to the following benefits: medical, dental and disability and 401(k).
On August 23, 2017, Dr. Sirgo executed a retirement agreement memorializing the terms of his voluntary retirement from our company, which was effective January 2, 2018. Pursuant to the retirement agreement, we and Dr. Sirgo agreed to terminate Dr. Sirgo’s employment agreement with us (collectively with the related confidentiality agreement between us and Dr. Sirgo) as of the retirement date, subject to those provisions of the employment agreement which survive termination (as the same were modified by the retirement agreement), including provisions related to confidentiality, non-solicitation and non-competition. (See Compensation Discussion and Analysis for details on Dr. Sirgo’s retirement agreement.)
Ernest R. De Paolantonio, CPA, MBA, Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and Treasurer - Mr. De Paolantonio’s current employment agreement, dated October 1, 2013 includes a base salary of $300,000, target bonus of up to 40% of his base salary (which is subject to modification by our Compensation Committee), and other employee benefits. Under the terms of his agreement, Mr. De Paolantonio received base salary in 2017 of $350,000 per year and a bonus of $112,000, which bonus was related to 2016 performance.
We may terminate Mr. De Paolantonio’s employment agreement without cause and Mr. De Paolantonio may resign without notice. We may immediately terminate Mr. De Paolantonio’s employment agreement for Good Cause (as defined in the agreement). Upon the termination of Mr. De Paolantonio’s employment for any reason, Mr. De Paolantonio will continue to receive payment of any base salary earned but unpaid through the date of termination and any other payment or benefit to which he is entitled under the applicable terms of any applicable company arrangements. If Mr. De Paolantonio is terminated during the term of the employment agreement other than for Good Cause (as defined in the employment agreement), or if Mr. De Paolantonio terminates his employment for Good Reason (as defined in the employment agreement), Mr. De Paolantonio is entitled to a lump sum severance payment equal to 1 times the sum of his annual base salary. In the event that such termination is within six months following a Change of Control (as defined in the employment agreement), the lump sum paid to Mr. De Paolantonio will equal to 1 times the sum of his then current annual base salary. In addition, Mr. De Paolantonio’s employment agreement will terminate prior to its scheduled expiration date in the event of Mr. De Paolantonio’s death or disability.
Mr. De Paolantonio’s employment agreement also included a 2-year non-competition and non-solicitation and confidentiality covenants on terms identical to the existing employment agreement. Under the terms of this agreement, he was also entitled to the following benefits: medical, dental and disability and 401(k).
Niraj Vasisht, Ph.D., Former Senior Vice President and Chief Technology Officer - Dr. Vasisht’s prior employment agreement, dated October 1, 2008, as amended, was subject to successive, automatic one-year extensions unless either party provided notice of non-extension to the other party at least 30 days prior to the end of the applicable term. The agreement included a base salary, target bonus of up to 40% of his base salary (which was subject to modification with the approval of our Compensation Committee and is now 50%), and other employee benefits. Under the terms of his agreement, Dr. Vasisht received base salary in 2017 of $310,000 per year and a bonus of $99,200, which related to 2016 performance.
Dr. Vasisht’s employment agreement also included a 2-year non-competition and non-solicitation and confidentiality covenants on terms identical to the existing employment agreement. Under the terms of this agreement, he was also entitled to the following benefits: medical, dental and disability and 401(k).
On January 12, 2018, Dr. Vasisht executed a retirement agreement memorializing the terms of his voluntary retirement from our company, which was effective February 4, 2018. Pursuant to the retirement agreement, we and Dr. Vasisht agreed to terminate Dr. Vasisht’s employment agreement with us (collectively with the related confidentiality agreement between us and Dr. Vasisht) as of the retirement date, subject to those provisions of the employment agreement which survive termination (as the same were modified by the retirement agreement), including provisions related to confidentiality, non-solicitation and non-competition. (See Compensation Discussion and Analysis for details on Dr. Vasisht’s retirement agreement.)
Scott M. Plesha, President - Mr. Plesha was promoted to the role as our President and his current employment agreement, dated December 20, 2017 includes a base salary of $365,000, target bonus of up to 45% of his base salary (which is subject to modification by our Compensation Committee), and other employee benefits.
93
Table of Contents
We may terminate Mr. Plesha’s employment agreement without cause and Mr. Plesha may resign without notice. We may immediately terminate Mr. Plesha’s employment agreement for Good Cause (as defined in the agreement). Upon the termination of Mr. Plesha’s employment for any reason, Mr. Plesha will continue to receive payment of any base salary earned but unpaid through the date of termination and any other payment or benefit to which he is entitled under the applicable terms of any applicable company arrangements. If Mr. Plesha is terminated during the term of the employment agreement other than for Good Cause (as defined in the employment agreement), or if Mr. Plesha terminates his employment for Good Reason (as defined in the employment agreement), Mr. Plesha is entitled to a lump sum severance payment equal to 1 times the sum of his annual base salary. In the event that such termination is within six months following a Change of Control (as defined in the employment agreement), the lump sum paid to Mr. Plesha will equal to 1 times the sum of his then current annual base salary. In addition, Mr. Plesha’s employment agreement will terminate prior to its scheduled expiration date in the event of Mr. Plesha’s death or disability.
Mr. Plesha’s employment agreement also included a 2-year non-competition and non-solicitation and confidentiality covenants on terms identical to the existing employment agreement. Under the terms of this agreement, he was also entitled to the following benefits: medical, dental and disability and 401(k).
Outstanding equity awards
The following table summarizes outstanding unexercised options, unvested stocks and equity incentive plan awards held by each of our name executive officers, as of December 31, 2017.
OUTSTANDING EQUITY AWARDS AT FISCAL YEAR-END
|
OPTION AWARDS |
STOCK AWARDS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) Exercisable |
Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) Unexercisable |
Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Unearned Options (#) |
Options Exercise Prices ($) |
Option Expiration Date |
Number of Shares or Units of Stock That Have Not Vested (#) |
Market Value of Shares or Units of Stock That Have Not Vested ($) |
Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Number of Unearned Shares, Units or Other Rights That Have Not Vested (#) |
Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Market or Payout Value of Unearned Shares, Units or Other Rights That Have Not vested ($) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mark A. Sirgo, Pharm.D |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 340,746 | (1) | 1,005,201 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 96,837 | (2) | 285,669 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 533,333 | (3)(6) | 1,573,332 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 275,000 | (4)(6) | 811,250 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 750,000 | (5)(6)(7) | 2,212,500 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25,000 | — | — | 3.47 | 7/20/21 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22,369 | — | — | 3.55 | 2/25/21 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 37,348 | — | — | 3.90 | 1/21/20 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25,000 | — | — | 5.40 | 7/22/19 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 100,000 | — | — | 4.83 | 4/30/19 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9,175 | — | — | 3.05 | 1/22/19 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 48,448 | — | — | 2.85 | 1/31/18 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ernest R. De Paolantonio, CPA MBA |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 33,048 | (1) | 97,492 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 34,391 | (3) | 101,453 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 60,000 | (4) | 177,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 55,659 | — | — | 5.39 | 10/17/23 | — | — | 190,000 | (5) | 560,500 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Niraj Vasisht, Ph.D. |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 99,952 | (1) | 294,858 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 66,666 | (3)(6) | 196,665 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 100,000 | (4)(6) | 295,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 325,000 | (5)(8) | 958,750 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14,297 | — | — | 1.96 | 2/15/22 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24,579 | — | — | 1.78 | 2/9/22 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12,105 | — | — | 3.55 | 2/25/21 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25,000 | — | — | 3.47 | 1/25/21 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17,329 | — | — | 2.43 | 7/21/20 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17,686 | — | — | 3.90 | 1/21/20 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20,000 | — | — | 2.54 | 10/1/18 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
94
Table of Contents
| (1) | Unvested stock awards consist of Restricted Stock Units from our Long-Term Incentive Plan (as defined under our 2011 Equity Incentive Plan, the “2011 EIP”) and which we refer to as Performance RSUs, which are rights to acquire shares of our common stock. |
| (2) | Unvested stock awards consist of Restricted Stock Units (as defined under the 2011 EIP) which are rights to acquire shares of our common stock. These unvested RSUs vest in thirds beginning February 2015. Mr. Sirgo’s remaining third was deferred until 2018. |
| (3) | Unvested stock awards consist of Restricted Stock Units (as defined under the 2011 EIP) which are rights to acquire shares of our common stock. These unvested RSUs vest in thirds beginning February 2016. Mr. Sirgo’s 2017 one-third was deferred until 2018. Mr. Sirgo’s and Mr. Vasisht’s remaining thirds have terminated pursuant to their respective Retirement Agreements (see note 6). |
| (4) | Unvested stock awards consist of Restricted Stock Units (as defined under the 2011 EIP) which are rights to acquire shares of our common stock. These unvested RSUs vest in thirds beginning February 2017. Mr. Sirgo’s 2017 one-third was deferred until 2018. Mr. Sirgo’s and Mr. Vasisht’s remaining two-thirds have terminated pursuant to their respective Retirement Agreements (see note 6). |
| (5) | Unvested stock awards consist of Restricted Stock Units (as defined under the 2011 EIP) which are rights to acquire shares of our common stock. One-half of which are time-based and one-half of which are performance-based, all of which vest over a three-year period beginning in February 2018. The performance-based RSUs provide for vesting if specified net revenue and operating income goals are achieved with respect to the annual fiscal years 2017 through 2019. Mr. Pursuant to Mr. Sirgo’s retirement agreement, his time-based awards (see note 6) and his performance-based awards (see note 7) have both terminated. Mr. Pursuant to Mr. Vasisht’s retirement agreement, his time-based awards (see note 6) and his performance-based awards (see note 8) have both terminated. |
| (6) | As of each of the respective Retirement Dates to, all previously granted Time Vesting RSUs issued to Mr. Sirgo and Mr. Vasisht pursuant to the Plan that are unvested as of the Retirement Dates terminated and, in lieu thereof, Mr. Sirgo and Mr. Vasisht shall each received a one-time issuance of fully vested shares of Common Stock under the Plan, the number of which was determined with reference to the Time Vesting RSUs being terminated by dividing (A) the Net Present Value of such Time Vesting RSUs by (B) the 30-day VWAP as of the Retirement Date. |
| (7) | As of the Retirement Date, all previously granted RSUs issued to Mr. Sirgo pursuant to the Plan which were to vest due to achievement of future performance milestones that are were unvested as of the Retirement Date shall terminate and, in lieu thereof, Mr. Sirgo shall receive a one-time issuance of 250,000 fully vested shares of Common Stock under the Plan as of the Retirement Date on January 2, 2018. |
| (8) | As of the Retirement Date, all previously granted RSUs issued to Mr. Vasisht pursuant to the Plan which were to vest due to achievement of future performance milestones that are were unvested as of the Retirement Date shall terminate and, in lieu thereof, Previously-awarded performance RSU’s shall continue to vest in accordance with the applicable equity incentive plan until December 31, 2018, at which time 60% of any unvested performance RSUs shall be deemed vested and the remaining 40% shall be deemed forfeited. |
Outstanding Equity Awards Narrative Disclosure
Amended and Restated 2001 Incentive Plan
In July 2011, our original Amended and Restated 2001 Incentive Plan expired. Options to purchase 1,938,039 shares of common stock were outstanding as of December 31, 2016 under the Amended and Restated 2001 Incentive Plan. Although the Amended and Restated 2001 Incentive Plan expired, the 1,938,039 options still outstanding under such plan are still exercisable. In April 2011, our board approved, and in July 2011, our stockholders approved a new 2011 Equity Incentive Plan, which is discussed below.
2011 Equity Incentive Plan
Our 2011 Equity Incentive Plan was originally comprised of 4,200,000 shares of our common stock. The purpose of the 2011 Equity Incentive Plan is: (i) to align our interests and recipients of options under the plan by increasing the proprietary interest of such recipients in our growth and success, and (ii) to advance our interests by providing additional incentives to officers, key employees and well-qualified non-employee directors and consultants who provide services to us, who are responsible for our management and growth, or otherwise contribute to the conduct and direction of our business, operations and affairs. The Compensation Committee of our board of directors administers our incentive plan, selects the persons to whom options are granted and fixes the terms of such options. In July 2013, 2014, 2015 and in December 2017, our stockholders approved increases to our 2011 Equity Incentive Plan in the amounts of 2,600,000, 2,000,000, 2,250,000 and 7,100,000, respectively.
Options may be awarded during the ten-year term of the plan to our employees (including employees who are directors), or consultants who are not employees and our other affiliates. Our plan provides for the grant of options that qualify as incentive stock options, or Incentive Stock Options, under Section 422A of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and options which are not
95
Table of Contents
Incentive Stock Options, or Non-Statutory Stock Options, as well as restricted stock and other awards. Only our employees or employees of our subsidiaries may be granted Incentive Stock Options. Our affiliates or consultants or others as may be permitted by our board of directors, may be granted Non-Statutory Stock Options.
Options to purchase 2,712,954 shares of our common stock at prices ranging from $1.76 to $16.47 are outstanding at December 31, 2017. There were no options granted during 2017 whose exercise price was lower than the estimated market price of the stock at the grant date.
Options issued during 2017 to directors and employees under the 2011 Equity Incentive Plan totaled 960,175 shares, at exercise prices ranging from $1.76 to $3.23.
Option Exercises and Stock Vested
The following information sets forth stock options exercised by the executive officers during the year ended December 31, 2017:
| OPTION AWARDS | STOCK AWARDS | |||||||||||||||
| Name |
Number of Shares Acquired on Exercise (#) |
Value Realized on Exercise ($) |
Number of Shares Acquired on Vesting (#) |
Value Realized on Vesting ($) |
||||||||||||
| Mark A. Sirgo, Pharm.D. |
151,373 | 112,300 | 524,418 | 1,087,790 | ||||||||||||
| Ernest R. De Paolantonio, CPA MBA |
— | — | 73,393 | 147,652 | ||||||||||||
| Niraj Vasisht, Ph.D. |
— | — | 159,787 | 319,576 | ||||||||||||
Pension Benefits
None of our employees participate in or have account balances in qualified or non-qualified defined benefit plans sponsored by us. Our Compensation Committee may elect to adopt qualified or non-qualified benefit plans in the future if it determines that doing so is in our company’s best interests.
Nonqualified Deferred Compensation
None of our employees participate in or have account balances in nonqualified defined contribution plans or other nonqualified deferred compensation plans maintained by us. Our Compensation Committee may elect to provide our officers and other employees with non-qualified defined contribution or other nonqualified deferred compensation benefits in the future if it determines that doing so is in our company’s best interests.
Grants of Plan-Based Awards in 2017
| Name |
Grant Date |
Estimated Future Payouts Under Non-Equity Incentive Plan Awards |
Estimated Future Payouts Under Equity Incentive Plan Awards |
All Awards: Number |
All Other Awards: Number |
Exercise or Base Price of Option |
Closing stock price on Award |
Grant Date Fair Value of Stock and Option |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Threshold ($) |
Target ($) |
Maximum ($) |
Threshold (#) (1) |
Target (#) |
Maximum (#) (2) |
Units (#) |
Options (#) |
Awards ($/Sh) |
date ($/Sh) |
Awards ($) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mark A. Sirgo, |
2/6/17 | 375,000 | 375,000 | $ | 1,387,500 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ernest R. De |
2/6/17 | 162,500 | 162,500 | $ | 601,250 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Niraj Vasisht, |
2/6/17 | 95,000 | 95,000 | $ | 351,500 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of time-based RSUs issued under our 2011 Equity Incentive Plan with a FMV of $1.85, which vest in ratably in thirds beginning February 2018. |
| (2) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of performance-based RSUs issued under our 2011 Equity Incentive Plan with a FMV of $1.85, which vest under certain performance criteria beginning February 2018. |
96
Table of Contents
| (3) | As of each of the respective Retirement Dates to, the stock awards disclosed in this item during 2017 related to time-vesting RSUs issued to Mr. Sirgo and Mr. Vasisht pursuant to the Plan terminated, and in lieu thereof, Mr. Sirgo and Mr. Vasisht each received a one-time issuance of fully vested shares of Common Stock under the Plan, the number of which was determined with reference to the time-vesting RSUs being terminated by dividing (A) the Net Present Value of such time-vesting RSUs by (B) the 30-day VWAP as of the Retirement Date. |
| (4) | As of the Retirement Date, the stock awards disclosed in this item during 2017 related to performance-based RSUs issued to Dr. Sirgo terminated and, in lieu thereof, Mr. Sirgo receive a one-time issuance of 250,000 fully vested shares of Common Stock under the Plan as of the Retirement Date on January 2, 2018. |
| (5) | As of the Retirement Date, the stock awards disclosed in this item during 2017 related to performance-based RSUs issued to Dr. Vasisht terminated and, in lieu thereof, performance RSUs shall continue to vest in accordance with the applicable equity incentive plan until December 31, 2018, at which time 60% of any unvested performance RSUs shall be deemed vested and the remaining 40% shall be deemed forfeited. |
Narrative to Grants of Plan Based Awards Table
See Compensation Discussion and Analysis above for complete description of the targets for payment of annual incentives, as well as performance criteria on which such payments were based.
Options granted to employees vest over 36 months beginning on the first anniversary of the grant date at which time 33% of such options vest. These options expire in 10 years and are outstanding for as long as the individual is an active employee. Employee options qualify as Incentive Stock Options.
Potential Payments Under Severance/Change in Control Arrangements
The table below sets forth potential payments payable to our current executive officers in the event of a termination of employment under various circumstances. For purposes of calculating the potential payments set forth in the table below, we have assumed that (i) the date of termination was December 31, 2017 and (ii) the stock price was $2.95, which was the closing market price of our common stock on December 29, 2017, the last business day of the 2017 fiscal year.
| Name |
If Company Terminates Executive Without Cause or Executive Resigns with Good Reason ($) |
Termination Following a Change in Control without Cause or Executive Resigns with Good Reason ($) |
||||||
| Mark A. Sirgo, Pharm.D. |
||||||||
| Cash Payment |
$ | 787,000 | (1) | $ | 1,023,000 | (1) | ||
| Acceleration of Options |
— | 4,845 | (3) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Cash and Benefits |
$ | 787,000 | $ | 1,027,845 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Ernest R. De Paolantonio, CPA MBA |
||||||||
| Cash Payment |
$ | 533,077 | (2) | $ | 358,077 | (2) | ||
| Acceleration of Options |
— | — | (3) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Cash and Benefits |
$ | 533,077 | $ | 358,077 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Niraj Vasisht, Ph.D. |
||||||||
| Cash Payment |
$ | 476,327 | (2) | $ | 708,827 | (2) | ||
| Acceleration of Options |
— | 60,123 | (3) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Cash and Benefits |
$ | 476,327 | $ | 768,950 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1) | Dr. Sirgo executed a retirement agreement on August 23, 2017 which was effective January 2, 2018. See Compensation Discussion and Analysis for details on Dr. Sirgo’s retirement agreement. |
| (1) | Includes severance payment and accrued and unused vacation time as of December 31, 2017. |
97
Table of Contents
| (2) | Determined by taking excess of the fair market value of our common stock on December 29, 2017, less the exercise price of each accelerated option. |
For each of our executive officers, in their employment agreements the term “change of control” means the occurrence of any one or more of the following events (it being agreed that, with respect to paragraphs (i) and (iii) of this definition below, a “change of control” shall not be deemed to have occurred if the applicable third party acquiring party is an “affiliate” of our company within the meaning of Rule 405 promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended):
(i) An acquisition (whether directly from our company or otherwise) of any voting securities of our company by any person or entity, immediately after which such person or entity has beneficial ownership of forty percent (40%) or more of the combined voting power of our then outstanding voting securities.
(ii) The individuals who, as of the date hereof, are members of our board of directors cease, by reason of a financing, merger, combination, acquisition, takeover or other non-ordinary course transaction affecting our company, to constitute at least fifty-one percent (51%) of the members of our board of directors; or
(iii) Approval by our board of directors and, if required, our stockholders of, or our execution of any definitive agreement with respect to, or the consummation of (it being understood that the mere execution of a term sheet, memorandum of understanding or other non-binding document shall not constitute a change of control):
(A) A merger, consolidation or reorganization involving our company, where either or both of the events described in clauses (i) or (ii) above would be the result;
(B) A liquidation or dissolution of or appointment of a receiver, rehabilitator, conservator or similar person for, or the filing by a third party of an involuntary bankruptcy against, our company; or
(C) An agreement for the sale or other disposition of all or substantially all of the assets of our company to any person or entity (other than a transfer to a subsidiary of our company).
The cash component (as opposed to option accelerations) of any change of control payment would be structured as a one-time cash severance payment.
CEO Pay Ratio – 15:1
We believe our executive compensation program must be consistent and internally equitable to motivate our employees to perform in ways that enhance shareholder value. We are committed to internal pay equity, and the Compensation Committee monitors the relationship between the pay of our executive officers and the pay of our non-executive employees. The Compensation Committee reviewed a comparison of Mark Sirgo’s, our Chief Executive Officer (which we refer to for these purposes as the CEO), annual total compensation in fiscal year 2017 to that of all other company employees for the same period. The calculation of annual total compensation of all employees was determined in the same manner as the “Total Compensation” shown for our CEO in the “Summary Compensation Table” on page 91 of this Report. Pay elements that were included in the annual total compensation for each employee are:
| • | salary received in fiscal year 2017; |
| • | annual bonus payment received for performance in fiscal year 2017; |
| • | grant date fair value of stock option exercises and RSU awards vested in fiscal year 2017; |
| • | company-paid 401(k) Plan match made during fiscal year 2017; |
| • | company-paid life insurance premiums during fiscal year 2017; and |
| • | auto allowance paid in fiscal year 2017. |
Our calculation includes all employees as of December 31, 2017. The annual total compensation of our CEO for 2017 includes a retirement payment (pursuant to his retirement agreement) and legal fees paid by our company in connection with the execution of the CEO’s retirement agreement.
We determined the compensation of our median employee by: (i) calculating the annual total compensation described above for each of our employees, (ii) ranking the annual total compensation of all employees except for the CEO from lowest to highest (a list of 90 employees), and (iii) since we have an even number of employees when not including the CEO, determining the average of the annual total compensation of the two employees ranked 46 and 47 on the list (“Median Employee”).
98
Table of Contents
The annual total compensation for fiscal year 2017 for our CEO was $2,405,516 and for the Median Employee was $159,578. We estimate that the resulting ratio of our CEO’s pay to the pay of our Median Employee for fiscal year 2017 is 15 to 1.
