Attached files
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015
or
o | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission File Number: 001-35462
Vantiv, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Delaware | 26-4532998 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
8500 Governor’s Hill Drive
Symmes Township, OH 45249
(Address of principal executive offices)
Registrant's telephone number, including area code: (513) 900-5250
Securities registered pursuant to 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
Class A Common Stock, $0.00001 par value | New York Stock Exchange | |
Securities registered pursuant to 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15 (d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports) and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer" and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer x | Accelerated filer o | |
Non-accelerated filer o | Smaller reporting company o | |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes o No x
As of June 30, 2015 (the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter), the aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was $5.5 billion.
As of December 31, 2015, there were 155,488,326 shares of the registrant’s Class A common stock outstanding and 35,042,826 shares of the registrant’s Class B common stock outstanding.
Documents Incorporated by Reference: |
Portions of the registrant's definitive Proxy Statement for the 2016 Annual Meeting of Stockholders are incorporated by reference in Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K as indicated. Such proxy statement will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days of the registrant's fiscal year ended December 31, 2015.
VANTIV, INC.
FORM 10-K
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2015
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page | |
2
NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K, including the sections entitled "Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" and "Risk Factors," contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933 and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. All statements other than statements of historical fact, including statements regarding our future results of operations and financial position, our business strategy and plans, our objectives for future operations, and any statements of a general economic or industry specific nature, are forward-looking statements. You can identify forward-looking statements by the fact that they do not relate strictly to historical or current facts. Words such as "anticipate," "estimate," "expect," "project," "plan," "intend," "believe," "may," "will," "continue," "could," "should," "can have," "likely," or the negative or plural of these words and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about future events and trends that we believe, based on information currently available to our management, may affect our financial condition, results of operations, business strategy, short-term and long-term business operations and objectives, and financial needs. These forward-looking statements are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and assumptions, including those described in the "Risk Factors" section of this report. Moreover, we operate in a very competitive and rapidly changing environment. New risks emerge from time to time. It is not possible for our management to predict all risks, nor can we assess the impact of all factors on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements we may make. In light of these risks, uncertainties and assumptions, the future events and trends discussed in this report may not occur and actual results could differ materially and adversely from those anticipated or implied in the forward-looking statements.
You should not rely upon forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. The events and circumstances reflected in the forward-looking statements may not be achieved or occur. Although we believe that the expectations and assumptions reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee future results, levels of activity, performance, or achievements. We undertake no obligation to publicly update any forward-looking statement after the date of this report, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise, or to conform these statements to actual results or revised expectations, except as may be required by law.
3
PART I
Item 1. Business
Vantiv, Inc., a Delaware corporation, is a holding company that conducts its operations through its majority-owned subsidiary, Vantiv Holding, LLC ("Vantiv Holding"). Vantiv, Inc., Vantiv Holding and their subsidiaries are referred to collectively as the "Company," "Vantiv," "we," "us" or "our," unless the context requires otherwise.
Business and Client Description
Vantiv is a leading payment processor differentiated by an integrated technology platform, breadth of distribution and superior cost structure. According to the Nilson Report, we are the second largest merchant acquirer and the largest PIN debit acquirer by number of transactions in the United States. Our integrated technology platform is differentiated from our competitors' multiple platform architectures. It enables us to efficiently provide a comprehensive suite of services to merchants and financial institutions of all sizes as well as to innovate, develop and deploy new services, while providing us with significant economies of scale. Our broad and varied distribution includes multiple sales channels, such as our direct and indirect sales forces and referral partner relationships, which provide us with a growing and diverse client base of merchants and financial institutions. We believe this combination of attributes provides us with competitive advantages that generate strong growth and profitability by enabling us to efficiently manage, update and maintain our technology, to utilize technology integration and value-added services to expand our new sales and distribution, and to realize significant operating leverage.
We offer a broad suite of payment processing services that enable our clients to meet their payment processing needs through a single provider, including in omni-channel environments that span point-of-sale, ecommerce and mobile devices. We enable merchants of all sizes to accept and process credit, debit and prepaid payments and provide them supporting value-added services, such as security solutions and fraud management, information solutions, and interchange management. We also provide mission critical payment services to financial institutions, such as card issuer processing, payment network processing, fraud protection, card production, prepaid program management, ATM driving and network gateway and switching services that utilize our proprietary Jeanie PIN debit payment network.
Merchant Services
We have a broad and diversified merchant client base. Our merchant client base includes approximately 800,000 merchant locations across the United States. In 2015, we processed approximately 19.0 billion transactions for these merchants. Our merchant client base has low client concentration and is heavily weighted in non-discretionary everyday spend categories, such as grocery and pharmacy, and includes large national retailers, including ten of the top 25 national retailers by revenue in 2014. We provide a comprehensive suite of payment processing services to our merchant services clients. We authorize, clear, settle and provide reporting for electronic payment transactions, as further discussed below.
Acquiring and Processing. We provide merchants with a broad range of credit, debit and prepaid payment processing services. We give them the ability to accept and process Visa, MasterCard, American Express, Discover and PIN debit network card transactions originated at the point of sale as well as for ecommerce and mobile transactions. This service includes all aspects of card processing, including authorization and settlement, customer service, chargeback and retrieval processing and network fee and interchange management.
Value-added Services. We offer value-added services that help our clients operate and manage their businesses including omni-channel acceptance, prepaid services and gift card solutions. We also provide security solutions such as point-to-point encryption and tokenization both at the point of sale and for ecommerce transactions.
Financial Institution Services
Our financial institution client base is also generally well diversified and includes approximately 1,400 financial institutions, including regional banks, community banks, credit unions and regional PIN debit networks. In 2015, we processed approximately 4.0 billion transactions for these financial institutions. We generally focus on small to mid-sized institutions with less than $15 billion in assets. Smaller financial institutions generally do not have the scale or infrastructure typical of large institutions and are more likely to outsource their payment processing needs. We provide integrated card issuer processing, payment network processing and value-added services to our financial institutions clients. These services are discussed further below.
4
Integrated Card Issuer and Processing. We process and service credit, debit, ATM and prepaid transactions. We process and provide statement production, collections and inbound/outbound call centers. Our card processing solution includes processing and other services such as card portfolio analytics, program strategy and support, fraud and security management and chargeback and dispute services. We also offer processing for specialized accounts, such as business cards, home equity lines of credit and health savings accounts. We provide authorization support in the form of online or batch settlement, as well as real-time transaction research capability and archiving and daily and monthly cardholder reports for statistical analysis.
Value-added Services. We provide additional services to our financial institution clients that complement our issuing and processing services. These services include fraud protection, card production, prepaid cards, ATM driving, portfolio optimization, data analytics and card program marketing. We also provide network gateway and switching services that utilize our Jeanie PIN network. Our Jeanie network offers real-time electronic payment, network bill payment, single point settlement, shared deposit taking and customer select PINs. Our Jeanie network includes approximately 7,600 ATMs, 26 million cardholders and 710 member financial institution clients.
Integrated Technology Platform
Our integrated technology platform provides our merchant and financial institution clients with differentiated payment processing solutions and provides us with significant strategic and operational benefits. Our clients access our processing solutions primarily through a single point of service, which is easy to use and enables our clients to acquire additional services as their business needs evolve. Small and mid-sized merchants are able to easily connect to our integrated technology platform using our application process interfaces, or APIs, software development kits, or SDKs, and other tools we make available to technology partners, which we believe enhances our capacity to sell to such merchants. Our integrated technology platform allows us to collect, manage and analyze data across both our Merchant Services and our Financial Institution Services segments that we can then package into information solutions for our clients. It provides insight into market trends and opportunities as they emerge, which enhances our ability to innovate and develop new value-added services, including security solutions and fraud management, and it allows us to easily deploy new solutions that span the payment processing value chain, such as ecommerce and mobile services, which are high growth market opportunities. It is highly scalable, which enables us to efficiently manage, update and maintain our technology, increase capacity and speed, and realize significant operating leverage. We believe our integrated technology platform is a key differentiator from payment processors that operate on multiple technology platforms and provides us with a significant competitive advantage.
Sales and Marketing
Our integrated technology platform enables us to provide a comprehensive suite of services to merchants and financial institutions of all sizes. We distribute our services through multiple sales channels that enable us to efficiently and effectively target a growing and diverse client base of merchants and financial institutions. Our sales channels include direct and indirect sales forces as well as referral partner relationships within our Merchant Services and Financial Institution Services segments as described below.
Merchant Services. We distribute our comprehensive suite of services to a broad range of merchants, including difficult to reach small and mid-sized merchants, through multiple sales channels as further discussed below.
• | Direct: Includes a national sales force that targets large national merchants, a regional and mid-market sales team that sells solutions to merchants and third party reseller clients, and a telesales operation that targets small and mid-sized merchants. |
• | Indirect: Includes Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) that target small and mid-sized merchants. |
• | Merchant Bank: Includes referral partner relationships with financial institutions that target their financial services customers as merchant referrals to us. |
• | Integrated Payments (IP): Includes referral partner relationships with independent software vendors (ISVs), value-added resellers (VARs), and payment facilitators that target their technology customers as merchant referrals to us. |
• | eCommerce: Includes a sales force that targets internet retail, online services and direct marketing merchants. |
These sales channels utilize multiple strategies and leverage relationships with referral partners that sell our solutions to small and mid-sized merchants. We offer certain of our services on a white-label basis which enables them to be marketed under our partners' brand. We select referral partners that enhance our distribution and augment our services with complimentary offerings. We believe our sales structure provides us with broad geographic coverage and access to various industries and verticals.
5
Financial Institution Services. We distribute our services by utilizing direct sales forces as well as a diverse group of referral partner relationships. These sales channels utilize multiple strategies and leverage relationships with core processors that sell our solutions to small and mid-sized financial institutions. We offer certain of our services on a white-label basis which enables them to be marketed under our client's brand. We select resellers that enhance our distribution and augment our services with complementary offerings. Our relationships with core processors are necessary for developing the processing environments required by our financial institution clients. Many of our core processing relationships are non-contractual and continue for so long as an interface between us and the core processor is needed to accommodate one or more common financial institution customers.
Our sales teams in both Merchant Services and Financial Institution Services are paid a combination of base salary and commission. As of December 31, 2015, we had approximately 1,000 full-time employees participating in sales and marketing, including sales support personnel. Commissions paid to our sales force are based upon a percentage of revenue from new business and cross-selling to existing clients. Residual payments to our referral partners are based upon a percentage of revenues earned from referred business. For the year ended December 31, 2015, combined sales force commissions and residual payments represent approximately 75% of total sales and marketing expenses, or $376.6 million.
Our History
We have a 40 year history of providing payment processing services. We operated as a business unit of Fifth Third Bank ("Fifth Third") until June 2009 when we separated as a stand-alone company, established our own organization, headquarters, brand, growth strategy and completed our initial public offering ("IPO") in March 2012. Since the separation, we have made substantial investments, including several key acquisitions, to enhance our integrated technology platform and reorganize our business to better align it with our market opportunities and broaden our geographic footprint beyond the markets traditionally served by Fifth Third Bank.
Industry Background
Electronic Payments
Electronic payments in the United States have evolved into a large and growing market with favorable secular trends that continue to increase the adoption and use of card-based payment services, such as those for credit, debit and prepaid cards.
This growth is driven by the shift from cash and checks towards card-based and other electronic forms of payment due to their greater convenience, security, enhanced services and rewards and loyalty features. We believe changing demographics and emerging trends, such as the adoption of new technologies and business models, including ecommerce, mobile commerce and prepaid services, will also continue to drive growth in electronic payments.
Payment Processing Industry
The payment processing industry is comprised of various processors that create and manage the technology infrastructure that enables electronic payments. Payment processors help merchants and financial institutions develop and offer electronic payment solutions to their customers, facilitate the routing and processing of electronic payment transactions and manage a range of supporting security, value-added and back office services. In addition, many large banks manage and process their card accounts in-house. This is collectively referred to as the payment processing value chain.
Many payment processors specialize in providing services in discrete areas of the payment processing value chain, which can result in merchants and financial institutions using payment processing services from multiple providers. A limited number of payment processors have capabilities or offer services in multiple parts of the payment processing value chain. We provide solutions across the payment processing value chain as a merchant acquirer, payment network, and as an issuer processor, primarily by utilizing our integrated technology platform to enable our clients to easily access a broad range of payment processing services as illustrated below:
6
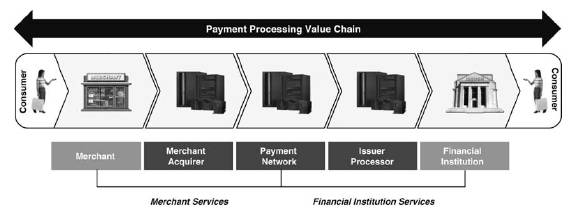
The payment processing value chain encompasses three key types of processing:
• | Merchant Acquiring Processing. Merchant acquiring processors sell electronic payment acceptance, processing and supporting services to merchants and third-party resellers. These processors route transactions originated by consumer transactions with the merchant, including in omni-channel environments that span point-of-sale, ecommerce and mobile devices, to the appropriate payment networks for authorization, known as "front-end" processing, and then ensure that each transaction is appropriately cleared and settled into the merchant's bank account, known as "back-end" processing. Many of these processors also provide specialized reporting, back office support, risk management and other value-added services to merchants. Merchant acquirers charge merchants based on a percentage of the value of each transaction on a per transaction basis. Merchant acquirers pay the payment network processors a routing fee per transaction and pass through interchange fees to the issuing financial institution. |
• | Payment Network Processing. Payment network processors, such as Visa, MasterCard and PIN debit payment networks, sell electronic payment network routing and support services to financial institutions that issue cards and merchant acquirers that provide transaction processing. Depending on their market position and network capabilities, these providers route credit, debit and prepaid card transactions from merchant acquiring processors to the financial institution that issued the card, and they ensure that the financial institution's authorization approvals are routed back to the merchant acquiring processor and that transactions are appropriately settled between the merchant's bank and the card-issuing financial institution. These providers also provide specialized risk management and other value-added services to financial institutions. Payment networks charge merchant acquiring processors and issuing financial institutions routing fees per transaction and monthly or annual maintenance fees and assessments. |
• | Issuer Card Processing. Issuer card processors sell electronic payment issuing, processing and supporting services to financial institutions. These providers authorize transactions received from the payment networks and ensure that each transaction is appropriately cleared and settled from the originating card account. These companies also provide specialized program management, reporting, outsourced customer service, back office support, risk management and other value-added services to financial institutions. Card processors charge issuing financial institutions fees based on the number of transactions processed and the number of cards that are managed. |
7
Emerging Trends and Opportunities in the Payment Processing Industry
The payment processing industry will continue to adopt new technologies, develop new products and services, evolve new business models and experience new market entrants and changes in the regulatory environment. In the near-term, as merchants and financial institutions seek services that help them enhance their own offerings to consumers, including acceptance and issuance of Europay-MasterCard-Visa (EMV) chip-based cards, other security and fraud management services, information services, and support for omni-commerce environments, we believe that payment processors may seek to develop additional capabilities and expand across the payment processing value chain to meet these demands and capture additional data and provide additional value per transaction. To facilitate this expansion and deliver more robust service offerings, we believe that payment processors will need to develop greater control over and integration of their technology platforms, to enable them to deliver and differentiate their offerings from other providers.
We believe that emerging, alternative electronic payment technologies will be adopted by merchants and other businesses. As a result, non-financial institution enterprises, such as mobile payment providers, internet, retail and social media companies, could become more active participants in the development of these alternative electronic payment technologies and facilitate the convergence of retail, online, mobile and social commerce applications, representing an attractive growth opportunity for the industry. We believe that payment processors that have an integrated business, provide solutions across the payment processing value chain and utilize broad distribution capabilities will be best positioned to provide processing services for emerging alternative electronic payment technologies and to successfully partner with new market entrants.
Competition
Merchant Services
Our competitors include financial institutions and well-established payment processing companies, including Bank of America Merchant Services, Chase Paymentech Solutions, Elavon Inc. (a subsidiary of U.S. Bancorp), First Data Corporation, Global Payments, Inc., Heartland Payment Systems, Inc., Total System Services, Inc. and WorldPay US, Inc. in our Merchant Services segment. Furthermore, we are facing new competitive pressure from non-traditional payments processors and other parties entering the payments industry, such as PayPal, Google, Apple, Alibaba and Amazon, who may compete in one or more of the functions performed in processing merchant transactions. The most significant competitive factors in this segment are price, breadth of features and functionality, data security, system performance and reliability, scalability, service capability and brand.
Financial Institution Services
In our Financial Institution Services segment, competitors include Fidelity National Information Services, Inc., First Data Corporation, Fiserv, Inc., Total System Services, Inc. and Visa Debit Processing Service. In addition to competition with direct competitors, we also compete with the capabilities of many larger potential clients to conduct their key payment processing applications in-house. The most significant competitive factors in this segment are price, system performance and reliability, breadth of services and functionality, data security, scalability, flexibility of infrastructure and servicing capability.
Our Strategy
We plan to grow our business over the course of the next few years, depending on market conditions, by continuing to execute on the following four key strategies:
• | Invest in and leverage our integrated business model and technology platform to strengthen and protect our core business; |
• | Broaden and deepen our distribution channels to grow our merchant and financial institutions client base; |
• | Differentiate through value-added services that address evolving client demands and provide additional cross-selling opportunities, including security and fraud management, information services, ease of connection and delivery, and support for omni-channel environments; and |
• | Enter new geographic markets through strategic partnerships or acquisitions that enhance our distribution channels, client base, and service capabilities. |
8
Financial Highlights
Revenue for the year ended December 31, 2015, increased 23% to $3,159.9 million from $2,577.2 million in 2014. Income from operations for the year ended December 31, 2015, increased 38% to $434.4 million from $314.7 million in 2014. Net income for the year ended December 31, 2015, increased 24% to $209.2 million from $169.0 million in 2014. Net income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. for the year ended December 31, 2015, increased 18% to $147.9 million from $125.3 million in 2014.
The following tables provide a summary of the results for our two segments, Merchant Services and Financial Institution Services, for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013.
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
Merchant Services | |||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 2,656,906 | $ | 2,100,367 | $ | 1,639,157 | |||||
Network fees and other costs | 1,321,312 | 1,033,801 | 801,463 | ||||||||
Net revenue | 1,335,594 | 1,066,566 | 837,694 | ||||||||
Sales and marketing | 478,736 | 367,998 | 286,200 | ||||||||
Segment profit | $ | 856,858 | $ | 698,568 | $ | 551,494 | |||||
Non-financial data: | |||||||||||
Transactions (in millions) | 18,959 | 16,262 | 13,333 | ||||||||
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||
Financial Institution Services | |||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 503,032 | $ | 476,836 | $ | 468,920 | |||||
Network fees and other costs | 156,890 | 140,864 | 133,978 | ||||||||
Net revenue | 346,142 | 335,972 | 334,942 | ||||||||
Sales and marketing | 25,213 | 28,355 | 25,844 | ||||||||
Segment profit | $ | 320,929 | $ | 307,617 | $ | 309,098 | |||||
Non-financial data: | |||||||||||
Transactions (in millions) | 4,032 | 3,815 | 3,613 | ||||||||
Refer to "Item 7 - Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" for more details.
Regulation
Various aspects of our business are subject to U.S. federal, state and local regulation. Failure to comply with regulations may result in the suspension or revocation of licenses or registrations, the limitation, suspension or termination of services and/or the imposition of civil and criminal penalties, including fines. Certain of our services are also subject to rules set by various payment networks, such as Visa and MasterCard. Many of these regulations and rules are more fully described below.
Dodd-Frank Act
In July 2010, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 was signed into law in the United States. The Dodd-Frank Act has resulted in significant structural and other changes to the regulation of the financial services industry. Among other things, the Dodd-Frank Act established the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, or CFPB, to regulate consumer financial services, including many offered by our clients.
The Dodd-Frank Act provided two immediately effective, self-executing statutory provisions limiting the ability of payment card networks to impose certain restrictions. The first provision allows merchants to set minimum dollar amounts (not
9
to exceed $10) for the acceptance of a credit card (and allows federal governmental entities and institutions of higher education to set maximum amounts for the acceptance of credit cards). The second provision allows merchants to provide discounts or incentives to entice consumers to pay with cash, checks, debit cards or credit cards, as the merchant prefers.
Separately, the "Durbin Amendment" to the Dodd-Frank Act provided that interchange fees that a card issuer or payment network receives or charges for debit transactions will now be regulated by the Federal Reserve and must be "reasonable and proportional" to the cost incurred by the card issuer in authorizing, clearing and settling the transaction. In addition, the Durbin Amendment contains prohibitions on network exclusivity and merchant routing restrictions.
Banking Regulation
Fifth Third Bank beneficially owns an equity interest representing approximately 18.4% of Vantiv Holding's voting power and equity interests (through their ownership of Vantiv Holding Class B units) and 18.4% of the voting interest in Vantiv, Inc. (through their ownership of our Class B common stock). Fifth Third Bank is an Ohio state-chartered bank and a member of the Federal Reserve System and is supervised and regulated by the Federal Reserve and the Ohio Division of Financial Institutions, or ODFI. Fifth Third Bank is a wholly-owned indirect subsidiary of Fifth Third Bancorp, which is a bank holding company, or BHC, which has elected to be treated as a financial holding company, or FHC, and is supervised and regulated by the Federal Reserve under the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, as amended, or BHC Act.
We continue to be deemed to be controlled by Fifth Third Bancorp and Fifth Third Bank for bank regulatory purposes and, therefore, remain subject to supervision and regulation by the Federal Reserve under the BHC Act and by the ODFI under applicable federal and state banking laws until Fifth Third Bancorp and Fifth Third Bank are no longer deemed to control us for bank regulatory purposes, which we do not generally have the ability to control and which will generally not occur until Fifth Third Bank has significantly reduced its equity interest in us, as well as certain other factors, including the extent to which we continue to maintain material business relationships with Fifth Third Bancorp and Fifth Third Bank. The ownership level at which the Federal Reserve would consider us no longer controlled by Fifth Third Bank for bank regulatory purposes will generally depend on the circumstances at that time and could be less than 5%. The circumstances and other factors that the Federal Reserve will consider will include, among other things, the extent of our relationships with Fifth Third Bank, including the various agreements entered into at the time of the separation from Fifth Third Bank and the Amended and Restated Vantiv Holding Limited Liability Company Agreement.
Because of the foregoing, in certain circumstances, prior approval of the Federal Reserve or the ODFI may be required before Fifth Third Bancorp, Fifth Third Bank or their subsidiaries for bank regulatory purposes, including us, can engage in permissible activities. The Federal Reserve has broad powers to approve, deny or refuse to act upon applications or notices for us to conduct new activities, acquire or divest businesses or assets, or reconfigure existing operations. Additionally, it may be difficult for us to engage in activities abroad or invest in a non-U.S. company. We and Fifth Third Bank may seek to engage in offshore activities through various entities and structures, each of which may require prior regulatory approval, the receipt of which cannot be assured, as well as continued banking regulation and limitations. The Federal Reserve and the ODFI have substantial discretion in this regard. We will need Fifth Third Bank's cooperation to form and operate any such entity for offshore activities, and the regulatory burdens imposed upon Fifth Third Bank may be too extensive to justify its establishment or continuation. If, after such an entity is formed, we or Fifth Third Bank are at any time unable to comply with any applicable regulatory requirements, the Federal Reserve or ODFI may impose additional limitations or restrictions on Fifth Third Bank's or our operations, which could potentially force us to limit the activities or dispose of the entity.
For as long as we are deemed to be controlled by Fifth Third Bancorp and Fifth Third Bank for bank regulatory purposes, we are subject to regulation, supervision, examination and potential enforcement action by the Federal Reserve and the ODFI and to certain banking laws, regulations and orders. Fifth Third Bancorp and Fifth Third Bank are required to file reports with the Federal Reserve and the ODFI on our behalf, and we are subject to examination by the Federal Reserve and the ODFI for the purposes of determining, among other things, our financial condition, the adequacy of our risk management and the financial and operational risks that we pose to the safety and soundness of Fifth Third Bank and Fifth Third Bancorp, and our compliance with federal and state banking laws applicable to us and our relationship and transactions with Fifth Third Bancorp and Fifth Third Bank. The Federal Reserve has broad authority to take enforcement actions against us if it determines that we are engaged in or are about to engage in unsafe or unsound banking practices or are violating or are about to violate a law, rule or regulation, or a condition imposed by or an agreement with, the Federal Reserve, and any enforcement actions taken against Fifth Third Bancorp or Fifth Third Bank may result in regulatory actions being applied to us or our activities in certain circumstances, even if the enforcement actions are unrelated to our conduct or business. For the most serious violations under federal banking laws, the Federal Reserve may impose civil money penalties and criminal penalties.
10
As a condition to Fifth Third Bank's investment in us, we are required under the Amended and Restated Vantiv Holding Limited Liability Company Agreement to limit our activities to those activities permissible for a national bank. Accordingly, under the Amended and Restated Vantiv Holding Limited Liability Company Agreement: (i) we are required to notify Fifth Third Bank before we engage in any activity, by acquisition, investment, organic growth or otherwise, that may reasonably require Fifth Third Bank or an affiliate of Fifth Third Bank to obtain regulatory approval, so that Fifth Third Bank can determine whether the new activity is permissible, permissible subject to regulatory approval or impermissible; and (ii) if a change in the scope of our business activities causes the ownership of our equity not to be legally permissible for Fifth Third Bank without first obtaining regulatory approvals, then we must use reasonable best efforts to assist Fifth Third Bank in obtaining the regulatory approvals, and if the change in the scope of our business activities is impermissible for Fifth Third Bank, then we will not engage in such activity.
We are subject to regulation and enforcement by the CFPB, created by the Dodd-Frank Act, because we are an affiliate of Fifth Third Bank for bank regulatory purposes and because we are a service provider to insured depository institutions with assets of $10 billion or more in connection with their consumer financial products and to entities that are larger participants in markets for consumer financial products and services such as prepaid cards. CFPB rules, examinations and enforcement actions may require us to adjust our activities and may increase our compliance costs. In addition to rulemaking authority over several enumerated federal consumer financial protection laws, the CFPB is authorized to issue rules prohibiting unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices by persons offering consumer financial products or services and those, such as us, who are service providers to such persons, and has authority to enforce these consumer financial protection laws and CFPB rules.
Collection Services State Licensing
Ancillary to our credit card processing business, we are subject to the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act and various similar state laws. We are authorized in 19 states to engage in debt administration and debt collection activities on behalf of some of our card issuing financial institution clients through calls and letters to the debtors in those states. We may seek licenses in other states to engage in similar activities in the future.
Association and Network Rules
While not legal or governmental regulation, we are subject to the network rules of Visa, MasterCard and other payment networks. The payment networks routinely update and modify their requirements. On occasion, we have received notices of non-compliance and fines, which have typically related to excessive chargebacks by a merchant or data security failures. Our failure to comply with the networks' requirements or to pay the fines they impose could cause the termination of our registration and require us to stop providing payment processing services.
Privacy and Information Security Regulations
We provide services that may be subject to privacy laws and regulations of a variety of jurisdictions. Relevant federal privacy laws include the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act of 1999, which applies directly to a broad range of financial institutions and indirectly, or in some instances directly, to companies that provide services to financial institutions. These laws and regulations restrict the collection, processing, storage, use and disclosure of personal information, require notice to individuals of privacy practices and provide individuals with certain rights to prevent the use and disclosure of protected information. These laws also impose requirements for safeguarding and proper destruction of personal information through the issuance of data security standards or guidelines. In addition, there are state laws restricting the ability to collect and utilize certain types of information such as Social Security and driver's license numbers. Certain state laws impose similar privacy obligations as well as obligations to provide notification of security breaches of computer databases that contain personal information to affected individuals, state officers and consumer reporting agencies and businesses and governmental agencies that own data.
Processing and Back-Office Services
As a provider of electronic data processing and back-office services to financial institutions we are also subject to regular oversight and examination by the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC), an interagency body of the FDIC, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, the Federal Reserve, the National Credit Union Administration and the CFPB. In addition, independent auditors annually review several of our operations to provide reports on internal controls for our clients' auditors and regulators. We are also subject to review under state laws and rules that regulate many of the same activities that are described above, including electronic data processing and back-office services for financial institutions and use of consumer information.
11
Anti-Money Laundering and Counter Terrorist Regulation
Our business is subject to U.S. federal anti-money laundering laws and regulations, including the Bank Secrecy Act, as amended by the USA PATRIOT Act of 2001, which we refer to collectively as the BSA. The BSA, among other things, requires money services businesses to develop and implement risk-based anti-money laundering programs, report large cash transactions and suspicious activity and maintain transaction records.
We are also subject to certain economic and trade sanctions programs that are administered by the Treasury Department's Office of Foreign Assets Control, or OFAC, that prohibit or restrict transactions to or from or dealings with specified countries, their governments and, in certain circumstances, their nationals, narcotics traffickers, and terrorists or terrorist organizations, as well as similar anti-money laundering, counter terrorist financing and proceeds of crime laws applicable to movements of currency and payments through electronic transactions and to dealings with certain specified persons.
We continually develop new compliance programs and enhance existing ones to monitor and address legal and regulatory requirements and developments.
Federal Trade Commission Act and Other Laws Impacting Our and our Customers' Business
All persons engaged in commerce, including, but not limited to, us and our merchant and financial institution customers are subject to Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act prohibiting unfair or deceptive acts or practices, or UDAP. In addition, there are other laws, rules and or regulations, including the Telemarketing Sales Act and the Unlawful Internet Gambling Enforcement Act of 2006, that may directly impact the activities of our merchant customers and in some cases may subject us, as the merchant's payment processor, to litigation, investigations, fees, fines and disgorgement of funds in the event we are deemed to have aided and abetted or otherwise provided the means and instrumentalities to facilitate the illegal activities of the merchant through our payment processing services. Various federal and state regulatory enforcement agencies including the Federal Trade Commission, or FTC, and the states' attorneys general have authority to take action against nonbanks that engage in UDAP or violate other laws, rules and regulations.
As a result of the increasingly uncertain regulatory and judicial environment surrounding Daily Fantasy Sports, we have decided to suspend processing for these transactions. Revenue from Daily Fantasy Sports is not material to our business or to our Merchant segment. If there is greater regulatory and judicial clarity, we may re-enter the space in the future. In the meantime, we remain firmly committed to processing for online and land-based gaming operators, including state lotteries and other regulated gaming activities where the regulatory and judicial framework are more clearly established.
Prepaid Services
Prepaid card programs managed by us are subject to various federal and state laws and regulations, which may include laws and regulations related to consumer and data protection, licensing, consumer disclosures, escheat, anti-money laundering, banking, trade practices and competition and wage and employment. For example, most states require entities engaged in money transmission in connection with the sale of prepaid cards to be licensed as a money transmitter with, and subject to examination by, that jurisdiction's banking department. In the future, we may have to obtain state licenses to expand our distribution network for prepaid cards, which licenses we may not be able to obtain. Furthermore, the Credit Card Accountability Responsibility and Disclosure Act of 2009 and the Federal Reserve's Regulation E impose requirements on general-use prepaid cards, store gift cards and electronic gift certificates. These laws and regulations are sometimes inconsistent and subject to judicial and regulatory challenge and interpretation, and therefore the extent to which these laws and rules have application to, and their impact on, us, financial institutions, merchants or others could change. Prepaid services may also be subject to the rules and regulations of Visa, MasterCard and other payment networks with which we and the card issuers do business. The programs in place to process these products generally may be modified by the payment networks in their discretion and such modifications could also impact us, financial institutions, merchants and others.
We are also registered with the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network of the U.S. Department of the Treasury, or FinCEN, as a "money services business-provider of prepaid access" and are subject to examination and review by FinCEN, primarily with respect to anti-money laundering issues.
Other
We are subject to the Housing Assistance Tax Act of 2008, which requires information returns to be made for each calendar year by merchant acquiring entities. In addition, we are subject to U.S. federal and state unclaimed or abandoned
12
property (escheat) laws in the United States which require us to turn over to certain government authorities the property of others we hold that has been unclaimed for a specified period of time such as account balances that are due to a merchant following discontinuation of its relationship with us.
The foregoing list of laws and regulations to which we are subject is not exhaustive, and the regulatory framework governing our operations changes continuously. The enactment of new laws and regulations may increasingly affect the operation of our business, directly and indirectly, which could result in substantial regulatory compliance costs, litigation expense, adverse publicity, the loss of revenue and decreased profitability.
