Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - Shiner International, Inc. | exhibit31-1.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - Shiner International, Inc. | exhibit32-1.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - Shiner International, Inc. | exhibit31-2.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - Shiner International, Inc. | exhibit32-2.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, DC 20549
FORM 10-K
[X] ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015
[ ] TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from _______________to _______________.
Commission File No. 001-33960
SHINER INTERNATIONAL,
INC.
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in Its Charter)
| Nevada | 98-0507398 |
| (State or Other Jurisdiction of | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| Incorporation or Organization) |
19th Floor, Didu Building, Pearl River Plaza
No. 2
North Longkun Road
Haikou, Hainan Province, China
570125
(Address of Principal Executive Offices, including zip
code)
011-86-898-68581104
(Registrant’s Telephone
Number, Including Area Code)
Securities registered under Section 12(b) of the Exchange Act:
| Common Stock, $0.001 par value | N/A |
| (Title of each class) | (Name of each exchange on which registered) |
Securities registered under Section 12(g) of the Exchange Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes [ ] No [X]
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes [ ] No [X]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes [X] No [ ]
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (Section 229.405) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. [X]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act (check one):
| Large accelerated filer [ ] | Accelerated filer [ ] |
| Non-accelerated filer [ ] | Smaller reporting company [X] |
| (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act).
Yes [ ] No [X]
As of April 6, 2016, there were 27,941,491 shares of the registrant's common stock outstanding.
As of June 30, 2015 (the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter), the aggregate market value of the shares of the registrant’s common stock held by non-affiliates was approximately $6.68 million. Shares of the registrant’s common stock held by each executive officer and director and each by each person who owns 10% or more of the outstanding common stock have been excluded from the calculation in that such persons may be deemed to be affiliates of the registrant. This determination of affiliate status is not necessarily a conclusive determination for other purposes.
Documents Incorporated by Reference
None.

Annual Report on Form 10-K
For the Year
Ended December 31, 2015
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
| PART I | ||
| Item 1. | Business | 5 |
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors | 17 |
| Unresolved Staff Comments | 31 | |
| Item 2. | Properties | 31 |
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings | 32 |
| Item 4. | Submission of Matters to a Vote of Security Holders | 32 |
| PART II | ||
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities | 33 |
| Item 6. | Selected Financial Data | 34 |
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 36 |
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk | 41 |
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | 41 |
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure | 41 |
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures | 41 |
| Item 9B. | Other Information | 42 |
| PART III | ||
| Item 10. | Directors and Executive Officers of the Registrant | 43 |
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation | 46 |
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters | 47 |
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions | 48 |
| Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services | 49 |
| PART IV | ||
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules | 50 |
| SIGNATURES | 55 | |
| EXHIBITS | ||
Special Note Regarding Forward Looking Statements
In addition to historical information, this report contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. We use words such as “believe,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “project,” “target,” “plan,” “optimistic,” “intend,” “aim,” “will” or similar expressions which are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Such statements include, among others, those concerning market and industry segment growth and demand and acceptance of new and existing products; any projections of sales, earnings, revenue, margins or other financial items; any statements of the plans, strategies and objectives of management for future operations; and any statements regarding future economic conditions or performance, as well as all assumptions, expectations, predictions, intentions or beliefs about future events. You are cautioned that any such forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and involve risks and uncertainties, as well as assumptions, which, if they were to ever materialize or prove incorrect, could cause the results of the Company to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. Potential risks and uncertainties include, among other things, the factors discussed in “Risk Factors” included elsewhere is this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Because the factors discussed in this report could cause our actual results or outcomes to differ materially from those expressed in any forward-looking statement made by us or on our behalf, you should not place undue reliance on any such forward-looking statement. Further, any forward-looking statement speaks only as of the date on which it is made, and we undertake no obligation to update any forward-looking statement or statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date on which such statement is made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events, except as required by law. New factors emerge from time to time, and it is not possible for us to predict which will arise. In addition, we cannot assess the impact of each factor on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statement.
Use of Terms
Except as otherwise indicated by the context, all references in this report to:
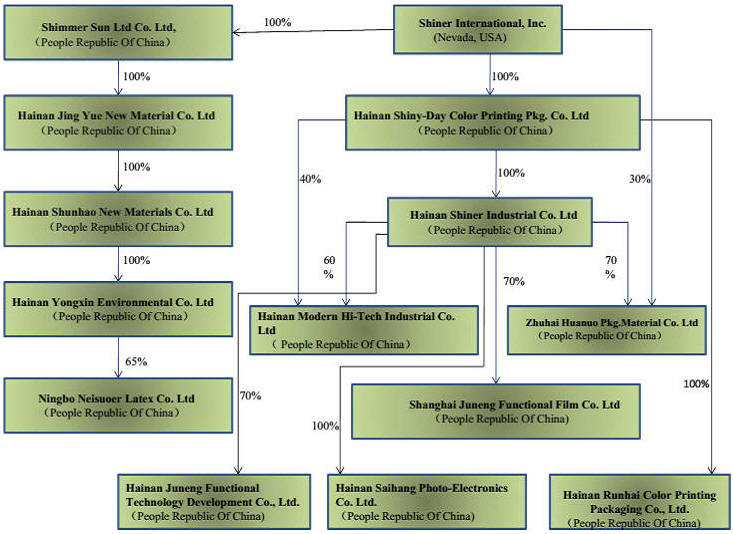
- “Shiner,” “Company,” “we,” “us” or “our” are to Shiner International, Inc., a Nevada corporation, and its direct and indirect subsidiaries: (i) Hainan Shiner Industrial Co., Ltd., or “Hainan Shiner,” (ii) Hainan Shiny-Day Color Printing Packaging Co., Ltd., or “Shiny-Day,” (iii) Hainan Modern Hi-Tech Industrial Co., Ltd., or “Hainan Modern,” (iv) Zhuhai Modern Huanuo Packaging Material Co., Ltd., or “Zhuhai Modern,” (v) Shimmer Sun Ltd., or “Shimmer Sun,” (vi) Hainan Jingyue New Material Co., Ltd., or “Jingyue,” (vii) Hainan Shunhao New Material Co., Ltd., or “Shunhao,” (viii) Hainan Yongxin Environmental Co., Ltd., or “Yongxin,” ,” (ix) Hainan Runhai Color Printing Packaging Co., or “Hainan Runhai,” (x) Hainan Saihang Photoelectric Co. Ltd., or “Hainan Saihang, ” (xi) Hainan Juneng Functional Film Co., or “Hainan Juneng” and (xii) Ningbo Neisuoer Latex Co., Ltd., or “Ningbo.”
- “SEC” are to the United States Securities and Exchange Commission;
- “Securities Act” are to the Securities Act of 1933, as amended; and “Exchange Act” are to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended;
- “RMB” are to Renminbi, the legal currency of China; and “US dollar,” “USD,” and “$” are to the legal currency of the United States; and
- “China,” “Chinese” and “PRC” are to the People’s Republic of China.
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS.
Overview
We were incorporated in Nevada in November 2003, but since July 2007, have been headquartered in Hainan, China. Through our operating subsidiaries, Hainan Shiner, Shiny-Day, Hainan Modern, Zhuhai Modern, Shimmer Sun, and Ningbo we manufacture and sell packaging and anti-counterfeit plastic film to manufacturers and producers in China. We sell anti-counterfeit film, coated film, and color printing, in international markets through a network of distributors and converters.
Our primary business consists of the manufacture and distribution of technology driven advanced packaging film products in five business segments: bi-axially oriented polypropylene, or BOPP, film for wrapping tobacco; water-based latex; coated film; color printed packaging; and advanced film. Our products are sold to customers in the food, tobacco, chemical, medical and pharmaceutical, personal care, electronics, automotive, construction, graphics, music and video publishing industries. Our current production capacity consists of: five coated film lines with a capacity of 15,000 tons a year; two BOPP tobacco film production lines with a capacity of 13,500 tons a year; one BOPP film production line with a capacity of 7,000 tons a year; three color printing lines; four anti-counterfeit film lines with a capacity of 2,500 tons a year; and two water-based latex reaction kettles with a capacity of 3,000 tons a year.
- 4 -
The table below shows the percentage of revenue by each of our business segments for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014:
| Percent of Total Revenue | ||||||
| Product | 2015 | 2014 | ||||
| BOPP tobacco film | 52% | 55% | ||||
| Water-based latex | 1% | 1% | ||||
| Coated film | 35% | 32% | ||||
| Color printed packaging | 5% | 5% | ||||
| Advanced film | 7% | 7% | ||||
| 100% | 100% | |||||
We have 49 patents issued by the State Intellectual Property Office of China. We have another 13 patent applications relating to our products and manufacturing processes pending. Although our patents and processes provide us a competitive advantage, we do not believe the loss of any single patent would have a material adverse effect on our business.
While our primary business consists of the manufacture and distribution of technology driven advanced packaging film products, we have historically advanced minimal funds to customers and other unrelated third parties that are non-interest bearing and payable upon demand. On April 17, 2014, Hainan Shiner, our primary operating subsidiary, drew down entirely on a RMB120 million (approximately $19.5 million) credit facility collateralized by the common stock of Hainan Shiner, our buildings and our land use rights. The facility bears interest at 7.35% per annum and is due and payable on April 17, 2017. Under the terms of the credit facility agreement, the proceeds of the funds borrowed under the credit facility are to be used solely for the construction of an office building and research facility at the Hainan Xiandai Packaging Industrial Park, and for the purchase of research and development equipment. However, on April 30, 2014, we loaned the entire proceeds of the credit facility to unrelated third parties. The business purpose for these loans was for us to make the spread between the amount of interest we pay on the credit facility and the amount of interest we can charge. Such parties have not provided us with significant collateral on such loans, other than a written guarantee from each of the borrowers and an unrelated fourth party. We do not consider this practice of lending money to third parties to be a new business segment as we deem this practice to be temporary. See our disclosures under Liquidity and Capital Resources for more information regarding our lending activities. During the twelve months ended December 31, 2015, approximately $13.1 million of these other receivables were outstanding.
Our principal executive offices are located at 19th Floor, Didu Building, Pearl River Plaza, No. 2 North Longkun Road, Haikou, Hainan Province, China 570125. Our telephone number is +86-898-68581104 and our website is www.shinerinc.com.
Corporate History and Structure
We were incorporated in Nevada on November 12, 2003 as Cartan Holdings Inc. Until July 23, 2007, we were an exploration stage company involved in the search for mineral deposits and owned a 100% undivided right, title and interest in and to the mineral property known as the “Cartan Mineral Claim,” which expired on December 15, 2007.
Acquisition of Shiny-Day
On July 23, 2007, we entered into a Share Exchange Agreement and Plan of Reorganization with Sino Palace Holdings Limited, or “Sino Palace,” a corporation formed under the laws of the BVI. Pursuant to the share exchange agreement, we acquired from Sino Palace all of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Shiny-Day, a PRC company, in exchange for the issuance of an aggregate of 16,500,000 shares of our common stock to the stockholders of Sino Palace. As a result of the acquisition, Shiny-Day and its subsidiaries, Zhuhai Modern and Shiner Industrial became our wholly-owned subsidiaries.
-
Shiny-Day, formed on March 19, 2004 and acquired on July 23, 2007 with a registered capital of $8,000,000, engages in the business of manufacturing and sales of color printing, plastic and rubber type products.
-
Shiner Industrial, formed on May 21, 2003 with a registered capital of RMB100,000 ($15,873), engages in the business of manufacture and sales of plastic film, packaging materials, PVDC latex and PVOH and R&D, manufacture, application and sales of anti-counterfeit film.
- 5 -
- Zhuhai Modern, formed on October 27, 2006 with a registered capital of RMB5,000,000 ($79,365), engages in the business of manufacturing and sales of color printing, plastic and rubber type products, and packaging materials and R&D for flexible packaging materials.
In late 2009, in an effort to improve efficiencies, reduce expenses and take advantage of favorable tax treatment, we consolidated the operations that were previously carried on by three of our subsidiaries – Hainan Shiner, Shiny-Day and Hainan Modern – into Shiner International. Shiny-Day and Hainan Modern are currently inactive subsidiaries of the Company.
Establishment of Shanghai Juneng
On September 20, 2010, we commenced operations of our 70% majority-owned subsidiary, Shanghai Juneng. The remaining 30% minority interest in Shanghai Juneng is held by Shanghai Shifu Material Co., Ltd., an unaffiliated third-party. Shanghai Juneng was formed on July 21, 2010 for the purpose of wholesale and retail sales of plastic film and packaging materials, chemical products, labels and anti-counterfeit film. Shanghai Juneng currently markets and sells food safety packaging products to domestic food producers.
Acquisition of Shimmer Sun
On May 2, 2011, we entered into an equity transfer agreement with Fu Zhiyong, pursuant to which we acquired Shimmer Sun from Fu Zhiyong for an aggregate purchase price of $3.2 million. The Company paid $1.3 million in cash and the remaining $1.9 million was recorded as “other payables” which was paid by September 30, 2011. As a result of the transaction, Shimmer Sun became our wholly-owned subsidiary and its subsidiaries and indirect subsidiaries, Jingyue, Shunhao, Yongxin and Ningbo became our indirect subsidiaries.
-
Jingyue, formed on January 25, 2011 with a registered capital of HK$3,900,000 ($495,237), engages in the sale of plastic film packaging, printing products, anti-counterfeit and packaging materials, water-based latex, and related consulting and technological services.
-
Shunhao, formed on March 15, 2011 with a registered capital of RMB2,500,000 ($396,825) , engages in the sale of plastic film, packaging and printing products, anti-counterfeit and packaging materials, water-based latex, and related consulting and technological services.
-
Yongxin, formed on April 15, 2011 with a registered capital of RMB2,000,000 ($317,460), engages in the sale of water- based latex, plastic film and packaging printing products, and R&D application and sale of anti- counterfeit technology products.
-
The acquisition gave Shiner a 65% controlling interest in Shimmer Sun’s subsidiary, Ningbo. Ningbo, formed on May 8, 2007 with a registered capital of RMB 2,080,000 ($330,158), engages in the manufacture, R&D and processing of PVDC latex series of products and being an import and export agent for latex products and technologies.
In the fourth quarter of 2014, the Company established a new subsidiary, Hainan Juneng Functional Technololgy Development Co., Ltd., through its operating subsidiary, Hainan Shiner. Hainan Juneng is owned 70% by Hainan Shiner and 30% by Hainan Rixin Hotel Management Co., Ltd, an unrelated third party. Hainan was formed to engage in the development, promotion and sale of functional thin film technology but has not conducted any business to date.
The Company also formed Hainan Runhai Color Printing Packaging Co. and Hainan Saihang Photoelectric Co. Ltd., in 2014. Hainan Runhai is a 100% subsidiary of Shiner Industrial and Hainan Saihang is a 100% subsidiary of Hainan Shiny-Day. Hainan Runhai was formed to engage in the development and sale of digital and electronic products but has not conducted any business to date.
The following chart reflects our organizational structure as of the date of this report:
- 6 -
Our Growth Strategy
Our principal business objective is to grow our market share in the flexible packaging film business and continue to expand domestically and internationally by pursuing the following key strategies:
-
Increase our market share by expanding our sales network and customer service. We believe the flexible packaging industry in China has substantial growth potential. In order to penetrate the key markets, we plan to set up a processing factory and warehouse in Shanghai. We plan to attract new customers and increase our market share by increasing our existing sales and marketing activities and strengthening our customer service within and outside of China. We plan to strengthen our customer service network by establishing a global customer service center located in Shanghai.
-
Continue to expand our production capacity with a focus on key geographic markets. We plan to increase our production capacity through potential acquisitions or installation of new production lines, or both, to meet the expected increase in the demand for our products. We foresee industry consolidation and believe we are well positioned to benefit from such a market trend. We believe we are in a position to acquire companies with advanced technology and a good customer base to expand our production capacity.
-
Strengthen our R&D capabilities, expand our product portfolio and improve our production efficiency. In order to maintain our competitiveness, we will continue to strengthen our R&D capabilities through staff training, equipment upgrades and collaborative R&D programs. We will focus our R&D efforts on the expansion of our product portfolio to meet the changing needs of our customers and the growing demands for packaging products. Moreover, we intend to develop technologies that would help us improve production efficiency and product quality while lowering production costs.
- 7 -
-
Strategically explore value-enhancing acquisitions and/or joint ventures to further grow our market share. To date, we have relied on organic expansion to achieve growth. We may strategically explore value-enhancing acquisitions and/or joint ventures to further grow our market share. We may also consider targeted acquisitions or investments where we stand to gain access to additional production capacity or proprietary technology relating to packaging, which we believe may further enhance our current products and services, and expand our position in key markets.
-
Further expand and penetrate selective international markets. We plan to continue our efforts to move beyond the PRC market and establish new sales offices in select markets to grow as a flexible packaging provider in 2012 and beyond. These new sales offices will allow us to maintain closer relationships and contacts with the end users of our products, improving our responsiveness and our ability to gather intelligence and feedback.
Industry Overview and Outlook
PRC Package Industry
We manufacture and distribute advanced packaging film products in China. China’s packaging industry has grown steadily since the mid-1980s with one of the highest growth rates in the international packaging market. Domestic consumption has always been considered by the Chinese government as one of the key drivers for national economic growth. Over the past several years, the Chinese government has released a number of industry policies and measures to encourage domestic consumption that would benefit the packaging industry. In July 2008, the Ministry of Finance of China established a fund to support the development of new and innovative products and technologies for the packaging industry, focusing on environmental protection, energy efficiency and renewable applications. China has been the second largest packaging market in the world since 2008. According to the China Packaging Federation, the Chinese packaging market reached over RMB1.0 trillion (approximately $147.5 billion) in 2009, over RMB1.4 trillion (approximately $216.7 billion) in 2011, and over RMB1.8 trillion (approximately $285.3 billion) in 2012. According to Euromonitor International’s Packaging Industry in China Report in January 2013, the packaging industry became China’s 14th largest industry sector and contributes about 2.7% of the country’s GDP.
Market Trends
With the mild recovery of the global economy, and growing consumer confidence in the Chinese domestic markets, we are cautiously optimistic that consumption of our products will continue to grow. We are experiencing an increase of inquiries from food manufacturers on how to comply with the Food Safety Law that went into effect in 2009. This renewed interest from manufacturers affects our entire breadth of products and we are confident this will lead to an overall improvement in our business. We believe we are well positioned to be the prime beneficiary of increased domestic consumption, a growing world economy, and increased market penetration as the full impact of the Food Safety Law requirements are realized.
We believe there are several positive trends that will continue to accelerate our growth, consumer demand for packaged goods, which offer convenience, quality, aesthetics and lifestyle branding will grow as Chinese consumers find themselves with increasing disposable income and as more purchases are made in supermarkets and away from wet markets and small independent food stores. We are well positioned to take advantage of these trends by providing retail foods and consumer goods manufacturers with beautiful printed flexible packaging.
-
Rapid Economic Growth and Rising Disposable Income. The growth of the flexible packaging industry is highly correlated with economic growth as the demand for packaging products is driven by improving demographic trends, including living standards and urbanization, as well as expanding industrial output. According to China National Bureau of Statistics, China is one of the fastest growing economies, its GDP having grown rapidly with a compound annual growth rate of 16.0% in the past five years. Per capita disposable income of urban households had a compound annual growth rate of 11.8% over the past ten years and per capita disposable income of rural households had a compound annual growth rate of 9.6% during the same period. China’s economy is expected to continue to grow in the next few years with an average GDP growth forecast of 8.4% from 2009 to 2014 by the World Bank.
-
High Growth of the Domestic Consumer Sectors. The main customers of the flexible packaging industry are consumer and industrial goods manufacturers that use corrugated paper cartons for packaging and shipping their products, including food and beverage, daily necessities, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. Catalyzed by the high growth of per capita disposable income and a series of favorable government policies, retail sales of consumer goods in China have grown rapidly and reached RMB18.4 trillion (approximately $2.8 trillion) in 2011, representing a compound annual growth rate (“CAGR”) of 17.1% from 2004, according to China National Bureau of Statistics. The continued robust growth in retail sales of consumer goods has had a significant positive impact on the demand for flexible packaging products.
- 8 -
- Substitution to Other Packaging Materials Due to Environmental Concerns. With environmental concerns becoming an increasingly important topic around the world, the Chinese government is demanding more environmentally friendly properties in packaging materials. Packaging materials are expected to be energy saving, toxic-free, reusable, degradable and multi-functional. Compared to packaging materials made of metal, plastic, wood or glass, flexible packaging film has always been regarded as relatively “greener packaging” due to its lighter weight and degradable qualifies, along with the ease of storage, shipment and processing.
Products
We produce customized, high-quality and competitively priced products used by manufacturers in a variety of applications, including producers of foods such as baked goods, beverages, candy and confections, dairy, fruits/vegetables and nuts, and consumer goods, like pharmaceuticals, tobacco, cosmetics and compact discs. Our packaging provides protection from tampering and contamination and preserves the texture, flavor and integrity of perishable items. In addition, we provide printing services for a variety of consumer products. Packaged goods require different porosity levels for humidity, gases, as well as fragrance and heat resistance barriers depending on whether the item is edible or a non-food product.
Flexible Packaging Material
We primarily use biaxially-oriented polypropylene (“BOPP”) as the base film from which more sophisticated films, such as advanced, coated and tobacco films are produced. There are multiple manufacturers of BOPP film in China qualified to meet international standards. BOPP refers to the manufacture of polypropylene films using an orienting system. BOPP is manufactured by three different processes, with resulting films having different properties. BOPP films are widely used in printing, lamination and over-wrap packaging. The main benefits of BOPP films are its stiffness, durability, high tensile strength and clear optics. The film is lightweight, non-toxic, odorless, transparent, glossy, temperature and moisture-resistant, and retains high barrier resistance, making it suitable for many forms of flexible packaging, printing, laminating, and other applications. We sell our products to packaging customers and distributors in China and throughout Asia, and have been expanding out international business in the Middle East, Australia, North America and Europe.
Upon request of our customers we may use different base films to create products customized to our customers’ needs. The base films include: biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate (“BoPET”), a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate (“PET”) that is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity and gas and aroma barrier properties; and biaxially-oriented polyamide film (“BOPA”), a nylon film used for its high tensile strength, high flex-/stress-crack and puncture resistance, barrier to gases, flavors and odors and high resistance to oil, greases, hydrocarbons and chemicals. Each base film can undergo one of three different processes to create films with different properties. A sequential or double bubble process is used for coating the films, in which a base film, generally a BOPP, BoPET or BOPA film is coated with a water-based latex compound. That compound is usually acrylic, Polyvinylidene Chloride (“PVDC”) or polyvinyl alcohol (“PVOH”), which enhance the moisture and oxygen barrier properties of the film while retaining its functionality. Films can be single or double coated with co-extruded structures, in transparent, opaque, or metalized varieties. In the metalized variety, the base film is usually coated with aluminum foil, which gives the film stronger insulation and anti-pressure properties.
Coated film is a functional packaging film in which a thin layer of polyolefin-based film is sealed either on one or both sides of the film with a varying type of chemical substance (coating layer). Depending on which coating layer is used, coated films have greater endurance and tensile strength and can be produced in heat-resistant, shrink-wrapped, peelable or other varieties. Coated film is a functional packaging film with moisture and oxygen barrier property, flavor and aroma preservation properties, as well as their superior clarity and printability. We currently produce 17 varieties of regular coated packaging films and can produce irregular coated packaging films according to the requirements of customers. As a result of these capabilities and our technology, we believe we provide the most diverse film product offering in China.
BOPP tobacco film is a box over-wrap film designed to meet the industry requirements for packaging appearance, product freshness and clear optics.
We provide color printing services that consist of surface printing and reverse printing services used mainly by consumer goods manufacturers and beverage companies. We provide printing services to our clients in our effort to provide value-added services and a one-stop-shop experience. Our printing capabilities span a range of products, such as food, drugs, cosmetics and chemicals. We use alcohol-soluble, benzene free printing ink to meet international environmental and safety standards.
- 9 -
Advanced Film
Advanced film is a specialty product derived from BOPP film and embossed with an advanced technology, multi-dimensional insignia that creates eye-catching images and makes it easier for user’s to increase brand identity. We use proprietary technology to develop specialized advanced film products. Losses from piracy and counterfeiting affect a wide number of industries including: music and video publishing, food, medicine, cosmetics, cigarettes and liquor. Advanced film is generally used in the packaging of high-end cigarettes, DVDs and other frequently imitated or pirated products.
Manufacturing
Our production facilities for packaging film are located in Haikou, Hainan Province in the PRC and our water-based latex production facilities are located in Ningbo, Zhejiang Province. Our production facilities are more fully discussed in Item 2, “Properties.”
Our products have been ISO9001:2000 accredited since 2003. We believe stringent quality control standards are crucial to our success and the continuous growth of our business. In order to maintain such standards, we conduct inspection at all stages during the production process. In that regard, we have adopted a quality management system covering the sourcing of raw materials, each stage of production, the delivery of final products, and post-sales quality control. We also provide employees with continuous training in order to help reduce the frequency of repeated errors. Below chart is our production process.
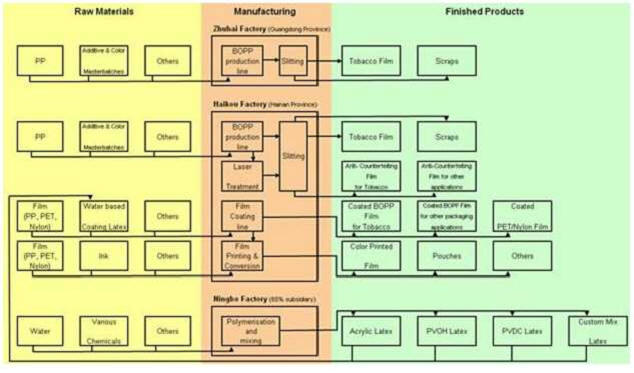
Our current production capacity consists of:
- five coated film lines with a total capacity of 15,000 tons a year;
- one BOPP tobacco film production line with a total capacity of 3,500 tons a year;
- one BOPP film production line with a total capacity of 10,000 tons a year;
- three color printing lines;
- four advanced film lines with a total capacity of 2,500 tons a year; and
- Two water-based latex reaction kettles with a total capacity of 3,000 tons a year.
Awards and Certifications
Our subsidiary, Shiner Industrial, has received the following awards and certificates, each of which, we believe, is an indication of our achievements, the quality of our products and makes us more attractive to potential customers and therefore a more competitive company both in the local and international markets:
- 10 -
| Date | Award/Certificate | Issuing Authority |
| November 2003 (1) | ISO 9001:2000 Certificate | China Certification Center for Quality Mark |
| September 2007 | Key High-Tech Enterprise of the National Torch Program | Ministry of Science and Technology |
| January 2010 | Awarded as one of the Top Ten Leading Enterprises in China food packaging industry | CNTV.COM, the website for China Network Television |
| December 2010 | Designated as “Advanced Enterprise of Chinese Plastic Industry” | China Packaging Federation |
| December 2010 | 2010 China Packaging Brand Excellence Award | China Packaging Federation |
| December 2010 | Key High-Tech Enterprise of the National Torch Program | Ministry of Science and Technology |
| May 2011 | Packaging Film Public R&D Platform | Hainan Provincial Department of Commerce |
| July 2011 | Hainan independent innovation excellent research and development team | Hainan Industry and Information Department |
| September 2011 | High and New Technology Enterprise Certificate | Provincial Science and Technology Department |
| November 2013 | National & Local Joint Engineering Research Center of Functional Film Technology | State Development and Reform Commission |
| November 2013 | The First List of national Intellectual Property demonstration enterprise | National Bureau of Intellectual Property |
| November 2013 | Science and Technical advanced unit for 2013 | National Bureau of Intellectual Property |
| (1) |
ISO 9000 certification has become an international reference for quality management requirements in business-to-business dealings. This certification enables us to compete on many more markets around the world and provides our customers with assurances about our quality, safety and reliability. |
Sales and Marketing
Our sales and marketing strategy focuses on establishing and maintaining a reputation for consistent and stable production of innovative high quality packaging film at competitive prices, providing dependable and efficient customer support services, and building stable and enduring relationships with our customers.
We sell our packaging film and services to dozens of food, beverage, and consumer goods manufacturers throughout the world, with a focus on the PRC market. Our customers are located in 20 provinces, three municipalities and three autonomous regions in the PRC. Our sales group is divided into two teams, a domestic sales team focusing on the PRC market and an international sales team focusing on the European, North American, Southeast Asian, Australasian and Middle Eastern markets. We currently have 30 full time sales representatives servicing our domestic and international customers. The majority of our sales professionals are university graduates and 10 of them have more than 10 years industry experience. We seek to expand our market share in the European and North American markets that we believe possess growth potential. Our domestic sales team is divided into five major sales regions in the PRC based on the location of our customers - Guangdong and Guangxi, Northwest China, Southwest China, Northeast China and Eastern China.
Our sales representatives maintain regular contact with customers to track product performance to ensure customer satisfaction. They are responsible for handling inquiries, processing and allocating orders to our production team, confirming orders and product specifications from customers, and providing after-sales services such as gathering market information and conducting surveys. In addition, these sales personnel are also responsible for handling ad hoc product inquiries and for cultivating relationships with potential new customers. Through regular contact with our customers, we are able to ascertain the current and future demand for existing products and the potential demand for new products.
In the international market, our sales team has adopted a strategic regional sales and marketing system and established an extensive sales and marketing network throughout North America, Europe and Southeast Asia. We have entered into preliminary letters of intent with potential representatives and agents in Southeast Asia, Europe, and the United States in relation to marketing and distribution of our products.
