Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.2 - EX-32.2 - Snap-on Inc | d308837dex322.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - Snap-on Inc | d308837dex321.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - Snap-on Inc | d308837dex312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - Snap-on Inc | d308837dex311.htm |
| EX-23 - EX-23 - Snap-on Inc | d308837dex23.htm |
| EX-21 - EX-21 - Snap-on Inc | d308837dex21.htm |
| EX-12 - EX-12 - Snap-on Inc | d308837dex12.htm |
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016, or
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission File Number 1-7724

(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 39-0622040 | |
| (State of incorporation) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| 2801 80th Street, Kenosha, Wisconsin | 53143 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip code) |
(262) 656-5200
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class |
Name of each exchange on which registered | |
| Common stock, $1.00 par value | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in a definitive proxy or information statement incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer ☒ Accelerated filer ☐ Non-accelerated filer ☐ Smaller reporting company ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates (excludes 503,411 shares held by directors and executive officers) computed by reference to the price ($158.00) at which common equity was last sold as of the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter (July 2, 2016) was $9.1 billion.
The number of shares of Common Stock ($1.00 par value) of the registrant outstanding as of February 3, 2017, was 57,970,318 shares.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K incorporates by reference certain information that will be set forth in Snap-on’s Proxy Statement, which is expected to first be mailed to shareholders on or about March 10, 2017, prepared for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders scheduled for April 27, 2017.
Table of Contents
| Page | ||||||||
| PART I | ||||||||
| Item 1 |
4 | |||||||
| Item 1A |
12 | |||||||
| Item 1B |
19 | |||||||
| Item 2 |
19 | |||||||
| Item 3 |
21 | |||||||
| Item 4 |
21 | |||||||
| PART II | ||||||||
| Item 5 |
21 | |||||||
| Item 6 |
25 | |||||||
| Item 7 |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
26 | ||||||
| Item 7A |
54 | |||||||
| Item 8 |
56 | |||||||
| Item 9 |
Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
56 | ||||||
| Item 9A |
56 | |||||||
| Item 9B |
58 | |||||||
| PART III | ||||||||
| Item 10 |
58 | |||||||
| Item 11 |
59 | |||||||
| Item 12 |
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
59 | ||||||
| Item 13 |
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
60 | ||||||
| Item 14 |
60 | |||||||
| PART IV | ||||||||
| Item 15 |
60 | |||||||
| Item 16 |
60 | |||||||
| 110 | ||||||||
| 112 | ||||||||
| 115 | ||||||||
| 119 | ||||||||
| 120 | ||||||||
| 2 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
PART I
Safe Harbor
Statements in this document that are not historical facts, including statements that (i) are in the future tense; (ii) include the words “expects,” “plans,” “targets,” “estimates,” “believes,” “anticipates,” or similar words that reference Snap-on Incorporated (“Snap-on” or “the company”) or its management; (iii) are specifically identified as forward-looking; or (iv) describe Snap-on’s or management’s future outlook, plans, estimates, objectives or goals, are forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Snap-on cautions the reader that any forward-looking statements included in this document that are based upon assumptions and estimates were developed by management in good faith and are subject to risks, uncertainties or other factors that could cause (and in some cases have caused) actual results to differ materially from those described in any such statement. Accordingly, forward-looking statements should not be relied upon as a prediction of actual results or regarded as a representation by the company or its management that the projected results will be achieved. For those forward-looking statements, Snap-on cautions the reader that numerous important factors, such as those listed below, as well as those factors discussed in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, particularly those in “Item 1A: Risk Factors,” could affect the company’s actual results and could cause its actual consolidated results to differ materially from those expressed in any forward-looking statement made by, or on behalf of, Snap-on.
These risks and uncertainties include, without limitation, uncertainties related to estimates, statements, assumptions and projections generally, and the timing and progress with which Snap-on can attain value through its Snap-on Value Creation Processes, including its ability to realize efficiencies and savings from its rapid continuous improvement and other cost reduction initiatives, improve workforce productivity, achieve improvements in the company’s manufacturing footprint and greater efficiencies in its supply chain, and enhance machine maintenance, plant productivity and manufacturing line set-up and change-over practices, any or all of which could result in production inefficiencies, higher costs and/or lost revenues. These risks also include uncertainties related to Snap-on’s capability to implement future strategies with respect to its existing businesses, its ability to refine its brand and franchise strategies, retain and attract franchisees, further enhance service and value to franchisees and thereby help improve their sales and profitability, introduce successful new products, successfully pursue, complete and integrate acquisitions, as well as its ability to withstand disruption arising from natural disasters, planned facility closures or other labor interruptions, the effects of external negative factors, including adverse developments in world financial markets, weakness in certain areas of the global economy (including as a result of the United Kingdom’s vote to exit the European Union), and significant changes in the current competitive environment, inflation, interest rates and other monetary and market fluctuations, changes in tax rates and regulations, and the impact of energy and raw material supply and pricing, including steel and gasoline, the amount, rate and growth of Snap-on’s general and administrative expenses, including health care and postretirement costs (resulting from, among other matters, U.S. health care legislation and its ongoing implementation or reform), continuing and potentially increasing required contributions to pension and postretirement plans, the impacts of non-strategic business and/or product line rationalizations, and the effects on business as a result of new legislation, regulations or government-related developments or issues, risks associated with data security and technological systems and protections, and other world or local events outside Snap-on’s control, including terrorist disruptions. Snap-on disclaims any responsibility to update any forward-looking statement provided in this document, except as required by law.
In addition, investors should be aware that generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“GAAP”) prescribe when a company should reserve for particular risks, including litigation exposures. Accordingly, results for a given reporting period could be significantly affected if and when a reserve is established for a major contingency. Reported results, therefore, may appear to be volatile in certain accounting periods.
Fiscal Year
Snap-on’s fiscal year ends on the Saturday that is on or nearest to December 31. Unless otherwise indicated, references in this document to “fiscal 2016” or “2016” refer to the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016; references to “fiscal 2015” or “2015” refer to the fiscal year ended January 2, 2016; and references to “fiscal 2014” or “2014” refer to the fiscal year ended January 3, 2015. Snap-on’s 2016 and 2015 fiscal years each contained 52 weeks of operating results; Snap-on’s 2014 fiscal year contained 53 weeks of operating results. References in this document to 2016, 2015 and 2014 year end refer to December 31, 2016, January 2, 2016, and January 3, 2015, respectively.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 3 |
Table of Contents
Snap-on was incorporated under the laws of the state of Wisconsin in 1920 and reincorporated under the laws of the state of Delaware in 1930. Snap-on is a leading global innovator, manufacturer and marketer of tools, equipment, diagnostics, repair information and systems solutions for professional users performing critical tasks. Products and services include hand and power tools, tool storage, diagnostics software, information and management systems, shop equipment and other solutions for vehicle dealerships and repair centers, as well as for customers in industries, including aviation and aerospace, agriculture, construction, government and military, mining, natural resources, power generation and technical education. Snap-on also derives income from various financing programs designed to facilitate the sales of its products and support its franchise business.
Snap-on markets its products and brands worldwide through multiple sales distribution channels in more than 130 countries. Snap-on’s largest geographic markets include the United States, Europe, Canada and Asia/Pacific. Snap-on reaches its customers through the company’s franchisee, company-direct, distributor and internet channels. Snap-on originated the mobile tool distribution channel in the automotive repair market.
The company began with the development of the original Snap-on interchangeable socket set in 1920 and subsequently pioneered mobile tool distribution in the automotive repair market, where fully stocked vans sell to professional vehicle technicians at their place of business. Today, Snap-on defines its value proposition more broadly, extending its reach “beyond the garage” to deliver a broad array of unique solutions that make work easier for serious professionals performing critical tasks. The company’s “coherent growth” strategy focuses on developing and expanding its professional customer base in its legacy automotive market, as well as in adjacent markets, additional geographies and other areas, including in critical industries, where the cost and penalties for failure can be high. In addition to its coherent growth strategy, Snap-on is committed to its “Value Creation Processes” – a set of strategic principles and processes designed to create value and employed in the areas of (i) safety; (ii) quality; (iii) customer connection; (iv) innovation; and (v) rapid continuous improvement (“RCI”). Snap-on’s RCI initiatives employ a structured set of tools and processes across multiple businesses and geographies intended to eliminate waste and improve operations. Savings from Snap-on’s RCI initiatives reflect benefits from a wide variety of ongoing efficiency, productivity and process improvements, including savings generated from product design cost reductions, improved manufacturing line set-up and change-over practices, lower-cost sourcing initiatives and facility consolidations.
Snap-on’s primary customer segments include: (i) commercial and industrial customers, including professionals in critical industries and emerging markets; (ii) professional vehicle repair technicians who purchase products through the company’s worldwide mobile tool distribution network; and (iii) other professional customers related to vehicle repair, including owners and managers of independent and original equipment manufacturer (“OEM”) dealership service and repair shops (“OEM dealerships”). Snap-on’s Financial Services customer segment includes: (i) franchisees’ customers and certain other customers of Snap-on who require financing for the purchase or lease of tools and diagnostics and equipment products on an extended-term payment plan; and (ii) franchisees who require financing for business loans and vehicle leases.
Snap-on’s business segments are based on the organization structure used by management for making operating and investment decisions and for assessing performance. Snap-on’s reportable business segments are: (i) the Commercial & Industrial Group; (ii) the Snap-on Tools Group; (iii) the Repair Systems & Information Group; and (iv) Financial Services. The Commercial & Industrial Group consists of business operations serving a broad range of industrial and commercial customers worldwide, including customers in the aerospace, natural resources, government, power generation, transportation and technical education market segments (collectively, “critical industries”), primarily through direct and distributor channels. The Snap-on Tools Group consists of business operations primarily serving vehicle service and repair technicians through the company’s worldwide mobile tool distribution channel. The Repair Systems & Information Group consists of business operations serving other professional vehicle repair customers worldwide, primarily owners and managers of independent repair shops and OEM dealerships, through direct and distributor channels. Financial Services consists of the business operations of Snap-on Credit LLC (“SOC”), the company’s financial services business in the United States, and Snap-on’s other financial services subsidiaries in those international markets where Snap-on has franchise operations. See Note 18 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on business segments and foreign operations.
| 4 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Snap-on evaluates the performance of its operating segments based on segment revenues, including both external and intersegment net sales, and segment operating earnings. Snap-on accounts for intersegment sales and transfers based primarily on standard costs with reasonable mark-ups established between the segments. Identifiable assets by segment are those assets used in the respective reportable segment’s operations. Corporate assets consist of cash and cash equivalents (excluding cash held at Financial Services), deferred income taxes and certain other assets. All significant intersegment amounts are eliminated to arrive at Snap-on’s consolidated financial results.
Recent Acquisitions
On November 16, 2016, Snap-on acquired Ryeson Corporation (d/b/a Sturtevant Richmont) for a preliminary cash purchase price of $12.9 million (or $12.5 million, net of cash acquired). The preliminary purchase price is subject to change based upon the finalization of a working capital adjustment that is expected to be completed in the first quarter of 2017. Sturtevant Richmont, based in Carol Stream, Illinois, designs, manufactures and distributes mechanical and electronic torque wrenches as well as wireless torque error proofing systems for a variety of industrial applications. The acquisition of Sturtevant Richmont enhanced and expanded Snap-on’s capabilities in providing solutions that address torque requirements, which are increasingly essential to critical mechanical performance. For segment reporting purposes, the results of operations and assets of Sturtevant Richmont have been included in the Commercial & Industrial Group since the acquisition date.
On October 31, 2016, Snap-on acquired Car-O-Liner Holding AB (“Car-O-Liner”) for a preliminary cash purchase price of $151.8 million (or $147.9 million, net of cash acquired). The preliminary purchase price is subject to change based upon the finalization of a working capital adjustment that is expected to be completed in the first quarter of 2017. Car-O-Liner, headquartered in Gothenburg, Sweden, designs and manufactures collision repair equipment, and information and truck alignment systems. The acquisition of Car-O-Liner complemented and increased Snap-on’s existing equipment and repair and service information product offerings, broadened its established capabilities in serving vehicle repair facilities and further expanded the company’s presence with repair shop owners and managers. For segment reporting purposes, substantially all of Car-O-Liner’s results of operations and assets have been included in the Repair Systems & Information Group since the acquisition date, with the remaining portions included in the Commercial & Industrial Group.
On July 27, 2015, Snap-on acquired the assets of Ecotechnics S.p.A. (“Ecotechnics”) for a cash purchase price of $11.8 million. Ecotechnics designs and manufactures vehicle air conditioning service equipment for OEM dealerships and the automotive aftermarket worldwide. The acquisition of the Ecotechnics product line complemented and increased Snap-on’s existing equipment product offering for OEM dealerships and independent automotive repair shops, broadened its established capabilities in serving vehicle repair facilities, and expanded the company’s presence with repair shop owners and managers.
On May 28, 2014, Snap-on acquired substantially all of the assets of Pro-Cut International, Inc. (“Pro-Cut”) for a cash purchase price of $41.3 million. Pro-Cut designs, manufactures and distributes on-car brake lathes, related equipment and accessories used in brake servicing by automotive repair facilities. The acquisition of the Pro-Cut product line complemented and increased Snap-on’s existing undercar equipment product offering, broadened its established capabilities in serving vehicle repair facilities and expanded the company’s presence with repair shop owners and managers.
For segment reporting purposes, the results of operations and assets of Ecotechnics and Pro-Cut have been included in the Repair Systems & Information Group since the respective acquisition dates.
Pro forma financial information has not been presented for any of these acquisitions as the net effects, individually and collectively, were neither significant nor material to Snap-on’s results of operations or financial position.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 5 |
Table of Contents
Information Available on the Company’s Website
Additional information regarding Snap-on and its products is available on the company’s website at www.snapon.com. Snap-on is not including the information contained on its website as a part of, or incorporating it by reference into, this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Snap-on’s Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Proxy Statements on Schedule 14A and Current Reports on Form 8-K, as well as any amendments to those reports, are made available to the public at no charge, other than an investor’s own internet access charges, through the Investor Information section of the company’s website at www.snapon.com. Snap-on makes such material available on its website as soon as reasonably practicable after it electronically files such material with, or furnishes it to, the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”). Copies of any materials the company files with the SEC can also be obtained free of charge through the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov. The SEC’s Public Reference Room can be contacted at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549, or by calling 1-800-732-0330. In addition, Snap-on’s (i) charters for the Audit, Corporate Governance and Nominating, and Organization and Executive Compensation Committees of the company’s Board of Directors; (ii) Corporate Governance Guidelines; and (iii) Code of Business Conduct and Ethics are available on the company’s website. Snap-on will also post any amendments to these documents, or information about any waivers granted to directors or executive officers with respect to the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, on the company’s website at www.snapon.com.
Products and Services
Tools, Diagnostics and Repair Information, and Equipment
Snap-on offers a broad line of products and complementary services that are grouped into three product categories: (i) tools; (ii) diagnostics and repair information; and (iii) equipment. Further product line information is not presented as it is not practicable to do so. The following table shows the consolidated net sales of these product categories for the last three years:
| Net Sales | ||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Product Category: |
||||||||||||
| Tools |
$ | 1,899.2 | $ | 1,910.1 | $ | 1,868.5 | ||||||
| Diagnostics and repair information |
748.2 | 689.6 | 689.5 | |||||||||
| Equipment |
783.0 | 753.1 | 719.7 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| $ | 3,430.4 | $ | 3,352.8 | $ | 3,277.7 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The tools product category includes hand tools, power tools and tool storage products. Hand tools include wrenches, sockets, ratchet wrenches, pliers, screwdrivers, punches and chisels, saws and cutting tools, pruning tools, torque measuring instruments and other similar products. Power tools include cordless (battery), pneumatic (air), hydraulic and corded (electric) tools, such as impact wrenches, ratchets, screwdrivers, drills, sanders, grinders and similar products. Tool storage includes tool chests, roll cabinets and other similar products. For many industrial customers, Snap-on creates specific, engineered solutions, including facility-level tool control and asset management hardware and software, custom kits in a wide range of configurations, and custom-built tools designed to meet customer requirements. The majority of products are manufactured by Snap-on and, in completing the product offering, other items are purchased from external manufacturers.
The diagnostics and repair information product category includes handheld and PC-based diagnostic products, service and repair information products, diagnostic software solutions, electronic parts catalogs, business management systems and services, point-of-sale systems, integrated systems for vehicle service shops, OEM purchasing facilitation services, and warranty management systems and analytics to help OEM dealerships manage and track performance.
The equipment product category includes solutions for the diagnosis and service of vehicles and industrial equipment. Products include wheel alignment equipment, wheel balancers, tire changers, vehicle lifts, test lane systems, collision repair equipment, vehicle air conditioning service equipment, brake service equipment, fluid exchange equipment, transmission troubleshooting equipment, safety testing equipment, battery chargers and hoists.
| 6 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Snap-on supports the sale of its diagnostics and vehicle service shop equipment by offering training programs as well as after-sales support for its customers, primarily focusing on the technologies and the application of specific products developed and marketed by Snap-on.
Products are marketed under a number of brand names and trademarks, many of which are well known in the vehicle service and industrial markets served. Some of the major trade names and trademarks and the products and services with which they are associated include the following:
| Names |
Products and Services | |
| Snap-on |
Hand tools, power tools, tool storage products (including tool control software and hardware), diagnostics, certain equipment and related accessories, mobile tool stores, websites, electronic parts catalogs, warranty analytics solutions, business management systems and services, OEM specialty tools and equipment development and distribution, and OEM facilitation services | |
| ATI |
Aircraft hand tools and machine tools | |
| BAHCO |
Saw blades, cutting tools, pruning tools, hand tools, power tools and tool storage | |
| Blackhawk |
Collision repair equipment | |
| Blue-Point |
Hand tools, power tools, tool storage, diagnostics, certain equipment and related accessories | |
| Cartec |
Safety testing, brake testers, test lane equipment, dynamometers, suspension testers, emission testers and other equipment | |
| Car-O-Liner |
Collision repair equipment, and information and truck alignment systems | |
| CDI |
Torque tools | |
| Challenger |
Vehicle lifts | |
| Ecotechnics |
Vehicle air conditioning service equipment | |
| Fish and Hook |
Saw blades, cutting tools, pruning tools, hand tools, power tools and tool storage | |
| Hofmann |
Wheel balancers, vehicle lifts, tire changers, wheel aligners, brake testers and test lane equipment | |
| Irimo |
Saw blades, cutting tools, hand tools, power tools and tool storage | |
| John Bean |
Wheel balancers, vehicle lifts, tire changers, wheel aligners, brake testers and test lane equipment | |
| Josam |
Heavy duty alignment and collision repair solutions | |
| Lindström |
Hand tools | |
| Mitchell1 |
Repair and service information, shop management systems and business services | |
| Nexiq |
Diagnostic tools, information and program distributions for fleet and heavy duty equipment | |
| Pro-Cut |
On-car brake lathes, related equipment and accessories | |
| Sandflex |
Hacksaw blades, bandsaws, saw blades, hole saws and reciprocating saw blades | |
| ShopKey |
Repair and service information, shop management systems and business services | |
| Sioux |
Power tools | |
| Sturtevant Richmont |
Torque tools | |
| Sun |
Diagnostic tools, wheel balancers, vehicle lifts, tire changers, wheel aligners, air conditioning products and emission testers | |
| TruckCam |
Commercial OEM factory solutions | |
| Williams |
Hand tools, tool storage, certain equipment and related accessories | |
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 7 |
Table of Contents
Financial Services
Snap-on also generates revenue from various financing programs that include: (i) installment sales and lease contracts arising from franchisees’ customers and certain other customers of Snap-on who require financing for the purchase or lease of tools and diagnostic and equipment products on an extended-term payment plan; and (ii) business loans and vehicle leases to franchisees. The decision to finance through Snap-on or another financing source is solely at the customer’s election. When assessing customers for potential financing, Snap-on considers various factors regarding ability to pay, including the customers’ financial condition, debt-servicing ability, past payment experience, and credit bureau and proprietary Snap-on credit model information, as well as the value of the underlying collateral.
Snap-on offers financing through SOC and the company’s international finance subsidiaries in those markets where Snap-on has franchise operations. Financing revenue from contract originations is recognized over the life of the underlying contracts, with interest computed primarily on the average daily balances of the underlying contracts.
Sales and Distribution
Snap-on markets and distributes its products and related services principally to professional tool and equipment users around the world. The two largest market sectors are the vehicle service and repair sector and the industrial sector.
Vehicle Service and Repair Sector
The vehicle service and repair sector has three main customer groups: (i) professional technicians who purchase tools and diagnostic and equipment products for use in their work; (ii) other professional customers related to vehicle repair, including owners and managers of independent repair shops and OEM dealerships who purchase tools and diagnostic and equipment products for use by multiple technicians within a service or repair facility; and (iii) OEMs.
Snap-on provides innovative tool, equipment and business solutions, as well as technical sales support and training, designed to meet technicians’ evolving needs. Snap-on’s mobile tool distribution system offers technicians the convenience of purchasing quality tools at their place of business with minimal disruption of their work routine. Snap-on also provides owners and managers of repair shops, where technicians work, with tools, diagnostic equipment, and repair and service information, including electronic parts catalogs and shop management products. Snap-on’s OEM facilitation business provides OEMs with products and services including tools, consulting and facilitation services, which include product procurement, distribution and administrative support to customers for their dealership equipment programs.
The vehicle service and repair sector is characterized by an increasing rate of technological change within motor vehicles, vehicle population growth and increasing vehicle life, and the resulting effects of these changes on the businesses of both our suppliers and customers. Snap-on believes it is a meaningful participant in the vehicle service and repair market sector.
Industrial Sector
Snap-on markets its products and services globally to a broad cross-section of commercial and industrial customers, including maintenance and repair operations; manufacturing and assembly facilities; various government agencies, facilities and operations, including military operations; vocational and technical schools; aviation and aerospace operations; oil and gas developers; mining operations; energy and power generation; equipment fabricators and operators; railroad manufacturing and maintenance; customers in agriculture; infrastructure construction companies; and other customers that require instrumentation, service tools and/or equipment for their product and business needs.
The industrial sector for Snap-on focuses on providing value-added products and services to an increasingly expanding global base of customers in critical industries. Through its experienced and dispersed sales organization, industrial “solutioneers” develop unique and highly valued productivity solutions for customers worldwide that leverage Snap-on’s product, service and development capabilities.
The industrial sector is characterized by a highly competitive, cost-conscious environment, and a trend toward customers making many of their tool and equipment purchases through one integrated supplier. Industrial customers increasingly require specialized solutions that provide repeatability and reliability in performing tasks of consequence that are specific to the particular end market in which they operate. Snap-on believes it is a meaningful participant in the industrial tools and equipment market sector.
| 8 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Distribution Channels
Snap-on serves customers primarily through the following channels of distribution: (i) the mobile van channel; (ii) company direct sales; (iii) distributors; and (iv) e-commerce. The following discussion summarizes Snap-on’s general approach for each channel, and is not intended to be all-inclusive.
Mobile Van Channel
In the United States, a significant portion of sales to the vehicle service and repair sector is conducted through Snap-on’s mobile franchise van channel. Snap-on’s franchisees primarily serve vehicle repair technicians and vehicle service shop owners, generally providing weekly contact at the customer’s place of business. Franchisees’ sales are concentrated in hand and power tools, tool storage products, shop equipment, and diagnostic and repair information products, which can easily be transported in a van or trailer and demonstrated during a brief sales call. Franchisees purchase Snap-on’s products at a discount from suggested list prices and resell them at prices established by the franchisee. U.S. franchisees are provided a list of calls that serves as the basis of the franchisee’s sales route. Snap-on’s franchisees also have the opportunity to add a limited number of additional franchises.
Snap-on charges nominal initial and ongoing monthly franchise fees. Franchise fee revenue, including nominal, non-refundable initial and ongoing monthly fees (primarily for sales and business training, and marketing and product promotion programs), is recognized as the fees are earned. Franchise fee revenue totaled $13.9 million, $12.7 million and $12.1 million in fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Snap-on also has a company-owned route program that is designed to: (i) provide another pool of potential field organization personnel; (ii) service customers in select new and/or open routes not currently serviced by franchisees; and (iii) allow Snap-on to pilot new sales and promotional ideas prior to introducing them to franchisees. As of 2016 year end, company-owned routes comprised less than 3% of the total route population; Snap-on may elect to increase or reduce the number of company-owned routes in the future.
In addition to its mobile van channel in the United States, Snap-on has replicated its U.S. franchise distribution model in certain other countries including the United Kingdom, Canada, Japan, Australia, Germany, Netherlands, South Africa, New Zealand, Belgium and Ireland. In many of these markets, as in the United States, purchase decisions are generally made or influenced by professional vehicle service technicians as well as repair shop owners and managers. As of 2016 year end, Snap-on’s worldwide route count was approximately 4,900, including approximately 3,500 routes in the United States.
Through SOC, financing is available to U.S. franchisees, including financing for van leases, working capital loans and loans to help enable new franchisees to fund the purchase of the franchise. In many international markets, Snap-on offers a variety of financing options to its franchisees and/or customer networks through its international finance subsidiaries. The decision to finance through Snap-on or another financing source is solely at the customer’s election.
Snap-on supports its franchisees with a field organization of regional offices, franchise performance teams, customer care centers and distribution centers. Snap-on also provides sales and business training, and marketing and product promotion programs, as well as customer and franchisee financing programs through SOC and the company’s international finance subsidiaries, all of which are designed to strengthen franchisee sales. National Franchise Advisory Councils in the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada and Australia, composed primarily of franchisees that are elected by franchisees, assist Snap-on in identifying and implementing enhancements to the franchise program.
Company Direct Sales
A significant proportion of shop equipment sales in North America under the John Bean, Hofmann, Blackhawk, Car-O-Liner, Challenger and Pro-Cut brands, diagnostic products under the Snap-on brand and information products under the Mitchell1 brand are made by direct and independent sales forces that have responsibility for national and other accounts. As the vehicle service and repair sector consolidates (with more business conducted by national chains and franchised service centers), Snap-on believes these larger organizations can be serviced most effectively by sales people who can demonstrate and sell the full line of diagnostic and equipment products and services. Snap-on also sells these products and services directly to OEMs and their franchised dealers.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 9 |
Table of Contents
Snap-on brand tools and equipment are marketed to industrial and governmental customers worldwide through both industrial sales associates and independent distributors. Selling activities focus on industrial customers whose main purchase criteria are quality and integrated solutions. As of 2016 year end, Snap-on had industrial sales associates and independent distributors primarily in the United States and in various European, Latin American, Middle Eastern, Asian and African countries, with the United States representing the majority of Snap-on’s total industrial sales.
Snap-on also sells software, services and solutions to the automotive, commercial, heavy duty, agriculture, power equipment and power sports segments. Products and services are marketed to targeted groups, including OEMs and their dealerships, fleets and individual repair shops. To effectively reach OEMs, which frequently have a multi-national presence, Snap-on has deployed focused business teams globally.
Distributors
Sales of certain tools and equipment are made through independent distributors who purchase the items from Snap-on and resell them to end users. Hand tools sold under the BAHCO, Fish and Hook, Irimo, Lindström, CDI, ATI, Sioux, Sturtevant Richmont and Williams brands and trade names, for example, are sold through distributors in Europe, North and South America, Asia and certain other parts of the world. Wheel service and other vehicle service equipment are sold through distributors primarily under brands including Hofmann, John Bean, Car-O-Liner, Challenger, Pro-Cut, Cartec, Blackhawk and Ecotechnics. Diagnostic and equipment products are marketed through distributors in South America and Asia, and through both a direct sales force and distributors in Europe under the Snap-on, Sun and Blue-Point brands.
E-commerce
Snap-on offers current and prospective customers online access to research and purchase products through its public website at www.snapon.com. The site features an online catalog of Snap-on hand tools, power tools, tool storage units and diagnostic equipment available to customers in the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada and Australia. E-commerce and certain other system enhancement initiatives are designed to improve productivity and further leverage the one-on-one relationships and service Snap-on has with its current and prospective customers. Sales through the company’s e-commerce distribution channel were not significant in any of the last three years.
Competition
Snap-on competes on the basis of its product quality and performance, product line breadth and depth, service, brand awareness and imagery, technological innovation and availability of financing (through SOC or its international finance subsidiaries). While Snap-on does not believe that any single company competes with it across all of its product lines and distribution channels, various companies compete in one or more product categories and/or distribution channels.
Snap-on believes it is a leading manufacturer and distributor of professional tools, tool storage, diagnostic and equipment products, and repair software and solutions, offering a broad line of these products to both vehicle service and industrial marketplaces. Various competitors target and sell to professional technicians in the vehicle service and repair sector through the mobile tool distribution channel. Snap-on also competes with companies that sell tools and equipment to vehicle service and repair technicians online and through retail stores, vehicle parts supply outlets and tool supply warehouses/distributorships. Within the power tools category and the industrial sector, Snap-on has various other competitors, including companies with offerings that overlap with other areas discussed herein. Major competitors selling diagnostics, shop equipment and information to vehicle dealerships and independent repair shops include OEMs and their proprietary electronic parts catalogs and diagnostics and information systems, and other companies that offer products serving this sector.
Raw Materials and Purchased Product
Snap-on’s supply of raw materials and purchased components are generally and readily available from numerous suppliers. Snap-on believes it has secured an ample supply of both bar and coil steel for the near future to ensure stable supply to meet material demands. The company does not currently anticipate experiencing any significant impact in 2017 from steel pricing or availability issues.
| 10 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Patents, Trademarks and Other Intellectual Property
Snap-on vigorously pursues and relies on patent protection to protect its intellectual property and position in its markets. As of 2016 year end, Snap-on and its subsidiaries held approximately 700 active and pending patents in the United States and approximately 1,600 active and pending patents outside of the United States. Sales relating to any single patent did not represent a material portion of Snap-on’s revenues in any of the last three years.
Examples of products that have features or designs that benefit from patent protection include wheel alignment systems, wheel balancers, tire changers, vehicle lifts, tool storage, tool control, collision measurement, test lanes, brake lathes, sealed ratchets, electronic torque instruments, ratcheting screwdrivers, emissions-sensing devices and diagnostic equipment.
Much of the technology used in the manufacture of vehicle service tools and equipment is in the public domain. Snap-on relies primarily on trade secret protection to protect proprietary processes used in manufacturing. Methods and processes are patented when appropriate. Copyright protection is also utilized when appropriate.
Trademarks used by Snap-on are of continuing importance to Snap-on in the marketplace. Trademarks have been registered in the United States and many other countries, and additional applications for trademark registrations are pending. Snap-on vigorously polices proper use of its trademarks. Snap-on’s right to manufacture and sell certain products is dependent upon licenses from others; however, these products under license do not represent a material portion of Snap-on’s net sales.
Domain names have become a valuable corporate asset for companies around the world, including Snap-on. Domain names often contain a trademark or service mark or even a corporate name and are often considered intellectual property. The recognition and value of the Snap-on name, trademark and domain name are core strengths of the company.
Snap-on strategically licenses the Snap-on brand to carefully selected manufacturing and distribution companies for items such as apparel, work boots, lighting and a variety of other goods, in order to further build brand awareness and market presence for the company’s strongest brand.
Environmental
Snap-on is subject to various environmental laws, ordinances, regulations, and other requirements of government authorities in the United States and other nations. At Snap-on, these environmental liabilities are managed through the Snap-on Environmental, Health and Safety Management System (“EH & SMS”), which is applied worldwide. The system is based upon continual improvement and is certified to ISO 14001:2004 and OHSAS 18001:2007, verified through Det Norske Veritas (DNV) Certification, Inc.
Snap-on believes that it complies with applicable environmental control requirements in its operations. Expenditures on environmental matters through EH & SMS have not had, and Snap-on does not for the foreseeable future expect them to have, a material effect upon Snap-on’s capital expenditures, earnings or competitive position.
Employees
Snap-on employed approximately 12,100 people at the end of January 2017; Snap-on employed approximately 11,500 people at the end of January 2016. The year-over-year increase in employees primarily reflects the Car-O-Liner and Sturtevant Richmont acquisitions.
Approximately 2,800 employees, or 23% of Snap-on’s worldwide workforce, are represented by unions and/or covered under collective bargaining agreements. The number of covered union employees whose contracts expire over the next five years approximates 2,100 employees in 2017, 500 employees in 2018, and 200 employees in 2019; there are no contracts currently scheduled to expire in 2020 or 2021. In recent years, Snap-on has not experienced any significant work slowdowns, stoppages or other labor disruptions.
There can be no assurance that these and other future contracts with Snap-on’s unions will be renegotiated upon terms acceptable to Snap-on.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 11 |
Table of Contents
Working Capital
Most of Snap-on’s businesses are not seasonal and their inventory needs are relatively constant. Snap-on did not have a significant backlog of orders at 2016 year end. In recent years, Snap-on has been using its working capital to fund, in part, the continued growth of the company’s financial services portfolio and the acquisitions discussed above.
Snap-on’s liquidity and capital resources and use of working capital are discussed herein in “Part II, Item 7, Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
As of 2016 year end, neither Snap-on nor any of its segments depend on any single customer, small group of customers or government for any material part of its revenues.
In evaluating the company, careful consideration should be given to the following risk factors, in addition to the other information included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including the Consolidated Financial Statements and the related notes. Each of these risk factors could adversely affect the company’s business, operating results, cash flows and/or financial condition, as well as adversely affect the value of an investment in the company’s common stock.
Economic conditions and world events could affect our operating results.
We, our franchisees and our customers, may be adversely affected by changing economic conditions, including conditions that may particularly impact specific regions. These conditions may result in reduced consumer and investor confidence, instability in the credit and financial markets, volatile corporate profits, and reduced business and consumer spending. We, our franchisees and our customers, and the economy as a whole, also may be affected by future world or local events outside our control, such as acts of terrorism, developments in the war on terrorism, conflicts in international situations and natural disasters, as well as government-related developments or issues. These factors may affect our results of operations by reducing our sales, margins and/or net earnings as a result of a slowdown in customer orders or order cancellations, impact the availability of raw materials and/or the supply chain, and could potentially lead to future impairment of our intangible assets. In addition, political and social turmoil related to international conflicts and terrorist acts may put pressure on economic conditions abroad. Unstable political, social and economic conditions may make it difficult for our franchisees, customers, suppliers and us to accurately forecast and plan future business activities. If such conditions persist, our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows could be negatively affected.
In June 2016, the United Kingdom voted in a referendum to exit the European Union (“Brexit”), which resulted in significant currency exchange rate fluctuations and volatility beginning late in the second quarter of fiscal 2016. Subject to parliamentary approval, the British government is expected to commence negotiations to determine the terms of Brexit. Given the lack of comparable precedent, the implications of Brexit, or how such implications might affect Snap-on, are unclear at this time. Brexit could, among other impacts, disrupt trade and the movement of goods, services and people between the United Kingdom and the European Union or other countries as well as create legal and global economic uncertainty. These and other potential implications could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
Raw material and energy price fluctuations and shortages (including steel and various fuel sources) could adversely affect the ability to obtain needed manufacturing materials and could adversely affect our results of operations.
The principal raw material used in the manufacture of our products is steel, which we purchase in competitive, price-sensitive markets. To meet Snap-on’s high quality standards, our steel needs range from specialized alloys, which are available only from a limited group of approved suppliers, to commodity types of alloys. These raw materials have historically exhibited price and demand cyclicality. Some of these materials have been, and in the future may be, in short supply, particularly in the event of mill shutdowns or production cut backs. As some steel alloys require specialized manufacturing procedures, we could experience inventory shortages if we were required to use an alternative manufacturer on short notice. Additionally, unexpected price increases for raw materials could result in higher prices to our customers or an erosion of the margins on our products.
| 12 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
We believe our ability to sell our products is also dependent on the number of vehicles on the road, the number of miles driven and the general aging of vehicles. These factors affect the frequency, type and amount of service and repair performed on vehicles by technicians, and therefore affect the demand for the number of technicians, the prosperity of technicians and, consequently, the demand technicians have for our tools, other products and services, and the value technicians place on those products and services. The use of other methods of transportation, including more frequent use of public transportation, could result in a decrease in the use of privately operated vehicles. A decrease in the use of privately operated vehicles may lead to fewer repairs and less demand for our products.
We use various energy sources to transport, produce and distribute products, and some of our products have components that are petroleum based. Petroleum and energy prices have periodically increased significantly over short periods of time; future volatility and changes may be caused by market fluctuations, supply and demand, currency fluctuations, production and transportation disruptions, world events and changes in governmental programs. Energy price increases raise both our operating costs and the costs of our materials, and we may not be able to increase our prices enough to offset these costs. Higher prices also may reduce the level of future customer orders and our profitability.
The performance of Snap-on’s mobile tool distribution business depends on the success of its franchisees.
Approximately 44% of our consolidated net revenues in 2016 were generated by the Snap-on Tools Group, which consists of Snap-on’s business operations primarily serving vehicle service and repair technicians through the company’s worldwide mobile tool distribution channel. Snap-on’s success is dependent on its relationships with franchisees, individually and collectively, as they are the primary sales and service link between the company and vehicle service and repair technicians, who are an important class of end users for Snap-on’s products and services. If our franchisees are not successful, or if we do not maintain an effective relationship with our franchisees, the delivery of products, the collection of receivables and/or our relationship with end users could be adversely affected and thereby negatively impact our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
In addition, if we are unable to maintain effective relationships with franchisees, Snap-on or the franchisees may choose to terminate the relationship, which may result in (i) open routes, in which end-user customers are not provided reliable service; (ii) litigation resulting from termination; (iii) reduced collections or increased write-offs of franchisee receivables owed to Snap-on; and/or (iv) reduced collections or increased write-offs of finance and contract receivables.
Exposure to credit risks of customers and resellers may make it difficult to collect receivables and could adversely affect operating results and financial condition.
The size of our financial services portfolio has increased significantly in recent years. A decline in industry and/or economic conditions could have the potential to weaken the financial position of some of our customers. If circumstances surrounding our customers’ ability to repay their credit obligations were to deteriorate and result in the write-down or write-off of such receivables, it would negatively affect our operating results for the period in which they occur and, if large, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Our inability to provide acceptable financing alternatives to end-user customers and franchisees could adversely impact our operating results.
An integral component of our business and profitability is our ability to offer competitive financing alternatives to end-user customers and franchisees. The lack of our ability to offer such alternatives or obtain capital resources or other financing to support our receivables on terms that we believe are attractive, whether resulting from the state of the financial markets, our own operating performance, or other factors, would negatively affect our operating results and financial condition. Adverse fluctuations in interest rates and/or our ability to provide competitive financing programs could also have an adverse impact on our revenue and profitability.
New, stricter and/or changed legislation and regulations may affect our business, reputation, results of operations and financial condition.
Increased legislative and regulatory activity and compliance burdens, including those associated with sales to our government, military and defense contractor customers, as well as a more stringent manner in which they are applied, could significantly impact our business and the economy as a whole.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 13 |
Table of Contents
Financial services businesses of all kinds are subject to increasing regulation and enforcement. In addition to potentially increasing the costs of doing business due to compliance obligations, new laws and regulations, or changes to existing laws and regulations, as well as the enforcement thereof, may affect the relationships between creditors and debtors, inhibit the rights of creditors to collect amounts owed to them, expand liability for certain actions or inactions, or limit the types of financial products or services offered, any or all of which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. Failure to comply with any of these laws or regulations could also result in civil, criminal, monetary and/or non-monetary penalties, damage to our reputation, and/or the incurrence of remediation costs.
These developments, and other potential future legislation and regulations, as well as the increasingly strict regulatory environment, including the growing international regulation of privacy rights, may also adversely affect the customers to which, and the markets into which, we sell our products, and increase our costs and otherwise negatively affect our business, reputation, results of operations and financial condition, including in ways that cannot yet be foreseen.
Failure to achieve expected investment returns on pension plan assets, as well as changes in interest rates or plan demographics, could adversely impact our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Snap-on sponsors various defined benefit pension plans (the “pension plans”). The assets of the pension plans are diversified in an attempt to mitigate the risk of a large loss. Required funding for the company’s domestic defined benefit pension plans is determined in accordance with guidelines set forth in the federal Employee Retirement Income Security Act (“ERISA”); foreign defined benefit pension plans are funded in accordance with local statutes or practice. Additional contributions to enhance the funded status of the pension plans can be made at the company’s discretion. However, there can be no assurance that the value of the pension plan assets, or the investment returns on those plan assets, will be sufficient to meet the future benefit obligations of such plans. In addition, during periods of adverse investment market conditions and declining interest rates, the company may be required to make additional cash contributions to the pension plans that could reduce our financial flexibility. Changes in plan demographics, including an increase in the number of retirements or changes in life expectancy assumptions, may also increase the costs and funding requirements of the obligations related to the company’s pension plans.