Intellectual Property
We rely on a combination of intellectual property laws, confidentiality procedures and contractual provisions to protect our proprietary technology and our brand. We have registered, and applied for the registration of, U.S. and international trademarks, service marks, and domain names. Additionally, we have filed U.S. and international patent applications covering certain of our proprietary technology relating to payment solutions, transaction processing and other matters. Over time, we have assembled and continue to assemble a portfolio of patents, trademarks, service marks, copyrights, domain names and trade secrets covering our products and services. Intellectual property is a component of our ability to be a leading payment services provider and any significant impairment of, or third-party claim against, our intellectual property rights could harm our business or our ability to compete.
Employees
As of December 31, 2015, we had 3,313 employees. As of December 31, 2015, this included 896 Merchant Services employees, 84 Financial Institution Services employees, 863 IT employees, 960 operations employees and 510 general and administrative employees. None of our employees are represented by a collective bargaining agreement. We believe that relations with our employees are good.
Corporate Information
We are a Delaware corporation incorporated on March 25, 2009. We completed our initial public offering in March 2012 and our Class A common stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol "VNTV". Our principal executive offices are located at 8500 Governor's Hill Drive, Symmes Township, Ohio 45249, and our telephone number is (513) 900-4811. Our website address is www.vantiv.com.
Available Information
We are subject to the informational requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and file or furnish reports, proxy statements, and other information with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC. You can read our SEC filings over the Internet at the SEC's website at www.sec.gov. Our filings with the SEC, including our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and any amendments to those reports, also are available free of charge on the investors section of our website at http://investors.vantiv.com when such reports are available on the SEC's website. Further corporate governance information, including our certificate of incorporation, bylaws, governance guidelines, board committee charters, and code of business conduct and ethics, is also available on the investors section of our website.
You may also read and copy any document we file with the SEC at its public reference facilities at 100 F Street, NE, Room 1580, Washington, DC 20549. You may also obtain copies of the documents at prescribed rates by writing to the Public Reference Section at the SEC at 100 F Street, NE, Room 1580, Washington, DC 20549. Please call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 for further information on the operation of the public reference facilities. The contents of the websites referred to above are not incorporated into this filing or in any other report or document we file with the SEC, and any references to these websites are intended to be inactive textual references only.
13
Item 1A. Risk Factors
Our business is subject to numerous risks. You should carefully consider the following risk factors and all other information contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and in our other filings with the SEC. Any of these risks could adversely affect our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
Risks Related to Our Business
If we cannot keep pace with rapid developments, changes and consolidation occurring in our industry and provide new services to our clients, the use of our services could decline, reducing our revenues.
The electronic payments market in which we operate is characterized by rapid technological change, new product and service introductions, including ecommerce services, mobile payment applications, and prepaid services, evolving industry standards, changing customer and consumer needs, the entrance of non-traditional competitors and periods of increased consolidation. In order to remain competitive in this rapidly evolving market, we are continually involved in a number of projects to develop new and innovative services. These projects carry risks, such as cost overruns, delays in delivery, performance problems and lack of market acceptance of new or innovated services. Any delay in the delivery of new services or the failure to differentiate our services or to accurately predict and address market demand could render our services less desirable, or even obsolete, to our clients.
In addition, the new or innovated services we develop are designed to process very complex transactions and provide information on those transactions, all at very high volumes and processing speeds. Any failure to deliver reliable, effective and secure services that meet the expectations of our clients could result in increased costs and/or a loss in business and revenues that could reduce our earnings. If we are unable to develop, adapt to or access technological changes or evolving industry standards on a timely and cost effective basis, our business, financial condition and results of operations would be materially adversely affected.
The payment processing industry is highly competitive, and we compete with certain firms that are larger and that have greater financial resources. Such competition could adversely affect the transaction and other fees we receive from merchants and financial institutions, and as a result, our margins, business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our competitors include financial institutions and well-established payment processing companies, including Bank of America Merchant Services, Chase Paymentech Solutions, Elavon Inc. (a subsidiary of U.S. Bancorp), First Data Corporation, Global Payments, Inc., Heartland Payment Systems, Inc., Total System Services, Inc. and WorldPay US, Inc. in our Merchant Services segment, and Fidelity National Information Services, Inc., First Data Corporation, Fiserv, Inc., Total System Services, Inc. and Visa Debit Processing Service in our Financial Institution Services segment. With respect to our Financial Institutions Services segment, in addition to competition with direct competitors, we also compete with the capabilities of many larger potential clients to conduct their key payment processing applications in-house.
Many of our competitors also have substantially greater financial, technological and marketing resources than we have. In addition, our competitors that are financial institutions or are affiliated with financial institutions, may not incur the sponsorship costs we incur for registration with the payment networks. Accordingly, these competitors may be able to offer more attractive fees to our current and prospective clients or other services that we do not provide. Competition could result in a loss of existing clients, and greater difficulty attracting new clients. Furthermore, if competition causes us to reduce the fees we charge in order to attract or retain clients, there is no assurance we can successfully control our costs in order to maintain our profit margins. One or more of these factors could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Furthermore, we are facing new competitive pressure from non-traditional payments processors and other parties entering the payments industry, such as PayPal, Google, Apple, Alibaba and Amazon, who may compete in one or more of the functions performed in processing merchant transactions. These companies have significant financial resources and robust networks and are highly regarded by consumers. If these companies gain a greater share of total electronic payments transactions or if we are unable to successfully react to changes in the industry spurred by the entry of these new market participants, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
14
Unauthorized disclosure of data, whether through cybersecurity breaches, computer viruses or otherwise, could expose us to liability, protracted and costly litigation and damage our reputation.
We have responsibility for certain third parties, including merchants, ISOs, third party service providers and other agents, which we refer to collectively as associated participants, under Visa, MasterCard and other payment network rules and regulations. We and certain of our associated participants process, store and/or transmit sensitive data, such as names, addresses, social security numbers, credit or debit card numbers, driver’s license numbers and bank account numbers, and we have ultimate liability to the payment networks and member financial institutions that register us with Visa, MasterCard and other payment networks for our failure or the failure of our associated participants to protect this data in accordance with payment network requirements. The loss of merchant or cardholder data by us or our associated participants could result in significant fines and sanctions by the payment networks or governmental bodies. A significant cybersecurity breach could also result in payment networks prohibiting us from processing transactions on their networks or the loss of our financial institution sponsorship that facilitates our participation in the payment networks, which would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
These concerns about security are increased when we transmit information over the Internet. The techniques used to obtain unauthorized access, disable or degrade service or sabotage systems change frequently and are often difficult to detect. We and our associated participants have been in the past and could be in the future, subject to breaches of security by hackers. In such circumstances, our encryption of data and other protective measures have not prevented and may not prevent unauthorized access service disruption or system sabotage. Although we have not incurred material losses or liabilities as a result of security breaches we or our associated participants have experienced, any future breach of our system or an associated participant could be material and harm our reputation, deter clients and potential clients from using our services, increase our operating expenses, expose us to uninsured losses or other liabilities, increase our risk of regulatory scrutiny, subject us to lawsuits, result in material penalties and fines under state and federal laws or by the payment networks, and adversely affect our continued payment network registration and financial institution sponsorship.
We cannot assure you that our arrangements with associated participants will prevent the unauthorized use or disclosure of data or that we would be reimbursed by associated participants in the event of unauthorized use or disclosure of data. Any such unauthorized use or disclosure of data could result in protracted and costly litigation, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our systems and our third party providers’ systems may fail due to factors beyond our control, which could interrupt our service, cause us to lose business and increase our costs.
We depend on the efficient and uninterrupted operation of numerous systems, including our computer systems, software, data centers and telecommunications networks, as well as the systems of third parties, in order to provide services to our clients. Our systems and operations and those of our third party providers, could be exposed to damage or interruption from, among other things, fire, natural disaster, power loss, telecommunications failure, unauthorized entry, security breach, computer viruses, defects and development delays. Our property and business interruption insurance may not be adequate to compensate us for all losses or failures that may occur. Defects in our systems or those of third parties, errors or delays in the processing of payment transactions, telecommunications failures or other difficulties could result in loss of revenues and clients, reputational harm, additional operating expenses in order to remediate the failures, fines imposed by payment networks and exposure to other losses or other liabilities.
We may not be able to continue to expand our share of the existing payment processing markets or expand into new markets which would inhibit our ability to grow and increase our profitability.
Our future growth and profitability depend upon the growth of the markets in which we currently operate and our ability to increase our penetration and service offerings within these markets, as well as the emergence of new markets for our services and our ability to penetrate these new markets. It is difficult to attract new clients because of potential disadvantages associated with switching payment processing vendors, such as transition costs, business disruption and loss of accustomed functionality. We seek to overcome these factors by making investments to enhance the functionality of our software and differentiate our services. However, there can be no assurance that our efforts will be successful, and this resistance may adversely affect our growth.
Our expansion into new markets is also dependent upon our ability to adapt our existing technology and offerings or to develop new or innovative applications to meet the particular service needs of each new market. In order to do so, we will need to anticipate and react to market changes and devote appropriate financial and technical resources to our development efforts, and there can be no assurance that we will be successful in these efforts.
15
Furthermore, in response to market developments, we may expand into new geographical markets and foreign countries in which we do not currently have any operating experience. We cannot assure you that we will be able to successfully expand in such markets or internationally due to our lack of experience and the multitude of risks associated with global operations or lack of appropriate regulatory approval.
Any acquisitions, partnerships or joint ventures that we make could disrupt our business and harm our financial condition.
Acquisitions, partnerships and joint ventures are part of our growth strategy. We evaluate, and expect in the future to evaluate potential strategic acquisitions of, and partnerships or joint ventures with, complementary businesses, services or technologies. However, we may not be able to successfully identify suitable acquisition, partnership or joint venture candidates in the future. In addition, for purposes of the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, as amended, or the BHC Act, we are deemed to be a subsidiary of Fifth Third Bank. For so long as we continue to be considered a subsidiary of a bank, we may only engage in activities that are permissible for the bank to engage in directly. These activities and restrictions may limit our ability to acquire other businesses, enter into other strategic transactions or expand into foreign countries.
If we do enter into acquisitions, partnerships and joint ventures, they may not provide us with the benefits we anticipate. We may not be able to successfully integrate any businesses, services or technologies that we acquire or with which we form a partnership or joint venture, or comply with applicable regulatory requirements. Furthermore, the integration of any acquisition, including our recent acquisitions, may divert management’s time and resources from our core business and disrupt our operations. Certain partnerships and joint ventures we make may also prevent us from competing for certain clients or in certain lines of business. To the extent we pay the purchase price of any acquisition in cash, it would reduce our cash reserves, and to the extent the purchase price is paid with our stock, it could be dilutive to our stockholders. To the extent we pay the purchase price with proceeds from the incurrence of debt, it would increase our already high level of indebtedness and could negatively affect our liquidity and restrict our operations.
If we fail to comply with the applicable requirements of the Visa, MasterCard or other payment networks, those payment networks could seek to fine us, suspend us or terminate our registrations through our financial institution sponsors. Fines could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations, and if these registrations are terminated, we may not be able to conduct our business.
In order to provide our transaction processing services, we are registered through our bank sponsorships with the Visa, MasterCard and other payment networks as service providers for member institutions. We and many of our clients are subject to payment network rules. If we or our associated participants do not comply with the payment network requirements, the payment networks could seek to fine us, suspend us or terminate our registrations. We have occasionally received notices of noncompliance and fines, which have typically related to excessive chargebacks by a merchant or data security failures on the part of a merchant. If we are unable to recover fines from or pass through costs to our merchants or other associated participants, we would experience a financial loss. The termination of our registration, or any changes in the payment network rules that would impair our registration, could require us to stop providing payment network services to the Visa, MasterCard or other payment networks, which would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Changes in payment network rules or standards could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Payment network rules are established and changed from time to time by each payment network as they may determine in their sole discretion and with or without advance notice to their participants. In some cases, payment networks compete with us, and their ability to modify and enhance their rules in their sole discretion may provide them an advantage in selling or developing their own services that may compete directly or indirectly with our services. Any changes in payment network rules or standards or the way they are implemented could increase our cost of doing business or limit our ability to provide transaction processing services to or through our clients and have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
16
If we cannot pass along to our merchants increases in interchange and other fees from payment networks, our operating margins would be reduced.
We pay interchange, assessment, transaction and other fees set by the payment networks to the card issuing financial institution and the payment networks for each transaction we process. From time to time, the payment networks increase the interchange fees and other fees that they charge payment processors and the financial institution sponsors. At their sole discretion, our financial institution sponsors have the right to pass any increases in interchange and other fees on to us and they have consistently done so in the past. We are generally permitted under the contracts into which we enter, and in the past we have been able to, pass these fee increases along to our merchants through corresponding increases in our processing fees. However, if we are unable to pass through these and other fees in the future, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If our agreements with financial institution sponsors and clearing service providers to process electronic payment transactions are terminated or otherwise expire and we are unable to renew existing or secure new sponsors or clearing service providers, we will not be able to conduct our business.
The Visa, MasterCard and other payment network rules require us to be sponsored by a member bank in order to process electronic payment transactions. Because we are not a bank, we are unable to directly access these payment networks. We are currently registered with the Visa, MasterCard and other payment networks through Fifth Third Bank and other sponsor banks. Our current agreement with Fifth Third Bank expires in June 2019. These agreements with Fifth Third Bank and other sponsors give them substantial discretion in approving certain aspects of our business practices, including our solicitation, application and qualification procedures for merchants and the terms of our agreements with merchants. Our financial institution sponsors’ discretionary actions under these agreements could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. We also rely on Fifth Third Bank and various other financial institutions to provide clearing services in connection with our settlement activities. Without these sponsorships or clearing services agreements, we would not be able to process Visa, MasterCard and other payment network transactions or settle transactions which would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. Furthermore, our financial results could be adversely affected if our costs associated with such sponsorships or clearing services agreements increase.
Increased merchant, financial institution or referral partner attrition and decreased transaction volume could cause our revenues to decline.
We experience attrition and declines in merchant and financial institution credit, debit or prepaid card processing volume resulting from several factors, including business closures, consolidations, loss of accounts to competitors, account closures that we initiate due to heightened credit risks, and reductions in our merchants' sales volumes. Our referral partners, many of which are not exclusive, such as merchant banks, ISVs, VARs, payment facilitators, ISOs and trade associations are strong contributors to our revenue growth in our Merchant Services segment. If an ISO or referral partner switches to another transaction processor, shuts down or becomes insolvent, we will no longer receive new merchant referrals from the ISO or referral partner, and we risk losing existing merchants that were originally enrolled by the ISO or referral partner. We cannot predict the level of attrition and decreased transaction volume in the future and our revenues could decline as a result of higher than expected attrition, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We are subject to economic and political risk, the business cycles and credit risk of our clients and the overall level of consumer, business and government spending, which could negatively impact our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The electronic payments industry depends heavily on the overall level of consumer, business and government spending. We are exposed to general economic conditions that affect consumer confidence, consumer spending, consumer discretionary income or changes in consumer purchasing habits. A sustained deterioration in general economic conditions, particularly in the United States, or increases in interest rates may adversely affect our revenues by reducing the number or average purchase amount of transactions made using electronic payments that we process. Furthermore, if economic conditions cause credit card issuers to tighten credit requirements, the negative effects on the use of electronic payments could be exacerbated. Since we have a certain amount of fixed and semi-fixed costs, including rent, debt service, processing contractual minimums and salaries, our ability to quickly adjust costs and respond to changes in our business and the economy is limited. As a result, changes in economic conditions could adversely impact our future revenues and profits.
17
In addition, a sustained deterioration in economic conditions could affect our merchants through a higher rate of closures or bankruptcies, resulting in lower revenues and earnings for us. In addition, our merchants and other associated participants are liable for any charges properly reversed by the card issuer on behalf of the cardholder and for any fines or penalties that may be assessed by payment networks. In the event that we are not able to collect such amounts from the associated participants, due to closure, insolvency or other reasons, we may be liable for any such charges.
Fraud by merchants or others could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We face potential liability for fraudulent electronic payment transactions initiated by merchants or other associated participants. Examples of merchant fraud include when a merchant or other party knowingly accepts payment by a stolen or counterfeit credit, debit or prepaid card, card number or other credentials records a false sales transaction utilizing a stolen or counterfeit card or credentials, processes an invalid card, or intentionally fails to deliver the merchandise or services sold in an otherwise valid transaction. In the event a dispute between a cardholder and a merchant is not resolved in favor of the merchant, the transaction is normally charged back to the merchant and the purchase price is credited or otherwise refunded to the cardholder. Failure to effectively manage risk and prevent fraud would increase our chargeback liability or other liability. In addition, beginning October 2015, merchants that cannot process EMV chip-based cards are held financially responsible for certain fraudulent transactions conducted using such cards. This will likely increase the amount of risk for merchants who are not yet EMV-compliant and could result in us having to seek increased chargebacks from such merchants. Increases in chargebacks or other liability could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
A decline in the use of credit, debit or prepaid cards as a payment mechanism for consumers or adverse developments with respect to the payment processing industry in general could have a materially adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If consumers do not continue to use credit, debit or prepaid cards as a payment mechanism for their transactions or if there is a change in the mix of payments between cash, alternative currencies and technologies, credit, debit and prepaid cards, or the corresponding methodologies used for each, which is adverse to us, it could have a materially adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. Moreover, if there is an adverse development in the payments industry in general, such as new legislation or regulation that makes it more difficult for our clients to do business, our business, financial condition and results of operations may be adversely affected.
If Fifth Third Bank fails or is acquired by a third party, it could place certain of our material contracts at risk, decrease our revenue, and transfer the ultimate voting power of Fifth Third Bank’s stock ownership in us (including any shares of Class A common stock that may be issued in exchange for Fifth Third Bank’s units in Vantiv Holding) to a third party.
Fifth Third Bank accounted for approximately 3% of our revenue during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, and is the provider of the services under our Clearing, Settlement and Sponsorship Agreement, Referral Agreement and Master Services Agreement. If Fifth Third Bank were to be placed into receivership or conservatorship, it could jeopardize our ability to generate revenue and conduct our business.
If Fifth Third Bank were to be acquired by a third party, it could affect certain of our contractual arrangements with them. For instance, in the event of a change of control or merger of Fifth Third Bank, our Clearing, Settlement and Sponsorship Agreement and our Referral Agreement provide that Fifth Third Bank may assign the contract to an affiliate or successor, in which case we would not have the right to terminate the contract regardless of such assignee’s ability to perform such services. Our Master Services Agreement provides that Fifth Third Bank would be in default under the agreement upon a change of control, in which case we would have the right to terminate the agreement effective upon 60 days' notice to Fifth Third Bank unless the surviving entity assumes Fifth Third Bank’s obligation and the level of fees paid to us pursuant to the Master Services Agreement remains equal or greater than fees paid to us prior to the change of control. In addition, the acquiring company may choose to terminate the terms of such contracts, requiring us to litigate if we believe such termination is not pursuant to contract terms, and find alternative clients, counterparties or sponsorships. The added expense of litigation and the inability to find suitable substitute clients or counterparties in a timely manner would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. Furthermore, such an acquisition would place in the hands of the acquiring third party the voting power of Fifth Third Bank’s stock ownership in Vantiv, Inc. (including any shares of Class A common stock that may be issued in exchange for Fifth Third Bank’s units in Vantiv Holding). We may not have a historical relationship with the acquiring party, and the acquiring party may be a competitor of ours or provide many of the same services that we provide. The acquiring party may vote its shares of our common stock or units in a manner adverse to us and our other stockholders.
18
Our risk management policies and procedures may not be fully effective in mitigating our risk exposure against all types of risks.
Our risk management policies and procedures may not be fully effective to identify, monitor and manage our risks. Some of our risk evaluation methods depend upon information provided by others and public information regarding markets, clients or other matters that are otherwise inaccessible by us. In some cases, however, that information may not be accurate, complete or up-to-date. If our policies and procedures are not fully effective or we are not always successful in capturing all risks to which we are or may be exposed, we may suffer harm to our reputation or be subject to litigation or regulatory actions that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We are subject to extensive government regulation, and any new laws and regulations, industry standards or revisions made to or interpretations of existing laws, regulations, or industry standards affecting the electronic payments industry and other industries in which we operate may have an unfavorable impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our business is impacted by numerous laws, regulations and examinations that affect us and our industry, many of which are discussed under "Item 1. Business - Regulation." In addition, the number of new and proposed regulations has increased significantly in recent years, particularly pertaining to interchange fees on credit and debit card transactions, which are paid to the card issuing financial institution. In particular, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, or the Dodd-Frank Act, significantly changed the payment processing industry by restricting amounts of debit card fees that certain issuing financial institutions can charge merchants and allowing merchants to set minimum dollar amounts for the acceptance of credit cards and offer discounts for different payment methods. These and other regulatory changes on our business and industry could negatively affect our business in a variety of ways including the number of debit transactions, and prices charged per transaction.
In the future, due to applicable law and regulation, we may have to obtain state licenses to expand our distribution network for prepaid cards. If we fail or are unable to comply with these requirements, our clients (or in certain instances, we) could be subject to the imposition of fines, other penalties or enforcement-related actions which may impact our ability to offer our credit issuer processing services, prepaid or other related services and could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. Because our business is highly regulated, it is very important to our business that our operations, policies and procedures comply with applicable laws, regulations and related requirements. Our failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations or adapt to changes in applicable laws and regulations, or a material increase in our compliance and other costs as a result of regulatory changes, could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, any failure to comply with laws and regulations, even if inadvertent, as well as rapidly evolving social expectations of corporate fairness, could damage our business or our reputation.
Governmental regulations designed to protect or limit access to consumer information could adversely affect our ability to effectively provide our services to merchants.
Governmental bodies in the United States and abroad have adopted, or are considering the adoption of, laws and regulations restricting the transfer of, and requiring safeguarding of, non-public personal information. For example, in the United States, all financial institutions must undertake certain steps to ensure the privacy and security of consumer financial information. Although we have limited our use of consumer information solely to providing services to other businesses and financial institutions, we are required by regulations and contracts with our merchants and financial institution clients to provide assurances regarding the confidentiality and security of non-public consumer information. These contracts require periodic audits by independent companies regarding our compliance with industry standards and also allow for similar audits regarding best practices established by regulatory guidelines. The compliance standards relate to our infrastructure, components and operational procedures designed to safeguard the confidentiality and security of non-public consumer personal information shared by our clients with us. Our ability to maintain compliance with these standards and satisfy these audits will affect our ability to attract and maintain business in the future. If we fail to comply with these regulations or requirements, we could be exposed to suits for breach of contract or to governmental proceedings. In addition, our client relationships and reputation could be harmed, and we could be inhibited in our ability to obtain new clients. If more restrictive privacy laws or rules are adopted by authorities in the future on the federal or state level, our compliance costs may increase, our opportunities for growth may be curtailed by our compliance capabilities or reputational harm and our potential liability for security breaches may increase, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
19
For purposes of federal and state banking laws, we are deemed to be controlled by Fifth Third Bank and Fifth Third Bancorp, and as such we are subject to supervision and examination by federal and state banking regulators, and our activities are limited to those permissible for Fifth Third Bank and Fifth Third Bancorp. We may therefore be restricted from engaging in new activities or businesses, whether organically or by acquisition. We are also subject to supervision and examination by the Federal Consumer Financial Protection Bureau.
As of December 31, 2015, Fifth Third Bank owned an equity interest representing approximately 18.4% of the voting and economic equity interest of Vantiv Holding and 18.4% of the voting interest in Vantiv, Inc.
We and Vantiv Holding historically have been, and are currently, deemed to be controlled by Fifth Third Bancorp and Fifth Third Bank and are therefore considered to be a subsidiary of Fifth Third Bank for purposes of relevant federal and state banking laws. We are therefore subject to regulation and supervision by the Federal Reserve and the Ohio Division of Financial Institutions, or the ODFI. We will remain subject to regulation and examination until Fifth Third Bancorp and Fifth Third Bank are no longer deemed to control us for bank regulatory purposes.
For as long as we are deemed to be controlled by Fifth Third Bancorp and Fifth Third Bank for bank regulatory purposes, we are subject to regulation, supervision, examination and potential enforcement action by the Federal Reserve and the ODFI and to most banking laws, regulations and orders that apply to Fifth Third Bancorp and Fifth Third Bank, including restrictions or approval requirements for certain activities or investments abroad. Any restrictions placed on Fifth Third Bancorp or Fifth Third Bank as a result of any supervisory actions may also restrict us or our activities in certain circumstances, even if these actions are unrelated to our conduct or business. Further, as long as we are deemed to be controlled by Fifth Third Bank, our activities are limited to those that are permissible for Fifth Third Bank to engage in, which include activities that are part of, or incidental to, the business of banking. Accordingly, we are subject to a covenant in the Amended and Restated Vantiv Holding Limited Liability Company Agreement that is intended to facilitate compliance by Fifth Third Bank with relevant federal and state banking laws.
In addition, new activities that we may wish to commence in the future may not be permissible for us under relevant federal or state banking laws, or may require prior regulatory approvals. More generally, the Federal Reserve has broad powers to approve, deny or refuse to act upon applications or notices for us to conduct new activities, acquire or divest businesses or assets, or reconfigure existing operations.
Because of the foregoing limitations, and in particular, Fifth Third Bank’s interest in us, it may be difficult for us to engage in activities abroad or invest in a non-U.S. company. We and Fifth Third Bank may seek to engage in offshore acquisitions and activities through various regulatory structures and entities, each of which will generally require prior regulatory approval. The Federal Reserve and the ODFI would therefore have substantial discretion as to whether any such regulatory structures or entities could be utilized, whether we would be permitted to operate or invest in a non-U.S. company, and under what conditions such structures or entities could operate.
We are subject to regulation and enforcement by the CFPB because we are an affiliate of Fifth Third Bank for bank regulatory purposes and because we are a service provider to insured depository institutions with assets of $10 billion or more in connection with their consumer financial products and to entities that are larger participants in markets for consumer financial products and services such as prepaid cards. CFPB rules and examinations may require us to adjust our activities and may increase our compliance costs, which could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Changes in tax laws or their interpretations, or becoming subject to additional international, U.S., state or local taxes that cannot be passed through to our merchants, could reduce our net income.
We are subject to tax laws in each jurisdiction where we do business. Changes in tax laws or their interpretations could decrease the amount of revenues we receive, the value of any tax loss carryforwards and tax credits recorded on our balance sheet and the amount of our cash flow, and have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations. Furthermore, companies in the electronic payments industry, including us, may become subject to incremental taxation in various tax jurisdictions. Taxing jurisdictions have not yet adopted uniform positions on this topic. If we are required to pay additional taxes and are unable to pass the tax expense through to our merchants, our costs would increase and our net income would be reduced.
20
The costs and effects of pending and future litigation, investigations or similar matters, or adverse facts and developments related thereto, could materially affect our business, financial position and results of operations.
We are involved in various litigation matters and from time to time may be involved in governmental or regulatory investigations or similar matters arising out of our current or future business. Our insurance or indemnities may not cover all claims that may be asserted against us, and any claims asserted against us, regardless of merit or eventual outcome, may harm our reputation. Furthermore, there is no guarantee that we will be successful in defending ourselves in pending or future litigation or similar matters under various laws. Should the ultimate judgments or settlements in any pending litigation or future litigation or investigation significantly exceed our insurance coverage, they could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We may not be able to successfully manage our intellectual property and may be subject to infringement claims.
Third parties may challenge, invalidate, circumvent, infringe or misappropriate our intellectual property, or such intellectual property may not provide us any competitive advantages, which could result in costly redesign efforts, discontinuance of certain service offerings or other competitive harm. Our competitors could also independently develop similar technology, duplicate our services or design around our intellectual property. We may be forced to litigate to enforce or determine the scope and enforceability of our intellectual property rights, trade secrets and know-how, which is expensive, could cause a diversion of resources and may not prove successful. Also, we may not be able to obtain or continue to obtain licenses and technologies from third parties on reasonable terms or at all. The loss of intellectual property protection or the inability to obtain third party intellectual property could harm our business and ability to compete.
We may also be subject to costly litigation in the event our services and technology infringe upon or otherwise violate a third party’s proprietary rights, or if a third party claims we have breached their copyright, trademark, license usage or other intellectual property rights. Any claim from third parties may result in a limitation on our ability to use the intellectual property subject to these claims. Additionally, we could be required to defend against individuals and groups who have been purchasing intellectual property assets for the sole purpose of making claims of infringement and attempting to extract settlements from companies like ours. Claims of intellectual property infringement also might require us to pay costly settlement or damage awards, or prevent us from marketing or selling certain of our services. If we cannot redesign affected services or license the infringed technology on reasonable terms or substitute similar technology from another source, our revenue and earnings could be adversely impacted.
Finally, we could be subject to suits by parties claiming ownership of what we believe to be open source software, which we use in connection with our technology and services. Despite our efforts to prevent it from occurring, we could be required to by some of our open source software licenses to publicly disclose all or part of the source code to such software and/or make available any derivative works of the open source code on unfavorable terms or at no cost. Any requirement to disclose our proprietary source code could be harmful to our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If we lose key personnel or are unable to attract, recruit, retain and develop qualified employees, our business, financial condition and results of operations may be adversely affected.
We are dependent upon the ability and experience of a number of our key personnel who have substantial experience with our operations, the rapidly changing payment processing industry and the selected markets in which we offer our services. The loss of the services of one or a combination of our senior executives or key managers, including Charles D. Drucker, our chief executive officer, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Additionally, in order for us to successfully compete and grow, we must attract, recruit, retain and develop the necessary personnel who can provide the needed expertise across the entire spectrum of our intellectual capital needs. We have hired significant numbers of new personnel in recent years and must continue to hire additional personnel to execute our strategic plans. However, the market for qualified personnel is competitive, and we may not succeed in recruiting additional personnel or may fail to effectively replace current personnel who depart. Failure to retain or attract key personnel could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our operating results are subject to seasonality, which could result in fluctuations in our quarterly net income.
We have experienced in the past, and expect to continue to experience, seasonal fluctuations in our revenues as a result of consumer spending patterns. Historically our revenues have been strongest in our fourth quarter, and weakest in our first quarter. This is due to the increase in the number and amount of electronic payment transactions related to seasonal retail events.
21
We may need to raise additional funds to finance our future capital needs, which may prevent us from growing our business.
We may need to raise additional funds to finance our future capital needs, including developing new services and technologies, and to fund ongoing operating expenses. We also may need additional financing earlier than we anticipate if we, among other things:
• | are required to pay significant settlements or fines; |
• | repurchase our common stock; or |
• | finance Vantiv, Inc.’s purchase of Class B units of Vantiv Holding from Fifth Third Bank upon the exercise of its right to put its Class B units of Vantiv Holding to Vantiv, Inc. in exchange for cash to the extent that we decide to purchase rather than exchange such units for Class A common stock. |
If we raise additional funds through the sale of equity securities, these transactions may dilute the value of our outstanding Class A common stock. We may also decide to issue securities, including debt securities that have rights, preferences and privileges senior to our Class A common stock. Any debt financing would increase our already high level of indebtedness and could negatively affect our liquidity and restrict our operations. We may be unable to raise additional funds on terms favorable to us or at all. If financing is not available or is not available on acceptable terms, we may be unable to fund our future needs. This may prevent us from increasing our market share, capitalizing on new business opportunities or remaining competitive in our industry.
We have a long sales cycle for many of our services, and if we fail to close sales after expending significant time and resources to do so, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
The initial installation and set-up of many of our services often involve significant resource commitments by our clients, particularly those with larger operational scale. Potential clients generally commit significant resources to an evaluation of available services and require us to expend substantial time (six to nine months is not uncommon), effort and money educating them as to the value of our services. We incur substantial costs in order to obtain each new customer. We may expend significant funds and management resources during a sales cycle and ultimately fail to close the sale. Our sales cycle may be extended due to our clients’ budgetary constraints or for other reasons. If we are unsuccessful in closing sales after expending significant funds and management resources or we experience delays, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Risks Related to Our Indebtedness and Organizational Structure
Our substantial indebtedness could adversely affect our ability to raise additional capital to fund our operations, limit our ability to react to changes in the economy or our industry, expose us to interest rate risk to the extent of our variable rate debt and prevent us from meeting our debt obligations.
