Attached files
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
_____________________
FORM 10-K
(MARK ONE)
|
[X]
|
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
|
|
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2015
|
|
|
or
|
|
|
[ ]
|
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
|
|
For the transition period from ___________ to ____________
|
|
Commission File No. 0-11676
_____________________
BEL FUSE INC.
206 Van Vorst Street
Jersey City, NJ 07302
(201) 432-0463
206 Van Vorst Street
Jersey City, NJ 07302
(201) 432-0463
(Address of principal executive offices and zip code)
(Registrant's telephone number, including area code)
|
NEW JERSEY
|
|
22-1463699
|
|
(State of incorporation)
|
|
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.)
|
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
Title of Each Class |
|
Name of Each Exchange
on which Registered |
|
Class A Common Stock ($0.10 par value)
|
|
NASDAQ Global Select Market
|
|
Class B Common Stock ($0.10 par value)
|
NASDAQ Global Select Market
|
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
|
Indicate by checkmark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
|
Yes [ ] |
No [X] |
|
Indicate by checkmark if the registrant is not required to file reports to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act.
|
Yes [ ]
|
No [X]
|
|
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
|
Yes [X]
|
No [ ]
|
|
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
|
Yes [X]
|
No [ ]
|
|
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K.
|
[X]
|
|
Indicate by checkmark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of large accelerated filer, accelerated filer and smaller reporting company in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
||
|
Large accelerated filer [ ]
|
Accelerated filer [X]
|
Non-accelerated filer [ ]
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company) |
Smaller reporting company [ ]
|
||
|
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act).
|
Yes [ ]
|
No [X]
|
|||
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity of the registrant held by non-affiliates (for this purpose, persons and entities other than executive officers and directors) of the registrant, as of the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter (June 30, 2015) was $221.0 million based on the closing sale price as reported on the NASDAQ Global Select Market.
|
Title of Each Class |
|
Number of Shares of Common Stock Outstanding as of March 1, 2016
|
|
Class A Common Stock
|
|
2,174,912
|
|
Class B Common Stock
|
9,701,977
|
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE:
Portions of Bel Fuse Inc.'s Definitive Proxy Statement for the 2016 Annual Meeting of Stockholders are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
|
BEL FUSE INC.
|
|||
|
Page
|
|||
|
Cautionary Notice Regarding Forward-Looking Information
|
1
|
||
|
Part I
|
|||
|
Item 1.
|
2
|
||
|
Item 1A.
|
7
|
||
|
Item 1B.
|
13
|
||
|
Item 2.
|
14
|
||
|
Item 3.
|
14
|
||
|
Item 4.
|
14
|
||
|
Part II
|
|||
|
Item 5.
|
|||
|
15
|
|||
|
Item 6.
|
17
|
||
|
Item 7.
|
|||
|
19
|
|||
|
Item 7A.
|
30
|
||
|
Item 8.
|
31
|
||
|
Item 9.
|
|||
|
71
|
|||
|
Item 9A.
|
71
|
||
|
Item 9B.
|
71
|
||
|
Part III
|
|||
|
Item 10.
|
72
|
||
|
Item 11.
|
72
|
||
|
Item 12.
|
|||
|
72
|
|||
|
Item 13.
|
72
|
||
|
Item 14.
|
72
|
||
|
Part IV
|
|||
|
Item 15.
|
73
|
||
|
75
|
|||
The terms the "Company," "Bel," "we," "us," and "our" as used in this Annual Report on Form 10-K ("Form 10-K") refer to Bel Fuse Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries unless otherwise specified.
The Company's consolidated operating results are affected by a wide variety of factors that could materially and adversely affect revenues and profitability, including the risk factors described in Item 1A of this Form 10-K. As a result of these and other factors, the Company may experience material fluctuations in future operating results on a quarterly or annual basis, which could materially and adversely affect its business, consolidated financial condition, operating results, and common stock prices. Furthermore, this document and other documents filed by the Company with the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC") contain certain forward-looking statements under the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 ("Forward-Looking Statements") with respect to the business of the Company. Forward-Looking Statements are necessarily subject to risks and uncertainties, many of which are outside our control, that could cause actual results to differ materially from these statements. Forward-Looking Statements can be identified by such words as "anticipates," "believes," "plans to," "assumes," "could," "should," "estimates," "expects," "intends," "potential," "seek," "predict," "may," "will" and similar expressions. These Forward-Looking Statements are subject to certain risks and uncertainties, including those detailed in Item 1A. of this Form 10-K, which could cause actual results to differ materially from these Forward-Looking Statements. The Company undertakes no obligation to publicly release the results of any revisions to these Forward-Looking Statements which may be necessary to reflect events or circumstances after the date hereof or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. Any Forward-Looking Statement made by the Company is based only on information currently available to us and speaks only as of the date on which it is made.
PART I
Bel Fuse Inc. designs, manufactures and markets a broad array of products that power, protect and connect electronic circuits. These products are primarily used in the networking, telecommunications, computing, military, aerospace, transportation and broadcasting industries. Bel's portfolio of products also finds application in the automotive, medical and consumer electronics markets.
With over 65 years in operation, Bel has reliably demonstrated the ability to succeed in a variety of product areas across a global platform. The Company has a strong track record of technical innovation working with the engineering teams of market leaders. Bel has consistently proven itself a valuable supplier to the foremost companies in its chosen industries by developing cost-effective solutions for the challenges of new product development. By combining our strength in product design with our own specially-designed manufacturing facilities, Bel has established itself as a formidable competitor on a global basis.
The Company, which is organized under New Jersey law, operates in one industry with three reportable operating segments, North America, Asia and Europe (representing 54%, 33% and 13% of the Company's 2015 sales, respectively). Bel's principal executive offices are located at 206 Van Vorst Street, Jersey City, New Jersey 07302; (201) 432-0463. The Company operates facilities in North America, Europe and Asia and trades on the NASDAQ Global Select Market (BELFA and BELFB). For information regarding Bel's three geographic operating segments, see Note 12, "Segments", of the notes to consolidated financial statements. Hereinafter, all references to "Note" will refer to the notes to consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8. "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Acquisitions have played a critical role in the growth of Bel and the expansion of both our product portfolio and our customer base and continue to be a key element in our growth strategy. We may, from time to time, purchase equity positions in companies that are potential merger candidates. We frequently evaluate possible merger candidates that would provide an expanded product and technology base that will allow us to expand the breadth of our product offerings to our strategic customers and/or provide an opportunity to reduce overall operating expense as a percentage of revenue. We also consider whether the merger candidates are positioned to take advantage of our lower cost offshore manufacturing facilities, and whether a cultural fit will allow the acquired company to be integrated smoothly and efficiently.
2014 Acquisitions
On June 19, 2014, we completed our acquisition of the Power Solutions business of Power-One ("Power Solutions") from ABB Ltd. for $109.9 million, net of cash acquired. Power Solutions is a leading provider of high-efficiency and high-density power conversion products for server, storage and networking equipment, industrial applications and power systems. Power Solutions offers a premier line of standard, modified-standard and custom designed AC/DC, DC/DC and other specific power conversion products for a variety of technologies in data centers, telecommunications and industrial applications. The acquisition of Power Solutions brought a complementary, industry-leading power product portfolio to Bel's existing line of power solutions and protection products, expanded our current customer base in the areas of server, storage and networking equipment and added industrial and additional transportation applications to the Company's product offering.
On July 25, 2014, we completed our acquisition of 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of the U.S. and U.K. Connectivity Solutions businesses from Emerson Electric Co. ("Emerson"). On August 29, 2014, we completed our acquisition of the Connectivity Solutions business in China from Emerson (collectively with the U.S. and U.K. portion of the transaction, "Connectivity Solutions"). The Company paid a total of $98.8 million for Connectivity Solutions, net of cash acquired and including a working capital adjustment. Connectivity Solutions is a leading provider of high‑performance RF/Microwave and Harsh Environment Optical Connectors and Assemblies for military, aerospace, wireless communications, data communications, broadcast and industrial applications. The acquisition of Connectivity Solutions enabled the Company to further expand into the aerospace and military markets where long-term product reliability resulting from highly engineered solutions is critical. The acquisition enhanced our position in the expanded beam fiber optic market place and significantly expanded our copper‑based product offerings with the addition of RF/Microwave components and assemblies.
The acquisitions of Power Solutions and Connectivity Solutions may hereafter be referred to collectively as either the "2014 Acquisitions" or the "2014 Acquired Companies".
2013 Acquisitions
On March 29, 2013, we completed our acquisition of 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Transpower Technologies (HK) Limited ("Transpower") and certain other tangible and intangible assets related to the Transpower magnetics business of TE Connectivity ("TE") for $21.0 million, net of cash acquired. The operations acquired are now doing business as TRP Connector ("TRP"). Transpower is the sole shareholder of Dongguan Transpower Electronic Products Co., Ltd. in the People's Republic of China ("PRC"). The Company's purchase of the TRP magnetics business consisted of the integrated connector module ("ICM") family of products, including RJ45, 10/100 Gigabit, 10G, PoE/PoE+, MRJ21 and RJ.5, a line of modules for smart-grid applications, and discrete magnetics.
On August 20, 2013, we completed our acquisition of Array, a manufacturer of aerospace and mil-spec connector products based in Miami, Florida, for $10.0 million in cash. The acquisition of Array expanded our portfolio of connector products and broadened our customer base for our other connector product offerings. Array has become part of Bel's interconnect product group under the Cinch Connectors business.
The acquisitions of TRP and Array may hereafter be referred to collectively as either the "2013 Acquisitions" or the "2013 Acquired Companies".
The 2013 Acquisitions and the 2014 Acquisitions were funded from cash on hand and/or borrowings.
Products
Bel's three reportable operating segments, North America, Asia and Europe, sell, or participate in the sale of, the following products:
Magnetic Solutions
Bel's Magnetics offers industry leading products. The Company's ICM products integrate RJ45 connectors with discrete magnetic components to provide a more robust part that allows customers to substantially reduce board space and inventory requirements. The Company's recent acquisition of the TE wire wound magnetics business broadens the ICM product line and provides access to strategically important customer programs. Power Transformers include standard and custom designs for use in industrial instrumentation, alarm and security systems, motion control, elevators, and medical products. All Power Transformers are designed to comply with international safety standards governing transformers. Bel's SMD Power Inductors include a selection of over 3,000 parts utilized in power supplies, DC-DC converters, LED lighting and other electronic applications. Discrete Components are magnetic devices that condition, filter and isolate the signal as it travels through network equipment, ensuring accurate data/voice/video transmission.
|
Product Line
|
Function
|
Applications
|
Brands Sold Under
|
|
|
Magnetic Solutions
|
Integrated Connector Modules (ICMs)
|
Condition, filter, and isolate the electronic signal to ensure accurate data/voice/video transmission and provide RJ45 and USB connectivity.
|
Network switches, routers, hubs, and PCs used in 10/100/1000 Gigabit Ethernet, Power over Ethernet (PoE), PoE Plus and home networking applications.
|
Bel, TRP, MagJack®
|
|
Power Transformers
|
Safety isolation and distribution.
|
Power supplies, alarm, fire detection, and security systems, HVAC, lighting and medical equipment. Class 2, three phase, chassis mount, and PC mount designs available.
|
Signal
|
|
|
SMD Power Inductors & SMPS Transformers
|
A passive component that stores energy in a magnetic field. Widely used in analog electronic circuitry.
|
Switchmode power supplies, DC-DC converters, LED lighting, automotive and consumer electronics.
|
Signal
|
|
|
Discrete Components-Telecom
|
Condition, filter, and isolate the electronic signal to ensure accurate data/voice/video transmission.
|
Network switches, routers, hubs, and PCs used in 10/100/1000 Gigabit Ethernet and Power over Ethernet (PoE).
|
Bel
|
Power Solutions & Protection
Bel's power conversion products include AC-DC power supplies, DC-DC converters and battery charging solutions. The DC-DC product offering consists of standard and custom isolated and non-isolated DC-DC converters designed specifically to power low voltage silicon devices or provide regulated mid-bus voltages. The need for converting one DC voltage to another is growing rapidly as developers of integrated circuits commonly adjust the supply voltage as a means of optimizing device performance. The DC-DC converters are used in data networking equipment, distributed power architecture, and telecommunication devices, as well as data storage systems, computers and peripherals. Opportunities for the DC-DC products also extend into industrial applications.
With the acquisition of the Power Solutions business from ABB in 2014, Bel's power solutions product portfolio, R&D capabilities and customer base were significantly expanded. Already a leader in DC/DC board mount products, since 2014 Bel has offered a sizeable portfolio of AC/DC products with industry leading efficiency and power density. The acquisition of Power Solutions also added considerable presence in the railway market and broader industrial markets with Melcher branded products. The Melcher brand is well known for reliability and performance in demanding applications.
Bel circuit protection products include board level fuses (miniature, micro and surface mount), and Polymeric PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) devices, designed for the global electronic and telecommunication markets. Fuses and PTC devices prevent currents in an electrical circuit from exceeding certain predetermined levels, acting as a safety valve to protect expensive components from damage by cutting off high currents before they can generate enough heat to cause smoke or fire. Additionally, PTC devices are resettable and do not have to be replaced before normal operation of the end product can resume.
|
Product Line
|
Function
|
Applications
|
Brands Sold Under
|
|
|
Power Solutions & Protection
|
Front-End Power Supplies
|
Provides the primary point of isolation between AC main line (input) and the low-voltage DC output that is used to power all electronics downstream
|
Servers, telecommunication, network and data storage equipment
|
Bel Power Solutions, Power-One
|
|
Board-Mount Power Products
|
These are designed to be mounted on a circuit board. These converters take input voltage and provide localized on-board power to low-voltage electronics.
|
Telecom (central office switches), networking and a broad range of industrial applications
|
Bel Power Solutions, Power-One, Melcher
|
|
|
Industrial Power Products
|
Converts between AC main line inputs and a wide variety of DC output voltages.
|
Rail, transportation, automation, test and measurement, medical, military and aerospace applications.
|
Bel Power Solutions, Power-One, Melcher
|
|
|
Module Products
|
Condition, filter, and isolate the electronic signal to ensure accurate data/voice/video transmission within a highly integrated, reduced footprint.
|
Broadband equipment, home networking, set top boxes, and telecom equipment supporting ISDN, T1/E1 and DSL technologies. Industrial applications include Smart Meters, Smart Grid communication platforms, vehicle communications and traffic management.
|
Bel
|
|
|
Circuit Protection
|
Protects devices by preventing current in an electrical circuit from exceeding acceptable levels.
|
Power supplies, cell phone chargers, consumer electronics, and battery protection.
|
Bel
|
Connectivity Solutions
Bel offers a comprehensive line of high speed and harsh environment copper and optical fiber connectors and integrated assemblies, which provide connectivity for a wide range of applications across multiple industries including commercial aerospace, military communications, network infrastructure, structured building cabling and several industrial applications. Bel's Stewart Connector business designs and deploys modular connector systems primarily used in high speed Telecom/Datacom applications. In January 2010, Bel completed the acquisition of Cinch Connectors. Cinch products are designed and manufactured for high reliablity/harsh enviroment applications. Cinch also possesses various enabling technologies and expertise with which to provide custom solutions and products. In 2012, the acquistions of Fiberco and GigaCom further enhanced the Cinch product offering with the addition of fiber optic connector and cable products optomized for harsh envirment applications. In 2013, the acquisition of Array further broadened the copper based product portfolio and expanded sales within the aerospace market. The acquisition of Connectivity Solutions in 2014 brought additional products and has strengthened our position with strategic OEM customers in the military, aerospace and networking segments. Connectivity Solutions is a leading innovator and producer of RF coaxial connectors and cables, harsh environment optical active and passive devices, and microwave components.
|
Product Line
|
Function
|
Applications
|
Brands Sold Under
|
|
|
Connectivity Solutions
|
Expanded Beam Fiber Optic Connectors, Cable Assemblies and Active Optical Devices (transceivers and media converters)
|
Harsh-environment, high-reliability, flight-grade optical connectivity for high-speed communications.
|
Military/aerospace, oil and gas well monitoring and exploration, broadcast, communications, RADAR
|
Stratos, Fibreco
|
|
Copper-based Connectors / Cable Assemblies-FQIS
|
Harsh-environment, high-reliability connectivity and fuel quantity monitoring (FQIS).
|
Commercial aerospace, avionics, smart munitions, communications, navigations and various industrial equipment
|
Cinch
|
|
|
RF Connectors, Cable Assemblies, Microwave Devices and Low Loss Cable
|
Connectors and cable assemblies designed to provide connectivity within radio frequency (RF) applications.
|
Military/aerospace, test and measurement, high-frequency and wireless communications
|
Johnson, Trompeter, Midwest Microwave, Semflex
|
|
|
RJ Connectors and Cable Assemblies
|
RJ45 and RJ11 connectivity for data/voice/video transmission.
|
Largely Ethernet applications including network routers, hubs, switches, and patch panels.
|
Stewart Connector
|
Sales and Marketing
We sell our products to customers throughout North America, Europe and Asia. Sales are made through one of three channels: direct strategic account managers, regional sales managers working with independent sales representative organizations or authorized distributors. Bel's strategic account managers are assigned to handle major accounts requiring global coordination.
Independent sales representatives and authorized distributors are overseen by the Company's sales management personnel located throughout the world. As of December 31, 2015, we had a sales and support staff of 233 persons that supported a network of sales representative organizations and non-exclusive distributors. We have written agreements with all of our sales representative organizations and most of our major distributors. These written agreements, terminable on short notice by either party, are standard in the industry.
Sales support functions have also been established and located in our international facilities to provide timely, efficient support for customers. This supplemental level of service, in addition to first-line sales support, enables us to be more responsive to customers' needs on a global level. Our marketing capabilities include product management which drives new product development, application engineering for technical support and marketing communications.
For information regarding customer concentrations, see "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations – Critical Accounting Policies and Other Matters – Revenue Recognition."
Research and Development ("R&D")
Our engineering groups are strategically located around the world to facilitate communication with and access to customers' engineering personnel. This collaborative approach enables partnerships with customers for technical development efforts. On occasion, we execute non-disclosure agreements with customers to help develop proprietary, next generation products destined for rapid deployment.
We also sponsor membership in technical organizations that allow our engineers to participate in developing standards for emerging technologies. It is management's opinion that this participation is critical in establishing credibility and a reputable level of expertise in the marketplace, as well as positioning the Company as an industry leader in new product development.
R&D costs are expensed as incurred and are included in cost of sales on the consolidated statements of operations. Generally, R&D is performed internally for the benefit of the Company. R&D costs include salaries, building maintenance and utilities, rents, materials, administration costs and miscellaneous other items. R&D expenses for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 amounted to $27.7 million, $21.5 million and $14.1 million, respectively.
Competition
We operate in a variety of markets, all of which are highly competitive. There are numerous independent companies and divisions of major companies that manufacture products that are competitive with one or more of our products.
Our ability to compete is dependent upon several factors including product performance, quality, reliability, depth of product line, customer service, technological innovation, design, delivery time and price. Overall financial stability and global presence also give us a favorable position in relation to many of our competitors. Management intends to maintain a strong competitive posture in the markets we serve by continued expansion of our product lines and ongoing investment in research, development and manufacturing resources.
Associates
As of December 31, 2015, we employed 7,971 full-time associates, a decrease of 239 full-time associates from December 31, 2014. At December 31, 2015, we employed 1,487 people at our North American facilities, 5,624 people at our Asian facilities and 860 people at our European facilities, excluding approximately 1,455 workers supplied by independent contractors. Our manufacturing facility in New York is represented by a labor union and all factory workers in the PRC, Worksop, England and Reynosa, Mexico are represented by unions. While the majority of our manufacturing associates are members of workers unions, approximately 471 associates worldwide are covered by collective bargaining agreements expiring within one year. We believe that our relations with our associates are satisfactory.
Raw Materials and Sourcing
We have multiple suppliers for most of the raw materials that we purchase. Where possible, we have contractual agreements with suppliers to assure a continuing supply of critical components.
With respect to those items which are purchased from single sources, we believe that comparable items would be available in the event that there was a termination of our existing business relationships with any such supplier. While such a termination could produce a disruption in production, we believe that the termination of business with any one of our suppliers would not have a material adverse effect on our long-term operations. Actual experience could differ materially from this belief as a result of a number of factors, including the time required to locate an alternative supplier, and the nature of the demand for our products. In the past, we have experienced shortages in certain raw materials, such as capacitors, ferrites and integrated circuits ("IC's"), when these materials were in great demand. Even though we may have more than one supplier for certain materials, it is possible that these materials may not be available to us in sufficient quantities or at the times desired by us. In the event that the current economic conditions have a negative impact on the financial condition of our suppliers, this may impact the availability and cost of our raw materials.
Backlog
We typically manufacture products against firm orders and projected usage by customers. Cancellation and return arrangements are either negotiated by us on a transactional basis or contractually determined. We estimate the value of the backlog of orders as of February 29, 2016 to be approximately $126.1 million as compared with a backlog of $150.4 million as of February 28, 2015. Management expects that substantially all of the Company's backlog as of February 29, 2016 will be shipped by December 31, 2016. Factors that could cause the Company to fail to ship all such orders by year-end include unanticipated supply difficulties, changes in customer demand and new customer designs. Due to these factors, backlog may not be a reliable indicator of the timing of future sales. See Item 1A of this Annual Report - "Risk Factors - Our backlog figures may not be reliable indicators."
Intellectual Property
We have acquired or been granted a number of patents in the U.S., Europe and Asia and have additional patent applications pending relating to our products. While we believe that the issued patents are defendable and that the pending patent applications relate to patentable inventions, there can be no assurance that a patent will be obtained from the applications or that our existing patents can be successfully defended. It is management's opinion that the successful continuation and operation of our business does not depend upon the ownership of patents or the granting of pending patent applications, but upon the innovative skills, technical competence and marketing and managerial abilities of our personnel. Our U.S. design patents have a life of 14 years and our U.S. utility patents have a life of 17 years from the date of issue or 20 years from filing of patent applications. Our existing patents expire on various dates from June 2016 to April 2033.
We utilize registered trademarks in the U.S., Europe and Asia to identify various products that we manufacture. The trademarks survive as long as they are in use and the registrations of these trademarks are renewed.
Available Information
We maintain a website at www.belfuse.com where we make available the proxy statements, press releases, registration statements and reports on Forms 3, 4, 8-K, 10-K and 10-Q that we and our insiders file with the SEC. These forms are made available as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC. Press releases are also issued via electronic transmission to provide access to our financial and product news, and we provide notification of and access to voice and internet broadcasts of our quarterly and annual results. Our website also includes investor presentations and corporate governance materials.
The risks described below should be carefully considered before making an investment decision. These are the risk factors that we consider to be the most significant risk factors, but they are not the only risk factors that should be considered in making an investment decision. This Form 10-K also contains Forward-Looking Statements that involve risks and uncertainties. See the "Cautionary Notice Regarding Forward-Looking Information," above. Our business, consolidated financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected by any of the risk factors described below, under "Cautionary Notice Regarding Forward-Looking Information" or with respect to specific Forward-Looking Statements presented herein. The trading price of our securities could decline due to any of these risks, and investors in our securities may lose all or part of their investment. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently believe to be immaterial may also materially adversely affect our business in the future.
We conduct business in a highly competitive industry.
Our business is largely in a highly competitive worldwide industry, with relatively low barriers to competitive entry. We compete principally on the basis of product performance, quality, reliability, depth of product line, customer service, technological innovation, design, delivery time and price. The industry in which we operate has become increasingly concentrated and globalized in recent years and our major competitors, some of which are larger than Bel, have significant financial resources and technological capabilities.
We may not be able to generate sufficient cash to service all of our indebtedness and may be forced to take other actions to satisfy our obligations under our indebtedness, which may not be successful.
Our ability to make scheduled payments on or refinance our debt obligations depends on our financial condition and operating performance, which are subject to prevailing economic and competitive conditions and to certain financial, business, legislative, regulatory and other factors beyond our control. We may be unable to maintain a level of cash flows from operating activities sufficient to permit us to pay the principal, premium, if any, and interest on our indebtedness.
If our cash flows and capital resources are insufficient to fund our debt service obligations, we could face substantial liquidity problems and could be forced to reduce or delay investments and capital expenditures or to dispose of material assets or operations, seek additional debt or equity capital or restructure or refinance our indebtedness. We may not be able to effect any such alternative measures on commercially reasonable terms or at all and, even if successful, those alternative actions may not allow us to meet our scheduled debt service obligations. Our credit agreement restricts our ability to dispose of assets and use the proceeds from those dispositions and may also restrict our ability to raise debt or equity capital to be used to repay other indebtedness when it becomes due. We may not be able to consummate those dispositions or to obtain proceeds in an amount sufficient to meet any debt service obligations then due.
In addition, we conduct a substantial portion of our operations through our subsidiaries, certain of which are not guarantors of our indebtedness. Accordingly, repayment of our indebtedness is dependent on the generation of cash flow by our subsidiaries and their ability to make such cash available to us, by dividend, debt repayment or otherwise. Unless they are guarantors of our indebtedness, our subsidiaries do not have any obligation to pay amounts due on indebtedness or to make funds available for that purpose. Our subsidiaries may not be able to, or may not be permitted to, make distributions to enable us to make payments in respect of our indebtedness. Each subsidiary is a distinct legal entity, and, under certain circumstances, legal and contractual restrictions may limit our ability to obtain cash from our subsidiaries. While the indenture governing certain of our senior notes, these notes and the credit agreement governing the senior secured credit facilities limit the ability of certain of our subsidiaries to incur consensual restrictions on their ability to pay dividends or make other intercompany payments to us, these limitations are subject to qualifications and exceptions. In the event that we do not receive distributions from our subsidiaries, we may be unable to make required principal and interest payments on our indebtedness.
Our inability to generate sufficient cash flows to satisfy our debt obligations, or to refinance our indebtedness on commercially reasonable terms or at all, would materially and adversely affect our consolidated financial position and results of operations.
If we cannot make scheduled payments on our debt, we will be in default, the lenders under the credit agreement could terminate their commitments to loan money, the lenders could foreclose against the assets securing their borrowings and we could be forced into bankruptcy or liquidation.
Our high level of indebtedness could negatively impact our access to the capital markets and our ability to satisfy financial covenants under our existing credit agreement.
We incurred substantial amounts of indebtedness to fund the acquisitions of Power Solutions and Connectivity Solutions in 2014, and we may need to incur additional indebtedness to finance operations or for other general corporate purposes. Our consolidated principal amount of outstanding indebtedness was $187.2 million at December 31, 2015, resulting in a leverage ratio of 2.98x adjusted EBITDA, as calculated in accordance with our credit agreement. Accordingly, our debt service requirements are significant in relation to our net sales and cash flow. This leverage exposes us to risk in the event of downturns in our business, in our industry or in the economy generally, and may impair our operating flexibility and our ability to compete effectively. Our current credit agreement requires us to maintain a certain covenant leverage ratio, and the ratio becomes more restrictive at set levels during the term. If we do not continue to satisfy this required ratio or receive waivers from our lenders, we will be in default under the credit agreement, which could result in an accelerated maturity of our debt obligations.
Our backlog figures may not be reliable indicators.
Many of the orders that comprise our backlog may be delayed, accelerated or canceled by customers without penalty. Customers may on occasion double order from multiple sources to ensure timely delivery when leadtimes are particularly long. Customers often cancel orders when business is weak and inventories are excessive. Therefore, we cannot be certain that the amount of our backlog equals or exceeds the level of orders that will ultimately be delivered. Our results of operations could be adversely impacted if customers cancel a material portion of orders in our backlog.
There are several factors which can cause us to lower our prices or otherwise cause our margins to suffer.
Our prices and/or margins could be substantially impacted by the following factors:
a) The average selling prices for our products tend to decrease over their life cycles, and customers put pressure on suppliers to lower prices even when production costs are increasing. Our profits suffer if we are not able to reduce our costs of production, introduce technological innovations as sales prices decline, or pass through cost increases to customers.
b) Any drop in demand for our products or increase in supply of competitive products could cause a dramatic drop in our average sales prices which in turn could result in a decrease in our gross margins. A shift in product mix could also have an unfavorable or favorable impact on our gross margins, depending upon the underlying raw material content and labor requirements of the associated products.
c) Increased competition from low cost suppliers around the world has put further pressures on pricing. We continually strive to lower our costs, negotiate better pricing for components and raw materials and improve our operating efficiencies. Profit margins will be materially and adversely impacted if we are not able to reduce our costs of production or introduce technological innovations when sales prices decline.
Our annual effective income tax rate can change materially as a result of changes in our mix of U.S. and foreign earnings and other factors, including changes in tax laws and changes made by regulatory authorities.
