Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32 - CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO 18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350 - AURA SYSTEMS INC | f10k2017ex32_aurasystems.htm |
| EX-31.2 - CFO CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002 - AURA SYSTEMS INC | f10k2017ex31-2_aurasystems.htm |
| EX-31.1 - CEO CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002 - AURA SYSTEMS INC | f10k2017ex31-1_aurasystems.htm |
| EX-16.1 - LETTER OF KABANI & COMPANY - AURA SYSTEMS INC | f10k2017ex16-1_aurasystems.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES
AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One)
☒ ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended February 28, 2017
OR
☐ TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from to
Commission file number 0-17249
AURA SYSTEMS, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 95-4106894 | |
| (State
or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S.
Employer Identification No.) |
10541 Ashdale St.,
Stanton, CA 90680
(Address of principal executive offices, zip code)
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (310) 643-5300
Name of each exchange on which registered: None
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: None
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: Common Stock
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer | ☐ | Accelerated filer | ☐ |
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | ☒ |
| Emerging growth company | ☐ | ||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
On August 31, 2016 the aggregate market value of the voting stock held by non-affiliates of the Registrant was $10,738,936. The aggregate market value has been computed by reference to the last sale price of the stock on August 31, 2016.
On August 30, 2017, the Registrant had 126,608,391 shares of common stock outstanding.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Report contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the federal securities laws. Statements other than statements of historical fact included in this Report, including the statements under the headings “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” “Business” and elsewhere in this Report regarding future events or prospects are forward-looking statements. The words “approximates,” “believes,” “forecast,” “expects,” “anticipates,” “estimates,” “intends,” “plans,” “would,” “could,” “should,” “seek,” “may,” or other similar expressions in this Report, as well as other statements regarding matters that are not historical fact, constitute forward-looking statements. We caution investors that any forward-looking statements presented in this Report are based on the beliefs of, assumptions made by, and information currently available to, us. Such statements are based on assumptions and the actual outcome will be affected by known and unknown risks, trends, uncertainties and factors that are beyond our control or ability to predict. Although we believe that our assumptions are reasonable, they are not guarantees of future performance and some may inevitably prove to be incorrect. As a result, our actual future results may differ from our expectations, and those differences may be material. Accordingly, investors should use caution in relying on forward-looking statements to anticipate future results or trends.
Some of the risks and uncertainties that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to differ materially from those expressed or implied by forward-looking statements include the following:
| ● | Our ability to generate positive cash flow from operations; |
| ● | Our ability to obtain additional financing to fund our operations; |
| ● | The impact of economic, political and market conditions on us and our customers; |
| ● | The impact of unfavorable results of legal proceedings; |
| ● | Our exposure to potential liability arising from possible errors and omissions, breach of fiduciary duty, breach of duty of care, waste of corporate assets and/or similar claims that may be asserted against us; |
| ● | Our ability to compete effectively against competitors offering different technologies; |
| ● | Our business development and operating development; |
| ● | Our expectations of growth in demand for our products; and |
| ● | Other risks described under the heading “Risk Factors”in Part I, Item 1A of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
We do not intend to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise except to the extent required by law. You should interpret all subsequent written or oral forward-looking statements attributable to us or persons acting on our behalf as being expressly qualified by the cautionary statements in this Report. As a result, you should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements.
References in this Report to “we”, “us”, “the Company,” “Aura” or “Aura Systems” means Aura Systems, Inc. As used herein, reference to “fiscal 2017” refers to the fiscal year ended February 28, 2017, reference to “fiscal 2016” refers to the fiscal year ended February 29, 2016, reference to “fiscal 2014” refers to the fiscal year ended February 28, 2014, reference to “fiscal 2015” refers to the fiscal year ended February 28, 2015 and reference to “fiscal 2018” refers to the fiscal year ending February 2018.
Introduction
The Company, a Delaware corporation, was founded in 1987. Prior to experiencing severe financial pressures that started in the second half of 2014 and which are further described below under “—Business Arrangements”, the Company designed, assembled, tested and sold our proprietary and patented Axial Flux induction machine (“AF”) known as the AuraGen® for industrial and commercial applications and the VIPER for military applications. Our patented system when applied as a generator uses the engine of a vehicle or any other prime mover to create mechanical energy and the AuraGen converts the mechanical energy to electric power. Our patented control system is used to deliver such power to the user. When used as an electric motor, our system delivers mechanical power to drive mechanical devices. During the first half of fiscal 2016, the Company significantly reduced operations due to lack of financial resources. During the second half of fiscal 2016 the Company’s operations were completely disrupted when the Company was forced to move from its facilities in Redondo Beach, California to a smaller facility in Stanton, California. Operations during the second half of fiscal 2016 were sporadic. During fiscal 2017, the Company suspended its engineering, manufacturing, sales, and marketing activities to focus on renegotiating numerous financial obligations with several Note holders.
Traditional induction machines are Radial Flux (“RF”) machines and are the workhorse of industry due to their robustness, attractive cost, and easy control. However, they are relatively heavy and bulky. Axial flux induction machines on the other hand, have all of the advantages of the radial flux machines, but with the advantage of higher energy density resulting in smaller, lighter machines with equivalent performance. Unlike permanent magnet (“PM”) machines, induction machines do not use any permanent magnets and therefore the controller can change the magnetic (B) fields since generally the magnetic (B) field is proportionate to the voltage divided by the frequency (V/f). It is generally accepted that for PM machines, as machine size grows, the magnetic losses increase proportionately and partial load efficiency drops. On the other hand,with induction machines, as the machine size grows, magnetic losses do not necessarily grow. Induction drives could offer an advantage when high-performance is desired. The peak efficiency of an induction drive will be somewhat lower than with PM machines, but average efficiency may actually increase.
The history of electric motors reveals that the earliest machines were in fact axial flux machines. However, after the first radial flux machines were demonstrated in the early 1900’s, such machines were accepted as mainstream configuration. The reason for shelving the axial flux machines were multifold and can be summarized as follows: (i) strong axial magnetic attraction force between the stator and the rotor, (ii) fabrication difficulties such as cutting the slots in laminated cores, (iii) high cost involved in manufacturing the laminated stator core, (iv) difficulties in assembling the machine and maintaining a uniform air gap and (v) providing a laminated rotor that can stand the large centrifugal forces. Modern techniques show that all of the historical objections for axial flux machines can be addressed with recent developments in the design of such machines, as well as, the design of the proper manufacturing processes and tooling.
The issue of the strong axial magnetic attraction force between the stator and the rotor was addressed by Aura’s patented approach of using a topology of two stators and a rotor sandwiched between them. This has been disclosed in Aura’s U.S. Patent 5,734,217 (March 1998 ), which expires in March 2018, and U.S. Patent 6,157,175 (Dec. 2000). In addition to other benefits, the topology is such that the axial forces on the bearings are very small and negligible.
The issues of fabrication difficulties and the high cost involved in manufacturing of the laminated stator cores were resolved years ago by Aura Systems using a technique involving punching the slots while rolling the steel. This approach creates a continuous punched steel ribbon at a cost that is lower than the traditional punched laminates because less material is wasted. The equipment required uses a closed loop control system that controls a precision step-motor and a punching press. Over the past 10 years, we have delivered thousands of units of our induction axial flux machines in the 5-16kW range and have not encountered technical issues that would appear to affect the use of the same techniques in any other size induction axial flux machines.
Many manufacturers of PM axial flux machines, as well as Aura Systems with its induction axial flux machines, have resolved the issues regarding difficulties in assembling the machine and maintaining a uniform air gap. Therefore this is no longer an issue.
| 1 |
Aura Systems Inc. has also developed a cast rotor for the axial flux machine as described in U.S. Patents 5,734,217 and 6,157,175. This rotor does not require any laminates and provides the structural integrity to withstand very large centrifugal forces, while at the same time provides the proper electric and magnetic properties.
As described above, Aura Systems developed the technology and manufacturing processes to overcome the traditional objections to axial flux machines. Once Aura Systems resolved the historical issues relating to the axial flux approach as described above, the next step was to develop a smart control system that provided for a total variable speed solution. A complete power generation system based on Aura’s axial flux generator and Aura’s unique smart controller is disclosed in Aura’s U.S. Patent 6,700,214 (March 2, 2004). Finally, Aura’s U.S. Patent 6,700,802 (March 2, 2004) disclosed a method where power from multi sources can be added to handle sudden power spikes such those that occur when a compressor, motor, pump, etcetera are turned on. In addition, patent 6,700,802 provides a very unique method (bi-directional Power supply) for uninterrupted seamless transition from generator power to battery pack power and back to generator power.
The AuraGen® /VIPER system is composed of three primary subsystems (i) the patented axial flux design alternator, (ii) the electronic control unit (“ECU”) and (iii) mounting kit that is a mechanical interface between the alternator and the prime mover. The architecture of our patented ECU is designed to separate the power generation from the power user, thus creating a flexible system that can support multi voltages simultaneously. The system architecture is based on having a direct current (“DC”) power bus that is used to excite the alternator and also to collect energy from the alternator. The user loads are supported from the power bus and not directly from the alternator. This immediately leads to a load following design where the demand on the alternator at any moment in time is equal to the demanded user load (up to the maximum alternator power capabilities). In addition, the output power is constructed from the power bus with either a PWM based inverter for alternating current (“AC”) output, and/or, a unique patented bi direction power supply (“BDPS”) that acts as a DC to DC converter to provide different DC voltages as an output. The BDPS provides the capability of adding power to the bus from a DC source such as batteries whenever sudden spikes or demands occur. The BDPS also provides the seamless transition to maintain the power bus when the prime mover is turned off (batteries are used to support the power bus).
After a lengthy development period, the Company began commercializing the AuraGen® in late 1999 and early 2000. Our first commercial product was a 5,000-watt 120/240V AC machine, in 2001; we subsequently added an 8,000-watt configuration and also introduced the BDPS that allowed us to provide simultaneously an AC/DC solution. In fiscal 2008, the Company introduced a system that generates up to 16,000-watts of continuous power by combining two 8,000 watts’ systems (dual system) and in fiscal 2010 introduced the TanGen system that combines two 8,000 watts systems on a single output shaft (two rotors on a single shaft). The Company is currently developing a 30,000-watt system consisting of two rotors on a single shaft (each one with 15,000 watts’ capability). As described above, the focus is on mobile power applications and thus requires an interface kit to the prime mover. Many of our applications are such that the AuraGen/VIPER is driven directly from a truck or SUV engine. The Company now has configurations available for more than 90 different engine types, including a majority of models of General Motors and Ford, some Chrysler models and numerous other engine models made by International, Isuzu, Nissan, Hino (Toyota), Mitsubishi, Caterpillar, Detroit Diesel, Cummins, and Freightliner. In addition, the Company has interface kits for numerous model of military HMMWV, as well as other military vehicles. Also, starting in fiscal 2008, the AuraGen/VIPER was installed on a number of U.S. Navy boats and on a number of the U.S. Coast Guard 44 ft. patrol boats. In addition to the usage of the vehicle engine as the prime mover, the Company has also developed numerous Power-Take-Off (“PTO”) interface kits for many different vehicle platforms and is also working with a number of customers on integrating our AuraGen/VIPER power solution with stand-alone engines known as Auxiliary-Power-Unit (“APU”) to be used in emergency rescue and electric vehicle applications.
Since March 2017, the Company has started to reexamine the market and identified key areas upon which to initially focus as the Company plans to restart operations. A key element of our business plan is focused on all-electric transport refrigeration. The market is well understood and both social and economic forces are providing an unprecedented opportunity to gain significant market share. Our immediate focus is on 20-k BTU/hr midsize trucks and the 50-k BTU/hr trailers. The market for new20-k BTU/hr midsize trucks is for approximately 15,000 new trucks per year and a significant retrofit market of the existing over 100,000 operating systems across North America. The market for new 50-k BTU/hr trailers is approximately 40,000 new units per year and also a significant retrofit market for the over 400,000 operating systems in North America. Another key element is the acceptance of our mobile power solution in military applications around the globe. Our near term focus is marketing efforts in the U.S., South Korea, Israel and China.
| 2 |
Business Arrangements
During the first half of fiscal 2016, the Company significantly reduced operations due to lack of financial resources. During the second half of fiscal 2016 the Company’s operations were disrupted when the Company was forced to move from its facilities in Redondo Beach, California to a smaller facility in Stanton, California. Operations during the second half of fiscal 2016 were sporadic. During fiscal 2017, the Company suspended its engineering, manufacturing, sales, and marketing activities to focus on renegotiating numerous financial obligations. During this time, the Company’s agreements with numerous customers, third party vendors, and organizations and entities material to the operation of the Company business were canceled, delayed or terminated. Based on informal discussions with various customers and vendors, management believes that many of the canceled or terminated agreements could be reinstated once the Company commences operating again. In March 2017, the Company signed a joint venture agreement with a Chinese company to build, service and distribute the AuraGen patented products in China. The Chinese partner owns 51% of the joint venture and the Company owns 49%. The Chinese partner contributed approximately $9.75 million for facility, equipment, and working capital of the joint venture and the Company is required to contribute $250,000. The joint venture is required to purchase the rotor and control software from the Company.
The AuraGen®/VIPER
The AuraGen® is composed of three basic subsystems. The first subsystem is the AF generator that is bolted to, and driven by, the vehicle’s engine, PTO, or any other prime mover. The second subsystem is the ECU, which filters and conditions the electricity to provide clean, steady voltages for both AC and DC power, and provides for variable speed applications as well as load following for increased efficiency. The third subsystem consists of mounting brackets and supporting components for installation and integration of the generator with the vehicle engine, PTO, or the prime mover.
Currently the Company has power solutions for three continuous power levels, (a) 5,000 watts AC/DC, (b) 8,000 watts AC/DC and (c) 16,000 watts AC/DC. All the AC power is pure sine wave with total harmonic distortion of less than 2.1% and is available in 120 VAC and/or 240 VAC and in some application 480 VAC. In addition, the power generated on all models can be partitioned to provide simultaneous AC and 14 or 28 volts of DC or only DC, if required by the user. The AuraGen power levels can be generated as the prime mover speed varies from idle to maximum rated speed. The VIPER (the military version of the AuraGen® system) includes as an option a complete power management system which (i) monitors in real time the batteries’ voltage and temperature, (ii) provides a partition of the power between AC and DC simultaneously with the ability to be programmed from all AC to all DC, (iii) monitors the RPM of the generator, (iv) monitors the temperatures of the generator and the ECU, (v) monitors the raw power generated, (vi) monitors both the AC and DC loads as to voltage and current, and (vii) provides programming of load prioritization and load shedding.
Mobile and Remote (not power grid connected) Power Industry
The mobile and remote power generation market is large and growing. There are four basic market segments (i) military, (ii) stationary but remote commercial/industrial, (iii) mobile commercial/industrial, and (iv) hybrid and electric vehicles. The military market place is also divided between mobile and stationary applications.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, in 2007 the U.S. motor and generator industry, for larger than one horsepower applications, recorded more than $9.5 billion in sales (U.S Census Bureau Industry Statistical Sampler).
We believe that one of the fastest growing segments in the military market place is On-Board-Exportable-Power (OBEP), which is electric power on vehicles that can be used to support other than vehicle functions. The driver for the increased demand for on board power are numerous advance weapon systems as well as increase in C4I functions (command, control, communication, computers and information). Currently, most on board power is provided by APUs that are (i) large fuel users, (ii) bulky, (iii) heavy and (iv) require constant maintenance. Militaries all over the world are seeking more efficient integrated power solutions for their vehicles.
| 3 |
Similar to the military demands, the commercial and industrial markets also require on board power to support modern computers, digital sensors and instruments as well as electrical driven tools. Current automotive alternators cannot supply the existing demanded power and thus the common solution is the use of APUs. These APUs are environmentally unfriendly, substantial users of fuel, heavy, bulky and require constant maintenance and scheduled service. Vehicles used in the telecommunications, utilities, public works, construction, catering, oil and gas industries, emergency/rescue, and recreational vehicles rely heavily on mobile power for their daily work. Hybrid and electric vehicles by their nature require significant amounts of on board power to charge batteries as well as to operate electric motors.
The traditional available solutions for mobile and remote power users are:
| ● | Gensets (AKA APUs), Gensets are standalone power generation units that are not incorporated into a vehicle and require external fuel, either gasoline or diesel, in order to generate electricity. Gensets (i) are generally noisy and cumbersome to transport because of their weight and size, (ii) typically run at constant speed to generate 50 or 60 Hz of AC power, (iii) must be operated at a significant part of the rated power to avoid wet staking, (iv) are significantly derated in the presence of harmonics in the loads and (v) require significant scheduled maintenance and service. Genset technology has been utilized since the 1950s. |
| ● | High-Output Alternators, High-output alternators are traditionally found in trucks and commercial vehicles and the vehicle’s engine is used as the prime mover. All high-output alternators provide their rated power at very high RPM and significantly less power at lower RPM. In addition, high-output alternators are generally only 30% efficient at the low RPM range and increase to 50% efficiency at the high end of the RPM range. The power generated by high-output alternators is 12 or 24 Volt DC and an inverter is required if AC power is needed. In addition, due to the low power output at low RPMs, in order to get significant power, a throttle controller is used to speed-up the engine. |
| ● | Inverters, Inverters are devices that invert DC to AC. Inverters as mobile power generators are traditionally used in low power requirements, typically less than 2,500 watts, and do not have the ability to recharge the batteries that are traditionally used as the source of power. Thus, typical inverter users require other means to recharge the used batteries such as “shore-power” or gensets. More recently dynamic inverters became available. Dynamic inverters use power from the alternator to augment power from the batteries and are able to achieve power levels in excess of 6,000 watts. Dynamic inverters introduce significant stresses on both the batteries and alternators, which causes significant life shortening for both. When the inverter is turned on, the alternator is switched off from the vehicle battery and tied into a transformer that uses electronic controls to change the DC alternator inputs to AC inverter output. A separate transformer winding provides battery charging so that fully regulated 120 Volt AC and 12 Volt DC power is available as long as the engine is running at high enough RPM to provide power for the load and the battery charging. All dynamic inverters require a high-output alternator to be able to output significant AC power. As is often the case, the limiting factor is the high-output alternator. In order to get stable output, a very accurate throttle controller is also needed to maintain steady speed on the engine. |
| ● | Permanent-Magnet Alternators. Recently a number of companies have introduced alternators using exotic permanent magnets. These alternators tend to have higher power generation capabilities than regular alternators at lower engine RPM. In order to be practical in an under-the–hood environment (200oF) active cooling must be added, since the magnets are demagnetized at approximately 176oF. There are other issues that require an active control system that will add and subtract magnetic field strength as the engine RPM increases. Currently, the vast majority of the magnets used for electric machines come from China. |
| ● | Fuel Cells. Fuel cells are solid-state devices that produce electricity by combining a fuel containing hydrogen with oxygen. They have a wide range of applications and can be used in place of the internal combustion engine and traditional lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries. The most widely deployed fuel cells cost about $2,000 per kilowatt. |
| ● | Batteries. Batteries convert stored chemical energy to electrical. |
| 4 |
Competition
The Company is involved in the application of its AuraGen technology to mobile power and, as such, faces substantial competition from companies offering different technologies. Over the last several years there have not been new significant developments in this industry.
Gensets AKA APU - Portable generators meet a large market need for auxiliary power. Millions of units per year are sold in North America alone, and millions more across the world to meet market demands for 1 to 20 Kilowatts of portable power. The market for these power levels addresses the commercial, leisure and residential markets, and divides essentially into: a) higher power, higher quality and higher price commercial level units; and b) lower power, lower quality and lower price level units. Gensets provide the strongest competition across the widest marketplace for auxiliary power. Onan, Honda and Kohler, among others, are well established and respected brand names in the genset market for auxiliary power generation. There are 44 registered genset-manufacturing companies in the U.S. with many more through Asia and, particularly, within China.
