Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-10.41 - EX-10.41 - SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS INC | scln-20151231ex10412e31a.htm |
| EX-10.40 - EX-10.40 - SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS INC | scln-20151231ex10404c96a.htm |
| EX-10.42 - EX-10.42 - SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS INC | scln-20151231ex10429b2e8.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS INC | scln-20151231xex321.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EX-21.1 - SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS INC | scln-20151231xex211.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS INC | scln-20151231xex312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS INC | scln-20151231xex311.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS INC | scln-20151231xex231.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EX-32.2 - SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS INC | scln-20151231xex322.htm |
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
|
☒ |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
|
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015 |
Or
|
☐ |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
For the transition period from to .
Commission file number 0-19825
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
|
Delaware |
94-3116852 |
|
(State or other jurisdiction of Incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
|
950 Tower Lane, Suite 900 Foster City, California |
94404 |
|
(Address of principal executive offices) |
(Zip Code) |
(650) 358-3456
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
Common Stock, $0.001 par value |
The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC. |
|
(Title of Class) |
(Name of each exchange on which registered) |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of Registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer or a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definition of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act (Check one):
|
Large accelerated filer |
☐ |
Accelerated filer |
☒ |
Non-accelerated filer |
☐ |
|
Smaller Reporting Company |
☐ |
|
|
|||||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of the voting stock held by non-affiliates of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. was approximately $489,624,000 as of June 30, 2015, based upon the closing price of SciClone Pharmaceuticals Inc.’s Common Stock on The NASDAQ Global Select Market on such date. Shares of Common Stock held by each executive officer and director have been excluded from the calculation because such persons may be deemed to be affiliates. This determination of affiliate status is not necessarily a conclusive determination for other purposes.
As of March 7, 2016, 49,624,211 shares of the Registrant’s Common Stock, $0.001 par value, were issued and outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Part III incorporates by reference from the definitive proxy statement for the Company’s 2016 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A not later than 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
PAGE NO. |
||||||
|
PART I. |
||||||
|
Item 1. |
4 |
|||||
|
Item 1A. |
16 |
|||||
|
Item 1B. |
35 |
|||||
|
Item 2. |
35 |
|||||
|
Item 3. |
35 |
|||||
|
Item 4. |
36 |
|||||
|
PART II. |
||||||
|
Item 5. |
37 |
|||||
|
Item 6. |
39 |
|||||
|
Item 7. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
40 |
||||
|
Item 7A. |
55 |
|||||
|
Item 8. |
56 |
|||||
|
57 |
||||||
|
58 |
||||||
|
59 |
||||||
|
60 |
||||||
|
61 |
||||||
|
62 |
||||||
|
63 |
||||||
|
Item 9. |
Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
88 |
||||
|
Item 9A. |
88 |
|||||
|
Item 9B. |
89 |
|||||
|
PART III. |
||||||
|
Item 10. |
89 |
|||||
|
Item 11. |
89 |
|||||
|
Item 12. |
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
90 |
||||
|
Item 13. |
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
90 |
||||
|
Item 14. |
90 |
|||||
|
PART IV. |
||||||
|
Item 15. |
90 |
|||||
|
95 |
||||||
As used in this Annual Report, the terms “we,” “us,” “our,” the “Company” and “SciClone” mean SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and its subsidiaries (unless the context indicates a different meaning). SciClone, SciClone Pharmaceuticals, the SciClone Pharmaceuticals design, the SciClone logo and ZADAXIN are registered trademarks of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. in the United States and numerous other countries. All other Company names and trademarks included in this Annual Report are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
2
NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. These forward-looking statements are based on our current expectations, estimates and projections about our business, industry, management’s beliefs and certain assumptions made by us. Words such as "may," "will," "would," "could," "should," "might," "believes," "estimates," "projects," "potential," "expects," "plans," "anticipates," "intends," "continues," "forecast," "designed," "goal," “unaudited,” “approximately” or the negative of those words or similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, including those statements we make regarding our future financial results. These statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that are difficult to predict and actual outcomes may differ materially.
These include risks and uncertainties relating to:
|
· |
our substantial dependence on sales of ZADAXIN in China; |
|
· |
government regulatory action affecting our Company or our drug products or our competitors' drug products in China, the US and other foreign countries, including the effect of government initiatives in China, particularly the Chinese government’s increasing regulation of the pharmaceutical industry through anti-corruption activities; |
|
· |
Chinese government regulatory actions intended to reduce pharmaceutical prices such as the reduction in the governmentally permitted maximum listed price for our products and increased oversight of the health care market and pharmaceutical industry; |
|
· |
prospects for ZADAXIN® and our plans for its enhancement and commercialization as well as our expectations regarding other products; |
|
· |
future size of the hepatitis B virus (“HBV”) and hepatitis C virus (“HCV”) and other markets, particularly in China; |
|
· |
anticipated product sales of current or anticipated products; |
|
· |
the sufficiency of our resources to complete clinical trials and other new product development initiatives; government regulatory actions that may affect product reimbursement, product pricing or otherwise affect the scope of our sales and marketing; the timing and outcome of clinical trials; |
|
· |
the dependence of our current and future revenue and prospects on third-party license, promotion or distribution agreements, including the need to renew such agreements, enter into similar agreements, or end arrangements that SciClone does not believe are beneficial; |
|
· |
the effects of the resolution of the SEC and DOJ matters and our ability to continue to comply with applicable regulations; |
|
· |
our ability to implement and maintain controls over our financial reporting; |
|
· |
operating an international business, particularly in China including pricing regulations, slow payment cycles and currency exchange fluctuations; |
|
· |
uncertainty in the prospects for unapproved products, including uncertainties as to pricing and competition and risks relating to the clinical trial process and related regulatory approval process and the process of initiating trials at, and enrolling patients at, clinical sites; |
|
· |
research and development and other expense levels; |
|
· |
the ability of our suppliers to continue financially viable production of our products; |
|
· |
the allocation of financial resources to certain trials and programs, and the outcome and expenses related to litigation; and |
|
· |
other factors discussed in this Report under Item 1A “Risk Factors” and Item 7 “Management Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations”. |
These statements are not guarantees of future performance and are subject to certain risks, uncertainties and assumptions that are difficult to predict. Therefore, our actual results could differ materially and adversely from those expressed in any forward-looking statements as a result of various factors including, but not limited to, those described under the caption “Risk Factors” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We undertake no obligation to revise or update publicly any forward-looking statements for any reason.
3
PART I
Overview
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (NASDAQ: SCLN) is a United States (“US”)-headquartered, China-focused, specialty pharmaceutical company with a substantial commercial business and a product portfolio of therapies for oncology, infectious diseases and cardiovascular disorders. We are focused on continuing to grow our revenue and profitability. Our business and corporate strategy is focused primarily on the People’s Republic of China (“China” or “PRC”) where we have built a solid reputation and established a strong brand through many years of experience marketing our lead product, ZADAXIN (thymalfasin). In addition, we have an established product promotion business model with large pharmaceutical partners and we are focused on establishing profitability in all of these collaborations. We believe our sales and marketing strengths position us to benefit from the long-term expansion of the pharmaceutical market in China. The Chinese pharmaceutical market currently ranks second among the global pharmaceutical markets, and had an estimated worth of $105 billion in 2014. It is forecasted to increase significantly to $200 billion by 2020. We seek to expand our presence in China and increase revenues by growing sales and profits of our current product portfolio, launching new products from our development pipeline, adding new, profitable product services agreements and leveraging our strong cash position to in-license additional products.
We operate in two segments which are generally based on the nature and location of our customers: 1) China and 2) the Rest of the World, which includes our US and Hong Kong operations.
We have two categories of revenues: “product sales revenues” and “promotion services revenues.” Our product sales revenues result from our proprietary and in-licensed products, including our lead product, ZADAXIN; DC Bead®, a product for the embolization of malignant hypervascularized tumors, for which we initiated sales and recorded product revenue beginning in the third quarter of 2015, and products from Pfizer International Trading (Shanghai) Ltd. (“Pfizer”). Through June 30, 2015, our product sales revenues also included Aggrastat®, an intervention cardiology product launched in China in 2009, in-licensed from Cardiome Pharma Corp (“Cardiome”). In August 2015, we and Cardiome mutually agreed to end our collaboration for Aggrastat, thereby terminating our exclusive distribution rights in China, and returning all rights to the product to Cardiome. We recorded Aggrastat revenues of $1.8 million, $1.1 million and $0 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively, and we do not expect to generate any further Aggrastat revenues. We do not anticipate that the termination of this agreement will adversely affect our profitability.
ZADAXIN has the highest margins in our portfolio as it is a premium product sold exclusively by SciClone. In addition, we anticipate that new marketed products, when and if introduced, can increase the future revenues and profitability of our pharmaceutical business in China over the coming years. Our “promotion services revenues” result primarily from fees we receive for exclusively promoting products in China for Baxter International, Inc. (“Baxter”). We recognize promotion services revenues as a percentage of our collaborators’ product sales revenue for these exclusively promoted products. Over time, as additional proprietary or in-licensed products come to the market, we aim to shift our product mix towards those products providing higher margins for us.
ZADAXIN is approved in over 30 countries and may be used for the treatment of HBV, HCV, and certain cancers, and as an immune system enhancer according to the local regulatory approvals we have in these countries. In China, thymalfasin is included in the treatment guidelines issued by the Ministry of Health (“MOH”) for liver cancer, as well as guidelines for treatment of chronic HBV (issued by both the Chinese Medical Association and the Asian-Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver) and invasive fungal infections of critically ill patients (issued by the Chinese Medical Association). Our sales force is focused on increasing sales to the country’s largest hospitals (class 3A with over 500 beds) as well as mid-size hospitals (class 2A). These hospitals serve Tier 1 and Tier 2 cities located mostly in the eastern part of China, which are the largest and generally have the most affluent populations. We are widening our market strategies by piloting e-commerce approaches to reaching customers. We are also seeking to expand the indications for which ZADAXIN could be used, including sepsis.
We initiated sales and recorded our first product revenue from DC Bead in the third quarter of fiscal 2015. The China Food and Drug Administration had approved the registration of DC Bead for the embolization of malignant hypervascularized tumors in August 2014. DC Bead may be used to treat liver cancer, a large and growing indication in China, and we believe our oncology sales team and academic marketing liaisons have established high quality relationships with medical professionals and institutions that specialize in cancer treatment, which we believe will be a valuable asset as we continue commercial sales of DC Bead. BioCompatibles UK Ltd.
4
(“BTG”) and SciClone previously entered into an agreement granting SciClone exclusive licensing and distribution rights to DC Bead in China. Under the agreement, we are purchasing DC Bead product from BTG.
We are also pursuing the registration of several other therapeutic products in China. These include: Loramyc®, a mucoadhesive tablet formulation of miconazole lauriad to treat oropharyngeal candidiasis; and RapidFilm®, an oral film formulation of ondansetron to treat nausea induced by chemotherapy.
Our agreement with Baxter is for a 5-year term, through December 2017, and our agreement with Pfizer is for a 5-year term, through June 2019. We are pursuing additional agreements to generate additional revenue. We continue to seek in-licensing arrangements for well-differentiated products at various stages of development that, if not yet approved, have a defined regulatory approval pathway in China. Our objective is to in-license products that provide us with higher margins, augmenting our product sales revenue and profitability, and we continue to explore opportunities to optimize our promotion services revenues.
In May 2015, Theravance Biopharma, Inc. (“Theravance Biopharma”) granted SciClone exclusive development and commercialization rights to VIBATIV® (telavancin) in China, as well as the Hong Kong SAR, the Macau SAR, Taiwan and Vietnam, in exchange for upfront and regulatory milestone payments totaling $6 million. SciClone will be responsible for all aspects of development and commercialization in the partnered regions, including pre- and post-launch activities and product registration. SciClone will initially develop VIBATIV for hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia, and additional indications may include complicated skin and skin structure infections and potentially bacteremia. Theravance Biopharma will sell to SciClone all clinical and commercial product required to develop and commercialize VIBATIV in China and our other licensed territories.
In December 2014, we entered into a strategic partnership with The Medicines Company for two cardiovascular products in China. The partnership includes an agreement granting us a license and the exclusive rights in China to promote two products including 1) Angiomax® (bivalirudin) for Injection, an anticoagulant indicated in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with provisional use of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor (GPI) and in patients with, or at risk of, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis syndrome undergoing PCI for which a Phase 3 registration trial was completed in China and is currently under review by the China Food and Drug Administration for marketing approval, and 2) Cleviprex® (clevidipine) Injectable Emulsion, a third-generation dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker indicated for the reduction of blood pressure when oral therapy is not feasible or desirable for which a clinical trial application (CTA) for China was filed in 2013. We received CTA approval from the China Food and Drug Administration (“CFDA”) in early 2016 and are preparing a clinical study. Under the terms of the agreement, we will be responsible for all aspects of commercialization, including pre-and post-launch activities, for both products in the China market (excluding Hong Kong and Macao). We have also agreed to participate in the China registration process for both products. Financial terms of the agreement, in addition to net sales royalties payable to The Medicines Company, include the following additional payments to The Medicines Company: an upfront payment made in the fourth quarter of 2014; a project support services fee; and regulatory/commercial success milestone payments of up to an aggregate of $50.5 million.
In June 2013, we entered into a license agreement with Taiwan Liposome Company (“TLC”) which granted us a license and the exclusive rights in China, Hong Kong and Macao to promote, market, distribute and sell ProFlow® for the treatment of peripheral arterial disease (“PAD”) and other indications. PAD is a serious cardiovascular condition in which blood flow to the limbs (usually the legs) is restricted due to arterial plaque build-up. Under the terms of the agreement, TLC will be responsible for the continued development including potential clinical trials and regulatory activities, as well as the manufacture and supply of ProFlow, and we will be responsible for all aspects of commercialization including pre-and post-launch activities. The agreement provides for the principal terms of the arrangement between SciClone and TLC, and in March 2014, the companies entered into a supplemental collaboration and license agreement. In November 2014, TLC was notified by the CFDA that ProFlow did not receive clinical trial approval and TLC is in the process of appealing the decision.
In May 2013, we entered into a framework agreement with Zensun (Shanghai) Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (“Zensun”) for the exclusive promotion, marketing, distribution and sale of NeucardinTM in China, Hong Kong and Macao. Neucardin is a novel, first-in-class therapeutic for the treatment of patients with intermediate to advanced heart failure, for which a New Drug Application (“NDA”) was submitted to and accepted for review by the CFDA in 2012. In December 2013, the CFDA informed Zensun that its Phase 2 data is insufficient, and has asked Zensun to submit a new NDA once the ongoing Phase 3 study reached its endpoints. As part of our agreement with Zensun, we agreed to loan up to $12 million to Zensun, of which $12 million had been loaned as of December
5
31, 2015 (refer to Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements appearing under Part II, Item 8 for further information regarding the Zensun loans).
For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, we recognized $7.5 million, $11 million and $5.0 million, respectively, in research and development expenses related to our in-license arrangements.
Recent governmental policy changes in China have eliminated national regulation of the maximum retail drug prices for most drugs effective as of June 1, 2015. Decisions by provincial authorities appear to be emerging as the primary governmental mechanism for price controls. As an example, the Zhejiang provincial authority announced a price limitation for sales of ZADAXIN in the province in April 2015 that became effective in May 2015. We were able to mitigate the impact of this price limitation by shifting an equitable portion of the burden of the price reduction to our distributor in our sales channel; accordingly, the impact of the price reduction through the year ended December 31, 2015 was $2.8 million. We anticipate that provincial pricing decisions will continue to be a significant factor in the China pharmaceutical market for the foreseeable future. The impact of such decisions on our future results is unpredictable, but we expect that pricing pressures on revenue in 2016 will be offset at least in significant part through sharing of the burden with our China distributor and potentially through volume increases. However, in the future, prices could be reduced to levels significantly below those that would prevail in an unregulated market, which may limit the growth of our revenues or cause them to decline.
As previously disclosed, since 2010 the US Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) and the US Department of Justice (“DOJ”) had each been conducting formal investigations of us regarding a range of matters, including the possibility of violations of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”). On February 4, 2016, we announced that we had entered into a settlement agreement with the SEC fully resolving the SEC’s investigation into possible violations of the FCPA. Under the terms of the settlement agreement, in February 2016 we paid a total of $12.8 million, including disgorgement, pre-judgment interest and a penalty as final settlement which was released from our restricted escrow account which we funded in the fourth quarter of 2015. This payment is in line with the charges we previously recorded and disclosed in our Form 10-Q filed with the SEC on August 10, 2015. As part of the agreement we neither admitted nor denied engagement in any wrongdoing and we agreed to give status reports to the SEC for the next three years on our continued remediation and implementation of anti-corruption compliance measures. The DOJ has also completed its related investigation and has declined to pursue any action (refer to Notes 18 and 22 to the consolidated financial statements appearing under Part II, Item 8 and “Legal Proceedings” in Part I, Item 3 for further information regarding the SEC and DOJ investigations).
BUILDING A LEADING INTERNATIONAL PHARMACEUTICAL BUSINESS
Our Established Business in China
In China, we have established product revenue and positive cash flow. We are committed to building on this base and introducing additional pharmaceutical products to meet the country’s evolving healthcare needs. China state leaders are continuing to implement a health care reform plan which, among other things, is seeking to expand patient access to pharmaceuticals. We believe the China pharmaceutical market may grow up to 10% annually over the next several years.
We launched ZADAXIN in China in 1996 and by 2015 our annual worldwide sales of this product reached more than $146 million, 96% of which were sales to China. Today, ZADAXIN is one of the largest imported pharmaceutical products in China, measured by revenue. We estimate our market share of thymalfasin by units is approximately 15%. Over the last decade, we have established a sales and marketing organization and strong importation relationships with distribution channels that have facilitated strong growth in sales, and profitability, and substantial cash flow. Through our extensive China sales organization of approximately 560 professionals including approximately 450 sales personnel, we believe we have developed a good reputation and relationships with physicians and administrators. We serve approximately 2,000 hospitals with approximately 300 of the largest hospitals in the major cities in China contributing approximately 80% of our business. We have built a strong commercial presence in liver disease, cancer and the intensive care setting. We are expanding geographically in China to position the Company for further growth. ZADAXIN has strong brand recognition and is positioned as a high-quality, imported product. ZADAXIN is approved in China for the treatment of HBV and for use as an immune system enhancer. It is also included in the treatment guidelines issued by the MOH for liver cancer. In China, orders for ZADAXIN are filled largely by distributors and sub-distributors which purchase ZADAXIN from our selected, established, government-licensed importing agents.
6
China accounted for approximately 96%, 97%, and 97% of our net revenues for each of the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. In 2015 and 2014, Sinopharm Holding Lingyun Biopharmaceutical (Shanghai) (“Sinopharm”) accounted for 97% and 94% of our net revenues, respectively. In 2013, Sinopharm and Sanofi Aventis S.A. accounted for 75% and 20% of our net revenues, respectively. No other customers accounted for more than 10% of our net revenues in those periods. As of December 31, 2015, approximately $38.3 million or 96% of our gross accounts receivable were attributable to Sinopharm.
The Chinese government is continuing its efforts to reduce overall health care costs, including pricing controls on pharmaceutical products. Individual provinces in China and, in some cases, individual hospitals can and have established pricing requirements for a product to be included on formulary lists. In some cases, these prices have been significantly lower than our distributors have been selling ZADAXIN, in which case we have been removed from formulary lists, which consequently has reduced sales to certain hospitals and could adversely affect our future sales. The price for pharmaceutical products is regulated in China. The process and timing for price restrictions is unpredictable. In addition, we are aware that ZADAXIN may be used on an off-label basis, and the Chinese government’s pricing, reimbursement or other actions might reduce such uses.
International Sales and Marketing
ZADAXIN is approved in over 30 countries, primarily in China and countries in the Pacific Rim, Latin America, Eastern Europe, and the Middle East regions. ZADAXIN’s approvals are principally for the treatment of HBV and as an immune system enhancer, with additional approvals in certain countries for the treatment of HCV, or as a chemotherapy immune enhancer for cancer patients with weakened immune systems. We sell ZADAXIN in various international markets through our wholly owned subsidiary, SciClone Pharmaceuticals International Ltd. (“SPIL”).
SPIL is registered in the Cayman Islands and its principal office is in Hong Kong. SPIL orders ZADAXIN from our European manufacturer and contracts with a third party for the storage of our finished goods inventory at warehousing facilities in Hong Kong. SPIL then distributes our product worldwide from these warehousing facilities based on purchase orders from our customers. Under our established distribution arrangements, local importers and distributors are responsible for the importation, inventory, distribution and invoicing of ZADAXIN after importation.
Product sales of $146.1 million, $126.1 million, and $96.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively, were from sales of ZADAXIN.
SciClone’s Lead Product ZADAXIN (Thymalfasin)
ZADAXIN is SciClone’s synthetic preparation of thymalfasin, scientifically referred to as thymosin alpha 1, a thymic peptide which circulates in the blood naturally and is instrumental in the immune response to certain cancers and infections. Published scientific and clinical studies have shown that thymalfasin helps to stimulate and direct the body’s immune response to eradicate infectious diseases, such as HBV, HCV, bacterial, and fungal infections; to fight certain cancers such as melanoma and liver cancer; and to enhance response to vaccines. Thymalfasin appears to be well tolerated, with few reports of significant side effects or toxicities associated with its use.
Thymalfasin elicits a variety of immune system responses. Acting on intracellular signaling pathways, thymalfasin increases the Th1 subset of T-helper cells that assist with fighting invading viruses and cancers and leads to a boost in production of antibodies in response to vaccines. Thymalfasin also results in decreased CD-4 cell differentiation into the Th2 subset of CD-4 helper cells that produce cytokines, such as IL-4, which are associated with persistence of viral infection, and stimulates several other components of the immune response that help the body attack and kill virally-infected or tumor cells.
7
Thymalfasin for Treatment of Sepsis
Clinical trials have shown that thymalfasin improves survival in patients in intensive care units being treated for sepsis from severe bacterial infections. One publication describes the results from a large, multicenter, single-blind, randomized, and controlled trial in 361 subjects in China. This study showed that the 28-day mortality from any cause was 26% in the ZADAXIN group, versus 35% in the control group, an effect that is clinically important (p = 0.062 non-stratified analysis, p = 0.049 log-rank). Greater improvement in the biomarker HLA-DR was also seen in subjects treated with ZADAXIN (p = 0.037). No serious drug-related adverse events were recorded. These data support the usefulness of ZADAXIN in treating severe sepsis.
Thymalfasin for Enhancement of Response to Vaccine
Clinical trials have demonstrated that thymalfasin increases response to influenza and hepatitis B vaccines in the elderly and in hemodialysis patients. In elderly subjects, thymalfasin was also shown to decrease the incidence of influenza from 19% in subjects given an influenza vaccine alone, to 6% in subjects receiving thymalfasin treatment in addition to the influenza vaccine. For these clinical trials, the treatment regimen involved 8 to 10 injections of 1.6 mg doses of thymalfasin. A clinical study conducted in 2009/2010 by Sigma-Tau Finanziaria, S.p.A. in Italy, however, showed that a higher dose of thymalfasin (3.2 or 6.4 mg) given only twice (seven days prior to vaccination and on the day of vaccination) was also effective. ZADAXIN in treatment led to a statistically significant increase in the percent of subjects who seroconverted to the H1N1 vaccine (MF59 adjuvanted monovalent vaccine, Focetria™ from Novartis), and an increase in total titers, when measured at 21 or 42 days after vaccination. While this effect was no longer seen at time points 84 and 168 days after vaccination, the enhancement effect of ZADAXIN provided a significant enhancing effect in the critical first six weeks following vaccination. These promising data further support the utility of thymalfasin for use in immune system enhancement.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND PROPRIETARY RIGHTS
Patents
We seek regulatory approval for our products in disease areas with high unmet medical need, significant market potential and where we have a proprietary position through patents covering use, manufacturing process, or composition of matter for our products. For our lead product ZADAXIN, we are the licensee or owner of patents and patent applications relating to thymalfasin and its use for a number of diseases. In particular, we are the licensee or owner of patents and applications in the US or China that are directed to thymalfasin therapy for the treatment of hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C as a monotherapy or in combination with other therapeutics, including drugs with or without regulatory approval for marketing. In China, patent number ZL99811382.4 has been granted for ZADAXIN for chronic hepatitis B that expires in 2019. In addition, we are the licensee or owner of several patents and applications in the US and internationally that are directed to thymalfasin therapy for immune system enhancement. The expiring patent terms for issued or to be issued patents are from 2025 to 2031. We are also the licensee or owner of several applications in China that are directed to thymalfasin therapy for the treatment of melanoma. The expiring patent term for these patents, if issued, is 2028. We are also the licensee or owner of patents in the US and China that are directed to thymalfasin therapy for reducing side effects of chemotherapy. The expiring patent terms for these issued patents are from 2020-2021. We have also applied for patents in the US and internationally that are directed to thymalfasin therapy for the treatment of severe sepsis and acute infection, as well as more specific patents for certain infections such as Aspergillus and severe acute respiratory syndrome (“SARS”). In addition, we have issued patents in the US and China directed to thymalfasin conjugates. We have also applied for patents in the US and internationally that are directed to thymalfasin therapy for purulent rhinosinusitis. Furthermore, we have applied for patents in the US and internationally that relate to use of thymalfasin as an immune system enhancer for the treatment of cancer. The expiring patent term for these patents, if issued, is 2035.
With respect to our issued patents in the US and Europe, we are also entitled to obtain a patent term extension to extend the patent expiration date. For example, in the US, we can apply for a patent term extension of up to five years for one of the patents covering ZADAXIN if ZADAXIN is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”). The exact duration of the extension depends on the time we spend in clinical trials as well as getting a new drug application approval from the FDA.
8
Proprietary Rights
In addition to patent protection, we intend to use other means to protect our proprietary rights. We may pursue marketing exclusivity periods that are available under regulatory provisions in certain countries, including the US, Europe, Japan, and China. For example, if we are the first to obtain market approval of a product, e.g., thymalfasin in the US, we would expect to receive at least five years of market exclusivity.
Furthermore, orphan drug exclusivity has been or may be sought where available. Such exclusivity has a term of seven years in the US and 10 years in Europe. We have obtained orphan drug designation for thymalfasin for the treatment of malignant melanoma and chronic hepatitis B in the US and for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in the US and in Europe. We own trademark registrations worldwide for ZADAXIN and other trademarks that appear on our commercial packaging and promotional literature. Copyrights for the commercial packaging may prevent counterfeit products or genuine but unauthorized products from entering a particular country by parallel importation. Brand and trademark protection are particularly important to us in China. We have implemented anti-counterfeiting measures on commercial packaging and we have registered the packaging with customs departments in countries where such procedures exist. We rely upon trade secrets, which we seek to protect in part by entering into confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, corporate partners, suppliers, and licensees.
MANUFACTURING
ZADAXIN is manufactured for us in Europe by third parties under exclusive contract manufacturing and supply agreements. We closely monitor production runs of ZADAXIN and conduct our own quality assurance audit programs. We believe the manufacturing facilities of our contract suppliers are in compliance with the FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices (“GMP”), and European equivalents of such standards. In order to sell ZADAXIN to the licensed importers in China, our manufacturers must 1) be approved by the Italian Ministry of Health (“AIFA”) and 2) be accepted by the CFDA, the Chinese regulatory agency, and we must obtain an Imported Drug License from the CFDA permitting the importation of ZADAXIN into China. The license must be renewed every five years, and our next renewal will be required in December 2017. If we change manufacturers, these changes must 1) be approved by AIFA in Italy and 2) be accepted by the CFDA, and we must obtain a new Imported Drug License from the CFDA.
In the event of the termination of an agreement with any single supplier, we believe that we would be able to enter into arrangements with other suppliers with similar terms. We do not intend at this time to acquire or establish our own dedicated manufacturing facilities for any of our products. We believe that our current manufacturing partners for ZADAXIN have enough manufacturing capacity to meet potential market demand. We also believe that we will be able to meet our clinical trial needs and market demand for our other drug candidates when needed with our current manufacturing partners and through pursuing new relationships with additional manufacturing partners.
COMPETITION
Our competition for sales of ZADAXIN in China is primarily from generic drug manufacturers located in China that sell their product at lower prices. We compete with them based on our reputation as a provider of high quality products, including the fact that our products are produced at US and western European GMP facilities.
Our competitors for existing and future products include pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, universities and other research institutions, in the US, China and other territories, that are actively engaged in research and development or marketing of products in the therapeutic areas we are pursuing. We believe that the principal competitive factors in this industry for a marketed drug include the efficacy, safety, price, therapeutic regimen, manufacturing, quality assurance and associated patents and the capabilities of its marketer.
Most of our competitors, particularly large pharmaceutical companies, have substantially greater financial, technical, regulatory, manufacturing, marketing and human resource capabilities than ours. Most of them also have extensive experience in undertaking the preclinical and clinical testing and in obtaining the regulatory approvals necessary to market drugs. Additional mergers and acquisitions in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries may result in even more resources being concentrated with our competitors.
9
For the treatment of HBV, current therapies being marketed by competitors include interferon alpha, in standard and pegylated forms, nucleoside analogues, such as lamivudine and entecavir, and nucleotide analogue adefovir. In addition to these products, in our largest market, China, ZADAXIN faces competition from other synthetic and generic biological extracts that are locally manufactured and significantly lower priced.
Future clinical trials may or may not show ZADAXIN or our other products in the market or in development to have advantages or value over such existing or future competitive products.
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
Research and development (“R&D”) expenses consist of independent R&D costs relating to the conduct of clinical trials and costs associated with in-licensing arrangements. R&D expenses were $12.3 million, $14.6 million, $8.0 million, for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. During 2015, 2014 and 2013, R&D expenses included $7.5 million, $11.0 million and $5.0 million, respectively, related to upfront and milestone payments made under our in-license arrangements.
During 2015, under our subsidiary SciClone Pharmaceuticals International (Cayman) Development Limited, we incorporated two further subsidiaries, SciClone Pharmaceuticals (Hong Kong) Development Company Ltd., and SciClone Pharmaceuticals (Shanghai) Development Company Ltd. Our development entities conduct various research and development activities including those relating to in-licensing arrangements and the conduct of clinical trials.
EMPLOYEES
As of December 31, 2015, we had approximately 590 employees: approximately 560 in China, approximately 20 in the US, and approximately 10 in other countries. From time to time, we engage the services of consultants worldwide with pharmaceutical and business backgrounds to assist in our product development and commercialization activities.
GOVERNMENT REGULATION
Regulation by governmental authorities in the US, China and other foreign countries is a significant factor in the manufacturing and marketing of our products, as well as in ongoing research and development activities and in pre-clinical and clinical trials and testing related to our products. Our products in clinical development in the US, China and other foreign countries are subject to approval by the FDA, the CFDA and similar regulatory authorities. Manufacturing establishments are subject to inspections by regulatory authorities at the federal, state and local level and must comply with current GMP as established in various jurisdictions. In complying with GMP standards, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money and effort in the area of production and quality assurance to ensure ongoing full technical compliance. We also conduct a separate review of products on an ongoing basis to test and maintain compliance with GMP standards.
China
In China, the pharmaceutical industry is subject to extensive government regulation and supervision. The regulatory framework addresses all aspects of operating in the pharmaceutical industry, including approval, pricing, re-imbursement, production, licensing and certification requirements and procedures, periodic renewal and reassessment processes, registration of new drugs and environmental protection.
The CFDA is the authority that monitors and supervises the administration of pharmaceutical products and medical appliances and equipment as well as food, health food and cosmetics in China. The primary responsibilities of the CFDA include:
|
· |
formulating administrative rules and policies concerning the supervision and administration of food, health food, cosmetics and the pharmaceutical industry; |
|
· |
evaluating, registering and approving of new drugs, generic drugs, imported drugs and traditional Chinese medicine; |
|
· |
approving and issuing permits for the manufacture and export/import of pharmaceutical products, medical appliances and equipment and approving the establishment of enterprises to be engaged in the manufacture and distribution of pharmaceutical products; and |
10
|
· |
examining and evaluating the safety of food, health food and cosmetics and handling significant accidents involving these products. |
The MOH is an authority at the ministerial level under the State Council and is primarily responsible for national public health and has administrative responsibility for the CFDA. The MOH performs a variety of tasks in relation to the health industry such as establishing social medical institutes, promulgating national regulations, and producing professional codes of ethics for public medical personnel. The MOH is also responsible for international issues, such as those pertinent to foreign companies and governments.
Drug Administration Laws and Regulations
The China Drug Administration Law and related regulations provide the legal framework for the establishment of pharmaceutical manufacturing enterprises, and pharmaceutical trading enterprises, and for the administration of pharmaceutical products, including the development and manufacturing of new drugs, the import of pharmaceuticals and the regulation of packaging, trademarking and advertising of pharmaceutical products in China.
Permits and Licenses for Importation, Manufacturing and Registration of Drugs
Imported Drug License. Our strategy to date has been to seek approval for the import into China of drugs approved in other markets. We must obtain an Imported Drug License from the CFDA to import a pharmaceutical product into China.
To qualify to receive an Imported Drug License from the CFDA, each manufacturing establishment must be registered with the FDA or European (“EMA”) regulatory authorities where the product is registered for sale and listed on the Certificate of Pharmaceutical Product (“CPP” or Country of Origin Approval). In general, the CFDA also requires that an imported drug must also have country of origin approval for the same indication for which an Imported Drug License is applied.
As a result, in order to obtain and maintain an Imported Drug License in China, we or our partners must also meet the regulatory requirements for the country of origin of the pharmaceutical products we import, or are seeking to import, into China.
The process for applying for and obtaining an Imported Drug License can be protracted and uncertain. In addition to the submission of clinical data from trials outside China, the CFDA may require additional clinical data, including from studies in China, and it may conduct its own inspection and testing of manufacturing facilities and of finished product. An Imported Drug License needs to be renewed every five years. Further, if the manufacturer of the pharmaceutical product changes, an additional approval is required from the CFDA, and approval will also have to be obtained in the country from which the product is imported.
For ZADAXIN, the CPP is in Italy, and was issued by the AIFA. The named manufacturer of ZADAXIN is Patheon Italia S.p.A. DC Bead is manufactured by Biocompatibles UK Ltd. and its Country of Origin approval is the United Kingdom. We and our partners need to maintain these approvals.
China requires that products with an Imported Drug License be imported through approved importing agents. At each port of entry, prior to moving the product forward to the distributors, government-licensed importing agents must process and evaluate each shipment to determine whether such shipment satisfies China's quality control requirements.
GMP Certificates. Our current products and our clinical candidates in China are all manufactured outside China and are subject to GMP standards in the country in which they are manufactured. Our manufacturers are subject to site inspections by the regulatory authorities in the jurisdictions in which they are located. The issuance and renewal of an Imported Drug License is dependent, among other things, upon maintaining manufacturing standards that comply with the GMP standards of a widely recognized regulatory authority, such as the FDA or EMEA.
If we were to manufacture product in China, or obtain product from Chinese contract manufacturers, such manufacturing would be subject to similar GMP standards established in China and administered by local authorities.
11
Distribution of Pharmaceutical Products
According to the China Drug Administration Law and related regulations, a manufacturer of pharmaceutical products in China can only engage in the trading of the pharmaceutical products that the manufacturer has produced itself. In addition, such manufacturer can only sell its products to:
|
· |
wholesalers and retailers holding pharmaceutical trading permits; |
|
· |
other holders of pharmaceutical manufacturing permits; or |
|
· |
medical practitioners holding medical practice permits. |
A pharmaceutical manufacturer in China is prohibited from selling its products to end-users, or individuals or entities other than holders of Pharmaceutical Trading Permits, the pharmaceutical manufacturing permits or the medical practice permits.
A pharmaceutical distributor (including wholesalers and retailers) must satisfy requirements as to: personnel with pharmaceutical expertise, appropriate warehousing and sanitary environments compatible with the distributed pharmaceutical products; quality management and compliance with regulations to ensure the quality of the distributed pharmaceutical products. Operations of pharmaceutical distributors must be conducted in accordance with the Pharmaceutical Operation Quality Management Rules and require a certificate from the CFDA. Pharmaceutical distributors must comply with record-keeping requirements regarding the products sold.
Price Controls
Prior to June 1, 2015, the price of pharmaceutical products in China was controlled and regulated by the Chinese government. The retail prices of pharmaceutical products included in the National Essential Drug List and the National Basic Medical Insurance Drugs, Work-Related Injury Insurance Drugs and Maternity Insurance Drugs Catalogue (the “Catalogue”), as well as those pharmaceutical products whose production or distribution are deemed to constitute monopolies were subject to price controls in the form of fixed prices or price ceilings. The prices of medicines that were not subject to price controls were determined at the discretion of the respective pharmaceutical companies.
With the promulgation of the Circular on Issuing the Opinions on Promoting Drug Price Reform jointly by the National Development and Reform Commission and several other government agencies (the “Circular”), starting from June 1, 2015, pharmaceutical products (other than anesthetics and Class I psychotropic drugs which are still subject to fixed ex-factory price and retail ceiling price controls) are no longer subject to price controls by the Chinese Government. Since the Circular is very new, it is not clear how exactly it will be implemented. Although most of the pharmaceutical products are no longer subject to fixed prices or price ceilings, the Chinese government could still influence the setting of the prices through the government bidding process and its management of the reimbursement system, as discussed below.
Reimbursement under the National Medical Insurance Program
The Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security (“MOHRSS”), together with other government authorities, determine which medicines are to be included in or removed from the Catalogue for the National Medical Insurance Program, as well as the category under which a medicine should fall in the Catalogue. There are two categories under the Catalogue: Category A and Category B. Category B medicines are generally more expensive than Category A medicines. A National Medical Insurance Program participant can be reimbursed for the full cost of a Category A medicine but only a certain percentage of a Category B medicine. Whether a medicine should be included in the Catalogue depends on a number of factors, including whether the medicine is used in large quantities and commonly prescribed, and whether it is considered to be important in meeting the basic healthcare needs of the general public.
Although the National Medical Insurance Program is designated as a national program, the implementation of the National Medical Insurance Program is delegated to various provincial governments, each of which has established its own medicine catalogue. A provincial government must include all Category A medicines listed in the Catalogue in its provincial medicine catalogue and may
12
not downgrade a nationally classified Category A medicine to Category B. For Category B medicines listed in the Catalogue, provincial governments have the discretion to add or subtract by no more than 15%.