Our overall effective income tax rate is equal to our total tax expense as a percentage of total earnings before tax. However, income tax expense and benefits are not recognized on a global basis but rather on a jurisdictional or legal entity basis. Losses in one jurisdiction may not be used to offset profits in other jurisdictions and may cause an increase in our tax rate. Changes in statutory tax rates and laws, as well as ongoing audits by domestic and international authorities, could affect the amount of income taxes and other taxes paid by us. For example, legislative proposals to change U.S. taxation of non-U.S. earnings could increase our effective tax rate. Also, changes in the mix of earnings (or losses) between jurisdictions and assumptions used in the calculation of income taxes, among other factors, could have a significant effect on our overall effective income tax rate. In addition, our effective tax rate would increase if we were unable to generate sufficient future taxable income in certain jurisdictions, or if we were otherwise required to increase our valuation allowances against our deferred tax assets.
We are subject to taxation in multiple jurisdictions. As a result, any adverse development in the tax laws of any of these jurisdictions or any disagreement with our tax positions could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated financial condition or results of operations.
We are subject to taxation in, and to the tax laws and regulations of, multiple jurisdictions as a result of the international scope of our operations and our corporate and financing structure. We are also subject to transfer pricing laws with respect to our intercompany transactions, including those relating to the flow of funds among our companies. Adverse developments in these laws or regulations, or any change in position regarding the application, administration or interpretation thereof, in any applicable jurisdiction, could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated financial condition or results of our operations. In addition, the tax authorities in any applicable jurisdiction, including the United States, may disagree with the positions we have taken or intend to take regarding the tax treatment or characterization of any of our transactions. If any applicable tax authorities, including U.S. tax authorities, were to successfully challenge the tax treatment or characterization of any of our transactions, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated financial condition or consolidated results of our operations.
In the PRC, we are challenged to match availability of workers and maintain leadtimes in line with customer demand for certain of our products, which demand has been highly volatile in recent years. This volatility can materially adversely affect Bel's results.
In the PRC, the availability of labor is cyclical and is significantly affected by the migration of workers in relation to the annual Lunar New Year holiday as well as economic conditions in the PRC. In addition, we have little visibility into the ordering habits of our customers and can be subjected to large and unpredictable variations in demand for our products. Accordingly, we must continually recruit and train new workers to replace those lost to attrition each year and to address peaks in demand that may occur from time to time. These recruiting and training efforts and related inefficiences, as well as overtime required in order to meet demand, can add volatility to the costs incurred by the Company for labor in the PRC.
We are dependent on our ability to develop new products.
Our future operating results are dependent, in part, on our ability to develop, produce and market new and more technologically advanced products. There are numerous risks inherent in this process, including the risks that we will be unable to anticipate the direction of technological change or that we will be unable to timely develop and bring to market new products and applications to meet customers' changing needs.
Our acquisitions may not produce the anticipated results.
A significant portion of our growth has been attributable to acquisitions. We cannot assure that we will identify or successfully complete transactions with suitable acquisition candidates in the future. If an acquired business fails to operate as anticipated or cannot be successfully integrated with our other businesses, our results of operations, enterprise value, market value and prospects could all be materially and adversely affected. Integration of new acquisitions into our consolidated operations may result in lower average operating results for the group as a whole, and may divert management's focus from the ongoing operations of the Company during the integration period.
Our strategy also focuses on the reduction of selling, general and administrative expenses through the integration or elimination of redundant sales facilities and administrative functions at acquired companies. The Company completed two acquisitions in 2013 and two acquisitions in 2014, as previously described in Item 1 of this Form 10-K. If we are unable to achieve our expectations with respect to these or future acquisitions, such inability could have a material and adverse effect on our results of operations. In connection with the 2013 Acquisitions, we have recorded $4.8 million of goodwill and $7.6 million of other intangible assets. In addition, we have recorded $105.4 million of goodwill and $73.2 million of other intangible assets in connection with the 2014 Acquisitions. If our acquisitions fail to perform up to our expectations, or if the value of goodwill or other intangible assets decreases as a result of weakened economic conditions, we could be required to record a non-cash loss from the impairment of these assets.
We may not achieve all of the expected benefits from our restructuring programs.
We have implemented a number of restructuring programs in the last few years. These programs include various cost savings, the consolidation of certain facilities and the reduction of headcount. We have made certain assumptions in estimating the anticipated savings we expect to achieve under such programs, which include the estimated savings from the elimination of certain headcount and the consolidation of facilities. These assumptions may turn out to be incorrect due to a variety of factors. In addition, our ability to realize the expected benefits from these programs is subject to significant business, economic and competitive uncertainties and contingencies, many of which are beyond our control. If we are unsuccessful in implementing these programs or if we do not achieve our expected results, our results of operations and cash flows could be adversely affected or our business operations could be disrupted.
The global nature of our operations exposes us to numerous risks that could materially adversely affect our consolidated financial condition and results of operations.
We operate in 15 countries, and our products are distributed in those countries as well as in other parts of the world. A large portion of our manufacturing operations are located outside of the United States and a large portion of our net sales are generated outside of the United States. Operations outside of the United States, particularly operations in developing regions, are subject to various risks that may not be present or as significant for our U.S. operations. Economic uncertainty in some of the geographic regions in which we operate, including developing regions, could result in the disruption of commerce and negatively impact cash flows from our operations in those areas.
Risks inherent in our international operations include:
|
•
|
|
foreign currency exchange controls and tax rates;
|
|
•
|
|
foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations, including devaluations;
|
|
•
|
|
the potential for changes in regional and local economic conditions, including local inflationary pressures;
|
|
•
|
|
restrictive governmental actions such as those on transfer or repatriation of funds and trade protection matters, including antidumping duties, tariffs, embargoes and prohibitions or restrictions on acquisitions or joint ventures;
|
|
•
|
|
changes in laws and regulations, including the laws and policies of the United States affecting trade and foreign investment;
|
|
•
|
|
the difficulty of enforcing agreements and collecting receivables through certain foreign legal systems;
|
|
•
|
|
variations in protection of intellectual property and other legal rights;
|
|
•
|
|
more expansive legal rights of foreign unions or works councils;
|
|
•
|
|
changes in labor conditions and difficulties in staffing and managing international operations;
|
|
•
|
|
social plans that prohibit or increase the cost of certain restructuring actions;
|
|
•
|
|
the potential for nationalization of enterprises or facilities; and
|
|
•
|
|
unsettled political conditions and possible terrorist attacks against U.S. or other interests.
|
In addition, there are potential tax inefficiencies and tax costs in repatriating funds from our non-U.S. subsidiaries.
These and other factors may have a material adverse effect on our international operations and, consequently, on our consolidated financial condition or consolidated results of operations.
The loss of certain substantial customers could materially and adversely affect us.
During the year ended December 31, 2015, sales to one direct customer exceeded 10% of our consolidated net sales. Hon Hai Precision Industry Company Ltd., a contract manufacturer utilized by various end customers, represented 13.2% of our 2015 consolidated net sales. We believe that the loss of this customer could have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position and consolidated results of operations. We have experienced significant concentrations in prior years. See Note 12, "Segments" for additional disclosures related to our significant customers.
We may experience labor unrest.
As we implement transfers of certain of our operations, we may experience strikes or other types of labor unrest as a result of lay-offs or termination of employees in higher labor cost countries. Our manufacturing facilities in New York State, the United Kingdom and Mexico are represented by labor unions and substantially all of our factory workers in the PRC are represented by government-sponsored unions.
We may experience labor shortages.
Government, economic, social and labor policies in the PRC may cause shortages of factory labor in areas where we have some of our products manufactured. If we are required to manufacture more of these products outside of the PRC as a result of such shortages, our margins will likely be materially adversely affected.
Our results of operations may be materially and adversely impacted by environmental and other regulations.
Our manufacturing operations, products and/or product packaging are subject to environmental laws and regulations governing air emissions; wastewater discharges; the handling, disposal and remediation of hazardous substances, wastes and certain chemicals used or generated in our manufacturing processes; employee health and safety labeling or other notifications with respect to the content or other aspects of our processes, products or packaging; restrictions on the use of certain materials in or on design aspects of our products or product packaging; and, responsibility for disposal of products or product packaging. More stringent environmental regulations may be enacted in the future, and we cannot presently determine the modifications, if any, in our operations that any such future regulations might require, or the cost of compliance with these regulations.
We may face risks relating to climate change that could have an adverse impact on our business.
Greenhouse gas ("GHG") emissions have increasingly become the subject of substantial international, national, regional, state and local attention. GHG emission regulations have been promulgated in certain of the jurisdictions in which we operate, and additional GHG requirements are in various stages of development. Such measures could require us to modify existing or obtain new permits, implement additional pollution control technology, curtail operations or increase our operating costs. Any additional regulation of GHG emissions, including a cap-and-trade system, technology mandate, emissions tax, reporting requirement or other program, could materially adversely affect our business.
Regulations related to conflict minerals will cause the Company to incur additional expenses and may have other adverse consequences.
The SEC has adopted inquiry, diligence and additional disclosure requirements related to certain minerals sourced from the Democratic Republic of the Congo and surrounding countries, or "conflict minerals", that are necessary to the functionality of a product manufactured, or contracted to be manufactured, by an SEC reporting company. The minerals that the rules cover are commonly referred to as "3TG" and include tin, tantalum, tungsten and gold. As a public company, Bel was required to make its first filing under these new rules on May 31, 2014. In such filing, Bel described the due diligence it had undertaken of its suppliers in an effort to determine the source of any conflict minerals used in its products or components. These due diligence requirements are ongoing, and Bel will continue to incur additional costs, which could be substantial, related to its due diligence and compliance process. In addition, the Company's supply chain is complex, and if it is not able to determine with certainty the source and chain of custody for all conflict minerals used in its products that are sourced from the Democratic Republic of the Congo and surrounding countries or determine that its products are "conflict free", then the Company may face reputational challenges with customers, investors or others. As there may be only a limited number of suppliers offering "conflict free" minerals, if the Company chooses to use only conflict minerals that are "conflict free" in its products and components, the Company cannot be sure that it will be able to obtain necessary materials from such suppliers in sufficient quantities or at competitive prices.
Our results may vary substantially from period to period.
Our revenues and expenses may vary significantly from one accounting period to another accounting period due to a variety of factors, including customers' buying decisions, our product mix, the volatility of raw material costs, the impact of competition, the impact of the Chinese New Year and general market and economic conditions. Such variations could significantly impact our stock price.
A shortage of availability or an increase in the cost of high-quality raw materials, components and other resources may adversely impact our ability to procure these items at cost effective prices and thus may negatively impact profit margins.
Our results of operations may be materially adversely impacted by difficulties in obtaining raw materials, supplies, power, labor, natural resources and any other items needed for the production of our products, as well as by the effects of quality deviations in raw materials and the effects of significant fluctuations in the prices of existing inventories and purchase commitments for these materials. Many of these materials and components are produced by a limited number of suppliers and their availability to us may be constrained by supplier capacity.
As product life cycles shorten and during periods of market slowdowns, the risk of materials obsolescence increases and this may materially and adversely impact our financial results.
Rapid shifts in demand for various products may cause some of our inventory of raw materials, components or finished goods to become obsolete.
The life cycles and demand for our products are directly linked to the life cycles and demand for the end products into which they are designed. Rapid shifts in the life cycles or demand for these end products due to technological shifts, economic conditions or other market trends may result in material amounts of either raw materials or finished goods inventory becoming obsolete. While the Company works diligently to manage inventory levels, rapid shifts in demand may result in obsolete or excess inventory and materially adversely impact financial results.
A loss of the services of the Company's executive officers or other skilled associates could negatively impact our operations and results.
The success of the Company's operations is largely dependent upon the performance of its executive officers, managers, engineers and sales people. Many of these individuals have a significant number of years of experience within the Company and/or the industry in which we compete and would be extremely difficult to replace. The loss of the services of any of these associates may materially and adversely impact our results of operations if we are unable to replace them in a timely manner.
Our stock price, like that of many technology companies, has been and may continue to be volatile.
The market price of our common stock may fluctuate as a result of variations in our quarterly operating results and other factors beyond our control. These fluctuations may be exaggerated if the trading volume of our common stock is low. The market price of our common stock may rise and fall in response to a variety of other factors, including:
|
·
|
announcements of technological or competitive developments;
|
|
·
|
general market or economic conditions;
|
|
·
|
market or economic conditions specific to particular geographical areas in which we operate;
|
|
·
|
acquisitions or strategic alliances by us or our competitors;
|
|
·
|
the gain or loss of a significant customer or order; or
|
|
·
|
changes in estimates of our financial performance or changes in recommendations by securities analysts regarding us or our industry
|
In addition, equity securities of many technology companies have experienced significant price and volume fluctuations even in periods when the capital markets generally are not distressed. These price and volume fluctuations often have been unrelated to the operating performance of the affected companies.
Our intellectual property rights may not be adequately protected under the current state of the law.
Our efforts to protect our intellectual property rights through patent, copyright, trademark and trade secret laws in the United States and in other countries may not prevent misappropriation, and our failure to protect our proprietary rights could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, operating results and future prospects. A third party could, without authorization, copy or otherwise appropriate our proprietary information. Our agreements with employees and others who participate in development activities could be breached, we may not have adequate remedies for any breach, and our trade secrets may otherwise become known or independently developed by competitors.
We may be sued by third parties for alleged infringement of their proprietary rights and we may incur defense costs and possibly royalty obligations or lose the right to use technology important to our business.
From time to time, we receive claims by third parties asserting that our products violate their intellectual property rights. Any intellectual property claims, with or without merit, could be time consuming and expensive to litigate or settle and could divert management attention from administering our business. A third party asserting infringement claims against us or our customers with respect to our current or future products may materially and adversely affect us by, for example, causing us to enter into costly royalty arrangements or forcing us to incur settlement or litigation costs.
As a result of protective provisions in the Company's certificate of incorporation, the voting power of certain officers, directors and principal shareholders may be increased at future meetings of the Company's shareholders.
The Company's certificate of incorporation provides that if a shareholder, other than shareholders subject to specific exceptions, acquires (after the date of the Company's 1998 recapitalization) 10% or more of the outstanding Class A common stock and does not own an equal or greater percentage of all then outstanding shares of both Class A and Class B common stock (all of which common stock must have been acquired after the date of the 1998 recapitalization), such shareholder must, within 90 days of the trigger date, purchase Class B common shares, in an amount and at a price determined in accordance with a formula described in the Company's certificate of incorporation, or forfeit its right to vote its Class A common shares. As of February 29, 2016, to the Company's knowledge, there was one shareholder of the Company's common stock with ownership in excess of 10% of Class A outstanding shares with no ownership of the Company's Class B common stock and with no basis for exception from the operation of the above-mentioned provisions. In order to vote its shares at Bel's next shareholders' meeting, this shareholder must either purchase the required number of Class B common shares or sell or otherwise transfer Class A common shares until its Class A holdings are under 10%. As of February 29, 2016, to the Company's knowledge, this shareholder owned 23.1% of the Company's Class A common stock and had not taken steps to either purchase the required number of Class B common shares or sell or otherwise transfer Class A common shares until its Class A holdings fall below 10%. Unless and until this situation is satisfied in a manner permitted by the Company's Restated Certificate of Incorporation, the subject shareholder will not be permitted to vote its shares of common stock.
To the extent that the voting rights of particular holders of Class A common stock are suspended as of times when the Company's shareholders vote due to the above-mentioned provisions, such suspension will have the effect of increasing the voting power of those holders of Class A common shares whose voting rights are not suspended. As of February 29, 2016, Daniel Bernstein, the Company's chief executive officer, beneficially owned 353,204 Class A common shares (or 21.1%) of the outstanding Class A common shares whose voting rights were not suspended, the Estate of Elliot Bernstein beneficially owned 82,357 Class A common shares (or 4.9%) of the outstanding Class A common shares whose voting rights were not suspended and all directors and executive officers as a group (which includes Daniel Bernstein, but does not include the Estate of Elliot Bernstein) beneficially owned 501,095 Class A common shares (or 29.9%) of the outstanding Class A common shares whose voting rights were not suspended.
Cyber risk and the failure to maintain the integrity of our operational or security systems or infrastructure, or those of third parties with which we do business, could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated financial condition and results of operations.
We could be subject to various types of information technology vulnerabilities, threats and targeted computer crimes which pose a risk to the security of our systems and networks and the confidentiality, availability and integrity of our data. Disruptions or failures in the physical infrastructure or operating systems that support our businesses and customers, or cyber-attacks or security breaches of our networks or systems, could result in the loss of customers and business opportunities, legal liability, regulatory fines, penalties or intervention, reputational damage, reimbursement or other compensatory costs, and additional compliance costs, any of which could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. While we attempt to mitigate these risks, our systems, networks, products, solutions and services remain potentially vulnerable to advanced and persistent threats. We also maintain and have access to sensitive, confidential or personal data or information in certain of our businesses that is subject to privacy and security laws, regulations and customer controls. Despite our efforts to protect such sensitive, confidential or personal data or information, our facilities and systems and those of our customers and third-party service providers may be vulnerable to security breaches, theft, misplaced or lost data, programming and/or human errors that could lead to the compromising of sensitive, confidential or personal data or information, improper use of our systems, software solutions or networks, unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification or destruction of information, defective products, production downtimes and operational disruptions, which in turn could adversely affect our consolidated financial condition and results of operations.
As a U.S. Government contractor, we are subject to a number of procurement rules and regulations.
We must comply with and are affected by laws and regulations relating to the award, administration, and performance of U.S. Government contracts. Government contract laws and regulations affect how we do business with our customers and, in some instances, impose added costs on our business. A violation of specific laws and regulations could result in the imposition of fines and penalties or the termination of our contracts or debarment from bidding on contracts. These fines and penalties could be imposed for failing to follow procurement integrity and bidding rules, employing improper billing practices or otherwise failing to follow cost accounting standards, receiving or paying kickbacks, or filing false claims. We have been, and expect to continue to be, subjected to audits and investigations by government agencies. The failure to comply with the terms of our government contracts could harm our business reputation. It could also result in our progress payments being withheld.
In some instances, these laws and regulations impose terms or rights that are more favorable to the government than those typically available to commercial parties in negotiated transactions. For example, the U.S. Government may terminate any of our government contracts and, in general, subcontracts, at its convenience as well as for default based on performance. Upon termination for convenience of a fixed-price type contract, we normally are entitled to receive the purchase price for delivered items, reimbursement for allowable costs for work-in-process, and an allowance for profit on work actually completed on the contract or adjustment for loss if completion of performance would have resulted in a loss. Upon termination for convenience of a Federal Government cost reimbursement contract, we normally are entitled to reimbursement of allowable costs plus a portion of the fee. Such allowable costs would normally include our cost to terminate agreements with our suppliers and subcontractors. The amount of the fee recovered, if any, is related to the portion of the work accomplished prior to termination and is determined by negotiation.
None.
The Company is headquartered in Jersey City, New Jersey, where it currently owns 19,000 square feet of office and warehouse space. In addition to its facilities in Jersey City, New Jersey, the Company leases 177,000 square feet in 15 facilities and owns properties of 168,000 square feet which are used primarily for management, financial accounting, engineering, sales and administrative support.
The Company also operated 23 manufacturing facilities in 7 countries as of December 31, 2015. Approximately 19% of the 2.7 million square feet the Company occupies is owned while the remainder is leased. See Note 16, "Commitments and Contingencies", for additional information pertaining to leases.
The following is a list of the locations of the Company's principal manufacturing facilities at December 31, 2015:
|
Location
|
Approximate
Square Feet
|
Owned/
Leased
|
Percentage
Used for
Manufacturing
|
||||||
|
Dongguan, People's Republic of China
|
650,000
|
Leased
|
28
|
%
|
|||||
|
Pingguo, People's Republic of China
|
251,000
|
Leased
|
71
|
%
|
|||||
|
Shanghai, People's Republic of China
|
32,000
|
Leased
|
70
|
%
|
|||||
|
Shenzhen, People's Republic of China
|
227,000
|
Leased
|
100
|
%
|
|||||
|
Zhongshan, People's Republic of China
|
315,000
|
Leased
|
86
|
%
|
|||||
|
Zhongshan, People's Republic of China
|
118,000
|
Owned
|
100
|
%
|
|||||
|
Zhongshan, People's Republic of China
|
78,000
|
Owned
|
100
|
%
|
|||||
|
Louny, Czech Republic
|
11,000
|
Owned
|
75
|
%
|
|||||
|
Dubnica nad Vahom, Slovakia
|
35,000
|
Owned
|
100
|
%
|
|||||
|
Dubnica nad Vahom, Slovakia
|
70,000
|
Leased
|
100
|
%
|
|||||
|
Worksop, England (a)
|
52,000
|
Leased
|
28
|
%
|
|||||
|
Great Dunmow, England
|
9,000
|
Leased
|
52
|
%
|
|||||
|
Chelmsford, United Kingdom
|
21,000
|
Leased
|
60
|
%
|
|||||
|
Dominican Republic
|
41,000
|
Leased
|
85
|
%
|
|||||
|
Cananea, Mexico
|
42,000
|
Leased
|
60
|
%
|
|||||
|
Reynosa, Mexico
|
77,000
|
Leased
|
56
|
%
|
|||||
|
Inwood, New York
|
39,000
|
Owned
|
40
|
%
|
|||||
|
Glen Rock, Pennsylvania
|
74,000
|
Owned
|
60
|
%
|
|||||
|
Waseca, Minnesota
|
124,000
|
Leased
|
83
|
%
|
|||||
|
McAllen, Texas
|
40,000
|
Leased
|
56
|
%
|
|||||
|
Miami, Florida
|
29,000
|
Leased
|
85
|
%
|
|||||
|
Melbourne, Florida
|
18,000
|
Leased
|
64
|
%
|
|||||
|
Mesa, Arizona
|
7,000
|
Leased
|
100
|
%
|
|||||
|
2,360,000
|
|||||||||
Of the space described above, 337,000 square feet is used for engineering, warehousing, sales and administrative support functions at various locations and 468,000 square feet is designated for dormitories, canteen and other employee related facilities in the PRC.
The Territory of Hong Kong became a Special Administrative Region ("SAR") of the PRC during 1997. The territory of Macao became a SAR of the PRC at the end of 1999. Management cannot presently predict what future impact, if any, this will have on the Company or how the political climate in the PRC will affect its contractual arrangements in the PRC. A significant portion of the Company's manufacturing operations and approximately 38.7% of its identifiable assets are located in Asia.
The information called for by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to the caption "Legal Proceedings" in Note 16, "Commitments and Contingencies."
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity and Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
|
(a)
|
Market Information
|
The Company's voting Class A Common Stock, par value $0.10 per share, and non-voting Class B Common Stock, par value $0.10 per share ("Class A" and "Class B," respectively), are traded on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the symbols BELFA and BELFB. The following table sets forth the high and low sales price range (as reported by The Nasdaq Stock Market Inc.) for the Common Stock on NASDAQ for each quarter during the past two years.
|
Class A
|
Class B
|
|||||||||||||||
|
High
|
Low
|
High
|
Low
|
|||||||||||||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2015
|
||||||||||||||||
|
First Quarter
|
$
|
24.66
|
$
|
18.17
|
$
|
27.53
|
$
|
18.79
|
||||||||
|
Second Quarter
|
23.38
|
17.33
|
23.23
|
17.35
|
||||||||||||
|
Third Quarter
|
20.95
|
14.19
|
23.77
|
16.46
|
||||||||||||
|
Fourth Quarter
|
21.80
|
14.29
|
23.73
|
16.16
|
||||||||||||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2014
|
||||||||||||||||
|
First Quarter
|
$
|
20.04
|
$
|
17.80
|
$
|
22.10
|
$
|
17.80
|
||||||||
|
Second Quarter
|
27.23
|
19.00
|
27.50
|
19.57
|
||||||||||||
|
Third Quarter
|
25.73
|
21.17
|
26.67
|
22.16
|
||||||||||||
|
Fourth Quarter
|
26.70
|
20.33
|
29.26
|
22.18
|
||||||||||||
(b) Holders
As of February 29, 2016, there were 56 registered shareholders of the Company's Class A Common Stock and 218 registered shareholders of the Company's Class B Common Stock. As of February 29, 2016, the Company estimates that there were 708 beneficial shareholders of the Company's Class A Common Stock and 2,390 beneficial shareholders of the Company's Class B Common Stock. At February 29, 2016, to the Company's knowledge, there was one shareholder of the Company's Class A common stock whose voting rights were suspended. This shareholder owned 23.1% of the Company's outstanding shares of Class A common stock. For additional discussion, see Item 1A – "Risk Factors – As a result of protective provisions in the Company's certificate of incorporation, the voting power of certain officers, directors and principal shareholders may be increased at future meetings of the Company's shareholders".
(c) Dividends
During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company declared dividends on a quarterly basis at a rate of $0.06 per Class A share of common stock and $0.07 per Class B share of common stock totaling $3.2 million, $3.2 million and $3.1 million, respectively. There are no contractual restrictions on the Company's ability to pay dividends provided the Company is not in default under its credit agreements immediately before such payment and after giving effect to such payment. On February 1, 2016, the Company paid a dividend to all shareholders of record at January 15, 2016 of Class A and Class B Common Stock in the total amount of $0.1 million ($0.06 per share) and $0.6 million ($0.07 per share), respectively. On February 17, 2016, Bel's Board of Directors declared a dividend in the amount of $0.06 per Class A common share and $0.07 per Class B common share which is scheduled to be paid on May 1, 2016 to all shareholders of record at April 15, 2016. The Company currently anticipates paying dividends quarterly in the future.
|
(d)
|
Common Stock Performance Comparisons
|
The following graph shows, for the five years ended December 31, 2015, the cumulative total return on an investment of $100 assumed to have been made on December 31, 2010 in our common stock. The graph compares this return ("Bel") with that of comparable investments assumed to have been made on the same date in: (a) the NASDAQ Stock Market (U.S. Companies) and (b) a group of companies within our industry.
Total return for each assumed investment assumes the reinvestment of all dividends on December 31 of the year in which the dividends were paid.
Comparison of 5 Year Cumulative Total Return
Assumes Initial Investment of $100
December 2015
Assumes Initial Investment of $100
December 2015
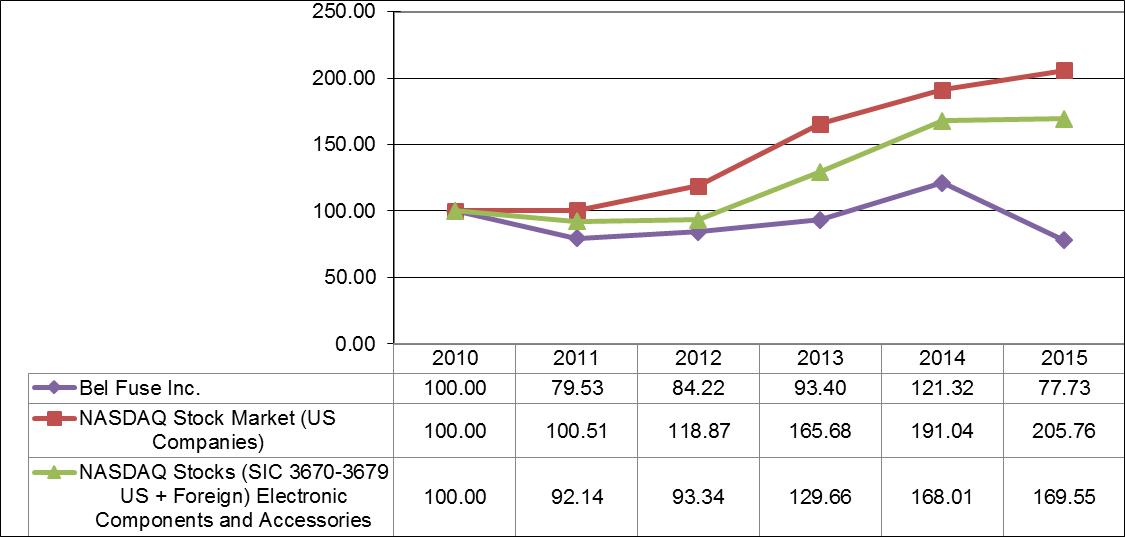
The following tables set forth selected consolidated financial data as of the dates and for the periods presented. The selected consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 and the selected consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 have been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements and related notes that we have included elsewhere in this Form 10-K. The selected financial data below includes the results of acquired companies from their respective acquisition dates. The selected consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 and the selected consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011 have been derived from audited consolidated financial statements that are not presented in this Form 10-K. The selected consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 and the selected consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 have been revised to reflect measurement period adjustments related to the 2012, 2013 and 2014 Acquisitions.