High Output Alternators - There are many high output alternator manufacturers and the prices vary from hundreds to thousands of dollars per unit. Some well-known manufacturers include: Delco-Remy, Bosh, Nippon Densu, Hitachi, Mitsubishi, Prestolite, EMP and Neihoff. Alternatorsprovide rated power at very high RPM and significantly less power at lower RPM. In addition, alternators are generally only 30% efficient at the low RPM range and increase to 50% efficiency at the high RPM range. The AuraGen/VIPER system (including mechanical linkages and belt) is over 80% efficient at the low RPM range and is approximately 75% efficient at the very high RPM range.
Inverters - There are many inverter manufacturers; across the globe the best known one is Xentrex. The pricing of industrial grade sine wave inverters is approximately $500 per kilowatt plus the cost of a high output alternator ($650) and a good throttle controller ($250).
Permanent-Magnet (“PM”) alternators. - A number of companies have introduced alternators using exotic NdFeB magnets (UQM technologies is one of the better known). These alternators tend to have higher power generation capabilities than regular alternators at lower RPM. Unfortunately, PM machines with NdFeB magnets are very sensitive to temperature and, unlike the AuraGen, cannot survive the typical under-the-hood environment (200oF+). In order to apply such devices for automotive applications one must add expensive and cumbersome active cooling since the magnets are demagnetized at approximately (176oF). To date, such machines have been used mostly in wind-power generation applications.
In addition to the temperature challenges of such machines, there are other issues involving active control of the magnetic field. A disadvantage of PM generators is the difficulty of output voltage regulation to compensate for speed and load variation due to the lack of a simple means of field control. In addition, in PM alternators as the machine size grows, the magnetic loses increase proportionally. Finally, PM machines are more expensive than induction machines.
Fuel Cells- Fuel cells are solid-state, devices that produce electricity by combining a fuel containing hydrogen with oxygen. They have a wide range of applications, and can be used in place of the internal combustion engine and traditional lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries. These systems are, however, generally prohibitively expensive, and the most widely deployed fuel cells cost about $1,500 per kilowatt.
Others - Symetron Technology by Raser Inc. is sometimes mistaken for a new form of motor or generator. The Symetron technology is a variable frequency motor/generator controller that uses numerous control schemes to optimize performance. The Symetron technology involves adaptive tuning to continuously optimize motor and system efficiency for the speed and torque operating point. When the system was tested in November 2006 the adaptive algorithm or table calculations were performed offline and then input to the controller.
The Symetron controller is a potential competitor to variable speed motor controllers provided by such companies as of ABB, or Baldor-Electric Co. The Symetron technology is not a new form of motor/generator.
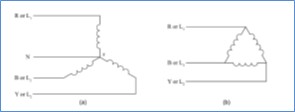 There
are a number of companies that advertise a “secret” approach for higher performance of inductive machines. Typically,
these claims are not proven and are based on changing the winding connections from Y to D or D to Y.
There
are a number of companies that advertise a “secret” approach for higher performance of inductive machines. Typically,
these claims are not proven and are based on changing the winding connections from Y to D or D to Y.
Axco in Finland briefly introduced axial flux machines similar to Aura’s. However, Axco stopped its pursue of patent protection in the U.S. when they discovered Aura’s patents. Furthermore, one of Axco scientist cites Aura’s approach in his PhD dissertation. Axco business is currently focused on large permanent magnets applications mostly related to large windmills.
| 5 |
Evans electric in Australia has recently introduced an axial flux machine with a complete conductive rotor. Such a machine was first introduced by Brinner more than 20 years ago and was abandoned because the rotor lacked the required rigidity to withstand the magnetic and centrifugal forces. The Brinner machine is cited in Aura’s patents.
Transport Refrigeration (“TRU”) - The main competitors for the all-electric TRU are traditional diesel based solutions provided by Thermo-king and Carrier. The diesel based comparable systems provided by Thermo-king and Carrier are somewhat less expensive than our AuraGen all-electric solution , however the diesel solutions require frequent maintenance and the utilization of a separate diesel engine that consumes considerable fuel every operating hour. In addition, the diesel solutions emit harmful emissions that have been recognized by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, California’s Air Resource Board and others as dangerous pollutants and are increasingly subject to federal and state regulations.
The economic and environmental benefits of the AuraGen solution are greatly amplified in transport refrigeration applications where a separate diesel engine is eliminated. An analysis of our solution for large refrigeration trucks (117,000 trucks across the nation) shows potential annual savings in excess of 26,000 tons of NMHC+NOx, 23,000 tons of CO and over to 1,400 tons of PM. The diesel fuel savings exceed 100,000,000 annual gallons. The above numbers are very conservative since they reflect: (i) the assumption that all refrigeration diesel engines already meet the Tier 4 EPA requirements and (ii) that there are no additional savings from idle reductions. Both assumptions are used as a lower bound for the anticipated savings.
Most of our competitors have greater financial, technical, and marketing resources than we have. They have larger budgets for research, new product development and marketing, and have long-standing customer relationships. We also compete with many larger and more established companies in the hiring and retention of qualified personnel. Our financial condition has limited our ability to market the AuraGen® aggressively.
The AuraGen® uses new technology and because our product is radically different from traditionally available mobile power solutions, users may require lengthy evaluation periods to gain confidence in the product. OEMs and large fleet users also typically require considerable time to make changes to their planning and production.
Targeted Markets
It is only recently that the Company has started to reexamine and identify key markets upon which to initially focus as the Company plans to restart operations.
(i) A key element of our business plan is focused on All-Electric Transport refrigeration. The market is well understood and both social and economic forces are providing an unprecedented opportunity to gain significant market share. Our immediate focus is on 20-k BTU/hr midsize trucks and the 50-k BTU/hr trailers.
(ii) Another element of our business plan is focused of our mobile power solution for military applications around the globe.
(iii) We plan to look for joint venture opportunities similar to the agreement we recently entered in China to explore other international opportunities.
Facilities, Manufacturing Process and Suppliers
As part of downsizing due to financial distress experienced by the Company as further described in “--Business Arrangements”, our current facilities consist of approximately 20,000 square feet in Stanton California and an additional storage facility for existing inventory. The Stanton facility is currently used for some assembly and testing of AuraGen/VIPER systems. The facility is rented on a month-to-month basis. The rent for the Stanton facility is $10,000 per month and the storage facility is additional $5,000 per month. The current Stanton facility is not sufficient to support the expected operations should the Company’s operations return to pre-2014 production levels. Accordingly, the Company is currently looking for a new facility of approximately 45,000 square feet that would be used for production, testing, and engineering for AuraGen/VIPER mobile power solution as well as needed office space for support staff. Prior to May 2015, we occupied a 69,000 square foot facility in Redondo Beach, California. The Redondo Beach facility was used for assembly and testing of products,as well as for general offices, engineering and warehousing. The rent for the Redondo Beach facility was approximately $60,000 per month.
| 6 |
As the Company is gearing up operations again, we need to renew relationships and contracts with our suppliers or locate suitable new suppliers for subassemblies and other components. Recently, the Company entered into discussions with several of its prior suppliers and is in the process of negotiating settlements of old payables and arranging new supply contracts.
Research and Development
We believe that ongoing research and development is important to the success of our product in order to utilize the most recent technology, develop additional products and additional uses for existing products, stay current with changes in vehicle manufacture and design and maintain an ongoing advantage over potential competition. Our engineering, research and development costs for fiscal 2017 were approximately $34,000 compared to approximately $0.4 million in fiscal 2016.
We stopped practically all research and development in the last two years due to severe cash shortfall; however, we did redesign the Electronic Control Unit (“ECU”) to include the latest state-of-the-art power electronics and processors. We set a modest budget of $400,000 for research and development in 2017 and $1.0 million budget for 2018 based on our anticipated resources. We believe that ongoing research and development is important to the success of our product in order to utilize the most recent technology, develop additional products and additional uses for existing products, stay current with changes in vehicle manufacture and design and maintain an ongoing advantage over potential competition.
Patents and Intellectual Property
Our intellectual property portfolio consists of trademarks, proprietary know-how and patents.
In the area of electromagnetic technology, we have developed numerous magnetic systems and designs that result in a significant increase of magnetic field density per unit volume that can be converted into useful power energy or work. This increase in field density is a factor of three to four, which, when incorporated into mechanical devices, could result in a significant reduction in size and cost of production for the same performance.
The applications of these technological advances are in machines used every day by industrial, commercial, and consumers. We have applied technology to numerous applications in industrial machines, such as generators, motors, actuators, and linear motors.
We hold the following patents: Nos. 5,734,217; 6,157,175; 6,700,214; 6,700,802; with expiration dates in 2018, 2020, 2024 and 2024 respectively. A provisional patent for a water-cooled AuraGen was granted in March 2013. Application 61/516,071 was filed January 2012 and claims allowed in March 2015, with an expiration date of March 2032.
The following applications are pending: Application 13/849,464 filed in March 2013; and Application 13/781,749 filed in March 2013.
Induction Machine
The basic patent covers a new form of induction machine with superior performance in a much smaller size than conventional machines. The solid cast rotor, the shaped magnetic field, the secondary conduction path through the steel and the axial magnetic orientations are key components of this innovation.
Control System
This system separates the power generation from the power delivery by introducing a 400 VDC buss. For each cycle of each phase, part of the cycle power is drawn from the bus to run the electronics and energize the coils, while during the other part of the cycle, power is delivered to charge up the buss. The control system must balance all the timing to effect zero voltage change to the buss under dynamic variations of frequency and loads. The ability to optimize in real time the slip frequency is a key innovation in motor and generator control for variable speed, variable frequency, and variable load systems.
| 7 |
Bi-Directional Power Supply (“BDP”)
The patented ICS system developed by Aura provides a new capability in power systems. The BDP allows a system to use multiple sources of power simultaneously. It is a key component in providing the ability to deliver both AC and DC power simultaneously, as well as the ability to handle large power surges without the need for a throttle controller.
At the end of fiscal 2013 and the first quarter of fiscal 2014, we filed five new patent applications related to the AuraGen. These new patent applications are specifically designed to cover the (i) integration of the AuraGen power solution with transport refrigeration, (ii) the interface kit of the AuraGen with prime movers, (iii) a water cooled AuraGen solution for situations where ventilation is not available, (iv) a unique cable system with safety protection to transfer high power between two moving objects, and (v) a unique clamping of power electronic components to heat sink to ensure good thermal conductivity.
Government Regulation
We are subject to laws and regulations that affect the Company’s activities, which include, but are not limited to, the areas of labor, intellectual property and ownership and infringement, tax, import and export requirements, environmental, and health and safety. As we recommence operations, our operations will again be subject to federal, state and local laws and regulations governing the occupational health and safety of our employees and wage regulations. For example, we are subject to the requirements of the federal Occupational Safety and Health Act, as amended, or OSHA, and comparable state laws that protect and regulate employee health and safety. We expect to expend resources to maintain compliance with OSHA requirements and industry best practices.
Employees
As of the date of this filing, other than our CEO Mr. Gagerman, the Company has no employees. However there are four independent contractors two of which are working to support the outside independent auditor, one who is working on redesigning the Electronic Control Unit for the AuraGen/VIPER and one who is helping dealing with the JV Agreement, and other technical matters. The independent contractors are used on an as need basis.
Significant Customers
We have no significant customers at this time. However, the Company has an initial commitment of approximately $1.25 million over the next eight months to deliver AuraGen systems and components to the Chinese Joint Venture partner to support their marketing efforts as the Joint Venture facilities are being readied. For additional information, see “Certain Subsequent Events—China Joint Venture.”
We had no sales during the fiscal year ended February 28, 2017. During the year ended February 29, 2016, we conducted business with two major customers whose sales comprised 55.9% and 22.0% of net sales, respectively. As of February 29, 2016, these customers accounted for 68.0% of net accounts receivable.
Backlog
There are no significant customers as of the date of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. However, the Company has an initial order of AuraGen systems and components representing approximately $1.25 million and deliverable during fiscal 2018 to a joint venture partner to support their marketing efforts as the joint venture facilities are being readied. Management believes that once the Company is operating again, a significant backlog will develop. No assurances, however, can be given how long it will take the Company, if at all, to develop a significant backlog. For additional information, see “Certain Subsequent Events—China Joint Venture.”
Raw Materials
The most important raw materials we use in manufacturing our products are steel, copper, and aluminum. Raw materials are purchased both domestically and outside the United States. We have no significant long-term supply contracts. When possible, we maintain a number of sources for our raw materials, which we believe contribute to our ability to obtain competitive pricing. The cost of some of our raw materials and shipping costs are dependent on petroleum cost. Higher material prices, cost of petroleum, and costs of sourced products could have an adverse effect on margins.
We enter into standard purchase agreements with certain foreign and domestic suppliers to source selected products. The terms of these arrangements are customary for the industry and do not contain any long-term contractual obligations on our behalf.
| 8 |
Certain Subsequent Events
Subsequent to the end of fiscal 2017, certain material developments have occurred relating to the business of the Company.
China Joint Venture - On January 27, 2017, we entered into a Sino-Foreign Cooperative Joint Venture Agreement (the “JV Agreement”) with Jiangsu AoLunTe Electrical Machinery Industrial Co., Ltd. (“AoLunTe”) pursuant to which the parties will establish a joint venture company (the “JV”) for the purposes of manufacturing and distributing our patented mobile power solution in the Peoples Republic of China (“PRC”). The business of the JV is limited to the manufacturing, marketing and sale, repair and maintenance of selected mobile power products for commercial and military use in the PRC only.
Pursuant to the JV Agreement, AoLunTe will own 51% of the JV and we will own 49%, and profits will be distributed based on the ownership interest of each party. AoLunTe will contribute the RMB equivalent of $500,000 US dollars in cash within 30 days after the Establishment Date (as defined), as well as tangible and intangible assets (including but not limited to equipment, land and facilities of the site for the JV) not later than 180 days after the Establishment Date valued at 9.25 million in US Dollars. The “Establishment Date” is the first business day after the JV’s receipt of the certificate of approval issued by the PRC governmental authority responsible for approving the JV Agreement and the Articles of Association of the JV. Such approval was granted in March 2017. Pursuant to the JV Agreement, we are required to contribute the RMB equivalent of $250,000 in US dollars within 45 days after the Establishment Date, as well as an exclusive, non-assignable, and royalty-free license in the PRC to use our intellectual property. We have made the required payment.
The JV shall be governed by a Board of Directors, consisting of three directors nominated by AoLunTe and three directors nominated by us. All “Major Decisions” of the Board, which are specified in a schedule to the JV Agreement, require the vote of two-thirds of the directors, including at least one director nominated by us and one director nominated by AoLunTe. All other decisions of the Board require the approval of a simple majority of directors. A general manager appointed by the Board upon the nomination by AoLunTe shall be responsible for the day-to-day operation and management of the JV, while quality control as well as the financial controller are to managed by individuals to be appointed by the Board upon our nomination, under the supervision of the Board.
The term of the JV Agreement is 30 years from the Establishment Date, subject to extension by mutual written agreement of the parties. The JV Agreement may be terminated sooner by the written agreement of the parties or in the event of certain specified events, including without limitation a material breach of the JV Agreement which is not remedied (if capable of remedy) within 30 days after written notice of such breach is provided to the other party.
Pursuant to the JV Agreement, AoLunTe will purchase from us $1,250,000 of product, payable in four payments after the Establishment Date in the amounts of $500,000, $250,000, $250,000, and $250,000. The fourth payment will be offset against a prior advance for products paid by AoLunTe to us.
AoLunTe is required by the JV Agreement to purchase 10 million shares of our Common Stock (such number being prior to a contemplated 1-for-7 reverse stock split by us, the “Reverse Split”) for an aggregate of $2,000,000 pursuant to a Securities Purchase Agreement, the form of which is attached to the JV Agreement. Pursuant to the terms of the Securities Purchase Agreement, the first installment of $1,000,000 was paid into a mutually-agreed escrow account and subsequently released from escrow in March 2017. The second installment of $1,000,000 was also paid into a mutually-agreed escrow account and is scheduled to be released to us following approval by our stockholders of resolutions electing a new board of directors and approving an amendment to our Certificate of Incorporation to effect the above-referenced 1-for-7 reverse stock split of our Common Stock. The shares of Common Stock to be sold to AoLunTe are being sold pursuant to Regulation S under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and will not be offered or sold to any U.S. person or for the account or benefit of any U.S. person prior to the end of the restricted period provided by Regulation S and any other applicable law.
| 9 |
Available Information
We file annual, quarterly and current reports and other information with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC” or the “Commission”). These materials can be inspected and copied at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. Copies of these materials may also be obtained by mail at prescribed rates from the SEC’s Public Reference Room at the above address. Information about the Public Reference Room can be obtained by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC also maintains a website at www.sec.gov that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC.
On our website, www.aurasystems.com, we provide free of charge our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and any amendments thereto, as soon as reasonably practicable after they have been electronically filed or furnished to the SEC. Information contained on our website is not part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K or our other filings with the SEC.
We have a history of losses, and we may not be profitable in any future period.
In each fiscal year since our reorganization in 2006, we have reported losses. Since the Company’s Chapter 11 Plan reorganization in 2006, we have spent considerable amounts on, among other things, building market awareness and infrastructure for sales and distribution, enhancing our engineering capabilities, perfecting an all electric refrigeration transport system for midsize trucks, developing a 16-18 kW product, and developing a nine-inch system capable of delivering approximately 4 kW of power. We continue to need substantial funds for the development of new products and in order to expand sales. However, sales of our products have not increased as we expected them to and may never increase to the level that we need to expand our operations, or even to sustain them. We can provide no assurance as to when, or if, we will recommence operations or be profitable in the future. Even if we recommence operations and achieve profitability, we may not be able to sustain it.
We will need additional capital in the future to meet our obligations and financing may not be available. During fiscal 2017, the Company suspended its engineering, manufacturing, sales, and marketing activities to focus on renegotiating numerous financial obligations. If we cannot obtain additional capital, we will not be able to recommence our operations.
As a result of our operating losses, we have financed our operations through sales of our debt and equity securities. During the first half of fiscal 2016, the Company significantly reduced operations due to lack of financial resources. During the second half of fiscal 2016 the Company’s operations were disrupted when the Company was forced to move from its facilities in Redondo Beach, California to a smaller facility in Stanton, California. During fiscal 2017, the Company suspended its engineering, manufacturing, sales, and marketing activities to focus on renegotiating numerous financial obligations. While we plan to recommence operations, expand sales and marketing and improve operations, we continue to operate at negative cash flow. Our ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon our ability to obtain additional operating capital and generating sufficient operating cash flow. If we are unable to obtain additional funding as and when we need it, we will not be able to recommence operations or undertake our planned expansion.
Our independent public accounting firm has included an explanatory paragraph in its opinion to the effect that there is substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
Our independent public accounting firm has included an explanatory paragraph in its opinion to the effect that there is substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. We do not have any sufficient committed sources of capital and do not know whether additional financing will be available when needed on terms that are acceptable, if at all. This going concern statement from our independent public accounting firm may discourage some investors from purchasing our stock or providing alternative capital financing. The failure to satisfy our capital requirements will adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
| 10 |
If we do not receive additional financing when and as needed, we may not be able to continue the research, development and commercialization of our technology and products. In that case, our business and results of operations would be materially and adversely affected.