- 11 -
We have refocused our marketing and sales strategy to match our customer focused business strategy. Our marketing activities are geared towards supporting the activities of our sales team by keeping abreast of industry trends, interacting with existing customers, cultivating new relationships and building brand awareness. By visiting our customers in the PRC regularly and nurturing close relationships it enables us to identify market trends, understand customers’ evolving needs, adjust and manage our production processes and proactively resolve customers’ issues and concerns. These regular contacts, visits, and interviews allow us to gain insight into the latest market trends and to capture business opportunities ahead of our competitors. We also distribute marketing materials we produce from time to time to our customers in person during such visits or otherwise by email or mail. Because of the attractive location of our plant and facilities in Haikou on Hainan Island, generally known as the “Hawaii” of China, we frequently invite potential customers to visit and inspect our operations first-hand and we also host many of the annual tobacco and other large industry management conventions.
We participate regularly in industry exhibitions and international trade fairs held in the PRC and internationally. To attract new customers and to maintain brand awareness in the industry, we regularly advertise our Company and products in industry magazines and on our own website. Members of our senior management team are frequent speakers at industry events and also give interviews to industry magazines from time to time to raise our profile.
Raw Materials and Suppliers
Major raw materials required in the manufacturing processes for our packaging products include petroleum-based resins and mixing chemicals, which are primarily supplied to us by large chemical companies. For these raw materials, we generally maintain purchase contracts for a period of up to six months. However, for many other materials, we can generally choose from multiple producers and such orders are placed on an “as-needed” monthly basis.
As all BOPP film is petroleum based, the effects of any short-term fluctuations in the price of oil will be averaged into the earnings over the period due to the cyclical nature of production, inventory and sales. Any long-term increases in the price of oil will have an adverse impact on our earnings. However, as there are currently no synthetics or substitute materials available in the market, management believes that any long-term increase in the price of oil will be made up for by an increase in sale prices by all film producers.
The base materials for many of Shiner Industrial’s products are derived from petroleum. Approximately 34% of the raw materials for Hainan Shiner’s BOPP tobacco film operation are imported from multi-national chemical companies such as Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd. In contrast, only about 4% of the raw materials for our coated films are imported because the current base BOPP film can be supplied through qualified domestic suppliers in China. All of the raw materials for our color printing operations are purchased domestically in China. There are numerous suppliers for these raw materials. We generally select a supplier based on the best combination of quality, price and service. There are no raw materials used in our color printing production process that are provided by any sole supplier.
BOPP is a major raw material for our flexible packaging films; our new BOPP film line produces sufficient basic BOPP film to satisfy our coated film production needs.
In general, we do not have long term contracts with our suppliers. We maintain relationships with two to three approved suppliers for each raw material purchased and generally experience no delay in meeting our production needs on a timely basis. Currently, raw materials are readily available and we expect to continue to successfully manage raw material supplies without significant supply interruptions. Our largest suppliers accounted for more than 12% of raw material purchases in 2015.
Customers
Our customers are composed mainly of consumer products manufacturers, distributors, printers and packaging industry distributers. About 80% of our customers are in China, with the remainder in Southeast Asia, Europe and North America. While most of our products are sold in the international market, our color printing business mainly serves customers in China who are looking for one-stop service to fulfill their printing and packaging needs by a single vendor.
- 12 -
Flexible Packaging Material
We are the leading producer of coated film in China, with approximately 30% market share of the Chinese domestic coated film output in 2015. Our domestic competitors exist only in the form of smaller rivals with an average annual capacity of several hundred metric tons. Approximately 70% of our sales are made directly to customers and the remaining 30% of our sales are made through domestic distributors servicing one-off, small-scale packaging operations. We believe we are the leading producer of coated films nationally, and enjoy a reputation both for first-rate quality and service. We maintain contracts with our larger customers generally for periods ranging from six months to one year. Smaller customers, those that constitute less than 2% of our overall sales are subject to pre-payment on all orders.
During 2015, our top 10 customers accounted for approximately 93% of our total international coated film sales, with an average sale of $680,000 per customer. Approximately 72% of our exported coated film is sold to printing and packaging companies located in Australia with the remainder sold to companies located in the United States, Europe, New Zealand and Turkey. Approximately 28% of our exported coated film sales are made to the “converter” industry, which represents mass packaging operations mainly in Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe that serve as packaging hubs for products sold in the US and European markets. Rolls of finished coated film are sent to the converters where they print, cut, fold, and insert re-sealable zips to form pouches for items such as dried fruits, nuts, beverages and dairy products like cheese and yogurt. Our largest international customer, Impak Films Pty. Ltd., an Australian packaging distributor, accounted for approximately 11% of our coated film sales and 4% of our total sales in 2015.
As tobacco remains one of the state-controlled industries in China, all of our domestic BOPP tobacco film sales are made to provincial cigarette manufacturers who can buy only from pre-approved domestic manufacturers meeting the quality and technical specifications as well as the standard price requirements of the Chinese government. We currently sell our BOPP tobacco film to 28 of 32 provincial cigarette manufacturers (representing approximately 70% of this market) and have contracts to sell over 5,000 metric tons of film per year to the state owned cigarette company of China.
The main customers of our color printing business are brand-name food and commodity companies in China that have strict requirements for quality and service. We believe our customers are also attracted to the one-stop service that we offer by fulfilling both their packaging film and printing requirements. Our largest customer, Chun Guang Foodstuff Co., Ltd., accounted for 40% of color printing sales in 2015.
Advanced Film
We introduced advanced film products in 2005 as a superior alternative to the industry’s hologram printed films.Our largest customer in the international market is Vietnam Tobacco Imports and Exports Co., or “Vintaba”, the tobacco production company of the Government of Vietnam. Vintaba accounted for approximately 54% of our advanced produce sales. A majority of our customers are brand name producers seeking to protect copyrights and reduce the occurrence of pirated product. According to the American Film Institute, the Chinese film market suffers a loss of $2.7 billion each year due to piracy, including the annual loss of $1.6 billion from piracy of CDs and DVDs.
At the Sixth Global Congress to Combat Counterfeiting & Piracy in February 2011, International Chamber of Commerce Secretary General Jean-Guy Carrier reported that “the total impact of illicit trade in “fakes” is staggering, with more than $1.0 trillion in annual losses to global economies, governments and consumers and potentially more than two million jobs at risk.” Reports from the Congress showed that the trade of counterfeit cigarettes currently accounts for 6% of the global tobacco trading and manufacturing and selling counterfeit cigarettes in the global market has reached approximately 150 billion units per year. According to new research of the Business Software Alliance, the percentage of counterfeit software in the global market increased to 45% in 2013 from 41% in 2008, resulting in more than $55 billion in losses to the industry.
Research and Development
We highly value our strong R&D support team. Our R&D team includes 28 engineers and technicians with each person holding a Bachelor’s or other advanced degree, and most of whom have direct or related field experience. Our R&D team strives to improve our production process, product quality and product compatibility to reinforce our competitive advantage in the market. In particular, our R&D efforts are focused on: (i) identifying processes that improve our cost-efficiency and our customers’ production efficiency; (ii) identifying alternative production materials to generate comparable performance at a lower cost to our customers.
Our R&D team is the first point of contact for customers in the event of quality related concerns and assists customers with identifying and resolving problems, offering effective and efficient solutions and facilitating discussion with our production team. Our R&D team has a long track record of experience in the flexible packaging industry and is capable of translating customer requests into solutions.
- 13 -
We built Hainan Film Engineering Center in Haikou, which has four well-equipped professional laboratories. In addition, we also set up R&D centers in both of our Hainan and Zhuhai locations. Our engineers have designed two of our coated film production lines. By designing our own production lines, we intend to reduce our fixed asset investment by approximately 35% and better meet our specific manufacturing needs. The director of our research department has over 15 years’ experience in the industry.
During 2015 and 2014, we spent approximately $2.6 million and $3.2 million respectively, on R&D projects with the majority expended on new product trials and experimental manufacturing techniques, including fog prevention and high heat shrinkable films.
In 2015, we spent approximately $1.6 million in the development of functional coatings of coated films and functional BOPP film. Functional coatings and film are designed to meet certain functional requirements of our customers and market, such as improved sealing and barrier properties. All R&D costs are funded through our operating cash flow and are expensed as incurred.
In addition to in-house R&D, we have sponsored several projects with research institutions and universities in China to which we retain all proprietary rights for the research funded by us. We also have a formal agreement with China’s Science & Technology University, Hainan University and Hainan Normal University through 2015 for which we have proprietary rights to all findings based upon dedicated research conducted on our behalf. We also have informal alliances with Fudan University in Shanghai, Sun Yat Sen University (Zhong Shan) in Guangzhou and Tsinghua University in Beijing.
Intellectual Property
We hold 49 patents on both products and production equipment that have been issued by the State Intellectual Property Office of China.
| Name of Patents | Patent No. | Issue Date | ||||
| Acrylic Acid Coated Film & Its Manufacturing Methods | ZL2005100777111.3 | Jan 31,2007 | ||||
| Two way stretched polypropylene film substrate with no bottom glue coating and Non bottom adhesive coating film | US 9068097 | Jun 30,2015 | ||||
| BOPP Shrinkable Monofilm & Its Manufacturing Methods | ZL03149870.1 | Nov 15,2006 | ||||
| Production System of Microwave Drying Coated Film | ZL03149871.X | March 22,2006 | ||||
| A Kind of Low heat-seal Coated Film | ZL2012205042172 | Mar 27,2013 | ||||
| A Kind of Transparent Coated Film apply to Sandwich Packing | ZL2012205041856 | Mar 27,2013 | ||||
| A kind of low temp. sealing high barrier coated film for heat sensitive food packing | ZL2012205041822 | Mar 27,2013 | ||||
| A kind of high barrier laminated film for air fresher packing | ZL201220471388.X | Mar 4,2013 | ||||
| A kind of Biax-oriented fringed BOPP | ZL201220459128.0 | Mar 12,2013 | ||||
| A kind of non primer coated film and its manufacturing method | ZL201010177656.2 | Apr 3,2013 | ||||
| A Kind of laminated Coated Film for ketchup bag packing | ZL2013200765856 | Jul 24,2013 | ||||
| A kind of heat sealable PVDC coated film manufacturing method | ZL201110119077.7 | Aug 21,2013 | ||||
| A Kind of Coated Film& Its Manufacturing Methods | ZL200510075370.2 | May 16,2007 | ||||
| BOPP Shrinkable Tobacco film & Its Manufacturing Methods | ZL01118669.0 | May 14, 2008 | ||||
| Manufacturing Methods for Heat Shrinkable Coated Films | ZL031498728 | March 27, 2009 | ||||
| A Kind of Heat-sealed BOPP Film | ZL200810177464.4 | March 24, 2010 | ||||
| Ultrathin biaxial stretching polypropylene film for rolling paper packaging & Its Manufacturing Methods | ZL201310033169.2 | May 6,2015 | ||||
| A Modified PVOH Coated Film for Print & Its Manufacturing Methods | ZL201010208100.5 | January 11, 2012 | ||||
| Methods for Producing Coated Film | US8007873B2 | August 30, 2011 | ||||
| A Kind of Ultraviolet-proof Coated Film Manufacturing Methods | ZL201010210692.4 | Jul 25,2012 | ||||
| A Kind of No Base Coated Film Manufacturing Methods | ZL200910215431.9 | Oct 10,2012 | ||||
| A kind of new film structure for fresh meat packing | ZL2013200925821 | Sep 25,2013 | ||||
| A vapor barrier type polyvinylidene chloride coated film manufacturing method | ZL201110119076.2 | Apr 09,2014 | ||||
| A plastic film coated with acrylic polyurethane rubber manufacturing method | ZL201210361249.6 | Apr 30,2014 | ||||
| A low shrinkage temperature of polyolefin heat shrinkable film and its manufacturing method | ZL201210570489.7 | Oct 01,2014 | ||||
| A kind of used for flour packaging composite membrane | ZL201420014511.4 | Oct 01,2014 | ||||
| Self-adhesive polyvinylidene chloride emulsion bottomless glue coating method and the implementation of the method of coating system | ZL201210572943.2 | Nov 26,2014 | ||||
| Chocolate thermal food coating film coating method and the implementation of the method of coating systems | ZL201210572302.7 | Jan 21, 2015 | ||||
| A low friction two-way stretch polypropylene heat sealing membrane and its manufacturing method | ZL201210569786.X | Feb 18, 2015 |
- 14 -
| Two-way stretch large size of polypropylene high shrinkable film cutting and winding process | ZL201210570488.2 | Feb 18, 2015 | ||||
| A high gloss two-way stretch polypropylene heat sealing membrane and its manufacturing method | ZL201210571747.3 | Jan 26, 2015 | ||||
| A holographic mould shrinkage film and its manufacturing method | ZL201210294383.9 | Jan 28,2015 | ||||
| A system used for double coating membrane flip | ZL201210572050.8 | Feb 04,2015 | ||||
| A plastic tag and its manufacturing method | ZL201310237880X | Feb 05,2015 | ||||
| A betelnut packaging composite membrane and its preparation method | ZL201310184488.3 | Feb 12,2015 | ||||
| A high resistance oxygen cooking polyvinylidene chloride resistant coating film and its manufacturing method | ZL201210294409.X | Mar 05,2015 | ||||
| A PET laser transfer film without slab joint and its preparation method | ZL201310254466.X | Mar 10,2015 | ||||
| A two-way stretch polypropylene heat sealing membrane and its manufacturing method | ZL201210570487.8 | Mar 12,2015 | ||||
| A kind of cigarette packing two-way stretch polypropylene shrinkable film and its manufacturing method and application | ZL201210570229.X | Mar 24,2015 | ||||
| A kind of Low temperature heat sealing high barrier coating film & Its Manufacturing Methods | ZL201210294382.4 | May 20,2015 | ||||
| Coating method for coating film of double coated PVDC emulsion in accordance with sandwich food package and Coating system | ZL201210572944.7 | Jun 6,2015 | ||||
| A kind of Method for producing bactericidal poly offset two vinyl chloride coating film | ZL201210294385.8 | Jun 24,2015 | ||||
| a kind of Polyolefin thermal shrinkage film with high shrinkage rate & Its Manufacturing Methods | ZL201210570571X | Jul 15,2015 | ||||
| A kind of Post curing method of polyvinyl alcohol coating film | ZL201210571976.5 | Oct 28,2015 | ||||
| A kind of Composite film for flour packaging & Its Manufacturing Methods | ZL201410011003.5 | Oct 28,2015 | ||||
| A kind of Latex feeding method in latex coating process for coating film and charging device | ZL201210571978.4 | Oct 28,2015 | ||||
| The recovery method of PVDC coating film | ZL201210571977X | Oct 28,2015 | ||||
| A kind of Bidirectional stretching polypropylene common cigarette packaging film & Its Manufacturing Methods | ZL201210570455.8 | Nov 18,2015 | ||||
| A kind of Cooking and cooking poly partial two vinyl chloride coating film & Its Manufacturing Methods | ZL201110202562.0 | Dec 16,2015 |
We have additional products and production equipment for which 50 patent applications are currently pending. Our current patents expire between 2015 and 2030. We also have two trademarks issued by the State Intellectual Property Office of China.
Employees
We have a centralized labor management system for our operating subsidiaries. Labor and employment affairs of each subsidiary are managed by our central human resources department. Currently, we have 393 full-time, and no part-time employees. The following table sets forth the number of our employees by function.
| Number of | |||
| Department | Employees | ||
| Executives | 15 | ||
| R&D | 28 | ||
| Human Resources | 4 | ||
| Manufacturing | 298 | ||
| Finance | 20 | ||
| Marketing & Sales | 25 | ||
| Other | 3 | ||
| Total | 393 |
Each employee must enter into multiple employment contracts, including a non-competition agreement, which are then filed with the municipal government. All employees receive a base monthly salary. Executive employees are also entitled to a year-end bonus based upon our overall performance results, seniority and individual performance and contribution to the Company. Production employees are entitled to a monthly bonus calculated on the basis of the quality of the products produced, and their respective contribution to volume, safe production, correct use of equipment and energy saving. Our production employees are not subject to collective bargaining agreements. However, we maintain a satisfactory working relationship with our employees, and we have not experienced any significant labor disputes or any difficulty in recruiting staff for our operations.
- 15 -
Our employees in China participate in a state pension plan mandated by Chinese municipal and provincial governments. Benefits include social security, pension benefits, and medical insurance. The Company contributes approximately 37% of annual salaries to the pension plan on behalf of all qualified employees.
We believe that we are in material compliance with relevant PRC labor laws.
Regulation
The Food Safety Law of the PRC, or the “Food Safety Law,” was enacted on February 28, 2009 by the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress and became effective on June 1, 2009. The Implementation Regulations of the Food Safety Law, or the “Implementation Regulations,” were subsequently promulgated on July 20, 2009 and were immediately effective.
Pursuant to the Food Safety Law and its Implementation Regulations, the Chinese government regulates food manufacturers (producers and processors) and operators (distributors and caterers), as well as manufacturers of (i) food additives, (ii) packaging materials, containers, detergents and disinfectants used with food and (iii) tools and equipment used in production and processing of food. Under this law, manufacturers who are engaged in the production of food, food additives and food related products must comply with applicable food safety standards and must satisfy inspection and approval procedures with regard to their products before sending them into the market. In addition, food manufacturers are required to check business permits and product qualification certificates of their suppliers from whom they purchase food materials, additives and related products and to inspect such products to ensure that they conform to applicable food safety standards. Any violation of the Food Safety Law and its Implementation Regulations may result in legal liabilities, such as warnings, fines, damages, or even in criminal liabilities for serious violations.
Shiner has been appointed a “Standards Creator” in Coated Film by the Standardization Administration of the PRC. As such, Shiner has been working closely with various government agencies to assist the regulatory authorities in drafting new packaging guidelines that that will help ensure a safe food supply as outlined in the Food Safety Law. It is our belief that large domestic Chinese food manufacturers will utilize coated film packaging to meet the requirements detailed in the Food Safety Law standards.
Additionally, our products are subject to regulation by agencies of the provincial government of Haikou responsible for food packaging and hygiene and the regulatory schemes of international governmental authorities governing the food safety, quality and hygiene of our customers. The safety, quality and hygiene requirements of many of our customers, especially those located internationally, exceed government requirements in China. Our PVDC and all coated films have already met FDA requirements, as well as the requirements for food products packaging sold in the European Economic Community, or the “EEC.”
Business registrations, our production processes, and certain products are certified on a regular basis and must be in compliance with the laws, rules and regulations of various governments and industry agencies. Our subsidiaries have been assessed and certified as meeting the requirements of ISO 9001:2000 for designing and manufacturing BOPP films, PVDC coated film, BOPP laser holographic advanced film for packaging by the SGS Group.
We are also subject to China’s National Environmental Protection Law as well as a number of other national and local laws and regulations regarding pollutant discharge for air, water and noise pollution. We believe we are in compliance with such laws and regulations.
In each of 2015 and 2014, we incurred expenses of approximately $15,000 to comply with governmental and environmental regulations in China.
Competition
We believe our expertise in manufacturing specialty films provides us a distinct advantage over competitors in China, most of whom are focused mainly on commodity films, such as BOPP, BoPET, PVC and BOPA. We are the leading producer of coated films in China with limited domestic competition only in the form of smaller rivals with an average annual capacity of several hundred metric tons. Internationally, we face competition from industry leaders such as DuPont Energy Co., Innovia Films Ltd. and Exxon Mobil Corporation. Each of these corporations has much larger production capacity than us and has a strong reputation as they have significant experience in the coated films market.
- 16 -
As tobacco remains a state-owned and operated industry in China, the government buys only from approved PRC domestic vendors and competition exists only in the form of other domestic film companies. In addition, each province is required to maintain two to three suppliers. Thus, competition among qualified players is limited. In the domestic market there are several qualified large producers including: Jiangsu Zhongda New Material Group Co., Ltd., Foshan Plastics Group Co., Ltd, Zhanjiang Packaging Enterprises Ltd., Yunnan Kunlene Film Industries Co., Ltd., Yunnan Hongta Plastics Co., Ltd., Hubei Firsta Packaging Co., Ltd. As we have attained certification as a government supplier, a certain level of annual sales is guaranteed to us from the government of China. In the international market, we face competition from large multi-nationals as well as Southeast Asian and Japanese firms. We believe we have a price advantage over our Western competitors due to our lower production costs.
Our advanced film is unique; as such we do not have a direct competitor for this product. However, established international producers such as Applied Extrusion Technologies, Inc. and Innovia Films Ltd. do produce their own advanced films based mainly on printed holograms, which are relatively simple to duplicate. Rather than direct competition, we are focusing on marketing efforts on awareness and educating buyers as to the superior quality of our products over these hologram-based counterfeit films.
We are the largest color printing service provider in Hainan province and rank approximately 20th in the overall Chinese market. Due to low operating costs, the printing industry is highly fragmented with approximately 4,000 soft packaging and printing companies in China. As a result, competition in China is fierce and industry margins are low. Accordingly, we maintain our printing services mainly as a convenience for current film customers who are more concerned with quality, service, and one-stop printing and packaging service than with price.
The primary barriers to enter the market include obtaining a printing license and significant capital investment in large-scale production facilities. We believe our competitive advantages over domestic players are better cost-efficiencies due to economies of scale and significant order volumes, long standing relationships with customers, advanced technologies and equipment deployed in our manufacturing process, high product quality with competitive cost structure and a well-known brand name. Our competitive advantages over international players include significant production capacity, a large existing customer base, the flexibility to customize our products, better local knowledge and connections in the PRC, lower price resulting from our lower cost structure and competitive product quality.
Competitive Strengths
We believe we are able to effectively compete in both the domestic Chinese and international markets by means of proven quality, cost advantages and a service team that supports our customers before, during and after the sale process in order to build long-term customer relationships. Our customer-oriented perspective permeates each business unit and is largely responsible for our ability to penetrate new markets and successfully build on sales to new customers.
-
Established long-term relationships with reputable customers in diversified end markets. We have established an extensive customer base in a wide variety of industries, including food, beverage, cigarette, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and other consumer and industrial goods. We believe this wide range of end markets reflects the strength of our experience and reputation as a qualified flexible packaging and advanced film producer, as well as the broad range of available markets for our products. Many of our customers are PRC’s Top 500 enterprises, and we believe we are well positioned to benefit from our established customer relationships.
-
Ability to provide customized products and solutions. As part of our differentiation strategy, we work closely with customers to understand and design innovative products based on our ability to formulate different blends of resins and additives to produce film with specific properties for our customers based on their unique requirements. This strategic advantage is difficult for our competitors to duplicate given the technological and manufacturing flexibility that it demands. As a result of our diverse, high quality product offering, we have been able to increase pricing of our certain coated film products.
-
One-stop service. We are able save customers both lead-time and costs by providing one-stop service in which we not only sell the film but also develop the production processes that produce the end packaging product.
-
Advanced production facilities and stringent quality control. We continually invest in our production capabilities and furnish our facilities with advanced equipment. Our products have been ISO9001:2000 accredited since 2003. We believe stringent quality control standards are crucial to our success and the continuous growth of our business. In order to maintain such standards, we conduct inspection at all stages during the production process. In that regard, we have adopted a quality management system covering the sourcing of raw materials, each stage of production, the delivery of final products, and post-sales quality control. We also provide employees with continuous training in order to help reduce the frequency of repeated errors.
- 17 -
- Strong R&D capabilities. We have an experienced R&D team of 22 professionals. The team has successfully developed new products and technologies, which have led to 16 patents and 10 pending patent applications. We also work with reputable academic and research institutions to undertake specific R&D projects. In 2006, we entered into a five-year research agreement with China’s Science & Technology University. Under the terms of this agreement, six professors, all holding advanced degrees, work in conjunction with our R&D team. Shiner owns the proprietary rights to all findings to dedicated research projects which are undertaken at our request. We pay the university estimated fees of $12,850 annually under this agreement. This agreement was renewed in 2010 for an additional five years under the same terms.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS.
An investment in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider the risks described below, together with all of the other information included in this report, before making an investment decision. If any of the following risks actually occurs, our business, financial condition or results of operations could suffer. In that case, the trading price of our common stock could decline, and you may lose all or part of your investment. You should read the section entitled “Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” above for a discussion of what types of statements are forward-looking statements, as well as the significance of such statements in the context of this report.
RISKS RELATED TO OUR BUSINESS
We could lose control of Hainan Shiner, our primary operating subsidiary, if we are unable to repay our loan or if we are unable to obtain a waiver for unsanctioned use of proceeds as a result of our temporary lending operations.
On April 17, 2014, Hainan Shiner, our primary operating subsidiary, drew down entirely on a RMB120 million (approximately $19.5 million) credit facility collateralized by the common stock of Hainan Shiner, our buildings and our land use rights. The facility bears interest at 7.35% per annum and is due and payable on April 17, 2017. Under the terms of the credit facility agreement, the proceeds of the funds borrowed under the credit facility are to be used solely for the construction of an office building and research facility at the Hainan Xiandai Packaging Industrial Park, and for the purchase of research and development equipment. However, on April 30, 2014, we loaned the entire proceeds of the credit facility to unrelated third parties as set forth below. Such parties have not provided us with significant collateral on such loans, other than a written guarantee from each of the borrowers and an unrelated fourth party. The use of the proceeds from the credit facility to provide such loans constitutes a breach under the credit facility agreement. Unless and until we obtain a waiver from the lender for such use of proceeds, the lender has the right to declare a breach of the trust agreement and enforce its right to ownership of the stock, buildings and land use rights of Hainan Shiner, our primary operating subsidiary. Furthermore, if any of the borrowers are unable to fulfill their obligations under our loans to them and their guarantees fail, we will be obligated to repay the credit facility in its entirety. If we are unable to repay this debt in full by the due date we could lose control of Hainan Shiner, our buildings and our land use rights. For more information regarding such third party loans see Note 3 to our financial statements.
We cannot be certain that our product innovations and marketing successes will continue.
We believe our past performance has been based on, and our future success will depend upon, in part, our ability to continue to improve our existing products through product innovation and to develop, market and produce new products. We cannot assure you that we will be successful in the introduction, marketing and production of new products or product innovations, or that we will develop and introduce in a timely manner innovations to our existing products which satisfy customer needs or achieve market acceptance. Although we have developed products that have met customers’ requirements in the past, there is no assurance that any of our R&D efforts will necessarily lead to any new or enhanced products or generate sufficient market share to justify commercialization. We must continually improve our current products and develop and introduce new or enhanced products that address the requirements of our customers and are competitive in terms of functionality, performance, quality and price in order to maintain and increase our market share. If our new products are unable to gain market acceptance, we would be forced to write-off the related inventory and would not be able to generate future revenue from our investment in R&D. In such event, we would be unable to increase our market share and achieve and sustain profitability. Our failure to develop new products and introduce them successfully and in a timely manner could harm our ability to grow our business and could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Our advanced technology may not satisfy the changing needs of our customers.
- 18 -
With any advanced product authentication technology, including the technology of our current and proposed products, there are risks that the technology may not successfully address all of our customers’ needs. While we have already established successful relationships with Chinese customers with regard to our products, our customers’ ultimate needs may change or vary, thus introducing variables which may affect the ability of our proposed products to address all of our customers’ ultimate technology needs in an economically feasible manner.
Our growth strategy and future success depends upon commercial acceptance of products incorporating technologies we have developed and are continuing to develop. Technological trends have had and will continue to have a significant impact on our business. Our results of operations and ability to remain competitive are largely based upon our ability to accurately anticipate customer and market requirements. Our success in developing, introducing and selling new and enhanced products depends upon a variety of factors, including:
- accurate technology and product selection;
- timely and efficient completion of product design and treatment;
- timely and efficient implementation of manufacturing processes;
- product performance; and
- product support and effective sales and marketing.
We may not be able to accurately forecast or respond to commercial and technological trends in the industries in which we operate.
We may not be able to keep pace with rapid technological changes in the advanced film product industry.
The advanced film product authentication industry is a relatively new industry and market, especially in China and other parts of Asia, and continues to evolve in terms of customer/market needs, applications, and technology. We believe we have hired or engaged personnel and outside consultants who have experience and are recognized within the industry to be experts. With respect to technology, while we continue to seek out and develop “next generation” technology through acquisition, strategic partnerships, and our own R&D, there is no guarantee that we will be able to keep pace with technological developments and market demands in this evolving industry and market. Technological changes, process improvements, or operating improvements that could adversely affect us include:
- development of new technologies by our competitors or counterfeiters;
- changes in product requirements of our customers; and
- improvements in the alternatives to our technologies.
We may not have sufficient funds to devote to R&D, or our R&D efforts may not be successful in developing products in the time, or with the characteristics, necessary to meet customer needs. If we do not adapt to such changes or improvements, our competitive position, operations and prospects would be materially affected.
Intense competition in the advanced and packaging markets may adversely affect our operating results.
We operate in highly competitive and rapidly evolving fields, and new developments are expected to continue at a rapid pace. We believe there are few barriers to entry into many of our markets. As a result, we may experience competition resulting from new manufacturers of various types of film in our product lines. Competitors may succeed in developing alternative technologies and products that are more effective, easier to use or less expensive than those which have been or are being developed by us or that would render our technology and products obsolete and non-competitive. Any of these actions by our competitors could adversely affect our sales.
In addition, we face competition from a substantial number of companies, which sell similar and substitute packaging products. Although we believe we have developed strategic relationships in China to best penetrate China’s market, we face competition from other providers, some of which have greater financial and human resources, have had a longer operating history, and have greater name recognition than we do. Many of these competitors have substantially greater financial and technical resources, production and marketing capabilities, and may have extensive production facilities, well-developed sales and marketing staffs and substantial financial resources. Competitive products are also available from a number of local manufacturers. This results in competition that is highly price sensitive. We also compete on the basis of quality, service, timely delivery and differentiation of product properties.
An increase in competition could result in material selling price reductions or loss of our market share. This could materially adversely affect our operations and financial condition.