Our pension plan obligations are affected by changes in market interest rates. Significant fluctuations in market interest rates have added, and may further add, volatility to our pension plan obligations. In periods of declining market interest rates, our pension plan obligations generally increase; in periods of increasing market interest rates, our pension plan obligations generally decrease. While our plan assets are broadly diversified, there are inherent market risks associated with investments; if adverse market conditions occur, our plan assets could incur significant or material losses. Since we may need to make additional contributions to address changes in obligations and/or a loss in plan assets, the combination of declining market interest rates, past or future plan asset investment losses, and/or changes in plan demographics could adversely impact our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
The company’s pension plan expense is comprised of the following factors: (i) service cost; (ii) interest on projected benefit obligations; (iii) expected return on plan assets; (iv) the amortization of prior service costs and credits; (v) effects of actuarial gains and losses; and (vi) settlement/curtailment costs, when applicable. The accounting for pensions involves the estimation of a number of factors that are highly uncertain. Certain factors, such as the interest on projected benefit obligations and the expected return on plan assets, are impacted by changes in market interest rates and the value of plan assets. A significant decrease in market interest rates and a decrease in the fair value of plan assets would increase net pension expense and may adversely affect the company’s future results of operations. See Note 11 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further information on the company’s pension plans.
Adverse developments in the credit and financial markets could negatively impact the availability of credit that we and our customers need to operate our businesses.
We depend upon the availability of credit to operate our business, including the financing of receivables from end-user customers that are originated by our financial services businesses. Our end-user customers, franchisees and suppliers also require access to credit for their businesses. At times in recent years, world financial markets have been unstable and subject to uncertainty. Adverse developments in the credit and financial markets, or unfavorable changes in Snap-on’s credit rating, could negatively impact the availability of future financing and the terms on which it might be available to Snap-on, its end-user customers, franchisees and suppliers. Inability to access credit or capital markets, or a deterioration in the terms on which financing might be available, could have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
| 14 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Increasing our financial leverage could affect our operations and profitability.
The maximum available credit under our multi-currency revolving credit facility is $700 million. The company’s leverage ratio may affect both our availability of additional capital resources as well as our operations in several ways, including:
| • | The terms on which credit may be available to us could be less attractive, both in the economic terms of the credit and the covenants stipulated by the credit terms; |
| • | The possible lack of availability of additional credit or access to the commercial paper market; |
| • | The potential for higher levels of interest expense to service or maintain our outstanding debt; |
| • | The possibility of additional borrowings in the future to repay our indebtedness when it comes due; and |
| • | The possible diversion of capital resources from other uses. |
While we believe we will have the ability to service our debt and obtain additional resources in the future if and when needed, that will depend upon our results of operations and financial position at the time, the then-current state of the credit and financial markets, and other factors that may be beyond our control. Therefore, we cannot give assurances that credit will be available on terms that we consider attractive, or at all, if and when necessary or beneficial to us.
Data security and information technology infrastructure and security are critical to supporting business objectives; failure of our systems to operate effectively could adversely affect our business and reputation.
We depend heavily on information technology infrastructure to achieve our business objectives and to protect sensitive information, and continually invest in improving such systems. Problems that impair or compromise this infrastructure, including due to natural disasters, power outages, major network failures, security breaches or malicious attacks, or during system upgrades and/or new system implementations, could impede our ability to record or process orders, manufacture and ship in a timely manner, account for and collect receivables, protect sensitive data of the company, our customers, our suppliers and business partners, or otherwise carry on business in the normal course. Any such events, if significant, could cause us to lose customers and/or revenue and could require us to incur significant expense to remediate, including as a result of legal or regulatory claims or proceedings, and could also damage our reputation. While we have taken steps to maintain adequate data security and address these risks and uncertainties by implementing security technologies, internal controls, network and data center resiliency, and redundancy and recovery processes, as well as by securing insurance, these measures may be inadequate.
In association with initiatives to better integrate business units, rationalize operating footprint and improve responsiveness to franchisees and customers, Snap-on is continually replacing and enhancing its global Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) management information systems. As we integrate, implement and deploy new information technology processes and enhance our common information infrastructure across our global operations, we could experience disruptions in our business that could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Failure to maintain effective distribution of products and services could adversely impact revenue, gross margin and profitability.
We use a variety of distribution methods to sell our products and services. Successfully managing the interaction of our distribution efforts to reach various potential customer segments for our products and services is a complex process. Moreover, since each distribution method has distinct risks, costs and gross margins, our failure to implement the most advantageous balance in the delivery model for our products and services could adversely affect our revenue and gross margins and therefore our profitability.
Risks associated with the disruption of manufacturing operations could adversely affect profitability or competitive position.
We manufacture a significant portion of the products we sell. Any prolonged disruption in the operations of our existing manufacturing facilities, whether due to technical or labor difficulties, facility consolidation or closure actions, lack of raw material or component availability, destruction of or damage to any facility (as a result of natural disasters, use and storage of hazardous materials or other events), or other reasons, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 15 |
Table of Contents
The inability to continue to introduce new products that respond to customer needs and achieve market acceptance could result in lower revenues and reduced profitability.
Sales from new products represent a significant portion of our net sales and are expected to continue to represent a significant component of our future net sales. We may not be able to compete effectively unless we continue to enhance existing products or introduce new products to the marketplace in a timely manner. Product improvements and new product introductions require significant financial and other resources, including significant planning, design, development, and testing at the technological, product and manufacturing process levels. Our competitors’ new products may beat our products to market, be more effective with more features, be less expensive than our products, and/or render our products obsolete. Any new products that we develop may not receive market acceptance or otherwise generate any meaningful net sales or profits for us relative to our expectations based on, among other things, existing and anticipated investments in manufacturing capacity and commitments to fund advertising, marketing, promotional programs and research and development.
The global tool, equipment, and diagnostics and repair information industries are competitive.
We face strong competition in all of our market segments. Price competition in our various industries is intense and pricing pressures from competitors and customers are increasing. In general, as a manufacturer and marketer of premium products and services, the expectations of Snap-on’s customers and its franchisees are high and continue to increase. Any inability to maintain customer satisfaction could diminish Snap-on’s premium image and reputation and could result in a lessening of our ability to command premium pricing. We expect that the level of competition will remain high in the future, which could limit our ability to maintain or increase market share or profitability.
Product liability claims and litigation could affect our business, reputation, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
The products that we design and/or manufacture, and/or the services we provide, can lead to product liability claims or other legal claims being filed against us. To the extent that plaintiffs are successful in showing that a defect in a product’s design, manufacture or warnings led to personal injury or property damage, or that our provision of services resulted in similar injury or damage, we may be subject to claims for damages. Although we are insured for damages above a certain amount, we bear the costs and expenses associated with defending claims, including frivolous lawsuits, and are responsible for damages up to the insurance retention amount. In addition to claims concerning individual products, as a manufacturer, we can be subject to costs, potential negative publicity and lawsuits related to product recalls, which could adversely impact our results of operations and damage our reputation.
Legal disputes could adversely affect our business, reputation, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
From time to time we are subject to legal disputes that are being litigated and/or settled in the ordinary course of business. Disputes or future lawsuits could result in the diversion of management’s time and attention away from business operations. Additionally, negative developments with respect to legal disputes and the costs incurred in defending ourselves could have an adverse impact on the company and its reputation. Adverse outcomes or settlements could also require us to pay damages, potentially in excess of amounts reserved, or incur liability for other remedies that could have a material adverse effect on our business, reputation, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Failure to adequately protect intellectual property could adversely affect our business.
Intellectual property rights are an important and integral component of our business. We attempt to protect our intellectual property rights through a combination of patent, trademark, copyright and trade secret laws, as well as licensing agreements and third-party nondisclosure and assignment agreements. Adverse determinations in a judicial or administrative proceeding could prevent us from manufacturing and selling our products or prevent us from stopping others from manufacturing and selling competing products. Failure to obtain or maintain adequate protection of our intellectual property rights for any reason could have a material adverse effect on our business.
| 16 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Foreign operations are subject to political, economic, currency exchange and other risks that could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Approximately 30% of our revenues in 2016 were generated outside of the United States. Future growth rates and success of our business depends in large part on continued growth in our non-U.S. operations, including growth in emerging markets and critical industries. Numerous risks and uncertainties affect our non-U.S. operations. These risks and uncertainties include political, economic and social instability, such as acts of war, civil disturbance or acts of terrorism, local labor conditions, changes in government policies and regulations, including imposition or increases in withholding and other taxes on remittances and other payments by international subsidiaries, as well as the exposure to liabilities under anti-corruption laws in various countries, such as the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, currency volatility, transportation delays or interruptions, sovereign debt uncertainties and difficulties in enforcement of contract and intellectual property rights, as well as natural disasters. Should the economic environment in our non-U.S. markets deteriorate from current levels, our results of operations and financial position could be materially impacted, including as a result of the effects of potential impairment write-downs of goodwill and/or other intangible assets related to these businesses.
The reporting currency for Snap-on’s consolidated financial statements is the U.S. dollar. Certain of the company’s assets, liabilities, expenses and revenues are denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. In preparing Snap-on’s Consolidated Financial Statements, those assets, liabilities, expenses and revenues are translated into U.S. dollars at applicable exchange rates. Increases or decreases in exchange rates between the U.S. dollar and other currencies affect the U.S. dollar value of those items, as reflected in the Consolidated Financial Statements. Substantial fluctuations in the value of the U.S. dollar could have a significant impact on the company’s financial condition and results of operations.
We are also affected by changes in inflation rates and interest rates. Additionally, cash generated in non-U.S. jurisdictions may be difficult to repatriate to the United States in a tax-efficient manner. Our foreign operations are also subject to other risks and challenges, such as the need to staff and manage diverse workforces, respond to the needs of multiple national and international marketplaces, and differing business climates and cultures in various countries.
We may not successfully integrate businesses we acquire, which could have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
The pursuit of growth through acquisitions, including participation in joint ventures, involves significant risks that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. These risks include:
| • | Loss of the acquired businesses’ customers; |
| • | Inability to integrate successfully the acquired businesses’ operations; |
| • | Inability to coordinate management and integrate and retain employees of the acquired businesses; |
| • | Unforeseen or contingent liabilities of the acquired businesses; |
| • | Large write-offs or write-downs, or the impairment of goodwill or other intangible assets; |
| • | Difficulties in implementing and maintaining consistent standards, controls, procedures, policies and information systems; |
| • | Failure to realize anticipated synergies, economies of scale or other anticipated benefits, or to maintain operating margins; |
| • | Strain on our personnel, systems and resources, and diversion of attention from other priorities; |
| • | Incurrence of additional debt and related interest expense; and |
| • | The dilutive effect in the event of the issuance of additional equity securities. |
The recognition of impairment charges on goodwill or other intangible assets would adversely impact our future financial condition and results of operations.
We have a substantial amount of goodwill and purchased intangible assets, almost all of which are booked in the Commercial & Industrial Group and in the Repair Systems & Information Group. We are required to perform impairment tests on our goodwill and other intangibles annually or at any time when events occur that could impact the value of our business segments. Our determination of whether impairment has occurred is based on a comparison of each of our reporting units’ fair market value with its carrying value. Significant and unanticipated changes in circumstances, such as significant and long-term adverse changes in business climate, adverse actions by regulators, unanticipated competition, the loss of key customers, and/or changes in technology or markets, could require a provision for impairment in a future period that could substantially impact our reported earnings and reduce our consolidated net worth and shareholders’ equity. Should the economic environment in these markets deteriorate, our results of operations and financial position could be materially impacted, including as a result of the effects of potential impairment write-downs of goodwill and/or other intangible assets related to these businesses.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 17 |
Table of Contents
Our operations expose us to the risk of environmental liabilities, costs, litigation and violations that could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and reputation.
Certain of our operations are subject to environmental laws and regulations in the jurisdictions in which they operate, which impose limitations on the discharge of pollutants into the ground, air and water and establish standards for the generation, treatment, use, storage and disposal of hazardous wastes. We must also comply with various health and safety regulations in the United States and abroad in connection with our operations. Failure to comply with any of these laws could result in civil and criminal, monetary and non-monetary penalties and damage to our reputation. In addition, we may incur costs related to remedial efforts or alleged environmental damage associated with past or current waste disposal practices. Legislation has been proposed, and governmental regulatory action has been both proposed and taken, that may significantly impact environmental compliance in the United States; these actions could increase our costs of production by raising the cost of energy as well as by further restricting emissions or other processes that we currently use in our operations. We cannot provide assurance that our costs of complying with current or future environmental protection and health and safety laws will not exceed our estimates.
The inability to successfully defend claims from taxing authorities could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
We conduct business in many countries, which requires us to interpret the income tax laws and rulings in each of those taxing jurisdictions. Due to the subjectivity of tax laws between those jurisdictions, as well as the subjectivity of factual interpretations, our estimates of income tax liabilities may differ from actual payments or assessments. Claims from taxing authorities related to these differences could have an adverse impact on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Failure to attract and retain qualified personnel could lead to a loss of revenue and/or profitability.
Snap-on’s success depends, in part, on the efforts and abilities of its senior management team and other key employees. Their skills, experience and industry contacts significantly benefit our operations and administration. The failure to attract and retain members of our senior management team and other key employees could have a negative effect on our operating results. In addition, transitions of important responsibilities to new individuals inherently include the possibility of disruptions to our business and operations, which could negatively affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
The steps taken to restructure operations, rationalize operating footprint, lower operating expenses and achieve greater efficiencies in the supply chain could disrupt business.
We have taken steps in the past, and expect to take additional steps in the future, intended to improve customer service and drive further efficiencies and reduce costs, some of which could be disruptive to our business. These actions, collectively across our operating groups, are focused on the following:
| • | Continuing to invest in initiatives focused on building a strong sales and operating presence in emerging growth markets; |
| • | Continuing to enhance service and value to our franchisees and customers; |
| • | Continuing to implement efficiency and productivity initiatives throughout the company to drive further efficiencies and reduce costs; |
| • | Continuing on the company’s existing path to improve and transform global manufacturing and the supply chain into a market-demand-based replenishment system with lower costs; |
| • | Continuing to invest in developing and marketing new, innovative, higher-value-added products and advanced technologies; |
| • | Extending our products and services into additional and/or adjacent markets or to new customers; and |
| • | Continuing to provide financing for, and grow our portfolio of, receivables within our financial services businesses. |
| 18 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
A failure to succeed in the implementation of any or all of these actions could result in an inability to achieve our financial goals and could be disruptive to the business.
In addition, any future reductions to headcount and other cost reduction measures may result in the loss of technical expertise and could adversely affect our research and development efforts as well as our ability to meet product development schedules. Efforts to reduce components of expense could result in the recording of charges for inventory and technology-related write-offs, workforce reduction costs or other charges relating to the consolidation or closure of facilities. If we were to incur a substantial charge to further these efforts, our earnings per share would be adversely affected in such period. If we are unable to effectively manage our cost reduction and restructuring efforts, our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows could be negatively affected.
Item 1B: Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Snap-on maintains leased and owned manufacturing (including software products), warehouse, distribution, research and development and office facilities throughout the world. Snap-on believes that its facilities currently in use are suitable and have adequate capacity to meet its present and foreseeable future demand. Snap-on’s facilities in the United States occupy approximately 3.3 million square feet, of which 75% is owned, including its corporate and general office facility located in Kenosha, Wisconsin. Snap-on’s facilities outside the United States occupy approximately 4.5 million square feet, of which approximately 71% is owned. Certain Snap-on facilities are leased through operating and capital lease agreements. See Note 15 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on the company’s operating and capital leases. Snap-on management continually monitors the company’s capacity needs and makes adjustments as dictated by market and other conditions.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 19 |
Table of Contents
The following table provides information about our corporate headquarters and financial services operations, and each of Snap-on’s principal active manufacturing locations and distribution centers (exceeding 50,000 square feet) as of 2016 year end:
| Location |
Principal Property Use |
Owned/Leased |
Segment* | |||
| U.S. Locations: |
||||||
| Elkmont, Alabama |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
SOT | |||
| Conway, Arkansas |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
RS&I | |||
| City of Industry, California |
Manufacturing |
Leased |
C&I | |||
| Poway, California |
Manufacturing and distribution |
Leased |
RS&I | |||
| San Jose, California |
Manufacturing and distribution |
Leased |
RS&I | |||
| Columbus, Georgia |
Distribution |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Crystal Lake, Illinois |
Distribution |
Owned and leased |
SOT | |||
| Libertyville, Illinois |
Financial services |
Leased |
FS | |||
| Algona, Iowa |
Manufacturing and distribution |
Owned |
SOT | |||
| Louisville, Kentucky |
Manufacturing and distribution |
Leased |
RS&I | |||
| Olive Branch, Mississippi |
Distribution |
Owned |
SOT | |||
| Carson City, Nevada |
Distribution |
Owned and leased |
SOT | |||
| Murphy, North Carolina |
Manufacturing and distribution |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Richfield, Ohio |
Manufacturing and distribution |
Owned |
RS&I | |||
| Robesonia, Pennsylvania |
Distribution |
Owned |
SOT | |||
| Elizabethton, Tennessee |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
SOT | |||
| Kenosha, Wisconsin |
Distribution and corporate |
Owned |
SOT, C&I, RS&I | |||
| Milwaukee, Wisconsin |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
SOT | |||
| Non-U.S. Locations: |
||||||
| Santo Tome, Argentina |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| New South Wales, Australia |
Distribution and financial services |
Leased |
SOT, FS | |||
| Minsk, Belarus |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Santa Bárbara d’Oeste, Brazil |
Manufacturing and distribution |
Owned |
RS&I | |||
| Calgary, Canada |
Distribution |
Leased |
SOT | |||
| Mississauga, Canada |
Distribution |
Leased |
SOT, RS&I | |||
| Beijing, China |
Manufacturing |
Leased |
C&I | |||
| Kunshan, China |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Xiaoshan, China |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Bramley, England |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Kettering, England |
Distribution and financial services |
Owned and leased |
SOT, C&I, FS | |||
| Sopron, Hungary |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
RS&I | |||
| Correggio, Italy |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
RS&I | |||
| Tokyo, Japan |
Distribution |
Leased |
C&I | |||
| Helmond, Netherlands |
Distribution |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Vila do Conde, Portugal |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Irun, Spain |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Placencia, Spain |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Vitoria, Spain |
Manufacturing and distribution |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Bollnäs, Sweden |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Edsbyn, Sweden |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Kungsör, Sweden |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
RS&I | |||
| Lidköping, Sweden |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
C&I | |||
| Örebro, Sweden |
Manufacturing |
Owned |
RS&I | |||
| * | Segment abbreviations: |
C&I – Commercial & Industrial Group
SOT – Snap-on Tools Group
RS&I – Repair Systems & Information Group
FS – Financial Services
| 20 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Snap-on is involved in various legal matters that are being litigated and/or settled in the ordinary course of business. Although it is not possible to predict the outcome of these legal matters, management believes that the results of these legal matters will not have a material impact on Snap-on’s consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Item 4: Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 5: Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Snap-on had 57,949,857 shares of common stock outstanding as of 2016 year end. Snap-on’s stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol “SNA.” At February 3, 2017, there were 5,040 registered holders of Snap-on common stock.
The high and low closing prices of Snap-on’s common stock during each fiscal quarter for the last two years were as follows:
| Common Stock High/Low Prices | ||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| Quarter |
High | Low | High | Low | ||||||||||||
| First |
$ | 168.53 | $ | 135.41 | $ | 148.29 | $ | 131.45 | ||||||||
| Second |
164.39 | 148.03 | 162.19 | 146.16 | ||||||||||||
| Third |
162.70 | 146.76 | 169.99 | 148.90 | ||||||||||||
| Fourth |
176.20 | 145.97 | 174.09 | 154.57 | ||||||||||||
Snap-on has paid consecutive quarterly cash dividends, without interruption or reduction, since 1939. Quarterly dividends in 2016 were $0.71 per share in the fourth quarter and $0.61 per share in each of the first three quarters ($2.54 per share for the year). Quarterly dividends in 2015 were $0.61 per share in the fourth quarter and $0.53 per share in each of the first three quarters ($2.20 per share for the year). Cash dividends paid in 2016 and 2015 totaled $147.5 million and $127.9 million, respectively. Snap-on’s Board of Directors (the “Board”) monitors and evaluates the company’s dividend practice quarterly and the Board may elect to increase, decrease or not pay a dividend on Snap-on common stock based upon the company’s financial condition, results of operations, cash requirements and future prospects of Snap-on and other factors deemed relevant by the Board.
See Note 13 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on securities authorized for issuance under equity compensation plans.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 21 |
Table of Contents
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The following chart discloses information regarding the shares of Snap-on’s common stock repurchased by the company during the fourth quarter of fiscal 2016, all of which were purchased pursuant to the Board’s authorizations that the company has publicly announced. Snap-on has undertaken stock repurchases from time to time to offset dilution created by shares issued for employee and franchisee stock purchase plans, stock options and other corporate purposes, as well as to repurchase shares when the company believes market conditions are favorable. The repurchase of Snap-on common stock is at the company’s discretion, subject to prevailing financial and market conditions.
|
Period |
Shares purchased |
Average price per share |
Shares purchased as part of publicly announced plans or programs |
Approximate value of shares that may yet be purchased under publicly announced plans or programs* |
||||||||||
| 10/02/16 to 10/29/16 |
65,000 | $ | 156.36 | 65,000 | $ | 201.2 million | ||||||||
| 10/30/16 to 11/26/16 |
61,000 | $ | 165.64 | 61,000 | $ | 217.0 million | ||||||||
| 11/27/16 to 12/31/16 |
140,000 | $ | 169.27 | 140,000 | $ | 207.2 million | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
| Total/Average |
266,000 | $ | 165.28 | 266,000 | N/A | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
N/A: Not applicable
| * | Subject to further adjustment pursuant to the 1996 Authorization described below, as of December 31, 2016, the approximate value of shares that may yet be purchased pursuant to the three outstanding Board authorizations discussed below is $207.2 million. |
| • | In 1996, the Board authorized the company to repurchase shares of the company’s common stock from time to time in the open market or in privately negotiated transactions (“the 1996 Authorization”). The 1996 Authorization allows the repurchase of up to the number of shares issued or delivered from treasury from time to time under the various plans the company has in place that call for the issuance of the company’s common stock. Because the number of shares that are purchased pursuant to the 1996 Authorization will change from time to time as (i) the company issues shares under its various plans; and (ii) shares are repurchased pursuant to this authorization, the number of shares authorized to be repurchased will vary from time to time. The 1996 Authorization will expire when terminated by the Board. When calculating the approximate value of shares that the company may yet purchase under the 1996 Authorization, the company assumed a price of $153.21, $170.58 and $171.27 per share of common stock as of the end of the fiscal 2016 months ended October 29, 2016, November 26, 2016, and December 31, 2016, respectively. |
| • | In 1998, the Board authorized the repurchase of an aggregate of $100 million of the company’s common stock (“the 1998 Authorization”). The 1998 Authorization will expire when the aggregate repurchase price limit is met, unless terminated earlier by the Board. |
| • | In 1999, the Board authorized the repurchase of an aggregate of $50 million of the company’s common stock (“the 1999 Authorization”). The 1999 Authorization will expire when the aggregate repurchase price limit is met, unless terminated earlier by the Board. |
| 22 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Other Purchases or Sales of Equity Securities
The following chart discloses information regarding transactions in shares of Snap-on’s common stock by Citibank, N.A. (“Citibank”) during the fourth quarter of 2016 pursuant to a prepaid equity forward agreement (the “Agreement”) with Citibank that is intended to reduce the impact of market risk associated with the stock-based portion of the company’s deferred compensation plans. The company’s stock-based deferred compensation liabilities, which are impacted by changes in the company’s stock price, increase as the company’s stock price rises and decrease as the company’s stock price declines. Pursuant to the Agreement, Citibank may purchase or sell shares of the company’s common stock (for Citibank’s account) in the market or in privately negotiated transactions. The Agreement has no stated expiration date and does not provide for Snap-on to purchase or repurchase its shares.
Citibank Sales of Snap-on Stock
|
Period |
Shares sold | Average price per share |
||||||
| 10/02/16 to 10/29/16 |
– | – | ||||||
| 10/30/16 to 11/26/16 |
3,800 | $ | 165.52 | |||||
| 11/27/16 to 12/31/16 |
3,000 | $ | 168.99 | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total/Average |
6,800 | $ | 167.05 | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 23 |
Table of Contents
Five-year Stock Performance Graph
The graph below illustrates the cumulative total shareholder return on Snap-on common stock since December 31, 2011, assuming that dividends were reinvested. The graph compares Snap-on’s performance to that of a Peer Group, Standard & Poor’s 500 Industrials Index (“S&P 500 Industrials”) and Standard & Poor’s 500 Stock Index (“S&P 500”). As a result of acquisitions and other transactions impacting companies that comprise the Peer Group listed below, Snap-on believes that the S&P 500 Industrials Index, of which Snap-on is a member, is a more relevant source of comparative performance. In accordance with SEC rules, Snap-on is presenting information for both the Peer Group and the S&P 500 Industrials Index this year; going forward, only the S&P 500 Industrials Index will be presented along with Snap-on and the S&P 500.
Snap-on Incorporated Total Shareholder Return (1)
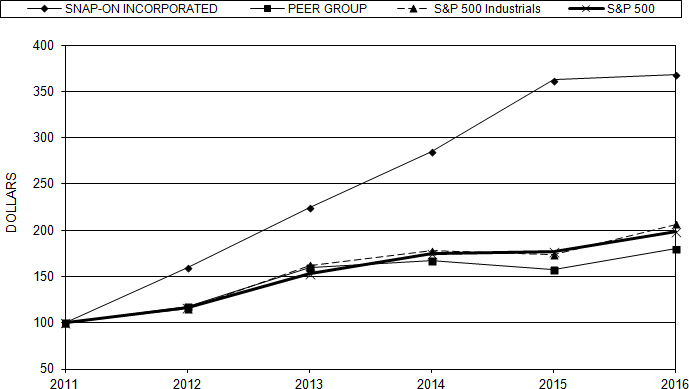
| Fiscal Year Ended (2) |
Snap-on Incorporated |
Peer Group (3) | S&P 500 Industrials |
S&P 500 | ||||||||||||
| December 31, 2011 |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 100.00 | $ | 100.00 | $ | 100.00 | ||||||||
| December 31, 2012 |
159.41 | 117.59 | 115.35 | 116.00 | ||||||||||||
| December 31, 2013 |
224.87 | 160.15 | 162.27 | 153.58 | ||||||||||||
| December 31, 2014 |
285.06 | 167.54 | 178.21 | 174.60 | ||||||||||||
| December 31, 2015 |
362.38 | 158.07 | 173.70 | 177.01 | ||||||||||||
| December 31, 2016 |
367.95 | 179.83 | 206.46 | 198.18 | ||||||||||||
| (1) | Assumes $100 was invested on December 31, 2011, and that dividends were reinvested quarterly. |
| (2) | The company’s fiscal year ends on the Saturday that is on or nearest to December 31 of each year; for ease of calculation, the fiscal year end is assumed to be December 31. |
| (3) | The Peer Group consists of: Stanley Black & Decker, Inc., Danaher Corporation, Emerson Electric Co., Genuine Parts Company, Newell Brands Inc., Pentair plc, SPX Corporation and W.W. Grainger, Inc. |
| 24 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Item 6: Selected Financial Data
The selected financial data presented below has been derived from, and should be read in conjunction with, the respective historical consolidated financial statements of the company, including the notes thereto, and “Part II, Item 7, Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” In the following table, “Total assets” was adjusted on a retrospective basis for all years presented to reflect the company’s 2016 adoption of Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2015-17, Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes (Topic 740). See Note 1 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on the company’s adoption of ASU No. 2015-17.
| Five-year Data |
||||||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions, except per share data) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||
| Results of Operations |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 3,430.4 | $ | 3,352.8 | $ | 3,277.7 | $ | 3,056.5 | $ | 2,937.9 | ||||||||||
| Gross profit |
1,709.6 | 1,648.3 | 1,584.3 | 1,472.9 | 1,390.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
1,054.1 | 1,053.7 | 1,048.7 | 1,012.4 | 980.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating earnings before financial services |
655.5 | 594.6 | 535.6 | 460.5 | 409.7 | |||||||||||||||
| Financial services revenue |
281.4 | 240.3 | 214.9 | 181.0 | 161.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Financial services expenses |
82.7 | 70.1 | 65.8 | 55.3 | 54.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating earnings from financial services |
198.7 | 170.2 | 149.1 | 125.7 | 106.7 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating earnings |
854.2 | 764.8 | 684.7 | 586.2 | 516.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
52.2 | 51.9 | 52.9 | 56.1 | 55.8 | |||||||||||||||
| Earnings before income taxes and equity earnings |
801.4 | 710.5 | 630.9 | 526.2 | 460.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
244.3 | 221.2 | 199.5 | 166.7 | 148.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Earnings before equity earnings |
557.1 | 489.3 | 431.4 | 359.5 | 312.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Equity earnings, net of tax |
2.5 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 2.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
559.6 | 490.6 | 432.1 | 359.7 | 314.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interests |
(13.2) | (11.9) | (10.2) | (9.4) | (8.5) | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to Snap-on |
546.4 | 478.7 | 421.9 | 350.3 | 306.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Financial Position |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 77.6 | $ | 92.8 | $ | 132.9 | $ | 217.6 | $ | 214.5 | ||||||||||
| Trade and other accounts receivable – net |
598.8 | 562.5 | 550.8 | 531.6 | 497.9 | |||||||||||||||
| Finance receivables – net (current) |
472.5 | 447.3 | 402.4 | 374.6 | 323.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Contract receivables – net (current) |
88.1 | 82.1 | 74.5 | 68.4 | 62.7 | |||||||||||||||
| Inventories – net |
530.5 | 497.8 | 475.5 | 434.4 | 404.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Property and equipment – net |
425.2 | 413.5 | 404.5 | 392.5 | 375.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term finance receivables – net |
934.5 | 772.7 | 650.5 | 560.6 | 494.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term contract receivables – net |
286.7 | 266.6 | 242.0 | 217.1 | 194.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
4,723.2 | 4,331.1 | 4,162.0 | 3,994.5 | 3,789.7 | |||||||||||||||
| Notes payable and current maturities of long-term debt |
301.4 | 18.4 | 56.6 | 113.1 | 5.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable |
170.9 | 148.3 | 145.0 | 155.6 | 142.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt |
708.8 | 861.7 | 862.7 | 858.9 | 970.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Total debt |
1,010.2 | 880.1 | 919.3 | 972.0 | 975.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Total shareholders’ equity attributable to Snap-on |
2,617.2 | 2,412.7 | 2,207.8 | 2,113.2 | 1,802.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Common Share Summary |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Weighted-average shares outstanding – diluted |
59.4 | 59.1 | 59.1 | 59.1 | 58.9 | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings per share attributable to Snap-on: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 9.40 | $ | 8.24 | $ | 7.26 | $ | 6.02 | $ | 5.26 | ||||||||||
| Diluted |
9.20 | 8.10 | 7.14 | 5.93 | 5.20 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends paid per share |
2.54 | 2.20 | 1.85 | 1.58 | 1.40 | |||||||||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity per basic share |
45.05 | 41.53 | 38.00 | 36.31 | 30.96 | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 25 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Item 7: Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Management Overview
References in this Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations to “organic sales” refer to sales from continuing operations calculated in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“GAAP”), excluding acquisition-related sales and the impact of foreign currency translation. Management evaluates the company’s sales performance based on organic sales growth, which primarily reflects growth from the company’s existing businesses as a result of increased output, customer base and geographic expansion, new product development and/or pricing, and excludes sales contributions from acquired operations the company did not own as of the comparable prior-year reporting period. The company’s organic sales disclosures also exclude the effects of foreign currency translation as foreign currency translation is subject to volatility that can obscure underlying business trends. Management believes that the non-GAAP financial measure of organic sales is meaningful to investors as it provides them with useful information to aid in identifying underlying growth trends in our businesses and facilitating comparisons of our sales performance with prior periods.
We believe our growth in 2016 demonstrates Snap-on’s continued progress in providing repeatability and reliability to a wide range of professional customers performing critical tasks in workplaces of consequence, as continued strengthening in the automotive repair sector combined with headwinds in certain industrial end markets that were most pronounced in the first half of the year. Leveraging capabilities already demonstrated in the automotive repair arena, our “coherent growth” strategy focuses on developing and expanding our professional customer base, not only in automotive repair, but in adjacent markets, additional geographies and other areas, including in critical industries, where the cost and penalties for failure can be high.
We believe our 2016 operating results also provide continued evidence that Snap-on’s value proposition of making work easier for serious professionals in workplaces of consequence is an ongoing strength as we move forward along our runways for coherent growth:
| • | Enhancing the franchise network, where we continued to focus on helping our franchisees extend their reach through innovative selling processes and productivity initiatives that break the traditional time and space barriers inherent in a mobile van; |
| • | Expanding in the vehicle repair garage, where we continued to make significant progress in connecting with customers and translating the resulting insights into innovation that solves specific challenges in the repair facility. For example, the October 31, 2016 acquisition of Car-O-Liner Holding AB (“Car-O-Liner”) broadened our established capabilities in serving vehicle repair facilities and further expanded our presence with repair shop owners and managers; |
| • | Further extending in critical industries, where we continued to grow our lines of products customized for specific industries, despite near-term challenges in certain industrial end markets; and |
| • | Building in emerging markets, where we continued to build manufacturing capacity, focused product lines and distribution capability. |
We also believe our year-over-year improvement in operating margin further validates the potential of our Snap-on Value Creation Processes – our suite of strategic principles and processes we employ every day designed to create value and employed in the areas of safety, quality, customer connection, innovation and rapid continuous improvement.
Our global financial services operations continue to serve a significant strategic role in offering financing options to our franchisees, to their customers, and to customers in other parts of our business. We expect that our global financial services business, which includes both Snap-on Credit LLC (“SOC”) in the United States and our other international finance subsidiaries, will continue to be a meaningful contributor to our operating earnings going forward.
Snap-on has significant international operations and is subject to risks inherent with foreign operations, including foreign currency translation fluctuations.
| 26 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Recent Acquisitions
On November 16, 2016, Snap-on acquired Ryeson Corporation (d/b/a Sturtevant Richmont) for a preliminary cash purchase price of $12.9 million (or $12.5 million, net of cash acquired). The preliminary purchase price is subject to change based upon the finalization of a working capital adjustment that is expected to be completed in the first quarter of 2017. Sturtevant Richmont, based in Carol Stream, Illinois, designs, manufactures and distributes mechanical and electronic torque wrenches as well as wireless torque error proofing systems for a variety of industrial applications. The acquisition of Sturtevant Richmont enhanced and expanded Snap-on’s capabilities in providing solutions that address torque requirements, which are increasingly essential to critical mechanical performance. For segment reporting purposes, the results of operations and assets of Sturtevant Richmont have been included in the Commercial & Industrial Group since the acquisition date.
On October 31, 2016, Snap-on acquired Car-O-Liner for a preliminary cash purchase price of $151.8 million (or $147.9 million, net of cash acquired). The preliminary purchase price is subject to change based upon the finalization of a working capital adjustment that is expected to be completed in the first quarter of 2017. Car-O-Liner, based in Gothenburg, Sweden, designs and manufactures collision repair equipment, and information and truck alignment systems. The acquisition of Car-O-Liner complemented and increased Snap-on’s existing equipment and repair and service information product offerings, broadened its established capabilities in serving vehicle repair facilities and further expanded the company’s presence with repair shop owners and managers. For segment reporting purposes, substantially all of Car-O-Liner’s results of operations and assets have been included in the Repair Systems & Information Group since the acquisition date, with the remaining portions included in the Commercial & Industrial Group.
On July 27, 2015, Snap-on acquired the assets of Ecotechnics S.p.A. (“Ecotechnics”) for a cash purchase price of $11.8 million. Ecotechnics designs and manufactures vehicle air conditioning service equipment for original equipment manufacturer (“OEM”) dealerships and the automotive aftermarket worldwide. The acquisition of the Ecotechnics product line complemented and increased Snap-on’s existing equipment product offering for OEM dealerships and independent automotive repair shops, broadened its established capabilities in serving vehicle repair facilities, and expanded the company’s presence with repair shop owners and managers.
On May 28, 2014, Snap-on acquired substantially all of the assets of Pro-Cut International Inc. (“Pro-Cut”) for a cash purchase price of $41.3 million. Pro-Cut designs, manufactures and distributes on-car brake lathes, related equipment and accessories used in brake servicing by automotive repair facilities. The acquisition of the Pro-Cut product line complemented and increased Snap-on’s existing undercar equipment product offering, broadened its established capabilities in serving vehicle repair facilities and expanded the company’s presence with repair shop owners and managers.
For segment reporting purposes, the results of operations and assets of Ecotechnics and Pro-Cut have been included in the Repair Systems & Information Group since the respective acquisition dates.
Pro forma financial information has not been presented for any of these acquisitions as the net effects, individually and collectively, were neither significant nor material to Snap-on’s results of operations or financial position.
Consolidated net sales of $3,430.4 million in 2016 increased $77.6 million, or 2.3%, from 2015 levels, reflecting a $96.2 million, or 2.9%, increase in organic sales (a non-GAAP financial measure that excludes acquisition-related sales and the impact of foreign currency translation) and $32.9 million of acquisition-related sales, partially offset by $51.5 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation.
Operating earnings before financial services of $655.5 million in 2016 were up $60.9 million, or 10.2%, from 2015 levels, reflecting contributions from higher sales and improved operating margins, including contributions from “Rapid Continuous Improvement” or “RCI” initiatives, partially offset by $21.5 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects.
Snap-on’s RCI initiatives employ a structured set of tools and processes across multiple businesses and geographies intended to eliminate waste and improve operations. Savings from Snap-on’s RCI initiatives reflect benefits from a wide variety of ongoing efficiency, productivity and process improvements, including savings generated from product design cost reductions, improved manufacturing line set-up and change-over practices, lower-cost sourcing initiatives and facility consolidations. Unless individually significant, it is not practicable to disclose each RCI activity that generated savings and/or segregate RCI savings embedded in sales volume increases.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 27 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (continued)
Operating earnings of $854.2 million in 2016 increased $89.4 million, or 11.7%, from $764.8 million last year. In 2016, net earnings attributable to Snap-on Incorporated were $546.4 million or $9.20 per diluted share. Net earnings attributable to Snap-on Incorporated in 2015 were $478.7 million or $8.10 per diluted share.
The Commercial & Industrial Group consists of business operations serving a broad range of industrial and commercial customers worldwide, including customers in the aerospace, natural resources, government, power generation, transportation and technical education market segments (collectively, “critical industries”), primarily through direct and distributor channels. Segment net sales of $1,148.3 million in 2016 decreased $15.3 million, or 1.3%, from 2015 levels, reflecting $20.6 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation partially offset by $4.2 million of acquisition-related sales and a $1.1 million, or 0.1%, organic sales gain. The organic sales increase primarily includes higher sales in the segment’s European-based hand tools business and in its Asia/Pacific and power tools operations, largely offset by lower sales to customers in critical industries, primarily in the international aerospace and natural resources market segments. Operating earnings of $168.0 million in 2016 decreased $1.4 million, or 0.8%, from 2015 levels, including $1.1 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects.
The Commercial & Industrial Group intends to continue building on the following strategic priorities in 2017:
| • | Continuing to invest in emerging market growth initiatives; |
| • | Expanding our business with existing customers and reaching new customers in critical industries and other market segments; |
| • | Broadening our product offering and engineered solutions designed particularly for critical industry segments; |
| • | Increasing our customer-connection-driven understanding of work across multiple industries; |
| • | Investing in innovation that, guided by that understanding of work, delivers an ongoing stream of productivity-enhancing solutions; and |
| • | Continuing to reduce structural and operating costs through RCI initiatives. |
The Snap-on Tools Group consists of business operations primarily serving vehicle service and repair technicians through the company’s worldwide mobile tool distribution channel. Segment net sales of $1,633.9 million in 2016 increased $65.2 million, or 4.2%, from 2015 levels, reflecting an $86.4 million, or 5.6%, organic sales gain partially offset by $21.2 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation. The organic sales increase includes higher sales in both the company’s U.S. and international franchise operations. Operating earnings of $281.1 million in 2016 increased $25.1 million, or 9.8%, from 2015 levels, primarily as a result of higher sales and savings from RCI initiatives, partially offset by $15.3 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects.
The Snap-on Tools Group made continued progress in 2016 on its fundamental, strategic initiatives to strengthen the franchise network and enhance franchisee profitability. In 2017, the Snap-on Tools Group intends to further build on the progress made in 2016, with specific initiatives focused on the following:
| • | Continuing to improve franchisee satisfaction, productivity, profitability and commercial health; |
| • | Developing new programs and products to expand market coverage, reaching new technicians and increasing penetration with existing customers; |
| • | Continuing to invest in new product innovation and development; and |
| • | Increasing operational flexibility in back office support functions, manufacturing and the supply chain through RCI initiatives and investment. |
By focusing on these areas, we believe that Snap-on, as well as its franchisees, will have the opportunity to continue to serve customers more effectively, more profitably and with improved satisfaction.