Our capital requirements have been and will continue to be significant. We anticipate that we will require substantial additional funds in excess of our current financial resources for research, development and commercialization of our technology and products, to obtain and maintain patents and other intellectual property rights in these technologies and products, and for working capital and other purposes, the timing and amount of which are difficult to ascertain. When and as we need additional funds, such funds may not be available on commercially reasonable terms or at all. If we cannot obtain additional funding when and as needed, our business and results of operation would be materially and adversely affected.
Market acceptance of our AuraGen® product line is uncertain. If a large enough market does not develop for our products, our business and the results of our operations will be materially and adversely affected.
Our business is dependent upon sales generated from our AuraGen®/VIPER family of products. This product line utilizes advanced technology and has only recently begun being used in the marketplace for selected applications. We are dependent on the broad acceptance by businesses and industry of our products. Because the market for our product line is emerging, the potential size of this market and the timing of its development cannot be predicted. A significant market may fail to develop or it may develop more slowly than we anticipate, either of which will have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
Our intellectual property rights are valuable, and any inability or failure to protect them could reduce the value of our products, services and brand, which would have a material adverse effect on our business.
Our patents, trademarks, and all of our other intellectual property rights are important assets for us. There are events that are outside of our control that pose a threat to our intellectual property rights. For example, effective intellectual property protection may not be available in every country in which our products and services are distributed or made available. Also, the efforts we have taken to protect our proprietary rights may not be sufficient or effective. The expiration of patents in our patent portfolio may also have an adverse effect on our business. Any significant impairment of our intellectual property rights could harm our business or our ability to compete. Protecting our intellectual property rights is costly and time consuming and we may need to resort to litigation to enforce our patent rights or to determine the scope and validity of third-party intellectual property rights. Some of our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of complex patent litigation more effectively than we can because they have substantially greater resources.
We seek to obtain patent protection for our innovations. It is possible, however, that some of these innovations may not be protectable. In addition, given the costs of obtaining patent protection, we may choose not to protect certain innovations that later turn out to be important. Furthermore, there is always the possibility, despite our efforts, that the scope of the protection gained will be insufficient or that an issued patent may be deemed invalid or unenforceable. Our inability or failure to protect our intellectual property rights could have a material adverse effect on our business by reducing the value of our products, services and brand.
We occasionally become subject to commercial disputes that could harm our business by distracting our management from the operation of our business, by increasing our expenses and, if we do not prevail, by subjecting us to potential monetary damages and other remedies.
From time to time we are engaged in disputes regarding our commercial transactions. These disputes could result in monetary damages or other remedies that could adversely impact our financial position or operations. Even if we prevail in these disputes, they may distract our management from operating our business and the cost of defending these disputes would reduce our operating results.
We are currently party to litigation with one of our directors relating to approximately $5.4 million and approximately 22 million warrants which the director claims are owed to him and his affiliates. An adverse ruling on these claims in this litigation would materially and adversely affect our business results or operating and financial condition, dilute our shareholders’ equity interests in the Company and could adversely effect our stock price.
The Company is presently engaged in a dispute with one of its directors, Robert Kopple, relating to approximately $5.4 million and approximately 22 million warrants which Mr. Kopple claims to be owed to him and his affiliates by the Company. In July 2017, Mr. Kopple filed suit against the Company as well as against other members of the Board of Directors in connection with these allegations. The Company believes that it has valid defenses in these matters and believes that no warrants are due to Mr. Kopple or his affiliates. The Company intends to vigorously defend against these claims. However, if Mr. Kopple were to prevail, an adverse ruling on these claims would materially and adversely affect our business results or operating and financial condition, dilute our shareholders’ equity interests in the Company and could adversely affect our stock price. See Item 3. “Legal Proceedings”, “Liquidity and Capital Resources” in “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information regarding the transactions under dispute.
| 11 |
Our business is not diversified. If we cannot increase market acceptance of our products, modify our products and services, or compete with new technologies, we may never be profitable.
We currently focus all of our resources on the successful commercialization of the AuraGen®/VIPER family of products. Because we have elected to focus our business on a single product line rather than diversifying into other areas, our success will be dependent upon the commercial success of these products. If we are unable to increase market acceptance of our products, if we are unable to modify our products and services on a timely basis so that we lose customers, or if new technologies make our technology obsolete, we may never be profitable.
Many of our competitors are larger and better financed than we are and have a greater presence in the marketplace. Our business may be adversely affected by industry competition.
Both in the U.S. and internationally, the industries in which we operate are extremely competitive. We face substantial competition from companies that have a long history of offering traditional auxiliary power units (portable generators), traditional automotive alternators, and inverters (a device that inverts battery direct current electricity to alternating current). Many of our competitors have substantially greater financial resources, spend considerably larger sums than we spend on research, new product development and marketing, and have long-standing customer relationships. Furthermore, we must compete with many larger and better-established companies in the hiring and retention of qualified personnel. Although we believe we have significant technological advantages over our competitors, realizing and maintaining such advantages will require us to develop customer relationships and will also depend on market acceptance of our products. We may not have the financial resources, technical expertise, or marketing and support capabilities to compete successfully, which would materially and adversely affect our business.
We may not be able to establish an effective distribution network or strategic OEM relationships, in which case our sales will not increase as expected and our financial condition and results of operations would be adversely affected.
We are in the early stages of developing our distribution network and establishing strategic relationships with original equipment manufacturer (OEM) customers. We may not be able to identify appropriate distributors or OEM customers on a timely basis. The distributors with which we partner may not focus adequate resources on selling our products or may otherwise be unsuccessful in selling them. In addition, we cannot assure you that we will be able to establish OEM relationships on favorable terms or at all. The lack of success of distributors or OEM customers in marketing our products would adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
If we are successful in executing our business plan, we expect our business to grow. Our failure to efficiently manage our growth could have an adverse affect on our business.
If we are successful in executing our business plan, we may experience growth in our business that could place a significant strain on our management and other resources. Our ability to manage this growth will require us to successfully assimilate new employees, improve existing management information systems and reorganize our operations. If we fail to manage growth efficiently, our business could be adversely affected.
We may experience delays in product shipments and increased product costs because we depend on third party manufacturers for certain product components. Delays in product shipment or an inability to replace certain suppliers could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
We currently have a limited capability to manufacture most of the AuraGen®/VIPER components on a commercial scale. Therefore, we rely extensively on subcontracts with third party manufacturers for such components. The use of third party manufacturers increases the risk of delay of shipments to our customers and increases the risk of higher costs if our manufacturers are not available when required. Our suppliers and manufacturers may not supply us with a sufficient amount of components or components of adequate quality, which would delay production of our product. We do not have written agreements with our suppliers. Furthermore, those suppliers who make our more technically difficult components may not be easily replaced. Any of these disruptions in the supply of components could have a material adverse effect on our business or results of operations.
Although we generally aim to use standard parts and components for our products, some of our components are currently available only from limited sources.
We may experience delays in production of the AuraGen®/VIPER if we fail to identify alternate vendors, or if any parts supply is interrupted or reduced or if there is a significant increase in production costs, each of which could materially adversely and affect our business and operations.
| 12 |
We will need to renew sources of component supplies to meet increases in demand for the AuraGen®/VIPER. There is no assurance that our suppliers can or will supply the components to us on favorable terms or at all.
In order to meet demand for AuraGen®/VIPER systems, we will need to renew contracts with our prior manufacturers and suppliers or locate other suitable manufacturers and suppliers. Although we believe that there are a number of potential manufacturers and suppliers of the components, we cannot guarantee that contracts for components can be obtained on favorable terms or at all. Any material adverse change in terms of the purchase of these components could increase our cost of goods.
We need to invest in tooling to have a more extensive line of products. If we cannot expand our tooling, it may not be possible for us to expand our operations.
We are currently limited in the products that we are able to manufacture because of the limitations of our tooling capabilities. In order to have a broader line of products that address industrial and commercial needs, we must make a significant investment in additional tooling. We do not currently have the required funds to acquire such tooling and no assurances can be given that we will have the required funds in the future. If we do not acquire the required funds for tooling we may not be able to expand our product line to meet industrial and commercial needs.
We are subject to government regulation that may restrict our ability to use certain suppliers outside the U.S. or to sell our products into certain countries. If we cannot obtain the required approval from government agencies, then our business may be adversely affected.
We depend on third party suppliers for our parts and components, some of which are located outside of the United States. In the event that some of these suppliers are barred from selling their products in the United States, or cannot meet other U.S. government regulations, we would need to locate other suppliers, which could delay or prevent us from shipping product to our customers. We use copper, steel and aluminum in our product and in the event of government regulations or restrictions of these materials we may experience a shortage of these materials to manufacture our product. Furthermore, U.S. law restricts us from selling products in some potential foreign markets without U.S. government approval. If we cannot obtain the required approvals from government agencies to obtain materials or contract with suppliers or if we are restricted by government regulation from selling our products into certain countries, our business may be adversely affected.
We face changes in global and local economic conditions that may adversely affect consumer demand and spending, our manufacturing operations or sources of merchandise and international operations.
Our industry is subject to variations in the general economy and to uncertainty regarding future economic prospects. Such uncertainty, as well as other variations in global economic conditions such as rising fuel costs, wage and benefit inflation, currency fluctuations, and increasing interest rates, may continue to cause inconsistent and unpredictable customer spending while increasing our own input costs. In addition, this downturn has had, and may continue to have, an unprecedented negative impact on the global credit markets. Credit has tightened significantly in the last several months, resulting in financing terms that are less attractive to borrowers, and in many cases, the unavailability of certain types of debt financing. These risks, as well as industrial accidents or work stoppages, could also severely disrupt our manufacturing operations, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial performance.
Our ability to obtain adequate supplies or to control our costs may be adversely affected by events affecting international commerce and businesses located outside the United States, including natural disasters, changes in international trade, central bank actions, changes in the relationship of the U.S. dollar versus other currencies, labor availability and cost, and other governmental policies of the U.S. and the countries from which we import our merchandise or in which we operate facilities. The inability to import products from certain foreign countries or the imposition of significant tariffs could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Acquisitions, joint ventures, and strategic alliances may have an adverse effect on our business.
We expect to continue entering into joint ventures and strategic alliances as part of our long-term business strategy. In March 2017, we entered into a joint venture agreement with a Chinese partner. This joint venture arrangement and other transactions and arrangements involve significant challenges and risks, including that they do not advance our business strategy, that we get an unsatisfactory return on our investment, that we have difficulty integrating and retaining new employees, business systems, and technology, or that they distract management from our other businesses. If an arrangement fails to adequately anticipate changing circumstances and interests of a party, it may result in early termination or renegotiation of the arrangement. The success of these transactions and arrangements will depend in part on our ability to leverage them to enhance our existing products and services or develop compelling new ones. It may take longer than expected to realize the full benefits from these transactions and arrangements, such as increased revenue, enhanced efficiencies, or increased market share, or the benefits may ultimately be smaller than we expected. These events could adversely affect our operating results or financial condition.
| 13 |
We rely on highly skilled personnel and, if we are unable to retain or motivate key personnel or hire qualified personnel, we may not be able to grow effectively.
Our performance is largely dependent on the talents and efforts of highly skilled individuals. Our future success depends on our continuing ability to identify, hire, develop, motivate, and retain highly skilled personnel for all areas of our organization. Our continued ability to compete effectively depends on our ability to attract new employees and to retain and motivate our existing employees. The incentives to attract, retain and motivate employees provided by our option grants or by future arrangements may not be as effective as in the past. If we do not succeed in attracting excellent personnel or retaining or motivating existing personnel, we may be unable to grow effectively.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None
As part of downsizing due to financial distress experienced by the Company as further described in “Business—Business Arrangements”, our current facilities consist of approximately 20,000 square feet in Stanton California and an additional storage facility in Canyon Country, California for existing inventory. The Stanton facility is currently used for some assembly and testing of AuraGen/VIPER systems. The facility is rented on a month-to-month basis. The rent for the Stanton facility is $10,000 per month and the storage facility is additional $5,000 per month. The current Stanton facility is not sufficient to support the expected operations should the Company’s operations return to pre-2014 production levels. Accordingly, the Company is currently looking for a new facility of approximately 45,000 square feet that would be used for production, testing, and engineering all related to the AuraGen/VIPER mobile power solution as well as needed office space for support staff. Prior to the middle of 2015, we occupied a 69,000 square foot facility in Redondo Beach, California. The Redondo Beach facility was used for assembly and testing using components that are produced by various suppliers as well as for general offices, engineering and warehousing. The rent for the Redondo Beach facility was approximately $60,000 per month.
| 14 |
We are subject to the legal proceedings and claims discussed below as well as certain other legal proceedings and claims that have not been fully resolved and that have arisen in the ordinary course of business. Our management evaluates our exposure to these claims and proceedings individually and in the aggregate and evaluates potential losses on such litigation if the amount of the loss is estimable and the loss is probable. However, the outcome of legal proceedings and claims brought against the Company is subject to significant uncertainty. Although management considers the likelihood of such an outcome to be remote, if one or more of these legal matters were resolved against the Company for amounts in excess of management’s expectations, the Company’s consolidated financial statements for that reporting period could be materially adversely affected. The Company settled certain matters subsequent to year end that did not individually or in the aggregate have a material impact on the Company’s financial condition or operating results.
In 2016, the Company was sued by a former employee for a work-related injury. The plaintiff is seeking $45,000. The Company has made the plaintiff a settlement offer which, as of the date of this filing,has not been accepted.
In November 2016, the Company was sued by a former customer for approximately $111,712 relating to an alleged failure by the Company to partially deliver against an advanced payment. In connection with its claims, the plaintiff has asserted that by virtue of the Company’s failure to fully deliver upon the contracted order, the plaintiff has obtained a perpetual worldwide license to utilize the Company’s actuator technology. The Company disputes the plaintiff’s claims and believes that it holds various claims against the plaintiff. In April 2017, the plaintiff’s action was involuntarily dismissed by the court although plaintiff sought to have the dismissal set aside on the grounds of attorney error. In June 2017, the court granted plaintiff’s motion and the Company intends to oppose this action and file a counterclaim.
Subsequent to year end, the Company’s former COO has been awarded approximately $238,000 in accrued salary and related charges by the California labor board. The Company believes that this award does not reflect the amount owed which is significantly lower and is exploring all its options and available remedies and is working toward an offer to settle this matter.
The Company and the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, Melvin Gagerman, are among several defendants named in a lawsuit filed by two secured creditors demanding repayment of loans totaling $125,000 plus accrued interest and exemplary damages. In January 2017, the Company entered into an agreement with all secured creditors other than the two plaintiffs. However, because secured creditors holding in excess of 97% of the issuable stock upon conversion have executed the agreement, the agreement is binding on all of the secured creditors, including the two plaintiffs. That agreement, among other provisions, waives all past events of default. It is the Company’s position that the two plaintiffs are not entitled to any payment or other relief at this time and therefore that they have no valid claim against the Company or Mr. Gagerman. In March 2017, plaintiffs moved for partial summary adjudication against the Company and Mr. Gagerman; however, the Court denied plaintiff’s motion. Thereafter, the Court sustained demurrers by Mr. Gagerman and the Company but granted plaintiffs leave to amend. In response to the plaintiffs’ second amended complaint, both the Company and Mr. Gagerman intend to further demurrer seeking dismissal of this action.
In June 2015, the landlord of the Company’s primary facility in Redondo Beach, California initiated litigation against us seeking to terminate the Company’s lease and require the Company to vacate the premises prior to the scheduled lease end. As a result of that litigation, the Company was forced to vacate its primary facility and relocate to its present facility in Stanton, California. To date, no action seeking damages or any other amount has been filed against the Company by the landlord, nor does the Company believe it has any further liability to the landlord.
The Company is presently engaged in a dispute with one of its directors, Robert Kopple, relating to approximately $5.4 million and approximately 22 million warrants which Mr. Kopple claims to be owed to him and his affiliates by the Company. In July 2017, Mr. Kopple filed suit against the Company as well as against current Directors Mr. Gagerman and Mr. Diaz-Verson together with former Directors Mr. Breslow and Mr. Howsmon in connection with these allegations. The Company believes that it has valid defenses in these matters and intends to vigorously defend against these claims. See “Liquidity and Capital Resources” in “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information regarding the transactions under dispute with Mr. Kopple.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
| 15 |
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Our shares are quoted on the OTC Bulletin Board under the symbol “AUSI”. Set forth below are high and low bid prices for our common stock for each quarterly period in the two most recent fiscal years. Such quotations reflect inter-dealer prices, without retail mark-up, markdown or commissions and may not necessarily represent actual transactions in the common stock. We had 6,279 stockholders of record as of August 21, 2017.
| Period | High | Low | ||||||
| Fiscal 2016 | ||||||||
| First Quarter ended May 31, 2015 | $ | 0.130 | $ | 0.0450 | ||||
| Second Quarter ended August 31, 2015 | $ | 0.070 | $ | 0.0340 | ||||
| Third Quarter ended November 30, 2015 | $ | 0.078 | $ | 0.0039 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter ended February 29, 2016 | $ | 0.180 | $ | 0.0382 | ||||
| Fiscal 2017 | ||||||||
| First Quarter ended May 31, 2016 | $ | 0.190 | $ | 0.051 | ||||
| Second Quarter ended August 31, 2016 | $ | 0.120 | $ | 0.055 | ||||
| Third Quarter ended November 30, 2016 | $ | 0.100 | $ | 0.035 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter ended February 28, 2017 | $ | 0.210 | $ | 0.015 | ||||
| Fiscal 2018 | ||||||||
| First Quarter ended May 31, 2017 | $ | 0.200 | $ | 0.085 | ||||
| Second Quarter ended August 31, 2017 | $ | 0.17 | $ | 0.06 | ||||
On August 30, 2017, the reported closing sales price for our common stock was $0.08.
Dividend Policy
We have not paid any dividends on our common stock and we do not anticipate paying any dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future.
Sales of Unregistered Securities
During the year ended February 28, 2017, we issued 950,000 shares of common stock in settlement of a note payable in the amount of $150,000 plus accrued interest of $15,288. Funds raised were for general corporate working capital purposes. All such securities were issued and sold in reliance on the exemption from registration contained in Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933, and the certificates representing such securities contain a restrictive legend reflecting the limitations on future transfer of those securities. The offer and sale of these securities was made without public solicitation or advertising. The investors represented to us that they were knowledgeable and sophisticated, and were experienced in business and financial matters so as to be capable of evaluating an investment in our securities and were an “accredited investor” within the meaning of Regulation D promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933. Each of these investors was afforded full access to information regarding our business.
Repurchases of Equity Securities
We did not repurchase any shares of our common stock during the fourth quarter of fiscal 2017.
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
As a smaller reporting company, we are not required to provide disclosure under this Item 6.
| 16 |
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Forward Looking Statements.
This Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations includes forward-looking statements. For cautions about relying on such forward-looking statements, please refer to the section entitled “Forward Looking Statements” at the beginning of this Report immediately prior to “Item 1”.
Overview
During the first half of fiscal 2016, the Company significantly reduced operations due to lack of financial resources. During the second half of fiscal 2016 the Company’s operations were disrupted when the Company was forced to move from its facilities in Redondo Beach, California to a smaller facility in Stanton, California. Operations during the second half of fiscal 2016 were sporadic. During fiscal 2017, the Company suspended its engineering, manufacturing, sales, and marketing activities to focus on renegotiating numerous financial obligations.