For information regarding the Company's acquisitions, see Note 2, "Acquisitions and Disposition."
|
Years Ended December 31,
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
2012
|
2011
|
||||||||||||||||
|
(In thousands of dollars, except per share data)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Selected Consolidated Statements of Operations Data: (a)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net sales
|
$
|
567,080
|
$
|
487,076
|
$
|
349,189
|
$
|
286,594
|
$
|
295,121
|
||||||||||
|
Cost of sales
|
458,253
|
399,721
|
286,952
|
240,115
|
244,749
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses
|
78,113
|
72,051
|
45,803
|
39,571
|
39,284
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation
|
2,815
|
2,717
|
1,879
|
1,767
|
1,709
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Litigation charges (b)
|
-
|
-
|
41
|
26
|
3,471
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Restructuring charges (c)
|
2,114
|
1,832
|
1,387
|
5,245
|
314
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Earnings before income taxes
|
25,732
|
9,770
|
15,165
|
997
|
7,872
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Net earnings
|
$
|
19,197
|
$
|
8,603
|
$
|
15,908
|
$
|
2,373
|
$
|
3,764
|
||||||||||
|
Reconciliation of net earnings to EBITDA (d):
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net earnings
|
$
|
19,197
|
$
|
8,603
|
$
|
15,908
|
$
|
2,373
|
$
|
3,764
|
||||||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization (e)
|
23,008
|
20,367
|
12,382
|
9,113
|
8,667
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Interest expense
|
7,588
|
3,978
|
156
|
16
|
-
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Income tax provision (benefit)
|
6,535
|
1,167
|
(743
|
)
|
(1,376
|
)
|
4,108
|
|||||||||||||
|
EBITDA (d)
|
$
|
56,328
|
$
|
34,115
|
$
|
27,703
|
$
|
10,126
|
$
|
16,539
|
||||||||||
|
Net earnings per share:
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Class A common share - basic and diluted
|
1.53
|
0.69
|
1.32
|
0.17
|
0.28
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Class B common share - basic and diluted
|
1.64
|
0.75
|
1.41
|
0.21
|
0.33
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Cash dividends declared per share:
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Class A common share
|
0.24
|
0.24
|
0.24
|
0.24
|
0.24
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Class B common share
|
0.28
|
0.28
|
0.28
|
0.28
|
0.28
|
|||||||||||||||
|
As of December 31,
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
2012
|
2011
|
||||||||||||||||
|
(In thousands of dollars, except percentages)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Selected Consolidated Balance Sheet Data and Ratios:
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents
|
$
|
85,040
|
$
|
77,138
|
$
|
62,123
|
$
|
71,262
|
88,241
|
|||||||||||
|
Working capital
|
163,428
|
188,854
|
137,174
|
144,530
|
165,264
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Goodwill
|
121,634
|
118,369
|
18,490
|
13,559
|
4,163
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Total assets
|
587,011
|
635,421
|
308,141
|
275,189
|
276,911
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Total debt
|
187,188
|
232,625
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Stockholders' equity
|
233,122
|
224,273
|
228,702
|
215,362
|
221,080
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Return on average total assets (f)
|
3.0
|
%
|
1.8
|
%
|
5.4
|
%
|
0.9
|
%
|
1.4
|
%
|
||||||||||
|
Return on average stockholders' equity (f)
|
8.2
|
%
|
3.8
|
%
|
7.3
|
%
|
1.1
|
%
|
1.7
|
%
|
||||||||||
|
(a)
|
See Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," for a discussion of the factors that contributed to our consolidated operating results and our consolidated cash flows for the three years ended December 31, 2015.
|
|
(b)
|
During 2011, the Company recorded litigation charges totaling $3.5 million related to the SynQor and Halo lawsuits. See Note 16, "Commitments and Contingencies," for further information on the SynQor lawsuit. The Halo lawsuit was resolved in 2011.
|
|
(c)
|
See Note 3, "Restructuring Activities," for further information on restructuring charges incurred during the three years ended December 31, 2015. During 2012, Bel initiated the closure of its Cinch North American manufacturing facility in Vinita, Oklahoma, and transition of the operations to Reynosa, Medico and a new facility in McAllen, Texas. The Company recorded $5.2 million related to this restructuring during 2012, comprised primarily of $3.2 million in severance costs, $1.4 million related to asset disposals and $0.6 million of other expenses. During 2011, the Company recorded restructuring costs associated with the realignment of its Cinch UK operations.
|
|
(d)
|
EBITDA is a non‑U.S. GAAP measure that is not a measure of performance under accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America ("U.S. GAAP"). EBITDA has limitations as an analytical tool and should not be considered in isolation from or as a substitute for U.S. GAAP information. It does not purport to represent any similarly titled U.S. GAAP information and is not an indicator of our performance under U.S. GAAP. EBITDA may not be comparable with similarly titled measures used by others. Investors are cautioned against placing undue reliance on this non-GAAP measure. Our management may assess our financial results both on a U.S. GAAP basis and on a non-U.S. GAAP basis. Non-U.S. GAAP financial measures provide management with additional means to understand and evaluate the core operating results and trends in our ongoing business.
|
|
(e)
|
Depreciation and amortization is included in both cost of sales and selling, general and administrative expenses on the consolidated statements of operations.
|
|
(f)
|
Returns on average total assets and stockholders' equity are computed for each year by dividing net earnings for such year by the average balances of total assets or stockholders' equity, as applicable, on the last day of each quarter during such year and on the last day of the immediately preceding year.
|
The information in this MD&A should be read in conjunction with the Company's consolidated financial statements and the notes related thereto. The discussion of results, causes and trends should not be construed to imply any conclusion that such results, causes or trends will necessarily continue in the future. See "Cautionary Notice Regarding Forward-Looking Information" above for further information. Also, when we cross reference to a "Note," we are referring to our "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements," unless the context indicates otherwise. All amounts and percentages are approximate due to rounding.
Overview
Our Company
We design, manufacture and market a broad array of products that power, protect and connect electronic circuits. These products are primarily used in the networking, telecommunications, computing, military, aerospace, transportation and broadcasting industries. Bel's portfolio of products also finds application in the automotive, medical and consumer electronics markets.
We operate through three geographic segments: North America, Asia and Europe. In 2015, 54% of the Company's revenues were derived from North America, 33% from Asia and 13% from its Europe operating segment. By product group, 38% of 2015 sales related to the Company's power solutions and protection products, 32% in connectivity solutions products and 30% in magnetic products.
Our operating expenses are driven principally by the cost of labor where the factories that Bel uses are located, the cost of the materials that we use and our ability to effectively and efficiently manage overhead costs. As labor and material costs vary by product line and region, any significant shift in product mix can have an associated impact on our costs of sales. Costs are recorded as incurred for all products manufactured. Such amounts are determined based upon the estimated stage of production and include labor cost and fringes and related allocations of factory overhead. Our products are manufactured at various facilities in the U.S., Mexico, Dominican Republic, England, Czech Republic, Slovakia and the PRC.
In the PRC, where we generally enter into processing arrangements with several independent third-party contractors and also have our own manufacturing facilities, the availability of labor is cyclical and is significantly affected by the migration of workers in relation to the annual Lunar New Year holiday as well as economic conditions in the PRC. In addition, we have little visibility into the ordering habits of our customers and we can be subjected to large and unpredictable variations in demand for our products. Accordingly, we must continually recruit and train new workers to replace those lost to attrition each year and be able to address peaks in demand that may occur from time to time. These recruiting and training efforts and related inefficiencies, and overtime required in order to meet demand, can add volatility to the costs incurred by us for labor in the PRC.
The consolidated results included in this MD&A include the results of acquired companies discussed above from their respective acquisition dates.
Key Factors Affecting our Business
The Company believes the key factors affecting Bel's 2015 and/or future results include the following:
|
·
|
Recent Acquisitions – The Company has completed four acquisitions since the first quarter of 2013. During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, the acquired companies have contributed a combined $309.0 million, $209.8 million and $68.6 million of sales, respectively, and a combined $19.6 million, $10.2 million and $8.4 million in income from operations, respectively.
|
|
·
|
Net Sales – Excluding the net sales contributions from the 2013 and 2014 Acquisitions as described above, the Company's net sales for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 were $258.1 million, $277.3 million and $280.6 million, respectively. By segment, excluding the net sales contributions from the 2013 and 2014 Acquisitions, net sales in Asia decreased by $18.4 million, European net sales were down by $2.7 million and sales in North America increased by $1.8 million in 2015 as compared to 2014. The decline in Bel's legacy business net sales resulted primarily from lower demand of its DC-DC converter, ICM and passive connector products as compared to 2014.
|
|
·
|
Product Mix – Material and labor costs vary by product line and any significant shift in product mix between higher- and lower-margin product lines will have a corresponding impact on the Company's gross margin percentage. As compared to the pre-2014 (legacy-Bel) business on average, the recently acquired Power Solutions business has lower margins and Connectivity Solutions has higher margins. Fluctuations in sales volume of Power Solutions or Connectivity Solutions products will have a corresponding impact on Bel's profit margins.
|
|
·
|
Pricing and Availability of Materials – Pricing and availability of components that constitute raw materials in our manufacturing processes have been stable for most of the Company's product lines, although lead times on certain electrical components continue to be extended. Pricing of electrical components during the year ended December 31, 2015 was flat compared to the same period of 2014. With regard to commodity pricing, the costs of certain commodities that are contained in components and other raw materials, such as gold and copper, were lower during 2015 as compared to 2014. Any fluctuations in component prices and other commodity prices associated with Bel's raw materials will have a corresponding impact on Bel's operating results.
|
|
·
|
Restructuring – The Company continued to implement restructuring programs throughout 2015 in connection with integrating the 2014 Acquisitions into the legacy-Bel structure and other cost savings and facility consolidation efforts. During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company incurred $2.1 million, $1.8 million and $1.4 million, respectively, in restructuring costs, primarily for severance and termination benefits. The measures implemented in 2015 are projected to result in incremental savings of $3 million to $4 million on an annualized basis, beginning in 2016. The Company will continue to review its operations for further cost containment opportunities and additional restructuring charges may be incurred in future quarters. The projected cost savings represent Forward-Looking Statements. See "Cautionary Notice Regarding Forward-Looking Information."
|
|
·
|
Labor Costs – Labor costs as a percentage of sales were 10.7% of sales in 2015 as compared to 12.1% of sales in 2014 and 14.5% of sales in 2013. The influx of the 2014 Acquisitions resulted in a lower consolidated labor cost as a percentage of sales as labor costs for the Power Solutions business in 2015 was 5.2% of their respective sales and Connectivity Solutions' labor costs were 7.0% of their respective sales.
|
|
·
|
Acquisition-Related Costs – The acquisitions of Power Solutions and Connectivity Solutions in 2014 gave rise to acquisition-related costs of $0.6 million in 2015 and $7.3 million in 2014, which includes professional fees for independent valuations and carve-out audits for each of the acquired companies. In addition to these costs, a combined $5.9 million of inventory step up costs were charged to cost of sales in 2014.
|
|
·
|
Impact of Foreign Currency – Since we are a U.S. domiciled company, we translate our foreign currency-denominated financial results into U.S. dollars. Due to the changes in the value of foreign currencies relative to the U.S. dollar, translating our financial results and the revaluation of certain intercompany transactions to and from foreign currencies to U.S. dollars may result in a favorable or unfavorable impact to our consolidated statements of operations and cash flows. The Company monitors changes in foreign currencies and implements pricing actions to help mitigate the impact that changes in foreign currencies may have on its operating results. See Selling, General and Administrative Expenses and Inflation and Foreign Currency Exchange below for further details.
|
|
·
|
Effective Tax Rate – The Company's effective tax rate will fluctuate based on the geographic segment in which our pretax profits are earned. Of the geographic segments in which we operate, the U.S. has the highest tax rates; Europe's tax rates are generally lower than U.S. tax rates; and Asia has the lowest tax rates of the Company's three geographical segments. See Note 9, "Income Taxes."
|
In the fourth quarter of 2015 as compared to the same quarter of 2014 and as compared to the trailing three quarters of 2015, Bel experienced a decrease in net sales that was reflective of industry trends. While we cannot control business conditions in the global markets, we took substantial steps during 2015 to strengthen relationships with the recently-acquired customer base, improve the quality of our products, increase efficiencies and reduce fixed costs. During the fourth quarter of 2015, we completed our facility consolidations in the Chicago area and successfully transitioned our Array operations from Miami to our existing facilities in McAllen, Texas and Reynosa, Mexico. In 2016, our profitability goals will be focused both on net sales growth and monitoring the cost structure of our business.
Summary by Operating Segment
Net sales to external customers by reportable operating segment for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 were as follows (dollars in thousands):
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
North America
|
$
|
304,328
|
54
|
%
|
$
|
217,258
|
45
|
%
|
$
|
116,548
|
33
|
%
|
||||||||||||
|
Asia
|
188,146
|
33
|
%
|
201,338
|
41
|
%
|
193,647
|
56
|
%
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Europe
|
74,606
|
13
|
%
|
68,480
|
14
|
%
|
38,994
|
11
|
%
|
|||||||||||||||
|
$
|
567,080
|
100
|
%
|
$
|
487,076
|
100
|
%
|
$
|
349,189
|
100
|
%
|
|||||||||||||
Net sales and income from operations by operating segment for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 were as set forth in the following table (dollars in thousands). Segment net sales are attributed to individual segments based on the geographic source of the billing for such customer sales.
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
||||||||||
|
Total segment sales:
|
||||||||||||
|
North America
|
$
|
329,304
|
$
|
248,007
|
$
|
128,472
|
||||||
|
Asia
|
295,751
|
275,765
|
225,151
|
|||||||||
|
Europe
|
148,735
|
114,748
|
40,742
|
|||||||||
|
Total segment sales
|
773,790
|
638,520
|
394,365
|
|||||||||
|
Reconciling item:
|
||||||||||||
|
Intersegment sales
|
(206,710
|
)
|
(151,444
|
)
|
(45,176
|
)
|
||||||
|
Net sales
|
$
|
567,080
|
$
|
487,076
|
$
|
349,189
|
||||||
|
Income (loss) from operations:
|
||||||||||||
|
North America
|
$
|
11,012
|
$
|
(4,531
|
)
|
$
|
(1,560
|
)
|
||||
|
Asia
|
8,175
|
13,090
|
15,356
|
|||||||||
|
Europe
|
9,413
|
4,913
|
1,251
|
|||||||||
|
$
|
28,600
|
$
|
13,472
|
$
|
15,047
|
|||||||
Net sales were favorably impacted in all segments in 2015 and 2014 due to the recent acquisitions. See Note 12, "Segments," for details on contributions from recent acquisitions to net sales and income from operations by segment.
Net Sales
The Company's net sales by major product line for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 were as follows (dollars in thousands):
|
Years Ended
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
December 31,
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Power solutions and protection
|
$
|
214,766
|
38
|
%
|
$
|
159,867
|
33
|
%
|
$
|
67,370
|
19
|
%
|
||||||||||||
|
Connectivity solutions
|
181,697
|
32
|
%
|
152,954
|
31
|
%
|
111,653
|
32
|
%
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Magnetic solutions
|
170,617
|
30
|
%
|
174,255
|
36
|
%
|
170,166
|
49
|
%
|
|||||||||||||||
|
$
|
567,080
|
100
|
%
|
$
|
487,076
|
100
|
%
|
$
|
349,189
|
100
|
%
|
|||||||||||||
2015 as Compared to 2014
Power Solutions and Protection:
The Power Solutions acquisition contributed incremental sales of $60.1 million to the power solutions and protection product line during 2015 as compared to 2014. Excluding the incremental impact of the Power Solutions acquisition, power solutions and protection net sales decreased by $5.2 million, or 8.8% in 2015 as compared to 2014. This decrease was primarily due to a reduction in demand of our legacy-Bel DC/DC products in 2015, resulting in a decrease in sales of $8.2 million during 2015 as compared to 2014. This was partially offset by an increase in sales of our custom module products of $2.5 million during the same timeframe.
Connectivity Solutions:
The Connectivity Solutions acquisition contributed incremental sales of $35.9 million to the connectivity solutions product line during 2015 as compared to 2014. Excluding the incremental impact of the Connectivity Solutions acquisition, connectivity solutions net sales decreased by $7.1 million, or 6.0%, during 2015 as compared to 2014 reflecting lower demand from our customers for these products. This decrease was primarily due to declines in sales volumes from our legacy-Bel passive connector products and Cinch products.
Magnetic Solutions:
The decreases in magnetic solutions' sales from 2014 to 2015 noted in the table above were primarily due to a reduction in sales volume of Bel's integrated connector module (ICM) products of $2.1 million during 2015 as compared to 2014 due to lower customer demand for these products.
2014 as Compared to 2013
The Company experienced increases in all product lines in 2014 as compared to 2013 due to the recent acquisitions. The increase in magnetic sales resulted from $2.1 million of incremental TRP sales (acquired in March 2013) and a higher volume of ICM sales of $3.5 million as compared to 2013. Power Solutions, acquired in June 2014, contributed $100.8 million in power solutions and protection sales, offset by an $11.3 million reduction in legacy-Bel's DC/DC sales. Connectivity Solutions, acquired in July and August 2014, accounted for $33.5 million of the increase in connectivity sales in 2014 and Array, acquired in August 2013, contributed an incremental $4.8 million to connectivity sales in 2014.
Cost of Sales
Cost of sales as a percentage of net sales for the three years ended December 31, 2015 consisted of the following:
|
Years Ended
|
||||||||||||
|
December 31,
|
||||||||||||
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
||||||||||
|
Material costs
|
43.6
|
%
|
44.9
|
%
|
42.5
|
%
|
||||||
|
Labor costs
|
10.7
|
%
|
12.1
|
%
|
14.5
|
%
|
||||||
|
Research and development expenses
|
4.9
|
%
|
4.4
|
%
|
4.0
|
%
|
||||||
|
Other expenses
|
21.6
|
%
|
20.7
|
%
|
21.2
|
%
|
||||||
|
Total cost of sales
|
80.8
|
%
|
82.1
|
%
|
82.2
|
%
|
||||||
2015 as Compared to 2014
Material costs as a percentage of sales decreased slightly in 2015 as compared to 2014. The decrease resulted from an improvement in Power Solutions material costs as a percentage of sales during 2015 (at 52.3%) versus 2014 (at 60%), as warranty claims incurred in the latter part of 2014 related to the Power Solutions business did not recur in 2015. A full year of sales related to the Connectivity Solutions business also contributed to lower material costs as a percentage of sales on a consolidated basis, as Connectivity Solutions' products carry a lower material content than legacy-Bel products.
Labor costs as a percentage of sales continued to decline in 2015 as compared to 2014 as a result of a full year of sales of Power Solutions and Connectivity Solutions products during 2015. As discussed below, the products of the 2014 Acquisitions carry a much lower labor content compared with the legacy-Bel products.
2014 as Compared to 2013
Material costs as a percentage of sales increased in 2014 due to the inclusion of the Power Solutions business, as those products have a higher material content (approximately 60% of sales) versus the legacy-Bel products. On a comparable basis to 2013, legacy-Bel's material costs as a percentage of sales decreased from 42.5% of sales to 41.5% of sales. This was due to the shift in sales noted above, as TRP and connectivity products carry a lower material content than Bel's DC/DC power products.
Labor costs as a percentage of sales declined with the inclusion of the 2014 Acquisitions, particularly Power Solutions, as their significant manufacturing sites are located in lower cost regions. Legacy-Bel's labor costs as a percentage of sales increased slightly from 2013. The PRC government mandated wage increases coupled with the strengthening of the Chinese currency further increased labor costs over the prior year. These increases were partially offset by the realization of cost savings in connection with the improvement in manufacturing efficiencies associated with the Cinch reorganization in 2013.
Research and Development ("R&D)
Included in cost of sales are R&D expenses of $27.7 million, $21.5 million and $14.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The majority of the increase over the past two years relates to the inclusion of R&D expenses of the 2013 and 2014 Acquired Companies, which have been included in Bel's results since their respective acquisition dates.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses ("SG&A")
2015 as Compared to 2014
SG&A expenses increased $6.1 million in 2015 as compared to 2014. This increase was primarily due to the inclusion of a full year of SG&A expenses related to the 2014 Acquisitions, which accounted for an additional $11.5 million in SG&A expenses in 2015. Legacy-Bel legal and professional fees were also higher by $1.3 million in 2015 due to incremental audit and tax work related to the 2014 Acquisitions performed in 2015. These increased expenses were offset by a reduction in acquisition-related costs of $6.9 million in 2015 as compared to 2014.
2014 as Compared to 2013
SG&A expenses increased $26.2 million in 2014 as compared to 2013. This increase was primarily due to the following:
|
·
|
the incremental impact of SG&A expenses related to the 2013 and 2014 Acquisitions of $19.1 million;
|
|
·
|
higher acquisition-related costs of $6.5 million related to the 2014 Acquisitions; and
|
|
·
|
an increase in salaries of $1.5 million.
|
These increases were partially offset by a $2.8 million reduction in incentive compensation expense in 2014 as compared to 2013 primarily due to lower profitability levels of the Company in 2014.
Restructuring Charges
The Company recorded restructuring charges of $2.1 million, $1.8 million and $1.4 million during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, in connection with its restructuring programs, as further described in Note 3, "Restructuring Activities."
Interest Expense
The Company incurred interest expense of $7.6 million and $4.0 million during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, primarily due to our outstanding borrowings under the Company's credit and security agreement used to fund the 2014 Acquisitions. See "Liquidity and Capital Resources" and Note 10, "Debt," for further information on the Company's outstanding debt.
Income Taxes
The Company's effective tax rate will fluctuate based on the geographic segment in which the pretax profits are earned. Of the geographic segments in which the Company operates, the U.S. has the highest tax rates; Europe's tax rates are generally lower than U.S. tax rates; and Asia has the lowest tax rates of the Company's three geographical segments. See Note 9, "Income Taxes."
2015 as Compared to 2014
The provision for income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 was $6.5 million and $1.2 million, respectively. The Company's earnings before income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2015 were $16.0 million greater than in 2014. The Company's effective tax rate was 25.4% and 11.9% for the year ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The change in the effective tax rate during 2015 as compared to 2014, was primarily attributed to an increase in U.S. taxes resulting from a significant increase in the North America segment's pre-tax income and an increase in Asia taxes resulting from taxes related to uncertain tax positions. In addition, there was a significant increase in the Europe segment income offset, in part, by a decrease in the Asia segment income which resulted in higher foreign taxes during 2015 compared to 2014. See Note 9, "Income Taxes."
2014 as Compared to 2013
The provision (benefit) for income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 was $1.2 million and ($0.7) million, respectively. The Company's earnings before income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2014 were $5.4 million lower than in 2013. The Company's effective tax rate was 11.9% and (4.9%) for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The change in the effective tax rate during 2014 as compared to 2013, is primarily attributable to the increase in US taxes despite a pretax loss in the North America segment from taxes related to valuation allowances and foreign acquired disregarded entity income and an increase in Asia taxes resulting from taxes related to uncertain tax positions. In addition, there was a significant increase in the Europe segment income offset in part by a decrease in the Asia segment income which resulted in higher foreign taxes during 2014 compared to 2013. Additionally, for the year ended December 31, 2013, the Company recognized an additional $0.4 million in R&E credits related to the year ended December 31, 2012 which offset the increase in the effective tax rate when comparing 2013 to 2014. See Note 9, "Income Taxes."
Other Tax Matters
The Company has a majority of its products manufactured on the mainland of the PRC, and Bel is not subject to corporate income tax on manufacturing services provided by third parties in the PRC. Hong Kong has a territorial tax system which imposes corporate income tax at a rate of 16.5% on income from activities solely conducted in Hong Kong.
The Company holds an offshore business license from the government of Macao. With this license, a Macao offshore company named Bel Fuse (Macao Commercial Offshore) Limited has been established to handle the Company's sales to third-party customers in Asia. Sales by this company consist of products manufactured in the PRC. This company is not subject to Macao corporate profit taxes which are imposed at a tax rate of 12%. Additionally, the Company established TRP International, a China Business Trust ("CBT"), when it acquired the TRP group, as previously discussed. Sales by the CBT consists of products manufactured in the PRC and sold to third-party customers inside and outside Asia. The CBT is not subject to PRC income taxes, which are generally imposed at a tax rate of 25%.
It is the Company's intention to repatriate substantially all net income from its wholly owned PRC subsidiary, Dongguan Transpower Electric Products Co., Ltd, a Chinese Limited Liability Company, to its direct Hong Kong parent Transpower Technologies (Hong Kong) Ltd. Applicable income and dividend withholding taxes have been reflected in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2015. However, U.S. deferred taxes need not be provided as there is no intention to repatriate such amounts to the U.S. Management's intention is to permanently reinvest the majority of the remaining earnings of foreign subsidiaries in the expansion of its foreign operations. Unrepatriated earnings, upon which U.S. income taxes have not been accrued, are approximately $143.4 million at December 31, 2015. Such unrepatriated earnings are deemed by management to be permanently reinvested. At December 31, 2015, the estimated federal income tax liability related to unrepatriated foreign earnings is $38.3 million under the current tax law.
Inflation and Foreign Currency Exchange
During the past three years, the effect of inflation on our consolidated financial position and results of operations was not material. We are exposed to market risk primarily from changes in foreign currency exchange rates. Historically, fluctuations of the U.S. dollar against other major currencies have not significantly affected our foreign operations as most sales have been denominated in U.S. dollars or currencies directly or indirectly linked to the U.S. dollar. Most significant expenses, including raw materials, labor and manufacturing expenses, are incurred primarily in U.S. dollars or the Chinese renminbi, and to a lesser extent in British pounds and Mexican pesos. The Chinese renminbi depreciated by approximately 1.4% in 2015 as compared to 2014. Future appreciation of the renminbi would result in the Company's incurring higher costs for all expenses incurred in the PRC. The Company's European entities, whose functional currencies are euros, British pounds and Czech korunas, enter into transactions which include sales that are denominated principally in euros, British pounds and various other European currencies, and purchases that are denominated principally in U.S. dollars and British pounds. Such transactions resulted in net realized and unrealized currency exchange gains (losses) of $5.1 million, $4.3 million and ($0.6) million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, which were included in SG&A expenses on the consolidated statements of operations. The currency exchange gains recorded in 2015 and 2014 were primarily due to the favorable impact of the depreciation of the Euro against the U.S. dollar on a $34 million intercompany loan. This loan was settled by the end of 2015. Translation of subsidiaries' foreign currency financial statements into U.S. dollars resulted in translation adjustments, net of taxes, of ($10.0) million, ($11.3) million and $1.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, which are included in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) on the consolidated balance sheets.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Our primary sources of cash are the collection of trade receivables generated from the sales of our products and services to our customers and amounts available under our existing lines of credit, including our credit facility. Our primary uses of cash are payments for operating expenses, investments in working capital, capital expenditures, interest, taxes, dividends, debt obligations and other long-term liabilities. We believe that our current liquidity position and future cash flows from operations will enable us to fund our operations, including all of the items mentioned above in the next twelve months.
At December 31, 2015 and 2014, $67.9 million and $67.2 million, respectively (or 80% and 87%, respectively), of cash and cash equivalents was held by foreign subsidiaries of the Company. Management's intention is to permanently reinvest the majority of these funds outside the U.S. and there are no current plans that would indicate a need to repatriate them to fund the Company's U.S. operations. In the event these funds were needed for Bel's U.S. operations, the Company would be required to accrue and pay U.S. taxes to repatriate these funds. See "Income Taxes" above for further details.
On June 19, 2014, the Company entered into a senior Credit and Security Agreement ("CSA") (see Note 10, "Debt," for additional details). The CSA contains customary representations and warranties, covenants and events of default and financial covenants that measure (i) the ratio of the Company's total funded indebtedness, on a consolidated basis, to the amount of the Company's consolidated EBITDA, as defined ("Leverage Ratio"), and (ii) the ratio of the amount of the Company's consolidated EBITDA to the Company's consolidated fixed charges ("Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio"). If an event of default occurs, the lenders under the CSA would be entitled to take various actions, including the acceleration of amounts due thereunder and all actions permitted to be taken by a secured creditor. At December 31, 2015, the Company was in compliance with its debt covenants, including its most restrictive covenant, the Leverage Ratio. The unused credit available under the credit facility at December 31, 2015 was $50.0 million, of which we had the ability to borrow $17.2 million without violating our Leverage Ratio covenant based on the Company's existing consolidated EBITDA.
In connection with its acquisitions of Power Solutions and Connectivity Solutions (see Note 2, "Acquisitions and Disposition"), the Company borrowed $235.0 million under the CSA during 2014. Scheduled principal payments of the long-term debt outstanding are included in "Contractual Obligations" below and in Note 10, "Debt."
For information regarding further commitments under the Company's operating leases, see Note 16, "Commitments and Contingencies.".
Cash Flows
During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company's cash and cash equivalents increased by $7.9 million. This resulted primarily from $65.8 million of cash provided by operating activities, including the impact of the changes in accounts receivable and inventories described below, proceeds of $9.0 million received from the NPS sale and related transactions and $4.2 million received for an acquisition-related settlement payment during 2015. This increase was partially offset by $23.0 million of net repayments under the revolving credit line, $22.4 million of repayments of long-term debt, $9.9 million paid for the purchase of property, plant and equipment and $3.2 million for payments of dividends. As compared to 2014, cash provided by operating activities increased by $43.3 million, partially due to a $10.1 increase in net earnings and a $2.6 increase in depreciation and amortization as 2015 contained a full year of expense for the 2014 Acquired Companies. The reduction in accounts receivable and inventory balances at December 31, 2015 as compared to December 31, 2014, described below, were also contributing factors to the increase in cash provided by operating activities during 2015.