The Repair Systems & Information Group consists of business operations serving other professional vehicle repair customers worldwide, primarily owners and managers of independent repair shops and OEM dealership service and repair shops (“OEM dealerships”), through direct and distributor channels. Segment net sales of $1,179.9 million in 2016 increased $66.7 million, or 6.0%, from 2015 levels, reflecting a $52.1 million, or 4.7%, organic sales gain and $28.7 million of acquisition-related sales, partially offset by $14.1 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation. The organic sales increase primarily reflects higher sales to independent repair shop owners and managers, as well as increased sales to OEM dealerships, including higher sales of diagnostic and repair information products, and increased sales of undercar equipment. Operating earnings of $297.8 million in 2016 increased $24.4 million, or 8.9%, from 2015 levels, primarily due to higher sales, including acquisition-related sales, and savings from RCI initiatives, partially offset by $5.1 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects.
| 28 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
The Repair Systems & Information Group intends to focus on the following strategic priorities in 2017:
| • | Expanding the product offering with new products and services, thereby providing more to sell to repair shop owners and managers; |
| • | Continuing software and hardware upgrades to further improve functionality, performance and efficiency; |
| • | Leveraging integration of software solutions; |
| • | Continuing productivity advancements through RCI initiatives and leveraging of resources; and |
| • | Increasing penetration in geographic markets, including emerging markets. |
Financial Services revenue was $281.4 million in 2016 and $240.3 million in 2015; originations of $1,075.7 million in 2016 increased $82.0 million, or 8.3%, from 2015 levels. In recent years, Snap-on has steadily grown its financial services portfolio by providing financing for new finance and contract receivables originated by our global financial services operations. In 2016, operating earnings from financial services of $198.7 million increased $28.5 million, or 16.7%, from $170.2 million last year, including $1.8 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects.
Financial Services intends to focus on the following strategic priorities in 2017:
| • | Delivering financial products and services that attract and sustain profitable franchisees and support Snap-on’s strategies for expanding market coverage and penetration; |
| • | Improving productivity levels and ensuring high quality in all financial products and processes through the use of RCI initiatives; and |
| • | Maintaining healthy portfolio performance levels. |
Cash Flows
Net cash provided by operating activities of $576.1 million in 2016 increased $68.9 million from $507.2 million in 2015 primarily due to $69.0 million of higher net earnings. Net cash provided by operating activities was $403.1 million in 2014.
Net cash used by investing activities of $473.4 million in 2016 included additions to finance receivables of $915.0 million, partially offset by collections of $671.7 million. It also included, on a preliminary basis, a total of $160.4 million (net of $4.3 million of cash acquired) for the acquisitions of Car-O-Liner and Sturtevant Richmont. Net cash used by investing activities of $306.4 million in 2015 included additions to finance receivables of $844.2 million, partially offset by collections of $624.8 million, as well as $11.8 million for the acquisition of Ecotechnics. Net cash used by investing activities of $273.2 million in 2014 included additions to finance receivables of $746.2 million, partially offset by collections of $591.4 million, as well as $41.3 million for the acquisition of Pro-Cut. Capital expenditures in 2016, 2015 and 2014 totaled $74.3 million, $80.4 million and $80.6 million, respectively. Capital expenditures in all three years included investments to support the company’s execution of its strategic growth initiatives and Value Creation Processes around safety, quality, customer connection, innovation and RCI.
Net cash used by financing activities of $116.0 million in 2016 included $147.5 million for dividend payments to shareholders and $120.4 million for the repurchase of 758,000 shares of Snap-on’s common stock, partially offset by $134.2 million of proceeds from a net increase in notes payable and other short-term borrowings and $41.8 million of proceeds from stock purchase and option plan exercises. Net cash used by financing activities of $236.7 million in 2015 included $127.9 million for dividend payments to shareholders, $110.4 million for the repurchase of 723,000 shares of Snap-on’s common stock and $34.0 million from a net decrease in notes payable and other short-term borrowings, partially offset by $41.6 million of proceeds from stock purchase and option plan exercises. Net cash used by financing activities of $212.1 million in 2014 included the repayment of $100 million of unsecured notes at maturity. Net cash used by financing activities in 2014 also included $107.6 million for dividend payments to shareholders and $79.3 million for the repurchase of 680,000 shares of Snap-on’s common stock, partially offset by $45.0 million of proceeds from a net increase in notes payable and other short-term borrowings and $33.0 million of proceeds from stock purchase and option plan exercises.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 29 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (continued)
Fiscal Year
Snap-on’s fiscal year ends on the Saturday that is on or nearest to December 31. Unless otherwise indicated, references in this Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations to “fiscal 2016” or “2016” refer to the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016; references to “fiscal 2015” or “2015” refer to the fiscal year ended January 2, 2016; and references to “fiscal 2014” or “2014” refer to the fiscal year ended January 3, 2015. References in this document to 2016, 2015 and 2014 year end refer to December 31, 2016, January 2, 2016, and January 3, 2015, respectively.
Snap-on’s 2016 and 2015 fiscal years each contained 52 weeks of operating results. Snap-on’s 2014 fiscal year contained 53 weeks of operating results; the impact of the additional week of operations was not material to Snap-on’s full year 2014 net sales or net earnings.
Results of Operations
2016 vs. 2015
Results of operations for 2016 and 2015 are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 3,430.4 | 100.0% | $ | 3,352.8 | 100.0% | $ | 77.6 | 2.3% | |||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(1,720.8) | -50.2% | (1,704.5) | -50.8% | (16.3) | -1.0% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
1,709.6 | 49.8% | 1,648.3 | 49.2% | 61.3 | 3.7% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(1,054.1) | -30.7% | (1,053.7) | -31.5% | (0.4) | – | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Operating earnings before financial services |
655.5 | 19.1% | 594.6 | 17.7% | 60.9 | 10.2% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Financial services revenue |
281.4 | 100.0% | 240.3 | 100.0% | 41.1 | 17.1% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Financial services expenses |
(82.7) | -29.4% | (70.1) | -29.2% | (12.6) | -18.0% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Operating earnings from financial services |
198.7 | 70.6% | 170.2 | 70.8% | 28.5 | 16.7% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Operating earnings |
854.2 | 23.0% | 764.8 | 21.3% | 89.4 | 11.7% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(52.2) | -1.4% | (51.9) | -1.4% | (0.3) | -0.6% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other income (expense) – net |
(0.6) | – | (2.4) | -0.1% | 1.8 | NM | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings before income taxes and equity earnings |
801.4 | 21.6% | 710.5 | 19.8% | 90.9 | 12.8% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
(244.3) | -6.6% | (221.2) | -6.2% | (23.1) | -10.4% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings before equity earnings |
557.1 | 15.0% | 489.3 | 13.6% | 67.8 | 13.9% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Equity earnings, net of tax |
2.5 | 0.1% | 1.3 | – | 1.2 | NM | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
559.6 | 15.1% | 490.6 | 13.6% | 69.0 | 14.1% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interests |
(13.2) | -0.4% | (11.9) | -0.3% | (1.3) | -10.9% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to Snap-on Inc. |
$ | 546.4 | 14.7% | $ | 478.7 | 13.3% | $ | 67.7 | 14.1% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
NM: Not meaningful
Percentage Disclosure: All income statement line item percentages below “Operating earnings from financial services” are calculated as a percentage of the sum of Net sales and Financial services revenue.
Net sales of $3,430.4 million in 2016 increased $77.6 million, or 2.3%, from 2015 levels, reflecting a $96.2 million, or 2.9%, organic sales gain and $32.9 million of acquisition-related sales, partially offset by $51.5 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation.
| 30 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Gross profit of $1,709.6 million in 2016 compared to $1,648.3 million last year. Gross margin (gross profit as a percentage of net sales) of 49.8% in 2016 improved 60 basis points (100 basis points (“bps”) equals 1.0 percent) from 49.2% last year as benefits from higher sales and savings from RCI initiatives were partially offset by 20 bps of unfavorable foreign currency effects. Restructuring costs included in gross profit were $0.8 million and zero in 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Operating expenses of $1,054.1 million in 2016 compared to $1,053.7 million last year. The operating expense margin (operating expenses as a percentage of net sales) of 30.7% in 2016 improved 80 bps from 31.5% last year primarily due to sales volume leverage and savings from RCI initiatives, 30 bps of lower stock-based (mark-to-market) compensation and other expenses, including lower costs associated with the company’s employee and franchisee stock purchase plans, and 20 bps of lower pension expense. Restructuring costs included in operating expenses were $0.1 million and zero in 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Operating earnings before financial services of $655.5 million in 2016, including $21.5 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $60.9 million, or 10.2%, as compared to $594.6 million last year. As a percentage of net sales, operating earnings before financial services of 19.1% in 2016 improved 140 bps from 17.7% last year.
Financial services revenue of $281.4 million in 2016 compared to revenue of $240.3 million last year. Financial services operating earnings of $198.7 million in 2016, including $1.8 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $28.5 million, or 16.7%, as compared to $170.2 million last year. The year-over-year increases in both revenue and operating earnings primarily reflect continued growth of the company’s financial services portfolio.
Operating earnings of $854.2 million in 2016, including $23.3 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $89.4 million, or 11.7%, from $764.8 million last year. As a percentage of revenues (net sales plus financial services revenue), operating earnings of 23.0% in 2016 improved 170 bps from 21.3% last year.
Interest expense of $52.2 million in 2016 increased $0.3 million from $51.9 million last year. See Note 9 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on Snap-on’s debt and credit facilities.
Other income (expense) – net was expense of $0.6 million and $2.4 million in 2016 and 2015, respectively. Other income (expense) – net reflects net losses and gains associated with hedging and currency exchange rate transactions, and interest income. See Note 16 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on other income (expense) – net.
Snap-on’s effective income tax rate on earnings attributable to Snap-on was 31.0% in 2016 and 31.7% in 2015. See Note 8 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on income taxes.
Net earnings attributable to Snap-on of $546.4 million, or $9.20 per diluted share, in 2016 increased $67.7 million, or $1.10 per diluted share, from 2015 levels. Net earnings attributable to Snap-on in 2015 were $478.7 million or $8.10 per diluted share.
Exit and Disposal Activities
In 2016, the company’s Repair Systems & Information Group recorded $0.9 million of severance costs for exit and disposal activities, all of which qualified for accrual treatment; no costs for exit and disposal activities were recorded in 2015. The exit and disposal accrual of $2.8 million as of 2016 year end is expected to be fully utilized in 2017. Snap-on anticipates funding the remaining cash requirements of its exit and disposal activities with available cash on hand, cash flows from operations and borrowings under the company’s existing credit facilities. The estimated costs for the exit and disposal activities were based on management’s best business judgment under prevailing circumstances.
Segment Results
Snap-on’s business segments are based on the organization structure used by management for making operating and investment decisions and for assessing performance. Snap-on’s reportable business segments are: (i) the Commercial & Industrial Group; (ii) the Snap-on Tools Group; (iii) the Repair Systems & Information Group; and (iv) Financial Services. The Commercial & Industrial Group consists of business operations serving a broad range of industrial and commercial customers worldwide, including customers in the aerospace, natural resources, government, power generation, transportation and technical education market segments (collectively, “critical industries”), primarily through direct and distributor channels. The Snap-on Tools Group consists of business operations primarily serving vehicle service and repair technicians through the company’s worldwide mobile tool distribution channel. The Repair Systems & Information Group consists of business operations serving other professional vehicle repair customers worldwide, primarily owners and managers of independent repair shops and OEM dealerships, through direct and distributor channels. Financial Services consists of the business operations of Snap-on’s finance subsidiaries.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 31 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (continued)
Snap-on evaluates the performance of its operating segments based on segment revenues, including both external and intersegment net sales, and segment operating earnings. Snap-on accounts for intersegment sales and transfers based primarily on standard costs with reasonable mark-ups established between the segments. Identifiable assets by segment are those assets used in the respective reportable segment’s operations. Corporate assets consist of cash and cash equivalents (excluding cash held at Financial Services), deferred income taxes and certain other assets. All significant intersegment amounts are eliminated to arrive at Snap-on’s consolidated financial results.
Commercial & Industrial Group
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External net sales |
$ | 863.0 | 75.2% | $ | 895.5 | 77.0% | $ | (32.5) | -3.6% | |||||||||||||||
| Intersegment net sales |
285.3 | 24.8% | 268.1 | 23.0% | 17.2 | 6.4% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment net sales |
1,148.3 | 100.0% | 1,163.6 | 100.0% | (15.3) | -1.3% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(698.3) | -60.8% | (717.1) | -61.6% | 18.8 | 2.6% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
450.0 | 39.2% | 446.5 | 38.4% | 3.5 | 0.8% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(282.0) | -24.6% | (277.1) | -23.8% | (4.9) | -1.8% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment operating earnings |
$ | 168.0 | 14.6% | $ | 169.4 | 14.6% | $ | (1.4) | -0.8% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Segment net sales of $1,148.3 million in 2016 decreased $15.3 million, or 1.3%, from 2015 levels, reflecting $20.6 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation partially offset by $4.2 million of acquisition-related sales and a $1.1 million, or 0.1%, organic sales gain. The organic sales increase primarily includes a mid single-digit gain in the segment’s European-based hand tools business and low single-digit increases in both the segment’s Asia/Pacific and power tools operations. These organic sales gains were largely offset by a mid single-digit decline in sales to customers in critical industries, primarily in the international aerospace and natural resources market segments.
Segment gross profit of $450.0 million in 2016 compared to $446.5 million last year. Gross margin of 39.2% in 2016 improved 80 bps from 38.4% last year primarily due to savings from RCI and other cost reduction initiatives, and 20 bps of favorable foreign currency effects.
Segment operating expenses of $282.0 million in 2016 compared to $277.1 million last year. The operating expense margin of 24.6% in 2016 increased 80 bps from 23.8% last year primarily due to higher costs, including costs associated with continued expansion initiatives in Asia, a 20 bps benefit realized in 2015 from a gain on the sale of a former manufacturing facility, and 10 bps of unfavorable foreign currency effects.
As a result of these factors, segment operating earnings of $168.0 million in 2016, including $1.1 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, decreased $1.4 million from 2015 levels. Operating margin (segment operating earnings as a percentage of segment net sales) for the Commercial & Industrial Group was 14.6% in both years.
Snap-on Tools Group
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Segment net sales |
$ | 1,633.9 | 100.0% | $ | 1,568.7 | 100.0% | $ | 65.2 | 4.2% | |||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(929.8) | -56.9% | (885.7) | -56.5% | (44.1) | -5.0% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
704.1 | 43.1% | 683.0 | 43.5% | 21.1 | 3.1% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(423.0) | -25.9% | (427.0) | -27.2% | 4.0 | 0.9% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment operating earnings |
$ | 281.1 | 17.2% | $ | 256.0 | 16.3% | $ | 25.1 | 9.8% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Segment net sales of $1,633.9 million in 2016 increased $65.2 million, or 4.2%, from 2015 levels, reflecting an $86.4 million, or 5.6%, organic sales gain partially offset by $21.2 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation. The organic sales increase includes mid single-digit gains in both the company’s U.S. and international franchise operations.
Segment gross profit of $704.1 million in 2016 compared to $683.0 million last year. Gross margin of 43.1% in 2016 declined 40 bps from 43.5% last year as 70 bps of unfavorable foreign currency effects were partially offset by benefits from higher sales.
Segment operating expenses of $423.0 million in 2016 compared to $427.0 million last year. The operating expense margin of 25.9% in 2016 improved 130 bps from 27.2% last year primarily due to sales volume leverage and savings from RCI and other cost reduction initiatives, as well as 20 bps of lower stock-based costs associated with the company’s franchisee stock purchase plan.
As a result of these factors, segment operating earnings of $281.1 million in 2016, including $15.3 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $25.1 million from 2015 levels. Operating margin for the Snap-on Tools Group of 17.2% in 2016 improved 90 bps from 16.3% last year.
Repair Systems & Information Group
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External net sales |
$ | 933.5 | 79.1% | $ | 888.6 | 79.8% | $ | 44.9 | 5.1% | |||||||||||||||
| Intersegment net sales |
246.4 | 20.9% | 224.6 | 20.2% | 21.8 | 9.7% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment net sales |
1,179.9 | 100.0% | 1,113.2 | 100.0% | 66.7 | 6.0% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(624.4) | -52.9% | (594.4) | -53.4% | (30.0) | -5.0% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
555.5 | 47.1% | 518.8 | 46.6% | 36.7 | 7.1% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(257.7) | -21.9% | (245.4) | -22.0% | (12.3) | -5.0% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment operating earnings |
$ | 297.8 | 25.2% | $ | 273.4 | 24.6% | $ | 24.4 | 8.9% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Segment net sales of $1,179.9 million in 2016 increased $66.7 million, or 6.0%, from 2015 levels, reflecting a $52.1 million, or 4.7%, organic sales gain and $28.7 million of acquisition-related sales, partially offset by $14.1 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation. The organic sales increase includes a high single-digit gain in sales of diagnostic and repair information products to independent repair shop owners and managers, and low single-digit increases in both sales of undercar equipment and sales to OEM dealerships.
Segment gross profit of $555.5 million in 2016 compared to $518.8 million last year. Gross margin of 47.1% in 2016 improved 50 bps from 46.6% last year, as benefits from higher sales and savings from RCI initiatives were partially offset by 10 bps of unfavorable currency effects. Restructuring costs included in gross profit were $0.8 million and zero in 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Segment operating expenses of $257.7 million in 2016 compared to $245.4 million last year. The operating expense margin of 21.9% in 2016 improved 10 bps from 22.0% last year primarily due to sales volume leverage and savings from RCI initiatives, partially offset by 20 bps of impact from the Car-O-Liner acquisition. Restructuring costs included in operating expenses were $0.1 million and zero in 2016 and 2015, respectively.
As a result of these factors, segment operating earnings of $297.8 million in 2016, including $5.1 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $24.4 million from 2015 levels. Operating margin for the Repair Systems & Information Group of 25.2% in 2016 improved 60 bps from 24.6% last year.
Financial Services
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial services revenue |
$ | 281.4 | 100.0% | $ | 240.3 | 100.0% | $ | 41.1 | 17.1% | |||||||||||||||
| Financial services expenses |
(82.7) | -29.4% | (70.1) | -29.2% | (12.6) | -18.0% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment operating earnings |
$ | 198.7 | 70.6% | $ | 170.2 | 70.8% | $ | 28.5 | 16.7% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 33 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (continued)
Financial services revenue of $281.4 million in 2016 increased $41.1 million, or 17.1%, from $240.3 million last year primarily reflecting $38.1 million of higher revenue as a result of continued growth of the company’s financial services portfolio and $2.7 million of increased revenue from higher average yields on finance receivables. In 2016 and 2015, the respective average yield on finance receivables was 18.0% and 17.8%, and the respective average yield on contract receivables was 9.4% and 9.5%. Originations of $1,075.7 million in 2016 increased $82.0 million, or 8.3%, from 2015 levels.
Financial services expenses primarily include personnel-related and other general and administrative costs, as well as provisions for credit losses. These expenses are generally more dependent on changes in the financial services portfolio than they are on the revenue of the segment. Financial services expenses of $82.7 million in 2016 increased from $70.1 million last year primarily due to changes in both the size of the portfolio and in the provisions for credit losses. As a percentage of the average financial services portfolio, financial services expenses were 4.9% and 4.8% in 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Financial services operating earnings of $198.7 million in 2016, including $1.8 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $28.5 million, or 16.7%, from 2015 levels.
See Note 1 and Note 3 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further information on financial services.
Corporate
Snap-on’s general corporate expenses in 2016 of $91.4 million decreased $12.8 million from $104.2 million last year. The year-over-year decrease in general corporate expenses primarily reflects $6.9 million of lower pension expense, $6.4 million of lower stock-based (mark-to-market) compensation expense and $2.3 million of lower stock-based costs associated with the company’s employee stock purchase plan, partially offset by $2.8 million of higher acquisition-related and other costs.
Fourth Quarter
Results of operations for the fourth quarters of 2016 and 2015 are as follows:
| Fourth Quarter | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 889.8 | 100.0% | $ | 851.7 | 100.0% | $ | 38.1 | 4.5% | |||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(445.9) | -50.1% | (439.4) | -51.6% | (6.5) | -1.5% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
443.9 | 49.9% | 412.3 | 48.4% | 31.6 | 7.7% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(267.8) | -30.1% | (250.0) | -29.3% | (17.8) | -7.1% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Operating earnings before financial services |
176.1 | 19.8% | 162.3 | 19.1% | 13.8 | 8.5% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Financial services revenue |
74.2 | 100.0% | 63.1 | 100.0% | 11.1 | 17.6% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Financial services expenses |
(22.6) | -30.5% | (18.1) | -28.7% | (4.5) | -24.9% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Operating earnings from financial services |
51.6 | 69.5% | 45.0 | 71.3% | 6.6 | 14.7% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Operating earnings |
227.7 | 23.6% | 207.3 | 22.7% | 20.4 | 9.8% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(13.1) | -1.4% | (13.0) | -1.4% | (0.1) | -0.8% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other income (expense) – net |
(0.3) | – | (0.5) | -0.1% | 0.2 | NM | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings before income taxes and equity earnings |
214.3 | 22.2% | 193.8 | 21.2% | 20.5 | 10.6% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
(64.9) | -6.7% | (59.3) | -6.5% | (5.6) | -9.4% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings before equity earnings |
149.4 | 15.5% | 134.5 | 14.7% | 14.9 | 11.1% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Equity earnings, net of tax |
0.3 | – | – | – | 0.3 | NM | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
149.7 | 15.5% | 134.5 | 14.7% | 15.2 | 11.3% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interests |
(3.4) | -0.3% | (3.1) | -0.3% | (0.3) | -9.7% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to Snap-on Inc. |
$ | 146.3 | 15.2% | $ | 131.4 | 14.4% | $ | 14.9 | 11.3% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
NM: Not meaningful
Percentage Disclosure: All income statement line item percentages below “Operating earnings from financial services” are calculated as a percentage of the sum of Net sales and Financial services revenue.
| 34 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Net sales of $889.8 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 increased $38.1 million, or 4.5%, from 2015 levels, reflecting a $30.0 million, or 3.6%, organic sales gain and $23.3 million of acquisition-related sales, partially offset by $15.2 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation.
Gross profit of $443.9 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 compared to $412.3 million last year. Gross margin of 49.9% in the quarter improved 150 bps from 48.4% last year primarily due to benefits from higher sales and savings from RCI initiatives.
Operating expenses of $267.8 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 compared to $250.0 million last year. The operating expense margin of 30.1% in the quarter increased 80 bps from 29.3% last year primarily due to 60 bps of higher acquisition-related and other expenses, including operating expenses for Car-O-Liner and Sturtevant Richmont, and a 30 bps benefit realized in the fourth quarter of 2015 primarily from a gain on the sale of a former manufacturing facility, partially offset by 20 bps of lower pension expense.
Operating earnings before financial services of $176.1 million in the fourth quarter of 2016, including $3.7 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $13.8 million, or 8.5%, as compared to $162.3 million last year. As a percentage of net sales, operating earnings before financial services of 19.8% in the quarter improved 70 bps from 19.1% last year.
Financial services revenue of $74.2 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 compared to revenue of $63.1 million last year. Financial services operating earnings of $51.6 million in the fourth quarter of 2016, including $0.6 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $6.6 million, or 14.7%, as compared to $45.0 million last year. The year-over-year increases in both revenue and operating earnings primarily reflect continued growth of the company’s financial services portfolio.
Operating earnings of $227.7 million in the fourth quarter of 2016, including $4.3 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $20.4 million, or 9.8%, from $207.3 million last year. As a percentage of revenues, operating earnings of 23.6% in the quarter improved 90 bps from 22.7% last year.
Interest expense of $13.1 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 increased $0.1 million from $13.0 million last year. See Note 9 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on Snap-on’s debt and credit facilities.
Other income (expense) – net was expense of $0.3 million and $0.5 million in the respective fourth quarters of 2016 and 2015. See Note 16 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on other income (expense) – net.
Snap-on’s fourth quarter effective income tax rate on earnings attributable to Snap-on was 30.8% in 2016 and 31.1% in 2015. See Note 8 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on income taxes.
Net earnings attributable to Snap-on of $146.3 million, or $2.47 per diluted share, in the fourth quarter of 2016 increased $14.9 million, or $0.25 per diluted share, from 2015 levels. Net earnings attributable to Snap-on in the fourth quarter of 2015 were $131.4 million or $2.22 per diluted share.
Segment Results
Commercial & Industrial Group
| Fourth Quarter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External net sales |
$ | 218.5 | 76.3% | $ | 212.0 | 75.2% | $ | 6.5 | 3.1% | |||||||||||||||
| Intersegment net sales |
67.8 | 23.7% | 69.8 | 24.8% | (2.0) | -2.9% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment net sales |
286.3 | 100.0% | 281.8 | 100.0% | 4.5 | 1.6% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(170.9) | -59.7% | (174.2) | -61.8% | 3.3 | 1.9% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
115.4 | 40.3% | 107.6 | 38.2% | 7.8 | 7.2% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(71.5) | -25.0% | (65.7) | -23.3% | (5.8) | -8.8% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment operating earnings |
$ | 43.9 | 15.3% | $ | 41.9 | 14.9% | $ | 2.0 | 4.8% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 35 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (continued)
Segment net sales of $286.3 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 increased $4.5 million, or 1.6%, from 2015 levels, reflecting a $6.5 million, or 2.4%, organic sales gain and $4.2 million of acquisition-related sales, partially offset by $6.2 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation. The organic sales increase primarily includes a high single-digit gain in the segment’s European-based hand tools business and a low single-digit increase to customers in critical industries, largely as a result of higher sales to the military. These organic sales gains were partially offset by a mid single-digit decline in the segment’s power tools operations and a low single-digit decline in the segment’s Asia/Pacific operations.
Segment gross profit of $115.4 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 compared to $107.6 million last year. Gross margin of 40.3% in the quarter improved 210 bps from 38.2% last year primarily due to benefits from higher sales and savings from RCI initiatives, and 100 bps of favorable foreign currency effects.
Segment operating expenses of $71.5 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 compared to $65.7 million last year. The operating expense margin of 25.0% in the quarter increased 170 bps from 23.3% last year primarily due to higher costs, including operating expenses for Car-O-Liner and Sturtevant Richmont, a 70 bps benefit realized in the fourth quarter of 2015 from a gain on the sale of a former manufacturing facility, and 10 bps of unfavorable foreign currency effects.
As a result of these factors, segment operating earnings of $43.9 million in the fourth quarter of 2016, including $1.8 million of favorable foreign currency effects, increased $2.0 million from 2015 levels. Operating margin for the Commercial & Industrial Group of 15.3% in the fourth quarter of 2016 improved 40 bps from 14.9% last year.
Snap-on Tools Group
| Fourth Quarter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Segment net sales |
$ | 417.5 | 100.0% | $ | 411.2 | 100.0% | $ | 6.3 | 1.5% | |||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(242.0) | -58.0% | (237.5) | -57.8% | (4.5) | -1.9% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
175.5 | 42.0% | 173.7 | 42.2% | 1.8 | 1.0% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(102.0) | -24.4% | (101.8) | -24.7% | (0.2) | -0.2% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment operating earnings |
$ | 73.5 | 17.6% | $ | 71.9 | 17.5% | $ | 1.6 | 2.2% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Segment net sales of $417.5 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 increased $6.3 million, or 1.5%, from 2015 levels, reflecting a $12.2 million, or 3.0%, organic sales gain partially offset by $5.9 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation. The organic sales increase includes a low single-digit gain in the company’s U.S. franchise operations and a mid single-digit gain in the company’s international franchise operations.
Segment gross profit of $175.5 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 compared to $173.7 million last year. Gross margin of 42.0% in the quarter declined 20 bps from 42.2% last year as 60 bps of unfavorable foreign currency effects were partially offset by benefits from higher sales.
Segment operating expenses of $102.0 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 compared to $101.8 million last year. The operating expense margin of 24.4% in the quarter improved 30 bps from 24.7% last year primarily due to sales volume leverage.
As a result of these factors, segment operating earnings of $73.5 million in the fourth quarter of 2016, including $3.8 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $1.6 million from 2015 levels. Operating margin for the Snap-on Tools Group of 17.6% in the fourth quarter of 2016 improved 10 bps from 17.5% last year.
| 36 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Repair Systems & Information Group
| Fourth Quarter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External net sales |
$ | 253.8 | 79.4% | $ | 228.5 | 81.4% | $ | 25.3 | 11.1% | |||||||||||||||
| Intersegment net sales |
66.0 | 20.6% | 52.1 | 18.6% | 13.9 | 26.7% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment net sales |
319.8 | 100.0% | 280.6 | 100.0% | 39.2 | 14.0% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(166.8) | -52.2% | (149.6) | -53.3% | (17.2) | -11.5% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
153.0 | 47.8% | 131.0 | 46.7% | 22.0 | 16.8% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(70.5) | -22.0% | (58.9) | -21.0% | (11.6) | -19.7% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment operating earnings |
$ | 82.5 | 25.8% | $ | 72.1 | 25.7% | $ | 10.4 | 14.4% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Segment net sales of $319.8 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 increased $39.2 million, or 14.0%, from 2015 levels, reflecting a $24.6 million, or 8.9%, organic sales gain and $19.1 million of acquisition-related sales, partially offset by $4.5 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation. The organic sales increase includes a double-digit gain in sales of diagnostic and repair information products to independent repair shop owners and managers, a mid single-digit increase in sales to OEM dealerships and a low single-digit gain in sales of undercar equipment.
Segment gross profit of $153.0 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 compared to $131.0 million last year. Gross margin of 47.8% in the quarter improved 110 bps from 46.7% last year primarily due to benefits from higher sales and savings from RCI initiatives.
Segment operating expenses of $70.5 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 compared to $58.9 million last year. The operating expense margin of 22.0% increased 100 bps from 21.0% last year primarily due to 90 bps of impact from the Car-O-Liner acquisition.
As a result of these factors, segment operating earnings of $82.5 million in the fourth quarter of 2016, including $1.7 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $10.4 million from 2015 levels. Operating margin for the Repair Systems & Information Group of 25.8% in the fourth quarter of 2016 improved 10 bps from 25.7% last year.
Financial Services
| Fourth Quarter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial services revenue |
$ | 74.2 | 100.0% | $ | 63.1 | 100.0% | $ | 11.1 | 17.6% | |||||||||||||||
| Financial services expenses |
(22.6) | -30.5% | (18.1) | -28.7% | (4.5) | -24.9% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment operating earnings |
$ | 51.6 | 69.5% | $ | 45.0 | 71.3% | $ | 6.6 | 14.7% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Financial services revenue of $74.2 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 increased $11.1 million, or 17.6%, from $63.1 million last year primarily reflecting $9.6 million of higher revenue as a result of continued growth of the company’s financial services portfolio and $1.3 million of increased revenue from higher average yields on finance receivables, partially offset by $0.1 million of lower revenue from lower average yields on contract receivables. In the fourth quarters of 2016 and 2015, the respective average yield on finance receivables was 18.2% and 17.8%, and the respective average yield on contract receivables was 9.3% and 9.5%. Originations of $260.3 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 increased $8.3 million, or 3.3%, from 2015 levels.
Financial services expenses primarily include personnel-related and other general and administrative costs, as well as provisions for credit losses. These expenses are generally more dependent on changes in the financial services portfolio than they are on the revenue of the segment. Financial services expenses of $22.6 million in the fourth quarter of 2016 increased from $18.1 million last year primarily due to changes in both the size of the portfolio and in the provisions for credit losses. As a percentage of the average financial services portfolio, financial services expenses were 1.3% and 1.2% in the fourth quarters of 2016 and 2015, respectively.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 37 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (continued)
Financial services operating earnings of $51.6 million in the fourth quarter of 2016, including $0.6 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $6.6 million, or 14.7%, from 2015 levels.
See Note 1 and Note 3 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further information on financial services.
Corporate
Snap-on’s fourth quarter 2016 general corporate expenses of $23.8 million increased $0.2 million from $23.6 million last year primarily due to higher acquisition-related and other costs partially offset by $1.6 million of lower pension expense.
2015 vs. 2014
Results of operations for 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2015 | 2014 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 3,352.8 | 100.0% | $ | 3,277.7 | 100.0% | $ | 75.1 | 2.3% | |||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(1,704.5) | -50.8% | (1,693.4) | -51.7% | (11.1) | -0.7% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
1,648.3 | 49.2% | 1,584.3 | 48.3% | 64.0 | 4.0% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(1,053.7) | -31.5% | (1,048.7) | -32.0% | (5.0) | -0.5% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Operating earnings before financial services |
594.6 | 17.7% | 535.6 | 16.3% | 59.0 | 11.0% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Financial services revenue |
240.3 | 100.0% | 214.9 | 100.0% | 25.4 | 11.8% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Financial services expenses |
(70.1) | -29.2% | (65.8) | -30.6% | (4.3) | -6.5% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Operating earnings from financial services |
170.2 | 70.8% | 149.1 | 69.4% | 21.1 | 14.2% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Operating earnings |
764.8 | 21.3% | 684.7 | 19.6% | 80.1 | 11.7% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(51.9) | -1.4% | (52.9) | -1.5% | 1.0 | 1.9% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other income (expense) – net |
(2.4) | -0.1% | (0.9) | – | (1.5) | NM | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings before income taxes and equity earnings |
710.5 | 19.8% | 630.9 | 18.1% | 79.6 | 12.6% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
(221.2) | -6.2% | (199.5) | -5.7% | (21.7) | -10.9% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings before equity earnings |
489.3 | 13.6% | 431.4 | 12.4% | 57.9 | 13.4% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Equity earnings, net of tax |
1.3 | – | 0.7 | – | 0.6 | NM | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
490.6 | 13.6% | 432.1 | 12.4% | 58.5 | 13.5% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interests |
(11.9) | -0.3% | (10.2) | -0.3% | (1.7) | -16.7% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to Snap-on Inc. |
$ | 478.7 | 13.3% | $ | 421.9 | 12.1% | $ | 56.8 | 13.5% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
NM: Not meaningful
Percentage Disclosure: All income statement line item percentages below “Operating earnings from financial services” are calculated as a percentage of the sum of Net sales and Financial services revenue.
Snap-on’s 2015 fiscal year contained 52 weeks of operating results. Snap-on’s 2014 fiscal year contained 53 weeks of operating results. The impact of the additional week of operations in fiscal 2014 was not material to Snap-on’s full year 2014 net sales or net earnings.
Net sales of $3,352.8 million in 2015 increased $75.1 million, or 2.3%, from 2014 levels, reflecting a $220.8 million, or 7.1%, organic sales gain and $12.0 million of acquisition-related sales, partially offset by $157.7 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation.
| 38 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Gross profit of $1,648.3 million in 2015 compared to $1,584.3 million in 2014. Gross margin of 49.2% in 2015 improved 90 bps from 48.3% in 2014 primarily due to benefits from higher sales and savings from RCI initiatives, as well as 20 bps of lower restructuring costs. Restructuring costs included in gross profit were zero and $5.7 million in 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Operating expenses of $1,053.7 million in 2015 compared to $1,048.7 million in 2014. The operating expense margin of 31.5% in 2015 improved 50 bps from 32.0% in 2014 primarily due to sales volume leverage and savings from RCI initiatives, partially offset by 20 bps of higher pension expense. Restructuring costs included in operating expenses were zero and $0.8 million in 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Operating earnings before financial services of $594.6 million in 2015, including $39.5 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $59.0 million, or 11.0%, as compared to $535.6 million in 2014. As a percentage of net sales, operating earnings before financial services of 17.7% in 2015 improved 140 bps from 16.3% in 2014.
Financial services revenue of $240.3 million in 2015 compared to revenue of $214.9 million in 2014. Financial services operating earnings of $170.2 million in 2015, including $2.6 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $21.1 million, or 14.2%, as compared to $149.1 million in 2014. The year-over-year increases in both revenue and operating earnings primarily reflect continued growth of the company’s financial services portfolio.
Operating earnings of $764.8 million in 2015, including $42.1 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $80.1 million, or 11.7%, from $684.7 million in 2014. As a percentage of revenues, operating earnings of 21.3% in 2015 improved 170 bps from 19.6% in 2014.
Interest expense of $51.9 million in 2015 decreased $1.0 million from $52.9 million in 2014. See Note 9 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on Snap-on’s debt and credit facilities.
Other income (expense) – net was expense of $2.4 million and $0.9 million in 2015 and 2014, respectively. See Note 16 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on other income (expense) – net.
Snap-on’s effective income tax rate on earnings attributable to Snap-on was 31.7% in 2015 and 32.1% in 2014. See Note 8 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on income taxes.
Net earnings attributable to Snap-on of $478.7 million, or $8.10 per diluted share, in 2015 increased $56.8 million, or $0.96 per diluted share, from 2014 levels. Net earnings attributable to Snap-on in 2014 were $421.9 million or $7.14 per diluted share.
Exit and Disposal Activities
Snap-on did not record any costs for exit and disposal activities in 2015; Snap-on recorded $6.5 million of costs for exit and disposal activities in 2014. See Note 7 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on Snap-on’s exit and disposal activities.
Segment Results
Commercial & Industrial Group
| (Amounts in millions) | 2015 | 2014 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External net sales |
$ | 895.5 | 77.0% | $ | 952.1 | 81.0% | $ | (56.6) | -5.9% | |||||||||||||||
| Intersegment net sales |
268.1 | 23.0% | 222.7 | 19.0% | 45.4 | 20.4% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment net sales |
1,163.6 | 100.0% | 1,174.8 | 100.0% | (11.2) | -1.0% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(717.1) | -61.6% | (725.1) | -61.7% | 8.0 | 1.1% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
446.5 | 38.4% | 449.7 | 38.3% | (3.2) | -0.7% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(277.1) | -23.8% | (291.1) | -24.8% | 14.0 | 4.8% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment operating earnings |
$ | 169.4 | 14.6% | $ | 158.6 | 13.5% | $ | 10.8 | 6.8% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 39 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (continued)
Segment net sales of $1,163.6 million in 2015 decreased $11.2 million, or 1.0%, from 2014 levels, reflecting $75.3 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation partially offset by a $64.1 million, or 5.8%, organic sales gain. The organic sales increase primarily included a double-digit gain in the segment’s power tools operations and high single-digit increases from both the segment’s European-based hand tools business and Asia/Pacific operations; sales to customers in critical industries were essentially flat, as sales gains in several market segments were generally offset by lower sales to customers in the oil and gas sector of our natural resources market segment.
Segment gross profit of $446.5 million in 2015 compared to $449.7 million in 2014. Gross margin of 38.4% in 2015 improved 10 bps from 38.3% in 2014, as savings from RCI initiatives were partially offset by a shift in sales that included higher volumes of lower gross margin products, including increased sales from the segment’s power tools and Asia/Pacific operations. Restructuring costs included in gross profit were zero and $1.0 million in 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Segment operating expenses of $277.1 million in 2015 compared to $291.1 million in 2014. The operating expense margin of 23.8% in 2015 improved 100 bps from 24.8% in 2014 primarily due to benefits from the sales shift noted above and a 20 bps gain from the sale of a former manufacturing facility. Restructuring costs included in operating expenses were zero and $0.4 million in 2015 and 2014, respectively.
As a result of these factors, segment operating earnings of $169.4 million in 2015, including $7.7 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $10.8 million from 2014 levels. Operating margin for the Commercial & Industrial Group of 14.6% in 2015 improved 110 bps from 13.5% in 2014.
Snap-on Tools Group
| (Amounts in millions) | 2015 | 2014 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Segment net sales |
$ | 1,568.7 | 100.0% | $ | 1,455.2 | 100.0% | $ | 113.5 | 7.8% | |||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(885.7) | -56.5% | (824.9) | -56.7% | (60.8) | -7.4% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
683.0 | 43.5% | 630.3 | 43.3% | 52.7 | 8.4% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(427.0) | -27.2% | (407.2) | -28.0% | (19.8) | -4.9% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment operating earnings |
$ | 256.0 | 16.3% | $ | 223.1 | 15.3% | $ | 32.9 | 14.7% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Segment net sales of $1,568.7 million in 2015 increased $113.5 million, or 7.8%, from 2014 levels, reflecting a $154.2 million, or 10.9%, organic sales gain partially offset by $40.7 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation. The organic sales increase included double-digit gains in both the company’s U.S. and international franchise operations.
Segment gross profit of $683.0 million in 2015 compared to $630.3 million in 2014. Gross margin of 43.5% in 2015 improved 20 bps from 43.3% in 2014 primarily due to benefits from higher sales and savings from RCI initiatives, partially offset by 90 bps of unfavorable foreign currency effects.
Segment operating expenses of $427.0 million in 2015 compared to $407.2 million in 2014. The operating expense margin of 27.2% in 2015 improved 80 bps from 28.0% in 2014 primarily due to sales volume leverage.