The amount in a participant’s individual medical insurance account varies, depending upon the amount of contributions from the participant and his or her employer. Generally, program participants who are from relatively wealthier eastern parts of China and relatively wealthier metropolitan centers have greater amounts in their individual accounts than those from less developed provinces.
Government Procurement
Most of the hospitals in China are State-owned. Pharmaceutical products covered by the National Medical Insurance Program are generally procured by the government through a tender process. The tender process is typically conducted by the provincial health authorities every year or every few years. A government-appointed committee reviews bids submitted by pharmaceutical companies and selects one or more products for the treatment of a particular medical condition. The selection is based on a number of factors, including bid price, quality and a manufacturer’s reputation and service. Once a product is selected by the committee, the state-owned hospitals in the province will purchase the product at the tender price submitted by the pharmaceutical company. However, starting from February 2015, the State Council had encouraged hospitals in some pilot cities to renegotiate the supply prices of the products selected to further drive down the price.
Healthcare Reform
The Chinese government is undertaking a major reform of its medical insurance system. The MOHRSS is responsible for the reform of the medical insurance system. At present, the medical insurance system consists of three basic medical insurances: (i) the Urban Employee Basic Medical Insurance Scheme, which is a mandatory health insurance program for urban employees and retirees; (ii) the Urban Resident Basic Medical Insurance Scheme, which is a voluntary program for other urban residents; and (iii) the New Rural Cooperative Medical Scheme, or NRCMS, which is a voluntary program for all rural residents. The coverage of China’s urban/rural basic medical insurance extended from approximately 10% in 2004 to approximately 94% and 100% in 2009 and 2013, respectively. As of December 31, 2014, the two urban insurance schemes covered 597 million urban residents and the NRCMS covered approximately 736 million rural residents. In addition, the budget and actual amount of medical and healthcare expenditures of the Ministry of Finance have been increasing since 2009, with both exceeding 900 billion Chinese Yuan Renminbi (“RMB”) in 2014.
Our Challenges
Our ability to successfully commercialize our products in China as well as in other parts of the world depends in part on the extent to which coverage and reimbursement to patients will be available from government health care programs, private health insurers and other third-party payors or organizations, as well as on the level of reimbursement. Significant uncertainty exists as to the reimbursement status of therapeutic products, such as ZADAXIN or other drugs we may develop. In most of the markets in which we are currently approved to sell ZADAXIN, reimbursement for ZADAXIN under government or private health insurance programs is not yet available. In many of these countries government resources and per capita income may be so low that our products would be prohibitively expensive and therefore will not be covered by government health insurance program.
In November 2009, thymalfasin, the generic chemical name for our pharmaceutical product ZADAXIN, was included as a Category B product in the Catalogue. However, since the Catalogue is amended every two years, there is no assurance that ZADAXIN will remain on the Catalogue with subsequent amendments. Furthermore, since the provinces have the discretion to exclude Category B products in the Catalogue from the provincial catalogue within certain limits, there is no assurance that ZADAXIN will be included in all the provincial catalogues. Even if ZADAXIN is included in the catalogue of a province, we may not be the successful bidder in the government bidding process.
13
US, Europe and Other Countries
The regulatory regime for the approval for drug distribution and marketing in the US and Europe is similar in many respects to the regulatory system in China. The steps required before a new drug may be distributed commercially generally include:
•conducting appropriate pre-clinical laboratory evaluations, including animal studies, in compliance with the FDA's Good Laboratory Practice (“GLP”) requirements, to assess the potential safety and efficacy of the product;
•submitting the results of these evaluations and tests to the FDA in an Investigational New Drug Application (“IND”), and receiving approval from the FDA that the clinical studies proposed under the IND are allowed to proceed;
•conducting adequate and well-controlled clinical trials in compliance with the FDA's Good Clinical Practice (“GCP”) requirements that establish the safety and efficacy of the product candidate for the intended use, typically in the same Phase 1, Phase 2 and Phase 3 steps described above for China;
•development of manufacturing processes that conform to FDA current Good Manufacturing Practices, or cGMPs, as confirmed by FDA inspection;
•submitting to the FDA the results of pre-clinical studies, clinical studies, and adequate data on chemistry, manufacturing and control information to ensure reproducible product quality batch after batch, in a New Drug Application (“NDA”) or Biologics License Application (“BLA”); and
•obtaining FDA approval of the NDA, including inspection and approval of the product manufacturing facility as compliant with cGMP requirements, prior to any commercial sale or shipment of the pharmaceutical agent.
After FDA approval has been obtained, the FDA requires post-marketing reporting to monitor the side effects of the drug. This may include phase 4 studies in which the drug is studied in an expanded patient population in a post-approval setting for continued monitoring of safety and sometimes continued efficacy.
We must comply with the regulations of each country in which we seek approval of and intend to market and sell any product.
AGREEMENTS WITH THIRD PARTIES
We hold license, promotion, distribution or marketing agreements with a number of parties for products currently marketed or under development, including an agreement with Biocompatibles UK Ltd (“Biocompatibles”) for the distribution of DC Bead® in China. We had agreements during 2015 with several companies for the distribution of certain products in China including the following significant agreements. We have additional license agreements with other parties.
MEDA Pharma GmbH & Co. KG (“MEDA”) Agreement. We are party to an agreement with MEDA for various products under development including Tramadol. See Part I, Item 3 “Legal Proceedings” regarding the status of our agreement with MEDA from whom we license Tramadol.
Baxter Healthcare Trading (Shanghai) Co. Ltd. (“Baxter”) Agreement. In June 2013, our subsidiary, NovaMed Pharmaceuticals (Shanghai) Co. Ltd. (“NovaMed Shanghai”), entered into an Amended and Restated Product Promotion Agreement with Baxter for the distribution of HoloxanTM, MesnaTM, and EndoxanTM in China effective January 1, 2013. Under the agreement, we market products from Baxter for sale in China, with a promotion fee specified in the agreement. To maintain our exclusive rights, we must meet certain unit volume requirements. The agreement will expire on December 31, 2017, unless renewed.
Pfizer International Trading (Shanghai) Ltd. (“Pfizer”) Agreement. In July 2014, our subsidiary, NovaMed Shanghai, renewed its promotion and distribution relationship with Pfizer by entering into an Import and Service Agreement for the continued distribution of several pharmaceutical products (currently MethotrexateTM, EstracytTM, and FarlutalTM) in China. Under the agreement, we must purchase product from Pfizer for sale in China at prices specified in the agreement. The purchase prices are subject to adjustment in certain circumstances. To maintain our exclusive rights, we must meet certain unit volume requirements. The agreement will expire June 30, 2019, unless renewed.
14
Correvio LLC Agreement (acquired by Cardiome Pharma Corp. (“Cardiome”) in November 2013). In December 2008, our subsidiary, NovaMed Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“NovaMed”), entered into a licensing and distribution agreement with Correvio LLC for the distribution of Aggrastat® in China. In August 2015, Cardiome and NovaMed mutually agreed to end their collaboration for Aggrastat, resulting in the Company’s obligation to return all rights to the product to Cardiome.
Zensun (Shanghai) Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (“Zensun”) Agreement. In May 2013, our subsidiary, SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Ltd. (“SciClone China”), entered into an agreement with Zensun granting SciClone China a license and the exclusive rights in China, Hong Kong and Macao to promote, market, distribute and sell Neucardin™, a novel, first-in-class therapeutic drug for the treatment of patients with intermediate to advanced chronic heart failure (CHF). The agreement provides for the principal terms of the arrangement between SciClone China and Zensun, and the companies have agreed to negotiate a supplemental license and supply agreement.
Taiwan Liposome Company (“TLC”) Agreement. In June 2013, we entered into an agreement with TLC granting us a license and the exclusive rights in China, Hong Kong and Macao to promote, market, distribute and sell ProFlow® for the treatment of peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and other indications. The agreement provides for the principal terms of our arrangement with TLC, and in March 2014, we entered into a collaboration and license agreement. In November 2014, TLC was notified by the CFDA that ProFlow did not received clinical trial approval and TLC is in the process of appealing the decision.
The Medicines Company Agreement. In December 2014, we entered into an agreement with The Medicines Company granting us a license and the exclusive rights in China to promote, market, distribute and sell two cardiovascular products: Angiomax®, an anticoagulant indicated in certain patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), and Cleviprex®, a third-generation dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker for the reduction of blood pressure.
Theravance Biopharma, Inc. In May 2015, we entered into an agreement with Theravance Biopharma granting us exclusive development and commercialization rights to VIBATIV® (telavancin) in China, as well as the Hong Kong SAR, the Macau SAR, Taiwan and Vietnam. Under the terms of the agreement Theravance Biopharma will sell to us all clinical and commercial product required to develop and commercialize VIBATIV in China and our other licensed territories.
Our continued distribution of approved products depends upon the continuation of these agreements and the renewal of the agreements upon expiration.
Information about Segment and Geographic Revenue
Additional information about segment and geographic revenue is set forth in Note 20 of our Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in Part II, Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
AVAILABLE INFORMATION
We file electronically with the SEC our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and current reports on Form 8-K pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. The public may read and copy any materials we file with the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, NE, Washington, DC 20549. The public may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC maintains an Internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC. The address of that site is http://www.sec.gov.
You may obtain a free copy of our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, on the day of filing with the SEC on our website on the World Wide Web at http://www.sciclone.com, by contacting the Investor Relations Department at our corporate offices by calling 800-724-2566 or by sending an e-mail message to investorrelations@sciclone.com.
15
You should carefully consider the risks described below, in addition to the other information in this report on Form 10-K, before making an investment decision. Each of these risk factors could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and operating results as well as adversely affect the value of an investment in our common stock.
Our stock price may be volatile, and an investment in our stock could suffer a decline in value.
Although we reported net income of $29.5 million, $25.2 million, $11.0 million, for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively, we have experienced significant operating losses in the past, and as of December 31, 2015, we had an accumulated deficit of approximately $118 million. If our operating expenses were to increase or if we were not able to increase or sustain revenue, we may not maintain profitability over the next 12 months.
The market price of our common stock has experienced, and may continue to experience, substantial volatility due to many factors, some of which we have no control over, including:
|
· |
government regulatory action affecting our Company or our drug products or our competitors' drug products in China, the US and other foreign countries, including the effect of government initiatives in China, particularly the Chinese government’s increasing regulation of the pharmaceutical industry through anti-corruption activities; |
|
· |
government regulatory action intended to reduce pharmaceutical prices such as the reduction in the governmentally permitted maximum listed price for our products and increased oversight of the health care market and pharmaceutical industry; |
|
· |
compliance by our employees with regulations that are applicable to sales and marketing activities, including the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act; |
|
· |
actual or anticipated fluctuations in our quarterly operating results, some of which may result from undertaking new clinical development projects, or from licensing or acquisition-related expenses including up-front fees, milestone payments, and other items; |
|
· |
progress and results of clinical trials and the regulatory approval process in Europe and in China; |
|
· |
timing and achievement of our corporate objectives; |
|
· |
charges related to expired inventory or bad debt; |
|
· |
terminations of, or changes in our agreements or relationships with collaborative partners; |
|
· |
announcements of technological innovations or new products by us or our competitors; |
|
· |
announcement and completion of corporate acquisition, merger, licensing or marketing arrangements, or sales of assets; |
|
· |
developments or disputes concerning patent or proprietary rights; |
|
· |
changes in the composition of our management team or Board of Directors; |
|
· |
changes in company assessments or financial estimates by securities analysts; |
|
· |
changes in assessments of our internal control over financial reporting; |
|
· |
general stock market conditions and fluctuations for the emerging growth and pharmaceutical market sectors; |
|
· |
unanticipated increases in our G&A expense due to legal and accounting expenses, including expenses relating to our dispute with MEDA, and arising out of matters relating to any additional or uncorrected control deficiency or related matters; |
|
· |
economic and political conditions in the US or abroad, particularly in China; |
|
· |
currency fluctuations between the RMB and US Dollar (“USD”) including recent RMB devaluation that has led to, and may continue to lead to, downward adjustments in our importer price if further devaluation continues; |
|
· |
broad financial market fluctuations in the US, Europe or Asia; and |
|
· |
More aggressive taxation policy by the government in China. |
16
Any acquisitions we may undertake involve a number of risks, and we may not realize all the anticipated benefits of an acquisition. We may acquire other companies or products that present risks similar to those stated above.
We may enter into other company or product acquisition transactions in the future which could present integration or other risks similar to those stated above and may also cause us to:
|
· |
issue common stock that would dilute our current shareholders’ percentage ownership; |
|
· |
assume liabilities, some of which may be unknown at the time of such acquisitions; |
|
· |
record goodwill and intangible assets that would be subject to impairment testing and potential periodic impairment charges; |
|
· |
incur amortization expenses related to certain intangible assets; and |
|
· |
incur large and immediate write-offs of in-process research and development costs; or become subject to litigation. |
Our revenue will continue to be substantially dependent on our sales of ZADAXIN in China.
Our product revenue is highly dependent on the sales of ZADAXIN in China. We anticipate that sales of ZADAXIN will continue to be a majority of our revenue for at least the next two years. For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013 approximately 96%, 96% and 95% of our ZADAXIN sales, respectively, were to customers in China. Sales of ZADAXIN in China may be limited due to the low average personal income, lack of patient cost reimbursement, poorly developed infrastructure and competition from other products, including generics. ZADAXIN sales growth in recent years has benefited from the rapidly growing Chinese economy and growing personal disposable income. Sales of ZADAXIN in China could be adversely affected by a slowing or downturn of the Chinese economy and from the recent and future decisions of provincial agencies’ pricing reform.
In China, ZADAXIN is approved for the treatment of hepatitis B virus (“HBV”) and as an immune system enhancer. We face competition from pharmaceutical companies who are aggressively marketing competing products for the treatment of HBV and for other indications where we believe ZADAXIN may be used on an off-label basis. In addition, several local companies are selling lower-priced, locally manufactured generic thymalfasin, which is a competitive product and is selling in substantial and increasing quantities. While generic products outsell ZADAXIN in unit volumes, we have been able to maintain a pricing advantage through the reputation of our imported, branded product. We believe such competition will continue with added new local manufacturers of generic thymalfasin and there could be a negative impact on the price and the volume of ZADAXIN sold in China, which would harm our business. Our efforts to in-license or acquire other pharmaceutical products for marketing in China and other markets may be unsuccessful or even if successful may not have a meaningful effect on our dependence on ZADAXIN sales in those markets.
Sales of ZADAXIN may fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter due to financing limitations on importers, changes in inventory levels at our customers, and surges in sales and inventories due to epidemics. Importers and distributors of ZADAXIN borrow funds in China from banks to purchase, hold and distribute ZADAXIN. Substantial increases in restrictions on fund availability and/or increases in borrowing costs could limit the ability of our importers and distributors to finance their import and distribution process. Further, our customers tend to purchase large orders, and inventory levels may fluctuate significantly as a result, or as a result of changes in the distribution channel, potentially affecting quarterly periodic results.
During the third quarter of 2012, we estimated that there was a substantial increase in ZADAXIN channel inventory levels and we believe that our sales to our customers exceeded the pace at which our customers were able to sell the ZADAXIN through to other parties, primarily hospital pharmacies. As a result, ZADAXIN revenues were lower in the first half of 2013, as compared to the same period of 2014. We believe channel inventory has returned to normal levels, and we continue to believe that we will grow demand for ZADAXIN through increased penetration in the market; however, we may not be successful or we may experience future fluctuations in channel inventory either of which could adversely affect our future ZADAXIN revenue.
We could experience fluctuations in channel inventory due to actual or expected epidemics. For example, during the second quarter of 2009, we experienced a strong upsurge in ZADAXIN sales, which we believe was attributable both to the increasing penetration of ZADAXIN within the Chinese market, as well as concerns in China from the H1N1 influenza virus. If distributors and hospitals that purchase ZADAXIN stockpile more ZADAXIN than needed for current use, our subsequent sales of ZADAXIN may suffer as distributors and hospitals use ZADAXIN already in their inventory before purchasing additional product from us. This could lead to uneven future revenue results for ZADAXIN and in turn materially impact our cash flows and business condition.
17
The Chinese government has previously imposed price restrictions on ZADAXIN and several of our oncology products. If we experience difficulties in our sales efforts as a result, our operating results and financial condition will be harmed.
The Chinese government is increasing its efforts to reduce overall health care costs, including pricing controls on pharmaceutical products. Individual provinces in China and, in some cases, individual hospitals can and have established pricing requirements for a product to be included on formulary lists. In some cases, these price limits have been significantly lower than prices at which our distributors have been selling ZADAXIN, in which case we have been removed from formulary lists, which consequently has reduced sales to certain hospitals and could adversely affect our future sales.
Recent governmental policy changes in China have eliminated national regulation of the maximum retail drug prices for most drugs, effective June 1, 2015. Decisions by provincial authorities are emerging as the primary governmental mechanism for price controls. As an example, the Zhejiang provincial authority announced a price limitation for sales of ZADAXIN in the province in April 2015 that became effective in May 2015; we were able to mitigate the impact of this price limitation by sharing the burden of the price reduction with our distributor. For fiscal 2015, we were able to mitigate the impact of this price limitation by shifting an equitable portion of the burden of the price reduction to our China distributor. We anticipate that provincial pricing decisions will continue to be a significant factor in the China pharmaceutical market for the foreseeable future. The impact of such decisions on our future results is unpredictable, but we expect that pricing pressures in 2016 will be offset at least in significant part through sharing of any potential further burden with our China distributor and potentially through volume increases. However, in the future, prices could be reduced to levels significantly below those that would prevail in an unregulated market, which may limit the growth of our revenues or cause them to decline.
The pricing regulations in China, whether operating at a national, provincial or institutional level, as well as regulation of the importation of pharmaceutical products, have reduced retail prices of, and our own revenue from, ZADAXIN and our other products, and we expect that pricing pressure will continue. While the regulatory mechanisms are changing and the ultimate outcome is uncertain, and while we have been able to mitigate the impact of prior price reductions on our overall business, prices could be reduced to levels significantly below those that would prevail in an unregulated market, limit the volume of product which may be imported and sold or place high import duties on the product, any of which may limit the growth of our revenues or cause them to decline.
While over the long term, we believe that the price reductions may positively affect our sales volumes and result in broader penetration into Tier 3 and Tier 2 cities in target geographies, potentially increasing our total sales revenues from these products, the process and timing for any price restrictions is unpredictable and further price reduction could be imposed that could adversely affect our business. In addition, our new contractual arrangement with our China distributor, Sinopharm, which commenced January 1, 2016, will result in the later recognition (relative to practices prevailing through December 31, 2015) of a portion of our revenue invoiced to Sinopharm in situations where the provincial tender price is greater relative to a referenced (baseline) tender price. This is due to a mechanism in the new contractual arrangement whereby the customer is invoiced at a lower base price relative to that prevailing in the previous agreement. The lower base price (as well as estimated price compensation payable due to the distributor for situations where the provincial tender price is lower than the referenced (baseline) tender price) will be recorded as revenue after the sale is completed. The distributor will then be invoiced for the portion of the price that may result from situations where the provincial tender price is greater than the referenced (baseline) tender price at a later time, and such amount will be recognized as revenue after the amount has been agreed to with the distributor. Although we do not expect this new arrangement to have a significant impact on annual revenue or the amount recognized on an annual basis, it may impact quarterly revenue amounts and timing, especially for the first quarter of 2016.
Our business strategy is dependent in part on our agreements with third parties for the rights to develop and commercialize products, or promote products, particularly in China. We have experienced challenges in maintaining some of our agreements and if we fail to enter into additional agreements, our business will suffer.
Our sales and marketing strategy in China depends significantly on agreements with third parties, and potentially on entering into additional agreements with third parties, or renegotiating agreements with third parties. Except for ZADAXIN, our rights to develop, market and sell our products in China, including licensed products and products currently promoted or sold by our subsidiaries, NovaMed and NovaMed Shanghai, are held by us under license, promotion, distribution or marketing agreements with third parties. These agreements for products include DC Bead, a product which we launched commercially in the third quarter of 2015, and products in the regulatory review process, including products in clinical trials that are held under license, distribution or marketing agreements. In addition, our success in the future may be dependent on entering into similar agreements with other parties and the
18
renewal of any such agreements. The third parties to these agreements are generally not under an obligation to renew the agreements. If any of these agreements are terminated, or if they are not renewed, our ability to distribute, or develop, the products or product candidates could be terminated and our business could be affected.
All of our products were originally obtained by us under licenses, promotion, distribution or similar third-party agreements. We do not conduct product discovery and our ability to bring new products to market is dependent upon our entering into additional acquisition, in-licensing, promotion or distribution agreements, particularly in China. The competition for attractive products is intense, and we cannot be certain that we will be able to negotiate in-license, promotion or distribution agreements for additional products in the future.
While in June 2013 we renewed our promotion agreement with Baxter for a 5-year term through December 2017 and in July 2014 we renewed our product distribution agreement with Pfizer for a 5-year term through June 2019, our promotion agreements with Sanofi were not renewed and expired on December 31, 2013. In addition, in August 2015, we and Cardiome mutually agreed to end our collaboration for Aggrastat, and return all rights to the product to Cardiome. We continue to assess the financial performance of the products we promote under our agreements and their overall value within our entire portfolio of products. Over time, we anticipate the product mix that we promote will change which may affect our revenues and profitability in the future. Terminations or failures to renew these or any other agreement as to some or all of the products covered by the agreement could result in a decline in revenue and in other costs including restructuring charges if a resulting revenue decline required us to reduce costs. On the other hand, if we are successful in negotiating better terms there may be a positive impact on our revenues and profitability.
If our products do not meet standards established by the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, we could lose our license to import products to China for commercial sale, which could negatively affect our revenues and operating results.
Our products are subject to standards established by the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, or ChP. The ChP is an official compendium of drugs in China and sets the standards of purity, description, test, dosage, precaution, storage and the strength for each drug in China. The ChP is revised from time to time, with the most recent revisions set forth in a 2015 edition. If our products fail to meet ChP specifications during routine customs testing as such specifications may be revised from time to time, our import drug licenses (IDLs), which allow the importation for commercial sale, may be revoked, which would result in a significant loss of revenue and materially adversely affect our business.
Our revenue will continue to be substantially dependent on our maintaining regulatory licenses and compliance with other regulations.
We have received regulatory approvals to import and market ZADAXIN in China and to manufacture ZADAXIN and export the product from Italy. In order to continue our sales to China, we need to maintain these approvals. Our license to import ZADAXIN into China needs to be renewed every five years and the next renewal is required in December 2017. Although renewals in the past were obtained successfully, there is no assurance that SciClone will receive renewals in the future when applied for or that the renewals will not be conditioned or limited in ways that limit our ability to sell ZADAXIN to China.
Our licenses to manufacture and export ZADAXIN from Italy are dependent upon our continuing compliance with regulations in Italy. Our business would be adversely affected if we are not able to maintain these approvals. In order to sell ZADAXIN to the licensed importers in China, our manufacturers must 1) be approved by the Italian Ministry of Health (“AIFA”) and 2) be accepted by the CFDA. Some manufacturing changes may require: 1) approval by AIFA in Italy and/or 2) be accepted by the CFDA, the Chinese equivalent of the FDA. In addition, we must obtain an IDL from the CFDA in order to sell ZADAXIN to the licensed importers in China. ZADAXIN registration in Italy has been essential to the renewal of our IDL from the CFDA permitting the importation of ZADAXIN into China. Our ability to continue to renew our IDL from the CFDA permitting the importation of ZADAXIN into China could be adversely affected, if we were to fail to maintain ZADAXIN registration in Italy. The CFDA, AIFA and other regulatory agencies may, and have, changed their internal administrative rules in ways that may delay or complicate the regulatory approval process. Those changes are not always disclosed or known to us and we may experience unexpected delays or additional costs as a result of such changes. Our product has been distributed in Italy through BioFutura Pharma Srl (“BioFutura”), a subsidiary of Sigma-Tau Finanziaria, S.p.A. (“Sigma-Tau”). In August 2012, we entered into an agreement with BioFutura to continue to distribute ZADAXIN for SciClone in Italy. However, if we are not able to continue this arrangement, we will need to establish alternative distribution operations in Italy to ensure continuing compliance with regulations in Italy and maintain our Italian licenses.
19
Our ZADAXIN sales and operations in China and in other parts of the world are subject to a number of risks and increasing regulations, including difficulties and delays in obtaining registrations, renewals of registrations, permits, pricing approvals and reimbursement, increasing regulation of product promotion and selling practices, unexpected changes in regulatory requirements and political instability.
Our resolution with government agencies in connection with violations by us of the US Foreign Corrupt Practices Act could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
As previously disclosed, since 2010 the SEC and the DOJ had each been conducting formal investigations of us regarding a range of matters, including possible violations of the FCPA, primarily related to certain historical sales and marketing activities with respect to our China operations. In response to these matters, our Board appointed the Special Committee to oversee our response to the government inquiry. Based on an initial review, the Special Committee decided to undertake an independent investigation as to matters reflected in and arising from the SEC and DOJ investigations in order to evaluate whether any violation of the FCPA or other laws occurred.
On February 4, 2016, we announced that we entered into a settlement agreement with the SEC fully resolving the SEC's investigation into possible violations of the FCPA and that the DOJ had also completed its related investigation and has declined to pursue any action. Under the terms of the settlement agreement with the SEC, SciClone paid a total of $12.8 million, including disgorgement, pre-judgment interest and a penalty. The payment is in line with the charges the Company previously recorded and disclosed in its Form 10-Q filed with the SEC on August 10, 2015. As part of the agreement, we neither admitted nor denied engagement in any wrongdoing and we agreed to give status reports to the SEC for the next three years on our continued remediation and implementation of anti-corruption compliance measures.
While we have resolved the previously pending matters with the SEC and DOJ, whether by virtue of announcement of the settlement agreement and the SEC Order or otherwise, we may be subject to investigations by foreign governments or further claims by third parties arising from conduct subject to the investigation or our other international operations. In addition, the remedial actions we have taken or may take as a result of such investigations may adversely affect our business in China and other countries, including adversely affecting our ability to obtain license renewals or other administrative approvals we require to conduct business in China and other countries.
Despite the resolution of the SEC and DOJ matters, we may be subject to additional investigations or regulatory actions in the future.
Despite the settlement of our SEC and DOJ matters, we may be subject to additional investigations in the future. We are unable to predict what ultimate consequences any investigation by any regulatory or law enforcement agency may have on us. Regulatory investigations that might be initiated in the future could result in substantial expenses, management diversion of attention, and harm to our business. If we fail to comply with regulations or to carry out controls on our Chinese or other foreign operations in a manner that satisfies all applicable laws, our business would be harmed. Any civil or criminal action commenced against us by a regulatory or law enforcement agency, including in China, could result in administrative orders against us, the imposition of significant penalties and/or fines against us, and/or the imposition of civil or criminal sanctions against certain of our officers, directors and/or employees.
If we fail to achieve or maintain an effective system of internal controls, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results. As a result, current and potential stockholders could lose confidence in our financial reporting, which would harm our business and the trading price of our stock.
Effective internal controls are necessary for us to provide reliable financial reports and to protect from fraudulent, illegal or unauthorized transactions. If we cannot establish effective controls and provide reliable financial reports, our business and operating results could be harmed. Moreover, as a US-based corporation doing business in China, these controls often need to satisfy the requirements of Chinese law as well as the requirements of US law which frequently differ in certain aspects. We have in the past discovered, and may in the future discover, areas of our internal controls that need improvement. For example, during the third quarter of 2012, our management determined that we had a material weakness in internal control over financial reporting related to the design and operation of our controls primarily associated with product returns reserves and the override of certain controls in the financial statement close process related to our NovaMed subsidiary. Furthermore, during the fourth quarter of 2012, our management determined that we had an additional indicator of the same material weakness related to the timing of revenue recognition for our Pfizer products and the override of related controls at our NovaMed subsidiary, and the corporate monitoring thereof. During fiscal
20
2014, we designed and implemented procedures to address the material weakness disclosed in our Annual Reports on Form 10-K for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 related to the design and operating effectiveness of certain corporate monitoring controls. Management designed and implemented corporate monitoring controls and other controls that provided increased oversight over our China operations, and has remediated the material weakness as of December 31, 2014. We continuously work on improvements to our internal controls and there can be no assurance that these or other material weaknesses will not occur in the future, or otherwise cause us to inaccurately report our financial statements. For example, the restatement of our financial statements for each of our first, second, and third quarters of 2012, and our financial statements for each of the second and third quarters of 2011 and the year ended December 31, 2011, were in part caused by the material weakness related to the design and operation of our controls disclosed as of December 31, 2012 discussed above. Any failure to implement and maintain controls over our financial reporting or difficulties encountered in the implementation of improvements in our controls, could cause us to fail to meet our reporting obligations. Any failure to improve our internal controls or to address identified weaknesses in the future, if they were to occur, could also cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information, which could have a negative impact on the trading price of our stock.
Compliance with changing regulations concerning corporate governance and public disclosure has resulted in and may continue to result in additional expenses. Changing laws, regulations and standards relating to corporate governance and public disclosure, including the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, new SEC regulations and The NASDAQ Stock Market rules, are creating uncertainty for companies such as ours and costs are increasing as a result of this uncertainty and other factors. We are committed to maintaining high standards of corporate governance and public disclosure. As a result, we intend to invest all reasonably necessary resources to comply with evolving standards, and this investment has and may continue to result in increased general and administrative expenses and a diversion of management time and attention from revenue-generating activities to compliance activities.
There can be no assurance that the strategic alternative process will result in pursuing or completing a particular transaction.
In early February 2016, we announced that our Board of Directors had initiated a process to identify, examine and consider a range of strategic alternatives available to us with a view to enhancing stockholder value and had engaged Lazard Freres & Co. LLC as its financial advisor to assist the Board in evaluating strategic alternatives. There can be no assurance that the evaluation of potential strategic alternatives will result in either pursuing any different strategic operational approach or completing any particular transaction. We also may not accurately assess the risks and uncertainties associated with engaging in a strategic alternative, and the anticipated benefits from pursuing any such alternative may not materialize. In addition, undertaking a strategic process could divert management’s time and focus from operating our business, potentially having adverse effects on our existing business relationships and our key employees.
We may not be able to effectively manage our employees and distribution network, and our reputation, business, prospects and brand may be materially and adversely affected by actions taken by our distributors and third-party marketing firms.
Our company policies prohibit our employees from making improper payments to hospitals or otherwise engaging in improper activities to influence the procurement decisions of hospitals, and we take remedial actions, including termination, when employees do not adhere to our policies. However, we may not be able to effectively ensure that every employee complies at all times with our policies. The compensation of our sales and marketing personnel is partially linked to their sales performance. Although we have made numerous changes to ensure compliance with our policies and to attempt to avoid any violation of law, we cannot assure you that employees will not violate the anticorruption laws of China, the US and other countries. Such violations, or allegations of such violations, could have a material adverse effect on our reputation, business, prospects and brand.
Furthermore, we have identified from time to time certain instances of improperly submitted expense reporting by our employees. Our employees may seek to create additional opportunities to engage in misappropriation or other employee malfeasance. If our controls and procedures to prevent such activities fail or are circumvented, our business would be negatively affected by, among other things, the related financial losses, diminished reputation and threat of litigation and regulatory inquiry and investigation.
We do not control, and therefore have limited ability to manage, the activities of third-parties who assist us in marketing and distributing our products. Our distributors or other third parties with whom we do business could take actions which violate the anti-corruption laws of China, the US or other countries. Failure to adequately manage our employees, and third parties and, or their non-compliance with employment, distribution or marketing agreements, could harm our corporate image among hospitals and end users
21
of our products and disrupt our sales, resulting in a failure to meet our sales goals. Furthermore, we could be liable for actions taken by our employees, distributors or third-party marketing or third-party firms, including any violations of applicable law in connection with the marketing or sale of our products, including China’s anticorruption laws and the FCPA of the US. In particular, if our employees, distributors or third-party marketing firms make any payments that are forbidden under China’s anticorruption laws or the FCPA, we could be subject to civil and criminal penalties imposed by the Chinese or US government.
Recently, the Chinese government has increased its anti-corruption measures. In the pharmaceutical industry, corrupt practices include, among others, acceptance of kickbacks, bribes or other illegal gains or benefits by the hospitals and medical practitioners from pharmaceutical manufacturers and distributors in connection with the prescription of certain pharmaceuticals. Our employees, affiliates, distributors or third-party marketing firms may violate these laws or otherwise engage in illegal practices with respect to their sales or marketing of our products or other activities involving our products. If our employees, affiliates, distributors or third-party marketing firms violate these laws, or are alleged to have violated these laws, we could be required to pay damages or fines, be subject to administrative actions or suffer additional consequences which could materially and adversely affect our ability to conduct business in China and our financial condition. In addition, Chinese laws regarding what types of payments to promote or sell our products are impermissible are not always clear, and local regulatory authorities enforcing these laws are not always consistent. As a result, we, our employees, affiliates, our distributors or third-party marketing firms could make certain payments in connection with the promotion or sale of our products or other activities involving our products which at the time are considered by us or them to be legal but are later deemed impermissible by the Chinese government, or we may be asked to make payments by local government authorities that may not be permissible under China’s anticorruption laws or the FCPA. Furthermore, our brand and reputation, our sales activities or the price of our common stock could be adversely affected if we become the target of any negative publicity as a result of actions taken by our employees, affiliates, distributors or third-party marketing firms.
Our independent registered public accounting firm serving as our external auditor is an audit firm which is not inspected by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (“PCAOB”), and, although they may be subject to other inspections, you do not have the benefits of PCAOB inspections.
Our incumbent independent auditors’ system of quality control and their individual audits are subject to review, inspection, or other outside assurance from time to time by member firms in the network of firms to which they belong, by peer accounting firms, or by regulatory or industry bodies in China (such as China’s securities regulator or the Chinese body representing certified public accountants). However, these various bodies or parties are distinct from the PCAOB, and their efforts may not be concentrated on audits of SEC registrants. Their reviews or inspections may be substantially different, or not comparable to, an inspection by the PCAOB. Auditors of companies that are registered with the SEC and traded publicly in the US, including our independent registered public accounting firm, must be registered with the PCAOB, and are required by the laws of the US to undergo regular inspections by the PCAOB to assess their compliance with the laws of the US and professional standards. Because our auditors are located in the People’s Republic of China, a jurisdiction where the PCAOB is currently unable to conduct inspections without the approval of the Chinese authorities, our auditors are not currently inspected by the PCAOB. This lack of PCAOB inspections in China prevents the PCAOB from regularly evaluating audits and quality control procedures of any auditors operating in China, including our auditors. As a result, investors in our equity securities may be deprived of the benefits of PCAOB inspections. The inability of the PCAOB to conduct inspections of auditors in China makes it more difficult to evaluate the effectiveness of our auditors’ audit procedures or quality control procedures as compared to other public company auditors outside of China that are subject to PCAOB inspections. As a result, investors in our stock may lose confidence in our reported financial information and procedures and the quality of our financial statements.
Proceedings instituted by the SEC against certain PRC-based accounting firms, including our independent registered public accounting firm, could result in financial statements being determined to not be in compliance with the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
In December 2012, the SEC brought administrative proceedings against five accounting firms, including our independent registered public accounting firm, in China, alleging that they had refused to produce audit work papers and other documents related to certain other China-based related companies under investigation by the SEC. On January 22, 2014, an initial administrative law decision was issued, censuring these accounting firms and suspending four of these firms from practicing before the SEC for a period of six months. The decision is neither final nor legally effective unless and until reviewed and approved by the SEC. On February 12, 2014, four of these PRC-based accounting firms, including our registered public accounting firm, appealed to the SEC against this sanction decision. In February 2015, the four PRC-based accounting firms agreed to a censure and to pay $500,000 each to the SEC to settle the dispute and avoid suspension of their ability to practice before the SEC and audit US- listed companies. The settlement
22
requires the firms to follow detailed procedures to seek to provide the SEC with access to Chinese firms’ audit documents via the China Securities Regulatory Commission. If the firms don’t follow the procedures, the SEC could impose penalties such as suspensions, or it could restart the current enforcement case administrative proceedings.
In the event that the SEC restarts the enforcement administrative proceedings, depending upon the final outcome, listed companies in the US with major PRC operations may find it difficult or impossible to retain auditors in respect of their operations in the PRC, which could result in financial statements being determined to not be in compliance with the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act. Moreover, any negative news about the proceedings against these audit firms may cause investor uncertainty regarding China-based, US-listed companies and the market price of our stock may be adversely affected.
If our independent registered public accounting firm were denied the ability to practice before the SEC and we were unable to timely find another registered public accounting firm to audit and issue an opinion on our financial statements, our financial statements could be determined not to be in compliance with the requirements of the Exchange Act of 1934. Such a determination could ultimately lead to the delisting of our shares from the Nasdaq Global Select Market or deregistration by the SEC, or both, which would substantially reduce or effectively terminate the trading of our stock in the US.
Our compliance with the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act may put us at a competitive disadvantage, while our failure to comply with the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act may result in substantial penalties.
As a US reporting company, we are required to comply with the FCPA. If our employees or other agents are found to have engaged in practices in violation of the FCPA, we could suffer severe penalties. Non-US companies, including some of our competitors, are not subject to the provisions of the FCPA. Corruption, extortion, bribery, pay-offs, theft and other fraudulent practices occur from time to time in mainland China. If our competitors engage in these practices, they may receive preferential treatment from personnel of some companies, giving our competitors an advantage in securing business or from government officials who might give them priority in their business dealings, which would put us at a disadvantage.
Retaliation from terminated employees may damage our reputation or lead to claims that could subject us to further regulatory action.
From time to time we have terminated the employment of certain employees for performance-related reasons, including, in particular, our policies intended to prevent corruption. Employees who are terminated may seek more favorable terms of separation by threatening to damage our reputation in the marketplace. Further, they may seek to retaliate against us by making so-called “whistleblower” claims under the provisions enacted by the Dodd-Frank Act that may entitle persons who report alleged wrong-doing to the SEC to cash rewards. We anticipate that these provisions will result in a significant increase in whistleblower claims across our industry, and dealing with such claims could generate significant expenses and take up significant management time, even for frivolous and non-meritorious claims. Any investigations of whistleblower claims may impose additional expense on us, may require the attention of senior management and members of the Board of Directors and may result in fines, adverse administrative sanctions or rulings and/or reputational damage whether or not we are deemed to have violated any regulations. Furthermore, terminated employees may also seek to retaliate against us by making claims against us to other regulatory agencies, including local regulatory authorities. Inquiries by local regulatory agencies about such claims, even if frivolous and non-meritorious, could also generate significant expenses and take up significant management and Board of Directors’ time.