During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company's cash and cash equivalents increased by $15.0 million. This resulted primarily from $22.5 million provided by operating activities, $215.0 million of proceeds from long-term debt and $23.0 million of proceeds from borrowing under the revolver, partially offset by, among other items, payments totaling $208.7 million, net of cash acquired, for the acquisitions of Power Solutions and Connectivity Solutions, $12.0 million of repayments under the revolving credit line, $5.4 million of repayments of long-term debt, $5.8 million paid in deferred financing costs, $9.0 million paid for the purchase of property, plant and equipment and $3.2 million for payments of dividends. As compared to 2013, cash provided by operating activities increased by $11.9 million, partially due to a $7.4 million increase in depreciation and amortization related to the inclusion of expense from the 2014 Acquisitions and additional depreciation and amortization on the fair value adjustments to tangible and intangible assets.
During the year ended December 31, 2013, the Company's cash and cash equivalents decreased by $9.1 million. This resulted primarily from $31.0 million of net cash payments for the acquisitions of TRP and Array, $6.9 million paid for the purchase of property, plant and equipment, $3.1 million for payments of dividends, $3.4 million for the repurchase of 178,643 shares of the Company's Class B common stock, and $1.3 million for the purchase of an intangible asset associated with the Radiall agreement, partially offset by, among other items, an increase in short-term borrowings of $12.0 million, a $13.0 million transfer out of restricted cash and $10.6 million provided by operating activities. As compared with 2012, cash provided by operating activities decreased by $1.0 million. During 2013, increased accounts receivable resulted in an operating cash outflow of $8.0 million. The increase in post-acquisition third-party receivables at TRP, which replaced receivables collected from TRP's pre-acquisition affiliates, accounted for $4.0 million of this increase, while receivables in the legacy-Bel portion of the Asia segment increased by $6.1 million. These increases were partially offset by lower receivables in North America and Europe. TRP's third-party receivables were $4.0 million higher than receivables from its former TE affiliates primarily due to higher gross margin and longer payment terms on third-party sales. The longer payment terms in TRP customer contracts acquired from the seller led to an increase of 3 days in overall days sales outstanding (DSO). The increase in legacy-Bel Asia receivables was largely due to a return to normal payment terms in 2013, following a period of shorter payment terms in connection with a new inventory stocking program that was implemented in 2012. Inventories increased by $6.5 million during 2013 primarily due to the expansion of a new stocking program in Asia, whereby certain customers now have quicker access to commonly-ordered parts.
Cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities and accounts receivable comprised approximately 29.2% and 27.8% of the Company's total assets at December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, respectively. The Company's current ratio (i.e., the ratio of current assets to current liabilities) was 2.3 to 1 and 2.6 to 1 at December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, respectively.
During the year ended December 31, 2015, accounts receivable decreased $12.2 million primarily due to lower sales volume in the fourth quarter of 2015 as compared to the fourth quarter of 2014. Days sales outstanding (DSO) declined to 59 days at December 31, 2015 from 62 days at December 31, 2014. Inventories decreased $13.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2015, which reflected the decline in sales volume. Inventory turns increased to 4.5 times per year at December 31, 2015 from 4.3 times per year at December 31, 2014. Accounts payable had a corresponding decrease of $10.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2015.
Contractual Obligations
The following table sets forth at December 31, 2015 the amounts of payments due under specific types of contractual obligations, aggregated by category of contractual obligation, for the time periods described below. This table excludes $42.2 million of unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2015, as we are unable to make reasonably reliable estimates of the future period or periods of cash settlements, if any, with the respective taxing authorities.
|
Payments due by period (dollars in thousands)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Contractual Obligations
|
Total
|
Less than 1 year
|
1-3
years |
3-5
years |
More than
5 years |
|||||||||||||||
|
Long-term debt obligations(1)
|
$
|
187,188
|
$
|
24,772
|
$
|
43,001
|
$
|
119,415
|
$
|
-
|
||||||||||
|
Interest payments due on long-term debt(2)
|
15,312
|
5,208
|
8,522
|
1,582
|
-
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Capital expenditure obligations
|
1,541
|
1,541
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Operating leases
|
23,430
|
7,924
|
9,079
|
4,216
|
2,211
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Raw material purchase obligations
|
42,607
|
42,452
|
155
|
-
|
-
|
|||||||||||||||
|
First quarter 2016 quarterly cash dividend declared
|
810
|
810
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Total
|
$
|
270,888
|
$
|
82,707
|
$
|
60,757
|
$
|
125,213
|
$
|
2,211
|
||||||||||
(1) Includes the $16.1 million scheduled mandatory principal payment for 2016 and a 2015 excess cash flow payment due in 2016, which is estimated at $8.6 million under the terms of the CSA.
(2) Includes interest payments required under our CSA related to our term loans and revolver balance. The interest rate in place under our CSA on December 31, 2015 was utilized and this calculation assumes obligations are repaid when due.
The Company is required to pay SERP obligations at the occurrence of certain events. As of December 31, 2015, $15.6 million is included in long-term liabilities as an unfunded pension obligation on the Company's consolidated balance sheet. Included in other assets at December 31, 2015 is the cash surrender value of company-owned life insurance and marketable securities held in a rabbi trust with an aggregate value of $12.2 million, which has been designated by the Company to be utilized to fund the Company's SERP obligations.
Critical Accounting Policies and Other Matters
The Company's consolidated financial statements include certain amounts that are based on management's best estimates and judgments. Estimates are used when accounting for amounts recorded in connection with mergers and acquisitions, including determination of the fair value of assets and liabilities. Additionally, estimates are used in determining such items as current fair values of goodwill and other intangible assets, as well as provisions related to product returns, bad debts, inventories, intangible assets, investments, SERP expense, income taxes and contingencies and litigation. The Company bases its estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions, including in some cases future projections, that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions. The following accounting policies require accounting estimates that have the potential for significantly impacting Bel's financial statements.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
In the normal course of business, we extend credit to our customers if they satisfy pre-defined credit criteria. We maintain an accounts receivable allowance for estimated losses resulting from the likelihood of failure of our customers to make required payments. An additional allowance may be required if the financial condition of our customers deteriorates. The allowance for doubtful accounts is maintained at a level that management assesses to be appropriate to absorb estimated losses in the accounts receivable portfolio. The allowance for doubtful accounts is reviewed at a minimum quarterly, and changes to the allowance are made through the provision for bad debts, which is included in SG&A expenses on our consolidated statements of operations. These changes may reflect changes in economic, business and market conditions. The allowance is increased by the provision for bad debts and decreased by the amount of charge-offs, net of recoveries.
The provision for bad debts charged against operating results is based on several factors including, but not limited to, a regular assessment of the collectability of specific customer balances, the length of time a receivable is past due and our historical experience with our customers. In circumstances where a specific customer's inability to meet its financial obligations is known, we record a specific provision for bad debt against amounts due, thereby reducing the receivable to the amount we reasonably assess will be collected. If circumstances change, such as higher than expected defaults or an unexpected material adverse change in a major customer's ability to pay, our estimates of recoverability could be reduced by a material amount. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company had allowance for doubtful accounts of $1.7 million and $2.0 million, respectively.
Inventory
The Company makes purchasing and manufacturing decisions principally based upon firm sales orders from customers, projected customer requirements and the availability and pricing of raw materials. Future events that could adversely affect these decisions and result in significant charges to the Company's operations include miscalculating customer requirements, technology changes which render certain raw materials and finished goods obsolete, loss of customers and/or cancellation of sales orders, stock rotation with distributors and termination of distribution agreements. The Company reduces the carrying value of its inventory for estimated obsolescence or unmarketable inventory by an amount equal to the difference between the cost of inventory and the estimated market value based on the aforementioned assumptions. When such inventory is subsequently used in the manufacturing process, the lower adjusted cost of the material is charged to cost of sales and the improved gross profit is recognized at the time the completed product is shipped and the sale is recorded. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company had reserves for excess or obsolete inventory of $7.1 million and $6.8 million, respectively. If actual market conditions are less favorable than those projected by management, additional inventory write-downs may be required.
Goodwill and Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets
Goodwill is reviewed for possible impairment at least annually on a reporting unit level during the fourth quarter of each year. A review of goodwill may be initiated before or after conducting the annual analysis if events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying value of goodwill may no longer be recoverable.
A reporting unit is the operating segment unless, at businesses one level below that operating segment — the "component" level — discrete financial information is prepared and regularly reviewed by management, and the component has economic characteristics that are different from the economic characteristics of the other components of the operating segment, in which case the component is the reporting unit.
While we are permitted to conduct a qualitative assessment to determine whether it is necessary to perform a two-step quantitative goodwill impairment test, for our annual goodwill impairment test in the fourth quarter of 2015 and in 2014, we performed a quantitative test for all of our reporting units.
The assets and liabilities of acquired businesses are recorded under the purchase method of accounting at their estimated fair values at the dates of acquisition. Goodwill represents the amount of consideration transferred in excess of fair values assigned to the underlying net assets of acquired businesses.
The goodwill impairment test involves a two-step process. In step one, we compare the fair value of each of our reporting units with goodwill to its carrying value, including the goodwill allocated to the reporting unit. If the fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying value, there is no indication of impairment and no further testing is required. If the fair value of the reporting unit is less than the carrying value, we must perform step two of the impairment test to measure the amount of impairment loss, if any. In step two, the reporting unit's fair value is allocated to all of the assets and liabilities of the reporting unit, including any unrecognized intangible assets, in a hypothetical analysis that calculates the implied fair value of goodwill in the same manner as if the reporting unit were being acquired in a business combination. If the implied fair value of the reporting unit's goodwill is less than the carrying value, the difference is recorded as an impairment loss.
We use a fair value approach to test goodwill for impairment. We must recognize a non-cash impairment charge for the amount, if any, by which the carrying amount of goodwill exceeds its implied fair value. We derive an estimate of fair values for each of our reporting units using a combination of an income approach and an appropriate market approach, each based on an applicable weighting. We assess the applicable weighting based on such factors as current market conditions and the quality and reliability of the data. Absent an indication of fair value from a potential buyer or similar specific transactions, we believe that the use of these methods provides a reasonable estimate of a reporting unit's fair value.
Fair value computed by these methods is arrived at using a number of factors, including projected future operating results, anticipated future cash flows, effective income tax rates, comparable marketplace data within a consistent industry grouping, and the cost of capital. There are inherent uncertainties, however, related to these factors and to our judgment in applying them to this analysis. Nonetheless, we believe that the combination of these methods provides a reasonable approach to estimate the fair value of our reporting units. Assumptions for sales, net earnings and cash flows for each reporting unit were consistent among these methods.
Income Approach Used to Determine Fair Values
The income approach is based upon the present value of expected cash flows. Expected cash flows are converted to present value using factors that consider the timing and risk of the future cash flows. The estimate of cash flows used is prepared on an unleveraged debt-free basis. We use a discount rate that reflects a market-derived weighted average cost of capital. We believe that this approach is appropriate because it provides a fair value estimate based upon the reporting unit's expected long-term operating and cash flow performance. The projections are based upon our best estimates of projected economic and market conditions over the related period including growth rates, estimates of future expected changes in operating margins and cash expenditures. Other significant estimates and assumptions include terminal value long-term growth rates, provisions for income taxes, future capital expenditures and changes in future cashless, debt-free working capital.
2015 Annual Goodwill Impairment Test
Critical assumptions that the Company used in performing the income approach for its reporting units in its 2015 annual goodwill impairment test included the following:
|
·
|
Applying a compounded annual growth rate for forecasted sales in our projected cash flows through 2020.
|
|
Reporting Unit
|
Compounded Annual Growth Rate
|
|||
|
North America
|
2.0
|
%
|
||
|
Asia
|
2.0
|
%
|
||
|
Europe
|
2.0
|
%
|
||
|
·
|
Applying a terminal value growth rate of 2% for our reporting units to reflect our estimate of stable and perpetual growth.
|
|
·
|
Determining an appropriate discount rate to apply to our projected cash flow results. This discount rate reflects, among other things, certain risks due to the uncertainties of achieving the cash flow results and the growth rates assigned. The discount rates applied were as follows:
|
|
Reporting Unit
|
Discount Rate
|
|||
|
North America
|
11.0
|
%
|
||
|
Asia
|
15.0
|
%
|
||
|
Europe
|
11.0
|
%
|
||
|
·
|
A weighting of the results of the income approach of 75% of our overall fair value calculation for each reporting unit.
|
Changes in any of these assumptions could materially impact the estimated fair value of our reporting units. Our forecasts take into account the near and long-term expected business performance, considering the long-term market conditions and business trends within the reporting units. For further discussion of the factors that could result in a change in our assumptions, see "Risk Factors" in this Form 10-K and our other filings with the SEC.
Market Approach Used to Determine Fair Values
The market approach estimates the fair value of the reporting unit by applying multiples of operating performance measures to the reporting unit's operating performance (the "Public Company Method"). These multiples are derived from comparable publicly-traded companies with similar investment characteristics to the reporting unit, and such comparables are reviewed and updated as needed annually. We believe that this approach is appropriate because it provides a fair value estimate using multiples from entities with operations and economic characteristics comparable to our reporting units and the Company.
The key estimates and assumptions that are used to determine fair value under this market approach includes trailing and future 12-month operating performance results and the selection of the relevant multiples to be applied. Under the Public Company Method, a control premium, or an amount that a buyer is usually willing to pay over the current market price of a publicly traded company, is applied to the calculated equity values to adjust the public trading value upward for a 100% ownership interest, where applicable.
In order to assess the reasonableness of the calculated fair values of our reporting units, we also compare the sum of the reporting units' fair values to our market capitalization and calculate an implied control premium (the excess of the sum of the reporting units' fair values over the market capitalization). We evaluate the control premium by comparing it to control premiums of recent comparable market transactions. If the implied control premium is not reasonable in light of these recent transactions, we will reevaluate our fair value estimates of the reporting units by adjusting the discount rates and/or other assumptions.
We applied a combined weighting of 25% to the market approach when determining the fair value of these reporting units.
If our assumptions and related estimates change in the future, or if we change our reporting unit structure or other events and circumstances change (such as a sustained decrease in the price of our common stock, a decline in current market multiples, a significant adverse change in legal factors or business climates, an adverse action or assessment by a regulator, heightened competition, strategic decisions made in response to economic or competitive conditions or a more-likely-than-not expectation that a reporting unit or a significant portion of a reporting unit will be sold or disposed of), we may be required to record impairment charges in future periods. Any impairment charges that we may take in the future could be material to our consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
See Note 4, "Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets," for details of our goodwill balance and the goodwill review performed in 2015.
Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets
The Company annually tests indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment on October 1, using a fair value approach, the relief-from-royalty method (a form of the income approach). No impairment was recognized as a result of the October 1, 2015 testing. At December 31, 2015, the Company's indefinite-lived intangible assets related solely to trademarks. Management has concluded that the fair value of its trademarks exceeds the associated carrying values at December 31, 2015 and that no impairment exists as of that date.
Long-Lived Assets and Other Intangible Assets
Property, plant and equipment represents an important component of the Company's total assets. The Company depreciates its property, plant and equipment on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Intangible assets with a finite useful life are amortized on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Management reviews long-lived assets and other intangible assets for potential impairment whenever significant events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. An impairment exists when the estimated undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use of an asset and its eventual disposition are less than its carrying amount. If an impairment exists, the resulting write-down would be the difference between the fair market value of the long-lived asset and the related net book value. No impairments related to long-lived assets or amortized intangible assets were recorded during the years ended December 31, 2015 or 2014.
Income Taxes
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases, as measured by enacted tax rates that are expected to be in effect in the periods when the deferred tax assets and liabilities are expected to be settled or realized. Significant judgment is required in determining the worldwide provisions for income taxes. Valuation allowances are provided for deferred tax assets where it is considered more likely than not that the Company will not realize the benefit of such asset. In the ordinary course of a global business, the ultimate tax outcome is uncertain for many transactions. It is the Company's policy not to recognize tax benefits arising from uncertain tax positions that may not be realized in future years as a result of an examination by tax authorities. The Company establishes the provisions based upon management's assessment of exposure associated with permanent tax differences and tax credits applied to temporary difference adjustments. The tax provisions are analyzed periodically (at least quarterly) and adjustments are made as events occur that warrant adjustments to those provisions. The accounting literature requires significant judgment in determining what constitutes an individual tax position as well as assessing the outcome of each tax position. Changes in judgment as to recognition or measurement of tax positions can materially affect the estimate of the effective tax rate and, consequently, affect our operating results.
Revenue Recognition
Revenue is recognized when the product has been delivered and title and risk of loss have passed to the customer, collection of the resulting receivable is deemed reasonably assured by management, persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists and the sale price is fixed and determinable.
Historically the Company has been successful in mitigating the risks associated with its revenue. Such risks include product warranty, creditworthiness of customers and concentration of sales among a few major customers.
The Company is not contractually obligated to accept returns from non-distributor customers except for defective products or in instances where the product does not meet the Company's quality specifications. If these conditions exist, the Company would be obligated to repair or replace the defective product or make a cash settlement with the customer. Distributors generally have the right to return up to 5% of their purchases depending on the products line for a specified period of time and are obligated to purchase an amount at least equal to the return. If the Company terminates a relationship with a distributor, the Company is obligated to accept as a return all of the distributor's inventory from the Company. The Company accrues an estimate for anticipated returns based on historical experience at the time revenue is recognized and adjusts such estimate as specific anticipated returns are identified. If a distributor terminates its relationship with the Company, the Company is not obligated to accept any inventory returns.
During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company had one customer with sales in excess of 10% of Bel's consolidated revenue. Management believes that the loss of this individual customer could have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position and results of operations. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company had sales of $74.8 million to Hon Hai Precision Industry Company Ltd., representing 13.2% of Bel's consolidated revenue. Sales to this customer are primarily in the Company's Asia operating segment.
Commitments and Contingencies — Litigation
On an ongoing basis, we assess the potential liabilities and costs related to any lawsuits or claims brought against us. We accrue a liability when we believe a loss is probable and when the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. Litigation proceedings are evaluated on a case-by-case basis considering the available information, including that received from internal and outside legal counsel, to assess potential outcomes. While it is typically very difficult to determine the timing and ultimate outcome of these actions, we use our best judgment to determine if it is probable that we will incur an expense related to the settlement or final adjudication of these matters and whether a reasonable estimation of the probable loss, if any, can be made. In assessing probable losses, we consider insurance recoveries, if any. We expense legal costs, including those legal costs expected to be incurred in connection with a loss contingency, as incurred. We have in the past adjusted existing accruals as proceedings have continued, been settled or otherwise provided further information on which we could review the likelihood of outflows of resources and their measurability, and we expect to do so in future periods. Due to the inherent uncertainties related to the eventual outcome of litigation and potential insurance recovery, it is possible that disputed matters may be resolved for amounts materially different from any provisions or disclosures that we have previously made.
Other Matters
The Company believes that it has sufficient cash reserves to fund its foreseeable working capital needs. It may, however, seek to expand such resources through bank borrowings, at favorable lending rates, from time to time. If the Company were to undertake another substantial acquisition for cash, the acquisition would either be funded with cash on hand or would be financed in part through cash on hand and in part through bank borrowings or the issuance of public or private debt or equity. If the Company borrows additional money to finance acquisitions, this would further decrease the Company's ratio of earnings to fixed charges, and could further impact the Company's material restrictive covenants, depending on the size of the borrowing and the nature of the target company. Under its existing credit facility, the Company is required to obtain its lender's consent for certain additional debt financing and to comply with other covenants, including the application of specific financial ratios, and may be restricted from paying cash dividends on its common stock. Depending on the nature of the transaction, the Company cannot assure investors that the necessary acquisition financing would be available to it on acceptable terms, or at all, when required. If the Company issues a substantial amount of stock either as consideration in an acquisition or to finance an acquisition, such issuance may dilute existing stockholders and may take the form of capital stock having preferences over its existing common stock.
New Financial Accounting Standards
The discussion of new financial accounting standards applicable to the Company is incorporated herein by reference to Note 1, "Description of Business and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies."
Fair Value of Financial Instruments — The estimated fair values of financial instruments have been determined by the Company using available market information and appropriate valuation methodologies. See Note 1, "Description of Business and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies."
The Company has not entered into, and does not expect to enter into, financial instruments for trading or hedging purposes. The Company does not currently anticipate entering into interest rate swaps and/or similar instruments.
The Company's carrying values of cash, cash equivalents, marketable securities, accounts receivable, restricted cash, accounts payable, accrued expenses and notes payable are a reasonable approximation of their fair value.
The Company enters into transactions denominated in U.S. Dollars, Hong Kong Dollars, the Chinese Renminbi, Euros, British Pounds, Mexican Pesos, the Czech Koruna, the Swiss Franc and other European currencies. Fluctuations in the U.S. dollar exchange rate against these currencies could significantly impact the Company's consolidated results of operations.
The Company believes that a change in the interest rate on our long-term debt of 1% would result in incremental annual interest expense of approximately $1.7 million on the Company's consolidated statement of operations.
See the consolidated financial statements listed in the accompanying Index to Consolidated Financial Statements for the information required by this item.
|
BEL FUSE INC.
|
|||
|
INDEX
|
|||
|
Financial Statements
|
Page
|
||
|
33
|
|||
|
34
|
|||
|
35
|
|||
|
36
|
|||
|
37
|
|||
|
38
|
|||
|
40
|
|||
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Bel Fuse Inc.