As a result of these factors, segment operating earnings of $256.0 million in 2015, including $21.3 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $32.9 million from 2014 levels. Operating margin for the Snap-on Tools Group of 16.3% in 2015 improved 100 bps from 15.3% in 2014.
Repair Systems & Information Group
| (Amounts in millions) | 2015 | 2014 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External net sales |
$ | 888.6 | 79.8% | $ | 870.4 | 79.5% | $ | 18.2 | 2.1% | |||||||||||||||
| Intersegment net sales |
224.6 | 20.2% | 224.8 | 20.5% | (0.2) | -0.1% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment net sales |
1,113.2 | 100.0% | 1,095.2 | 100.0% | 18.0 | 1.6% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(594.4) | -53.4% | (590.9) | -54.0% | (3.5) | -0.6% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
518.8 | 46.6% | 504.3 | 46.0% | 14.5 | 2.9% | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(245.4) | -22.0% | (253.1) | -23.1% | 7.7 | 3.0% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment operating earnings |
$ | 273.4 | 24.6% | $ | 251.2 | 22.9% | $ | 22.2 | 8.8% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 40 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Segment net sales of $1,113.2 million in 2015 increased $18.0 million, or 1.6%, from 2014 levels, reflecting a $51.8 million, or 4.9%, organic sales gain and $12.0 million of acquisition-related sales, partially offset by $45.8 million of unfavorable foreign currency translation. The organic sales increase primarily included mid single-digit gains in sales of undercar equipment, sales to OEM dealerships, and sales of diagnostic and repair information products to independent repair shop owners and managers.
Segment gross profit of $518.8 million in 2015 compared to $504.3 million in 2014. Gross margin of 46.6% in 2015 improved 60 bps from 46.0% in 2014 primarily due to contributions from higher sales and savings from RCI initiatives, and 40 bps of lower restructuring costs. These gross margin improvements were partially offset by a shift in sales that included higher volumes of lower gross margin products, including increased essential tool and facilitation sales to OEM dealerships. Restructuring costs included in gross profit were zero and $4.7 million in 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Segment operating expenses of $245.4 million in 2015 compared to $253.1 million in 2014. The operating expense margin of 22.0% in 2015 improved 110 bps from 23.1% in 2014 primarily due to sales volume leverage, including benefits from the sales shift noted above, and savings from RCI initiatives. Restructuring costs included in operating expenses were zero and $0.4 million in 2015 and 2014, respectively.
As a result of these factors, segment operating earnings of $273.4 million in 2015, including $10.5 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $22.2 million from 2014 levels. Operating margin for the Repair Systems & Information Group of 24.6% in 2015 improved 170 bps from 22.9% in 2014.
Financial Services
| (Amounts in millions) | 2015 | 2014 | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial services revenue |
$ | 240.3 | 100.0% | $ | 214.9 | 100.0% | $ | 25.4 | 11.8% | |||||||||||||||
| Financial services expenses |
(70.1) | -29.2% | (65.8) | -30.6% | (4.3) | -6.5% | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Segment operating earnings |
$ | 170.2 | 70.8% | $ | 149.1 | 69.4% | $ | 21.1 | 14.2% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Financial services revenue of $240.3 million in 2015 increased $25.4 million, or 11.8%, from $214.9 million in 2014 primarily reflecting $23.0 million of higher revenue as a result of continued growth of the company’s financial services portfolio and $2.2 million of increased revenue from higher average yields on finance receivables. In 2015 and 2014, the average yield on finance receivables was 17.8% and 17.6%, respectively, and the average yield on contract receivables was 9.5% in both years. Originations of $993.7 million in 2015 increased $105.1 million, or 11.8%, from 2014 levels.
Financial services expenses of $70.1 million in 2015 compared to $65.8 million in 2014. As a percentage of the average financial services portfolio, financial services expenses were 4.8% and 5.1% in 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Financial services operating earnings of $170.2 million in 2015, including $2.6 million of unfavorable foreign currency effects, increased $21.1 million, or 14.2%, from 2014 levels.
See Note 1 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further information on financial services.
Corporate
Snap-on’s general corporate expenses in 2015 of $104.2 million increased $6.9 million from $97.3 million in 2014 primarily due to $7.9 million of higher pension expense.
Non-GAAP Supplemental Data
The following non-GAAP supplemental data is presented for informational purposes to provide readers with insight into the information used by management for assessing the operating performance of Snap-on Incorporated’s (“Snap-on”) non-financial services (“Operations”) and “Financial Services” businesses.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 41 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (continued)
The supplemental Operations data reflects the results of operations and financial position of Snap-on’s tools, diagnostic and equipment products, software and other non-financial services operations with Financial Services on the equity method. The supplemental Financial Services data reflects the results of operations and financial position of Snap-on’s U.S. and international financial services operations. The financing needs of Financial Services are met through intersegment borrowings and cash generated from Operations; Financial Services is charged interest expense on intersegment borrowings at market rates. Income taxes are charged to Financial Services on the basis of the specific tax attributes generated by the U.S. and international financial services businesses. Transactions between the Operations and Financial Services businesses were eliminated to arrive at the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Non-GAAP Supplemental Consolidating Data – Supplemental Statements of Earnings information for 2016, 2015 and 2014 is as follows:
| Operations* | Financial Services | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 3,430.4 | $ | 3,352.8 | $ | 3,277.7 | $ | – | $ | – | $ | – | ||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(1,720.8) | (1,704.5) | (1,693.4) | – | – | – | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
1,709.6 | 1,648.3 | 1,584.3 | – | – | – | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(1,054.1) | (1,053.7) | (1,048.7) | – | – | – | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Operating earnings before financial services |
655.5 | 594.6 | 535.6 | – | – | – | ||||||||||||||||||
| Financial services revenue |
– | – | – | 281.4 | 240.3 | 214.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Financial services expenses |
– | – | – | (82.7) | (70.1) | (65.8) | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Operating earnings from financial services |
– | – | – | 198.7 | 170.2 | 149.1 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Operating earnings |
655.5 | 594.6 | 535.6 | 198.7 | 170.2 | 149.1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(51.9) | (51.4) | (52.2) | (0.3) | (0.5) | (0.7) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Intersegment interest income (expense) – net |
72.2 | 62.7 | 56.7 | (72.2) | (62.7) | (56.7) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other income (expense) – net |
(0.7) | (2.4) | (0.8) | 0.1 | – | (0.1) | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Earnings before income taxes and equity earnings |
675.1 | 603.5 | 539.3 | 126.3 | 107.0 | 91.6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
(197.7) | (181.9) | (165.8) | (46.6) | (39.3) | (33.7) | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Earnings before equity earnings |
477.4 | 421.6 | 373.5 | 79.7 | 67.7 | 57.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Financial services – net earnings attributable to Snap-on |
79.7 | 67.7 | 57.9 | – | – | – | ||||||||||||||||||
| Equity earnings, net of tax |
2.5 | 1.3 | 0.7 | – | – | – | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
559.6 | 490.6 | 432.1 | 79.7 | 67.7 | 57.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interests |
(13.2) | (11.9) | (10.2) | – | – | – | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to Snap-on |
$ | 546.4 | $ | 478.7 | $ | 421.9 | $ | 79.7 | $ | 67.7 | $ | 57.9 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
* Snap-on with Financial Services on the equity method.
| 42 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Non-GAAP Supplemental Consolidating Data – Supplemental Balance Sheet Information as of 2016 and 2015 year end is as follows:
| Operations* | Financial Services | |||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||
| ASSETS |
||||||||||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 77.5 | $ | 92.7 | $ | 0.1 | $ | 0.1 | ||||||||
| Intersegment receivables |
15.0 | 15.9 | – | – | ||||||||||||
| Trade and other accounts receivable – net |
598.2 | 562.2 | 0.6 | 0.3 | ||||||||||||
| Finance receivables – net |
– | – | 472.5 | 447.3 | ||||||||||||
| Contract receivables – net |
7.9 | 8.0 | 80.2 | 74.1 | ||||||||||||
| Inventories – net |
530.5 | 497.8 | – | – | ||||||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets |
122.4 | 111.5 | 1.1 | 1.2 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total current assets |
1,351.5 | 1,288.1 | 554.5 | 523.0 | ||||||||||||
| Property and equipment – net |
423.8 | 412.1 | 1.4 | 1.4 | ||||||||||||
| Investment in Financial Services |
288.7 | 251.8 | – | – | ||||||||||||
| Deferred income tax assets |
49.1 | 40.6 | 23.7 | 19.8 | ||||||||||||
| Intersegment long-term notes receivable |
584.7 | 398.7 | – | – | ||||||||||||
| Long-term finance receivables – net |
– | – | 934.5 | 772.7 | ||||||||||||
| Long-term contract receivables – net |
11.2 | 12.1 | 275.5 | 254.5 | ||||||||||||
| Goodwill |
895.5 | 790.1 | – | – | ||||||||||||
| Other intangibles – net |
184.6 | 195.0 | – | – | ||||||||||||
| Other assets |
47.9 | 49.9 | 0.1 | 1.0 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 3,837.0 | $ | 3,438.4 | $ | 1,789.7 | $ | 1,572.4 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| * | Snap-on with Financial Services on the equity method. |
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 43 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (continued)
Non-GAAP Supplemental Consolidating Data – Supplemental Balance Sheet Information (continued):
| Operations* | Financial Services | |||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY |
||||||||||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Notes payable and current maturities of long-term debt |
$ | 151.4 | $ | 18.4 | $ | 150.0 | $ | – | ||||||||
| Accounts payable |
170.3 | 148.2 | 0.6 | 0.1 | ||||||||||||
| Intersegment payables |
– | – | 15.0 | 15.9 | ||||||||||||
| Accrued benefits |
52.8 | 52.1 | – | – | ||||||||||||
| Accrued compensation |
85.7 | 86.9 | 4.1 | 4.1 | ||||||||||||
| Franchisee deposits |
66.7 | 64.4 | – | – | ||||||||||||
| Other accrued liabilities |
292.1 | 277.4 | 22.8 | 25.0 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total current liabilities |
819.0 | 647.4 | 192.5 | 45.1 | ||||||||||||
| Long-term debt and intersegment long-term debt |
– | – | 1,293.5 | 1,260.4 | ||||||||||||
| Deferred income tax liabilities |
13.1 | 14.1 | – | 0.2 | ||||||||||||
| Retiree health care benefits |
36.7 | 37.9 | – | – | ||||||||||||
| Pension liabilities |
246.5 | 227.8 | – | – | ||||||||||||
| Other long-term liabilities |
86.5 | 80.5 | 15.0 | 14.9 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total liabilities |
1,201.8 | 1,007.7 | 1,501.0 | 1,320.6 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total shareholders’ equity attributable to Snap-on |
2,617.2 | 2,412.7 | 288.7 | 251.8 | ||||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interests |
18.0 | 18.0 | – | – | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total equity |
2,635.2 | 2,430.7 | 288.7 | 251.8 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total liabilities and equity |
$ | 3,837.0 | $ | 3,438.4 | $ | 1,789.7 | $ | 1,572.4 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| * | Snap-on with Financial Services on the equity method. |
| 44 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Snap-on’s growth has historically been funded by a combination of cash provided by operating activities and debt financing. On January 17, 2017, Snap-on repaid $150 million of unsecured 5.50% notes (the “2017 Notes”) upon maturity with available cash and cash generated from issuances of commercial paper. Snap-on believes that its cash from operations and collections of finance receivables, coupled with its sources of borrowings and available cash on hand, are sufficient to fund its currently anticipated requirements for scheduled debt payments (including the January 15, 2018 repayment of $250 million of unsecured 4.25% notes at maturity (the “2018 Notes”)), payments of interest and dividends, new receivables originated by our financial services businesses, capital expenditures, working capital, the funding of pension plans, and funding for share repurchases and acquisitions, as they arise.
Due to Snap-on’s credit rating over the years, external funds have been available at an acceptable cost. As of the close of business on February 3, 2017, Snap-on’s long-term debt and commercial paper were rated, respectively, A3 and P-2 by Moody’s Investors Service; A- and A-2 by Standard & Poor’s; and A and F1 by Fitch Ratings. Snap-on believes that its current credit arrangements are sound and that the strength of its balance sheet affords the company the financial flexibility, including through access to financial markets for potential new financing, to respond to both internal growth opportunities and those available through acquisitions. However, Snap-on cannot provide any assurances of the availability of future financing or the terms on which it might be available, or that its debt ratings may not decrease.
The following discussion focuses on information included in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets.
As of 2016 year end, working capital (current assets less current liabilities) of $894.5 million decreased $224.1 million from $1,118.6 million as of 2015 year end primarily as a result of the inclusion of the 2017 Notes and $130 million of outstanding commercial paper borrowings in “Notes payable and current maturities of long-term debt,” partially offset by the other net changes in working capital discussed below. As of 2015 year end, the 2017 Notes were included in “Long-term debt” on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheet as their scheduled maturity was in excess of one year of the 2015 year-end balance sheet date.
The following represents the company’s working capital position as of 2016 and 2015 year end:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 77.6 | $ | 92.8 | ||||
| Trade and other accounts receivable – net |
598.8 | 562.5 | ||||||
| Finance receivables – net |
472.5 | 447.3 | ||||||
| Contract receivables – net |
88.1 | 82.1 | ||||||
| Inventories – net |
530.5 | 497.8 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets |
116.5 | 106.3 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current assets |
1,884.0 | 1,788.8 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Notes payable and current maturities of long-term debt |
(301.4) | (18.4) | ||||||
| Accounts payable |
(170.9) | (148.3) | ||||||
| Other current liabilities |
(517.2) | (503.5) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current liabilities |
(989.5) | (670.2) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Working capital |
$ | 894.5 | $ | 1,118.6 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Cash and cash equivalents of $77.6 million as of 2016 year end decreased $15.2 million from 2015 year-end levels primarily due to (i) the funding of $915.0 million of new finance receivables; (ii) the funding of $160.4 million, net of cash acquired, for the acquisitions of Car-O-Liner and Sturtevant Richmont; (iii) dividend payments to shareholders of $147.5 million; (iv) the repurchase of 758,000 shares of the company’s common stock for $120.4 million; and (v) the funding of $74.3 million of capital expenditures. These decreases in cash and cash equivalents were partially offset by (i) $671.7 million of cash from collections of finance receivables; (ii) $576.1 million of cash generated from operations, net of $60.0 million of discretionary cash contributions to the company’s domestic pension plans; (iii) $134.2 million of net proceeds from notes payable and other short-term borrowings; and (iv) $41.8 million of cash proceeds from stock purchase and option plan exercises.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 45 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (continued)
Of the $77.6 million of cash and cash equivalents as of 2016 year end, $59.0 million was held outside of the United States. Snap-on maintains non-U.S. funds in its foreign operations to (i) provide adequate working capital; (ii) satisfy various regulatory requirements; and/or (iii) take advantage of business expansion opportunities as they arise. The repatriation of cash from certain foreign subsidiaries could have adverse net tax consequences on the company should Snap-on be required to pay and record U.S. income taxes and foreign withholding taxes on such funds. Alternatively, the repatriation of cash from certain other foreign subsidiaries could result in favorable net tax consequences for the company. Snap-on periodically evaluates its cash held outside the United States and may pursue opportunities to repatriate certain foreign cash amounts to the extent that it does not incur unfavorable net tax consequences.
Trade and other accounts receivable – net of $598.8 million as of 2016 year end increased $36.3 million from 2015 year-end levels primarily due to higher sales and an increase in days sales outstanding, and $21.5 million of receivables related to the Car-O-Liner and Sturtevant Richmont acquisitions, partially offset by $13.8 million of foreign currency translation. Days sales outstanding (trade and other accounts receivable – net as of the respective period end, divided by the respective trailing 12 months sales, times 360 days) was 63 days at 2016 year end and 60 days at 2015 year end.
The current portions of net finance and contract receivables of $560.6 million as of 2016 year end compared to $529.4 million at 2015 year end. The long-term portions of net finance and contract receivables of $1,221.2 million as of 2016 year end compared to $1,039.3 million at 2015 year end. The combined $213.1 million increase in net current and long-term finance and contract receivables over 2015 year-end levels is primarily due to continued growth of the company’s financial services portfolio, partially offset by $15.1 million of foreign currency translation.
Inventories – net of $530.5 million as of 2016 year end increased $32.7 million from 2015 year-end levels primarily due to $21.5 million of inventories related to the Car-O-Liner and Sturtevant Richmont acquisitions, as well as to support continued higher customer demand and new product introductions, partially offset by $17.8 million of foreign currency translation. As of 2016 and 2015 year end, inventory turns (trailing 12 months of cost of goods sold, divided by the average of the beginning and ending inventory balance for the trailing 12 months) were 3.3 turns and 3.5 turns, respectively. Inventories accounted for using the first-in, first-out (“FIFO”) method as of 2016 and 2015 year end approximated 59% and 57%, respectively, of total inventories. All other inventories are accounted for using the last-in, first-out (“LIFO”) method. The company’s LIFO reserve was $73.2 million and $73.3 million as 2016 and 2015 year end, respectively.
Notes payable and current maturities of long-term debt of $301.4 million as of 2016 year end consisted of $150 million of the 2017 Notes, $130 million of commercial paper borrowings and $21.4 million of other notes. Notes payable at 2015 year end totaled $18.4 million and there were no commercial paper borrowings outstanding. As of 2015 year end, the 2017 Notes were included in “Long-term debt” on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheet as their scheduled maturity was in excess of one year of the 2015 year-end balance sheet date.
Average notes payable outstanding, including commercial paper borrowings, were $49.3 million and $78.5 million in 2016 and 2015, respectively. The weighted-average interest rate of 7.09% in 2016 increased from 4.36% last year primarily due to higher interest rates on local borrowings in emerging growth markets (where interest rates are generally higher). Average commercial paper borrowings were $26.6 million and $52.2 million in 2016 and 2015, respectively, and the weighted-average interest rate of 0.73% in 2016 increased from 0.41% last year. At 2016 year end, the weighted-average interest rate on outstanding notes payable of 2.85% compared with 15.82% at 2015 year end. The 2016 year-end rate benefited from lower interest rates on commercial paper borrowings. The 2015 year-end rate reflected higher rates on local borrowings in emerging growth markets; no commercial paper was outstanding at 2015 year end.
Accounts payable of $170.9 million as of 2016 year end increased $22.6 million from 2015 year-end levels primarily due to the timing of payments and $10.9 million of accounts payable related to the Car-O-Liner and Sturtevant Richmont acquisitions, partially offset by $3.8 million of foreign currency translation.
Other accrued liabilities of $307.9 million as of 2016 year end increased $11.9 million from 2015 year-end levels primarily due to a $7.6 million increase in derivative liabilities and $6.4 million of other accrued liabilities related to the Car-O-Liner and Sturtevant Richmont acquisitions, partially offset by $8.3 million of foreign currency translation.
| 46 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Long-term debt of $708.8 million as of 2016 year end consisted of (i) $250 million of the 2018 Notes; (ii) $200 million of unsecured 6.70% notes that mature in 2019; (iii) $250 million of unsecured 6.125% notes that mature in 2021; and (iv) $8.8 million of other long-term debt, including fair value adjustments related to interest rate swaps. As of 2016 year end, the 2018 Notes were included in “Long-term debt” on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheet as their scheduled maturity was in excess of one year of the 2016 year-end balance sheet date.
Snap-on has a five-year, $700 million multi-currency revolving credit facility that terminates on December 15, 2020 (the “Credit Facility”); as of December 31, 2016, no amounts were outstanding under the Credit Facility. Borrowings under the Credit Facility bear interest at varying rates based on Snap-on’s then-current, long-term debt ratings. The Credit Facility’s financial covenant requires that Snap-on maintain, as of each fiscal quarter end, either (i) a ratio not greater than 0.60 to 1.00 of consolidated net debt (consolidated debt net of certain cash adjustments) to the sum of such consolidated net debt plus total equity and less accumulated other comprehensive income or loss (the “Debt Ratio”); or (ii) a ratio not greater than 3.50 to 1.00 of such consolidated net debt to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization and certain other adjustments for the preceding four fiscal quarters then ended (the “Debt to EBITDA Ratio”). Snap-on may, up to two times during any five-year period during the term of the Credit Facility (including any extensions thereof), increase the maximum Debt Ratio to 0.65 to 1.00 and/or increase the maximum Debt to EBITDA Ratio to 3.75 to 1.00 for four consecutive fiscal quarters in connection with certain material acquisitions (as defined in the related credit agreement). As of 2016 year end, the company’s actual ratios of 0.24 and 1.02, respectively, were both within the permitted ranges set forth in this financial covenant. Snap-on generally issues commercial paper to fund its financing needs on a short-term basis and uses the Credit Facility as back-up liquidity to support such commercial paper issuances.
Snap-on’s Credit Facility and other debt agreements also contain certain usual and customary borrowing, affirmative, negative and maintenance covenants. As of 2016 year end, Snap-on was in compliance with all covenants of its Credit Facility and other debt agreements.
Snap-on believes it has sufficient available cash and access to both committed and uncommitted credit facilities to cover its expected funding needs on both a short-term and long-term basis. Snap-on manages its aggregate short-term borrowings so as not to exceed its availability under the revolving Credit Facility. Snap-on believes that it can access short-term debt markets, predominantly through commercial paper issuances and existing lines of credit, to fund its short-term requirements and to ensure near-term liquidity. Snap-on regularly monitors the credit and financial markets and may take advantage of what it believes are favorable market conditions to issue long-term debt to further improve its liquidity and capital resources in 2017. Near-term liquidity requirements for Snap-on include scheduled debt payments (including the repayment of the 2018 Notes; as noted above, the 2017 Notes were repaid on January 17, 2017), payments of interest and dividends, funding to support new receivables originated by our financial services businesses, capital expenditures, working capital, the funding of pension plans, and funding for share repurchases and acquisitions, as they arise. Snap-on intends to make contributions of $7.1 million to its foreign pension plans and $2.3 million to its domestic pension plans in 2017, as required by law. Depending on market and other conditions, Snap-on may make discretionary cash contributions to its pension plans in 2017.
Snap-on’s long-term financing strategy is to maintain continuous access to the debt markets to accommodate its liquidity needs, including the use of commercial paper, additional fixed-term debt and/or securitizations.
The following discussion focuses on information included in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows.
Operating Activities
Net cash provided by operating activities of $576.1 million in 2016 increased $68.9 million from $507.2 million in 2015 primarily due to $69.0 million of higher net earnings. Net cash provided by operating activities was $403.1 million in 2014.
Depreciation expense was $61.4 million in 2016, $57.8 million in 2015 and $54.8 million in 2014. Amortization expense was $24.2 million in 2016 and $24.7 million in both 2015 and 2014. See Note 6 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on goodwill and other intangible assets.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 47 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (continued)
Investing Activities
Net cash used by investing activities of $473.4 million in 2016 included additions to finance receivables of $915.0 million, partially offset by collections of $671.7 million. Net cash used by investing activities of $306.4 million in 2015 included additions to finance receivables of $844.2 million, partially offset by collections of $624.8 million. Net cash used by investing activities of $273.2 million in 2014 included additions to finance receivables of $746.2 million, partially offset by collections of $591.4 million. Finance receivables are comprised of extended-term installment payment contracts to both technicians and independent shop owners (i.e., franchisees’ customers) to enable them to purchase tools and diagnostic and equipment products on an extended-term payment plan, generally with average payment terms approaching four years.
Net cash used by investing activities in 2016 also included, on a preliminary basis, a total of $160.4 million (net of $4.3 million of cash acquired) for the acquisitions of Car-O-Liner and Sturtevant Richmont. Net cash used by investing activities in 2015 included $11.8 million for the acquisition of Ecotechnics. Net cash used by investing activities in 2014 included $41.3 million for the acquisition of Pro-Cut. See Note 2 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on acquisitions.
Capital expenditures in 2016, 2015 and 2014 totaled $74.3 million, $80.4 million and $80.6 million, respectively. Capital expenditures in all three years included continued investments related to the company’s execution of its strategic Value Creation Processes and strategic growth initiatives. The company also invested in (i) new product, efficiency, safety and cost reduction initiatives that are intended to expand and improve its manufacturing capabilities worldwide; (ii) new production and machine tooling to enhance manufacturing operations, as well as ongoing replacements of manufacturing and distribution equipment, particularly in the United States; (iii) the ongoing replacement and enhancement of the company’s global enterprise resource planning (ERP) management information systems; and (iv) improvements in the company’s corporate headquarters and research and development facilities in Kenosha, Wisconsin. Capital expenditures in 2015 also included the purchase of a previously leased manufacturing facility in the United Kingdom. Snap-on believes that its cash generated from operations, as well as its available cash on hand and funds available from its credit facilities will be sufficient to fund the company’s capital expenditure requirements in 2017.
Financing Activities
Net cash used by financing activities of $116.0 million in 2016 included $134.2 million of proceeds from a net increase in notes payable and other short-term borrowings. Net cash used by financing activities of $236.7 million in 2015 included the net repayment of $34.0 million of notes payable and other short-term borrowings. Net cash used by financing activities of $212.1 million in 2014 included the repayment of $100 million of unsecured notes at maturity, partially offset by $45.0 million of proceeds from a net increase in notes payable and other short-term borrowings.
Proceeds from stock purchase and option plan exercises totaled $41.8 million in 2016, $41.6 million in 2015 and $33.0 million in 2014. Snap-on has undertaken stock repurchases from time to time to offset dilution created by shares issued for employee and franchisee stock purchase plans, stock options and other corporate purposes. In 2016, Snap-on repurchased 758,000 shares of its common stock for $120.4 million under its previously announced share repurchase programs. As of 2016 year end, Snap-on had remaining availability to repurchase up to an additional $207.2 million in common stock pursuant to its Board of Directors’ (the “Board”) authorizations. The purchase of Snap-on common stock is at the company’s discretion, subject to prevailing financial and market conditions. Snap-on repurchased 723,000 shares of its common stock for $110.4 million in 2015 and Snap-on repurchased 680,000 shares of its common stock for $79.3 million in 2014. Snap-on believes that its cash generated from operations, available cash on hand, and funds available from its credit facilities, will be sufficient to fund the company’s share repurchases, if any, in 2017.
| 48 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Snap-on has paid consecutive quarterly cash dividends, without interruption or reduction, since 1939. Cash dividends paid in 2016, 2015 and 2014 totaled $147.5 million, $127.9 million and $107.6 million, respectively. On November 3, 2016, the company announced that its Board increased the quarterly cash dividend by 16.4% to $0.71 per share ($2.84 per share annualized). Quarterly dividends in 2016 were $0.71 per share in the fourth quarter and $0.61 per share in the first three quarters ($2.54 per share for the year). Quarterly dividends in 2015 were $0.61 per share in the fourth quarter and $0.53 per share in the first three quarters ($2.20 per share for the year). Quarterly dividends in 2014 were $0.53 per share in the fourth quarter and $0.44 per share in the first three quarters ($1.85 per share for the year).
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Cash dividends paid per common share |
$ | 2.54 | $ | 2.20 | $ | 1.85 | ||||||
| Cash dividends paid as a percent of prior-year retained earnings |
4.9% | 4.8% | 4.6% | |||||||||
Snap-on believes that its cash generated from operations, available cash on hand and funds available from its credit facilities will be sufficient to pay dividends in 2017.
Off-Balance-Sheet Arrangements
Except as included below in the section labeled “Contractual Obligations and Commitments” and Note 15 to the Consolidated Financial Statements, the company had no off-balance-sheet arrangements as of 2016 year end.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
A summary of Snap-on’s future contractual obligations and commitments as of 2016 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | Total | 2017 | 2018-2019 | 2020-2021 | 2022 and thereafter |
|||||||||||||||
| Contractual obligations: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Notes payable and current maturities of long-term debt |
$ | 301.4 | $ | 301.4 | $ | – | $ | – | $ | – | ||||||||||
| Long-term debt |
708.8 | – | 450.0 | 258.8 | – | |||||||||||||||
| Interest on fixed rate debt |
111.9 | 39.7 | 46.6 | 25.6 | – | |||||||||||||||
| Operating leases |
81.5 | 23.0 | 32.2 | 15.8 | 10.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Capital leases |
20.2 | 3.7 | 6.2 | 4.7 | 5.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Purchase obligations |
54.0 | 45.8 | 8.2 | – | – | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 1,277.8 | $ | 413.6 | $ | 543.2 | $ | 304.9 | $ | 16.1 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
On January 17, 2017, Snap-on repaid the 2017 Notes (included in the table above) upon maturity with available cash and cash generated from issuances of commercial paper.
Snap-on intends to make contributions of $7.1 million to its foreign pension plans and $2.3 million to its domestic pension plans in 2017, as required by law. Depending on market and other conditions, Snap-on may make discretionary cash contributions to its pension plans in 2017. Snap-on has not presented estimated pension and postretirement funding contributions in the table above as the funding can vary from year to year based on changes in the fair value of the plan assets and actuarial assumptions; see Note 11 and Note 12 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on the company’s benefit plans and payments.
Due to the uncertainty of the timing of settlements with taxing authorities, Snap-on is unable to make reasonably reliable estimates of the period of cash settlement of unrecognized tax benefits for its remaining uncertain tax liabilities. As a result, $9.4 million of unrecognized tax benefits have been excluded from the table above; see Note 8 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on income taxes.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 49 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (continued)
Environmental Matters
Snap-on is subject to various federal, state and local government requirements regulating the discharge of materials into the environment or otherwise relating to the protection of the environment. Snap-on’s policy is to comply with these requirements and the company believes that, as a general matter, its policies, practices and procedures are properly designed to prevent unreasonable risk of environmental damage, and of resulting financial liability, in connection with its business. Some risk of environmental damage is, however, inherent in some of Snap-on’s operations and products, as it is with other companies engaged in similar businesses.
Snap-on is and has been engaged in the handling, manufacture, use and disposal of many substances classified as hazardous or toxic by one or more regulatory agencies. Snap-on believes that, as a general matter, its handling, manufacture, use and disposal of these substances are in accordance with environmental laws and regulations. It is possible, however, that future knowledge or other developments, such as improved capability to detect substances in the environment or increasingly strict environmental laws and standards and enforcement policies, could bring into question the company’s handling, manufacture, use or disposal of these substances.
New Accounting Standards
See Note 1 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on new accounting standards.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The Consolidated Financial Statements and related notes contain information that is pertinent to management’s discussion and analysis. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. These estimates are generally based on historical experience, current conditions and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily available from other sources, as well as identifying and assessing our accounting treatment with respect to commitments and contingencies. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
In addition to the company’s significant accounting policies described in Note 1 to the Consolidated Financial Statements, Snap-on considers the following policies and estimates to be the most critical in understanding the judgments that are involved in the preparation of the company’s consolidated financial statements and the uncertainties that could impact the company’s financial position, results of operations and cash flows.
Impairment of Goodwill and Other Indefinite-lived Intangible Assets: Goodwill and other indefinite-lived intangible assets are tested for impairment annually or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the assets might be impaired. Annual impairment tests are performed by the company in the second quarter of each year using information available as of fiscal April month end.
Snap-on evaluates the recoverability of goodwill by estimating the future discounted cash flows of the businesses to which the goodwill relates. Estimated cash flows and related goodwill are grouped at the reporting unit level. The company has determined that its reporting units for testing goodwill impairment are its operating segments or components of an operating segment that constitute a business for which discrete financial information is available and for which segment management regularly reviews the operating results. Within its four reportable operating segments, the company has identified 11 reporting units.
Snap-on evaluates the recoverability of goodwill by utilizing an income approach that estimates the fair value of the future discounted cash flows of the reporting units to which the goodwill relates. The future projections, which are based on both past performance and the projections and assumptions used in the company’s operating plans, are subject to change as a result of changing economic and competitive conditions. This approach reflects management’s internal outlook at the reporting units, which management believes provides the best determination of value due to management’s insight and experience with the reporting units. Significant estimates used by management in the discounted cash flows methodology include estimates of future cash flows based on expected growth rates, price increases, working capital levels, expected benefits from RCI initiatives, and a weighted-average cost of capital that reflects the specific risk profile of the reporting unit being tested. The company’s methodologies for valuing goodwill are applied consistently on a year-over-year basis; the assumptions used in performing the second quarter 2016 impairment calculations were evaluated in light of then-current market and business conditions. Snap-on continues to believe that the future discounted cash flow valuation model provides the most reasonable and meaningful fair value estimate based upon the reporting units’ projections of future operating results and cash flows and replicates how market participants would value the company’s reporting units in an orderly transaction.
| 50 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
In the event the fair value of a reporting unit is less than the carrying value, including goodwill, the company would then perform an additional assessment that would compare the implied fair value of goodwill with the carrying amount of goodwill. The determination of implied fair value of goodwill would require management to compare the estimated fair value of the reporting unit to the estimated fair value of the assets and liabilities of the reporting unit; if necessary, the company may consult with valuation specialists to assist with the assessment of the estimated fair value of the assets and liabilities of the reporting unit. If the implied fair value of the goodwill is less than the carrying value, an impairment loss would be recorded.
Snap-on also evaluates the recoverability of its indefinite-lived trademarks by utilizing an income approach that estimates the fair value of the future discounted cash flows of each of its trademarks. The future projections, which are based on both past performance and the projections and assumptions used in the company’s operating plans, are subject to change as a result of changing economic and competitive conditions. Significant estimates used by management in the discounted cash flows methodology include estimates of future cash flows based on expected growth and royalty rates, expected synergies, and a weighted-average cost of capital that reflects the specific risk profile of the trademark being tested. The company’s methodologies for valuing trademarks are applied consistently on a year-over-year basis; the assumptions used in performing the second quarter 2016 impairment calculations were evaluated in light of then-current market and business conditions. Snap-on continues to believe that the future discounted cash flow valuation model provides the most reasonable and meaningful fair value estimate based upon the trademarks’ projected future cash flows and replicates how market participants would value the company’s trademarks in an orderly transaction.
Inherent in fair value determinations are significant judgments and estimates, including material assumptions about future revenue, profitability and cash flows, the company’s operational plans and its interpretation of current economic indicators. Should the operations of the businesses with which goodwill or other indefinite-lived intangible assets are associated incur significant declines in profitability and cash flow due to significant and long-term deterioration in macroeconomic, industry and market conditions, the loss of key customers, changes in technology or markets, significant changes in key personnel or litigation, a significant and sustained decrease in share price and/or other events, including effects from the sale or disposal of a reporting unit, some or all of the recorded goodwill or other indefinite-lived intangible assets could be subject to impairment and could result in a material adverse effect on Snap-on’s financial position or results of operations.
Snap-on completed its annual impairment testing of goodwill and other indefinite-lived intangible assets in the second quarter of 2016, the results of which did not result in any impairment. As of 2016 year end, the company has no accumulated impairment losses. Although the company consistently uses the same methods in developing the assumptions and estimates underlying the fair value calculations, such estimates are uncertain by nature and can vary from actual results. In performing its annual impairment testing the company performed a sensitivity analysis on the material assumptions used in the discounted cash flow valuation models for each of its 11 reporting units. Based on the company’s second quarter 2016 impairment testing and assuming a hypothetical 10% decrease in the estimated fair values of each of its 11 reporting units, the hypothetical fair value of each of the company’s 11 reporting units would have been greater than its carrying value. See Note 6 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further information about goodwill and other intangible assets.
Pension Benefits: The pension benefit obligation and related pension expense are calculated in accordance with GAAP and are impacted by certain actuarial assumptions. Changes in these assumptions are primarily influenced by factors outside of Snap-on’s control, such as changes in economic conditions, and can have a significant effect on the amounts reported in the financial statements. Snap-on believes that the two most critical assumptions are (i) the expected return on plan assets; and (ii) the assumed discount rate.
Snap-on’s domestic pension plans have a long-term investment horizon and a total return strategy that emphasizes a capital growth objective. In 2016, the long-term investment performance objective for Snap-on’s domestic plans’ assets was to achieve net of expense returns that met or exceeded the 7.6% domestic expected return on plan assets assumption. Snap-on uses a three-year, market-related value asset method of amortizing the difference between actual and expected returns on its domestic plans’ assets. As of 2016 year end, Snap-on’s domestic pension plans’ assets comprised approximately 86% of the company’s worldwide pension plan assets.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 51 |
Table of Contents
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (continued)
Based on forward-looking capital market expectations, Snap-on selected an expected return on plan assets assumption for its U.S. pension plans of 7.5%, a decrease of 10 bps from 2016, to be used in determining pension expense for 2017. In estimating the domestic expected return on plan assets, Snap-on utilizes a nominal returns forecasting method. For each asset class, future returns are estimated by identifying the premium of riskier asset classes over lower risk alternatives. The methodology constructs expected returns using a “building block” approach to the individual components of total return. These forecasts are stated in both nominal and real (after inflation) terms. This process first considers the long-term historical return premium based on the longest set of data available for each asset class. These premiums, calculated using the geometric mean, are then adjusted based on current relative valuation levels, macro-economic conditions, and the expected alpha related to active investment management. The asset return assumption is also adjusted by an implicit expense load for estimated administrative and investment-related expenses. Since asset allocation is a key determinant of expected investment returns, the current and expected mix of plan assets are also considered when setting the assumption.
Pension expense increases as the expected rate of return on plan assets decreases. Lowering the expected rate of return assumption for Snap-on’s domestic pension plans’ assets by 50 bps would have increased Snap-on’s 2016 domestic pension expense by approximately $4.7 million.
The objective of Snap-on’s discount rate assumption is to reflect the rate at which the pension benefits could be effectively settled. In making this determination, the company takes into account the timing and amount of benefits that would be available under the plans. The domestic discount rate as of 2016 and 2015 year end was selected based on a cash flow matching methodology developed by the company’s outside actuaries and which incorporates a review of current economic conditions. This methodology matches the plans’ yearly projected cash flows for benefits and service costs to those of hypothetical bond portfolios using high-quality, AA rated or better, corporate bonds from either Moody’s Investors Service or Standard & Poor’s credit rating agencies available at the measurement date. This technique calculates bond portfolios that produce adequate cash flows to pay the plans’ projected yearly benefits and then selects the portfolio with the highest yield and uses that yield as the recommended discount rate.
The selection of the 4.5% weighted-average discount rate for Snap-on’s domestic pension plans as of 2016 year end (compared to 4.7% as of 2015 year end) represents the single rate that produces the same present value of cash flows as the estimated benefit plan payments. Lowering Snap-on’s domestic discount rate assumption by 50 bps would have increased Snap-on’s 2016 domestic pension expense and projected benefit obligation by approximately $6.7 million and $65.3 million, respectively. As of 2016 year end, Snap-on’s domestic projected benefit obligation comprised approximately 83% of Snap-on’s worldwide projected benefit obligation. The weighted-average discount rate for Snap-on’s foreign pension plans of 2.9% (compared to 3.7% as of 2015 year end) represents the single rate that produces the same present value of cash flows as the estimated benefit plan payments. Lowering Snap-on’s foreign discount rate assumption by 50 bps would have increased Snap-on’s 2016 foreign pension expense and projected benefit obligation by approximately $1.7 million and $23.4 million, respectively.
Actuarial gains and losses in excess of 10 percent of the greater of the projected benefit obligation or market-related value of assets are amortized on a straight-line basis over the average remaining service period of active participants or over the average remaining life expectancy for plans with primarily inactive participants. Prior service costs and credits resulting from plan amendments are amortized in equal annual amounts over the average remaining service period of active participants or over the average remaining life expectancy for plans with primarily inactive participants.
To determine the 2017 net periodic benefit cost, Snap-on is using weighted-average discount rates for its domestic and foreign pension plans of 4.5% and 2.9%, respectively, and an expected return on plan assets for its domestic pension plans of 7.5%. The expected returns on plan assets for foreign pension plans ranged from 1.8% and 6.3% as of 2016 year end. The net change in these two key assumptions from those used in 2016 is expected to increase pension expense in 2017. Other factors, such as changes in plan demographics and discretionary contributions, may further increase or decrease pension expense in 2017. See Note 11 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further information on pension plans.
| 52 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Allowances for Doubtful Accounts on Finance and Contract Receivables: The allowances for doubtful accounts on finance and contract receivables are maintained at levels management believes are adequate to cover probable losses inherent in Snap-on’s finance and contract receivables portfolios as of the measurement date. The allowances represent management’s estimate of the losses inherent in the company’s receivables portfolios based on ongoing assessments and evaluations of collectability and historical loss experience. Determination of the proper level of allowances by portfolio requires management to exercise significant judgment about the timing, frequency and severity of losses that could materially affect the provision for doubtful accounts and, as a result, net earnings. The allowances take into consideration numerous quantitative and qualitative factors that include receivable type, historical loss experience, loss migration, delinquency trends, collection experience, current economic conditions and credit risk characteristics. Some of these factors are influenced by items such as the customers’ financial condition, debt-servicing ability, past payment experience, and credit bureau and proprietary Snap-on credit model information, as well as the value of the underlying collateral. Changes in economic conditions and assumptions, including the resulting credit quality metrics relative to the performance of the finance and contract receivables portfolios, create uncertainty and could result in changes to both the allowances and provisions for doubtful accounts.