Compensation of Directors Summary Table
DIRECTOR COMPENSATION
| Name (a) | Fees Earned or Paid in Cash ($) |
Stock Awards ($) (11) |
Option Awards ($) |
Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation ($) |
Non-Qualified Deferred Compensation Earnings ($) |
All Other Compensation ($) |
Total ($) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Frank E. O’Donnell, Jr. |
313,250 | (1) | 351,915 | (2) | — | — | — | 18,432 | (3) | 683,597 | ||||||||||||||||||
| William B. Stone |
87,500 | 98,000 | (4) | 43,000 | (5) | — | — | — | 228,500 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Samuel P. Sears, Jr. |
70,000 | 84,000 | (6) | 32,250 | (7) | — | — | — | 186,250 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Thomas W. D’Alonzo |
55,000 | 84,000 | (6) | 32,250 | (7) | — | — | — | 171,250 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Charles J. Bramlage |
57,500 | 84,000 | (6) | 32,250 | (7) | — | — | — | 173,750 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Barry I. Feinberg |
55,000 | 84,000 | (6) | 32,250 | (7) | — | — | — | 171,250 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Timothy C. Tyson |
52,500 | 20,482 | (8) | 7,865 | (9) | — | — | — | 80,847 | |||||||||||||||||||
| William M. Watson (10) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Compensation for serving as Executive Chairman through May 2017 and subsequently as Chairman, which includes $132,000 as bonus, which relates to 2016 performance but was contingent upon board approval which occurred March 2017. |
| (2) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of 2,520 RSUs in 2017 with a FMV of $2.00 under our LTIP and 375,000 unvested RSUs issued as executive grants in 2017 with a FMV of $1.85 which vest in thirds beginning in 2018. Does not include 170,828 unvested RSUs to be issued under our LTIP upon the achievement of certain performance criteria and 375,000 performance-based RSUs that vests under certain performance criteria which were granted in 2017. |
| (3) | Includes $18,432 in health benefits paid in 2017. |
| (4) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of 35,000 RSUs issued in 2017 with a FMV of $2.80 for serving on the board which half vested in 2017 and the remaining half vest in 2018. |
| (5) | The stock options disclosed in this item consists of 20,000 options granted in 2017 with a FMV of $2.15 for serving on the board which half vested in 2017 and the remaining half vest in 2018. |
| (6) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of 30,000 RSUs issued in 2017 with a FMV of $2.80 for serving on the board which half vested in 2017 and the remaining half vest in 2018. |
| (7) | The stock options disclosed in this item consists of 15,000 options granted in 2017 with a FMV of $2.15 for serving on the board which half vested in 2017 and the remaining half vest in 2018. |
| (8) | The stock awards disclosed in this item consists of 7,315 RSUs issued in 2017 with a FMV of $2.80 for serving on the board which half vested in 2017 and the remaining half vest in 2018. |
| (9) | The stock options disclosed in this item consists of 3,658 options granted in 2017 with a FMV of $2.15 for serving on the board which half vested in 2017 and the remaining half vest in 2018. |
| (10) | Mr. Watson joined our board in December 2017. |
| (11) | The reported amounts represent the aggregate grant date fair value of the awards computed in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board Account Standards Codification Topic 718, Stock Compensation, as modified or supplemented, or FASB ASC Topic 718. |
Narrative to Director Compensation
The Compensation Committee of our board of directors reviews the Director Remuneration Policy, which establishes the compensation our directors earn for serving on our board of directors and individual committees. The policy follows (all annual cash retainers are paid quarterly in arrears):
| • | $45,000 annual cash retainer to each board member. |
| • | $10,000 annual cash retainer to the Lead Director. |
| • | $20,000 annual cash retainer to the Chairman of the Audit Committee. |
| • | $15,000 annual cash retainer to the Chairman of the Compensation Committee. |
| • | $10,000 annual cash retainer to the Chairman of the Nominating & Corporate Governance Committee. |
| • | $10,000 annual cash retainer to each non-Chairman Audit Committee member. |
99
Table of Contents
| • | $7,500 annual cash retainer to each non-Chairman Compensation Committee member. |
| • | $5,000 annual cash retainer to each non-Chairman Nominating & Corporate Governance Committee member. |
| • | $7,500 annual cash retainer to each Special Committee member. |
| • | 30,000 restricted stock units of our common stock per year, to each director. |
| • | 5,000 additional restricted stock units of our common stock per year to the Lead Director. |
| • | 15,000 stock options of our common stock per year, to each director. |
| • | 5,000 additional stock options of our common stock per year to the Lead Director. |
| • | New directors will earn a pro-rated portion (based on months to be served in the fiscal year in which they join) of cash and restricted stock units. |
Options granted to directors expire in 10 years and are outstanding for the life of the option. Director options qualify as Non-Statutory Stock Options. The total number of options granted during the year ended December 31, 2017 was 83,658, of which 41,829 vested during the first open window upon issuance in August 2017 and 41,829 vests in August 2018.
The total number of RSUs granted during the year ended December 31, 2017 was 162,315, of which 81,158 vested during the first open window upon issuance in August 2017 and 81,158 vests in August 2018.
Performance Long Term Incentive Plan
In December 2012, by unanimous written consent following significant planning and discussion (as well as discussion with our outside compensation consultant Radford), the Committee approved the LTIP. The LTIP is designed as an incentive for our senior management (including our NEOs) to generate revenue for our company.
The LTIP consists of RSUs (as defined under our 2011 Equity Incentive Plan) which are rights to acquire shares of our common stock. All Performance RSUs granted under the LTIP will be granted under our 2011 Equity Incentive Plan (as the same may be amended, supplemented or superseded from time to time) as “Performance Compensation Awards” under such plan. The participants in the LTIP are either NEOs or senior officers of our company.
The term of the LTIP began with our fiscal year ended December 31, 2012 and lasts through our fiscal year ended December 31, 2019. The total number of Performance RSUs covered by the LTIP is 1,078,000, of which 978,000 were awarded in 2012 and 35,000 were awarded November 2015 (the remaining 319,676 Performance RSUs being reserved for future hires, which includes forfeitures). A total of 9,958, 23,853, 21,356, 4,447 and 8,986 RSUs vested during the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The Performance RSUs under the LTIP did not vest upon granting, but instead are subject to potential vesting each year over the 8 year term of the LTIP depending on the achievement of revenue by our company, as reported in our Annual Report on Form 10-K. Performance RSUs will be valued on the day of issuance and will vest annually on the last day preceding the first open window after filing our Annual Report on Form 10-K based on the revenue achieved during the prior fiscal year as a proportion of the total cumulative revenue target for the entire term of the LTIP (which we call the Predefined Cumulative Revenue). Predefined Cumulative Revenue is a predefined aggregate revenue target for the entire term of the LTIP that was determined by the Committee in conjunction with our executive management. The Predefined Cumulative Revenue may be adjusted by the Committee upon the occurrence of extraordinary corporate events during the term of the LTIP (such as acquisitions by our company of revenue generating businesses or assets).
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
None of our executive officers serves as a member of the Compensation Committee of our board of directors, or other committee serving an equivalent function. None of the members of our Compensation Committee has ever been our employee or one of our officers.
100
Table of Contents
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters. |
The following table sets forth, as of March 13, 2018, by: (i) each of our directors, (ii) all persons who, to our knowledge, are the beneficial owners of more than 5% of the outstanding shares of common stock, (iii) each of the executive officers, and (iv) all of our directors and executive officers, as a group. Each person named in this table has sole investment power and sole voting power with respect to the shares of common stock set forth opposite such person’s name, except as otherwise indicated. Unless otherwise indicated, the address for each person listed below is in care of BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc., 4131 ParkLake Avenue, Suite #225, Raleigh, NC 27612.
|
Name and Address of Beneficial Owner |
Amount and Nature of Beneficial Ownership |
Percentage of Class as of March 13, 2018(1) |
||||||
| Broadfin Capital, LLC (2) |
4,634,119 | 7.93 | % | |||||
| Stonepine Capital Management (3) |
3,645,461 | 6.24 | % | |||||
| Mark A. Sirgo, Pharm.D.(4) |
2,519,553 | 4.29 | % | |||||
| Frank E. O’Donnell, Jr., M.D.(5) |
530,174 | * | ||||||
| Scott M. Plesha (6) |
141,698 | * | ||||||
| Ernest R. De Paolantonio, CPA MBA (7) |
152,123 | * | ||||||
| Samuel P. Sears, Jr (8) |
117,863 | * | ||||||
| Thomas W. D’Alonzo (9) |
183,879 | * | ||||||
| Barry I. Feinberg (10) |
143,500 | * | ||||||
| Timothy C. Tyson (11) |
6,487 | * | ||||||
| William M. Watson (12) |
1,500 | * | ||||||
| All Directors and Officers as a group (9 persons) |
3,796,777 | 6.44 | % | |||||
| * | Less than 1% |
| (1) | Based on 58,221,869 shares of common stock outstanding as of March 13, 2018 and shares beneficially owned by the referenced parties as described below. |
| (2) | Based on 13G/A filed with the SEC on February 13, 2018 by Broadfin Capital, LLC. |
| (3) | Based on 13G/A filed with the SEC on February 13, 2018 by Stonepoint Capital Management |
| (4) | Includes 2,300,661 shares owned by Dr. Sirgo, our Vice Chairman. Includes options to purchase 218,892 shares of common stock, all of which are currently exercisable. Does not include 285,305 shares of unvested RSUs which vest in March 2018. Does not include 340,746 unvested RSUs potentially issuable under our LTIP if certain pre-determined company revenue targets are achieved. Dr. Sirgo’s address is 606 Wayne Drive, Raleigh, NC. 27609. |
| (5) | Dr. O’Donnell is our Chairman of the Board and a Director. Excludes 167,500 shares owned by The Francis E. O’Donnell, Jr. Irrevocable Trust #1, of which Dr. O’Donnell’s sister, Kathleen O’Donnell, is trustee, and as to which Dr. O’Donnell disclaims beneficial interest. This number includes 271,299 shares owned by Dr. O’Donnell and options to purchase 145,000 shares of our common stock, all of which is currently exercisable. Does not include an aggregate of 457,833 shares of unvested RSUs which vest in thirds from September 2018 to March 2021. Does not include 232,500 shares of unvested RSUs potentially issuable in thirds if certain pre-determined company revenue targets are achieved. Also, does not include 170,828 shares of unvested RSUs potentially issuable under our LTIP if certain pre-determined company revenue targets are achieved. Dr. O’Donnell’s address is 865 Longboat Club Road, Longboat Key FL. 34228. |
| (6) | Mr. Plesha is our President. This number includes 141,698 shares owned by Mr. Plesha. Does not include an aggregate of 147,265 shares of unvested RSUs which vest in thirds from March 2018 to March 2021. Also, does not include 87,500 shares of unvested RSUs potentially issuable in thirds if certain pre-determined company revenue targets are achieved. Mr. Plesha’s address is 1410 Smythe Street, Daniel Island, SC. 29492. |
| (7) | Mr. De Paolantonio is our Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and Treasurer. Includes 96,464 shares owned by Mr. De Paolantonio. Includes options to purchase 55,659 shares of common stock, all of which are currently exercisable. Does not include an aggregate of 259,391 shares of unvested RSUs which vest in thirds from March 2018 to March 2021. Does not include 165,000 shares of unvested RSUs potentially issuable in thirds if certain pre-determined company revenue targets are achieved. Also, does not include 33,048 shares of unvested RSUs potentially issuable under our LTIP if certain pre-determined company revenue targets are achieved. Mr. De Paolantonio’s address is 4209 Lassiter Mill Road, Raleigh, NC. 27609. |
| (8) | Mr. Sears is a Director. Includes 82,863 shares owned and options to purchase 35,000 shares of our common stock, all of which are currently exercisable. Excludes options to purchase 7,500 shares of common stock which are not currently exercisable. Does not include 15,000 shares of unvested RSUs which will vest August 2018. Mr. Sears’ address is 2 Spring Avenue, S. Hamilton, MA. 01982. |
101
Table of Contents
| (9) | Mr. D’Alonzo is a Director. Includes 161,379 shares owned and options to purchase 22,500 shares of our common stock, all of which are currently exercisable. Excludes options to purchase 7,500 shares of common stock which are not currently exercisable. Does not include 15,000 shares of unvested RSUs which will vest August 2018. Mr. D’Alonzo’s address is 81 Seagate Drive, Unit 503, Naples, FL. 34103. |
| (10) | Dr. Feinberg is a Director. Includes 121,000 shares owned and options to purchase 22,500 shares of our common stock, all of which are currently exercisable. Excludes options to purchase 7,500 shares of common stock which are not currently exercisable. Does not include 15,000 shares of unvested RSUs which will vest August 2018. Dr. Feinberg’s address is 3 Somerset Downs, St. Louis, MO. 63124. |
| (11) | Timothy C. Tyson is a Director. Includes 4,658 shares owned and options to purchase 1,829 shares of our common stock, all of which are currently exercisable. Excludes options to purchase 1,829 shares of common stock which are not currently exercisable. Does not include 4,657 shares of unvested RSUs which will vest August 2018. Mr. Tyson’s address is 6 Point Road, Norwalk, CT. 06854. |
| (12) | William M. Watson became a Director December 2017. Includes 1,500 shares owned. Mr. Watson’s address is 4905 Caspar Whitney Pl. #401, Tampa, Fl. 33616. |
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
The following table indicates shares of common stock authorized for issuance under our 2011 Equity Incentive Plan as of December 31, 2017:
| Plan category |
Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights (1) |
Weighted- average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights (2) |
Number of securities remaining available for future issuance |
|||||||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders |
9,555,869 | $ | 3.68 | 5,216,763 | ||||||||
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Total |
9,555,869 | $ | 3.68 | — | ||||||||
| (1) | Includes 890,693 shares of common stock underlying options previously granted under our Amended and Restated 2001 Incentive Plan, which are still exercisable despite the fact that such plan expired July 2011. |
| (2) | Weighted average exercise price does not include restricted stock units. |
102
Table of Contents
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence. |
As of December 31, 2001, our board of directors appointed an audit committee consisting of independent directors. This committee, among other duties, is charged to review, and if appropriate, ratify all agreements and transactions which had been entered into with related parties, as well as review and ratify all future related party transactions. The audit committee and/or our independent directors independently reviewed, ratified and/or approved, as the case may be, the agreements described below. From time to time, after compliance with our internal policies and procedures, we have entered into related party contracts, some of which were amended subsequently in accordance with the same policies and procedures.
The following is a listing of our related party transactions:
On November 30, 2000, we entered into an agreement with Biotech Specialty Partners, LLC, or BSP, an emerging alliance of early stage biotechnology and specialty pharmaceutical companies. BSP to date has not distributed any pharmaceutical products. Under this agreement, BSP will serve as a nonexclusive distributor of our products in consideration of a ten (10%) percent discount to the wholesale price, which our board of directors has determined to be commercially reasonable. BSP has waived its rights under this agreement with respect to Arius’ products which include the BEMA® technology. Hopkins Capital Group, which is affiliated with Dr. Frank E. O’Donnell, Jr., our Chairman of the Board and a director, are affiliated as stockholders, and Dr. O’Donnell is a member of the management of BSP.
As a matter of corporate governance policy, we have not and will not make loans to officers or loan guarantees available to “promoters” as that term is commonly understood by the SEC and state securities authorities.
We believe that the terms of the above transactions with affiliates were as favorable to us or our affiliates as those generally available from unaffiliated third parties. At the time of certain of the above referenced transactions, we did not have sufficient disinterested directors to ratify or approve the transactions; however, the present board of directors includes five independent directors which constitute a majority as required by NASDAQ Stock Market rules. We believe that William M Watson, Samuel P. Sears, Jr., Thomas W. D’Alonzo, Barry I. Feinberg and Timothy C. Tyson qualify as independent directors for NASDAQ Stock Market purposes.
All future transactions between us and our officers, directors or five percent stockholders, and respective affiliates will be on terms no less favorable than could be obtained from unaffiliated third parties and will be approved by a majority of our independent directors who do not have an interest in the transactions and who had access, at our expense, to our legal counsel or independent legal counsel.
To the best of our knowledge, other than as set forth above, there were no material transactions, or series of similar transactions, or any currently proposed transactions, or series of similar transactions, to which we were or are to be a party, in which the amount involved exceeds $120,000, and in which any director or executive officer, or any security holder who is known by us to own of record or beneficially more than 5% of any class of our common stock, or any member of the immediate family of any of the foregoing persons, has an interest.
| Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services. |
Audit Fees. The aggregate fees billed by Cherry Bekaert LLP for professional services rendered for the audit of our annual financial statements, review of the financial information included in our Forms 10-Q for the respective periods and other required filings with the SEC for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 totaled $188,500 and $179,500, respectively. The above amounts include interim procedures and audit fees, as well as attendance at audit committee meetings.
Audit-Related Fees. The aggregate fees billed by Cherry Bekaert LLP for audit-related fees for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 were $149,839 and $53,800, respectively. The fees were provided in consideration of services consisting of review and update procedures associated with registration statements and other SEC filings, as well as the 2017 audit of the BELBUCA® asset acquisition.
Tax Fees. The aggregate fees billed by Cherry Bekaert LLP for professional services rendered for tax compliance for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 were $42,460 and $2,650, respectively. The fees were provided in consideration of services consisting of preparation of tax returns and related tax advice.
103
Table of Contents
All Other Fees. None
The Audit Committee of our board of directors has established its pre-approval policies and procedures, pursuant to which the Audit Committee approved the foregoing audit and non-audit services provided by Cherry Bekaert LLP in 2017. Consistent with the Audit Committee’s responsibility for engaging our independent auditors, all audit and permitted non-audit services require pre-approval by the Audit Committee. The full Audit Committee approves proposed services and fee estimates for these services. The Audit Committee chairperson has been designated by the Audit Committee to approve any audit-related services arising during the year that were not pre-approved by the Audit Committee. Any non-audit service must be approved by the full Audit Committee. Services approved by the Audit Committee chairperson are communicated to the full Audit Committee at its next regular meeting and the Audit Committee reviews services and fees for the fiscal year at each such meeting. Pursuant to these procedures, the Audit Committee approved the foregoing services provided by Cherry Bekaert LLP.
104
Table of Contents
| Item 15. | Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules. |
The following exhibits are filed with this Report.
105
Table of Contents
106
Table of Contents
| * | Filed herewith |
| + | Confidential treatment has been granted for certain portions of this exhibit pursuant to 17 C.F.R. Sections 200.8(b)(4) and 240.24b-2. |
| # | A signed original of this written statement required by Section 906 has been provided to the Company and will be retained by the Company and furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission or its staff upon request. |
| ‡ | Confidential treatment extension of confidential treatment previously granted for certain portions of this exhibit pursuant to 17 C.F.R. Sections 200.8(b)(4) and 240.24b-2 is currently pending with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| (1) | Previously filed with Form SB-2, Amendment No. 2, dated February 1, 2002. |
| (2) | Previously filed with PRE14A, dated June 17, 2003. |
| (3) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated August 26, 2004. |
| (4) | Previously filed as Annex A to Schedule 14A, dated June 27, 2006. |
| (5) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated August 9, 2006. |
| (6) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated February 23, 2007. |
| (7) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated September 10, 2007. |
| (8) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated July 28, 2008. |
| (9) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, January 6, 2009. |
| (10) | Previously filed with Form 10-K, March 20, 2009. |
| (11) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, July 23, 2010. |
| (12) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, October 8, 2010. |
| (13) | Previously filed with PRE14A, dated June 1, 2011 |
| (14) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated July 25, 2011. |
| (15) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated September 19, 2012. |
| (16) | Previously filed with DEF14A, dated June 12, 2013 |
| (17) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated November 28, 2012. |
| (18) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated October 23, 2013. |
| (19) | Previously filed with DEF14A, dated June 10, 2014. |
107
Table of Contents
| (20) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated October 31, 2014. |
| (21) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated January 28, 2015. |
| (22) | Previously filed with Form 10-K, dated March 16, 2015. |
| (23) | Previously filed with DEF14A, dated June 5, 2015. |
| (24) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated December 18, 2015. |
| (25) | Previously filed with Form 10-K, dated March 10, 2016. |
| (26) | Previously filed with Form 10-Q, dated August 9, 2016. |
| (27) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated February 27, 2017. |
| (28) | Previously filed with Form 10-K, dated March 16, 2017. |
| (29) | Previously filed with Form 8-K/A No.2, dated June 1, 2017. |
| (30) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated August 29, 2017. |
| (31) | Previously filed with Form 8-K/A, dated September 1, 2017. |
| (32) | Previously filed with DEF14A, dated November 1, 2017. |
| (33) | Previously filed with Form 10-Q, dated November 9, 2017. |
| (34) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated November 17, 2017. |
| (35) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated December 22, 2017. |
| (36) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated Janaury 18, 2018. |
| (37) | Previously filed with Form 8-K, dated February 6, 2018. |
| Item 16. | Form 10-K Summary. |
Not applicable.
108
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC.
F-1
Table of Contents
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc.
Opinions on the Financial Statements and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc. and Subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2017, the related notes, and Schedule II – Valuation and Qualifying Accounts and Reserves (the “financial statements”). We also have audited the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2017, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
Emphasis of Matter
As discussed in Note 2 to the financial statements, during 2017, the Company experienced negative cash flows of approximately $10.8 million and, at December 31, 2017, the Company had incurred cumulative net losses of approximately $305.1 million. Management’s plans in regard to this matter are described in Note 2.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report of Internal Control over Financial Reporting included in Item 9A – Controls and Procedures in the Company’s 2017 Annual Report on Form 10-K. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements and an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud, and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audits of the financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
F-2
Table of Contents
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Cherry Bekaert LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2003.