- 19 -
We are a major purchaser of many commodities that we use for raw materials in the manufacturing process of our products, and price changes for the commodities we depend on may adversely affect our profitability.
With the rapid growth of China’s economy, the demand for certain raw materials is great while the supply may be more limited. This may affect our ability to secure the necessary raw materials we need in a cost-effective manner, including chemicals and other items needed for production of our products at the volume of purchase orders that we anticipate receiving.
For example, the PET resin used in our coated film products is currently used as a raw material in China’s textile industry, and the market prices of PET resin may fluctuate due to changes in supply and demand conditions in that industry. Any sudden shortage of supply of, or significant increase in demand for, PET resin and additives may result in higher market prices and thereby increase our cost of sales. The prices of PET resin and additives are, to a certain extent, affected by the price movement of crude oil.
If there is a significant increase in the cost of our raw materials and we are unable to pass on such increase to our customers on a timely basis or at all, our profit margins and results of operations will be adversely affected.
Petroleum prices impact our operating results.
Petroleum is the prime ingredient in many plastics that we use to make many of our products. We estimate that an increase in the price of crude oil of $10.00 per barrel could cause our gross margin to decline by up to 6% on the sale of these products. There has been some increase in the cost of our raw materials as a result of an increase in crude oil prices throughout the year. Current political unrest in the Middle East has resulted in an increase in the price of crude oil and may result in further increases in the price of crude oil.
We may not be able to adequately protect our technology and other proprietary rights.
Our success will depend in part on our ability to obtain and protect our products, methods, processes and other technologies, to preserve our trade secrets, and to operate without infringing on the proprietary rights of third parties both domestically in China and abroad. We rely on patents, trademarks and licenses to protect our intellectual property. We also have patent applications pending in China, and have worked and continue to work closely with China’s patent officials to preserve our intellectual property rights. If we are unable to adequately protect or enforce our intellectual property rights with respect to our products, methods, processes and other technologies, our prospects for revenue growth could be significantly diminished. Additionally, if our products, methods, processes and other technologies infringe on the intellectual property rights of other parties, we could incur substantial costs.
Our ability to compete in our markets and to achieve future revenue growth will depend, in significant part, on our ability to protect our proprietary technology and operate without infringing upon the intellectual property rights of others. The legal regime in China for the protection of intellectual property rights is still at its early stage of development. Intellectual property protection became a national effort in China in 1979 when China adopted its first statute on the protection of trademarks. Since then, China has adopted its Patent Law, Trademark Law and Copyright Law and promulgated related regulations such as Regulation on Computer Software Protection, Regulation on the Protection of Layout Designs of Integrated Circuits and Regulation on Internet Domain Names. China has also acceded to various international treaties and conventions in this area, such as the Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property, Patent Cooperation Treaty, Madrid Agreement and its Protocol Concerning the International Registration of Marks. In addition, when China became a party to the World Trade Organization in 2001, China amended many of its laws and regulations to comply with the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights. Despite many laws and regulations promulgated and other efforts made by China over the years to tighten up its regulation and protection of intellectual property rights, private parties may not enjoy intellectual property rights in China to the same extent as they would in many Western countries, including the US, and enforcement of such laws and regulations in China have not achieved the levels reached in those countries. Both the administrative agencies and the court system in China are not well-equipped to deal with violations or handle the nuances and complexities between compliant technological innovation and non-compliant infringement.
There is no assurance that the measures that we have put into place to protect our intellectual property rights will be sufficient. As the number of patents, trademarks, copyrights and other intellectual property rights in our industry increases, and as the coverage of these rights and the functionality of the products in the market further overlap, we believe business entities in our industry may face more frequent infringement claims. Litigation to enforce our intellectual property rights could result in substantial costs and may not be successful. If we are not able to successfully defend our intellectual property rights, we might lose rights to technology that we need to conduct and develop our business. This may seriously harm our business, operating results and financial condition, and enable our competitors to use our intellectual property to compete against us.
Entry of new BOPP and advanced film producers in China may increase the supply of, and decrease the prices of, BOPP and advanced film in the industry, and hence lead to a decline in our profit margins.
- 20 -
We believe we are currently one of the few producers of BOPP and advanced film in China with R&D capabilities. Our past financial performance is attributable to our market position in the industry. Over time, there may be new entrants into our industry, whether as a result of increased access to the production technology of BOPP and advanced film or otherwise. Accordingly, we may experience increased competition, and the entry of new BOPP and advanced film producers will also lead to an increase in the industry supply of BOPP and advanced film resulting in more competitive pricing. We may have to price our products in response to competitive market conditions and this may lead to a decline in our profit margins. In the event that we are unable to successfully compete or retain effective control over the pricing of our products, our profit margins will decrease and our revenues and net income may also decrease.
In addition, China has gradually lifted its import restrictions, lowered import tariffs and relaxed foreign investment restrictions after its entry into the World Trade Organization in December 2001. This may lead to increased competition from foreign companies in our industry, some of which are significantly larger and financially stronger than us. If we fail to compete effectively with these companies in the future, our current business and future growth potential could be adversely affected.
With respect to our BOPP tobacco film and other flexible packaging materials, we have a large amount of sales concentrated in a small number of customers.
Any decrease in the demand for our flexible packaging materials, particularly our BOPP tobacco film, will significantly affect our financial performance. Although demand for our BOPP tobacco film has gradually been increasing, any significant fall in the consumption of tobacco, in particular, whether as a result of health concerns or otherwise, could result in a decline in the sales of our products and adversely impact our financial condition, business and operation.
A disruption in the supply of utilities, fire or other calamity at our manufacturing plants would disrupt production of our products and adversely affect our sales.
Our films are manufactured solely at our production facilities located in Haikou City and Zhuhai City in China. While we have not experienced any calamities in the past which disrupted production, any disruption in the supply of utilities, in particular, electricity or power supply or any outbreak of fire, flood or other calamity resulting in significant damage at our facilities, would severely affect our production capabilities. As a result, we could incur substantial liabilities that could reduce or eliminate the funds available for product development, or result in a loss of equipment and properties. While we maintain insurance policies covering losses with respect to damage to our properties, machinery and inventories of raw materials and products, we cannot assure you that our insurance would be sufficient to cover all of our potential losses.
We have limited experience in operating outside mainland China, and failure to achieve our international marketing and sales strategy may have an adverse effect on our business growth in the future.
Our future growth depends, to a considerable extent, on our ability to develop both the domestic and overseas markets. We are currently exploring new business opportunities outside mainland China for our products. We have a limited number of customers outside China, mainly in the US and Europe. However, we have limited experience in operating outside mainland China, including dealing with foreign regulatory environments and market practices, and cannot guarantee that we will be able to penetrate any international market. In connection with our initial efforts to expand overseas, we have encountered many obstacles, including cultural and linguistic differences, difficulties in keeping abreast of market, business and technical developments in foreign jurisdictions, and political and social disturbances. Failure in the development of international markets may have an adverse effect on our business growth in the future.
Compliance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and related corporate governance and public disclosure requirements have resulted in significant additional expense.
Changing laws, regulations, and standards relating to corporate governance and public disclosure, including the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and the associated SEC regulations have resulted in significant additional expense as well as a diversion of management time and attention from revenue-generating activities to compliance activities. If our efforts to comply with new or changed laws, regulations, and standards differ from the activities intended by regulatory or governing bodies, we might be subject to lawsuits or sanctions or investigation by regulatory authorities, such as the SEC, and our reputation may be harmed.
- 21 -
We are subject to many environmental and safety regulations that may result in unanticipated costs or liabilities, that could reduce our profitability.
We are subject to extensive federal, local and foreign laws, regulations, rules and ordinances relating to pollution, protection of the environment and the generation, storage, handling, transportation, treatment, disposal and remediation of hazardous substances and waste materials. Actual or alleged violations of environmental laws or permit requirements could result in restrictions or prohibitions on plant operations, substantial civil or criminal sanctions, as well as, under some environmental laws, the assessment of strict liability and/or joint and several liability. Moreover, changes in environmental regulations could inhibit or interrupt our operations, or require us to modify our facilities or operations. Accordingly, environmental or regulatory matters may cause us to incur significant unanticipated losses, costs or liabilities that could reduce our profitability.
In addition, we could incur significant expenditures in order to comply with existing or future environmental or safety laws. Capital expenditures and costs relating to environmental or safety matters will be subject to evolving regulatory requirements and will depend on the timing of the promulgation and enforcement of specific standards which impose requirements on our operations. Capital expenditures and costs beyond those currently anticipated may therefore be required under existing or future environmental or safety laws.
Furthermore, we may be liable for the costs of investigating and cleaning up environmental contamination on or from our properties or at off-site locations where we disposed of or arranged for the disposal or treatment of hazardous materials or from disposal activities that pre-dated our purchase of our businesses. We may therefore incur additional costs and expenditures beyond those currently anticipated to address all such known and unknown situations under existing and future environmental laws. In 2013, we incurred expenses of approximately $15,000 to comply with environmental and safety laws.
Failure to adequately comply with hygiene and food safety standards set by the PRC may disrupt our operations.
In accordance with the laws and regulations of the PRC, we are required to comply with applicable hygiene and food safety standards, including the standards set forth in the Food Safety Law, and any rules and regulations promulgated by the central Chinese government or local provincial governments thereunder. Failure to comply with these laws, rules and regulations, could require us to temporarily or permanently suspend some or all of our production operations, which could disrupt our operations and adversely affect our revenues and profitability.
PRC food safety and hygiene laws may become more onerous, which may adversely affect our operations and financial performance and lead to an increase in our costs which we may be unable to pass on to our customers.
As a manufacturer of food-related products, we are subject to extensive governmental regulation. For example, we are subject to the Food Safety Law (“FSL”) and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder. We cannot assure stockholders that in the future the PRC food safety and hygiene laws will not become more onerous, providing for stricter and more comprehensive monitoring and regulation of food-related product manufacturers, which may lead to an increase in our costs of complying with such regulations resulting in a material adverse effect on its results of operations. In 2013, we incurred expenses of approximately $10,000 to comply with the FSL
Concerns with the safety and quality of packaged food products could cause consumers to avoid such products and our customers to stop producing packaged food products.
We could be adversely affected if consumers lose confidence in the safety and quality of packaged food products. Adverse publicity about these types of concerns, such as the publicity concerning the use of the substance melamine in milk and infant formula, may discourage consumers from buying packaged food products, which would reduce or eliminate the need for our food packaging, causing production disruptions. Any negative change in customer perceptions about the safety and quality of packaged food products could adversely affect our business and financial condition.
Increased consumption tax on cigarettes may materially impact our tobacco film sales
On May 1, 2009, the central Chinese government raised the consumption tax on cigarettes in an effort to curb smoking and increase state revenues. The consumption tax was raised by between 6% and 11% and is based on the sales price of the cigarettes – the higher the sales price the higher the percentage of consumption tax. This tax hike, together with a new 5% tax on cigarette wholesalers, which became effective on May 1, 2009, may negatively impact the cigarette manufacturing business in China and, depending on the severity of the impact thereon, may create a severe softening of our sales in the tobacco film market. Coupled with the decrease in our sales as a result of the economic crisis, the new tobacco-related taxes may have a material adverse effect on both our sales price and volume for the foreseeable future.
- 22 -
Deterioration of economic conditions could negatively impact our business.
Our business may be adversely affected by changes in global economic conditions, including inflation, interest rates, availability of capital markets, consumer spending rates, energy availability and costs (including fuel surcharges) and the effects of governmental initiatives to manage economic conditions. Any such changes could adversely affect the demand for our products or the cost and availability of our needed raw materials, thereby negatively affecting our financial results.
The recent disruptions in credit and other financial markets and deterioration of global economic conditions, could, among other things:
- make it more difficult or costly for us to obtain financing for our operations or investments or to finance debt in the future;
- impair the financial condition of some of our customers or suppliers, thereby increasing bad debts or non-performance by suppliers; and
- negatively impact demand for our products, which could result in a reduction of sales, operating income and cash flows.
RISKS RELATED TO CONDUCTING OUR BUSINESS IN CHINA
We are subject to international economic and political risks over which we have little or no control and may be unable to alter our business practice in time to avoid the possibility of reduced revenues.
A substantial portion of our business is conducted in China. Doing business outside the US, particularly in China, subjects us to various risks including changing economic and political conditions, major work stoppages, exchange controls, currency fluctuations, armed conflicts and unexpected changes in United States and foreign laws relating to tariffs, trade restrictions, transportation regulations, foreign investments and taxation. We have no control over most of these risks and may be unable to anticipate changes in international economic and political conditions. Therefore, we may be unable to alter our business practices in time to avoid the possibility of reduced revenues.
China’s economic policies could affect our business.
Generally, all of our assets are located in China and a substantial amount of our revenue is derived from our operations in China. Accordingly, our results of operations and prospects are subject, to a significant extent, to the economic, political and legal developments in China.
While China’s economy has experienced significant growth in the past twenty years, such growth has been uneven, both geographically and among various sectors of the economy. China’s government has implemented various measures to encourage economic growth and guide the allocation of resources. Some of these measures benefit the overall economy of China, but they may also have a negative effect on us. For example, operating results and financial condition may be adversely affected by the government control over capital investments or changes in tax regulations. The economy of China has been changing from a planned economy to a more market-oriented economy. In recent years, China government has implemented measures emphasizing the utilization of market forces for economic reform, the reduction of state ownership of productive assets, and the establishment of corporate governance in business enterprises; however, a substantial portion of productive assets in China are still owned by our government. In addition, China government continues to play a significant role in regulating industry development by imposing industrial policies. It also exercises significant control over China’s economic growth through the allocation of resources, the control of payment of foreign currency-denominated obligations, the setting of monetary policy and the provision of preferential treatment to particular industries or companies.
We may have difficulty establishing adequate management, legal and financial controls in China.
China historically has not adopted a Western style of management and financial reporting concepts and practices, as well as in modern banking, computer and other control systems. We may have difficulty in hiring and retaining a sufficient number of qualified employees to work in China. As a result of these factors, we may experience difficulty in establishing management, legal and financial controls, collecting financial data and preparing financial statements, books of account and corporate records and instituting business practices that meet Western standards.
- 23 -
Our bank accounts are not insured or protected against loss.
We maintain our cash with various banks and trust companies located in China. Our cash accounts are not insured or otherwise protected. Should any bank or trust company holding our cash deposits become insolvent, or if we are otherwise unable to withdraw funds, we would lose the cash on deposit with that particular bank or trust company.
As we have limited business insurance coverage in China, any loss which we suffer may not be insured or may be insured to only a limited extent.
The insurance industry in China is still in an early state of development and insurance companies located in China offer limited business insurance products. In the event of damage or loss to our properties, our insurance may not provide as much coverage as if we were insured by insurance companies in the United States.
Tax laws and regulations in China are subject to substantial revision, some of which may adversely affect our profitability.
China’s tax system is in a state of flux, and it is anticipated that China’s tax regime will be altered in the coming years. Tax benefits that we presently enjoy may not be available in the wake of these changes, and we could incur tax obligations to our government that are significantly higher than anticipated. These increased tax obligations could negatively impact our financial condition and our revenues, gross margins, profitability and results of operations may be adversely affected as a result.
Certain tax exemptions that we presently enjoy in China are scheduled to expire over the next several years.
Since a substantial portion of our operations are located in a privileged economic zone, we are entitled to certain tax benefits. These tax benefits are presently scheduled to expire over the next several years. For example, Zhuhai presently has a 50% exemption from federal tax through December 31, 2013. As these exemptions expire, our income tax expenses will increase, reducing our net income below what it would be if we continued to enjoy these exemptions.
We may face judicial corruption in China.
Another obstacle to foreign investment in China is corruption. There is no assurance that we will be able to obtain recourse in any legal disputes with suppliers, customers or other parties with whom we conduct business, if desired, through China’s poorly developed and sometimes corrupt judicial systems.
If relations between the United States and China worsen, investors may be unwilling to hold or buy our stock and our stock price may decrease.
At various times during recent years, the United States and China have had significant disagreements over political and economic issues. Controversies may arise in the future between these two countries. Any political or trade controversies between the United States and China, whether or not directly related to our business, could reduce the price of our common stock.
The government of China could change its policies toward private enterprise or even nationalize or expropriate private enterprises, which could result in the total loss of our and your investment.
Our business is subject to significant political and economic uncertainties and may be affected by political, economic and social developments in China. Over the past several years, the government of China has pursued economic reform policies including the encouragement of private economic activity and greater economic decentralization. The government of China may not continue to pursue these policies or may significantly alter them to our detriment from time to time with little, if any, prior notice.
Changes in policies, laws and regulations or in their interpretation or the imposition of confiscatory taxation, restrictions on currency conversion, restrictions or prohibitions on dividend payments to stockholders, or devaluations of currency could all cause a decline in the price of our common stock, should a market for our common stock ever develop. Nationalization or expropriation could even result in the total loss of your investment.
The nature and application of many laws of China create an uncertain environment for business operations and they could have a negative effect on us.
The legal system in China is a civil law system. Unlike the common law system, the civil law system is based on written statutes and decided legal cases have little value as precedents. In 1979, China began to promulgate a comprehensive system of laws and has since introduced many laws and regulations to provide general guidance on economic and business practices in China and to regulateforeign investment. Progress has been made in the promulgation of laws and regulations dealing with economic matters such as corporate organization and governance, foreign investment, commerce, taxation and trade. The promulgation of new laws, changes of existing laws and the abrogation of local regulations by national laws could cause a decline in the price of our common stock. Since these laws, regulations and legal requirements are relatively recent, their interpretation and enforcement involve significant uncertainty.
- 24 -
As we import goods into and export goods out of China, fluctuation of the RMB may affect our financial condition by affecting the volume of cross-border money flow.
Although we use the United States dollar (“USD”) for financial reporting purposes, many of the transactions effected by our operating subsidiaries are denominated in RMB. The value of the RMB fluctuates and is subject to changes in China’s political and economic conditions. We do not currently engage in hedging activities to protect against foreign currency risks. Even if we chose to engage in such hedging activities, we may not be able to do so effectively. Future movements in the exchange rate of the RMB could adversely affect our financial condition as we may suffer financial losses when transferring money raised outside of China into the country or when paying vendors for services performed outside of China.
We may not be able to obtain regulatory approvals for our products.
The manufacture and sale of our products in China are regulated by China and the local provincial governments. Although our licenses and regulatory filings are current, the uncertain legal environment in China and our industry may be vulnerable to local government agencies or other parties who wish to renegotiate the terms and conditions of, or terminate their agreements or other understandings with us.
It will be extremely difficult to acquire jurisdiction and enforce liabilities against our officers, directors and assets based in China.
As our executive officers and several of our directors, including the chairman of our Board of Directors, are Chinese citizens, it may be difficult, if not impossible, to acquire jurisdiction over these persons in the event a lawsuit is initiated against us and/or our officers and directors by a stockholder or group of stockholders in the United States. Also, because our operating subsidiaries and assets are located in China, it may be extremely difficult or impossible for one to access those assets to enforce judgments rendered against us or our directors or executive officers by United States courts. In addition, the courts in China may not permit the enforcement of judgments arising out of United States federal and state corporate, securities or similar laws. Accordingly, United States investors may not be able to enforce judgments against us for violation of United States securities laws.
Recent PRC regulations relating to acquisitions of PRC companies by foreign entities may create regulatory uncertainties that could restrict or limit our ability to operate. Our failure to obtain required prior approval for the share exchange, reverse merger and the listing and trading of our common stock could have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results, reputation and trading price of our common stock.
The PRC State Administration of Foreign Exchange, or “SAFE,” issued a public notice in November 2005, known as Circular 75, concerning the use of offshore holding companies controlled by PRC residents in mergers and acquisitions in China. This circular requires that (1) a PRC resident shall register with a local branch of the SAFE before he or she establishes or controls an overseas special purpose vehicle, or “SPV,” for the purpose of overseas equity financing (including convertible debt financing); (2) when a PRC resident contributes the assets of or his or her equity interests in a domestic enterprise to an SPV, or engages in overseas financing after contributing assets or equity interests to an SPV, such PRC resident must register his or her interest in the SPV and any changes in such interest with a local branch of the SAFE; and (3) when the SPV undergoes a material change outside of China, such as a change in share capital or merger or acquisition, the PRC resident shall, within 30 days from the occurrence of the event that triggers the change, register such change with a local branch of the SAFE. In addition, SAFE issued updated internal implementing rules, or the Implementing Rules in relation to Circular 75. The Implementing Rules were promulgated and became effective on May 29, 2007. Such Implementing Rules provide more detailed provisions and requirements regarding the overseas investment foreign exchange registration procedures. However, even after the promulgation of Implementing Rules there still exist uncertainties regarding the SAFE registration for PRC residents’ interests in overseas companies. If any PRC resident stockholder of a SPV fails to make the required SAFE registration and amended registration, the onshore PRC subsidiaries of that offshore company may be prohibited from distributing their profits and the proceeds from any reduction in capital, share transfer or liquidation to the offshore entity. Our PRC resident beneficial holders have not completed such approvals and registrations required by the SAFE regulations. Failure to comply with the SAFE registration and amendment requirements described above could result in liability under PRC laws for evasion of applicable foreign exchange restrictions. Because of uncertainty in how the SAFE notice will be interpreted and enforced, we cannot be sure how it will affect our business operations or future plans. For example, our PRC subsidiaries’ ability to conduct foreign exchange activities, such as the remittance of dividends and foreign currency-denominated borrowings, may be subject to compliance with the SAFE notice by our PRC resident beneficial holders over whom we have no control. In addition, we cannot assure you that such PRC residents will be able to complete the necessary approval and registration procedures required by the SAFE regulations. Failure by any PRC resident beneficial holder to register as required with the relevant branch of SAFE could subject these PRC resident beneficial holders to fines or legal sanctions, restrict our overseas or cross-border investment activities, limit our PRC subsidiaries’ ability to make distributions or pay dividends or affect our ownership structure, which could adversely affect our business and prospects.
- 25 -
On August 8, 2006, the PRC Ministry of Commerce (“MOFCOM”), joined by the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council, the State Administration of Taxation, the State Administration for Industry and Commerce, the China Securities Regulatory Commission (“CSRC”) and SAFE, released a substantially amended version of the Provisions for Foreign Investors to Merge with or Acquire Domestic Enterprises (the “Revised M&A Regulations”), which took effect September 8, 2006. These new rules significantly revised China’s regulatory framework governing onshore-to-offshore restructurings and foreign acquisitions of domestic enterprises. These new rules signify greater PRC government attention to cross-border merger, acquisition and other investment activities, by confirming MOFCOM as a key regulator for issues related to mergers and acquisitions in China and requiring MOFCOM approval of a broad range of merger, acquisition and investment transactions. Further, the new rules establish reporting requirements for acquisition of control by foreigners of companies in key industries, and reinforce the ability of the Chinese government to monitor and prohibit foreign control transactions in key industries.
Among other things, the Revised M&A Regulations include new provisions that purport to require that an offshore special purpose vehicle, or a SPV, formed for listing purposes and controlled directly or indirectly by PRC companies or individuals must obtain the approval of the CSRC prior to the listing and trading of such SPV’s securities on an overseas stock exchange. On September 21, 2006, the CSRC published on its official website procedures specifying documents and materials required to be submitted to it by SPVs seeking CSRC approval of their overseas listings. However, the application of this PRC regulation remains unclear with no consensus currently existing among the leading PRC law firms regarding the scope and applicability of the CSRC approval requirement.
According to the M&A Regulations, a “Related Party Acquisition” is defined as having taken place when a PRC business that is owned by PRC individual(s) is sold to a non-PRC entity that is established or controlled, directly or indirectly, by those same PRC individual(s). Under the M&A Regulations, any Related Party Acquisition must be approved by MOFCOM and any indirect arrangement or series of arrangements which achieves the same end result without the approval of MOFCOM is a violation of PRC law.
The PRC regulatory authorities may take the view that the acquisition by us from Sino Palace of all of the issued and outstanding capital stock of each of Shiner Industrial and Shiny-day, Hainan Hi-Tech and Zhuhai in exchange for the issuance of an aggregate of 16,500,000 shares of our common stock to the stockholders of Sino Palace was a Related Party Acquisition, because at the end of these transactions, PRC individuals become majority owners and effective controlling parties of a foreign entity that acquired ownership of PRC subsidiaries. If the PRC regulatory authorities take the view that the acquisition of the PRC subsidiaries constituted a Related Party Acquisition without the approval of the national offices of MOFCOM, they could invalidate our acquisition and ownership of these entities. Additionally, the PRC regulatory authorities may take the view that the share exchange constitutes a transaction which requires the prior approval of the CSRC. If this takes place, we would attempt to find a way to re-establish control of the PRC subsidiaries’ business operations through a series of contractual arrangements rather than an outright purchase of PRC subsidiaries. But we cannot assure you that any such contractual arrangements will be protected by PRC law or that the Company can receive as complete or effective economic benefit and overall control of the PRC subsidiaries’ business than if the Company had direct ownership of these subsidiaries. In addition, we cannot assure you that any such contractual arrangements can be successfully effected under PRC law. If we cannot obtain MOFCOM or CSRC approval if required by the PRC regulatory authorities to do so, and if we cannot put in place or enforce relevant contractual arrangements as an alternative and equivalent means of control of PRC subsidiaries, our business and financial performance will be materially adversely affected.
If the CSRC approval is not obtained, we may face regulatory actions or other sanctions from the CSRC or other PRC regulatory agencies. These regulatory agencies may impose fines and penalties on our operations in the PRC, limit our operating privileges in the PRC, delay or restrict the repatriation of the proceeds from any financings into the PRC, or take other actions that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, reputation and prospects, as well as the trading price of our common stock. The CSRC or other PRC regulatory agencies also may take actions requiring us, or making it advisable for us, to halt the proposed public offering before settlement and delivery of the common stock offered thereby. Consequently, if investors engage in market trading or other activities in anticipation of and prior to settlement and delivery, they do so at the risk that settlement and delivery may not occur.
Any uncertainties and/or negative publicity regarding this CSRC approval requirement could have a material adverse effect on the trading price of our common stock. Furthermore, published news reports in China recently indicated that the CSRC may have curtailed or suspended overseas listings for Chinese private companies. These news reports have created further uncertainty regarding the approach that the CSRC and other PRC regulators may take with respect to us.
- 26 -
It is uncertain how our business operations or future strategy will be affected by the interpretations and implementation of the aforementioned rules and regulations. It is anticipated that application of the new rules will be subject to significant administrative interpretation, and we will need to closely monitor how MOFCOM and other ministries apply the rules to ensure that our domestic and offshore activities continue to comply with PRC law. Given the uncertainties regarding interpretation and application of the new rules, we may need to expend significant time and resources to maintain compliance.
Our labor costs are likely to increase as a result of changes in Chinese labor laws.
We expect to experience an increase in our cost of labor due to recent changes in Chinese labor laws which are likely to increase costs further and impose restrictions on our relationship with our employees. In June 2007, the National People’s Congress of the PRC enacted new labor law legislation called the Labor Contract Law and more strictly enforcing existing labor laws. The new labor law, which became effective on January 1, 2008, amended and formalized workers’ rights concerning overtime hours, pensions, layoffs, employment contracts and the role of trade unions. Generally, this labor law increased our cost of labor. In addition, under the new law, employees who either have worked for the Company for 10 years or more or who have had two consecutive fixed-term contracts must be given an “open-ended employment contract” that, in effect, constitutes a lifetime, permanent contract, which is terminable only in the event the employee materially breaches the Company’s rules and regulations or is in serious dereliction of his duty. Such non-cancelable employment contracts will substantially increase its employment related risks and limit the Company’s ability to downsize its workforce in the event of an economic downturn. No assurance can be given that the Company will not in the future be subject to labor strikes or that it will not have to make other payments to resolve future labor issues caused by the new laws.
Furthermore, there can be no assurance that the labor laws will not change further or that their interpretation and implementation will vary, which may have a negative effect upon our business and results of operations.
Inflation in the PRC could negatively affect our profitability and growth.
While the PRC economy has experienced rapid growth, such growth has been uneven among various sectors of the economy and in different geographical areas of the country. Rapid economic growth can lead to growth in the money supply and rising inflation. Furthermore, in order to control inflation in the past, the PRC government has imposed controls on bank credits, limits on loans for fixed assets and restrictions on state bank lending. In January 2010, the Chinese government took steps to tighten the availability of credit including ordering banks to increase the amount of reserves they hold and to reduce or limit their lending. The implementation of such policies may impede economic growth. In 2004, the People’s Bank of China, or the PBOC, the PRC’s central bank, raised interest rates for the first time in nearly a decade and indicated in a statement that the measure was prompted by inflationary concerns in the Chinese economy. Since then, the PBOC has raised rates to restrain inflation and limit the risk of asset bubbles, including the most recent rate hikes in connection with the global economic crisis. Repeated rises in interest rates by the PBOC would likely slow economic activity in China which could, in turn, materially increase our costs and also reduce demand for our products and services.
Failure to comply with the United States Foreign Corrupt Practices Act could subject us to penalties and other adverse consequences.
As our ultimate holding company is a Nevada corporation, we are subject to the United States Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, which generally prohibits United States companies from engaging in bribery or other prohibited payments to foreign officials for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business. Foreign companies, including some that may compete with us, are not subject to these prohibitions. Corruption, extortion, bribery, pay-offs, theft and other fraudulent practices may occur from time-to-time in the PRC. We can make no assurance, however, that our employees or other agents will not engage in such conduct for which we might be held responsible. If our employees or other agents are found to have engaged in such practices, we could suffer severe penalties and other consequences that may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Any outbreak of the Swine Flu (H1N1), severe acute respiratory syndrome, or SARS, the Avian Flu, or another widespread public health problem in the PRC could adversely affect our operations.