We may incur unexpected charges relating to our operations.
Although we have generally experienced minimal product returns and our customers have historically paid all invoiced amounts, we could incur future charges relating to inventory that expires or as a result of customer failures to pay invoiced amounts timely or in full. For example, we recorded $0.5 million of bad debt expense in general and administrative expense for the first quarter of 2015 related to one customer whose accounts receivable are uncertain of collection. In addition, we recorded $2.4 million to bad debt expense for the year ended December 31, 2013 related to one customer whose accounts receivable were significantly past due and for which collectability was uncertain at that time. Although we subsequently collected $1.5 million of these receivables in fiscal 2014 and a further $0.4 million in the second quarter of 2015, there still remains $0.5 million awaiting collection that is fully reserved. We also recorded charges of $2.1 million during the year ended December 31, 2014 for potential inventory obsolescence related to Aggrastat. We have had and could also experience additional charges for potential inventory obsolescence related to other products if we are unable to sell units that are nearing their expiration dates, or for bad debt if other distributors do not pay outstanding receivables in full. Those or similar future events would have an adverse impact upon our operating results.
23
We are at risk of additional securities class action and derivative lawsuits.
Securities class action and derivative lawsuits are often filed against public companies following a decline in the market price of their securities. After our announcement regarding SEC and DOJ investigations in 2010, we and certain of our officers and directors were named as parties in purported stockholder class actions and derivative lawsuits. Those class action lawsuits were dismissed and we have settled those derivative lawsuits. Our stock price declined following the announcement of a restatement of our financial statements for fiscal 2011 and the first three quarters of fiscal 2012, and that our predecessor independent auditing firm had elected not to stand for reappointment for the 2013 fiscal year. Soon after that announcement, we and certain of our officers and directors were named as parties in a purported derivative lawsuit relating to the restatement, which was subsequently dismissed in its entirety. We may experience stock price volatility in the future related to other matters. This risk is especially relevant for us because biotechnology companies have experienced greater than average stock price volatility in recent years. We may be named in additional litigation, which could require significant management time and attention and result in significant legal expenses and may result in an unfavorable outcome, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. Such litigation could result in additional substantial costs and a diversion of management's and the Board of Directors’ attention and resources, which could harm our business.
We may not be able to successfully develop or commercialize our products.
We have numerous products under development in China, some of which were acquired in the NovaMed acquisition and others which were in-licensed by us. In recent years, we have in-licensed several additional product candidates for each of which our future development expenses and milestone payments could be material.
Clinical trials are inherently risky and may reveal that our product candidates are ineffective or have unanticipated side effects and/or drug interactions that may significantly decrease the likelihood of regulatory approval. For example, in March 2012, we announced the discontinuation of our phase 2b clinical trial evaluating SCV-07 for the delayed onset of oral mucositis. This decision was based on the results of a pre-planned interim analysis that indicated that the trial would not meet the pre-specified efficacy endpoints, and we have no plans to proceed with further development of SCV-07 at this time.
The regulatory approval processes in the US, Europe and China are demanding, lengthy and expensive. We have committed significant resources, including capital and time, to develop and seek approval for products under development, and if we do not obtain approvals we are seeking, we may be unable to achieve any revenue from these products. All new drugs, including our product candidates, are subject to extensive and rigorous regulation by the FDA, CFDA and similar regulatory agencies. These regulations govern, among other things, the development, testing, manufacturing, labeling, storage, pre-market approval, importation, advertising, promotion, sale and distribution of our products. These regulations may change from time to time and new regulations may be adopted.
Satisfaction of government regulations may take several years and the time needed to satisfy them varies substantially based on the type, complexity and novelty of the pharmaceutical product. As a result, government regulation may cause us to delay the introduction of, or prevent us from marketing, our existing or potential products for a considerable period of time and impose costly procedures on our activities. We have experienced delays in the regulatory process, and there exists risk that we may not receive approval of in-licensed products currently in the regulatory process. In addition, the Chinese government is increasing its efforts to reduce overall health care costs, including pricing controls on pharmaceutical products. We cannot determine what the potential government pricing constraints are likely to be for products in development in advance. Therefore, we may be required to abandon the development or commercialization of a product after significant effort and expense if we determine at any time that trends in government pricing constraints will make the commercialization of a product unprofitable.
To fully develop these products and other products we may acquire, substantial resources are required for extensive research, development, pre-clinical testing, clinical trials, and manufacturing scale-up and regulatory approval prior to the potential products being ready for sale. We cannot assure that our efforts will produce commercially viable products. We face significant technological risks inherent in developing these products. We may also abandon some or all of our proposed products before they become commercially viable. We are obligated to make a milestone payment upon regulatory approval of certain products under development. If any of our products, even if developed and approved, cannot be successfully commercialized in a timely manner, our business will be harmed and the price of our stock may decline.
24
Market acceptance of any product that is successfully developed and approved will depend on many factors, including our ability to convince prospective customers to use our products as an alternative to other treatments and therapies. In addition, doctors must opt to use treatments involving our products. If doctors elect to use a different course of treatment, demand for our drug products would be reduced. In addition, for certain products we may need to convince partners to manufacture or market our products. Failure to do any of the above will lead to an unfavorable outcome on the results of our operations.
Our sales are concentrated in China and we face risks relating to operating in China, including risks due to changes in the regulatory environment, slow payment cycles and exposure to fluctuations in the Chinese economy.
A significant portion of our revenue and profit is derived from operations in China. Consequently, our overall financial results are dependent on this market, and our business is exposed to risks there. In addition to the risks relating to pricing previously discussed above, these risks also include changes in economic conditions (including wage and cost inflation, currency exchange rates, consumer spending and employment levels), tax rates, laws, changes in the regulatory environment, increased competition and potential noncompliance with local laws and regulations. Risks also include changing consumer product preferences and preferred sales channels, as well as our ability to accommodate such changing preferences. Certain risks and uncertainties of doing business in China are solely within the control of the Chinese government, and Chinese law regulates the scope of our foreign investments and business conducted within China. Any significant or prolonged deterioration in China’s relations with the United States and other countries could adversely affect our China business. There are also uncertainties regarding the interpretation and application of laws and regulations and the enforceability of intellectual property and contract rights in China. There can be no assurance as to the future effect of any such risks and uncertainties on our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
In addition to the risk relating to pricing regulations and other risks related to operating in China, as discussed above, we experience other issues with managing sales operations in China including long payment cycles, potential difficulties in timely accounts receivable collection and, especially from significant customers, fluctuations in the timing and amount of orders and the adverse effect of any of these issues on our business could be increased due to the concentration of our business with a small number of distributors. Problems with collections from, or sales to, any one of those distributors could materially adversely affect our results. Operations in foreign countries including China also expose us to risks relating to difficulties in enforcing our proprietary rights, currency fluctuations and adverse or deteriorating economic conditions. If we experience problems with these matters, or if significant regulatory limitations are imposed on our ability to terminate employees and on the related costs, political, economic or regulatory changes occur, our results could be adversely affected. During the third quarter of 2014, we wrote-off $1.1 million of $3.5 million in fully reserved accounts receivable related to one customer. For that customer, we received $1.5 million in payments on fully reserved accounts receivable in 2014 and a further $0.4 million in the second quarter of 2015, and the remaining fully reserved accounts receivable balance of $0.5 million as of December 31, 2015 is substantially delinquent. Although we entered into a settlement agreement with this customer in October 2014, and the customer had a binding obligation to pay us the remaining $0.5 million by December 31, 2015, we did not receive the payment as of December 31, 2015 and there can be no assurance if we are not paid and we pursue legal action what the timing or result of such action would be.
Our operations throughout the world including China are potentially subject to the laws and regulations of the US including the FCPA, in addition to the laws and regulations of the other countries. Regulation in China of the activities in the pharmaceutical industry has increased and may continue to undergo significant and unanticipated changes. A number of companies have faced significant expenses or fines as a result of the increasing regulation of, and enforcement activity regarding, the pharmaceutical industry. The Chinese government has recently made arrests of pharmaceutical company employees for allegedly illegal sales and marketing activities. Recent or future arrests of sales personnel, doctors or others in the pharmaceutical industry, whether or not the individuals violated laws or regulations, could impact the operations and results of pharmaceutical companies in China, including our own. The Chinese government has also been investigating the costs to manufacture approximately 40 pharmaceutical products sold in China. While SciClone was not involved in either of these actions, these actions may be an indication of heightened Chinese government oversight of the pharmaceutical industry, and of multinational pharmaceutical companies in particular. Such activities could have long-term implications for the pharmaceutical industry in China including increased pricing pressure and a heightened level of government oversight and investigations, either of which could adversely affect the industry as a whole or individual companies, including SciClone.
25
Our business is sensitive to the economy in China. A downturn in the Chinese economy could materially and adversely affect our revenues and results of operations.
Any slowdown in China’s economic development might lead to tighter credit markets, increased market volatility, sudden drops in business and consumer confidence and dramatic changes in business and consumer behaviors. Economic growth rates in China are slowing and there has been significant volatility in the stock indexes within China. The Chinese government is believed to take an active role in influencing stock indexes and in many other areas, but there is no assurance that growth rates will not continue to decline. Slowing growth in China, stock market volatility and uncertainty in economic conditions, may cause a decline in sales of ZADAXIN or negatively impact our other products. A decline is demand for our products in China could materially and adversely affect our revenues and results of operations.
The Company could be subject to changes in its tax rates, the adoption of new US or international tax legislation or exposure to additional tax liabilities which could have a negative impact on our financial position and results of operations.
Currently all of our revenue is generated from customers located outside the US, and a substantial portion of our assets, including employees, are located outside the US. US income taxes and foreign withholding taxes have not been provided on undistributed earnings of non-US subsidiaries, because such earnings are intended to be indefinitely reinvested in the operations of those subsidiaries. The US government may propose initiatives that would substantially reduce our ability to defer US taxes including: repealing deferral of US taxation of foreign earnings, eliminating utilization or substantially reducing our ability to claim foreign tax credits, and eliminating various tax deductions until foreign earnings are repatriated to the US. If any of these proposals are constituted into legislation, they could increase our US income tax liability and as a result have a negative impact on our financial position and results of operations.
Chinese healthcare regulation and the Chinese market are changing rapidly and we may modify our strategy in response to those changes and we cannot assure you that we will be successful in implementing changes.
The Chinese healthcare and regulatory environment have changed and are likely to continue to change in response to Chinese government policies and other factors. We intend to evaluate and make modifications to our strategy in response to these changes. We intend to continue our strategies of growing business in China by expanding ZADAXIN sales, entering into new promotional agreements, and seeking of products that have been approved outside China, but we may implement additional strategies, including expanding our capabilities in China to develop earlier stage products in-licensed from third parties in China or elsewhere. If we make significant additions or changes to our strategy, we may not be successful in implementing such changes, or the Chinese market may change in unexpected directions to which we are not able to respond timely.
We may lose market share or otherwise fail to compete effectively in the intensely competitive pharmaceutical industry.
Competition in the pharmaceutical industry in China is intense, and we believe that competition will increase. Our success depends on our ability to compete in this industry, but we cannot assure you that we will be able to successfully compete with our competitors. Increased competitive pressure could lead to intensified price-based competition resulting in lower prices and margins, which would hurt our operating results. We cannot assure you that we will compete successfully against our competitors or that our competitors, or potential competitors, will not develop drugs or other treatments for our targeted indications that will be superior to ours.
We depend on sales to China, and global conditions could negatively affect our operating results or limit our ability to expand our operations in and outside of China. Changes in China’s political, social, regulatory and economic environment may affect our financial performance.
Our business is concentrated in China. Heightened tensions resulting from the current geopolitical conditions in the Middle East, North Korea and elsewhere could worsen, causing disruptions in foreign trade, which would harm our sales. In particular, our commercial product is manufactured in Europe and distributed by us from our operations in Hong Kong. Any disruption of our supply and distribution activities due to geopolitical conditions could decrease our sales and harm our operating results. In addition, while we continue our efforts to expand our operations in and outside of China, disruptions in our marketing or distribution efforts could delay or limit our ability to expand. We have had distributors with whom our accounts receivable collectability has become uncertain where, in addition to the charges that may result from the collectability of the accounts receivable, we may experience delays in our efforts to expand our operations and lose business to our competitors from any resulting disruption.
26
With respect to China, our financial performance may be affected by changes in China’s political, social, regulatory and economic environment. The role of the Chinese central and local governments in the Chinese economy is significant. Chinese policies toward economic liberalization, and laws and policies affecting foreign companies, currency exchange rates and other matters could change, resulting in greater restrictions on our ability to do business in China. Any imposition of surcharges or any increase in Chinese tax rates could hurt our operating results. The Chinese government could revoke, terminate or suspend our license for national security and similar reasons or in the event our employees, affiliates, distributors or third-party marketing firms violate Chinese anticorruption laws, or are alleged to have violated these laws, without compensation to us. If the government of China were to take any of these actions, we would be prevented from conducting all or part of our business. Any failure on our part to comply with governmental regulations could result in the loss of our ability to market our products in China.
Because of China's tiered method of importing and distributing finished pharmaceutical products, our quarterly results may vary substantially from one period to the next; we are dependent upon Sinopharm as the exclusive importer of ZADAXIN.
Imported products in China, including ZADAXIN and NovaMed’s imported products, are distributed through a tiered method to import and distribute finished pharmaceutical products. Promoted products are typically sold from our partner companies within China to the primary distributor with the following distribution being the same for imported as well as promoted products. At each port of entry, and prior to moving the product forward to the distributors, government-licensed importing agents must process and evaluate each imported product shipment to determine whether it satisfies China's quality assurance requirements. In order to efficiently manage this process, the importing agents typically place large, and therefore relatively few, orders within an annual period. Therefore, sales to an importing agent can vary substantially from quarter to quarter depending on the size and timing of the orders, which has in the past and may in the future cause our quarterly results to fluctuate. We rely on Sinopharm to supply our ZADAXIN sales. Our receivables from Sinopharm are material, and if we were unable to collect receivables from Sinopharm or any other importer, our business and cash-flow would be adversely affected. In 2012, we also relied on another distributor to supply our ZADAXIN product. Receivables from this importer are $0.5 million as of December 31, 2015 that are more than one year past due and fully reserved, and if we were unable to collect these receivables, our business and cash flows would be adversely affected.
Generally, our importers are not obligated to place purchase orders for our product, and if they determined for any reason not to place purchase orders, we would need to seek alternative licensed importers, which could cause fluctuations in our revenue. As a result of our agreement granting certain exclusive importation rights to Sinopharm for ZADAXIN, we are dependent upon Sinopharm’s performance of its obligations under that agreement. We have a long-standing and, we believe excellent, relationship with Sinopharm; however, if Sinopharm were unable to adequately perform its obligations under, or breached, the agreement our business would be adversely affected.
The existence of counterfeit pharmaceutical products in China’s pharmaceutical retail market may damage our brand and reputation and have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Certain medicine products distributed or sold in China’s pharmaceutical retail market, including those appearing to be our products, may be counterfeit. Counterfeit products are products sold under the same or very similar brand names and/or have a similar appearance to genuine products. Counterfeit products, including counterfeit pharmaceutical products, are a significant problem in China and we have experienced counterfeiting of our products. Such counterfeit products divert sales from genuine products, often are of lower cost, often are of lower quality (having different ingredients or formulations, for example), and have the potential to damage the reputation for quality and effectiveness of the genuine product. The counterfeit pharmaceutical product regulation control and enforcement system in China is not able to completely eliminate production and sale of counterfeit pharmaceutical products. To increase our ability to prevent counterfeiting, we have taken several actions, including enhancements of our product labeling to implement industry-leading labeling technology and implementation of product tracking applications. However we cannot eliminate counterfeiting and, any sale of counterfeit products resulting in adverse side effects to consumers may subject us to negative publicity and expenses. It could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We may be subject to currency exchange rate fluctuations, which could adversely affect our financial performance.
The majority of our sales have been in US dollars, although a portion of our sales are denominated in RMB. Per our previous contractual arrangement with Sinopharm through December 31, 2015, and a renewed contractual arrangement with Sinopharm (our sole importer and distributor for ZADAXIN in China) which took effect January 1, 2016, our sales of ZADAXIN to Sinopharm have been and continue to be denominated in US dollars. However, the established importer price may be adjusted quarterly based upon
27
exchange rate fluctuations between the US dollar and RMB. In recent months the RMB has experienced devaluation; accordingly, our importer price has been and can continue to be adjusted downward as denominated in US dollars. Our purchases with contract manufacturers are denominated in US dollars and euros and costs of our marketing efforts in China are paid in local currency. In addition, we have certain cash balances and other assets and liabilities denominated in euros, RMB and Hong Kong dollars. Fluctuation in the US dollar exchange rate with local currency directly affects the customer's cost for our product. In particular, a stronger US dollar vis-à-vis the local currency would tend to have an adverse effect on sales and potentially on collection of accounts receivable. China currently maintains the value of the RMB in a narrow currency trading band that may or may not fluctuate based on government policy. For example, in August 2015, the Chinese government devalued the RMB and may further devalue the RMB at any time. This devaluation has resulted in the strengthening of the US dollar and may reflect a weakening of the Chinese economy. Depending on market conditions and the state of the Chinese economy, China has intervened in the foreign exchange market in the past to prevent significant short-term fluctuations in the RMB exchange rate, and it could make future adjustments, including moving to a managed float system, with opportunistic interventions. This reserve diversification may negatively impact the US dollar and US interest rates. A trend to a stronger US dollar would erode margins earned by our Chinese importers and prompt them to ask us to lower our prices. A weaker US dollar would increase our in-country China operating expenses, and with the addition of NovaMed, our China operating expenses have increased. We are subject to currency exchange rate fluctuations as a result of expenses incurred by our foreign operations. In particular, one of our supply arrangements under which we purchase finished products is denominated in euros and costs of our operations in China are paid in local currency. Consequently, changes in exchange rates could unpredictably and adversely affect our operating results and could result in exchange losses. To date, we have not hedged against the risks associated with fluctuations in exchange rates and, therefore, exchange rate fluctuations could have a material adverse impact on our future operating results and stock price.
We cannot predict the safety profile of the use of ZADAXIN or other drugs we may develop or market particularly when used in combination with other drugs.
While ZADAXIN has an excellent safety profile, we cannot predict whether ZADAXIN or any product we market may have unexpected safety issues in a particular patient population or when used in new indications. In addition, we cannot predict how ZADAXIN or other drugs we may develop or market will work with other drugs, including causing possible adverse side effects not directly attributable to the other drugs that could compromise the safety profile of ZADAXIN or other drugs we may develop or market when used in certain combination therapies. We are exploring new indications for ZADAXIN and there is a risk that new safety issues could appear in these new patient populations.
As we introduce new products, such as DC Bead, to the market in China, there may be adverse safety events related to those products. Adverse safety events may have a negative impact on our business. Discovery of safety issues with our products could create product liability and could cause additional regulatory scrutiny and requirements for additional labeling, withdrawal of products from the market, and the imposition of fines or criminal penalties. Adverse safety events may also damage physician and patient confidence in our products and our reputation. Any of these could result in liabilities, loss of revenue, material write-offs of inventory, material impairments of goodwill and fixed assets, material restructuring charges and other adverse impacts on our results of operations.
Regulatory authorities are making greater amounts of stand-alone safety information directly available to the public through periodic safety update reports, patient registries and other reporting requirements. The reporting of adverse safety events involving our products or products similar to ours and public rumors about such events may increase claims against us and may also cause our product sales or stock price to decline or experience periods of volatility.
If third-party reimbursement is not available or patients cannot otherwise pay for ZADAXIN or other drugs we may develop, we may not be able to successfully market them.
Significant uncertainty exists as to the reimbursement status of therapeutic products, such as ZADAXIN or other drugs we may develop. We cannot assure you that third-party insurance coverage and reimbursement will be available for therapeutic products we might develop. Although ZADAXIN receives some limited reimbursement in certain provinces in China, we cannot assure you that we will be able to maintain existing reimbursements or increase third-party payments for ZADAXIN or obtain third-party payments for other products that we sell or develop in China. The failure to obtain or maintain third-party reimbursement for our products would harm our business. Further, we cannot assure you that additional limitations will not be imposed in the future in the US or elsewhere on drug coverage and reimbursement due to proposed health care reforms. In many emerging markets where we have marketing rights to ZADAXIN, but where government resources and per capita income may be so low that our products will be prohibitively expensive, we may not be able to market our products on economically favorable terms, if at all.
28
Recent efforts by governmental and third-party payers to contain or reduce health care costs and the announcement of legislative proposals and reforms to implement government controls has caused us to reduce the prices at which we market our drugs in China, and additional reforms, if they were to occur, could cause us to further reduce our prices which could reduce our gross margins and may harm our business.
We rely on third parties who are our sole source suppliers for our clinical trial and commercial products and their inability to deliver products that meet our quality-control standards could delay or harm one or more important areas of our business including our sales, clinical trials or the regulatory approval process.
We rely on third parties, who are subject to regulatory oversight, to supply our commercial products. Any deficiencies or shortages in supply of our commercial products would adversely affect our ability to realize our sales plans. For example, the manufacturing of the raw material and the processing to finished product of ZADAXIN is done in few batches in any given three-month period and any manufacturing errors have the potential to require a product recall. We currently have only one approved finished vial manufacturer and two approved active pharmaceutical ingredient (“API”) suppliers. If we experience a problem with the manufacturer or our suppliers, our sales may suffer. We have each experienced difficulties with obtaining product from manufacturers in the past. During 2012, we experienced limitations on supply of several products we were promoting (each of which we no longer market) and the growth in the sales of those products was affected. During 2011, we experienced manufacturing delays related to repairs for general, non-production-related facilities equipment at one of our API suppliers. During 2010, we experienced difficulties validating upgrades to equipment with one of our API manufacturers. Although we are taking steps to ensure that such problems do not continue, there is no assurance that we will either be successful in doing so with our current supplier or be able to timely and cost-effectively qualify new suppliers for this component. Manufacturing interruptions or failure or delay of product to meet quality assurance specifications could adversely affect shipments and recognition of sales of our products in any period and impair our relationships with customers and our competitive position and may increase the cost of material produced. In addition, each of the products that are marketed through our NovaMed subsidiary is manufactured by, or obtained from, a single source.
We also rely on third parties, who are subject to regulatory oversight, to supply drug product. For example, ONXEO (formerly BioAlliance) is the sole supplier of Loramyc. Any unanticipated deficiencies in this supplier, or the suppliers of our raw materials, and/or recall of the manufacturing lots could also impede commercialization of our products and impair our competitive position. In addition, any unanticipated deficiencies in suppliers used in our clinical trials could delay the trials or detract from the integrity of the trial data and its potential use in future regulatory filings. In addition, manufacturing interruptions or failure to comply with regulatory requirements by any of these suppliers could significantly delay clinical development of potential products and reduce third-party or clinical researcher interest and support of proposed trials.
If our thymalfasin API or ZADAXIN products are not shipped and stored at precision temperatures, the products could become damaged, which could negatively affect our sales and operating results.
Thymalfasin API and ZADAXIN are temperature sensitive products. SciClone relies on third-party organizations to provide controlled temperature shipping logistics services from the point of ownership transfer from the API contract manufacturer to the point where thymalfasin API is converted to ZADAXIN drug product, and from the ZADAXIN drug product manufacturing site to our storage locations in Hong Kong and then to China. Although some temperature excursions are allowable and thymalfasin and ZADAXIN are relatively stable when exposed to temperatures higher than recommended, if any third-party logistics or equipment provider fails to perform their required oversight duties with respect to temperature control or a shipment is delayed in transit for a prolonged period of time, the thymalfasin API or ZADAXIN drug product could become unsuitable for subsequent processing or commercial use. Although we have not experienced cold chain interruptions in the past and our distributor in China may maintain several months supply of our product, were our cold chain distribution or warehouse capability to be interrupted, our ability to timely deliver finished product to China could be adversely affected, which in turn could materially adversely affect our sales and operating results.
We rely on third parties for development of our products and the inability of any of these parties to reliably, timely or cost-effectively provide us with their obligated services could materially harm the timing of bringing our products to market and accordingly adversely affect our business.
We rely on third parties, such as contract research organizations, medical institutions, clinical investigators, contract laboratories, and collaborative partners in the conduct of clinical trials for our product candidates. If these parties, whom we do not control, do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or regulatory obligations or meet expected deadlines or choose not to continue their
29
relationship with us, if the third parties need to be replaced, or if the quality or accuracy of the data they obtain is compromised due to the failure to adhere to our clinical protocols or regulatory requirements or for other reasons, our pre-clinical or clinical activities may be extended, delayed, suspended or terminated, and we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for, or successfully commercialize our product candidates.
Commercialization of some of our products depends on collaborations with others. If our collaborators are not successful, or if we are unable to find future collaborators, we may not be able to properly develop and commercialize our products.
We depend in part on our distributors and business partners to develop or promote our drugs, and if they are not successful in their efforts or fail to do so, our business will suffer. We generally do not have control over the amount and timing of resources that our business partners devote to our collaborative efforts, and some have not always performed as or when expected. If they do not perform their obligations as we expect, particularly obligations regarding clinical trials, our development expenses would increase and the development or sale of our products could be limited or delayed, which could hurt our business and cause our stock price to decline. In addition, our relationships with these companies may not be successful. Disputes may arise with our collaborators, including disputes over ownership rights to intellectual property, know-how or technologies developed with our collaborators. We may not be able to negotiate similar additional arrangements in the future to develop and commercialize ZADAXIN or other products.
If we are unable to retain our key personnel, or are unable to attract and retain additional, highly skilled and experienced personnel, including the ability to expand our sales staff, our business will suffer.
We are highly dependent upon our ability to attract and retain qualified personnel because of the specialized, scientific and worldwide nature of our business. We are also dependent on our ability to appropriately staff these personnel in appropriate positions as our business fluctuates. Further, our efforts to in-license or acquire, develop and commercialize product candidates for China may require the addition of clinical and regulatory personnel and the expansion of, or changes in our sales and marketing operation. In addition, we assign numerous key responsibilities to a limited number of individuals, and we would experience difficulty in finding immediate replacements for any of them were any one of them to choose to leave employment with us. There is intense competition for qualified management, scientific, clinical, regulatory, and sales and marketing personnel in the pharmaceutical industry.
There is significant turnover in the industry, in China in particular, and we have also experienced turnover in our sales personnel and key employees. We may not be able to attract and retain the qualified personnel we need to grow and develop our business globally.
We have terminated personnel for violations of our policies and procedures as well as for lack of performance. Our future success will depend in part on our retaining key personnel and on recruiting additional senior sales and other personnel in China. We are continuously recruiting executives and other level personnel to address departures and to expand and strengthen our China operations.
Conversely, if we need to reduce the size of a particular aspect of our business, including if we have contracts that are not renewed or renegotiated for products we market or promote, we are also dependent on our ability to make such adjustments while retaining suitably skilled personnel. For example, we reduced the size of our sales force as a result of the expiration of our agreement with Sanofi at the end of 2013. In addition, we have taken corrective measures based on the findings of our Special Committee relating to its investigation of matters relating to the FCPA and have taken, and expect to continue to take, corrective measures relating to managements’ evaluation of internal control over financial reporting which could have adverse effects on our business, including the loss of personnel, and changes in marketing, sales and educational practices or programs. If we were unable to attract and retain qualified personnel as needed or promptly replace those employees who are critical to our sales, development and other operations, and in particular senior executives, our financial results and operations would be adversely affected. At this time, we do not maintain “key person” life insurance for any of our personnel.
We may need to obtain additional funding to support our long-term product development, including funding of in-licensed products, and commercialization programs.
We believe our existing cash and cash equivalents and ongoing revenue generating business operations will be sufficient to support our current operating plan for at least the next 12 months. We may use cash to acquire additional product rights or for future acquisitions. Our ability to achieve and sustain operating profitability is dependent on numerous factors including our ability to achieve increasing sales of ZADAXIN and DC Bead in China, and for our other products including those products we acquired as a result of the NovaMed acquisition and the execution and successful completion of clinical trials in China. Further, we may use cash to
30
fund products we in-license. We cannot assure you that such funds from operating activities will be sufficient, or that we will attain profitable operations in future periods. In addition, we intend to develop other products and we may need additional funds in the future to support such development and to support future growth and achieve profitability. If we need to raise additional funds in the future and such funds are not available on reasonable terms, if at all, our commercialization efforts may be impeded, our revenues may be limited and our operating results may suffer.
We are subject to the risk of increased income taxes which could reduce our future operating income.
We have structured our operations in a manner designed to maximize income in countries where:
|
· |
tax incentives have been extended to encourage foreign investment; or |
|
· |
income tax rates are low. |
Our taxes could increase if certain tax holidays or incentives are not renewed upon expiration, or if tax rates applicable to us in such jurisdictions are otherwise increased. For example, on March 16, 2007, the Chinese government passed a unified enterprise income tax law which became effective on January 1, 2008. Among other things, the law cancels many income tax incentives previously applicable to one of our subsidiaries in China. The law provides a transition rule which increased the tax rate of one of our subsidiaries in China over a 5-year period to 25% by 2012. The law also increased the standard withholding rate on earnings distributions to between 5% and 10% depending on the residence of the shareholder. The ultimate effect of these and other changes in Chinese tax laws on our overall tax rate will be affected by, among other things, our China income, the manner in which China interprets, implements and applies the new tax provisions, and by our ability to qualify for any exceptions or new incentives.
In addition, the Company and its subsidiaries are regularly subject to tax return audits and examinations by various taxing jurisdictions, particularly in the US and China. In determining the adequacy of our provision for income taxes, we regularly assess the likelihood of adverse outcomes resulting from tax examinations. While it is often difficult to predict the final outcome or the timing of the resolution of a tax examination, we believe that our reserves for uncertain tax positions reflect the outcome of tax positions that are more likely than not to occur. However, we cannot be certain that the final determination of any tax examinations will not be materially different than that which is reflected in our income tax provisions and accruals. Should additional taxes be assessed as a result of a current or future examination, there could be a material adverse effect on our tax provision, operating results, financial position and cash flows in the period or periods for which that determination is made.
If we fail to protect our products, technologies and trade secrets, we may not be able to successfully use, manufacture, market or sell our products, or we may fail to advance or maintain our competitive position, and we have limited intellectual property protection in China.
Our success depends significantly on our ability to obtain and maintain meaningful patent protection for our products and technologies and to preserve our trade secrets. Our pending patent applications may not result in the issuance of patents in the future. Our patents or patent applications may not have priority over others' applications. Our existing patents and additional patents that may be issued, if any, may not provide a competitive advantage to us or may be invalidated or circumvented by our competitors. Others may independently develop similar products or design around patents issued or licensed to us. Patents issued to, or patent applications filed by, other companies could harm our ability to use, manufacture, market or sell our products or maintain our competitive position with respect to our products. Although many of our patents relating to thymalfasin have expired, including composition of matter patents, we have rights to other patents and patent applications relating to thymalfasin and thymalfasin analogues, including method of use patents with respect to the use of thymalfasin for certain indications. Additionally, thymalfasin has received Orphan Drug designation in the US for the treatment of stage 2b through stage 4 melanoma, for the treatment of chronic active hepatitis B, for the treatment of DiGeorge anomaly with immune defects, and for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. If other parties develop generic forms of thymalfasin for other indications, including conducting clinical trials for such indications, our patents and other rights might not be sufficient to prohibit them from marketing and selling such generic forms of thymalfasin or their brands of thymalfasin. If other parties develop analogues or derivatives of thymalfasin, our patents and other rights might not be sufficient to prohibit them from marketing these analogues or derivatives.
Pharmaceutical products are either not patentable or have only recently become patentable in some of the countries in which we market or may market thymalfasin. We do not have composition patent claims directed to the thymalfasin that is currently marketed in China, our largest market, although we do have other type of patent claims, pending or issued, directed to other aspects of thymalfasin therapy. Other companies market generic thymalfasin in China, potentially in violation of our patent, trademark or other rights which,
31
to date, we have defended by informing physicians and hospitals of the practice. Past enforcement of intellectual property rights in many of these countries, including China in particular, has been limited or non-existent. Future enforcement of patents and proprietary rights in many other countries will likely be problematic or unpredictable. Moreover, the issuance of a patent in one country does not assure the issuance of a similar patent in another country. Claim interpretation and infringement laws vary by nation, so the extent of any patent protection is uncertain and may vary in different jurisdictions.
If we are involved in intellectual property claims and litigation, the proceedings may divert our resources and subject us to significant liability for damages, substantial litigation expense and the loss of our proprietary rights.
Our commercial success depends in part on our not infringing valid, enforceable patents or proprietary rights of third parties, and not breaching any licenses that may relate to our technologies and products. In addition, we may not be aware of all patents or patent applications that may impact our ability to make, use or sell any of our potential products. For example, US patent applications may be kept confidential for 12 or more months while pending in the Patent and Trademark Office, and patent applications filed in foreign countries are often first published nine months or more after filing. It is possible that we may unintentionally infringe these patents or other patents or proprietary rights of third parties. We may in the future receive notices claiming infringement from third parties as well as invitations to take licenses under third-party patents. Any legal action against us or our collaborative partners claiming damages and seeking to enjoin commercial activities relating to our products and processes affected by third-party rights may require us or our collaborative partners to obtain licenses in order to continue to manufacture or market the affected products and processes. Our efforts to defend against any of these claims, regardless of merit, would require us to devote resources and attention that could have been directed to our operations and growth plans. In addition, these actions may subject us to potential liability for damages. We or our collaborative partners may not prevail in a patent action and any license required under a patent may not be made available on commercially acceptable terms, or at all. Any conflicts resulting from the patent rights of others could significantly reduce the coverage of our patents and limit our ability to obtain meaningful patent protection.
If other companies obtain patents with conflicting claims, we may be required to obtain licenses to those patents or develop or obtain alternate technology to manufacture or market the affected products and processes. We may not be able to obtain any such licenses on acceptable terms or at all. Any failure to obtain such licenses could delay or prevent us from pursuing the development or commercialization of our potential products. Our efforts to defend against any of these claims would require us to devote resources and attention that could have been directed to our operations and growth plans.
We may need to initiate litigation, which could be time-consuming and expensive, to enforce our proprietary rights or to determine the scope and validity of others' rights. If litigation results, a court may find our patents or those of our licensors invalid or may find that we have infringed on a competitor's rights. If any of our competitors have filed patent applications in the US that claim technology we also have invented, the Patent and Trademark Office may require us to participate in expensive interference proceedings to determine who has the right to a patent for the technology. These actions may subject us to potential liability for damages. We or our collaborative partners may not prevail in a patent action and any license required under a patent may not be made available on commercially acceptable terms, or at all.
Substantial sales of our stock or the exercise or conversion of options may impact the market price of our common stock.
While we do not have any plans to issue common stock other than with respect to equity compensation, future issuances of substantial amounts of our common stock could adversely affect the market price of our common stock. Similarly, if we raise additional funds through the issuance of common stock or securities convertible into or exercisable for common stock or sell equity in a subsidiary, the percentage ownership of our present stockholders of the respective entities will be reduced and the price of our common stock may fall.
Our cash and cash equivalents are subject to certain risks which could materially adversely affect our overall financial position.
We invest our cash and cash equivalents in accordance with an established internal policy and customarily in instruments which historically have been highly liquid and carried relatively low risk. However, with turmoil in the credit markets, similar types of investments have experienced losses in value or liquidity issues which differ from their historical pattern. For example, we routinely have invested in money market funds with large financial institutions. One or more of these funds could experience losses or liquidity problems and, although to date some of the largest financial institutions who sponsor such funds have offset similar losses, there is no assurance that our financial institutions would either not incur losses or would offset any losses were they to occur.
32
Any adjustment to decrease the ratings of our investments by a statistical rating organization (such as Moody’s or Standard and Poor’s) may have a negative impact on the value of our investments.
Should any of our cash investments permanently lose value or have their liquidity impaired, it would have a material and adverse effect on our overall financial position by imperiling our ability to fund our operations and forcing us to seek additional financing sooner than we would otherwise and such financing may not be available on commercially attractive terms.
In addition, financial instruments may subject us to a concentration of credit risk. Most of our cash and cash equivalents are held by a limited number of financial institutions. To date, we have not experienced any losses on our deposits of cash and cash equivalents. However, if any of these instruments permanently lost value or have their liquidity impaired, it would also have a material and adverse effect on our overall financial position by imperiling our ability to fund our operations and forcing us to seek additional financing sooner than we would otherwise and such financing may not be available on commercially attractive terms.
We expect that we may need to transfer capital to NovaMed Shanghai from time to time to fund its operations. We need to obtain regulatory approval from China’s State Administration of Foreign Exchange (“SAFE”) in order to make such transfers and there can be no assurance that we will be able to obtain such approval in a timely manner. We have been able to fund the operations of NovaMed Shanghai to date through commercial credit facilities or through intercompany loans, but we could face difficulties in the future if our efforts to improve profitability and cash flow in NovaMed Shanghai are not successful, or if we are unable to obtain SAFE approval or obtain further funding for NovaMed Shanghai.
Furthermore, a majority of our cash is held by our foreign subsidiaries. Such cash is used to fund the operating activities of our foreign subsidiaries and for further investment in foreign operations. Based on our current operating plan, we do not anticipate the need to repatriate undistributed earnings of cash and cash equivalents held by our foreign subsidiaries accumulated through December 31, 2015, but we do anticipate a need to repatriate a portion of future foreign earnings to fund our US operations which will result in the need to accrue for US income taxes on those future foreign earnings that we anticipate repatriating from our foreign subsidiaries.
Our loans receivable are subject to certain risks which could materially adversely affect our financial position.
As part of our May 2013 license and supply agreement with Zensun, we agreed to loan up to $12 million to Zensun, of which $12 million had been loaned as of December 31, 2015. The proceeds of the loans are to be used for working capital and general corporate purposes by Zensun. As security for the loan agreements, Zensun pledged its entire equity interest in its subsidiary Shanghai Dongxin Biochemical Technology Co. Ltd. (whose assets include real property) to us. If the real property which comprises the majority of the value of all of the assets pledged as security were to suffer a decrease in its value due to macroeconomic conditions or local market-specific factors impacting commercial real estate market values, such a fact may represent an indication of loan impairment. If these loans were to become impaired and the loans could not be collected, our financial position could be negatively impacted with a charge to operations for the amount of any unpaid principal and interest.