Raleigh, North Carolina
March 15, 2018
F-3
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(U.S. DOLLARS, IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE AND PER SHARE AMOUNTS)
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||
| Cash |
$ | 21,195 | $ | 32,019 | ||||
| Accounts receivable, net |
8,852 | 2,967 | ||||||
| Inventory, net |
6,091 | 3,368 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
3,610 | 4,136 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current assets |
39,748 | 42,490 | ||||||
| Property and equipment, net |
3,778 | 4,230 | ||||||
| Goodwill |
2,715 | 2,715 | ||||||
| BELBUCA® license and distribution rights intangible asset, net |
40,500 | — | ||||||
| Other intangible assets, net |
1,360 | 2,285 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total assets |
$ | 88,101 | $ | 51,720 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) | ||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
$ | 26,149 | $ | 17,572 | ||||
| Deferred revenue, current |
— | 1,716 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current liabilities |
26,149 | 19,288 | ||||||
| Notes payable |
47,660 | 29,272 | ||||||
| Deferred revenue, long-term |
— | 20,000 | ||||||
| Other long-term liabilities |
5,415 | 825 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities |
79,224 | 69,385 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Notes 6 and 17) |
||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity (deficit): |
||||||||
| Preferred Stock, $.001 par value; 5,000,000 shares authorized; 2,093,155 shares of Series A Non-Voting Convertible Preferred Stock outstanding at both December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively |
2 | 2 | ||||||
| Common Stock, $.001 par value; 75,000,000 shares authorized; 55,904,072 and 54,133,511 shares issued; 55,888,581 and 54,118,020 shares outstanding at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively |
56 | 54 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
313,922 | 292,667 | ||||||
| Treasury stock, at cost, 15,491 shares |
(47 | ) | (47 | ) | ||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(305,056 | ) | (310,341 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
8,877 | (17,665 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
$ | 88,101 | $ | 51,720 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-4
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(U.S. DOLLARS, IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE AND PER SHARE AMOUNTS)
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Revenues: |
||||||||||||
| Product sales |
$ | 34,922 | $ | 8,266 | $ | 4,157 | ||||||
| Product royalty revenues |
5,070 | 3,646 | 1,406 | |||||||||
| Research and development reimbursements |
799 | 1,134 | 909 | |||||||||
| Contract revenue |
21,194 | 2,500 | 41,759 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total revenues |
61,985 | 15,546 | 48,231 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cost of sales |
19,496 | 11,258 | 8,101 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Expenses: |
||||||||||||
| Research and development |
13,040 | 18,878 | 20,624 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
58,869 | 49,345 | 54,685 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total expenses |
71,909 | 68,223 | 75,309 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Loss from operations |
(29,420 | ) | (63,935 | ) | (35,179 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Interest expense, net |
(8,577 | ) | (3,267 | ) | (2,518 | ) | ||||||
| Bargain purchase gain |
27,336 | — | — | |||||||||
| Other (expense) income, net |
(26 | ) | 64 | 25 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Loss before income taxes |
$ | (10,687 | ) | $ | (67,138 | ) | $ | (37,672 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income tax benefit |
15,972 | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders |
$ | 5,285 | $ | (67,138 | ) | $ | (37,672 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Basic: |
||||||||||||
| Weighted average common stock shares outstanding |
55,355,802 | 53,679,134 | 52,384,876 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Basic earnings (loss) per share |
$ | 0.10 | $ | (1.25 | ) | $ | (0.72 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted: |
||||||||||||
| Diluted weighted average common stock shares outstanding |
56,402,479 | 53,679,134 | 52,384,876 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted earnings (loss) per share |
$ | 0.09 | $ | (1.25 | ) | $ | (0.72 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-5
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT)
(U.S. DOLLARS, IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE DATA)
| Preferred Stock Series A |
Common Stock | Additional Paid-In Capital |
Treasury Stock |
Accumulated Deficit |
Total Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances, January 1, 2015 |
2,139,000 | $ | 2 | 51,603,070 | $ | 52 | $ | 259,920 | $ | (47 | ) | $ | (205,531 | ) | $ | 54,396 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | 14,249 | — | — | 14,249 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock option exercise |
— | — | 223,923 | — | 755 | — | — | 755 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock awards |
— | — | 857,677 | 1 | — | — | — | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant exercises |
— | — | 284 | — | 1 | — | — | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Short swing profit return |
— | — | — | — | 6 | — | — | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conversion of preferred shares to common shares |
(45,845 | ) | — | 45,845 | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity financing costs |
— | — | — | — | (40 | ) | — | — | (40 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (37,672 | ) | (37,672 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Balances, December 31, 2015 |
2,093,155 | $ | 2 | 52,730,799 | $ | 53 | $ | 274,891 | $ | (47 | ) | $ | (243,203 | ) | $ | 31,696 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | 14,931 | — | — | 14,931 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock option exercise |
— | — | 147,426 | — | 297 | — | — | 297 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock awards |
— | — | 592,065 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common stock issuance upon retirement |
— | — | 663,221 | 1 | 2,459 | — | — | 2,460 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of warrants |
— | — | — | — | 49 | — | — | 49 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity financing costs |
— | — | — | — | 40 | — | — | 40 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (67,138 | ) | (67,138 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Balances, December 31, 2016 |
2,093,155 | $ | 2 | 54,133,511 | $ | 54 | $ | 292,667 | $ | (47 | ) | $ | (310,341 | ) | $ | (17,665 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | 14,801 | — | — | 14,801 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock option exercise |
— | — | 202,519 | — | 439 | — | — | 439 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock awards |
— | — | 1,568,042 | 2 | (2 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of warrants |
— | — | — | — | 6,017 | — | — | 6,017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 5,285 | 5,285 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Balances, December 31, 2017 |
2,093,155 | $ | 2 | 55,904,072 | $ | 56 | $ | 313,922 | $ | (47 | ) | $ | (305,056 | ) | $ | 8,877 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-6
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(U.S. DOLLARS, IN THOUSANDS)
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 5,285 | $ | (67,138 | ) | $ | (37,672 | ) | ||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash flows from operating activities |
||||||||||||
| Depreciation |
693 | 437 | 329 | |||||||||
| Accretion of debt discount and loan costs |
2,392 | 397 | 500 | |||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
5,425 | 971 | 970 | |||||||||
| Provision for inventory obsolescence |
243 | — | — | |||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
14,801 | 14,931 | 14,249 | |||||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
(15,972 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Bargain purchase gain |
(27,336 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable |
(5,884 | ) | (862 | ) | 670 | |||||||
| Inventories |
2,448 | (810 | ) | (730 | ) | |||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets |
526 | (203 | ) | (1,365 | ) | |||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
6,644 | (1,546 | ) | 5,055 | ||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
(21,716 | ) | (159 | ) | 14,262 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash flows used in operating activities |
(32,451 | ) | (53,982 | ) | (3,732 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Investing activities: |
||||||||||||
| BELBUCA® acquisition |
(5,853 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Purchase of equipment |
(11 | ) | (405 | ) | (701 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash flows used in investing activities |
(5,864 | ) | (405 | ) | (701 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Financing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from sales of securities, net of costs incurred |
— | 40 | (40 | ) | ||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options |
439 | 297 | 755 | |||||||||
| Issuance of common stock |
— | 2,460 | — | |||||||||
| Issuance of warrants |
— | 49 | — | |||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of common stock warrants |
— | — | 1 | |||||||||
| Payment on note payable |
(30,000 | ) | — | (3,335 | ) | |||||||
| Proceeds from notes payable |
60,000 | — | 20,667 | |||||||||
| Return of short swing profits |
— | — | 6 | |||||||||
| Payment of deferred financing fees |
(2,948 | ) | — | (533 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash flows from financing activities |
27,491 | 2,846 | 17,521 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents |
(10,824 | ) | (51,541 | ) | 13,088 | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year |
32,019 | 83,560 | 70,472 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year |
$ | 21,195 | $ | 32,019 | $ | 83,560 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash paid for interest |
$ | 5,285 | $ | 2,870 | $ | 1,885 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-7
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
SUPPLEMENTAL CASH FLOW INFORMATION
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS EXCEPT SHARE DATA)
Non-cash Financing and Investing Activities:
The Company recorded the fair value of the bargain purchase price of the BELBUCA® acquisition totaling $27.3 million to income during the year ended December 31, 2017 in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“GAAP”) (see note 7, Business Combinations and BELBUCA® Acquisition).
The Company recorded the fair value of warrants totaling $6.0 million to equity with an offsetting amount to Notes payable in connection with the CRG Term Loan Agreement (as defined in note 11) during the year ended December 31, 2017 in accordance with GAAP (see note 14, Stockholders’ Equity).
The Company converted 45,845 shares of Series A Preferred to equal shares of the Company’s common stock during the year ended December 31, 2015.
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-8
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 1. | Nature of business and summary of significant accounting policies: |
Organization
BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) was incorporated in the State of Indiana on January 6, 1997 and reincorporated as a Delaware corporation in 2002. The Company’s subsidiaries are Arius Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Arius One”) and Arius Two, Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Arius Two”), each of which are wholly-owned, and its majority-owned subsidiary, Bioral Nutrient Delivery, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (“BND”).
The Company is a specialty pharmaceutical company with a focus in the areas of pain management and addiction medicine. The Company is utilizing its novel and proprietary BioErodible MucoAdhesive (BEMA®) technology and other drug delivery technologies to develop and commercialize, either on its own or in partnership with third parties, new applications of proven therapies aimed at addressing important unmet medical needs. The Company’s development strategy has focused on utilization of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (“FDA”) 505(b)(2) approval process to obtain more timely and efficient approval of new formulations of previously approved therapeutics.
As used herein, the Company’s common stock, par value $.001 per share, is referred to as the “Common Stock”.
Principles of consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company, Arius One, Arius Two and BND. For each period presented BND has been an inactive subsidiary. All significant inter-company balances and transactions have been eliminated.
Significant accounting policies:
Use of estimates in financial statements
The preparation of the accompanying consolidated financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the period. Actual results could differ from those estimates. The Company reviews all significant estimates affecting the consolidated financial statements on a recurring basis and records the effect of any necessary adjustments prior to their issuance. Significant estimates of the Company include: revenue recognition, sales allowances such as returns of product sold, government program rebates, customer coupon redemptions, wholesaler/pharmacy discounts, product service fees, rebates and chargebacks, sales bonuses, stock-based compensation, determination of fair values of assets and liabilities relating to business combinations, and deferred income taxes.
Reacquisition of BELBUCA®
On December 7, 2016, the Company entered into an agreement (the “Termination Agreement”) with Endo Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Endo”) terminating Endo’s licensing of rights to the Company’s BELBUCA® (buprenorphine) buccal film product (“BELBUCA®”). The closing of the Termination Agreement, and the formal termination of the BELBUCA® license to Endo and closing of the transactions further described below occurred on January 6, 2017 (see note 7, Business Combinations and BELBUCA® Acquisition).
Reclassification
Certain amounts were reclassified between Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable and Accrued Expenses for the year ended December 31, 2016 Consolidated Balance Sheet and in the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 to conform to current year presentation to reflect the right of offset and practice of settling certain liabilities with our wholesale customers. Certain amounts were also reclassified between Accounts Payable and Accrued Liabilities in note 3, for the year ended December 31, 2016 to conform to current year presentation. The Company also reclassified certain amounts between Machinery & Equipment and Idle Equipment in note 4, for the year ended December 31, 2016. These reclassifications had no effect on the previously reported net cash flows from operations, activities or net losses.
F-9
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 1. | Nature of business and summary of significant accounting policies (continued): |
Certain risks, concentrations and uncertainties
The Company relies on certain materials used in its development and third-party manufacturing processes, most of which are procured from three contract manufacturers and two active pharmaceutical ingredient (“API”) suppliers for BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®. The Company purchases its pharmaceutical ingredients pursuant to long-term supply agreements with a limited number of suppliers. The failure of a supplier, including a subcontractor, to deliver on schedule could delay or interrupt the development or commercialization process and thereby adversely affect the Company’s operating results. In addition, a disruption in the commercial supply of or a significant increase in the cost of the API from any of these sources could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® business, which would affect the Company’s financial position and results of operations.
In addition, the Company utilizes only two contract manufacturers to create the BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® laminates and only one contract manufacturer to package the laminates into final product. Although the Company has long term supply agreements with these two vendors, any problems or regulatory issues at either of these vendors could create significant BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® supply delays. Amounts due to these vendors represented approximately 22.8% and 5.6% of total accounts payable as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Key components used in the manufacture of ONSOLIS® are currently provided by a limited number of suppliers. This could result in the Company’s inability to timely obtain an adequate supply of required components and reduce control over pricing, quality and timely delivery. Also, if the supply of any components is interrupted, components from alternative suppliers may not be available in sufficient volumes within required time frames, if at all, to meet the Company’s obligations under certain supply agreements. This could delay timely commercialization efforts causing the Company’s obligations to not be fulfilled.
The Company sells its BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® products primarily to large national wholesalers, which in turn may resell the products to smaller or regional wholesalers, retail pharmacies, chain drug stores, government agencies and other third parties. The following table lists the Company’s customers that individually comprise greater than 10% of total accounts receivable:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| Customers |
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
| Customer A |
47 | % | 36 | % | ||||
| Customer B |
22 | % | 28 | % | ||||
| Customer C |
26 | % | 28 | % | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
95 | % | 92 | % | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
These three customers accounted for 92%, 91% and 90% of total annual sales during the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 respectively.
Cash
The Company places cash on deposit with financial institutions in the United States. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation covers $0.25 million for substantially all depository accounts. As of December 31, 2017, the Company had approximately $21.2 million, which exceeded these insured limits. As of December 31, 2016, the Company had approximately $32.0 million, which exceeded these insured limits.
Accounts receivable
The Company typically requires its customers to remit payments within the first 30 to 37 days, depending on the customer and the products purchased. In addition, the Company offers wholesale distributors a prompt payment discount if they make payments within these deadlines. This discount is generally 2% but may be higher in some instances due to product launches or customer and/or industry expectations. Because the Company’s wholesale distributors typically take the prompt payment discount, the Company accrues 100% of the prompt payment discounts, based on the gross amount of each invoice, at the time
F-10
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 1. | Nature of business and summary of significant accounting policies (continued): |
of sale, and the Company applies earned discounts at the time of payment. The allowance for prompt payment discounts was $0.2 million and $0.05 million as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
The Company performs ongoing credit evaluations and does not require collateral. As appropriate, the Company establishes provisions for potential credit losses. As such, there were no allowances for doubtful accounts as of December 31, 2017 or 2016. The Company writes off accounts receivable when management determines they are uncollectible and credits payments subsequently received on such receivables to bad debt expense in the period received. Write-offs during the years ending December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 were $0, $0.02 million and $0, respectively.
Inventory
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or net realizable value with costs determined for each batch under the first-in, first-out method and specifically allocated to remaining inventory. Inventory consists of raw materials, work in process and finished goods. Raw materials include amounts of active pharmaceutical ingredient for a product to be manufactured, work in process includes the bulk inventory of laminate (the Company’s drug delivery film) prior to being packaged for sale, and finished goods include pharmaceutical products ready for commercial sale.
On a quarterly basis, the Company analyzes its inventory levels and records allowances for inventory that has become obsolete, inventory that has a cost basis more than the expected net realizable value and inventory that is more than expected demand based upon projected product sales. The Company recorded $0.2 million in inventory obsolescence as of December 31, 2017. There were no allowances recorded as of December 31, 2016.
Inventory is composed of the following at December 31:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Raw Materials & Supplies |
$ | 1,338 | $ | 978 | ||||
|
Work-in-process |
3,135 | 1,660 | ||||||
| Finished Goods |
1,861 | 730 | ||||||
| Finished Goods Reserve |
(243 | ) | — | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Inventories |
$ | 6,091 | $ | 3,368 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Property and equipment
The Company records property and equipment at cost less accumulated depreciation, which is computed on a straight-line basis over its estimated useful lives, generally 3 to 10 years.
The Company evaluates the carrying value of the idle equipment when events or changes in circumstances indicate the related carrying amount may not be recoverable. During the year ended December 31, 2017, $0.7 million of idle equipment was placed back into production to support manufacturing of BELBUCA®. During the year ended December 31, 2016, $3.7 million of idle equipment related to the postponement of the U.S. relaunch of ONSOLIS® (see note 6) was re-tooled, put into production and prepared to manufacture BUNAVAIL® to meet product demand in 2016. There was no impairment of equipment recorded during the year ended December 31, 2017 or 2016.
Intangibles and goodwill
The Company reviews intangible assets with finite lives (“other intangible assets”) for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. The Company uses an estimate of the undiscounted cash flows over the remaining life of its other intangible assets, or related group of assets where applicable, in measuring whether the assets to be held and used will be realizable. In the event of impairment, the Company would discount the future cash flows using its then estimated incremental borrowing rate to estimate the amount of the impairment.
There were no impairment charges recognized on finite lived intangibles in 2017, 2016 or 2015.
F-11
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 1. | Nature of business and summary of significant accounting policies (continued): |
Intangible assets with finite useful lives are amortized over the estimated useful lives as follows:
| Estimated Useful Lives | ||
|
| ||
| Licenses |
15 years | |
| BELBUCA® license and distribution rights |
10 years | |
| U.S. product rights |
8-12 years | |
| EU product rights |
7-11 years |
Goodwill is evaluated for impairment at least annually or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount may not be recoverable. During the evaluation of the potential impairment of goodwill, either a qualitative or a quantitative assessment may be performed. If a qualitative evaluation determines that it is more likely than not that no impairment exists, then no further analysis is performed. If a qualitative evaluation is unable to determine whether it is more likely than not that impairment has occurred, a quantitative evaluation is performed. If the carrying value exceeds the fair value, an impairment charge is recorded based on that difference. There were no goodwill impairment charges in 2017, 2016 or 2015.
Deferred revenue
Consistent with the Company’s revenue recognition policy, deferred revenue represents cash received in advance for licensing fees, consulting, research and development services and related supply agreements. Such payments are reflected as deferred revenue until recognized under the Company’s revenue recognition policy. Deferred revenue is classified as current if management believes the Company will be able to recognize the deferred amount as revenue within twelve months of the balance sheet date.
Deferred revenue is recognized when the product is sold to the end user, based upon prescriptions filled. To estimate product sold to end users, the Company relies on third-party information, including prescription data and information obtained from significant distributors with respect to their inventory levels and sales to customers. Deferred revenue is recorded net of estimated allowances for rebates, price adjustments, chargebacks, prompt payment and other discounts. Estimated allowances are recorded and classified as accrued expenses in the accompanying balance sheets as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 (see note 3).
The Company deferred sales, until January 1, 2017, of BUNAVAIL® and recognized such revenue when the product was sold through to the end user. There were no product sales by the Company of BELBUCA® before January 2017. As of December 31, 2016, the Company had $1.7 million of deferred revenue related to sales to wholesalers for which future returns could not be reasonably estimated at the time of sale. There were no deferred sales as of December 31, 2017.
Revenue recognition
Net product sales
Beginning in the first quarter of 2017, the Company had determined that it had sufficient experience with BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® to estimate its returns at time of ex-factory sales. The Company recognizes revenue when it is realized or realizable and earned. Revenue is realized or realizable and earned when all the following criteria are met: (a) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; (b) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; (c) the Company’s price to the buyer is fixed or determinable; and (d) collectability is reasonably assured. The Company sells its products primarily to large national wholesalers, which have the right to return the products they purchase. The Company recognizes revenue from sales transactions where the buyer has the right to return the product at the time of sale only if (1) the Company’s price to the buyer is substantially fixed or determinable at the date of sale, (2) the buyer has paid the Company, or the buyer is obligated to pay the Company and the obligation is not contingent on resale of the product, (3) the buyer’s obligation to the Company would not be changed in the event of theft or physical destruction or damage of the product, (4) the buyer acquiring the product for resale has economic substance apart from any provided by the Company, (5) the Company does not have significant obligations for future performance to directly bring about resale of the product by the buyer, and (6) the amount of future returns can be reasonably estimated. The Company recognizes product sales net of estimated allowances for rebates, price adjustments, returns, chargebacks and prompt payment discounts. Given the sufficient experience with BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®, the Company
F-12
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 1. | Nature of business and summary of significant accounting policies (continued): |
can reasonably estimate the amount of future product returns, and therefore, the risk of estimating product returns has been substantially eliminated. The effect in income from operations and on net income is that the Company can recognize revenue earlier on the sell-in method, net of a provision for estimated returns, since the Company can record revenue once sold to the wholesaler rather than waiting until the product is sold to the end user on a sell-through basis.
The Company establishes allowances for estimated rebates, chargebacks and product returns based on numerous qualitative and quantitative factors, including:
| • | the number of and specific contractual terms of agreements with customers; |
| • | estimated levels of inventory in the distribution channel; |
| • | historical rebates, chargebacks and returns of products; |
| • | direct communication with customers; |
| • | anticipated introduction of competitive products or generics; |
| • | anticipated pricing strategy changes by the Company and/or its competitors; |
| • | analysis of prescription data gathered by a third-party prescription data provider; |
| • | the impact of changes in state and federal regulations; and |
| • | the estimated remaining shelf life of products. |
In its analyses, the Company uses prescription data purchased from a third-party data provider to develop estimates of historical inventory channel sell-through. The Company utilizes an internal analysis to compare historical net product shipments to estimated historical prescriptions written. Based on that analysis, management develops an estimate of the quantity of product in the channel which may be subject to various rebate, chargeback and product return exposures. To estimate months of ending inventory in the Company’s distribution channel, the Company divides estimated ending inventory in the distribution channel by the Company’s recent prescription data, not considering any future anticipated demand growth beyond the succeeding quarter. Monthly for each product line, the Company prepares an internal estimate of ending inventory units in the distribution channel by adding estimated inventory in the channel at the beginning of the period, plus net product shipments for the period, less estimated prescriptions written for the period. This is done for each product line by applying a rate of historical activity for rebates, chargebacks and product returns, adjusted for relevant quantitative and qualitative factors discussed above, to the potential exposed product estimated to be in the distribution channel.
Product returns-Consistent with industry practice, the Company offers contractual return rights that allow its customers to return the products within an 18-month period that begins six months prior to and ends twelve months after expiration of the products.
Rebates- The liability for government program rebates is calculated based on historical and current rebate redemption and utilization rates contractually submitted by each program’s administrator.
Price adjustments and chargebacks-The Company’s estimates of price adjustments and chargebacks are based on its estimated mix of sales to various third-party payers, which are entitled either contractually or statutorily to discounts from the Company’s listed prices of its products. If the sales mix to third-party payers is different from the Company’s estimates, the Company may be required to pay higher or lower total price adjustments and/or chargebacks than it had estimated, and such differences may be significant.
The Company, from time to time, offers certain promotional product-related incentives to its customers. These programs include certain product incentives to pharmacy customers and other sales stocking allowances. The Company has voucher programs for BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® whereby the Company offers a point-of-sale subsidy to retail consumers. The Company estimates its liabilities for these voucher programs based on the actual redemption rates as reported to the Company by a third-party claims processing organization. The Company accounts for the costs of these special promotional programs as price adjustments, which are a reduction of gross revenue.