Management utilizes established policies and procedures in an effort to ensure the estimates and assumptions are well controlled, reviewed and consistently applied. As of December 31, 2016, the ratios of the allowances for doubtful accounts to finance and contract receivables (the “allowance ratios”) were 3.34% and 1.03%, respectively. As of January 2, 2016, the respective allowance ratios were 3.04% and 1.25%. While management believes it exercises prudent judgment and applies reasonable assumptions in establishing its estimates for allowances for finance and contract receivables, there can be no assurance that changes in economic conditions or other factors would not adversely impact the financial health of our customers and result in changes to the estimates used in the allowance calculations. For reference, a 100 bps increase in the allowance ratios for both finance and contract receivables as of December 31, 2016, would have increased Snap-on’s 2016 provision expense and related allowances for doubtful accounts by approximately $14.6 million and $3.8 million, respectively.
For additional information on Snap-on’s allowances for doubtful accounts, see Note 1 and Note 3 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Outlook
Snap-on expects to make continued progress in 2017 along its defined runways for coherent growth, leveraging capabilities already demonstrated in the automotive repair arena and developing and expanding its professional customer base, not only in automotive repair, but in adjacent markets, additional geographies and other areas, including extending in critical industries, where the cost and penalties for failure can be high. In pursuit of these initiatives, Snap-on expects that capital expenditures in 2017 will be in a range of $80 million to $90 million. Snap-on also anticipates that its full year 2017 effective income tax rate will be comparable to its 2016 full year rate.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 53 |
Table of Contents
Item 7A: Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Market, Credit and Economic Risks
Market risk is the potential economic loss that may result from adverse changes in the fair value of financial instruments. Snap-on is exposed to market risk from changes in interest rates and foreign currency exchange rates, including as a result of the recent weakening of the British pound vis-à-vis the U.S. dollar following the United Kingdom’s referendum vote to exit from the European Union. Snap-on is also exposed to market risk associated with the stock-based portion of its deferred compensation plans. Snap-on monitors its exposure to these risks and attempts to manage the underlying economic exposures through the use of financial instruments such as foreign currency forward contracts, interest rate swap agreements, treasury lock agreements and prepaid equity forward agreements (“equity forwards”). Snap-on does not use derivative instruments for speculative or trading purposes. Snap-on’s broad-based business activities help to reduce the impact that volatility in any particular area or related areas may have on its operating earnings as a whole. Snap-on’s management takes an active role in the risk management process and has developed policies and procedures that require specific administrative and business functions to assist in the identification, assessment and control of various risks.
Foreign Currency Risk Management
Snap-on has significant international operations and is subject to certain risks inherent with foreign operations that include currency fluctuations. Foreign currency exchange risk exists to the extent that Snap-on has payment obligations or receipts denominated in currencies other than the functional currency, including intercompany loans denominated in foreign currencies. To manage these exposures, Snap-on identifies naturally offsetting positions and then purchases hedging instruments to protect the residual net exposures. See Note 10 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on foreign currency risk management.
Interest Rate Risk Management
Snap-on aims to control funding costs by managing the exposure created by the differing maturities and interest rate structures of Snap-on’s borrowings through the use of interest rate swap agreements. Treasury lock agreements are used from time to time to manage the potential change in interest rates in anticipation of the possible issuance of fixed rate debt. See Note 10 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information on interest rate risk management.
Snap-on utilizes a Value-at-Risk (“VAR”) model to determine the potential one-day loss in the fair value of its interest rate and foreign exchange-sensitive financial instruments from adverse changes in market factors. The VAR model estimates were made assuming normal market conditions and a 95% confidence level. Snap-on’s computations are based on the inter-relationships among movements in various currencies and interest rates (variance/co-variance technique). These inter-relationships were determined by observing interest rate and foreign currency market changes over the preceding quarter.
The estimated maximum potential one-day loss in fair value, calculated using the VAR model, as of 2016 and 2015 year end was $0.4 million and $0.6 million, respectively, on interest rate-sensitive financial instruments, and $0.8 million and $0.5 million, respectively, on foreign currency-sensitive financial instruments. The VAR model is a risk management tool and does not purport to represent actual losses in fair value that will be incurred by Snap-on, nor does it consider the potential effect of favorable changes in market factors.
Stock-based Deferred Compensation Risk Management
Snap-on aims to manage market risk associated with the stock-based portion of its deferred compensation plans through the use of equity forwards. Equity forwards are used to aid in offsetting the potential mark-to-market effect on stock-based deferred compensation from changes in Snap-on’s stock price. Since stock-based deferred compensation liabilities increase as the company’s stock price rises and decrease as the company’s stock price declines, the equity forwards are intended to mitigate the potential impact on deferred compensation expense that may result from such mark-to-market changes. See Note 10 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information on stock-based deferred compensation risk management.
| 54 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Credit Risk
Credit risk is the possibility of loss from a customer’s failure to make payments according to contract terms. Prior to extending credit, each customer is evaluated, taking into consideration various factors, including the customer’s financial condition, debt-servicing ability, past payment experience, credit bureau information, and other financial and qualitative factors that may affect the customer’s ability to repay, as well as the value of the underlying collateral. Credit risk is also monitored regularly through the use of internal proprietary custom scoring models to evaluate each transaction at the time of the application for credit and by periodically updating those credit scores for ongoing monitoring purposes. Snap-on evaluates credit quality through the use of an internal proprietary measuring system that provides a framework to analyze finance and contract receivables on the basis of risk factors of the individual obligor as well as transaction specific risk. The finance and contract receivables are typically monitored through an asset quality review process that closely monitors past due accounts and initiates a progressive collection action process when appropriate.
Counterparty Risk
Snap-on is exposed to credit losses in the event of non-performance by the counterparties to its various financial agreements, including its foreign currency forward contracts, interest rate swap agreements, treasury lock agreements and prepaid equity forward agreements. Snap-on does not obtain collateral or other security to support financial instruments subject to credit risk, but monitors the credit standing of the counterparties and generally enters into agreements with financial institution counterparties with a credit rating of A- or better. Snap-on does not anticipate non-performance by its counterparties, but cannot provide assurances.
Economic Risk
Economic risk is the possibility of loss resulting from economic instability in certain areas of the world. Snap-on continually monitors its exposure in these markets; for example, the company will be monitoring the potential effects of the United Kingdom’s referendum vote to exit from the European Union, although it is too soon to know what effects the results of the referendum will have on the world economy or the company. Inflation has not had a significant impact on the company.
As a result of the above market, credit and economic risks, net earnings and revenues in any particular period may not be representative of full-year results and may vary significantly from year to year.
Commodity Risk
Snap-on is a purchaser of certain commodities such as steel, natural gas and electricity. The company is also a purchaser of components and parts that are integrated into the company’s end products, as well as the purchaser of certain finished goods, all of which may contain various commodities including steel, aluminum, nickel, copper and others. Snap-on’s supply of raw materials and purchased components are generally and readily available from numerous suppliers.
The principal raw material used in the manufacture of the company’s products is steel, which the company purchases in competitive, price-sensitive markets. To meet Snap-on’s high quality standards, the company’s steel needs range from specialized alloys, which are available only from a limited group of approved suppliers, to commodity types of alloys. These raw materials have historically exhibited price and demand cyclicality. Some of these materials have been, and in the future may be, in short supply, particularly in the event of mill shutdowns or production cut backs. As some steel alloys require specialized manufacturing procedures, Snap-on could experience inventory shortages if it were required to use an alternative manufacturer on short notice. Additionally, unexpected price increases for raw materials could result in higher prices to Snap-on’s customers or an erosion of the margins on its products.
Snap-on believes its ability to sell product is also dependent on the number of vehicles on the road, the number of miles driven and the general aging of vehicles. These factors affect the frequency, type and amount of service and repair performed on vehicles by technicians, and therefore affect the demand for the number of technicians, the prosperity of the technicians and, consequently, the demand technicians have for the company’s tools, other products and services, and the value technicians place on those products and services. The use of other methods of transportation, including more frequent use of public transportation, could result in a decrease in the use of privately operated vehicles. A decrease in the use of privately operated vehicles may lead to fewer repairs and less demand for the company’s products.
To the extent that commodity prices increase and the company does not have firm pricing agreements with its suppliers, the company may experience margin declines to the extent that it is not able to increase the selling prices of its products.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 55 |
Table of Contents
Item 8: Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
The financial statements and schedules are listed in Item 15(a) and are incorporated by reference into this Item 8.
Item 9: Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A: Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Snap-on maintains a system of disclosure controls and procedures that is designed to provide reasonable assurance that material information relating to the company and its consolidated subsidiaries is timely communicated to the officers who certify Snap-on’s financial reports and to other members of senior management and the Board, as appropriate.
In accordance with Rule 13a-15(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”), the company’s management evaluated, with the participation of the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, the effectiveness of the design and operation of the company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) as of December 31, 2016 and, as permitted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board auditing standards, excluded from its assessment the company’s October 31, 2016, acquisition of Car-O-Liner Holding AB (which represented less than 4% of total assets at December 31, 2016, and less than 1% of 2016 net sales). Based upon their evaluation of these disclosure controls and procedures, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that the disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of December 31, 2016, to ensure that information required to be disclosed by the company in the reports it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time period specified in the Securities and Exchange Commission rules and forms, and to ensure that information required to be disclosed by the company in the reports it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to the company’s management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Changes in Internal Control
There has not been any change in the company’s internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2016, that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the company’s internal control over financial reporting (as such term is defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)).
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended). Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we evaluated the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013). As permitted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board auditing standards, the company’s October 31, 2016, acquisition of Car-O-Liner Holding AB (which represented less than 4% of total assets at December 31, 2016, and less than 1% of 2016 net sales) was excluded from the scope of management’s assessment of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016. Based on this assessment, the company’s management believes that, as of December 31, 2016, our internal control over financial reporting was effective at a reasonable assurance level. The company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, has been audited by Deloitte & Touche LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in its attestation report, which is included herein.
Our management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, does not expect that our internal control over financial reporting will prevent all error or fraud. Because of inherent limitations, a system of internal control over financial reporting can provide only reasonable assurance and may not prevent or detect misstatements. Further, because of changes in conditions, the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting may vary over time.
| 56 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of
Snap-on Incorporated:
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Snap-on Incorporated and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. As described in Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting, management excluded from its assessment the internal control over financial reporting at Car-O-Liner Holding AB, which was acquired on October 31, 2016, and whose financial statements constitute less than 4% of the Company’s total assets as of December 31, 2016, and less than 1% of the Company’s 2016 net sales. Accordingly, our audit did not include the internal control over financial reporting at Car-O-Liner Holding AB. The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company’s principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the company’s board of directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including the possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements due to error or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on the criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements of the Company as of and for the year ended December 31, 2016, and our report dated February 9, 2017 expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements.
| /s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP |
||
| Milwaukee, Wisconsin February 9, 2017 |
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 57 |
Table of Contents
None.
PART III
Item 10: Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
Incorporated by reference to sections entitled “Item 1: Election of Directors,” “Corporate Governance Practices and Board Information” and “Other Information” in Snap-on’s 2017 Annual Meeting Proxy Statement, which is expected to be mailed to shareholders on or about March 10, 2017 (the “2017 Proxy Statement”).
The Section 16(a) filing compliance disclosure pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is contained in Snap-on’s 2017 Proxy Statement in the section entitled “Other Information – Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance,” and is incorporated herein by reference.
Information regarding Snap-on’s executive officers, including their ages, business experience (for at least the last five years) and titles as of December 31, 2016, is presented below:
Nicholas T. Pinchuk (70) – Chairman of the Board of Directors since 2009, President and Chief Executive Officer since December 2007 and President and Chief Operating Officer from April to December 2007. Senior Vice President and President – Worldwide Commercial & Industrial Group from 2002 to 2007. Prior to joining Snap-on, Mr. Pinchuk held various positions, including President of Global Refrigeration Operations and President of Asia Pacific Operations, at Carrier Corporation, a producer of air conditioning, heating and refrigeration systems, and a subsidiary of United Technologies Corporation. Mr. Pinchuk serves on the board of directors of Columbus McKinnon Corporation.
Aldo J. Pagliari (62) – Senior Vice President – Finance and Chief Financial Officer since 2010.
Anup R. Banerjee (66) – Senior Vice President, Human Resources and Chief Development Officer since 2015, and President, Commercial Group from 2011 to 2015.
Iain Boyd (54) – Vice President, Operations Development since 2015. Vice President – Human Resources from 2007 to 2015.
Constance R. Johnsen (59) – Vice President and Controller since 2003.
Thomas L. Kassouf (64) – Senior Vice President and President – Snap-on Tools Group since 2010.
Jeanne M. Moreno (62) – Vice President and Chief Information Officer since 2005.
Irwin M. Shur (58) – Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary since 2008.
Thomas J. Ward (64) – Senior Vice President and President – Repair Systems & Information Group since 2010.
There is no family relationship among the executive officers and there has been no involvement in legal proceedings during the past ten years that would be material to the evaluation of the ability or integrity of any of the executive officers. Executive officers may either be elected by the Board or may be appointed by the Chief Executive Officer at the regular meeting of the Board that follows the Annual Shareholders’ Meeting, which is ordinarily held in April each year, or at such other times as new positions are created or vacancies must be filled.
| 58 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Code of Ethics and Website Disclosure
Snap-on has adopted a written code of ethics that applies to its Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, Vice President and Controller, and all other financial officers and executives performing similar functions. Snap-on has posted a copy of the code of ethics in the Investors/Corporate Governance section on the company’s website at www.snapon.com. Snap-on will also post any amendments to these documents, or information about any waivers granted to directors or executive officers with respect to the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, on the company’s website at www.snapon.com.
Snap-on intends to satisfy the disclosure requirements under Item 10 of Form 8-K regarding amendments to, or waivers from, the code of ethics by posting such information in the “Investors” section of its corporate website at www.snapon.com.
Item 11: Executive Compensation
The information required by Item 11 is contained in Snap-on’s 2017 Proxy Statement in the sections entitled “Executive Compensation,” “Board Compensation,” “Compensation Committee Report,” and “Other Information” and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12: Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The following table sets forth information about Snap-on’s equity compensation plans at 2016 year end:
| Plan category |
Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights (a) |
Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights (b) |
Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a)) (c) |
|||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders |
3,366,358 (1) | $ 103.03 (2) | 5,059,920 (3) | |||||
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders |
53,439 (4) | Not Applicable | – (5) | |||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
| Total |
3,419,797 | $ 103.03 (2) | 5,059,920 (5) | |||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
| (1) | Includes (i) options to acquire 589,784 shares granted under the 2001 Incentive Stock and Awards Plan (the “2001 Plan”); (ii) options and stock appreciation rights to acquire 2,724,530 shares granted under the 2011 Incentive Stock and Awards Plan (the “2011 Plan,” and collectively with the 2001 Plan, the “Incentive Plans”); and (iii) 52,044 shares represented by deferred share units under the Directors’ Fee Plan. Excludes 50,528 shares issuable in connection with the vesting of restricted stock units and restricted stock under the 2001 Plan, and 288,072 shares issuable in connection with the vesting of performance share awards, restricted stock units and restricted stock under the 2011 Plan. Also excludes shares of common stock that may be issuable under the employee and franchisee stock purchase plans. |
| (2) | Reflects only the weighted-average exercise price of outstanding stock options and stock appreciation rights granted under the Incentive Plans and does not include shares represented by deferred share units under the Directors’ Fee Plan and shares issuable in connection with the vesting of restricted stock units or performance units under the Incentive Plans for which there are no exercise prices. Also excludes shares of common stock that may be issuable under the employee and franchisee stock purchase plans. |
| (3) | Includes (i) 4,121,252 shares reserved for issuance under the 2011 Plan; (ii) 158,105 shares reserved for issuance under the Directors’ Fee Plan; and (iii) 780,563 shares reserved for issuance under the employee stock purchase plan. |
| (4) | Consists of deferred share units under Snap-on’s Deferred Compensation Plan, which allows elected and appointed officers of Snap-on to defer all or a percentage of their respective annual salary and/or incentive compensation. The deferred share units are payable in shares of Snap-on common stock on a one-for-one basis and are calculated at fair market value. Shares of common stock delivered under the Deferred Compensation Plan are previously issued shares reacquired and held by Snap-on. |
| (5) | The Deferred Compensation Plan provides that Snap-on will make available, as and when required, a sufficient number of shares of common stock to meet the needs of the plan. It further provides that such shares shall be previously issued shares reacquired and held by Snap-on. |
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 59 |
Table of Contents
The additional information required by Item 12 is contained in Snap-on’s 2017 Proxy Statement in the sections entitled “Executive Compensation,” “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management,” and “Other Information,” and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13: Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
Incorporated by reference to the sections entitled “Corporate Governance Practices and Board Information – Board Information” and “Other Information – Transactions with the Company” in Snap-on’s 2017 Proxy Statement.
Item 14: Principal Accounting Fees and Services
Incorporated by reference to the section entitled “Deloitte & Touche LLP Fee Disclosure” in Snap-on’s 2017 Proxy Statement.
PART IV
Item 15: Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules
| Item 15(a): | Documents Filed as Part of This Report: |
1. List of Financial Statements
Unless otherwise indicated, references to “fiscal 2016” or “2016” refer to the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016; references to “fiscal 2015” or “2015” refer to the fiscal year ended January 2, 2016; and references to “fiscal 2014” or “2014” refer to the fiscal year ended January 3, 2015. References to 2016, 2015 and 2014 year end refer to December 31, 2016, January 2, 2016, and January 3, 2015, respectively.
The following consolidated financial statements of Snap-on and the Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm thereon, are filed as part of this report:
| • | Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
| • | Consolidated Statements of Earnings for the 2016, 2015 and 2014 fiscal years. |
| • | Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the 2016, 2015 and 2014 fiscal years. |
| • | Consolidated Balance Sheets as of 2016 and 2015 year end. |
| • | Consolidated Statements of Equity for the 2016, 2015 and 2014 fiscal years. |
| • | Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the 2016, 2015 and 2014 fiscal years. |
| • | Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
2. Financial Statement Schedules
All schedules are omitted because they are not applicable, or the required information is included in the consolidated financial statements or notes thereto.
3. List of Exhibits
The exhibits filed with or incorporated by reference in this report are as specified in the exhibit index included herein.
None.
| 60 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of
Snap-on Incorporated:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Snap-on Incorporated and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2016, and January 2, 2016, and the related consolidated statements of earnings, comprehensive income, equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2016. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Snap-on Incorporated and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2016, and January 2, 2016, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2016, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on the criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated February 9, 2017 expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
| /s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP |
||
| Milwaukee, Wisconsin February 9, 2017 |
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 61 |
Table of Contents
Snap-on Incorporated – Consolidated Statements of Earnings
| (Amounts in millions, except per share data) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 3,430.4 | $ | 3,352.8 | $ | 3,277.7 | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
(1,720.8) | (1,704.5) | (1,693.4) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Gross profit |
1,709.6 | 1,648.3 | 1,584.3 | |||||||||
| Operating expenses |
(1,054.1) | (1,053.7) | (1,048.7) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Operating earnings before financial services |
655.5 | 594.6 | 535.6 | |||||||||
| Financial services revenue |
281.4 | 240.3 | 214.9 | |||||||||
| Financial services expenses |
(82.7) | (70.1) | (65.8) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Operating earnings from financial services |
198.7 | 170.2 | 149.1 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Operating earnings |
854.2 | 764.8 | 684.7 | |||||||||
| Interest expense |
(52.2) | (51.9) | (52.9) | |||||||||
| Other income (expense) – net |
(0.6) | (2.4) | (0.9) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Earnings before income taxes and equity earnings |
801.4 | 710.5 | 630.9 | |||||||||
| Income tax expense |
(244.3) | (221.2) | (199.5) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Earnings before equity earnings |
557.1 | 489.3 | 431.4 | |||||||||
| Equity earnings, net of tax |
2.5 | 1.3 | 0.7 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net earnings |
559.6 | 490.6 | 432.1 | |||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to noncontrolling interests |
(13.2) | (11.9) | (10.2) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net earnings attributable to Snap-on Incorporated |
$ | 546.4 | $ | 478.7 | $ | 421.9 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net earnings per share attributable to Snap-on Incorporated: |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 9.40 | $ | 8.24 | $ | 7.26 | ||||||
| Diluted |
9.20 | 8.10 | 7.14 | |||||||||
| Weighted-average shares outstanding: |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
58.1 | 58.1 | 58.1 | |||||||||
| Effect of dilutive securities |
1.3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted |
59.4 | 59.1 | 59.1 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
| 62 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Snap-on Incorporated – Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss): |
||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 559.6 | $ | 490.6 | $ | 432.1 | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss): |
||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation* |
(99.2) | (110.8) | (128.8) | |||||||||
| Unrealized cash flow hedges, net of tax: |
||||||||||||
| Reclassification of cash flow hedges from accumulated other comprehensive loss |
8.8 | – | – | |||||||||
| Reclassification of cash flow hedges to net earnings |
(0.3) | (0.3) | (0.3) | |||||||||
| Defined benefit pension and postretirement plans: |
||||||||||||
| Net prior service costs and credits and unrecognized loss |
(93.3) | (48.3) | (136.1) | |||||||||
| Income tax benefit |
30.7 | 19.4 | 47.9 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net of tax |
(62.6) | (28.9) | (88.2) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Amortization of net prior service costs and credits and unrecognized loss included in net periodic benefit cost |
30.1 | 38.0 | 22.0 | |||||||||
| Income tax benefit |
(11.1) | (14.0) | (8.1) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net of tax |
19.0 | 24.0 | 13.9 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total comprehensive income |
425.3 | 374.6 | 228.7 | |||||||||
| Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
(13.2) | (11.9) | (10.2) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Comprehensive income attributable to Snap-on Incorporated |
$ | 412.1 | $ | 362.7 | $ | 218.5 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| * | There is no reclassification adjustment as there was no sale or liquidation of any foreign entity during any period presented. |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 63 |
Table of Contents
Snap-on Incorporated – Consolidated Balance Sheets
| Fiscal Year End | ||||||||
| (Amounts in millions, except share data) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| ASSETS |
||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 77.6 | $ | 92.8 | ||||
| Trade and other accounts receivable – net |
598.8 | 562.5 | ||||||
| Finance receivables – net |
472.5 | 447.3 | ||||||
| Contract receivables – net |
88.1 | 82.1 | ||||||
| Inventories – net |
530.5 | 497.8 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets |
116.5 | 106.3 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current assets |
1,884.0 | 1,788.8 | ||||||
| Property and equipment – net |
425.2 | 413.5 | ||||||
| Deferred income tax assets |
72.8 | 60.4 | ||||||
| Long-term finance receivables – net |
934.5 | 772.7 | ||||||
| Long-term contract receivables – net |
286.7 | 266.6 | ||||||
| Goodwill |
895.5 | 790.1 | ||||||
| Other intangibles – net |
184.6 | 195.0 | ||||||
| Other assets |
39.9 | 44.0 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total assets |
$ | 4,723.2 | $ | 4,331.1 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY |
||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||
| Notes payable and current maturities of long-term debt |
$ | 301.4 | $ | 18.4 | ||||
| Accounts payable |
170.9 | 148.3 | ||||||
| Accrued benefits |
52.8 | 52.1 | ||||||
| Accrued compensation |
89.8 | 91.0 | ||||||
| Franchisee deposits |
66.7 | 64.4 | ||||||
| Other accrued liabilities |
307.9 | 296.0 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current liabilities |
989.5 | 670.2 | ||||||
| Long-term debt |
708.8 | 861.7 | ||||||
| Deferred income tax liabilities |
13.1 | 14.3 | ||||||
| Retiree health care benefits |
36.7 | 37.9 | ||||||
| Pension liabilities |
246.5 | 227.8 | ||||||
| Other long-term liabilities |
93.4 | 88.5 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities |
2,088.0 | 1,900.4 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 15) |
||||||||
| Equity |
||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity attributable to Snap-on Incorporated: |
||||||||
| Preferred stock (authorized 15,000,000 shares of $1 par value; none outstanding) |
– | – | ||||||
| Common stock (authorized 250,000,000 shares of $1 par value; issued 67,400,250 and 67,392,545 shares, respectively) |
67.4 | 67.4 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
317.3 | 296.3 | ||||||
| Retained earnings |
3,384.9 | 2,986.9 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(498.5) | (364.2) | ||||||
| Treasury stock at cost (9,450,393 and 9,306,499 shares, respectively) |
(653.9) | (573.7) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total shareholders’ equity attributable to Snap-on Incorporated |
2,617.2 | 2,412.7 | ||||||
| Noncontrolling interests |
18.0 | 18.0 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total equity |
2,635.2 | 2,430.7 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities and equity |
$ | 4,723.2 | $ | 4,331.1 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
| 64 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Snap-on Incorporated – Consolidated Statements of Equity
| Shareholders’ Equity Attributable to Snap-on Incorporated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions, except share data) | Common Stock |
Additional Paid-in Capital |
Retained Earnings |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss |
Treasury Stock |
Noncontrolling Interests |
Total Equity | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 28, 2013 |
$ | 67.4 | $ | 225.1 | $ | 2,324.1 | $ | (44.8) | $ | (458.6) | $ | 17.2 | $ | 2,130.4 | ||||||||||||||
| Net earnings for 2014 |
– | – | 421.9 | – | – | 10.2 | 432.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss |
– | – | – | (203.4) | – | – | (203.4) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends – $1.85 per share |
– | – | (107.6) | – | – | – | (107.6) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock compensation plans |
– | 15.7 | – | – | 34.6 | – | 50.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Share repurchases – 680,000 shares |
– | – | – | – | (79.3) | – | (79.3) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from certain stock options |
– | 13.9 | – | – | – | – | 13.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividend reinvestment plan and other |
– | – | (1.2) | – | – | (9.9) | (11.1) | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at January 3, 2015 |
67.4 | 254.7 | 2,637.2 | (248.2) | (503.3) | 17.5 | 2,225.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings for 2015 |
– | – | 478.7 | – | – | 11.9 | 490.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss |
– | – | – | (116.0) | – | – | (116.0) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends – $2.20 per share |
– | – | (127.9) | – | – | – | (127.9) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock compensation plans |
– | 23.3 | – | – | 40.0 | – | 63.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Share repurchases – 723,000 shares |
– | – | – | – | (110.4) | – | (110.4) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from certain stock options |
– | 18.3 | – | – | – | – | 18.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividend reinvestment plan and other |
– | – | (1.1) | – | – | (11.4) | (12.5) | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at January 2, 2016 |
67.4 | 296.3 | 2,986.9 | (364.2) | (573.7) | 18.0 | 2,430.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings for 2016 |
– | – | 546.4 | – | – | 13.2 | 559.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss |
– | – | – | (134.3) | – | – | (134.3) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends – $2.54 per share |
– | – | (147.5) | – | – | – | (147.5) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock compensation plans |
– | 21.0 | – | – | 40.2 | – | 61.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Share repurchases – 758,000 shares |
– | – | – | – | (120.4) | – | (120.4) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other |
– | – | (0.9) | – | – | (13.2) | (14.1) | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2016 |
$ | 67.4 | $ | 317.3 | $ | 3,384.9 | $ | (498.5) | $ | (653.9) | $ | 18.0 | $ | 2,635.2 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 65 |
Table of Contents
Snap-on Incorporated – Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 559.6 | $ | 490.6 | $ | 432.1 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to net cash provided (used) by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Depreciation |
61.4 | 57.8 | 54.8 | |||||||||
| Amortization of other intangibles |
24.2 | 24.7 | 24.7 | |||||||||
| Provision for losses on finance receivables |
44.0 | 31.6 | 27.4 | |||||||||
| Provision for losses on non-finance receivables |
7.5 | 13.6 | 14.3 | |||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
31.0 | 39.8 | 38.1 | |||||||||
| Excess tax benefits from stock-based compensation |
– | (18.3) | (13.9) | |||||||||
| Deferred income tax provision (benefit) |
1.3 | (5.1) | 3.2 | |||||||||
| Loss (gain) on sales of assets |
0.2 | (2.1) | 0.4 | |||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of effects of acquisitions: |
||||||||||||
| Increase in trade and other accounts receivable |
(41.0) | (44.7) | (57.4) | |||||||||
| Increase in contract receivables |
(31.9) | (34.6) | (37.5) | |||||||||
| Increase in inventories |
(32.7) | (43.3) | (61.1) | |||||||||
| Increase in prepaid and other assets |
(11.9) | (28.2) | (50.9) | |||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in accounts payable |
16.3 | 4.7 | (7.0) | |||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in accruals and other liabilities |
(51.9) | 20.7 | 35.9 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
576.1 | 507.2 | 403.1 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Investing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Additions to finance receivables |
(915.0) | (844.2) | (746.2) | |||||||||
| Collections of finance receivables |
671.7 | 624.8 | 591.4 | |||||||||
| Capital expenditures |
(74.3) | (80.4) | (80.6) | |||||||||
| Acquisitions of businesses, net of cash acquired |
(160.4) | (11.8) | (41.3) | |||||||||
| Disposals of property and equipment |
2.2 | 3.5 | 0.8 | |||||||||
| Other |
2.4 | 1.7 | 2.7 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash used by investing activities |
(473.4) | (306.4) | (273.2) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Financing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Repayment of long-term debt |
– | – | (100.0) | |||||||||
| Proceeds from notes payable |
4.5 | 7.1 | 4.9 | |||||||||
| Repayments of notes payable |
(5.3) | (6.3) | (1.6) | |||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in other short-term borrowings |
135.0 | (34.8) | 41.7 | |||||||||
| Cash dividends paid |
(147.5) | (127.9) | (107.6) | |||||||||
| Purchases of treasury stock |
(120.4) | (110.4) | (79.3) | |||||||||
| Proceeds from stock purchase and option plans |
41.8 | 41.6 | 33.0 | |||||||||
| Excess tax benefits from stock-based compensation |
– | 18.3 | 13.9 | |||||||||
| Other |
(24.1) | (24.3) | (17.1) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash used by financing activities |
(116.0) | (236.7) | (212.1) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents |
(1.9) | (4.2) | (2.5) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Decrease in cash and cash equivalents |
(15.2) | (40.1) | (84.7) | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year |
92.8 | 132.9 | 217.6 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year |
$ | 77.6 | $ | 92.8 | $ | 132.9 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Supplemental cash flow disclosures: |
||||||||||||
| Cash paid for interest |
$ | (51.0) | $ | (50.8) | $ | (52.8) | ||||||
| Net cash paid for income taxes |
(247.3) | (191.9) | (191.2) | |||||||||
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
| 66 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Note 1: Summary of Accounting Policies
Principles of consolidation and presentation: The Consolidated Financial Statements include the accounts of Snap-on Incorporated and its wholly-owned and majority-owned subsidiaries (collectively, “Snap-on” or “the company”).
Snap-on accounts for investments in unconsolidated affiliates where Snap-on has a greater than 20% but less than 50% ownership interest under the equity method of accounting. Investments in unconsolidated affiliates of $15.2 million as of December 31, 2016, and $13.3 million as of January 2, 2016, are included in “Other assets” on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets; no equity investment dividends were received in any period presented. In the normal course of business, the company may purchase products or services from, or sell products or services to, unconsolidated affiliates; purchases from unconsolidated affiliates were $12.9 million, $13.4 million and $15.6 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, and sales to unconsolidated affiliates were $0.2 million in 2016 and zero in both 2015 and 2014. The Consolidated Financial Statements do not include the accounts of the company’s independent franchisees. Snap-on’s Consolidated Financial Statements are prepared in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“GAAP”). All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated.
Fiscal year accounting period: Snap-on’s fiscal year ends on the Saturday that is on or nearest to December 31. The 2016 fiscal year ended on December 31, 2016 (“2016”) and contained 52 weeks of operating results. The 2015 fiscal year ended on January 2, 2016 (“2015”) and contained 52 weeks of operating results. The 2014 fiscal year ended on January 3, 2015 (“2014”) and contained 53 weeks of operating results; the impact of the additional week of operations was not material to Snap-on’s 2014 net sales or net earnings.
Use of estimates: The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Financial instruments: The fair value of the company’s derivative financial instruments is generally determined using quoted prices in active markets for similar assets and liabilities. The carrying value of the company’s non-derivative financial instruments either approximates fair value, due to their short-term nature, or the amount disclosed for fair value is based upon a discounted cash flow analysis or quoted market values. See Note 10 for further information on financial instruments.
Revenue recognition: Snap-on recognizes revenue from the sale of tools and diagnostic and equipment products when contract terms are met, the price is fixed or determinable, collectability is reasonably assured and a product is shipped or risk of ownership has been transferred to and accepted by the customer. For sales contingent upon customer acceptance, revenue recognition is deferred until such obligations are fulfilled. Estimated product returns are recorded as a reduction in reported revenues at the time of sale based upon historical product return experience and gross profit margin adjusted for known trends. Provisions for customer volume rebates, discounts and allowances are also recorded as a reduction of reported revenues at the time of sale based on historical experience and known trends. Revenue related to maintenance, extended warranty and subscription agreements is recognized over the terms of the respective agreements.
Snap-on also recognizes revenue related to multiple element arrangements, including sales of hardware, software and software-related services. When a sales arrangement contains multiple elements, such as hardware and software products and/or services, Snap-on uses the relative selling price method to allocate revenues between hardware and software elements. For software elements that are not essential to the hardware’s functionality and related software post-contract customer support, vendor specific objective evidence (“VSOE”) of fair value is used to further allocate revenue to each element based on its relative fair value and, when necessary, the residual method is used to assign value to the delivered elements when VSOE only exists for the undelivered elements. The amount assigned to the products or services is recognized when the product is delivered and/or when the services are performed. In instances where the product and/or services are performed over an extended period, as is the case with subscription agreements or the providing of ongoing support, revenue is generally recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the agreement, which generally ranges from 12 to 60 months.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 67 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
Franchise fee revenue, including nominal, non-refundable initial fees, is recognized upon the granting of a franchise, which is when the company has performed substantially all initial services required by the franchise agreement. Franchise fee revenue also includes ongoing monthly fees (primarily for sales and business training as well as marketing and product promotion programs) that are recognized as the fees are earned. Franchise fee revenue totaled $13.9 million, $12.7 million and $12.1 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Financial services revenue: Snap-on also generates revenue from various financing programs that include: (i) installment sales and lease contracts arising from franchisees’ customers and certain other customers of Snap-on who require financing for the purchase or lease of tools and diagnostic and equipment products on an extended-term payment plan; and (ii) business loans and vehicle leases to franchisees. These financing programs are offered through Snap-on’s wholly owned finance subsidiaries. Financial services revenue consists primarily of interest income on finance and contract receivables and is recognized over the life of the underlying contracts, with interest computed primarily on the average daily balances of the underlying contracts.
The decision to finance through Snap-on or another financing source is solely at the election of the customer. When assessing customers for potential financing, Snap-on considers various factors regarding ability to pay including the customers’ financial condition, debt-servicing ability, past payment experience, and credit bureau and proprietary Snap-on credit model information, as well as the value of the underlying collateral. For finance and contract receivables, Snap-on assesses these factors through the use of credit quality indicators consisting primarily of customer credit risk scores combined with internal credit risk grades, collection experience and other internal metrics.
Financial services lease arrangements: Snap-on accounts for its financial services leases as direct financing or sales-type leases. The company determines the gross investment in the lease as the present value of the minimum lease payments using the interest rate implicit in the lease, net of amounts, if any, included therein for executor costs to be paid by Snap-on, together with any profit thereon. The difference between the gross investment in the lease and the related undiscounted minimum lease payments for the leased property is reported as unearned finance charges. Unearned finance charges are amortized to income over the life of the contract. The default covenants included in the lease arrangements are usual and customary, consistent with industry practice, and do not impact the lease classification. Except in circumstances where the company has concluded that a lessee’s financial condition has deteriorated, the other default covenants under Snap-on’s lease arrangements are objectively determinable.
Research and engineering: Snap-on incurred research and engineering costs of $53.4 million, $49.3 million and $52.4 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Research and engineering costs are included in “Operating expenses” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
Internally developed software: Costs incurred in the development of software that will ultimately be sold are capitalized from the time technological feasibility has been attained and capitalization ceases when the related product is ready for general release. During 2016, 2015 and 2014, Snap-on capitalized $10.8 million, $14.9 million and $19.0 million, respectively, of such costs. Amortization of capitalized software development costs, which is included in “Cost of goods sold” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings, was $13.8 million in 2016, $14.0 million in 2015 and $13.6 million in 2014. Unamortized capitalized software development costs of $47.4 million as of 2016 year end and $50.4 million as of 2015 year end are included in “Other intangibles – net” on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Internal-use software: Costs that are incurred in creating software solutions and enhancements to those solutions are capitalized only during the application development stage of the project.
Shipping and handling: Amounts billed to customers for shipping and handling are included as a component of sales. Costs incurred by Snap-on for shipping and handling are included as a component of cost of goods sold when the costs relate to manufacturing activities. In 2016, 2015 and 2014, Snap-on incurred shipping and handling charges of $43.1 million, $39.0 million and $40.3 million, respectively, that were recorded in “Cost of goods sold” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings. Shipping and handling costs incurred in conjunction with selling or distribution activities are included as a component of operating expenses. Shipping and handling charges were $81.2 million in 2016 and $78.5 million in both 2015 and 2014; these charges were recorded in “Operating expenses” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
| 68 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Advertising and promotion: Production costs of future media advertising are deferred until the advertising occurs. All other advertising and promotion costs are expensed when incurred. For 2016, 2015 and 2014, advertising and promotion expenses totaled $52.6 million, $54.9 million and $51.4 million, respectively. Advertising and promotion costs are included in “Operating expenses” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
Warranties: Snap-on provides product warranties for specific product lines and accrues for estimated future warranty costs in the period in which the sale is recorded. See Note 15 for information on warranties.
Foreign currency: The financial statements of Snap-on’s foreign subsidiaries are translated into U.S. dollars. Assets and liabilities of foreign subsidiaries are translated at current rates of exchange, and income and expense items are translated at the average exchange rates for the period. The resulting translation adjustments are recorded directly into “Accumulated other comprehensive loss” on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets. Foreign exchange transactions, net of foreign currency hedges, resulted in pretax losses of $1.3 million, $2.7 million and $1.5 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Foreign exchange transaction gains and losses are reported in “Other income (expense) – net” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
Income taxes: Current tax assets and liabilities are based upon an estimate of taxes refundable or payable for each of the jurisdictions in which the company is subject to tax. In the ordinary course of business, there is inherent uncertainty in quantifying income tax positions. Snap-on assesses income tax positions and records tax benefits for all years subject to examination based upon management’s evaluation of the facts, circumstances and information available at the reporting dates. For those tax positions where it is more-likely-than-not that a tax benefit will be sustained, Snap-on records the largest amount of tax benefit with a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement with a taxing authority that has full knowledge of all relevant information. For those income tax positions where it is not more-likely-than-not that a tax benefit will be sustained, no tax benefit is recognized in the financial statements. When applicable, associated interest and penalties are recognized as a component of income tax expense. Accrued interest and penalties are included within the related tax asset or liability on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Deferred income taxes are provided for temporary differences arising from differences in bases of assets and liabilities for tax and financial reporting purposes. Deferred income taxes are recorded on temporary differences using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the temporary differences are expected to reverse. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when, in the opinion of management, it is more-likely-than-not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. See Note 8 for further information on income taxes.
Per share data: Basic earnings per share calculations were computed by dividing net earnings attributable to Snap-on Incorporated by the corresponding weighted-average number of common shares outstanding for the period. The dilutive effect of the potential exercise of outstanding options and stock-settled stock appreciation rights (“SARs”) to purchase common shares is calculated using the treasury stock method. As of both December 31, 2016, and January 2, 2016, there were 1,600 awards outstanding that were anti-dilutive; as of January 3, 2015, there were no outstanding awards that were anti-dilutive. Performance-based equity awards are included in the diluted earnings per share calculation based on the attainment of the applicable performance metrics to date. Snap-on had dilutive securities totaling 1,307,914 shares, 1,016,969 shares and 921,050 shares, as of the end of 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. See Note 13 for further information on equity awards.
Stock-based compensation: Snap-on recognizes the cost of employee services in exchange for awards of equity instruments based on the grant date fair value of those awards. That cost, based on the estimated number of awards that are expected to vest, is recognized on a straight-line basis over the period during which the employee is required to provide the service in exchange for the award. No compensation cost is recognized for awards for which employees do not render the requisite service. The grant date fair value of employee stock options and similar instruments is estimated using the Black-Scholes valuation model.