We have a high level of indebtedness. As of December 31, 2015, we had total indebtedness of $3.1 billion. For the year ended December 31, 2015, total payments under our annual debt service obligations, including interest and principal, were approximately $215 million. Our high degree of leverage could have significant negative consequences, including:
• | increasing our vulnerability to adverse economic, industry or competitive developments; |
• | requiring a substantial portion of cash flow from operations to be dedicated to the payment of principal and interest on our indebtedness, thereby reducing our ability to use our cash flow to fund our operations, capital expenditures and future business opportunities; |
• | exposing us to the risk of increased interest rates because certain of our borrowings, including our borrowings under our senior secured credit facilities, are at variable rates of interest; |
• | making it more difficult for us to comply with the obligations of our debt instruments, including restrictive covenants and borrowing conditions, which could result in an event of default under the agreements governing such indebtedness; |
• | restricting us from making strategic acquisitions or causing us to make non-strategic divestitures; |
• | making it more difficult for us to obtain payment network sponsorship and clearing services from financial institutions; |
22
• | limiting our ability to obtain additional financing for working capital, capital expenditures, product development, debt service requirements, acquisitions and general corporate or other purposes; and |
• | limiting our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business or market conditions and placing us at a competitive disadvantage compared to our competitors who are less highly leveraged and who, therefore, may be able to take advantage of opportunities that our leverage prevents us from exploiting. |
The majority of our indebtedness consists of indebtedness under our senior secured credit facilities consisting of a term A loan which matures in 2019 and a term B loan which matures in 2021. We may not be able to refinance our senior secured credit facilities or any other indebtedness because of our high level of debt, debt incurrence restrictions under our debt agreements or because of adverse conditions in credit markets generally.
Despite our high indebtedness level, we still may be able to incur significant additional amounts of debt, which could further exacerbate the risks associated with our substantial indebtedness. Although our senior secured credit facilities contain restrictions on the incurrence of additional indebtedness, these restrictions are subject to a number of significant qualifications and exceptions, and under certain circumstances, the amount of indebtedness that could be incurred in compliance with these restrictions could be substantial. For example, we may incur up to $425 million of additional debt pursuant to an incremental facility under our senior secured credit facilities, subject to certain terms and conditions.
Our use of derivative financial instruments may not be successful in managing our interest rate risks and could result in material financial losses by us.
To the extent that we hedge our exposure to fluctuations in interest rates, we forgo the benefits we would otherwise experience if interest rates were to change in our favor. Developing an effective strategy for dealing with movements in interest rates is complex, and no strategy can completely insulate us from risks associated with such fluctuations. In addition, a counterparty to the arrangement could default on its obligation, thereby exposing us to credit risk. Further, we may have to repay certain costs, such as transaction fees or breakage costs, if we terminate these arrangements. Finally, our interest rate risk management activities could expose us to substantial losses if interest rates move materially differently from management's expectations. As a result, we cannot assure that our interest rate hedging arrangements will effectively manage our interest rate sensitivity or have the desired beneficial impact on our results of operations or financial condition.
Our balance sheet includes significant amounts of goodwill and intangible assets. The impairment of a significant portion of these assets would negatively affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our balance sheet includes goodwill and intangible assets that represent 65% of our total assets at December 31, 2015. These assets consist primarily of goodwill and customer relationship intangible assets associated with our acquisitions. Additional acquisitions would also result in our recognition of additional goodwill and intangible assets. Under current accounting standards, we are required to amortize certain intangible assets over the useful life of the asset, while goodwill is not amortized. On at least an annual basis, we assess whether there have been impairments in the carrying value of goodwill and certain intangible assets. If the carrying value of the asset is determined to be impaired, then it is written down to fair value by a charge to operating earnings. An impairment of a significant portion of goodwill or intangible assets could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
We are party to tax receivable agreements and the amounts we may be required to pay under these agreements are expected to be significant. In certain cases, payments under the tax receivable agreements may be accelerated and/or significantly exceed the actual benefits we realize in respect of the tax attributes subject to the tax receivable agreements.
We are party to tax receivable agreements ("TRAs") as further described in "Item 7 - Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations." The payments we will be required to make under these TRAs are expected to be substantial. As of December 31, 2015, we have a liability recorded of approximately $1.0 billion associated with the TRAs. Because payments under the TRAs are determined based on realized cash savings resulting from the underlying tax attributes, a period of declining profitability would result in a corresponding reduction in our TRA payments. We will incur additional liabilities in connection with any future purchases by us of units in Vantiv Holding from Fifth Third Bank or from the future exchange of units by Fifth Third Bank for cash or shares of our Class A common stock. If Fifth Third Bank had exchanged its remaining Class B units of Vantiv Holding, had exercised the remaining warrant and exchanged the Class C units of Vantiv Holding, all for shares of Class A common stock on December 31, 2015, we would have recorded an additional full and undiscounted TRA obligation of approximately $1.1 billion. This estimate is subject to material change based on changes in Fifth Third Bank’s tax basis in the partnership interest, changes in tax rates, or significant changes in our stock price. It is possible that future transactions or events, including changes in tax rates, could increase or decrease the actual tax benefits
23
realized and the corresponding TRA payments. There may be a material adverse effect on our liquidity if, as a result of timing discrepancies or otherwise, distributions to us by Vantiv Holding are not sufficient to permit us to make payments under the TRAs.
The TRAs provide that, upon certain mergers, asset sales, other forms of business combination or certain other changes of control, our obligations to make payments with respect to tax benefits would be based on certain assumptions, including that we would have sufficient taxable income to fully use the NOLs or deductions arising from increased tax basis of assets. As a result, upon a merger or other change of control, we could be required to make payments under the TRAs that are greater than 85% of our actual tax savings.
We may elect to terminate any or all of the remaining TRAs prior to the time they terminate in accordance with their terms. If we were to so elect, or if we materially breach a material obligation in the TRAs and we do not cure such breach within a specified time period, we would be required to make an immediate payment equal to the present value of the anticipated future tax benefits taken into account under the TRAs. In these circumstances, the anticipated future tax benefits would be determined under certain assumptions that in general assume that we would recognize the greatest amount of benefits at the earliest time. As a result, the payments we would be required to make could exceed 85% of the tax savings that we actually realize from the increased tax basis and/or the NOLs, and we could be required to make those payments significantly in advance of the time the tax savings arise.
If the Internal Revenue Service, or the IRS, challenges the tax basis increases or NOLs that give rise to payments under the TRAs and the tax basis increases or NOLs are subsequently disallowed, our payments under the TRAs could exceed our actual tax savings, and we may not be able to recoup payments under the TRAs that were calculated on the assumption that the disallowed tax savings were available.
We are a holding company and our principal assets are our interests in Vantiv Holding, and we depend on dividends, distributions and other payments from Vantiv Holding to meet any existing or future debt service and other obligations and to pay dividends, if any, and taxes and other expenses.
We are a holding company and conduct all of our operations through Vantiv Holding and its subsidiaries. We have no material assets other than our ownership of units of Vantiv Holding. To the extent that we need funds and Vantiv Holding is restricted from making distributions to us under applicable law or regulation, or by the terms of Vantiv Holding’s indebtedness, or Vantiv Holding is otherwise unable to provide such funds, it could materially adversely affect our liquidity and, consequently, our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Fifth Third Bank has interests that could present potential conflicts with our and our other stockholders’ interests.
Fifth Third Bank has the ability to pursue, for its own accounts, business line or acquisition opportunities that may be similar or complementary to our business, and as a result, those opportunities may not be available to us. Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation contains provisions renouncing any interest or expectancy we may have in certain corporate opportunities held by or known to our directors affiliated with Fifth Third Bank. Accordingly, the interests of Fifth Third Bank may supersede ours, causing it or its affiliates to compete against us or to pursue opportunities instead of us, for which we would have no recourse. Such actions on the part of Fifth Third Bank and inaction on our part could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Some provisions of Delaware law and our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws may deter third parties from acquiring us and diminish the value of our Class A common stock.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws provide for, among other things:
• | restrictions on the ability of our stockholders to call a special meeting and the business that can be conducted at such meeting; |
• | prohibition on the ability of our stockholders to remove directors elected by the holders of our Class A common stock without cause; |
• | our ability to issue additional shares of Class A common stock and to issue preferred stock with terms that the board of directors may determine, in each case without stockholder approval (other than as specified in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation); |
• | the absence of cumulative voting in the election of directors; |
24
• | supermajority approval requirements for amending or repealing provisions in the amended and restated certificate of incorporation and bylaws; |
• | a classified board of directors; |
• | a prohibition on action by written consent of stockholders; and |
• | advance notice requirements for stockholder proposals and nominations. |
These provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws may discourage, delay or prevent a transaction involving a change in control of our company that is in the best interest of our stockholders. Even in the absence of a takeover attempt, the existence of these provisions may adversely affect the prevailing market price of our Class A common stock if they are viewed as discouraging future takeover attempts. These provisions could also make it more difficult for stockholders to nominate directors for election to our board of directors and take other corporate actions.
Risks Related to the Ownership of our Class A Common Stock
Future sales of our Class A common stock or securities convertible into or exchangeable for Class A common stock could depress the market price of our Class A common stock.
Sales of substantial amounts of our Class A common stock in the public market, or the perception that such sales could occur, could adversely affect the market price of our Class A common stock. As of December 31, 2015, we had 155,488,326 shares of Class A common stock outstanding. Subject to compliance with applicable documentation, which includes the Exchange Agreement and may include the Warrant, Fifth Third Bank could acquire up to 42,834,782 shares of our Class A common stock. Pursuant to the Registration Rights Agreement, Fifth Third Bank is entitled to certain demand and "piggyback" registration rights and any shares of our Class A common stock that are sold by Fifth Third Bank pursuant to such a registration would become eligible for sale in the public market without restriction. In addition, we have filed registration statements on Form S-8 relating to an aggregate of 39,750,519 shares of our Class A common stock that we have issued or may issue in the future pursuant to employee benefit plans. These shares may be sold in the public market upon issuance and once vested, subject to the terms of the equity incentive plan and applicable award agreements.
Failure to maintain effective systems of internal control over financial reporting and disclosure controls and procedures could adversely affect the trading price of our common stock.
Effective internal control over financial reporting is necessary for us to provide accurate financial information. If we are unable to adequately maintain effective internal control over financial reporting, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results, which could cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information and negatively affect the trading price of our common stock. Furthermore, we cannot be certain that our internal control over financial reporting and disclosure controls and procedures will prevent all possible error and fraud. Because of inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of error or fraud, if any, in our company have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision-making can be faulty and that breakdowns can occur because of simple error or mistake, which could have an adverse impact on our business.
The price of our Class A common stock may be volatile.
Securities markets worldwide have experienced, and are likely to continue to experience, significant price and volume fluctuations. This market volatility, as well as general economic, market or political conditions could reduce the market price of our Class A common stock regardless of our results of operations. The trading price of our Class A common stock is likely to be highly volatile and could be subject to wide price fluctuations in response to various factors, including, among other things, the risk factors described in this section of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and other factors beyond our control. Factors affecting the trading price of our common stock will include:
• | market conditions in the broader stock market; |
• | actual or anticipated variations in our quarterly financial and operating results; |
• | variations in operating results of similar companies; |
• | introduction of new services by us, our competitors or our clients |
• | issuance of new, negative or changed securities analysts’ reports or recommendations or estimates; |
• | investor perceptions of us and the industries in which we or our clients operate; |
25
• | sales, or anticipated sales, of our stock, including sales by existing stockholders; |
• | additions or departures of key personnel; |
• | regulatory or political developments; |
• | stock-based compensation expense under applicable accounting standards; |
• | litigation and governmental investigations; and |
• | changing economic conditions. |
These and other factors may cause the market price and demand for shares of our Class A common stock to fluctuate substantially, which may limit or prevent investors from readily selling their shares of Class A common stock and may otherwise negatively affect the liquidity of our Class A common stock. In addition, in the past, when the market price of a stock has been volatile, holders of that stock have sometimes instituted securities class action litigation against the company that issued the stock. Securities litigation against us, regardless of the merits or outcome, could result in substantial costs and divert the time and attention of our management from our business, which could significantly harm our business, profitability and reputation.
We have not declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock since our initial public offering, and we do not intend to in the foreseeable future.
We have not declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock since our initial public offering, and we do not intend to in the foreseeable future. We currently intend to retain our future earnings, if any, to repay indebtedness and to support our general corporate purposes. We are a holding company that does not conduct any business operations of our own. As a result, our ability to pay cash dividends on our common stock, if any, is dependent upon cash dividends and distributions and other transfers from Vantiv Holding. The amounts available to us to pay cash dividends are also restricted by our subsidiaries’ debt agreements, and, to the extent that we require additional funding, the sources of such additional funding may prohibit the payment of a dividend. As a result, appreciation in the price of our Class A common stock, if any, will be the only source of gain on an investment in our Class A common stock.
26
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None
Item 2. Properties
Our principal place of business is our corporate headquarters located at 8500 Governor's Hill Drive, Symmes Township, Cincinnati, Ohio 45249.
In addition to our corporate headquarters, as of December 31, 2015 we leased operational, sales, and administrative facilities in Arizona, California, Colorado, Florida, Illinois, Kentucky, Massachusetts and Texas and owned a facility in Colorado. As of December 31, 2015, we leased data center facilities in Colorado, Kentucky and Michigan. We believe that our facilities are suitable and adequate for our business as presently conducted, however, we periodically review our facility requirements and may acquire new space to meet the needs of our business or consolidate and dispose of facilities that are no longer required.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
From time to time, we are involved in various litigation matters arising in the ordinary course of our business. While it is impossible to ascertain the ultimate resolution or range of financial liability with respect to these contingent matters, management believes none of these matters, either individually or in the aggregate, would have a material adverse effect on us.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable
27
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Price Range of Common Stock
Our Class A common stock has traded on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol "VNTV" since March 22, 2012. Prior to that date, there was no public trading market for our Class A common stock. Our initial public offering of Class A common stock was priced at $17.00 per share on March 21, 2012. There is currently no established public trading market for our Class B common stock. The information presented in the table below represents the high and low sales prices per share of Class A common stock as reported on the NYSE for the periods indicated.
2014 | High | Low | ||||||
First Quarter | $ | 34.42 | $ | 29.05 | ||||
Second Quarter | $ | 33.74 | $ | 28.45 | ||||
Third Quarter | $ | 34.90 | $ | 30.25 | ||||
Fourth Quarter | $ | 35.11 | $ | 29.35 | ||||
2015 | High | Low | ||||||
First Quarter | $ | 39.11 | $ | 32.99 | ||||
Second Quarter | $ | 41.09 | $ | 37.16 | ||||
Third Quarter | $ | 47.02 | $ | 38.20 | ||||
Fourth Quarter | $ | 53.46 | $ | 44.46 | ||||
There were approximately 50 holders of record of our Class A common stock and one holder of our Class B common stock as of January 31, 2016.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The following table sets forth information regarding shares of Class A common stock repurchased by us during the three months ended December 31, 2015:
Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased (1)(2) | Average Price Paid per Share | Total Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs (2) | Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs (in millions) (2) | ||||||||||
October 1, 2015 to October 31, 2015 | 874,436 | $ | 45.11 | 869,651 | $ | 74.6 | ||||||||
November 1, 2015 to November 30, 2015 | 2,463 | $ | 51.11 | — | $ | 74.6 | ||||||||
December 1, 2015 to December 31, 2015 | 125 | $ | 47.25 | — | $ | 74.6 | ||||||||
(1) | Includes shares of Class A common stock surrendered to us to satisfy tax withholding obligations in connection with the vesting of restricted stock awards. |
(2) | On February 12, 2014, our board of directors authorized a program to repurchase up to $300 million of our Class A common stock. During the three months ended December 31, 2015, we repurchased approximately 870,000 shares of Class A common stock for approximately $39.3 million. The repurchases occurred in the open market and pursuant to a trading plan under Rule 10b5-1 of the Exchange Act. The share repurchase program has no expiration date and may be suspended or discontinued at any time without notice. |
28
Dividend Policy
Since our initial public offering, we have not declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock, and we do not intend to in the foreseeable future. We are a holding company that does not conduct any business operations of our own. As a result, our ability to pay cash dividends on our common stock, if any, is dependent upon cash dividends and distributions and other transfers from Vantiv Holding. The amounts available to us to pay cash dividends are subject to the covenants and restrictions in our subsidiaries' loan agreements. Any future determination as to the declaration and payment of dividends, if any, will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend on then existing conditions, including our financial condition, operating results, legal and contractual restrictions, capital requirements, business prospects and other factors our board of directors may deem relevant.
Vantiv Holding paid aggregate tax distributions to or on behalf of its equity holders including Fifth Third Bank of $12.9 million, $22.9 million and $41.2 million, respectively, for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, pursuant to the terms of the Amended and Restated Vantiv Holding Limited Liability Company Agreement. Vantiv Holding will continue to make tax distributions to its equity holders in accordance with the Amended and Restated Vantiv Holding Limited Liability Company Agreement.
Stock Performance Graph
The following graph shows a comparison from March 22, 2012 (the date our Class A common stock commenced trading on the NYSE) through December 31, 2015 of the cumulative total return for our Class A common stock, the S&P 500 Index and the S&P Information Technology Index. Data for the S&P 500 Index and the S&P Information Technology Index assume reinvestment of dividends. Note that historic stock price performance is not necessarily indicative of future stock price performance.
29
COMPARISON OF 45 MONTH CUMULATIVE TOTAL RETURN*
Among Vantiv, Inc., the S&P 500 Index, and the S&P Information Technology Index
*$100 invested on 3/22/12 in stock or 2/29/12 in index, including reinvestment of dividends.
Fiscal year ending December 31.
Fiscal year ending December 31.
This performance graph shall not be deemed "soliciting material" or to be "filed" with the Securities and Exchange Commission for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or otherwise subject to the liabilities under that Section, and shall not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any filing of Vantiv, Inc. under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
The following table sets forth our historical financial and other data for the periods and as of the dates indicated. We derived the statement of income data for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 and our balance sheet data as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 from our audited financial statements for such periods included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The statement of income data for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011 and the balance sheet data as of December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 are derived from our audited financial statements that are not included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The results indicated below are not necessarily indicative of our future performance. You should read this information together with "Item 7 - Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" and "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
30
Year Ended December 31, 2015 | Year Ended December 31, 2014 | Year Ended December 31, 2013 | Year Ended December 31, 2012 | Year Ended December 31, 2011 | |||||||||||||||
(in thousands, except per share data) | |||||||||||||||||||
Statement of income data: | |||||||||||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 3,159,938 | $ | 2,577,203 | $ | 2,108,077 | $ | 1,863,239 | $ | 1,622,421 | |||||||||
Network fees and other costs | 1,478,202 | 1,174,665 | 935,441 | 840,597 | 756,735 | ||||||||||||||
Sales and marketing | 503,949 | 396,353 | 312,044 | 280,644 | 236,917 | ||||||||||||||
Other operating costs | 284,066 | 242,439 | 200,630 | 158,374 | 143,420 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative | 182,369 | 173,986 | 121,707 | 118,231 | 86,870 | ||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 276,942 | 275,069 | 185,453 | 160,538 | 155,326 | ||||||||||||||
Income from operations | 434,410 | 314,691 | 352,802 | 304,855 | 243,153 | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense-net | (105,736 | ) | (79,701 | ) | (40,902 | ) | (54,572 | ) | (111,535 | ) | |||||||||
Non-operating income (expense) | (31,268 | ) | 177 | (20,000 | ) | (92,672 | ) | (14,499 | ) | ||||||||||
Income before applicable income taxes | 297,406 | 235,167 | 291,900 | 157,611 | 117,119 | ||||||||||||||
Income tax expense | 88,177 | 66,177 | 83,760 | 46,853 | 32,309 | ||||||||||||||
Net income | 209,229 | 168,990 | 208,140 | 110,758 | 84,810 | ||||||||||||||
Less: Net income attributable to non-controlling interests | (61,283 | ) | (43,698 | ) | (74,568 | ) | (53,148 | ) | (48,570 | ) | |||||||||
Net income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. | $ | 147,946 | $ | 125,292 | $ | 133,572 | $ | 57,610 | $ | 36,240 | |||||||||
Net income per share attributable to Vantiv, Inc. Class A common stock: | |||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 1.02 | $ | 0.88 | $ | 0.96 | $ | 0.50 | $ | 0.40 | |||||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.95 | $ | 0.75 | $ | 0.87 | $ | 0.47 | $ | 0.40 | |||||||||
Shares used in computing net income per share of Class A common stock: | |||||||||||||||||||
Basic | 145,044,577 | 141,936,933 | 138,836,314 | 116,258,204 | 89,515,617 | ||||||||||||||
Diluted | 200,934,442 | 199,170,813 | 206,027,557 | 122,747,362 | 89,515,617 | ||||||||||||||
As of December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | |||||||||||||||
(in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
Balance sheet data: | |||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 197,096 | $ | 411,568 | $ | 171,427 | $ | 67,058 | $ | 370,549 | |||||||||
Total assets | 6,465,426 | 6,336,083 | 4,189,553 | 3,979,529 | 3,489,710 | ||||||||||||||
Total long-term liabilities | 3,944,981 | 4,072,164 | 2,327,918 | 1,665,826 | 1,793,270 | ||||||||||||||
Non-controlling interests | 272,278 | 397,573 | 408,391 | 626,309 | 632,022 | ||||||||||||||
Total equity | 1,225,066 | 1,300,586 | 1,176,322 | 1,444,235 | 1,255,720 | ||||||||||||||
31
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
This management's discussion and analysis provides a review of the results of operations, financial condition and liquidity and capital resources of Vantiv, Inc. ("Vantiv", "we", "us", "our" or the "company" refer to Vantiv, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries) and outlines the factors that have affected recent results, as well as those factors that may affect future results. Our actual results in the future may differ materially from those anticipated in these forward looking statements as a result of many factors, including those set forth under "Risk Factors," Forward Looking Statements" and elsewhere in this report. The following discussion and analysis should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and related notes included in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" of this report.
Overview
Vantiv is the second largest merchant acquirer and the largest PIN debit acquirer by number of transactions, according to the Nilson Report, and a leading payment processor in the United States differentiated by our integrated technology platform, breadth of distribution and superior cost structure. Our integrated technology platform enables us to efficiently provide a comprehensive suite of services to both merchants and financial institutions of all sizes as well as to innovate, develop and deploy new services, while providing us with significant economies of scale. Our broad and varied distribution provides us with a growing and diverse client base of merchants and financial institutions. Our merchant client base includes approximately 800,000 merchant locations across the United States and is heavily-weighted in non-discretionary everyday spend categories where spending has generally been more resilient during economic downturns. In 2015, we processed approximately 19.0 billion transactions for these merchants. Our financial institution client base includes approximately 1,400 financial institutions, including regional banks, community banks, credit unions and regional PIN debit networks. In 2015, we processed approximately 4.0 billion transactions for these financial institutions. See Item 1 - Business for a more detailed discussion of the business overview.
Executive Overview
Revenue for the year ended December 31, 2015 increased 23% to $3,159.9 million from $2,577.2 million in 2014.
Income from operations for the year ended December 31, 2015 increased 38% to $434.4 million from $314.7 million in 2014.
Net income for the year ended December 31, 2015 increased 24% to $209.2 million from $169.0 million in 2014. Net income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. for the year ended December 31, 2015 increased 18% to $147.9 million from $125.3 million in 2014. See the "Results of Operations" section of this Management's Discussion and Analysis for a discussion of our financial results.
Strategic Capital Deployment
The highly recurring nature of our revenues and significant cost structure advantages provided by our integrated technology platform enable our business to generate high levels of free cash flow. As a result, we maintain a balanced and strategic focus on capital allocation with priorities of investing in our business for growth and returning capital to shareholders. In-line with these priorities, the following events during 2015 signify our efforts to strategically deploy capital to our shareholders:
• | In January 2015, we made an early principal payment of $200 million on our term B loan. See Note 6 - Long-Term Debt in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" for more information about the early principal payment. |
• | In July 2015, we entered into a Repurchase Addendum to Tax Receivable Agreement (the "TRA Addendum") with each of the Mercury Payment Systems, LLC ("Mercury") pre-acquisition owners ("TRA Holders"), which terminated and settled a portion of our obligations under the Mercury TRA, in consideration for a cash payment of $44.8 million that was paid on a pro rata basis to the Mercury TRA Holders. In addition, under the terms of the TRA Addendum, we are granted call options and the Mercury TRA Holders are granted put options to settle the remaining obligations under the Mercury TRA. See Note 7 - Tax Receivable Agreements in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" for more information about the TRA transaction. |
• | In October 2015, we entered into a tax receivable purchase addendum with Fifth Third to terminate a portion of our obligations owed to Fifth Third under the Fifth Third TRA. Under the terms of the tax receivable repurchase |
32
addendum, we paid approximately $49 million to Fifth Third to settle approximately $140 million of obligations under the Fifth Third TRA. See Note 7 - Tax Receivable Agreements in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" for more information about the TRA transaction.
• | In December 2015, we entered into a warrant cancellation agreement (the "Warrant Cancellation Agreement") with Fifth Third Bank to cancel a portion of the warrant that was issued to Fifth Third on June 30, 2009. The Warrant Cancellation Agreement canceled the rights under the warrant to purchase approximately 4.8 million Class C Units of Vantiv Holding for aggregate consideration of $200 million paid by us to Fifth Third. At the time of the Warrant Cancellation Agreement, the 4.8 million Class C Units cancelled would have been equivalent to approximately 3.2 million dilutive shares on a full quarterly basis. See Note 9 - Controlling and Non-controlling Interests in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" for more information about the warrant cancellation. |
• | Throughout 2015 we repurchased approximately 4.4 million shares of our Class A common stock for approximately $200.4 million under various programs approved by our board of directors. See Note 12 - Capital Stock in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" for more information about the share repurchases. |
Recent Acquisition
On June 13, 2014, we acquired Mercury for approximately $1.68 billion in cash and $192.5 million in contingent consideration related to the Mercury TRA entered into with the Mercury TRA Holders as part of the acquisition of Mercury. We funded the acquisition by borrowing an additional $1.7 billion through an amendment and refinancing of our senior secured credit facilities. Mercury is a payment technology and service leader whose solutions are integrated into point-of-sale software applications and brought to market through dealer and developer partners. This acquisition helps to accelerate our growth in the integrated payments channel. The operations of Mercury are included in our Merchant Services segment operating results.
Our Segments, Revenue and Expenses
Segments
We report our results of operations in two segments, Merchant Services and Financial Institution Services. We evaluate segment performance based upon segment profit, which is defined as net revenue, which represents total revenue less network fees and other costs, less sales and marketing expense attributable to that segment. See Item 1 - Business for a more detailed discussion of the business segments.
Revenue
We generate revenue primarily by processing electronic payment transactions. Set forth below is a description of our revenues by segment and factors impacting segment revenues.
Our Merchant Services segment revenues are primarily derived from processing credit and debit card transactions. Merchant Services revenue is primarily comprised of fees charged to businesses, net of interchange fees, for payment processing services, including authorization, capture, clearing, settlement and information reporting of electronic transactions. The fees charged consist of either a percentage of the dollar volume of the transaction or a fixed fee, or both, and are recognized at the time of the transaction. Merchant Services revenue also includes a number of revenue items that are incurred by us and are reimbursable as the costs are passed through to and paid by our clients. These items primarily consist of Visa, MasterCard and other payment network fees. In addition, for sales through referral partners in which we are the primary party to the contract with the merchant, we record the full amount of the fees collected from the merchant as revenue. Associated residual payments made to referral partners are included in sales and marketing expenses. Merchant Services revenue also includes revenue from ancillary services such as fraud management, equipment sales and terminal rent. Revenue in our Merchant Services segment is impacted primarily by transaction volume, average transaction size, the mix of merchant types in our client portfolio, the performance of our merchant clients and the effectiveness of our distribution channels.
Our Financial Institution Services revenues are primarily derived from debit, credit and ATM card transaction processing, ATM driving and support, and PIN debit processing services. Financial Institution Services revenue associated with processing transactions includes per transaction and account related fees, card production fees and fees generated from our Jeanie network. Financial Institution Services revenue is impacted by the number of financial institutions using our services as well as their transaction volume. The number of financial institutions in the United States has declined as a result of prevailing economic conditions and consolidation, as well as other market and regulatory pressures. These factors have contributed to industry-wide pricing compression of the fees that financial institutions are willing to pay for payment processing. Since 2011,
33
pricing compression in the Financial Institution Services segment has represented on average 3% or less of segment net revenue on an annual basis.
Network Fees and Other Costs
Network fees and other costs primarily consist of pass through expenses incurred by us in connection with providing processing services to our clients, including Visa and MasterCard network association fees, payment network fees, third party processing expenses, telecommunication charges, postage and card production costs.
Net Revenue
Net revenue is revenue, less network fees and other costs and reflects revenue generated from the services we provide to our clients. Management uses net revenue to assess our operating performance. We believe that net revenue, when reviewed together with revenue, is meaningful to our investors in order to understand our performance.
Expenses
Set forth below is a brief description of the components of our expenses, aside from the network fees and other costs discussed above:
• | Sales and marketing expense primarily consists of salaries and benefits paid to sales personnel, sales management and other sales and marketing personnel, residual payments made to ISOs and referral partners and advertising and promotional costs. |
• | Other operating costs primarily consist of salaries and benefits paid to operational and IT personnel, costs associated with operating our technology platform and data centers, information technology costs for processing transactions, product development costs, software consulting fees and maintenance costs. |
• | General and administrative expenses primarily consist of salaries and benefits paid to executive management and administrative employees, including finance, human resources, product development, legal and risk management, share-based compensation costs, equipment and occupancy costs and consulting costs. |
• | Depreciation and amortization expense consists of our depreciation expense related to investments in property, equipment and software as well as our amortization of intangible assets, principally customer relationships acquired in connection with the acquisition of a majority interest in Vantiv Holding in June 2009 and our subsequent acquisitions. |
• | Interest expense—net consists primarily of interest on borrowings under our senior secured credit facilities less interest income earned on our cash and cash equivalents. |
• | Income tax expense represents federal, state and local taxes based on income in multiple jurisdictions. |
• | Non-operating income (expense) during the year ended December 31, 2015 primarily relates to the change in the fair value of the Mercury TRA entered into as part of the acquisition of Mercury. The 2014 amount primarily relates to a benefit recorded as a result of a reduction in certain TRA liabilities, partially offset by the refinancing of the Company’s senior secured credit facilities in June 2014 and the change in fair value of the Mercury TRA. The 2013 amount relates to the refinancing of the Company's senior secured credit facilities in May 2013. |
Non-Controlling Interest
As a result of the non-controlling ownership interests in Vantiv Holding held by Fifth Third, our results of operations include net income attributable to non-controlling interests. Future sales or redemptions of ownership interests in Vantiv Holding by Fifth Third will continue to reduce the amount recorded as non-controlling interest and increase net earnings attributable to our Class A stockholders. In addition, net income attributable to non-controlling interests includes the non-controlling interest related to a joint venture with a bank partner. Net income attributable to non-controlling interests for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 was $61.3 million, $43.7 million and $74.6 million, respectively. See Note 9 - Controlling and Non-controlling Interests in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" for more information.
34
Factors and Trends Impacting Our Business and Results of Operations
We expect a number of factors will impact our business, results of operations and financial condition. In general, our revenue is impacted by the number and dollar volume of card based transactions which in turn are impacted by general economic conditions, consumer spending and the emergence of new technologies and payment types, such as ecommerce, mobile payments, and prepaid cards. In our Merchant Services segment, our net revenues are impacted by the mix of the size of merchants that we provide services to as well as the mix of transaction volume by merchant category. In our Financial Institution Services segment, our net revenues are also impacted by the mix of the size of financial institutions to which we provide services as well as consolidation and market and industry pressures, which have contributed and are expected to continue to contribute to pricing compression of payment processing fees in this segment. We also expect our results of operations to be impacted by the factors discussed below.
Pro Forma Adjusted Net Income
We use pro forma adjusted net income for financial and operational decision making as a means to evaluate period-to-period comparisons of our performance and results of operations. Pro forma adjusted net income is also incorporated into performance metrics underlying certain share-based payments issued under the 2012 Vantiv, Inc. Equity Incentive Plan and our annual incentive plan. We believe pro forma adjusted net income provides useful information about our performance and operating results, enhances the overall understanding of past financial performance and future prospects and allows for greater transparency with respect to key metrics used by management in its financial and operational decision making.
In calculating pro forma adjusted net income, we make certain non-GAAP adjustments, as well as pro forma adjustments, to adjust our GAAP operating results for the items discussed below. This non-GAAP measure should be considered together with GAAP operating results.
Non-GAAP Adjustments
Transition, Acquisition and Integration Costs
In connection with our acquisitions, we incurred costs associated with the acquisitions and related integration activities, consisting primarily of consulting fees for advisory, conversion and integration services and related personnel costs. Additionally, our expenses include costs associated with a one-time signing bonus issued to certain employees that transferred to us from Fifth Third Bank in connection with our separation from Fifth Third Bank in June 2009. This signing bonus contained a five-year vesting period beginning on the date of the separation. Also included in these expenses are costs related to employee termination benefits and other transition activities. These transition, acquisition and integration costs are included in other operating costs and general and administrative expenses.