Prompt payment discounts-The Company typically offers its wholesale customers a prompt payment discount of 2% as an incentive to remit payments within the first 30 to 37 days after the invoice date depending on the customer and the products purchased.
F-13
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 1. | Nature of business and summary of significant accounting policies (continued): |
Gross to net accruals-A significant majority of the Company’s gross to net adjustments to gross product revenues are the result of accruals for its voucher program and Medicaid rebates, with most of those programs having an accrual to payment cycle of anywhere from one to three months. In addition to this relatively short accrual to payment cycle, the Company receives daily information from the wholesalers regarding their sales of the Company’s products and actual on hand inventory levels of its products. This enables the Company to execute accurate provisioning procedures. Consistent with the pharmaceutical industry, the accrual to payment cycle for returns is longer and can take several years depending on the expiration of the related products.
License and development agreements
The Company periodically enters into license and development agreements to develop and commercialize its products. The arrangements typically are multi-deliverable arrangements that are funded through upfront payments, milestone payments and other forms of payment. The Company currently has multiple license and development agreements that are described in notes 6, 8 and 9. Depending on the nature of the contract these revenues are classified as research and development reimbursements or contract revenue.
Deferred cost of sales
Prior to January 1, 2017, the Company deferred its cost of sales relating to BUNAVAIL® sales at time of ex-factory sales. These costs were recognized when the product was sold through to the end user. Beginning January 1, 2017, cost of sales for BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® are recognized when sold to the wholesaler from our distribution center.
The Company incurred $1.7 million of deferred costs of sales for the year ended December 31, 2016, which is included in other current assets in the accompanying balance sheets. There was no deferred cost of sales for the year ended December 31, 2017.
Cost of sales
Cost of sales includes the direct costs attributable to the production of BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®. It includes raw materials, production costs at the Company’s three contract manufacturing sites, quality testing directly related to the products, and depreciation on equipment that the Company has purchased to produce BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®. It also includes any batches not meeting specifications and raw material yield losses. Yield losses and batches not meeting specifications are expensed as incurred. Prior to January 1, 2017, cost of sales was recognized as actual product was sold through to the end user. Beginning January 1, 2017, cost of sales is recognized when sold to the wholesaler from our distribution center.
For BREAKYL™ and PAINKYL™ (the Company’s out-licensed breakthrough cancer pain therapies), cost of sales includes all costs related to creating the product at the Company’s contract manufacturing location in Germany. The Company’s contract manufacturer bills the Company for the final product, which includes materials, direct labor costs, and certain overhead costs as outlined in applicable supply agreements. Cost of sales also includes royalty expenses that the Company owes to third parties.
Research and development expenses
Research and development expenses consist of product development expenses incurred in identifying, developing and testing product candidates. Product development expenses consist primarily of labor, benefits and related employee expenses for personnel directly involved in product development activities; fees paid to professional service providers for monitoring and analyzing clinical trials; expenses incurred under joint development agreements; regulatory costs; costs of contract research and manufacturing of inventory used in testing and clinical trials; and the cost of facilities used by the Company’s product development personnel.
Product development expenses are expensed as incurred and reflect costs directly attributable to product candidates in development during the applicable period and to product candidates for which the Company has discontinued development. Additionally, product development expenses include the cost of qualifying new current Good Manufacturing Practice (“cGMP”) third-party manufacturers for the Company’s product candidates, including expenses associated with any related technology transfer. All indirect costs (such as salaries, benefits or other costs related to the Company’s accounting, legal, human resources, purchasing, information technology and other general corporate functions) associated with individual product candidates are included in general and administrative expenses. Research and development expenses were $13.0 million, $18.9 million and $20.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2016 respectively.
F-14
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 1. | Nature of business and summary of significant accounting policies (continued): |
Advertising
Advertising costs, which include promotional expenses and the cost of placebo samples, are expensed as incurred. Advertising expenses were $3.8 million, $4.2 million and $4.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively, and are included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Shipping and handling costs
Shipping and handling costs, which include expenses from our wholesalers, are expensed as incurred. Shipping and handling costs were $0.2 million, $0.05 and $0.05 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively, and are included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Stock-based compensation
The Company has a stock-based compensation plan under which various types of equity-based awards are granted, including stock options, restricted stock units (RSUs) and performance-based RSUs. The fair value of stock option and RSUs, which are subject only to service conditions with graded vesting, are recognized as compensation expense, generally on a straight-line basis over the service period, net of estimated forfeitures. Forfeitures are recognized as they occur. The fair values of performance-based RSUs are recognized as compensation expense from the grant date to the end of the performance period. The Company uses the fair-value based method to determine compensation for all arrangements under which employees and others receive shares of stock or equity instruments (warrants and options). The grant date fair value of an RSU equals the closing price of our common stock on the trading day preceding the grant date. The fair value of each option and warrant is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes valuation model that uses assumptions for expected volatility, expected dividends, expected term, and the risk-free interest rate. Expected volatility is based on historical volatility of the Company’s Common Stock and other factors estimated over the expected term of the options. The expected term of options granted is derived using the “simplified method” which computes expected term as the average of the sum of the vesting term plus the contract term. The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield.
In applying the Black-Scholes options-pricing model, assumptions are as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||
| Expected price volatility |
68.76%-78.79% | 62.65%-80.78% | 73.00%-76.78% | |||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.77%-2.05% | 0.56%-1.70% | 1.25%-1.68% | |||
| Weighted average expected life in years |
6 years | 6 years | 6 years | |||
| Dividend yield |
— | — | — |
The Company estimated fair values of derivative financial instruments using the Black-Scholes option valuation technique because it embodied all of the requisite assumptions (including trading volatility, estimated terms and risk-free rates) necessary to fairly value these instruments. In addition, option-based techniques were highly volatile and sensitive to changes in the Company’s trading market price which was high-historical volatility. Since derivative financial instruments were initially and subsequently carried at fair values, the Company’s operating results reflected the volatility in these estimates and assumption changes.
Recent accounting pronouncements
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers,” which supersedes the revenue recognition requirements of Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 605, “Revenue Recognition” and most industry-specific guidance on revenue recognition throughout the ASC. The standard’s core principle is that a company will recognize revenue when it transfers promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. In doing so, companies will need to use more judgment and make more estimates than under today’s guidance. In August 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-14, which defers the effective date of ASU 2014-09 for all entities by one year. Accordingly, public business entities should apply the guidance in ASU 2014-09 to annual reporting periods (including interim periods within those periods) beginning after December 15, 2017. The standard may be applied retrospectively to each prior period presented (full retrospective method) or retrospectively with the cumulative effect recognized as of the date of initial application (modified retrospective method).
F-15
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 1. | Nature of business and summary of significant accounting policies (continued): |
The Company used the modified retrospective approach upon adoption of this guidance effective January 1, 2018 using a cumulative effect adjustment to accumulated deficit. The Company utilized a comprehensive approach to assess the impact of the guidance on its contract portfolio. The Company reviewed its current accounting policies and practices to identify potential differences resulting from the application of the new requirements to its revenue contracts, including evaluation of performance obligations in the contract, estimating the amount of variable consideration to include in the transaction price, allocating the transaction price to each separate performance obligation and accounting treatment of costs to obtain and fulfill contracts. In addition, the Company will update certain disclosures, as applicable, included in our financial statements to meet the requirements of the new guidance beginning in January 1, 2018. Under the new guidance, the Company is required to evaluate the impact of estimating variable consideration related to our product sales and licensing contracts. The Company will use the expected value method to estimate the total revenue of the contract, constrained by the probability that there would not be a significant revenue reversal in a future period. The Company will continue to evaluate the expected value of revenue over the term of the contract and adjust revenue recognition as appropriate. Based on this evaluation, the adoption will not have a material impact on the Company’s financial position, results of operations, cash flows, accounting policies, business processes, internal controls or disclosures.
The FASB’s new leases standard, ASU 2016-02 Leases (Topic 842), was issued on February 25, 2016. ASU 2016-02 is intended to improve financial reporting about leasing transactions. The ASU affects all companies and other organizations that lease assets such as real estate, airplanes, and manufacturing equipment. The ASU will require organizations that lease assets referred to as “Lessees” to recognize on the balance sheet the assets and liabilities for the rights and obligations created by those leases. An organization is to provide disclosures designed to enable users of financial statements to understand the amount, timing, and uncertainty of cash flows arising from leases. These disclosures include qualitative and quantitative requirements concerning additional information about the amounts recorded in the financial statements. Under the new guidance, a lessee will be required to recognize assets and liabilities for leases with lease terms of more than 12 months. Consistent with current GAAP, the recognition, measurement, and presentation of expenses and cash flows arising from a lease by a lessee primarily will depend on its classification as a finance or operating lease. However, unlike current GAAP which requires only capital leases to be recognized on the balance sheet, the new ASU will require both types of leases (i.e. operating and capital leases) to be recognized on the balance sheet. The FASB lessee accounting model will continue to account for both types of leases. The capital lease will be accounted for in substantially the same manner as capital leases are accounted for under existing GAAP. The operating lease will be accounted for in a manner similar to operating leases under existing GAAP, except that lessees will recognize a lease liability and a lease asset for all of those leases. The new standard requires a modified-retrospective approach to adoption and is effective for interim and annual periods beginning on January 1, 2019, but may be adopted earlier. The Company expects to adopt this standard beginning in 2019. The Company does not expect that this standard will have a material impact on its consolidated statements of operations, but the Company does expect that upon adoption, this standard will impact the carrying value of its assets and liabilities on its consolidated balance sheets as a result of the requirement to record right-of-use assets and corresponding lease obligations for current operating leases. In addition, the standard will require that the Company update its systems, processes and controls it uses to track, record and account for its lease portfolio.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-01, Business Combinations (Topic 805): Clarifying the Definition of a Business. The amendments in this update provide a screen to determine when an integrated set of assets and activities (a “set”) is not a business. The screen requires that when substantially all of the fair value of the gross assets acquired (or disposed of) is concentrated in a single identifiable asset or a group of similar identifiable assets, the set is not a business. The new standard also requires that a business include at least one substantive process and narrows the definition of outputs. The new guidance will be applied prospectively and is effective for the Company for interim and annual periods beginning on January 1, 2018 and early adoption is permitted. The Company expects to adopt this standard beginning in 2018. Adoption of this new standard may result in more transactions being accounted for as asset acquisitions versus business combinations; however, the impact to the Company’s consolidated financial statements will depend on the facts and circumstances of future transactions.
F-16
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 1. | Nature of business and summary of significant accounting policies (continued): |
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU Update No. 2017-04, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Simplifying the Test of Goodwill Impairment. This ASU simplifies the accounting for goodwill impairment for all entities by requiring impairment charges to be based on the first step of the goodwill impairment test under ASC 350. Under previous guidance, if the fair value of a reporting unit is lower than its carrying amount (Step 1), an entity calculates any impairment charge by comparing the implied fair value of goodwill with its carrying amount (Step 2). The implied fair value of goodwill is calculated by deducting the fair value of all assets and liabilities of the reporting unit from the reporting unit’s fair value as determined in Step 1. To determine the implied fair value of goodwill, entities estimate the fair value of any unrecognized intangible assets (including in-process research and development) and any corporate-level assets or liabilities that were included in the determination of the carrying amount and fair value of the reporting unit in Step 1. Under this new guidance if a reporting unit’s carrying value exceeds its fair value, an entity will record an impairment charge based on that difference with such impairment charge limited to the amount of goodwill in the reporting unit. This ASU does not change the guidance on completing Step 1 of the goodwill impairment test. An entity will still be able to perform today’s optional qualitative goodwill impairment assessment before determining whether to proceed to Step 1. This ASU will be applied prospectively and is effective for annual and interim impairment tests performed in periods beginning after December 15, 2019 for public business enterprises. Early adoption is permitted for annual and interim goodwill impairment testing dates after January 1, 2017. The Company adopted this guidance during the year ended December 31, 2017 and determined that ASU 2017-04 did not have any impact on its consolidated financial statements.
| 2. | Liquidity: |
At December 31, 2017, the Company had cash of approximately $21.2 million. The Company used $32.5 million of cash in operations during the year-ended December 31, 2017 and had stockholders’ equity of $8.9 million, versus stockholders’ deficit of $17.7 million at December 31, 2016. The Company expects that it has sufficient cash to manage the business as currently planned into the second quarter of 2019, which includes access to additional capital through CRG Servicing LLC (“CRG”) from the CRG loan of $15 million if it satisfies the third draw requirements (see note 11) as well as equity markets if the Company chooses or a combination of both that would provide sufficient capital necessary to support the commercialization of BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL®. This estimation assumes that the Company does not otherwise face unexpected events, costs or contingencies, any of which could affect the Company’s cash requirements from time to time. As a result of the Company’s late filing of certain financing information related to its reacquisition of BELBUCA® in 2017, the Company is unable to utilize its universal shelf registration statement and associated at-the-market offering program until April 2018.
Additional capital will be required to support the continued commercialization of the Company’s BELBUCA® and BUNAVAIL® products, the reformulation project for and the anticipated commercial relaunch of ONSOLIS®, the potential continued development of Buprenorphine Extended Release Injection or other products which may be acquired or licensed by the Company, and for general working capital requirements. Based on product development timelines and agreements with the Company’s development partners, the ability to scale up or reduce personnel and associated costs are factors considered throughout the product development life cycle. Available resources may be consumed more rapidly than currently anticipated, potentially resulting in the need for additional funding. Additional funding, capital or loans (including, without limitation, milestone or other payments from commercialization agreements) may be unavailable on favorable terms, if at all.
F-17
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 3. | Accounts payable and accrued liabilities: |
The following table represents the components of accounts payable and accrued liabilities as of December 31:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 12,236 | $ | 9,397 | ||||
| Accrued rebates |
5,648 | 3,842 | ||||||
| Accrued compensation and benefits |
3,472 | 2,052 | ||||||
| Accrued acquisition costs |
2,311 | — | ||||||
| Accrued returns |
915 | — | ||||||
| Accrued royalties |
488 | 518 | ||||||
| Accrued clinical trial costs |
234 | 615 | ||||||
| Accrued legal |
216 | 490 | ||||||
| Accrued manufacturing costs |
— | 200 | ||||||
| Accrued sales and marketing costs |
— | 193 | ||||||
| Accrued other |
629 | 265 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total accounts payable and accrued expenses |
$ | 26,149 | $ | 17,572 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
As of December 31, 2017, three vendors comprised 39% of the accounts payable balance. As of December 31, 2016, two vendors comprised 28% of the accounts payable balance.
| 4. | Property and equipment: |
Property and equipment, summarized by major category, consist of the following as of December 31:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Machinery & equipment |
$ | 5,428 | $ | 4,476 | ||||
| Computer equipment & software |
399 | 464 | ||||||
| Office furniture & equipment |
169 | 202 | ||||||
| Leasehold improvements |
44 | 53 | ||||||
| Idle equipment |
766 | 1,486 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
6,806 | 6,681 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Less accumulated depreciation |
(3,028 | ) | (2,451 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total property, plant & equipment, net |
$ | 3,778 | $ | 4,230 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Depreciation expense for years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 was approximately $0.7 million, $0.4 million and $0.3 million, respectively.
| 5. | Other intangible assets: |
Other intangible assets, net, consisting of product rights and licenses are summarized as follows:
| December 31, 2017 |
Gross Carrying Value |
Accumulated Amortization |
Intangible Assets, net |
Weighted average Useful Life |
||||||||||||
| Product rights |
$ | 6,050 | $ | (4,881 | ) | $ | 1,169 | 1.21 | ||||||||
| BELBUCA® license and distribution rights |
45,000 | (4,500 | ) | 40,500 | 8.50 | |||||||||||
| Licenses |
1,900 | (1,709 | ) | 191 | 0.54 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total intangible assets |
$ | 52,950 | $ | (11,090 | ) | $ | 41,860 | 10.25 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| December 31, 2016 |
Gross Carrying Value |
Accumulated Amortization |
Intangible Assets, net |
Weighted average Useful Life |
||||||||||||
| Product rights |
$ | 9,050 | $ | (7,052 | ) | $ | 1,998 | 9.11 | ||||||||
| Licenses |
1,900 | (1,613 | ) | 287 | 1.84 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total intangible assets |
$ | 10,950 | $ | (8,665 | ) | $ | 2,285 | 10.95 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
F-18
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 5. | Other intangible assets (continued): |
The Company incurred amortization expense on other intangible assets of approximately $5.4 million, $1.0 million and $1.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Estimated aggregate future amortization expenses for other intangible assets for each of the next five years and thereafter are as follows:
| Years ending December 31, | ||||
| 2018 |
$ | 5,157 | ||
| 2019 |
5,157 | |||
| 2020 |
4,547 | |||
| 2021 |
4,500 | |||
| 2022 |
4,500 | |||
| Thereafter |
17,999 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 41,860 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| 6. | License and development agreements: |
The Company periodically enters into license and development agreements to develop and commercialize its products. The arrangements typically are multi-deliverable arrangements that are funded through upfront payments, milestone payments, royalties and other forms of payment to the Company. The Company’s most significant license and development agreements are as follows:
Meda license, development and supply agreements
In August 2006 and September 2007, the Company entered into certain agreements with Meda AB (“Meda”) a subsidiary of Mylan N.V., a Swedish company to develop and commercialize the Company’s ONSOLIS® product, a drug treatment for breakthrough cancer pain delivered utilizing the Company’s BEMA® technology. The agreements related to the United States, Mexico and Canada (“Meda U.S. Agreements”) and to certain countries in Europe (“Meda EU Agreements”). They carry license terms that commenced on the date of first commercial sale in each respective territory and end on the earlier of the entrance of a generic product to the market or upon expiration date of the last to expire Orange Book listed patents which currently is July 23, 2027.
The Company has determined that it is acting as a principal under the Meda Agreements and, as such, will record product supply revenue, research and development services revenue and other services revenue amounts on a gross basis in the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
On March 12, 2012, the Company announced the postponement of the U.S. relaunch of ONSOLIS® following the initiation of the class-wide Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (“REMS”) until the product formulation could be modified to address two appearance-related issues. Such appearance-related issues involved the formation of microscopic crystals and a fading of the color in the mucoadhesive layer, and as previously reported the Company has since worked with FDA to reformulate ONSOLIS® to address these issues. In August 2015, the Company announced the FDA approval of the new formulation. The Company identified a new supplier and requested guidance from the FDA on specific requirements for obtaining approval to supply product from this new vendor. Based on the Company’s current estimates, the Company will be able to submit the necessary documentation to the FDA for qualification of the new manufacturer in the first quarter of 2018.
On January 27, 2015, the Company announced that it had entered into an assignment and revenue sharing agreement with Meda to return to the Company the marketing authorization for ONSOLIS® in the U.S. and the right to seek marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® in Canada and Mexico. In connection with the return to the Company by Meda of the U.S. marketing authorization in January 2015, the remaining U.S.-related deferred revenue of $1.0 million was recorded as contract revenue during the year ended December 31, 2015. On February 27, 2016, the Company entered into an extension of the assignment and revenue sharing agreement to extend the period until December 31, 2016, which terminated on May 11, 2016 upon the signing of the Termination and Revenue Sharing Agreement (“the Agreement”).
Simultaneously on May 11, 2016, the Company and Collegium executed a definitive License and Development Agreement (the “License Agreement”) under which the Company had granted to Collegium the exclusive rights to develop and commercialize ONSOLIS® in the U.S. See “Collegium License and Development Agreement” below.
F-19
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 6. | License and development agreements (continued): |
Collegium license and development agreement
On May 11, 2016, the Company and Collegium executed a License Agreement under which the Company granted Collegium the exclusive rights to develop and commercialize ONSOLIS® in the U.S.
Under the terms of the License Agreement, Collegium was responsible for the manufacturing, distribution, marketing and sales of ONSOLIS® in the U.S. The Company was obligated to use commercially reasonable efforts to continue the transfer of manufacturing to the anticipated manufacturer for ONSOLIS® and to submit a corresponding Prior Approval Supplement (the “Supplement”) to the FDA with respect to the current NDA for ONSOLIS®. Following approval of the Supplement, the NDA and manufacturing responsibility for ONSOLIS® (including the manufacturing relationship with the Company’s manufacturer, subject to the Company entering into an appropriate agreement with such manufacturer that is acceptable and assignable to Collegium) would have been transferred to Collegium.
On December 8, 2017, the Company received the required 90-day notice from Collegium regarding termination of the License Agreement and the effective date of termination was March 8, 2018. The Company is assessing its commercial options for ONSOLIS®.
Pursuant to the Collegium Agreement, the Company has received the following payments:
| • | a $2.5 million upfront non-refundable payment, payable to the Company within 30 days of execution of the License Agreement (received June 2016); |
| • | reimbursement to the Company for a pre-determined amount of the remaining expenses associated with the ongoing transfer of the manufacturing of ONSOLIS®; |
ONSOLIS® was originally licensed to, and launched in the U.S. by, Meda. In January 2015, the Company entered into an assignment and revenue sharing agreement (the “ARS Agreement”) with Meda pursuant to which Meda transferred the marketing authorizations for ONSOLIS® in the United States back to the Company. Under the ARS Agreement, financial terms were established that enable Meda to share a significant portion of the proceeds of milestone and royalty payments received by the Company from any new North American partnership for ONSOLIS® that may be executed by the Company. The execution of the License Agreement between the Company and Collegium also required the execution of a definitive termination agreement between the Company and Meda embodying those royalty-sharing terms, returning ONSOLIS®-related assets and rights in the U.S., Canada, and Mexico to the Company, and including certain other provisions. In addition, the Company’s royalty obligations to CDC IV, LLC (“CDC IV”) and its assignees will remain in effect. CDC IV provided funding for the development of ONSOLIS® in the past.
Endo license and development agreement
In January 2012, the Company entered into a License and Development Agreement with Endo Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Endo”) pursuant to which the Company granted Endo an exclusive commercial world-wide license to develop, manufacture, market and sell the Company’s BELBUCA® product and to complete U.S. development of such product candidate for purposes of seeking FDA approval (the “Endo Agreement”). BELBUCA® is for the management of pain severe enough to require daily, around-the-clock, long-term opioid treatment and for which alternative treatment options are inadequate.