Our ability to utilize our tax attributes may be limited by an “ownership change”.
Our ability to use our tax attributes, such as our US federal income tax net operating loss carryforwards and our tax credit carryforwards, may be substantially restricted if we have had in the past, or have in the future, an “ownership change” as defined in Section 382 of the US Internal Revenue Code. An ownership change occurs if increases in the percentage of our stock held by “5-percent shareholders” (within the meaning of Section 382, which provides that certain public groups can be treated as 5-percent shareholders) collectively exceed more than fifty percent, comparing the lowest percentage of stock owned by each 5-percent shareholder at any time during the testing period (which is generally a three-year rolling period) to the percentage of stock owned by the 5-percent shareholder immediately after the close of any owner shift testing date. Our repurchases of our Common Stock, issuances of any additional significant amounts of our Common Stock for future acquisitions or other transactions and trading in our stock by stockholders, may have increased the possibility that in the future we could experience an ownership change. Trading by our stockholders, stock repurchases or other transactions could, in the future, cause an ownership change, resulting in an annual limitation on utilization of our tax attributes. If our tax attribute usage is subject to limitation and if we are profitable, our future cash flows could be adversely affected due to an increased tax liability.
33
Anti-takeover provisions in our charter documents and under Delaware law may make an acquisition of us, which may be beneficial to our stockholders, more difficult.
Certain anti-takeover provisions of Delaware law and our charter documents as currently in effect may make a change in control of our company more difficult, even if a change in control would be beneficial to our stockholders. Our charter documents contain certain anti-takeover provisions, including provisions in our certificate of incorporation providing that stockholders may not cumulate votes, stockholders' meetings may be called by stockholders only if they hold 25% or more of our common stock and provisions in our bylaws providing that the stockholders may not take action by written consent. Additionally, our Board of Directors has the authority to issue 10 million shares of preferred stock and to determine the terms of those shares of stock without any further action by the stockholders. The rights of holders of our common stock are subject to the rights of the holders of any preferred stock that may be issued. The issuance of preferred stock could make it more difficult for a third-party to acquire a majority of our outstanding voting stock. Delaware law also prohibits corporations from engaging in a business combination with any holders of 15% or more of their capital stock until the holder has held the stock for three years unless, among other possibilities, the Board of Directors approves the transaction. Our Board of Directors may use these provisions to prevent changes in the management and control of our company. Also, on December 18, 2006, our Board of Directors declared a dividend distribution of one Preferred Stock Purchase Right (collectively, the “Rights”) for each outstanding share of our Common Stock, each Right which entitles the registered holder to purchase from the Company one one-thousandth of a share of the Company’s Series D Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value, at a price of $25.00 pursuant to a Rights Agreement dated as of December 19, 2006, between the Company and Mellon Investor Services LLC, that expires December 19, 2016. The Rights have certain anti-takeover effects. Under certain circumstances the Rights could cause substantial dilution to a person or group who attempts to acquire the Company on terms not approved by our Board of Directors. Although the Rights should not interfere with an acquisition of the Company approved by the Board, the Rights may have the effect of delaying and perhaps improving the terms of an acquisition for our stockholders, or deterring an acquisition of the Company. Also, under applicable Delaware law, our Board of Directors may adopt additional anti-takeover measures in the future.
We may be subject to product liability lawsuits, and our insurance may be inadequate to cover damages.
Clinical trials of any of our current and potential products or the actual commercial sales of our product may expose us to liability claims from the use of these products. We currently carry product liability insurance. However, we cannot be certain that we will be able to maintain insurance on acceptable terms, if at all, for clinical and commercial activities, that any insurance we have will cover any particular claim that is asserted, or that the insurance would be sufficient to cover any potential product liability claim or recall. If we fail to have sufficient coverage, our business, results of operations and cash flows could be adversely affected.
If we are unable to comply with environmental and other laws and regulations, our business may be harmed.
We are subject to various federal, state and local laws, regulations and recommendations relating to the use, manufacture, storage, handling and disposal of hazardous materials and waste products (including radioactive compounds and infectious disease agents), as well as safe working conditions, laboratory and manufacturing practices and the experimental use of animals. The extent of government regulation that might result from future legislation or administrative action in these areas cannot be accurately predicted.
We do not currently maintain hazardous materials at our facilities. While we outsource our research and development programs involving the controlled use of biohazardous materials, if in the future we conduct these programs ourselves, we might be required to incur significant cost to comply with environmental laws and regulations. Further, in the event of an accident, we would be liable for any damages that result, and the liability could exceed our resources.
Our business and operations are subject to the risks of being based in particular locations known for earthquakes, other natural catastrophic disasters and service interruptions.
Our corporate headquarters are located in the Silicon Valley area of Northern California, a region known for seismic activity. Although we maintain a disaster recovery policy that includes storage of important corporate data in a different geographic region of the US, all of our significant corporate data is stored in our headquarters facility and accordingly, a significant natural disaster, such as an earthquake, could have a material adverse impact on our business, operating results, and financial condition. Most of our sales are into China for which we maintain our warehouses for finished goods in Hong Kong, which can experience severe typhoon storms, earthquakes or other natural catastrophic disasters. Although our distributors in China may maintain several months supply of our product, were our warehouse capability to be interrupted, either through a natural disaster such as flooding or through a service interruption, such as a lack of electricity to power required air conditioning, our ability to timely deliver finished product to China could be adversely affected which in turn would materially adversely affect our sales and ensuing operating results.
34
We may be affected by climate change and market or regulatory responses to climate change.
Climate change, including the impact of global warming, could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity if it were to disrupt the demand, supply or delivery of product, management of our business, or result in cost increases as a result of government regulation.
Security breaches and other disruptions could compromise our information and expose us to liability, which would cause our business and reputation to suffer.
In the ordinary course of our business, we store sensitive data, including intellectual property, our proprietary business information, certain information regarding our business partners, and personally identifiable information of our employees, in our computer networks. The secure maintenance and transmission of this information is critical to our operations and reputation. Despite our security measures, our information technology and infrastructure may be vulnerable to attacks by hackers or breached due to employee error, malfeasance or other disruptions. Although we have not been adversely affected in any significant manner, we have experienced problems with information security in the past which we believe is primarily due to breaches of security by current or former employees gaining access to restricted information. Any such breach could compromise our computer networks and the information stored there could be accessed, publicly disclosed, lost or stolen. Although we have purchased cyber liability insurance, any such access, disclosure or other loss of information could result in legal claims or proceedings, liability under laws that protect the privacy of personal information, and regulatory penalties, and damage our reputation, any of which could adversely affect our business and competitive position.
Item 1B.Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
We currently lease approximately 11,900 square feet of office space for our corporate headquarters in Foster City, California, approximately 40,600 square feet of office space in China, primarily in Beijing and Shanghai, and lease approximately 6,100 square feet of combined office space in Hong Kong and Vietnam. We believe that our existing facilities will be adequate for our current needs and that additional space will be available as needed.
As previously disclosed, since 2010 the SEC and the DOJ had each been conducting formal investigations of us regarding a range of matters, including the possibility of violations of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”), primarily related to certain historical sales and marketing activities with respect to our China operations. In response to these matters, our Board appointed a Special Committee of independent directors (the “Special Committee”) to oversee our response to the government inquiry. Based on an initial review, the Special Committee decided to undertake an independent investigation as to matters reflected in and arising from the SEC and DOJ investigations in order to evaluate whether any violation of the FCPA or other laws occurred.
As previously disclosed, we entered into a settlement agreement with the SEC that fully resolved the SEC’s investigation. Under the terms of the settlement agreement, we paid a total of $12.8 million in February 2016, including disgorgement, pre-judgment interest and a penalty. The payment is in line with the charges we previously recorded and disclosed in our Form 10-Q filed with the SEC on August 10, 2015. As part of the agreement, we neither admitted nor denied engagement in any wrongdoing and we agreed to give status reports to the SEC for the next three years on our continued remediation and implementation of anti-corruption compliance measures. The DOJ has also completed its related investigation and has declined to pursue any action.
As previously disclosed, we have taken, and continue to take certain steps to enhance our existing anti-bribery compliance efforts, including (i) evaluating and expanding our training of employees regarding understanding and compliance with laws including the FCPA and other anti-bribery laws and regulations, (ii) evaluating existing compliance and anti-bribery policies and guidelines and preparing new, more detailed policies and guidelines for implementation after review by our Board of Directors and/or committees of the Board of Directors, (iii) implementing a pre-approval policy for certain expenses including payments for, or reimbursement of, travel and entertainment expenses, and sponsorships of certain third-party events, (iv) establishing an automated system for recording and approving travel and entertainment expenditures, and (v) hiring a Vice President of Compliance and an Internal Audit Director to monitor and enforce compliance with our policies. Also, upon the recommendation of the Special Committee, the Audit Committee of
35
the Board has retained a third-party consultant to observe and make recommendations regarding our FCPA compliance. We will continue to emphasize the importance of compliance and ethical business conduct.
NovaMed was a party to a Distribution and Supply Agreement with MEDA originally entered into in 2007. Following our acquisition of NovaMed in 2011, MEDA claimed it had a right to terminate the agreement under a change of control provision. NovaMed does not believe that MEDA had a right of termination under the agreement. NovaMed filed an application for binding arbitration with the China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission (“CIETAC”) on July 26, 2012. On April 2, 2014, CIETAC issued the final Award of the Arbitral Tribunal. The Arbitral Tribunal found that MEDA did have a right to terminate the agreement upon a change of control, but that MEDA must make reasonable reimbursement to NovaMed before any product rights are returned to MEDA. The amount that must be paid includes $333,333 as “unjust enrichment” plus an amount for reasonable compensation for such services provided by NovaMed to MEDA. The amount of such payment for services was not determined by the Arbitral Tribunal, but was left to be determined by NovaMed. On April 30, 2014, NovaMed informed MEDA that its determination of reasonable compensation for its services was $3,314,629, including the $333,333 for unjust enrichment. MEDA made a counter offer and the parties were attempting to resolve the matter without an additional arbitration proceeding. In December 2014, NovaMed filed a “Request for Second Arbitration” with CIETAC in order to enforce its right to compensation. The arbitration case is pending with CIETAC and no hearing has taken place yet. The amount of any final payment to NovaMed remains uncertain, and as such the Company has not recognized it as a gain contingency.
Item 4.Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
36
PART II
Item 5.Market for the Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Our common stock trades on The NASDAQ Global Select Market of the NASDAQ Stock Market under the symbol “SCLN.”
The following table sets forth the high and low sales prices per share for the quarterly periods indicated, as reported by The NASDAQ Stock Market. The quotations shown represent inter-dealer prices without adjustment for retail markups, markdowns, or commissions, and may not necessarily reflect actual transactions.
|
Price Range |
|||||
|
Common Stock |
|||||
|
High |
Low |
||||
|
2015 |
|||||
|
4th quarter |
$ |
10.94 |
$ |
6.70 | |
|
3rd quarter |
11.71 | 6.47 | |||
|
2nd quarter |
9.87 | 8.07 | |||
|
1st quarter |
9.65 | 7.01 | |||
|
2014 |
|||||
|
4th quarter |
$ |
9.14 |
$ |
6.59 | |
|
3rd quarter |
7.40 | 4.68 | |||
|
2nd quarter |
5.39 | 4.24 | |||
|
1st quarter |
5.34 | 4.25 | |||
Stockholders
As of March 7, 2016, there were approximately 200 holders of record of our common stock and 49,624,211 shares of common stock issued and outstanding. Because many of our shares of common stock are held by brokers and other institutions on behalf of stockholders we are unable to estimate the total number of stockholders represented by these record holders.
Dividends
We have not paid any dividends on our common stock during the fiscal years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013 and do not currently have plans to pay any cash dividends.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
The information required by Item 201(d) of Regulation S-K is incorporated by reference from the section entitled “Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans” in Part III, Item 12 of this Form 10-K.
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchasers
There were no common stock repurchases for the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015. As of December 31, 2015, the Company had repurchased $78.1 million under the authorized $80.5 million stock repurchase program that expired December 31, 2015.
37
Performance Graph
This performance graph shall not be deemed “soliciting material” or to be “filed” with the SEC for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act, or otherwise subject to the liabilities under that Section, and shall not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any of our filings under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act.
The following line graph compares the annual percentage change in (i) the cumulative total stockholder return on the Company’s Common Stock since December 31, 2010, with (ii) the cumulative total return on (a) The NASDAQ Composite Index and (b) the NASDAQ Biotechnology Index. The comparison assumes (i) an investment of $100 on December 31, 2010 in each of the foregoing indices and (ii) reinvestment of dividends, if any. The stock price performance shown on the graph below is not necessarily indicative of future stock price performance.
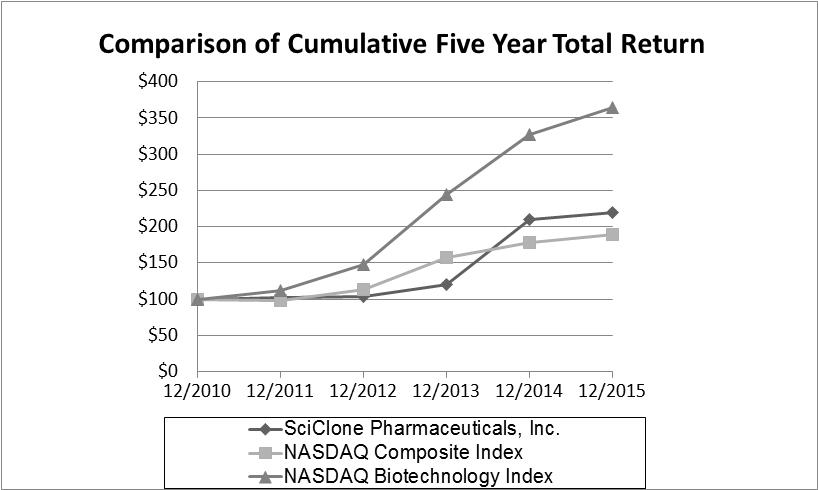
38
Item 6.Selected Financial Data
This section presents selected historical financial data for each of the last five fiscal years and is qualified by reference to and should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and notes thereto included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The selected balance sheet data as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 and the selected statement of operations data for each year ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013 have been derived from our audited financial statements that are included elsewhere in this report. The selected balance sheet data as of December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011 and the selected statement of operations data for each year ended December 31, 2012 and 2011 have been derived from our audited financial statements not included in this report. Historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected in the future.
|
Year Ended December 31, |
||||||||||||||
|
(in thousands, except per share data) |
||||||||||||||
|
2015(1) |
2014 |
2013(1) |
2012(2) |
2011(3) |
||||||||||
|
Statement of Operations data: |
||||||||||||||
|
Total net revenues |
$ |
157,257 |
$ |
134,790 |
$ |
127,058 |
$ |
156,269 |
$ |
132,565 | ||||
|
Net income |
$ |
29,463 |
$ |
25,208 |
$ |
10,964 |
$ |
9,620 |
$ |
28,122 | ||||
|
Basic net income per share |
$ |
0.59 |
$ |
0.49 |
$ |
0.20 |
$ |
0.17 |
$ |
0.51 | ||||
|
Diluted net income per share |
$ |
0.56 |
$ |
0.48 |
$ |
0.20 |
$ |
0.16 |
$ |
0.49 | ||||
|
Shares used in computing: |
||||||||||||||
|
Basic net income per share |
49,797 | 51,277 | 53,587 | 56,637 | 55,110 | |||||||||
|
Diluted net income per share |
52,173 | 52,684 | 54,936 | 58,483 | 57,387 | |||||||||
|
As of December 31, |
||||||||||||||
|
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||||
|
2015(1) |
2014 |
2013(1) |
2012(2) |
2011(3) |
||||||||||
|
Balance Sheet data: |
||||||||||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ |
101,403 |
$ |
86,228 |
$ |
85,803 |
$ |
84,228 |
$ |
66,654 | ||||
|
Restricted cash in escrow for SEC settlement |
12,826 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|||||||||
|
Accounts receivable, net of allowance |
39,363 | 40,268 | 39,771 | 38,109 | 38,465 | |||||||||
|
Inventories |
10,976 | 10,703 | 15,238 | 10,424 | 11,141 | |||||||||
|
Deferred tax assets |
299 | 326 | 6 | 369 | 1,788 | |||||||||
|
Total current assets |
168,521 | 140,197 | 143,417 | 137,329 | 119,694 | |||||||||
|
Intangible assets, net |
— |
— |
— |
— |
45,185 | |||||||||
|
Goodwill |
32,979 | 34,521 | 35,357 | 34,313 | 33,868 | |||||||||
|
Total assets |
216,619 | 181,831 | 179,859 | 174,071 | 200,844 | |||||||||
|
Borrowings |
— |
— |
1,651 | 1,445 | 2,500 | |||||||||
|
Contingent consideration |
— |
— |
— |
— |
15,400 | |||||||||
|
Deferred revenue |
174 | 596 | 2,915 |
— |
— |
|||||||||
|
Deferred tax liabilities |
— |
— |
— |
153 | 8,407 | |||||||||
|
Other long-term liabilities |
87 | 114 | 44 | 237 | 469 | |||||||||
|
Total stockholders’ equity |
179,712 | 155,274 | 146,595 | 143,022 | 150,119 | |||||||||
|
(1) |
We recorded a charge of $2.0 million for 2013 related to the possibility of a settlement, and recorded an additional charge of $10.8 million associated with the SEC settlement for 2015. Refer to Part I, Item 3 for further information regarding the SEC and DOJ investigations. |
|
(2) |
During fiscal 2012, we identified an impairment indicator with respect to our intangible assets related to our promotion and distribution contract rights and recorded losses of approximately $42.7 million to recognize the full impairment. We recorded a benefit for income tax of approximately $6.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2012 due to the impairment of intangible assets, which resulted in a reversal of deferred tax liabilities. This was partially offset by the impact of recognizing a full valuation allowance on any remaining NovaMed deferred tax assets. In addition, we recorded a non-cash gain of $15.4 million related to the contingent consideration because revenue and EBITDA targets of NovaMed were not achieved. |
|
(3) |
On April 18, 2011, we acquired NovaMed Pharmaceuticals, Inc. ("NovaMed") for approximately $24.6 million in cash and 8,298,110 shares of SciClone common stock and a contingent right to receive additional cash consideration (“the contingent consideration”) of up to $43.0 million based upon achievement of revenue and earnings targets for the 2011 and 2012 fiscal years. Commencing April 18, 2011, the Company’s financial statements include the assets, liabilities, and operating results of NovaMed. |
39
Item 7.Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
This Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations should be read in conjunction with the “Selected Financial Data” and our consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. This Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations and other parts of this Annual Report on Form 10-K contain forward-looking statements which involve risks and uncertainties. See “Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” and “Risk Factors” contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (NASDAQ: SCLN) is a United States (“US”)-headquartered, China-focused, specialty pharmaceutical company with a substantial commercial business and a product portfolio of therapies for oncology, infectious diseases and cardiovascular disorders. We are focused on continuing to grow our revenue and profitability. Our business and corporate strategy is focused primarily on the People’s Republic of China (“China” or “PRC”) where we have built a solid reputation and established a strong brand through many years of experience marketing our lead product, ZADAXIN® (thymalfasin). In addition, we have an established product promotion business model with large pharmaceutical partners and we are focused on establishing profitability in all of these collaborations. We believe our sales and marketing strengths position us to benefit from the long-term expansion of the pharmaceutical market in China. The Chinese pharmaceutical market currently ranks second among the global pharmaceutical markets, and had an estimated worth of $105 billion in 2014. It is forecasted to increase significantly to $200 billion by 2020. We seek to expand our presence in China and increase revenues by growing sales and profits of our current product portfolio, launching new products from our development pipeline, adding new, profitable product services agreements and leveraging our strong cash position to in-license additional products.
We operate in two segments which are generally based on the nature and location of our customers: 1) China and 2) the Rest of the World, which includes our US and Hong Kong operations.
We have two categories of revenues: “product sales revenues” and “promotion services revenues.” Our product sales revenues result from our proprietary and in-licensed products, including our lead product, ZADAXIN; DC Bead®, a product for the embolization of malignant hypervascularized tumors, for which we initiated sales and recorded product revenue beginning in the third quarter of 2015, and products from Pfizer International Trading (Shanghai) Ltd. (“Pfizer”). Through June 30, 2015, our product sales revenues also included Aggrastat®, an intervention cardiology product launched in China in 2009, in-licensed from Cardiome Pharma Corp (“Cardiome”). In August 2015, we and Cardiome mutually agreed to end our collaboration for Aggrastat, thereby terminating our exclusive distribution rights in China, and returning all rights to the product to Cardiome. We recorded Aggrastat revenues of $1.8 million, $1.1 million and $0 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively, and we do not expect to generate any further Aggrastat revenues. We do not anticipate that the termination of this agreement will adversely affect our profitability.
ZADAXIN has the highest margins in our portfolio as it is a premium product sold exclusively by SciClone. In addition, we anticipate that new marketed products, when and if introduced, can increase the future revenues and profitability of our pharmaceutical business in China over the coming years. Our “promotion services revenues” result primarily from fees we receive for exclusively promoting products in China for Baxter International, Inc. (“Baxter”). We recognize promotion services revenues as a percentage of our collaborators’ product sales revenue for these exclusively promoted products. Over time, as additional proprietary or in-licensed products come to the market, we aim to shift our product mix towards those products providing higher margins for us.
ZADAXIN is approved in over 30 countries and may be used for the treatment of HBV, HCV, and certain cancers, and as an immune system enhancer according to the local regulatory approvals we have in these countries. In China, thymalfasin is included in the treatment guidelines issued by the Ministry of Health (“MOH”) for liver cancer, as well as guidelines for treatment of chronic HBV (issued by both the Chinese Medical Association and the Asian-Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver) and invasive fungal infections of critically ill patients (issued by the Chinese Medical Association). Our sales force is focused on increasing sales to the country’s largest hospitals (class 3A with over 500 beds) as well as mid-size hospitals (class 2A). These hospitals serve Tier 1 and Tier 2 cities located mostly in the eastern part of China, which are the largest and generally have the most affluent populations. We are widening our market strategies by piloting e-commerce approaches to reach customers. We are also seeking to expand the indications for which ZADAXIN could be used, including sepsis.
40
We initiated sales and recorded our first product revenue from DC Bead in the third quarter of fiscal 2015. The China Food and Drug Administration had approved the registration of DC Bead for the embolization of malignant hypervascularized tumors in August 2014. DC Bead may be used to treat liver cancer, a large and growing indication in China, and we believe our oncology sales team and academic marketing liaisons have established high quality relationships with medical professionals and institutions that specialize in cancer treatment, which we believe will be a valuable asset as we continue commercial sales of DC Bead. BioCompatibles UK Ltd. (“BTG”) and SciClone previously entered into an agreement granting SciClone exclusive licensing and distribution rights to DC Bead in China. Under the agreement, we are purchasing DC Bead product from BTG.
We are also pursuing the registration of several other therapeutic products in China. These include: Loramyc®, a mucoadhesive tablet formulation of miconazole lauriad to treat oropharyngeal candidiasis; and RapidFilm®, an oral film formulation of ondansetron to treat nausea induced by chemotherapy.
Our agreement with Baxter is for a 5-year term, through December 2017, and our agreement with Pfizer is for a 5-year term, through June 2019. We are pursuing additional agreements to generate additional revenue. We continue to seek in-licensing arrangements for well-differentiated products at various stages of development that, if not yet approved, have a defined regulatory approval pathway in China. Our objective is to in-license products that provide us with higher margins, augmenting our product sales revenue and profitability, and we continue to explore opportunities to optimize our promotion services revenues.
In May 2015, Theravance Biopharma, Inc. (“Theravance Biopharma”) granted SciClone exclusive development and commercialization rights to VIBATIV® (telavancin) in China, as well as the Hong Kong SAR, the Macau SAR, Taiwan and Vietnam, in exchange for upfront and regulatory milestone payments totaling $6 million. SciClone will be responsible for all aspects of development and commercialization in the partnered regions, including pre- and post-launch activities and product registration. SciClone will initially develop VIBATIV for hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia, and additional indications may include complicated skin and skin structure infections and potentially bacteremia. Theravance Biopharma will sell to SciClone all clinical and commercial product required to develop and commercialize VIBATIV in China and our other licensed territories.
In December 2014, we entered into a strategic partnership with The Medicines Company for two cardiovascular products in China. The partnership includes an agreement granting us a license and the exclusive rights in China to promote two products including 1) Angiomax® (bivalirudin) for Injection, an anticoagulant indicated in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with provisional use of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor (GPI) and in patients with, or at risk of, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis syndrome undergoing PCI for which a Phase 3 registration trial was completed in China and is currently under review by the China Food and Drug Administration for marketing approval, and 2) Cleviprex® (clevidipine) Injectable Emulsion, a third-generation dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker indicated for the reduction of blood pressure when oral therapy is not feasible or desirable for which a clinical trial application (CTA) for China was filed in 2013. We received CTA approval from the China Food and Drug Administration (“CFDA”) in early 2016 and are preparing a clinical study. Under the terms of the agreement, we will be responsible for all aspects of commercialization, including pre-and post-launch activities, for both products in the China market (excluding Hong Kong and Macao). We have also agreed to participate in the China registration process for both products. Financial terms of the agreement, in addition to net sales royalties payable to The Medicines Company, include the following additional payments to The Medicines Company: an upfront payment made in the fourth quarter of 2014; a project support services fee; and regulatory/commercial success milestone payments of up to an aggregate of $50.5 million.
In June 2013, we entered into a license agreement with Taiwan Liposome Company (“TLC”) which granted us a license and the exclusive rights in China, Hong Kong and Macao to promote, market, distribute and sell ProFlow® for the treatment of peripheral arterial disease (“PAD”) and other indications. PAD is a serious cardiovascular condition in which blood flow to the limbs (usually the legs) is restricted due to arterial plaque build-up. Under the terms of the agreement, TLC will be responsible for the continued development including potential clinical trials and regulatory activities, as well as the manufacture and supply of ProFlow, and we will be responsible for all aspects of commercialization including pre-and post-launch activities. The agreement provides for the principal terms of the arrangement between SciClone and TLC, and in March 2014, the companies entered into a supplemental collaboration and license agreement. In November 2014, TLC was notified by the CFDA that ProFlow did not receive clinical trial approval and TLC is in the process of appealing the decision.
In May 2013, we entered into a framework agreement with Zensun (Shanghai) Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (“Zensun”) for the exclusive promotion, marketing, distribution and sale of NeucardinTM in China, Hong Kong and Macao. Neucardin is a novel,
41
first-in-class therapeutic for the treatment of patients with intermediate to advanced heart failure, for which a New Drug Application (“NDA”) was submitted to and accepted for review by the CFDA in 2012. In December 2013, the CFDA informed Zensun that its Phase 2 data is insufficient, and has asked Zensun to submit a new NDA once the ongoing Phase 3 study reached its endpoints. As part of our agreement with Zensun, we agreed to loan up to $12 million to Zensun, of which $12 million had been loaned as of December 31, 2015 (refer to Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements appearing under Part II, Item 8 for further information regarding the Zensun loans).
For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, we recognized $7.5 million, $11 million and $5.0 million, respectively, in research and development expenses related to our in-license arrangements.
Recent governmental policy changes in China have eliminated national regulation of the maximum retail drug prices for most drugs effective as of June 1, 2015. Decisions by provincial authorities appear to be emerging as the primary governmental mechanism for price controls. As an example, the Zhejiang provincial authority announced a price limitation for sales of ZADAXIN in the province in April 2015 that became effective in May 2015. We were able to mitigate the impact of this price limitation by shifting an equitable portion of the burden of the price reduction to our distributor in our sales channel; accordingly, the impact of the price reduction through the year ended December 31, 2015 was $2.8 million. We anticipate that provincial pricing decisions will continue to be a significant factor in the China pharmaceutical market for the foreseeable future. The impact of such decisions on our future results is unpredictable, but we expect that pricing pressures on revenue in 2016 will be offset at least in significant part through sharing of the burden with our China distributor and potentially through volume increases. However, in the future, prices could be reduced to levels significantly below those that would prevail in an unregulated market, which may limit the growth of our revenues or cause them to decline. In addition, our new contractual arrangement with Sinopharm Holding Lingyun Biopharmaceutical (Shanghai) Co. Ltd (Sinopharm), our China distributor for ZADAXIN, which commenced January 1, 2016 will result in the later recognition (relative to practices prevailing through December 31, 2015) of a portion of our revenue invoiced to Sinopharm in situations where the provincial tender price is greater relative to a referenced (baseline) tender price. This is due to a mechanism in the new contractual arrangement whereby the customer is invoiced at a lower base price relative to that prevailing in the previous agreement. The lower base price (as well as estimated price compensation payable due to the distributor for situations where the provincial tender price is lower than the referenced (baseline) tender price) will be recorded as revenue after the sale is completed. The distributor will then be invoiced for the portion of the price that may result from situations where the provincial tender price is greater than the referenced (baseline) tender price at a later time, and such amount will be recognized as revenue after the amount has been agreed to with the distributor. Although we do not expect this new arrangement to have a significant impact on annual revenue or the amount recognized on an annual basis, it may impact quarterly revenue amounts and timing, especially for the first quarter of 2016.
As previously disclosed, since 2010 the US Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) and the US Department of Justice (“DOJ”) had each been conducting formal investigations of us regarding a range of matters, including the possibility of violations of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”). On February 4, 2016, we announced that we have entered into a settlement agreement with the SEC fully resolving the SEC’s investigation into possible violations of the FCPA. Under the terms of the settlement agreement, in February 2016 we paid a total of $12.8 million, including disgorgement, pre-judgment interest and a penalty as final settlement which was released from our restricted escrow account which we funded in the fourth quarter of 2015. This payment is in line with the charges we previously recorded and disclosed in our Form 10-Q filed with the SEC on August 10, 2015. As part of the agreement we neither admitted nor denied engagement in any wrongdoing and we agreed to give status reports to the SEC for the next three years on our continued remediation and implementation of anti-corruption compliance measures. The DOJ has also completed its related investigation and has declined to pursue any action (refer to Notes 18 and 22 to the consolidated financial statements appearing under Part II, Item 8 and “Legal Proceedings” in Part I, Item 3 for further information regarding the SEC and DOJ investigations).
We believe our cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2015 and ongoing revenue generating business operations will be sufficient to support our current operating plan for at least the next 12 months. Our results may fluctuate from quarter to quarter and we may report losses in the future.
42
Results of Operations
Revenues:
The following table summarizes the year over year changes in our product sales and promotion services revenues (in thousands):
|
Years Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||
|
2015 |
Change |
2014 |
Change |
2013 |
|||||||||
|
Product Sales, net |
$ |
154,329 | 17% |
$ |
131,973 | 33% |
$ |
99,414 | |||||
|
Promotion Services |
2,928 | 4% | 2,817 |
-90% |
27,644 | ||||||||
|
Total Net Revenues |
$ |
157,257 | 17% |
$ |
134,790 | 6% |
$ |
127,058 | |||||
Product sales were $154.3 million, $132.0 million, and $99.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. The increase of $22.4 million, or 17%, for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to 2014, was primarily attributable to an increase in ZADAXIN unit sales and stronger demand for certain oncology products. ZADAXIN sales were $146.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to $126.1 million for the prior year, an increase of $20.0 million, or 16%, which mainly related to a 21% increase in volume sold, offset partially by a 5% decrease in selling price mainly related to a decrease in the list price of ZADAXIN in the Zhejiang province since May 2015. Product sales for the year ended December 31, 2015, also included Pfizer product sales and initial immaterial DC Bead revenue.
The increase in product sales of $32.6 million, or 33%, for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to 2013, was primarily attributable to an increase in ZADAXIN unit sales and stronger demand for certain oncology products. ZADAXIN sales were $126.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to $96.3 million for the prior year, an increase of $29.8 million, or 31%, which mainly related to an increase in volume sold, and to a lesser extent related to an increase in selling price. We believe our ZADAXIN product revenues in the first half of fiscal 2013 were adversely affected by the increase in channel inventory we experienced in the third quarter of 2012. We believe channel inventory for ZADAXIN has returned to normalized levels.
We anticipate that ZADAXIN revenues in 2016 will be higher than 2015, although our revenues are subject to exchange rate fluctuations and provincial adjustments to tender (retail level, government approved) prices which we cannot predict. The majority of our sales have been in US dollars, although a portion of our sales are denominated in RMB. Per our previous contractual arrangement with Sinopharm through December 31, 2015, and a renewed contractual arrangement with Sinopharm (our sole importer and distributor for ZADAXIN in China) which took effect January 1, 2016, our sales of ZADAXIN to Sinopharm have been and continue to be denominated in US dollars. However, the established importer price may be adjusted quarterly based upon exchange rate fluctuations between the US dollar and RMB. Our China ZADAXIN sales revenues are subject to exchange rate risk, and in recent months the RMB has experienced devaluation. In addition, per our previous contractual arrangement with Sinopharm during the year ended December 31, 2015, and a renewed contractual arrangement with Sinopharm which took effect January 1, 2016, our contracted sales prices to Sinopharm are subject to adjustment based on changes in tender prices within the province territories. In addition, our new contractual arrangement with Sinopharm which commenced January 1, 2016 will result in the later recognition (relative to practices prevailing through December 31, 2015) of a portion of our revenue invoiced to Sinopharm in situations where the provincial tender price is greater relative to a referenced (baseline) tender price. This is due to a mechanism in the new contractual arrangement whereby the customer is invoiced at a lower base price relative to that prevailing in the previous agreement. The lower base price (as well as estimated price compensation payable due to the distributor for situations where the provincial tender price is lower than the referenced (baseline) tender price) will be recorded as revenue after the sale is completed. The distributor will then be invoiced for the portion of the price that may result from situations where the provincial tender price is greater than the referenced (baseline) tender price at a later time, and such amount will be recognized as revenue after the amount has been agreed to with the distributor. Although we do not expect this new arrangement to have a significant impact on annual revenue or the amount recognized on an annual basis, it may impact quarterly revenue amounts and timing, especially for the first quarter of 2016.
Recent governmental policy changes in China have eliminated national regulation of the maximum retail drug prices for most drugs effective as of June 1, 2015. Decisions by provincial authorities appear to be emerging as the primary governmental mechanism for price controls. As an example, the Zhejiang provincial authority announced a price limitation for sales of ZADAXIN in the province in April 2015 that became effective in May 2015. Changes in provincial drug prices for ZADAXIN in the provinces could impact our future sales revenues.
43
In China, pharmaceutical products are imported and distributed through a tiered method of distribution. For our proprietary product ZADAXIN, we manufacture our product using our US and European contract manufacturers, and we generate our product sales revenue through sales of ZADAXIN product to Sinopharm. Sinopharm acts as an importer, and also as the top “tier” of the distribution system (“Tier 1”) in China. Our ZADAXIN sales occur when Sinopharm purchases product from us without any right of return except for replacement of product in the event of damaged product or quality control issues. Passage of title and risk of loss are transferred to Sinopharm at the time of arrival of a shipment at its destination. After the sale, Sinopharm clears products through China import customs, sells directly to large hospitals and holds additional product it has purchased in inventory for sale to the next tier in the distribution system. The second-tier (“Tier 2”) distributors are responsible for the further sale and distribution of the products they purchase from the importer, either through sales of product directly to the retail level (hospitals and pharmacies), or to third-tier (“Tier 3”) local or regional distributors who, in turn, sell products to hospitals and pharmacies.
Promotion services revenue was $2.9 million, $2.8 million, and $27.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively, and related to products promoted under agreements with Baxter and Sanofi Aventis S.A. (“Sanofi”). Promotion services revenue increased $0.1 million or 4% for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to 2014, related to an increase in EndoxanTM (Baxter) product sales. Promotion services revenue decreased $24.8 million or 90% for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to 2013, related to the expiration of our promotional agreements with Sanofi as of December 31, 2013.
Our promotion agreements with Sanofi, consisting of individual promotional agreements for certain pharmaceutical products and supplementary agreements extending the terms thereof, were not renewed and expired on December 31, 2013. NovaMed Pharmaceuticals (Shanghai) Co. Ltd. (“NovaMed Shanghai”) and Sanofi negotiated a settlement of certain amounts in dispute, effective as of July 14, 2014, and NovaMed Shanghai received approximately 22 million RMB (approximately $3.5 million) in August 2014 as final payment from Sanofi. The terms of the settlement resulted in the recognition of promotion services revenue, for the second quarter of 2014, of approximately $0.2 million of Sanofi revenue that had been deferred in the fourth quarter of 2013. The remaining approximately $2.6 million of deferred revenue that had been deferred in the fourth quarter of 2013 was reversed with an equivalent write-down of accounts receivable. This contemporaneous write-down of accounts receivable and deferred revenue had no impact on net income for the second quarter of 2014 or for the year ended December 31, 2014. Our revenues for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, with Sanofi were $0, $0.2 million, and $25.0 million, respectively.
Our Baxter promotion agreement is for a 5-year term, through December 2017. Our Pfizer product distribution agreement is for a 5-year term, through June 2019. In August 2015, we and Cardiome, from whom we licensed Aggrastat®, mutually agreed to end our collaboration for Aggrastat, and return all rights to the product to Cardiome. We recorded Aggrastat revenues of $1.8 million, $1.1 million and $0 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively, and we do not expect to generate any further Aggrastat revenues. We do not anticipate that the termination of this agreement will adversely affect our profitability.
We continue to assess the financial performance of the products we promote and distribute under our agreements and their overall value within our entire portfolio of products. Over time, we anticipate the product mix that we promote will change, which may affect our revenues and profitability in the future. If any of these agreements are determined to no longer be beneficial to us and are allowed to expire, or if third parties will not renegotiate, renew or extend the agreements on terms acceptable to us, our revenues would be adversely affected and our profitability may be adversely or beneficially affected. On the other hand, if we are successful in negotiating better terms, there may be a positive impact on our revenues and profitability.
All of our promotion services revenue and a majority of our product revenues related to our China segment. Total China revenues were $151.6 million, $130.3 million, and $122.6 million, or 96%, 97% and 97% of sales for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. Rest of the World segment revenues were $5.7 million, $4.5 million, and $4.4 million, or 4%, 3%, and 3%, for each of the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and related to sales of ZADAXIN product.