The Company has been successful in restructuring its secured debt and has reached an agreement with its secured creditors whereby all defaults and penalties have been waived and 80% of the secured debt will be converted into shares of the Company’s common stock as soon as the Company holds an annual meeting of stockholders to elect a new board of directors. The balance (the remaining 20%), is to be paid to the secured creditors in cash if the Company raises at least $4.0 million in proceeds through new equity offering. Upon conversion, the converting secured creditors will receive approximately 3.9 million new common shares in exchange for approximately $5.73 million of converting debt.
The Company has also been successful in restructuring approximately $27.5 million of unsecured debt. Various unsecured creditors have agreed to waive all defaults and penalties, to forgive an aggregate of approximately $9.3 million in debt, and convert an aggregate of approximately $15.2 million of unsecured debt into approximately 10.2 million common shares. As of the date of this filing, Robert Kopple, the Company’s Vice Chairman of the Board, is the only significant unsecured note holder that has not agreed to restructure his debt. Mr. Kopple claims to be owed approximately $5.4 million on terms significantly preferable to other similarly-situated unsecured creditors. Mr. Kopple has not accepted the Company’s offer to restructure this debt to-date.
Reverse Stock Split – The Company intends to file a proxy statement and hold an annual meeting of stockholders during 2017, seeking, among other things, stockholder approval of the Reverse Split. Currently the aggregate number of shares of our common stock outstanding, when combined with the number of shares of our common stock issuable upon the exercise of outstanding warrants or options or upon the conversion of convertible debt exceeds the authorized number of shares of our common stock provided for in our certificate of incorporation. Since the Reverse Split would not affect the authorized number of shares of our common stock, all outstanding warrants, options and convertible debt could be exercised or converted, as applicable, and we could also issue additional shares of common stock in the future.
The Company is planning to restart operations with a new board of directors and a new management team as soon as the Company holds its stockholders meeting to elect the new board and approve the Reverse Split. Currently the Company has a contractual agreement for $1.25 million of orders for the Auragen/VIPER product to fill during the next eight months and anticipates that is may receive significant additional orders once the Company is back in operation.
| 17 |
Our business is based on the exploitation of our patented mobile power solution known as the AuraGen for commercial and industrial applications and the VIPER for military applications. Our business model consists of three major components; (i) sales and marketing, (ii) engineering, and (iii) customer service and support.
(i) Our sales and marketing approach is composed of direct sales in North America and the use of agents, distributors and joint ventures for sales internationally. In North America, our primary focus is in (a) transport refrigeration, and (b) U.S. Military applications.
(ii) The second component of our business model is focused on the engineering support for the sales activities described above. The engineering support consists of the introduction of new features for our AuraGen/VIPER solution such as higher power, different voltages, three phase options, shore power systems, higher current solutions as well as interface kits for different platforms. After suspending engineering, manufacturing, sales, and marketing activities to focus on renegotiating numerous financial obligations in fiscal 2017, we expect modest engineering activities budgeted at approximately $400,000 during the fiscal 2018 year.
(iii) The third component of our business model is customer service. In fiscal 2018, we expect to rehire several previously trained field engineers to support our product in North America. In addition, we are working closely with our Chinese Joint Venture partner to train their staff to support our products overseas.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our management’s discussion and analysis of our financial conditions and results of operations are based upon our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. The preparation of financial statements requires management to make estimates and disclosures on the date of the financial statements. On an on-going basis, we evaluate our estimates, including, but not limited to, those related to revenue recognition. We use authoritative pronouncements, historical experience and other assumptions as the basis for making judgments. Actual results could differ from those estimates. We believe that the following critical accounting policies affect our more significant judgments and estimates in the preparation of our consolidated financial statements.
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s revenue recognition policies are in compliance with Staff accounting bulletin (SAB) 104. Sales revenue is recognized at the date of shipment to customers when a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and collect-ability is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are satisfied are recorded as unearned revenue.
We recognize revenue for product sales upon shipment and when title is transferred to the customer. When Aura performs the installation of the product, revenue and cost of sales are recognized when the installation is complete. We have in the past earned a portion of our revenues from license fees and recorded those fees as income when we fulfilled our obligations under the particular agreement.
Terms of our sales generally provide for Shipment from our facilities to customers free on board (FOB) point of shipment. Title passes to customers at the time the products leave our warehouse.
The Company does not offer a general right of return on any of its sales and considers all sales as final. While some sales are for evaluative purposes, such sales are deemed final by the Company. The customers’ evaluation is for such customers to determine if there is a benefit to them to outfit additional vehicles in their fleets.
The only potential post-delivery obligation the Company might have is for the installation of the unit. However, the unit is typically delivered at the time of installation, and the billing is done when the installation is complete. The Company does not utilize bill and hold. The Company does provide customers with a warranty; however, due to the low sales volume to date, the amount has not been material and is expensed as incurred.
Inventory Valuation and Classification
Inventories are valued at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out) or market, on a standard cost basis. We review the components of inventory on a regular basis for excess or obsolete inventory based on estimated future usage and sales. The Company has not operated and therefore has not produced product since late 2015. As a result, while the Company believes that a significant portion of the inventory has value, we are unable to substantiate it’s demand and market value and as a result have elected to reserve it in its entirety as of February 28, 2016 and February 28, 2017.
| 18 |
Valuation of Long-Lived Assets
Long-lived assets, consisting primarily of property and equipment, and patents and trademarks, comprise a small portion of our total assets. Long-lived assets are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that their carrying values may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets is measured by a comparison of the carrying value of an asset to the future net cash flows expected to be generated by those assets. Net cash flows are estimated based on expectations as to the realize-ability of the asset. Factors that could trigger a review include significant changes in the manner of an asset’s use or our overall strategy.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company accounts for stock-based compensation under the provisions of FASB ASC 718, “Compensation – Stock Compensation”, which requires the measurement of all share-based payments to employees, including grants of employee stock options, using a fair value based method and the recording of such expense in the consolidated statements of operations.
The Company accounts for stock option and warrant grants issued and vesting to non-employees in accordance with FASB ASC 505-50, “Equity Based Payments to Non-Employees”, whereas the fair value of the equity based compensation is based upon the measurement date as determined at the earlier of either (a) the date at which a performance commitment is reached or (b) at the date at which the necessary performance to earn the equity instruments is complete.
For the past, several years and in accordance with established public company accounting practice, the Company has consistently utilized the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to calculate the fair value of stock options and warrants issued as compensation, primarily to management, employees, and directors. The Black-Scholes option-pricing model is a widely-accepted method of valuation that public companies typically utilize to calculate the fair value of options and warrants that they issue in such circumstances.
Research and Development
Research and development costs are expensed as incurred.
Specific asset categories are treated as follows:
Accounts Receivable: We record an allowance for doubtful accounts based on management’s expectation of collect-ability of current and past due accounts receivable.
Property, Plant and Equipment: We depreciate our property and equipment over various useful lives ranging from five to ten years. Adjustments are made as warranted when market conditions and values indicate that the current value of an asset is less than its net book value.
Patents and trademarks: As our business depends on using new technology to create new products, impairments in patents can be triggered by changed expectations regarding the foreseeable commercial production of products underlying such patents.
When we determine that an asset is impaired, we measure any such impairment by discounting an asset’s realizable value to the present using a discount rate appropriate to the perceived risk in realizing such value. When we determine that an impaired asset has no foreseeable realizable value, we write such asset down to zero.
| 19 |
Results of Operations
Fiscal 2017 compared to Fiscal 2016
Revenues
Net revenues in fiscal 2017 decreased to $0 from $183,032 in fiscal 2016. The decrease is attributable to a lack of financial resources causing us to substantially curtail operational activities.
Cost of Goods
Cost of goods sold in fiscal 2017 decreased to $0 from $170,996 in fiscal 2016. The decrease is attributable to the curtailment of our activities as noted above.
Engineering, Research and Development
Engineering, research and development costs decreased $361,517 to $34,210 in fiscal 2017 from $395,727 in fiscal 2016. While we had planned for an increase in engineering, research and development in fiscal 2017, the lack of resources noted above prevented us from implementing our plan.
Selling, General and Administrative Expense
Selling, general and administrative increased $540,566 to $3,522,347 in fiscal 2017 from $2,981,781 in fiscal 2016. The increase is due to the expensing of approximately $2.25 million in rent expense related to the facility the company vacated, which offset the reduction in expenses due to the curtailment of activities resulting from our lack of financial resources.
Non-Operating Income and Expense
Net interest expense increased $948,777 to $4,246,831 in fiscal 2017 from $3,298,054 in fiscal 2016 due to increased interest accrual.
Net Income/Loss
The increase in our net loss of $1,126,366 to $7,731,333 in fiscal 2017 from $6,604,967 in fiscal 2016 is a result of the curtailment of corporate activities as noted above, offset by the expensing of future rent due resulting from the vacating of our former facility as noted above.
Fiscal 2016 compared to Fiscal 2015
Revenues
Net revenues in fiscal 2016 decreased $972,779 to $183,032 from $1,155,811 in fiscal 2015, a decrease of 84%. The decrease is attributable to a lack of financial resources causing us to substantially curtail activities.
Cost of Goods
Cost of goods sold in fiscal 2016 decreased $319,383 to $170,996 from $490,379 in fiscal 2015. The decrease is attributable to the curtailment of our activities as noted above.
Engineering, Research and Development
Engineering, research and development costs decreased $449,408 to $395,727 in fiscal 2016 from $845,135 in fiscal 2015. While we had planned for an increase in engineering, research and development in fiscal years 2017 and 2018, the lack of resources noted above prevented us from implementing our plan.
Selling, General and Administrative Expense
Selling, general and administrative expenses decreased $5,916,385 to $2,981,781 in fiscal 2016 from $8,898,166 in fiscal 2015. The decrease is due to the curtailment of corporate activities as noted above.
Non-Operating Income and Expenses
Net interest expense increased to $3,298,054 in fiscal 2016 from $3,214,963 in fiscal 2015, an increase of $83,091 due to our increased debt levels. Other income increased to $58,559 in fiscal 2016 from $5,580 in fiscal 2015.
Net Income/Loss
Our net loss in fiscal 2016 decreased to $6,604,967 from $12,287,252 in fiscal 2015, a decrease of $5,682,285, primarily as a result of the curtailment of corporate activities as noted above.
| 20 |
Liquidity and Capital Resources
In fiscal 2017, we incurred losses of approximately $7.7 million and had negative cash flows from operations of $1.1 million. As of February 28, 2017, the total amount owing to Mr. Kopple, a Board member, is $5,567,624 plus accrued interest of $1,658,661. We also owe approximately $15 million plus accrued interest of $8.68 million to Mr. Breslow, another board member. We do not currently have the resources to repay any of the above.
At February 28, 2017, we had cash of approximately $256,000, compared to cash of approximately $22,000 at February 29, 2016. Working capital at February 28, 2017 was a negative $52.8 million as compared to a negative $41.3 million at the end of the prior fiscal year. Accrued expenses increased $0.5 million due to an increase in accrued interest of approximately $0.5 million. At February 28, 2017, we had no accounts receivable, compared to approximately $22,000 at February 29, 2016. In fiscal 2017 we made no acquisitions of property and equipment.
During the year ended February 28, 2017, we issued 950,000 shares of common stock in settlement of a note payable in the amount of $150,000 plus accrued interest of $15,288.
In the past, in order to maintain liquidity, we have relied upon external sources of financing, principally equity financing and private indebtedness. We have no bank line of credit and require additional debt or equity financing to fund ongoing operations. Currently, we have binding commitments from third parties to provide $2.1 million in financing in the form of equity as soon as the stockholders meeting is held. We cannot assure you that additional financing will be available at the times or in the amounts required. Based on a cash flow analysis performed by management, we estimate that the Company will need an additional $2.5 million to support the Company’s operations for the fiscal year ending February 28, 2018. The issuance of additional shares of equity in connection with such financing could dilute the interests of our existing stockholders, and such dilution could be substantial. If we cannot raise the needed funds, we would also be forced to make further substantial reductions in our operating expenses, which could adversely affect our ability to implement our current business plan and ultimately our viability as a company.
Amendment to 2013 Securities Purchase Agreement – On January 30, 2017, the Company entered into an agreement with five of our secured creditors (the “Signatories”), pursuant to which a Securities Purchase Agreement dated May 6, 2013 (the “2013 Purchase Agreement”) among the Company, the Signatories, and two other parties was amended (the “Amended Agreement”).
Pursuant to the 2013 Purchase Agreement, we offered and sold convertible notes (the “Original Notes”) and warrants (the “Original Warrants”) to the Signatories and the two other parties (collectively, the “Buyers”). The Buyers purchased an aggregate of approximately $4.9 million principal amount of convertible notes and warrants to purchase shares of common stock. As part of the 2013 transaction, we entered into a security agreement dated on or about May 7, 2013 (the “Original Security Agreement”) with the Buyers pursuant to which the Buyers were granted a security interest in all of Company’s assets except for its patents and other intellectual properties in order to secure performance of the convertible notes.
The 2013 Purchase Agreement, as well as the related transaction documents can be amended by a written instrument signed by the Company and those Buyers holding or having the right to acquire at least 75% of the shares of Company’s common stock issuable upon conversion of the convertible notes and exercise of the warrants and any such amendment is binding equally on all Buyers. The Amended Agreement amends the 2013 Purchase Agreement and the Original Security Agreement, replaces the convertible notes with “Amended Notes” and replaces the warrants with “Amended Warrants.” Pursuant to the Amended Agreement, the Company is obligated to file with the SEC a preliminary proxy statement for a stockholders meeting at which the Company will seek stockholder approval of resolutions to (i) elect a new board of at least five directors, (ii) approve a reverse stock split of up to 1-for-7 (the “Reverse Split”), and (iii) if, and to the extent required by applicable law, to approve the issuances granted to the Buyers under the Amended Agreement. The Company is obligated to use its best efforts to solicit stockholder approval of these resolutions, and must hold the stockholder meeting promptly following the mailing of the definitive proxy statement. In addition, the Amendment waives any and all events of default under the 2013 Purchase Agreement and related transaction documents existing on or prior to January 30, 2017 and amends the defaults and remedies section of the 2013 Purchase Agreement.
| 21 |
The Amended Notes provide that all accrued and unpaid interest on the Original Notes through October 31, 2016 be added to the principal amount of the Amended Notes. The Amended Notes bear interest at the rate of 0% until May 1, 2017 and 5% per annum thereafter, subject to reduction to comply with applicable law, and mature in 60 months from the effective date of the Reverse Split. Upon certain financings, the Company is obligated to make a payment to the holders of the Amended Notes in the amount of 20% of the outstanding Notes. Immediately upon the effectiveness of the Reverse Split, there shall be a mandatory conversion of 80% of the then-unpaid principal of and all of the then accrued but unpaid interest on the Amended Notes. After the effectiveness of the Reverse Split, and so long as any portion of the Amended Notes are outstanding, the holders thereof may voluntarily convert the unpaid principal and interest thereon into the Company’s common stock at the conversion price of $1.40 per share.
The Signatories hold or have the right to acquire at least 97% of the shares of Company’s common stock issuable upon conversion of the Original Notes and exercise of the Original Warrants. Two secured creditors, who together hold or have the right to acquire less than 3% of the Company’s common stock issuable upon conversion of the Original Notes and exercise of the Original Warrants, did not sign the amendment and have named the Company and the Company’s Chief Executive Officer among several defendants in a lawsuit demanding repayment of loans totaling $125,000 plus accrued interest and exemplary damages. However, in that secured creditors holding in excess of 97% of the shares of Company’s common stock issuable upon conversion of the Original Notes and exercise of the Original Warrants under the 2013 Purchase Agreement have executed the amendment, the 2013 Purchase Agreement provides that the Amendment is binding on all of the secured creditors, including the two plaintiffs in the lawsuit. Management believes that the two plaintiffs have no valid claim against the Company or our Chief Executive Officer. In March 2017, plaintiffs moved for partial summary adjudication against the Company and our Chief Executive Officer; however, the Court denied plaintiffs’ motion. Both the Company and Mr. Gagerman have filed demurrers seeking dismissal of this action, which remain pending at this time. See “Item 3. Legal Proceedings” above.
Establishment of the Special Committee of the Board - In September 2016, our Board of Directors appointed a special committee comprised of disinterested directors to negotiate with Mr. Breslow and Mr. Kopple, who at the time were both interested board members, in an effort to reach a settlement on the obligations that Messrs. Breslow and Kopple claim are due to them, as discussed in more detail below. The Special Committee was granted full power and authority to act in the name of the entire Board in negotiating with Mssrs. Breslow and Kopple in the best interest, and for the benefit of, the Company’s stockholders, and in approving (or rejecting) the terms of any proposed transactions with these individuals.
Breslow Debt Refinancing Agreement - Warren Breslow served as a director of the Company from 2006 to 2017. He resigned his position on our board in March 2017. During the period from 2006 through 2016, Mr. Breslow and his affiliates made various temporary advances to the Company of $15,930,041 aggregate amount advanced over the years (the “Original Advances”). Interest on the Original Advances was at a rate of 10% per annum. As of January 24, 2017, there was an outstanding balance of $23,603,852 which represents outstanding principal in the amount of $14,930,041 together with accrued and unpaid interest in the amount of $8,673,811.
On January 24, 2017, the Special Committee approved, and the Company entered into, a Debt Refinancing Agreement (the “Breslow Refinancing Agreement”) with Warren Breslow and the Survivor’s Trust under the Warren L. Breslow Trust (collectively, the “Breslow Parties”), and issued an unsecured convertible promissory note (the “Breslow Note”). At the time of the Original Advances and the entering into of the Breslow Refinancing Agreement and at all times in between, Breslow was a director of the Company and, in addition, beneficially owns approximately 6% of Company’s common stock. Mr. Breslow is also a trustee of the Survivor’s Trust under the Warren L. Breslow Trust.
Pursuant to the Breslow Refinancing Agreement, the parties agreed that, as of the date thereof, the Company owed the Breslow Parties outstanding principal in the amount of $14,930,041, together with accrued and unpaid interest in the amount of $8,673,811, or a total of $23,603,852.
| 22 |
Pursuant to the Breslow Refinancing Agreement, the Breslow Parties have canceled and forgiven all accrued interest through the date of the Breslow Refinancing Agreement, have waived all existing events of default relating to the outstanding indebtedness, and have agreed that all instruments or other agreements evidencing or pertaining to the outstanding indebtedness shall be cancelled and shall be superseded and replaced in their entirety by a new promissory note (the “New Breslow Note”) issued by the Company concurrently with, and as a condition of, the Breslow Refinancing Agreement. The New Breslow Note was issued in the principal amount of $14,930,041 (the “Restructured Principal”), bears interest on the Restructured Principal at a rate equal to 0% for the first six months, and 5% per annum thereafter. However, in the event of an event of default (as defined in the New Breslow) Note, the interest rate shall become 18% per annum. The entire unpaid balance of the Note is due on the 60th month anniversary of the date of issuance, and may be prepaid or redeemed in whole or in part without premium or penalty. With certain exceptions, if an event of default occurs and is continuing, the holder of the New Breslow Note may, without notice, declare the outstanding Restructured Principal and accrued and unpaid interest thereon to be immediately due and payable.
If stockholder approval of the Reverse Split and, if required, the transactions with the Breslow Parties, are not obtained within twelve months after the date of the Breslow Refinancing Agreement, the Breslow Refinancing Agreement and the New Breslow Note shall be rescinded and shall be of no further force or effect; provided however, that if the Breslow Parties fail to vote all of the voting securities of the Company beneficially owned by them in favor of such proposals such rescission will not apply.