Pursuant to the Endo Agreement, Endo had obtained all rights necessary to complete the clinical and commercial development of BELBUCA® and to sell the product worldwide. Although Endo had obtained all such necessary rights, the Company had agreed under the Endo Agreement to be responsible for the completion of certain clinical trials regarding BELBUCA® (and to provide clinical trial materials for such trials) necessary to submit a New Drug Application (“NDA”) to the FDA to obtain approval of BELBUCA® in the U.S. Such NDA was submitted to the FDA in December 2014, was accepted by the FDA February 2015 and was approved by the FDA in October 2015. The Company was responsible for development activities through the filing of the NDA in the U.S., while Endo was responsible for the development following the NDA submission as well as the manufacturing, distribution, marketing and sales of BELBUCA® on a worldwide basis. In addition, Endo was responsible for all filings required to obtain regulatory approval of BELBUCA®.
F-20
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 6. | License and development agreements (continued): |
Pursuant to the Endo Agreement, the Company has received the following recent payments:
| • | $10 million upon FDA acceptance of filing NDA (earned in February 2015); |
| • | $50 million upon regulatory approval, earned in October 2015 and received in November 2015. Of the $50 million received in November 2015, $20 million related to a patent extension and was recorded as deferred revenue because all or a portion of such $20 million was contingently refundable to Endo if a third party generic product was introduced in the U.S. during the patent extension period from 2020 to 2027. However, due to the Company and Endo entering into a Termination Agreement on December 7, 2016 which terminated the BELBUCA® license to Endo effective January 6, 2017, the deferred $20 million was recognized as revenue in January 2017. (See note 7, Business Combinations and BELBUCA® Acquisition). |
The Company had assessed its arrangement with Endo and the Company’s deliverables thereunder at inception to determine: (i) the separate units of accounting for revenue recognition purposes, (ii) which payments should be allocated to which of those units of accounting and (iii) the appropriate revenue recognition pattern or trigger for each of those payments. The assessment requires subjective analysis and requires management to make judgments, estimates and assumptions about whether deliverables within multiple-element arrangements are separable and, if so, to determine the amount of arrangement consideration to be allocated to each unit of accounting.
The Company was reimbursed by Endo for certain research and development costs when these costs went beyond set thresholds as outlined in the Endo Agreement. Endo reimbursed the Company for this spending at cost and the Company received no mark-up or profit. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recognized $0.9 million of reimbursable expenses related to the Endo Agreement, which is recorded as research and development reimbursement revenue. There was no research and development reimbursement revenue during the years ended December 31, 2017 or 2016, since the program ended in 2015.
F-21
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 6. | License and development agreements (continued): |
On October 26, 2015, the Company and Endo announced that the FDA approved BELBUCA® (on October 23, 2015). FDA approval of BELBUCA® triggered a milestone payment to the Company from Endo of $50 million pursuant to the Endo Agreement, less approximately $6.0 million of the aforementioned cumulative pre-payments received and recorded in deferred revenue, current in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet. The Company received payment of such milestone in November 2015 and deferred $20 million of the $50 million payment because all or a portion of the $20 million was contingently refundable to Endo if a third party generic product was introduced in the U.S. during the patent extension period from 2020 to 2027 at year ended December 31, 2016. The remaining $30 million of the $50 million payment was recognized as revenue during the year ended December 31, 2015. However, due to the Company and Endo entering into a Termination Agreement on December 7, 2016 which terminated the BELBUCA® license to Endo effective January 6, 2017, the deferred $20 million was recognized as revenue in January 2017. (See note 7, Business Combinations and BELBUCA® Acquisition).
| 7. | Business combination and BELBUCA® acquisition: |
On December 7, 2016, the Company and Endo entered into the Termination Agreement to terminate Endo’s licensing rights for BELBUCA®. The transaction closed on January 6, 2017. At the closing date, the Company purchased from Endo the following net assets (the “net assets”): (i) current BELBUCA® product inventory and work-in-progress, (ii) material manufacturing contracts related to BELBUCA®, (iii) BELBUCA®-related domain names and trademarks (including the BELBUCA® trademark), (iv) BELBUCA® -related manufacturing equipment, and (v) all pre-approval regulatory submissions, including any Investigational New Drug Applications and New Drug Applications, regulatory approvals and post-approval regulatory submissions concerning BELBUCA®. The purchase price for the net assets (the “Asset Purchase Price”) was equal to the sum of: (i) the aggregate book value of the portion of the transferred product inventory forecasted to be used or sold by the Company, (ii) the aggregate book value of work-in-progress inventory, and (iii) the assumption of any assumed liabilities. Together with the Asset Purchase Price, pursuant to the terms of the Termination Agreement, the Company will also pay to Endo a fee in the amount of $5 million in consideration for (i) Endo’s agreement not to compete for a period of two years from the closing date of the termination agreement and (ii) Endo’s waiver of its right to sell product for twelve months following the closing of the termination agreement.
At the closing date, the Company accepted transfer of the net assets and assumed and agreed to discharge when due all applicable liabilities assumed by the Company, which consisted of post-closing obligations for liabilities and payments associated with the net assets, the assumed contracts related to the net assets and applicable taxes (with the obligation for pre-closing and other certain liabilities resulting from the acts or omissions of Endo being retained by Endo). The Asset Purchase Price, together with all other payments (including a non-compete covenant payment) due to Endo under the Termination Agreement, was payable to Endo in cash in four quarterly installments on the last calendar day of each quarter in 2017. Furthermore, the Company is not responsible for future royalties or milestone payments to Endo and Endo is not obligated to any future milestone payments to the Company. The Termination Agreement contains customary representations and warranties and mutual releases and indemnification.
At the closing date, the Company and Endo entered into a Transition Services Agreement which governed the post-closing rights and responsibilities of the Company and Endo in connection with the license termination and the transfer of the Assets to the Company. Under this agreement, the Company and Endo agreed to the handling of transition matters such as managing customer contracts, BELBUCA® price reporting, payments, returns and rebates, and customer and managed care relations. In connection therewith, Endo has agreed to provide to the Company an agreed upon number of work hours to be provided by Endo personnel during the transition for certain of these transition services and other assistance with respect to the transition of BELBUCA® to the Company.
The BELBUCA® acquisition was accounted for as a business combination in accordance with ASC No. 805, Business Combinations which, among other things, requires assets acquired and liabilities assumed to be measured at their acquisition date fair values. Determining the fair value of certain acquired assets and liabilities is subjective in nature and often involves the use of significant estimates and assumptions, including, but not limited to, the selection of appropriate valuation methodology, projected revenue, expenses and cash flows, weighted average cost of capital, discount rates, and estimates of terminal values. The Company believes the estimates used are reasonable and the significant effects of the BELBUCA® acquisition are properly reflected.
F-22
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 7. | Business combination and BELBUCA® acquisition (continued): |
The following table summarizes the consideration paid to acquire BELBUCA® and the estimated values of assets acquired and liabilities assumed in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet based on their fair values on January 6, 2017 (the date of the Endo Closing):
| Asset purchase price: |
||||
| Deferred cash consideration to Endo |
$ | 7,536 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Total asset purchase price |
$ | 7,536 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Estimated fair value of assets acquired: |
||||
| Current BELBUCA® product inventory and work-in process |
$ | 5,412 | ||
| BELBUCA®-related manufacturing equipment |
432 | |||
| License and distribution rights intangible assets |
45,000 | |||
| Deferred tax liability |
(15,972 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Amount attributable to assets acquired |
$ | 34,872 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Bargain purchase gain |
$ | (27,336 | ) | |
|
|
|
Inventories acquired included raw materials, work-in-progress and finished goods. The fair value of the acquired finished goods inventory was estimated by adjusting the anticipated selling price costs to sell and an appropriate profit on selling activities. For work-in-process, in addition to those inputs used to estimate the fair value of finished goods, the cost and estimated profit on completing the manufacturing are also included. The fair value of the raw materials represent cost to acquire the materials from suppliers.
The fair value of the equipment was determined by consideration of replacement cost and equipment condition and was assigned a useful life of seven years. The fair value of the license and distribution rights intangible assets as amortized in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets were estimated primarily using the “income method,” which starts with a forecast of all expected future cash flows. Some of the more significant assumptions inherent in the development of intangible asset values, from the perspective of a market participant, include: the amount and timing of projected future cash flows (including net revenue, cost of sales, commercial expenses, research and development costs and working capital requirements) as well as estimated contributory asset charges; the discount rate selected to measure the risks inherent in the future cash flows; and the assessment of the asset’s life cycle and the competitive trends impacting the asset, among other factors. The license and distribution rights intangible assets will be amortized over ten years, which approximates the current, remaining patent life of the BELBUCA® -related intellectual property.
As a result of the business combination, the Company recognized a deferred tax liability of $16.0 million. This deferred tax liability was netted against its deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2017. Because a full valuation allowance has been provided against the Company’s deferred tax assets as it is considered more likely than not that they will not be utilized, the Company released a corresponding amount of its valuation allowance during the year ended December 31, 2017 and recognized a $16.0 million tax benefit in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations.
During the year ended December 31, 2017, the Company recorded the asset acquisition as a bargain purchase gain of $27.3 million in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations.
Pro forma impact of acquisition of BELBUCA®
The following pro forma combined results of operations are provided for the year ended December 31, 2016, as though the BELBUCA® acquisition had been completed as of January 1, 2016. These supplemental pro forma results of operations are provided for illustrative purposes only and do not purport to be indicative of the actual results that would have been achieved by the combined company for the period presented or that may be achieved by the combined company in the future. The pro forma results of operations do not include any cost savings or other synergies that resulted, or may result, from the BELBUCA® acquisition or any estimated costs that will be incurred to integrate the BELBUCA® product line, nor do they reflect the bargain purchase gain recognized. Future results may vary significantly from the results in this pro forma information because of future events and transactions, as well as other factors.
F-23
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 7. | Business combination and BELBUCA® acquisition (continued): |
| (in thousands, except per share data) | December 31, 2016 (unaudited) |
|||
| Revenue |
$ | 25,010 | ||
| Net loss |
$ | (201,769 | ) | |
| Pro forma net loss per common share |
||||
| Basic |
$ | (3.76 | ) | |
| Diluted |
$ | (3.76 | ) | |
The Company’s historical financial information was adjusted to give effect to the pro forma events that were directly attributable to the BELBUCA® acquisition and factually supportable. The unaudited pro forma consolidated results include historical revenues and expenses of assets acquired in the acquisition with the following adjustments:
| • | Adjustment to recognize incremental amortization expense based on the fair value of intangibles acquired; |
| • | Adjustment to recognize incremental depreciation expense for equipment acquired in the acquisition. |
Endo launched BELBUCA® in February 2016, therefore, pro forma impact of acquisition during the year ended December 31, 2015 is not applicable.
| 8. | License obligations: |
Arcion license agreement
On March 26, 2013, the Company entered into a license agreement with Arcion Therapeutics, Inc. (the “Arcion Agreement”) pursuant to which Arcion granted to the Company an exclusive commercial world-wide license, with rights of sublicense, under certain patent and other intellectual property rights related to in-process research and development to develop, manufacture, market, and sell gel products containing clonidine (or a derivative thereof) for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy (“PDN”) and other indications (the “Arcion Products”).
On December 13, 2016, the Company announced that its Phase 2b clinical study assessing the efficacy and safety of Clonidine Topical Gel failed to show a statistically significant difference in pain relief between Clonidine Topical Gel and placebo. As a result, the Company has discontinued further development of the product as of December 31, 2016.
Evonik definitive development and exclusive license option agreement:
On October 27, 2014, the Company entered into a definitive Development and Exclusive License Option Agreement (the “Development Agreement”) with Evonik Corporation, (“Evonik”) to develop and commercialize an injectable, extended release, microparticle formulation of buprenorphine for the treatment of opioid dependence (the “Evonik Product”). Under the Development Agreement, the Company also has the right to pursue development of the Evonik Product for pain management.
Under the Development Agreement, Evonik has also granted to the Company two exclusive options to acquire exclusive worldwide licenses, with rights of sublicense, to certain patents and other intellectual property rights of Evonik to develop and commercialize certain products containing buprenorphine. If these options are exercised, such licenses would be memorialized in the Evonik License Agreement (as defined below).
Pursuant to the Development Agreement, Evonik is responsible for using commercially reasonable efforts to develop a formulation for the Evonik Product in accordance with a work plan mutually agreed upon by the parties (the “Evonik Project”). Should the Evonik Project proceed past the formulation stage, Evonik also has the right to manufacture clinical and commercial supplies of Evonik Product, such manufacturing arrangement to be negotiated by the parties in good faith in a formal License and Supply Agreement(s) (the “Evonik License Agreement”), with such Evonik License Agreement covering Evonik’s intellectual property rights to be entered into between the parties if certain conditions are met and terms are mutually agreed upon.
Should Evonik and the Company enter into the License Agreement following the attainment of a Phase 1 ready formulation of the Evonik Product for one or both of the opioid dependence or pain management indications, the Company would pay Evonik a non-refundable, non-creditable one-time payment in conjunction with certain future regulatory filings and approvals and royalties on net sales of the Evonik Product.
F-24
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 8. | License obligations (continued): |
The Development Agreement contains customary termination provisions, and the Company may additionally terminate the Development Agreement at any time after the completion of certain enumerated tasks as provided in the Development Agreement, for any reason or no reason, by providing written notice of termination to Evonik. Upon termination of the Development Agreement, Evonik will be paid any amounts owed to Evonik in accordance with the estimated budget for work performed under the Development Agreement through the effective date of termination, including any reasonable, documented, non-cancelable third-party costs and any reasonable, documented wind-down costs reasonably incurred by Evonik in connection with the Evonik Project. Should the Company terminate for reasons other than for a material, uncured breach by Evonik or Evonik’s bankruptcy, Evonik shall have the right to use any and all data and intellectual property generated under the Evonik Project for any purpose.
This product candidate is currently in the pre-clinical stage of development. An Investigational New Drug Application (“IND”) for opioid dependence was filed in the fourth quarter 2016.
| 9. | Other license agreements and acquired product rights: |
Purdue license and supply agreement:
On July 12, 2017, the Company, along with Purdue Pharma, an Ontario limited partnership (“Purdue”), announced that they had executed an exclusive agreement granting to Purdue the licensing, distribution, marketing and sale rights related to BELBUCA® in Canada. Financial terms of the Purdue agreement include: (i) total upfront and other cash milestone payments (relating to marketing authorization transfer and certain other marketing- and sales-related milestones) of up to an aggregate of CAD 4.5 million, including approximately CAD 1.5 million (0.5 million CAD and 1.0 million CAD received August 2017 and October 2017, respectfully); (ii) a low double digit percent royalty payable quarterly by Purdue to the Company based on Canadian net sales of BELBUCA®, which royalty rate is subject to adjustment in certain circumstances; (iii) an annual royalty fee commencing a period of time after the commercial launch of BELBUCA® in Canada, which fee is creditable against royalties payable by Purdue and subject to reduction in certain circumstances; and (iv) payment by Purdue of certain costs incurred to obtain and transfer the marketing authorization for BELBUCA® in Canada, a portion of which will be reimbursed by the Company as a reduction of royalties payable by Purdue.
Pursuant to the agreement, the royalty from Purdue to the Company terminates on the later of (a) the first date on which there is not at least one valid claim of the licensed patents in the territory covering any licensed product or (b) February 14th of the calendar year immediately following the first complete calendar year following the tenth anniversary of first commercial sale in which net sales total less than a predetermined amount.
On September 12, 2017, the Company announced Health Canada had granted market authorization to formally transfer the Drug Identification Number (DIN) ownership of BELBUCA® in Canada to Purdue. This approval triggered a milestone payment to the Company in the amount of CAD 1 million, which was received October 2017.
On January 30, 2018, the Company and Purdue announced that BELBUCA® is now commercially available in Canada. The first commercial sale of BELBUCA® in Canada triggered a milestone payment to the Company from Purdue in the amount of CAD 1 million, which the Company received March 2018.
Kunwha license agreement
In May 2010, the Company entered into a License and Supply Agreement (the “Kunwha License Agreement”) with Kunwha to develop, manufacture, sell and distribute the Company’s BEMA® Fentanyl product in the Republic of Korea (the “Kunwha Territory”). BEMA® Fentanyl is marketed as ONSOLIS® in North America. The Kunwha License Agreement was for a term beginning on May 26, 2010 until the date of expiration of the patents, or July 23, 2027, whichever is later.
Under the terms of the Kunwha License Agreement, Kunwha was granted exclusive licensing rights for BEMA® Fentanyl in the Kunwha Territory, while the Company will retain all other licensing rights to the Licensed Product not previously granted to third parties. Kunwha paid to the Company an upfront payment of $0.3 million (net of taxes approximating $0.25 million) and was responsible to make certain milestone payments which could have aggregated up to $1.3 million (net of taxes approximating $1.1 million). In August 2015, Kunwha paid to the Company a milestone payment of $0.3 million toward the aggregate total of $1.3 million, however, the Kunwha License Agreement was terminated on August 31, 2015.
F-25
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 9. | Other license agreements and acquired product rights (continued): |
TTY license and supply agreement
On October 7, 2010, the Company announced a license and supply agreement with TTY Biopharm Co., Ltd. (“TTY”) for the exclusive rights to develop and commercialize BEMA® Fentanyl in the Republic of China, Taiwan. The agreement results in potential milestone payments to the Company of up to $1.3 million, which include an upfront payment of $0.3 million that was received in 2010. In addition, the Company will receive an ongoing royalty based on net sales. TTY will be responsible for the regulatory filing of BEMA® Fentanyl in Taiwan as well as future commercialization in that territory. The term of the agreement with TTY is for the period from October 4, 2010 until the date fifteen years after first commercial sale unless the agreement is extended in writing or earlier terminated as provided for in the agreement.
On July 29, 2013, the Company announced the regulatory approval of BEMA® Fentanyl in Taiwan, where the product will be marketed under the brand name PAINKYL™. The approval in Taiwan resulted in a milestone payment of $0.3 million to the Company, which was received in the third quarter 2013.
The Company received cumulative payments totaling $1.2 million and $0.9, all which related to royalties based on product purchased in Taiwan by TTY of PAINKYL™. Such amounts are recorded as contract revenue in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. There were no payments received from TTY during 2015.
Agreement with Par Pharmaceuticals
In conjunction with the aforementioned Endo Termination Agreement, on December 7, 2016, the Company also entered into a distribution agreement (the “Distribution Agreement”) with Par Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Par”) for the distribution of an authorized generic BELBUCA® product (the “Generic Product”) after the launch of a generic BELBUCA® product by a third party. The Distribution Agreement covers distribution within the entire United States, has an initial term of three years (the “Initial Term”) after the launch of a generic BELBUCA® product by a third party, an initial automatic renewal period of two years, and additional automatic one-year renewal periods thereafter (such two-year period and each one-year period, a “Renewal Term”), which will occur unless either party provides written notice of termination an agreed upon period of time prior to the expiration of the Initial Term or any Renewal Term. In exchange for distribution rights of the Generic Product, Par will pay to the Company an agreed upon base purchase price and a deferred purchase price equal to a percentage of profit (as such term is specifically agreed to in the Distribution Agreement) with respect to units of each dosage strength of Generic Product. During the term of the Distribution Agreement, Par is precluded from manufacturing for sale in the United States, or distributing in the United States, any equivalent product, provided that nothing prohibits Par from continuing or undertaking to develop any equivalent product or selling such equivalent product outside of the U.S. The Distribution Agreement contains customary termination provisions for bankruptcy, withdrawal of product from the market, and regulatory and legislative changes, as well as a termination right for insufficient profits or Par’s acquisition by or of a party challenging the Company’s patents with respect to BELBUCA®.
| 10. | Note payable (Midcap loan): |
On May 29, 2015, the Company entered into a $30 million secured loan facility (the “Loan”) with MidCap Financial Trust, as agent and lender (“MidCap”), pursuant to the terms and conditions of that certain Amended and Restated Credit and Security Agreement, dated as of May 29, 2015 (the “Credit Agreement”), between the Company and MidCap (the “MidCap Credit Agreement”).
On February 21, 2017, the Company entered into a term loan agreement (the “Term Loan Agreement”) with CRG, as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the lenders named in the Term Loan Agreement (the “Lenders”). The Company utilized approximately $29.4 million of the initial loan proceeds under the Term Loan Agreement to repay all the amounts owed by the Company under the MidCap Credit Agreement. Upon the repayment of all amounts owed by the Company under the MidCap Credit Agreement, all commitments under the MidCap Credit Agreement were terminated and all security interests granted by the Company and its subsidiary guarantors under the MidCap Credit Agreement were released (see note 11, Term Loan Agreement (CRG)). Certain warrants issued to MidCap and its affiliates in May 2016 related to the extension of the interest only period under the MidCap Credit Agreement remain outstanding as of December 31, 2017 and will expire, if not earlier exercised in May 2021. Such warrants are exercisable for 84,986 shares of Common Stock at an exercise price of $3.53 per share. During the year ended December 31, 2017, $0.7 million of deferred loan costs arising out of the MidCap Credit Agreement were expensed and recorded as interest expense in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations.
F-26
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 11. | Term loan agreement (CRG): |
Pursuant to the Term Loan Agreement, the Company borrowed $45.0 million from the Lenders as of the Closing Date, and may be eligible to borrow up to an additional $30.0 million in two tranches of $15.0 million each contingent upon achievement of certain conditions, including: (i) in the case of the first tranche, representing the second potential draw under the Loan Agreement (the “Second Draw”), satisfying both (a) certain minimum net revenue thresholds on or before September 30, 2017 or December 31, 2017 and (b) a certain minimum market capitalization threshold for a period of time prior to the funding of the Second Draw (provided, that if the Company does not achieve the minimum net revenue thresholds necessary for the Second Draw but does achieve a certain minimum market capitalization threshold for a period of time prior to December 31, 2017, the Company would be eligible for a Second Draw funding in the amount of $5.0 million); and (ii) in the case of the second tranche, representing the third potential draw under the Loan Agreement (the “Third Draw”), satisfying both (a) certain minimum net revenue thresholds on or before June 30, 2018 or September 30, 2018 and (b) a certain minimum market capitalization threshold for a period of time prior to the funding of the Third Draw. On December 26, 2017, the Company was eligible and elected to receive the Second Draw for gross proceeds of $15.0 million.