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, sales to Sinopharm in China accounted for approximately 97% and 94% of our revenues, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2013, sales to Sinopharm and Sanofi in China accounted for approximately 75% and 20% of our revenues, respectively, (prior to the expiration of our promotion agreements with Sanofi). Our experience with our largest customer has been good and we anticipate that we will continue to sell a majority of our product to them.
44
Cost of Product Sales:
The following table summarizes the year over year changes in our cost of product sales (in thousands):
|
Years Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||
|
2015 |
Change |
2014 |
Change |
2013 |
|||||||||
|
Cost of Product Sales |
$ |
22,348 |
-3% |
$ |
23,002 | 30% |
$ |
17,668 | |||||
Cost of product sales was $22.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to $23.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, a decrease of $0.7 million. The decrease in cost of sales of $0.7 million, or 3%, for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to 2014 was primarily attributable to a $2.9 million decrease in cost of product sales of Aggrastat as we had recorded a provision of $2.1 million for excess Aggrastat inventory during the year ended December 31, 2014 that didn’t recur for the year ended December 31, 2015. It was also attributable to our receipt in the fourth quarter of 2015 of $1.1 million for reimbursement for Aggrastat inventory returned that we had previously fully written off in 2014, which was recorded as a reduction in cost of product sales. These decreases in cost of product sales were partially offset by increases in cost of product sales related to ZADAXIN and certain oncology product sales due to increased volume sold. Cost of product sales also increased related to initial DC Bead sales in the second half of 2015.
The increase in cost of sales of $5.3 million, or 30%, for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to 2013, was attributable to a $2.0 million increase in ZADAXIN cost of product sales related primarily to an increase in ZADAXIN unit sales and a $3.3 million increase in Aggrastat and oncology cost of sales as a result of higher sales volume of Aggrastat and certain oncology products. Cost of sales for Aggrastat product also increased for the year ended December 31, 2014 related to a provision of $2.1 million for excess Aggrastat inventory expected to expire and $0.2 million associated with Aggrastat inventory shipped within six months of expiration.
ZADAXIN cost of sales were $18.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to $17.5 million and $15.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Gross margin for ZADAXIN was 87.3% for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to 86.1% and 83.9% for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The increase in gross margin for ZADAXIN for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, compared to the year ended December 31, 2013, was due primarily to higher production volume lowering per unit overhead costs and manufacturing efficiencies.
We expect our ZADAXIN cost of product sales and gross margins to fluctuate from period to period depending on the level of sales and price of our products, the absorption of product-related fixed costs, currency exchange fluctuations, any charges associated with excess or expiring finished product inventory, and the timing of other inventory period costs such as manufacturing process improvements for the goal of future cost reductions.
Overall, we expect our gross margin percentages in 2016 to be lower than 2015, based on lower selling prices as set by one province, with indications of others to follow, as well as the unfavorable impact of currency exchange fluctuations.
Sales and Marketing (“S&M”):
The following table summarizes the year over year changes in our sales and marketing expenses (in thousands):
|
Years Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||
|
2015 |
Change |
2014 |
Change |
2013 |
|||||||||
|
Sales and Marketing |
$ |
53,961 | 11% |
$ |
48,477 |
-12% |
$ |
55,240 | |||||
S&M expenses were $54.0 million, $48.5 million, and $55.2 million, for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. S&M expenses increased by $5.5 million, or 11%, for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to 2014, related to growth in our S&M efforts for ZADAXIN and DC Bead. S&M expenses decreased by $6.8 million, or 12%, for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to 2013, related to the expiration of the Sanofi distribution agreements and the reduction in costs associated with marketing the products under the Sanofi agreements. The reductions in S&M expenses for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to 2013, were partially offset by increases in our S&M efforts for ZADAXIN in 2014.
45
We anticipate total S&M expenses for the year ending December 31, 2016 to be higher than those incurred for the year ended December 31, 2015 related to growth in our S&M efforts for ZADAXIN.
Research and Development (“R&D”):
The following table summarizes the year over year changes in our R&D expenses (in thousands):
|
Years Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||
|
2015 |
Change |
2014 |
Change |
2013 |
|||||||||
|
Research and Development |
$ |
12,314 |
-16% |
$ |
14,581 | 81% |
$ |
8,044 | |||||
R&D expenses were $12.3 million, $14.6 million, and $8.0 million, for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, we recorded $7.5 million, $11.0 million and $5.0 million, respectively, in R&D expenses related to upfront and milestone costs under our in-license arrangements. In addition, during the year ended December 31, 2015, R&D expenditures included R&D expenditures related to in-licensing agreements with certain business partners and R&D activities in China. During the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, R&D expenses also included costs incurred related to preparation for a potential sepsis clinical study for ZADAXIN we were contemplating which has not been continued.
The major components of R&D expenses include salaries and other personnel-related expenses, including associated stock-based compensation, facility-related expenses, depreciation of facilities and equipment, license-related fees, services performed by clinical research organizations and research institutions and other outside service providers.
We anticipate our R&D expenses to increase in 2016 compared to 2015 related to potential license fee payments, milestone payments expected to occur under license arrangements, and related to research and development activities in China.
General and Administrative (“G&A”):
The following table summarizes the year over year changes in our G&A expenses (in thousands):
|
Years Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||
|
2015 |
Change |
2014 |
Change |
2013 |
|||||||||
|
General and Administrative |
$ |
27,897 | 23% |
$ |
22,746 |
-30% |
$ |
32,496 | |||||
G&A expenses were $27.9 million, $22.7 million, and $32.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. G&A expenses for the year ended December 31, 2015 increased by $5.2 million, or 23%, compared to the year ended December 31, 2014 mainly related to a China legal-entity restructuring plan which we are in the process of implementing, higher professional consulting fees for business development strategy, higher stock-based compensation expense, and lower credits to bad debt expense for recovery of previously written off accounts receivable, offset by lower legal expenses related to our investigations with the SEC and DOJ and lower accounting fees.
G&A expenses for the year ended December 31, 2014 decreased by $9.8 million, or 30%, compared to the year ended December 31, 2013, mainly related to a decrease in legal fees associated with the government investigations, MEDA Pharma GmbH & Co KG (“MEDA”) arbitration and other corporate matters. During the year ended December 31, 2014, G&A expenses also reflected credits to bad debt expense for $1.5 million in recovery of previously fully reserved substantially delinquent accounts receivable balances from a particular customer that had been fully reserved prior to 2014. During the year ended December 31, 2013, we recorded an additional $2.4 million in bad debt expense related to significantly past due accounts receivable from the customer noted above in order to fully reserve such receivables. The increase in bad debt expense was determined as a result of continual negotiations that indicated the accounts receivable balance may not be recoverable. Additional increases in G&A expenses for the year ended December 31, 2013, included higher professional expenses of approximately $5.3 million related to legal matters associated with the government investigations and our ongoing improvements to our FCPA compliance efforts, and approximately $1.1 million mainly related to accounting matters associated with the restatement of our consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2011 and certain quarters of 2012 and 2011 and matters involving consultation with the Securities and Exchange Commission related to one aspect of our accounting for one of our contracts, as well as higher general and administrative personnel-related costs and higher legal costs related to other general corporate matters.
46
We expect our G&A expenses in 2016 to increase compared to 2015 related to growth in our business. As previously disclosed in our Form 8-K issued in early February 2016, our Board is evaluating a range of strategic transactions with a view to enhancing shareholder value. We may incur certain G&A expenses in connection with this evaluation.
Restructuring Charges:
For the year ended December 31, 2013, we recorded $1.2 million to restructuring charges to reflect planned reductions in our China segment related to our sales force and the one-time termination benefits for approximately 175 employees as a result of the non-renewal of the Sanofi promotion agreement as of December 31, 2013. The amounts provided were paid in 2014.
SEC Settlement Expense:
We recorded a charge of $2.0 million in the fourth quarter of 2013 related to the possibility of a settlement with the SEC and DOJ regarding their investigation into possible violations of the FCPA by us, and we recorded additional charges totaling $10.8 million associated with the SEC settlement in 2015. In February 2016, we entered into a settlement agreement with the SEC fully resolving the SEC’s investigation into possible violations of the FCPA. Under the terms of the settlement agreement, in February 2016 we paid $12.8 million, including disgorgement, pre-judgement interest and a penalty as final settlement. As part of the agreement, we neither admitted nor denied engagement in any wrongdoing and we agreed to give status reports to the SEC for the next three years on our continued remediation and implementation of anti-corruption compliance measures. The DOJ has also completed its related investigation and has declined to pursue any actions. Refer to Part I, Item 3 “Legal Proceedings” and Part II, Item 8, Note 18 “Contingencies” and Note 22 “Subsequent Events” for further information on this matter.
Other Income:
On July 8, 2013, we and the representatives of the former stockholders of NovaMed entered into a “Confidential Escrow Settlement Agreement” pursuant to which we retained approximately $0.8 million in cash and 342,300 shares of our common stock, having a combined fair value of approximately $2.6 million on the settlement date. As a result, we recorded $2.6 million in the year ended December 31, 2013 to other income related to this settlement.
Provision for Income Tax:
The provision for income tax relates to our foreign operations in China. The provision for income tax was $0.8 million, $1.2 million and $2.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Tax expense decreased $0.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared to 2014, mainly related to a reduction in our liabilities for uncertain tax positions (and associated accrued interest) in China due to certain tax years becoming closed to assessment due to the statute of limitations.
The tax provision decreased $1.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to the year ended December 31, 2013, principally due to a reduction of approximately $0.2 million in our liabilities for uncertain tax positions (and associated accrued interest) due to certain tax years becoming closed to assessment due to the statute of limitations. Tax expense was also lower for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to 2013, as a result of lower taxable income related to our China operations.
The statutory tax rate in China was 25% in 2015, 2014 and 2013. We expect the provision for income tax to increase for the year ending December 31, 2016, compared to the year ended December 31, 2015 due to growth in our China operations.
As of December 31, 2015, we had net operating loss carryforwards for US federal income tax purposes of approximately $114.2 million that expire in the years 2020 through 2035, and had approximately $52 million in net operating loss carryforwards related to our NovaMed Shanghai subsidiary that expire in the years 2016-2020. As of December 31, 2015, we had US federal research and development, orphan drug and investment tax credit carryforwards of approximately $12.2 million that expire in the years 2018 through 2035.
Because of the “change in ownership” provisions of the Internal Revenue Code, a portion of our net operating loss carryforwards and tax credit carryforwards may be subject to an annual limitation regarding their utilization against taxable income in future periods. As a result of the annual limitation, a portion of these carryforwards may expire before ultimately becoming available to reduce future income tax liabilities.
47
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We continue to closely manage our liquidity and capital resources. We rely on our operating cash flows, and cash and cash equivalents to provide for our liquidity requirements. We believe that we have the ability to meet our liquidity needs for at least the next 12 months to fund our working capital requirements of our operations, including investments in our business, and to fund our business development activities.
The following tables summarize our cash and investments and our cash flow activities as of the end of, and for each of, the years presented (in thousands):
|
As of December 31, |
|||||
|
2015 |
2014 |
||||
|
Cash and investments |
$ |
101,403 |
$ |
86,303 | |
As of December 31, 2015, we had $101.4 million in cash and cash equivalents, in addition to the $12.8 million of restricted cash held in escrow for the SEC settlement, of which $98.5 million was located in subsidiaries of the Company outside the US. Cash and cash equivalents held by subsidiaries outside the US are held primarily in US dollars. Such cash and cash equivalents are used to fund the operating activities of our foreign subsidiaries and for further investment in foreign operations, which may include in-licensing new products, particularly for China, and for potential acquisitions. In the fourth quarter of 2015, we repatriated $12.8 million in funds via a special dividend distribution from our foreign subsidiary as a result of the need to fund an escrow facility for our SEC settlement (as previously described). This dividend distribution was made from the current year earnings and profits of our foreign subsidiary, which was not part of the cumulative pool of undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014.
We have determined that as of December 31, 2015, $176.2 million of accumulated undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries, after the payment of the dividend which was satisfied entirely out of current year earnings and profits, continues to be indefinitely reinvested outside of the US. In making this determination, the following attributes were considered: (i) the expected future needs of the foreign subsidiaries, including working capital, capital expenditures, as well as additional investments to support the infrastructure in our China subsidiaries and (ii) additional investments to support our expansion in the China market as well as planned product licensing transactions. Upon distribution of our foreign undistributed earnings, we may be subject to US federal and state income taxes. Based on our current operating plan, we do not anticipate the need to repatriate undistributed earnings of cash and cash equivalents held by foreign subsidiaries accumulated as of December 31, 2015, but we do anticipate a need to repatriate a portion of future foreign earnings to fund our US operations. We will accrue for US income taxes on future foreign earnings that we anticipate repatriating from our foreign subsidiaries.
|
Years Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
|
2015 |
2014 |
2013 |
|||||||
|
Cash provided by (used in): |
|||||||||
|
Operating activities |
$ |
32,507 |
$ |
27,609 |
$ |
9,502 | |||
|
Investing activities |
$ |
(9,010) |
$ |
(6,203) |
$ |
55 | |||
|
Financing activities |
$ |
(8,419) |
$ |
(20,806) |
$ |
(8,353) | |||
Net cash provided by operating activities was $32.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 and primarily reflected the net income for the period, adjusted for non-cash items such as stock-based compensation expense, provisions for doubtful accounts, depreciation and amortization expense, and changes in operating assets and liabilities. We reserved an amount of $0.5 million in the first quarter of 2015 as a bad debt charge recorded in general and administrative expense related to a customer whose receivable balance was past due which we subsequently wrote off when we determined it to be uncollectible during the fourth quarter of 2015. Accounts payable and accrued liabilities increased $9.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 as compared to the prior year’s period, mainly related to the additional $10.8 million SEC settlement expense recorded to operating expense related to the settlement with the SEC. Restricted cash in escrow for the SEC settlement increased $12.8 million related to the $12.8 million SEC settlement amount deposited in escrow during the fourth quarter of 2015.
Net cash provided by operating activities was $27.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 and primarily reflected the net income for the period, adjusted for non-cash items such as stock-based compensation expense, provisions for expiring inventory, depreciation and amortization expense, and changes in operating assets and liabilities. As of December 31, 2014, we had accounts
48
receivable totaling approximately $0.9 million from a single customer, which were substantially delinquent and which we were actively trying to collect, and for which we had recorded a reserve of $0.9 million. We entered into a settlement agreement with the customer in October 2014 to collect the remaining balance (refer to Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements appearing under Part II, Item 8). Accounts receivable increased $3.3 million mainly related to an increase in ZADAXIN sales. Inventory decreased $5.9 million mainly related to ZADAXIN inventory sales during the first half of 2014 exceeding our purchase levels, excluding approximately $2.9 million in Pfizer and Aggrastat inventory not yet paid for as of December 31, 2014. Accounts payable and accrued liabilities decreased $5.9 million mainly related to sales and marketing and manufacturing expense payments made during the year ended December 31, 2014.
Net cash provided by operating activities was $9.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2013 and primarily reflected the net income for the period, adjusted for non-cash items such as stock-based compensation expense, depreciation and amortization expense, non-cash escrow share settlement, loss on maturity of available-for-sale investments, provision for losses on accounts receivable, and changes in operating assets and liabilities. Accounts receivable increased $4.0 million related to an increase in our ZADAXIN sales during the fourth quarter of 2013, compared to the same quarter of 2012 when there was excess inventory of ZADAXIN in the channel. Inventory increased $4.7 million due to the completion our new manufacturing process and processing of new batches.
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities was ($9.0) million, ($6.2) million, and $0.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, purchases of property and equipment were $1.8 million, $1.5 million, and $0.3 million, respectively. In addition, for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2013, we received proceeds of $0.1 million and $0.4 million from the sale or maturity of our short-term investments or available-for-sale securities, net of purchases. In addition, as part of our license and supply agreement with Zensun, we agreed to loan up to $12 million in total to Zensun under two separate loan agreements. Pursuant to these agreements, we loaned $7.25 million in the first half of 2015, and $4.75 million to Zensun during the second half of 2014 (such lendings are further described in Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements appearing under Part II, Item 8), which is reflected in the $9.0 million and $6.2 million of net cash used in investing activities for 2015 and 2014, respectively. The proceeds of the loans are to be used for working capital and general corporate purposes by Zensun. To secure the loans, Zensun pledged its entire equity interest in its subsidiary, Shanghai Dongxin Biochemical Technology Co. Ltd. (whose assets include real property) to SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Ltd (“SPIL China”).
Net cash used in financing activities was $8.4 million, $20.8 million, and $8.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, we used $12.8 million, $24.4 million, and $12.5 million, respectively, to repurchase and retire approximately 1.5 million, 3.8 million, and 2.4 million shares of our common stock under our stock repurchase program. For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, we also received $4.4 million, $5.2 million, and $1.7 million of proceeds, respectively, from the issuances of common stock made under our stock award plans. For the year ended December 31, 2013, our subsidiary borrowed $0.6 million and repaid $2.0 million under its loan agreement with Shanghai Pudong Development Bank Co. Ltd that expired August 29, 2013. All amounts borrowed were repaid by the expiration date. Restricted cash of $2.3 million was released during the year ended December 31, 2013, that had been used to secure a letter of credit related to a loan agreement.
In December 2013, our subsidiary, NovaMed Shanghai, entered into a 10.0 million RMB revolving line of credit facility (approximately $1.6 million USD) and a maximum 15.0 million RMB loan facility (approximately $2.4 million USD) secured by its accounts receivable with Shanghai Pudong Development Bank Co. Ltd. (the “Credit Facility”). In June 2014, NovaMed Shanghai repaid the 10.0 million RMB (approximately $1.6 million USD) under the Credit Facility. The Credit Facility expired on November 30, 2014 and all amounts borrowed were repaid by the expiration date.
49
The following summarizes our other future contractual obligations as of December 31, 2015 (in thousands):
|
Payments Due by Period |
|||||||||||||||
|
Less than |
More Than |
||||||||||||||
|
Contractual Obligations |
Total |
1 Year |
1-3 Years |
3-5 Years |
5 Years |
||||||||||
|
Operating leases (1) |
$ |
5,200 |
$ |
2,421 |
$ |
2,013 |
$ |
766 |
$ |
— |
|||||
|
Purchase obligations (2) |
11,844 | 11,844 |
— |
— |
— |
||||||||||
|
Uncertain tax positions (3) |
3,462 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
||||||||||
|
Total |
$ |
20,506 |
$ |
14,265 |
$ |
2,013 |
$ |
766 |
$ |
— |
|||||
|
(1) |
These are future minimum rental commitments for office space and copiers leased under non-cancelable operating lease arrangements. |
|
(2) |
These consist of purchase obligations with manufacturers and distributors. |
|
(3) |
As we are not able to reasonably estimate the timing of the payments or the amount by which our obligations for unrecognized tax benefits will increase or decrease over time, the related balances have not been reflected in the ”Payments Due by Period” section of the table. |
Under our $80.5 million stock repurchase program, we repurchased and retired 1,526,306 shares at a cost of $12.8 million during the year ended December 31, 2015 bringing the total repurchases since the program’s inception to approximately 13.2 million shares at a cost of $78.1 million through December 31, 2015. Our stock repurchase program expired December 31, 2015 and is currently under strategic review by the Board.
We recorded a charge of $2.0 million in the fourth quarter of 2013 related to the possibility of a settlement with the SEC and DOJ regarding their investigation into possible violations of the FCPA by us. Based on our discussions with the SEC, we recorded an additional $10.8 million in SEC settlement to operating expense for the year ended December 31, 2015, bringing the total loss to the government in penalties, fines and/or other remedies to $12.8 million. In February 2016, we entered into a settlement agreement with the SEC fully resolving the SEC’s investigation into possible violations of the FCPA. Under the terms of the agreement, in February 2016, we paid $12.8 million including disgorgement, pre-judgement interest and a penalty from our restricted escrow account that we funded in the fourth quarter of 2015. As part of the agreement, we neither admitted nor denied engagement in any wrongdoing and we agreed to give status reports to the SEC for the next three years on our continued remediation and implementation of anti-corruption compliance measures. The DOJ has also completed its related investigation and has declined to pursue any action. Refer to Part I, Item 3 “Legal Proceedings” and Part II, Item 8, Notes 18 and 22 for further information on this matter.
Under our license agreements with third parties we have agreed to various milestone payments related to regulatory and commercial success and other achievements that may require substantial payments in the future.
We believe that our existing cash and cash equivalents and ongoing revenue generating business operations will be sufficient to support our current operating plan for at least the next 12 months. We have no current commitments to offer and sell any securities that may be offered or sold pursuant to a registration statement. To the extent that we raise additional capital by issuing equity securities, our stockholders may experience dilution. Debt financing, if available, may subject us to restrictive covenants and significant interest costs. To the extent that we raise additional funds through collaboration and licensing arrangements, we would be required to relinquish some rights to our technologies, product candidates or marketing territories. Additional financing or collaboration and licensing arrangements may not be available when needed either at all or on favorable terms.
We intend to continue to explore alternatives for financing to provide additional flexibility in managing our operations, in-licensing new products, particularly for China, and potential acquisitions, as may be required. In addition, as previously disclosed, our Board is evaluating a range of strategic transactions with a view to enhancing stockholder value. The unavailability or the inopportune timing of any financing could prevent or delay our long-term product development and commercialization programs, either of which could hurt our business. We cannot assure you that funds from financings, if any, will be sufficient to in-license additional products. The need, timing and amount of any such financing would depend upon numerous factors, including the status of the pending regulatory investigations and pending litigations, the level and price of our products, the timing and amount of manufacturing costs related to our products, the availability of complementary products, technologies and businesses, the initiation and continuation of preclinical and clinical trials and testing, the timing of regulatory approvals, developments in relationships with existing or future
50
collaborative parties, the status of competitive products, and various alternatives for financing. We have not determined the timing or structure of any transaction.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not have any off-sheet balance sheet arrangements.
Critical Accounting Policies and Significant Judgments and Estimates
General
We have identified the policies below as critical to our business operations and the understanding of our results of operations. The impact and any associated risks related to these policies on our business operations are discussed throughout “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” where such policies affect our reported and expected financial results. For a detailed discussion on the application of these and other accounting policies, see Note 1 in the “Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements” in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Our consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, which require us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amount of assets and liabilities, disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of our financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. On an on-going basis, we evaluate the relevance of our estimates and judgments. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other market-specific assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. There can be no assurance that actual results will not differ from those estimates.
Revenue Recognition
We recognize revenue when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, services have been rendered or delivery has occurred, the price to the buyer is fixed or determinable and collectability is reasonably assured.
Product Revenue. We recognize product revenue from selling manufactured ZADAXIN product at the time of delivery. Sales of ZADAXIN to Sinopharm are recognized upon the arrival of a shipment to its destination when title and risk of loss to the product are transferred to them. We also earn product revenue from purchasing medical products from pharmaceutical companies and selling them directly to importers or distributors. We recognize revenue related to these products based on the “sell-in” method, when the medical products have been delivered to the importers or distributors. Payments by the importing agents and distributors are not contingent upon sale to the end user by the importing agents or distributors.
Promotion Services Revenue. We recognize promotion services revenue after designated medical products are delivered to the distributors as specified in the promotion services contracts, which marks the period when marketing and promotion services have been rendered, and the revenue recognition criteria are met. In certain arrangements, we were required to return or refund a portion of promotion services fees received during interim periods from pharmaceutical customers if defined annual sales targets were not achieved. Under our agreements with these customers, if the agreement was terminated, and provided such targets had been met on a “pro rata” basis at the date of contract termination, we were entitled to retain the amounts paid. Due to these contractual provisions, we recognized revenue during interim periods without reduction for amounts subject to refund based on Method 2 of Accounting Standards Codification 605-20-S99-1, “Accounting for Management Fees Based on a Formula.”
Revenue Reserve. We maintain a revenue reserve for product returns based on estimates of the amount of product to be returned by our customers which is based on historical patterns, analysis of market demand and/or a percentage of sales based on industry trends, and management’s evaluation of specific factors that may increase the risk of product returns. Importing agents or distributors do not have contractual rights of return except under limited terms regarding product quality. However, we are expected to replace products that have expired or are deemed to be damaged or defective when delivered. The calculation of the product returns reserve requires estimates and involves a high degree of subjectivity and judgment. As a result of the uncertainties involved in estimating the product returns reserve, there is a possibility that materially different amounts could be reported under different conditions or using different assumptions. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, our revenue reserves were approximately $0.1 million; the reserves were recorded as accrued liabilities on our consolidated balances sheets.
51
We evaluate our returns reserve quarterly and adjust it when events indicate that a change in estimate is appropriate. Changes in estimates could materially affect our results of operations or financial position. It is possible that we may need to adjust our estimates in future periods.
Accounts Receivable Reserve
We record a receivable reserve based on a specific review of our overdue invoices. Our estimate for a reserve is determined after considering our existing contractual payment terms, payment patterns of our customers and individual customer circumstances, the age of any outstanding receivables and our current customer relationships. Accounts receivable are charged off at the point when they are considered uncollectible.
As of December 31, 2015, we had a receivable reserve of $0.6 million. In October 2014, our subsidiary, SPIL China, executed an agreement with a particular customer providing for settlement of a $3.0 million receivable balance. The terms of the settlement agreement resulted in the write-off of $1.1 million in previously fully reserved accounts receivable with an equivalent charge-off of the allowance for bad debt, which had no impact on net income in 2014, as the subsequent agreement provided direct evidence that the $1.1 million previously reserved will not be collected in the future. Of the remaining $1.9 million receivable balance, $0.4 million and $1.0 million were collected in 2015 and 2014, respectively, per the terms of the settlement agreement, and these gains on recovery were recorded as reductions to general and administrative expense for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. As of December 31, 2015, a balance of $0.5 million remained uncollected from the same customer but remained fully reserved. We recognized $0.5 million of bad debt expense in general and administrative expense during the first quarter of 2015 related to past due receivables from another customer, due to uncertainty regarding the collectability of the customer’s outstanding receivable balance. We wrote-off the $0.5 million of past due accounts receivable from this customer during the fourth quarter of 2015 as uncollectible.
Inventories
Our inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market (net realizable value), with cost determined on a first-in, first-out basis and include amounts related to materials, labor and overhead. In assessing the ultimate realization of inventories, we are required to make judgments as to future demand requirements and compare that with the current inventory levels. If our current assumptions about future production or inventory levels and demand were to change or if actual market conditions are less favorable than those projected by management, inventory write-downs may be required, which could negatively impact our gross margins and results of operations. If obsolete or excess items are observed and there are no alternate uses for the inventory, we will record a write-down to net realizable value in the period that the impairment is first recognized. During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, we recorded inventory write-downs of $0, $2.1 million, $0, respectively, principally related to carrying value reductions for excess Aggrastat product. As we have discontinued this product, remaining inventory is zero at December 31, 2015.
Goodwill
We account for goodwill in accordance with ASC Topic 805, and ASC Topic 350, Intangibles — Goodwill and Other. ASC Topic 805 requires that the acquisition method of accounting be used for all business combinations and specifies the criteria that must be met in order for intangible assets acquired in a business combination to be recognized and reported apart from goodwill. Goodwill is tested for impairment at least annually or whenever events or circumstances occur that indicate impairment might have occurred or circumstances suggest that the carrying value of these assets may not be recoverable and the undiscounted cash flows estimated to be generated by those assets are less than the carrying amounts of those assets in accordance with ASC Topic 350. Judgment regarding the existence of impairment indicators will be based on operating results, changes in the manner of our use of the acquired assets or our overall business strategy, and market and economic trends.
Goodwill relates to our China segment which focuses on our primary pharmaceutical distribution market, consisting of the NovaMed business and the legacy China business of the Company, which represent a single reporting unit. For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, we tested for goodwill impairment by quantitatively comparing the fair value of the reporting unit to its carrying amounts - step one of the two-step impairment test. We estimated the fair value of the China reporting unit using a discounted cash flow model. This valuation approach considers a number of factors that include, but are not limited to, expected future cash flows, growth rates, discount rates, and requires us to make certain assumptions and estimates regarding industry economic factors and future profitability of our business. Although we believe our assumptions are reasonable, actual results may vary significantly and may expose us to impairment charges in the future. Our methodology for determining fair value remained consistent for the periods presented. If we determine that the carrying value of our reporting unit exceeds its fair value, we would then calculate
52
the implied fair value of the reporting unit goodwill as compared to its carrying value to determine the appropriate impairment charge. After completing our annual impairment review for the reporting unit as of December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, and our interim impairment review during the third quarter of 2013, as a result of the notification by Sanofi of the non-renewal of our promotional agreements with them at the end of their terms on December 31, 2013, we concluded that goodwill was not impaired in 2015, 2014, or 2013.
Loans Receivable
Loans receivable consist of two loans to one third party (see Note 6). Loans are initially recorded, and continue to be carried, at unpaid principal balances under “other assets” on the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2015 and 2014. Carried balances are subsequently adjusted for payments of principal or adjustments to the allowance for loan losses to account for any impairment. Interest income is recognized over the term of the loans and is calculated using the simple-interest method, as the loans do not have associated premium or discount. If the loans were to experience impairment, interest income would not be recognized unless the likelihood of further loss was remote.
Management considers impairment to exist when, based on current information or factors (such as payment history, value of collateral, and assessment of the counterparty’s current creditworthiness), it is probable that principal and interest payments will not be collected according to the contractual agreements. Management considers a loan payment delinquent when not received by the due date.
Management assessed the credit worthiness of the counterparty by reviewing available borrower financial information and substantiation of the value of the pledged security interest in the course of preparing our consolidated financial statements. Management also considered in its analysis that the borrower was compliant with the terms of the loans, that interest payments have been timely made, and that available reliable evidence indicated that the market value of the pledged security was greater than the loan receivable balance. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, management concluded the loans receivable were not impaired, and there was no allowance for loan losses.
Contingent Liabilities
We record as liabilities estimated amounts for litigation, claims or other legal actions that are probable and can be reasonably estimated. The likelihood of a material change in these estimated reserves is dependent on the possible outcome of settlement negotiations, regulatory or judicial review and the development of facts and circumstances in extended litigation, which could change claims or assessments when both the amount and range of loss on some outstanding litigation is uncertain. We disclose in the footnotes of the financial statements when we are unable to make a reasonable estimate of a material liability that could result from unfavorable outcomes. As events occur, we will assess the potential liability related to any pending litigation, claims or other legal actions and adjust our estimates accordingly.
Stock-Based Compensation
We record stock-based compensation costs relating to share-based payment transactions, including stock options, restricted stock units (“RSUs”), performance restricted stock units (“PSUs”) and employee stock purchase plans (“ESPP”). Stock-based compensation expense for stock options and the employee stock purchase plan is estimated at the date of grant based on the fair value of the award using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. Stock-based compensation expense for RSUs and PSUs is estimated at the date of grant based on the number of shares granted and the quoted price of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. Stock-based compensation expense values for stock options, RSUs and the ESPP plan are recognized as expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period, net of estimated forfeitures. We recognize expense related to the performance stock options and PSUs over the implicit service period if it is probable that the performance goals will be achieved. If it is subsequently determined that the performance goals are not probable of achievement, the expense related to the performance stock options or PSUs is reversed. The share-based payment awards that are ultimately expected to vest are recognized as expense ratably (as the awards vest) over the requisite service period, which is generally one or four years for stock options and RSUs and three months for ESPP. We estimate pre-vesting forfeitures at the time of grant by analyzing historical data and revise those estimates in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates. The total expense recognized over the vesting period will only be for those awards that ultimately vest.
The option-pricing models require the use of certain subjective assumptions, including the expected volatility of the market price of the underlying stock and the expected term of the award. Expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of our stock.
53
Expected term is derived from historical data on employee exercises and terminations. We review our valuation assumptions at each grant date, and, as a result, valuation assumptions used to value stock-based compensation of awards granted in future periods may change.
Income Taxes
Income taxes are accounted for under the liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the difference between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities as measured by the enacted tax rates that will be in effect when these differences reverse. We provide a valuation allowance against deferred tax assets if, based upon the available evidence, it is more-likely-than-not that the deferred tax assets will not be realized. Realization of our deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income, the timing and amount of which are uncertain. The tax years 1995-2015 remain open to examination by the major US taxing jurisdictions to which we are subject. The Internal Revenue Service completed their examinations of our 2008, 2009 and 2011 US Federal tax returns with no additional tax assessments or proposed adjustments relating to taxable income for any years. Our China income tax returns are generally subject to examination for a period of five years and those years remain open to examination.
We record liabilities related to uncertain tax positions in accordance with the guidance that clarifies the accounting for uncertainty in income taxes recognized in an enterprise’s financial statements by prescribing a minimum recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. We do not believe any such uncertain tax positions currently pending will have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial statements, although an adverse resolution of one or more of these uncertain tax positions in any period could have a material impact on the results of operations for that period.
Restructuring Costs
When necessary, we record expense for the estimated costs of restructuring activities. The liability recorded for restructuring costs contains uncertainties because management is required to make assumptions and to apply judgment to estimate the amounts and timing of future settlement payments and the timing of such payments. When making these assumptions, management considers a number of factors including the number of employees involved and the related benefits included in the restructuring plan, and historical settlement experience. We do not believe there is a reasonable likelihood that there will be a material change in the estimates or assumptions we use to calculate our restructuring liabilities. However, if actual results are not consistent with our estimates or assumptions, we may be exposed to losses or gains which would have an impact on the results of operations for that period.
New Accounting Standards Updates
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2014-09, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers" (“ASU 2014-09”), which contains new accounting literature relating to how and when a company recognizes revenue. Under ASU 2014-09, a company will recognize revenue when it transfers promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods and services. ASU 2014-09 is effective for our fiscal year beginning January 1, 2018, which reflects a one year deferral approved by the FASB in July 2015, with early application permitted provided that the effective date is not earlier than the original effective date. We are in the process of determining what impact, if any, the adoption of ASU 2014-09 will have on our financial statements and related disclosures. The standard permits the use of either the full retrospective or modified retrospective transition method. We have not yet selected a transition method nor have we determined the effect of the standard on our ongoing financial reporting.
In July 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-11, "Inventory (Topic 330): Simplifying the Measurement of Inventory" (“ASU 2015-11”) which applies to inventory that is measured using first-in, first-out ("FIFO") or average cost. Under the updated guidance, an entity should measure inventory that is within scope at the lower of cost and net realizable value, which is the estimated selling prices in the ordinary course of business, less reasonably predictable costs of completion, disposal and transportation. Subsequent measurement is unchanged for inventory that is measured using last-in, first-out ("LIFO"). This ASU is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and should be applied prospectively with early adoption permitted at the beginning of an interim or annual reporting period. We have evaluated the impact of adopting this guidance and have concluded we will likely have no effect on the financial statements as our adjustments already reflect the concept of net realizable value. Inventory provisions are generally full write-downs for the affected inventory.
54
In November 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-17, "Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes." This ASU amends existing guidance to require that deferred income tax liabilities and assets be classified as noncurrent in a classified balance sheet, and eliminates the prior guidance which required an entity to separate deferred tax liabilities and assets into a current amount and a noncurrent amount in a classified balance sheet. The amendments in this ASU are effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those annual periods. Earlier application is permitted as of the beginning of an interim or annual period. Additionally, the new guidance may be applied either prospectively to all deferred tax liabilities and assets or retrospectively to all periods presented. We have not yet selected an adoption method. The impact of adopting this guidance is not expected to be material to our consolidated financial statements given our deferred tax amounts.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02 “Leases”. Under the new guidance, lessees will be required to recognize a lease liability and a lease asset for all leases, including operating leases, with a term greater than 12 months on its balance sheet. The update also expands the required quantitative and qualitative disclosures surrounding leases. This update is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018 and interim periods within those fiscal years, with earlier application permitted. We are evaluating the impact of the adoption of this update on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
Item 7A.Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk
We do not hold any derivative financial instruments for speculation or trading purposes. The majority of our sales have been in US dollars, although a portion of our sales are denominated in RMB. Per our previous contractual arrangement with Sinopharm through December 31, 2015, and a renewed contractual arrangement with Sinopharm (our sole importer and distributor for ZADAXIN in China) which took effect January 1, 2016, our sales of ZADAXIN to Sinopharm have been and continue to be denominated in US dollars. However, the established importer price may be adjusted quarterly based upon exchange rate fluctuations between the US dollar and RMB. In recent months the RMB has experienced devaluation, which has led to, and may continue to lead to, downward adjustments in our importer price if further devaluation continues. While our revenue may be negatively affected, our expenses are also positively impacted as a substantial portion of our expenses are denominated in RMB. Our purchases with contract manufacturers are denominated in US dollars and euros and costs of our marketing efforts in China are paid in local currency.
In addition, we have certain cash balances and other assets and liabilities denominated in euros, RMB and Hong Kong dollars. As a result, we are exposed to foreign currency rate fluctuations, and we do not hedge against the risk associated with such fluctuations. Consequently, changes in exchange rates could result in material exchange losses and could unpredictably, materially and adversely affect our operating results and stock price. A hypothetical 1% increase or decrease in foreign exchange rates would result in an approximate $0.1 million increase or decrease in our financial assets and liabilities denominated in euros, RMB and Hong Kong dollars, as of December 31, 2015 and 2014. These potential changes are based on sensitivity analyses performed on our financial position as of December 31, 2015 and 2014. Actual results may differ materially.
Interest Rate Risk
The primary objective of our investment activities is to preserve principal while at the same time maximizing yields without significantly increasing risk. To achieve this objective, we invest in money market funds, term deposits, commercial paper, corporate bonds, US treasury, or government agency notes; our investments are most frequently classified as cash equivalents. We are also invested in a loan to a business partner; however, the purpose for such loan is to facilitate the business relationship and it is not principally for investment purposes. Our investment securities may be subject to interest rate risk and could decrease in value if market interest rates rise. To minimize this risk, we primarily hold securities that are short-term in duration and maintain an average maturity of less than one year. We believe that our exposure to interest rate risk is not significant and a 1% movement in market interest rates would not have a significant impact to the total value of our investment portfolio as of December 31, 2015 or 2014.