There have been recent outbreaks of the highly pathogenic Swine Flu, caused by the H1N1 virus, in certain regions of the world, including parts of China, where all of our manufacturing facilities are located and where all of our sales occur. Our business is dependent upon our ability to continue to manufacture and distribute our products, and an outbreak of the Swine Flu, or a renewed outbreak of SARS, the Avian Flu, or another widespread public health problem in China, could have a negative effect on our operations. Any such outbreak could have an impact on our operations as a result of:
- 27 -
- quarantines or closures of our manufacturing or distribution facilities or offices;
- quarantines or closures of the manufacturing or distribution facilities or officers of our suppliers or customers;
- the sickness or death of our key officers and employees; and
- a general slowdown in the Chinese economy.
Any of the foregoing events or other unforeseen consequences of public health problems could adversely affect our operations.
We face risks related to natural disasters, terrorist attacks or other events in China that could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
Our business could be materially and adversely affected by natural disasters, terrorist attacks or other events in China. The Hainan province in which we operate is prone to typhoons and flooding. Earthquakes, tsunamis and other storms that may occur in China may impact our distribution capabilities and those of our suppliers. Any future natural disasters, terrorist attacks or other events in China could cause severe disruptions to our operations, as well as those of our suppliers and customers, which could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
Because our business is located in the PRC, we may have difficulty establishing adequate management, legal and financial controls, which we are required to do in order to comply with US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (“US GAAP”) and securities laws, and which could cause a materially adverse impact on our financial statements, the trading of our common stock and our business.
PRC companies have historically not adopted a Western style of management and financial reporting concepts and practices, which includes strong corporate governance, internal controls and, computer, financial and other control systems. Most of our middle and top management staff are not educated and trained in the Western system, and we may have difficulty hiring new employees in the PRC with experience and expertise relating to US GAAP and US public-company reporting requirements. In addition, we may have difficulty in hiring and retaining a sufficient number of qualified employees to work in the PRC. As a result of these factors, we may experience difficulty in establishing management, legal and financial controls, collecting financial data and preparing financial statements, books of account and corporate records and instituting business practices that meet Western standards. Therefore, we may, in turn, experience difficulties in implementing and maintaining adequate internal controls as required under Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. This may result in significant deficiencies or material weaknesses in our internal controls which could impact the reliability of our financial statements and prevent us from complying with SEC rules and regulations and the requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. Any such deficiencies, material weaknesses or lack of compliance could result in restatements of our historical financial information, cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information, have an adverse impact on the trading price of our common stock, adversely affect our ability to access the capital markets and our ability to recruit personnel, lead to the delisting of our securities from the stock exchange on which they are traded, lead to litigation claims, thereby diverting management’s attention and resources, and which may lead to the payment of damages to the extent such claims are not resolved in our favor, lead to regulatory proceedings, which may result in sanctions, monetary or otherwise, and have a materially adverse effect on our reputation and business.
Contract drafting, interpretation and enforcement in China involve significant uncertainty.
We have entered into numerous contracts governed by PRC law, many of which are material to our business. As compared with contracts in the United States, contracts governed by PRC law tend to contain less detail and are not as comprehensive in defining contracting parties’ rights and obligations. As a result, contracts in China are more vulnerable to disputes and legal challenges. In addition, contract interpretation and enforcement in China is not as developed as in the United States, and the result of any contract dispute is subject to significant uncertainties. Therefore, we cannot assure you that we will not be subject to disputes under our material contracts, and if such disputes arise, we cannot assure you that we will prevail.
Under the new Enterprise Tax Law, we may be classified as a “resident enterprise” of China for tax purpose, which may subject us and/or our subsidiaries to PRC income tax on taxable global income.
Under the new PRC Enterprise Income Tax Law (the “New EIT Law”) and its implementing rules, both of which became effective on January 1, 2008. Under the New EIT Law, enterprises are classified as resident enterprises and non-resident enterprises. An enterprise established outside of China with its “de facto management bodies” located within China is considered a “resident enterprise,” meaning that it can be treated in a manner similar to a Chinese domestic enterprise for enterprise income tax purposes.
The implementing rules of the New EIT Law define de facto management body as a managing body that in practice exercises “substantial and overall management and control over the production and operations, personnel, accounting, and properties” of the enterprise. Due to the short history of the New EIT law and lack of applicable legal precedents, it remains unclear how the PRC tax authorities will determine the PRC tax resident treatment of a foreign company such as us, with all of the members of its management located in China. If the PRC tax authorities determine that we are a “resident enterprise” for PRC enterprise income tax purposes, we may be subject to the enterprise income tax at a rate of 25% on our worldwide taxable income, as well as PRC enterprise income tax reporting obligations.
- 28 -
We are actively monitoring the possibility of “resident enterprise” treatment for the applicable tax years and are evaluating appropriate organizational changes to avoid this treatment, to the extent possible. If we are required to pay income tax on our worldwide income at the 25% tax rate, the amount of dividends we could, if any, pay to our stockholders would be materially reduced.
If we were treated as a “resident enterprise” by PRC tax authorities, we would be subject to taxation in both the US and China, and our PRC tax may not be credited against our US tax. As a result of the New EIT Law, our historical operating results will not be indicative of our operating results for future periods and the value of our common stock.
Dividends we receive from our subsidiaries located in the PRC may be subject to PRC withholding tax.
If we are not treated as a resident enterprise under the New EIT Law, then dividends that we receive from our Chinese subsidiaries may be subject to PRC withholding tax. The New EIT Law provides that an income tax rate of 20% may be applicable to dividends payable to non-resident investors, which (i) do not have an establishment or place of business in the PRC or (ii) have an establishment or place of business in the PRC but the relevant income is not effectively connected with the establishment or place of business, to the extent such dividends are derived from sources within the PRC. The State Council of the PRC reduced such rate to 10% through the implementation regulations of the New EIT Law. Further, pursuant to the Double Tax Avoidance Arrangement between Hong Kong and Mainland China and the Notice on Certain Issues with Respect to the Enforcement of Dividend Provisions in Tax Treaties issued on February 20, 2009 by the State Administration of Taxation, if the Hong Kong resident enterprise owns more than 25% of the equity interest in a company in China incessantly within 12 months immediately prior to obtaining dividend from such company, the 10% withholding tax on the dividends the Hong Kong resident enterprise received from such company in China is reduced to 5%.
However, based on the Notice on Certain Issues with Respect to the Enforcement of Dividend Provisions in Tax Treaties, if the relevant PRC tax authorities determine, in their discretion, that a company benefits from such reduced income tax rate due to a structure or arrangement that is primarily tax-driven, such PRC tax authorities may adjust the preferential tax treatment; and based on the Notice on the Comprehension and Recognition of Beneficial Owner in Tax Treaties issued on October 27, 2009 by the State Administration of Taxation, funnel companies, which are established for the purpose of evading or reducing tax, transferring or accumulating profits, shall not be recognized as beneficial owner, and thus, are not entitled to the abovementioned reduced income tax rate of 5% under the Double Tax Avoidance Arrangement. If we are required under the New EIT Law to pay income tax for any dividends we receive from our PRC subsidiaries, or if our PRC subsidiaries are determined by PRC government authority as receiving benefits from reduced income tax rate due to a structure or arrangement that is primarily tax-driven, it would materially and adversely affect the amount of dividends, if any, we may pay to our stockholders.
Dividends payable by us to our foreign investors and any gain on the sale of our shares may be subject to taxes under PRC tax laws.
If dividends payable to stockholders by the Company are treated as income derived from sources within China, then the dividends that stockholders receive from us, and any gain on the sale or transfer of our shares, may be subject to taxes under PRC tax laws.
Under the New EIT Law, PRC enterprise income tax at the rate of 20% is applicable to dividends payable by us to our investors that are non-resident enterprises which (i) do not have an establishment or place of business in the PRC or (ii) have an establishment or place of business in the PRC but the relevant income is not effectively connected with the establishment or place of business, to the extent such dividends are derived from sources within the PRC. The State Council of the PRC reduced such rate to 10% through the implementation regulations of the New EIT Law. Similarly, any gain realized on the transfer of our shares by such investors is also subject to a 10% PRC income tax if such gain is regarded as income derived from sources within China and the Company is considered as a resident enterprise which is domiciled in China for tax purpose. If we are required under the New EIT Law to withhold PRC income tax on our dividends payable to our foreign stockholders or investors who are non-resident enterprises, or if you are required to pay PRC income tax on the transfer or our shares under the circumstances mentioned above, the value of your investment in our shares may be materially and adversely affected.
In January 2009, the State Administration of Taxation promulgated the Provisional Measures for the Administration of Withholding of Enterprise Income Tax for Non-resident Enterprises (“Measures”), pursuant to which, the entities which have the direct obligation to make the following payment to a non-resident enterprise shall be the relevant tax withholders for such non-resident enterprise, and such payment includes: incomes from equity investment (including dividends and other return on investment), interests, rents, royalties, and incomes from assignment of property as well as other incomes subject to enterprise income tax received by non-resident enterprises in China. Further, the Measures provides that in case of equity transfer between two non-resident enterprises which occurs outside China, the non-resident enterprise which receives the equity transfer payment shall, by itself or engage an agent to, file tax declaration with the PRC tax authority located at place of the PRC company whose equity has been transferred, and the PRC company whose equity has been transferred shall assist the tax authorities to collect taxes from the relevant non-resident enterprise. However, it is unclear whether the Measures refer to the equity transfer by a non-resident enterprise which is a direct or an indirect stockholder of the said PRC company. Given these Measures, there is a possibility that the Company may have an obligation to withhold income tax in respect of the dividends paid to non-resident enterprise investors.
- 29 -
Furthermore, non-resident individual investors may be required to pay PRC individual income tax at a rate of 20% on interests or dividends payable to the investors or any capital gains realized from the transfer of shares if such gains are deemed income derived from sources within the PRC. Under the PRC Individual Income Tax Law, or IIT Law, non-resident individual refers to an individual who has no domicile in China and does not stay in the territory of China or who has no domicile in China and has stayed in the territory of China for less than one year. Pursuant to the IIT Law and its implementation rules, for purposes of the PRC capital gains tax, the taxable income will be the balance of the total income obtained from the transfer of the shares minus all the costs and expenses that are permitted under PRC tax laws to be deducted from the income. If we are considered a ’‘resident enterprise’’ and relevant competent PRC tax authorities consider dividends we could pay with respect to our shares and the gains realized from the transfer of our shares to be income derived from sources within the PRC, such gains earned by non-resident individuals may be subject to PRC withholding tax at a rate of 20%. If we are required under PRC law to withhold PRC income tax on dividends payable to our non-PRC investors that are non-resident individuals or if you are required to pay PRC income tax on the transfer of our shares, the value of your investment in our shares may be materially and adversely affected.
We will not be able to complete an acquisition of prospective acquisition targets in the PRC unless their financial statements can be reconciled to US GAAP in a timely manner.
Companies based in the PRC may not have properly kept financial books and records that may be reconciled with US GAAP. If we attempt to acquire a significant PRC target company and/or its assets, we would be required to obtain or prepare financial statements of the target that are prepared in accordance with and reconciled to US GAAP. Federal securities laws require that a business combination meeting certain financial significance tests require the public acquirer to prepare and file historical and/or pro forma financial statement disclosure with the SEC. These financial statements must be prepared in accordance with, or be reconciled to US GAAP and the historical financial statements must be audited in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), or PCAOB. If a proposed acquisition target does not have financial statements that have been prepared in accordance with, or that can be reconciled to, US GAAP and audited in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB, we will not be able to acquire that proposed acquisition target. These financial statement requirements may limit the pool of potential acquisition targets with which we may acquire and hinder our ability to expand our retail operations.
We face uncertainty from China’s “Circular on Strengthening the Administration of Enterprise Income Tax on Non-Resident Enterprises’ Share Transfer” that was released in December 2009 with retroactive effect from January 1, 2008.
The Chinese State Administration of Taxation released a circular (“Circular 698”) on December 10, 2009 that addresses the transfer of shares by nonresident companies. Circular 698, which is effective retroactively to January 1, 2008, may have a significant impact on many companies that use offshore holding companies to invest in China. Pursuant to Circular 698, where the withholding agent does not withhold in accordance with laws or cannot perform the withholding obligation, the non-resident enterprises shall file a tax declaration with the PRC tax authority located at place of the resident enterprise whose equity has been transferred, within seven days since the date of equity transfer provided under the contracts.
Where a foreign investor indirectly transfers equity interests in a Chinese resident enterprise by selling the shares in an offshore holding company, and the latter is located in a country or jurisdiction where the effective tax burden is less than 12.5% or where the offshore income of his, her, or its residents is not taxable, the foreign investor is required to provide the tax authority in charge of that Chinese resident enterprise with the relevant information within 30 days of the transfers. Moreover, where a foreign investor indirectly transfers equity interests in a Chinese resident enterprise through an abuse of form of organization and there are no reasonable commercial purposes such that the corporate income tax liability is avoided, the PRC tax authority will have the power to re-assess the nature of the equity transfer and deny the existence of the offshore holding company that is used for tax planning purposes.
There is uncertainty as to the application of Circular 698. For example, while the term “indirectly transfer” is not defined, it is understood that the relevant PRC tax authorities have jurisdiction regarding requests for information over a wide range of foreign entities having no direct contact with China. Moreover, the relevant authority has not yet promulgated any formal provisions or formally declared or stated how to calculate the effective tax in the country or jurisdiction and to what extent and the process of the disclosure to the tax authority in charge of that Chinese resident enterprise. In addition, there are not any formal declarations with regard to how to decide abuse of form of organization and reasonable commercial purpose, which can be utilized by us to balance if our company complies with the Circular 698. As a result, we may become at risk of being taxed under Circular 698 and we may be required to expend valuable resources to comply with Circular 698 or to establish that we should not be taxed under Circular 698, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
- 30 -
RISKS RELATED TO OUR SECURITIES
There is not now, and there may not ever be, an active market for our common stock and we cannot assure you that the common stock will become liquid or that it will be listed on a securities exchange.
There currently is no active market for our common stock. We plan to list our common stock as soon as practicable. However, we cannot assure you that we will be able to meet the initial listing standards of any stock exchange, or that we will be able to maintain any such listing. Until our common stock is listed on an exchange, we expect that it would be eligible to continue being quoted in the over-the-counter market maintained by the OTC Markets Group Inc. In this venue, however, an investor may find it difficult to obtain accurate quotations as to the market value of the common stock and trading of our common stock may be extremely sporadic. For example, several days may pass before any shares may be traded. A more active market for the common stock may never develop. In addition, if we failed to meet the criteria set forth in SEC regulations, various requirements would be imposed by law on broker-dealers who sell our securities to persons other than established customers and accredited investors. Consequently, such regulations may deter broker-dealers from recommending or selling the common stock, which may further affect its liquidity. This would also make it more difficult for us to raise additional capital.
We are subject to penny stock regulations and restrictions that may affect our ability to sell our securities on the secondary market.
The SEC has adopted regulations that generally define “penny stock” to be an equity security that has a market price of less than $5.00 per share, subject to specific exemptions. The market price of our common stock is less than $5.00 per share and therefore is a “penny stock.” Brokers or dealers effecting transactions in “penny stock” must disclose certain information concerning the transaction, obtain a written agreement from the purchaser and determine that the purchaser is reasonably suitable to purchase the securities. These rules may restrict the ability of brokers or dealers to sell our common stock and may affect your ability to sell shares. In addition, so long as our common stock is quoted in the “pink sheets” (as is currently the case), investors will find it difficult to obtain accurate quotations of the stock, and may find few buyers to purchase such stock and few market makers to support its price.
Future sales of shares of our common stock by our stockholders could cause our stock price to decline.
We cannot predict the effect, if any, that market sales of shares of our common stock or the availability of shares of common stock for sale will have on the market price prevailing from time to time. Sales of shares of our common stock in the public market covered under an effective registration statement, or the perception that those sales may occur, could cause the trading price of our common stock to decrease or become lower than it might be in the absence of those sales or perceptions.
Shares eligible for future sale may adversely affect the market for our common stock.
As of December 31, 2015, we had outstanding 90,000 shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of outstanding stock options at a weighted average exercise price of $0.95 per share, and 521,664 shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of our outstanding warrants at a weighted average exercise price of $1.70 per share. If or when these securities are exercised into shares of our common stock, the number of our shares of common stock outstanding will increase. Increases in the number of our outstanding shares and any sales of shares could have an adverse effect on the trading activity and market price of our common stock.
In addition, from time to time, certain of our shareholders may be eligible to sell all, or a portion of, their shares of common stock by means of ordinary brokerage transactions in the open market pursuant to Rule 144, promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933, or under effective resale prospectuses. Any substantial sale of our common stock pursuant to Rule 144 or any resale prospectus may have an adverse effect on the market price of our securities.
We may issue additional shares of our capital stock or debt securities to raise capital or complete acquisitions, which would reduce the equity interest of our stockholders.
- 31 -
Our articles of incorporation authorize the issuance of up to 75,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $.001 per share. There are currently 47,396,664 authorized and unissued shares of our common stock that have not been reserved and are available for future issuance. Although we have no commitments as of the date of this offering to issue our securities, we may issue a substantial number of additional shares of our common stock to complete a business combination, to raise capital or to compensate our employees and/or directors. The issuance of additional shares of our common stock:
- may significantly reduce the equity interest of investors in this offering; and
- may adversely affect prevailing market prices for our common stock.
Our directors and senior management own a significant amount of our common stock, giving them influence or control in corporate transactions and other matters, and their interests could differ from those of other stockholders.
The Chairman of our board of directors owns approximately 41.22% of our outstanding common stock and, together with our other directors and senior management, they own approximately 41.65% of our outstanding common stock. As a result, they are in a position to significantly influence the outcome of matters requiring a stockholder vote, including the election of directors, the adoption of any amendment to our articles of incorporation or bylaws, and the approval of significant corporate transactions. Their control may delay or prevent a change of control on terms favorable to our other stockholders and may adversely affect your voting and other stockholders rights.
The ability of our Chinese operating subsidiaries to pay dividends may be restricted due to foreign exchange control and other regulations of China.
Under applicable PRC regulations, foreign-invested enterprises in China may pay dividends only out of their accumulated profits, if any, determined in accordance with PRC accounting standards and regulations. In addition, a foreign-invested enterprise in China is required to set aside at least 10% of its after-tax profit based on PRC accounting standards each year to its general reserves until the accumulative amount of such reserves reach 50% of its registered capital. These reserves are not distributable as cash dividends. The board of directors of a foreign-invested enterprise has the discretion to allocate a portion of its after-tax profits to staff welfare and bonus funds, which may not be distributed to equity owners except in the event of liquidation.
Furthermore, the ability of our Chinese operating subsidiaries to pay dividends may be restricted due to the foreign exchange control policies and availability of cash balance of the Chinese operating subsidiaries. Because substantially all of our operations are conducted in China and a substantial majority of our revenues are generated in China, a majority of our revenue being earned and currency received are denominated in RMB. RMB is subject to the exchange control regulation in China, and, as a result, we may unable to distribute any dividends outside of China due to PRC exchange control regulations that restrict our ability to convert RMB into USD.
Our inability to receive dividends or other payments from our Chinese operating subsidiaries could adversely limit our ability to grow, make investments or acquisitions that could be beneficial to our business, pay dividends, or otherwise fund and conduct our business. The funds of our Chinese operating subsidiaries may not be readily available to us to satisfy obligations which have been incurred outside the PRC, which could adversely affect our business and prospects or our ability to meet our cash obligations. Accordingly, if we do not receive dividends from our Chinese operating subsidiaries, our liquidity, financial condition and ability to make dividend distributions to our stockholders will be materially and adversely affected.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS.
None.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES.
All land in China is owned by the State. Individuals and companies are permitted to acquire rights to use land or land use rights for specific purposes. In the case of land used for industrial purposes, the land use rights are granted for a period of 50 years. This period may be renewed at the expiration of the initial and any subsequent terms. Granted land use rights are transferable and may be used as security for borrowings and other obligations.
We currently have land use rights of approximately 40.32 acres consisting of manufacturing facilities, warehouse and office buildings in China. The chart below lists all facilities owned by us.
- 32 -
| Size of Land | |||
| Location | Type of Facility | (Acre) | |
| 19th Floor, Didu Building, Pearl River Plaza, No. 2 North Longkun Road, Haikou, Hainan Province | Principal executive offices | 0.23 | |
| Taipingpo, Yongxing Town, Xiuying District, Haikou, Hainan Province | Manufacturing facilities and warehouse | 11.90 | |
| Shiziling Feidi Industrial Park, Haikou, Hainan Province | Manufacturing facilities | 25.00 | |
| Pingshasan Road, Pingsha Town, Jinwan District, Zhuhai, Guangdong Province | Manufacturing facilities | 3.13 | |
| Room 307, 3rd Floor, Unit 3, Lane 1800, Xinsongjiang Road, Songjiang District, Shanghai | Sales office | 0.06 |
Hainan Factories
We have been granted the right to use three plots of land in Haikou City by the Municipal Administration of China for state-owned land. With respect to two of these plots, our rights run through January 2059 and, with respect to the third plot, our rights run through October 2060. Our original Hainan Factory currently has one BOPP tobacco film production line with total capacity of 3,500 metric tons per year, three advanced film lines with an annual capacity of 1,000 metric tons, three coated film lines with an annual capacity of 6,000 metric tons and two 8-color printing lines. Our original Hainan Factory consists of four buildings dedicated to film production and administrative offices. We made one-time payment of RMB 2,667,879 (approximately $322,013) for the right to use the land.
In 2009, we purchased a plot of land and entered into a 10-year lease for an adjacent, then-undeveloped, plot from Hainan Xiandai Keji Group, in the Hainan Shiziling Feidi Industrial Park and began construction of a new manufacturing facility there. We completed phase 1 of construction on our new manufacturing facility in Hainan in May 2010 and have successfully begun operations. The new facility in Hainan is a well-designed industrial park, with a total factory space of approximately 500,000 square feet. The new plant allows us to consolidate operations and processes from three separate locations into this central location; which will provide immediate operational efficiencies, improved quality control and cost savings. We believe this new facility provides us with the opportunity to better serve international customers and puts Shiner in a better competitive position to win new business. We have no rental obligations for this property through 2013.
We built a new BOPP tobacco film production line that was launched in the fourth quarter of 2011. The new line is in a fully automated plant equipped with state-of-the-art production machinery from Germany and England. This additional production line started running at the beginning of 2013, increasing our annual BOPP tobacco film capacity by an additional 10,000 metric tons.
Zhuhai Factory
We completed the construction of our Zhuhai Factory in 2006 to meet the growing demand for BOPP films. The Zhuhai Factory is equipped with one BOPP film production line with an annual capacity of 7,000 metric tons, two coated film lines with an annual capacity of 9,000 metric tons, one advanced film line with an annual capacity of 1,500 metric tons and one 10-color printing line. We lease the Zhuhai Factory for approximately $387,000 per year and our lease runs through 2016.
Shanghai Sales Office
On September 20, 2010, Shanghai Juneng opened a new sales office in Shanghai. Through this office we are pursuing sales opportunities among the domestic food safety packaging markets and targeting China’s leading food producers. Shanghai Juneng leases this office for approximately $10,000 per year under a lease that runs until 2015.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS.
From time to time, we may become involved in various lawsuits and legal proceedings, which arise in the ordinary course of business. However, litigation is subject to inherent uncertainties, and an adverse result in these or other matters may arise from time to time that may harm business. We are currently not aware of any such legal proceedings or claims that will have, individually or in the aggregate, a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or operating results.
- 33 -
ITEM 4. MINING SAFETY DISCLOSURES.
None.
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER REPURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES.
Market Information
Through September 14, 2012, our common stock was traded on the Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol “BEST.” Now, our common stock is quoted on QB tier of the over-the-counter electronic bulletin board maintained by the OTC Markets LLC under the same symbol. The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the quarterly high and low selling prices for our common stock as reported by the OTC Markets.
| For the Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||
| High | Low | High | Low | |||||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 0.35 | $ | 0.22 | $ | 0.50 | $ | 0.23 | ||||
| Second Quarter | 0.33 | 0.17 | 0.54 | 0.28 | ||||||||
| Third Quarter | 0.39 | 0.21 | 0.41 | 0.27 | ||||||||
| Fourth Quarter | 0.39 | 0.21 | 0.44 | 0.21 | ||||||||
On April 6, 2015, the closing price of our common stock as reported on the OTC Markets was $0.17 per share.
Holders
As of April 6, 2016, there were 27,941,491 shares of our common stock outstanding held by approximately 47 stockholders of record. The number of our stockholders of record excludes any estimate by us of the number of beneficial owners of shares held in street name, the accuracy of which cannot be guaranteed.
Dividend Policy
Except for dividends paid to those persons who held shares of our common stock prior to the consummation of the share exchange transaction discussed in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we have not paid any cash dividends on our common stock and we have no intention of paying cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Whether we will declare and pay dividends in the future will be determined by our board of directors at their discretion, subject to certain limitations imposed under Nevada corporate law. In addition, our ability to pay dividends may be affected by the foreign exchange controls in China. The timing, amount and form of dividends, if any, will depend on, among other things, our results of operations, financial condition, cash requirements and other factors deemed relevant by our board of directors.
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
The following table provides information as of December 31, 2014 about our common stock that may be issued upon the exercise of options and rights granted to employees or members of our Board of Directors:
- 34 -
| Plan Category | (a) Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights |
(b) Weighted- average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights |
(c) Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a) |
||||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | 120,000 | $ | 1.03 | - | |||||
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | - | $ | - | - | |||||
| Total | 120,000 | $ | 1.03 | - |
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities; Use of Proceeds from Registered Securities
None.
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA.
Not required.
- 35 -
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS.
Overview
We were incorporated in Nevada in November 2003, but since July 2007, have been headquartered in Hainan, China. Through our operating subsidiaries, Hainan Shiner, Shiny-Day, Hainan Modern, Zhuhai Modern, Shimmer Sun, and Ningbo we manufacture and sell packaging and anti-counterfeit plastic film to manufacturers and producers in China. We sell anti-counterfeit film, coated film, and color printing, in international markets through a network of distributors and converters.
Our primary business consists of the manufacture and distribution of technology driven advanced packaging film products in five business segments: bi-axially oriented polypropylene, or BOPP, film for wrapping tobacco; water-based latex; coated film; color printed packaging; and advanced film. Our products are sold to customers in the food, tobacco, chemical, medical and pharmaceutical, personal care, electronics, automotive, construction, graphics, music and video publishing industries. Our current production capacity consists of: five coated film lines with a capacity of 15,000 tons a year; two BOPP tobacco film production lines with a capacity of 13,500 tons a year; one BOPP film production line with a capacity of 7,000 tons a year; three color printing lines; four anti-counterfeit film lines with a capacity of 2,500 tons a year; and two water-based latex reaction kettles with a capacity of 3,000 tons a year.
The table below shows the percentage of revenue by each of our business segments for the three and year ended December 31, 2015 and 2014:
| Percent of Revenue | ||||||
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| BOPP tobacco film | 52.5% | 57.4% | ||||
| Water-based latex | 0.6% | 0.6% | ||||
| Coated film | 35.0% | 30.8% | ||||
| Color printing | 5.2% | 4.6% | ||||
| Advanced film | 6.7% | 6.6% | ||||
| 100.0% | 100.0% | |||||
We have 49 patents issued by the State Intellectual Property Office of China and have 13 patent applications relating to our products and manufacturing processes pending. Although our patents and processes provide us a competitive advantage, we do not believe the loss of any single patent would have a material adverse effect on our business.
While our primary business consists of manufacture and distribution of technology driven advanced packaging film products, we have historically advanced minimal funds to customers and other unrelated third parties that are non-interest bearing and payable upon demand. In 2014 we decided to temporarily expand our advances to unrelated third parties. On April 17, 2014, Hainan Shiner, our primary operating subsidiary, drew down entirely on a RMB120 million (approximately $19.5 million) credit facility collateralized by the common stock of Hainan Shiner, our buildings and our land use rights. The facility bears interest at 7.35% per annum and is due and payable on April 17, 2017. Under the terms of the credit facility agreement, the proceeds of the funds borrowed under the credit facility are to be used solely for the construction of an office building and research facility at the Hainan Xiandai Packaging Industrial Park, and for the purchase of research and development equipment. However, on April 30, 2014, we loaned the entire proceeds of the credit facility to unrelated third parties. The business purpose for these loans was for us to make the spread between the amount of interest we pay on the credit facility and the amount of interest we can charge. Such parties have not provided us with significant collateral on such loans, other than a written guarantee from each of the borrowers and an unrelated fourth party. We do not consider this practice of lending money to third parties to be a new business segment as we deem this practice to be temporary. See our disclosures under Liquidity and Capital Resources for more information regarding our lending activities. During the year ended December 31, 2015, approximately $35.9 million of these other receivables were repaid.
Our principal executive offices are located at 19th Floor, Didu Building, Pearl River Plaza, No. 2 North Longkun Road, Haikou, Hainan Province, China 570125. Our telephone number is +86-898-68581104 and our website is www.shinerinc.com.
Principal Factors Affecting Our Financial Performance
We believe that the following factors will continue to affect our financial performance:
- Global Economic Fragility – The ongoing turmoil in the global economy may have an impact on our business and our financial condition, and we may face challenges if economic conditions do not improve. These economic conditions impact levels of consumer spending, which have deteriorated and may remain depressed for the foreseeable future. If demand for our products fluctuates as a result of these economic conditions or otherwise, our revenue and gross margin could be harmed.
- 36 -
- Fuel Prices – Significant fluctuations in fuel prices could have both a positive and negative effect on our business and operations. Significant fluctuations in world fuel prices could significantly increase the price of shipping or transporting our products which we may not be able to pass on to our customers.