Share-Based Compensation
We have granted share-based awards to certain employees and members of our board of directors and intend to continue to grant additional share-based awards in the future. Share-based compensation is included in general and administrative expense. See Note 13 - Share-Based Compensation Plans in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
Intangible Amortization Expense
These expenses represent amortization of intangible assets acquired through business combinations and customer portfolio and related asset acquisitions. For the year ended December 31, 2014, intangible amortization expense also included a $34.3 million charge related to phasing out a trade name.
Non-operating Income (Expense)
Non-operating expense was $31.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, which primarily related to the change in fair value of the Mercury TRA. Non-operating income was $0.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, which consisted of a benefit recorded as a result of a reduction in certain TRA liabilities of $41.3 million, partially offset by $26.5 million in expenses related to the refinancing of our senior secured credit facilities in June 2014 and expense of $14.6 million related to the change in fair value of the Mercury TRA.
35
Pro Forma Adjustments
Income Tax Expense Adjustments
Our effective tax rate reported in our results of operations reflects the impact of our non-controlling interest not being taxed at the statutory corporate tax rate. For purposes of calculating pro forma adjusted net income, income tax expense is adjusted to reflect an effective tax rate assuming conversion of Fifth Third's non-controlling interests into shares of Class A common stock, including the income tax effect of the non-GAAP adjustments described above. The adjusted effective tax rate was 36.0% for the year ended December 31, 2015 and 36.5% for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Tax Adjustments
In addition to the adjustment described above, income tax expense is also adjusted for the cash tax benefits resulting from certain tax attributes, primarily the amortization of tax intangible assets resulting from or acquired with our acquisitions, the tax basis step up associated with our separation from Fifth Third and the purchase or exchange of Class B units of Vantiv Holding, net of payment obligations under TRAs established at the time of our IPO and in connection with our acquisition of Mercury. Additionally, as a result of the Mercury TRA Addendum and the Fifth Third TRA Addendum entered into during 2015 as discussed in Note 7 - Tax Receivable Agreements in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" we reflect the retention of the cash tax benefits resulting from the realization of the tax attributes underlying each respective TRA in pro forma adjusted net income. The estimate of the cash tax benefits is based on the consistent and highly predictable realization of the underlying tax attributes.
The following table provides a schedule of the tax adjustments discussed above which are reflected in the pro forma adjusted net income table below:
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
2015 | 2014 | |||||||
Fifth Third Tax Benefit (a) | $ | 41,701 | $ | 37,989 | ||||
Mercury Tax Benefit (b) | 25,230 | 23,796 | ||||||
Total Tax Benefits | 66,931 | 61,785 | ||||||
Less: TRA payments (c) | (56,891 | ) | (52,517 | ) | ||||
TRA Tax Benefits (d) | 10,040 | 9,268 | ||||||
Acquired Tax Benefits (e) | 48,146 | 37,194 | ||||||
Pro Forma Tax Benefits (f) | $ | 58,186 | $ | 46,462 | ||||
(a) Represents the cash tax benefits which are shared with Fifth Third Bank (85%) pursuant to a TRA.
(b) Represents the cash tax benefits shared with Mercury former shareholders (85%) pursuant to a TRA.
(c) Represents the amount of the TRA payment to be made to Fifth Third Bank and Mercury shareholders (85% payment).
(d) Represents the 15% benefit that we retain for the shared tax benefits related to the TRAs.
(e) Represents the tax benefits wholly owned by us, acquired through acquisition or termination of TRAs in which we retain 100% of the benefit.
(f) Represents the net cash tax benefit retained by us from the use of the tax attributes, as reflected in the Pro forma Tax Adjustments.
36
The table below provides a reconciliation of GAAP income before applicable income taxes to pro forma adjusted net income for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
(in thousands) | |||||||
Income before applicable income taxes | $ | 297,406 | $ | 235,167 | |||
Non-GAAP Adjustments: | |||||||
Transition, acquisition and integration costs | 62,583 | 38,482 | |||||
Share-based compensation | 30,492 | 42,171 | |||||
Intangible amortization | 191,441 | 198,563 | |||||
Non-operating (income) expense | 31,268 | (177 | ) | ||||
Non-GAAP Adjusted Income Before Applicable Taxes | 613,190 | 514,206 | |||||
Pro Forma Adjustments: | |||||||
Income tax expense adjustment | (220,748 | ) | (187,685 | ) | |||
Tax adjustments | 58,186 | 46,462 | |||||
Less: JV non-controlling interest | (1,501 | ) | (622 | ) | |||
Pro Forma Adjusted Net Income | $ | 449,127 | $ | 372,361 | |||
Results of Operations
The following tables set forth our statements of income in dollars and as a percentage of net revenue for the periods presented.
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 3,159,938 | $ | 2,577,203 | $ | 582,735 | 23 | % | ||||||
Network fees and other costs | 1,478,202 | 1,174,665 | 303,537 | 26 | ||||||||||
Net revenue | 1,681,736 | 1,402,538 | 279,198 | 20 | ||||||||||
Sales and marketing | 503,949 | 396,353 | 107,596 | 27 | ||||||||||
Other operating costs | 284,066 | 242,439 | 41,627 | 17 | ||||||||||
General and administrative | 182,369 | 173,986 | 8,383 | 5 | ||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 276,942 | 275,069 | 1,873 | 1 | ||||||||||
Income from operations | $ | 434,410 | $ | 314,691 | $ | 119,719 | 38 | % | ||||||
Non-financial data: | ||||||||||||||
Transactions (in millions) | 22,991 | 20,077 | 15 | % | ||||||||||
As a Percentage of Net Revenue | Year Ended December 31, | ||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||
Net revenue | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | |
Sales and marketing | 30.0 | 28.3 | |||
Other operating costs | 16.9 | 17.3 | |||
General and administrative | 10.8 | 12.4 | |||
Depreciation and amortization | 16.5 | 19.6 | |||
Income from operations | 25.8 | % | 22.4 | % | |
37
Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2015 Compared to Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2014
Revenue
Revenue increased 23% to $3,159.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $2,577.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase was due to transaction growth of 15%, primarily in the Merchant Services segment which includes the impact of the Mercury acquisition and expansion in our merchant bank and integrated payments channels, which contributed to higher net revenue per transaction.
Network Fees and Other Costs
Network fees and other costs increased 26% to $1,478.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $1,174.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase was due primarily to transaction growth of 15%, including the impact of the Mercury acquisition, and to a lesser extent an increase in third party processing costs in connection with the Mercury acquisition.
Net Revenue
Net revenue, which is revenue less network fees and other costs, increased 20% to $1,681.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $1,402.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 due to the factors discussed above.
Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing expense increased 27% to $503.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $396.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase was primarily attributable to the Mercury acquisition, higher sales and marketing personnel and related costs and higher residual payments to referral partners in connection with increased revenue.
Other Operating Costs
Other operating costs increased 17% to $284.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $242.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase was primarily attributable to the Mercury acquisition and an increase in information technology spend. Also contributing to the increase was a $11.1 million increase in transition, acquisition and integration costs due to our recent acquisitions.
General and Administrative
General and administrative expenses increased 5% to $182.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $174.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase was primarily attributable to the Mercury acquisition, continued investment in our infrastructure in support of growth initiatives, and an increase in acquisition and integration costs of $13.0 million, partially offset by a decrease in share-based compensation of $11.7 million. In addition, synergies and operating leverage has decelerated the increase of general and administrative expenses as a percentage of net revenue.
Depreciation and Amortization
Depreciation expense associated with our property, equipment and software increased 9% to $76.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $70.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase during the year reflects depreciation expense associated with increased capital expenditures largely related to our continued investment in information technology infrastructure in support of growth initiatives, as well as assets acquired in connection with the Mercury acquisition.
Amortization expense associated with intangible assets, which consist primarily of customer relationship intangible assets, decreased 2% to $200.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $205.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. A $34.3 million charge related to phasing out a trade name during the year ended December 31, 2014 more than offset an increase in amortization expense associated with intangible assets acquired in connection with the Mercury acquisition.
38
Income from Operations
Income from operations increased 38% to $434.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $314.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Interest Expense—Net
Interest expense—net increased to $105.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $79.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase in interest expense—net is primarily attributable to our June 2014 debt refinancing, which resulted in an increase in the amount of outstanding debt, as well as an increase in the applicable interest rates. The increase in outstanding debt was used to fund the acquisition of Mercury.
Non-Operating Income (Expense)
Non-operating expenses were $31.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, primarily relating to the change in fair value of the Mercury TRA entered into as part of the acquisition of Mercury. Non-operating income was $0.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, which consisted of a benefit recorded as a result of a reduction in certain TRA liabilities of $41.3 million, partially offset by $26.5 million in expenses related to the refinancing of our senior secured credit facilities in June 2014 and expense of $14.6 million related to the change in fair value of the Mercury TRA.
Income Tax Expense
Income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2015 was $88.2 million compared to $66.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, reflecting effective rates of 29.6% and 28.1%, respectively. Our effective rate reflects the impact of our non-controlling interest not being taxed at the statutory corporate tax rates. The increase in our effective tax rate reflects the 2014 favorable impact of cumulative deductions related to Internal Revenue Code Section 199, which allows for the deduction of a portion of the income related to domestically produced computer software and the impact to deferred taxes due to a change in state tax rates. As our non-controlling interest declines to the point Vantiv Holding is a wholly-owned subsidiary, we expect our effective rate to increase to approximately 36.0%.
Segment Results
The following tables provide a summary of the components of segment profit for our two segments for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014.
Merchant Services
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 2,656,906 | $ | 2,100,367 | $ | 556,539 | 26 | % | ||||||
Network fees and other costs | 1,321,312 | 1,033,801 | 287,511 | 28 | ||||||||||
Net revenue | 1,335,594 | 1,066,566 | 269,028 | 25 | ||||||||||
Sales and marketing | 478,736 | 367,998 | 110,738 | 30 | ||||||||||
Segment profit | $ | 856,858 | $ | 698,568 | $ | 158,290 | 23 | % | ||||||
Non-financial data: | ||||||||||||||
Transactions (in millions) | 18,959 | 16,262 | 17 | % | ||||||||||
Net Revenue
Net revenue in this segment increased 25% to $1,335.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $1,066.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase during the year ended December 31, 2015 was due primarily to transaction growth of 17%, including the impact of the Mercury acquisition and expansion in our merchant bank and integrated payments channels, which contributed to higher net revenue per transaction. On a pro forma organic basis, net revenue would have increased 14% for the year ended December 31, 2015 when compared to the year ended December 31, 2014 if we had owned Mercury throughout both years.
39
Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing expense increased 30% to $478.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $368.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase was primarily attributable to the Mercury acquisition, higher sales and marketing personnel and related costs and higher residual payments to referral partners in connection with increased revenue.
Financial Institution Services
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 503,032 | $ | 476,836 | $ | 26,196 | 5 | % | ||||||
Network fees and other costs | 156,890 | 140,864 | 16,026 | 11 | ||||||||||
Net revenue | 346,142 | 335,972 | 10,170 | 3 | ||||||||||
Sales and marketing | 25,213 | 28,355 | (3,142 | ) | (11 | ) | ||||||||
Segment profit | $ | 320,929 | $ | 307,617 | $ | 13,312 | 4 | % | ||||||
Non-financial data: | ||||||||||||||
Transactions (in millions) | 4,032 | 3,815 | 6 | % | ||||||||||
Net Revenue
Net revenue in this segment increased 3% to $346.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $336.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase during the year ended December 31, 2015 was due primarily to an increase in transactions and value-added services revenue. This increase was partially offset by a decrease in net revenue per transaction, which was driven by pricing compression and shift in the mix of our client portfolio, resulting in a lower rate per transaction.
Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing expense decreased $3.1 million to $25.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 from $28.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2014 Compared to Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2013
The following tables set forth our statements of income in dollars and as a percentage of net revenue for the periods presented.
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 2,577,203 | $ | 2,108,077 | $ | 469,126 | 22 | % | ||||||
Network fees and other costs | 1,174,665 | 935,441 | 239,224 | 26 | ||||||||||
Net revenue | 1,402,538 | 1,172,636 | 229,902 | 20 | ||||||||||
Sales and marketing | 396,353 | 312,044 | 84,309 | 27 | ||||||||||
Other operating costs | 242,439 | 200,630 | 41,809 | 21 | ||||||||||
General and administrative | 173,986 | 121,707 | 52,279 | 43 | ||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 275,069 | 185,453 | 89,616 | 48 | ||||||||||
Income from operations | $ | 314,691 | $ | 352,802 | $ | (38,111 | ) | (11 | )% | |||||
Non-financial data: | ||||||||||||||
Transactions (in millions) | 20,077 | 16,946 | 18 | % | ||||||||||
40
As a Percentage of Net Revenue | Year Ended December 31, | ||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||
Net revenue | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | |
Sales and marketing | 28.3 | 26.6 | |||
Other operating costs | 17.3 | 17.1 | |||
General and administrative | 12.4 | 10.4 | |||
Depreciation and amortization | 19.6 | 15.8 | |||
Income from operations | 22.4 | % | 30.1 | % | |
Revenue
Revenue increased 22% to $2,577.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $2,108.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase was due primarily to transaction growth of 18%, including the impact of our recent acquisitions, which expanded our integrated payments and ecommerce channels and have contributed to higher revenue per transaction.
Network Fees and Other Costs
Network fees and other costs increased 26% to $1,174.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $935.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase was due primarily to transaction growth of 18%, including the impact of our recent acquisitions, and to a lesser extent an increase in third party processing costs.
Net Revenue
Net revenue, which is revenue less network fees and other costs, increased 20% to $1,402.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $1,172.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2013 due to the factors discussed above.
Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing expense increased 27% to $396.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $312.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase was attributable to our recent acquisitions, higher sales and marketing personnel and related costs and higher residual payments to referral partners as a result of increased revenue.
Other Operating Costs
Other operating costs increased 21% to $242.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $200.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase was primarily attributable to our recent acquisitions and an increase in information technology infrastructure in support of growth initiatives. Also contributing to the increase was a $6.9 million increase in transition, acquisition and integration costs.
General and Administrative
General and administrative expenses increased 43% to $174.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $121.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase was primarily attributable to our recent acquisitions, continued investment in our infrastructure in support of growth initiatives, and increases in acquisition and integration costs and share-based compensation of $16.5 million and $12.4 million, respectively.
Depreciation and Amortization
Depreciation expense associated with our property, equipment and software increased 23% to $70.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $56.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase during the year reflects depreciation expense associated with increased capital expenditures largely related to our continued investment in information technology infrastructure in support of growth initiatives, as well as assets acquired in connection with our recent acquisitions.
41
Amortization expense associated with intangible assets, which consist primarily of customer relationship intangible assets, increased 59% to $205.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $128.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase during the year is due to a $34.3 million charge related to phasing out a trade name and amortization expense related to intangible assets acquired in connection with our recent acquisitions, primarily consisting of amortization of customer relationship intangible assets.
Income from Operations
Income from operations decreased 11% to $314.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $352.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2013.
Interest Expense-Net
Interest expense—net increased to $79.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $40.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase in interest expense—net is primarily attributable to our June 2014 debt refinancing, which resulted in an increase in the amount of outstanding debt of approximately $1.7 billion, as well as an increase in the applicable interest rates. The increase in outstanding debt was used to fund the acquisition of Mercury.
Non-Operating Expenses
Non-operating income (expense) was $0.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, which consisted of a benefit recorded as a result of a reduction in certain TRA liabilities of $41.3 million, partially offset by $26.5 million in expenses related to the refinancing of our senior secured credit facilities in June 2014 and expense of $14.6 million related to the change in fair value of the Mercury TRA. Non-operating expenses were $20.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2013, which consisted of charges related to the refinancing of our senior secured credit facilities in May 2013.
Income Tax Expense
Income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2014 was $66.2 million compared to $83.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2013, reflecting effective rates of 28.1% and 28.7%, respectively. Our effective rate reflects the impact of our non-controlling interest not being taxed at the statutory corporate tax rates. The decrease in our effective tax rate reflects the favorable impact of deductions related to Internal Revenue Code Section 199, which allows for the deduction of a portion of the income related to domestically produced computer software. This was partially offset by a decrease in non-controlling interests, which have been reduced over the last two years in connection with secondary offerings in May and August 2013 and June 2014.
Segment Results
The following tables provide a summary of the components of segment profit for our two segments for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
Merchant Services
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 2,100,367 | $ | 1,639,157 | $ | 461,210 | 28 | % | ||||||
Network fees and other costs | 1,033,801 | 801,463 | 232,338 | 29 | ||||||||||
Net revenue | 1,066,566 | 837,694 | 228,872 | 27 | ||||||||||
Sales and marketing | 367,998 | 286,200 | 81,798 | 29 | ||||||||||
Segment profit | $ | 698,568 | $ | 551,494 | $ | 147,074 | 27 | % | ||||||
Non-financial data: | ||||||||||||||
Transactions (in millions) | 16,262 | 13,333 | 22 | % | ||||||||||
42
Net Revenue
Net revenue in this segment increased 27% to $1,066.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $837.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase during the year ended December 31, 2014 was due primarily to transaction growth of 22%, including the impact of our recent acquisitions, which expanded our integrated payments and ecommerce channels and contributed to higher net revenue per transaction.
Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing expense increased 29% to $368.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $286.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase was primarily attributable to our recent acquisitions, higher sales and marketing personnel and related costs and higher residual payments to referral partners as a result of increased revenue.
Financial Institution Services
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 476,836 | $ | 468,920 | $ | 7,916 | 2 | % | ||||||
Network fees and other costs | 140,864 | 133,978 | 6,886 | 5 | ||||||||||
Net revenue | 335,972 | 334,942 | 1,030 | — | ||||||||||
Sales and marketing | 28,355 | 25,844 | 2,511 | 10 | ||||||||||
Segment profit | $ | 307,617 | $ | 309,098 | $ | (1,481 | ) | — | % | |||||
Non-financial data: | ||||||||||||||
Transactions (in millions) | 3,815 | 3,613 | 6 | % | ||||||||||
Net Revenue
Net revenue in this segment increased slightly to $336.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $334.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The slight increase during the year ended December 31, 2014 was due primarily to an increase in transactions and value-added services revenue. This increase was partially offset by a decrease in net revenue per transaction, which was driven by continued pricing compression and a continuing shift in the mix of our client portfolio, resulting in a lower rate per transaction.
Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing expense increased 10% to $28.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $25.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2013, due primarily to personnel related costs associated with our product initiatives.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Our liquidity is funded primarily through cash provided by operations, debt and a line of credit, which is generally sufficient to fund our operations, planned capital expenditures, tax distributions made to our non-controlling interest holders, required payments under TRAs, debt service and acquisitions. Payments under the TRAs are determined based on realized cash savings resulting from the underlying tax attributes. Excluding the call and put structure in the Mercury TRA Addendum discussed in Note 7 - Tax Receivable Agreements in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," a period of declining profitability would result in a corresponding reduction in our TRA payments, thus resulting in the TRA having a minimal effect on our liquidity and capital resources. As of December 31, 2015, our principal sources of liquidity consisted of $197.1 million of cash and cash equivalents and $425.0 million of availability under the revolving portion of our senior secured credit facilities. Our total indebtedness, including capital leases, was $3.1 billion as of December 31, 2015.
During 2015, we continued to repurchase shares of our Class A common stock under various programs approved by our board of directors. We repurchased approximately 4.4 million shares for approximately $200.4 million under these programs during the year ended December 31, 2015. We have approximately $75 million of share repurchase authority remaining as of December 31, 2015 under a program authorized by the board of directors on February 12, 2014 to repurchase up to an additional $300 million of our Class A common stock.
43
Purchases under the repurchase program are allowed from time to time in the open market, in privately negotiated transactions, or otherwise. The manner, timing, and amount of any purchases are determined by management based on an evaluation of market conditions, stock price, and other factors. The share repurchase program has no expiration date and we may discontinue purchases at any time that management determines additional purchases are not warranted.
In connection with our IPO, we entered into the Exchange Agreement with Fifth Third, under which Fifth Third has the right, from time to time, to exchange their units in Vantiv Holding for shares of our Class A common stock or, at our option, cash. If we choose to satisfy the exchange in cash, we anticipate that we will fund such exchange through cash from operations, funds available under the revolving portion of our senior secured credit facilities, equity financings or a combination thereof.
We do not intend to pay cash dividends on our Class A common stock in the foreseeable future. Vantiv, Inc. is a holding company that does not conduct any business operations of its own. As a result, Vantiv, Inc.’s ability to pay cash dividends on its common stock, if any, is dependent upon cash dividends and distributions and other transfers from Vantiv Holding. The amounts available to Vantiv, Inc. to pay cash dividends are subject to the covenants and distribution restrictions in its subsidiaries’ loan agreements.
In addition to principal needs for liquidity discussed above, our strategy includes investing in and leveraging our integrated business model and technology platform, broadening and deepening our distribution channels, entry into new geographic markets and development of additional payment processing services. Our near-term priorities for capital allocation include debt reduction, share repurchases and investing in our operations to support organic growth. Long-term priorities remain unchanged and include investing for growth through strategic acquisitions and returning excess capital to shareholders.
We anticipate that to the extent that we require additional liquidity, it will be funded through the incurrence of other indebtedness, equity financings or a combination thereof. We cannot assure you that we will be able to obtain this additional liquidity on reasonable terms, or at all. Additionally, our liquidity and our ability to meet our obligations and fund our capital requirements are also dependent on our future financial performance, which is subject to general economic, financial and other factors that are beyond our control. Accordingly, we cannot assure you that our business will generate sufficient cash flow from operations or that future borrowings will be available under our credit facilities or otherwise to meet our liquidity needs. If we decide to pursue one or more significant acquisitions, we may incur additional debt or sell additional equity to finance such acquisitions.
Cash Flows
The following table presents a summary of cash flows from operating, investing and financing activities for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 (in thousands).
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 757,878 | $ | 592,905 | $ | 480,622 | |||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (126,727 | ) | (1,798,956 | ) | (228,298 | ) | |||||
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (845,623 | ) | 1,446,192 | (147,955 | ) | ||||||
Cash Flow from Operating Activities
Net cash provided by operating activities was $757.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 as compared to $592.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase is due primarily to an increase in net income, changes in working capital including the favorable impact of year-over-year changes in accounts receivable, prepaid and other assets and other liabilities, partially offset by customer incentives.
Net cash provided by operating activities was $592.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 as compared to $480.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase is due primarily to changes in working capital, principally due to the favorable impact of year-over-year changes in net settlement assets and obligations and accounts payable and accrued expenses. Settlement assets and obligations can fluctuate due to seasonality as well as the day of the month end.
44
Cash Flow from Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities was $126.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 as compared to $1,799.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The decrease was primarily due to the acquisition of Mercury in the prior year.
Net cash used in investing activities was $1,799.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 as compared to $228.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase was primarily due to the acquisition of Mercury as well as an increase in capital expenditures and the acquisition of customer portfolios and related assets.
Cash Flow from Financing Activities
Net cash used in financing activities was $845.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 as compared to net cash provided by financing activities of $1,446.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. Cash used in financing activities during the year ended December 31, 2015 consisted primarily of the repayment of debt and capital leases, including the early principal payment of $200 million on the term B loan on January 6, 2015, the Warrant Cancellation Agreement with Fifth Third, repurchases of Class A common stock, payments made under the tax receivable agreements and addendums and distributions to non-controlling interests.
Net cash provided by financing activities was $1,446.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 as compared to net cash used in financing activities of $148.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. Cash provided by financing activities during the year ended December 31, 2014 consisted primarily of proceeds from the June 2014 refinancing, partially offset by the repayment of existing debt and related debt issuance costs, repurchases of Class A common stock and distributions to non-controlling interests. Cash used in financing activities during the year ended December 31, 2013 primarily reflects the net impact of the May 2013 debt refinancing, share repurchases and the settlement of certain TRA obligations as discussed above. Cash used in financing activities during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 also reflects $22.9 million and $41.2 million, respectively, of distributions made to our non-controlling interest holders.
Credit Facilities
At December 31, 2015, we have $1.9 billion and $1.2 billion outstanding under our term A and term B loans, respectively, and there were no outstanding borrowings on our revolving credit facility. See additional discussion in Note 6 - Long-Term Debt in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
On June 13, 2014, Vantiv, LLC completed a debt refinancing by entering into an amended and restated loan agreement ("Amended Loan Agreement"). The Amended Loan Agreement requires us to maintain a leverage ratio no greater than established thresholds (based upon the ratio of total funded debt to consolidated EBITDA, as defined in the loan agreement) and a minimum interest coverage ratio (based upon the ratio of consolidated EBITDA to interest expense), which are tested quarterly based on the last four fiscal quarters. The required financial ratios become more restrictive over time, with the specific ratios required by period set forth in the below table.
Period | Leverage Ratio (must not exceed) | Interest Coverage Ratio (must exceed) | ||
September 30, 2014 to March 31, 2015 | 6.50 to 1.00 | 4.00 to 1.00 | ||
June 30, 2015 to September 30, 2016 | 6.25 to 1.00 | 4.00 to 1.00 | ||
December 31, 2016 to September 30, 2017 | 5.50 to 1.00 | 4.00 to 1.00 | ||
December 31, 2017 to September 30, 2018 | 4.75 to 1.00 | 4.00 to 1.00 | ||
December 31, 2018 and thereafter | 4.25 to 1.00 | 4.00 to 1.00 | ||
As of December 31, 2015, we were in compliance with these covenants with a leverage ratio of 3.87 to 1.00 and an interest coverage ratio of 8.26 to 1.00.
Interest Rate Swaps
As of December 31, 2015, we have a total of 14 outstanding interest rate swaps that were designated as cash flow hedges of interest rate risk. See Note 8 - Derivatives in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" for more information about the interest rate swaps.
45
Tax Receivable Agreements
We entered into several TRAs in which we agree to make payments to various parties of 85% of the federal, state, local and foreign income tax benefits realized by us as a result of certain tax deductions. Payments under the TRAs will be based on our tax reporting positions and are only required to the extent we realize cash savings as a result of the underlying tax attributes. The cash savings realized by us are computed by comparing our actual income tax liability to the amount of such taxes we would have been required to pay had there been no deductions related to the tax attributes discussed below. We will retain the benefit of the remaining 15% of the cash savings associated with the TRAs. We currently have the following TRAs:
• | A TRA with pre-IPO investors for its use of NOLs and other tax attributes existing at the IPO date, all of which is currently held by Fifth Third. |
• | A TRA with Fifth Third in which we realize tax deductions as a result of the increases in tax basis from the purchase of Vantiv Holding units or from the exchange of Vantiv Holding units for cash or shares of Class A common stock, as well as the tax benefits attributable to payments made under such TRA. |
• | A TRA with Mercury shareholders as part of the acquisition of Mercury as a result of the increase in tax basis of the assets of Mercury resulting from the acquisition and the use of the net operating losses and other tax attributes of Mercury that were acquired as part of the acquisition. |
All TRA obligations are recorded based on the full and undiscounted amount of the expected future payments, except for the Mercury TRA which represents contingent consideration relating to an acquired business, and is recorded at fair value for financial reporting purposes. The following table reflects TRA activity and balances for the year ended December 31, 2015 (in thousands):
Balance as of December 31, 2014 | 2015 TRA Payment | 2015 TRA Settlements | 2015 Secondary Offering | Purchase Accounting Adjustment | Change in Value | Balance as of December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
TRA with Fifth Third Bank | $ | 620,062 | $ | (22,805 | ) | $ | (140,024 | ) | $ | 376,597 | $ | — | $ | (769 | ) | $ | 833,061 | ||||||||||
Mercury TRA | 152,420 | — | (44,800 | ) | — | 54,647 | 28,940 | 191,207 | |||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 772,482 | $ | (22,805 | ) | $ | (184,824 | ) | $ | 376,597 | $ | 54,647 | $ | 28,171 | $ | 1,024,268 | |||||||||||
During 2015, we terminated a portion of our obligations under the Mercury TRA. In addition to the Mercury TRA settlement presented in the table above, the Mercury TRA Addendum contains the following provisions to acquire a significant portion of the remaining Mercury TRA:
• | Beginning December 1st of each of 2015, 2016, 2017, and 2018, and ending June 30th of 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019, respectively, we are granted call options (collectively, the "Call Options") pursuant to which certain of our additional obligations under the Mercury TRA would be terminated in consideration for cash payments of $41.4 million, $38.1 million, $38.0 million, and $43.0 million, respectively. |
• | In the unlikely event we do not exercise the relevant Call Option, the Mercury TRA Holders are granted put options beginning July 10th and ending July 25th of each of 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019, respectively (collectively, the "Put Options"), pursuant to which certain of our additional obligations would be terminated in consideration for cash payments with similar amounts to the Call Options. |
The timing and/or amount of aggregate payments due under the TRAs may vary based on a number of factors, including the amount and timing of the taxable income we generate in the future and the tax rate then applicable, the use of loss carryovers and amortizable basis. Payments under the TRAs, if necessary, are required to be made no later than January 5th of the second year immediately following the taxable year in which the obligation occurred. We made a payment under the TRA obligations of approximately $53.5 million in January 2016. The January 2016 payment is recorded as current portion of tax receivable agreement obligations on the accompanying consolidated statement of financial position. The term of the TRAs will continue until all such tax benefits have been utilized or expired, unless we exercise our right to terminate the TRA for an amount based on the agreed payments remaining to be made under the agreement.
If Fifth Third Bank had exchanged its remaining Class B units of Vantiv Holding, had exercised the remaining warrant and exchanged the Class C units of Vantiv Holding, all for shares of Class A common stock on December 31, 2015, we would have recorded an additional full and undiscounted TRA obligation of approximately $1.1 billion. This estimate is subject to
46
material change based on changes in Fifth Third Bank’s tax basis in the partnership interest, changes in tax rates, or significant changes in our stock price.
See additional discussion in Note 7 - Tax Receivable Agreements in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
Contractual Obligations
The following table summarizes our contractual obligations and commitments as of December 31, 2015:
Payments Due By Period | |||||||||||||||||||
Total | Less than 1 year | 1 - 3 Years | 3 - 5 Years | More than 5 Years | |||||||||||||||
(in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
Operating leases | $ | 44,175 | $ | 9,539 | $ | 12,472 | $ | 8,814 | $ | 13,350 | |||||||||
Capital leases | 30,876 | 8,454 | 17,938 | 4,484 | — | ||||||||||||||
Borrowings(1) | 3,471,113 | 205,893 | 503,766 | 1,621,377 | 1,140,077 | ||||||||||||||
Purchase commitments: | |||||||||||||||||||
Technology and telecommunications(2) | 59,826 | 32,742 | 21,772 | 5,312 | — | ||||||||||||||
Processing Services(3) | 3,945 | 1,945 | 1,760 | 240 | — | ||||||||||||||
Other | 23,758 | 12,920 | 10,750 | 88 | — | ||||||||||||||
Obligations under TRAs(4) | 1,076,450 | 94,855 | 191,816 | 140,867 | 648,912 | ||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 4,710,143 | $ | 366,348 | $ | 760,274 | $ | 1,781,182 | $ | 1,802,339 | |||||||||
(1) | Represents principal and variable interest payments due under our senior secured credit facilities and our loan agreement for our corporate headquarters facility as of December 31, 2015. Interest payments are as follows: $89.4 million for less than 1 year; $168.2 million for 1 - 3 years; $106.9 million for 3 - 5 years and $21.2 million for more than 5 years. Variable interest payments were calculated using interest rates as of December 31, 2015. |
(2) | Includes obligations related to software licenses, software maintenance support and telecommunication and network services. |
(3) | We have agreements with third-party processors to provide gateway authorization and other processing services. These agreements require us to submit a minimum number of transactions for processing. If we submit a number of transactions that is less than the minimum, we are required to pay the third party processor's fees that they would have received if we had submitted the required minimum number of transactions. Processing services includes amounts due under network sponsorship agreements. |
(4) | Represents estimated TRA payments to various parties and cash payments to exercise the call options pursuant to which certain additional obligations of the Company under the Mercury TRA would be terminated. See Note 7 - Tax Receivable Agreements in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" for more details. |
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based upon our audited consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate our critical estimates giving consideration to a combination of factors, including historical experience, current conditions and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
The accounting policies we believe to be most critical to understanding our financial results and condition and that require complex and subjective management judgments are discussed below.