Jersey City, New Jersey
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Bel Fuse Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), stockholders' equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2015. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15. We also have audited the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The Company's management is responsible for these consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management's Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule and an opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the consolidated financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall consolidated financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company's principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the company's board of directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including the possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements due to error or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of Bel Fuse Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2015, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, such financial statement schedule of Bel Fuse Inc. and subsidiaries, when considered in relation to the basic consolidated financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein. Also, in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015, based on the criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
New York, New York
March 11, 2016
|
BEL FUSE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
|
||||||||
|
(dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
|
||||||||
|
December 31,
|
December 31,
|
|||||||
|
2015
|
2014
|
|||||||
|
(Revised)
|
||||||||
|
ASSETS
|
||||||||
|
Current assets:
|
||||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents
|
$
|
85,040
|
$
|
77,138
|
||||
|
Accounts receivable - less allowance for doubtful accounts
|
||||||||
|
of $1,747 and $1,989 at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively
|
86,268
|
99,605
|
||||||
|
Inventories
|
98,510
|
113,630
|
||||||
|
Other current assets
|
15,636
|
20,283
|
||||||
|
Total current assets
|
285,454
|
310,656
|
||||||
|
Property, plant and equipment, net
|
57,611
|
69,261
|
||||||
|
Intangible assets, net
|
87,827
|
95,502
|
||||||
|
Goodwill
|
121,634
|
118,369
|
||||||
|
Deferred income taxes
|
3,321
|
7,933
|
||||||
|
Other assets
|
31,164
|
33,700
|
||||||
|
Total assets
|
$
|
587,011
|
$
|
635,421
|
||||
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
Current liabilities:
|
||||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
$
|
49,798
|
$
|
61,926
|
||||
|
Accrued expenses
|
38,323
|
42,588
|
||||||
|
Current maturities of long-term debt
|
24,772
|
13,438
|
||||||
|
Other current liabilities
|
9,133
|
3,850
|
||||||
|
Total current liabilities
|
122,026
|
121,802
|
||||||
|
Long-term liabilities:
|
||||||||
|
Long-term debt
|
162,416
|
219,187
|
||||||
|
Liability for uncertain tax positions
|
40,295
|
39,767
|
||||||
|
Minimum pension obligation and unfunded pension liability
|
15,576
|
14,205
|
||||||
|
Deferred income taxes
|
13,002
|
15,739
|
||||||
|
Other long-term liabilities
|
574
|
448
|
||||||
|
Total liabilities
|
353,889
|
411,148
|
||||||
|
Commitments and contingencies
|
||||||||
|
Stockholders' equity:
|
||||||||
|
Preferred stock, no par value, 1,000,000 shares authorized; none issued
|
-
|
-
|
||||||
|
Class A common stock, par value $.10 per share, 10,000,000 shares
|
||||||||
|
authorized; 2,174,912 shares outstanding at each date (net of
|
||||||||
|
1,072,769 treasury shares)
|
217
|
217
|
||||||
|
Class B common stock, par value $.10 per share, 30,000,000 shares
|
||||||||
|
authorized; 9,701,977 and 9,686,777 shares outstanding, respectively
|
||||||||
|
(net of 3,218,307 treasury shares)
|
970
|
969
|
||||||
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
24,440
|
21,626
|
||||||
|
Retained earnings
|
229,371
|
213,409
|
||||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income
|
(21,876
|
)
|
(11,948
|
)
|
||||
|
Total stockholders' equity
|
233,122
|
224,273
|
||||||
|
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity
|
$
|
587,011
|
$
|
635,421
|
||||
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
|
||||||||
|
BEL FUSE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
|
||||||||||||
|
(dollars in thousands, except per share data)
|
||||||||||||
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
||||||||||||
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
||||||||||
|
(Revised)
|
||||||||||||
|
Net sales
|
$
|
567,080
|
$
|
487,076
|
$
|
349,189
|
||||||
|
Cost of sales
|
458,253
|
399,721
|
286,952
|
|||||||||
|
Selling, general and administrative expenses
|
78,113
|
72,051
|
45,803
|
|||||||||
|
Restructuring charges
|
2,114
|
1,832
|
1,387
|
|||||||||
|
Income from operations
|
28,600
|
13,472
|
15,047
|
|||||||||
|
Interest expense
|
(7,588
|
)
|
(3,978
|
)
|
(156
|
)
|
||||||
|
Interest income and other, net
|
4,720
|
276
|
274
|
|||||||||
|
Earnings before provision (benefit) for income taxes
|
25,732
|
9,770
|
15,165
|
|||||||||
|
Provision (benefit) for income taxes
|
6,535
|
1,167
|
(743
|
)
|
||||||||
|
Net earnings available to common shareholders
|
$
|
19,197
|
$
|
8,603
|
$
|
15,908
|
||||||
|
Net earnings per common share:
|
||||||||||||
|
Class A common shares - basic and diluted
|
$
|
1.53
|
$
|
0.69
|
$
|
1.32
|
||||||
|
Class B common shares - basic and diluted
|
$
|
1.64
|
$
|
0.75
|
$
|
1.41
|
||||||
|
Weighted-average shares outstanding:
|
||||||||||||
|
Class A common shares - basic and diluted
|
2,175
|
2,175
|
2,175
|
|||||||||
|
Class B common shares - basic and diluted
|
9,698
|
9,491
|
9,240
|
|||||||||
|
Dividends paid per common share:
|
||||||||||||
|
Class A common shares
|
$
|
0.24
|
$
|
0.24
|
$
|
0.24
|
||||||
|
Class B common shares
|
$
|
0.28
|
$
|
0.28
|
$
|
0.28
|
||||||
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
|
||||||||||||
|
BEL FUSE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
|
||||||||||||
|
(dollars in thousands)
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
|||||||||||
|
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
|||||||||
|
|
(Revised)
|
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Net earnings
|
$
|
19,197
|
$
|
8,603
|
$
|
15,908
|
||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Other comprehensive (loss) income:
|
||||||||||||
|
Currency translation adjustment, net of taxes of ($194), ($219) and $77
|
(9,954
|
)
|
(11,255
|
)
|
977
|
|||||||
|
Reclassification adjustment for gain (loss) on sale of marketable
|
||||||||||||
|
securities included in net earnings, net of tax of $-, $- and ($37)
|
-
|
-
|
(61
|
)
|
||||||||
|
Unrealized holding (losses) gains on marketable securities arising during
|
||||||||||||
|
the period, net of taxes of $5, $90 and $45
|
5
|
147
|
87
|
|||||||||
|
Change in unfunded SERP liability, net of taxes of $2, ($631) and
|
||||||||||||
|
$457, respectively
|
21
|
(1,485
|
)
|
1,069
|
||||||||
|
Other comprehensive (loss) income
|
(9,928
|
)
|
(12,593
|
)
|
2,072
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive income (loss)
|
$
|
9,269
|
$
|
(3,990
|
)
|
$
|
17,980
|
|||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
|
||||||||||||
|
BEL FUSE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(dollars in thousands)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Accumulated
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Other
|
Class A
|
Class B
|
Additional
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Retained
|
Comprehensive
|
Common
|
Common
|
Paid-In
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Total
|
Earnings
|
(Loss) Income
|
Stock
|
Stock
|
Capital
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2012
|
$
|
215,362
|
$
|
195,183
|
$
|
(1,427
|
)
|
$
|
217
|
$
|
937
|
$
|
20,452
|
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cash dividends declared on Class A common stock
|
(522
|
)
|
(522
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cash dividends declared on Class B common stock
|
(2,576
|
)
|
(2,576
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of restricted common stock
|
-
|
16
|
(16
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Forfeiture of restricted common stock
|
-
|
(2
|
)
|
2
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Repurchase/retirement of Class B common stock
|
(3,356
|
)
|
(18
|
)
|
(3,338
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of taxes of $77
|
977
|
977
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Unrealized holding gains on marketable securities
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
arising during the year, net of taxes of $45
|
87
|
87
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Reclassification adjustment for unrealized holding
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
gains included in net earnings, net of taxes of ($37)
|
(61
|
)
|
(61
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Reduction in APIC pool associated with tax
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
deficiencies related to restricted stock awards
|
(65
|
)
|
(65
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation expense
|
1,879
|
1,879
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Change in unfunded SERP liability, net of taxes of $457
|
1,069
|
1,069
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net earnings
|
15,908
|
15,908
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2013
|
$
|
228,702
|
$
|
207,993
|
$
|
645
|
$
|
217
|
$
|
933
|
$
|
18,914
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cash dividends declared on Class A common stock
|
(522
|
)
|
(522
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cash dividends declared on Class B common stock
|
(2,665
|
)
|
(2,665
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of restricted common stock
|
-
|
38
|
(38
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Forfeiture of restricted common stock
|
-
|
(2
|
)
|
2
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of taxes of ($219)
|
(11,255
|
)
|
(11,255
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Unrealized holding gains on marketable securities
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
arising during the year, net of taxes of $90
|
147
|
147
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Increase in APIC pool associated with tax
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
benefits related to restricted stock awards
|
31
|
31
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation expense
|
2,717
|
2,717
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Change in unfunded SERP liability, net of taxes of ($631)
|
(1,485
|
)
|
(1,485
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net earnings
|
8,603
|
8,603
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2014 (Revised)
|
$
|
224,273
|
$
|
213,409
|
$
|
(11,948
|
)
|
$
|
217
|
$
|
969
|
$
|
21,626
|
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cash dividends declared on Class A common stock
|
(522
|
)
|
(522
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cash dividends declared on Class B common stock
|
(2,713
|
)
|
(2,713
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of restricted common stock
|
-
|
8
|
(8
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Forfeiture of restricted common stock
|
-
|
(7
|
)
|
7
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of taxes of ($194)
|
(9,954
|
)
|
(9,954
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Unrealized holding gains on marketable securities
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
arising during the year, net of taxes of $5
|
5
|
5
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Increase in APIC pool associated with tax
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
benefits related to restricted stock awards
|
0
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation expense
|
2,815
|
2,815
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Change in unfunded SERP liability, net of taxes of $2
|
21
|
21
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net earnings
|
19,197
|
19,197
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2015
|
$
|
233,122
|
$
|
229,371
|
$
|
(21,876
|
)
|
$
|
217
|
$
|
970
|
$
|
24,440
|
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
BEL FUSE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
|
||||||||||||
|
(dollars in thousands)
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
Years Ended December 31,
|
|||||||||||
|
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
|||||||||
|
|
(Revised)
|
|||||||||||
|
Cash flows from operating activities:
|
||||||||||||
|
Net earnings
|
$
|
19,197
|
$
|
8,603
|
$
|
15,908
|
||||||
|
Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to net cash
|
||||||||||||
|
provided by operating activities:
|
||||||||||||
|
Depreciation and amortization
|
23,009
|
20,367
|
12,382
|
|||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation
|
2,815
|
2,717
|
1,879
|
|||||||||
|
Amortization of deferred financing costs
|
1,432
|
699
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
Deferred income taxes
|
(356
|
)
|
(2,691
|
)
|
(877
|
)
|
||||||
|
Other, net
|
(1,419
|
)
|
(3,651
|
)
|
407
|
|||||||
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities:
|
||||||||||||
|
Accounts receivable
|
12,187
|
1,382
|
(8,025
|
)
|
||||||||
|
Inventories
|
12,951
|
9,121
|
(6,538
|
)
|
||||||||
|
Other current assets
|
846
|
693
|
1,702
|
|||||||||
|
Other assets
|
2,161
|
(450
|
)
|
(62
|
)
|
|||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
(10,022
|
)
|
(3,890
|
)
|
1,485
|
|||||||
|
Accrued expenses
|
(3,154
|
)
|
(10,170
|
)
|
(7,670
|
)
|
||||||
|
Other liabilities
|
(295
|
)
|
423
|
165
|
||||||||
|
Income taxes payable
|
6,437
|
(696
|
)
|
(175
|
)
|
|||||||
|
Net cash provided by operating activities
|
65,789
|
22,457
|
10,581
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Cash flows from investing activities:
|
||||||||||||
|
Purchase of property, plant and equipment
|
(9,891
|
)
|
(9,042
|
)
|
(6,940
|
)
|
||||||
|
Purchase of intangible asset
|
-
|
(1,336
|
)
|
|||||||||
|
Purchase of marketable securities
|
-
|
(2,936
|
)
|
-
|
||||||||
|
Purchase of company-owned life insurance
|
(2,820
|
)
|
(2,820
|
)
|
(2,820
|
)
|
||||||
|
Cash transferred from (to) restricted cash
|
-
|
-
|
12,993
|
|||||||||
|
Payments for acquisitions, net of cash acquired
|
-
|
(208,693
|
)
|
(30,994
|
)
|
|||||||
|
Proceeds from cash surrender of COLI policies
|
-
|
5,756
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
Proceeds from sale of marketable securities
|
2,820
|
-
|
2,820
|
|||||||||
|
Proceeds from disposal/sale of property, plant and equipment
|
77
|
65
|
96
|
|||||||||
|
Net cash used in investing activities
|
(9,814
|
)
|
(217,670
|
)
|
(26,181
|
)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
(continued)
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
|
||||||||||||
|
BEL FUSE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
|
||||||||||||
|
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS (Continued)
|
||||||||||||
|
(dollars in thousands)
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
|||||||||||
|
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
|||||||||
|
|
(Revised)
|
|||||||||||
|
Cash flows from financing activities:
|
||||||||||||
|
Dividends paid to common shareholders
|
(3,238
|
)
|
(3,160
|
)
|
(3,111
|
)
|
||||||
|
Deferred financing costs
|
(15
|
)
|
(5,756
|
)
|
-
|
|||||||
|
Borrowings under revolving credit line
|
12,500
|
23,000
|
12,000
|
|||||||||
|
Repayments under revolving credit line
|
(35,500
|
)
|
(12,000
|
)
|
-
|
|||||||
|
(Reduction) increase in notes payable
|
(123
|
)
|
(161
|
)
|
506
|
|||||||
|
Proceeds from long-term debt
|
-
|
215,000
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
Repayments of long-term debt
|
(22,438
|
)
|
(5,375
|
)
|
-
|
|||||||
|
Purchase and retirement of Class B common stock
|
-
|
-
|
(3,356
|
)
|
||||||||
|
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities
|
(48,814
|
)
|
211,548
|
6,039
|
||||||||
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash
|
741
|
(1,320
|
)
|
422
|
||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents
|
7,902
|
15,015
|
(9,139
|
)
|
||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents - beginning of year
|
77,138
|
62,123
|
71,262
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Cash and cash equivalents - end of year
|
$
|
85,040
|
$
|
77,138
|
$
|
62,123
|
||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Supplemental cash flow information:
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Cash paid (received) during the year for:
|
||||||||||||
|
Income taxes, net of refunds received
|
$
|
580
|
$
|
4,686
|
$
|
(474
|
)
|
|||||
|
Interest payments
|
$
|
6,153
|
$
|
3,210
|
$
|
156
|
||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Details of acquisition (see Note 2):
|
||||||||||||
|
Fair value of identifiable net assets acquired
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
130,747
|
$
|
34,541
|
||||||
|
Goodwill
|
-
|
105,402
|
4,812
|
|||||||||
|
Fair value of net assets acquired
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
236,149
|
$
|
39,353
|
||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Fair value of consideration transferred
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
236,149
|
$
|
39,353
|
||||||
|
Less: Cash acquired in acquisition
|
-
|
(27,456
|
)
|
(8,359
|
)
|
|||||||
|
Cash paid for acquisition, net of cash acquired
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
208,693
|
$
|
30,994
|
||||||
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
|
||||||||||||
BEL FUSE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
AS OF AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2015, 2014 AND 2013
1. DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Bel Fuse Inc. and subsidiaries ("Bel," the "Company," "we," "us," and "our") design, manufacture and sell a broad array of products that power, protect and connect electronic circuits. These products are used in the networking, telecommunication, high-speed data transmission, commercial aerospace, military, broadcasting, transportation and consumer electronic industries around the world. We manage our operations geographically through our three reportable operating segments: North America, Asia and Europe.
On June 19, 2014, we completed our acquisition of 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of the Power-One Power Solutions business ("Power Solutions") of ABB Ltd. On July 25, 2014, we completed our acquisition of 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of the U.S. and U.K. Connectivity Solutions businesses from Emerson Electric Co. ("Emerson"). On August 29, 2014, we completed our acquisition of the Connectivity Solutions business in China from Emerson (collectively with the U.S. and U.K. portion of the transaction, "Connectivity Solutions"). The acquisitions of Power Solutions and Connectivity Solutions may hereafter be referred to collectively as either the "2014 Acquisitions" or the "2014 Acquired Companies".
On March 29, 2013, we completed our acquisition of 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Transpower Technologies (HK) Limited ("Transpower") and certain other tangible and intangible assets related to the Transpower magnetics business of TE Connectivity ("TE"). These operations are now doing business as TRP Connector ("TRP"). On August 20, 2013, we completed our acquisition of 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Array Connector Corporation ("Array"). The acquisitions of TRP and Array may hereafter be referred to collectively as either the "2013 Acquisitions" or the "2013 Acquired Companies".
Accordingly, as of the respective acquisition dates, all of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed were recorded at their preliminary fair values and the Company's consolidated results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 include the operating results of the acquired companies from their respective acquisition dates through the respective period end dates. The accompanying consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2014 has been revised to reflect certain adjustments affecting the consolidated statements of operations including the acquisition-date fair values related to property, plant and equipment and various other balance sheet accounts of the 2014 Acquired Companies. Other adjustments with no impact to the consolidated statement of operations have been recorded as of and for the year ended December 31, 2015. The consolidated statements of operations, stockholders' equity and cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 reflect measurement period adjustments related to the 2014 and 2013 Acquisitions. The measurement period adjustments in the aggregate were not considered material to the condensed consolidated financial statements. See Note 2, "Acquisitions and Disposition," for further details.
All amounts included in the tables to these notes to consolidated financial statements, except per share amounts, are in thousands.
Principles of Consolidation - The consolidated financial statements include all of the accounts of the Company and its wholly owned subsidiaries, including businesses acquired since their respective dates of acquisition. All intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates - The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America ("U.S. GAAP") requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. On an on-going basis, we evaluate our estimates, including but not limited to those related to product returns, provisions for bad debt, inventories, goodwill, intangible assets, investments, Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan ("SERP") expense, income taxes, contingencies and litigation. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
Cash Equivalents - Cash equivalents include short-term investments in money market funds and certificates of deposit with an original maturity of three months or less when purchased.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts - We maintain an allowance for doubtful accounts for estimated losses from the inability of our customers to make required payments. We determine our allowance by both specific identification of customer accounts where appropriate and the application of historical loss experience to non-specific accounts.
Business Combinations – We account for business combinations by recognizing the assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, and any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree at the acquisition date, measured at their fair values as of that date, with limited exceptions specified in the accounting literature. Acquisition-related costs, including restructuring costs, are recognized separately from the acquisition and will generally be expensed as incurred.
Effects of Foreign Currency – In non-U.S. locations that are not considered highly inflationary, we translate the balance sheets at the end of period exchange rates with translation adjustments accumulated in stockholders' equity on our consolidated balance sheets. We translate the statements of operations at the average exchange rates during the applicable period. The Company incurred net realized and unrealized currency exchange gains (losses) of $5.1 million, $4.3 million and ($0.6) million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, which were included in net earnings.
Concentration of Credit Risk - Financial instruments which potentially subject us to concentrations of credit risk consist principally of accounts receivable and temporary cash investments. We grant credit to customers that are primarily original equipment manufacturers and to subcontractors of original equipment manufacturers based on an evaluation of the customer's financial condition, without requiring collateral. Exposure to losses on receivables is principally dependent on each customer's financial condition. We control our exposure to credit risk through credit approvals, credit limits and monitoring procedures and establish allowances for anticipated losses. See Note 12, "Segments," for disclosures regarding significant customers.
We place temporary cash investments with quality financial institutions and commercial issuers of short-term paper and, by policy, limit the amount of credit exposure in any one financial instrument.
Inventories - Inventories are stated at the lower of weighted-average cost or market. Costs related to inventories include raw materials, direct labor and manufacturing overhead which are included in cost of sales on the consolidated statements of operations. The Company utilizes the average cost method in determining amounts to be removed from inventory.
Revenue Recognition – Revenue is recognized when the product has been delivered and title and risk of loss has passed to the customer, collection of the resulting receivable is deemed reasonably assured by management, persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists and the sales price is fixed and determinable. Substantially all of our shipments are FCA (free carrier), which provides for title to pass upon delivery to the customer's freight carrier. Some product is shipped DDP/DDU with title passing when the product arrives at the customer's dock. DDP is defined as Delivered Duty Paid by the Company and DDU is Delivered Duty Unpaid by the Company.
For certain customers, we provide consigned inventory, either at the customer's facility or at a third-party warehouse. Sales of consigned inventory are recorded when the customer withdraws inventory from consignment.
The Company is not contractually obligated to accept returns except for defective product or in instances where the product does not meet the Company's product specifications. However, the Company may permit its customers to return product for other reasons. In these instances, the Company would generally require a significant cancellation penalty payment by the customer. The Company estimates such returns, where applicable, based upon management's evaluation of historical experience, market acceptance of products produced and known negotiations with customers. Such estimates are deducted from sales and provided for at the time revenue is recognized.
Product Warranties – Warranties vary by product line and are competitive for the markets in which the Company operates. Warranties generally extend for one to three years from the date of sale. The Company reviews its warranty liability quarterly based on an analysis of actual expenses and failure rates accompanied with estimated future costs and projected failure rate trends. Factors taken into consideration when evaluating our warranty reserve are (i) historical claims for each product, (ii) volume increases, (iii) life of warranty, (iv) historical warranty repair costs and (v) other factors. To the extent that actual experience differs from our estimate, the provision for product warranties will be adjusted in future periods. Actual warranty repair costs are charged against the reserve balance as incurred. See Note 11, "Accrued Expenses."
Finite-Lived Intangible Assets – Intangible assets with finite lives are stated at cost less accumulated amortization. Amortization is calculated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the asset.
Goodwill and Other Indefinite-lived Intangible Assets– Goodwill represents the excess of the aggregate of the following (1) consideration transferred, (2) the fair value of any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree and, (3) if the business combination is achieved in stages, the acquisition-date fair value of our previously held equity interest in the acquiree over the net of the acquisition-date amounts of the identifiable assets acquired and the liabilities assumed.
We evaluate goodwill and other indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment annually as of October 1 or more frequently if impairment indicators arise in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") Topic 350, "Intangibles – Goodwill and Other".
The Company tests goodwill for impairment using a fair value approach at the reporting unit level. A reporting unit is an operating segment or one level below an operating segment for which discrete financial information is available and reviewed regularly by management. Our reporting units are geographical in nature and are North America, Asia and Europe. Assets and liabilities of the Company have been assigned to the reporting units to the extent they are employed in or are considered a liability related to the operations of the reporting unit and are considered in determining the fair value of the reporting unit. Reporting units with similar economic characteristics are aggregated for purposes of the goodwill impairment test.
The goodwill impairment test is a two-step process. If the fair value of a reporting unit exceeds its carrying amount, goodwill of the reporting unit is considered not impaired and the second step of the impairment test is unnecessary. If the carrying amount of a reporting unit exceeds its fair value, the second step of the goodwill impairment test is performed to measure the amount of impairment loss, if any. The second step of the goodwill impairment test, used to measure the amount of impairment loss, compares the implied fair value of goodwill associated with each reporting unit with the carrying amount of that goodwill. If the carrying amount of goodwill associated with a reporting unit exceeds the implied fair value of that goodwill, an impairment loss shall be recognized in an amount equal to that excess. No impairment was recognized as a result of the October 1, 2015 and 2014 testing. See Note 4, "Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets."
The Company tests indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment using the relief-from-royalty method (a form of the income approach). No impairment was recognized as a result of the October 1, 2015 testing. See Note 4, "Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets."
Evaluation of Long-lived Assets – Management reviews long-lived assets for potential impairment whenever significant events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. An impairment exists when the carrying amount of the long-lived asset is not recoverable and exceeds its fair value. The carrying amount of a long-lived asset is not recoverable if it exceeds the sum of the estimated undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use and eventual disposition of the asset. If an impairment exists, the resulting writedown would be the difference between fair market value of the long-lived asset and the related net book value
Depreciation - Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are calculated primarily using the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the asset. The estimated useful lives primarily range from 3 to 39 years for buildings and leasehold improvements, and from 3 to 15 years for machinery and equipment.
Income Taxes - We account for income taxes under the asset and liability method, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the consolidated financial statements. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the differences between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
We record net deferred tax assets to the extent we believe these assets will more-likely-than-not be realized. In making such determination, we consider all available positive and negative evidence, including future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, projected future taxable income, tax planning strategies and recent financial operations. We have established valuation allowances for deferred tax assets that are not likely to be realized. In the event we were to determine that we would be able to realize our deferred income tax assets in the future in excess of our net recorded amount, we would adjust the valuation allowance, which would reduce the provision for income taxes.
We establish reserves for tax contingencies when, despite the belief that our tax return positions are fully supported, it is probable that certain positions may be challenged and may not be fully sustained. The tax contingency reserves are analyzed on a quarterly basis and adjusted based upon changes in facts and circumstances, such as the conclusion of federal and state audits, expiration of the statute of limitations for the assessment of tax, case law and emerging legislation. Our effective tax rate includes the effect of tax contingency reserves and changes to the reserves as considered appropriate by management.
Earnings per Share – We utilize the two-class method to report our earnings per share. The two-class method is an earnings allocation formula that determines earnings per share for each class of common stock according to dividends declared and participation rights in undistributed earnings. The Company's Certificate of Incorporation, as amended, states that Class B common shares are entitled to dividends at least 5% greater than dividends paid to Class A common shares, resulting in the two-class method of computing earnings per share. In computing earnings per share, the Company has allocated dividends declared to Class A and Class B based on amounts actually declared for each class of stock and 5% more of the undistributed earnings have been allocated to Class B shares than to the Class A shares on a per share basis. Basic earnings per common share are computed by dividing net earnings by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per common share, for each class of common stock, are computed by dividing net earnings by the weighted-average number of common shares and potential common shares outstanding during the period. There were no potential common shares outstanding during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 or 2013 which would have had a dilutive effect on earnings per share.
The earnings and weighted average shares outstanding used in the computation of basic and diluted earnings per share are as follows:
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
||||||||||
|
Numerator:
|
||||||||||||
|
Net earnings
|
$
|
19,197
|
$
|
8,603
|
$
|
15,908
|
||||||
|
Less dividends declared:
|
||||||||||||
|
Class A
|
522
|
522
|
522
|
|||||||||
|
Class B
|
2,713
|
2,665
|
2,576
|
|||||||||
|
Undistributed earnings
|
$
|
15,962
|
$
|
5,416
|
$
|
12,810
|
||||||
|
Undistributed earnings allocation - basic and diluted:
|
||||||||||||
|
Class A undistributed earnings
|
$
|
2,809
|
$
|
970
|
$
|
2,346
|
||||||
|
Class B undistributed earnings
|
13,153
|
4,446
|
10,464
|
|||||||||
|
Total undistributed earnings
|
$
|
15,962
|
$
|
5,416
|
$
|
12,810
|
||||||
|
Net earnings allocation - basic and diluted:
|
||||||||||||
|
Class A net earnings
|
$
|
3,331
|
$
|
1,492
|
$
|
2,868
|
||||||
|
Class B net earnings
|
15,866
|
7,111
|
13,040
|
|||||||||
|
Net earnings
|
$
|
19,197
|
$
|
8,603
|
$
|
15,908
|
||||||
|
Denominator:
|
||||||||||||
|
Weighted average shares outstanding:
|
||||||||||||
|
Class A - basic and diluted
|
2,175
|
2,175
|
2,175
|
|||||||||
|
Class B - basic and diluted
|
9,698
|
9,491
|
9,240
|
|||||||||
|
Net earnings per share:
|
||||||||||||
|
Class A - basic and diluted
|
$
|
1.53
|
$
|
0.69
|
$
|
1.32
|
||||||
|
Class B - basic and diluted
|
$
|
1.64
|
$
|
0.75
|
$
|
1.41
|
||||||
Research and Development ("R&D") - Our engineering groups are strategically located around the world to facilitate communication with and access to customers' engineering personnel. This collaborative approach enables partnerships with customers for technical development efforts. On occasion, we execute non-disclosure agreements with our customers to help develop proprietary, next generation products destined for rapid deployment. R&D costs are expensed as incurred, and are included in cost of sales on the consolidated statements of operations. Generally, R&D is performed internally for the benefit of the Company. R&D costs include salaries, building maintenance and utilities, rents, materials, administration costs and miscellaneous other items. R&D expenses for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 amounted to $27.7 million, $21.5 million and $14.1 million, respectively. The majority of the increase over the past two years relates to the inclusion of R&D expenses of the 2013 and 2014 Acquired Companies, which have been included in Bel's results since their respective acquisition dates.
Fair Value Measurements - We utilize the accounting guidance for fair value measurements and disclosures for all financial assets and liabilities and nonfinancial assets and liabilities that are recognized or disclosed at fair value in the consolidated financial statements on a recurring basis or on a nonrecurring basis during the reporting period. The fair value is an exit price, representing the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants based upon the best use of the asset or liability at the measurement date. The Company utilizes market data or assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability. The accounting guidance establishes a three-tier fair value hierarchy, which prioritizes the inputs used in measuring fair value. These tiers are defined as follows:
Level 1 - Observable inputs such as quoted market prices in active markets
Level 2 - Inputs other than quoted prices in active markets that are either directly or indirectly observable
Level 3 - Unobservable inputs about which little or no market data exists, therefore requiring an entity to develop its own assumptions
For financial instruments such as cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable, accrued expenses and notes payable, the carrying amount approximates fair value because of the short maturities of such instruments. See Note 5, "Fair Value Measurements," for additional disclosures related to fair value measurements.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
Recently Adopted Accounting Standards
In April 2014, the FASB issued guidance for the reporting of discontinued operations, which also contains new disclosure requirements for both discontinued operations and other disposals that do not meet the definition of a discontinued operation. This guidance was adopted by the Company effective January 1, 2015. The effects of this guidance will depend on future disposals by the Company.
In November 2014, the FASB issued guidance on pushdown accounting for business combinations. This amendment provides an acquired entity with an option to apply pushdown accounting in its separate financial statements upon occurrence of an event in which an acquirer obtains control of the acquired entity. This amendment was effective on November 18, 2014. The effects of this standard will depend on any future events whereby we obtain control of an entity and elect to apply pushdown accounting.
In July 2013, the FASB issued revised guidance to address the diversity in practice related to the financial statement presentation of unrecognized tax benefits when a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward exists. The Company adopted this guidance on January 1, 2014, on a prospective basis. The adoption did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
Accounting Standards Issued But Not Yet Adopted
In February 2016, the FASB issued guidance to provide a new comprehensive model for lease accounting. Under this guidance, lessees and lessors should apply a "right-of-use" model in accounting for all leases (including subleases) and eliminate the concept of operating leases and off-balance sheet leases. This guidance is effective for annual periods and interim periods within those annual periods beginning after December 15, 2018. Early adoption is permitted. Management is currently evaluating the impact that this guidance will have on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
In November 2015, the FASB issued guidance which will require entities to present deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities as noncurrent on the consolidated balance sheet. The guidance simplifies the current guidance, which requires entities to separately present deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities as current and noncurrent on the consolidated balance sheet. This guidance may be applied either prospectively or retrospectively and is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, with early adoption permitted. The adoption of this guidance is not expected to have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
In September 2015, the FASB issued guidance which simplifies the accounting for measurement period adjustments related to business combinations, which eliminates the requirement for an acquirer in a business combination to account for measurement period adjustments retrospectively. Under this guidance, acquirers must recognize measurement period adjustments in the period in which they determine the amounts, including the effect on earnings of any amount they would have recorded in previous periods if the accounting had been completed at the acquisition date. This guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2015, with early adoption permitted. Measurement period adjustments of any future acquisitions will be accounted for under this new guidance.
In July 2015, the FASB issued guidance which requires entities to measure most inventory at the lower of cost and net realizable value, thereby simplifying the current guidance under which an entity must measure inventory at the lower of cost or market. The update is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods therein. Early application is permitted. Management is currently evaluating the impact that this guidance will have on the Company's consolidated financial statements, if any.
In April 2015, the FASB issued guidance on simplifying the balance sheet presentation of debt issuance costs. The update requires debt issuance costs related to a recognized debt liability be presented in the balance sheet as a direct deduction from the carrying amount of the related debt liability instead of being presented as an asset. Debt disclosures will include the face amount of the debt liability and the effective interest rate. In August 2015, the FASB amended this guidance for debt issuance costs associated with line-of-credit arrangements to reflect that the SEC would not object to the deferral and presentation of debt issuance costs as an asset and subsequent amortization of debt issuance costs over the term of the line-of-credit arrangement, whether or not there are any outstanding borrowings on the line-of-credit arrangement. The update requires retrospective application and represents a change in accounting principle. The update is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2015. Early application is permitted. Management does not believe that the adoption of this guidance will have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial position or results of operations.
In January 2015, the FASB issued guidance on simplifying the income statement presentation by eliminating the concept of extraordinary items. Extraordinary items are events and transactions that are distinguished by their unusual nature and by the infrequency of their occurrence. Eliminating the extraordinary classification simplifies income statement presentation by altogether removing the concept of extraordinary items from consideration. This amendment is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2015. The adoption of this standard is not expected to have a material impact on our consolidated financial position or results of operations.
In August 2014, the FASB issued guidance on the presentation of financial statements when there is substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern. The amendment requires that an entity's management evaluate whether there are conditions or events, considered in the aggregate, that raise substantial doubt about the entity's ability to continue as a going concern within one year after the date that the financial statements are issued. If conditions or events raise substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern, additional disclosure is required to enable users of the financial statements to understand the conditions or events, management's evaluation of the significance of those conditions and events and management's plans that are intended to alleviate or management's plans that have alleviated substantial doubt. The amendment is effective for annual periods ending after December 15, 2016, and for annual periods and interim periods thereafter. Early application is permitted. Management does not believe that the adoption of this guidance will have any material impact on the Company's consolidated financial position or results of operations.
In June 2014, the FASB issued guidance on stock compensation. The amendment requires that a performance target that affects vesting and that could be achieved after the requisite service period be treated as a performance condition. A reporting entity should apply existing guidance in Topic 718 as it relates to awards with performance conditions that affect vesting to account for such awards. Compensation cost should be recognized in the period in which it becomes probable that the performance target will be achieved and should represent the compensation cost attributable to the period(s) for which the requisite service has already been rendered. The amendment is effective for annual reporting periods (including interim reporting periods within those periods) beginning after December 15, 2015. Earlier adoption is permitted. Management does not believe that the adoption of this guidance will have any impact on the Company's consolidated financial position or results of operations.
In May 2014, the FASB issued guidance on the accounting for revenue from contracts with customers that will supersede most existing revenue recognition guidance, including industry-specific guidance. The core principle requires an entity to recognize revenue to depict the transfer of goods and services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. In addition, the guidance requires enhanced disclosures regarding the nature, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from an entity's contracts with customers. This guidance allows for both retrospective and prospective methods of adoption and is effective for periods beginning after December 15, 2016. On July 9, 2015, the FASB decided to defer the effective date of this guidance by one year to annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, however, early adoption as of the original effective date will be permitted. Management is currently evaluating the impact that this guidance will have on the Company's consolidated financial statements, if any, including which transition method it will adopt.
|
2.
|
ACQUISITIONS AND DISPOSITION
|
2014 Acquisitions:
On June 19, 2014, the Company completed its acquisition of Power Solutions for $109.9 million, net of cash acquired. Power Solutions is a leading provider of high-efficiency and high-density power conversion products for server, storage and networking equipment, industrial applications and power systems. In connection with its acquisition of Power Solutions from ABB Ltd., the Company acquired a 49% interest in a joint venture in the People's Republic of China ("PRC"). The Company has assigned no value to this investment. See Note 18, "Related Party Transactions," for additional information. During the second quarter of 2015, the Company finalized the valuation of the Power Solutions acquisition as further detailed in the table below. At the conclusion of the measurement period, which was one year after the acquisition date, there were certain working capital and tax related items outstanding with ABB Ltd. The working capital item was settled with ABB Ltd. during the third quarter of 2015, which was after the conclusion of the measurement period and, as a result, the Company recognized $4.2 million of other income on the consolidated statements of operations. See Note 9, "Income Taxes," for further information on the tax related items outstanding with ABB Ltd.