After the payoff of the MidCap Credit Agreement (see note 10), the Company is utilizing the initial proceeds under the Term Loan Agreement (after deducting loan origination costs and broker and other fees) of approximately $13.7 million, plus any additional amounts that may be borrowed in the future, for general corporate purposes and working capital. The Term Loan Agreement has a six-year term with three years of interest-only payments (which can be extended to four years if the Company achieves certain net revenue and market capitalization thresholds prior to December 31, 2019), after which quarterly principal and interest payments will be due through the December 31, 2022 maturity date. Interest on the amounts borrowed under the Term Loan Agreement accrues at an annual fixed rate of 12.50%, 3.5% of which (i.e., a resultant 9.0% rate) may be deferred during the interest-only period by adding such amount to the aggregate principal loan amount. On each borrowing date (including the Closing Date), the Company is required to pay CRG a financing fee based on the loan drawn on that date. The Company is also required to pay the Lenders a final payment fee equivalent to 9% of the original loan amount upon repayment of the Loans in full, in addition to prepayment amounts described below.
The Company may prepay all or a portion of the outstanding principal and accrued unpaid interest under the Term Loan Agreement at any time upon prior notice to the Lenders subject to a certain prepayment fees during the first five years of the term (which fees are lowered over time) and no prepayment fee thereafter. In certain circumstances, including a change of control and certain asset sales or licensing transactions, the Company is required to prepay all or a portion of the loan, including the applicable prepayment premium on the amount of the outstanding principal to be prepaid.
As security for its obligations under the Term Loan Agreement, on the funding date of the initial borrowing, the Company and the Subsidiary Guarantors entered into a security agreement with CRG whereby the Company and the subsidiary guarantors of the Company under the Term Loan Agreement (the “Subsidiary Guarantors”) granted to CRG, as collateral agent for the Lenders, a lien on substantially all of its assets including intellectual property (subject to certain exceptions). The Term Loan Agreement requires the Company to maintain minimum cash and cash equivalents balance and, each year through the end of 2022, to meet a minimum net annual revenue threshold. The Company is in compliance as of December 31, 2017. In the event that the Company does not meet the minimum net annual revenue threshold, then the Company can satisfy the requirement for that year by raising two (2) times the shortfall by way of raising equity or subordinated debt.
The Term Loan Agreement also contains customary affirmative and negative covenants for a credit facility of this size and type, including covenants that limit or restrict the Company’s ability to, among other things (but subject in each case to negotiated exceptions), incur indebtedness, grant liens, merge or consolidate, dispose of assets, make investments, make acquisitions, enter into transactions with affiliates, pay dividends or make distributions, license intellectual property rights on an exclusive basis or repurchase stock.
The Term Loan Agreement includes customary events of default that include, among other things, non-payment, inaccuracy of representations and warranties, covenant breaches, a material adverse change (as defined in the Term Loan Agreement), cross default to material indebtedness or material agreements, bankruptcy and insolvency, material judgments and a change of control. The occurrence and continuance of an event of default could result in the acceleration of the obligations under the Term Loan Agreement. Under certain circumstances, a default interest rate of an additional 4.00% per annum will apply on all outstanding obligations during the existence of an event of default under the Term Loan Agreement.
F-27
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 11. | Term loan agreement (CRG) (continued): |
The following table represents future maturities of the CRG obligation as of December 31, 2017:
| 2018 |
$ | — | ||
| 2019 |
— | |||
| 2020 |
20,054 | |||
| 2021 |
20,054 | |||
| 2022 |
20,054 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total maturities |
$ | 60,162 | ||
| Unamortized discount and loan costs |
(12,502 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Total CRG obligation |
$ | 47,660 | ||
|
|
|
In connection with the initial borrowing made under the Term Loan Agreement, the Company issued to CRG and certain of its affiliates five separate warrants to purchase an aggregate of 1,701,583 shares of the Common Stock (the “CRG Warrants”). The CRG Warrants are exercisable any time prior to February 21, 2027 at a price of $2.38 per share, with typical provisions for cashless exercises. The exercise of the CRG Warrants could have a dilutive effect to the Common Stock to the extent that the market price per share of the Common Stock, as measured under the terms of the CRG Warrants, exceeds the exercise price of the CRG Warrants. CRG is also entitled to receive a smaller amount of similar warrants concurrently with the funding, if applicable, of the Third Draw.
In connection with the Second Draw, the Company issued to CRG and certain of its affiliates warrants to purchase an aggregate of 349,452 shares of the Company’s common stock (the “CRG Second Draw Warrants”). The CRG Second Draw Warrants are exercisable any time prior to December 26, 2027, at a price of $3.42 per share, with typical provisions for cashless exercise and stock-based anti-dilution protection. The exercise of the CRG Second Draw Warrants could have a dilutive effect to the Company’s common stock to the extent that the market price per share of the Company’s common stock, as measured under the terms of the CRG Second Draw Warrants, exceeds the exercise price of the CRG Warrants.
| 12. | Segment reporting: |
The Company operates in a single industry engaging in the development and commercialization of pharmaceutical products principally in the areas of pain management and addiction. Accordingly, the Company’s business is classified as a single reportable segment.
The following table presents net sales by product for each of the years ended December 31 (in thousands):
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| BELBUCA® |
$ | 26,980 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| BUNAVAIL® |
7,942 | 8,266 | 4,157 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net product sales |
$ | 34,922 | $ | 8,266 | $ | 4,157 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 13. | Income taxes: |
On December 22, 2017, the United States enacted major tax reform legislation, Public Law No. 115-97, commonly referred to as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (or 2017 Tax Act). The 2017 Tax Act, among other changes, lowers the general corporate income tax rate to 21% for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, transitions U.S. international taxation from a worldwide tax system to a territorial system, and provides for a one-time transition tax on the mandatory deemed repatriation of cumulative foreign earnings as of December 31, 2017, which is not applicable to the Company. The Company has calculated its best estimate of the impact of the 2017 Tax Act in its income tax provision during the year ended December 31, 2017, in accordance with its understanding of the 2017 Tax Act and guidance available as of the date of this filing and does not believe it will be material to its results of operations. The provisional amount related to the remeasurement of certain deferred tax assets and liabilities is based on the tax rates at which they are expected to reverse in the future. The estimated amount recorded related to the remeasurement of these balances was an income tax benefit of $33.1 million, offset entirely by the reduction in the Company’s valuation allowance.
F-28
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 13. | Income taxes (continued): |
On December 22, 2017, Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 118 (“SAB 118”) was issued to address the application of US GAAP in situations when a registrant does not have the necessary information available, prepared, or analyzed (including computations) in reasonable detail to complete the accounting for certain income tax effects of the 2017 Tax Act. In accordance with SAB 118, the Company has determined that the $33.1 million of the deferred tax income offset by the reduction in valuation allowance recorded in connection with the re-measurement of certain deferred tax assets and liabilities and the expectation the transition tax is immaterial are reasonable estimates at December 31, 2017.
In addition, North Carolina reduced its corporate income tax rate from 4% to 3% in 2017. This resulted in a tax benefit of $1.7 million, offset by a reduction in the Company’s valuation allowance.
The Company recorded an income tax benefit of $16.0 million in 2017. This benefit was associated with the release of the Company’s valuation allowance triggered by the recognition of deferred tax liabilities recorded as part of the Endo BELBUCA® transaction (See note 7, Business Combinations and BELBUCA® Acquisition). The Company did not record income tax expense or pay any income tax in 2016 as it had incurred a net operating loss. The Company has recognized valuation allowances for all deferred tax assets for years ending 2017 and 2016. Reconciliation of the Federal statutory income tax rate of 34% to the effective rate is as follows:
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Federal statutory income (benefit) tax rate |
(34.00 | %) | 34.00 | % | 34.00 | % | ||||||
| 2017 Tax Act, net deferred tax remeasurement |
(626.73 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| State taxes, net of federal benefit |
(2.01 | ) | 2.88 | 3.45 | ||||||||
| Stock compensation |
(5.18 | ) | (0.61 | ) | — | |||||||
| Permanent differences-other |
(13.39 | ) | (1.00 | ) | (4.66 | ) | ||||||
| North Carolina tax rate change |
(32.75 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Research and development (“R&D”) credit |
5.54 | 0.98 | 0.95 | |||||||||
| Valuation release for bargain purchase gain |
(302.23 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Other |
(1.36 | ) | (0.47 | ) | 0.64 | |||||||
| Decrease (increase) in valuation allowance |
709.88 | (35.78 | ) | (34.38 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (302.23 | %) | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | % | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The tax effects of temporary differences and net operating losses that give rise to significant components of deferred tax assets and liabilities consist of the following:
| December 31, | ||||||||
|
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) |
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
| Deferred revenue |
$ | — | $ | 7,377 | ||||
| Basis difference in equipment |
(587 | ) | (1,084 | ) | ||||
| Basis difference in intangibles |
(8,288 | ) | 1,201 | |||||
| Accrued liabilities and other |
654 | 550 | ||||||
| R&D credit |
11,882 | 11,589 | ||||||
| AMT credit |
79 | 79 | ||||||
| Stock options |
6,115 | 5,697 | ||||||
| Net operating loss carry-forward |
61,660 | 83,621 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 71,515 | 109,030 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Less: valuation allowance |
(71,515 | ) | (109,030 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | — | $ | — | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The Company is required to reduce any deferred tax asset by a valuation allowance if, based on an assessment of positive and negative evidence, including estimates of future taxable income necessary to realize future deductible amounts, it is more likely than not (a likelihood of more than 50 percent) that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The valuation allowance should be sufficient to reduce the deferred tax asset to the amount which is more likely than not to be realized. As a result, the Company recorded a valuation allowance with respect to all of the Company’s deferred tax assets. The change in the valuation allowance for the year ended December 31, 2017 independent of the impact of the 2017 Tax Act was $(4.4 million). In addition to the remeasurement of the net deferred tax assets due to the 2017 Tax Act, the
F-29
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 13. | Income taxes (continued): |
valuation allowance decreased in 2017 due primarily to changes in the intangible assets and deferred revenue offset partially by stock compensation and an increase in the Company’s net operating loss carryforwards.
The Company has a federal net operating loss carry forward (“NOLs”) of approximately $263 million as of December 31, 2017. Under Section 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code, if an ownership change occurs with respect to a “loss corporation”, as defined, there are annual limitations on the amount of the NOLs and other deductions which are available to the Company. The portion of the NOLs incurred prior to May 16, 2006 is subject to this limitation. As such, the use of these NOLs to offset taxable income is limited to approximately $1.5 million per year. The Company’s State NOLS are approximately $292 million as of December 31, 2017. These loss carryforwards expire between 2024 and 2037 for federal and 2030 for state purposes. Management has evaluated all other tax positions that could have a significant effect on the financial statements and determined that the Company has no uncertain income tax positions at December 31, 2017.
One or more of the Company’s legal entities file income tax returns in the U.S. federal jurisdiction and various U.S. state jurisdictions. The Company’s income tax returns are subject to audit by the tax authorities in those jurisdictions. Significant disputes may arise with authorities involving issues of the timing and amount of deductions, the use of tax credits and allocations of income and expenses among various tax jurisdictions because of differing interpretations of tax laws, regulations and the interpretation of the relevant facts. The Company is no longer subject to U.S. federal or state tax examinations for years ended on or before December 31, 2013.
| 14. | Stockholders’ equity: |
Common Stock
On July 2, 2015, the Company filed a shelf registration statement which registered up to $150 million of the Company’s securities for potential future issuance, and such registration statement was declared effective on July 13, 2015. Concurrent with the filing of the registration statement, the Company established an “at-the-market” offering program utilizing the universal shelf registration for up to $40 million of Common Stock. Due to the Company’s late filing of certain financing information related to its reacquisition of BELBUCA®, the Company is unable to utilize its universal shelf registration statement and associated at-the-market offering program until April 2018.
On December 16, 2015, the Company and Dr. Andrew Finn entered into a retirement agreement (the “Retirement Agreement”) setting forth their mutual understandings regarding Dr. Finn’s retirement from the Company. Pursuant to the Retirement Agreement, all unvested RSUs previously issued under the Company’s equity incentive plans and held by Dr. Finn as of the retirement date were cancelled and, in lieu thereof, Dr. Finn was awarded a one-time issuance of shares of Common Stock based upon a net present valuation of the cancelled RSUs as set forth in the Retirement Agreement (which resulted in an issuance in January 2016 of 513,221 shares of Common Stock).
Following its review of the Company’s corporate performance for 2015, the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors approved in early 2016, equity awards for 2015 in the form of RSUs to its named executive officers (including Dr. Finn) and other senior executives in amounts at or below the 25th% percentile of the Company’s peer group. Dr. Finn, who retired on December 31, 2015, received an immediate award of 150,000 shares of Common Stock in fulfillment of the Company’s contractual obligation to him under the Retirement Agreement. Such shares were issued in March 2016.
During the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, Company employees, directors and affiliates exercised approximately 0.2 million, 0.1 million and 0.2 million stock options, respectively, with net proceeds to the Company of approximately $0.4 million, 0.3 million and $0.8 million, respectively.
Preferred Stock
The Company had authorized five million “blank check” shares of $.001 par value convertible preferred stock. On December 3, 2012, the Company closed a registered direct offering, issuance and sale of Series A Preferred. The final amount of Series Preferred issued in the offering was an aggregate of 2,709,300 shares of Series A Preferred. In the event of the Company’s liquidation, dissolution or winding up, holders of the Series A Preferred will receive a payment equal to $.001 per share of Series A Preferred before any proceeds are distributed to the holders of common stock. After the payment of this preferential amount, and subject to the rights of holders of any class or series of capital stock hereafter created specifically ranking by its terms senior to the Series A Preferred, the holders of Series A Preferred will participate ratably in the distribution of any remaining assets with the common stock and any other class or series of our capital stock hereafter created that participates with the common stock in such distributions.
F-30
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 14. | Stockholders’ equity (continued): |
At December 31, 2017, 2,093,155 shares of Series A Preferred were outstanding and 2,290,700 shares of “blank check” preferred stock remain authorized but undesignated. During the year ended December 31, 2015, 45,845 shares of Series A Preferred were converted to equal shares of the Company’s common stock. There were no conversions of Series A Preferred during the years ended December 31, 2017 or 2016.
Restricted stock units
During the year ended December 31, 2017, 2,357,315 RSUs, were granted to members of the Company’s executive officers, board of directors and employees, with a fair market value of approximately $4.7 million. The fair value of restricted units is determined using quoted market prices of the Common Stock and the number of shares expected to vest. These RSUs were issued under the Company’s 2011 Equity Incentive Plan, as amended, and vest as following: (i) For executive officers, half of the grant vests in equal installments over three years and the remaining half vests subject to performance criteria over three years, (ii) for employees, the grants vest in full June 2018, (iii) and for the board of directors grants vest one-half in August 2017 and one-half in August 2018.
Restricted stock activity during the year ended December 31, 2017 was as follows:
| Number of Restricted Shares |
Weighted Average Fair Market Value Per RSU |
|||||||
| Outstanding at January 1, 2017 |
4,584,297 | $ | 7.29 | |||||
| Granted: |
||||||||
| Executive officers |
1,640,000 | 1.85 | ||||||
| Directors |
162,315 | 2.80 | ||||||
| Employees |
555,000 | 2.10 | ||||||
| Vested |
(1,568,042 | ) | 2.17 | |||||
| Forfeitures |
(666,675 | ) | 2.71 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2017 |
4,706,895 | $ | 5.20 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Performance Long Term Incentive Plan
In December 2012, the Company’s Board of Directors (the “Board”) approved the BDSI Performance Long Term Incentive Plan (“LTIP”). The LTIP is designed as an incentive for the Company’s senior management to generate revenue for the Company. The LTIP consists of RSUs (which are referred to in this context as Performance RSUs) which are rights to acquire shares of Common Stock. All Performance RSUs granted under the LTIP will be granted under the Company’s 2011 Equity Incentive Plan (as the same may be amended, supplemented or superseded from time to time) as “Performance Compensation Awards” under such plan. The participants in the LTIP are either named executive officers or senior officers of the Company.
The term of the LTIP began with the Company’s fiscal year ended December 31, 2012 and lasts through the fiscal year ending December 31, 2019. The total number of Performance RSUs covered by the LTIP is 1,078,000, of which 978,000 were awarded in 2012 (with 100,000 Performance RSUs being reserved for future hires and of that reserve, 35,000 Performance RSUs were awarded in 2015). No additional Performance RSUs were awarded in 2016 or 2017. The Performance RSUs under the LTIP did not vest upon granting, but instead are subject to potential vesting each year over the 8-year term of the LTIP depending on the achievement of pre-defined revenue amounts by the Company, as reported in its Annual Report on Form 10-K. During the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, a total of 9,958, 13,347 and 21,356 RSUs vested, respectively, subject to performance criteria.
F-31
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 14. | Stockholders’ equity (continued): |
Stock options
The Company has a 2011 Equity Incentive Plan. During the 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (the “Annual Meeting”), stockholders approved an amendment to the Company’s 2011 Equity Incentive Plan to increase the number of shares of common stock authorized for issuance under the plan by 7,100,000 shares from 11,050,000 to 18,150,000.
An additional 890,693 shares of Common Stock underlying options previously granted under the Company’s Amended and Restated 2001 Incentive Plan remain outstanding and exercisable as of December 31, 2017. The Company’s Amended and Restated 2001 Incentive Plan expired in July 2011 and no new securities may be issued thereunder. Options may be awarded during the ten-year term of the 2011 Equity Incentive Plan to Company employees, directors, consultants, sales force and other affiliates.
Stock option activity for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 is as follows:
| Number of Shares |
Weighted Average Exercise Price Per Share |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
||||||||||
| Outstanding at January 1, 2015 |
3,196,100 | $ | 4.32 | $ | 22,881 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Granted in 2015: |
||||||||||||
| Others |
684,629 | 8.14 | ||||||||||
| Exercised |
(235,480 | ) | 3.52 | |||||||||
| Forfeitures |
(247,720 | ) | 12.65 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2015 |
3,397,529 | $ | 5.42 | $ | 3,124 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Granted in 2016: |
||||||||||||
| Officers and Directors |
95,000 | $ | 2.34 | |||||||||
| Others |
558,373 | 3.12 | ||||||||||
| Exercised |
(147,425 | ) | 2.01 | |||||||||
| Forfeitures |
(434,486 | ) | 13.17 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2016 |
3,468,991 | $ | 4.14 | $ | 0 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Granted in 2017: |
||||||||||||
| Officers and Directors |
83,658 | $ | 2.64 | |||||||||
| Others |
873,017 | 1.96 | ||||||||||
| Exercised |
(202,519 | ) | 2.17 | |||||||||
| Forfeitures |
(1,510,193 | ) | 5.13 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2017 |
2,712,954 | $ | 2.98 | $ | 1,190 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Options outstanding at December 31, 2017 are as follows:
| Range of Exercise Prices |
Number Outstanding |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
||||||||||||
| $1.00 – 5.00 |
2,192,695 | 5.53 | $ | 2.72 | ||||||||||||
| $5.01 – 10.00 |
430,149 | 5.38 | $ | 6.29 | ||||||||||||
| $10.01 – 15.00 |
48,358 | 7.14 | $ | 13.13 | ||||||||||||
| $15.01 – 20.00 |
41,500 | 6.75 | $ | 16.27 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 2,712,954 | $ | 1,190 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
F-32
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 14. | Stockholders’ equity (continued): |
Options exercisable at December 31, 2017 are as follows:
| Range of Exercise Prices |
Number Outstanding |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
||||||||||||
| $1.00 – 5.00 |
1,400,022 | 3.48 | $ | 3.04 | ||||||||||||
| $5.01 – 10.00 |
345,257 | 5.43 | $ | 6.28 | ||||||||||||
| $10.01 – 15.00 |
35,439 | 7.13 | $ | 13.15 | ||||||||||||
| $15.01 – 20.00 |
41,500 | 6.75 | $ | 16.27 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 1,822,218 | $ | 561 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
The weighted average grant date fair value of options granted during the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 was $1.46, $1.75 and $4.99, respectively. There were no options granted during the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 or 2015 whose exercise price was lower than the estimated market price of the stock at the grant date.
Nonvested stock options as of December 31, 2017, and changes during the year then ended, are as follows:
| Nonvested Shares |
Shares | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value |
Intrinsic Value |
|||||||||
| Nonvested at January 1, 2017 |
829,431 | |||||||||||
| Granted |
960,175 | |||||||||||
| Vested |
(363,701 | ) | ||||||||||
| Forfeited |
(540,421 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Nonvested at December 31, 2017 |
885,484 | $ | 2.70 | $ | 629 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
As of December 31, 2017, there was approximately $5.5 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to unvested share-based compensation awards granted. These costs will be expensed over the next three years.
Stock-based compensation
During the year ended December 31, 2017, a total of 956,675 options to purchase Common Stock, with an aggregate fair market value of approximately $1.4 million, were granted to Company employees, directors and contractors. The options granted have a term of 10 years from the grant date and vest ratably between a one and three-year period. The fair value of each option is amortized as compensation expense evenly through the vesting period.
The Company’s stock-based compensation expense is allocated between research and development and selling, general and administrative as follows as of December 31:
| Stock-based compensation expense |
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
| Research and Development |
$ | 1.6 | $ | 2.5 | $ | 4.2 | ||||||
| Selling, General and Administrative |
$ | 13.2 | $ | 12.4 | $ | 10.0 | ||||||
Warrants:
The Company has granted warrants to purchase shares of Common Stock. Warrants may be granted to affiliates in connection with certain agreements.
During the year ended December 31, 2016, the Company granted warrants to purchase 84,986 shares of Common Stock at an exercise price of $3.53 per share to Midcap and its affiliates in connection with the Company’s extension agreement with MidCap. The warrants were valued using the Black-Scholes Model, which fair value is approximately $0.05 million. As of December 31, 2017, 84,986 warrants remain outstanding.
F-33
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 14. | Stockholders’ equity (continued): |
In February 2017, the Company granted warrants to purchase 1,701,583 shares of Common Stock at an exercise price of $2.38 per share to CRG and certain of its affiliates in connection with the Company’s term loan agreement with CRG. The warrants were valued using the Black-Scholes Model, which fair value is approximately $4.5 million.
In December 2017, the Company granted warrants to purchase 349,451 shares of Common Stock at an exercise price of $3.42 per share to CRG and certain of its affiliates in connection with the Company’s 2nd tranche funding from its term loan agreement with CRG. The warrants were valued using the Black-Scholes Model, which fair value is approximately $1.5 million. As of December 31, 2017, a cumulative of 2,051,034 to CRG and affiliates remain outstanding.
| 15. | Earnings per common share: |
The following is a reconciliation of the numerators and denominators of the basic and diluted earnings per common share computations for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015.