Revenue Recognition
We have contractual agreements with our clients that set forth the general terms and conditions of the relationship including line item pricing, payment terms and contract duration. Revenues are recognized as earned (i.e., for transaction based fees, when the underlying transaction is processed) in conjunction with ASC 605, Revenue Recognition. ASC 605, Revenue Recognition, establishes guidance as to when revenue is realized or realizable and earned by using the following criteria: (1) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; (2) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; (3) the seller’s price is fixed or determinable; and (4) collectibility is reasonably assured.
47
We follow guidance provided in ASC 605-45, Principal Agent Considerations. ASC 605-45, Principal Agent Considerations, states that the determination of whether a company should recognize revenue based on the gross amount billed to a customer or the net amount retained is a matter of judgment that depends on the facts and circumstances of the arrangement and that certain factors should be considered in the evaluation. We recognize processing revenues net of interchange fees, which are assessed to our merchant customers on all processed transactions. Interchange rates are not controlled by us, in which we effectively act as a clearing house collecting and remitting interchange fee settlement on behalf of issuing banks, debit networks, credit card associations and its processing customers. All other revenue is reported on a gross basis, as we contract directly with the end customer, assume the risk of loss and have pricing flexibility.
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
In accordance with ASC 350, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other, we test goodwill for impairment for our two reporting units (Merchant Services and Financial Institution Services) on an annual basis, or when events occur or circumstances change that would indicate the fair value of a reporting unit is below its carrying value. These reporting units are also the segments for which we report financial results. If the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value, an impairment loss is recorded to the extent that fair value of the goodwill within the reporting unit is less than its carrying value. We performed our most recent annual goodwill impairment test for all reporting units as of July 31, 2015 using market data and discounted cash flow analysis. Based on this analysis, it was determined that the fair value of all reporting units was substantially in excess of the carrying value.
Intangible assets consist of acquired customer relationships, trade names and customer portfolios and related assets that are amortized over their estimated useful lives. We review finite lived intangible assets for possible impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that carrying amounts may not be recoverable.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have no off-balance sheet financing arrangements.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure About Market Risk
We are exposed to interest rate risk in connection with our senior secured credit facilities, which are subject to variable interest rates.
As of December 31, 2015 we had a total of 14 outstanding interest rate swaps. Of the 14 outstanding swaps, 8 of them cover an exposure period from June 2015 through June 2017 and have a combined notional balance of $1.2 billion (amortizing to $1.1 billion). The remaining 6 interest rate swaps cover an exposure period from January 2016 through January 2019 and have a combined notional balance of $500 million. As of December 31, 2015, we had $1.9 billion of variable rate debt not subject to a fixed rate swap effective at December 31, 2015.
Based on the amount outstanding under our senior secured credit facilities at December 31, 2015, a change in one percentage point in variable interest rates, after the effect of our interest rate swaps effective at December 31, 2015, would cause an increase or decrease in interest expense of $19.0 million on an annual basis.
48
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements
Page | ||
Vantiv, Inc. and Subsidiaries | ||
49
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Vantiv, Inc.
Symmes Township, Ohio
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of financial position of Vantiv, Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, and the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2015. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15. These financial statements and financial statement schedule are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the financial statements and financial statement schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Vantiv, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2015, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, such financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic consolidated financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015, based on the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated February 10, 2016 expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
Cincinnati, Ohio
February 10, 2016
50
Vantiv, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(In thousands, except share data)
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||
Revenue: | ||||||||||||
External customers | $ | 3,079,506 | $ | 2,496,899 | $ | 2,028,681 | ||||||
Related party revenues | 80,432 | 80,304 | 79,396 | |||||||||
Total revenue | 3,159,938 | 2,577,203 | 2,108,077 | |||||||||
Network fees and other costs | 1,478,202 | 1,174,665 | 935,441 | |||||||||
Sales and marketing | 503,949 | 396,353 | 312,044 | |||||||||
Other operating costs | 284,066 | 242,439 | 200,630 | |||||||||
General and administrative | 182,369 | 173,986 | 121,707 | |||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 276,942 | 275,069 | 185,453 | |||||||||
Income from operations | 434,410 | 314,691 | 352,802 | |||||||||
Interest expense—net | (105,736 | ) | (79,701 | ) | (40,902 | ) | ||||||
Non-operating income (expense) | (31,268 | ) | 177 | (20,000 | ) | |||||||
Income before applicable income taxes | 297,406 | 235,167 | 291,900 | |||||||||
Income tax expense | 88,177 | 66,177 | 83,760 | |||||||||
Net income | 209,229 | 168,990 | 208,140 | |||||||||
Less: Net income attributable to non-controlling interests | (61,283 | ) | (43,698 | ) | (74,568 | ) | ||||||
Net income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. | $ | 147,946 | $ | 125,292 | $ | 133,572 | ||||||
Net income per share attributable to Vantiv, Inc. Class A common stock: | ||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 1.02 | $ | 0.88 | $ | 0.96 | ||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.95 | $ | 0.75 | $ | 0.87 | ||||||
Shares used in computing net income per share of Class A common stock: | ||||||||||||
Basic | 145,044,577 | 141,936,933 | 138,836,314 | |||||||||
Diluted | 200,934,442 | 199,170,813 | 206,027,557 | |||||||||
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
51
Vantiv, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(In thousands)
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||
Net income | $ | 209,229 | $ | 168,990 | $ | 208,140 | ||||||
Other comprehensive income, net of tax: | ||||||||||||
Gain (loss) on cash flow hedges and other | (8,209 | ) | (6,172 | ) | 663 | |||||||
Comprehensive income | 201,020 | 162,818 | 208,803 | |||||||||
Less: Comprehensive income attributable to non-controlling interests | (58,510 | ) | (41,558 | ) | (74,967 | ) | ||||||
Comprehensive income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. | $ | 142,510 | $ | 121,260 | $ | 133,836 | ||||||
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
52
Vantiv, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
(In thousands, except share data)
December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | ||||||
Assets | |||||||
Current assets: | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 197,096 | $ | 411,568 | |||
Accounts receivable—net | 680,033 | 607,674 | |||||
Related party receivable | 3,999 | 6,164 | |||||
Settlement assets | 143,563 | 135,422 | |||||
Prepaid expenses | 31,147 | 26,906 | |||||
Other | 61,661 | 27,002 | |||||
Total current assets | 1,117,499 | 1,214,736 | |||||
Customer incentives | 57,984 | 39,210 | |||||
Property, equipment and software—net | 308,009 | 281,715 | |||||
Intangible assets—net | 863,066 | 1,034,692 | |||||
Goodwill | 3,366,528 | 3,291,366 | |||||
Deferred taxes | 731,622 | 429,623 | |||||
Other assets | 20,718 | 44,741 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 6,465,426 | $ | 6,336,083 | |||
Liabilities and equity | |||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses | $ | 364,878 | $ | 299,771 | |||
Related party payable | 4,698 | 2,035 | |||||
Settlement obligations | 677,502 | 501,042 | |||||
Current portion of note payable to related party | 10,353 | 10,353 | |||||
Current portion of note payable | 106,148 | 106,148 | |||||
Current portion of tax receivable agreement obligations to related parties | 31,232 | 22,789 | |||||
Current portion of tax receivable agreement obligations | 64,227 | — | |||||
Deferred income | 14,470 | 5,480 | |||||
Current maturities of capital lease obligations | 7,931 | 8,158 | |||||
Other | 13,940 | 7,557 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 1,295,379 | 963,333 | |||||
Long-term liabilities: | |||||||
Note payable to related party | 181,169 | 191,521 | |||||
Note payable | 2,762,469 | 3,085,716 | |||||
Tax receivable agreement obligations to related parties | 801,829 | 597,273 | |||||
Tax receivable agreement obligations | 126,980 | 152,420 | |||||
Capital lease obligations | 21,801 | 14,779 | |||||
Deferred taxes | 15,836 | 24,380 | |||||
Other | 34,897 | 6,075 | |||||
Total long-term liabilities | 3,944,981 | 4,072,164 | |||||
Total liabilities | 5,240,360 | 5,035,497 | |||||
Commitments and contingencies (See Note 10 - Commitments, Contingencies and Guarantees) | |||||||
Equity: | |||||||
Class A common stock, $0.00001 par value; 890,000,000 shares authorized; 155,488,326 shares outstanding at December 31, 2015; 145,455,008 shares outstanding at December 31, 2014 | 1 | 1 | |||||
Class B common stock, no par value; 100,000,000 shares authorized; 35,042,826 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2015; 43,042,826 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2014 | — | — | |||||
Preferred stock, $0.00001 par value; 10,000,000 shares authorized; no shares issued and outstanding | — | — | |||||
Paid-in capital | 553,145 | 629,353 | |||||
Retained earnings | 476,304 | 328,358 | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (9,204 | ) | (3,768 | ) | |||
Treasury stock, at cost; 2,593,242 shares at December 31, 2015 and 2,173,793 shares at December 31, 2014 | (67,458 | ) | (50,931 | ) | |||
Total Vantiv, Inc. equity | 952,788 | 903,013 | |||||
Non-controlling interests | 272,278 | 397,573 | |||||
Total equity | 1,225,066 | 1,300,586 | |||||
Total liabilities and equity | $ | 6,465,426 | $ | 6,336,083 | |||
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
53
Vantiv, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In thousands)
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Operating Activities: | |||||||||||
Net income | 209,229 | $ | 168,990 | $ | 208,140 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization expense | 276,942 | 240,802 | 185,453 | ||||||||
Write-off of intangible asset | — | 34,267 | — | ||||||||
Amortization of customer incentives | 18,256 | 12,032 | 10,139 | ||||||||
Amortization and write-off of debt issuance costs | 8,376 | 31,956 | 24,427 | ||||||||
Share-based compensation expense | 30,492 | 42,171 | 29,729 | ||||||||
Deferred taxes | 55,280 | 32,469 | 31,340 | ||||||||
Excess tax benefit from share-based compensation | (16,707 | ) | (13,420 | ) | (5,464 | ) | |||||
Tax receivable agreements non-cash items | 28,171 | (25,838 | ) | — | |||||||
Other | (945 | ) | — | 491 | |||||||
Change in operating assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||
Accounts receivable and related party receivable | (70,194 | ) | (94,326 | ) | (71,614 | ) | |||||
Net settlement assets and obligations | 168,319 | 157,663 | 93,318 | ||||||||
Customer incentives | (32,892 | ) | (17,108 | ) | (13,034 | ) | |||||
Prepaid and other assets | 11,324 | (25,557 | ) | (5,127 | ) | ||||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 57,861 | 53,172 | (7,250 | ) | |||||||
Payable to related party | 2,663 | (433 | ) | 756 | |||||||
Other liabilities | 11,703 | (3,935 | ) | (682 | ) | ||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 757,878 | 592,905 | 480,622 | ||||||||
Investing Activities: | |||||||||||
Purchases of property and equipment | (84,730 | ) | (103,179 | ) | (61,578 | ) | |||||
Acquisition of customer portfolios and related assets | (41,997 | ) | (29,596 | ) | (7,892 | ) | |||||
Purchase of investments | — | (7,487 | ) | (3,174 | ) | ||||||
Cash used in acquisitions, net of cash acquired | — | (1,658,694 | ) | (155,654 | ) | ||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (126,727 | ) | (1,798,956 | ) | (228,298 | ) | |||||
Financing Activities: | |||||||||||
Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt | — | 3,443,000 | 1,850,000 | ||||||||
Borrowings on revolving credit facility | 177,000 | — | — | ||||||||
Repayment of debt and capital lease obligations | (503,462 | ) | (1,870,540 | ) | (1,304,966 | ) | |||||
Payment of debt issuance costs | — | (38,092 | ) | (26,288 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from exercise of Class A common stock options | 13,630 | 4,492 | — | ||||||||
Warrant termination | (200,219 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Repurchase of Class A common stock | (200,406 | ) | (59,364 | ) | (503,225 | ) | |||||
Repurchase of Class A common stock (to satisfy tax withholding obligations) | (16,527 | ) | (17,801 | ) | (15,224 | ) | |||||
Settlement of certain tax receivable agreements | (94,022 | ) | — | (112,562 | ) | ||||||
Payments under tax receivable agreements | (22,805 | ) | (8,639 | ) | — | ||||||
Excess tax benefit from share-based compensation | 16,707 | 13,420 | 5,464 | ||||||||
Distribution to non-controlling interests | (12,892 | ) | (22,911 | ) | (41,154 | ) | |||||
(Decrease) increase in cash overdraft | (2,627 | ) | 2,627 | — | |||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (845,623 | ) | 1,446,192 | (147,955 | ) | ||||||
Net (decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents | (214,472 | ) | 240,141 | 104,369 | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents—Beginning of period | 411,568 | 171,427 | 67,058 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents—End of period | $ | 197,096 | $ | 411,568 | $ | 171,427 | |||||
Cash Payments: | |||||||||||
Interest | $ | 98,971 | $ | 70,751 | $ | 37,975 | |||||
Taxes | 6,565 | 35,157 | 46,198 | ||||||||
Non-cash Items: | |||||||||||
Issuance of tax receivable agreements to related parties | $ | 376,597 | $ | 109,400 | $ | 329,400 | |||||
Issuance of tax receivable agreement as contingent consideration | — | 137,860 | — | ||||||||
Assets acquired under capital lease obligations | — | 12,997 | 20,345 | ||||||||
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
54
Vantiv, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF EQUITY
(In thousands)
Accumulated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Common Stock | Other | Non- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | Class A | Class B | Treasury Stock | Paid-in | Retained | Comprehensive | Controlling | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Capital | Earnings | Income (Loss) | Interests | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Beginning Balance, January 1, 2015 | $ | 1,300,586 | 145,455 | $ | 1 | 43,043 | $ | — | 2,174 | $ | (50,931 | ) | $ | 629,353 | $ | 328,358 | $ | (3,768 | ) | $ | 397,573 | |||||||||||||||||||
Net income | 209,229 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 147,946 | — | 61,283 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of Class A common stock under employee stock plans, net of forfeitures | 13,630 | 1,523 | — | — | — | — | — | 13,630 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tax benefit from employee share-based compensation | 16,707 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 16,707 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of Class A common stock (to satisfy tax withholding obligation) | (16,527 | ) | (419 | ) | — | — | — | 419 | (16,527 | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warrant retirement | (144,568 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (129,173 | ) | — | — | (15,395 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of Class A common stock and cancellation of Class B common stock in connection with secondary offering | — | 8,000 | — | (8,000 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of Class A common stock | (200,406 | ) | (4,446 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | (200,406 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Termination of certain tax receivable agreements | 58,191 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 58,191 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Partial exercise of warrant | — | 5,375 | — | — | — | — | — | 25,022 | — | — | (25,022 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of tax receivable agreements | (21,167 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (21,167 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized loss on hedging activities and other, net of tax | (8,209 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (5,436 | ) | (2,773 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution to non-controlling interests | (12,892 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (12,892 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation | 30,492 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 23,588 | — | — | 6,904 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reallocation of non-controlling interests of Vantiv Holding due to change in ownership | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 137,400 | — | — | (137,400 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ending Balance, December 31, 2015 | $ | 1,225,066 | 155,488 | $ | 1 | 35,043 | $ | — | 2,593 | $ | (67,458 | ) | $ | 553,145 | $ | 476,304 | $ | (9,204 | ) | $ | 272,278 | |||||||||||||||||||
55
Vantiv, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF EQUITY
(In thousands)
Accumulated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Common Stock | Other | Non- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | Class A | Class B | Treasury Stock | Paid-in | Retained | Comprehensive | Controlling | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Capital | Earnings | Income (Loss) | Interests | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Beginning Balance, January 1, 2014 | $ | 1,176,322 | 141,759 | $ | 1 | 48,823 | $ | — | 1,607 | $ | (33,130 | ) | $ | 597,730 | $ | 203,066 | $ | 264 | $ | 408,391 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | 168,990 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 125,292 | — | 43,698 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of Class A common stock under employee stock plans, net of forfeitures | 4,492 | 419 | — | — | — | — | — | 4,492 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tax benefit from employee share-based compensation | 13,420 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 13,420 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of Class A common stock (to satisfy tax withholding obligation) | (17,801 | ) | (567 | ) | — | — | — | 567 | (17,801 | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of Class A common stock and cancellation of Class B common stock in connection with secondary offering | — | 5,780 | — | (5,780 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of Class A common stock | (59,364 | ) | (1,936 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | (59,364 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of tax receivable agreements | (17,400 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (17,400 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized loss on hedging activities and other, net of tax | (6,172 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (4,032 | ) | (2,140 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Formation of joint venture | 18,839 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 18,839 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution to non-controlling interests | (22,911 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (22,911 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation | 42,171 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 32,103 | — | — | 10,068 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reallocation of non-controlling interests of Vantiv Holding due to change in ownership | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 58,372 | — | — | (58,372 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ending Balance, December 31, 2014 | $ | 1,300,586 | 145,455 | $ | 1 | 43,043 | $ | — | 2,174 | $ | (50,931 | ) | $ | 629,353 | $ | 328,358 | $ | (3,768 | ) | $ | 397,573 | |||||||||||||||||||
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
56
Vantiv, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF EQUITY
(In thousands)
Accumulated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Common Stock | Other | Non- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | Class A | Class B | Treasury Stock | Paid-in | Retained | Comprehensive | Controlling | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Capital | Earnings | Income | Interests | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Beginning Balance, January 1, 2013 | $ | 1,444,235 | 142,244 | $ | 1 | 70,219 | $ | — | 978 | $ | (17,906 | ) | $ | 766,337 | $ | 69,494 | $ | — | $ | 626,309 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | 208,140 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 133,572 | — | 74,568 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of Class A common stock upon vesting of restricted stock units | — | 4 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tax benefit from employee share-based compensation | 5,464 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 5,464 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of Class A common stock (to satisfy tax withholding obligation) | (15,224 | ) | (629 | ) | — | — | — | 629 | (15,224 | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of Class A common stock and cancellation of Class B common stock in connection with secondary offering | — | 21,396 | — | (21,396 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of Class A common stock | (503,225 | ) | (20,904 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | (503,225 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of tax receivable agreements | (93,000 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (93,000 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Termination of certain tax receivable agreements | 140,694 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 140,694 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized gain on hedging activities, net of tax | 663 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 264 | 399 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Distribution to non-controlling interests | (41,154 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (41,154 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation | 29,729 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 21,239 | — | — | 8,490 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Forfeitures of restricted stock awards | — | (352 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reallocation of non-controlling interests of Vantiv Holding due to change in ownership | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 260,221 | — | — | (260,221 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ending Balance, December 31, 2013 | $ | 1,176,322 | 141,759 | $ | 1 | 48,823 | $ | — | 1,607 | $ | (33,130 | ) | $ | 597,730 | $ | 203,066 | $ | 264 | $ | 408,391 | ||||||||||||||||||||
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
57
Vantiv, Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. BASIS OF PRESENTATION AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Description of Business
Vantiv, Inc., a Delaware corporation, is a holding company that conducts its operations through its majority-owned subsidiary, Vantiv Holding, LLC ("Vantiv Holding"). Vantiv, Inc. and Vantiv Holding are referred to collectively as the "Company," "Vantiv," "we," "us" or "our," unless the context requires otherwise.
The Company provides electronic payment processing services to merchants and financial institutions throughout the United States of America. The Company markets its services through diverse distribution channels, including national, regional and mid-market sales teams, third-party reseller clients and a telesales operation. The Company also has relationships with a broad range of referral partners that include merchant banks, independent software vendors ("ISVs"), value-added resellers ("VARs"), payment facilitators, independent sales organizations ("ISOs") and trade associations as well as arrangements with core processors.
Segments
The Company’s segments consist of the Merchant Services segment and the Financial Institution Services segment. The Company’s Chief Executive Officer ("CEO"), who is the chief operating decision maker ("CODM"), evaluates the performance and allocates resources based on the operating results of each segment. Below is a summary of each segment:
• | Merchant Services—Provides merchant acquiring and payment processing services to large national merchants, regional and small-to-mid sized businesses. Merchant services are sold to small to large businesses through diverse distribution channels. Merchant Services includes all aspects of card processing including authorization and settlement, customer service, chargeback and retrieval processing and interchange management. |
• | Financial Institution Services—Provides card issuer processing, payment network processing, fraud protection, card production, prepaid program management, automated teller machine ("ATM") driving and network gateway and switching services that utilize the Company’s proprietary Jeanie debit payment network to a diverse set of financial institutions, including regional banks, community banks, credit unions and regional personal identification number ("PIN") networks. Financial Institution Services also provides statement production, collections and inbound/outbound call centers for credit transactions, and other services such as credit card portfolio analytics, program strategy and support, fraud and security management and chargeback and dispute services. |
Basis of Presentation and Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include those of Vantiv, Inc. and all subsidiaries thereof, including its majority-owned subsidiary, Vantiv Holding, LLC. The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America ("U.S. GAAP"). All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated.
As of December 31, 2015, Vantiv, Inc. and Fifth Third owned interests in Vantiv Holding of 81.61% and 18.39%, respectively (see Note 9 - Controlling and Non-controlling Interests for changes in non-controlling interests).
The Company accounts for non-controlling interests in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") 810, Consolidation. Non-controlling interests primarily represent Fifth Third's minority share of net income or loss of and equity in Vantiv Holding. Net income attributable to non-controlling interests does not include expenses incurred directly by Vantiv, Inc., including income tax expense attributable to Vantiv, Inc. All of the Company’s non-controlling interests are presented after Vantiv Holding income tax expense in the accompanying consolidated statements of income as "Net income attributable to non-controlling interests." Non-controlling interests are presented as a component of equity in the accompanying consolidated statements of financial position.
58
Sponsorship
In order to provide electronic payment processing services, Visa, MasterCard and other payment networks require sponsorship of non-financial institutions by a member clearing bank. In June 2009, the Company entered into a ten-year agreement with Fifth Third (the "Sponsoring Member"), to provide sponsorship services to the Company. The Company also has agreements with certain other banks that provide sponsorship into the card networks.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amount of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Revenue Recognition
The Company has contractual agreements with its clients that set forth the general terms and conditions of the relationship including line item pricing, payment terms and contract duration. Revenues are recognized as earned (i.e., for transaction based fees, when the underlying transaction is processed) in conjunction with ASC 605, Revenue Recognition. ASC 605, Revenue Recognition, establishes guidance as to when revenue is realized or realizable and earned by using the following criteria: (1) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; (2) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; (3) the seller’s price is fixed or determinable; and (4) collectibility is reasonably assured.
The Company follows guidance provided in ASC 605-45, Principal Agent Considerations, which states that the determination of whether a company should recognize revenue based on the gross amount billed to a customer or the net amount retained is a matter of judgment that depends on the facts and circumstances of the arrangement and that certain factors should be considered in the evaluation. The Company recognizes processing revenues net of interchange fees, which are assessed to the Company’s merchant customers on all processed transactions. Interchange rates are not controlled by the Company, which effectively acts as a clearing house collecting and remitting interchange fee settlement on behalf of issuing banks, debit networks, credit card associations and its processing customers. All other revenue is reported on a gross basis, as the Company contracts directly with the end customer, assumes the risk of loss and has pricing flexibility.
The Company generates revenue primarily by processing electronic payment transactions. Set forth below is a description of the Company’s revenue by segment.
Merchant Services
The Company’s Merchant Services segment revenue is primarily derived from processing credit and debit card transactions. Merchant Services revenue is primarily comprised of fees charged to businesses, net of interchange fees, for payment processing services, including authorization, capture, clearing, settlement and information reporting of electronic transactions. The fees charged consist of either a percentage of the dollar volume of the transaction or a fixed fee, or both, and are recognized at the time of the transaction. Merchant Services revenue also includes a number of revenue items that are incurred by the Company and are reimbursable as the costs are passed through to and paid by the Company’s clients. These items primarily consist of Visa, MasterCard and other payment network fees. In addition, for sales through ISOs and certain other referral sources in which the Company is the primary party to the contract with the merchant, the Company records the full amount of the fees collected from the merchant as revenue. Merchant Services segment revenue also includes revenue from ancillary services such as fraud management, equipment sales and terminal rent. Merchant Services revenue is recognized as services are performed.
Financial Institution Services
The Company’s Financial Institution Services segment revenues are primarily derived from debit, credit and ATM card transaction processing, ATM driving and support, and PIN debit processing services. Financial Institution Services revenue associated with processing transactions includes per transaction and account related fees, card production fees and fees generated from the Company’s Jeanie network. Financial Institution Services revenue related to card transaction processing is recognized when consumers use their client-issued cards to make purchases. Financial Institution Services also generates
59
revenue through other services, including statement production, collections and inbound/outbound call centers for credit transactions and other services such as credit card portfolio analytics, program strategy and support, fraud and security management and chargeback and dispute services. Financial Institution Services revenue is recognized as services are performed.
Financial Institution Services provides certain services to Fifth Third. Revenues related to these services are included in the accompanying statements of income as related party revenues.
Expenses
Set forth below is a brief description of the components of the Company’s expenses:
• | Network fees and other costs primarily consist of pass through expenses incurred by the Company in connection with providing processing services to its clients, including Visa and MasterCard network association fees, payment network fees, third party processing fees, telecommunication charges, postage and card production costs. |
• | Sales and marketing expense primarily consists of salaries and benefits paid to sales personnel, sales management and other sales and marketing personnel, residual payments made to ISOs and referral partners, and advertising and promotional costs. |
• | Other operating costs primarily consist of salaries and benefits paid to operational and IT personnel, costs associated with operating the Company’s technology platform and data centers, information technology costs for processing transactions, product development costs, software consulting fees and maintenance costs. |
• | General and administrative expenses primarily consist of salaries and benefits paid to executive management and administrative employees, including finance, human resources, product development, legal and risk management, share-based compensation costs, equipment and occupancy costs and consulting costs. |
• | Non-operating income (expense): |
◦ | The 2015 amount primarily relates to the change in the fair value of the Mercury TRA entered into as part of the acquisition of Mercury (see Note 7 - Tax Receivable Agreements). |
◦ | The 2014 amount consists of non-operating income of $41.3 million related to a benefit recorded as a result of a reduction in certain TRA liabilities (see Note 7 - Tax Receivable Agreements), partially offset by non-operating expenses of $41.1 million related to the refinancing of our senior secured credit facilities in June 2014 (see Note 6 - Long-Term Debt) and the change in fair value of the Mercury TRA (see Note 7 - Tax Receivable Agreements). |
◦ | The 2013 amount relates to the refinancing of the Company's senior secured credit facilities in May 2013 (see Note 6 - Long-Term Debt). |
Share-Based Compensation
The Company expenses employee share-based payments under ASC 718, Compensation—Stock Compensation, which requires compensation cost for the grant-date fair value of share-based payments to be recognized over the requisite service period. The Company estimates the grant date fair value of the share-based awards issued in the form of options using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The fair value of restricted stock awards and performance awards is measured based on the market price of the Company’s stock on the grant date. See Note 13 - Share-Based Compensation Plans for further discussion.
Earnings Per Share
Basic earnings per share is computed by dividing net income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. by the weighted average shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per share is computed by dividing net income attributable to Vantiv, Inc., adjusted as necessary for the impact of potentially dilutive securities, by the weighted-average shares outstanding during the period and the impact of securities that would have a dilutive effect on earnings per share. See Note 16 - Net Income Per Share for further discussion.
60
Income Taxes
Vantiv, Inc. is taxed as a C corporation for U.S. income tax purposes and is therefore subject to both federal and state taxation at a corporate level.
Income taxes are computed in accordance with ASC 740, Income Taxes, and reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the financial reporting carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and the corresponding income tax amounts. The Company has deferred tax assets and liabilities and maintains valuation allowances where it is more likely than not that all or a portion of deferred tax assets will not be realized. To the extent the Company determines that it will not realize the benefit of some or all of its deferred tax assets, such deferred tax assets will be adjusted through the Company’s provision for income taxes in the period in which this determination is made. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company had recorded no valuation allowances against deferred tax assets. See Note 14 - Income Taxes for further discussion of income taxes.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash on hand and investments with original maturities of three months or less (that are readily convertible to cash) are considered to be cash equivalents. Cash equivalents consist primarily of overnight EuroDollar sweep accounts which are maintained at reputable financial institutions with high credit quality and therefore are considered to bear minimal credit risk.
Accounts Receivable—net
Accounts receivable primarily represent processing revenues earned but not collected. For a majority of its customers, the Company has the authority to debit the client’s bank accounts through the Federal Reserve’s Automated Clearing House; as such, collectibility is reasonably assured. The Company records a reserve for doubtful accounts when it is probable that the accounts receivable will not be collected. The Company reviews historical loss experience and the financial position of its customers when estimating the allowance. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the allowance for doubtful accounts was not material to the Company’s statements of financial position.
Customer Incentives
Customer incentives represent signing bonuses paid to customers. Customer incentives are paid in connection with the acquisition or renewal of customer contracts, and are therefore deferred and amortized using the straight-line method based on the contractual agreement. Related amortization is recorded as contra-revenue.
Property, Equipment and Software—net
Property, equipment and software consists of the Company’s facilities, furniture and equipment, software, land and leasehold improvements. These assets are depreciated on a straight-line basis over their respective useful lives, which are 15 to 40 years for the Company’s facilities and related improvements, 2 to 10 years for furniture and equipment, 3 to 5 years for software and 3 to 10 years for leasehold improvements or the lesser of the estimated useful life of the improvement or the term of lease. Also included in property, equipment and software is work in progress consisting of costs associated with software developed for internal use which has not yet been placed in service.
The Company capitalizes certain costs related to computer software developed for internal use and amortizes such costs on a straight-line basis over an estimated useful life of 5 years. Research and development costs incurred prior to establishing technological feasibility are charged to operations as such costs are incurred. Once technological feasibility has been established, costs are capitalized until the software is placed in service.
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
In accordance with ASC 350, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other, the Company tests goodwill for impairment for each reporting unit on an annual basis, or when events occur or circumstances indicate the fair value of a reporting unit is below its carrying value. If the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value, an impairment loss is recorded to the extent that fair value of the goodwill within the reporting unit is less than its carrying value. The Company performed its most recent annual goodwill impairment test for all reporting units as of July 31, 2015 using market data and discounted cash flow analyses. Based on this analysis, it was determined that the fair value of all reporting units were substantially in excess of the
61
carrying value. There have been no other events or changes in circumstances subsequent to the testing date that would indicate impairment of these reporting units as of December 31, 2015.
Intangible assets consist of acquired customer relationships, trade names and customer portfolios and related assets that are amortized over their estimated useful lives. The Company reviews finite lived intangible assets for possible impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that carrying amounts may not be recoverable. As of December 31, 2015, there have been no such events or circumstances that would indicate potential impairment of finite lived intangible assets. Subsequent to the Mercury acquisition in June 2014, the Company decided to phase out an existing trade name used in the ISO channel within the Merchant Services segment. As a result of this decision, the remaining useful life was changed from indefinite to definite which resulted in the Company recording a charge to amortization expense of $34.3 million during the quarter ended June 30, 2014. The remaining fair value is being amortized on a straight-line basis over the remaining estimated useful life of two years.
Settlement Assets and Obligations
Settlement assets and obligations result from Financial Institution Services when funds are transferred from or received by the Company prior to receiving or paying funds to a different entity. This timing difference results in a settlement asset or obligation. The amounts are generally collected or paid the following business day.
The settlement assets and obligations recorded by Merchant Services represent intermediary balances due to differences between the amount the Sponsoring Member receives from the card associations and the amount funded to the merchants. Such differences arise from timing differences, interchange expenses, merchant reserves and exception items. In addition, certain card associations limit the Company from accessing or controlling merchant settlement funds and, instead, require that these funds be controlled by the Sponsoring Member. The Company follows a net settlement process whereby, if the settlement received from the card associations precedes the funding obligation to the merchant, the Company temporarily records a corresponding liability. Conversely, if the funding obligation to the merchant precedes the settlement from the card associations, the amount of the net receivable position is recorded by the Company, or in some cases, the Sponsoring Member may cover the position with its own funds in which case a receivable position is not recorded by the Company.
Derivatives
The Company accounts for derivatives in accordance with ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging. This guidance establishes accounting and reporting for derivative instruments, including certain derivative instruments embedded in other contracts, and for hedging activities. All derivatives, whether designated in hedging relationships or not, are required to be recorded on the statement of financial position at fair value. If the derivative is designated as a fair value hedge, the changes in the fair value of the derivative and the hedged item will be recognized in earnings. If the derivative is designated as a cash flow hedge, the effective portion of the change in the fair value of the derivative will be recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) ("AOCI") and will be recognized in the statement of income when the hedged item affects earnings. The Company does not enter into derivative financial instruments for speculative purposes.