On July 25, 2014, the Company completed its acquisition of the U.S. and U.K. entities of Connectivity Solutions. On August 29, 2014, the China portion of the transaction closed. The Company paid a total of $98.8 million for Connectivity Solutions, net of cash acquired and including a working capital adjustment. Connectivity Solutions is a leading provider of high‑performance RF/Microwave and Harsh Environment Optical Connectors and Assemblies for military, aerospace, wireless communications, data communications, broadcast and industrial applications. During the third quarter of 2015, the Company finalized its valuation of the Connectivity Solutions acquisition as further detailed in the table below.
During the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company incurred $0.6 million and $7.3 million of acquisition-related costs, respectively, associated with the 2014 Acquisitions primarily for audit-related costs, investment banker fees and legal fees. These costs are included in selling, general and administrative expenses on the consolidated statements of operations.
Fair Value Estimate of Assets Acquired and Liabilities Assumed
The table below depicts the Company's final purchase price allocation for the 2014 Acquisitions as of the respective acquisition dates.
|
Power Solutions
|
Connectivity Solutions
|
2014 Acquisitions
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
June 19, 2014
|
July 25, 2014/
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(As Reported at
|
Measurement
|
June 19,
|
August 29, 2014(a)
|
Measurement
|
July 25, 2014/
|
Acquisition-Date
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
December 31,
|
Period
|
2014
|
(As Reported at
|
Period
|
August 29, 2014
|
Fair Values
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2014)
|
|
Adjustments
|
(Revised)
|
December 31, 2014)
|
Adjustments
|
(Revised)
|
(Revised)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cash
|
$
|
20,912
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
20,912
|
$
|
6,544
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
6,544
|
$
|
27,456
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Accounts receivable
|
29,389
|
-
|
29,389
|
9,375
|
-
|
9,375
|
38,764
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Inventories
|
36,429
|
-
|
36,429
|
17,632
|
-
|
17,632
|
54,061
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Other current assets
|
7,350
|
-
|
7,350
|
2,615
|
(1,761
|
)
|
(c)
|
854
|
8,204
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Property, plant and equipment
|
28,175
|
(1,060
|
)
|
(b)
|
27,115
|
9,900
|
-
|
9,900
|
37,015
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Intangible assets
|
33,220
|
-
|
33,220
|
40,000
|
-
|
40,000
|
73,220
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Other assets
|
19,171
|
-
|
19,171
|
2,345
|
2,388
|
(c)
|
4,733
|
23,904
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Total identifiable assets
|
174,646
|
(1,060
|
)
|
173,586
|
88,411
|
627
|
89,038
|
262,624
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Accounts payable
|
(26,180
|
)
|
-
|
(26,180
|
)
|
(10,682
|
)
|
-
|
(10,682
|
)
|
(36,862
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Accrued expenses
|
(25,545
|
)
|
-
|
(25,545
|
)
|
(5,307
|
)
|
76
|
(5,231
|
)
|
(30,776
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Other current liabilities
|
223
|
-
|
223
|
(57
|
)
|
946
|
(c)
|
889
|
1,112
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Noncurrent liabilities
|
(42,062
|
)
|
(4,623
|
)
|
(c)
|
(46,685
|
)
|
(17,314
|
)
|
(1,352
|
)
|
(c)
|
(18,666
|
)
|
(65,351
|
)
|
||||||||||||||
|
Total liabilities assumed
|
(93,564
|
)
|
(4,623
|
)
|
(98,187
|
)
|
(33,360
|
)
|
(330
|
)
|
(33,690
|
)
|
(131,877
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Net identifiable assets acquired
|
81,082
|
(5,683
|
)
|
75,399
|
55,051
|
297
|
55,348
|
130,747
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Goodwill
|
49,710
|
5,683
|
55,393
|
50,306
|
(297
|
)
|
50,009
|
105,402
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net assets acquired
|
$
|
130,792
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
130,792
|
$
|
105,357
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
105,357
|
$
|
236,149
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Cash paid
|
$
|
130,792
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
130,792
|
$
|
105,357
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
105,357
|
$
|
236,149
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Assumption of liability
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Fair value of consideration
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
transferred
|
130,792
|
-
|
130,792
|
105,357
|
-
|
105,357
|
236,149
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Deferred consideration
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Total consideration paid
|
$
|
130,792
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
130,792
|
$
|
105,357
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
105,357
|
$
|
236,149
|
||||||||||||||||
|
(a)
|
The Company acquired the U.S. and U.K. entities of Connectivity Solutions on July 25, 2014 and the China entity of Connectivity Solutions on August 29, 2014. These values represent the fair values as of the respective acquisition dates.
|
|
(b)
|
Represents the purchase accounting adjustments reflecting the finalization of the acquisition-date fair values of property, plant and equipment associated with completion of third-party valuations.
|
|
(c)
|
Primarily represents the impact to deferred taxes reflecting the finalization of the allocation of identifiable intangible assets acquired.
|
Of the goodwill noted above, $17.7 million of goodwill associated with Power Solutions and $3.2 million of goodwill associated with Connectivity Solutions will be deductible for U.S. income tax purposes.
The results of operations of the 2014 Acquired Companies have been included in the Company's consolidated financial statements for the period subsequent to their respective acquisition dates. During the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, the 2014 Acquired Companies contributed revenue of $230.3 million and $134.3 million, respectively, and operating income (loss) of approximately $10.3 million and ($2.5) million, respectively, to the Company's consolidated financial results.
The following unaudited pro forma information presents a summary of the combined results of operations of the Company and the aggregate results of TRP, Array, Power Solutions and Connectivity Solutions for the periods presented as if the 2013 Acquisitions had occurred on January 1, 2012 and the 2014 Acquisitions had occurred on January 1, 2013, along with certain pro forma adjustments. These pro forma adjustments give effect to the amortization of certain definite-lived intangible assets, adjusted depreciation based upon estimated fair value of assets acquired, interest expense and amortization of deferred financing costs related to the financing of the business combinations, and related tax effects. The 2014 unaudited pro forma net earnings for the year ended December 31, 2014 were adjusted to exclude $14.9 million ($9.8 million after tax) of non-recurring expenses, including audit, legal and other transaction fees, IT migration costs and employee-related expenses, which were incurred in connection with the 2013 and 2014 Acquisitions. The 2013 unaudited pro forma net earnings were adjusted to include these charges in addition to an estimated non-recurring expense related to a fair value adjustment to acquisition-date inventory of $5.9 million ($4.1 million after tax) during the year ended December 31, 2013, respectively. The 2013 results reflected below include merger-related charges incurred by Power Solutions in connection with its acquisition by ABB in July 2013. The pro forma results do not reflect the realization of any potential cost savings, or any related integration costs. Certain cost savings may result from these acquisitions; however, there can be no assurance that these cost savings will be achieved. The unaudited pro forma results are presented for illustrative purposes only and are not necessarily indicative of the results that would have actually been obtained if the acquisitions had occurred on the assumed dates, nor is the pro forma data intended to be a projection of results that may be obtained in the future.
|
Year Ended
|
||||||||
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2014
|
2013
|
|||||||
|
Revenue
|
$
|
629,132
|
$
|
710,937
|
||||
|
Net earnings
|
11,705
|
(65,299
|
)
|
|||||
|
Earnings per Class A common share - basic and diluted
|
0.94
|
(5.52
|
)
|
|||||
|
Earnings per Class B common share - basic and diluted
|
1.02
|
(5.77
|
)
|
|||||
2013 Acquisitions:
On March 29, 2013, the Company completed its acquisition of TRP for $21.0 million, net of cash acquired. The Company's purchase of TRP consisted of the integrated connector module ("ICM") family of products, including RJ45, 10/100 Gigabit, 10G, PoE/PoE+, MRJ21 and RJ.5, a line of modules for smart-grid applications, and discrete magnetics.
On August 20, 2013, the Company completed its acquisition of Array, a manufacturer of aerospace and mil-spec connector products based in Miami, Florida, for $10.0 million in cash. The acquisition of Array expands the Company's portfolio of connector products that can be offered to the combined customer base, and provides an opportunity to sell other products that Bel manufactures to Array's customers. Array has become part of Bel's Cinch Connector business.
During the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company incurred $0.1 million and $0.7 million, respectively, of combined acquisition-related costs associated with the 2013 Acquisitions. These costs are included in selling, general and administrative expense in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
The purchase accounting related to the 2013 Acquisitions was finalized within one year of the respective acquisition dates. The contributions to revenue and operating income from the 2013 Acquisitions is detailed in Note 12, "Segments."
|
3.
|
RESTRUCTURING ACTIVITIES
|
Activity and liability balances related to restructuring costs for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2015 are as follows:
|
|
2014
|
2015
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Liability at
|
Cash Payments
|
Liability at
|
Cash Payments
|
Liability at
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
December 31,
|
New
|
and Other
|
December 31,
|
New
|
and Other
|
December 31,
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
2013
|
Charges
|
Settlements
|
2014
|
Charges
|
Settlements
|
2015
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Severance costs
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
1,778
|
$
|
(1,778
|
)
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
1,144
|
$
|
(1,034
|
)
|
$
|
110
|
||||||||||||
|
Other restructuring costs
|
-
|
54
|
(54
|
)
|
-
|
626
|
(626
|
)
|
-
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Total
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
1,832
|
$
|
(1,832
|
)
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
1,770
|
$
|
(1,660
|
)
|
$
|
110
|
||||||||||||
During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company's restructuring charges included costs related to reductions in headcount and consolidation and relocation of certain facilities and offices in North America, Asia and Europe and additional headcount reductions at Cinch US, Array and the U.S. and Asia locations of Connectivity Solutions. During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company incurred severance costs associated with restructuring of management and sales teams after the acquisitions of Power Solutions and Connectivity Solutions.
During 2012, Bel initiated the closure of its Cinch North American manufacturing facility in Vinita, Oklahoma, and transition of the operations to Reynosa, Mexico and a new facility in McAllen, Texas. The Cinch restructuring continued into early 2013 and the Company incurred $1.4 million of restructuring costs in 2013 related to these efforts, as detailed in the table above. These amounts are classified as restructuring charges on the consolidated statements of operations.
|
4.
|
GOODWILL AND OTHER INTANGIBLE ASSETS
|
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price and related acquisition costs over the fair value assigned to the net tangible and other intangible assets acquired in a business acquisition.
Other intangible assets include patents, technology, license agreements, non-compete agreements and trademarks. Amounts assigned to these intangible assets have been determined by management. Management considered a number of factors in determining the allocations, including valuations and independent appraisals. Trademarks have indefinite lives and are reviewed for impairment on an annual basis. Other intangible assets, excluding trademarks, are being amortized over 2 to 24 years.
The changes in the carrying value of goodwill classified by reportable operating segment for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
|
|
Total
|
North America
|
Asia
|
Europe
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at January 1, 2014
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Goodwill, gross
|
45,431
|
18,865
|
14,107
|
12,459
|
||||||||||||
|
Accumulated impairment charges
|
(26,941
|
)
|
(14,066
|
)
|
(12,875
|
)
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
Goodwill, net
|
$
|
18,490
|
$
|
4,799
|
$
|
1,232
|
$
|
12,459
|
||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Goodwill allocation related to acquisitions
|
100,812
|
51,011
|
36,155
|
13,646
|
||||||||||||
|
Measurement period adjustments
|
(496
|
)
|
(496
|
)
|
-
|
-
|
||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation
|
(437
|
)
|
-
|
(210
|
)
|
(227
|
)
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2014:
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Goodwill, gross
|
145,310
|
69,380
|
50,052
|
25,878
|
||||||||||||
|
Accumulated impairment charges
|
(26,941
|
)
|
(14,066
|
)
|
(12,875
|
)
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
Goodwill, net
|
$
|
118,369
|
$
|
55,314
|
$
|
37,177
|
$
|
25,878
|
||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Measurement period adjustments
|
4,590
|
(6,016
|
)
|
4,351
|
6,255
|
|||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation
|
(1,325
|
)
|
-
|
129
|
|
(1,454
|
)
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2015:
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Goodwill, gross
|
148,575
|
63,364
|
54,532
|
30,679
|
||||||||||||
|
Accumulated impairment charges
|
(26,941
|
)
|
(14,066
|
)
|
(12,875
|
)
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
Goodwill, net
|
$
|
121,634
|
$
|
49,298
|
$
|
41,657
|
$
|
30,679
|
||||||||
During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company recorded $100.8 million of goodwill related to the 2014 Acquisitions. An additional $4.6 million of goodwill related to the 2014 Acquisitions, including finalization of goodwill allocation by reporting unit, was recorded during the measurement period in 2015.
During the fourth quarters of 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company completed step one of our annual goodwill impairment test for our reporting units We concluded that the fair value of each of the Company's reporting units exceeded the respective carrying values and that there was no indication of impairment in 2015, 2014 or 2013.
We estimated the fair value of these reporting units using a weighting of fair values derived from income and market approaches. Under the income approach, we determine the fair value of a reporting unit based on the present value of estimated future cash flows. Cash flow projections are based on management's estimates of revenue growth rates and operating margins, taking into consideration industry and market conditions. The discount rate used is based on a weighted average cost of capital adjusted for the relevant risk associated with the characteristics of the business and the projected cash flows. The market approach estimates fair value based on market multiples of revenue and earnings derived from comparable publicly traded companies with similar operating and investment characteristics as the reporting unit.
The excess of estimated fair values over carrying value, including goodwill for each of our reporting units that had goodwill as of the 2015 annual impairment test were the following:
|
Reporting Unit
|
% by Which Estimated Fair Value Exceeds Carrying Value
|
|||
|
North America
|
11.4
|
%
|
||
|
Asia
|
20.2
|
%
|
||
|
Europe
|
18.4
|
%
|
||
As noted above, the fair value determined under step one of the goodwill impairment test completed in the fourth quarter of 2015 exceeded the carrying value for each reporting unit. Therefore, there was no impairment of goodwill. However, if the fair value decreases in future periods, the Company may fail step one of the goodwill impairment test and be required to perform step two. In performing step two, the fair value would have to be allocated to all of the assets and liabilities of the reporting unit. Therefore, any potential goodwill impairment charge would be dependent upon the estimated fair value of the reporting unit at that time and the outcome of step two of the impairment test. The fair values of the assets and liabilities of the reporting unit, including the intangible assets, could vary depending on various factors.
The future occurrence of a potential indicator of impairment, such as a decrease in expected net earnings, adverse equity market conditions, a decline in current market multiples, a decline in our common stock price, a significant adverse change in legal factors or business climates, an adverse action or assessment by a regulator, unanticipated competition, strategic decisions made in response to economic or competitive conditions, or a more-likely-than-not expectation that a reporting unit or a significant portion of a reporting unit will be sold or disposed of, could require an interim assessment for some or all of the reporting units before the next required annual assessment. In the event of significant adverse changes of the nature described above, it may be necessary for us to recognize a non-cash impairment of goodwill, which could have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial condition and results of operations.
Other Intangible Assets
The components of intangible assets other than goodwill are as follows:
|
December 31, 2015
|
December 31, 2014
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Gross Carrying
|
Accumulated
|
Net Carrying
|
Gross Carrying
|
Accumulated
|
Net Carrying
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Amount
|
Amortization
|
Amount
|
Amount
|
Amortization
|
Amount
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Patents, licenses and technology
|
$
|
39,388
|
$
|
7,932
|
$
|
31,456
|
$
|
38,872
|
$
|
4,297
|
$
|
34,575
|
||||||||||||
|
Customer relationships
|
44,894
|
5,735
|
39,159
|
45,836
|
3,062
|
42,774
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Non-compete agreements
|
2,753
|
1,838
|
915
|
2,781
|
1,050
|
1,731
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Trademarks
|
16,338
|
41
|
16,297
|
16,624
|
202
|
16,422
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
$
|
103,373
|
$
|
15,546
|
$
|
87,827
|
$
|
104,113
|
$
|
8,611
|
$
|
95,502
|
|||||||||||||
The Company tests indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment using a fair value approach, the relief-from-royalty method (a form of the income approach). At December 31, 2015, the Company's indefinite-lived intangible assets related to the trademarks acquired in the Power Solutions, Connectivity Solutions, Cinch and Fibreco acquisitions. The Company completed its annual indefinite-lived intangible assets impairment test during the fourth quarter of 2015, noting no impairment. Management has concluded that the fair value of these trademarks exceeded the related carrying values at December 31, 2015 and that no impairment existed as of that date.
Amortization expense was $7.0 million, $5.4 million and $1.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Estimated amortization expense for intangible assets for the next five years is as follows:
|
December 31,
|
Amortization Expense
|
|||
|
2016
|
$
|
6,759
|
||
|
2017
|
6,325
|
|||
|
2018
|
6,084
|
|||
|
2019
|
6,084
|
|||
|
2020
|
6,052
|
|||
|
5.
|
FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
|
As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company held certain financial assets that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis. These consisted of securities that are among the Company's investments in a rabbi trust which are intended to fund the Company's Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan ("SERP") obligations, and other marketable securities described below. The securities that are held in the rabbi trust are categorized as available-for-sale securities and are included as other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets at December 31, 2015 and 2014. The gross unrealized gains associated with the investments held in the rabbi trust were $0.7 million and $0.7 million at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Such unrealized gains are included, net of tax, in accumulated other comprehensive income.
As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, our available-for-sale securities, which primarily consist of investments held in a rabbi trust of $3.6 million and $6.5 million, respectively, are measured at fair value using quoted prices in active markets for identical assets (Level 1) inputs. The Company does not have any financial assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis categorized as Level 3, and there were no transfers in or out of Level 1, Level 2 or Level 3 during 2015 or 2014. There were no changes to the Company's valuation techniques used to measure asset fair values on a recurring or nonrecurring basis during 2015.
There were no financial assets accounted for at fair value on a nonrecurring basis as of December 31, 2015 or 2014.
The Company has other financial instruments, such as cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, restricted cash, accounts payable, accrued expenses and notes payable, which are not measured at fair value on a recurring basis but are recorded at amounts that approximate fair value due to their liquid or short-term nature. The fair value of the Company's long-term debt is estimated using a discounted cash flow method based on interest rates that are currently available for debt issuances with similar terms and maturities. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the estimated fair value of long-term debt was $188.1 million and $233.3 million, respectively, compared to a carrying amount of $187.2 million and $232.6 million, respectively. The Company did not have any other financial liabilities within the scope of the fair value disclosure requirements as of December 31, 2015.
Nonfinancial assets and liabilities, such as goodwill, indefinite-lived intangible assets and long-lived assets, are accounted for at fair value on a nonrecurring basis. These items are tested for impairment upon the occurrence of a triggering event or in the case of goodwill, on at least an annual basis. See Note 4, "Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets," for further information about goodwill and other indefinite-lived intangible assets.
|
6.
|
OTHER ASSETS
|
At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company has obligations of $15.6 million and $14.2 million, respectively, associated with its SERP. As a means of informally funding these obligations, the Company has invested in life insurance policies related to certain employees and marketable securities held in a rabbi trust. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, these assets had a combined value of $12.2 million and $12.3 million, respectively.
Company-Owned Life Insurance
Investments in company-owned life insurance policies ("COLI") were made with the intention of utilizing them as a long-term funding source for the Company's SERP obligations. However, the cash surrender value of the COLI does not represent a committed funding source for these obligations. Any proceeds from these policies are subject to claims from creditors. The cash surrender value of the COLI of $8.5 million and $5.8 million at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, is included in other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. During 2015, the Company sold $2.8 million of marketable securities within the rabbi trust and utilized the proceeds to purchase additional COLI. The volatility in global equity markets in recent years has also had an effect on the cash surrender value of the COLI policies. The Company recorded (expense) income to account for the (decrease) increase in cash surrender value in the amount of ($0.1) million, $0.2 million and $0.7 million during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. These fluctuations in the cash surrender value were allocated between cost of sales and selling, general and administrative expenses on the consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013. The allocation is consistent with the costs associated with the long-term employee benefit obligations that the COLI is intended to fund.
Other Investments
At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company held, in the aforementioned rabbi trust, available-for-sale investments at a cost of $2.9 million and $5.8 million, respectively. Together with the COLI described above, these investments are intended to fund the Company's SERP obligations and are classified as other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The Company monitors these investments for impairment on an ongoing basis. As discussed above, the Company sold $2.8 million of its SERP investments during 2015. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the fair market value of these investments was $3.6 million and $6.5 million, respectively. The gross unrealized gain of $0.7 million and $0.7 million at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, has been included, net of tax, in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss).
|
7.
|
INVENTORIES
|
The components of inventories are as follows:
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2015
|
2014
|
|||||||
|
Raw materials
|
$
|
42,036
|
$
|
51,638
|
||||
|
Work in progress
|
16,908
|
16,128
|
||||||
|
Finished goods
|
39,566
|
45,864
|
||||||
|
Inventories
|
$
|
98,510
|
$
|
113,630
|
||||
|
8.
|
PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET
|
Property, plant and equipment, net consist of the following:
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2015
|
2014
|
|||||||
|
Land
|
$
|
2,240
|
$
|
3,293
|
||||
|
Buildings and improvements
|
29,346
|
31,067
|
||||||
|
Machinery and equipment
|
116,921
|
117,178
|
||||||
|
Construction in progress
|
4,949
|
4,764
|
||||||
|
153,456
|
156,302
|
|||||||
|
Accumulated depreciation
|
(95,845
|
)
|
(87,041
|
)
|
||||
|
Property, plant and equipment, net
|
$
|
57,611
|
$
|
69,261
|
||||
Depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 was $16.0 million, $15.0 million and $10.5 million, respectively.
9. INCOME TAXES
At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company has approximately $42.2 million and $40.0 million, respectively, of liabilities for uncertain tax positions ($1.9 million and $0.2 million, respectively, included in income taxes payable on the consolidated balance sheets and $40.3 million and $39.8 million, respectively, included in liability for uncertain tax positions on the consolidated balance sheets) which, if recognized, would reduce the Company's effective tax rate.
The Company and its subsidiaries file income tax returns in the U.S. federal jurisdiction and various states and foreign jurisdictions. The Company is no longer subject to U.S. federal examinations by tax authorities for years before 2012 and for state examinations before 2009. Regarding foreign subsidiaries, the Company is no longer subject to examination by tax authorities for years before 2005 in Asia and generally 2008 in Europe. The Company is currently under examination by the taxing authorities in Germany for the tax years 2011-2013.
As a result of the expiration of the statutes of limitations for specific jurisdictions, it is reasonably possible that the related unrecognized benefits for tax positions taken regarding previously filed tax returns may change materially from those recorded as liabilities for uncertain tax positions in the Company's consolidated financial statements at December 31, 2015. A total of $1.9 million of previously recorded liabilities for uncertain tax positions relates principally to the 2012 tax year. The statute of limitations related to these liabilities is scheduled to expire on September 15, 2016. Additionally, a total of $0.2 million of previously recorded liabilities for uncertain tax positions relating to the 2010 tax year were reversed during the year ended December 31, 2015. This was offset by an increase to the liability for uncertain tax positions in the amount of $3.2 million, of which $2.1 million relates to interest and penalties on the uncertain tax positions acquired from Power Solutions, which is included in the consolidated statement of operations during the year ended December 31, 2015. A total of $0.8 million of previously recorded liabilities for uncertain tax positions relating to 2010 were reversed during the year ended December 31, 2014.
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of the liability for uncertain tax positions, including the portion included in income taxes payable, is as follows:
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
||||||||||
|
Liability for uncertain tax positions - January 1
|
$
|
39,970
|
$
|
2,189
|
$
|
2,711
|
||||||
|
Additions based on tax positions
|
||||||||||||
|
related to the current year
|
3,241
|
2,732
|
28
|
|||||||||
|
Additions relating to acquisitions
|
-
|
35,874
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
Translation adjustment
|
(844
|
)
|
-
|
-
|
||||||||
|
Settlement/expiration of statutes of limitations
|
(209
|
)
|
(825
|
)
|
(550
|
)
|
||||||
|
Liability for uncertain tax positions - December 31
|
$
|
42,158
|
$
|
39,970
|
$
|
2,189
|
||||||
As part of the acquisition of Power Solutions the Company acquired a $35.9 million liability for uncertain tax positions. Of this amount, $12.0 million relates to an ongoing claim by the Arezzo Revenue Agency in Italy concerning certain tax matters related to what was then Power-One Asia Pacific Electronics Shenzhen Co. Ltd. (now Bel Power Solutions Asia Pacific Electronics Shenzhen Co. Ltd.) for the years 2004 through 2006, as further described in Note 16, "Commitments and Contingencies." The Company also acquired a liability for additional uncertain tax positions related to various tax matters for the years 2007 through 2013. Resolution of these tax matters are being actively pursued with the applicable taxing authority. From the date of acquisition through December 31, 2015, the Company has recorded $3.4 million of interest and penalties pertaining to this issue and will continue to accrue approximately $2.1 million annually until the issues are resolved.
The Company's policy is to recognize interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions as a component of the current provision for income taxes. During the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company recognized $2.5 million and $1.6 million, respectively, in interest and penalties in the consolidated statements of operations. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recognized a benefit of an immaterial amount for the reversal of such interest and penalties. The Company has approximately $4.0 million and $1.6 million accrued for the payment of interest and penalties at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, which is included in both income taxes payable and liability for uncertain tax positions in the consolidated balance sheets.
The Company's total income (loss) before provision (benefit) for income taxes included earnings (loss) from domestic operations of $6.1 million, ($9.2) million and ($1.2) million for 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and earnings before provision (benefit) for income taxes from foreign operations of $19.6 million, $19.0 million and $16.3 million for 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
The provision (benefit) for income taxes consists of the following:
|
Years Ended December 31,
|
||||||||||||
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
||||||||||
|
Current:
|
||||||||||||
|
Federal
|
$
|
1,494
|
$
|
402
|
$
|
(1,099
|
)
|
|||||
|
Foreign
|
5,327
|
3,281
|
1,120
|
|||||||||
|
State
|
70
|
175
|
113
|
|||||||||
|
6,891
|
3,858
|
134
|
||||||||||
|
Deferred:
|
||||||||||||
|
Federal
|
1,019
|
(2,698
|
)
|
(865
|
)
|
|||||||
|
State
|
(64
|
)
|
(407
|
)
|
65
|
|||||||
|
Foreign
|
(1,311
|
)
|
414
|
(77
|
)
|
|||||||
|
(356
|
)
|
(2,691
|
)
|
(877
|
)
|
|||||||
|
$
|
6,535
|
$
|
1,167
|
$
|
(743
|
)
|
||||||
A reconciliation of taxes on income computed at the U.S. federal statutory rate to amounts provided is as follows:
|
Years Ended December 31,
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
$
|
|
%
|
$
|
|
%
|
$
|
|
%
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Tax provision computed at the
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
federal statutory rate
|
$
|
9,006
|
35
|
%
|
$
|
3,420
|
35
|
%
|
$
|
5,309
|
35
|
%
|
||||||||||||
|
Increase (decrease) in taxes resulting from:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Different tax rates applicable to foreign operations
|
(5,353
|
)
|
(21
|
%)
|
(4,458
|
)
|
(46
|
%)
|
(4,677
|
)
|
(31
|
%)
|
||||||||||||
|
Increase in (reversal of) liability for uncertain
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
tax positions - net
|
3,032
|
12
|
%
|
1,907
|
20
|
%
|
(522
|
)
|
(3
|
%)
|
||||||||||||||
|
Utilization of research and experimentation, solar and foreign
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
tax credits
|
(349
|
)
|
(1
|
%)
|
(508
|
)
|
(5
|
%)
|
(1,049
|
)
|
(7
|
%)
|
||||||||||||
|
State taxes, net of federal benefit
|
56
|
0
|
%
|
(183
|
)
|
(2
|
%)
|
117
|
1
|
%
|
||||||||||||||
|
Current year (reversal) increase in U.S. valuation allowances
|
(343
|
)
|
(1
|
%)
|
335
|
3
|
%
|
49
|
0
|
%
|
||||||||||||||
|
Federal tax on profit of foreign disregarded entities
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
net of deferred tax
|
872
|
3
|
%
|
770
|
8
|
%
|
-
|
0
|
%
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Other, including qualified production activity credits, SERP/COLI
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
income, under/(over) accruals, unrealized foreign exchange gains
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
and amortization of purchase accounting intangibles
|
(386
|
)
|
(2
|
%)
|
(116
|
)
|
(1
|
%)
|
30
|
0
|
%
|
|||||||||||||
|
Tax (benefit) provision computed at the Company's
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
effective tax rate
|
$
|
6,535
|
25
|
%
|
$
|
1,167
|
12
|
%
|
$
|
(743
|
)
|
(5
|
%)
|
|||||||||||
The Company holds an offshore business license from the government of Macao. With this license, a Macao offshore company named Bel Fuse (Macao Commercial Offshore) Limited has been established to handle the Company's sales to third-party customers in Asia. Sales by this company consist of products manufactured in the PRC. This company is not subject to Macao corporate profit taxes which are imposed at a tax rate of 12%. Additionally, the Company established TRP International, a China Business Trust ("CBT"), when it acquired the TRP group, as previously discussed. Sales by the CBT consists of products manufactured in the PRC and sold to third-party customers inside and outside Asia. The CBT is not subject to PRC income taxes, which are generally imposed at a tax rate of 25%.