Results of Operations
The following summary of our results of operations should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and the notes thereto for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 included herein. The following tables set forth key components of our results of operations for the periods indicated, both in dollars and as a percentage of sales revenue and key components of our revenue for the periods indicated in dollars and percentages.
Comparison of Years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
The following table summarizes the results of our operations during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 and provides information regarding the dollar and percentage increase or (decrease) in such periods:
|
|
Years Ended December 31, | $ | % | |||||||||
|
|
2015 | 2014 | Change | Change | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Revenues |
$ | 76,331,519 | $ | 101,117,821 | $ | (24,786,302 | ) | -24.5% | ||||
|
Cost of goods sold |
59,694,988 | 85,284,144 | (25,589,156 | ) | -30.0% | |||||||
|
Gross profit |
16,636,531 | 15,833,677 | 802,854 | 5.1% | ||||||||
|
Selling expenses |
4,096,456 | 4,355,567 | (259,111 | ) | -5.9% | |||||||
|
General and administrative expenses |
11,654,538 | 7,025,634 | 4,628,904 | 65.9% | ||||||||
|
Income from operations |
885,537 | 4,452,476 | (3,566,939 | ) | -80.1% | |||||||
|
Other income (expense), net |
994,041 | 2,100,948 | (1,106,907 | ) | -52.7% | |||||||
|
Interest income |
2,334,276 | 2,192,067 | 142,209 | 6.5% | ||||||||
|
Interest expense |
(3,782,252 | ) | (3,628,174 | ) | (154,078 | ) | 4.2% | |||||
|
Exchange loss |
(154,737 | ) | (34,017 | ) | (120,720 | ) | 354.9% | |||||
|
Income tax expense |
962,688 | 1,022,512 | (59,824 | ) | -5.9% | |||||||
|
Net income (loss) attributed to noncontrolling interest |
(109,015 | ) | 3,841 | (112,856 | ) | -2938.2% | ||||||
|
Net income (loss) attributed to Shiner |
$ | (576,808 | ) | $ | 4,056,947 | $ | (4,633,755 | ) | -114.2% | |||
Revenues
Revenues for the year ended December 31, 2015 decreased $24.8 million (or 24.5%), to $76.3 million, compared to $101.1 million in 2014. The decrease was primarily attributable to decreased revenues generated from sales in all five of our segments, but largely from our BOPP tobacco segment. During the year ended December 31, 2015, revenue from BOPP tobacco decreased $17.9 million (or 30.9%) to $40.1 million, down from $58.1 million; revenue from coated film decreased $4.4 million (or 14.2%) to $26.7 million, down from $31.1 million; revenue from color printing decreased $0.7 million (or 14.7%) to $3.9 million, down from $4.6 million; and revenue from advanced film decreased $1.6 million (or 23.4%) to $5.1 million, down from $6.7 million. During 2015, our domestic (China Mainland) sales decreased as a percentage of total sales from 88.6% in 2014 to 87.2% in 2015. The decrease in revenue for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to the same period in 2014, was largely due to decrease in revenues during the 2015 first quarter as a direct result of the declining economic growth in China during that period. In addition, Chinese regulators have intensified supervision of consumer products resulting in an impact on consumer purchasing. During the fourth quarter of 2015, the Company also stopped accepting orders for product lines that were only marginally profitable which resulted in a reduction in revenue.
Cost of Goods Sold
For the year ended December 31, 2015, COGS decreased $25.6 million (or 30.0 %), from $85.3 million in the 2014, to $59.7 million in 2015. COGS for the year ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 were 78.2% and 84.3% of our revenues, respectively. The decrease in COGS as a percentage of revenues for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to the year ended December 31, 2014, was a result of lower raw material costs.
- 37 -
Gross Profit
Our gross profit for the year ended December 31, 2015 was $16.6 million, with a profit margin of 21.8%, a 6.2% increase from 15.7% for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase in gross profit percentage was a result of lower raw material costs caused by the decline in oil prices worldwide.
Selling Expenses
For the year ended December 31, 2015, our selling expenses decreased by $0.3 million (or 5.9%) to $4.1 million, compared to $4.4 million in 2014. The decrease in selling expenses was mainly due to a decrease in logistics expenses.
General and Administrative (“G&A”) Expenses
For the year ended December 31, 2015, our G&A expenses increased by $4.6 million (or 65.9 %) to $11.7 million, compared to $7.0 million in 2014. G&A expenses include rent, management and staff salaries, insurance, accounting, legal, and R&D expenses. The significant increase in G&A expenses is due to a write down of advances to suppliers in the fourth quarter of 2015.
Other Income, net
For the year ended December 31, 2015, other income decreased by $1.1 million (or 52.7 %), to $1.0 million in 2015, compared to $2.1 million in 2014. The change in other income (expense) is mainly due to a decrease in subsidy income.
Interest Income
For the year ended December 31, 2015, interest income increased by $0.1 million (or 6.5%) to $2.3 million, compared to $2.2 million in the 2014 period. The net increase in interest income is primarily due to an increase in interest charged on other receivables in connection with loans to unrelated third parties. During 2014, we borrowed RMB120 million, or approximately $19.5 million, at a 7.35% interest under a line of credit agreement and then lent these and other funds to unrelated third parties at interest rates ranging from 12% to 16%.
Interest Expense
For the year ended December 31, 2015, interest expense increased by $0.2 million (or 4.2%) to $3.8 million, compared to $3.6 million in 2014. The increase in interest expense is primarily due to the increase in the average amount of short-term and long-term loans outstanding throughout 2015, compared to 2014. During 2014 we borrowed RMB120 million, or approximately $19.5 million, at a 7.35% interest under a line of credit agreement and then lent the funds to unrelated third parties at interest rates ranging from 12% to 16%.
Income Tax Expense
For the year ended December 31, 2015, we recorded a tax provision of $1.0 million, compared to $1.0 million in the 2014 period. Our effective tax rates for 2015 and 2014 were 348% and 20%, respectively. The effective rate in 2015 is much higher than the statutory rate due to losses incurred by some of our subsidiaries that we were not able to offset income generated by other subsidiaries for tax purposes. The effective rate in 2014 was lower than the statutory rate due to tax holidays enjoyed by some of our subsidiaries.
Net Income (Loss)
Due to the factors explained above, for the year ended December 31, 2015, we generated a net loss attributed to Shiner of $0.6 million, compared to net income attributed to Shiner of $4.1 million in 2014.
Foreign Currency Translation gain (loss)
Foreign currency translation loss for the year ended December 31, 2015 was $1.8 million, an increase of $1.6 million, compared to $0.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The significant loss in 2015 was attributable to the significant decrease in the RMB-US exchange rate that occurred during the year ended December 31, 2015.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
At December 31, 2015, we had $0.8 million in cash and equivalents on hand, compared to $5.7 million at December 31, 2014. We had working capital deficit of $3.5 million at December 31, 2015, compared to $10.1 million at December 31, 2014. The primary reason for the decrease working capital deficit is the pay down of a long-term loan, currently in default that is classified as a current liability.
- 38 -
Our principal demands for liquidity are: increasing capacity, purchasing raw materials, sales distribution and the possible acquisition of new subsidiaries in our industry, as well as other general corporate purposes.
Below is a tabular summary of our cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2015 and 2014:
|
|
Years Ended December 31, | |||||
|
|
2015 | 2014 | ||||
|
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities |
$ | (2,486,693 | ) | $ | 8,065,476 | |
|
Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
21,395,687 | (38,621,126 | ) | |||
|
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
(23,797,816 | ) | 27,189,853 | |||
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and equivalents |
7,840 | (59,818 | ) | |||
|
Net decrease in cash and equivalents |
(4,880,982 | ) | (3,425,615 | ) | ||
|
Cash and equivalents at beginning of period |
5,710,373 | 9,135,988 | ||||
|
Cash and equivalents at end of period |
$ | 829,391 | $ | 5,710,373 | ||
Operating Activities
Net cash used in operating activities during the year ended December 31, 2015 was $2.5 million, a decrease of $10.6 million, compared to cash provided by operating activities during the year ended December 31, 2014 of $8.1 million. The decrease in cash used in operating activities during the year ended December 31, 2015 was primarily attributable to the changes in working capital components, particularly the significant increase in inventory and other receivables, and an increase in accounts payable and unearned revenue in the 2015 period.
Investing Activities
Net cash provided by investing activities during the year ended December 31, 2015 was $21.4 million, an increase of $60.0 million, compared to cash used in investing activities of $38.6 million in 2014. During 2015, we received $35.9 million from the repayment of other receivables and issued $21.1 million in new receivables, compared to the issuance of $38.6 million of other receivables and receiving $8.9 million from the repayment of other receivables in 2014.
Financing Activities
Net cash used in financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2015 was $23.8 million, a decrease of $51.0 million, compared to cash provided by financing activities of $27.2 million in 2014. During the 2015 period, we repaid $69.1 million of short-term loans and $8.8 million of long-term loans and borrowed an additional $53.5 million from short-term loans. During the 2014 period, we repaid $61.0 million of short-term loans and borrowed an additional $71.1 million from short-term loans and $19.5 million from long-term loans.
Assets
Our total assets as of December 31, 2015 were $91.5 million, a decrease of $37.7 million, compared to $129.1 million as of December 31, 2014. The decrease was primarily due to the decrease of other receivables, current, of $14.6 million, other non-current receivables of $7.3 million, restricted cash of $7.7 million, cash and equivalents of $4.9 million, advances to suppliers of $4.1 million and property and equipment of $3.8 million, offset by an increase in inventory of $2.0 million and an increase in accounts receivable of $2.4 million. The decrease in other receivables (both current and long-term) is due to the repayment of amounts loaned in 2014. (See Note 3 to the financial statements). We have historically advanced minimal funds to customers and other unrelated third parties that are non-interest bearing and payable upon demand. However, in 2014 we decided to temporarily expand our advances to unrelated third parties. The decrease in restricted cash is due to the lenders requirements to keep less cash in restricted accounts. The decrease in property and equipment is due to depreciation expense. The decrease in cash is due to the timing of collections of receivables and payment of payables. The decrease in advances to suppliers is due to us not placing as many orders of inventory. The increase in accounts receivable is due to the timing of the collection of customer balances. The increase in inventory is due to the decrease in inventory sold during the last quarter of 2015.
Liabilities
Our total liabilities as of December 31, 2015 were $57.3 million, a decrease of $35.8 million, compared $93.1 million as of December 31, 2014. The decrease from period to period was principally due to a decrease in long-term loans of $9.9 million and other payables of $8.3 million; a decrease in accounts payable of $1.9 million; and a decrease in short-term loans of $17.0 million; offset by an increase in unearned revenue of $1.3 million.
- 39 -
The decrease in long-term loans is due to our repayment of RMB40 million (approximately $6.4 million) of an RMB 120 million credit facility pursuant to a Trust Agreement between Hainan Shiner, our primary operating subsidiary, and Zhongrong International Trust Co., Ltd., or Zhongrong, on April 17, 2014. The credit facility bears interest at 7.35% per annum, is due on April 17, 2017 and is collateralized by the common stock of Hainan Shiner, our buildings and our land use rights. We intend to meet our liquidity requirements under this Trust Agreement, including capital expenditures related to the purchase of equipment, purchase of raw materials, and the expansion of our business, through cash flow provided by operations, and our current credit facilities. Under the terms of the Trust Agreement, the proceeds of the funds borrowed were to be used solely for the construction of an office building and research facility at the Hainan Xiandai Packaging Industrial Park and for the purchase of research and development equipment, however, on April 30, 2014, we loaned the entire proceeds of the credit facility to unrelated third parties who have provided no collateral on such loans other than a written guarantee from each of the borrowers and an unrelated fourth party. As such, Zhongrong has the right to declare a breach of the Trust Agreement and enforce its right to ownership of the stock, buildings and land use rights of Hainan Shiner, our primary operating subsidiary. We have not been able to obtain a waiver for the violation of the use of proceeds provision of the Trust Agreement, therefore the remaining amount due under this credit facility of RMB 80 million (approximately $12.3 million) is being shown as a current liability. If Zhongrong calls the loan due to the violation of the agreement, we will attempt to negotiate a waiver, or request additional time in order to collect the amounts due from unrelated third parties or to obtain other financing to repay the loan.
The decrease in other payables is due to a decrease in amounts due to two companies with which we are engaged in business. The decrease in short-term loans is due to the paid own of loans and not borrowing as much in additional loans in 2015. The decrease in accounts payable is due to the timing of payments to our vendors. The decrease in unearned revenue is due to shipping products to customers that had given us a deposit on their orders.
Loan Commitments
In addition to the Trust Agreement disclosed under Liabilities, on August 2, 2010, Hainan Shiner, our wholly owned subsidiary, entered into a credit facility with the Hainan Branch of the Bank of China. The credit facility is comprised of a seven-year RMB70 million, or $11.1 million, secured revolving credit facility. On each of January 24, February 10, February 16, February 17, March 25, November 30, December 23, 2011 and March 19, 2012, Hainan Shiner made withdrawals on the credit facility of $2.5 million, $2.6 million, $2.2 million, $1.2 million, $0.4 million, $0.2 million, $0.5 million and $1.1 million, respectively. Hainan Shiner may only use the loan proceeds to improve the technology of its BOPP film and to purchase certain equipment necessary for these improvements. Proceeds under the facility not used for these purposes may be subject to a misappropriation penalty interest rate of 100% of the current interest rate (6.6% at December 31, 2015) on the loan. The initial interest rate on each withdrawal from the facility is the 5-year benchmark lending rate announced by the People’s Bank of China on the date of such withdrawal, and is subject to adjustment every 12 months based upon this benchmark. Additional interest is paid on any overdue loan under this credit facility of 50% of the current interest rate on the loan. Hainan Shiner and certain of its affiliates, including the Company, provided guarantees and certain land use rights, buildings, and property as collateral under this facility. The credit facility includes financial covenants that prohibit Hainan Shiner from making distributions to its sole shareholder if (a) its after-tax net income for the fiscal year is zero or negative, (b) its after-tax net income is insufficient to make up its accumulated loss for the last several fiscal years, (c) its income before tax is not utilized in paying off the capital, interest and expense of the lender, or (d) the income before tax is insufficient to pay the capital, interest and expense of the lender. As of December 31, 2015, the outstanding balance under this credit facility was RMB 30 million or $4.6 million.
Except as set forth above, as at December 31, 2015, the Company is in compliance with all its obligations under the foregoing loan commitments.
Dividends
Our Chinese subsidiaries have restrictions on the payment of dividends to us. China has currency and capital transfer regulations that may require our Chinese subsidiaries to comply with complex regulations for the movement of capital. These regulations include a public notice issued in October 2005 by the State Administration of Foreign Exchange (“SAFE”) requiring PRC residents, including both legal and natural persons, to register with the competent local SAFE branch before establishing or controlling any company outside of China. Although we believe our Chinese subsidiaries are in compliance with these regulations, should these regulations or the interpretation of them by courts or regulatory agencies change, we may not be able to pay dividends outside of China.
Obligations under Material Contracts
- 40 -
We have no material payment obligations other than the loan commitments disclosed above.
Obligations under Material Contracts
We have no material payment obligations other than the loan commitments disclosed above.
Contractual Obligations
Our significant contractual obligations as of December 31, 2015 are as follows:
| Payments due by Period | |||||||||||||||
| Less than | One to | Three to | More Than | ||||||||||||
| One Year | Three Years | Five Years | Five Years | Total | |||||||||||
| Short-term loan | $ | 21,728,100 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 21,728,100 | |||||
| Long-term loans | 12,328,000 | 4,623,000 | - | - | 16,951,000 | ||||||||||
| Interest on loan obligations | 1,597,561 | 670,334 | - | - | 2,267,895 | ||||||||||
| Total | $ | 35,653,661 | $ | 5,293,334 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 40,946,995 | |||||
Critical Accounting Policies
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“US GAAP”) requires our management to make assumptions, estimates and judgments that affect the amounts reported, including the notes thereto, and related disclosures of commitments and contingencies, if any. We have identified certain accounting policies that are significant to the preparation of our financial statements. These accounting policies are important for an understanding of our financial condition and results of operation. Critical accounting policies are those that are most important to the portrayal of our financial conditions and results of operations and require management’s difficult, subjective, or complex judgment, often as a result of the need to make estimates about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain and may change in subsequent periods. Certain accounting estimates are particularly sensitive because of their significance to financial statements and because of the possibility that future events affecting the estimate may differ significantly from management’s current judgments.
Accounts Receivable, net
The Company maintains reserves for potential credit losses on accounts receivable. Management reviews the composition of accounts receivable and analyzes historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customer payment patterns to evaluate the adequacy of these reserves. Reserves are recorded primarily on a specific identification basis.
Inventory, net
Inventory is valued at the lower of cost (determined on a weighted average basis) or market. Management compares the cost of inventory with this market value and allowance is made to write down inventory to market value, if lower.
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s revenue recognition policies comply with the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 605, “Revenue Recognition.” Sales revenue is recognized at the date of shipment to customers when a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and collectability is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are satisfied are recorded as unearned revenue.
Sales revenue consists of the invoiced value of goods, which is net of value-added tax (“VAT”). All of the Company’s products are sold in the PRC and are subject to Chinese VAT of 17% of the gross sales price. This VAT may be offset by VAT paid by the Company on raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing their end product. The Company recorded VAT payable and VAT receivable net of payments in the financial statements. The VAT tax return is filed offsetting the payables against the receivables.
Sales and purchases are recorded net of VAT collected and paid. VAT taxes are not affected by the income tax holiday.
- 41 -
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company records stock-based compensation in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718, “Compensation – Stock Compensation.” ASC Topic 718 requires companies to measure compensation cost for stock-based employee compensation at fair value (“FV”) at the grant date and recognize the expense over the employee’s requisite service period. The Company recognizes in the statement of operations the grant-date FV of stock options and other equity-based compensation issued to employees and non-employees.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 740, “Income Taxes.” ASC Topic 740 requires a company to use the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes, whereby deferred tax assets are recognized for deductible temporary differences, and deferred tax liabilities are recognized for taxable temporary differences. Temporary differences are the differences between the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and their tax bases. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when, in the opinion of management, it is more likely than not that some portion, or all of, the deferred tax assets will not be realized. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are adjusted for the effects of changes in tax laws and rates on the date of enactment.
Under FASB ASC Topic 740, a tax position is recognized as a benefit only if it is “more likely than not” that the tax position would be sustained in a tax examination, with a tax examination being presumed to occur. The amount recognized is the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than 50% likely of being realized on examination. For tax positions not meeting the “more likely than not” test, no tax benefit is recorded. The adoption had no effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Basic and Diluted Earnings Per Share
Earnings per share (“EPS”) is calculated in accordance with the FASB ASC Topic 260, “Earnings Per Share.” Basic EPS is based upon the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted EPS is based on the assumption that all dilutive convertible shares and stock warrants were converted or exercised. Dilution is computed by applying the treasury stock method. Under this method, warrants are assumed to be exercised at the beginning of the period (or at the time of issuance, if later), and as if funds obtained thereby were used to purchase common stock at the average market price during the period.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2014, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (ASU 2014-09) , which supersedes nearly all existing revenue recognition guidance under U.S. GAAP. The core principle of ASU 2014-09 is to recognize revenues when promised goods or services are transferred to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which an entity expects to be entitled for those goods or services. ASU 2014-09 defines a five step process to achieve this core principle and, in doing so, more judgment and estimates may be required within the revenue recognition process than are required under existing U.S. GAAP. The standard is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods therein, using either of the following transition methods: (i) a full retrospective approach reflecting the application of the standard in each prior reporting period with the option to elect certain practical expedients, or (ii) a retrospective approach with the cumulative effect of initially adopting ASU 2014-09 recognized at the date of adoption (which includes additional footnote disclosures). Early adoption is not permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of the pending adoption of ASU 2014-09 on its consolidated financial statements and has not yet determined the method by which it will adopt the standard beginning January 1, 2017.
In August, 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-14, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Deferral of the Effective Date. The amendment in this ASU defers the effective date of ASU No. 2014-09 for all entities for one year. Public business entities, certain not-for-profit entities, and certain employee benefit plans should apply the guidance in ASU 2014-09 to annual reporting periods beginning December 15, 2017, including interim reporting periods within that reporting period. Earlier application is permitted only as of annual reporting periods beginning after December 31, 2016, including interim reporting periods with that reporting period.
In February, 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-02, Consolidation (Topic 810): Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis. ASU 2015-02 provides guidance on the consolidation evaluation for reporting organizations that are required to evaluate whether they should consolidate certain legal entities such as limited partnerships, limited liability corporations, and securitization structures (collateralized debt obligations, collateralized loan obligations, and mortgage-backed security transactions). ASU 2015-02 is effective for periods beginning December 15, 2015. The adoption of ASU 2015-02 is not expected to have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements. Early adoption is permitted.
In September, 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-16, Business Combinations (Topic 805). Topic 805 requires that an acquirer retrospectively adjust provisional amounts recognized in a business combination, during the measurement period. To simplify the accounting for adjustments made to provisional amounts, the amendments in the Update require that the acquirer recognize adjustments to provisional amounts that are identified during the measurement period in the reporting period in which the adjustment amount is determined. The acquirer is required to also record, in the same period’s financial statements, the effect on earnings of changes in depreciation, amortization, or other income effects, if any, as a result of the change to the provisional amounts, calculated as if the accounting had been completed at the acquisition date. In addition an entity is required to present separately on the face of the income statement or disclose in the notes to the financial statements the portion of the amount recorded in current-period earnings by line item that would have been recorded in previous reporting periods if the adjustment to the provisional amounts had been recognized as of the acquisition date. ASU 2015-16 is effective for fiscal years beginning December 15, 2015. The adoption of ASU 2015-016 is not expected to have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
- 42 -
In November 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-17, Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes. The new guidance requires that all deferred tax assets and liabilities, along with any related valuation allowance, be classified as noncurrent on the balance sheet. This update is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016 and interim periods within those annual periods. The Company does not anticipate the adoption of this ASU will have a significant impact on its consolidated financial position, results of operations, or cash flows.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842). The guidance in ASU No. 2016-02 supersedes the lease recognition requirements in ASC Topic 840, Leases (FAS 13). ASU 2016-02 requires an entity to recognize assets and liabilities arising from a lease for both financing and operating leases, along with additional qualitative and quantitative disclosures. ASU 2016-02 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the effect this standard will have on its consolidated financial statements.
Other recent accounting pronouncements issued by the FASB, including its Emerging Issues Task Force, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, and the Securities and Exchange Commission did not or are not believed by management to have a material impact on the Company's present or future financial statements.
Seasonality of Our Sales
The first quarter of the calendar year is typically the slowest season of the year for us due to the Chinese New Year holiday. During this period, accounts receivable collection tends to be very slow and we also need to purchase raw materials to prepare for upcoming busier seasons.
Inflation
Inflation does not materially affect our business or the results of our operations.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of December 31, 2015, we did not have any off-balance sheet arrangements.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK.
We are exposed to market risks related to changes in interest rates and foreign currency exchange rates, however, we believe those risks to be not material in relation to our operations. We do not have any derivative financial instruments.
Interest Rate Risk
As of December 31, 2014, we held no money market securities or short term available for sale marketable securities. Due to the short term duration of our investment portfolio, an immediate 10% change in interest rates would not have a material effect on the fair market value of our portfolio. Therefore, we would not expect our operating results or cash flows to be affected to any significant degree by the effect of a sudden change in market interest rates on our securities portfolio.
Foreign Currency Exchange Risk
All of our revenues are denominated in RMB and, as a result, we have certain exposure to foreign currency exchange risk with respect to current revenues. A majority of our expenses are payable in foreign currency. We do not use forward exchange contracts to hedge exposures denominated in foreign currencies or any other derivative financial instruments for trading or speculative purposes. The effect of an immediate 10% change in exchange rates would not have a material impact on our future operating results or cash flows.
- 43 -
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA.
The full text of our audited consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 begins on page F-1 of this report.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE.
None
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES.
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, under the supervision and with the participation of our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, has performed an evaluation of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”)) as of the end of the period covered by this report, as required by Rule 13a-15(b) under the Exchange Act. Disclosure controls and procedures are those controls and procedures designed to provide that the information required to be disclosed in our Exchange Act filings is (1) recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules, regulations and related forms, and (2) accumulated and communicated to management, including our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Based on that evaluation, our chief executive officer and chief financial officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting.
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act). Internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). Internal control over financial reporting includes policies and procedures that:
| 1) |
Pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; | |
| 2) |
Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP, and that our receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and/or our board of directors; and | |
| 3) |
Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on the interim or annual consolidated financial statements. |
Under the supervision and with the participation of our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of Shiner’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, using the criteria established inInternal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“Treadway”).
Based on this evaluation, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective and that there was no material weakness or significant deficiency discovered as of December 31, 2014.
Inherent Limitations of Internal Controls
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect all errors or misstatements and all fraud. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the policies and procedures are met. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
- 44 -
This annual report does not include an attestation report of the company’s registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting. Management’s report was not subject to attestation by the company’s registered public accounting firm pursuant to temporary rules of the SEC that permit the company to provide only management’s report in this annual report.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There have not been any changes in our internal control over financial reporting (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act) during the fourth quarter of 2014 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION.
None.
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE.
Information about our Board of Directors
The size of our Board of Directors has been set at five directors by action of the Board of Directors. Set forth below are the names, ages, principal occupations, and length of service of each of the members of our Board of Directors. In addition, we briefly describe the particular experience, qualifications, attributes or skills that led our Board of Directors to conclude that the person should serve as a director of Shiner.
| Yuet Ying | 61 |
Mr. Ying has served as Chairman of our Board of Directors since July 2007. Prior to that, Mr. Ying served as chairman and a director of Sino Palace Holdings Limited, Shiner’s predecessor, from January 2004 to July 2007. He served as chairman of Hainan Modern Technology Group from 1996 to December 2003. Mr. Ying holds a Bachelor’s Degree in Management from the Institute of the CPC Party School and an Advanced certificate of M.B.A. studies from Renmin People’s University. Mr. Ying is the father-in-law of Qingtao Xing, the President and Chief Executive Officer of Shiner. Mr. Ying’s history of leadership experience in the technology industry and his business education were significant to the decision to nominate him and remain important in his role as Chairman. |
|
| ||
| Jian Fu | 50 |
Mr. Fu joined our Board of Directors in July 2007. He currently serves as Shiner’s Executive Vice President of Manufacturing. From July 2007 until February 2010, he served as our Chief Executive Officer. Prior to that, Mr. Fu served as chief executive officer and a director of Sino Palace Holdings Limited, Shiner’s predecessor, from January 2004 to July 2007. He worked at Hainan Plastic Industrial Co., Ltd. as Vice Chairman of the Hainan Modern Technology Group from 1998 to December 2003 and as General Manager from 1985 to 1997. Mr. Fu holds a undergraduate degree in Plastic Engineering Technique from South China Institute of Technology and an Advanced Certificate of M.B.A. studies from Renmin University. Mr. Fu’s engineering experience and technological acumen, along with his knowledge of Shiner’s operations and previous executive experience, are attributes we value in our directors. |
|
| ||
| Zhenhuan Yuan | 47 |
Mr. Yuan joined our Board of Directors in July 2010. He is the founding-partner of Sunstone International LLC, a California based investment advisory and management firm. He is also the Senior Vice President of Cunat Inc., a real estate investment and management company. Mr. Yuan served as the Vice President at Fortress Investment Group for the Shanghai Office from 2008 to 2009, where he was in charge of acquisitions and asset management. From 2006 to 2008, Mr. Yuan worked for Jones Lang LaSalle in China, where he was responsible for sourcing, negotiating and underwriting real estate investment deals in the region. Mr. Yuan received a bachelor of engineering degree from Harbin Institute of Technology and his M.B.A. degree from Cornell University. Mr. Yuan is fluent in English, Chinese and Japanese. Mr. Yuan’s extensive business background and understanding of Chinese culture and business were attributes that Shiner considered important in connection with his nomination to the Board and service on each of the Board’s standing committees and as the Company’s Audit Committee Chair. |
- 45 -
Composition of the Board
Our Board of Directors oversees our business and affairs and monitors the performance of management. Management is responsible for the day-to-day operations of our company. As of the date of this proxy statement, our board has three directors. Our board has determined that Mr. Yuan is an “independent director” within the meaning of the rules promulgated by the SEC.
During 2015, the board met 6 times and acted by unanimous consent 4 times. We had three standing committees in 2015 - an audit committee, a compensation committee and a nominating committee. Each of our directors attended at least 80% of the meetings of the board and meetings of the committees on which they served that were held in 2015 during the term of their service on the board and each committee. We strongly encourage our Board of Directors to attend our annual meeting of stockholders.
Committees of the Board
The table below provides 2015 membership and meeting information for each of the committees.
| Name Audit | Compensation | Nominating | |
| Jian Fu | |||
| Yuet Ying | |||
| Zhenhuan Yuan | X* | X* | X |
| 2014 Meetings | 4 | 0 | 2 |
| 2014 Consents | 4 | 0 | 2 |
| * Committee Chair |
Audit Committee
The Audit Committee is responsible for: monitoring the quality, reliability and integrity of the accounting policies and financial statements of Shiner; overseeing our compliance with legal and regulatory requirements; reviewing the independence, qualifications and performance of our internal and external auditors; overseeing the performance of Shiner’s internal audit function and independent auditors; reviewing and monitoring the provisions of non-audit services performed by our independent auditors; and preparing a committee report as required by the SEC to be included in our annual proxy statement. Our Board of Directors has made an affirmative determination that each member of the Audit Committee (a) is an “independent director” as that term is defined by Nasdaq Marketplace Rules and (b) satisfies Nasdaq Marketplace Rules relating to financial literacy and experience.