Immediately upon the Reverse Split becoming effective, $11,930,041 of the Restructured Principal shall automatically be converted into 7,948,097 shares of the Company’s common stock. In addition, at any time after the effective date of the Reverse Split, and so long as any portion of the New Breslow Note remains outstanding, the holder thereof shall be entitled to convert any portion thereof then outstanding (together with accrued and unpaid interest) into shares of our common stock, at a conversion price of $1.40 per share, subject to adjustment from time to time in the event of any stock split, reverse stock split or similar subdivision or combination, other than the Reverse Split. To date, the shareholders have not approved the Reverse Stock Split.
Kopple Debt - Robert Kopple, who has been a director of the Company since September 2013, claims that the Company owes him and certain affiliated parties an aggregate of approximately $3.46 million in principal and interest, in excess of $1.57 million in accrued interest, and warrants to purchase 22,917,200 shares of our common stock at a price of $0.10 per share, as a result of various loans made by Mr. Kopple and his affiliates (collectively, the “Kopple Parties”) to the Company between 2013 and 2016. Mr. Kopple has served as Vice Chairman of the Board since his appointment in 2013.
On or about March 23, 2013, the Kopple Parties made various cash advances to the Company in the aggregate original principal amount of $2,500,000, evidenced by an unsecured convertible note (the “Original Kopple Note”) with the right to convert outstanding principal and accrued and unpaid interest at $0.50 per share. On or around June 20, 2014, $500,000 of the Original Kopple Note was reclassified as a short-term note, the principal amount of the Original Kopple Note was reduced from $2.5 million to $2.0 million and the Original Kopple Note was amended to provide that an event of default under the June 2014 Agreement (as described and defined below) would also constitute an event of default under the Original Kopple Note.
Also in June 2014, the Company entered into a Financing Letter of Agreement (the “June 2014 Agreement”) with two affiliate entities of Mr. Kopple, KF Business Ventures and the Kopple Family Partnership (the “Additional Kopple Parties”), pursuant to which the Additional Kopple Parties loaned us an additional $1,000,000 (the “June 2014 Loan”). In connection with the June 2014 Loan, Mr. Kopple also added $202,205 in penalties and accrued interest, credited the Company with $200,000 for amounts previously repaid by the Company and consolidated several earlier advances into a single new note (the “June 2014 Kopple Note”) in the principal amount of $2,915,206 and bearing simple interest at a rate of 10% per annum. The Company was also required to obtain a subordination agreement from the Breslow Parties in favor of the Kopple Parties with respect to the June 2014 Kopple Note.
| 23 |
Pursuant to the June 2014 Agreement, the Kopple Parties also placed various restrictions on our ability to raise additional capital, hire qualified personnel and pay certain expenses without his prior approval for so long as the principal amount of his note remained outstanding. The June 2014 Kopple Note also required us to issue Mr. Kopple a stock purchase warrant (the “June 2014 Kopple Warrant”) to purchase approximately 5.8 million shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $0.10 per share, to be exercisable for seven years. Additionally, if we borrowed funds, issued capital stock or rights to acquire or convert into capital stock, or granted rights in respect to territories to any person for cash consideration of more than $5 million in the aggregate after the date of the June 2014 Kopple Note, we would be required to pay the entire amount of such cash consideration in excess of $5 million as a mandatory prepayment of the June 2014 Kopple Note. Additionally, Mr. Kopple required a default provision providing that in the event that the entire outstanding balance of the June 2014 Kopple Note was not paid in full prior to October 1, 2014, then for each consecutive calendar month during the period beginning October 1, 2014 and ending March 31, 2015, the Company would issue to Mr. Kopple additional stock purchase warrants, each to purchase 2,915,206 shares of our common stock, up to a maximum aggregate of approximately 17.5 million shares of our common stock, at $0.10 per share (the “Kopple Penalty Warrants”), the Kopple Penalty Warranties to be exercisable for seven years from the time of their respective issuances. In addition to the Kopple Penalty Warrants, the default provision under the June 2014 Kopple Note provides for a 5% late charge on the total amount due plus 15% per year interest. The Company did not repay the Kopple Parties the amounts loaned to the Company, and the Company has not yet done so. Additionally, the Company has not issued any of the Kopple Penalty Warrants and management believes that Mr. Kopple is not entitled to receive them. The Company has also cancelled the June 2014 Kopple Warrant.
See “Item 3. Legal Proceedings” included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for information regarding the dispute with Mr. Kopple regarding these transactions.
Unsecured Creditor Agreements - During the period from 2013 through 2015, a number of investors made various temporary advances to the Company in the aggregate amount of $3,273,057 (the “Original Advances”). Interest on the Original Advances was at a rate of 10% per annum. As of February 28, 2017, there was an outstanding balance of $3,940,444 which represents outstanding principal in the amount of $3,273,057 together with accrued and unpaid interest in the amount of $667,387. Subsequent to fiscal year end, the Company entered into several Debt Refinancing Agreements (collectively, the “Refinancing Agreements”) with debt holders holding $2,811,520 outstanding principal, plus accrued interest in the amount of $612,888, or a total outstanding obligation in the amount of $3,424,408. The Refinancing Agreements waive all events of default, cancel and forgive all accrued interest and provide for new five-year 5% convertible notes (the “Refinancing Notes”) in the aggregate principal amount of $2,811,520, with no interest for first six months and 5% per year thereafter. Upon the approval of the Reverse Split by the stockholders the Refinancing Notes will be converted into 1,940,415 shares of our common stock. The Refinancing Notes also contain various default provisions related to the timely payment of the principal and interest when due, and in case of the Company filing for bankruptcy protection. The default provisions call for default interest rate of 18% per annum and acceleration of the Notes.
We consider the transactions described above with Mr. Breslow and Mr. Kopple to be related transactions.
Going Concern.
Our independent auditor has expressed doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern and believes that our ability is dependent on our ability to implement our business plan, raise capital and generate revenues. See Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm on page F-1, together with the Company’s audited consolidated financial statements for the fiscal year ended February 28, 2017.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
As a smaller reporting company, we are not required to provide the information required by this Item 7A.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
See Index to Consolidated Financial Statements at page F-1.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
Not applicable.
| 24 |
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company maintains disclosure controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in reports filed under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the specified time periods. For the last 3 fiscal years, these control and procedures broke down due to insufficient capital to maintain such controls and procedures. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by the Company in the reports that it files or submits under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is accumulated and communicated to its management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. As of the end of the period covered by this report, the Company’s management evaluated, with the participation of the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures. Based on the evaluation, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that these controls and procedures were ineffective for the last 3 fiscal years in ensuring that information requiring disclosure is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified by the SEC’s rules and forms.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the Company’s fiscal quarter ended February 28, 2017, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Inherent Limitations on Effectiveness of Controls
The Company does not expect that its disclosure controls and procedures or its internal control over financial reporting will prevent all errors and all fraud. A control procedure, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable not absolute assurance that the objectives of the control procedure are met. Because of the inherent limitations in all control procedures, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within the Company have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision-making can be faulty, and that breakdowns can occur because of simple error or mistake. Additionally, controls can be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people, or by management override of the control. The design of any control procedure also is based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions; over time, controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. Because of the inherent limitations in a cost-effective control procedure, misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and not be detected.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The Company’s management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with United States generally accepted accounting principles. Internal control over financial reporting includes policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with United States generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisitions, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of February 28, 2017. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”) in Internal Control-Integrated Framework. Based on this assessment, and on those criteria, management concluded that, due to the material weaknesses identified below, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was ineffective as of February 28, 2017.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the Company’s annual or interim financial statements would not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. The specific material weaknesses identified by our management relate to limited resources and inadequate number of personnel in our accounting and financial reporting group due to insufficient capital to maintain such resources. Management has determined that our internal audit function is also significantly deficient due to insufficient resources to perform internal audit functions. This was further evidenced by our inability to timely file our annual reports on Form 10-K for the fiscal years ended February 28, 2015, February 29, 2016 and February 28, 2017 and our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q for the fiscal quarters ended May 31, 2015, August 31, 2015, November 30, 2015, May 31, 2016, August 31 2016, November 30, 2016 and May 31, 2017.
Management plans to remediate these weaknesses by prioritizing the allocation of financial and personnel resources to ensure that the Company’s accounting and financial reporting groups are sufficiently able to effectuate information requiring disclosure being recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified by the SEC’s rules and forms. Since February 28, 2017, the Company has engaged a registered public accounting firm to complete the required audit of the Company’s financial statements and is in the process of filing all outstanding periodic reports with the SEC.
None
| 25 |
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Directors and Executive Officers
The following table sets forth the names, ages and offices of all of our directors and management. Our officers are appointed by, and serve at the pleasure of, the Board of Directors. The stockholders at the annual meeting elect our directors to serve until the next meeting.
| Name | Age | Title | ||
| Melvin Gagerman | 74 | Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and Director | ||
| Warren Breslow* | 74 | Director, Chairman of the Audit Committee, Member of the Nominating Committee and Compensation Committee | ||
| Salvador Diaz-Verson, Jr. | 61 | Director, Chairman of the Compensation Committee, Member of the Audit Committee and Nominating Committee | ||
| Robert Kopple | 72 | Director |
* Mr. Breslow resigned as a director in March 2017.
Biographical information with respect to our directors and management is provided below.
Melvin Gagerman. Mr. Gagerman is a CPA and has been a director and our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer since we emerged from Chapter 11 proceedings on January 31, 2006. As Chief Executive Officer Mr. Gagerman formulates policies, defines our values, directs the operations of the business and defines our corporate culture. He is also responsible for overseeing our other executive officers. Mr. Gagerman has many years of experience in performing these duties and a strong background in accounting and financing. Prior to joining Aura, Mr. Gagerman served as the Chief Executive Officer of a number of companies including Surface Protection Industries and Applause. Mr. Gagerman has also served as Managing Partner of Good, Gagerman & Berns, an accounting firm, National Audit Partner for Laventhol and Horwath, and Audit Supervisor at Coopers and Lybrand. As the Chairman of the Board, Mr. Gagerman’s background and experience provides the Board with a solid understanding of the business issues and financial planning and execution required by the business. Mr. Gagerman is currently serving as our Chief Financial Officer while we search for a permanent candidate for that position.
Warren Breslow. Mr. Breslow is a CPA and has been a director and Chairman of the Audit Committee since we emerged from Chapter 11 bankruptcy proceedings on January 31, 2006. Mr. Breslow is the General Partner and Chief Financial Officer of Goldrich & Kest Industries (“G & K Industries”). He joined G & K Industries in 1972 as controller and assumed his current position as General Partner and Chief Financial Officer in 1974. As General Partner and Chief Financial Officer of G & K Industries, Mr. Breslow oversees the financial aspects of its construction activity, as well as its management operations and information systems center. He is also the past president and a lifetime member of the board of directors of the Stephen S. Wise Temple, and supports numerous charitable and civic organizations. Prior to his association with G & K Industries, Mr. Breslow was a manager with the international accounting firm of Laventhol & Horwath. Mr. Breslow resigned as a director in March 2017.
| 26 |
Salvador Diaz-Verson, Jr. Mr. Diaz-Verson has served as a director since June 2007. He previously served as one of our directors from 1997-2005. Mr. Diaz-Verson is the founder, Chairman and President of Diaz-Verson Capital Investments, Inc., and was a registered investment advisor with the Securities and Exchange Commission until 2009. Mr. Diaz-Verson served as President and member of the board of directors of American Family Corporation (AFLAC, INC.) from 1976 until 1992. Mr. Diaz-Verson served as Executive Vice President and Chief Investment Officer of American Family Life Assurance Company, a subsidiary of AFLAC, INC. He is currently Chairman of Miramar Securities. Mr. Diaz-Verson has received two presidential appointments to the Christopher Columbus Fellowship Foundation; first by President George H.W. Bush in 1992 and subsequently by President Clinton in 2000. Mr. Diaz-Verson is a trustee of the Florida State University Foundation and is a national trustee of the Boys and Girls Club of America. He also serves as a trustee of Clark Atlanta University. Mr. Diaz-Verson is a graduate of Florida State University and was selected as a director in view of his lengthy experience in managing companies and his knowledge of capital investments.
Robert Kopple. Mr. Kopple is an investor, businessman, and lawyer. He is a founding partner in a law firm based in Los Angeles, California specializing in taxation and business law. Mr. Kopple manages interests in real estate and operating companies and has provided equity and debt financing for a number of companies. Mr. Kopple has served as a director since September 2013 and is a significant investor in Aura.
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
Our shares of common stock are registered under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, and therefore our executive officers and directors and persons who beneficially own more than 10% of a registered class of our equity securities to file with the SEC initial statements of beneficial ownership, reports of changes in ownership and annual reports concerning their ownership of our common shares and other equity securities, on Forms 3, 4 and 5 respectively. Executive officers, directors and greater than 10% stockholders are required by the Securities and Exchange Commission regulations to furnish us with copies of all Section 16(a) reports they file. Based on our review of the copies of such forms received by us, and to the best of our knowledge, no executive officers, directors and persons holding greater than 10% of our issued and outstanding stock have filed the required reports during the year ended February 28, 2017.
Code of Ethics
We have adopted a Code of Ethics applicable to the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and all other members of the Company’s Finance Department. This Code of Ethics is posted on the Company’s website within a broader Code of Business Conduct and Ethics at www.aurasystems.com in the Investor Relations section. We intend to satisfy the disclosure requirement under Item 10 of Form 8-K regarding an amendment to, or a waiver from, the provision of our Code of Ethics that applies to our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller, or persons performing similar functions and that relates to any element of such provision of our Code of Ethics by posting such information on our website within four business days of the date of such amendment or waiver. In the case of a waiver, the nature of the waiver, the name of the person to whom the waiver was granted and the date of the waiver will also be disclosed.
Family Relationships
None of our directors or executive officers is related to one another.
Legal Proceedings
To the best of our knowledge, except as described elsewhere in this report with respect to Mr. Kopple, none of our executive officers or directors is a party to any material proceedings adverse to the Company, has any material interest adverse to the Company or has, during the past ten years:
| ● | been convicted in a criminal proceeding or been subject to a pending criminal proceeding (excluding traffic violations and other minor offenses); |
| 27 |
| ● | had any bankruptcy petition filed by or against him/her or any business of which he/she was a general partner or executive officer, either at the time of the bankruptcy or within two years prior to that time; |
| ● | been subject to any order, judgment, or decree, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any court of competent jurisdiction, permanently or temporarily enjoining, barring, suspending or otherwise limiting his/her involvement in any type of business, securities, futures, commodities or banking activities; |
| ● | been found by a court of competent jurisdiction (in a civil action), the Securities and Exchange Commission or the Commodity Futures Trading Commission to have violated a federal or state securities or commodities law, and the judgment has not been reversed, suspended, or vacated; |
| ● | been subject to, or party to, any judicial or administrative order, judgment, decree , or finding, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, relating to an alleged violation of (i) any Federal or State securities or commodities law or regulation, (ii) any law or regulation respecting financial institutions or insurance companies including, but not limited to, a temporary or permanent injunction, order of disgorgement or restitution, civil money penalty or temporary or permanent cease-and-desist order, or removal or prohibition order or (iii) any law or regulation prohibiting mail or wire fraud or fraud in connection with any business entity; or been the subject of, or a party to, any sanction or order, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any self-regulatory organization (as defined in Section 3(a)(26) of the Exchange Act (15 U.S.C. 78c(a)(26))), any registered entity (as defined in Section 1(a)(29) of the Commodity Exchange Act (7 U.S.C. 1(a)(29))), or any equivalent exchange, association, entity or organization that has disciplinary authority over its members or persons associated with a member. |
Committees of the Board of Directors
The Board maintains the following committees to assist it in discharging its oversight responsibilities.
Audit Committee. The Audit Committee does not have a formal charter but is responsible primarily for overseeing the services performed by our independent registered public accounting firm, evaluating our accounting policies and system of internal controls, and reviewing our annual and quarterly reports before filing with the Securities and Exchange Commission. The sole current member of the Audit Committee is Mr. Salvador Diaz-Verson. Mr. Breslow had also been a member of the Audit Committee prior to his resignation as a director in March 2017. The Board of Directors has determined that the Audit Committee does not have a member who is an “audit committee financial expert” as such term is defined by the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission. While the Board recognizes that the Board member serving on the Audit Committee does not meet the qualifications required of an “audit committee financial expert,” the Board believes that the appointment of a new director to the Board of Directors and to the Audit Committee at this time is not necessary as the level of financial knowledge and experience of the current member of the Audit Committee, including such member’s ability to read and understand fundamental financial statements, is sufficient to adequately discharge the Audit Committee’s responsibilities.
Compensation Committee. The Compensation Committee does not have a formal charter but reviews and recommends to the full Board the amounts and types of compensation to be paid to the Chairman and Chief Executive Officer; reviews and approves the amounts and types of compensation to be paid to our other executive officers and the non-employee directors; reviews and approves, on behalf of the Board, salary, bonus and equity guidelines for our other employees; and administers our 2006 Stock Option Plan. The Compensation Committee is currently comprised solely of Mr. Diaz-Verson. Mr. Breslow had also been a member of the Compensation Committee prior to his resignation as a director in March 2017. Mr. Breslow has provided loans to us in the aggregate principal amount of $14,930,041. For a discussion about Mr. Breslow’s loans to us, see “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Results of Operations – Liquidity” and “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions”.
Nominating Committee. The Nominating Committee does not have a formal charter but assists the Board in identifying qualified individuals to become directors, determines the composition of the Board and its committees, monitors the process to assess the Board’s effectiveness and helps develop and implement our corporate governance guidelines. The Nominating Committee also considers nominees proposed by stockholders. The Nominating Committee currently consists of Mr. Diaz-Verson.
Special Committee. In September 2016, the Board of Directors appointed Messrs. Gagerman and Diaz-Verson to a Special Committee to seek to negotiate restructuring agreements with each of Mr. Breslow and Mr. Kopple, to review the Company’s relationships with each of Mr. Breslow and Mr. Kopple, to independently assess the transactions with each of Mr. Breslow and Mr. Kopple, and to undertake such other inquiries and investigations, and make such recommendations, as the Special Committee considers in the best interests of the Company and its stockholders as a whole. See the Related Transactions disclosure under “Liquidity and Capital Resources” in “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| 28 |
Director Compensation
Although we do not currently compensate our directors in cash for their service as members of our Board of Directors, the Board may, in its discretion, elect to compensate directors for attending Board and Committee meetings and to reimburse directors for out-of-pocket expenses incurred in connection with attending such meetings. Additionally, our directors are eligible to receive stock options under the 2011 Directors and Executive Officer Stock Option Plan. During fiscal 2017, no Directors received any stock options. There are no payments due to any directors upon their resignation or retirement as members of the Board.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The following table summarizes all compensation earned for the fiscal years ended February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, to the individual who served as our chief executive officer during fiscal 2017. We had no other officers who would qualify as “named executive officers” as such term is defined in Item 402 of Regulation S-K and serving in such capacity at any time during the year ended February 28, 2017 (the “Named Executive Officers”).