As of December 31, 2015, the Company has gross foreign income tax net operating losses ("NOL") of $21.0 million, foreign tax credits of $0.3 million and capital loss carryforwards of $0.2 million which amount to a total of $5.2 million of deferred tax assets. The Company has established valuation allowances totaling $5.2 million against these deferred tax assets. In addition, the Company has gross federal and state income tax NOLs of $17.8 million, including $3.8 million of NOLs acquired from Array and $10.0 million of NOLs acquired from Connectivity Solutions, which amount to $5.3 million of deferred tax assets and tax credit carryforwards of $1.3 million. The Company has established valuation allowances of $0.3 million and $1.1 million, respectively, against these deferred tax assets. The foreign NOL's can be carried forward indefinitely, the NOL acquired from Array expires at various times during 2026 – 2027, the NOL acquired from Connectivity Solutions expire at various times during 2022-2033, the state NOL's expire at various times during 2015 – 2031 and the tax credit carryforwards expire at various times during 2025 - 2034.
Upon the acquisition of Power Solutions and Connectivity Solutions, there were net deferred tax assets of $2.2 million and $1.2 million, respectively, arising from various temporary differences and net operating loss carry forward acquired. In connection with the 2014 Acquisitions, the Company was required to complete a fair market value report of property, plant and equipment and intangibles. As a result of that report, the Company established deferred tax liabilities at the date of acquisition in the amount of $3.1 million and $16.4 million, respectively, for the Power Solutions and Connectivity Solutions acquisitions. At December 31, 2015, a net deferred tax liability of $11.2 million remains on the consolidated balance sheet for the 2014 Acquisitions.
The Company has made elections to step up the tax basis to fair value under IRC Section 338(g) for the Power Solutions acquisition and for a single jurisdiction with respect to the Connectivity Solutions acquisition. The elections made under Section 338(g) only affect U.S. income taxes (not those of the foreign country where the acquired entities were incorporated).
Upon the acquisition of TRP, TRP had a deferred tax asset in the amount of $2.2 million arising from various timing differences related to depreciation and accrued expenses. Upon the acquisition of Array, Array had a deferred tax liability of $0.7 million arising from timing differences related to depreciation and a deferred tax asset of $2.1 million arising from the NOL acquired. In connection with the 2013 Acquisitions, the Company was required to complete a fair market value report of property, plant and equipment and intangibles. As a result of that report, the Company established deferred tax liabilities at the date of acquisition in the amount of $0.6 million and $1.0 million respectively for the TRP and Array acquisitions. At December 31, 2015, a net deferred tax asset of $1.9 million remains on the consolidated balance sheet for the 2013 Acquisitions.
The Company did not make any election to step up the tax basis of the 2013 Acquisitions to fair value under IRC Section 338(g).
On July 31, 2012, the Company completed its acquisition of 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Fibreco Ltd. ("Fibreco"). Upon the acquisition of Fibreco, Fibreco had a deferred tax liability in the amount of $0.1 million arising from various timing differences.
On March 9, 2012, the Company completed its acquisition of 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of GigaCom Interconnect AB ("GigaCom"). On September 12, 2012, the Company completed its acquisition of 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of Powerbox Italia S.r.L. and its subsidiary, Powerbox Design (collectively, "Powerbox", now merged to form Bel Power Europe S.r.l.). The acquisitions of GigaCom, Fibreco and Powerbox are hereafter be referred to collectively as the "2012 Acquisitions."
In connection with the 2012 Acquisitions, the Company was required to complete a fair market value report of property, plant and equipment and intangibles. As a result of that report, the Company established deferred tax liabilities at the date of acquisition in the amount of $1.7 million, $0.6 million and $0.4 million, respectively for the Fibreco, GigaCom and Powerbox acquisitions. At December 31, 2015, a deferred tax liability of $2.0 million remains on the consolidated balance sheet for the 2012 Acquisitions.
The Company has made elections under Internal Revenue Code ("IRC") Section 338(g) to step up the tax basis of the 2012 Acquisitions to fair value. The elections made under Section 338(g) only affect U.S. income taxes (not those of the foreign country where the acquired entities were incorporated).
It is the Company's intention to repatriate substantially all net income from its wholly owned PRC subsidiary, Dongguan Transpower Electric Products Co., Ltd, a Chinese Limited Liability Company, to its direct Hong Kong parent Transpower Technologies (Hong Kong) Ltd. Applicable income and dividend withholding taxes have been reflected in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2015. However, U.S. deferred taxes need not be provided as there is no intention to repatriate such amounts to the U.S. Management's intention is to permanently reinvest the majority of the remaining earnings of foreign subsidiaries in the expansion of its foreign operations. Unrepatriated earnings, upon which U.S. income taxes have not been accrued, are approximately $143.4 million at December 31, 2015. Such unrepatriated earnings are deemed by management to be permanently reinvested. At December 31, 2015, the estimated federal income tax liability related to unrepatriated foreign earnings is $38.3 million under the current tax law.
Components of deferred income tax assets are as follows:
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2015
|
2014
|
|||||||
|
Tax Effect
|
Tax Effect
|
|||||||
|
(Revised)
|
||||||||
|
Deferred tax assets:
|
||||||||
|
State tax credits
|
$
|
902
|
$
|
954
|
||||
|
Unfunded pension liability
|
1,327
|
1,301
|
||||||
|
Reserves and accruals
|
4,349
|
2,095
|
||||||
|
Federal, state and foreign net operating loss
|
||||||||
|
and credit carryforwards
|
10,953
|
15,361
|
||||||
|
Depreciation
|
880
|
962
|
||||||
|
Amortization
|
814
|
995
|
||||||
|
Acquired deferred taxes
|
-
|
10,775
|
||||||
|
Other accruals
|
9,622
|
3,253
|
||||||
|
Total deferred tax assets
|
28,847
|
35,696
|
||||||
|
Deferred tax liabilities:
|
||||||||
|
Reserves and accruals
|
64
|
68
|
||||||
|
Depreciation
|
2,391
|
707
|
||||||
|
Amortization
|
23,772
|
21,062
|
||||||
|
Acquired deferred taxes
|
-
|
8,053
|
||||||
|
Other accruals
|
857
|
1,522
|
||||||
|
Total deferred tax liabilities
|
27,084
|
31,412
|
||||||
|
Valuation allowance
|
6,635
|
6,692
|
||||||
|
Net deferred tax assets/(liabilities)
|
$
|
(4,872
|
)
|
$
|
(2,408
|
)
|
||
On December 31, 2013, under the "American Taxpayer Relief Act" ("ATRA"), the Research and Experimentation credit ("R&E") expired. On December 16, 2014, the R&E credit was extended back to January 1, 2014 and the Company recognized $0.3 million in R&E credits during the fourth quarter of 2014. During December, 2015, the PATH Act was approved which permanently extends the R&E credit retroactive to the end of 2014.
The Company continues to monitor proposed legislation affecting the taxation of transfers of U.S. intangible property and other potential tax law changes.
|
10.
|
DEBT
|
On June 19, 2014, the Company entered into a senior Credit and Security Agreement with KeyBank National Association ("KeyBank"), as administrative agent and lender, which was amended on June 30, 2014 principally to add a syndicate of additional lenders (as so amended, the "Credit and Security Agreement" or "CSA"). The maturity date of the CSA is June 18, 2019.
The CSA consists of (i) a $50 million revolving credit facility ("Revolver"), (ii) a $145 million term loan facility ("Term Loan") and (iii) a $70 million delayed draw term loan ("DDTL"). Under the terms of the CSA, the Company is entitled, subject to the satisfaction of certain conditions, to request additional commitments under the revolving credit facility or term loans in the aggregate principal amount of up to $100 million to the extent that existing or new lenders agree to provide such additional commitments and/or term loans.
The obligations of the Company under the CSA are guaranteed by certain of the Company's material U.S. subsidiaries (together with the Company, the "Loan Parties") and are secured by a first priority security interest in substantially all of the existing and future personal property of the Loan Parties, certain material real property of the Loan Parties and certain of the Loan Parties' material U.S. subsidiaries, including 65% of the voting capital stock of certain of the Loan Parties' direct foreign subsidiaries.
The borrowings under the CSA will bear interest at a rate equal to, at the Company's option, either (1) LIBOR, plus a margin ranging from 1.75% per annum to 3.00% per annum depending on the Company's leverage ratio, or (2)(a) an "Alternate Base Rate," which is the highest of (i) the federal funds rate plus 0.50%, (ii) KeyBank's prime rate and (iii) the LIBOR rate with a maturity of one month plus 1.00%, plus (b) a margin ranging from 0.75% per annum to 2.00% per annum, depending on the Company's leverage ratio. The interest rate in effect at December 31, 2015 was 3.19%, which consisted of LIBOR of 0.44% plus the Company's margin of 2.75%. The interest rate in effect at December 31, 2014 was 2.94%, which consisted of LIBOR of 0.19% plus the Company's margin of 2.75%.
The CSA contains customary representations and warranties, covenants and events of default and financial covenants that measure (i) the ratio of the Company's total funded indebtedness, on a consolidated basis, to the amount of the Company's consolidated EBITDA, as defined, ("Leverage Ratio") and (ii) the ratio of the amount of the Company's consolidated EBITDA to the Company's consolidated fixed charges ("Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio"). If an event of default occurs, the lenders under the CSA would be entitled to take various actions, including the acceleration of amounts due thereunder and all actions permitted to be taken by a secured creditor. At December 31, 2015, the Company was in compliance with its debt covenants, including its most restrictive covenant, the Leverage Ratio. The unused credit available under the credit facility at December 31, 2015 was $50.0 million.
Concurrent with its entry into the CSA on June 19, 2014, the Company borrowed $145.0 million under the Term Loan to complete its acquisition of Power Solutions. In July 2014, in connection with the acquisition of Connectivity Solutions, the Company borrowed an additional $90.0 million under the CSA ($70.0 million through the DDTL and $20.0 million under the Revolver). During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company recorded $5.8 million in deferred financing costs which will be amortized over the five-year term.
In connection with its outstanding borrowings and amortization of the deferred financing costs described above, the Company incurred $7.6 million and $4.0 million of interest expense during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, borrowings outstanding related to the term loans (Term Loan and DDTL combined) were $187.2 million and $209.6 million, respectively, and borrowings outstanding under the revolver were $0 and $23.0 million, respectively.
Scheduled principal payments of the long-term debt outstanding at December 31, 2015 are as follows (in thousands):
|
2016(1)
|
$
|
24,772
|
||
|
2017
|
18,813
|
|||
|
2018
|
24,188
|
|||
|
2019
|
119,415
|
|||
|
Total long-term debt
|
187,188
|
|||
|
Less: Current maturities of long-term debt
|
(24,772
|
)
|
||
|
Noncurrent portion of long-term debt
|
$
|
162,416
|
(1) Includes an estimated $8.6 million excess cash flow payment due in 2016 based on 2015 results as per
the terms of the CSA.
At December 31, 2013, the Company maintained a $30 million line of credit with Bank of America (the "Credit Agreement"), which was due to expire on October 14, 2016. At December 31, 2013, the borrowings under the line of credit amounted to $12.0 million. During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company repaid the full $12.0 million balance outstanding and terminated the Credit Agreement.
11. ACCRUED EXPENSES
Accrued expenses consist of the following:
|
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
|||||||
|
|
2015
|
2014
|
||||||
|
Sales commissions
|
$
|
2,824
|
$
|
3,017
|
||||
|
Subcontracting labor
|
1,942
|
2,217
|
||||||
|
Salaries, bonuses and related benefits
|
15,672
|
17,964
|
||||||
|
Warranty accrual
|
3,659
|
6,032
|
||||||
|
Other
|
14,226
|
13,358
|
||||||
|
|
$
|
38,323
|
$
|
42,588
|
||||
A tabular presentation of the activity within the warranty accrual account for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 is presented below:
|
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
|||||||
|
|
2015
|
2014
|
||||||
|
Balance, beginning of year
|
$
|
6,032
|
$
|
-
|
||||
|
Warranty accruals acquired in 2014 Acquisitions
|
-
|
4,397
|
||||||
|
Charges and costs accrued
|
2,892
|
3,834
|
||||||
|
Adjustments related to pre-existing warranties
|
||||||||
|
(including changes in estimates)
|
(1,208
|
)
|
(66
|
)
|
||||
|
Less: Repair costs incurred
|
(2,932
|
)
|
(2,061
|
)
|
||||
|
Less: Cash settlements
|
(1,000
|
)
|
-
|
|||||
|
Currency translation
|
(125
|
)
|
(72
|
)
|
||||
|
Balance, end of year
|
$
|
3,659
|
$
|
6,032
|
||||
12. SEGMENTS
The Company operates in one industry with three reportable operating segments, which are geographic in nature. The segments consist of North America, Asia and Europe. The primary criteria by which financial performance is evaluated and resources are allocated are net sales and income from operations. The following is a summary of key financial data:
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
||||||||||
|
Net Sales to External Customers:
|
||||||||||||
|
North America
|
$
|
304,328
|
$
|
217,258
|
$
|
116,548
|
||||||
|
Asia
|
188,146
|
201,338
|
193,647
|
|||||||||
|
Europe
|
74,606
|
68,480
|
38,994
|
|||||||||
|
$
|
567,080
|
$
|
487,076
|
$
|
349,189
|
|||||||
|
Net Sales:
|
||||||||||||
|
North America
|
$
|
329,304
|
$
|
248,007
|
$
|
128,472
|
||||||
|
Asia
|
295,751
|
275,765
|
225,151
|
|||||||||
|
Europe
|
148,735
|
114,748
|
40,742
|
|||||||||
|
Less intercompany
|
||||||||||||
|
net sales
|
(206,710
|
)
|
(151,444
|
)
|
(45,176
|
)
|
||||||
|
$
|
567,080
|
$
|
487,076
|
$
|
349,189
|
|||||||
|
Income (Loss) from Operations:
|
||||||||||||
|
North America
|
$
|
11,012
|
$
|
(4,531
|
)
|
$
|
(1,560
|
)
|
||||
|
Asia
|
8,175
|
13,090
|
15,356
|
|||||||||
|
Europe
|
9,413
|
4,913
|
1,251
|
|||||||||
|
$
|
28,600
|
$
|
13,472
|
$
|
15,047
|
|||||||
|
Total Assets:
|
||||||||||||
|
North America
|
$
|
247,436
|
$
|
314,565
|
$
|
117,261
|
||||||
|
Asia
|
231,063
|
251,240
|
148,780
|
|||||||||
|
Europe
|
108,512
|
69,616
|
42,100
|
|||||||||
|
$
|
587,011
|
$
|
635,421
|
$
|
308,141
|
|||||||
|
Capital Expenditures:
|
||||||||||||
|
North America
|
$
|
2,425
|
$
|
3,862
|
$
|
2,064
|
||||||
|
Asia
|
4,888
|
4,089
|
4,551
|
|||||||||
|
Europe
|
2,578
|
1,091
|
325
|
|||||||||
|
$
|
9,891
|
$
|
9,042
|
$
|
6,940
|
|||||||
|
Depreciation and Amortization Expense:
|
||||||||||||
|
North America
|
$
|
10,841
|
$
|
7,986
|
$
|
4,282
|
||||||
|
Asia
|
8,706
|
8,391
|
6,540
|
|||||||||
|
Europe
|
3,462
|
3,990
|
1,560
|
|||||||||
|
$
|
23,009
|
$
|
20,367
|
$
|
12,382
|
|||||||
Net Sales – Segment net sales are attributed to individual segments based on the geographic source of the billing for such customer sales. Intercompany sales include finished products manufactured in foreign countries which are then transferred to the United States and Europe for sale; finished goods manufactured in the United States which are transferred to Europe and Asia for sale; and semi-finished components manufactured in the United States which are sold to Asia for further processing. Income from operations represents net sales less operating costs and expenses and does not include any amounts related to intercompany transactions.
The following items are included in the segment data presented above:
Recent Acquisitions – At December 31, 2015 and 2014, Power Solutions' total assets of $199.2 million and $203.1 million, respectively, and Connectivity Solutions' total assets of $134.2 million and $133.1 million, respectively, are included in the table above. See Note 2, "Acquisitions and Disposition," for further information on the 2014 Acquisitions.
The acquisitions in 2014 and 2013 contributed to Bel's segment net sales and income from operations as follows:
|
Year Ended
|
||||||||||||
|
December 31,
|
||||||||||||
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
||||||||||
|
Net Sales to External Customers:
|
||||||||||||
|
North America:
|
||||||||||||
|
Power Solutions
|
$
|
131,215
|
$
|
73,530
|
$
|
-
|
||||||
|
Connectivity Solutions
|
57,903
|
28,242
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
Array (a)
|
4,729
|
6,842
|
2,074
|
|||||||||
|
193,847
|
108,614
|
2,074
|
||||||||||
|
Asia:
|
||||||||||||
|
Power Solutions
|
1,026
|
3,401
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
Connectivity Solutions
|
4,872
|
2,469
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
TRP
|
71,215
|
66,082
|
65,141
|
|||||||||
|
77,113
|
71,952
|
65,141
|
||||||||||
|
Europe:
|
||||||||||||
|
Power Solutions
|
28,685
|
23,882
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
Connectivity Solutions
|
6,634
|
2,812
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
TRP
|
2,700
|
2,498
|
1,407
|
|||||||||
|
38,019
|
29,192
|
1,407
|
||||||||||
|
Net sales from 2013-2014 acquisitions
|
308,979
|
209,758
|
68,622
|
|||||||||
|
Income (loss) from operations:
|
||||||||||||
|
North America:
|
||||||||||||
|
Power Solutions
|
2,320
|
(777
|
)
|
-
|
||||||||
|
Connectivity Solutions
|
2,803
|
(2,808
|
)
|
-
|
||||||||
|
Array (a)
|
(311
|
)
|
(801
|
)
|
(936
|
)
|
||||||
|
4,812
|
(4,386
|
)
|
(936
|
)
|
||||||||
|
Asia:
|
||||||||||||
|
Power Solutions
|
(2,074
|
)
|
(3,851
|
)
|
-
|
|||||||
|
Connectivity Solutions
|
(329
|
)
|
493
|
-
|
||||||||
|
TRP
|
9,269
|
13,152
|
9,007
|
|||||||||
|
6,866
|
9,794
|
9,007
|
||||||||||
|
Europe:
|
||||||||||||
|
Power Solutions
|
6,799
|
4,574
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
Connectivity Solutions
|
731
|
(168
|
)
|
-
|
||||||||
|
TRP
|
351
|
366
|
289
|
|||||||||
|
7,881
|
4,772
|
289
|
||||||||||
|
Total income (loss) from operations
|
||||||||||||
|
from 2013-2014 acquisitions
|
$
|
19,559
|
$
|
10,180
|
$
|
8,360
|
||||||
|
(a)
|
2015 net sales and loss from operations noted for Array reflect 2015 activity through September 30, 2015. Array was merged into the Company's Cinch Connector business during the fourth quarter of 2015.
|
Restructuring Charges – The following restructuring charges are included in income (loss) from operations by segment. See Note 3, "Restructuring Activities," for further information on the Company's restructuring efforts.
|
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
|||||||||
|
North America
|
$
|
1,452
|
$
|
1,539
|
$
|
963
|
||||||
|
Asia
|
352
|
-
|
249
|
|||||||||
|
Europe
|
310
|
293
|
175
|
|||||||||
|
|
$
|
2,114
|
$
|
1,832
|
$
|
1,387
|
||||||
Entity-Wide Information
The following is a summary of entity-wide information related to the Company's net sales to external customers by geographic area and by major product line.
|
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
|||||||||
|
Net Sales by Geographic Location:
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
United States
|
$
|
304,328
|
$
|
217,258
|
$
|
116,548
|
||||||
|
Macao
|
182,248
|
195,469
|
193,647
|
|||||||||
|
United Kingdom
|
27,552
|
22,852
|
16,538
|
|||||||||
|
Germany
|
16,314
|
18,663
|
16,585
|
|||||||||
|
Switzerland
|
18,050
|
15,236
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
All other foreign countries
|
18,588
|
17,598
|
5,871
|
|||||||||
|
Consolidated net sales
|
$
|
567,080
|
$
|
487,076
|
$
|
349,189
|
||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Net Sales by Major Product Line:
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
Power solutions and protection
|
$
|
214,766
|
$
|
159,867
|
$
|
67,370
|
||||||
|
Connectivity solutions
|
181,697
|
152,954
|
111,653
|
|||||||||
|
Magnetic solutions
|
170,617
|
174,255
|
170,166
|
|||||||||
|
Consolidated net sales
|
$
|
567,080
|
$
|
487,076
|
$
|
349,189
|
||||||
The following is a summary of long-lived assets by geographic area as of December 31, 2015 and 2014:
|
2015
|
2014
|
|||||||
|
Long-lived Assets by Geographic Location:
|
||||||||
|
United States
|
$
|
35,967
|
$
|
43,760
|
||||
|
People's Republic of China (PRC)
|
37,796
|
42,323
|
||||||
|
Slovakia
|
7,758
|
8,101
|
||||||
|
Switzerland
|
4,006
|
4,935
|
||||||
|
United Kingdom
|
2,016
|
2,537
|
||||||
|
All other foreign countries
|
1,232
|
1,305
|
||||||
|
Consolidated long-lived assets
|
$
|
88,775
|
$
|
102,961
|
||||
Long-lived assets consist of property, plant and equipment, net and other assets of the Company that are identified with the operations of each geographic area.
The territory of Hong Kong became a Special Administrative Region ("SAR") of the PRC in the middle of 1997. The territory of Macao became a SAR of the PRC at the end of 1999. Management cannot presently predict what future impact this will have on the Company, if any, or how the political climate in the PRC will affect the Company's contractual arrangements in the PRC. A significant portion of the Company's manufacturing operations and approximately 38.7% of its identifiable assets are located in Asia.
Net Sales to Major Customers
The Company had net sales to one customer in excess of ten percent of consolidated net sales in each of 2015 and 2014. The net sales associated with this customer was $74.8 million in 2015 (13.2% of sales) and $76.4 million in 2014 (15.7% of sales). The Company had net sales to two customers in excess of ten percent of consolidated net sales in 2013. The combined net sales from these two customers was $103.3 million (29.6% of total sales) during the year ended December 31, 2013. Net sales related to these significant customers were primarily reflected in the Asia operating segment during each of the three years discussed.
13. RETIREMENT FUND AND PROFIT SHARING PLAN
The Company maintains the Bel Fuse Inc. Employees' Savings Plan, a defined contribution plan that is intended to meet the applicable requirements for tax-qualification under sections 401(a) and (k) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the "Code"). The Employees' Savings Plan allows eligible employees to voluntarily contribute a percentage of their eligible compensation, subject to Code limitations, which contributions are matched by the Company. For plan years beginning on and after January 1, 2012, the Company's matching contributions are made in cash and are equal to 100% of the first 1% of compensation contributed by participants, and 50% of the next 5% of compensation contributed by participants. Prior to January 1, 2012, the Company's matching and profit sharing contributions were made in the form of shares of Bel Fuse Inc. Class A and Class B common stock. The expense for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 amounted to $1.2 million, $0.8 million and $0.4 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2015, the plan owned 13,928 and 169,989 shares of Bel Fuse Inc. Class A and Class B common stock, respectively.
The Company's subsidiaries in Asia have a retirement fund covering substantially all of their Hong Kong based full-time employees. Eligible employees contribute up to 5% of salary to the fund. In addition, the Company must contribute a minimum of 5% of eligible salary, as determined by Hong Kong government regulations. The Company currently contributes 7% of eligible salary in cash or Company stock. The expense for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 amounted to approximately $0.3 million in each year. As of December 31, 2015, the plan owned 3,323 and 17,342 shares of Bel Fuse Inc. Class A and Class B common stock, respectively.
The SERP is designed to provide a limited group of key management and highly compensated employees of the Company with supplemental retirement and death benefits. Participants in the SERP are selected by the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors. The SERP initially became effective in 2002 and was amended and restated in April 2007 to conform with applicable requirements of Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code and to modify the provisions regarding benefits payable in connection with a change in control of the Company. The Plan is unfunded. Benefits under the SERP are payable from the general assets of the Company, but the Company has established a rabbi trust which includes certain life insurance policies in effect on participants as well as other investments to partially cover the Company's obligations under the Plan. See Note 6, "Other Assets," for further information on these assets.
The benefits available under the Plan vary according to when and how the participant terminates employment with the Company. If a participant retires (with the prior written consent of the Company) on his normal retirement date (65 years old, 20 years of service, and 5 years of Plan participation), his normal retirement benefit under the Plan would be annual payments equal to 40% of his average base compensation (calculated using compensation from the highest five consecutive calendar years of Plan participation), payable in monthly installments for the remainder of his life. If a participant retires early from the Company (55 years old, 20 years of service, and five years of Plan participation), his early retirement benefit under the Plan would be an amount (i) calculated as if his early retirement date were in fact his normal retirement date, (ii) multiplied by a fraction, with the numerator being the actual years of service the participant has with the Company and the denominator being the years of service the participant would have had if he had retired at age 65, and (iii) actuarially reduced to reflect the early retirement date. If a participant dies prior to receiving 120 monthly payments under the Plan, his beneficiary would be entitled to continue receiving benefits for the shorter of (i) the time necessary to complete 120 monthly payments or (ii) 60 months. If a participant dies while employed by the Company, his beneficiary would receive, as a survivor benefit, an annual amount equal to (i) 100% of the participant's annual base salary at date of death for one year, and (ii) 50% of the participant's annual base salary at date of death for each of the following four years, each payable in monthly installments. The Plan also provides for disability benefits, and a forfeiture of benefits if a participant terminates employment for reasons other than those contemplated under the Plan. The expense related to the Plan for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 amounted to $1.5 million, $1.3 million and $1.3 million, respectively.
Net Periodic Benefit Cost
The net periodic benefit cost related to the SERP consisted of the following components during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013:
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
||||||||||
|
Service Cost
|
$
|
552
|
$
|
542
|
$
|
556
|
||||||
|
Interest Cost
|
567
|
541
|
448
|
|||||||||
|
Net amortization
|
366
|
182
|
307
|
|||||||||
|
Net periodic benefit cost
|
$
|
1,485
|
$
|
1,265
|
$
|
1,311
|
||||||
Obligations and Funded Status
Summarized information about the changes in plan assets and benefit obligation, the funded status and the amounts recorded at December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
Summarized information about the changes in plan assets and benefit obligation, the funded status and the amounts recorded at December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
|
|
2015
|
2014
|
||||||
|
Fair value of plan assets, January 1
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
-
|
||||
|
Company contributions
|
85
|
16
|
||||||
|
Benefits paid
|
(85
|
)
|
(16
|
)
|
||||
|
Fair value of plan assets, December 31
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
-
|
||||
|
Benefit obligation, January 1
|
14,205
|
10,830
|
||||||
|
Service cost
|
552
|
542
|
||||||
|
Interest cost
|
567
|
541
|
||||||
|
Benefits paid
|
(85
|
)
|
(16
|
)
|
||||
|
Actuarial (gains) losses
|
337
|
2,308
|
||||||
|
Benefit obligation, December 31
|
$
|
15,576
|
$
|
14,205
|
||||
|
Underfunded status, December 31
|
$
|
(15,576
|
)
|
$
|
(14,205
|
)
|
||
The Company has recorded the 2015 and 2014 underfunded status as a long-term liability on the consolidated balance sheets. The accumulated benefit obligation for the SERP was $12.7 million as of December 31, 2015 and $12.1 million as of December 31, 2014. The aforementioned company-owned life insurance policies and marketable securities held in a rabbi trust had a combined value of $12.2 million and $12.3 million at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. See Note 6, "Other Assets," for additional information on these investments.
The estimated net loss and prior service cost for the defined benefit pension plan that will be amortized from accumulated other comprehensive loss into net periodic benefit cost over the next fiscal year is $0.4 million. The Company expects to make contributions of $0.1 million to the SERP in 2016. The Company had no net transition assets or obligations recognized as an adjustment to other comprehensive income and does not anticipate any plan assets being returned to the Company during 2016, as the plan has no assets.