Our Board of Directors has adopted a written Audit Committee charter, a copy of which may be viewed on the “Annual Meeting” page of our website located at www.shinerinc.com/annualmeeting.html or a printed copy may be obtained by making a written request to Ms. Cindy Gong, Corporate Secretary of Shiner International, Inc., at 19/F, Didu Building, Pearl River Plaza, No. 2 North Longkun Road, Haikou, Hainan Province, China 570125.
Audit Committee Financial Expert
The Board of Directors has examined the composition of the Audit Committee in light of the regulations under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (“Exchange Act”) applicable to audit committees. Based upon this examination, the Board of Directors has determined that our Audit Committee is comprised of an “independent” director within the meaning of the Exchange Act and the rules and regulations thereunder. Mr. Yuan qualifies as an “audit committee financial expert” as that term is defined in applicable regulations of the SEC.
- 46 -
Compensation Committee
The Compensation Committee is responsible for recommending compensation arrangements for our executive officers; evaluating the performance of our chief executive officer; and administering our compensation plans. All members of the Compensation Committee are independent under the standards for independence established by the applicable Nasdaq Marketplace Rules. Our Board of Directors has adopted a written compensation committee charter, a copy of which may be viewed on the “Annual Meeting” page of our website located at www.shinerinc.com/annualmeeting.html or a printed copy may be obtained by making a written request to Ms. Cindy Gong, Corporate Secretary of Shiner International, Inc., at 19/F, Didu Building, Pearl River Plaza, No. 2 North Longkun Road, Haikou, Hainan Province, China 570125.
Nominating Committee
The Nominating Committee is responsible for, among other thing, assisting the board in identifying individuals qualified to become members of the board and executive officers, selecting, or recommending that the board select, director nominees for election as directors by the stockholders, developing and recommending to the Board a set of effective governance policies and procedures applicable to Shiner, and recommending to the board director nominees for each committee. Our Nominating Committee is comprised of an “independent” director within the meaning of the Exchange Act and the rules and regulations thereunder. The Nominating Committee acts under a written charter adopted by our Board of Directors (a copy of which may be viewed on the “Annual Meeting” page of our website located atwww.shinerinc.com/annualmeeting.html or a printed copy may be obtained by making a written request to Ms. Cindy Gong, Corporate Secretary of Shiner International, Inc., at 19/F, Didu Building, Pearl River Plaza, No. 2 North Longkun Road, Haikou, Hainan Province, China 570125).
Procedure for Stockholder Nominations of Directors
Nominations for the election of directors may only be made by the Board of Directors in consultation with its nominating committee. A stockholder of record may recommend to the committee a candidate for consideration as a nominee. The committee will consider a stockholder nominee only if a stockholder provides written notice to: Shiner International, Inc., 19/F, Didu Building, Pearl River Plaza, No. 2 North Longkun Road, Haikou, Hainan Province, China 570125), Attention: Corporate Secretary for the Nominating Committee, with a copy to our counsel, William W. Uchimoto, Esq., Stevens & Lee, P.C., 1818 Market Street, 29th Floor, Philadelphia, PA 19103-1702, not later than 120 days prior to the anniversary of the mailing of the proxy statement for the prior year’s annual meeting of stockholders. Each such notice must include the name, address and telephone number of the potential nominee; a detailed biography of the potential nominee; and evidence of stock ownership by the presenting stockholder, including the number of shares owned. Nominees properly proposed by eligible stockholders will be evaluated by the nominating committee in the same manner as nominees identified by the committee. To date, no stockholder or group of stockholders has put forth any director nominees.
Executive Officers
Our executive officers, in addition to Mr. Fu, are listed below:
| Qingtao Xing | 38 |
Mr. Xing has been our Chief Executive Officer since February 22, 2010. Mr. Xing became President of Shiner in May 2008, having joined Shiner in January 2008, serving as Shiner’s Vice President for strategic initiatives. Prior to joining Shiner, Mr. Xing worked as a project development associate for LaSalle Investment Management from July 2007 to January 2008, as managing partner of New Frontiers Investment Management from May 2007 to January 2008 and as a summer intern for Citigroup Property Investors in Hong Kong during 2006. Mr. Xing received his master of professional studies degree from Cornell University in 2007 and holds a bachelor’s degree from Tongji University. Prior to attending Cornell, Mr. Xing was associated with two real estate companies in China, which developed residential and commercial properties. Mr. Xing is the son-in-law of our Chairman, Mr. Ying. |
|
| ||
| Xue Zhu Xu | 53 |
Ms. Xu is our interim Chief Financial Officer and Corporate Controller. Ms. Xu served as our Chief Financial Officer from July 2007 until February 2010. Prior to that, Ms. Xu served as chief financial officer of Sino Palace Holdings Limited, Shiner’s predecessor, from January 2004 to July 2007. She worked at Hisense Company Limited as chief financial officer from 1996 to December 2003. From 1990 to 1996 Ms. Xu worked as an accounting manager at Hainan Hisense Group. She worked as the accounting manager in Hainan WenChang Foreign Trade Co. from 1981 to 1990. Ms. Xu graduated from Hainan Supply and Marketing School in 1981 with a bachelor’s degree in accounting. She received an Advanced certificate of MBA studies from Renmin University in 2004. |
- 47 -
| Ming Biao Li | 49 |
Mr. Li has served as our Chief Operating Officer since January 1, 2008, having served as our vice president of technology from July 2007 through December 2007. Prior to that, Mr. Li served as general manager of our subsidiary, Hainan Shiner Industrial Co., Ltd., from January 2003 to March 2005 and as its Chairman from July 2004 to July 2007. He served as general manager of our subsidiary, Hainan Shiny-day Color Printing Packaging Co., Ltd., from September 2003 to May 2004. From October 1997 to December 2002, he worked in Hainan Weilin Electron Co. as general manager. Mr. Li served as section chief of the Project Investment and Evaluation group of the Guangxi Auto & Tractor Research Institution from 1995 to 1997. From 1990 to 1995, he headed up the automated equipment group at the Guangxi Auto & Tractor Research Institution. Mr. Li graduated from Tsinghua University in 1987 with a Bachelor’s degree in Automotive Engineering. He later obtained his Master’s in Transport Engineering from Beijing University in 1991. |
Code of Conduct
We have adopted a code of conduct that applies to our chief executive officer, chief financial officer and all of our other officers, employees and directors, a copy of which may be viewed on the “Corporate Governance” page of our website located atwww.shinerinc.com/inves_cg.html or a printed copy may be obtained by making a written request to Ms. Cindy Gong, Corporate Secretary of Shiner International, Inc., at 19/F, Didu Building, Pearl River Plaza, No. 2 North Longkun Road, Haikou, Hainan Province, China 570125.
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act requires directors, executive officers and persons who are the beneficial owners of more than 10% of our common stock to file reports of their ownership and changes in ownership of our equity securities with the SEC. The reporting persons are required by SEC regulation to furnish us with copies of all Section 16 reports they file. Based on a review of the copies of such forms furnished to us and other written representations that no other reports were required during the year ended December 31, 2014, we believe our directors, executive officers and greater than ten percent beneficial owners timely filed all Section 16(a) reports required during the year ended December 31, 2015.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION.
Summary Compensation Table
The following table shows the compensation of each of our named executives in 2015. Our named executives are: our chief executive officer and president, Mr. Qingtao Xing; our interim chief financial officer and corporate controller, Ms. XueZhu Xu; and our next two most highly compensated executive officers - our executive vice president of manufacturing, Mr. Jian Fu, and our chief operating officer, Mr. MingBao Li.
- 48 -
| Change in | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Equity | Value and | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incentive | Nonqualified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock | Option | Plan | Deferred | All Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name and | Salary | Awards | Awards | Bonus | Compensation | Compensation | Compensation | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Principal Position | Year | ($)* | ($) | ($) | ($)* | ($) | Earnings ($) | ($) | Total ($)* | ||||||||||||||||||
| Qingtao Xing, President and Chief Executive Officer |
2015 2014 2013 |
9166 9143 9054 |
36494 36494 36494 |
45660 45637 45548 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Xuezhu Xu, Interim Chief Financial Officer and Corporate Controller |
2015 2014 2013 |
8505 8478 8371 |
17089 17089 17089 |
25594 25567 25460 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jian Fu, Executive Vice President of Manufacturing |
2015 2014 2013 |
8890 8812 8730 |
20980 20980 20980 |
29870 29792 29710 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| MingBiao Li, Chief Operating Officer |
2015 2014 2013 |
8509 8461 8267 |
20443 20443 20443 |
28952 28904 28710 |
| * |
Each of the named executive officer were paid their salaries and bonuses in RMB and the amounts in the foregoing table represent the US dollar equivalent based on a conversion rate of $1= RMB 6.4936 and RMB 6.1190 at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. |
Narrative Disclosure to Summary Compensation Table
Compensation paid to our named executives in 2015 consisted solely of cash salary and bonus. However, in the future, our named executive officers may be eligible to receive other forms of compensation.
Historically, we have not provided our named executives with perquisites or other personal benefits. Additionally, we do not provide any company-sponsored retirement benefits or deferred compensation programs to any employee, including the named executive officers (other than a mandatory state pension scheme in which all of our employees in the People’s Republic of China participate), because it is not customary to provide such benefits and programs in the People’s Republic of China.
We maintain employment agreements with each of our named executive officers. The terms of these employment agreements generally provide that the employment relationship must comply with the laws and regulations of the People’s Republic of China. These agreements do not specifically provide any payments in the event of a change in control of Shiner or the executive’s termination, other than payments that may be required pursuant to Chinese labor laws.
Mr. Fu and Ms. Xu are subject to a two-year non-compete under their employment agreements. The non-compete prohibits them from working for any other organization which provides the same kind of products or services as Shiner and from competing with Shiner for its employees and customers.
Director Compensation
The following table provides information concerning the compensation of our non-executive directors for the year ended December 31, 2015.
| Change in | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Value and | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Nonqualified | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Equity | Deferred | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Fees Earned or | Stock | Option | Incentive Plan | Compensation | All Other | ||||||||||||||||
| Paid in Cash | Awards | Awards | Compensation | Earnings | Compensation | Total | |||||||||||||||
| ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | ($) | |||||||||||||||
| Jian Fu (1) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Yuet Ying (1) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Zhenhuan Yuan | 20,000 | — | — | — | — | — | 20,000 |
- 49 -
Narrative to Director Compensation Table
Mr. Fu is executive officers of Shiner and did not receive any compensation for serving on our Board of Directors. Mr. Ying elected to forego any compensation for his board service for the 2015 fiscal year. The only non-executive director received a $5,000 quarterly cash retainer.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS.
The following table sets forth information regarding beneficial ownership of our common stock as of April 6, 2016 (i) by each person who is known by us to beneficially own more than 5% of our common stock; (ii) by each of our officers and directors; and (iii) by all of our officers and directors as a group. Unless otherwise specified, the address of each of the persons set forth below is in care of Shiner International, Inc., 19th Floor, Didu Building, Pearl River Plaza, No. 2 North Longkun Road, Haikou, Hainan Province, 570125, People’s Republic of China.
| Amount | ||||||||
| &Nature of | Percent | |||||||
| Name & Address of Beneficial | Beneficial | of | ||||||
| Owner | Office, If Any | Title of Class | Ownership(1) | Class(2) | ||||
| Officers and Directors | ||||||||
| Yuet Ying | Director | Common Stock, $0.001 par value | 11,518,408 | 41.22% | ||||
| Jian Fu (3) | Chief Executive Officer and Director | Common Stock, $0.001 par value | 51,000 | * | ||||
| Qingtao Xing | Chief Financial Officer and Board Chair | Common Stock, $0.001 par value | - | * | ||||
| XueZhu Xu (4) | Chief Operating Officer | Common Stock, $0.001 par value | 40,000 | * | ||||
| MingBao Li | Director | Common Stock, $0.001 par value | - | * | ||||
| Zhenhuan Yuan (5) | Non-Executive and Non- Voting Director | 30,000 | * | |||||
| All Officers and Directors as a group (5 persons named above) | - | - | 11,639,408 | 41.65% | ||||
| 5% Security Holders | ||||||||
| First Wilshire Securities Management, Inc. (6) 1224 East Green Street, Suite 200, Pasadena, California 91106 | Common Stock, $0.001 par value | 2,420,544 | 8.66% | |||||
| Yuet Ying | Common Stock, $0.001 par value | 11,518,408 | 41.22% | |||||
_______________
* Less than 1 percent
| (1) |
In computing the number and percentage of shares beneficially owned by a person, shares that may be acquired by such person within 60 days of March 27, 2015 are counted as outstanding, while these shares are not counted as outstanding for computing the percentage ownership of any other person. |
| (2) |
Beneficial ownership has been determined in accordance with Rule 13d-3 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. Unless otherwise noted, we believe that all persons named in the table have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of common stock beneficially owned by them. At the close of business on March 27, 2015, we had 27,941,491 shares of common stock outstanding. |
| (3) |
The shares reported include 51,000 shares held by Mr. Fu’s spouse; Mr. Fu disclaims beneficial ownership of all of these shares. |
| (4) |
The shares reported include 40,000 shares held by Ms. Xu’s daughter; Ms. Xu disclaims beneficial ownership of all of these shares. |
| (5) |
The shares reported include 30,000 shares issuable upon the exercise of vested options granted to Mr. Yuan on September 12, 2011. The options have an exercise price of $0.80 per share and expire on December 8, 2017. |
| (6) |
This information is derived from a Schedule 13G/A filed by First Wilshire Securities Management, Inc. ("First Wilshire"), a registered broker-dealer, on February 15, 2011. Matthew Dunn, First Wiltshire's Chief Compliance Officer is deemed to have dispositive power with respect to these 988,880. |
- 50 -
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE.
Transactions with Related Persons
Other than as described below, we are not a party to any transactions required to be disclosed pursuant to Item 404 of Regulation S-K, including any transaction or series of transactions between us and any officer, director or affiliates of Shiner that has an aggregate value in excess of $120,000, or 1% of the average of our total assets for the last two completed fiscal years.
On April 30, 2014, one of the Company's PRC subsidiaries, Hainan Modern Hi-Tech Industrial Co. Ltd., entered into a loan agreement with Rixin Hotel Management Co. Ltd., pursuant to which Hainan Modern loaned approximately $3,015,807 to Rixin, at a rate of 12%. At the time this transaction was entered into, Rixin was an unrelated third party; however, in the fourth quarter of 2014, the Company formed a new, subsidiary, Hainan Juneng, that is owned 70% by the Company and 30% by Rixin, thereby rendering Rixin a related party. The outstanding balance of the loan at December 31, 2015, was $3,015,807 and the loan is repayable in full on April 21, 2017. The Company in turn has a payable due to Rixin for cash advances during the 2014 period. The advances have no fixed repayment date and bear a 12% interest rate. There was an outstanding balance of $3,604,947 at December 31, 2015.
Related Party Transaction Approval Policy
It is our policy that the Audit Committee review and approve in advance all related party transactions that are required to be disclosed pursuant to Item 404 of Regulation S-K promulgated by the SEC. If advance approval is not feasible, the Audit Committee must approve or ratify the transaction at the next scheduled meeting of the committee. Transactions required to be disclosed pursuant to Item 404 include any transaction or series of transactions between Shiner and any officer, director or certain affiliates of Shiner which has an aggregate value in excess of the lesser of $120,000, or 1% of the average of our total assets for the last two completed fiscal years. In reviewing related party transactions, the Audit Committee evaluates all material facts about the transaction, including the nature of the transaction, the benefit provided to Shiner, whether the transaction is on commercially reasonable terms that would have been available from an unrelated third-party and any other factors necessary to its determination that the transaction is fair to Shiner. To identify related party transactions, each year, we submit and require our directors and officers to complete director and officer questionnaires identifying any transaction with us or any of our subsidiaries in which the officer or director or their family members have an interest.
Director Independence
Our board has determined that each of Messrs. Antonoplos, Cunat, and Yuan are “independent directors” within the meaning of applicable Nasdaq Stock Market rules and the rules promulgated by the SEC.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES.
Audit and Related Fees
The following table sets forth fees billed to us by MJF & Associates, APC for professional services rendered for 2015 and 2014:
- 51 -
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Audit Fees | $ | 72,500 | $ | 71,500 | ||
| Audit-Related Fees | - | - | ||||
| Tax Fees | - | - | ||||
| All Other Fees | - | - | ||||
| Total | $ | 72,500 | $ | 71,500 |
Audit Fees. This category includes the aggregate fees billed for professional services rendered for the audits of our consolidated financial statements for fiscal years 2015 and 2014, respectively, for the reviews of the financial statements included in our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and for services that are normally provided by MJF & Associates, APC and by Goldman Kurland and Mohidin, LLP, respectively, in connection with statutory and regulatory filings or engagements for the relevant year.
Audit-Related Fees. This category includes the aggregate fees billed during the period for years 2015 and 2014, respectively, for assurance and related services by MJF & Associates, APC and by Goldman Kurland and Mohidin LLP, respectively, that are reasonably related to the performance of the audits or reviews of the financial statements and are not reported above under “Audit Fees.” These amounts generally consist of fees for due diligence accounting consultation with respect to our agreed-upon procedure reports.
Tax Fees. This category includes tax preparation, tax compliance and tax advice.
All Other Fees. This category includes all accounting services which are not included in the foregoing categories.
Policy for Pre-Approval of Audit and Non-audit Services
Under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, all audit and non-audit services performed by our auditors must be approved in advance by our Board of Directors to assure that such services do not impair the auditors’ independence from us. The Audit Committee has adopted an approval policy regarding the approval of audit and non-audit services provided by the independent accountants, which approval policy describes the procedures and the conditions pursuant to which the Audit Committee may grant general pre-approval for services proposed to be performed by our independent accountants. All services provided by our independent accountants, both audit and non-audit, must be pre-approved by the Audit Committee. Our Audit Committee has delegated to the chairman of the audit committee the authority to grant pre-approvals of non-audit services provided by MJF & Associates, APC. The decisions of the Chairman of the Audit Committee to pre-approve such a service are required to be reported to the audit committee at its next regularly scheduled meeting.
In determining whether to approve a particular audit or permitted non-audit service, the Audit Committee (or the Chairman thereof) will consider, among other things, whether such service is consistent with maintaining the independence of the independent accountant. The Audit Committee (or the Chairman thereof) will also consider whether the independent accountant is best positioned to provide the most effective and efficient service to our Company and whether the service might be expected to enhance our ability to manage or control risk or improve audit quality.
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES.
Financial Statements and Schedules
The financial statements are set forth under Item 8 of this annual report on Form 10-K. Financial statement schedules have been omitted since they are either not required, not applicable, or the information is otherwise included.
Exhibits
| Exhibit | Description of Exhibit | |
|
2.1 |
Share Exchange Agreement by and between Sino Palace Holdings Limited and Cartan Holdings Inc. dated as of July 23, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on July 27, 2007). |
- 52 -
| 2.2 |
Return to Treasury Agreement between Cartan Holdings, Inc. and Zubeda Mohamed-Lakhani, dated as of July 23, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.2 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on July 27, 2007). | |
| 3.1 |
Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on July 27, 2007). | |
| 3.2 |
Amended and Restated Bylaws (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on July 27, 2007). | |
| 4.1 |
Specimen Stock Certificate (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on July 27, 2007). | |
| 10.1 |
Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of September 30, 2007, between Shiner and the investors signatory thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of Shiner’s Registration Statement on Form SB-2 (Commission File No. 333- 148304), filed with the SEC on December 21, 2007). | |
| 10.2 |
Form of Common Stock Purchase Warrant (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of Shiner’s Registration Statement on Form SB-2 (Commission File No. 333-148304), filed with the SEC on December 21, 2007). | |
| 10.3 |
Form of Stock Option Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of Shiner’s Registration Statement on Form SB-2 (Commission File No. 333-148304), filed with the SEC on December 21, 2007). | |
| 10.4 |
Employment Agreement, dated January 1, 2008, by and between Shiner and Jian Fu (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 of Shiner’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on March 28, 2008). | |
| 10.5 |
Employment Agreement, dated January 1, 2008, by and between Shiner and Xuezhu Xu (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 of Shiner’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on March 28, 2008). | |
| 10.6 |
Employment Agreement, dated January 1, 2008, by and between Shiner and Mingbiao Li (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 of Shiner’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on March 28, 2008). | |
| 10.7 |
Employment Agreement, dated February 11, 2010, by and between Shiner and Jeffrey T. Roney (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on February 26, 2009). | |
| 10.8 |
Employment Agreement, dated February 3, 2010, by and between Shiner and Qingtao Xing (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 of Shiner’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on March 25, 2010). | |
| 10.9 |
Articles of Association of Shanghai Juneng Functional Film Company, Ltd., a joint venture between Shiner and Shanghai Shifu Film Material, Co., Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on September 21, 2010). | |
| 10.10 |
Credit Facility between Hainan Shiner Industrial Co., Ltd. and the Hainan Branch of the Bank of China, dated June 29, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 of Shiner’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on November 15, 2010). | |
| 10.11 |
Securities Purchase Agreement for Non-US Persons, dated as of December 28, 2010, between the Company and the Investors thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on December 29, 2010). | |
| 10.12 |
Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of December 28, 2010, between the Company and the Investors thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on December 29, 2010). |
- 53 -
| 10.13 |
Form of Warrant of the Company (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8- K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on December 29, 2010). | |
|
| ||
| 10.14 |
Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of December 28, 2010, by and between the Company and the Investors (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on December 29, 2010). | |
|
| ||
| 10.15 |
Amendment to Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of January 10, 2011, between the Company and the Investors thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on January 14, 2011). | |
|
| ||
| 10.16 |
Share Transfer Agreement, dated as of May 2, 2011, by and between Fu Zhiyong and Shiner International, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.3 of the Company's quarterly report on Form 10-Q filed with the SEC on May 16, 2011) | |
|
| ||
| 10.17 |
English Translation of Trust Contract on Stock Rights Usufruct, dated April 17, 2014, between Zhongrong International Trust Co., Ltd and Hainan Shiner Industrial Co., Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 of the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on April 20, 2015). | |
|
| ||
| 10.18 |
English Translation of Loan Agreement, dated April 30, 2014, between Hainan Shiny-Day Color Printing Packaging Co., Ltd. and Hainan Jinhong Trading Co. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18 of the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on April 20, 2015). | |
|
| ||
| 10.19 |
English Translation of Loan Agreement, dated April 30, 2014, between Hainan Shiny-Day Color Printing Packaging Co., Ltd. and Hainan Modern Construction Engineering Co. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.19 of the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on April 20, 2015). | |
|
| ||
| 10.20 |
English Translation of Loan Agreement, dated April 30, 2014, between Hainan Shiny-Day Color Printing Packaging Co., Ltd. and Hainan Dingfeng Trading Co. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 of the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on April 20, 2015). | |
|
| ||
| 10.21 |
English Translation of Loan Agreement, dated April 30, 2014, between Hainan Modern Hi-Tech Industrial Co., Ltd. and Rixin Hotel Management Co., Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 of the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on April 20, 2015). | |
|
| ||
| 10.22 |
English Translation of Trust Loan Contract, dated April 30, 2014, among Hainan Modern Hi-Tech Industrial Co., Ltd., Ping An Bank Co., Ltd. Haikou Branch, and Hainan Modern Meiju Investment Co., Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 of the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on April 20, 2015). | |
|
| ||
| 21 |
List of Subsidiaries (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 21 of the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on April 20, 2015). | |
|
| ||
| 31.1* |
Certifications of Chief Executive Officer Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
|
| ||
| 31.2* |
Certifications of Chief Financial Officer Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
|
| ||
| 32.1* |
Certification of Chief Executive Officer Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
|
| ||
| 32.2* |
Certification of Chief Financial Officer Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
|
| ||
| 101** |
Interactive data files pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T |
________________
* Filed herewith
** Pursuant to Rule
405 of Regulation S-T, the following financial information from the Company’s
Annual Report on Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2015, is formatted
in XBRL interactive data files: (i) Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December
31, 2015 and 2014; (ii) Consolidated Statements of Operations and Other
Comprehensive Loss for the Years Ended December 31, 2015 and 2014; (iii)
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity for the Years Ended December 31,
2015 and 2014; (iv) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended
December 31, 2015 and 2014; and (vi) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Pursuant to Rule 406T of Regulation S-T, these interactive data files are deemed
not filed or part of a registration statement or prospectus for purposes of Sections 11 or 12 of the Securities
Act of 1933, as amended, or for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Act of
1934, as amended, and otherwise are not subject to liability under those
sections.
- 54 -
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized on the 15th day of April, 2016.
Shiner International, Inc.