The Black-Scholes valuation model requires the input of subjective assumptions, including the expected life of the stock-based award and stock price volatility. The assumptions used are management’s best estimates, but the estimates involve inherent uncertainties and the application of management judgment. As a result, if other assumptions had been used, the recorded stock-based compensation expense could have been materially different from that depicted in the financial statements. See Note 13 for further information on stock-based compensation.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 69 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
Derivatives: Snap-on utilizes derivative financial instruments, including foreign currency forward contracts, interest rate swap agreements, treasury lock agreements and prepaid equity forward agreements to manage its exposures to foreign currency exchange rate risks, interest rate risks, and market risk associated with the stock-based portion of its deferred compensation plans. Snap-on accounts for its derivative instruments at fair value. Snap-on does not hold or issue financial instruments for speculative or trading purposes. See Note 10 for further information on derivatives.
Cash equivalents: Snap-on considers all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. There were no cash equivalents as of 2016 and 2015 year ends.
Receivables and allowances for doubtful accounts: All trade, finance and contract receivables are reported on the Consolidated Balance Sheets at their outstanding principal balance adjusted for any charge-offs and net of allowances for doubtful accounts. Finance and contract receivables also include accrued interest and contract acquisition costs, net of contract acquisition fees.
Snap-on maintains allowances for doubtful accounts to absorb probable losses inherent in its portfolio of receivables. The allowances for doubtful accounts represent management’s estimate of the losses inherent in the company’s receivables portfolio based on ongoing assessments and evaluations of collectability and historical loss experience. In estimating losses inherent in each of its receivable portfolios (trade, finance and contract receivables), Snap-on uses historical loss experience rates by portfolio and applies them to a related aging analysis. Determination of the proper level of allowances by portfolio requires management to exercise significant judgment about the timing, frequency and severity of credit losses that could materially affect the provision for credit losses and, as a result, net earnings. The allowances take into consideration numerous quantitative and qualitative factors that include receivable type, historical loss experience, loss migration, delinquency trends, collection experience, current economic conditions and credit risk characteristics as follows:
| • | Snap-on evaluates the collectability of receivables based on a combination of various financial and qualitative factors that may affect its customers’ ability to pay. These factors may include customers’ financial condition, debt-servicing ability, past payment experience, and credit bureau and proprietary Snap-on credit model information, as well as the value of the underlying collateral. |
| • | For finance and contract receivables, Snap-on assesses quantitative and qualitative factors through the use of credit quality indicators consisting primarily of collection experience and other internal metrics as follows: |
| • | Collection experience – Snap-on conducts monthly reviews of credit and collection performance for each of its finance and contract receivable portfolios focusing on data such as delinquency trends, non-performing assets, and charge-off and recovery activity. These reviews allow for the formulation of collection strategies and potential collection policy modifications in response to changing risk profiles in the finance and contract receivable portfolios. |
| • | Other internal metrics – Snap-on maintains a system that aggregates credit exposure by customer, risk classification and geographical area, among other factors, to further monitor changing risk profiles. |
Management performs detailed reviews of its receivables on a monthly and/or quarterly basis to assess the adequacy of the allowances based on historical and current trends and other factors affecting credit losses and to determine if any impairment has occurred. A receivable is impaired when it is probable that all amounts related to the receivable will not be collected according to the contractual terms of the agreement. Additions to the allowances for doubtful accounts are maintained through adjustments to the provision for credit losses, which are charged to current period earnings; amounts determined to be uncollectable are charged directly against the allowances, while amounts recovered on previously charged-off accounts increase the allowances. Net charge-offs include the principal amount of losses charged-off as well as charged-off interest and fees. Recovered interest and fees previously charged-off are recorded through the allowances for doubtful accounts and increase the allowances. Finance receivables are assessed for charge-off when an account becomes 120 days past due and are charged-off typically within 60 days of asset repossession. Contract receivables related to equipment leases are generally charged-off when an account becomes 150 days past due, while contract receivables related to franchise finance and van leases are generally charged-off up to 180 days past the asset return date. For finance and contract receivables, customer bankruptcies are generally charged-off upon notification that the associated debt is not being reaffirmed or, in any event, no later than 180 days past due.
| 70 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Snap-on does not believe that its trade accounts, finance or contract receivables represent significant concentrations of credit risk because of the diversified portfolio of individual customers and geographical areas. See Note 3 for further information on receivables and allowances for doubtful accounts.
Other accrued liabilities: Supplemental balance sheet information for “Other accrued liabilities” as of 2016 and 2015 year end is as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Income taxes |
$ | 21.4 | $ | 28.5 | ||||
| Accrued restructuring |
2.8 | 4.1 | ||||||
| Accrued warranty |
16.0 | 16.4 | ||||||
| Deferred subscription revenue |
43.0 | 40.7 | ||||||
| Accrued property, payroll and other taxes |
36.1 | 39.7 | ||||||
| Accrued selling and promotion expense |
24.7 | 23.3 | ||||||
| Other |
163.9 | 143.3 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total other accrued liabilities |
$ | 307.9 | $ | 296.0 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Inventories: Snap-on values its inventory at the lower of cost or market and adjusts for the value of inventory that is estimated to be excess, obsolete or otherwise unmarketable. Snap-on records allowances for excess and obsolete inventory based on historical and estimated future demand and market conditions. Allowances for raw materials are largely based on an analysis of raw material age and actual physical inspection of raw material for fitness for use. As part of evaluating the adequacy of allowances for work-in-progress and finished goods, management reviews individual product stock-keeping units (SKUs) by product category and product life cycle. Cost adjustments for each product category/product life-cycle state are generally established and maintained based on a combination of historical experience, forecasted sales and promotions, technological obsolescence, inventory age and other actual known conditions and circumstances. Should actual product marketability and raw material fitness for use be affected by conditions that are different from management estimates, further adjustments to inventory allowances may be required.
Snap-on adopted the “last-in, first-out” (“LIFO”) inventory valuation method in 1973 for its U.S. locations. Snap-on’s U.S. inventories accounted for on a LIFO basis consist of purchased product and inventory manufactured at the company’s heritage U.S. manufacturing facilities (primarily hand tools and tool storage). Since Snap-on began acquiring businesses in the 1990’s, the company has used the “first-in, first-out” (“FIFO”) inventory valuation methodology for acquisitions; the company does not adopt the LIFO inventory valuation methodology for new acquisitions. See Note 4 for further information on inventories.
Property and equipment: Property and equipment is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are provided on a straight-line basis over estimated useful lives. Major repairs that extend the useful life of an asset are capitalized, while routine maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred. Capitalized software included in property and equipment reflects costs related to internally developed or purchased software for internal use and is amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives. Long-lived assets are evaluated for impairment when events or circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the long-lived asset may not be recoverable. See Note 5 for further information on property and equipment.
Goodwill and other intangible assets: Goodwill and other indefinite-lived assets are tested for impairment annually or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the assets might be impaired. Annual impairment tests are performed by the company in the second quarter of each year using information available as of fiscal April month end. Snap-on evaluates the existence of goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible asset impairment on the basis of whether the assets are fully recoverable from projected, discounted cash flows of the related reportable unit or asset. Intangible assets with finite lives are amortized over their estimated useful lives using straight-line and accelerated methods depending on the nature of the particular asset. See Note 6 for further information on goodwill and other intangible assets.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 71 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
New accounting standards
In March 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2016-09, Compensation – Stock Compensation (Topic 718) – Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting, which is intended to simplify several aspects of the accounting for stock-based compensation transactions, including the income tax consequences, classification of awards as either equity or liabilities, and classification on the statements of cash flows. Snap-on adopted this ASU as of January 3, 2016. Prior to adoption, excess tax benefits or expense related to stock-based compensation transactions were recognized in “Additional paid-in capital” on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets; following adoption, all excess tax benefits or expense related to stock-based compensation transactions are recognized prospectively as income tax benefits or expense in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings. In addition, the excess tax benefits or expense from stock-based compensation transactions previously included in “Financing activities” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows are prospectively included on that statement as a component of “Net earnings.” To eliminate diversity in practice, the ASU also requires that cash payments to tax authorities in connection with shares withheld to meet employees’ statutory tax withholding requirements are to be included retrospectively, for all periods presented, in financing activities on the statements of cash flows. The adoption of this ASU did not have a significant impact on the company’s Consolidated Financial Statements.
In November 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-17, Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes (Topic 740), to simplify the presentation of deferred income taxes by requiring that all deferred tax liabilities and assets be classified as long term on the balance sheet. Snap-on adopted this ASU as of April 2, 2016. Upon adoption, Snap-on retrospectively reclassified $109.9 million of current “Deferred income tax assets,” $45.9 million of long-term “Deferred income tax assets,” and $0.3 million of current deferred income tax liabilities (included in “Other accrued liabilities”) to long-term “Deferred income tax liabilities” on the accompanying 2015 year-end Consolidated Balance Sheet. Due to the jurisdictional netting of non-current deferred tax assets and liabilities, Snap-on’s overall assets and liabilities were reduced by $155.8 million on the revised 2015 year-end Consolidated Balance Sheet.
In September 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-16, Business Combinations (Topic 805), to simplify the accounting and disclosures for entities that report provisional amounts for items in a business combination for which the accounting is incomplete at the end of the reporting period in which the business combination occurred. The ASU, which was effective for Snap-on at the beginning of its 2016 fiscal year, requires that an acquirer recognize adjustments to provisional amounts identified during the measurement period in the reporting period in which the adjustment amounts are determined as if the accounting had been completed at the acquisition date. Entities are required to present separately on the face of the income statement or disclose in the notes to the financial statements the amounts recorded in current-period earnings (by line item) that would have been recorded in previous reporting periods if the adjustments to the provisional amounts had been recognized as of the acquisition date. The adoption of this ASU did not have a significant impact on the company’s Consolidated Financial Statements.
In May 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-07, Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosures for Investments in Certain Entities That Calculate Net Asset Value per Share (or Its Equivalent), which removed the requirement to categorize within the fair value hierarchy all investments for which fair value is measured using the net asset value (“NAV”) per share practical expedient. The ASU also removed the requirement to make certain disclosures for all investments that are eligible to be measured at fair value using the NAV per share practical expedient. Rather, those disclosures are limited to investments for which the entity has elected to measure the fair value using the practical expedient. Entities are required to apply the provisions of this ASU retrospectively to all periods presented. Snap-on adopted ASU No. 2015-07 at the beginning of its 2016 fiscal year. In Note 11 and Note 12, certain investments within the company’s pension and postretirement plan assets that are measured at fair value using the NAV per share (or its equivalent) practical expedient have not been classified in the fair value hierarchy. The adoption of this ASU did not have a significant impact on the company’s Consolidated Financial Statements.
In October 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-16, Income Taxes (Topic 740) – Intra-Entity Transfers of Assets Other Than Inventory. The ASU eliminates the requirement to defer the recognition of current and deferred income taxes for an intra-entity asset transfer until the asset has been sold to an outside party. Under the new guidance, an entity should recognize the income tax consequences of an intra-entity transfer of an asset other than inventory when the transfer occurs. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years; early adoption is permitted as of the beginning of an annual reporting period for which financial statements (interim or annual) have not been issued or made available for issuance (i.e., the first interim period if an entity issues interim financial statements). The amendments in this ASU are to be applied on a modified retrospective basis through a cumulative-effect adjustment directly to retained earnings at the time of adoption. The company is currently assessing the impact this ASU will have on its consolidated financial statements.
| 72 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-15, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230), which adds and/or clarifies guidance on the classification of certain cash receipts and payments in the statement of cash flows. The new guidance is intended to reduce diversity in practice in how certain transactions are classified in the statement of cash flows. This ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years; early adoption is permitted. The company is currently assessing the impact this ASU will have on its consolidated statements of cash flows.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13, Financial Instruments – Credit Losses (Topic 326), to require the measurement of expected credit losses for financial instruments held at the reporting date based on historical experience, current conditions and reasonable forecasts. The main objective of this ASU is to provide financial statement users with more decision-useful information about the expected credit losses on financial instruments and other commitments to extend credit held by a reporting entity at each reporting date. ASU No. 2016-13 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, including interim periods within those fiscal years; the ASU allows for early adoption as of the beginning of an interim or annual reporting period beginning after December 15, 2018. The company is currently assessing the impact this ASU will have on its consolidated financial statements.
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606), which outlines a single comprehensive model for entities to use in accounting for revenue arising from contracts with customers and supersedes most current revenue recognition guidance, including industry-specific guidance. Topic 606 is based on the principle that an entity should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. Topic 606 also requires additional disclosure about the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from customer contracts, including significant judgments and changes in judgments and assets recognized from costs incurred to fulfill a contract.
In December 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-20, Technical Corrections and Improvements to Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, which clarified the guidance in Topic 606 on assessing certain aspects of the new revenue standard, including loan guarantee fees, contract cost impairment testing, provisions for loan losses, disclosure of remaining and prior-period performance obligations, contract modifications, contract assets and receivables, refund liabilities, advertising costs and other items. The amendments in this ASU did not change the core principles of the guidance in Topic 606.
In May 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-12, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) – Narrow-Scope Improvements and Practical Expedients, which clarified the guidance in Topic 606 on assessing collectibility, presentation of sales taxes, noncash consideration, and completed contracts and contract modifications at transition. The amendments in this ASU did not change the core principles of the guidance in Topic 606.
In April 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-10, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) – Identifying Performance Obligations and Licensing, which clarified the identification of performance obligations and the licensing implementation guidance in Topic 606. The amendments in this ASU did not change the core principles of the guidance in Topic 606.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-08, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) – Principal versus Agent Considerations (Reporting Revenue Gross versus Net). ASU No. 2016-08 clarified the principal-versus-agent implementation guidance in Topic 606 that requires an entity to determine whether the nature of its promise to provide goods or services to a customer is performed in a principal or agent capacity and to recognize revenue in a gross or net manner based on its principal/agent designation. The amendments in this ASU did not change the core principles of the guidance in Topic 606.
Entities may early adopt Topic 606 only as of annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim reporting periods within that reporting period. Entities have the option of adopting this standard using either a full retrospective approach or a modified retrospective approach (i.e., through a cumulative-effect adjustment directly to retained earnings at the time of adoption).
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 73 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
Snap-on commenced its assessment of Topic 606 during the second half of 2014 and developed a comprehensive project plan that included representatives from across the company’s business segments. The project plan included analyzing the standard’s impact on the company’s various revenue streams, comparing its historical accounting policies and practices to the requirements of the new standard, and identifying potential differences from applying the requirements of the new standard to its contracts. In addition, the company is in the process of identifying and implementing appropriate changes to its business processes, systems and controls to support revenue recognition and disclosures under Topic 606.
As of December 31, 2016, and subject to the potential effects of any new related ASUs issued by the FASB in 2017, as well as the company’s evaluation of new transactions and contracts, the company has substantially completed its evaluation of the expected impact of adopting Topic 606 and anticipates that the adoption of this standard will not have a significant impact on the company’s consolidated financial statements. The company presently expects to adopt Topic 606 at the beginning of its 2018 fiscal year using the modified retrospective approach.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842), to increase transparency and comparability among organizations by recognizing lease assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet and disclosing key information about leasing arrangements. The ASU is intended to represent an improvement over previous GAAP, which did not require lease assets and lease liabilities to be recognized for most leases. This ASU, which supersedes most current lease guidance, affects any entity that enters into a lease (as that term is defined in the ASU), with some specified scope exemptions. ASU No. 2016-02 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years; the ASU allows for early adoption as of the beginning of an interim or annual reporting period. The company is currently assessing the impact this ASU will have on its consolidated financial statements.
Note 2: Acquisitions
On November 16, 2016, Snap-on acquired Ryeson Corporation (d/b/a Sturtevant Richmont) for a preliminary cash purchase price of $12.9 million (or $12.5 million, net of cash acquired). The preliminary purchase price is subject to change based upon the finalization of a working capital adjustment that is expected to be completed in the first quarter of 2017. Sturtevant Richmont, based in Carol Stream, Illinois, designs, manufactures and distributes mechanical and electronic torque wrenches as well as wireless torque error proofing systems for a variety of industrial applications. For segment reporting purposes, the results of operations and assets of Sturtevant Richmont have been included in the Commercial & Industrial Group since the acquisition date.
As of December 31, 2016, and subject to the finalization of the working capital adjustment in the first quarter of 2017, the company has completed the majority of the purchase accounting valuations for the acquired net assets, including the identification of $3.7 million of non-amortized trademarks, of Sturtevant Richmont. On a preliminary basis, the $3.2 million excess of the Sturtevant Richmont purchase price over the fair value of the net assets acquired was recorded in “Goodwill” on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets. The company does not expect any of the goodwill will be deductible for tax purposes.
On October 31, 2016, Snap-on acquired Car-O-Liner Holding AB (“Car-O-Liner”) for a preliminary cash purchase price of $151.8 million (or $147.9 million, net of cash acquired). The preliminary purchase price is subject to change based upon the finalization of a working capital adjustment that is expected to be completed in the first quarter of 2017. Car-O-Liner, headquartered in Gothenburg, Sweden, designs and manufactures collision repair equipment, and information and truck alignment systems. For segment reporting purposes, substantially all of Car-O-Liner’s results of operations and assets have been included in the Repair Systems & Information Group since the acquisition date, with the remaining portions included in the Commercial & Industrial Group.
As of December 31, 2016, the purchase accounting valuations for the acquired net assets of Car-O-Liner, including intangible assets, were not complete. Given the timing and complexity of this acquisition, the presentation of Car-O-Liner in Snap-on’s 2016 Consolidated Financial Statements, including the allocation of the purchase price, has been prepared on a preliminary basis and changes to the allocations will occur as fair value estimates of the acquired net assets are determined. The company anticipates completing the purchase accounting valuations for Car-O-Liner during the first half of 2017. On a preliminary basis, the $128.1 million excess of the Car-O-Liner purchase price over the net assets acquired was recorded in “Goodwill” on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets. The company does not expect any of the goodwill will be deductible for tax purposes.
| 74 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
The following is a summary of the preliminary values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed of Car-O-Liner as of the acquisition date:
| (Amounts in millions) | Amount | |||
| Assets acquired: |
||||
| Cash |
$ | 3.9 | ||
| Trade and other accounts receivable |
17.4 | |||
| Inventories |
18.0 | |||
| Property and equipment |
7.6 | |||
| Goodwill |
128.1 | |||
| Other assets |
2.7 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total assets acquired |
177.7 | |||
| Liabilities assumed: |
||||
| Accounts payable |
9.8 | |||
| Accrued expenses |
9.3 | |||
| Pension liabilities |
4.3 | |||
| Other liabilities |
2.5 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total liabilities assumed |
25.9 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Preliminary net assets acquired |
$ | 151.8 | ||
|
|
|
|||
The post-acquisition revenues and earnings for the Sturtevant Richmont and Car-O-Liner acquisitions, individually and collectively, were neither significant nor material to Snap-on’s 2016 results of operations.
On July 27, 2015, Snap-on acquired the assets of Ecotechnics S.p.A. (“Ecotechnics”) for a cash purchase price of $11.8 million. Ecotechnics designs and manufactures vehicle air conditioning service equipment for original equipment manufacturer (“OEM”) dealerships and the automotive aftermarket worldwide.
On May 28, 2014, Snap-on acquired substantially all of the assets of Pro-Cut International, Inc. (“Pro-Cut”) for a cash purchase price of $41.3 million. Pro-Cut designs, manufactures and distributes on-car brake lathes, related equipment and accessories used in brake servicing by automotive repair facilities.
For segment reporting purposes, the results of operations and assets of Ecotechnics and Pro-Cut have been included in the Repair Systems & Information Group since the respective acquisition dates.
Pro forma financial information has not been presented for any of these acquisitions as the net effects, individually and collectively, were neither significant nor material to Snap-on’s results of operations or financial position. See Note 6 for further information on goodwill and other intangible assets.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 75 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
Note 3: Receivables
Trade and Other Accounts Receivable
Snap-on’s trade and other accounts receivable primarily arise from the sale of tools and diagnostic and equipment products to a broad range of industrial and commercial customers and to Snap-on’s independent franchise van channel on a non-extended-term basis with payment terms generally ranging from 30 to 120 days.
The components of Snap-on’s trade and other accounts receivable as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Trade and other accounts receivable |
$ | 612.8 | $ | 579.2 | ||||
| Allowances for doubtful accounts |
(14.0) | (16.7) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total trade and other accounts receivable – net |
$ | 598.8 | $ | 562.5 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Finance and Contract Receivables
Snap-on Credit LLC (“SOC”), the company’s financial services operation in the United States, originates extended-term finance and contract receivables on sales of Snap-on’s products sold through the U.S. franchisee and customer network and to certain other customers of Snap-on; Snap-on’s foreign finance subsidiaries provide similar financing internationally. Interest income on finance and contract receivables is included in “Financial services revenue” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
Snap-on’s finance receivables are comprised of extended-term installment payment contracts to both technicians and independent shop owners (i.e., franchisees’ customers) to enable them to purchase tools and diagnostic and equipment products on an extended-term payment plan, generally with average payment terms approaching four years. Contract receivables, with payment terms of up to 10 years, are comprised of extended-term installment payment contracts to a broad base of customers worldwide, including shop owners, both independents and national chains, for their purchase of tools and diagnostic and equipment products. Contract receivables also include extended-term installment loans to franchisees to meet a number of financing needs, including working capital loans, loans to enable new franchisees to fund the purchase of the franchise and van leases. Finance and contract receivables are generally secured by the underlying tools and/or diagnostic or equipment products financed and, for installment loans to franchisees, other franchisee assets.
The components of Snap-on’s current finance and contract receivables as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Finance receivables, net of unearned finance charges of $17.0 million and $16.9 million, respectively |
$ | 488.1 | $ | 460.7 | ||||
| Contract receivables, net of unearned finance charges of $15.6 million and $15.1 million, respectively |
89.3 | 83.5 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
577.4 | 544.2 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Allowances for doubtful accounts: |
||||||||
| Finance receivables |
(15.6) | (13.4) | ||||||
| Contract receivables |
(1.2) | (1.4) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
(16.8) | (14.8) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current finance and contract receivables – net |
$ | 560.6 | $ | 529.4 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Finance receivables – net |
$ | 472.5 | $ | 447.3 | ||||
| Contract receivables – net |
88.1 | 82.1 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current finance and contract receivables – net |
$ | 560.6 | $ | 529.4 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 76 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
The components of Snap-on’s finance and contract receivables with payment terms beyond one year as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Finance receivables, net of unearned finance charges of $13.0 million and $10.9 million, respectively |
$ | 967.5 | $ | 797.5 | ||||
| Contract receivables, net of unearned finance charges of $21.5 million and $21.1 million, respectively |
289.4 | 269.6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
1,256.9 | 1,067.1 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Allowances for doubtful accounts: |
||||||||
| Finance receivables |
(33.0) | (24.8) | ||||||
| Contract receivables |
(2.7) | (3.0) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
(35.7) | (27.8) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total long-term finance and contract receivables – net |
$ | 1,221.2 | $ | 1,039.3 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Finance receivables – net |
$ | 934.5 | $ | 772.7 | ||||
| Contract receivables – net |
286.7 | 266.6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total long-term finance and contract receivables – net |
$ | 1,221.2 | $ | 1,039.3 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Long-term finance and contract receivables installments, net of unearned finance charges, as of 2016 and 2015 year end are scheduled as follows:
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | Finance Receivables |
Contract Receivables |
Finance Receivables |
Contract Receivables |
||||||||||||
| Due in Months: |
||||||||||||||||
| 13 – 24 |
$ | 380.9 | $ | 69.5 | $ | 361.0 | $ | 65.1 | ||||||||
| 25 – 36 |
296.9 | 60.2 | 252.8 | 56.6 | ||||||||||||
| 37 – 48 |
196.8 | 49.7 | 137.8 | 46.5 | ||||||||||||
| 49 – 60 |
92.9 | 37.7 | 45.9 | 35.0 | ||||||||||||
| Thereafter |
– | 72.3 | – | 66.4 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | 967.5 | $ | 289.4 | $ | 797.5 | $ | 269.6 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Delinquency is the primary indicator of credit quality for finance and contract receivables. Receivable balances are considered delinquent when contractual payments become 30 days past due.
Finance receivables are generally placed on nonaccrual status (nonaccrual of interest and other fees) (i) when a customer is placed on repossession status; (ii) upon receipt of notification of bankruptcy; (iii) upon notification of the death of a customer; or (iv) in other instances in which management concludes collectability is not reasonably assured. Finance receivables that are considered nonperforming include receivables that are on nonaccrual status and receivables that are generally more than 90 days past due.
Contract receivables are generally placed on nonaccrual status (i) when a receivable is more than 90 days past due or at the point a customer’s account is placed on terminated status regardless of its delinquency status; (ii) upon notification of the death of a customer; or (iii) in other instances in which management concludes collectability is not reasonably assured. Contract receivables that are considered nonperforming include receivables that are on nonaccrual status and receivables that are generally more than 90 days past due.
The accrual of interest and other fees is resumed when the finance or contract receivable becomes contractually current and collection of all remaining contractual amounts due is reasonably assured. Finance and contract receivables are evaluated for impairment on a collective basis. A receivable is impaired when it is probable that all amounts related to the receivable will not be collected according to the contractual terms of the applicable agreement. Impaired finance and contract receivables are covered by the company’s respective allowances for doubtful accounts and are charged-off against the allowances when appropriate. As of 2016 and 2015 year end, there were $24.9 million and $18.2 million, respectively, of impaired finance receivables, and there were $2.0 million and $1.7 million, respectively, of impaired contract receivables.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 77 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
It is the general practice of Snap-on’s financial services business to not engage in contract or loan modifications. In limited instances, Snap-on’s financial services business may modify certain impaired receivables in troubled debt restructurings. The amount and number of restructured finance and contract receivables as of 2016 and 2015 year end were immaterial to both the financial services portfolio and the company’s results of operations and financial position.
The aging of finance and contract receivables as of 2016 and 2015 year end is as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 30-59 Days Past Due |
60-90 Days Past Due |
Greater Than 90 Days Past Due |
Total Past Due |
Total Not Past Due |
Total | Greater Than 90 Days Past Due and Accruing |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 year end: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Finance receivables |
$ | 15.1 | $ | 9.8 | $ | 17.0 | $ | 41.9 | $ | 1,413.7 | $ | 1,455.6 | $ | 13.2 | ||||||||||||||
| Contract receivables |
1.4 | 0.9 | 1.4 | 3.7 | 375.0 | 378.7 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 year end: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Finance receivables |
$ | 12.1 | $ | 7.6 | $ | 11.9 | $ | 31.6 | $ | 1,226.6 | $ | 1,258.2 | $ | 9.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Contract receivables |
1.3 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 3.3 | 349.8 | 353.1 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
The amount of performing and nonperforming finance and contract receivables based on payment activity as of 2016 and 2015 year end is as follows:
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | Finance Receivables |
Contract Receivables |
Finance Receivables |
Contract Receivables |
||||||||||||
| Performing |
$ | 1,430.7 | $ | 376.7 | $ | 1,240.0 | $ | 351.4 | ||||||||
| Nonperforming |
24.9 | 2.0 | 18.2 | 1.7 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | 1,455.6 | $ | 378.7 | $ | 1,258.2 | $ | 353.1 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
The amount of finance and contract receivables on nonaccrual status as of 2016 and 2015 year end is as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Finance receivables |
$ | 11.7 | $ | 9.3 | ||||
| Contract receivables |
1.5 | 1.5 | ||||||
The following is a rollforward of the allowances for doubtful accounts for finance and contract receivables for 2016 and 2015:
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | Finance Receivables |
Contract Receivables |
Finance Receivables |
Contract Receivables |
||||||||||||
| Allowances for doubtful accounts: |
||||||||||||||||
| Beginning of year |
$ | 38.2 | $ | 4.4 | $ | 32.7 | $ | 3.5 | ||||||||
| Provision |
44.0 | 1.0 | 31.6 | 2.5 | ||||||||||||
| Charge-offs |
(39.8) | (1.8) | (31.7) | (1.9) | ||||||||||||
| Recoveries |
6.2 | 0.4 | 5.9 | 0.4 | ||||||||||||
| Currency translation |
– | (0.1) | (0.3) | (0.1) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| End of year |
$ | 48.6 | $ | 3.9 | $ | 38.2 | $ | 4.4 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 78 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
The following is a rollforward of the combined allowances for doubtful accounts related to trade and other accounts receivable, as well as finance and contract receivables, for 2016, 2015 and 2014:
| (Amounts in millions) | Balance at Beginning of Year |
Expenses | Deductions (1) | Balance at End of Year |
||||||||||||
| Allowances for doubtful accounts: |
||||||||||||||||
| 2016 |
$ | 59.3 | $ | 51.5 | $ | (44.3) | $ | 66.5 | ||||||||
| 2015 |
52.4 | 45.1 | (38.2) | 59.3 | ||||||||||||
| 2014 |
46.0 | 41.7 | (35.3) | 52.4 | ||||||||||||
| (1) | Represents write-offs of bad debts, net of recoveries, and the net impact of currency translation. |
Note 4: Inventories
Inventories by major classification as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Finished goods |
$ | 467.4 | $ | 437.9 | ||||
| Work in progress |
42.7 | 42.9 | ||||||
| Raw materials |
93.6 | 90.3 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total FIFO value |
603.7 | 571.1 | ||||||
| Excess of current cost over LIFO cost |
(73.2) | (73.3) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total inventories – net |
$ | 530.5 | $ | 497.8 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Inventories accounted for using the FIFO method approximated 59% and 57% of total inventories as of 2016 and 2015 year end, respectively. The company accounts for its non-U.S. inventory on the FIFO method. As of 2016 year end, approximately 33% of the company’s U.S. inventory was accounted for using the FIFO method and 67% was accounted for using the LIFO method. There were no LIFO inventory liquidations in 2016, 2015 or 2014.
Note 5: Property and Equipment
Property and equipment (which are carried at cost) as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Land |
$ | 19.1 | $ | 19.7 | ||||
| Buildings and improvements |
309.4 | 297.9 | ||||||
| Machinery, equipment and computer software |
809.6 | 780.3 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Property and equipment – gross |
1,138.1 | 1,097.9 | ||||||
| Accumulated depreciation and amortization |
(712.9) | (684.4) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Property and equipment – net |
$ | 425.2 | $ | 413.5 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The estimated service lives of property and equipment are principally as follows:
| Buildings and improvements |
3 to 50 years | |
| Machinery, equipment and computer software |
2 to 15 years |
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 79 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
The cost and accumulated depreciation of property and equipment under capital leases as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Buildings and improvements |
$ | 20.5 | $ | 20.1 | ||||
| Accumulated depreciation |
(12.3) | (11.0) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net book value |
$ | 8.2 | $ | 9.1 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Depreciation expense was $61.4 million, $57.8 million and $54.8 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Note 6: Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
The changes in the carrying amount of goodwill by segment for 2016 and 2015 are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | Commercial & Industrial Group |
Snap-on Tools Group |
Repair Systems & Information Group |
Total | ||||||||||||
| Balance as of 2014 year end |
$ | 275.9 | $ | 12.5 | $ | 522.3 | $ | 810.7 | ||||||||
| Currency translation |
(22.8) | – | (4.0) | (26.8) | ||||||||||||
| Acquisition |
– | – | 6.2 | 6.2 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Balance as of 2015 year end |
$ | 253.1 | $ | 12.5 | $ | 524.5 | $ | 790.1 | ||||||||
| Currency translation |
(16.4) | – | (9.5) | (25.9) | ||||||||||||
| Acquisitions |
5.7 | – | 125.6 | 131.3 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Balance as of 2016 year end |
$ | 242.4 | $ | 12.5 | $ | 640.6 | $ | 895.5 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Goodwill of $895.5 million as of 2016 year end includes, on a preliminary basis, $131.3 million of non-tax-deductible goodwill from the 2016 acquisitions of Car-O-Liner and Sturtevant Richmont. The preliminary goodwill from Car-O-Liner of $128.1 million as of 2016 year end is distributed as follows: $125.6 million in the Repair Systems & Information Group and $2.5 million in the Commercial & Industrial Group. The preliminary goodwill from Sturtevant Richmont of $3.2 million as of 2016 year end is included in the Commercial & Industrial Group. The preliminary purchase prices for the Car-O-Liner and Sturtevant Richmont acquisitions are subject to the finalization of working capital adjustments that are expected to be completed in the first quarter of 2017. See Note 2 for additional information on acquisitions.
As the purchase accounting valuations for the acquired net assets of Car-O-Liner were not complete as of December 31, 2016, the allocation of the purchase price, and resulting goodwill, has been prepared on a preliminary basis and changes to the allocations will occur as fair value estimates of the acquired net assets, including intangible assets, are determined.
Additional disclosures related to other intangible assets as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | Gross Carrying Value |
Accumulated Amortization |
Gross Carrying Value |
Accumulated Amortization |
||||||||||||
| Amortized other intangible assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Customer relationships |
$ | 142.6 | $ | (86.0) | $ | 146.2 | $ | (79.7) | ||||||||
| Developed technology |
17.7 | (17.7) | 18.9 | (18.9) | ||||||||||||
| Internally developed software |
165.7 | (118.3) | 156.0 | (105.6) | ||||||||||||
| Patents |
31.9 | (21.5) | 30.1 | (20.9) | ||||||||||||
| Trademarks |
2.8 | (1.8) | 2.6 | (1.7) | ||||||||||||
| Other |
7.2 | (2.2) | 7.6 | (1.9) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
367.9 | (247.5) | 361.4 | (228.7) | ||||||||||||
| Non-amortized trademarks |
64.2 | – | 62.3 | – | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total other intangible assets |
$ | 432.1 | $ | (247.5) | $ | 423.7 | $ | (228.7) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 80 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
The gross carrying value of non-amortized trademarks as of 2016 year end includes $3.7 million related to the Sturtevant Richmont acquisition.
Significant and unanticipated changes in circumstances, such as declines in profitability and cash flow due to significant and long-term deterioration in macroeconomic, industry and market conditions, the loss of key customers, changes in technology or markets, significant changes in key personnel or litigation, a significant and sustained decrease in share price and/or other events, including effects from the sale or disposal of a reporting unit, could require a provision for impairment of goodwill and/or other intangible assets in a future period. As of 2016 year end, the company had no accumulated impairment losses.
The weighted-average amortization periods related to other intangible assets are as follows:
| In Years | ||
| Customer relationships |
15 | |
| Internally developed software |
3 | |
| Patents |
8 | |
| Trademarks |
6 | |
| Other |
39 |
Snap-on is amortizing its customer relationships on both an accelerated and straight-line basis over a 15 year weighted-average life; the remaining intangibles are amortized on a straight-line basis. The weighted-average amortization period for all amortizable intangibles on a combined basis is 11 years.
The company’s customer relationships generally have contractual terms of three to five years and are typically renewed without significant cost to the company. The weighted-average 15 year life for customer relationships is based on the company’s historical renewal experience. Intangible asset renewal costs are expensed as incurred.
The aggregate amortization expense was $24.2 million in 2016 and $24.7 million in both 2015 and 2014. Based on current levels of amortizable intangible assets and estimated weighted-average useful lives, estimated annual amortization expense is expected to be $23.2 million in 2017, $20.8 million in 2018, $17.5 million in 2019, $13.9 million in 2020, and $12.2 million in 2021.
Note 7: Exit and Disposal Activities
In 2016, the company’s Repair Systems & Information Group recorded $0.9 million of severance costs for exit and disposal activities, all of which qualified for accrual treatment; no costs for exit and disposal activities were recorded in 2015. In 2014, Snap-on recorded $6.5 million of severance costs for exit and disposal activities, all of which qualified for accrual treatment. The exit and disposal accrual of $2.8 million as of 2016 year end is expected to be fully utilized in 2017. Snap-on anticipates funding the remaining cash requirements of its exit and disposal activities with available cash on hand, cash flows from operations and borrowings under the company’s existing credit facilities. The estimated costs for the exit and disposal activities were based on management’s best business judgment under prevailing circumstances.
Note 8: Income Taxes
The source of earnings before income taxes and equity earnings consisted of the following:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| United States |
$ | 644.0 | $ | 578.4 | $ | 481.1 | ||||||
| Foreign |
157.4 | 132.1 | 149.8 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 801.4 | $ | 710.5 | $ | 630.9 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 81 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
The provision (benefit) for income taxes consisted of the following:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Current: |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
$ 175.9 | $ 165.8 | $ 137.6 | |||||||||
| Foreign |
39.9 | 40.8 | 41.2 | |||||||||
| State |
27.2 | 19.7 | 17.5 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total current |
243.0 | 226.3 | 196.3 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Deferred: |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
6.3 | (8.7) | 10.0 | |||||||||
| Foreign |
(6.7) | 3.9 | (8.2) | |||||||||
| State |
1.7 | (0.3) | 1.4 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total deferred |
1.3 | (5.1) | 3.2 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total income tax provision |
$ 244.3 | $ 221.2 | $ 199.5 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| The following is a reconciliation of the statutory federal income tax rate to Snap-on’s effective tax rate: |
||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Statutory federal income tax rate |
35.0% | 35.0% | 35.0% | |||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in tax rate resulting from: |
||||||||||||
| State income taxes, net of federal benefit |
2.4 | 2.3 | 2.2 | |||||||||
| Noncontrolling interests |
(0.6) | (0.6) | (0.5) | |||||||||
| Repatriation of foreign earnings |
(0.1) | (3.0) | (0.4) | |||||||||
| Change in valuation allowance for deferred tax assets |
(1.0) | 0.1 | (0.9) | |||||||||
| Adjustments to tax accruals and reserves |
0.3 | 0.8 | 0.5 | |||||||||
| Foreign rate differences |
(2.1) | (1.9) | (2.2) | |||||||||
| Domestic production activities deduction |
(1.9) | (1.9) | (2.0) | |||||||||
| Excess tax benefits related to equity compensation |
(1.8) | – | – | |||||||||
| Other |
0.3 | 0.3 | (0.1) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Effective tax rate |
30.5% | 31.1% | 31.6% | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Snap-on’s effective income tax rate on earnings attributable to Snap-on Incorporated was 31.0% in 2016, 31.7% in 2015, and 32.1% in 2014. The effective tax rate for 2016 included tax benefits from the reversal of deferred tax asset valuation allowances that are now expected to be realized in future years, as well as tax benefits associated with the January 3, 2016 adoption of ASU No. 2016-09; these tax benefits were partially offset by tax contingency reserves established for certain non-U.S. tax audits. See Note 1 for further information on the company’s adoption of ASU No. 2016-09.
| 82 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Temporary differences that give rise to the net deferred income tax asset (liability) as of 2016, 2015 and 2014 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Long-term deferred income tax assets (liabilities): |
||||||||||||
| Inventories |
$ 33.3 | $ 29.4 | $ 29.2 | |||||||||
| Accruals not currently deductible |
77.7 | 71.1 | 72.7 | |||||||||
| Tax credit carryforward |
15.1 | 10.2 | – | |||||||||
| Employee benefits |
108.1 | 101.2 | 91.5 | |||||||||
| Net operating losses |
42.8 | 44.4 | 53.5 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
(209.8) | (199.3) | (191.2) | |||||||||
| Valuation allowance |
(21.7) | (32.0) | (34.8) | |||||||||
| Equity-based compensation |
24.3 | 22.7 | 19.6 | |||||||||
| Cash flow hedge |
(5.5) | – | – | |||||||||
| Other |
(4.6) | (1.6) | (5.7) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net deferred income tax asset |
$ 59.7 | $ 46.1 | $ 34.8 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
As of 2016 year end, Snap-on had tax net operating loss carryforwards totaling $253.8 million as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | State | Federal | Foreign | Total | ||||||||||||
| Year of expiration: |
||||||||||||||||
| 2017-2021 |
$ – | $ – | $ 37.6 | $ 37.6 | ||||||||||||
| 2022-2026 |
0.3 | – | 6.5 | 6.8 | ||||||||||||
| 2027-2031 |
122.1 | – | 37.6 | 159.7 | ||||||||||||
| 2032-2036 |
– | – | – | – | ||||||||||||
| Indefinite |
– | – | 49.7 | 49.7 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total net operating loss carryforwards |
$ 122.4 | $ – | $ 131.4 | $ 253.8 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
A valuation allowance totaling $21.7 million, $32.0 million and $34.8 million as of 2016, 2015 and 2014 year end, respectively, has been established for deferred income tax assets primarily related to certain subsidiary loss carryforwards that may not be realized. For the year ended December 31, 2016, the net valuation allowance decreased by $10.3 million primarily due to a non-U.S. subsidiary having, in part, attained three years of cumulative pretax income and, as a result, management concluded there is sufficient positive evidence that it is more-likely-than-not that additional deferred taxes are realizable. Realization of the net deferred income tax assets is dependent on generating sufficient taxable income prior to their expiration. Although realization is not assured, management believes it is more-likely-than-not that the net deferred income tax assets will be realized. The amount of the net deferred income tax assets considered realizable, however, could change in the near term if estimates of future taxable income during the carryforward period fluctuate.