Summary Compensation Table
| Name and Principal Position | Fiscal Year | Salary ($) | Option Awards ($) | Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation | All Other Compensation ($) | Total ($) | ||||||||||||||||
| Melvin Gagerman (1) | 2017 | 0 | (2) | - | - | 0 | (3) | 0 | ||||||||||||||
Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer | 2016 | 360,000 | - | - | $ | 44,961 | (4) | 404,961 | (5) | |||||||||||||
| (1) | Mr. Gagerman was elected Chairman and Chief Financial Officer effective February 1, 2006 and was elected President and Chief Executive Officer effective May 25, 2006. | |
| (2) | For additional information, see “--Employment Contracts, Termination of Employment Contracts and Change in Control Arrangements” below. | |
| (3) | No bonuses or stock awards were granted to the above individuals for fiscal 2017. No amounts are indicated for perquisites and other personal benefits as the value provided did not exceed $10,000. | |
| (4) | Represents $24,000 in automobile allowance, $13,022 for the cost of life and long term care insurance premiums, and $7,939 in medical expense reimbursements. | |
| (5) | Mr. Gagerman’s salary of $360,000 for fiscal 2016 was not paid but was accrued. |
| 29 |
Outstanding Equity Awards at 2017 Fiscal Year-End
The following table summarizes certain information regarding the number and value of all options to purchase our common stock held by our named executive officer for the year ended February 28, 2017. No stock awards or equity incentive plan awards were issued or outstanding during fiscal 2017.
2017 OUTSTANDING EQUITY AWARDS AT FISCAL YEAR END
| Option Awards | ||||||||||||||||||
Number of (#) | Number of (#) | Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Unearned Options | Option Exercise Price | Option Expiration | ||||||||||||||
Name | Exercisable | Unexercisable | (#) | ($) | Date | |||||||||||||
| Melvin Gagerman | 1,100,000 | 0 | -- | $ | 0.75 | 2/28/20 | ||||||||||||
| Melvin Gagerman | 1,400,000 | 0 | -- | $ | 0.75 | 6/2/21 | ||||||||||||
| Melvin Gagerman | 1,000,000 | 0 | -- | $ | 1.00 | 8/25/16 | ||||||||||||
Option Exercises and Stock Vesting During 2017
No stock options were exercised during fiscal 2017 by the individuals named in the Summary Compensation Table. No stock awards were issued or outstanding during fiscal 2017.
Employment Contracts, Termination of Employment Contracts and Change in Control Arrangements
We do not currently have any employment agreements with any of our Named Executive Officers.
In fiscal 2016, Mr. Gagerman was entitled to a base salary of $360,000 per year, which was accrued by the Company but not paid to Mr. Gagerman due to the Company’s inability to pay Mr. Gagerman any salary. It is expected that the Company will pay Mr. Gagerman the amount he is due for prior services when and if the Company generates sufficient revenue to do so. There is no agreement to pay Mr. Gagerman for his services in fiscal 2017; however, the Board has the discretion to pay Mr. Gagerman for services he renders to the Company if the Company generates sufficient revenue to do so.
Potential Payments to the Named Executive Officers Upon Termination or Change in Control
None of the named executive officers is entitled to any payments or benefits upon termination, whether by change in control or otherwise, other than benefits available generally to all employees.
Director Compensation During Fiscal 2017
Although we do not currently compensate our directors for their service as members of our Board of Directors, the Board may, at its discretion, compensate directors for attending board and committee meetings and reimburse the directors for out-of-pocket expenses incurred in connection with attending such meetings. Our directors are also eligible to receive stock option grants under our 2006 employee stock option plan and Director Warrants authorized under our Chapter 11 Plan of Reorganization.
| 30 |
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT
The following table sets forth, to the extent of our knowledge, certain information regarding our common stock owned as of August 30, 2017 (i) by each person who is known to be the beneficial owner of more than 5% of our outstanding common stock, (ii) by each of our Directors and the named executive officers in the Summary Compensation Table, and (iii) by all Directors and current executive officers as a group:
Beneficial Ownership Table
| Beneficial Owner | Number
of Shares of Common Stock | Percent
of Common Stock (1) | ||||||
| Melvin Gagerman (2) | 7,796,801 | 6.1 | % | |||||
| Warren Breslow (3) | 6,287,966 | 4.9 | % | |||||
| Salvador Diaz-Verson, Jr. (4) | 790,934 | * | ||||||
| Robert Kopple(5) | 25,349,089 | 20.0 | % | |||||
| All current executive officers and Directors as a group (three)(6) | 33,936,824 | 26.1 | % | |||||
| 5% Stockholders | ||||||||
| None other than the Directors named above | ||||||||
* Less than 1% of outstanding shares.
| (1) | Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission. The calculation of the percentage of beneficial ownership is based upon 126,608,391shares of common stock outstanding on August 30, 2017. In computing the number of shares beneficially owned by any stockholder and the percentage ownership of such stockholder, shares of common stock which may be acquired by a such stockholder upon exercise or conversion of warrants or options which are currently exercisable or exercisable within 60 days of August 30, 2017, are deemed to be exercised and outstanding. Such shares, however, are not deemed outstanding for purposes of computing the beneficial ownership percentage of any other person. Shares issuable upon exercise of warrants and options which are subject to stockholder approval are not deemed outstanding for purposes of determining beneficial ownership. Except as indicated by footnote, to our knowledge, the persons named in the table above have the sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of common stock shown as beneficially owned by them. |
| (2) | Includes 5,675,258 warrants and options exercisable within 60 days of August 30, 2017. |
| (3) | Includes 4,923,901 warrants and options exercisable within 60 days of August 30, 2017. Mr. Breslow resigned as a director in March 2017. |
| (4) | Includes 723,489 warrants and options exercisable within 60 days of August 30, 2017. |
| (5) | Based on a Schedule 13D filed by Mr. Kopple with the SEC on September 11, 2013. The business address of Mr. Kopple is 10866 Wilshire Blvd., Suite 1500, Los Angeles, California 90024. The Company is also presently engaged in a dispute with Mr. Kopple that includes a claim regarding approximately 22.9 million warrants which Mr. Kopple claims to be owed to him and his affiliates by the Company. The Company believes that it has valid defenses against Mr. Kopple’s claims and that no warrants are issuable to Mr. Kopple. Accordingly, the amount reflected herein does not include the warrants in dispute. See Item 3. “Legal Proceedings”, “Liquidity and Capital Resources” in “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information regarding the transactions under dispute. |
| (6) | Excludes Mr. Breslow, who resigned from the Board of Directors in March 2017. |
The mailing address for each of the officers and directors is c/o Aura Systems, Inc., 10541 Ashdale St., Stanton, CA 90680.
| 31 |
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans as of February 28, 2017
Equity Compensation Plan Information as of February 28, 2017
| |
Number of Securities to be Issued Upon Exercise of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights | Weighted-average Exercise Price of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights | Number of Securities Remaining Available for Future Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans (Excluding Securities Reflected in Column (a) | |||||||||
| Plan Category | (a) | (b) | (c) | |||||||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders (1) | 7,224,000 | $ | 0.76 | 11,767,258 | ||||||||
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | 15,550,000 | $ | 0.75 | 3,441,258 | ||||||||
| (1) | Reflects options under the 2006 Stock Option Plan. The 2006 Stock Option Plan authorizes the Company to grant stock options exercisable for up to an aggregate number of shares of common stock equal to the greater of (i) 3,000,000 shares of common stock, or (ii) 10% of the number of shares of common stock outstanding from time to time. The numbers in this table are as of February 28, 2017. |
For additional information regarding options and warrants, see Note 10 to our financial statements appearing elsewhere in this report.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
Related Transactions
See the related transactions disclosure under “Liquidity and Capital Resources” in “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Review and Approval of Related Party Transactions
Our Audit Committee is responsible for the review and approval of all related party transactions required to be disclosed to the public under SEC rules. This procedure, which is contained in the written charter of our Audit Committee, has been established by our Board of Directors in order to serve the interests of our shareholders. Related party transactions are reviewed and approved by the Audit Committee on a case-by-case basis. Under existing, unwritten policy no related party transaction can be approved by the Audit Committee unless it is first determined that the terms of such transaction is on terms no less favorable to us than could be obtained from an unaffiliated third party on an arms-length basis and is otherwise in our best interest.
See the Related Transactions disclosure under “Liquidity and Capital Resources” in “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Director Independence
Using the definition of “independence” included in the listing rules of The Nasdaq Stock Market, our Board has determined that director Mr. Diaz-Verson is independent.
| 32 |
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND DISCLOSURES
The following table sets forth the aggregate fees billed to us by KSP Group, Inc. for the years ended February 28, 2017, and February 29, 2016:
| Year Ended | ||||||||
| February 28, 2017 | February 29, 2016 | |||||||
| Audit Fees | $ | 32,000 | $ | 47,500 | ||||
| Audit-related fees | - | - | ||||||
| Tax fees | - | - | ||||||
| All other fees | - | - | ||||||
| Total | $ | 32,000 | $ | 47,500 | ||||
As defined by the SEC, (i) “audit fees” are fees for professional services rendered by our principal accountant for the audit of our annual financial statements and review of financial statements included in our Form 10-K, or for services that are normally provided by the accountant in connection with statutory and regulatory filings or engagements for those fiscal years; (ii) “audit-related fees” are fees for assurance and related services by our principal accountant that are reasonably related to the performance of the audit or review of our financial statements and are not reported under “audit fees;” (iii) “tax fees” are fees for professional services rendered by our principal accountant for tax compliance, tax advice, and tax planning; and (iv) “all other fees” are fees for products and services provided by our principal accountant, other than the services reported under “audit fees,” “audit-related fees,” and “tax fees.”
Audit Fees
Services provided to us by KSP Group, Inc. with respect the audit of our annual financial statements and review of our annual reports on Form 10-K and for reviews of the financial statements included in our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q for the first three quarters of the years ended February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016.
Audit Related Fees
KSP Group, Inc. did not provide any professional services to us during fiscal 2017 or fiscal 2016 which would constitute “audit related fees”.
Tax Fees
KSP Group, Inc. did not provide any professional services to us during fiscal 2017 or fiscal 2016 which would constitute “tax fees”.
All Other Fees
KSP Group, Inc. did not provide any professional services to us during fiscal 2017 or fiscal 2016 which would constitute “other fees”.
On February 8, 2017, Kabani & Company, Inc. (“Kabani”) resigned as the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, effective as of February 8, 2017.
Kabani served as the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm for the Company’s fiscal years ended February 28, 2014, and February 28, 2013. The reports of Kabani on the Company’s financial statements for the years ended February 28, 2014, and February 28, 2013 did not contain an adverse opinion or disclaimer of opinion and were not qualified or modified as to uncertainty, audit scope, or accounting principles.
| 33 |
During the fiscal years ended February 28, 2014, and February 28, 2013 and through September 18, 2017, there were no disagreements with Kabani on any matter of accounting principles or practices, financial statement disclosure, or auditing scope or procedure, which disagreements if not resolved to the satisfaction of Kabani would have caused it to make reference to the subject matter of the disagreements in connection with its reports. During the fiscal years ended February 28, 2014, and February 28, 2013 and through September 18, 2017, there have been no reportable events (as defined in Item 304(a)(1)(v) of Regulation S-K).
The Company requested that Kabani review the disclosures contained herein and asked Kabani to furnish the Company with a letter addressed to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission containing any new information, clarification of the Company’s expression of Kabani’s views, or the respects in which Kabani does not agree with the statements contained herein. A copy of the letter is filed as Exhibit 16.1 hereto.
In February 2017, the Company engaged KSP Group, Inc. (“KSP”) as the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm for the fiscal years ending February 28, 2015, February 29, 2016 and February 28, 2017. The decision to appoint KSP was approved by the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors.
During the two most recent fiscal years and during the subsequent interim period from March 1, 2017 through September 18, 2017, neither the Company nor anyone on its behalf consulted KSP regarding either (i) the application of accounting principles to a specified transaction, either completed or proposed, or the type of audit opinion that might be rendered on the Company’s financial statements, and neither a written report nor oral advice was provided to the Company that KSP concluded was an important factor considered by the Company in reaching a decision as to any accounting, auditing or financial reporting issue, or (ii) any matter that was either the subject of a “disagreement” or a “reportable event,” each as defined in Regulation S-K Item 304(a)(1)(v), respectively.
Policy on Audit Committee Pre-Approval of Audit and Permissible Non-Audit Services of Independent Auditors
Under the SEC’s rules, the Audit Committee is required to pre-approve the audit and permissible non-audit services performed by the independent registered public accounting firm in order to ensure that they do not impair the auditors’ independence. The SEC’s rules specify the types of non-audit services that an independent auditor may not provide to its audit client and establish the Audit Committee’s responsibility for administration of the engagement of the independent registered public accounting firm.
Consistent with the SEC’s rules, the Audit Committee pre-approves all audit and permissible non-audit services provided by our independent auditors. These services may include audit services, audit-related services, tax and other services. Pre-approval is generally provided for up to one year, and any pre-approval is detailed as to the particular service or category of services and is generally subject to a specific budget. The independent auditors and management are required to periodically report to the Audit Committee regarding the extent of services provided by the independent auditors in accordance with this pre-approval, and the fees for the services performed to date. The Audit Committee may also pre-approve particular services on a case-by-case basis. During fiscal 2017 and 2016 all services provided by KSP Group, Inc. were pre-approved by the Audit Committee in accordance with this policy.
There were no hours expended on the principal accountant’s engagement to audit the registrant’s financial statements for the most recent fiscal year that were attributed to work performed by persons other than the principal accountant’s full-time, permanent employees.
| 34 |
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
Documents filed as part of this Form 10-K:
1. Financial Statements
See Index to Consolidated Financial Statements at page F-1
2. Financial Statement Schedules
See Index to Consolidated Financial Statements at page F-1
3. Exhibits
INDEX TO EXHIBITS
Description of Documents
| 35 |
| 36 |
| * | Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| ** | See Item 3. “Legal Proceedings” and Item 12. “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for information on the dispute with Mr. Kopple regarding these exhibits. |
| In accordance with SEC Release 33-8238, Exhibit 32.1 and 32.2 are being furnished and not filed. |
| Furnished herewith. XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language) information is furnished and not filed or a part of a registration statement or prospectus for purposes of Sections 11 or 12 of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, is deemed not filed for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and otherwise is not subject to liability under these sections. |
None.
| 37 |
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15 (d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| AURA SYSTEMS, INC. | ||
| Dated: | September 18, 2017 | |
| By: | /s/ Melvin Gagerman | |
| Melvin Gagerman | ||
| Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the date indicated.
| Signatures | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Melvin Gagerman | Chief Executive Officer and Acting Chief Financial Officer | September 18, 2017 | ||
| Melvin Gagerman | (Principal Executive Officer, Principal
Financial Officer, Principal Accounting Officer) |
|||
| /s/ Salvador Diaz-Verson, Jr. | Director | September 18, 2017 | ||
| Salvador Diaz-Verson, Jr. | ||||
| Director | ||||
| Robert Kopple |
| 38 |
Index to Financial Statements
| F-1 |
 |
5757 W Century Blvd, Suite 303, Los Angeles, CA 90045
Tel +1(310) 568-1628 Fax +1(310) 410-0371 |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders
Aura Systems, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying balance sheets of Aura Systems, Inc. (a Delaware corporation), (the “Company”) as of February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, and the related statements of operations, stockholders' equity (deficit), and cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended February 28, 2017. The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audit included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Aura Systems, Inc. as of February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the two year period ended February 28, 2017 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As more fully described in Note 11 to the financial statements, the Company has historically incurred substantial losses from operations, and the Company may not have sufficient working capital or outside financing available to meet its planned operating activities over the next twelve months. These conditions raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans regarding these matters are described in Note 11. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of these uncertainties.

Los Angeles, California
September 11, 2017
| F-2 |
BALANCE SHEETS
| As of February 28, | As of February 29, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current assets: | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 255,869 | $ | 22,175 | ||||
| Accounts receivable, net | - | 2,115 | ||||||
| Other current assets | 2,894 | 16,282 | ||||||
| Total current assets | 258,763 | 40,572 | ||||||
| Deposits | 3,500 | 90,213 | ||||||
| Property, plant, and equipment, net | - | - | ||||||
| Total assets | $ | 262,263 | $ | 130,785 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT | ||||||||
| Current liabilities: | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 4,943,559 | $ | 1,823,776 | ||||
| Accrued expenses | 5,939,251 | 5,389,883 | ||||||
| Customer advances | 641,751 | 641,751 | ||||||
| Notes payable | 4,776,938 | 3,927,468 | ||||||
| Convertible note payable and accrued interest-related party, net of discount | 2,920,172 | - | ||||||
| Convertible notes payable, net of discount | 4,177,283 | 2,720,700 | ||||||
| Notes payable and accrued interest- related party | 29,669,693 | 26,869,911 | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | 53,068,647 | 41,373,489 | ||||||
| Convertible note payable, net of discount | - | 1,366,922 | ||||||
| Convertible note payable and accrued interest-related party, net of discount | - | 2,560,425 | ||||||
| Total liabilities | 53,068,647 | 45,300,836 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies | ||||||||
| Stockholders’ deficit: | ||||||||
| Common stock, $0.0001 par value; 150,000,000 shares authorized at February 28, 2017 and 2016; 113,991,432 and 113,041,432 issued and outstanding at February 28, 2017 and, 2016, respectively | 11,399 | 11,304 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 410,499,597 | 410,404,692 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (463,317,380 | ) | (455,586,047 | ) | ||||
| Total stockholders’ deficit | (52,806,384 | ) | (45,170,051 | ) | ||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit | $ | 262,263 | $ | 130,785 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-3 |
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
| For the Year ended February 28, 2017 | For the Year ended February 29, 2016 | |||||||
| Net revenues | $ | 0 | $ | 183,032 | ||||
| Cost of goods sold | 0 | 170,996 | ||||||
| Gross profit | 0 | 12,036 | ||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||
| Engineering, research and development | 34,210 | 395,727 | ||||||
| Selling, general, and administrative | 3,522,347 | 2,981,781 | ||||||
| Total operating expenses | 3,556,557 | 3,377,508 | ||||||
| Loss from operations | (3,556,557 | ) | (3,365,472 | ) | ||||
| Other income (expense): | ||||||||
| Interest expense, net | (4,246,831 | ) | (3,298,054 | ) | ||||
| Other income net | 72,055 | 58,559 | ||||||
| Total other expense | (4,174,776 | ) | (3,239,495 | ) | ||||
| Net Loss | $ | (7,731,333 | ) | $ | (6,604,967 | ) | ||
| Basic and diluted loss per share | $ | (0.07 | ) | $ | (0.06 | ) | ||
| *Weighted-average shares outstanding | 113,925,405 | 113,041,432 | ||||||
* Basic and diluted weighted average number of shares outstanding are equivalent because the effect of dilutive securities is anti-dilutive.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
| F-4 |
STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
FOR THE YEARS ENDED FEBRUARY 28, 2017 AND FEBRUARY 29, 2016
| Common Stock Shares | Common Stock Amount | Additional Paid-In Capital | Accumulated Deficit | Total Stockholders’ Deficit | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance, February 28, 2015 | 113,041,432 | $ | 11,304 | $ | 410,404,692 | $ | (448,981,080 | ) | $ | (38,565,084 | ) | |||||||||
| Net Loss | (6,604,967 | ) | (6,604,967 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Balance, February 29, 2016 | 113,041,432 | $ | 11,304 | $ | 410,404,692 | $ | (455,586,047 | ) | $ | (45,170,051 | ) | |||||||||
| Shares issued for note payable | 950,000 | 95 | 94,905 | 95,000 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net Loss | (7,731,333 | ) | (7,731,333 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance, February 28, 2017 | 113,991,432 | $ | 11,399 | $ | 410,499,597 | $ | (463,317,380 | ) | $ | (52,806,384 | ) | |||||||||
| F-5 |
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| For the Years Ended February 28, 2017 | For the Years Ended February 29, 2016 | |||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (7,731,333 | ) | $ | (6,604,967 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | - | 945 | ||||||
| Amortization of debt discount | 250,505 | 256,439 | ||||||
| Gain on settlement of debt | (70,288 | ) | - | |||||
| (Increase) decrease in: | ||||||||
| Accounts receivable | 2,115 | 56,842 | ||||||
| Other current assets | 100,101 | 54,239 | ||||||
| Increase (decrease) in: | ||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 6,483,111 | 4,351,074 | ||||||
| Customer advances | - | 177,684 | ||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | (965,790 | ) | (1,675,745 | ) | ||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||
| Purchase of property, plant, and equipment | - | - | ||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||
| Proceeds from notes payable | 999,470 | 459,410 | ||||||
| Proceeds from notes payable - related party | 200,014 | 1,203,654 | ||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 1,199,484 | 1,663,064 | ||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 233,694 | (12,680 | ) | |||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year | 22,175 | 34,855 | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of year | $ | 255,869 | $ | 22,175 | ||||
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | ||||||||
| Interest paid | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
| Income taxes paid | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
Supplemental schedule of non-cash financing and investing activities:
None
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
| F-6 |
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FEBRUARY 29, 2016
NOTE 1 - ORGANIZATION AND OPERATIONS
Aura Systems, Inc., (“Aura”, “We” or the “Company”) a Delaware corporation, was founded to engage in the development, commercialization, and sales of products, systems, and components, using its patented and proprietary electromagnetic technology. Aura develops and sells AuraGen® axial flux mobile induction power systems to the industrial, commercial, and defense mobile power generation markets. In addition, we also sell our developed and patented High Force Electromagnetic Linear Actuators.