New Accounting Pronouncements
In November 2015, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2015-17, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes. The update simplifies the presentation of deferred income taxes by requiring that deferred tax liabilities and assets be classified as noncurrent in the balance sheet. The update is effective for public companies for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The guidance may be adopted prospectively or retrospectively and early adoption is permitted. As of December 31, 2015, the Company has elected to early adopt this ASU on a prospective basis and therefore, prior years were not retrospectively adjusted.
In April 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-03, Interest - Imputation of Interest (Subtopic 835-30): Simplifying the Presentation of Debt Issuance Costs. The update requires debt issuance costs related to a recognized debt liability to be presented in the balance sheet as a direct deduction from the carrying amount of the related debt liability instead of being presented as an asset. Amortization of the costs will continue to be reported as interest expense. In August 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-15, Interest - Imputation of Interest (Subtopic 835-30): Presentation and Subsequent Measurement of Debt Issuance Costs Associated with Line-of-Credit Arrangements. The update provides additional guidance to ASU 2015-03, which did not address presentation or subsequent measurement of debt issuance costs related to line-of-credit arrangements. The update noted that the SEC staff would not object to an entity deferring and presenting debt issuance costs as an asset and
62
subsequently amortizing the deferred debt issuance costs ratably over the term of the line-of-credit arrangement, regardless of whether there are any outstanding borrowings on the line-of-credit arrangement. These updates require retrospective application and represent a change in accounting principle. The change in accounting principle, resulting from the Company's adoption of this ASU, has been implemented and the results are not material to the Company's consolidated statement of financial position.
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, "Revenue From Contracts With Customers." The ASU supersedes the revenue recognition requirements in ASC 605, Revenue Recognition. The new standard provides a five-step analysis of transactions to determine when and how revenue is recognized, based upon the core principle that revenue is recognized to depict the transfer of goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. The new standard also requires additional disclosures regarding the nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from contracts with customers. The new standard, as amended, is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted. The amendment allows companies to use either a full retrospective or a modified retrospective approach to adopt this ASU. The Company is currently evaluating which transition approach to use and assessing the impact of the adoption of this principle on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
2. BUSINESS COMBINATIONS
Acquisition of Mercury Payment Systems, LLC
On June 13, 2014, the Company completed the acquisition of Mercury Payment Systems, LLC ("Mercury"), acquiring all of the outstanding voting interest. Mercury was a payment technology and service leader whose solutions are integrated into point-of-sale software applications and brought to market through dealer and developer partners. This acquisition helps to accelerate the Company's growth in the integrated payments channel.
During the second quarter of 2015, the Company recorded measurement period adjustments to the trade name and to the Mercury TRA. The adjustment to the trade name, which is included in intangible assets below, is based on a change in the underlying assumptions used to value the trade name due to the refinement of estimates. The trade name was initially assigned a value of $59.1 million and a weighted average estimated useful life of 9.5 years utilizing the relief from royalty method. As a result of a change in the underlying assumptions due to the refinement of estimates, the Company assigned the trade name a value of $15.0 million based on a weighted average estimated useful life of 2.5 years. The adjustment to the Mercury TRA is due to a change in the inputs used in determining the fair value of the TRA as a result of refining estimates. Both measurement period adjustments are reflected in the table below and have no effect on the accompanying statement of income.
The following is the estimated fair value of the purchase price for Mercury (in thousands):
Cash purchase price paid at closing | $ | 1,681,179 | |
Fair value of contingent consideration related to a TRA | 192,507 | ||
Total purchase price | $ | 1,873,686 | |
63
The acquisition was accounted for as a business combination under ASC 805, Business Combinations ("ASC 805"). The purchase price was allocated to the assets acquired and the liabilities assumed based on the estimated fair value at the date of acquisition. The excess of the purchase price over the fair value of the net assets acquired was allocated to goodwill, a significant portion of which is deductible for tax purposes. Goodwill, assigned to Merchant Services, consists primarily of the acquired workforce and growth opportunities, none of which qualify as an intangible asset. The final purchase price allocation is as follows (in thousands):
Cash acquired | $ | 22,485 | |
Current assets | 47,421 | ||
Property, equipment and software | 32,257 | ||
Intangible assets | 347,000 | ||
Goodwill | 1,422,916 | ||
Deferred tax assets | 43,054 | ||
Other non-current assets | 767 | ||
Current and non-current liabilities | (42,214 | ) | |
Total purchase price | $ | 1,873,686 | |
Simultaneously and in connection with the completion of the Mercury acquisition, the Company entered into a Tax Receivable Agreement (the "Mercury TRA") with pre-acquisition owners of Mercury ("Mercury TRA Holders"). See Note 7 - Tax Receivable Agreements for further discussion of the Mercury TRA. The Mercury TRA is considered contingent consideration under ASC 805 as it is part of the consideration payable to the former owners of Mercury. In accordance with ASC 805, the contingent consideration is initially measured at fair value at the acquisition date and recorded as a liability. The Mercury TRA liability is therefore recorded at fair value based on estimates of discounted future cash flows associated with estimated payments to the Mercury TRA Holders. The liability recorded by the Company for the Mercury TRA obligations will be re-measured at fair value at each reporting date with the change in fair value recognized in earnings as a non-operating expense.
Intangible assets consist of customer relationship assets of $332.0 million and a trade name of $15.0 million having weighted average estimated useful lives of 10 years and 2.5 years, respectively. The trade name was valued utilizing a relief from royalty method.
The Company incurred transaction and integration expenses of approximately $17.9 million during the year ended December 31, 2014 in conjunction with the acquisition of Mercury, which are included within general and administrative expenses and other operating costs on the accompanying consolidated statement of income. From the acquisition date of June 13, 2014 through December 31, 2014, revenue included in the accompanying statement of income for the year ended December 31, 2014 attributable to Mercury was approximately $217 million. Net income for the period could not be determined due to integration activities that were implemented subsequent to the acquisition.
Under the terms of the Mercury transaction agreement, the Company replaced unvested employee stock options held by certain employees of Mercury. The number of replacement stock options was based on a conversion factor into equivalent stock options of the Company on the acquisition date. The weighted average fair value of the replacement options was $32.1 million and was calculated on the acquisition date using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The portion of the fair value of the replacement awards related to services provided prior to the acquisition of $17.7 million was part of the consideration transferred to acquire Mercury. The remaining portion of the fair value is associated with future service and will be recognized as expense over the future service period. See additional discussion in Note 13 - Share-Based Compensation Plans.
64
The following unaudited pro forma information shows the Company’s results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 as if the Mercury acquisition had occurred January 1, 2013. The unaudited pro forma information is presented for informational purposes only and is not necessarily indicative of what would have occurred if the acquisition had been made as of that date, nor is it intended to be indicative of future operating results.
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||
2014 | 2013 | ||||||
(in thousands, except share data) | |||||||
Total revenue | $ | 2,737,024 | $ | 2,435,234 | |||
Income from operations | 322,746 | 354,517 | |||||
Net income including non-controlling interests | 174,797 | 155,145 | |||||
Net income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. | 129,630 | 95,819 | |||||
Net income per share attributable to Vantiv, Inc. Class A common stock: | |||||||
Basic | $ | 0.91 | $ | 0.69 | |||
Diluted | $ | 0.78 | $ | 0.61 | |||
Shares used in computing net income per share of Class A common stock: | |||||||
Basic | 141,936,933 | 138,836,314 | |||||
Diluted | 199,170,813 | 206,027,557 | |||||
The unaudited pro forma results include certain pro forma adjustments that were directly attributable to the business combination as follows:
• | additional amortization expense that would have been recognized relating to the acquired intangible assets, |
• | adjustment of interest expense to reflect the additional borrowings of the Company in conjunction with the acquisition and removal of Mercury historical debt, and |
• | a reduction in non-operating expenses for the year ended December 31, 2014 and a corresponding increase for the year ended December 31, 2013 for acquisition-related transaction costs and debt refinancing costs incurred by the Company. |
Acquisition of Element Payment Services, Inc.
On July 31, 2013, the Company completed the acquisition of Element Payment Services, Inc. ("Element"), acquiring all of the outstanding voting interest. Element was a provider of integrated payment processing solutions. This acquisition provides the Company with strategic capabilities to partner with integrated point-of-sale developers and dealers and positions the Company to increase its presence in the integrated payments channel.
The acquisition was accounted for as a business combination under ASC 805. The purchase price was allocated to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on the estimated fair value at the date of acquisition. The excess of the purchase price over the fair value of the net assets acquired was allocated to goodwill, none of which is deductible for tax purposes. Goodwill, assigned to Merchant Services, consists primarily of the acquired workforce and growth opportunities, none of which qualifies as an identifiable intangible asset. The final purchase price allocation is as follows (in thousands):
Current assets | $ | 11,359 | ||
Equipment and software | 8,193 | |||
Goodwill | 135,068 | |||
Customer relationship intangible assets | 29,300 | |||
Trade name | 500 | |||
Current liabilities | (8,189 | ) | ||
Deferred tax liabilities | (13,772 | ) | ||
Total purchase price | $ | 162,459 | ||
Customer relationship intangible assets and the trade name have weighted average useful lives of 10 years and 1 year, respectively.
65
The pro forma results of the Company reflecting the acquisition of Element were not material to our financial results and therefore have not been presented.
3. PROPERTY, EQUIPMENT AND SOFTWARE
A summary of the Company's property, equipment and software is as follows (in thousands):
Estimated Useful Life | December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | ||||||||
Land | N/A | $ | 6,401 | $ | 6,401 | |||||
Building and improvements | 15 - 40 years | 33,938 | 33,454 | |||||||
Furniture and equipment | 2 - 10 years | 134,191 | 116,065 | |||||||
Software | 5 years | 319,866 | 259,495 | |||||||
Leasehold improvements | 3 - 10 years | 8,885 | 8,753 | |||||||
Work in progress | 45,061 | 60,309 | ||||||||
Accumulated depreciation | (240,333 | ) | (202,762 | ) | ||||||
Total | $ | 308,009 | $ | 281,715 | ||||||
Depreciation and amortization expense related to property, equipment and software for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 was $76.6 million, $70.0 million and $56.8 million, respectively.
4. GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Changes in the carrying amount of goodwill, by business segment, are as follows (in thousands):
Merchant Services | Financial Institution Services | Total | ||||||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2013 | $ | 1,368,763 | $ | 574,850 | $ | 1,943,613 | ||||||
Goodwill attributable to acquisition of Mercury | 1,347,753 | — | 1,347,753 | |||||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2014 | 2,716,516 | 574,850 | 3,291,366 | |||||||||
Goodwill attributable to acquisition of Mercury (1) | 75,162 | — | 75,162 | |||||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2015 | $ | 2,791,678 | $ | 574,850 | $ | 3,366,528 | ||||||
(1) Amount represents adjustments to goodwill associated with the acquisition of Mercury as a result of the finalization of purchase accounting.
Intangible assets consist of acquired customer relationships, trade names and customer portfolios and related assets. The useful lives of customer relationships are determined based on forecasted cash flows, which include estimates for customer attrition associated with the underlying portfolio of customers acquired. The customer relationships acquired in conjunction with acquisitions are amortized based on the pattern of cash flows expected to be realized taking into consideration expected revenues and customer attrition, which are based on historical data and the Company's estimates of future performance. These estimates result in accelerated amortization on certain acquired intangible assets.
Indefinite lived trade names are reviewed for impairment on an annual basis or whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount may not be recoverable. Subsequent to the Mercury acquisition in June 2014, the Company decided to phase out an existing trade name used in the ISO channel. The trade name was originally expected to remain in use for the foreseeable future and therefore was deemed an indefinite lived intangible asset not subject to amortization. As a result of this decision, the remaining useful life was changed from indefinite to definite which resulted in the Company recording a charge to amortization expense of $34.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2014. The trade name was revalued utilizing an income approach using the relief-from-royalty method. The revised fair value of $6.7 million is being amortized on a straight-line basis over the remaining estimated useful life of two years.
The Company reviews finite lived intangible assets for possible impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that carrying amounts may not be recoverable.
66
As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company's finite lived intangible assets consisted of the following (in thousands):
December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
Customer relationship intangible assets | $ | 1,596,581 | $ | 1,596,581 | ||||
Trade name | 21,733 | 65,833 | ||||||
Customer portfolios and related assets | 129,734 | 57,383 | ||||||
Patents | 366 | — | ||||||
1,748,414 | 1,719,797 | |||||||
Less accumulated amortization on: | ||||||||
Customer relationship intangible assets | 821,580 | 655,017 | ||||||
Trade name | 14,350 | 5,105 | ||||||
Customer portfolios and related assets | 49,418 | 24,983 | ||||||
885,348 | 685,105 | |||||||
$ | 863,066 | $ | 1,034,692 | |||||
Customer portfolios and related assets acquired during the year ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, have weighted-average amortization periods of 4.8 years and 4.2 years, respectively. Amortization expense on intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 was $200.4 million, $205.1 million and $128.6 million, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2014, intangible amortization expense included the $34.3 million charge related to the phasing out of a trade name discussed above.
The estimated amortization expense of intangible assets for the next five years is as follows (in thousands):
2016 | $ | 192,296 | ||
2017 | 171,382 | |||
2018 | 161,930 | |||
2019 | 153,530 | |||
2020 | 81,470 | |||
5. CAPITAL LEASES
The Company has various lease agreements for equipment that are classified as capital leases. The cost and accumulated depreciation of equipment under capital leases included in the accompanying statements of financial position within property and equipment were $36.6 million and $4.4 million, respectively, as of December 31, 2015 and $33.4 million and $8.3 million, respectively, as of December 31, 2014. Depreciation expense associated with capital leases for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013 was $7.8 million, $6.0 million and $6.7 million, respectively.
67
The future minimum lease payments required under capital leases and the present value of net minimum lease payments as of December 31, 2015 are as follows (in thousands):
Amount | ||||
2016 | $ | 8,454 | ||
2017 | 8,969 | |||
2018 | 8,969 | |||
2019 | 4,484 | |||
Total minimum lease payments | 30,876 | |||
Less: Amount representing interest | (1,144 | ) | ||
Present value of minimum lease payments | 29,732 | |||
Less: Current maturities of capital lease obligations | (7,931 | ) | ||
Long-term capital lease obligations | $ | 21,801 | ||
6. LONG-TERM DEBT
As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company’s long-term debt consisted of the following (in thousands):
December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | ||||||
$2,050.0 million term A loan, maturing on June 13, 2019, and bearing interest at a variable base rate (LIBOR) plus a spread rate (200 basis points) (total rate of 2.33% at December 31, 2015) and amortizing on a basis of 1.25% per quarter during each of the first twelve quarters, 1.875% per quarter during the next four quarters and 2.50% during the next three quarters with a balloon payment due at maturity | $ | 1,896,250 | $ | 1,998,750 | |||
$1,400.0 million term B loan, maturing on June 13, 2021, and bearing interest at a variable base rate (LIBOR) with a floor of 75 basis points plus a spread rate (300 basis points) (total rate of 3.75% at December 31, 2015) and amortizing on a basis of 0.25% per quarter, with a balloon payment due at maturity | 1,179,000 | 1,393,000 | |||||
$10.1 million leasehold mortgage, expiring on August 10, 2021 and bearing interest payable monthly at a fixed rate (rate of 6.22% at December 31, 2015) | 10,131 | 10,131 | |||||
Less: Current portion of note payable and current portion of note payable to related party | (116,501 | ) | (116,501 | ) | |||
Less: Original issue discount | (6,024 | ) | (8,143 | ) | |||
Less: Debt issuance costs | (19,218 | ) | — | ||||
Note payable and note payable to related party | $ | 2,943,638 | $ | 3,277,237 | |||
2014 Debt Refinancing
On June 13, 2014, Vantiv, LLC completed a debt refinancing by entering into an amended and restated loan agreement ("Amended Loan Agreement"). The Amended Loan Agreement provides for senior secured credit facilities comprised of a $2.05 billion term A loan, a $1.4 billion term B loan and a $425 million revolving credit facility. Proceeds from the refinancing were primarily used to fund the Mercury acquisition and repay the prior term A loan discussed below with an outstanding balance of approximately $1.8 billion as of the date of refinancing. The prior revolving credit facility was also terminated. The maturity date and debt service requirements relating to the new term A and term B loans are listed in the table above. The new revolving credit facility matures in June 2019 and includes a $100 million swing line facility and a $40 million letter of credit facility. The commitment fee rate for the unused portion of the revolving credit facility is 0.375% per year. The Company borrowed $177 million under its revolving credit facility in December 2015 and repaid the amount prior to year-end. There were no outstanding borrowings on the revolving credit facility at December 31, 2015 and 2014.
As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, Fifth Third held $191.5 million and $201.9 million, respectively, of the term A loans, which are presented as note payable to related party on the consolidated statements of financial position.
On January 6, 2015, the Company made an early principal payment of $200 million on the term B loan. The Company expensed approximately $1.8 million in non-operating expenses related to the write-off of deferred financing fees and OID in connection with the early principal payment. At December 31, 2015, deferred financing fees of approximately $19.2 million
68
and OID of approximately $6.0 million are recorded as a reduction of note payable in the accompanying consolidated statement of financial position as a result of implementing the change in accounting principle discussed in ASU 2015-03 under New Accounting Pronouncements in Note 1 - Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies.
As a result of the Company's 2014 debt refinancing, the Company expensed approximately $26.5 million, which consisted primarily of the write-offs of unamortized deferred financing fees and original issue discount ("OID") associated with the component of the refinancing accounted for as a debt extinguishment and certain third party costs incurred in connection with the refinancing. Amounts expensed in connection with the refinancing are recorded as a component of non-operating expenses in the accompanying consolidated statement of income for the year ended December 31, 2014. At December 31, 2014, deferred financing fees of approximately $25.5 million and OID of approximately $8.1 million are recorded as a component of other non-current assets and as a reduction of note payable, respectively, in the accompanying consolidated statement of financial position. Fifth Third participated in the debt both prior and subsequent to the refinancing pursuant to terms and conditions consistent with third-party lenders, and therefore the refinancing of the component of the Company's debt held by Fifth Third was treated consistently with the overall refinancing.
2013 Debt Refinancing
In May 2013, the Company entered into a $1.85 billion term A loan (the "2013 term A loan"), of which a portion of the proceeds were used to repay outstanding debt under the Company's 2012 refinanced debt agreement with an aggregate outstanding balance of approximately $1.2 billion as of the date of refinancing. The related revolving credit facility was also terminated. In addition to the 2013 term A loan, the new debt agreement included a $250 million revolving credit facility. The revolving credit facility originally matured in May 2018 and included a $75 million swing line facility and a $40 million letter of credit facility. The commitment fee rate for the unused portion of the revolving credit facility was 0.375% per year.
As a result of the Company's 2013 debt refinancing, the Company expensed approximately $20.0 million, which consisted primarily of the write-offs of unamortized deferred financing fees and original issue discount associated with the component of the refinancing accounted for as a debt extinguishment. Amounts expensed in connection with the refinancing are recorded as a component of non-operating expenses in the accompanying consolidated statement of income for the year ended December 31, 2013. Fifth Third participated in the debt both prior and subsequent to the refinancing pursuant to terms and conditions consistent with third-party lenders, and therefore the refinancing of the component of the Company's debt held by Fifth Third was treated consistently with the overall refinancing.
Guarantees and Security
The Company's debt obligations at December 31, 2015 are unconditional and are guaranteed by Vantiv Holding and certain of Vantiv Holding’s existing and subsequently acquired or organized domestic subsidiaries. The refinanced debt and related guarantees are secured on a first-priority basis (subject to liens permitted under the Amended Loan Agreement) by substantially all the capital stock (subject to a 65% limitation on pledges of capital stock of foreign subsidiaries and domestic holding companies of foreign subsidiaries) and personal property of Vantiv Holding and any obligors as well as any real property in excess of $10 million in the aggregate held by Vantiv Holding or any obligors (other than Vantiv Holding), subject to certain exceptions.
Covenants
There are certain financial and non-financial covenants contained in the Amended Loan Agreement for the refinanced debt, which are tested on a quarterly basis. The financial covenants require maintenance of certain leverage and interest coverage ratios. At December 31, 2015, the Company was in compliance with these financial covenants.
7. TAX RECEIVABLE AGREEMENTS
The Company entered into several TRAs in which the Company agrees to make payments to various parties of 85% of the federal, state, local and foreign income tax benefits realized by the Company as a result of certain tax deductions. Payments under the TRAs will be based on the tax reporting positions of the Company and are only required to the extent the Company realizes cash savings as a result of the underlying tax attributes. The cash savings realized by the Company are computed by comparing the actual income tax liability of the Company to the amount of such taxes the Company would have been required to pay had there been no deductions related to the tax attributes discussed below. The Company will retain the benefit of
69
the remaining 15% of the cash savings associated with the TRAs. The Company has entered into the following three TRAs:
• | TRAs with pre-IPO investors for its use of NOLs and other tax attributes existing at the IPO date, all of which is currently held by Fifth Third. |
• | TRAs with Fifth Third, Advent and JPDN Enterprises, LLC ("JPDN"), an affiliate of Charles D. Drucker, our Chief Executive Officer, in which the Company realizes tax deductions as a result of the increases in tax basis from the purchase of Vantiv Holding units or from the exchange of Vantiv Holding units for cash or shares of Class A common stock, as well as the tax benefits attributable to payments made under such TRAs. |
• | A TRA with Mercury shareholders as part of the acquisition of Mercury as a result of the increase in tax basis of the assets of Mercury resulting from the acquisition and the use of the net operating losses and other tax attributes of Mercury that were acquired as part of the acquisition. |
Obligations recorded pursuant to the TRAs are based on estimates of future taxable income and future tax rates. On an annual basis, the Company evaluates the assumptions underlying the TRA obligations. As a result of this process, obligations under the tax receivable agreements with Fifth Third were adjusted in 2014 to reflect the impact of tax planning strategies implemented during the year which are expected to reduce the amount of future obligations. The Company recorded a benefit of $41.3 million in non-operating income (expense) during the year ended December 31, 2014 as a result of the reduction in the TRA obligations with Fifth Third.
As discussed in Note 2 - Business Combinations, the Company entered into the Mercury TRA and recorded a liability of $192.5 million for the Mercury TRA and non-operating expenses of $28.9 million and $14.6 million related to the change in fair value of the Mercury TRA during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
From time to time, the Company enters into repurchase addendums to the TRA agreements. The following table presents the Company's TRA settlements and the impact of these settlements on the Company's consolidated statement of financial position (in thousands):
TRA | Settlement Date | Cash Buyout Payment | Balance Sheet Obligation Prior to Settlement | Deferred Taxes and Other | Net Gain Recorded in Equity | |||||||||||||
Advent & JPDN | October 2013 | $ | (112,562 | ) | $ | 254,400 | $ | 1,144 | $ | 140,694 | ||||||||
Mercury | July 2015 | (44,800 | ) | 44,800 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Fifth Third | October 2015 | (48,866 | ) | 140,024 | 32,967 | 58,191 | ||||||||||||
In addition to the Mercury TRA settlement presented in the table above, the Mercury TRA Addendum contains the following provisions to acquire a significant portion of the remaining Mercury TRA:
• | Beginning December 1st of each of 2015, 2016, 2017, and 2018, and ending June 30th of 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019, respectively, the Company is granted call options (collectively, the "Call Options") pursuant to which certain additional obligations of the Company under the Mercury TRA would be terminated in consideration for cash payments of $41.4 million, $38.1 million, $38.0 million, and $43.0 million, respectively. |
• | In the unlikely event the Company does not exercise the relevant Call Option, the Mercury TRA Holders are granted put options beginning July 10th and ending July 25th of each of 2016, 2017, 2018, and 2019, respectively (collectively, the "Put Options"), pursuant to which certain additional obligations of the Company would be terminated in consideration for cash payments with similar amounts to the Call Options. |
Except to the extent the Company’s obligations under the Mercury TRA have been terminated and settled in full in accordance with the terms of the Mercury TRA Addendum, the Mercury TRA will remain in effect, and the parties thereto will continue to have all rights and obligations thereunder.
70
The Company’s President, Integrated Payments, is a Mercury TRA Holder. Pursuant to the initial payment under the Mercury TRA Addendum, this individual is entitled to receive an aggregate of $0.6 million, and could receive as much as an additional $2.2 million with respect to payments made pursuant to the Mercury TRA Addendum.
All TRA obligations are recorded based on the full and undiscounted amount of the expected future payments, except for the Mercury TRA which represents contingent consideration relating to an acquired business, and is recorded at fair value for financial reporting purposes (see Note 15 - Fair Value Measurements). The following table reflects TRA activity and balances for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 (in thousands):
Balance as of December 31, 2012 | 2013 Secondary Offerings | 2013 TRA Settlements | Balance as of December 31, 2013 | ||||||||||||
TRA with Fifth Third Bank | $ | 165,100 | $ | 329,400 | $ | — | $ | 494,500 | |||||||
TRA with Advent | 183,800 | — | (183,800 | ) | — | ||||||||||
TRA with all pre-IPO investors | 134,100 | — | (68,900 | ) | 65,200 | ||||||||||
TRA with JPDN | 1,700 | — | (1,700 | ) | — | ||||||||||
Total | $ | 484,700 | $ | 329,400 | $ | (254,400 | ) | $ | 559,700 | ||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2013 | 2014 TRA Payment | 2014 Secondary Offering | Acquisition of Mercury | Change in Value | Balance as of December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||
TRA with Fifth Third Bank | $ | 559,700 | $ | (8,639 | ) | $ | 109,400 | $ | — | $ | (40,399 | ) | $ | 620,062 | |||||||||
Mercury TRA | — | — | — | 137,860 | 14,560 | 152,420 | |||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 559,700 | $ | (8,639 | ) | $ | 109,400 | $ | 137,860 | $ | (25,839 | ) | $ | 772,482 | |||||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2014 | 2015 TRA Payment | 2015 TRA Settlements | 2015 Secondary Offering | Purchase Accounting Adjustment | Change in Value | Balance as of December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
TRA with Fifth Third Bank | $ | 620,062 | $ | (22,805 | ) | $ | (140,024 | ) | $ | 376,597 | $ | — | $ | (769 | ) | $ | 833,061 | ||||||||||
Mercury TRA | 152,420 | — | (44,800 | ) | — | 54,647 | 28,940 | 191,207 | |||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 772,482 | $ | (22,805 | ) | $ | (184,824 | ) | $ | 376,597 | $ | 54,647 | $ | 28,171 | $ | 1,024,268 | |||||||||||
As a result of the secondary offerings and exchange of units of Vantiv Holding discussed in Note 12 - Capital Stock, the Company recorded the following (in thousands):
Secondary Offerings by Year | TRA Liability | Deferred Tax Asset | Net Equity | |||||||||
2015 | $ | 376,597 | $ | 355,430 | $ | 21,167 | ||||||
2014 | 109,400 | 92,000 | 17,400 | |||||||||
2013 | 329,400 | 236,400 | 93,000 | |||||||||
The timing and/or amount of aggregate payments due under the TRAs may vary based on a number of factors, including the amount and timing of the taxable income the Company generates in the future and the tax rate then applicable, the use of loss carryovers and amortizable basis. Payments under the TRAs, if necessary, are required to be made no later than January 5th of the second year immediately following the taxable year in which the obligation occurred. Therefore, the Company was not required to make any payments under the TRAs during the year ended December 31, 2013. The first contractually obligated payment under the TRA obligations of approximately $8.6 million was paid during January 2014. An additional payment under the TRA obligations of approximately $22.8 million was paid during January 2015. Additionally, the Company made a payment under the TRA obligations of approximately $53.5 million in January 2016. The January 2016 payment is recorded as current portion of tax receivable agreement obligations on the accompanying consolidated statement of financial position. The term of the TRAs will continue until all such tax benefits have been utilized or expired, unless the Company exercises its right to terminate the TRA for an amount based on the agreed payments remaining to be made under the agreement.
71
8. DERIVATIVES AND HEDGING ACTIVITIES
Risk Management Objective of Using Derivatives
The Company enters into derivative financial instruments to manage differences in the amount, timing and duration of its known or expected cash payments related to its variable-rate debt. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company’s derivative instruments consisted of interest rate swaps, which hedged the variable rate debt by converting floating-rate payments to fixed-rate payments. These swaps are designated as cash flow hedges for accounting purposes.
Accounting for Derivative Instruments
The Company recognizes derivatives in other current and non-current assets or liabilities in the accompanying consolidated statements of financial position at their fair values. Refer to Note 15 - Fair Value Measurements for a detailed discussion of the fair value of its derivatives. The Company designates its interest rate swaps as cash flow hedges of forecasted interest rate payments related to its variable-rate debt.
The Company formally documents all relationships between hedging instruments and underlying hedged transactions, as well as its risk management objective and strategy for undertaking hedge transactions. This process includes linking all derivatives that are designated as cash flow hedges to forecasted transactions. A formal assessment of hedge effectiveness is performed both at inception of the hedge and on an ongoing basis to determine whether the hedge is highly effective in offsetting changes in cash flows of the underlying hedged item. Hedge effectiveness is assessed using a regression analysis. If it is determined that a derivative ceases to be highly effective during the term of the hedge, the Company will discontinue hedge accounting for such derivative.
The Company’s interest rate swaps qualify for hedge accounting under ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging. Therefore, the effective portion of changes in fair value were recorded in AOCI and will be reclassified into earnings in the same period during which the hedged transactions affected earnings.
Cash Flow Hedges of Interest Rate Risk
The Company's objectives in using interest rate derivatives are to add stability to interest expense and to manage its exposure to interest rate movements. To accomplish these objectives, the Company uses interest rate swaps as part of its interest rate risk management strategy. As of December 31, 2015, the Company had a total of 14 outstanding interest rate swaps that were designated as cash flow hedges of interest rate risk. Of the 14 outstanding interest rate swaps, 8 of them cover an exposure period from June 2015 through June 2017 and have a combined notional balance of $1.2 billion (amortizing to $1.1 billion). The remaining 6 interest rate swaps cover an exposure period from January 2016 through January 2019 and have a combined notional balance of $500 million. Fifth Third is the counterparty to 5 of the 14 outstanding interest rate swaps with notional balances ranging from $293.8 million to $250.0 million.
The Company does not offset derivative positions in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. The table below presents the fair value of the Company’s derivative financial instruments designated as cash flow hedges included within the accompanying consolidated statements of financial position (in thousands):
Consolidated Statement of Financial Position Location | December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
Interest rate swaps | Other long-term assets | $ | — | $ | 104 | ||||
Interest rate swaps | Other current liabilities | 9,343 | 5,205 | ||||||
Interest rate swaps | Other long-term liabilities | 9,885 | 2,283 | ||||||
Any ineffectiveness associated with such derivative instruments will be recorded immediately as interest expense in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. As of December 31, 2015, the Company estimates that $10.0 million will be reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income as an increase to interest expense during the next 12 months.
72
The table below presents the pre-tax effect of the Company’s interest rate swaps on the accompanying consolidated statements of comprehensive income for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Derivatives in cash flow hedging relationships: | |||||||||||
Amount of gain (loss) recognized in OCI (effective portion) (1) | $ | (18,836 | ) | $ | (11,240 | ) | $ | 244 | |||
Amount of loss reclassified from accumulated OCI into earnings (effective portion) | (6,990 | ) | (3,040 | ) | (573 | ) | |||||
Amount of loss recognized in earnings (2) | — | (1 | ) | — | |||||||
(1) | "OCI" represents other comprehensive income. |
(2) | For the year ended December 31, 2014, amount represents hedge ineffectiveness. |
Credit Risk Related Contingent Features
The Company has agreements with each of its derivative counterparties that contain a provision where if the Company defaults on any of its indebtedness, then the Company could also be declared in default on its derivative obligations.
As of December 31, 2015, the fair value of derivatives in a net liability position, which includes accrued interest but excludes any adjustment for nonperformance risk, related to these agreements was $20.4 million. As of December 31, 2015, the Company had not posted any collateral related to these agreements. If the Company had breached any of these provisions at December 31, 2015, it could have been required to settle its obligations under the agreements at their termination value of $20.4 million.
9. CONTROLLING AND NON-CONTROLLING INTERESTS
The Company has various non-controlling interests that are accounted for in accordance with ASC 810, Consolidation ("ASC 810"). As discussed in Note 1 - Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, Vantiv, Inc. owns a controlling interest in Vantiv Holding, and therefore consolidates the financial results of Vantiv Holding and its subsidiaries and records non-controlling interest for the economic interests in Vantiv Holding held by Fifth Third. The Exchange Agreement entered into prior to the IPO provides for a 1 to 1 ratio between the units of Vantiv Holding and the common stock of Vantiv, Inc.