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Basic: |
||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders |
$ | 5,285 | $ | (67,138 | ) | $ | (37,672 | ) | ||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding |
55,355,802 | 53,679,134 | 52,384,876 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Basic earnings (loss) per common share |
$ | 0.10 | $ | (1.25 | ) | $ | (0.72 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted: |
||||||||||||
| Effect of dilutive securities: |
||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders |
5,285 | (67,138 | ) | (37,672 | ) | |||||||
| Adjustment to income for dilutive options and warrants |
— | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 5,285 | (67,138 | ) | (37,672 | ) | ||||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding |
55,355,802 | 53,679,134 | 52,384,876 | |||||||||
| Effect of dilutive options and warrants |
1,046,677 | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding |
56,402,479 | 53,679,134 | 52,384,876 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted earnings (loss) per common share |
$ | 0.09 | $ | (1.25 | ) | $ | (0.72 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Basic earnings per common share is calculated using the weighted average shares of Common Stock outstanding during the period. Common equivalent shares from stock options, RSUs, warrants and convertible preferred stock using the treasury stock method, are also included in the diluted per share calculations unless the effect of inclusion would be antidilutive. During the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, outstanding stock options, RSUs, warrants and convertible preferred stock of 6,531,346, 10,228,929 and 9,788,838, respectively, were not included in the computation of diluted earnings per common share, because to do so would have had an antidilutive effect because the outstanding exercise prices were greater than the average market price of the common shares during the relevant periods.
F-34
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 15. | Earnings per common share (continued): |
The following is the total outstanding options, RSUs and warrants for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Options, RSUs, warrants and convertible preferred stock to purchase Common Stock |
9,555,869 | 10,228,929 | 9,788,838 | |||||||||
| 16. | Retirement plan: |
The Company sponsors a defined contribution retirement plan under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code. The plan covers all employees who meet certain eligibility and participation requirements. Participants may contribute up to 90% of their eligible earnings, as limited by law. The Company makes a matching contribution equal to 100% on the first 5% of participant contributions to the plan. The Company made contributions of approximately $0.5 million, $0.4 million and $0.2 million in years, 2017, 2016 and 2015.
| 17. | Retirement agreements: |
Sirgo retirement agreement
On August 23, 2017, Dr. Sirgo, the Company’s former President and Chief Executive Officer and current Vice Chairman, executed a retirement agreement (which is referred to as the Sirgo Retirement Agreement) memorializing the terms of Dr. Sirgo’s voluntary retirement from the Company, which was effective January 2, 2018 (which is referred to as the Sirgo Retirement Date, with the period from August 23, 2017 to the Sirgo Retirement Date being referred to herein as the Sirgo Transition Period). During the Sirgo Transition Period and following the Sirgo Retirement Date, Dr. Sirgo served and will continue to serve as Vice Chairman of the Company‘s board of directors.
Pursuant to the Sirgo Retirement Agreement, Dr. Sirgo served as the Company’s President and Chief Executive Officer during the Sirgo Transition Period. By entering into the Sirgo Retirement Agreement, the Company and Dr. Sirgo agreed to terminate Dr. Sirgo’s employment agreement with the Company, dated August 24, 2004, as amended by that First Amendment thereto (collectively with the related confidentiality agreement between the Company and Sirgo, the Sirgo Employment Agreement) as of the Sirgo Retirement Date, subject to those provisions of the Sirgo Employment Agreement which survive termination (as the same were modified by the Sirgo Retirement Agreement), including provisions related to confidentiality, non-solicitation and non-competition.
In connection with his retirement from the Company, and in consideration of his many years of service to the Company (and in lieu of any similar benefits provided for in the Sirgo Employment Agreement), Dr. Sirgo has received or will receive the following benefits pursuant to the Sirgo Retirement Agreement:
| (i) | a cash payment of $0.8 million (less applicable withholdings) which was paid in September 2017; and |
| (ii) | an additional cash payment equal to $0.8 million (less applicable withholdings) which was paid in January 2018. |
In addition, pursuant to the Sirgo Retirement Agreement:
| (i) | as of the Sirgo Retirement Date, all previously vested options held by Sirgo to purchase shares of Common Stock will continue for the life of such options (as opposed to such options terminating on the 90 th day following the Sirgo Retirement Date, as provided for in the Plan; |
| (ii) | Dr. Sirgo will be entitled to receive his ordinary year end equity bonus award (in the form of RSUs) for his service as an officer during 2017, as determined by the Compensation Committee of the Board (or the Sirgo 2017 Equity Award); provided, however, that (A) with respect to RSUs which by their terms would vest with the passage of time (or Time Vesting RSUs), Dr. Sirgo shall receive a number of shares of Common Stock equal to (1) the Net Present Value (as defined in the Sirgo Retirement Agreement) of the Time Vesting RSUs that would have been issued to Dr. Sirgo for the Sirgo 2017 Equity Award had he not retired divided by (2) the 30-day volume weighted average price of the Common Stock (or the 30-day VWAP) as of the date of issuance of the Sirgo 2017 Equity Bonus; and (B) with respect to RSUs which by their terms would vest based on future performance (or Performance Vesting RSUs), Dr. Sirgo shall receive a number of shares of Common Stock determined by multiplying the number of Performance Vesting RSUs that would have been issued to Dr. Sirgo for the Sirgo 2017 Equity Award had he not retired by 0.66; |
F-35
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 17. | Retirement agreements (continued): |
| (iii) | as of the Sirgo Retirement Date, all previously granted Time Vesting RSUs issued to Dr. Sirgo pursuant to the Plan that are unvested as of the Sirgo Retirement Date shall terminate and, in lieu thereof, Dr. Sirgo shall receive a one-time issuance of fully vested shares of Common Stock under the Plan, the number of which will be determined with reference to the Time Vesting RSUs being terminated by dividing (A) the Net Present Value of such Time Vesting RSUs by (B) the 30-day VWAP as of the Sirgo Retirement Date, which resulted in the issuance of 795,730 shares that were issued to Dr. Sirgo in January 2018, and all previously granted RSUs issued to Sirgo pursuant to the Plan which vest due to achievement of future performance milestones that are unvested as of the Sirgo Retirement Date shall terminate and, in lieu thereof, Dr. Sirgo shall receive a one-time issuance of 250,000 fully vested shares of Common Stock under the Plan, which were issued to Sirgo in January 2018; and |
| (iv) | Dr. Sirgo will continue to be entitled to receive (if applicable) one hundred percent (100%) of his regular award of vested Common Stock (or the LTIP Stock) under the LTIP, with the amount of such LTIP Stock to be determined and issued in accordance with the terms and provisions of the LTIP. The issuance of the LTIP Stock to Dr. Sirgo as provided for above shall occur, if applicable, concurrently with the issuance of LTIP Stock to the Company’s officers, but no later than March 15, 2018. Should Dr. Sirgo voluntarily resign from the Board, in each case prior to payment of any amount of LTIP Stock, Dr. Sirgo’s right to receive LTIP Stock from and after that time shall terminate. In the event a Change in Control (as defined in the Sirgo Retirement Agreement) occurs on or within twelve (12) months following the Retirement Date with a company with whom Dr. Sirgo had contact about a potential transaction in his capacity as an employee of the Company prior to the Sirgo Retirement Date, then the Company shall issue to Dr. Sirgo, as an additional retirement benefit, fully vested shares of Common Stock in an amount equal to the number of shares Dr. Sirgo would have received pursuant to the LTIP had he remained employed with us through the Change in Control. |
For purposes of the Sirgo Retirement Agreement, the term “Change of Control” means the occurrence of any one or more of the following events (it being agreed that, with respect to paragraphs (i) and (iii) of this definition below, a “Change of Control” shall not be deemed to have occurred if the applicable third party acquiring party is an “affiliate” of the Company within the meaning of Rule 405 promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended):
| (i) | an acquisition (whether directly from the Company or otherwise) of any voting securities of the Company (or the Voting Securities) by any “Person” (as the term person is used for purposes of Section 13(d) or 14(d) of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (or the 1934 Act)), immediately after which such Person has “Beneficial Ownership” (within the meaning of Rule 13d-3 promulgated under the 1934 Act) of forty percent (40%) or more of the combined voting power of the Company’s then outstanding Voting Securities. |
| (ii) | the individuals who, as of the date hereof, are members of the Company’s board of directors cease, by reason of a financing, merger, combination, acquisition, takeover or other non-ordinary course transaction affecting the Company, to constitute at least fifty-one percent (51%) of the members of the Company’s board of directors; or |
| (iii) | approval by the Company’s board of directors and, if required, the Company’s stockholders, or execution by us of any definitive agreement with respect to, or the consummation of (it being understood that the mere execution of a term sheet, memorandum of understanding or other non-binding document shall not constitute a Change of Control): |
(A) a merger, consolidation or reorganization involving the Company, where either or both of the events described in clauses (i) or (ii) above would be the result;
(B) a liquidation or dissolution of or appointment of a receiver, rehabilitator, conservator or similar person for, or the filing by a third party of an involuntary bankruptcy against, the Company; or
(C) an agreement for the sale or other disposition of all or substantially all of the assets of the Company to any Person (other than a transfer to a subsidiary of the Company).”
The Sirgo Retirement Agreement also contains other customary provisions, including provisions for Dr. Sirgo’s continuing participation in certain company employee benefit plans, mutual releases of claims by the Company and Dr. Sirgo (subject to certain exceptions) and a covenant of cooperation.
F-36
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 17. | Retirement agreements (continued): |
Vasisht retirement agreement
On January 12, 2018, Niraj Vasisht, the Company’s former Senior Vice President and Chief Technology Officer, executed a Retirement Agreement (which is referred to as the Vasisht Retirement Agreement) memorializing the terms of Dr. Vasisht’s voluntary retirement from the Company, which was effective February 4, 2018 (which is referred to as the Vasisht Retirement
Date, with the period from January 12, 2018, to the Vasisht Retirement Date being referred to herein as the Vasisht Transition Period).
Pursuant to the Vasisht Retirement Agreement, Dr. Vasisht continued to serve as the Company’s Senior Vice President and Chief Technology Officer during the Vasisht Transition Period. By entering into the Vasisht Retirement Agreement, the Company and Dr. Vasisht agreed to terminate Vasisht’s employment agreement with the Company, dated October 8, 2008 (collectively with the related confidentiality agreement between the Company and Vasisht, the Vasisht Employment Agreement) as of the Vasisht Retirement Date, subject to those provisions of the Vasisht Employment Agreement which survive termination (as the same were modified by the Vasisht Retirement Agreement), including provisions related to confidentiality, non-solicitation and non-competition.
In connection with his retirement from the Company, and in consideration of his service to the Company (and in lieu of any similar benefits provided for in the Vasisht Employment Agreement), Dr. Vasisht received or will receive the following benefits pursuant to the Vasisht Retirement Agreement:
| (i) | a cash separation payment of $0.33 million (less applicable withholdings), in two equal payments of $0.165 million each: the first payment paid January 19, 2018, the second payment to be paid on April 1, 2018; |
| (ii) | an additional cash payment equal to $0.02 million (less applicable withholdings) paid on January 19, 2018, in consideration for a previously deferred raise in Dr. Vasisht’s base salary; |
| (iii) | if a Change of Control (as defined in the Vasisht Employment Agreement) occurs before July 1, 2018, Dr. Vasisht will be entitled to the cash payments provided for in Paragraph 4(d) of the Vasisht Employment Agreement (namely, a cash payment equal to: (A) Dr. Vasisht’s annual base salary plus an amount equal to fifty percent (50%) of his such salary multiplied by (B) 1.5), but less the separation payments made under the Vasisht Retirement Agreement; and |
| (iv) | for a period of 12 months from the Vasisht Retirement Date, Dr. Vasisht will serve as a consultant to the Company as requested from time to time during such period with respect to the Company’s research and development operations at the rate of $200 per hour. |
In addition, pursuant to the Vasisht Retirement Agreement:
| (i) | as of the Vasisht Retirement Date, all previously vested options held by Dr. Vasisht to purchase shares of Common Stock will continue for the life of such options (as opposed to such options terminating on the 90th day following the Vasisht Retirement Date, as provided for in the Plan; |
| (ii) | Vasisht will be entitled to receive his ordinary year end equity bonus award (in the form of RSUs) for his service as an officer of the Company during 2017, as determined by the Compensation Committee (or the Vasisht 2017 Equity Award); provided, however, that (A) with respect to Time Vesting RSUs, Dr. Vasisht shall receive a number of shares of Common Stock equal to (1) the Net Present Value (as defined in the Vasisht Retirement Agreement) of the Time Vesting RSUs that would have been issued to Dr. Vasisht for the Vasisht 2017 Equity Award had he not retired divided by (2) the 30-day VWAP as of the date of issuance of the Vasisht 2017 Equity Bonus; and (B) with respect to Performance Vesting RSUs, Vasisht shall receive a number of shares of Common Stock determined by multiplying the number of Performance Vesting RSUs that would have been issued to Dr. Vasisht for the 2017 Equity Award had he not retired by 0.66, which calculation resulted in a net issuance of 198,129 shares of Common Stock, which were issued to Dr. Vasisht February 2018; |
| (iii) | Dr. Vasisht shall receive one hundred percent (100%) of his regular award of vested LTIP Stock under the LTIP, with the amount of such LTIP Stock to be determined and issued in accordance with the terms and provisions of the LTIP, in consideration for his work in 2017, and Dr. Vasisht shall also be considered for a bonus in consideration for his work in 2017 in accordance with the normal procedures and conditions for award of a bonus; and |
F-37
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 17. | Retirement agreements (continued): |
| (iv) | as of the Vasisht Retirement Date, all previously granted Time Vesting RSUs issued to Dr. Vasisht pursuant to the Plan that are unvested as of the Vasisht Retirement Date shall terminate and, in lieu thereof, Vasisht shall receive a one-time issuance of fully vested shares of Common Stock under the Plan, the number of which will be determined with reference to the Time Vesting RSUs being terminated by dividing (A) the Net Present Value of such Time Vesting RSUs by (B) the 30-day VWAP as of the Vasisht Retirement Date which resulted in the issuance of 309,162 shares that were issued to Dr. Vasisht in February 2018 All previously granted Performance Vesting RSUs that are unvested as of the Vasisht Retirement Date will continue to vest until December 31, 2018, at which time 60% of the unvested Performance RSUs shall vest and 40% of the unvested Performance RSUs shall be deemed forfeited. |
The Vasisht Retirement Agreement also contains other customary provisions, including provisions for Dr. Vasisht’s continuing participation in certain company benefit plans, mutual releases of claims by the Company and Dr. Vasisht (subject to certain exceptions) and a non-disparagement covenant.
| 18. | Commitments and contingencies: |
Operating leases
Since November 2007, the Company has leased space for their corporate offices. Lease expense for the corporate office was $0.3 million, $0.3 million and $0.3 million for each of the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The Company leased new space for their corporate offices, which began March 2015 for 89 months.
The future minimum commitment on the new operating lease at December 31, 2017 is as follows:
| Years ending December 31, |
||||
| 2018 |
$ | 341 | ||
| 2019 |
351 | |||
| 2020 |
360 | |||
| 2021 |
370 | |||
| 2022 |
219 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 1,641 | |||
|
|
|
|||
Indemnifications
The Company’s directors and officers are indemnified against costs and expenses related to stockholder and other claims (i.e., only actions taken in their capacity as officers and directors) that are not covered by the Company’s directors and officers insurance policy. This indemnification is ongoing and does not include a limit on the maximum potential future payments, nor are there any recourse provisions or collateral that may offset the cost.
On February 5, 2018, the Company entered into indemnification agreements (the “Indemnification Agreements”) with each member of its board of directors (each, an “Indemnitee”). The form of Indemnification Agreement was approved by the board of directors.
The Indemnification Agreements are intended to clarify and supplement the indemnification rights and obligations of the Indemnitees and Company already included in the Company’s Certificate of Incorporation, as amended, and Second Amended and Restated Bylaws, and generally provide that, subject to certain exceptions specified in the Indemnification Agreements, the Company will indemnify the Indemnitee to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law in the event the Indemnitee becomes subject to or a participant in certain claims or proceedings as a result of the Indemnitee’s service as a director or officer. The Company will also, subject to certain exceptions and repayment conditions, be obligated to advance to the Indemnitee specified indemnifiable expenses incurred in connection with such claims or proceedings. No events have occurred as of the date of this report which would trigger any liability under the agreements.
Post marketing requirements
On October 5, 2017, the Company entered a subsequent party acknowledgement relating to its participation in the Opioid PMR Consortium (the “OPC”). The participants are member companies, collectively undertaking various observational and clinical studies to satisfy certain post-marketing requirements by the FDA as holders of a NDA for extended-release and long-acting opioid analgesics. As a requirement of joining the OPC, the Company was required to pay its share of the previous expenses incurred and funded by the existing member companies. The Company’s pro-rata share of such expenses totaled approximately
F-38
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 18. | Commitments and contingencies (continued): |
$4.3 million, which was paid during the fourth quarter of 2017. Ongoing expenses will be shared equally by the member companies and paid monthly from 2018 through 2020.
Certain rights of CDC IV
The Company and CDC IV are parties to the CDLA pursuant to which CDC IV has previously provided funds to the Company for the development of the Company’s ONSOLIS® product. CDC IV is entitled to receive a mid-single digit royalty based on net sales of ONSOLIS®, including minimum royalties of $375,000 per quarter beginning in the second full year following commercial launch. The royalty term expires upon the latter of expiration of the patent or generic entry into a particular country.
In September 2007, in connection with CDC IV’s consent to the North American Meda transaction, the Company, among other transactions with CDC IV, granted CDC IV a 1% royalty on net sales of the next BEMA® product, which was BUNAVAIL®. CDC IV’s right to the royalty shall immediately terminate at any time if annual net sales of BUNAVAIL® equal less than $7.5 million in any calendar year following the third anniversary of initial launch of the product and CDC IV receives $0.02 million in three (3) consecutive quarters as payment for CDC IV’s one percent (1%) royalty during such calendar year.
The Company records such royalties as costs of sales occur.
In April 2016, CDC IV exercised its right pursuant to the Royalty Purchase and Amendment Agreement to exchange its royalty rights to the next BEMA® product which was BUNAVAIL®, in favor of royalty rights to the Substitute BEMA® product which is BELBUCA® (the CDC IV Option).
Litigation related to ONSOLIS®
On November 2, 2010, Aquestive filed an action against the Company and its commercial partners for ONSOLIS® in the Federal District Court of New Jersey (the DNJ) for alleged patent infringement and false marking. The Company was formally served in this matter on January 19, 2011. Aquestive claimed that the Company’s manufacturing process for ONSOLIS®, which has never been disclosed publicly and which the Company and its partners maintain as a trade secret, infringes on its’588 Patent. Of note, the BEMA® technology itself was not at issue in the case, nor is BELBUCA® or BUNAVAIL®, but rather only the manner in which ONSOLIS®, which incorporates the BEMA® technology, is manufactured. Pursuant to its complaint, Aquestive was seeking an unspecified amount of damages, attorney’s fees and an injunction preventing future infringement of Aquestive’s patents.
The Company strongly refuted as without merit Aquestive’s assertion of patent infringement, which relates to the Company’s confidential, proprietary manufacturing process for ONSOLIS®. On September 12, 2011, the Company filed a request for inter partes reexamination in the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) of Aquestive’s ’588 Patent demonstrating that all claims of such patent were anticipated by or obvious in the light of prior art references, including several prior art references not previously considered by the USPTO, and thus invalid. On September 16, 2011, the Company filed a motion for stay pending the outcome of the reexamination proceedings, which subsequently was granted.
In November 2011, the USPTO rejected all 191 claims of Aquestive’s ’588 Patent. On January 20, 2012, the Company filed requests for reexamination before the USPTO of Aquestive’s ’891 Patent, and’292 Patent, the two additional patents asserted by Aquestive, demonstrating that all claims of those two patents were anticipated by or obvious in the light of prior art references, including prior art references not previously considered by the USPTO, and thus invalid. The USPTO granted the requests for reexamination with respect to Aquestive’s ’292 and ’891 Patents. In its initial office action in each, the USPTO rejected every claim in each patent.
As expected, in the ’891 Patent and ’292 Patent Ex Parte Reexamination proceedings, Aquestive amended the claims several times and made multiple declarations and arguments in an attempt to overcome the rejections made by the USPTO. These amendments, declarations and other statements regarding the claim language significantly narrowed the scope of their claims in these two patents. In the case of the ’891 Patent, not one of the original claims survived reexamination and five separate amendments were filed confirming the Company’s position that the patent was invalid. Additionally, the Company believes that arguments and admissions made by Aquestive prevent it from seeking a broader construction during any subsequent litigation by employing arguments or taking positions that contradict those made during prosecution.
A Reexamination Certificate for Aquestive’s ’891 Patent in its amended form was issued August 21, 2012 (the ’891C1 Patent). A Reexamination Certificate for Aquestive’s ’292 Patent in its amended form was issued on July 3, 2012 (t’292C1 Patent).
F-39
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 18. | Commitments and contingencies (continued): |
These actions by the USPTO confirm the invalidity of the original patents and through the narrowing of the claims in the reissued patents strengthens the Company’s original assertion that its products and technologies do not infringe on Aquestive’s original patents.
On June 12, 2013, despite the Company’s previously noted success in the prior ex parte reexaminations for the ’292 and ’891 Patents, the Company filed requests for inter partes reviews (“IPRs”) on the narrowed yet reexamined patents, the ’292 C1 and ’891 C1 Patents, to challenge their validity and continue to strengthen its position. On November 13, 2013, the USPTO decided not to institute the two IPRs for the ’891 C1 and ’292 C1 Patents. The USPTO’s decision was purely on statutory grounds and based on a technicality (in that the IPRs were not filed within what the UPSTO determined to be the statutory period) rather than substantive grounds. Thus, even though the IPRs were not instituted, the USPTO decision preserves the Company rights to raise the same arguments at a later time (e.g., during litigation). Regardless, the Company’s assertion that its products and technologies do not infringe the original ’292 and ’891 Patents and, now, the reexamined ’891 C1 and ’292 C1 Patents remains the same.
Importantly, in the case of Aquestive’s ’588 Patent, after the reexamination proceedings (and its appeals process), on April 17, 2014, the PTAB issued a Decision on Appeal affirming the Examiner’s rejection (and confirming the invalidity) of all the claims of the ’588 Patent. Aquestive did not request a rehearing by the May 17, 2014 due date for making such a request and did not further appeal the Decision to the Federal Court of Appeals by the June 17, 2014 due date for making such an appeal. Subsequently, on August 5, 2014, the USPTO issued a Certificate of Reexamination cancelling the ‘588 Patent claims.