| By: | /s/ Qingtao Xing |
| Name: Qingtao Xing | |
| Title: President and Chief Executive Officer | |
| (Principal Executive Officer) | |
| By: | /s/ XueZhuXu |
| Name: XueZhuXu | |
| Title: Interim Chief Financial Officer | |
| (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
In accordance with the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Qingtao Xing | President and Chief Executive Officer | April 15, 2016 | ||
| Qingtao Xing | ||||
| /s/XueZhu Xu | Interim Chief Financial Officer | April 15, 2016 | ||
| XueZhu Xu | (Chief Accounting Officer) | |||
| /s/ Yuet Ying | Chairman of the Board of Directors | April 15, 2016 | ||
| Yuet Ying | ||||
| /s/ Jian Fu | Director | April 15, 2016 | ||
| Jian Fu | ||||
| /s/ Zhenhuan Yuan | Director | April 15, 2016 | ||
| Zhenhuan Yuan |
- 55 -
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND
2014
Table of Contents
| Page | |
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | F-1 |
| Financial Statements: | |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 | F-2 |
| Consolidated Statements of Operations and Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) for the Years | F-3 |
| Ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 | F-4 |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 | F-5 |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | F-6 |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Shiner International, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of Shiner International, Inc. as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss), stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for the year then ended. Shiner International, Inc.’s management is responsible for these financial statements. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Shiner International, Inc. as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for the year then ended in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
MJF & Associates
Los Angeles, California
April 14, 2016
F-1
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND
SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
DECEMBER 31, 2015
AND 2014
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| ASSETS | ||||||
| CURRENT ASSETS: | ||||||
| Cash and equivalents | $ | 829,391 | $ | 5,710,373 | ||
| Restricted cash | 219,605 | 7,972,290 | ||||
| Accounts receivable, net | 10,051,326 | 7,656,456 | ||||
| Other receivables | 5,959,283 | 20,563,087 | ||||
| Advances to suppliers | 19,402,658 | 23,529,482 | ||||
| Notes receivable | 341,843 | 35,794 | ||||
| Inventory, net | 11,990,551 | 9,983,143 | ||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 381,129 | 238,317 | ||||
| Total current assets | 49,175,786 | 75,688,942 | ||||
| Property and equipment, net | 22,018,192 | 25,872,633 | ||||
| Construction in progress | 7,434,263 | 7,007,576 | ||||
| Advance for purchase of equipment | 404,632 | 727,764 | ||||
| Other non-current receivables | 11,485,998 | 18,797,707 | ||||
| Intangible assets, net | 973,372 | 1,051,243 | ||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 91,492,243 | $ | 129,145,865 | ||
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | ||||||
| CURRENT LIABILITIES: | ||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 7,032,147 | $ | 8,968,199 | ||
| Other payables | 9,890,606 | 18,177,999 | ||||
| Unearned revenue | 1,610,508 | 272,135 | ||||
| Accrued payroll | 110,477 | 139,274 | ||||
| Short-term loans | 21,728,100 | 38,744,022 | ||||
| Long-term loan, currently in default | 12,328,000 | 19,524,000 | ||||
| Total current liabilities | 52,699,838 | 85,825,629 | ||||
| Long-term loans | 4,623,000 | 7,321,500 | ||||
| Total liabilities | 57,322,838 | 93,147,129 | ||||
| Commitments and contingencies | ||||||
| EQUITY: | ||||||
| Shiner stockholders' equity: | ||||||
| Common
stock, par value $0.001; 75,000,000 shares
authorized, 27,603,336 shares issued and 27,541,491 shares outstanding |
27,603 | 27,603 | ||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 14,336,456 | 14,336,456 | ||||
| Treasury stock (61,845 shares) | (58,036 | ) | (58,036 | ) | ||
| Other comprehensive income | 4,849,974 | 6,611,234 | ||||
| Statutory reserve | 4,247,524 | 4,085,752 | ||||
| Retained earnings | 10,490,793 | 11,229,373 | ||||
| Total Shiner stockholders' equity | 33,894,314 | 36,232,382 | ||||
| Noncontrolling interest | 275,091 | (233,646 | ) | |||
| Total equity | 34,169,405 | 35,998,736 | ||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | $ | 91,492,243 | $ | 129,145,865 |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-2
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND
SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME AND OTHER COMPREHENSIVE
INCOME (LOSS)
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Net revenue | $ | 76,331,519 | $ | 101,117,821 | ||
| Cost of goods sold | 59,694,988 | 85,284,144 | ||||
| Gross profit | 16,636,531 | 15,833,677 | ||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||
| Selling | 4,096,456 | 4,355,567 | ||||
| General and administrative | 11,654,538 | 7,025,634 | ||||
| Total operating expenses | 15,750,994 | 11,381,201 | ||||
| Income from operations | 885,537 | 4,452,476 | ||||
| Non-operating income (expense): | ||||||
| Other income, net | 994,041 | 2,100,948 | ||||
| Interest income | 2,334,276 | 2,192,067 | ||||
| Interest expense | (3,782,252 | ) | (3,628,174 | ) | ||
| Exchange loss | (154,737 | ) | (34,017 | ) | ||
| Total non-operating income (expense) | (608,672 | ) | 630,824 | |||
| Income before income tax | 276,865 | 5,083,300 | ||||
| Income tax expense | 962,688 | 1,022,512 | ||||
| Net income (loss) | (685,823 | ) | 4,060,788 | |||
| Net income (loss) attributed to noncontrolling interest | (109,015 | ) | 3,841 | |||
| Net income (loss) attributed to Shiner | $ | (576,808 | ) | $ | 4,056,947 | |
| Comprehensive income (loss): | ||||||
| Net income | $ | (685,823 | ) | $ | 4,060,788 | |
| Foreign currency translation loss | (1,778,038 | ) | (197,740 | ) | ||
| Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | (2,463,861 | ) | $ | 3,863,048 | |
| Weighted average shares outstanding : | ||||||
| Basic | 27,541,491 | 27,541,491 | ||||
| Diluted | 27,541,491 | 27,541,491 | ||||
| Earnings per share attributed to Shiner common stockholders: | ||||||
| Basic | $ | (0.02 | ) | $ | 0.15 | |
| Diluted | $ | (0.02 | ) | $ | 0.15 |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-3
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
| Additional | Other | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock | Paid-in | Treasury | Comprehensive | Statutory | Retained | Stockholders' | Noncontrolling | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Capital | Stock | Income | Reserve | Earnings | Equity | Interest | Equity | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2013 | 27,603,336 | $ | 27,603 | $ | 14,336,456 | $ | (58,036 | ) | $ | 6,810,734 | $ | 3,644,905 | $ | 7,613,273 | $ | 32,374,935 | $ | (288,057 | ) | 32,086,878 | ||||||||||
| Contribution by non-controlling interest | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 48,810 | 48,810 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation loss | - | - | - | - | (199,500 | ) | - | - | (199,500 | ) | 1,760 | (197,740 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Net income | - | - | - | - | - | - | 4,056,947 | 4,056,947 | 3,841 | 4,060,788 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Transfer from statutory reserve | - | - | - | - | - | 440,847 | (440,847 | ) | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2014 | 27,603,336 | 27,603 | 14,336,456 | $ | (58,036 | ) | 6,611,234 | 4,085,752 | 11,229,373 | 36,232,382 | (233,646 | ) | 35,998,736 | |||||||||||||||||
| Contribution by non-controlling interest | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 634,530 | 634,530 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation loss | - | - | - | - | (1,761,260 | ) | - | - | (1,761,260 | ) | (16,778 | ) | (1,778,038 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Net income | - | - | - | - | - | - | (576,808 | ) | (576,808 | ) | (109,015 | ) | (685,823 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Transfer from statutory reserve | - | - | - | - | - | 161,772 | (161,772 | ) | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2015 | 27,603,336 | $ | 27,603 | $ | 14,336,456 | $ | (58,036 | ) | $ | 4,849,974 | $ | 4,247,524 | $ | 10,490,793 | $ | 33,894,314 | $ | 275,091 $ | 34,169,405 | |||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-4
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND
SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
YEARS
ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | ||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | (685,823 | ) | $ | 4,060,788 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net
income (loss) to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: |
||||||
| Depreciation | 3,174,300 | 4,090,837 | ||||
| Amortization | 23,245 | 23,549 | ||||
| Gain on sale and write off of assets | ||||||
| Change in working capital components: | ||||||
| Accounts receivable | (2,917,069 | ) | 2,694,465 | |||
| Other receivables | 699,231 | 1,907,256 | ||||
| Inventory | (2,640,930 | ) | 572,600 | |||
| Notes receivable | (320,930 | ) | 612,951 | |||
| Advances to suppliers | 3,090,585 | 2,762,178 | ||||
| Other assets | (71,964 | ) | 83,340 | |||
| Accounts payable | (1,596,316 | ) | (2,962,077 | ) | ||
| Unearned revenue | 1,385,563 | (4,265,083 | ) | |||
| Other payables | (2,604,244 | ) | (1,533,041 | ) | ||
| Accrued payroll | (22,341 | ) | 17,713 | |||
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | (2,486,693 | ) | 8,065,476 | |||
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | ||||||
| Payments for property and equipment | (1,115,894 | ) | (3,337,756 | ) | ||
| Increase (decrease) in restricted cash | 7,640,522 | (5,582,245 | ) | |||
| Issuance of other receivables | (21,075,510 | ) | (38,576,072 | ) | ||
| Payment on other receivable | 35,946,569 | 8,874,947 | ||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | 21,395,687 | (38,621,126 | ) | |||
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | ||||||
| Repayment of short-term loans | (69,060,994 | ) | (61,022,677 | ) | ||
| Proceeds from short-term loans | 53,461,648 | 71,080,220 | ||||
| Repayment of long-term loans | (8,833,000 | ) | (2,440,500 | ) | ||
| Proceeds from long-term loans | - | 19,524,000 | ||||
| Contribution by non-controlling interest | 634,530 | 48,810 | ||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | (23,797,816 | ) | 27,189,853 | |||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and equivalents | 7,840 | (59,818 | ) | |||
| NET DECREASE IN CASH AND EQUIVALENTS | (4,880,982 | ) | (3,425,615 | ) | ||
| CASH AND EQUIVALENTS, BEGINNING BALANCE | 5,710,373 | 9,135,988 | ||||
| CASH AND EQUIVALENTS, ENDING BALANCE | $ | 829,391 | $ | 5,710,373 | ||
| SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION: | ||||||
| Interest paid | $ | 3,502,103 | $ | 4,116,273 | ||
| Income taxes paid | $ | - | $ | 172,462 |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-5
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
Note 1 - Organization and Basis of Presentation
Organization and Line of Business
Shiner International, Inc. (the “Company” or “Shiner”) was incorporated in the State of Nevada on November 12, 2003. The Company, through its subsidiaries manufactures Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene (“BOPP”) tobacco film, coated films, color printing products, advanced film, and water based coatings selling to customers throughout the People’s Republic of China (“China” or “PRC”), Asia, Australia, Europe, the Middle East and North America. Our products are sold to companies in the following industries: food, tobacco, chemical, agribusiness, medical, pharmaceutical, personal care, electronics, automotive, construction, graphics, music and video publishing and other consumer goods.
Except as otherwise indicated by the context, all references in this report to “Shiner,” “Company,” “we,” “us” or “our” are to Shiner International, Inc. and its direct and indirect subsidiaries: (i) Hainan Shiner Industrial Co., Ltd., or “Hainan Shiner,” (ii) Hainan Shiny-Day Color Printing Packaging Co., Ltd., or “Shiny-Day,” (iii) Hainan Modern Hi-Tech Industrial Co., Ltd., or “Hainan Modern,” (iv) Zhuhai Modern Huanuo Packaging Material Co., Ltd., or “Zhuhai Modern,” (v) Shimmer Sun Ltd., or “Shimmer Sun,” (vi) Hainan Jingyue New Material Co., Ltd., or “Jingyue,” (vii) Hainan Shunhao New Material Co., Ltd., or “Shunhao,” (viii) Hainan Yongxin Environmental Co., Ltd., or “Yongxin,” (ix) Hainan Runhai Color Printing Packaging Co., or “Hainan Runhai,” (x) Hainan Saihang Photoelectric Co. Ltd., or “Hainan Saihang, ” (xi) Hainan Juneng Functional Film Co., or “Hainan Juneng” and (xii) Ningbo Neisuoer Latex Co., Ltd., or “Ningbo.”
The Company has historically advanced minimal funds to customers and other unrelated third parties that are non-interest bearing and payable upon demand. However, in 2014 the Company decided to temporarily expand its advances to unrelated third parties. On April 17, 2014, Hainan Shiner, the Company’s primary operating subsidiary, drew down entirely on a RMB120 million (approximately $19.5 million) credit facility collateralized by the common stock of Hainan Shiner, buildings and land use rights. The facility bears interest at 7.35% per annum and is due and payable on April 17, 2017. Under the terms of the credit facility agreement, the proceeds of the funds borrowed under the credit facility are to be used solely for the construction of an office building and research facility at the Hainan Xiandai Packaging Industrial Park, and for the purchase of research and development equipment. However, on April 30, 2014, the Company loaned the entire proceeds of the credit facility to unrelated third parties (See Note 3). The business purpose for these loans was for the Company to make the spread between the amount of interest it pays on the credit facility and the amount of interest it can charge. Such parties have not provided the Company with significant collateral on such loans, other than a written guarantee from each of the borrowers and an unrelated fourth party. The Company does not consider this practice of lending money to third parties to be a new business segment as we deem this practice to be temporary.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Shiner and its subsidiaries as follows:
| Place | Percentage | ||||||||
| Subsidiary | Incorporated | Owned | Parent | ||||||
| Shiner International, Inc. |
Nevada, USA |
- | |||||||
| Hainan Shiner |
China |
100% |
Shiner International, Inc. |
||||||
| Shiny-Day |
China |
100% |
Shiner International, Inc. |
||||||
| Hainan Modern |
China |
100% |
Shiny-Day/Hainan Shiner |
||||||
| Zhuhai Modern |
China |
100% |
Hainan Shiner/Shiner International, Inc. |
||||||
| Shimmer Sun |
China |
100% |
Shiner International, Inc. |
||||||
| Jingyue |
China |
100% |
Shimmer Sun Limited |
||||||
| Shunhao |
China |
100% |
Jingyue |
||||||
| Yongxin |
China |
100% |
Shunhao |
||||||
| Hainan Runhai |
China |
100% |
Shiny-Day |
||||||
| Hainan Saihang |
China |
100% |
Hainan Shiner |
||||||
| Hainan Juneng |
China |
50% |
Hainan Shiner |
||||||
| Ningbo |
China |
65% |
Yongxin |
F-6
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
The accompanying consolidated financial statements were prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“US GAAP”). The Company’s functional currency is the Chinese Yuan Renminbi (“RMB”); however, the accompanying consolidated financial statements were translated and presented in United States Dollars (“$” or “USD”).
Noncontrolling Interest
On May 2, 2011, Shiner acquired 100% of the stock of Shimmer Sun for $3.2 million. The Company paid $1.3 million in cash and the remaining $1.9 million was recorded as “other payables’ which was paid by September 30, 2011. The acquisition gave Shiner a 65% controlling interest in Shimmer Sun’s subsidiary, Ningbo. The transaction was accounted for under the acquisition method of accounting, with the purchase price allocated based on the fair value (“FV”) of the individual assets acquired and liabilities assumed.
In the fourth quarter of 2014, the Company set up a new subsidiary, Hainan Juneng, originally owned 70% by Hainan Shiner and 30% by an unrelated third party. During the quarter ended March 31, 2015 another unrelated third party purchased additional stock from Hainan for RMB 3,900,000 ($634,530). As of December 31, 2015, the Company owns 50% of Hainan Juneng and two other parties own the remaining 50%. The 50% owned by the third parties is presented as noncontrolling interest.
The Company follows Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 810, “Consolidation,” which governs the accounting for and reporting of non-controlling interests (“NCIs”) in partially owned consolidated subsidiaries and the loss of control of subsidiaries. Certain provisions of this standard indicate, among other things, that NCIs be treated as a separate component of equity, not as a liability, that increases and decreases in the parent’s ownership interest that leave control intact be treated as equity transactions rather than as step acquisitions or dilution gains or losses, and that losses of a partially owned consolidated subsidiary be allocated to the NCI even when such allocation might result in a deficit balance. This standard also required changes to certain presentation and disclosure requirements.
The net income attributed to the NCI is separately designated in the accompanying consolidated statements of income and other comprehensive income (loss).
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Shiner International, Inc. and its subsidiaries. All significant intercompany transactions and balances were eliminated in consolidation.
Foreign Currency Translation
The accounts of the Company’s Chinese subsidiaries are maintained in RMB and the accounts of the US parent company are maintained in USD. The accounts of the Chinese subsidiaries are translated into USD in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 830, “Foreign Currency Matters” with the RMB as the functional currency. According to ASC Topic 830, all assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rate on the balance sheet date, stockholders’ equity is translated at historical rates and statement of operations items are translated at the weighted average exchange rate for the period. The resulting translation adjustments are reported under other comprehensive income in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 220, “Comprehensive Income.” Gains and losses resulting from the translations of foreign currency transactions and balances are reflected in the consolidated statement of operations and other comprehensive income (loss).
F-7
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
Note 2 - Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Going Concern
These consolidated financial statements have been prepared on a going concern basis, which implies the Company will continue to realize its assets and discharge its liabilities in the normal course of business. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company was in violation of certain loan covenants which required the entire loan amount to be shown as a current liability. These consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments to the recoverability and classification of recorded asset amounts and classification of liabilities that might be necessary should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern.
On April 17, 2014, Hainan Shiner drew down entirely on a RMB120 million (approximately $19.5 million) credit facility collateralized by the common stock of Hainan Shiner, buildings and land use rights. The facility bears interest at 7.35% per annum and is due and payable on April 17, 2017. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company repaid RMB 40 million (approximately $6.4 million) of this credit facility. Under the terms of the credit facility agreement, the proceeds of the funds borrowed under the credit facility are to be used solely for the construction of an office building and research facility at the Hainan Xiandai Packaging Industrial Park, and for the purchase of research and development equipment. However, on April 30, 2014, the Company loaned the entire proceeds of the credit facility to unrelated third parties. Such parties have not provided the Company with significant collateral on such loans, other than a written guarantee from each of the borrowers and an unrelated fourth party. The use of the proceeds from the credit facility to provide such loans constitutes a breach under the credit facility agreement. The Company has not obtained a waiver from the lender for such use of proceeds and the lender has the right to declare a breach of the trust agreement and enforce its right to ownership of the stock, buildings and land use rights of Hainan Shiner. Furthermore, if the borrowers are unable to fulfill their obligations under the Company’s loans to them and their guarantees fail, the Company will be obligated to repay the credit facility in its entirety. If the Company is unable to repay this debt in full by the due date it could lose control of Hainan Shiner, certain buildings and land use rights. Finally, the Company’s inability to obtain a waiver for the violation of the loan agreement resulted in the amount due under this credit facility being shown as a current liability. If the lender calls the loan due to the violation of the trust agreement, the Company will attempt to negotiate a waiver from the current lender or request additional time to repay the loan to allow the Company time to collect the amounts due from the unrelated third parties, or to obtain other financing to repay this lender.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with US GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash and Equivalents
Cash and equivalents include cash on hand and cash in time deposits, certificates of deposit and all highly liquid debt instruments with original maturities of three months or less.
Restricted Cash
Restricted cash consists of monies restricted by the Company’s lenders related to its outstanding debt obligations.
Accounts Receivable, net
The Company maintains reserves for potential credit losses on accounts receivable. Management reviews the composition of accounts receivable and analyzes historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customer payment patterns to evaluate the adequacy of these reserves. Reserves are recorded primarily on a specific identification basis. Based on historical collection activity, the Company had allowances of $1,845,038 and $1,576,952 at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
F-8
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
Other Receivables
Other receivables consist of amounts due from customers that are non-interest bearing and payable upon demand and amounts due from other unrelated third parties that bear interest and have specific repayment dates - (See Note 3).
Advances to Suppliers
To ensure a steady supply of raw materials, the Company is required from time to time to make cash advances when placing its purchase orders. Management determined no reserve was necessary for advances to suppliers. The advances to suppliers are interest free and unsecured.
Notes Receivable
Notes receivable consist of bank notes received from customers as payment of their accounts receivable. The notes are guaranteed by banks and bear no interest. The notes are generally due within twelve months from the date of issuance.
Inventory, net
Inventory is valued at the lower of the inventory’s cost (weighted average basis) or the current market price of the inventory. Management compares the cost of inventory with its market value and an allowance is made to write down inventory to market value, if lower.
Property and Equipment, net
Property and equipment are stated at cost. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred; additions, renewals and improvements are capitalized. When property and equipment are retired or otherwise disposed of, the related cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from the respective accounts, and any gain or loss is included in operations. Depreciation of property and equipment is provided using the straight-line method for substantially all assets with estimated lives as follows:
| Operating equipment | 10 years |
| Vehicles | 8 years |
| Office equipment | 5 years |
| Buildings and improvements | 20 years |
Construction in Progress and Government Grants
Construction in progress (“CIP”) mainly consists of amounts expended to build a manufacturing workshop in Hainan, including a product line for a BOPP tobacco line. The costs incurred and capitalized as construction in progress at December 31, 2015 and 2014 include facility and equipment. Once the project is completed, it will be transferred from “Construction in progress” to “Property and equipment.” The total cost of the new Hainan manufacturing workshop and the BOPP tobacco line is expected to be $25.1 million. The first phase of the project was completed during 2010.
In October 2009, the Company received a government grant for the above project of RMB29.1 million (or $4.3 million based on the exchange rate at December 31, 2009) from the Hainan Province Finance Bureau (“HPFB”). The Company is required to provide detailed expenses of the construction project to the HPFB. At December 31, 2015 and 2014 respectively, RMB17.8 million ($2.8 million based on the exchange rate at December 31, 2015) and RMB20.8 million ($3.4 million based on the exchange rate at December 31, 2014) was recorded in “Other payables” on the accompanying consolidated financial statements (Note 7). The government grant is being amortized into other income over the useful life of the asset on the same basis used to depreciate the asset. For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company amortized $467,346 and $469,965, respectively, into “Other income.”
F-9
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
In December 2011, the Company received a government grant of RMB14.0 million (or $2.2 million based on the exchange rate as of December 31, 2011) from the Haikou Finance Bureau (“HFB”) for the adjustment and expansion of our operations and related capital expenditures for construction and equipment purchases. The Company is required to provide detailed expenses of the construction project to HFB. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, RMB8.6 million ($1.3 million based on the exchange rate at December 31, 2015) and RMB10.0 million ($1.6 million based on the exchange rate at December 31, 2014) was recorded in “Other payables” on the accompanying consolidated financial statements (Note 7). The government grant is being amortized into other income over the useful life of the asset on the same basis used to depreciate the asset. For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company amortized $224,840 and $227,780, respectively, into “Other income.”
In January 2012, the Company received a government grant of RMB1.8 million (or $0.3 million based on the exchange rate as of January 31, 2012) from the HFB for the adjustment and expansion of our operation and related capital expenditures for construction and equipment purchase. The Company is required to provide detailed expenses of the construction project to the HFB. At the end of the project, the government will determine if the funds were used in accordance with the grant. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the grant was recorded in “Other payables” on the accompanying consolidated financial statements (Note 7). If the government determines the funds were used for their intended purpose, the government grant is then amortized into “Other income” over the useful life of the asset on the same basis being used to depreciate the asset.
A rollfoward of the CIP from December 31, 2013 to December 31, 2015 is below:
| CIP at December 31, 2013 | $ | 6,251,585 | |
| Transfers to property and equipment | (820,347 | ) | |
| Additions during 2014 | 1,614,528 | ||
| Foreign currency translation | (38,190 | ) | |
| CIP at December 31, 2014 | 7,007,576 | ||
| Transfers to property and equipment | - | ||
| Additions during 2015 | 830,589 | ||
| Foreign currency translation | (403,902 | ) | |
| CIP at December 31, 2015 | $ | 7,434,263 |
Long-Lived Assets
The Company applies FASB ASC Topic 360, “Property, Plant, and Equipment,” which addresses financial accounting and reporting for the impairment or disposal of long-lived assets. ASC Topic 360 requires impairment losses to be recorded on long-lived assets used in operations when indicators of impairment are present and the undiscounted cash flows estimated to be generated by those assets are less than the assets’ carrying amounts. In that event, a loss is recognized based on the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the FV of the long-lived assets. Loss on long-lived assets to be disposed of is determined in a similar manner, except that FVs are reduced to recognize the cost of disposal. Based on its review, the Company believes that as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, there was no significant impairment of its long-lived assets.
Intangible Assets, net
Intangible assets consist of rights to use three plots of land in Haikou City granted by the Municipal Administration of China for state-owned land. For two of these plots, the Company’s rights run through January 2059 and, for the third, through October 2060. The Company also acquired a patent with the acquisition of Shimmer Sun that is being amortized over 10 years. The Company evaluates intangible assets for impairment, at least on an annual basis and whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable from its estimated future cash flows. Recoverability of intangible and other long-lived assets is measured by comparing their net book value to the related projected undiscounted cash flows from these assets, considering a number of factors including past operating results, budgets, economic projections, market trends and product development cycles. If the net book value of the asset exceeds the related undiscounted cash flows, the asset is considered impaired, and a second test is performed to measure the amount of impairment loss. No impairment adjustment was required at December 31, 2015 and 2014.
F-10
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
For certain of the Company’s financial instruments, including cash and equivalents, restricted cash, accounts receivable, advances to suppliers, accounts payable, accrued liabilities and short-term debt, the carrying amounts approximate their FVs due to their short maturities. In addition, the Company has long-term debt with financial institutions. The carrying amounts of the line of credit and other long-term liabilities approximate their FVs based on current rates of interest for instruments with similar characteristics.
FASB ASC Topic 820, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures,” requires disclosure of the FV of financial instruments held by the Company. FASB ASC Topic 825, “Financial Instruments,” defines FV, and establishes a three-level valuation hierarchy for disclosures of FV measurement that enhances disclosure requirements for FV measures. The carrying amounts reported in the consolidated balance sheets for receivables and current liabilities each qualify as financial instruments and are a reasonable estimate of their FVs because of the short period of time between the origination of such instruments and their expected realization and their current market rate of interest. The three levels of valuation hierarchy are defined as follows:
| • |
Level 1 inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets. | |
|
| ||
| • |
Level 2 inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, quoted prices for identical or similar assets in inactive markets, and inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument. | |
|
| ||
| • |
Level 3 inputs to the valuation methodology use one or more unobservable inputs which are significant to the FV measurement. |
The Company analyzes all financial instruments with features of both liabilities and equity under FASB ASC Topic 480, “Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity,” and FASB ASC Topic 815, “Derivatives and Hedging.” As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, the Company did not identify any assets and liabilities required to be presented on the balance sheet at FV.
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s revenue recognition policies comply with FASB ASC Topic 605, “Revenue Recognition.” Sales revenue is recognized at the date of shipment to customers when a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and collectability is reasonably assured. Payments received before all of the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are satisfied are recorded as unearned revenue.
Sales revenue consists of the invoiced value of goods, which is net of value-added tax (“VAT”). All of the Company’s products sold in the PRC are subject to Chinese VAT of 17% of the gross sales price. This VAT may be offset by VAT paid by the Company on raw materials and other materials included in the cost of producing their end product. The Company recorded VAT payable and VAT receivable net of payments in the financial statements. The VAT tax return is filed offsetting the payables against the receivables. Sales and purchases are recorded net of VAT collected and paid. VAT taxes are not affected by the income tax holiday.
F-11
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
Sales returns and allowances was $0 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014. The Company does not provide unconditional right of return, price protection or any other concessions to its dealers or other customers.
Other Income
The Company recognizes other income in the period it has earned the revenue and collectability is reasonably assured. Other income for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 consists primarily of subsidy income received from Chinese Government Agencies for developing technology and research and development. The Company must manage the funds according to government requirements. The Company recognizes the income over the useful life of the asset for which the subsidy was received.
Advertising Costs
The Company expenses the cost of advertising as incurred. Advertising costs for 2015 and 2014 were not significant.
Research and Development
The Company expenses its research and development (“R&D”) costs as incurred. R&D costs included in general and administrative expenses for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 were $2,587,262 and $3,159,619, respectively.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company records stock-based compensation in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718, “Compensation – Stock Compensation.” ASC Topic 718 requires companies to measure compensation cost for stock-based employee compensation at FV at the grant date and recognize the expense over the employee’s requisite service period. The Company recognizes in the consolidated statement of operations and other comprehensive income the grant-date FV of stock options and other equity-based compensation issued to employees and non-employees. There were 60,000 options outstanding as of December 31, 2015 and 2014.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 740, “Income Taxes.” ASC Topic 740 requires a company to use the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes, whereby deferred tax assets are recognized for deductible temporary differences, and deferred tax liabilities are recognized for taxable temporary differences. Temporary differences are the differences between the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and their tax bases. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when, in the opinion of management, it is more likely than not that some portion, or all of, the deferred tax assets will not be realized. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are adjusted for the effects of changes in tax laws and rates on the date of enactment.
Under ASC Topic 740, a tax position is recognized as a benefit only if it is “more likely than not” that the tax position would be sustained in a tax examination, with a tax examination being presumed to occur. The amount recognized is the largest amount of tax benefit that is more than 50% likely of being realized on examination. For tax positions not meeting the “more likely than not” test, no tax benefit is recorded.
Basic and Diluted Earnings (Loss) Per Share
Earnings (loss) per share is calculated in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 260, “Earnings Per Share.” Basic earnings per share (“EPS”) is based on the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted EPS is based on the assumption that all dilutive convertible shares and stock warrants were converted or exercised. Dilution is computed by applying the treasury stock method. Under this method, warrants are assumed to be exercised at the beginning of the period (or at the time of issuance, if later), and as if funds obtained thereby were used to purchase common stock at the average market price during the period. There were 60,000 options and 0 warrants outstanding as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 with weighted-average exercise prices of $0.80. All options were excluded from the diluted loss per share for 2015 due to the anti-dilutive effect. The following is a reconciliation of the number of shares (denominator) used in the basic and diluted EPS computations for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014:
F-12
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||
| Per | Per | |||||||||||
| Share | Share | |||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||
| Basic earnings (loss) per share | 27,541,491 | $ | (0.02 | ) | 27,541,491 | $ | 0.15 | |||||
| Effect of dilutive stock options and warrants | - | - | - | - | ||||||||
| Diluted earnings (loss) per share | 27,541,491 | $ | (0.02 | ) | 27,541,491 | $ | 0.15 | |||||
Foreign Currency Transactions and Comprehensive Income
US GAAP requires recognized revenue, expenses, gains and losses to be included in net income. Certain statements, however, require entities to report specific changes in assets and liabilities, such as gain or loss on foreign currency translation, as a separate component of the equity section of the balance sheet. Such items, along with net income, are components of comprehensive income. The functional currency of the Company’s Chinese subsidiaries is the RMB. Translation gains of $4,849,974 and $6,611,234 at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, are classified as an item of other comprehensive income in the stockholders’ equity section of the consolidated balance sheets.
Statement of Cash Flows
In accordance with FASB ASC Topic 230, “Statement of Cash Flows,” cash flows from the Company’s operations are calculated based on the local currencies using the average translation rates. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the consolidated statements of cash flows will not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the consolidated balance sheets.
Segment Reporting
FASB ASC Topic 280, “Segment Reporting,” requires use of the “management approach” model for segment reporting. The management approach model is based on the way a company’s management organizes segments within the company for making operating decisions and assessing performance. The Company determined it has five reportable segments. See Note 15.
Dividends
The Company's Chinese subsidiaries have restrictions on the payment of dividends to the Company. China has currency and capital transfer regulations that may require the Company's Chinese subsidiaries to comply with complex regulations for the movement of capital. These regulations include a public notice issued in October 2005 by the State Administration of Foreign Exchange (“SAFE”) requiring PRC residents, including both legal and natural persons, to register with the competent local SAFE branch before establishing or controlling any company outside of China. Although the Company believes its Chinese subsidiaries are in compliance with these regulations, should these regulations or the interpretation of them by courts or regulatory agencies change, the Company may not be able to pay dividends outside of China.
F-13
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
Reclassifications
Certain prior period amounts were reclassified to conform to the manner of presentation in the current period. These reclassifications had no effect on the net loss or stockholders’ equity.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2014, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (ASU 2014-09) , which supersedes nearly all existing revenue recognition guidance under U.S. GAAP. The core principle of ASU 2014-09 is to recognize revenues when promised goods or services are transferred to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which an entity expects to be entitled for those goods or services. ASU 2014-09 defines a five step process to achieve this core principle and, in doing so, more judgment and estimates may be required within the revenue recognition process than are required under existing U.S. GAAP. The standard is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods therein, using either of the following transition methods: (i) a full retrospective approach reflecting the application of the standard in each prior reporting period with the option to elect certain practical expedients, or (ii) a retrospective approach with the cumulative effect of initially adopting ASU 2014-09 recognized at the date of adoption (which includes additional footnote disclosures). Early adoption is not permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of the pending adoption of ASU 2014-09 on its consolidated financial statements and has not yet determined the method by which it will adopt the standard beginning January 1, 2017.
In August, 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-14, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Deferral of the Effective Date. The amendment in this ASU defers the effective date of ASU No. 2014-09 for all entities for one year. Public business entities, certain not-for-profit entities, and certain employee benefit plans should apply the guidance in ASU 2014-09 to annual reporting periods beginning December 15, 2017, including interim reporting periods within that reporting period. Earlier application is permitted only as of annual reporting periods beginning after December 31, 2016, including interim reporting periods with that reporting period.
In February, 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-02, Consolidation (Topic 810): Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis. ASU 2015-02 provides guidance on the consolidation evaluation for reporting organizations that are required to evaluate whether they should consolidate certain legal entities such as limited partnerships, limited liability corporations, and securitization structures (collateralized debt obligations, collateralized loan obligations, and mortgage-backed security transactions). ASU 2015-02 is effective for periods beginning December 15, 2015. The adoption of ASU 2015-02 is not expected to have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements. Early adoption is permitted.
In September, 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-16, Business Combinations (Topic 805). Topic 805 requires that an acquirer retrospectively adjust provisional amounts recognized in a business combination, during the measurement period. To simplify the accounting for adjustments made to provisional amounts, the amendments in the Update require that the acquirer recognize adjustments to provisional amounts that are identified during the measurement period in the reporting period in which the adjustment amount is determined. The acquirer is required to also record, in the same period’s financial statements, the effect on earnings of changes in depreciation, amortization, or other income effects, if any, as a result of the change to the provisional amounts, calculated as if the accounting had been completed at the acquisition date. In addition an entity is required to present separately on the face of the income statement or disclose in the notes to the financial statements the portion of the amount recorded in current-period earnings by line item that would have been recorded in previous reporting periods if the adjustment to the provisional amounts had been recognized as of the acquisition date. ASU 2015-16 is effective for fiscal years beginning December 15, 2015. The adoption of ASU 2015-016 is not expected to have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In November 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-17, Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes. The new guidance requires that all deferred tax assets and liabilities, along with any related valuation allowance, be classified as noncurrent on the balance sheet. This update is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016 and interim periods within those annual periods. The Company does not anticipate the adoption of this ASU will have a significant impact on its consolidated financial position, results of operations, or cash flows.