The following is a reconciliation of the beginning and ending amounts of unrecognized tax benefits for 2016, 2015 and 2014:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Unrecognized tax benefits at beginning of year |
$ 7.2 | $ 6.4 | $ 4.6 | |||||||||
| Gross increases – tax positions in prior periods |
2.5 | 1.7 | 2.1 | |||||||||
| Gross decreases – tax positions in prior periods |
(0.3) | (0.5) | – | |||||||||
| Gross increases – tax positions in the current period |
0.5 | 0.5 | 1.8 | |||||||||
| Settlements with taxing authorities |
– | – | (1.6) | |||||||||
| Lapsing of statutes of limitations |
(0.5) | (0.9) | (0.5) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Unrecognized tax benefits at end of year |
$ 9.4 | $ 7.2 | $ 6.4 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 83 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
The unrecognized tax benefits of $9.4 million, $7.2 million and $6.4 million as of 2016, 2015 and 2014 year end, respectively, would impact the effective income tax rate if recognized. As of December 31, 2016, unrecognized tax benefits of $3.4 million, $2.4 million and $3.6 million were included in “Deferred income tax assets,” “Other accrued liabilities” and “Other long-term liabilities,” respectively, on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheet. Interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits are recorded in income tax expense. As of 2016, 2015 and 2014 year end, the company had provided for $0.9 million, $0.5 million and $0.5 million, respectively, of accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits. During 2016, the company increased the reserve attributable to interest and penalties associated with unrecognized tax benefits by a net $0.4 million. As of December 31, 2016, $0.4 million and $0.5 million of accrued interest and penalties were included in “Other accrued liabilities” and “Other long-term liabilities,” respectively, on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheet.
Snap-on and its subsidiaries file income tax returns in the United States and in various state, local and foreign jurisdictions. It is reasonably possible that certain unrecognized tax benefits may either be settled with taxing authorities or the statutes of limitations for such items may lapse within the next 12 months, causing Snap-on’s gross unrecognized tax benefits to decrease by a range of zero to $4.0 million. Over the next 12 months, Snap-on anticipates taking certain tax positions on various tax returns for which the related tax benefit does not meet the recognition threshold. Accordingly, Snap-on’s gross unrecognized tax benefits may increase by a range of zero to $1.2 million over the next 12 months for uncertain tax positions expected to be taken in future tax filings.
With few exceptions, Snap-on is no longer subject to U.S. federal and state/local income tax examinations by tax authorities for years prior to 2011, and Snap-on is no longer subject to non-U.S. income tax examinations by tax authorities for years prior to 2010.
The undistributed earnings of all non-U.S. subsidiaries totaled $800.6 million, $624.1 million and $619.1 million as of 2016, 2015 and 2014 year end, respectively. Snap-on has not provided any deferred taxes on these undistributed earnings as it considers the undistributed earnings to be permanently invested. Determination of the amount of unrecognized deferred income tax liability related to these earnings is not practicable.
Note 9: Short-term and Long-term Debt
Short-term and long-term debt as of 2016 and 2015 year end consisted of the following:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| 5.50% unsecured notes due 2017 |
$ | 150.0 | $ | 150.0 | ||||
| 4.25% unsecured notes due 2018 |
250.0 | 250.0 | ||||||
| 6.70% unsecured notes due 2019 |
200.0 | 200.0 | ||||||
| 6.125% unsecured notes due 2021 |
250.0 | 250.0 | ||||||
| Other debt* |
160.2 | 30.1 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 1,010.2 | 880.1 | |||||||
| Less: notes payable and current maturities of long-term debt: |
||||||||
| Current maturities of long-term debt |
$ | (150.0) | $ | – | ||||
| Commercial paper borrowings |
(130.0) | – | ||||||
| Other notes |
(21.4) | (18.4) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (301.4) | (18.4) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total long-term debt |
$ | 708.8 | $ | 861.7 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
* Includes fair value adjustments related to interest rate swaps.
| 84 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
The annual maturities of Snap-on’s long-term debt and notes payable over the next five years are $301.4 million in 2017 (including $150 million of unsecured 5.50% notes due January 2017 (the “2017 Notes”) that were repaid upon maturity), $250 million on January 15, 2018, $200 million in 2019, no maturities in 2020, and $250 million in 2021. As of 2016 year end, the $250 million of 4.25% unsecured notes that mature on January 15, 2018, are included in “Long-term debt” on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheet as their scheduled maturity was in excess of one year of the 2016 year-end balance sheet date. See Note 20 regarding the January 2017 repayment of the 2017 Notes.
Average notes payable outstanding, including commercial paper borrowings, were $49.3 million and $78.5 million in 2016 and 2015, respectively. The weighted-average interest rate of 7.09% in 2016 increased from 4.36% last year primarily due to higher interest rates on local borrowings in emerging growth markets (where interest rates are generally higher). Average commercial paper borrowings were $26.6 million and $52.2 million in 2016 and 2015, respectively, and the weighted-average interest rate of 0.73% in 2016 increased from 0.41% last year. At 2016 year end, the weighted-average interest rate on outstanding notes payable of 2.85% compared with 15.82% at 2015 year end. The 2016 year-end rate benefited from lower interest rates on commercial paper borrowings. The 2015 year-end rate reflected higher rates on local borrowings in emerging growth markets; no commercial paper was outstanding at 2015 year end.
Snap-on has a five-year, $700 million multi-currency revolving credit facility that terminates on December 15, 2020 (the “Credit Facility”); as of December 31, 2016, no amounts were outstanding under the Credit Facility. Borrowings under the Credit Facility bear interest at varying rates based on Snap-on’s then-current, long-term debt ratings. The Credit Facility’s financial covenant requires that Snap-on maintain, as of each fiscal quarter end, either (i) a ratio not greater than 0.60 to 1.00 of consolidated net debt (consolidated debt net of certain cash adjustments) to the sum of such consolidated net debt plus total equity and less accumulated other comprehensive income or loss (the “Debt Ratio”); or (ii) a ratio not greater than 3.50 to 1.00 of such consolidated net debt to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization and certain other adjustments for the preceding four fiscal quarters then ended (the “Debt to EBITDA Ratio”). Snap-on may, up to two times during any five-year period during the term of the Credit Facility (including any extensions thereof), increase the maximum Debt Ratio to 0.65 to 1.00 and/or increase the maximum Debt to EBITDA Ratio to 3.75 to 1.00 for four consecutive fiscal quarters in connection with certain material acquisitions (as defined in the related credit agreement). As of 2016 year end, the company’s actual ratios of 0.24 and 1.02, respectively, were both within the permitted ranges set forth in this financial covenant. Snap-on generally issues commercial paper to fund its financing needs on a short-term basis and uses the Credit Facility as back-up liquidity to support such commercial paper issuances.
Note 10: Financial Instruments
Derivatives: All derivative instruments are reported in the Consolidated Financial Statements at fair value. Changes in the fair value of derivatives are recorded each period in earnings or on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets, depending on whether the derivative is designated and effective as part of a hedged transaction. Gains or losses on derivative instruments recorded in Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) (“Accumulated OCI”) must be reclassified to earnings in the period in which earnings are affected by the underlying hedged item and the ineffective portion of all hedges must be recognized in earnings in the period that such portion is determined to be ineffective.
The criteria used to determine if hedge accounting treatment is appropriate are (i) the designation of the hedge to an underlying exposure; (ii) whether or not overall risk is being reduced; and (iii) if there is a correlation between the value of the derivative instrument and the underlying hedged item. On the date a derivative contract is entered into, Snap-on designates the derivative as a fair value hedge, a cash flow hedge, a hedge of a net investment in a foreign operation, or a natural hedging instrument whose change in fair value is recognized as an economic hedge against changes in the value of the hedged item. Snap-on does not use derivative instruments for speculative or trading purposes.
The company is exposed to global market risks, including the effects of changes in foreign currency exchange rates, interest rates, and the company’s stock price, and therefore uses derivatives to manage financial exposures that occur in the normal course of business. The primary risks managed by using derivative instruments are foreign currency risk, interest rate risk and stock-based deferred compensation risk.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 85 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
Foreign currency risk management: Snap-on has significant international operations and is subject to certain risks inherent with foreign operations that include currency fluctuations. Foreign currency exchange risk exists to the extent that Snap-on has payment obligations or receipts denominated in currencies other than the functional currency, including intercompany loans denominated in foreign currencies. To manage these exposures, Snap-on identifies naturally offsetting positions and then purchases hedging instruments to protect the residual net exposures. Snap-on manages most of these exposures on a consolidated basis, which allows for netting of certain exposures to take advantage of natural offsets. Foreign currency forward contracts (“foreign currency forwards”) are used to hedge the net exposures. Gains or losses on net foreign currency hedges are intended to offset losses or gains on the underlying net exposures in an effort to reduce the earnings volatility resulting from fluctuating foreign currency exchange rates. Snap-on’s foreign currency forwards are typically not designated as hedges. The fair value changes of these contracts are reported in earnings as foreign exchange gain or loss, which is included in “Other income (expense) – net” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
As of 2016 year end, Snap-on had $144.4 million of net foreign currency forward buy contracts outstanding comprised of buy contracts including $55.0 million in euros, $53.6 million in British pounds, $47.0 million in Swedish kronor, $9.0 million in Hong Kong dollars, $7.0 million in South Korean won, $5.5 million in Singapore dollars, $4.9 million in Mexican pesos, $4.6 million in Norwegian kroner, and $6.4 million in other currencies, and sell contracts comprised of $16.6 million in Japanese yen, $11.8 million in Canadian dollars, $4.4 million in Australian dollars, $4.0 million in Brazilian real, and $11.8 million in other currencies. As of 2015 year end, Snap-on had $98.3 million of net foreign currency forward buy contracts outstanding comprised of buy contracts including $52.0 million in euros, $31.4 million in British pounds, $23.4 million in Swedish kronor, $12.9 million in Singapore dollars, $6.2 million in South Korean won, $5.5 million in Mexican pesos and $8.7 million in other currencies, and sell contracts comprised of $18.4 million in Canadian dollars, $9.7 million in Japanese yen, $4.2 million in Australian dollars and $9.5 million in other currencies.
Interest rate risk management: Snap-on aims to control funding costs by managing the exposure created by the differing maturities and interest rate structures of Snap-on’s borrowings through the use of interest rate swap agreements (“interest rate swaps”) and treasury lock agreements (“treasury locks”).
Interest rate swaps: Snap-on enters into interest rate swaps to manage risks associated with changing interest rates related to the company’s fixed rate borrowings. Interest rate swaps are accounted for as fair value hedges. The differentials paid or received on interest rate swaps are recognized as adjustments to “Interest expense” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings. The effective portion of the change in fair value of the derivative is recorded in “Long-term debt” on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets, while any ineffective portion is recorded as an adjustment to “Interest expense” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings. The notional amount of interest rate swaps outstanding and designated as fair value hedges was $100 million as of both 2016 and 2015 year end.
Treasury locks: Snap-on entered into a treasury lock in November 2016 to manage the potential change in interest rates in anticipation of the possible issuance of fixed rate debt; the treasury lock expires on February 28, 2017. Treasury locks are accounted for as cash flow hedges. The effective differentials to be paid or received on treasury locks related to the anticipated issuance of fixed rate debt are initially recorded in Accumulated OCI. As of 2016 year end, an unrecognized gain of $8.8 million has been recorded in Accumulated OCI on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheet. Upon the issuance of debt, the related amount in Accumulated OCI will be released over the term of the debt and recognized as an adjustment to interest expense on the consolidated statements of earnings. The notional amount of treasury locks outstanding and designated as cash flow hedges as of December 31, 2016, was $250 million; there were no treasury locks outstanding as of January 2, 2016, and no treasury locks were settled in 2016 or 2015.
Stock-based deferred compensation risk management: Snap-on aims to manage market risk associated with the stock-based portion of its deferred compensation plans through the use of prepaid equity forward agreements (“equity forwards”). Equity forwards are used to aid in offsetting the potential mark-to-market effect on stock-based deferred compensation from changes in Snap-on’s stock price. Since stock-based deferred compensation liabilities increase as the company’s stock price rises and decrease as the company’s stock price declines, the equity forwards are intended to mitigate the potential impact on deferred compensation expense that may result from such mark-to-market changes. As of 2016 and 2015 year end, Snap-on had equity forwards in place intended to manage market risk with respect to 104,400 shares and 107,900 shares, respectively, of Snap-on common stock associated with its deferred compensation plans.
| 86 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Fair value measurements: Snap-on has derivative assets and liabilities related to interest rate swaps, treasury locks, foreign currency forwards and equity forwards that are measured at Level 2 fair value on a recurring basis. The fair values of derivative instruments included within the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | Balance Sheet Presentation |
Asset Derivatives Fair Value |
Liability Derivatives Fair Value |
Asset Derivatives Fair Value |
Liability Derivatives Fair Value |
|||||||||||||
| Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate swaps |
Other assets |
$ | 9.8 | $ | – | $ | 12.9 | $ | – | |||||||||
| Treasury locks |
Other assets |
14.3 | – | – | – | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 24.1 | – | 12.9 | – | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency forwards |
Prepaid expenses |
$ | 4.4 | $ | – | $ | 2.8 | $ | – | |||||||||
| Foreign currency forwards |
Other accrued |
– | 13.5 | – | 5.9 | |||||||||||||
| Equity forwards |
Prepaid expenses |
17.9 | – | 18.5 | – | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 22.3 | 13.5 | 21.3 | 5.9 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total derivative instruments |
$ | 46.4 | $ | 13.5 | $ | 34.2 | $ | 5.9 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
As of 2016 and 2015 year end, the fair value adjustment to long-term debt related to the interest rate swaps was $9.8 million and $12.9 million, respectively.
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between participants at the measurement date. Level 2 fair value measurements for derivative assets and liabilities are measured using quoted prices in active markets for similar assets and liabilities. Interest rate swaps are valued based on the six-month LIBOR swap rate for similar instruments. Treasury locks are valued based on the 10-year U.S. treasury interest rate. Foreign currency forwards are valued based on exchange rates quoted by domestic and foreign banks for similar instruments. Equity forwards are valued using a market approach based primarily on the company’s stock price at the reporting date. The company did not have any derivative assets or liabilities measured at Level 1 or Level 3, nor did it implement any changes in its valuation techniques as of and for its 2016 and 2015 years ended.
The effect of derivative instruments designated as fair value hedges as included in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings is as follows:
| Effective Portion of Gain Recognized in Income |
||||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | Statement of Earnings Presentation |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||
| Derivatives designated as fair value hedges: |
||||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate swaps |
Interest expense | $ | 2.9 | $ | 3.7 | $ | 4.0 | |||||||||||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 87 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
The effect of derivative instruments designated as cash flow hedges as included in Accumulated OCI on the Consolidated Balance Sheets and the Consolidated Statements of Earnings is as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | Effective Portion of Gain Recognized in Accumulated OCI |
Effective Portion of Gain Reclassified from Accumulated OCI into Income |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | Statement of Earnings Presentation |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives designated as cash flow hedges: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury locks |
$ | 8.8 | $ | – | $ | – | |
Interest expense |
|
$ | 0.3 | $ | 0.3 | $ | 0.3 | |||||||||||||
The effects of derivative instruments not designated as hedging instruments as included in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings are as follows:
| Gain (Loss) Recognized in Income |
||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | Statement of Earnings Presentation |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||
| Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: | ||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency forwards |
|
Other income (expense) – net |
|
$ | (7.4) | $ | (15.5) | $ | (19.3) | |||||||
| Equity forwards |
Operating expenses | 0.8 | 4.7 | 3.6 | ||||||||||||
Snap-on’s foreign currency forwards are typically not designated as hedges for financial reporting purposes. The fair value changes of foreign currency forwards not designated as hedging instruments are reported in earnings as foreign exchange gain or loss in “Other income (expense) – net” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings. In 2016, the $7.4 million derivative loss was partially offset by transaction gains on net exposures of $6.1 million, resulting in a net foreign exchange loss of $1.3 million. In 2015, the $15.5 million derivative loss was partially offset by transaction gains on net exposures of $12.8 million, resulting in a net foreign exchange loss of $2.7 million. In 2014, the $19.3 million derivative loss was partially offset by transaction gains on net exposures of $17.8 million, resulting in a net foreign exchange loss of $1.5 million. The resulting net foreign exchange losses are included in “Other income (expense) – net” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings. See Note 16 for additional information on “Other income (expense) – net.”
Snap-on’s equity forwards are not designated as hedges for financial reporting purposes. Fair value changes of both the equity forwards and related stock-based (mark-to-market) deferred compensation liabilities are reported in “Operating expenses” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings. The $0.8 million derivative gain recognized in 2016 was partially offset by $0.3 million of mark-to-market deferred compensation expense. The $4.7 million derivative gain recognized in 2015 was largely offset by $4.6 million of mark-to-market deferred compensation expense. The $3.6 million derivative gain recognized in 2014 was offset by $3.6 million of mark-to-market deferred compensation expense.
As of 2016 year end, the maximum maturity date of any fair value hedge was five years. During the next 12 months, Snap-on expects to reclassify into earnings net gains from Accumulated OCI of approximately $0.2 million after tax at the time the underlying hedge transactions are realized.
Counterparty risk: Snap-on is exposed to credit losses in the event of non-performance by the counterparties to its various financial agreements, including its foreign currency forward contracts, interest rate swap agreements, treasury lock agreements and prepaid equity forward agreements. Snap-on does not obtain collateral or other security to support financial instruments subject to credit risk, but monitors the credit standing of the counterparties and generally enters into agreements with financial institution counterparties with a credit rating of A- or better. Snap-on does not anticipate non-performance by its counterparties, but cannot provide assurances.
Fair value of financial instruments: The fair values of financial instruments that do not approximate the carrying values in the financial statements as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | Carrying Value | Fair Value |
Carrying Value |
Fair Value |
||||||||||||
| Finance receivables – net |
$ | 1,407.0 | $ | 1,631.2 | $ | 1,220.0 | $ | 1,381.9 | ||||||||
| Contract receivables – net |
374.8 | 409.7 | 348.7 | 380.2 | ||||||||||||
| Long-term debt, notes payable and current maturities of long-term debt |
1,010.2 | 1,076.7 | 880.1 | 961.1 | ||||||||||||
| 88 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
The following methods and assumptions were used in estimating the fair value of financial instruments:
| • | Finance and contract receivables include both short-term and long-term receivables. The fair value estimates of finance and contract receivables are derived utilizing discounted cash flow analyses performed on groupings of receivables that are similar in terms of loan type and characteristics. The cash flow analyses consider recent pre-payment trends where applicable. The cash flows are discounted over the average life of the receivables using a current market discount rate of a similar term adjusted for credit quality. Significant inputs to the fair value measurements of the receivables are unobservable and, as such, are classified as Level 3. |
| • | Fair value of long-term debt and current maturities of long-term debt was estimated, using Level 2 fair value measurements, based on quoted market values of Snap-on’s publicly traded senior debt. The carrying value of long-term debt includes adjustments related to fair value hedges. The fair value of notes payable approximates such instruments’ carrying value due to their short-term nature. |
| • | The fair value of all other financial instruments, including trade and other accounts receivable, accounts payable and other financial instruments, approximates such instruments’ carrying value due to their short-term nature. |
Note 11: Pension Plans
Snap-on has several non-contributory defined benefit pension plans covering most U.S. employees and certain employees in foreign countries. Snap-on also has foreign contributory defined benefit pension plans covering certain foreign employees. Retirement benefits are generally provided based on employees’ years of service and average earnings or stated amounts for years of service. Normal retirement age is 65, with provisions for earlier retirement.
The status of Snap-on’s pension plans as of 2016 and 2015 year end is as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Change in projected benefit obligation: |
||||||||
| Benefit obligation at beginning of year |
$ | 1,279.4 | $ | 1,325.9 | ||||
| Service cost |
19.3 | 20.0 | ||||||
| Interest cost |
56.5 | 53.2 | ||||||
| Plan participant contributions |
1.0 | 1.1 | ||||||
| Benefits paid |
(63.2) | (62.4) | ||||||
| Actuarial loss (gain) |
94.7 | (40.8) | ||||||
| Foreign currency impact |
(26.3) | (17.6) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Benefit obligation at end of year |
$ | 1,361.4 | $ | 1,279.4 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Change in plan assets: |
||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year |
$ | 1,049.2 | $ | 1,103.4 | ||||
| Actual return (loss) on plan assets |
73.5 | (17.8) | ||||||
| Plan participant contributions |
1.0 | 1.1 | ||||||
| Employer contributions |
68.7 | 39.2 | ||||||
| Benefits paid |
(63.2) | (62.4) | ||||||
| Foreign currency impact |
(18.4) | (14.3) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Fair value of plan assets at end of year |
$ | 1,110.8 | $ | 1,049.2 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Unfunded status at end of year |
$ | (250.6) | $ | (230.2) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 89 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
Amounts recognized in the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Other assets |
$ | 0.6 | $ | 2.1 | ||||
| Accrued benefits |
(4.7) | (4.5) | ||||||
| Pension liabilities |
(246.5) | (227.8) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net liability |
$ | (250.6) | $ | (230.2) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Amounts included in Accumulated OCI on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Net loss, net of tax of $160.6 million and $141.4 million, respectively |
$ | (297.0) | $ | (253.7) | ||||
| Prior service credit, net of tax of $1.3 million and$1.7 million, respectively |
2.2 | 2.8 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | (294.8) | $ | (250.9) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The accumulated benefit obligation for Snap-on’s pension plans as of 2016 and 2015 year end was $1,283.1 million and $1,231.2 million, respectively.
The projected benefit obligation, accumulated benefit obligation and fair value of plan assets for Snap-on’s pension plans in which the accumulated benefit obligation exceeds the fair value of plan assets as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Projected benefit obligation |
$ | 1,312.1 | $ | 1,128.4 | ||||
| Accumulated benefit obligation |
1,238.7 | 1,097.6 | ||||||
| Fair value of plan assets |
1,061.0 | 906.5 | ||||||
The components of net periodic benefit cost and changes recognized in “Other comprehensive income (loss)” (“OCI”) are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Net periodic benefit cost: |
||||||||||||
| Service cost |
$ | 19.3 | $ | 20.0 | $ | 18.0 | ||||||
| Interest cost |
56.5 | 53.2 | 57.3 | |||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets |
(81.0) | (79.0) | (73.3) | |||||||||
| Amortization of unrecognized loss |
31.3 | 38.6 | 22.8 | |||||||||
| Amortization of prior service credit |
(1.1) | (0.9) | (0.8) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net periodic benefit cost |
$ | 25.0 | $ | 31.9 | $ | 24.0 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Changes in benefit obligations recognized in OCI, net of tax: |
||||||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | 43.3 | $ | 6.3 | $ | 72.0 | ||||||
| Prior service cost |
0.6 | 0.7 | 0.5 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total recognized in OCI |
$ | 43.9 | $ | 7.0 | $ | 72.5 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 90 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Amounts in Accumulated OCI that are expected to be amortized as net expense into net periodic benefit cost during 2017 are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | Amount | |||
| Amortization of unrecognized loss |
$ | 27.6 | ||
| Amortization of prior service credit |
(1.1) | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total to be recognized in net periodic benefit cost |
$ | 26.5 | ||
|
|
|
|||
The worldwide weighted-average assumptions used to determine Snap-on’s full-year pension costs are as follows:
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Discount rate |
4.5% | 4.1% | 5.1% | |||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets |
7.4% | 7.4% | 7.4% | |||||||||
| Rate of compensation increase |
3.6% | 3.6% | 3.6% | |||||||||
The worldwide weighted-average assumptions used to determine Snap-on’s projected benefit obligation as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Discount rate |
4.2% | 4.5% | ||||||
| Rate of compensation increase |
3.4% | 3.6% | ||||||
The objective of Snap-on’s discount rate assumption is to reflect the rate at which the pension benefits could be effectively settled. In making this determination, the company takes into account the timing and amount of benefits that would be available under the plans. The domestic discount rate as of 2016 and 2015 year end was selected based on a cash flow matching methodology developed by the company’s outside actuaries and which incorporates a review of current economic conditions. This methodology matches the plans’ yearly projected cash flows for benefits and service costs to those of hypothetical bond portfolios using high-quality, AA rated or better, corporate bonds from either Moody’s Investors Service or Standard & Poor’s credit rating agencies available at the measurement date. This technique calculates bond portfolios that produce adequate cash flows to pay the plans’ projected yearly benefits and then selects the portfolio with the highest yield and uses that yield as the recommended discount rate.
The weighted-average discount rate for Snap-on’s domestic pension plans of 4.5% represents the single rate that produces the same present value of cash flows as the estimated benefit plan payments. Lowering Snap-on’s domestic discount rate assumption by 50 basis points (100 basis points (“bps”) equals 1.0 percent) would have increased Snap-on’s 2016 domestic pension expense and projected benefit obligation by approximately $6.7 million and $65.3 million, respectively. As of 2016 year end, Snap-on’s domestic projected benefit obligation comprised approximately 83% of Snap-on’s worldwide projected benefit obligation. The weighted-average discount rate for Snap-on’s foreign pension plans of 2.9% represents the single rate that produces the same present value of cash flows as the estimated benefit plan payments. Lowering Snap-on’s foreign discount rate assumption by 50 bps would have increased Snap-on’s 2016 foreign pension expense and projected benefit obligation by approximately $1.7 million and $23.4 million, respectively.
Actuarial gains and losses in excess of 10 percent of the greater of the projected benefit obligation or market-related value of assets are amortized on a straight-line basis over the average remaining service period of active participants or over the average remaining life expectancy for plans with primarily inactive participants. Prior service costs and credits resulting from plan amendments are amortized in equal annual amounts over the average remaining service period of active participants or over the average remaining life expectancy for plans with primarily inactive participants.
As a practical expedient, Snap-on uses the calendar year end as the measurement date for its plans. Snap-on funds its pension plans as required by governmental regulation and may consider discretionary contributions as conditions warrant. Snap-on intends to make contributions of $7.1 million to its foreign pension plans and $2.3 million to its domestic pension plans in 2017, as required by law. Depending on market and other conditions, Snap-on may make discretionary cash contributions to its pension plans in 2017.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 91 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
The following benefit payments, which reflect expected future service, are expected to be paid as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | Amount | |||
| Year: |
||||
| 2017 |
$ | 68.8 | ||
| 2018 |
70.6 | |||
| 2019 |
73.2 | |||
| 2020 |
76.0 | |||
| 2021 |
78.8 | |||
| 2022-2026 |
438.2 | |||
Snap-on’s domestic pension plans have a long-term investment horizon and a total return strategy that emphasizes a capital growth objective. The long-term investment performance objective for Snap-on’s domestic plans’ assets is to achieve net of expense returns that meet or exceed the 7.5% domestic long-term return on plan assets assumption used for reporting purposes. Snap-on uses a three-year, market-related value asset method of amortizing the difference between actual and expected returns on its domestic plans’ assets. As of 2016 year end, Snap-on’s domestic pension plans’ assets comprised approximately 86% of the company’s worldwide pension plan assets.
The basis for determining the overall expected long-term return on plan assets assumption is a nominal returns forecasting method. For each asset class, future returns are estimated by identifying the premium of riskier asset classes over lower risk alternatives. The methodology constructs expected returns using a “building block” approach to the individual components of total return. These forecasts are stated in both nominal and real (after inflation) terms. This process first considers the long-term historical return premium based on the longest set of data available for each asset class. These premiums, which are calculated using the geometric mean, are then adjusted based on current relative valuation levels, macro-economic conditions, and the expected alpha related to active investment management. The asset return assumption is also adjusted by an implicit expense load for estimated administrative and investment-related expenses.
For risk and correlation assumptions, the actual experience for each asset class is reviewed for the longest time period available. Expected relationships for a 10 to 20 year time horizon are determined based upon historical results, with adjustments made for material changes.
Investments are diversified to attempt to minimize the risk of large losses. Since asset allocation is a key determinant of expected investment returns, assets are periodically rebalanced to the targeted allocation to correct significant deviations from the asset allocation policy that are caused by market fluctuations and cash flow. Asset/liability studies are conducted periodically to determine if any revisions to the strategic asset allocation policy are necessary.
Snap-on’s domestic pension plans’ target allocation and actual weighted-average asset allocation by asset category and fair value of plan assets as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| Target | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Asset category: |
||||||||||||
| Equity securities |
50% | 51% | 49% | |||||||||
| Debt securities and cash and cash equivalents |
35% | 39% | 39% | |||||||||
| Real estate and other real assets |
5% | 1% | 2% | |||||||||
| Hedge funds |
10% | 9% | 10% | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
100% | 100% | 100% | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Fair value of plan assets (Amounts in millions) |
$ | 957.1 | $ | 892.3 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
The fair value measurement hierarchy prioritizes the inputs used to measure fair value. The hierarchy gives the highest priority (“Level 1”) to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities and the lowest priority (“Level 3”) to unobservable inputs. Fair value measurements primarily based on observable market information are given a “Level 2” priority.
| 92 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Certain equity and debt securities are valued at quoted per share or unit market prices for which an official close or last trade pricing on an active exchange is available and are categorized as Level 1 in the fair value hierarchy. If quoted market prices are not readily available for specific securities, values are estimated using quoted prices of securities with similar characteristics and are categorized as Level 2 in the fair value hierarchy. Insurance contracts are valued at the present value of the estimated future cash flows promised under the terms of the insurance contracts and are categorized as Level 2 in the fair value hierarchy.
Commingled equity securities and commingled multi-strategy funds are valued at the NAV per share or unit multiplied by the number of shares or units held as of the measurement date, as reported by the fund managers. The share or unit price is quoted on a private market and is based on the value of the underlying investments, which are primarily based on observable inputs; such investments that are measured at fair value using the NAV per share (or its equivalent) practical expedient have not been classified in the fair value hierarchy.
Private equity partnership funds, hedge funds, and real estate and other real assets are valued at the NAV as reported by the fund managers. Private equity partnership funds, certain hedge funds, and certain real estate and other real assets are valued based on the proportionate interest or share of net assets held by the pension plan, which is based on the estimated fair market value of the underlying investments. Certain other hedge funds and real estate and other real assets are valued at the NAV per share or unit multiplied by the number of shares or units held as of the measurement date, based on the estimated value of the underlying investments as reported by the fund managers. These investments are measured at fair value using the NAV per share (or its equivalent) practical expedient and have not been classified in the fair value hierarchy.
The company regularly reviews fund performance directly with its investment advisor and the fund managers, and performs qualitative analysis to corroborate the reasonableness of the reported NAVs. For funds for which the company did not receive a year-end NAV, the company recorded an estimate of the change in fair value for the latest period based on return estimates and other fund activity obtained from the fund managers.
The columns labeled “Investments Measured at NAV” in the following tables reflect certain investments that are measured at fair value using the NAV per share (or its equivalent) practical expedient and have not been categorized in the fair value hierarchy. The fair value amounts presented in these tables are intended to permit a reconciliation of the fair value hierarchy to the pension plan assets.
The following is a summary, by asset category, of the fair value and the level within the fair value hierarchy of Snap-on’s domestic pension plans’ assets as of 2016 year end:
| (Amounts in millions) | Quoted Prices for Identical Assets (Level 1) |
Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) |
Investments Measured at NAV |
Total | ||||||||||||
| Asset category: |
||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 20.4 | $ | – | $ | – | $ | 20.4 | ||||||||
| Equity securities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Domestic |
66.0 | – | – | 66.0 | ||||||||||||
| Foreign |
74.7 | – | – | 74.7 | ||||||||||||
| Commingled funds – domestic |
– | – | 191.3 | 191.3 | ||||||||||||
| Commingled funds – foreign |
– | – | 117.7 | 117.7 | ||||||||||||
| Private equity partnerships |
– | – | 34.2 | 34.2 | ||||||||||||
| Debt securities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Government |
139.2 | 0.9 | – | 140.1 | ||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds |
– | 214.6 | – | 214.6 | ||||||||||||
| Real estate and other real assets |
– | – | 10.4 | 10.4 | ||||||||||||
| Hedge funds |
– | – | 87.7 | 87.7 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | 300.3 | $ | 215.5 | $ | 441.3 | $ | 957.1 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 93 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
The following is a summary, by asset category, of the fair value and the level within the fair value hierarchy of Snap-on’s domestic pension plans’ assets as of 2015 year end:
| (Amounts in millions) | Quoted Prices for Identical Assets (Level 1) |
Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) |
Investments Measured at NAV |
Total | ||||||||||||
| Asset category: |
||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 21.3 | $ | – | $ | – | $ | 21.3 | ||||||||
| Equity securities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Domestic |
53.9 | – | – | 53.9 | ||||||||||||
| Foreign |
61.7 | – | – | 61.7 | ||||||||||||
| Commingled funds – domestic |
– | – | 169.3 | 169.3 | ||||||||||||
| Commingled funds – foreign |
– | – | 110.0 | 110.0 | ||||||||||||
| Private equity partnerships |
– | – | 43.7 | 43.7 | ||||||||||||
| Debt securities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Government |
133.0 | – | – | 133.0 | ||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds |
– | 195.8 | – | 195.8 | ||||||||||||
| Real estate and other real assets |
– | – | 17.4 | 17.4 | ||||||||||||
| Hedge funds |
– | – | 86.2 | 86.2 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | 269.9 | $ | 195.8 | $ | 426.6 | $ | 892.3 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Snap-on’s primary investment objective for its foreign pension plans’ assets is to meet the projected obligations to the beneficiaries over a long period of time, and to do so in a manner that is consistent with the company’s risk tolerance. The foreign asset allocation policies consider the company’s financial strength and long-term asset class risk/return expectations, since the obligations are long term in nature. The company believes the foreign pension plans’ assets, which are managed locally by professional investment firms, are well diversified.
The expected long-term rates of return on foreign plans’ assets, which ranged from 1.8% to 6.3% as of 2016 year end, reflect management’s expectations of long-term average rates of return on funds invested to provide benefits included in the plans’ projected benefit obligation. The expected returns are based on outlooks for inflation, fixed income returns and equity returns, asset allocations and investment strategies. Differences between actual and expected returns on foreign pension plans’ assets are recorded as an actuarial gain or loss and amortized accordingly.
Snap-on’s foreign pension plans’ target allocation and actual weighted-average asset allocation by asset category and fair value of plan assets as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| Target | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Asset category: |
||||||||||||
| Equity securities* |
39% | 41% | 40% | |||||||||
| Debt securities* and cash and cash equivalents |
36% | 36% | 36% | |||||||||
| Insurance contracts and hedge funds |
25% | 23% | 24% | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
100% | 100% | 100% | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Fair value of plan assets (Amounts in millions) |
$ | 153.7 | $ | 156.9 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| * | Includes commingled funds – multi-strategy |
| 94 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
The following is a summary, by asset category, of the fair value and the level within the fair value hierarchy of Snap-on’s foreign pension plans’ assets as of 2016 year end:
| (Amounts in millions) | Quoted Prices for Identical Assets (Level 1) |
Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) |
Investments Measured at NAV |
Total | ||||||||||||
| Asset category: |
||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 0.7 | $ | – | $ | – | $ | 0.7 | ||||||||
| Commingled funds – multi-strategy |
– | – | 117.4 | 117.4 | ||||||||||||
| Insurance contracts |
– | 21.3 | – | 21.3 | ||||||||||||
| Hedge fund |
– | – | 14.3 | 14.3 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | 0.7 | $ | 21.3 | $ | 131.7 | $ | 153.7 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
The following is a summary, by asset category, of the fair value and the level within the fair value hierarchy of Snap-on’s foreign pension plans’ assets as of 2015 year end:
| (Amounts in millions) | Quoted Prices for Identical Assets (Level 1) |
Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) |
Investments Measured at NAV |
Total | ||||||||||||
| Asset category: |
||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 0.2 | $ | – | $ | – | $ | 0.2 | ||||||||
| Commingled funds – multi-strategy |
– | – | 119.0 | 119.0 | ||||||||||||
| Insurance contracts |
– | 19.8 | – | 19.8 | ||||||||||||
| Hedge fund |
– | – | 17.9 | 17.9 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | 0.2 | $ | 19.8 | $ | 136.9 | $ | 156.9 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Snap-on has several 401(k) plans covering certain U.S. employees. Snap-on’s employer match to the 401(k) plans is made with cash contributions. For 2016, 2015 and 2014, Snap-on recognized $8.2 million, $7.0 million and $6.5 million, respectively, of expense related to its 401(k) plans.
Note 12: Postretirement Plans
Snap-on provides health care benefits for certain retired U.S. employees. Employees retiring prior to 1989 were eligible for retiree medical coverage upon reaching early retirement age, with no retiree contributions required. Benefits are paid based on deductibles and percentages of covered expenses and take into consideration payments made by Medicare and other insurance coverage.
Since 1989, U.S. retirees have been eligible for comprehensive major medical plans. Benefits are paid based on deductibles and percentages of covered expenses, and plan provisions allow for benefit and coverage changes. Most retirees are required to pay the entire cost of the coverage, but Snap-on may elect to subsidize the cost of coverage under certain circumstances.
Snap-on has a Voluntary Employees Beneficiary Association (“VEBA”) trust for the funding of existing postretirement health care benefits for certain non-salaried retirees in the United States; all other retiree health care plans are unfunded.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 95 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
The status of Snap-on’s U.S. postretirement health care plans as of 2016 and 2015 year end is as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Change in accumulated postretirement benefit obligation: |
||||||||
| Benefit obligation at beginning of year |
$ 55.6 | $ 62.0 | ||||||
| Service cost |
0.1 | 0.1 | ||||||
| Interest cost |
2.2 | 2.2 | ||||||
| Plan participant contributions |
0.5 | 0.9 | ||||||
| Benefits paid |
(4.4) | (5.4) | ||||||
| Actuarial gain |
(0.8) | (4.2) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Benefit obligation at end of year |
$ 53.2 | $ 55.6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Change in plan assets: |
||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year |
$ 13.7 | $ 14.7 | ||||||
| Actual return on plan assets |
0.5 | – | ||||||
| Plan participant contributions |
0.5 | 0.9 | ||||||
| Employer contributions |
2.9 | 3.5 | ||||||
| Benefits paid |
(4.4) | (5.4) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Fair value of plan assets at end of year |
$ 13.2 | $ 13.7 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Unfunded status at end of year |
$ (40.0) | $ (41.9) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Amounts recognized in the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Accrued benefits |
$ (3.3) | $ (4.0) | ||||||
| Retiree health care benefits |
(36.7) | (37.9) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net liability |
$ (40.0) | $ (41.9) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Amounts included in Accumulated OCI on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Net gain, net of tax of $2.9 million in both years |
$ 4.8 | $ 4.5 | ||||||
The components of net periodic benefit cost and changes recognized in OCI are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Net periodic benefit cost: |
||||||||||||
| Service cost |
$ 0.1 | $ 0.1 | $ 0.1 | |||||||||
| Interest cost |
2.2 | 2.2 | 2.5 | |||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets |
(0.9) | (1.0) | (1.1) | |||||||||
| Amortization of unrecognized (gain) loss |
(0.1) | 0.3 | – | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net periodic benefit cost |
$ 1.3 | $ 1.6 | $ 1.5 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Changes in benefit obligations recognized in OCI, net of tax: |
||||||||||||
| Net (gain) loss |
$ (0.3) | $ (2.1) | $ 1.8 | |||||||||
| 96 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Snap-on expects to recognize $0.4 million of prior unrecognized gains, included in Accumulated OCI on the accompanying 2016 Consolidated Balance Sheet, in net periodic benefit cost during 2017.
The weighted-average discount rate used to determine Snap-on’s postretirement health care expense is as follows:
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Discount rate |
4.1% | 3.6% | 4.2% | |||||||||
The weighted-average discount rate used to determine Snap-on’s accumulated benefit obligation is as follows:
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Discount rate |
4.1% | 4.1% | ||||||
The methodology for selecting the year-end 2016 and 2015 weighted-average discount rate for the company’s domestic postretirement plans was to match the plans’ yearly projected cash flows for benefits and service costs to those of hypothetical bond portfolios using high-quality, AA rated or better, corporate bonds from either Moody’s Investors Service or Standard & Poor’s credit rating agencies available at the measurement date. As a practical expedient, Snap-on uses the calendar year end as the measurement date for its plans.
For 2017, the actuarial calculations assume a pre-65 health care cost trend rate of 5.9% and a post-65 health care cost trend rate of 6.6%, both decreasing gradually to 4.5% in 2038 and thereafter. As of 2016 year end, a one-percentage-point increase in the health care cost trend rate for future years would increase the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation by approximately $0.6 million and the aggregate of the service cost and interest cost components by less than $0.1 million. Conversely, a one-percentage-point decrease in the health care cost trend rate for future years would decrease the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation by $0.6 million and the aggregate of the service cost and interest rate components by less than $0.1 million.