Based on the Company’s original assertion that its proprietary manufacturing process for ONSOLIS® does not infringe on patents held by Aquestive, and the denial and subsequent narrowing of the claims on the two reissued patents Aquestive has asserted against us while the third has had all claims rejected by the USPTO, the Company remains confident in its original stated position regarding this matter. Thus far, the Company has proven that the “original” ’292 and ’891 patents in light of their reissuance with fewer and narrower claims were indeed invalid and the third and final patent, the ’588 patent, was invalid as well with all its claims cancelled. Given the outcomes of the ‘292, ‘891 and ‘588 reexamination proceedings, at a January 22, 2015 status meeting, the Court decided to lift the stay and grant the Company’s request for the case to proceed on an expedited basis with a Motion for Summary Judgment to dismiss the action. On September 25, 2015, the Company’s motion for summary judgment was ordered and the case was subsequently closed. The Company was found to be entitled to absolute intervening rights as to both patents in suit, the ‘292 and ‘891 patents and its ONSOLIS® product is not liable for infringing the patents prior to July 3, 2012 and August 21, 2012, respectively. In October 2015, Aquestive appealed the decision of the court to the Federal Circuit. The Company had no reason to believe the outcome would be different and was prepared to vigorously defend the appeal. Aquestive, however, subsequently decided to withdraw the appeal. On February 25, 2016, Aquestive filed an Unopposed Motion For Voluntary Dismissal Of Appeal, which was granted by the court on February 26, 2016 and the case dismissed. Thus, the district court’s grant of the Summary Judgement of Intervening Rights stands. The possibility exists that Aquestive could file another suit alleging infringement of the ‘292 and ’891 patents. The Company continues to believe, however, that ONSOLIS® and its other products relying on the BEMA® technology, including BUNAVAIL® and BELBUCA®, do not infringe any amended, reexamined claim from either patent.
Litigation related to BUNAVAIL®
RB and Aquestive
On October 29, 2013, Reckitt Benckiser, Inc., RB Pharmaceuticals Limited, and Aquestive (collectively, the RB Plaintiffs) filed an action against the Company relating to its BUNAVAIL® product in the United States District Court for the Eastern District of North Carolina for alleged patent infringement. BUNAVAIL® is a drug approved for the maintenance treatment of opioid dependence. The RB Plaintiffs claim that the formulation for BUNAVAIL®, which has never been disclosed publicly, infringes its patent ’832 Patent.
On May 21, 2014, the Court granted the Company’s motion to dismiss. In doing so, the Court dismissed the case in its entirety. The RB Plaintiffs did not appeal the Court Decision by the June 21, 2014 due date and therefore, the dismissal will stand and the RB Plaintiffs lose the ability to challenge the Court Decision in the future. The possibility exists, however, that the RB Plaintiffs could file another suit alleging infringement of the ‘832 Patent. If this occurs, based on the Company’s original position that its BUNAVAIL® product does not infringe the ‘832 Patent, the Company would defend the case vigorously (as the Company has done so previously), and the Company anticipates that such claims against them ultimately would be rejected.
F-40
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 18. | Commitments and contingencies (continued): |
On September 20, 2014, based upon the Company’s position and belief that its BUNAVAIL® product does not infringe any patents owned by the RB Plaintiffs, the Company proactively filed a declaratory judgment action in the United States District Court for the Eastern District of North (EDNC) Carolina, requesting the Court to make a determination that its BUNAVAIL® product does not infringe the RB Plaintiffs’ ‘080 Patent and the ‘378 Patent. With the declaratory judgment, there is an automatic stay in proceedings. The RB Plaintiffs may request that the stay be lifted, but they have the burden of showing that the stay should be lifted. For the ‘832 Patent, the January 15, 2014 IPR was instituted and in June 2015, all challenged claims were rejected for both anticipation and obviousness. In August 2015, the RB Plaintiffs filed an appeal to the Federal Circuit. The Federal Circuit affirmed the USPTO’s decision, and the RB Plaintiffs then filed a Petition for Panel Rehearing and for Rehearing En Banc, which was denied. A mandate issued on October 25, 2016, pursuant to Rule 41(a) of the Federal Rules of Appellate Procedure, meaning that a petition for certiorari to the Supreme Court is no longer possible for the RB Plaintiffs. The ‘832 IPR was finally resolved with the invalidation of claims 15-19. For the ‘080 Patent, all claims have been rejected in an inter partes reexamination and the rejection of all claims as invalid over the prior art has been affirmed on appeal by the PTAB in a decision dated March 27, 2015. In May 2015, the RB Plaintiffs filed a response after the decision to which the Company filed comments. In December 2015, the PTAB denied Aquestive’s request to reopen prosecution, but provided Aquestive an opportunity to file a corrected response. Aquestive filed the request in December 2015 and the Company subsequently filed comments on December 23, 2015. The PTAB issued a communication on July 7, 2016 denying Aquestive’s request to reopen prosecution of the rejections of all claims over the prior art. On January 31, 2017, the PTAB issued a final decision maintaining an additional new ground of rejection in addition to the previous grounds of invalidity. As such, all claims remain finally rejected on multiple grounds. If a request for rehearing is not filed within 30 days, the decision will become final as to the PTAB. Thereafter, if Aquestive does not appeal to the Federal Circuit, the decision will be final and all claims will be cancelled. For the ‘378 Patent, an IPR was filed on June 1, 2014, but an IPR was not instituted.
However, in issuing its November 5, 2014 decision not to institute the IPR, the PTAB construed the claims of the ‘378 Patent narrowly. As in prior litigation proceedings, the Company believes these IPR and the reexamination filings will provide support for maintaining the stay until the IPR and reexamination proceedings conclude. Indeed, given the PTAB’s narrow construction of the claims of the ‘378 Patent, the Company filed a motion to withdraw the ‘378 Patent from the case on December 12, 2014. In addition, the Company also filed a joint motion to continue the stay (with RB Plaintiffs) in the proceedings on the same day. Both the motion to withdraw the ‘378 Patent from the proceedings and motion to continue the stay were granted.
On September 22, 2014, the RB Plaintiffs filed an action against the Company (and its commercial partner) relating to the Company’s BUNAVAIL® product in the United States District Court for the District of New Jersey for alleged patent infringement. The RB Plaintiffs claim that BUNAVAIL®, whose formulation and manufacturing processes have never been disclosed publicly, infringes its ‘167 Patent. As with prior actions by the RB Plaintiffs, the Company believes this is another anticompetitive attempt by the RB Plaintiffs to distract the Company’s efforts from commercializing BUNAVAIL®. The Company strongly refutes as without merit the RB Plaintiffs’ assertion of patent infringement and will vigorously defend the lawsuit. On December 12, 2014, the Company filed a motion to transfer the case from New Jersey to North Carolina and a motion to dismiss the case against our commercial partner. The Court issued an opinion on July 21, 2015 granting the Company motion to transfer the venue to the Eastern District of North Carolina (“ENDC”) but denying its motion to dismiss the case against the Company’s commercial partner as moot. The Company has also filed a Joint Motion to Stay the case in North Carolina at the end of April 2016, which was granted by the court on May 5, 2016. Thus, the case is now stayed until a final resolution of the ‘167 IPRs in the USPTO. The Company will continue to vigorously defend this case in the EDNC.
In a related matter, on October 28, 2014, the Company filed multiple IPR requests on the ’167 Patent demonstrating that certain claims of such patent were anticipated by or obvious in light of prior art references, including prior art references not previously considered by the USPTO, and thus, invalid. The USPTO instituted three of the four IPR requests and we filed a request for rehearing for the non-instituted IPR. The final decisions finding all claims patentable were issued in March 2016 and the Company filed a Request for Reconsideration in the USPTO in April 2016, which was denied in September 2016 and appealed to Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit (Fed. Cir.) in November 2016. The appeal is currently proceeding in the Federal Circuit with final briefing completed August 7, 2017 and oral argument held February 7, 2018. The Company anticipates receiving a final decision from the Federal Circuit sometime in 2018. Regardless of the outcome of the appeal, the Company believes that BUNAVAIL® will be found not to infringe the claims of the ‘167 patent.
On January 22, 2014, Aquestive filed a Petition for IPR on US Patent No. 7,579,019 (the ‘019 Patent). The Petition asserted that the claims of the ‘019 Patent are alleged to be unpatentable over certain prior art references. The IPR was instituted on August 6, 2014. An oral hearing was held in April 2015 and a decision upholding all seven claims was issued August 5, 2015. In September 2015, Aquestive requested that the PTAB rehear the IPR. On December 19, 2016, the PTAB issued a final decision denying Aquestive’s request for rehearing. Aquestive did not file a notice of appeal to the Federal Circuit by February 20, 2017, and therefore, the PTAB’s decision upholding all claims of the Company’s ‘019 patent are final and unappealable.
F-41
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 18. | Commitments and contingencies (continued): |
On January 13, 2017, Aquestive filed a complaint in the United States District Court for the District of New Jersey alleging BELBUCA® infringes the ‘167 patent. In lieu of answering the complaint, the Company filed motions to dismiss the complaint and, in the alternative, to transfer the case to the EDNC. Briefing on the motions was completed on June 21, 2017. On July 25, 2017, the Court administratively terminated the case pending the parties submission of a joint stipulation of transfer because the District of New Jersey was an inappropriate venue. This case has been transferred to Delaware District Court. On October 31, 2017 the Company filed motions to dismiss the complaint and, in the alternative, to transfer the case to the EDNC. Briefing on the motions was completed on December 1, 2017. The Company anticipates receiving a final decision from the District Court in the 2nd quarter of 2018. The Company strongly refutes as without merit Aquestive’s assertion of patent infringement and will vigorously defend the lawsuit.
Teva Pharmaceuticals (formerly Actavis)
On February 8, 2016, the Company received a notice relating to a Paragraph IV certification from Teva Pharmaceuticals (“Teva”) (formerly Actavis Laboratories UT, Inc.) seeking to find invalid three Orange Book listed patents (the “Patents”) relating specifically to BUNAVAIL®. The Paragraph IV certification relates to an Abbreviated New Drug Application (the “ANDA”) filed by Actavis with the FDA for a generic formulation of BUNAVAIL®. The Patents subject to Teva’s certification are U.S. Patent Nos. 7,579,019 (“the ’019 Patent”), the ’866 Patent and the ’177 Patent. Under the Food Drug and Cosmetic Act, as amended by the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, as amended (the “Hatch-Waxman Amendments”), after receipt of a valid Paragraph IV notice, the Company may, and in this case did, bring a patent infringement suit in federal district court against Teva within 45 days from the date of receipt of the certification notice. On March 18, 2016, the Company filed a complaint in Delaware against Teva, thus the Company is entitled to receive a 30 month stay on the FDA’s ability to give final approval to any proposed products that reference BUNAVAIL®. The 30-month stay is expected to preempt any final approval by the FDA on Teva’s ANDA until at least August of 2018.
The Company has asserted three different patents against Teva, the ’019 patent, the ‘866 patent, and the ’177 patent. Teva did not raise non-infringement positions with regard to the ’019 and the ’866 patents in its Paragraph IV certification. Teva did raise a non-infringement position on the ’177 patent due to its assertion that the backing layer for its generic product does not have a pH within the claimed range claimed in the patent. The Company asserted in its complaint that Teva infringed the ‘177 patent either literally or under the doctrine of equivalents.
The Company believes that Teva is unlikely to prevail on its claims that the ’019, ’866, and ’177 Patents are invalid, and, as the Company has done in the past, intends to vigorously defend its intellectual property. Each of the three patents carry the presumption of validity and, the ‘019 Patent has already been the subject of an unrelated IPR before the USPTO under which the Company, and all claims of the ‘019 Patent survived. Aquestive’s request for rehearing of the final IPR decision regarding the ‘019 Patent was denied by the USPTO on December 19, 2016. Aquestive did not file a timely appeal at the Federal Circuit.
On December 20, 2016 the USPTO issued U.S. Patent No. 9,522,188 (“the ’188 patent”), and this patent was properly listed in the Orange Book as covering the BUNAVAIL® product. On February 23, 2017 Teva sent a Paragraph IV certification adding the 9,522,188 to its ANDA. An amended Complaint will be filed, adding the ’188 patent to the current litigation.
On January 31, 2017, the Company received a notice relating to a Paragraph IV certification from Teva relating to Teva’s ANDA on additional strengths of BUNAVAIL®. On March 16, 2017, the Company brought suit against Teva and its parent company on these additional strengths within 45 days from the receipt of the notice in Delaware. As in the original case brought by Actavis, the Company is again entitled to receive a 30 month stay on the FDA’s ability to give final approval to any proposed products that reference the additional strengths of BUNAVAIL®. The 30-month stay is expected to extend until at least August of 2019. On June 20, 2017, the Court entered orders staying both BUNAVAIL® suits at the request of the parties.
On May 23, 2017, the USPTO issued U.S. Patent 9,655,843 (the “’843 Patent”), and this patent was properly listed in the Orange Book as covering the BUNAVAIL® product.
Finally, on October 12, 2017, the Company announced that it had entered into a settlement agreement with Teva that resolved the Company’s BUNAVAIL® patent litigation against Teva pending in the U.S. District Court for the District of Delaware. As part of the Settlement Agreement, which is subject to review by the U.S. Federal Trade Commission and the U.S. Department of Justice, the Company has entered into a non-exclusive license agreement with Teva that permits Teva to first begin selling its generic version of BUNAVAIL® in the U.S. on July 23, 2028 or earlier under certain circumstances. Other terms of the agreement are confidential.
F-42
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
| 18. | Commitments and contingencies (continued): |
Litigation related to BELBUCA®
The Company received notices regarding Paragraph IV certifications from Teva on November 8, 2016, November 10, 2016, and December 22, 2016, seeking to find invalid two Orange Book listed patents (the “Patents”) relating specifically to BELBUCA®. The Paragraph IV certifications relate to three ANDAs filed by Teva with the FDA for a generic formulation of BELBUCA®. The Patents subject to Teva’s certification were U.S. Patent Nos. 7,579,019 (“the ’019 Patent”) and 8,147,866 (“the ’866 Patent”). Under the Hatch-Waxman Amendments, after receipt of a valid Paragraph IV notice, the Company may, and in this case did, bring a patent infringement suit in federal district court against Teva within 45 days from the date of receipt of the certification notice. The Company filed complaints in Delaware against Teva on December 22, 2016 and February 3, 2017, thus the Company was entitled to receive a 30 month stay on the FDA’s ability to give final approval to any proposed products that reference BELBUCA®. The 30-month stay was expected to preempt any final approval by the FDA on Teva’s ANDA Nos. 209704 and 209772 until at least May of 2019 and for Teva’s ANDA No. 209807 until at least June of 2019.
The Company asserted two different patents against Teva, the ’019 Patent and the ’866 Patent. Teva did not contest infringement of the claims of the ’019 Patent and also did not contest infringement of the claims of the ’866 Patent that cover BELBUCA® in its Paragraph IV certifications.
The Company believed that Teva was unlikely to prevail on its claims that the ’019 and ’866 Patents are invalid, and, as the Company has done in the past, vigorously defended its intellectual property. Both of the patents carry the presumption of validity, and the ’019 Patent has already been the subject of an unrelated IPR before the USPTO under which the Company prevailed, and all claims of the ‘019 Patent survived. Aquestive’s request for rehearing of the final IPR decision regarding the ’019 Patent was denied by the USPTO on December 19, 2016. Aquestive did not file a timely appeal at the Federal Circuit.
On May 23, 2017, the USPTO issued U.S. Patent 9,655,843 (the “’843 Patent”), and this patent was properly listed in the Orange Book as covering the BELBUCA® product.
On August 28, 2017, the Court entered orders staying both BELBUCA® suits at the request of the parties. On October 18, 2017, the Court entered orders continuing the stay in both BELBUCA® suits at the request of the parties. On December 19, 2017, the Court entered orders continuing the stay in both BELBUCA® suits at the request of the parties.
Finally, on February 6, 2018, the Company announced that it had entered into a settlement agreement with Teva that resolved the Company’s BELBUCA® patent litigation against Teva pending in the U.S. District Court for the District of Delaware. As part of the settlement agreement, which is subject to review by the U.S. Federal Trade Commission and the U.S. Department of Justice, the Company granted Teva a non-exclusive license (for which the Company will receive no current or future payments) that permits Teva to first begin selling the generic version of the Company’s BELBUCA® product in the U.S. on January 23, 2027 or earlier under certain circumstances (including, for example, upon (i) the delisting of the patents-in-suit from the U.S. FDA Orange Book, (ii) the granting of a license by the Company to a third party to launch another generic form of BELBUCA® at a date prior to January 23, 2027, or (iii) the occurrence of certain conditions regarding BELBUCA® market share).
F-43
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. DOLLARS IN THOUSANDS)
SELECTED QUARTERLY RESULTS (UNAUDITED)
The following table sets forth certain quarterly financial data for the periods indicated (in thousands, except per share data):
| Quarter Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| March 31, 2017 |
June 30, 2017 |
September 30, 2017 |
December 31, 2017 |
|||||||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 29,478 | $ | 8,744 | $ | 11,253 | $ | 12,510 | ||||||||
| Gross profit |
23,833 | 4,573 | 6,808 | 7,275 | ||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
7,903 | (12,987 | ) | (10,045 | ) | (14,291 | ) | |||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
48,325 | (14,879 | ) | (11,951 | ) | (16,210 | ) | |||||||||
| Basic income (loss) per share |
0.89 | (0.27 | ) | (0.21 | ) | (0.31 | ) | |||||||||
| Diluted income (loss) per share |
0.87 | (0.27 | ) | (0.21 | ) | (0.30 | ) | |||||||||
| Quarter Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| March 31, 2016 |
June 30, 2016 |
September 30, 2016 |
December 31, 2016 |
|||||||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 3,040 | $ | 5,004 | $ | 3,571 | $ | 3,931 | ||||||||
| Gross profit |
490 | 910 | 1,257 | 1,631 | ||||||||||||
| Loss from operations |
(17,942 | ) | (15,594 | ) | (15,199 | ) | (15,200 | ) | ||||||||
| Net loss |
(18,733 | ) | (16,486 | ) | (15,977 | ) | (15,942 | ) | ||||||||
| Basic loss per share |
(0.35 | ) | (0.31 | ) | (0.30 | ) | (0.29 | ) | ||||||||
| Diluted loss per share |
(0.35 | ) | (0.31 | ) | (0.30 | ) | (0.29 | ) | ||||||||
| Quarter Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| March 31, 2015 |
June 30, 2015 |
September 30, 2015 |
December 31, 2015 |
|||||||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 13,054 | $ | 1,733 | $ | 1,235 | $ | 32,209 | ||||||||
| Gross profit |
11,930 | (888 | ) | (464 | ) | 29,552 | ||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
(7,800 | ) | (18,681 | ) | (19,652 | ) | 10,954 | |||||||||
| Net (loss) income |
(8,193 | ) | (19,211 | ) | (20,439 | ) | 10,171 | |||||||||
| Basic (loss) income per share |
(0.16 | ) | (0.37 | ) | (0.39 | ) | 0.20 | |||||||||
| Diluted (loss) income per share |
(0.16 | ) | (0.37 | ) | (0.39 | ) | 0.20 | |||||||||
F-44
Table of Contents
BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
SCHEDULE II – VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS AND RESERVES
| Balance at beginning of the period |
Charged to income |
Charged to other accounts |
Deductions | Balance at the end of the period |
||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Description |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Valuation allowance for deferred tax assets |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2017: |
$ | 109,030 | $ | (37,515 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 71,515 | |||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2016: |
$ | 84,960 | $ | 24,070 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 109,030 | ||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2015: |
$ | 72,061 | $ | 12,899 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 84,960 | ||||||||||
| Allowance for rebates |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2017: |
$ | 3,842 | $ | 17,236 | $ | (132 | ) | $ | (15,298 | ) | $ | 5,648 | ||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2016: |
$ | 4,470 | $ | (1,204 | ) | $ | 11,501 | $ | (10,925 | ) | $ | 3,842 | ||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2015: |
$ | 939 | $ | 2,118 | $ | 6,360 | $ | (4,947 | ) | $ | 4,470 | |||||||||
| Allowance for price adjustments and chargebacks |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2017: |
$ | 602 | $ | 6,738 | $ | (3 | ) | $ | (3,412 | ) | $ | 3,925 | ||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2016: |
$ | 383 | $ | 36 | $ | 1,711 | $ | (1,528 | ) | $ | 602 | |||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2015: |
$ | 400 | $ | (2,118 | ) | $ | 3,259 | $ | (1,158 | ) | $ | 383 | ||||||||
| Allowance for inventory obsolescence |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2017: |
$ | — | $ | 243 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 243 | ||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2016: |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2015: |
$ | — | $ | 213 | $ | (213 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||
F-45
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
In accordance with Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| BIODELIVERY SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL, INC. | ||||||
| Date: March 15, 2018 | By: | /S/ SCOTT M. PLESHA | ||||
| Name: | Scott M. Plesha | |||||
| Title: | President | |||||
| (Principal Executive Officer) | ||||||
| By: | /s/ ERNEST R. DE PAOLANTONIO | |||||
| Name: | Ernest R. De Paolantonio | |||||
| Title: | Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and Treasurer | |||||
| (Principal Accounting Officer) | ||||||
In accordance with the Exchange Act, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Person |
Capacity |
Date | ||
| /S/ FRANK E. O’DONNELL, JR. |
Chairman of the Board |
March 15, 2018 | ||
| Francis E. O’Donnell, Jr. | ||||
| /S/ SCOTT M. PLESHA |
President |
March 15, 2018 | ||
| Scott M. Plesha | ||||
| /S/ MARK A. SIRGO |
Vice Chairman |
March 15, 2018 | ||
| Mark A. Sirgo | ||||
| /S/ SAMUEL P. SEARS, JR. |
Director |
March 15, 2018 | ||
| Samuel P. Sears, Jr. | ||||
| /S/ THOMAS W. D’ALONZO |
Director |
March 15, 2018 | ||
| Thomas W. D’Alonzo | ||||
| /S/ BARRY FEINBERG |
Director |
March 15, 2018 | ||
| Barry Feinberg | ||||
| /S/ TIMOTHY TYSON |
Director |
March 15, 2018 | ||
| Timothy Tyson | ||||
| /S/ WILLIAM M. WATSON |
Director |
March 15, 2018 | ||
| William M. Watson | ||||
S-1