The following benefit payments, which reflect expected future service, are expected to be paid:
|
Years Ending
|
||||
|
December 31,
|
||||
|
2016
|
$
|
129
|
||
|
2017
|
280
|
|||
|
2018
|
280
|
|||
|
2019
|
532
|
|||
|
2020
|
647
|
|||
|
2021 - 2025
|
4,662
|
|||
The following gross amounts are recognized net of tax in accumulated other comprehensive loss:
|
2015
|
2014
|
|||||||
|
Prior service cost
|
$
|
866
|
$
|
1,048
|
||||
|
Net loss
|
3,465
|
3,302
|
||||||
|
$
|
4,331
|
$
|
4,350
|
|||||
Actuarial Assumptions
The weighted average assumptions used in determining the periodic net cost and benefit obligation information related to the SERP are as follows:
|
|
2015
|
|
2014
|
|
2013
|
|
Net periodic benefit cost
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discount rate
|
4.00%
|
5.00%
|
4.00%
|
||
|
Rate of compensation increase
|
3.00%
|
3.00%
|
3.00%
|
||
|
Benefit obligation
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discount rate
|
4.25%
|
4.00%
|
5.00%
|
||
|
Rate of compensation increase
|
3.00%
|
|
3.00%
|
|
3.00%
|
14. SHARE-BASED COMPENSATION
The Company has an equity compensation program (the "Program") which provides for the granting of "Incentive Stock Options" within the meaning of Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, non-qualified stock options and restricted stock awards. The Company believes that such awards better align the interest of its employees with those of its shareholders. The 2011 Equity Compensation Plan provides for the issuance of 1.4 million shares of the Company's Class B common stock. At December 31, 2015, 750,600 shares remained available for future issuance under the 2011 Equity Compensation Plan.
The Company records compensation expense in its consolidated statements of operations related to employee stock-based options and awards. The aggregate pretax compensation cost recognized for stock-based compensation amounted to approximately $2.8 million, $2.7 million and $1.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and related solely to restricted stock awards. The Company did not use any cash to settle any equity instruments granted under share-based arrangements during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the only instruments issued and outstanding under the Program related to restricted stock awards.
Restricted Stock Awards
The Company provides common stock awards to certain officers and key employees. The Company grants these awards, at its discretion, from the shares available under the Program. Unless otherwise provided at the date of grant or unless subsequently accelerated, the shares awarded are earned in 25% increments on the second, third, fourth and fifth anniversaries of the award, respectively, and are distributed provided the employee has remained employed by the Company through such anniversary dates; otherwise the unearned shares are forfeited. The market value of these shares at the date of award is recorded as compensation expense on the straight-line method over the five-year periods from the respective award dates, as adjusted for forfeitures of unvested awards. During 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company issued 84,000 shares, 378,000 shares and 162,200 shares of the Company's Class B common stock, respectively, under a restricted stock plan to various officers and employees.
A summary of the restricted stock activity under the Program as of December 31, 2015 is presented below:
|
|
Weighted Average
|
||||||||
|
Restricted Stock
|
Weighted Average
|
Remaining
|
|||||||
|
Awards
|
Shares
|
Award Price
|
Contractual Term
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||||
|
Outstanding at January 1, 2015
|
643,275
|
$
|
21.52
|
3.8 years
|
|||||
|
Granted
|
84,000
|
23.05
|
|
||||||
|
Vested
|
(94,450
|
)
|
18.96
|
|
|||||
|
Forfeited
|
(68,800
|
)
|
22.99
|
|
|||||
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2015
|
564,025
|
$
|
22.00
|
3.2 years
|
|||||
As of December 31, 2015, there was $8.1 million of total pretax unrecognized compensation cost included within additional paid-in capital related to non-vested stock based compensation arrangements granted under the restricted stock award plan. That cost is expected to be recognized over a period of 4.4 years.
The Company's policy is to issue new shares to satisfy restricted stock awards. Currently the Company believes that substantially all restricted stock awards will vest.
15. COMMON STOCK
In July 2012, the Board of Directors of the Company authorized the purchase of up to $10 million of the Company's outstanding Class B common shares. As of December 31, 2013, the Company had cumulatively purchased and retired 547,366 Class B common shares at a cost of approximately $10.0 million. No shares of Class A or Class B common stock were repurchased during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014.
As of December 31, 2014, according to regulatory filings, there was one shareholder of the Company's common stock (other than shareholders subject to specific exceptions) with ownership in excess of 10% of Class A outstanding shares with no ownership of the Company's Class B common stock. In accordance with the Company's certificate of incorporation, the Class B Protection clause is triggered if a shareholder owns 10% or more of the outstanding Class A common stock and does not own an equal or greater percentage of all then outstanding shares of both Class A and Class B common stock (all of which common stock must have been acquired after the date of the 1998 recapitalization). In such a circumstance, such shareholder must, within 90 days of the trigger date, purchase Class B common shares, in an amount and at a price determined in accordance with a formula described in the Company's certificate of incorporation, or forfeit its right to vote its Class A common shares. As of December 31, 2015, to the Company's knowledge, this shareholder had not purchased any Class B shares to comply with these requirements. In order to vote its shares at Bel's next shareholders' meeting, this shareholder must either purchase the required number of Class B common shares or sell or otherwise transfer Class A common shares until its Class A holdings are under 10%. As of December 31, 2015, to the Company's knowledge, this shareholder owned 23.1% of the Company's Class A common stock in the aggregate and had not taken steps to either purchase the required number of Class B common shares or sell or otherwise transfer Class A common shares until its Class A holdings fall below 10%. Unless and until this situation is satisfied in a manner permitted by the Company's Restated Certificate of Incorporation, the subject shareholder will not be permitted to vote its shares of common stock.
Throughout 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company declared cash dividends on a quarterly basis at a rate of $0.06 per Class A share of common stock and $0.07 per Class B share of common stock. The Company declared and paid cash dividends totaling $3.2 million in 2015, $3.2 million in 2014 and $3.1 million in 2013. There are no contractual restrictions on the Company's ability to pay dividends provided the Company is not in default under its credit agreements immediately before such payment and after giving effect to such payment.
16. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Leases
The Company leases various facilities under operating leases expiring through December 2023. Some of these leases require the Company to pay certain executory costs (such as insurance and maintenance).
Future minimum lease payments for operating leases are approximately as follows:
|
Year Ending
|
||||
|
December 31,
|
||||
|
2016
|
$
|
7,924
|
||
|
2017
|
5,870
|
|||
|
2018
|
3,209
|
|||
|
2019
|
2,184
|
|||
|
2020
|
2,032
|
|||
|
Thereafter
|
2,211
|
|||
|
$
|
23,430
|
|||
Rental expense for all leases was approximately $8.8 million, $7.5 million and $4.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Other Commitments
The Company submits purchase orders for raw materials to various vendors throughout the year for current production requirements, as well as forecasted requirements. Certain of these purchase orders relate to special purpose material and, as such, the Company may incur penalties if an order is cancelled. The Company had outstanding purchase orders related to raw materials in the amount of $42.6 million and $50.4 million at December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, respectively. The Company also had outstanding purchase orders related to capital expenditures in the amount of $1.5 million and $3.7 million at December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, respectively.
Legal Proceedings
The Company was a defendant in a lawsuit captioned SynQor, Inc. v. Artesyn Technologies, Inc., et al. brought in the United States District Court, Eastern District of Texas in November 2007 ("SynQor I case"). The plaintiff alleged that eleven defendants, including Bel, infringed its patents covering certain power products. With respect to the Company, the plaintiff claimed that the Company infringed its patents related to unregulated bus converters and/or point-of-load (POL) converters used in intermediate bus architecture power supply systems. The case initially went to trial in December 2010. A decision was ultimately rendered in November 2013 in favor of the plaintiff, and the Company released a payment to SynQor of $10.9 million. The Company subsequently received a $2.1 million payment from one of its customers related to an indemnification agreement and reimbursement of certain legal fees.
In a related matter, on September 29, 2011, the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Texas ordered SynQor, Inc.'s continuing causes of action for post-verdict damages to be severed from the original action and assigned to a new case number. The new action captioned SynQor, Inc. v. Artesyn Technologies, Inc., et al. (Case Number 2:11cv444) is a patent infringement action for damages in the form of lost profits and reasonable royalties for the period beginning January 24, 2011 ("SynQor II case"). SynQor, Inc. also seeks enhanced damages. The Company has an indemnification agreement in place with one of its customers specifically covering post-verdict damages related to this case. This case went to trial on July 30, 2013. In April 2014, a final judgment was rendered in this case, whereby the Company was assessed an additional $0.7 million in post-verdict damages. This amount was paid by the Company in July 2014 and was subsequently reimbursed by one of its customers under the terms of the indemnification agreement referenced above. SynQor filed an appeal of the final judgment in May 2014. The appeals court heard oral arguments from the parties on this matter on March 2, 2015. The matter was settled as to all further damages and claims relating to the appeal in early 2016 with no further payment required from the Company.
The Company is a plaintiff in a lawsuit captioned Bel Fuse Inc. et al. v. Molex Inc. brought in the United District Court of New Jersey in April 2013. The Company claims that Molex infringed three of the Company's patents related to integrated magnetic connector products. Molex filed a motion to dismiss the complaint on August 6, 2013. The Company filed an amended complaint and response on August 20, 2013. Molex withdrew its original Motion to Dismiss and filed a second, revised Motion to Dismiss on September 6, 2013. The Company filed its response on October 7, 2013. The Court denied Molex's revised Motion to Dismiss on June 16, 2014. In June 2014, Molex initiated an Inter Partes Review (IPR) at the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office for one of the three patents associated with this case. The Company and Molex executed an agreement in September 2014 to terminate the IPR and to withdraw one of the patents from the district court litigation. The Parties settled the case involving the two remaining patents for $0.5 million in September 2015 and the case was subsequently dismissed by the Court in October 2015. The Company recognized the settlement amount in net sales on the consolidated statements of operations.
In connection with the acquisition of Power Solutions, there is an ongoing claim by the Arezzo Revenue Agency in Italy concerning certain tax matters related to what was then Power-One Asia Pacific Electronics Shenzhen Co. Ltd. (now Bel Power Solutions Asia Pacific Electronics Shenzhen Co. Ltd, or "BPS China") for the years 2004 to 2006. In September 2012, the Tax Court of Arezzo ruled in favor of BPS China and cancelled the claim. In February 2013, the Arezzo Revenue Agency filed an appeal of the Tax Court's ruling. The hearing of the appeal was held on October 2, 2014. On October 13, 2014, BPS China was informed of the Regional Tax Commission of Florence ruling which was in favor of the Arezzo Revenue Agency and against BPS China. The estimated liability related to this matter is approximately $12.0 million and has been included as a liability for uncertain tax positions on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. As Bel is fully indemnified in this matter per the terms of the stock purchase agreement with ABB, a corresponding other asset for indemnification is also included in other assets on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets at December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014.
The Company is not a party to any other legal proceeding, the adverse outcome of which is likely to have a material adverse effect on the Company's consolidated financial condition or results of operations.
17. ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE (LOSS) INCOME
The components of accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income as of December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 are summarized below:
|
2015
|
2014
|
2013
|
||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment
|
$
|
(19,305
|
)
|
$
|
(9,351
|
)
|
$
|
1,904
|
||||
|
Unrealized holding gain on available-for-sale
|
||||||||||||
|
securities, net of taxes of $265, $259 and $169 as of
|
||||||||||||
|
December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013
|
434
|
429
|
282
|
|||||||||
|
Unfunded SERP liability, net of taxes of ($1,327), ($1,325)
|
||||||||||||
|
and ($693) as of December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013
|
(3,005
|
)
|
(3,026
|
)
|
(1,541
|
)
|
||||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income
|
$
|
(21,876
|
)
|
$
|
(11,948
|
)
|
$
|
645
|
||||
Changes in accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income by component during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows. All amounts are net of tax.
|
Unrealized Holding
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Foreign Currency
|
Gains on
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Translation
|
Available-for-
|
Unfunded
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Adjustment
|
Sale Securities
|
SERP Liability
|
Total
|
||||||||||||||
|
Balance at January 1, 2014
|
1,904
|
282
|
(1,541
|
)
|
645
|
||||||||||||
|
Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications
|
(11,255
|
)
|
147
|
(1,667
|
)
|
(12,775
|
)
|
||||||||||
|
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
comprehensive income (loss)
|
-
|
-
|
182
|
(a)
|
182
|
||||||||||||
|
Net current period other comprehensive income (loss)
|
(11,255
|
)
|
147
|
(1,485
|
)
|
(12,593
|
)
|
||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2014
|
$
|
(9,351
|
)
|
$
|
429
|
$
|
(3,026
|
)
|
$
|
(11,948
|
)
|
||||||
|
Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications
|
(9,954
|
)
|
5
|
(233
|
)
|
(10,182
|
)
|
||||||||||
|
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
comprehensive income (loss)
|
254
|
(a)
|
254
|
||||||||||||||
|
Net current period other comprehensive income (loss)
|
(9,954
|
)
|
5
|
21
|
(9,928
|
)
|
|||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2015
|
$
|
(19,305
|
)
|
$
|
434
|
$
|
(3,005
|
)
|
$
|
(21,876
|
)
|
||||||
|
(a)
|
This reclassification relates to the amortization of prior service costs and gains/losses associated with the Company's SERP plan. This expense is allocated between cost of sales and selling, general and administrative expense based upon the employment classification of the plan participants.
|
18. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
The Company maintains minority ownership in a joint venture in the PRC. See Note 2, "Acquisitions and Disposition." The joint venture may purchase raw components and other goods from the Company and may sell finished goods to the Company as well as to other third parties. The Company purchased $1.5 million and $4.3 million of inventory from the joint venture during the year ended December 31, 2015 and during the period from its acquisition date of June 19, 2014 through December 31, 2014, respectively. At December 31, 2015, the Company owed the joint venture approximately $0.5 million, which is included in accounts payable on the accompanying consolidated balance sheet.
-68-
19. SELECTED QUARTERLY DATA (UNAUDITED)
Quarterly results for the year ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are summarized as follows:
|
|
2015
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
First
|
Second
|
Third
|
Fourth
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
Quarter(a)
|
Quarter
|
Quarter
|
Quarter
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Net sales
|
$
|
142,015
|
$
|
145,658
|
$
|
144,161
|
$
|
135,246
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Cost of sales
|
115,202
|
(a) |
117,098
|
116,749
|
109,203
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Net earnings
|
5,320
|
(a) |
6,062
|
4,920
|
2,895
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Net earnings per share:
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Class A common share - basic and diluted
|
$
|
0.43
|
(a) |
$
|
0.49
|
$
|
0.39
|
$
|
0.23
|
|||||||||
|
Class B common share - basic and diluted
|
$
|
0.45
|
(a) |
$
|
0.52
|
$
|
0.42
|
$
|
0.25
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
First
|
Second
|
Third
|
Fourth
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
Quarter
|
Quarter
|
Quarter
|
Quarter(b)
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Net sales
|
$
|
82,646
|
$
|
99,439
|
$
|
156,341
|
$
|
148,650
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Cost of sales
|
68,576
|
81,493
|
128,561
|
121,091
|
(b) | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Net earnings
|
2,503
|
3,065
|
1,261
|
1,774
|
(b) | |||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Earnings per share:
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Class A common share - basic and diluted
|
$
|
0.20
|
$
|
0.25
|
$
|
0.10
|
$
|
0.14
|
(b) | |||||||||
|
Class B common share - basic and diluted
|
$
|
0.22
|
$
|
0.27
|
$
|
0.11
|
$
|
0.15
|
(b) | |||||||||
|
(a)
|
Revised from 10-Q disclosures to reflect immaterial measurement period adjustments related to the 2014 Acquisitions. First quarter 10-Q reflected cost of sales of $114.9 million, net earnings of $5.6 million, earnings per Class A common share of $0.45 per share and earnings per Class B common share of $0.48 per share.
|
|
(b)
|
Revised from the disclosure in the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2014 to reflect immaterial measurement period adjustments related to the 2014 Acquisitions. The 2014 10-K reflected, for the fourth quarter of 2014, cost of sales of $120.8 million, net earnings of $2.0 million, earnings per Class A common share of $0.16 per share and earnings per Class B common share of $0.17 per share.
|
|
BEL FUSE INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
SCHEDULE II - VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
(Amounts in thousands)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Column A
|
Column B
|
Column C
|
Column D
|
Column E
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Additions
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Balance at
|
(1)
|
|
(2)
|
|
Balance
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
beginning
|
Charged to costs
|
Charged to other
|
Deductions
|
at end
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Description
|
of period
|
and expenses
|
accounts (b)
|
(a)
|
of period
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Year ended December 31, 2015:
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Allowance for doubtful accounts
|
$
|
1,989
|
$
|
295
|
$
|
303
|
$
|
(840
|
)
|
$
|
1,747
|
|||||||||
|
Allowance for excess and obsolete inventory
|
$
|
6,809
|
$
|
2,186
|
$
|
(59
|
) |
$
|
(3,668
|
)
|
$
|
5,268
|
||||||||
|
Deferred tax assets - valuation allowances
|
$
|
6,692
|
$
|
456
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
(513
|
)
|
$
|
6,635
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Year ended December 31, 2014:
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Allowance for doubtful accounts
|
$
|
941
|
$
|
1,434
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
(386
|
)
|
$
|
1,989
|
|||||||||
|
Allowance for excess and obsolete inventory
|
$
|
3,941
|
$
|
4,438
|
$
|
(1
|
)
|
$
|
(1,569
|
)
|
$
|
6,809
|
||||||||
|
Deferred tax assets - valuation allowances
|
$
|
1,955
|
$
|
4,766
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
(29
|
)
|
$
|
6,692
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Year ended December 31, 2013:
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Allowance for doubtful accounts
|
$
|
743
|
$
|
325
|
$
|
50
|
$
|
(177
|
)
|
$
|
941
|
|||||||||
|
Allowance for excess and obsolete inventory
|
$
|
5,490
|
$
|
(85
|
)
|
$
|
7
|
$
|
(1,471
|
)
|
$
|
3,941
|
||||||||
|
Deferred tax assets - valuation allowances
|
$
|
1,874
|
$
|
308
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
(227
|
)
|
$
|
1,955
|
|||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
(a) Write-offs
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
(b) Includes foreign currency translation adjustments
|
||||||||||||||||||||
None.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
During the fourth quarter of 2015, the Company's management, including the principal executive officer and principal financial officer, supervised and participated in the evaluation of the Company's disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934) related to the recording, processing, summarization, and reporting of information in the Company's periodic reports that the Company files with the SEC. These disclosure controls and procedures have been designed to ensure that material information relating to the Company, including its subsidiaries, is made known to the Company's management, including these officers, by other of the Company's employees, and that this information is recorded, processed, summarized, evaluated, and reported, as applicable, within the time periods specified in the SEC's rules and forms.
In designing and evaluating the disclosure controls and procedures, the Company recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the above objectives have been met. Notwithstanding these limitations, the Company believes that its disclosure controls and procedures are designed and are operating to provide reasonable assurances of achieving their objectives.
Based on their evaluation as of December 31, 2015, the Company's principal executive officer and principal financial officer have concluded that the Company's disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934) are effective to ensure that the information required to be disclosed by the Company in the reports that the Company files or submits under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms.
Management's Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The Company's management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(f). Under the supervision and with the participation of the Company's management, including the Company's principal executive officer and principal financial officer, the Company conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
Based on the Company's evaluation under the framework in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013), the Company's management concluded that the Company's internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2015.
The Company's independent registered public accounting firm, Deloitte & Touche LLP, has audited the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015 and has expressed an unqualified opinion in their report which is included in Item 8 herein.
Changes in Internal Controls Over Financial Reporting
There has not been any change in our internal control over financial reporting during the three months ended December 31, 2015 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
None.
The Registrant incorporates by reference herein information to be set forth in its definitive proxy statement for its 2016 annual meeting of shareholders that is responsive to the information required with respect to this item.
The Registrant has adopted a code of ethics for its directors, executive officers and all other senior financial personnel. The code of ethics, as amended from time to time, is available on the Registrant's website under Corporate Governance. The Registrant will also make copies of its code of ethics available to investors upon request. Any such request should be sent by mail to Bel Fuse Inc., 206 Van Vorst Street, Jersey City, NJ 07302 Attn: Colin Dunn or should be made by telephone by calling Colin Dunn at 201-432-0463.
The Registrant incorporates by reference herein information to be set forth in its definitive proxy statement for its 2016 annual meeting of shareholders that is responsive to the information required with respect to this Item.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The Registrant incorporates by reference herein information to be set forth in its definitive proxy statement for its 2016 annual meeting of shareholders that is responsive to the remaining information required with respect to this Item.
The table below depicts the securities authorized for issuance under the Company's equity compensation plans.
Equity Compensation Plan Information
|
Plan Category
|
Number of Securities to be Issued Upon Exercise of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights
(a) |
Weighted Average Exercise Price of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights
(b) |
Number of Securities Remaining Available for Future Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans (Excluding Securities Reflected in Column (a))
(c) |
|||||||||
|
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders:
|
||||||||||||
|
2011 Equity Compensation Plan
|
-
|
$
|
-
|
750,600
|
||||||||
|
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|||||||||
|
Totals
|
-
|
$
|
-
|
750,600
|
||||||||
The Registrant incorporates by reference herein information to be set forth in its definitive proxy statement for its 2016 annual meeting of shareholders that is responsive to the information required with respect to this Item.
The Registrant incorporates by reference herein information to be set forth in its definitive proxy statement for its 2016 annual meeting of shareholders that is responsive to the information required with respect to this Item.
PART IV
|
Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules
(a) Documents filed as a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K:
(1) Financial Statements
See Index to Consolidated Financial Statements and Schedule of this Form 10-K.
(2) Financial Statement Schedule
See Schedule II — Valuation and Qualifying Accounts — Years Ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
(3) Exhibits
|
|||
|
Exhibit No.:
|
|||
|
3.1
|
Restated Certificate of Incorporation, as amended, is incorporated by reference to (i) Restated Certificate of Incorporation filed as Exhibit 3.1 of the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 1998 and (ii) Certificate of Amendment to the Company's Restated Certificate of Incorporation filed as Exhibit 3.1 of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1999.
|
||
|
3.2
|
By-laws, as amended and restated on May 13, 2014, are incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 of the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the six months ended June 30, 2014.
|
||
|
10.1†
|
2002 Equity Compensation Program. Incorporated by reference to the Registrant's proxy statement for its 2002 annual meeting of shareholders.
|
||
|
10.2
|
Credit and Guaranty Agreement, dated as of February 12, 2007, by and among Bel Fuse Inc., as Borrower, the Subsidiary Guarantors party thereto and the Bank of America, N.A., as Lender. Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 16, 2007 and incorporated herein by reference.
|
||
|
10.3†
|
Amended and Restated Bel Fuse Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, dated as of April 17, 2007. Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 23, 2007 and incorporated herein by reference.
|
||
|
10.4
|
Stock and Asset Purchase Agreement between Bel Fuse Inc. and Tyco Electronics Corporation, dated as of November 28, 2012. Filed as Exhibit 2.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 4, 2012 and incorporated herein by reference.
|
||
|
10.5
|
First Amendment to Credit and Guaranty Agreement dated as of April 30, 2008, by and among Bel Fuse Inc., as Borrower, the Subsidiary Guarantors party thereto and the Bank of America, N.A., as Lender. Filed as Exhibit 10.6 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009 and incorporated herein by reference.
|
||
|
10.6
|
Second Amendment to Credit and Guaranty Agreement dated as of June 30, 2009, by and among Bel Fuse Inc., as Borrower, the Subsidiary Guarantors party thereto and the Bank of America, N.A., as Lender. Filed as Exhibit 10.7 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009 and incorporated herein by reference.
|
||
|
10.7
|
Third Amendment to Credit and Guaranty Agreement dated as of January 29, 2010, by and among Bel Fuse Inc., as Borrower, the Subsidiary Guarantors party thereto and the Bank of America, N.A., as Lender. Filed as Exhibit 10.9 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009 and incorporated herein by reference.
|
||
|
10.8
|
Fourth Amendment to Credit and Guaranty Agreement dated as of September 27, 2010, by and among Bel Fuse Inc., as Borrower, the Subsidiary Guarantors party thereto and the Bank of America, N.A., as Lender. Filed as Exhibit 10.9 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference.
|
||
|
10.9
|
Fifth Amendment to Credit and Guaranty Agreement dated as of February 16, 2011, by and among Bel Fuse Inc., as Borrower, the Subsidiary Guarantors party thereto and the Bank of America, N.A., as Lender. Filed as Exhibit 10.10 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference.
|
||
|
10.10†
|
2011 Equity Compensation Program. Incorporated by reference to the Registrant's proxy statement for its 2011 annual meeting of shareholders.
|
||
|
10.11
|
Sixth Amendment to Credit and Guaranty Agreement dated as of November 8, 2013, by and among Bel Fuse Inc., as Borrower, the Subsidiary Guarantors party thereto and the Bank of America, N.A., as Lender. Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the nine months ended September 30, 2013 and incorporated herein by reference.
|
||
|
10.12
|
Stock Purchase Agreement dated as of April 24, 2014, by and among Bel Fuse Inc., Power-One, Inc. and PWO Holdings B.V. Filed as Exhibit 2.1 to the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the three months ended March 31, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference.
|
||
|
10.13
|
Stock Purchase Agreement dated as of May 16, 2014, by and among Bel Fuse Inc. and Emerson Electric Co. Filed as Exhibit 2.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on May 22, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference.
|
||
|
10.14
|
Credit and Security Agreement dated June 19, 2014, as amended and restated as of June 30, 2014, by and among Bel Fuse Inc., as Borrower, and KeyBank National Association, as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and Issuing Lender, and the other lenders identified therein. Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on July 7, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference.
|
||
|
11.1
|
A statement regarding the computation of earnings per share is omitted because such computation can be clearly determined from the material contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
|
||
|
12.1*
|
Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges.
|
||
|
21.1*
|
Subsidiaries of the Registrant.
|
||
|
23.1*
|
Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.
|
||
|
24.1*
|
Power of attorney (included on the signature page)
|
||
|
31.1*
|
Certification of the Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
|
||
|
31.2*
|
Certification of the Vice President of Finance pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
|
||
|
32.1**
|
Certification of the Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes - Oxley Act of 2002.
|
||
|
32.2**
|
Certification of the Vice-President of Finance pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
|
||
|
101.INS*
|
XBRL Instance Document
|
||
|
101.SCH*
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document
|
||
|
101.CAL*
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document
|
||
|
101.DEF*
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document
|
||
|
101.LAB*
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document
|
||
|
101.PRE*
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document
|
* Filed herewith.
** Submitted herewith.
† Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
BEL FUSE INC.
(Registrant)
|
By:
|
/s/ Daniel Bernstein
|
|
Daniel Bernstein
|
|
|
President and Chief Executive Officer
|
|
|
Dated: March 11, 2016
|
KNOW ALL MEN BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints Daniel Bernstein and Colin Dunn as his/her attorney-in-fact and agent, with full power of substitution and resubstitution, for him/her and in his/her name, place, and stead, in any and all capacities, to sign and file any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, with all exhibits thereto and hereto, and other documents with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorney-in-fact and agent, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite or necessary to be done in and about the premises, as fully to all intents and purposes as he/she might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents, or any of them, or their or his substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
Signature
|
Title
|
Date
|
||
|
/s/ Daniel Bernstein
|
President, Chief Executive Officer
|
March 11, 2016
|
||
|
Daniel Bernstein
|
and Director
|
|||
|
/s/ Howard Bernstein
|
Director
|
March 11, 2016
|
||
|
Howard B. Bernstein
|
||||
|
/s/ Robert H. Simandl
|
Director
|
March 11, 2016
|
||
|
Robert H. Simandl
|
||||
|
/s/ Peter Gilbert
|
Director
|
March 11, 2016
|
||
|
Peter Gilbert
|
||||
|
/s/ John Tweedy
|
Director
|
March 11, 2016
|
||
|
John Tweedy
|
||||
|
/s/ John Johnson
|
Director
|
March 11, 2016
|
||
|
John Johnson
|
||||
|
/s/ Avi Eden
|
Director
|
March 11, 2016
|
||
|
Avi Eden
|
||||
|
/s/ Mark Segall
|
Director
|
March 11, 2016
|
||
|
Mark Segall
|
||||
|
/s/ Norman Yeung
|
Director
|
March 11, 2016
|
||
|
Norman Yeung
|
|
/s/ Eric Nowling
|
Director
|
March 11, 2016
|
||
|
Eric Nowling
|
||||
|
/s/ Colin Dunn
|
Vice President of Finance and Secretary
|
March 11, 2016
|
||
|
Colin Dunn
|
(Principal Financial Officer and Principal
|
|||
|
Accounting Officer)
|