55
Item 8.Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
PAGE NO. |
|||||
|
57 |
|||||
|
58 |
|||||
|
59 |
|||||
|
60 |
|||||
|
61 |
|||||
|
62 |
|||||
|
63 |
|||||
56
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(1) present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and its subsidiaries at December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2015 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In addition, in our opinion, the financial statement schedule listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(2), presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein when read in conjunction with the related consolidated financial statements. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company's management is responsible for these financial statements and financial statement schedule, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9(a). Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements, on the financial statement schedule, and on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers Zhong Tian LLP
Shanghai, the People’s Republic of China
March 11, 2016
57
SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
||
|
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
101,403 |
|
$ |
86,228 |
|
Restricted cash in escrow for SEC settlement (Notes 18 and 22) |
|
|
12,826 |
|
|
— |
|
Accounts receivable, net of allowances of $594 and $998 as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively |
|
|
39,363 |
|
|
40,268 |
|
Inventories |
|
|
10,976 |
|
|
10,703 |
|
Short-term investments |
|
|
— |
|
|
75 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
3,654 |
|
|
2,597 |
|
Deferred tax assets |
|
|
299 |
|
|
326 |
|
Total current assets |
|
|
168,521 |
|
|
140,197 |
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
2,651 |
|
|
1,848 |
|
Goodwill |
|
|
32,979 |
|
|
34,521 |
|
Other assets |
|
|
12,468 |
|
|
5,265 |
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
216,619 |
|
$ |
181,831 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable |
|
$ |
4,495 |
|
$ |
5,311 |
|
Accrued and other current liabilities |
|
|
32,151 |
|
|
20,536 |
|
Deferred revenue |
|
|
174 |
|
|
596 |
|
Total current liabilities |
|
|
36,820 |
|
|
26,443 |
|
Other long-term liabilities |
|
|
87 |
|
|
114 |
|
Commitments and contingencies (Notes 10 and 18) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stockholders’ equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred stock; $0.001 par value; 10,000,000 shares authorized; no shares issued and outstanding |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
Common stock; $0.001 par value; 100,000,000 shares authorized; 49,533,835 and 49,948,897 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively |
|
|
50 |
|
|
50 |
|
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
296,086 |
|
|
287,108 |
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income |
|
|
2,070 |
|
|
3,264 |
|
Accumulated deficit |
|
|
(118,494) |
|
|
(135,148) |
|
Total stockholders’ equity |
|
|
179,712 |
|
|
155,274 |
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
|
$ |
216,619 |
|
$ |
181,831 |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
58
SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(In thousands, except per share amounts)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Product sales, net |
|
$ |
154,329 |
|
$ |
131,973 |
|
$ |
99,414 |
|
|
Promotion services |
|
|
2,928 |
|
|
2,817 |
|
|
27,644 |
|
|
Total net revenues |
|
|
157,257 |
|
|
134,790 |
|
|
127,058 |
|
|
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of product sales |
|
|
22,348 |
|
|
23,002 |
|
|
17,668 |
|
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
53,961 |
|
|
48,477 |
|
|
55,240 |
|
|
Research and development |
|
|
12,314 |
|
|
14,581 |
|
|
8,044 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
27,897 |
|
|
22,746 |
|
|
32,496 |
|
|
Restructuring charges |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
1,181 |
|
|
SEC settlement expense (Notes 18 and 22) |
|
|
10,826 |
|
|
— |
|
|
2,000 |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
|
127,346 |
|
|
108,806 |
|
|
116,629 |
|
|
Income from operations |
|
|
29,911 |
|
|
25,984 |
|
|
10,429 |
|
|
Non-operating income (expense): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest and investment income |
|
|
869 |
|
|
161 |
|
|
85 |
|
|
Interest and investment expense |
|
|
— |
|
|
(48) |
|
|
(103) |
|
|
Other (expense) income, net |
|
|
(510) |
|
|
280 |
|
|
2,795 |
|
|
Income before provision for income tax |
|
|
30,270 |
|
|
26,377 |
|
|
13,206 |
|
|
Provision for income tax |
|
|
807 |
|
|
1,169 |
|
|
2,242 |
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
29,463 |
|
$ |
25,208 |
|
$ |
10,964 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic net income per share |
|
$ |
0.59 |
|
$ |
0.49 |
|
$ |
0.20 |
|
|
Diluted net income per share |
|
$ |
0.56 |
|
$ |
0.48 |
|
$ |
0.20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted-average shares used in computing: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic net income per share |
|
|
49,797 |
|
|
51,277 |
|
|
53,587 |
|
|
Diluted net income per share |
|
|
52,173 |
|
|
52,684 |
|
|
54,936 |
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
59
SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(In thousands)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|||
|
Net income |
|
$ |
29,463 |
|
$ |
25,208 |
|
$ |
10,964 |
|
Other comprehensive income, net of income tax: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Available-for-sale securities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unrealized loss and foreign currency translation arising during the period on foreign currency denominated available-for-sale securities |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(4) |
|
Reclassification adjustment for losses included in net income |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
71 |
|
Net change |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
67 |
|
Foreign currency translation |
|
|
(1,194) |
|
|
(912) |
|
|
1,121 |
|
Total other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
(1,194) |
|
|
(912) |
|
|
1,188 |
|
Total comprehensive income |
|
$ |
28,269 |
|
$ |
24,296 |
|
$ |
12,152 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
60
SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(In thousands)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional |
|
Other |
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
||
|
|
Common stock |
|
|
Paid-in |
|
Comprehensive |
|
Accumulated |
|
Stockholders’ |
|
||||||
|
|
Shares |
|
Amount |
|
|
Capital |
|
Income (Loss) |
|
Deficit |
|
Equity |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance as of January 1, 2013 |
54,484 |
|
$ |
54 |
|
$ |
274,387 |
|
$ |
2,988 |
|
$ |
(134,407) |
|
$ |
143,022 |
|
|
Net income |
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
10,964 |
|
|
10,964 |
|
|
Other comprehensive income |
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
1,188 |
|
|
— |
|
|
1,188 |
|
|
Escrow shares received in settlement and immediately retired |
(342) |
|
|
— |
|
|
(1,866) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(1,866) |
|
|
Issuance of common stock from exercise of stock options, restricted stock units, and employee stock purchase plan |
634 |
|
|
— |
|
|
1,705 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
1,705 |
|
|
Compensation related to stock-based awards |
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
4,101 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
4,101 |
|
|
Repurchase of common stock |
(2,404) |
|
|
(2) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(12,517) |
|
|
(12,519) |
|
|
Balance as of December 31, 2013 |
52,372 |
|
|
52 |
|
|
278,327 |
|
|
4,176 |
|
|
(135,960) |
|
|
146,595 |
|
|
Net income |
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
25,208 |
|
|
25,208 |
|
|
Other comprehensive loss |
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(912) |
|
|
— |
|
|
(912) |
|
|
Issuance of common stock from exercise of stock options, restricted stock units, and employee stock purchase plan, net |
1,399 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
5,212 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
5,214 |
|
|
Compensation related to stock-based awards |
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
3,569 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
3,569 |
|
|
Repurchase of common stock |
(3,822) |
|
|
(4) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(24,396) |
|
|
(24,400) |
|
|
Balance as of December 31, 2014 |
49,949 |
|
|
50 |
|
|
287,108 |
|
|
3,264 |
|
|
(135,148) |
|
|
155,274 |
|
|
Net income |
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
29,463 |
|
|
29,463 |
|
|
Other comprehensive loss |
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(1,194) |
|
|
— |
|
|
(1,194) |
|
|
Issuance of common stock from exercise of stock options, restricted stock units, and employee stock purchase plan, net |
1,111 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
4,390 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
4,392 |
|
|
Compensation related to stock-based awards |
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
4,588 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
4,588 |
|
|
Repurchase of common stock |
(1,526) |
|
|
(2) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(12,809) |
|
|
(12,811) |
|
|
Balance as of December 31, 2015 |
49,534 |
|
$ |
50 |
|
$ |
296,086 |
|
$ |
2,070 |
|
$ |
(118,494) |
|
$ |
179,712 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
61
SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In thousands)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|||
|
Operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
29,463 |
|
$ |
25,208 |
|
$ |
10,964 |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-cash expense related to stock-based compensation |
|
|
4,441 |
|
|
3,465 |
|
|
4,007 |
|
Non-cash escrow share settlement |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(1,866) |
|
Provision for doubtful accounts |
|
|
541 |
|
|
— |
|
|
2,540 |
|
Provision for expiring inventory |
|
|
— |
|
|
2,099 |
|
|
— |
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
931 |
|
|
852 |
|
|
860 |
|
Loss on maturity of available-for-sale investment |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
75 |
|
Loss on disposal of fixed assets |
|
|
3 |
|
|
26 |
|
|
17 |
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
12 |
|
|
(321) |
|
|
191 |
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable, net |
|
|
306 |
|
|
(3,276) |
|
|
(3,999) |
|
Inventories |
|
|
1,432 |
|
|
5,382 |
|
|
(4,685) |
|
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
|
|
(1,020) |
|
|
(277) |
|
|
(202) |
|
Restricted cash in escrow for SEC settlement (Notes 18 and 22) |
|
|
(12,826) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
Accounts payable |
|
|
(2,295) |
|
|
(5,485) |
|
|
(134) |
|
Accrued and other current liabilities |
|
|
11,997 |
|
|
(414) |
|
|
(1,006) |
|
Deferred revenue |
|
|
(422) |
|
|
340 |
|
|
2,873 |
|
Other long-term liabilities |
|
|
(56) |
|
|
10 |
|
|
(133) |
|
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
|
32,507 |
|
|
27,609 |
|
|
9,502 |
|
Investing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from the maturity of available-for-sale securities or short-term investments |
|
|
75 |
|
|
— |
|
|
379 |
|
Loans to third party (Note 6) |
|
|
(7,250) |
|
|
(4,751) |
|
|
— |
|
Purchases of property and equipment |
|
|
(1,835) |
|
|
(1,452) |
|
|
(324) |
|
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities |
|
|
(9,010) |
|
|
(6,203) |
|
|
55 |
|
Financing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Repurchase of common stock including commissions |
|
|
(12,811) |
|
|
(24,400) |
|
|
(12,519) |
|
Repayment of credit facilities |
|
|
— |
|
|
(1,620) |
|
|
(2,035) |
|
Proceeds from borrowing on credit facilities |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
2,196 |
|
Decrease in restricted cash related to loan facility |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
2,300 |
|
Proceeds from issuances of common stock, net |
|
|
4,392 |
|
|
5,214 |
|
|
1,705 |
|
Net cash used in financing activities |
|
|
(8,419) |
|
|
(20,806) |
|
|
(8,353) |
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
97 |
|
|
(175) |
|
|
371 |
|
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
15,175 |
|
|
425 |
|
|
1,575 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period |
|
|
86,228 |
|
|
85,803 |
|
|
84,228 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents, end of period |
|
$ |
101,403 |
|
$ |
86,228 |
|
$ |
85,803 |
|
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income taxes paid related to foreign operations |
|
$ |
1,509 |
|
$ |
944 |
|
$ |
2,237 |
|
Interest and unused line fees paid related to borrowings |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
48 |
|
$ |
81 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
62
SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1 — The Company and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Description of Business
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“SciClone” or the “Company”), incorporated in 1990, is a United States (“US”)-headquartered, China-focused, specialty pharmaceutical company with a substantial commercial business in China and a product portfolio of therapies for oncology and infectious diseases. The Company’s lead product, ZADAXIN® (thymalfasin) is approved in over 30 countries and may be used for the treatment of hepatitis B (HBV), hepatitis C (HCV), and certain cancers according to the local regulatory approvals, and for use as an immune system enhancer. In addition to ZADAXIN, SciClone markets approximately 7 partnered and in-licensed products in China. SciClone is also pursuing the registration of several other therapeutic products in China.
Presentation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly owned subsidiaries. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated from the consolidated financial statements.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with US generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make informed estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and accompanying notes. Actual results could differ materially from those estimates.
Cash Equivalents and Investments
Cash equivalents consist of highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less on the date of purchase. The Company records its investments at fair value, as determined by available information on the consolidated balance sheet date. The Company’s investment portfolio as of December 31, 2015 consisted of money market funds that were included in cash and cash equivalents.
Unrealized gains or losses on available-for-sale securities are included in accumulated other comprehensive income on the consolidated balance sheets. Realized gains and losses and declines in value judged to be other-than-temporary on available-for-sale securities are included in earnings. The amortized cost of securities is adjusted for amortization of premiums and accretion of discounts to maturity and is included in earnings. The cost of securities sold is based on the specific identification method.
Available-for-sale investments are evaluated for impairment each reporting period. An investment is considered impaired if the fair value of the investment is less than its cost. If, after consideration of all available evidence to evaluate the realizable value of its investment, impairment is determined to be other-than-temporary, then an impairment loss is recognized in the consolidated statement of income. No such losses were recorded in the periods presented.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value must maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. Fair value measurements are based on a three-tier hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs used to measure fair value. The three levels of input are:
Level 1 - Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2 - Inputs other than Level 1 that are observable, either directly or indirectly, such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities; quoted prices in markets that are not active; or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities.
63
Level 3 - Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities.
Where quoted prices are available in an active market, the Company determines fair value based on quoted market prices, and classifies these values in level 1 of the valuation hierarchy. If quoted market prices are not available, fair values are based on observable inputs such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities; quoted prices in markets that are not active; or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities and are classified in level 2 of the valuation hierarchy. When quoted prices and observable inputs are unavailable, fair values are based on cash flow models and are classified in level 3 of the valuation hierarchy. The cash flow models use inputs specific to the asset or liabilities including estimates for interest rates and discount rates including yields of comparable traded instruments adjusted for illiquidity and other risk factors, amount of cash flows and expected holding periods of the assets and liabilities. These inputs reflect the Company’s assumptions about the assumptions market participants would use in pricing the assets and liabilities including assumptions about risk developed based on the best information available in the circumstances. The Company’s assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurements requires judgment, and may materially affect the valuation of the assets and liabilities being measured and their placement within the fair value hierarchy.
Other financial instruments, including accrued short-term liabilities, are carried at cost, which the Company believes approximates fair value because of the short-term maturity of these instruments.
Concentration of Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to a concentration of credit risk consist of cash, cash equivalents, investments, accounts receivable and loans receivable. The Company is exposed to credit risk in the event of default by the institutions holding the cash, cash equivalents and investments, and by customers and partners in the event of default by the customer or partner to pay the amounts due to the Company on receivables and loans receivables, respectively, to the extent of the amounts recorded on the consolidated balance sheet. Most of the Company’s cash and cash equivalents are held by financial institutions that the Company believes are of high credit quality. At times, deposits may exceed government insured limits. The Company has not experienced any losses on its deposits of cash and cash equivalents.
In China, pharmaceutical products are imported and distributed through a tiered method of distribution. For the Company’s proprietary product ZADAXIN, the Company manufactures its product using its US and European contract manufacturers, and it generates its product sales revenue through sales of ZADAXIN products to Sinopharm Holding Lingyun Biopharmaceutical (Shanghai) Co. Limited (“Sinopharm”). Sinopharm acts as an importer, and also as the top “tier” of the distribution system (“Tier 1”) in China. The Company’s ZADAXIN sales occur when the importer purchases product from the Company, without any right of return except for replacement of product in the events of damaged product or quality control issues. As the Company bears risk of loss until delivery has occurred, revenue is not recognized until the shipment reaches its destination. After the Company’s sale of ZADAXIN to the importer, Sinopharm clears products through China import customs, sells directly to large hospitals and holds additional product it has purchased in inventory for sale to the next tier in the distribution system. The second-tier (“Tier 2”) distributors are responsible for the further sale and distribution of the products they purchase from the importer, either through sales of product directly to the retail level (hospitals and pharmacies), or to third-tier (“Tier 3”) local or regional distributors who, in turn, sell products to hospitals and pharmacies. The Company’s other product sales revenues result from the sale of the Company’s in-licensed products to importing agents and distributors.
Promotion services revenues result from fees received for exclusively promoting products for certain pharmaceutical partners. These importing agents, distributors and partners are the Company’s customers.
Customers that exceeded 10% of the Company’s total net revenue and related to our China segment were as follows:
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
||||||
|
2015 |
2014 |
2013 |
||||
|
Customer A |
97% | 94% | 75% | |||
|
Customer B |
— |
— |
20% | |||
64
Product sales of $146.1 million or 95%, $126.1 million or 96%, and $96.3 million or 97%, for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, related to sales of ZADAXIN. As of December 31, 2015, approximately $38.3 million, or 96%, of the Company's gross accounts receivable was attributable to one customer, Sinopharm, in China. The Company generally does not require collateral from its customers. The Company maintains reserves for potential credit losses and such actual losses may vary significantly from its estimates.
The Company currently relies on two suppliers to provide key components to its ZADAXIN manufacturing supply. Although there are a limited number of manufacturers who would be able to meet the requirements to manufacture these components, the Company believes that other suppliers could provide similar components on comparable terms. A change in suppliers, however, could cause a delay in manufacturing and a possible loss of sales, which would affect operating results adversely.
Per the Company’s previous contractual arrangement with Sinopharm through December 31, 2015, and a renewed contractual arrangement with Sinopharm (the Company’s sole distributor for ZADAXIN in China) which took effect January 1, 2016, the Company’s sales of ZADAXIN to Sinopharm have been and continue to be denominated in US dollars. However, the established importer price may be adjusted quarterly based upon exchange rate fluctuations between the US dollar and Chinese Yuan Renminbi (“RMB”). A significant portion of the Company’s other revenues and expenses are denominated in RMB and a significant portion of the Company’s assets and liabilities are denominated in RMB and are exposed to foreign exchange risk. In recent months, the RMB has experienced devaluation. Such devaluation may negatively affect the US dollar value of revenues, albeit on a lagging basis, pursuant to the periodic adjustments described above. RMB is not freely convertible into foreign currencies. In China, foreign exchange transactions are required by law to be transacted only by authorized financial institutions at the exchange rates quoted by People’s Bank of China. Remittances in currencies other than RMB by the Company in China require certain supporting documentation in order to affect the remittance.
Accounts Receivable Reserve
The Company records a receivable reserve based on a specific review of its overdue invoices. The Company’s estimate for a reserve is determined after considering its existing contractual payment terms, payment patterns of its customers and individual customer circumstances, the age of any outstanding receivables and its current customer relationships. Accounts receivable are charged off at the point when they are considered uncollectible.
As of December 31, 2015, the Company had a receivable reserve of $0.6 million. In October 2014, the Company’s subsidiary, SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Ltd (“SPIL China”) executed an agreement with a particular customer providing for settlement of a $3.0 million receivable balance. The terms of the settlement agreement resulted in the write-off of $1.1 million in previously fully reserved accounts receivable with an equivalent charge-off of the allowance for bad debt, which had no impact on net income in 2014. Of the remaining $1.9 million receivable balance, $0.4 million and $1.0 million were collected in 2015 and 2014, respectively, per the terms of the settlement agreement, and these gains on recovery were recorded as reductions to general and administrative expense for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. As of December 31, 2015, a balance of $0.5 million remained uncollected from the same customer but remained fully reserved. The Company recognized $0.5 million of bad debt expense in general and administrative expense during the first quarter of 2015 related to past due receivables from another customer, due to uncertainty regarding the collectability of the customer’s outstanding receivable balance. The Company wrote-off the $0.5 million of past due accounts receivable from this customer during the fourth quarter of 2015 as uncollectible.
Inventories
Inventories consist of raw materials, work in progress and finished goods products. Inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market (net realizable value), with cost determined on a first-in, first-out basis, and include amounts related to materials, labor and overhead. The Company periodically reviews the inventory in order to identify excess and obsolete items. If obsolete or excess items are observed and there are no alternate uses for the inventory, the Company will record a write-down to net realizable value in the period that the impairment is first indicated. During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, the Company recorded inventory write-downs of $0, $2.1 million, and $0, respectively, principally related to carrying value reductions for excess Aggrastat® product. As of December 31, 2015, there was zero remaining Aggrastat product in inventory following a discontinuation of the product. (Refer to Note 17 for further information regarding the discontinuation of Aggrastat.)
65
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is recorded over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets on the straight-line basis. Office furniture and fixtures are generally amortized over five years, office equipment and computer software are generally amortized over three years, and the Company’s vehicle is being amortized over four years. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of the estimated useful life or lease term on the straight-line basis. The Company’s policy is to identify and record impairment losses, if necessary, on property and equipment when events and circumstances indicate that the assets might be impaired and the undiscounted cash flows estimated to be generated by those assets are less than the carrying amounts of those assets.
Goodwill
The Company accounted for the acquisition of NovaMed Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“NovaMed”) in 2011 under the acquisition method of accounting in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 805, Business Combinations. Under the acquisition method of accounting, the total acquisition-date fair value of the assets and liabilities are recognized as of the closing date. The excess of the fair value of the total consideration transferred over the acquisition-date fair value of net tangible and intangible assets and liabilities assumed was allocated to goodwill. Goodwill is tested for impairment at least annually, or whenever events or circumstances occur that indicate impairment might have occurred in accordance with ASC Topic 350, Intangibles — Goodwill and Other. Goodwill relates to the Company’s China segment which focuses on the Company’s primary pharmaceutical distribution market, consisting of the NovaMed business and the legacy China business, which represent a single reporting unit. As of December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company tested its goodwill for impairment by quantitatively comparing the fair value of the reporting unit to its carrying amount - step one of the two-step impairment test. The Company bypassed the optional qualitative screening test in proceeding directly to step one of the two-step impairment test. In addition, during the third quarter of fiscal 2013, the Company performed an interim goodwill impairment analysis to determine if the goodwill was impaired as a result of the non-renewal of the Sanofi Aventis S.A. (“Sanofi”) promotional agreements as of December 31, 2013, by comparing the fair value of the reporting unit to its carrying amount. The Company estimates the fair value of the China reporting unit using a discounted cash flow model. This valuation approach considers a number of factors that include, but are not limited to, expected future cash flows, growth rates, discount rates, and requires the Company to make certain assumptions and estimates regarding industry economic factors and future profitability of the Company’s business. If the Company determines that the carrying value of its reporting unit exceeds its fair value, the Company would then calculate the implied fair value of the reporting unit goodwill as compared to its carrying value to determine the appropriate impairment charge. After completing the Company’s impairment review for the reporting unit during the third quarter of 2013, and as of December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, the Company concluded that goodwill was not impaired in any of these years.
Loans Receivable
Loans receivable are due from a single third party (see Note 6). Loans are initially recorded, and continue to be carried, at unpaid principal balances under “other assets” on the consolidated balance sheet. Carried balances are subsequently adjusted for payments of principal or adjustments to the allowance for loan losses to account for any impairment. Interest income is recognized over the term of the loans and is calculated using the simple-interest method, as the loans do not have associated premium or discount. If the loans were to experience impairment, interest income would not be recognized unless the likelihood of further loss was remote.
Although the measurement basis is unpaid principal (as adjusted for subsequent payments or impairment), not fair value, the loans receivable would qualify as Level 3 measurements under the fair value hierarchy due to the presence of significant unobservable inputs related to the counterparty, which is a private entity.
Management considers impairment to exist when, based on current information or factors (such as payment history, value of collateral, and assessment of the counterparty’s current creditworthiness), it is probable that principal and interest payments will not be collected according to the contractual agreements. Management considers a loan payment delinquent when not received by the due date. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, management concluded the loans receivable were not impaired, and there was no allowance for loan losses.
66
Accrued Expenses
The Company makes estimates of its accrued expenses as of each balance sheet date in its consolidated financial statements based on facts and circumstances known to them. Examples of estimated accrued expenses include fees paid to contract research organizations and investigative sites in connection with clinical trials, fees paid to contract manufacturers in connection with the production of materials, and professional services. The Company periodically confirms the accuracy of its estimates with selected service providers and makes adjustments, if necessary, in the periods identified.
Expenses related to clinical trials charged to research and development expense generally are accrued based on estimates of work performed or the level of patient enrollment and activities according to the protocols and agreements. The Company makes adjustments, if necessary, in the periods identified to reflect actual levels of work performed, and such adjustments have historically not been material. The financial terms of these agreements are subject to negotiation and vary from contract to contract and may result in uneven payment flows. Payments under certain contracts depend on factors such as the achievement of certain events, the successful enrollment of patients, and the completion of portions of the clinical trial or similar conditions. The objective of the Company’s accrual policy is to match the recording of expenses to the actual services received and efforts expended. The Company monitors planned protocols, work performed, patient enrollment levels and related activities to the extent possible and adjusts estimates accordingly.
The Company records as liabilities estimated amounts for litigation, claims or other legal actions that are probable and can be reasonably estimated. The likelihood of a material change in these estimated reserves is dependent on the possible outcome of settlement negotiations, regulatory or judicial review and the development of facts and circumstances in extended litigation which could change claims or assessments when both the amount and range of loss on some outstanding litigation is uncertain. The Company discloses in the footnotes to the financial statements when it is unable to make a reasonable estimate of a material liability that is reasonably possible to result from unfavorable outcomes. As events occur, the Company assesses the potential liability related to any pending litigation, claims or other legal actions and adjusts its estimates accordingly. Such adjustments could materially impact its financial statements.
Foreign Currency Translation
The Company translates the assets and liabilities of its foreign subsidiaries stated in local functional currencies to US dollars at the rates of exchange in effect at the end of the period. Revenues and expenses are translated using average rates of exchange in effect during the period. Goodwill, and certain other balances, are generally recorded in the local currency which is the functional currency of the Company’s subsidiaries located in China. As a result, the carrying value of goodwill and certain other balances may fluctuate with the value of the RMB as compared to the US dollar. Gains and losses from the translation of financial statements denominated in foreign currencies are included as a separate component of accumulated other comprehensive income in the statement of stockholders' equity.
The Company records foreign currency transactions at the exchange rate prevailing at the date of the transaction with resultant gains and losses being included in results of operations. Foreign currency transaction losses were $0.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. For the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, foreign currency transaction gains and losses were not significant.
Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, services have been rendered or delivery has occurred, the price to the buyer is fixed or determinable and collectability is reasonably assured.
Product Revenue. The Company recognizes product revenue from selling manufactured ZADAXIN product at the time of delivery. Sales of ZADAXIN to Sinopharm are recognized upon the arrival of a shipment to its destination when title and risk of loss to the product are transferred. The Company also earns product revenue from purchasing medical products from pharmaceutical companies and selling them directly to importers or distributors. The Company recognizes revenue related to these products based on the “sell-in” method, when the medical products have been delivered to the importers or distributors. Payments by the importing agents and distributors are not contingent upon sale to the end user by the importing agents or distributors.
67
Promotion Services Revenue. The Company recognizes promotion services revenue after designated medical products are delivered to the distributors as specified in a promotion services contract, which marks the period when marketing and promotion services have been rendered and the revenue recognition criteria are met. Per the Company’s arrangement with Sanofi, the Company was required to return or refund a portion of promotion services fees received during interim periods if defined annual sales targets were not achieved. Under the Company’s agreements with this customer, if an agreement was terminated, and provided such targets had been met on a “pro rata” basis at the date of contract termination, the Company was entitled to retain the amounts paid. Due to the ability to retain amounts paid upon contract termination, provided applicable targets had been met on a “pro rata” basis at any interim date, the Company elected to recognize revenue during interim periods without reduction for amounts subject to refund based on Method 2 of Accounting Standards Codification 605-20-S99-1, “Accounting for Management Fees Based on a Formula.”
The Company’s promotion agreements with Sanofi, consisting of individual promotional agreements for certain pharmaceutical products and supplementary agreements extending the terms thereof, were not renewed and expired on December 31, 2013. NovaMed Pharmaceuticals (Shanghai) Co. Ltd. (“NovaMed Shanghai”) and Sanofi negotiated a settlement of certain amounts in dispute, effective July 14, 2014, and NovaMed Shanghai received approximately 22 million RMB (approximately $3.5 million) in August 2014 as final payment from Sanofi. The terms of the settlement resulted in the recognition of promotion services revenue for the second quarter of 2014 of approximately $0.2 million of Sanofi revenue that had been deferred in the fourth quarter of 2013. The remaining approximately $2.6 million of deferred revenue originally recorded during the fourth quarter of 2013, was reversed with an equivalent write-down of accounts receivable. This contemporaneous write-down of accounts receivable and deferred revenue had no impact on net income during the second quarter of 2014 or the year ended December 31, 2014.
Revenue Reserve: The Company generally maintains a revenue reserve for product returns based on estimates of the amount of product to be returned by its customers which are based on historical patterns, analysis of market demand and/or a percentage of sales based on industry trends, and management’s evaluation of specific factors that may increase the risk of product returns. Importing agents or distributors do not have contractual rights of return except under limited terms regarding product quality. However, the Company is expected to replace products that have expired or are deemed to be damaged or defective when delivered. The calculation of the revenue reserve requires estimates and involves a high degree of subjectivity and judgment. As a result of the uncertainties involved in estimating the revenue reserve, there is a possibility that materially different amounts could be reported under different conditions or using different assumptions.
As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company’s revenue reserves were $0.1 million on its consolidated balance sheets.
The Company evaluates the need for a returns reserve quarterly and adjusts it when events indicate that a change in estimate is appropriate. Changes in estimates could materially affect the Company’s results of operations or financial position. It is possible that the Company may need to adjust its estimates in future periods.
Sales Tax and Surcharge Expense
Sales taxes and surcharge costs are expensed as incurred and are included in sales and marketing expense. The Company is generally subject to a 5-6.42% business tax and surcharge for services provided related to marketing products under the relevant taxation laws in China. Sales tax and surcharge costs amounted to approximately $3.4 million, $2.5 million, and $3.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development costs are expensed as incurred. These costs include salaries and other personnel-related expenses, including associated stock-based compensation, facility-related expenses, depreciation of facilities and equipment, upfront payments under in-licensing agreements with certain business partners and other license-related fees, and services performed by clinical research organizations and research institutions and other outside service providers.
Shipping and Handling Costs
Shipping and handling costs incurred for inventory purchases and product shipments are included in cost of product sales for all periods presented.
68
Advertising Expenses
Advertising costs are expensed as incurred and are included in sales and marketing expenses for all periods presented. Advertising expenses for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, were $4.1 million, $2.6 million, and $1.1 million, respectively.
Legal Costs
Legal costs related to loss contingencies are expensed to general and administrative expense as incurred.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company records stock-based compensation costs relating to share-based payment transactions, including stock options, restricted stock units (“RSUs”), performance restricted stock units (“PSUs”) and the employee stock purchase plan (“ESPP”). Stock-based compensation expense for stock options and the employee stock purchase plan is estimated at the date of grant based on the fair value of the award using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. Stock-based compensation expense for RSUs and PSUs are estimated at the date of grant based on the number of shares granted and the quoted price of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. Stock-based compensation expense values for stock options, RSUs and the ESPP are recognized as expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period, net of estimated forfeitures. The stock-based compensation costs that are ultimately expected to vest are recognized as expense ratably (as the awards vest) over the requisite service period, which is generally one or four years for stock options and RSUs and three months for the ESPP. The Company estimates pre-vesting forfeitures at the time of grant by analyzing historical data and revises those estimates in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates. The total expense recognized over the vesting period will only be for those awards that ultimately vest. The Company recognizes expense related to the PSUs and performance stock options over the implicit service period if it is probable that the performance goals will be achieved. If it is subsequently determined that the performance goals are not probable of achievement, the expense related to the PSUs or performance stock options is reversed.
Income Taxes
Income taxes are accounted for under the liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the difference between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities as measured by the enacted tax rates that will be in effect when these differences reverse. The Company provides a valuation allowance against net deferred tax assets if, based upon the available evidence, it is more-likely-than-not that the deferred tax assets will not be realized. When the Company establishes or reduces the valuation allowance against its deferred tax assets, its provision for income taxes will increase or decrease, respectively, in the period such determination is made.
The Company records liabilities related to uncertain tax positions in accordance with the guidance that clarifies the accounting for uncertainty in income taxes recognized in an enterprise’s financial statements by prescribing a minimum recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The Company does not believe any such uncertain tax positions currently pending will have a material adverse effect on its consolidated financial statements, although an adverse resolution of one or more of these uncertain tax positions in any period could have a material impact on the results of operations for that period. The Company’s policy is to recognize interest and penalties related to the liabilities for uncertain tax positions as a component of income tax expense. The amount of accrued interest related to tax positions taken on the Company’s tax returns and included in accrued and other current liabilities was $1.7 million and $1.5 million, as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The amount of interest recognized as tax expense related to uncertain tax positions in the consolidated statements of income was $0.2 million, $0.3 million and $0.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Net Income Per Share
Basic net income per share has been computed by dividing net income by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding for the period. Diluted net income per share is computed by dividing net income by the weighted-average number of common equivalent shares outstanding for the period. Diluted net income per share includes any dilutive impact from outstanding stock options, stock awards and the ESPP using the treasury stock method.
69
The following is a reconciliation of the numerator and denominators of the basic and diluted net income per share computations for the years ended December 31 (in thousands, except per share amounts):
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Numerator: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
29,463 |
|
$ |
25,208 |
|
$ |
10,964 |
|
Denominator: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted-average shares outstanding used to compute basic net income per share |
|
|
49,797 |
|
|
51,277 |
|
|
53,587 |
|
Effect of dilutive securities |
|
|
2,376 |
|
|
1,407 |
|
|
1,349 |
|
Weighted-average shares outstanding used to compute diluted net income per share |
|
|
52,173 |
|
|
52,684 |
|
|
54,936 |
|
Basic net income per share |
|
$ |
0.59 |
|
$ |
0.49 |
|
$ |
0.20 |
|
Diluted net income per share |
|
$ |
0.56 |
|
$ |
0.48 |
|
$ |
0.20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, approximately 1,151,537, 3,541,071, and 3,378,063 shares, respectively, related to outstanding stock options were excluded from the calculation of diluted net income per share because the effect from the assumed exercise of these options calculated under the treasury stock method would have been anti-dilutive. In addition, for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, outstanding stock options and awards for 312,500, 50,000, and 50,171 shares, respectively, subject to performance conditions were excluded from the calculation of diluted net income per share because the performance criteria had not been or were not probable to be met.
Segment Information
The Company operates in two segments (refer to Note 20).
Revision
In the consolidated statement of cash flows, the Company reduced the line item “Inventories” and increased the line item “Provision for expiring inventory” in the amount of $0.5 million within the reconciling adjustments to arrive at net cash provided by operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2014 to correct an error in the prior year presentation. This revision had no impact on cash provided by operating activities. The amount of the error was not material to the annual period of 2014.
New Accounting Standards Updates
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update 2014-09, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers" (“ASU 2014-09”), which contains new accounting literature relating to how and when a company recognizes revenue. Under ASU 2014-09, a company will recognize revenue when it transfers promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods and services. ASU 2014-09 is effective for the Company’s fiscal year beginning January 1, 2018, which reflects a one year deferral approved by the FASB in July 2015, with early application permitted provided that the effective date is not earlier than the original effective date. The Company is in the process of determining what impact, if any, the adoption of ASU 2014-09 will have on its financial statements and related disclosures. The standard permits the use of either the full retrospective or modified retrospective transition method. The Company has not yet selected a transition method nor has it determined the effect of the standard on its ongoing financial reporting.
In July 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-11, "Inventory (Topic 330): Simplifying the Measurement of Inventory" (“ASU 2015-11”) which applies to inventory that is measured using first-in, first-out ("FIFO") or average cost. Under the updated guidance, an entity should measure inventory that is within scope at the lower of cost and net realizable value, which is the estimated selling prices in the ordinary course of business, less reasonably predictable costs of completion, disposal and transportation. Subsequent measurement is unchanged for inventory that is measured using last-in, first-out ("LIFO"). This ASU is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and should be applied prospectively with early adoption permitted at the beginning of an interim or annual reporting period. The Company has evaluated the impact of adopting this guidance and has
70
concluded it will likely have no effect on the financial statements as the Company’s adjustments already reflect the concept of net realizable value. Inventory provisions are generally full write-downs for the affected inventory.
In November 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-17, "Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes”. This ASU amends existing guidance to require that deferred income tax liabilities and assets be classified as noncurrent in a classified balance sheet, and eliminates the prior guidance which required an entity to separate deferred tax liabilities and assets into a current amount and a noncurrent amount in a classified balance sheet. The amendments in this ASU are effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those annual periods. Earlier application is permitted as of the beginning of an interim or annual period. Additionally, the new guidance may be applied either prospectively to all deferred tax liabilities and assets or retrospectively to all periods presented. The Company has not yet selected an adoption method. The impact of adopting this guidance is not expected to be material to the consolidated financial statements given the Company’s deferred tax amounts.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02 “Leases”. Under the new guidance, lessees will be required to recognize a lease liability and a lease asset for all leases, including operating leases, with a term greater than 12 months on its balance sheet. The update also expands the required quantitative and qualitative disclosures surrounding leases. This update is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018 and interim periods within those fiscal years, with earlier application permitted. The Company is evaluating the impact of the adoption of this update on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
Note 2 — Available-for-Sale Investment
The Company realized $0.1 million in losses related to the maturity of its Italian state bonds for the year ended December 31, 2013 which were reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income and included in non-operating expenses.
Note 3 — Fair Value Measurements
The following tables represent the Company’s fair value hierarchy for its financial assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis (in thousands):
|
Fair Value Measurements as of December 31, 2015 Using |
|||||||||||||
|
Quoted Prices in |
Significant |
||||||||||||
|
Active Markets |
Other |
Significant |
|||||||||||
|
for |
Observable |
Unobservable |
Balance |
||||||||||
|
Identical Assets |
Inputs |
Inputs |
as of |
||||||||||
|
Description |
(Level 1) |
(Level 2) |
(Level 3) |
December 31, 2015 |
|||||||||
|
Money market funds |
$ |
19,678 |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
19,678 | |||||
|
Total |
$ |
19,678 |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
19,678 | |||||
|
Fair Value Measurements as of December 31, 2014 Using |
|||||||||||||
|
Quoted Prices in |
Significant |
||||||||||||
|
Active Markets |
Other |
Significant |
|||||||||||
|
for |
Observable |
Unobservable |
Balance |
||||||||||
|
Identical Assets |
Inputs |
Inputs |
as of |
||||||||||
|
Description |
(Level 1) |
(Level 2) |
(Level 3) |
December 31, 2014 |
|||||||||
|
Certificate of deposit |
$ |
— |
$ |
75 |
$ |
— |
$ |
75 | |||||
|
Money market funds |
19,678 |
— |
— |
19,678 | |||||||||
|
Total |
$ |
19,678 |
$ |
75 |
$ |
— |
$ |
19,753 | |||||
71
Note 4 — Inventories
Inventories consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
December 31, |
||||||
|
2015 |
2014 |
|||||
|
Raw materials |
$ |
3,871 |
$ |
5,009 | ||
|
Work in progress |
535 | 761 | ||||
|
Finished goods |
6,570 | 4,933 | ||||
|
Total |
$ |
10,976 |
$ |
10,703 | ||
As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company had $3.3 million and $3.1 million, respectively, in inventory held at distributors related to non–ZADAXIN products.