NOTE 2 - SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s revenue recognition policies are in compliance with Staff accounting bulletin (SAB) 104. Sales revenue is recognized at the date of shipment to customers when a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and collect-ability is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are satisfied are recorded as unearned revenue.
We recognize revenue for product sales upon shipment and when title is transferred to the customer. When Aura performs the installation of the product, revenue and cost of sales are recognized when the installation is complete. We have in the past earned a portion of our revenues from license fees and recorded those fees as income when we fulfilled our obligations under the particular agreement.
Terms of our sales generally provide for Shipment from our facilities to customers FOB point of shipment. Title passes to customers at the time the products leave our warehouse.
The Company does not offer a general right of return on any of its sales and considers all sales as final. However, if a customer determines that a different system configuration would better suit their application, we will allow them to exchange the system and bill them the incremental cost, or credit them if there is a decrease in the system cost. While some sales are for evaluative purposes, they are still considered final sales. The customers’ evaluation is for them to determine if there is a benefit to them to outfit additional vehicles in their fleets.
The only potential post delivery obligation the Company might have is for the installation of the unit. However, the unit is typically delivered at the time of installation, and the billing is done when the installation is complete. Any discounts that are offered are done as a reduction of the invoiced amount at the time of billing. The Company does not utilize bill and hold. The Company does provide customers with a warranty; however, due to the low sales volume to date, the amount has not been material and is expensed as incurred.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and equivalents include cash on hand and cash in time deposits, certificates of deposit and all highly liquid debt instruments with original maturities of three months or less. We have not experienced any losses in such accounts and believe we are not exposed to any significant risk on cash and cash equivalents.
Accounts Receivable
The Company grants credit to its customers generally in the form of short-term trade accounts receivable. Accounts receivable are stated at the amount that management expects to collect from outstanding balances. When appropriate, management provides for probable uncollectible amounts through an allowance for doubtful accounts. Management primarily determines the allowance based on the aging of accounts receivable balances, historical write-off experience, customer concentrations, customer creditworthiness and current industry and economic trends. Balances that are still outstanding after management has used reasonable collection efforts are written off through a charge to the allowance for doubtful accounts and a credit to accounts receivable.
| F-7 |
Inventories
Inventories are valued at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out) or market, on a standard cost basis. We review the components of inventory on a regular basis for excess or obsolete inventory based on estimated future usage and sales. As further described in Note 3, due to historical reasons, we are holding inventories in excess of what we expect to sell in the next fiscal year. The Company has not operated and therefore has not produced product since late 2015. As a result, while the Company believes that a significant portion of the inventory has value, we are unable to substantiate its demand and market value and as a result have elected to reserve it in its entirety as of February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016.
Property, Plant, and Equipment
Property, plant, and equipment, including leasehold improvements, are recorded at cost, less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation is provided using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets as follows:
| Machinery and equipment | 5 to 10 years | |
| Furniture and fixtures | 7 years |
Improvements to leased property are amortized over the lesser of the life of the lease or the life of the improvements.
Maintenance and minor replacements are charged to expense as incurred. Gains and losses on disposals are included in the results of operations.
Patents and Trademarks
We capitalize the cost of obtaining or acquiring patents and trademarks. Amortization of patent and trademark costs is provided for by the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets.
Valuation of Long-Lived Assets
The Company accounts for the impairment of long-lived assets, such as fixed assets, patents and trademarks, under the provisions of Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification (“FASB ASC”) 360, “Property, Plant, and Equipment”, which establishes the accounting for impairment of long-lived tangible and intangible assets other than goodwill and for the disposal of a business. Pursuant to FASB ASC 360, we review for impairment when facts or circumstances indicate that the carrying value of long-lived assets to be held and used may not be recoverable. If such facts or circumstances are determined to exist, an estimate of the undiscounted future cash flows produced by the long-lived asset, or the appropriate grouping of assets, is compared to the carrying value to determine whether impairment exists. If an asset is determined to be impaired, the loss is measured based on various valuation techniques, including a discounted value of estimated future cash flows. We report impairment costs as a charge to operations at the time it is recognized. As of the year ended February 28, 2017, all long-lived assets have been fully depreciated.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company accounts for stock-based compensation under the provisions of FASB ASC 718, “Compensation – Stock Compensation”, which requires the measurement of all share-based payments to employees, including grants of employee stock options, using a fair value based method and the recording of such expense in the consolidated statements of operations.
The Company accounts for stock option and warrant grants issued and vesting to non-employees in accordance with FASB ASC 505-50, “Equity Based Payments to Non-Employees”, whereas the fair value of the equity based compensation is based upon the measurement date as determined at the earlier of either (a) the date at which a performance commitment is reached or (b) at the date at which the necessary performance to earn the equity instruments is complete.
| F-8 |
For the past several years and in accordance with established public company accounting practice, the Company has consistently utilized the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to calculate the fair value of stock options and warrants issued as compensation, primarily to management, employees, and directors. The Black-Scholes option-pricing model is a widely-accepted method of valuation that public companies typically utilize to calculate the fair value of options and warrants that they issue in such circumstances.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
We measure our financial assets and liabilities in accordance with the requirements of FASB ASC 825 “Financial Instruments”. The carrying values of accounts receivable, accounts payable, current notes payable, accrued expenses and other liabilities approximate fair value due to the short-term maturities of these instruments. The carrying amounts of long-term convertible notes payable approximate their respective fair values because of their current interest rates payable and other features of such debt in relation to current market conditions.
Shipping and handling expenses
We record all shipping and handling billings to a customer as revenue earned for the goods provided in accordance with FASB ASC 605-45-45-19, “Shipping and Handling Fees and Costs”. We include shipping and handling expenses in selling, general and administrative expense. Shipping and handling expenses amounted to $0 and $30,079 for the years ended February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, respectively.
Advertising Expense
Advertising costs are charged to expense as incurred and were immaterial for the years ended February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016.
Research and Development
Research and development costs are expensed as incurred. These costs include the expenses incurred in the development of products such as the 375amp ECU, the TanGen (dual generator), the eight inch generator, the 30 kW unit and the refrigeration system.
Income Taxes
We account for income taxes in accordance with FASB ASC 740, “Income Taxes”. Under FASB ASC 740, deferred income taxes are recognized for the tax consequences in future years of differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their financial statement reporting amounts at each period end based on enacted tax laws and statutory tax rates applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to affect taxable income. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized. The provision for income taxes represents the tax expense for the period, if any, and the change during the period in deferred tax assets and liabilities.
We have significant income tax net operating losses; however, due to the uncertainty of the realize-ability of the related deferred tax asset and other deferred tax assets, a valuation allowance equal to the amount of deferred tax assets has been established at February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016.
FASB ASC 740 also provides criteria for the recognition, measurement, presentation and disclosure of uncertain tax positions. A tax benefit from an uncertain position may be recognized only if it is “more likely than not” that the position is sustainable based on its technical merit.
| F-9 |
Earnings (Loss) per Share
We utilize FASB ASC 260, “Earnings per Share.” Basic earnings (loss) per share is computed by dividing earnings (loss) available to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted earnings (loss) per share is computed similar to basic earnings (loss) per share except that the denominator is increased to include additional common shares available upon exercise of stock options and warrants using the treasury stock method, except for periods of operating loss for which no common share equivalents are included because their effect would be anti-dilutive.
Estimates
The preparation of financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Major Customers
During the year ended February 28, 2017, we did not have any sales to customers. During the year ended February 29, 2016, we conducted business with two major customers whose sales comprised 55.9% and 22% of net sales, respectively. As of February 29, 2016, these customers accounted for more than 90% of net accounts receivable.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In April 2015, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2015-03, Interest–Imputation of Interest (Subtopic 835-30) (“ASU 2015-03”), which changes the presentation of debt issuance costs in financial statements. ASU 2015-03 requires an entity to present such costs in the balance sheet as a direct deduction from the related debt liability rather than as an asset. Amortization of the costs will continue to be reported as interest expense. It is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016. Early adoption is permitted. The new guidance will be applied retrospectively to each prior period presented. The Company is currently in the process of evaluating the impact of adoption of ASU 2015-03 on its balance sheets.
In January 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) 2016-01, which amends the guidance in U.S. GAAP on the classification and measurement of financial instruments. Changes to the current guidance primarily affect the accounting for equity investments, financial liabilities under the fair value option, and the presentation and disclosure requirements for financial instruments. In addition, the ASU clarifies guidance related to the valuation allowance assessment when recognizing deferred tax assets resulting from unrealized losses on available-for-sale debt securities. The new standard is effective for fiscal years and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2017, and upon adoption, an entity should apply the amendments by means of a cumulative-effect adjustment to the balance sheet at the beginning of the first reporting period in which the guidance is effective. Early adoption is not permitted except for the provision to record fair value changes for financial liabilities under the fair value option resulting from instrument-specific credit risk in other comprehensive income. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of adopting this guidance.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842) to increase transparency and comparability among organizations by recognizing lease assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet and disclosing key information about leasing arrangements. Topic 842 affects any entity that enters into a lease, with some specified scope exemptions. The guidance in this Update supersedes Topic 840, Leases. The core principle of Topic 842 is that a lessee should recognize the assets and liabilities that arise from leases. A lessee should recognize in the statement of financial position a liability to make lease payments (the lease liability) and a right-of-use asset representing its right to use the underlying asset for the lease term. For public companies, the amendments in this Update are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years. We are currently evaluating the impact of adopting ASU No. 2016-02 on our financial statements.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-08, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Principal versus Agent Considerations (Reporting Revenue Gross versus Net) that clarifies how to apply revenue recognition guidance related to whether an entity is a principal or an agent. ASU 2016-08 clarifies that the analysis must focus on whether the entity has control of the goods or services before they are transferred to the customer and provides additional guidance about how to apply the control principle when services are provided and when goods or services are combined with other goods or services. The effective date for ASU 2016-08 is the same as the effective date of ASU 2014-09 as amended by ASU 2015-14, for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those years. The Company has not yet determined the impact of ASU 2016-08 on its financial statements.
| F-10 |
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-09, Compensation – Stock Compensation, or ASU No. 2016-09. The areas for simplification in this Update involve several aspects of the accounting for share-based payment transactions, including the income tax consequences, classification of awards as either equity or liabilities, and classification on the statement of cash flows. For public entities, the amendments in this Update are effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those annual periods. Early adoption is permitted in any interim or annual period. If an entity early adopts the amendments in an interim period, any adjustments should be reflected as of the beginning of the fiscal year that includes that interim period. An entity that elects early adoption must adopt all of the amendments in the same period. Amendments related to the timing of when excess tax benefits are recognized, minimum statutory withholding requirements, forfeitures, and intrinsic value should be applied using a modified retrospective transition method by means of a cumulative-effect adjustment to equity as of the beginning of the period in which the guidance is adopted. Amendments related to the presentation of employee taxes paid on the statement of cash flows when an employer withholds shares to meet the minimum statutory withholding requirement should be applied retrospectively. Amendments requiring recognition of excess tax benefits and tax deficiencies in the income statement and the practical expedient for estimating expected term should be applied prospectively. An entity may elect to apply the amendments related to the presentation of excess tax benefits on the statement of cash flows using either a prospective transition method or a retrospective transition method. We are currently evaluating the impact of adopting ASU No. 2016-09 on our financial statements.
In April 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-10, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Identifying Performance Obligations and Licensing, which provides further guidance on identifying performance obligations and improves the operability and understandability of licensing implementation guidance. The effective date for ASU 2016-10 is the same as the effective date of ASU 2014-09 as amended by ASU 2015-14, for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those years. In May 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-12 “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) - Narrow-Scope Improvements and Practical Expedients,” which amends the guidance on transition, collectability, non-cash consideration, and the presentation of sales and other similar taxes. ASU 2016-12 clarifies that, for a contract to be considered completed at transition, all (or substantially all) of the revenue must have been recognized under legacy GAAP. In addition, ASU 2016-12 clarifies how an entity should evaluate the collectability threshold and when an entity can recognize nonrefundable consideration received as revenue if an arrangement does not meet the standard’s contract criteria. The standard allows for both retrospective and modified retrospective methods of adoption. The Company has not yet determined the impact of ASU 2016-10 on its financial statements.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, “Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Statements,” which requires companies to measure credit losses utilizing a methodology that reflects expected credit losses and requires consideration of a broader range of reasonable and supportable information to inform credit loss estimates. ASU 2016-13 is effective for annual reporting periods, and interim periods therein, beginning after December 15, 2019 (fiscal year 2021 for the Company). The Company has not yet determined the potential effects of the adoption of ASU 2016-13 on its Financial Statements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-15, “Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments,” which aims to eliminate diversity in practice in how certain cash receipts and cash payments are presented and classified in the statement of cash flows under Topic 230, Statement of Cash Flows, and other Topics. ASU 2016-15 is effective for annual reporting periods, and interim periods therein, beginning after December 15, 2017 (fiscal year 2019 for the Company). The Company has not yet determined the potential effects of the adoption of ASU 2016-15 on its Financial Statements.
| F-11 |
NOTE 3 - INVENTORIES
Inventories at February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016 consisted of the following:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Raw materials | $ | 1,872,720 | $ | 1,858,347 | ||||
| Finished goods | 1,568,188 | 1,558,554 | ||||||
| 3,440,908 | 3,416,901 | |||||||
| Inventory reserve | (3,440,908 | ) | (3,416,901 | ) | ||||
| Current portion | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | ||||
Inventories consist primarily of components and completed units for the Company’s AuraGen® product.
Early in our AuraGen® program, we determined it was most cost-effective to outsource production of components and subassemblies to volume-oriented manufacturers, rather than produce these parts in house. As a result of this decision, and based on then anticipated sales, we purchased, prior to fiscal 2001, a substantial inventory of components at volume prices, most of which was then assembled into finished AuraGen® units. Since sales did not meet such expectations, we have been selling product from this inventory for several years. Management has analyzed its inventories based on its current business plan, current potential orders for future delivery, and pending proposals with prospective customers and has determined we do not expect to realize all of its inventories within the next year. As described in Note 2 above while the Company believes the inventory has significant value it has elected to fully reserve the inventory due to the inability of determining the demand and, therefore, fair market value at February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016.
NOTE 4 - OTHER CURRENT ASSETS
Other current assets of $2,895 and $16,283 are primarily comprised of vendor advances of $2,895 and $16,283 as of February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, respectively.
NOTE 5 - PROPERTY, PLANT, AND EQUIPMENT
Property, plant, and equipment at February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016 consists of the following:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Machinery and equipment | $ | 964,111 | $ | 964,111 | ||||
| Furniture and fixtures | 163,302 | 163,302 | ||||||
| 1,127,413 | 1,127,413 | |||||||
| Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | (1,127,413 | ) | (1,127,413 | ) | ||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
Depreciation and amortization expense was $0 and $945 for the years ended February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, respectively.
| F-12 |
NOTE 6 - NOTES PAYABLE
Notes payable consisted of the following:
| February 28, 2017 | February 29, 2016 | |||||||
| Demand notes payable, at 10% and 16% | $ | 3,782,468 | $ | 3,927,468 | ||||
| Convertible Promissory Note dated August 10, 2012, due August 10, 2017, convertible into shares of our common stock at a price of $0.76 per share. The note carries an interest rate of 7% with interest only payments due on the 10th of each month with the principal payment due on the maturity date. | 972,632 | 910,488 | ||||||
| Convertible Promissory Note dated October 2, 2012, due October 2, 2017, convertible into shares of our common stock at a price of $0.76 per share. The note carries an interest rate of 7% with interest only payments due on the 2nd of each month with the principal payment due on the maturity date. | 483,951 | 456,434 | ||||||
| Senior secured convertible notes dated May 7, 2013, due May 7, 2014, convertible into shares of our common stock at a price of $0.75 per share. The notes carry an interest rate of 12% with interest due on the last day of the month. The note was not repaid when originally due. | 2,395,700 | 2,395,700 | ||||||
| Senior secured convertible notes dated June 20, 2013, due June 20, 2014, convertible into shares of our common stock at a price of $0.50 per share. The note was not repaid when originally due. | 325,000 | 325,000 | ||||||
| Convertible notes dated April 2016 thru February 2017. The notes carry an interest rate of 5% and might be converted into the company shares of common if the shareholders approve a 7:1 reverse stock split. | 994,470 | - | ||||||
| 8,994,221 | 8,015,090 | |||||||
| Less: Current portion | $ | 8,994,221 | $ | 6,648,168 | ||||
| Long-term portion | $ | - | $ | 1,366,922 | ||||
CONVERTIBLE DEBT
On May 7, 2013, the Company transferred 4 notes payable with a total principal value of $1,000,000 together with accrued interest, and consulting fees to a senior secured convertible note with a principal value of $1,087,000 and warrants to Kenmont Capital Partners. This new note has a 1-year maturity date and is convertible into shares of common stock at the conversion price of $0.75 per share. The warrants entitle the holder to acquire 1,449,333 shares of common stock, have an initial exercise price of $0.75 per share, and have a 7-year term. The Company recorded $342,020 as a discount, which will be amortized over the life of the note.
On May 7, 2013, the Company transferred 2 note payables with a total principal value of $550,000 together with accrued interest to a senior secured convertible note with a principal value of $558,700 and warrants to LPD Investments, Ltd. This new note has a 1-year maturity date and is convertible into shares of common stock at the conversion price of $0.75 per share. The warrants entitle the holder to acquire 744,933 shares of common stock, have an initial exercise price of $0.75 per share, and have a 7-year term. The Company recorded $175,793 as a discount, which will be amortized over the life of the note.
On May 7, 2013, the Company entered into an agreement with an individual for the sale of a secured convertible note payable in the original principal amount of $750,000 and warrants. This note has a 1-year maturity date and is convertible into shares of common stock at the conversion price of $0.75 per share. The warrants entitle the holder to acquire 1,000,000 shares of common stock, have an initial exercise price of $0.75 per share, and have a 7-year term. The Company recorded $235,985 as a discount, which will be amortized over the life of the note.