The following benefit payments, which reflect expected future service, are expected to be paid as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | Amount | |||
| Year: |
||||
| 2017 |
$ | 4.4 | ||
| 2018 |
4.5 | |||
| 2019 |
4.6 | |||
| 2020 |
4.8 | |||
| 2021 |
4.8 | |||
| 2022-2026 |
23.9 | |||
The objective of the VEBA trust is to achieve net of expense returns that meet or exceed the 6.6% long-term return on plan assets assumption used for reporting purposes. Investments are diversified to attempt to minimize the risk of large losses. Since asset allocation is a key determinant of expected investment returns, assets are periodically rebalanced to the targeted allocation to correct significant deviations from the asset allocation policy that are caused by market fluctuations and cash flow.
The basis for determining the overall expected long-term return on plan assets assumption is a nominal returns forecasting method. For each asset class, future returns are estimated by identifying the premium of riskier asset classes over lower risk alternatives. The methodology constructs expected returns using a “building block” approach to the individual components of total return. These forecasts are stated in both nominal and real (after inflation) terms. This process first considers the long-term historical return premium based on the longest set of data available for each asset class. These premiums, which are calculated using the geometric mean, are then adjusted based on current relative valuation levels and macro-economic conditions. The asset return assumption is also adjusted by an implicit expense load for estimated administrative and investment-related expenses.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 97 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
Snap-on’s VEBA plan target allocation and actual weighted-average asset allocation by asset category and fair value of plan assets as of 2016 and 2015 year end are as follows:
| Target | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Asset category: |
||||||||||||
| Debt securities and cash and cash equivalents |
46% | 45% | 44% | |||||||||
| Equity securities |
29% | 28% | 27% | |||||||||
| Hedge funds |
25% | 27% | 29% | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
100% | 100% | 100% | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Fair value of plan assets (Amounts in millions) |
$ | 13.2 | $ | 13.7 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
The fair value measurement hierarchy prioritizes the inputs used to measure fair value. The hierarchy gives the highest priority (Level 1) to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities and the lowest priority (Level 3) to unobservable inputs. Fair value measurements primarily based on observable market information are given a Level 2 priority.
Debt securities are valued at quoted per share or unit market prices for which an official close or last trade pricing on an active exchange is available and are categorized as Level 1 in the fair value hierarchy.
Equity securities are valued at the NAV per share or unit multiplied by the number of shares or units held as of the measurement date, as reported by the fund managers. The share or unit price is quoted on a private market and is based on the value of the underlying investments, which are primarily based on observable inputs; such investments that are measured at fair value using the NAV per share (or its equivalent) practical expedient have not been classified in the fair value hierarchy.
Hedge funds are stated at the NAV per share or unit (based on the estimated fair market value of the underlying investments) multiplied by the number of shares or units held as of the measurement date, as reported by the fund managers. These investments are measured at fair value using the NAV per share (or its equivalent) practical expedient and have not been classified in the fair value hierarchy.
The company regularly reviews fund performance directly with its investment advisor and the fund managers, and performs qualitative analysis to corroborate the reasonableness of the reported NAVs. For funds for which the company did not receive a year-end NAV, the company recorded an estimate of the change in fair value for the latest period based on return estimates and other fund activity obtained from the fund managers.
The columns labeled “Investments Measured at NAV” in the following tables are measured at fair value using the NAV per share (or its equivalent) practical expedient and have not been categorized in the fair value hierarchy. The fair value amounts presented in these tables are intended to permit a reconciliation of the fair value hierarchy to the VEBA plan assets.
The following is a summary, by asset category, of the fair value and the level within the fair value hierarchy of the VEBA plan assets as of 2016 year end:
| (Amounts in millions) | Quoted Prices for Identical Assets (Level 1) |
Investments Measured at NAV |
Total | |||||||||
| Asset category: |
||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 0.7 | $ | – | $ | 0.7 | ||||||
| Debt securities |
5.3 | – | 5.3 | |||||||||
| Equity securities |
– | 3.6 | 3.6 | |||||||||
| Hedge fund |
– | 3.6 | 3.6 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 6.0 | $ | 7.2 | $ | 13.2 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 98 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
The following is a summary, by asset category, of the fair value and the level within the fair value hierarchy of the VEBA plan assets as of 2015 year end:
| (Amounts in millions) | Quoted Prices for Identical Assets (Level 1) |
Investments Measured at NAV |
Total | |||||||||
| Asset category: |
||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 0.1 | $ | – | $ | 0.1 | ||||||
| Debt securities |
6.0 | – | 6.0 | |||||||||
| Equity securities |
– | 3.7 | 3.7 | |||||||||
| Hedge fund |
– | 3.9 | 3.9 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 6.1 | $ | 7.6 | $ | 13.7 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Note 13: Stock-based Compensation and Other Stock Plans
The 2011 Incentive Stock and Awards Plan (the “2011 Plan”) provides for the grant of stock options, performance awards, stock appreciation rights (“SARs”) and restricted stock awards (which may be designated as “restricted stock units” or “RSUs”). No further grants are being made under its predecessor, the 2001 Incentive Stock and Awards Plan (the “2001 Plan”), although outstanding awards under the 2001 Plan will continue until exercised, vested, forfeited or expired. As of 2016 year end, the 2011 Plan had 4,121,252 shares available for future grants. The company uses treasury stock to deliver shares under both the 2001 and 2011 Plans.
Net stock-based compensation expense was $31.0 million in 2016, $39.8 million in 2015 and $38.1 million in 2014. Cash received from stock purchase and option plan exercises was $41.8 million in 2016, $41.6 million in 2015 and $33.0 million in 2014. The tax benefit realized from both the exercise and vesting of share-based payment arrangements was $24.8 million in 2016, $26.4 million in 2015 and $22.3 million in 2014.
Stock Options
Stock options are granted with an exercise price equal to the market value of a share of Snap-on’s common stock on the date of grant and have a contractual term of ten years. Stock option grants vest ratably on the first, second and third anniversaries of the date of grant.
The fair value of each stock option award is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes valuation model. The company uses historical data regarding stock option exercise and forfeiture behaviors for different participating groups to estimate the period of time that options granted are expected to be outstanding. Expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of the company’s stock for the length of time corresponding to the expected term of the option. The expected dividend yield is based on the company’s historical dividend payments. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. treasury yield curve on the grant date for the expected term of the option.
The following weighted-average assumptions were used in calculating the fair value of stock options granted during 2016, 2015 and 2014, using the Black-Scholes valuation model:
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Expected term of option (in years) |
5.05 | 4.76 | 4.52 | |||||||||
| Expected volatility factor |
22.17% | 24.13% | 26.76% | |||||||||
| Expected dividend yield |
1.77% | 2.04% | 2.40% | |||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.04% | 1.38% | 1.30% | |||||||||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 99 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
A summary of stock option activity during 2016 is presented below:
| Shares (in thousands) |
Exercise Price per Share* |
Remaining Contractual Term* (in years) |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value (in millions) |
|||||||||||||
| Outstanding at beginning of year |
2,811 | $ | 88.62 | |||||||||||||
| Granted |
644 | 138.04 | ||||||||||||||
| Exercised |
(416) | 74.10 | ||||||||||||||
| Forfeited or expired |
(28) | 133.11 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Outstanding at end of year |
3,011 | 100.78 | 6.6 | $ | 212.3 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Exercisable at end of year |
1,776 | 76.51 | 5.3 | 168.3 | ||||||||||||
| * | Weighted-average |
The weighted-average grant date fair value of options granted was $22.99 in 2016, $25.64 in 2015 and $20.19 in 2014. The intrinsic value of options exercised was $35.2 million in 2016, $37.6 million in 2015 and $24.6 million in 2014. The fair value of stock options vested was $12.7 million in 2016, $9.9 million in 2015 and $9.6 million in 2014.
As of 2016 year end, there was $16.6 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested stock options that is expected to be recognized as a charge to earnings over a weighted-average period of 1.5 years.
Performance Awards
Performance awards, which are granted as performance share units and performance-based RSUs, are earned and expensed using the fair value of the award over a contractual term of three years based on the company’s performance. Vesting of the performance awards is dependent upon performance relative to pre-defined goals for revenue growth and return on net assets for the applicable performance period. For performance achieved above specified levels, the recipient may earn additional shares of stock, not to exceed 100% of the number of performance awards initially granted.
The performance share units have a three-year performance period based on the results of the consolidated financial metrics of the company. The performance-based RSUs have a one-year performance period based on the results of the consolidated financial metrics of the company followed by a two-year cliff vesting schedule, assuming continued employment.
The fair value of performance awards is calculated using the market value of a share of Snap-on’s common stock on the date of grant and assumed forfeitures based on recent historical experience; in recent years, forfeitures have not been significant. The weighted-average grant date fair value of performance awards granted during 2016, 2015 and 2014 was $138.83, $139.30 and $102.11, respectively. Vested performance share units totaled 61,149 shares as of 2016 year end, 94,186 shares as of 2015 year end and 130,764 shares as of 2014 year end. Performance share units related to 94,186 shares, 130,764 shares and 146,313 shares were paid out in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Earned performance share units are generally paid out following the conclusion of the applicable performance period upon approval by the Organization and Executive Compensation Committee of the company’s Board of Directors (the “Board”).
Based on the company’s 2016 performance, 45,502 RSUs granted in 2016 were earned; assuming continued employment, these RSUs will vest at the end of fiscal 2018. Based on the company’s 2015 performance, 64,327 RSUs granted in 2015 were earned; assuming continued employment, these RSUs will vest at the end of fiscal 2017. Based on the company’s 2014 performance, 78,585 RSUs granted in 2014 were earned; these RSUs vested as of fiscal 2016 year end and were paid out shortly thereafter.
| 100 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Changes to the company’s non-vested performance awards in 2016 are as follows:
| Shares (in thousands) |
Fair Value Price per Share* |
|||||||
| Non-vested performance awards at beginning of year |
265 | $ | 124.16 | |||||
| Granted |
97 | 138.83 | ||||||
| Vested |
(136) | 109.43 | ||||||
| Cancellations and other |
(19) | 112.14 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Non-vested performance awards at end of year |
207 | 141.94 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| * | Weighted-average |
As of 2016 year end, there was $13.7 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested performance awards that is expected to be recognized as a charge to earnings over a weighted-average period of 1.6 years.
Stock Appreciation Rights (“SARs”)
The company also issues stock-settled and cash-settled SARs to certain key non-U.S. employees. SARs have a contractual term of ten years and vest ratably on the first, second and third anniversaries of the date of grant. SARs are granted with an exercise price equal to the market value of a share of Snap-on’s common stock on the date of grant.
Stock-settled SARs are accounted for as equity instruments and provide for the issuance of Snap-on common stock equal to the amount by which the company’s stock has appreciated over the exercise price. Stock-settled SARs have an effect on dilutive shares and shares outstanding as any appreciation of Snap-on’s common stock value over the exercise price will be settled in shares of common stock. Cash-settled SARs provide for the cash payment of the excess of the fair market value of Snap-on’s common stock price on the date of exercise over the grant price. Cash-settled SARs have no effect on dilutive shares or shares outstanding as any appreciation of Snap-on’s common stock over the grant price is paid in cash and not in common stock.
The fair value of stock-settled SARs is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes valuation model. The fair value of cash-settled SARs is revalued (mark-to-market) each reporting period using the Black-Scholes valuation model based on Snap-on’s period-end stock price. The company uses historical data regarding SARs exercise and forfeiture behaviors for different participating groups to estimate the expected term of the SARs granted based on the period of time that similar instruments granted are expected to be outstanding. Expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of the company’s stock for the length of time corresponding to the expected term of the SARs. The expected dividend yield is based on the company’s historical dividend payments. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. treasury yield curve in effect as of the grant date (for stock-settled SARs) or reporting date (for cash-settled SARs) for the length of time corresponding to the expected term of the SARs.
The following weighted-average assumptions were used in calculating the fair value of stock-settled SARs granted during 2016, 2015 and 2014, using the Black-Scholes valuation model:
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Expected term of stock-settled SARs (in years) |
4.03 | 4.72 | 4.49 | |||||||||
| Expected volatility factor |
20.09% | 23.66% | 25.64% | |||||||||
| Expected dividend yield |
1.66% | 2.04% | 2.40% | |||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.11% | 1.50% | 1.50% | |||||||||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 101 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
Changes to the company’s stock-settled SARs in 2016 are as follows:
| Stock-settled SARs (in thousands) |
Exercise Price per Share* |
Remaining Contractual Term* (in years) |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value (in millions) |
|||||||||||||
| Outstanding at beginning of year |
269 | $ | 113.70 | |||||||||||||
| Granted |
101 | 138.05 | ||||||||||||||
| Exercised |
(26) | 89.10 | ||||||||||||||
| Forfeited or expired |
(41) | 103.29 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Outstanding at end of year |
303 | 125.38 | 7.9 | $ | 13.9 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Exercisable at end of year |
106 | 106.50 | 7.0 | 6.8 | ||||||||||||
| * | Weighted-average |
The weighted-average grant date fair value of stock-settled SARs granted was $19.47 in 2016, $25.37 in 2015 and $19.55 in 2014. The intrinsic value of stock-settled SARs exercised was $1.9 million in 2016, $1.0 million in 2015 and $0.1 million in 2014. The fair value of stock-settled SARs vested was $2.1 million in 2016, $1.4 million in 2015 and $0.6 million in 2014.
As of 2016 year end there was $2.4 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested stock-settled SARs that is expected to be recognized as a charge to earnings over a weighted-average period of 1.5 years.
The following weighted-average assumptions were used in calculating the fair value of cash-settled SARs granted during 2016, 2015 and 2014, using the Black-Scholes valuation model:
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Expected term of cash-settled SARs (in years) |
3.11 | 3.10 | 3.53 | |||||||||
| Expected volatility factor |
19.53% | 18.14% | 23.92% | |||||||||
| Expected dividend yield |
1.56% | 1.69% | 2.11% | |||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.47% | 1.31% | 1.07% | |||||||||
The intrinsic value of cash-settled SARs exercised was $3.3 million in 2016, $11.0 million in 2015 and $5.5 million in 2014. The fair value of cash-settled SARs vested during 2016, 2015 and 2014 was $0.2 million, $4.6 million and $5.9 million, respectively.
Changes to the company’s non-vested cash-settled SARs in 2016 are as follows:
| Cash-settled SARs (in thousands) |
Fair Value Price per Share* |
|||||||
| Non-vested cash-settled SARs at beginning of year |
7 | $ | 51.71 | |||||
| Granted |
4 | 39.51 | ||||||
| Vested |
(4) | 61.42 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Non-vested cash-settled SARs at end of year |
7 | 40.83 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| * | Weighted-average |
As of 2016 year end there was $0.3 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested cash-settled SARs that is expected to be recognized as a charge to earnings over a weighted-average period of 1.5 years.
| 102 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Restricted Stock Awards – Non-employee Directors
The company awarded 7,145 shares, 8,640 shares and 10,398 shares of restricted stock to non-employee directors in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The fair value of the restricted stock awards is expensed over a one year vesting period based on the fair value on the date of grant. All restrictions for the restricted stock generally lapse upon the earlier of the first anniversary of the grant date, the recipient’s death or disability or in the event of a change in control, as defined in the 2011 Plan. If termination of the recipient’s service occurs prior to the first anniversary of the grant date for any reason other than death or disability, the shares of restricted stock would be forfeited, unless otherwise determined by the Board.
Directors’ Fee Plan
Under the Directors’ 1993 Fee Plan, as amended, non-employee directors may elect to receive up to 100% of their fees and retainer in shares of Snap-on’s common stock. Directors may elect to defer receipt of all or part of these shares. For 2016, 2015 and 2014, issuances under the Directors’ Fee Plan totaled 2,579 shares, 2,747 shares and 21,533 shares, respectively, of which 2,019 shares, 1,969 shares and 20,483 shares, respectively, were deferred. As of 2016 year end, shares reserved for issuance to directors under this plan totaled 158,105 shares.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
Substantially all Snap-on employees in the United States and Canada are eligible to participate in an employee stock purchase plan. The purchase price of the company’s common stock to participants is the lesser of the mean of the high and low price of the stock on the beginning date (May 15) or ending date (the following May 14) of each plan year. For 2016, 2015 and 2014, issuances under this plan totaled 27,156 shares, 57,324 shares and 56,582 shares, respectively. As of 2016 year end, shares reserved for issuance under this plan totaled 780,563 shares and Snap-on held participant contributions of approximately $2.4 million. Participants are able to withdraw from the plan at any time prior to the ending date and receive back all contributions made during the plan year. Compensation expense for plan participants was zero in 2016, $2.3 million in 2015 and $1.5 million in 2014.
Franchisee Stock Purchase Plan
All franchisees in the United States and Canada are eligible to participate in a franchisee stock purchase plan. The purchase price of the company’s common stock to participants is the lesser of the mean of the high and low price of the stock on the beginning date (May 15) or ending date (the following May 14) of each plan year. For 2016, 2015 and 2014, issuances under this plan totaled 42,867 shares, 74,001 shares and 74,502 shares, respectively. As of 2016 year end, shares reserved for issuance under this plan totaled 613,469 shares and Snap-on held participant contributions of approximately $4.6 million. Participants are able to withdraw from the plan at any time prior to the ending date and receive back all contributions made during the plan year. The company recognized a mark-to-market benefit of $0.2 million in 2016; mark-to-market expense for plan participants was $2.9 million in 2015 and $1.7 million in 2014.
Note 14: Capital Stock
Snap-on has undertaken repurchases of Snap-on common stock from time to time to offset dilution created by shares issued for employee and franchisee stock purchase plans, stock awards and other corporate purposes. Snap-on repurchased 758,000 shares, 723,000 shares and 680,000 shares in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. As of 2016 year end, Snap-on has remaining availability to repurchase up to an additional $207.2 million in common stock pursuant to Board authorizations. The purchase of Snap-on common stock is at the company’s discretion, subject to prevailing financial and market conditions.
Cash dividends paid in 2016, 2015 and 2014 totaled $147.5 million, $127.9 million and $107.6 million, respectively. Cash dividends per share in 2016, 2015 and 2014 were $2.54, $2.20 and $1.85, respectively. On February 9, 2017, the company’s Board declared a quarterly dividend of $0.71 per share, payable on March 10, 2017, to shareholders of record on February 24, 2017.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 103 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
Note 15: Commitments and Contingencies
Snap-on leases facilities, office equipment and vehicles under non-cancelable operating and capital leases that extend for varying amounts of time. Snap-on’s future minimum lease commitments under these leases, net of sub-lease rental income, are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | Operating
Leases |
Capital Leases |
||||||
| Year: |
||||||||
| 2017 |
$ | 23.0 | $ | 3.7 | ||||
| 2018 |
18.3 | 3.3 | ||||||
| 2019 |
13.9 | 2.9 | ||||||
| 2020 |
9.4 | 2.6 | ||||||
| 2021 |
6.4 | 2.1 | ||||||
| 2022 and thereafter |
10.5 | 5.6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total minimum lease payments |
$ | 81.5 | $ | 20.2 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Less: amount representing interest |
(1.5) | |||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total present value of minimum capital lease payments |
$ | 18.7 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
Amounts included in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets for the present value of minimum capital lease payments as of 2016 year end are as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | |||
| Other accrued liabilities |
$ | 3.3 | ||
| Other long-term liabilities |
15.4 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total present value of minimum capital lease payments |
$ | 18.7 | ||
|
|
|
|||
Rent expense for worldwide facilities, office equipment and vehicles, net of sub-lease rental income, was $31.2 million, $29.4 million and $30.6 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Snap-on provides product warranties for specific product lines and accrues for estimated future warranty cost in the period in which the sale is recorded. Snap-on calculates its accrual requirements based on historic warranty loss experience that is periodically adjusted for recent actual experience, including the timing of claims during the warranty period and actual costs incurred. Snap-on’s product warranty accrual activity for 2016, 2015 and 2014 is as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Warranty accrual: |
||||||||||||
| Beginning of year |
$ | 16.4 | $ | 17.3 | $ | 17.0 | ||||||
| Additions |
12.8 | 13.3 | 14.6 | |||||||||
| Usage |
(13.2) | (14.2) | (14.3) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| End of year |
$ | 16.0 | $ | 16.4 | $ | 17.3 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Approximately 2,800 employees, or 23% of Snap-on’s worldwide workforce, are represented by unions and/or covered under collective bargaining agreements. The number of covered union employees whose contracts expire over the next five years approximates 2,100 employees in 2017, 500 employees in 2018, and 200 employees in 2019; there are no contracts currently scheduled to expire in 2020 or 2021. In recent years, Snap-on has not experienced any significant work slowdowns, stoppages or other labor disruptions.
Snap-on is involved in various legal matters that are being litigated and/or settled in the ordinary course of business. Although it is not possible to predict the outcome of these legal matters, management believes that the results of these legal matters will not have a material impact on Snap-on’s consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
| 104 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Note 16: Other Income (Expense) – Net
“Other income (expense) – net” on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Earnings consists of the following:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Interest income |
$ | 0.6 | $ | 0.5 | $ | 0.5 | ||||||
| Net foreign exchange loss |
(1.3) | (2.7) | (1.5) | |||||||||
| Other |
0.1 | (0.2) | 0.1 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total other income (expense) – net |
$ | (0.6) | $ | (2.4) | $ | (0.9) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Note 17: Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The following is a summary of net changes in Accumulated OCI by component and net of tax for 2016 and 2015:
| (Amounts in millions) | Foreign Currency Translation |
Cash Flow Hedges |
Defined Benefit Pension and Postretirement Plans |
Total | ||||||||||||
| Balance as of 2014 year end |
$ | (7.7) | $ | 1.0 | $ | (241.5) | $ | (248.2) | ||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss before reclassifications |
(110.8) | – | (28.9) | (139.7) | ||||||||||||
| Amounts reclassified from Accumulated OCI |
– | (0.3) | 24.0 | 23.7 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net other comprehensive loss |
(110.8) | (0.3) | (4.9) | (116.0) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Balance as of 2015 year end |
$ | (118.5) | $ | 0.7 | $ | (246.4) | $ | (364.2) | ||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications |
(99.2) | 8.8 | (62.6) | (153.0) | ||||||||||||
| Amounts reclassified from Accumulated OCI |
– | (0.3) | 19.0 | 18.7 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net other comprehensive income (loss) |
(99.2) | 8.5 | (43.6) | (134.3) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Balance as of 2016 year end |
$ | (217.7) | $ | 9.2 | $ | (290.0) | $ | (498.5) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
The reclassifications out of Accumulated OCI in 2016 and 2015 are as follows:
| Details about Accumulated OCI Components |
Amounts Reclassified from Accumulated OCI |
Statement of Earnings | ||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| Gains on cash flow hedges: |
||||||||||
| Treasury locks |
$ | 0.3 | $ | 0.3 | Interest expense | |||||
| Income tax expense |
– | – | Income tax expense | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net of tax |
0.3 | 0.3 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Amortization of net unrecognized losses and prior service credits |
(30.1) | (38.0) | See footnote below* | |||||||
| Income tax benefit |
11.1 | 14.0 | Income tax expense | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net of tax |
(19.0) | (24.0) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total reclassifications for the period, net of tax |
$ | (18.7) | $ | (23.7) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| * | These Accumulated OCI components are included in the computation of net periodic pension and postretirement health care costs; see Note 11 and Note 12 for further information. |
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 105 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
Note 18: Segments
Snap-on’s business segments are based on the organization structure used by management for making operating and investment decisions and for assessing performance. Snap-on’s reportable business segments are: (i) the Commercial & Industrial Group; (ii) the Snap-on Tools Group; (iii) the Repair Systems & Information Group; and (iv) Financial Services. The Commercial & Industrial Group consists of business operations serving a broad range of industrial and commercial customers worldwide, including customers in the aerospace, natural resources, government, power generation, transportation and technical education market segments (collectively, “critical industries”), primarily through direct and distributor channels. The Snap-on Tools Group consists of business operations primarily serving vehicle service and repair technicians through the company’s worldwide mobile tool distribution channel. The Repair Systems & Information Group consists of business operations serving other professional vehicle repair customers worldwide, primarily owners and managers of independent repair shops and original equipment manufacturer (“OEM”) dealership service and repair shops (“OEM dealerships”), through direct and distributor channels. Financial Services consists of the business operations of Snap-on’s finance subsidiaries.
Snap-on evaluates the performance of its operating segments based on segment revenues, including both external and intersegment net sales, and segment operating earnings. Snap-on accounts for intersegment sales and transfers based primarily on standard costs with reasonable mark-ups established between the segments. Identifiable assets by segment are those assets used in the respective reportable segment’s operations. Corporate assets consist of cash and cash equivalents (excluding cash held at Financial Services), deferred income taxes and certain other assets. All significant intersegment amounts are eliminated to arrive at Snap-on’s consolidated financial results.
Neither Snap-on nor any of its segments depend on any single customer, small group of customers or government for more than 10% of its revenues.
Financial Data by Segment:
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Net sales: |
||||||||||||
| Commercial & Industrial Group |
$ | 1,148.3 | $ | 1,163.6 | $ | 1,174.8 | ||||||
| Snap-on Tools Group |
1,633.9 | 1,568.7 | 1,455.2 | |||||||||
| Repair Systems & Information Group |
1,179.9 | 1,113.2 | 1,095.2 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Segment net sales |
3,962.1 | 3,845.5 | 3,725.2 | |||||||||
| Intersegment eliminations |
(531.7) | (492.7) | (447.5) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total net sales |
$ | 3,430.4 | $ | 3,352.8 | $ | 3,277.7 | ||||||
| Financial Services revenue |
281.4 | 240.3 | 214.9 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total revenues |
$ | 3,711.8 | $ | 3,593.1 | $ | 3,492.6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Operating earnings: |
||||||||||||
| Commercial & Industrial Group |
$ | 168.0 | $ | 169.4 | $ | 158.6 | ||||||
| Snap-on Tools Group |
281.1 | 256.0 | 223.1 | |||||||||
| Repair Systems & Information Group |
297.8 | 273.4 | 251.2 | |||||||||
| Financial Services |
198.7 | 170.2 | 149.1 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Segment operating earnings |
945.6 | 869.0 | 782.0 | |||||||||
| Corporate |
(91.4) | (104.2) | (97.3) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Operating earnings |
854.2 | 764.8 | 684.7 | |||||||||
| Interest expense |
(52.2) | (51.9) | (52.9) | |||||||||
| Other income (expense) – net |
(0.6) | (2.4) | (0.9) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Earnings before income taxes and equity earnings |
$ | 801.4 | $ | 710.5 | $ | 630.9 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 106 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Financial Data by Segment (continued):
| (Amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||
| Commercial & Industrial Group |
$ | 907.1 | $ | 901.6 | ||||||||
| Snap-on Tools Group |
668.1 | 646.7 | ||||||||||
| Repair Systems & Information Group |
1,211.0 | 1,041.6 | ||||||||||
| Financial Services |
1,789.7 | 1,572.4 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total assets from reportable segments |
4,575.9 | 4,162.3 | ||||||||||
| Corporate |
212.3 | 203.6 | ||||||||||
| Elimination of intersegment receivables |
(65.0) | (34.8) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 4,723.2 | $ | 4,331.1 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Capital expenditures: |
||||||||||||
| Commercial & Industrial Group |
$ | 19.3 | $ | 31.0 | $ | 28.5 | ||||||
| Snap-on Tools Group |
38.3 | 38.1 | 36.9 | |||||||||
| Repair Systems & Information Group |
13.1 | 9.0 | 10.6 | |||||||||
| Financial Services |
0.6 | 1.0 | 0.4 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total from reportable segments |
71.3 | 79.1 | 76.4 | |||||||||
| Corporate |
3.0 | 1.3 | 4.2 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total capital expenditures |
$ | 74.3 | $ | 80.4 | $ | 80.6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Depreciation and amortization: |
||||||||||||
| Commercial & Industrial Group |
$ | 20.7 | $ | 20.1 | $ | 20.8 | ||||||
| Snap-on Tools Group |
27.6 | 24.9 | 21.4 | |||||||||
| Repair Systems & Information Group |
33.9 | 34.0 | 33.7 | |||||||||
| Financial Services |
0.6 | 0.7 | 0.9 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total from reportable segments |
82.8 | 79.7 | 76.8 | |||||||||
| Corporate |
2.8 | 2.8 | 2.7 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total depreciation and amortization |
$ | 85.6 | $ | 82.5 | $ | 79.5 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Revenues by geographic region:* |
||||||||||||
| United States |
$ | 2,588.8 | $ | 2,483.9 | $ | 2,288.9 | ||||||
| Europe |
654.4 | 635.0 | 701.9 | |||||||||
| All other |
468.6 | 474.2 | 501.8 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total revenues |
$ | 3,711.8 | $ | 3,593.1 | $ | 3,492.6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Long-lived assets:** |
||||||||
| United States |
$ | 1,048.6 | $ | 1,033.3 | ||||
| Sweden |
218.8 | 114.5 | ||||||
| All other |
237.9 | 250.8 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total long-lived assets |
$ | 1,505.3 | $ | 1,398.6 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| * | Revenues are attributed to countries based on the origin of the sale. |
| ** | Long-lived assets consist of Property and equipment – net, Goodwill, and Other intangibles – net. |
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 107 |
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
Products and Services: Snap-on derives net sales from a broad line of products and complementary services that are grouped into three categories: (i) tools; (ii) diagnostics and repair information; and (iii) equipment. The tools product category includes Snap-on’s hand tools, power tools and tool storage products. The diagnostics and repair information product category includes handheld and PC-based diagnostic products, service and repair information products, diagnostic software solutions, electronic parts catalogs, and business management systems and services to help owners and managers of independent repair shops and OEM dealerships manage and track performance. The equipment product category includes solutions for the diagnosis and service of vehicles and industrial equipment. Through its financial services businesses, Snap-on also derives revenue from various financing programs designed to facilitate the sales of its products and support its franchise business. Further product line information is not presented as it is not practicable to do so.
The following table shows the consolidated net sales and revenues of these product groups in the last three years:
(Amounts in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Net sales: |
||||||||||||
| Tools |
$ | 1,899.2 | $ | 1,910.1 | $ | 1,868.5 | ||||||
| Diagnostics and repair information |
748.2 | 689.6 | 689.5 | |||||||||
| Equipment |
783.0 | 753.1 | 719.7 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total net sales |
$ | 3,430.4 | $ | 3,352.8 | $ | 3,277.7 | ||||||
| Financial services revenue |
281.4 | 240.3 | 214.9 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total revenues |
$ | 3,711.8 | $ | 3,593.1 | $ | 3,492.6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 108 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
Note 19: Quarterly Data (unaudited)
| (Amounts in millions, except per share data) | First Quarter |
Second Quarter |
Third Quarter |
Fourth Quarter |
Total | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 834.2 | $ | 872.3 | $ | 834.1 | $ | 889.8 | $ | 3,430.4 | ||||||||||
| Gross profit |
415.3 | 431.3 | 419.1 | 443.9 | 1,709.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Financial services revenue |
66.3 | 69.3 | 71.6 | 74.2 | 281.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Financial services expenses |
(19.3) | (19.8) | (21.0) | (22.6) | (82.7) | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
131.3 | 143.4 | 135.2 | 149.7 | 559.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to Snap-on Incorporated |
128.3 | 140.1 | 131.7 | 146.3 | 546.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Earnings per share – basic |
2.21 | 2.41 | 2.27 | 2.52 | 9.40 | |||||||||||||||
| Earnings per share – diluted |
2.16 | 2.36 | 2.22 | 2.47 | 9.20 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends paid per share |
0.61 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.71 | 2.54 | |||||||||||||||
| First Quarter |
Second Quarter |
Third Quarter |
Fourth Quarter |
Total | ||||||||||||||||
| 2015 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 827.8 | $ | 851.8 | $ | 821.5 | $ | 851.7 | $ | 3,352.8 | ||||||||||
| Gross profit |
410.1 | 419.0 | 406.9 | 412.3 | 1,648.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Financial services revenue |
57.4 | 58.7 | 61.1 | 63.1 | 240.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Financial services expenses |
(17.1) | (17.3) | (17.6) | (18.1) | (70.1) | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
113.2 | 123.0 | 119.9 | 134.5 | 490.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings attributable to Snap-on Incorporated |
110.5 | 120.0 | 116.8 | 131.4 | 478.7 | |||||||||||||||
| Earnings per share – basic |
1.90 | 2.07 | 2.01 | 2.26 | 8.24 | |||||||||||||||
| Earnings per share – diluted |
1.87 | 2.03 | 1.98 | 2.22 | 8.10 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends paid per share |
0.53 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.61 | 2.20 | |||||||||||||||
Note 20: Subsequent Event
On January 17, 2017, Snap-on repaid the 2017 Notes upon maturity with an aggregate of $150 million of available cash and cash generated from issuances of commercial paper.
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 109 |
Table of Contents
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, Snap-on has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
||||||
| By: | /s/ Nicholas T. Pinchuk | Date: February 9, 2017 | ||||
| Nicholas T. Pinchuk, Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer |
||||||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of Snap-on and in the capacities and on the date indicated.
| /s/ Nicholas T. Pinchuk | Date: February 9, 2017 | |||||
| Nicholas T. Pinchuk, Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer |
||||||
| /s/ Aldo J. Pagliari | Date: February 9, 2017 | |||||
| Aldo J. Pagliari, Principal Financial Officer, Senior Vice President – Finance and Chief Financial Officer |
||||||
| /s/ Constance R. Johnsen | Date: February 9, 2017 | |||||
| Constance R. Johnsen, Principal Accounting Officer, Vice President and Controller |
||||||
| 110 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of Snap-on and in the capacities and on the date indicated.
| By: | /s/ David C. Adams | Date: February 9, 2017 | ||||
| David C. Adams, Director |
||||||
| By: | /s/ Karen L. Daniel | Date: February 9, 2017 | ||||
| Karen L. Daniel, Director |
||||||
| By: | /s/ Ruth Ann M. Gillis | Date: February 9, 2017 | ||||
| Ruth Ann M. Gillis, Director |
||||||
| By: | /s/ James P. Holden | Date: February 9, 2017 | ||||
| James P. Holden, Director |
||||||
| By: | /s/ Nathan J. Jones | Date: February 9, 2017 | ||||
| Nathan J. Jones, Director |
||||||
| By: | /s/ Henry W. Knueppel | Date: February 9, 2017 | ||||
| Henry W. Knueppel, Director |
||||||
| By: | /s/ W. Dudley Lehman | Date: February 9, 2017 | ||||
| W. Dudley Lehman, Director |
||||||
| By: | /s/ Nicholas T. Pinchuk | Date: February 9, 2017 | ||||
| Nicholas T. Pinchuk, Director |
||||||
| By: | /s/ Gregg M. Sherrill | Date: February 9, 2017 | ||||
| Gregg M. Sherrill, Director |
||||||
| By: | /s/ Donald J. Stebbins | Date: February 9, 2017 | ||||
| Donald J. Stebbins, Director |
||||||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 111 |
Table of Contents
| (3) |
(a) |
Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Snap-on Incorporated, as amended through April 25, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to Snap-on’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended September 28, 2013 (Commission File No. 1-7724)) | ||
| (b) |
Bylaws of Snap-on Incorporated, as amended and restated as of April 25, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to Snap-on’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated April 25, 2013 (Commission File No. 1-7724)) | |||
| (4) |
(a) |
Indenture, dated as of January 8, 2007, between Snap-on Incorporated and U.S. Bank National Association as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit (4)(b) to Form S-3 Registration Statement (Registration No. 333-139863)) | ||
| (b) |
Officer’s Certificate, dated as of February 24, 2009, providing for the $200,000,000 6.70% Notes due 2019 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to Snap-on’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated February 19, 2009 (Commission File No. 1-7724)) | |||
| (c) |
Officer’s Certificate, dated as of August 14, 2009, providing for the $250,000,000 6.125% Notes due 2021 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Snap-on’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated August 11, 2009 (Commission File No. 1-7724)) | |||
| (d) |
Officer’s Certificate, dated as of December 14, 2010, providing for the $250,000,000 4.25% Notes due 2018 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Snap-on’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated December 9, 2010 (Commission File No. 1-7724)) | |||
Except for the foregoing, Snap-on and its subsidiaries have no unregistered long-term debt agreement for which the related outstanding debt exceeds 10% of consolidated total assets as of December 31, 2016. Copies of debt instruments for which the related debt is less than 10% of consolidated total assets will be furnished to the Commission upon request.
| (10) |
Material Contracts | |||
| (a) |
Amended and Restated Snap-on Incorporated 2001 Incentive Stock and Awards Plan (Amended and Restated as of April 27, 2006, as further amended on August 6, 2009) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Snap-on’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended October 3, 2009 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** (superseded except as to outstanding awards) | |||
| (b) |
Snap-on Incorporated 2011 Incentive Stock and Awards Plan (Amended and Restated as of April 30, 2015) (incorporated by reference to Appendix A to Snap-on’s Definitive Proxy Statement for its 2015 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on March 12, 2015 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (c) |
Form of Restated Executive Agreement between Snap-on Incorporated and each of its executive officers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Snap-on’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated January 31, 2008 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (d)(1) |
Form of Indemnification Agreement between Snap-on Incorporated and certain executive officers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Snap-on’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 1, 2011 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (d)(2) |
Form of Indemnification Agreement between Snap-on Incorporated and directors (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Snap-on’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 1, 2011 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (e)(1) |
Amended and Restated Snap-on Incorporated Directors’ 1993 Fee Plan (as amended through August 5, 2010) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Snap-on’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended October 2, 2010 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (e)(2) |
Amendment to Amended and Restated Snap-on Incorporated Directors’ 1993 Fee Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(e)(2) to Snap-on’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 28, 2013 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| 112 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
Table of Contents
| (f)(1) |
Snap-on Incorporated Deferred Compensation Plan (as amended and restated as of September 1, 2011) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(g) to Snap-on’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (f)(2) |
Amendment to Snap-on Incorporated Deferred Compensation Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(f)(2) to Snap-on’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 28, 2013 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (g) |
Snap-on Incorporated Supplemental Retirement Plan for Officers (as amended through June 11, 2010) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Snap-on’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended July 3, 2010 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (h) |
Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement under the 2001 Incentive Stock and Awards Plan (and accompanying Non-Qualified Stock Option Grant Offer Letter) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Snap-on’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2007 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (i) |
Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement for Directors under the 2001 Incentive Stock and Awards Plan (and accompanying Restricted Stock Unit Offer Letter) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Snap-on’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended October 3, 2009 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (j) |
Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement under the 2011 Incentive Stock and Awards Plan (and accompanying Non-Qualified Stock Option Grant Offer Letter) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Snap-on’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended October 1, 2011 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (k) |
Form of Performance Share Unit Award Agreement under the 2011 Incentive Stock and Awards Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Snap-on’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2012 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (l) |
Form of Restricted Unit Award Agreement for Executive Officers under the 2011 Incentive Stock and Awards Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Snap-on’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2012 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (m) |
Form of Restricted Unit Award Agreement for Directors under the 2011 Incentive Stock and Awards Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Snap-on’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2012 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (n) |
Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement for Directors under the 2011 Incentive Stock and Awards Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Snap-on’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 30, 2013 (Commission File No. 1-7724))** | |||
| (o) |
Second Amended and Restated Five Year Credit Agreement, dated as of December 15, 2015, among Snap-on Incorporated and the lenders and agents listed on the signature pages thereof, and J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Citigroup Global Markets Inc. and U.S. Bank National Association as joint lead arrangers and joint bookrunners (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Snap-on’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated December 15, 2015 (Commission File No. 1-7724)) | |||
| 2016 ANNUAL REPORT | 113 |
Table of Contents
| (12) |
Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges | |
| (14) |
Snap-on Incorporated Section 406 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act Code of Ethics (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10(aa) to Snap-on’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 3, 2004 (Commission File No. 1-7724)) | |
| (21) |
Subsidiaries of the Corporation | |
| (23) |
Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | |
| (31.1) |
Certification of the Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
| (31.2) |
Certification of the Principal Financial Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
| (32.1) |
Certification of Chief Executive Officer Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
| (32.2) |
Certification of Principal Financial Officer Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
| (101.INS) |
XBRL Instance Document*** | |
| (101.SCH) |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document*** | |
| (101.CAL) |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document*** | |
| (101.DEF) |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document*** | |
| (101.LAB) |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document*** | |
| (101.PRE) |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document*** | |
| * | Filed electronically or incorporated by reference as an exhibit to this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Copies of any materials the company files with the SEC can also be obtained free of charge through the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov. The SEC’s Public Reference Room can be contacted at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549, or by calling the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 1-800-732-0330. |
| ** | Represents a management compensatory plan or agreement. |
| *** | Attached as Exhibit 101 to this report are the following documents formatted in XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language): (i) Consolidated Statements of Earnings for the twelve months ended December 31, 2016, January 2, 2016, and January 3, 2015; (ii) Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the twelve months ended December 31, 2016, January 2, 2016, and January 3, 2015; (iii) Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2016, and January 2, 2016; (iv) Consolidated Statements of Equity for the twelve months ended December 31, 2016, January 2, 2016, and January 3, 2015; (v) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the twelve months ended December 31, 2016, January 2, 2016, and January 3, 2015; and (vi) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
| 114 | SNAP-ON INCORPORATED |