Note 5 — Property and Equipment
Property and equipment consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
December 31, |
||||||
|
2015 |
2014 |
|||||
|
Construction in process |
$ |
18 |
$ |
30 | ||
|
Office equipment |
3,172 | 2,059 | ||||
|
Leasehold improvements |
1,281 | 791 | ||||
|
Office furniture and fixtures |
1,377 | 1,463 | ||||
|
Software |
897 | 763 | ||||
|
Vehicle |
67 | 70 | ||||
|
Gross property and equipment |
6,812 | 5,176 | ||||
|
Less accumulated depreciation |
(4,161) | (3,328) | ||||
|
Net property and equipment |
$ |
2,651 |
$ |
1,848 | ||
Depreciation expense was $0.9 million for each of the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013.
Note 6 — Loans Receivable
As part of the Company’s May 2013 license and supply agreement with Zensun (Shanghai) Science & Technology Co. Ltd (“Zensun”), the Company previously agreed to loan up to $12 million to Zensun. The entry into the license and supply agreement in the second quarter of 2013, pursuant to which the Company licensed the exclusive rights to promote, market, distribute, and sell NeucardinTM, a chronic heart failure product under development by Zensun (such rights licensed for the People’s Republic of China, Hong Kong and Macao) is more fully described in Note 16.
Pursuant to its agreement to loan funds, the Company loaned $12 million to Zensun. The extension of credit and funding to Zensun was accomplished through two of the Company's subsidiaries, SPIL China, and SciClone Pharmaceuticals (China) Ltd. (“SciClone China”).
With respect to lender SciClone China, Zensun can make RMB-denominated borrowings for up to RMB 1,550,000 using an entrustment mechanism with a bank as an intermediary. In the third quarter of 2014, SciClone China entered into an entrusted loan agreement for RMB 1,550,000 (approximately US$239,000 as of December 31, 2015) with Zensun, using a major Chinese bank as the lending agent. SciClone China is the principal and ultimately bears the credit risk, not the bank. The loan bears interest at a fixed rate of 7.5% per annum and Zensun is subject to obligations of the borrower as specified in the loan agreements. The loan term is sixty-six months. All outstanding principal and interest balances must be repaid by the maturity date, with prepayments permitted without penalty upon prior notice.
With respect to lender SPIL China, Zensun could request US-dollar denominated borrowings up to $11.75 million. As of December 31, 2015, borrowings totaling $11.75 million had been requested by Zensun and paid by SPIL China with $4.5 million lent in the second half of 2014 and $7.25 million lent in the second quarter of 2015. These borrowings bear interest at a fixed rate of 7.5%
72
per annum payable annually in arrears at each interest payment date as defined in the overall loan agreement. These borrowings mature on September 26, 2017, with an option electable by Zensun to extend for two additional years provided certain conditions are met. All outstanding balances must be repaid by the maturity date, with prepayments permitted without penalty upon prior notice.
The proceeds of the separate but related loans are to be used for working capital and general corporate purposes by Zensun. To secure the loans, Zensun pledged its entire equity interest in its subsidiary, Shanghai Dongxin Biochemical Technology Co. Ltd. (whose assets include real property) to SPIL China.
Management, on the basis of (i) a creditworthiness evaluation using recent Zensun financial information, (ii) consideration of evidence of the market value of the pledged security indicating such market value exceeded the outstanding loan principal, and (iii) consideration of Zensun’s compliance with the terms of the loans and timely payments of interest, concluded there were no indications of loan impairment at December 31, 2015 or 2014; accordingly, there is no allowance for losses.
The two loans are included in “other assets” on the Company’s consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2015 and 2014. Interest income on the loans amounted to $0.8 million and $0.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, and is included in interest and investment income in the consolidated statements of income. The Company estimates the fair value of the loans receivable approximates $12.7 million as of December 31, 2015, based upon prevailing market rates of interest as published by major Chinese banks.
Note 7 — Goodwill
The following table represents the changes in goodwill for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 (in thousands):
|
Balance as of January 1, 2013 |
$ |
34,313 |
|
Translation adjustments |
1,044 | |
|
Balance as of December 31, 2013 |
$ |
35,357 |
|
Translation adjustments |
(836) | |
|
Balance as of December 31, 2014 |
$ |
34,521 |
|
Translation adjustments |
(1,542) | |
|
Balance as of December 31, 2015 |
$ |
32,979 |
Note 8 — Accrued Liabilities
The following is a summary of accrued liabilities (in thousands):
|
December 31, |
||||||
|
2015 |
2014 |
|||||
|
Accrued sales and marketing expenses |
$ |
8,511 |
$ |
5,383 | ||
|
Accrued taxes, tax reserves and interest |
4,323 | 5,208 | ||||
|
Accrued compensation and benefits |
4,341 | 4,176 | ||||
|
Accrued SEC settlement loss (Notes 18 and 22) |
12,826 | 2,000 | ||||
|
Accrued professional fees |
1,130 | 1,819 | ||||
|
Accrued license fee |
— |
1,000 | ||||
|
Accrued manufacturing costs |
444 | 95 | ||||
|
Other |
576 | 855 | ||||
|
Total |
$ |
32,151 |
$ |
20,536 | ||
Note 9 — Escrow Settlement Agreement
On October 16, 2012, the Company made a claim against the former stockholders of NovaMed pursuant to the acquisition agreement relating to its acquisition of NovaMed. As a result of the Company’s claim, approximately $1.4 million in cash that was held in escrow and 622,363 shares of the Company’s common stock that were held in escrow were not released to the former NovaMed stockholders pending the outcome of the Company’s claim. The claim related to damages the Company incurred as a result of misrepresentations made by NovaMed regarding various matters, including the estimated product return reserves for Aggrastat
73
product on the date of the acquisition, and related expenses and damages. On July 8, 2013, the Company and the representatives of the former stockholders of NovaMed entered into a “Confidential Escrow Settlement Agreement” pursuant to which the Company retained approximately $0.8 million in cash and 342,300 shares of its common stock, having a combined value of approximately $2.6 million on the settlement date that was recorded to other income during the year ended December 31, 2013. As of December 31, 2013, the Company had canceled and retired the shares.
Note 10 — Commitments
Purchase Obligations
Under agreements with certain of the Company’s pharmaceutical partners, the Company is committed to certain annual minimum product purchases where the contract is subject to termination if the annual minimum order is not met. As of December 31, 2015, the Company did not have any material unmet purchase obligations.
Leases
In May 2007, the Company entered into a non-cancelable operating lease agreement for its corporate headquarters ("the Lease”) effective from July 1, 2007 through June 30, 2014. In September 2008, the Company entered into an amendment to the Lease for additional office space (“the Amendment”) that expired on June 30, 2014. Both the Lease and Amendment contained rent escalations of approximately 4% and 6% per year, respectively. In December 2013, the Company entered into a second amendment to the Lease extending the term of the lease for an additional four years through June 30, 2018, with an option to renew for an additional five year period. Beginning on July 1, 2014, the second amendment reduced the amount of leased office space from approximately 21,517 square feet leased to approximately 11,886 square feet. It also reduced the monthly base rent of $120,824 to $51,704 in the first year, with rent escalations of approximately 3% per year. In addition, the Company received a rent abatement for the first four months of the extended lease term.
The Company is recognizing the rental expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term. Under the terms of the Lease and the Amendment, the Company was provided allowances in the amounts of approximately $0.2 million and $0.5 million, respectively, towards the cost of its leasehold improvements and as an incentive to rent, respectively. The Company has recorded these allowances as deferred rent which is being amortized over the lease term as a reduction of rent expense. The Lease requires the Company to pay insurance and taxes and its pro-rata share of operating expenses.
In June 2014, the Company entered into a non-cancelable operating lease agreement for its primary office space in China (“the China Lease”) for a fixed lease term from October 15, 2014 through April 14, 2018, with options to renew for an additional two years. The Company is recognizing the rental expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term. The leases require the Company to pay insurance and its pro-rata share of operating expenses.
The Company also leases other office facilities and equipment outside the US under non-cancelable operating lease agreements. Through May 2014, the Company also subleased certain office facilities to a third party. Rent expense for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, was $2.1 million, $2.2 million, and $2.9 million, respectively, net of sublease income. Future minimum lease payments under non-cancelable facility and equipment operating lease agreements as of December 31, 2015, were as follows (in thousands):
|
Minimum Lease |
||||
|
Year ended: |
Payments |
|||
|
2016 |
$ |
2,421 | ||
|
2017 |
2,013 | |||
|
2018 |
766 | |||
|
2019 |
— |
|||
|
2020 |
— |
|||
|
$ |
5,200 | |||
Note 11 — Restructuring Charges
In December 2013, the Company announced a plan to significantly reduce its workforce by approximately 175 employees, from approximately 650 full-time employees, primarily in sales and marketing that were included in the Company's China segment. The restructuring was decided as a result of the non-renewal of the Company’s distribution agreement with Sanofi as of December 31,
74
2013. The decision resulted in severance-related charges of approximately $1.2 million recognized to restructuring expense in the consolidated statement of income for the year ended December 31, 2013.
Note 12 — Income Taxes
The Company recorded income tax provisions of $0.8 million, $1.2 million, and $2.2 million, for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively, related to its operations in China. Tax expense decreased for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, compared to 2013, mainly related to a reduction in the Company’s liabilities (and associated accrued interest) for uncertain tax positions in China due to certain tax years becoming closed to assessment due to the statute of limitations and as a result of lower taxable income related to its China operations. The Company’s statutory tax rate in China was 25% in 2015, 2014 and 2013. The Company has not recorded any significant US federal or state income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013.
During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015, the Company repatriated a special dividend distribution of $12.8 million from its foreign subsidiary related to the SEC settlement expense (as further described in Note 18) from the current year earnings and profits of its foreign subsidiaries, which were not part of the cumulative pool of undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014. The Company recorded US federal income taxes for this income as a component of the 2015 income tax provision; however, the net effect of the special dividend distribution on the 2015 income tax provision was zero as the incremental taxable income (as well as the nondeductible applicable SEC settlement expenses) were fully offset by deductible operating expenses. The Company determined that as of December 31, 2015, $176.2 million of accumulated undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries, exclusive of the dividend repatriation which was entirely satisfied out of current year earnings and profits, continues to be indefinitely reinvested outside of the US. Accordingly, taxes have not been provided on this amount of accumulated undistributed earnings. Upon any distribution of accumulated undistributed earnings, the Company may be subject to US federal and state income taxes, although determining the amount is not practicable as it is dependent on a variety of factors, including, but not limited to, the amounts of US tax loss carryforwards and tax credit carryforwards available at the time of the repatriation.
Based on the Company’s current liquid resources and future operating plan, it does not need to repatriate undistributed earnings held by foreign subsidiaries accumulated through December 31, 2015. However, to meet future operating needs, the Company does anticipate repatriating a portion of future annual foreign earnings in a forthcoming annual period. The Company plans to accrue for US income taxes on future foreign earnings that it anticipates repatriating from its foreign subsidiaries beginning in 2016. However, the Company has significant accumulated net operating loss and tax credit carryforwards available to offset any tax liability on a dividend distribution from its foreign subsidiaries.
The domestic and foreign components of income (loss) before provision for tax for the years ended December 31 are as follows (in thousands):
|
2015 |
2014 |
2013 |
|||||||
|
Domestic |
$ |
(17,017) |
$ |
(8,496) |
$ |
(17,168) | |||
|
Foreign |
47,287 | 34,873 | 30,374 | ||||||
|
Pre-tax income |
$ |
30,270 |
$ |
26,377 |
$ |
13,206 | |||
A reconciliation of tax at the statutory federal income tax rate of 34% to the actual tax provision for the years ended December 31 is as follows (in thousands):
|
2015 |
2014 |
2013 |
|||||||
|
Tax at federal statutory rate |
$ |
10,382 |
$ |
8,968 |
$ |
4,490 | |||
|
Foreign income taxed at different rates |
(15,210) | (10,788) | (8,383) | ||||||
|
Federal tax effect of dividend from foreign subsidiary |
4,317 |
— |
— |
||||||
|
Effect of uncertain tax positions |
(126) | 127 | 297 | ||||||
|
Change in valuation allowance |
1,092 | 2,672 | 5,254 | ||||||
|
Stock-based compensation |
(86) | 2 | (87) | ||||||
|
Non deductible expenses |
189 | 189 | 670 | ||||||
|
Other |
249 | (1) | 1 | ||||||
|
Provision for income tax |
$ |
807 |
$ |
1,169 |
$ |
2,242 | |||
75
The provision for income taxes for the years ended December 31 consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
2015 |
2014 |
2013 |
|||||||
|
Federal |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
|||
|
State |
1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
|
Foreign |
793 | 1,489 | 2,032 | ||||||
|
Total current |
794 | 1,490 | 2,033 | ||||||
|
Federal |
— |
— |
— |
||||||
|
State |
— |
— |
— |
||||||
|
Foreign |
13 | (321) | 209 | ||||||
|
Total deferred |
13 | (321) | 209 | ||||||
|
Provision for income tax |
$ |
807 |
$ |
1,169 |
$ |
2,242 | |||
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes.
Significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities as of December 31 are as follows (in thousands):
|
2015 |
2014 |
||||||||
|
Deferred tax assets: |
|||||||||
|
Net operating loss carryforwards |
$ |
38,679 |
$ |
37,513 | |||||
|
Research and development credit carryforwards |
10,650 | 10,615 | |||||||
|
Intangibles |
382 | 395 | |||||||
|
Other |
2,692 | 2,527 | |||||||
|
Gross deferred tax assets |
52,403 | 51,050 | |||||||
|
Valuation allowance |
(52,104) | (50,724) | |||||||
|
Total deferred tax assets |
299 | 326 | |||||||
|
Deferred tax liabilities: |
|||||||||
|
Other |
— |
— |
|||||||
|
Total deferred tax liabilities |
— |
— |
|||||||
|
Net deferred tax assets |
$ |
299 |
$ |
326 | |||||
Realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the Company generating future taxable income, the timing and amount of which are uncertain. Accordingly, the deferred tax assets have been largely offset by a valuation allowance. The valuation allowance increased by approximately $1.4 million, $3.4 million, and $4.4 million, in the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. Approximately $3.8 million of the valuation allowance relates to benefits associated with stock option deductions that, when recognized, will be credited directly to stockholders' equity.
As of December 31, 2015, the Company had US federal net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $114.2 million that expire in the years 2020 through 2035, and US federal research and development, orphan drug and investment tax credit carryforwards of approximately $12.2 million that expire in the years 2018 through 2035. As of December 31, 2015, the Company had approximately $52 million in net operating loss carryforwards related to its NovaMed Shanghai subsidiary that expire in the years 2016 through 2020. As of December 31, 2015, the Company had state net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $25.9 million that expire in the years 2016 through 2030, if not utilized, and state research and development tax credit carryforwards of approximately $2.2 million that do not expire.
Utilization of the Company’s net operating loss and credit carryforwards may be subject to substantial annual limitation due to the ownership change limitations provided by the Internal Revenue Code and similar state provisions. Such annual limitation could result in the expiration of the net operating loss and credit carryforwards before utilization.
As of December 31, 2015, the unrecognized tax benefit was $5.5 million, of which $1.8 million, if recognized would affect the effective tax rate, and $3.7 million, if recognized, would be offset by a change in the valuation allowance. Accrued interest associated with the liability for unrecognized tax benefits was $1.7 million as of December 31, 2015. A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefit for the years ended December 31 is as follows (in thousands):
76
|
2015 |
2014 |
2013 |
|||||||
|
Balance beginning of period |
$ |
5,876 |
$ |
6,138 |
$ |
6,053 | |||
|
Tax positions related to current year: |
|||||||||
|
Additions for current year items |
14 | 32 | 36 | ||||||
|
Additions for prior year items |
— |
— |
88 | ||||||
|
Lapse of statute of limitations |
(288) | (206) | (115) | ||||||
|
Changes for foreign currency translation |
(132) | (88) | 76 | ||||||
|
Balance end of period |
$ |
5,470 |
$ |
5,876 |
$ |
6,138 | |||
Tax years 1995-2015 remain open to examination by the major US taxing jurisdictions to which the Company is subject. The Internal Revenue Service concluded its examinations of the Company’s 2011, 2009 and 2008 US federal tax returns with no additional tax assessments or proposed adjustments relating to taxable income for any years. The Company’s China operations are generally subject to examination under China tax law for a period of five years and those five years remain open for examination. The outcome of income tax examinations is uncertain, and the amounts ultimately paid, if any, on resolution of any issues raised by the taxing authorities may differ materially from the amounts accrued for each year. The Company anticipates that its liability for unrecognized tax benefits will decrease over the next 12 months on account of expiries of statutes of limitations associated with certain tax jurisdictions, and that such decreases will favorably impact the effective tax rate.
Note 13 — Stockholders’ Equity
Stock Award Plans
The Company’s 2015 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2015 Plan”) became effective on June 11, 2015 and superseded the 2005 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2005 Plan”) and the 2004 Outside Directors Stock Option Plan (the “2004 Director Plan”), when those plans terminated upon the adoption of the 2015 Plan. The 2015 Plan authorizes the Company to issue up to 6,550,000 shares increased by not more than 3,000,000 additional shares that were subject to options and other awards outstanding under the 2005 Plan and 2004 Director Plan, to the extent that such awards expire or are forfeited for any reason after the effective date of the 2015 Plan. The 2015 Plan permits the grant of incentive stock options, nonstatutory stock options, RSUs, PSUs and other forms of equity compensation. Under the 2015 Plan, options are exercisable upon conditions determined by the Board of Directors and expire ten years from the date of grant. Options have exercise prices equal to the grant date fair market value of a share of Company common stock and vest over time, generally four years, or on achievement of certain performance conditions. See Stock-Based Compensation.
The Company’s 2005 Plan had authorized up to 13,600,000 shares of common stock for issuance. The 2005 Plan permitted the grant of incentive stock options, nonstatutory stock options, RSUs, PSUs and other forms of equity compensation. Under the terms of the 2005 Plan, options are exercisable upon conditions determined by the Board of Directors and expire ten years from the date of grant. Options have exercise prices equal to the grant date fair market value of a share of Company common stock and vest over time, generally four years, or on achievement of certain performance conditions. See Stock-Based Compensation. As of December 31, 2015, no shares of common stock were available for future issuance of new awards under the 2005 Plan. Although the 2005 Plan has terminated, the outstanding stock options relating to it are fully valid and are governed by the terms of the 2005 Plan.
The Company’s 2004 Director Plan authorized up to 1,765,000 shares of common stock for issuance. The 2004 Director Plan automatically granted nonqualified stock options to nonemployee directors on their appointment or first election to the Company’s Board of Directors (“Initial Grant”) and annually on their reelection to the Board of Directors at the Company’s Annual Meeting of Stockholders (“Annual Grant”). Under the 2004 Director Plan, options have exercise prices equal to the grant date fair market value of a share of Company common stock and expire ten years from the date of grant. Initial Grants became exercisable in three equal annual installments beginning on the first anniversary of the date of grant, and Annual Grants became exercisable in twelve equal monthly installments from the date of grant, subject in each case to the Director’s continuous service on the Company’s Board of Directors. As of December 31, 2015, no shares of common stock were available for future issuance of new awards under the 2004 Director Plan. Although the 2004 Director Plan has terminated, the outstanding stock options relating to it are fully valid and are governed by the terms of the 2004 Director Plan.
Certain stock option awards are subject to accelerated vesting if there is a change in control.
77
The Company issues new shares on exercise of stock options, for release of RSUs and PSUs and for issuance of stock under its ESPP.
Stock-Based Compensation
The following table summarizes the stock-based compensation expenses included in the Company’s consolidated statements of income (in thousands):
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
|
2015 |
2014 |
2013 |
|||||||
|
Sales and marketing |
$ |
869 |
$ |
1,031 |
$ |
1,113 | |||
|
Research and development |
210 | 104 | 122 | ||||||
|
General and administrative |
3,362 | 2,330 | 2,772 | ||||||
|
$ |
4,441 |
$ |
3,465 |
$ |
4,007 | ||||
Compensation cost capitalized in inventory was approximately $0.1 million for each of the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013. There has been no income tax benefit recognized in the income statement for share-based compensation arrangements as the arrangements relate to an entity with accumulated and ongoing tax net operating losses.
Valuation Assumptions
The fair value of awards granted under the Company’s stock option and ESPP plans is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option valuation model with the following weighted-average assumptions for the years ended December 31:
|
2015 |
2014 |
2013 |
||||||
|
Risk-free interest rate: |
||||||||
|
Time-based stock options |
1.52 |
% |
1.61 |
% |
1.02 |
% |
||
|
Performance-based stock options |
N/A |
N/A |
1.22 | |||||
|
ESPP |
0.07 | 0.04 | 0.06 | |||||
|
Volatility factor of the market price of the Company's common stock: |
||||||||
|
Time-based stock options |
52.08 |
% |
57.96 |
% |
64.12 |
% |
||
|
Performance-based stock options |
N/A |
N/A |
63.20 | |||||
|
ESPP |
53.73 | 42.50 | 37.36 | |||||
|
Weighted-average expected life (years): |
||||||||
|
Time-based stock options |
5.30 | 5.00 | 5.10 | |||||
|
Performance-based stock options |
N/A |
N/A |
5.04 | |||||
|
ESPP |
0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | |||||
|
Dividend yield |
0.00 |
% |
0.00 |
% |
0.00 |
% |
||
The risk-free interest rate is based on the US Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant. The expected dividend yield is based on the Company’s history and expectations of no dividend payouts. Expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of the Company’s stock. The expected term of options granted is derived from historical data on employee exercises and terminations.
78
Stock Options
The following table summarizes stock option activity as of December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, and changes during the years then ended are presented below (in thousands, except per share and term amounts):
|
Options Outstanding |
|||||||||
|
Weighted- |
Weighted- |
||||||||
|
Average |
Average |
||||||||
|
Number |
Exercise |
Remaining |
Aggregate |
||||||
|
of |
Price Per |
Contractual |
Intrinsic |
||||||
|
Shares |
Share |
Term (Years) |
Value |
||||||
|
Balance as of January 1, 2013 |
5,998 |
$ |
4.05 | 6.06 |
$ |
5,575 |
|||
|
Options forfeited |
(966) | 5.45 | |||||||
|
Options granted |
1,637 | 4.76 | |||||||
|
Options exercised |
(574) | 2.82 | |||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2013 |
6,095 |
$ |
4.14 | 5.66 |
$ |
7,199 |
|||
|
Options forfeited |
(705) | 5.10 | |||||||
|
Options granted |
1,740 | 4.85 | |||||||
|
Options exercised |
(1,233) | 4.43 | |||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2014 |
5,897 |
$ |
4.17 | 6.08 |
$ |
27,066 |
|||
|
Options forfeited |
(262) | 5.77 | |||||||
|
Options granted |
1,414 | 8.83 | |||||||
|
Options exercised |
(1,022) | 4.48 | |||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2015 |
6,027 |
$ |
5.14 | 6.07 |
$ |
24,462 |
|||
|
Vested and expected to vest after December 31, 2015 |
5,564 |
$ |
4.97 | 5.84 |
$ |
23,556 |
|||
|
Exercisable as of December 31, 2015 |
3,600 |
$ |
3.91 | 4.35 |
$ |
19,030 |
|||
During 2013, the Company extended the period in which two of the Company’s Board members could exercise their outstanding vested stock options following the cessation of their service to the Company from ninety days to the second anniversary of the date of cessation of service which was on June 27, 2013. The Company recorded expense of approximately $0.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2013 related to these modifications. In addition, the Company extended the period in which two former employees of the Company could exercise their outstanding vested stock options following the cessation of their service to the Company from ninety days to the one year anniversary of the date of cessation of their services. The Company recorded expense of approximately $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2013 related to these modifications.
The Company has granted certain performance-based options to purchase shares of the Company’s common stock at an exercise price equal to the closing price of a share of the Company’s common stock as of the grant date. The options will fully vest on meeting a performance goal within an established time frame. If the performance goal is met for the option within the established time frame, the option generally has a ten-year term measured from the date of grant. If the performance goal is not met within the established time frame, the option expires in its entirety. The Company recognizes expense related to a performance-based option over the period of time the Company determines that it is probable that the performance goal will be achieved. If it is subsequently determined that the performance goal is not probable of achievement, the expense related to the performance-based option is reversed. For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, the Company recognized approximately $20,000, $0.1 million, and $39,000, respectively, of expense related to performance-based options.
The weighted-average fair value of stock options granted for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, was $4.18, $2.43, and $2.56, respectively. The intrinsic value of options at time of exercise was $4.7 million, $2.4 million, and $1.3 million, for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. The estimated fair value of options vested for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013 was $3.9 million, $3.2 million, and $3.8 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2015, unamortized compensation expense related to unvested options was approximately $5.5 million, net of forfeitures. The weighted average period over which compensation expense related to these options will be recognized is approximately 2.45 years. Cash received from stock option exercises was $4.6 million, $5.5 million, and $1.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively.
79
RSUs and PSUs
The following table summarizes RSU and PSU activity as of December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013 and changes during the years then ended are presented below (in thousands):
|
RSUs and PSUs |
|||||||||
|
Outstanding |
|||||||||
|
Number |
Aggregate |
||||||||
|
of |
Intrinsic |
||||||||
|
Shares |
Value |
||||||||
|
Balance as of January 1, 2013 |
260 |
$ |
1,121 |
||||||
|
Awarded |
170 | ||||||||
|
Vested/Released |
(39) | ||||||||
|
Forfeited |
(23) | ||||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2013 |
368 |
$ |
1,857 |
||||||
|
Awarded |
7 | ||||||||
|
Vested/Released |
(212) | ||||||||
|
Forfeited |
(4) | ||||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2014 |
159 |
$ |
1,393 |
||||||
|
Awarded |
688 | ||||||||
|
Vested/Released |
(105) | ||||||||
|
Forfeited |
— |
||||||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2015 |
742 |
$ |
6,822 |
||||||
|
Vested and expected to vest after December 31, 2015 |
552 |
$ |
5,077 |
||||||
|
Exercisable as of December 31, 2015 (Vested and deferred) |
— |
— |
|||||||
The RSUs generally vest 25% approximately one year after grant date with the remaining shares vesting either approximately annually or quarterly in equal installments over a three-year period, depending on the terms of the grant. The PSUs will vest and be released on meeting specified performance goals (including revenue and product expansion targets) within an established time frame. If the performance goals are not met within the established time frame, the PSUs will expire. The Company recognizes expense related to the PSUs over the implicit service period if it is probable that the performance goals will be achieved. If it is subsequently determined that the performance goals are not probable of achievement, the expense related to the PSUs is reversed. For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company recorded approximately $0.1 million, $0 and $0, respectively, of expense related to the PSUs. The weighted average fair value at grant date of the RSUs and PSUs was $8.95, $4.52, and $4.98, for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. As of December 31, 2015, there was approximately $2.5 million of unrecognized compensation cost, net of forfeitures, related to non-vested RSUs and PSUs, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average remaining period of approximately 2.1 years.
ESPP
As of December 31, 2015, 1,300,000 shares of the Company’s common stock are reserved for issuance under the Company’s ESPP that expires July 25, 2016. Under the terms of the ESPP, eligible employees may choose to have up to 15% of their salary withheld to purchase the Company's common stock and may purchase up to 1,000 shares per offering period. Each offering under the ESPP is for a three-month period. The purchase price of the stock issued under the ESPP will be equal to 85% of the lower of the fair market value of a share of common stock on the first day of the offering or on the final day of the offering period. As of December 31, 2015, 432,795 shares of common stock were available for issuance under the ESPP.
Repurchase of Common Stock
The Company’s Board of Directors authorized an $80.5 million share repurchase program that expired December 31, 2015. The Company repurchased and retired 1,526,306, 3,822,434, and 2,404,034, shares at a cost of $12.8 million, $24.4 million, and $12.5 million, during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. As of December 31, 2015, the Company had repurchased $78.1 million of the $80.5 million share repurchase program authorized by the Board for share repurchases.
80
Repurchased shares have been retired and constitute authorized but unissued shares. Upon repurchase, the Company eliminated the par value associated with the retired shares, and the excess price of the repurchase above par value was charged to retained earnings (accumulated deficit).
Stockholder Rights Agreement
On December 18, 2006, the Company’s Board of Directors declared a dividend distribution of one Preferred Stock Purchase Right (collectively, the “Rights”) for each outstanding share of the Company’s Common Stock, each Right which entitles the registered holder to purchase from the Company one one-thousandth of a share of the Company’s Series D Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value, at a price of $25.00 pursuant to a Rights Agreement dated as of December 19, 2006, between the Company and Mellon Investor Services LLC (the “Rights Agreement”). The Rights, which will initially trade with the Common Stock, become exercisable when a person or group acquires 15% or more of the Company’s Common Stock without prior Board approval. In that event, the Rights permit the Company’s stockholders, other than the acquirer, to purchase the Company’s Common Stock having a market value of twice the exercise price of the Rights, in lieu of the Preferred Stock. Alternatively, when the Rights become exercisable, the Company’s Board of Directors may authorize the issuance of one share of the Company’s Common Stock in exchange for each Right that is then exercisable. In addition, in the event of certain business combinations, the Rights permit the purchase of the Common Stock of an acquirer at a 50% discount. Rights held by the acquirer will become null and void in each case. Prior to a person or group acquiring 15%, the Rights can be redeemed for $0.001 each by action of the Board. The Rights expire on December 19, 2016. The Rights Agreement includes a requirement that a committee of independent directors evaluate the Rights Agreement at least every three years.
Note 14 — Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Changes in the composition of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013 are as follows (in thousands):
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Currency |
|
Available-for-Sale |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Translation |
|
Investments |
|
Total |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balances as of January 1, 2013 |
|
$ |
3,055 |
|
$ |
(67) |
|
$ |
2,988 |
|
Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications |
|
|
1,121 |
|
|
(4) |
|
|
1,117 |
|
Amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) to other (expense) income, net |
|
|
— |
|
|
71 |
|
|
71 |
|
Net other comprehensive income |
|
|
1,121 |
|
|
67 |
|
|
1,188 |
|
Balances as of December 31, 2013 |
|
|
4,176 |
|
|
— |
|
|
4,176 |
|
Other comprehensive loss |
|
|
(912) |
|
|
— |
|
|
(912) |
|
Balances as of December 31, 2014 |
|
|
3,264 |
|
|
— |
|
|
3,264 |
|
Other comprehensive loss |
|
|
(1,194) |
|
|
— |
|
|
(1,194) |
|
Balances as of December 31, 2015 |
|
$ |
2,070 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
2,070 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note 15 — 401(k) Plan
The Company has a pre-tax savings plan covering most US employees, which qualifies under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code. Under the plan, eligible employees may contribute a portion of their pre-tax salary, subject to certain limitations. The Company contributes and matches 50% of the employee contributions. Company contributions, which can be terminated at the Company's discretion, were approximately $0.2 million, $0.1 million, and $0.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively.
81
Note 16 — Licensing Agreements
Theravance Biopharma, Inc. (“Theravance Biopharma”)
In May 2015, Theravance Biopharma granted the Company exclusive development and commercialization rights to VIBATIV® (telavancin) in China, as well as the Hong Kong SAR, the Macau SAR, Taiwan and Vietnam, in exchange for upfront and regulatory milestone payments totaling $6 million. SciClone will be responsible for all aspects of development and commercialization in the partnered regions, including pre- and post-launch activities and product registration. Theravance Biopharma will sell to SciClone all clinical and commercial product required to develop and commercialize VIBATIV in China and the Company’s other licensed territories.
The Medicines Company
In December 2014, the Company entered into a strategic partnership for two cardiovascular products in China. The partnership includes an agreement granting SciClone a license and the exclusive rights in China to promote two products of The Medicines Company including Angiomax® (bivalirudin) for Injection for which a Phase 3 registration trial was completed in China and is currently under review by the China Food and Drug Administration for marketing approval, and Cleviprex® (clevidipine) Injectable Emulsion, for which a clinical trial application (CTA) for China was filed in 2013. Under the terms of the agreement, SciClone will be responsible for all aspects of commercialization, including pre-and post-launch activities, for both products in the China market (excluding Hong Kong and Macao). SciClone has also agreed to participate in the China registration process for both products. Financial terms of the agreement, in addition to net sales royalties payable to The Medicines Company, include the following additional payments to The Medicines Company: an upfront payment; a product support services fee; and regulatory/commercial success milestone payments of up to an aggregate of $50.5 million.
Zensun
On May 13, 2013, the Company, through a designated affiliate, entered into a framework agreement with Zensun for the exclusive promotion, marketing, distribution and sale of NeucardinTM in China, Hong Kong and Macao. Neucardin is a novel, first-in-class therapeutic for the treatment of patients with intermediate to advanced heart failure, for which a New Drug Application was submitted to and accepted for review by the China Food and Drug Administration (“CFDA”) in 2012. The China Food and Drug Administration informed Zensun in 2014 that its Phase 2 clinical study data is insufficient, and has asked Zensun to submit a New Drug Application once the ongoing Phase 3 clinical study reaches its endpoints.
The Zensun framework agreement provides the principal terms of the arrangement and the two parties have also entered into a supplemental license and supply agreement.
Subject to certain conditions, the Company has agreed to make payments of up to $18.5 million to Zensun, consisting of an upfront payment amount and further amounts on the achievement of certain milestones, including the approval of a new drug application for Neucardin™, the granting of a manufacturing license, good manufacturing practices certificate and drug approval number in China. The Company has agreed under certain conditions to make milestone payments to Zensun of $10 million if approval is received for a new device to deliver Neucardin™ and up to $25 million if approval is received for the use of Neucardin™ in additional indications.
Zensun will be responsible for manufacture of the product and the Company has agreed to purchase the product exclusively from Zensun for the duration of the agreement.
In addition, the Company agreed to provide a collateralized loan to Zensun of up to approximately $12.0 million. Refer to Note 6 “Loans Receivable” for further information on the loans to Zensun.
Taiwan Liposome Company (“TLC”)
In June 2013, the Company entered into an agreement with TLC granting the Company a license and the exclusive rights in China, Hong Kong and Macao to promote, market, distribute and sell ProFlow® for the treatment of peripheral arterial disease (“PAD”) and other indications. Under the terms of the agreement, TLC will be responsible for the continued development, including potential clinical trials and regulatory activities, as well as the manufacture and supply of ProFlow, and the Company will be
82
responsible for all aspects of commercialization including pre-and post-launch activities. In November 2014, TLC was notified by the CFDA that ProFlow did not receive clinical trial approval and TLC is in the process of appealing the decision.
The agreement provides for the principal terms of the arrangement between SciClone and TLC, and in March 2014, the companies entered into a collaboration and license agreement. Financial terms of the agreement include clinical and regulatory milestone payments and sales milestone payments up to an aggregate of $39.5 million.
For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company recorded upfront and milestone payments totaling $7.5 million, $11.0 million and $5.0 million, respectively, in research and development expense related to its licensing arrangements.
Note 17 — Termination of Collaboration with Cardiome Pharma Corp. (“Cardiome”)
In August 2015, Cardiome, from whom the Company licensed marketing and commercialization rights to the heart medication Aggrastat®, and the Company mutually agreed to end their collaboration for Aggrastat and terminate the Company’s exclusive distributorship in China for the product, resulting in the Company’s obligation to return all rights to the product to Cardiome. The Company recorded Aggrastat revenues of $1.8 million, $1.1 million, and $0 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively, and the Company does not expect to generate any further Aggrastat revenues.
The terms of the agreement include up to $750,000 in transition payments to be received by the Company from Cardiome over approximately a one year period and require Cardiome to repurchase Aggrastat inventory held by the Company at its original purchase price. Transition payments in the amount of $450,000 were collected from Cardiome during the second half of fiscal 2015 and were recorded as a credit to general and administrative expenses. During the fourth quarter of 2015, the Company received $1.1 million from Cardiome for repurchased inventory. The Company recorded the $1.1 million for reimbursement for inventory returned as a reduction in cost of product sales since all of such inventory had previously been written down to zero.
For the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded a liability of $0.6 million, and a corresponding offset to revenue and cost of goods sold, related to Aggrastat product due to expire in mid-2016 that it expects to repurchase from its customer in connection with the termination of its agreement with Cardiome. Under the terms of the agreement, Cardiome is not obliged to repurchase this inventory already sold to the Company’s distributors. The Company does not expect to resell this inventory.
Note 18 — Contingencies
Legal Matters
The Company is a party to various legal proceedings and subject to government investigations, as noted in this section below. All legal proceedings and any government investigations are subject to inherent uncertainties, unfavorable rulings or other adverse events which could occur. Unfavorable outcomes could include substantial monetary damages or awards, injunctions or other remedies, and if any of these were to occur, the possibility exists for a material adverse impact on the Company’s business, results of operations, financial position, and overall trends. The Company might also conclude that settling one or more such matters is in the best interests of its stockholders and its business, and any such settlement could include substantial payments.
As previously disclosed, since 2010 the SEC and the US Department of Justice (“DOJ”) had each been conducting formal investigations of the Company regarding a range of matters, including the possibility of violations of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”), primarily related to certain historical sales and marketing activities with respect to the Company’s China operations. In response to these matters, the Company’s Board appointed a Special Committee of independent directors (the “Special Committee”) to oversee its response to the government inquiry. Based on an initial review, the Special Committee decided to undertake an independent investigation as to matters reflected in and arising from the SEC and DOJ investigations in order to evaluate whether any violation of the FCPA or other laws occurred.
The Company previously recorded a charge to operating expenses in the fourth quarter of 2013 in the amount of $2.0 million for the accrual of an estimated loss associated with the SEC and DOJ investigations based on the available information at the time. In the second quarter of 2015, the Company recorded an additional charge to operating expenses of $10.8 million based on an agreement in principle reached with the SEC which had not yet been finalized, bringing the accrued liability to $12.8 million.