On June 20, 2013, the Company entered into an agreement with four individuals for the sale of secured convertible notes payable in the original amount of $325,000 and warrants. These Notes have a 1-year maturity date and are convertible into shares of common stock at the conversion price of $0.50 per share. The warrants entitle the holders to acquire 433,334 shares of common stock, have an initial exercise price of $0.75 per share, and have a 7-year term. The Company recorded $63,622 as a discount, which will be amortized over the life of the notes.
On August 19, 2013, the Company entered into an agreement with a member of its Board of Directors for the sale of $2,500,000 of unsecured convertible notes payable and warrants. These notes carry a base interest rate of 9.5%, have a 4-year maturity date and are convertible into shares of common stock at the conversion price of $0.50 per share. The warrants entitle the holder to acquire 5,000,000 shares of common stock, have an initial exercise price of $0.75 per share and have a 7-year term. The Company recorded $667,118 as a discount, which will be amortized over the life of the note.
All convertible notes payable are due within twelve months or have not been paid when originally due.
| F-13 |
CONVERTIBLE PROMISSORY NOTES
At February 28, 2013, the three other unsecured convertible promissory notes payable amounted to $1,447,938, net of discounts of $402,063. These convertible notes bear interest at 7% per annum, and are convertible into common stock of the Company at $0.76 per share (as well as variable conversion rates as described below). These notes are due on August 10, 2017, October 2, 2017, and January 4, 2013. On May 7, 2013, the note due on January 4, 2013 was converted into a portion of the note due June 15, 2013, which carries an interest rate of 12%.
7% Convertible Promissory Notes:
On August 10, 2012 the Company entered into an agreement with an individual for the sale of an unsecured convertible promissory note in the original principal amount of $1,000,000. This convertible promissory note is due and payable on August 10, 2017 and bears a interest rate is 7% per annum. Interest on the unpaid principal amount of this note is payable monthly in arrears on the tenth day of each calendar month commencing September 10, 2012. Interest is computed on the actual number of days elapsed over a 360-day year. The Holder has the right to convert any outstanding and unpaid principal portion of this convertible promissory note into shares of common stock. The company recorded $310,723 as a debt discount, which will be amortized over the life of the note.
On October 2, 2012 the Company entered into an agreement with an individual for the sale of an unsecured convertible promissory note in the original principal amount of $500,000. This convertible promissory note is due and payable on October 2, 2017 and bears an interest rate is 7% per annum. Interest on the unpaid principal amount of this note is payable monthly in arrears on the second day of each calendar month commencing November 2, 2012. Interest is computed on the actual number of days elapsed over a 360-day year. The Holder has the right to convert any outstanding and unpaid principal portion of this convertible promissory note into shares of common stock. The company recorded $137,583 as a debt discount, which will be amortized over the life of the note.
On January 30, 2017 the Company entered into an agreement entitled First Amendment to Transaction Documents with five of seven of its secured creditors. These creditors hold a security interest in all of the Company’s assets except for its patents and other intellectual properties. The original agreement dated May 7, 2013 provided that if the holders of at least 75% of the stock issuable upon conversion of the convertible notes votes to amend the agreement, then such amendments will be binding on all the secured creditors. The five secured creditors signing the amendment total in excess of 95% of the issuable stock upon conversion and, therefore the agreement is binding on all seven of the secured creditors. The amended agreement provided that all accrued and unpaid interest will be added to the principal amount, the amended note will bear no interest from November 1, 2016 to May 1, 2016 and 16% per annum thereafter. Upon stockholder approval of a 1-for-7 reverse stock split and the election of a new Board of Directors, 80% of the total secured debt, including accrued interest, will be converted into shares of common stock; a new five-year unsecured convertible promissory note bearing 5% interest per annum will be issued for the remaining 20% balance. The amended note also provides for early payoff under certain conditions and contains various default provisions. The agreement was further amended subsequent to year end to extend the time for the Company to file a preliminary proxy statement.
On February 21, 2017 the Company entered into debt refinancing agreements with several debt holder relating to aggregate unsecured debt totaling $2,237,456 including interest of $489,466. This refinancing agreements waives any past events of default and provides for new five-year convertible notes which bear no interest for the first six months and 5% annually thereafter. Upon stockholder approval of a 1-for-7 reverse stock split, these notes will be converted into a total of 1,164,555 shares of common stock. The notes also provide various default provisions.
As of February 28, 2017, the shareholders have not approved any reverse stock split.
| F-14 |
NOTE 7 - RELATED PARTIES TRANSACTIONS
On January 24, 2017 the Company entered into a Debt Refinancing Agreement with Mr. Breslow, a Director of the Company. Pursuant to this agreement, both Mr. Breslow and the Company acknowledged that total debt owed to Mr. Breslow was $23,872,614 including $8,890,574 of accrued interest. Mr. Breslow agreed to cancel and forgive all interest due, waive any past events of default and sign a new, five-year unsecured convertible note, in the amount of $14,930,041. This new note bears no interest for the first six months and interest of 5% per annum thereafter, payable monthly in arrears. This new note also provides various default provisions. The refinancing agreement further provides that $11,982,041 of Mr. Breslow’s new note will be converted into 7,403,705 shares of common stock upon stockholder approval of a 1-for-7 reverse stock split within one year of entering into that agreement; the remaining balance may thereafter be converted at any time. In the absence of stockholder approval of a 1-for-7 reverse stock split within one year, the refinancing agreement will become null and void. The Company has elected to continue to accrue interest on this agreement until such time as the 1-for-7 reverse stock split has been approved. As of February 28, 2017, the shareholders have not approved the reverse stock split.
At February 28, 2017, the balance in Notes Payable and accrued interest-related party, current, includes $14,982,041 of unsecured notes payable plus accrued interest of $8,890,574 to Mr. Breslow, a member of our Board of Directors, payable on demand, bearing interest at a rate of 10% per annum. The balance of $14,880,372 plus accrued interest of $7,680,164 as of February 29, 2016. During the years ended February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, interest amounting to $993,647 and $1,459,374 respectively, was incurred on these notes. Related Parties Transactions also includes $82,000 of unsecured notes payable plus accrued interest of $29,141 and $23,704 to our CEO pursuant to a demand note entered into on April 5, 2014and an unsecured note payable to Mr. Kopple, another member of our Board of Directors in the total amount of $3,587,322 and $3,418,738 plus accrued interest of $2,098,616 and $784,934 pursuant to 10% demand note payable as of February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, respectively. At February 28, 2017, the balance in Convertible note payable and accrued interest-related party, long term, includes $2,000,000 of secured convertible notes payable plus accrued interest of $920,172 to Mr. Kopple.
NOTE 8 - ACCRUED EXPENSES
Accrued expenses at February 28, 2017 and February 28, 2016 consisted of the following:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Accrued payroll and related expenses | $ | 3,099,842 | $ | 3,148,841 | ||||
| Accrued rent | 202,036 | 218,025 | ||||||
| Accrued interest | 2,562,375 | 1,933,017 | ||||||
| Other | 75,000 | 90,000 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 5,939,252 | $ | 5,389,883 | ||||
Accrued payroll and related expenses consists of salaries and vacation time accrued but not paid to employees due to our lack of financial resources.
| F-15 |
NOTE 9 - COMMITMENTS & CONTINGENCIES
Leases
In September, 2014, we entered into lease for a facility of approximately 69,000 square feet. The lease is for a term of seven years, has an option to extend for five years, and carries an initial base rent of $46,871.72. In accordance with the terms of the lease, the Company is responsible for common area charges. Rent expense charged to operations amounted to $674,876and $603,440 for the years ended February 29,2016 and February 28, 2015, respectively. The Company moved out of the facility in June 2015 to a much smaller facility in Stanton California. In the new Stanton California facility, the Company is on a month-to-month lease. During the next 12 months, the Company plans to move to a new, larger facility.
Joint Venture
On January 27, 2017, the Company entered into a joint venture (JV) agreement with a Chinese company to manufacture, market and distribute certain mobile power products based on Aura’s patented technology solely for the Peoples Republic of China territories. The JV is owned 49% by the Company and 51% by the Chinese company. The Company has contributed $250,000 and a license to specific technology and the Chinese company is required to contribute $9,750,000. In addition, the Chinese company will invest $2,000,000 in Aura at $0.20 per share for a total of 10,000,000 shares of common stock. Additionally, the Chinese company will purchase a minimum of $1,250,000 of product supported by letters of credit for distribution until the joint venture factory is built, equipped, and staffed. In order to assure proper training of joint venture personnel, Aura has also committed to supply instructional personnel for six months at no cost other than reimbursement for travel, room and board. The agreement was subject to the approval of the Chinese Government which was received in April, 2017.
Contingencies
We are subject to the legal proceedings and claims discussed below as well as certain other legal proceedings and claims that have not been fully resolved and that have arisen in the ordinary course of business. Our management evaluates our exposure to these claims and proceedings individually and in the aggregate and evaluates potential losses on such litigation if the amount of the loss is estimable and the loss is probable. However, the outcome of legal proceedings and claims brought against the Company is subject to significant uncertainty. Although management considers the likelihood of such an outcome to be remote, if one or more of these legal matters were resolved against the Company for amounts in excess of management’s expectations, the Company’s consolidated financial statements for that reporting period could be materially adversely affected. The Company settled certain matters subsequent to year end that did not individually or in the aggregate have a material impact on the Company’s financial condition or operating results.
Subsequent to year end, the Company was sued in 2016 by a former employee for a work-related injury. The plaintiff is seeking $45,000. The Company has made the plaintiff a settlement offer which, as of the date of this filing, has not been accepted.
Subsequent to year end, the Company was sued by a customer for an alleged failure to partially deliver against an advanced payment of approximately $120,000. The Company has made the plaintiff a settlement offer which, as of the date of this filing, has not been accepted.
Subsequent to year end, the Company’s former COO has been awarded approximately $238,000 in accrued salary and related charges by the California labor board. The Company has made the plaintiff a settlement offer which, as of the date of this filing, has not been accepted.
Subsequent to year end, the Company and the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, Melvin Gagerman, are among several defendants named in a lawsuit filed by two secured creditors demanding repayment of loans totaling $125,000 plus accrued interest and exemplary damages. In January 2017, the Company entered into an agreement with all secured creditors other than the two plaintiffs which became binding on all of the secured creditors, including the two plaintiffs. That agreement, among other provisions, waives all past events of default. It is the Company’s position that the two plaintiffs are not entitled to any payment or other relief at this time and therefore that they have no valid claim against the Company or Mr. Gagerman. In March 2017, plaintiffs moved for partial summary adjudication against the Company and Mr. Gagerman which was denied by the Court. Thereafter, the Court sustained demurrers by Mr. Gagerman and the Company but granted plaintiffs leave to amend. In response to the plaintiffs’ second amended complaint, both the Company and Mr. Gagerman intend to further demurrer seeking dismissal of this action.
In June 2015, the landlord of the Company’s primary facility in Redondo Beach, California initiated litigation against us seeking to terminate the Company’s lease and require the Company to vacate the premises prior to the scheduled lease end. As a result of that litigation, the Company was forced to vacate its primary facility and relocate to its present facility in Stanton, California. To date, no action seeking damages or any other amount has been filed against the Company by the landlord, nor does the Company believe it has any further liability to the landlord.
| F-16 |
NOTE 10 - STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
Common Stock
At February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, we had 150,000,000 shares of $0.0001 par value common stock authorized for issuance. During the year ended February 28, 2017 we issued 950,000 shares of common stock in settlement of a note payable in the amount of $150,000 plus accrued interest of $15,288. During the year ended February 29, 2016, we did not issue any shares of common stock.
Employee Stock Options
In September, 2006, our Board of Directors adopted the 2006 Employee Stock Option Plan, subject to shareholder approval, which was obtained at a special shareholders meeting in 2011. Under the Plan, the Company may grant options for up to the greater of Three Million (3,000,000) or 10% of the number of shares of the Common Stock of Aura from time to time outstanding. The exercise price of each option shall be at least equal to the fair market value of such shares on the date of grant. The term of the options may not be greater than ten years, and they typically vest over a three-year period.
During the year ended February 28, 2017, no employee options were granted by the Company.
The Company incurred stock options related expenses of $0 and $0, during the years ended February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, respectively.
Activity in this plan is as follows:
| 2006 Plan | ||||||||||||
| Weighted-Average Exercise Price | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | Number of Options | ||||||||||
| Outstanding, February 28, 2015 | $ | 0.75-$1.00 | $ | 0.00 | 7,777,000 | |||||||
| Granted | - | - | ||||||||||
| Cancelled | $ | 0.75 | (553,000 | ) | ||||||||
| Outstanding, February 29, 2016 | $ | 0.75-$1.00 | $ | 0.00 | 7,224,000 | |||||||
| Granted | - | - | ||||||||||
| Cancelled | $ | 0.75 | - | |||||||||
| Outstanding, February 28, 2017 | $ | 0.75-$1.00 | 7,224,000 | |||||||||
The exercise prices for the options outstanding at February 28, 2017, and information relating to these options is as follows:
| Options Outstanding | Exercisable Options | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Range of Exercise Price | Number | Weighted Average Remaining Life | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Weighted Average Remaining Life | Number | Weighted Average Exercise Price | ||||||||||||||||
| $0.75-$1.00 | 7,224,000 | 3 years | $ | 0.79 | 3 years | 7,224,000 | $ | 0.79 | ||||||||||||||
The weighted average fair values of the options on the date of grant for the year ended February 29, 2016 and February 28, 2015 were nil per share and $0.0 per share, respectively.
| F-17 |
Warrants
Activity in issued and outstanding warrants is as follows:
| Number of Shares | Exercise Prices | |||||||
| Outstanding, February 29, 2016 | 35,626,208 | $ | 0.10-$1.50 | |||||
| Granted | - | - | ||||||
| Exercised | - | - | ||||||
| Expired | (9,172,187 | ) | $ | 1.50 | ||||
| Outstanding, February 28, 2017 | 26,454,021 | $ | 0.10-$1.00 | |||||
The exercise prices for the warrants outstanding at February 28, 2017, and information relating to these warrants is as follows:
| Range of Exercise Prices | Stock Warrants Outstanding | Stock Warrants Exercisable | Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Life | Weighted-Average Exercise Price of Warrants Outstanding | Weighted-Average Exercise Price of Warrants Exercisable | Intrinsic Value | ||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 0.10-$0.75 | 18,381,012 | 18,381,012 | 49 months | $ | 0.56 | $ | 0.56 | $ | 0.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| $ | 0.75 | 1,082,734 | 1,082,734 | 48 months | $ | 0.75 | $ | 0.75 | $ | 0.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| $ | 0.75 | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 38 months | $ | 0.75 | $ | 0.75 | $ | 0.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| $ | 0.75-$1.00 | 5,990,275 | 5,990,275 | 33 months | $ | 0.77 | $ | 0.77 | $ | 0.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| 26,454,021 | 26,454,021 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTE 11 - GOING CONCERN
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. During the years ended February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, the Company incurred losses of $7,731,333 and $6,604,967, respectively and had negative cash flows from operating activities of $965,790 and $1,675,745, respectively.
If the Company is unable to generate profits and is unable to continue to obtain financing for its working capital requirements, it may have to curtail its business sharply or cease business altogether.
Substantial additional capital resources will be required to fund continuing expenditures related to our research, development, manufacturing and business development activities. The Company’s continuation as a going concern is dependent upon its ability to generate sufficient cash flow to meet its obligations on a timely basis, to retain its current financing, to obtain additional financing, and ultimately to attain profitability.
During the next twelve months we intend to restart operations of our AuraGen/VIPER business both domestically and internationally. At the next shareholders meeting the shareholders will vote for an entire new slate of five board candidates. The new board when elected will hire a new management team. In addition, we plan to acquire a new facility of approximately 45,000 square feet for operations, as well as, rebuild the engineering QA and sales teams to support the operation. We anticipate being able to fund these additions in the upcoming fiscal year.
NOTE 12 - INCOME TAXES
The Company did not record any income tax expense due to the net loss during the years ended February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016. The actual tax benefit differs from the expected tax benefit computed by applying the combined United States corporate tax rate and the State of California tax rate of 40% to loss before income taxes as follows for the years ended February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Current: | ||||||||
| Federal | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
| State | 800 | 800 | ||||||
| Total | 800 | 800 | ||||||
| Deferred | ||||||||
| Federal | - | - | ||||||
| State | - | - | ||||||
| Total | - | - | ||||||
| Total Income Tax Provision | $ | 800 | $ | 800 | ||||
| F-18 |
The provision for income tax is included with other expense in the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Expected tax benefit | 34.0 | % | 34.0 | % | ||||
| State income taxes, net of federal benefit | 6.0 | 6.0 | ||||||
| Changes in valuation allowance | (40.0 | ) | (40.0 | ) | ||||
| Total | - | % | - | % | ||||
The following table summarizes the significant components of our deferred tax asset at February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Deferred tax asset | ||||||||
| Primarily relating to net operating loss carry-forwards, but also reserves for inventory and accounts receivable, stock-based compensation and other | 115,000,000 | 113,000,000 | ||||||
| Valuation allowance | (115,000,000 | ) | (113,000,000 | ) | ||||
| Net deferred tax asset | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
We recorded an allowance of 100% for deferred tax assets due to the uncertainty of its realization.
At February 28, 2017, we had operating loss carry-forwards of approximately $338,000,000 for federal purposes, which expire through 2037, and $55,000,000 for state purposes, which expire through 2022.
We follow FASB ASC 740 related to uncertain tax positions. Under FASB ASC 740, the impact of an uncertain tax position on the income tax return must be recognized at the largest amount that is more-likely-than-not to be sustained upon audit by the relevant taxing authority. An uncertain income tax position will not be recognized if it has less than a 50% likelihood of being sustained. At February 29, 2016 and February 28, 2015, we have no unrecognized tax benefits.
Our continuing practice is to recognize interest and/or penalties related to income tax matters in income tax expense. As of February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, we have no accrued interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions.
We are subject to taxation in the U.S. and California. Our tax years for 2012 and forward are subject to examination by our tax authorities. We are not currently under examination by any tax authority.
NOTE 13 - EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS
We sponsor two employee benefit plans: The Employee Stock Ownership Plan (the “ESOP”) and a 401(k) plan.
The ESOP is a qualified discretionary employee stock ownership plan that covers substantially all employees. We did not make any contributions to the ESOP during the years ended February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, respectively.
| F-19 |
We sponsor a voluntary, defined contribution 401(k) plan. The plan provides for salary reduction contributions by employees and matching contributions by us of 100% of the first 4% of the employees’ pre-tax contributions. The matching contributions included in expense were $0 and $0 for the years ended February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016, respectively.
NOTE 14 - SEGMENT INFORMATION
We are a United States based company providing advanced technology products to various industries. The principal markets for our products are North America, Europe, and Asia. All of our operating long-lived assets are located in the United States. We operate in one segment.
Total net revenues from customer geographical segments are as follows for the years ended February 28, 2017 and February 29, 2016:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| United States | $ | - | $ | 13,341 | ||||
| Canada | 2,800 | |||||||
| Europe | 210 | |||||||
| Other | 55,979 | |||||||
| Asia | 137,384 | |||||||
| Total | $ | - | $ | 183,032 | ||||
NOTE 15 - SUBSEQUENT EVENTS:
The Company is presently engaged in a dispute with one of its directors, Robert Kopple, relating to approximately $5.4 million and approximately 22 million warrants which Mr. Kopple claims to be owed to him and his affiliates by the Company. In July 2017, Mr. Kopple filed suit against the Company as well as against current Directors Mr. Gagerman and Mr. Diaz-Verson together with former Directors Mr. Breslow and Mr. Howsmon in connection with these allegations. The Company believes that it has valid defenses in these matters and intends to vigorously defend against these claims.
F-20