In May 2014, the Company entered into a joint venture with a bank partner which provides customers a comprehensive suite of payment solutions. Vantiv Holding owns 51% and the bank partner owns 49% of the joint venture. The joint venture is consolidated by the Company in accordance with ASC 810, with the associated non-controlling interest included in “Net income attributable to non-controlling interests" in the consolidated statements of income. The bank partner contributed a merchant asset portfolio to the joint venture valued at $18.8 million which was recorded to non-controlling interests in the 2014 consolidated statement of equity.
73
As of December 31, 2015, Vantiv, Inc.’s interest in Vantiv Holding was 81.61%. Changes in units and related ownership interest in Vantiv Holding are summarized as follows:
Vantiv, Inc. | Fifth Third | Total | ||||||
As of December 31, 2013 | 141,758,681 | 48,822,826 | 190,581,507 | |||||
% of ownership | 74.38 | % | 25.62 | % | ||||
Fifth Third exchange of Vantiv Holding units for shares of Class A common stock in connection with June 2014 secondary offering | 5,780,000 | (5,780,000 | ) | — | ||||
Share repurchases | (1,936,400 | ) | — | (1,936,400 | ) | |||
Equity plan activity (1) | (147,273 | ) | — | (147,273 | ) | |||
As of December 31, 2014 | 145,455,008 | 43,042,826 | 188,497,834 | |||||
% of ownership | 77.17 | % | 22.83 | % | ||||
Fifth Third exchange of Vantiv Holding units for shares of Class A common stock in connection with December 2015 secondary offering | 8,000,000 | (8,000,000 | ) | — | ||||
Fifth Third exchange of Class C units of Vantiv Holding for shares of Class A common stock in connection with partial warrant exercise | 5,374,592 | — | 5,374,592 | |||||
Share repurchases | (4,445,551 | ) | — | (4,445,551 | ) | |||
Equity plan activity (1) | 1,104,277 | — | 1,104,277 | |||||
As of December 31, 2015 | 155,488,326 | 35,042,826 | 190,531,152 | |||||
% of ownership | 81.61 | % | 18.39 | % | ||||
(1) | Includes stock issued under the equity plans less Class A common stock withheld to satisfy employee tax withholding obligations upon vesting or exercise of employee equity awards and forfeitures of restricted Class A common stock awards. |
As a result of the changes in ownership interests in Vantiv Holding, adjustments of $137.4 million and $58.4 million were recognized during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, in order to reflect the portion of net assets of Vantiv Holding attributable to non-controlling unit holders based on changes in the proportionate ownership interests in Vantiv Holding during those periods.
The table below provides a reconciliation of net income attributable to non-controlling interests based on relative ownership interests as discussed above (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 209,229 | $ | 168,990 | $ | 208,140 | |||||
Items not allocable to non-controlling interests: | |||||||||||
Vantiv, Inc. expenses (1) | 55,111 | 7,725 | 58,520 | ||||||||
Vantiv Holding net income | $ | 264,340 | $ | 176,715 | $ | 266,660 | |||||
Net income attributable to non-controlling interests of Fifth Third (2) | $ | 58,938 | $ | 43,022 | $ | 74,568 | |||||
Net income attributable to joint venture non-controlling interest (3) | 2,345 | 676 | — | ||||||||
Total net income attributable to non-controlling interests | $ | 61,283 | $ | 43,698 | $ | 74,568 | |||||
(1) Primarily represents income tax expense related to Vantiv, Inc. and TRA related expense (credits) (see Note 7 - Tax Receivable Agreements).
(2) Net income attributable to non-controlling interests of Fifth Third reflects the allocation of Vantiv Holding’s net income based on the proportionate ownership interests in Vantiv Holding held by the non-controlling unit holders. The net income attributable to non-controlling unit holders reflects the changes in ownership interests summarized in the table above.
(3) | Reflects net income attributable to the non-controlling interest of the joint venture. |
In connection with the separation from Fifth Third, Fifth Third received a warrant that allows for the purchase of up to 20.4 million Class C Non-Voting Units of Vantiv Holding. The warrant is currently exercisable, in whole or in part, and from time to time. The warrant expires upon the earliest to occur of June 30, 2029 or a change of control where the price paid per unit in such change of control minus the exercise price of the warrant is less than zero. Fifth Third is entitled to purchase the
74
underlying Units of the warrant at a price of $15.98 per unit. The warrant was valued at approximately $65.4 million at June 30, 2009, the issuance date, using a Black-Scholes option valuation model using probability weighted scenarios. The warrant is recorded as a component of the non-controlling interest on the accompanying statements of financial position.
On December 2, 2015, the Company entered into a warrant cancellation agreement (the "Warrant Cancellation Agreement") with Fifth Third to cancel a portion of the warrant. The Warrant Cancellation Agreement cancels the rights under the warrant to purchase 4.8 million Class C Units of Vantiv Holding for aggregate consideration of $200 million paid by the Company to Fifth Third.
Following the effectiveness of the Warrant Cancellation Agreement discussed above, Fifth Third net exercised a portion of the remaining warrants to purchase 5.4 million Class C Units of Vantiv Holding.
After giving effect to the above transactions, at December 31, 2015, Fifth Third holds the rights to purchase 7.8 million Class C Units of Vantiv Holding under the warrant at an exercise price of $15.98 per unit.
10. COMMITMENTS, CONTINGENCIES AND GUARANTEES
Leases
The Company leases office space under non-cancelable operating leases that expire between January 2016 and December 2045. Future minimum commitments under these leases are as follows (in thousands):
Year Ending December 31, | ||||
2016 | $ | 9,539 | ||
2017 | 7,250 | |||
2018 | 5,222 | |||
2019 | 4,941 | |||
2020 | 3,873 | |||
Thereafter | 13,350 | |||
Total | $ | 44,175 | ||
Rent expense for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 was approximately $11.6 million, $9.9 million and $7.0 million, respectively.
Legal Reserve
From time to time, the Company is involved in various litigation matters arising in the ordinary course of its business. While it is impossible to ascertain the ultimate resolution or range of financial liability with respect to these contingent matters, management believes none of these matters, either individually or in the aggregate, would have a material effect upon the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
11. EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS
The Company offers a defined contribution savings plan to virtually all Company employees. The plan provides for elective, tax-deferred participant contributions and Company matching contributions.
Expenses associated with the defined contribution savings plan for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 were $9.1 million, $7.3 million and $5.9 million, respectively.
12. CAPITAL STOCK
Common Stock
Under the Company’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation, the Company is authorized to issue 890,000,000 shares of Class A common stock with a par value of $0.00001 per share and 100,000,000 shares of Class B
75
common stock with no par value per share. The Class A and Class B common stock each provide holders with one vote on all matters submitted to a vote of stockholders; however, the holders of shares of Class B common stock shall be limited to voting power, including voting power associated with any Class A common stock held, of 18.5% at any time other than in connection with a stockholder vote with respect to a change of control. Also, holders of Class B common stock do not have any of the economic rights (including rights to dividends and distributions upon liquidation) provided to the holders of Class A common stock. The holders of Class B common stock hold one share of Class B common stock for each Vantiv Holding Class B unit they hold. The Class B units of Vantiv Holding may be exchanged for shares of Class A common stock on a one-for-one basis or, at the Company's option, for cash equal to the fair value of the shares tendered for exchange. Upon exchange of any Class B units of Vantiv Holding, an equal number of shares of Class B common stock automatically will be cancelled. The Class A common stock and Class B common stock vote together as a single class, except that the holders of Class B common stock are entitled to elect a number of the Company's directors equal to the percentage of the voting power of all of the outstanding common stock represented by the Class B common stock but not exceeding 18.5% of the board of directors. Fifth Third holds all of the issued and outstanding Class B common stock.
As of December 31, 2015, 155,488,326 shares of Class A common stock and 35,042,826 shares of Class B common stock were issued and outstanding.
Secondary Offerings
In May 2013, a secondary offering took place in which selling shareholders sold 40.7 million shares of Vantiv, Inc. Class A common stock. In August and November 2013, secondary offerings took place in which selling shareholders sold 20.0 million and 15.0 million shares, respectively, of Vantiv, Inc. Class A common stock. The Company did not receive any proceeds from these sales.
In March 2014, a secondary offering took place in which Advent sold its remaining 18.8 million shares of the Company's Class A common stock. In June 2014, a secondary offering took place in which Fifth Third sold 5.8 million shares of the Company's Class A common stock. The Company did not receive any proceeds from these sales.
On December 8, 2015, subsequent to the Warrant Cancellation Agreement and the Partial Warrant Exercise described in Note 9 - Controlling and Non-controlling Interests, a secondary offering took place in which Fifth Third sold 13.4 million shares of the Company's Class A common stock. The Company did not receive any proceeds from this sale.
Share Repurchases
In connection with the May 2013 secondary offering discussed above, the Company repurchased approximately 17.5 million shares of its Class A common stock for approximately $400 million. The repurchased shares were retired and accounted for as a reduction to equity in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. In connection with the share repurchase, the Company incurred costs of approximately $0.6 million, which are also reflected as a reduction to equity in the accompanying consolidated statement of equity.
On October 22, 2013, the Company's board of directors approved a program to repurchase up to $137 million of the Company's Class A common stock. During the year ended December 31, 2013, approximately 3.5 million shares were repurchased under this program for approximately $103 million. During the year ended December 31, 2014, approximately 1.1 million shares were repurchased for approximately $34 million, which completed the repurchases under this authorization. The repurchased shares were immediately retired.
On February 12, 2014, the Company's board of directors approved a program to repurchase up to an additional $300 million of the Company's Class A common stock. Purchases under the program may be made from time to time in the open market, in privately negotiated transactions, or otherwise. The manner, timing, and amount of any purchases are determined by management based on an evaluation of market conditions, stock price, and other factors. The share repurchase program has no expiration date and the Company may discontinue purchases at any time that management determines additional purchases are not warranted. During the year ended December 31, 2014, approximately 828,000 shares were repurchased under this program for approximately $25 million. During the year ended December 31, 2015, approximately 4.4 million shares were repurchased for approximately $200 million. The repurchased shares were immediately retired. There is approximately $75 million of share repurchase authority remaining as of December 31, 2015.
76
Preferred Stock
Under the Company’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation, the Company is authorized to issue 10,000,000 shares of preferred stock with a par value of $0.00001 per share. As of December 31, 2015, there was no preferred stock outstanding.
Dividend Restrictions
The Company does not intend to pay cash dividends on its Class A common stock in the foreseeable future. Vantiv, Inc. is a holding company that does not conduct any business operations of its own. As a result, Vantiv, Inc.’s ability to pay cash dividends on its common stock, if any, is dependent upon cash dividends and distributions and other transfers from Vantiv Holding. The amounts available to Vantiv, Inc. to pay cash dividends are subject to the covenants and distribution restrictions in its subsidiaries’ loan agreements. As a result of the restrictions on distributions from Vantiv Holding and its subsidiaries, essentially all of the Company's consolidated net assets are held at the subsidiary level and are restricted as of December 31, 2015.
13. SHARE-BASED COMPENSATION PLANS
The company accounts for share-based compensation plans in accordance with ASC 718, Compensation-Stock Compensation, which requires compensation expense for the grant-date fair value of share-based payments to be recognized over the requisite service period.
2012 Equity Incentive Plan
The 2012 Equity Incentive Plan was adopted by the Company’s board of directors in March 2012. The 2012 Equity Incentive Plan provides for grants of stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock and restricted stock units, performance awards and other stock-based awards. The maximum number of shares of Class A common stock available for issuance pursuant to the 2012 Equity Incentive Plan is 35.5 million shares.
Restricted Stock Awards
The Company grants restricted stock awards to certain employees which vest based on the recipient's continued employment or service to the Company ("Time Awards").
The Company also grants restricted stock awards to certain employees subject to the achievement of certain financial performance measures ("Performance Awards"). These Performance Awards typically vest on the third anniversary of the grant date. Participants have the right to earn 0% to 200% of the target number of shares of the Company’s Class A common stock, determined by the level of achievement of the financial performance measures during the performance period.
The weighted-average grant date fair value of the restricted stock awards is based on the quoted fair market value of our common stock on the grant date. The total grant date fair value of restricted stock awards vested was $18.0 million, $20.1 million and $22.4 million in 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
The following table presents the number and weighted-average grant date fair value of the restricted stock awards for the year ended December 31, 2015:
Restricted Class A Common Stock - Time Awards | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | Restricted Class A Common Stock - Performance Awards | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | ||||||||||
Non-vested at December 31, 2014 | 240,087 | $ | 4.01 | 1,013,211 | $ | 17.00 | |||||||
Granted | 153,327 | 38.74 | 347,934 | 37.82 | |||||||||
Vested | (202,477 | ) | 4.07 | (1,013,211 | ) | 17.00 | |||||||
Forfeited | (24,483 | ) | 8.82 | (15,094 | ) | 37.10 | |||||||
Non-vested at December 31, 2015 | 166,454 | $ | 35.22 | 332,840 | $ | 37.86 | |||||||
77
Restricted Stock Units
The Company issues restricted stock units to directors and certain employees, which typically vest on the first anniversary of the grant date (for directors) and in equal annual increments over three to four years beginning on the first anniversary of the date of grant (for employees). The grant date fair value of the restricted stock units is based on the quoted fair market value of our common stock at the award date. The total grant date fair value of restricted stock units vested was $6.8 million, $3.7 million and $0.1 million in 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
The following table presents the number and weighted-average grant date fair value of the restricted stock units for the year ended December 31, 2015:
Restricted Stock Units | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | |||||
Non-vested at December 31, 2014 | 980,495 | $ | 26.41 | |||
Granted | 435,594 | 38.42 | ||||
Vested | (258,480 | ) | 26.41 | |||
Forfeited | (169,602 | ) | 29.03 | |||
Non-vested at December 31, 2015 | 988,007 | $ | 31.24 | |||
Stock Options
The Company grants stock options to certain key employees. The stock options vest in 25% annual increments beginning on the first anniversary of the date of grant, subject to the participant's continued service through each such vesting date. All stock options are nonqualified stock options and expire on the tenth anniversary of the grant date.
During the year ended December 31, 2014, under the terms of the Mercury transaction agreement, the Company replaced unvested employee stock options held by certain employees of Mercury. The number of replacement stock options was based on a conversion factor into equivalent stock options of the Company on the acquisition date. The weighted average fair value of the replacement options was calculated on the acquisition date using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The replacement stock options typically vest over four and a half years with 22.22% of the awards vesting after one year and the remainder in quarterly increments, subject to the participant's continued service through each such vesting date. Per the applicable option agreement, if a participant is terminated without cause within the prescribed acceleration period (which range from 12 to 24 months following the acquisition), then such replacement options shall immediately become fully vested and exercisable at the time of such termination to the extent not then vested and not previously cancelled. The replacement options are nonqualified stock options and expire on the tenth anniversary of the grant date. See Note 2 - Business Combinations for additional details.
78
The following table summarizes stock option activity for the year ended December 31, 2015:
Stock Options | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term (Years) | Aggregate Intrinsic Value (in thousands) | |||||||||
Outstanding options at December 31, 2014 | 2,732,760 | $ | 21.10 | 8.40 | $ | 35,039 | ||||||
Granted | 707,738 | 37.10 | ||||||||||
Exercised | (777,204 | ) | 17.54 | $ | 17,531 | |||||||
Expired | — | — | ||||||||||
Forfeited | (353,051 | ) | 24.11 | |||||||||
Outstanding options at December 31, 2015 | 2,310,243 | $ | 26.74 | 8.01 | $ | 47,780 | ||||||
Options exercisable at December 31, 2015 | 540,231 | $ | 21.20 | 7.28 | $ | 14,166 | ||||||
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, the total grant date fair value of options vested was $13.9 million and $10.2 million, respectively. There were no options vested or exercisable during 2013. The weighted-average grant date fair value was estimated by the Company using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the assumptions below:
2014 | ||||||||
2015 | Vantiv Grant | Mercury Replacement Options | 2013 | |||||
Number of options granted | 707,738 | 710,297 | 1,750,519 | 659,938 | ||||
Weighted average exercise price | $37.10 | $31.02 | $10.18 - $29.79 | $21.95 | ||||
Expected option life at grant (in years) | 6.25 | 6.25 | 3.00 - 6.00 | 6.25 | ||||
Expected volatility | 26.33% | 25.00% | 24.80% - 30.80% | 30.60% | ||||
Expected dividend yield | —% | —% | —% | —% | ||||
Risk-free interest rate | 1.67% | 1.93% | 0.93% - 1.96% | 1.15% | ||||
Fair value | $11.04 | $9.07 | $17.75 - $22.10 | $7.10 | ||||
The expected option life represents the period of time the stock options are expected to be outstanding and is based on the "simplified method" allowed under SEC guidance. The Company used the "simplified method" due to the lack of sufficient historical exercise data to provide a reasonable basis upon which to otherwise estimate the expected life of the stock options. Since the Company's publicly traded stock history is relatively short, expected volatility is based on the Company's historical volatility and the historical volatility of a group of peer companies. The Company does not intend to pay cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Consequently, the Company used an expected dividend yield of zero. The risk-free interest rate was based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of the grant.
Performance Share Units
The Company issues performance share units to certain employees subject to the achievement of certain financial performance measures. These performance share units vest on the third anniversary of the grant date. Participants have the right to earn 0% to 200% of the target number of shares of the Company’s Class A common stock, determined by the level of achievement of the financial performance measures during the three year performance period. In 2015 the Company also issued performance share units to certain employees subject to the achievement of certain financial and non-financial performance measures through 2018.
Additionally, associated with an acquisition in 2013 the Company issued performance share units to certain employees subject to the achievement of certain financial and non-financial performance measures through 2016.
The weighted-average grant date fair value of the performance share units is based on the quoted fair market value of our common stock on the grant date. For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, total grant date fair value of performance share units vested was $0.8 million and $1.9 million, respectively. There were no performance share units vested during 2013.
79
The following table presents the number and weighted-average grant date fair value of the performance share units for the year ended December 31, 2015:
Performance Share Units | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | |||||
Non-vested at December 31, 2014 | 508,097 | $ | 27.76 | |||
Granted | 122,134 | 39.16 | ||||
Vested | (26,358 | ) | 31.60 | |||
Forfeited | (131,355 | ) | 30.51 | |||
Non-vested at December 31, 2015 | 472,518 | $ | 29.73 | |||
The share-based compensation expense related to the performance share units granted in 2013 ("2013 PSUs") was initially estimated based on target performance and was adjusted as appropriate throughout the performance period based on the shares expected to be earned at that time. The 2013 PSUs are included in the table above as non-vested at December 31, 2015 at target, or 100%. On February 1, 2016, the Compensation Committee of our Board of Directors certified the achievement of the performance goals for the 2013 PSUs, which had a performance period of January 1, 2013 to December 31, 2015, at the maximum 200% of the target number of shares (173,714 shares incremental to those included in the table above for the 2013 PSUs).
For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, total share-based compensation expense was $30.5 million, $42.2 million and $29.7 million, respectively. Related tax benefits recorded in the accompanying consolidated statements of income totaled $8.8 million in 2015, $12.9 million in 2014 and $8.5 million in 2013. At December 31, 2015, there was approximately $51.1 million of unrecognized share-based compensation expense, which is expected to be recognized over a remaining weighted-average period of approximately 2.6 years.
14. INCOME TAXES
In accordance with ASC Topic 740, Income Taxes, income taxes are recognized for the amount of taxes payable for the current year and for the impact of deferred tax liabilities and assets, which represent future tax consequences of events that have been recognized differently in the financial statements than for tax purposes. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are established using the enacted statutory tax rates and are adjusted for any changes in such rates in the period of change. Vantiv, Inc. is taxed as a C Corporation, which is subject to both federal and state taxation at a corporate level. Therefore, tax expense and deferred tax assets and liabilities reflect such status.
The following is a summary of applicable income taxes (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||
Current income tax expense: | ||||||||||||
U.S. income taxes | $ | 28,586 | $ | 29,234 | $ | 48,494 | ||||||
State and local income taxes | 4,311 | 4,474 | 3,926 | |||||||||
Total current tax expense | 32,897 | 33,708 | 52,420 | |||||||||
Deferred income tax expense: | ||||||||||||
U.S. income taxes | 55,553 | 36,070 | 30,264 | |||||||||
State and local income taxes | (273 | ) | (3,601 | ) | 1,076 | |||||||
Total deferred tax expense | 55,280 | 32,469 | 31,340 | |||||||||
Applicable income tax expense | $ | 88,177 | $ | 66,177 | $ | 83,760 | ||||||
80
A reconciliation of the U.S. income tax rate and the Company's effective tax rate for all periods is provided below:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
Federal statutory tax rate | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | |||
State taxes-net of federal benefit | 2.7 | 2.6 | 2.7 | ||||||
Effect of changes in deferred tax rates | (1.9 | ) | (3.1 | ) | — | ||||
Non-controlling interest | (5.9 | ) | (5.6 | ) | (8.5 | ) | |||
Other-net | (0.3 | ) | (0.8 | ) | (0.5 | ) | |||
Effective tax rate | 29.6 | % | 28.1 | % | 28.7 | % | |||
Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are comprised of the following as of December 31 (in thousands):
2015 | 2014 | |||||||
Deferred tax assets | ||||||||
Net operating losses | $ | 25,569 | $ | 29,296 | ||||
Employee benefits | 55 | 46 | ||||||
Other assets | 2,316 | 813 | ||||||
Other accruals and reserves | 79,925 | 55,427 | ||||||
Partnership basis | 728,532 | 430,525 | ||||||
Deferred tax assets | 836,397 | 516,107 | ||||||
Deferred tax liabilities | ||||||||
Property and equipment | (9,840 | ) | (7,849 | ) | ||||
Goodwill and intangible assets | (109,988 | ) | (98,675 | ) | ||||
Deferred tax liability | (119,828 | ) | (106,524 | ) | ||||
Deferred tax asset-net | $ | 716,569 | $ | 409,583 | ||||
As part of the acquisitions of NPC Group, Inc. ("NPC") and Mercury, the Company acquired federal and state tax loss carryforwards. As of December 31, 2015, the cumulative federal and state tax loss carryforwards were approximately $58.5 million and $106.5 million, respectively. Federal tax loss carryforwards will expire between 2027 and 2034, and state tax loss carryforwards will expire between 2016 and 2035.
The partnership basis included in the above table is the result of a difference between the tax basis and book basis of Vantiv, Inc.'s investment in Vantiv Holding. Vantiv Holding, a partnership for tax purposes, has an Internal Revenue Code election in place to adjust the tax basis of partnership property to fair market value related to the portion of the partnership interest transferred, through an exchange of units of Vantiv Holding by its members. Included in partnership basis in the table above are deferred tax assets resulting from the increase in tax basis generated by the exchange of units of Vantiv Holding by Fifth Third and JPDN in connection with the IPO and subsequent secondary offerings. See Note 7 - Tax Receivable Agreements for discussion of deferred tax assets as a result of the secondary offerings and exchange of units of Vantiv Holding.
Deferred tax assets are reviewed to determine whether the available evidence allows the Company to recognize the tax benefits. To the extent that a tax asset is not expected to be realized, the Company records a valuation allowance against the deferred tax assets. The Company has recorded no valuation allowance during the years ended December 31, 2015 or 2014.
A provision for federal, state and local income taxes has been recorded on the statements of income for the amounts of such taxes the Company is obligated to pay or amounts refundable to the Company. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company recorded an income tax receivable of approximately $53.2 million and $9.4 million, respectively, which is included in other current assets on the Company's consolidated statements of financial position.
The Company accounts for uncertainty in income taxes under ASC 740, Income Taxes. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company had no material uncertain tax positions. If a future liability does arise related to uncertainty in income taxes, the Company has elected an accounting policy to classify interest and penalties, if any, as income tax expense.
81
Accordingly, a loss contingency is recognized when it is probable that a liability has been incurred as of the date of the financial statements and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. Any amount recognized would be subject to estimate and management judgment with respect to the likely outcome of each uncertain tax position. The amount that is ultimately sustained for an individual uncertain tax position or for all uncertain tax positions in the aggregate could differ from the amount recognized.
15. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. The Company uses the hierarchy prescribed in ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement, based upon the available inputs to the valuation and the degree to which they are observable or not observable in the market. The three levels in the hierarchy are as follows:
• | Level 1 Inputs—Quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets that are accessible as of the measurement date. |
• | Level 2 Inputs—Inputs other than quoted prices within Level 1 that are observable either directly or indirectly, including but not limited to quoted prices in markets that are not active, quoted prices in active markets for similar assets or liabilities and observable inputs other than quoted prices such as interest rates or yield curves. |
• | Level 3 Inputs—Unobservable inputs reflecting the Company’s own assumptions about the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability, including assumptions about risk. |
The following table summarizes assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 (in thousands):
2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Fair Value Measurements Using | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
Assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate swaps | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 104 | $ | — | |||||||||||
Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate swaps | $ | — | $ | 19,228 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 7,488 | $ | — | |||||||||||
Mercury TRA | — | — | 191,207 | — | — | 152,420 | |||||||||||||||||
Interest Rate Swaps
The Company uses interest rate swaps to manage interest rate risk. The fair value of interest rate swaps is determined using the market standard methodology of netting the discounted future fixed cash receipts (or payments) and the discounted expected variable cash payments (or receipts). The variable cash payments (or receipts) are based on the expectation of future interest rates (forward curves) derived from observed market interest rate curves. In addition, to comply with the provisions of ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements, credit valuation adjustments, which consider the impact of any credit enhancements to the contracts, are incorporated in the fair values to account for potential nonperformance risk. In adjusting the fair value of its interest rate swaps for the effect of nonperformance risk, the Company has considered any applicable credit enhancements such as collateral postings, thresholds, mutual puts, and guarantees.
Although the Company determined that the majority of the inputs used to value its interest rate swaps fell within Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy, the credit valuation adjustments associated with its interest rate swaps utilized Level 3 inputs, such as estimates of current credit spreads to evaluate the likelihood of default by itself and its counterparties. However, as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company assessed the significance of the impact of the credit valuation adjustments on the overall valuation of its interest rate swaps and determined that the credit valuation adjustment was not significant to the overall valuation of its interest rate swaps. As a result, the Company classified its interest rate swap valuations in Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy. See Note 8 - Derivatives and Hedging Activities for further discussion of the Company’s interest rate swaps.
82
Mercury TRA
The Mercury TRA is considered contingent consideration as it is part of the consideration payable to the former owners of Mercury. Such contingent consideration is measured at fair value and is based on significant inputs not observable in the market, which is classified in Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy. The Mercury TRA is recorded at fair value based on estimates of discounted future cash flows associated with the estimated payments to the Mercury TRA Holders. The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of the Mercury TRA are the discount rate, projections of taxable income and effective tax rates. Significant increases (decreases) in any of those inputs in isolation would result in a significantly lower (higher) fair value measurement. The liability recorded is re-measured at fair value at each reporting period with the change in fair value recognized in earnings as a non-operating expense. See Note 2 - Business Combinations and Note 7 - Tax Receivable Agreements for further discussion of the Mercury TRA including the roll forward of the fair value.
The following table summarizes carrying amounts and estimated fair values for financial assets and liabilities, excluding assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis, as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 (in thousands):
2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||
Carrying Amount | Fair Value | Carrying Amount | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
Note payable | $ | 3,060,139 | $ | 3,064,989 | $ | 3,393,738 | $ | 3,310,181 | |||||||
We consider that the carrying value of cash and cash equivalents, receivables, accounts payable and accrued expenses approximates fair value (level 1) given the short-term nature of these items. The fair value of the Company’s note payable was estimated based on rates currently available to the Company for bank loans with similar terms and maturities and is classified in Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy.
16. NET INCOME PER SHARE
Basic net income per share is calculated by dividing net income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. by the weighted-average shares of Class A common stock outstanding during the period.
Diluted net income per share is calculated assuming that Vantiv Holding is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Vantiv, Inc., therefore eliminating the impact of Fifth Third's non-controlling interest. Pursuant to the Exchange Agreement, the Class B units of Vantiv Holding ("Class B units"), which are held by Fifth Third and represent the non-controlling interest in Vantiv Holding, are convertible into shares of Class A common stock on a one-for-one basis. Based on this conversion feature, diluted net income per share is calculated assuming the conversion of the Class B units on an "if-converted" basis. Due to the Company's structure as a C corporation and Vantiv Holding's structure as a pass-through entity for tax purposes, the numerator in the calculation of diluted net income per share is adjusted accordingly to reflect the Company's income tax expense assuming the conversion of the Fifth Third non-controlling interest into Class A common stock. The adjusted effective tax rate used in the calculation was 36.0%, 36.5% and 38.5% for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. As of December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, there were approximately 35.0 million, 43.0 million and 48.8 million Class B units outstanding, respectively.
In addition to the Class B units discussed above, potentially dilutive securities during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 included restricted stock awards, the warrant held by Fifth Third which allows for the purchase of Class C units of Vantiv Holding (the "Fifth Third Warrant"), stock options and performance share units. During the year ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, approximately 472,518, 508,097 and 430,490, respectively, performance share units have been excluded as the applicable performance metrics had not been met as of the reporting dates.
The shares of Class B common stock do not share in the earnings or losses of the Company and are therefore not participating securities. Accordingly, basic and diluted net income per share of Class B common stock has not been presented.
83
The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted net income per share (in thousands, except share data):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Basic: | |||||||||||
Net income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. | $ | 147,946 | $ | 125,292 | $ | 133,572 | |||||
Shares used in computing basic net income per share: | |||||||||||
Weighted-average Class A common shares | 145,044,577 | 141,936,933 | 138,836,314 | ||||||||
Basic net income per share | $ | 1.02 | $ | 0.88 | $ | 0.96 | |||||
Diluted: | |||||||||||
Consolidated income before applicable income taxes | $ | 297,406 | $ | 235,167 | $ | 291,900 | |||||
Income tax expense excluding impact of non-controlling interest | 107,066 | 85,836 | 112,382 | ||||||||
Net income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. | $ | 190,340 | $ | 149,331 | $ | 179,518 | |||||
Shares used in computing diluted net income per share: | |||||||||||
Weighted-average Class A common shares | 145,044,577 | 141,936,933 | 138,836,314 | ||||||||
Weighted-average Class B units of Vantiv Holding | 42,521,087 | 45,472,332 | 57,906,592 | ||||||||
Warrant | 11,866,595 | 10,121,483 | 7,522,801 | ||||||||
Restricted stock awards | 696,273 | 1,321,890 | 1,751,816 | ||||||||
Stock options | 545,180 | 318,175 | 10,034 | ||||||||
Performance share units | 260,730 | — | — | ||||||||
Diluted weighted-average shares outstanding | 200,934,442 | 199,170,813 | 206,027,557 | ||||||||
Diluted net income per share | $ | 0.95 | $ | 0.75 | $ | 0.87 | |||||
84
17. ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
The activity of the components of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) related to cash flow hedging and other activities for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 is presented below (in thousands):
Total Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
AOCI Beginning Balance | Pretax Activity | Tax Effect | Net Activity | Attributable to non-controlling interests | Attributable to Vantiv, Inc. | AOCI Ending Balance | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net change in fair value recorded in accumulated OCI | $ | (5,288 | ) | $ | (18,836 | ) | $ | 5,490 | $ | (13,346 | ) | $ | 4,298 | $ | (9,048 | ) | $ | (14,336 | ) | |||||||||
Net realized loss reclassified into earnings (a) | 1,732 | 6,990 | (2,065 | ) | 4,925 | (1,525 | ) | 3,400 | 5,132 | |||||||||||||||||||
Other | (212 | ) | 212 | — | 212 | — | 212 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net change | $ | (3,768 | ) | $ | (11,634 | ) | $ | 3,425 | $ | (8,209 | ) | $ | 2,773 | $ | (5,436 | ) | $ | (9,204 | ) | |||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net change in fair value recorded in accumulated OCI | $ | (5 | ) | $ | (11,240 | ) | $ | 3,114 | $ | (8,126 | ) | $ | 2,843 | $ | (5,283 | ) | $ | (5,288 | ) | |||||||||
Net realized loss reclassified into earnings (a) | 269 | 3,040 | (874 | ) | 2,166 | (703 | ) | 1,463 | 1,732 | |||||||||||||||||||
Other | — | (212 | ) | — | (212 | ) | — | (212 | ) | (212 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Net change | $ | 264 | $ | (8,412 | ) | $ | 2,240 | $ | (6,172 | ) | $ | 2,140 | $ | (4,032 | ) | $ | (3,768 | ) | ||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net change in fair value recorded in accumulated OCI | $ | — | $ | 244 | $ | 3 | $ | 247 | $ | (252 | ) | $ | (5 | ) | $ | (5 | ) | |||||||||||
Net realized loss reclassified into earnings (a) | — | 573 | (157 | ) | 416 | (147 | ) | 269 | 269 | |||||||||||||||||||
Net change | $ | — | $ | 817 | $ | (154 | ) | $ | 663 | $ | (399 | ) | $ | 264 | $ | 264 | ||||||||||||
(a) The reclassification adjustment on cash flow hedge derivatives affected the following lines in the accompanying consolidated statements of income:
OCI Component | Affected line in the accompanying consolidated statements of income | ||||||||||
Pretax activity(1) | Interest expense-net | ||||||||||
Tax effect | Income tax expense | ||||||||||
OCI attributable to non-controlling interests | Net income attributable to non-controlling interests | ||||||||||
(1) The years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, reflect amounts of losses reclassified from AOCI into earnings, representing the effective portion of the hedging relationships, and are recorded in interest expense-net. | |||||||||||
18. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
In connection with the Company's separation from Fifth Third on June 30, 2009, the Company entered into various agreements which provide for services provided to or received from Fifth Third. Subsequent to the separation from Fifth Third, the Company continues to enter into various business agreements with Fifth Third. Transactions under these agreements are discussed below and throughout these notes to the accompanying consolidated financial statements. As discussed in Note 1 - Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, Fifth Third currently holds 35,042,826 shares of Class B common stock representing 18.4% of the voting interests in Vantiv, Inc. and 35,042,826 Class B units of Vantiv Holding representing a 18.4% ownership interest in Vantiv Holding. In addition, in connection with the separation from Fifth Third, Fifth Third received a warrant that allows for the purchase of up to 20.4 million Class C Non-Voting Units of Vantiv Holding. As discussed in Note 9 - Controlling and Non-Controlling Interests, as a result of the Warrant Cancellation Agreement and the Fifth Third net exercise of a portion of the remaining warrant, at December 31, 2015, Fifth Third holds the rights to purchase 7,791,956 Class C Units of Vantiv Holding under the warrant.