83
On October 7, 2015, the Company deposited $12.8 million in an interest-bearing escrow account that it established related to the agreement in principle regarding a proposed settlement of FCPA-related matters with the staff of the SEC, creating a cash restriction at the time of deposit. On February 4, 2016, the Company announced that it has entered into a settlement agreement with the SEC fully resolving the SEC’s investigation into possible violations of the FCPA. Under the terms of the settlement agreement, in February 2016 the Company paid to the SEC a total of $12.8 million which was released from its escrow account, including disgorgement, pre-judgment interest and a penalty as final settlement. This payment is in line with the charges the Company previously recorded and disclosed as summarized above. As part of the agreement the Company neither admitted nor denied engagement in any wrongdoing and the Company agreed to give status reports to the SEC for the next three years on its continued remediation and implementation of anti-corruption compliance measures. The DOJ has also completed its related investigation and has declined to pursue any action.
NovaMed was a party to a Distribution and Supply Agreement with MEDA Pharma GmbH & Co. KG (“MEDA”). Following the Company’s acquisition of NovaMed, MEDA claimed it had a right to terminate the agreement under a change of control provision. NovaMed does not believe that MEDA had a right of termination under the agreement. NovaMed filed an application for binding arbitration with the China International Economic and Trade Arbitration Commission (“CIETAC”) on July 26, 2012. On April 2, 2014, CIETAC issued the final Award of the Arbitral Tribunal. The Arbitral Tribunal found that MEDA did have a right to terminate the agreement upon a change of control, but that MEDA must make reasonable reimbursement to NovaMed before any product rights are returned to MEDA. The amount that must be paid includes $333,333 as “unjust enrichment” plus an amount for reasonable compensation for such services provided by NovaMed to MEDA. The amount of such payment for services was not determined by the Arbitral Tribunal, but was left to be determined by NovaMed. On April 30, 2014, NovaMed informed MEDA that its determination of reasonable compensation for its services was $3,314,629, including the $333,333 for unjust enrichment. MEDA made a counter offer and the parties were attempting to resolve the matter without an additional arbitration proceeding. In December 2014, NovaMed filed a “Request for Second Arbitration” with CIETAC in order to enforce its right to compensation. The arbitration case is pending with CIETAC and no hearing has taken place yet. The amount of any final payment to NovaMed remains uncertain, and as such the Company has not recognized it as a gain contingency.
Note 19 — Credit Facility
In December 2013, the Company’s subsidiary, NovaMed Shanghai entered into a 10.0 million RMB revolving line of credit facility (approximately $1.6 million USD) and a maximum 15.0 million RMB loan facility (approximately $2.4 million USD) with Shanghai Pudong Development Bank Co. Ltd. (“the Credit Facility”) that was secured by its accounts receivable. The Credit Facility bore interest on borrowed funds at the People’s Bank of China 6-month base rate plus 15% (6.44% in 2014 and 2013) on outstanding balances. The Credit Facility expired November 30, 2014, and all amounts borrowed were repaid by the expiration date. For the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company paid interest of approximately $48,000 related to the Credit Facility.
Note 20 — Segment Information and Geographic Data
The Company reports segment information based on the internal reporting used by management for evaluating segment performance based on management’s estimates of the appropriate allocation of resources to segments.
The Company operates and manages its business primarily on a geographic basis. Accordingly, the Company determined its operating segments and reporting units, which are generally based on the nature and location of its customers, to be 1) China, and 2) Rest of the World, including the US and Hong Kong.
The Company evaluates the performance of its operating segments based on revenues and operating income (loss). Revenues for geographic segments are generally based on the location of customers. Operating income (loss) for each segment includes revenues, related cost of sales and operating expenses directly attributable to the segment. Operating income (loss) for each segment excludes non-operating income and expense.
84
Summary information by operating segments is as follows (in thousands):
|
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||
|
2015 |
2014 |
2013 |
|||||||||
|
Revenue: |
|||||||||||
|
China |
$ |
151,573 |
$ |
130,311 |
$ |
122,616 | |||||
|
Rest of the World (including the US and Hong Kong) |
5,684 | 4,479 | 4,442 | ||||||||
|
Total net revenues |
$ |
157,257 |
$ |
134,790 |
$ |
127,058 | |||||
|
Income (loss) from operations: |
|||||||||||
|
China |
$ |
52,892 |
(1) |
$ |
35,630 |
(3) |
$ |
30,557 |
(4) |
||
|
Rest of the World (including the US and Hong Kong) |
(22,981) |
(2) |
(9,646) | (20,128) |
(5) |
||||||
|
Total income from operations |
$ |
29,911 |
$ |
25,984 |
$ |
10,429 | |||||
|
Non-operating income (expense): |
|||||||||||
|
China |
$ |
349 |
$ |
412 |
$ |
233 | |||||
|
Rest of the World (including the US and Hong Kong) |
10 | (19) | 2,544 |
(6) |
|||||||
|
Total non-operating income |
$ |
359 |
$ |
393 |
$ |
2,777 | |||||
|
Income (loss) before provision for income tax: |
|||||||||||
|
China |
$ |
53,241 |
$ |
36,042 |
$ |
30,790 | |||||
|
Rest of the World (including the US and Hong Kong) |
(22,971) | (9,665) | (17,584) | ||||||||
|
Total income before provision for income tax |
$ |
30,270 |
$ |
26,377 |
$ |
13,206 | |||||
|
(1) |
Operating income for the China segment for the year ended December 31, 2015 includes upfront and milestone payments totaling $5.5 million related to the Company’s licensing arrangements. |
|
(2) |
Operating loss for the Rest of the World segment for the year ended December 31, 2015 includes a milestone payment totaling $2.0 million related to the Company’s licensing arrangements. Operating loss for the Rest of the World segment also includes $10.8 million of expense that the Company recorded for the year ended December 31, 2015 associated with the SEC settlement related to the Company’s investigations with the SEC and DOJ. Refer to Part II, Item 8, Note 18 “Contingencies” and Note 22 “Subsequent Events” for further information regarding the SEC and DOJ investigations. |
|
(3) |
Operating income for the China segment for the year ended December 31, 2014 includes upfront payments totaling $11.0 million related to the Company’s licensing arrangements. |
|
(4) |
Operating income for the China segment for the year ended December 31, 2013 includes upfront payments totaling $5.0 million related to the Company’s licensing arrangements and $1.2 million in restructuring charges related to the non-renewal of the Company’s promotional agreements with Sanofi. |
|
(5) |
Operating loss for the Rest of the World segment includes $2.0 million of expense that the Company recorded for the year ended December 31, 2013 to reflect the Company’s estimate of a probable loss incurred related to potential penalties, fines and/or other remedies related to the SEC and DOJ investigations. |
|
(6) |
Non-operating income (expense) for the Rest of the World segment for the year ended December 31, 2013 includes the escrow settlement of $2.6 million recorded to other income. |
Long-lived assets by operating segment are as follows (in thousands):
|
December 31, |
||||||
|
Long-lived assets: |
2015 |
2014 |
||||
|
China |
$ |
46,315 |
$ |
41,092 | ||
|
Rest of the World (including the US and Hong Kong) |
1,783 | 542 | ||||
|
Total long-lived assets |
$ |
48,098 |
$ |
41,634 | ||
85
Note 21 — Selected Quarterly Financial Data (unaudited)
|
Three Months Ended |
|||||||||||||
|
(in thousands, except per share amounts) |
|||||||||||||
|
March 31, |
June 30, |
September 30, |
December 31, |
||||||||||
|
2015 |
2015 |
2015 |
2015 |
||||||||||
|
Product sales, net |
$ |
33,168 |
$ |
37,202 |
$ |
41,986 |
$ |
41,973 | |||||
|
Promotion services revenue |
400 | 744 | 894 | 890 | |||||||||
|
Cost of product sales |
4,597 | 5,681 | 6,853 | 5,217 |
(2) |
||||||||
|
Net income (loss) |
8,962 | (4,022) |
(1) |
11,979 | 12,544 |
(2) |
|||||||
|
Basic net income (loss) per share |
$ |
0.18 |
$ |
(0.08) |
$ |
0.24 |
$ |
0.25 | |||||
|
Diluted net income (loss) per share |
$ |
0.17 |
$ |
(0.08) |
$ |
0.23 |
$ |
0.24 | |||||
|
Three Months Ended |
|||||||||||||
|
(in thousands, except per share amounts) |
|||||||||||||
|
March 31, |
June 30, |
September 30, |
December 31, |
||||||||||
|
2014 |
2014 |
2014 |
2014 |
||||||||||
|
Product sales, net |
$ |
26,064 |
$ |
31,551 |
$ |
33,621 |
$ |
40,737 | |||||
|
Promotion services revenue |
501 | 962 | 666 | 688 | |||||||||
|
Cost of product sales |
4,561 | 5,011 | 6,005 | 7,425 | |||||||||
|
Net income |
4,134 | 9,640 | 7,915 | 3,519 |
(3) |
||||||||
|
Basic net income per share |
$ |
0.08 |
$ |
0.19 |
$ |
0.16 |
$ |
0.07 | |||||
|
Diluted net income per share |
$ |
0.08 |
$ |
0.18 |
$ |
0.15 |
$ |
0.07 | |||||
|
(1) |
During the three months ended June 30, 2015, the Company recorded upfront payments totaling $5.5 million in research and development expense related to its licensing arrangements. In addition, during the three months ended June 30, 2015, the Company recorded an additional charge of $10.8 million of operating expense, in addition to the $2.0 million charge recorded in the fourth quarter of 2013, to reflect the Company’s total SEC settlement expense incurred related to penalties, fines and/or other remedies related to the SEC and DOJ investigations of $12.8 million. Refer also to Notes 18 and 22 for more information on the SEC and DOJ investigations. |
|
(2) |
During the three months ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded a milestone payment totaling $2.0 million in research and development expense related to its licensing arrangements, and recorded a $1.1 million and $0.3 million reduction to cost of product sales and general and administrative expense, respectively, related to return of inventory and other items as part of its termination of collaboration with Cardiome. Refer also to Note17 for more information related to this termination. |
|
(3) |
During the three months ended December 31, 2014, the Company recorded upfront payments totaling $11.0 million in research and development expense related to its licensing arrangements. |
SEC Settlement and DOJ Investigation Update: On February 4, 2016, the Company announced that it has entered into a settlement agreement with the SEC fully resolving the SEC’s investigation into possible violations of the FCPA. Under the terms of the settlement agreement, in February 2016 the Company paid a total of $12.8 million, including disgorgement, pre-judgment interest and a penalty as final settlement that was released from its restricted escrow account funded in the fourth quarter of 2015. This payment is in line with the charges the Company previously recorded and disclosed as further described in Note 18. As part of the agreement, the Company neither admitted nor denied engagement in any wrongdoing and the Company agreed to give status reports to the SEC for the next three years on its continued remediation and implementation of anti-corruption compliance measures. The DOJ has also completed its related investigation and has declined to pursue any action.
86
Sinopharm Agreement: Effective January 1, 2016, the Company’s new contractual arrangement with its China importer and distributor for ZADAXIN, Sinopharm, will result in the later recognition (relative to practices prevailing through December 31, 2015) of a portion of the Company’s revenue invoiced to Sinopharm related to situations where the provincial tender price is greater relative to a referenced (baseline) tender price. This is due to a mechanism in the new contractual arrangement whereby the customer is invoiced at a lower base price relative to that prevailing in the previous agreement. The lower base price (as well as estimated price compensation payable due to the distributor for situations where the provincial tender price is lower than the referenced (baseline) tender price) will be recorded as revenue after the sale is completed. The distributor will then be invoiced for the portion of the price that may result from situations where the provincial tender price is greater than the referenced (baseline) tender price at a later time, and such amount will be recognized as revenue after the amount has been agreed to with the distributor. This new arrangement may impact quarterly revenue amounts and timing, especially for the first quarter of 2016.
87
Item 9.Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
Not applicable.
Item 9A.Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Disclosure controls and procedures are controls and other procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our reports filed or submitted under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the Securities and Exchange Commission’s rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our reports filed under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to management, including our President and Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and our Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”), as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. As of the end of the period covered by this report, management carried out an evaluation under the supervision and with the participation of the CEO and the CFO of the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures in ensuring that material information required to be disclosed in the Company’s reports filed or submitted under the Exchange Act, has been made known to them in a timely fashion. Based on this evaluation, the CEO and CFO concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures are effective as of December 31, 2015.
Management's Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. A control system, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the internal control system are met. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, we assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015, based on the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”) in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013). Based on the results of our assessment, our management concluded that the Company maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015.
PricewaterhouseCoopers Zhong Tian LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, has audited the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015 as stated in their report, which is referenced in the index appearing under Item 8.
Changes in Internal Controls
Our management, including our CEO and CFO, has evaluated any changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the quarter ended December 31, 2015, and has concluded that there was no change during such quarter that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
88
None.
PART III
Certain information required by Part III is incorporated by reference from our definitive Proxy in connection with the solicitation of proxies for our 2016 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (the “Proxy Statement”) or in an amendment to this Annual Report on Form 10-K to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, in each case, not later than 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this report, and certain information therein is incorporated in this report by reference.
Item 10.Directors, Executive Officers, and Corporate Governance
The information required by Item 401 of Regulation S-K is incorporated by reference from the Proxy Statement under the caption “Proposal No. 1 Election of Directors – Nominees,” and “Proposal No. 1 Corporate Governance – Board Meetings and Committees.” Information relating to the executive officers of the Company is incorporated by reference from the Proxy Statement under the caption “Executive Compensation and Other Matters – Executive Officers”.
The information required by Item 405 of Regulation S-K is incorporated by reference from the Proxy Statement under the caption “Executive Compensation and Other Matters – Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance”.
Code of Ethics
We have adopted a code of business conduct and ethics, and a policy providing for the reporting of potential violations of the code, for directors, officers (including our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller) and employees, known as the Corporate Code of Conduct and Ethics (including “Whistleblowing in the case of Violations of the Company Policies”) (the “Code of Conduct”). The Code of Conduct is available on our website at www.sciclone.com under the section “Investor Relations – Corporate Governance”. We intend to satisfy the disclosure requirement under Item 5.05 of Form 8-K regarding amendment to, or waiver from, a provision of our Code of Conduct and by posting such information on the website address and location specified above. Additionally, stockholders may request a free copy of the Code of Conduct by contacting the Investor Relations Department at our corporate offices by calling 800-724-2566 or by sending an e-mail message to investorrelations@sciclone.com.
Item 11.Executive Compensation
The information required by this Item 11 is incorporated by reference from the Proxy Statement under the captions “Executive Compensation and Other Matters” and “Corporate Governance.”
89
Item 12.Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
The following table provides certain information regarding our compensation plans in effect as of December 31, 2015 (in thousands, except per share amounts):
|
Number of |
Weighted- |
Number of securities |
||||
|
securities |
average exercise |
remaining available for |
||||
|
to be issued upon |
price of |
future issuance under |
||||
|
exercise of |
outstanding |
equity compensation |
||||
|
outstanding |
options, |
plans (excluding |
||||
|
options, warrants |
warrants and |
securities |
||||
|
and rights |
rights |
reflected in column (a)) |
||||
|
(a) |
(b) |
(c) |
||||
|
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders: |
||||||
|
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan |
— |
— |
433 | |||
|
2004 Outside Directors Stock Option Plan |
717 |
$ |
3.92 |
— |
||
|
2005 Equity Incentive Plan |
5,838 |
$ |
5.16 |
— |
||
|
2015 Equity Incentive Plan |
213 |
$ |
8.88 | 6,527 | ||
|
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders: |
— |
— |
— |
|||
|
Total |
6,768 |
$ |
5.14 | 6,960 | ||
The information required by Item 403 of Regulation S-K is incorporated by reference from the Proxy Statement under the caption “Executive Compensation and Other Matters – Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management.”
Item 13.Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this Item 13 is incorporated by reference from the Proxy Statement under the captions “Executive Compensation and Other Matters – Transactions with Related Persons” and “Corporate Governance – Director Independence.”
Item 14.Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information required by this Item 14 is incorporated by reference from the Proxy Statement under the caption “Proposal No. 4 Ratification of Appointment of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm – Principal Accountant Fees.”
PART IV
Item 15.Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules
Item 15 (a).The following documents are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K:
(1) Financial Statements. The following financial statements of the Company are contained in Item 8, Part II on pages 57-87 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K:
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2015 and 2014.
Consolidated Statements of Income for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2015.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2015.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity for each of the three years ended December 31, 2015.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2015.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
90
(2) Financial Statement Schedules. The following schedule required to be filed by Item 8 of this form and Item 15(d) is contained on page 96 of this Report:
Schedule II – Valuation and Qualifying Accounts for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2015.
All other schedules have been omitted because they are either inapplicable or the required information has been given in the consolidated financial statements or the notes thereto.
(3) Exhibits.
Refer to Item 15(b) below.
Item 15 (b). Exhibits.
Exhibits (numbered in accordance with Item 601 of Regulation S-K):
|
|
|
|
Exhibit |
|
|
Number |
Description |
|
3(i).1(1) |
Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation. |
|
3(i).2(13) |
Certificate of Amendment to the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation. |
|
3(i).3(7) |
Certificate of Designation, Preferences and Rights of the Terms of the Series D Preferred Stock, as filed by SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware as of December 22, 2006. |
|
3(ii).1(8) |
Amended and Restated Bylaws. |
|
4(6) |
Rights Agreement, effective as of December 19, 2006, between the Company and Mellon Investor Services LLC, as rights agent (including as Exhibit A the form of Certificate of Designation, Preferences and Rights of the Series D Preferred Stock, as Exhibit B the form of Right Certificate, and as Exhibit C the Summary of Terms of Rights Agreement). |
|
10.1(16)** |
Registrant’s 2005 Equity Incentive Plan, effective as of June 7, 2005, as amended on June 25, 2012. |
|
10.2(5)** |
Registrant’s 2004 Outside Directors Stock Option Plan, as amended on June 7, 2005 and as further amended on February 22, 2007. |
|
10.3(2)** |
Form of Indemnity Agreement by and between the Registrant and each director and executive officer of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.4(3)* |
Manufacturing and Supply Agreement between SciClone Pharmaceuticals International Ltd. and Patheon Italia S.p.A. dated as of November 1, 2002. |
|
10.5(4)** |
Employment Agreement between SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Friedhelm Blobel, Ph.D. dated as of April 23, 2006 and effective as of June 2, 2006. |
|
10.6(9)* |
Manufacturing Supply Agreement Between SciClone Pharmaceuticals International Ltd. and Lonza Sales Ltd., executed as of May 23, 2008. |
|
10.7(10)** |
Amendment No. 1 to Employment Agreement between Dr. Friedhelm Blobel and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. dated April 7, 2009. |
|
10.8(11)** |
The SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan, as amended. |
|
10.9(14)** |
Description of Executive Incentive Plan. |
|
10.10(12)* |
Amendment No. 1 to Manufacturing and Supply Agreement between SciClone Pharmaceuticals International Ltd. and Lonza Sales Ltd., effective December 31, 2010. |
|
10.11(12)** |
Amendment No. 2 to Employment Agreement between Dr. Friedhelm Blobel and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. effective May 4, 2010. |
|
10.12(14)* |
Re-Exportation Agreement between SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Ltd., Sinopharm Holding Hong Kong Co., Limited and Sinopharm Holding Lingyun Biopharmaceutical (Shanghai) Co. Limited effective January 1, 2013. |
91
|
10.13(15)** |
Employment Agreement effective April 1, 2013 by and between Hong Zhao and NovaMed Pharmaceuticals (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., an affiliate of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.14(15)** |
Sign On Bonus Letter effective April 1, 2013 by and between Hong Zhao and NovaMed Pharmaceuticals (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., an affiliate of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.15(17)** |
Employment Agreement effective July 16, 2013 by and between Wilson W. Cheung and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.16(17)* |
Framework Agreement effective May 13, 2013 between Zensun (Shanghai) Science & Technology Co., Ltd and SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Ltd. |
|
10.17(17)* |
Framework Agreement effective June 25, 2013 between Taiwan Liposome Company and SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Ltd. |
|
10.18(18)** |
Employment Agreement effective October 15, 2013 by and between Raymond Low and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.19(19) |
Second Amendment, dated December 20, 2013, between SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and CA-Metro Center Limited Partnership. |
|
10.20(20) ** |
Employment Agreement effective February 9, 2014 by and between Chun Cai Meng and SciClone Pharmaceuticals Hong Kong Ltd. |
|
10.21(21)** |
Description of Executive Long-Term Incentive Program. |
|
10.22(22)** |
Form of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Notice of Grant of Performance Restricted Stock Units (Performance-Based RSUs for US Participant) and Performance Restricted Stock Units Agreement (Performance-Based RSUs for US Participant) dated April 3, 2015 entered into between Friedhelm Blobel and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.23(22)** |
Form of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Notice of Grant of Restricted Stock Units (Time-Based RSUs for US Participant) and Restricted Stock Units Agreement (Time-Based RSUs for US Participant) dated April 3, 2015 entered into between Friedhelm Blobel and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.24(22)** |
Form of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Notice of Grant of Performance Restricted Stock Units (Performance-Based RSUs for US Participant) and Performance Restricted Stock Units Agreement (Performance-Based RSUs for US Participant) dated April 3, 2015 entered into between Wilson W. Cheung and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.25(22)** |
Form of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Notice of Grant of Restricted Stock Units (Time-Based RSUs for US Participant) and Restricted Stock Units Agreement (Time-Based RSUs for US Participant) dated April 3, 2015 entered into between Wilson W. Cheung and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.26(22)** |
Form of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Notice of Grant of Performance Restricted Stock Units (Performance-Based RSUs for PRC Participant) and Performance Restricted Stock Units Agreement (Performance-Based RSUs for PRC Participant) dated April 3, 2015 entered into between Hong Zhao and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.27(22)** |
Form of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Notice of Grant of Restricted Stock Units (Time-Based RSUs for PRC Participant) and Restricted Stock Units Agreement (Time-Based RSUs for PRC Participant) dated April 3, 2015 entered into between Hong Zhao and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.28(23)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2015 Equity Incentive Plan. |
|
10.29(24)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Friedhelm Blobel and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective June 16, 2015. |
|
10.30(24)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Wilson W. Cheung and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective June 16, 2015. |
|
10.31(24)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Robert King and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective June 30, 2015. |
|
10.32(24)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Raymond Low and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective June 30, 2015. |
|
10.33(25)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Lan Xie and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective July 31, 2015. |
|
10.34(25)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Hong Zhao and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective July 31, 2015. |
92
|
10.35(25)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Chun Cai Meng and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective July 31, 2015. |
|
10.36(25)** |
Form of Stock Option Agreement for 2015 Equity Incentive Plan (US Participant). |
|
10.37(25)** |
Form of Stock Option Agreement for 2015 Equity Incentive Plan (PRC Participant). |
|
10.38(25)** |
Form of Restricted Stock Units Agreement for 2015 Equity Incentive Plan (US Participant). |
|
10.39(25)** |
Form of Restricted Stock Units Agreement for 2015 Equity Incentive Plan (PRC Participant). |
|
10.40(26)* |
Letter Agreement supplementing the 2016 Import Agreement by and between SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Limited and Sinopharm Holding Lingyun Biopharmaceutical (Shanghai) Co. Limited effective November 12, 2015. |
|
10.41(26)* |
Letter Agreement modifying the Re-Exportation Agreement by and among SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Limited, Sinopharm Holding Hong Kong International Limited and Sinopharm Holding Lingyun Biopharmaceutical (Shanghai) Co. Limited effective November 13, 2015. |
|
10.42(26)* |
2016 Import and Distribution Agreement between SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Limited and Sinopharm Holding Lingyun Biopharmaceuticals (Shanghai) Co. Limited effective January 1, 2016. |
|
14 |
See “Code of Ethics” in Item 10: Executive Officers and Directors, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
|
21.1(26) |
Subsidiaries of Registrant. |
|
23.1(26) |
Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
|
24.1(26) |
Power of Attorney. See page 95. |
|
31.1(26) |
Certification of Principal Executive Officer Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
31.2(26) |
Certification of Chief Financial Officer Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
32.1(27) |
Certification Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
32.2(27) |
Certification Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
101(26) |
The following materials from Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2015, formatted in Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) includes: (i) Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 (ii) Consolidated Statements of Income for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, (iii) Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, (iv) Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, (v) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 2015, 2014 and 2013 and (vi) Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
Certain information in this exhibit has been omitted and filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to a confidential treatment request under 17 C.F.R. Sections 200.80(b)(4), 200.83 and 230.46. |
|
** |
Management compensatory plan or arrangement. |
|
(1) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on July 28, 2003. |
|
(2) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2003, filed on October 31, 2003. |
|
(3) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2003, filed on March 15, 2004. |
|
(4) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 25, 2006. |
|
(5) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2007, filed on August 8, 2007. |
|
(6) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 22, 2006. |
|
(7) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 28, 2006. |
93
|
(8) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 16, 2014. |
|
(9) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2008, filed on August 1, 2008. |
|
(10) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 8, 2009. |
|
(11) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2010, filed on August 9, 2010. |
|
(12) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010, filed on March 31, 2011. |
|
(13) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on July 6, 2011. |
|
(14) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2012, filed on April 1, 2013. |
|
(15) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2013, filed on August 9, 2013. |
|
(16) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 13, 2012. |
|
(17) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2013, filed on August 9, 2013. |
|
(18) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended September 30, 2013, filed on November 12, 2013. |
|
(19) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 2, 2014. |
|
(20) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2014, filed on May 12, 2014. |
|
(21) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 6, 2015. |
|
(22) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2015, filed on May 11, 2015. |
|
(23) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 17, 2015. |
|
(24) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2015, filed on August 10, 2015. |
|
(25) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended September 30, 2015, filed on November 9, 2015. |
|
(26) |
Filed herewith. |
|
(27) |
Furnished herewith. |
Item 15 (c). See Item 15(a) above.
94
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this Report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
|
||
|
|
SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. |
||
|
|
|
||
|
Date: March 11, 2016 |
/s/ Wilson W. Cheung |
||
|
|
Wilson W. Cheung Senior Vice President, Finance and Chief Financial Officer |
||
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints Friedhelm Blobel, Ph.D. and Wilson W. Cheung, and each of them, his attorneys-in-fact and agents, each with the power of substitution and resubstitution, for him in any and all capacities, to sign any amendment to this Report on Form 10-K, and to file the same, with exhibits thereto and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting to said attorneys-in-fact and agents, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary, to be done in connection therewith, as fully as to all intents and purposes as he might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents, or either of them, or their or his substitute or substitutes, may do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this Report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
Signature |
|
Title |
|
Date |
|
/S/ FRIEDHELM BLOBEL, PH.D. (Friedhelm Blobel, Ph.D.) |
|
President and Chief Executive Officer, Director (Principal Executive Officer) |
|
March 11, 2016 |
|
/S/ WILSON W. CHEUNG (Wilson W. Cheung) |
Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
March 11, 2016 |
||
|
/S/ JON S. SAXE (Jon S. Saxe) |
|
Chairman of the Board of Directors |
|
March 11, 2016 |
|
/S/ NANCY T. CHANG, PH.D. (Nancy T. Chang, Ph.D.) |
|
Director |
|
March 11, 2016 |
|
/S/ RICHARD J. HAWKINS (Richard J. Hawkins) |
|
Director |
|
March 11, 2016 |
|
/S/ GREGG A LAPOINTE (Gregg A. Lapointe) |
|
Director |
|
March 11, 2016 |
|
/S/ SIMON LI (Simon Li) |
|
Director |
|
March 11, 2016 |
95
SCHEDULE II – VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
SCICLONE PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
Receivables and Product Returns Reserves (in thousands):
|
Balance at |
Charges for |
Deductions for |
Deductions for |
Balance at |
|||||||||||
|
Beginning of |
Amounts |
Amounts |
Amounts |
End of |
|||||||||||
|
Period |
Reserved |
Recovered |
Written Off |
Period |
|||||||||||
|
Receivables Reserve: |
|||||||||||||||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2015 |
$ |
(998) |
$ |
(541) |
$ |
400 |
$ |
545 |
$ |
(594) | |||||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2014 |
$ |
(3,587) |
$ |
— |
$ |
1,500 |
$ |
1,089 |
$ |
(998) | |||||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2013 |
$ |
(1,046) |
$ |
(2,541) |
(1) |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
(3,587) | ||||
|
Balance at |
Charges for |
Deductions for |
Deductions for |
Balance at |
|||||||||||
|
Beginning of |
Amounts |
Amounts |
Amounts |
End of |
|||||||||||
|
Period |
Reserved |
Recovered |
Paid |
Period |
|||||||||||
|
Reserve for Product Returns: |
|||||||||||||||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2015 |
$ |
(66) |
$ |
(134) |
$ |
— |
$ |
66 |
$ |
(134) | |||||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2014 |
$ |
— |
$ |
(66) |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
$ |
(66) | |||||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2013 |
$ |
(123) |
$ |
— |
$ |
123 |
$ |
— |
$ |
— |
|||||
|
(1) |
For the year ended December 31, 2013, the charges for amounts reserved included $2.5 million of general and administrative expense related to bad debt that was uncertain of collection. |
96
INDEX TO EXHIBITS
|
|
|
|
Exhibit |
|
|
Number |
Description |
|
3(i).1(1) |
Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation. |
|
3(i).2(13) |
Certificate of Amendment to the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation. |
|
3(i).3(7) |
Certificate of Designation, Preferences and Rights of the Terms of the Series D Preferred Stock, as filed by SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware as of December 22, 2006. |
|
3(ii).1(8) |
Amended and Restated Bylaws. |
|
4(6) |
Rights Agreement, effective as of December 19, 2006, between the Company and Mellon Investor Services LLC, as rights agent (including as Exhibit A the form of Certificate of Designation, Preferences and Rights of the Series D Preferred Stock, as Exhibit B the form of Right Certificate, and as Exhibit C the Summary of Terms of Rights Agreement). |
|
10.1(16)** |
Registrant’s 2005 Equity Incentive Plan, effective as of June 7, 2005, as amended on June 25, 2012. |
|
10.2(5)** |
Registrant’s 2004 Outside Directors Stock Option Plan, as amended on June 7, 2005 and as further amended on February 22, 2007. |
|
10.3(2)** |
Form of Indemnity Agreement by and between the Registrant and each director and executive officer of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.4(3)* |
Manufacturing and Supply Agreement between SciClone Pharmaceuticals International Ltd. and Patheon Italia S.p.A. dated as of November 1, 2002. |
|
10.5(4)** |
Employment Agreement between SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Friedhelm Blobel, Ph.D. dated as of April 23, 2006 and effective as of June 2, 2006. |
|
10.6(9)* |
Manufacturing Supply Agreement Between SciClone Pharmaceuticals International Ltd. and Lonza Sales Ltd., executed as of May 23, 2008. |
|
10.7(10)** |
Amendment No. 1 to Employment Agreement between Dr. Friedhelm Blobel and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. dated April 7, 2009. |
|
10.8(11)** |
The SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan, as amended. |
|
10.9(14)** |
Description of Executive Incentive Plan. |
|
10.10(12)* |
Amendment No. 1 to Manufacturing and Supply Agreement between SciClone Pharmaceuticals International Ltd. and Lonza Sales Ltd., effective December 31, 2010. |
|
10.11(12)** |
Amendment No. 2 to Employment Agreement between Dr. Friedhelm Blobel and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. effective May 4, 2010. |
|
10.12(14)* |
Re-Exportation Agreement between SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Ltd., Sinopharm Holding Hong Kong Co., Limited and Sinopharm Holding Lingyun Biopharmaceutical (Shanghai) Co. Limited effective January 1, 2013. |
|
10.13(15)** |
Employment Agreement effective April 1, 2013 by and between Hong Zhao and NovaMed Pharmaceuticals (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., an affiliate of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.14(15)** |
Sign On Bonus Letter effective April 1, 2013 by and between Hong Zhao and NovaMed Pharmaceuticals (Shanghai) Co. Ltd., an affiliate of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.15(17)** |
Employment Agreement effective July 16, 2013 by and between Wilson W. Cheung and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.16(17)* |
Framework Agreement effective May 13, 2013 between Zensun (Shanghai) Science & Technology Co., Ltd and SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Ltd. |
|
10.17(17)* |
Framework Agreement effective June 25, 2013 between Taiwan Liposome Company and SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Ltd. |
|
10.18(18)** |
Employment Agreement effective October 15, 2013 by and between Raymond Low and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
97
|
10.19(19) |
Second Amendment, dated December 20, 2013, between SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and CA-Metro Center Limited Partnership. |
|
10.20(20) ** |
Employment Agreement effective February 9, 2014 by and between Chun Cai Meng and SciClone Pharmaceuticals Hong Kong Ltd. |
|
10.21(21)** |
Description of Executive Long-Term Incentive Program. |
|
10.22(22)** |
Form of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Notice of Grant of Performance Restricted Stock Units (Performance-Based RSUs for US Participant) and Performance Restricted Stock Units Agreement (Performance-Based RSUs for US Participant) dated April 3, 2015 entered into between Friedhelm Blobel and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.23(22)** |
Form of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Notice of Grant of Restricted Stock Units (Time-Based RSUs for US Participant) and Restricted Stock Units Agreement (Time-Based RSUs for US Participant) dated April 3, 2015 entered into between Friedhelm Blobel and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.24(22)** |
Form of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Notice of Grant of Performance Restricted Stock Units (Performance-Based RSUs for US Participant) and Performance Restricted Stock Units Agreement (Performance-Based RSUs for US Participant) dated April 3, 2015 entered into between Wilson W. Cheung and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.25(22)** |
Form of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Notice of Grant of Restricted Stock Units (Time-Based RSUs for US Participant) and Restricted Stock Units Agreement (Time-Based RSUs for US Participant) dated April 3, 2015 entered into between Wilson W. Cheung and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.26(22)** |
Form of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Notice of Grant of Performance Restricted Stock Units (Performance-Based RSUs for PRC Participant) and Performance Restricted Stock Units Agreement (Performance-Based RSUs for PRC Participant) dated April 3, 2015 entered into between Hong Zhao and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.27(22)** |
Form of SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Notice of Grant of Restricted Stock Units (Time-Based RSUs for PRC Participant) and Restricted Stock Units Agreement (Time-Based RSUs for PRC Participant) dated April 3, 2015 entered into between Hong Zhao and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
|
10.28(23)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2015 Equity Incentive Plan. |
|
10.29(24)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Friedhelm Blobel and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective June 16, 2015. |
|
10.30(24)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Wilson W. Cheung and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective June 16, 2015. |
|
10.31(24)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Robert King and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective June 30, 2015. |
|
10.32(24)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Raymond Low and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective June 30, 2015. |
|
10.33(25)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Lan Xie and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective July 31, 2015. |
|
10.34(25)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Hong Zhao and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective July 31, 2015. |
|
10.35(25)** |
SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retention Agreement by and between Chun Cai Meng and SciClone Pharmaceuticals, Inc., effective July 31, 2015. |
|
10.36(25)** |
Form of Stock Option Agreement for 2015 Equity Incentive Plan (US Participant). |
|
10.37(25)** |
Form of Stock Option Agreement for 2015 Equity Incentive Plan (PRC Participant). |
|
10.38(25)** |
Form of Restricted Stock Units Agreement for 2015 Equity Incentive Plan (US Participant). |
|
10.39(25)** |
Form of Restricted Stock Units Agreement for 2015 Equity Incentive Plan (PRC Participant). |
|
10.40(26)* |
Letter Agreement supplementing the 2016 Import Agreement by and between SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Limited and Sinopharm Holding Lingyun Biopharmaceutical (Shanghai) Co. Limited effective November 12, 2015. |
98
|
10.41(26)* |
Letter Agreement modifying the Re-Exportation Agreement by and among SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Limited, Sinopharm Holding Hong Kong International Limited and Sinopharm Holding Lingyun Biopharmaceutical (Shanghai) Co. Limited effective November 13, 2015. |
|
10.42(26)* |
2016 Import and Distribution Agreement between SciClone Pharmaceuticals International China Holding Limited and Sinopharm Holding Lingyun Biopharmaceuticals (Shanghai) Co. Limited effective January 1, 2016. |
|
14 |
See “Code of Ethics” in Item 10: Executive Officers and Directors, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
|
21.1(26) |
Subsidiaries of Registrant. |
|
23.1(26) |
Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
|
24.1(26) |
Power of Attorney. See page 95. |
|
31.1(26) |
Certification of Principal Executive Officer Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
31.2(26) |
Certification of Chief Financial Officer Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
32.1(27) |
Certification Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
32.2(27) |
Certification Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
101(26) |
The following materials from Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2015, formatted in Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) includes: (i) Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 (ii) Consolidated Statements of Income for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, (iii) Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, (iv) Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, (v) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 2015, 2014 and 2013 and (vi) Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
Certain information in this exhibit has been omitted and filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to a confidential treatment request under 17 C.F.R. Sections 200.80(b)(4), 200.83 and 230.46. |
|
** |
Management compensatory plan or arrangement. |
|
(1) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on July 28, 2003. |
|
(2) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2003, filed on October 31, 2003. |
|
(3) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2003, filed on March 15, 2004. |
|
(4) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 25, 2006. |
|
(5) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2007, filed on August 8, 2007. |
|
(6) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 22, 2006. |
|
(7) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 28, 2006. |
|
(8) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 16, 2014. |
|
(9) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2008, filed on August 1, 2008. |
|
(10) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 8, 2009. |
|
(11) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2010, filed on August 9, 2010. |
|
(12) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010, filed on March 31, 2011. |
|
(13) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on July 6, 2011. |
99
|
(14) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2012, filed on April 1, 2013. |
|
(15) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2013, filed on August 9, 2013. |
|
(16) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 13, 2012. |
|
(17) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2013, filed on August 9, 2013. |
|
(18) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended September 30, 2013, filed on November 12, 2013. |
|
(19) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 2, 2014. |
|
(20) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2014, filed on May 12, 2014. |
|
(21) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 6, 2015. |
|
(22) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2015, filed on May 11, 2015. |
|
(23) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 17, 2015. |
|
(24) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2015, filed on August 10, 2015. |
|
(25) |
Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended September 30, 2015, filed on November 9, 2015. |
|
(26) |
Filed herewith. |
|
(27) |
Furnished herewith. |
100