F-14
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842). The guidance in ASU No. 2016-02 supersedes the lease recognition requirements in ASC Topic 840, Leases (FAS 13). ASU 2016-02 requires an entity to recognize assets and liabilities arising from a lease for both financing and operating leases, along with additional qualitative and quantitative disclosures. ASU 2016-02 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the effect this standard will have on its consolidated financial statements.
Other recent accounting pronouncements issued by the FASB, including its Emerging Issues Task Force, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, and the Securities and Exchange Commission did not or are not believed by management to have a material impact on the Company's present or future financial statements.
Note 3 – Other Receivables
Other receivables at December 31, 2015 and 2014 consisted of the following:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Due from various unrelated customers, non-interest bearing and due upon demand | $ | 511,649 | $ | 1,289,628 | ||
| Due April 30, 2015 from Hainan Jinhong, an unrelated third party, with interest at 5% | - | 4,335,598 | ||||
| Due April 30, 2015 from Hainan Modern Construction Company, an unrelated third party, with interest at 10% | - | 7,990,197 | ||||
| Due April 30, 2015 from Dingfeng, an unrelated third party, with interest at 5% | - | 6,947,664 | ||||
| Due April 21, 2017 from Rixin Hotel Management, an unrelated third party, with interest at 12%* | 2,825,578 | 3,015,807 | ||||
| Due April 21, 2017 from Xiandai Meiju, an unrelated third party, with interest at 16% | 8,660,420 | 15,781,900 | ||||
| Due May 1, 2016 from Hainan Dingfeng Trading Co., an unrelated third party, with interest at 0% | 1,232,800 | - | ||||
| Due May 1, 2016 from Hainan Jinhong, an unrelated third party, with interest at 0% | 339,020 | - | ||||
| Due April 30, 2016 from Rixin Hotel Management, a related party, with interest at 0% | 3,875,814 | - | ||||
| Total other receivables | 17,445,281 | 39,360,794 | ||||
| Current portion | 5,959,283 | 20,563,087 | ||||
| Non-current portion | $ | 11,485,998 | $ | 18,797,707 |
* At the time this transaction was entered into, Rixin Hotel Management was an unrelated third party; however, in the fourth quarter of 2014, the Company formed a new subsidiary, Hainan Juneng, that is owned 50% by the Company, 22% by Rixin Hotel Management and 28% by an unrelated third party.
Note 4 – Inventory, net
Inventory at December 31, 2015 and 2014 consisted of the following:
F-15
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Raw Material | $ | 4,831,858 | $ | 3,544,464 | ||
| Work in process | 1,473,871 | 1,220,588 | ||||
| Finished goods | 6,333,103 | 5,968,467 | ||||
| Total Inventory | 12,638,832 | 10,733,519 | ||||
| Less: Obsolescence reserve | (648,281 | ) | (750,376 | ) | ||
| Inventory, net | $ | 11,990,551 | $ | 9,983,143 |
Note 5 – Property and Equipment, net
Property and equipment at December 31, 2015 and 2014 consisted of the following:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Operating equipment | $ | 25,030,991 | $ | 25,856,799 | ||
| Vehicles | 655,413 | 691,990 | ||||
| Office equipment | 144,376 | 146,193 | ||||
| Buildings | 12,041,660 | 12,700,884 | ||||
| Total property and equipment | 37,872,440 | 39,395,866 | ||||
| Less accumulated depreciation | (15,854,248 | ) | (13,523,233 | ) | ||
| Property and equipment, net | $ | 22,018,192 | $ | 25,872,633 |
Note 6 - Intangible Assets
Intangible assets at December 31, 2015 and 2014 consisted of the following:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Right to use land | $ | 1,129,970 | $ | 1,193,031 | ||
| Less: Accumulated amortization | (156,598 | ) | (141,788 | ) | ||
| Intangible assets, net | $ | 973,372 | $ | 1,051,243 |
Pursuant to the regulations, the PRC government owns all land. The Company has recognized the amounts paid for the acquisition of rights to use the land as an intangible asset and amortizing such rights over the period the Company has use of the land, which range from 54 to 57 years.
Amortization of intangible assets is as follows, by years from December 31, 2015:
| Year ending December 31, | |||
| 2016 | $ | 22,599 | |
| 2017 | 22,599 | ||
| 2018 | 22,599 | ||
| 2019 | 22,599 | ||
| 2020 | 22,599 | ||
| Thereafter | 860,377 | ||
| $ | 973,372 |
F-16
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
Note 7 – Other Payables
Other payables at December 31, 2015 and 2014 consisted of the following:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Government grant for Shi Zi Ling workshop | $ | 2,765,325 | $ | 3,393,109 | ||
| Government grant for structure and equipment | 1,330,397 | 1,632,423 | ||||
| Government grant for expansion and equipment | 275,069 | 290,420 | ||||
| Taxes Payable | 1,954,864 | 1,985,966 | ||||
| Due to Rixin Hotel Management | 3,071,629 | 3,243,050 | ||||
| Due to Hainan Dingfeng | - | 5,126,991 | ||||
| Miscellaneous payables | 493,322 | 2,506,040 | ||||
| $ | 9,890,606 | $ | 18,177,999 |
The $2,765,325, $1,330,397 and $275,069 payables at December 31, 2015 are liabilities recorded pursuant to the funds received as part of government grants. See “Construction in Progress and Government Grants” in Note 2.
Note 8 - Short-term Loans
Short-term loans at December 31, 2015 and 2014 consisted of the following:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Due February 14, 2015 with interest of 4.5% | $ | - | $ | 332,766 | ||
| Due February 20, 2015 with interest of 4.5% | - | 56,635 | ||||
| Due March 8, 2015 with interest of 4.5% | - | 499,998 | ||||
| Due March 28, 2015, with interest of 6.6% | - | 1,627,000 | ||||
| Due March 28, 2015, with interest of 6.6% | - | 3,254,000 | ||||
| Due April 28, 2015 with interest of 6.6% | - | 3,254,000 | ||||
| Due April 30, 2015 with interest of 6.72% | - | 2,928,600 | ||||
| Due May 30, 2015 with interest of 6.6% | - | 1,627,000 | ||||
| Due June 25, 2015 with interest of 6.6% | - | 1,627,000 | ||||
| Due June 25, 2015 with interest of 6.16% | - | 1,545,650 | ||||
| Due June 30, 2015 with interest of 6.16% | - | 1,301,600 | ||||
| Due August 28, 2015 with interest of 7.2% | - | 3,254,000 | ||||
| Due November 25, 2015 with interest of 6.72% | - | 813,500 | ||||
| Due November 28, 2015 with interest of 6.72% | - | 3,254,000 | ||||
| Due December 17, 2015 with interest of 6.2% | - | 4,067,500 | ||||
| Due December 19, 2015 with interest of 6.2% | - | 2,440,500 | ||||
| Due December 22, 2015 with interest of 5.6% | - | 2,928,600 | ||||
| Due February 10, 2016 with interest of 6.2% | 770,500 | - | ||||
| Due February 15, 2016 with interest of 6.7% | 3,082,000 | - | ||||
| Due March 9, 2016 with interest of 5.8% | 1,463,950 | - | ||||
| Due March 13, 2016 with interest of 5.9% | 770,500 | - | ||||
| Due March 19, 2016 with interest of 5.9% | 2,311,500 | - | ||||
| Due April 10, 2016 with interest of 5.9% | 3,082,000 | - | ||||
| Due May 20, 2016 with interest of 5.9% | 1,541,000 | - | ||||
| Due June 8, 2016 with interest of 5.9% | 1,541,000 | - | ||||
| Due June 8, 2016 with interest of 5.9% | 1,541,000 | - | ||||
| Due June 17, 2016 with interest of 5.9% | 1,541,000 | - | ||||
| Due June 20, 2016 with interest of 5.4% | 2,234,450 | |||||
| Due June 28, 2016 with interest of 5.4% | 924,600 | |||||
| Various bank acceptance bills payable on various dates through March 27, 2016 | 924,600 | 3,931,673 | ||||
| $ | 21,728,100 | $ | 38,744,022 |
F-17
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
All short-term loans are collateralized by Company buildings and equipment.
Note 9 - Long-term Loans
Long-term loans at December 31, 2015 and 2014 consisted of the following:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Due January 24, 2018, with interest of 6.60% | $ | 4,623,000 | $ | 7,321,500 | ||
| Credit line due April 18, 2017, with interest of 7.35% (see Note 3) | 12,328,000 | 19,524,000 | ||||
| 16,951,000 | 26,845,500 | |||||
| Long-term loans, currently in default | (12,328,000 | ) | (19,524,000 | ) | ||
| Long-term loans | $ | 4,623,000 | $ | 7,321,500 |
All long-term loans are collateralized by Company buildings and land use rights. The credit line due April 18, 2017 is also collateralized by all the capital stock of Hainan Shiner, the Company’s primary operating subsidiary. Aggregate future maturities of long-term loans at December 31, 2015 are as follows:
| Year ending December 31, | |||
| 2016 | $ | - | |
| 2017 | 12,328,000 | ||
| 2018 | 4,623,000 | ||
| $ | 16,951,000 |
The weighted average interest rate on long-term loans is 7.15% .
On August 2, 2010, Hainan Shiner entered into a credit facility with the Hainan Branch of the Bank of China. It is a secured revolving credit facility of RMB70 million (or $11.1 million based on the exchange rate on December 31, 2010) for seven years. Under the credit facility, Hainan Shiner may only use the loan proceeds to improve the technology of its BOPP film and to purchase certain equipment necessary for this improvement. Proceeds under the facility not used for these purposes would be subject to a misappropriation penalty interest rate that is 100% of the current interest rate on the loan.
The initial interest rate on each withdrawal from the facility is the 5-year benchmark lending rate announced by the People’s Bank of China on the date of such withdrawal, and is subject to adjustment every 12 months based upon the benchmark. Additional interest is paid on an overdue loan under this credit facility at 50% of the current interest rate on the loan. Hainan Shiner and certain of its affiliates, including the Company, have provided guarantees and certain land use rights, buildings, and property as collateral under this facility.
The credit facility includes covenants that prohibit Hainan Shiner from making distributions to the Company, its sole shareholder, if (a) its after-tax net income for the fiscal year is zero or negative, (b) its after-tax net income is insufficient to make up its accumulated loss, (c) its income before tax is not utilized in paying off the capital, interest and expense of the lender, or (d) its income before tax is insufficient to pay the capital, interest and expense of the lender.
F-18
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
As of December 31, 2015, the outstanding balance under this credit facility was RMB30 million or $4.6 million.
The Company also has a RMB120 million (approximately $19.5 million) credit facility that it drew down in its entirety on April 17, 2014. The credit facility is collateralized by the stock of Hainan Shiner, bears interest at 7.35% per annum and is due on April 17, 2017. Under the terms of the credit facility agreement, the proceeds of the funds borrowed under this credit facility are to be used solely for the construction of an office building and research facility at the Hainan Xiandai Packaging Industrial Park and for the purchase of research and development equipment, however, the Company has loaned the entire proceeds of the credit facility to unrelated third parties who have no collateral on such loans other than a guarantee from each of the borrowers and an unrelated fourth party (See Note 3). During the year ended December 31, 2015, some of the loans made to unrelated third parties were repaid. The Company has not been able to obtain a waiver for the violation of the loan agreement, therefore the amount due under this credit facility is being shown as a current liability, as the lender will retain the right to declare a breach of the credit agreement and enforce its right to ownership of the stock, buildings and land use rights of Hainan Shiner, the Company’s primary operating subsidiary. Except as set forth above, as at December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company is in compliance with all its obligations under the foregoing loan commitments. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company repaid approximately $7.2 million of this credit facility.
Note 10 - Stock Options and Warrants
Stock Options
The following is a summary of the Company’s stock option activity for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014:
| Weighted | ||||||||||
| Average | ||||||||||
| Exercise | Aggregate | |||||||||
| Options | Price | Intrinsic | ||||||||
| Outstanding | Price | Value | ||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2013 | 90,000 | $ | 0.95 | $ | - | |||||
| Granted | - | |||||||||
| Canceled/ Expired | (30,000 | ) | 1.25 | |||||||
| Exercised | - | |||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2014 | 60,000 | $ | 0.80 | $ | - | |||||
| Granted | - | |||||||||
| Canceled/ Expired | - | |||||||||
| Exercised | - | |||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2015 | 60,000 | $ | 0.80 | $ | - | |||||
| Exercisable at December 31, 2015 | 60,000 | $ | 0.80 | $ | - |
The number and weighted average exercise prices of all options outstanding as of December 31, 2015, are as follows:
| Options Outstanding | ||||||||||
| Weighted | ||||||||||
| Weighted | Average | |||||||||
| Number | Average | Remaining | ||||||||
| Range of | Outstanding | Exercise | Contractual Life | |||||||
| Exercise Price | December 31, 2015 | Price | (Years) | |||||||
| $0.80 | 60,000 | $ | 0.80 | 0.94 | ||||||
| 60,000 | ||||||||||
F-19
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
The number and weighted average exercise prices of all options exercisable as of December 31, 2015, are as follows:
| Options Exercisable | ||||||||||
| Weighted | ||||||||||
| Weighted | Average | |||||||||
| Number | Average | Remaining | ||||||||
| Range of | Outstanding | Exercise | Contractual Life | |||||||
| Exercise Price | December 31, 2015 | Price | (Years) | |||||||
| $0.80 | 60,000 | $ | 0.80 | 0.94 | ||||||
| 60,000 | ||||||||||
Note 11 - Income Taxes
Local PRC Income Tax
Pursuant to the tax laws of the PRC, general enterprises are subject to income tax at 25%.
The Company operates in a privileged economic zone which entitles it to certain tax benefits (tax holiday). Hainan Shiner has a tax rate of 15% from January 1, 2009 to December 31, 2014 since it is recognized as a high-tech enterprise. Hainan Shiner acquired all of the assets of Shiny-Day and Modern in 2009, partially in response to the expiration of the tax holiday.
Income tax expense reflected in the consolidated statements of operations and other comprehensive loss consist of the following for 2015 and 2014:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Current expense: | ||||||
| Federal | $ | - | $ | - | ||
| State | - | - | ||||
| Foreign | 962,688 | 1,022,512 | ||||
| 962,688 | 1,022,512 | |||||
| Deferred expense: | ||||||
| Federal | - | - | ||||
| State | - | - | ||||
| Foreign | - | - | ||||
| - | - | |||||
| Total income tax expense | $ | 962,688 | $ | 1,022,512 |
The components of deferred income tax assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Deferred tax assets: | ||||||
| Net operating loss | $ | 674,000 | $ | 630,000 | ||
| Total deferred tax assets | 674,000 | 630,000 | ||||
| Less valuation allowance | (674,000 | ) | (630,000 | ) | ||
| $ | - | $ | - |
A reconciliation of tax at US federal statutory rate to provision for income tax recorded in the financial statements for 2015 and 2014 is as follows:
F-20
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Tax provision (benefit) at statutory rate | 34% | 34% | ||||
| Foreign tax rate difference | (9)% | (9)% | ||||
| US and Chinese current NOL for which no benefit is realized | 323% | (12)% | ||||
| Effect of tax holiday | 0% | 7% | ||||
| Effective rate | 348% | 20% |
If the Company had not been exempt from income taxes due to operating in a privileged economic zone, for 2014 net income would have been decreased by $363,000. The net effect on EPS had income tax been applied at the regular rates would have been $0.01.
Foreign pretax income (loss) approximated $(557,509) and $4,157,000 for 2015 and 2014, respectively. Pretax earnings of a foreign subsidiary are subject to US taxation when effectively repatriated. The Company provides income taxes on the undistributed earnings of non-US subsidiaries except to the extent such earnings are indefinitely invested outside the US. At December 31, 2015, $15,871,000 of accumulated undistributed earnings of non-US subsidiaries was indefinitely invested. At the existing US federal income tax rate, additional taxes of $2,608,000 would have to be provided if such earnings were remitted currently.
Note 12 - Employee Welfare Plans
The expense for employee common welfare was $90,141 and $107,344 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Note 13 - Statutory Common Welfare Fund
As stipulated by the Company Law of the PRC, net income after taxation can only be distributed as dividends after appropriation has been made for the following:
| i. |
Making up cumulative prior years’ losses, if any; | |
| ii. |
Allocations to the “statutory surplus reserve” of at least 10% of income after tax, as determined under PRC accounting rules and regulations, until the reserve reaches 50% of the Company’s registered capital; | |
| iii. |
Allocations of 5% to 10% of income after tax, as determined under PRC accounting rules and regulations, to the Company’s “statutory common welfare fund,” which is established for the purpose of providing employee facilities and other collective benefits to the Company’s employees; and | |
| iv. |
Allocations to the discretionary surplus reserve, if approved in the stockholders’ general meeting. |
The Company appropriated $161,772 and $440,847 as reserve for the statutory surplus reserve and statutory common welfare fund for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Note 14 - Current Vulnerability Due to Certain Concentrations
There were no customers that exceeded 10% of the Company’s sales for either year ended December 31, 2015 or 2014.
One vendor provided 11% of the Company’s raw material purchases for the year ended December 31, 2015. One vendor provided 11% of the Company’s raw material purchases for the year ended December 31, 2014. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company owed this vendor $0 and $0, respectively.
The Company’s operations are carried out in the PRC. Accordingly, the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations may be influenced by the political, economic and legal environments in the PRC and by the general state of the PRC’s economy. The Company’s business may be influenced by changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, currency conversion and remittance abroad, and rates and methods of taxation, among other things.
F-21
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
Note 13 – Commitments and Contingencies
At December 31, 2015, the Company was contingently liable to banks for discounted notes receivable and to vendors for endorsed notes receivable of $2,332,186.
Note 15 – Segment Information
The Company has five segments: BOPP tobacco films, water-based latex, coated film, color printed packaging and advanced film. The water-based latex is one of the raw materials used in coated film to make the packaging more environmental friendly and the barrier property better.
The following tables summarize the Company’s segment information for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014:
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||
| Revenues from unrelated entities | ||||||
| Tobacco film | $ | 40,116,262 | $ | 58,090,157 | ||
| Water-based latex | 463,833 | 632,053 | ||||
| Coated film | 26,698,220 | 31,100,464 | ||||
| Color printing | 3,945,283 | 4,625,718 | ||||
| Advanced film | 5,107,921 | 6,669,429 | ||||
| $ | 76,331,519 | $ | 101,117,821 | |||
| Intersegment revenues | ||||||
| Tobacco film | $ | 2,581,689 | $ | 1,184,944 | ||
| Water-based latex | 42,827 | 43,387 | ||||
| Coated film | 1,718,168 | 679,784 | ||||
| Color printing | 253,899 | 101,108 | ||||
| Advanced film | 328,721 | 145,778 | ||||
| $ | 4,925,304 | $ | 2,155,001 | |||
| Total revenues | ||||||
| Tobacco film | $ | 42,697,951 | $ | 59,275,101 | ||
| Water-based latex | 506,660 | 675,440 | ||||
| Coated film | 28,416,388 | 31,780,248 | ||||
| Color printing | 4,199,182 | 4,726,826 | ||||
| Advanced film | 5,436,642 | 6,815,207 | ||||
| Less Intersegment revenues | (4,925,304 | ) | (2,155,001 | ) | ||
| $ | 76,331,519 | $ | 101,117,821 | |||
| Income (loss) from operations | ||||||
| Tobacco film | $ | 3,576,842 | $ | 5,135,083 | ||
| Water-based latex | 147,209 | 201,360 | ||||
| Coated film | (1,537,022 | ) | 191,081 | |||
F-22
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
| Color printing | (885,096 | ) | (695,747 | ) | ||
| Advanced film | (218,401 | ) | (213,317 | ) | ||
| Holding Company | (197,995 | ) | (165,984 | ) | ||
| $ | 885,537 | $ | 4,452,476 | |||
| Interest income | ||||||
| Tobacco film | $ | 1,188,682 | $ | 1,181,676 | ||
| Water-based latex | 13,744 | 13,777 | ||||
| Coated film | 791,094 | 677,909 | ||||
| Color printing | 116,903 | 100,829 | ||||
| Advanced film | 151,353 | 145,376 | ||||
| Holding Company | 72,500 | 72,500 | ||||
| $ | 2,334,276 | $ | 2,192,067 | |||
| Interest expense | ||||||
| Tobacco film | $ | 2,286,746 | $ | 2,193,336 | ||
| Water-based latex | 23,787 | 22,815 | ||||
| Coated film | 907,049 | 869,997 | ||||
| Color printing | 183,522 | 176,026 | ||||
| Advanced film | 383,967 | 368,283 | ||||
| Holding Company | (2,819 | ) | (2,283 | ) | ||
| $ | 3,782,252 | $ | 3,628,174 | |||
| Income tax expense | ||||||
| Tobacco film | $ | 482,481 | $ | 545,455 | ||
| Water-based latex | - | - | ||||
| Coated film | 403,088 | 392,818 | ||||
| Color printing | - | - | ||||
| Advanced film | 77,119 | 84,239 | ||||
| Holding Company | - | - | ||||
| $ | 962,688 | $ | 1,022,512 | |||
| Net income (loss) | ||||||
| Tobacco film | $ | 2,453,278 | $ | 3,235,489 | ||
| Water-based latex | 137,166 | 189,526 | ||||
| Coated film | (1,674,283 | ) | 1,668,979 | |||
| Color printing | (951,716 | ) | (791,407 | ) | ||
| Advanced film | (455,092 | ) | (78,098 | ) | ||
| Holding Company | (195,176 | ) | (163,701 | ) | ||
| $ | (685,823 | ) | $ | 4,060,788 | ||
| Provision for depreciation | ||||||
| Tobacco film | $ | 1,907,807 | $ | 2,462,726 | ||
| Water-based latex | 36,301 | 40,097 | ||||
| Coated film | 756,741 | 976,852 | ||||
| Color printing | 153,111 | 197,646 | ||||
| Advanced film | 320,340 | 413,516 | ||||
| Holding Company | - | - | ||||
| $ | 3,174,300 | $ | 4,090,837 |
F-23
SHINER INTERNATIONAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES
TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2015 AND 2014
| As of | As of | |||||
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||
| Total Assets | 2015 | 2014 | ||||
| Tobacco film | $ | 48,472,654 | $ | 71,293,886 | ||
| Water-based latex | 657,568 | 657,568 | ||||
| Coated film | 19,226,916 | 28,279,069 | ||||
| Color printing | 3,890,165 | 5,721,679 | ||||
| Advanced film | 8,139,035 | 11,970,944 | ||||
| Holding Company | 11,105,905 | 11,222,719 | ||||
| $ | 91,492,243 | $ | 129,145,865 |
Note 16 - Geographical Sales
The geographical distribution of Shiner’s revenue for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 is as follows:
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||
|
Geographical Areas |
2015 | 2014 | ||||
|
Chinese Mainland |
$ | 66,554,075 | $ | 89,634,221 | ||
| Asia (outside Mainland China) | 4,658,546 | 5,514,238 | ||||
| Australia | 2,764,349 | 3,569,645 | ||||
| North America | 1,201,851 | 896,518 | ||||
| Middle East | 641,039 | 449,136 | ||||
| Europe | 347,563 | 938,884 | ||||
| South America | 164,096 | 115,179 | ||||
| $ | 76,331,519 | $ | 101,117,821 | |||
F-24
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Exhibit | Description of Exhibit | |
| 2.1 |
Share Exchange Agreement by and between Sino Palace Holdings Limited and Cartan Holdings Inc. dated as of July 23, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on July 27, 2007). | |
|
| ||
| 2.2 |
Return to Treasury Agreement between Cartan Holdings, Inc. and Zubeda Mohamed-Lakhani, dated as of July 23, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.2 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on July 27, 2007). | |
|
| ||
| 3.1 |
Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on July 27, 2007). | |
|
| ||
| 3.2 |
Amended and Restated Bylaws (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on July 27, 2007). | |
|
| ||
| 4.1 |
Specimen Stock Certificate (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on July 27, 2007). | |
|
| ||
| 10.1 |
Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of September 30, 2007, between Shiner and the investors signatory thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of Shiner’s Registration Statement on Form SB-2 (Commission File No. 333- 148304), filed with the SEC on December 21, 2007). | |
|
| ||
| 10.2 |
Form of Common Stock Purchase Warrant (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of Shiner’s Registration Statement on Form SB-2 (Commission File No. 333-148304), filed with the SEC on December 21, 2007). | |
|
| ||
| 10.3 |
Form of Stock Option Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of Shiner’s Registration Statement on Form SB-2 (Commission File No. 333-148304), filed with the SEC on December 21, 2007). | |
|
| ||
| 10.4 |
Employment Agreement, dated January 1, 2008, by and between Shiner and Jian Fu (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 of Shiner’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on March 28, 2008). | |
|
| ||
| 10.5 |
Employment Agreement, dated January 1, 2008, by and between Shiner and Xuezhu Xu (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 of Shiner’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on March 28, 2008). | |
|
| ||
| 10.6 |
Employment Agreement, dated January 1, 2008, by and between Shiner and Mingbiao Li (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 of Shiner’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on March 28, 2008). | |
|
| ||
| 10.7 |
Employment Agreement, dated February 11, 2010, by and between Shiner and Jeffrey T. Roney (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on February 26, 2009). | |
|
| ||
| 10.8 |
Employment Agreement, dated February 3, 2010, by and between Shiner and Qingtao Xing (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 of Shiner’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on March 25, 2010). | |
|
| ||
| 10.9 |
Articles of Association of Shanghai Juneng Functional Film Company, Ltd., a joint venture between Shiner and Shanghai Shifu Film Material, Co., Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on September 21, 2010). | |
|
| ||
| 10.10 |
Credit Facility between Hainan Shiner Industrial Co., Ltd. and the Hainan Branch of the Bank of China, dated June 29, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 of Shiner’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on November 15, 2010). |
| 10.11 |
Securities Purchase Agreement for Non-US Persons, dated as of December 28, 2010, between the Company and the Investors thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on December 29, 2010). | |
|
| ||
| 10.12 |
Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of December 28, 2010, between the Company and the Investors thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on December 29, 2010). | |
|
| ||
| 10.13 |
Form of Warrant of the Company (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8- K (Commission File No. 001-33960) filed with the SEC on December 29, 2010). | |
|
| ||
| 10.14 |
Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of December 28, 2010, by and between the Company and the Investors (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on December 29, 2010). | |
|
| ||
| 10.15 |
Amendment to Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of January 10, 2011, between the Company and the Investors thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 of Shiner’s Current Report on Form 8-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on January 14, 2011). | |
|
| ||
| 10.16 |
Share Transfer Agreement, dated as of May 2, 2011, by and between Fu Zhiyong and Shiner International, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.3 of the Company's quarterly report on Form 10-Q filed with the SEC on May 16, 2011) | |
|
| ||
| 10.17 |
English Translation of Trust Contract on Stock Rights Usufruct, dated April 17, 2014, between Zhongrong International Trust Co., Ltd. and Hainan Shiner Industrial Co., Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 of the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on April 20, 2015). | |
|
| ||
| 10.18 |
English Translation of Loan Agreement, dated April 30, 2014, between Hainan Shiny-Day Color Printing Packaging Co., Ltd. and Hainan Jinhong Trading Co. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18 of the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on April 20, 2015). | |
|
| ||
| 10.19 |
English Translation of Loan Agreement, dated April 30, 2014, between Hainan Shiny-Day Color Printing Packaging Co., Ltd. and Hainan Modern Construction Engineering Co. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.19 of the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on April 20, 2015). | |
|
| ||
| 10.20 |
English Translation of Loan Agreement, dated April 30, 2014, between Hainan Shiny-Day Color Printing Packaging Co., Ltd. and Hainan Dingfeng Trading Co. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 of the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on April 20, 2015). | |
|
| ||
| 10.21 |
English Translation of Loan Agreement, dated April 30, 2014, between Hainan Modern Hi-Tech Industrial Co., Ltd. and Rixin Hotel Management Co., Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 of the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on April 20, 2015). | |
|
| ||
| 10.22 |
English Translation of Trust Loan Contract, dated April 30, 2014, among Hainan Modern Hi-Tech Industrial Co., Ltd., Ping An Bank Co., Ltd. Haikou Branch, and Hainan Modern Meiju Investment Co., Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 of the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K (Commission File No. 001- 33960) filed with the SEC on April 20, 2015). | |
|
| ||
| 21 |
List of Subsidiaries | |
|
| ||
| 31.1* |
Certifications of Chief Executive Officer Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
|
| ||
| 31.2* |
Certifications of Chief Financial Officer Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
|
| ||
| 32.1* |
Certification of Chief Executive Officer Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
|
| ||
| 32.2* |
Certification of Chief Financial Officer Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
|
| ||
| 101** |
Interactive data files pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T |
________________________________
* Filed herewith
** Pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T, the following financial information from the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2015, is formatted in XBRL interactive data files: (i) Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2015 and 2014; (ii) Consolidated Statements of Operations and Other Comprehensive Loss for the Years Ended December 31, 2015 and 2014; (iii) Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2015 and 2014; (iv) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2015 and 2014; and (vi) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. Pursuant to Rule 406T of Regulation S-T, these interactive data files are deemed not filed or part of a registration statement or prospectus for purposes of Sections 11 or 12 of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Act of 1934, as amended, and otherwise are not subject to liability under those sections.