85
Debt Agreements
As discussed in Note 6 - Long-Term Debt, the Company had certain debt arrangements outstanding and available from Fifth Third. For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, interest expense associated with these arrangements was $4.4 million, $5.4 million and $7.3 million, respectively, and commitment fees were $0.2 million, $0.2 million and $0.3 million, respectively.
Master Lease Agreement/Master Sublease Agreement
On July 1, 2009, the Company entered into a five-year Master Lease Agreement and a five-year Master Sublease Agreement with Fifth Third and certain of its affiliates, that remains in effect in accordance with its terms, for the lease or sublease of a number of office and/or data center locations. Related party rent expense was approximately $3.8 million, $3.8 million and $3.6 million, respectively, for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013.
Referral Agreement
On June 30, 2009, the Company entered into an exclusive referral arrangement with Fifth Third. Commercial and retail merchant clients of Fifth Third and its subsidiary depository institutions that request merchant (credit or debit card) acceptance services are referred exclusively to us. In return for these referrals and the resulting merchant relationships, we make ongoing incentive payments to Fifth Third. The agreement also provides for our referral of prospective banking clients to Fifth Third, in return for certain incentive payments. This agreement terminates in June 2019. Costs associated with this agreement totaled $0.3 million, $0.3 million and $0.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Clearing, Settlement and Sponsorship Agreement and Treasury Management Agreement
As discussed in Note 1 - Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, Fifth Third is a member of the Visa, MasterCard and other payment network associations. Fifth Third is the Company's primary sponsor into the respective card associations. Fifth Third also provides access to certain cash and treasury management services to the Company. For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company paid Fifth Third approximately $2.3 million, $2.8 million and $2.2 million, respectively, for these services. As discussed in Note 1 - Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, the Company holds certain cash and cash equivalents on deposit at Fifth Third. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, approximately $149.7 million and $362.8 million, respectively, was held on deposit at Fifth Third. Interest income on such amounts during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 was approximately $1.7 million and $1.4 million, respectively. The interest income on such amounts during 2015 was immaterial.
Transition Services Agreement
In conjunction with the Company's separation from Fifth Third, the Company entered into a transition services agreement ("TSA") with Fifth Third. The TSA terminated on October 31, 2011. Subsequent to such date, the Company continues to receive certain non-material services from Fifth Third. The total for services provided by Fifth Third for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 were $0.4 million, $0.5 million and $0.5 million, respectively.
19. SEGMENT INFORMATION
Segment operating results are presented below (in thousands). The results reflect revenues and expenses directly related to each segment. The Company does not evaluate performance or allocate resources based on segment asset data, and therefore such information is not presented.
Segment profit reflects total revenue less network fees and other costs and sales and marketing costs of the segment. The Company’s CODM evaluates this metric in analyzing the results of operations for each segment.
86
Year Ended December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||
Merchant Services | Financial Institution Services | Total | |||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 2,656,906 | $ | 503,032 | $ | 3,159,938 | |||||
Network fees and other costs | 1,321,312 | 156,890 | 1,478,202 | ||||||||
Sales and marketing | 478,736 | 25,213 | 503,949 | ||||||||
Segment profit | $ | 856,858 | $ | 320,929 | $ | 1,177,787 | |||||
Year Ended December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||
Merchant Services | Financial Institution Services | Total | |||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 2,100,367 | $ | 476,836 | $ | 2,577,203 | |||||
Network fees and other costs | 1,033,801 | 140,864 | 1,174,665 | ||||||||
Sales and marketing | 367,998 | 28,355 | 396,353 | ||||||||
Segment profit | $ | 698,568 | $ | 307,617 | $ | 1,006,185 | |||||
Year Ended December 31, 2013 | |||||||||||
Merchant Services | Financial Institution Services | Total | |||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 1,639,157 | $ | 468,920 | $ | 2,108,077 | |||||
Network fees and other costs | 801,463 | 133,978 | 935,441 | ||||||||
Sales and marketing | 286,200 | 25,844 | 312,044 | ||||||||
Segment profit | $ | 551,494 | $ | 309,098 | $ | 860,592 | |||||
A reconciliation of total segment profit to the Company’s income before applicable income taxes is as follows (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Total segment profit | $ | 1,177,787 | $ | 1,006,185 | $ | 860,592 | |||||
Less: Other operating costs | (284,066 | ) | (242,439 | ) | (200,630 | ) | |||||
Less: General and administrative | (182,369 | ) | (173,986 | ) | (121,707 | ) | |||||
Less: Depreciation and amortization | (276,942 | ) | (275,069 | ) | (185,453 | ) | |||||
Less: Interest expense—net | (105,736 | ) | (79,701 | ) | (40,902 | ) | |||||
Less: Non-operating income (expense) | (31,268 | ) | 177 | (20,000 | ) | ||||||
Income before applicable income taxes | $ | 297,406 | $ | 235,167 | $ | 291,900 | |||||
87
20. QUARTERLY CONSOLIDATED RESULTS OF OPERATIONS (UNAUDITED)
The following table sets forth our unaudited results of operations on a quarterly basis for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014.
Dec 31, 2015 | Sep 30, 2015 | Jun 30, 2015 | Mar 31, 2015 | Dec 31, 2014 | Sep 30, 2014 | Jun 30, 2014 | Mar 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 852,334 | $ | 815,998 | $ | 785,995 | $ | 705,611 | $ | 733,785 | $ | 697,109 | $ | 608,731 | $ | 537,578 | |||||||||||||||
Network fees and other costs | 399,159 | 385,548 | 362,349 | 331,146 | 331,635 | 316,592 | 277,392 | 249,046 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net revenue | 453,175 | 430,450 | 423,646 | 374,465 | 402,150 | 380,517 | 331,339 | 288,532 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Sales and marketing | 132,488 | 132,481 | 122,925 | 116,055 | 116,169 | 111,233 | 90,507 | 78,444 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Other operating costs | 72,213 | 66,563 | 76,551 | 68,739 | 64,657 | 60,659 | 56,754 | 60,369 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
General and administrative | 45,974 | 41,492 | 47,060 | 47,843 | 47,406 | 45,422 | 48,552 | 32,606 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 70,843 | 70,638 | 67,659 | 67,802 | 70,893 | 65,289 | 89,041 | 49,846 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Income from operations | $ | 131,657 | $ | 119,276 | $ | 109,451 | $ | 74,026 | $ | 103,025 | $ | 97,914 | $ | 46,485 | $ | 67,267 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 70,392 | $ | 59,148 | $ | 52,693 | $ | 26,996 | $ | 81,741 | $ | 42,845 | $ | 3,313 | $ | 41,091 | |||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to Vantiv, Inc. | $ | 50,929 | $ | 41,492 | $ | 36,536 | $ | 18,989 | $ | 68,579 | $ | 29,986 | $ | (1,409 | ) | $ | 28,136 | ||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) per share attributable to Vantiv, Inc. Class A common stock: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.35 | $ | 0.29 | $ | 0.25 | $ | 0.13 | $ | 0.48 | $ | 0.21 | $ | (0.01 | ) | $ | 0.20 | ||||||||||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.31 | $ | 0.27 | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.13 | $ | 0.35 | $ | 0.20 | $ | (0.01 | ) | $ | 0.18 | ||||||||||||||
Our results of operations are subject to seasonal fluctuations in our revenue as a result of consumer spending patterns. Historically our revenues have been the strongest in the fourth quarter and weakest in our first quarter.
* * * * *
88
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2015. The term "disclosure controls and procedures," as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, means controls and other procedures of a company that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports it files or submits under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is accumulated and communicated to the company’s management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives. Based on the evaluation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2015, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that, as of such date, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act. Our internal control system is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also controls deemed effective now may become inadequate in the future because of changes in conditions, or because compliance with the policies or procedures has deteriorated or been circumvented.
Under the supervision and with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, our management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015. In making this assessment, management used the criteria established in the Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (the "COSO criteria"). Based on management’s assessment and the COSO criteria, management believes that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2015.
Deloitte & Touche LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, has audited the consolidated financial statements included in this Form 10-K and, as part of the audit, has issued a report, included herein, on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the three months ended December 31, 2015 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
89
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Vantiv, Inc.
Symmes Township, Ohio
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Vantiv, Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2015, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The Company's management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company's principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the company's board of directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including the possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements due to error or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015, based on the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule as of and for the year ended December 31, 2015 of the Company and our report dated February 10, 2016 expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements and financial statement schedule.
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
Cincinnati, Ohio
February 10, 2016
90
Item 9B. Other Information
None
91
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to Vantiv's Proxy Statement for its 2016 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015.
We have adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics that applies to all of our directors, officers and employees, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer. The Code of Business Conduct and Ethics is available on our website (http://investors.vantiv.com) under "Corporate Governance." We will also provide a copy of these documents to any person, without charge, upon request, by writing to us at Vantiv, Inc., Investor Relations Department, 8500 Governor's Hill Drive, Symmes Township, Ohio 45249. We intend to satisfy the disclosure requirement under Item 5.05 of Form 8-K regarding an amendment to, or waiver from, a provision of our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics by posting such information on our website at the address and the location specified above.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this item will be set forth in the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Securities Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
Except as included below regarding equity compensation plan information, the information required by this item will be set forth in the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Equity Compensation Plan Information
The following table sets forth information as of December 31, 2015 regarding the Company's equity compensation plans. The only plan pursuant to which the Company may currently make additional equity grants is the Vantiv, Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan.
[a] | [b] | [c] | |||||
Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights (1) | Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights | Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column [a]) | |||||
Plan category | |||||||
Equity compensation plans approved by stockholders | 3,125,824 | $30.47 | 25,808,526 | (2) | |||
Equity compensation plans not approved by stockholders | — | — | — | ||||
Total | 3,125,824 | $30.47 | 25,808,526 | (2)(3) | |||
(1) | Column [a] includes the following outstanding equity-based awards: |
• | 1,603,495 stock options; |
• | 1,049,811 restricted stock units; and |
• | 472,518 performance share units. |
(2) | The 2012 Equity Incentive Plan had 35.5 million shares initially authorized for issuance. In addition to these 35.5 million shares, the following shares will become available for grant under the 2012 Equity Incentive Plan, and, to the extent such shares became available as of December 31, 2015, they are included in the table above as available for grant: (i) shares covered by outstanding awards under the 2012 Equity Incentive Plan that are forfeited or otherwise terminated or settled in cash or other property rather than settled through the issuance of shares; and (ii) shares that are used to pay the exercise price of stock options and shares used to pay withholding taxes on equity awards generally. |
(3) | Additionally, at the time of the acquisition of Mercury Payment Systems, LLC, the Company registered and issued 1.8 million shares under the Mercury Payment Systems, LLC 2010 Unit Incentive Plan, as Restated and Assumed by |
92
Vantiv, Inc. The awards issued were stock options, which have been excluded in the table above. As of December 31, 2015 there were 706,748 outstanding options remaining with a weighted-average exercise price of $16.85.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions and Director Independence
The information required by this item will be set forth in the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information required by this item will be set forth in the Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
93
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
(a)(1) Consolidated Financial Statements
Our consolidated financial statements are set forth in "Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" of this report.
(a)(2) Financial Statement Schedules
Schedule I - Condensed Financial Information of Registrant
All other financial statement schedules have been omitted because they are not applicable, not material or the required information is presented in the financial statements or the notes thereto.
(a)(3) Exhibits
See the Exhibit Index immediately following the signature page of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, which is incorporated herein by reference.
94
SCHEDULE I - Condensed Financial Information of Registrant
Vantiv, Inc.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME (PARENT COMPANY ONLY)
(In thousands)
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||
General and administrative | $ | 745 | $ | 181 | $ | — | ||||||
Income (loss) from operations | (745 | ) | (181 | ) | — | |||||||
Non-operating income (expense), net | (359 | ) | 40,399 | — | ||||||||
Income before income taxes and equity in net income of subsidiaries | (1,104 | ) | 40,218 | — | ||||||||
Income tax expense | 54,007 | 47,943 | 58,520 | |||||||||
Loss before equity in net income of subsidiaries | (55,111 | ) | (7,725 | ) | (58,520 | ) | ||||||
Equity in net income of subsidiaries | 203,057 | 133,017 | 192,092 | |||||||||
Net income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. | $ | 147,946 | $ | 125,292 | $ | 133,572 | ||||||
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Parent Company only).
95
SCHEDULE I - Condensed Financial Information of Registrant
Vantiv, Inc.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (PARENT COMPANY ONLY)
(In thousands)
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||
Net income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. | $ | 147,946 | $ | 125,292 | $ | 133,572 | ||||||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | (5,436 | ) | (4,032 | ) | 264 | |||||||
Comprehensive income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. | $ | 142,510 | $ | 121,260 | $ | 133,836 | ||||||
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Parent Company only).
96
SCHEDULE I - Condensed Financial Information of Registrant
Vantiv, Inc.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION (PARENT COMPANY ONLY)
(In thousands)
December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | ||||||
Assets | |||||||
Current assets: | |||||||
Tax refund receivable | $ | 51,998 | $ | 9,714 | |||
Receivable from subsidiaries | — | 27,016 | |||||
Total current assets | 51,998 | 36,730 | |||||
Investment in subsidiaries | 1,008,907 | 1,056,716 | |||||
Deferred taxes | 731,258 | 429,629 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 1,792,163 | $ | 1,523,075 | |||
Liabilities and equity | |||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses | $ | 795 | $ | — | |||
Payable to subsidiaries | 5,519 | — | |||||
Current portion of tax receivable agreement obligations to related parties | 31,232 | 22,789 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 37,546 | 22,789 | |||||
Long-term liabilities: | |||||||
Tax receivable agreement obligations to related parties | 801,829 | 597,273 | |||||
Total long-term liabilities | 801,829 | 597,273 | |||||
Total liabilities | 839,375 | 620,062 | |||||
Equity: | |||||||
Total Vantiv, Inc. equity | 952,788 | 903,013 | |||||
Total liabilities and equity | $ | 1,792,163 | $ | 1,523,075 | |||
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Parent Company only).
97
SCHEDULE I - Condensed Financial Information of Registrant
Vantiv, Inc.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS (PARENT COMPANY ONLY)
(In thousands)
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Operating Activities: | |||||||||||
Net income attributable to Vantiv, Inc. | $ | 147,946 | $ | 125,292 | $ | 133,572 | |||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: | |||||||||||
Equity in net income of subsidiaries | (203,057 | ) | (133,017 | ) | (192,092 | ) | |||||
Deferred taxes | 24,662 | 27,395 | 13,658 | ||||||||
Tax receivable agreements non-cash items | (769 | ) | (40,399 | ) | — | ||||||
Distributions from subsidiaries | 68,892 | 58,551 | 126,895 | ||||||||
Excess tax benefit from share-based compensation | (16,707 | ) | (13,420 | ) | (5,464 | ) | |||||
Change in operating assets and liabilities, net | 28,834 | (9,151 | ) | 10,497 | |||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 49,801 | 15,251 | 87,066 | ||||||||
Investing Activities: | |||||||||||
Proceeds from sale of Class A units in Vantiv Holding | 216,933 | 77,165 | 518,449 | ||||||||
Purchase of Class A units in Vantiv Holding | (13,630 | ) | (4,492 | ) | — | ||||||
Net cash provided by investing activities | 203,303 | 72,673 | 518,449 | ||||||||
Financing Activities: | |||||||||||
Advances from subsidiaries, net | 5,519 | (20,032 | ) | 20,032 | |||||||
Proceeds from exercise of Class A common stock options | 13,630 | 4,492 | — | ||||||||
Repurchase of Class A common stock | (200,406 | ) | (59,364 | ) | (503,225 | ) | |||||
Repurchase of Class A common stock (to satisfy tax withholding obligations) | (16,527 | ) | (17,801 | ) | (15,224 | ) | |||||
Settlement of certain tax receivable agreements | (49,222 | ) | — | (112,562 | ) | ||||||
Payments under tax receivable agreements | (22,805 | ) | (8,639 | ) | — | ||||||
Excess tax benefit from share-based compensation | 16,707 | 13,420 | 5,464 | ||||||||
Net cash used in financing activities | (253,104 | ) | (87,924 | ) | (605,515 | ) | |||||
Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents | — | — | — | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents—Beginning of period | — | — | — | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents—End of period | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Cash Payments: | |||||||||||
Taxes | $ | 2,323 | $ | 28,583 | $ | 31,874 | |||||
Non-cash Items: | |||||||||||
Issuance of tax receivable agreements | $ | 376,597 | $ | 109,400 | $ | 329,400 | |||||
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Parent Company only).
98
SCHEDULE I - Condensed Financial Information of Registrant
Vantiv, Inc.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (PARENT COMPANY ONLY)
1. BASIS OF PRESENTATION
For Vantiv, Inc.'s presentation (Parent Company only), the investment in subsidiaries is accounted for using the equity method. The condensed parent company financial statements and notes should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and notes of Vantiv, Inc. appearing in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Vantiv, Inc., is a holding company that does not conduct any business operations of its own and therefore its assets consist primarily of investments in subsidiaries. Vantiv Inc.'s cash inflows are primarily from cash dividends and distributions and other transfers from Vantiv Holding. Vantiv, Inc. may not be able to access cash generated by its subsidiaries in order to fulfill cash commitments or to pay cash dividends on its common stock. The amounts available to Vantiv, Inc. to fulfill cash commitments or to pay cash dividends are also subject to the covenants and distribution restrictions in its subsidiaries’ loan agreements. For a discussion on the tax receivable agreements, see Note 7- Tax Receivable Agreements in the consolidated financial statements and notes of Vantiv, Inc. appearing in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
99
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
VANTIV, INC. | |||
Dated: | February 10, 2016 | By: | /s/ CHARLES D. DRUCKER |
Name: Charles D. Drucker | |||
Title: President and Chief Executive Officer | |||
Dated: | February 10, 2016 | By: | /s/ CHRISTOPHER THOMPSON |
Name: Christopher Thompson | |||
Title: SVP, Controller and Chief Accounting Officer | |||
100
POWER OF ATTORNEY
Each person whose signature appears below hereby constitutes and appoints Charles D. Drucker, Mark L. Heimbouch and Nelson F. Greene, and each of them, as his or her true and lawful attorneys-in-fact and agents, with full power of substitution and resubstitution and full power to act without the other, for him or her and in his or her name, place and stead, in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and to file the same, with all exhibits thereto, and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorneys-in-fact and agents, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done in connection therewith, as fully to all intents and purposes as he or she might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming that all said attorneys-in-fact and agents, or any of them or their or his or her substitute or substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated:
Signature | Title | Date | ||
/s/ CHARLES D. DRUCKER | Chief Executive Officer, President and Director | February 10, 2016 | ||
Charles D. Drucker | (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
/s/ MARK L. HEIMBOUCH | Sr. Executive Vice President and Chief Operating & Financial Officer and Director | February 10, 2016 | ||
Mark L. Heimbouch | (Principal Financial Officer) | |||
/s/ JEFFREY STIEFLER | Chairman | February 10, 2016 | ||
Jeffrey Stiefler | ||||
/s/ LEE ADREAN | Director | February 10, 2016 | ||
Lee Adrean | ||||
/s/ TAYFUN TUZUN | Director | February 10, 2016 | ||
Tayfun Tuzun | ||||
/s/ GARY L. LAUER | Director | February 10, 2016 | ||
Gary L. Lauer | ||||
/s/ KEVIN COSTELLO | Director | February 10, 2016 | ||
Kevin Costello | ||||
/s/ DAVID KARNSTEDT | Director | February 10, 2016 | ||
David Karnstedt | ||||
/s/ LARS ANDERSON | Director | February 10, 2016 | ||
Lars Anderson | ||||
/s/ LISA HOOK | Director | February 10, 2016 | ||
Lisa Hook | ||||
/s/ BOON SIM | Director | February 10, 2016 | ||
Boon Sim | ||||
101
EXHIBIT INDEX
Exhibit | Incorporated by Reference | |||||||||
Number | Exhibit Description | Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | |||||
2.1 | Master Investment Agreement among Fifth Third Bank, Fifth Third Financial Corporation, Advent-Kong Blocker Corp., Vantiv Holding, LLC (f/k/a FTPS Holding, LLC) and Vantiv, LLC (f/k/a Fifth Third Processing Solutions, LLC) dated March 27, 2009 and as amended June 30, 2009. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 2.1 | November 10, 2011 | |||||
2.2 | Agreement and Plan of Merger by and among NPC Group, Inc., FTPS-BG Acquisition Corp., Vantiv, LLC (f/k/a Fifth Third Processing Solutions, LLC), and National Processing Holdings, LLC dated September 15, 2010. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 2.2 | November 10, 2011 | |||||
2.3 | Recapitalization Agreement by and among Vantiv, Inc., Vantiv Holding, LLC, Fifth Third Bank, FTPS Partners, LLC, JPDN Enterprises, LLC and the Vantiv, Inc. stockholders party thereto. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 2.1 | May 8, 2012 | |||||
2.4 | Membership Interest Purchase Agreement, dated as of October 26, 2012, by and among National Processing Company, Vantiv, LLC, Litle & Co. LLC, Litle Holdings LLC, the members named therein and Thomas J. Litle IV, as members' representative. | S-1 | 333-185222 | 2.4 | November 30, 2012 | |||||
2.5 | Transaction Agreement, dated as of May 12, 2014, by and among Vantiv, Inc., National Processing Company, Mars Merger Sub, LLC, Vantiv, LLC, SLP III Quicksilver Feeder I, L.P., Mercury Payment Systems, LLC and Silver Lake Partners III DE, L.P. | 8-K | 001-35462 | 2.1 | May 16, 2014 | |||||
3.1 | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Vantiv, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 3.1 | May 8, 2012 | |||||
3.2 | Amended and Restated Bylaws of Vantiv, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 3.2 | October 30, 2014 | |||||
4.1 | Form of Class A Common Stock Certificate. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 4.1 | March 14, 2012 | |||||
10.1 | Second Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of Vantiv Holding, LLC. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.1 | May 8, 2012 | |||||
10.2 | Advancement Agreement by and among Vantiv Holding, LLC and Vantiv, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.2 | May 8, 2012 | |||||
10.3 | Exchange Agreement among Vantiv, Inc., Vantiv Holding, LLC, Fifth Third Bank, FTPS Partners, LLC and such other holders of Class B Units and Class C Non-Voting Units from time to time party thereto. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.3 | May 8, 2012 | |||||
10.4 | Registration Rights Agreement by and among Vantiv, Inc. and the stockholders party thereto. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.4 | May 8, 2012 | |||||
10.5 | Warrant issued by Vantiv Holding, LLC (f/k/a FTPS Holding, LLC) to Fifth Third Bank. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.5 | May 8, 2012 | |||||
10.6 | Tax Receivable Agreement by and among Vantiv, Inc., Fifth Third Bank and FTPS Partners, LLC. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.6 | May 8, 2012 | |||||
10.7 | Tax Receivable Agreement by and among Vantiv, Inc., the Advent Stockholders and Advent International Corporation. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.7 | May 8, 2012 | |||||
10.7.1 | Tax Receivable Termination Agreement, dated October 23, 2013, by and among Vantiv, Inc., the Advent Stockholders and Advent International Corporation. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.1 | October 24, 2013 | |||||
10.8 | Tax Receivable Agreement by and between Vantiv, Inc. and JPDN Enterprises, LLC. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.8 | May 8, 2012 | |||||
10.8.1 | Tax Receivable Termination Agreement, dated October 23, 2013, by and between Vantiv, Inc. and JPDN Enterprises, LLC. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.2 | October 24, 2013 | |||||
10.9 | Tax Receivable Agreement by and among Vantiv, Inc., Fifth Third Bank, FTPS Partners, LLC, the Advent Stockholders, Advent International Corporation and JPDN Enterprises, LLC. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.9 | May 8, 2012 | |||||
10.10 | Amendment and Restatement Agreement, dated as of June 13, 2014, among Vantiv, LLC, Vantiv Holding, LLC, the other Loan Parties, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent, and the other agents and lenders party thereto. | 8-K | 001-35462 | 10.1 | June 19, 2014 | |||||
10.11 | Amended and Restated Loan Agreement, dated as of June 13, 2014, by and among Vantiv, LLC, various lenders from time to time party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. as Administrative Agent, and the other agents party thereto. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.2 | July 31, 2014 | |||||
10.12+ | Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement under the Vantiv, Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan for Holders of Phantom Units under the Vantiv Holding, LLC Management Phantom Equity Plan. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 10.24 | March 5, 2012 | |||||
102
10.12.1+ | Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement under the Vantiv, Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan for the Chief Executive Officer. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 10.38 | March 14, 2012 | |||||
10.12.2+ | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement for Non-Employee Directors Under the Vantiv, Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 10.39 | March 14, 2012 | |||||
10.12.3+ | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement for Carlos Lima under the Vantiv, Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan. | 10-K | 001-35462 | 10.15 | February 20, 2013 | |||||
10.12.4+ | Form of Stock Option Grant Notice and Option Agreement under the Vantiv, Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.1 | May 6, 2013 | |||||
10.12.5+ | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Grant Notice and Restricted Stock Unit Agreement under the Vantiv, Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.2 | May 6, 2013 | |||||
10.12.6+ | Form of Performance Share Unit Award Notice and Performance Share Unit Agreement under the Vantiv, Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.3 | May 6, 2013 | |||||
10.12.7+ | Revised Form of Performance Share Award Notice and Performance Share Agreement under the Vantiv, Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan. | |||||||||
10.13+ | Amended and Restated Offer Letter, dated as of March 15, 2012, by and between Vantiv, LLC and Charles D. Drucker. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 10.26 | March 16, 2012 | |||||
10.14+ | Amended and Restated Offer Letter, dated as of February 27, 2012, by and between Vantiv, LLC and Mark L. Heimbouch. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 10.27 | March 14, 2012 | |||||
10.15+ | Amended and Restated Offer Letter, dated as of February 27, 2012, by and between Vantiv, LLC and Royal Cole. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 10.35 | March 14, 2012 | |||||
10.16+ | Offer Letter, dated as of August 9, 2013, by and between Vantiv, LLC and Daniela Mielke | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.1 | April 30, 2015 | |||||
10.17+ | Offer Letter, dated as of May 12, 2014, by and between Vantiv, LLC and Matt Taylor | |||||||||
10.17.1+ | Offer Letter, dated as of November 14, 2014, by and between Vantiv, LLC and Kimberly Martin | |||||||||
10.18+ | Non-Competition, Non-Solicitation and Confidentiality Agreement made as of June 30, 2009, by and between Vantiv, LLC and Charles D. Drucker. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 10.28 | March 5, 2012 | |||||
10.19+ | Form of Vantiv, LLC Non-Competition, Non-Solicitation and Confidentiality Agreement for executive officers. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 10.29 | March 5, 2012 | |||||
10.20+ | Form of Indemnification Agreement. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 10.37 | March 16, 2012 | |||||
10.21† | Referral Agreement, dated June 30, 2009, by and between Vantiv, LLC and Fifth Third Bancorp. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 10.11 | March 14, 2012 | |||||
10.22† | Master Services Agreement, dated as of June 30, 2009, by and between Fifth Third Bancorp and Vantiv, LLC. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 10.12 | March 14, 2012 | |||||
10.22.1† | Amendment No. 1 to the Master Services Agreement between Vantiv, LLC and Fifth Third Bancorp. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 10.13 | March 14, 2012 | |||||
10.23† | Clearing, Settlement and Sponsorship Services Agreement, dated June 30, 2009, by and between Vantiv, LLC and Fifth Third Bank. | S-1/A | 333-177875 | 10.14 | March 14, 2012 | |||||
10.24 | Stock Repurchase Agreement, dated as of May 6, 2013 | 8-K | 001-35462 | 10.1 | May 9, 2013 | |||||
10.25 | Tax Receivable Agreement, dated as of May 12, 2014, by and among NPC Group, Inc.; Silver Lake Partners III DE, LP; SLP III Quicksilver Feeder I, LP; Silver Lake Technology Investors III, L.P.; MPS 1, Inc.; Mercury Payment Systems II, LLC; Vantiv, LLC; and certain other parties listed on Schedule B thereto. | 8-K | 001-35462 | 10.3 | June 19, 2014 | |||||
10.26+ | Mercury Payment Systems, LLC 2010 Unit Incentive Plan, as Restated and Assumed by Vantiv, Inc. | S-8 | 333-196911 | 4.3 | June 19, 2014 | |||||
10.27+ | Form of Restricted Share Grant Notice and Restricted Share Agreement under the Vantiv, Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.3 | April 30, 2015 | |||||
10.28+ | Form of Performance Share Grant Notice and Performance Share Agreement under the Vantiv, Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.4 | April 30, 2015 | |||||
10.29 | Repurchase Addendum to Tax Receivable Agreement, dated as of July 24, 2015 by and among NPC Group, Inc.; Silver Lake Partners III DE, L.P.; SLP III Quicksilver Feeder I, L.P.; Silver Lake Technology Associates III, L.P.; Silver Lake Technology Investors III, L.P.; Durango FI, LLC (f/k/a MPS 1, Inc.); Mercury Payment Systems II, LLC; Vantiv, LLC; and certain other parties listed on Schedule A thereto. | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.1 | July 29, 2015 | |||||
10.30 | Tax Receivable Purchase Addendum, dated as of October 23, 2015, by and between Vantiv, Inc. and Fifth Third Bank | 10-Q | 001-35462 | 10.1 | October 28, 2015 | |||||
10.31 | Warrant Cancellation Agreement, dated as of December 2, 2015, by and between Vantiv Holding, LLC and Fifth Third Bank | 8-K | 001-35462 | 10.1 | December 2, 2015 | |||||
103
10.32+ | Employee Stock Purchase Plan, amended as of October 27, 2015 | |||||||||
10.33+ | Amended and Restated Executive Severance Plan, dated as of November 8, 2015 | |||||||||
10.34+ | Vantiv, Inc. 2012 Equity Incentive Plan, dated as of November 8, 2015 | |||||||||
11.1 | Statement re computation of per share earnings (incorporated by reference to Notes to the Financial Statements included in Part II of this Report). | |||||||||
21.1 | Subsidiaries of the Registrant. | |||||||||
23.1 | Consent of Deloitte & Touche LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. | |||||||||
24.1 | Power of Attorney (included on signature page). | |||||||||
31.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rules 13a-14(a) and 15d-14(a), as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |||||||||
31.2 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rules 13a-14(a) and 15d-14(a), as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |||||||||
32 | Certifications of Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |||||||||
101 | Interactive Data Files. | |||||||||
† | Confidential treatment granted as to certain portions by the SEC. |
+ | Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan. |
104
